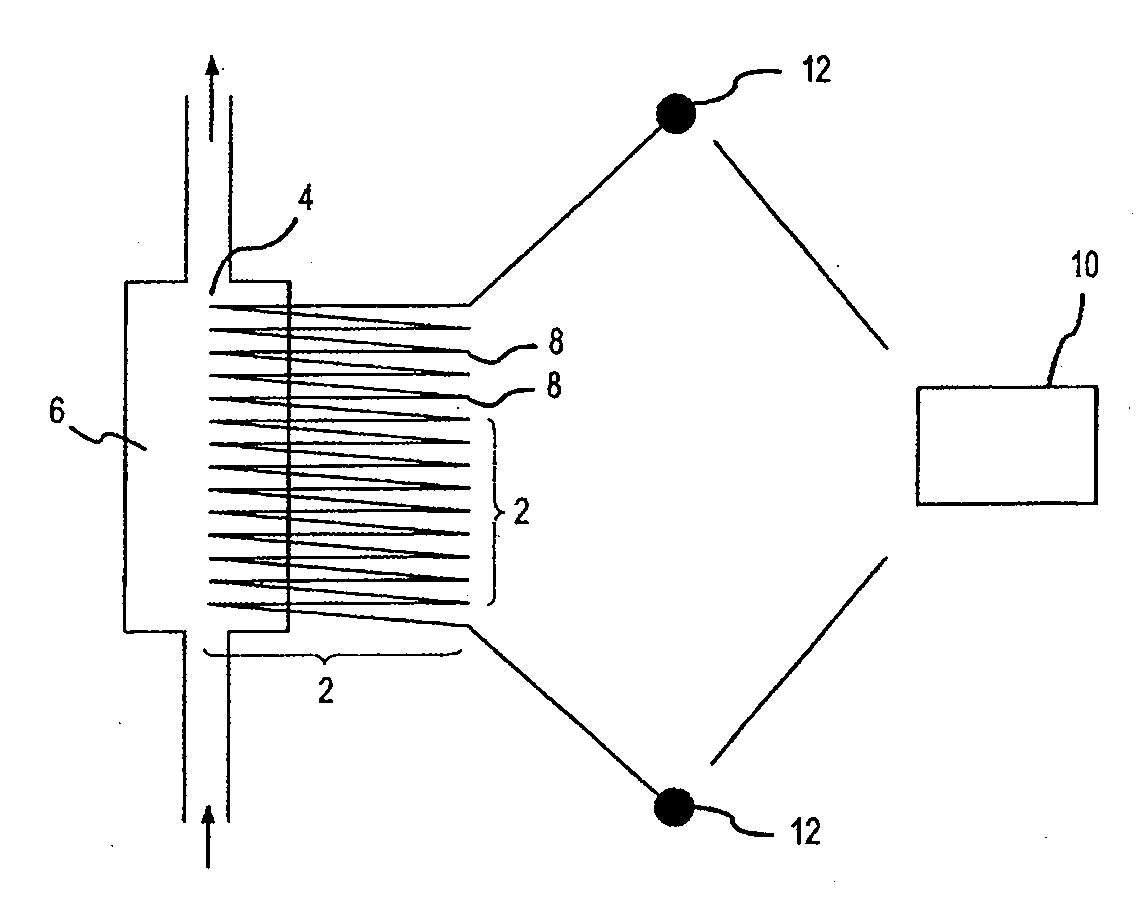
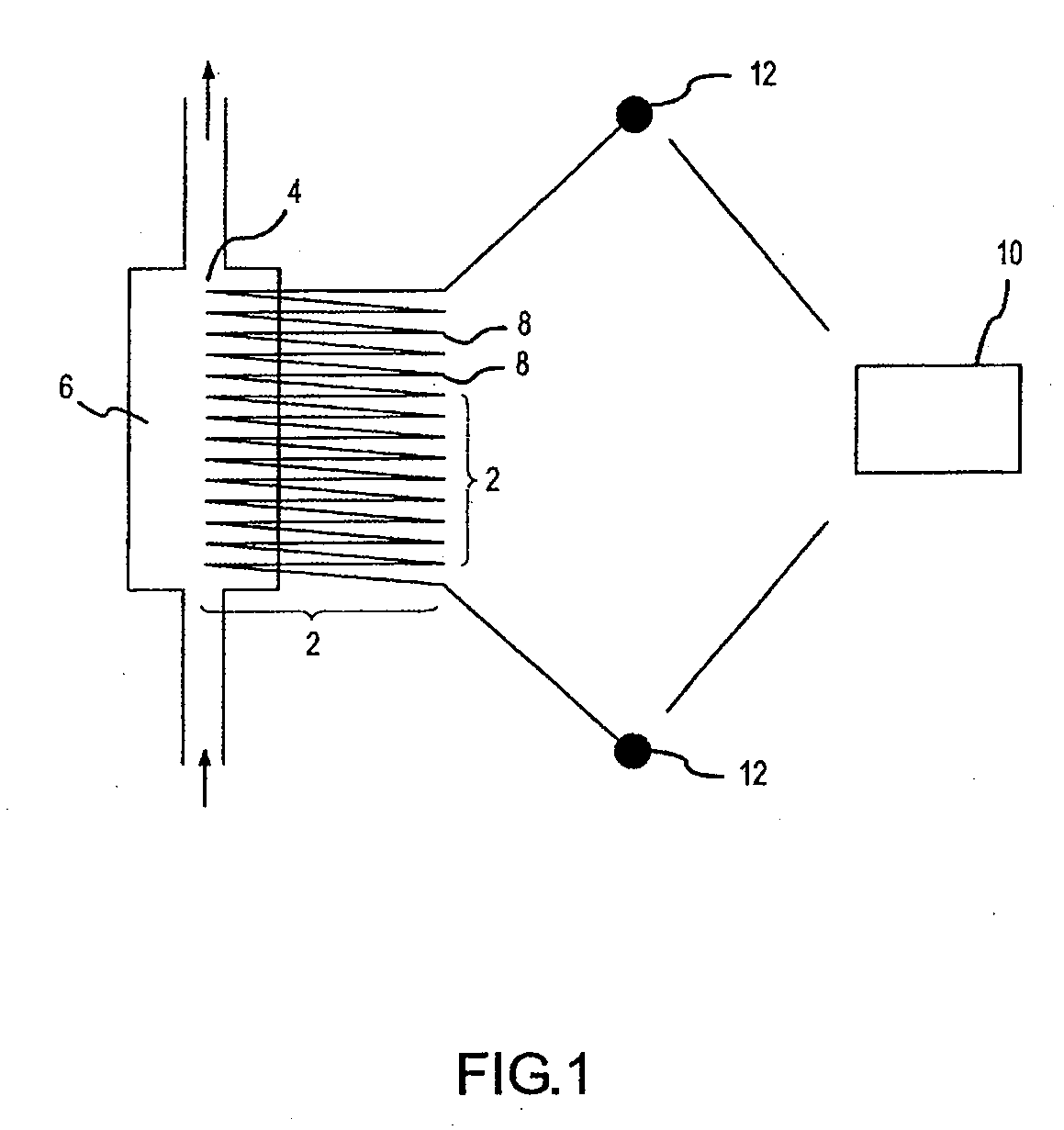
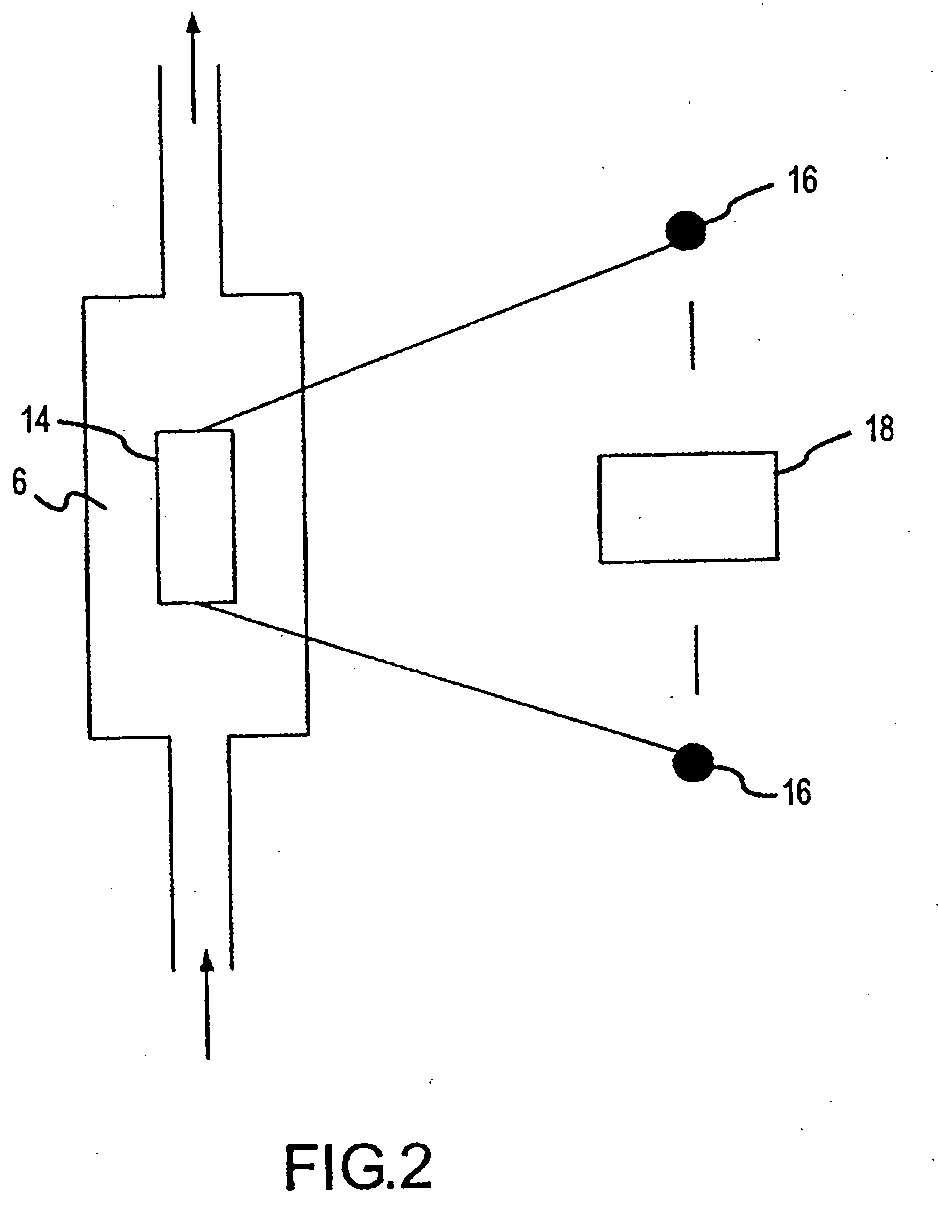
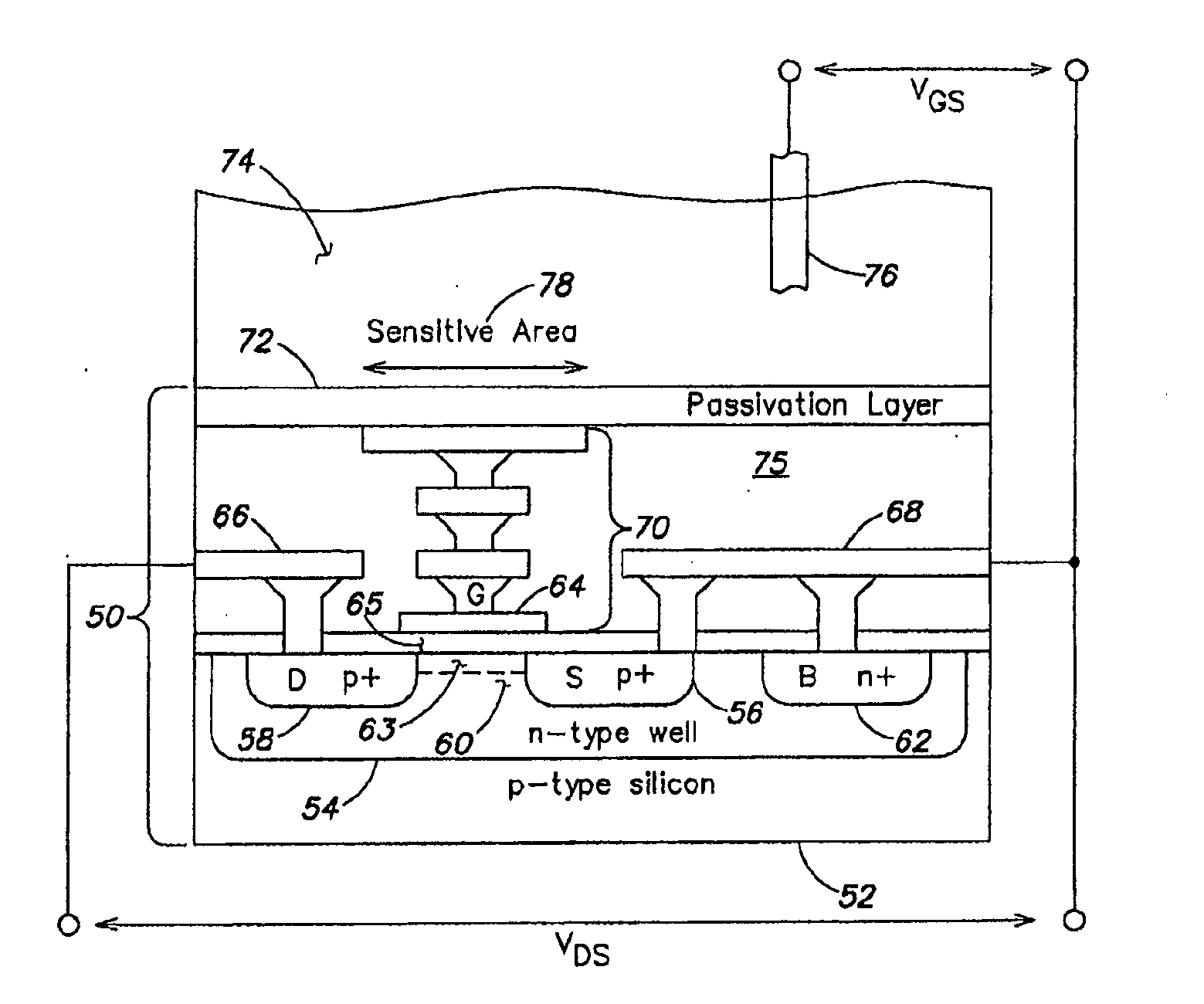
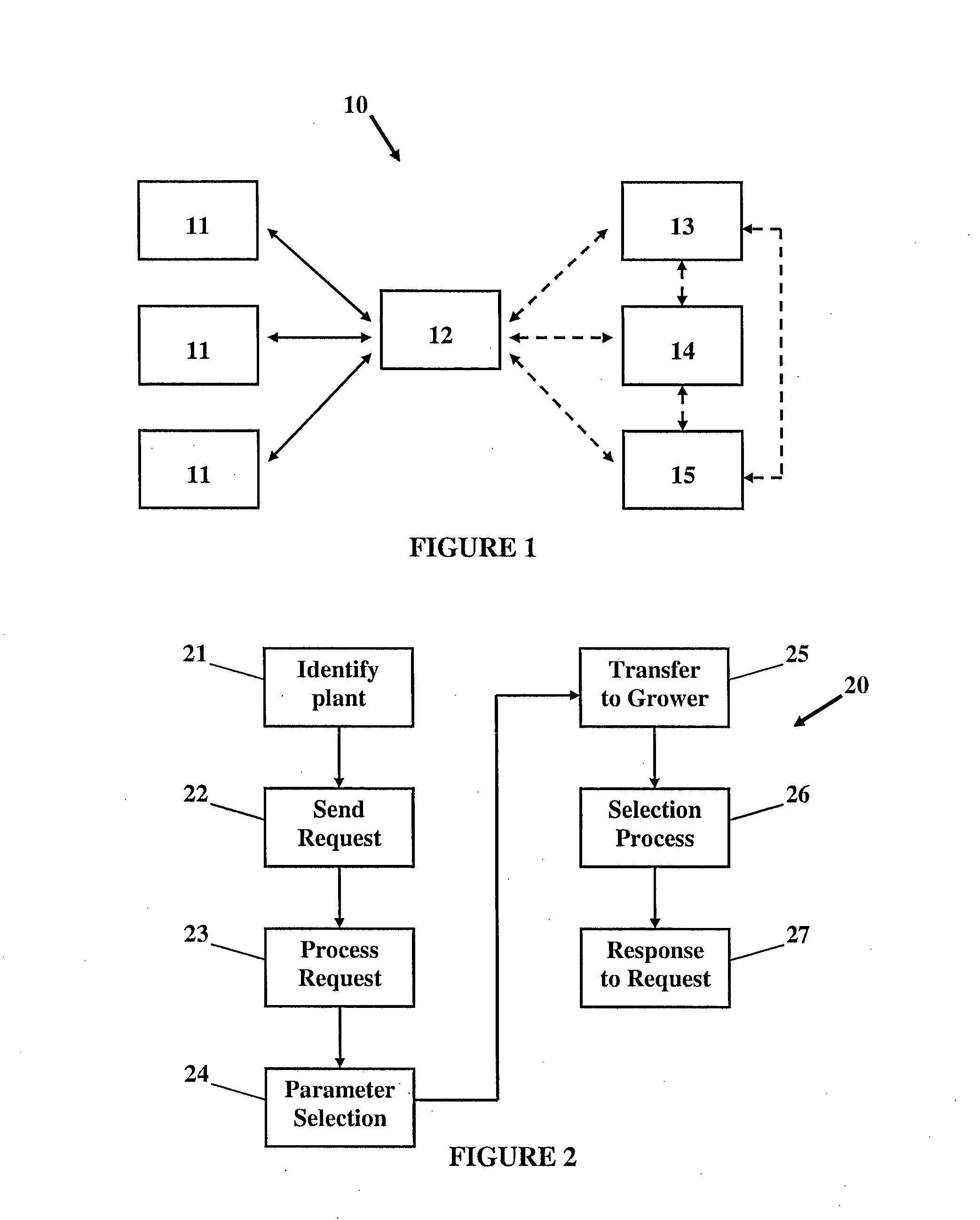
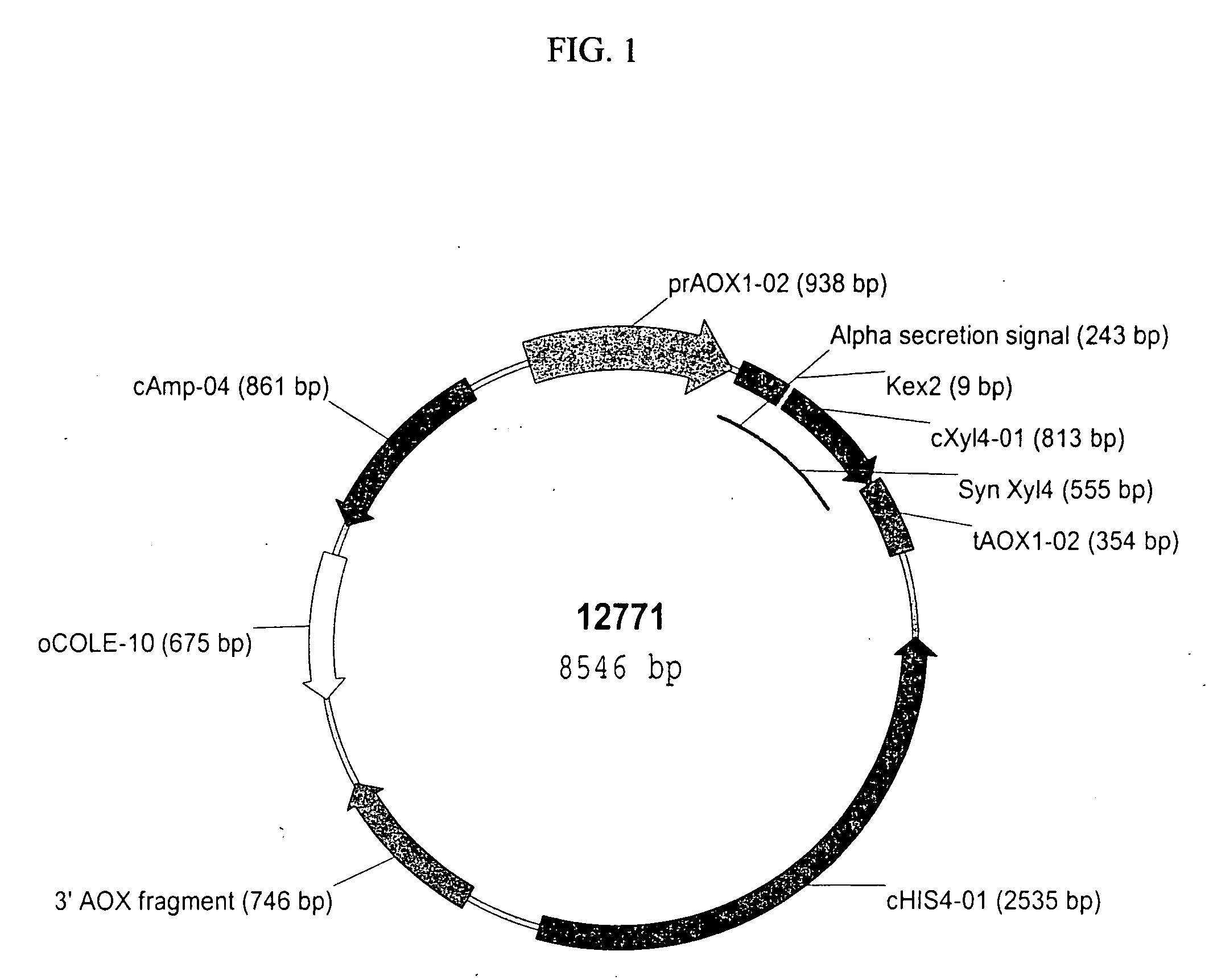
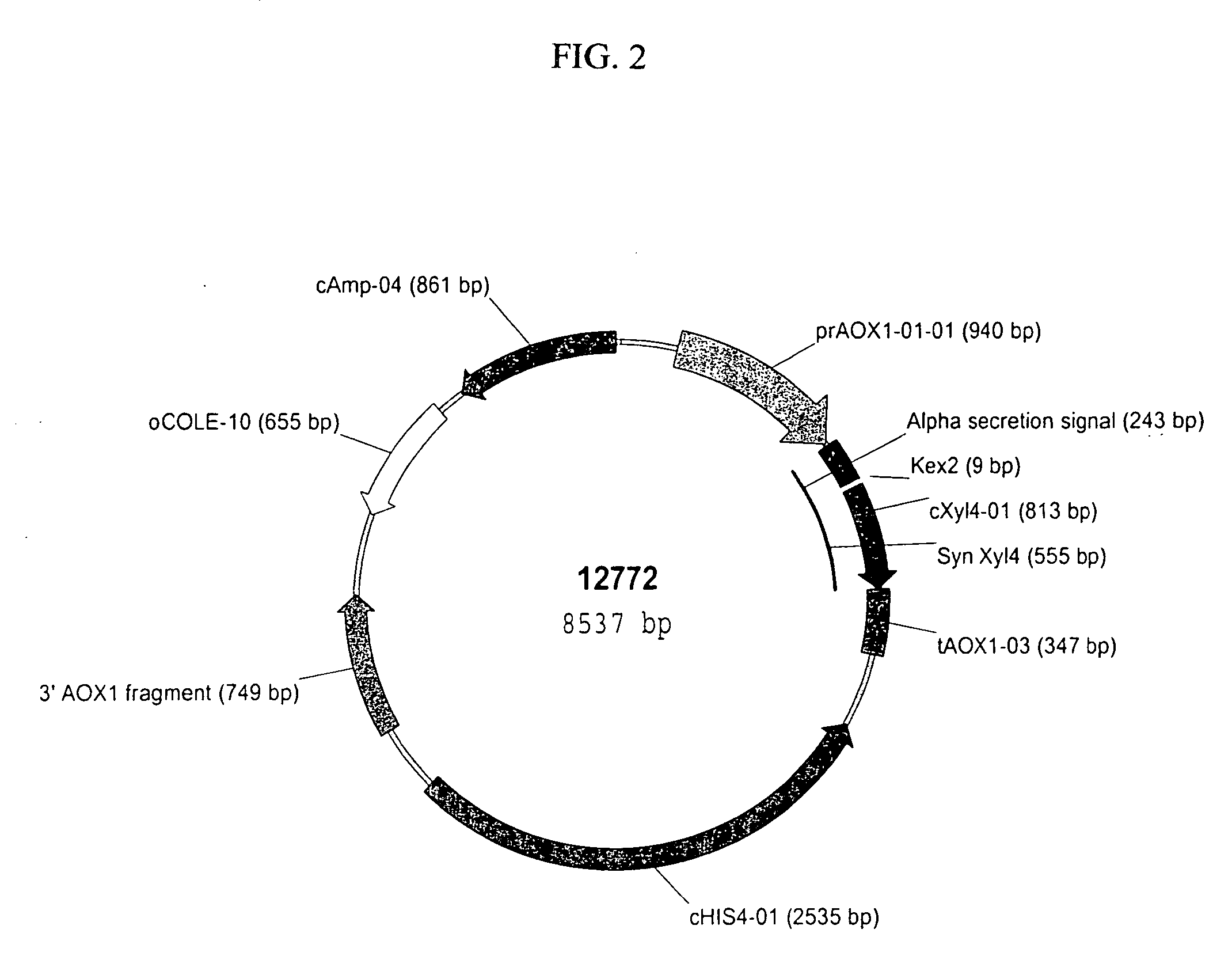
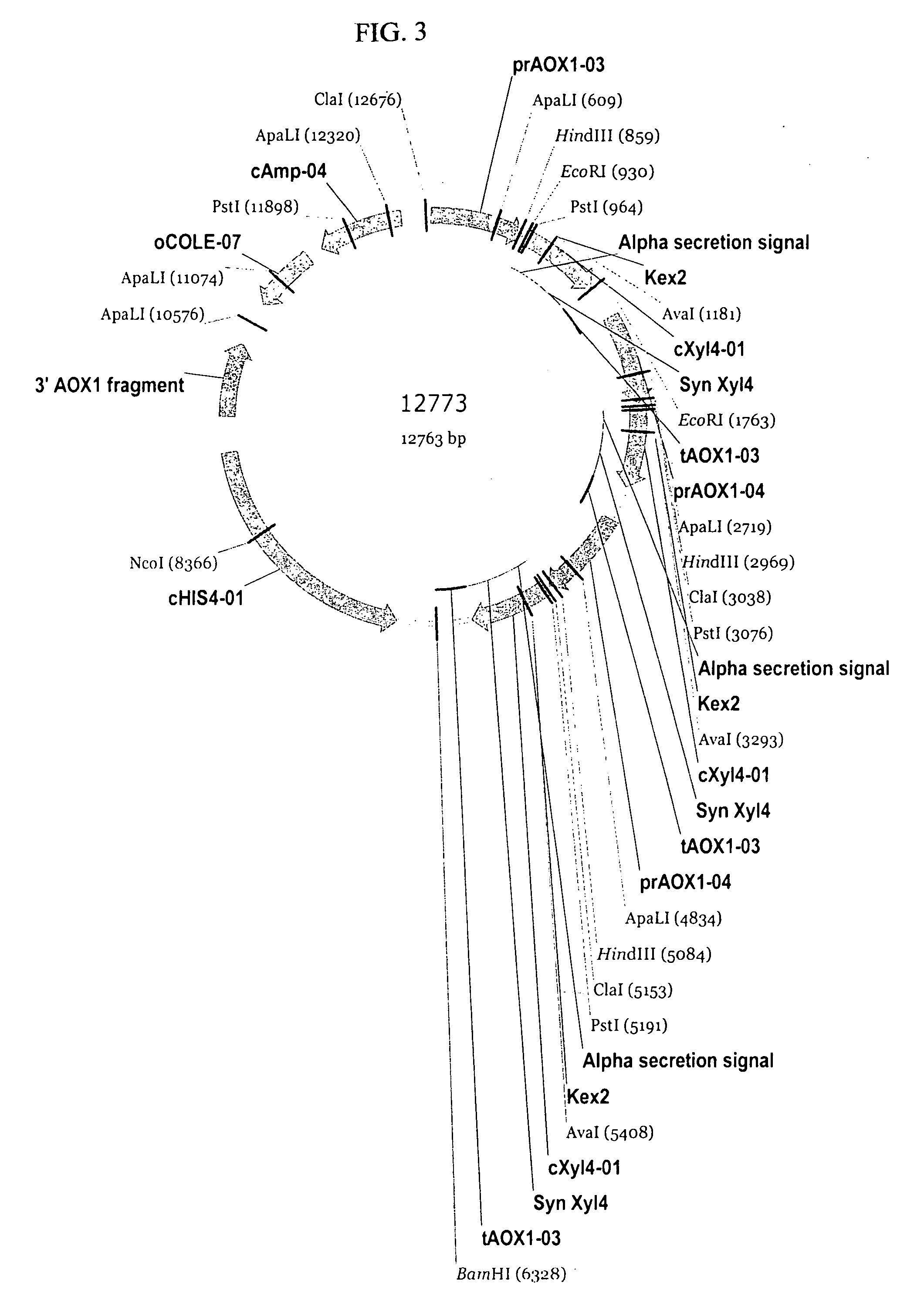
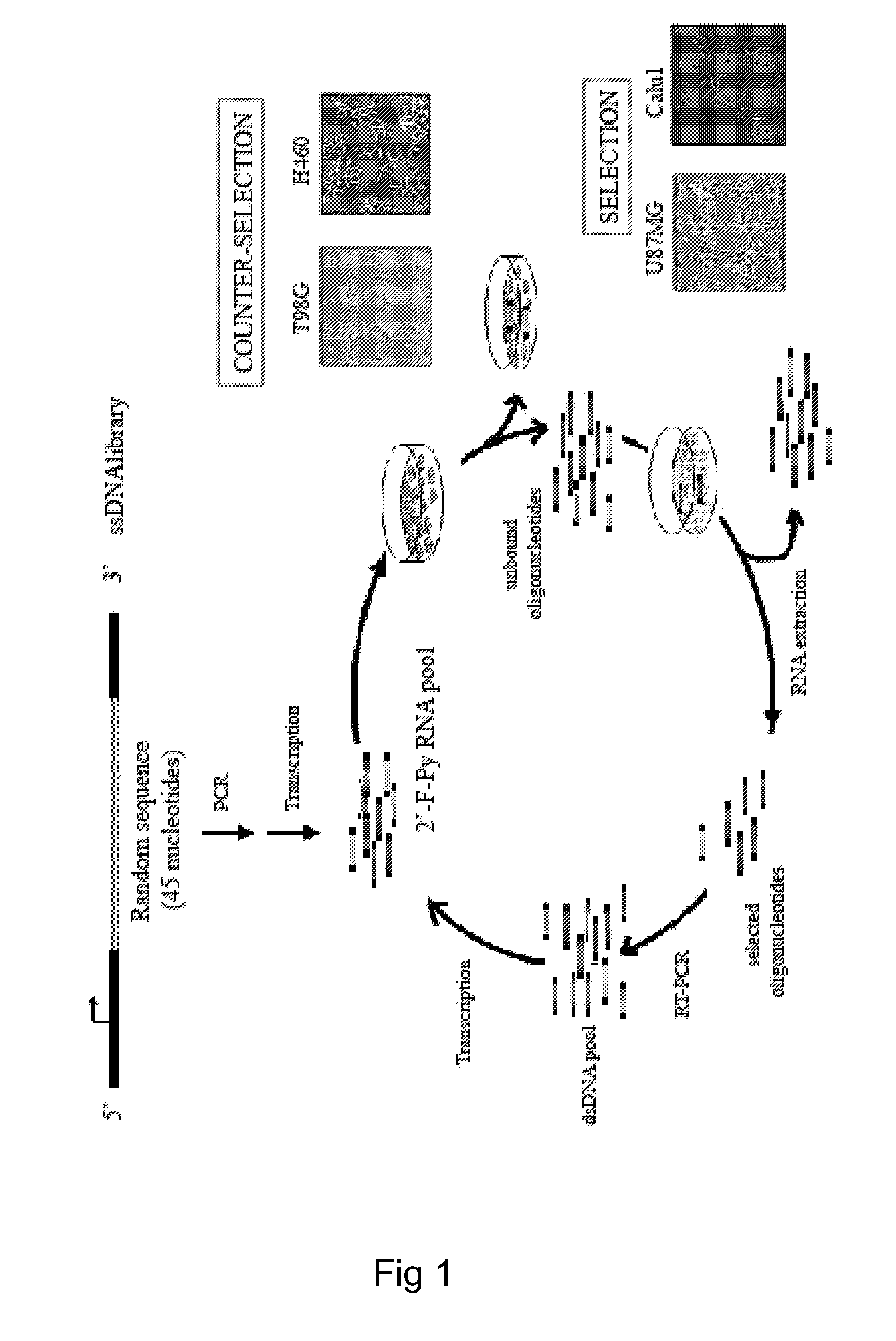
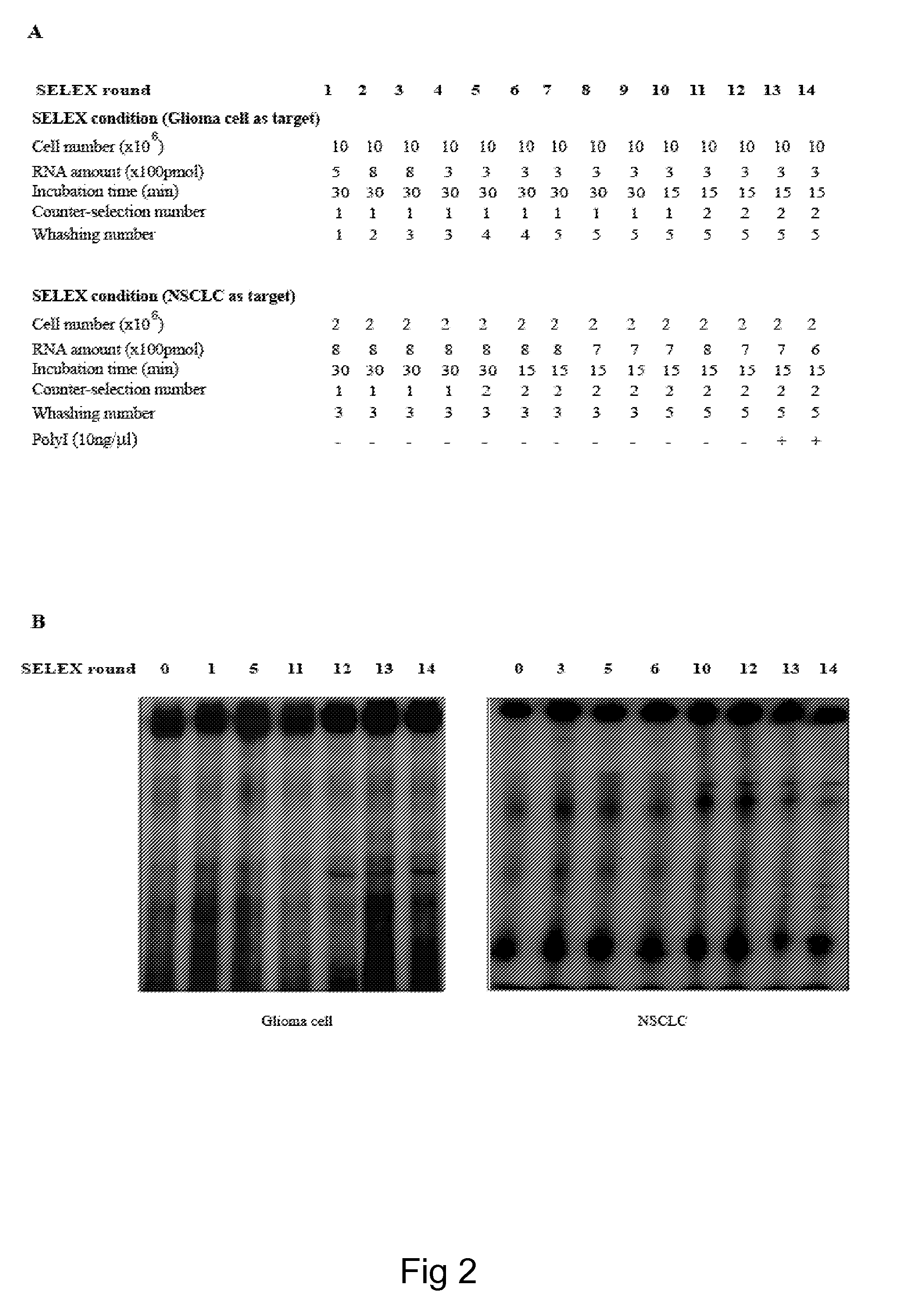
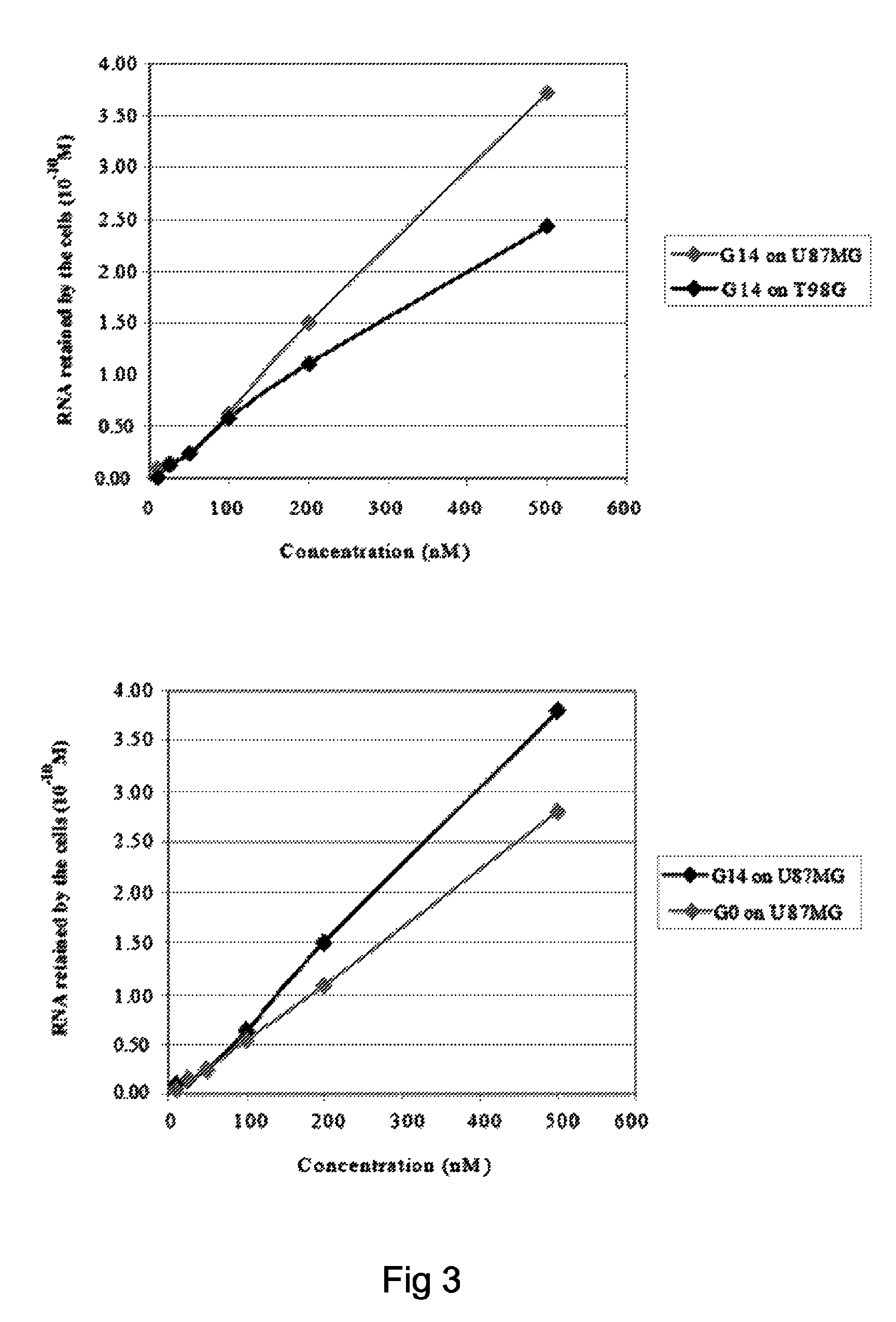
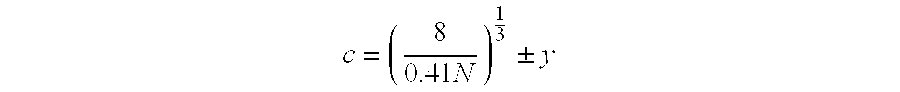Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
193results about "Directed macromolecular evolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
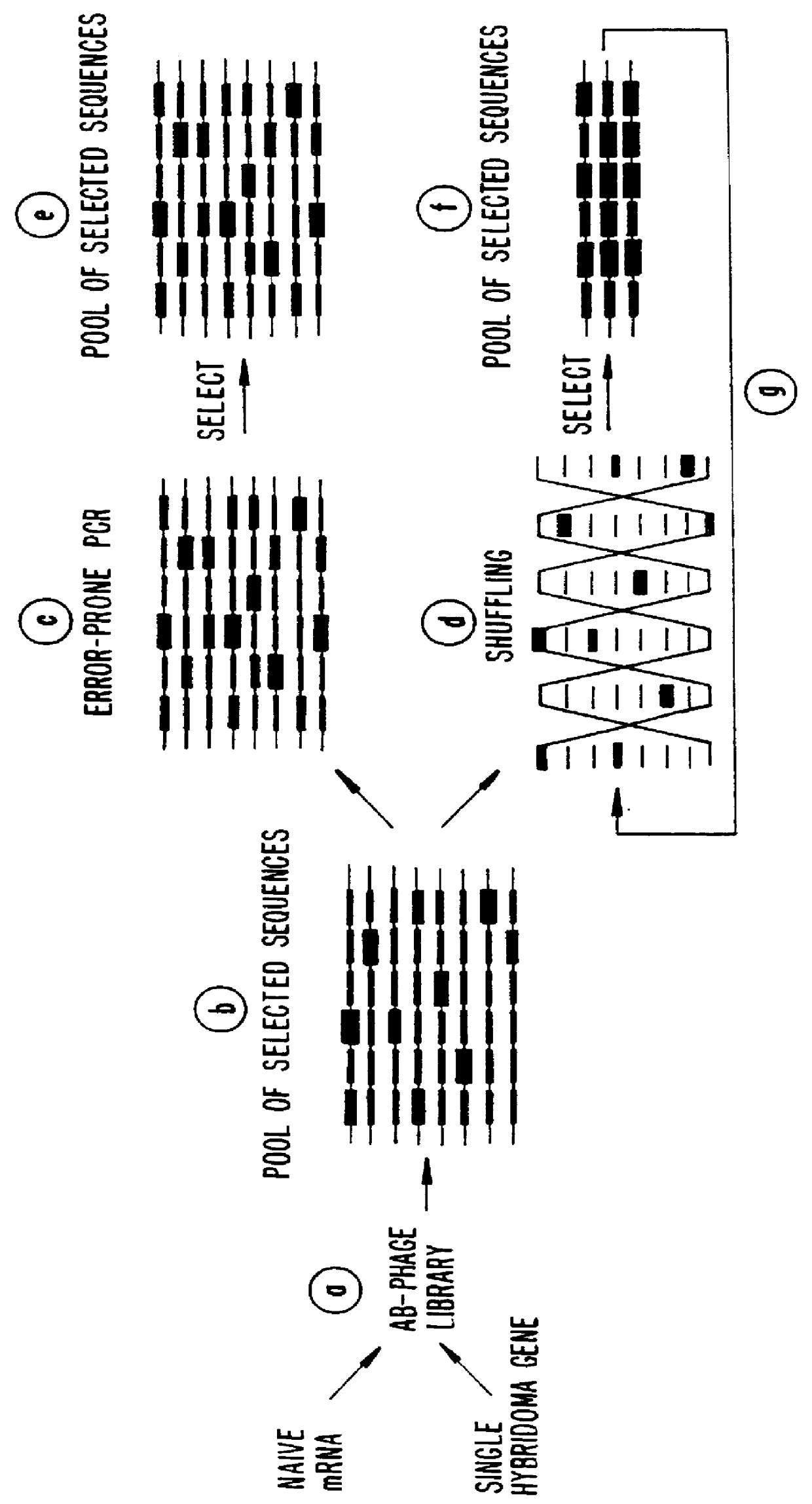
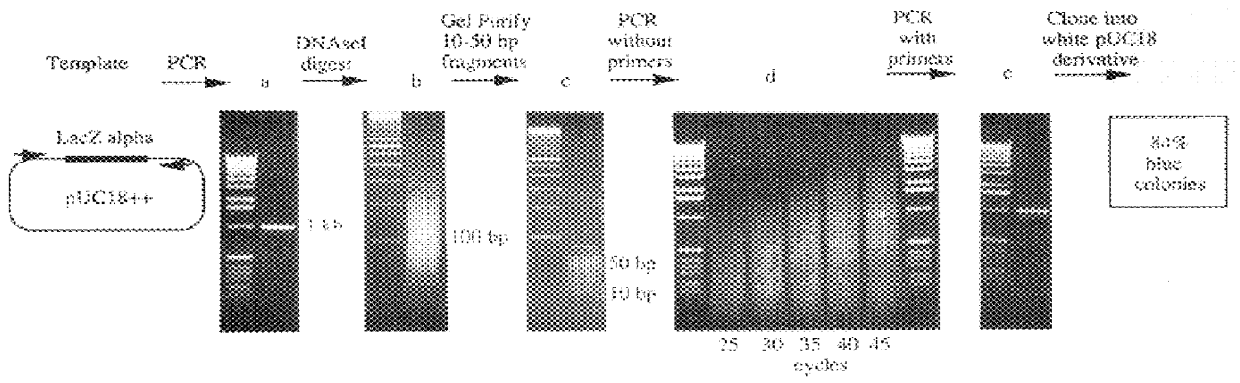
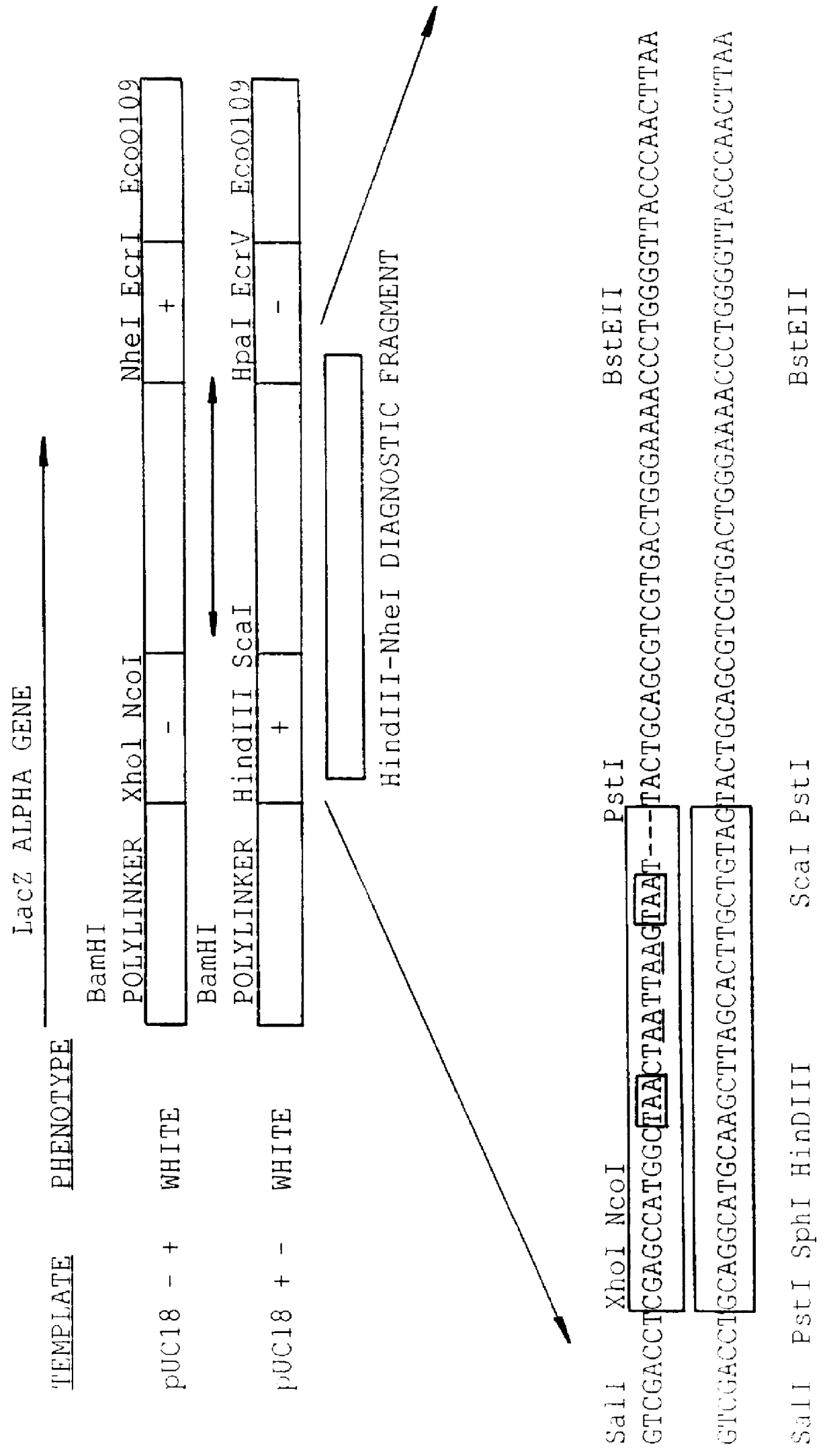
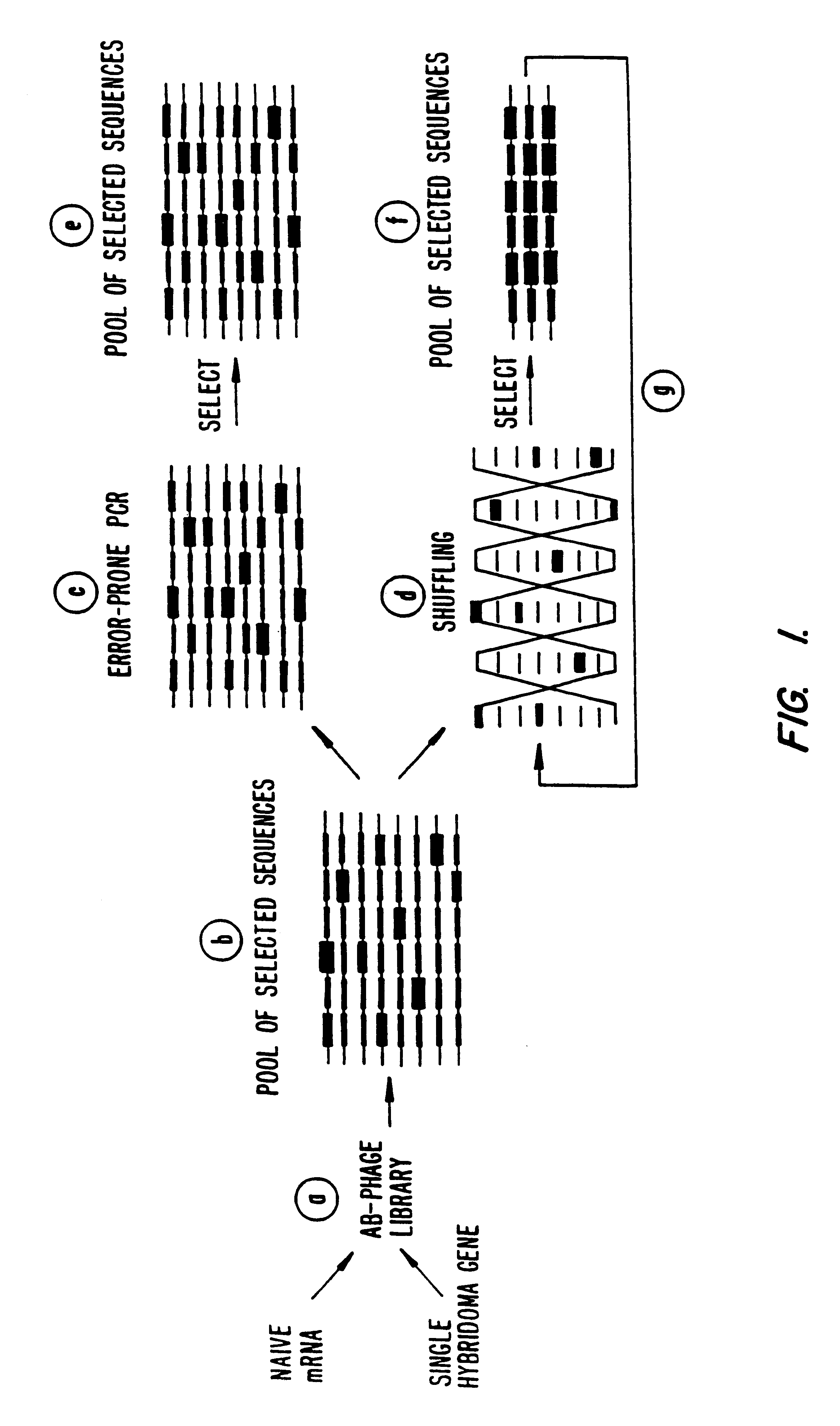
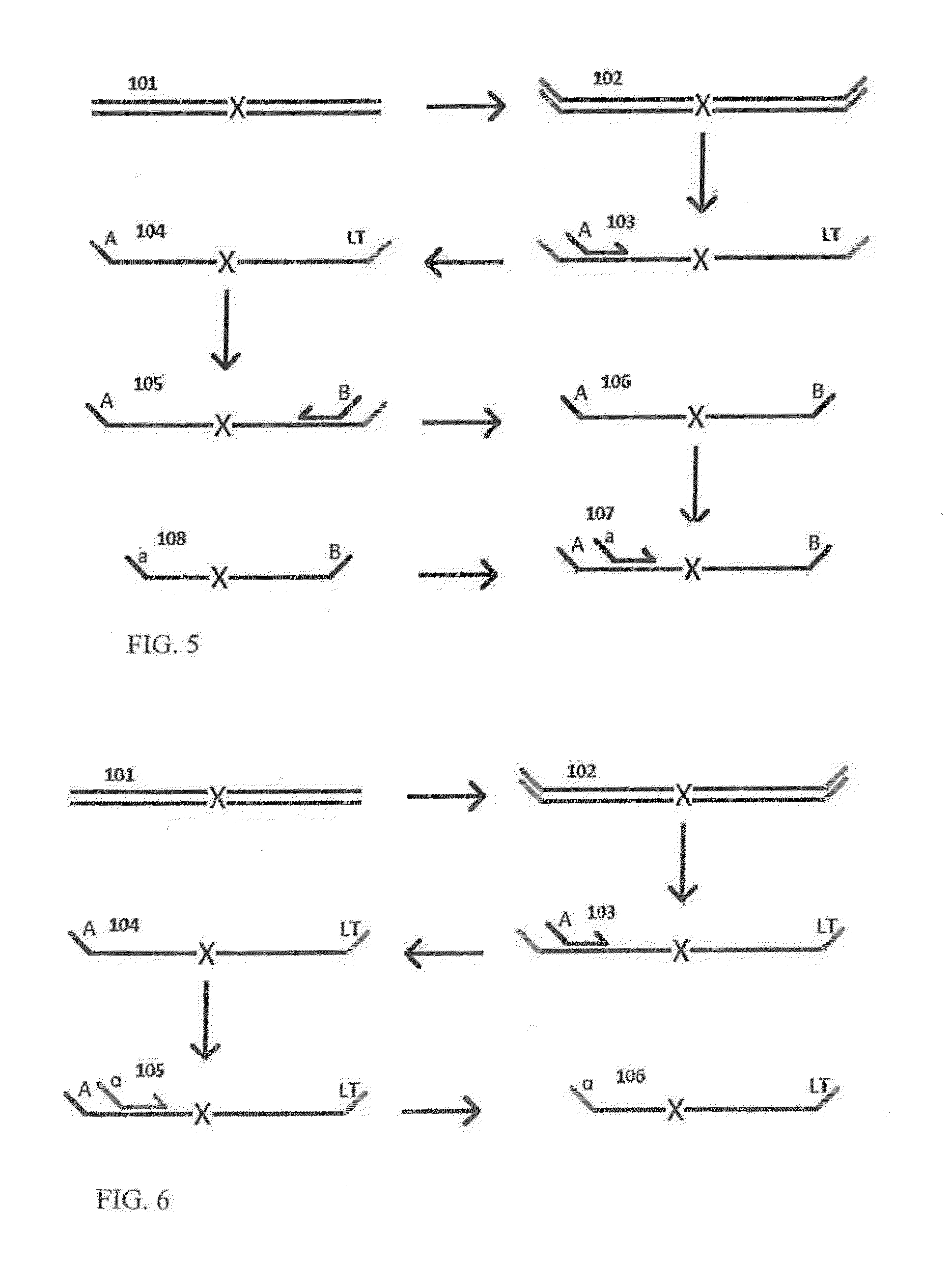
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6117679ALess immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
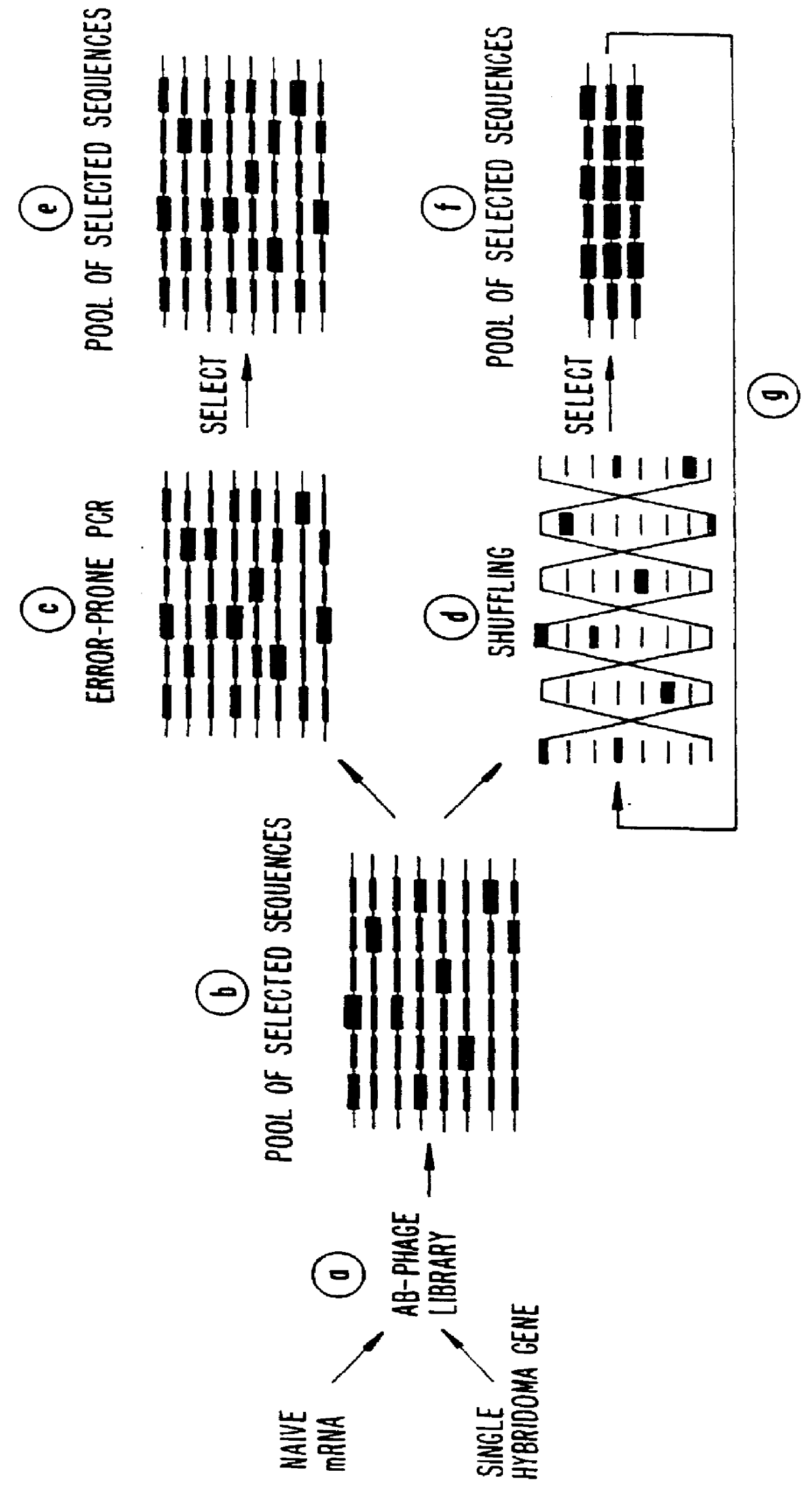
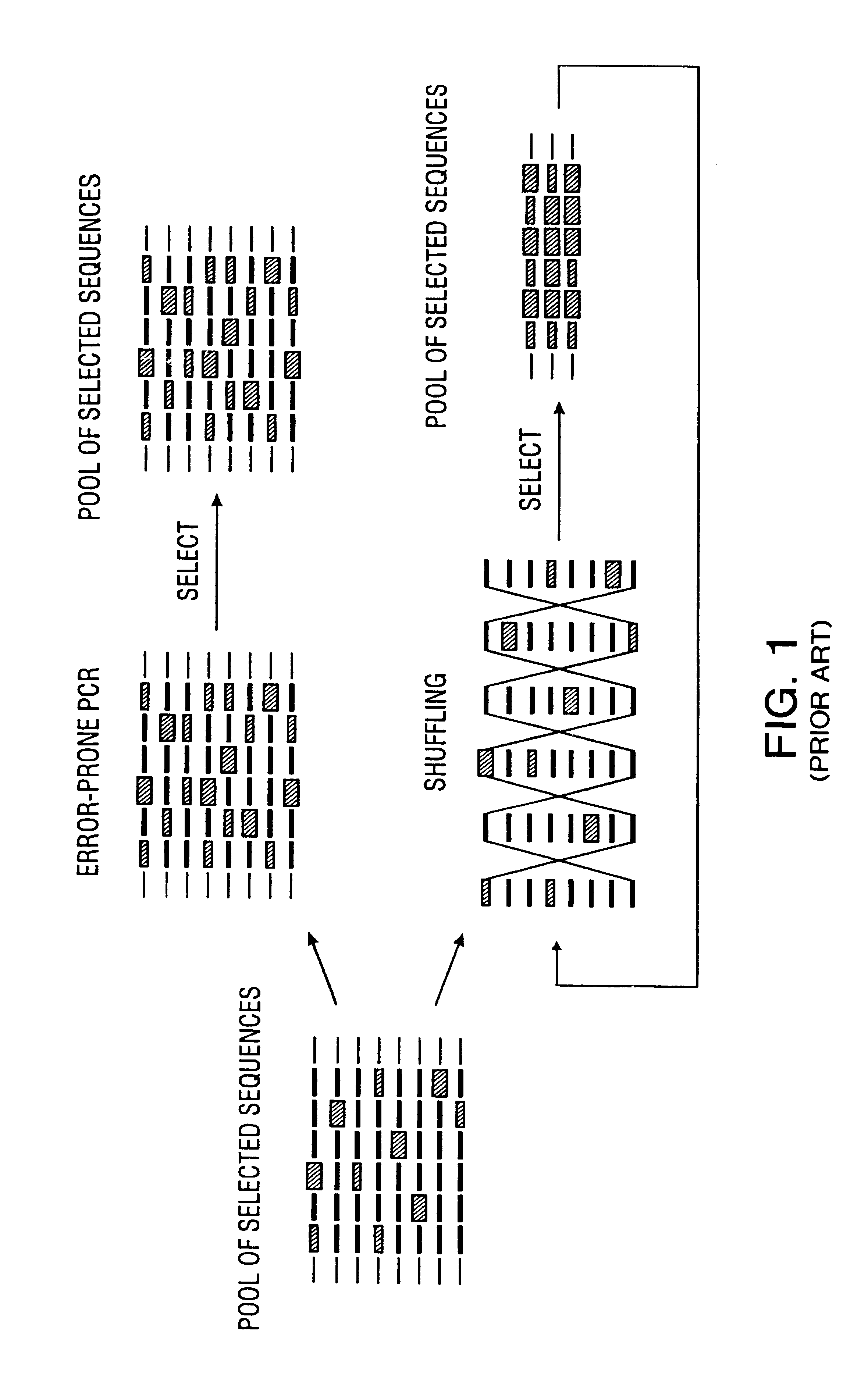
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6180406B1Less immunogenicLibrary screeningDirected macromolecular evolutionMutated proteinNucleic acid sequencing
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Methods for generating polynucleotides having desired characteristics by iterative selection and recombination
InactiveUS6165793ALess immunogenicDirected macromolecular evolutionImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinNucleotide
A method for DNA reassembly after random fragmentation, and its application to mutagenesis of nucleic acid sequences by in vitro or in vivo recombination is described. In particular, a method for the production of nucleic acid fragments or polynucleotides encoding mutant proteins is described. The present invention also relates to a method of repeated cycles of mutagenesis, shuffling and selection which allow for the directed molecular evolution in vitro or in vivo of proteins.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
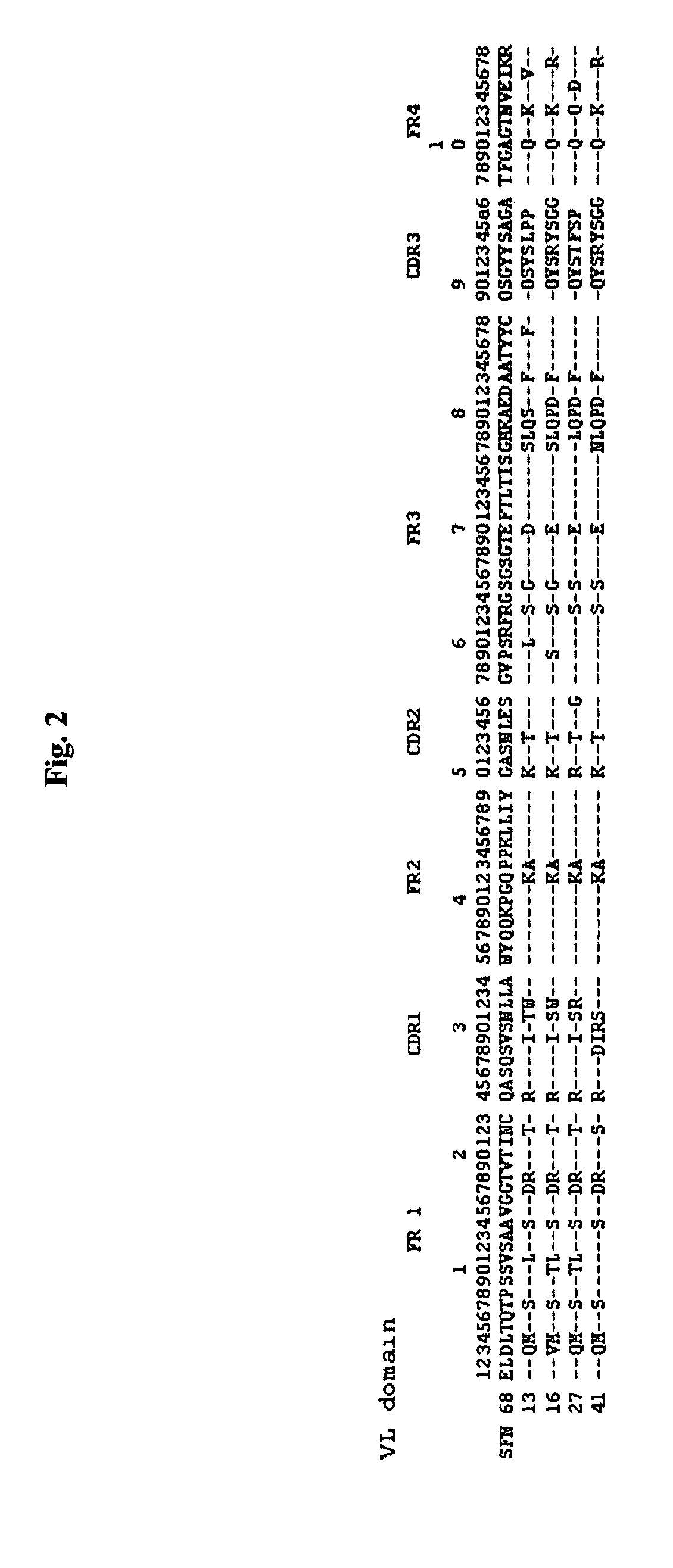
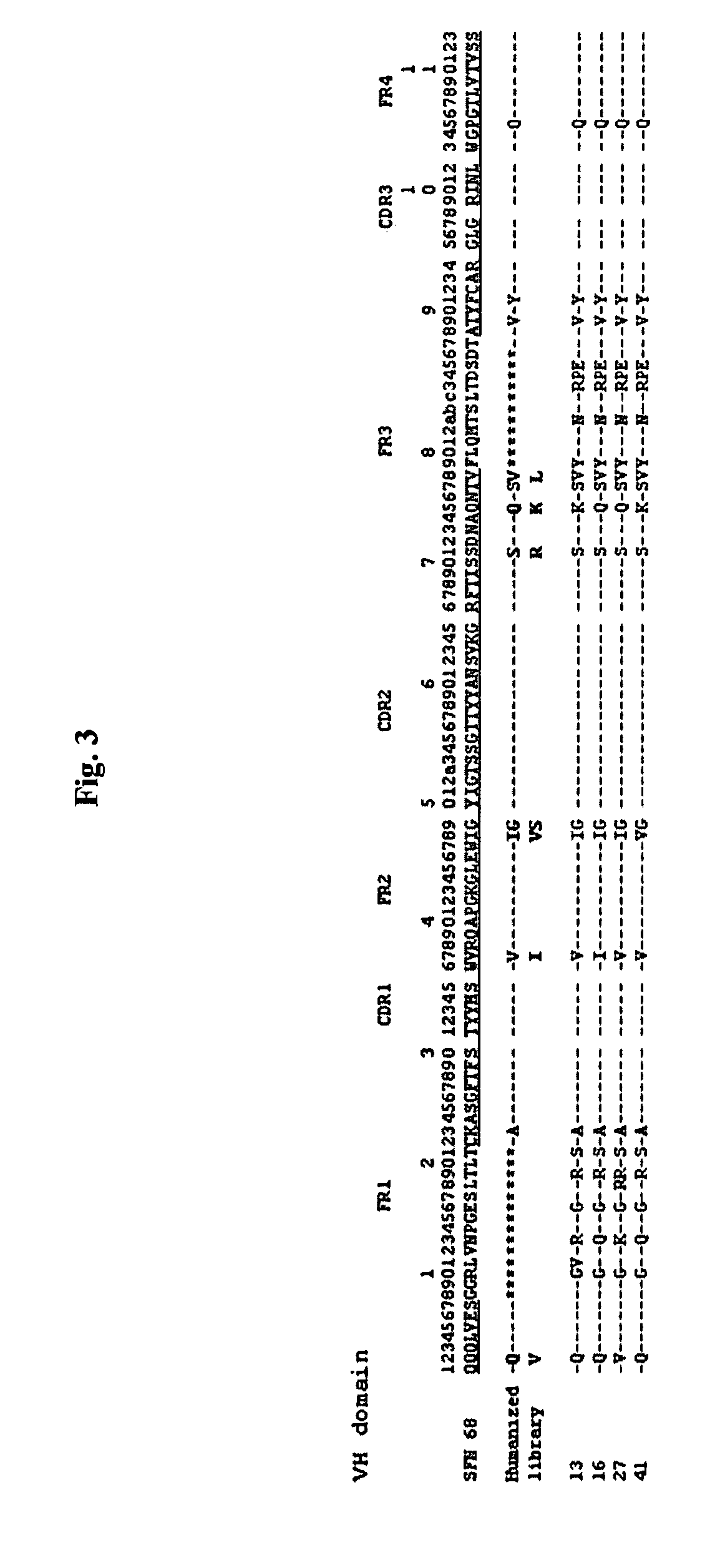
Antibody specificity transfer using minimal essential binding determinants
The present invention provides methods of making antibodies having the binding specificity of a reference antibody. Antibodies generated by the methods of the inventions have at least one minimal essential binding specificity determinant from a heavy chain or light chain CDR3 from the reference antibody. The method can be used, e.g., in humanization procedures. The invention also provides libraries and antibodies made in accordance with the methods.
Owner:HUMANIGEN INC
Method of Determining The Nucleotide Sequence of Oligonucleotides and DNA Molecules
InactiveUS20080213770A1Eliminate needHigh puritySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceOligonucleotide primers
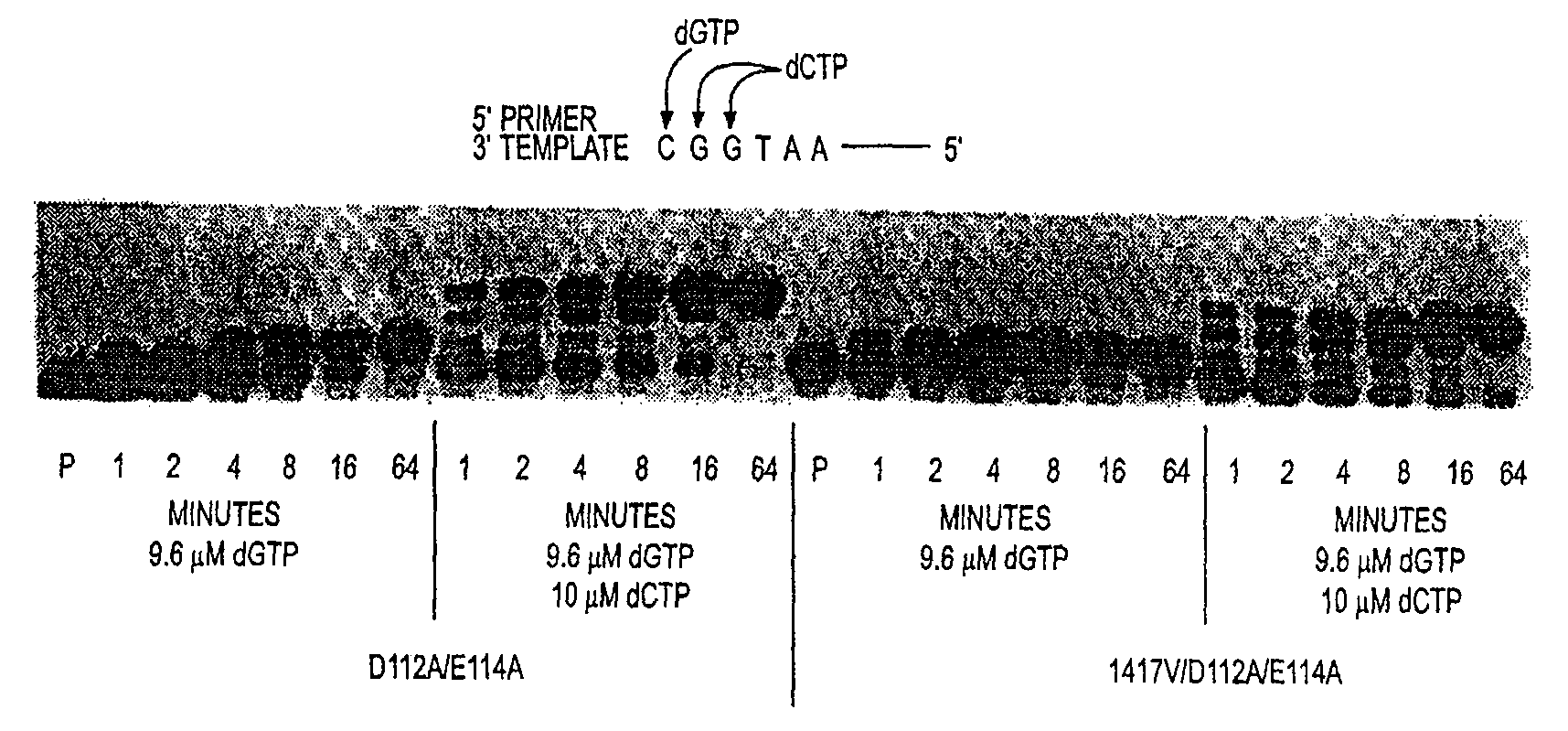
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Methods and apparatus for measuring analytes using large scale fet arrays
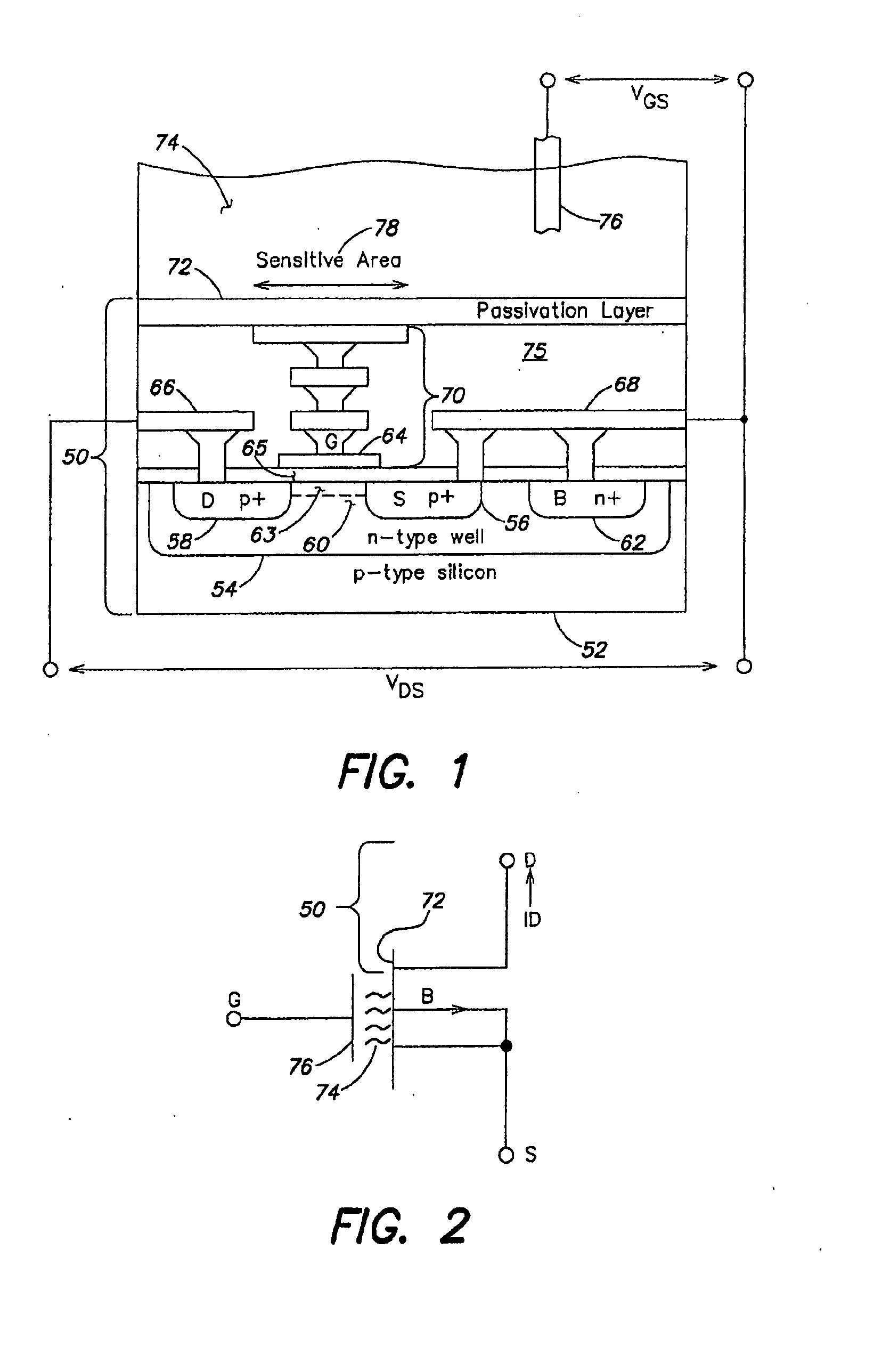
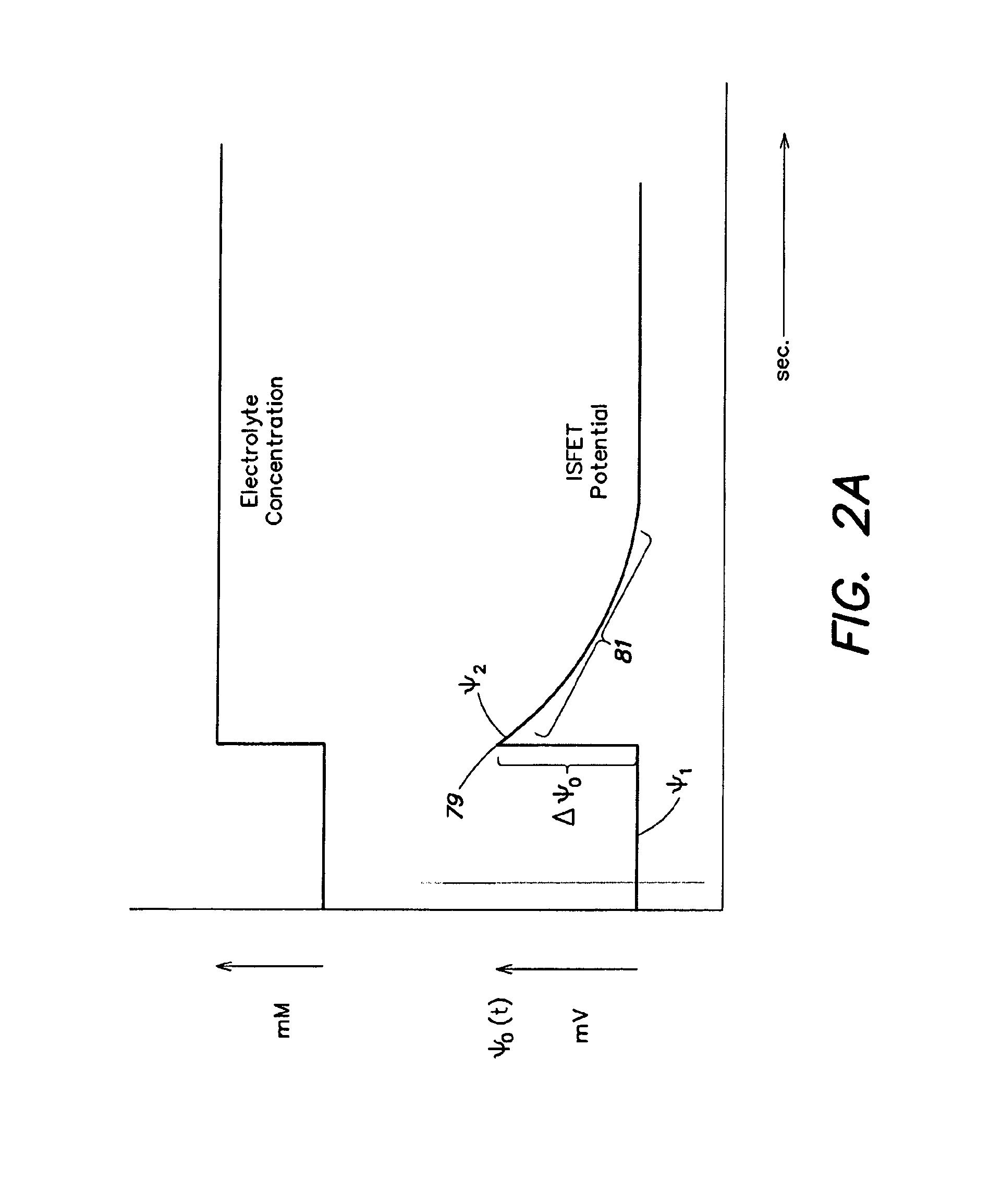
ActiveUS20110217697A1Constant voltageFacilitate rapid acquisition of dataWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementCMOSOrganismal Process
Methods and apparatus relating to very large scale FET arrays for analyte measurements. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes. In one example, chemFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in the concentration of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi), hydrogen ions, and nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method of determining the nucleotide sequence of oligonucleotides and DNA molecules
InactiveUS7875440B2Eliminate needHigh puritySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersFluorescence
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
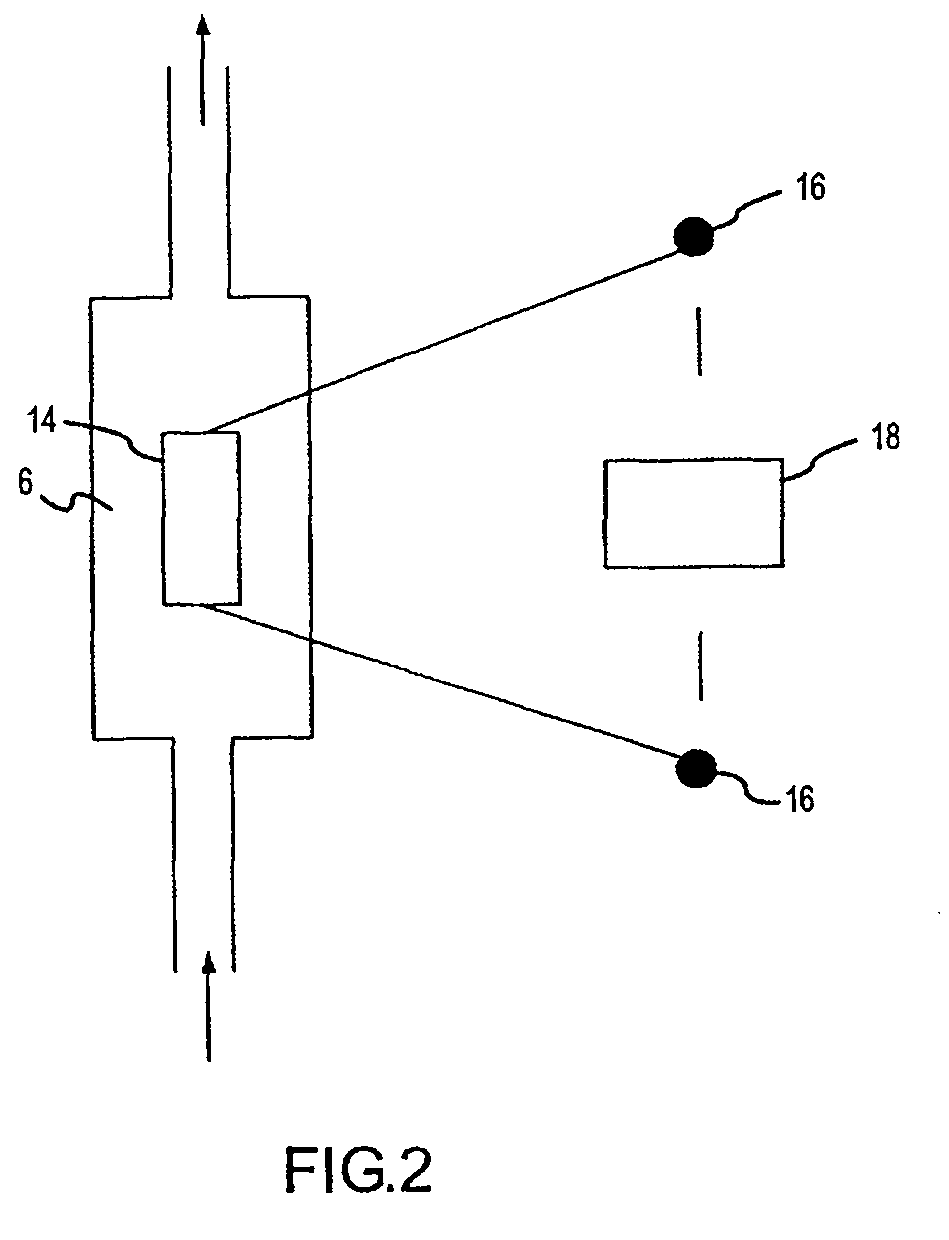
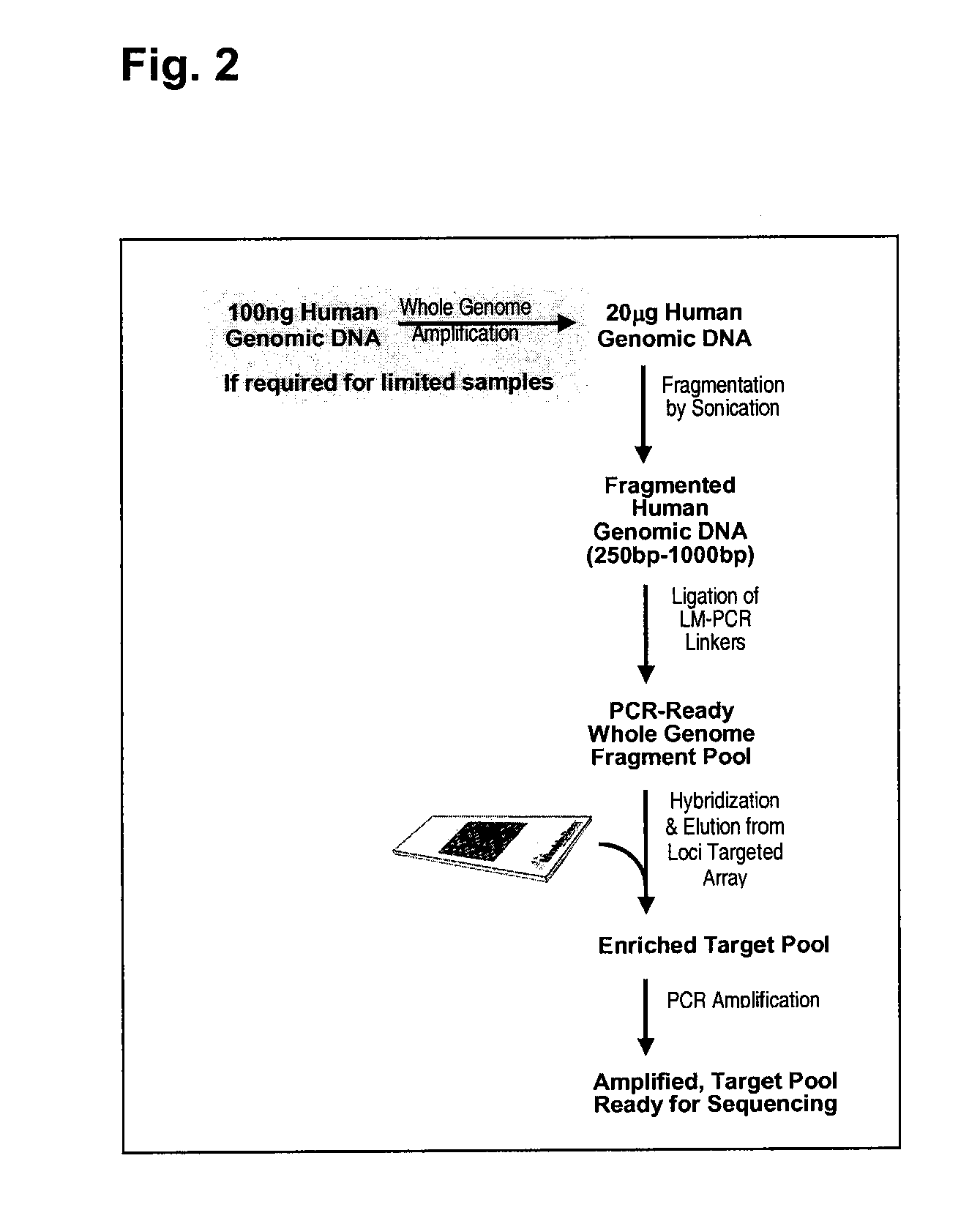
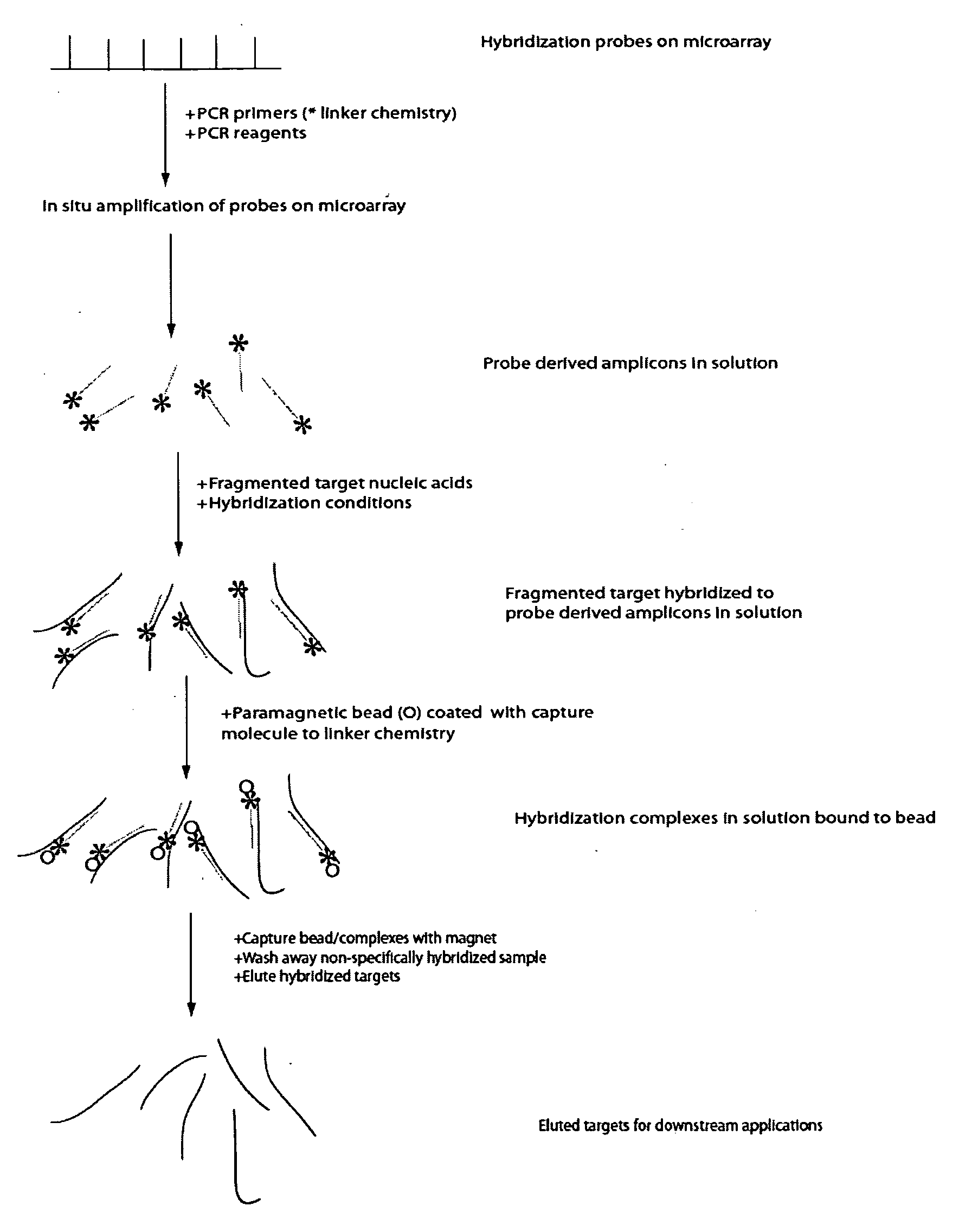
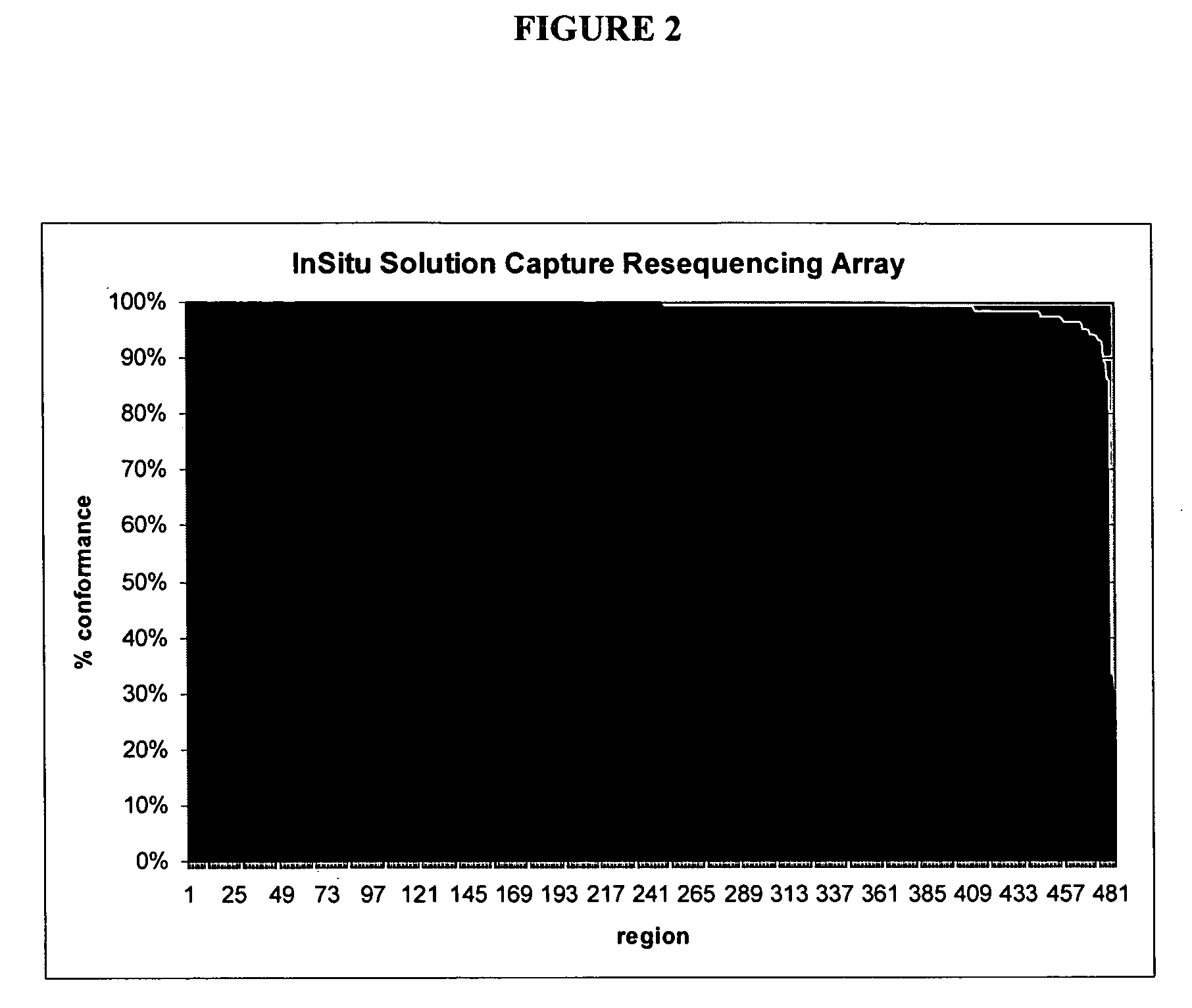
Methods and systems for solution based sequence enrichment
ActiveUS20120046175A1Significant complexityEasy to analyzeSugar derivativesLibrary tagsBase sequenceBioinformatics
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
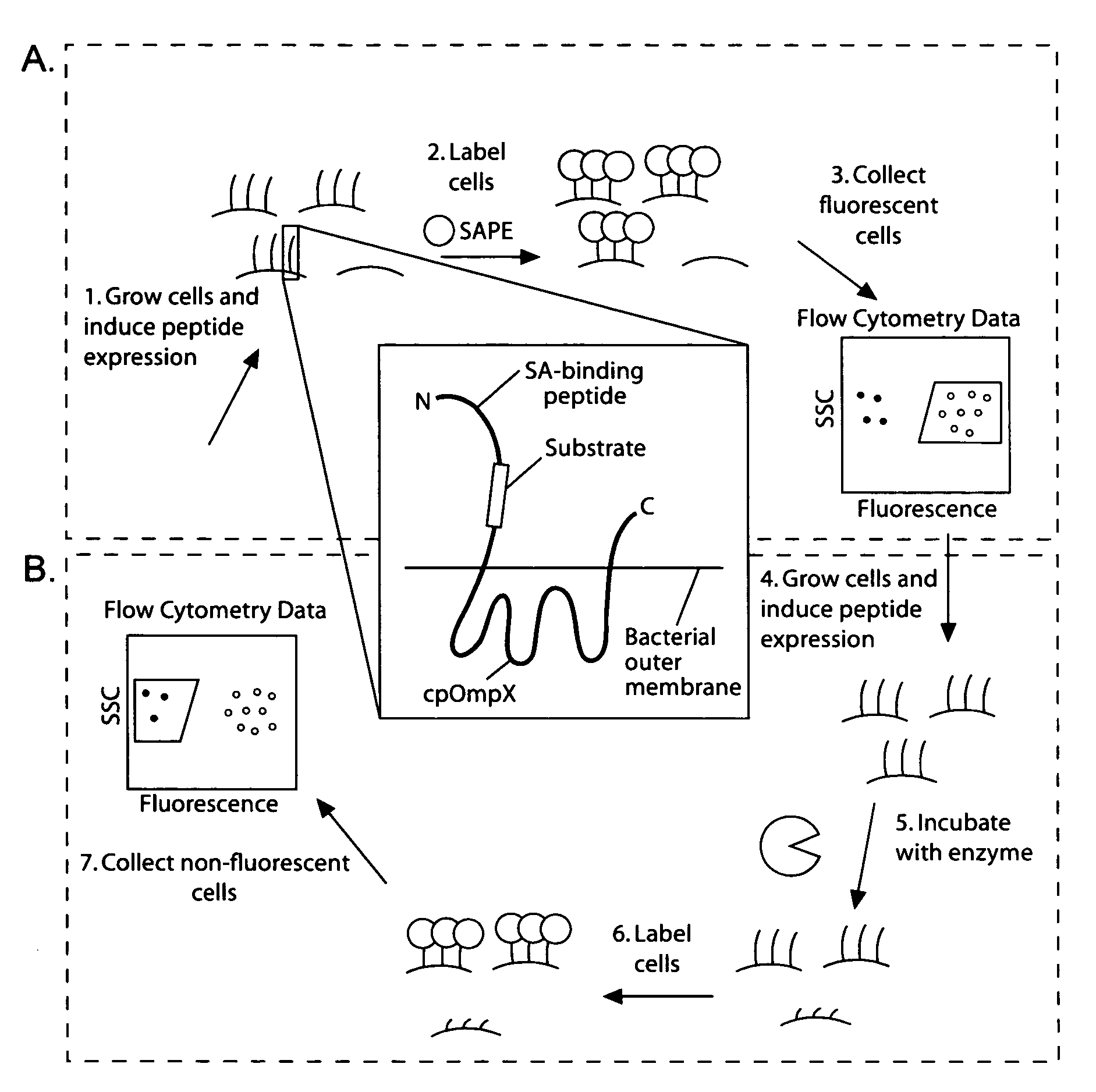
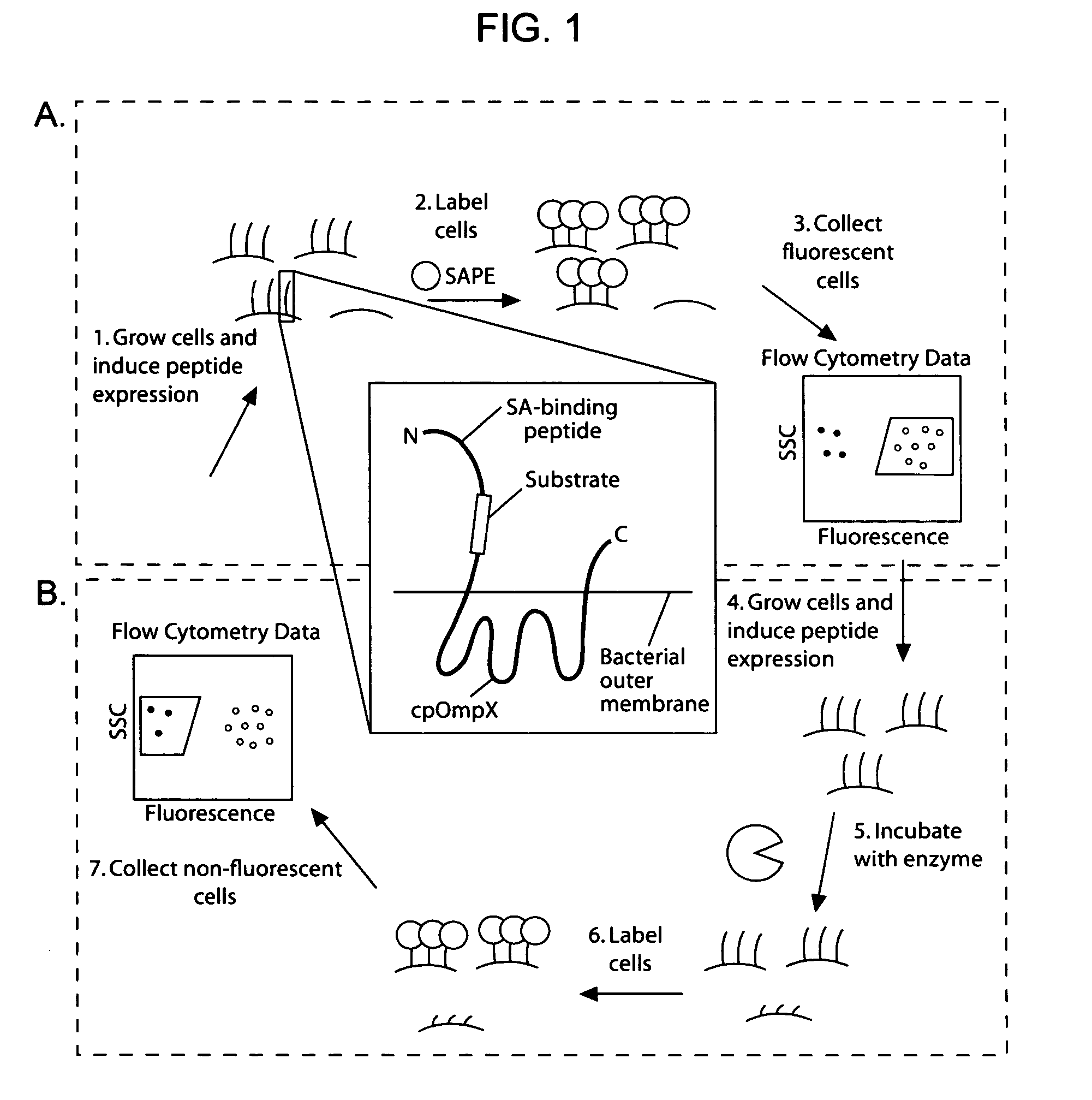
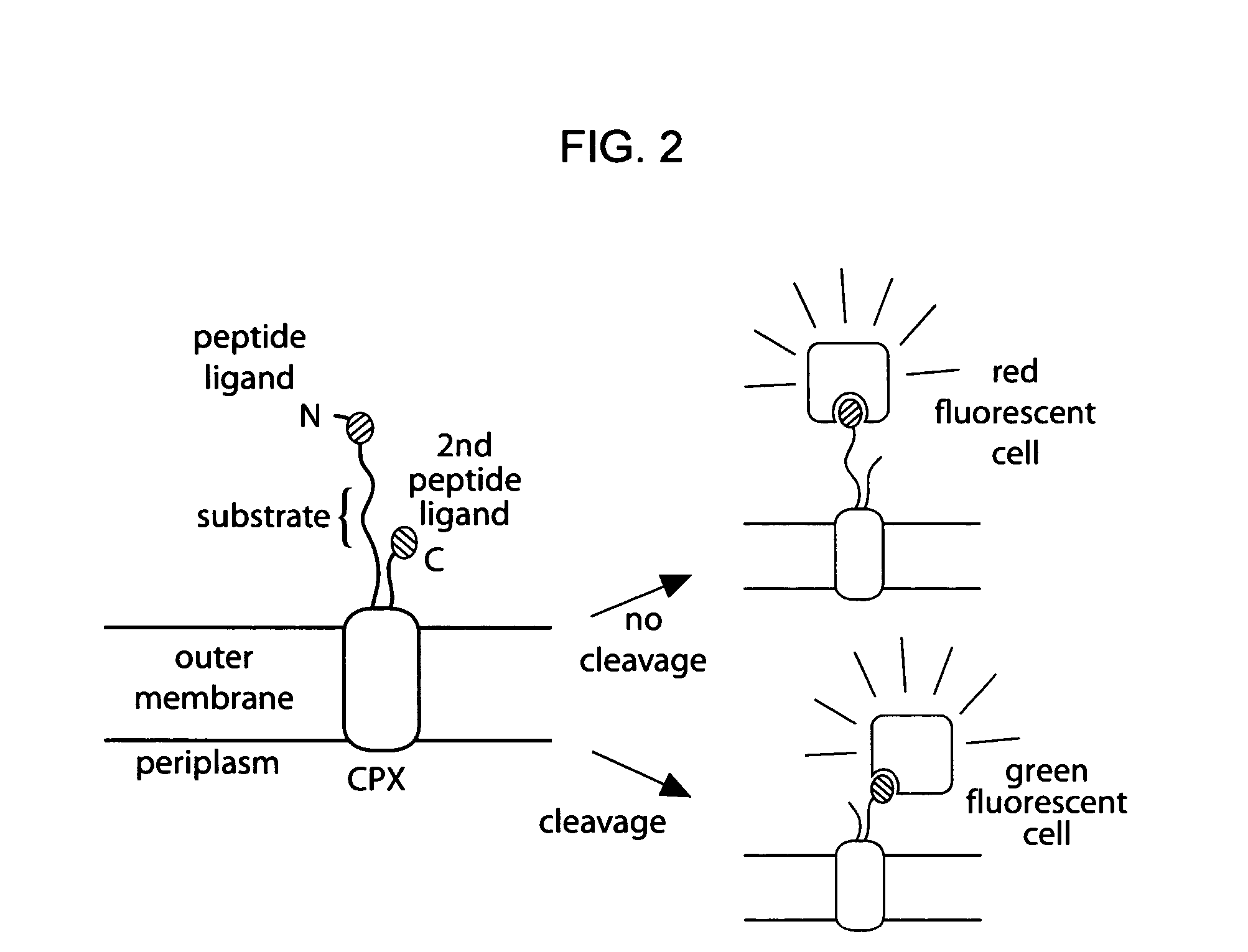
Cellular libraries of peptide sequences (CLiPS) and methods of using the same
The present invention provides compositions including peptide display scaffolds that present at least one candidate peptide and at least one detectable moiety in at least one of the N-terminal and C-terminal candidate peptide presenting domains that when expressed in a cell are accessible at a surface of the cell outermembrane. In addition, the present invention also provides kits and methods for screening a library of cells presenting the candidate peptides in peptide display scaffolds to identify a ligand for an enzyme.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
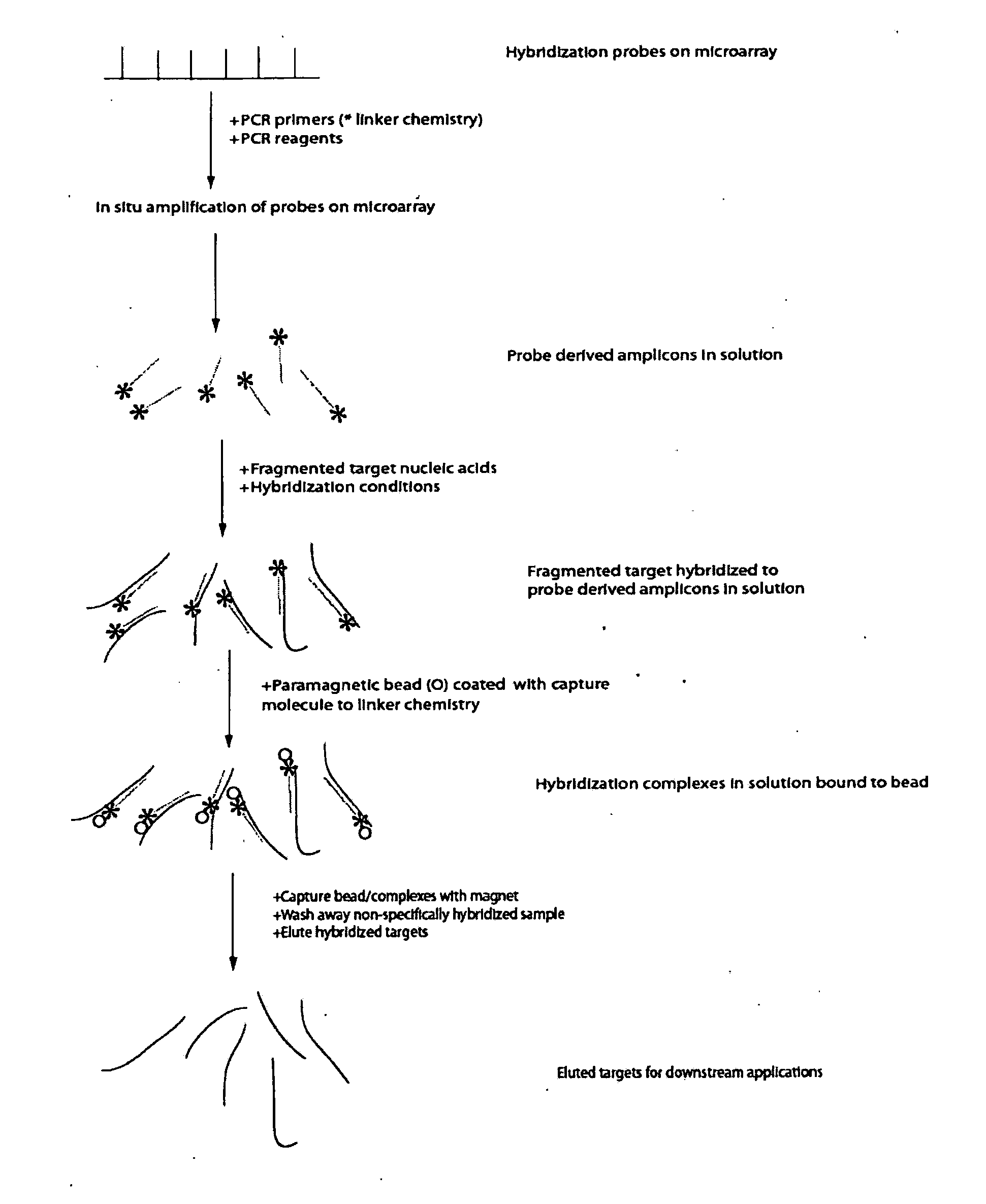
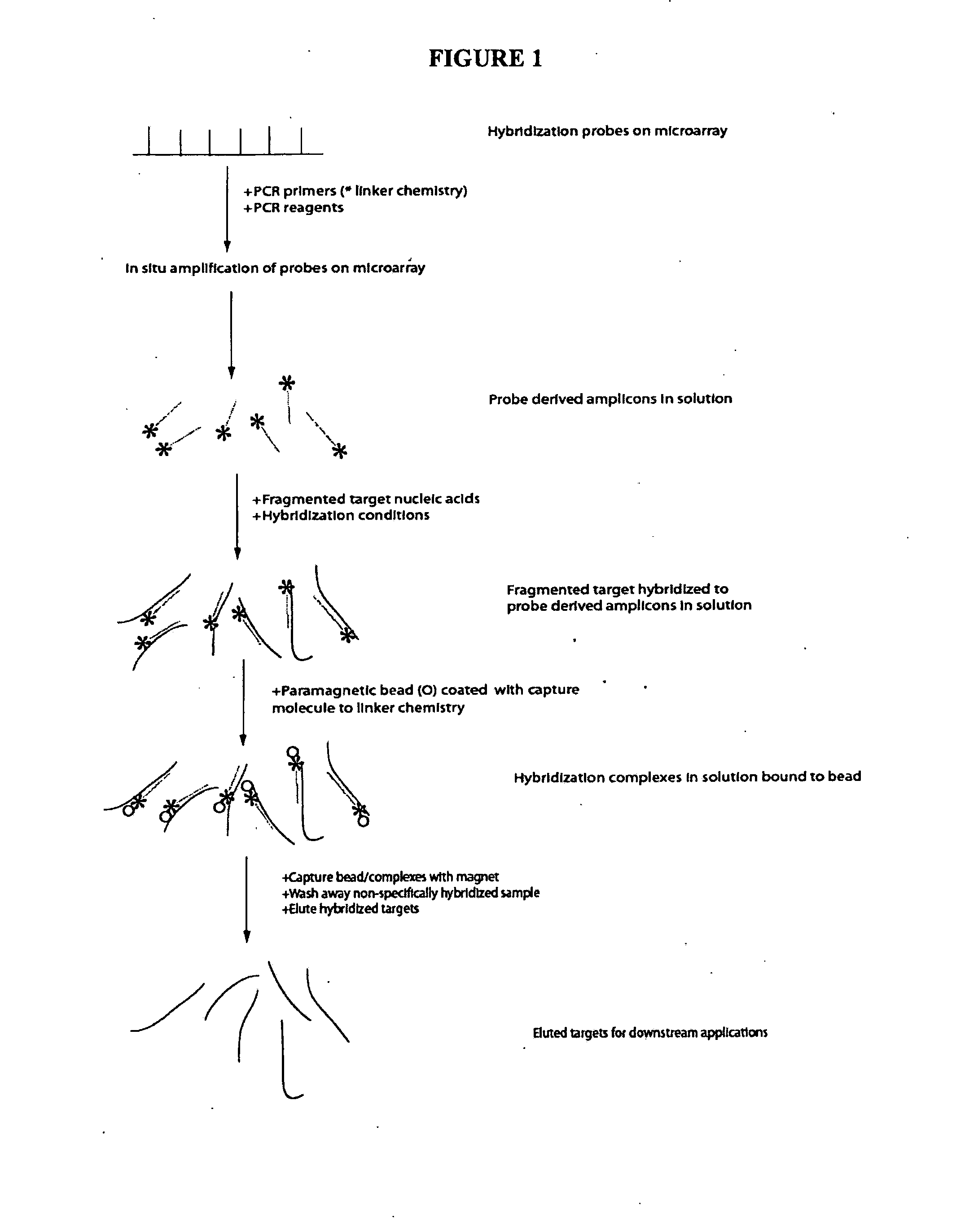
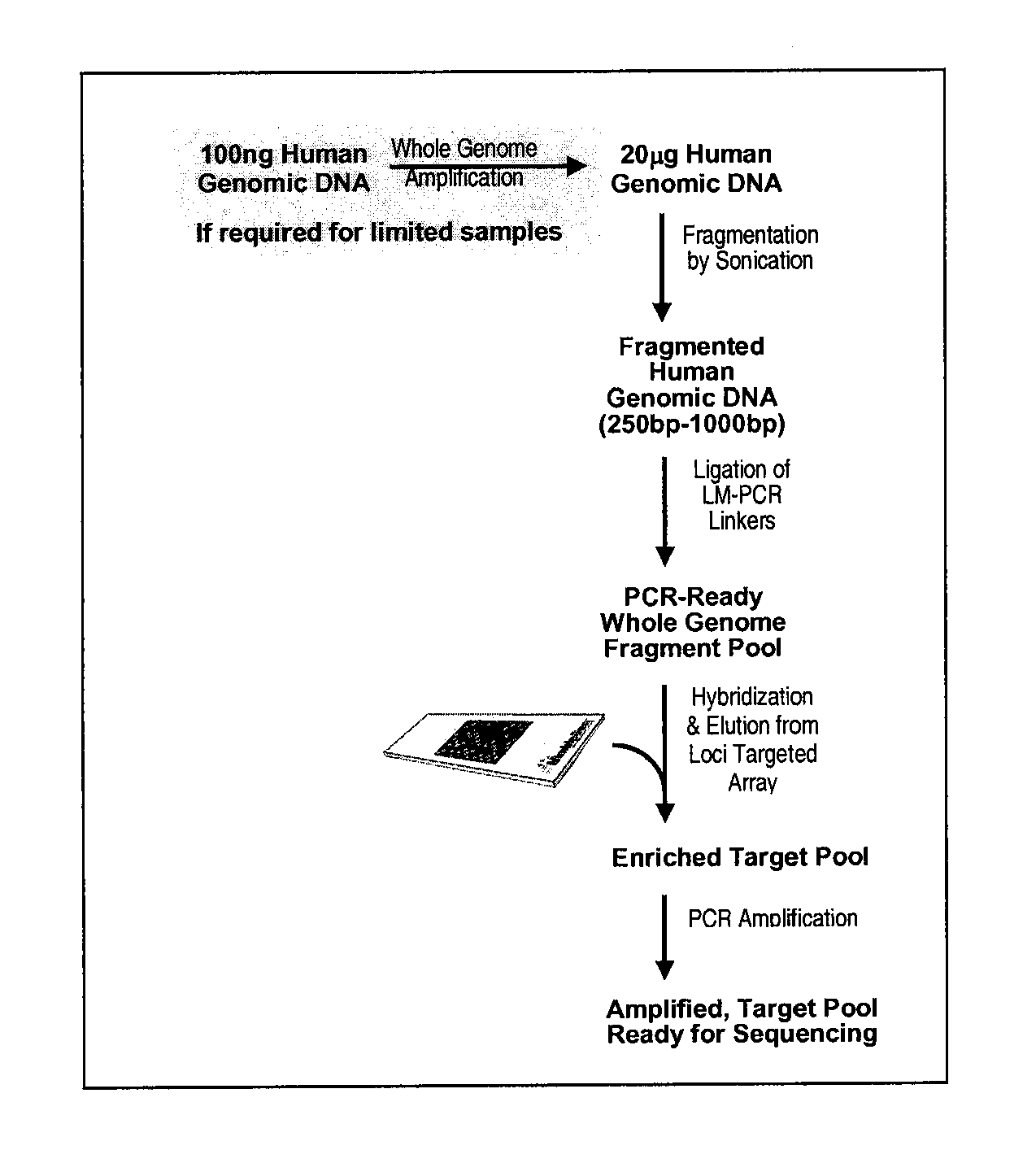
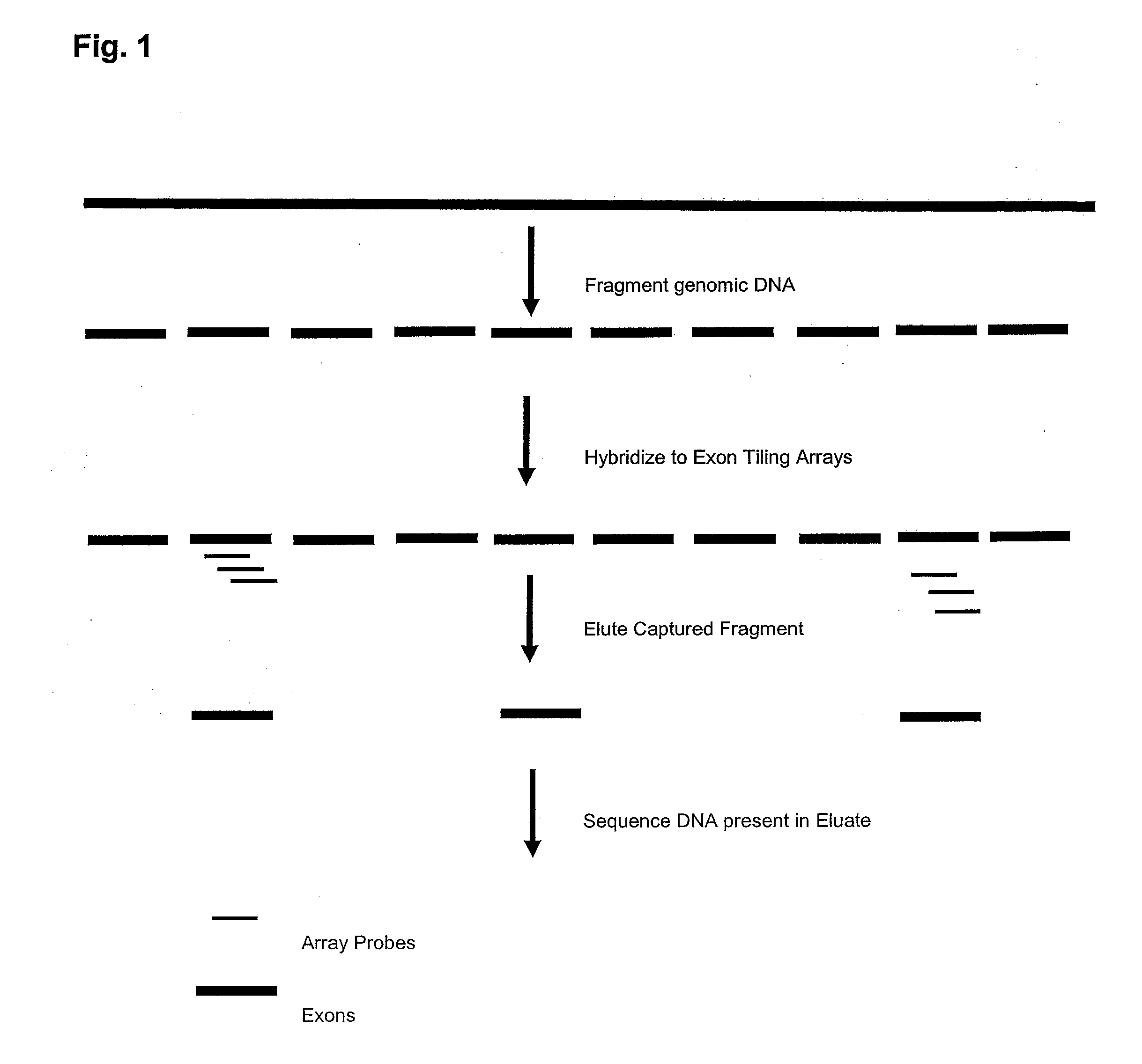
Enrichment and sequence analysis of genomic regions
InactiveUS20080194414A1Significant complexityFacilitate subsequent processingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSequence analysisAs Directed
The present invention provides novel methods for reducing the complexity of preferably a genomic sample for further analysis such as direct DNA sequencing, resequencing or SNP calling. The methods use pre-selected immobilized oligonucleotide probes to capture target nucleic acid molecules from a sample containing denatured, fragmented (genomic) nucleic acids for reducing the genetic complexity of the original population of nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:ALBERT THOMAS J +8
Highly multiplex PCR methods and compositions
InactiveUS20140094373A1High copy numberMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMultiplexDimer
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Single cell bar-coding for antibody discovery
Owner:ABVITRO LLC
Method of DNA shuffling with polynucleotides produced by blocking or interrupting a synthesis or amplification process
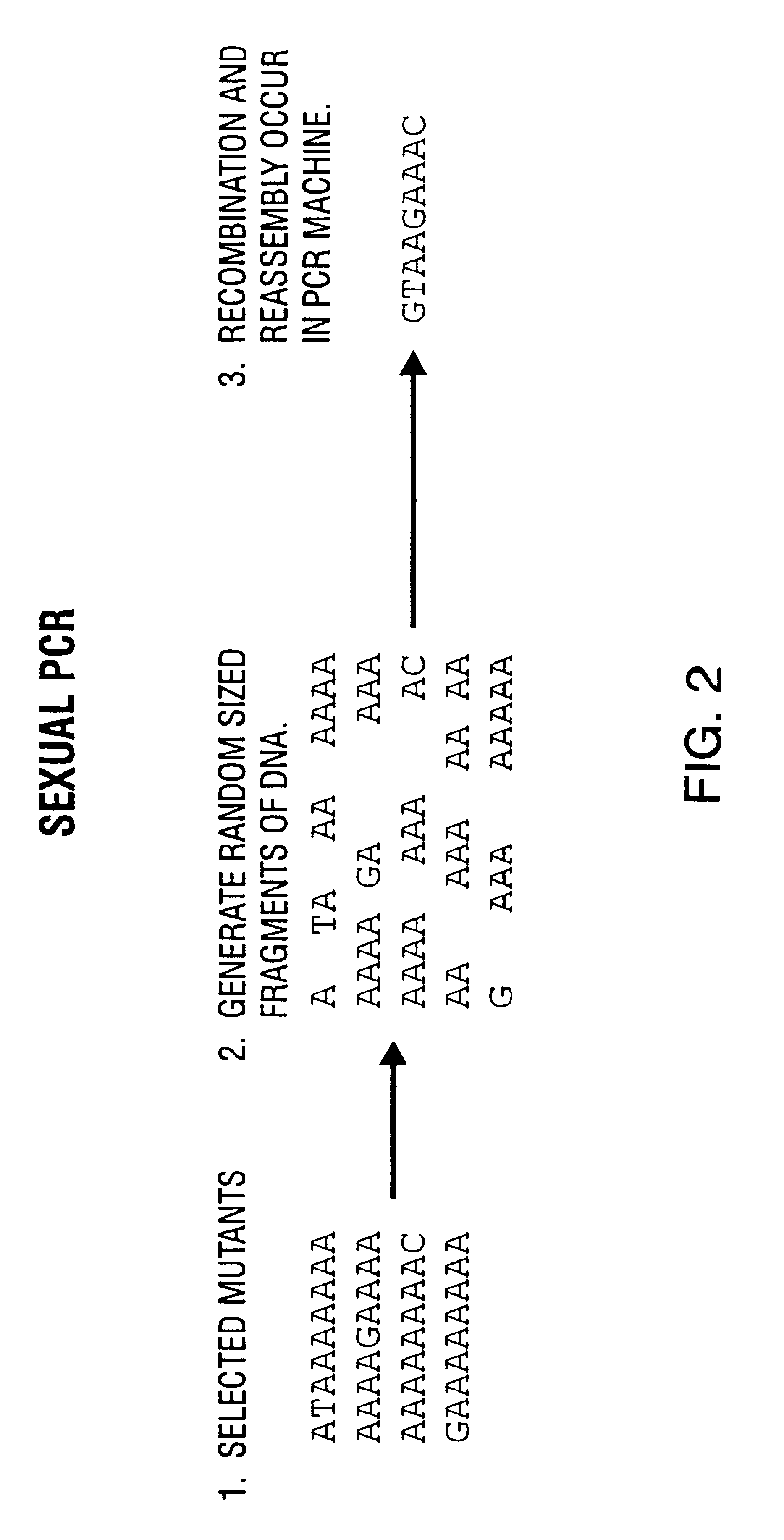
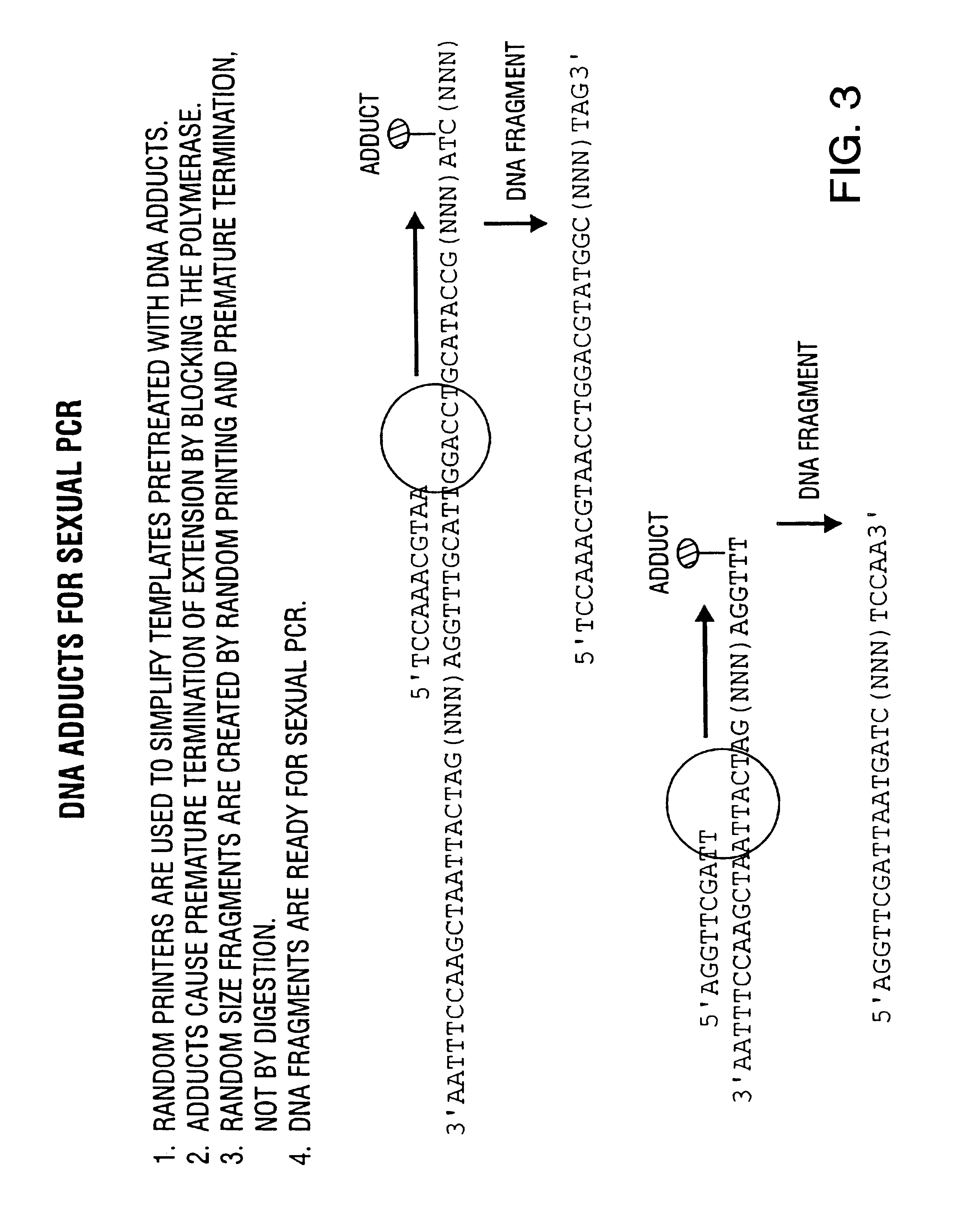
Disclosed is a process of performing Sexual PCR which includes generating random polynucleotides by interrupting or blocking synthesis or amplification process to slow or halt synthesis or amplification of at least one polynucleotides, optionally amplifying the polynucleotides, and reannealing the polynucleotides to produce random mutant polynucleotides. Also provided are vector and expression vehicles including such mutant polynucleotides, polypeptides expressed by the mutant polynucleotides and a method for producing random polypeptides.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
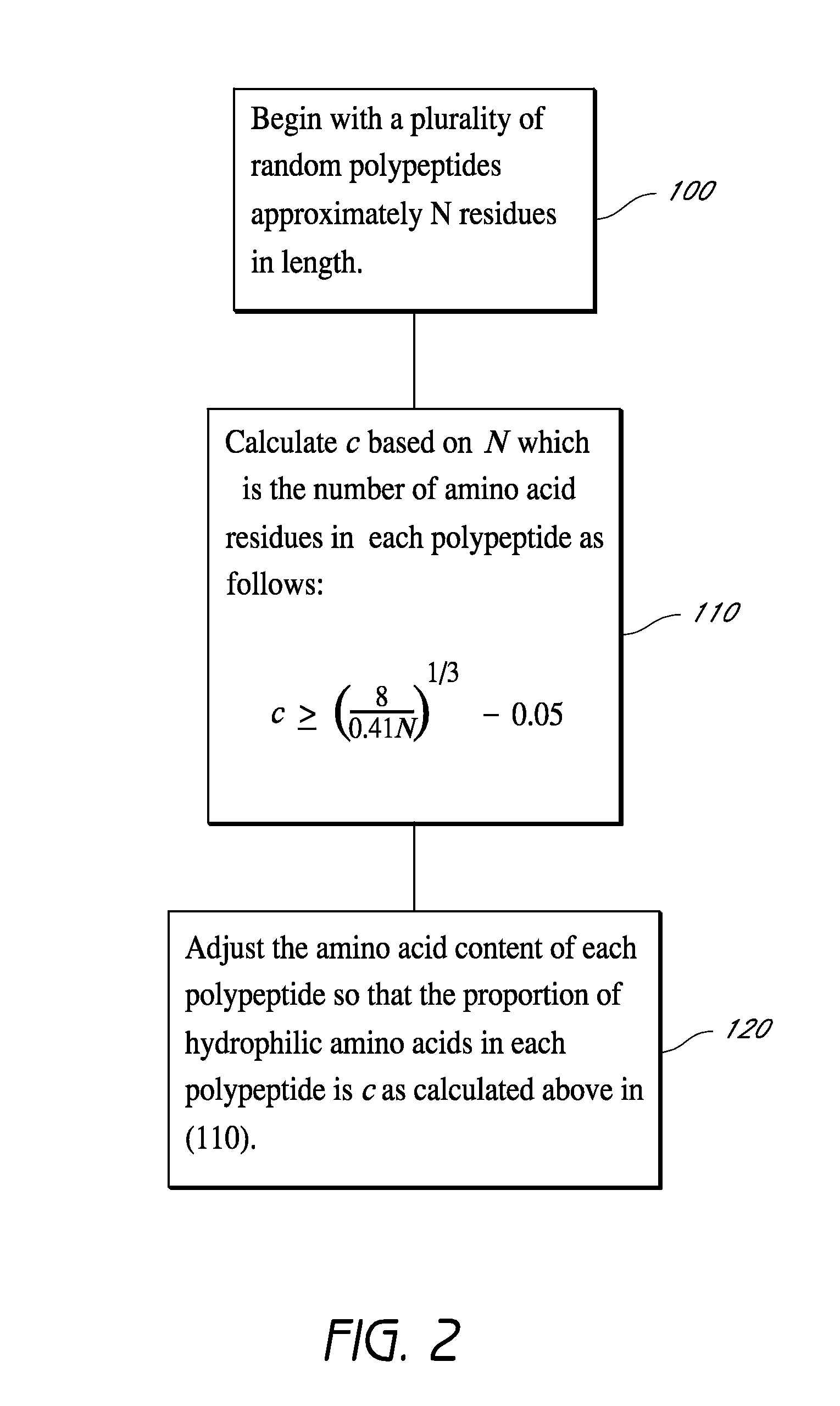
GENERATION OF LIBRARY OF SOLUBLE RANDOM POLYPEPTIDES LINKED TO mRNA
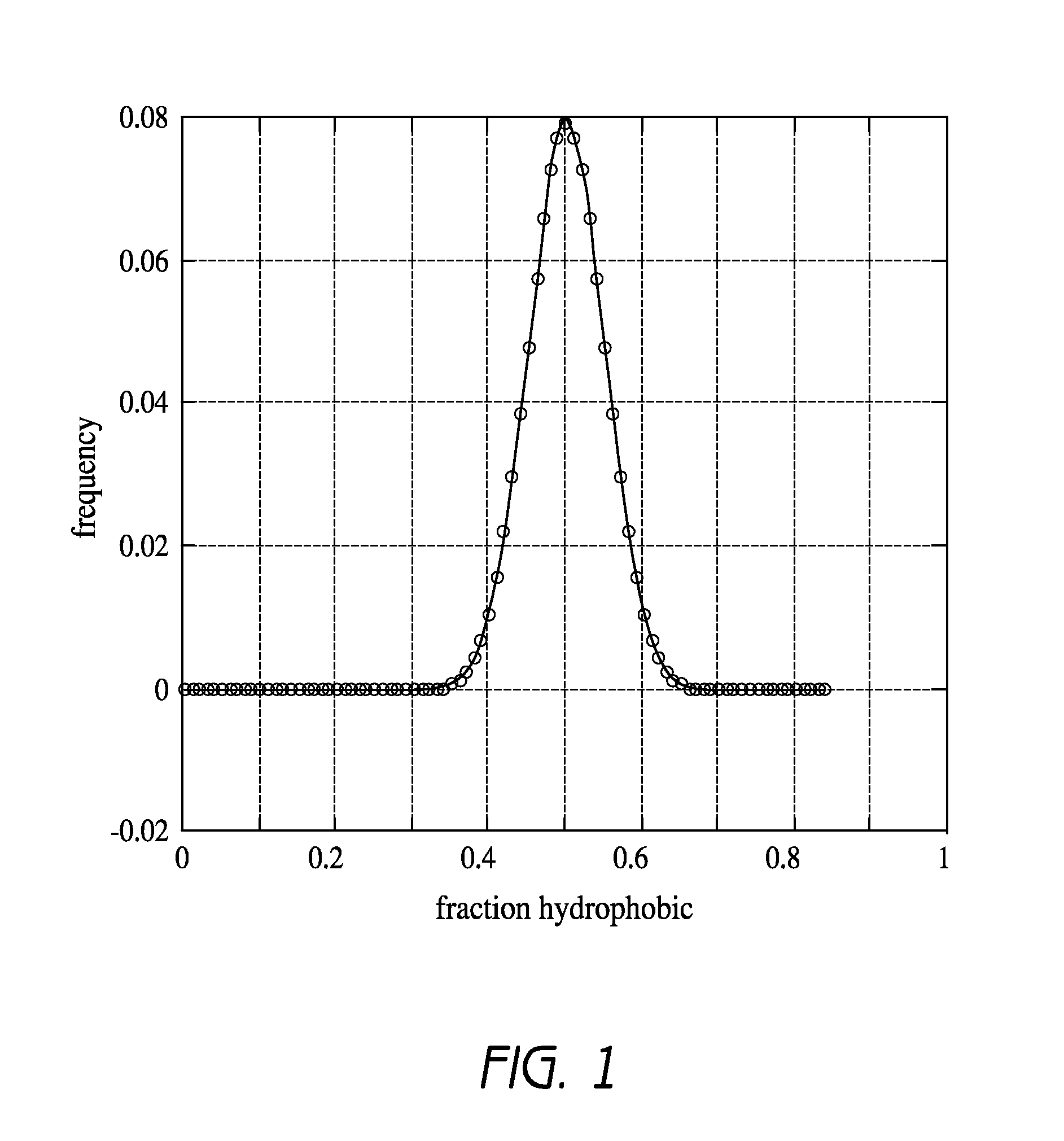
Methods and compositions are provided for producing libraries of soluble random polypeptides. In the methods, the fraction of hydrophilic residues in the polypeptide is controlled so as to maintain the solubility of the polypeptide constructs.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
Compositions and methods for the identification and selection of nucleic acids and polypeptides
InactiveUS20050089913A1Efficient rapid identification selectionQuickly and accurately identify and selectPeptide librariesGenetic material ingredientsComputational biologyPsoralen
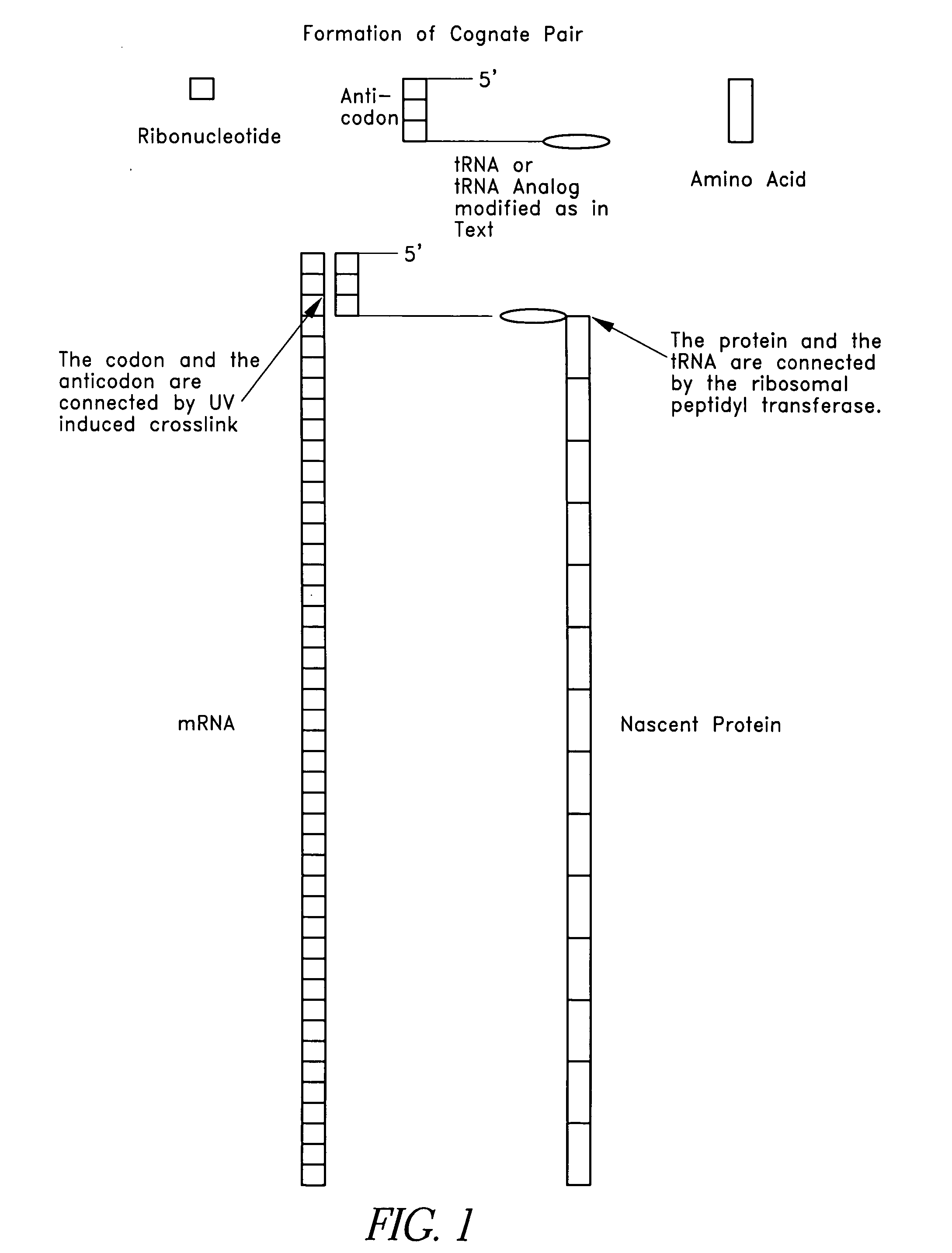
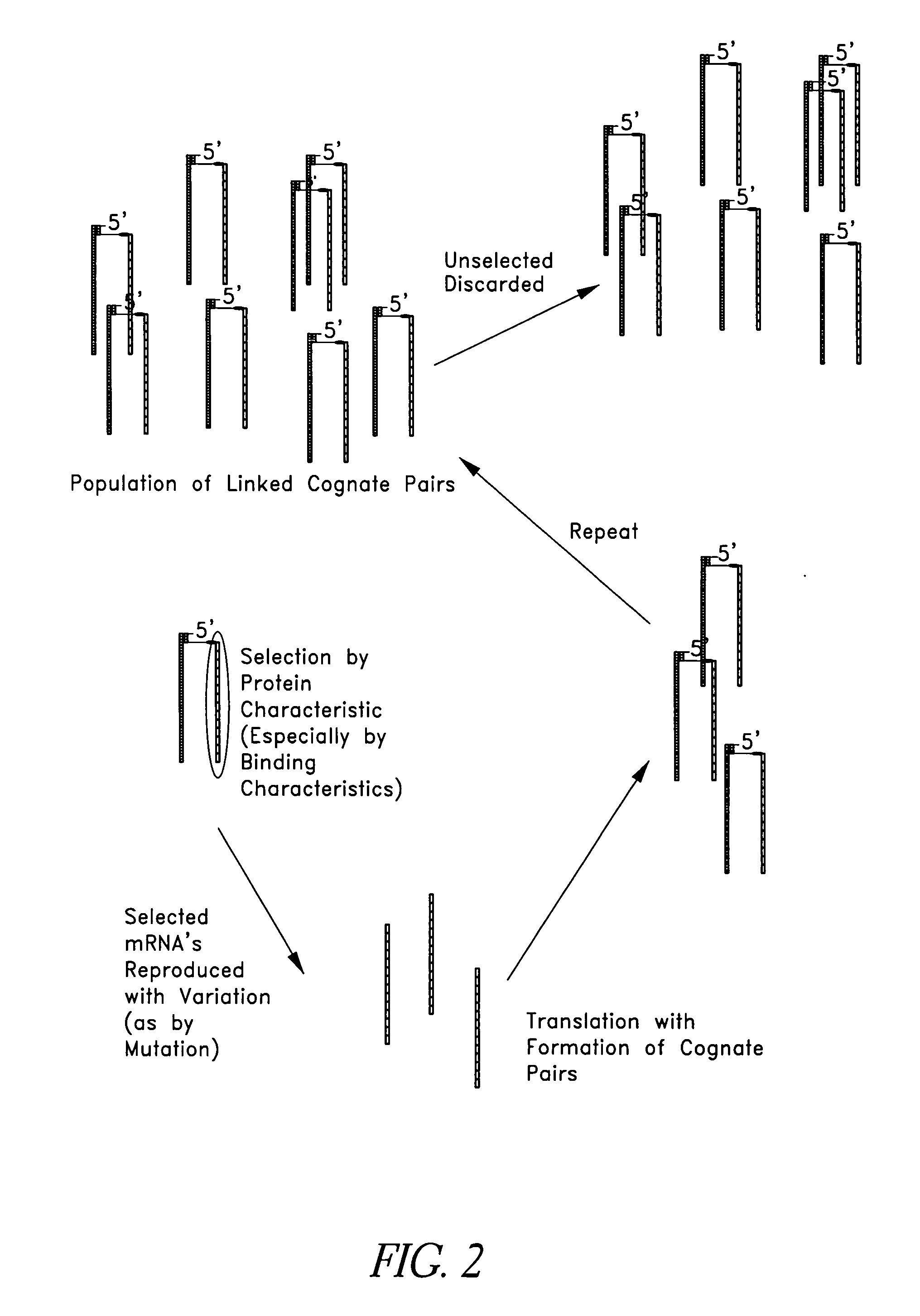
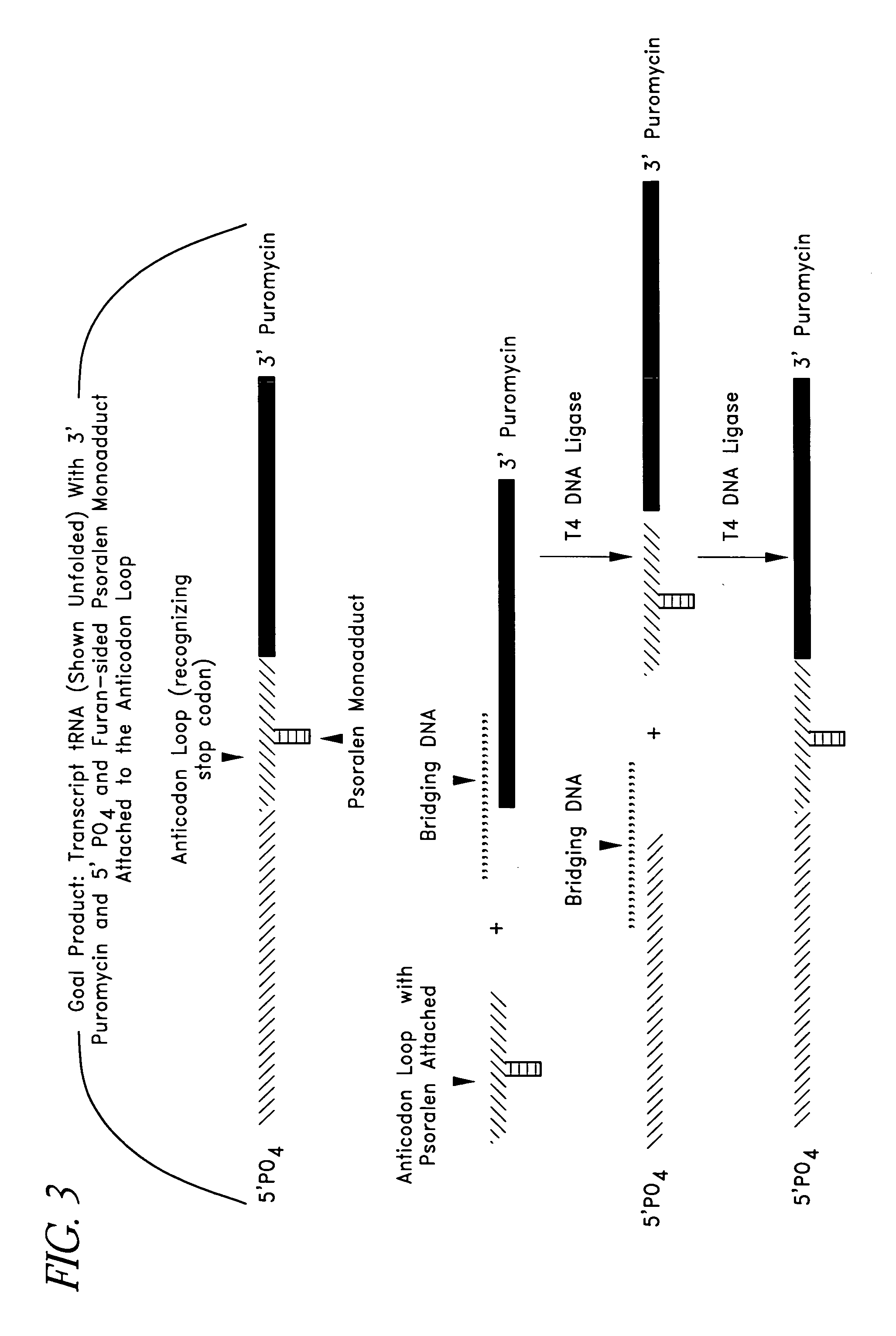
This invention relates generally to systems and methods for identifying and selecting, desired proteins or nucleic acid molecules by linking mRNA, with known or unknown sequences, to its translated protein to form a cognate pair. The cognate pair is selected based upon desired properties of the protein or the nucleic acid. This method also includes the evolution of a desired protein or nucleic acid molecule by amplifying the nucleic acid portion of the selected cognate pair, introducing variation into the nucleic acid, translating the nucleic acid, attaching the nucleic acid to its protein to form a second cognate pair, and re-selecting this cognate pair based upon desired properties. Modified mRNAs operable to crosslink to tRNAs are also provided. Methods of producing a psoralen monoadduct or a crosslink are also provided.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
Evolving new molecular function
InactiveUS7491494B2High selectivityEnhance covalent bond formationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBio moleculesChemical reaction
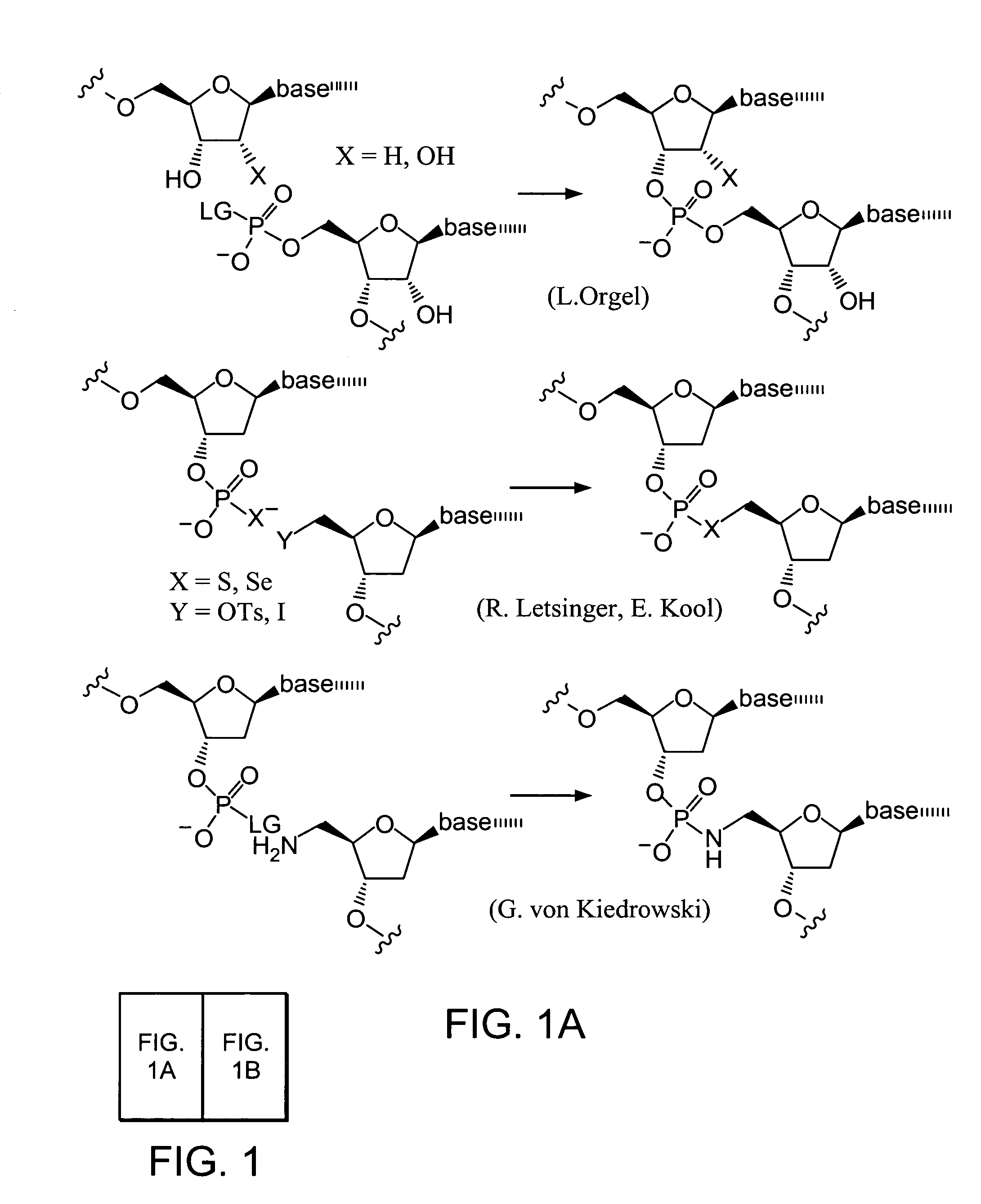
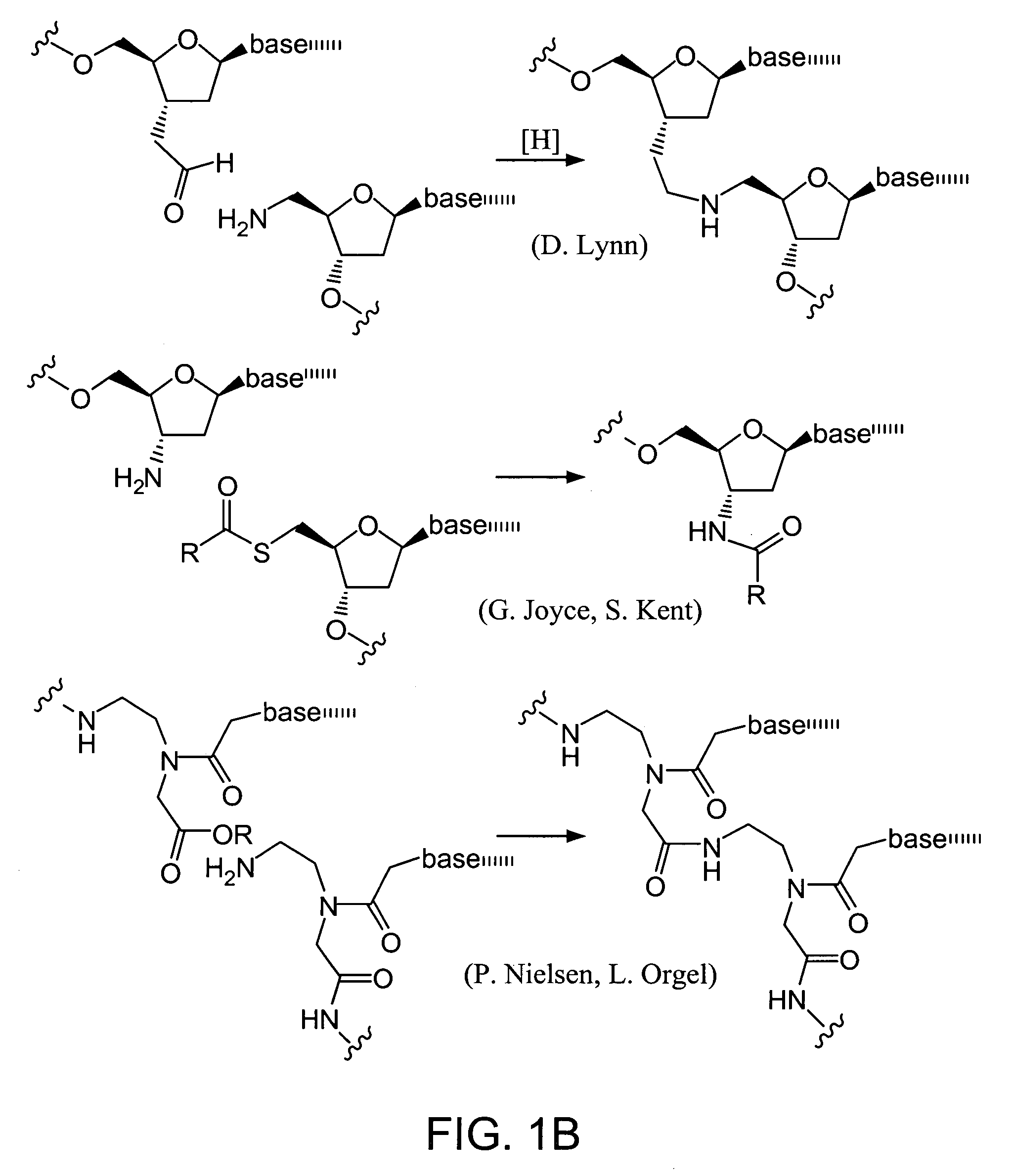
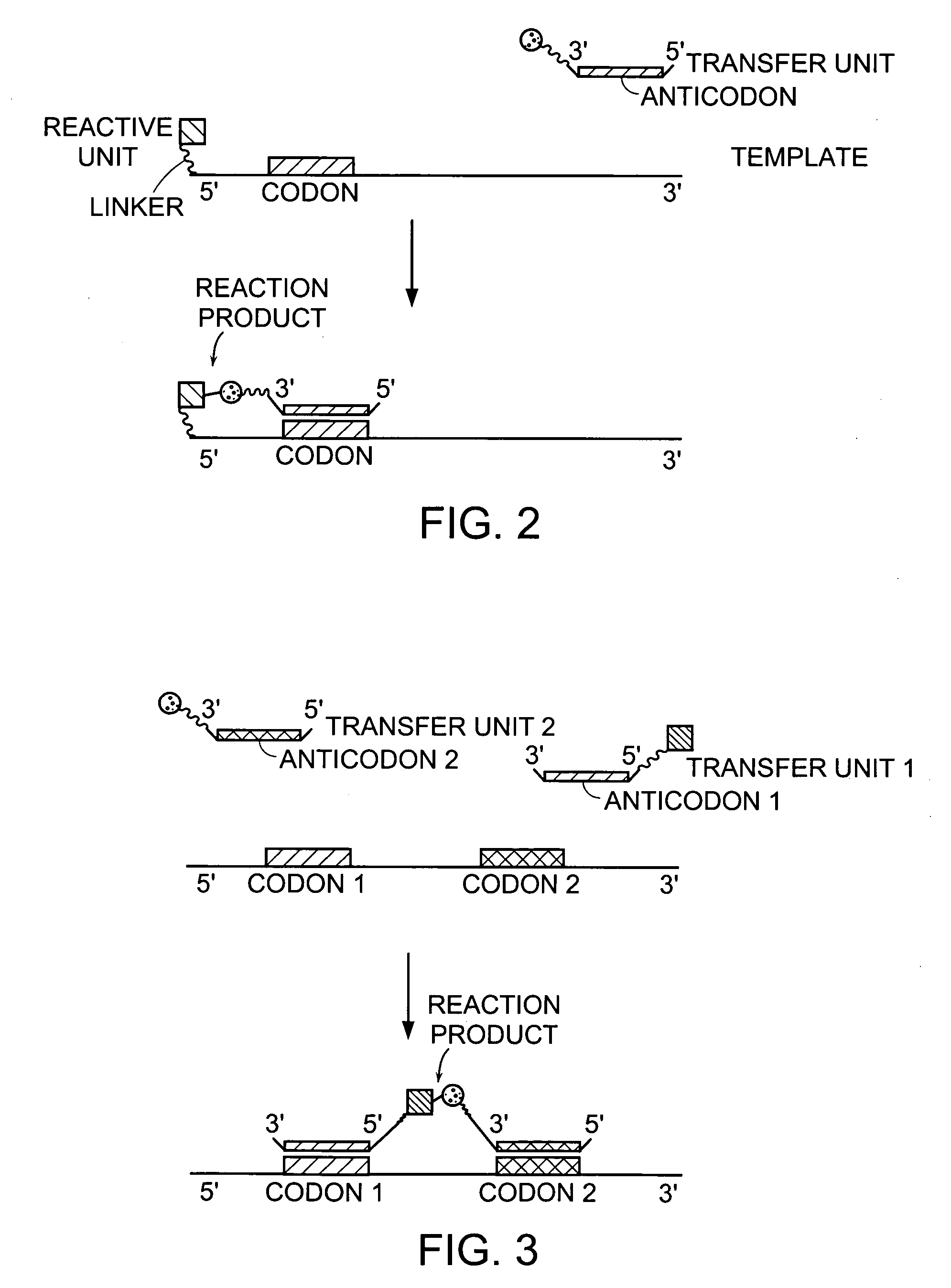
Nature evolves biological molecules such as proteins through iterated rounds of diversification, selection, and amplification. The power of Nature and the flexibility of organic synthesis are combined in nucleic acid-templated synthesis. The present invention provides a variety of template architectures for performing nucleic acid-templated synthesis, methods for increasing the selectivity of nucleic acid-templated reactions, methods for performing stereoselective nucleic acid-templated reactions, methods of selecting for reaction products resulting from nucleic acid-templated synthesis, and methods of identifying new chemical reactions based on nucleic acid-templated synthesis.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Screening methods
Owner:BIOCONSORTIA
Microbially expressed xylanases and their use as feed additives and other uses
The present invention relates to codon-optimized xylanase coding sequences and the expression of xylanases in microbes and yeast. The invention further relates to using multiple copies of the xylanase expression construct for high levels of protein expression. The invention also relates to the use of xylanases as feed or food additives. The invention also relates to methods of expression of enzymes to increase thermotolerance by expressing them in organisms that glycosylate proteins compared to expression that the same enzyme without the glycosylation. Further, the invention relates to methods of preparing feed, enzyme feed additives, and methods of reducing the feed conversion ration or increasing weight gain of animals.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Methods and systems for solution based sequence enrichment
InactiveUS20090105081A1Significant complexityEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementDirected macromolecular evolutionBase sequenceBioinformatics
Owner:ROCHE NIMBLEGEN
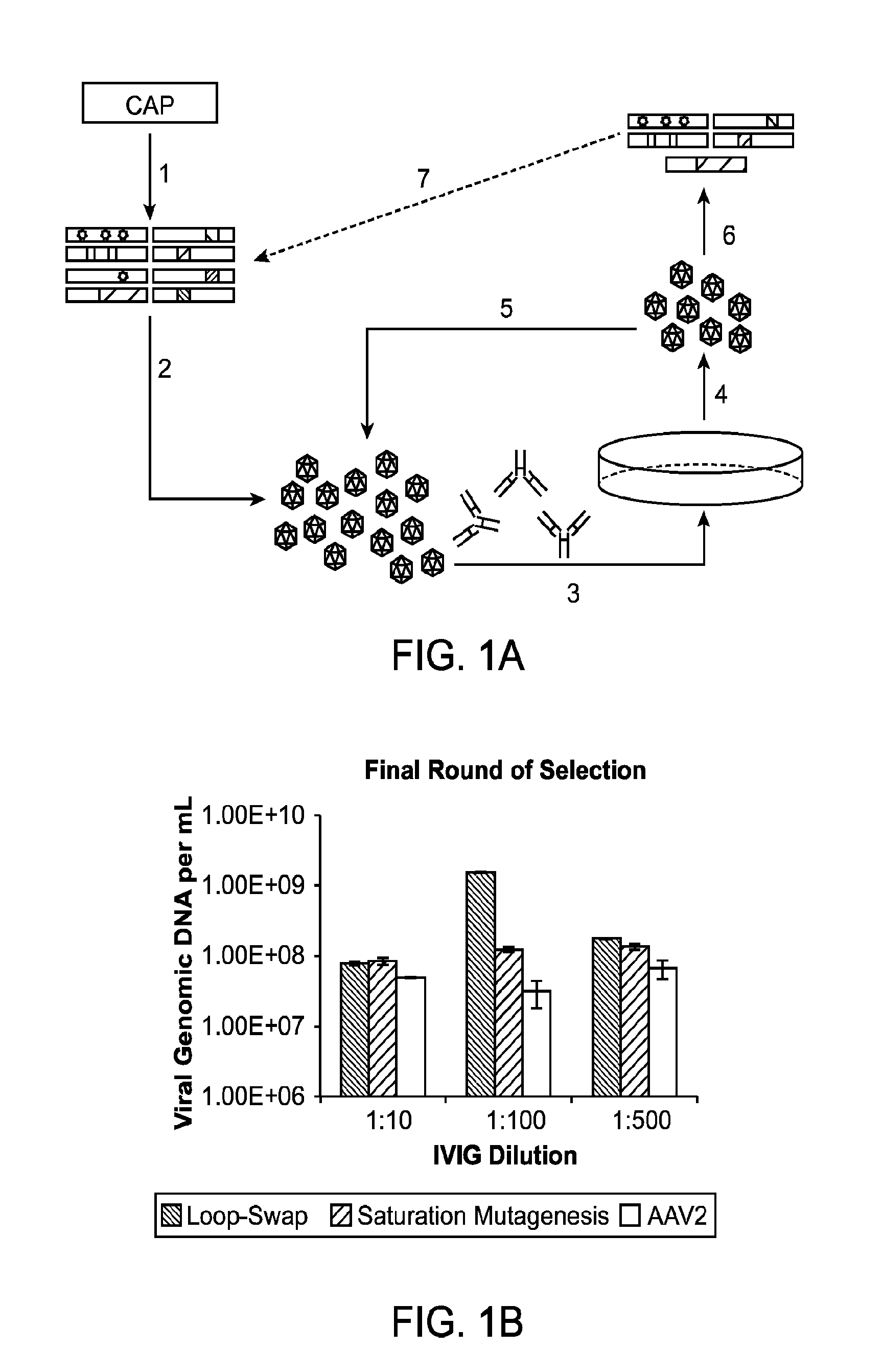
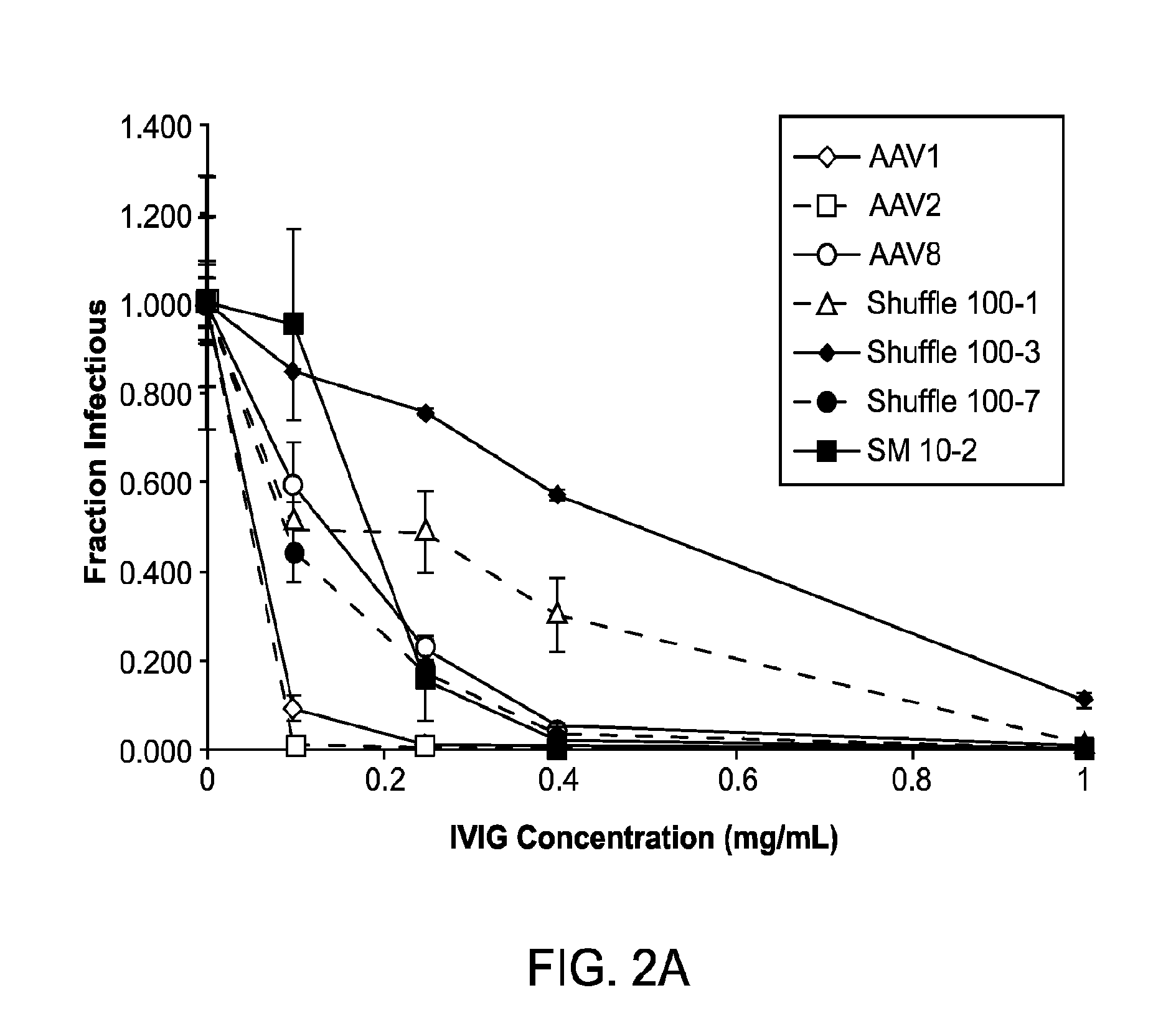
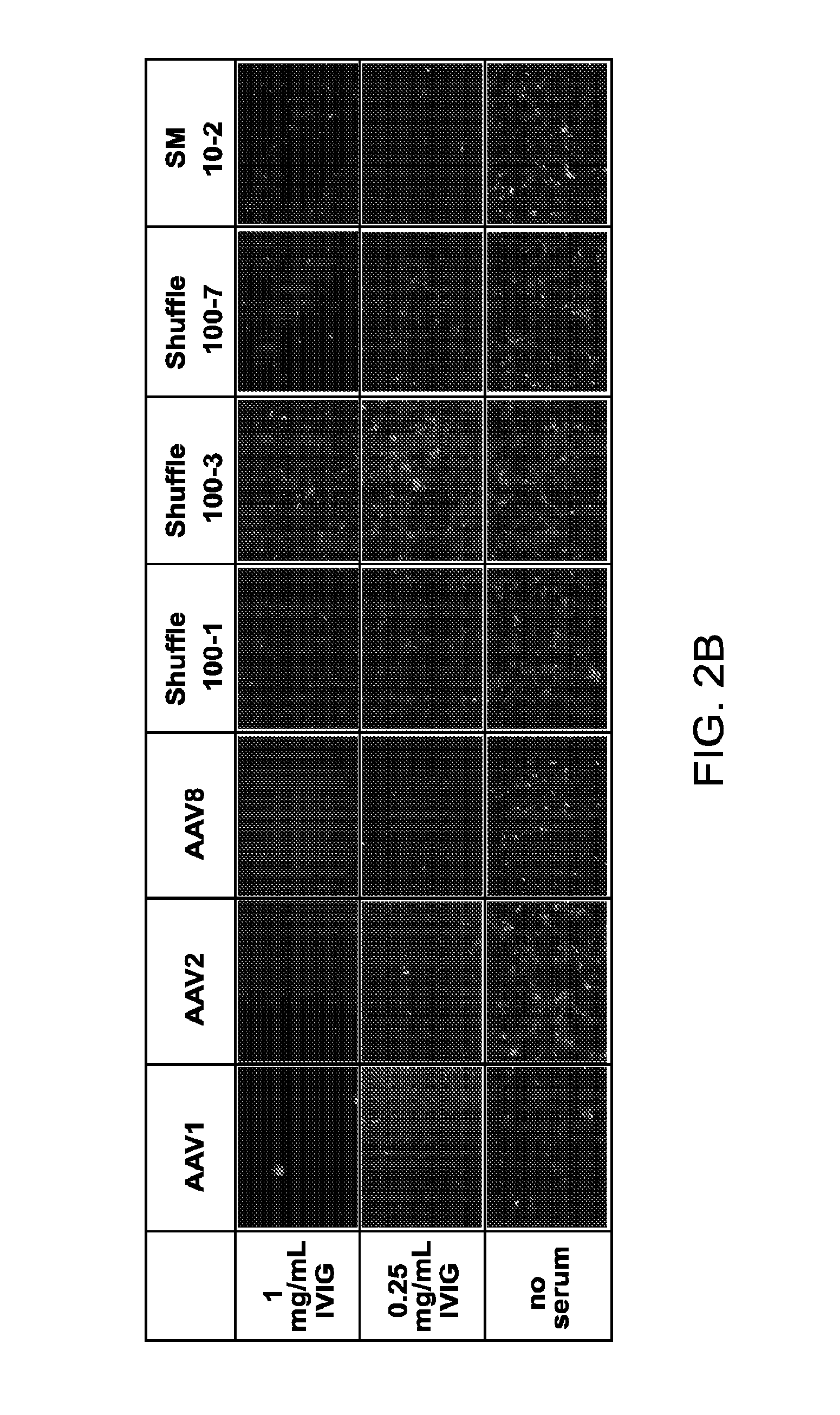
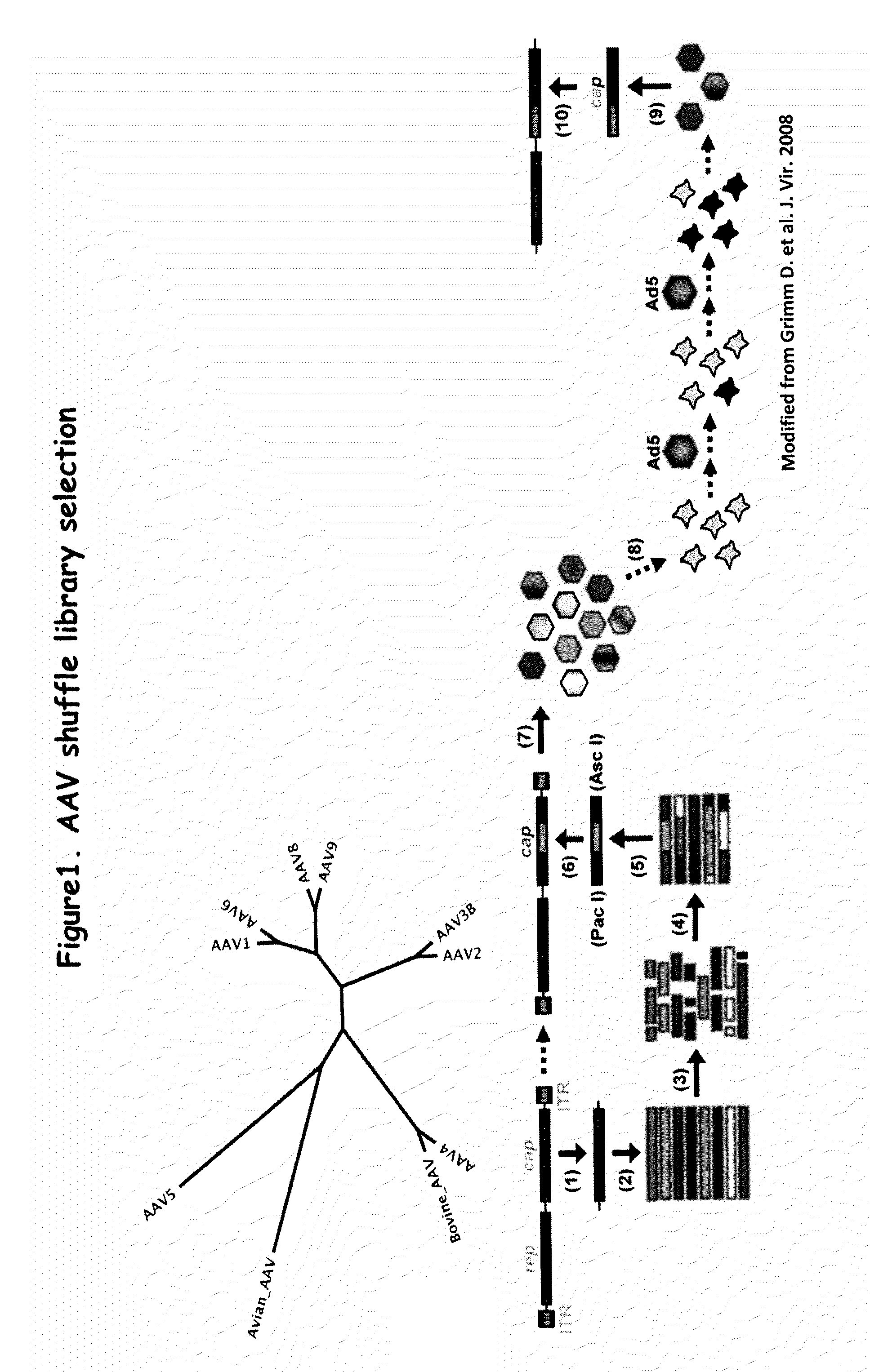
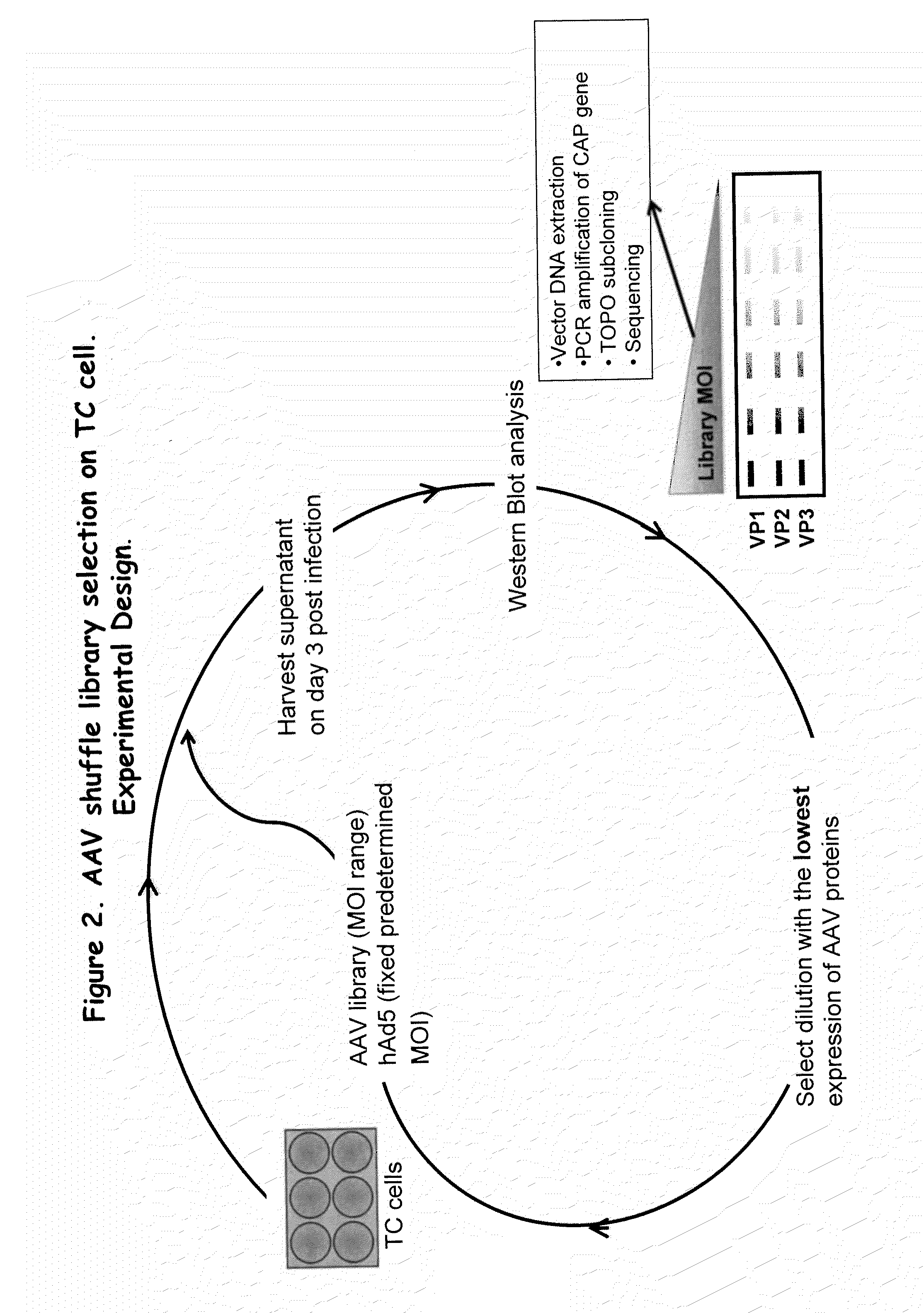
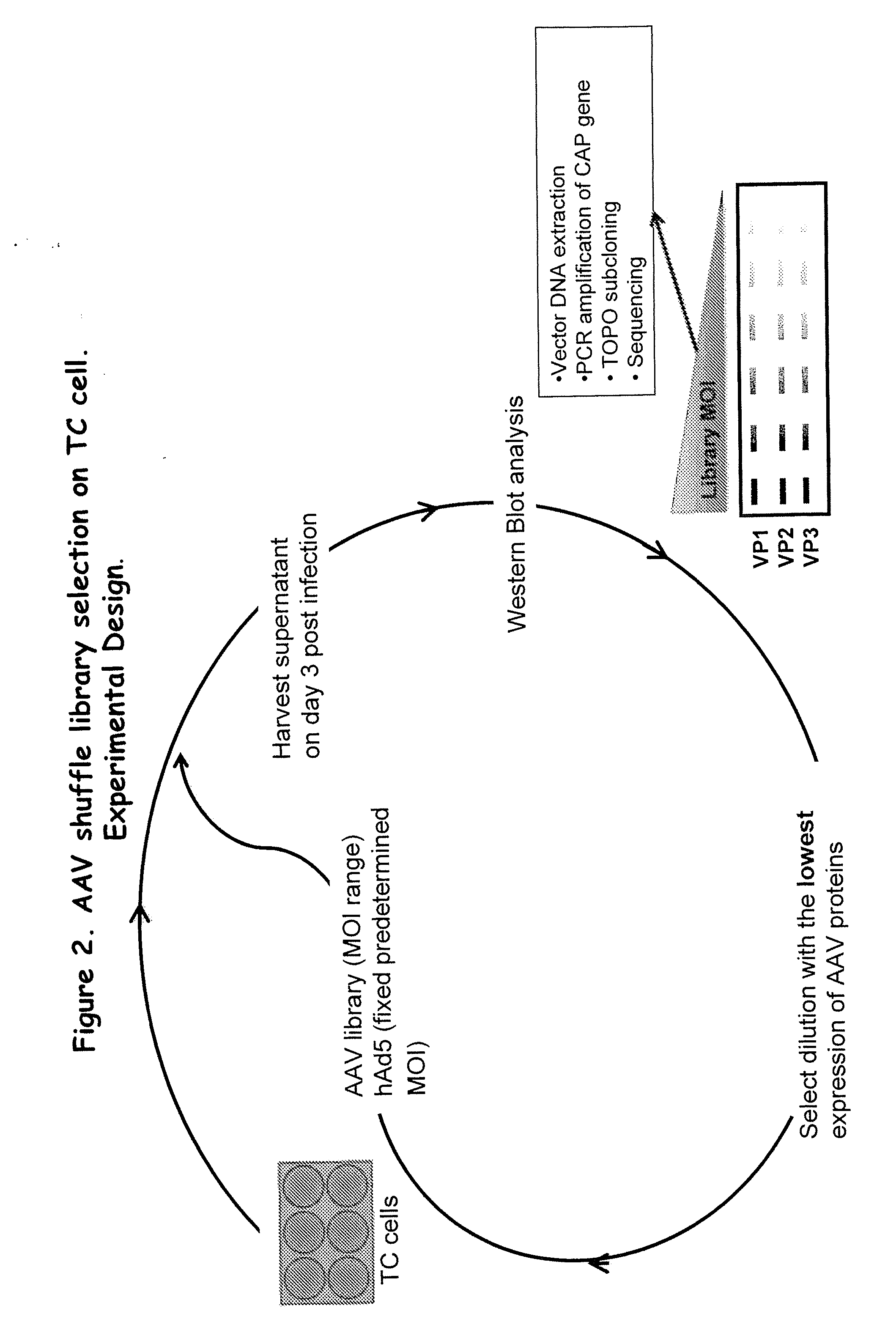
Adeno-associated virus variants and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20160017295A1Improve the immunityEfficient deliveryAntibacterial agentsVirusesHeterologousGene product
The present disclosure provides infectious recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) virions that comprise a variant capsid protein and a heterologous nucleic acid. The present disclosure further provides the variant adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid proteins (and / or a nucleic acid encoding the variant AAV capsid proteins), which confer to an infectious rAAV virion an increased resistance to human AAV neutralizing antibodies. The present disclosure further provides host cells comprising an infectious rAAV virion and / or a nucleic acid encoding a subject variant AAV capsid protein. The present disclosure further provides methods of delivering a heterologous nucleic acid to a target cell where the target cell is contacted with a subject infectious rAAV virion. The present disclosure further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Aav capsid proteins for nucleic acid transfer
ActiveUS20130059732A1Wide host rangeSufficient infection levelVirus peptidesDirected macromolecular evolutionCapsidBiology
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Universal fibronectin type iii bottom-side binding domain libraries
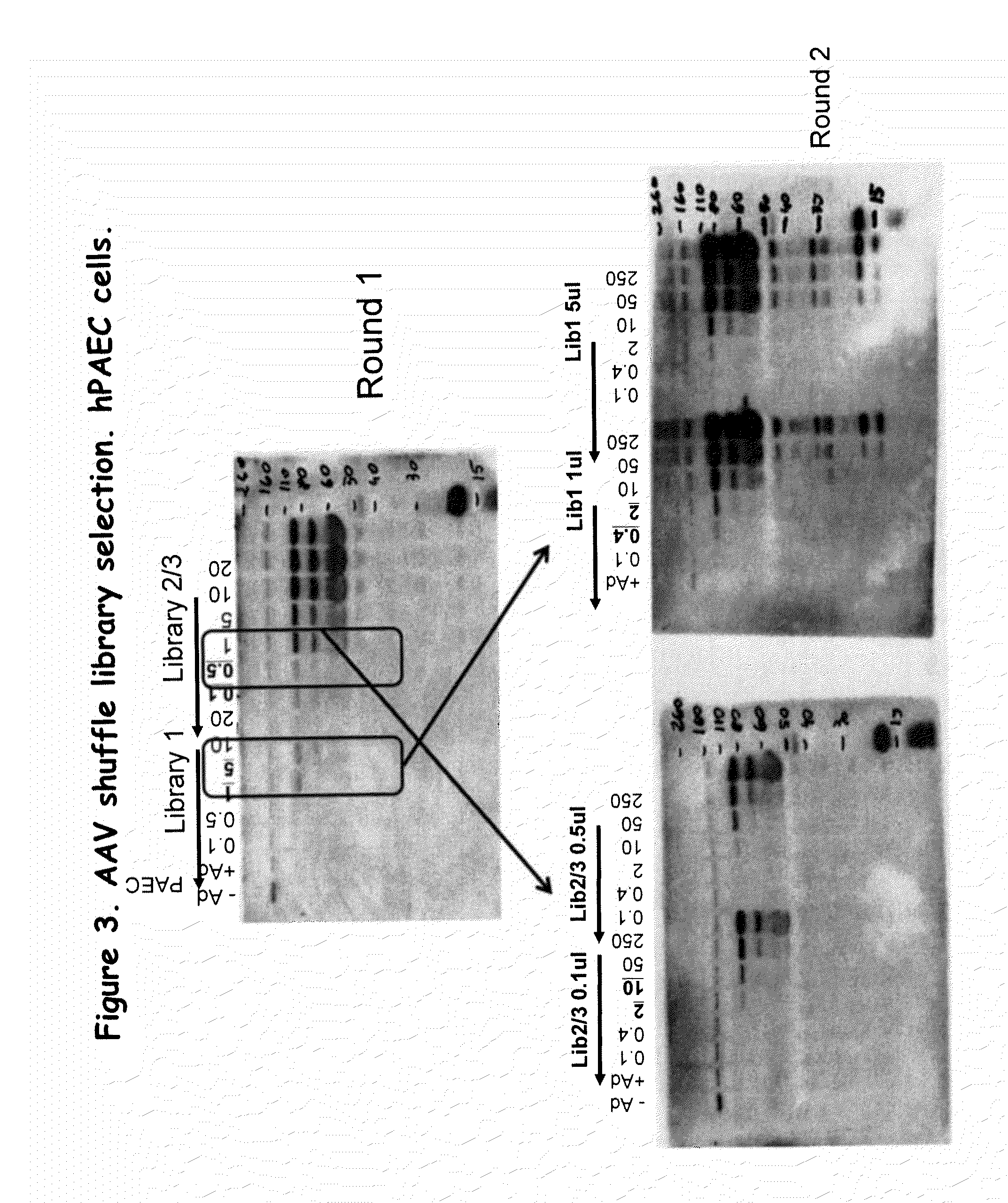
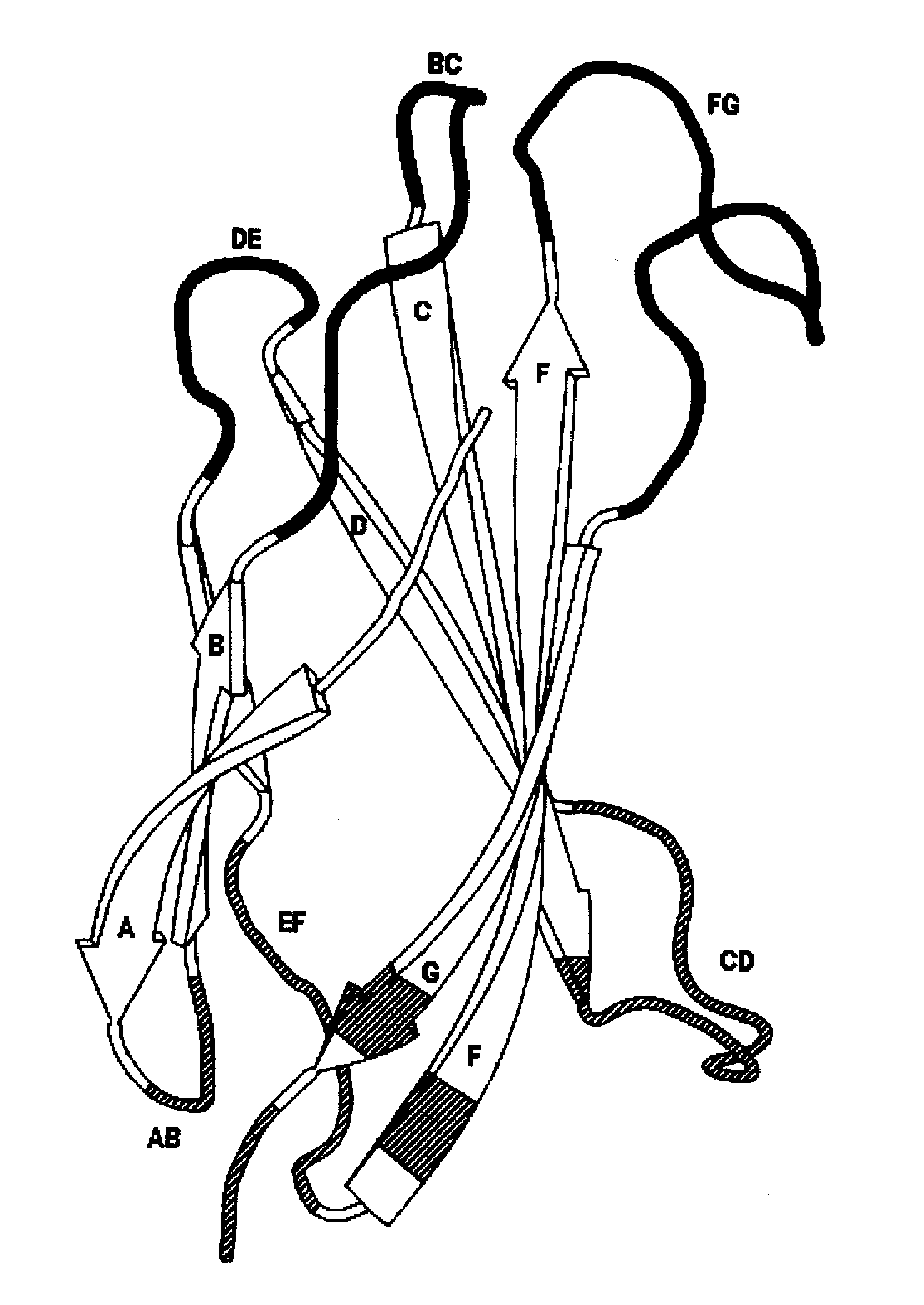
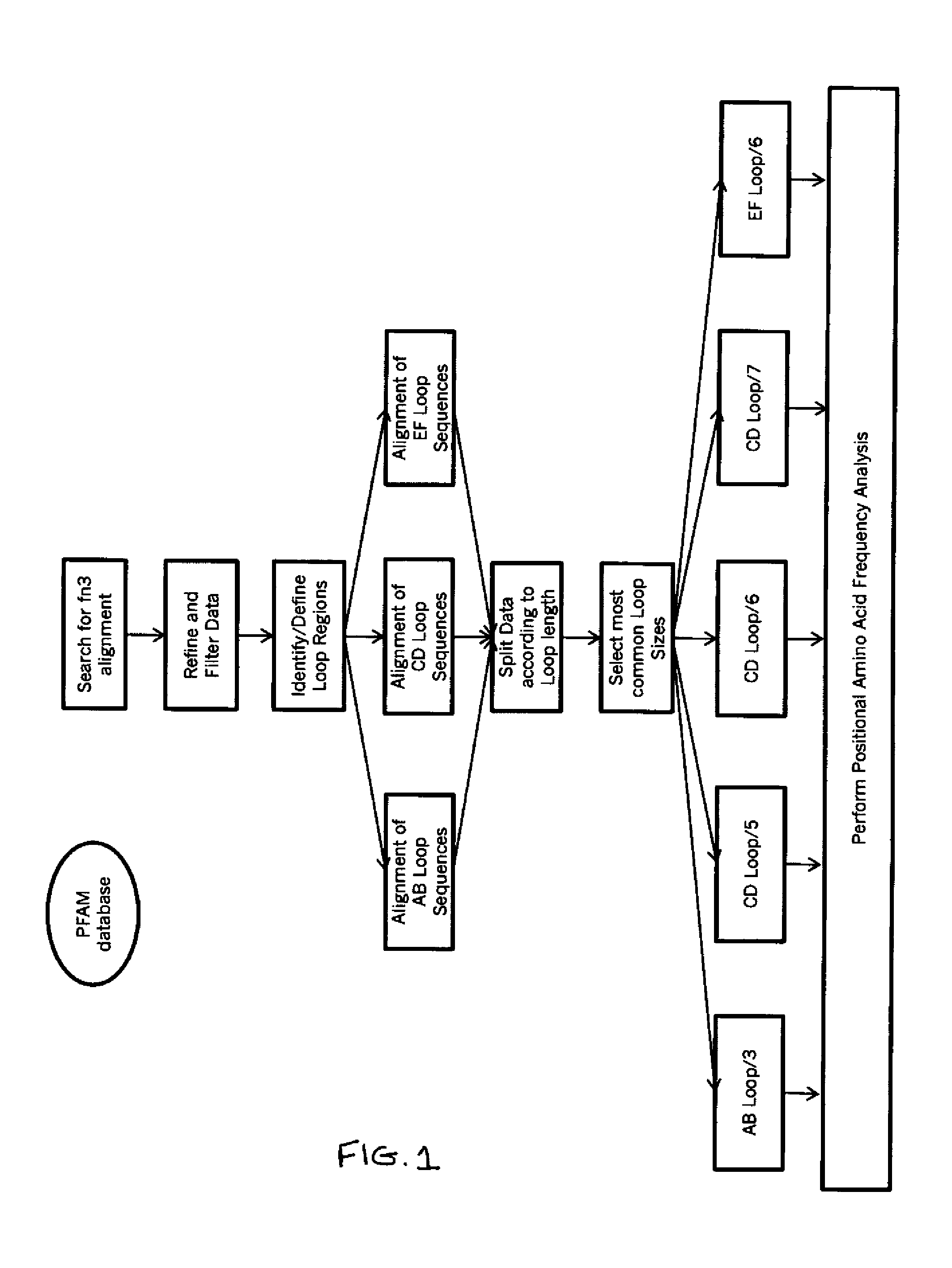
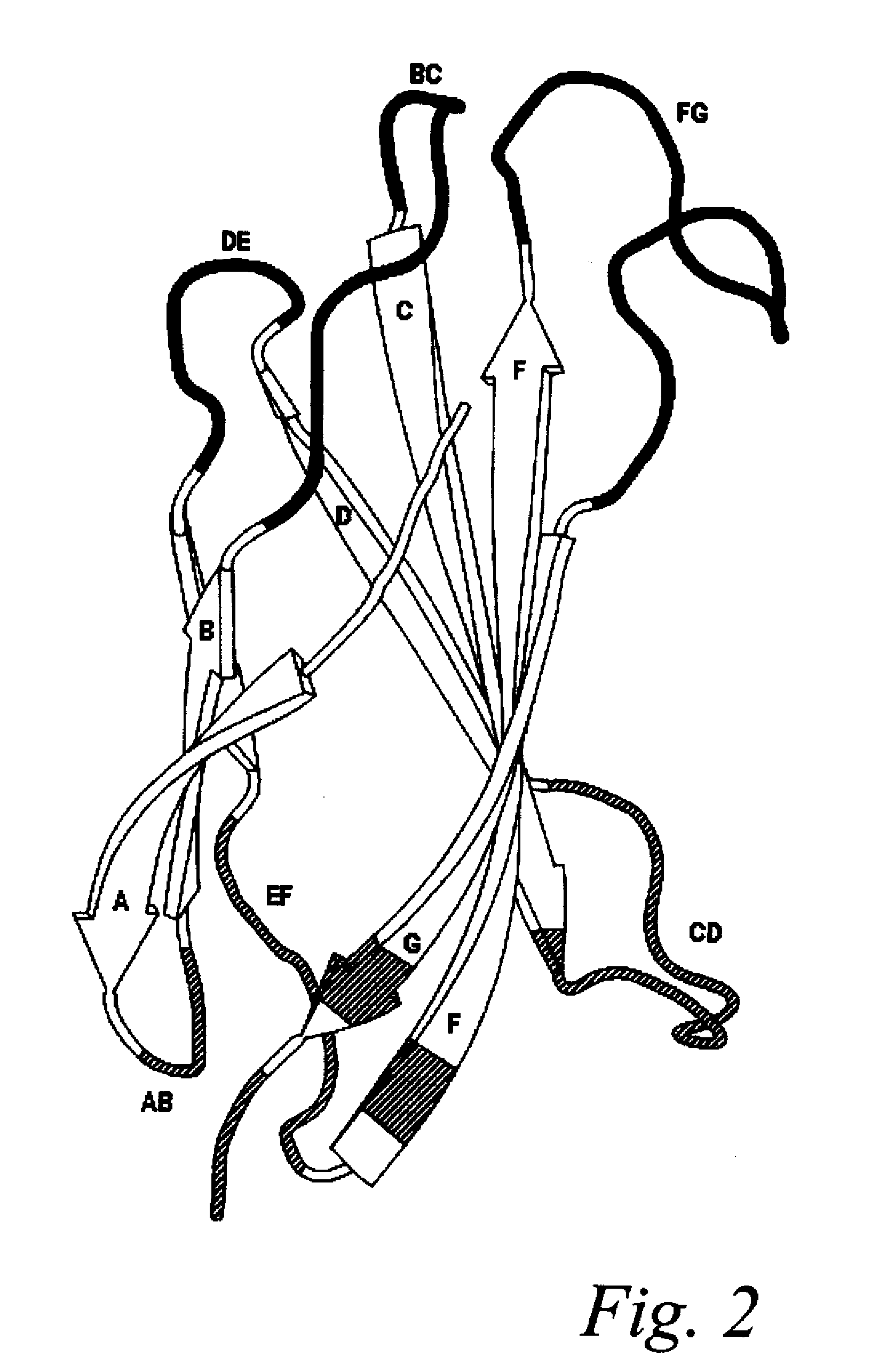
The invention pertains to a natural-variant combinatorial library of fibronectin Type 3 domain (Fn3) polypeptides useful in screening for the presence of one or more polypeptides having a selected binding or enzymatic activity. The library polypeptides include (a) regions A, AB, B, C, CD, D, E, EF, F, and G having wildtype amino acid sequences of a selected native fibronectin Type 3 polypeptide or polypeptides, and (b) loop regions AB, CD, and EF having selected lengths (Bottom Loops). The Fn3 may also have loop regions BC, DE, and FG having wildtype amino acid sequences, having selected lengths, or mutagenized amino acid sequences (Top Loops).
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method for obtaining oligonucleotide aptamers and uses thereof
The present invention relates to a method for obtaining nucleic acid aptamers that bind to cancer cell-surface epitopes, to the aptamers generated using this method and their use for therapeutic, diagnostic and prognostic purposes.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Antibody specificity transfer using minimal essential binding determinants
The present invention provides methods of making antibodies having the binding specificity of a reference antibody. Antibodies generated by the methods of the inventions have at least one minimal essential binding specificity determinant from a heavy chain or light chain CDR3 from the reference antibody. The method can be used, e.g., in humanization procedures. The invention also provides libraries and antibodies made in accordance with the methods.
Owner:HUMANIGEN INC
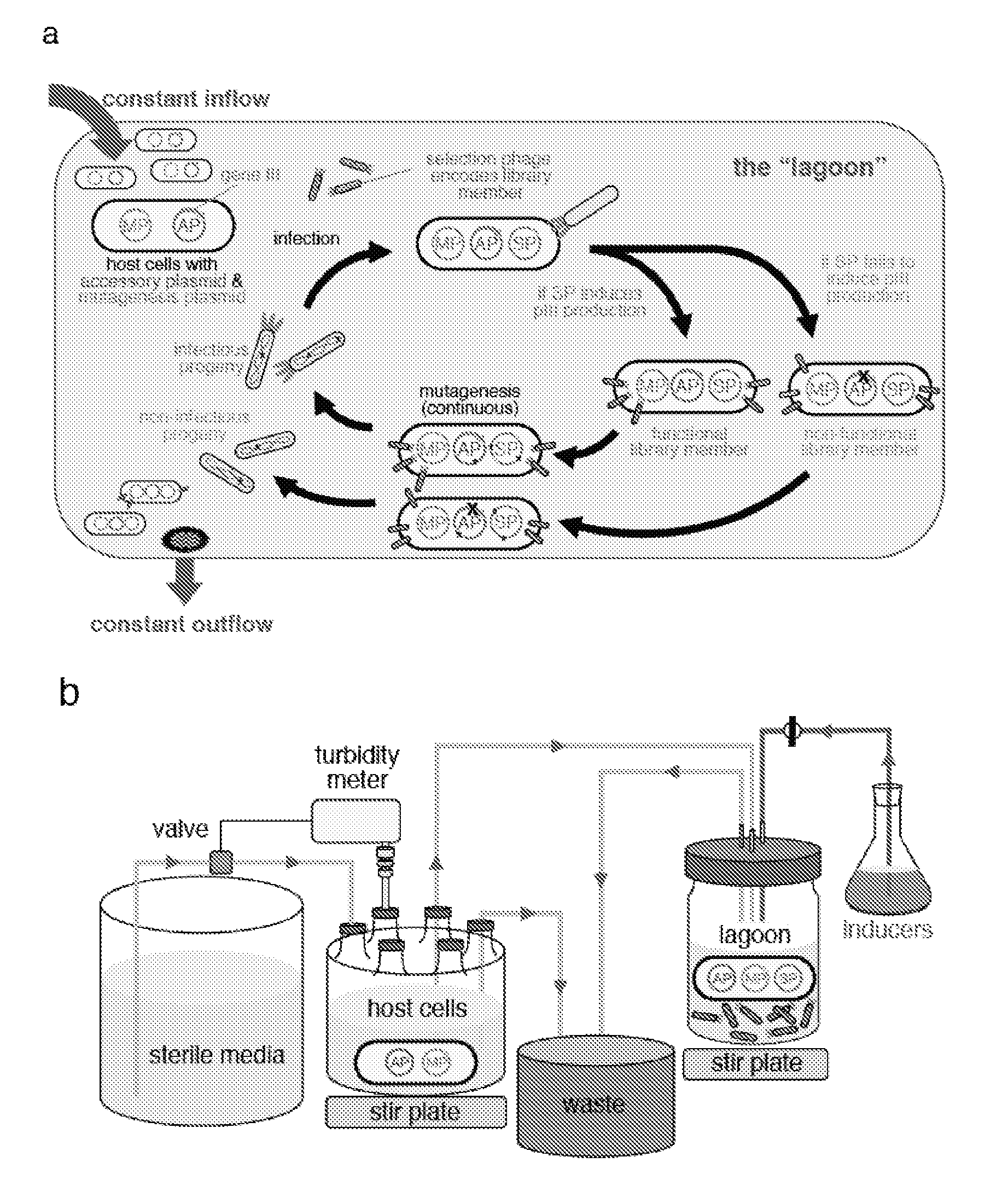
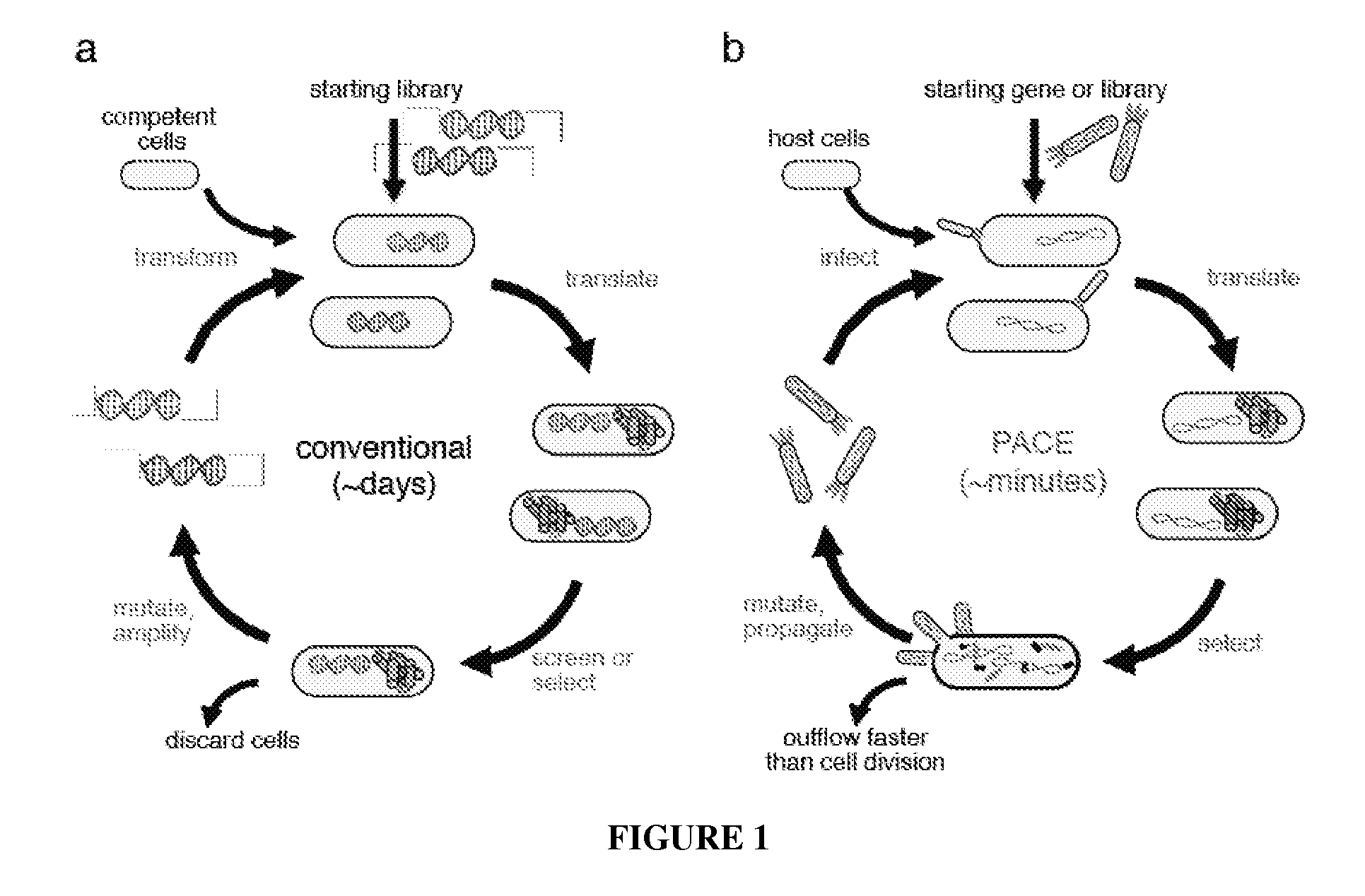
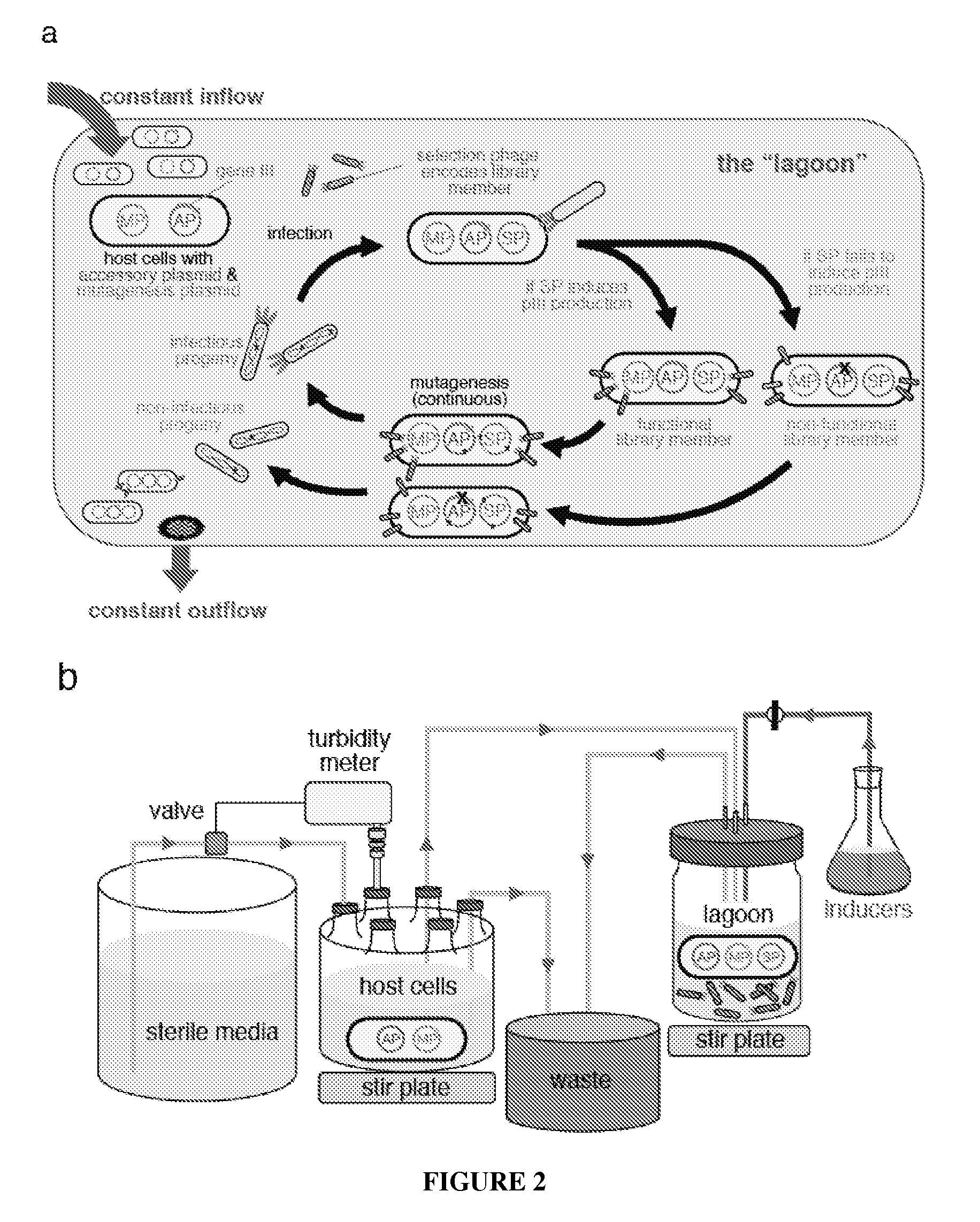
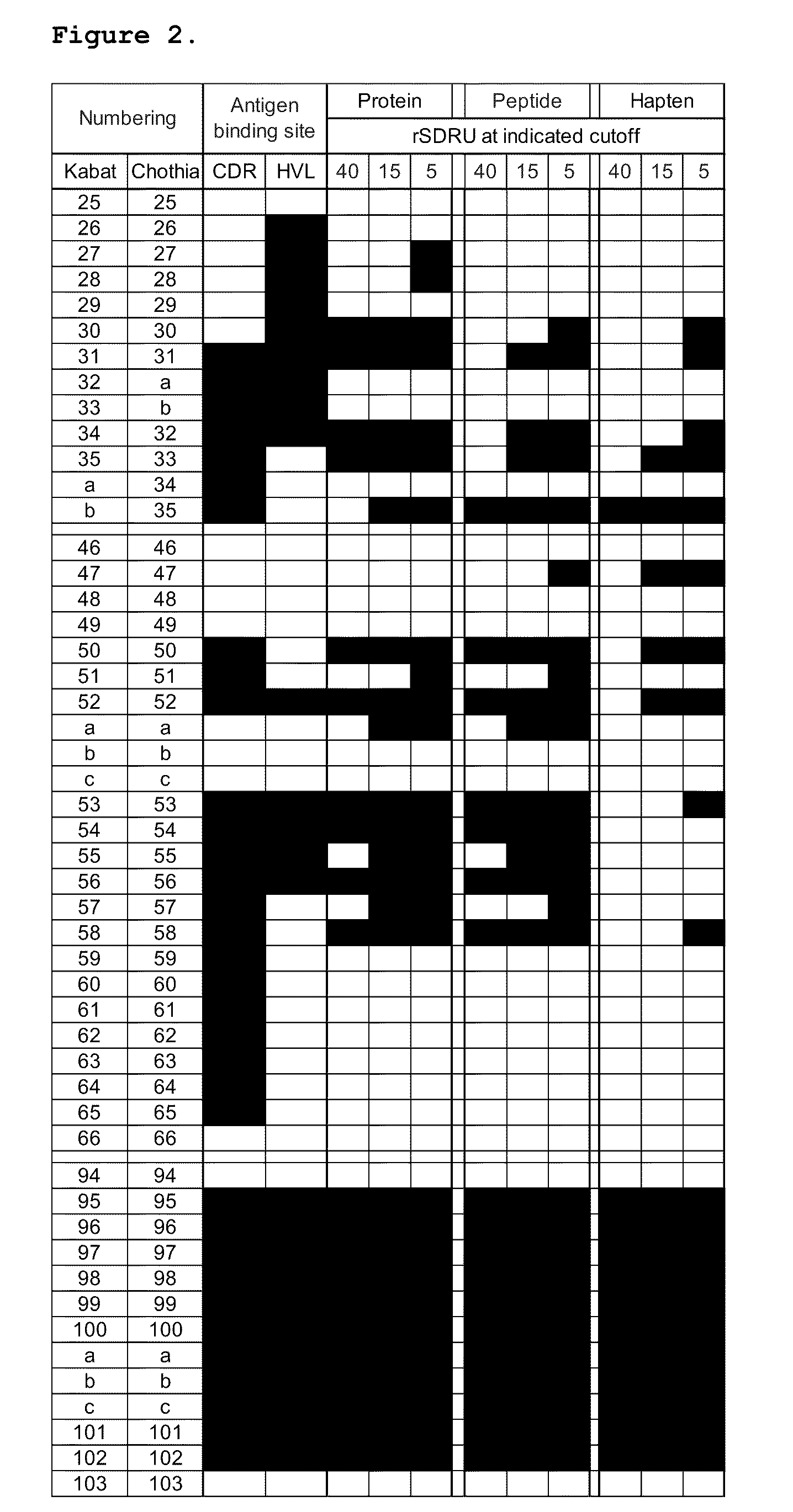
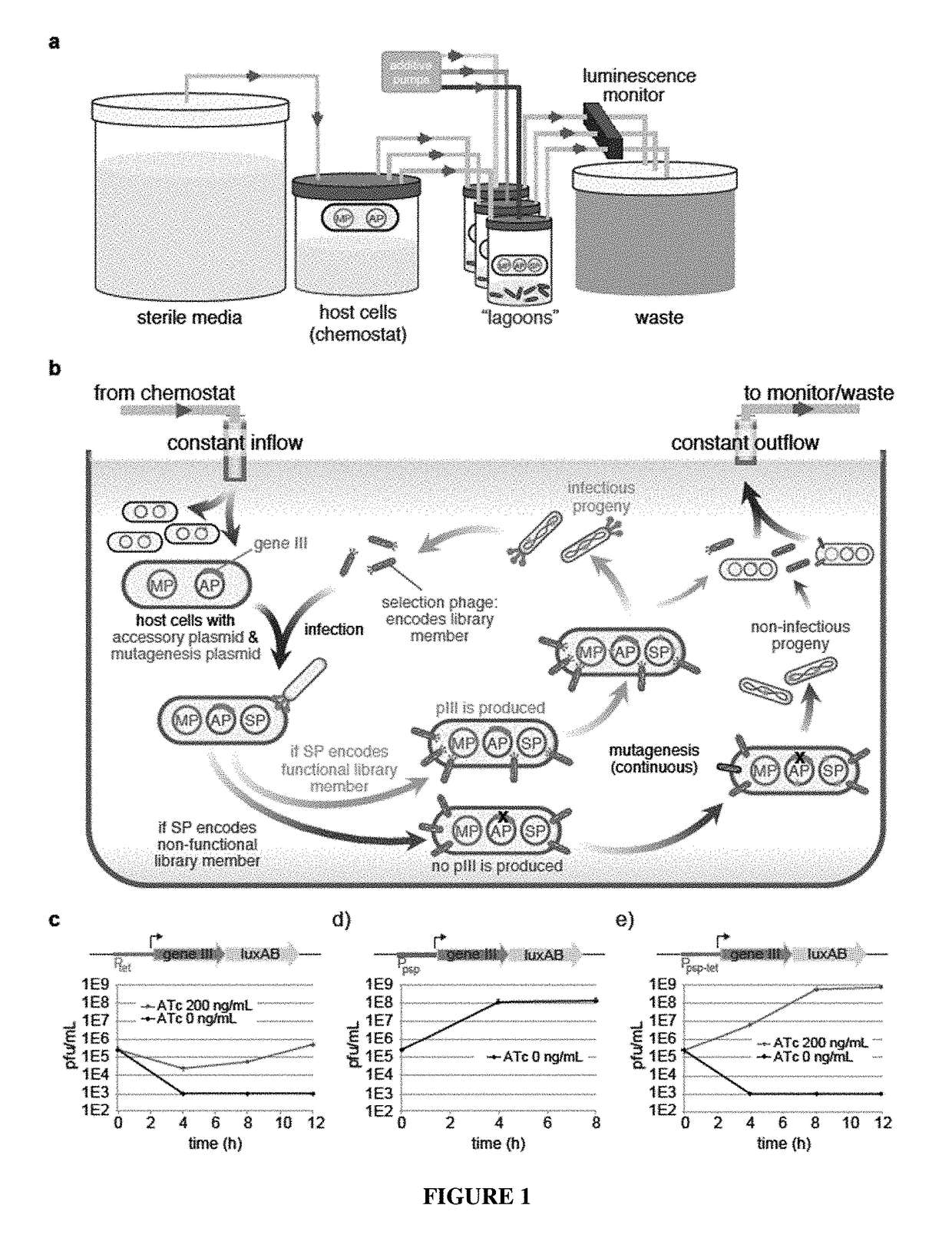
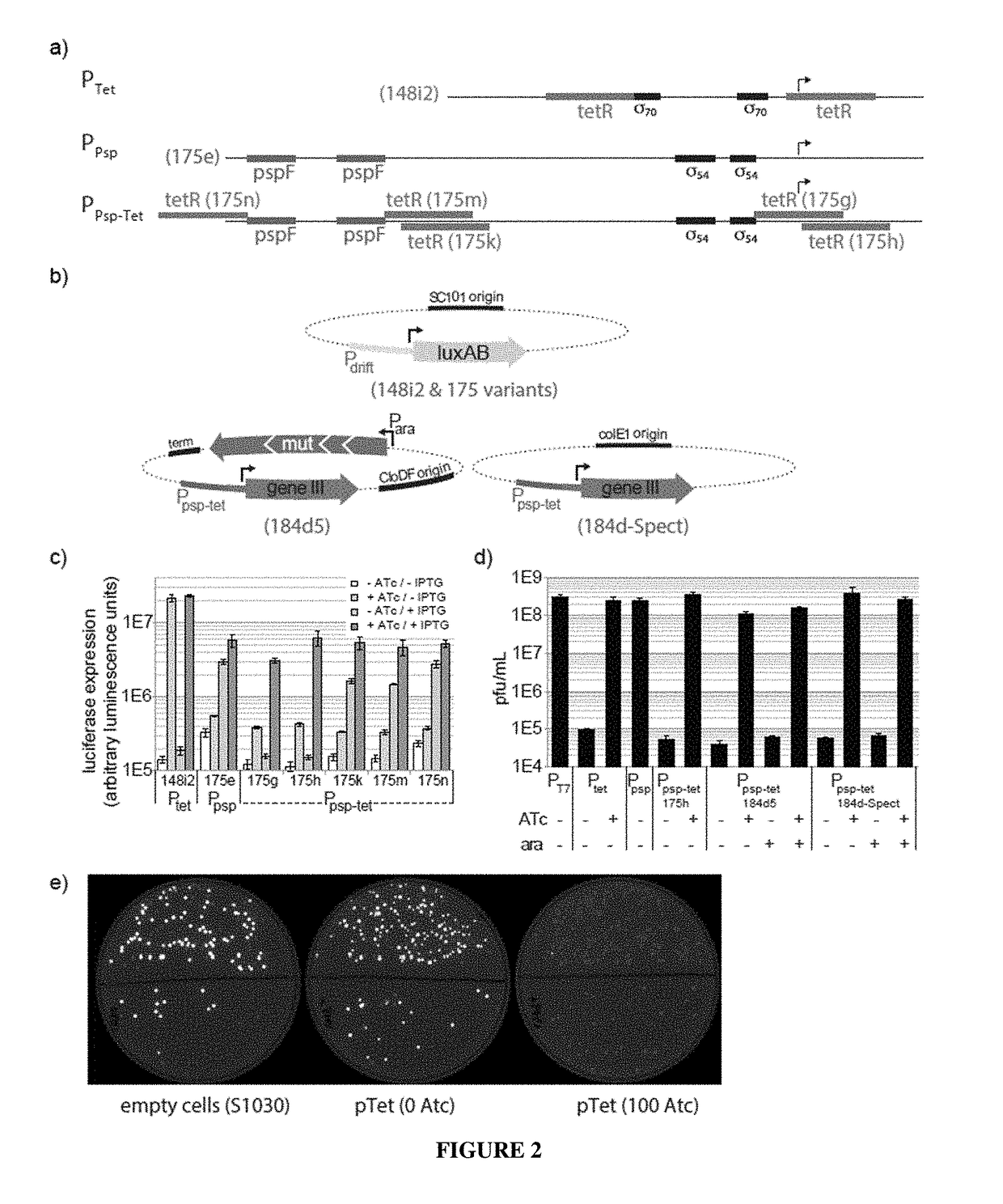
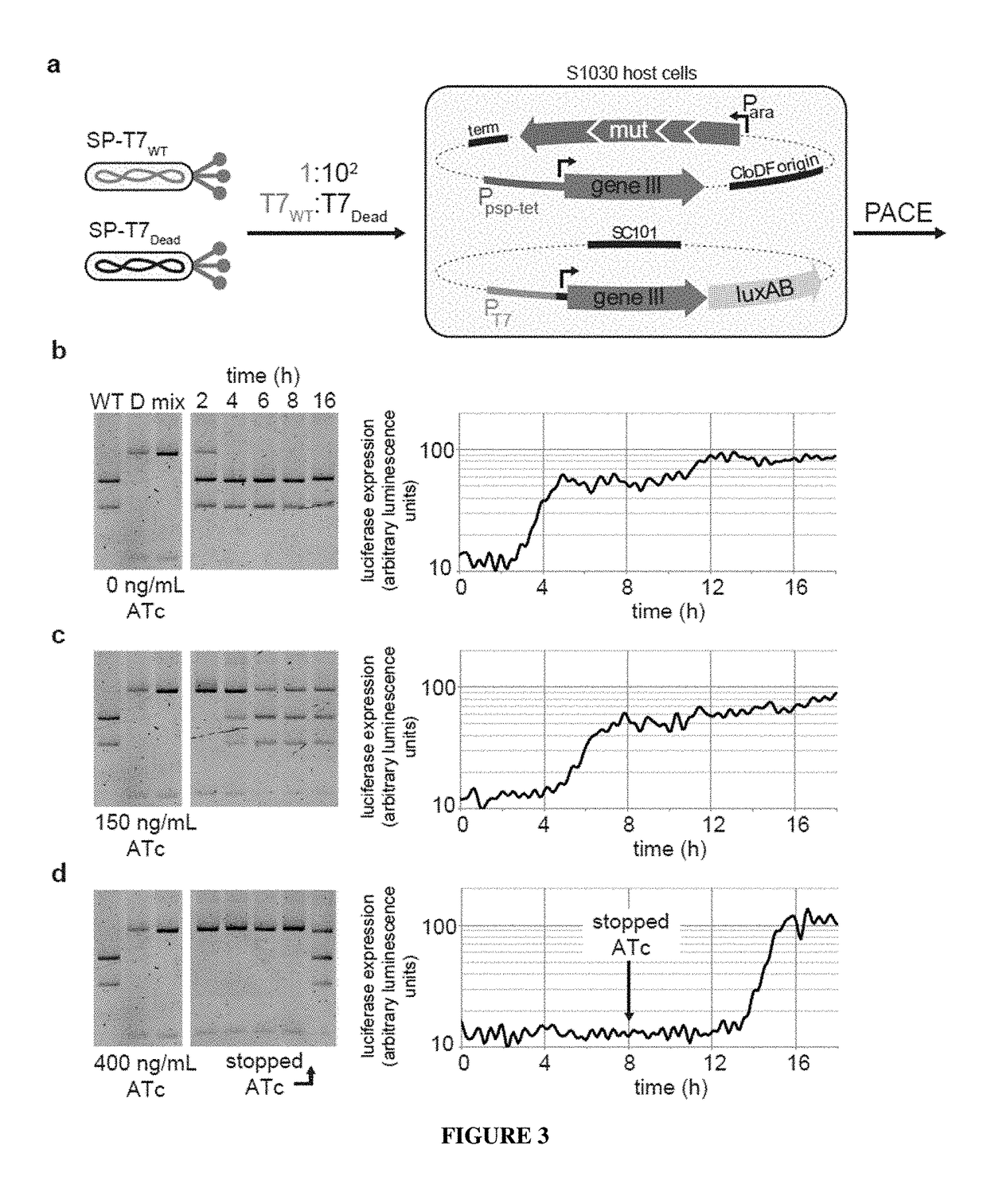
Continuous directed evolution
ActiveUS9394537B2Accelerating evolutionVirus peptidesDirected macromolecular evolutionViral vectorVirus
The invention provides systems, methods, reagents, apparatuses, vectors, and host cells for the continuous evolution of nucleic acids. For example, a lagoon is provided in which a population of viral vectors comprising a gene of interest replicates in a stream of host cells, wherein the viral vectors lack a gene encoding a protein required for the generation of infectious viral particles, and wherein that gene is expressed in the host cells under the control of a conditional promoter, the activity of which depends on a function of the gene of interest to be evolved. Some aspects of this invention provide evolved products obtained from continuous evolution procedures described herein. Kits containing materials for continuous evolution are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Conductivity Detector For Fluids
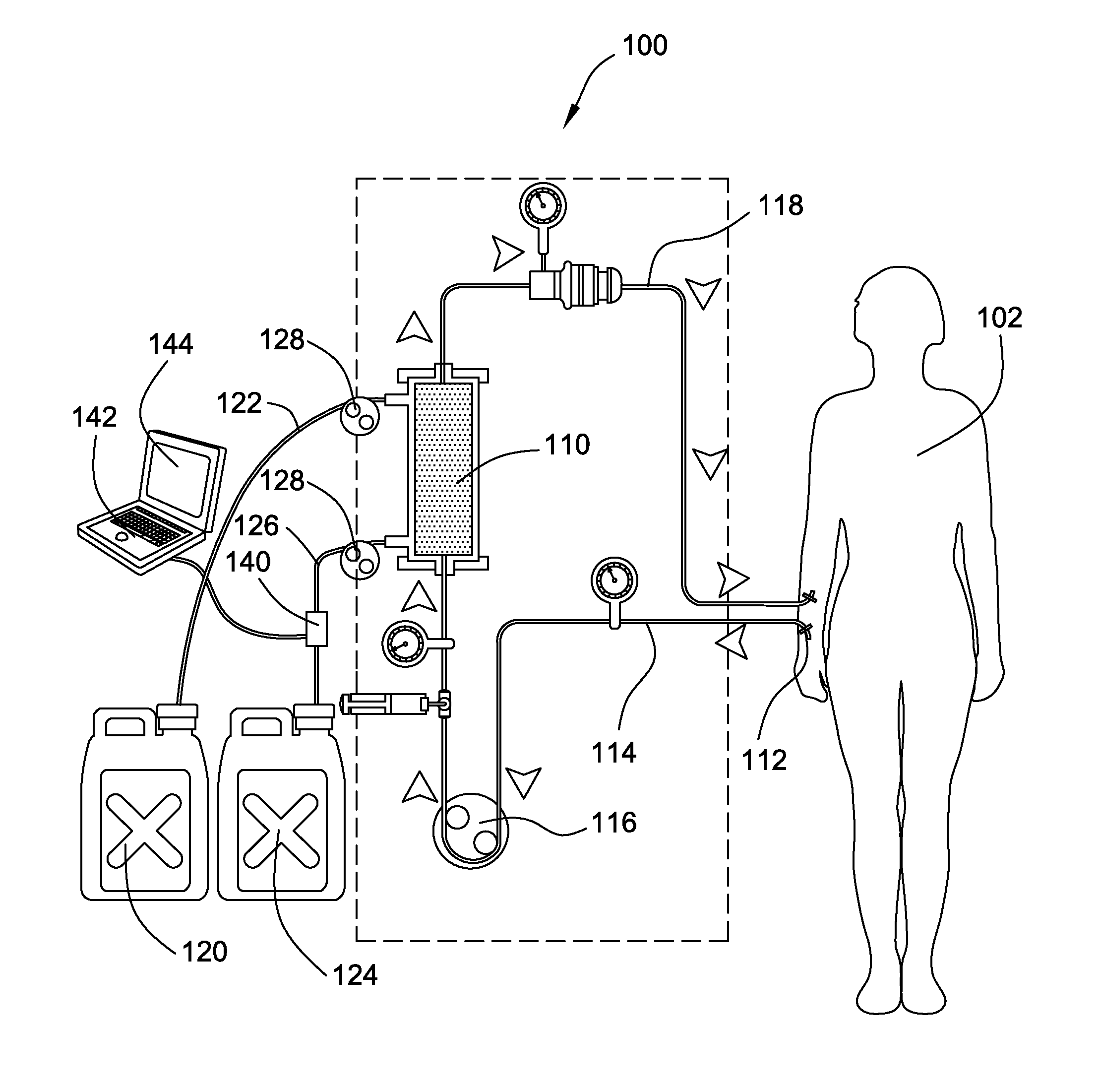
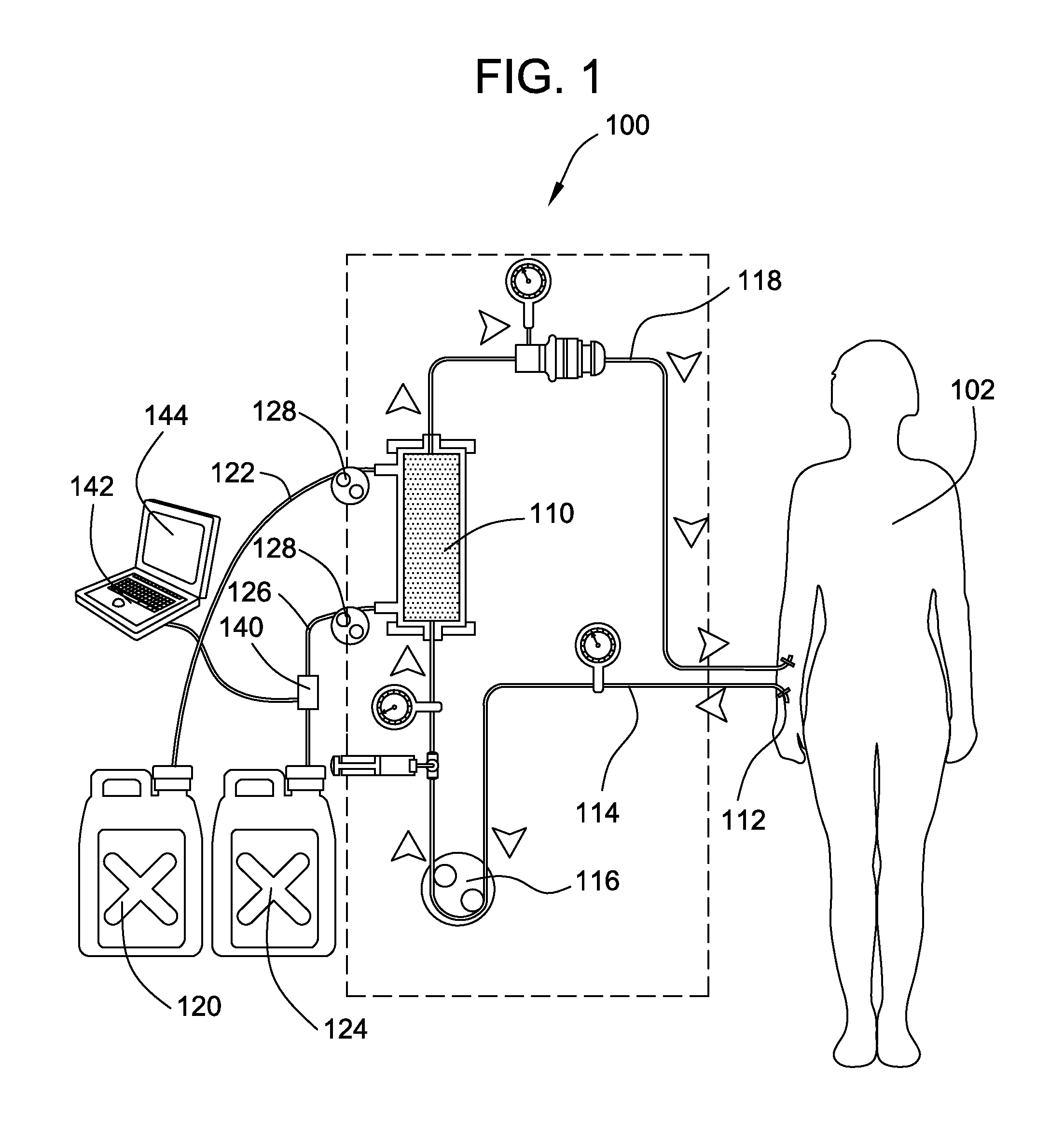
ActiveUS20120068723A1Accurate measurementAvoid foulingVolume/mass flow measurementVoltage-current phase angleCapacitanceHemodialysis
A conductivity detector detects the electrical conductivity of a fluid under analysis for determining chemical or physical properties of the fluid that are related its electrical properties. Such conductivity detectors may find use in, for example, hemodialysis systems for analyzing the effectiveness of the hemodialysis treatment. In an aspect, to improve accuracy of the conductivity measurements, the detector utilizes four-wire resistance measurement methods. In another aspect, to avoid fouling or contamination of the electrodes, the detector utilizes capacitively-coupled contactless conductivity detection (C4D) methods so that the electrodes are physically unconnected to the fluid contained in a fluid chamber. In a possible further aspect, the fluid chamber may be a disposable component removable from the electrodes. The conductivity detector can include other features such as calibration circuits and features for electrically isolating the fluid under detection from the fluid in the rest of the system.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Methods of Affinity Maturing Antibodies
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Negative selection and stringency modulation in continuous evolution systems
ActiveUS10179911B2High selectivityStrong specificityFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPositive selectionBiology
Strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits for phage-assisted continuous evolution are provided herein. These include strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits allowing for stringency modulation to evolve weakly active or inactive biomolecule variants, negative selection of undesired properties, and / or positive selection of desired properties.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Aav capsid proteins for nucleic acid transfer
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
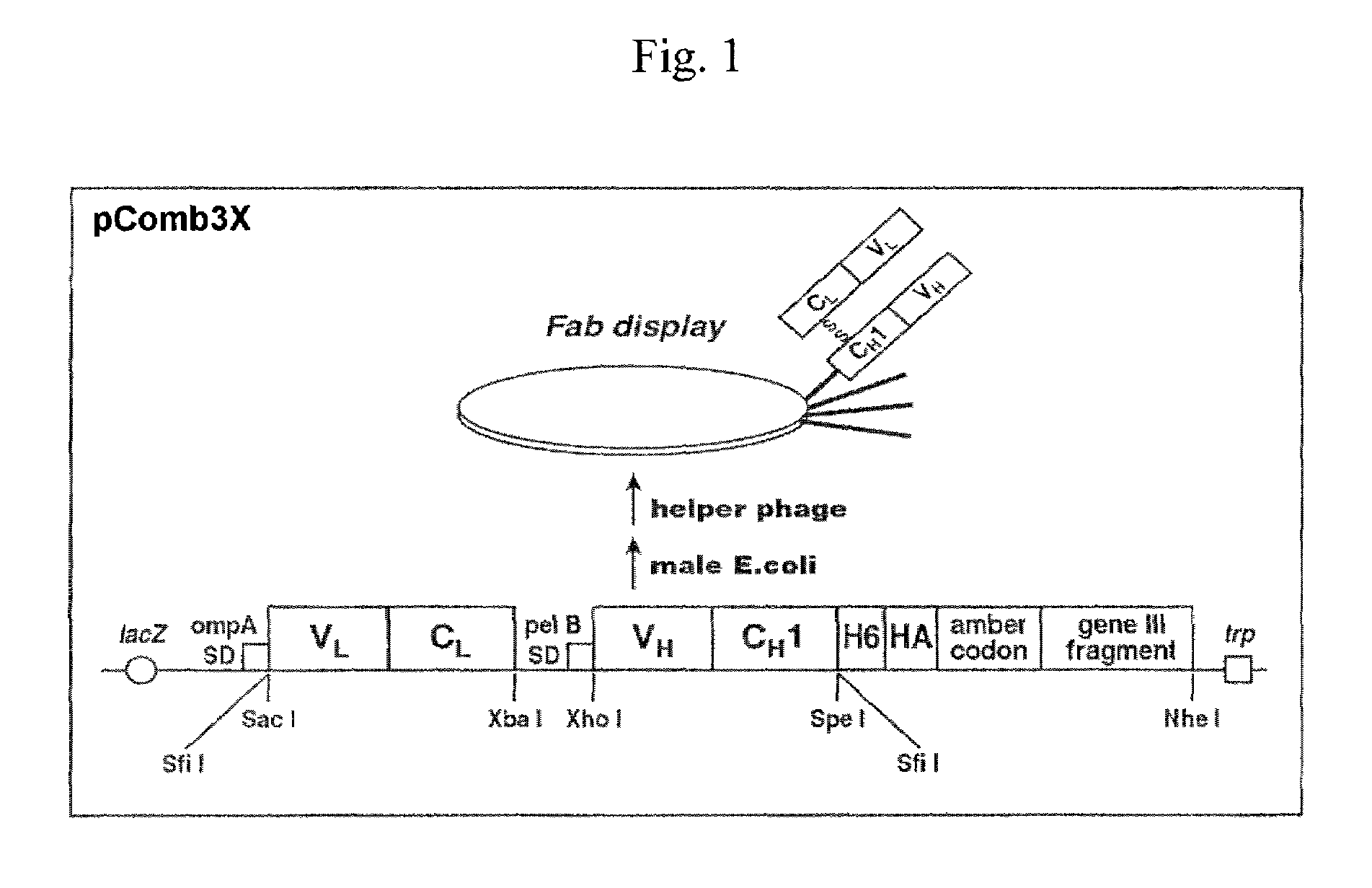
Anti-HGF/SF humanized antibody
The inventive anti-HGF / SF humanized antibody prepared by displaying on the surface of a phage an anti-HGF / SF chimeric Fab library comprising a set of human antibody light chain variable region (VL) and human antibody heavy chain variable region (VH) which are grafted with heavy chain complementary determining regions (HCDRs) of an anti-HGF / SF antibody of an animal other than human, has the equal or greater binding affinity than that of the parent anti-HGF / SF antibody, the neutralizing activity inhibiting the binding of HGF / SF to its receptor, cMET while having the reduced immunogenicity in human. Therefore, the inventive anti-HGF / SF humanized antibody can be used for preventing and treating diseases effectively, e.g., cancers, by the action of binding HGF / SF to cMET.
Owner:DONG A ST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com