Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
9236 results about "Least squares" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The method of least squares is a standard approach in regression analysis to approximate the solution of overdetermined systems, i.e., sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns. "Least squares" means that the overall solution minimizes the sum of the squares of the residuals made in the results of every single equation.
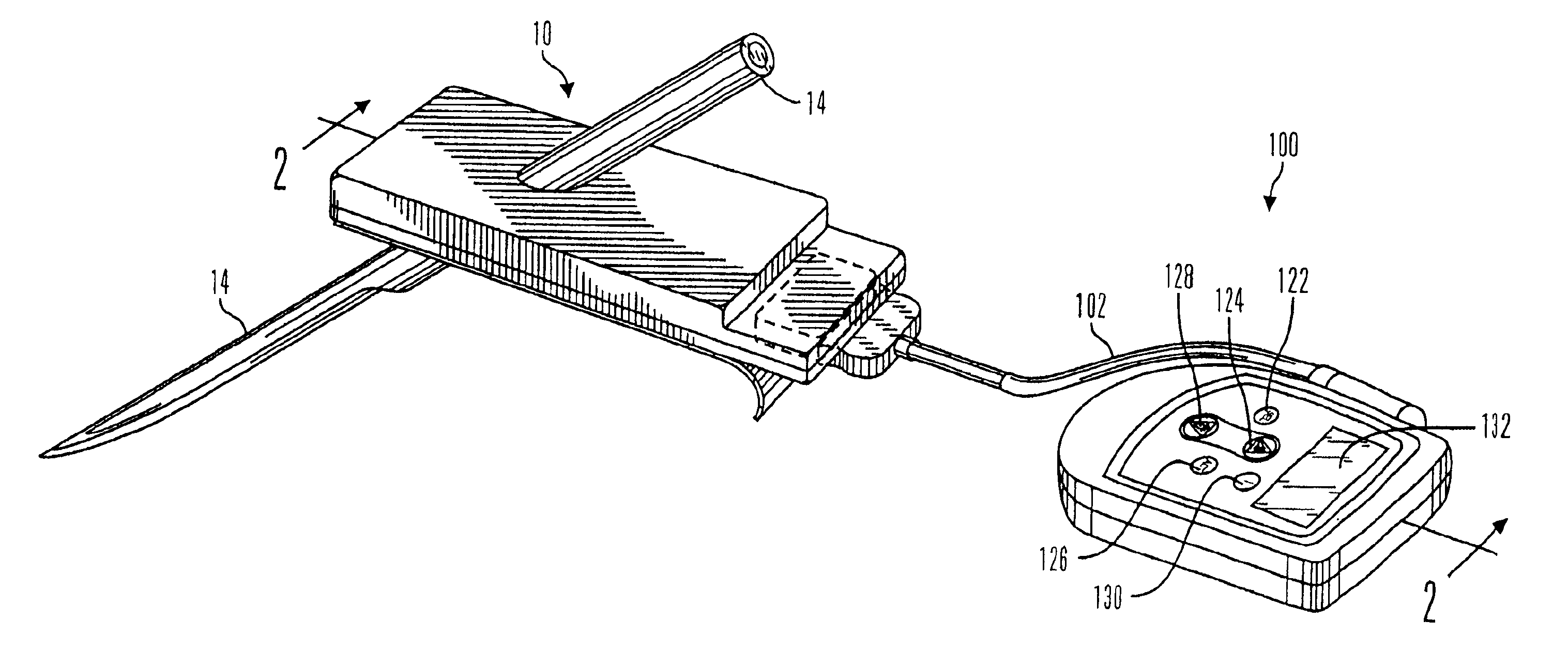
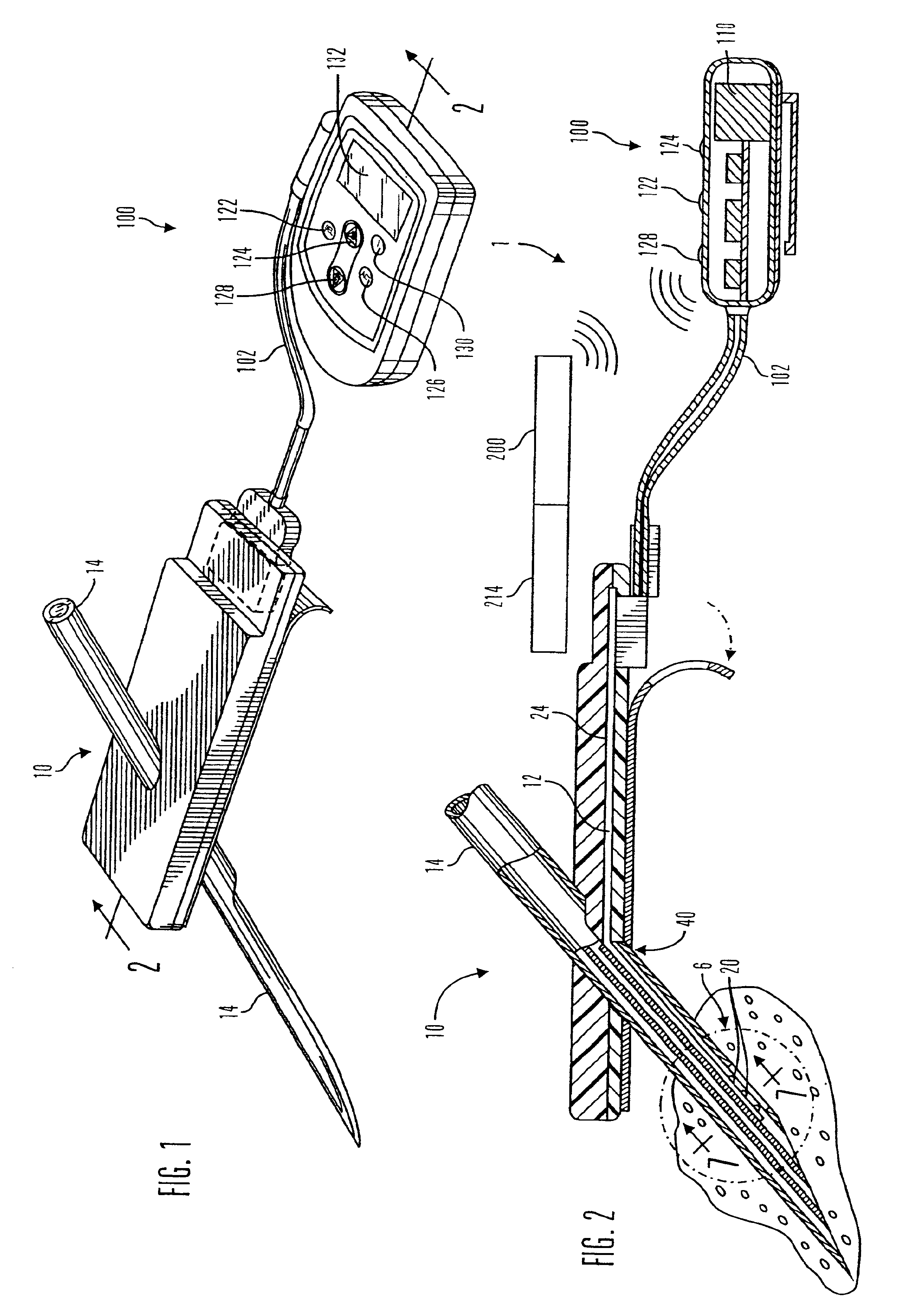
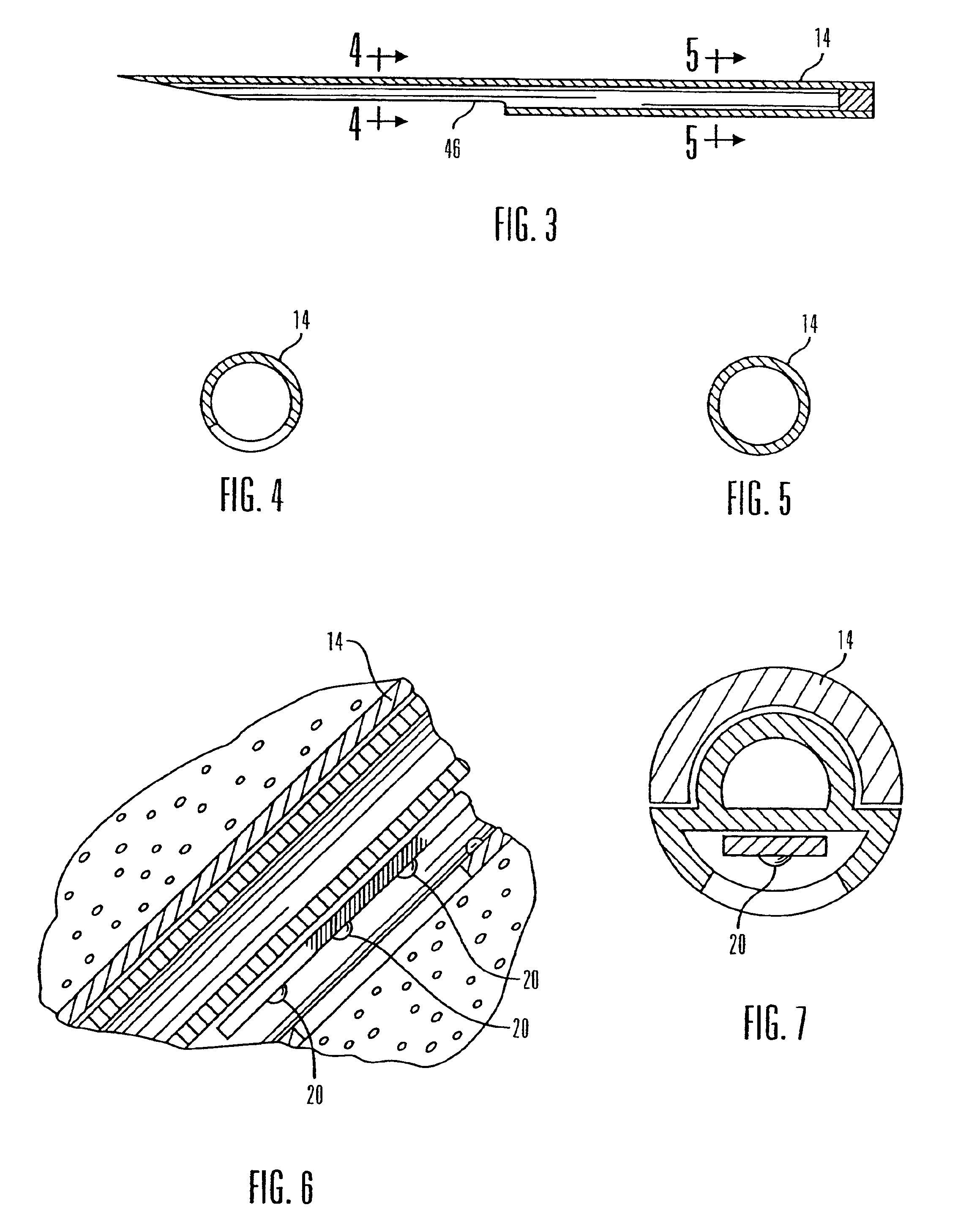
Real time self-adjusting calibration algorithm
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
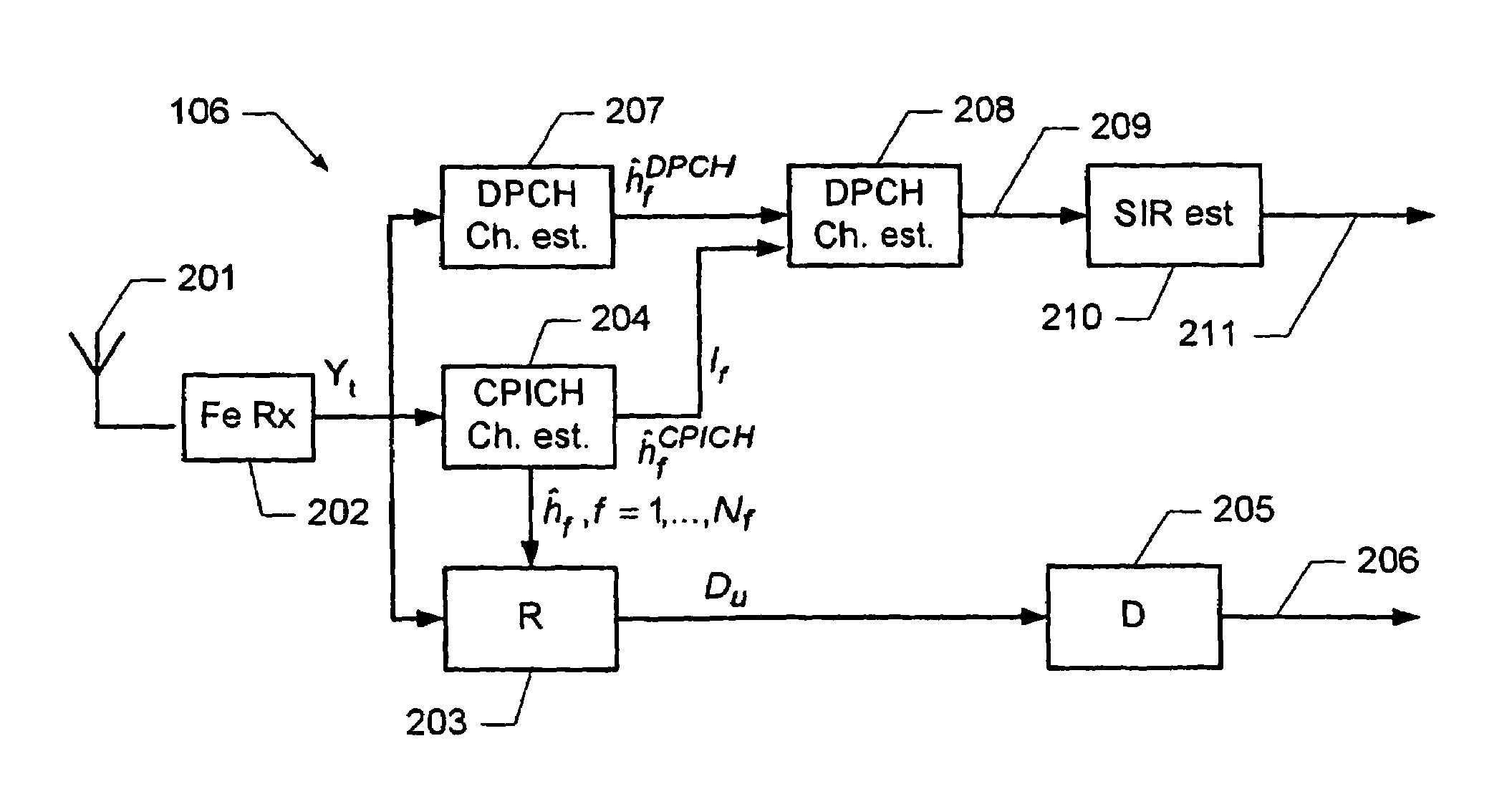
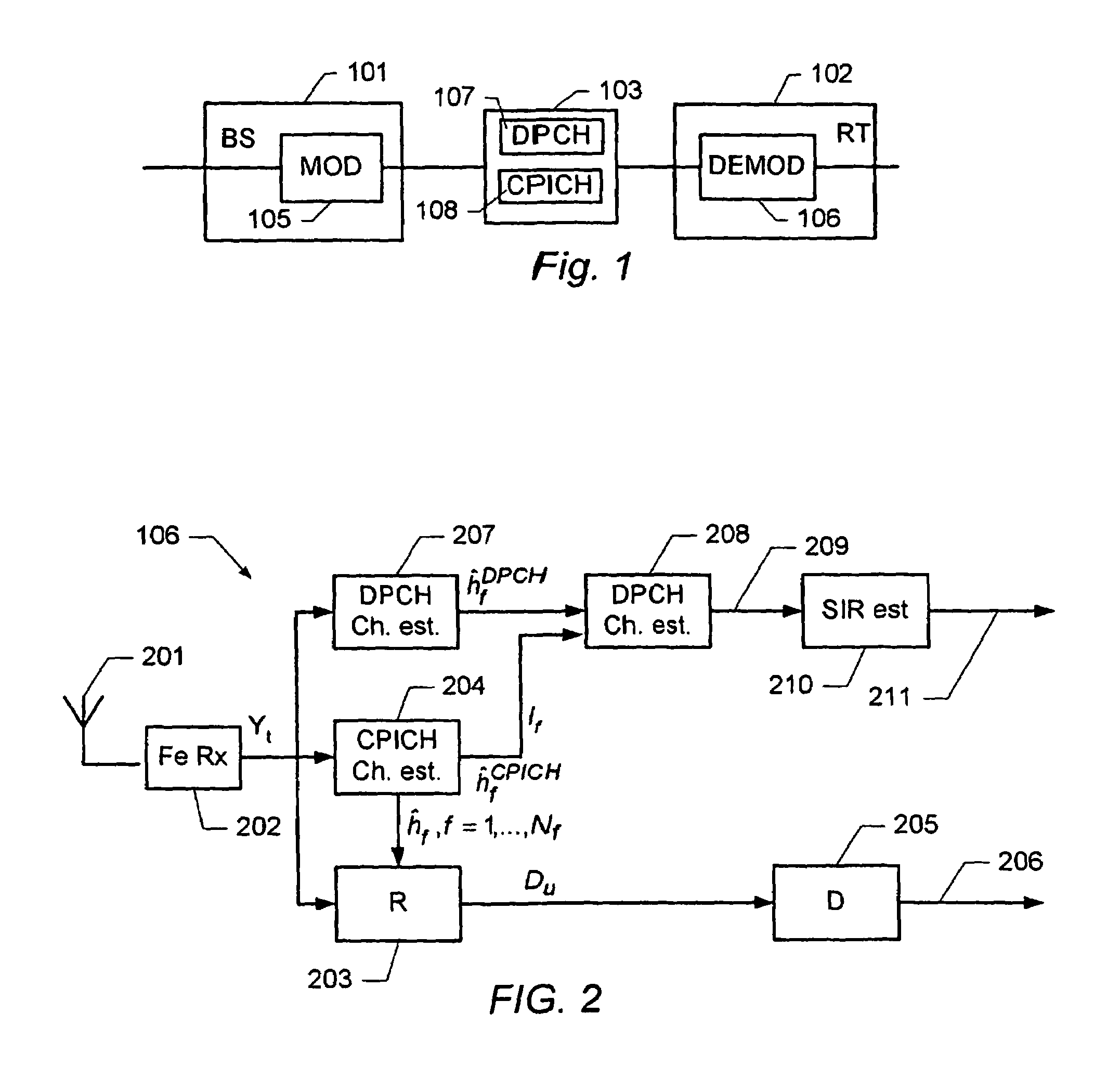
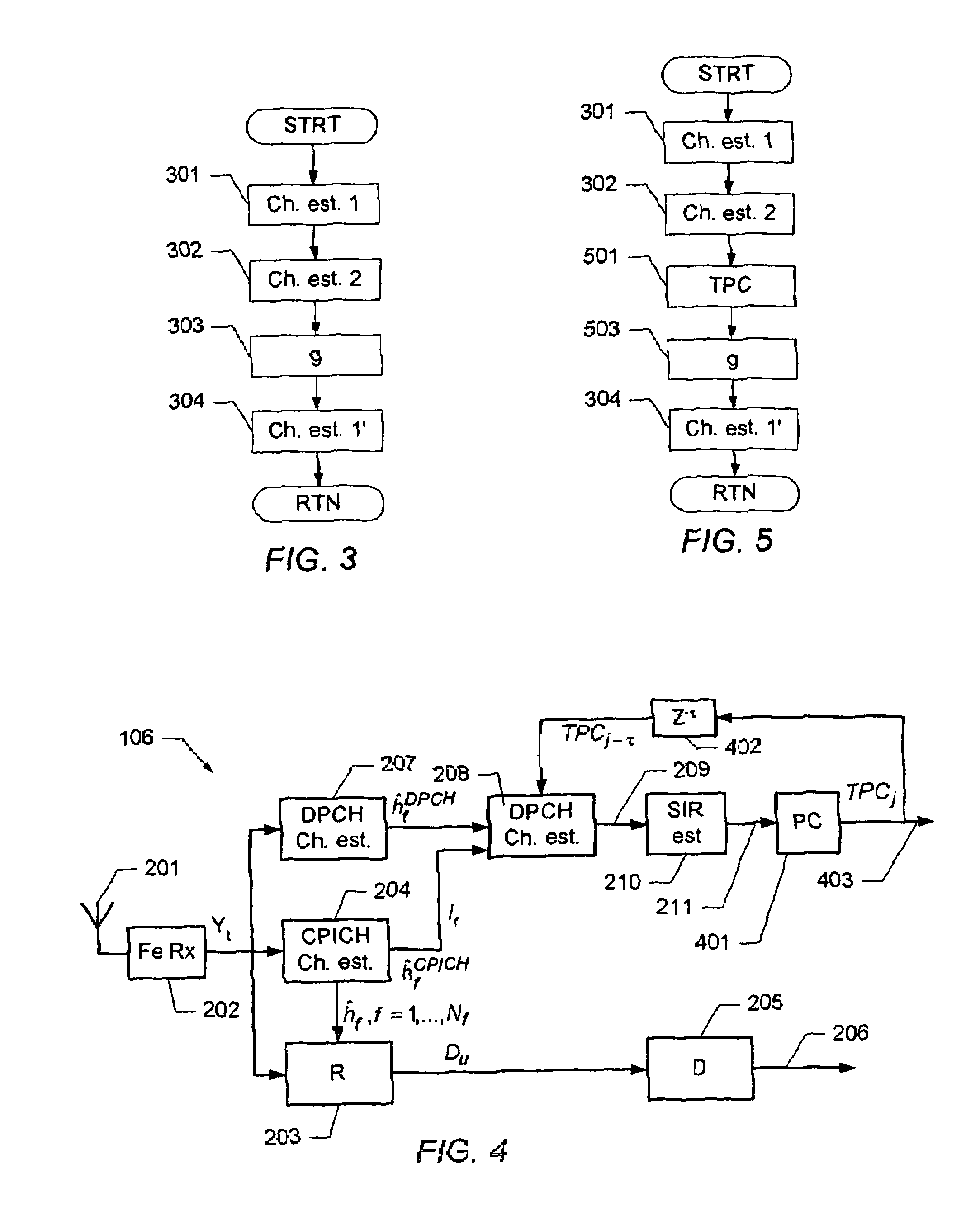
Determination of a channel estimate of a transmission channel
ActiveUS7561637B2Good estimateChannel estimate for one of the channels is improvedMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationCommunications systemTransmission channel
A method of determining a channel estimate of a first transmission channel in a communications system. The method comprises deriving a first set of channel estimates from symbols received through said first transmission channel; deriving a second set of channel estimates from symbols received through a second transmission channel in the communications system; determining a scale factor between the first and second sets of channel estimates from a least squares error criterion; and determining the channel estimate of the first transmission channel as a channel estimate of the second transmission channel scaled by the determined scale factor.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Real time self-adjusting calibration algorithm
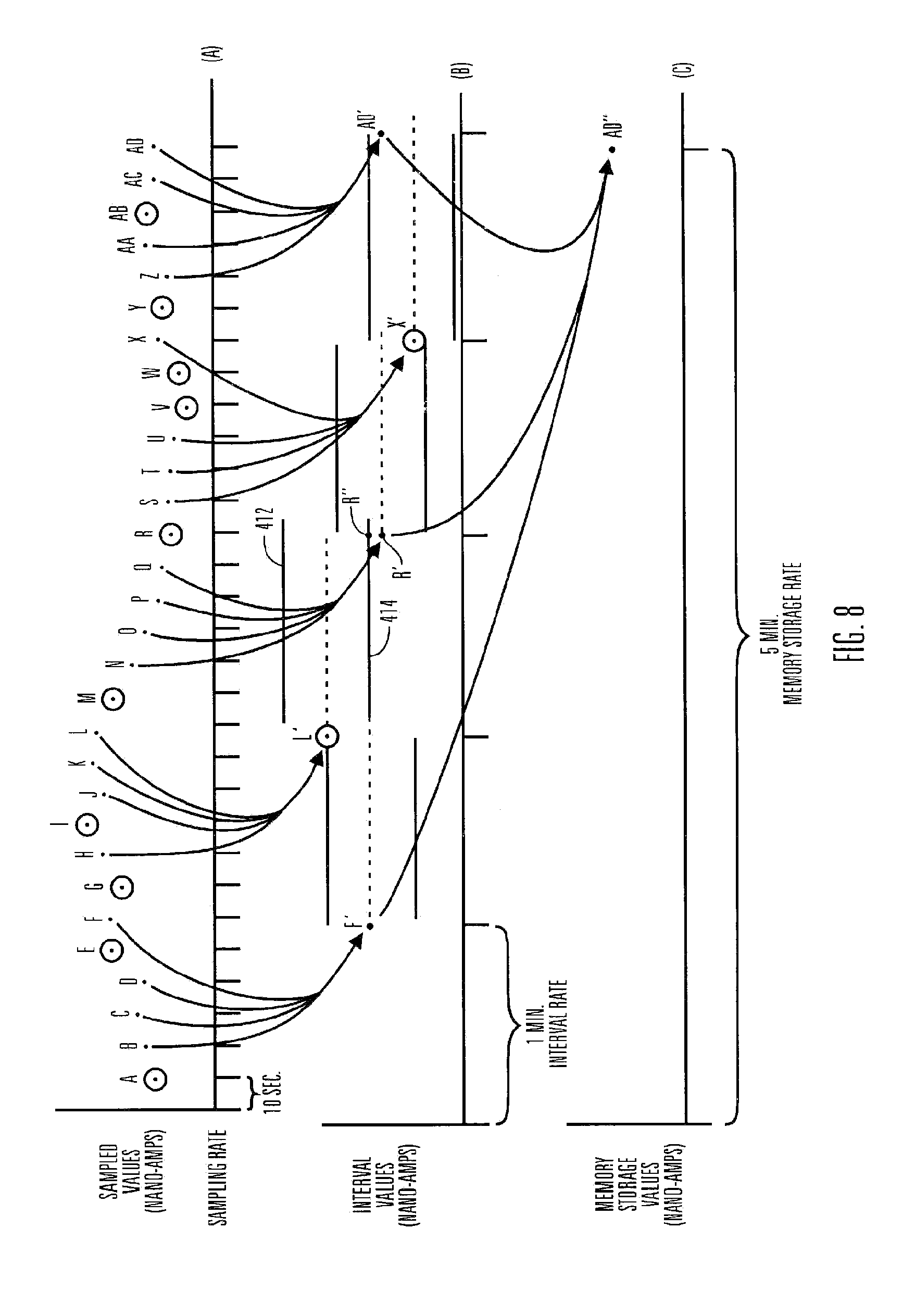
A method of calibrating glucose monitor data includes collecting the glucose monitor data over a period of time at predetermined intervals. It also includes obtaining at least two reference glucose values from a reference source that temporally correspond with the glucose monitor data obtained at the predetermined intervals. Also included is calculating the calibration characteristics using the reference glucose values and corresponding glucose monitor data to regress the obtained glucose monitor data. And, calibrating the obtained glucose monitor data using the calibration characteristics is included. In preferred embodiments, the reference source is a blood glucose meter, and the at least two reference glucose values are obtained from blood tests. In additional embodiments, calculation of the calibration characteristics includes linear regression and, in particular embodiments, least squares linear regression. Alternatively, calculation of the calibration characteristics includes non-linear regression. Data integrity may be verified and the data may be filtered.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Dual mode tracking system
InactiveUS6353406B1Memory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsData warehouseDual mode
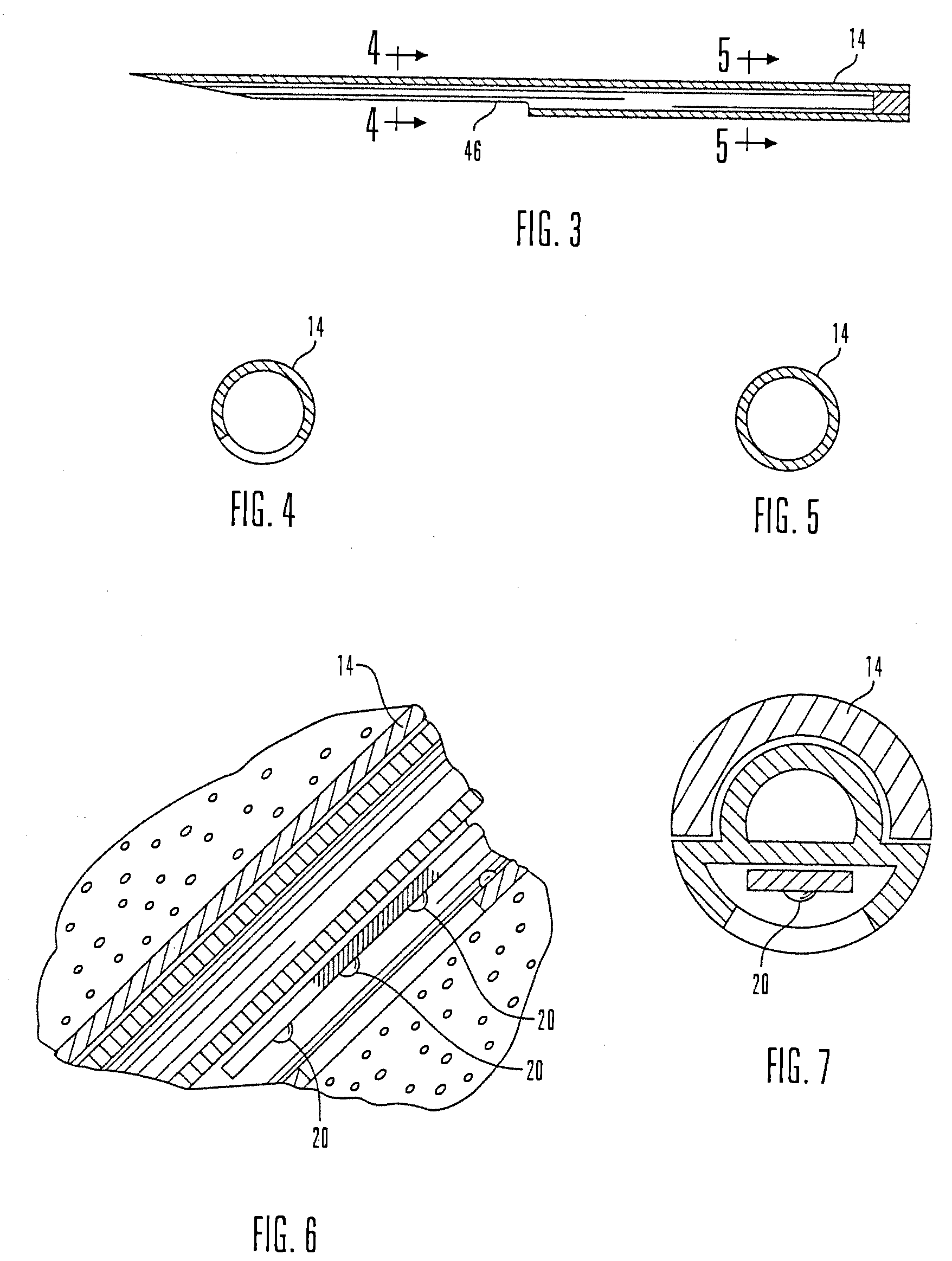
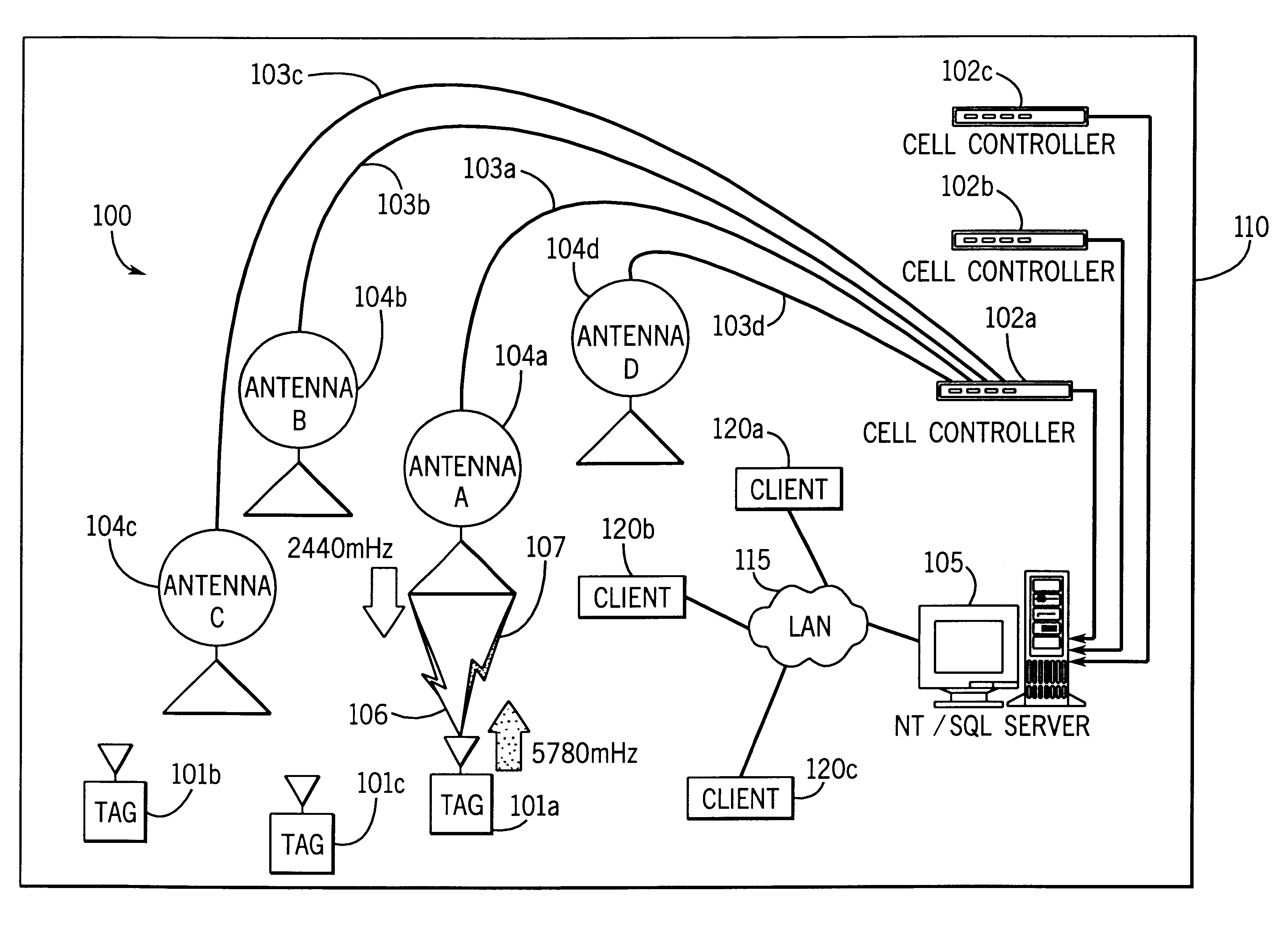
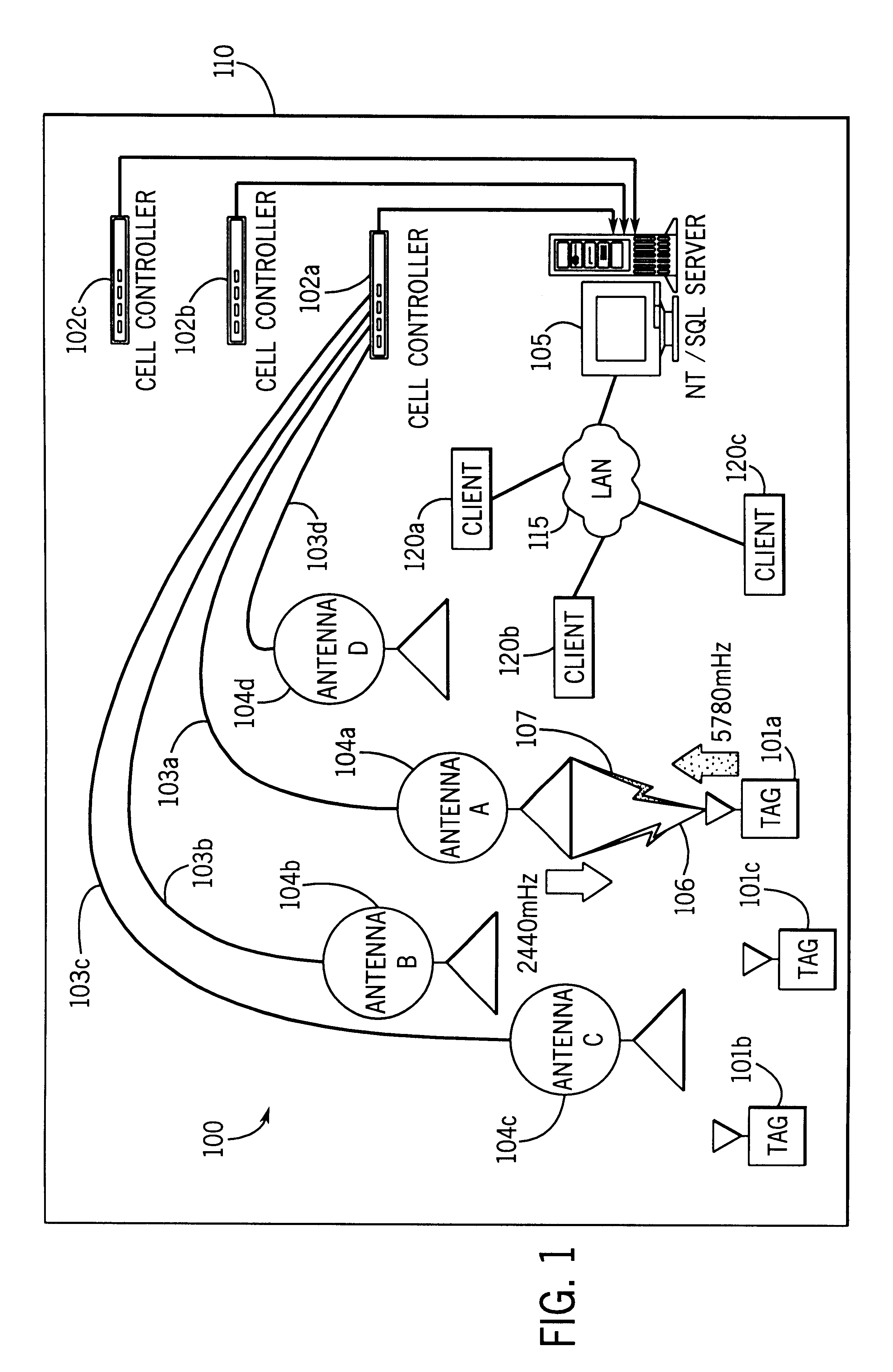
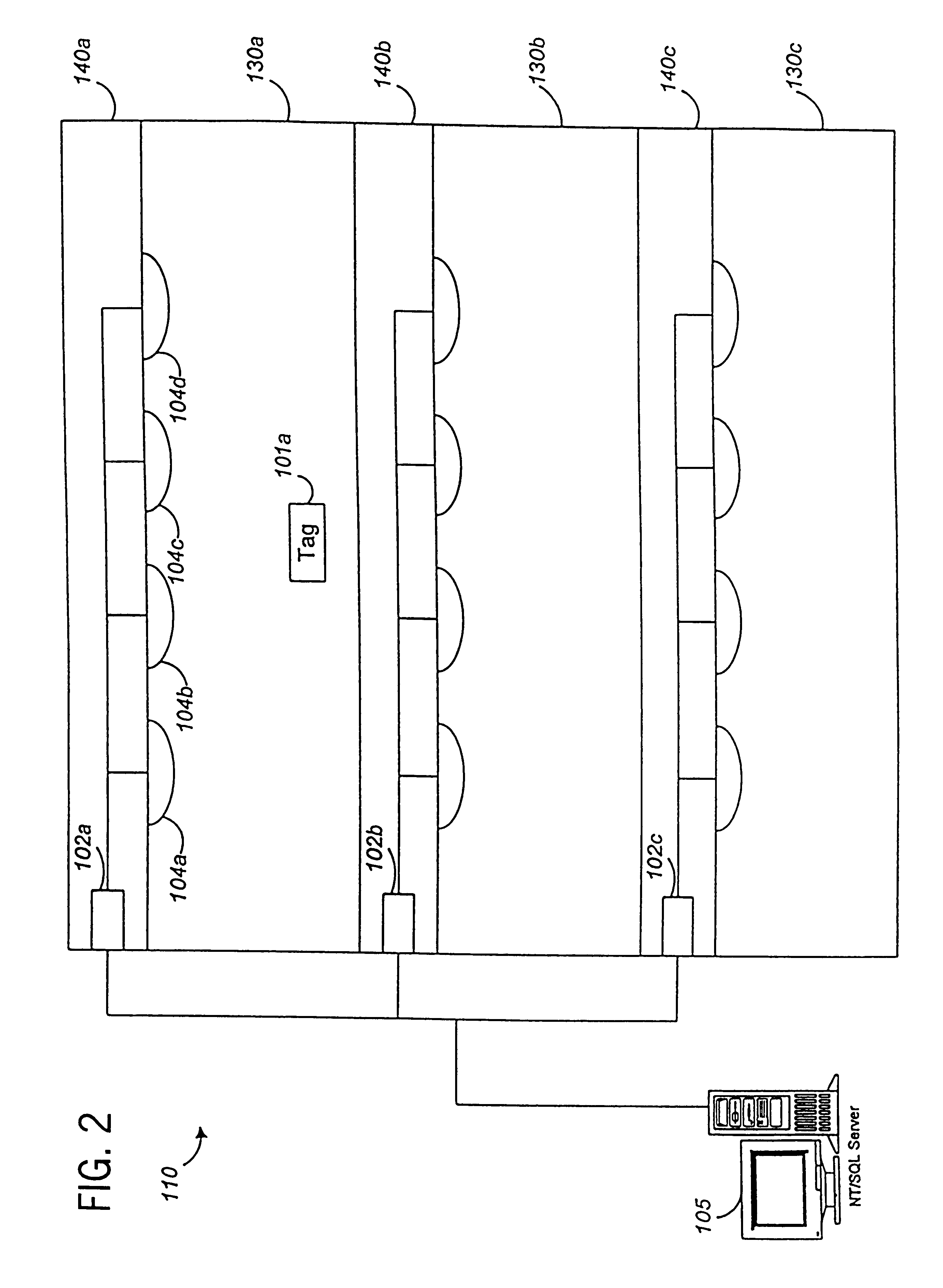
System for tracking mobile tags. Cell controllers with multiple antenna modules generate a carrier signal which is received by the tags. Tags shift the frequency of the carrier signal, modulate an identification code onto it, and transmit the resulting tag signal at randomized intervals. The antennas receive and process the response, and determine the presence of the tags by proximity and triangulation. The recursive-least squares (RLS) technique is used in filtering received signals. Distance of a tag from an antenna is calculated by measuring the round trip signal time. The cell controllers send data from the antenna to a host computer. The host computer collects the data and resolves them into positional estimates. Data are archived in a data warehouse, such as an SQL Server. Also disclosed is an article tracking system that supports both active and passive tags with a cell controller able to read both passive and active tag signals.
Owner:RF TECH +1
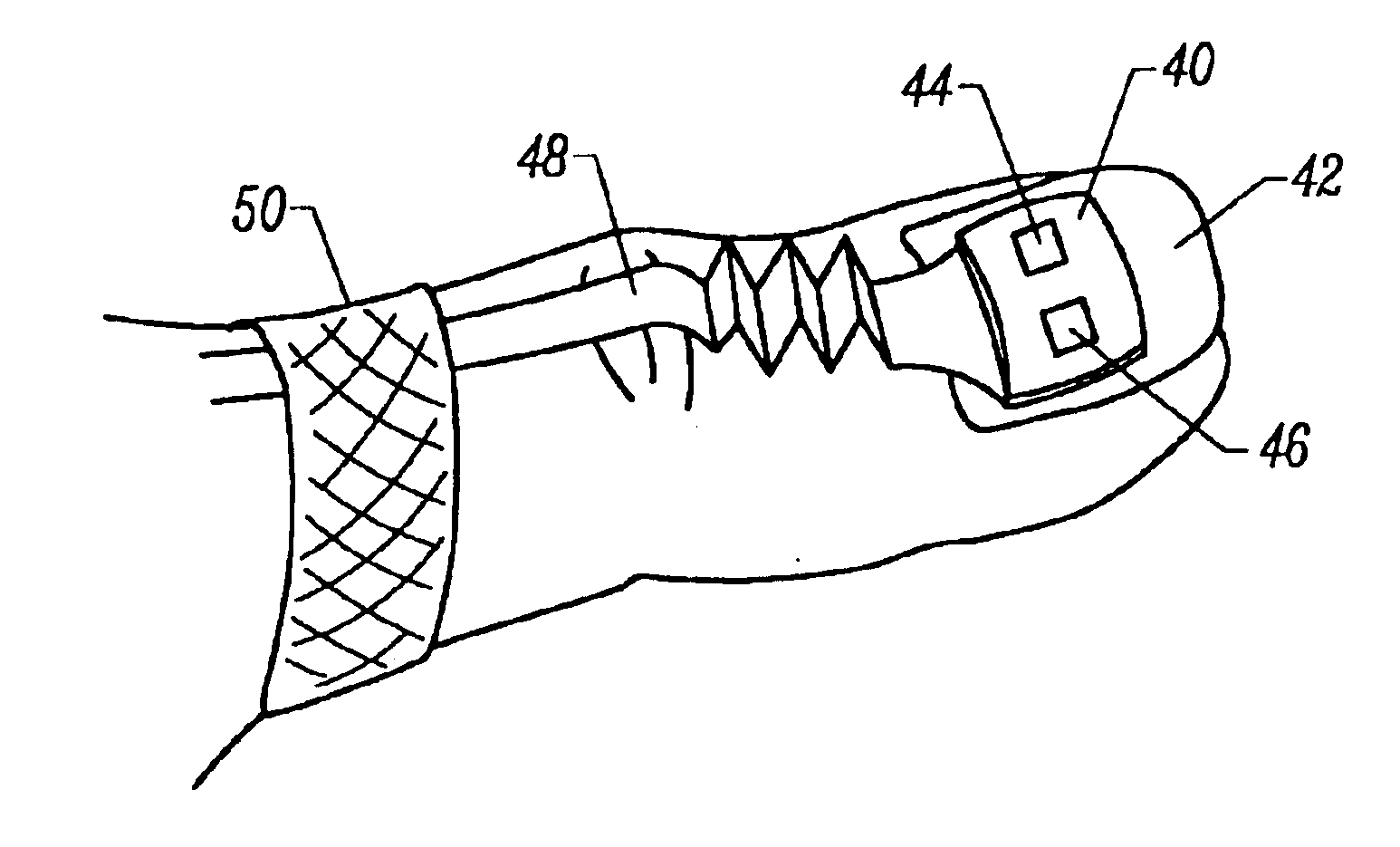
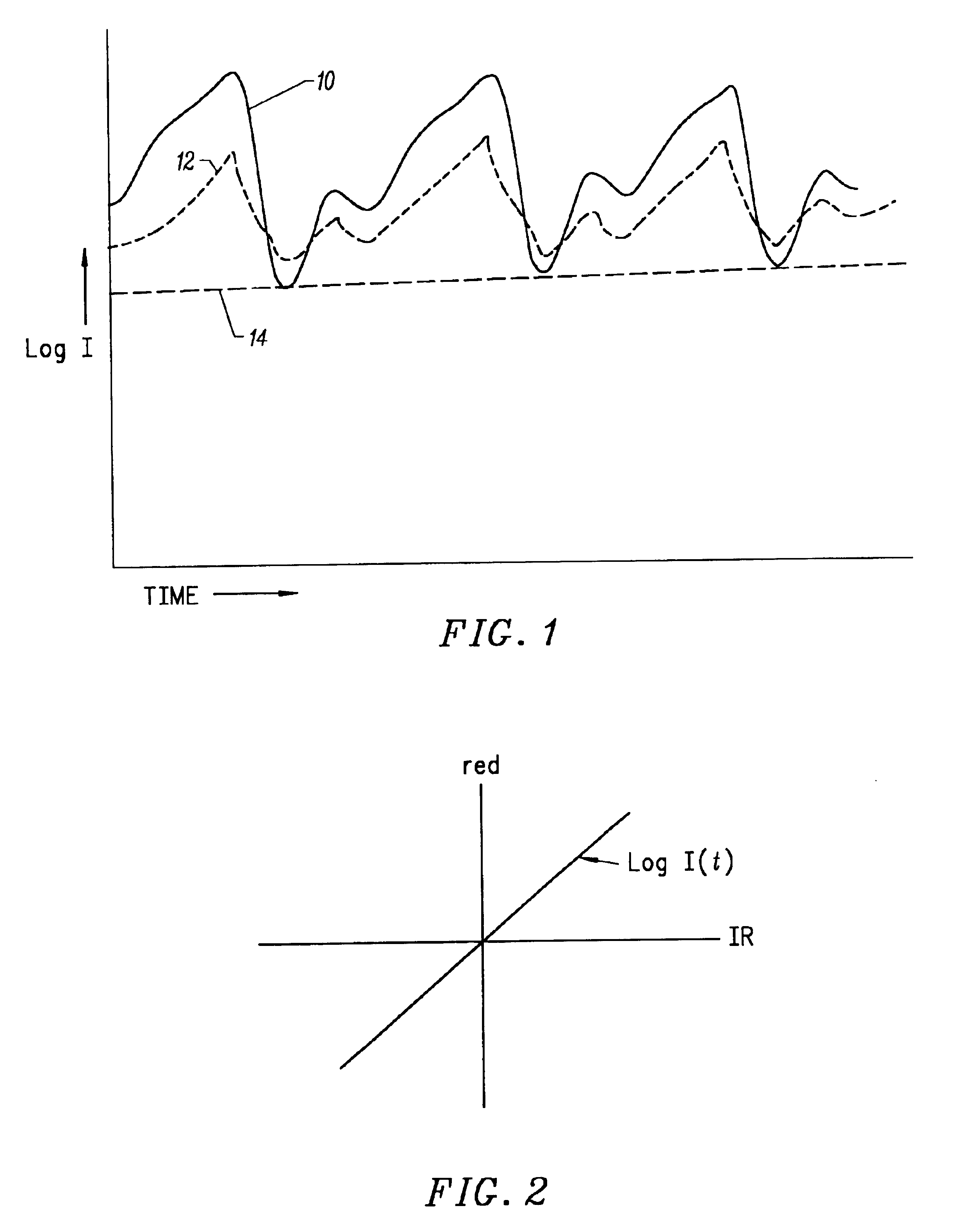
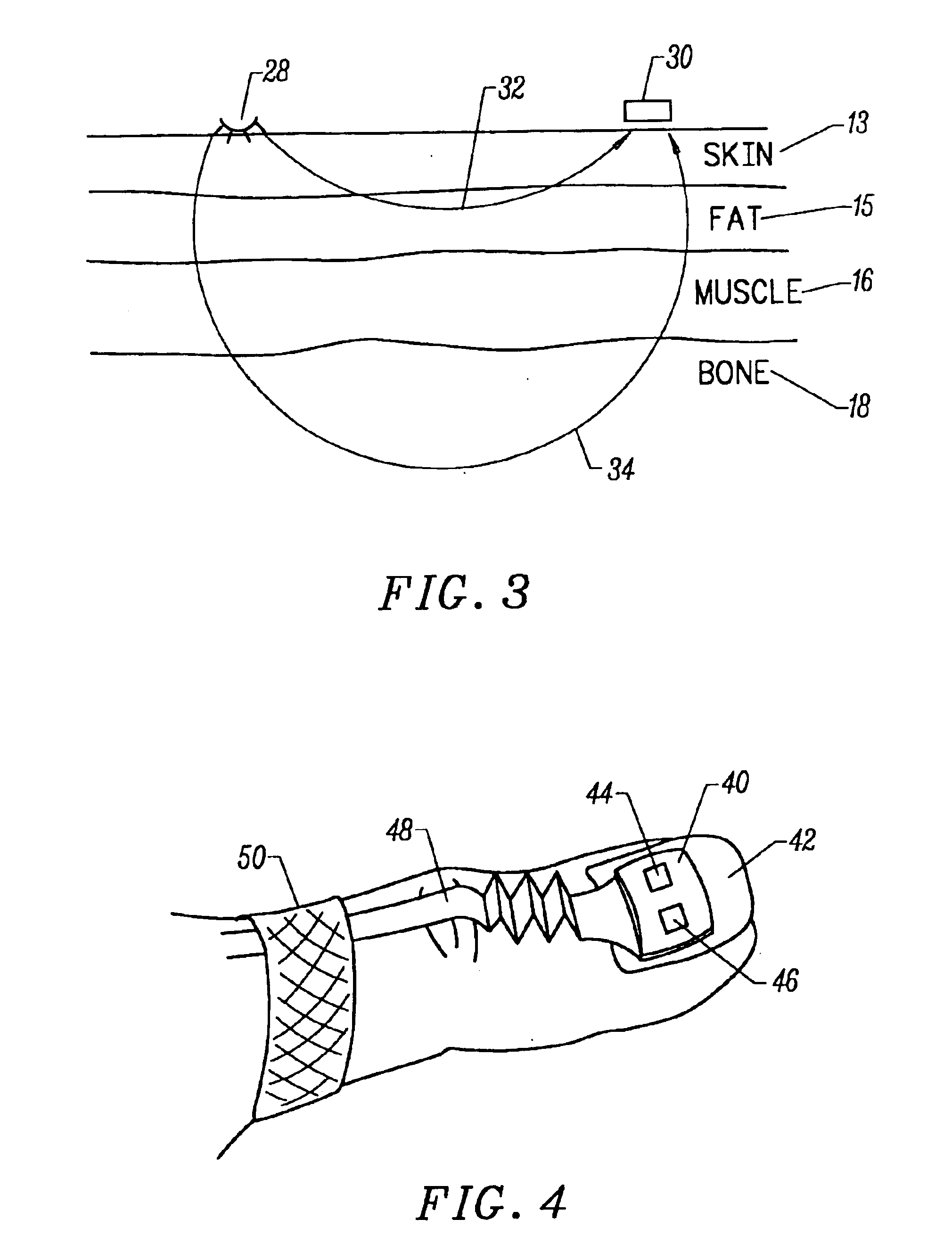
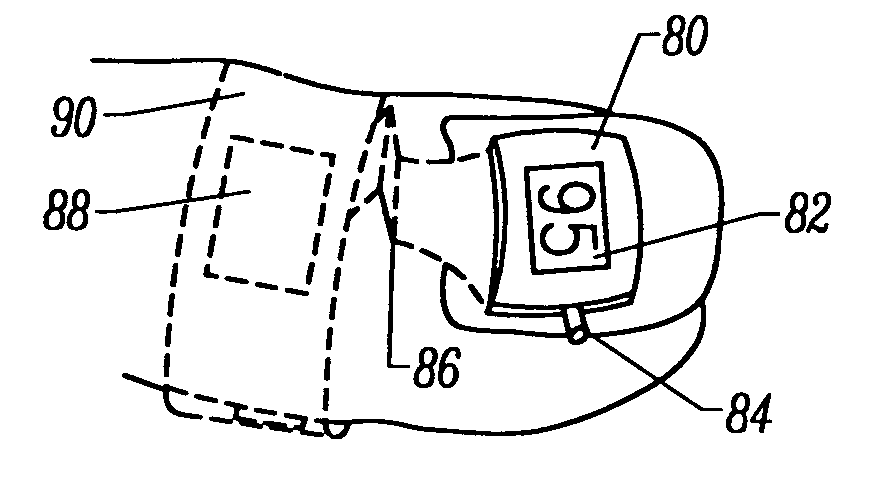
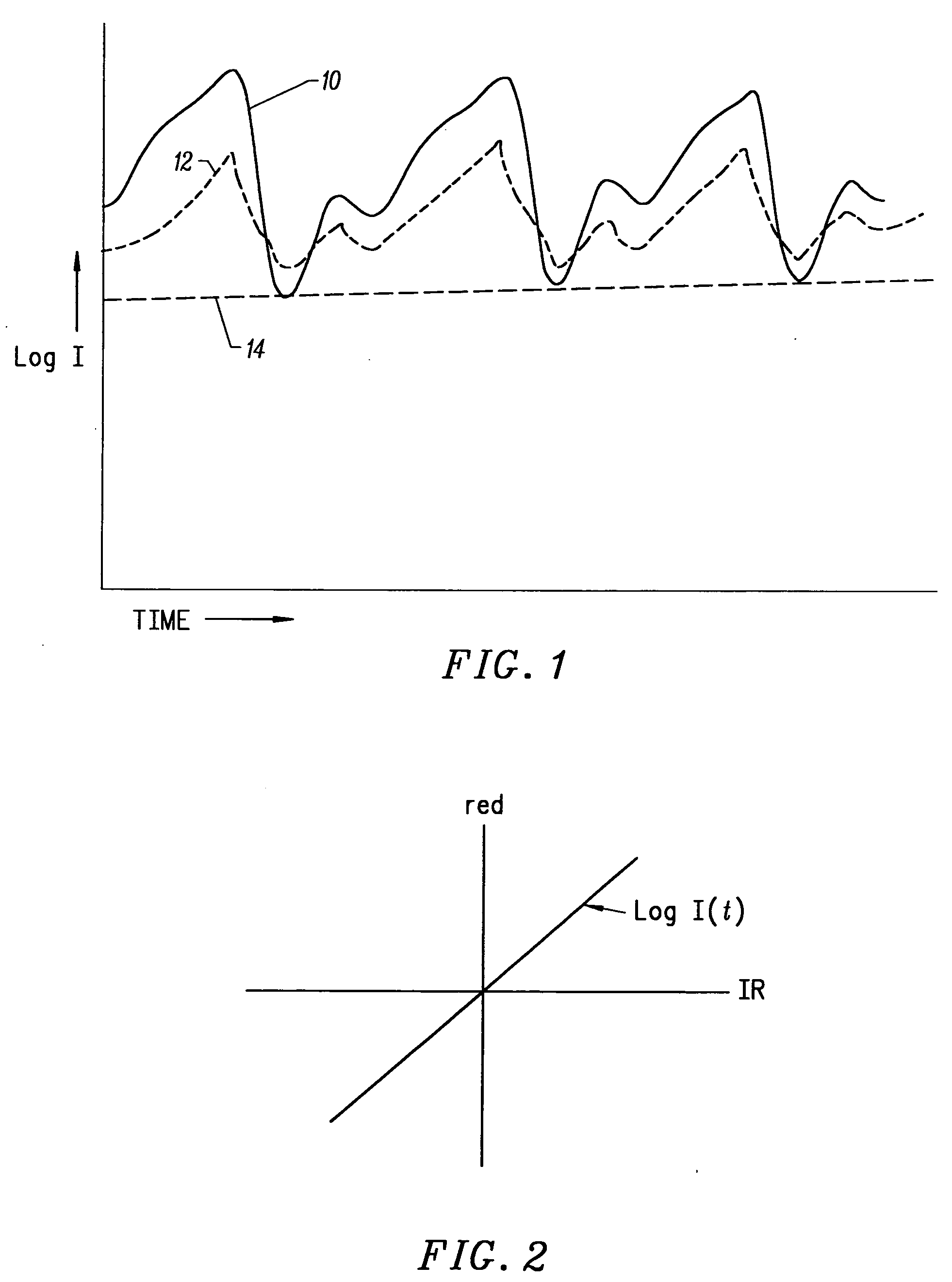
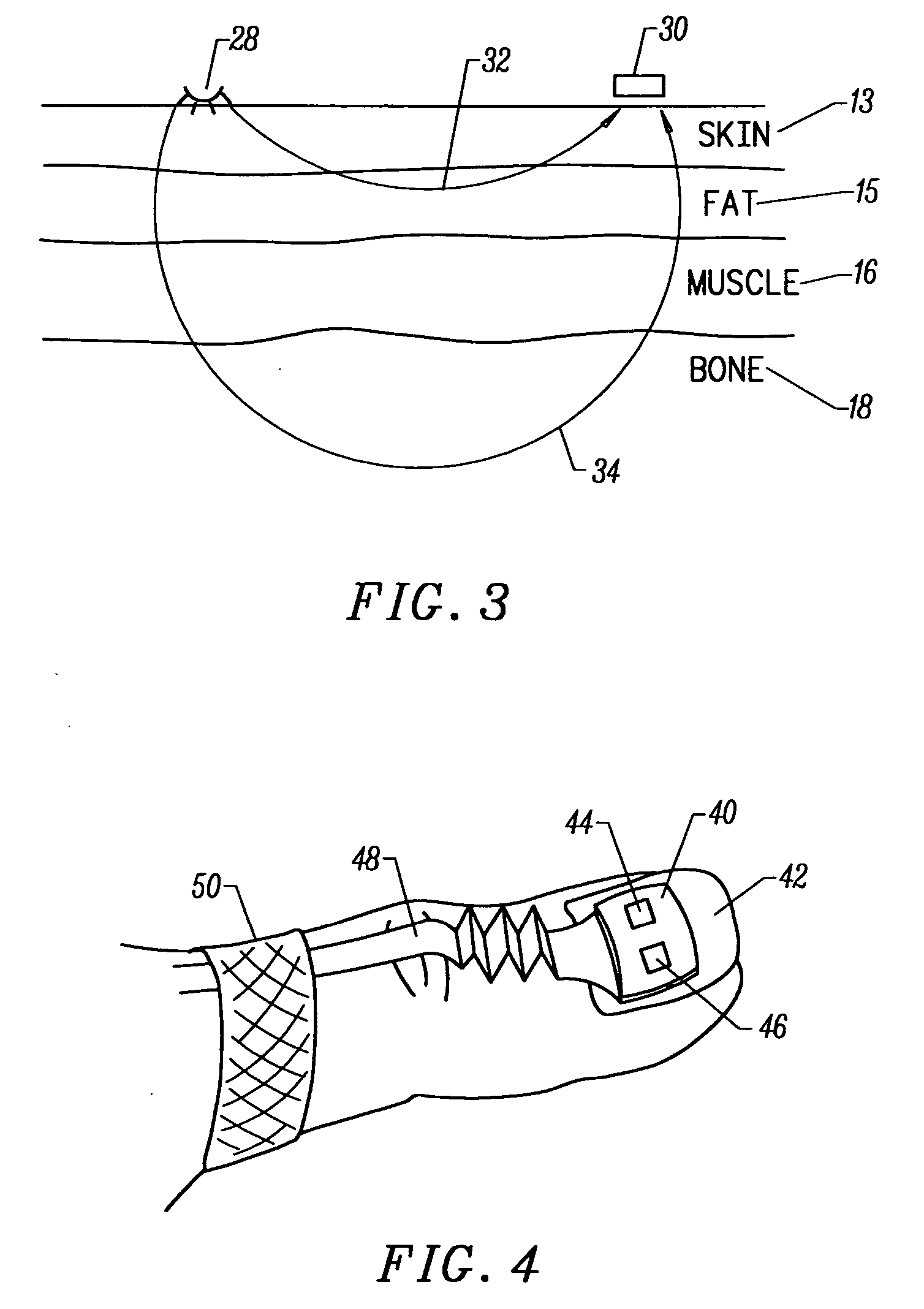
Motion compatible sensor for non-invasive optical blood analysis
InactiveUS6845256B2Limit differential phase errorLow profileSensorsBlood characterising devicesClassical mechanicsPulse oximetry
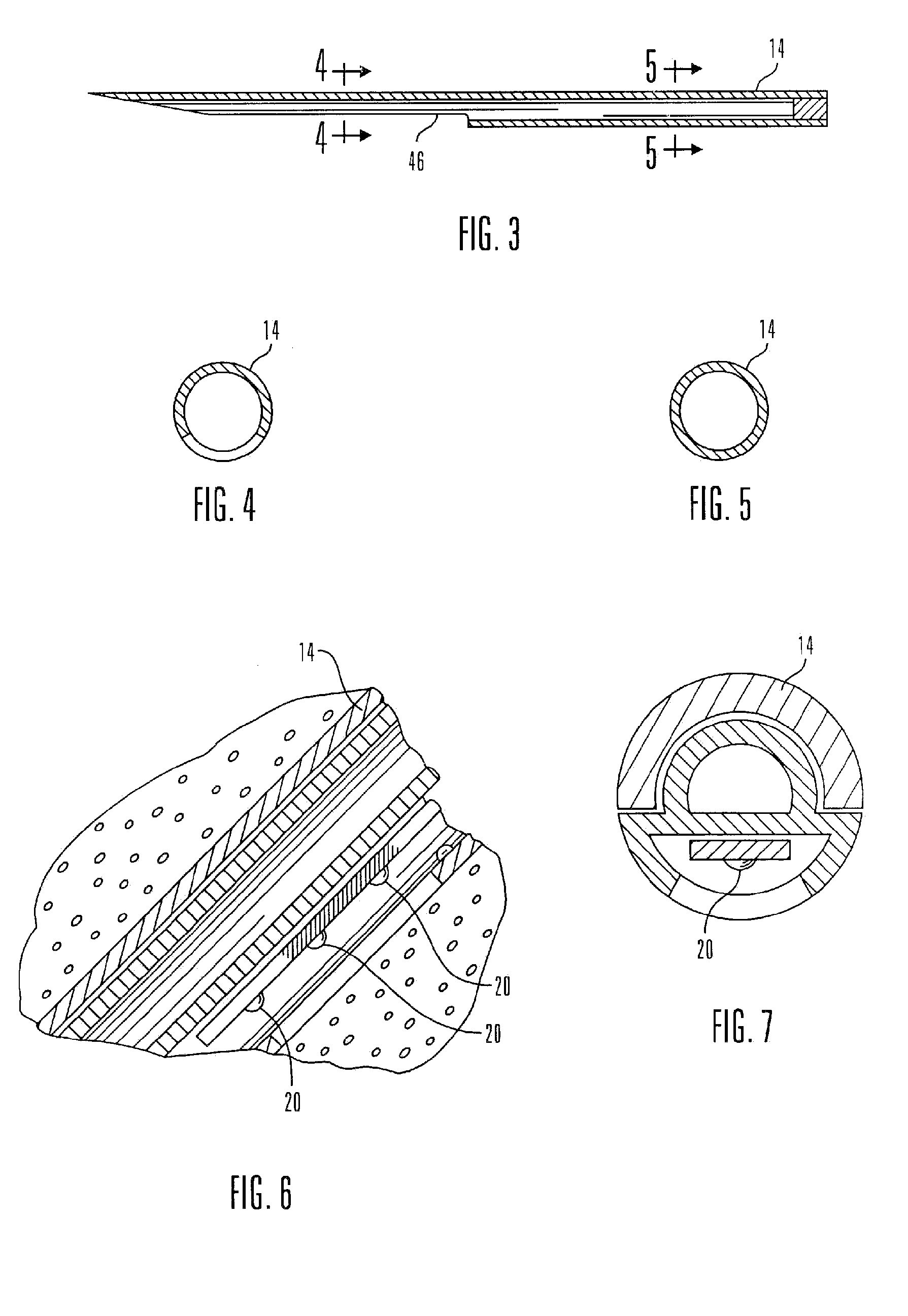
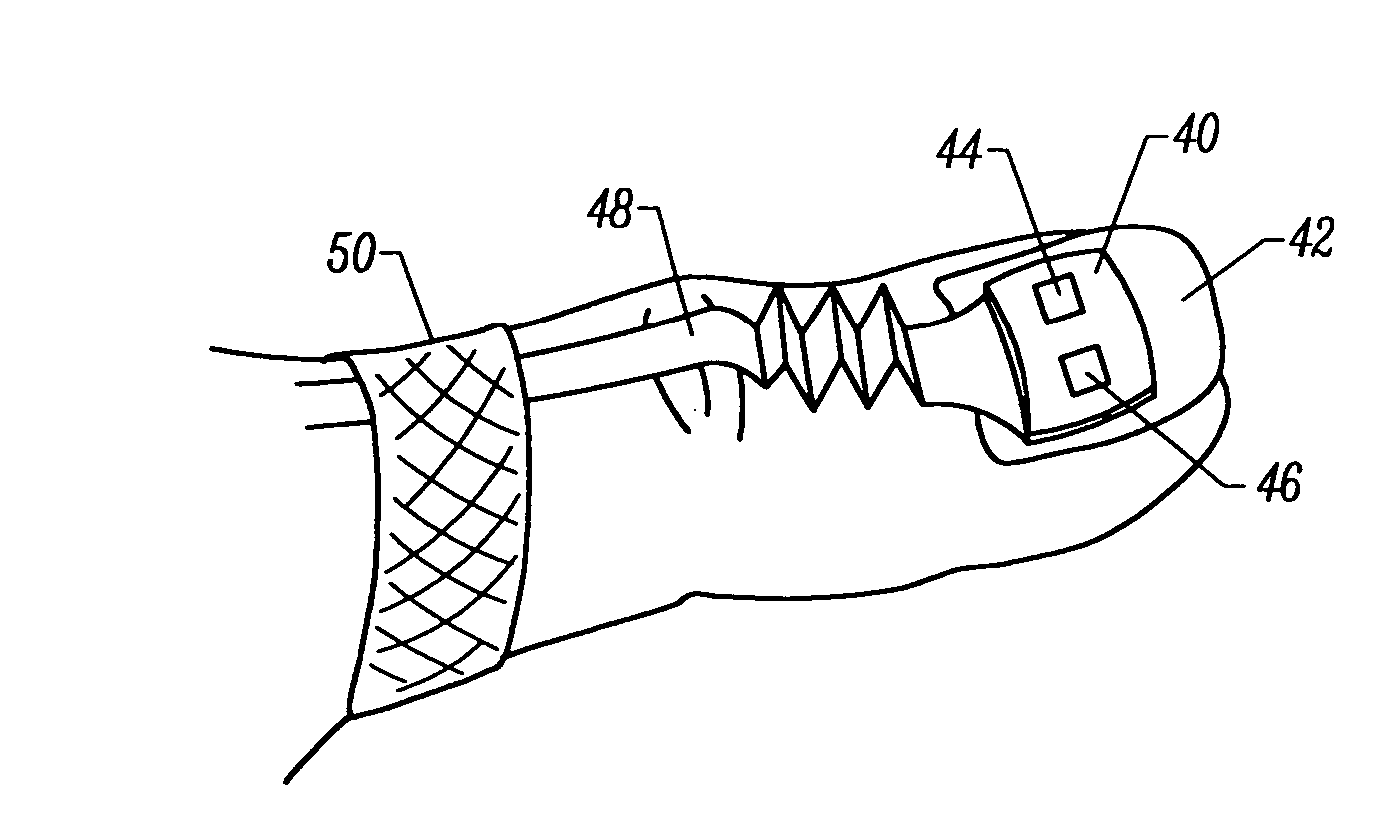
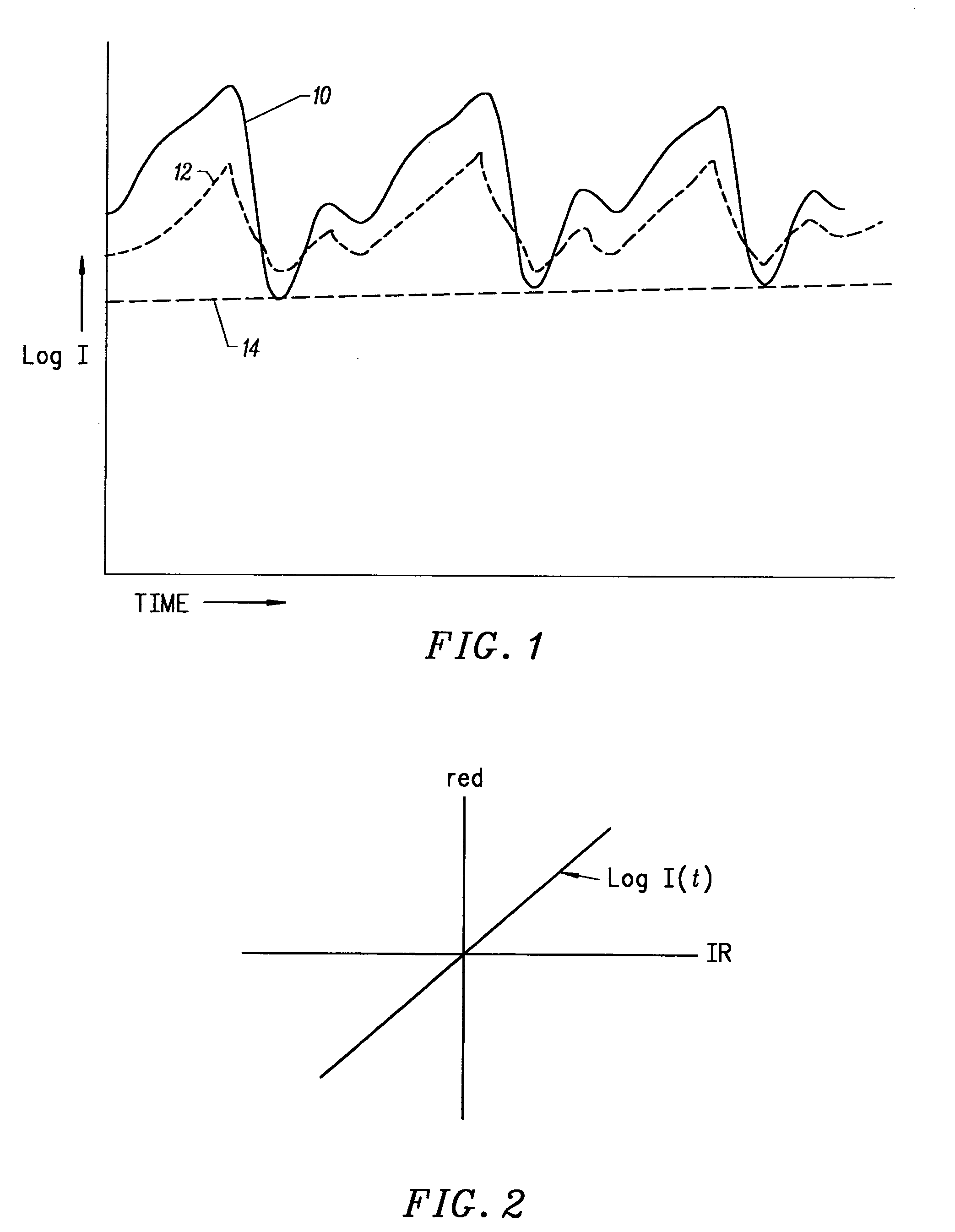
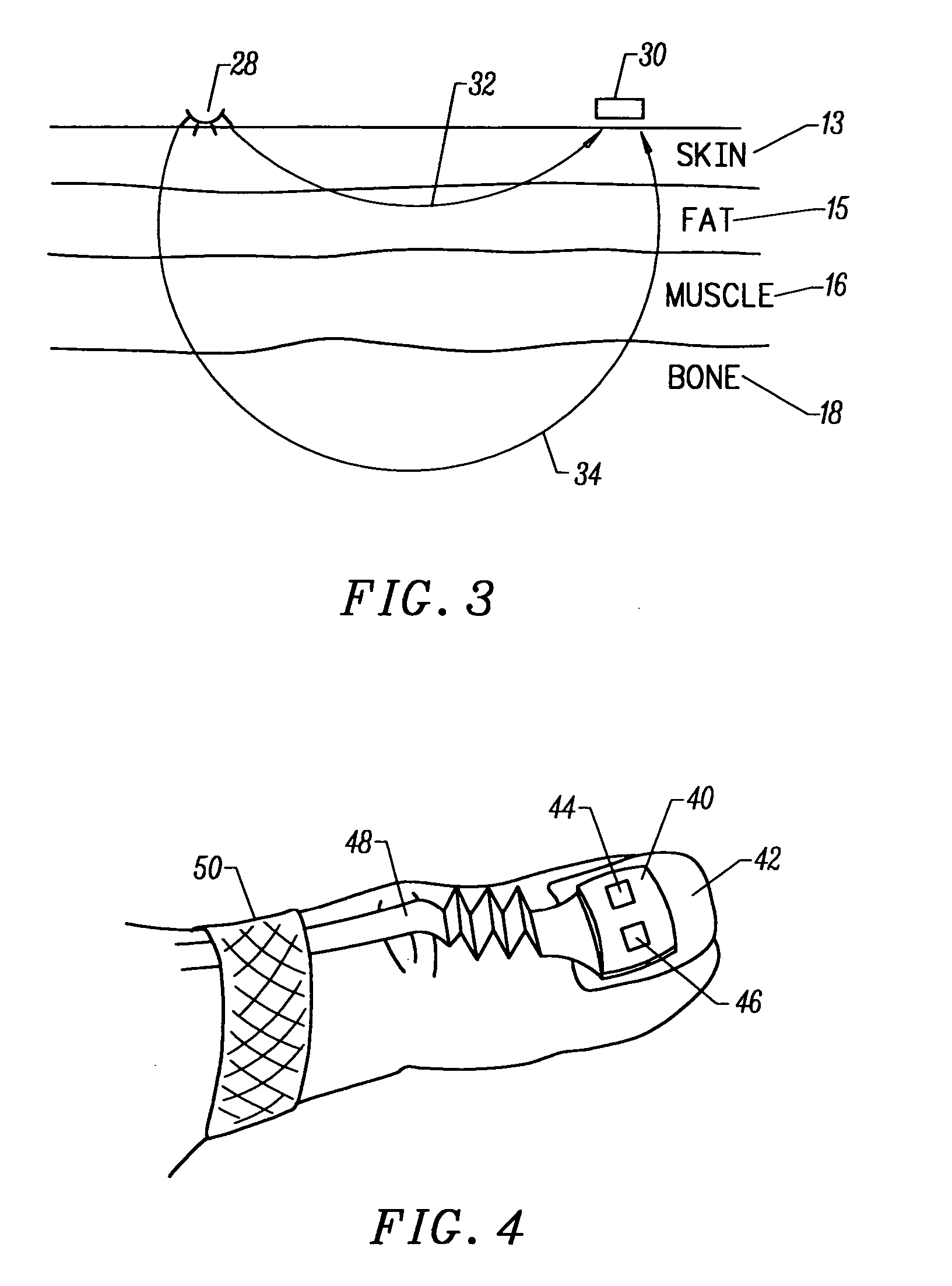
A non-invasive optical sensor which uses the motion signal to calculate the physiological characteristic being measured. For pulse oximetry, a least squares or a ratio-of-ratios technique can be applied to the motion signal itself. This is made possible by selecting a site on the patient where variations in motion produce signals of two wavelengths which are sufficiently correlated. In particular, it has been determined that a sensor placed on a nail, in particular a thumbnail, exhibits the characteristics of having the red and infrared signals correlated when used for pulse oximetry, and the resulting signals correlate to arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:NELL COR PURITAN BENNETT INC (US)
Modified Sensor Calibration Algorithm
ActiveUS20090112478A1Reduce weightQuick changeTesting/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsData integrityGlucose polymers
A method of calibrating glucose monitor data includes collecting the glucose monitor data over a period of time at predetermined intervals, obtaining reference glucose values from a reference source that temporally correspond with the glucose monitor data obtained at the predetermined intervals, calculating the calibration characteristics using the reference glucose values and corresponding glucose monitor data to regress the obtained glucose monitor data, and calibrating the obtained glucose monitor data using the calibration characteristics. In additional embodiments, calculation of the calibration characteristics includes linear regression and, in particular embodiments, least squares linear regression. Alternatively, calculation of the calibration characteristics includes non-linear regression. Data integrity may be verified and the data may be filtered. Further, calibration techniques may be modified during a fast rate of change in the patient's blood glucose level to increase sensor accuracy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Motion compatible sensor for non-invasive optical blood analysis
InactiveUS20050070773A1Low profileReduce quality problemsSensorsBlood characterising devicesClassical mechanicsPulse oximetry
A non-invasive optical sensor which uses the motion signal to calculate the physiological characteristic being measured. For pulse oximetry, a least squares or a ratio-of-ratios technique can be applied to the motion signal itself. This is made possible by selecting a site on the patient where variations in motion produce signals of two wavelengths which are sufficiently correlated. In particular, it has been determined that a sensor placed on a nail, in particular a thumbnail, exhibits the characteristics of having the red and infrared signals correlated when used for pulse oximetry, and the resulting signals correlate to arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:NELLCOR PURITAN BENNETT LLC
De-embedment of optical component characteristics and calibration of optical receivers using rayleigh backscatter
InactiveUS6947147B2Accurate analysisIncrease the number ofPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringFiber
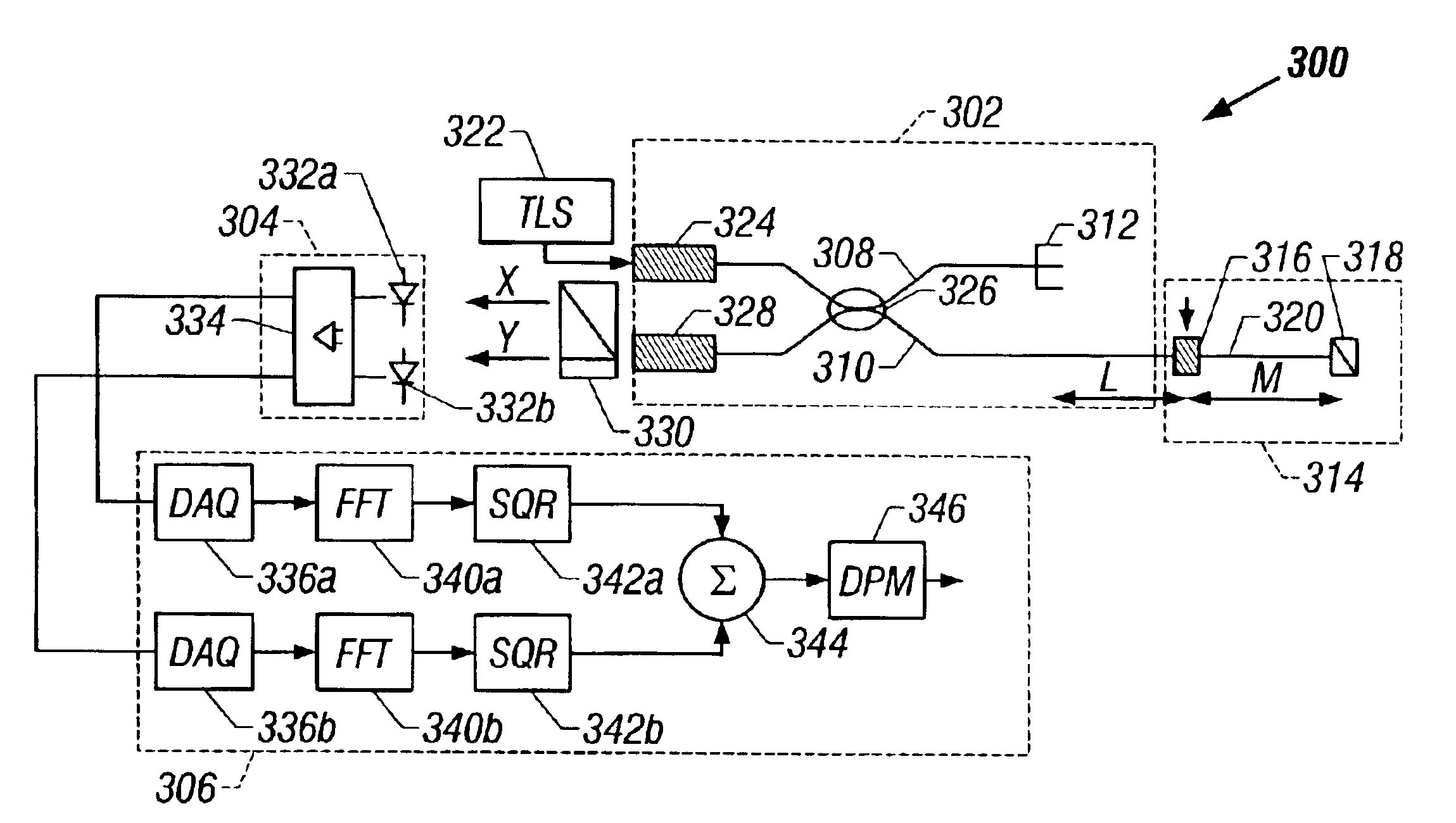
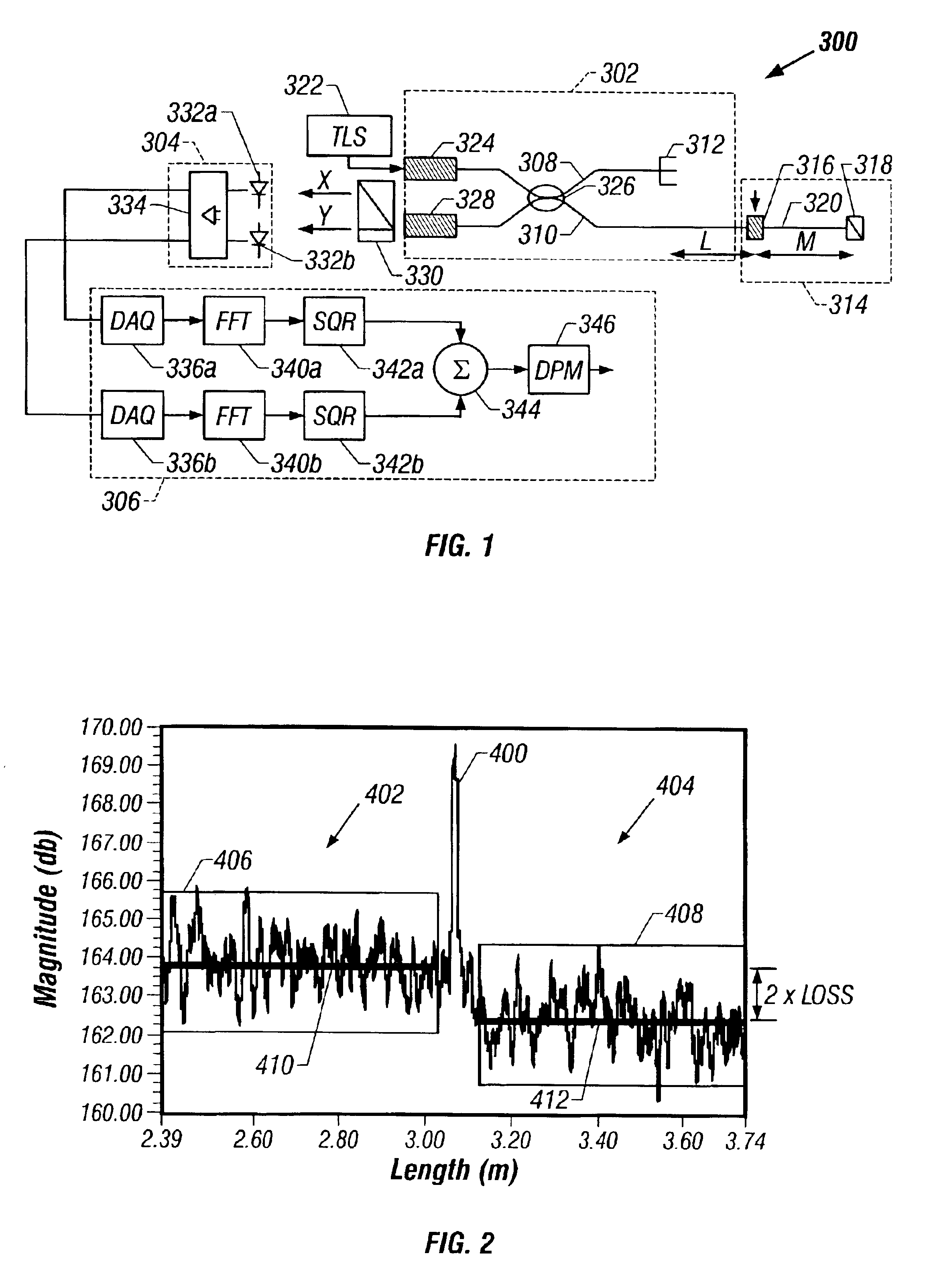
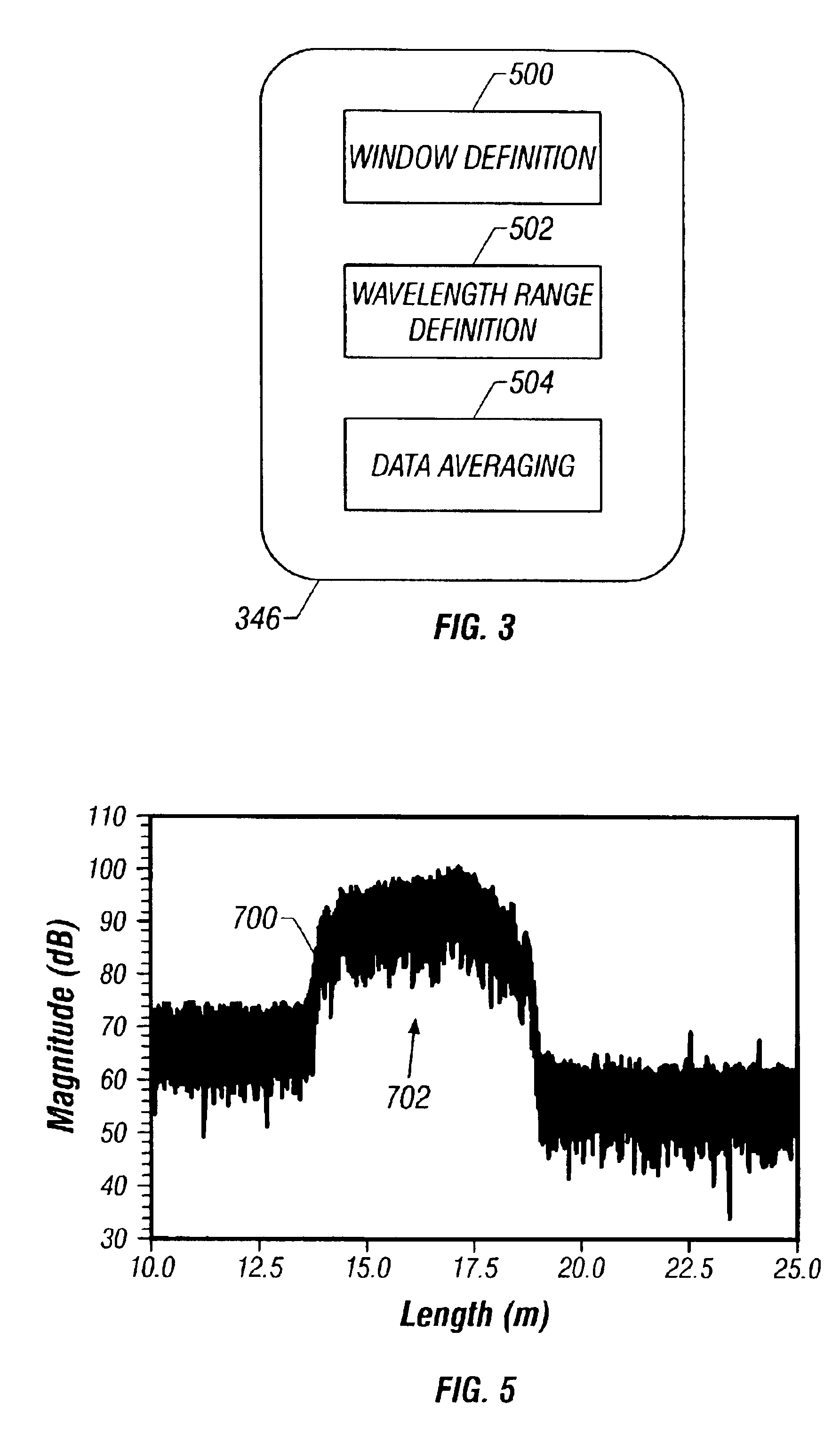
Method and system are disclosed for de-embedding optical component characteristics from optical device measurements. In particular, the invention uses frequency domain averaging of the RBS on both sides of an optical component to determine one or more of its optical characteristics. Where the RBS has a slope (e.g., as in the case of a lossy fiber), a frequency domain least square fit can be used to determine the optical component characteristics. In addition, the invention uses a reference DUT to correct for variations in the frequency response of the photoreceiver. A reference interferometer is used in the invention to correct for sweep non-linearity of the TLS. The optical component characteristics are then de-embedded from optical device measurements to provide a more precise analysis of the optical device.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Motion compatible sensor for non-invasive optical blood analysis
InactiveUS20050070775A1Low profileReduce quality problemsSensorsBlood characterising devicesClassical mechanicsPulse oximetry
A non-invasive optical sensor which uses the motion signal to calculate the physiological characteristic being measured. For pulse oximetry, a least squares or a ratio-of-ratios technique can be applied to the motion signal itself. This is made possible by selecting a site on the patient where variations in motion produce signals of two wavelengths which are sufficiently correlated. In particular, it has been determined that a sensor placed on a nail, in particular a thumbnail, exhibits the characteristics of having the red and infrared signals correlated when used for pulse oximetry, and the resulting signals correlate to arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:NELL COR PURITAN BENNETT INC (US)
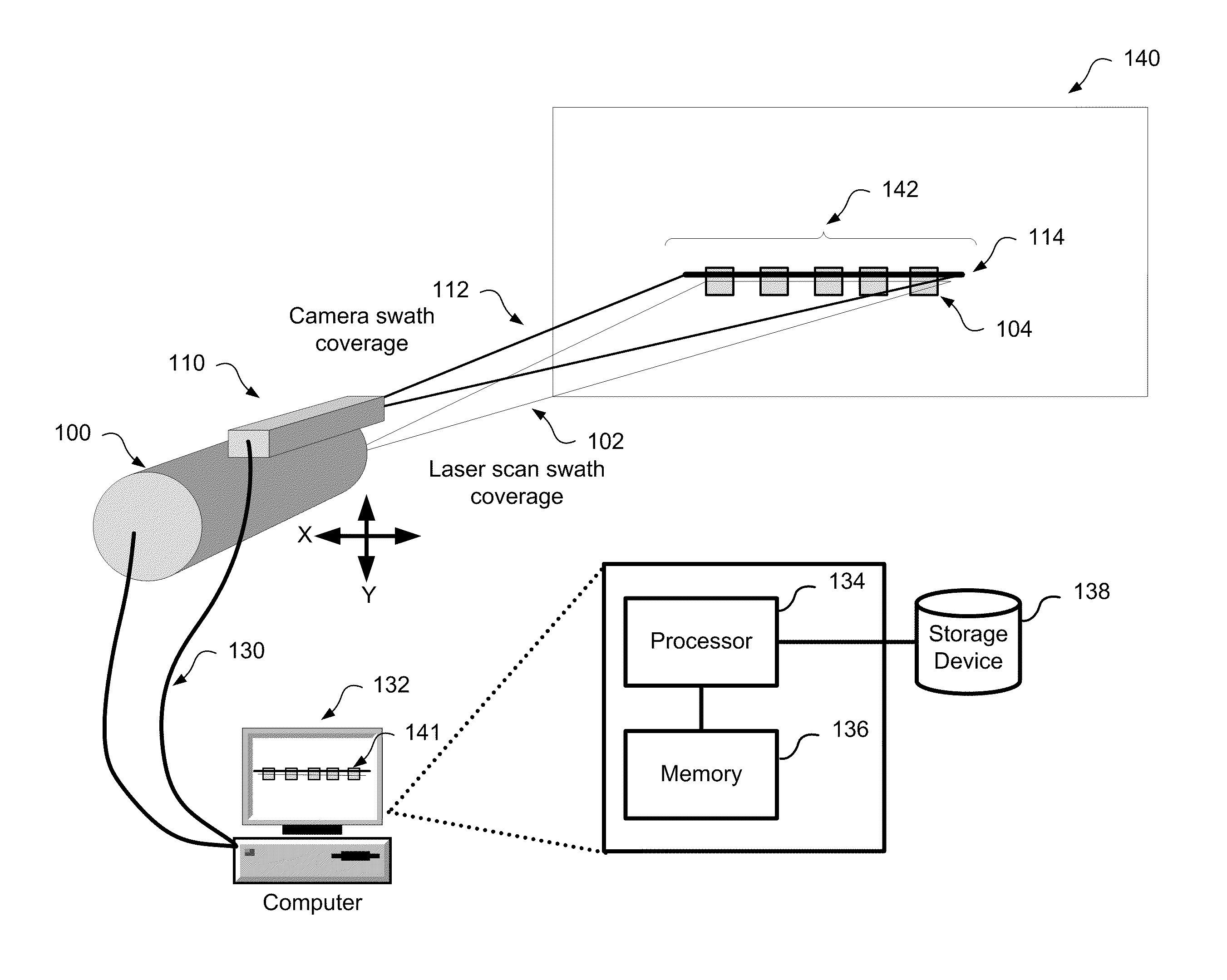
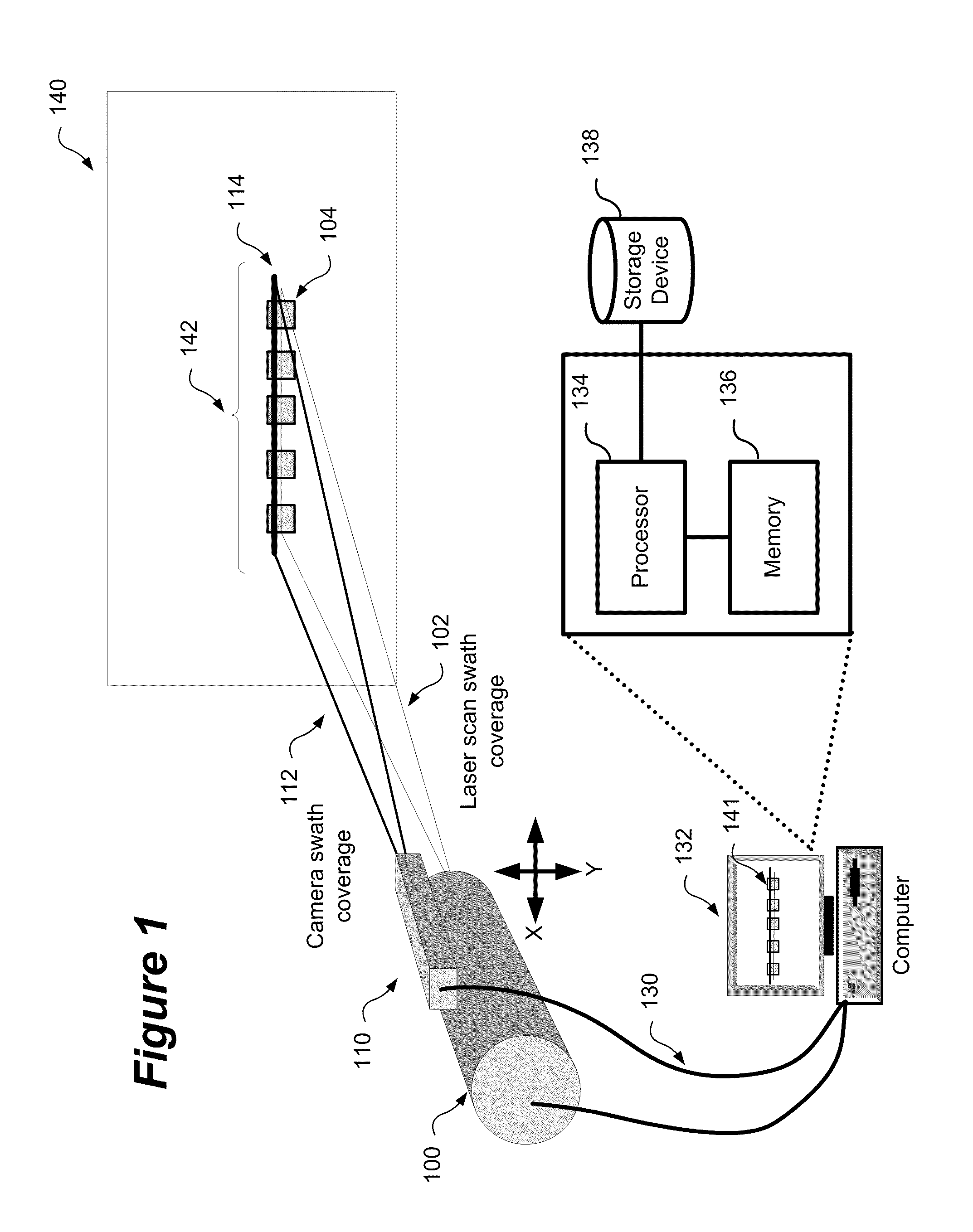
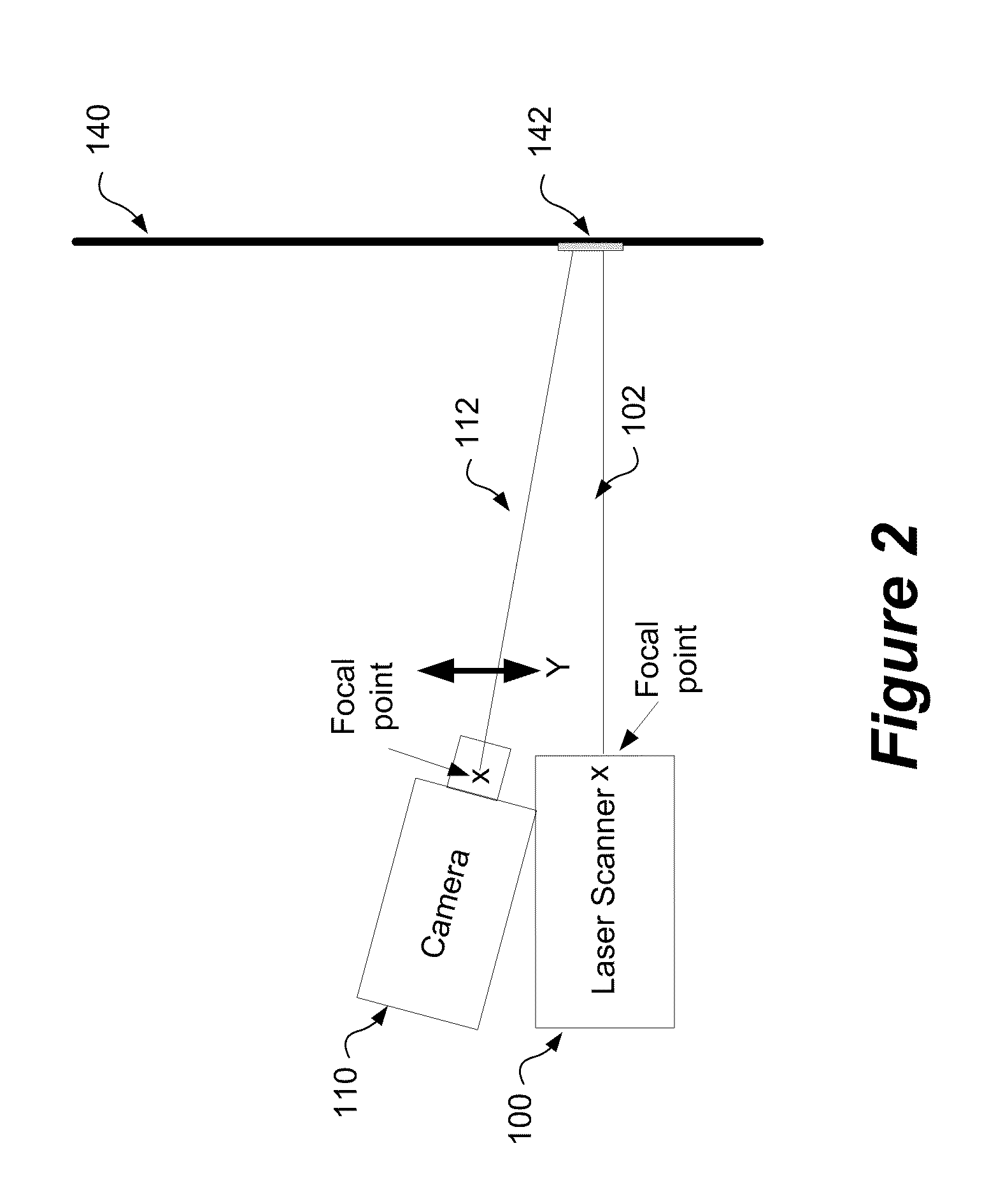
Method and system for aligning a line scan camera with a lidar scanner for real time data fusion in three dimensions
An apparatus and method for aligning a line scan camera with a Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) scanner for real-time data fusion in three dimensions is provided. Imaging data is captured at a computer processor simultaneously from the line scan camera and the laser scanner from target object providing scanning targets defined in an imaging plane perpendicular to focal axes of the line scan camera and the LiDAR scanner. X-axis and Y-axis pixel locations of a centroid of each of the targets from captured imaging data is extracted. LiDAR return intensity versus scan angle is determined and scan angle locations of intensity peaks which correspond to individual targets is determined. Two axis parallax correction parameters are determined by applying a least squares. The correction parameters are provided to post processing software to correct for alignment differences between the imaging camera and LiDAR scanner for real-time colorization for acquired LiDAR data.
Owner:AMBERCORE SOFTWARE
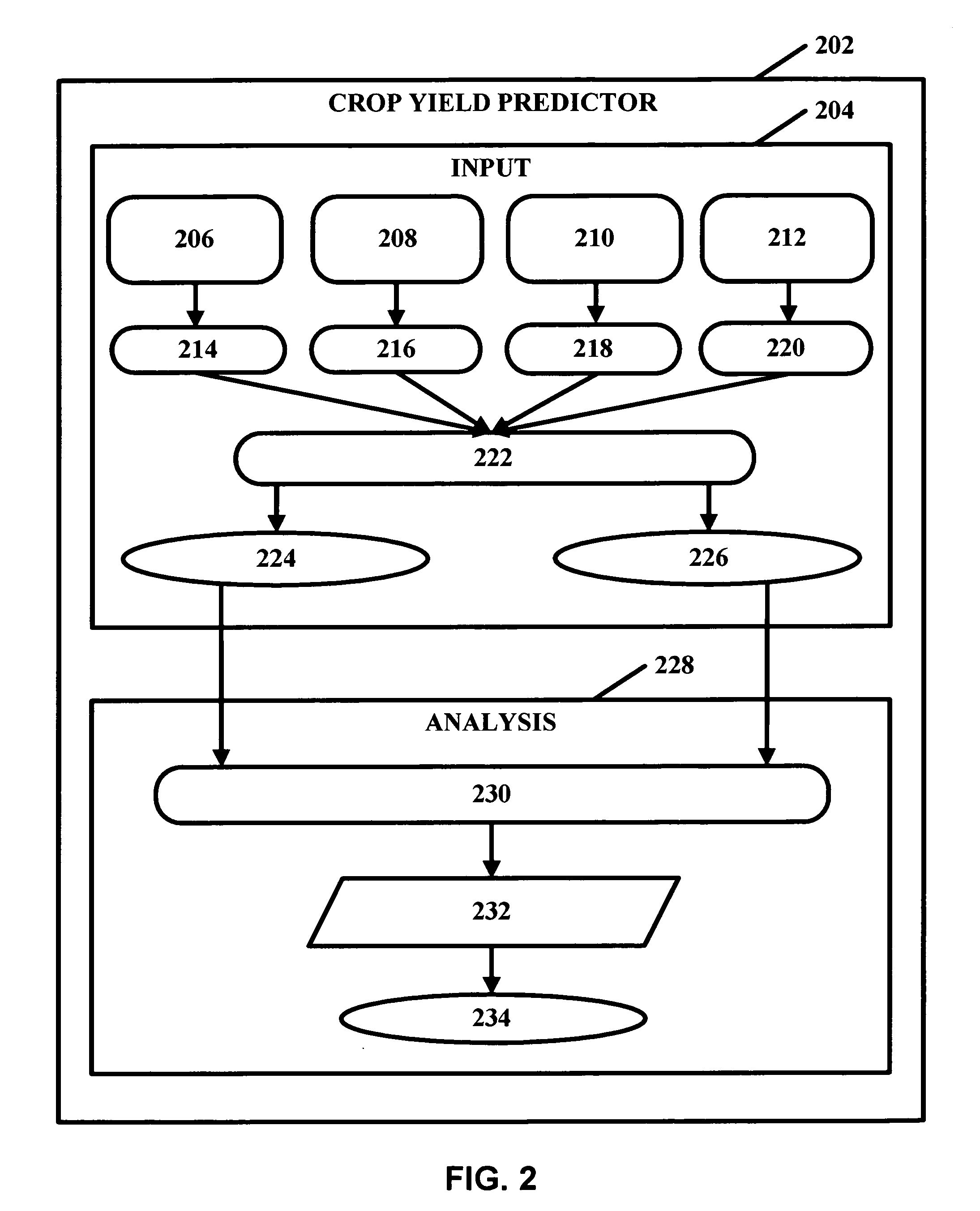
Crop yield prediction
InactiveUS20050234691A1Climate change adaptationAnalogue computers for chemical processesNon linear methodsEngineering
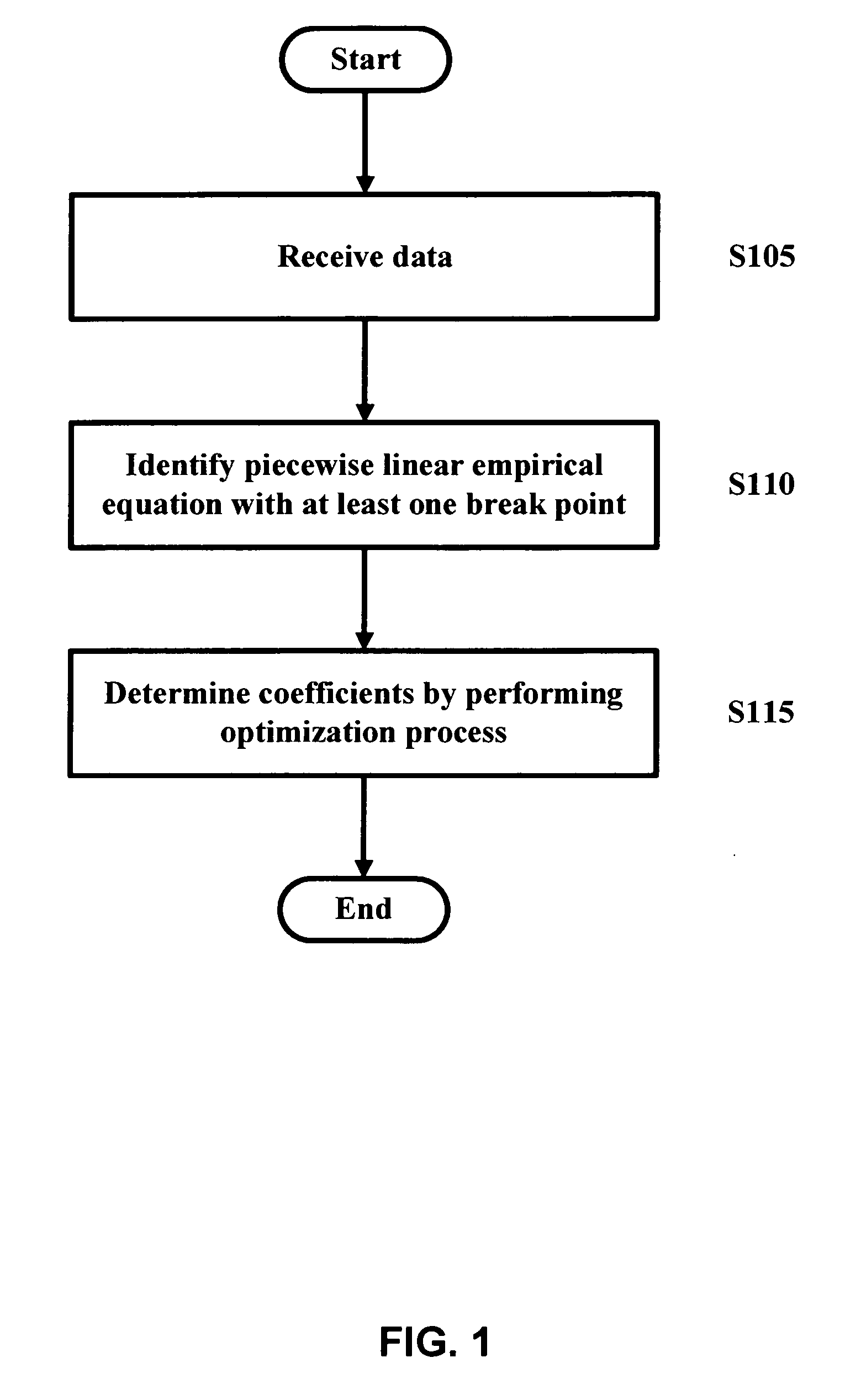
Crop yield may be assessed and predicted using a piecewise linear regression method with break point and various weather and agricultural parameters, such as NDVI, surface parameters (soil moisture and surface temperature) and rainfall data. These parameters may help aid in estimating and predicting crop conditions. The overall crop production environment can include inherent sources of heterogeneity and their nonlinear behavior. A non-linear multivariate optimization method may be used to derive an empirical crop yield prediction equation. Quasi-Newton method may be used in optimization for minimizing inconsistencies and errors in yield prediction. Minimization of least square loss function through iterative convergence of pre-defined empirical equation can be based on piecewise linear regression method with break point. This non-linear method can achieve acceptable lower residual values with predicted values very close to the observed values. The present invention can be modified and tailored for different crops worldwide.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
Geometry calibration algorithm for large flat module detector CT scanner
ActiveUS9398890B2The process is simple and effectiveSmall sizeComputerised tomographsTomographyCt scannersComputer science
A method for geometric calibration of a CT scanner, including, for each row of at least one row of detector cells, establishing a complete geometric description of the CT scanner, including at least one unknown geometric parameter, establishing a description of a forward projection function using the complete geometric description, acquiring actual projection coordinates of a calibration phantom placed in a scanning field of view (SFOV) on a current row of detector cells and corresponding to a plurality of angles, acquiring calculated projection coordinates of the calibration phantom on the current row of detector cells and corresponding to the plurality of angles using the description of the forward projection function, and acquiring a calibrated value for the at least one unknown geometric parameter by evaluating the at least one unknown geometric parameter based on the acquired actual projection coordinates and calculated projection coordinates via a nonlinear least square fitting algorithm.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
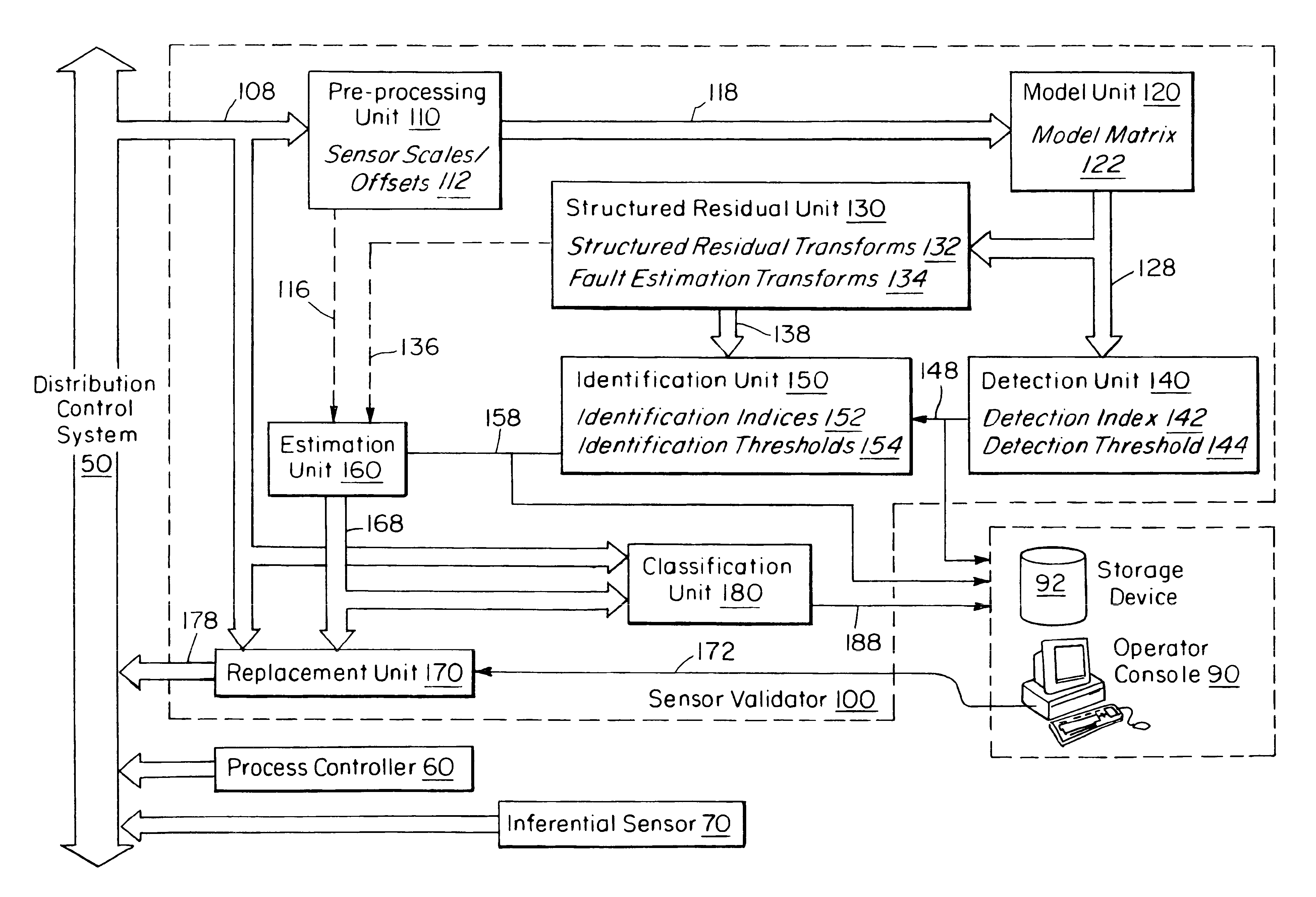
Sensor validation apparatus and method
An apparatus and method is disclosed for detecting, identifying, and classifying faults occurring in sensors measuring a process. A variety of process models can be used such as first principles models, dynamic multivariable predictive control models, from data using statistical methods such as partial least squares (PLS) or principal component analysis. If faults are identified in one or more sensors, the apparatus and method provide replacement values for the faulty sensors so that any process controllers and process monitoring systems that use these sensors can remain in operation during the fault period. The identification of faulty sensors is achieved through the use of a set of structured residual transforms that are uniquely designed to be insensitive to specific subsets of sensors, while being maximally sensitive to sensors not in the subset. Identified faults are classified into one of the types Complete Failure, Bias, Drift, Precision Loss, or Unknown.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
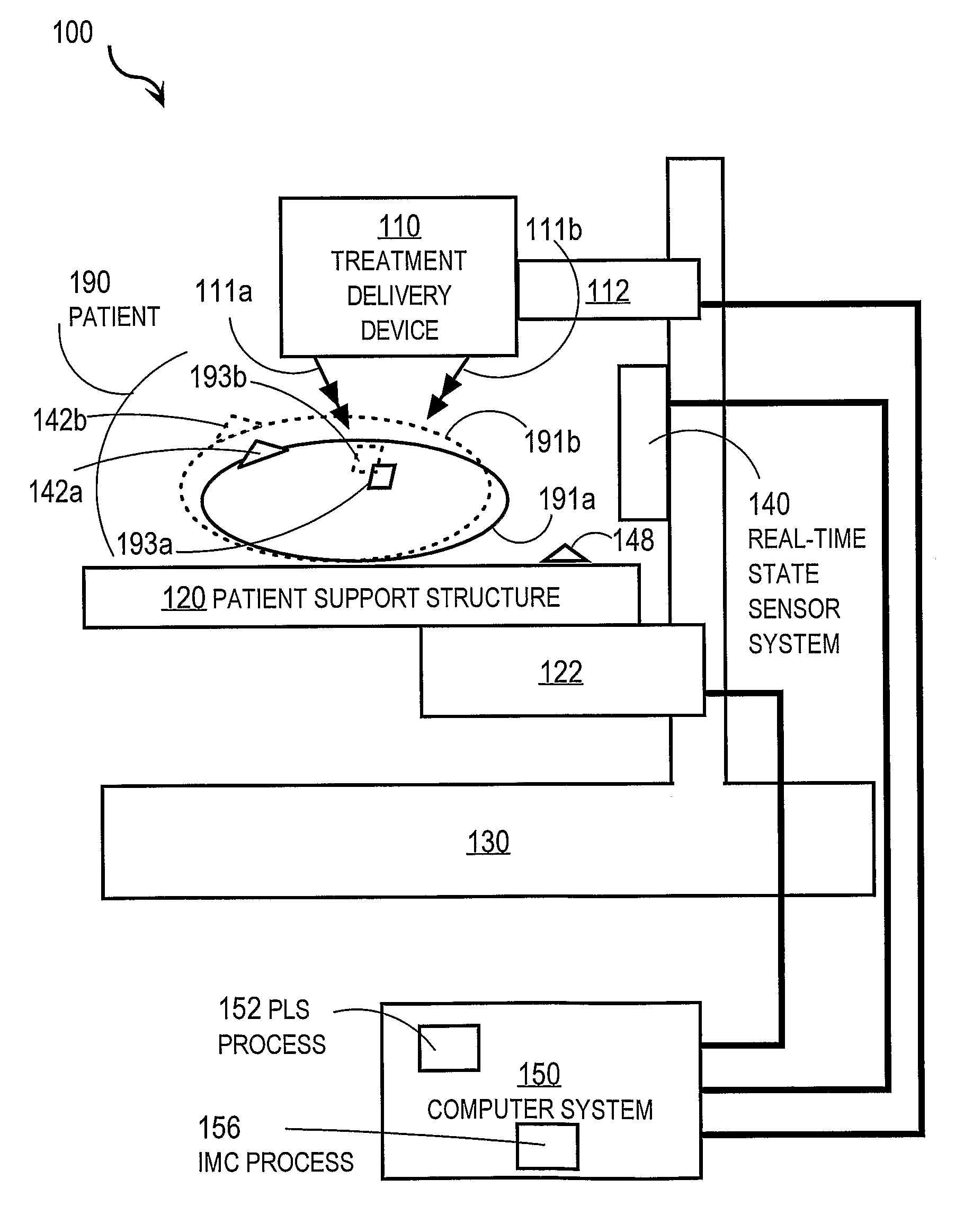
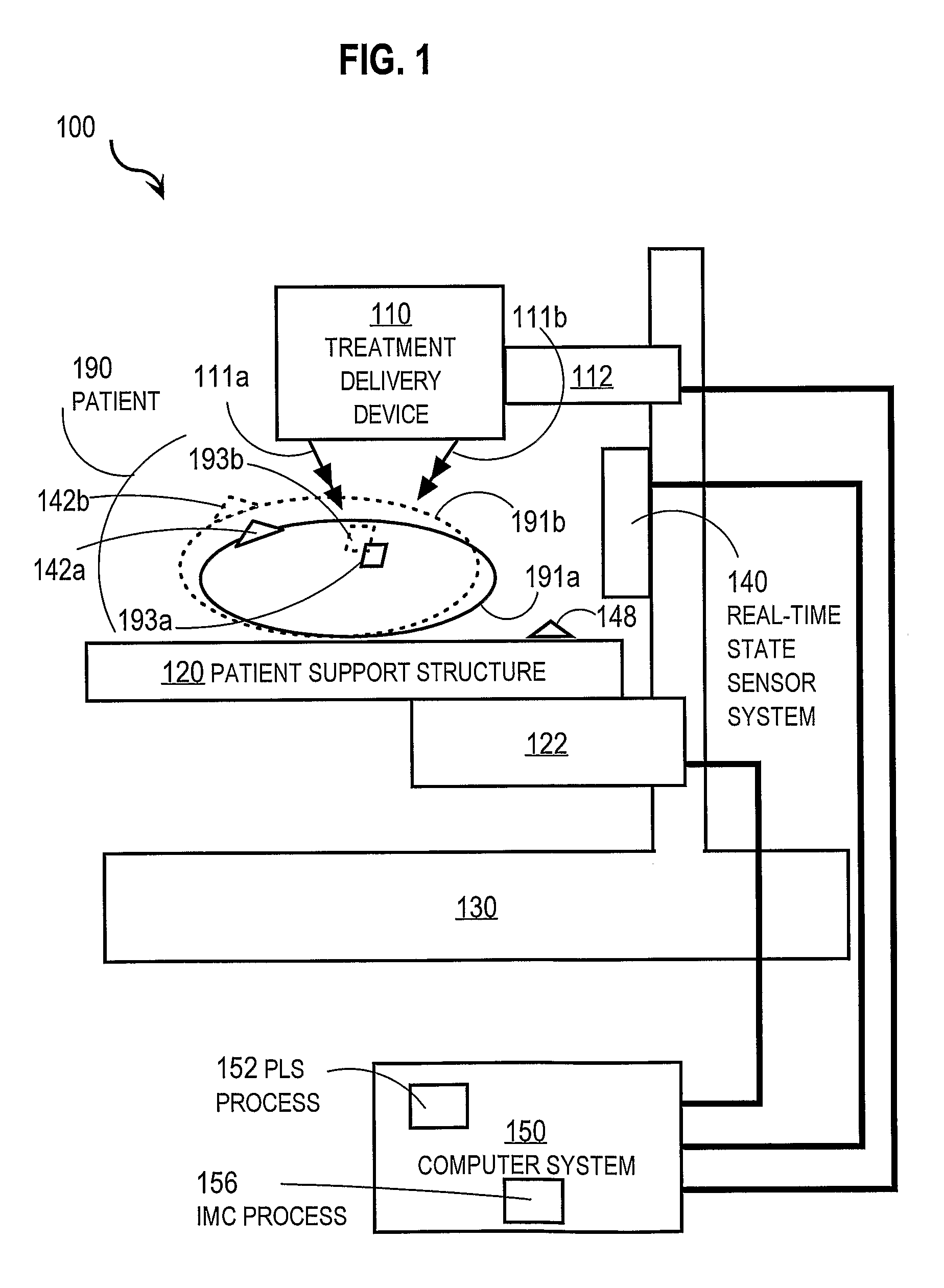
Techniques For Compensating Movement of a Treatment Target in a Patient
ActiveUS20080212737A1Reduce deliveryConvenient treatmentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTreatment deliveryMedicine
Techniques for improving treatment delivered to a target site in a patient include delivering a treatment from a treatment delivery device to a target site in a patient supported by a patient support structure. During the delivery of treatment, a state of the patient is measured to produce real-time measurement data. Measuring the state is non-invasive; and the measured state is a correlated surrogate for position of the target site. Compensating movement data is determined based on the real-time measurement data to cause the target site to maintain a particular spatial relationship with the treatment delivery device. Either the treatment delivery device, or the support structure, or both, are moved based on the compensating movement data. When the delivery device alone is moved, the correlation between measured state and target site is based on partial least squares applied to pre-treatment measurements of both.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
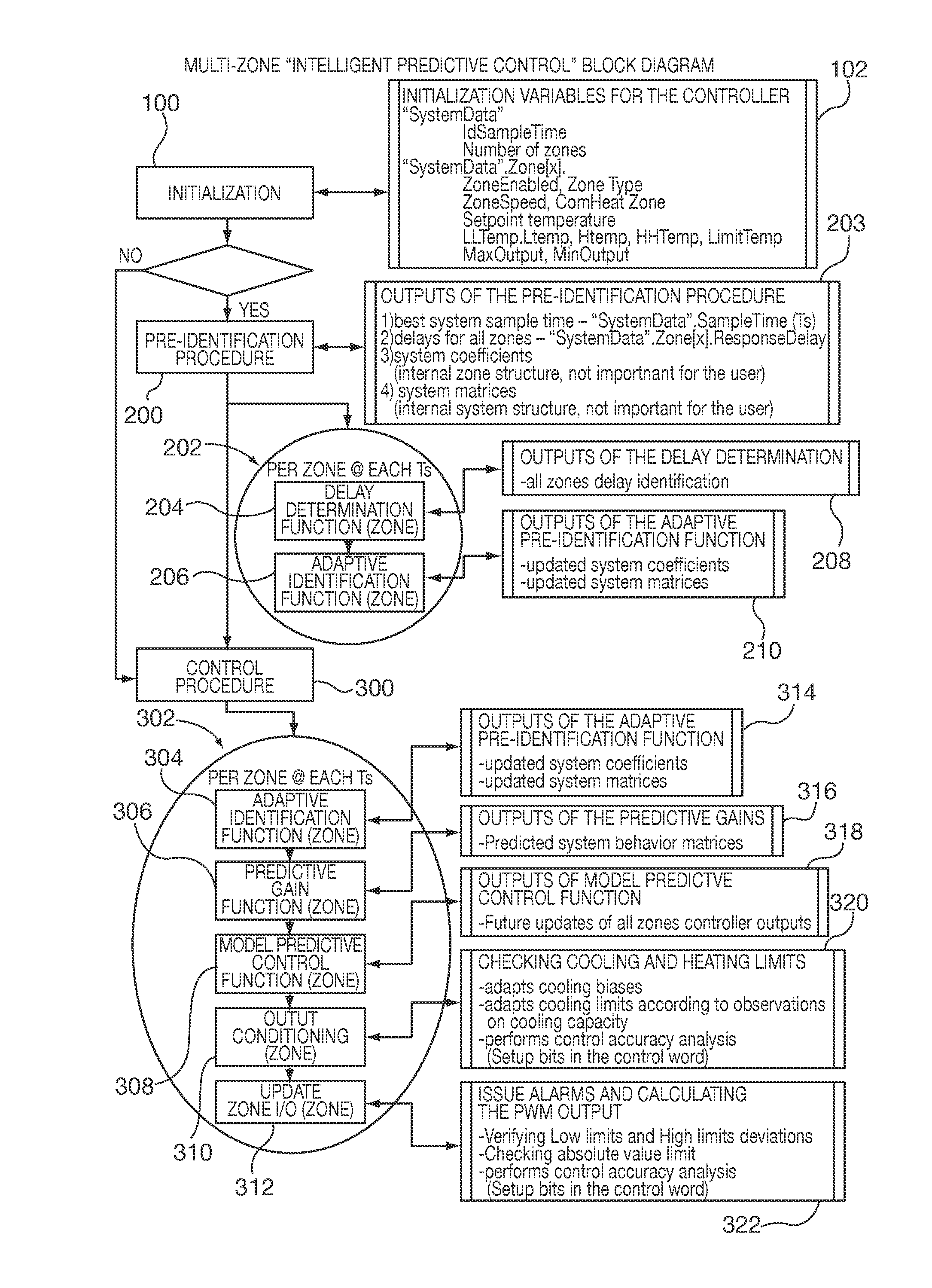
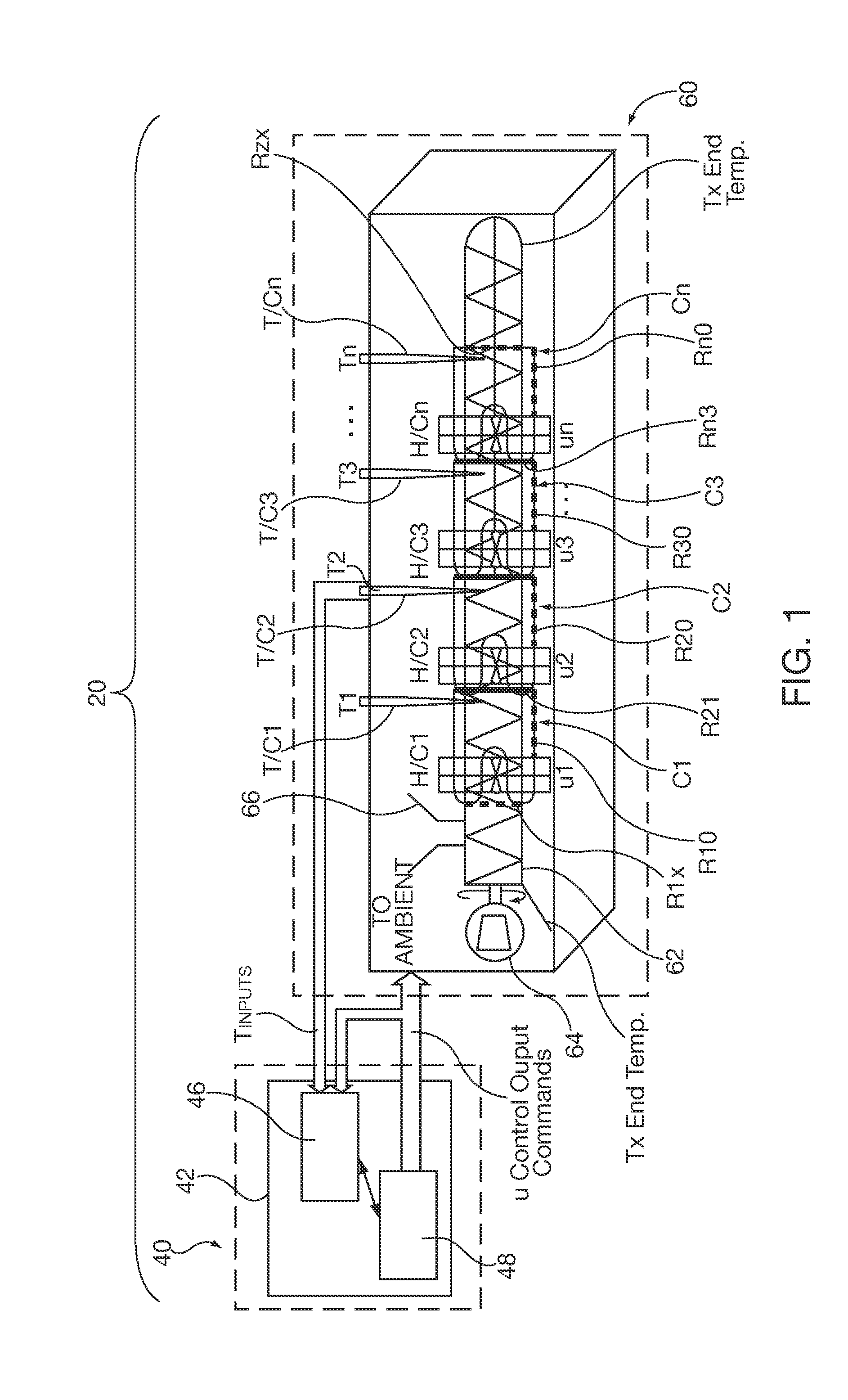
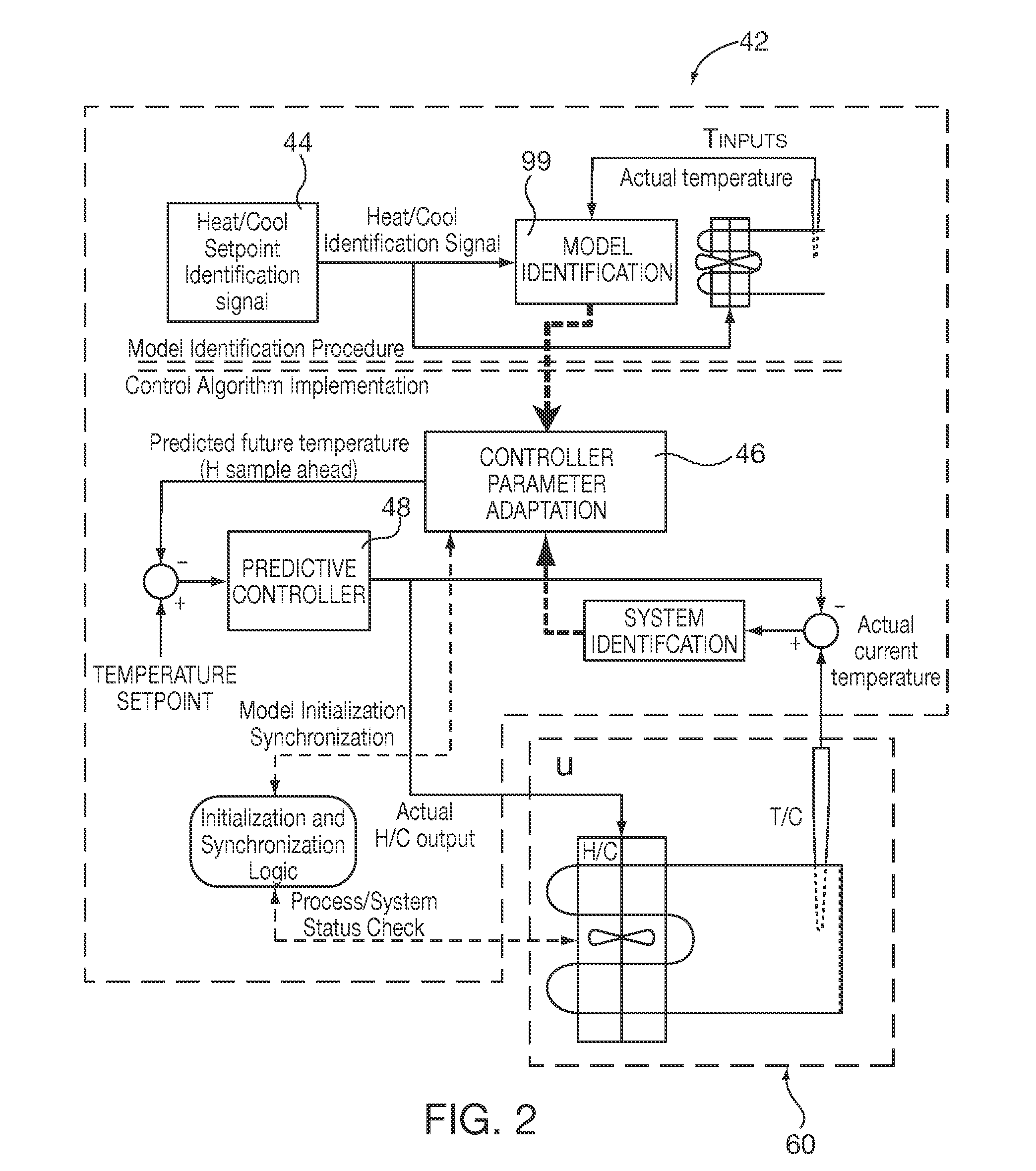
Method and apparatus of a self-configured, model-based adaptive, predictive controller for multi-zone regulation systems
InactiveUS20110022193A1Easy to addPrecise processingSampled-variable control systemsTravelling carriersHorizonPlastic injection molding
A control system simultaneously controls a multi-zone process with a self-adaptive model predictive controller (MPC), such as temperature control within a plastic injection molding system. The controller is initialized with basic system information. A pre-identification procedure determines a suggested system sampling rate, delays or “dead times” for each zone and initial system model matrix coefficients necessary for operation of the control predictions. The recursive least squares based system model update, control variable predictions and calculations of the control horizon values are preferably executed in real time by using matrix calculation basic functions implemented and optimized for being used in a S7 environment by a Siemens PLC. The number of predictions and the horizon of the control steps required to achieve the setpoint are significantly high to achieve smooth and robust control. Several matrix calculations, including an inverse matrix procedure performed at each sample pulse and for each individual zone determine the MPC gain matrices needed to bring the system with minimum control effort and variations to the final setpoint. Corrective signals, based on the predictive model and the minimization criteria explained above, are issued to adjust system heating / cooling outputs at the next sample time occurrence, so as to bring the system to the desired set point. The process is repeated continuously at each sample pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
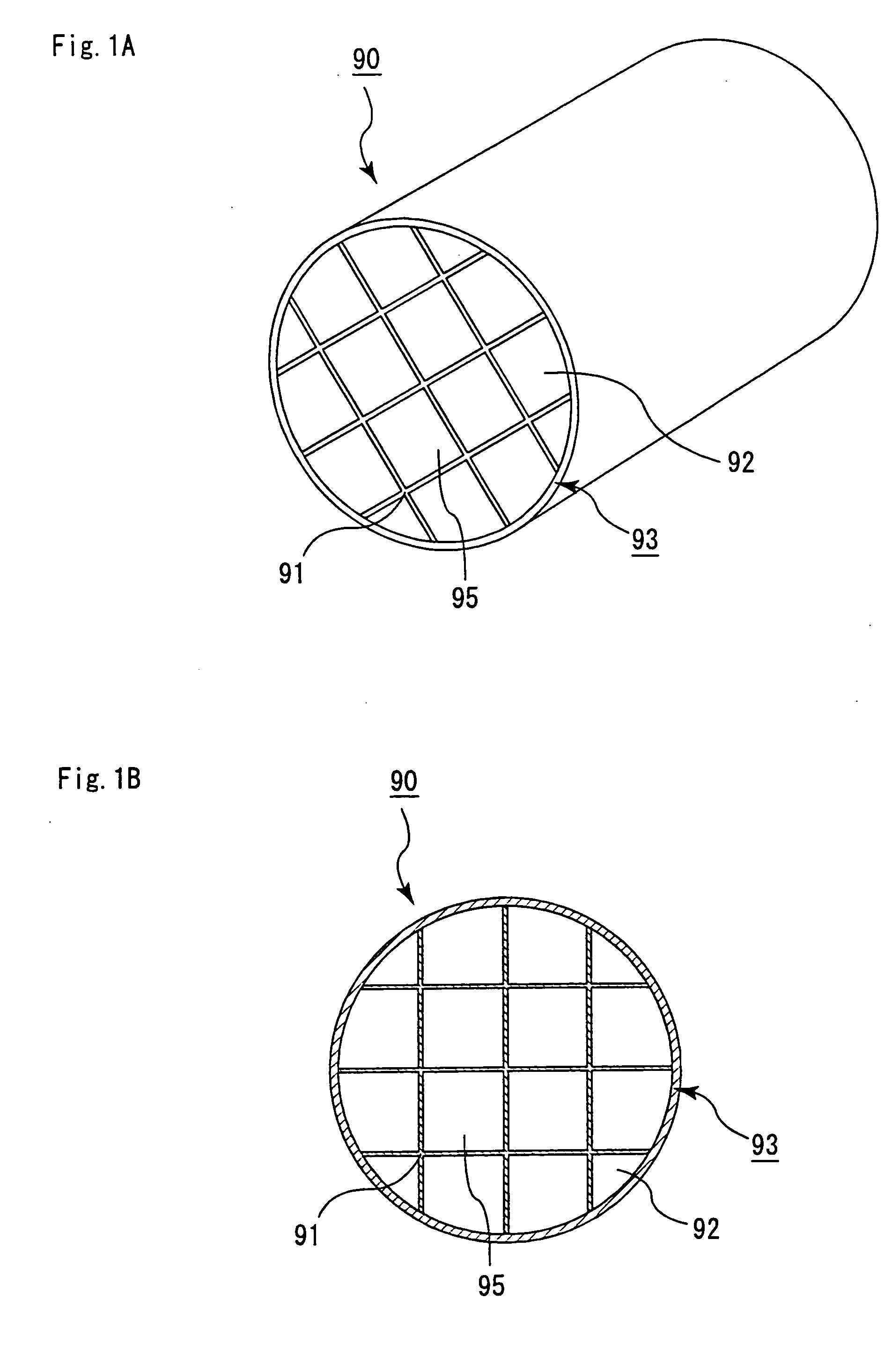
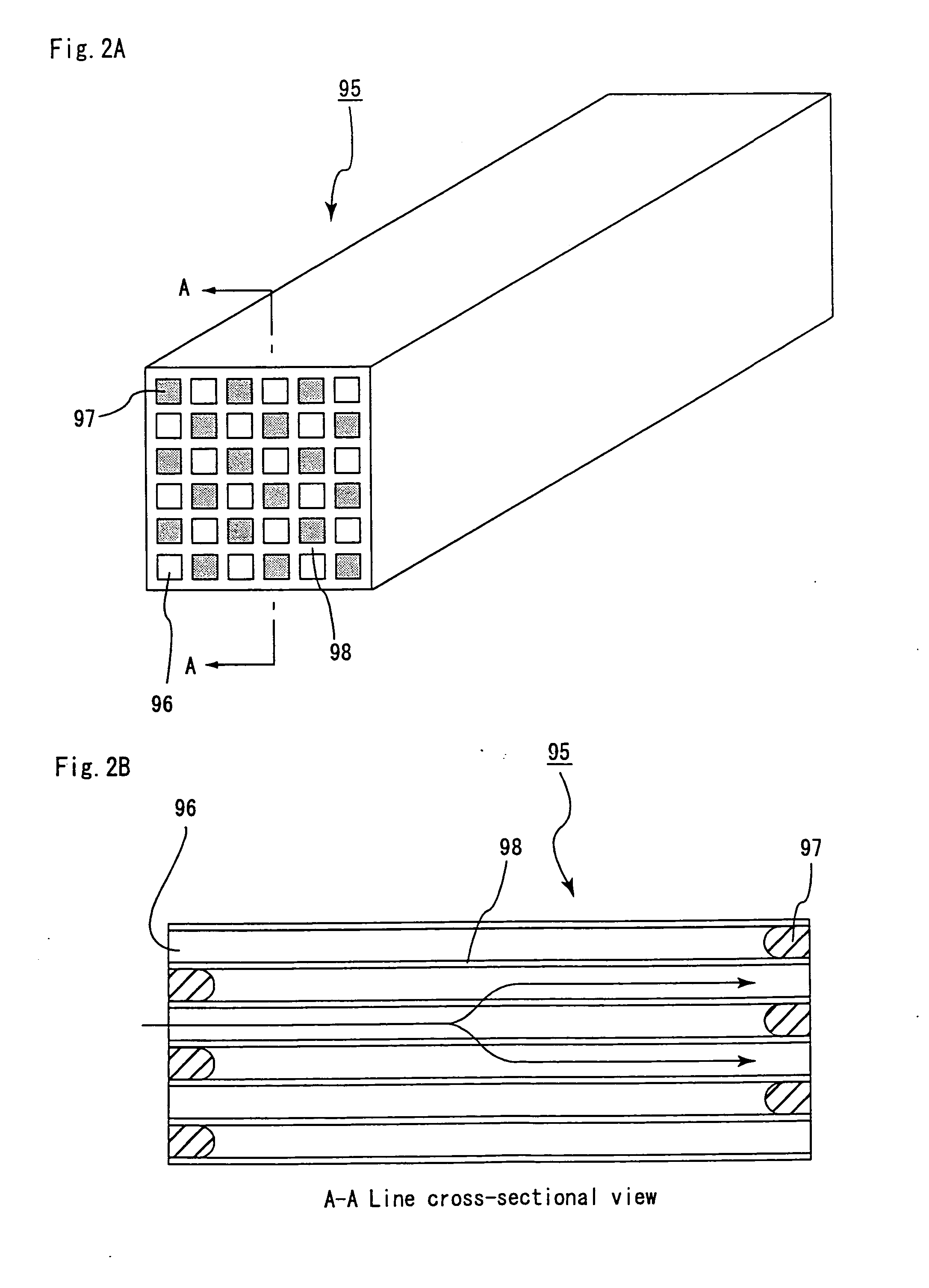
Honeycomb structural body, manufacturing method of the honeycomb structural body, and exhaust gas purifying device
ActiveUS20050229565A1High strengthIncreased durabilityCombination devicesCatalyst protectionLeast squaresHoneycomb structure
A honeycomb structural body comprising: a pillar-shaped ceramic block and a sealing material provided on an outer peripheral portion of said ceramic block, each of them having irregularities formed on an outer peripheral face wherein: when a least square curve is determined by a least square method on the basis of points constituting the contour of a cross-section, a center-of-gravity is defined as c1, a distance between a minimum concentric circumscribed curve having c1 and the center-of-gravity c1 is defined as D1, a distance between a maximum concentric inscribed curve having c1 and the center-of-gravity c1 is defined as D2, and the following inequality is satisfied: about 0.3 mm≦(D1−D2); same definition is applied to said ceramic block, a center-of-gravity thereof is defined as c2, a distance between a minimum concentric circumscribed curve having c2 and the center-of-gravity c2 is defined as D3, a distance between a maximum concentric inscribed curve having c2 and the center-of-gravity c2 is defined as D4, and the following inequality is satisfied: about 0.5 mm≦(D3−D4)≦about 7.0 mm.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
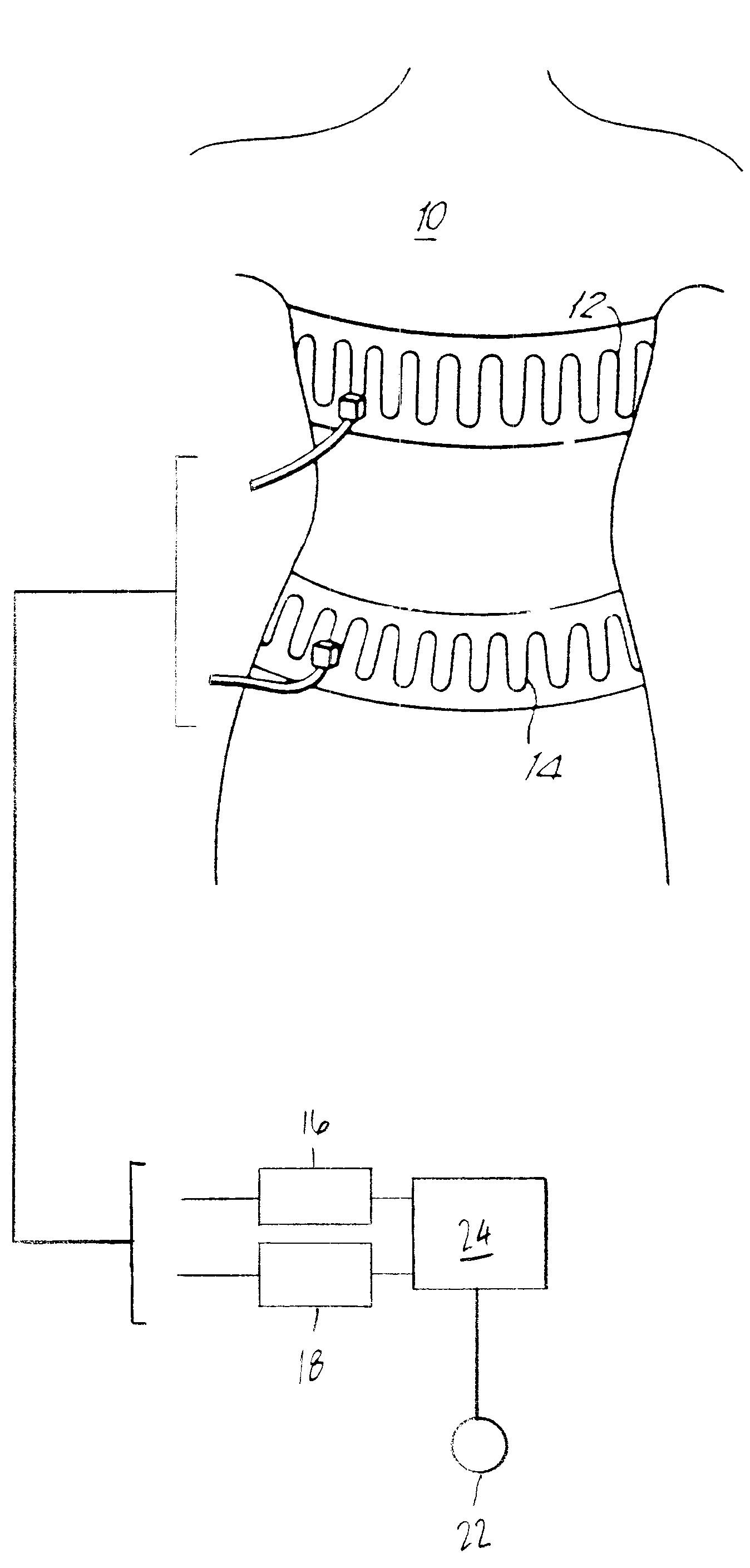
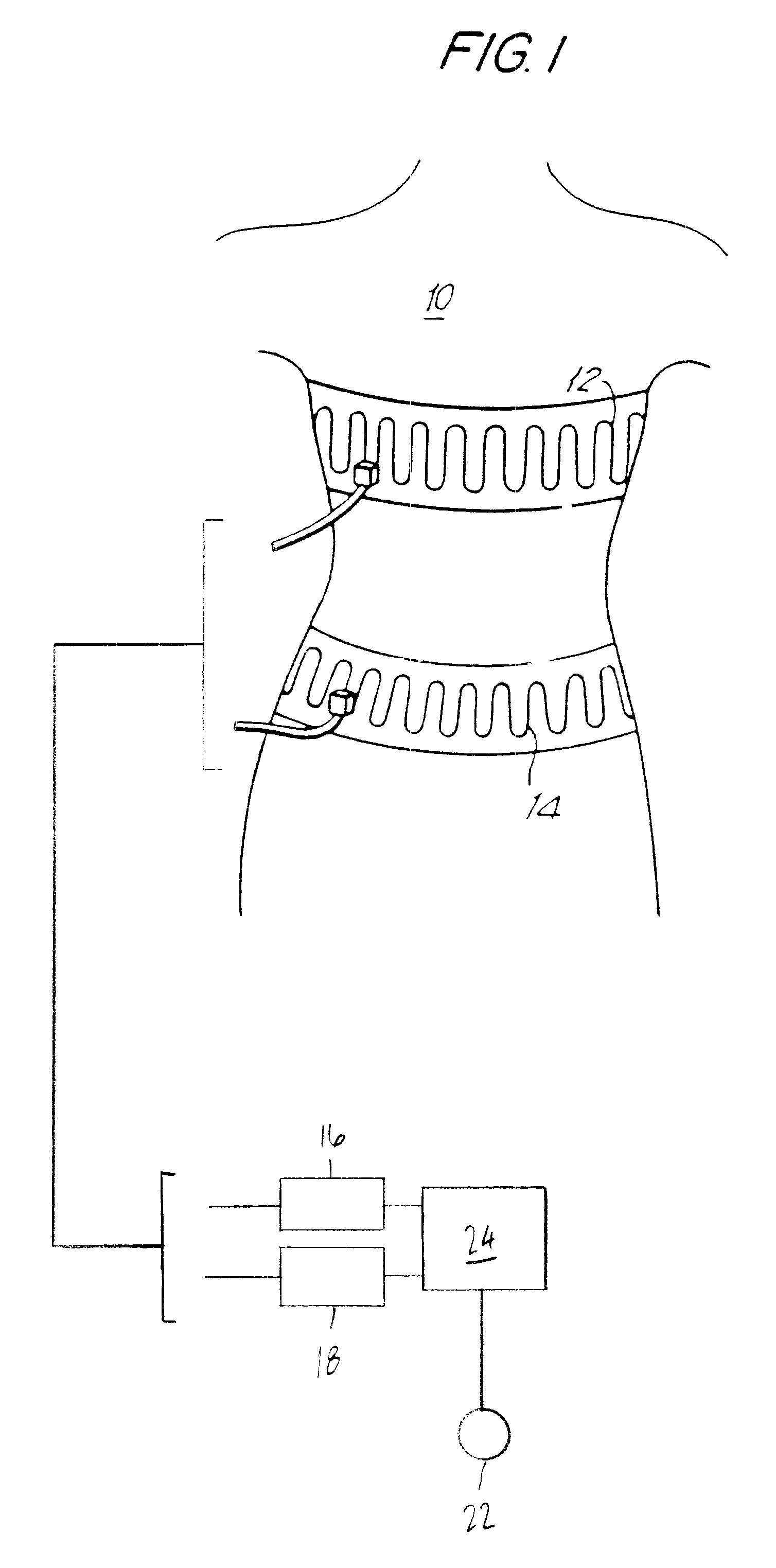
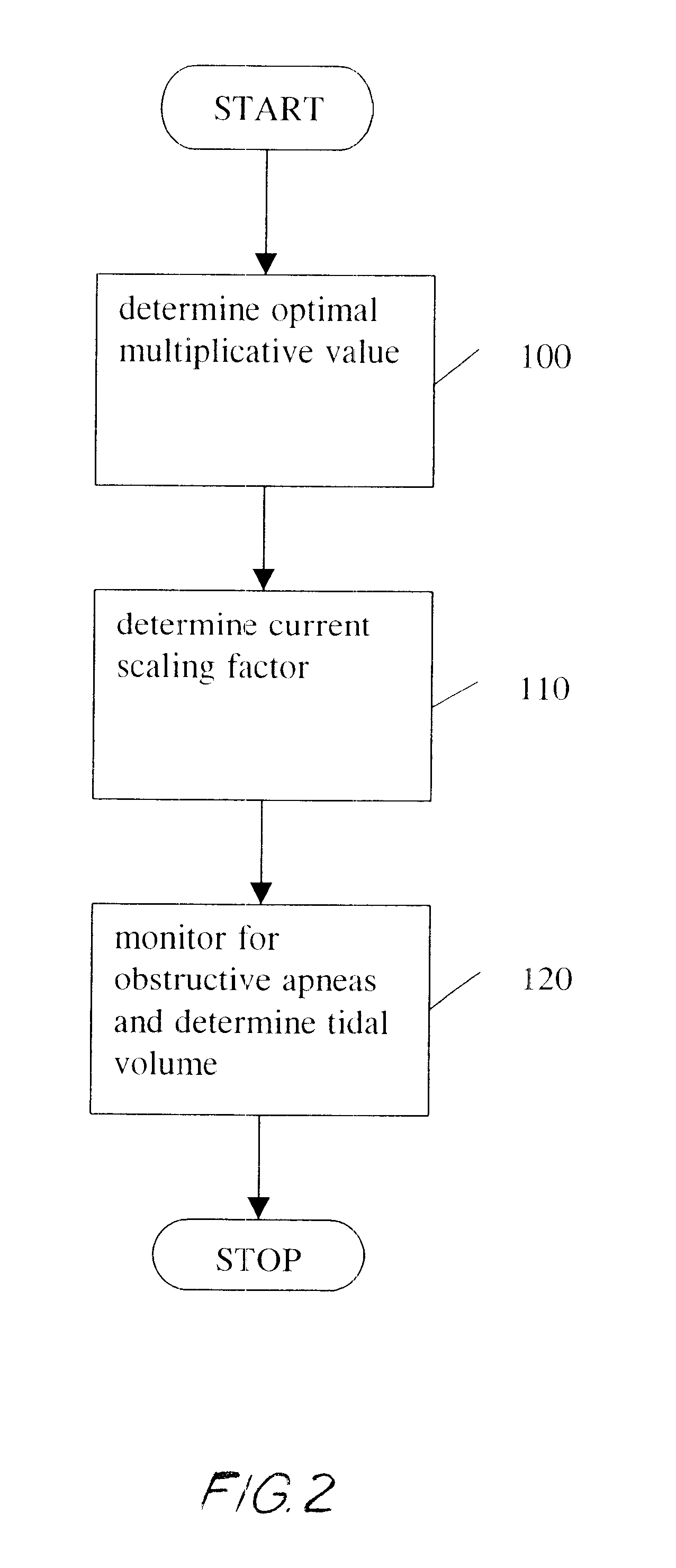
Quantitative calibration of breathing monitors with transducers placed on both rib cage and abdomen
A method for calibrating non-invasive breathing monitors with sensors placed on the rib-cage and abdomen of a subject includes determining an initial scaling factor and an optimal multiplicative factor for the readings of the rib-cage and abdomen sensors using one of a least squares, linear regression, or multi-linear regression techniques. A current scaling factor is determined on a periodic basis using qualitative device calibration techniques. The current scaling factor is used to monitor breathing and diagnose obstructive apneas. Furthermore, the optimal multiplicative and the current scaling factor are used to determine the current tidal volume.
Owner:ADIDAS +1
Remote high-precision independent combined navigation locating method
InactiveCN101270993AImprove drop point (hit) accuracyHigh resolutionInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSynthetic aperture radarNavigation system
The invention relates to a remote high precision autonomous integrated navigation and positioning method, which is characterized in that a Strapdown Inertial Navigation System (SINS) is used as a main navigation system during the whole flight course of the aircraft, assisted by 3D high precision position and attitude angle information provided by celestial navigation system (CNS) based on the least square differential correction in boost phase (or middle segment). In reentry phase (terminal), using the characteristics of synthetic aperture radar (SAR), such as strong penetration capability, high resolving precision and all-weather, the SINS can be corrected through accurate location information and course information provided by SAR scene matching after motion compensation when the aircraft reentry into atmospheres, so the impact point (hit) accuracy of the aircraft can be increased and the invention has remarkable effects of eliminating or decreasing non-guidance error. The invention has advantages of autonomy and high precision, which can be used for improving remote ballistic missile, remote cruise missile, navigation and positioning accuracy of remote aircraft, such as long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicle, etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
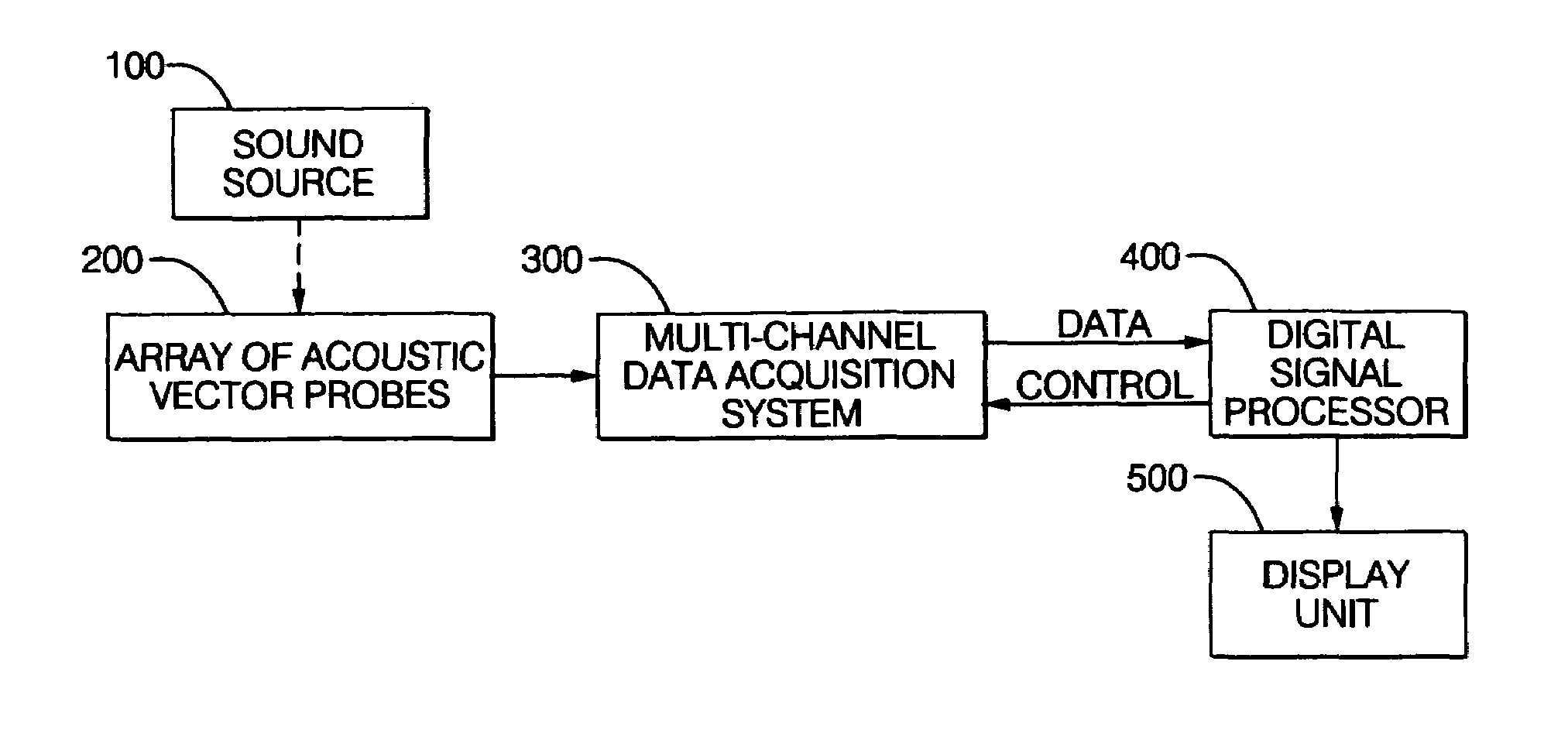
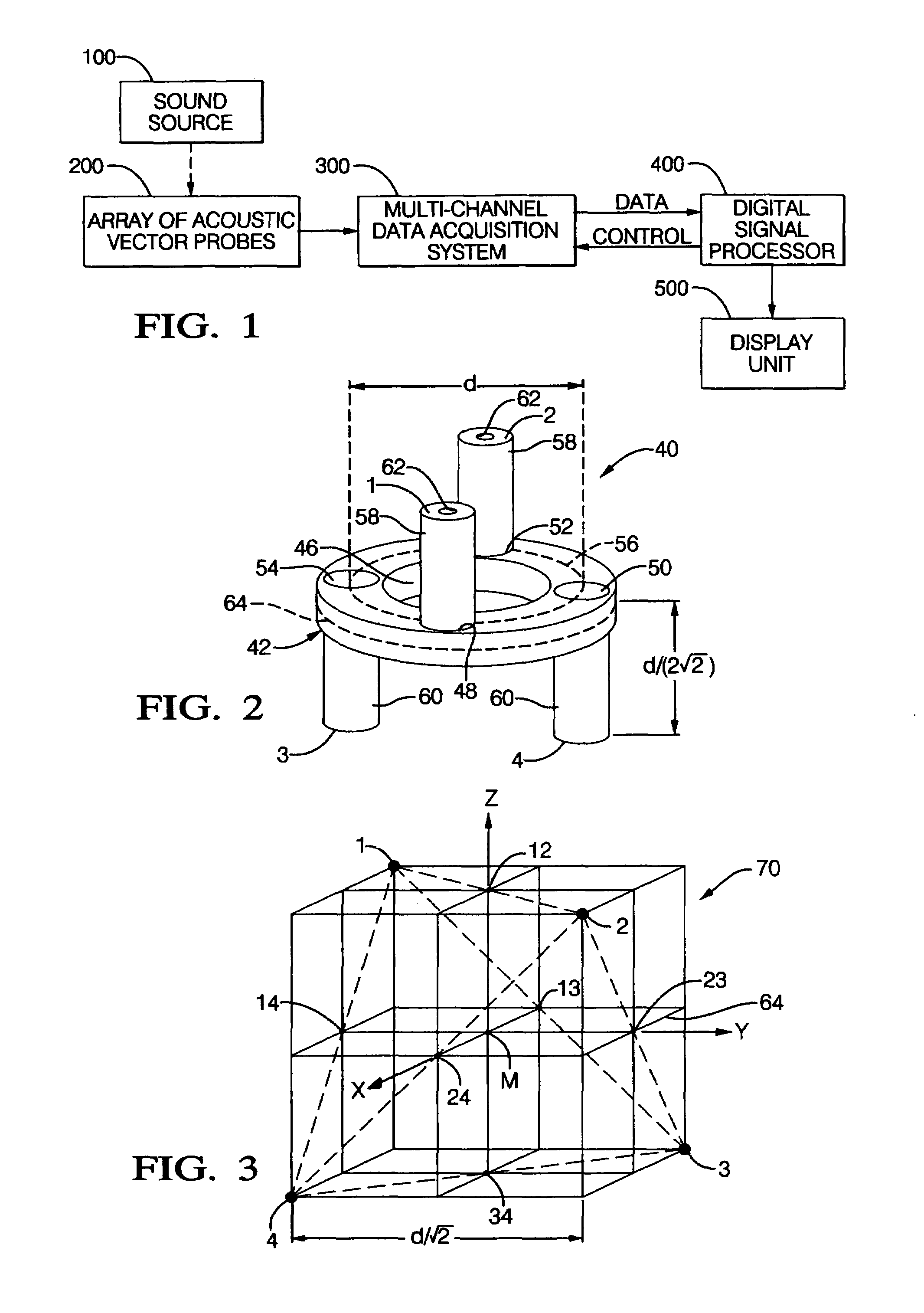
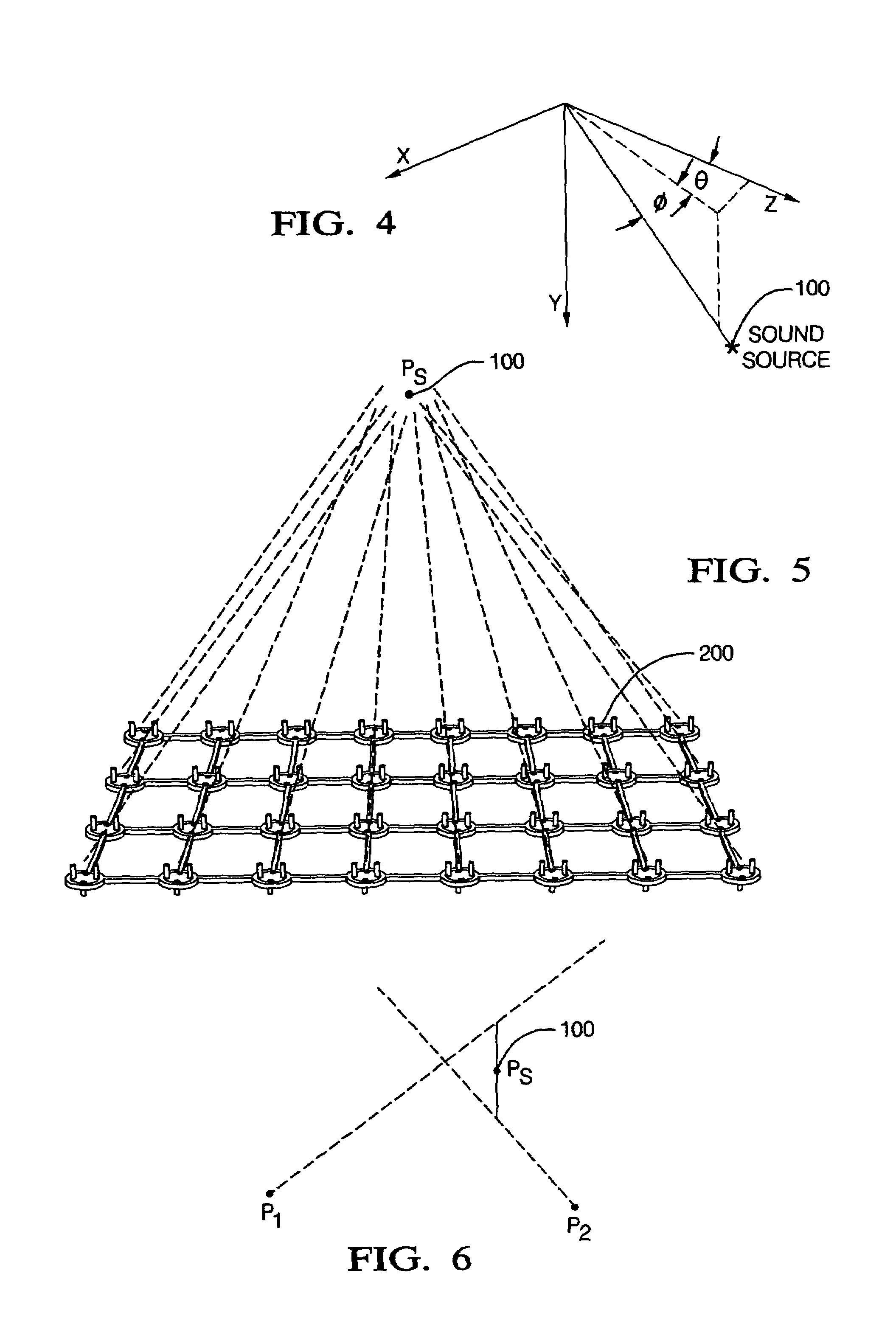
Sound source location and quantification using arrays of vector probes
InactiveUS7054228B1Well formedSmall, rugged and inexpensiveMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationSound source locationSound sources
Owner:HICKLING ROBERT
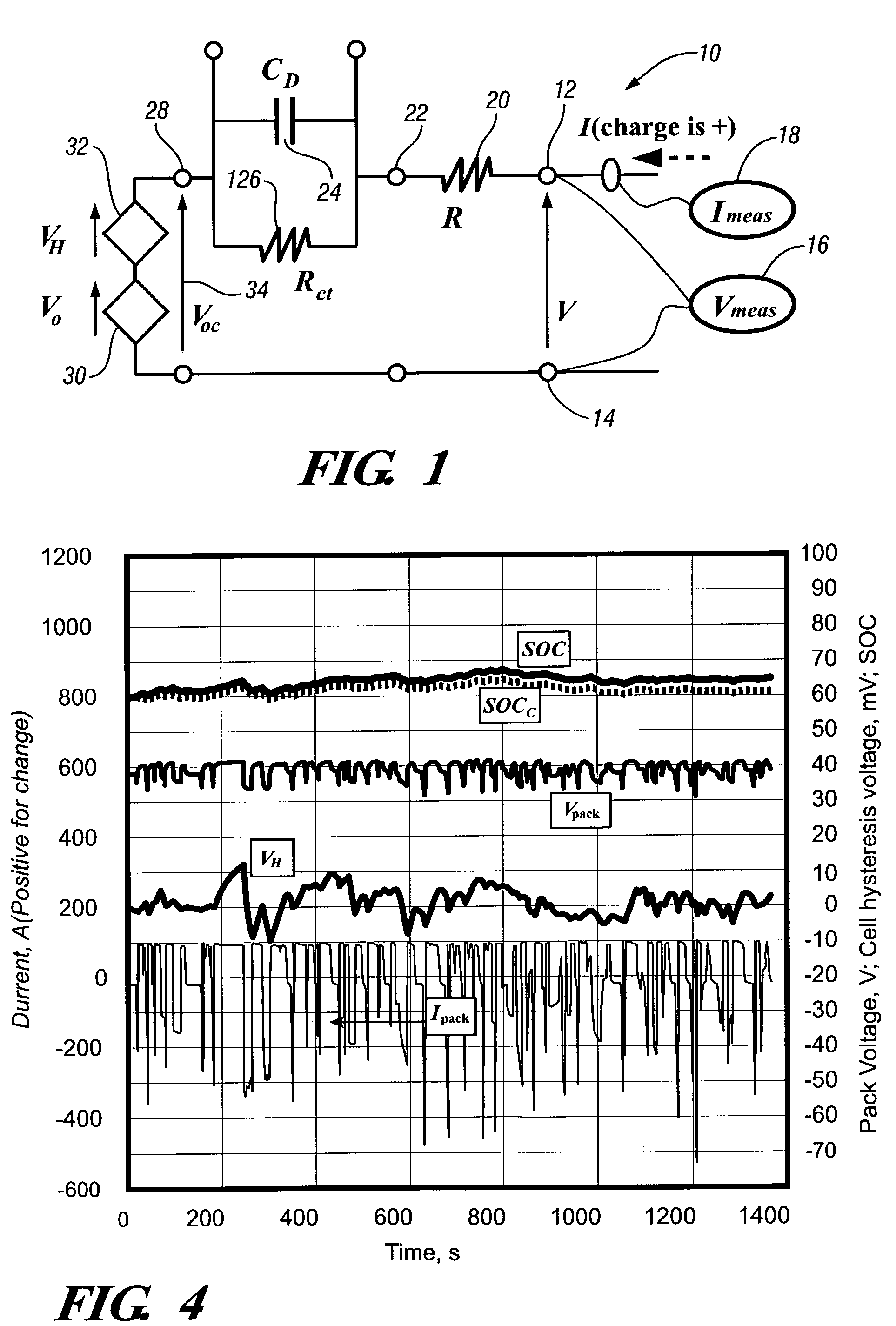
Method and apparatus for generalized recursive least-squares process for battery state of charge and state of health
InactiveUS7324902B2Current/voltage measurementTesting electric installations on transportBattery state of chargeState of health
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
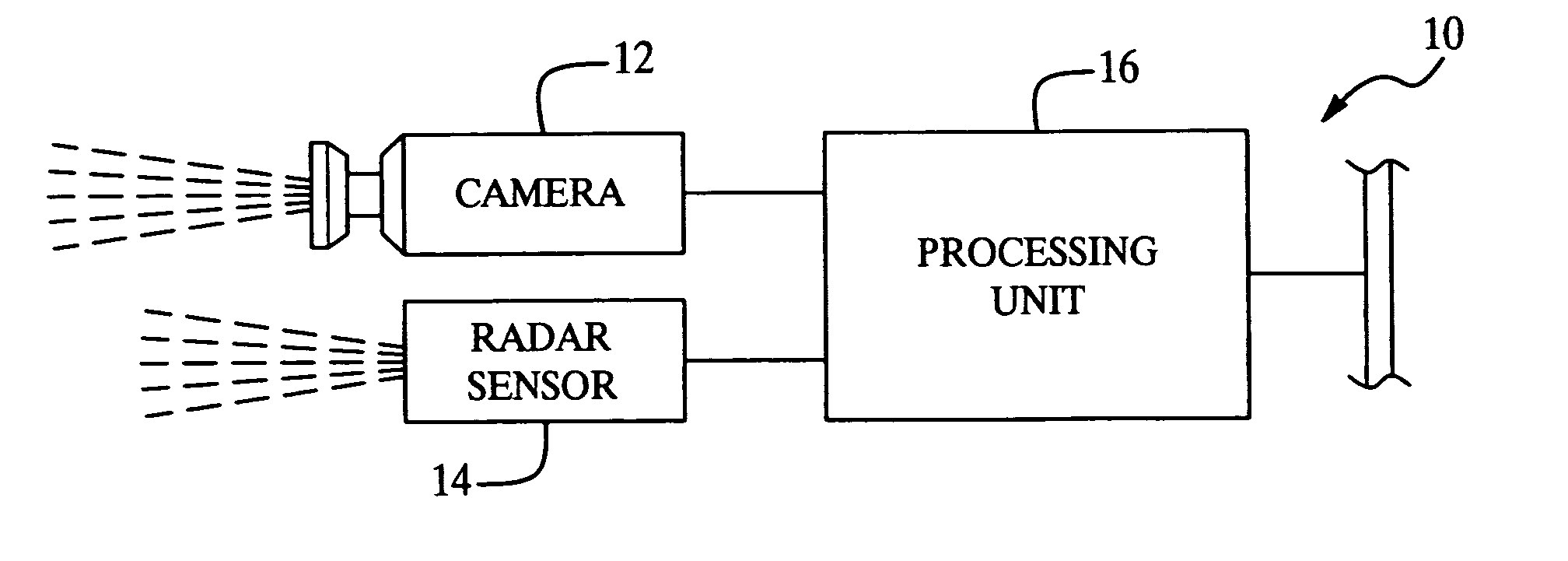
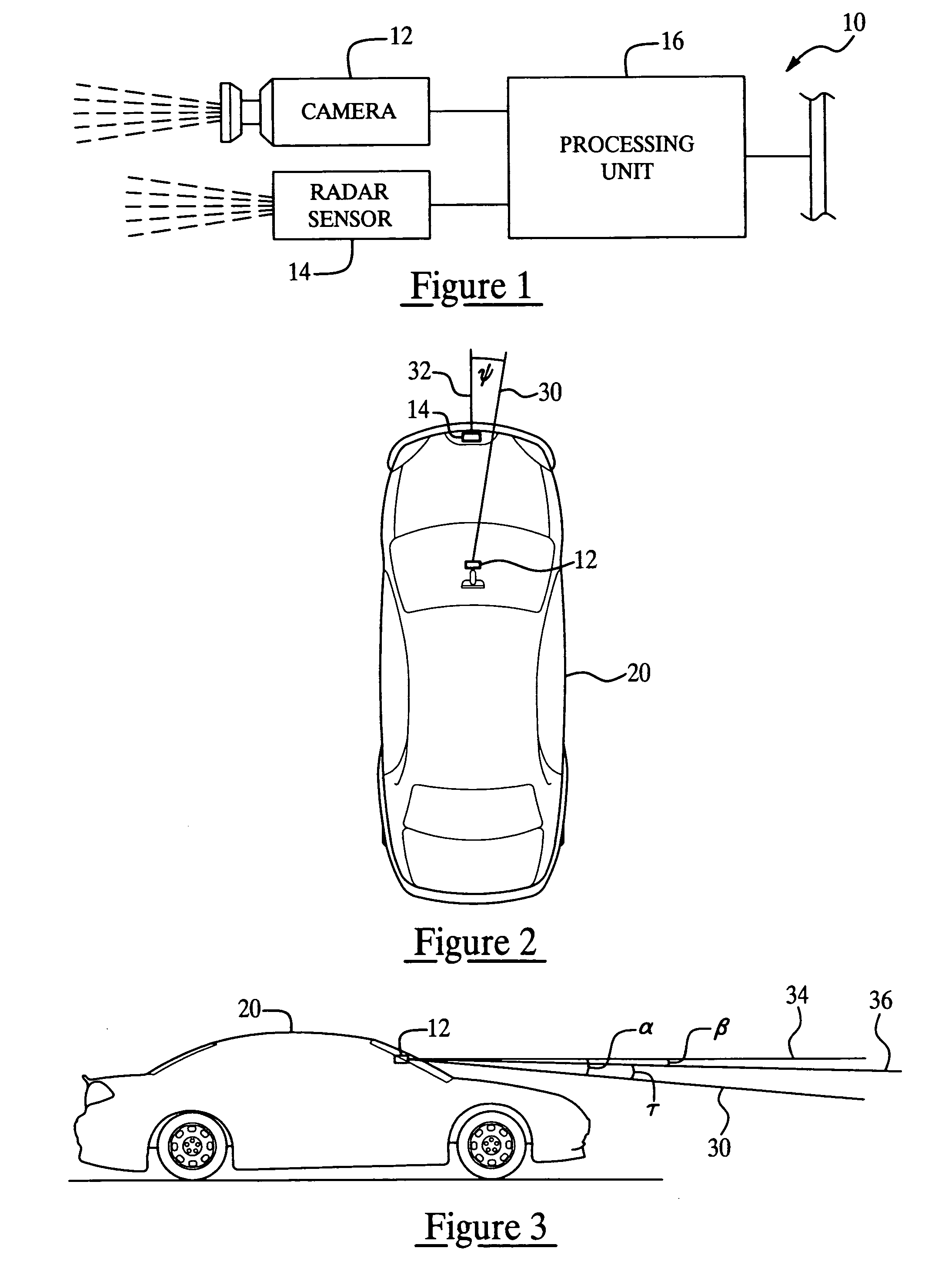
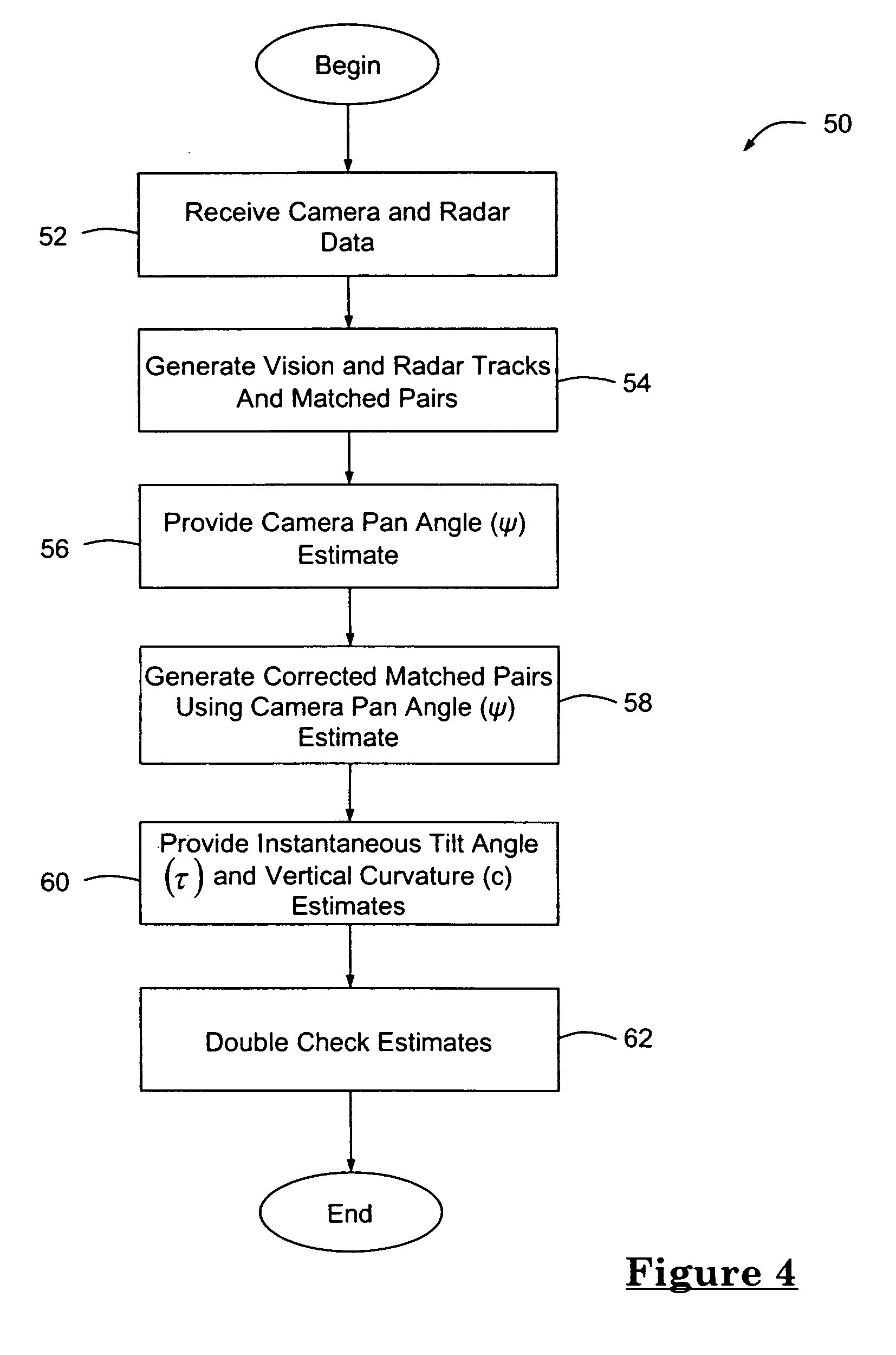
Method for estimating unknown parameters for a vehicle object detection system
InactiveUS20070055446A1Efficient solutionEasy to optimizeAnti-collision systemsComplex mathematical operationsRadarProcessing element
A method for estimating unknown parameters (pan angle (ψ), instantaneous tilt angle (τ) and road geometry of an upcoming road segment) for a vehicle object detection system. The vehicle object detection system is preferably a forward looking, radar-cued vision system having a camera, a radar sensor and an processing unit. The method first estimates the pan angle (ψ), then corrects the coordinates from a radar track so that pan angle (ψ) can be treated as zero, and finally solves a least squares problem that determines best estimates for instantaneous tilt angle (τ) and road geometry. Estimating these parameters enables the vehicle object detection system to identify, interpret and locate objects in a more accurate and efficient manner.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
OFDM channel estimation in the presence of interference
InactiveUS6487253B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsBaseband system detailsEngineeringOfdm channel estimation
Systems and methods for estimating channel response in the presence of interference. Interference and / or noise present on received training symbols is estimated. Based on the measured noise and / or interference, a weighting among training symbols is developed. Channel response is then estimated based on a weighted least squares procedure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
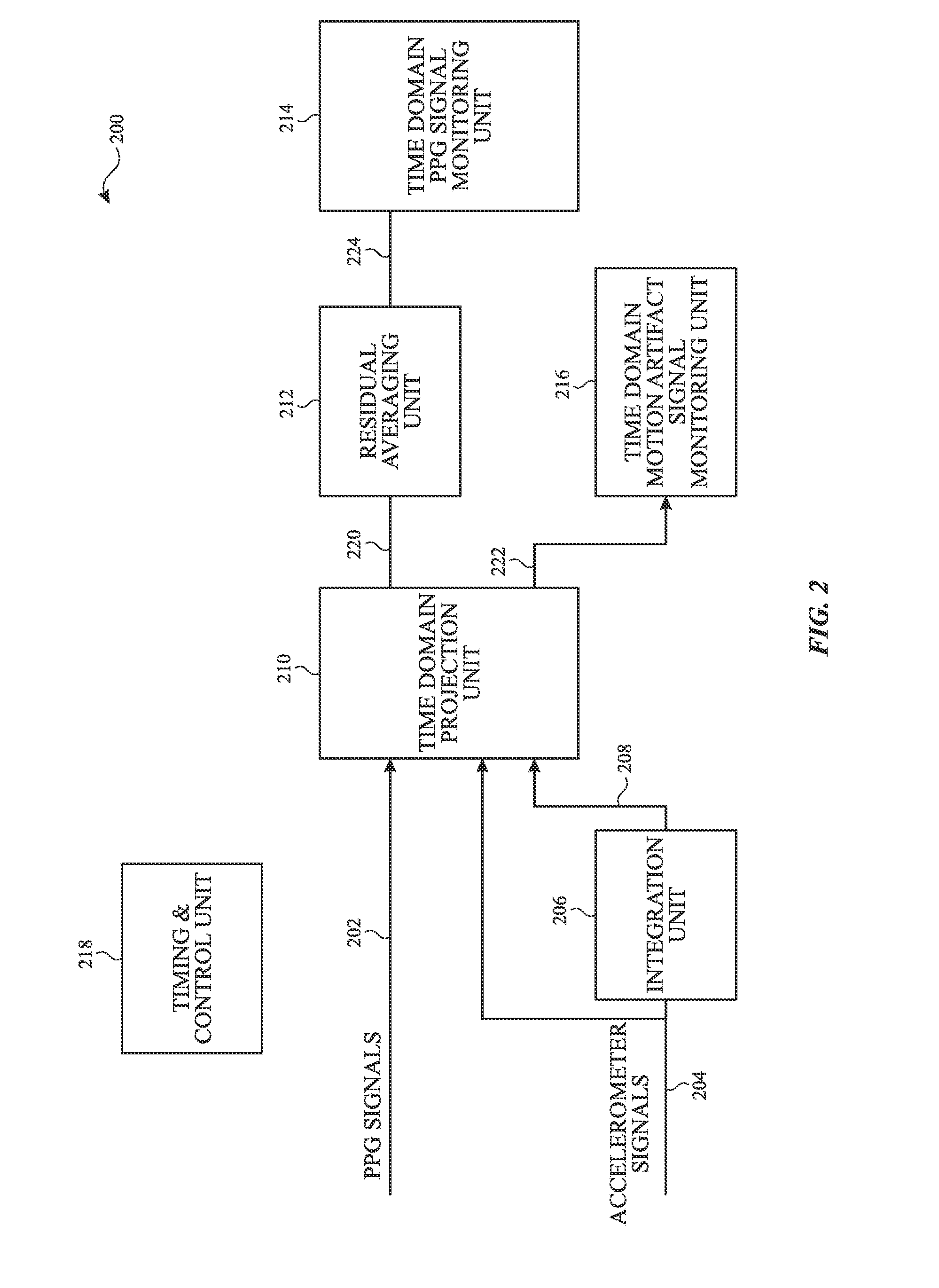
Motion artifact removal by time domain projection
An algorithm for removing motion artifacts from the PPG signal in the time domain to determine heart rate is disclosed. A device for determining a heart rate of a user can include a heart rate sensor configured to generate heart rate signals when positioned on or adjacent to a user's skin, an accelerometer configured to generate one or more acceleration signals, and processing circuitry configured to remove, in a time domain, motion artifacts from the heart rate signals based on the acceleration signals. In some examples, the removal of motion artifacts can also be based on mean-centered, variance-scaled integrated acceleration signals. In some examples, the processing circuitry can be configured to remove motion artifacts using a least squares algorithm to identify a best representation of acceleration and integrated acceleration signals in the heart rate signals.
Owner:APPLE INC
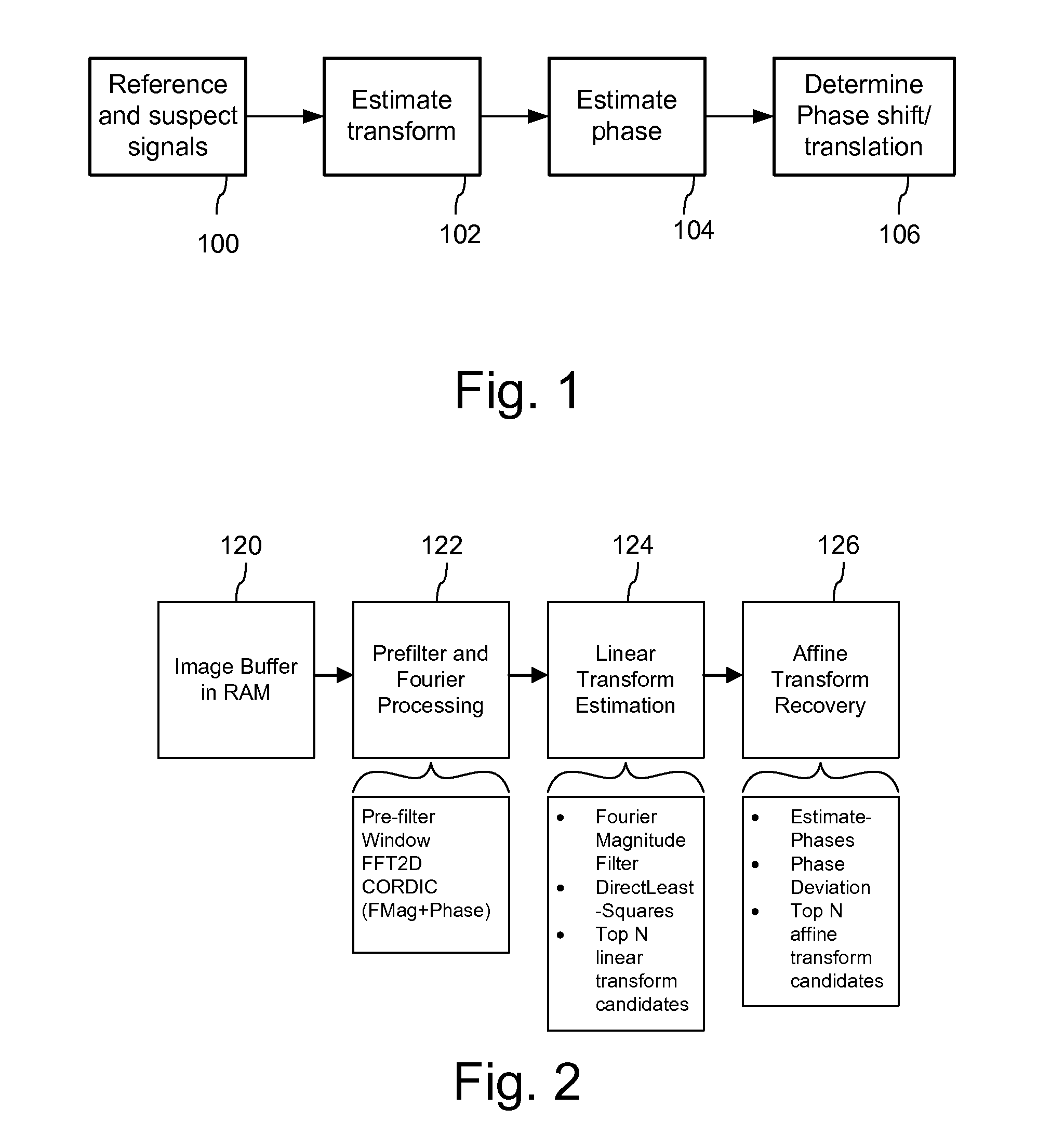
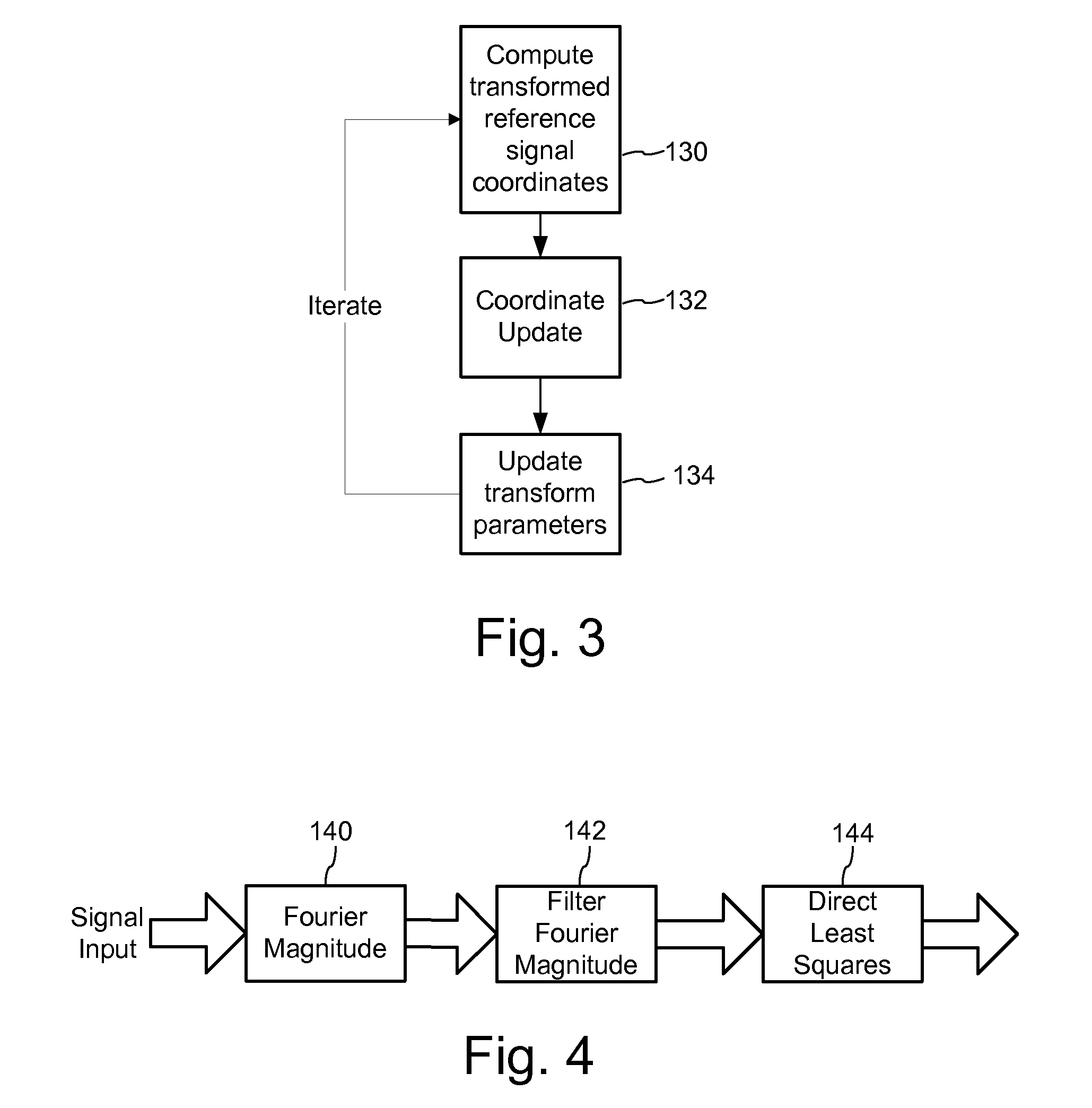
Signal Processors and Methods for Estimating Transformations Between Signals with Least Squares
ActiveUS20120078989A1Computed accurately and efficientlyAccurate detectionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmLeast squares
Signal processing devices and methods estimate transforms between signals using a least squares technique. From a seed set of transform candidates, a direct least squares method applies a seed transform candidate to a reference signal and then measures correlation between the transformed reference signal and a suspect signal. For each candidate, update coordinates of reference signal features are identified in the suspect signal and provided as input to a least squares method to compute an update to the transform candidate. The method iterates so long as the update of the transform provides a better correlation. At the end of the process, the method identifies a transform or set of top transforms based on a further analysis of correlation, as well as other results.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
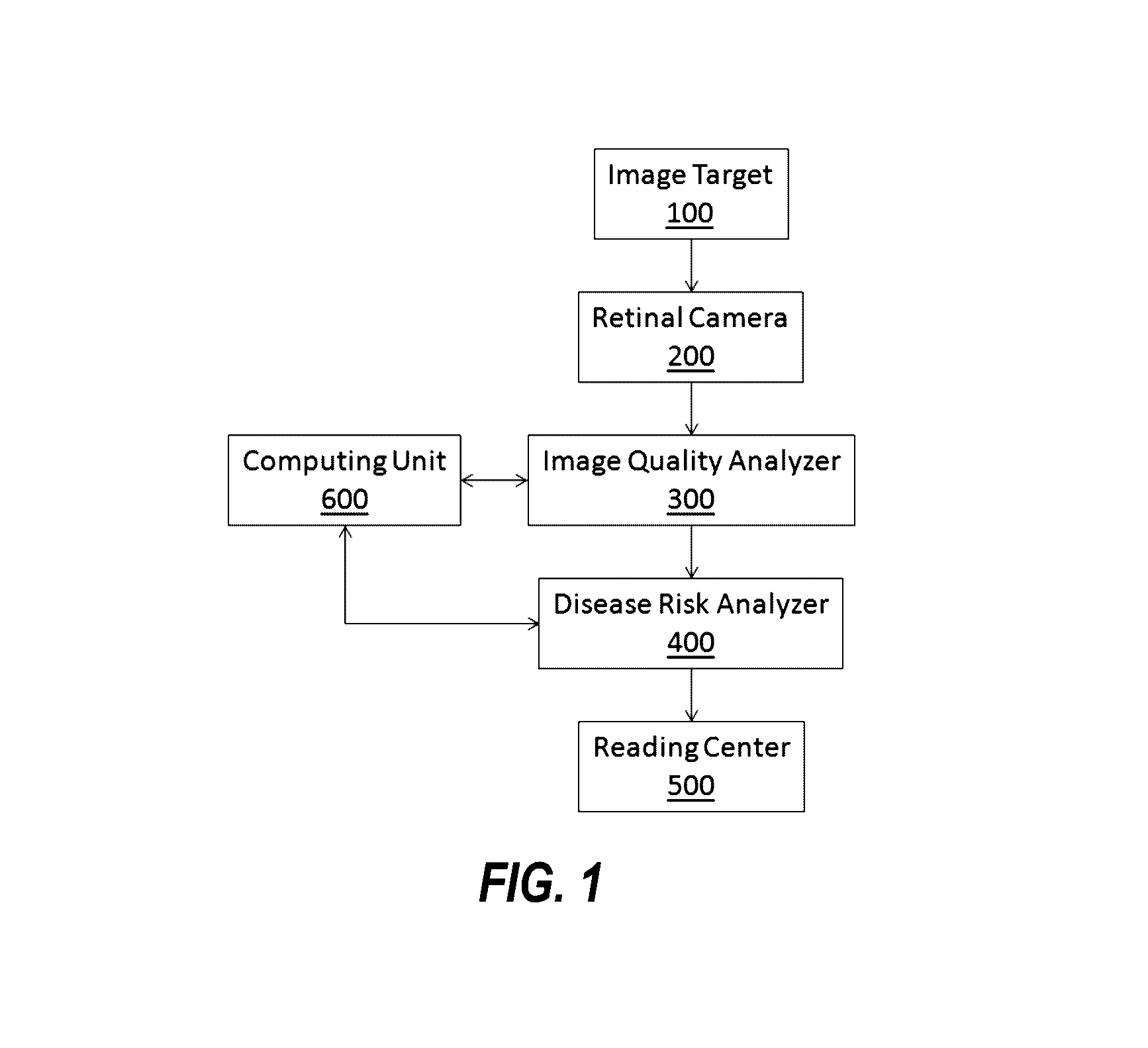
System and methods for automatic processing of digital retinal images in conjunction with an imaging device
Systems and methods of obtaining and recording fundus images by minimally trained persons, which includes a camera for obtaining images of a fundus of a subject's eye, in combination with mathematical methods to assign real time image quality classification to the images obtained based upon a set of criteria. The classified images will be further processed if the classified images are of sufficient image quality for clinical interpretation by machine-coded and / or human-based methods. Such systems and methods can thus automatically determine whether the quality of a retinal image is sufficient for computer-based eye disease screening. The system integrates global histogram features, textural features, and vessel density, as well as a local non-reference perceptual sharpness metric. A partial least square (PLS) classifier is trained to distinguish low quality images from normal quality images.
Owner:VISIONQUEST BIOMEDICAL
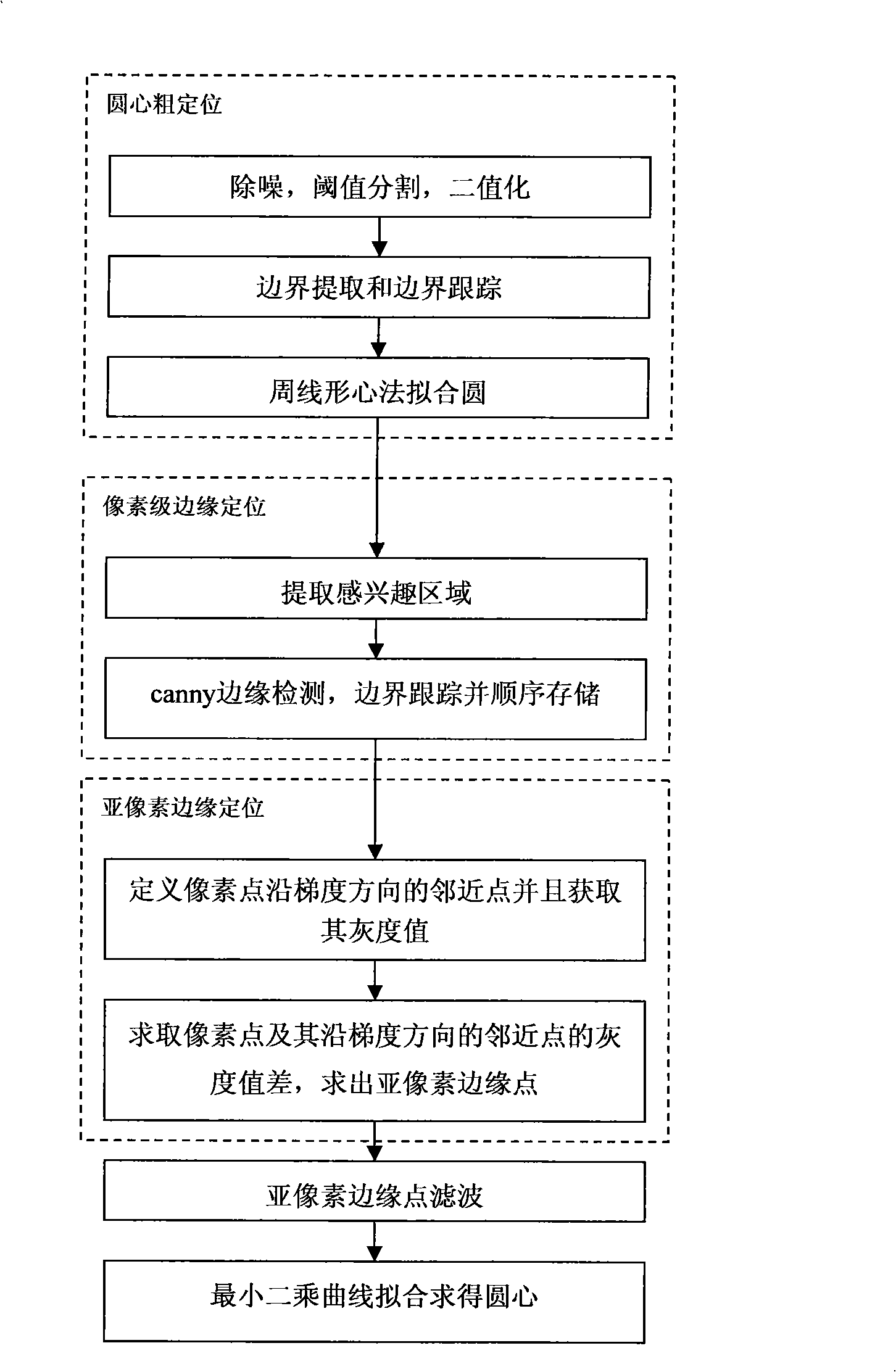
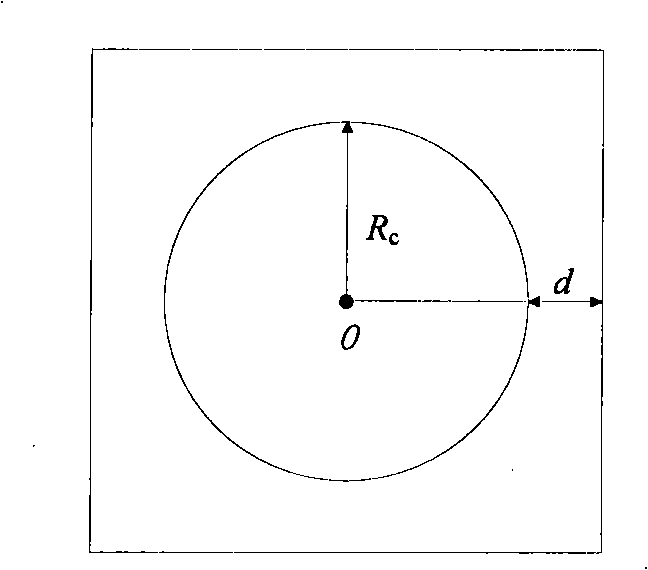
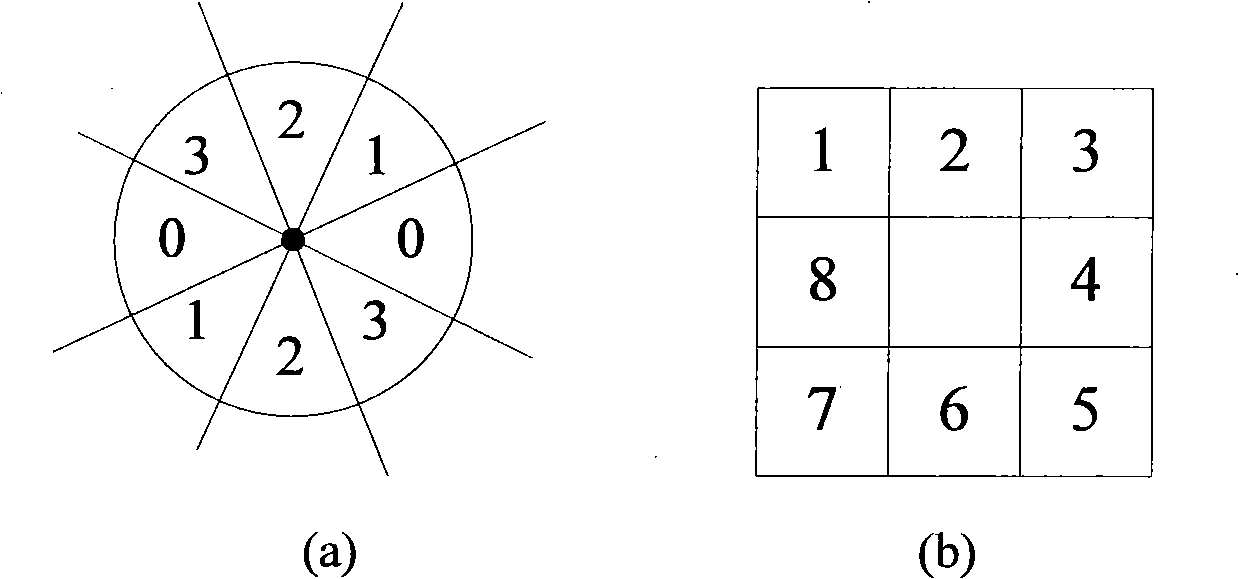
Circular target circular center positioning method
InactiveCN101334263AIncrease speedSimple calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansMeasurement precisionLeast squares
The invention discloses a circle center locating method of a circular target, mainly relating to a great deal of target identification and target location. Firstly, rough circle center location is carried out to an image by using a simple contour centroid method, a key square region is extracted as a region of interest according to the information of a rough location circle center and a rough location radius, and pixel-level edge location is carried out to the circular target in the region of interest by a canny operator; then sub-pixel location is carried out to the circular target according to the geometric features and the gray information of the circle, therefore, a precise coordinate of sub-pixel edge points is obtained; after that, a curvature filtering method and an average filtering method are respectively used for filtering 'isolated points' and noise occurring in the sub-pixel edge points; finally, a least squares method is utilized to fit a circle to the filtered sub-pixel edge points so as to obtain the final circular center and radius. The method not only effectively improves the precision of circle center location, but also improves the robustness thereof, thus further improving the measurement precision of a measurement system and perfecting the stability of the measurement system.
Owner:南通欧特建材设备有限公司 +1
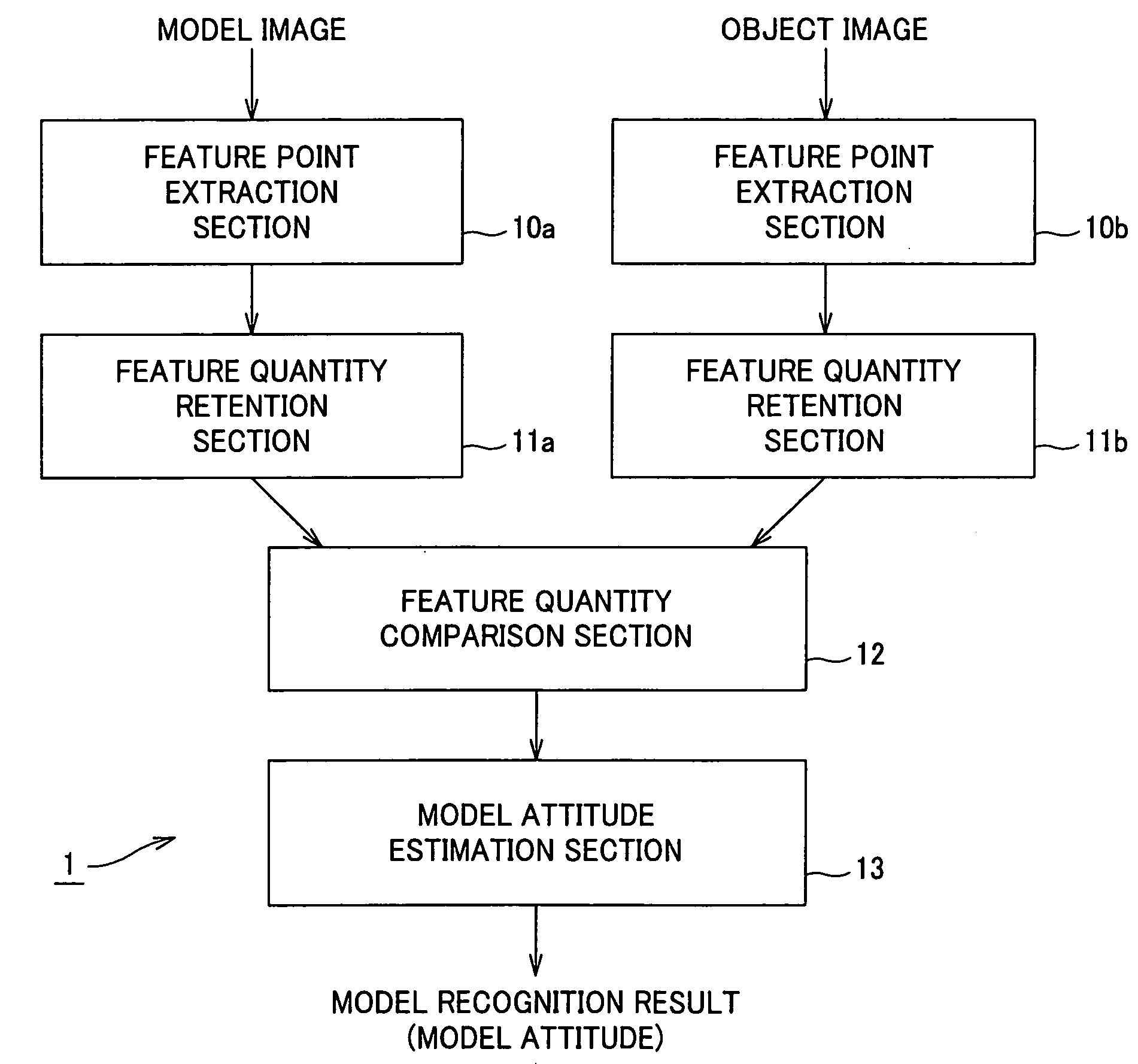
Image recognition device and method, and robot device
InactiveUS20050213818A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTransformation parameterRelevant feature
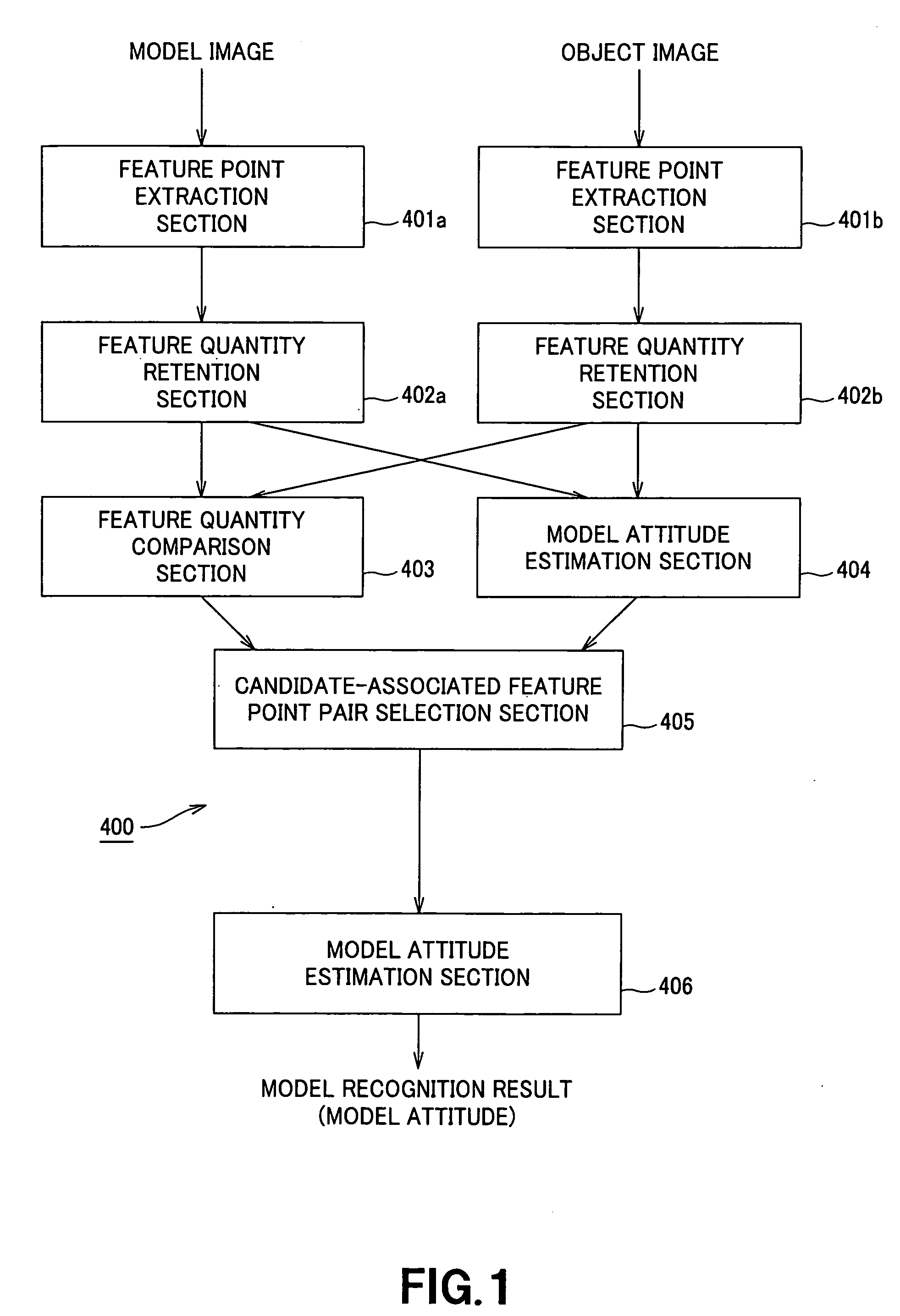
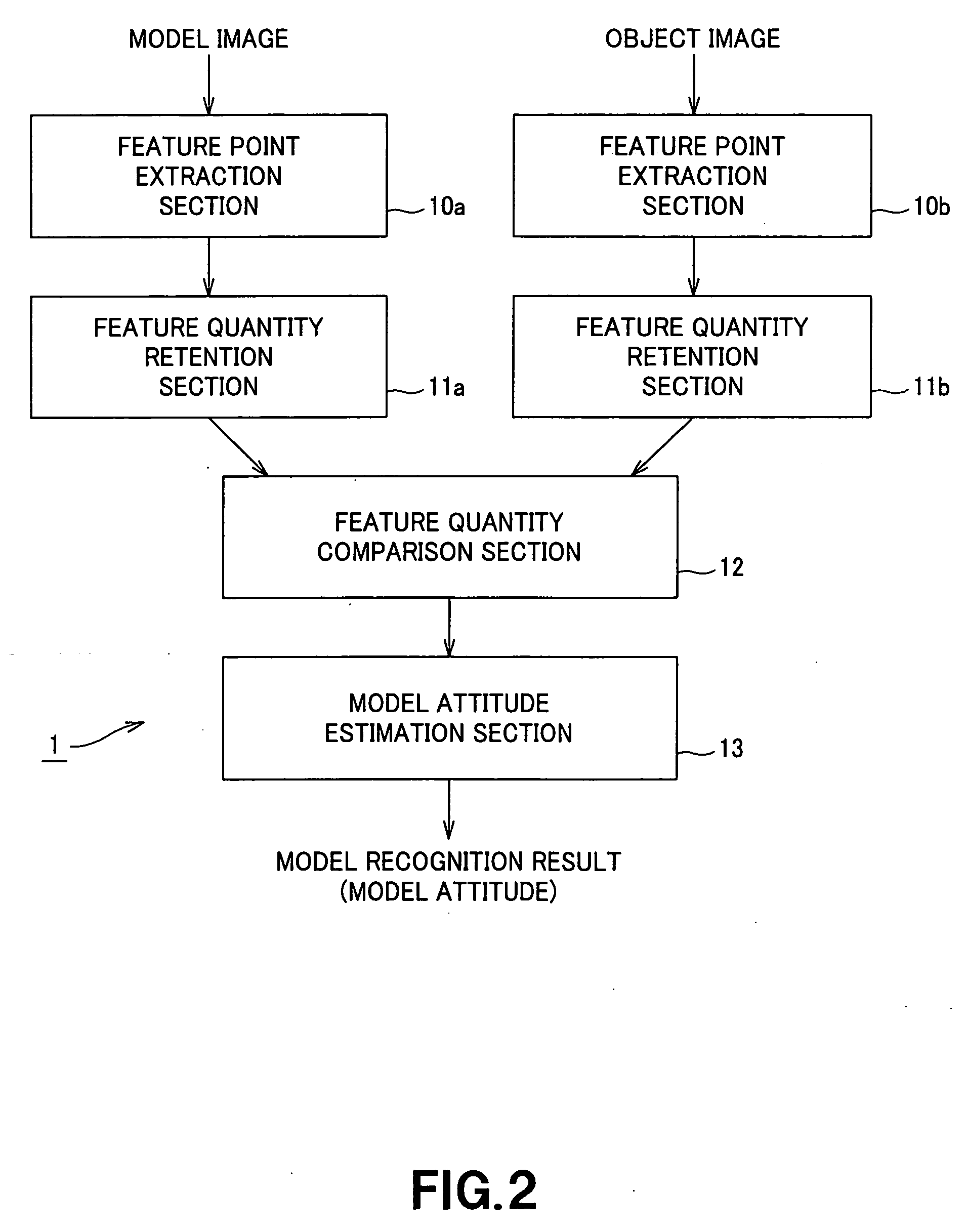
In an image recognition apparatus (1), feature point extraction sections (10a) and (10b) extract feature points from a model image and an object image. Feature quantity retention sections (11a) and (11b) extract a feature quantity for each of the feature points and retain them along with positional information of the feature points. A feature quantity comparison section (12) compares the feature quantities with each other to calculate the similarity or the dissimilarity and generates a candidate-associated feature point pair having a high possibility of correspondence. A model attitude estimation section (13) repeats an operation of projecting an affine transformation parameter determined by three pairs randomly selected from the candidate-associated feature point pair group onto a parameter space. The model attitude estimation section (13) assumes each member in a cluster having the largest number of members formed in the parameter space to be an inlier. The model attitude estimation section (13) finds the affine transformation parameter according to the least squares estimation using the inlier and outputs a model attitude determined by this affine transformation parameter.
Owner:SONY CORP
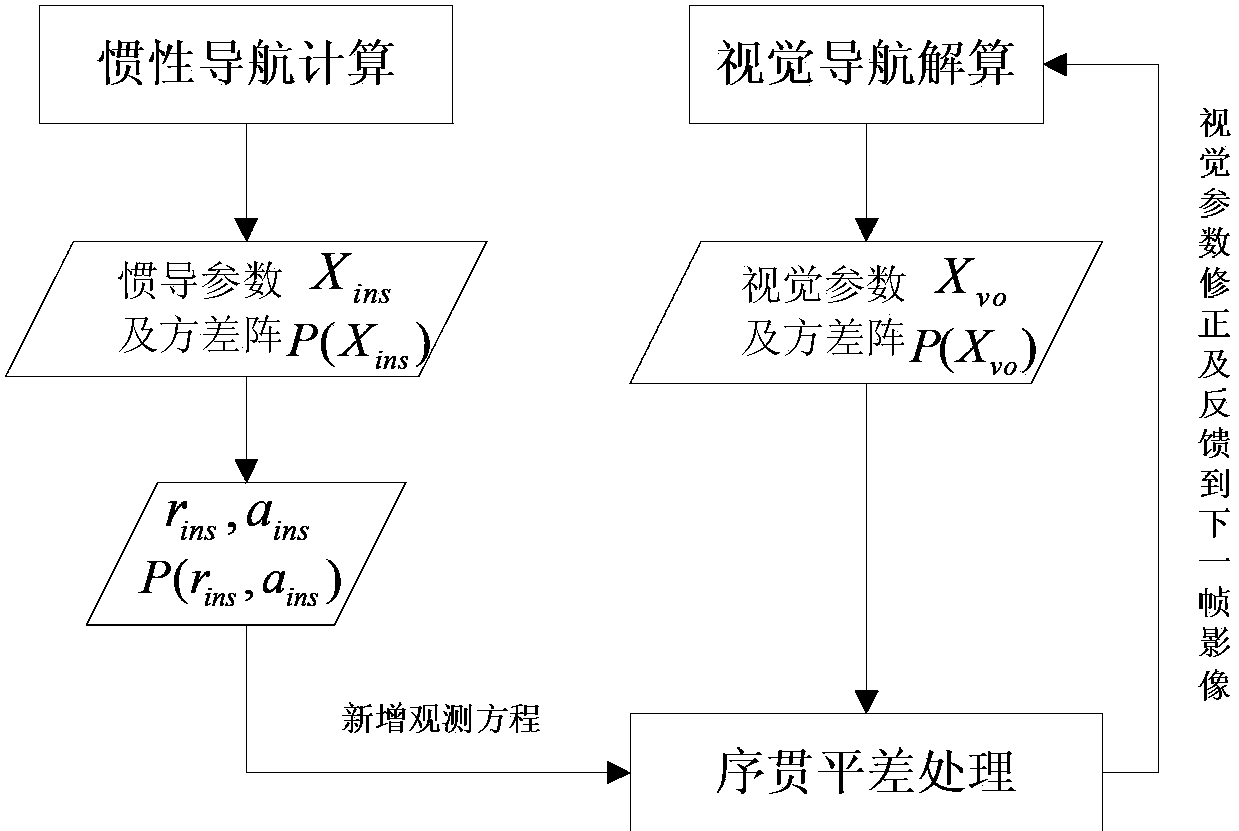
Visual navigation/inertial navigation full combination method
InactiveCN103424114AHigh precisionReduce precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputer visionLeast squares
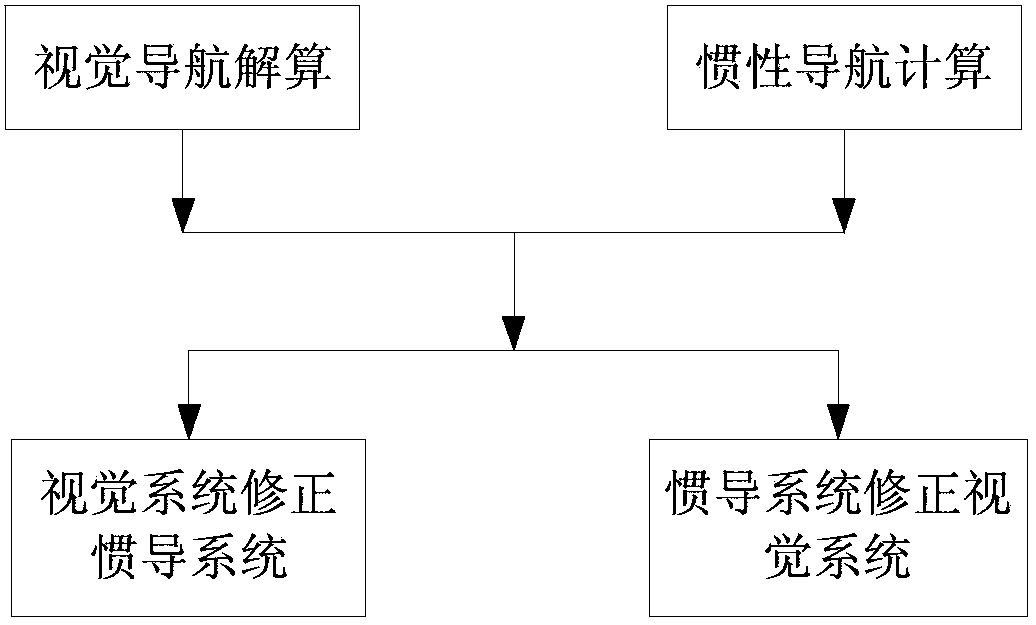
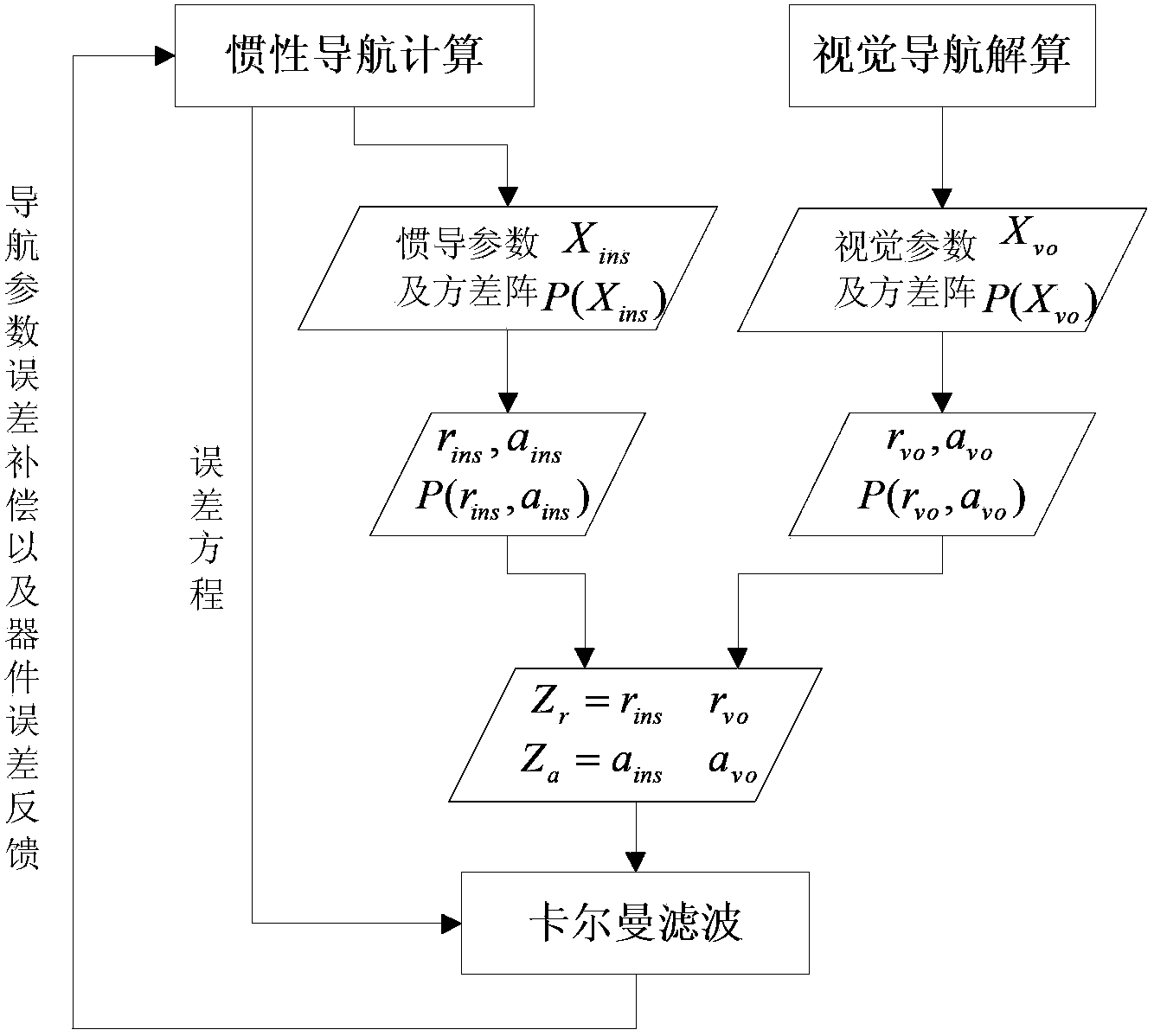
The invention relates to a visual navigation / inertial navigation full combination method. The method comprises the following steps: first, calculation of visual navigation: observation equations are listed based on collinearity equations, carrier positions and attitude parameters are obtained through the least square principle and adjustment,, and variance-covariance arrays among the parameters are calculated; second, calculation of inertial navigation: navigation calculation is carried out in the local horizontal coordinates, carrier positions, speeds and attitude parameters of each moment are obtained, variance-covariance arrays among the parameters are calculated; third, correction of the inertial navigation system through the visual system: by means of the Kalman filtering, navigation parameter errors and device errors of the inertial navigation system are estimated, and subjected to compensation and feedback correction, and therefore the optimal estimated values of all the parameters of the inertial navigation system are obtained; fourth, correction of the visual system through the inertial navigation system: all the parameters of the visual system are corrected through the sequential adjustment treatment. Compared to the prior art, the method has advantages of rigorous theories, stable performances, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
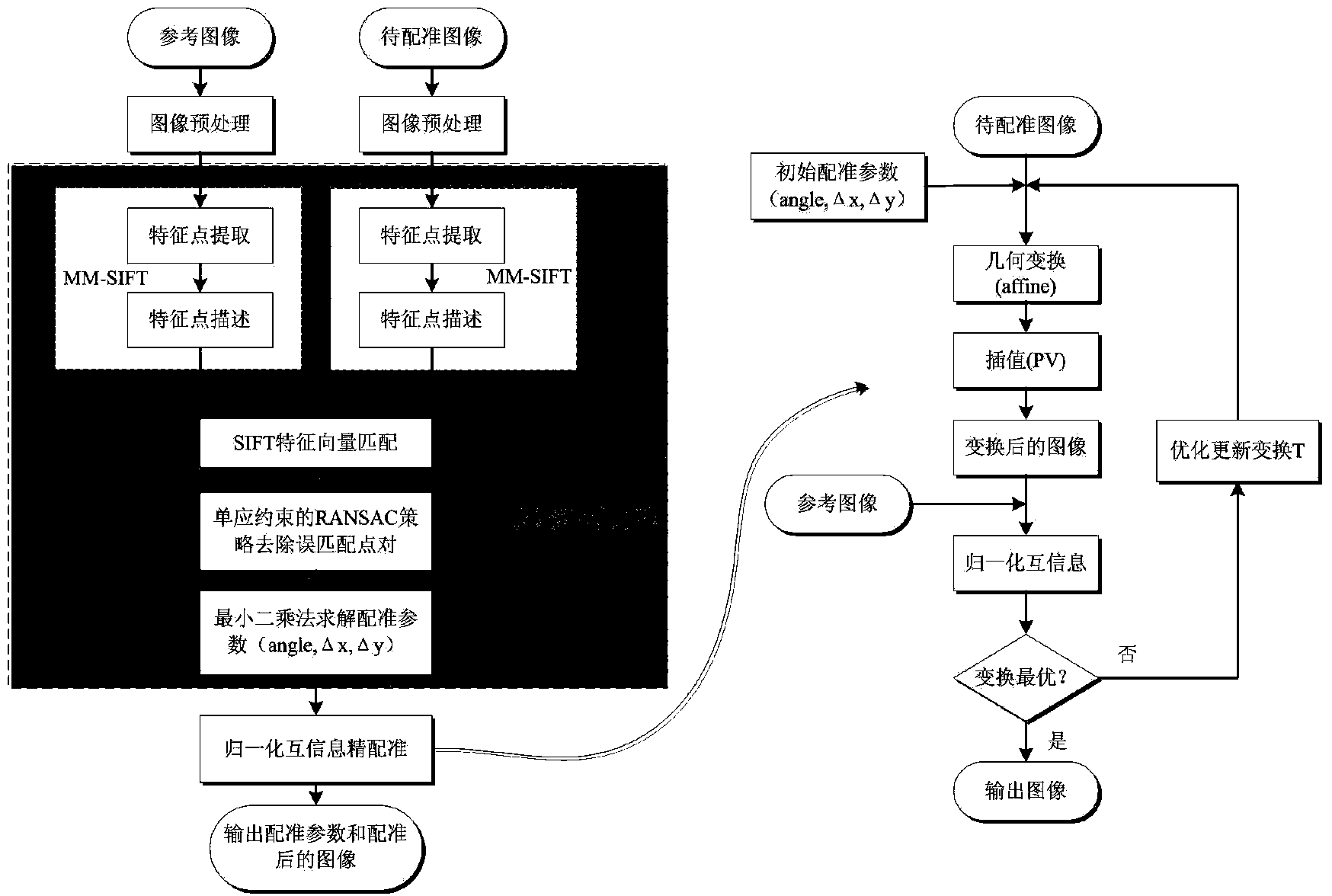
SAR image registration method based on SIFT and normalized mutual information
ActiveCN103839265AShorten the timeEnsure follow-up registration accuracyImage analysisFeature vectorNormalized mutual information
The invention provides an SAR image registration method based on SIFT and normalized mutual information. The method includes the steps that firstly, a standard image I1 and an image to be registered I2 are input and are respectively pre-processed; secondly, features of the pre-processed image I1 and features of the pre-processed image I2 are extracted according to the MM-SIFT method to acquire initial feature point pairs Fc and SIFT feature vectors Fv1 and Fv2; thirdly, initial matching is carried out through the Fv1 and the Fv2; fourthly, the Fc is screened for the second time according to the RANSAC strategy of a homography matrix model, final correct matching point pairs Fm are acquired, and a registration parameter pr is worked out according to the least square method; fifthly, I2 is subjected to space conversion through affine transformation, and a roughly-registered image I3 is acquired through interpolation and resampling; sixthly, pr serves as the initial value of normalization information registration, I1 and I2 are subjected to fine registration through the normalized mutual information method, a final registration parameter pr1 is worked out, and a registered image I4 is output. The method can be quickly, effectively and stably carried out, and SAR image registration precision and robustness are improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
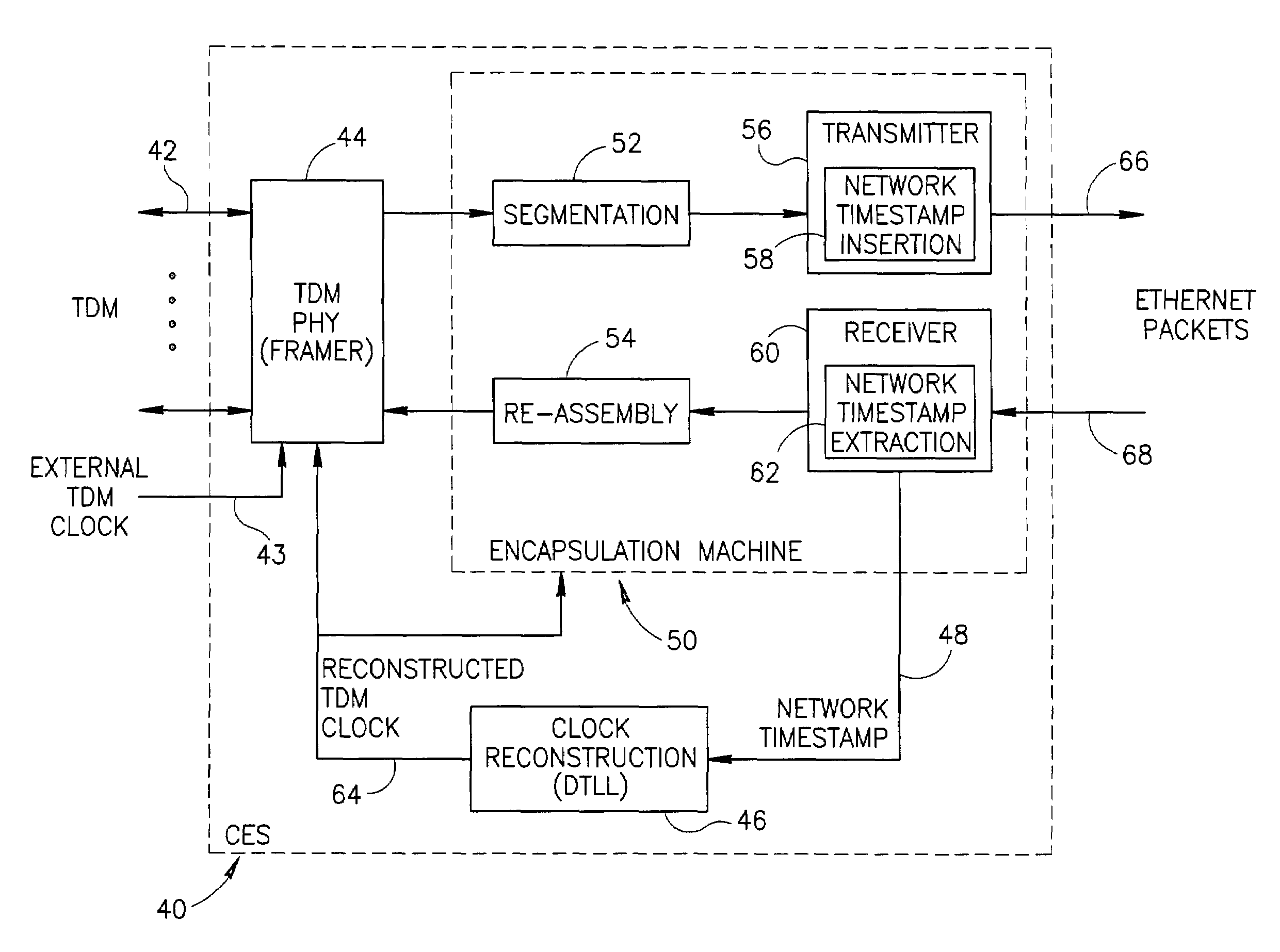
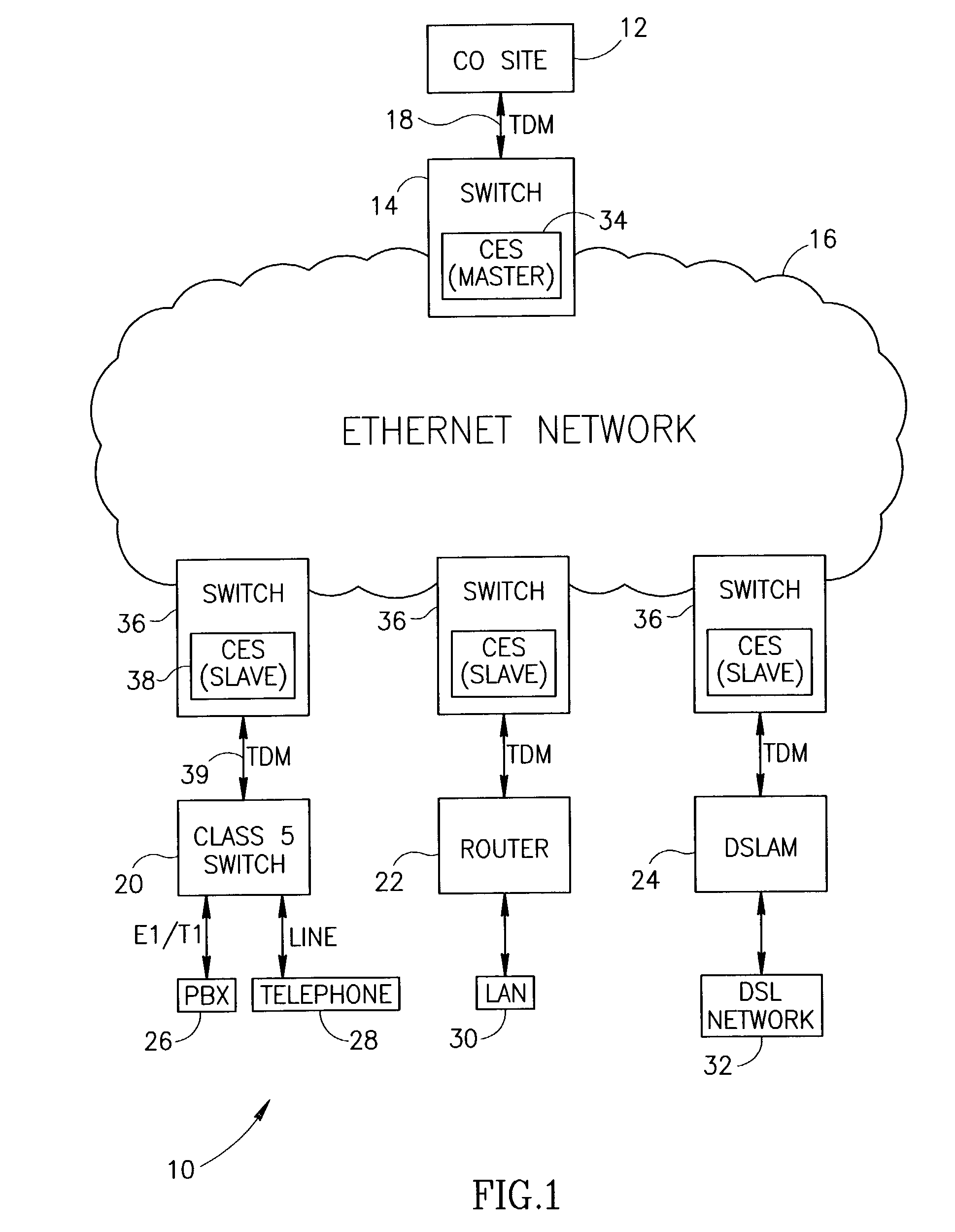
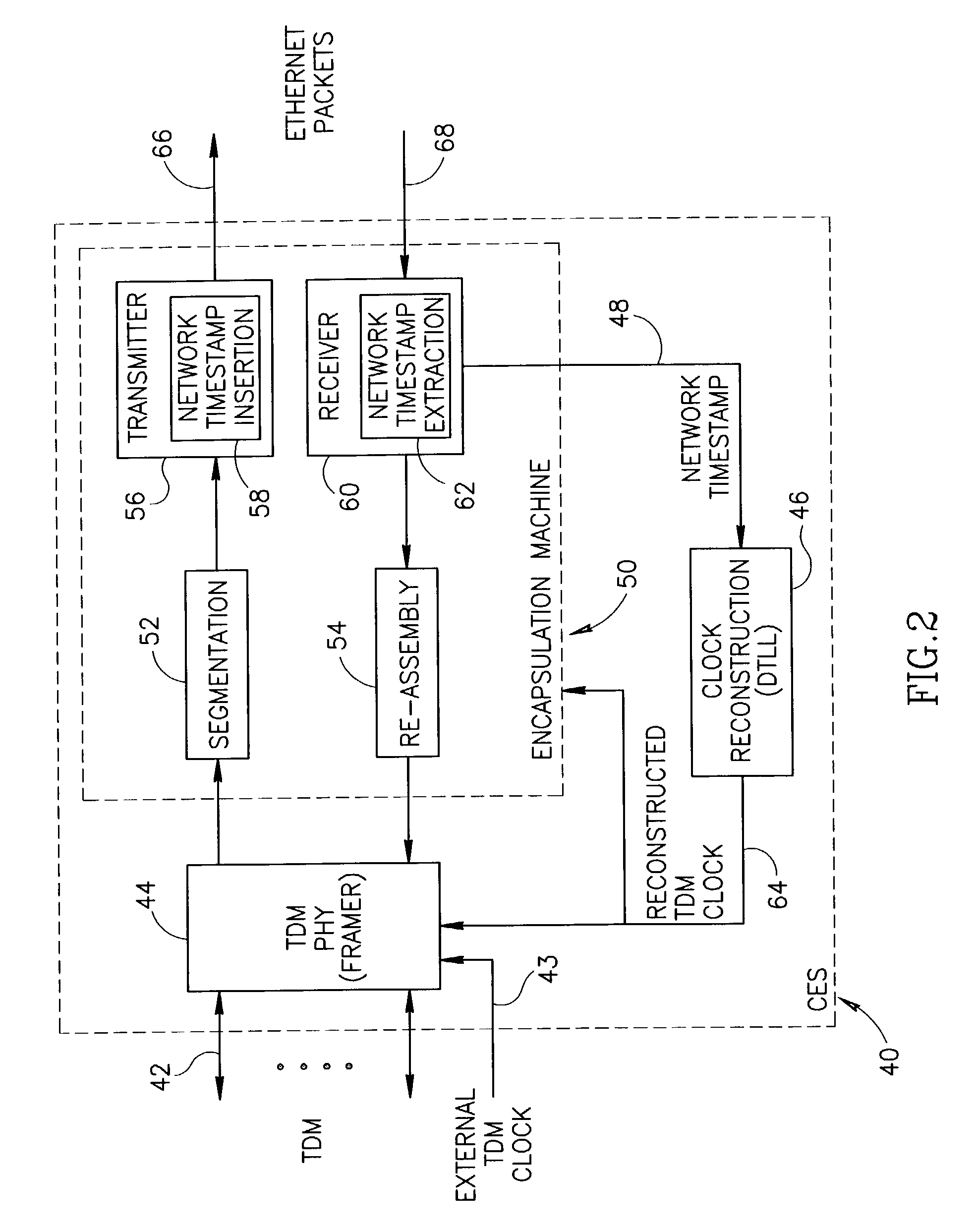
Clock reconstruction for time division multiplexed traffic transported over asynchronous ethernet networks
A clock reconstruction mechanism for synchronous TDM communications traffic transported over asynchronous networks such as Ethernet networks. The invention is applicable to edge switches in Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) that transport legacy TDM traffic using a Circuit Emulation Services (CES) module whereby TDM traffic is encapsulated and transported across the Ethernet network where it is de-encapsulated and clocked out to the destination. The mechanism encapsulates the input TDM data stream into Ethernet packets and inserts a network timestamp within the packet. At the destination CES, a local timestamp is generated for each received packet as it is received. The network timestamp is extracted and input along with the local timestamp to a Digital Time Locked Loop (DTLL) which is operative to accurately reconstruct the original transmit TDM clock. The filter in the DTLL performs a Least Squares Regression (LSR) algorithm and Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filter algorithm to generate a clock control signal for adjusting the clock generated.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING III +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com