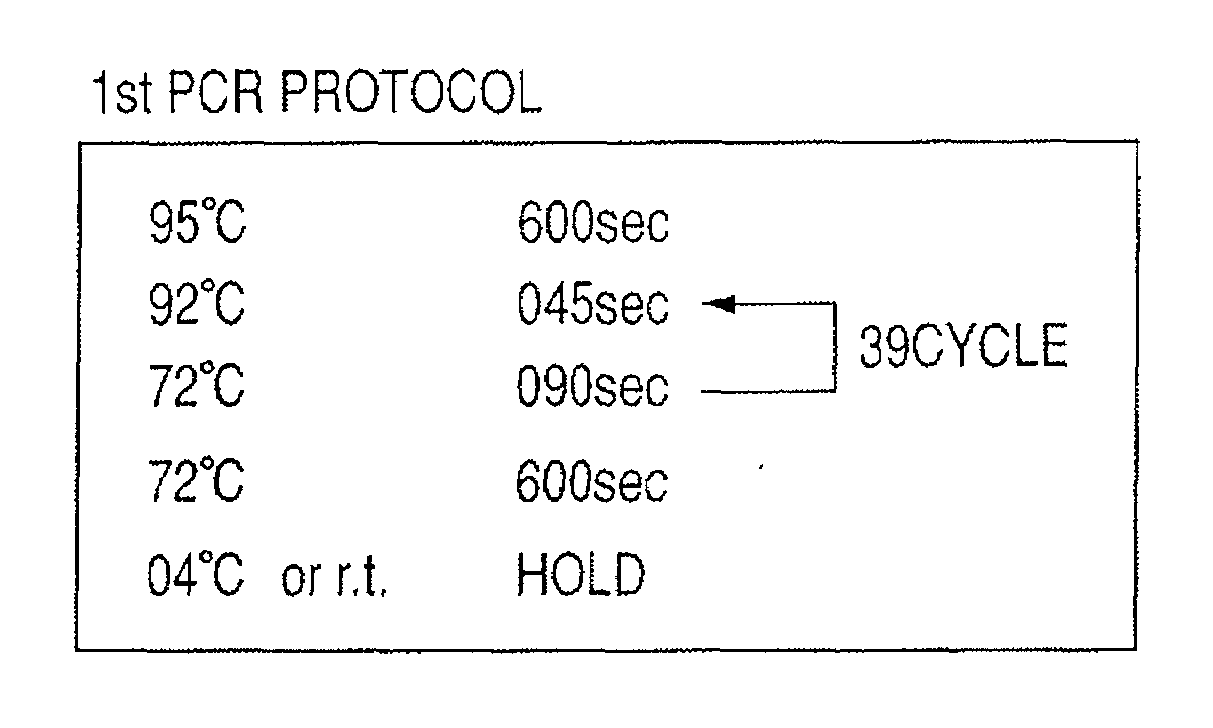
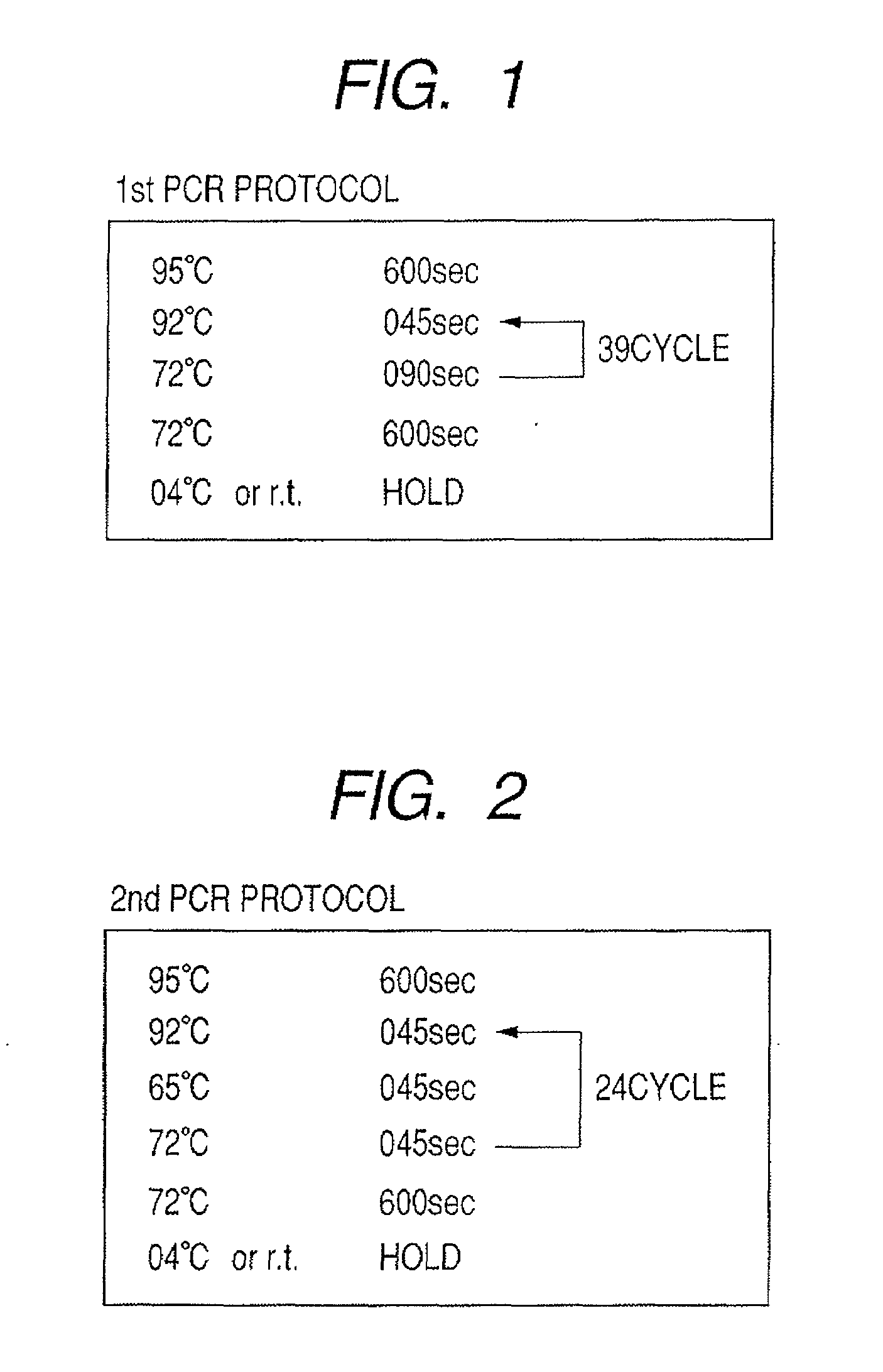
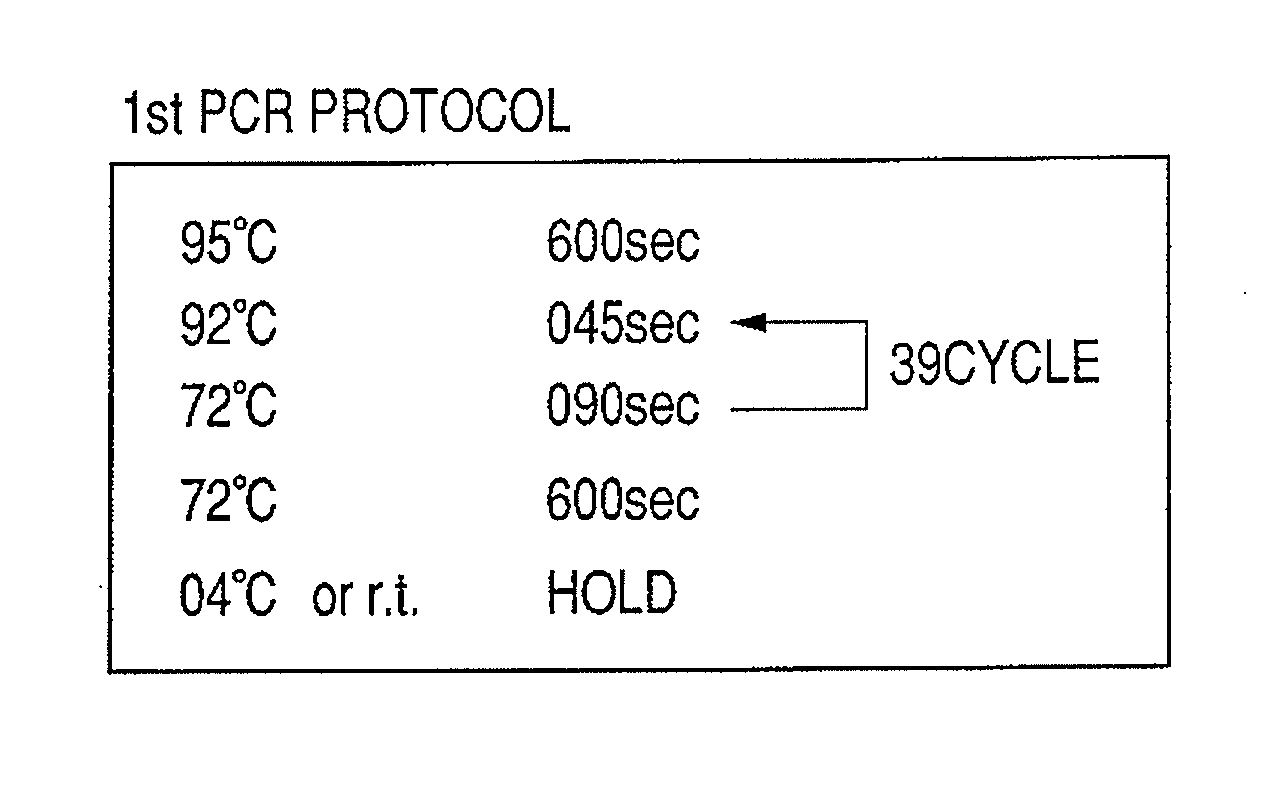
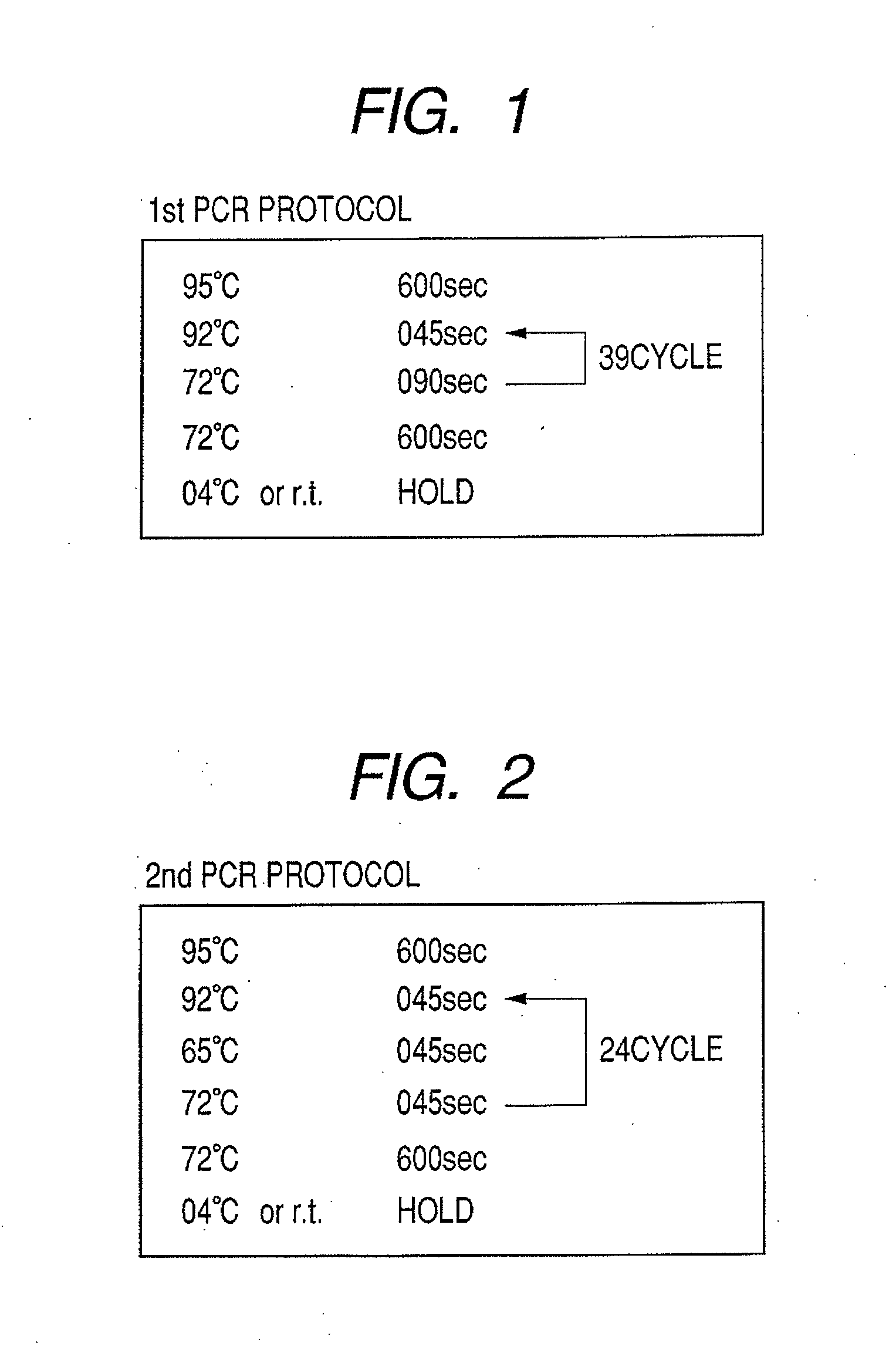
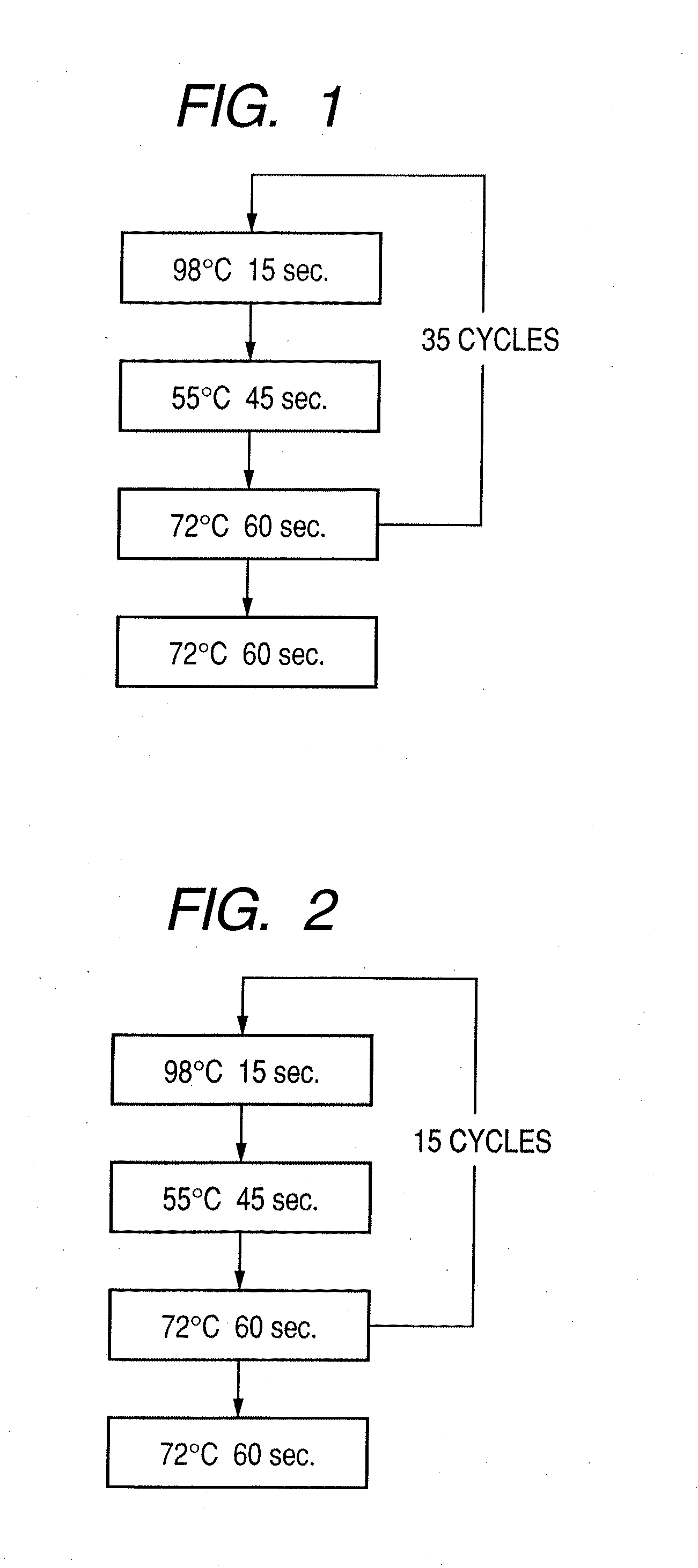
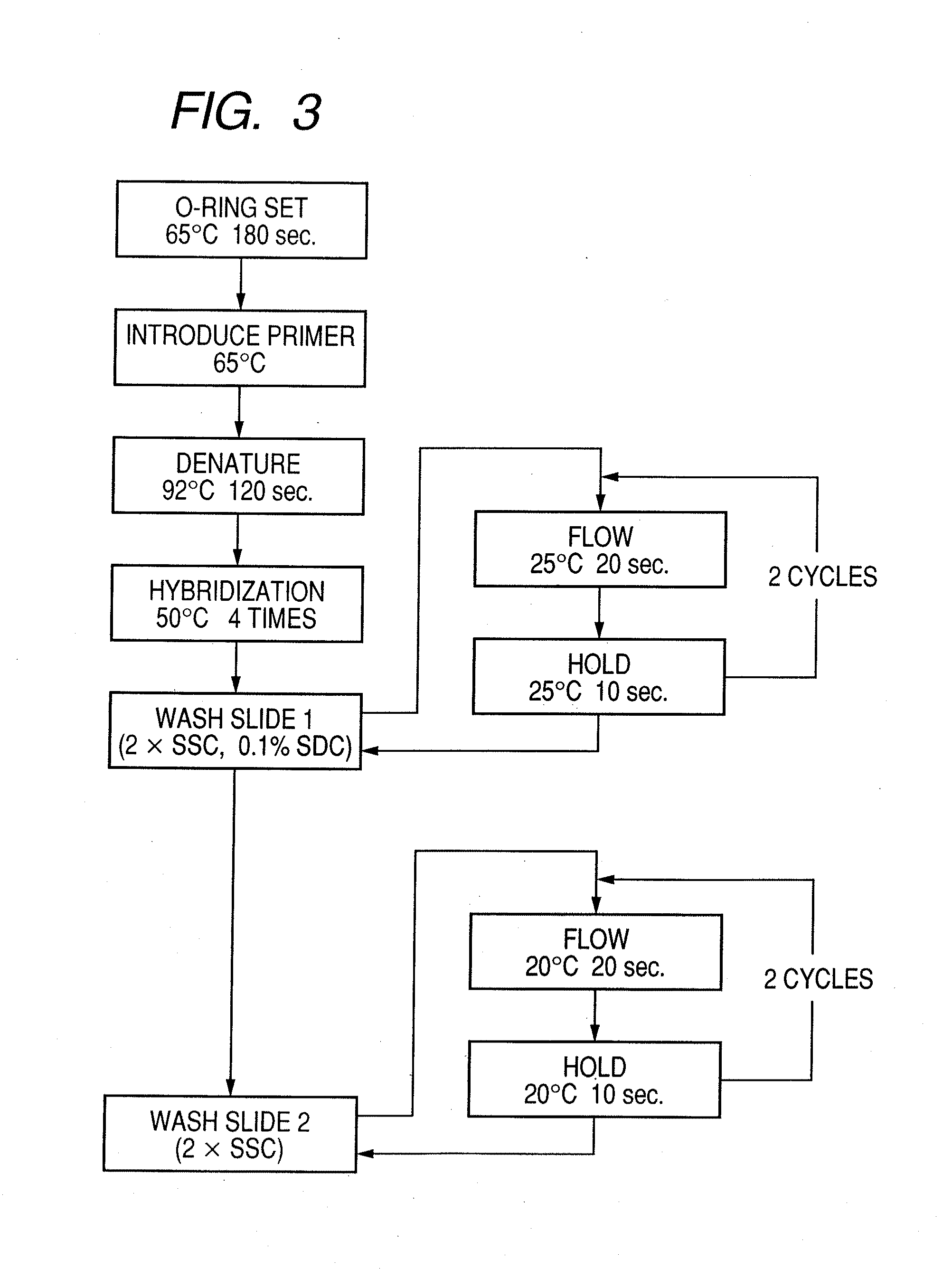
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3162 results about "Base sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polynucleotides for causing RNA interference and method for inhibiting gene expression using the same
InactiveUS20080113351A1High RNA interference effectLittle riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBase JNucleotide
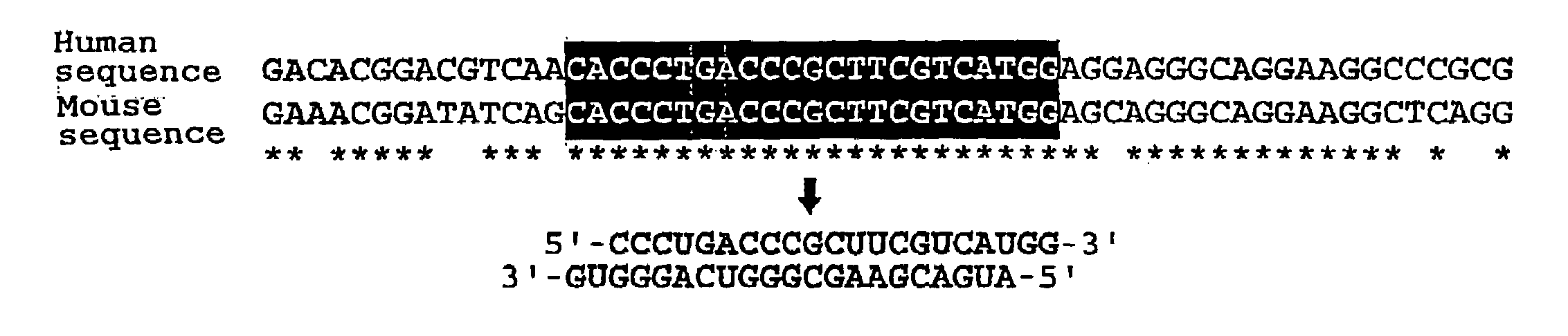
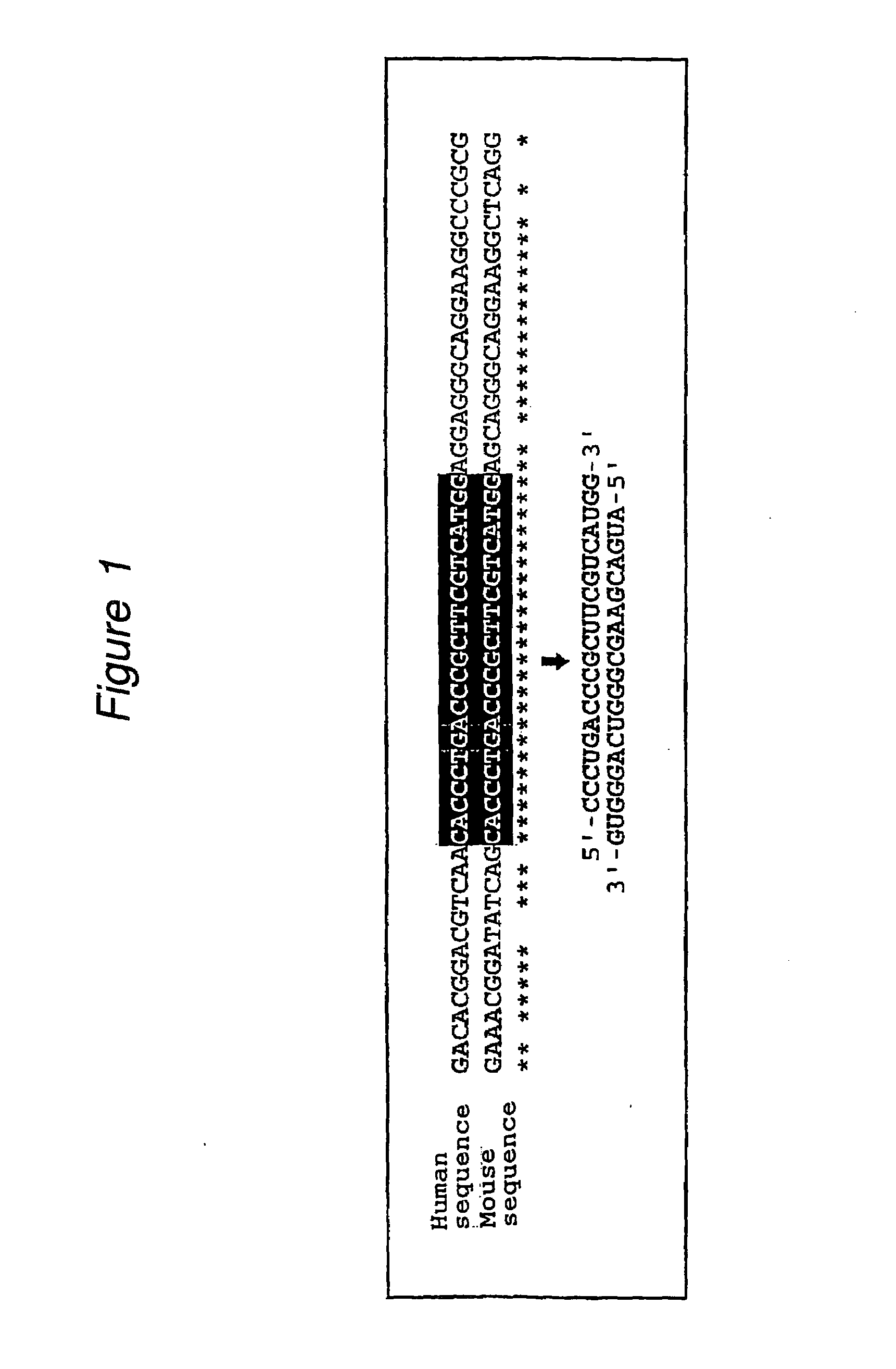
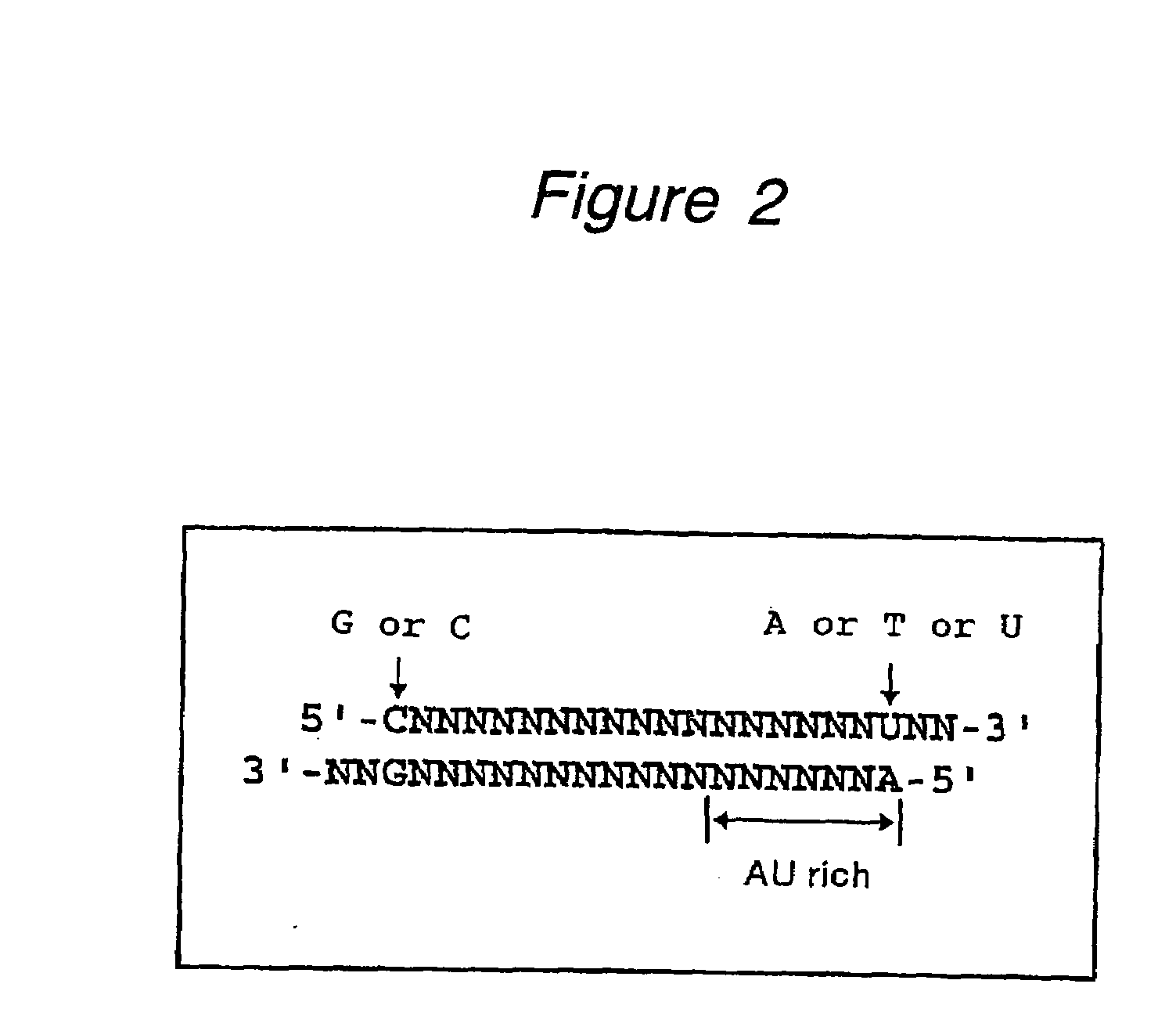
The present invention provides a polynucleotide that not only has a high RNA interference effect on its target gene, but also has a very small risk of causing RNA interference against a gene unrelated to the target gene. A sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene for RNA interference and, based on the search results, a polynucleotide capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.:(a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil,(b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine,(c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and(d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:ALPHAGEN
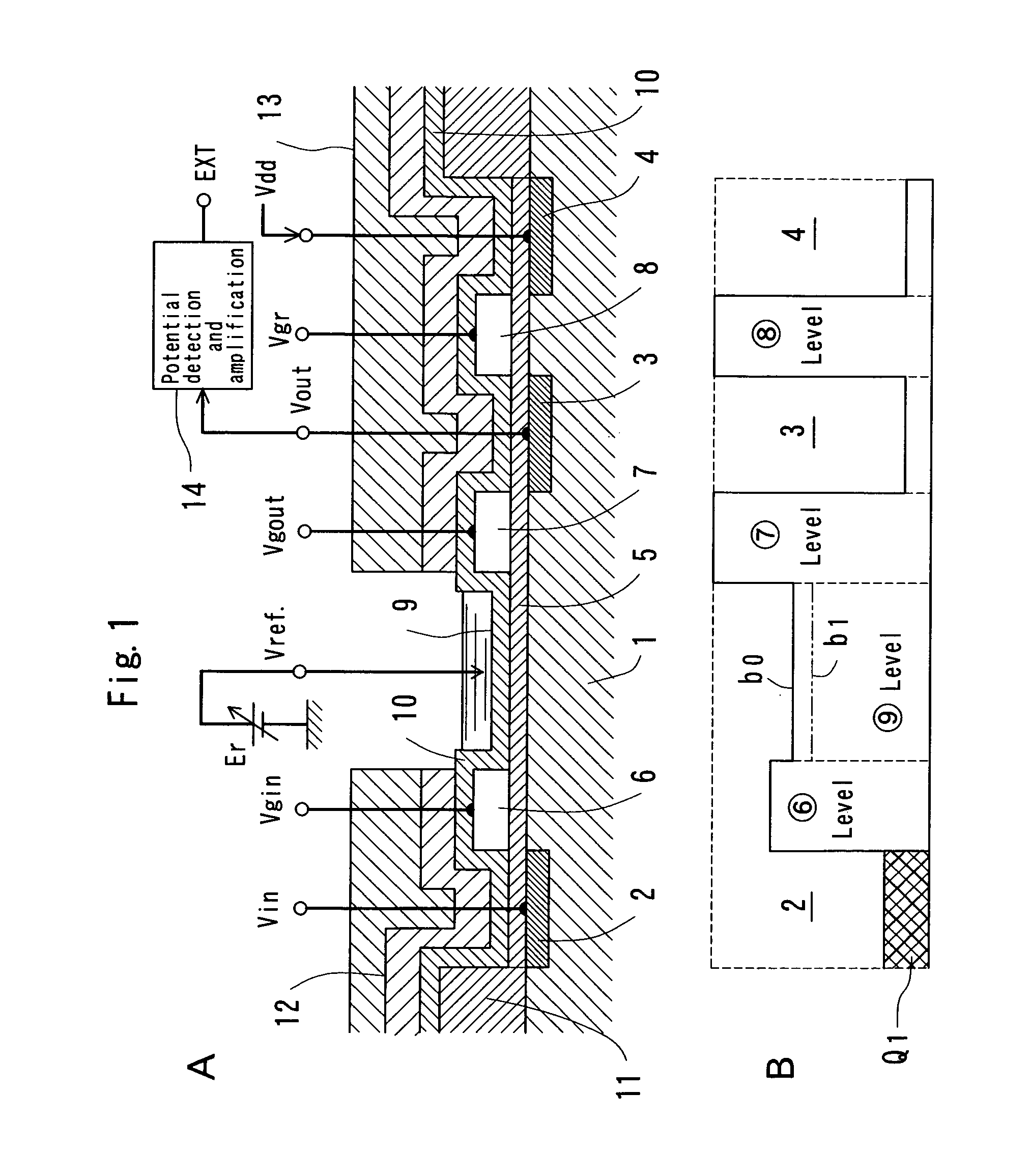
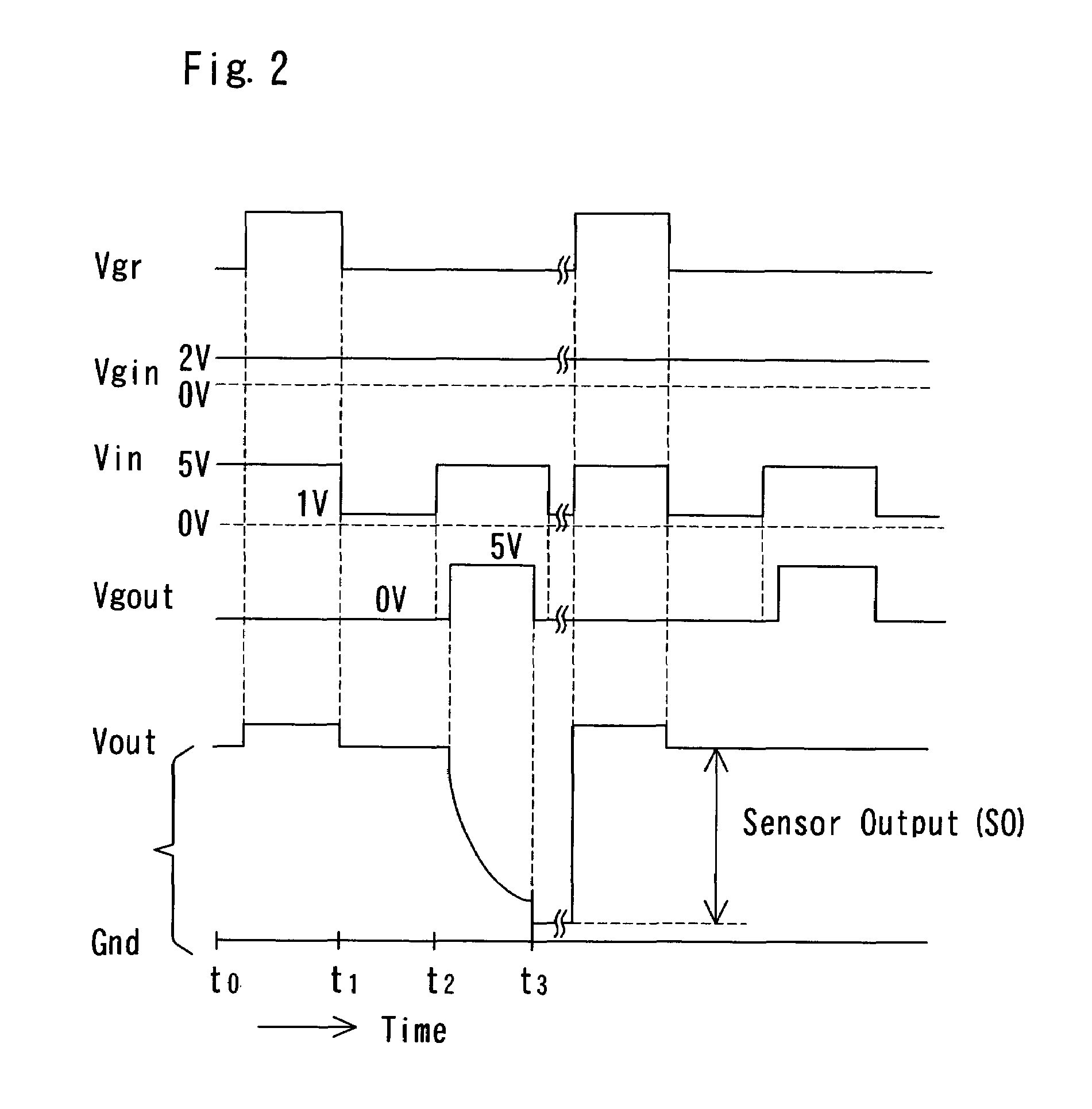
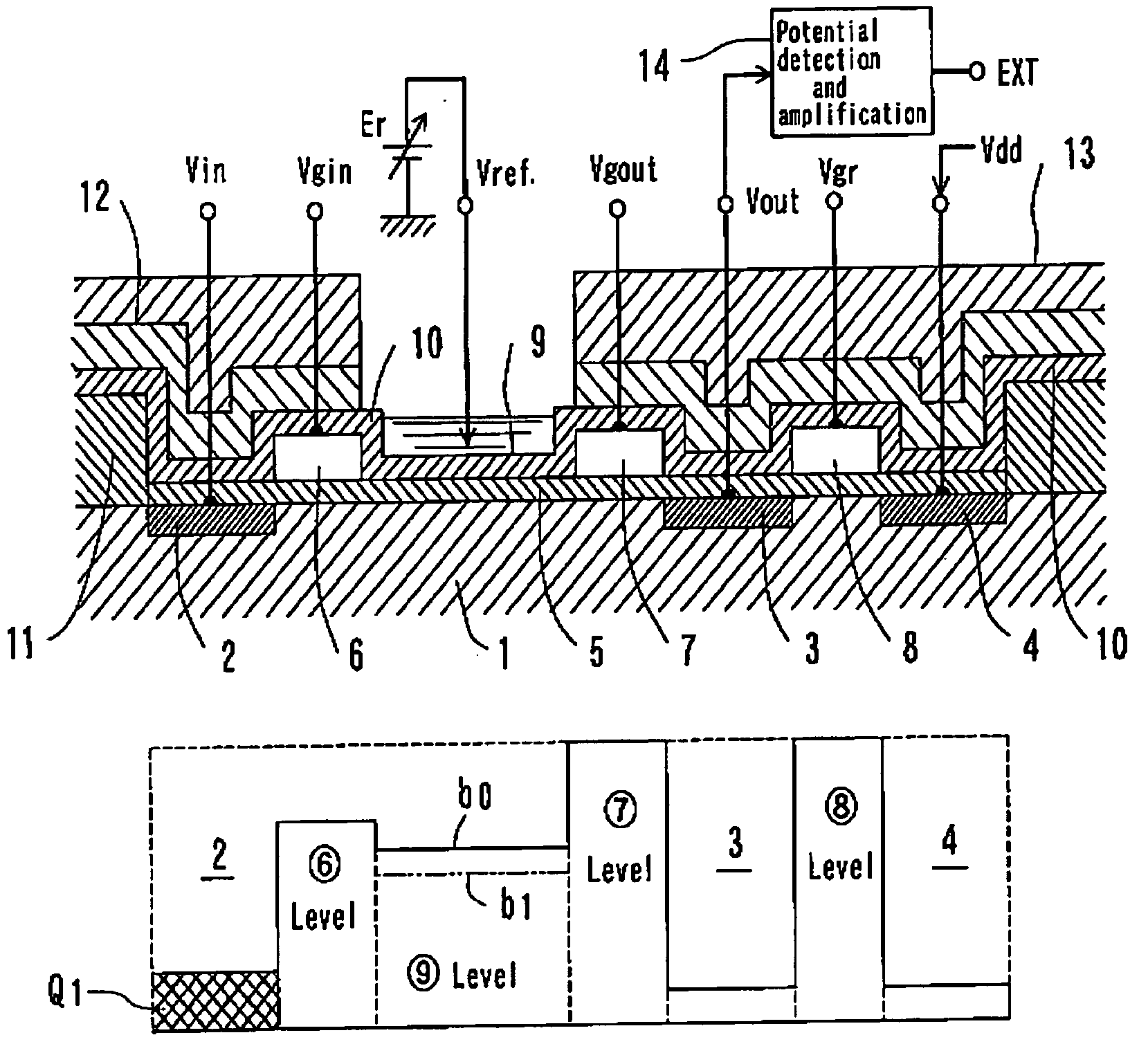
FET type sensor, ion density detecting method comprising this sensor, and base sequence detecting method
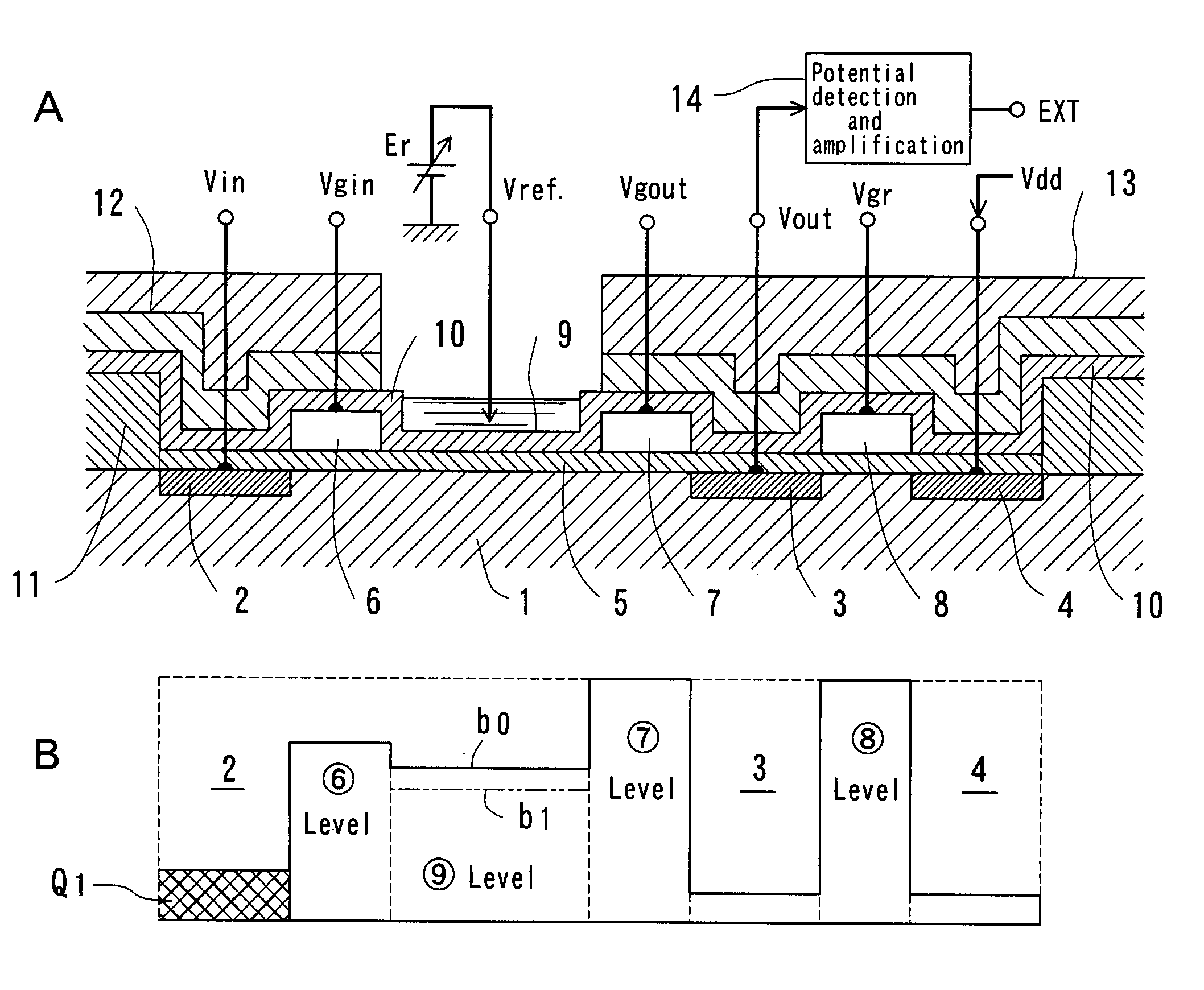
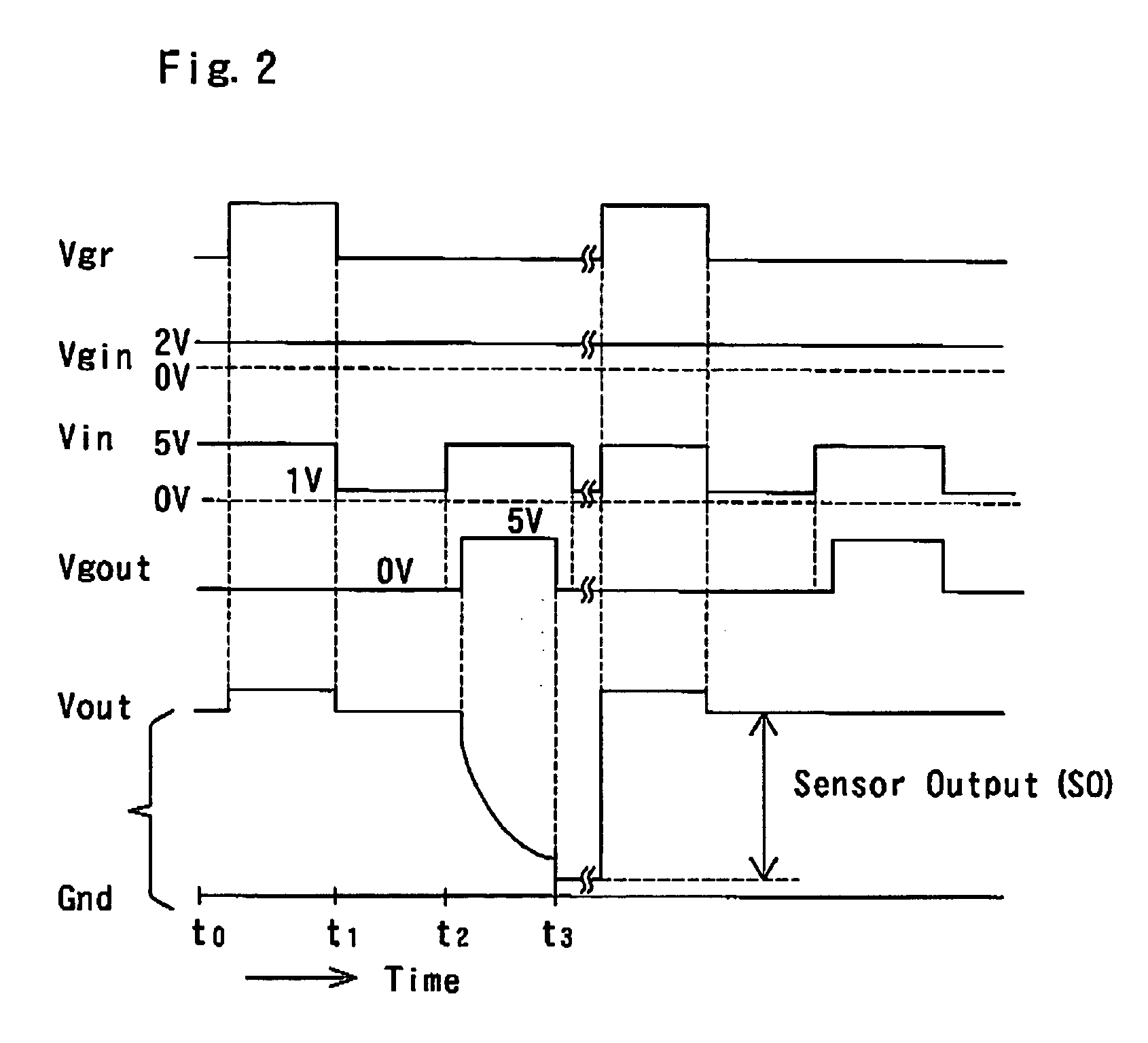
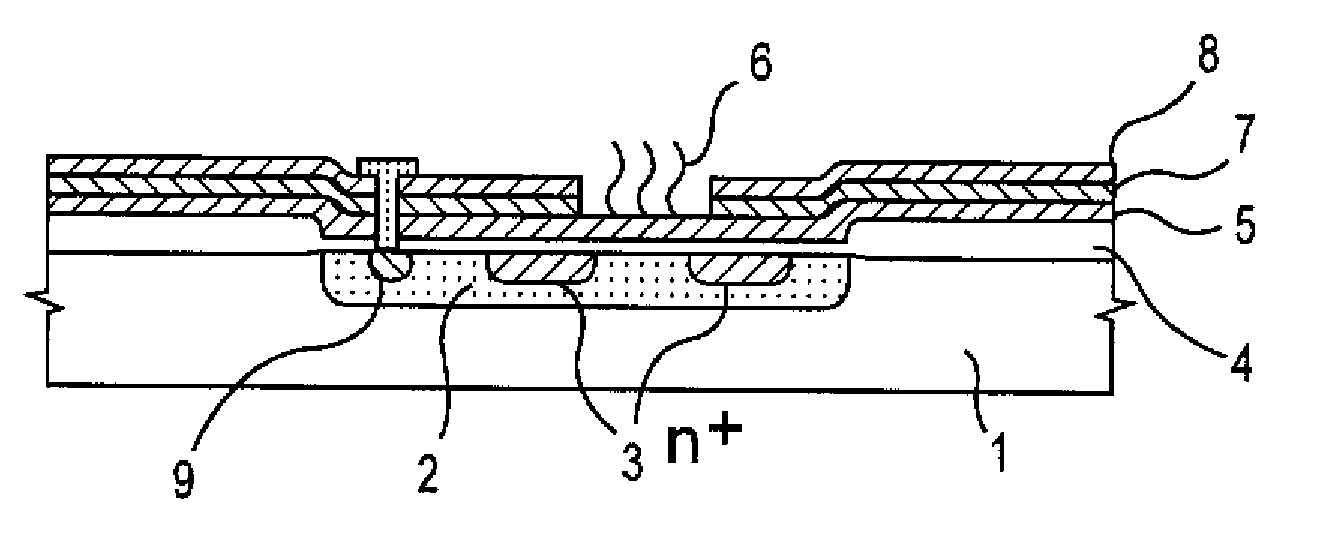
InactiveUS7049645B2Low costSure easyTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusionIon density
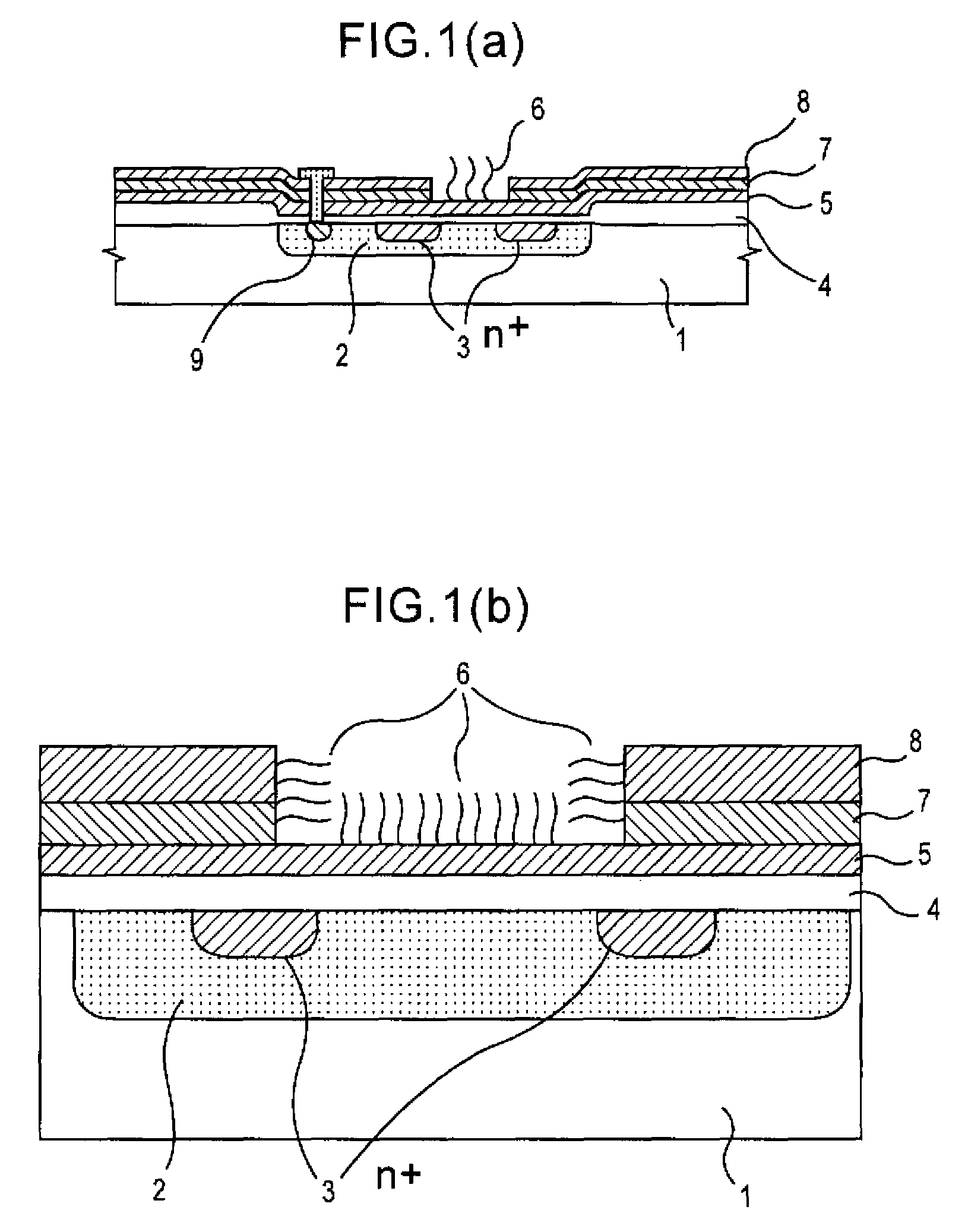
The surface of a semiconductor substrate (1) comprises an input diode section (2) and a floating diffusion section (3) consisting of a diffusion region reverse to the substrate in conductivity type, an input gate (6) and an output gate (7) fixed on an insulation film (5) extending from an input diode section to a floating diffusion section, a sensing section (9) consisting of an ion sensitive film fixed on the insulation film extending from the input.
Owner:BAIO TSUKUSU +1
Reference Signal Resource Allocation for Single User MIMO
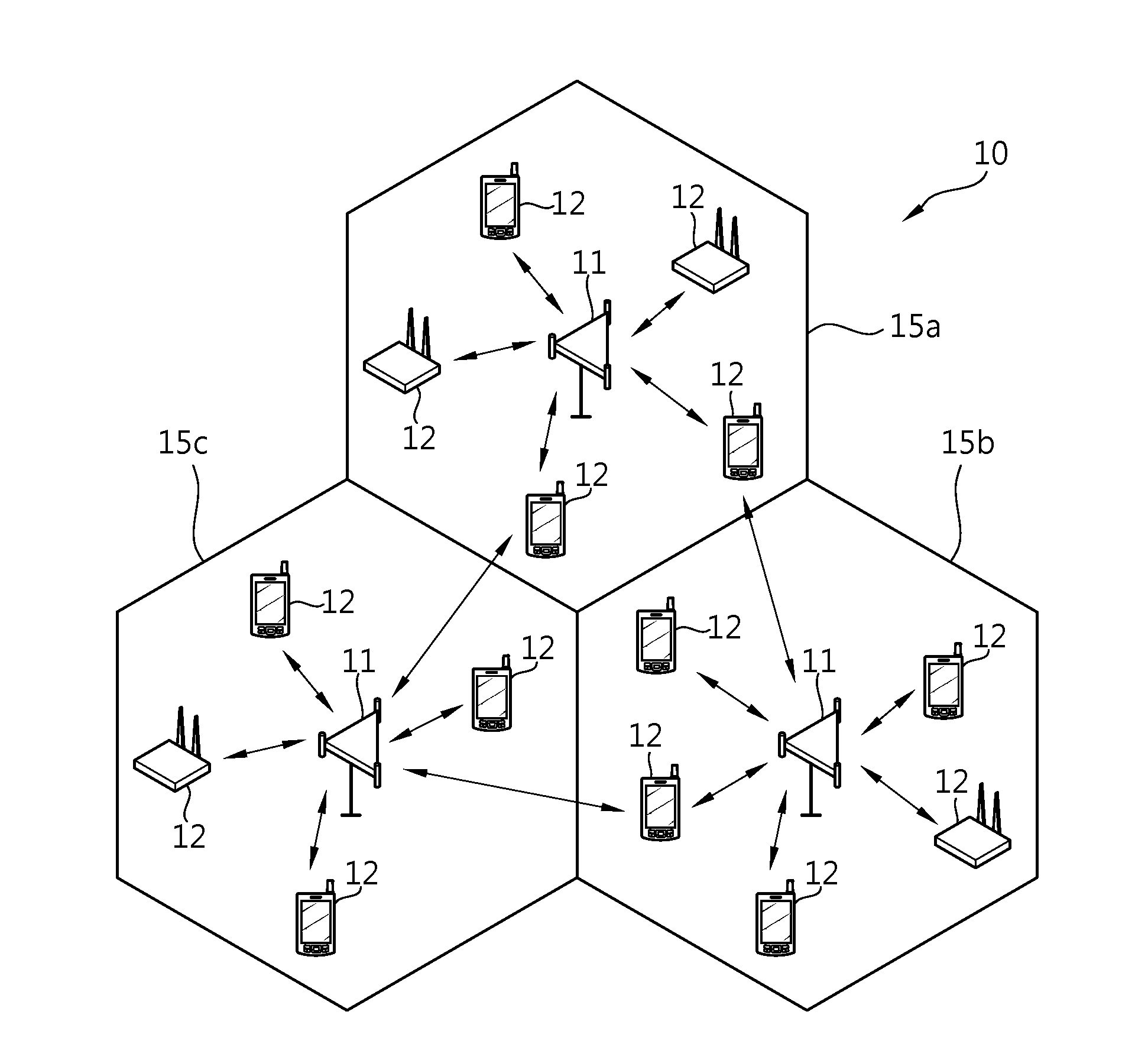
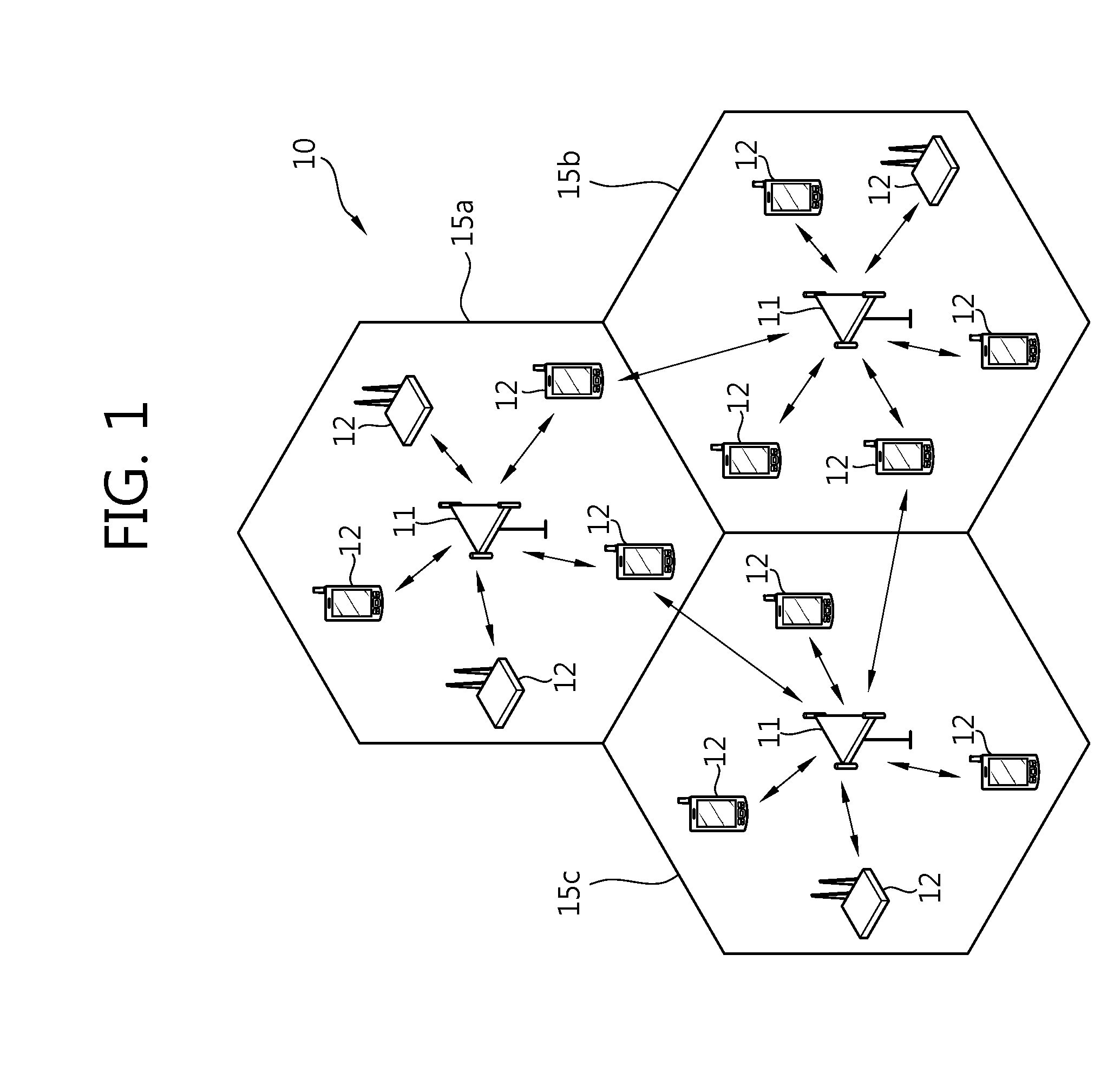
ActiveUS20100034312A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationTelecommunicationsMimo transmission
Transmission with multiple antennas in a wireless network is performed by transmitting a plurality of reference sequences (RS) from a UE. A first RS s1[k] is produced using a first cyclic shift and a base sequence s0[k], wherein k={1, 2 . . . K} is an element index. A second RS s2[k] is produced using a second cyclic shift and s0[k]. A first symbol sequence x1[k] is produced using at least s1[k] and s2[k], for at least one k. A second symbol sequence x2[k] is produced using at least s1[k] and s2[k], for at least one k. x1[k] is transmitted using a first transmit antenna and x2[k] is transmitted using a second transmit antenna.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
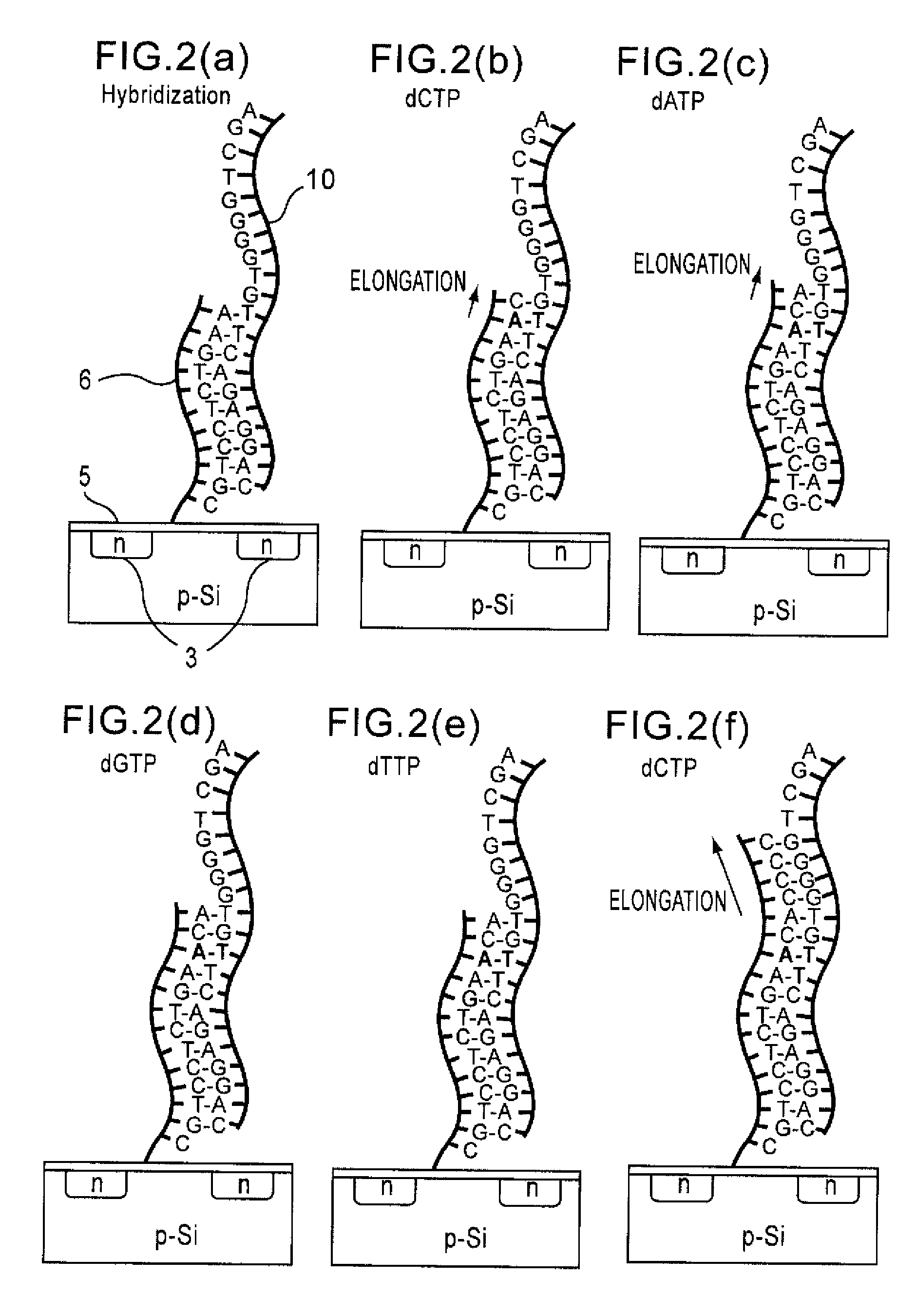
Method of analyzing DNA sequence using field-effect device, and base sequence analyzer
ActiveUS7888013B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
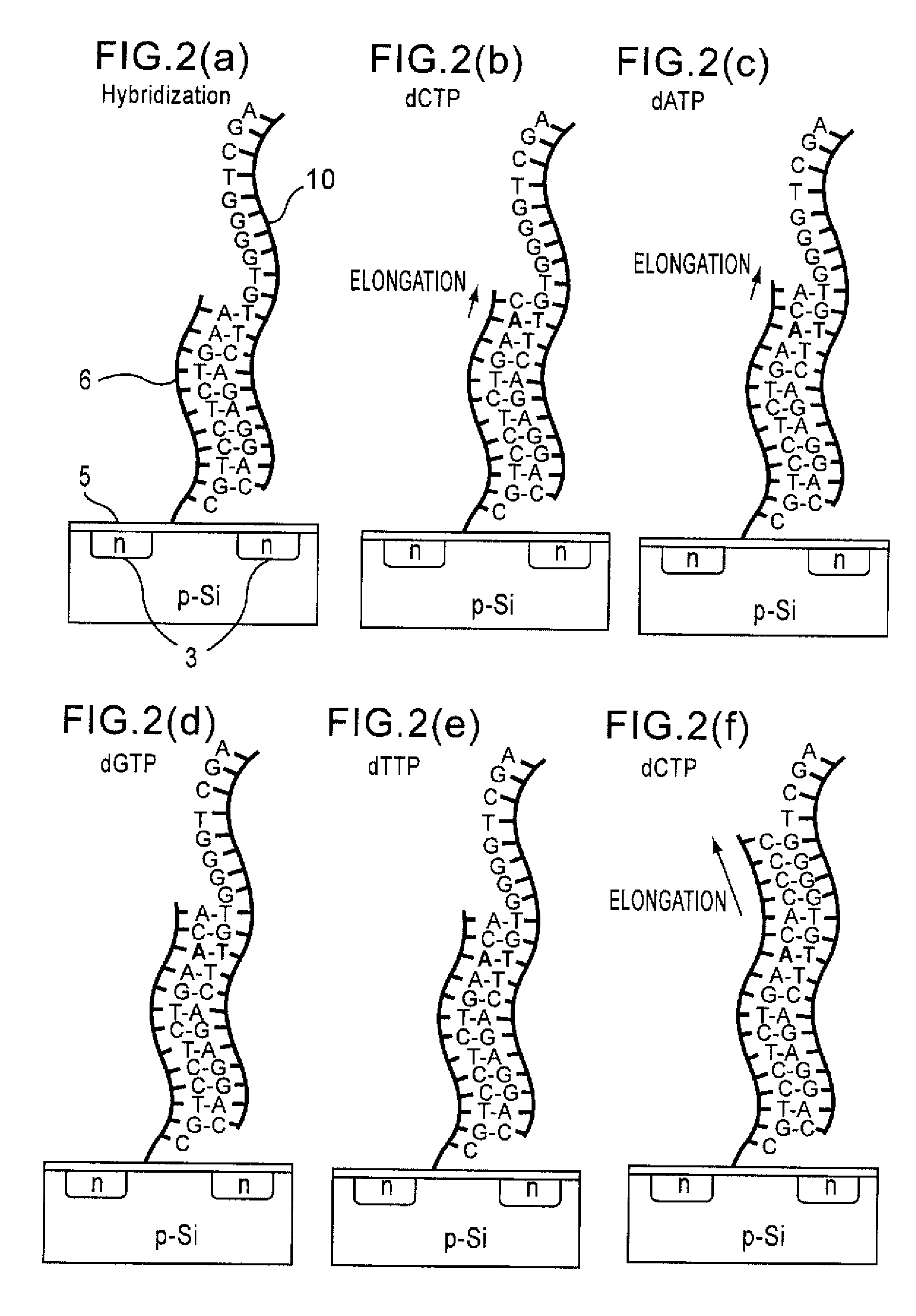
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
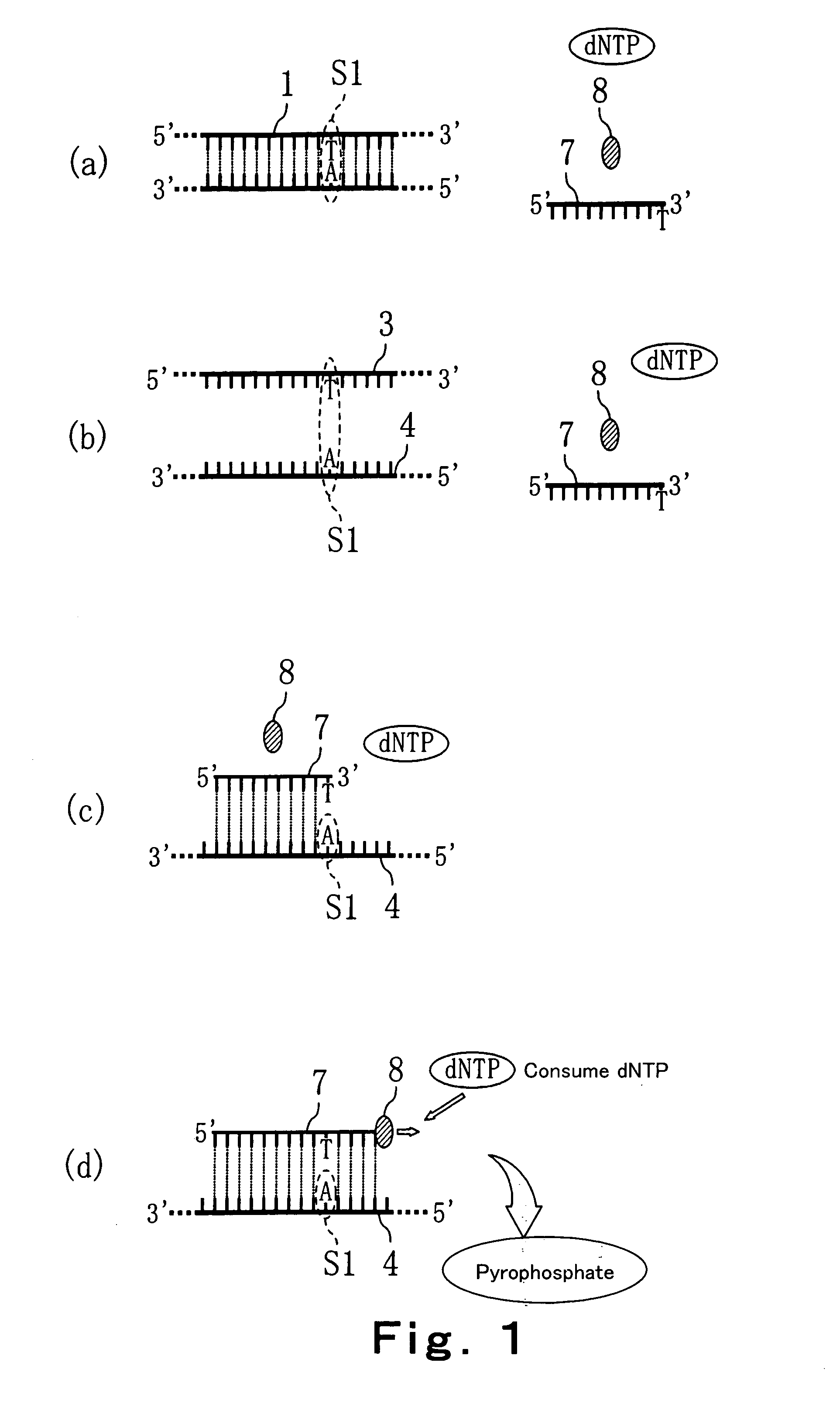
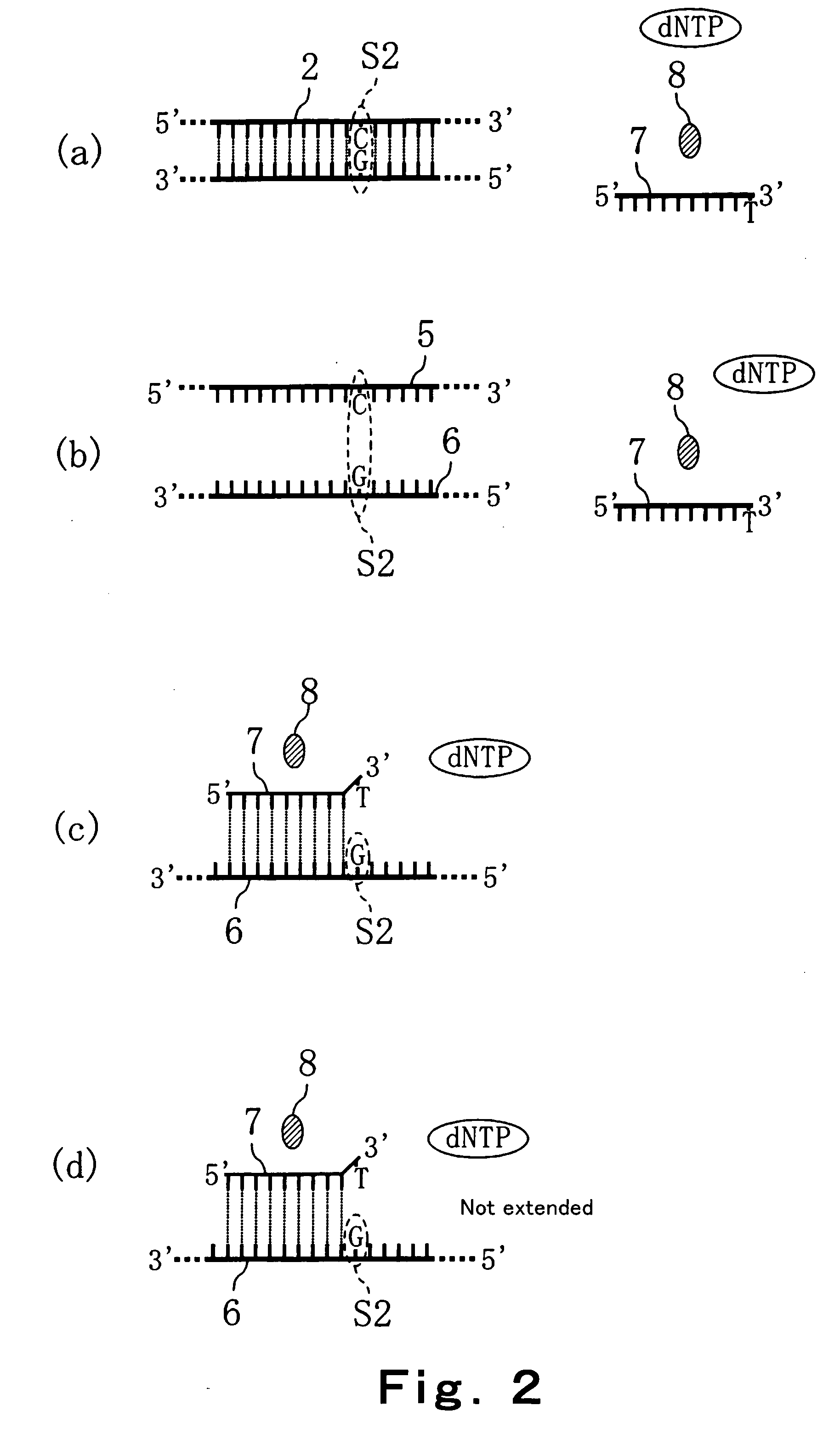
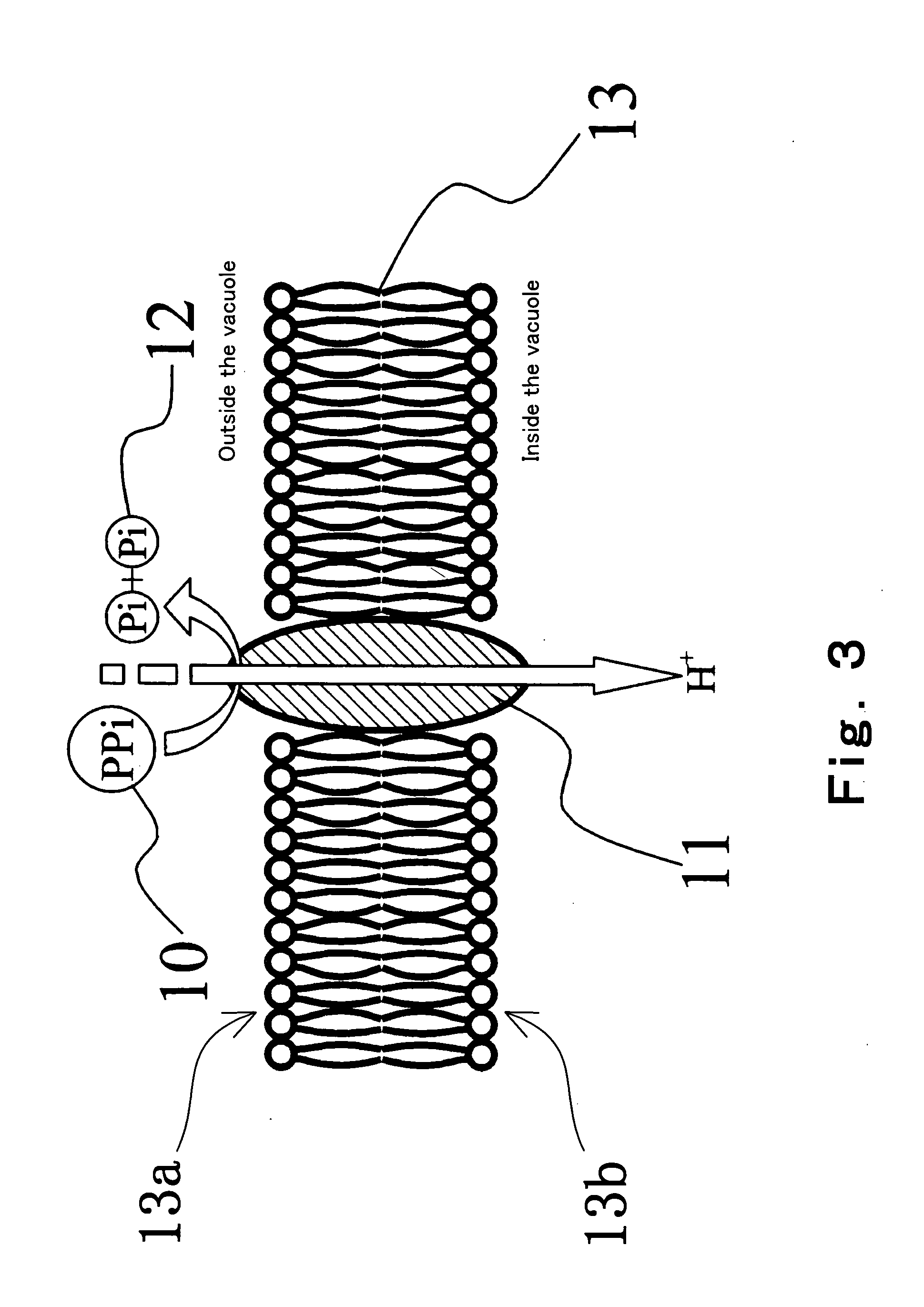
Method of detecting primer extension reaction, method of discriminating base type, device for discriminating base type, device for detecting pyrophosphate, method of detecting nucleic acid and tip for introducing sample solution
InactiveUS20050032075A1Decrease of H+ concentrationImprove concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBase JNucleotide
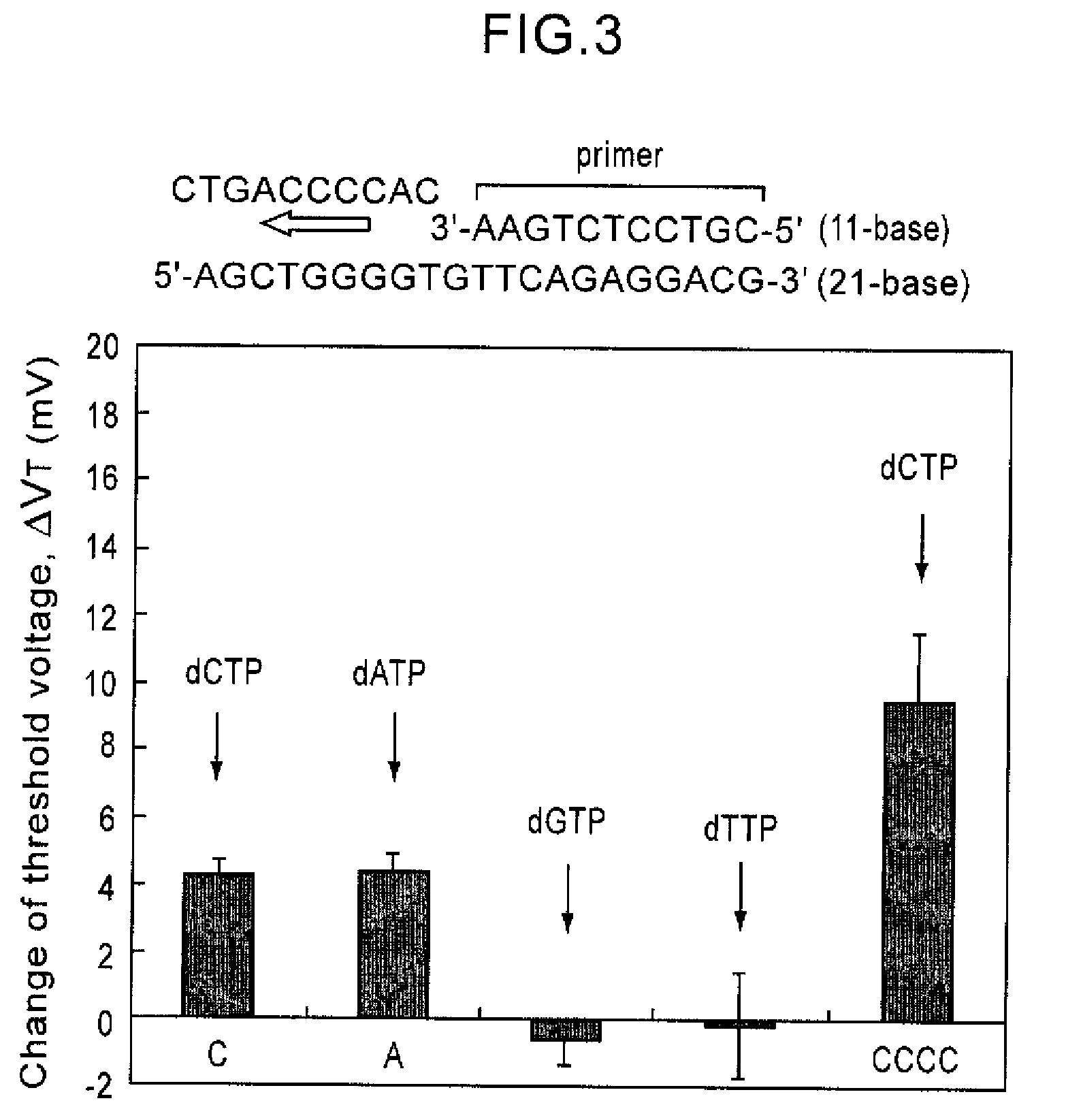
Convenient techniques for discriminating the base type in a base sequence of a nucleic acid are provided. The technique includes the step (a) of preparing a sample solution containing a nucleic acid, a primer having a base sequence that includes a complementary binding region which complementarily binds to the nucleic acid, and a nucleotide; the step (b) of allowing the sample solution to stand under a condition to cause an extension reaction of the primer, and producing pyrophosphate when the extension reaction is caused; the step (c) of bringing the sample solution into contact with the front face of a H+ hardly permeable membrane having H+-pyrophosphatase, which penetrates from front to back of the membrane, of which active site that hydrolyzes pyrophosphate being exposed to the front face; the step (d) of measuring the H+ concentration of at least either one of the solution at the front face side of the H+ hardly permeable membrane or the solution at the back face side of the H+ hardly permeable membrane, in a state where the H+-pyrophosphatase is immersed in the solution; the step (e) of detecting the extension reaction on the basis of the result of measurement in the step (d) ; and the step (f) of discriminating the base type in the base sequence of the nucleic acid on the basis of the result of detection in the step (e).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
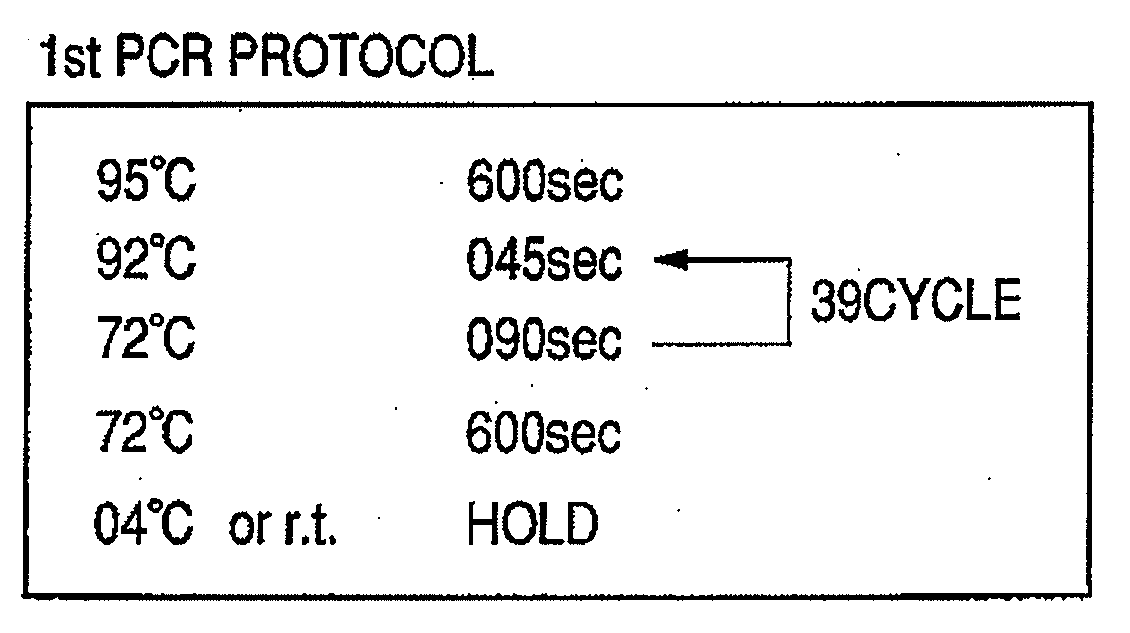
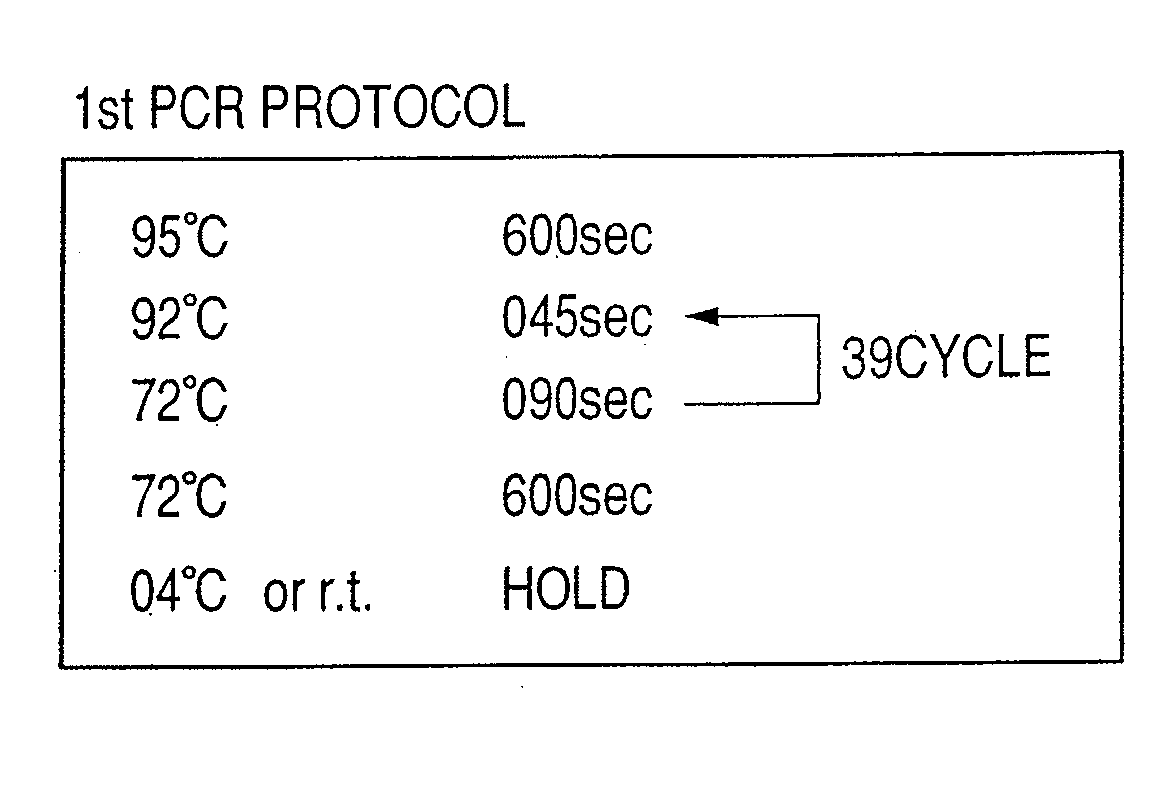
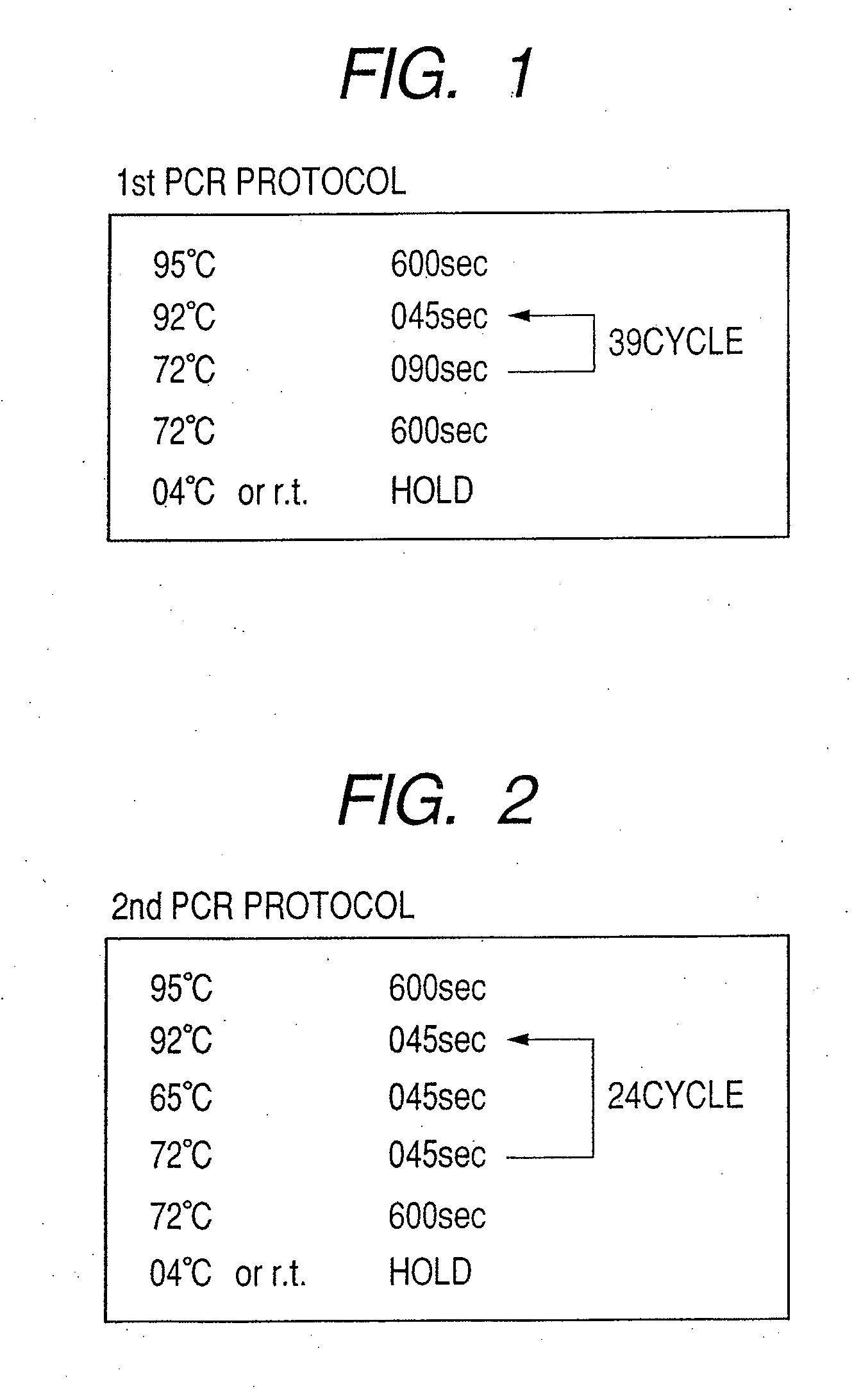
Polymerase chain reaction of DNA of which base sequence is completely unidentified
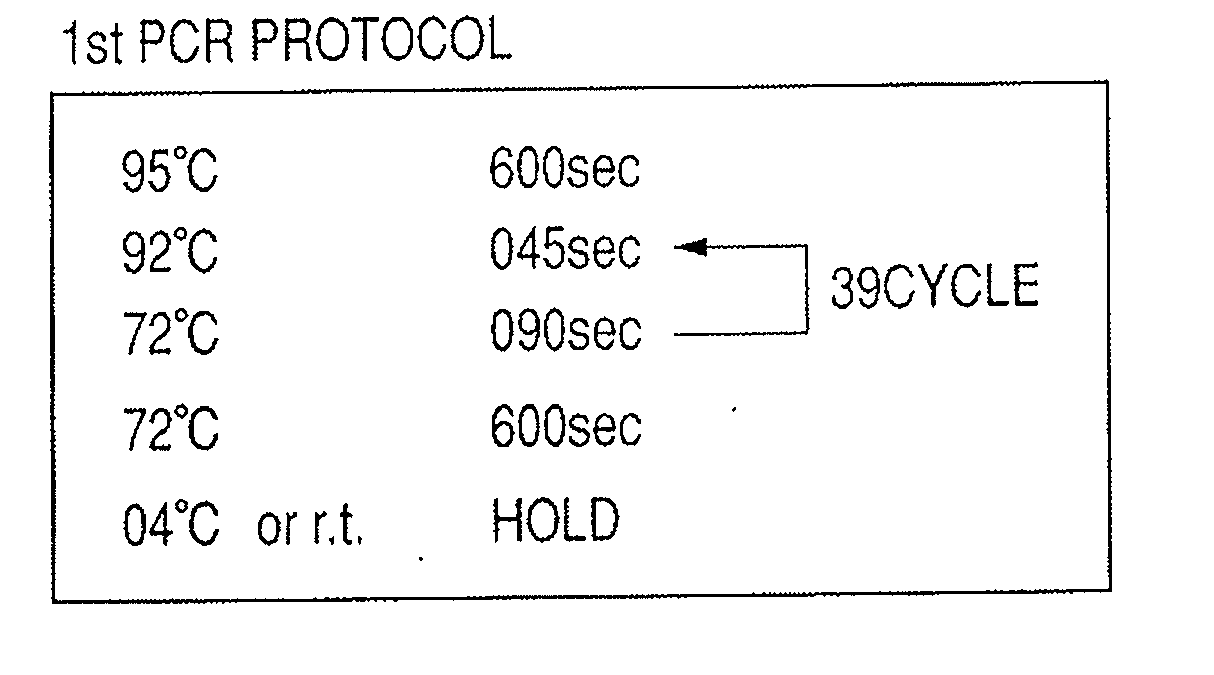
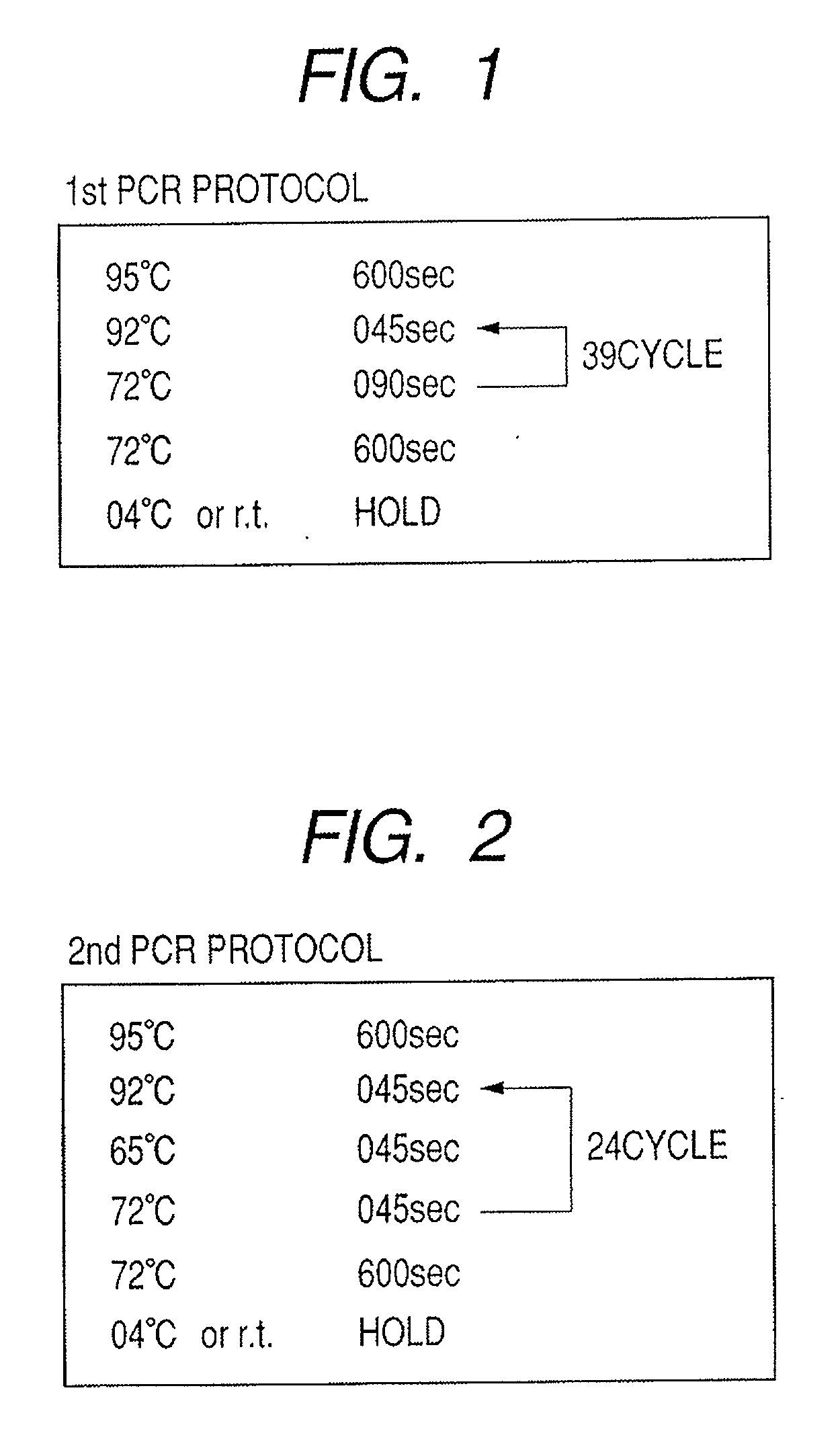
The present invention relates to a process for amplifying DNA of an organism. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a process for amplifying DNA of an organism through Polymerase Chain Reaction(PCR) without any information regarding a primer needed for amplifying DNA of an organism.
Owner:BIONEER
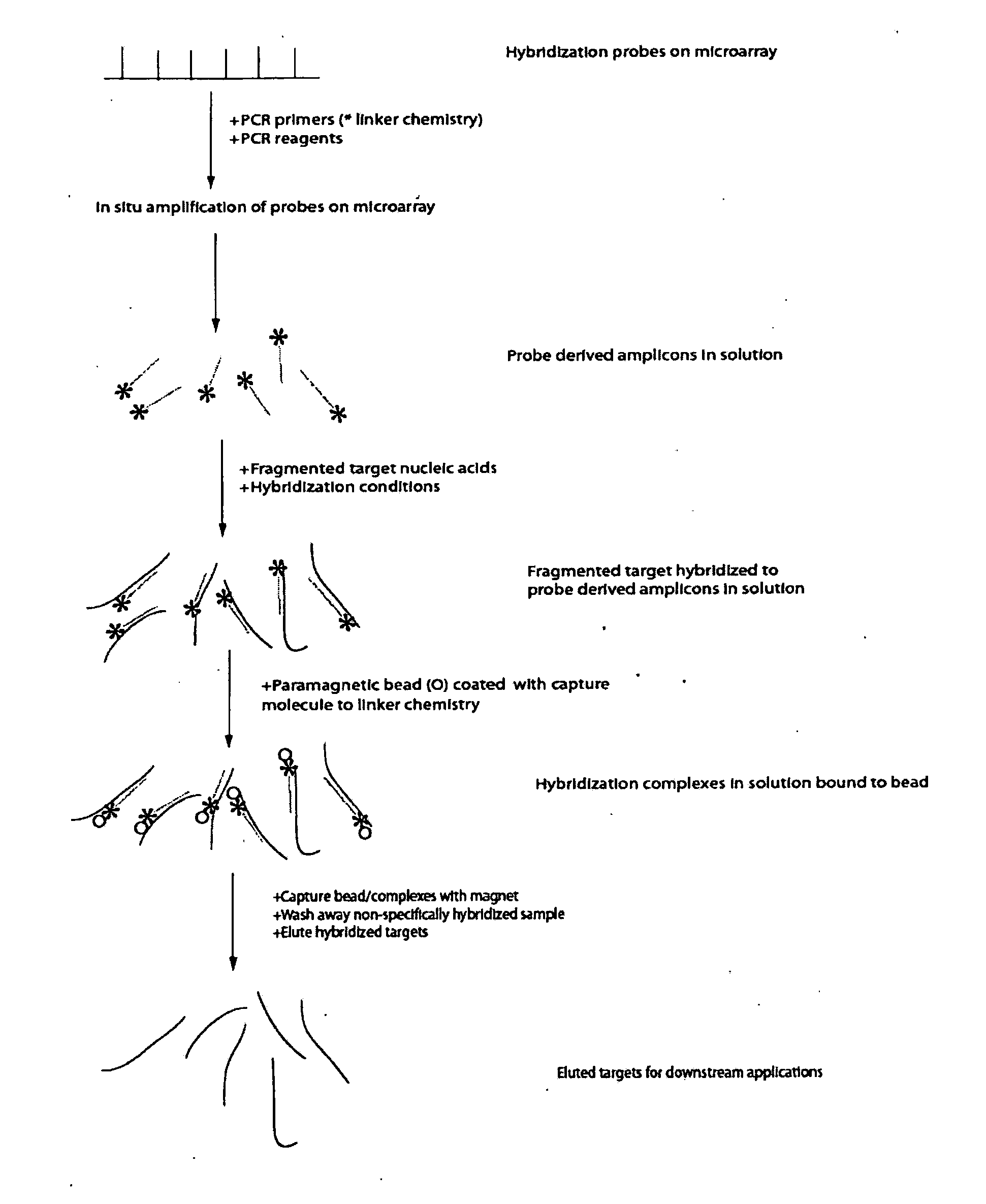
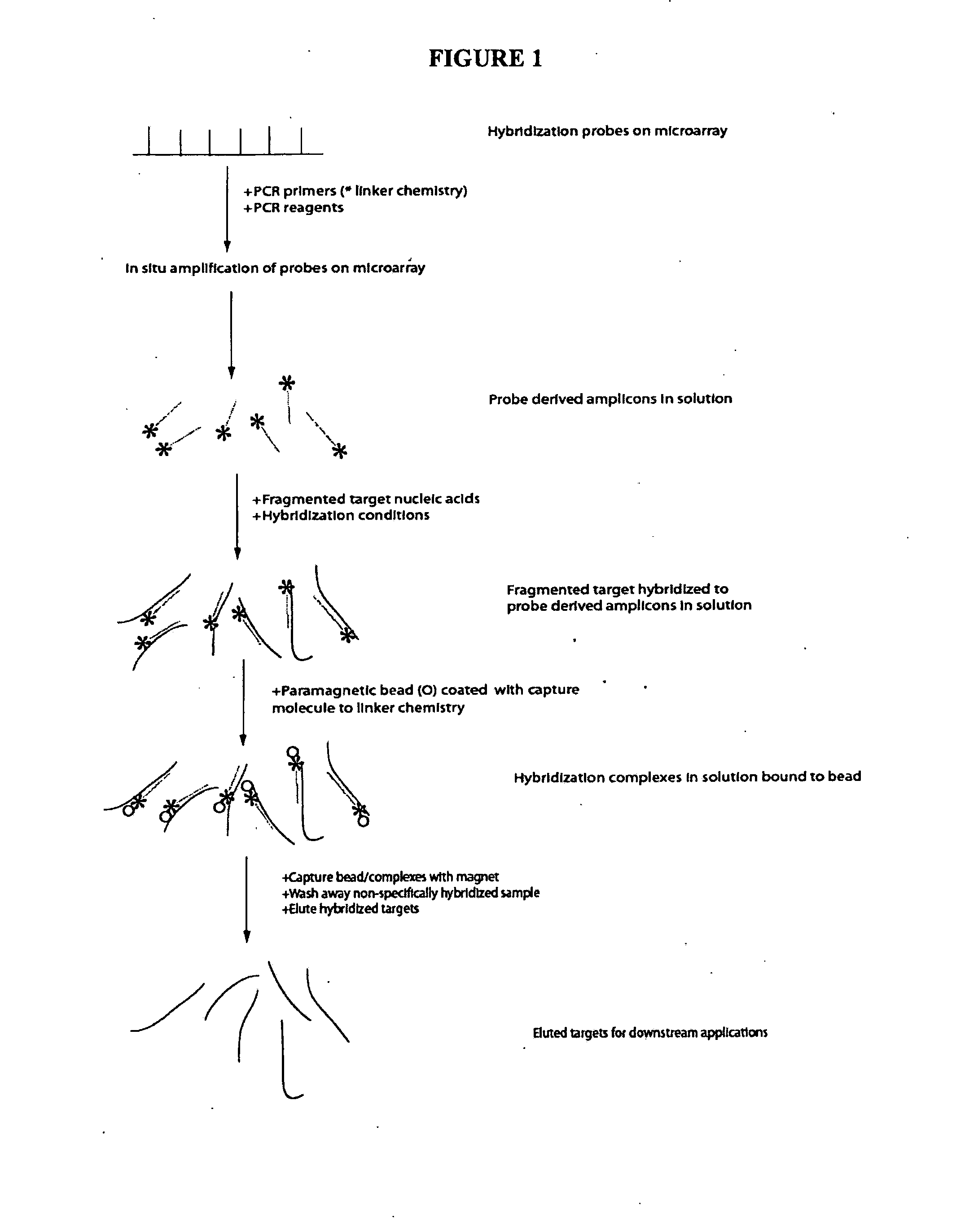
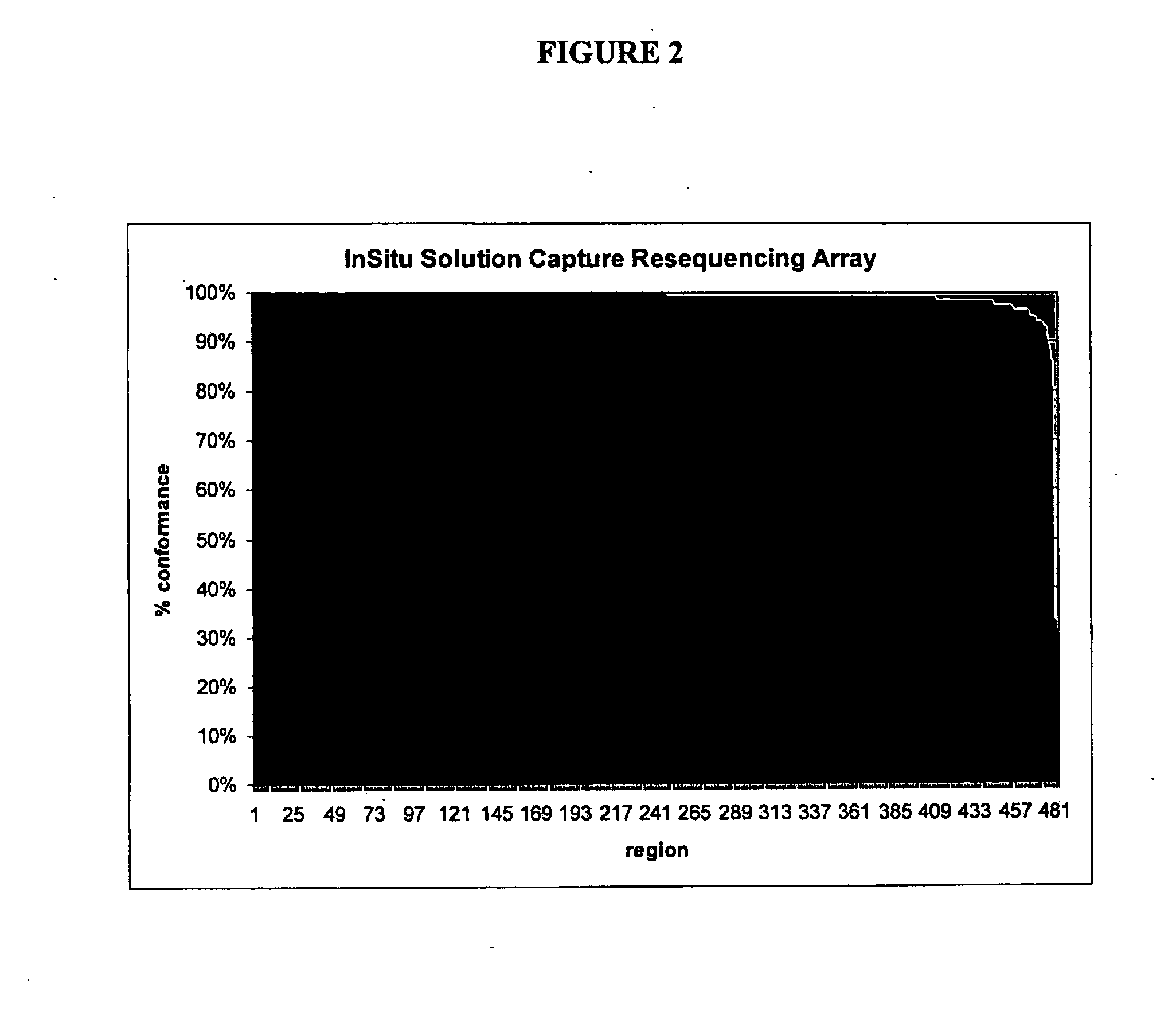
Methods and systems for solution based sequence enrichment
ActiveUS20120046175A1Significant complexityEasy to analyzeSugar derivativesLibrary tagsBase sequenceBioinformatics
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
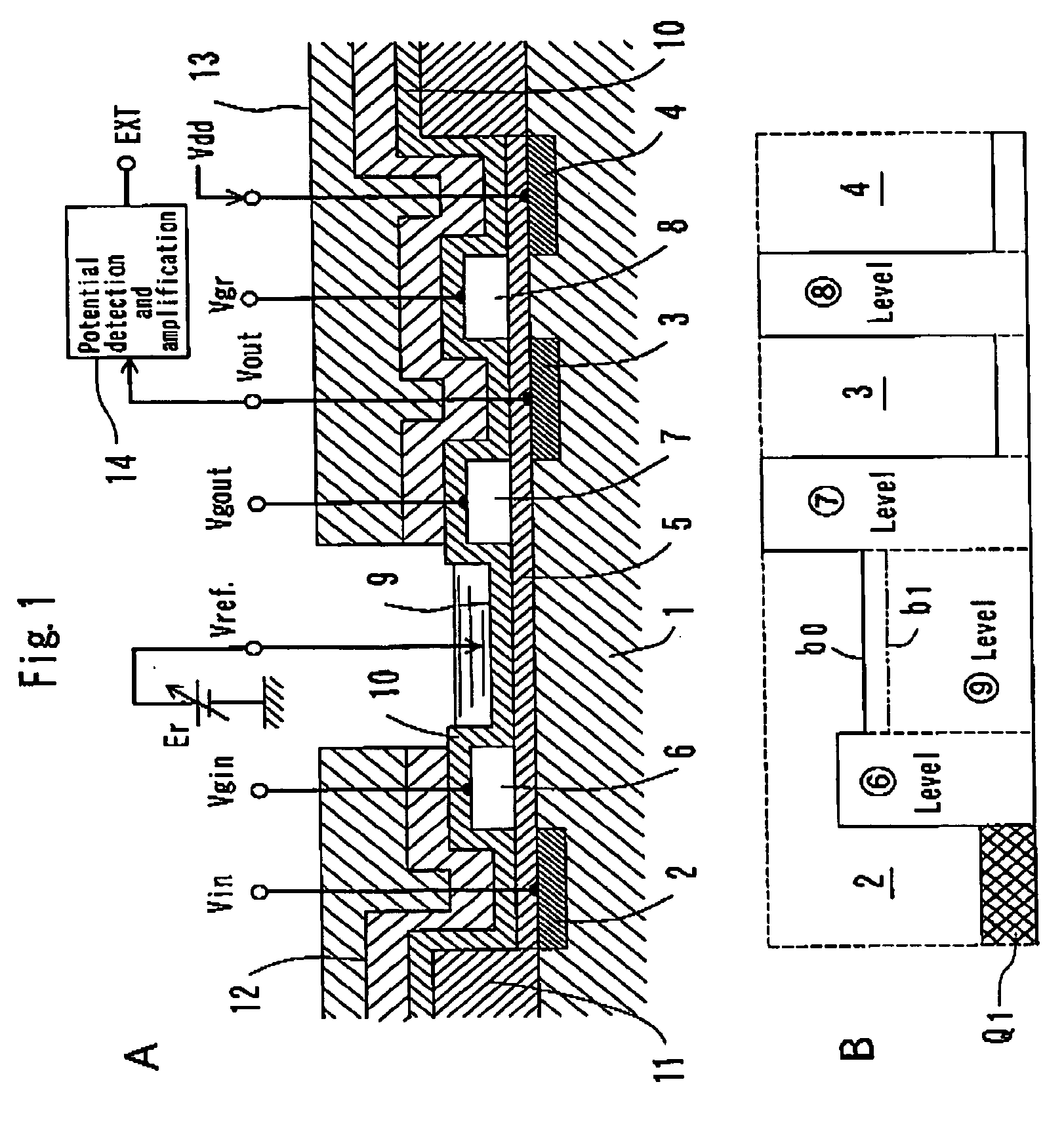
Fet type sensor, ion density detecting method comprising this sensor, and base sequence detecting method
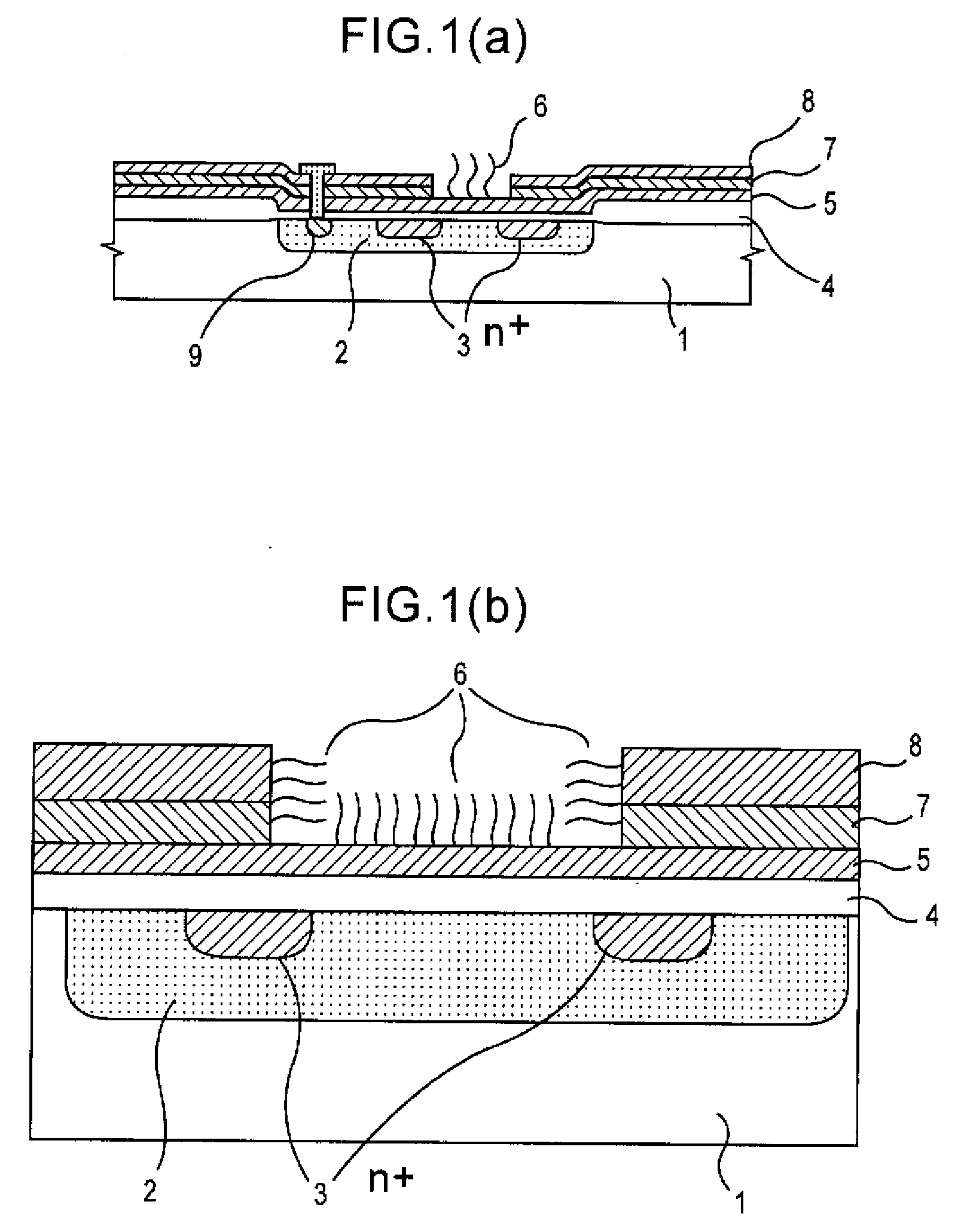
InactiveUS20050062093A1Accurate detectionLow costTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusionIon density
The surface of a semiconductor substrate (1) comprises an input diode section (2) and a floating diffusion section (3) consisting of a diffusion region reverse to the substrate in conductivity type, an input gate (6) and an output gate (7) fixed on an insulation film (5) extending from an input diode section to a floating diffusion section, a sensing section (9) consisting of an ion sensitive film fixed on the insulation film extending from the input.
Owner:BAIO TSUKUSU +1
Method for producing polymers
InactiveUS6586211B1Effective studyEfficient and rapid designMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsDouble strandPolymer
The invention relates to a method for producing polymers, in particular synthetic nucleic acid double strands of optional sequence, comprising the steps:(a) provision of a support having a surface area which contains a plurality of individual reaction areas,(b) location-resolved synthesis of nucleic acid fragments having in each case different base sequences in several of the individual reaction areas, and(c) detachment of the nucleic acid fragments from individual reaction areas.
Owner:CODEX DNA INC
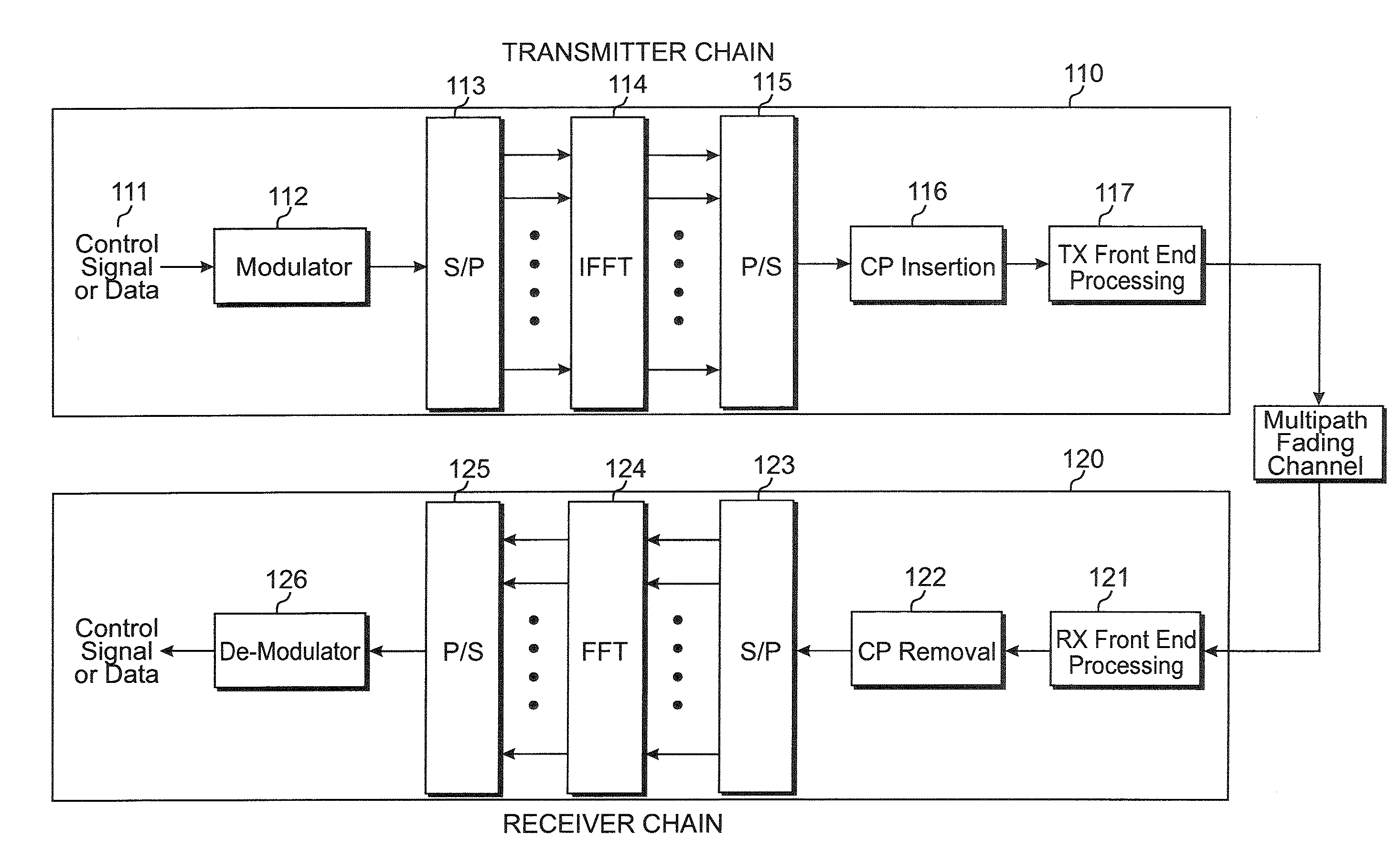
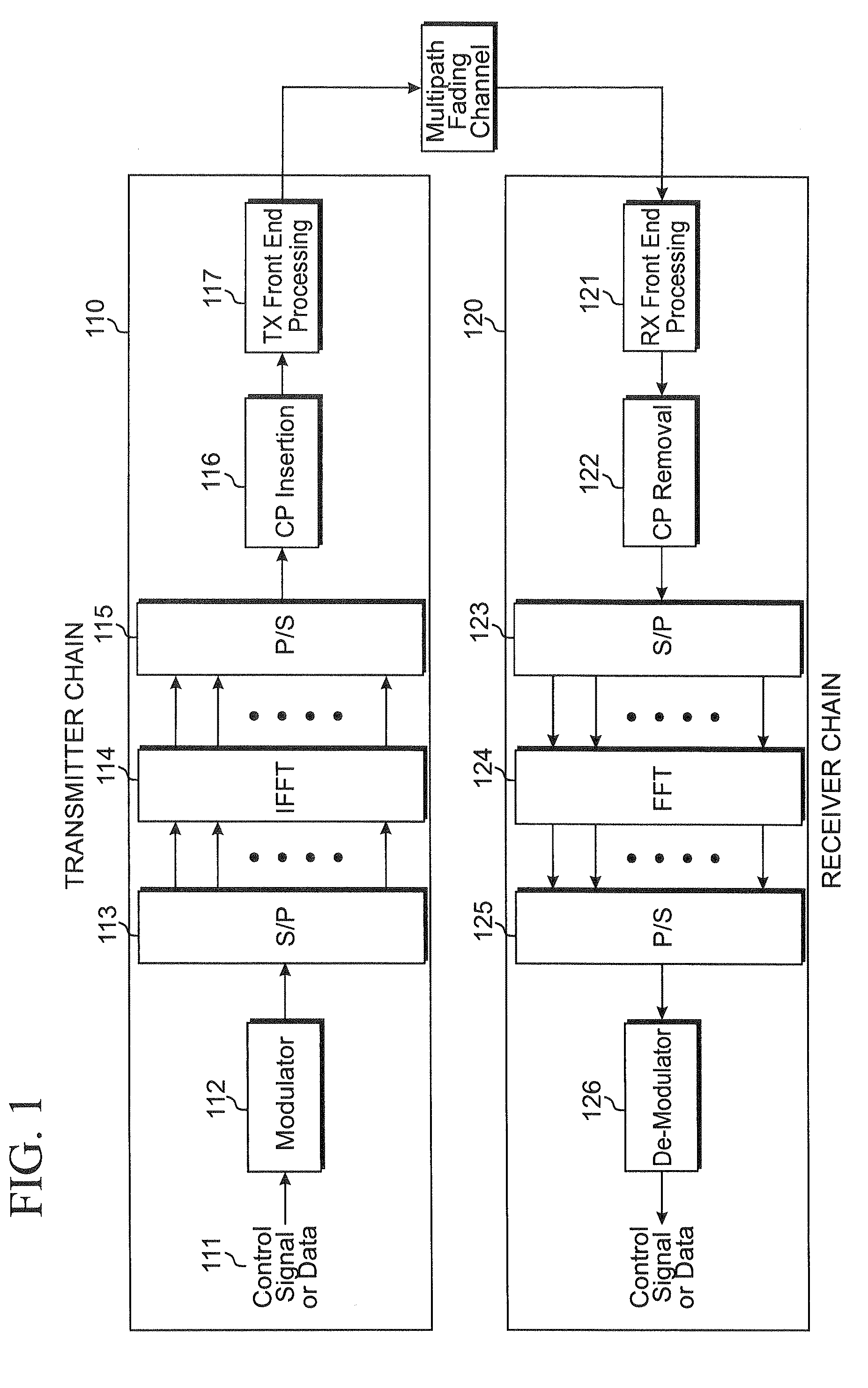
Method of transmitting control signal in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090290538A1Guaranteed normal transmissionImprove system performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemResource block
A method of transmitting a control signal in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes acquiring a resource index, the number of cyclic shifts (CSs) and a CS interval, wherein the number of CSs is an integer multiple of the CS interval, determining a CS index based on the number of CSs and the CS interval, generating a cyclically shifted sequence by cyclically shifting a base sequence by a CS amount obtained from the CS index, generating a modulated sequence based on the cyclically shifted sequence and a symbol for a control signal and transmitting the modulated sequence after mapping the modulated sequence to a resource block obtained from the resource index.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Antisense composition and method for treating cancer
A method and composition for treating colorectal cancer is disclosed. The method involves administering to a subject, a therapeutically effective amount of a morpholino antisense compound (i) having a nuclease-resistant backbone, (ii) capable of uptake by target cancer cells in the subject, (iii) containing between 10-40 nucleotide bases, and (iv) having a base sequence effective to hybridize to a region of processed or preprocessed human SNAIL RNA transcript.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Method of Analyzing Dna Sequence Using Field-Effect Device, and Base Sequence Analyzer
ActiveUS20080286767A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
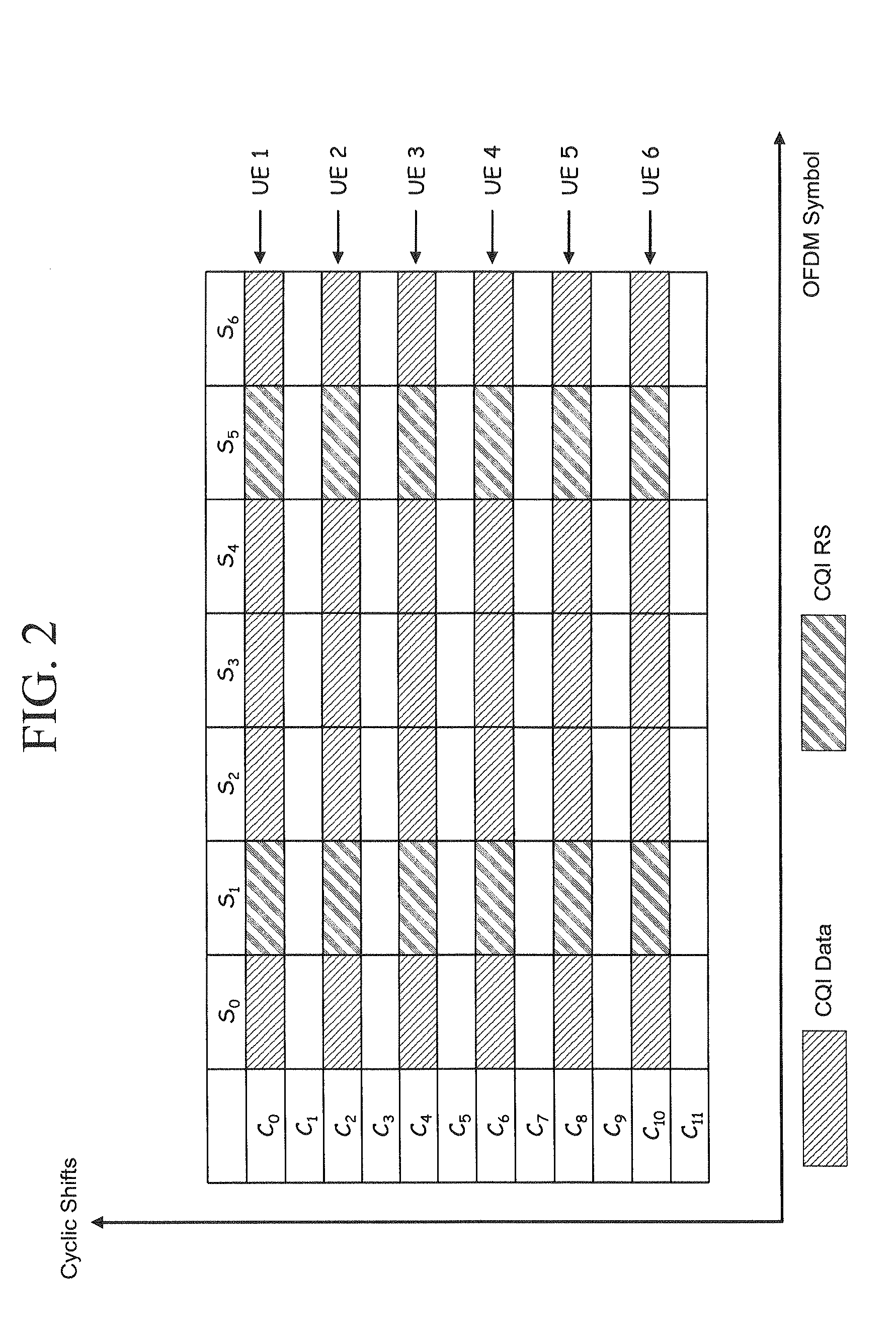
Resource remapping and regrouping in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090092148A1Efficiently remappingTransmission path divisionSignal allocationCell specificCommunications system
Methods and apparatus for remapping and regrouping transmission resources in a wireless communication system. First, a set of new permutation algorithms based on Galois field operation is proposed. Then the proposed algorithms and the known Pruned Bit Reversal Ordering (PBRO) algorithm are applied to several of various resource mapping schemes, including slot or symbol level Orthogonal Cover (OC) / Cyclic Shift (CS) mapping, cell-specific slot-level and symbol-level CS hopping patterns, and subframe and slot level base sequence hopping patterns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mass label linked hybridisation probes
InactiveUS20050042625A1Increase the number ofEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHybridization probeMass spectrometry
An array of hybridization probes, each of which comprises a mass label linked to a known base sequence of predetermined length, wherein each mass label of the array, optionally together with the known base sequence, is relatable to that base sequence by mass spectrometry.
Owner:XZILLION
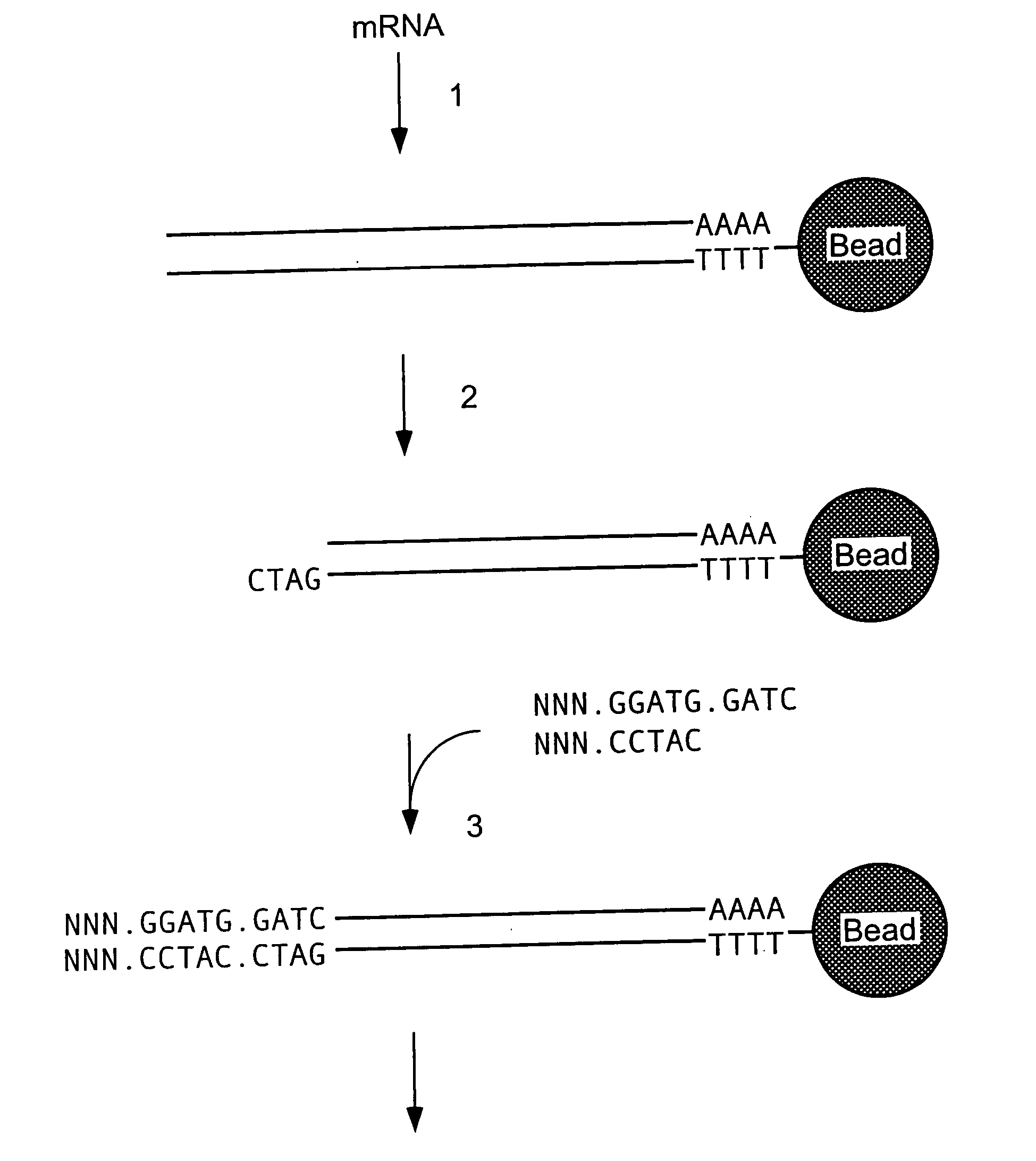
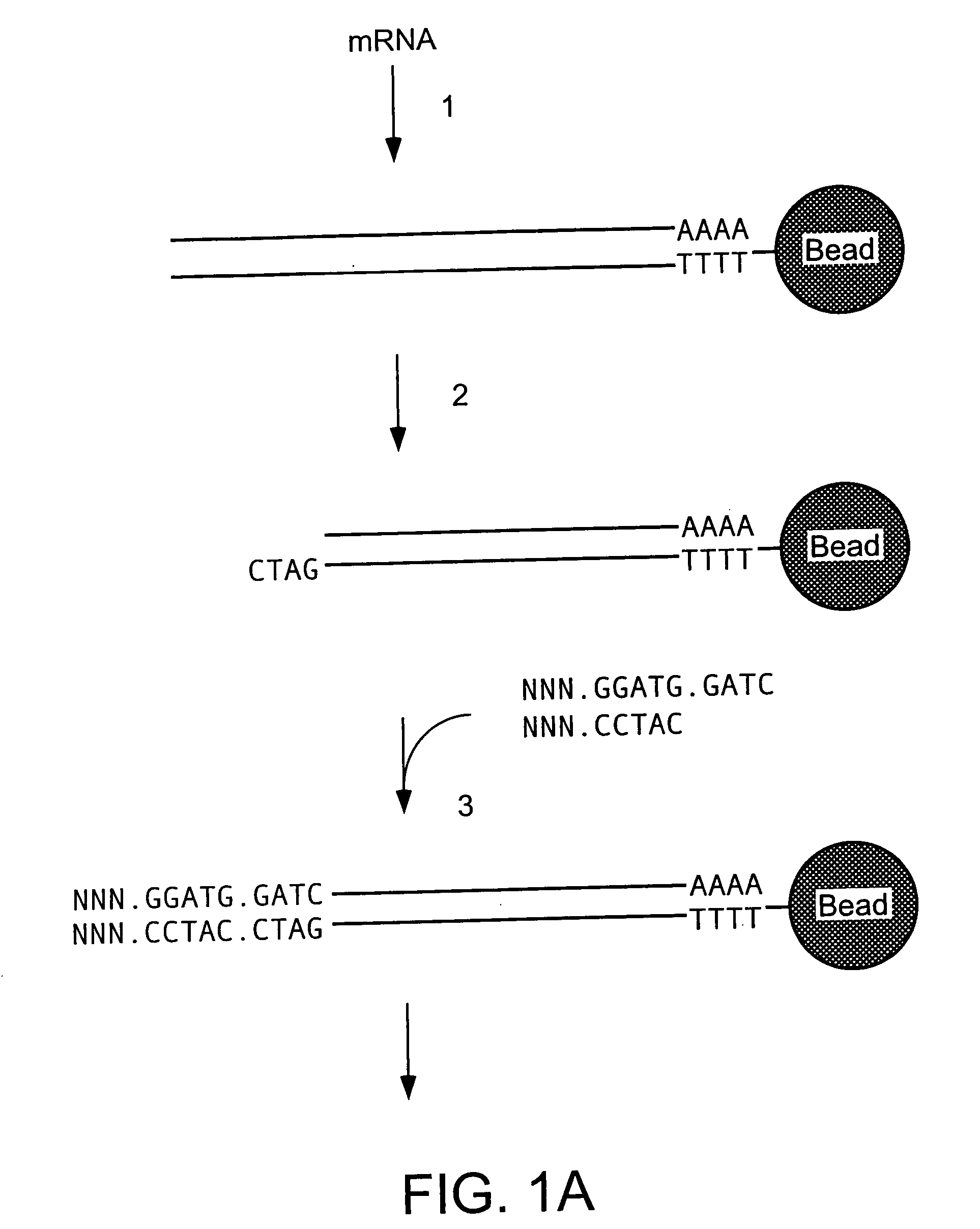
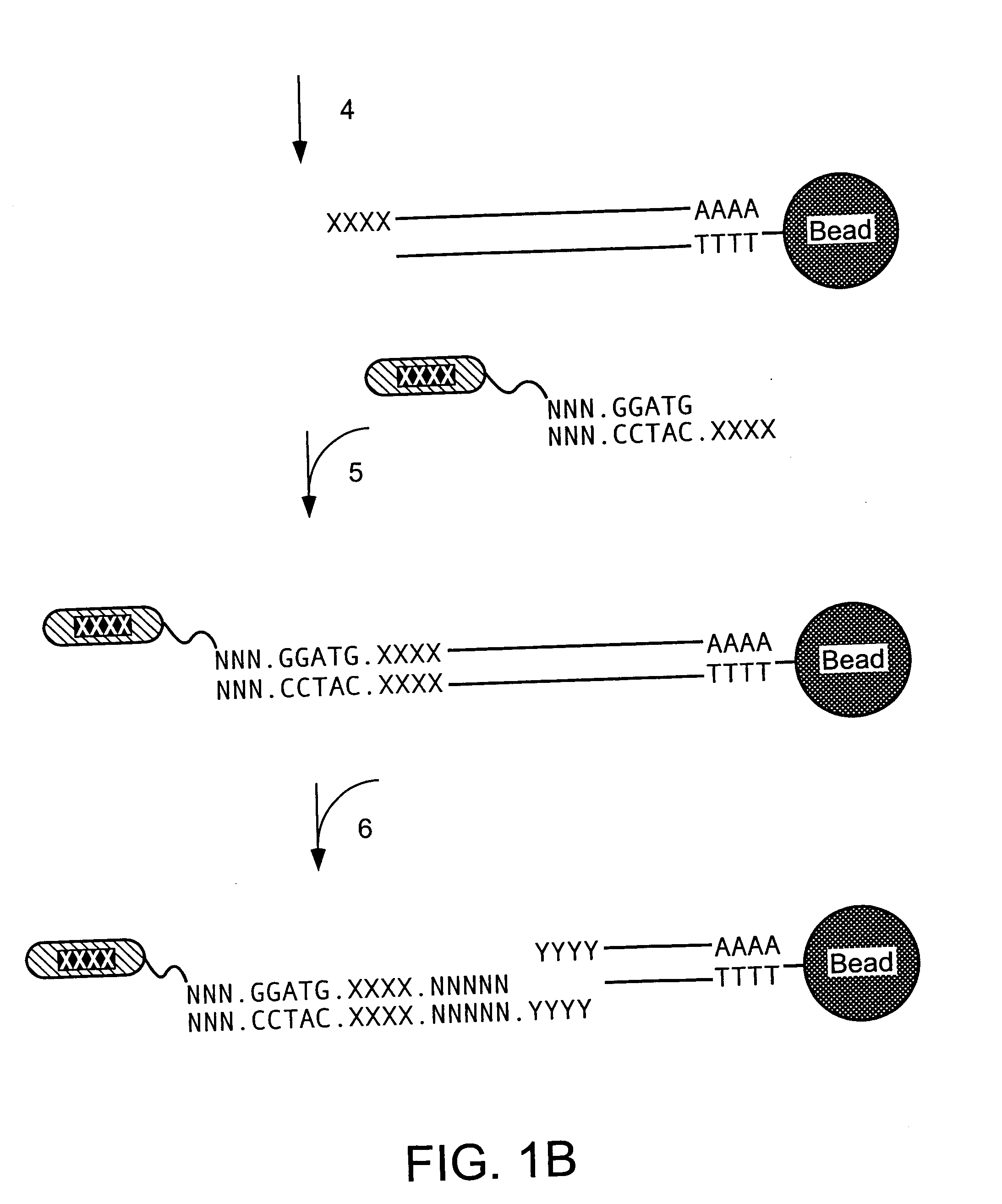
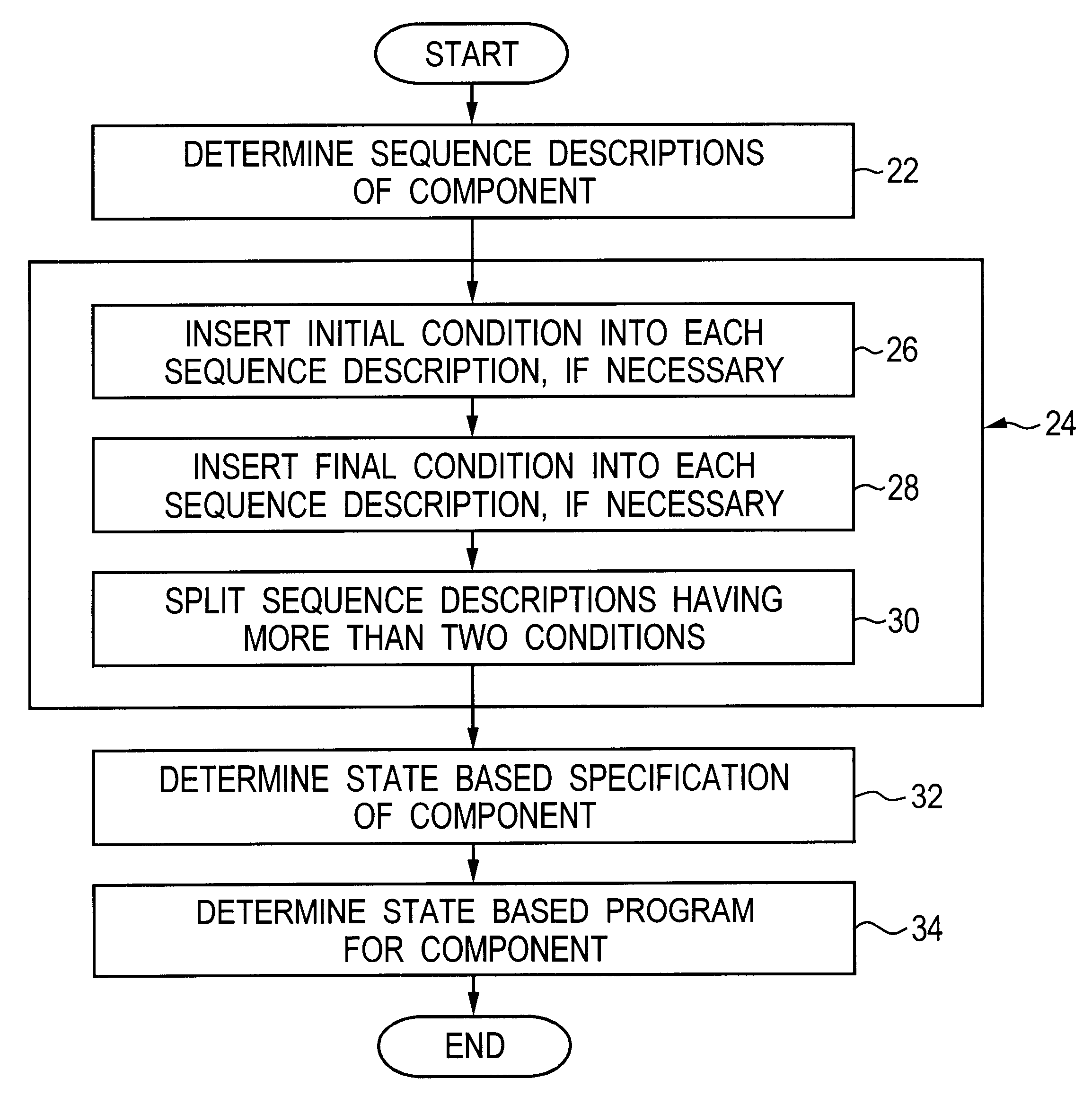
Automatically generating a program
InactiveUS6405361B1Reduce processDecrease necessary effortRequirement analysisSpecific program execution arrangementsTheoretical computer scienceBase sequence
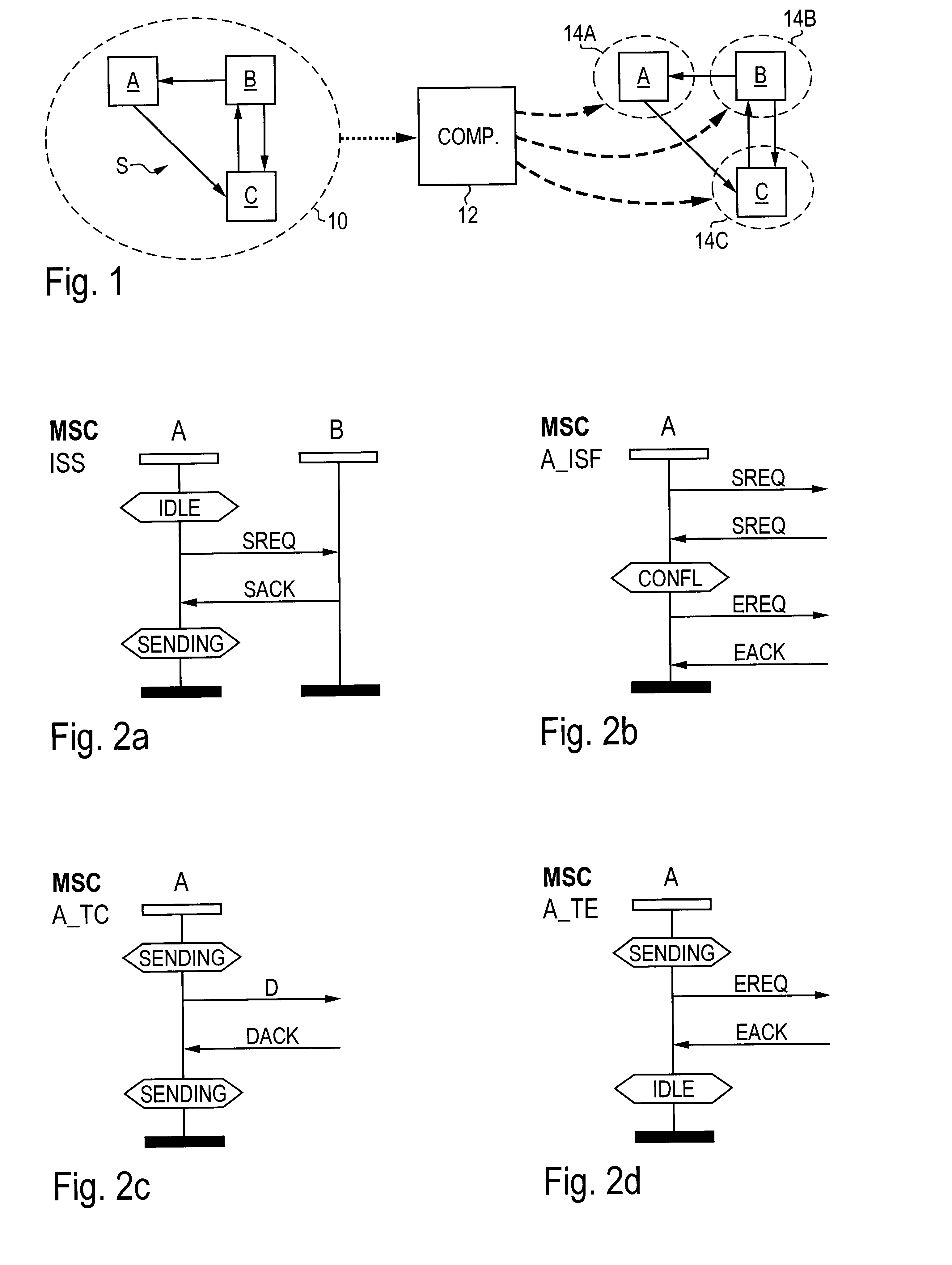
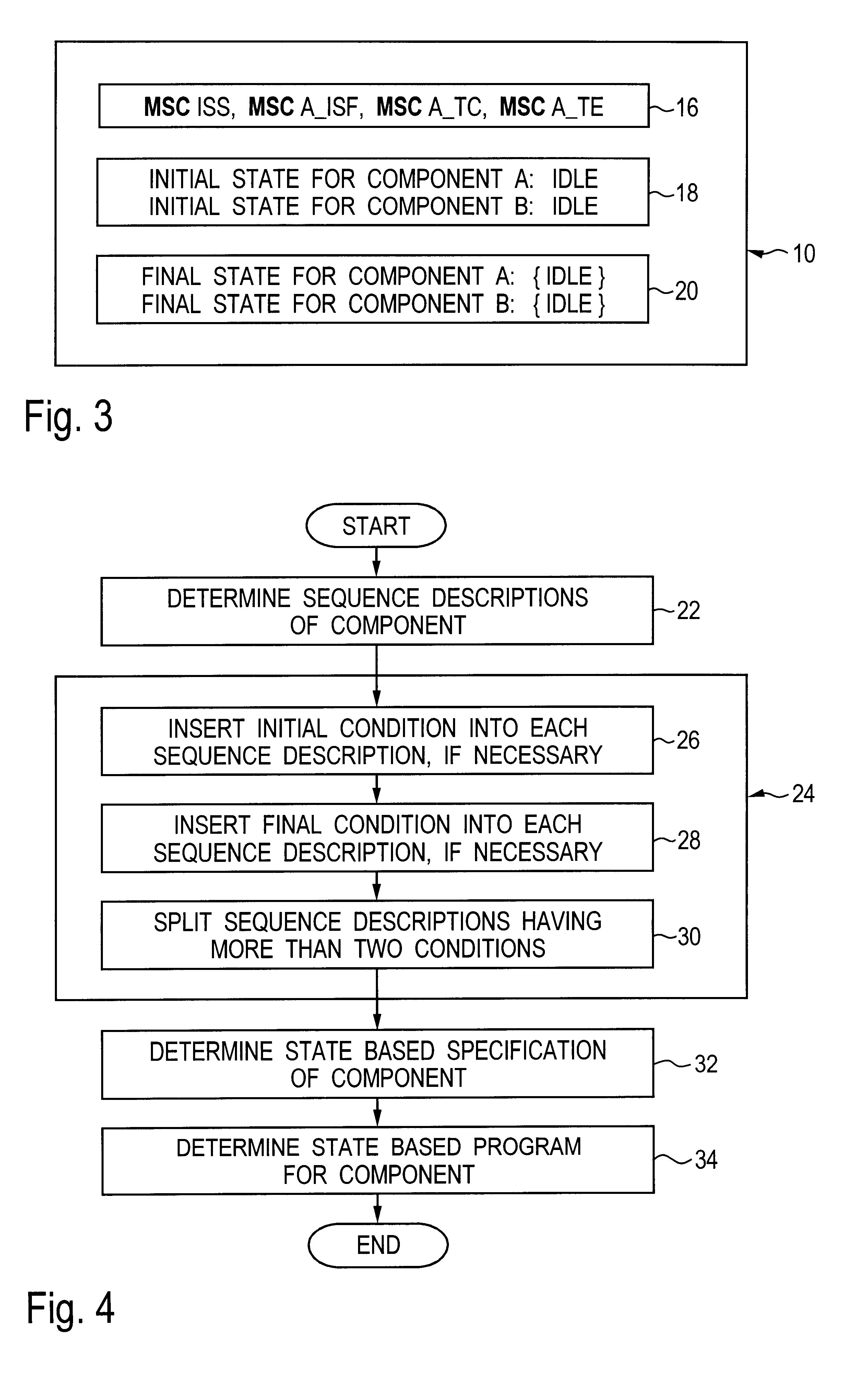
A method, an apparatus and a computer program product are described for automatically generating a state-based program for a component of a system consisting of a plurality of components communicating with each other, wherein the program is generated from a specification of the system, the specification comprising interaction-based sequence descriptions of the system. According to the present invention, all sequence descriptions of said component are determined, the sequence descriptions are normalized, a state-based specification of said component is determined from the normalized sequence descriptions, and the state-based program for the component is determined from the state-based specification. The present invention facilitates the process of program development since the costly, manual development of a state-based program from the specification of a system is automated at least to a substantial degree.
Owner:BROY MANFRED +2
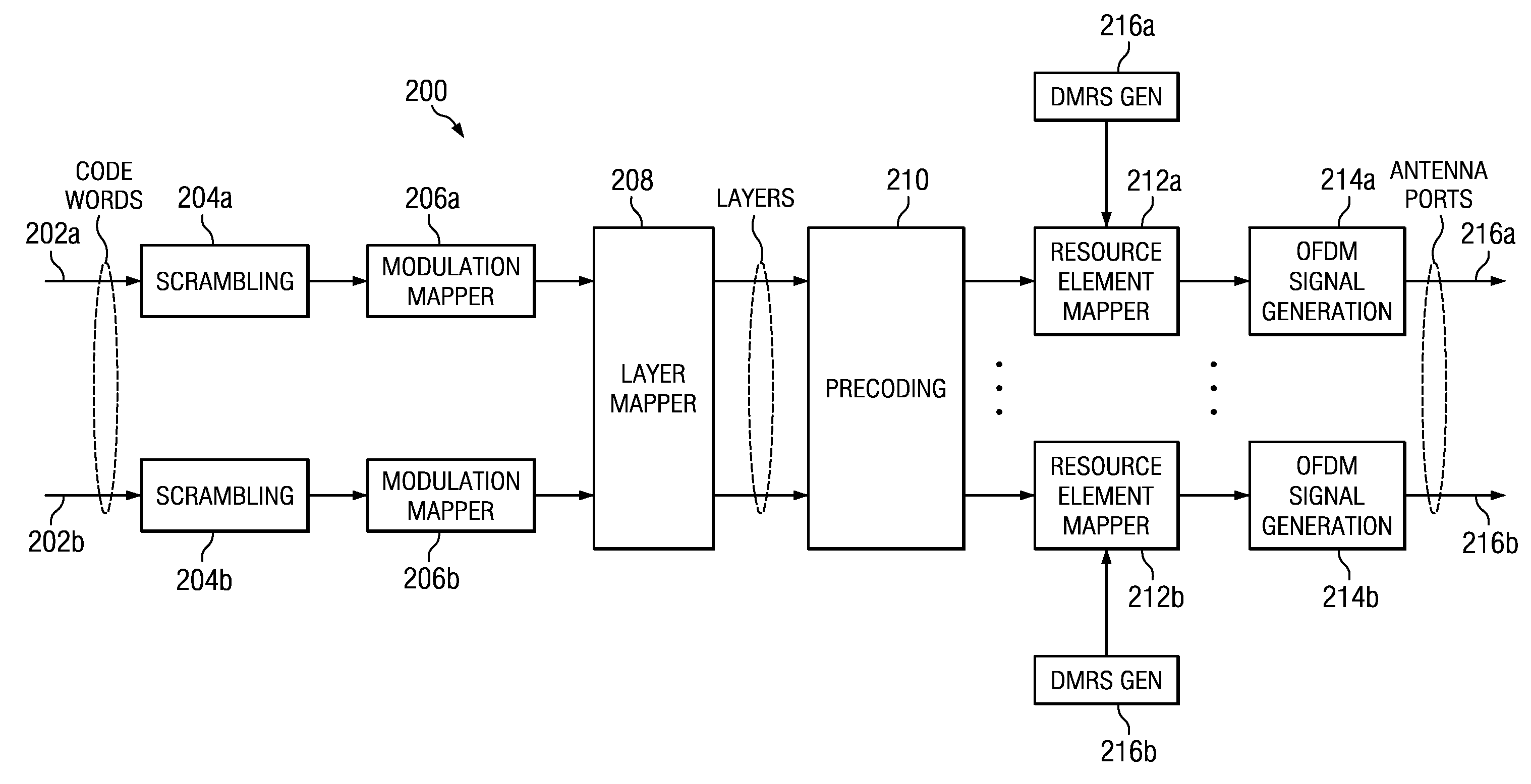
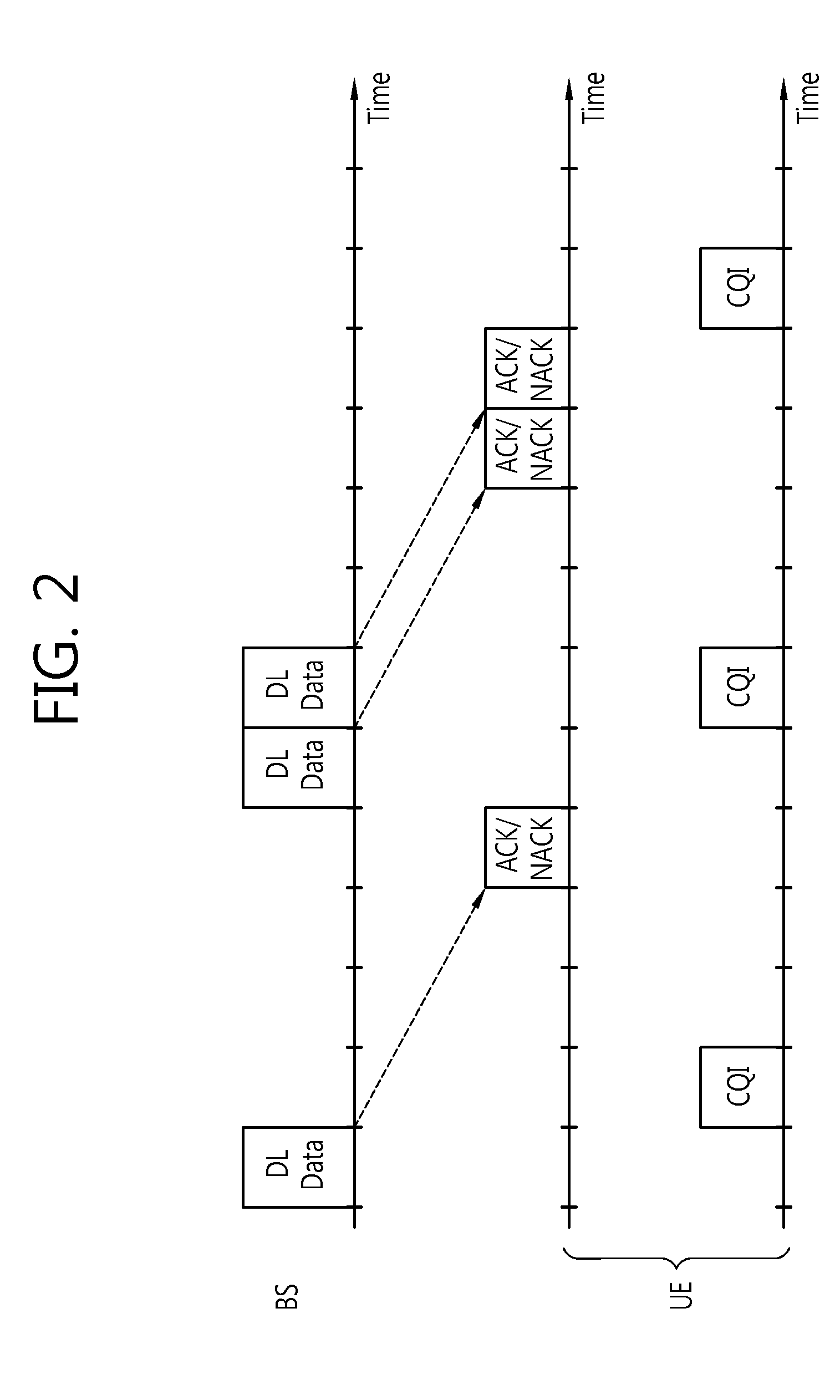
Apparatus and method for uplink transmission in wireless communication systems
ActiveUS20130077569A1Power managementWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemUplink transmission
An apparatus and method for a User Equipment in a wireless network including at least one Base Station (BS) are provided. The method includes receiving an Information Element (IE) for configuring at least one of a PUSCH power control method and a PUSCH DMRS generation method from the BS, determining a state of the IE, and transmitting a PUSCH and a DMRS for the PUSCH according to the state of the IE. A transmission power of the PUSCH is controlled and a base sequence for the PUSCH DMRS is generated according to the state of the IE. When the state of the IE indicates a first state, the transmission power of the PUSCH is determined according to a first power control equation. When the state of the IE indicates a second state, the transmission power of the PUSCH is determined according to a second power control equation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
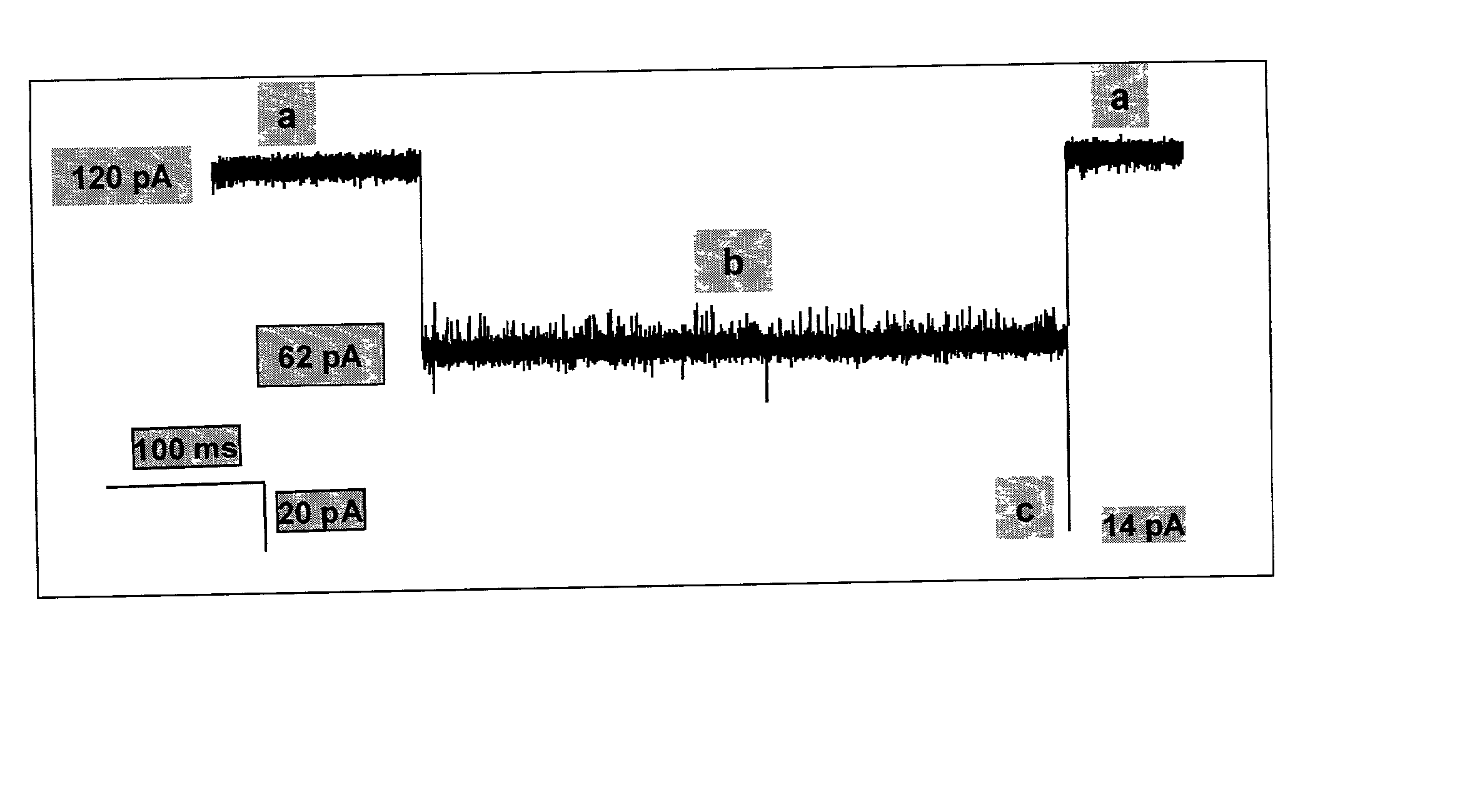
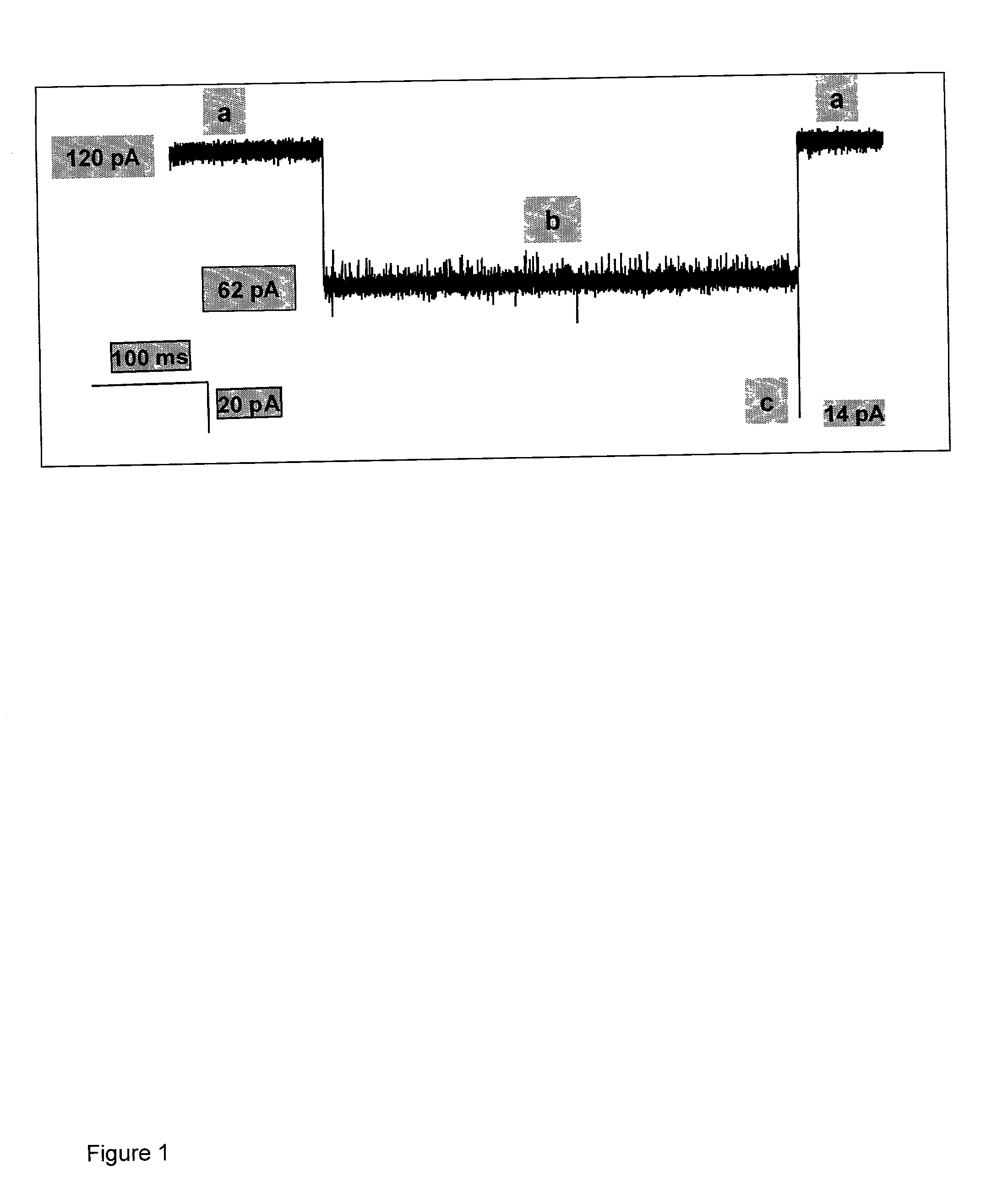
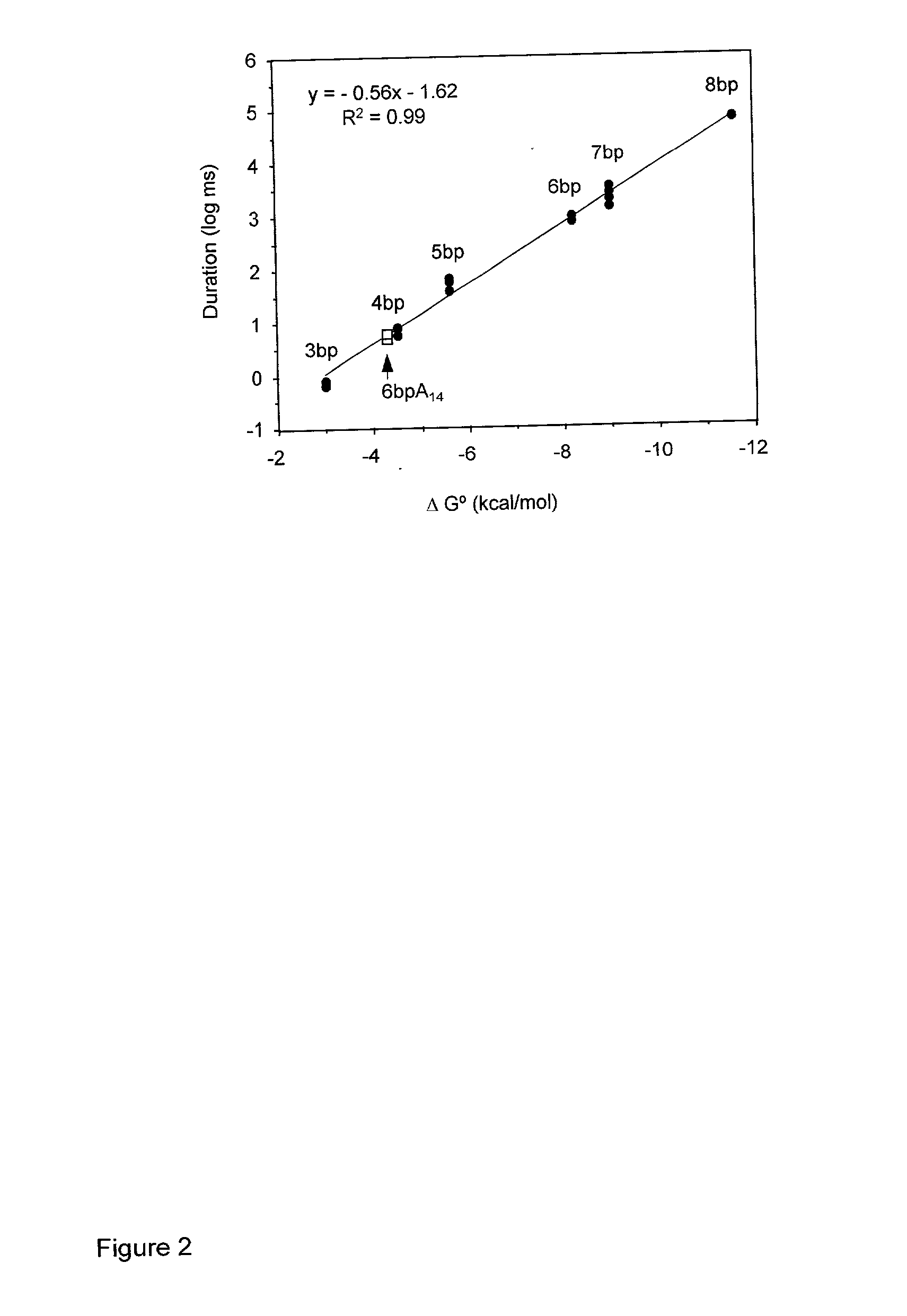
Methods and devices for characterizing duplex nucleic acid molecules
Methods and devices are provided for characterizing a duplex nucleic acid, e.g., a duplex DNA molecule. In the subject methods, a fluid conducting medium that includes a duplex nucleic acid molecule is contacted with a nanopore under the influence of an applied electric field and the resulting changes in current through the nanopore caused by the duplex nucleic acid molecule are monitored. The observed changes in current through the nanopore are then employed as a set of data values to characterize the duplex nucleic acid, where the set of data values may be employed in raw form or manipulated, e.g., into a current blockade profile. Also provided are nanopore devices for practicing the subject methods, where the subject nanopore devices are characterized by the presence of an algorithm which directs a processing means to employ monitored changes in current through a nanopore to characterize a duplex nucleic acid molecule responsible for the current changes. The subject methods and devices find use in a variety of applications, including, among other applications, the identification of an analyte duplex DNA molecule in a sample, the specific base sequence at a single nulceotide polymorphism (SNP), and the sequencing of duplex DNA molecules.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20080124733A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesMicrobiology
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 90 to 91 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Nuclear based expression of genes for production of biofuels and process co-products in algae
Various embodiments provide, for example, vectors, expression cassettes, and cells useful for transgenic expression of nucleic acid sequences. In various embodiments, vectors can contain nuclear-based sequences of unicellular photosynthetic bioprocess organisms for the production of food- and feed-stuffs, oils, biofuels, starches, raw materials, pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals.
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST
Probe set, probe immobilized carrier and gene examination method
InactiveUS20070134702A1Improve accuracyThe process is fast and accurateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismMicrobiology
A probe and a primer capable of collectively detecting microorganisms of the same species while differentiating microorganisms of other species with an object of classification by species of fungus. An oligonucleotide probe for detecting an infectious etiologic microorganism gene includes at least one base sequence selected from the base sequences belonging to one group of the following first to ninth groups. The base sequence groups of first to ninth groups are: first group (SEQ ID NOS:1 to 5); second group (SEQ ID NOS:6 to 10); third group (SEQ ID NOS:11 to 15); fourth group (SEQ ID NOS:16 to 21); fifth group (SEQ ID NOS:22 to 26); sixth group (SEQ ID NOS:27 to 31); seventh group (SEQ ID NOS:32 to 36); eighth group (SEQ ID NOS:37 to 41); and ninth group (SEQ ID NOS:42 to 46).
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20080113365A1Quickly and precisely detectAccurate identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInfectious DisorderNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 76 to 77 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20080113363A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementInfectious DisorderNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 70 to 72 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Screening method for gene variation
InactiveUS6924103B2Quick fixBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsScreening methodA-DNA
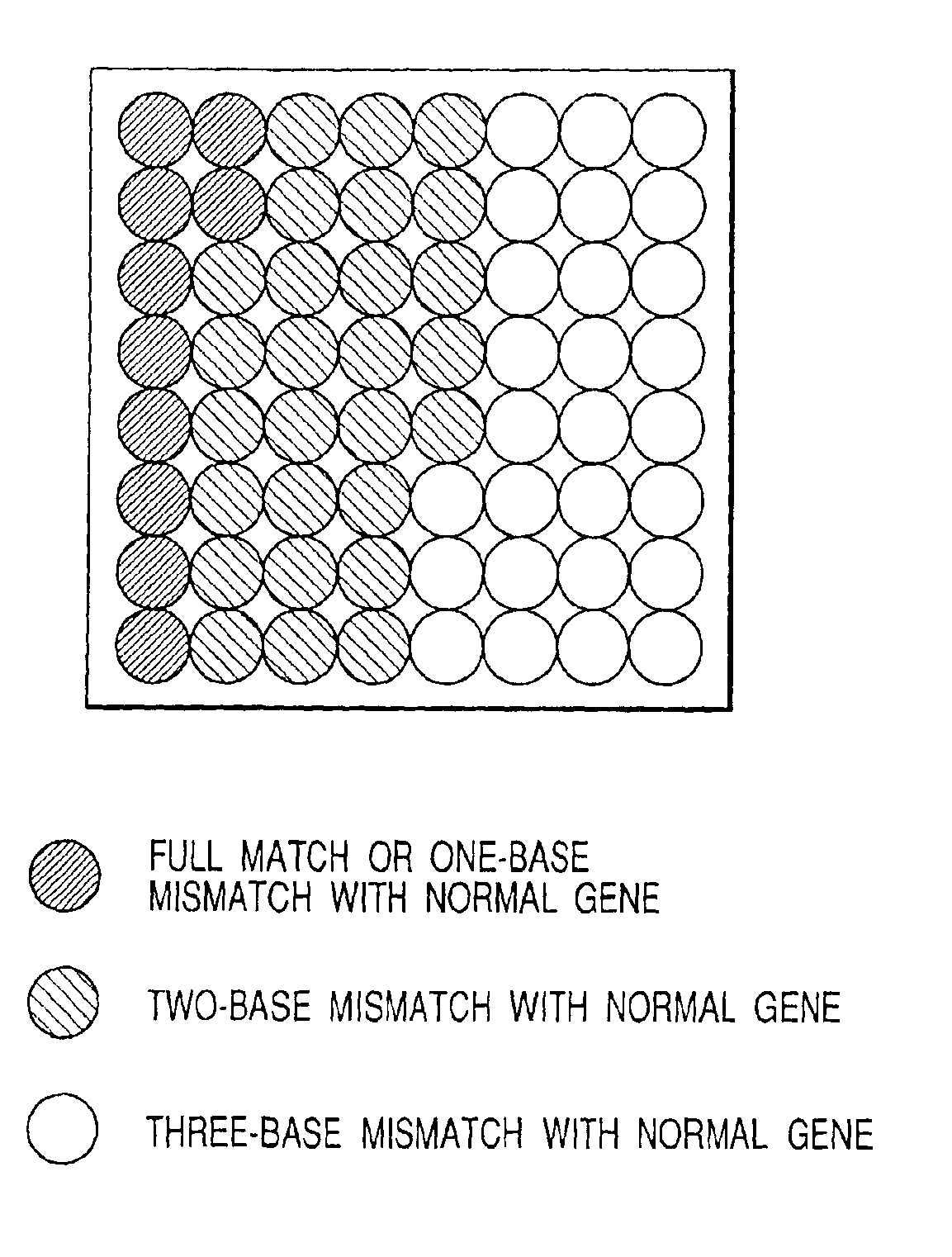
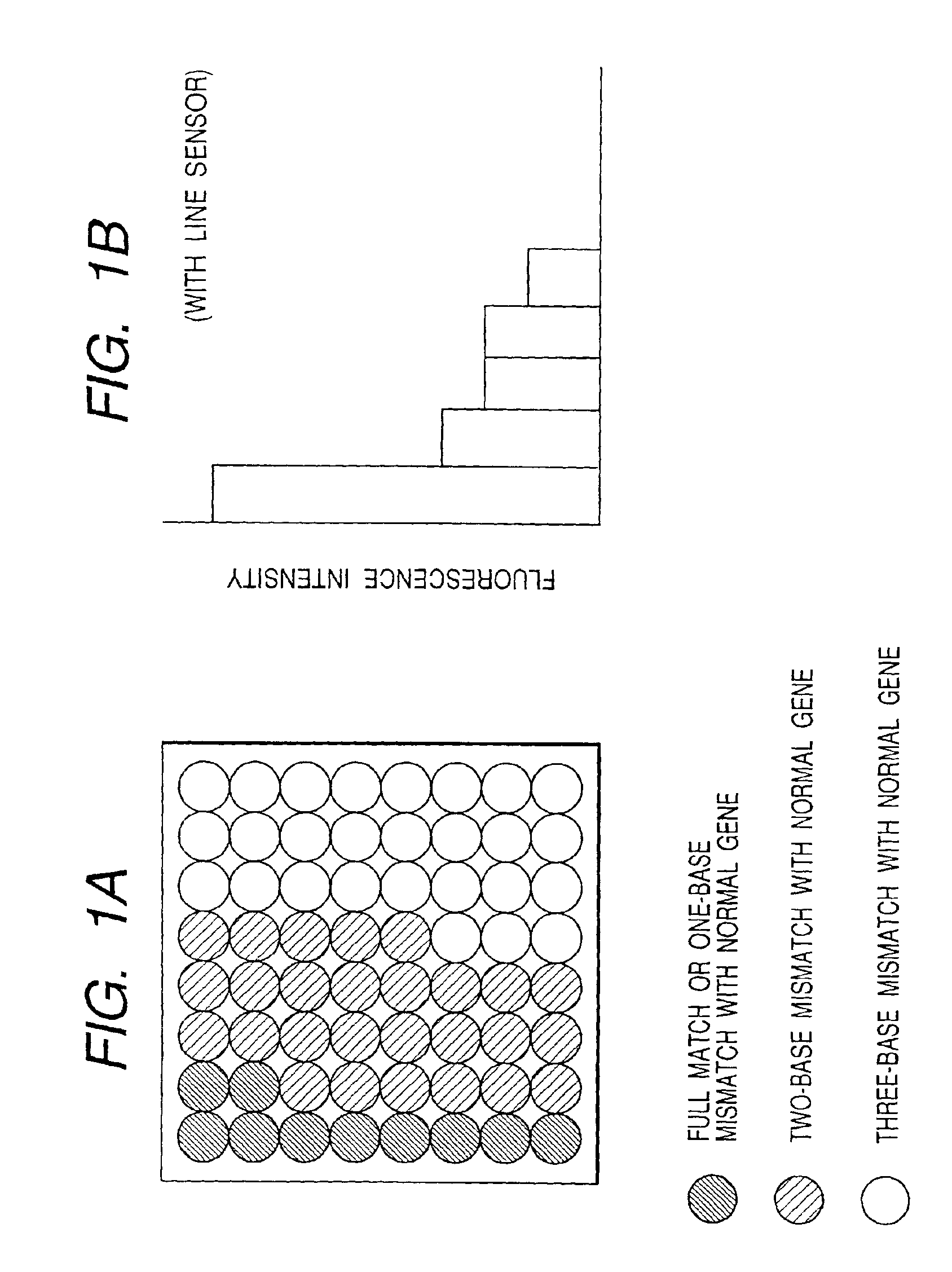
A method for screening presence or absence of a variation in a region of a nucleic acid which comprises the steps of (a) preparing a sample containing a test nucleic acid corresponding to the region, (b) preparing a probe having a base sequence fully complementary to a normal sequence of the region, and a plurality of probes each having at least one base not complementary to the normal sequence, (c) fixing the probes in separate regions on a surface of a substrate to prepare a DNA array substrate, (d) reacting the test nucleic acid with the probes on the DNA array substrate, (e) measuring signals in each region where the signals are originated from respective hybrids formed between the test nucleic acid and one of the probes, and (f) calling variation in the test nucleic acid using a pattern of total signals of all regions.
Owner:CANON KK
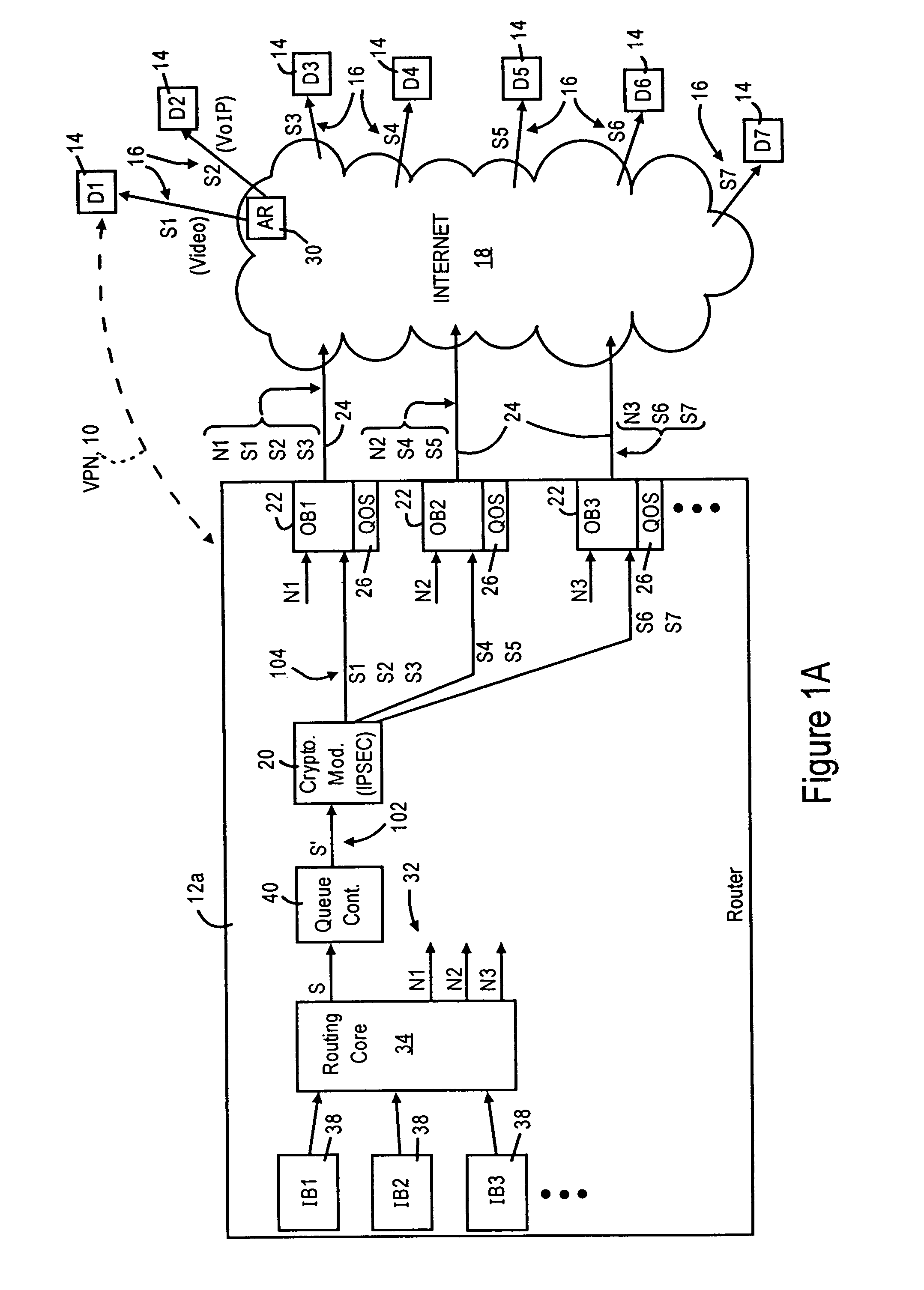
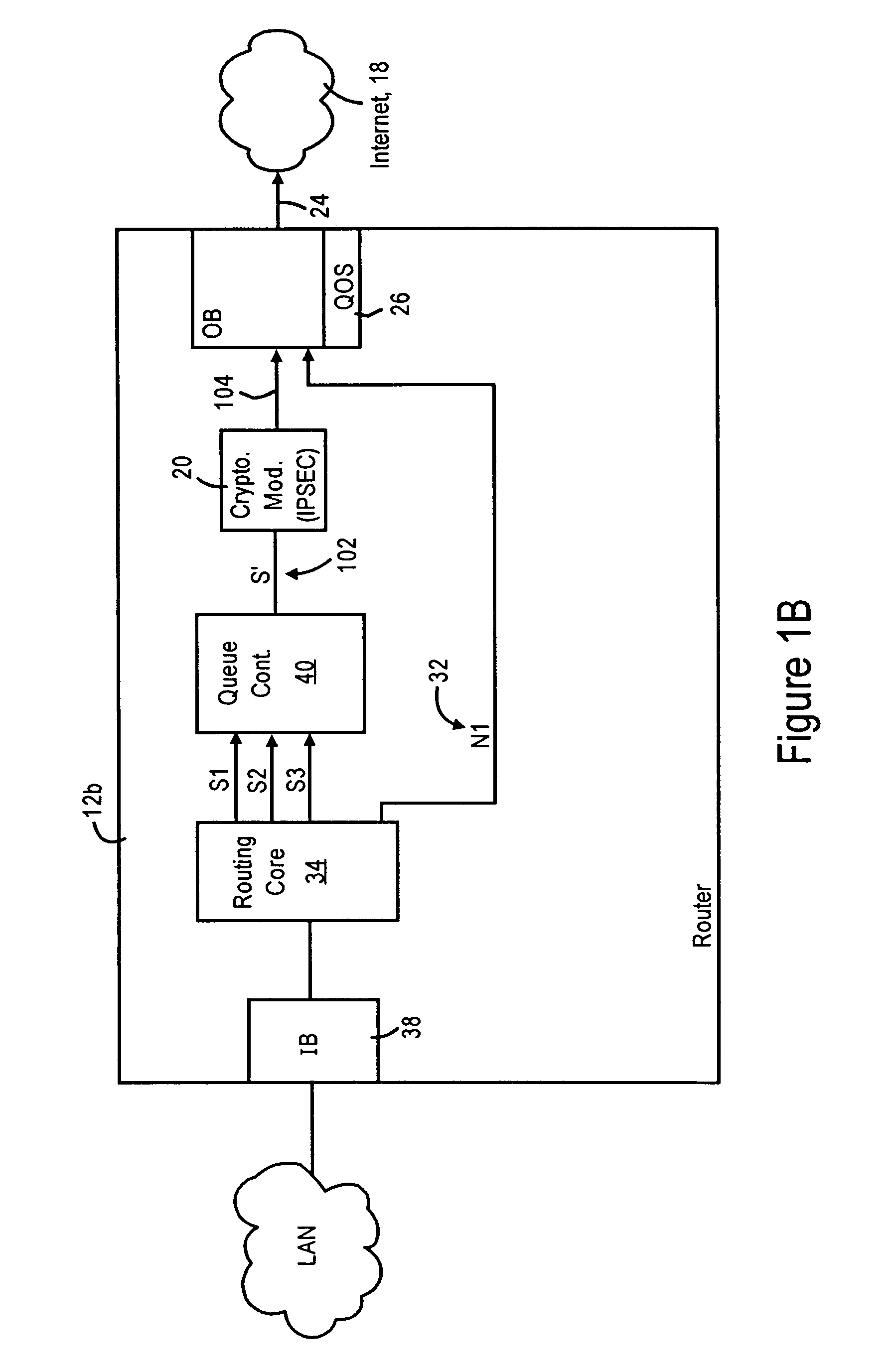
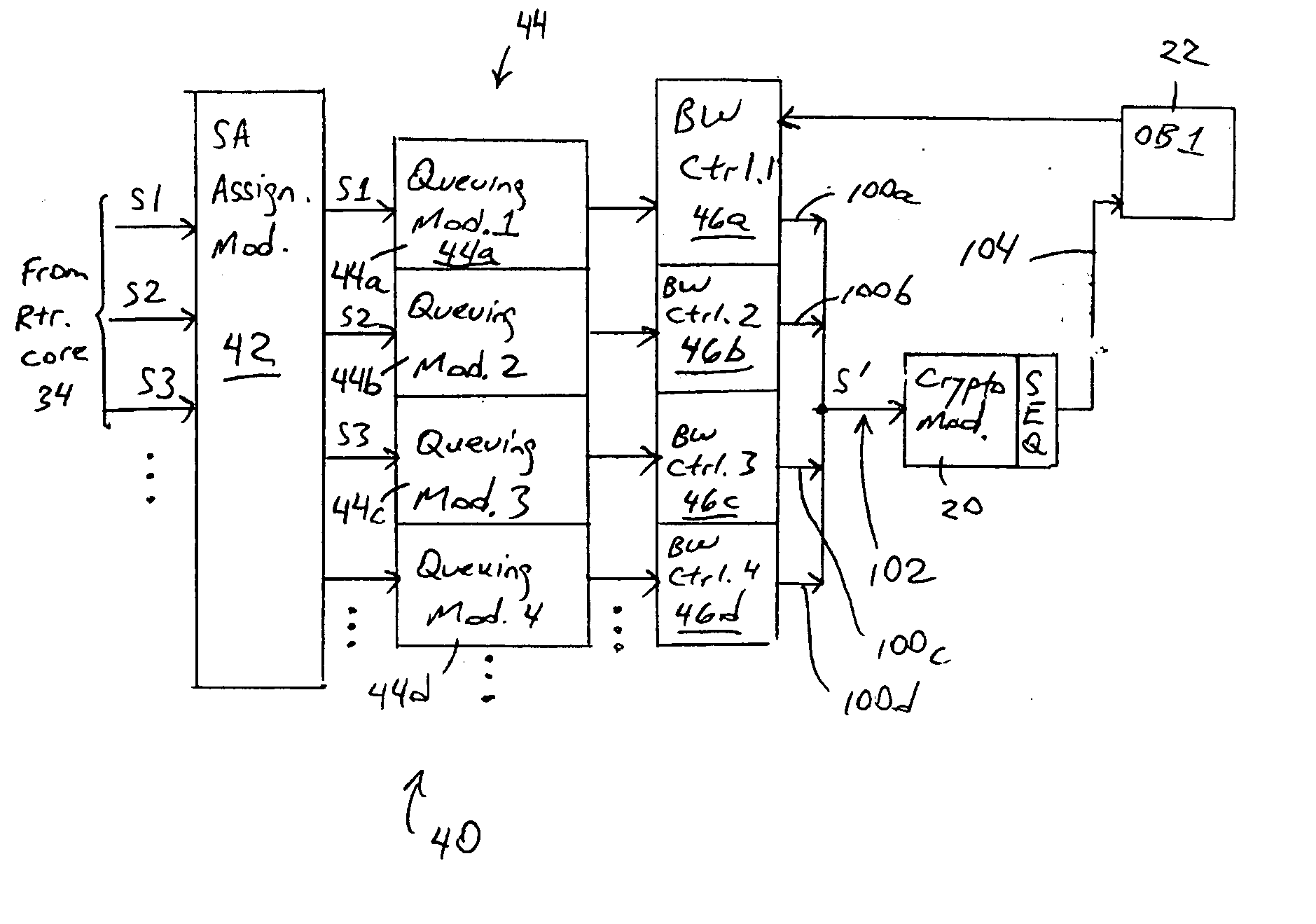
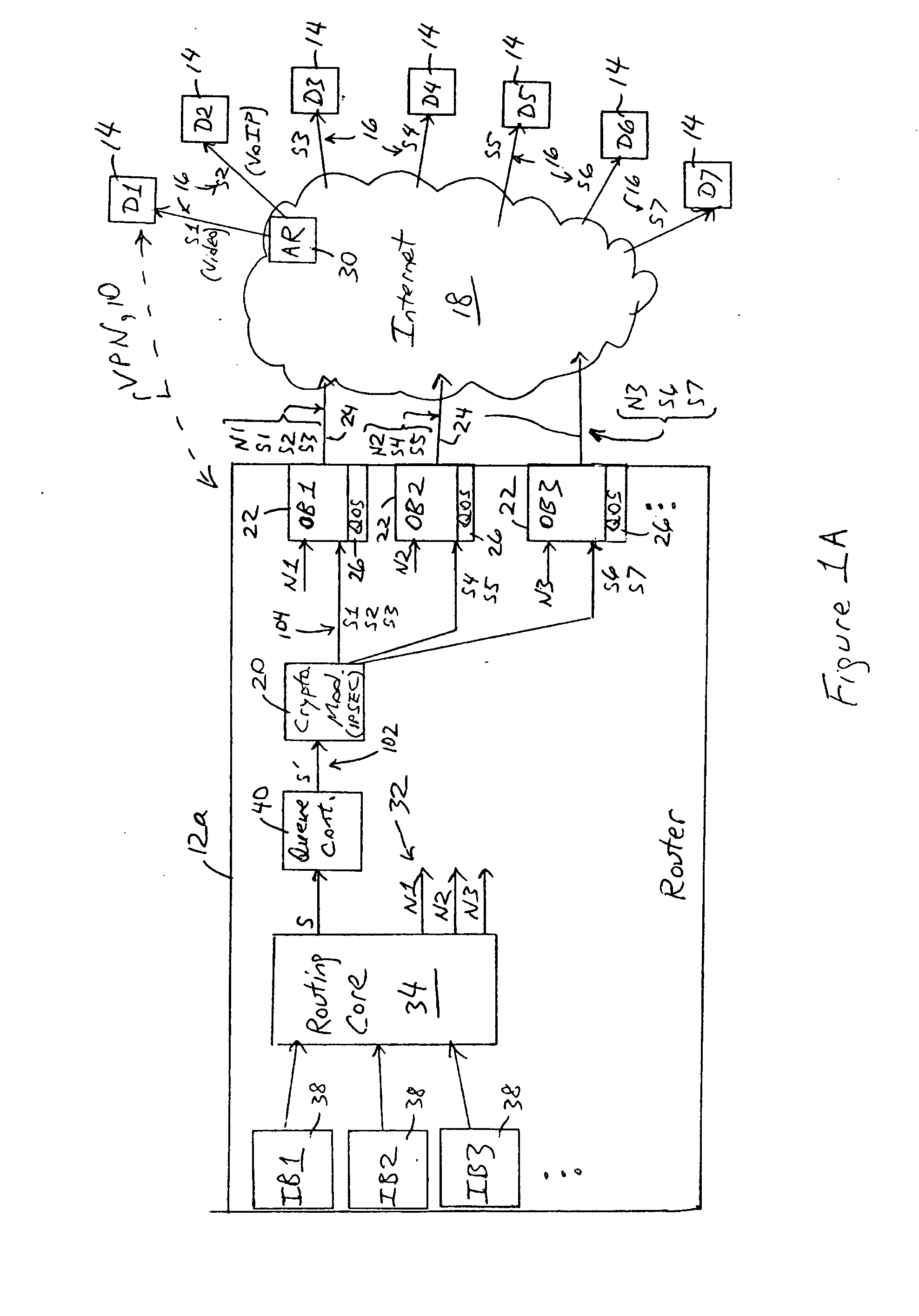
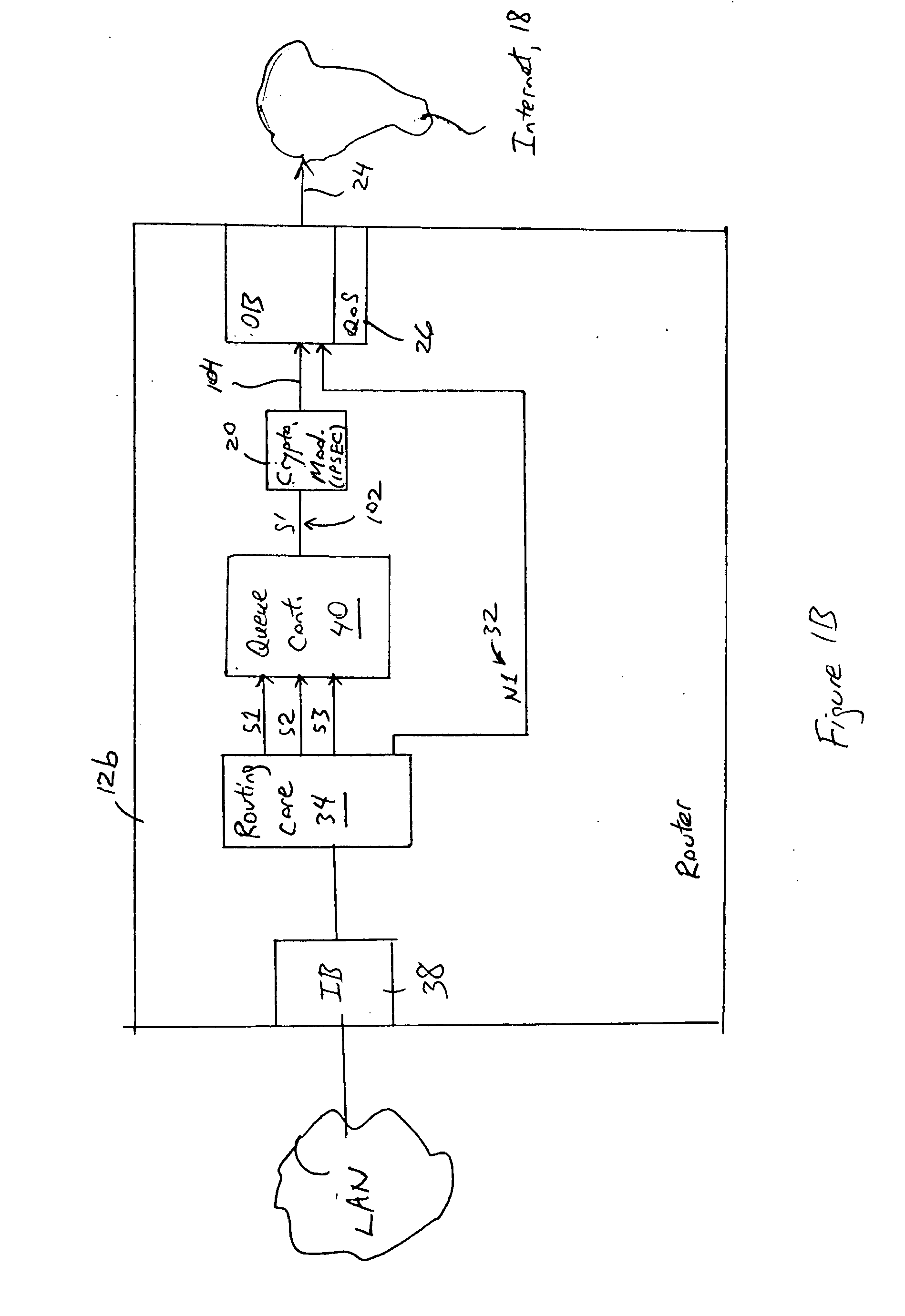
Arrangement in an IP node for preserving security-based sequences by ordering IP packets according to quality of service requirements prior to encryption
ActiveUS7389357B2Guaranteed service qualityMinimizes packet lossMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksQuality of serviceService level requirement
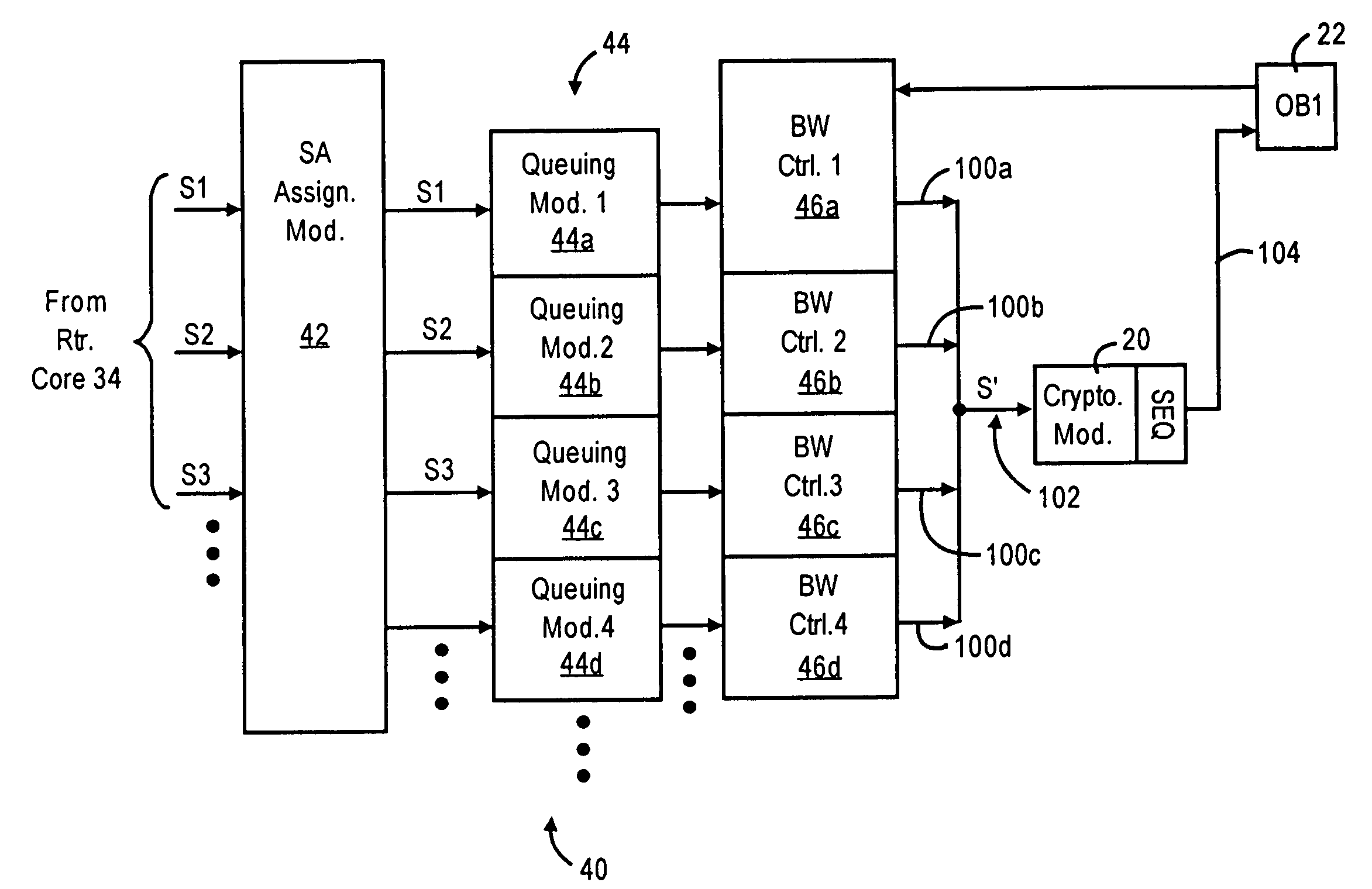
A router has at least one outbound interface configured for establishing multiple IP-based secure connections (i.e., tunnels) with respective destinations based on transmission of encrypted data packets via the IP-based secure connections. The encrypted data packets are generated by a cryptographic module, where each encrypted packet successively output from the cryptographic module includes a corresponding successively-unique sequence number. The supply of data packets to the cryptographic module is controlled by a queue controller: the queue controller assigns, for each secure connection, a corresponding queuing module configured for outputting a group of data packets associated with the corresponding secure connection according to a corresponding assigned maximum output bandwidth. Each queuing module also is configured for reordering the corresponding group of data packets according to a determined quality of service policy and the corresponding assigned maximum output bandwidth.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20080113366A1Quickly and precisely detectAccurate identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInfectious DisorderNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 68 to 69 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20080161192A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 87 to 89 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Identifier and nucleic acid amplification method of verification using the same
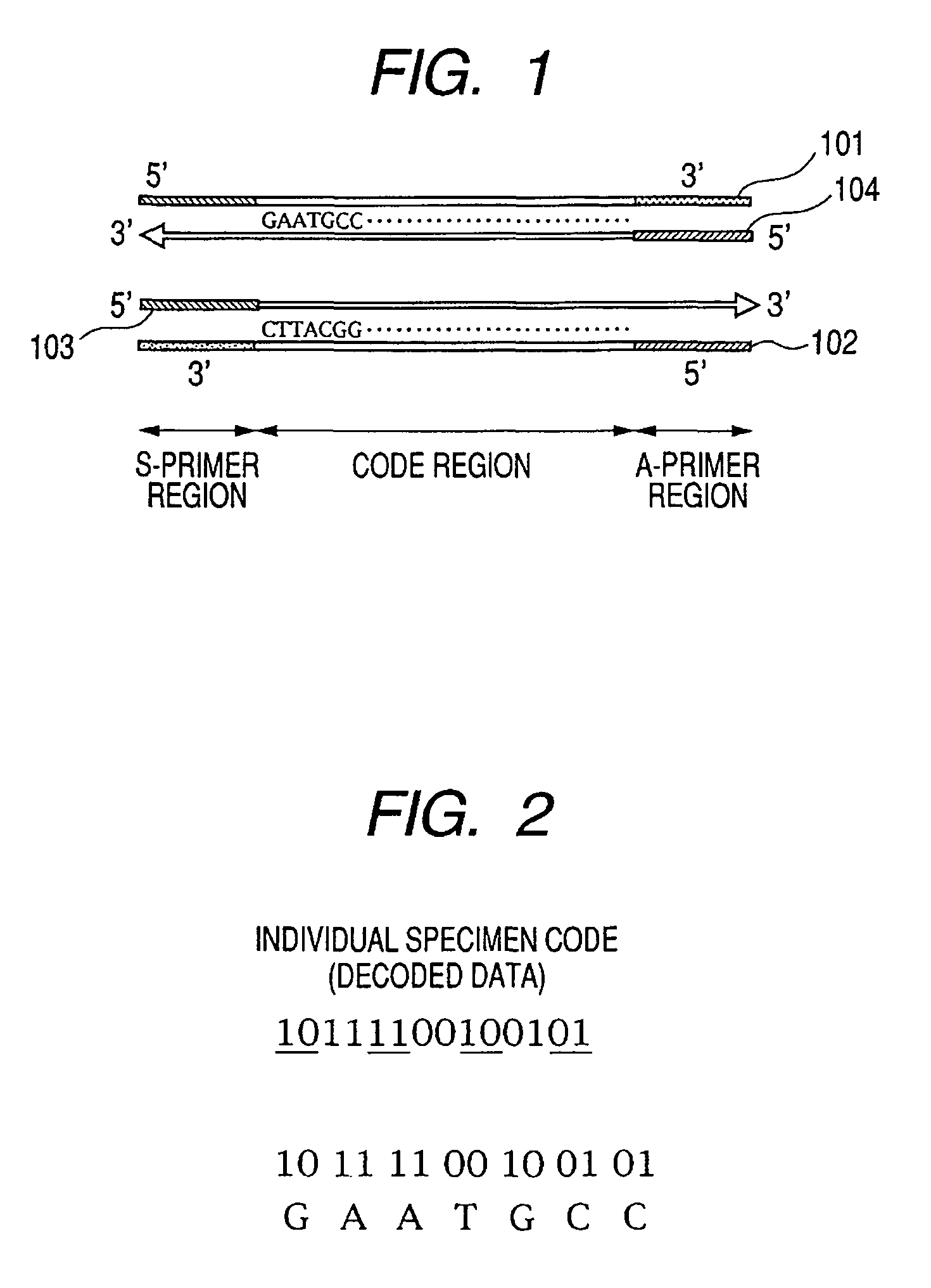
InactiveUS8101346B2Improve test efficiencyEasy to specifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyBase sequence
Owner:CANON KK
Arrangement in an IP node for preserving security-based sequences by ordering IP packets according to quality of service requirements prior to encryption
ActiveUS20050182833A1Guaranteed service qualityMinimizes packet lossMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksQuality of serviceService level requirement
A router has at least one outbound interface configured for establishing multiple IP-based secure connections (i.e., tunnels) with respective destinations based on transmission of encrypted data packets via the IP-based secure connections. The encrypted data packets are generated by a cryptographic module, where each encrypted packet successively output from the cryptographic module includes a corresponding successively-unique sequence number. The supply of data packets to the cryptographic module is controlled by a queue controller: the queue controller assigns, for each secure connection, a corresponding queuing module configured for outputting a group of data packets associated with the corresponding secure connection according to a corresponding assigned maximum output bandwidth. Each queuing module also is configured for reordering the corresponding group of data packets according to a determined quality of service policy and the corresponding assigned maximum output bandwidth.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299575A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080286792A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com