Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
244 results about "Ion density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
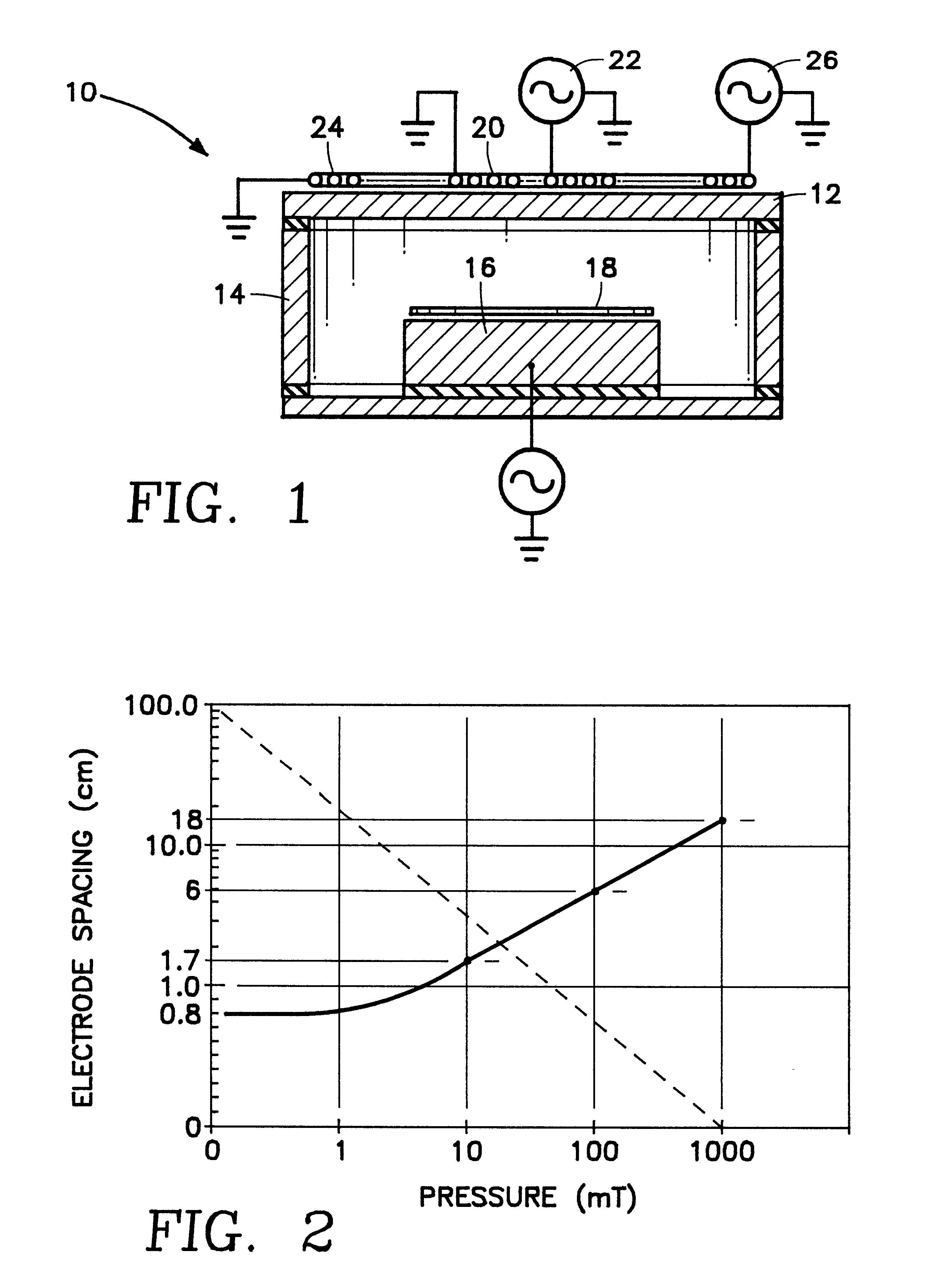
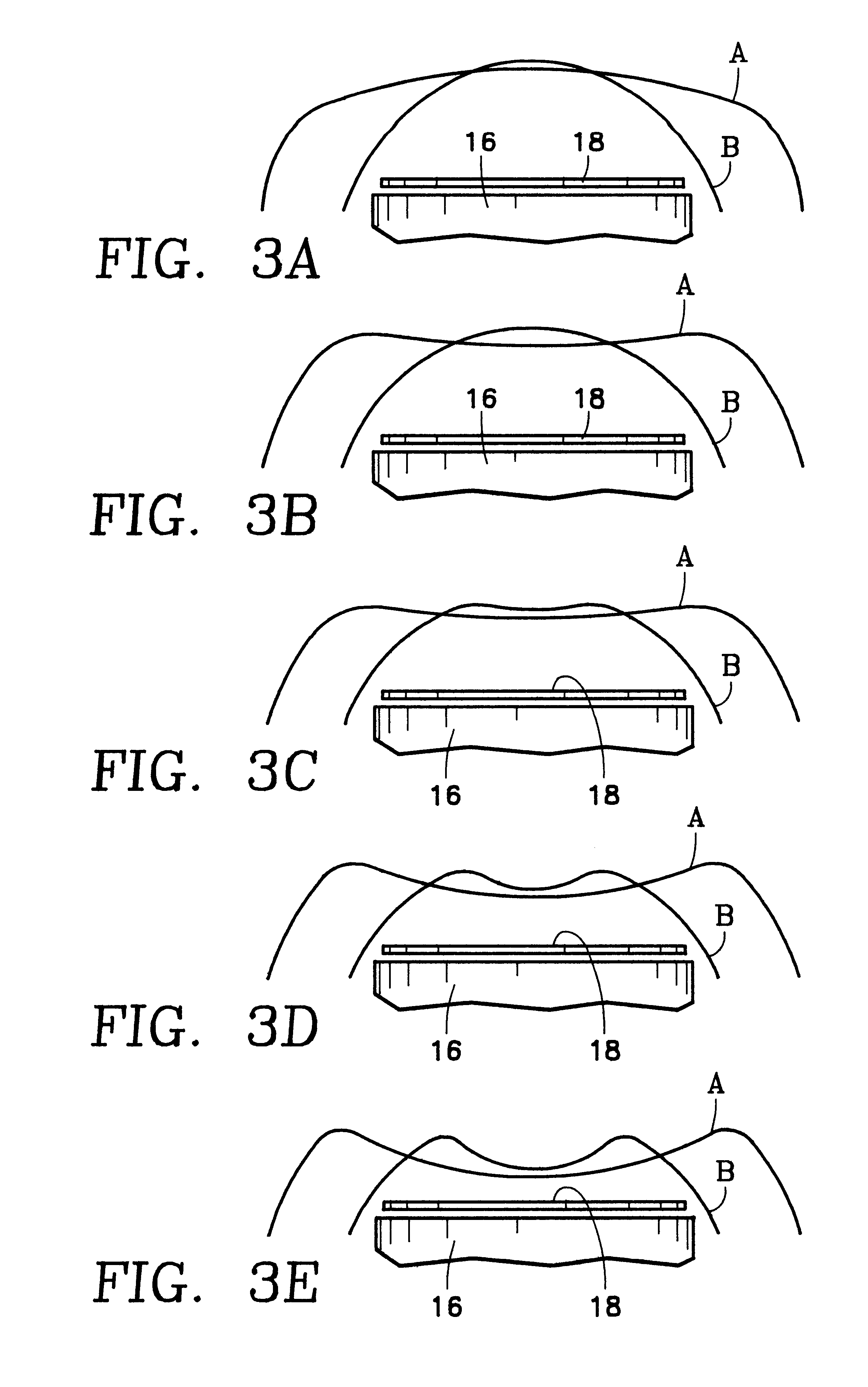
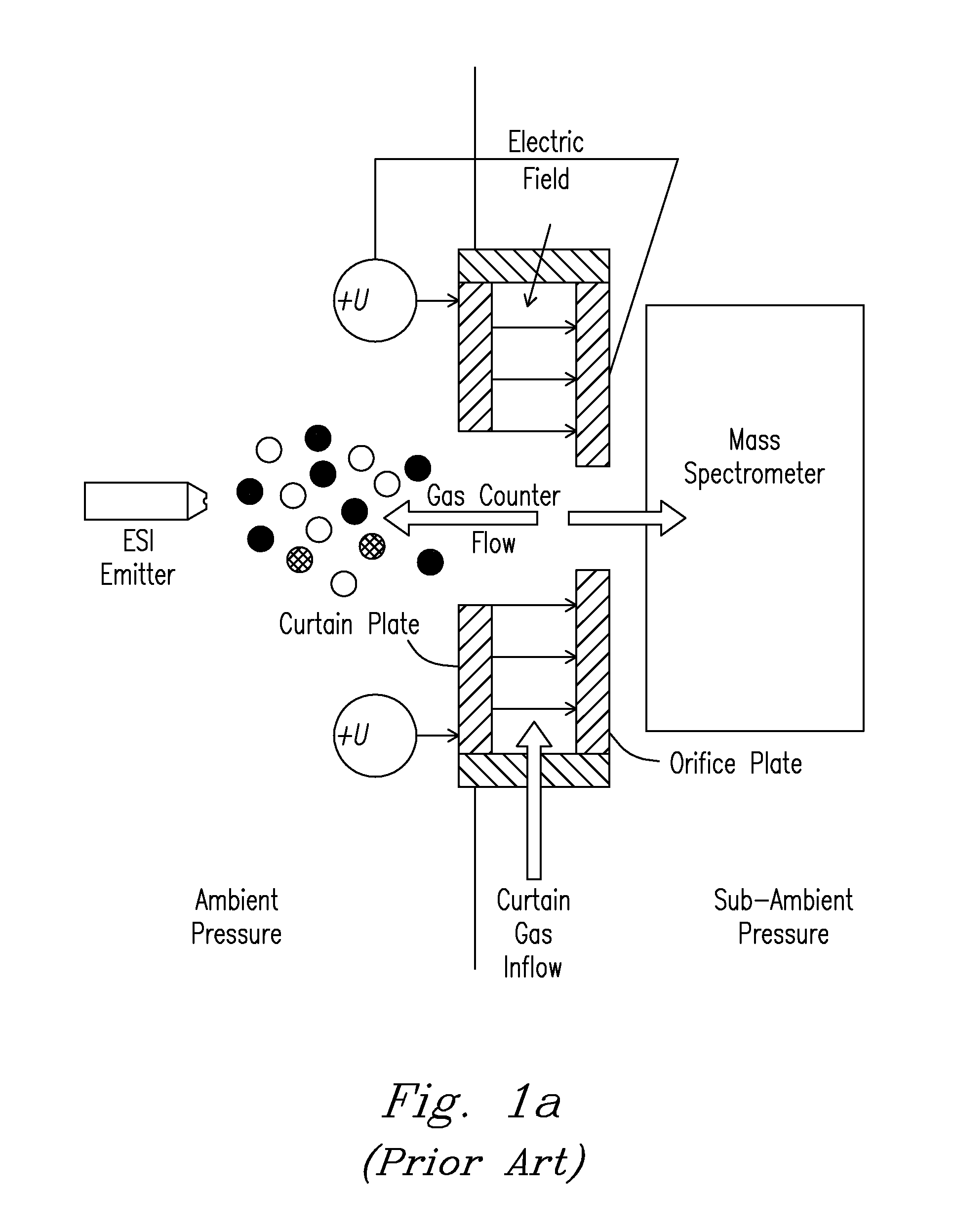
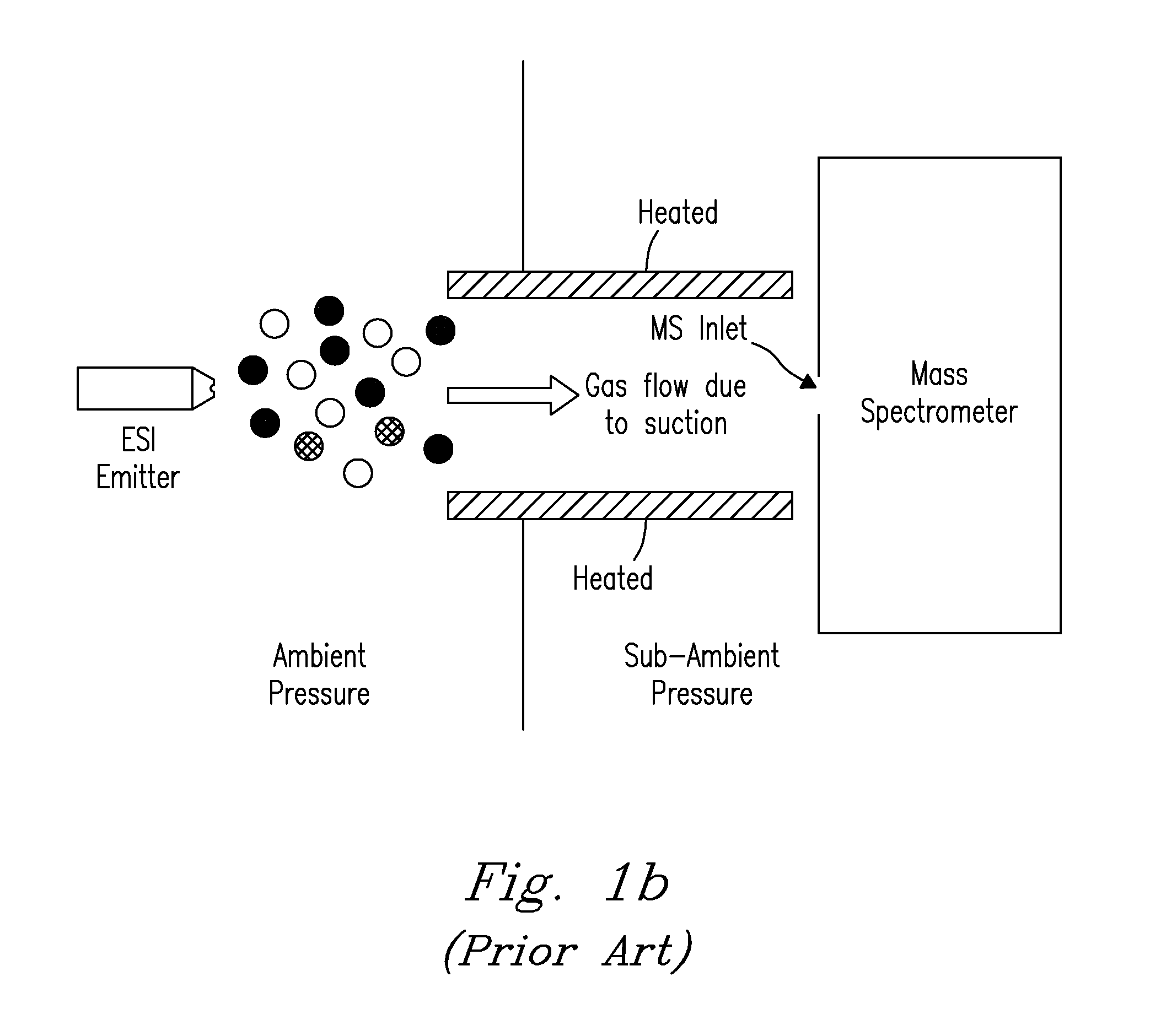
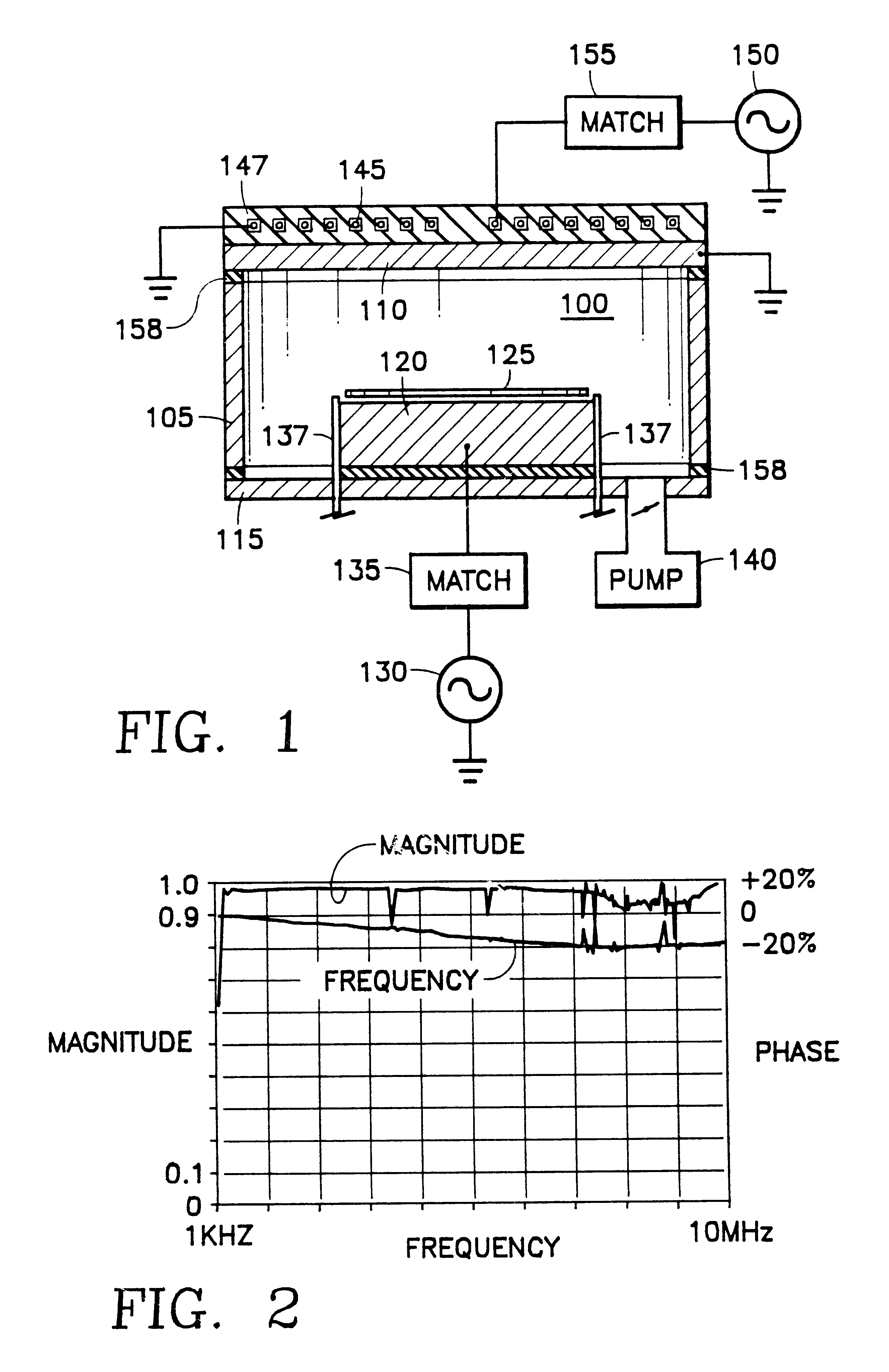
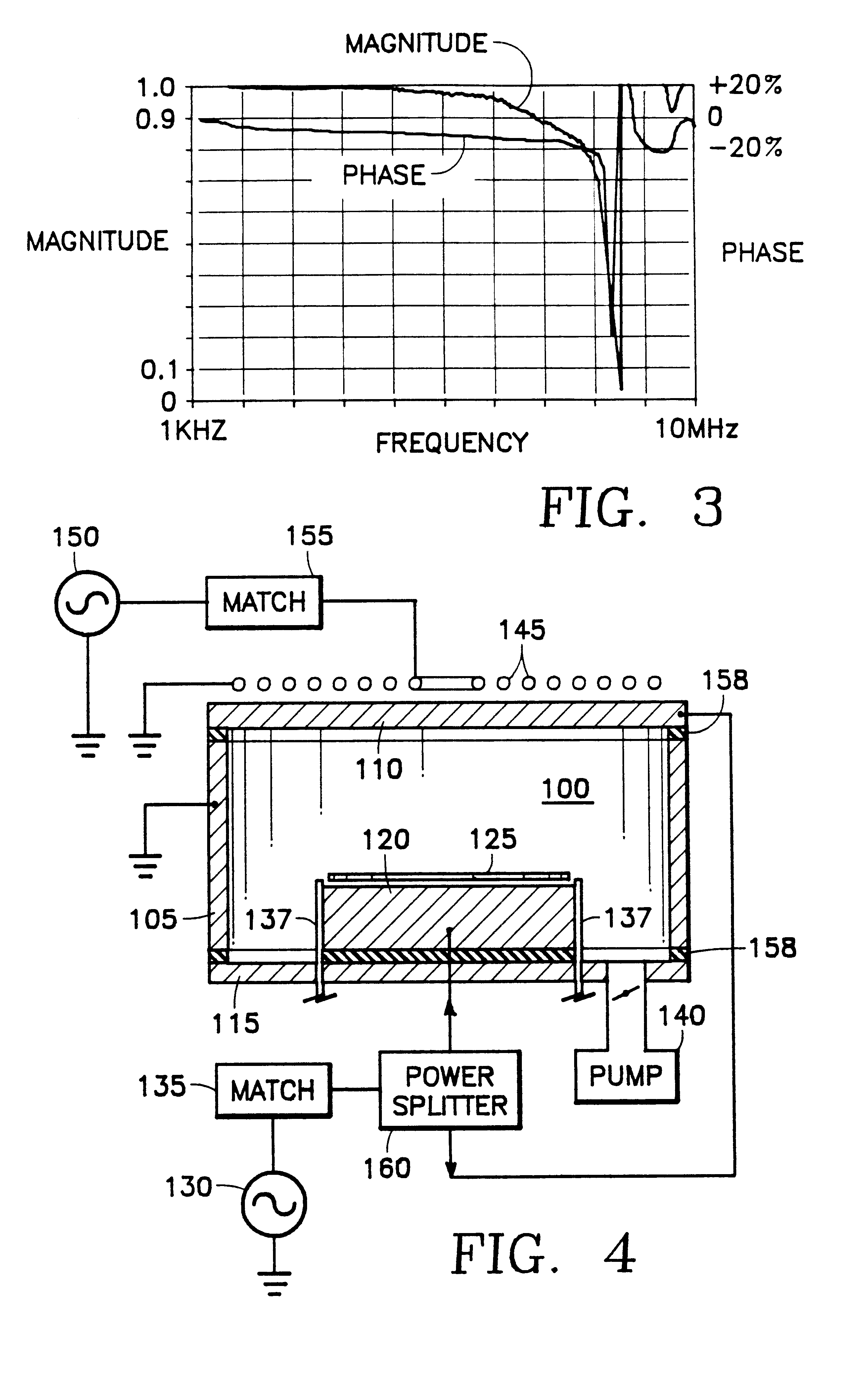
Its height was found to be related to ion density in a linear way. This density was measured by using the transient current technique. We conclude that ion density can be determined by measuring optical response.
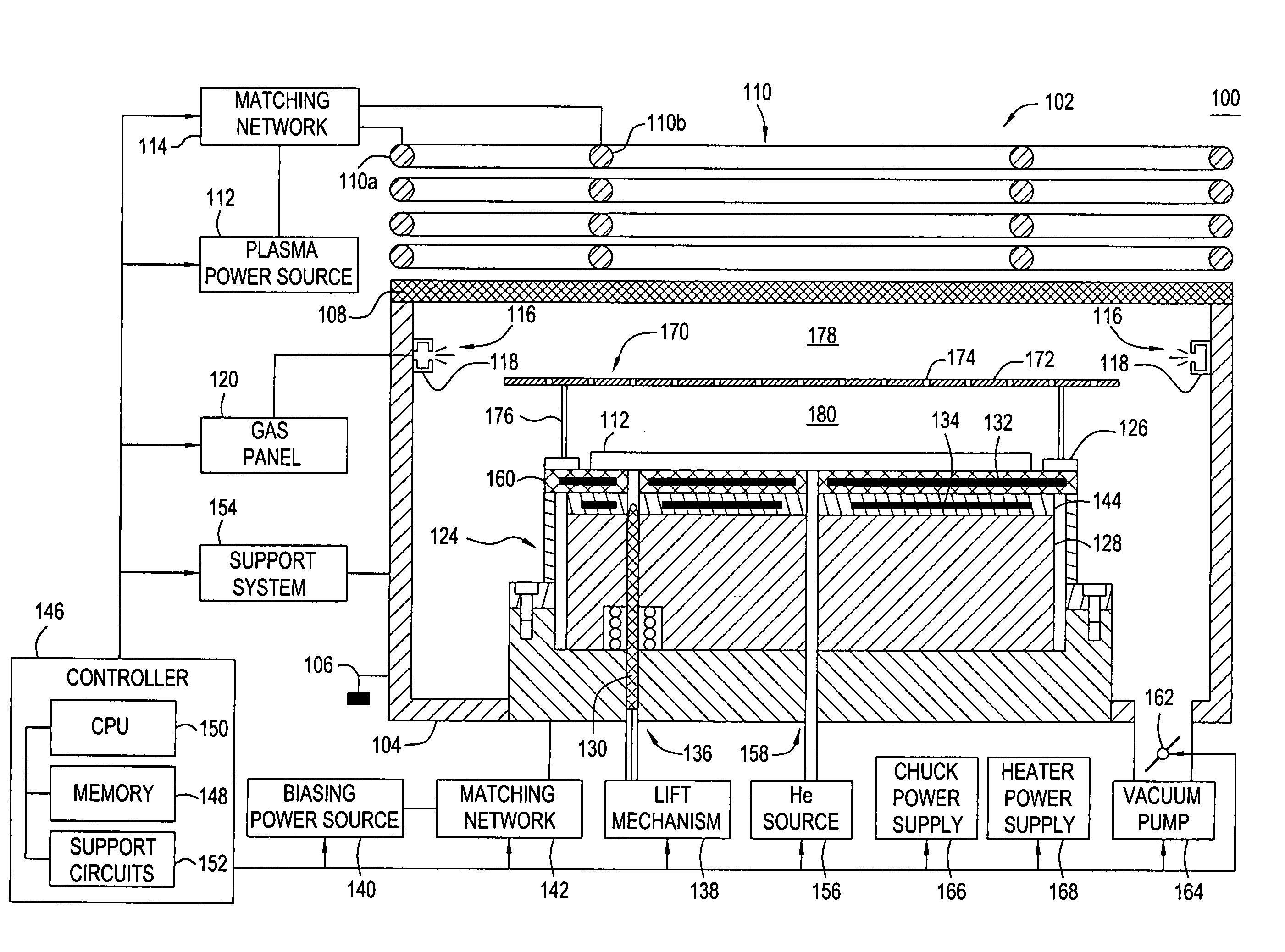
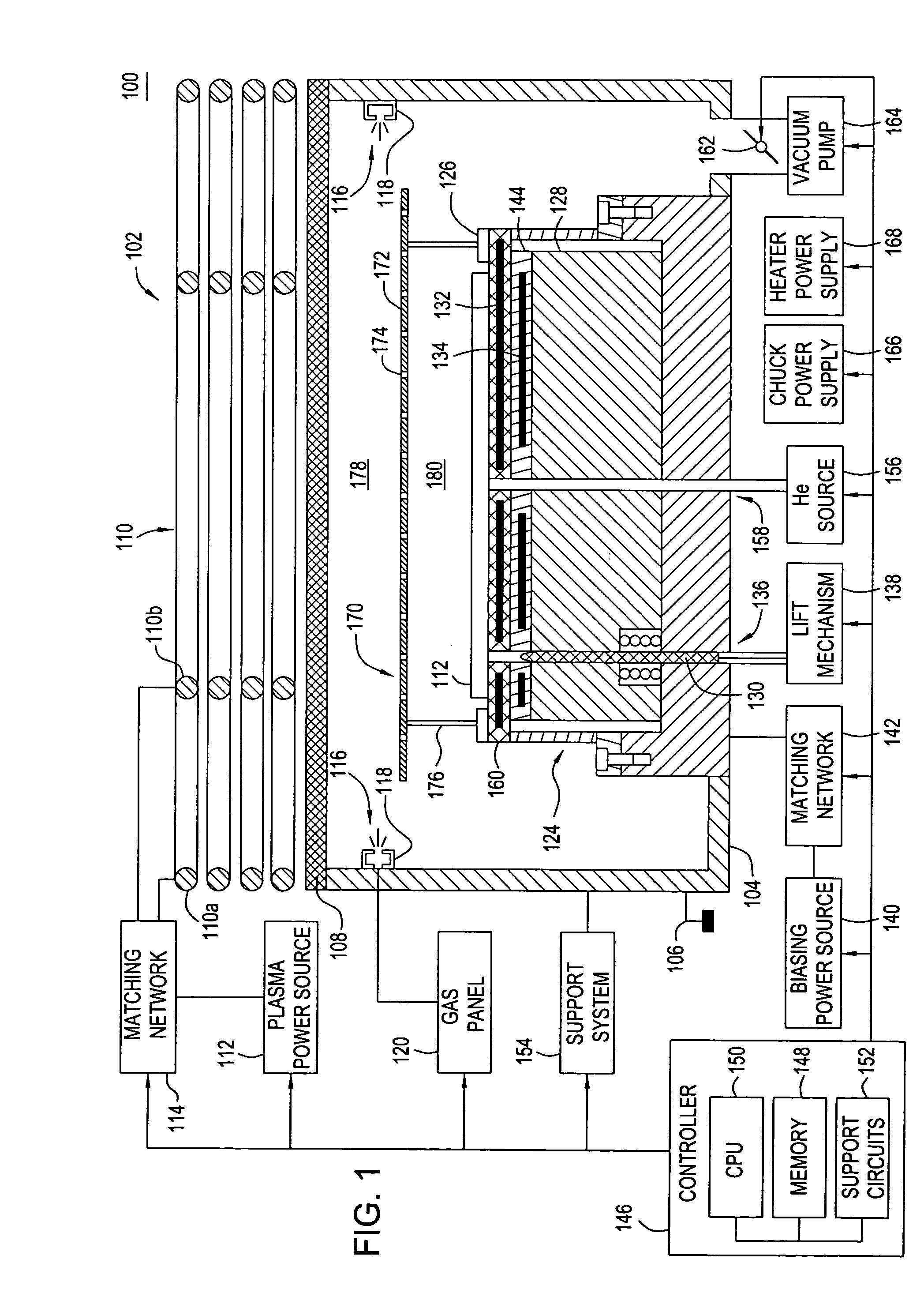
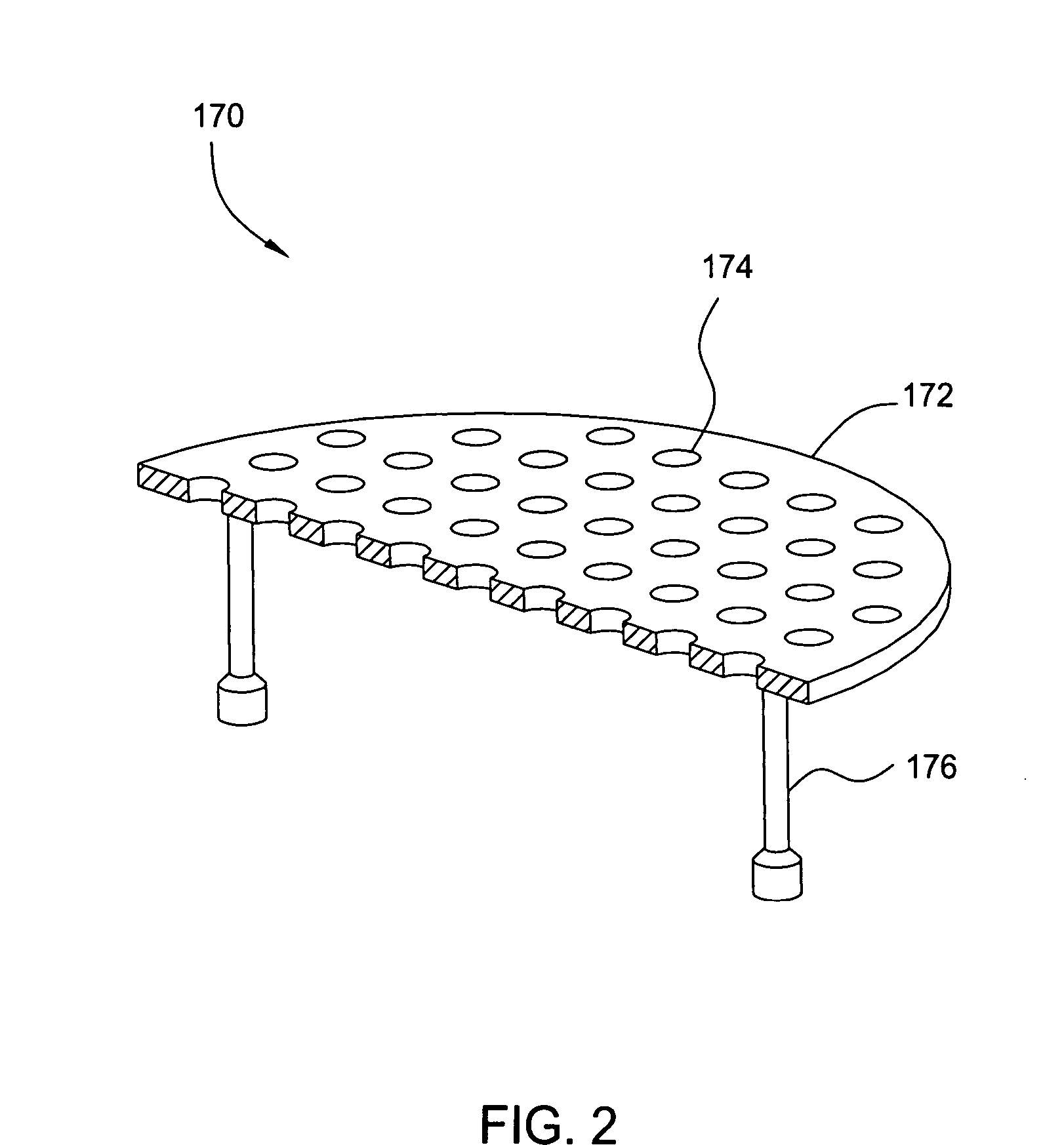
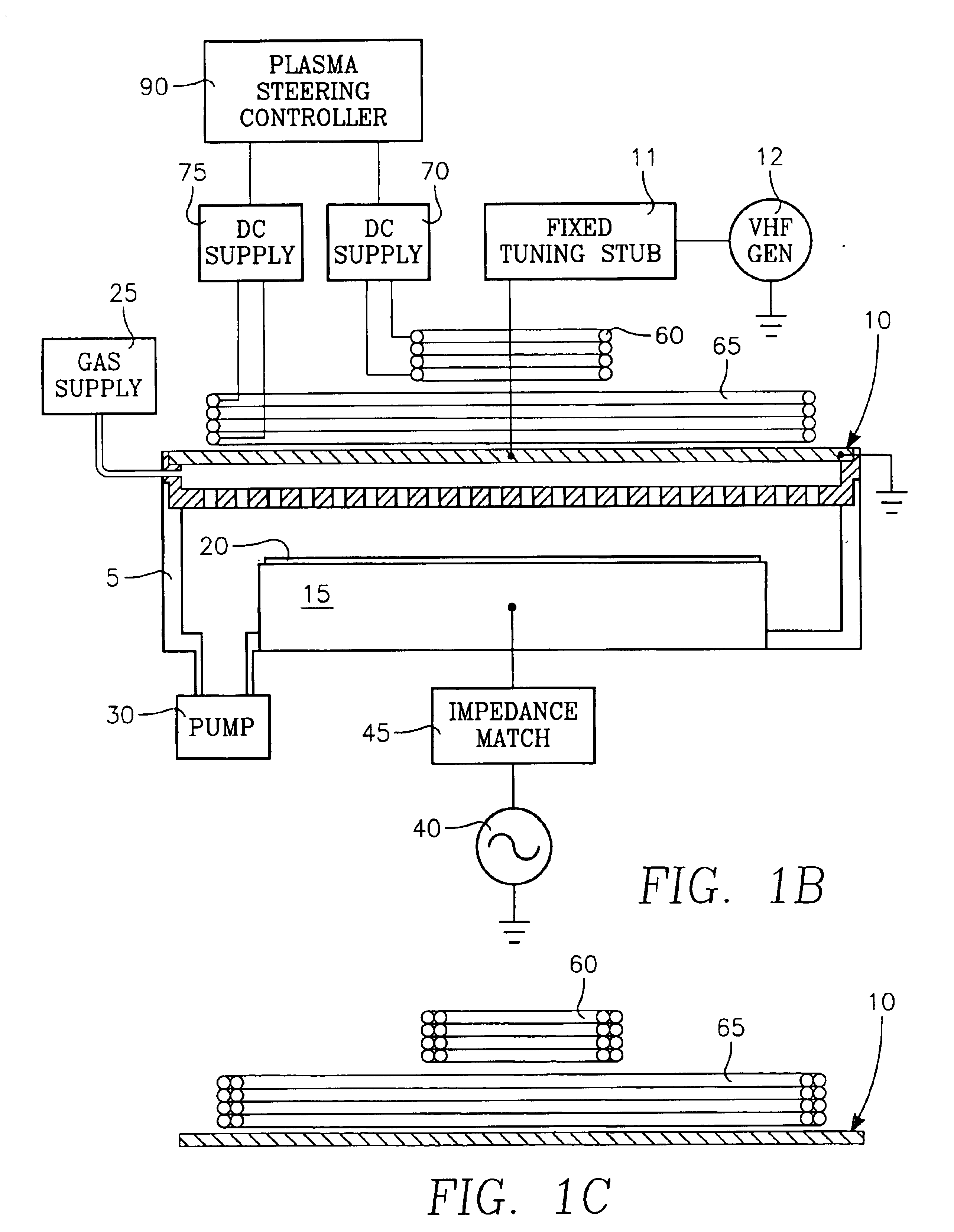
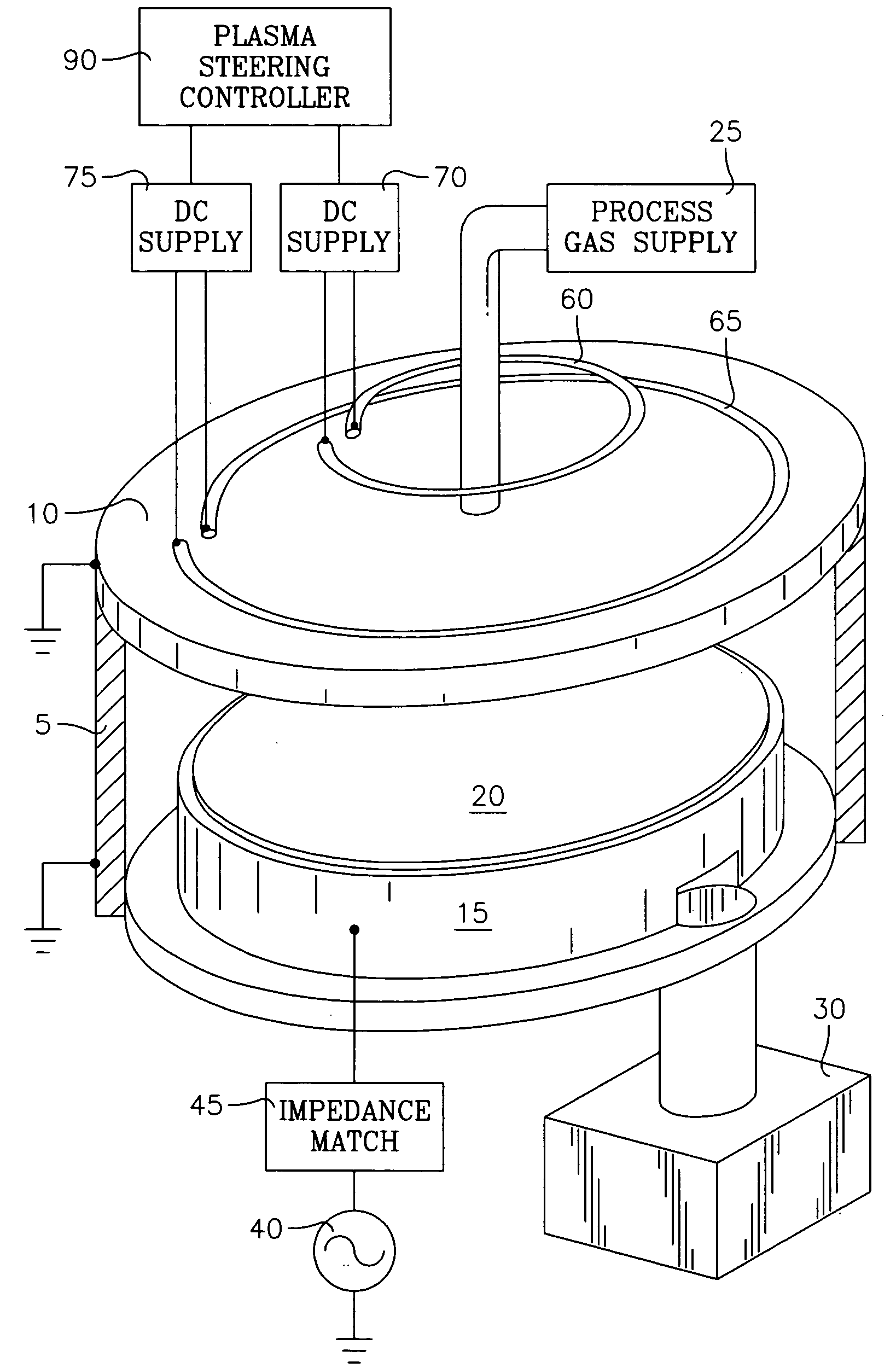
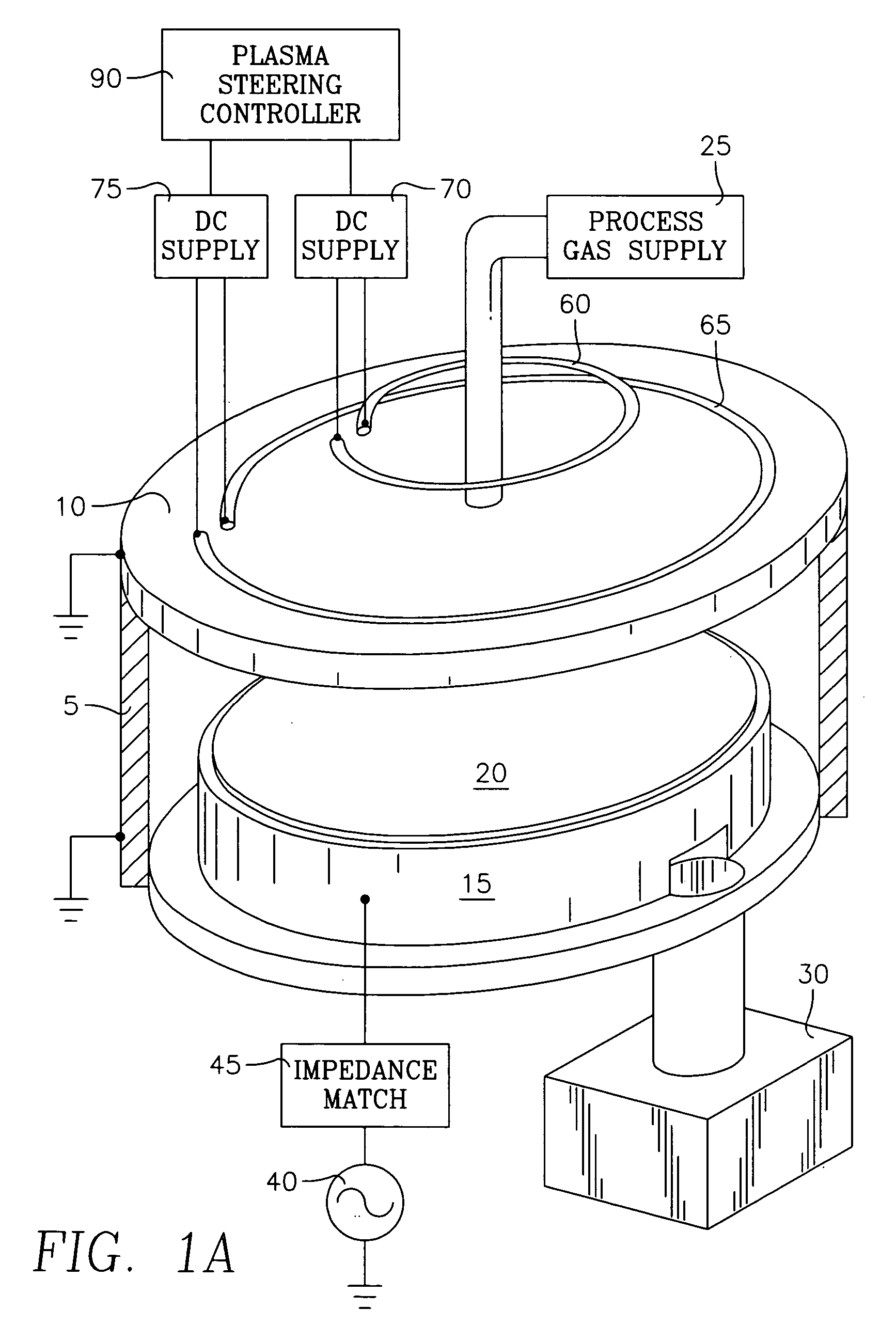
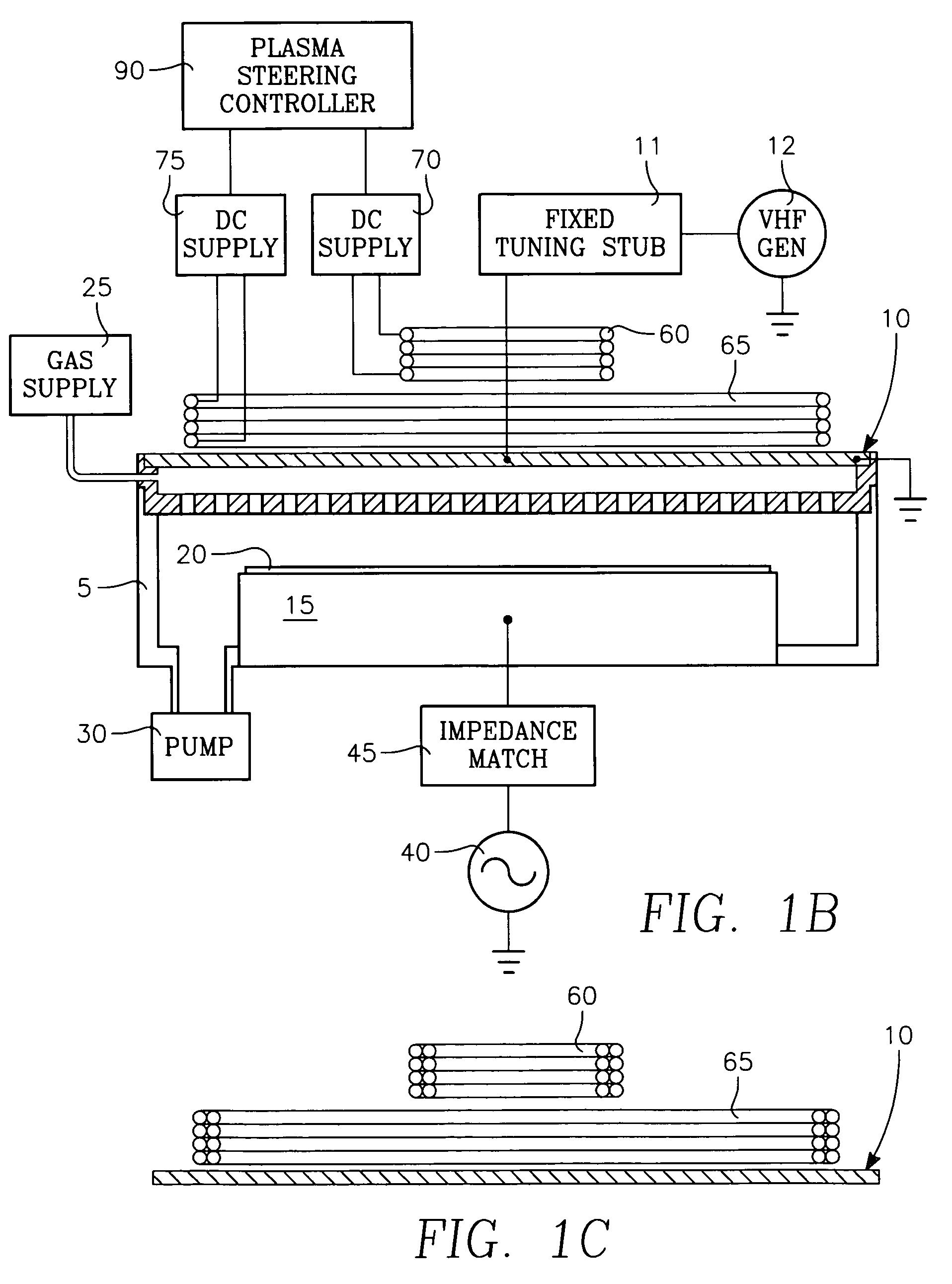
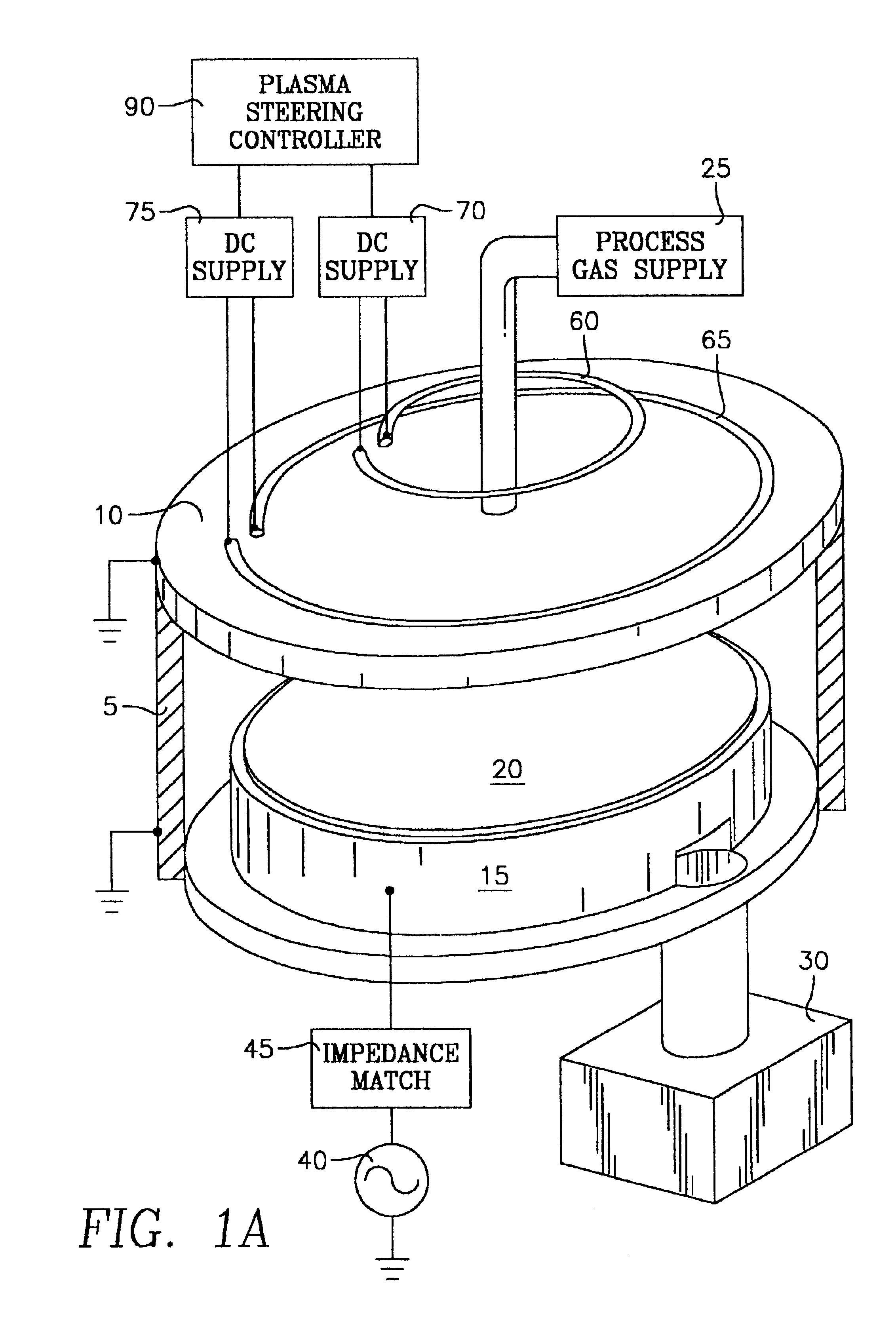
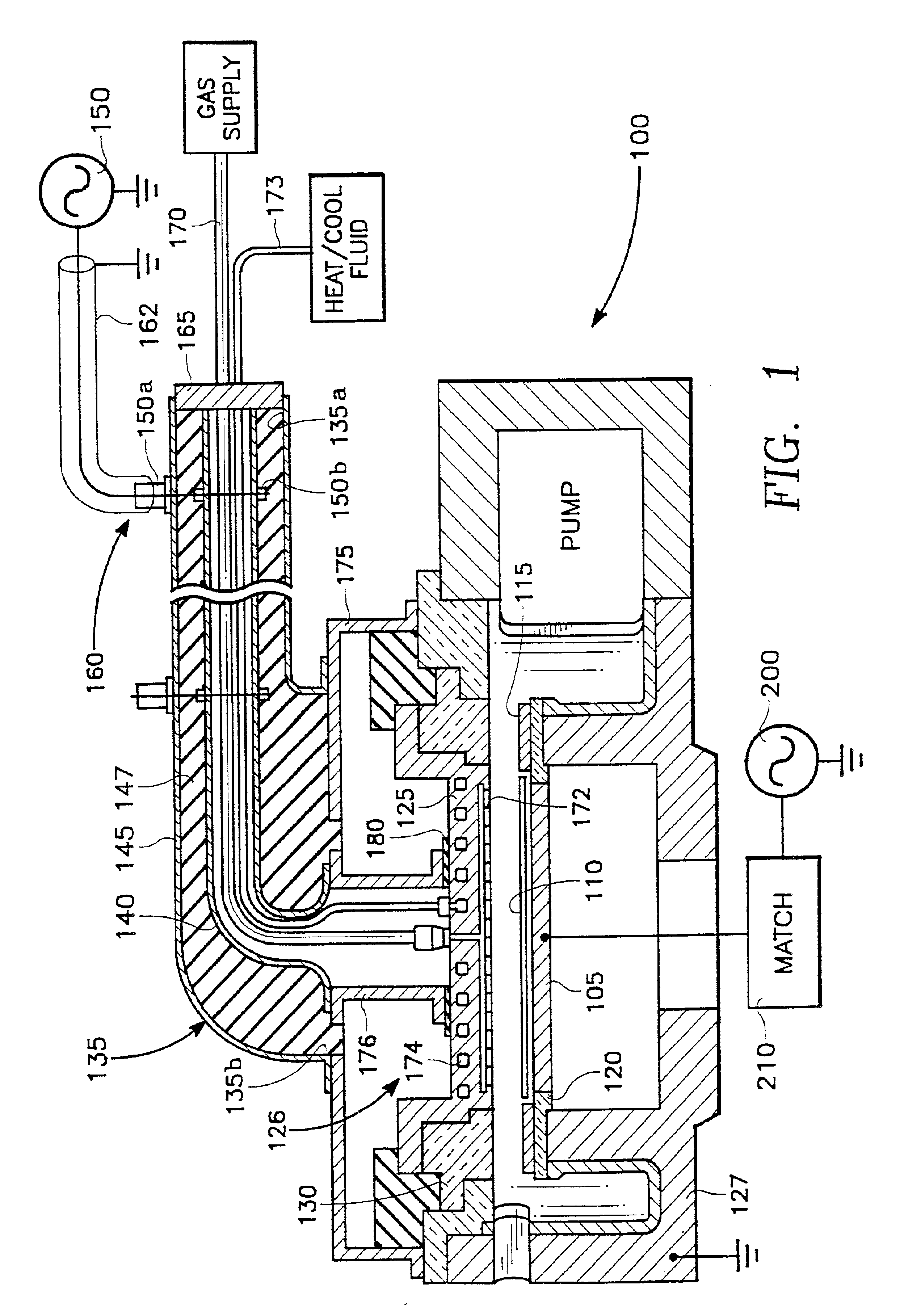
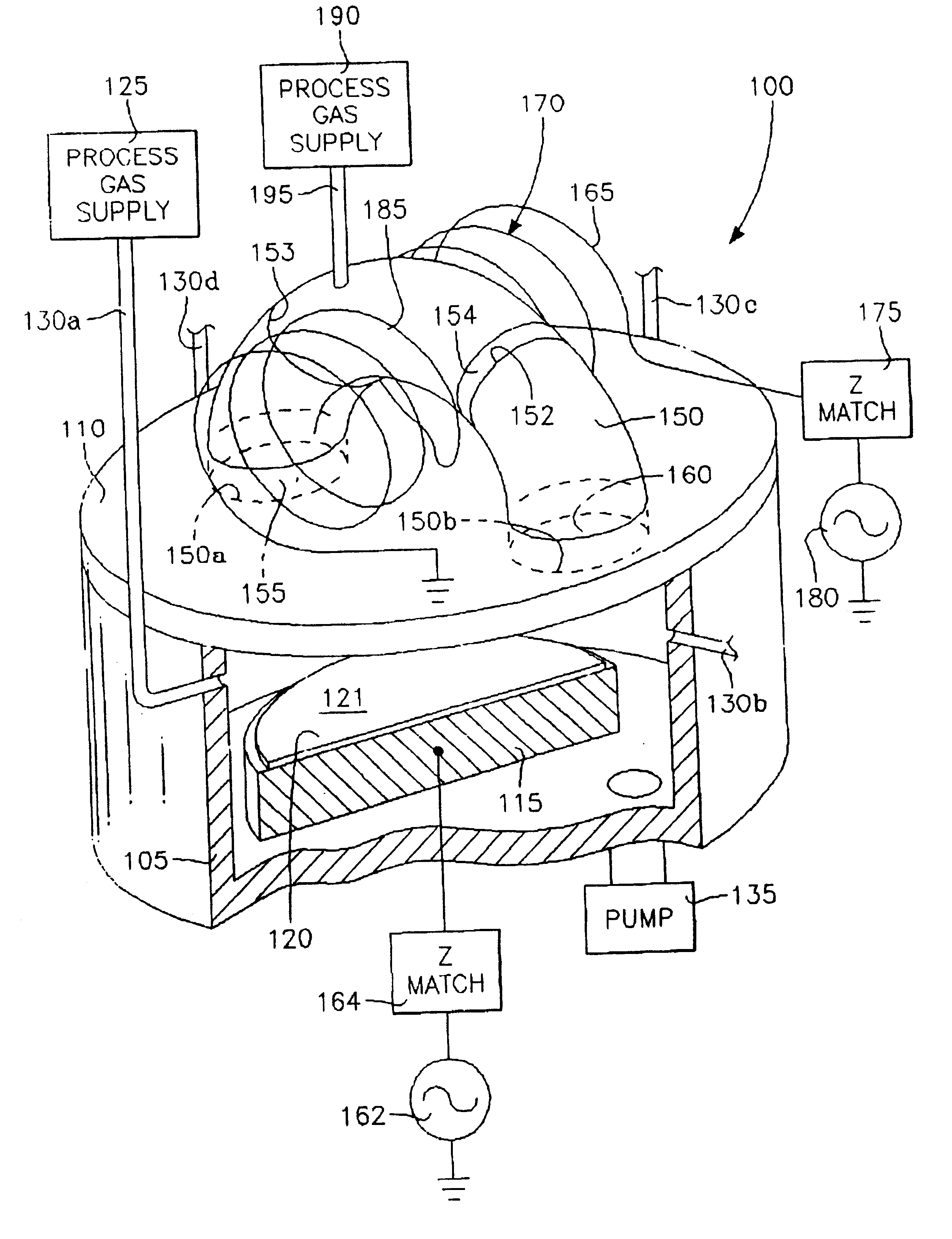
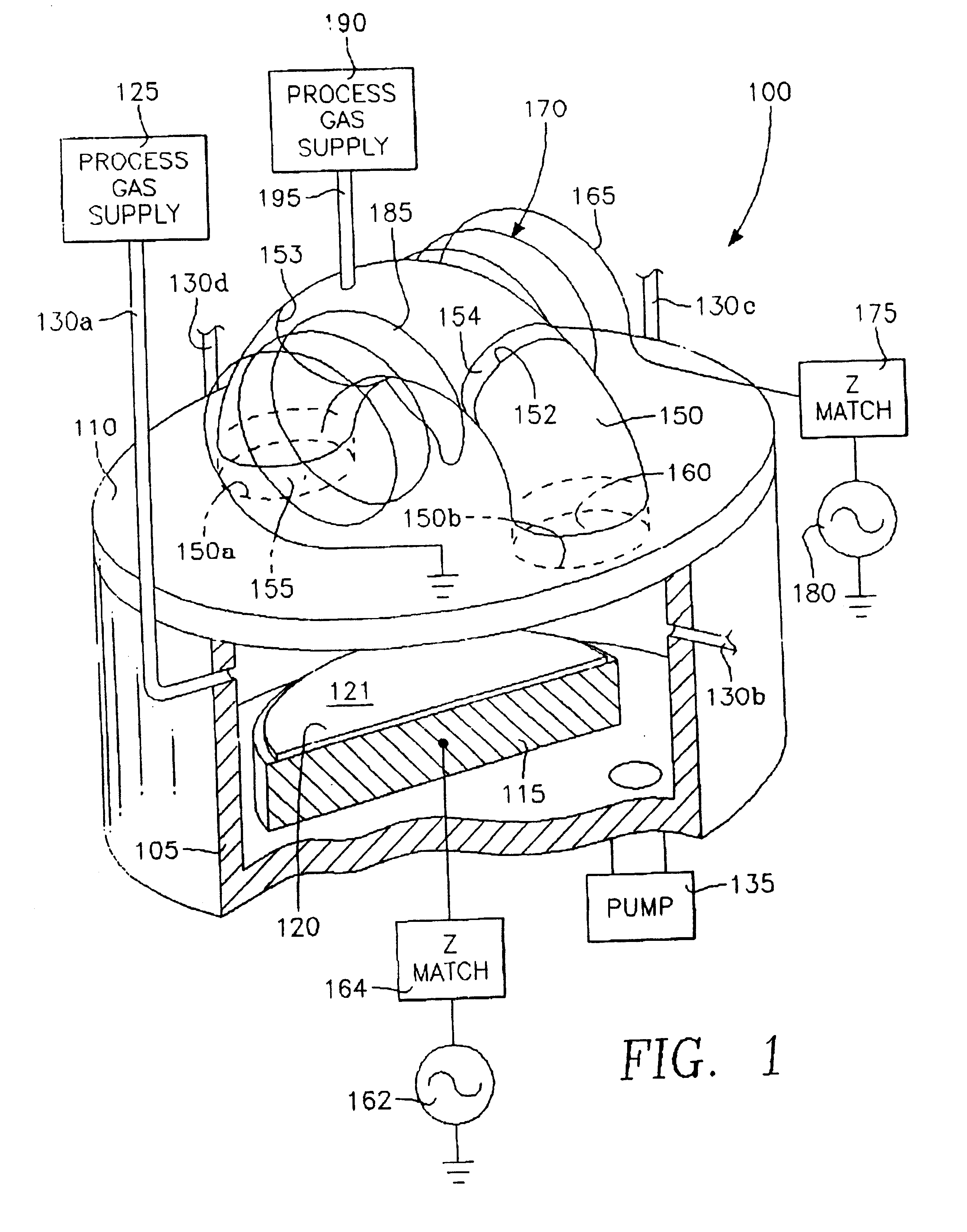
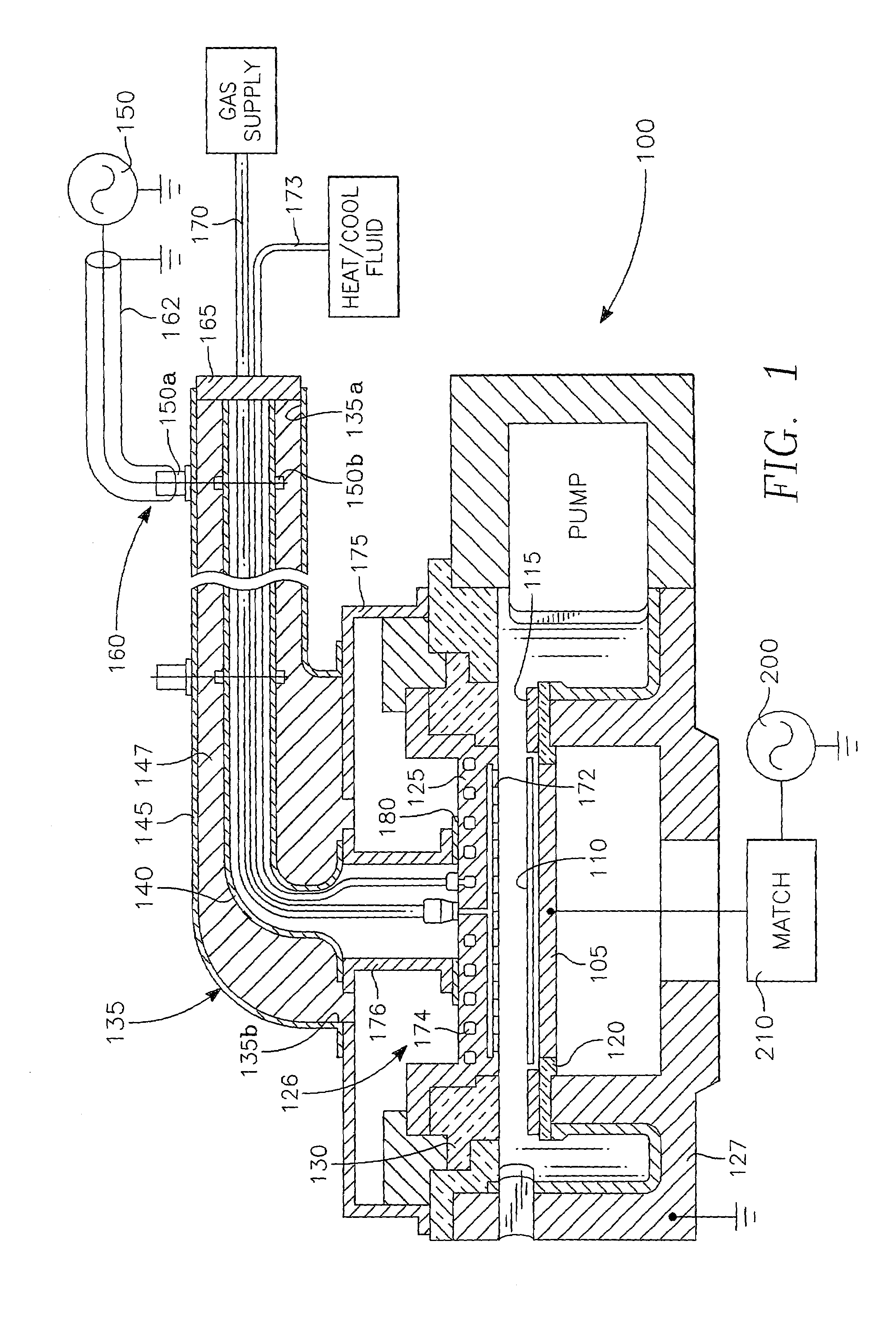
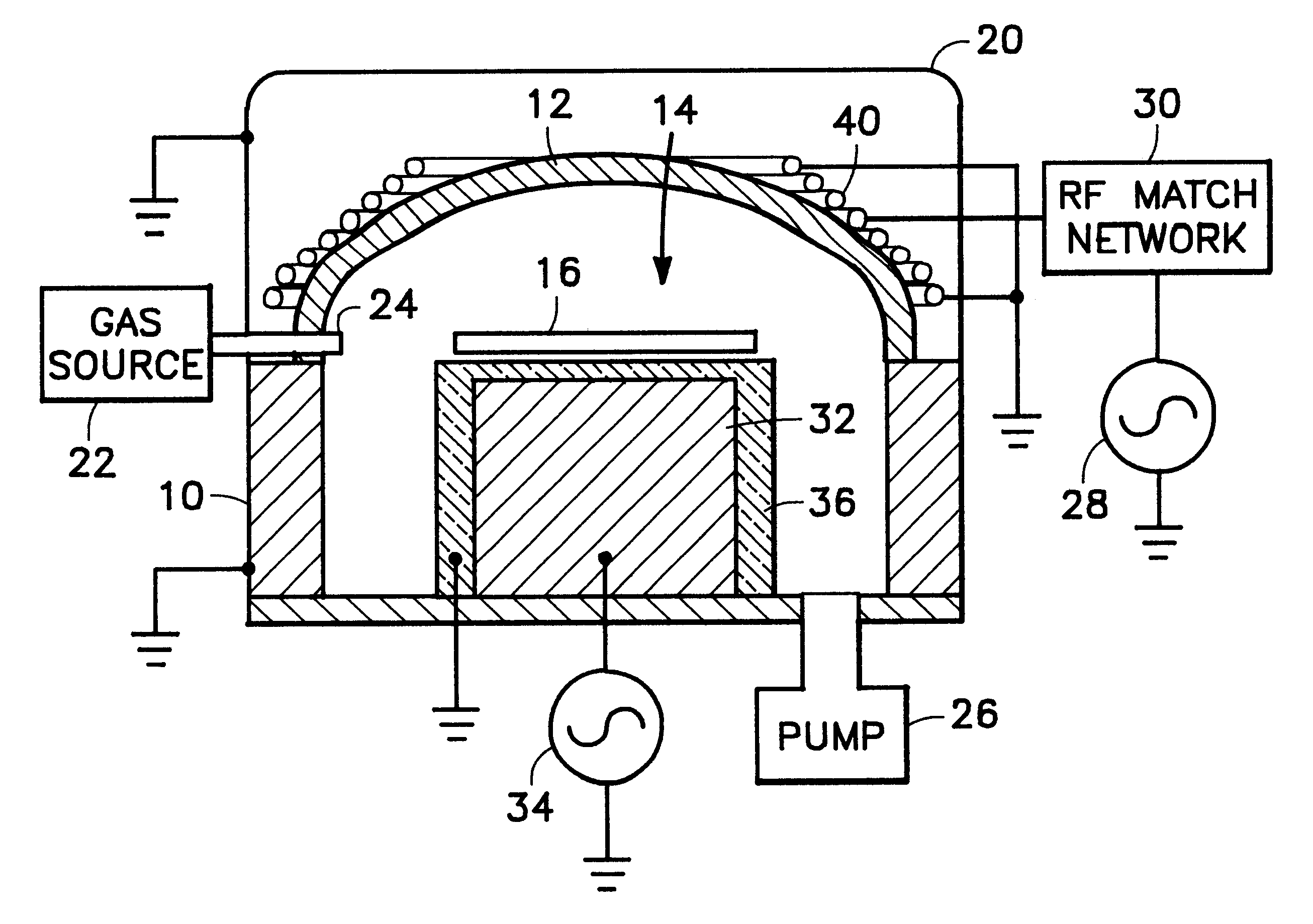
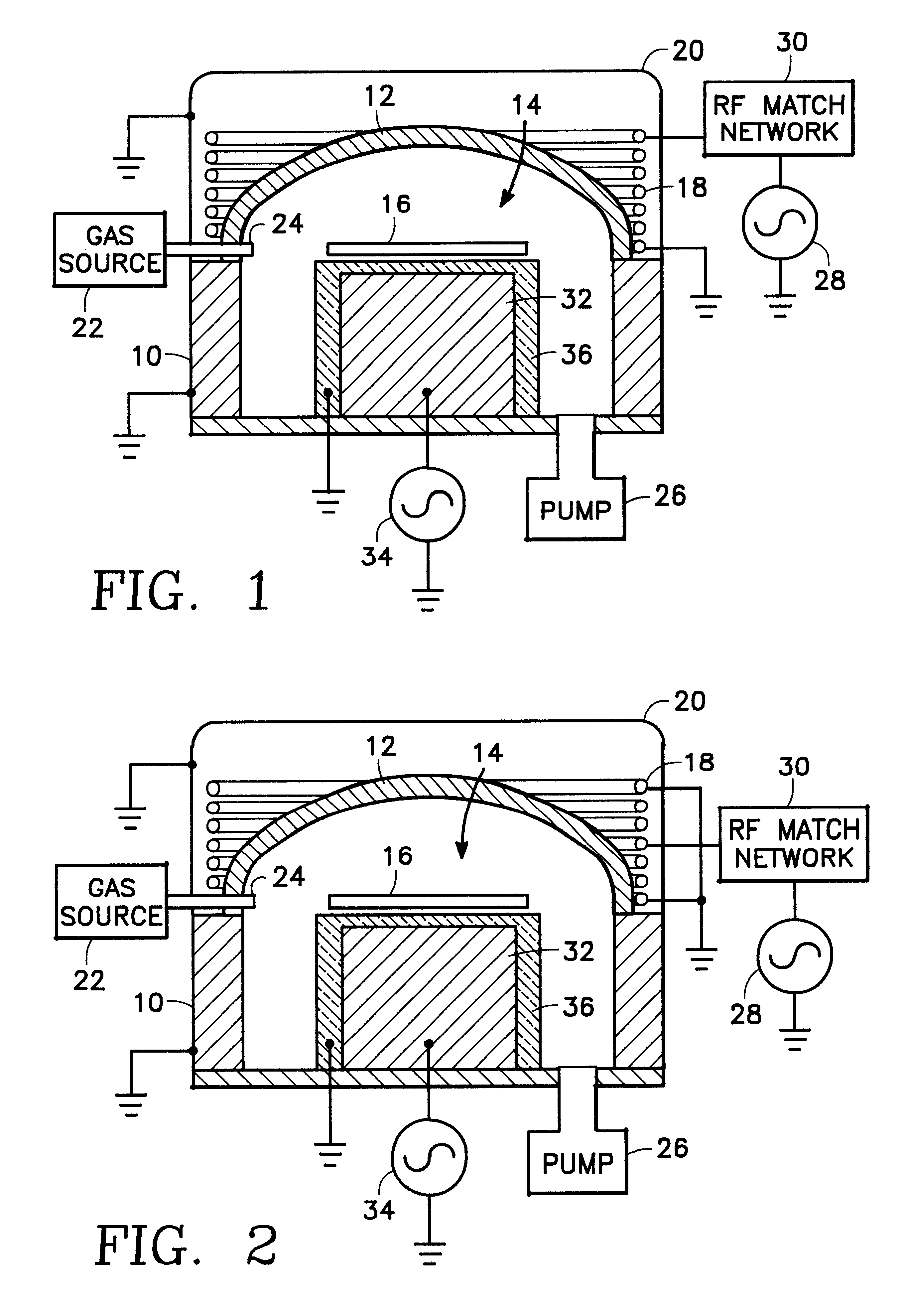
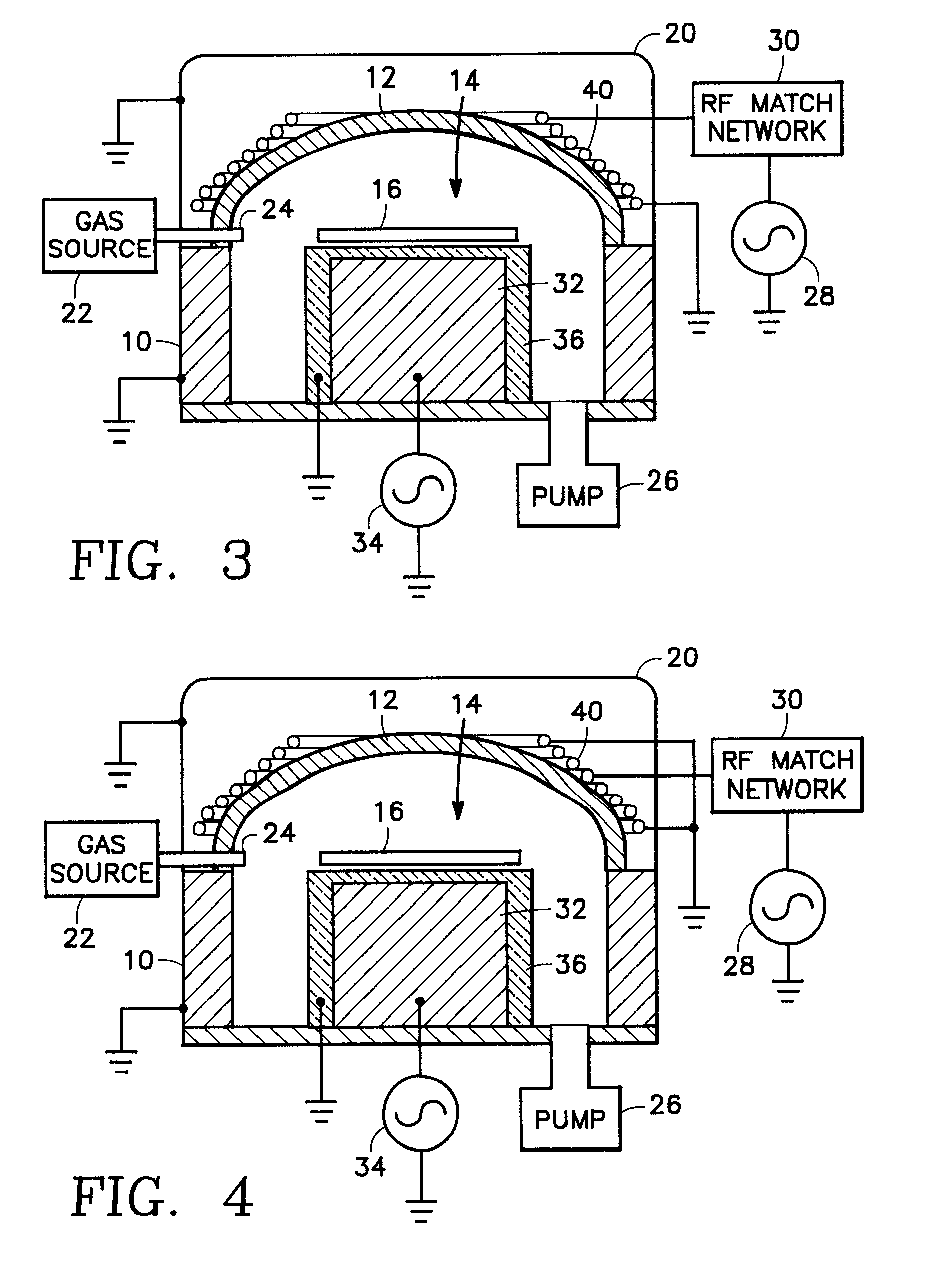
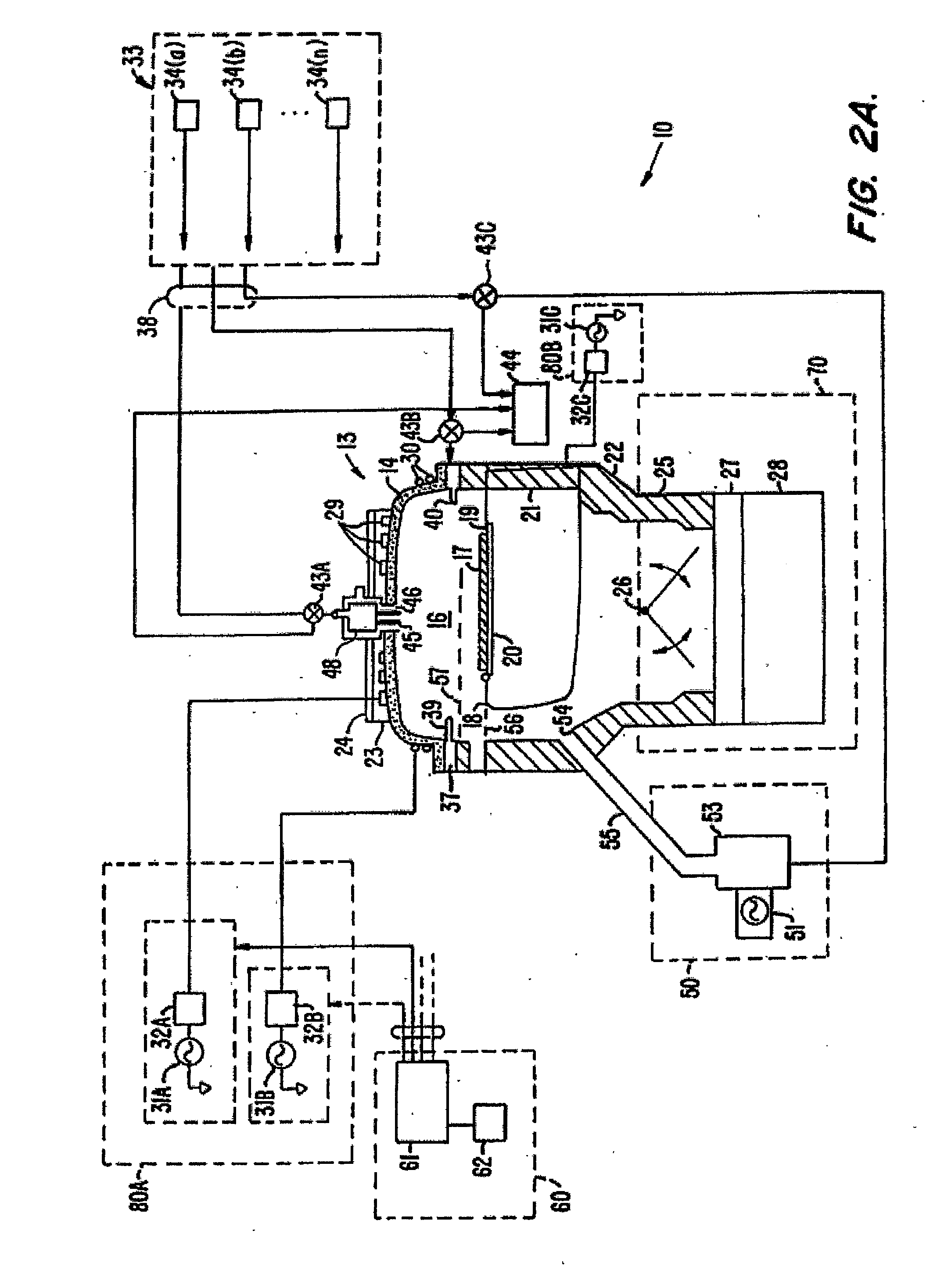
Method and apparatus for stable plasma processing
A method and apparatus for etching a substrate using a spatially modified plasma is provided herein. In one embodiment, the method includes providing a process chamber having a plasma stabilizer disposed above a substrate support pedestal. A substrate is placed upon the pedestal. A process gas is introduced into the process chamber and a plasma is formed from the process gas. The substrate is etched with a plasma having an ion density to radical density ratio defined by the plasma stabilizer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
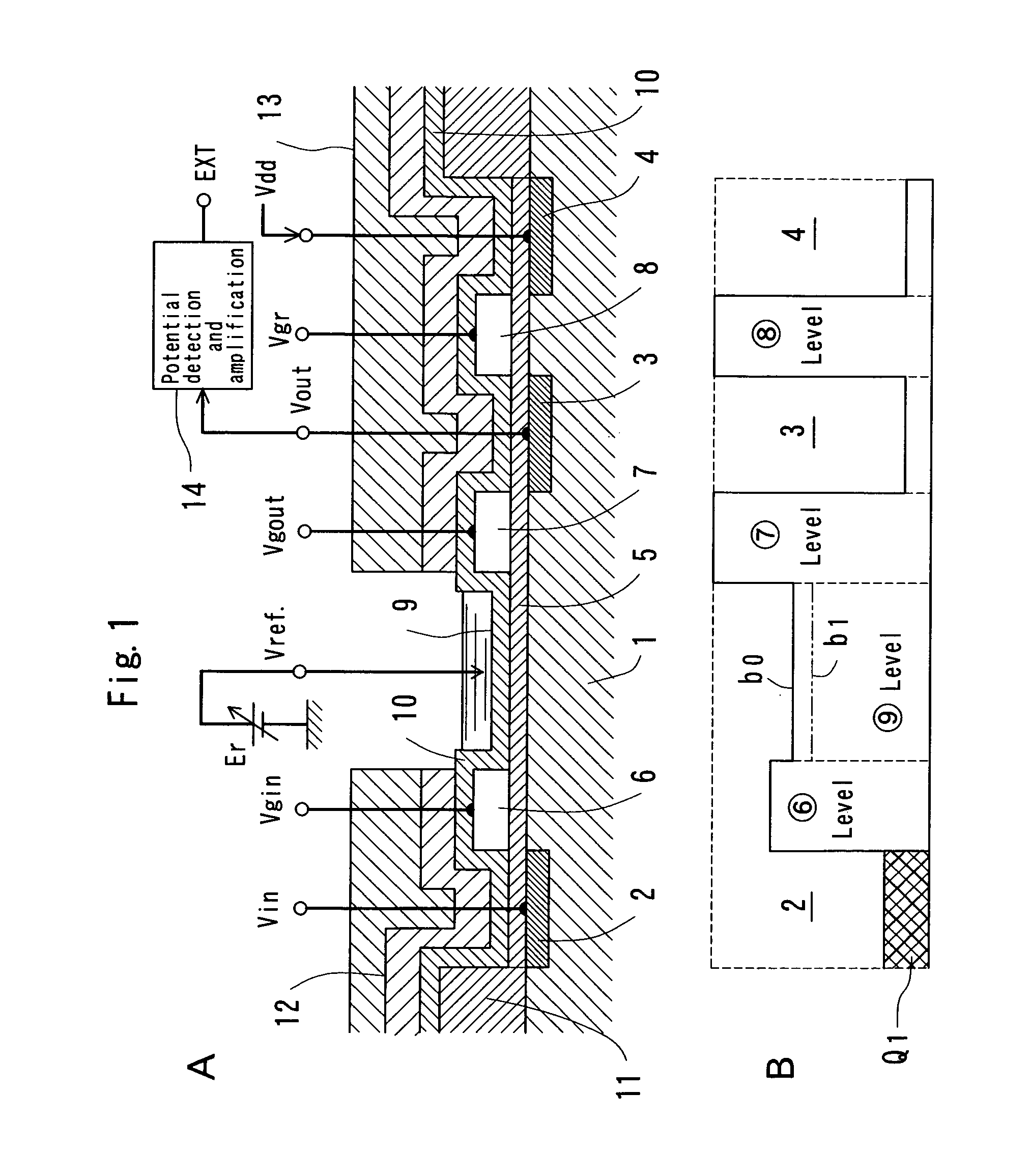
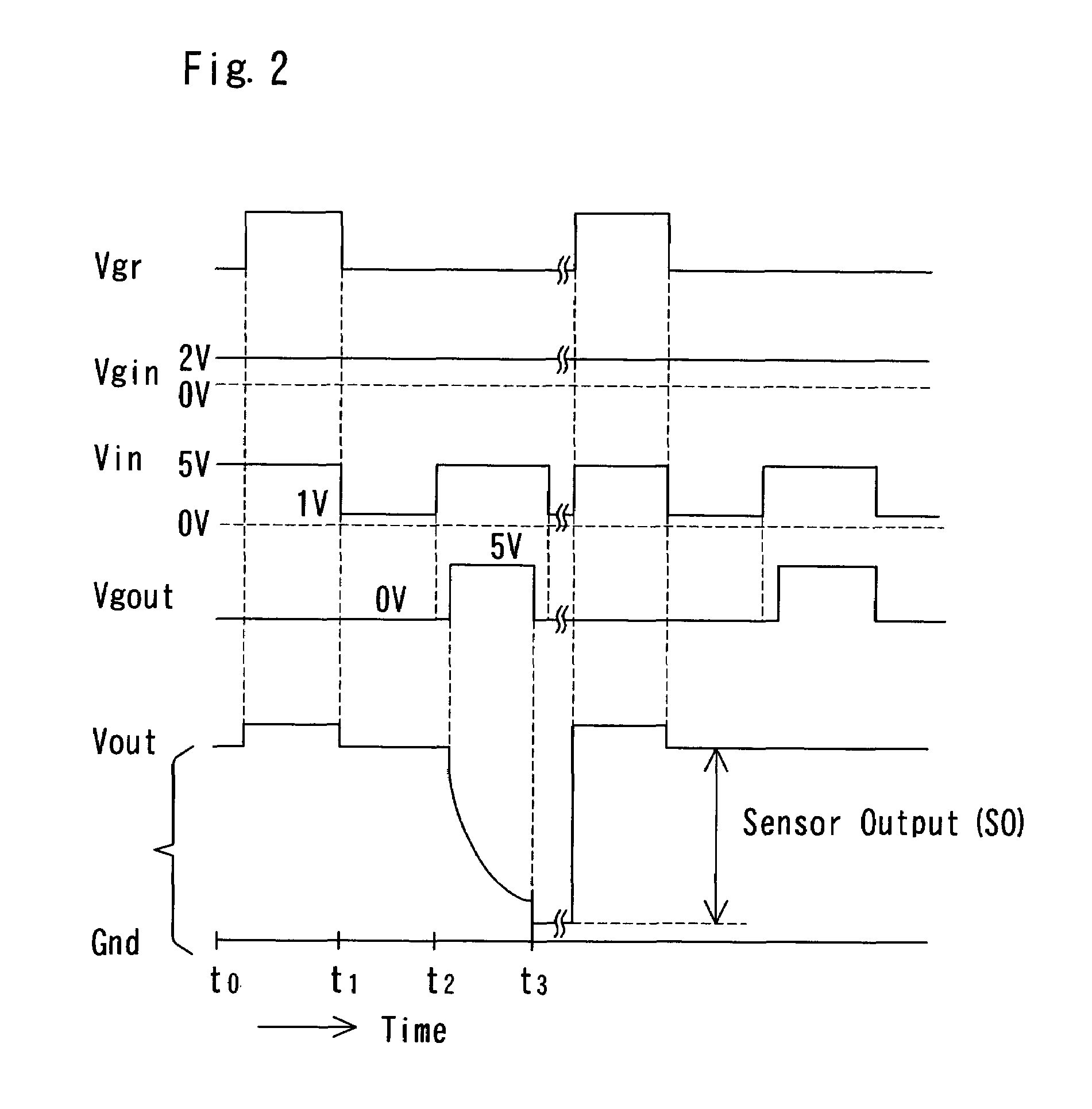
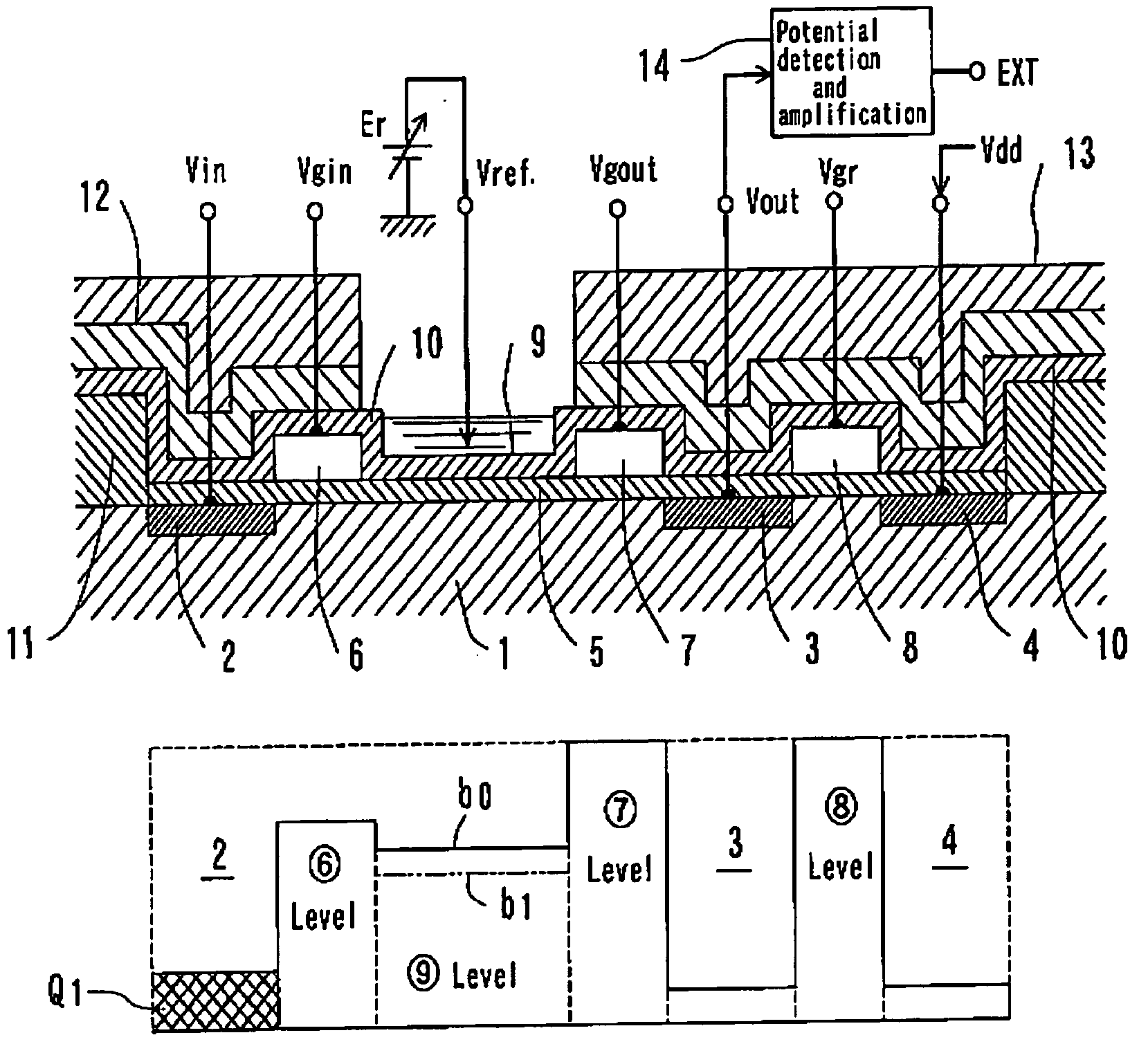
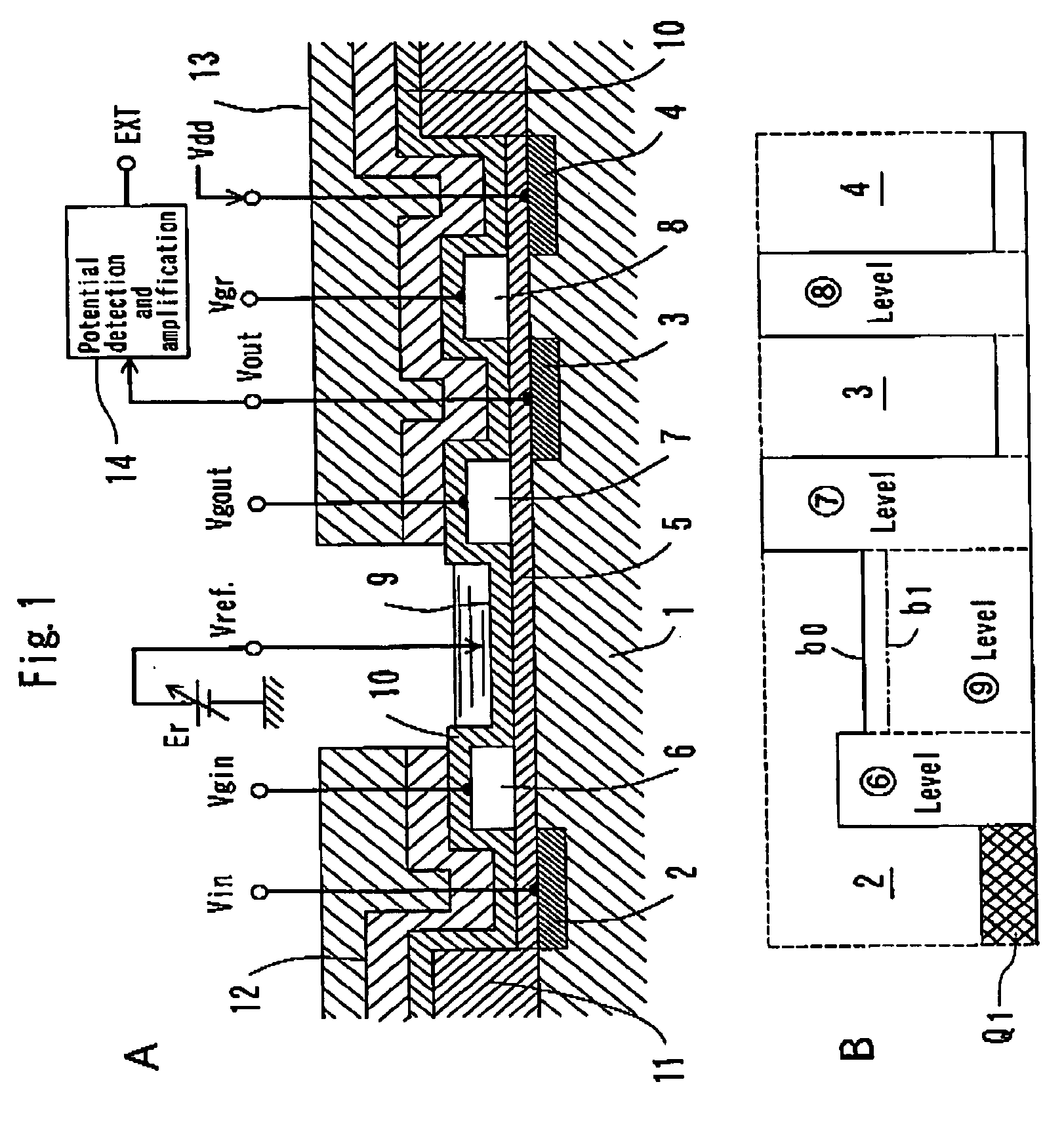
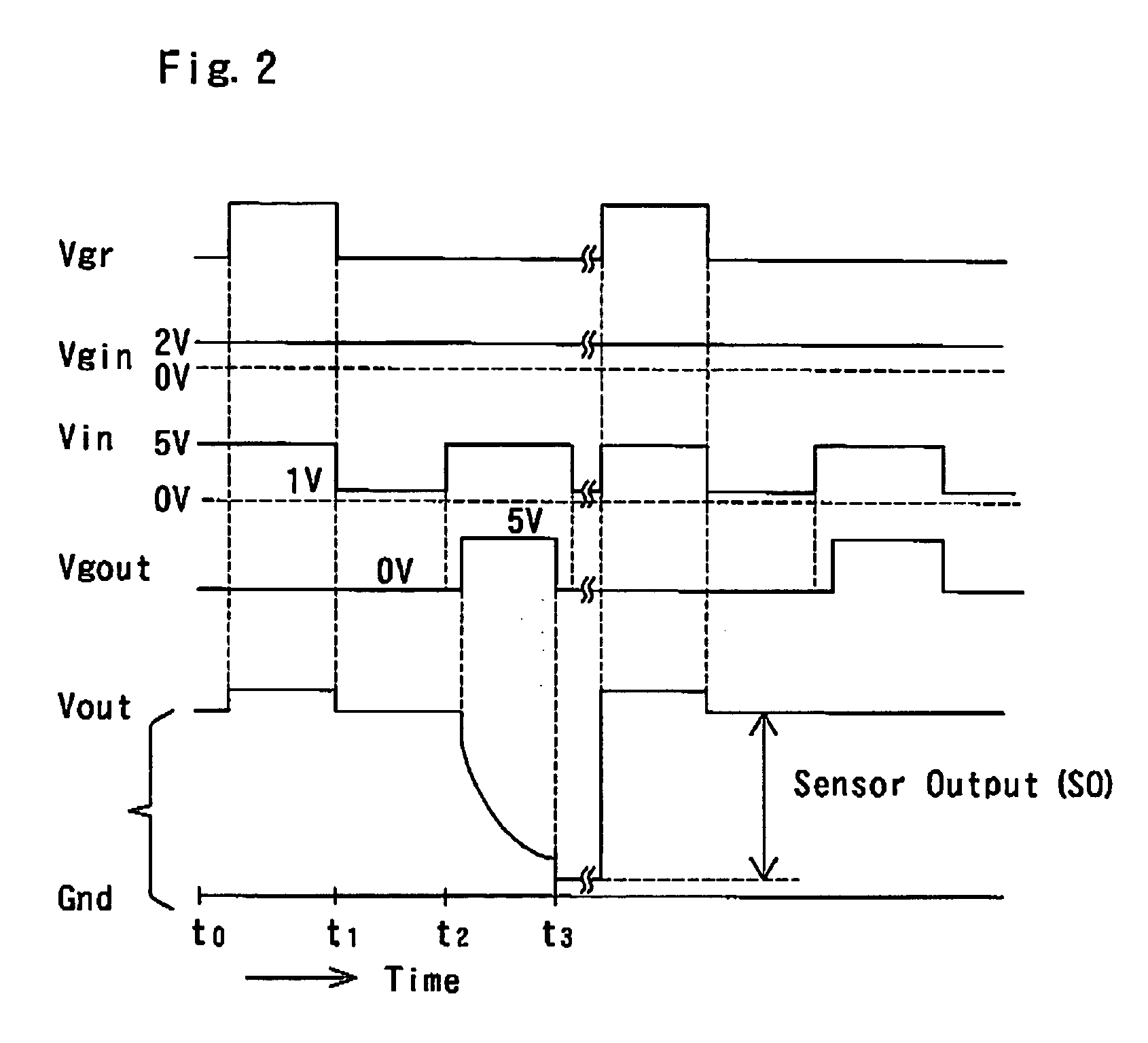
FET type sensor, ion density detecting method comprising this sensor, and base sequence detecting method
InactiveUS7049645B2Low costSure easyTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusionIon density
The surface of a semiconductor substrate (1) comprises an input diode section (2) and a floating diffusion section (3) consisting of a diffusion region reverse to the substrate in conductivity type, an input gate (6) and an output gate (7) fixed on an insulation film (5) extending from an input diode section to a floating diffusion section, a sensing section (9) consisting of an ion sensitive film fixed on the insulation film extending from the input.
Owner:BAIO TSUKUSU +1
Capacitively coupled plasma reactor with uniform radial distribution of plasma
InactiveUS6900596B2Enhances plasma ion density uniformityImprove density uniformityElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A plasma reactor for processing a semiconductor wafer includes a side wall and an overhead ceiling defining a chamber, a workpiece support cathode within the chamber having a working surface facing the ceiling for supporting a semiconductor workpiece, process gas inlets for introducing a process gas into the chamber and an RF bias power generator having a bias power frequency. There is a bias power feed point at the working surface and an RF conductor is connected between the RF bias power generator and the bias power feed point at the working surface. A dielectric sleeve surrounds a portion of the RF conductor, the sleeve having an axial length along the RF conductor, a dielectric constant and an axial location along the RF conductor, the length, dielectric constant and location of the sleeve being such that the sleeve provides a reactance that enhances plasma ion density uniformity over the working surface. In accordance with a further aspect, the reactor can include an annular RF coupling ring having an inner diameter corresponding generally to a periphery of the workpiece, the RF coupling ring extending a sufficient portion of a distance between the working surface and the overhead electrode to enhance plasma ion density near a periphery of the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Fet type sensor, ion density detecting method comprising this sensor, and base sequence detecting method
InactiveUS20050062093A1Accurate detectionLow costTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusionIon density
The surface of a semiconductor substrate (1) comprises an input diode section (2) and a floating diffusion section (3) consisting of a diffusion region reverse to the substrate in conductivity type, an input gate (6) and an output gate (7) fixed on an insulation film (5) extending from an input diode section to a floating diffusion section, a sensing section (9) consisting of an ion sensitive film fixed on the insulation film extending from the input.
Owner:BAIO TSUKUSU +1
Capacitively coupled plasma reactor with magnetic plasma control
InactiveUS20050001556A1Plasma uniformity can be improvedImprove uniformityElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsCapacitanceAxis of symmetry
A plasma reactor includes a vacuum enclosure including a side wall and a ceiling defining a vacuum chamber, and a workpiece support within the chamber and facing the ceiling for supporting a planar workpiece, the workpiece support and the ceiling together defining a processing region between the workpiece support and the ceiling. Process gas inlets furnish a process gas into the chamber. A plasma source power electrode is connected to an RF power generator for capacitively coupling plasma source power into the chamber for maintaining a plasma within the chamber. The reactor further includes at least a first overhead solenoidal electromagnet adjacent the ceiling, the overhead solenoidal electromagnet, the ceiling, the side wall and the workpiece support being located along a common axis of symmetry. A current source is connected to the first solenoidal electromagnet and furnishes a first electric current in the first solenoidal electromagnet whereby to generate within the chamber a magnetic field which is a function of the first electric current, the first electric current having a value such that the magnetic field increases uniformity of plasma ion density radial distribution about the axis of symmetry near a surface of the workpiece support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Capacitively coupled plasma reactor with magnetic plasma control
InactiveUS6853141B2Plasma uniformity can be improvedImprove uniformityElectric arc lampsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceAxis of symmetry
A plasma reactor includes a vacuum enclosure including a side wall and a ceiling defining a vacuum chamber, and a workpiece support within the chamber and facing the ceiling for supporting a planar workpiece, the workpiece support and the ceiling together defining a processing region between the workpiece support and the ceiling. Process gas inlets furnish a process gas into the chamber. A plasma source power electrode is connected to an RF power generator for capacitively coupling plasma source power into the chamber for maintaining a plasma within the chamber. The reactor further includes at least a first overhead solenoidal electromagnet adjacent the ceiling, the overhead solenoidal electromagnet, the ceiling, the sidewall and the workpiece support being located along a common axis of symmetry. A current source is connected to the first solenoidal electromagnet and furnishes a first electric current in the first solenoidal electromagnet whereby to generate within the chamber a magnetic field which is a function of the first electric current, the first electric current having a value such that the magnetic field increases uniformity of plasma ion density radial distribution about the axis of symmetry near a surface of the workpiece support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
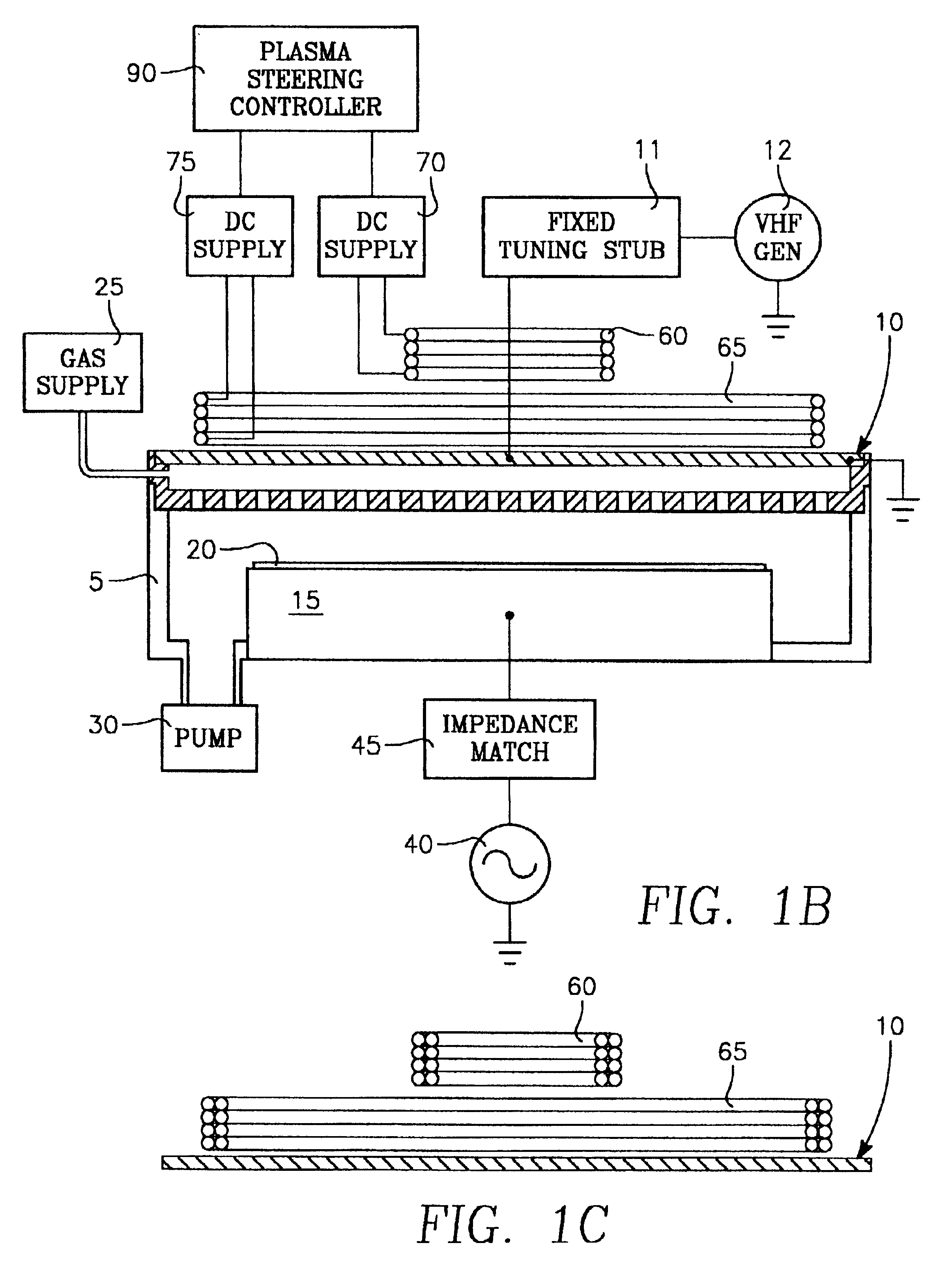
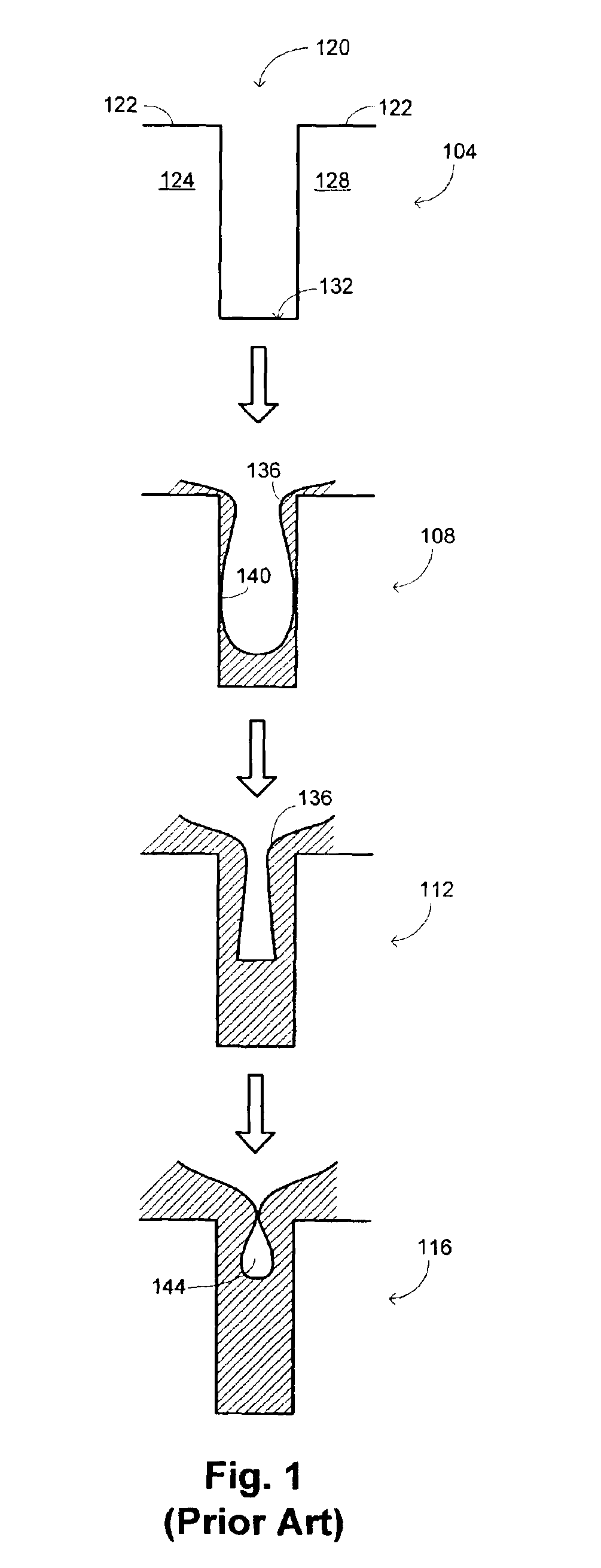
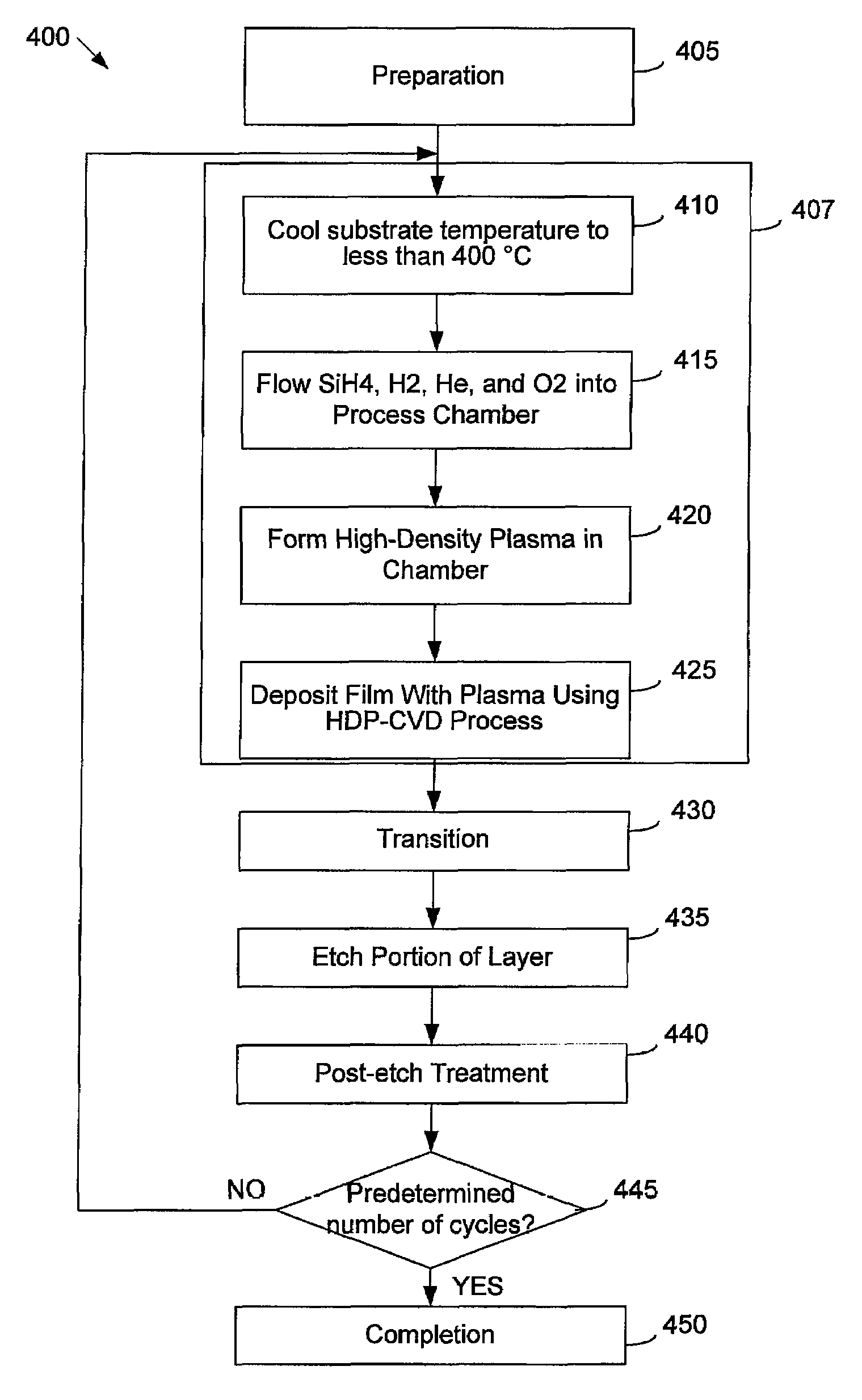
In-situ-etch-assisted HDP deposition using SiF4 and hydrogen
InactiveUS6903031B2Reduce concentrationImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenIon density
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
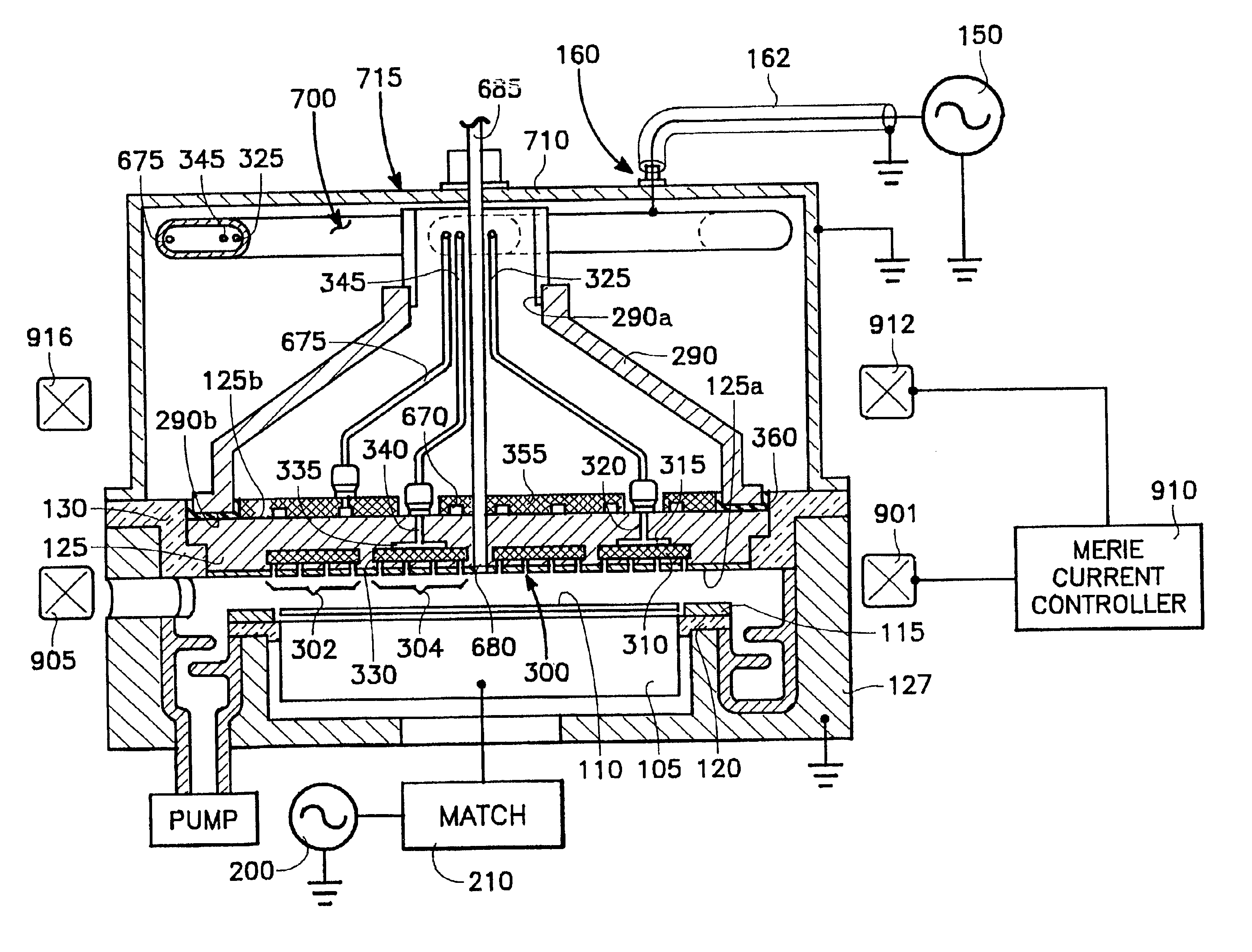
Merie plasma reactor with overhead RF electrode tuned to the plasma with arcing suppression
InactiveUS6894245B2Improve plasma ion density distribution uniformitySufficient capacitanceElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsCapacitanceIon density
A plasma reactor for processing a semiconductor workpiece, includes a reactor chamber having a chamber wall and containing a workpiece support for holding the semiconductor support, the electrode comprising a portion of the chamber wall, an RF power generator for supplying power at a frequency of the generator to the overhead electrode and capable of maintaining a plasma within the chamber at a desired plasma ion density level. The overhead electrode has a capacitance such that the overhead electrode and the plasma formed in the chamber at the desired plasma ion density resonate together at an electrode-plasma resonant frequency, the frequency of the generator being at least near the electrode-plasma resonant frequency. The reactor further includes a set of MERIE magnets surrounding the plasma process area overlying the wafer surface that produce a slowly circulating magnetic field which stirs the plasma to improve plasma ion density distribution uniformity.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of processing a workpiece using an externally excited torroidal plasma source
InactiveUS6410449B1Increase ion densityIncrease plasma densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma currentIon density
A method of processing a workpiece in a plasma reactor includes establishing a torroidal path for a plasma current to flow that passes near and transverse to the surface of said workpiece, maintaining a plasma current in the torroidal path by applying RF power to a portion of the torroidal path away from the surface of the workpiece, and increasing the ion density of the plasma current in the vicinity of the workpiece by constricting the area of a portion of the torroidal path overlying the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
In-situ-etch-assisted HDP deposition using SiF4 and hydrogen
ActiveUS20050048801A1Good gapfill characteristicReduce fluorine concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenIon density
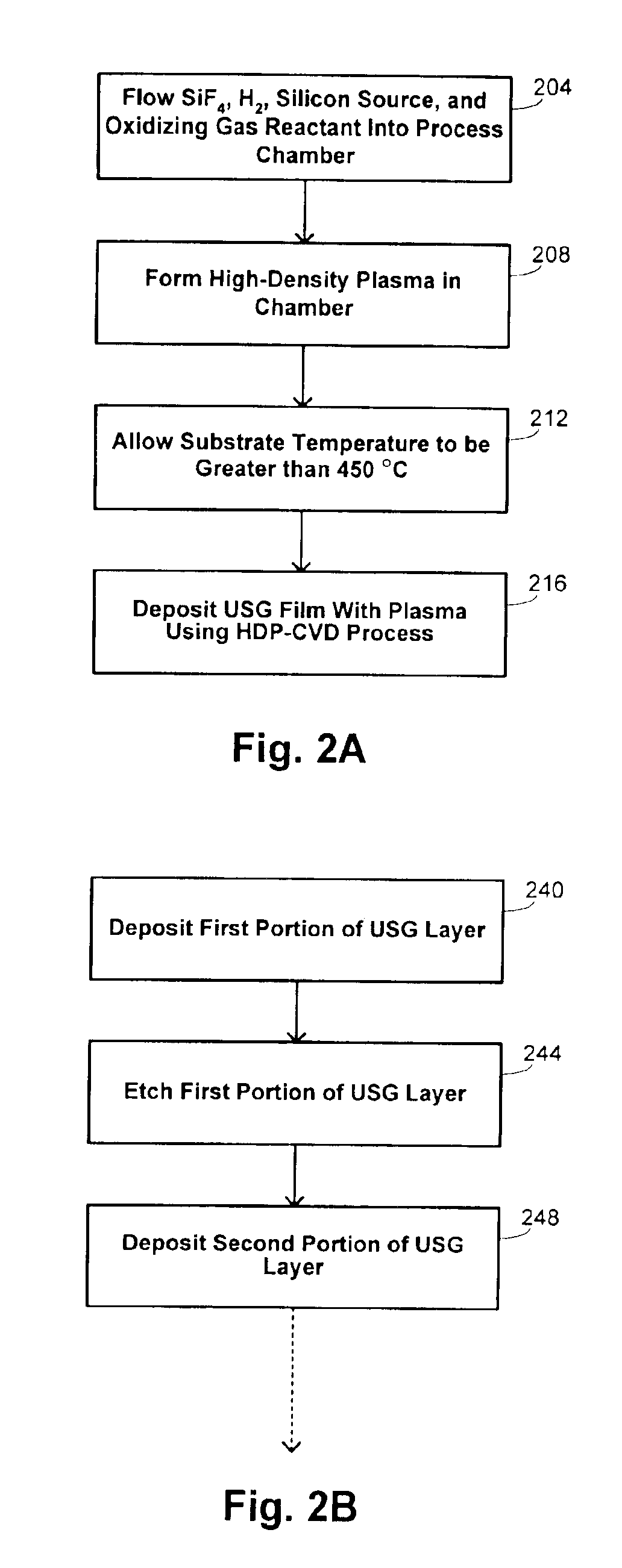
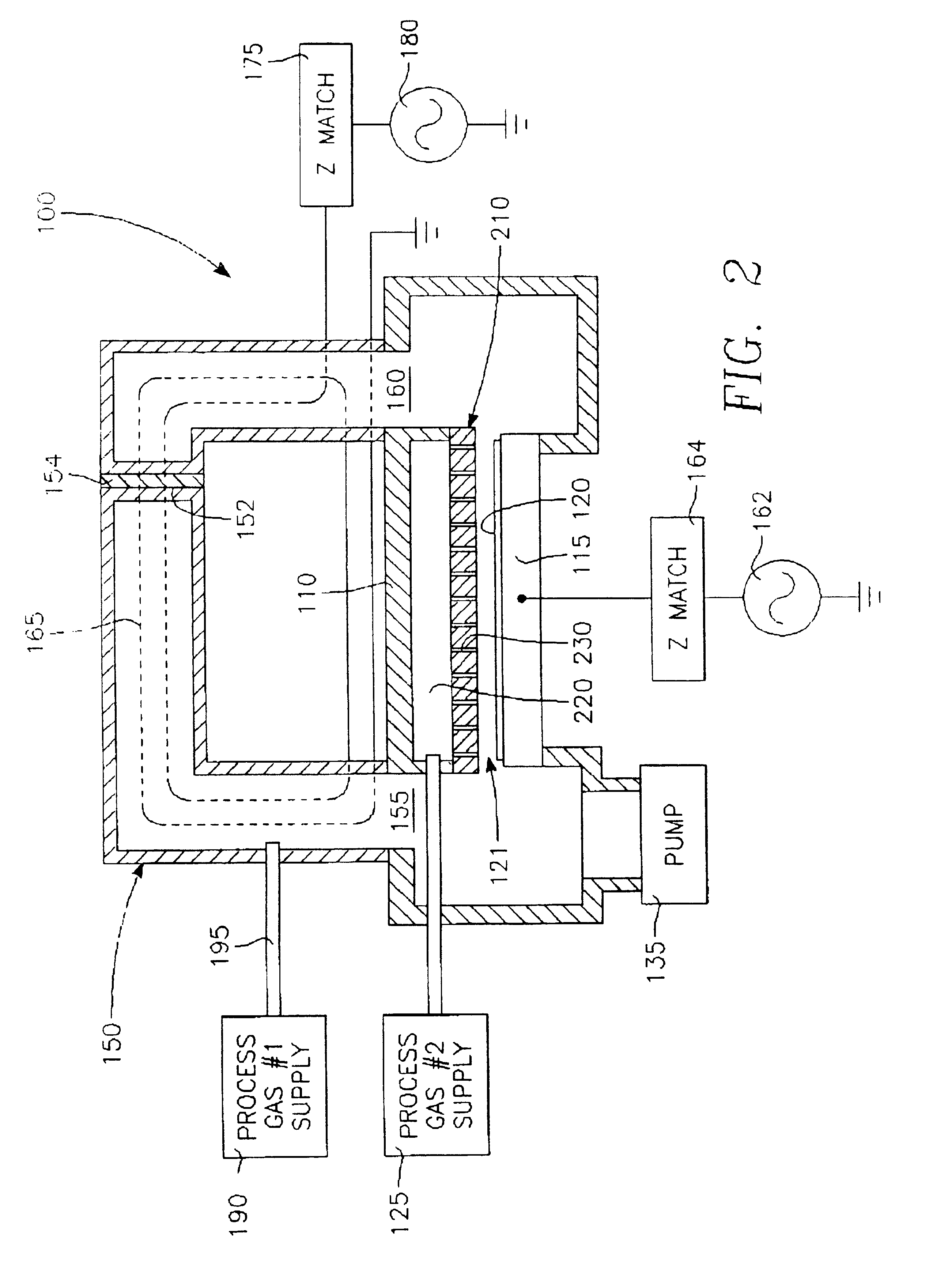
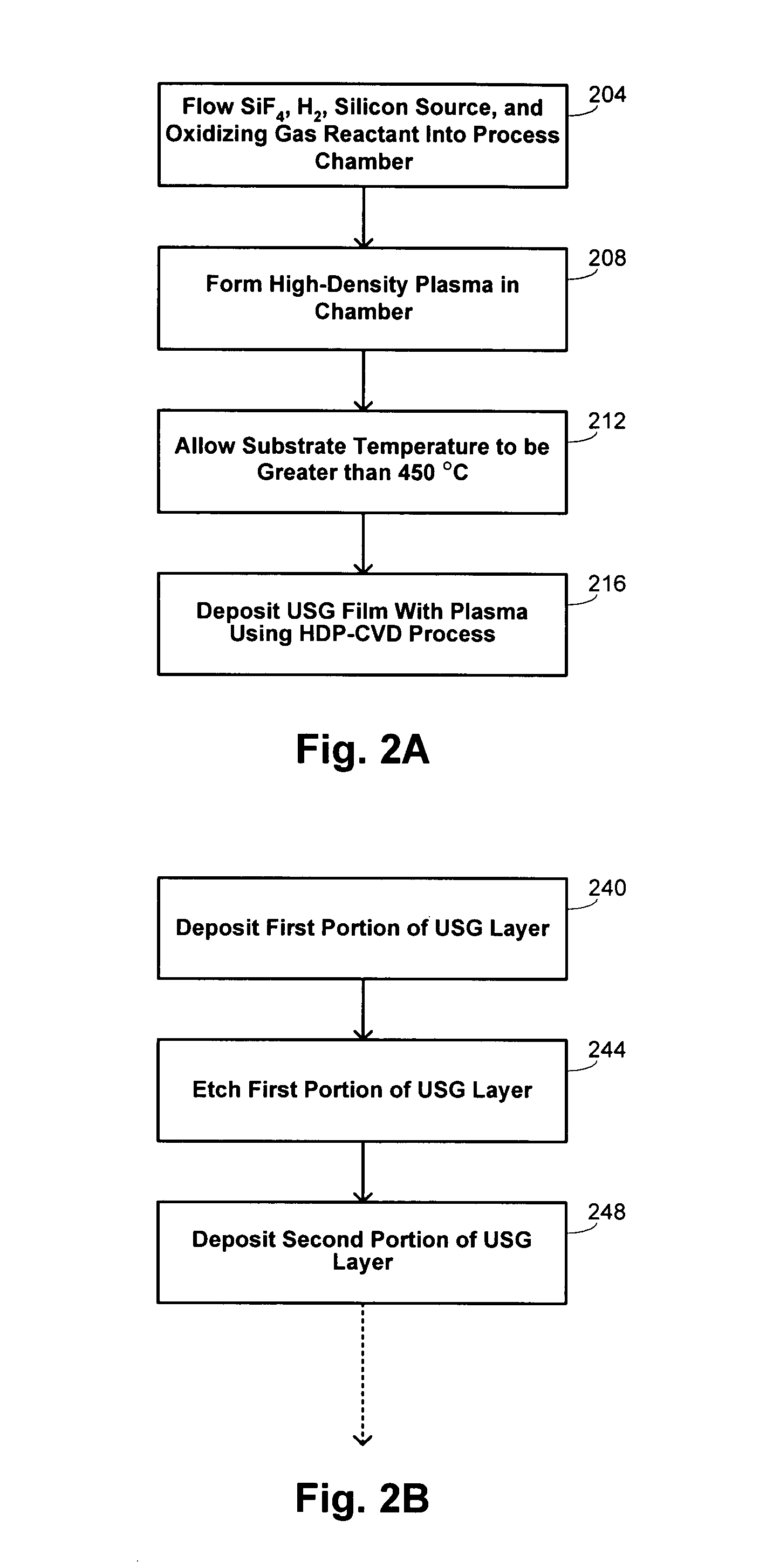
A process is provided for depositing an undoped silicon oxide film on a substrate disposed in a process chamber. A process gas that includes SiF4, H2, a silicon source, and an oxidizing gas reactant is flowed into the process chamber. A plasma having an ion density of at least 1011 ions / cm3 is formed from the process gas. The undoped silicon oxide film is deposited over the substrate with the plasma using a process that has simultaneous deposition and sputtering components. A temperature of the substrate during such depositing is greater than 450° C.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
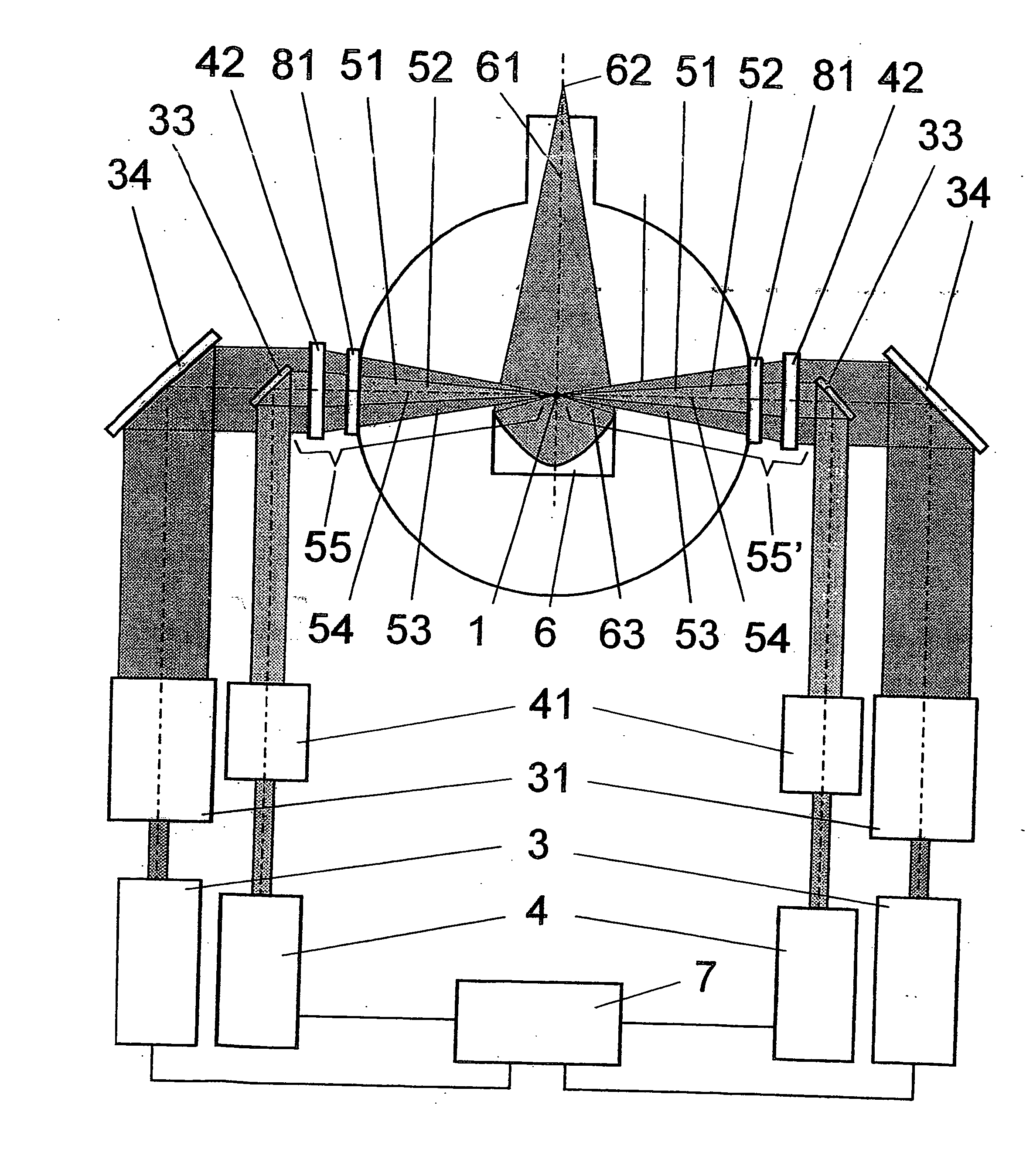
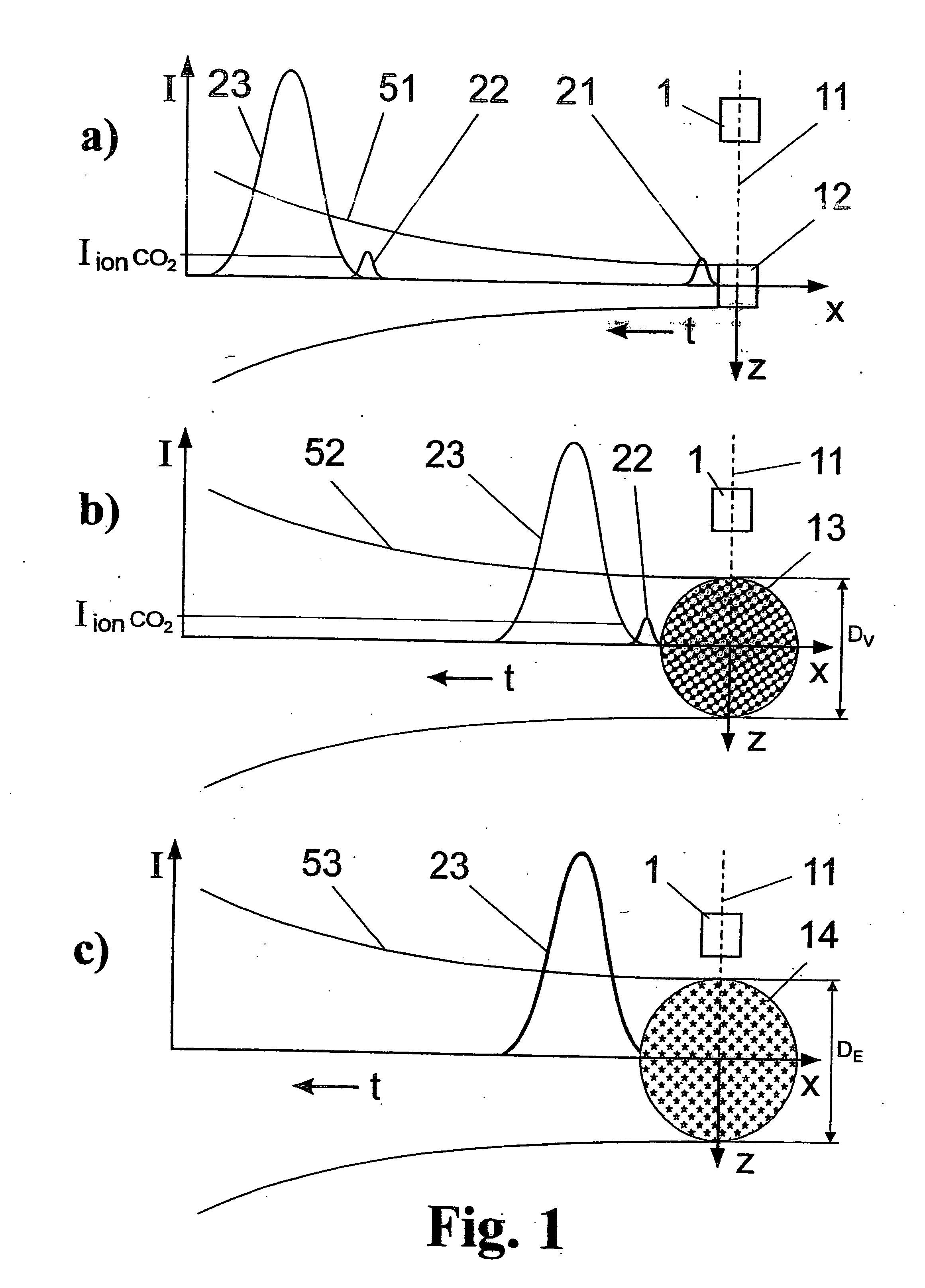
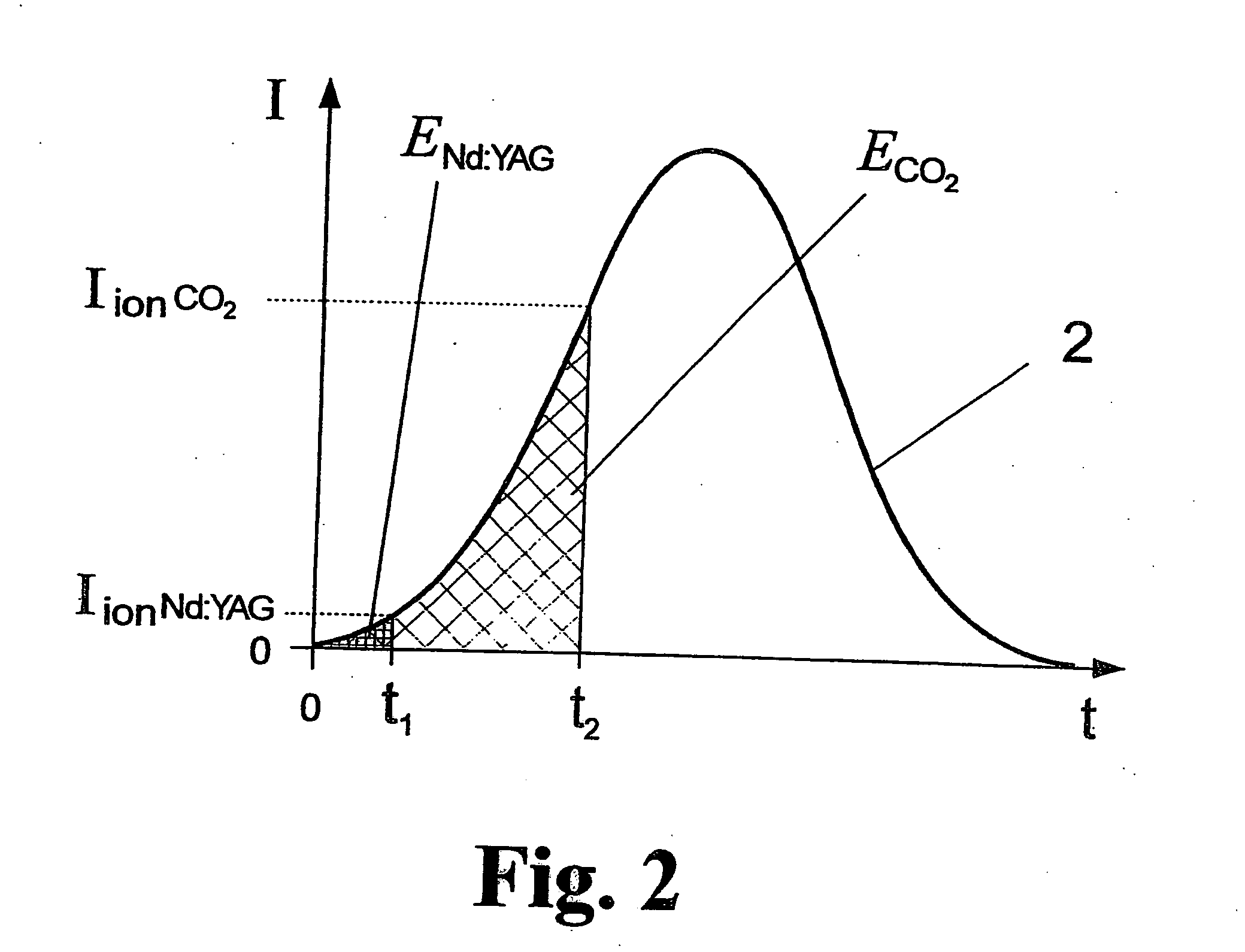
Method and arrangement for the efficient generation of short-wavelength radiation based on a laser-generated plasma
InactiveUS20060215712A1Losses in the main pulse (e.g., due to transmission) are minimizedLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialIon densityElectromagnetic radiation
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for the efficient generation of intensive short-wavelength radiation based on a plasma. The object of the invention is to find a novel possibility for the generation of intensive short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation, particularly EUV radiation, which permits the excitation of a radiation-emitting plasma with economical gas lasers (preferably CO2 lasers). This object is met, according to the invention, in that a first prepulse for reducing the target density is followed by at least a second prepulse which generates free electrons in the target by multiphoton ionization after a virtually complete recombination of free electrons generated by the first prepulse has taken place due to a long-lasting expansion of the target for reducing the target density, and the main pulse of a gas laser with a low critical electron density typical for its wavelength is directed to the target immediately after the second prepulse when the second prepulse in the expanded target, whose ion density corresponds to the critical electron density of the gas laser, has created enough free electrons so that an efficient avalanche ionization is triggered by the main pulse of the gas laser until reaching the ionization level for the desired radiation emission of the plasma.
Owner:XTREME TECH
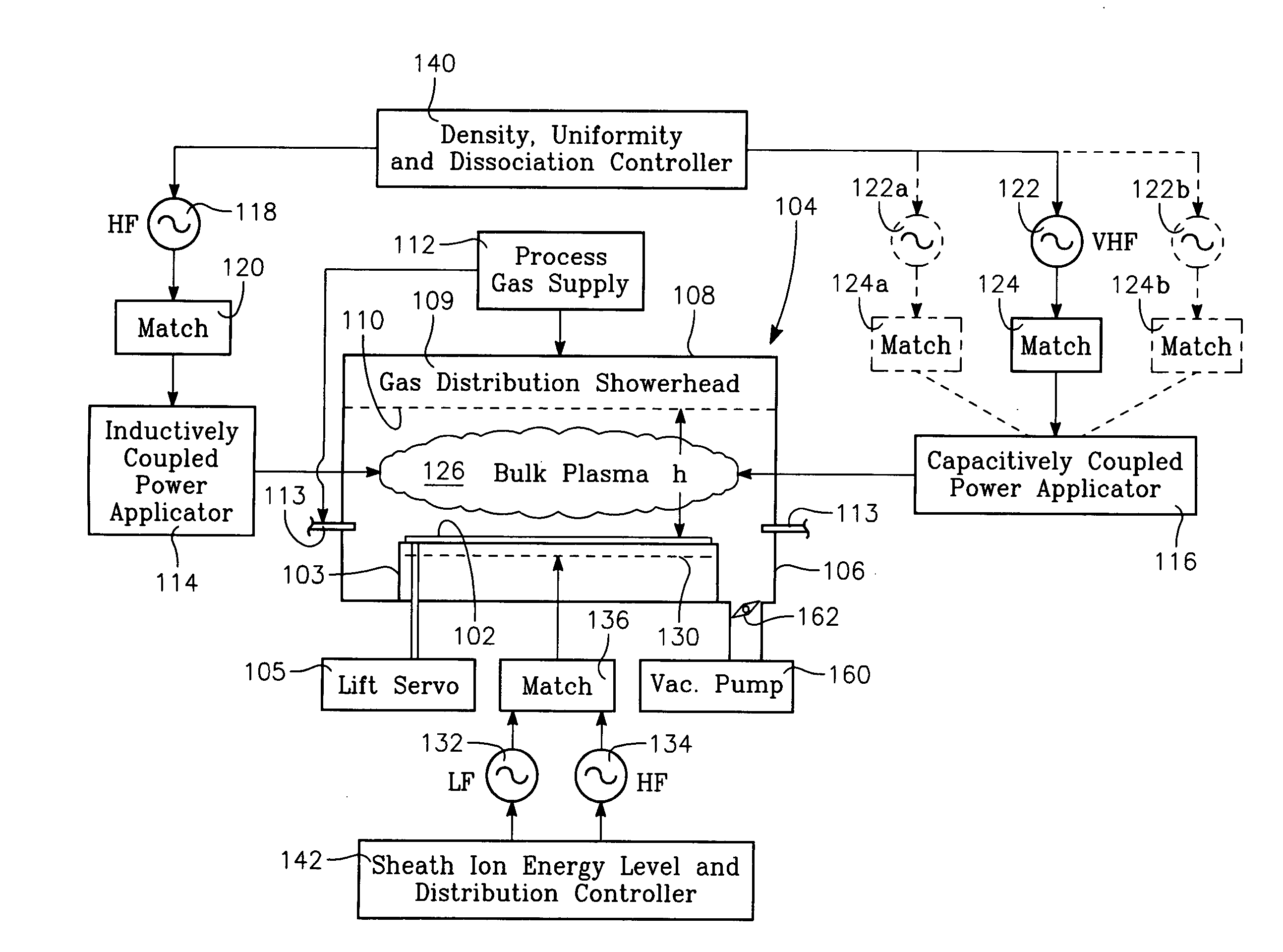
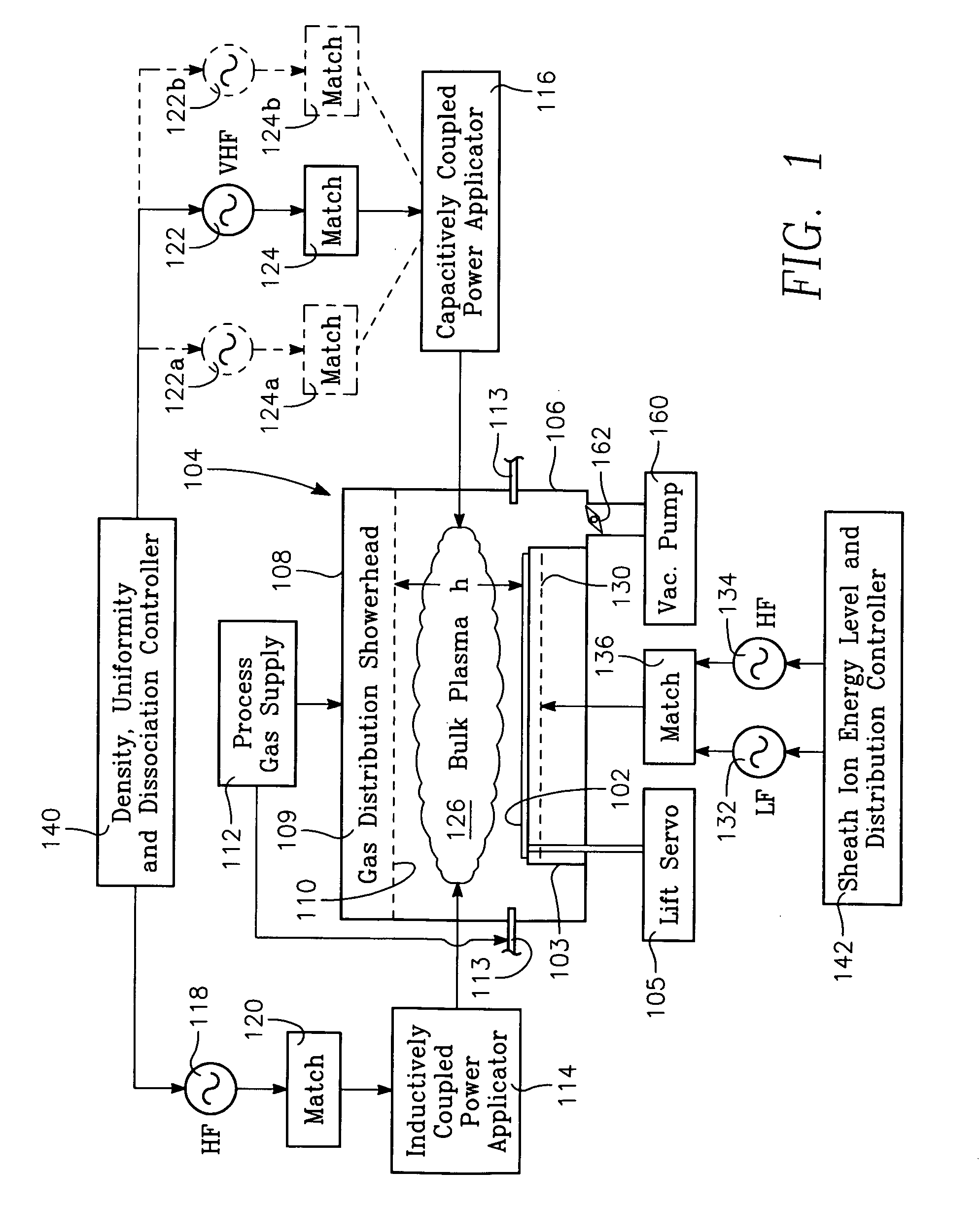
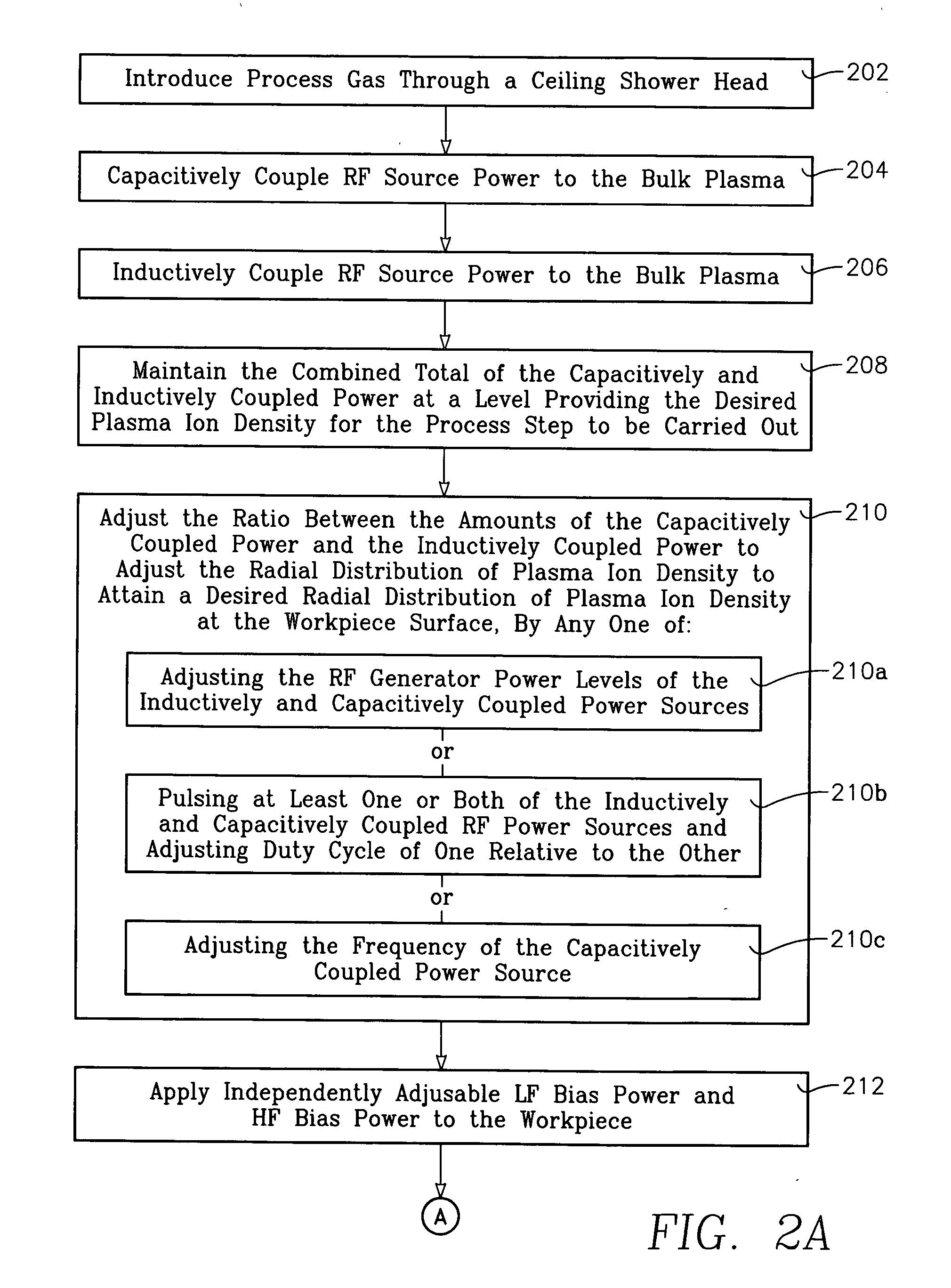
Process using combined capacitively and inductively coupled plasma sources for controlling plasma ion radial distribution
InactiveUS20070247074A1Increase ratingsIncrease ion densityElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsCapacitanceInductively coupled plasma
A method of processing a workpiece in the chamber of a plasma reactor includes introducing a process gas into the chamber, capacitively coupling VHF plasma source power into a process region of the chamber that overlies the wafer while inductively coupling RF plasma source power into the process region. A particular plasma ion density level is established by maintaining the total amount of plasma source power inductively and capacitively coupled into the process region at a level that provides the desired plasma ion density. The plasma ion density radial distribution in the process region is controlled by adjusting the ratio between the amounts of the (VHF) capacitively coupled power and the inductively coupled power while continuing to maintain the level of total plasma source power. The method can also include applying independently adjustable LF bias power and HF bias power to the workpiece and adjusting the average value and population distribution of ion energy at the surface of the workpiece by adjusting the proportion between the LF and HF bias powers. The VHF capacitively coupled power may be applied from the ceiling or from the wafer support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High pressure high non-reactive diluent gas content high plasma ion density plasma oxide etch process
InactiveUS6238588B1Increase pressureHigh strengthElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsHigh plasmaOxygen
The invention is embodied in a method of processing a semiconductor workpiece in a plasma reactor chamber, including supplying a polymer and etchant precursor gas containing at least carbon and fluorine into the chamber at a first flow rate sufficient of itself to maintain a gas pressure in the chamber in a low pressure range below about 20 mT, supplying a relatively non-reactive gas into the chamber at second flow rate sufficient about one half or more of the total gas flow rate into the chamber, in combination with the first flow rate of the precursor gas, to maintain the gas pressure in the chamber in a high pressure range above 20 mT, and applying plasma source power into the chamber to form a high ion density plasma having an ion density in excess of 1010 ions per cubic centimeter. In one application of the invention, the workpiece includes an oxygen-containing overlayer to be etched by the process and a non-oxygen-containing underlayer to be protected from etching, the precursor gas dissociating in the plasma into fluorine-containing etchant species which etch the oxygen-containing layer and carbon-containing polymer species which accumulate on the non-oxygen-containing underlayer. Alternatively, the high pressure range may be defined as a pressure at which the skin depth of the inductive field exceeds {fraction (1 / 10)} of the gap between the inductive antenna and the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
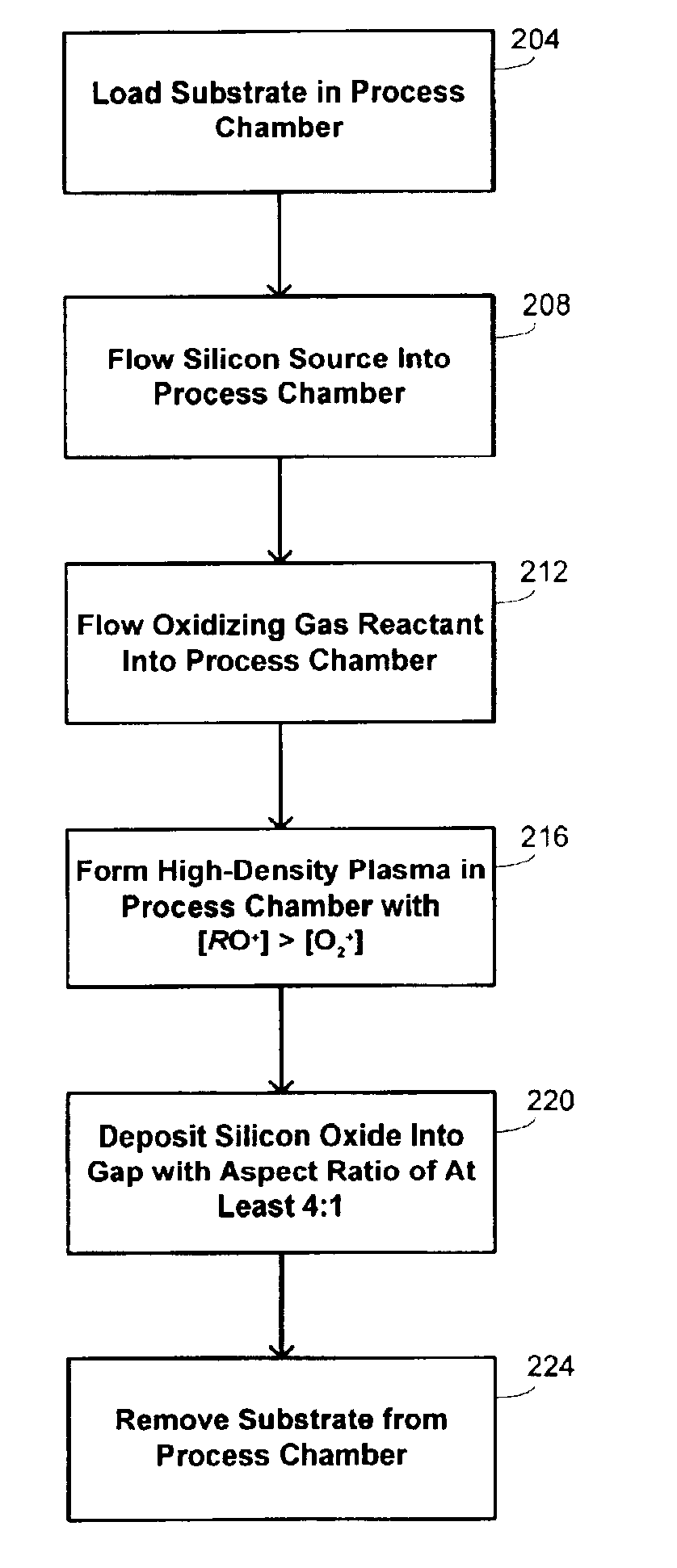
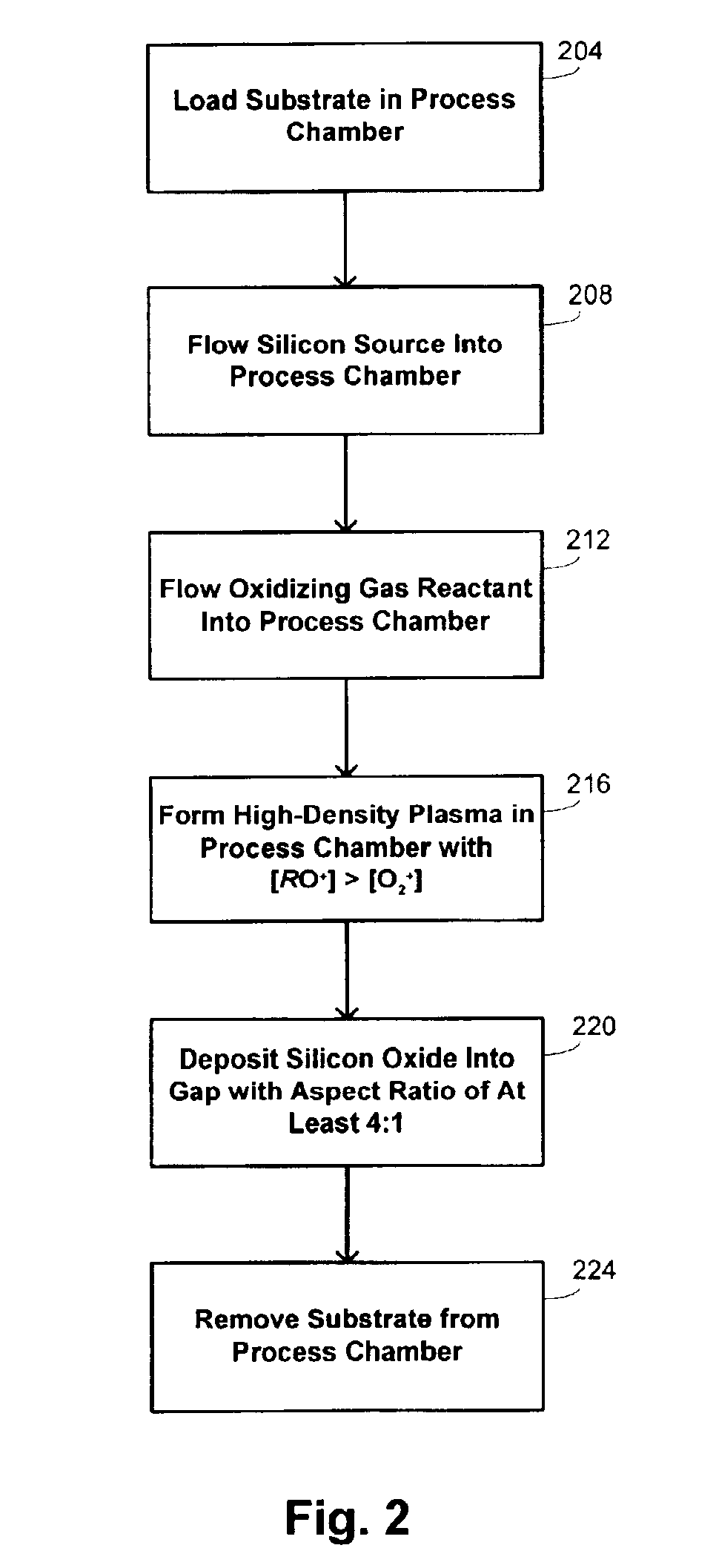
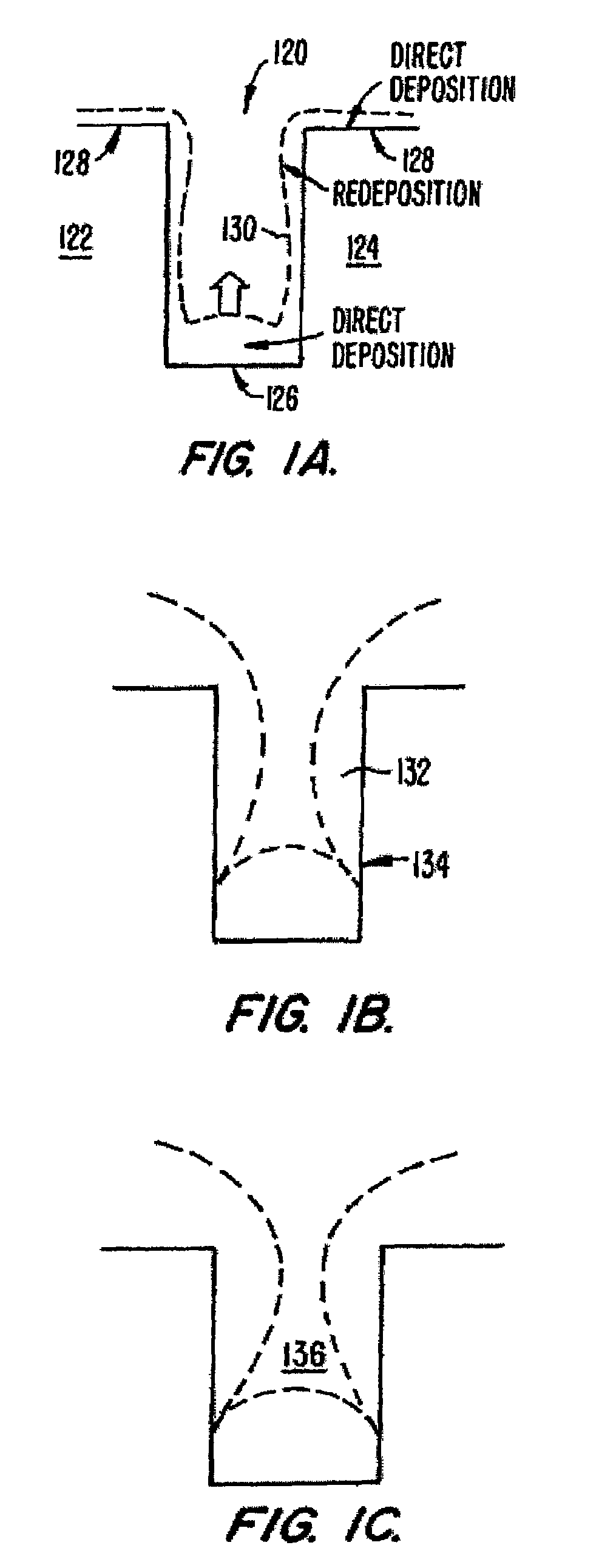
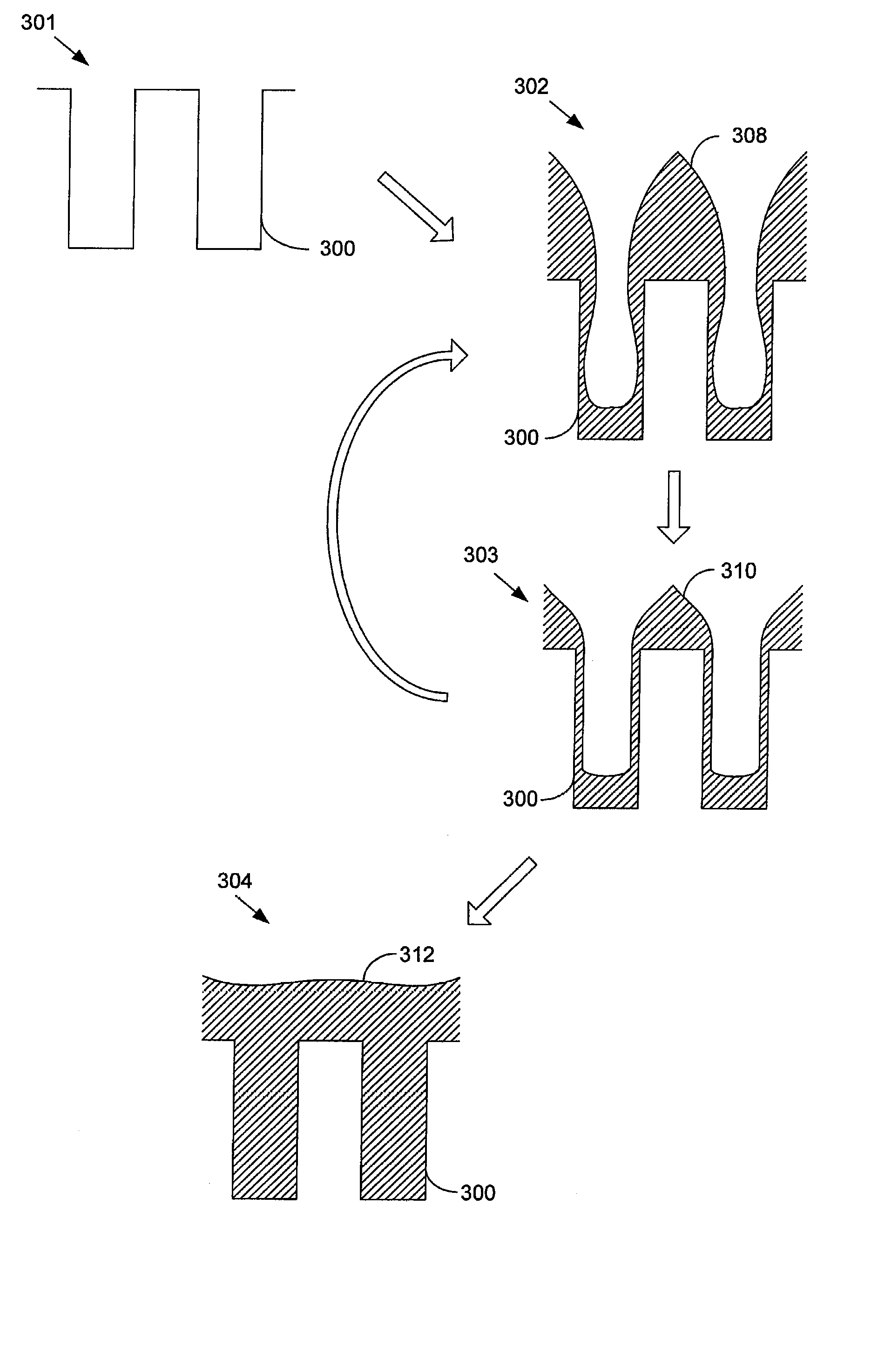
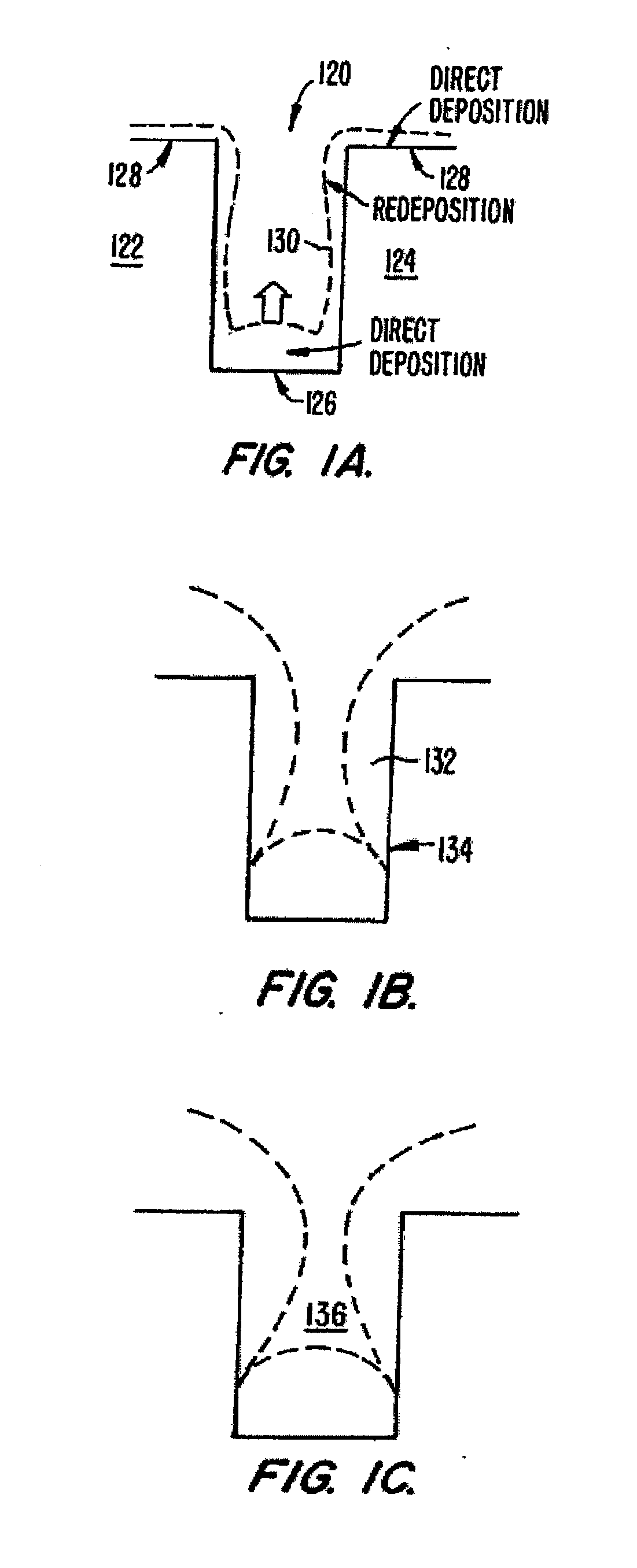
Methods and systems for high-aspect-ratio gapfill using atomic-oxygen generation
InactiveUS6958112B2Improved redeposition characteristicReduce the impactVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon densitySilicon oxide
Methods and systems are provided for depositing silicon oxide in a gap on a substrate. The silicon oxide is formed by flowing a process gas into a process chamber and forming a plasma having an overall ion density of at least 1011 ions / cm3. The process gas includes H2, a silicon source, and an oxidizing gas reactant, and deposition into the gap is achieved using a process that has simultaneous deposition and sputtering components. The probability of forming a void is reduced by ensuring that the plasma has a greater density of ions having a single oxygen atom than a density of ions having more than one oxygen atom.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
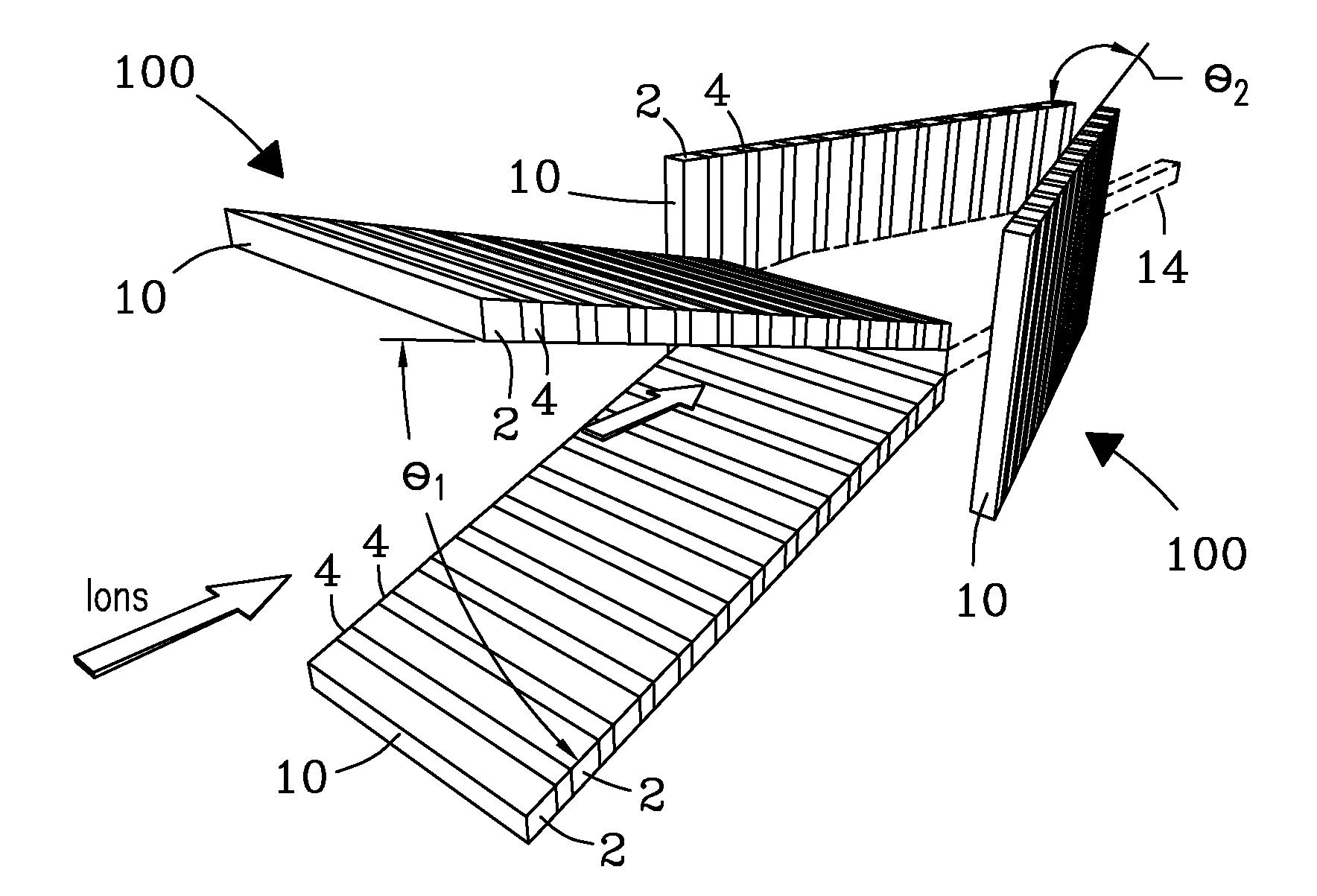
Microchip and wedge ion funnels and planar ion beam analyzers using same
ActiveUS20120261570A1Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionMicroscopic scaleMeasurement precision
Electrodynamic on funnels confine, guide, or focus ions in gases using the Dehmelt potential of oscillatory electric field. New funnel designs operating at or close to atmospheric gas pressure are described. Effective on focusing at such pressures is enabled by fields of extreme amplitude and frequency, allowed in microscopic gaps that have much higher electrical breakdown thresholds in any gas than the macroscopic gaps of present funnels. The new microscopic-gap funnels are useful for interfacing atmospheric-pressure ionization sources to mass spectrometry (MS) and on mobility separation (IMS) stages including differential IMS or FAIMS, as well as IMS and MS stages in various configurations. In particular, “wedge” funnels comprising two planar surfaces positioned at an angle and wedge funnel traps derived therefrom can compress on beams in one dimension, producing narrow belt-shaped beams and laterally elongated cuboid packets. This beam profile reduces the ion density and thus space-charge effects, mitigating the adverse impact thereof on the resolving power, measurement accuracy, and dynamic range of MS and IMS analyzers, while a greater overlap with coplanar light or particle beams can benefit spectroscopic methods.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Plasma reactor with overhead RF electrode tuned to the plasma with arcing suppression
InactiveUS7030335B2Sufficient capacitanceAvoid insufficient thicknessCellsElectric discharge tubesCapacitanceIon density
A plasma reactor for processing a semiconductor workpiece, includes a reactor chamber having a chamber wall and containing a workpiece support for holding the semiconductor workpiece, an overhead electrode overlying said workpiece support, the electrode comprising a portion of said chamber wall, an RF power generator for supplying power at a frequency of said generator to said overhead electrode and capable of maintaining a plasma within said chamber at a desired plasma ion density level. The overhead electrode has a capacitance such that said overhead electrode and the plasma formed in said chamber at said desired plasma ion density resonate together at an electrode-plasma resonant frequency, said frequency of said generator being at least near said electrode-plasma resonant frequency. The reactor further includes an insulating layer formed on a surface of said overhead electrode facing said workpiece support, a capacitive insulating layer between said RF power generator and said overhead electrode, and a metal foam layer overlying and contacting a surface of said overhead electrode that faces away from said workpiece support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
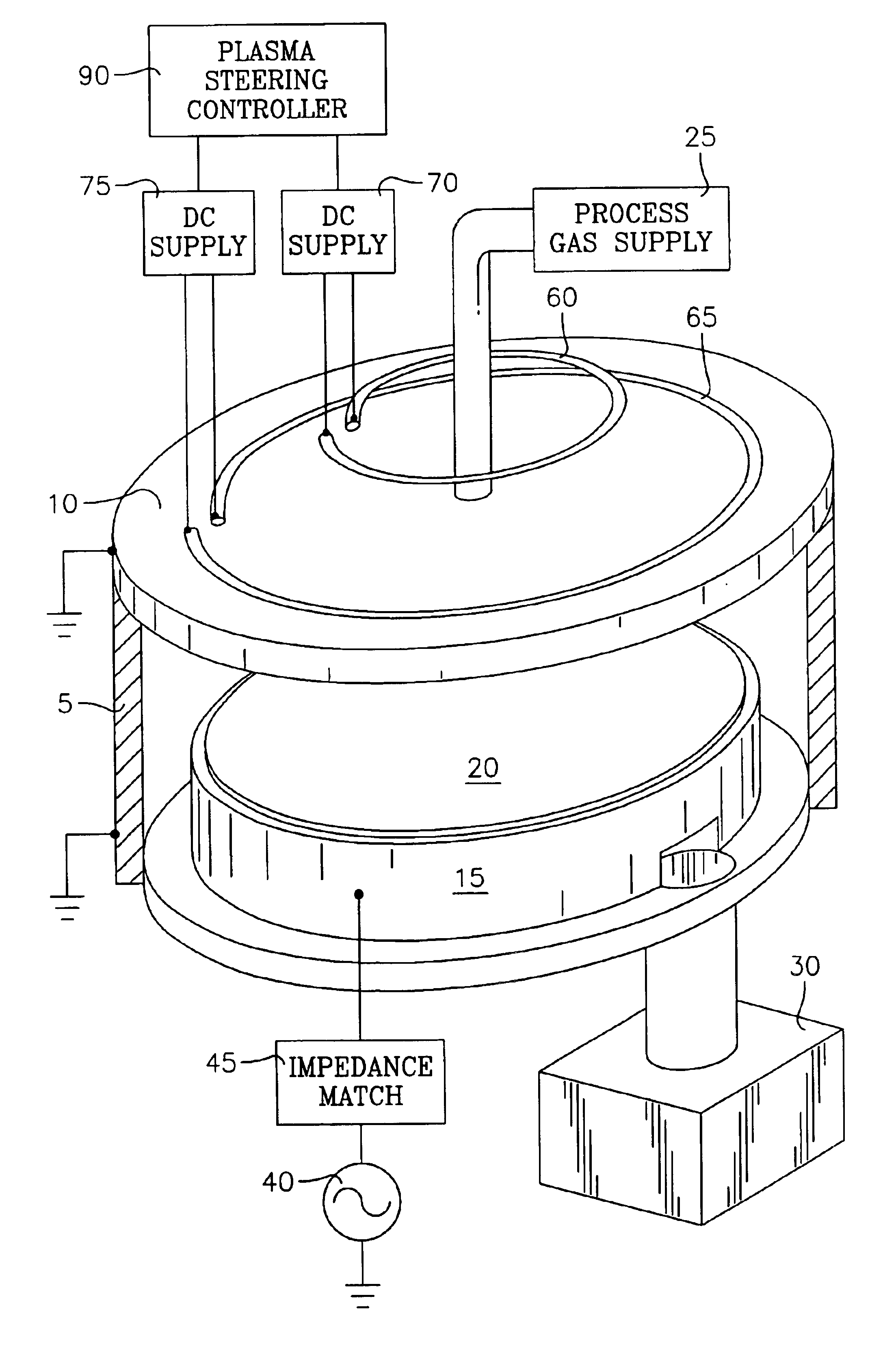
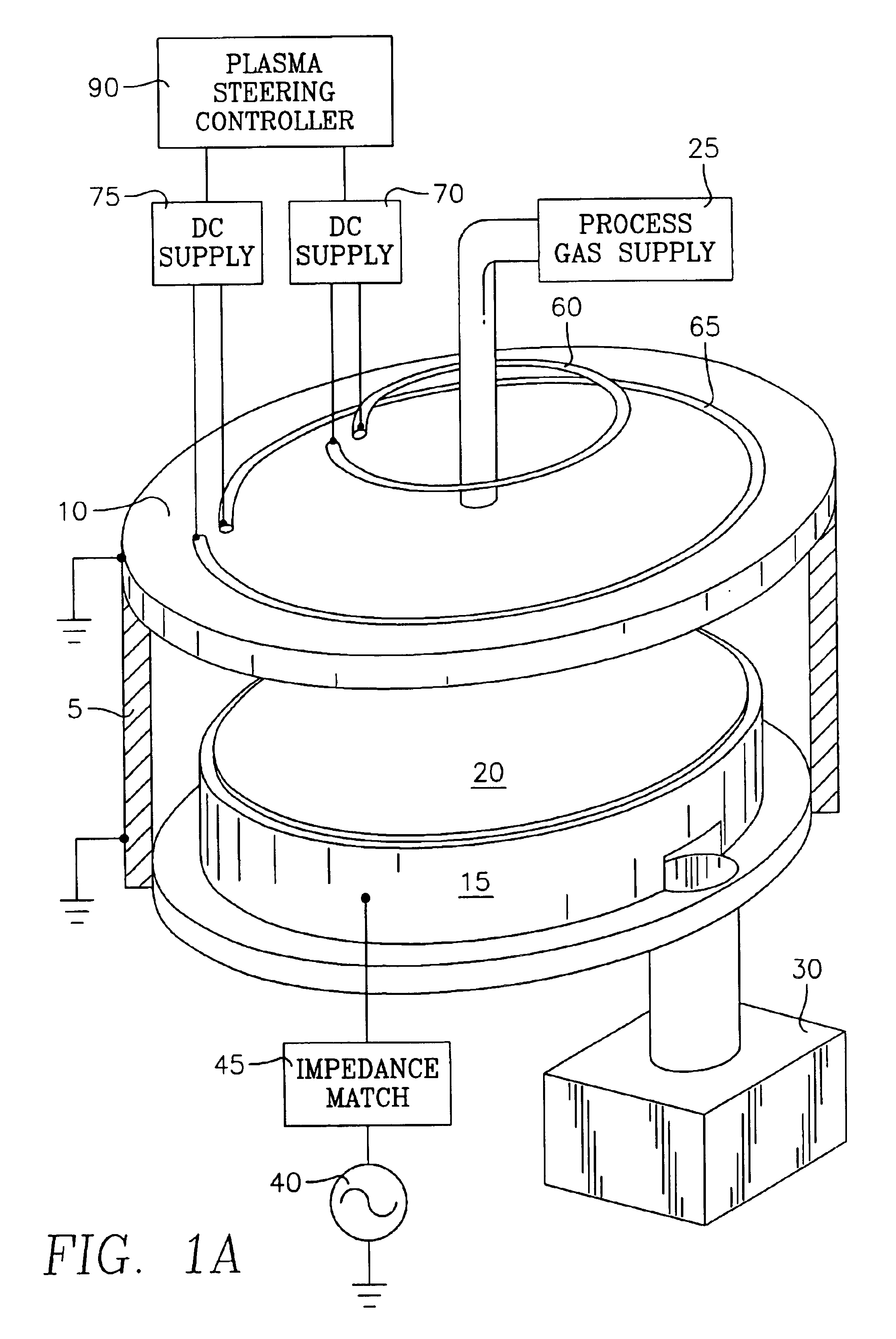
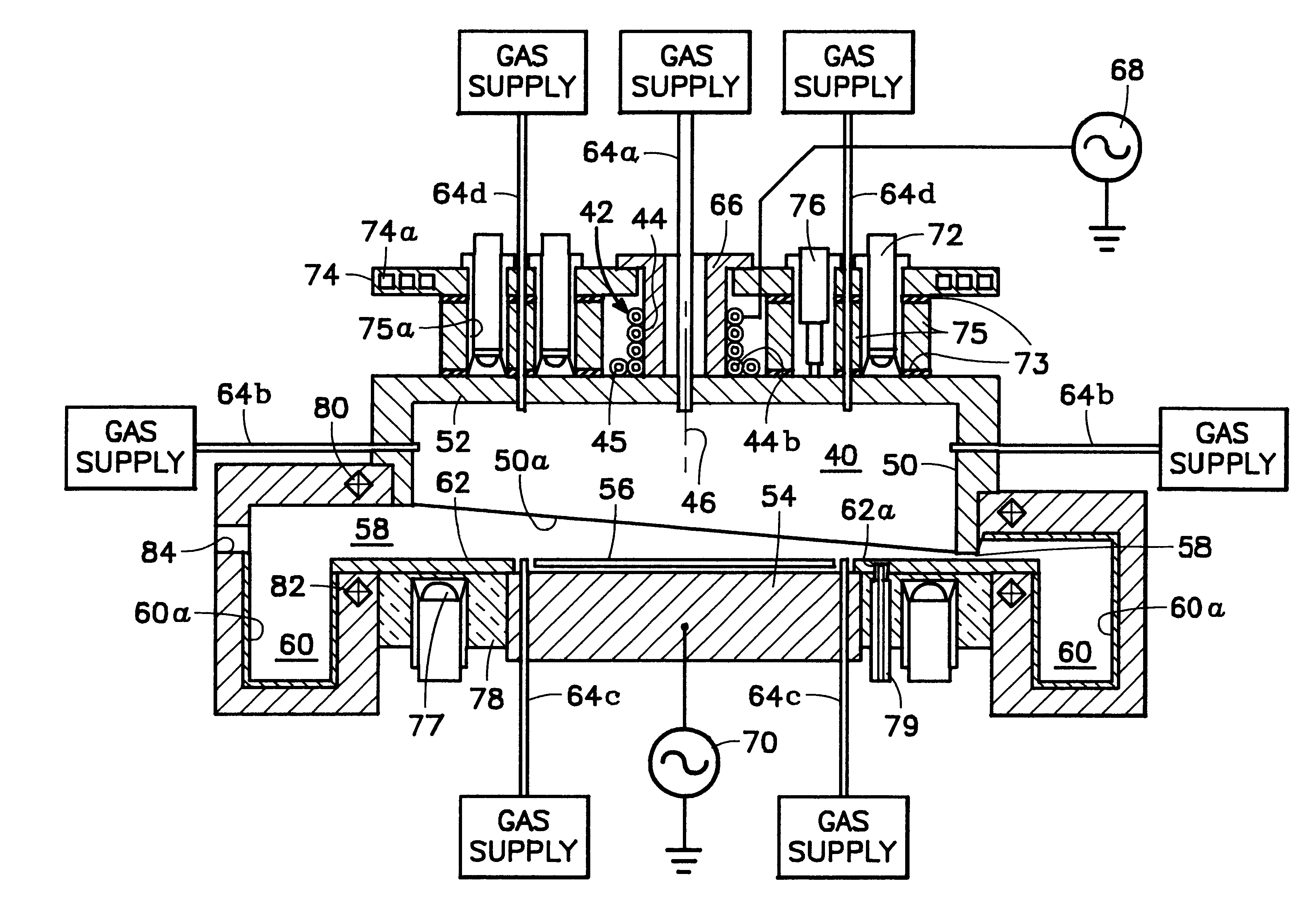
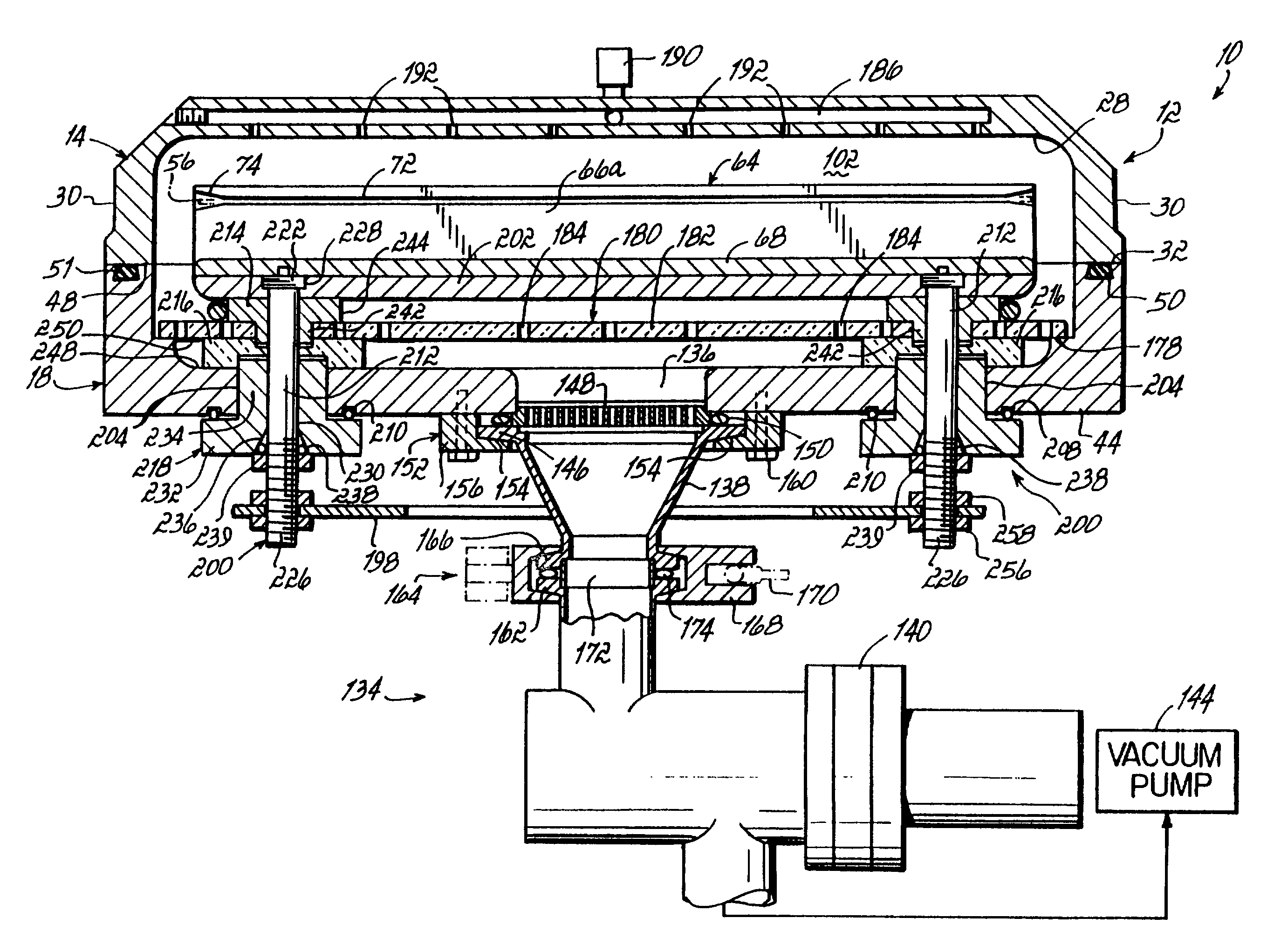
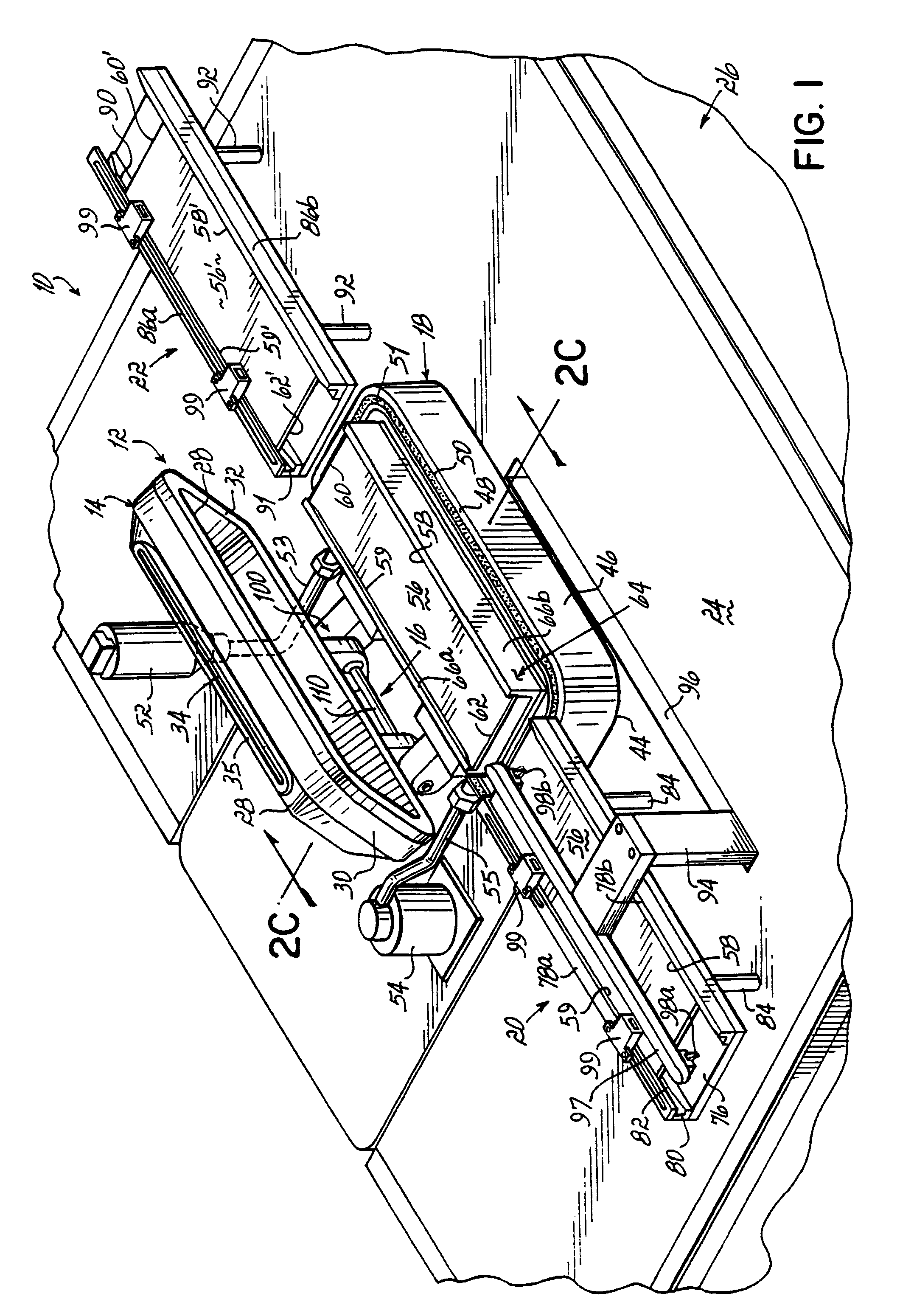
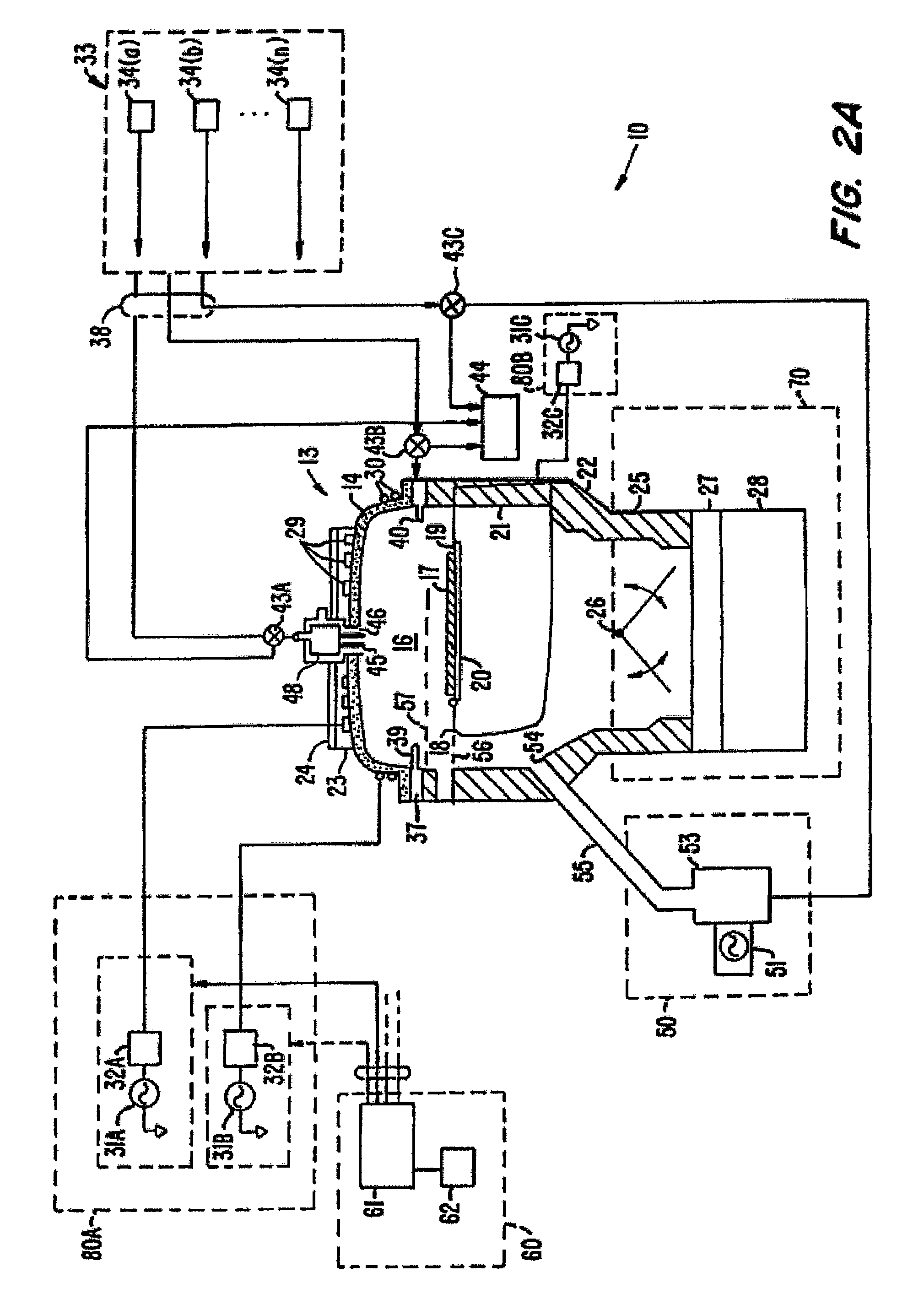
High-speed symmetrical plasma treatment system
InactiveUS6972071B1High pump rateHighly uniform and symmetrical distributionCellsElectric discharge tubesIon densityEngineering
A plasma treatment system (10) and related methods for rapidly treating a workpiece (56) with ions from a plasma having an ion density that is reproducibly uniform and symmetrical. The processing chamber (12) of the plasma treatment system (10) includes a chamber (14) lid having a symmetrical array of apertures (192) and further includes a vacuum distribution baffle (180), which are both configured to uniformly disperse a process gas adjacent the surface of the workpiece (56). The uniform dispersion of process gas and a symmetrical placement of the workpiece within the chamber (12) contribute to providing a uniformly dense plasma of ions adjacent the workpiece (56). A treatment system control (304) automates the operation of the system and controls the flow of process gas, evacuation of the chamber, and the application of the plasma excitation power to minimize the length of a treatment cycle and to optimize the uniformity of the plasma treatment.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
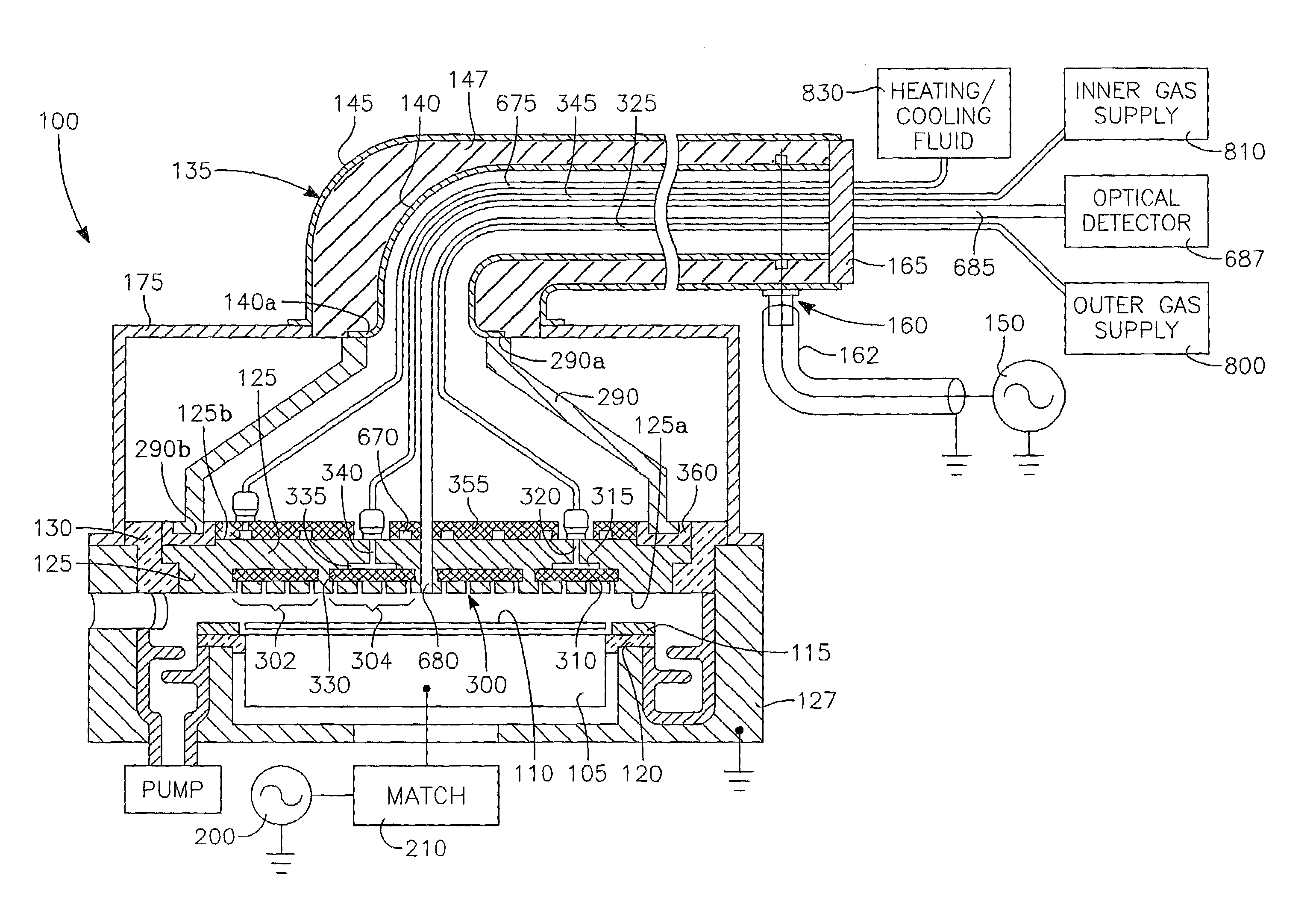
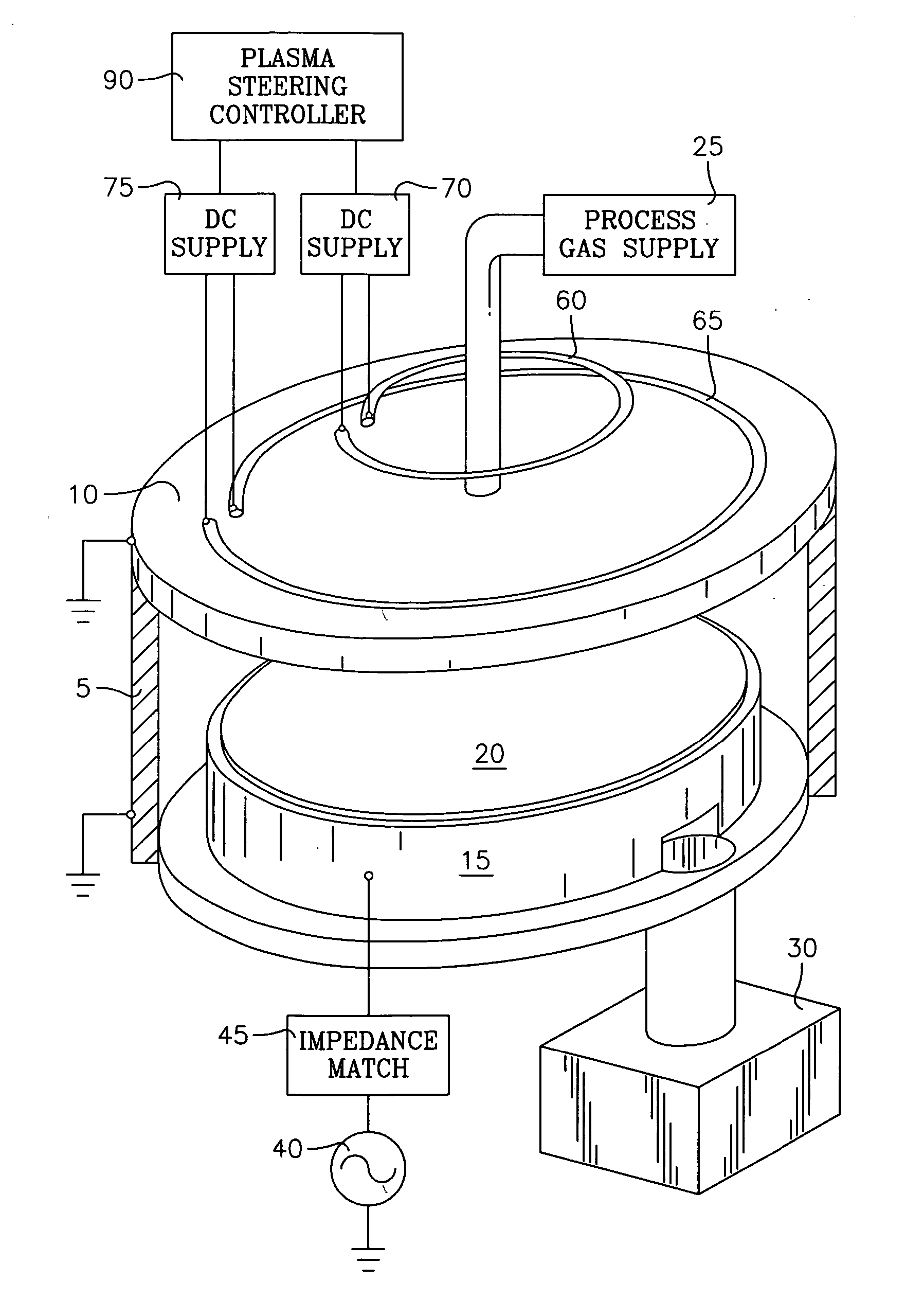
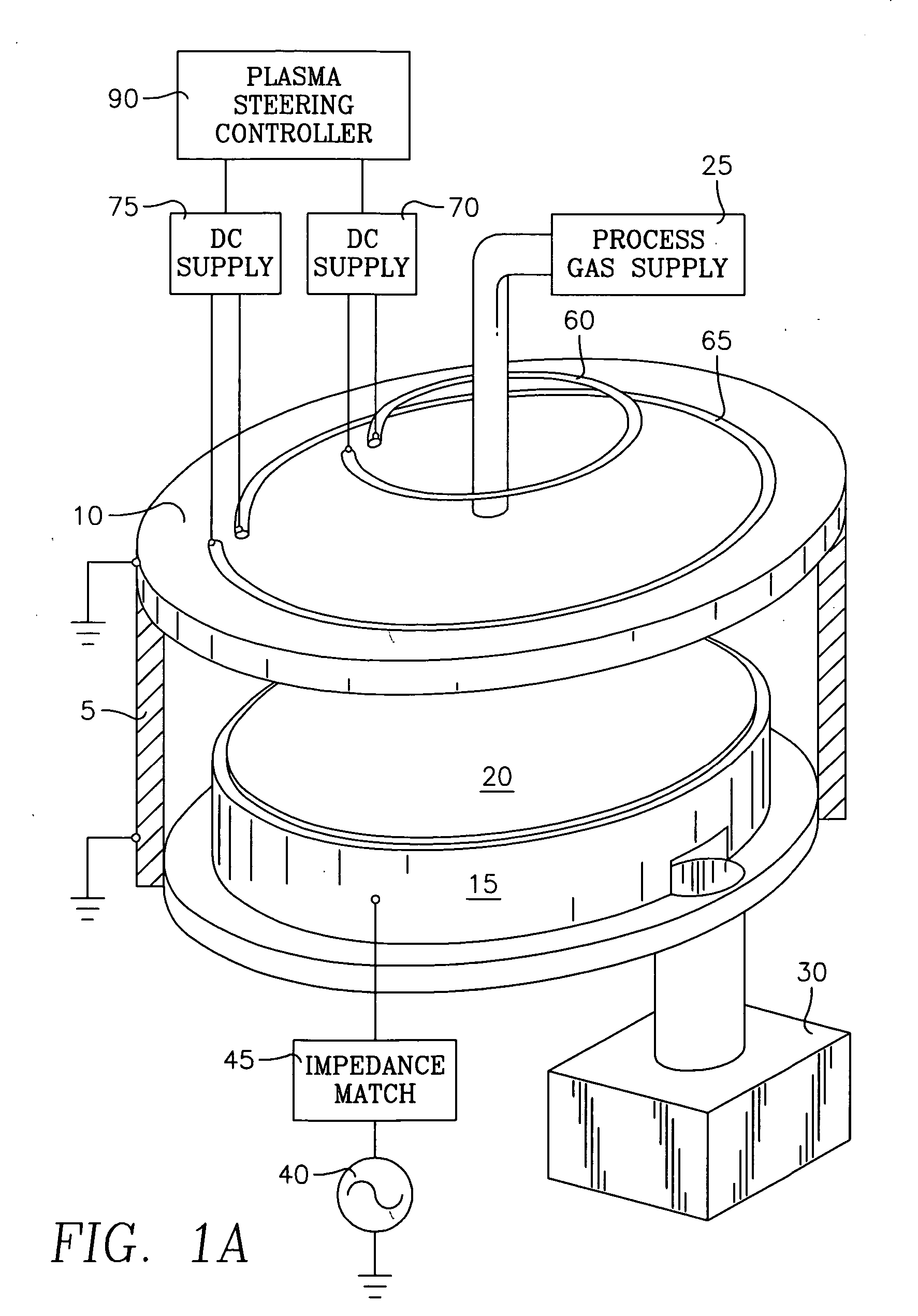
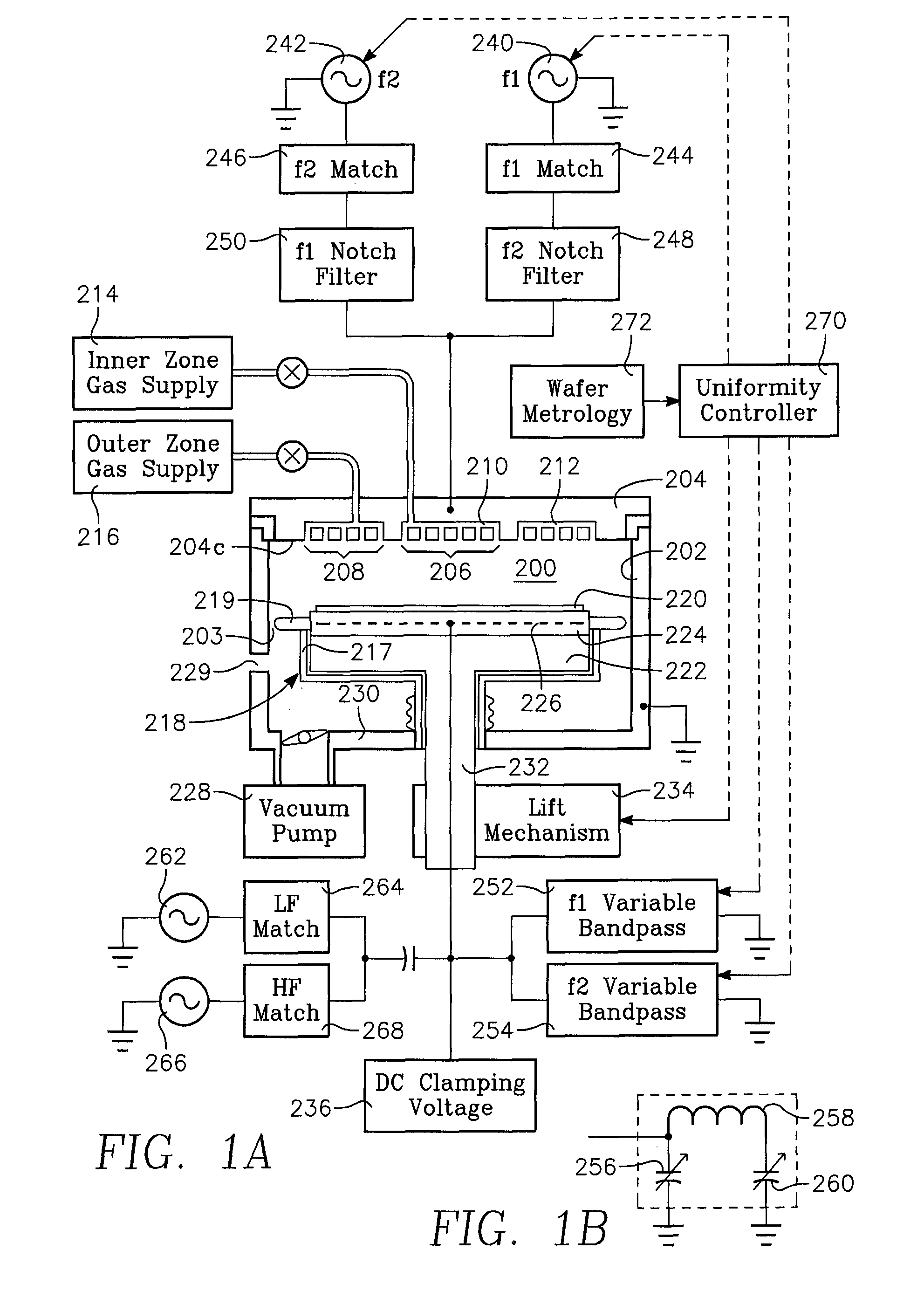
Method of controlling a chamber based upon predetermined concurrent behavoir of selected plasma parameters as a function of selected chamber paramenters
InactiveUS20070095788A1Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsIon densityEngineering
The invention involves a method of processing a workpiece on workpiece support pedestal in a plasma reactor chamber in accordance with user-selected values of plural (i.e., N) plasma parameters by controlling plural chamber parameters. The plasma parameters may be selected from of a group including ion density, wafer voltage, etch rate, wafer current and possibly other plasma parameters. The chamber parameters may be selected from a group including source power, bias power, chamber pressure, magnet coil current of different coils, gas flow rate in different gas injection zones, gas species composition in different gas injection zones, and possibly other chamber parameters. The method begins with a first step carried out for each one of the selected plasma parameters. This first step consists of fetching from a memory a relevant surface of constant value corresponding to the user-selected value of the one plasma parameter, the surface being defined in a N-dimensional space of which each of the N chamber parameters is a dimension. This step further includes determining an intersection of these relevant surfaces, the intersection corresponding to a target value of each of the N chamber parameter. The method further includes setting each of the N chamber parameters to the corresponding target value.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Integrated process modulation (IPM) a novel solution for gapfill with HDP-CVD
InactiveUS7524750B2Reduce moistureAvoid attackElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHalogenIon density
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
RF plasma reactor with hybrid conductor and multi-radius dome ceiling
InactiveUS6270617B1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAxis of symmetryElectrical conductor
An RF plasma reactor for processing a semiconductor wafer in a reactor chamber with a multi-radius dome-shaped ceiling and a gas inlet for supplying a process gas into the chamber includes an overhead RF signal applicator near the ceiling for applying an RF signal into the chamber through the ceiling to maintain a plasma of the process gas in the chamber, the plasma having a radial ion density distribution near the plane of the pedestal which is center-high for a greater height of the ceiling above the pedestal and is center-low for a lesser height, the height of the ceiling being intermediate the greater and lesser heights such that the radial ion density distribution is neither center-high nor center-low. In another aspect of the invention, the RF signal applicator has an annular distribution characterized by an effective mean radius, the plasma having a radial ion density distribution with respect to an axis of symmetry of the ceiling which is center-high for a lesser mean radius of the signal applicator and center-low for a greater mean radius of the signal applicator, the mean radius of the signal applicator being intermediate the greater and lesser mean radii such that the radial ion density distribution is neither center-high nor center-low.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Integrated process modulation (IPM) a novel solution for gapfill with hdp-cvd
InactiveUS20070243693A1Reduce moistureAvoid attackSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectric discharge tubesHalogenIon density
A process is provided for depositing an silicon oxide film on a substrate disposed in a process chamber. A process gas that includes a halogen source, a fluent gas, a silicon source, and an oxidizing gas reactant is flowed into the process chamber. A plasma having an ion density of at least 1011 ions / cm3 is formed from the process gas. The silicon oxide film is deposited over the substrate with a halogen concentration less than 1.0%. The silicon oxide film is deposited with the plasma using a process that has simultaneous deposition and sputtering components. The flow rate of the halogen source to the process chamber to the flow rate of the silicon source to the process chamber is substantially between 0.5 and 3.0.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Parallel-plate electrode plasma reactor having an inductive antenna and adjustable radial distribution of plasma ion density
InactiveUS6524432B1Minimize interactionAvoid flowElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsParallel plate
There is disclosed a plasma reactor for processing a semiconductor workpiece such as a wafer, including a chamber having an overhead ceiling with a three-dimensional shape such as a hemisphere or dome. The reactor further includes an inductive antenna over the ceiling which may be conformal or nonconformal in shape with the ceiling. The ceiling may be a semiconductor material so that it can function as both a window for the inductive field of the antenna as well as an electrode which can be grounded, or to which RF power may be applied or which may be allowed to float electrically. The reactor includes various features which allow the radial distribution of the plasma ion density across the wafer surface to be adjusted to an optimum distribution for processing uniformity across the wafer surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Microchip and wedge ion funnels and planar ion beam analyzers using same
ActiveUS8299443B1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMicroscopic scaleMeasurement precision
Electrodynamic ion funnels confine, guide, or focus ions in gases using the Dehmelt potential of oscillatory electric field. New funnel designs operating at or close to atmospheric gas pressure are described. Effective ion focusing at such pressures is enabled by fields of extreme amplitude and frequency, allowed in microscopic gaps that have much higher electrical breakdown thresholds in any gas than the macroscopic gaps of present funnels. The new microscopic-gap funnels are useful for interfacing atmospheric-pressure ionization sources to mass spectrometry (MS) and ion mobility separation (IMS) stages including differential IMS or FAIMS, as well as IMS and MS stages in various configurations. In particular, “wedge” funnels comprising two planar surfaces positioned at an angle and wedge funnel traps derived therefrom can compress ion beams in one dimension, producing narrow belt-shaped beams and laterally elongated cuboid packets. This beam profile reduces the ion density and thus space-charge effects, mitigating the adverse impact thereof on the resolving power, measurement accuracy, and dynamic range of MS and IMS analyzers, while a greater overlap with coplanar light or particle beams can benefit spectroscopic methods.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
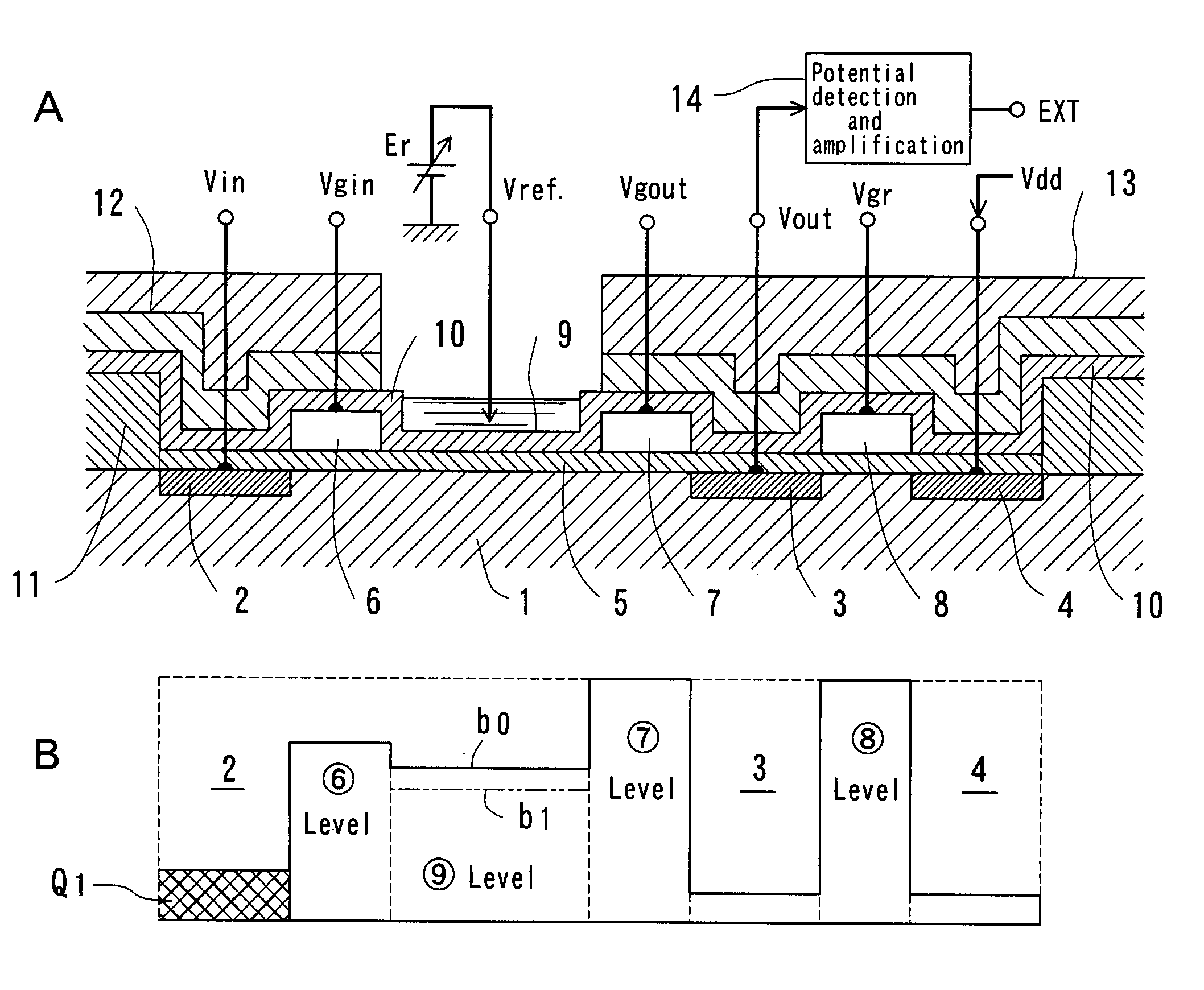
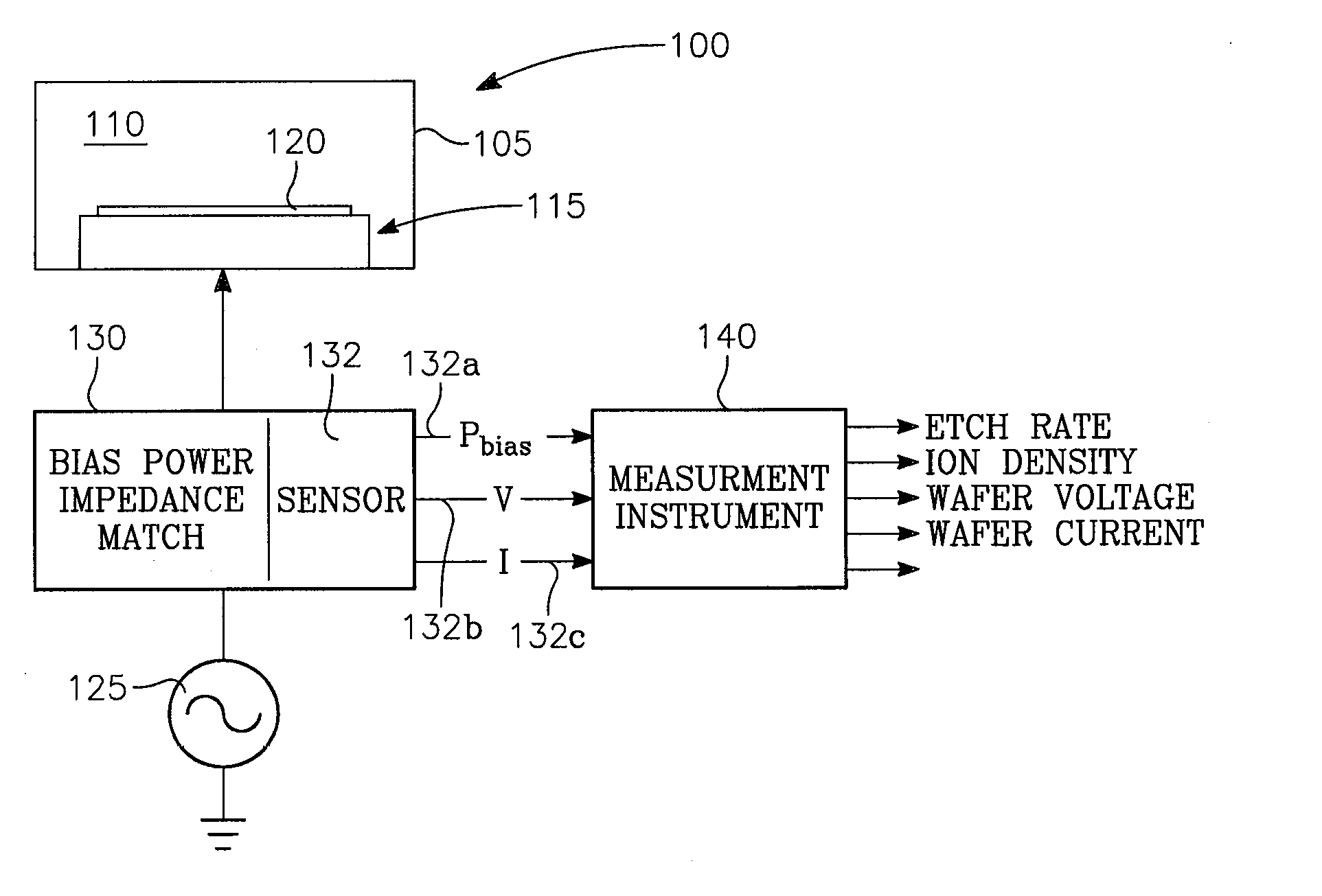
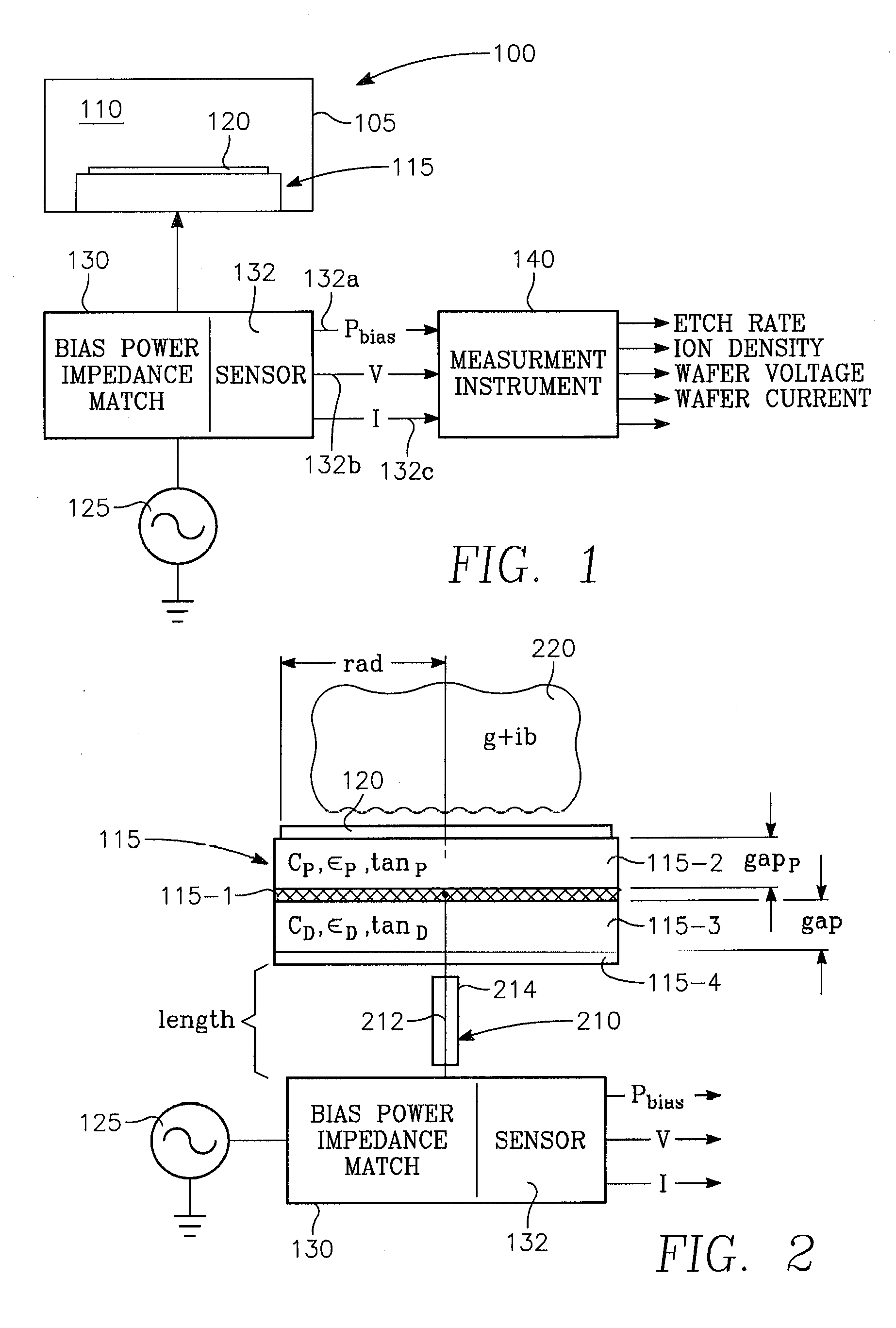
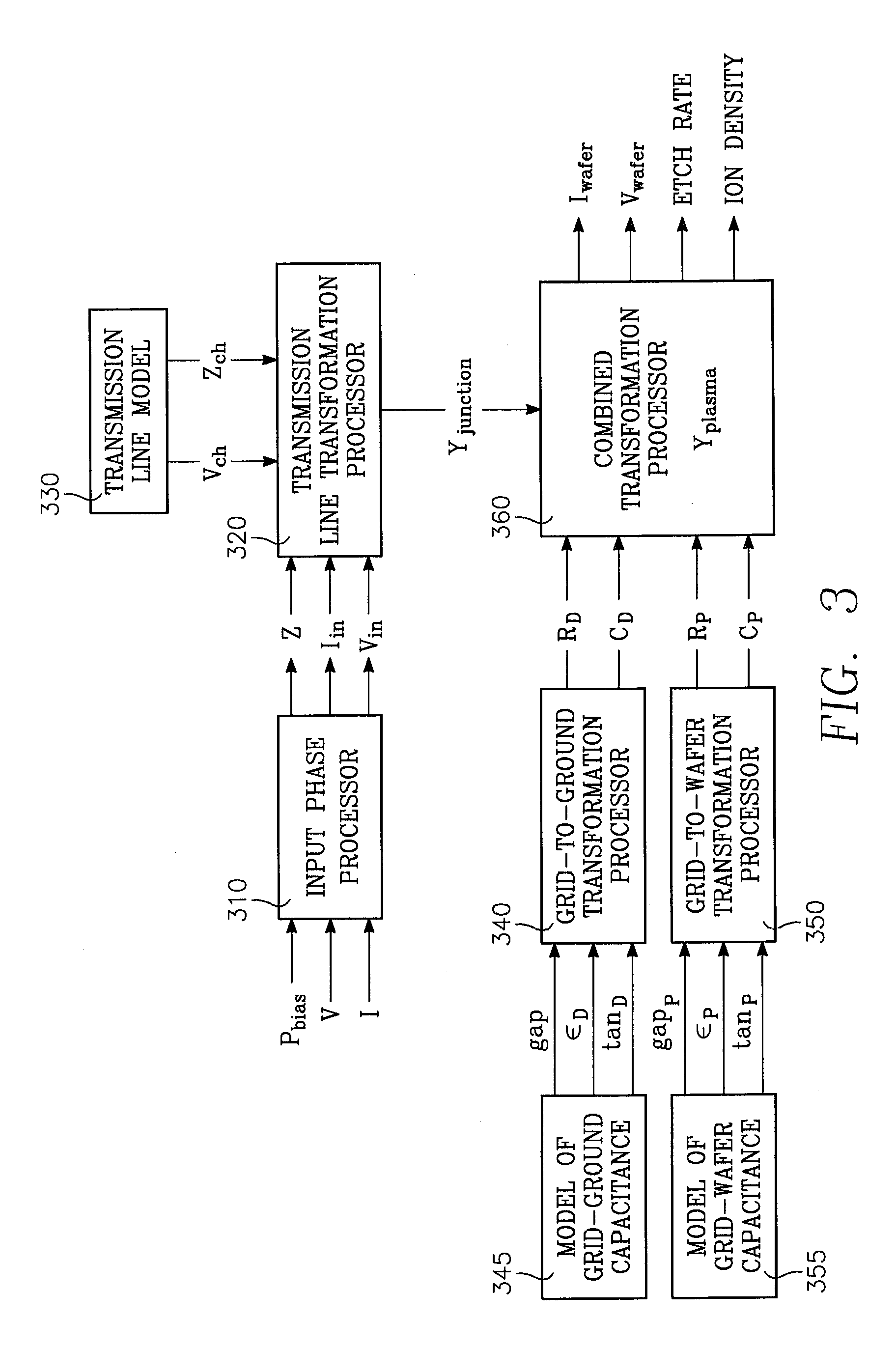
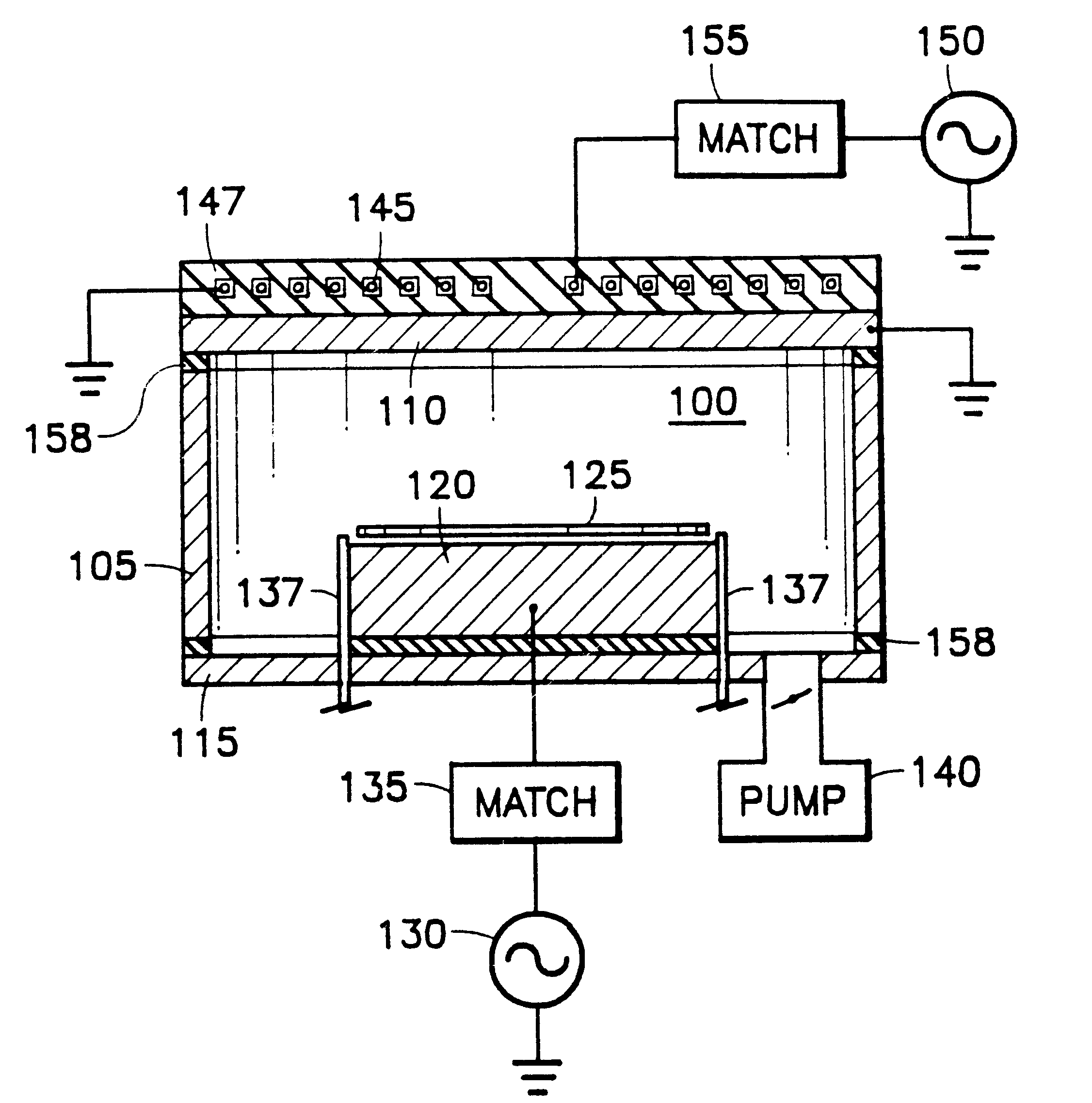
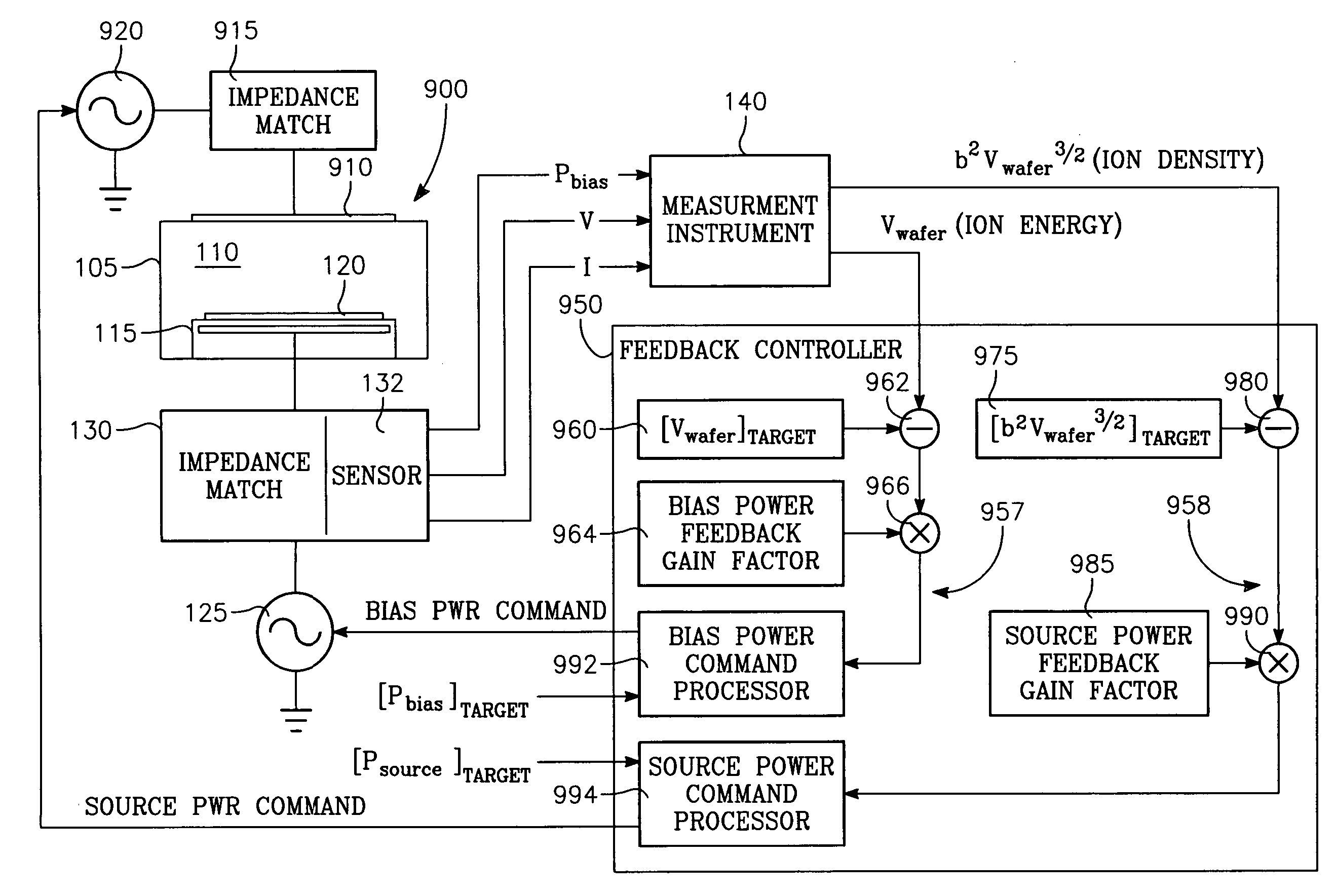
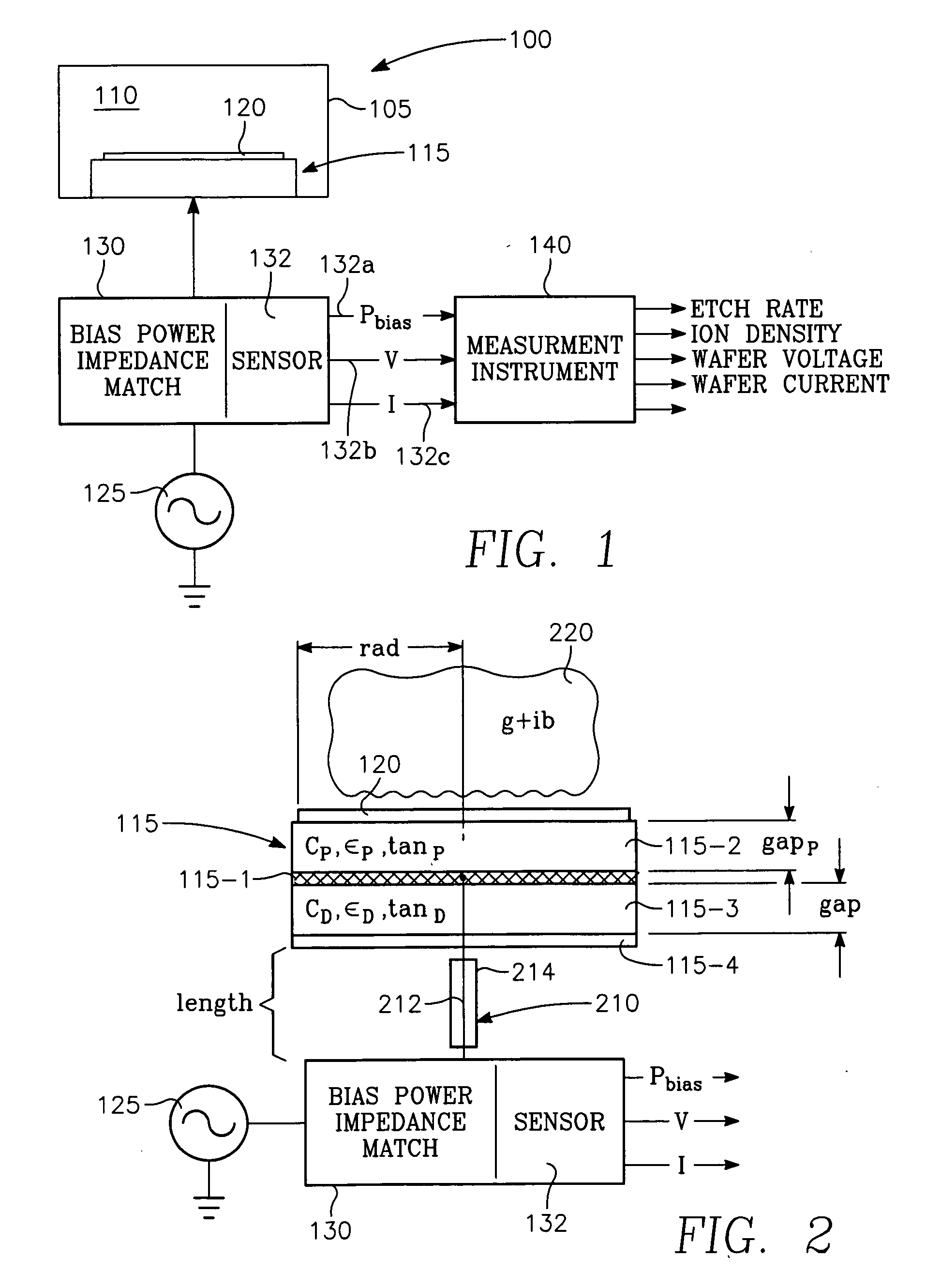
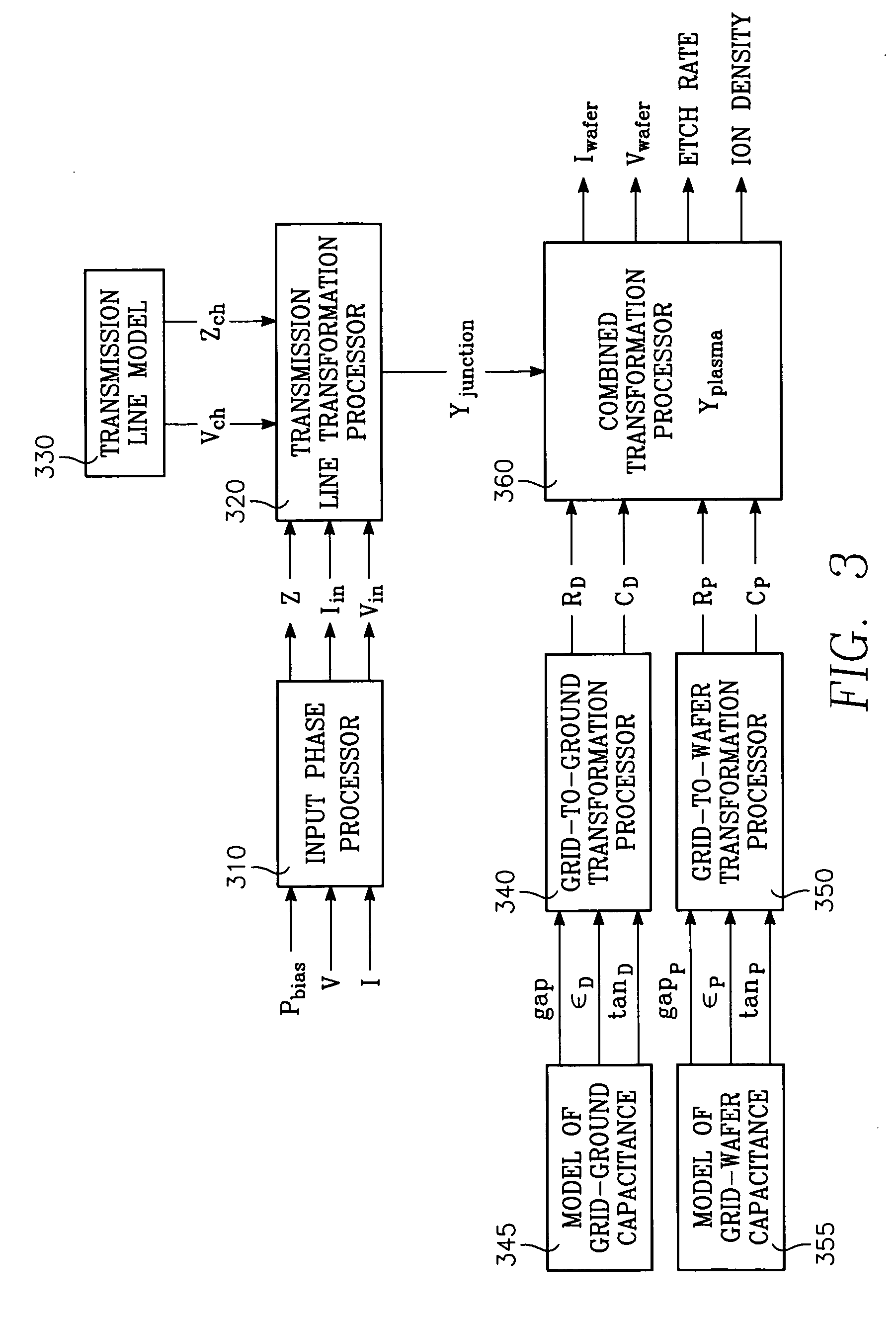
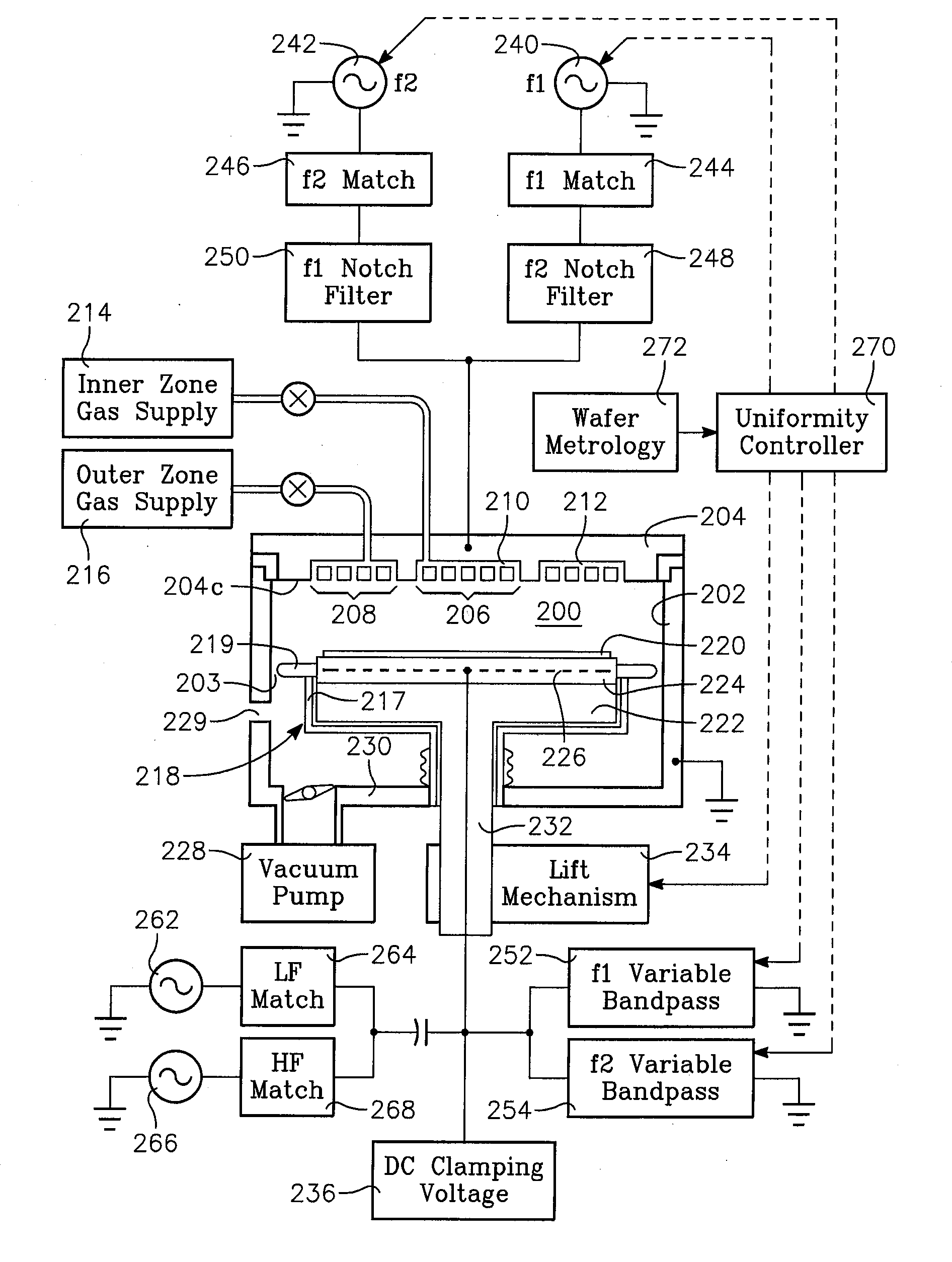
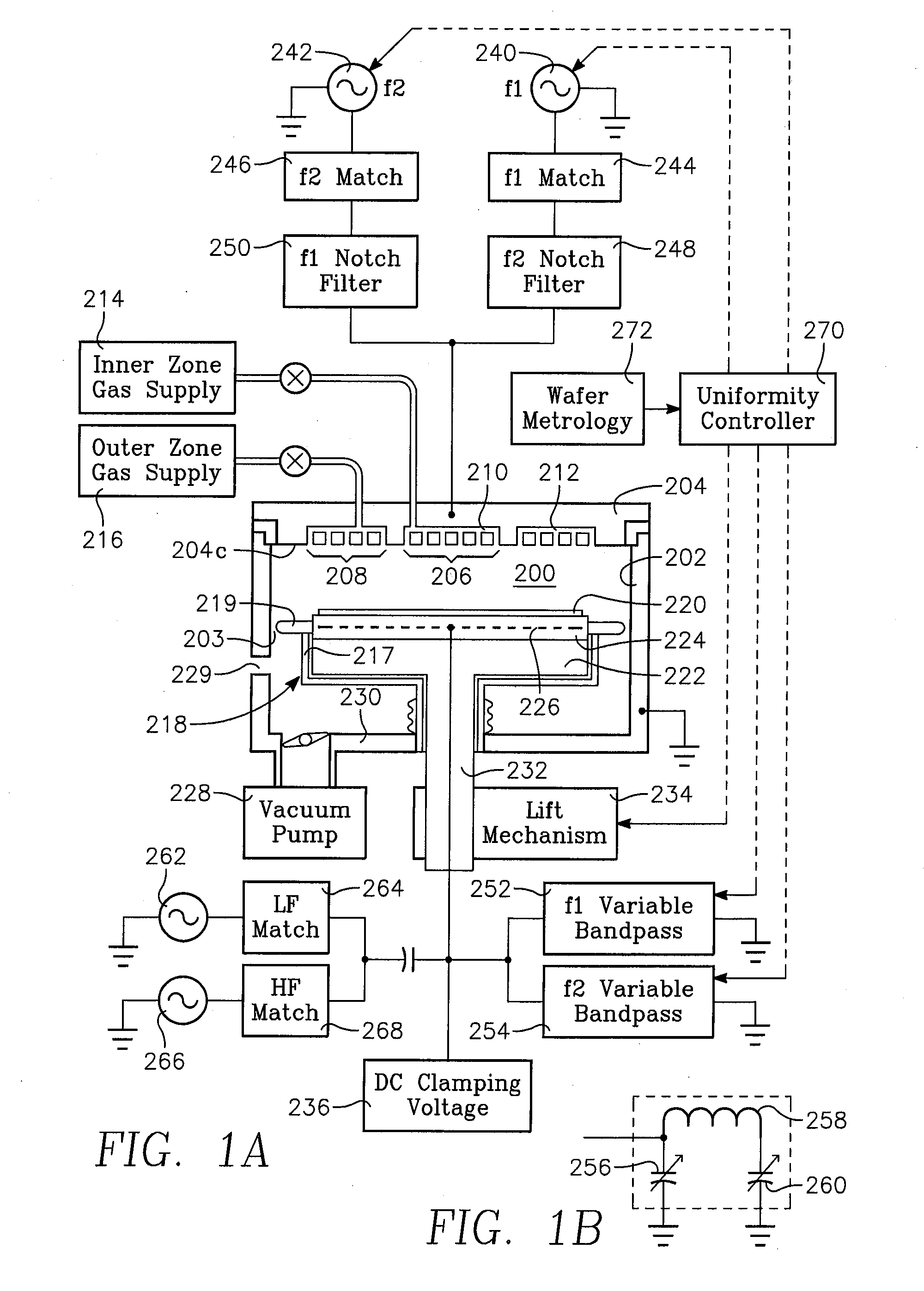
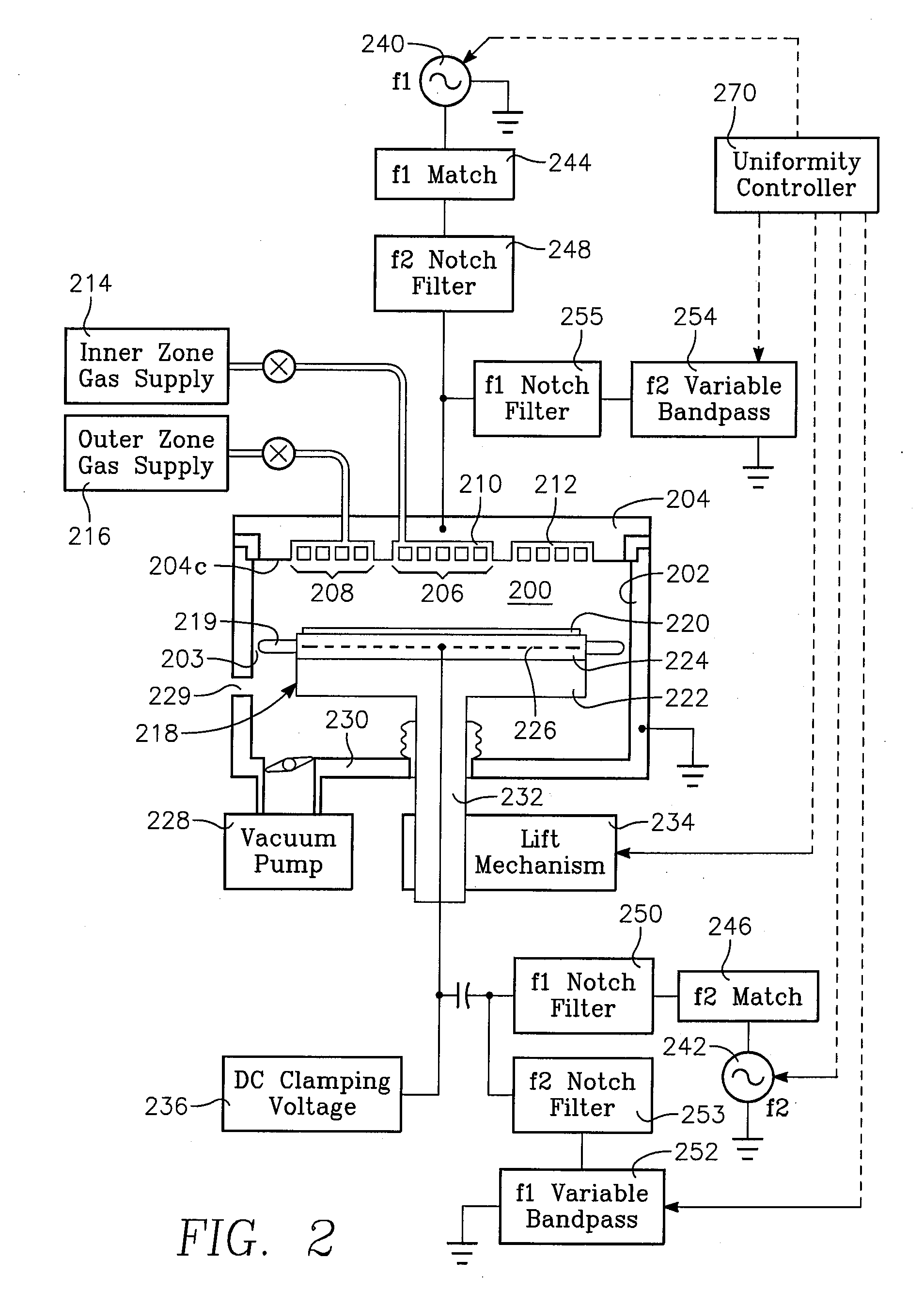
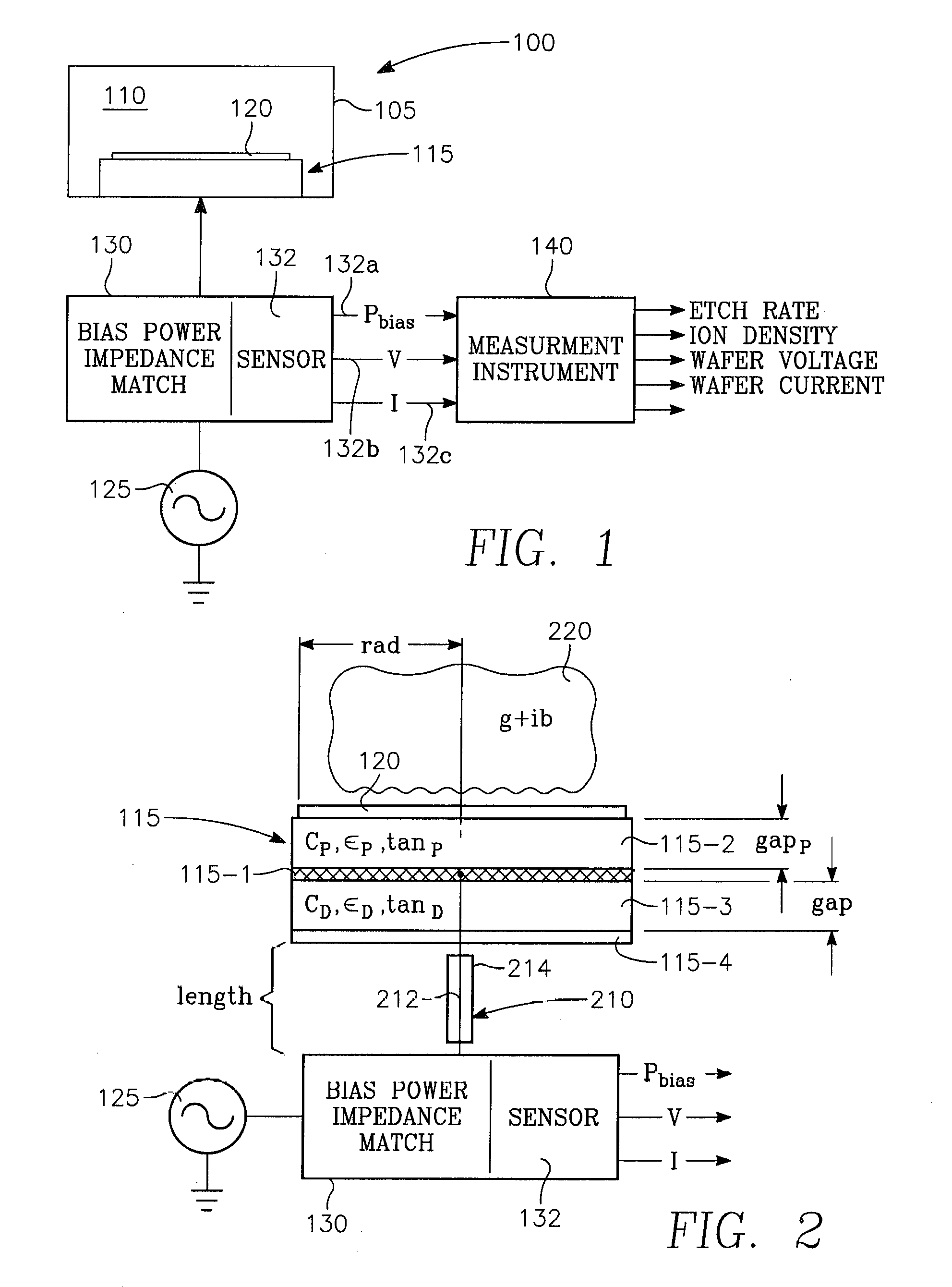
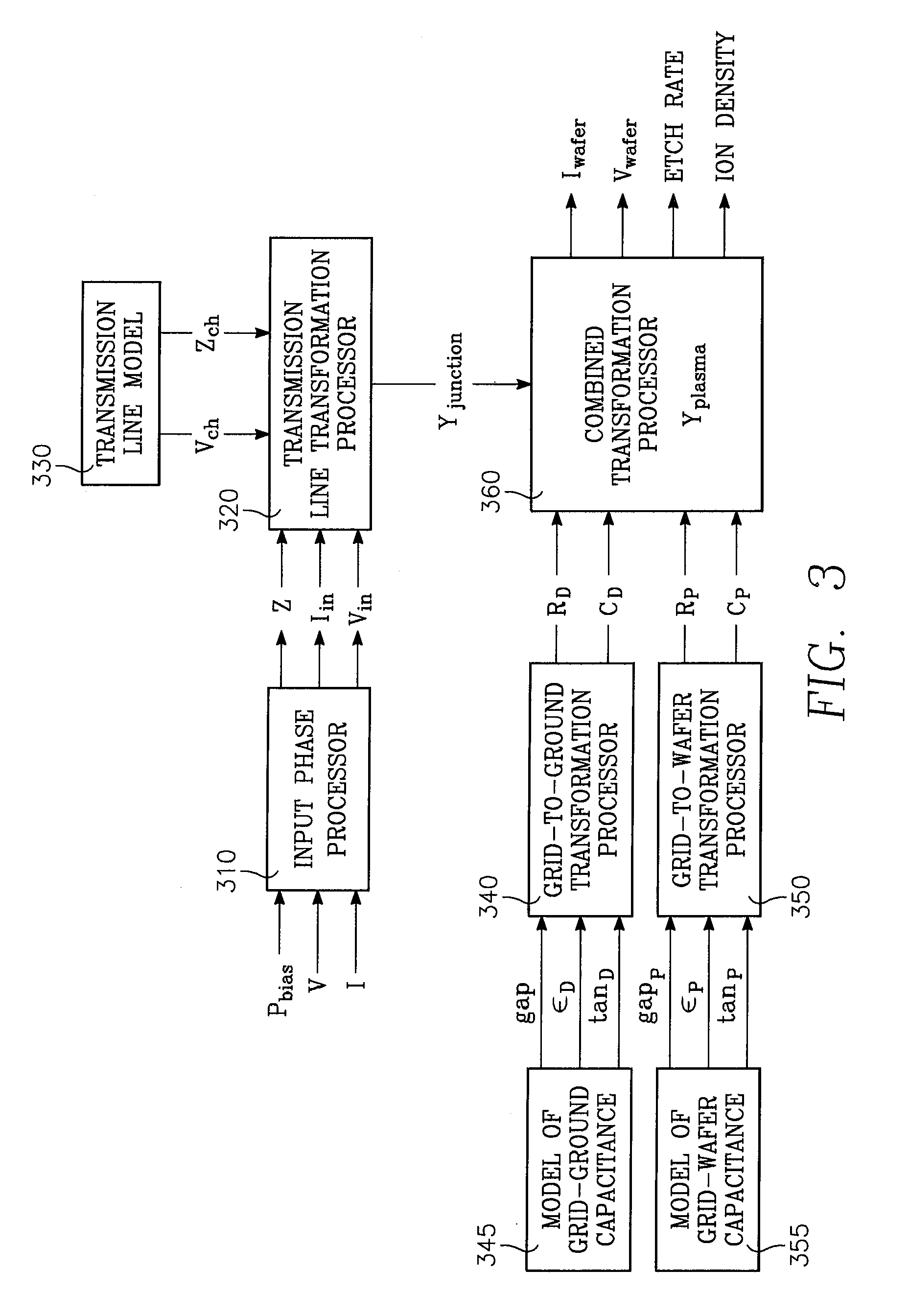
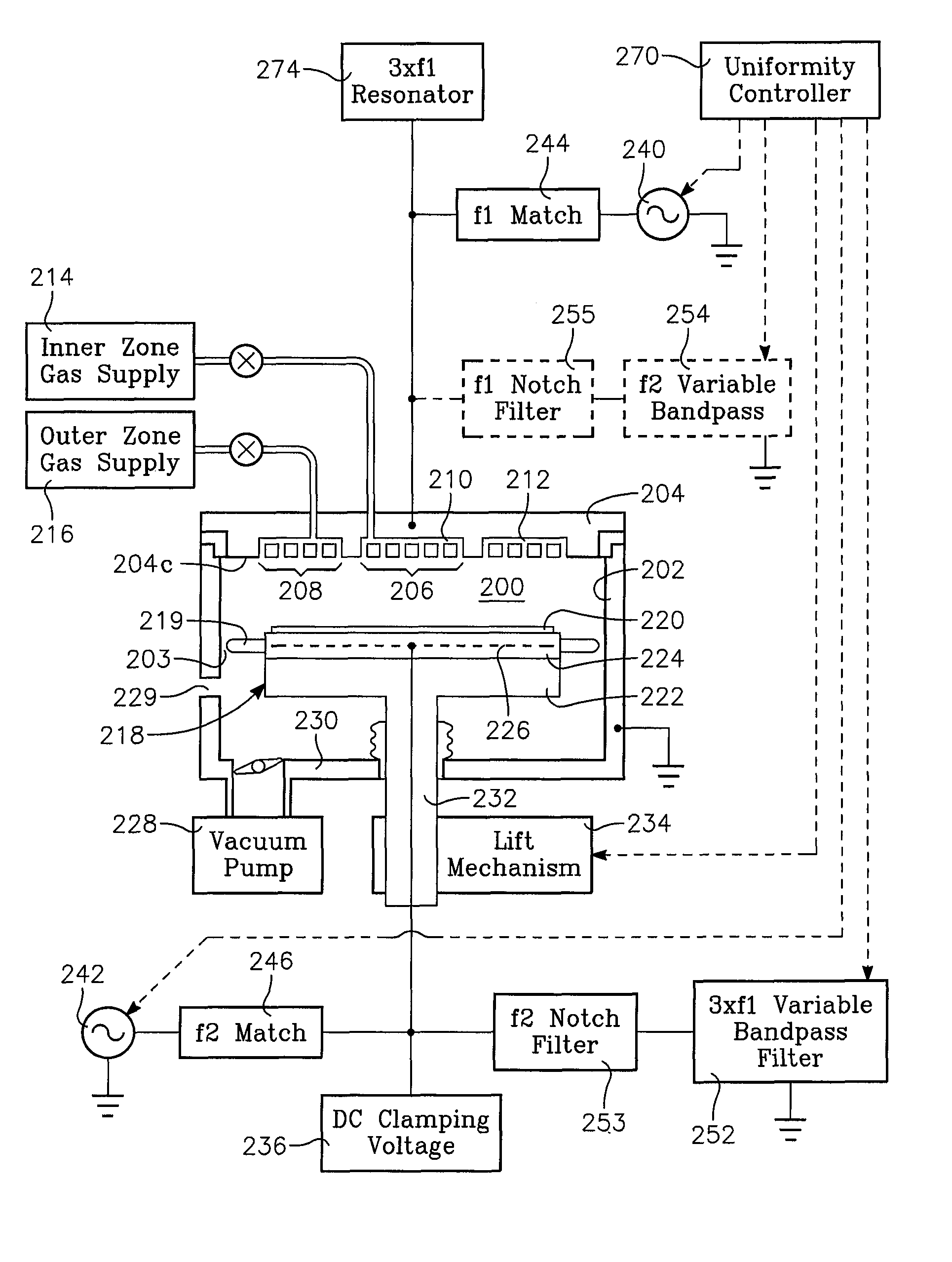
Method of determining plasma ion density, wafer voltage, etch rate and wafer current from applied bias voltage and current
ActiveUS20060278608A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesImpedance matchingShunt capacitance
Plasma parameters such as plasma ion density, wafer voltage, etch rate and wafer current in the chamber are determined from external measurements on the applied RF bias electrical parameters such as voltage and current. The method includes sensing RF parameters corresponding to an input impedance, an input current and an input voltage at the input of the impedance match element to a transmission line coupled between the bias generator and the wafer pedestal. The method continues by computing a junction admittance of a junction between the transmission line and the electrode within the wafer pedestal from the input impedance, input current and input voltage and from parameters of the transmission line. The method further includes providing shunt electrical quantities of a shunt capacitance between the electrode and a ground plane, and providing load electrical quantities of a load capacitance between the electrode and a wafer on the pedestal. The method further includes computing at least one of the plasma parameters from the junction admittance, the shunt electrical quantities, the load electrical quantities and a frequency of RF bias power applied to the electrode.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Capacitively coupled plasma reactor with magnetic plasma control
InactiveUS20060157201A1Improve uniformityElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceAxis of symmetry
A plasma reactor includes a vacuum enclosure including a side wall and a ceiling defining a vacuum chamber, and a workpiece support within the chamber and facing the ceiling for supporting a planar workpiece, the workpiece support and the ceiling together defining a processing region between the workpiece support and the ceiling. Process gas inlets furnish a process gas into the chamber. A plasma source power electrode is connected to an RF power generator for capacitively coupling plasma source power into the chamber for maintaining a plasma within the chamber. The reactor further includes at least a first overhead solenoidal electromagnet adjacent the ceiling, the overhead solenoidal electromagnet, the ceiling, the side wall and the workpiece support being located along a common axis of symmetry. A current source is connected to the first solenoidal electromagnet and furnishes a first electric current in the first solenoidal electromagnet whereby to generate within the chamber a magnetic field which is a function of the first electric current, the first electric current having a value such that the magnetic field increases uniformity of plasma ion density radial distribution about the axis of symmetry near a surface of the workpiece support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming carbon film, method of manufacturing magnetic recording medium, and apparatus for forming carbon film
InactiveUS20100028563A1High hardnessReduce thicknessSpark gapsMagnetic layer protectionCarbon filmInternal pressure
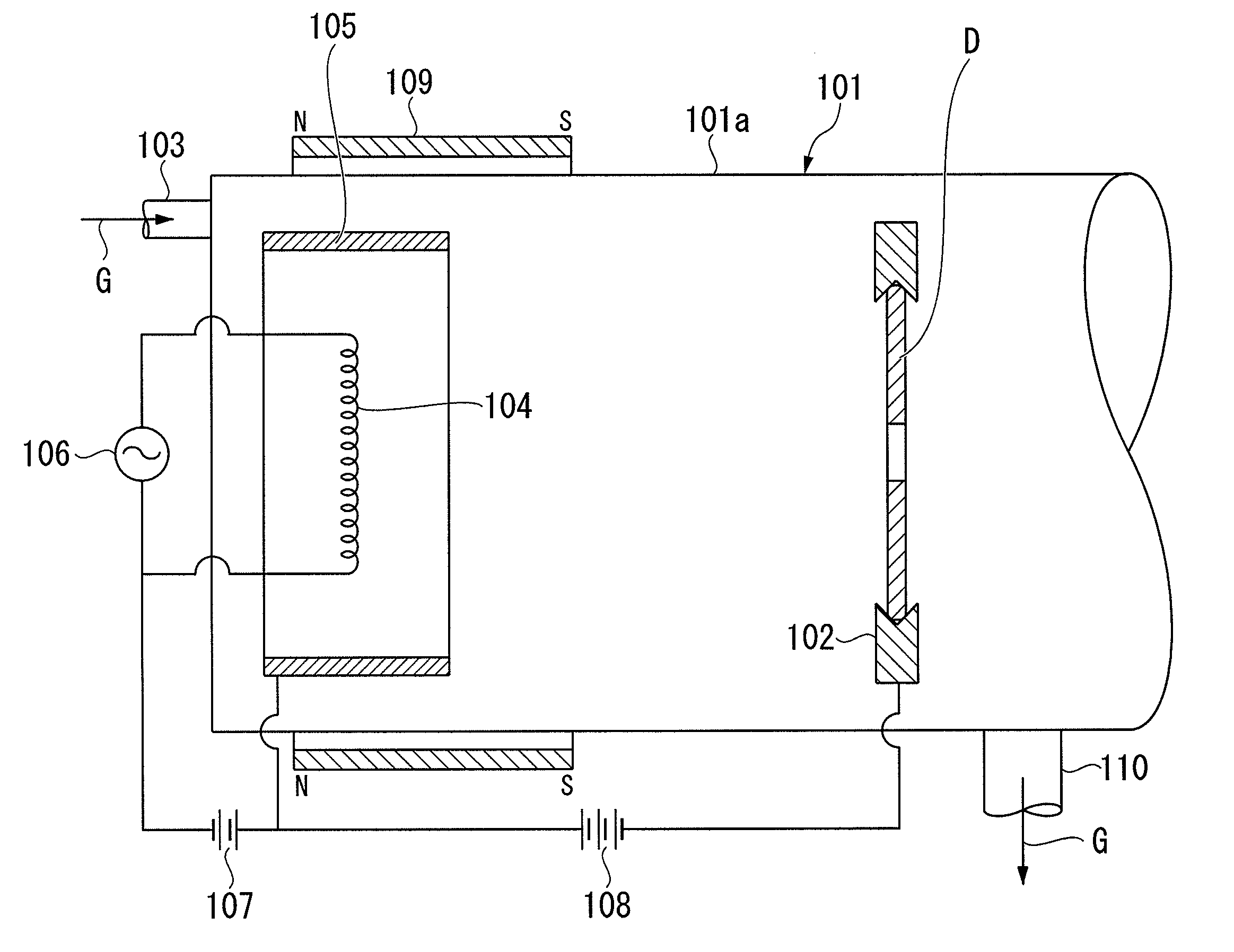
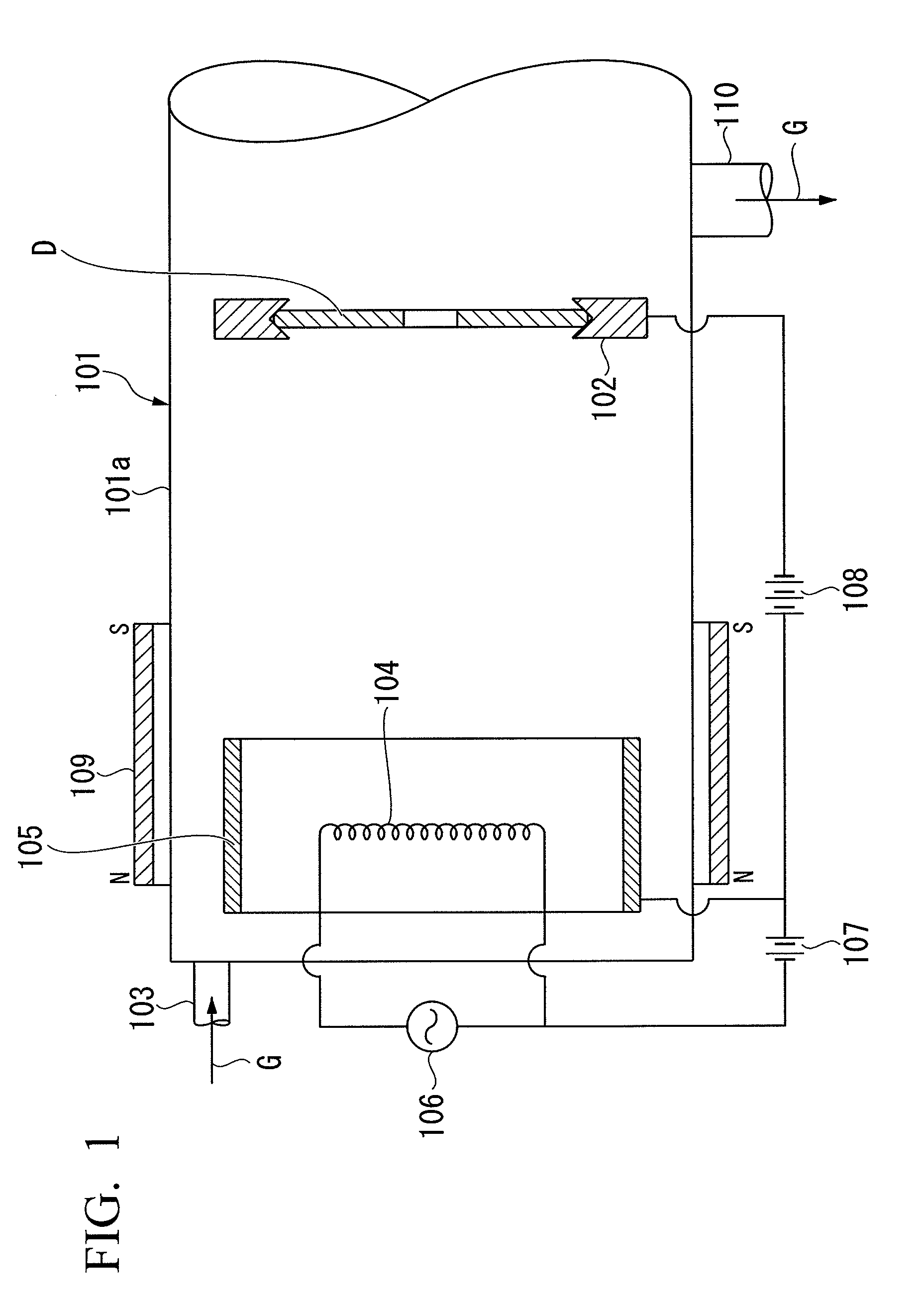
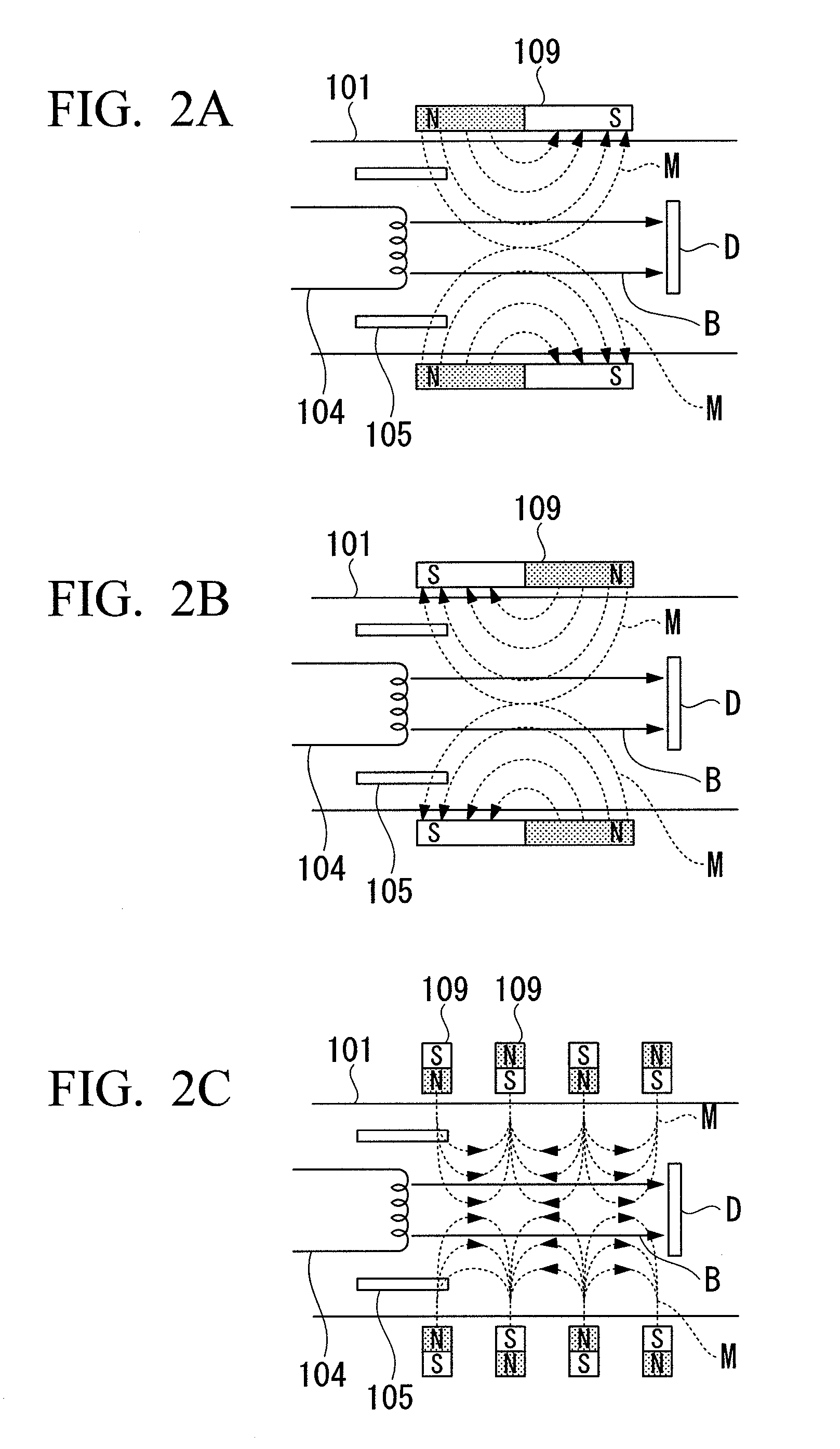
The present invention provides a carbon film forming method capable of forming a dense carbon film with high hardness. The carbon film forming method includes: introducing a raw material gas G including carbon into a deposition chamber 101 whose internal pressure is reduced; ionizing the raw material gas G using a discharge between a filament-shaped cathode electrode 104 heated by electrical power and an anode electrode 105 provided around the cathode electrode; and accelerating and radiating the ionized gas to the surface of a substrate D. A magnetic field is applied by a permanent magnet 109 to increase the ion density of the ionized gas accelerated and radiated to the surface of the substrate D. In this way, it is possible to form a carbon film with high hardness and high density on the surface of the substrate D.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO HD SINGAPORE PTE
Plasma process uniformity across a wafer by controlling RF phase between opposing electrodes
InactiveUS20080180028A1Increase currentReduce trafficElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsWaferingIon density
A method is provided for processing a workpiece in a plasma reactor chamber. The method includes coupling, to a plasma in the chamber, power of an RF frequency via a ceiling electrode and coupling, to the plasma, power of at least approximately the same RF frequency via a workpiece support electrode. The method also includes providing an edge ground return path. The method further includes adjusting the proportion between (a) current flow between said electrodes and (b) current flow to the edge ground return path from said electrodes, to control plasma ion density distribution uniformity over the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of characterizing a chamber based upon concurrent behavior of selected plasma parameters as a function of plural chamber parameters
InactiveUS20070080138A1Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsIon densityEngineering
The invention involves a method of characterizing a plasma reactor chamber through the behavior of many selected plasma parameters as functions of many selected chamber parameters. The plasma parameters may be selected from a group including ion density, wafer voltage, etch rate and wafer current or other plasma parameters. The chamber parameters are selected from a group including source power, bias power, chamber pressure, magnetic coil current in different magnetic coils, gas flow rates in different gas injection zones and species composition of the gas in different gas injection zones.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Liquid crystal tropism agent, liquid crystal tropism film and liquid crystal display element
ActiveCN101470303AIncrease ion densityImprove long-term reliabilityLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsCrystallographyLiquid-crystal display
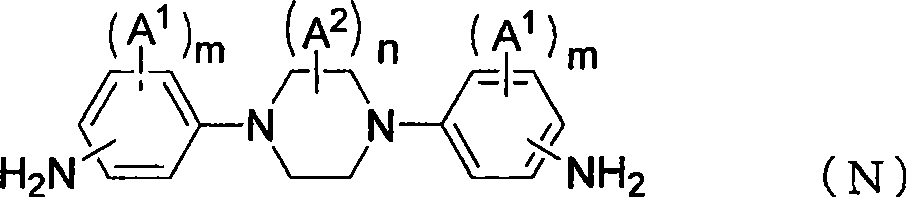
The present invention provides a liquid crystal display component which can represent the necessary ion density and realize long-term stability of the ion density, a liquid crystal aligning film which represents necessary ion density and realizes the long-term stability of ion density in the liquid display component, and a liquid crystal aligning agent which can form the liquid crystal aligning film. According to the invention, the liquid crystal aligning film is formed by the liquid crystal aligning agent which comprises the polyamic acid or the derivative thereof, and furthermore the liquidcrystal aligning film is used in the liquid crystal display component. The polyamic acid is the reaction product of specific diamine and tetracarboxylic dianhydride, wherein the specific diamine comprises piperazine.
Owner:JNC CORP +1
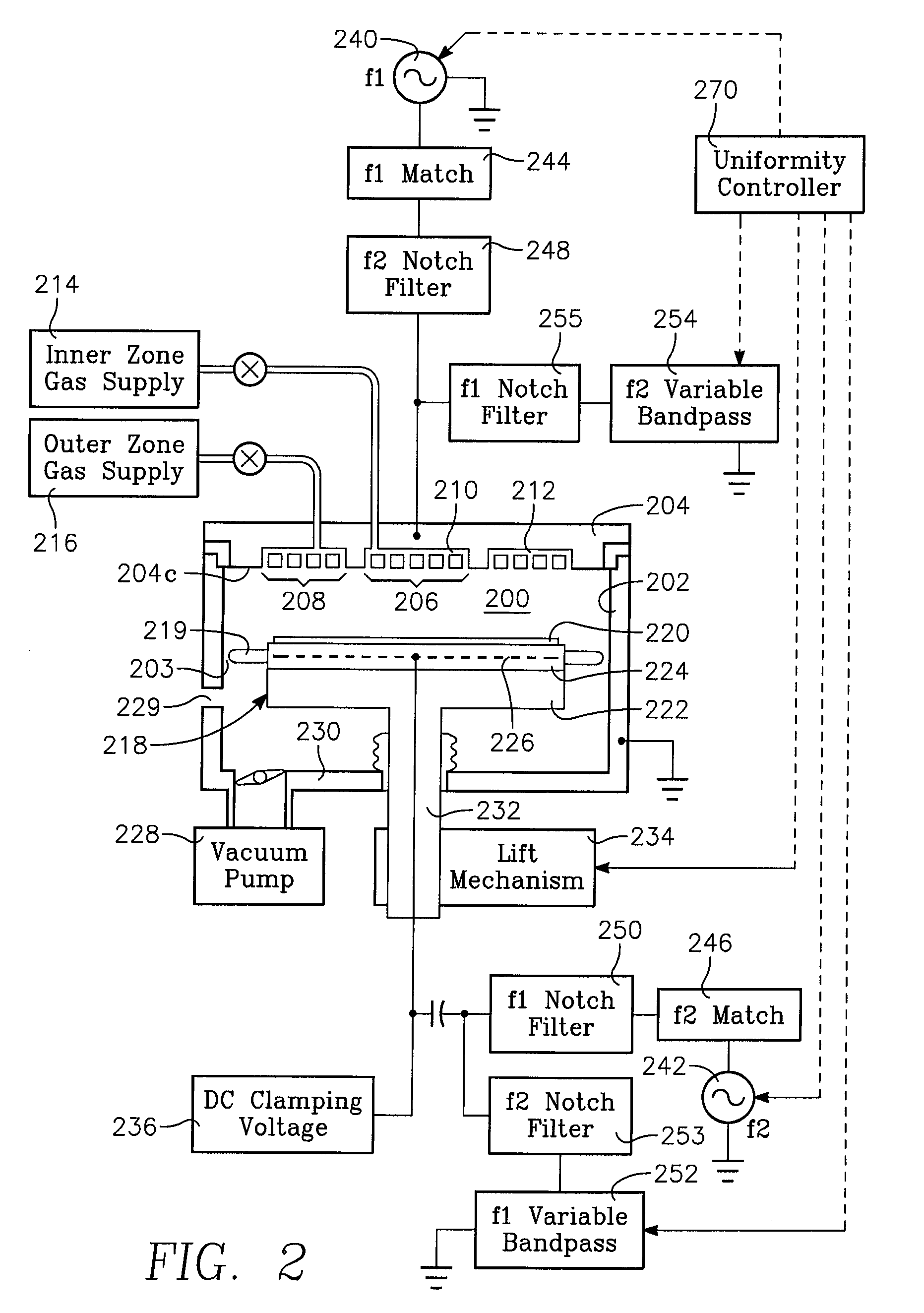
Method of processing a workpiece in a plasma reactor with variable height ground return path to control plasma ion density uniformity
InactiveUS7968469B2Increase and decrease tendencyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon densityEngineering
A method for processing a workpiece in a plasma reactor chamber includes coupling RF power at a first VHF frequency f1 to a plasma via one of the electrodes of the chamber, and providing a center ground return path for RF current passing directly between the ceiling electrode and the workpiece support electrode for the frequency f1. The method further includes providing a variable height edge ground annular element and providing a ground return path through the edge ground annular element for the frequency f1. The method controls the uniformity of plasma ion density distribution by controlling the distance between the variable height edge ground annular element and one of: (a) height of ceiling electrode or (b) height of workpiece support electrode.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com