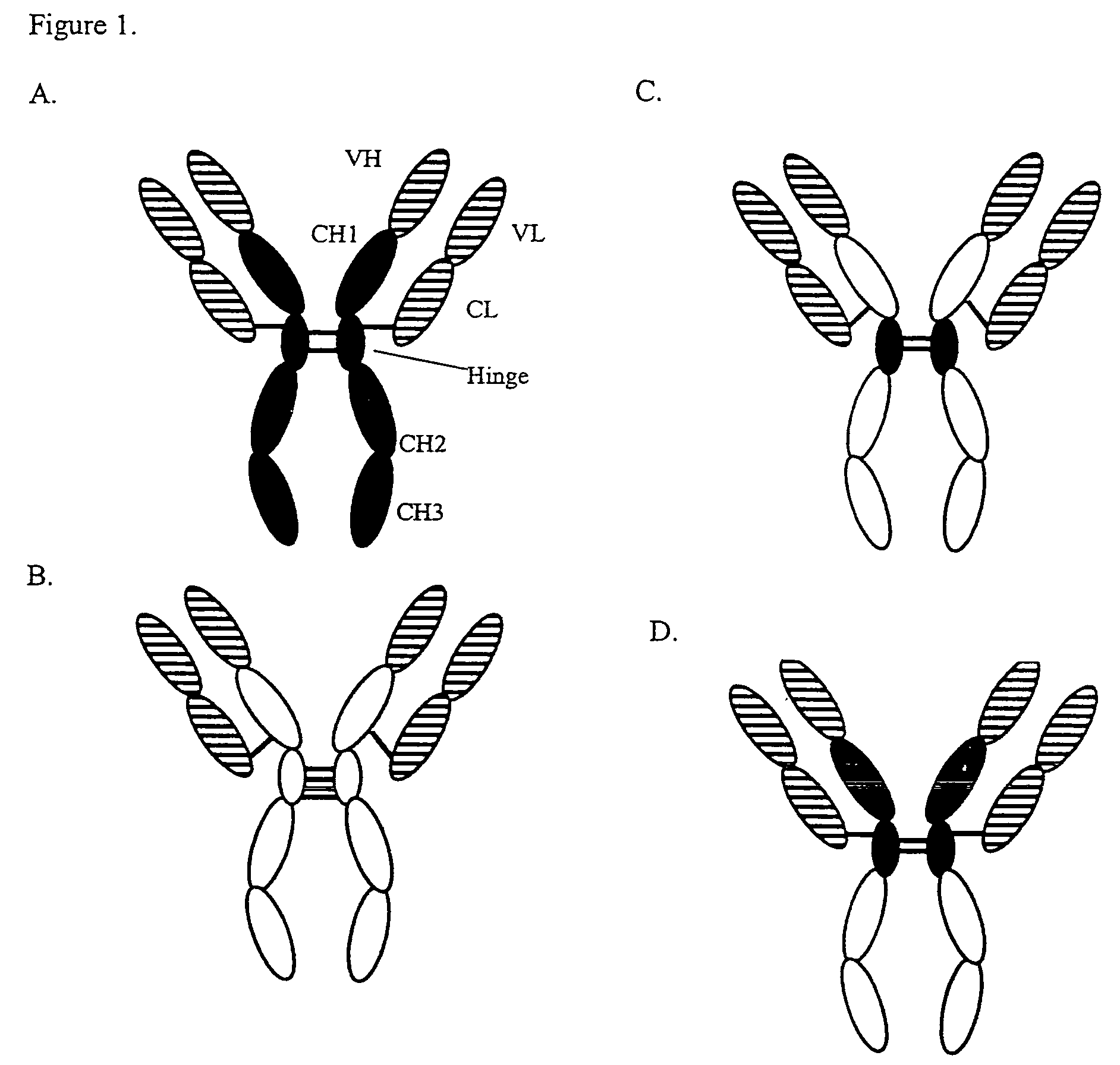
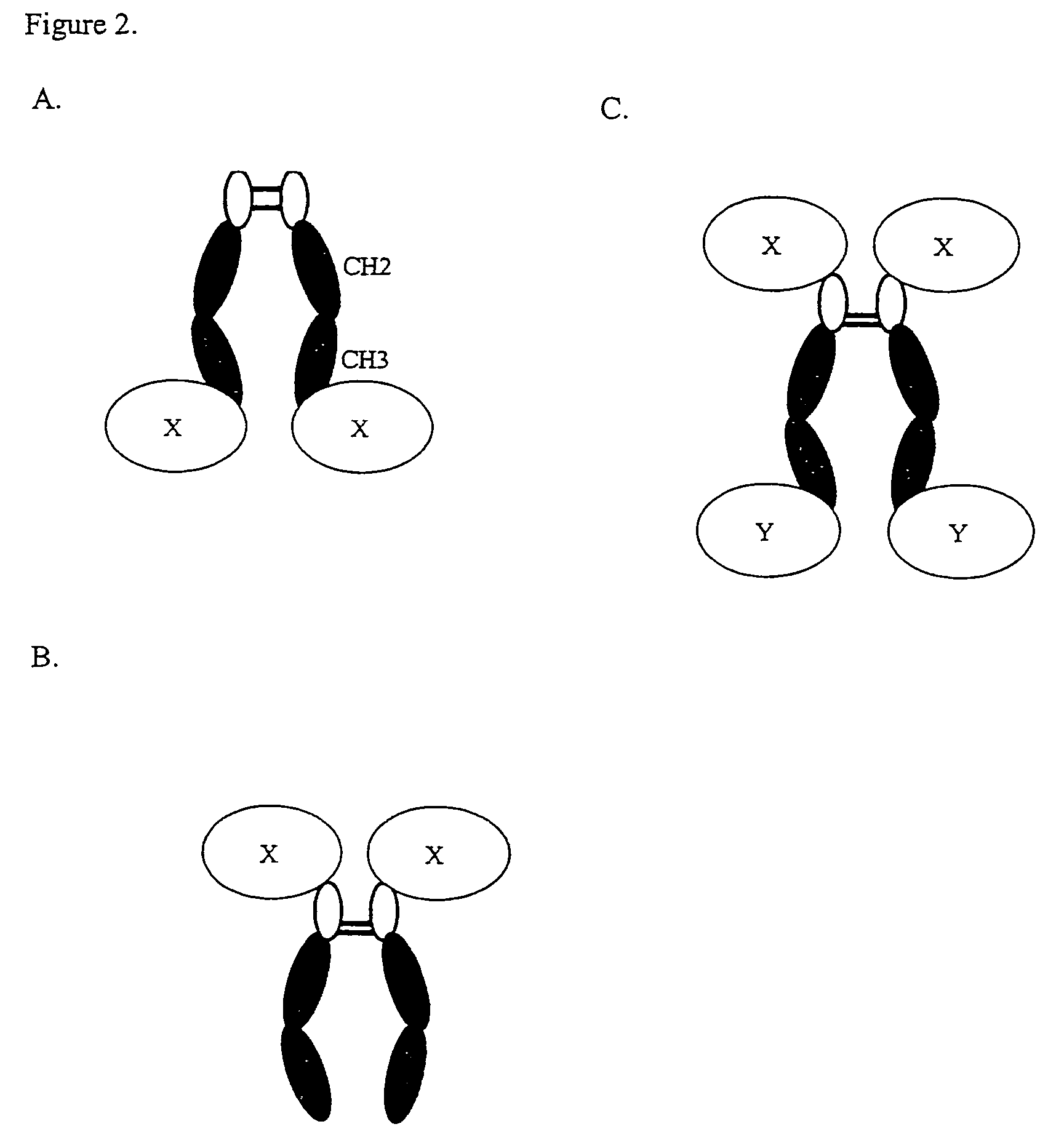
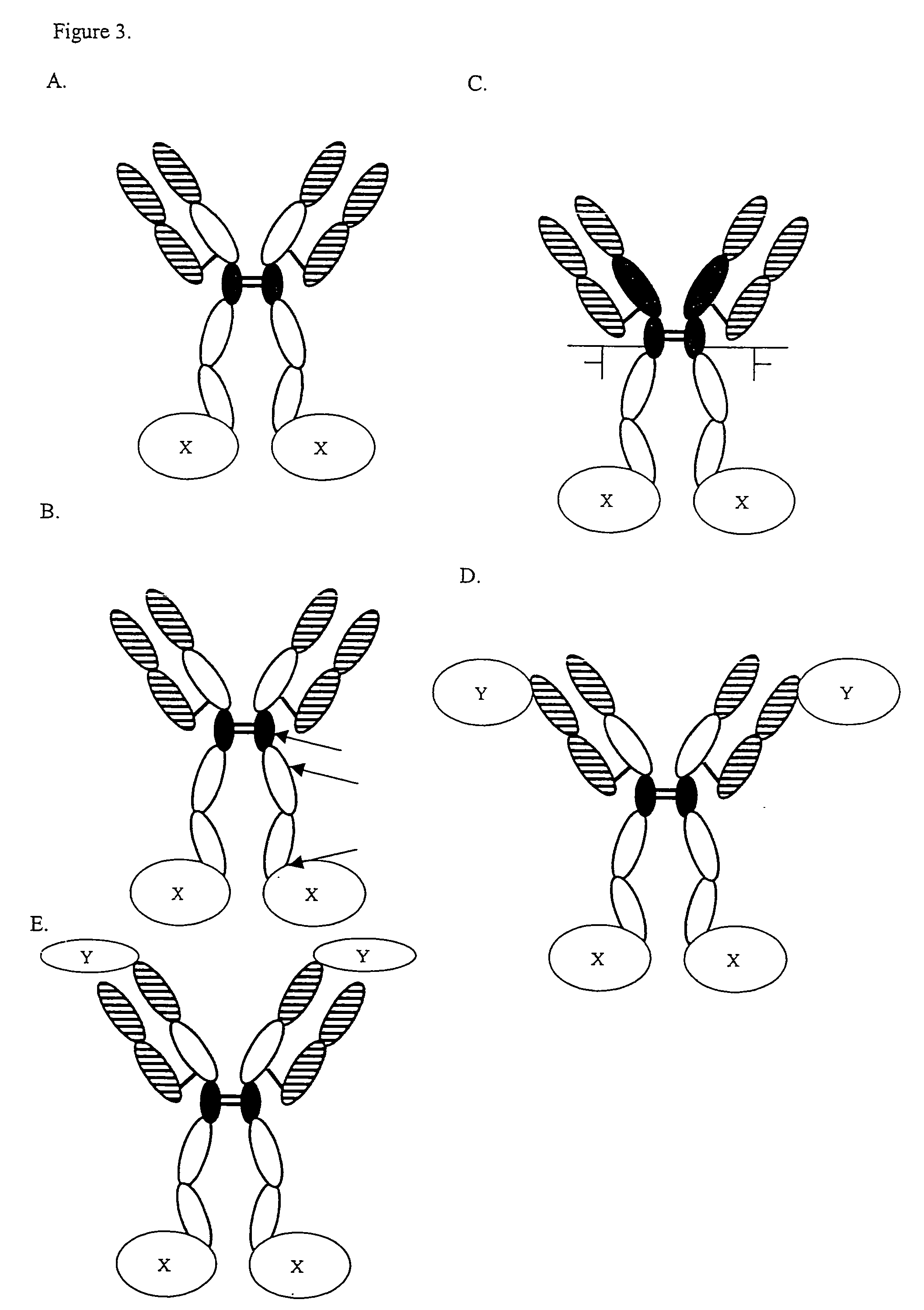
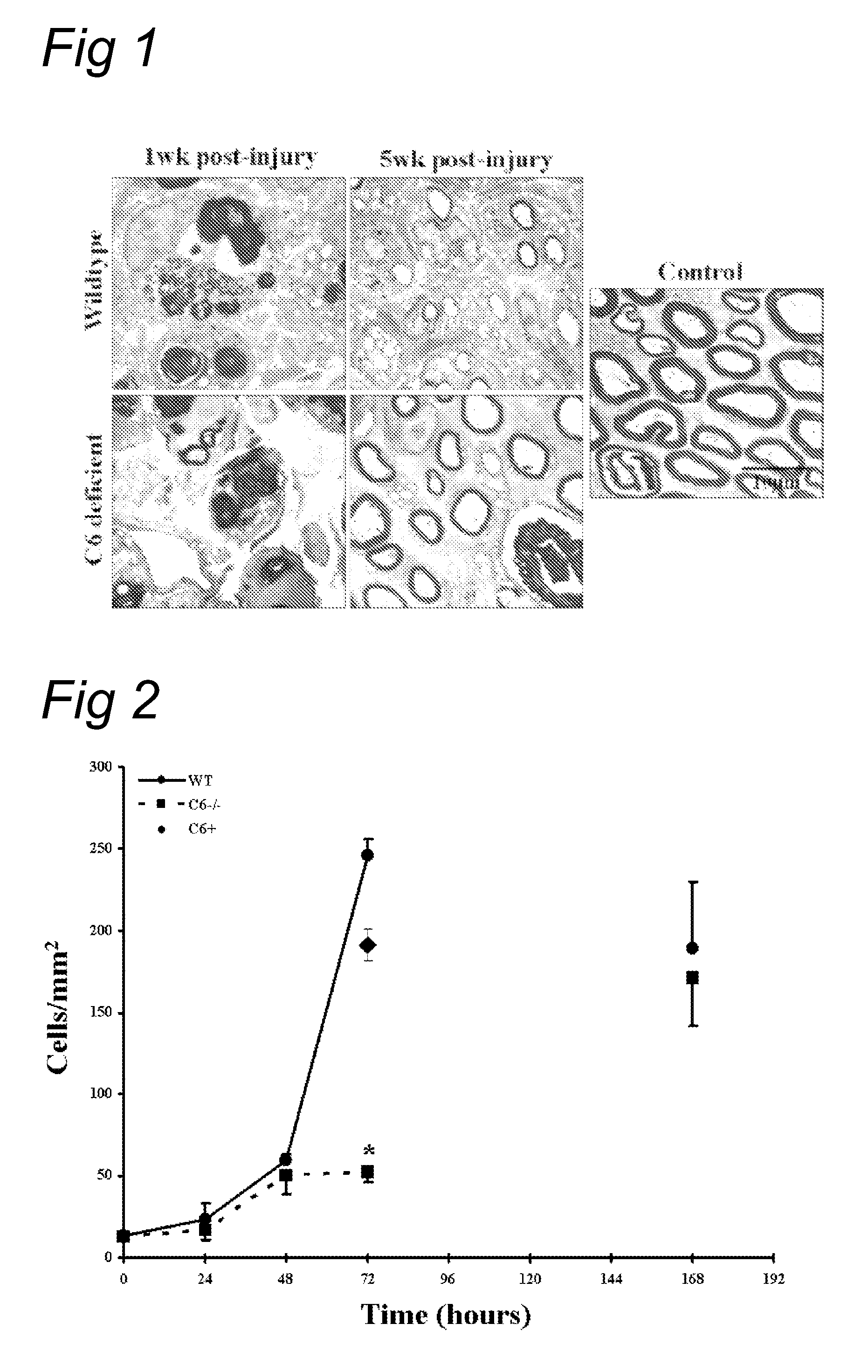
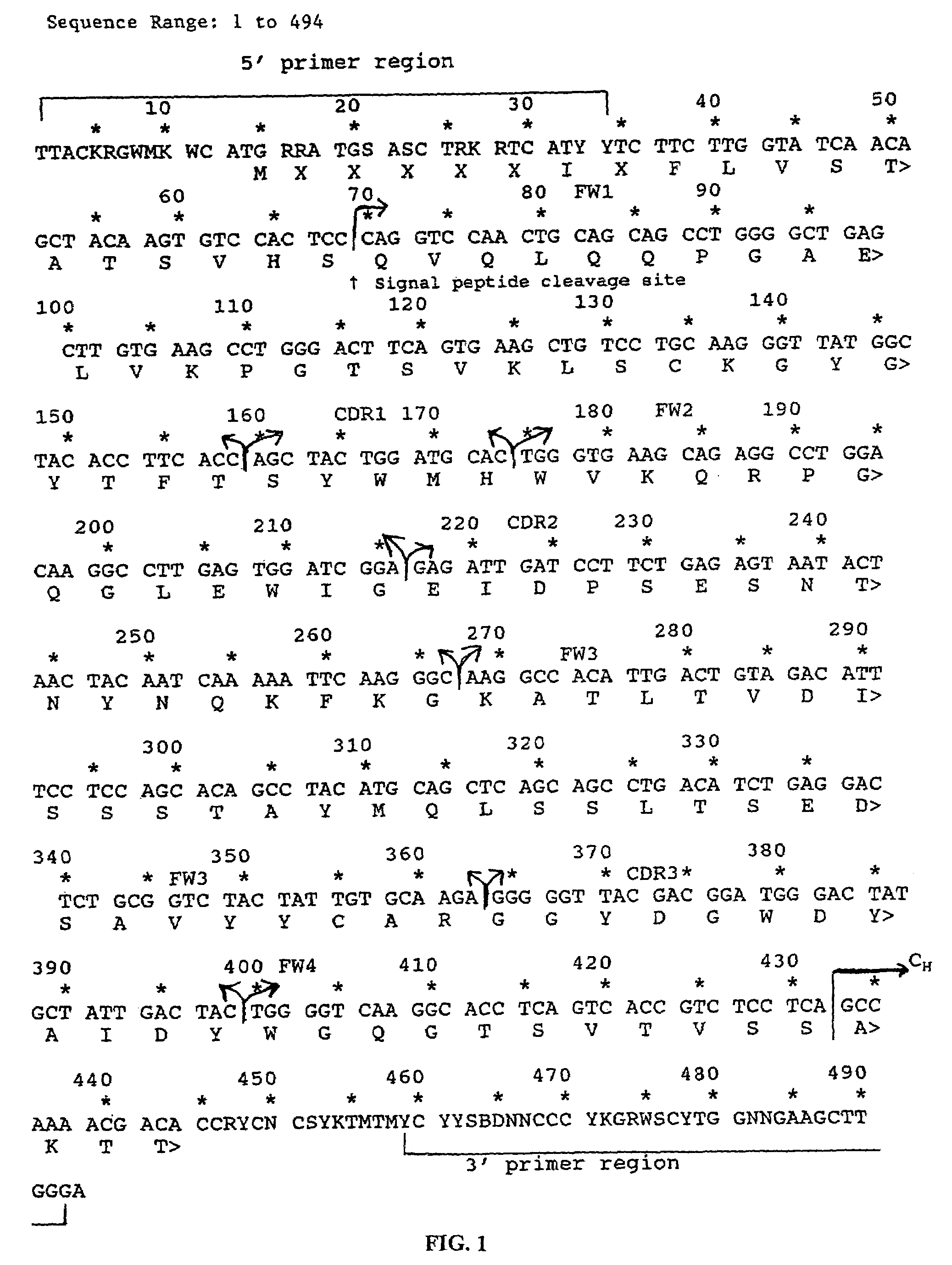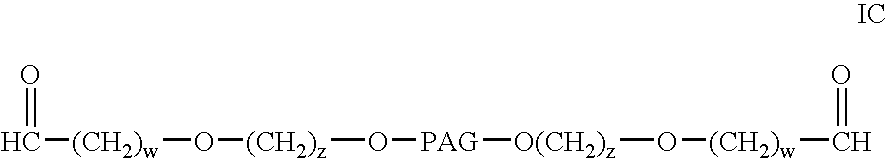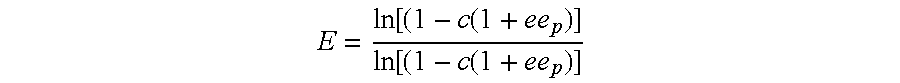Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
102results about How to "Less immunogenic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
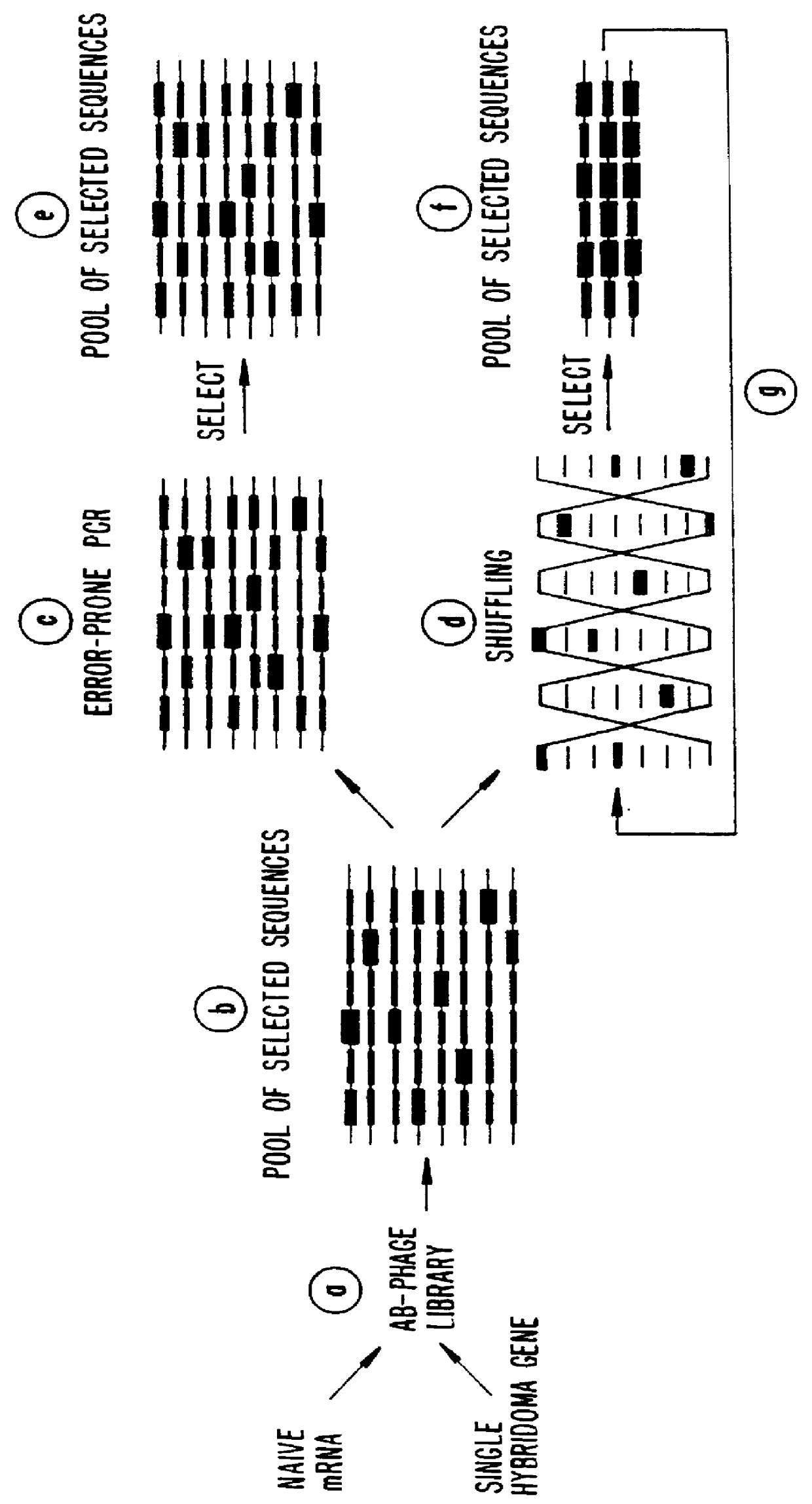
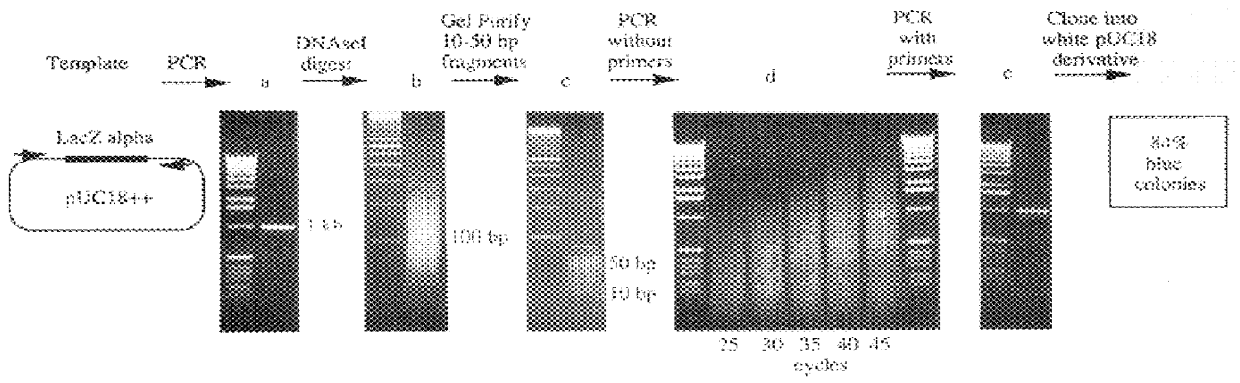
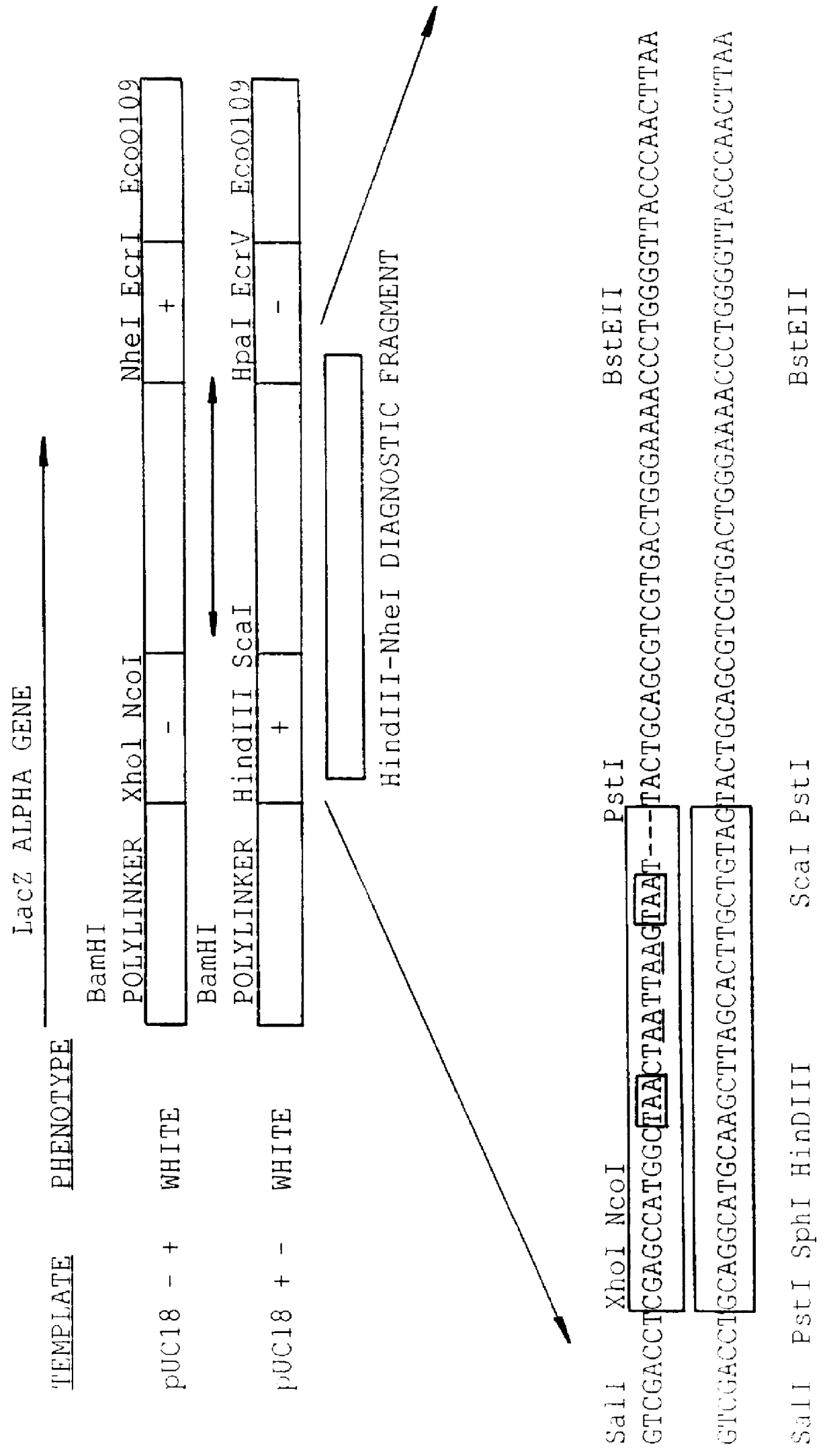
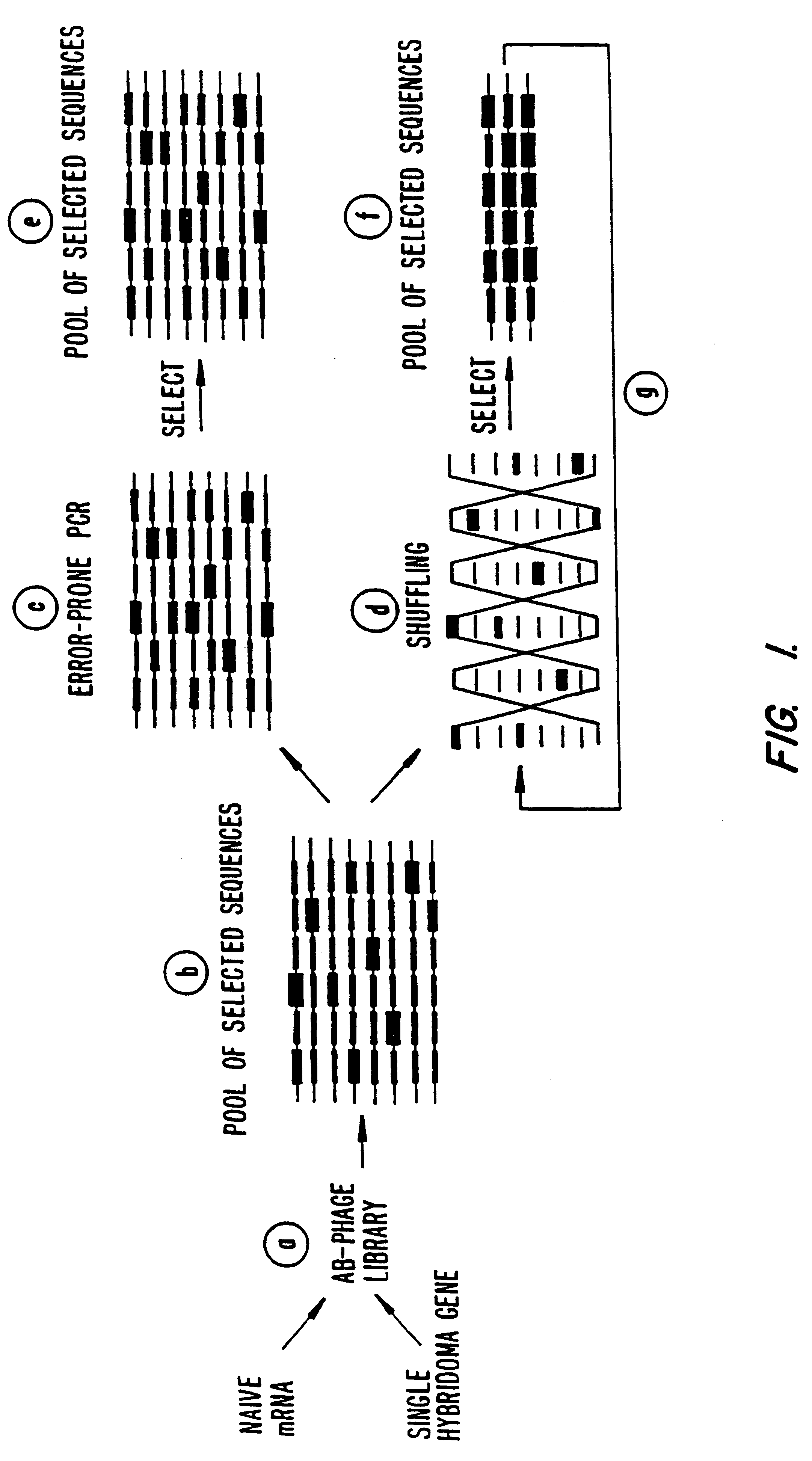
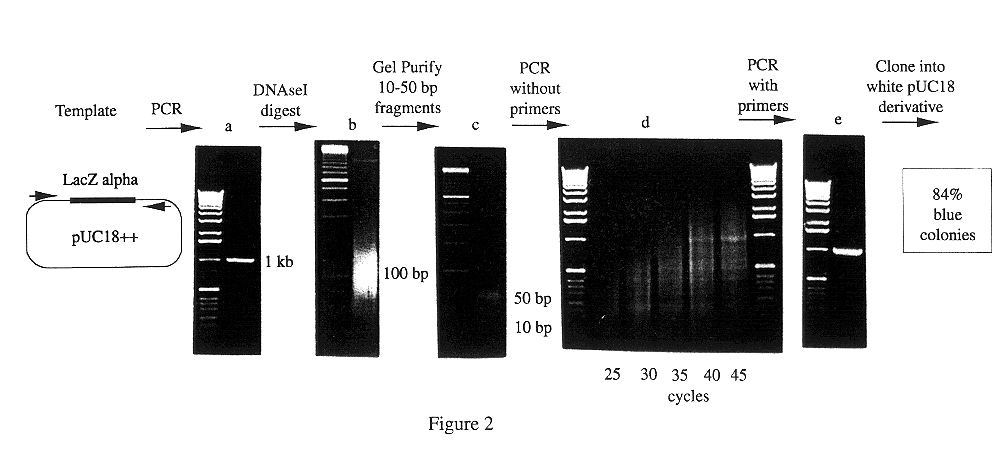
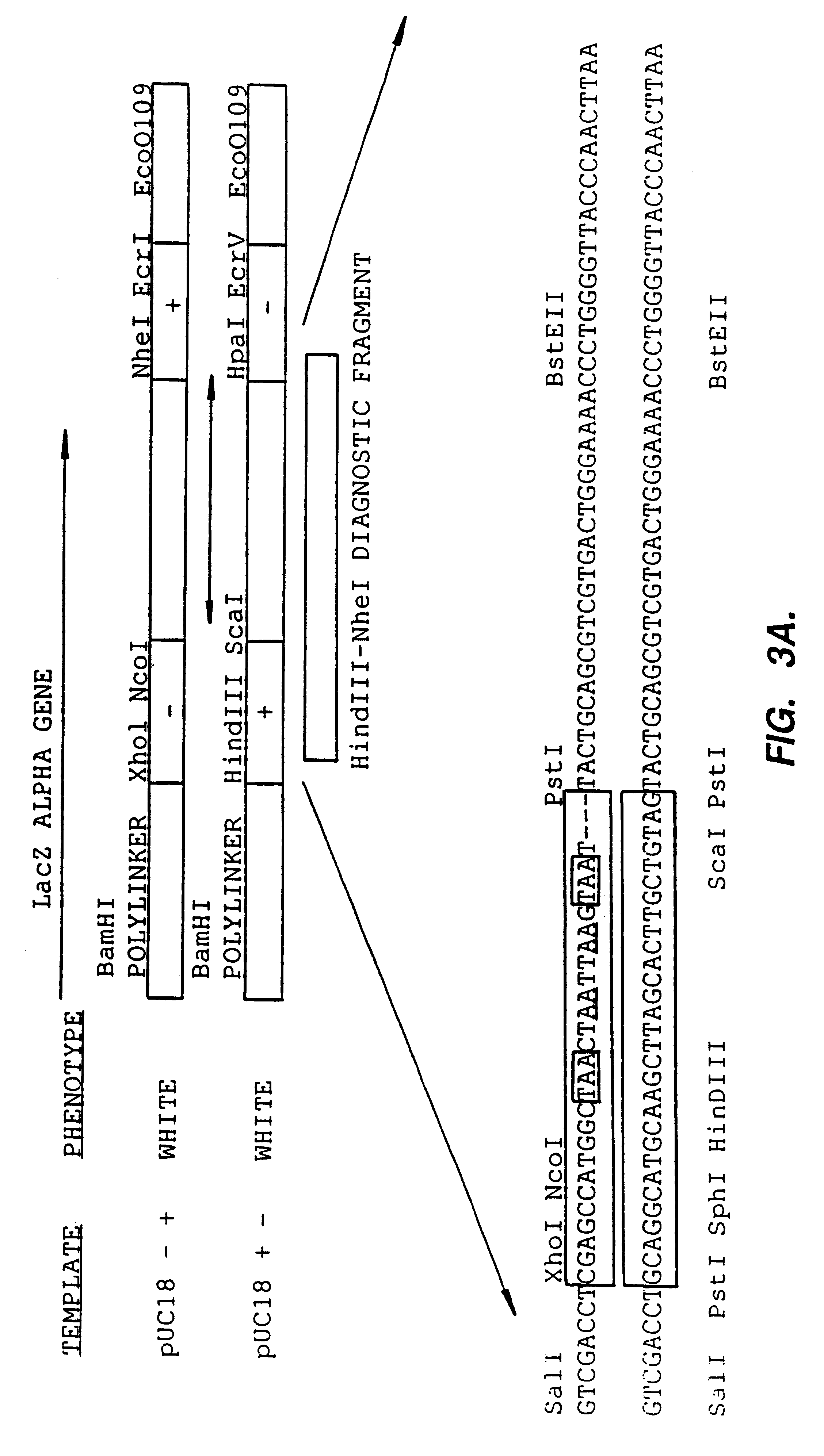
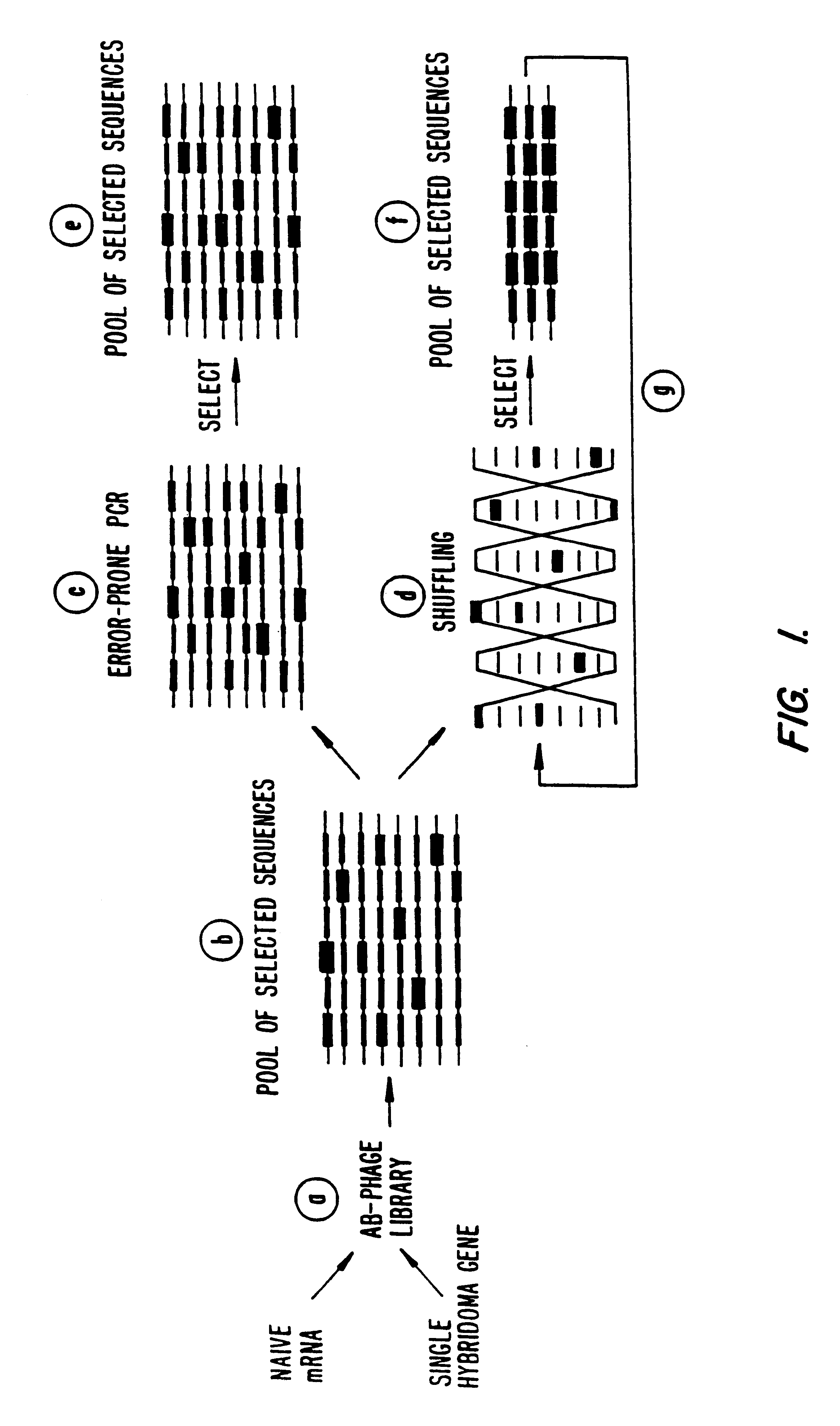
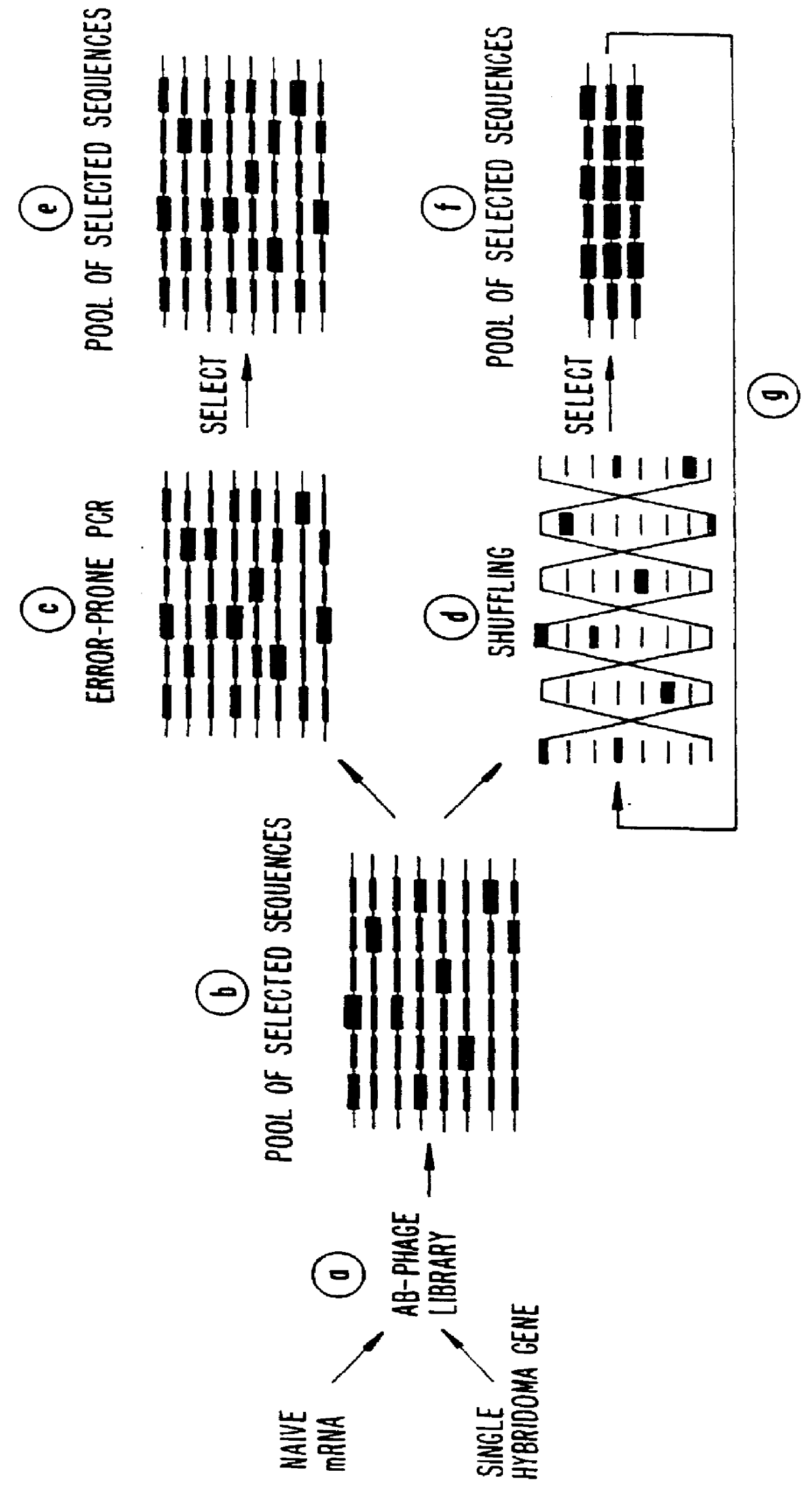
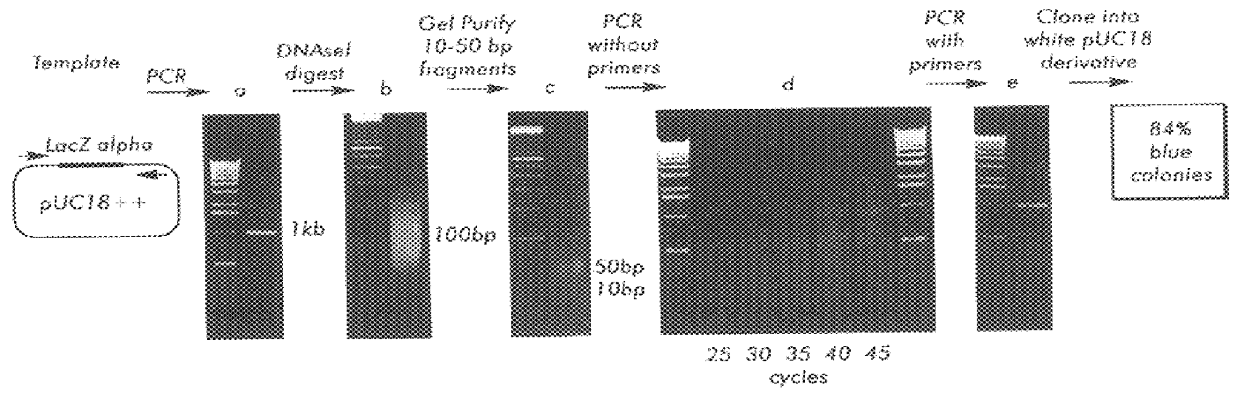
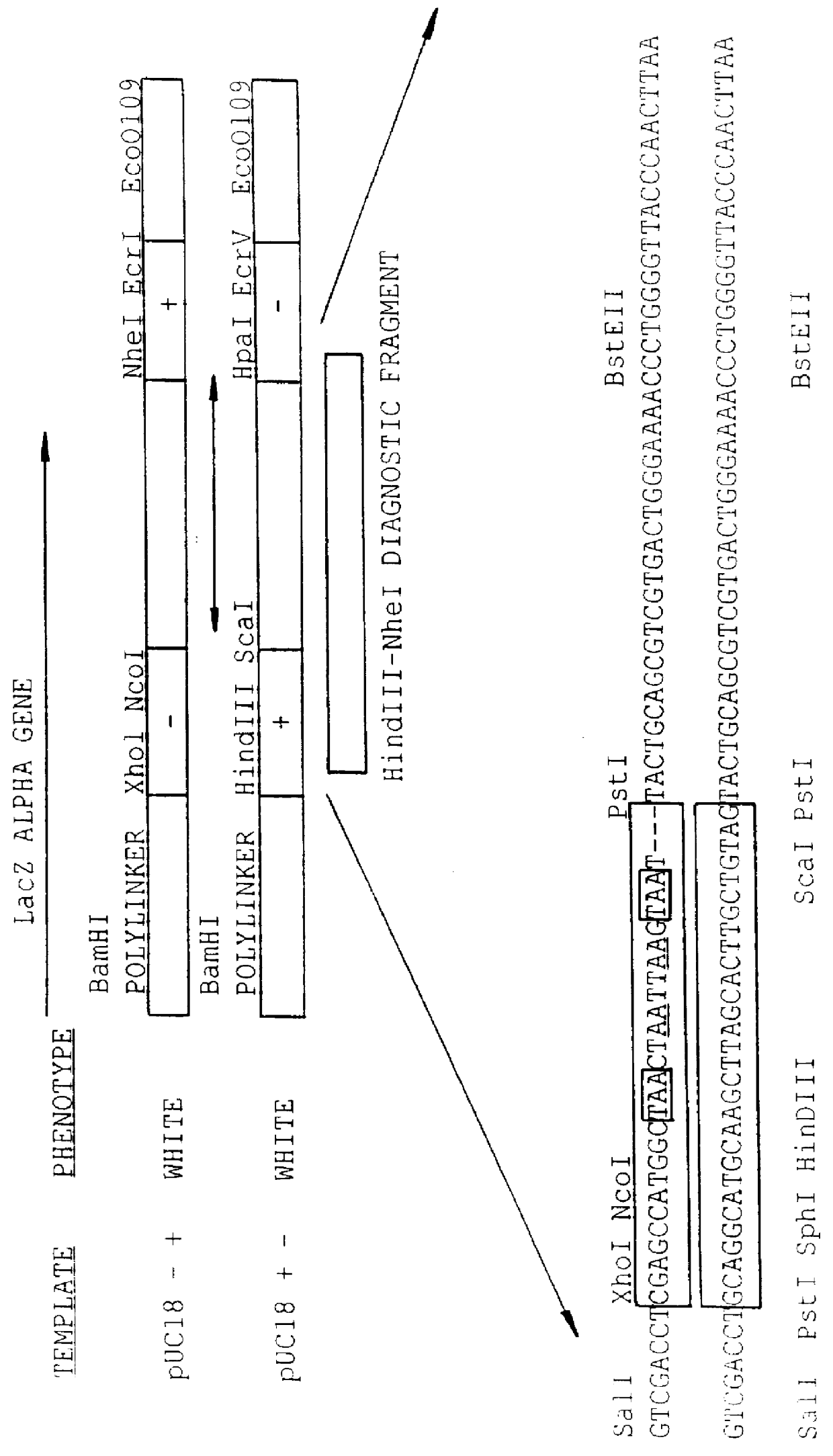
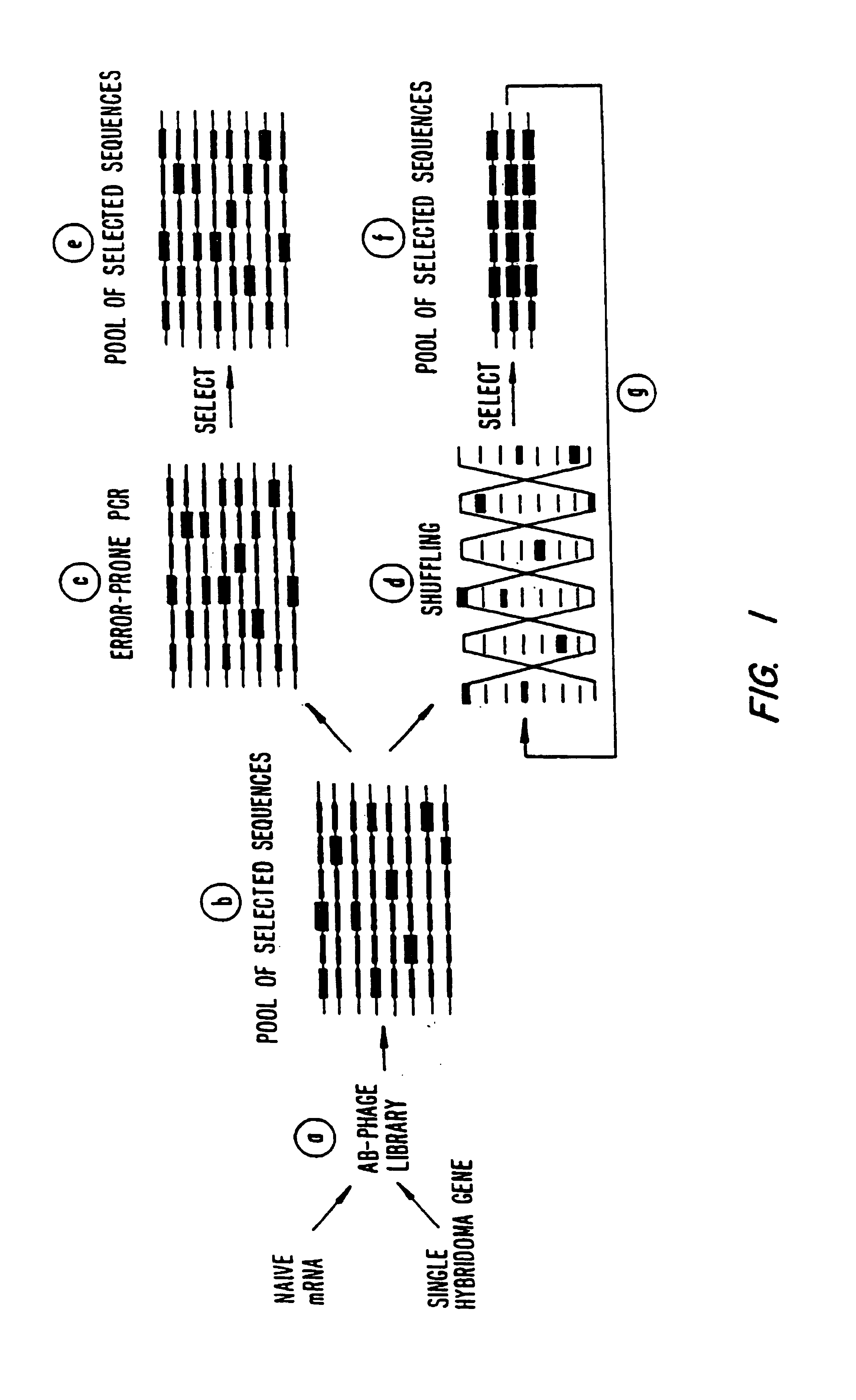
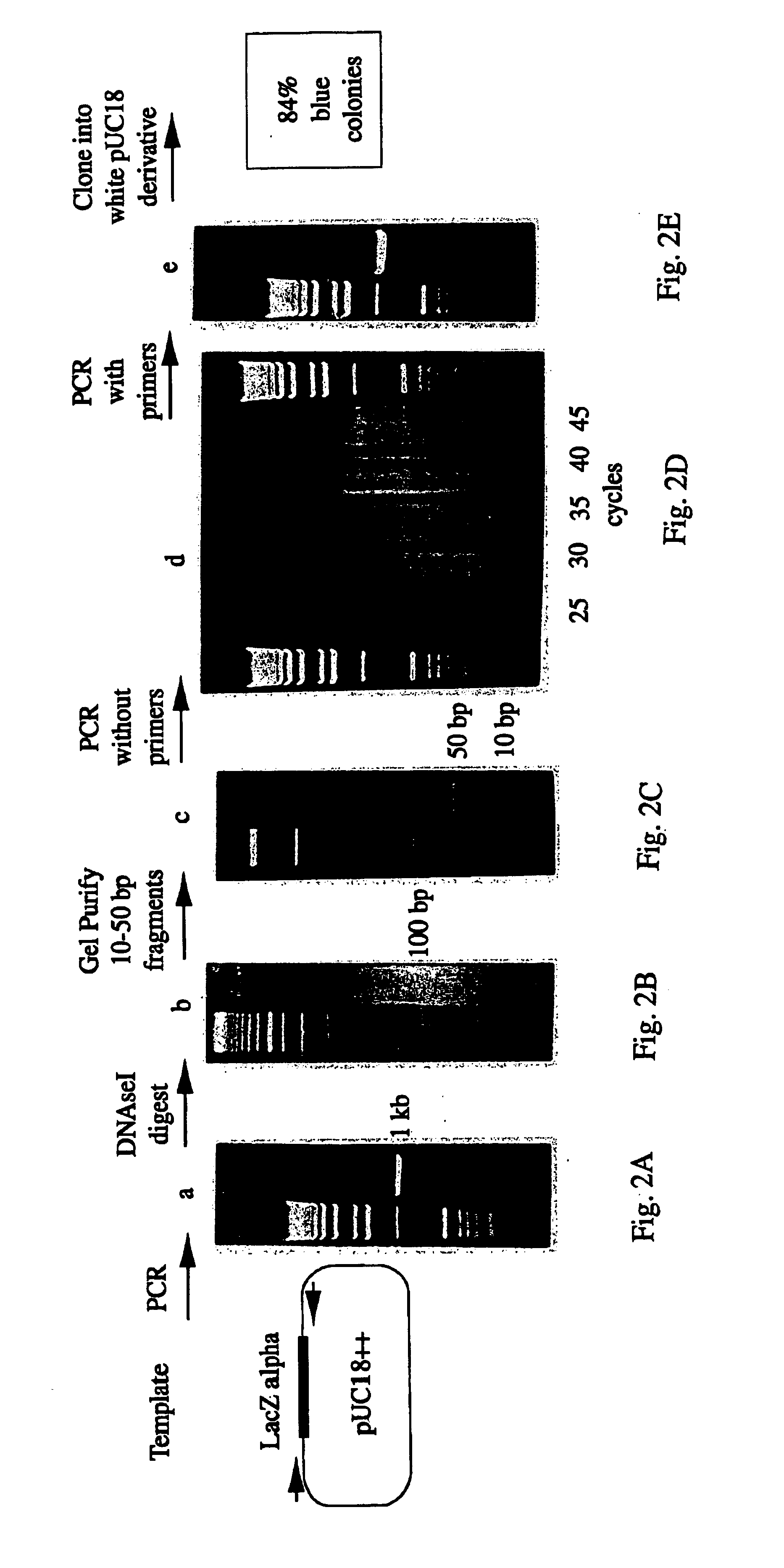
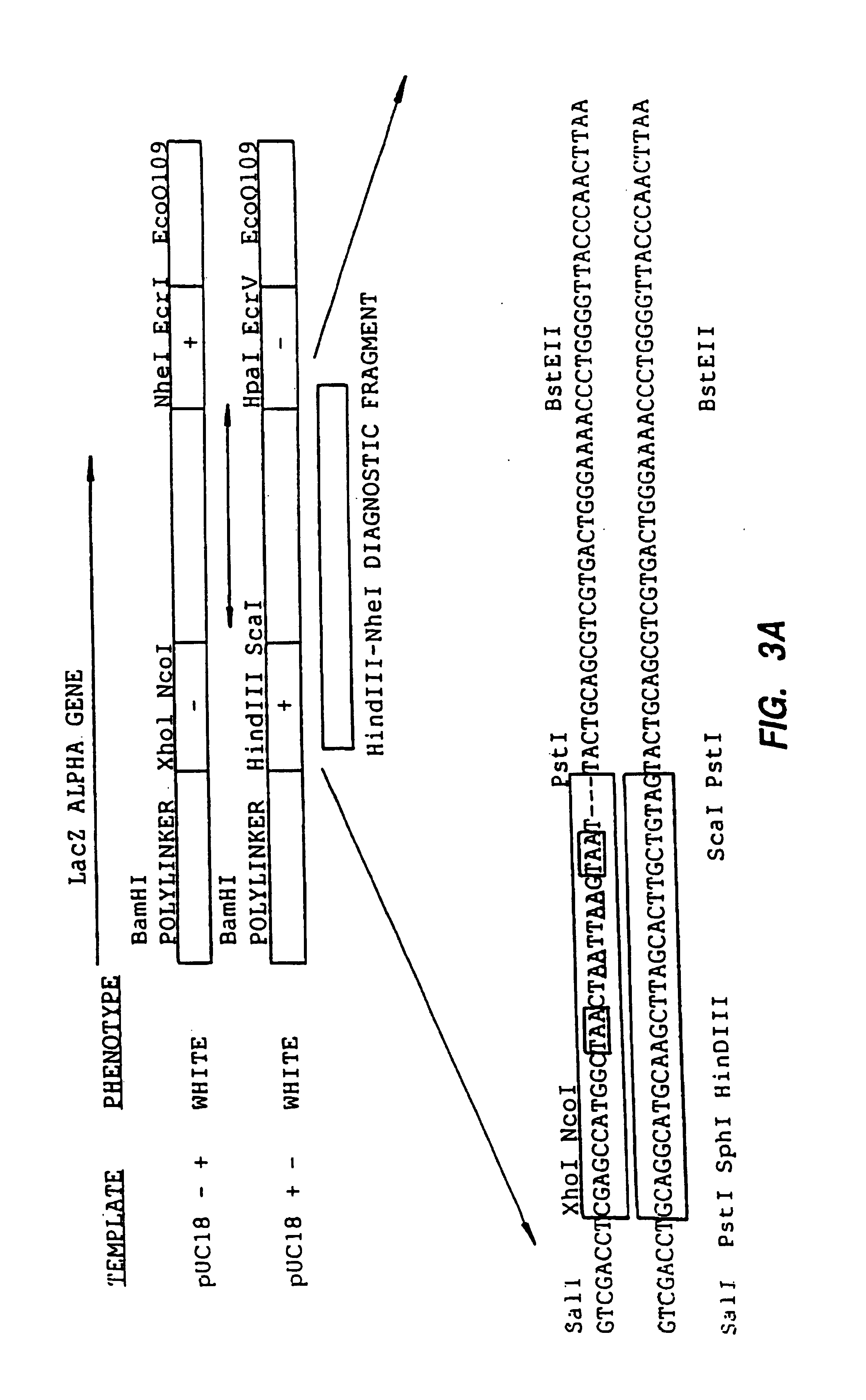
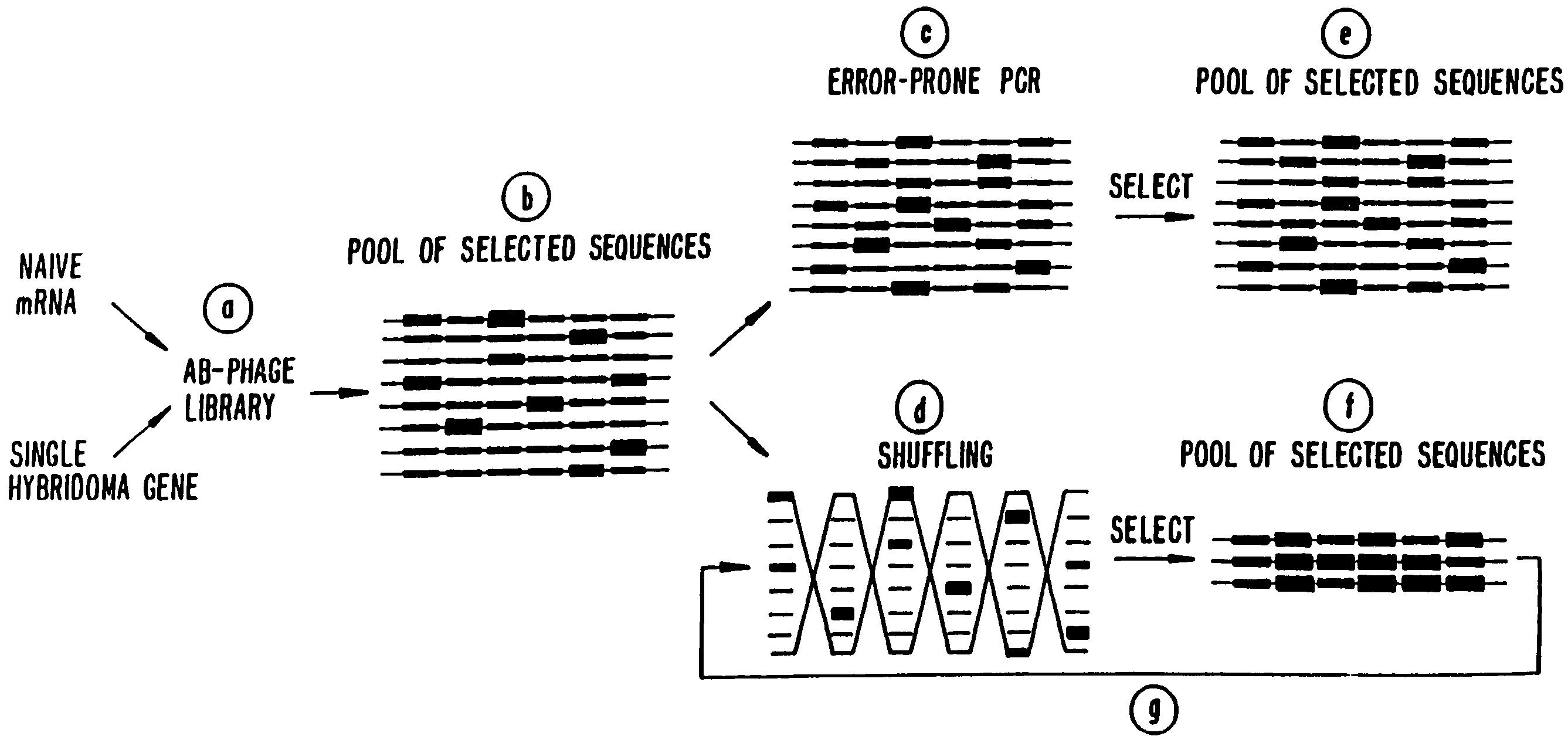
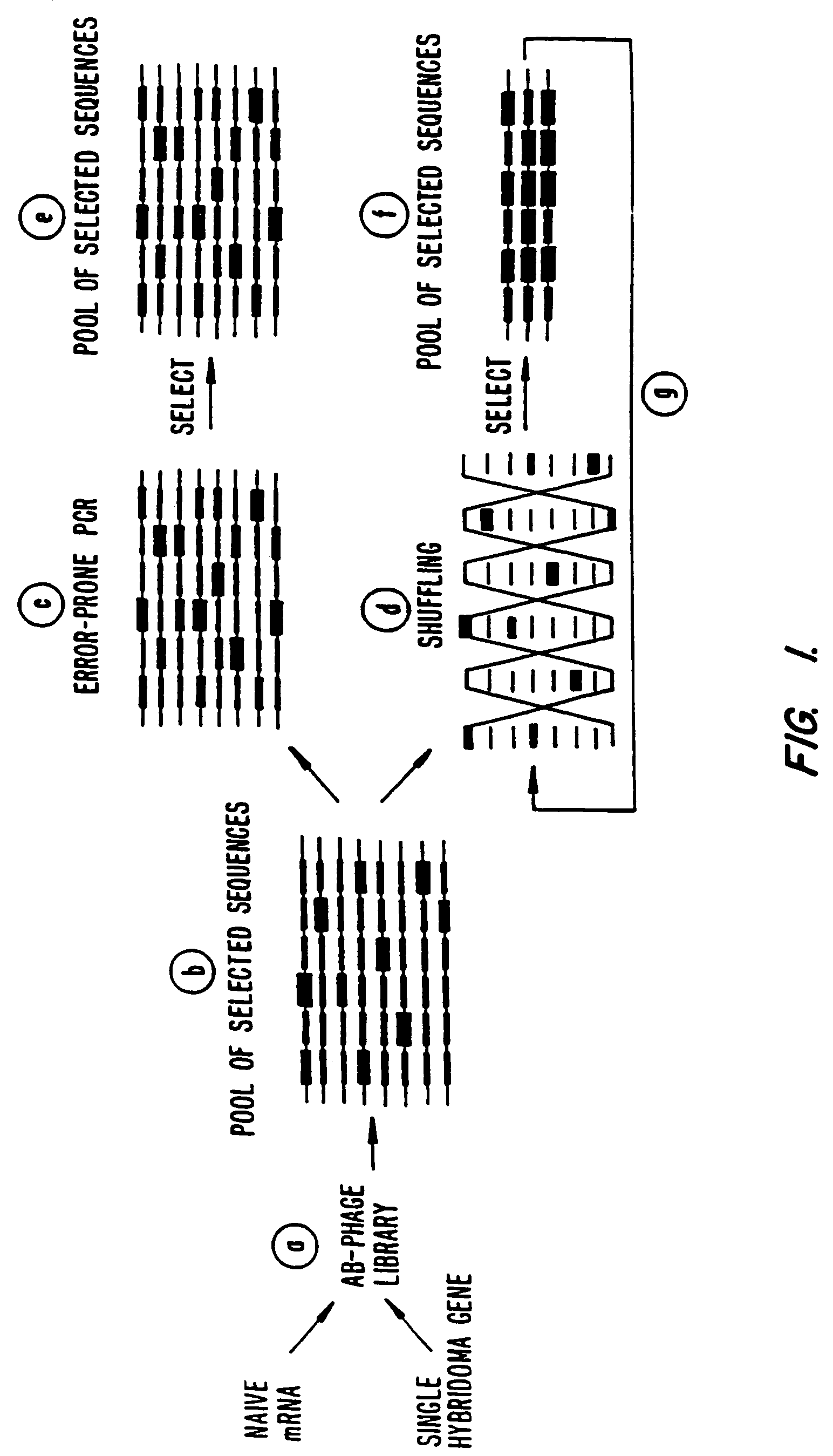
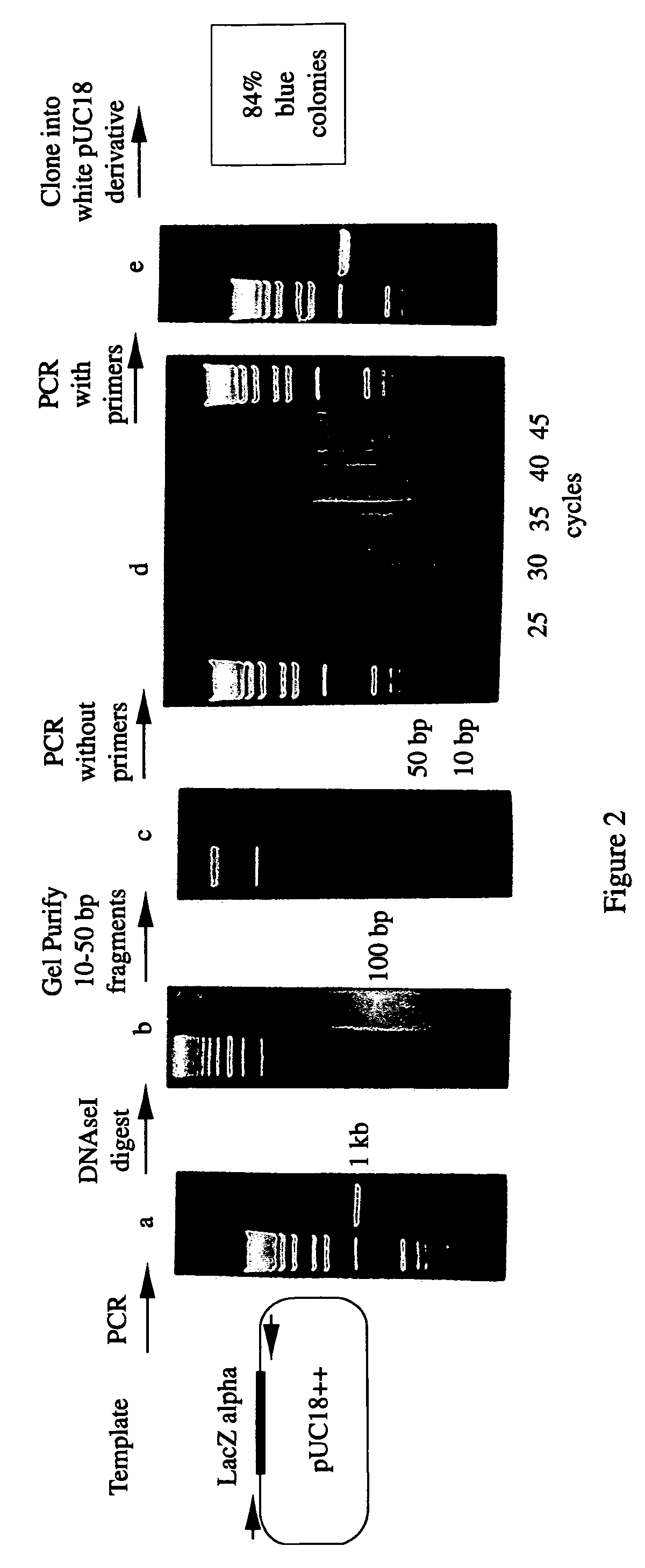
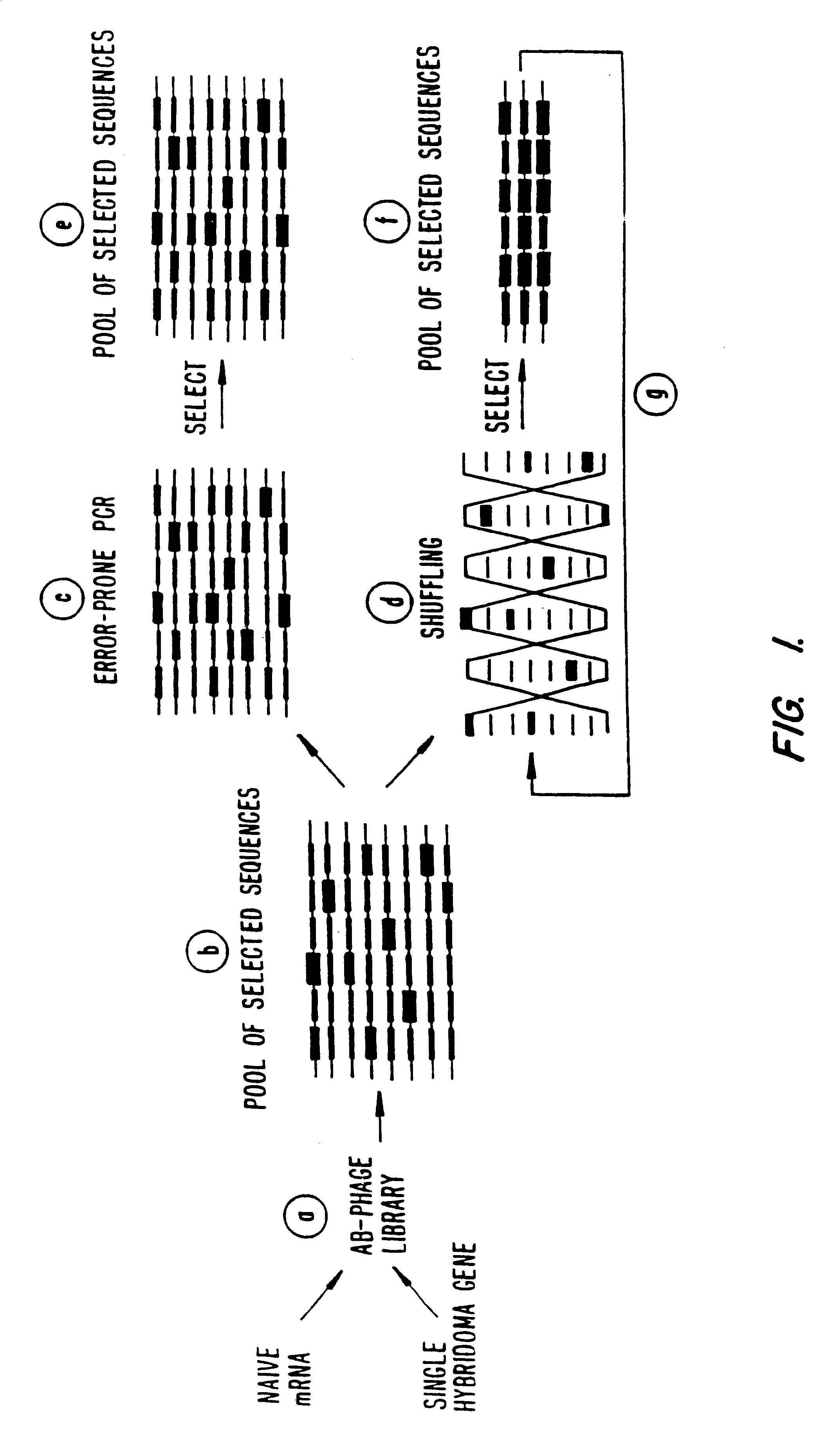
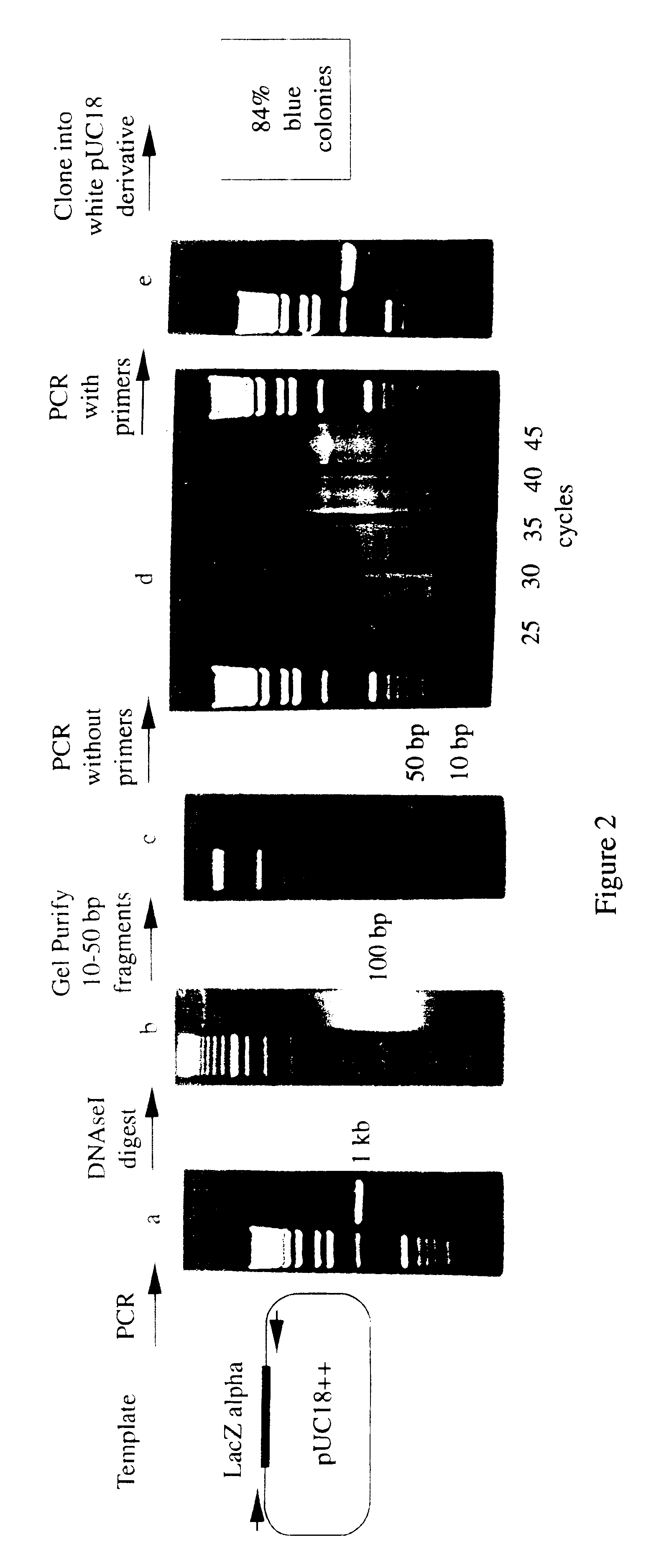
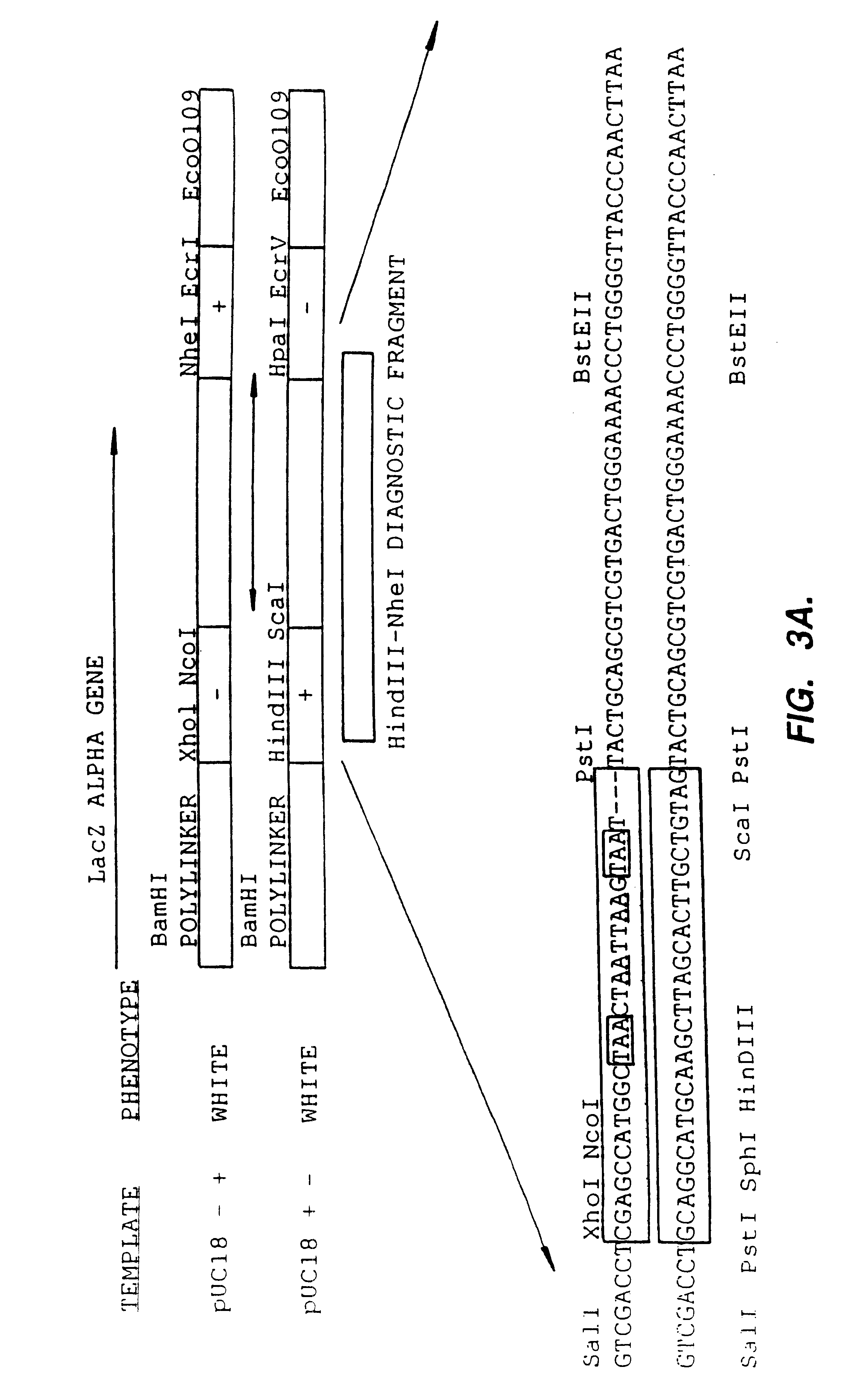
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6180406B1Less immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6165793ALess immunogenicDirected macromolecular evolutionImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Human Anti-pd-1, pd-l1, and pd-l2 antibodies and uses therefor
ActiveUS20110271358A1Reduced antigen binding affinityLess immunogenicAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticTransplant rejectionAutoimmune disease
The present invention is based, in part, on the identification of novel human anti-PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 antibodies. Accordingly, the invention relates to compositions and methods for diagnosing, prognosing, and treating conditions that would benefit from modulating PD-1, PD-L1, and / or PD-L2 activity (e.g., persistent infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, asthma, transplant rejection, inflammatory disorders and tumors) using the novel human anti-PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 antibodies described herein.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +2
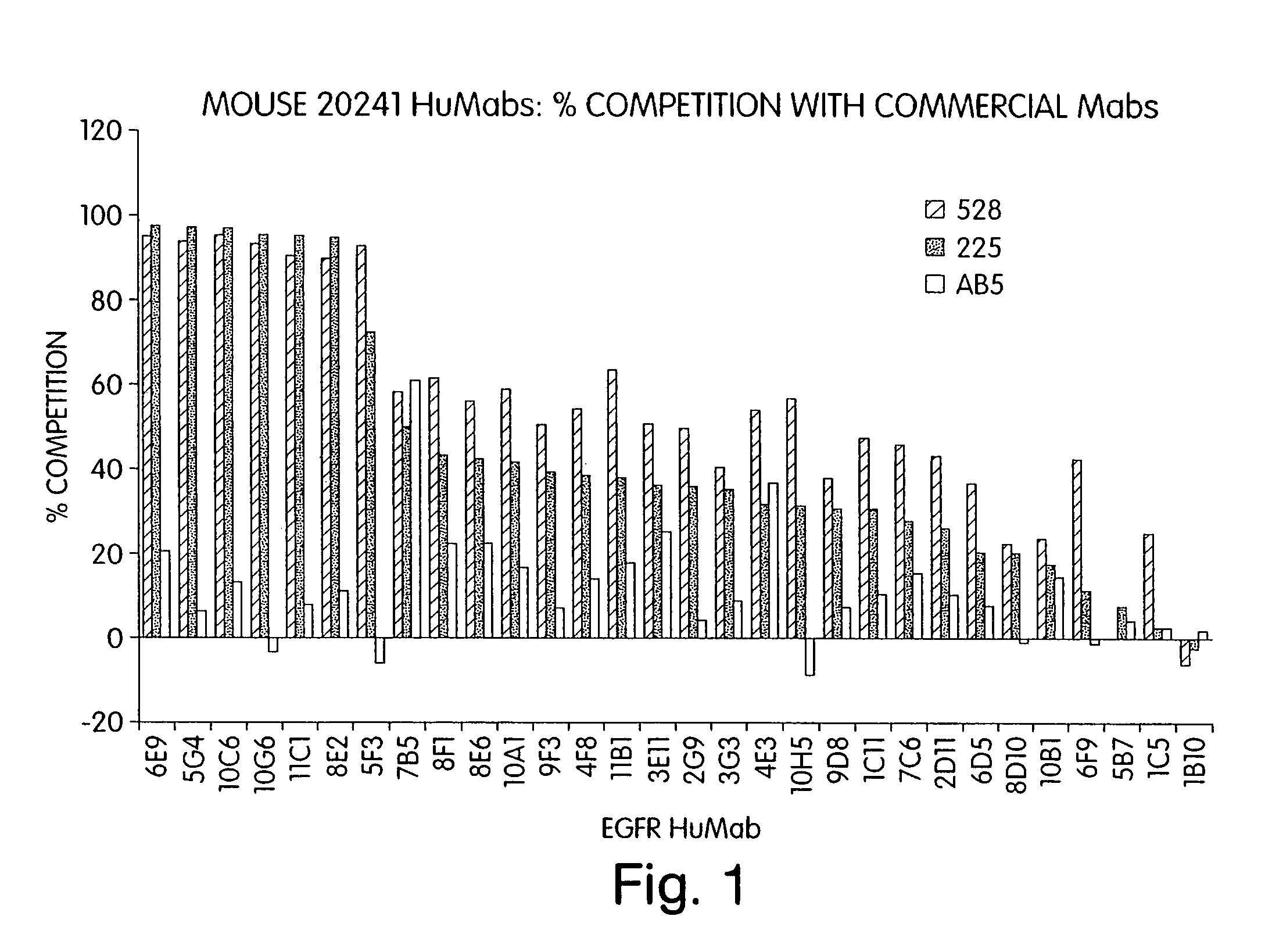
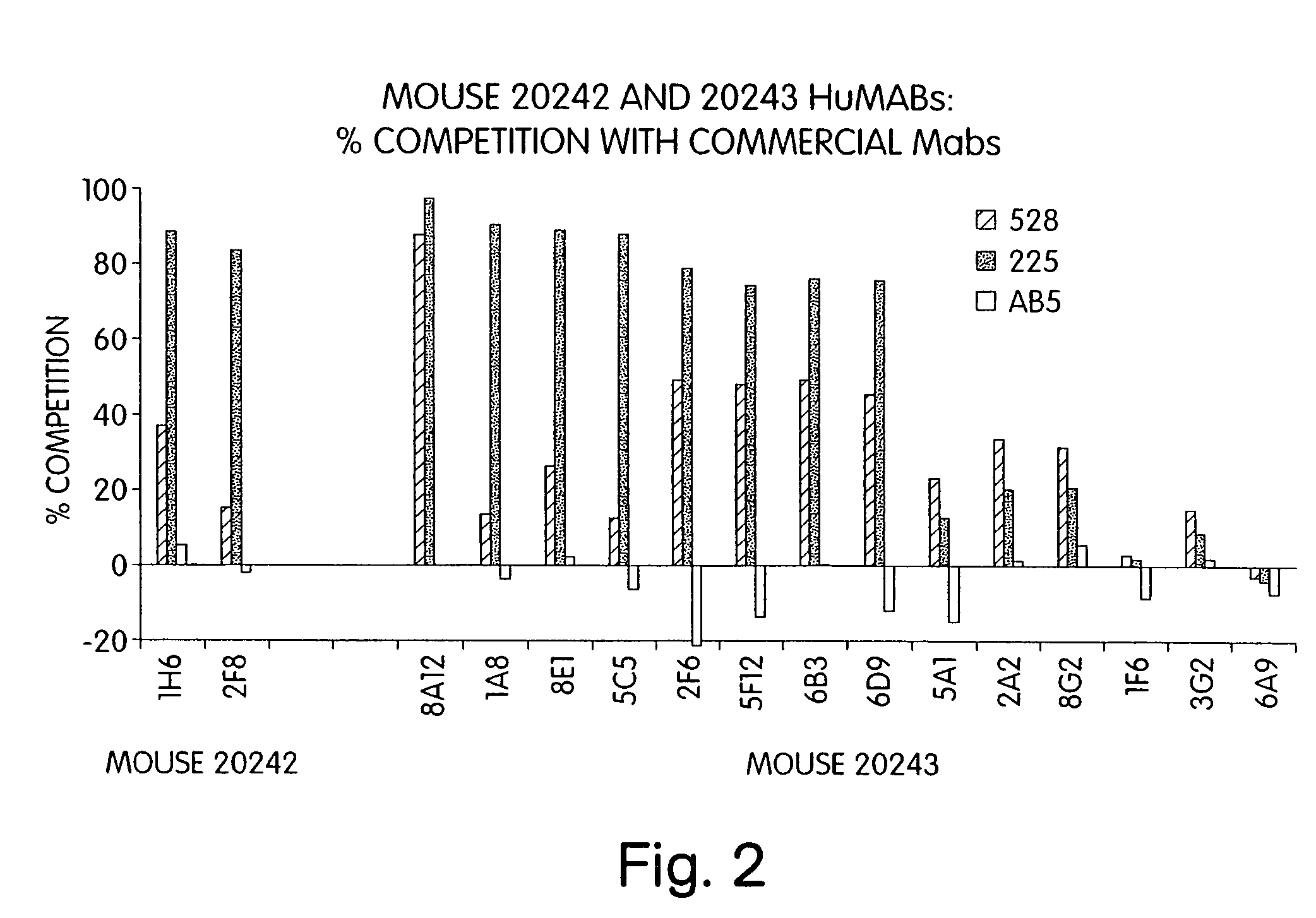
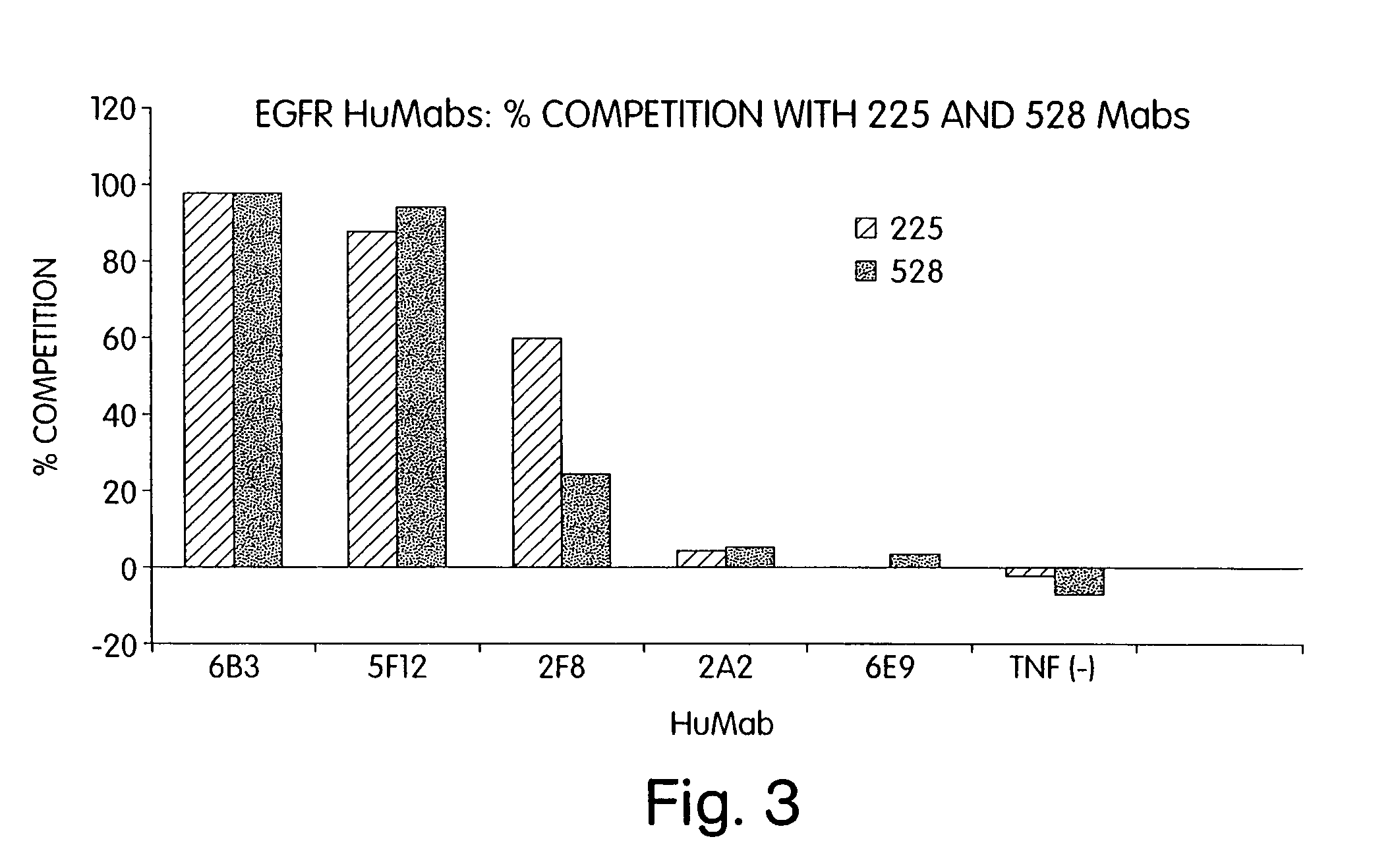
Human monoclonal antibodies to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
InactiveUS7247301B2Less immunogenicReduce adverse side effectsInorganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsV(D)J recombinationHuman epidermal growth factor receptor
Isolated human monoclonal antibodies which specifically bind to human EGFR, and related antibody-based compositions and molecules, are disclosed. The human antibodies can be produced by a transfectoma or in a non-human transgenic animal, e.g., a transgenic mouse, capable of producing multiple isotypes of human monoclonal antibodies by undergoing V-D-J recombination and isotype switching. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the human antibodies, non-human transgenic animals and hybridomas which produce the human antibodies, and therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the human antibodies.
Owner:GENMAB INC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6995017B1Enhance rate of recombinationEnhancing recombinationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS7288375B2Less immunogenicPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6518065B1Less immunogenicImmunoglobulinsLibrary member identificationMutated proteinNucleotide
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
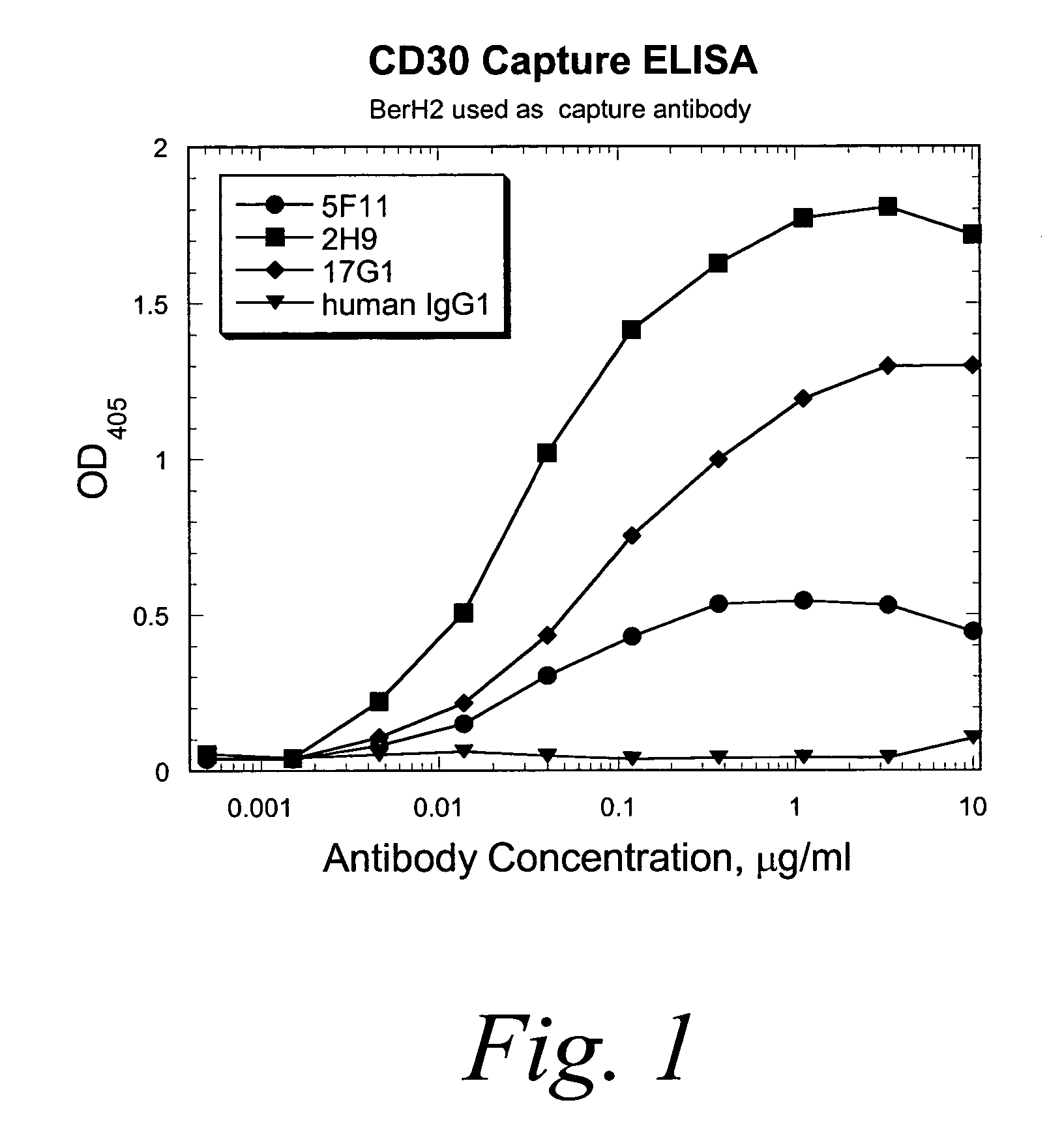
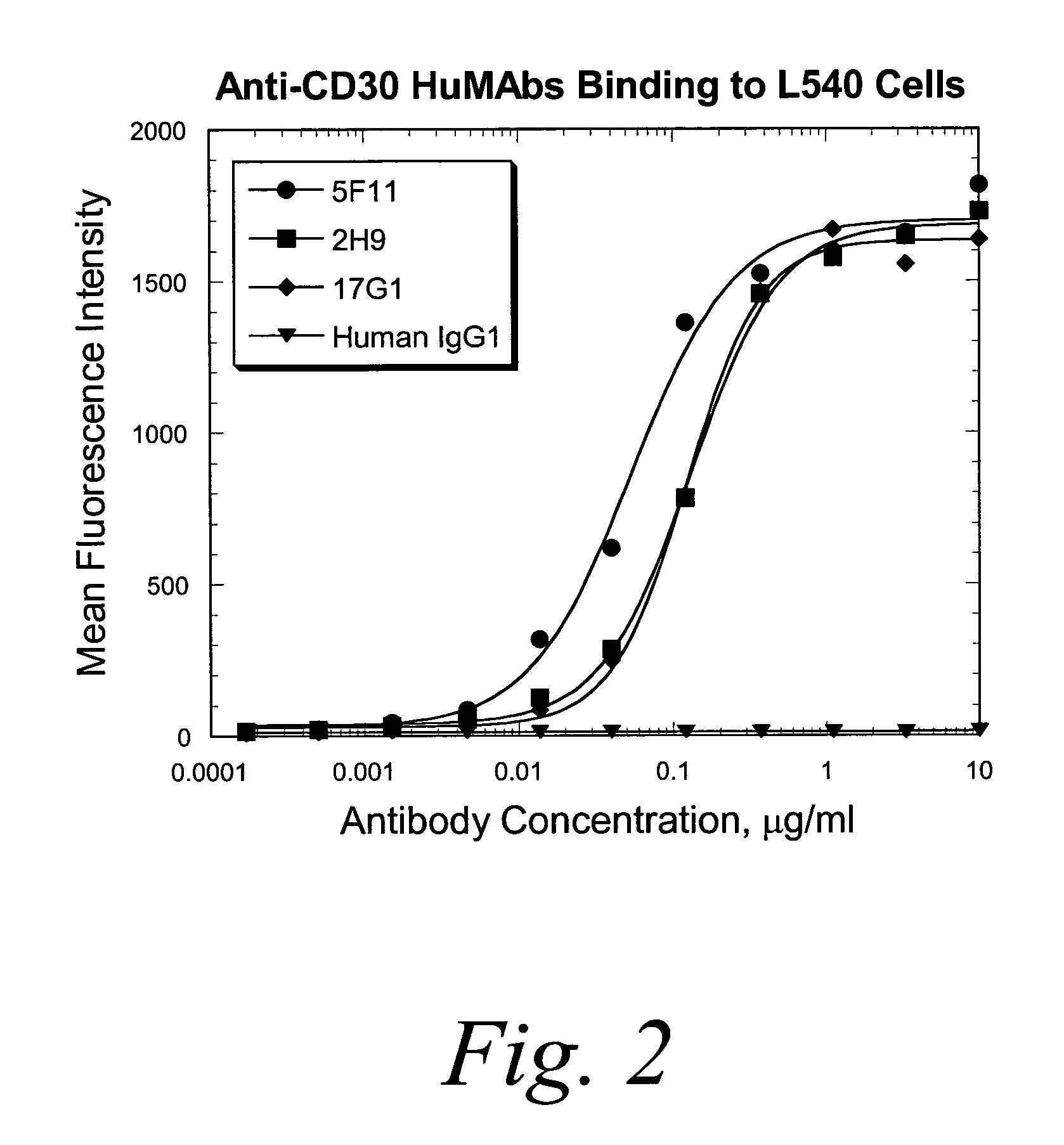
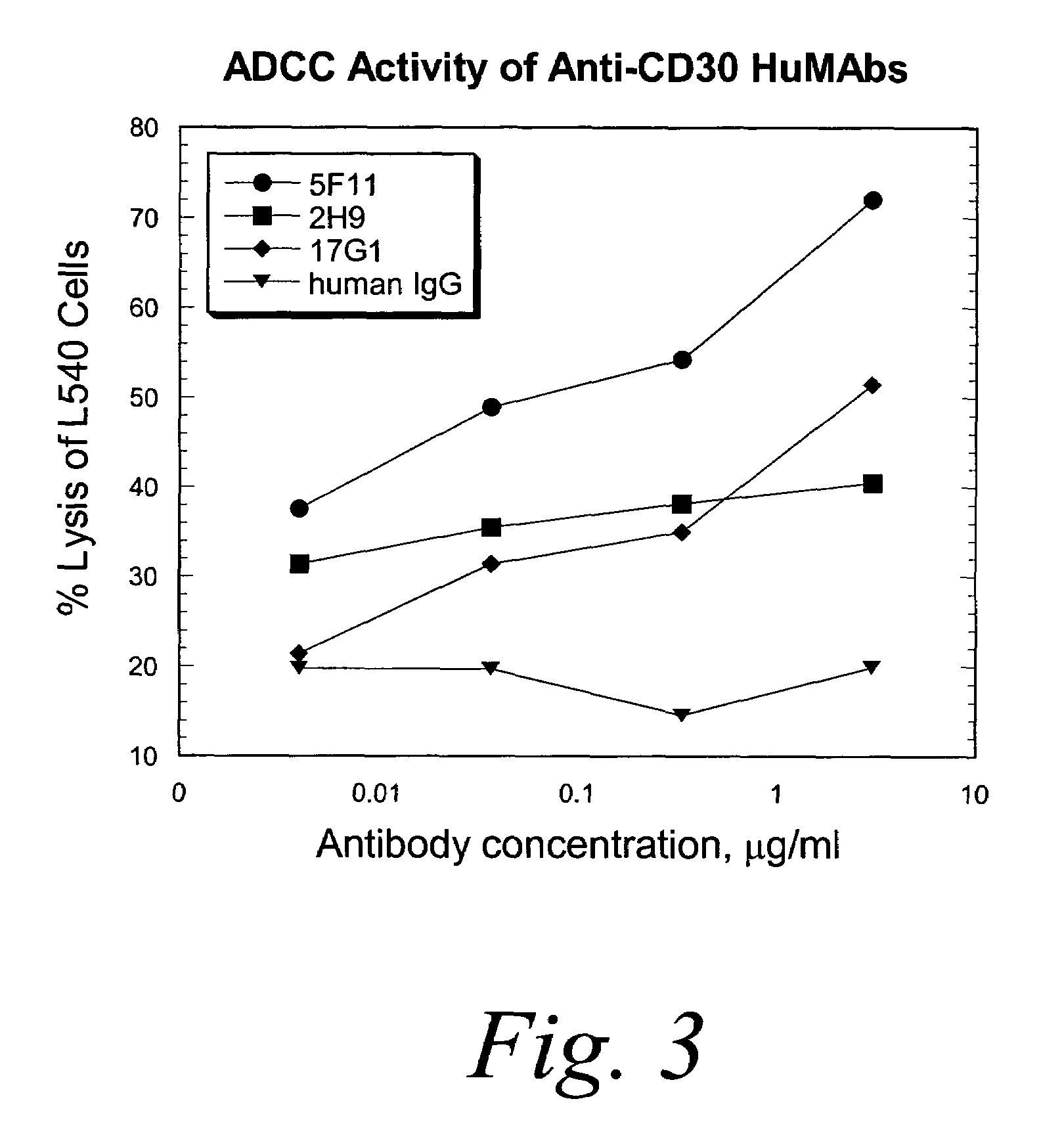
Human monoclonal antibodies against CD30
ActiveUS7387776B2Good curative effectInhibit growth/mediate killingAntipyreticAnalgesicsV(D)J recombinationBispecific antibody
Isolated human monoclonal antibodies which bind to CD30 (e.g., human CD30) are disclosed. The human antibodies can be produced in a non-human transgenic animal, e.g., a transgenic mouse, capable of producing multiple isotypes of human monoclonal antibodies by undergoing V-D-J recombination and isotype switching. Also disclosed are derivatives of the human antibodies (e.g., bispecific antibodies and immunoconjugates), pharmaceutical compositions comprising the human antibodies, non-human transgenic animals and hybridomas which produce the human antibodies, and therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the human antibodies.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
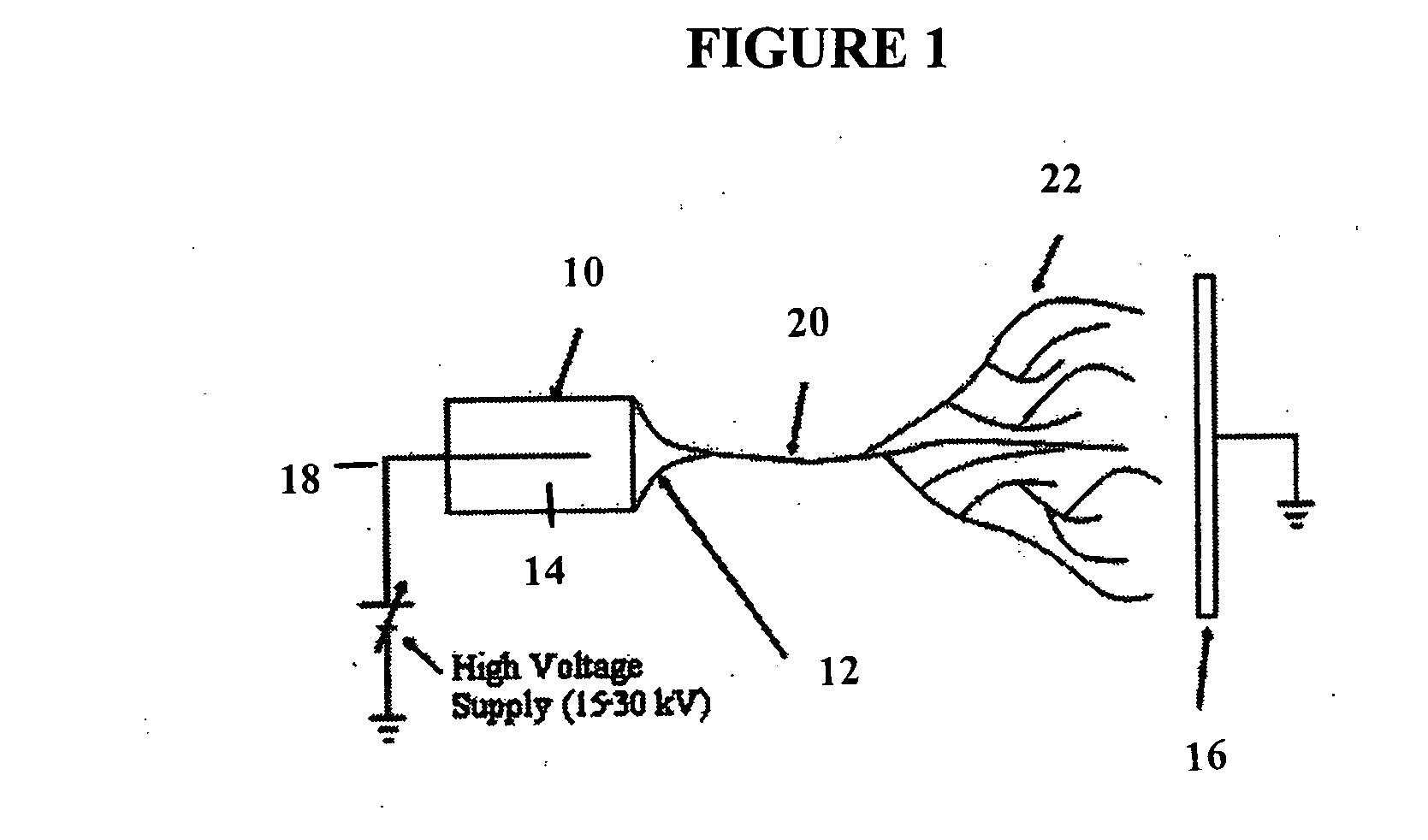
Electrospun cell matrices
InactiveUS20060204539A1Function increaseFiber sizeMonocomponent protein artificial filamentElectro-spinningElectrospinningUltimate tensile strength
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for preparing electrospun matrices comprising at least one natural biological material component and at least one synthetic polymer material. The natural component makes the matrices highly biocompatible while the molecular weight polymer component can impart additional strength mechanical strength to the scaffold and / or improve ease of manufacture by increasing viscosity and spinning characteristics of the solution during electrospining.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
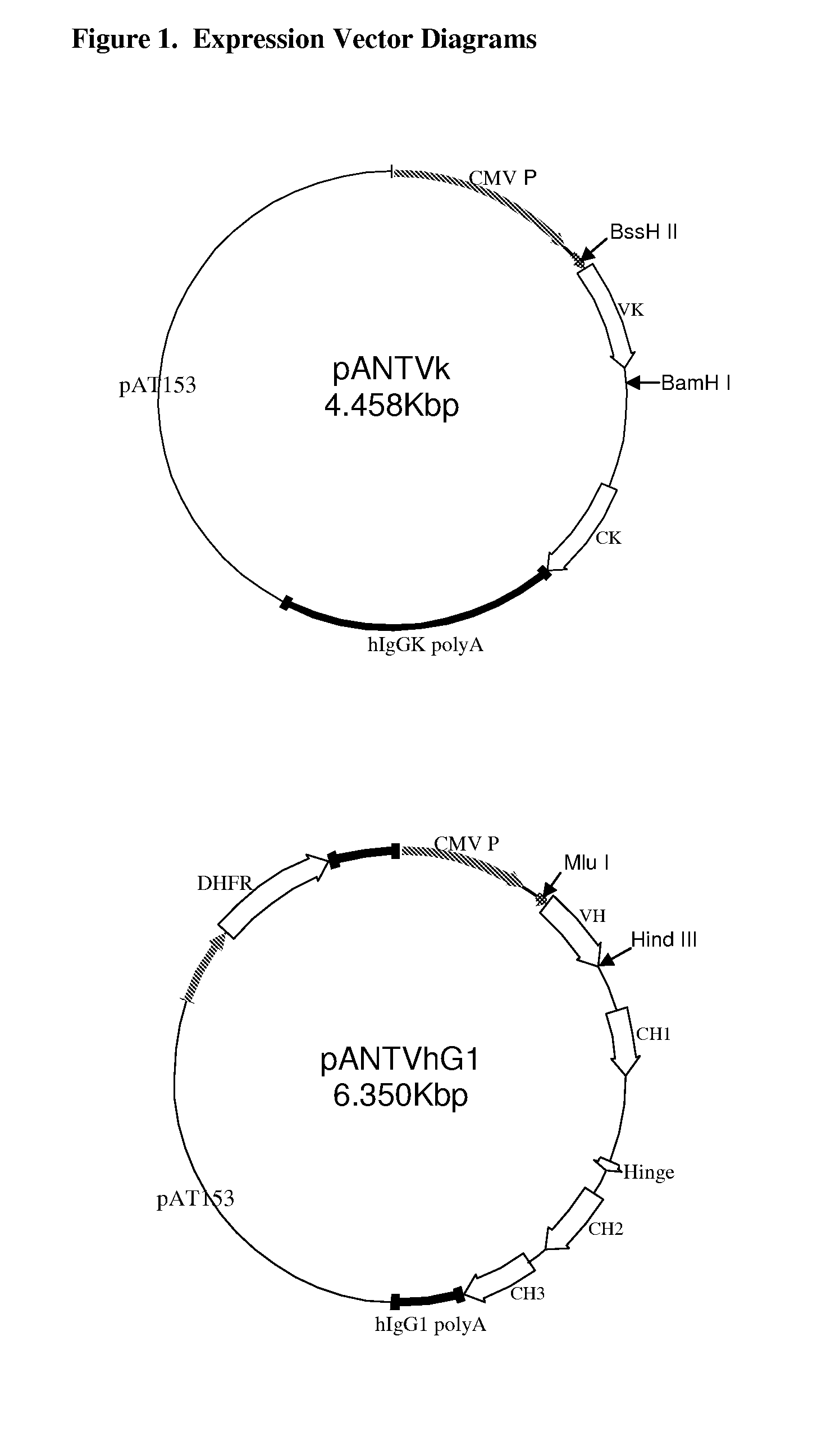
Expression technology for proteins containing a hybrid isotype antibody moiety
Disclosed are methods and compositions for efficiently expressing antibody fusion proteins. Antibody fusion proteins of the invention include a hybrid antibody moiety containing sequences from more than one type of antibody and / or mutant antibody sequences. Hybrid antibody fusion proteins of the invention may be produced at high levels and may combine functional properties characteristic of different antibody types in addition to functional properties of a non-antibody moiety.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
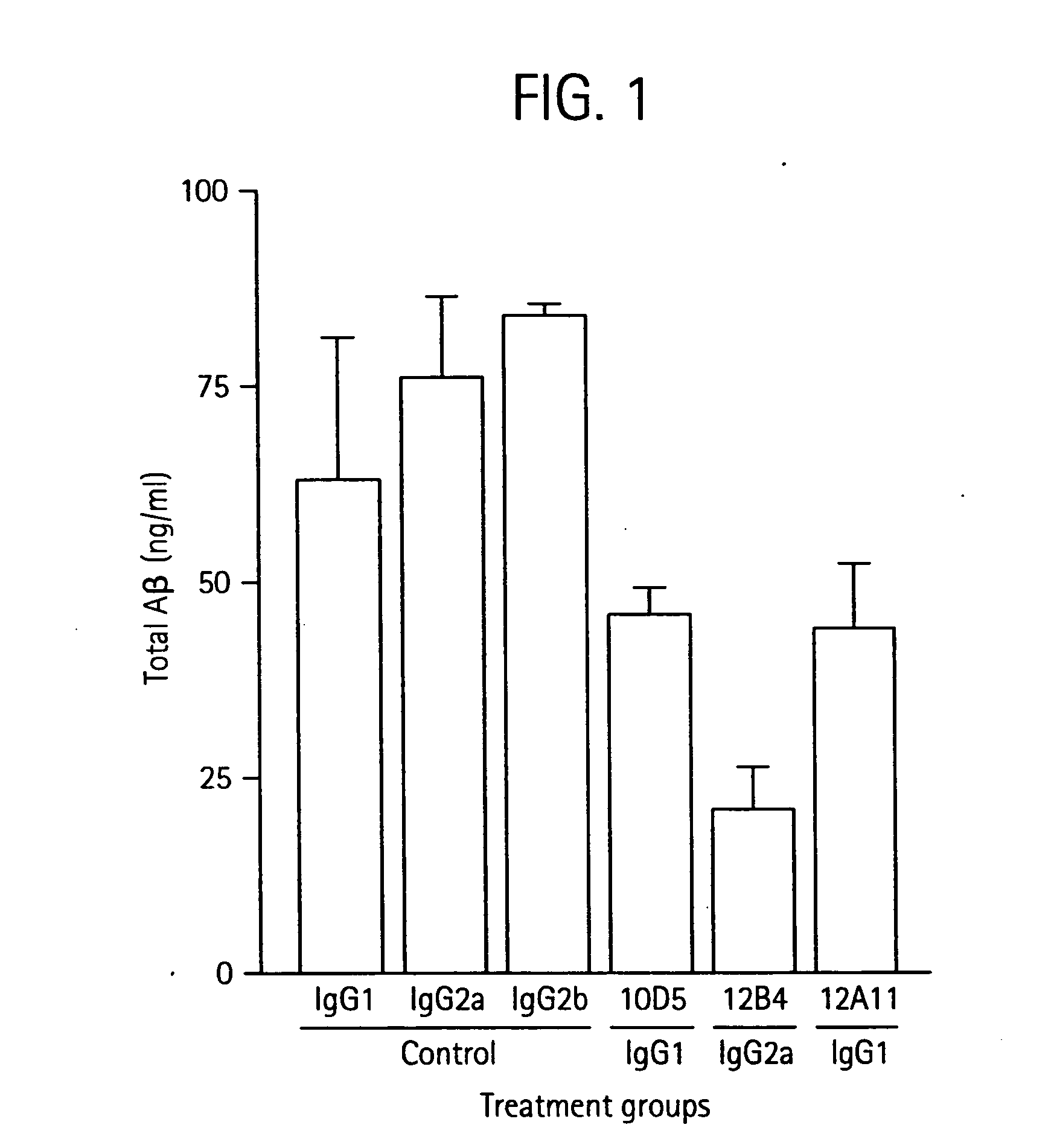
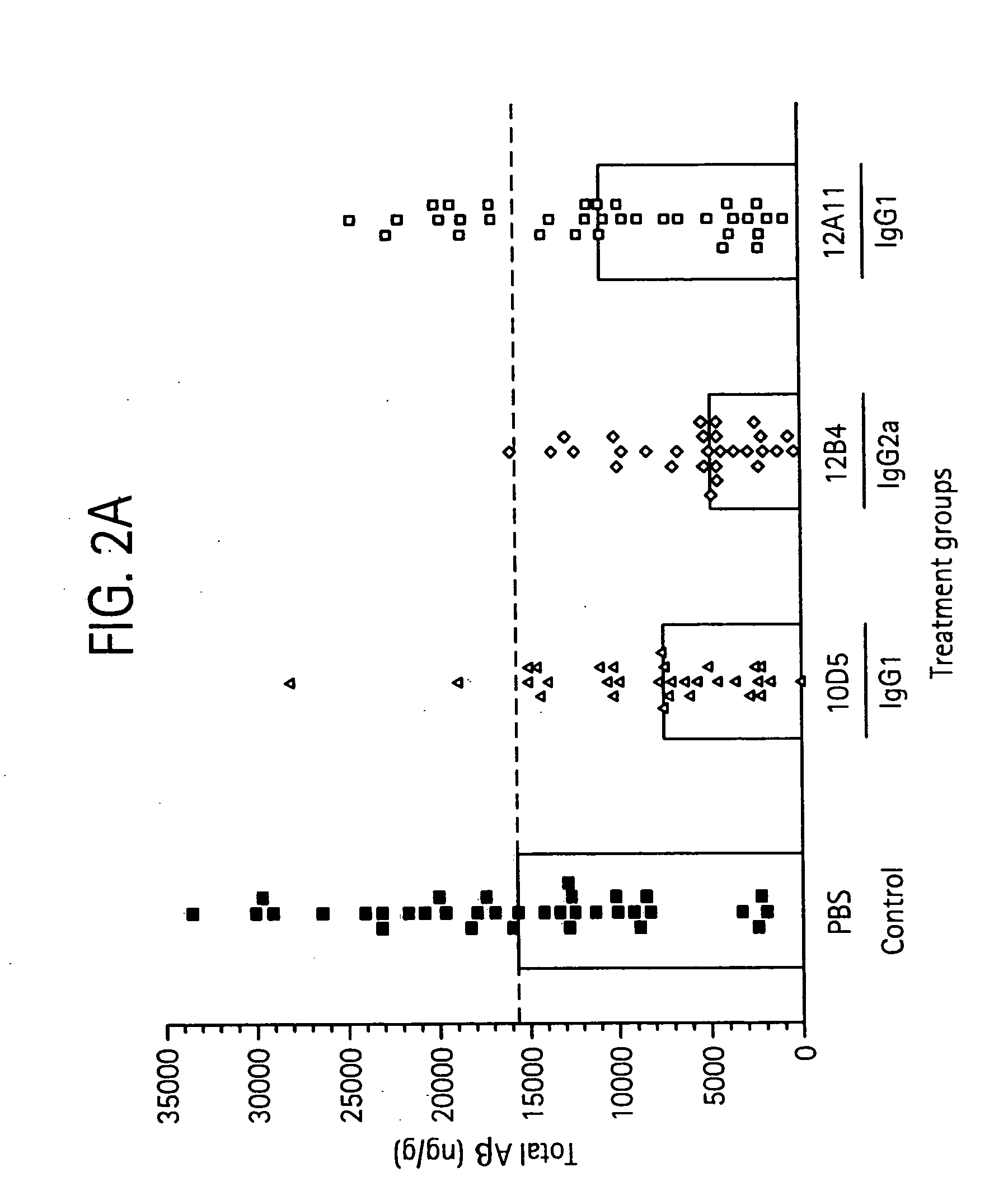
Humanized Abeta antibodies for use in improving cognition
InactiveUS20060198851A1Increase awarenessReduce the burden onNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of diseases associated with beta amyloid (Aβ). Preferred agents include antibodies, e.g., humanized antibodies specific for Aβ.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
Humanized immunoglobulin reactive with α4β7 integrin
InactiveUS7147851B1Reduce inflammationLess immunogenicFungiBacteriaComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
The present invention relates to humanized immunoglobulins having binding specificity for α4β7 integrin, comprising an antigen binding region of nonhuman origin (e.g., rodent) and at least a portion of an immunoglobulin of human origin (e.g., a human framework region, a human constant region). In one embodiment, the humanized immunoglobulin can compete with murine Act-1 for binding to human α4β7 integrin. In a preferred embodiment, the antigen binding region of the humanized immunoglobulin comprises each of the complementarity determining regions of the light and heavy chains of the murine Act-1 antibody.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Human monoclonal antibodies against Bacillus anthracis protective antigen
ActiveUS7456264B2Avoid infectionNeutralizing activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAntigenV(D)J recombination
Isolated human monoclonal antibodies which bind to Anthrax protective antigen are disclosed. The human antibodies can be produced in a non-human transgenic animal, e.g., a transgenic mouse, capable of producing multiple isotypes of human monoclonal antibodies by undergoing V-D-J recombination and isotype switching. Also disclosed are derivatives of the human antibodies (e.g., bispecific antibodies and immunoconjugates), pharmaceutical compositions comprising the human antibodies, non-human transgenic animals and hybridomas which produce the human antibodies, and therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the human antibodies.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
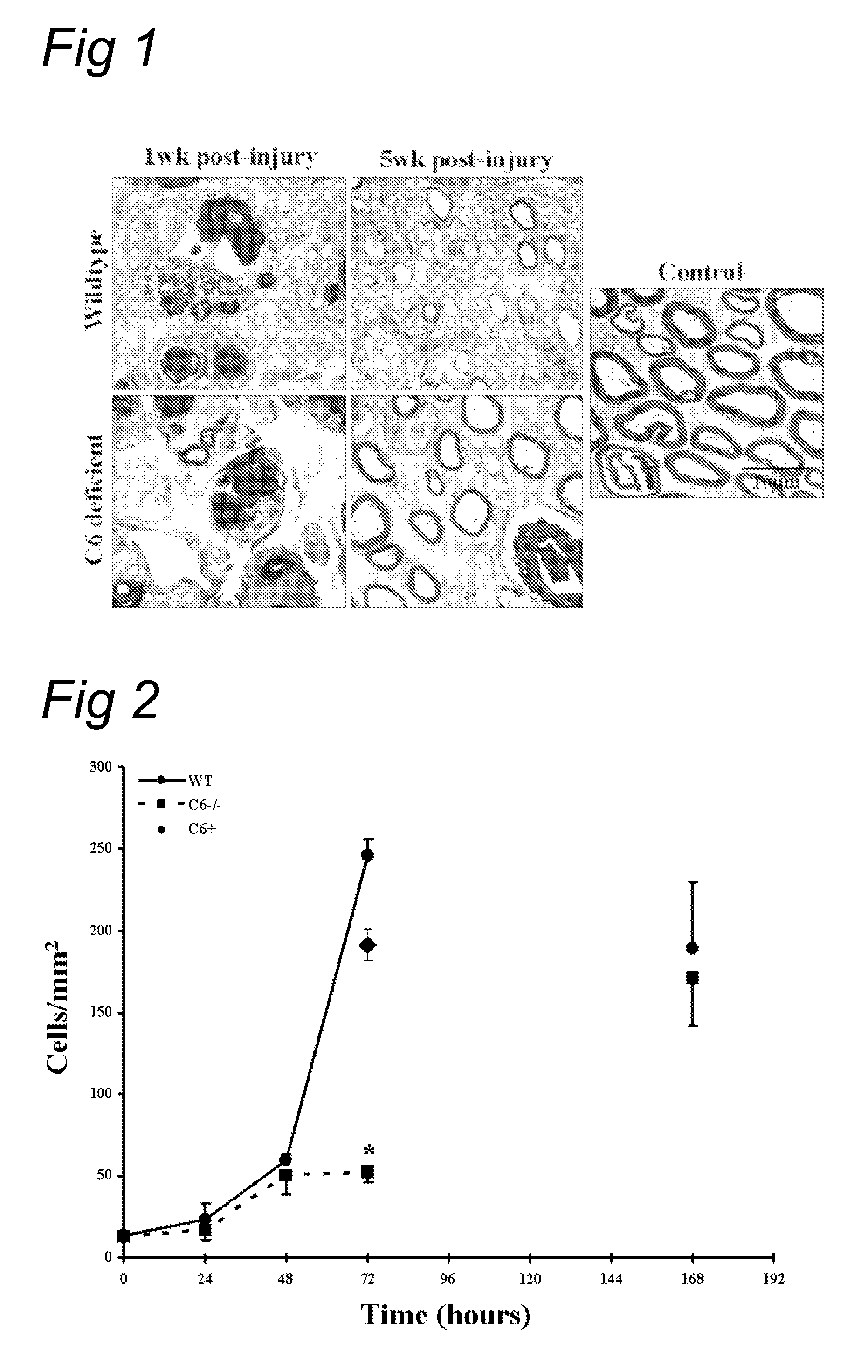
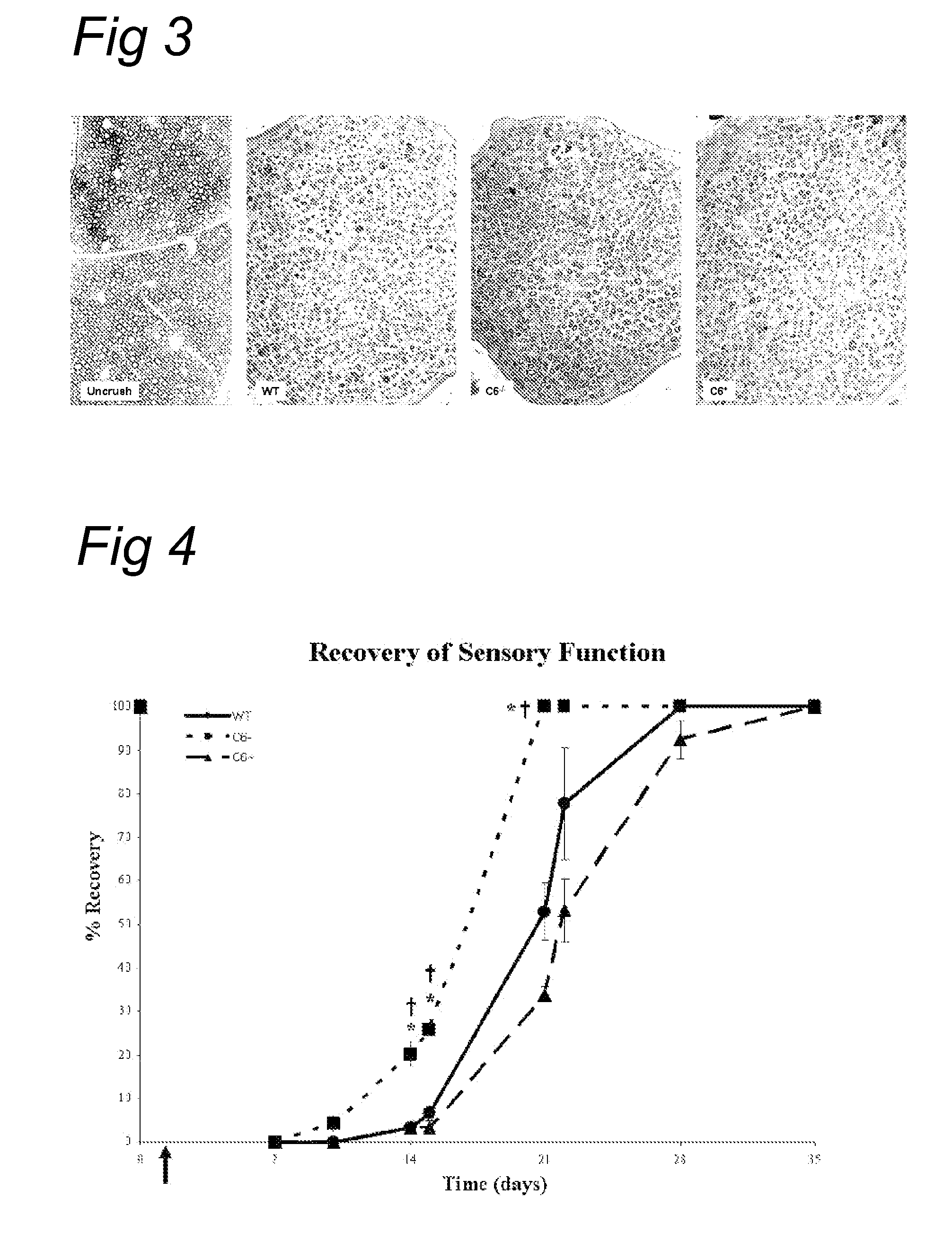
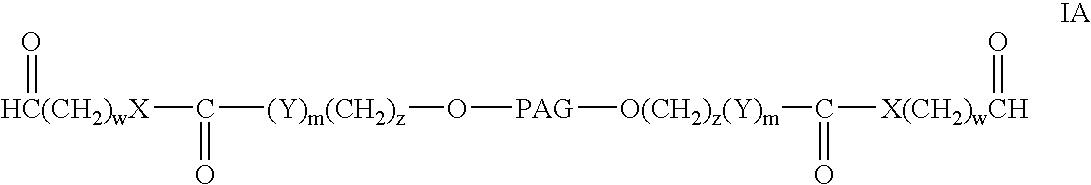
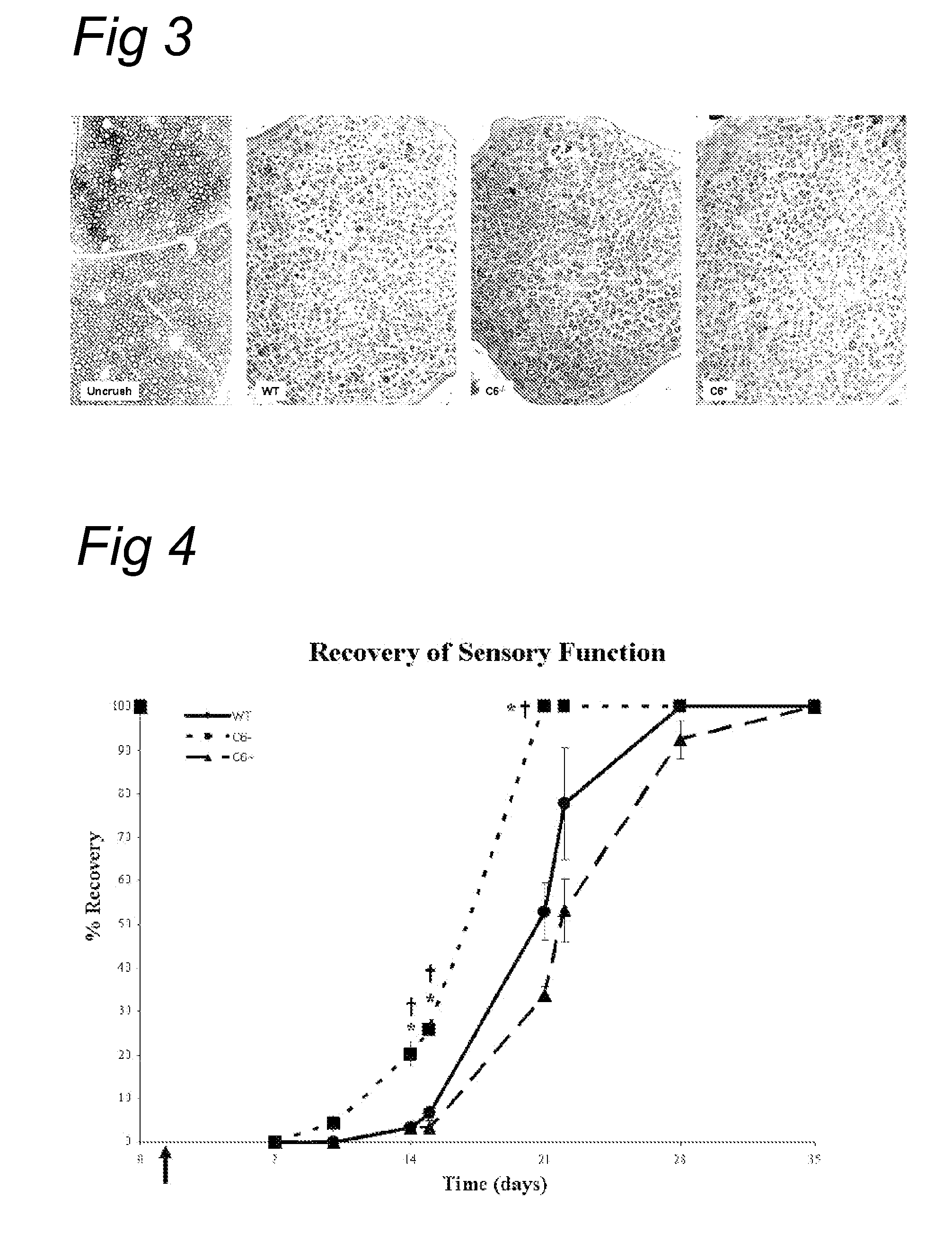
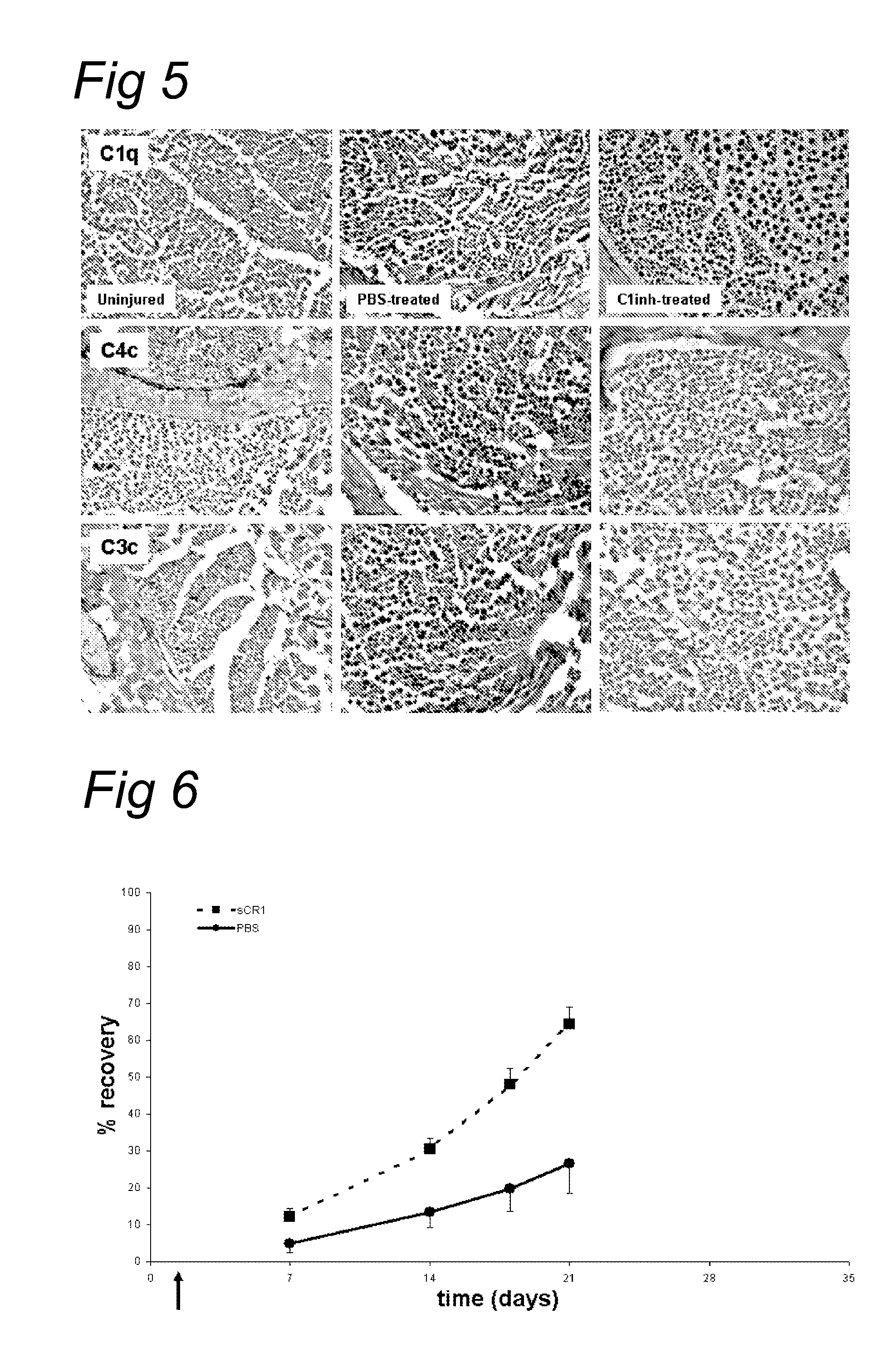
Complement inhibition for improved nerve regeneration
ActiveUS20100143344A1Improve regenerative abilityPromote regenerationBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates to methods and medicaments used for treating conditions that require axonal regeneration, e.g. in mammals affected by injury or disease of the central or peripheral nervous system. The medicaments used in these methods facilitate axonal regeneration by inhibition of the complement system. Conditions requiring axonal regeneration that may be treated in accordance with the invention include physical injuries as well as neurodegenerative disorders of the peripheral or central nervous system.
Owner:REGENESANCE
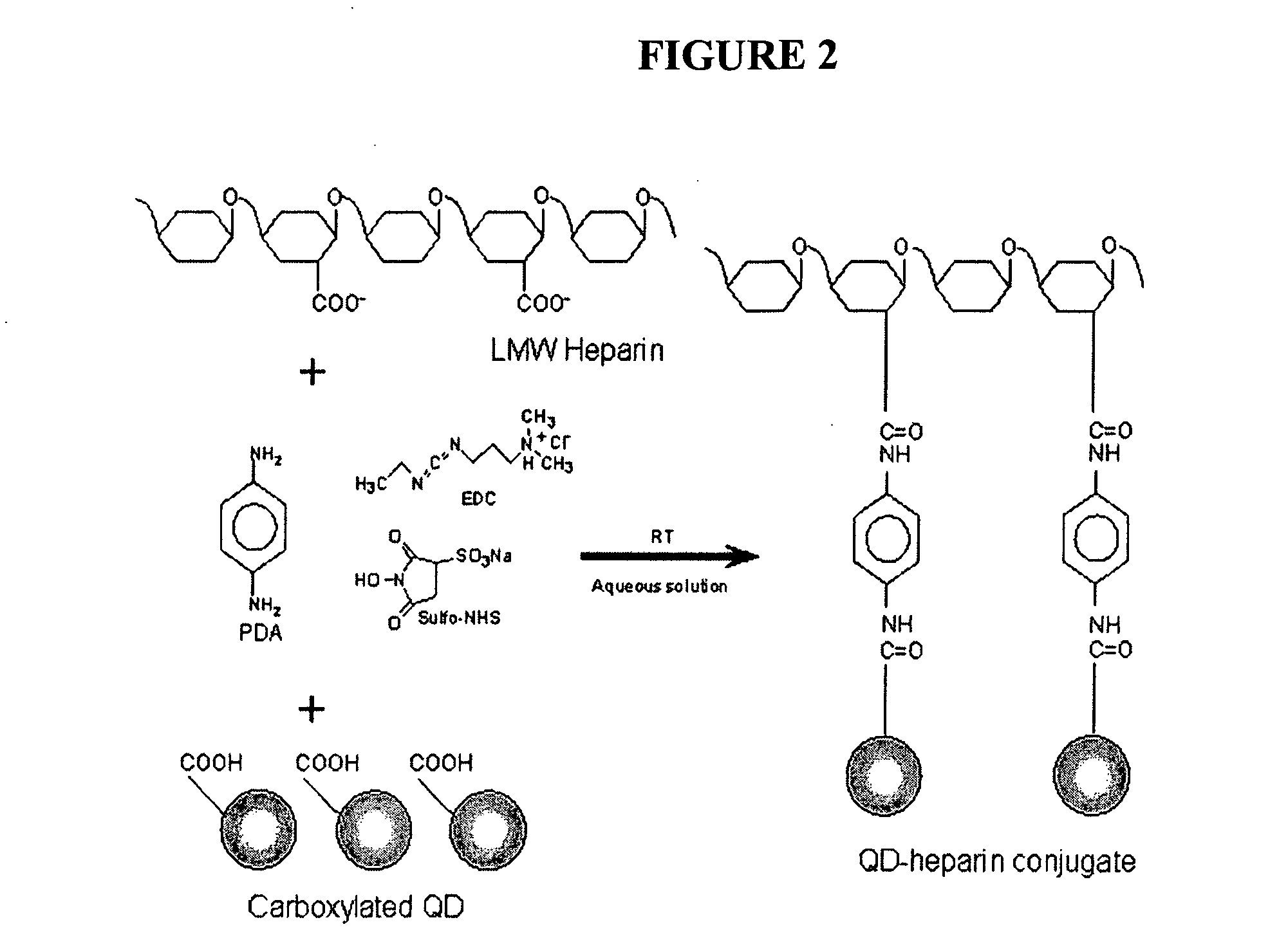
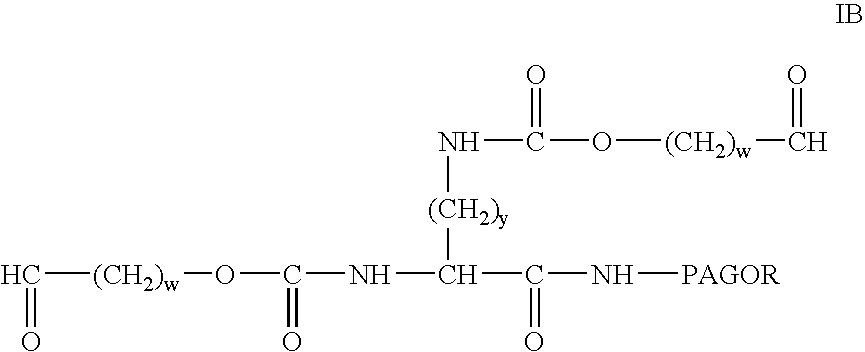
Bifunctional polyethylene glycol derivatives
InactiveUS20040115165A1Linkage stabilityDifficult to purifyOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProtein insertionActive protein
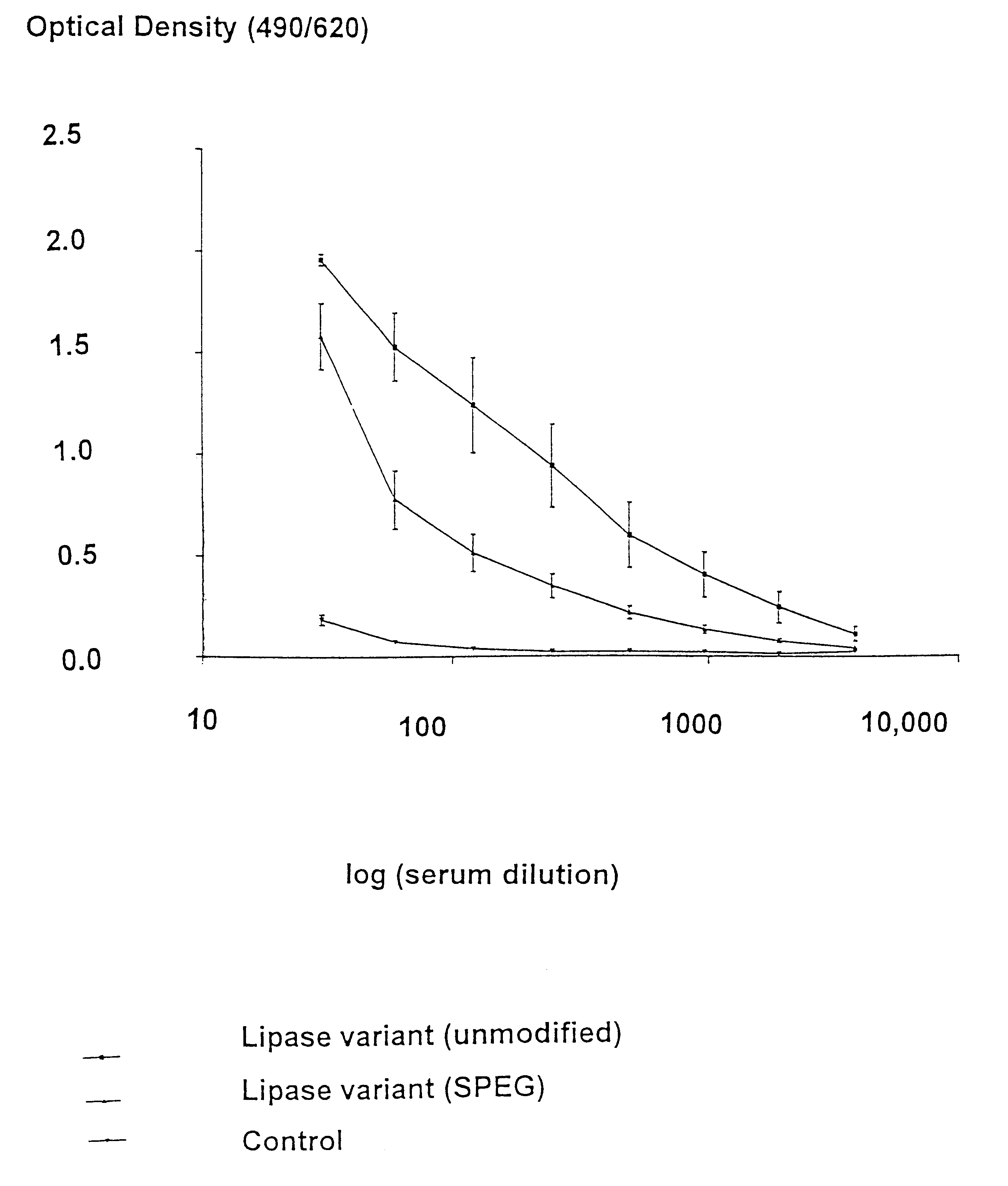
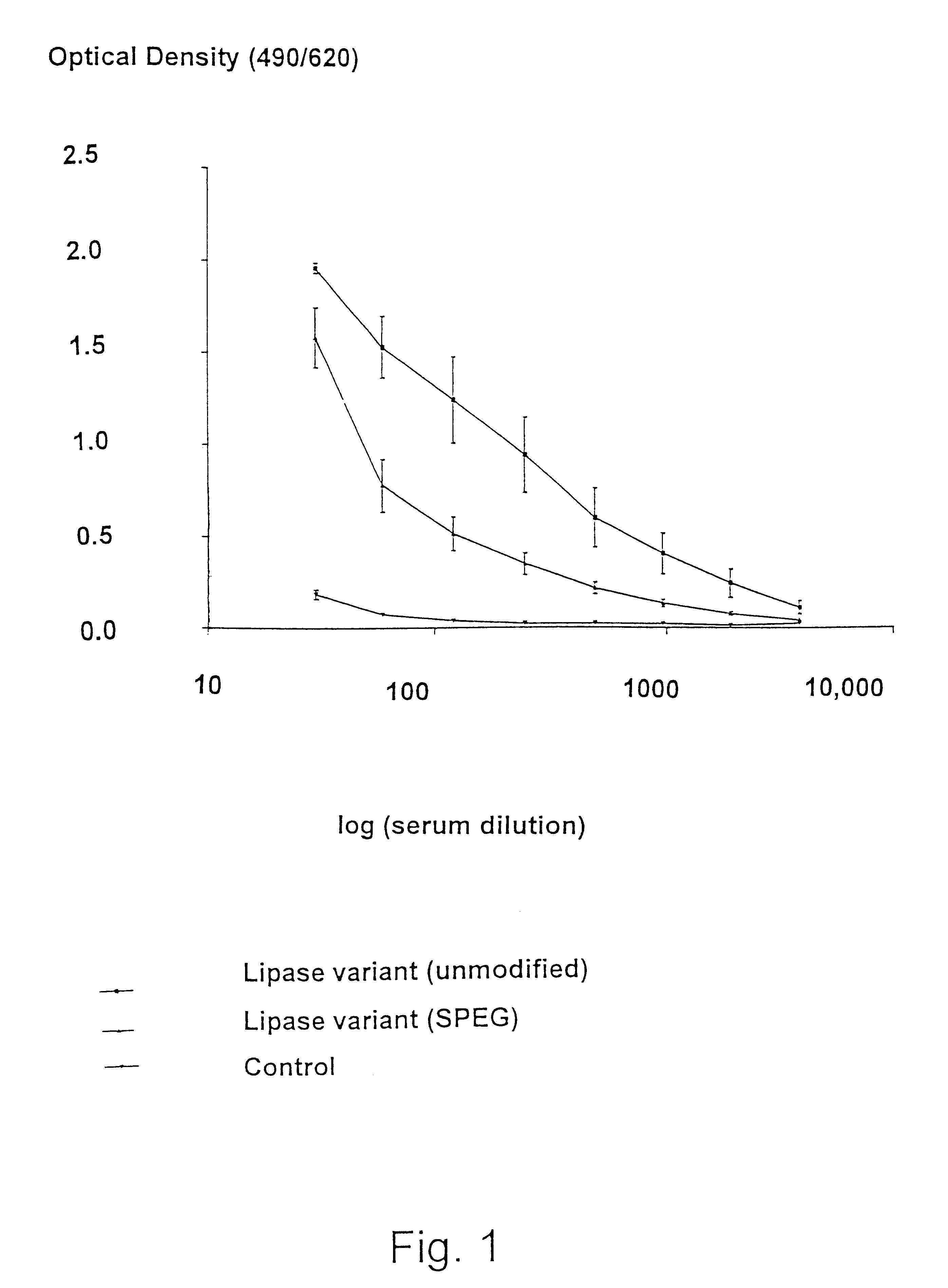
The present invention provides novel heterobifunctional and monobifunctional polyethylene glycol derivatives for the pegylation of therapeutically active proteins. The heterobifunctional PEGs which bear two different functional groups as well as the monobifunctional PEGs which contain two similar functional groups, may be used for cross-linking purposes. The cross-linking may be intramolecular between two areas within the same molecule or intermolecular between two separate molecules. The pegylated protein conjugates that are produced, retain a substantial portion of their therapeutic activity and are less immunogenic than the protein from which the conjugate is derived. New syntheses for preparing such bifunctional derivatives are described.
Owner:SUN BIO INC
Modified antibodies to prostate-specific membrane antigen and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060062793A1Less immunogenicHigh affinityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCancer cellAntigen Binding Fragment
Modified antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, to the extracellular domain of human prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) are provided. The modified anti-PSMA antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, have been rendered less immunogenic compared to their unmodified counterparts to a given species, e.g., a human. Pharmaceutical compositions including the aforesaid antibodies, nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors and host cells for making such antibodies and fragments are also disclosed. Methods of using the antibodies of the invention to detect human PSMA, or to ablate or kill a PSMA-expressing cell, e.g., a PSMA-expressing cancer or prostatic cell, either in vitro or in vivo, are also provided.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
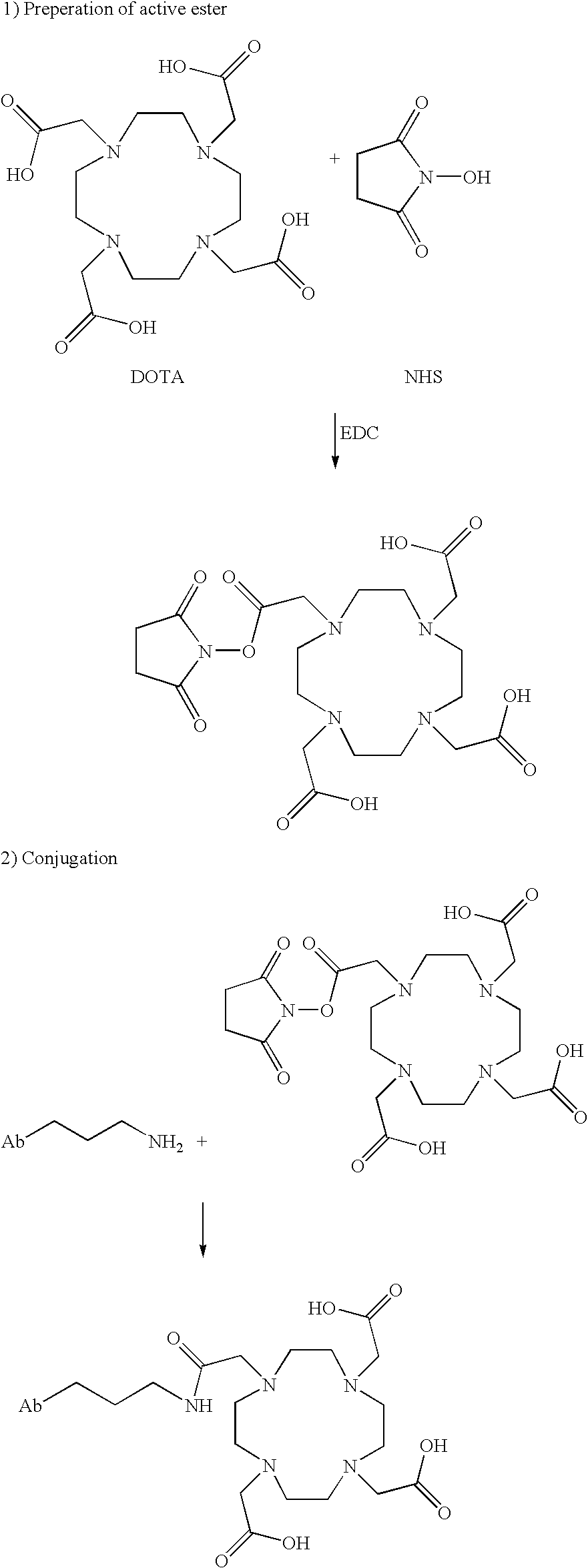
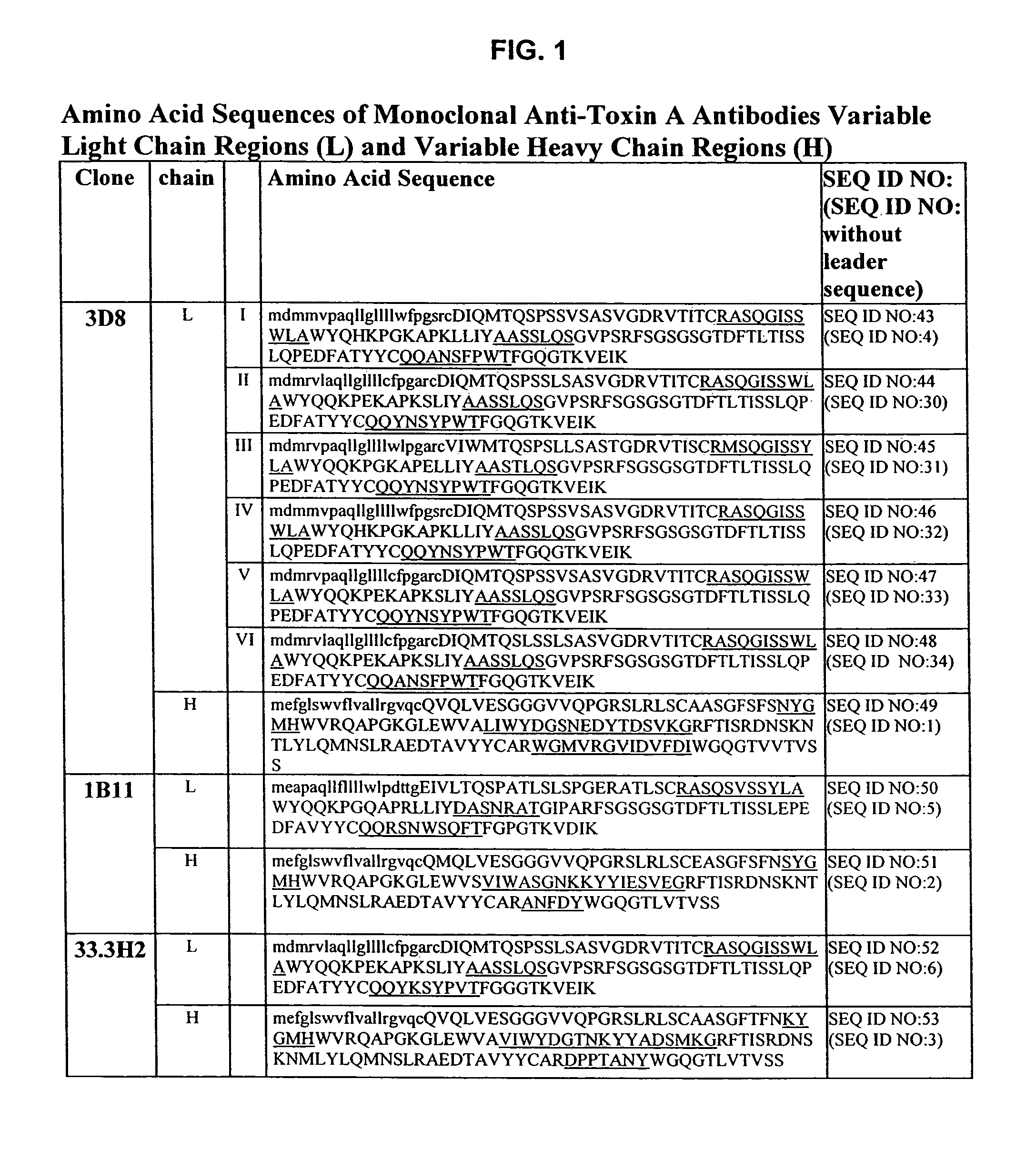
Antibodies against Clostridium difficile toxins and uses thereof
ActiveUS7625559B2High affinityLess immunogenicAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin AClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF +2
Expression technology for proteins containing a hybrid isotype antibody moiety
Disclosed are methods and compositions for efficiently expressing antibody fusion proteins. Antibody fusion proteins of the invention include a hybrid antibody moiety containing sequences from more than one type of antibody and / or mutant antibody sequences. Hybrid antibody fusion proteins of the invention may be produced at high levels and may combine functional properties characteristic of different antibody types in addition to functional properties of a non-antibody moiety.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Complement inhibition for improved nerve regeneration
ActiveUS8703136B2Improve regenerative abilityPromote regenerationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates to methods and medicaments used for treating conditions that require axonal regeneration, e.g. in mammals affected by injury or disease of the central or peripheral nervous system. The medicaments used in these methods facilitate axonal regeneration by inhibition of the complement system. Conditions requiring axonal regeneration that may be treated in accordance with the invention include physical injuries as well as neurodegenerative disorders of the peripheral or central nervous system.
Owner:REGENESANCE
Antibodies against Clostridium difficile toxins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050287150A1High affinityLess immunogenicAntibacterial agentsBacteriaClostridium difficileClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF +2
Human monoclonal antibodies against CD20
Isolated human monoclonal antibodies which bind to and inhibit human CD20, and related antibody-based compositions and molecules, are disclosed. The human antibodies can be produced by a transfectoma or in a non-human transgenic animal, e.g., a transgenic mouse, capable of producing multiple isotypes of human monoclonal antibodies by undergoing V-D-J recombination and isotype switching. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the human antibodies, non-human transgenic animals and hybridomas which produce the human antibodies, and therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the human antibodies.
Owner:GENMAB AS
Combinatorial screening of mixed populations of organisms
InactiveUS7018793B1Quick filterLess immunogenicSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganismGenus
Provided is a method of screening gene libraries derived from a mixed population of organisms for a bioactivity or biomolecule of interest. The mixed population of organisms can be a cultured population or an uncultured population from, for example, the environment. Also provided are methods of screening isolates or enriched populations of organisms, which isolates include a population that is spatially, temporally, or hierarchical, for example, of a particular species, genus, family, or class of organisms. Identified clones containing a biomolecule or bioactivity of interest can be further variegated or the DNA contained in the clone can be variegated to create novel biomolecules or bioactivities of interest.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Modified enzymes having polymer conjugates
InactiveUS6623950B1Low immunogenicityReduce allergiesOrganic detergent compounding agentsBacteriaVaccine ImmunogenicityEnzyme
The present invention relates to polypeptide-polymer conjugates having added and / or removed one or more attachment groups for coupling polymeric molecules on the surface of the polypeptide structure, a method for preparing polypeptide-polymer conjugates of the invention, the use of said conjugates for reducing the immunogenicity and allergenicity and compositions comprising said conjugate.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Electrospun Cell Matrices
ActiveUS20100129450A1Function increaseFiber sizeMonocomponent protein artificial filamentPowder deliveryElectrospinningUltimate tensile strength
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for preparing electrospun matrices comprising at least one natural biological material component and at least one synthetic polymer material. The natural component makes the matrices highly biocompatible while the molecular weight polymer component can impart additional strength mechanical strength to the scaffold and / or improve ease of manufacture by increasing viscosity and spinning characteristics of the solution during electrospining.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
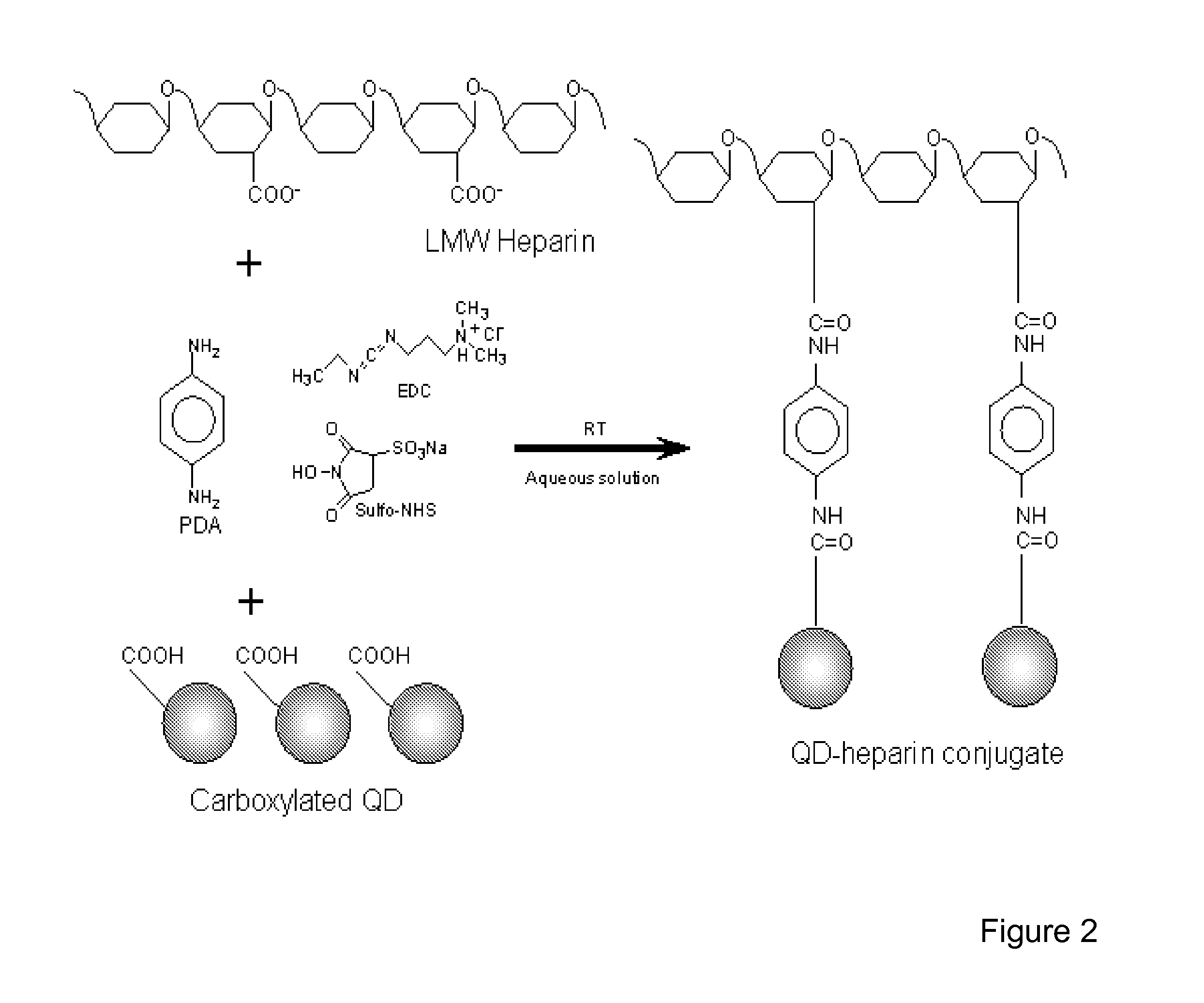
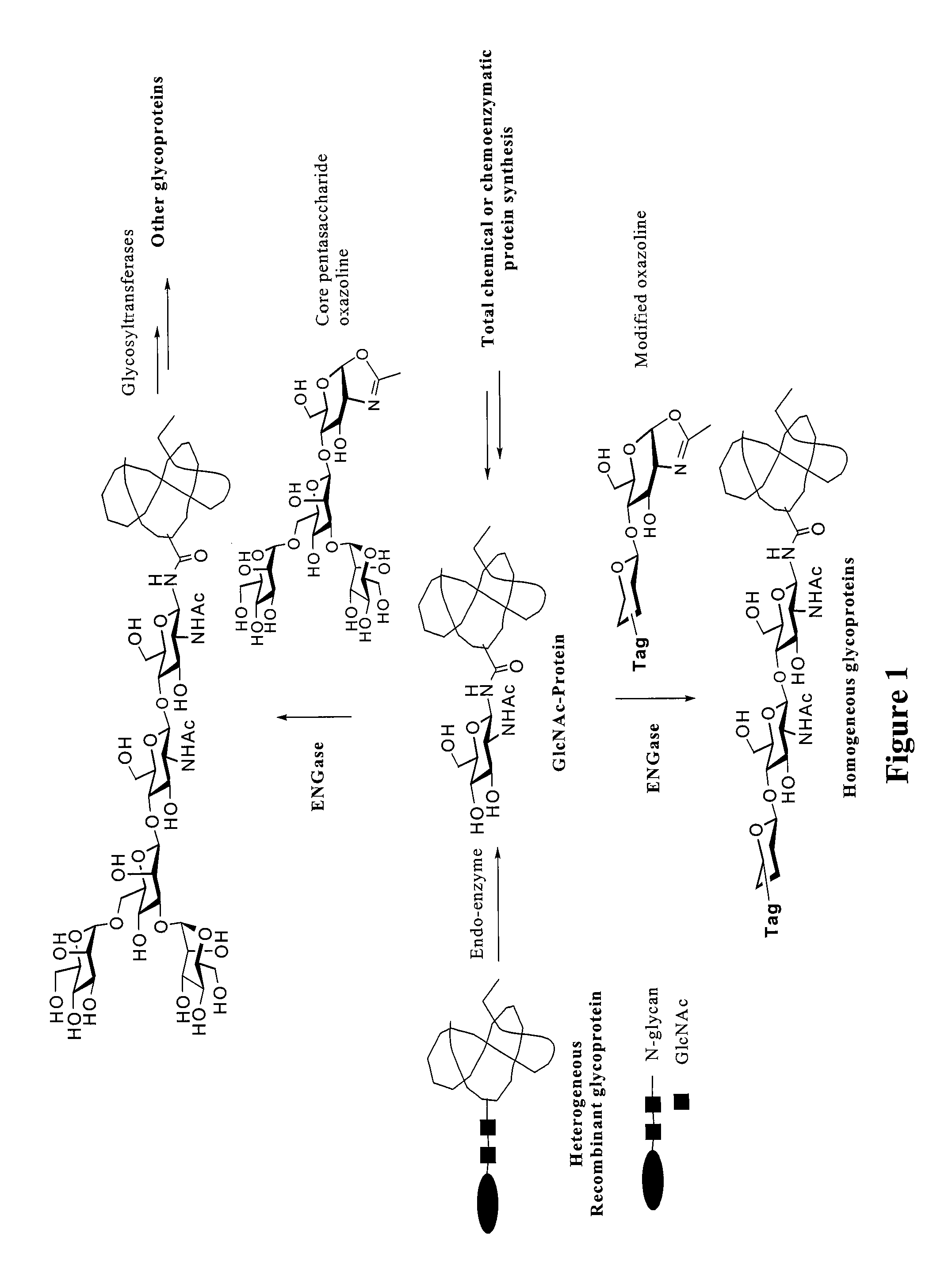
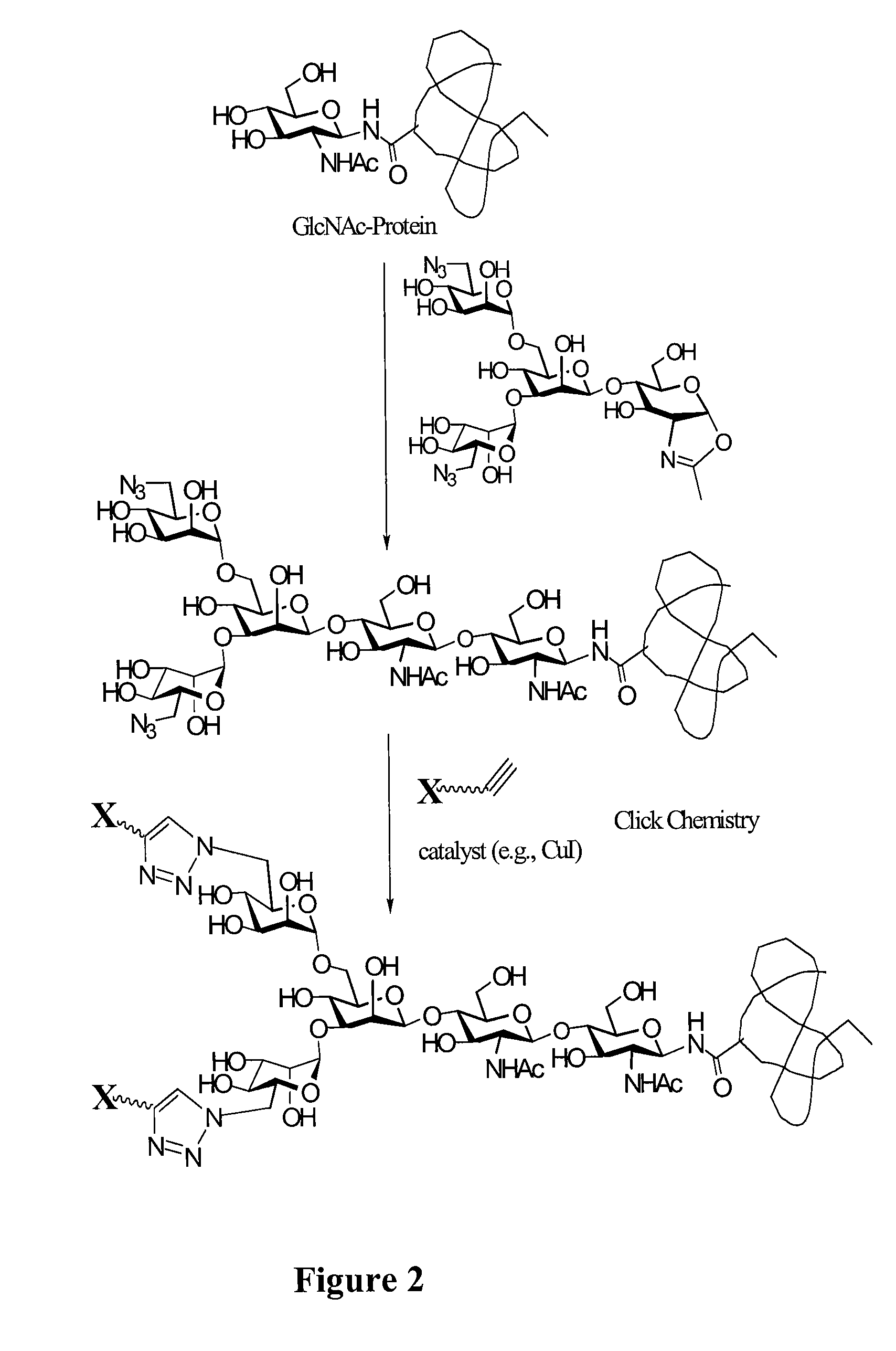
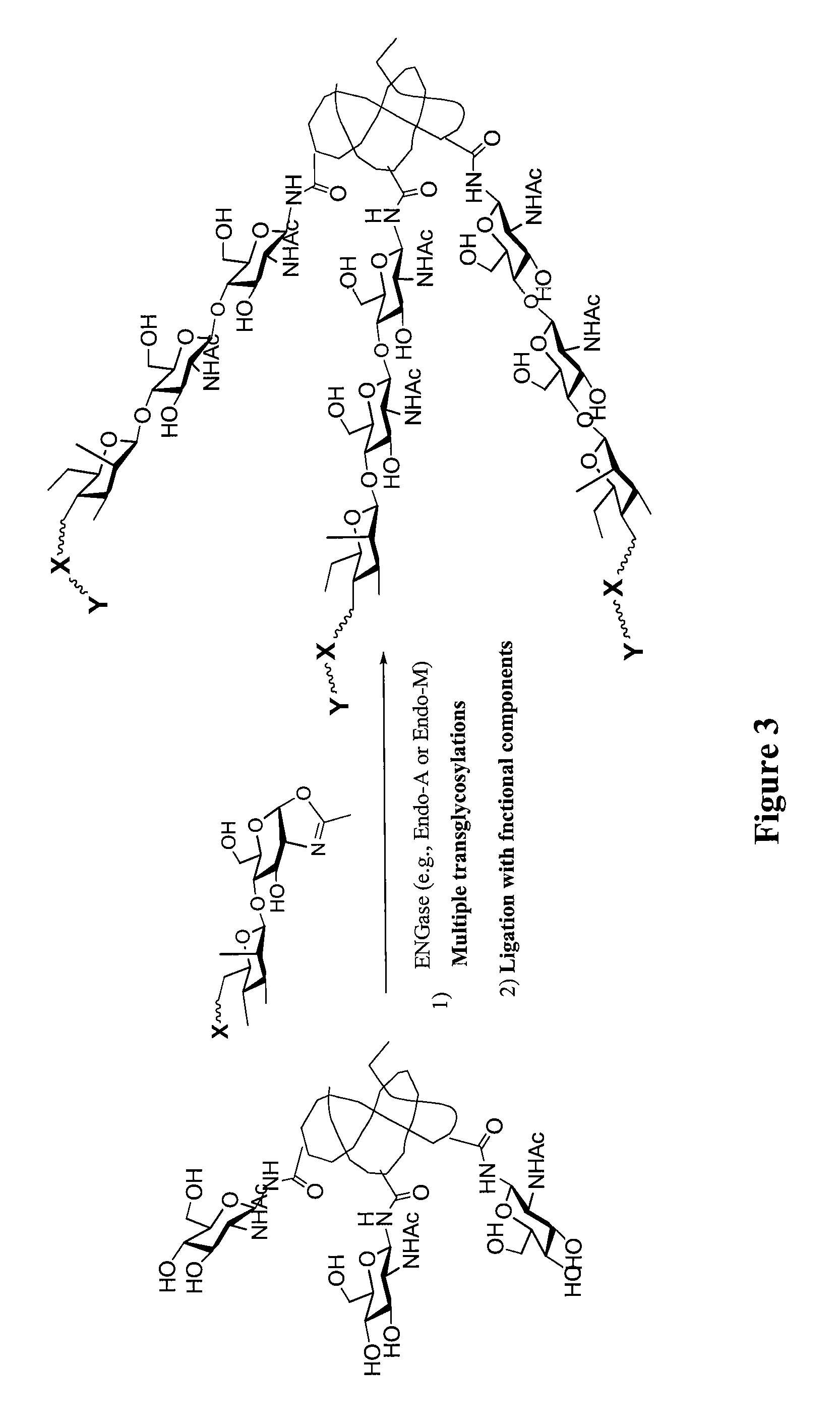
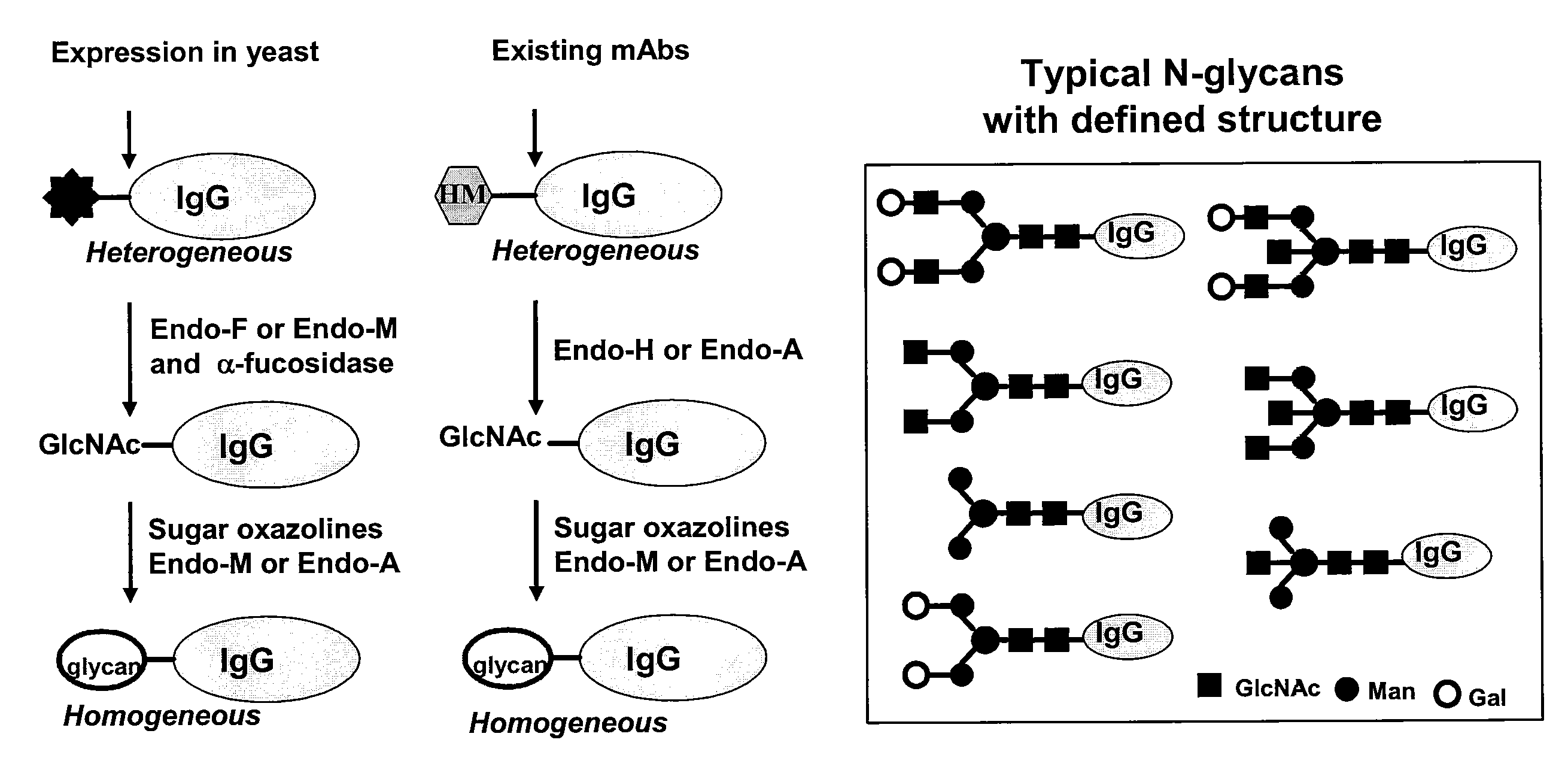
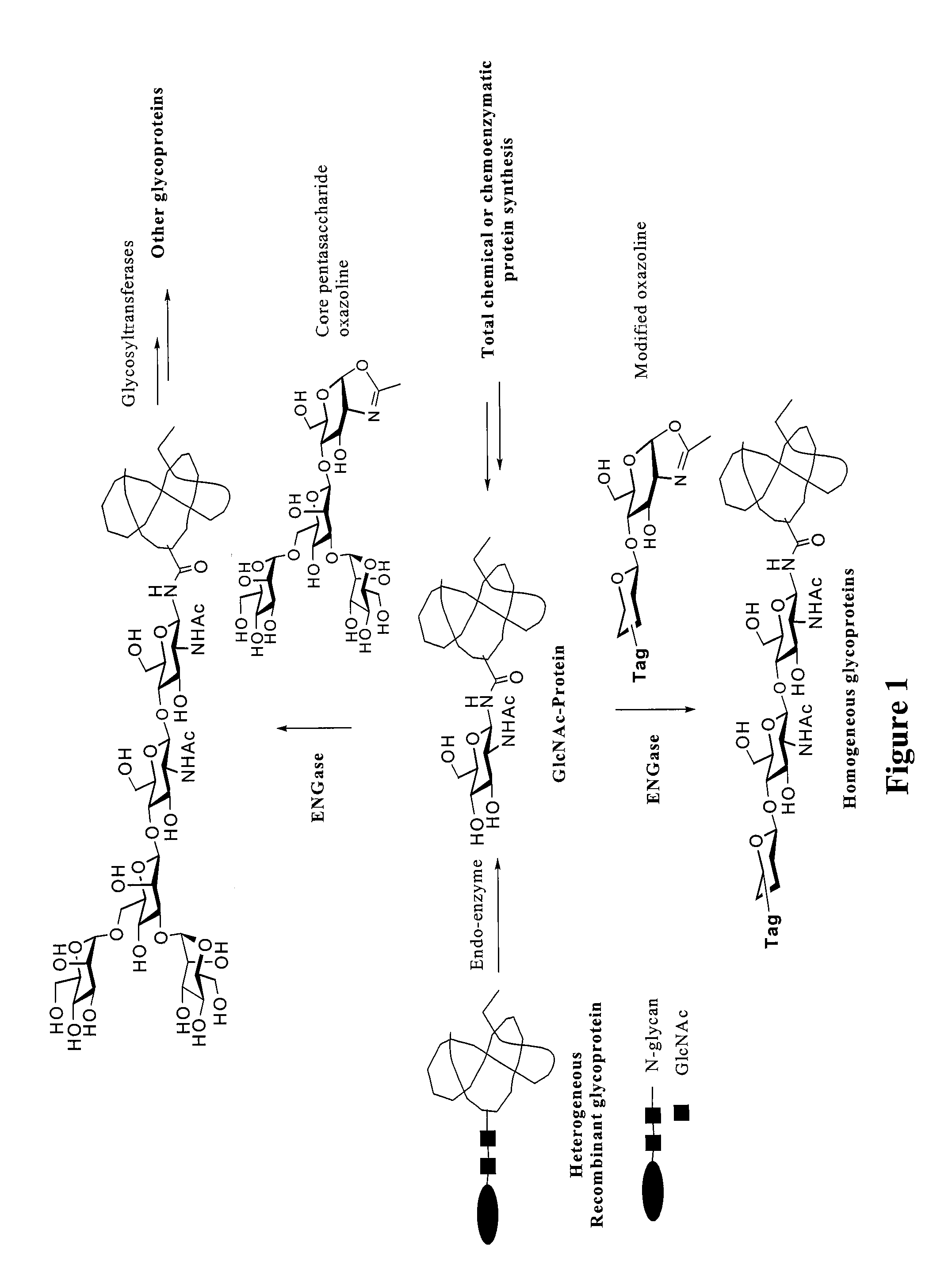
Glycoprotein synthesis and remodeling by enzymatic transglycosylation
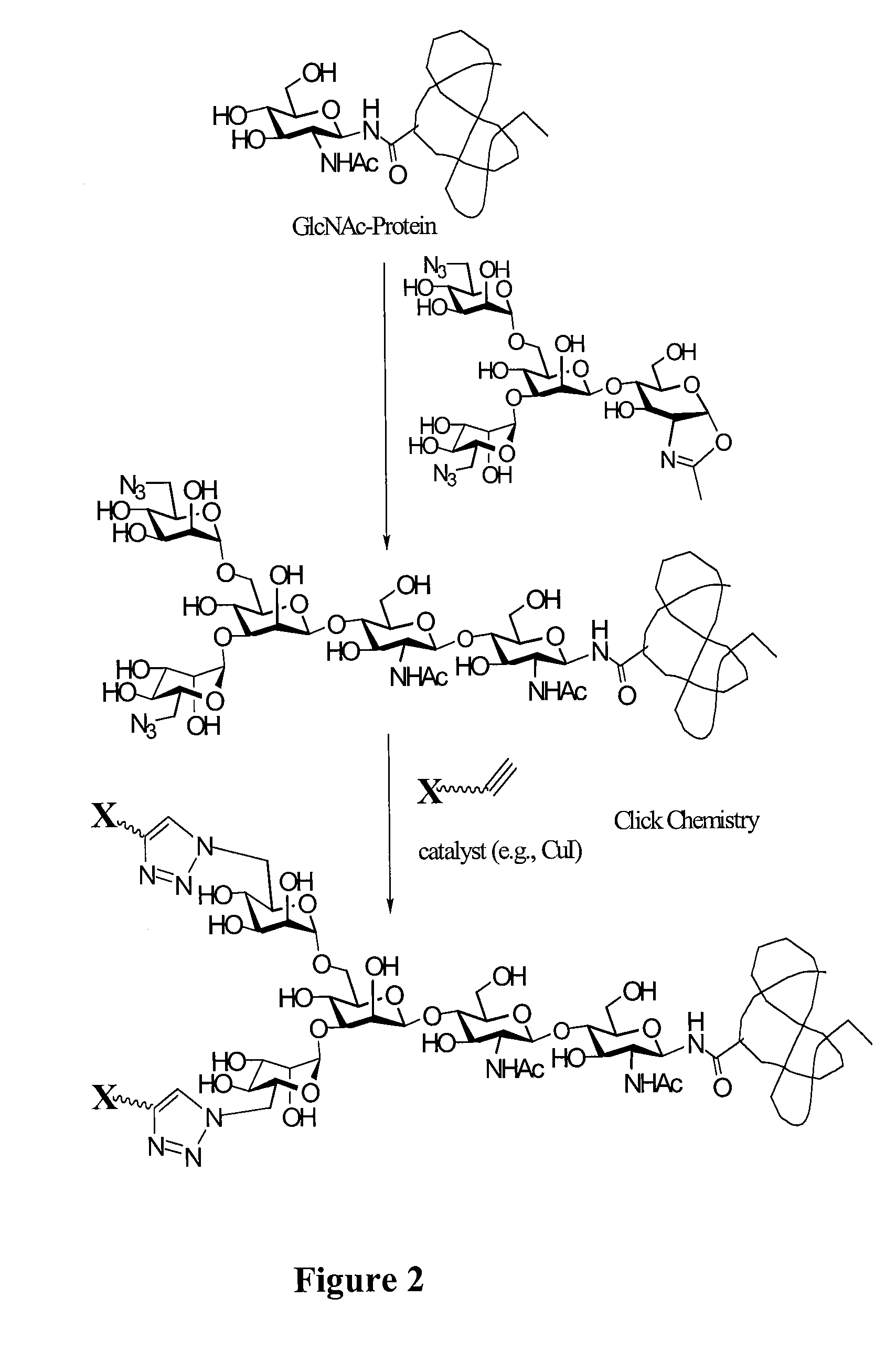
ActiveUS7807405B2Prolonged half-life-timeLess immunogenicVirus peptidesPeptide preparation methodsHalf-lifeGlycopeptide
A chemoenzymatic method for the preparation of a homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide, including (a) providing an acceptor selected from the group consisting of GlcNAc-protein and GlcNAc-peptide; and (b) reacting the acceptor with a donor substrate including an activated oligosaccharide moiety, in the presence of a catalyst comprising endoglycosidase (ENGase), to transfer the oligosaccharide moiety to the acceptor and yield the homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide. The donor substrate includes, in a specific implementation, a synthetic oligosaccharide oxazoline. A related method of glycoprotein or glycopeptide remodeling with a predetermined natural N-glycan or a tailor-made oligosaccharide moiety, and a method of remodeling an antibody including a heterogeneous sugar chain, are also described. The disclosed methodology enables glycoprotein drugs to be modified for prolonged half-life in vivo, reduced immunogenicity, and enhanced in vivo activity, and for targeting and drug delivery.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
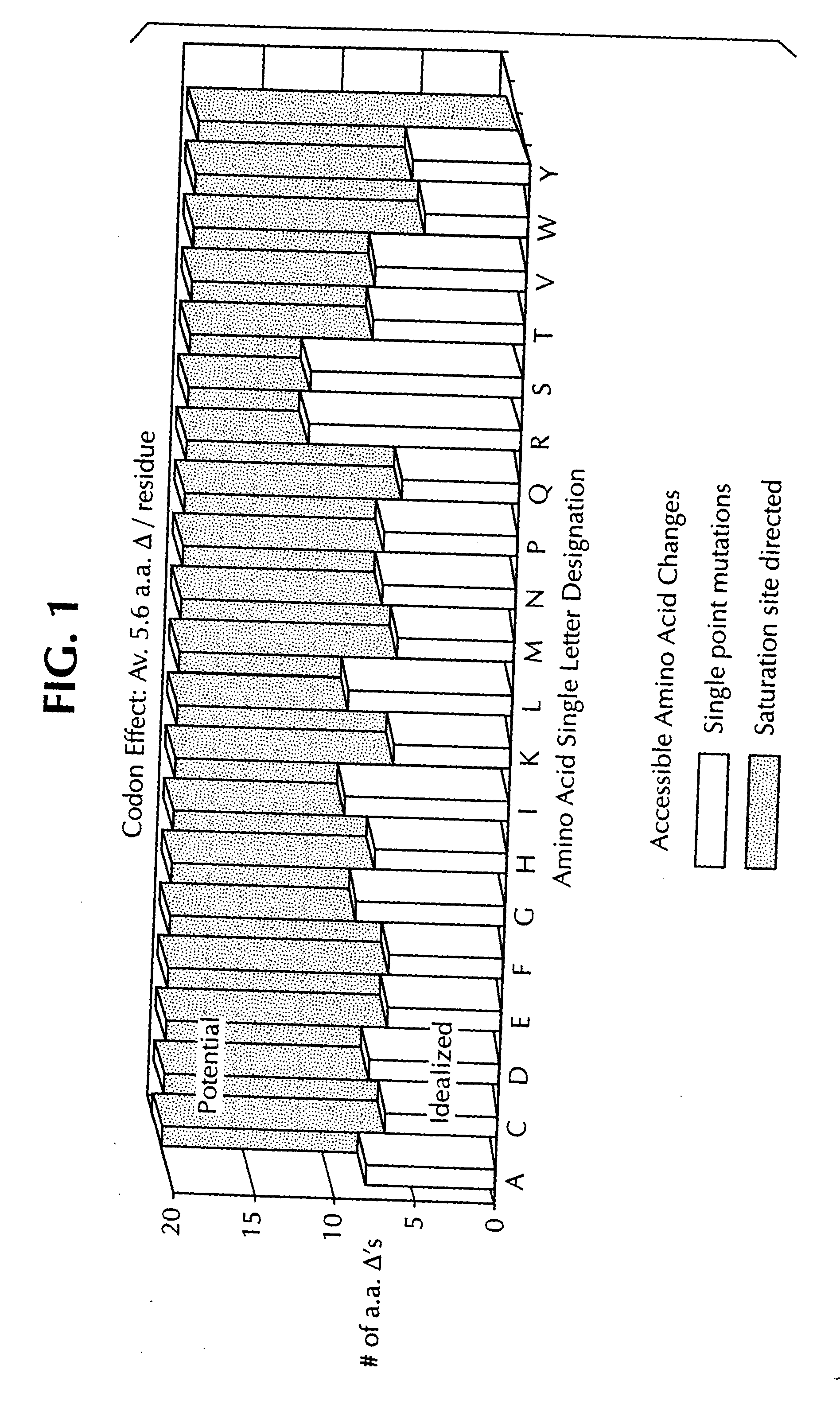
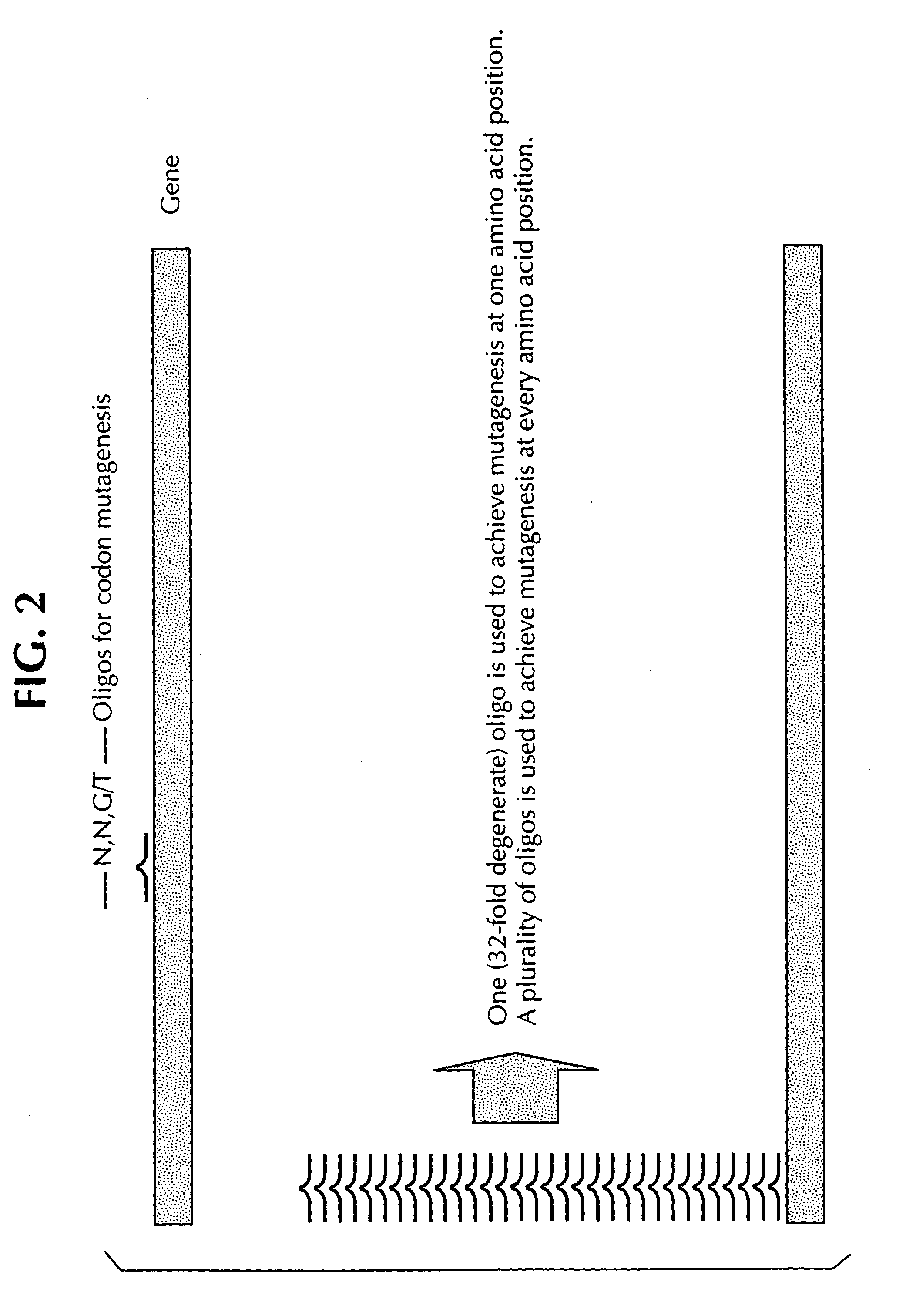
Saturation mutagenesis in directed evolution
InactiveUS20050100985A1Reduce complexityHigh activityHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideCombined use
Disclosed is a rapid and facilitated method of producing from a parentlal template polynucleotide, a set of mutagenized progeny polynculeotides whereby at each original codon position there is produced at least one substitute codon encoding each of the 20 naturally encoded amino acids. Accordingly, there is also provided a method of producing from a parental template polypeptide, a set of mutagenized progeny polypeptides wherein each of the 20 naturally encoded amino acids is represented at each original amino acid position. The method provided is termed site-saturation mutagenesis, or simply saturation mutagenesis, and can be used in combination with other mutagenization processes, such as, for example, a process wherein two or more related polynucleotides are introduced into a suitable host cell such that a hybrid polynucleotide is generated by recombination and reductive reassortment. Also provided are vector and expression vehicles incuding such polynucleotides, polypeptides expressed by the hybrid polynucleotides and a method for screening for hybrid polypeptides.
Owner:SHORT JAY
Glycoprotein synthesis and remodeling by enzymatic transglycosylation
ActiveUS20080138855A1Prolonged half-life-timeLess immunogenicImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDepsipeptidesHalf-lifeGlycopeptide
A chemoenzymatic method for the preparation of a homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide, including (a) providing an acceptor selected from the group consisting of GlcNAc-protein and GlcNAc-peptide; and (b) reacting the acceptor with a donor substrate including an activated oligosaccharide moiety, in the presence of a catalyst comprising endoglycosidase (ENGase), to transfer the oligosaccharide moiety to the acceptor and yield the homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide. The donor substrate includes, in a specific implementation, a synthetic oligosaccharide oxazoline. A related method of glycoprotein or glycopeptide remodeling with a predetermined natural N-glycan or a tailor-made oligosaccharide moiety, and a method of remodeling an antibody including a heterogeneous sugar chain, are also described. The disclosed methodology enables glycoprotein drugs to be modified for prolonged half-life in vivo, reduced immunogenicity, and enhanced in vivo activity, and for targeting and drug delivery.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Human monoclonal antibodies against interleukin 8 (IL-8)
ActiveUS7282568B2More therapeutically effectiveLess immunogenicNervous disorderAntipyreticV(D)J recombinationInterleukin 8
Isolated human monoclonal antibodies which bind to IL-8 (e.g., human IL-8) are disclosed. The human antibodies can be produced in a hybridoma, transfectoma or in a non-human transgenic animal, e.g., a transgenic mouse, capable of producing multiple isotypes of human monoclonal antibodies by undergoing V-D-J recombination and isotype switching. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the human antibodies, non-human transgenic animals, hybridomas, and transfectomas which produce the human antibodies, and therapeutic and diagnostic methods for using the human antibodies.
Owner:CORMORANT PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com