Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11640 results about "Wafering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
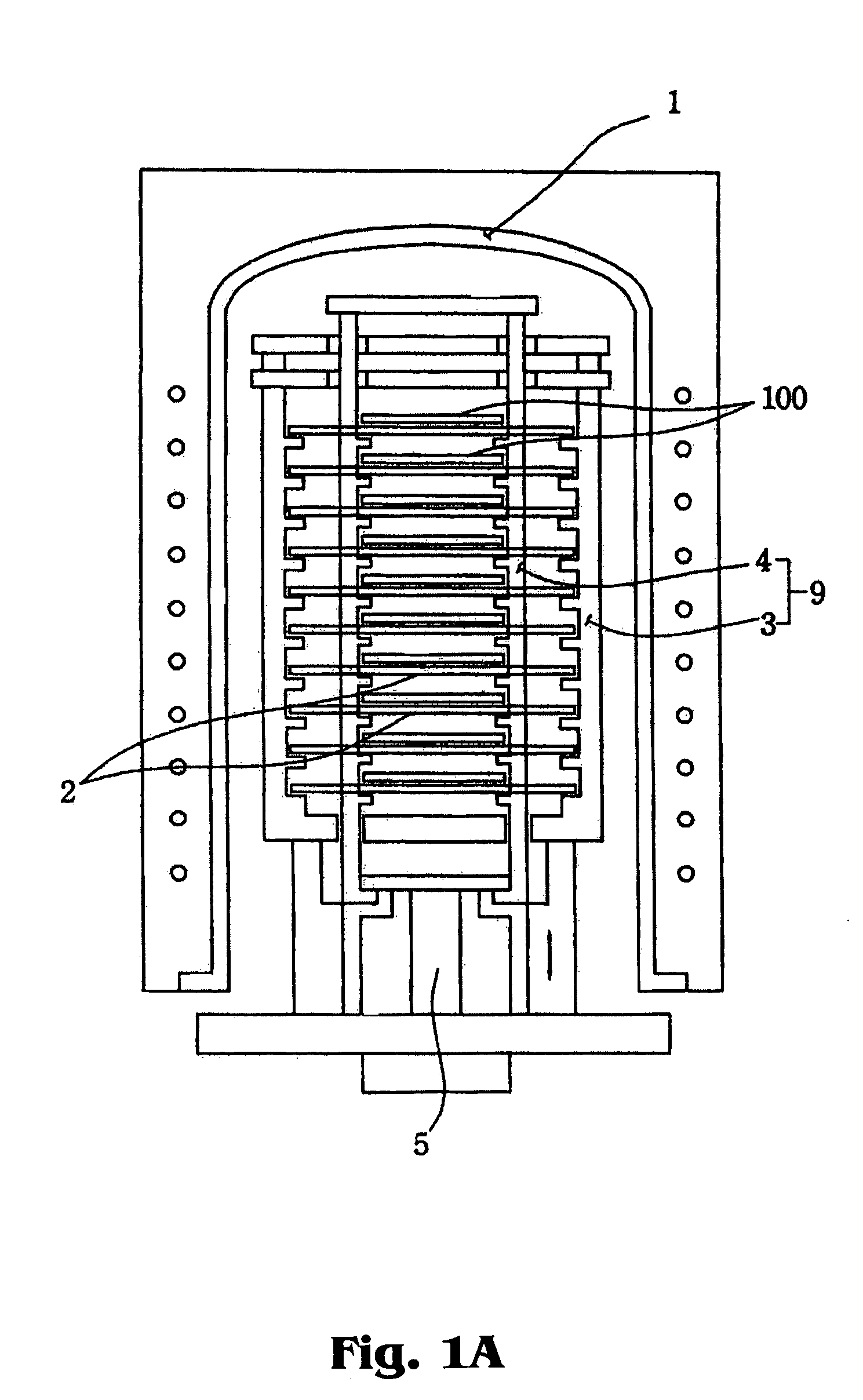
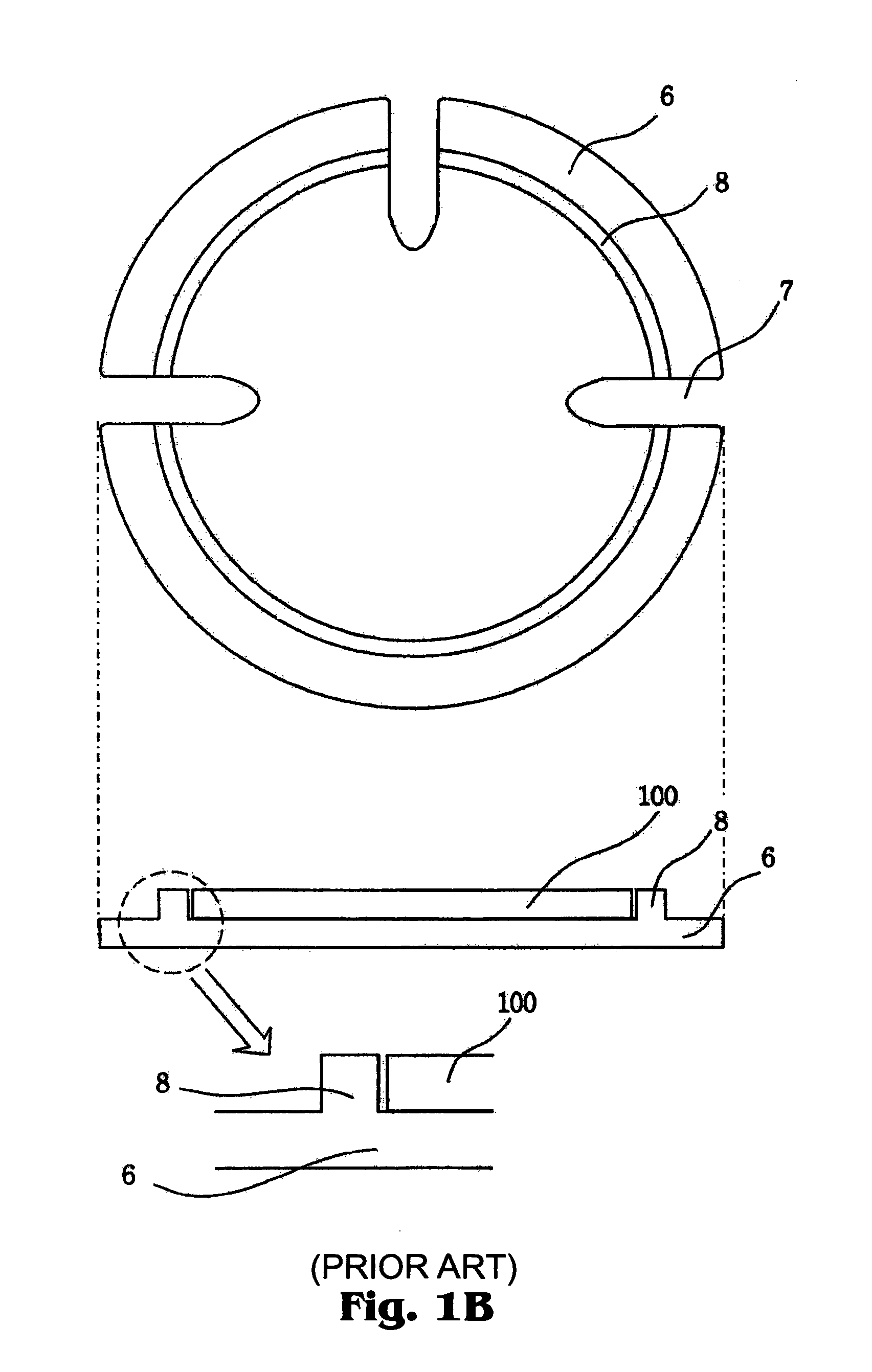
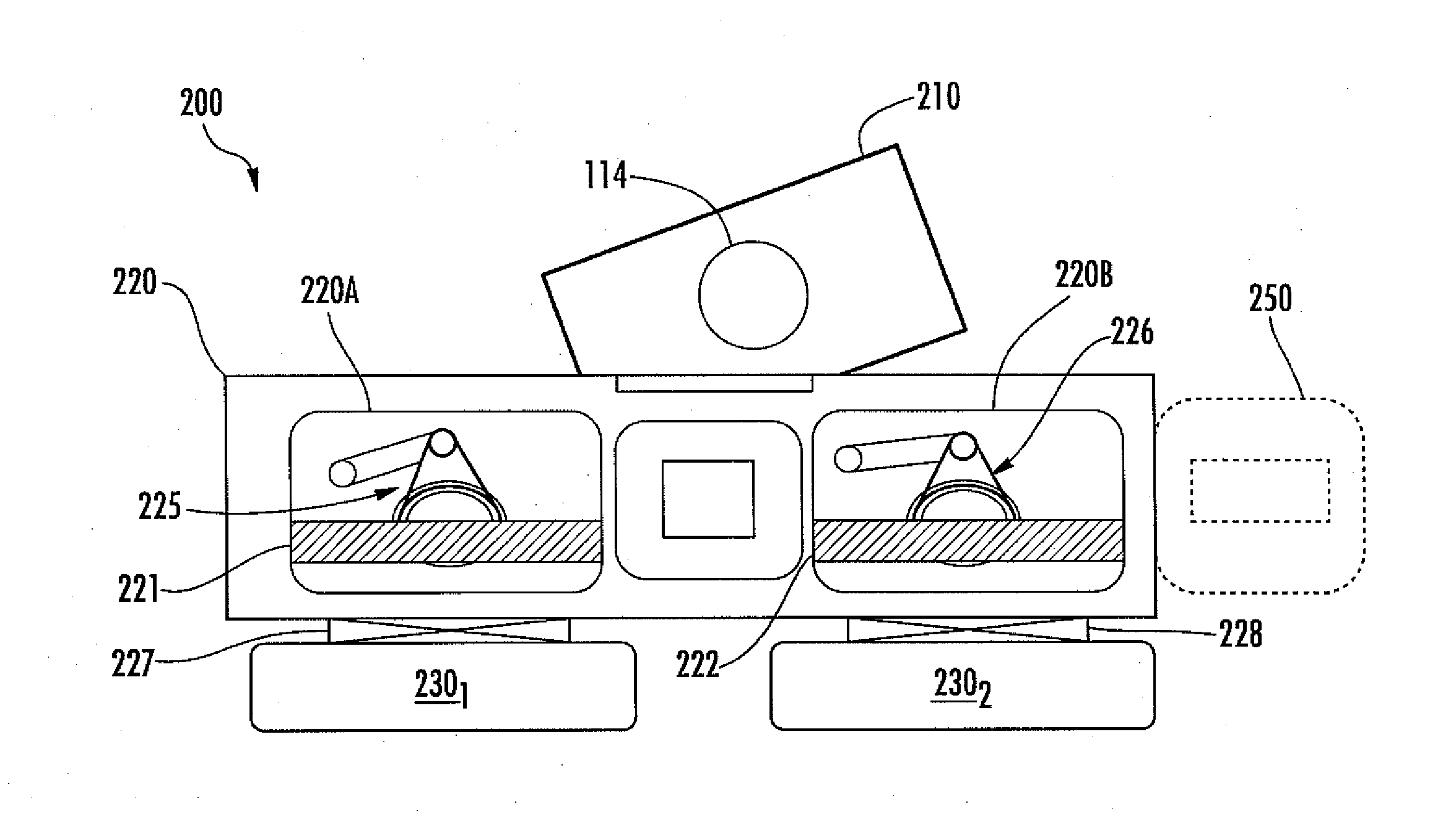
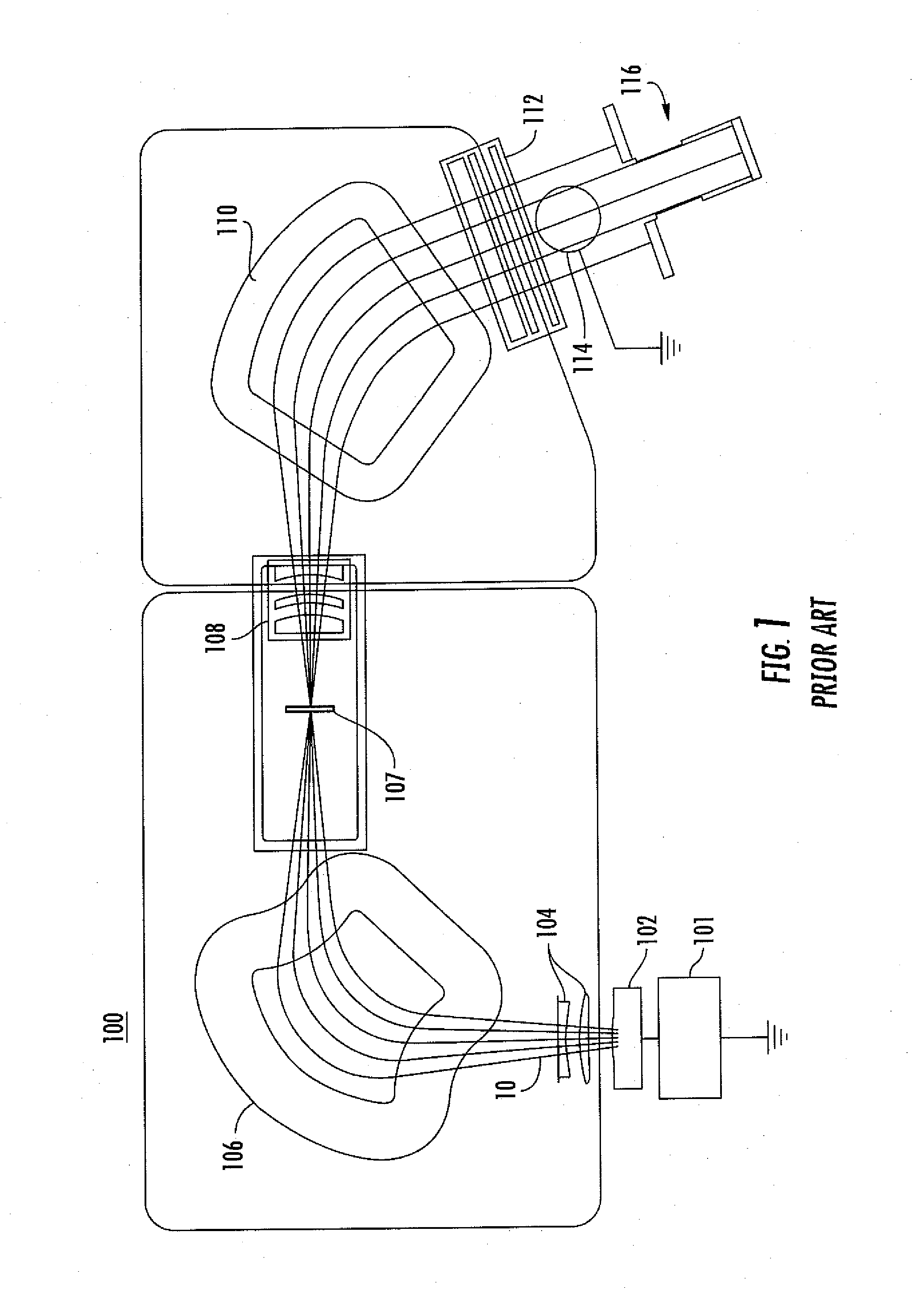
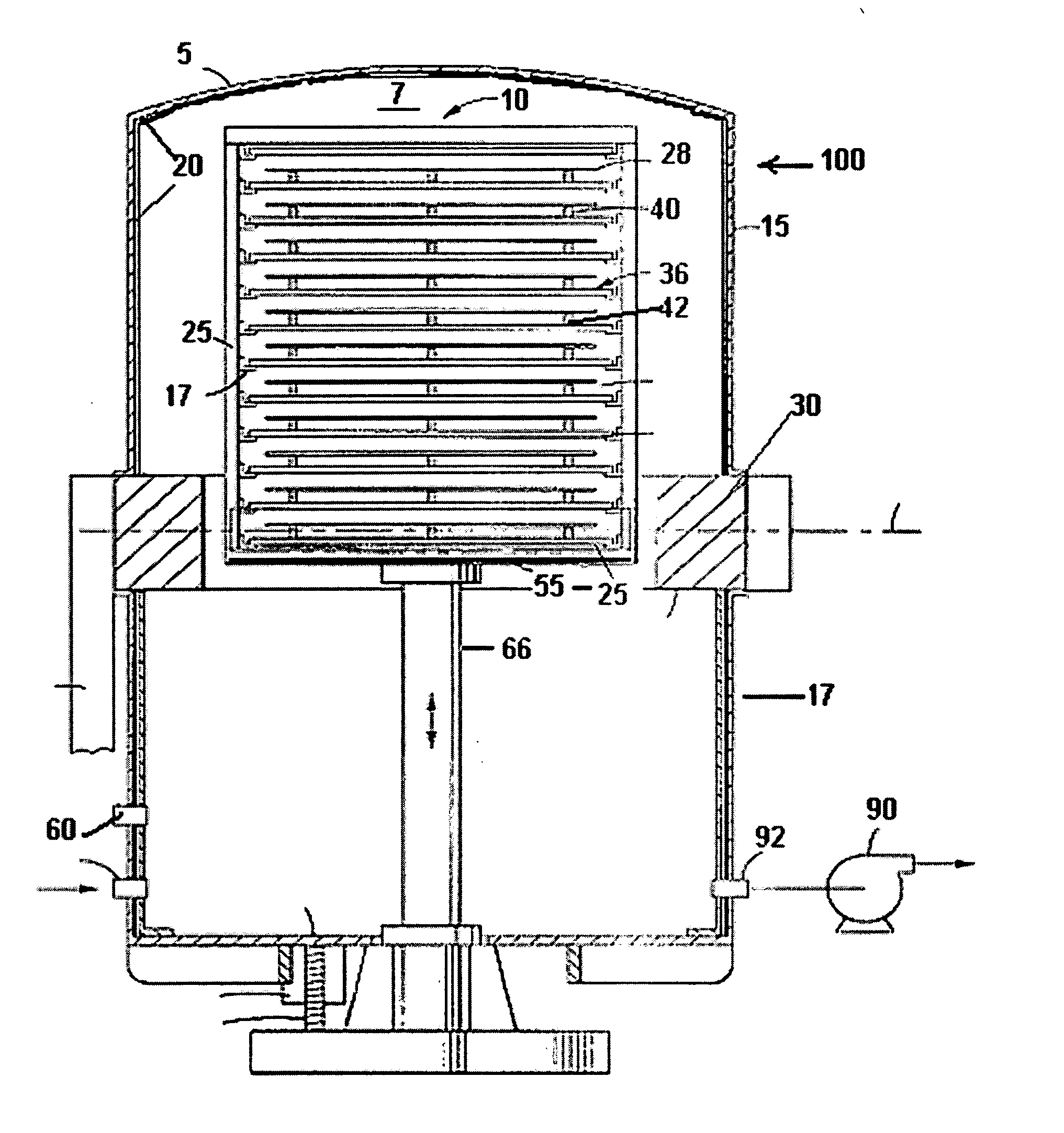
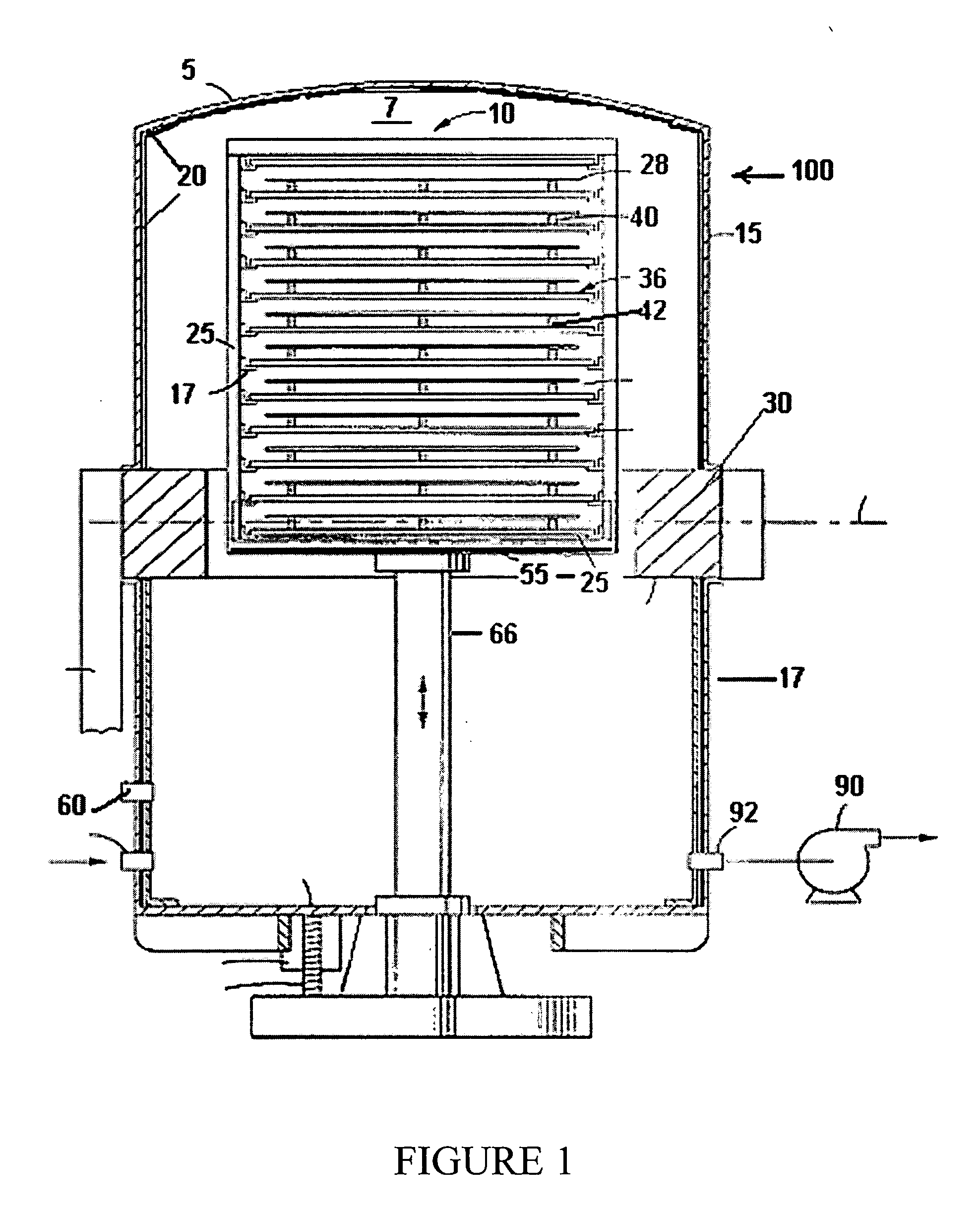
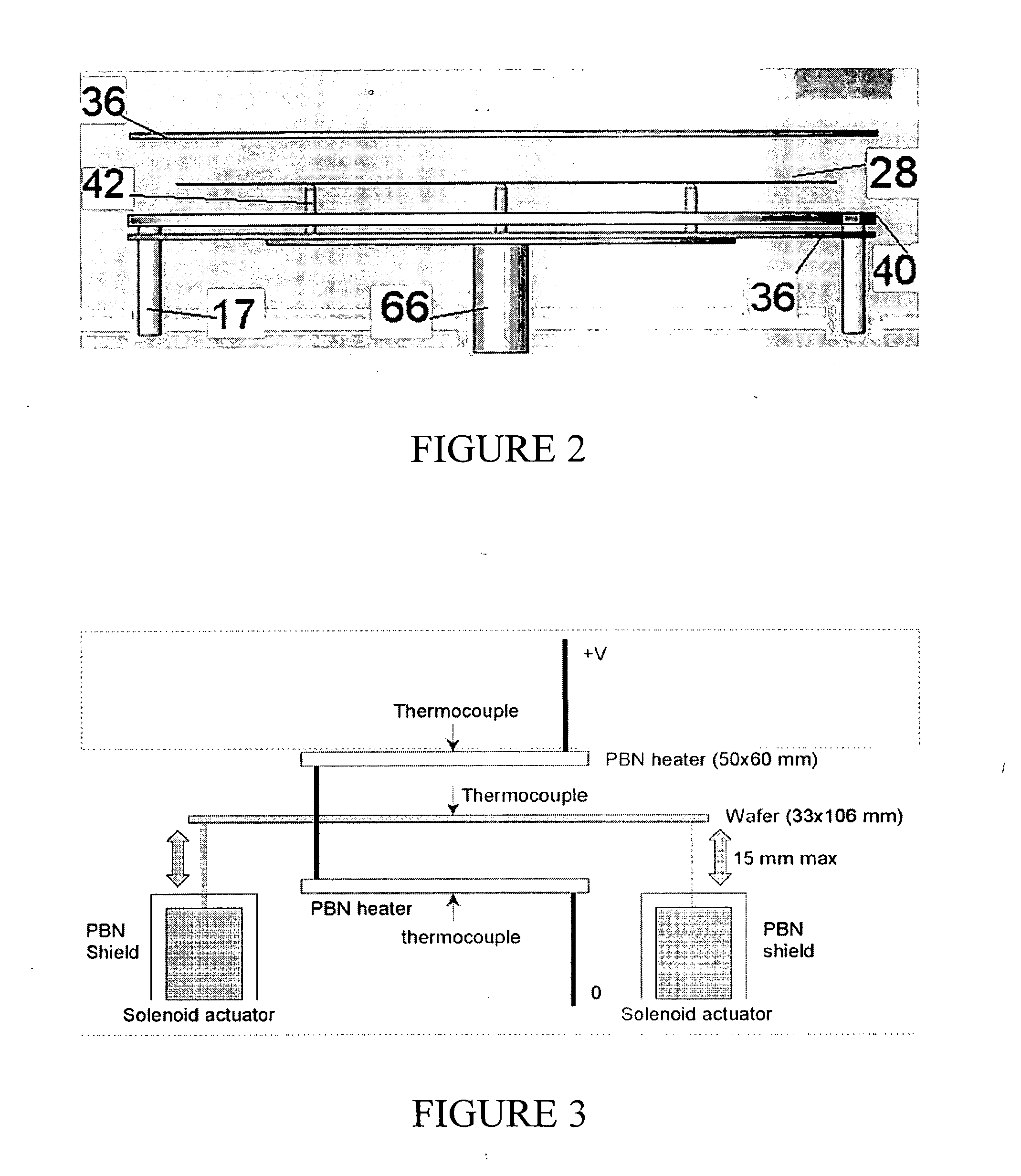
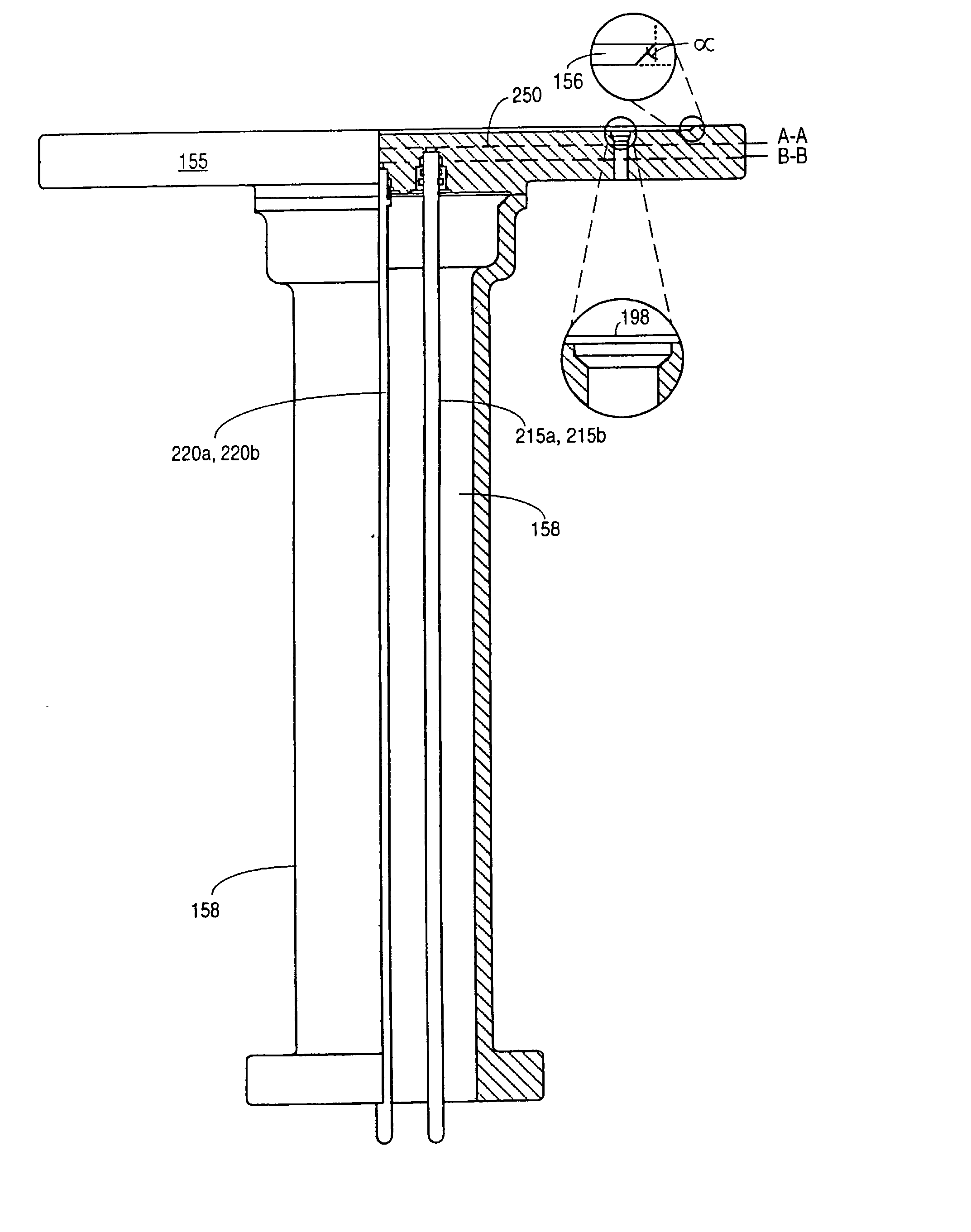
Wafering is the process by which a silicon crystal (boule) is made into wafers. This process is usually carried out by a multi-wire saw which cuts multiple wafers from the same crystal at the same time. These wafers are then polished to the desired degree of flatness and thickness.
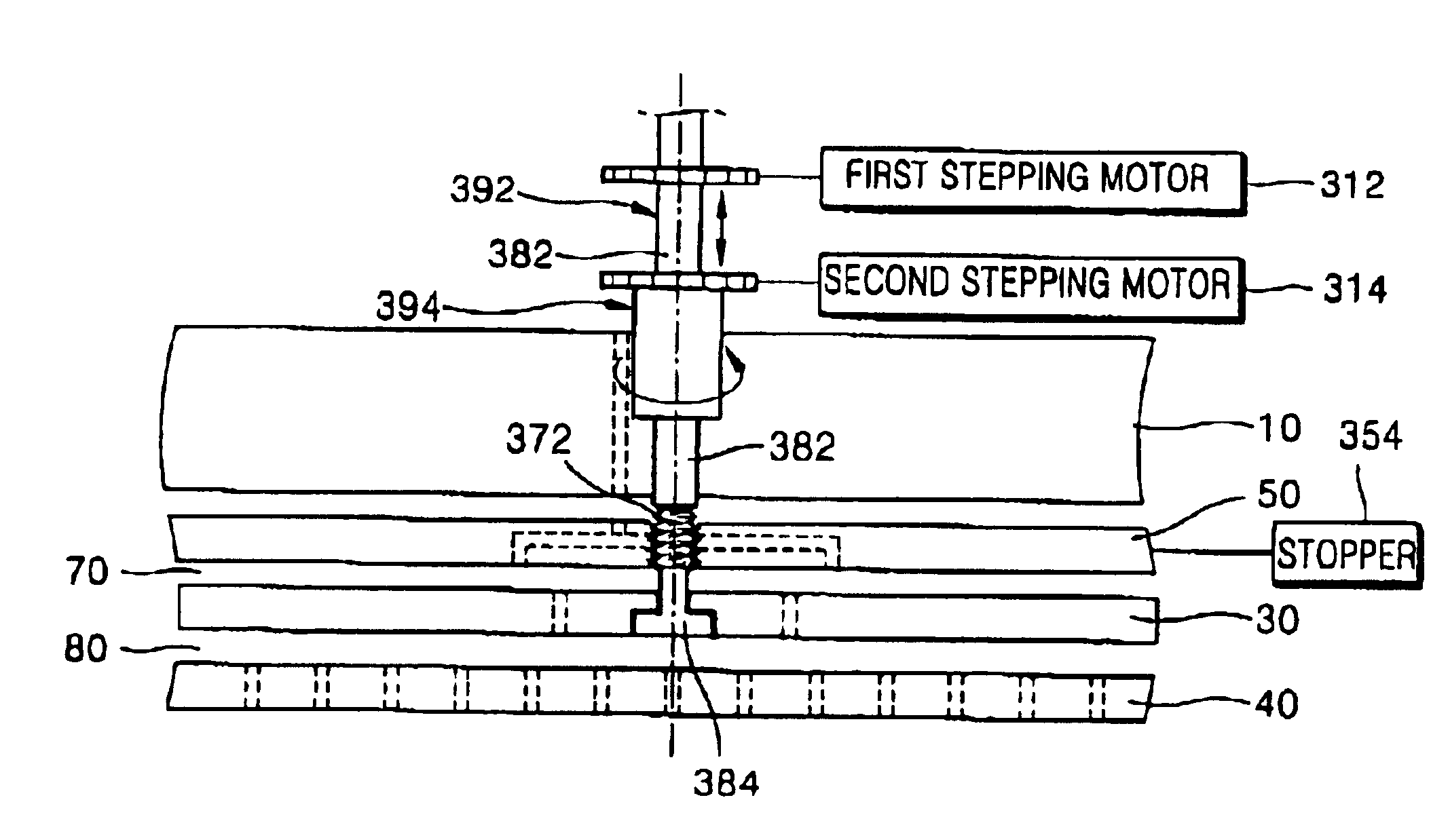
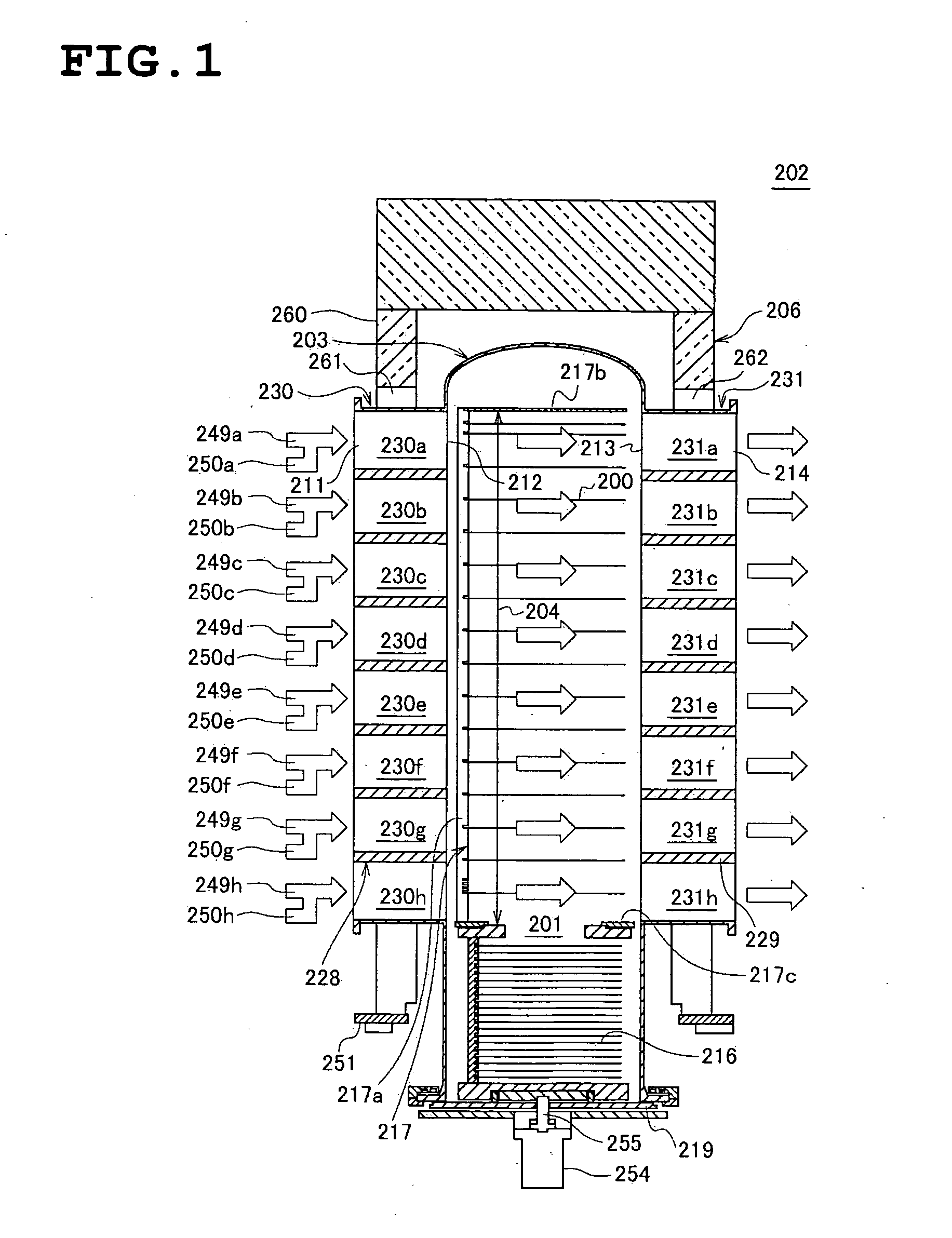
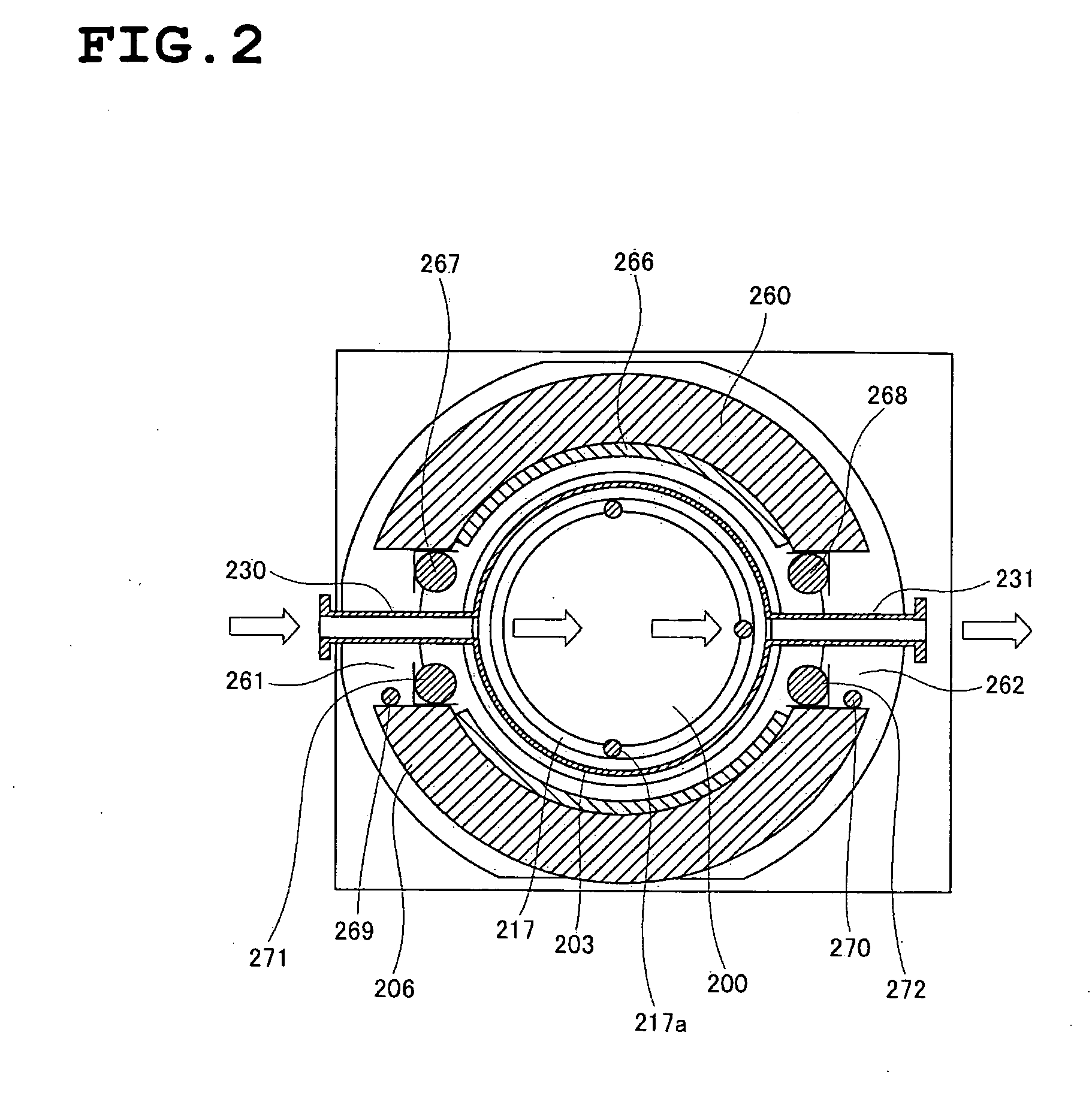
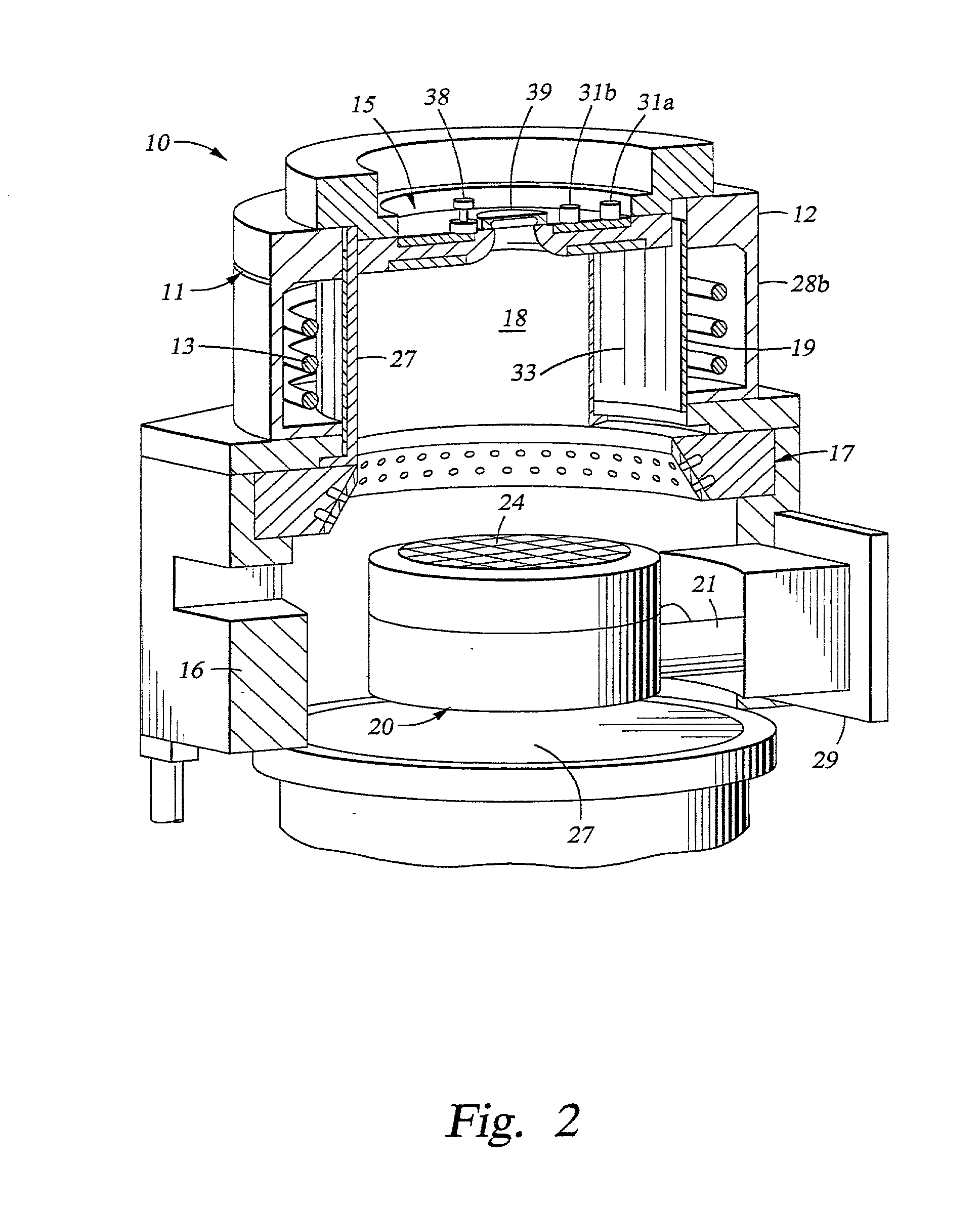
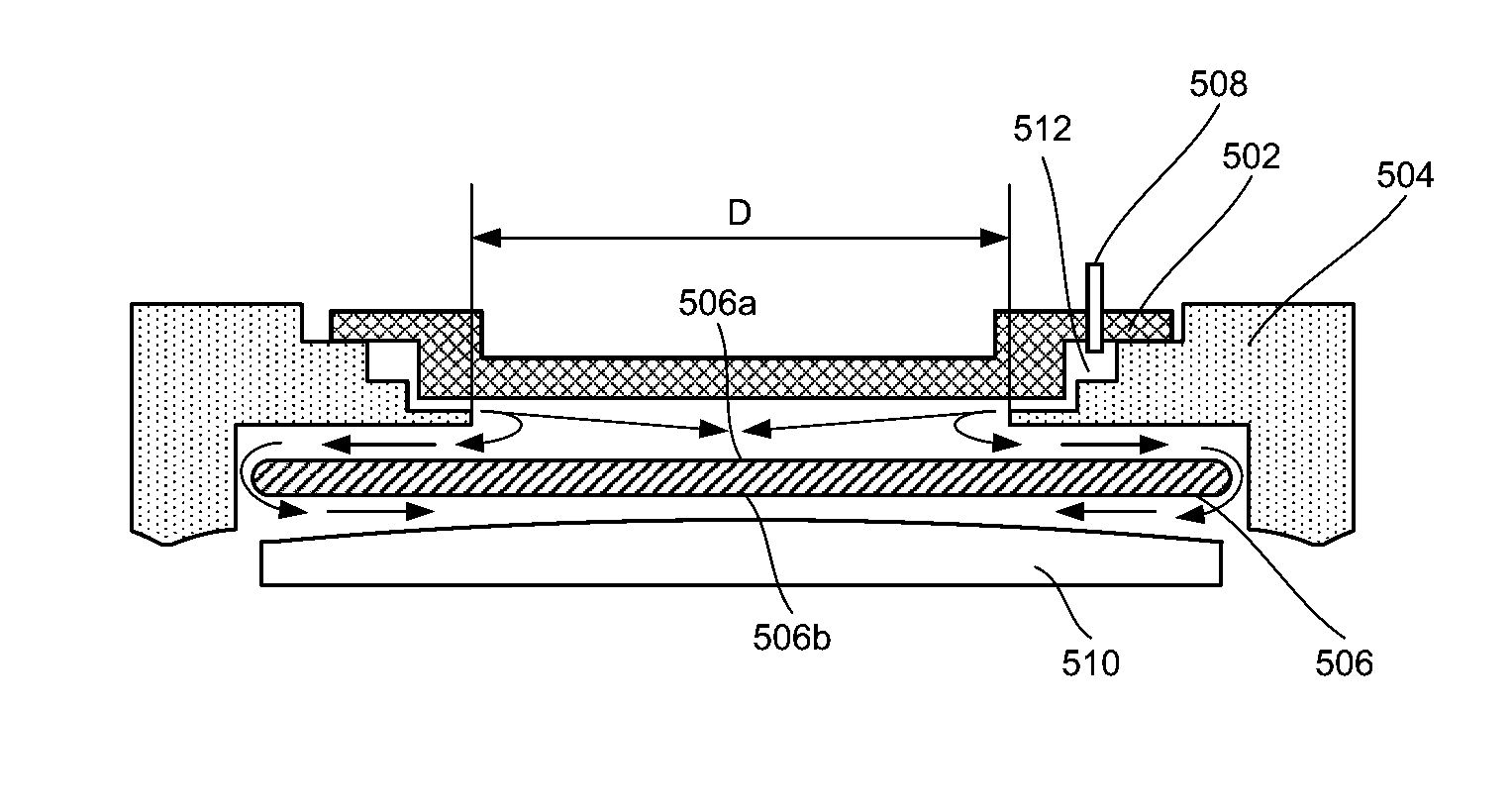
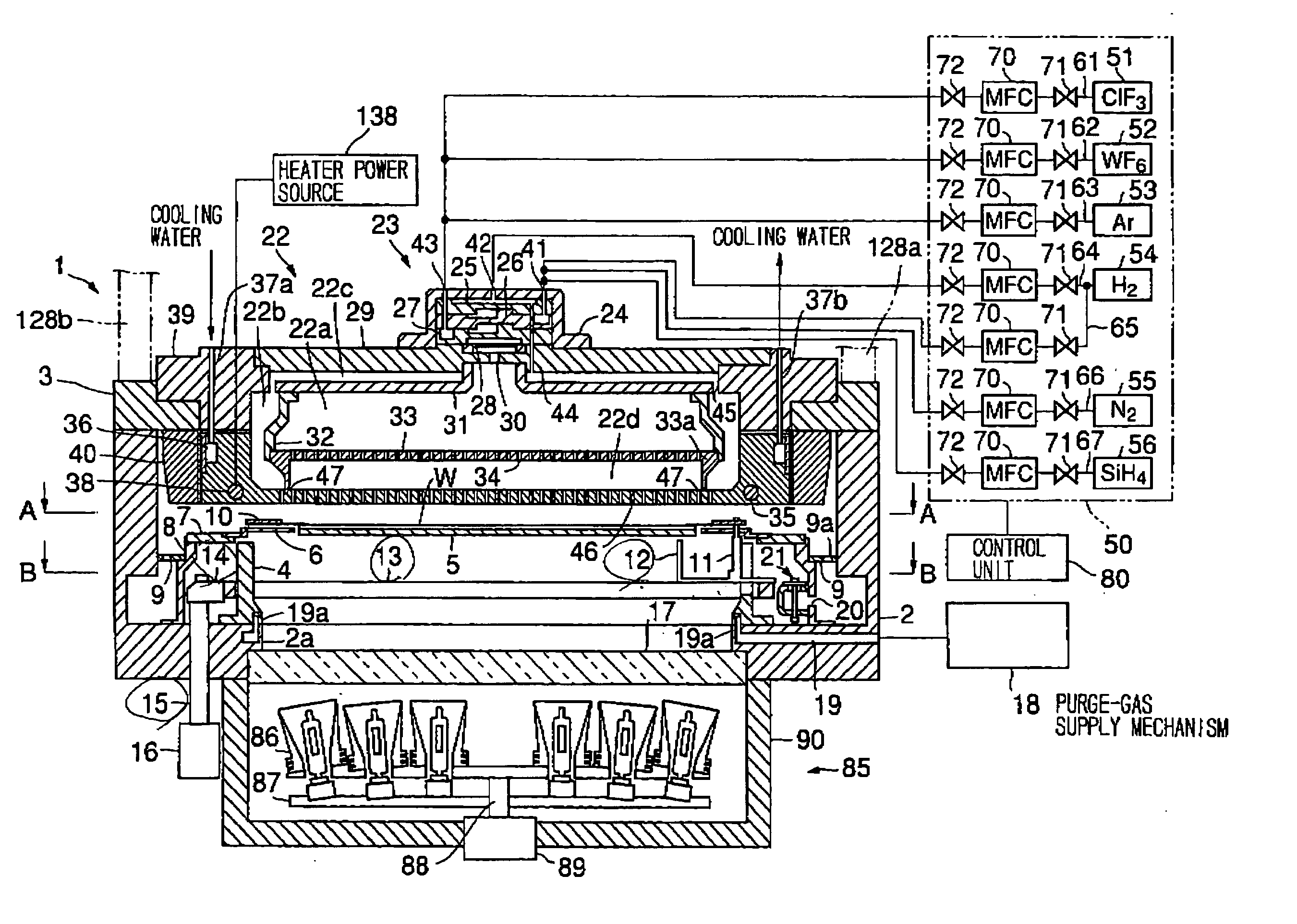
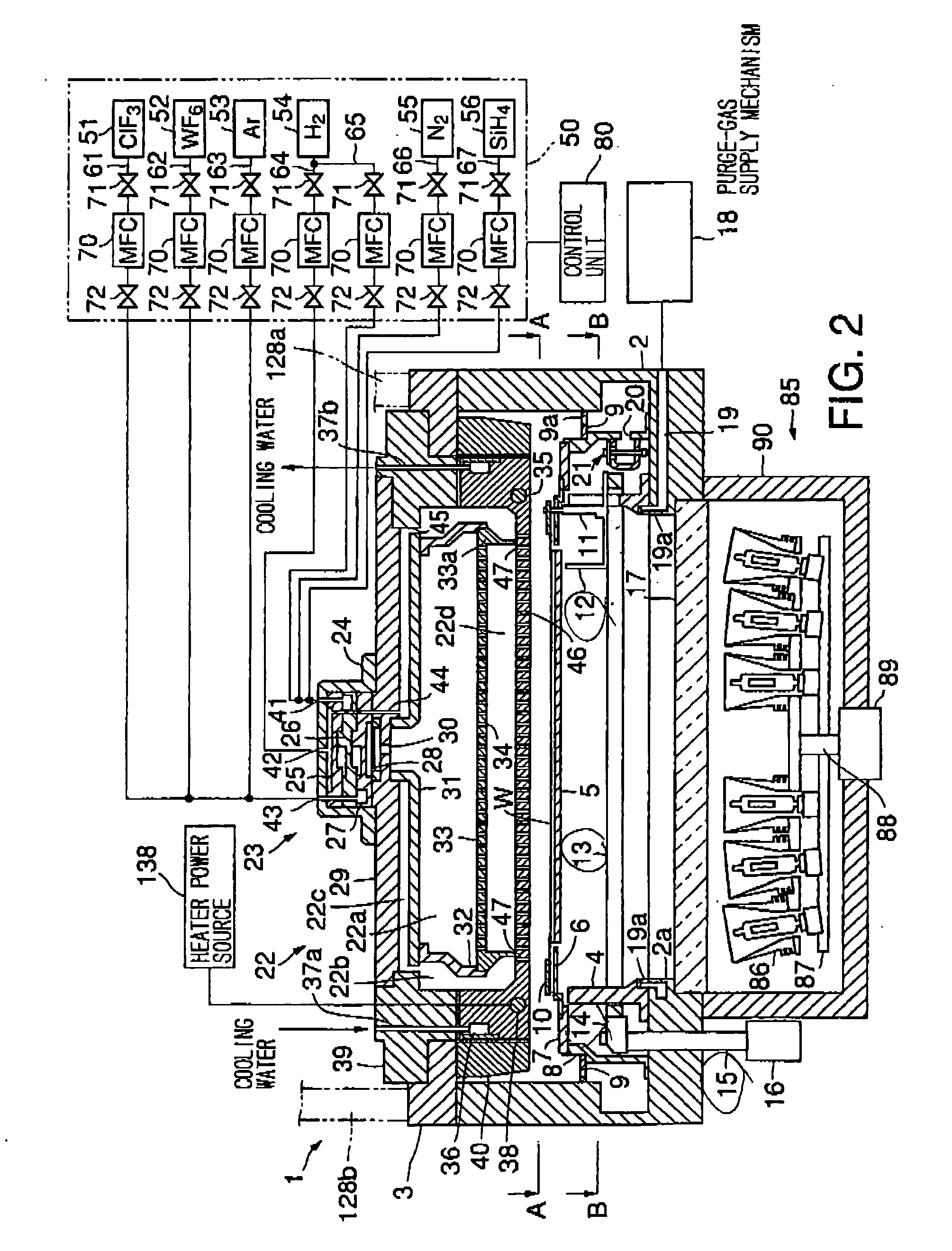
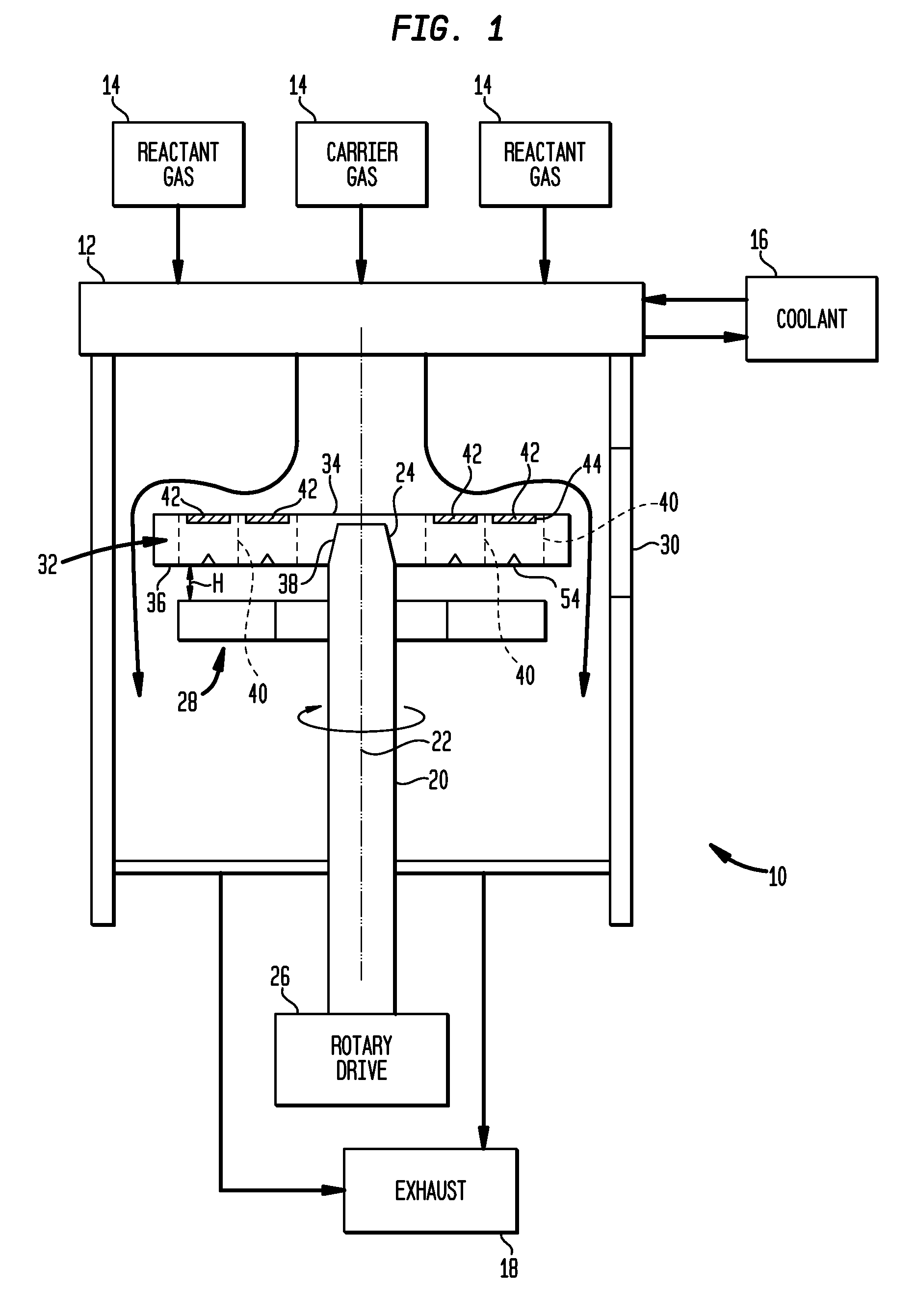
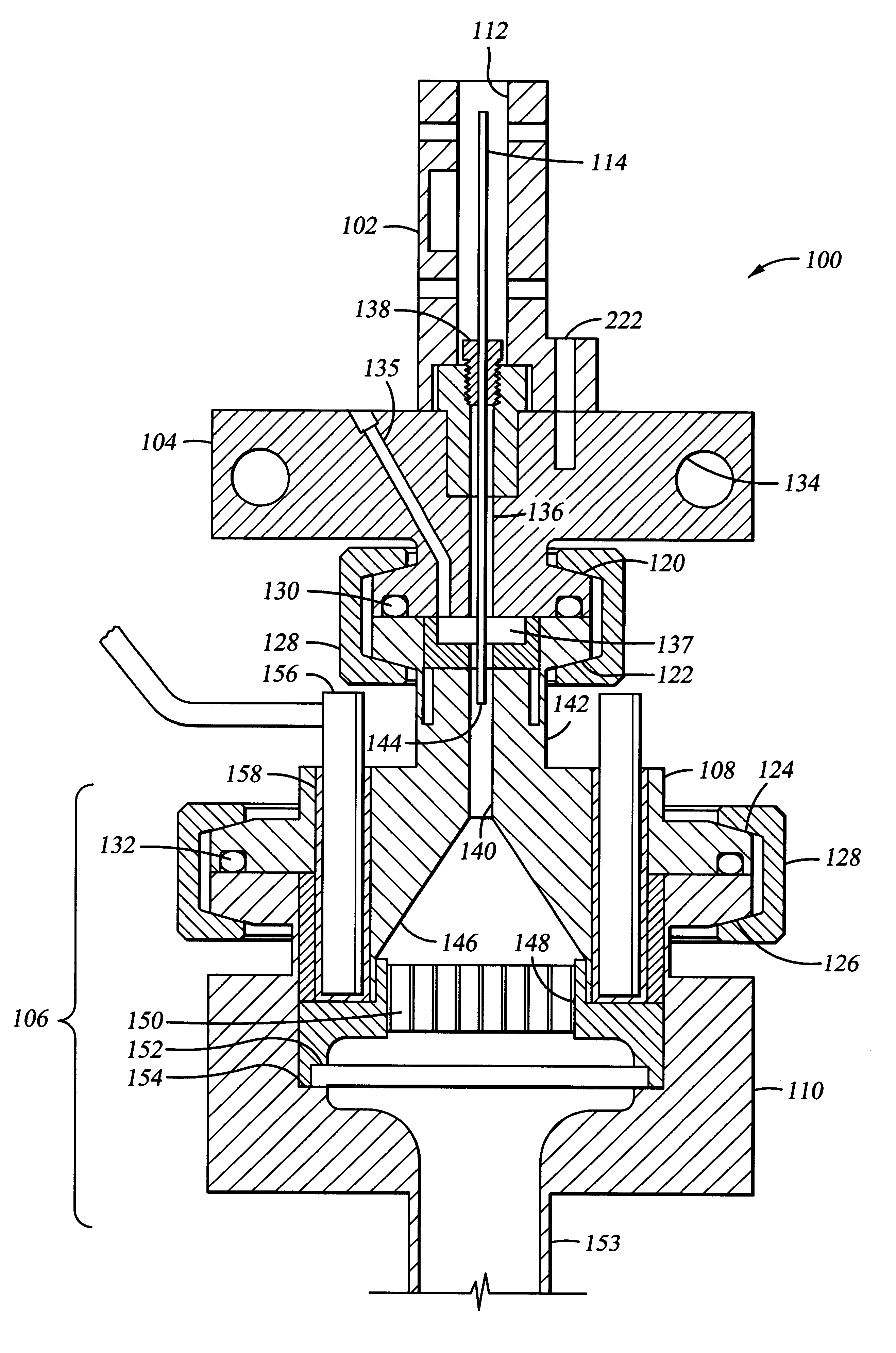
Shower head of a wafer treatment apparatus having a gap controller
InactiveUS6872258B2Improve uniformityEtch rate be optimizedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingProcess regionSemiconductor
A shower head for adjusting distribution of a reactant gas in a process region of a semiconductor manufacturing reaction chamber, wherein a top plate has a gas port for introducing the reactant gas into the reaction chamber; a face plate, having through holes, disposed opposite the process region; a first baffle plate, having through holes, disposed between the top plate and the face plate and capable of moving up or down, wherein the first baffle plate has a top surface that defines a first gap for forming a first lateral flow passage; a second baffle plate, having through holes, disposed between the first baffle plate and the face plate and capable of moving up or down, wherein the second baffle plate has a top surface that defines a second gap for forming a second lateral flow passage; and a gap controller for determining widths of the first and second gaps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
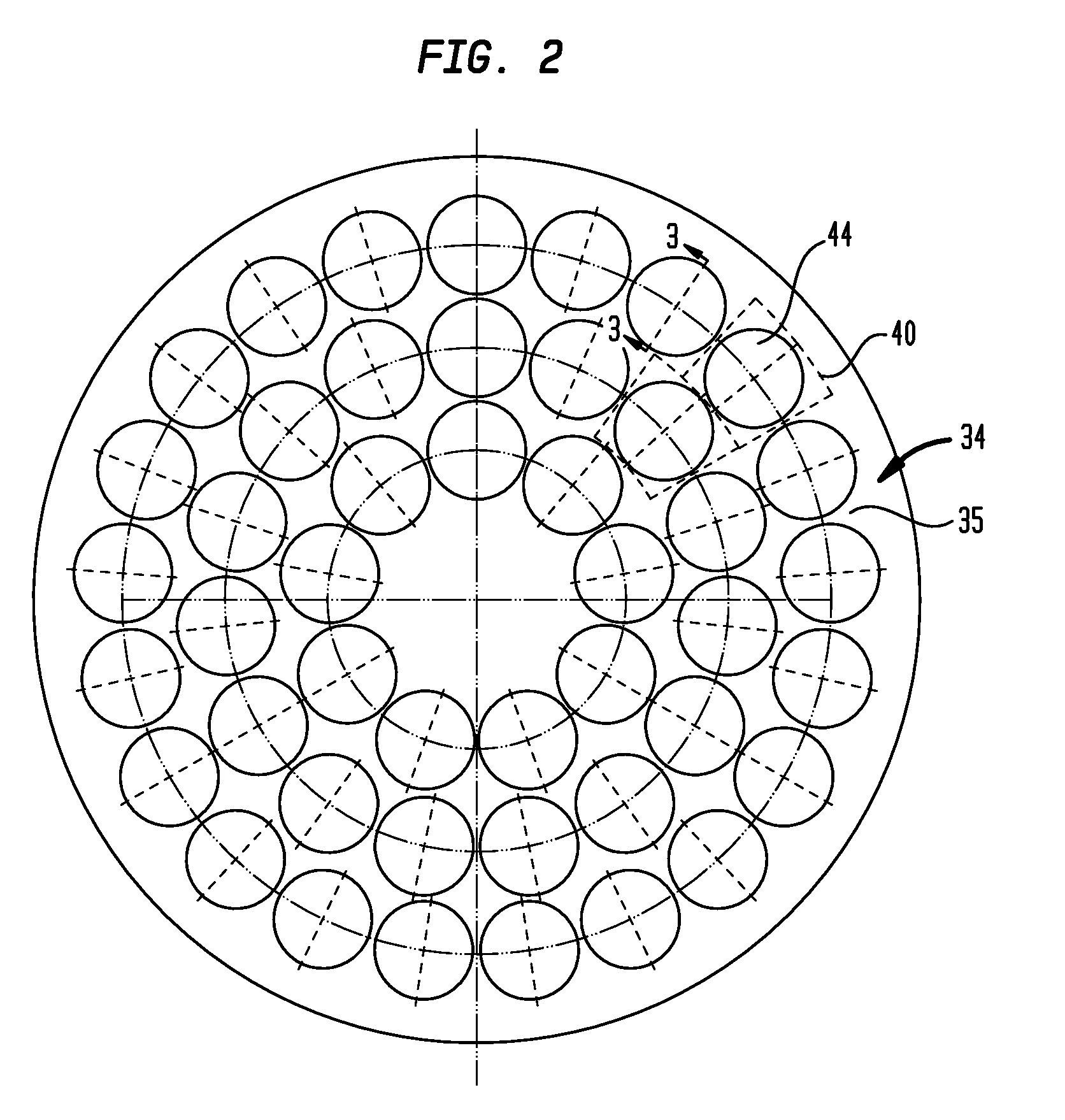
Substrate processing apparatus, method of manufacturing semiconductor device, and reaction vessel
InactiveUS20080173238A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingIn planeProduct gas
A substrate processing apparatus that affords improved uniformity to in-plane wafer and interwafer film thickness of a large number of wafers on which a film is simultaneously formed, having: a reaction tube having in an interior thereof a processing chamber in which a plurality of substrates disposed in a direction perpendicular to a substrate processing surface can be processed; and a heating device provided to surround an outer circumference of the reaction tube, a gas inlet tube being provided on a side face of the reaction tube in a region for processing a substrate inside the reaction tube, so as to reach at least an outside of the heating device; and a gas spouting port being disposed in this gas inlet tube in a slit form so as to straddle at least a plurality of the substrates in a direction perpendicular to the substrate processing surface, for spouting gas from the gas inlet tube into the processing chamber.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
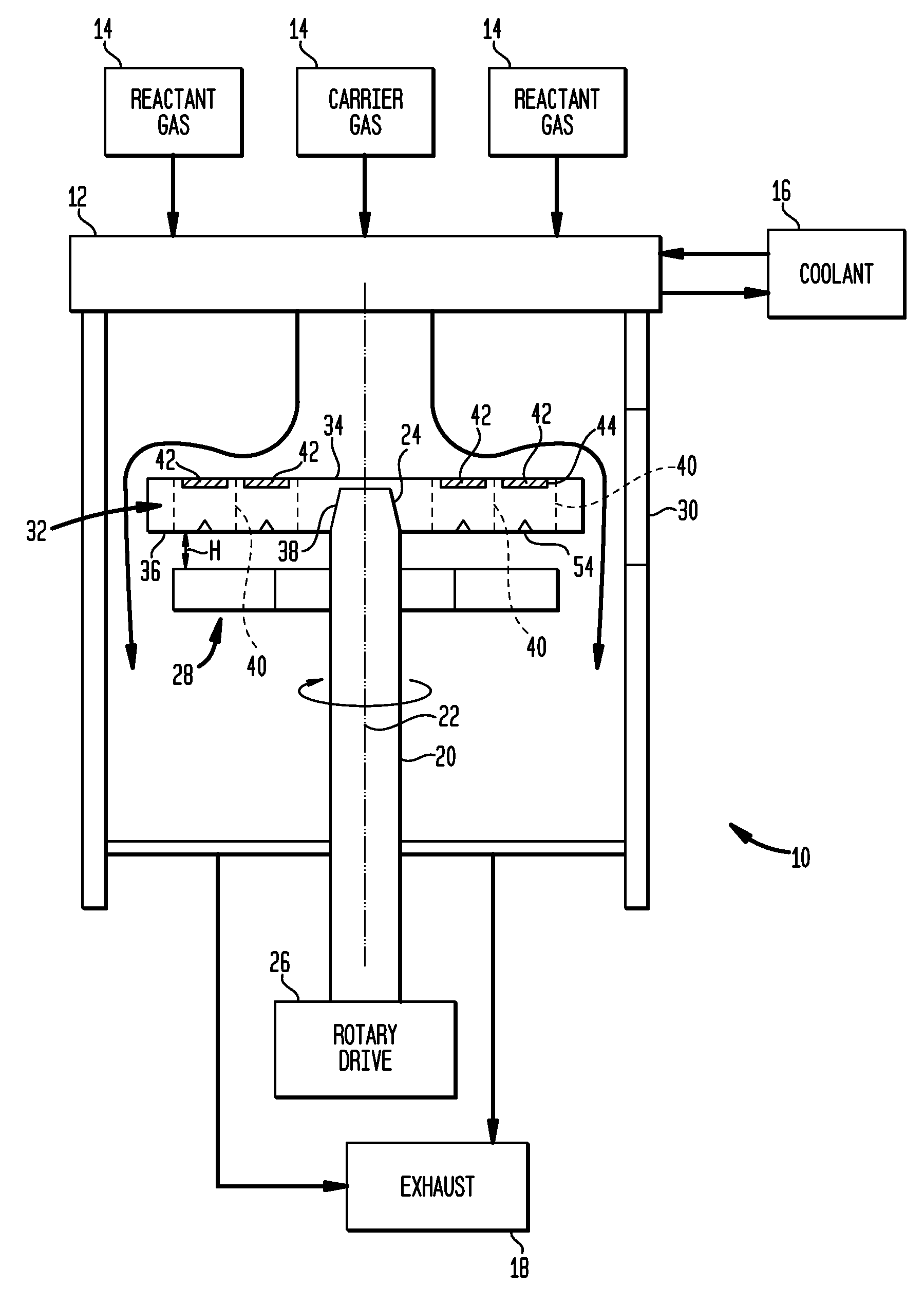
Plasma enhanced chemical processing reactor and method
InactiveUS20020078893A1Improve film qualityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical treatmentReactive gas
A plasma enhanced chemical processing reactor and method. The reactor includes a plasma chamber including a first gas injection manifold and a source of electromagnetic energy. The plasma chamber is in communication with a process chamber which includes a wafer support and a second gas manifold. The plasma generated in the plasma chamber extends into the process chamber and interacts with the reactive gases to deposit a layer of material on the wafer. The reactor also includes a vacuum system for exhausting the reactor. The method includes the steps of generating a plasma within the plasma chamber, introducing at least one gaseous chemical into the process chamber proximate to the wafer support and applying r.f. gradient to induce diffusion of the plasma to the area proximate the wafer support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Substrate Processing Apparatus and Substrate Mount Table Used in the Apparatus
InactiveUS20100162956A1Achieving temperature uniformityEliminate the effects ofElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInternal pressureSusceptor
Disclosed is a susceptor which achieves uniform temperature distribution of a wafer placed on the susceptor, and also disclosed is a substrate processing apparatus provided with the susceptor. An annular recess 12a is formed in an intermediate portion between the central portion and the peripheral portion of a wafer support surface of the susceptor 12. Due to the provision of the recess, the substrate heating effect by thermal radiation from the susceptor is suppressed in the intermediate portion. The geometrical dimension of the recess is determined taking the chamber internal pressure into consideration.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
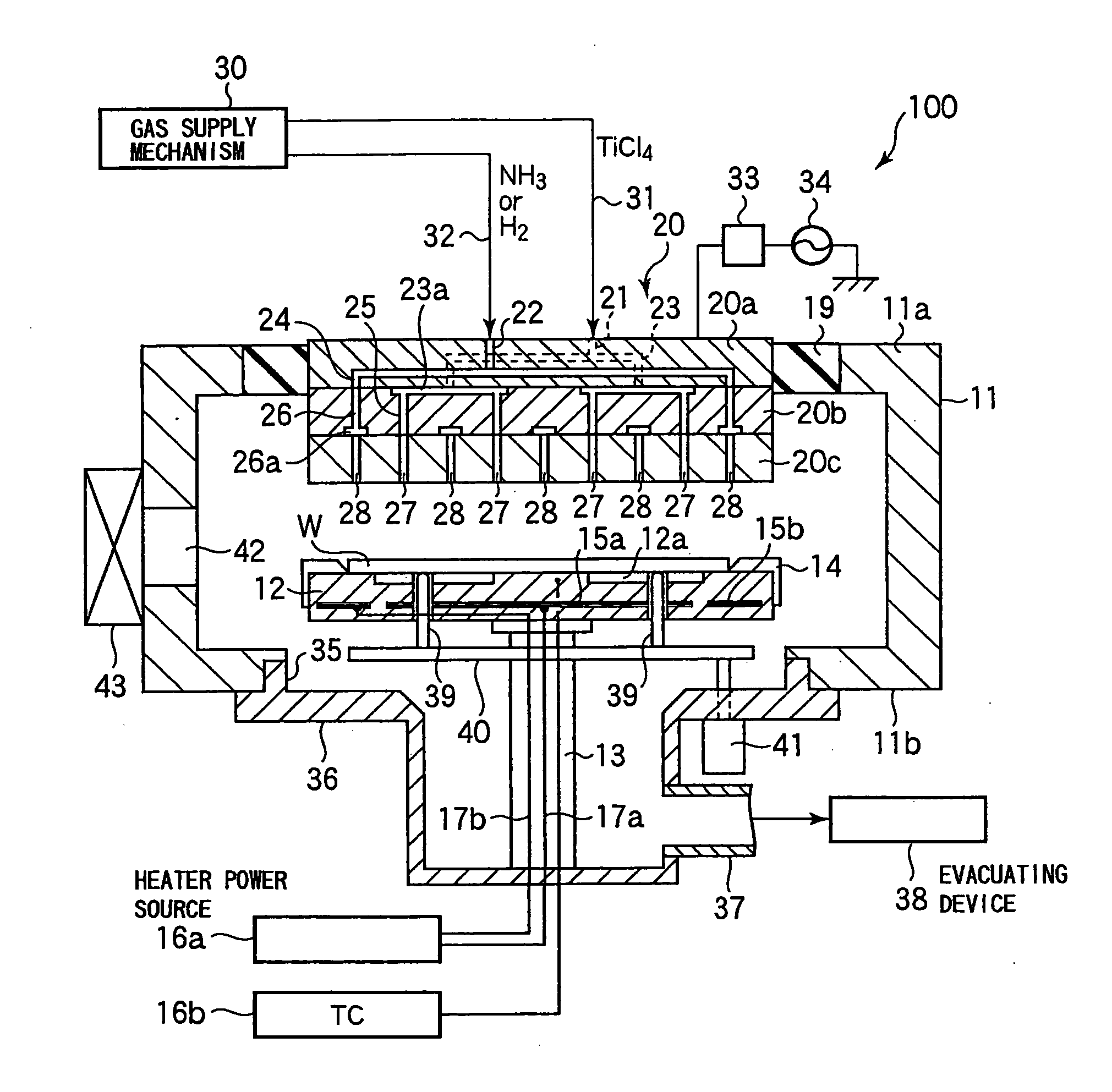
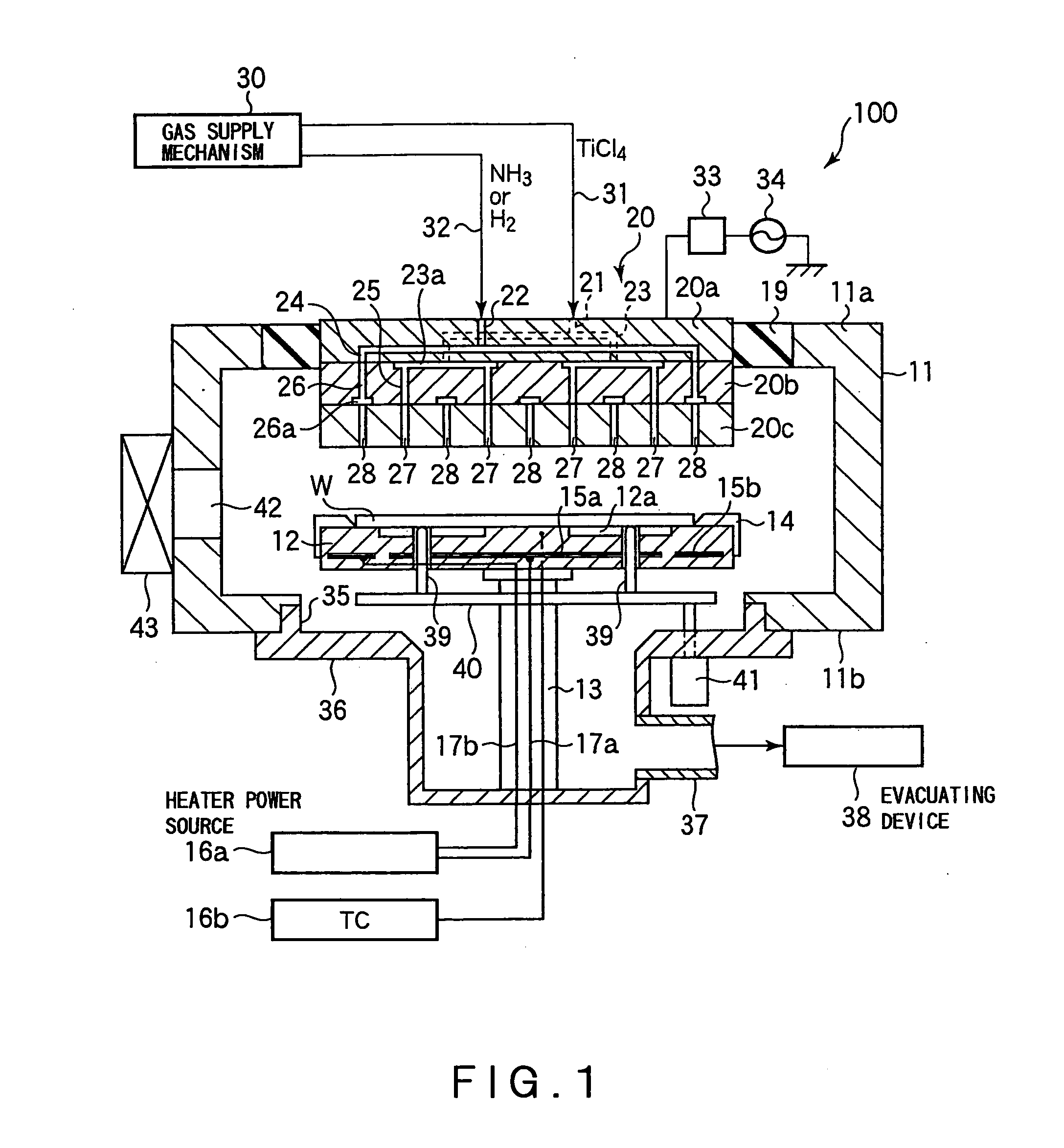
In-situ atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS20070037412A1Improve uniformityImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingWaferingHafnium
An in situ method for forming a HfO2 high-k dielectric layer in a batch wafer processing system. The method comprises first loading a plurality of wafers into a process chamber, and then pre-treating the plurality of wafers in the process chamber with a first oxidizer. After pre-treating the wafers, and without removing the wafers from the process chamber, the method then comprises depositing HfO2 on the plurality of wafers by atomic layer deposition, which comprises a plurality of deposition cycles, each cycle comprising alternating exposure of the plurality of wafers in the process chamber to a second oxidizer and a hafnium precursor. The hafnium precursor is selected from hafnium tert-butoxide (HTB) or hafnium tetra-diethylamide (TDEAH).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
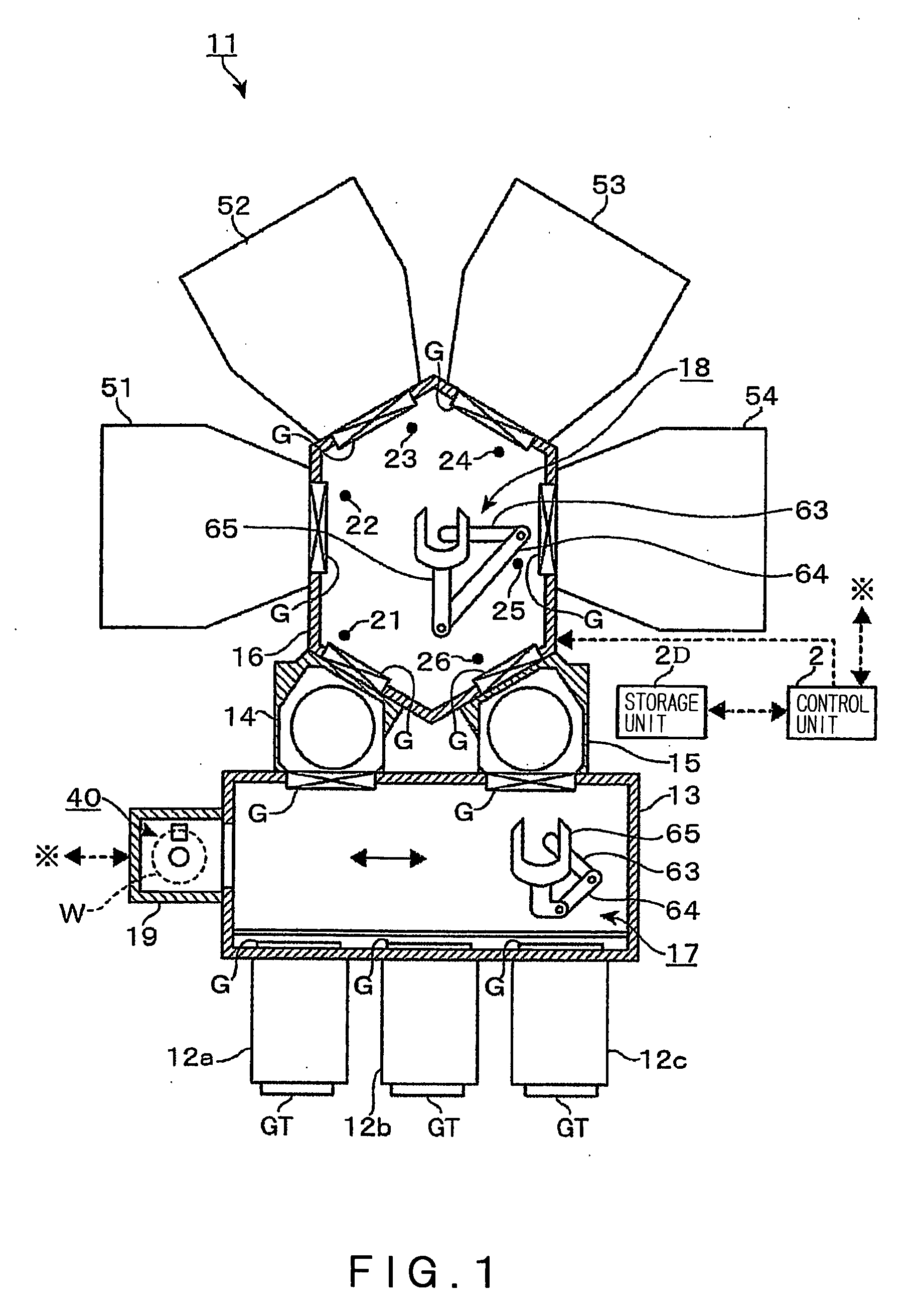
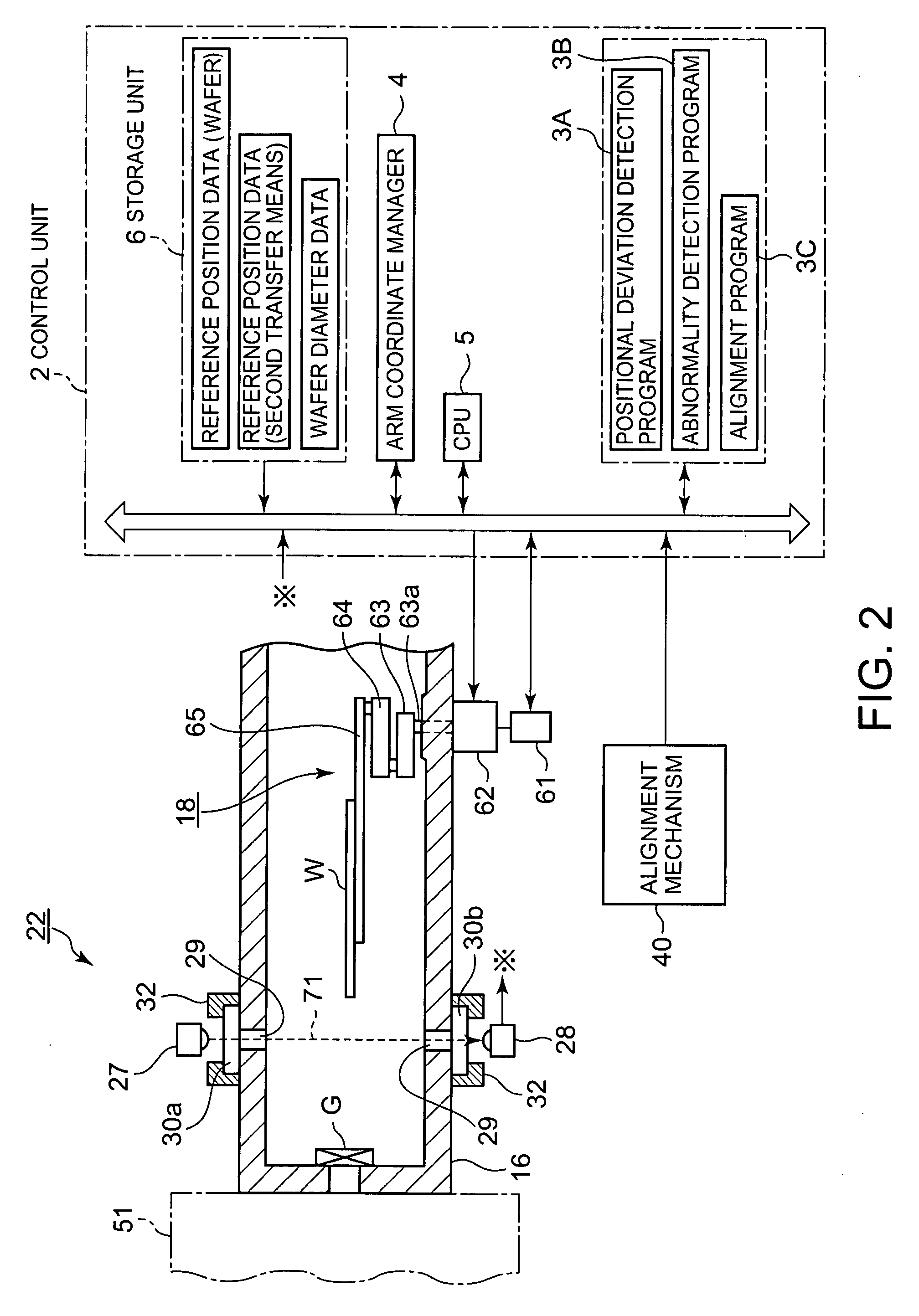
Wafer transfer apparatus, wafer transfer method and storage medium
ActiveUS20090053023A1Low costOptimize layoutDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringLight emission
One sensor constituted of a light emission element and a light-receiving element is provided in a path through which a wafer is transferred. The sensor is positioned so that the wafer passes through an area between the light emission element and the light-receiving element. Coordinates of the center of the wafer are calculated based on encoder values obtained when the wafer starts passing through the sensor and when the wafer completes passing through the sensor, position data of wafer transfer means corresponding to the encoder value, and the diameter of the wafer; and thereby the amount of positional deviation of the center of the wafer from a reference position is calculated.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
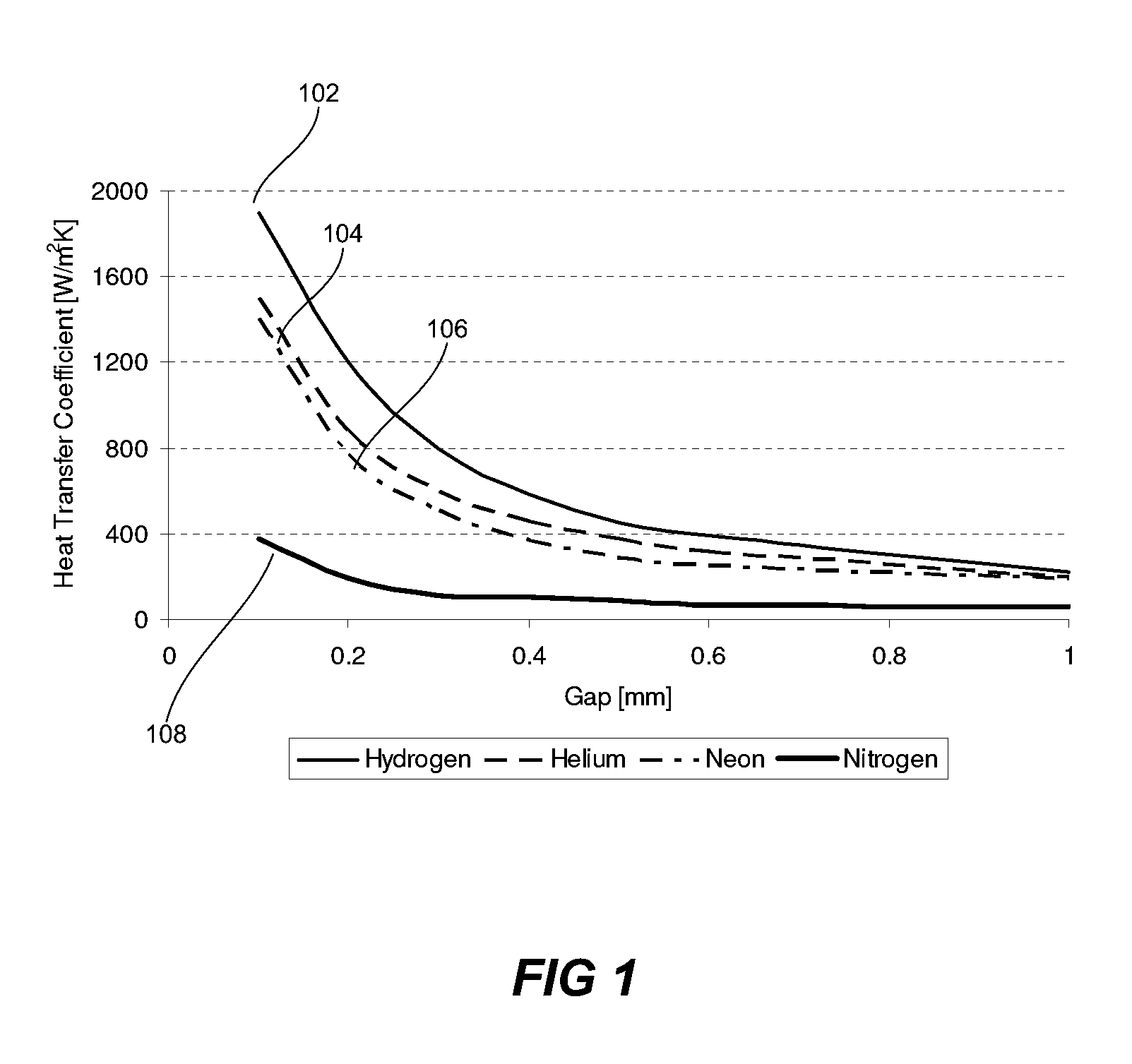
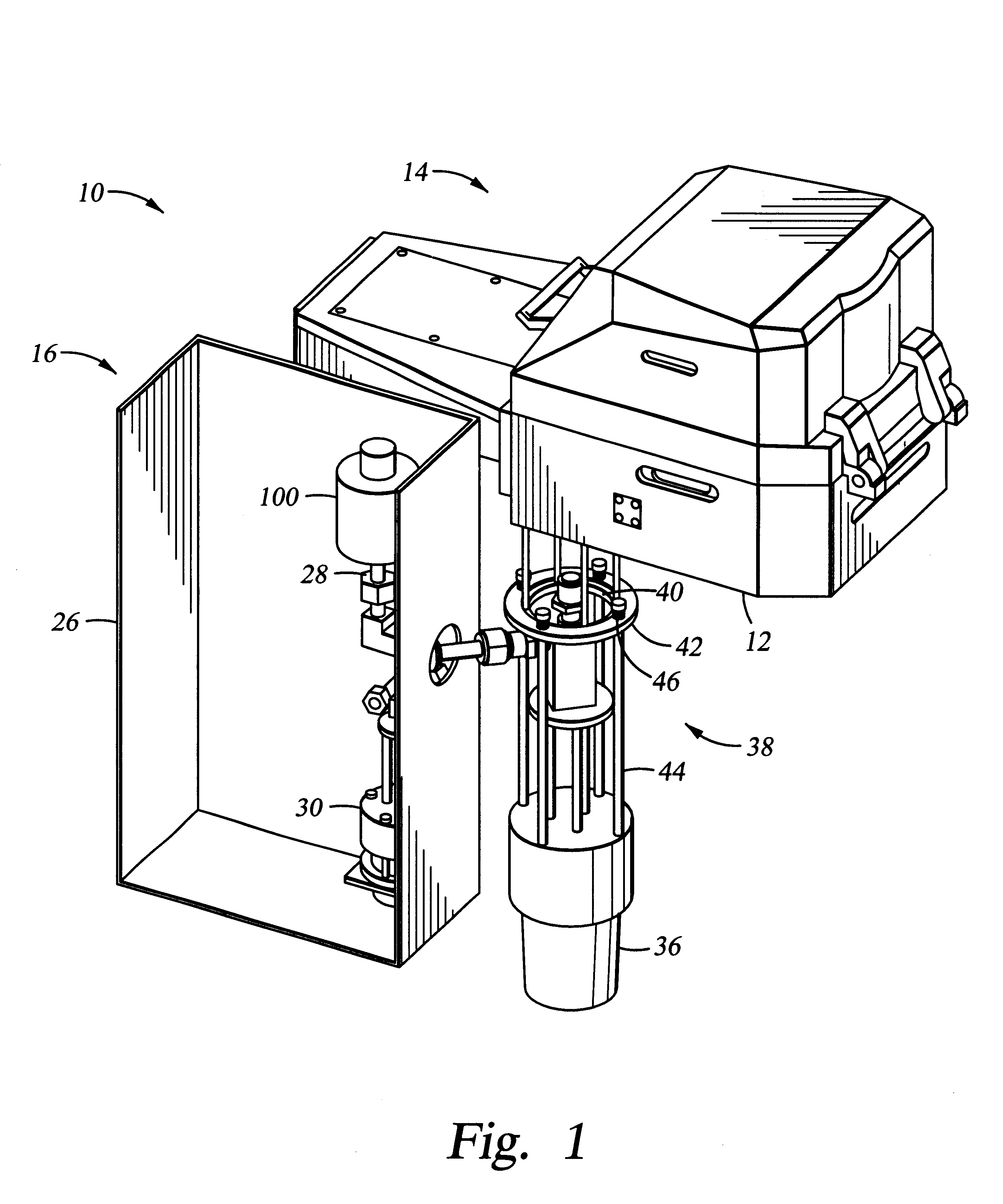
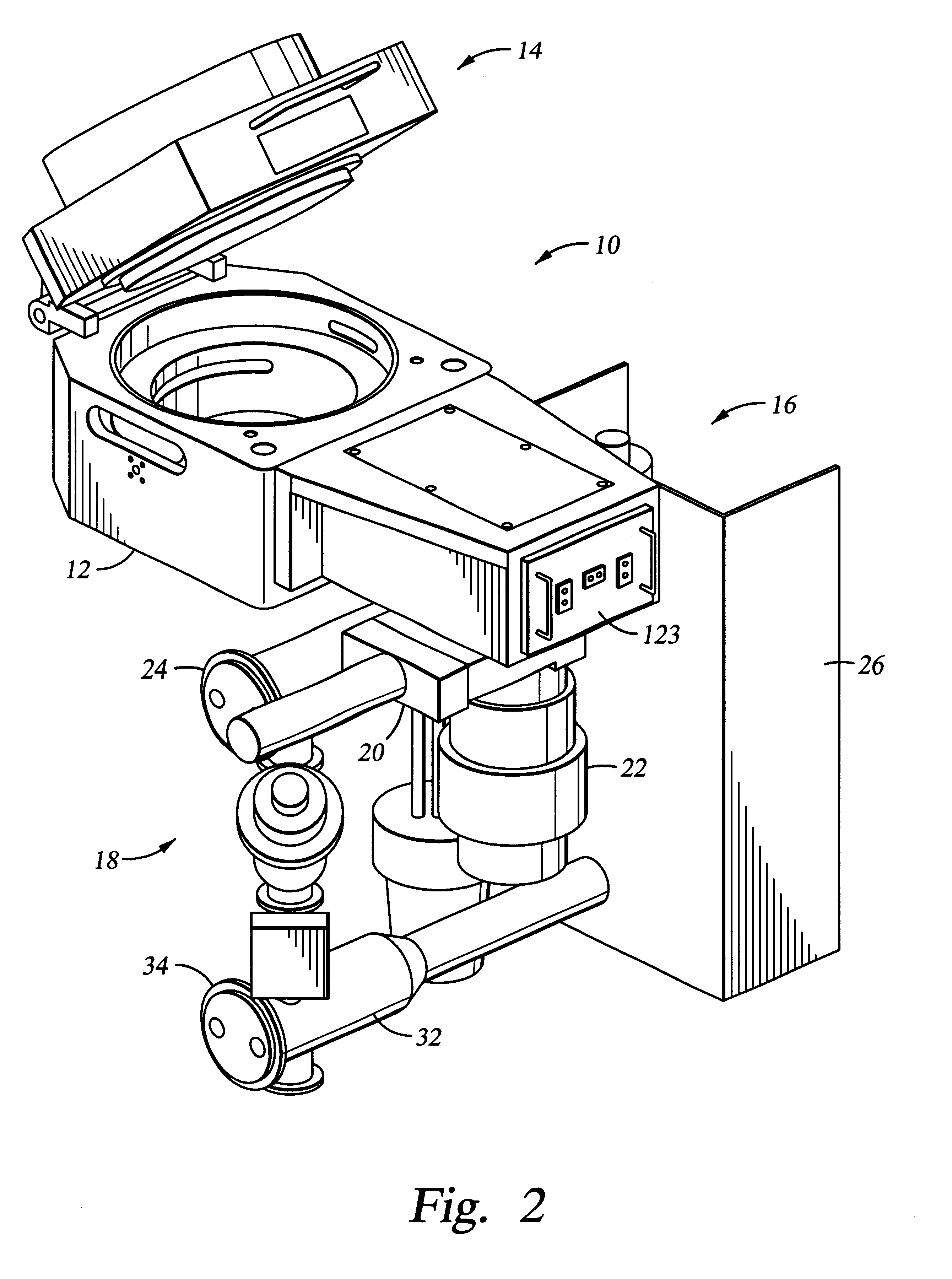
Minimum contact area wafer clamping with gas flow for rapid wafer cooling
ActiveUS8033771B1Reduce CooldownSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConveyor partsNitrogenEngineering
Apparatuses and methods for cooling and transferring wafers from low pressure environment to high pressure environment are provided. An apparatus may include a cooling pedestal and a set of supports for holding the wafer above the cooling pedestal. The average gap between the wafer and the cooling pedestal may be no greater than about 0.010 inches. Venting gases may be used to increase the pressure inside the apparatus during the transfer. In certain embodiment, venting gases comprise nitrogen.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Plasma reactor apparatus with multiple gas injection zones having time-changing separate configurable gas compositions for each zone
ActiveUS8231799B2Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsGas compositionEngineering
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor manufacturing system and wafer holder for semiconductor manufacturing system
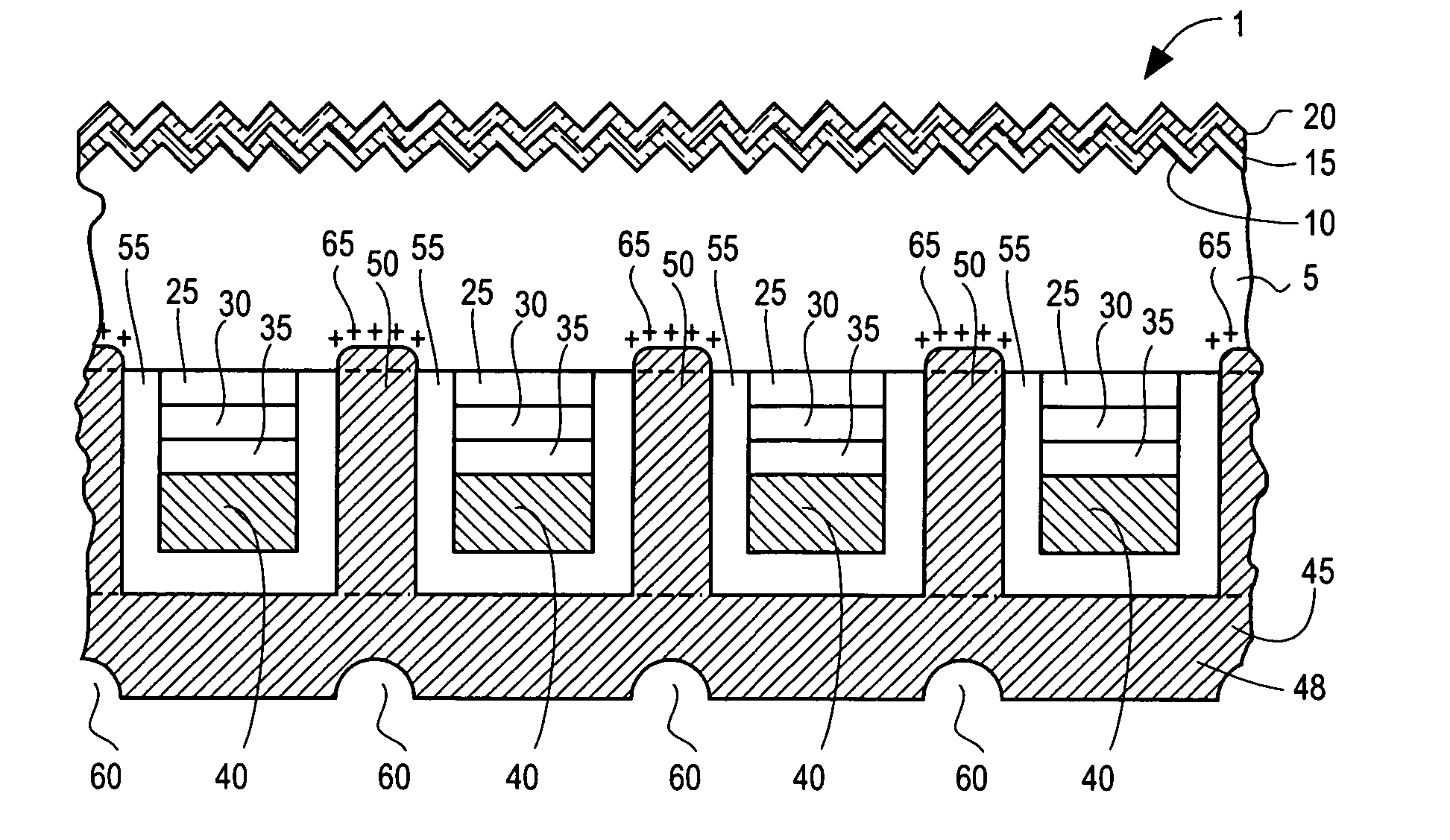
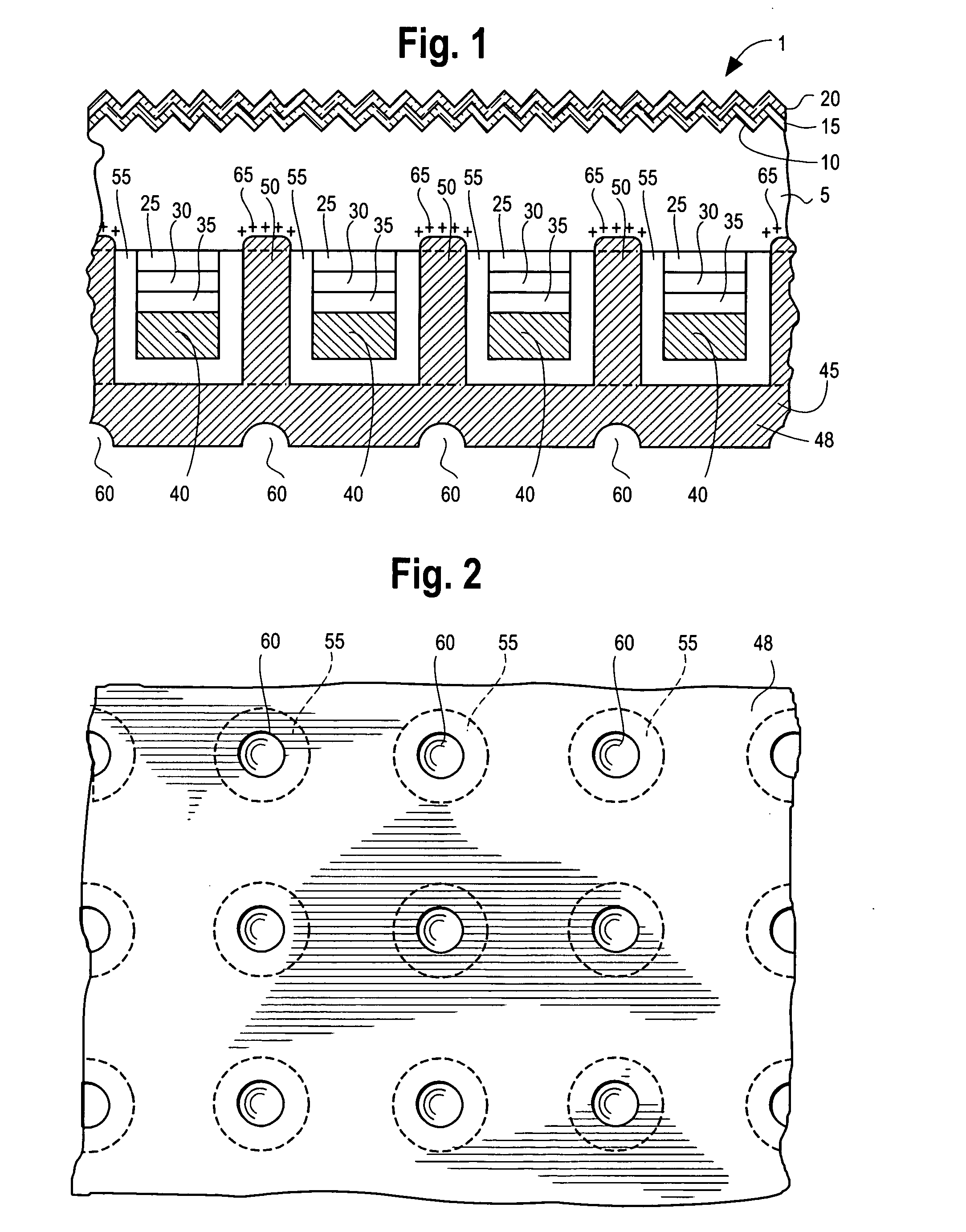
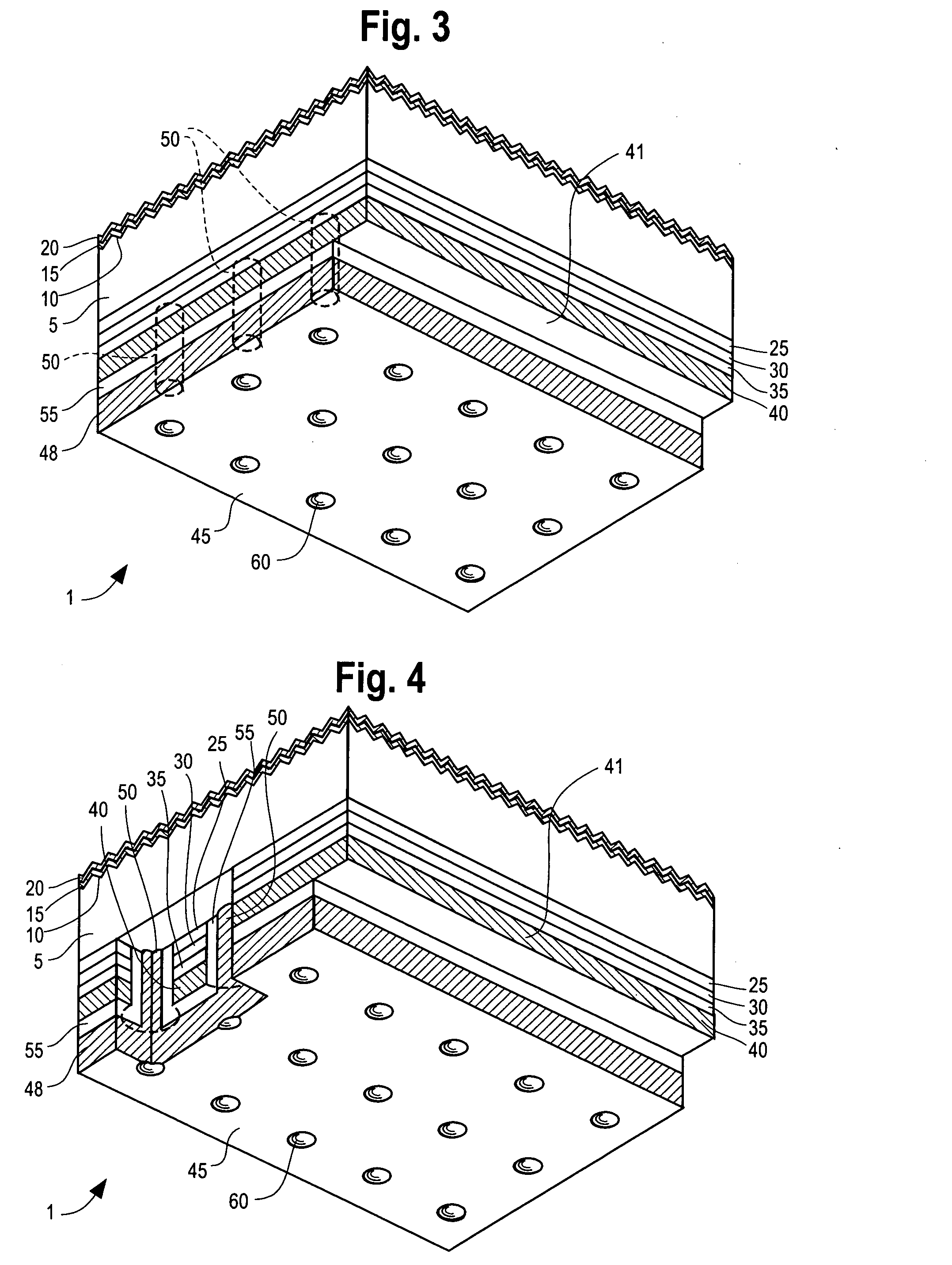
InactiveUS7207763B2Improves yield and productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlatesWaferingEngineering
A semiconductor manufacturing system and wafer holder for a semiconductor manufacturing system which prevents a semiconductor wafer from being exposed to a process reaction and which includes a reaction tube for providing a sealed process space and a dual boat and which prevents the backside deposition by the wafer holder. The wafer holder includes a holder body to hide the backside of the semiconductor wafer during a process in the reaction tube and a wafer lifter having a portion that can be disengaged from and coupled to the holder body so that a lower portion of the semiconductor wafer is supported by the dual boat and so that the semiconductor wafer can be lifted up from the wafer body when the semiconductor wafer is loaded and unloaded. A separation boundary between the holder body and the wafer lifter includes a gas inflow interception surface to hinder reaction gas from flowing through the separation boundary.
Owner:TERASEMICON CO LTD
In vacuum optical wafer heater for cryogenic processing
ActiveUS20110143461A1Prevent unwanted condensationConveyorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringMoisture
A vacuum assembly used for warming processed substrates above the dew point to prevent unwanted moisture on the processed substrate surfaces as well as reducing negative impact on manufacturing throughput. The vacuum assembly includes a processing chamber, a substrate handling robot, and a heater which may be an optical heater. The processing chamber is configured to cryogenically process one or more substrates. The transfer chamber is connected to the processing chamber and houses the substrate handling robot. The substrate handling robot is configured to displace one or more substrates from the processing chamber to the transfer chamber. The heater is connected to the transfer chamber above the substrate handling robot such that the heater emits energy incident on the substrate when the substrate handling robot displaces the substrate in the transfer chamber.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Method and apparatus for detecting a wafer's posture on a susceptor
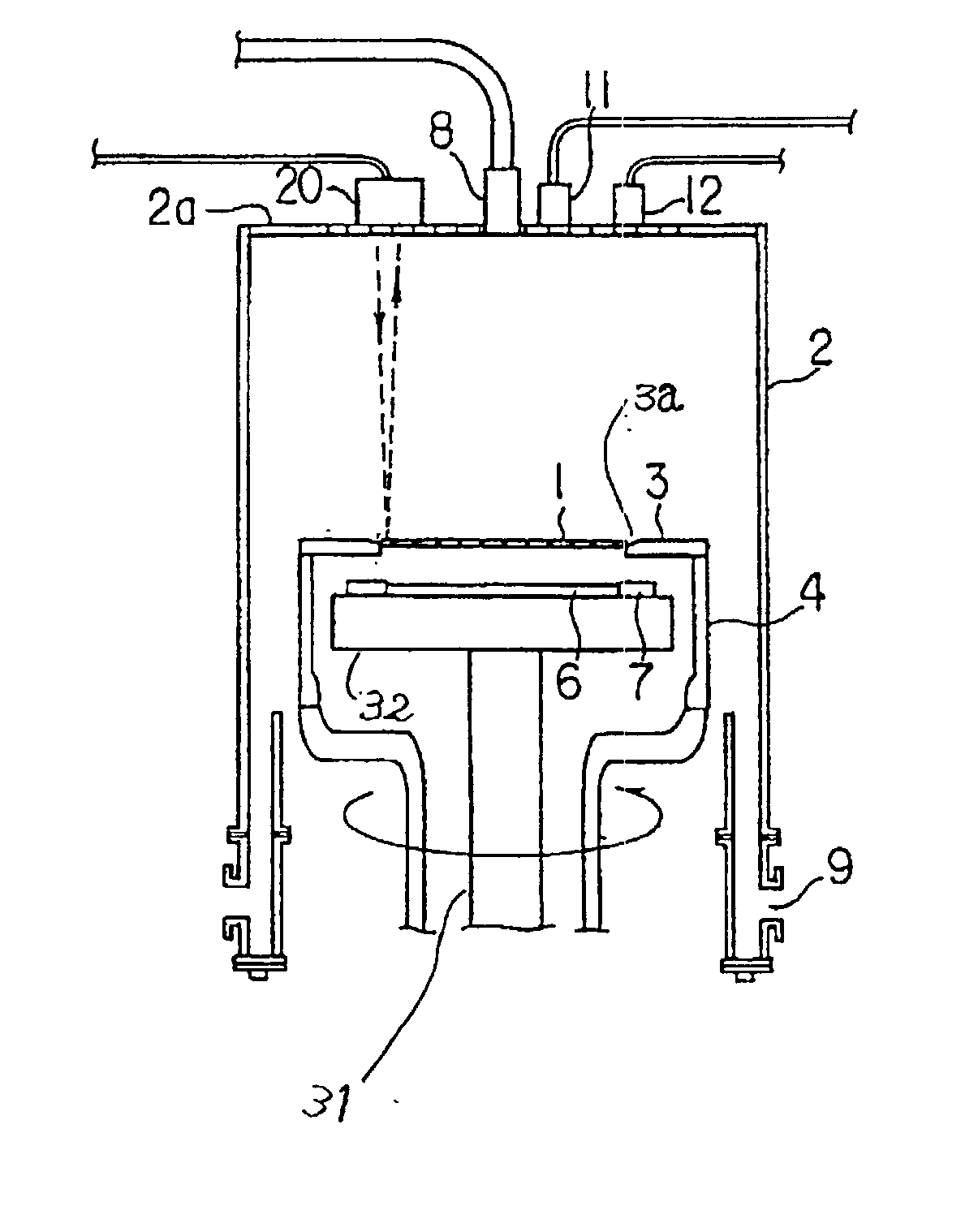
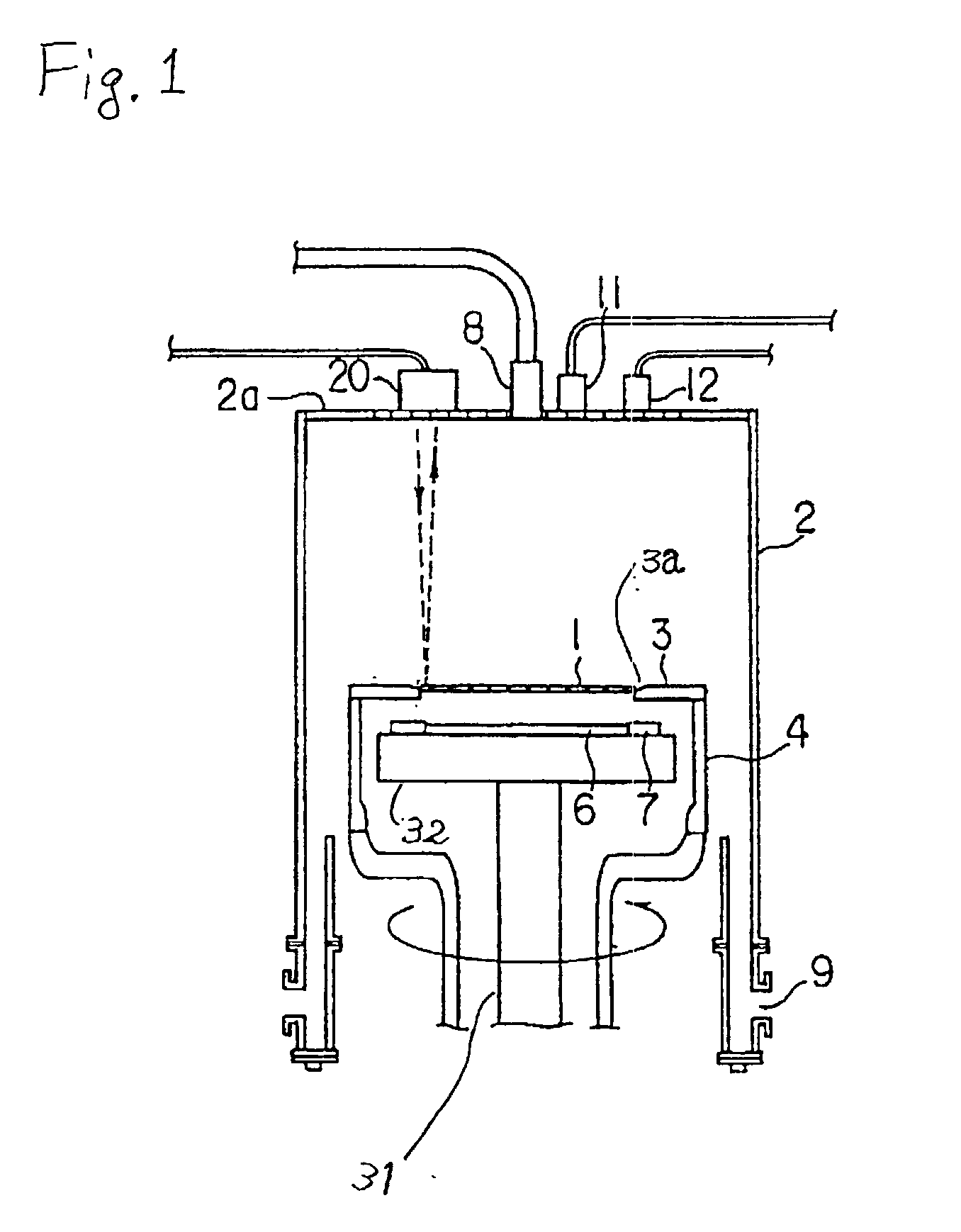
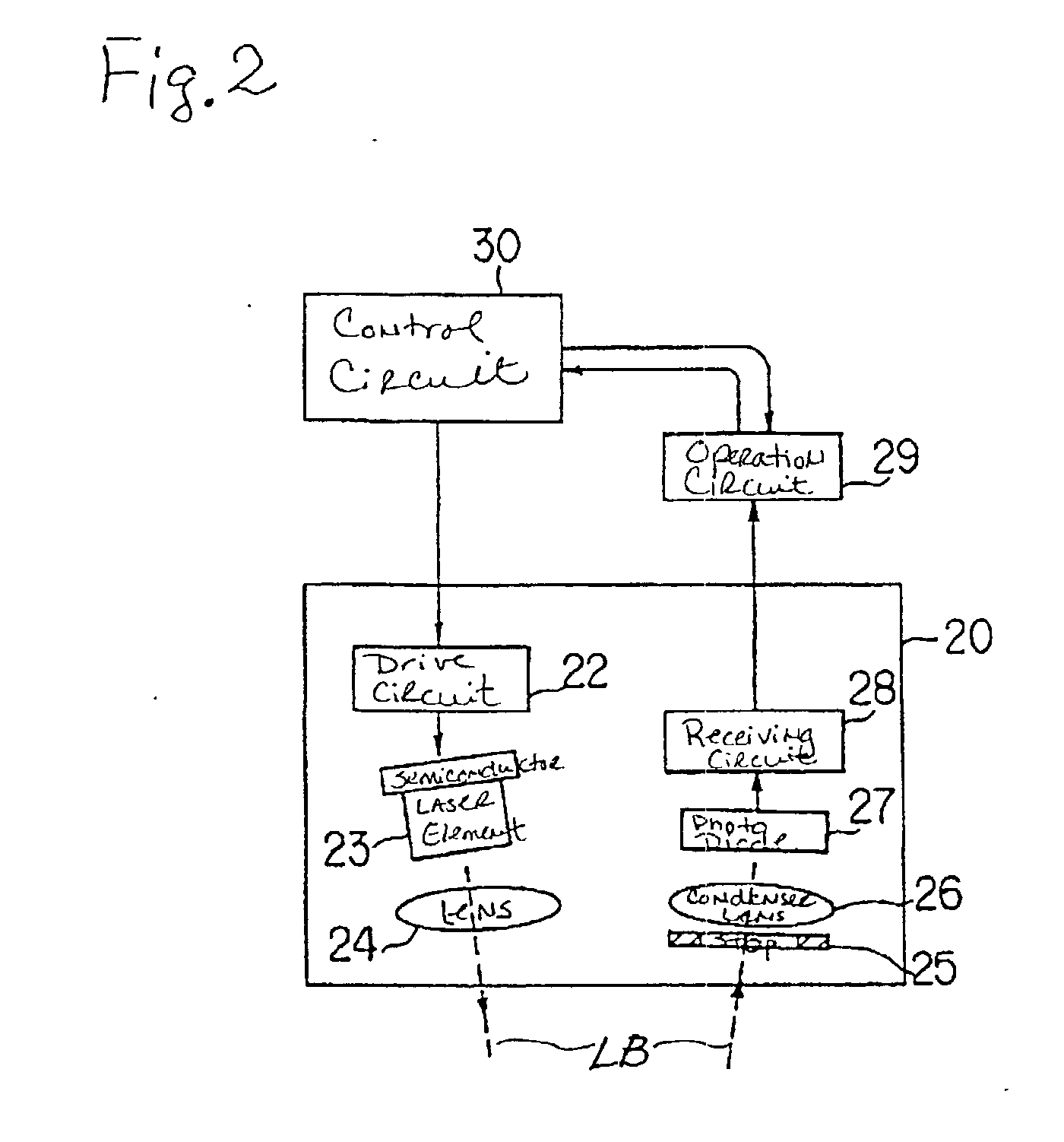
InactiveUS20030042419A1Improve accuracyControl quantityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansWaferingSusceptor
An apparatus used for an epitaxial vapor growing arrangement and for detecting whether a wafer is properly seated within a susceptor contained therein. The apparatus includes a semiconductor laser element that generates a laser beam which irradiates the wafer's surface. The apparatus, further, includes a combination of a stop mechanism, a condenser lens and a photo diode, which detects the laser beam reflected from the wafer surface and an operation circuit, which determines the wafer's posture on the susceptor. During operation, the reflected laser beam focuses on a receiving surface of the photo diode through the condenser lens. The operation circuit then compares the output signal from the photo diode with a preset reference value for discriminating the slope of the wafer.
Owner:TOSHIBA MASCH CO LTD
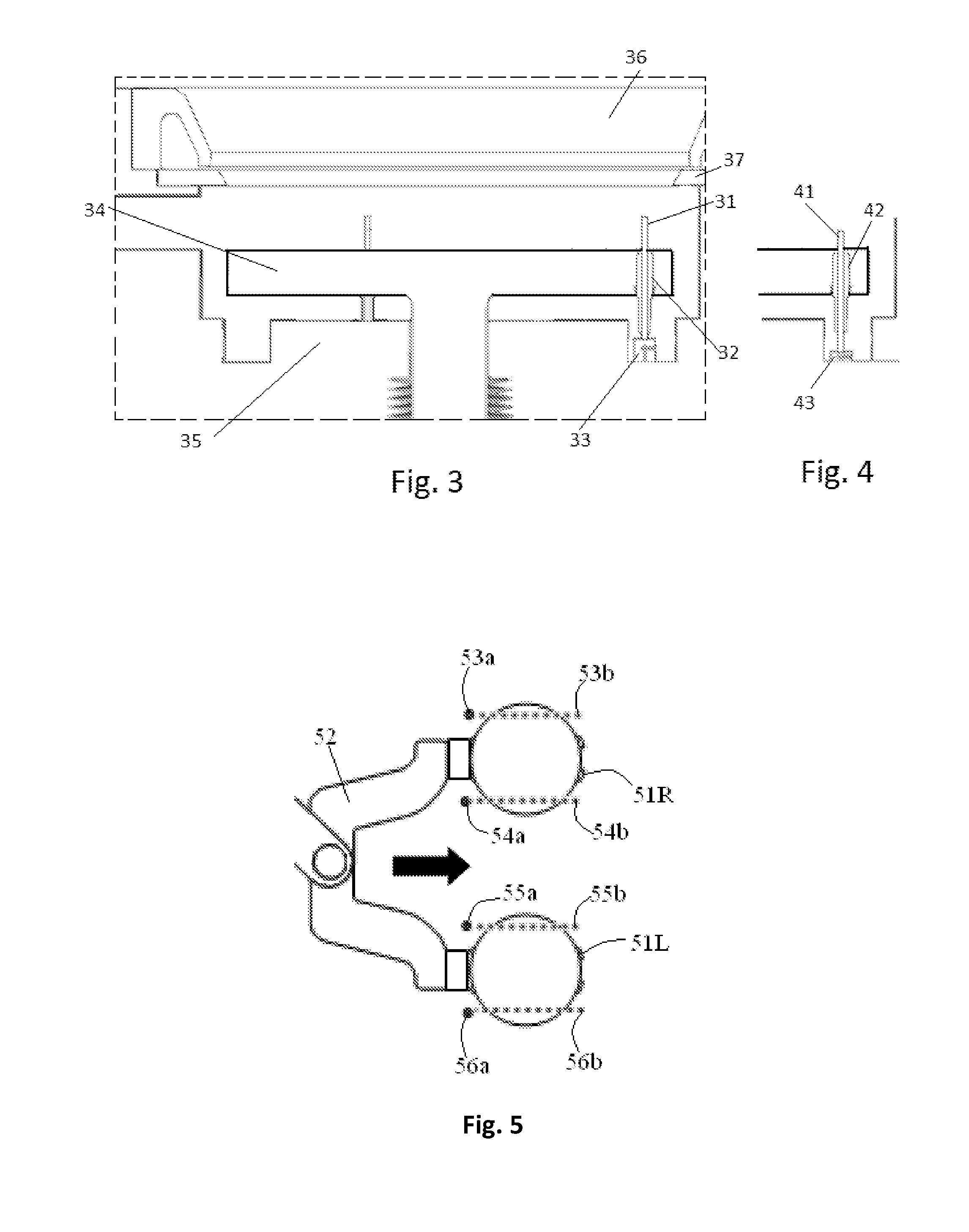
Gas treating device and gas treating method
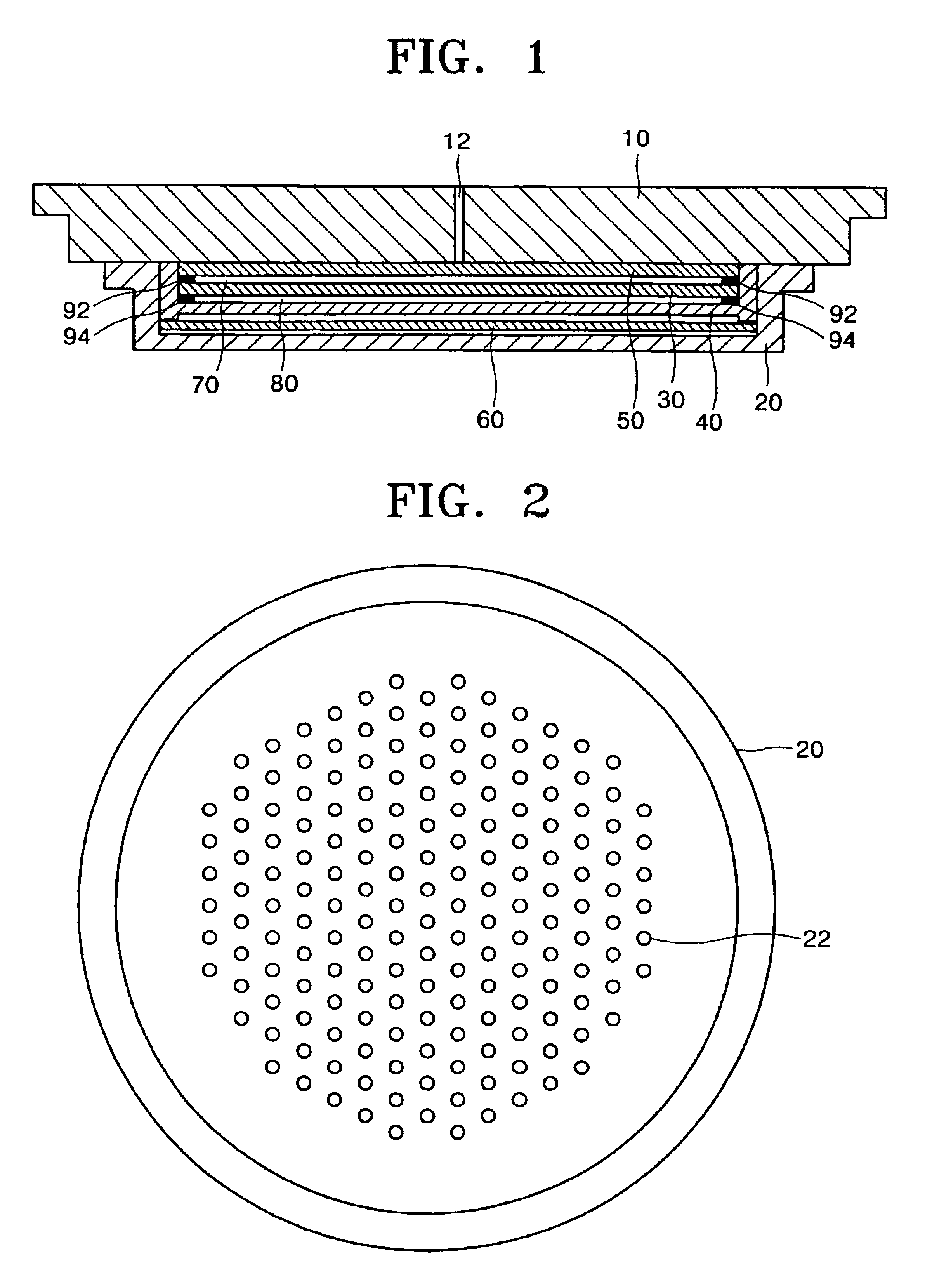
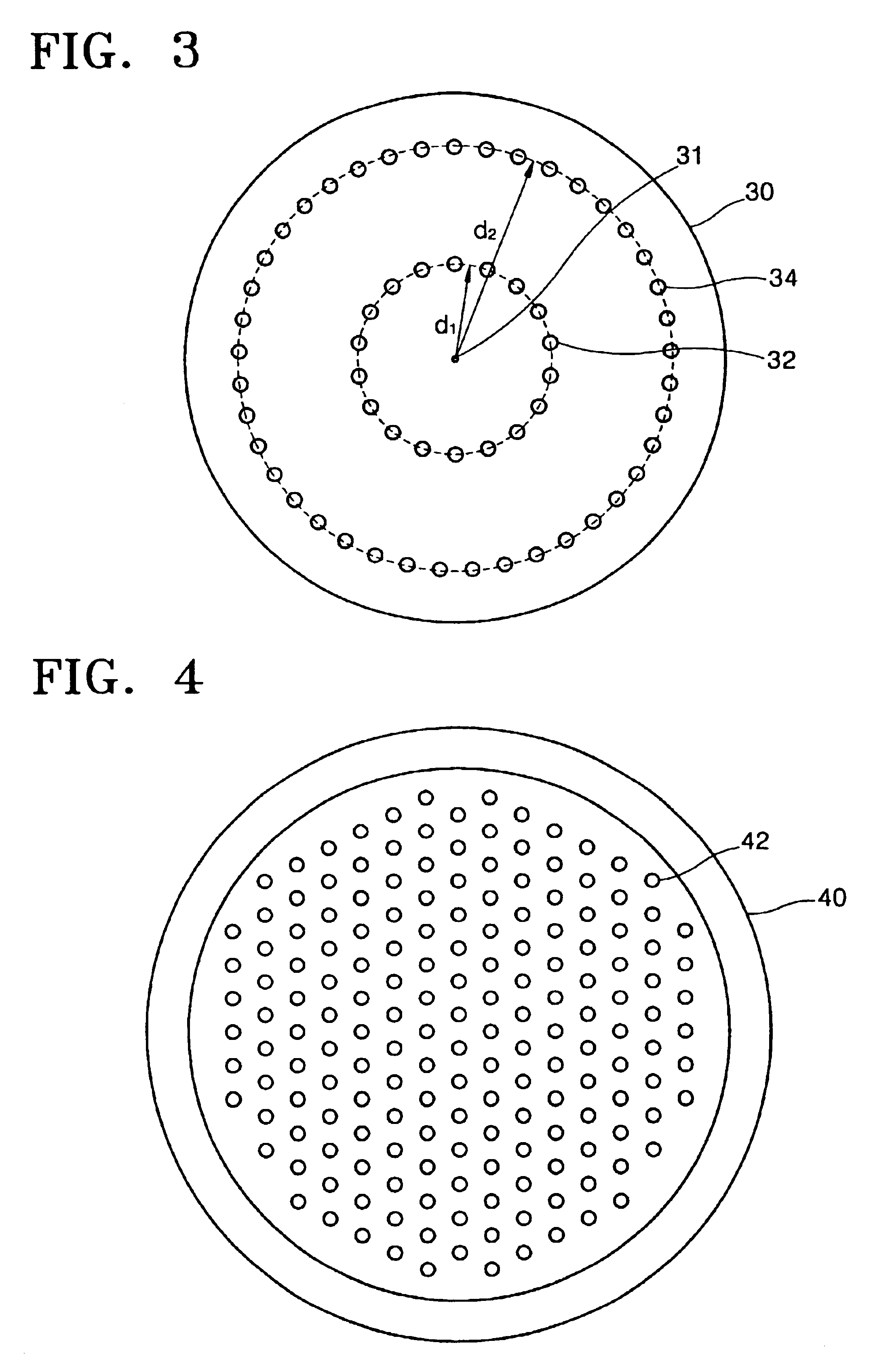
InactiveUS20050003600A1Inhibition formationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas supplyShower
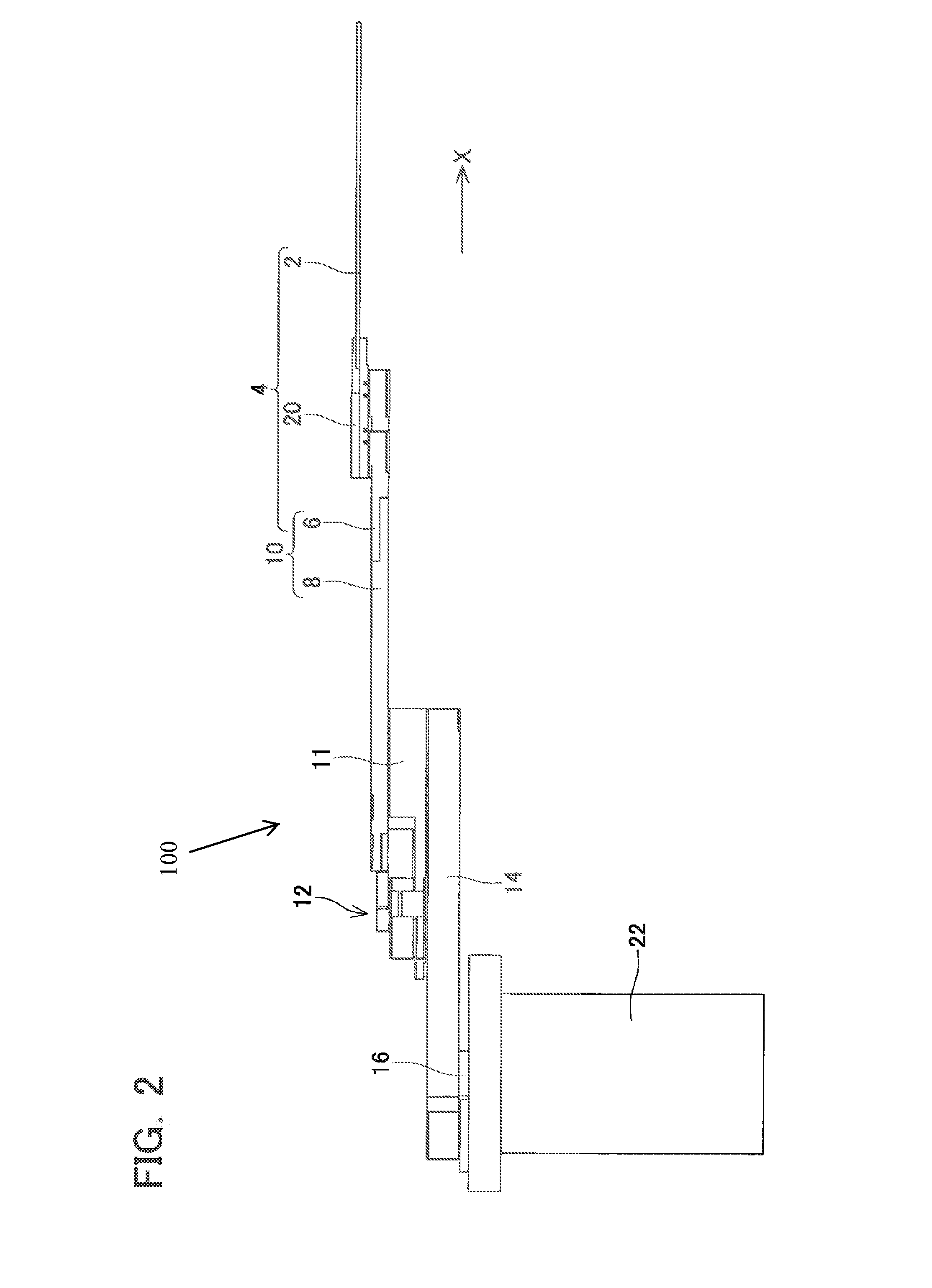
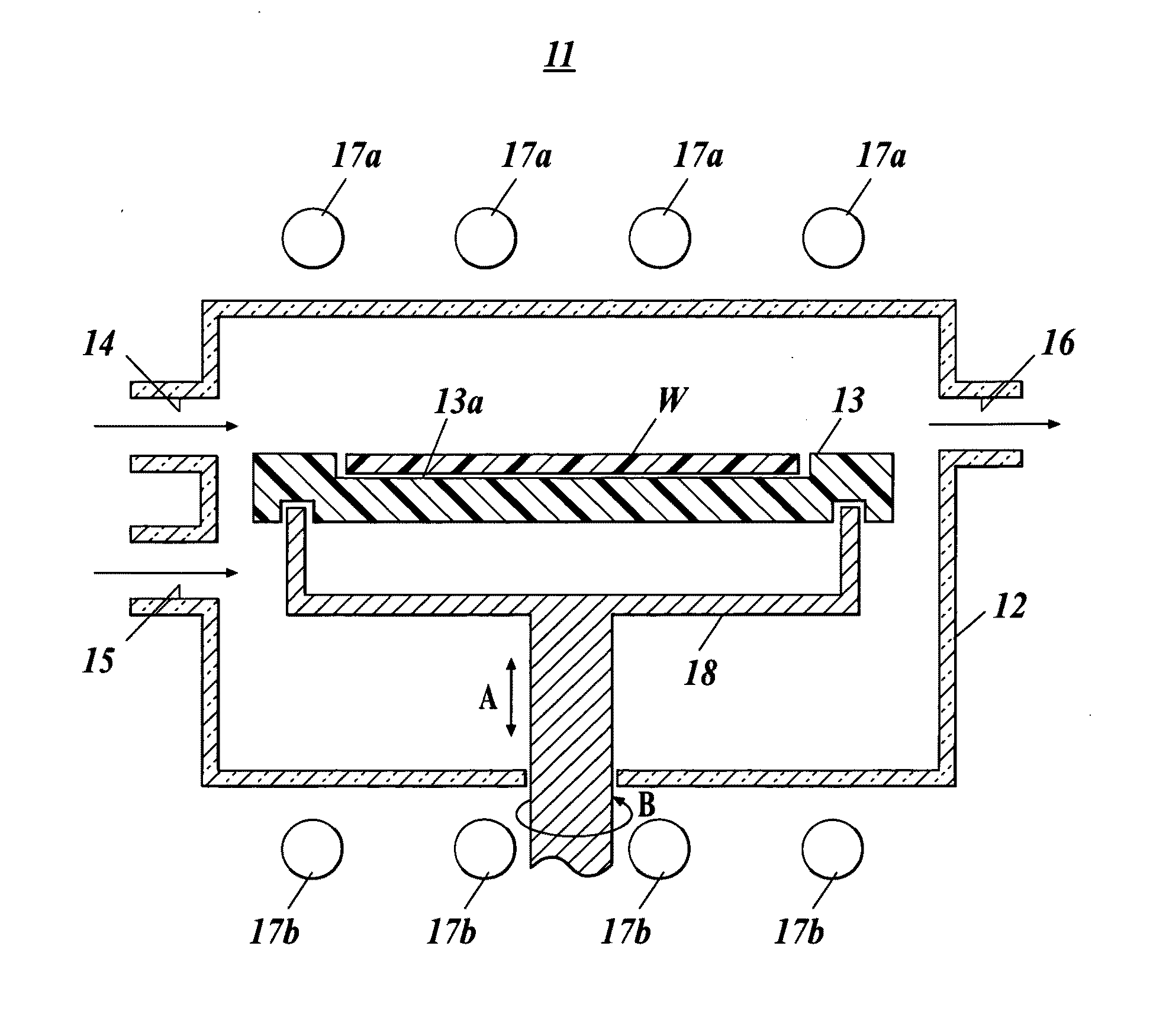
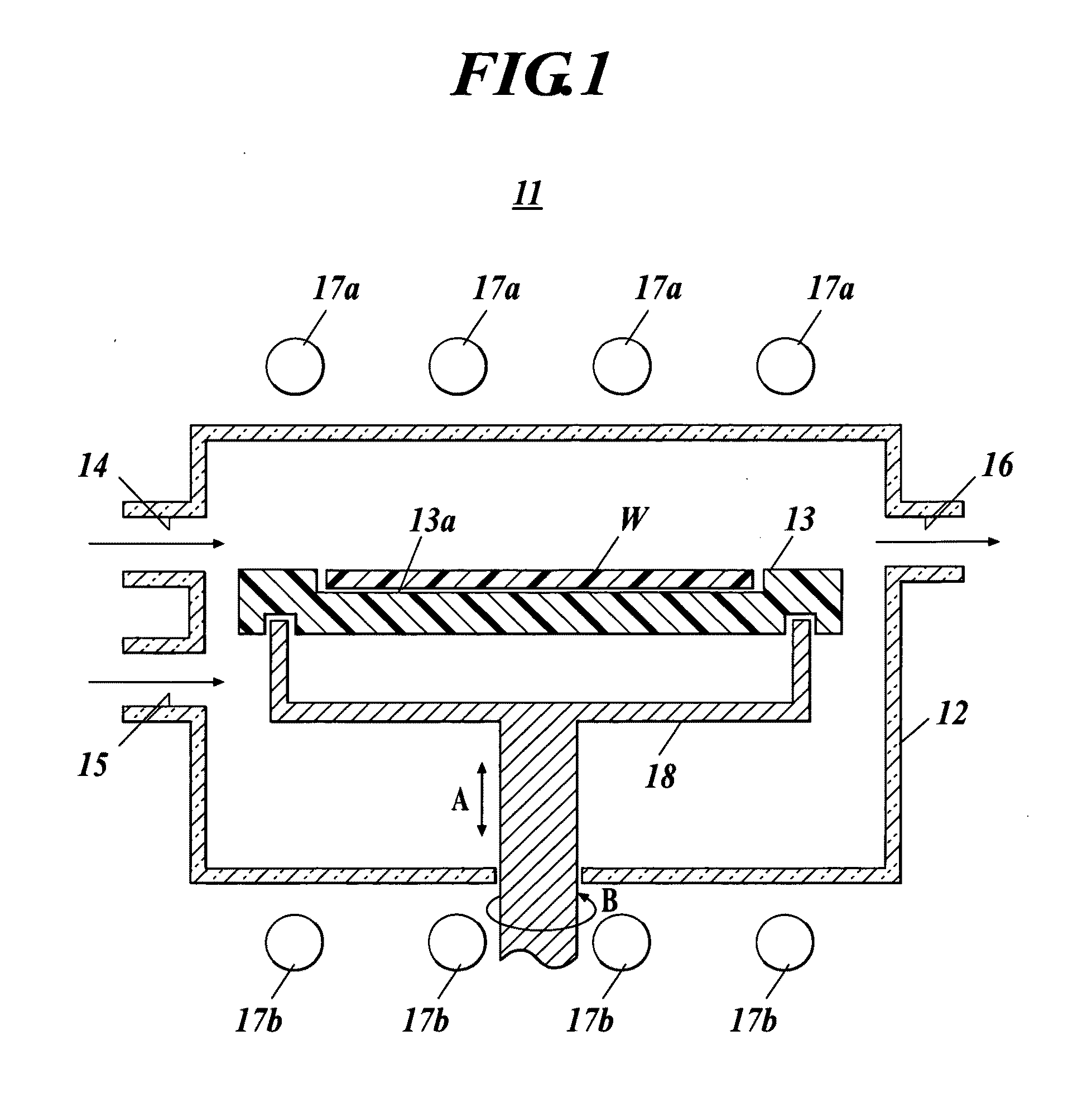
A gas processing apparatus 1 includes a processing container 2 for applying a processing to a wafer W while using a processing gas, a mount table 5 arranged in the processing container 2 to mount the wafer W, a shower head 22 arranged corresponding to the wafer W on the mount table 5 to discharge the processing gas into the processing container 2 and exhausting means 132 for exhausting the interior of the processing container 2. The shower head 22 has first gas discharging holes 46 arranged corresponding to the wafer W mounted on the mount table 5 and second gas discharging holes 47 arranged around the first gas discharging holes 46 independently to discharge the processing gas to the peripheral part of the wafer W. Thus, with a uniform gas supply to a substrate, it is possible to perform a uniform gas processing.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Wafer carrier with varying thermal resistance
InactiveUS20100055318A1Minimize contactImprove temperature uniformityLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringRadiant heat transfer
In chemical vapor deposition apparatus, a water carrier (32) has a top surface (34) holding the wafers and a bottom surface (36) heated by radiant heat transfer from a heating element (28). The bottom surface (36) of the wafer carrier is non-planar due to features such as depressions (54) so that the wafer carrier has different thickness at different locations. The thicker portions of the wafer carrier have higher thermal resistance. Differences in thermal resistance at different locations counteract undesired non-uniformities in heat transfer to the wafer. The wafer carrier may have pockets with projections (553, 853) for engaging spaced-apart locations on the edges of the wafer.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
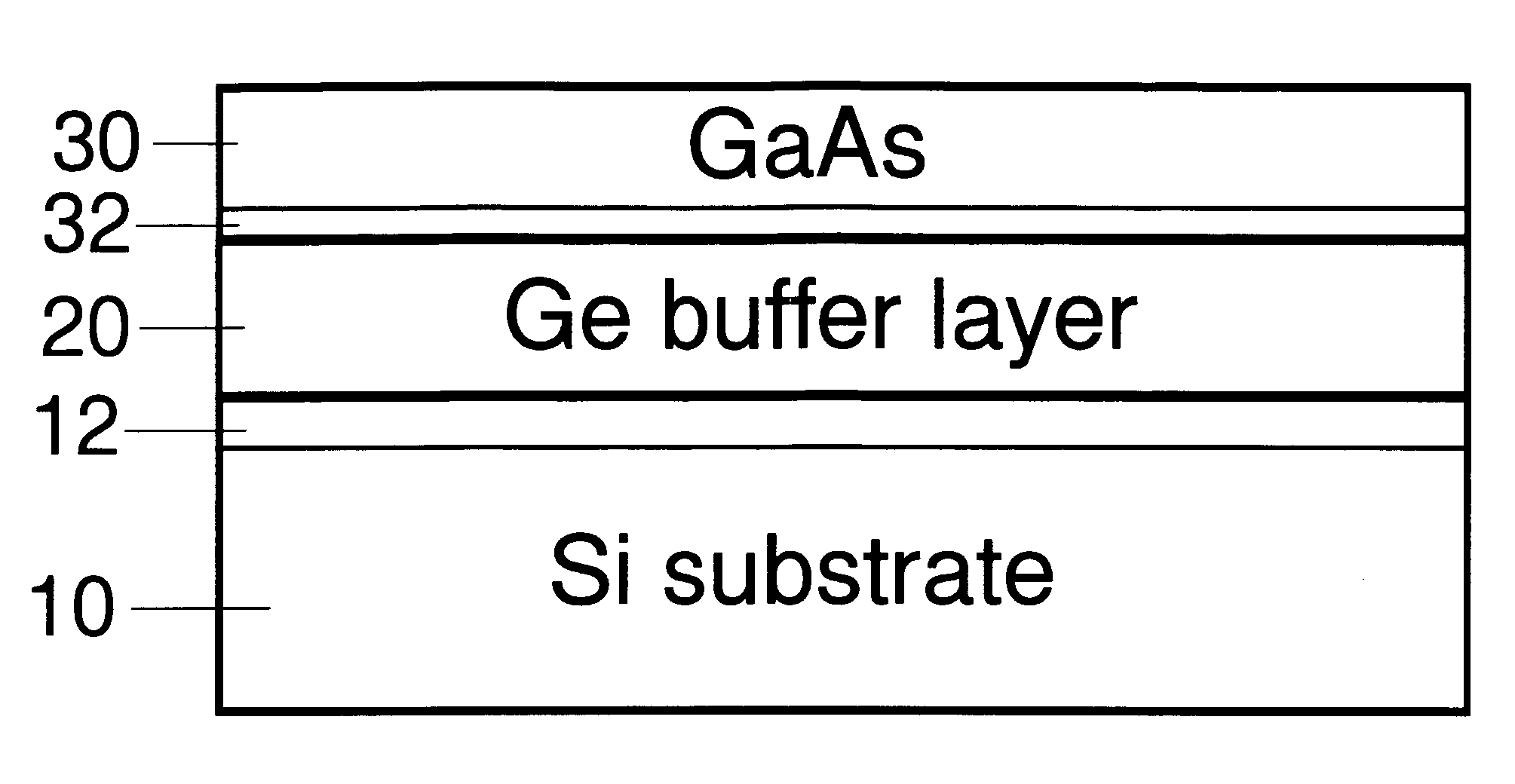
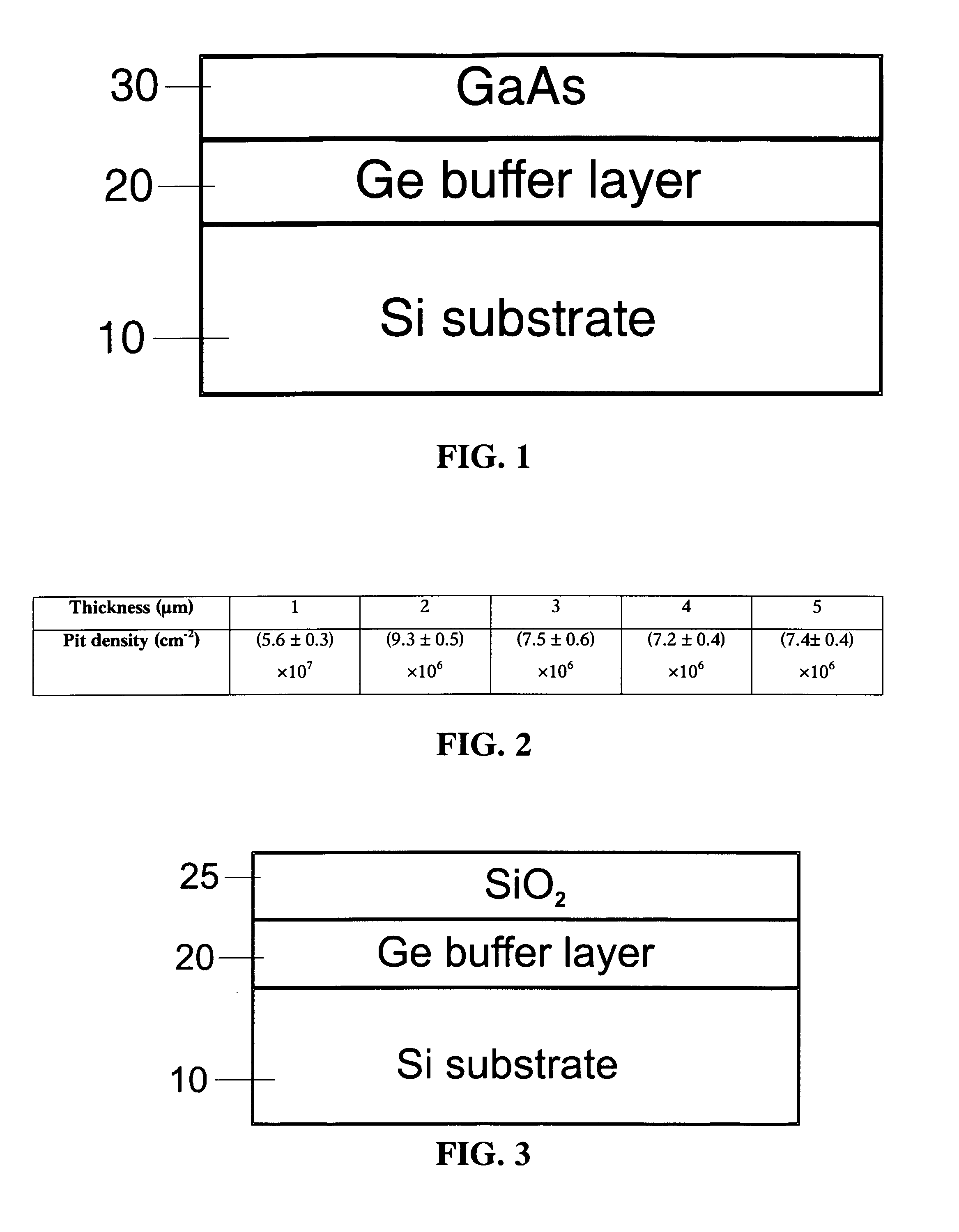
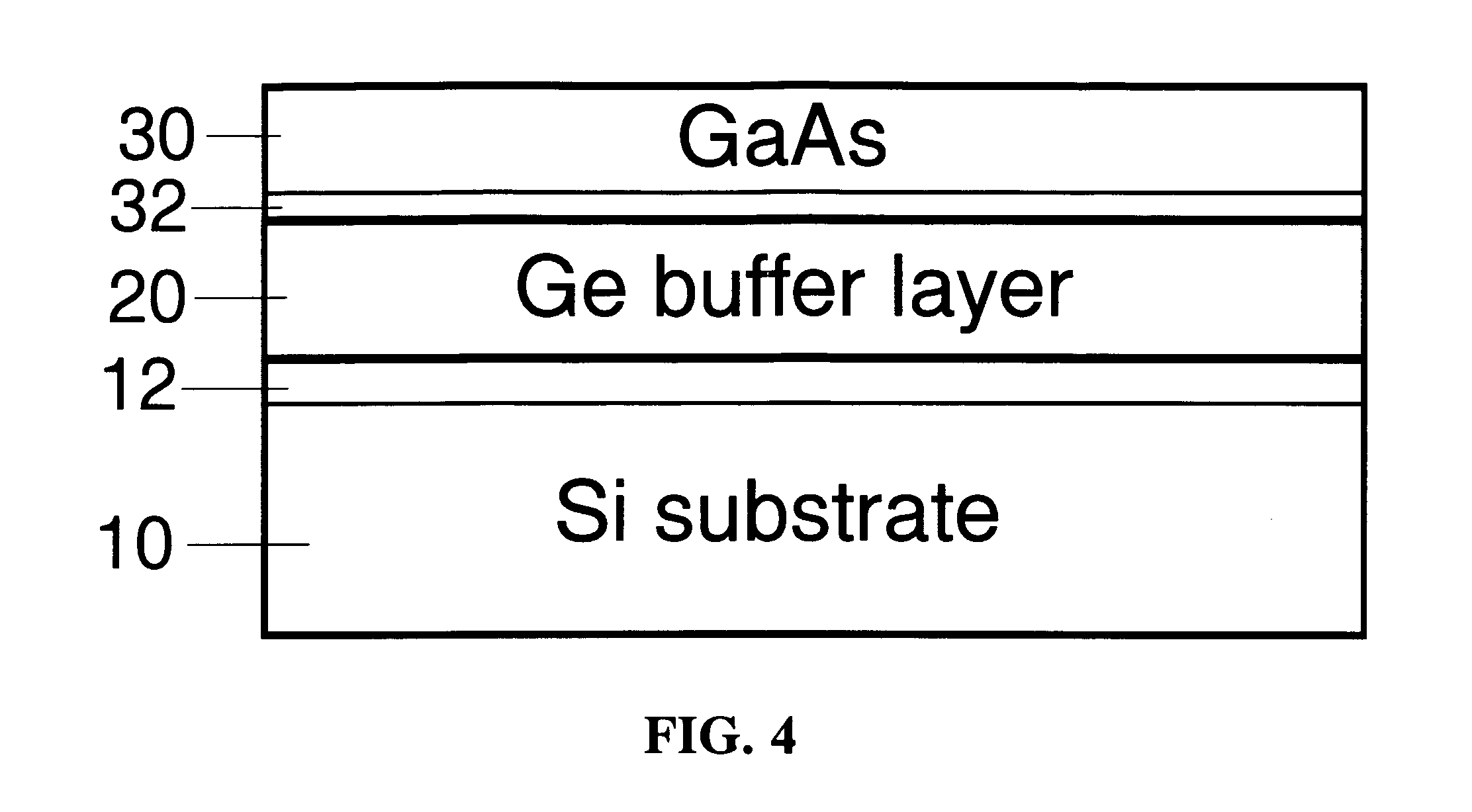
Method for Producing Virtual Ge Substrates for III/V-Integration on Si(001)
InactiveUS20070231488A1Fast epitaxial growthCheap methodSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorSolar cell
Relaxed germanium buffer layers can be grown economically on misoriented silicon wafers by low-energy plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, in conjunction with thermal annealing and / or patterning, the buffer layers can serve as high-quality virtual substrates for the growth of crack-free GaAs layers suitable for high-efficiency solar cells, lasers and field effect transistors.
Owner:DICHROIC CELL
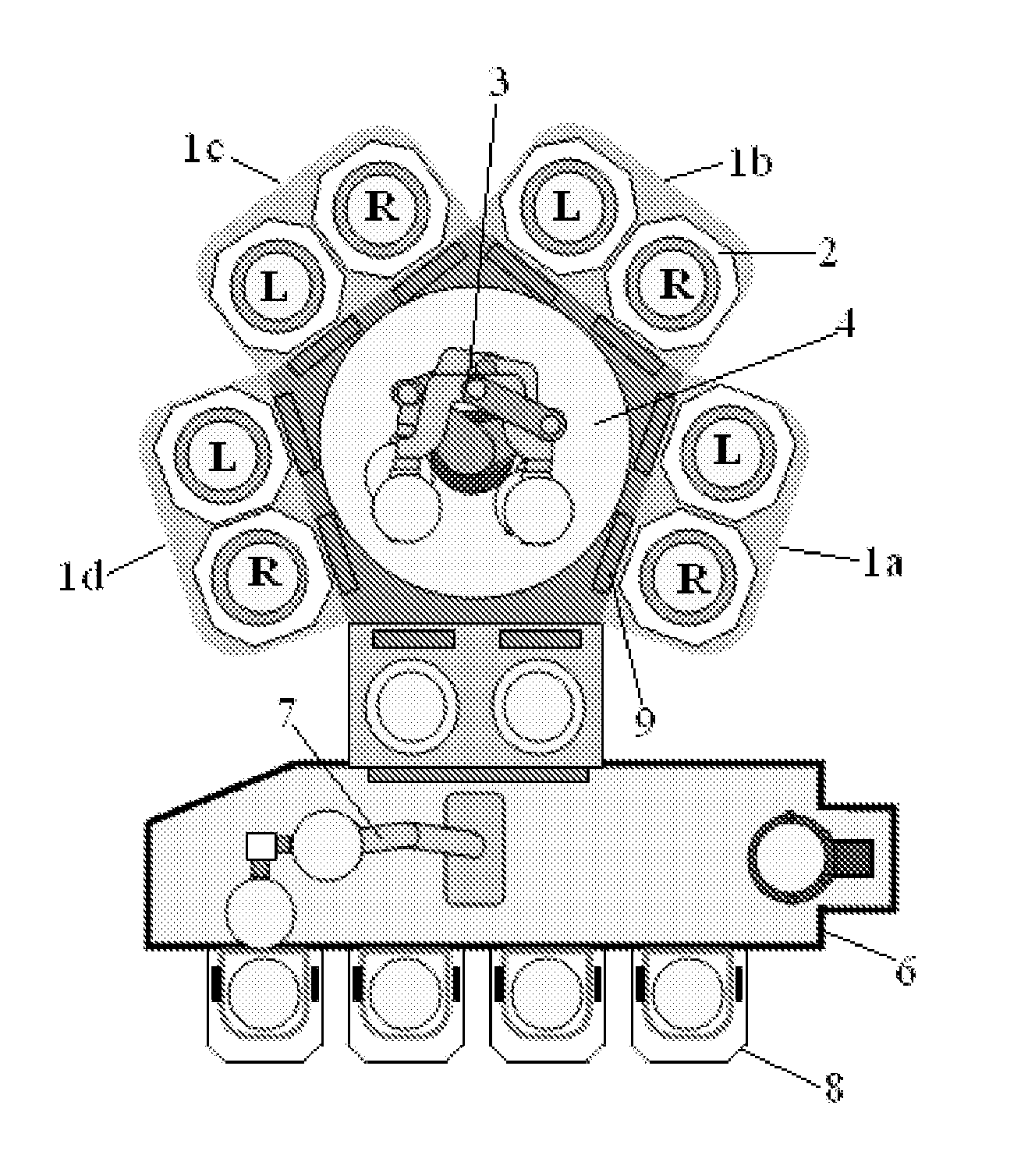
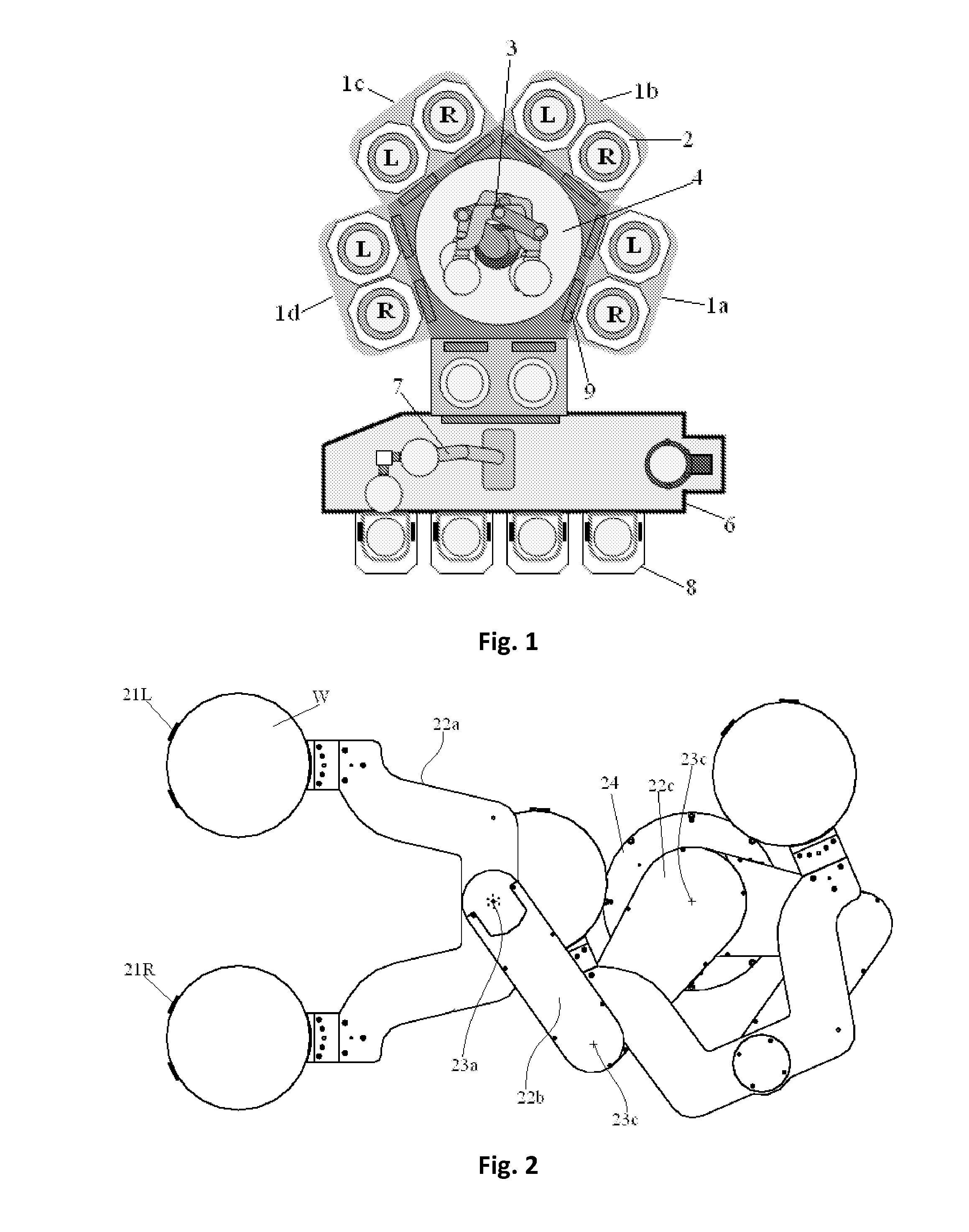
Method for Positioning Wafers in Multiple Wafer Transport
ActiveUS20120325148A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingSusceptor
A method for positioning wafers in dual wafer transport, includes: simultaneously moving first and second wafers placed on first and second end-effectors to positions over lift pins protruding from first and second susceptors, respectively; and correcting the positions of the first and second wafers without moving any of the lift pins relative to the respective susceptors or without moving the lift pins relative to each other, wherein when the first and second wafers are moved to the respective positions, the distance between the first wafer and tips of the lift pins of the first susceptor is substantially smaller than the distance between the second wafer and tips of the lift pins of the second susceptor.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Fast heating and cooling wafer handling assembly and method of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS20060127067A1Muffle furnacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceThermal control
A thermal control device for wafer processing which comprises a) a platform for placement of an object of various sizes to be heated, b) at least a shaft extending substantially transverse to the platform; and c) a plurality of resistance heating elements patterned in a plurality of circuits defining at least one zone for independent controlled heating of objects of varying sizes on the platform.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-zone resistive heater
InactiveUS20030062359A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHot plates heating arrangementsHeating elementWafering
A heating apparatus including a stage comprising a surface having an area to support a wafer and a body, a shaft coupled to the stage, and a first and a second heating element. The first heating element is disposed within a first plane of the body of the stage. The second heating element is disposed within a second plane of the body of the stage at a greater distance from the surface of the stage than the first heating element, and the second heating element is offset from the first heating element in a plane substantially parallel to at least one of the first plane and the second plane.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High volume delivery system for gallium trichloride
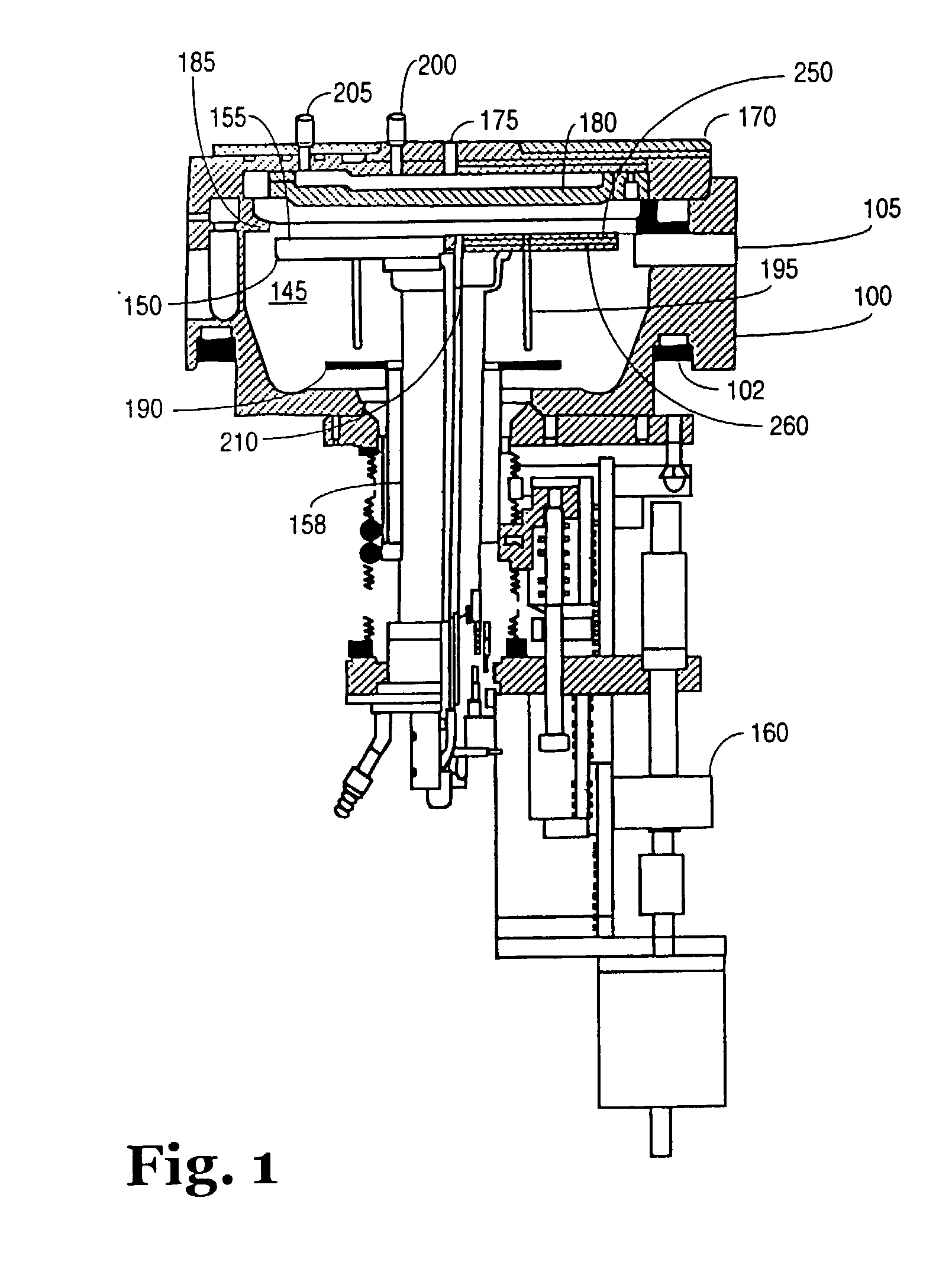
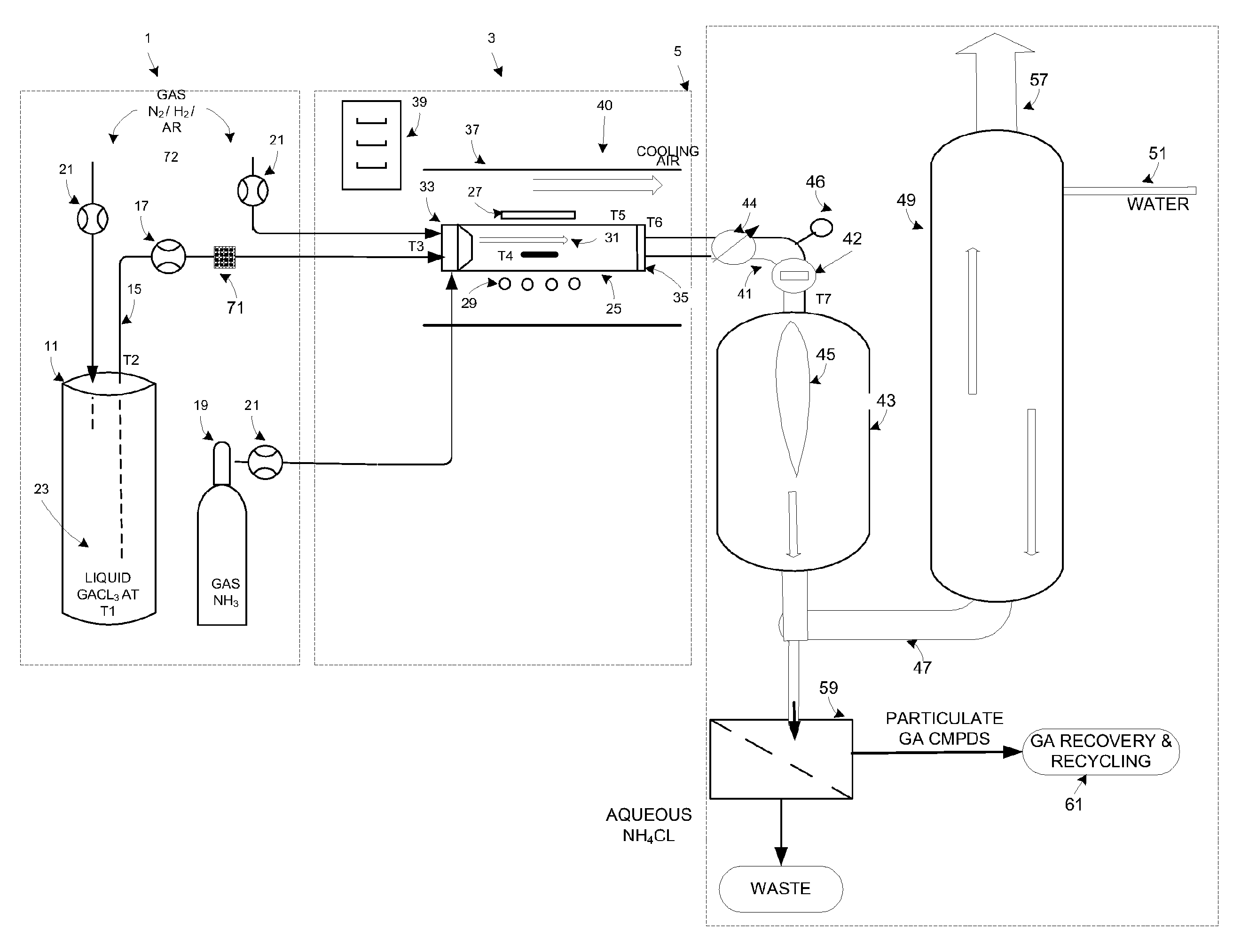
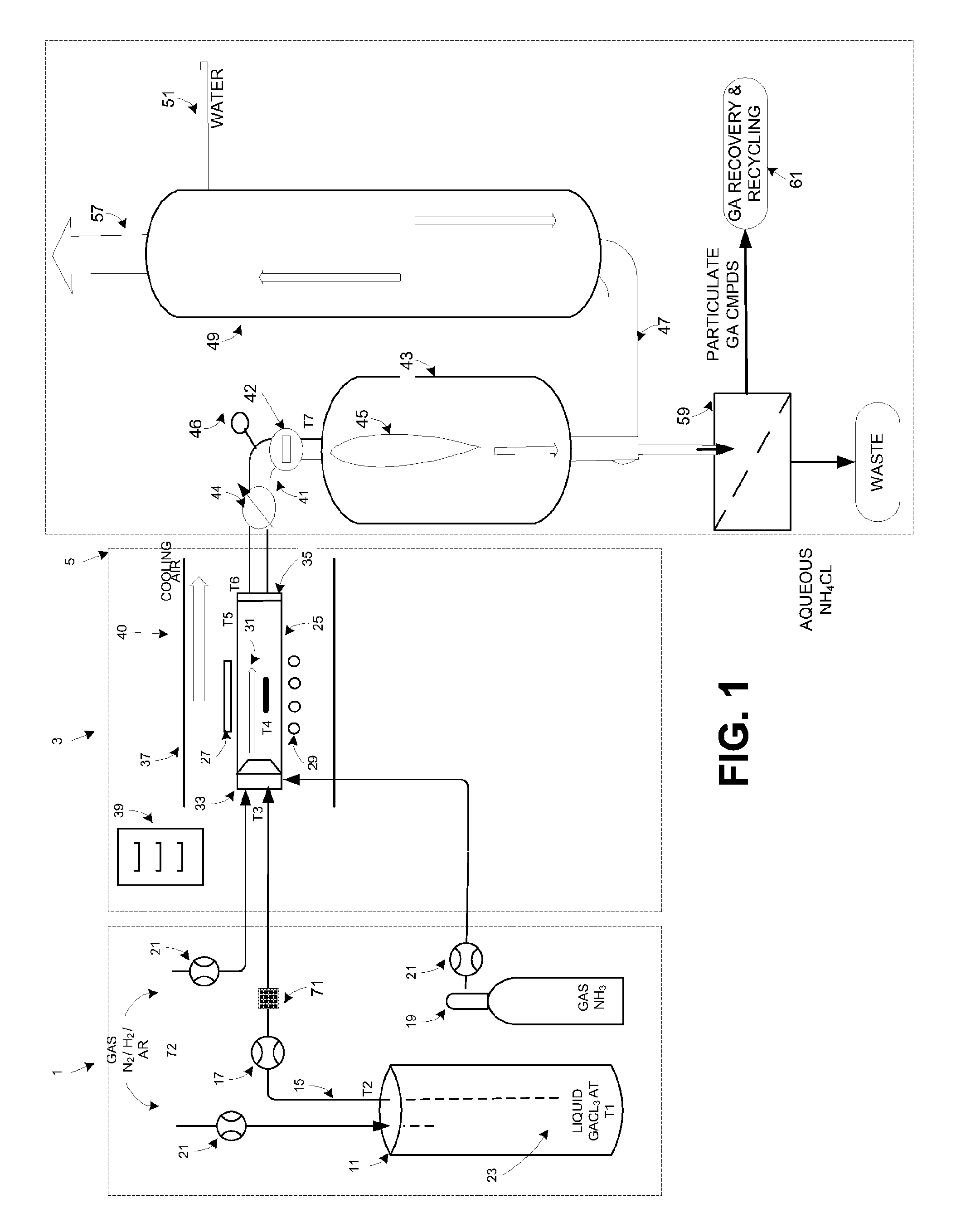
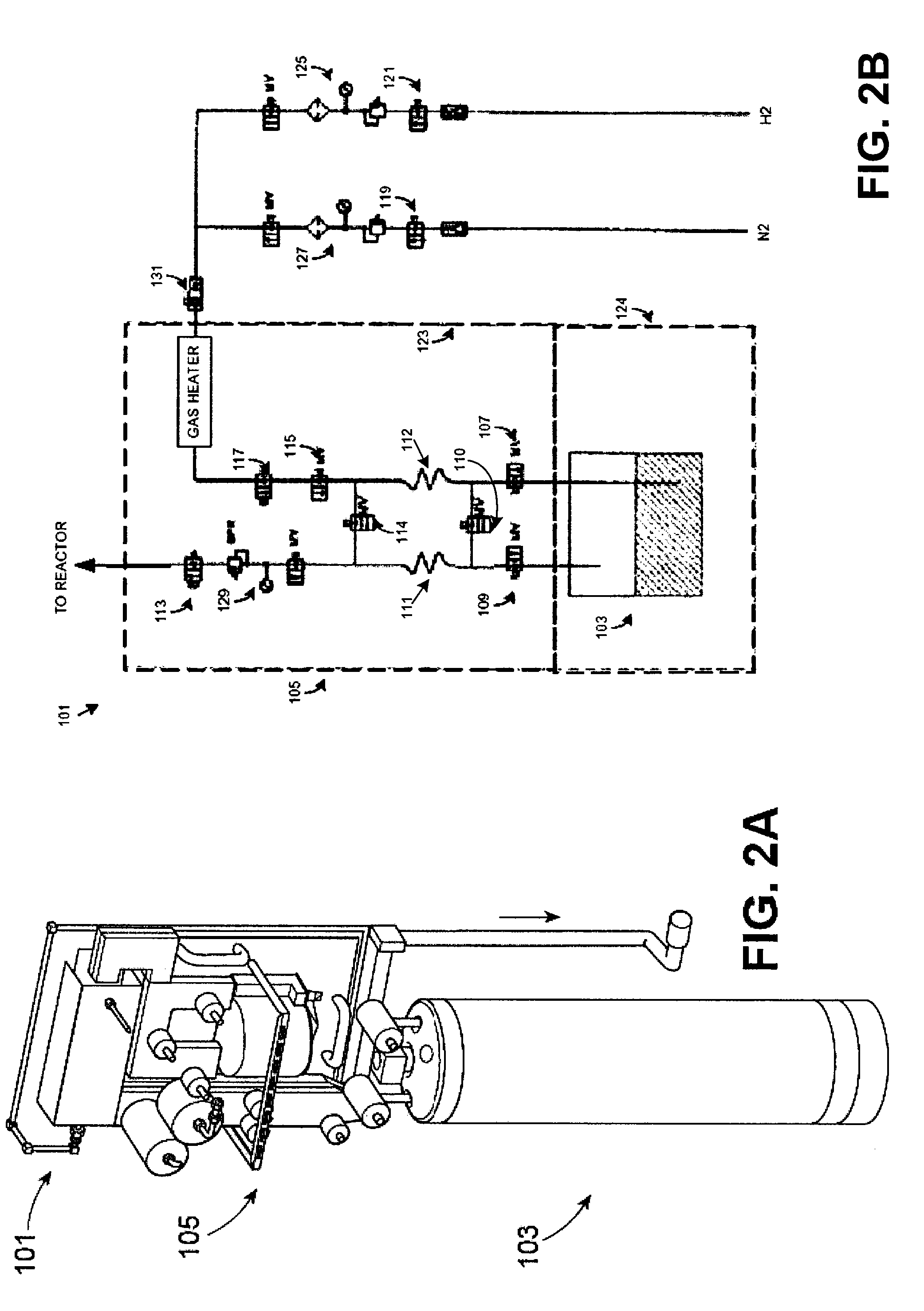
InactiveUS20090223441A1High manufacturing processEasy to prepare in large batchesPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh volume manufacturingSemiconductor materials
The present invention is related to the field of semiconductor processing equipment and methods and provides, in particular, methods and equipment for the sustained, high-volume production of Group III-V compound semiconductor material suitable for fabrication of optic and electronic components, for use as substrates for epitaxial deposition, for wafers and so forth. In preferred embodiments, these methods and equipment are optimized for producing Group III-N (nitrogen) compound semiconductor wafers and specifically for producing GaN wafers. Specifically, the precursor is provided at a mass flow of at least 50 g Group III element / hour for a time of at least 48 hours to facilitate high volume manufacture of the semiconductor material. Advantageously, the mass flow of the gaseous Group III precursor is controlled to deliver the desired amount.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Back-contact photovoltaic cells
A photovoltaic cell comprising a wafer comprising a semiconductor material of a first conductivity type, the wafer comprising a first light receiving surface and a second surface opposite the first surface; a first passivation layer positioned over the first surface of the wafer; a first electrical contact positioned over the second surface of the wafer; a second electrical contact positioned over the second surface of the wafer and separated electrically from the first electrical contact; a second passivation layer positioned over the second surface of the wafer in the region on the wafer that is at least between the first electrical contact and the second surface of the wafer; and a layer comprising a semiconductor material of a conductivity opposite the conductivity of the wafer and positioned in the region between the second passivation layer and the first contact.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Chemical vapor deposition vaporizer
InactiveUS6210485B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMachines/enginesIntegrated circuitEvaporator
The invention relates to an apparatus and process for the vaporization of liquid precursors and deposition of a film on a suitable substrate. Particularly contemplated is an apparatus and process for the vaporization of a metal-oxide film, such as a barium, strontium, titanium oxide (BST) film, for deposition on a silicon wafer to make integrated circuit capacitors useful in high capacity dynamic memory modules. The vaporizer comprises thermally controlled components which are adapted for easy assembly and disassembly. A main vaporizing section provides a large heated surface for flash vaporization. A high conductance blocker is disposed at a lower end of the vaporizer to provide an extended vaporization surface. Optionally, a filter may be employed to capture unvaporized precursor droplets.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
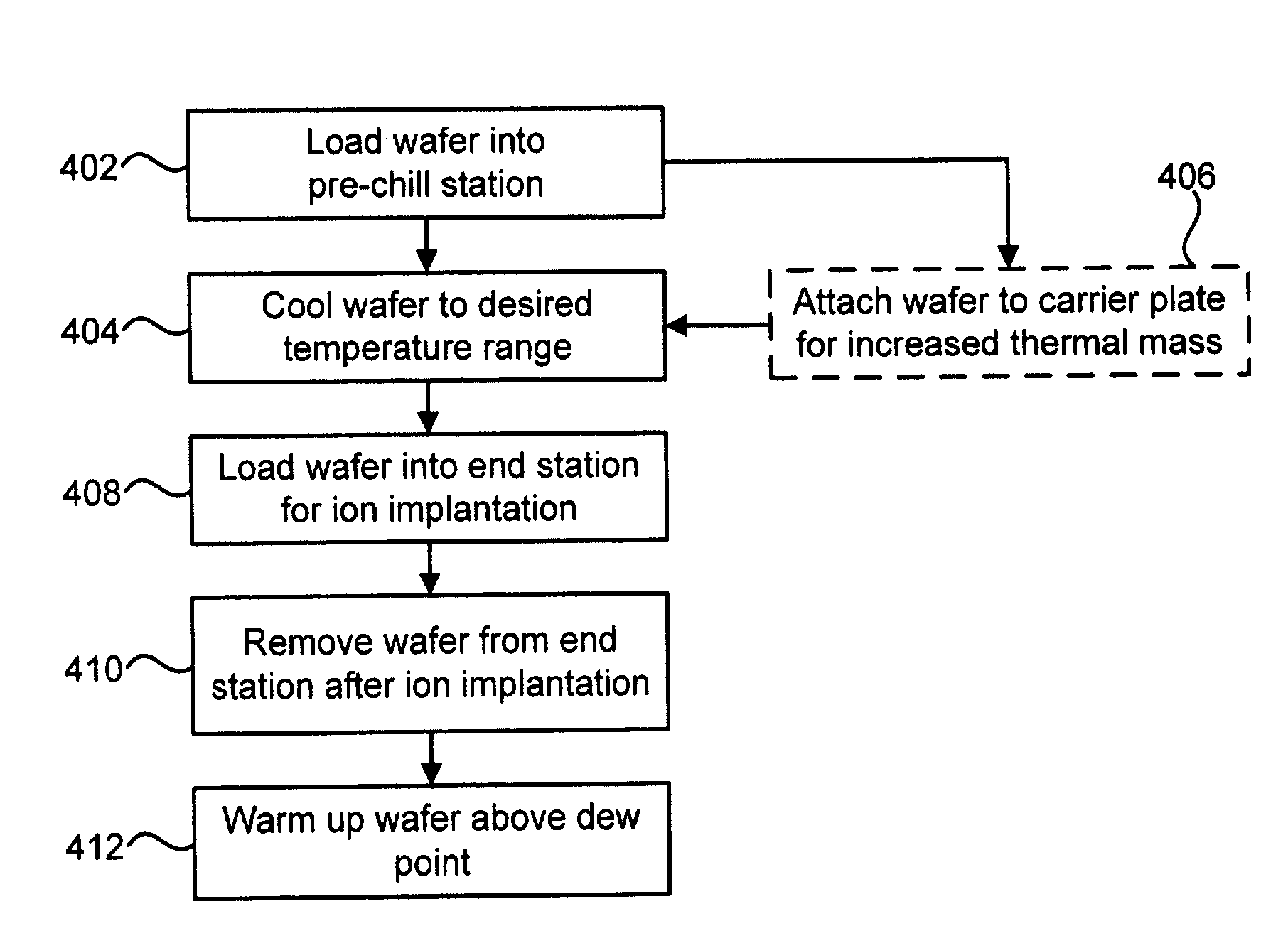
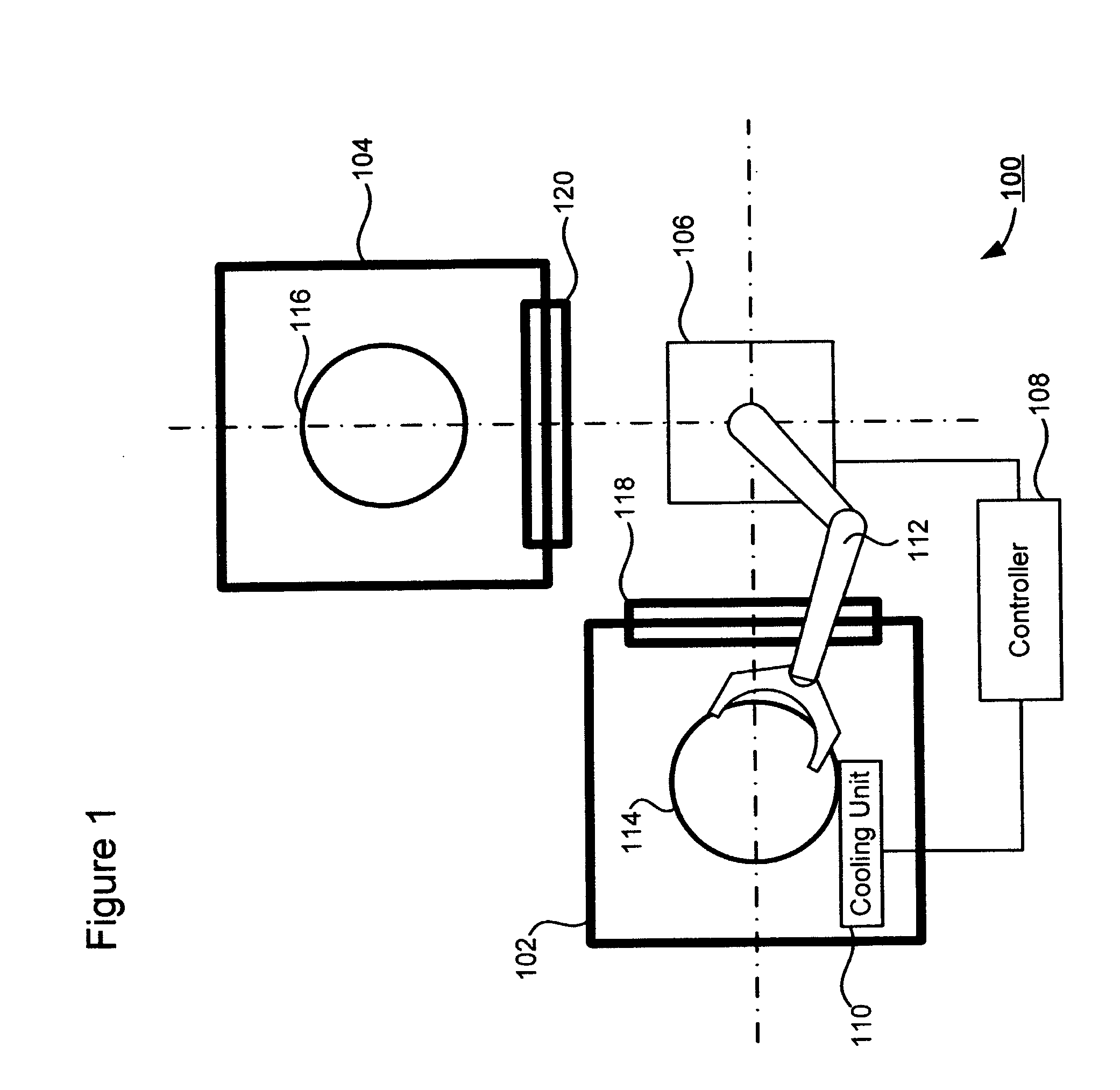
Technique for low-temperature ion implantation
ActiveUS20080044938A1Avoid overall overheatingFacilitate tilting and rotationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesEngineeringIon implantation
A technique for low-temperature ion implantation is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as an apparatus for low-temperature ion implantation. The apparatus may comprise a pre-chill station located in proximity to an end station in an ion implanter. The apparatus may also comprise a cooling mechanism within the pre-chill station. The apparatus may further comprise a loading assembly coupled to the pre-chill station and the end station. The apparatus may additionally comprise a controller in communication with the loading assembly and the cooling mechanism to coordinate loading a wafer into the pre-chill station, cooling the wafer down to a predetermined temperature range, and loading the cooled wafer into the end station where the cooled wafer undergoes an ion implantation process.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
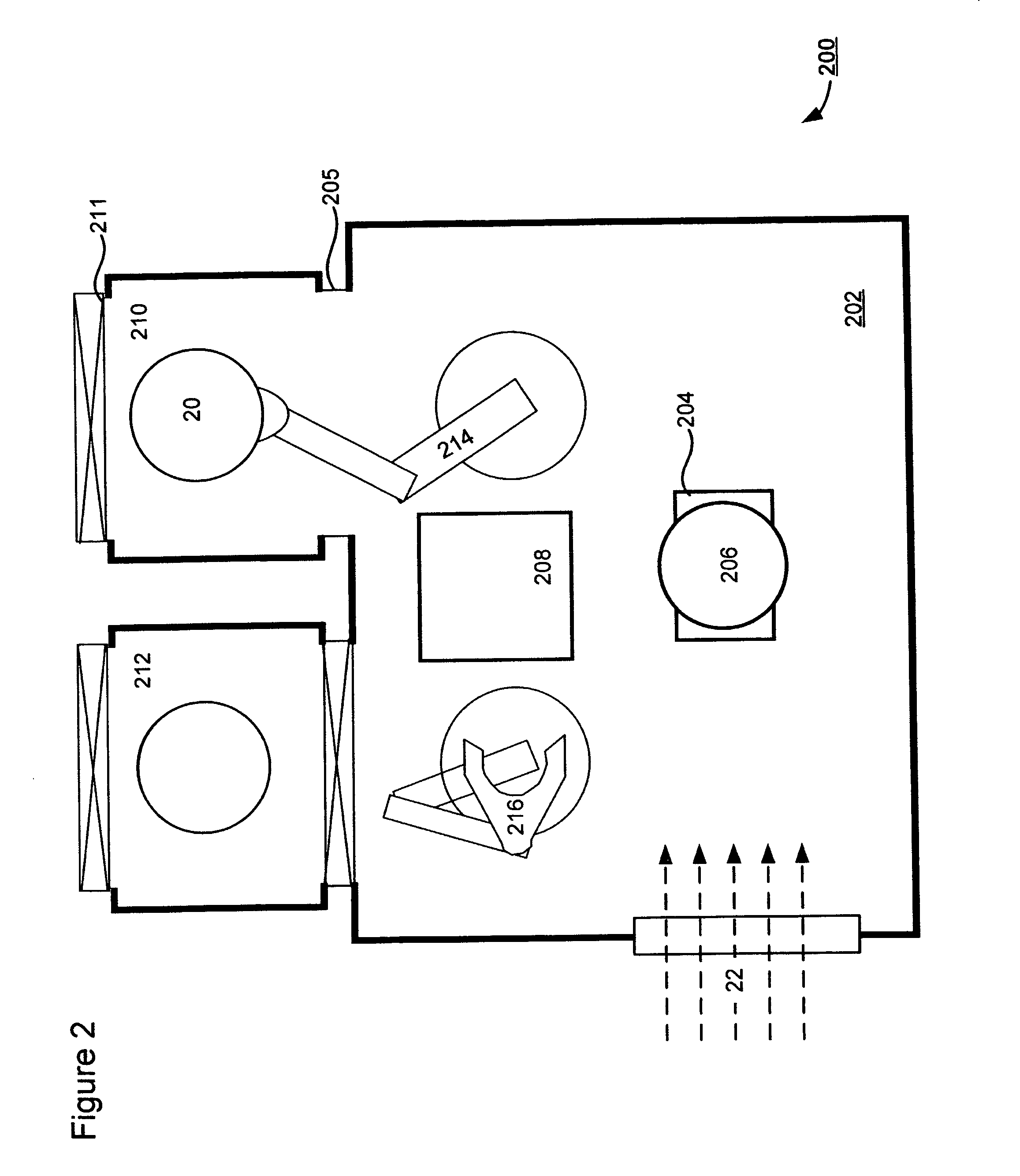
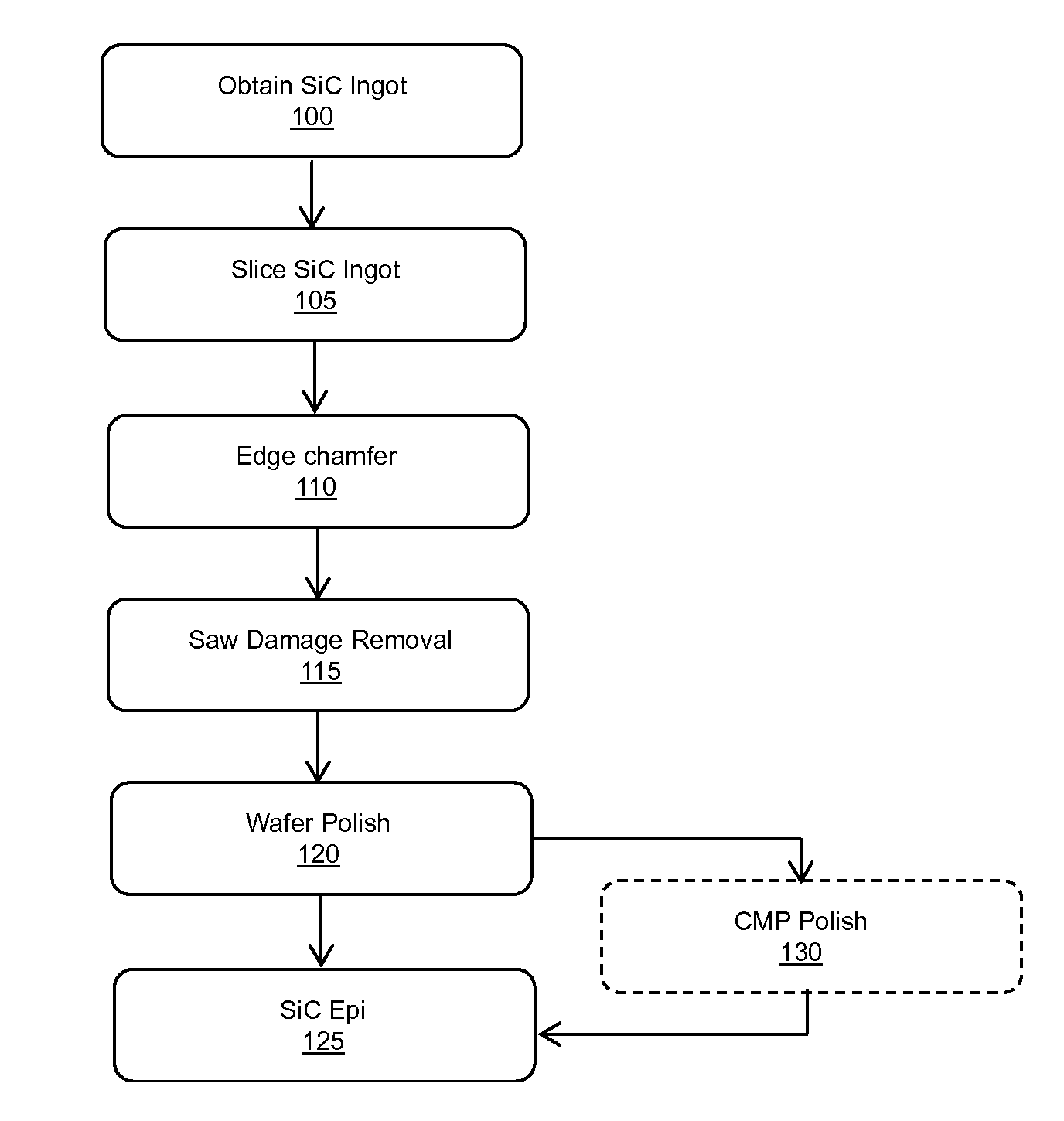
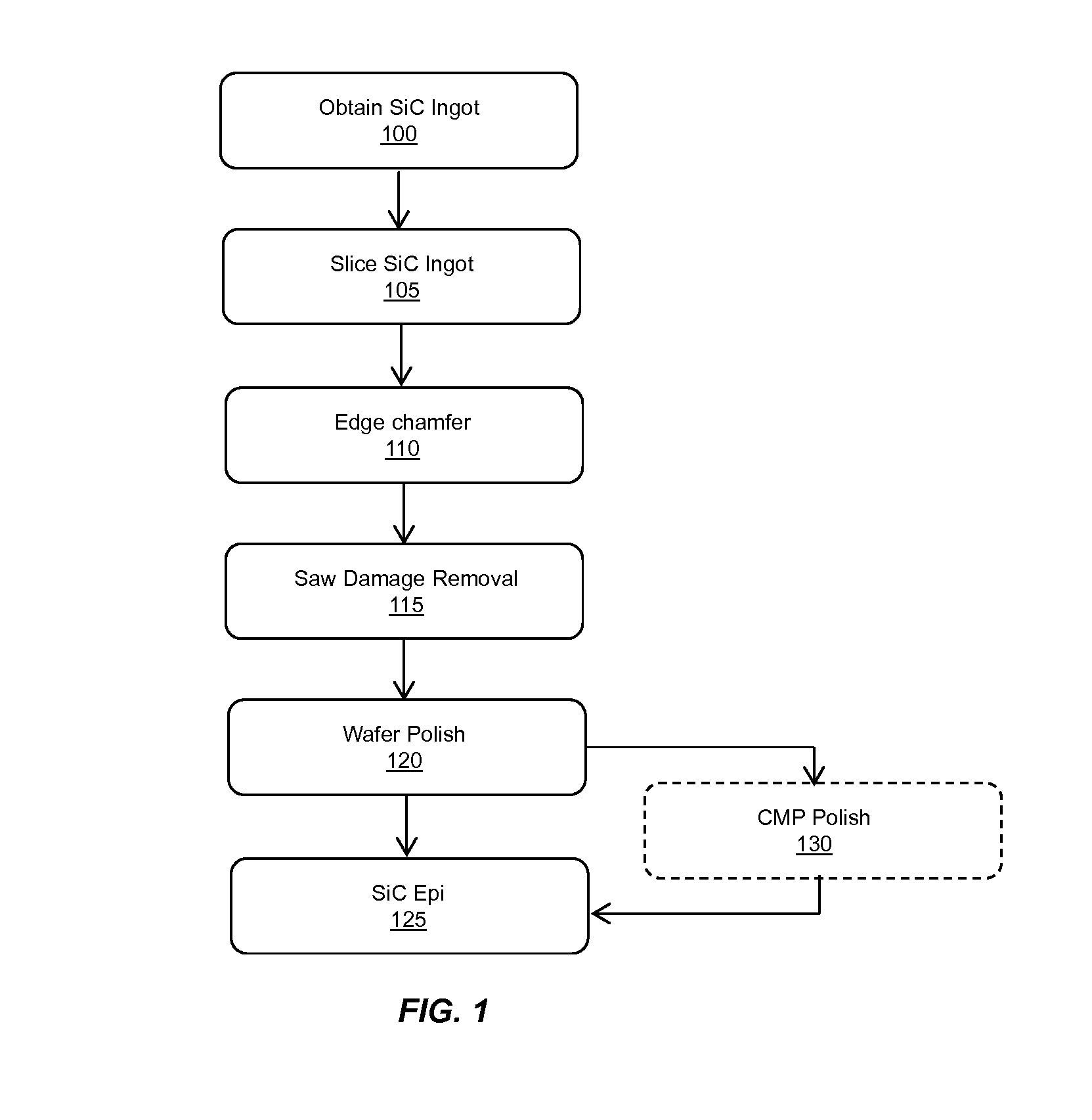
Flat sic semiconductor substrate
ActiveUS20140117380A1Efficient polishingImprove performanceEdge grinding machinesPolycrystalline material growthCrystallographyWafering
Methods for manufacturing silicon carbide wafers having superior specifications for bow, warp, total thickness variation (TTV), local thickness variation (LTV), and site front side least squares focal plane range (SFQR). The resulting SiC wafer has a mirror-like surface that is fit for epitaxial deposition of SiC. The specifications for bow, warp, total thickness variation (TTV), local thickness variation (LTV), and site front side least squares focal plane range (SFQR) of the wafer are preserved following the addition of the epitaxy layer.
Owner:SK SILTRON CSS LLC
Self-Centering Wafer Carrier System For Chemical Vapor Deposition
ActiveUS20160372321A1Increase probabilityQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseCarrier system
A self-centering wafer carrier system for a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) reactor includes a wafer carrier comprising an edge. The wafer carrier at least partially supports a wafer for CVD processing. A rotating tube comprises an edge that supports the wafer carrier during processing. An edge geometry of the wafer carrier and an edge geometry of the rotating tube being chosen to provide a coincident alignment of a central axis of the wafer carrier and a rotation axis of the rotating tube during process at a desired process temperature.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Robot arm
ActiveUS20130084156A1Precise positioningPollution suppressionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationWafering
The robot arm of the present application is a robot arm that transports semiconductor wafers. The robot arm includes a hand, a lower arm link, and an upper arm link. The hand is connected to the lower arm link via a first joint. The upper arm link is connected to the lower arm link via a second joint. In the robot arm of the present application, the lower arm link is capable of being separated at a location between the first joint and the second joint.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
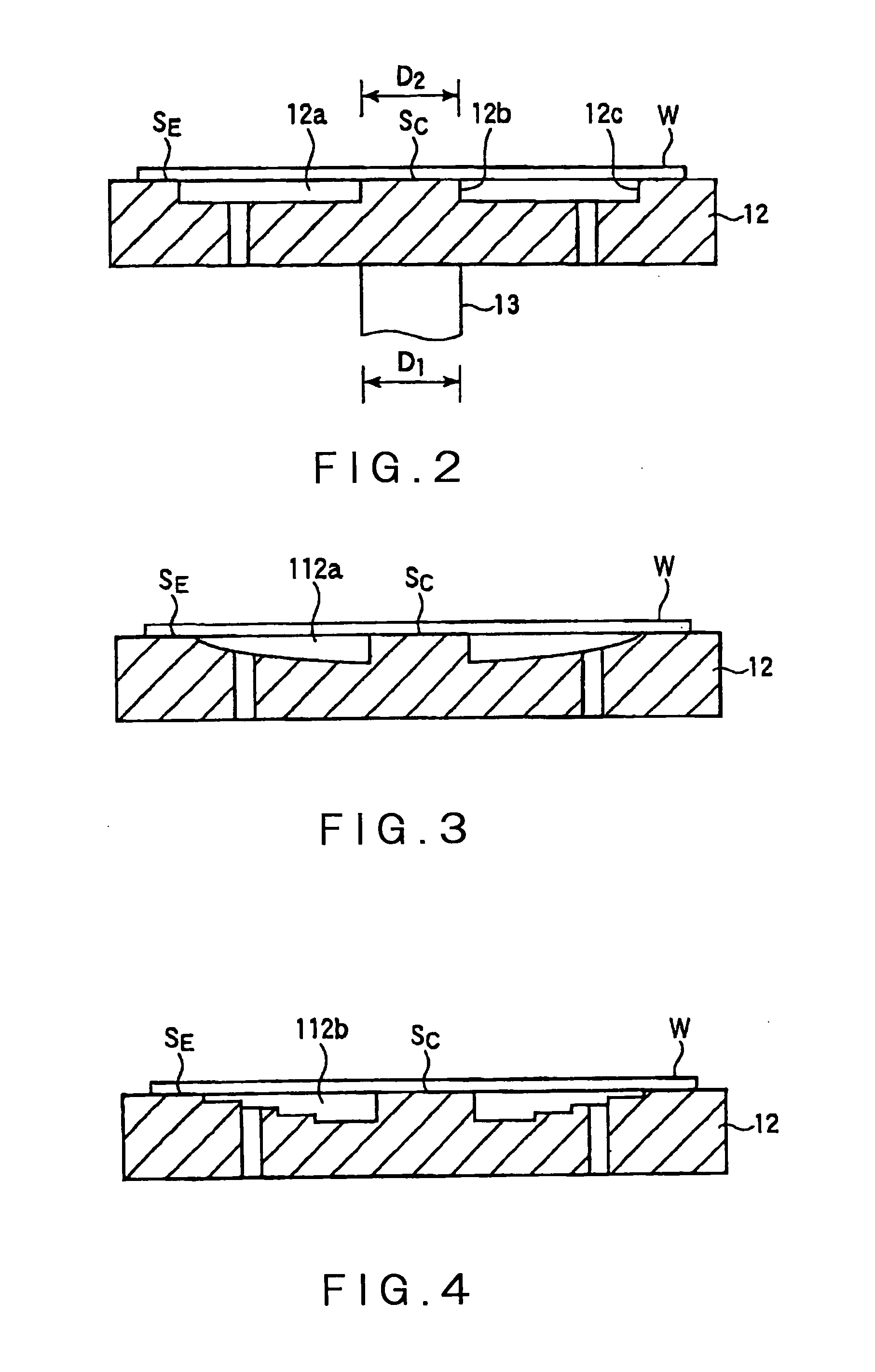
Susceptor and method for manufacturing silicon epitaxial wafer
ActiveUS20100129990A1Avoid stickingPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsSusceptorWafering
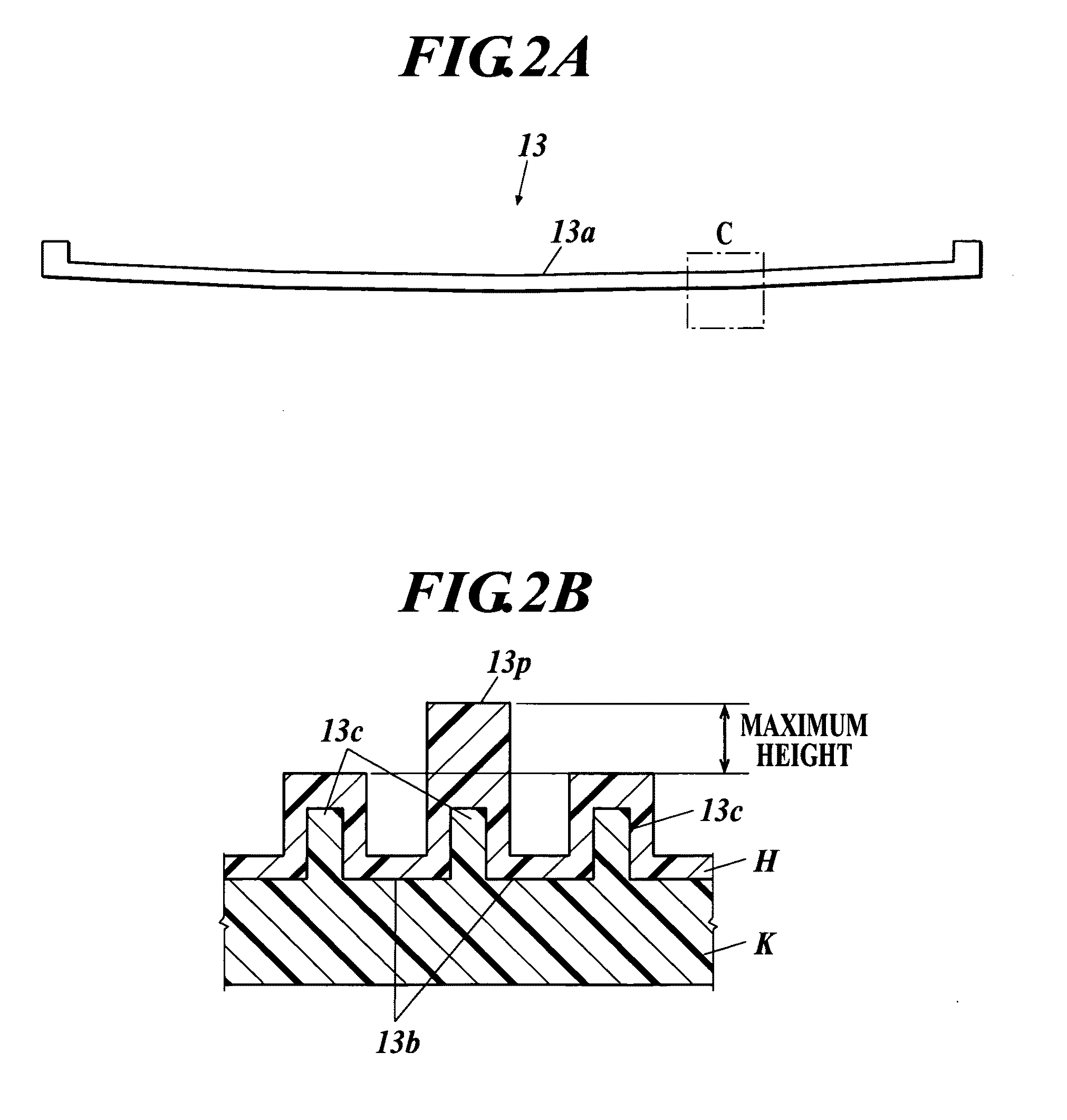
Provided is a susceptor 13 for manufacturing an epitaxial wafer, comprising a mesh-like groove 13b on a mount face on which a silicon substrate W is to be mounted, wherein a coating H of silicon carbide is formed on the mount face, and the coating has a surface roughness of 1 μm or more in centerline average roughness Ra and a maximum height of a protrusion 13p generated in forming the coating H of 5 μm or less. Thus, defects such as warping and slip as well as adhesion of the silicon substrate to the susceptor are prevented.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Method for positioning wafers in multiple wafer transport
ActiveUS9793148B2Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingSusceptor
A method for positioning wafers in dual wafer transport, includes: simultaneously moving first and second wafers placed on first and second end-effectors to positions over lift pins protruding from first and second susceptors, respectively; and correcting the positions of the first and second wafers without moving any of the lift pins relative to the respective susceptors or without moving the lift pins relative to each other, wherein when the first and second wafers are moved to the respective positions, the distance between the first wafer and tips of the lift pins of the first susceptor is substantially smaller than the distance between the second wafer and tips of the lift pins of the second susceptor.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method for depositing silicon-free carbon-containing film as gap-fill layer by pulse plasma-assisted deposition
ActiveUS10388513B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseSilicon
A Si-free C-containing film having filling capability is deposited by forming a viscous polymer in a gas phase by striking an Ar, He, or N2 plasma in a chamber filled with a volatile hydrocarbon precursor that can be polymerized within certain parameter ranges which define mainly partial pressure of precursor during a plasma strike, and wafer temperature.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
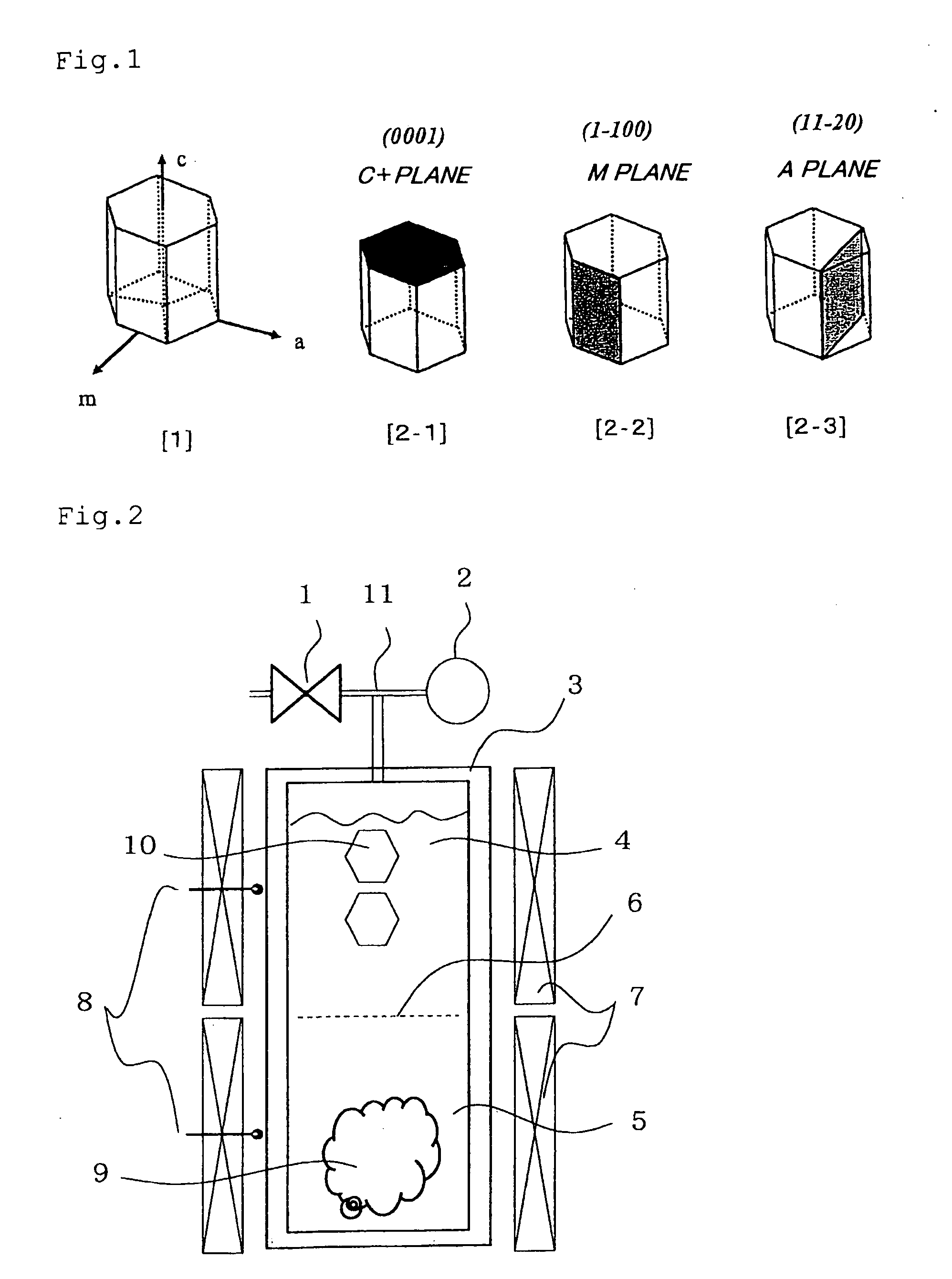
Method for producing nitride semiconductor, crystal growth rate increasing agent, single crystal nitride, wafer and device
InactiveUS20100104495A1Improve performanceIncrease probabilityPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNitrogenCrystal structure
A method for producing a nitride semiconductor, comprising controlling temperature and pressure in a autoclave containing a seed having a hexagonal crystal structure, a nitrogen element-containing solvent, a raw material substance containing a metal element of Group 13 of the Periodic Table, and a mineralizer so as to put said solvent into a supercritical state and / or a subcritical state and thereby ammonothermally grow a nitride semiconductor crystal on the surface of said seed, wherein the crystal growth rate in the m-axis direction on said seed is 1.5 times or more the crystal growth rate in the c-axis direction on said seed. By the method, a nitride semiconductor having a large-diameter C plane or a nitride semiconductor thick in the m-axis direction can be efficiently and simply produced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +1
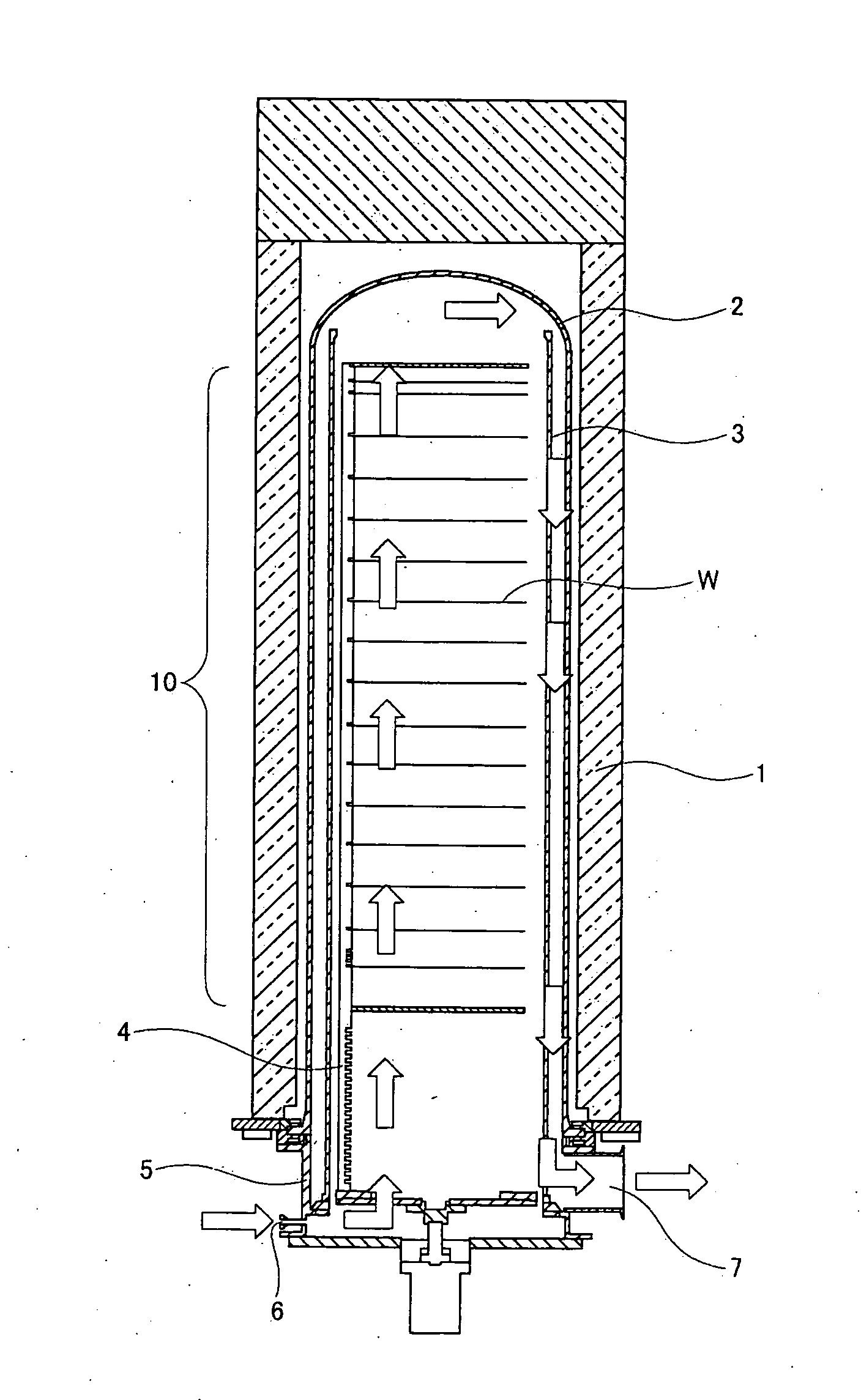
Gas injectors for a vertical furnace used in semiconductor processing
InactiveUS6929699B2Simple designStable positionChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringProduct gas
Improved long gas injectors for a vertical furnace used in semiconductor wafer processing are useful to minimize particulate contamination in the wafer processing area of the furnace, and minimize distortion of the long injectors during thermal excursions. The improved injectors are fabricated with a stabilizing quartz standoff positioned near the onset of the vertical portion of the injector tube which adds support to the long tube. Thickness of the standoff is calculated to define and enforce a specified separation distance between liner and injector, as well as to provide dual alignment points at the base of the liner and at the tip of the injector.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Silicon-on-insulator vertical array device trench capacitor DRAM
InactiveUS6566177B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringBottle
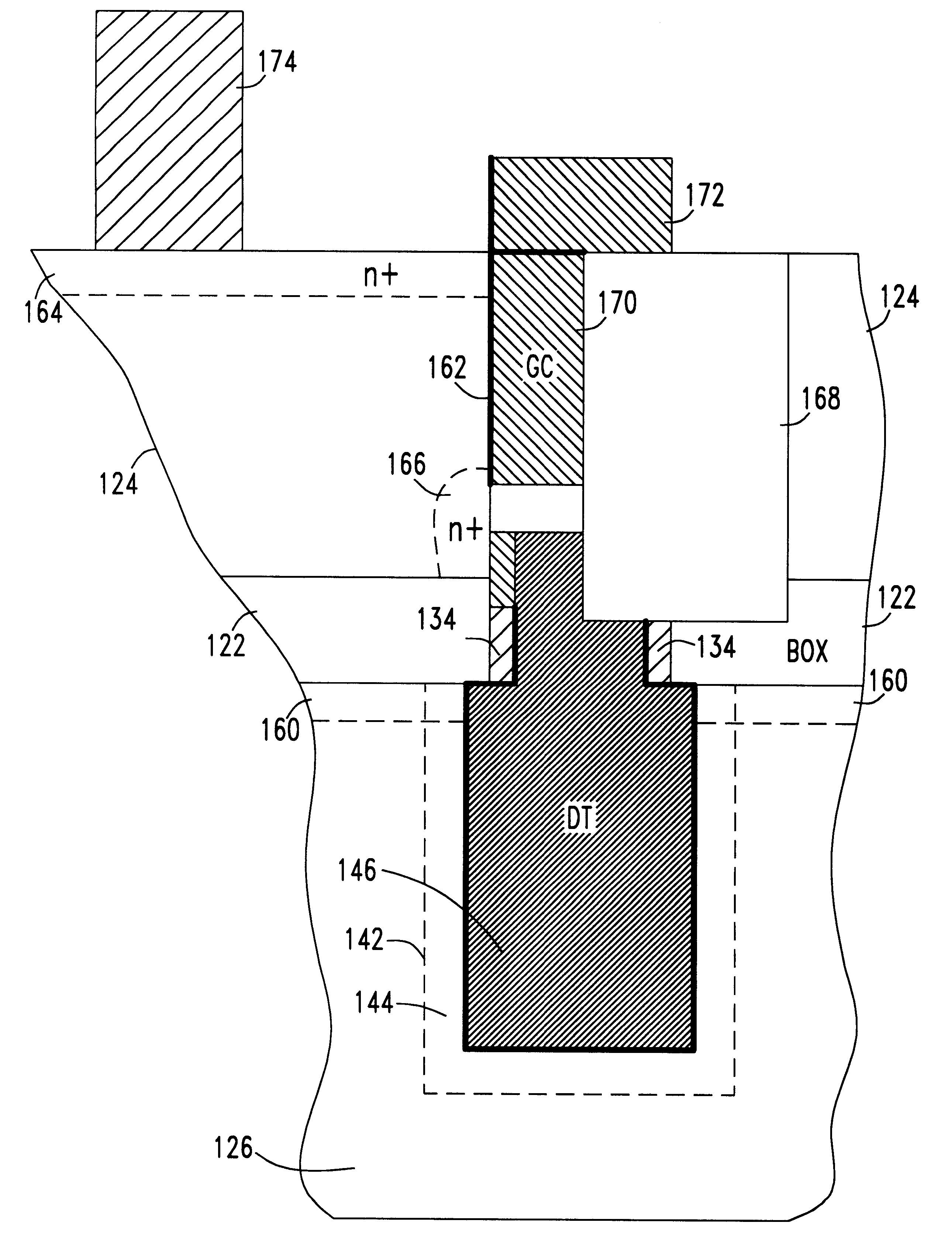
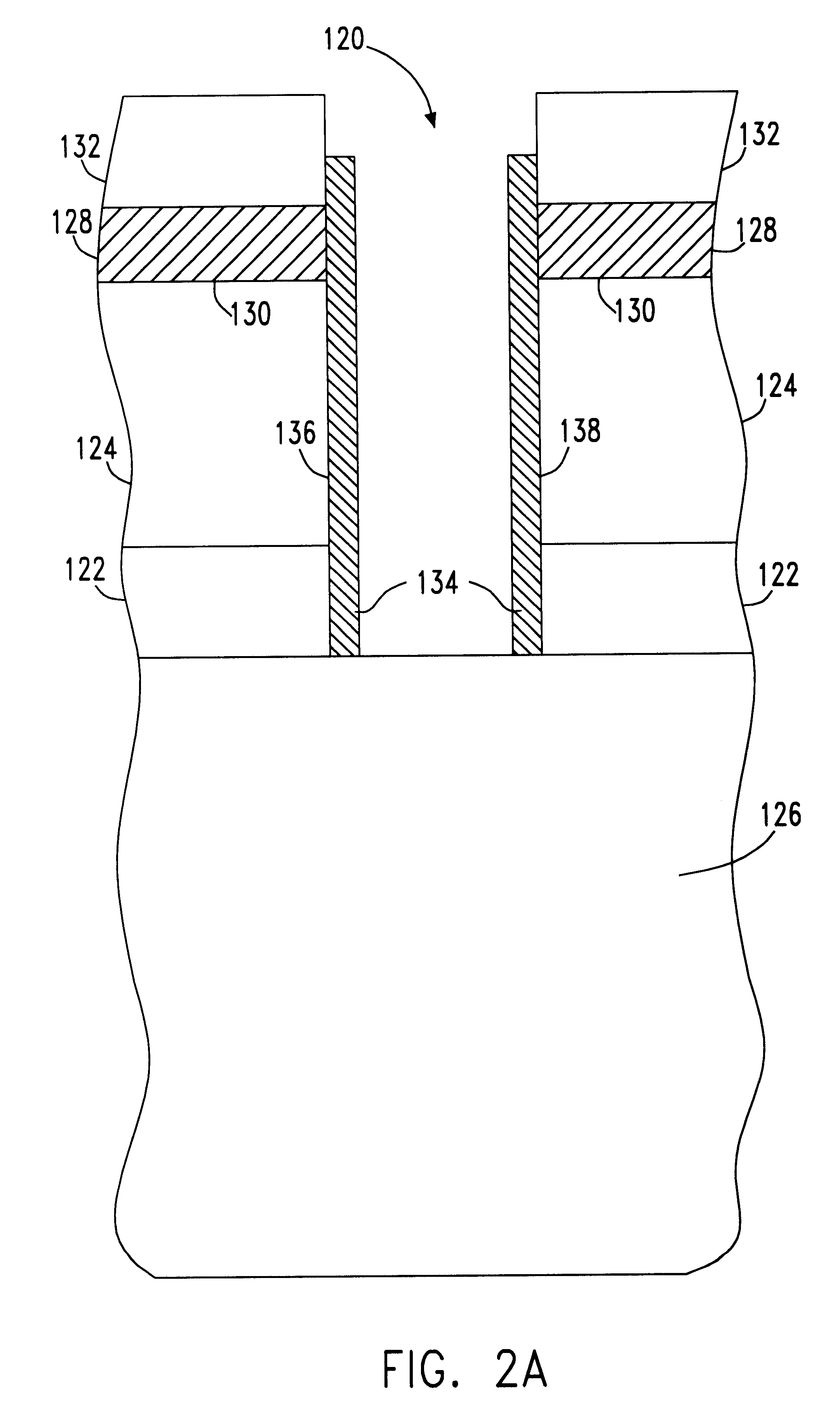
A silicon on insulator (SOI) dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell and array and method of manufacture. The memory cell includes a trench storage capacitor connected by a self aligned buried strap to a vertical access transistor. A buried oxide layer isolates an SOI layer from a silicon substrate. The trench capacitor is formed in the substrate and the access transistor is formed on a sidewall of the SOI layer. A polysilicon strap connected to the polysilicon plate of the storage capacitor provides a self-aligned contact to the source of the access transistor. Initially, the buried oxide layer is formed in the wafer. Deep trenches are etched, initially just through the SOI layer and the BOX layer. Protective sidewalls are formed in the trenches. Then, the deep trenches are etched into the substrate. The volume in the substrate is expanded to form a bottle shaped trench. A polysilicon capacitor plate is formed in the deep trenches and conductive polysilicon straps are formed in the trenches between the capacitor plates and the SOI sidewalls. Device regions are defined in the wafer and a sidewall gate is formed in the deep trenches. Shallow trenches isolation (STI) is used to isolate and define cells. Bitlines and wordlines are formed on the wafer.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com