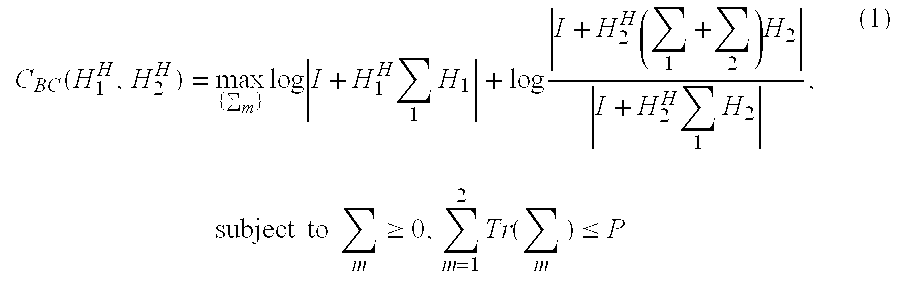Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1595 results about "Covariance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. If the greater values of one variable mainly correspond with the greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for the lesser values, (i.e., the variables tend to show similar behavior), the covariance is positive. In the opposite case, when the greater values of one variable mainly correspond to the lesser values of the other, (i.e., the variables tend to show opposite behavior), the covariance is negative. The sign of the covariance therefore shows the tendency in the linear relationship between the variables. The magnitude of the covariance is not easy to interpret because it is not normalized and hence depends on the magnitudes of the variables. The normalized version of the covariance, the correlation coefficient, however, shows by its magnitude the strength of the linear relation.
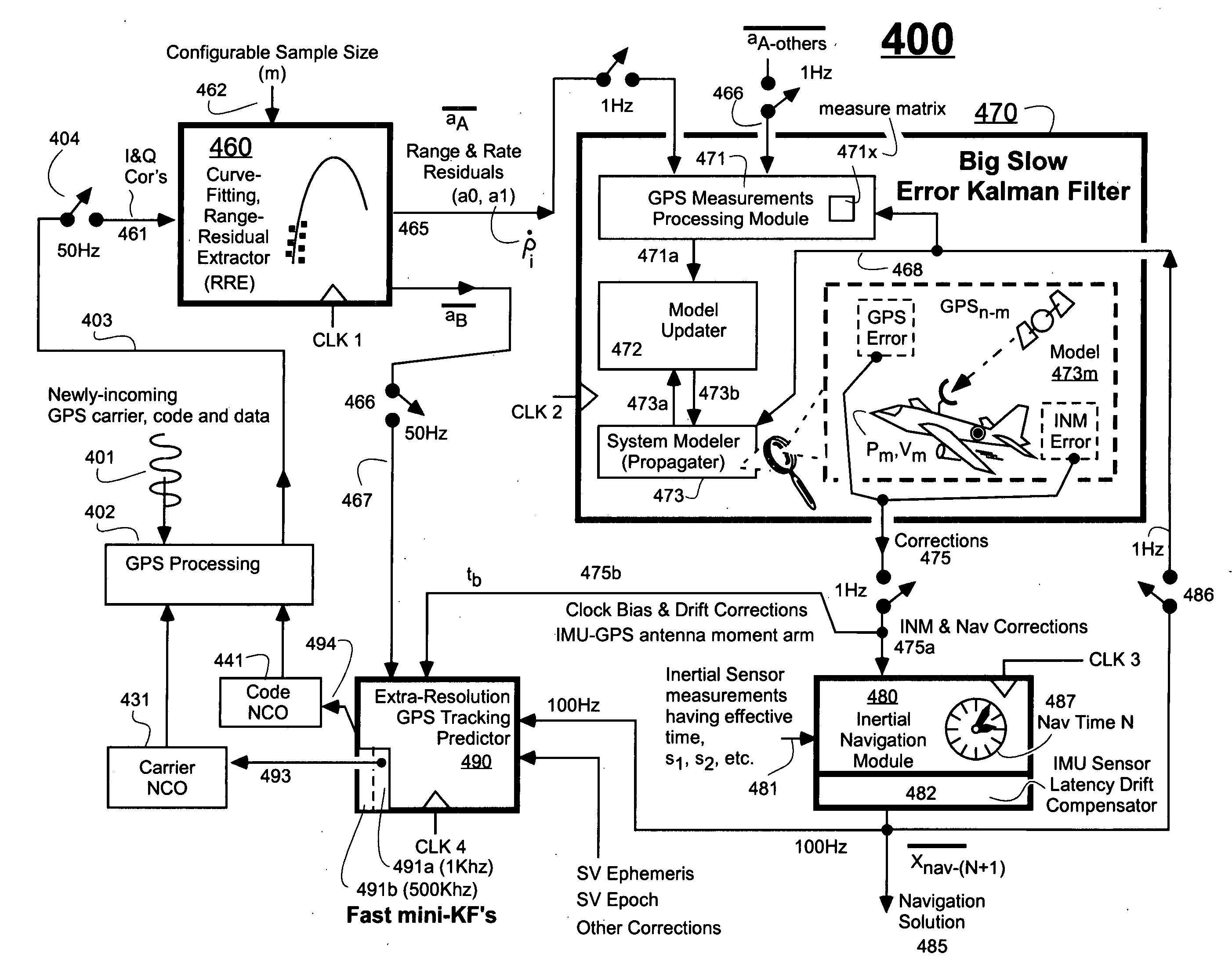
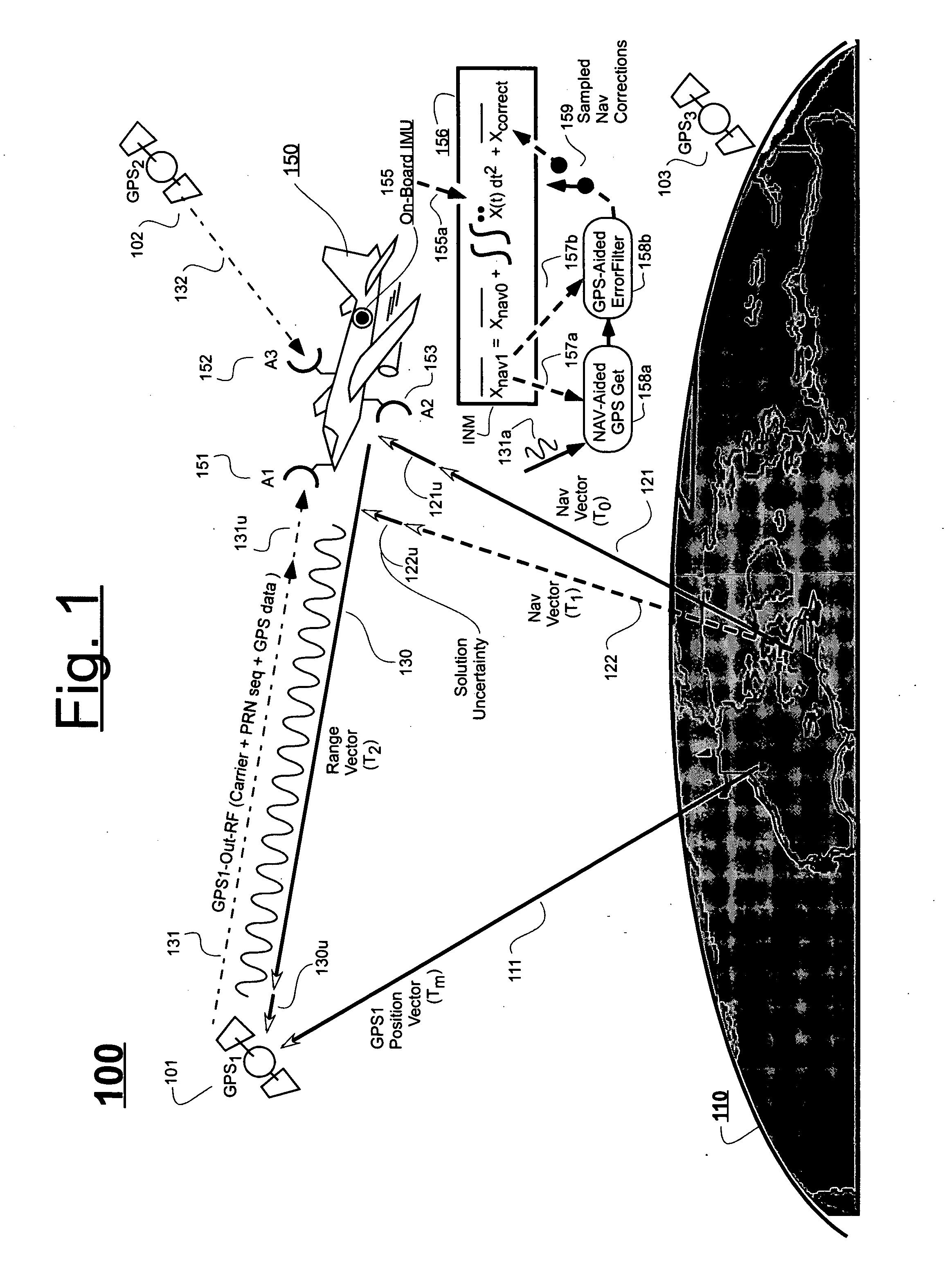
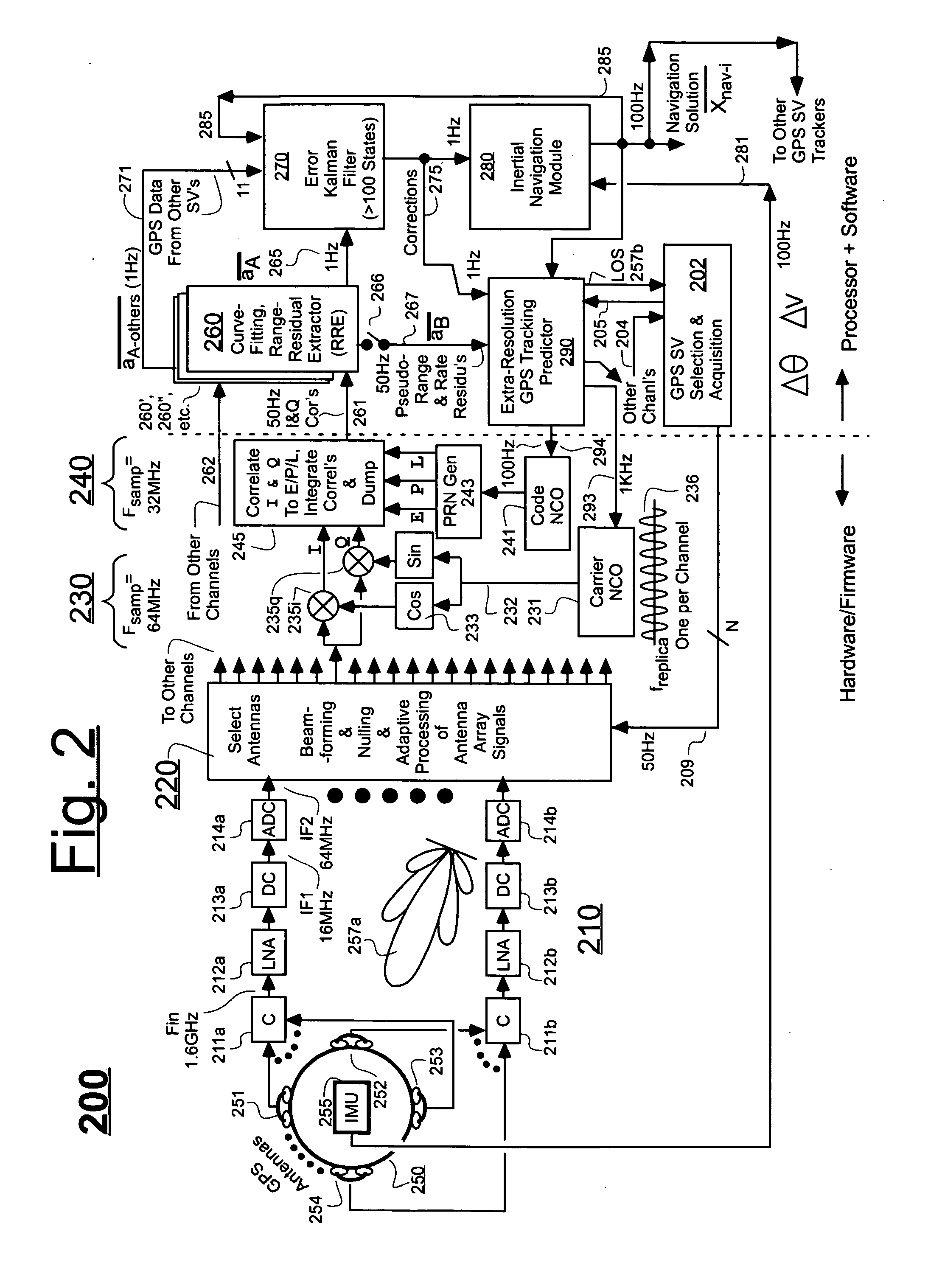
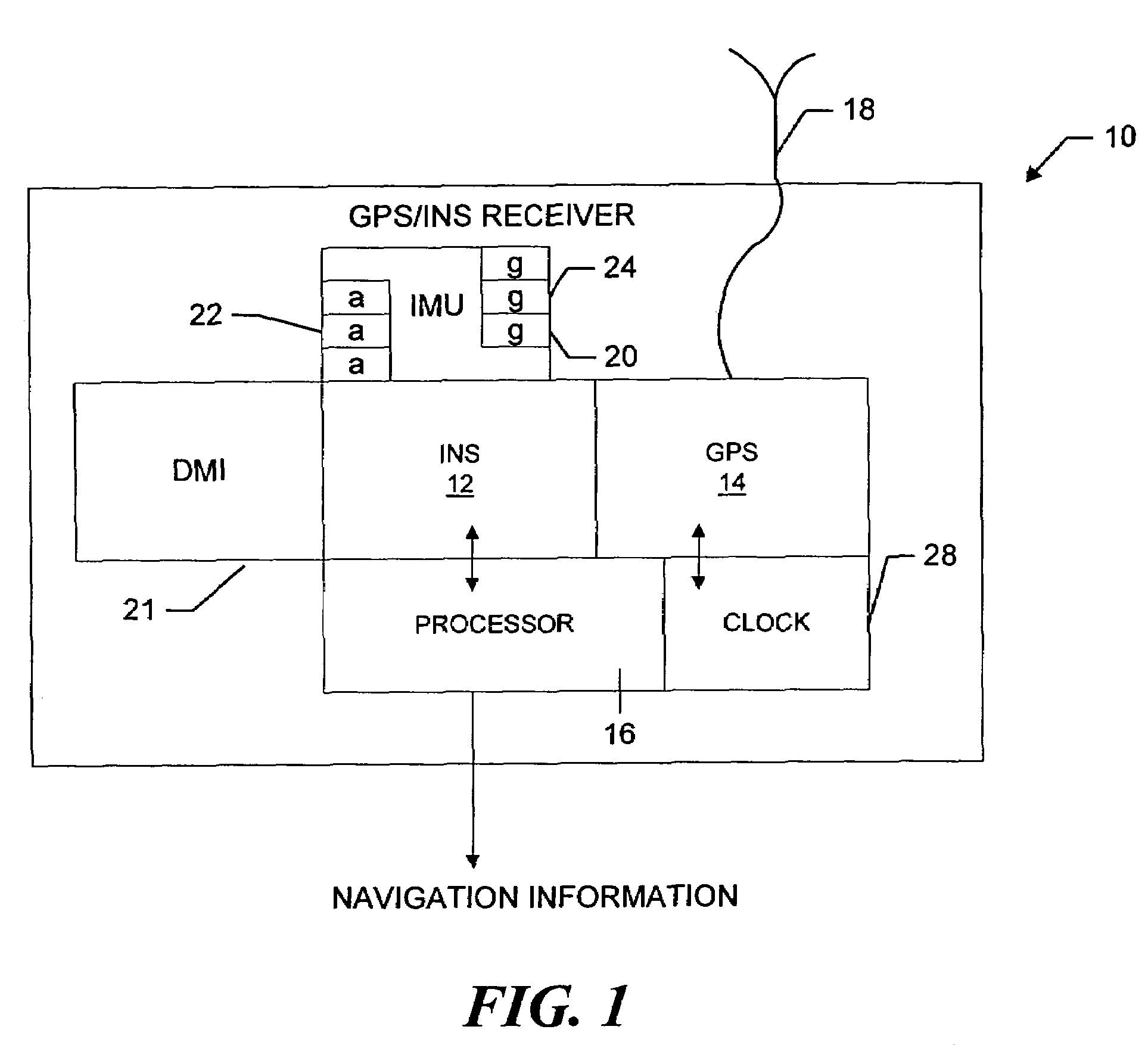
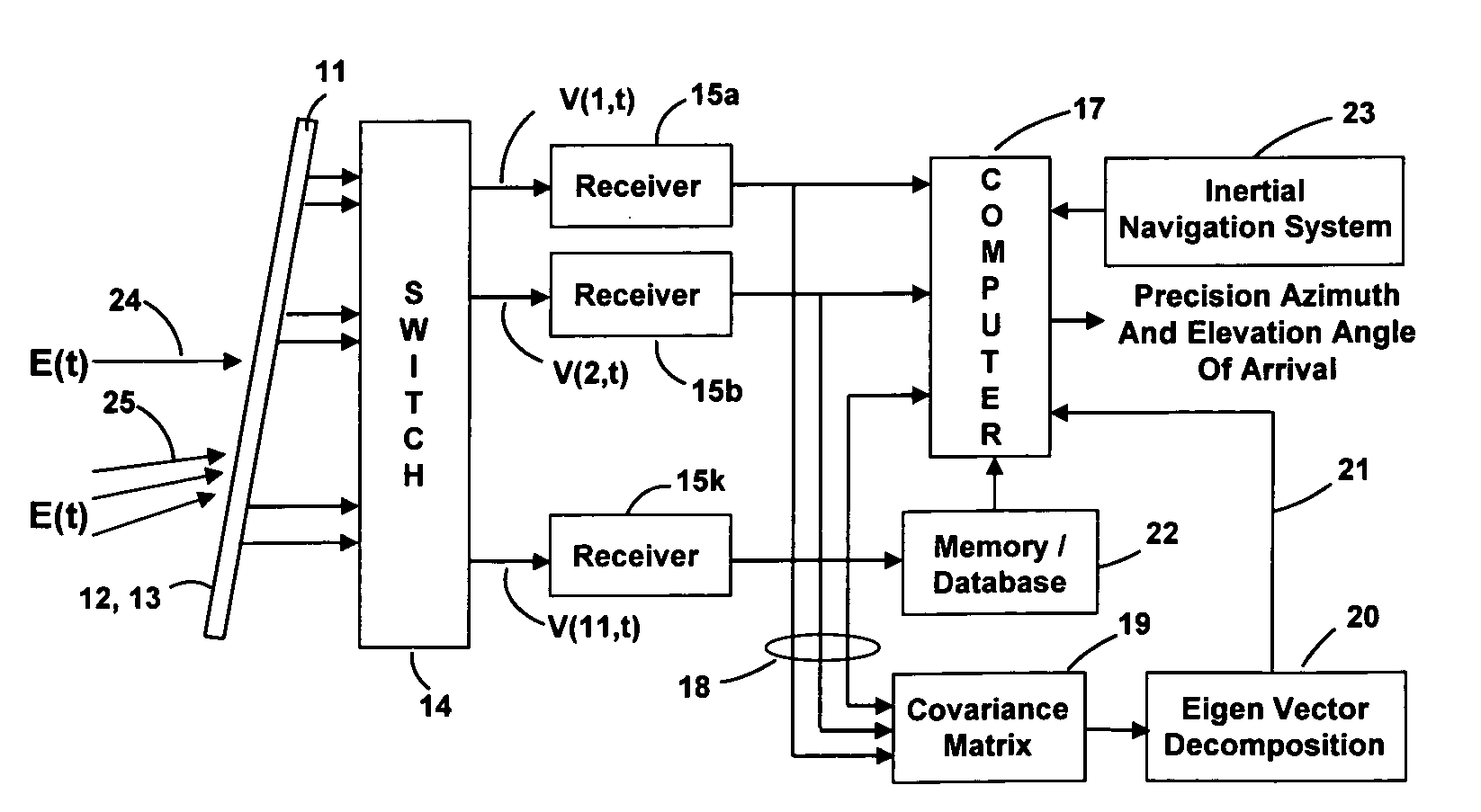
Ultra-tightly coupled GPS and inertial navigation system for agile platforms
InactiveUS20070118286A1Cancel noiseReduce computing timeDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCurve fittingCarrier signal
An Ultra-Tightly Coupled GPS-inertial navigation system for use in a moving agile platform includes a range residual extractor that uses best curve fitting of a third order polynomial for estimating range residual. The curve-fitted residual is used to update an error Kalman filter. The error Kalman filter includes correction for navigation solution, and IMU and GPS parameters. The navigation solution together with GPS parameter corrections are used in a Tracking Predictor to generate high-sampling-rate carrier and code replicas. The curve-fitting error covariance indicates signal to noise ratio for the tracked GPS signal and may be used for early indication of interference or jamming.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
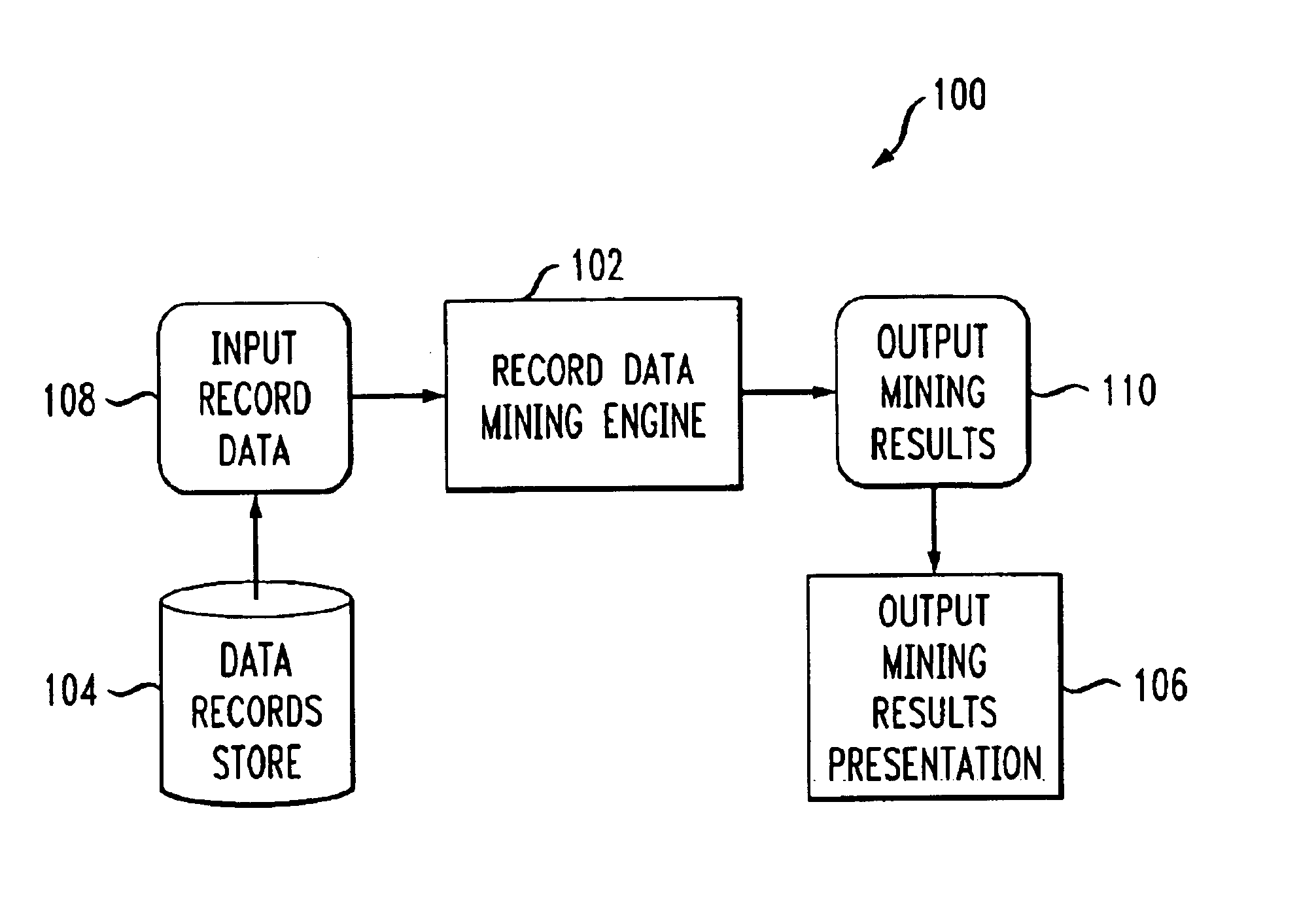
Method and apparatus for data mining to discover associations and covariances associated with data
ActiveUS7043476B2Efficient and effectiveData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData dredgingHigh dimensionality
Data mining techniques are provided which are effective and efficient for discovering useful information from an amorphous collection or data set of records. For example, the present invention provides for the mining of data, e.g., of several or many records, to discover interesting associations between entries of qualitative text, and covariances between data of quantitative numerical types, in records. Although not limited thereto, the invention has particular application and advantage when the data is of a type such as clinical, pharmacogenomic, forensic, police and financial records, which are characterized by many varied entries, since the problem is then said to be one of “high dimensionality” which has posed mathematical and technical difficulties for researchers. This is especially true when considering strong negative associations and negative covariance, i.e., between items of data which may so rarely come together that their concurrence is never seen in any record, yet the fact that this is not expected is of potential great interest.
Owner:IBM CORP
Photoplethysmography (PPG) device and the method thereof
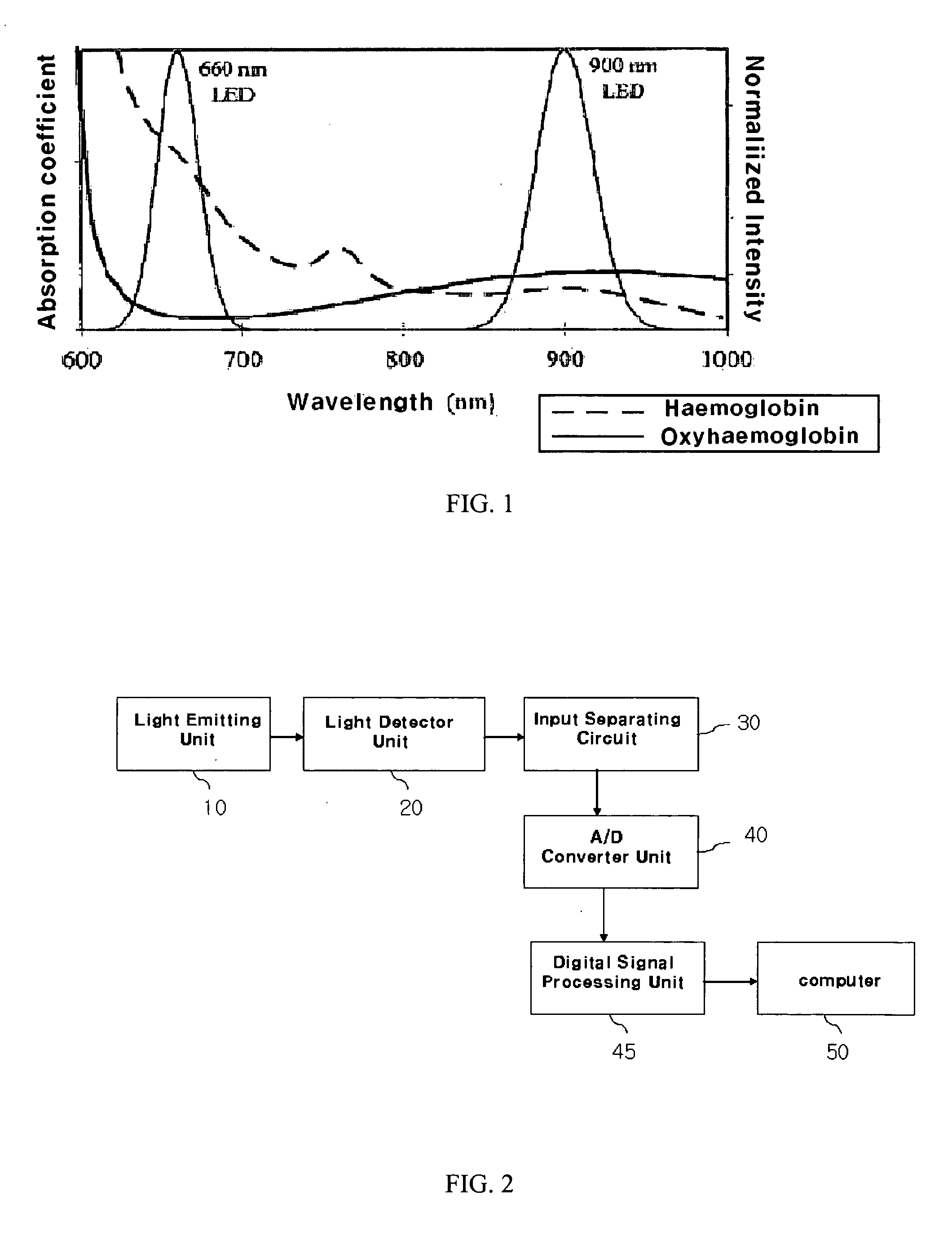
ActiveUS7336982B2Improve performanceReduce Motion ArtifactsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAcquired characteristicCovariance
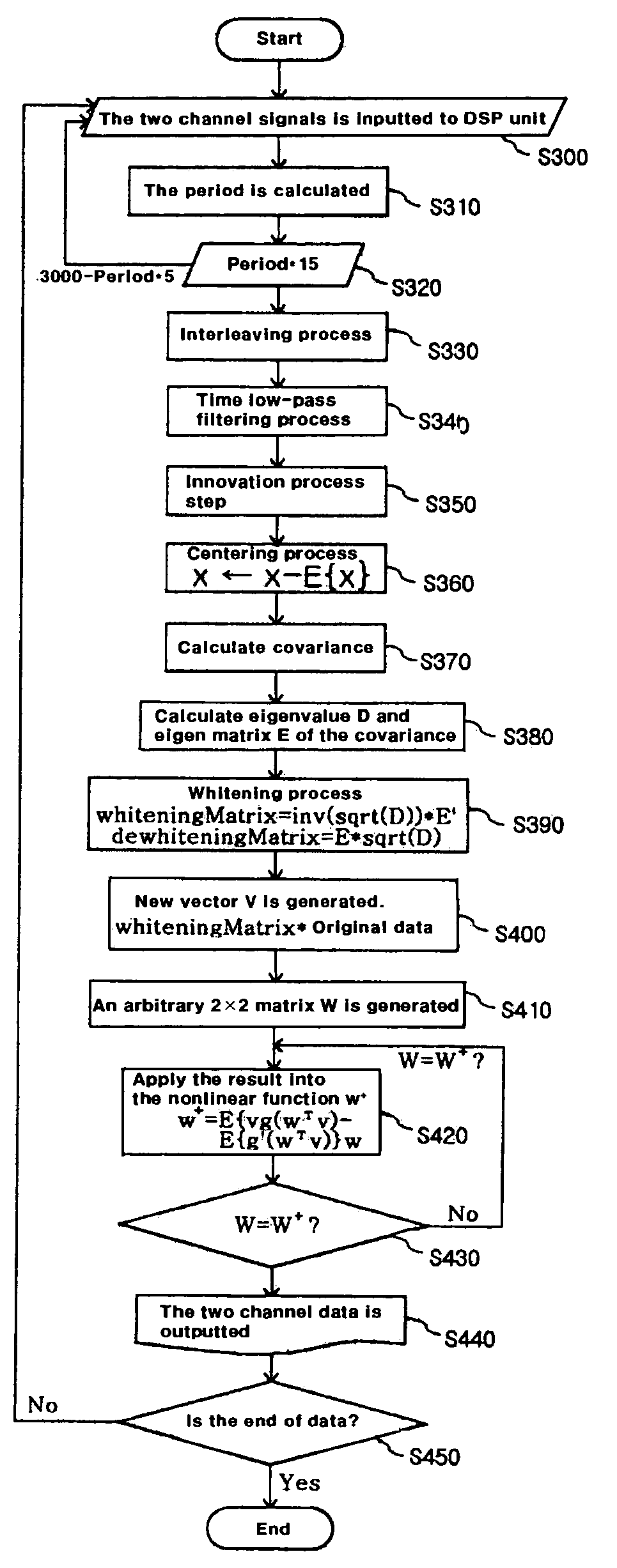
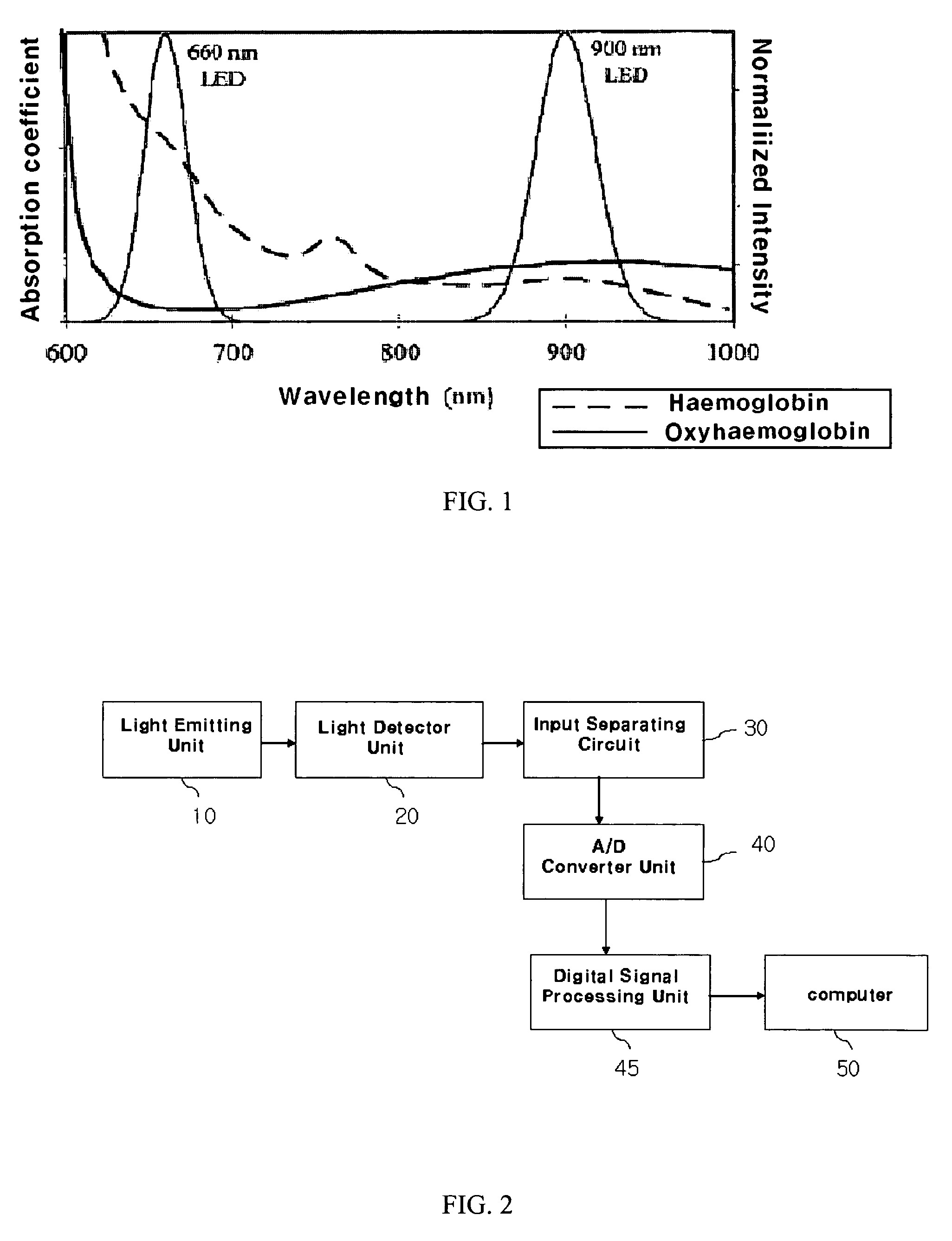
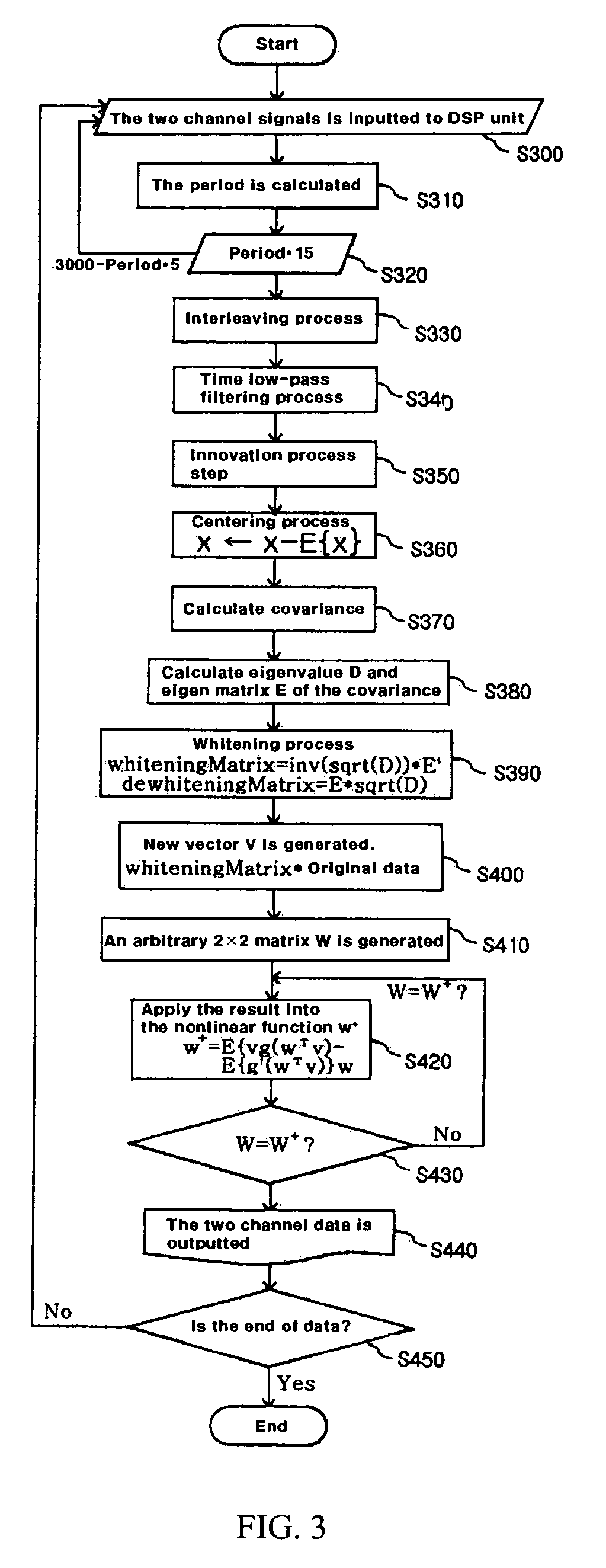
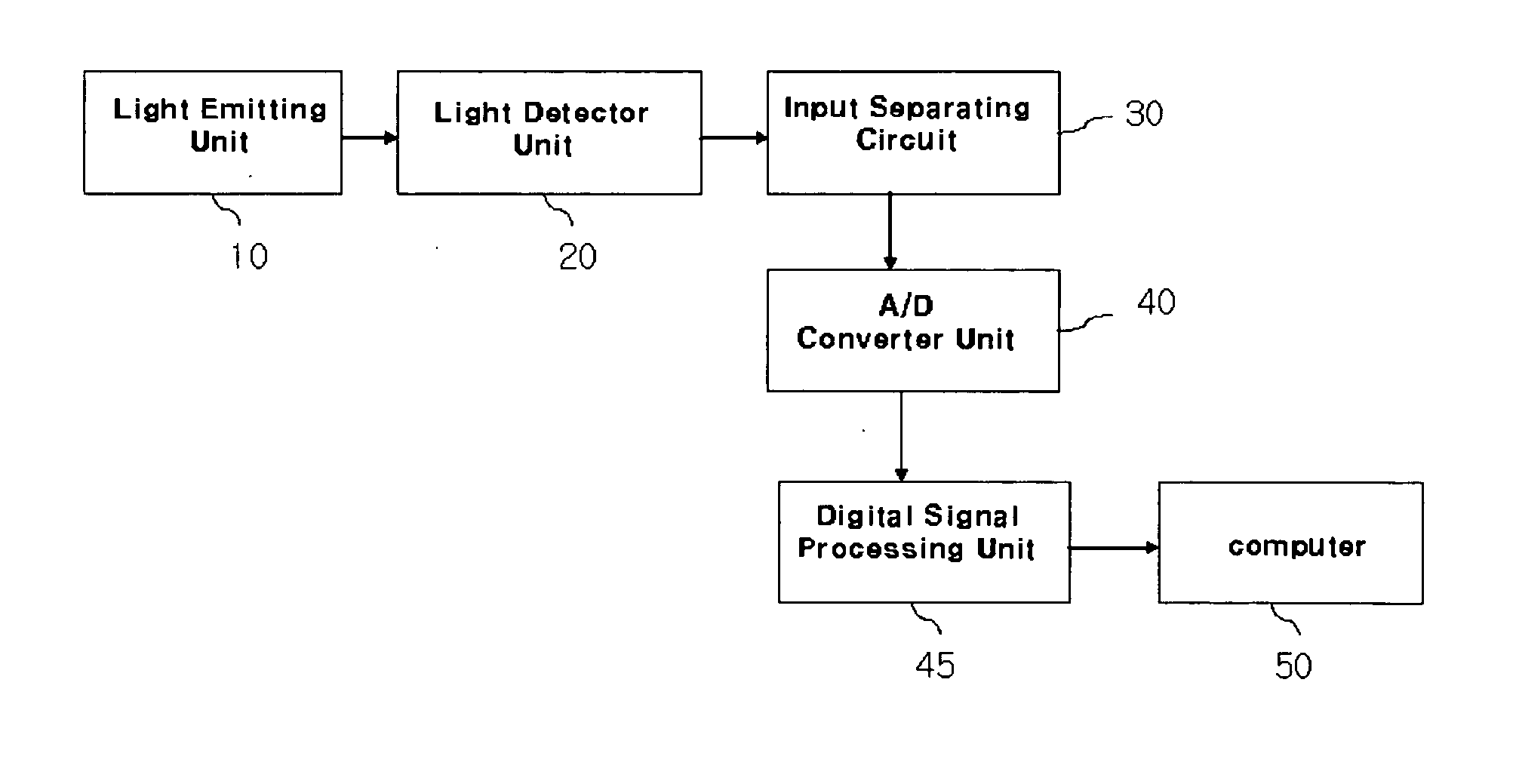
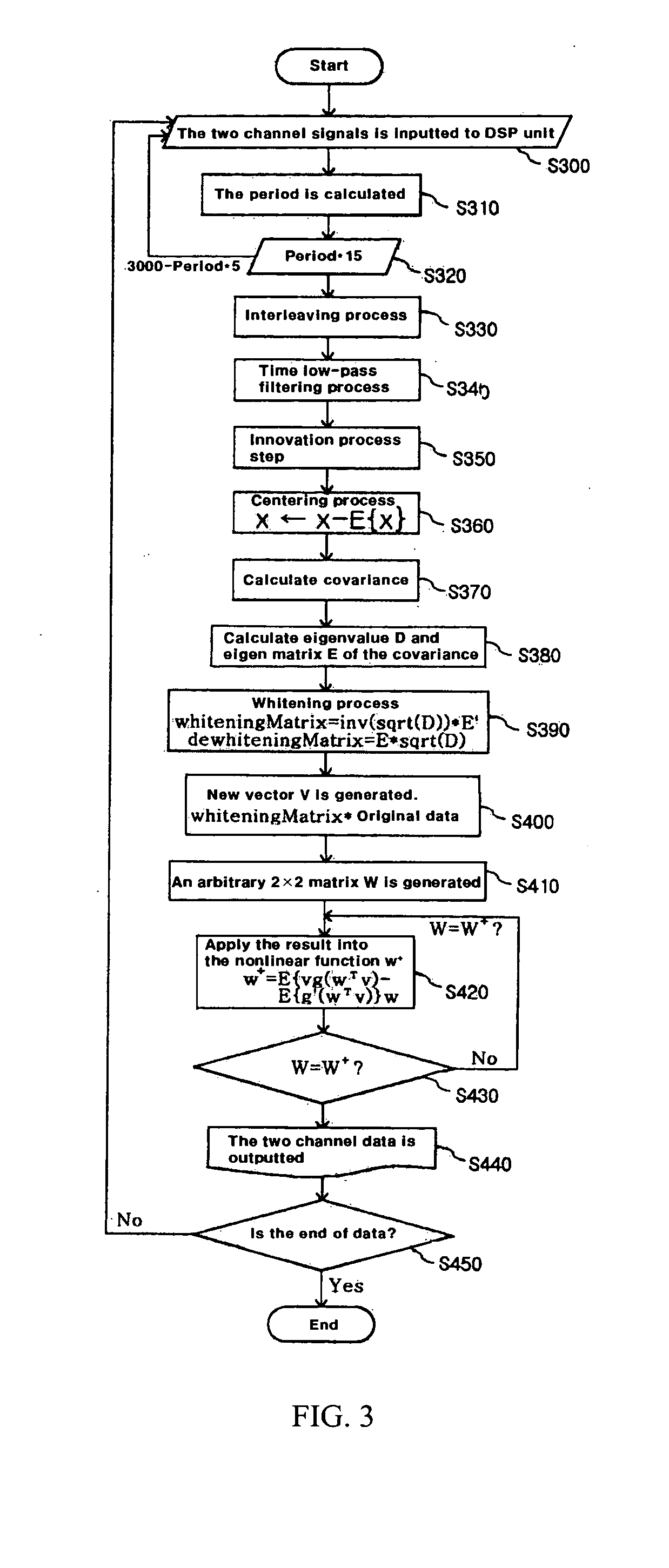
A method of measuring Photoplethysmography (PPG) signals may comprise detecting dual wavelength illumination from a light detector so as to provide detected signals, converting the detected signals into digital signals so as to provide digital signals, reducing noises from the digital signals and increasing independency between the digital signals so as to provide preprocessed signals, subtracting the average value from the preprocessed signals so as to provide adjusted signals, obtaining whitening matrix based on covariance, eigen value, and eigen matrix obtained from the adjusted signals, and restoring data using the whitening matrix.
Owner:SILICON MITUS
Method and apparatus for coexistence
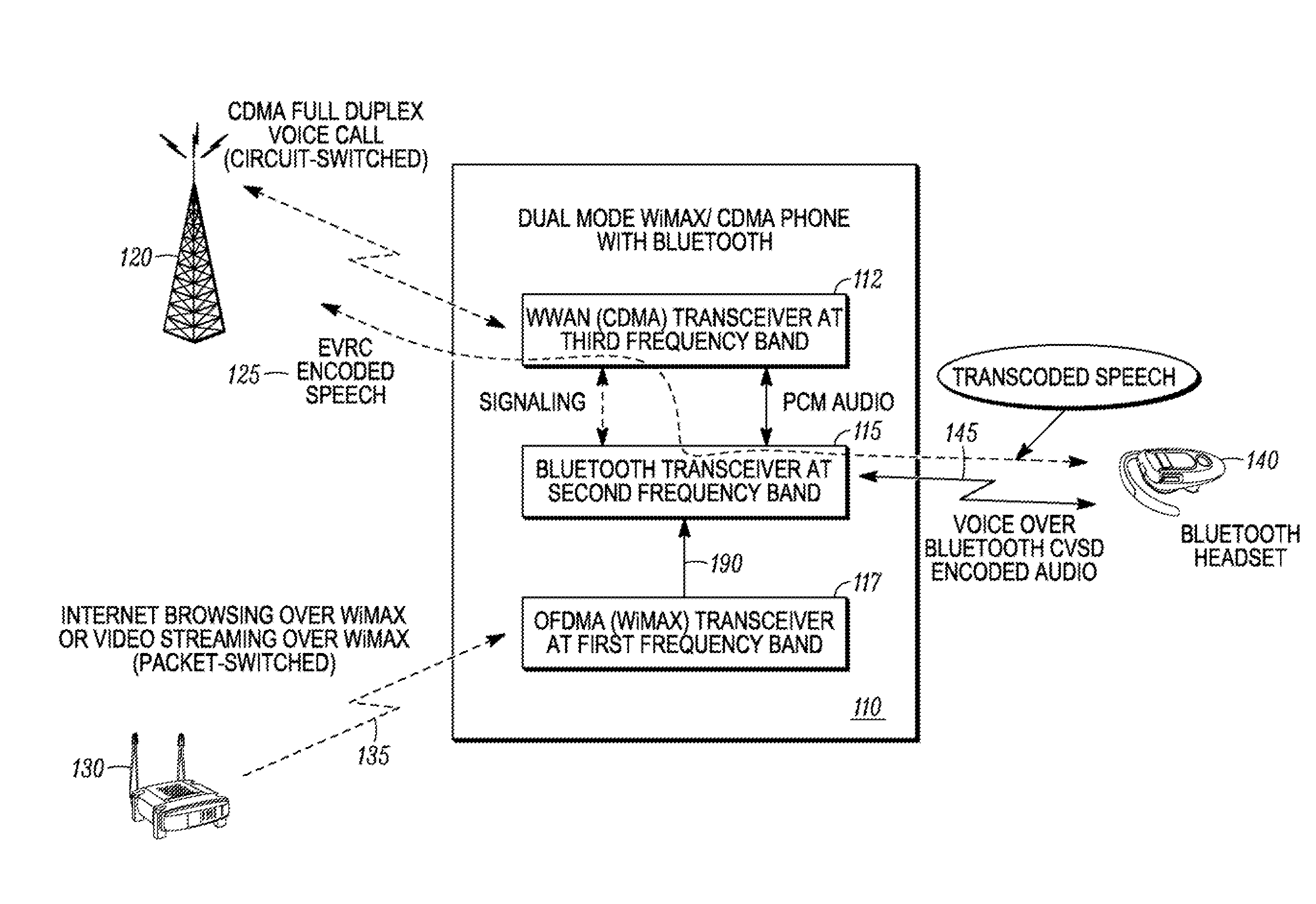
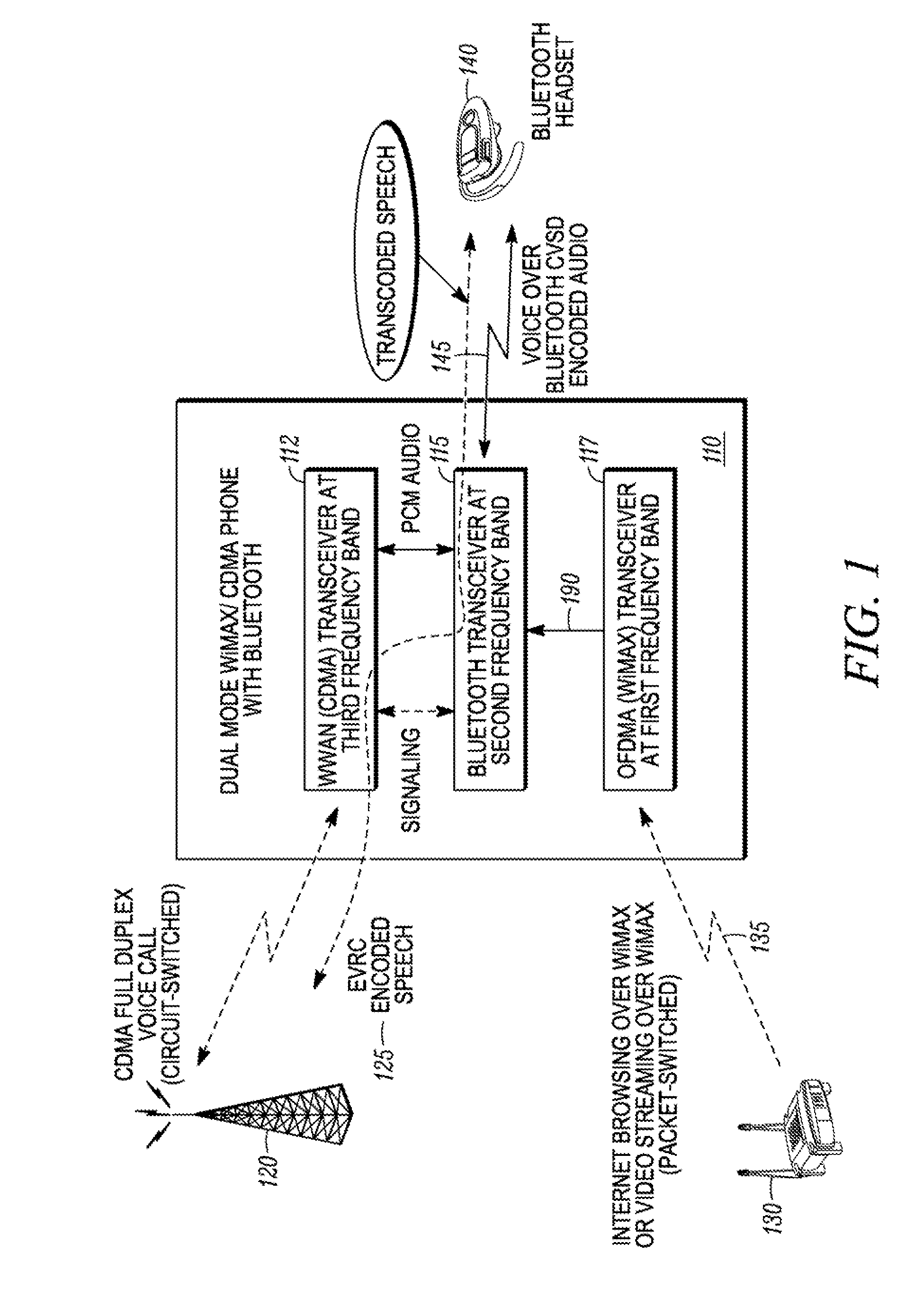
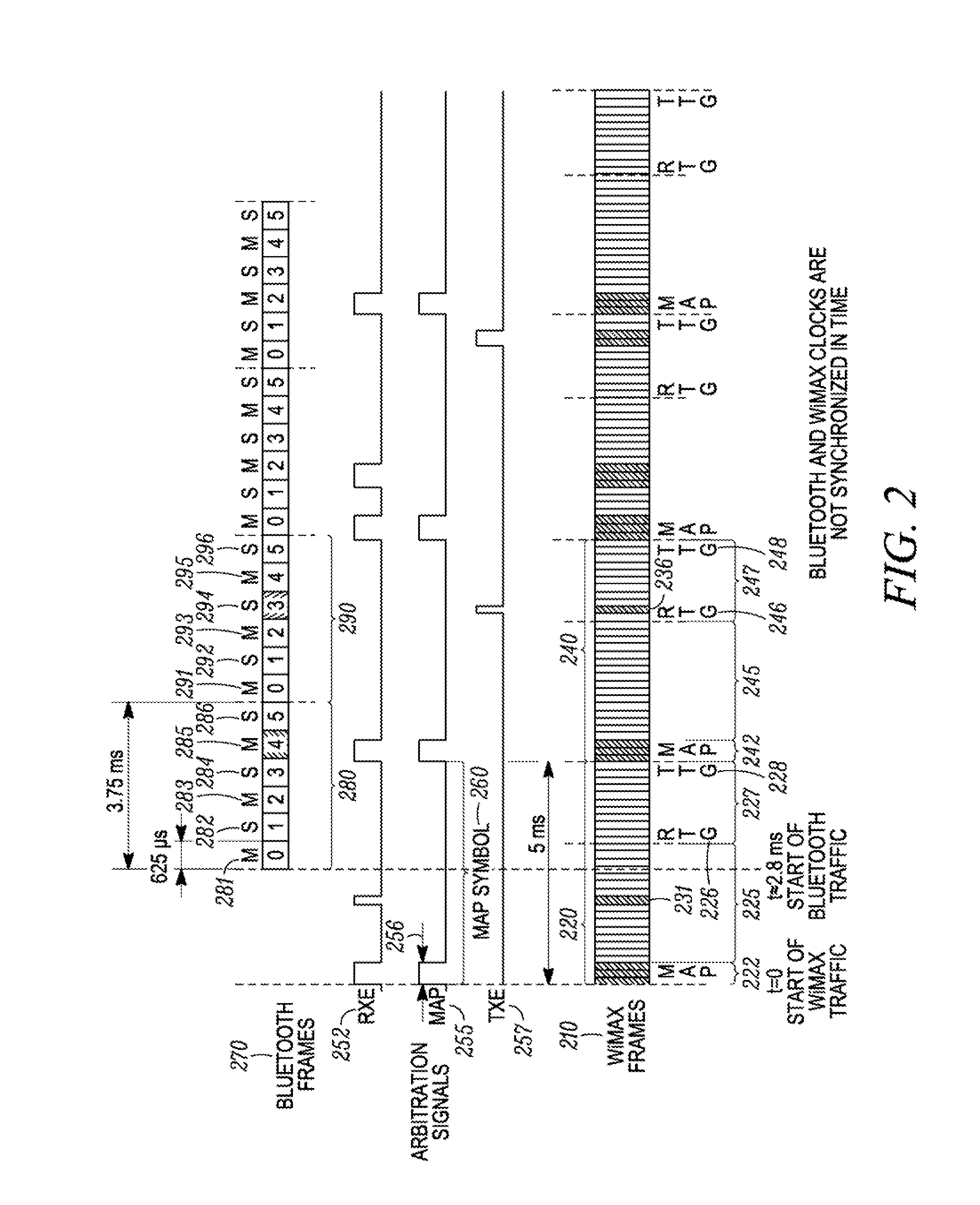
A method for coexistence of an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) receiver (117) such as a WiMAX receiver with a synchronous frame-based transmitter (115) such as a Bluetooth transmitter within a mobile station (110) receives an estimated media access protocol (MAP′) signal indicating when a MAP message is expected to be received by the OFDMA receiver (117) and uses it at a Bluetooth shutdown signal (190) at least when a MAP message is expected to be received. The MAP′ signal can be taken directly from the ODFMA transceiver (117) or it may be produced through analysis of a receiver-enable (RXE) signal that includes not only MAP symbols but also downlink data symbols. The RXE signal can be analyzed using interrupt-and-timer, Fast Fourier Transform, covariance, and / or delay-locked loop techniques to extract historical MAP symbol information and generate expected MAP symbol information. Shutting down a Bluetooth transmitter during expected MAP message receipt permits the OFDMA receiver to maintain synchronicity with an access point while not requiring the Bluetooth transmitter to shut down every time the OFDMA receiver expects to receive an OFDMA symbol.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Photoplethysmography (PPG) device and the method thereof
ActiveUS20050058456A1Improve performanceReduce Motion ArtifactsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAcquired characteristicCovariance
A method of measuring Photoplethysmography (PPG) signals may comprise detecting dual wavelength illumination from a light detector so as to provide detected signals, converting the detected signals into digital signals so as to provide digital signals, reducing noises from the digital signals and increasing independency between the digital signals so as to provide preprocessed signals, subtracting the average value from the preprocessed signals so as to provide adjusted signals, obtaining whitening matrix based on covariance, eigen value, and eigen matrix obtained from the adjusted signals, and restoring data using the whitening matrix.
Owner:SILICON MITUS
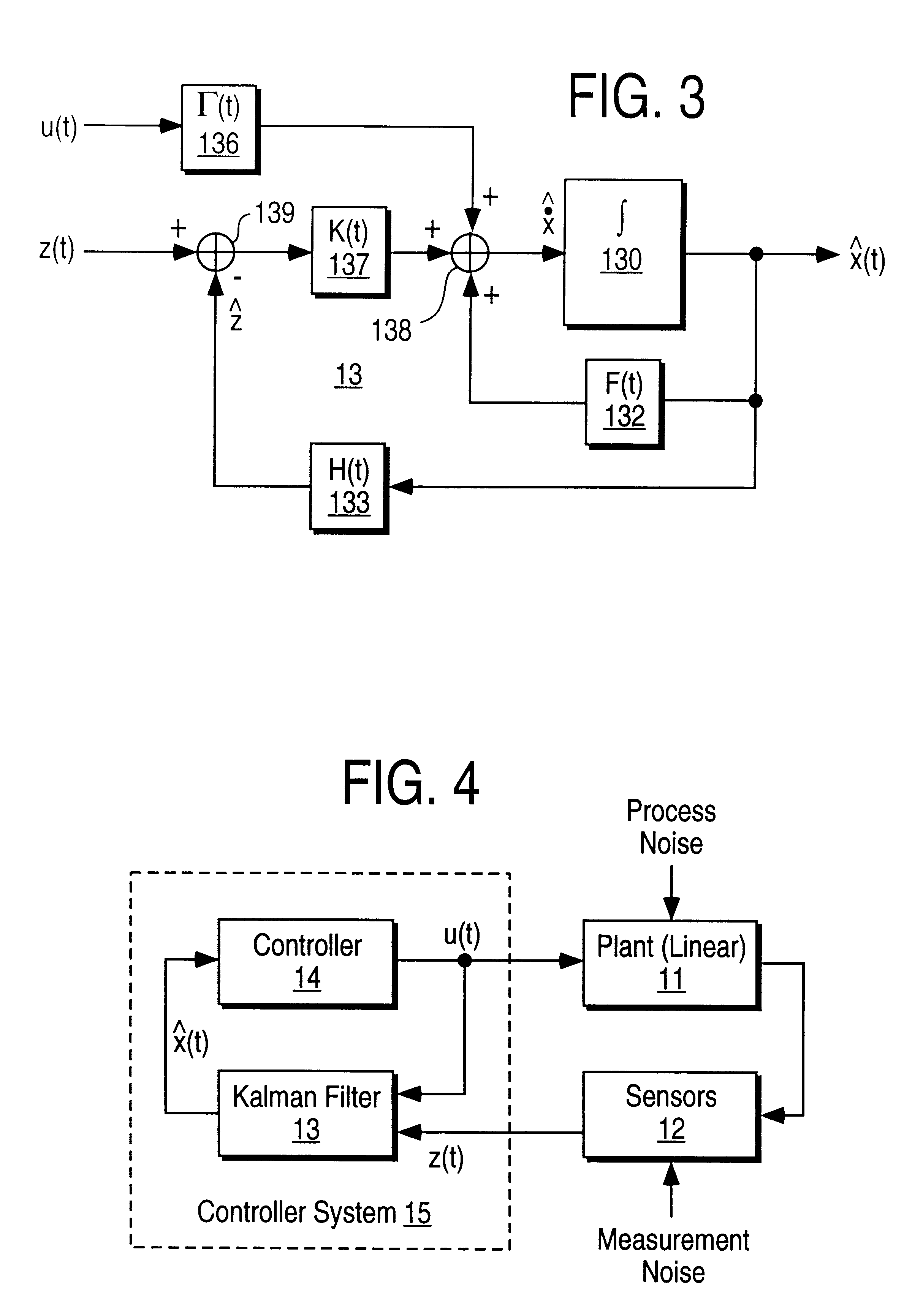
Method for real-time nonlinear system state estimation and control
InactiveUS6285971B1Computation using non-denominational number representationAdaptive controlOperating pointEngineering
A method for the estimation of the state variables of nonlinear systems with exogenous inputs is based on improved extended Kalman filtering (EKF) type techniques. The method uses a discrete-time model, based on a set of nonlinear differential equations describing the system, that is linearized about the current operating point. The time update for the state estimates is performed using integration methods. Integration, which is accomplished through the use of matrix exponential techniques, avoids the inaccuracies of approximate numerical integration techniques. The updated state estimates and corresponding covariance estimates use a common time-varying system model for ensuring stability of both estimates. Other improvements include the use of QR factorization for both time and measurement updating of square-root covariance and Kalman gain matrices and the use of simulated annealing for ensuring that globally optimal estimates are produced.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
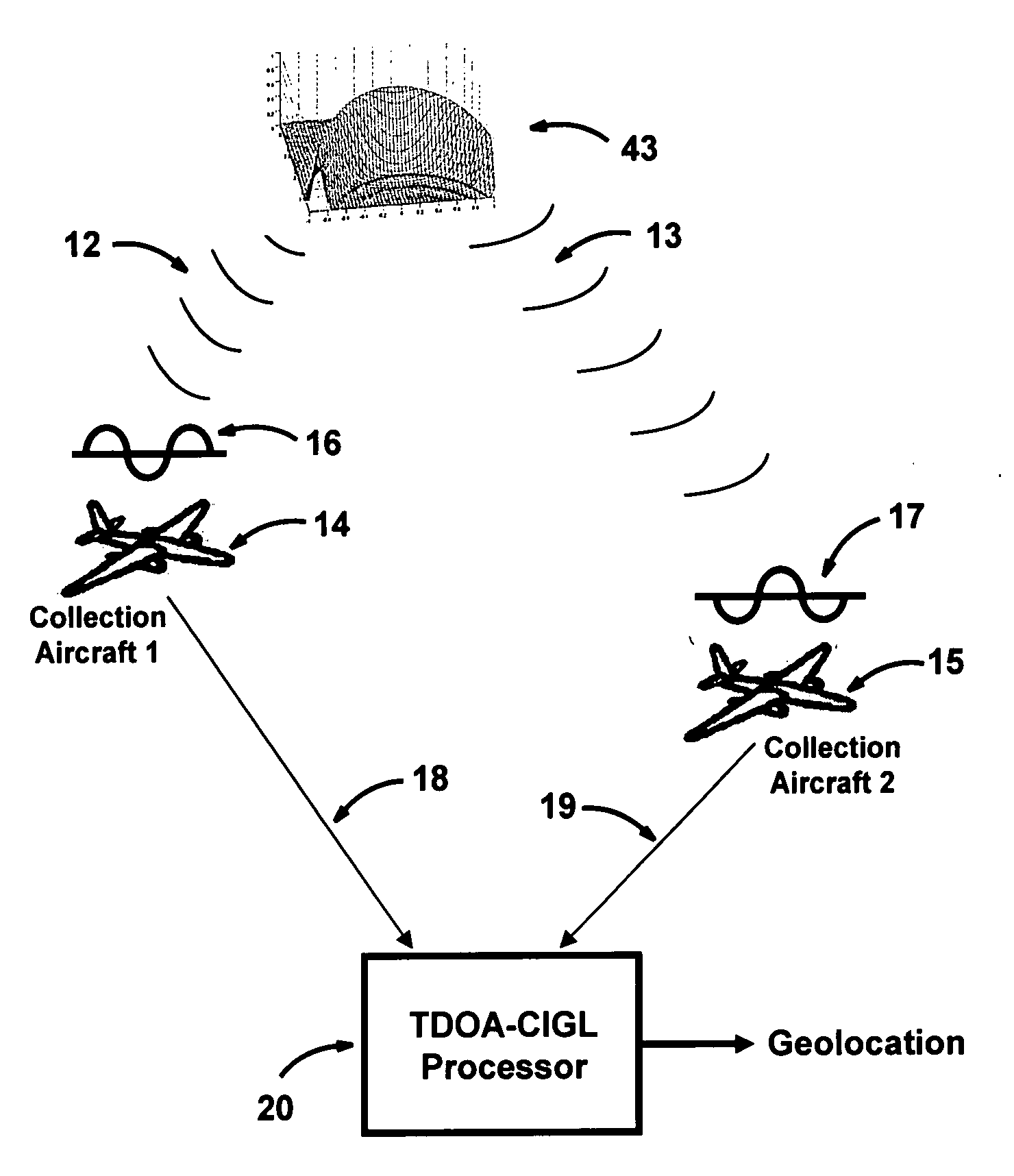
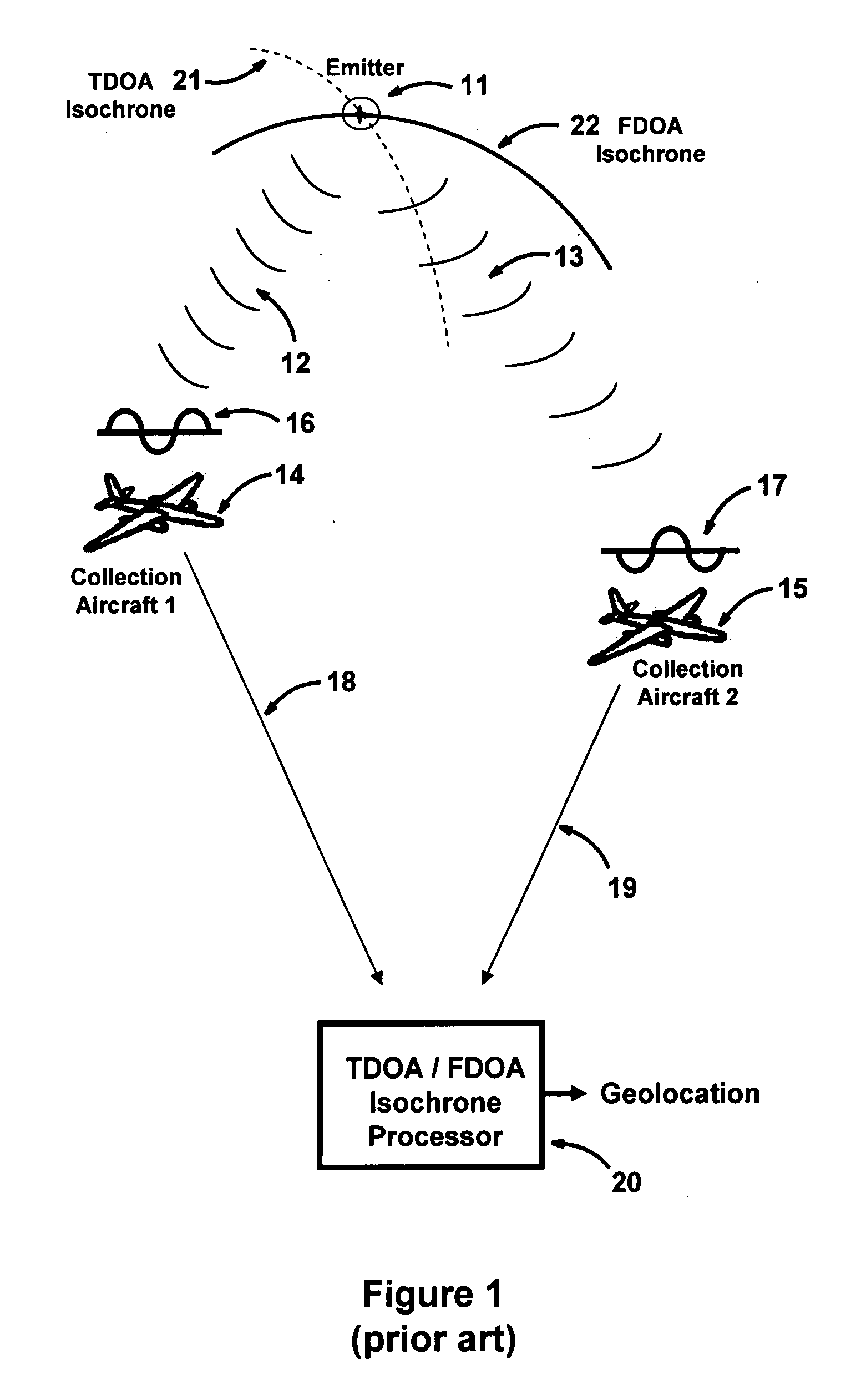
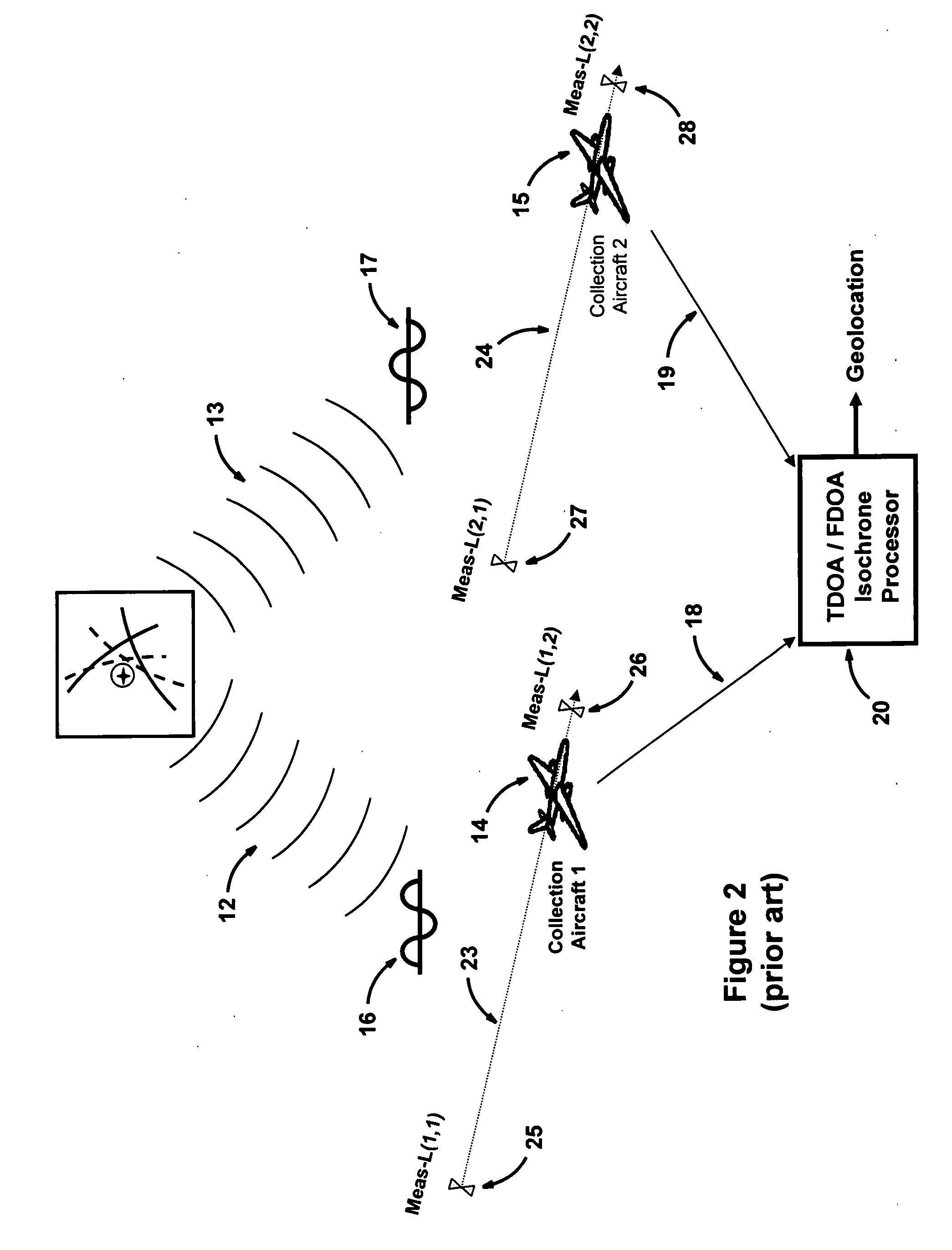
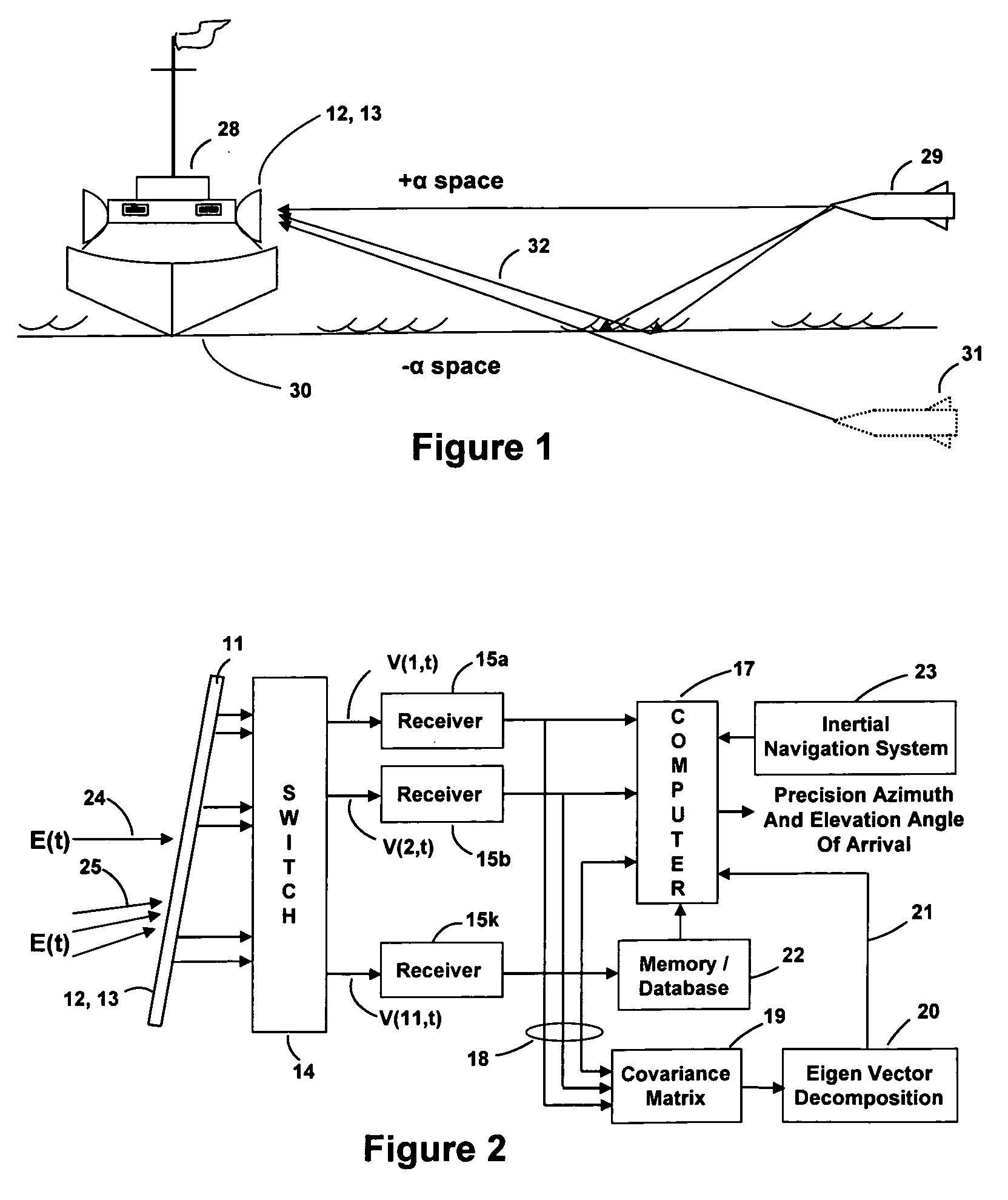
Multiplatform TDOA correlation interferometer geolocation
ActiveUS20080186235A1Improve geolocation accuracyGeographical information is accurateDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationData setGeolocation
A radio geolocation system is described in which a plurality of moving platforms such as aircraft concurrently receive a signal from a remote transmitter and the geolocation of the transmitter is determined. At each platform every thirty seconds a plurality of samples of the received signal are taken over a one second period. The samples are digitized and a time and GPS location stamp are added to each sample. The digitized samples with time and location stamps from all platforms are transmitted to a central location and stored in covariance matrices, one matrix per one second sample period. The signal samples in each matrix are processed utilizing a unique algorithm to generate a data set which defines a correlation surface. The data from a plurality of data sets are summed together on a point by point basis and normalized to yield a summation data set which defines a summation correlation surface. The summation correlation surface has a well defined peak that defines the geolocation of the remote transmitter.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
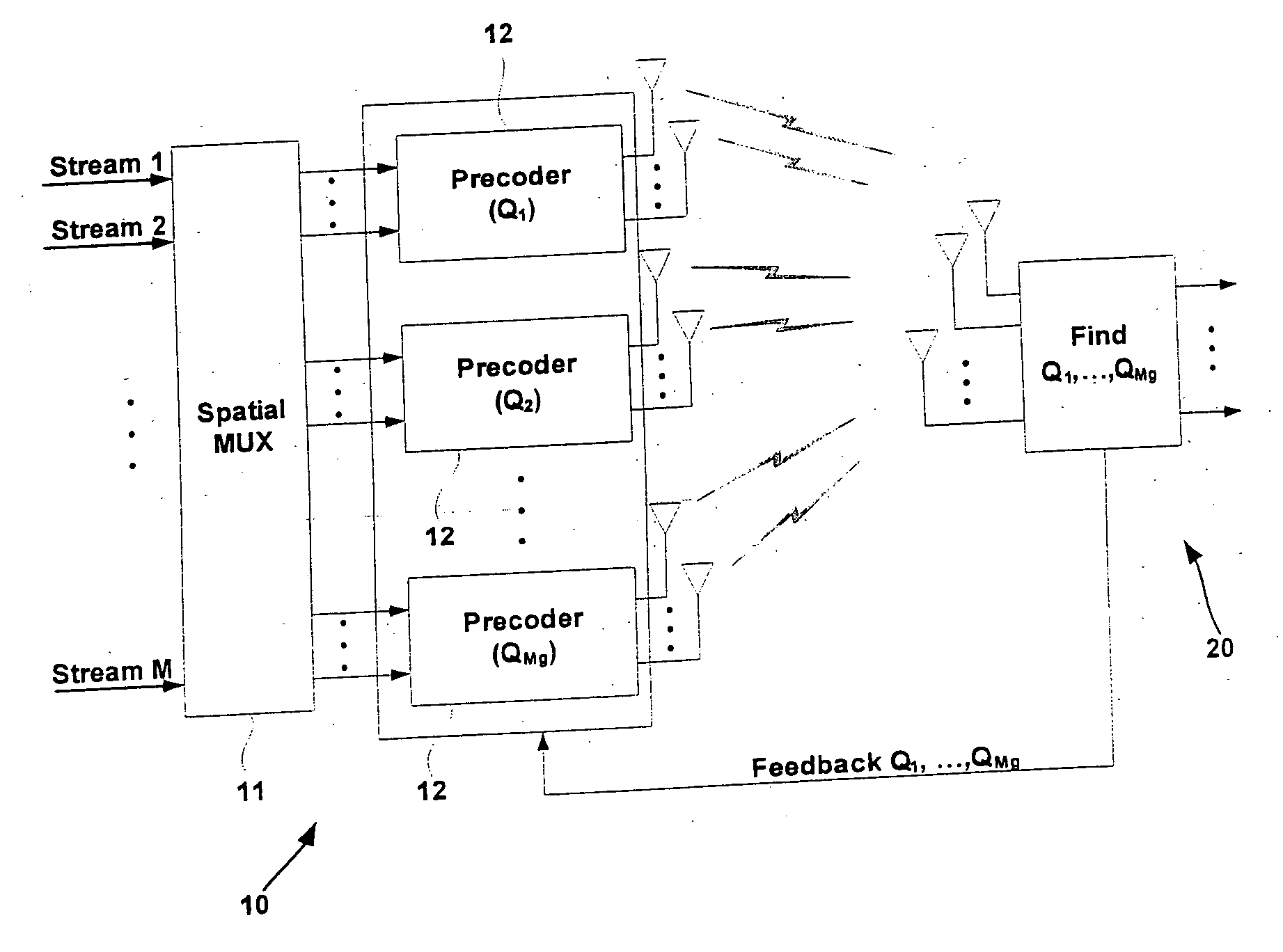
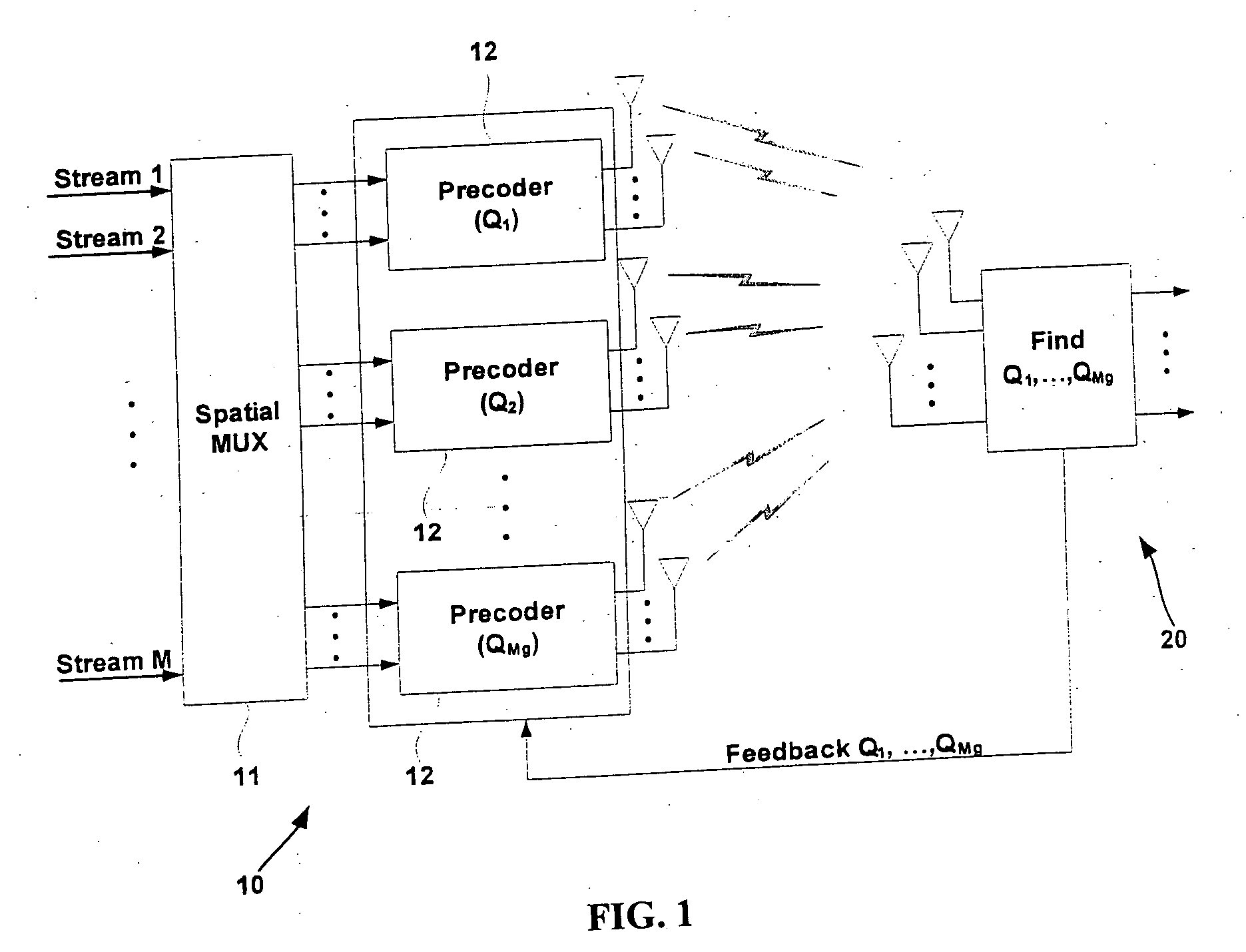
Beam and power allocation method for MIMO communication system
InactiveUS20060098754A1Maximizing rate capabilityReduce the amount requiredPower managementDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemData stream
A beam and power allocation method for a MIMO system transmitting multiple data streams from a transmitter having a plurality of transmit antennas to a receiver having at least two receive antennas, the transmit antennas being grouped based on feedback information from the receiver, includes obtaining covariance matrices for respective transmit antenna group, and allocating beam and power to the transmit antenna groups according to the covariance matrices of the respective antenna groups. The power allocation method can be adapted to various partial beamforming techniques by generalizing the optimization problem as a function of transmit covariance matrices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
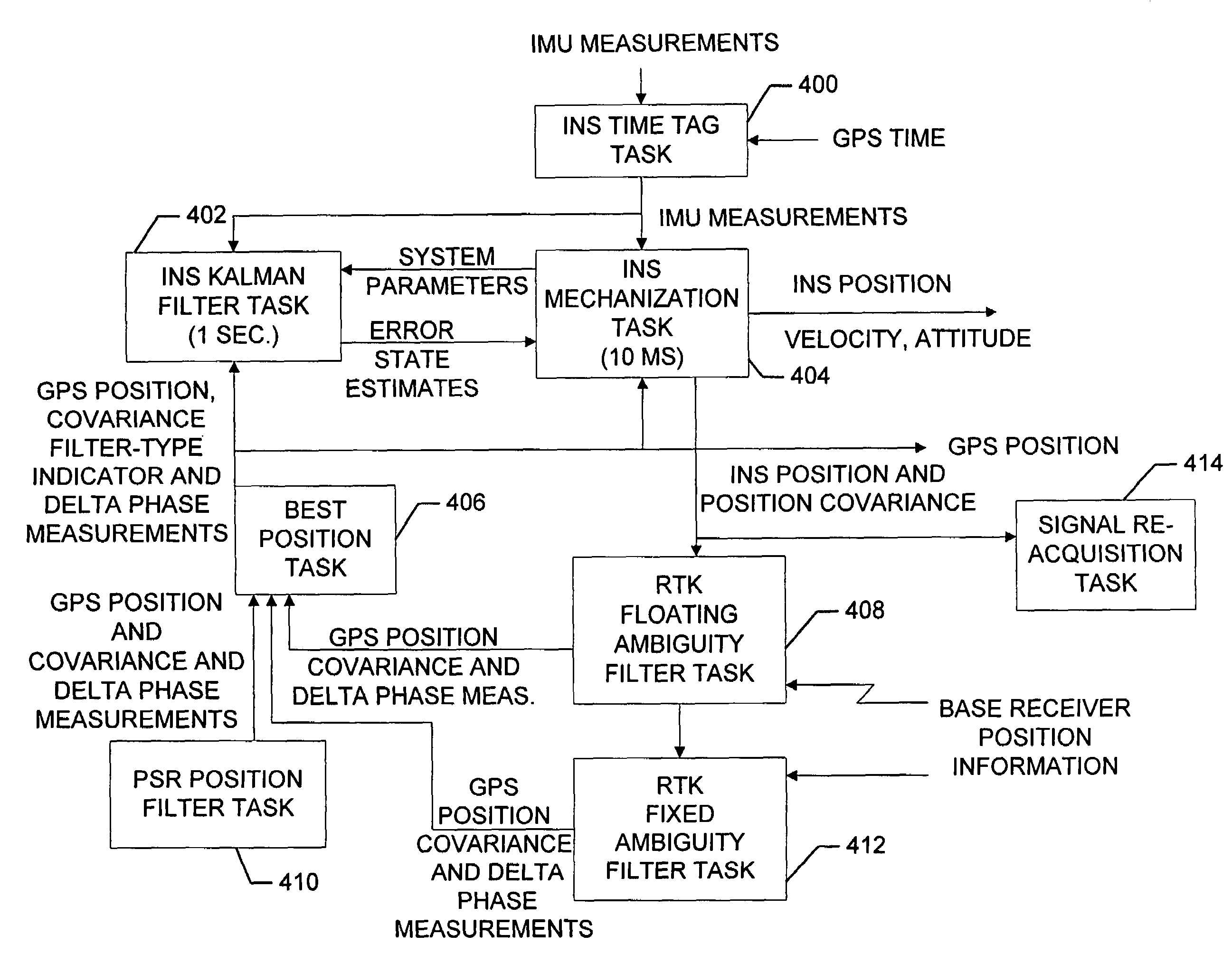
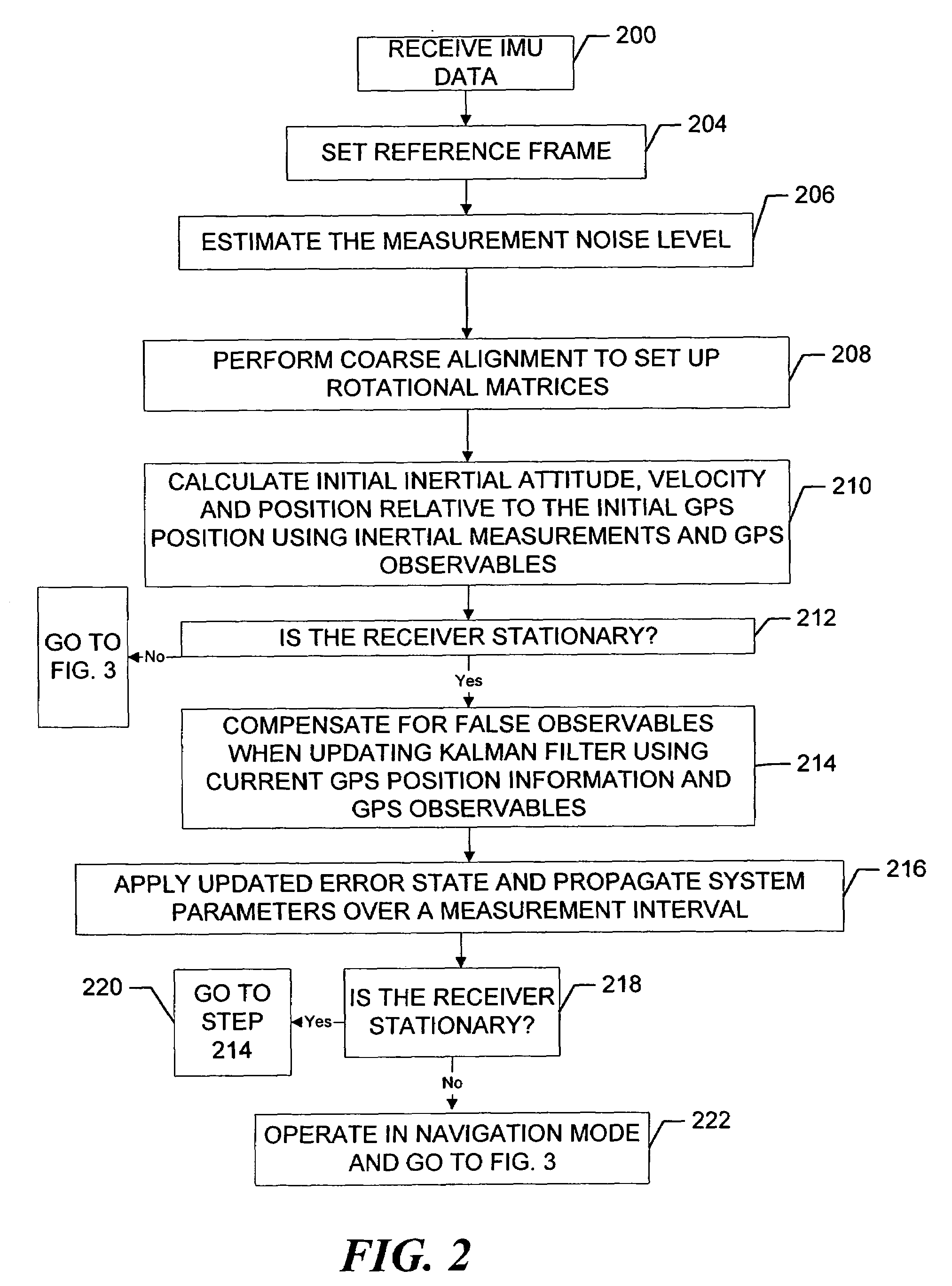
Inertial GPS navigation system with modified kalman filter
ActiveUS7193559B2Eliminate the effects ofShorten the timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPhase differenceDirect observation
An inertial (“INS”) / GPS receiver includes an INS sub-system which incorporates, into a modified Kalman filter, GPS observables and / or other observables that span previous and current times. The INS filter utilizes the observables to update position information relating to both the current and the previous times, and to propagate the current position, velocity and attitude related information. The GPS observable may be delta phase measurements, and the other observables may be, for example, wheel pick-offs (or counts of wheel revolutions) that are used to calculate along track differences, and so forth. The inclusion of the measurements in the filter together with the current and the previous position related information essentially eliminates the effect of system dynamics from the system model. A position difference can thus be formed that is directly observable by the phase difference or along track difference measured between the previous and current time epochs. Further, the delta phase measurements can be incorporated in the INS filter without having to maintain GPS carrier ambiguity states. The INS sub-system and the GPS sub-system share GPS and INS position and covariance information. The receiver time tags the INS and any other non-GPS measurement data with GPS time, and then uses the INS and GPS filters to produce INS and GPS position information that is synchronized in time. The GPS / INS receiver utilizes GPS position and associated covariance information and the GPS and / or other observables in the updating of the INS filter. The INS filter, in turn, provides updated system error information that is used to propagate inertial current position, velocity and attitude information. Further, the receiver utilizes the inertial position, velocity and covariance information in the GPS filters to speed up GPS satellite signal re-acquisition and associated ambiguity resolution operations
Owner:NOVATEL INC
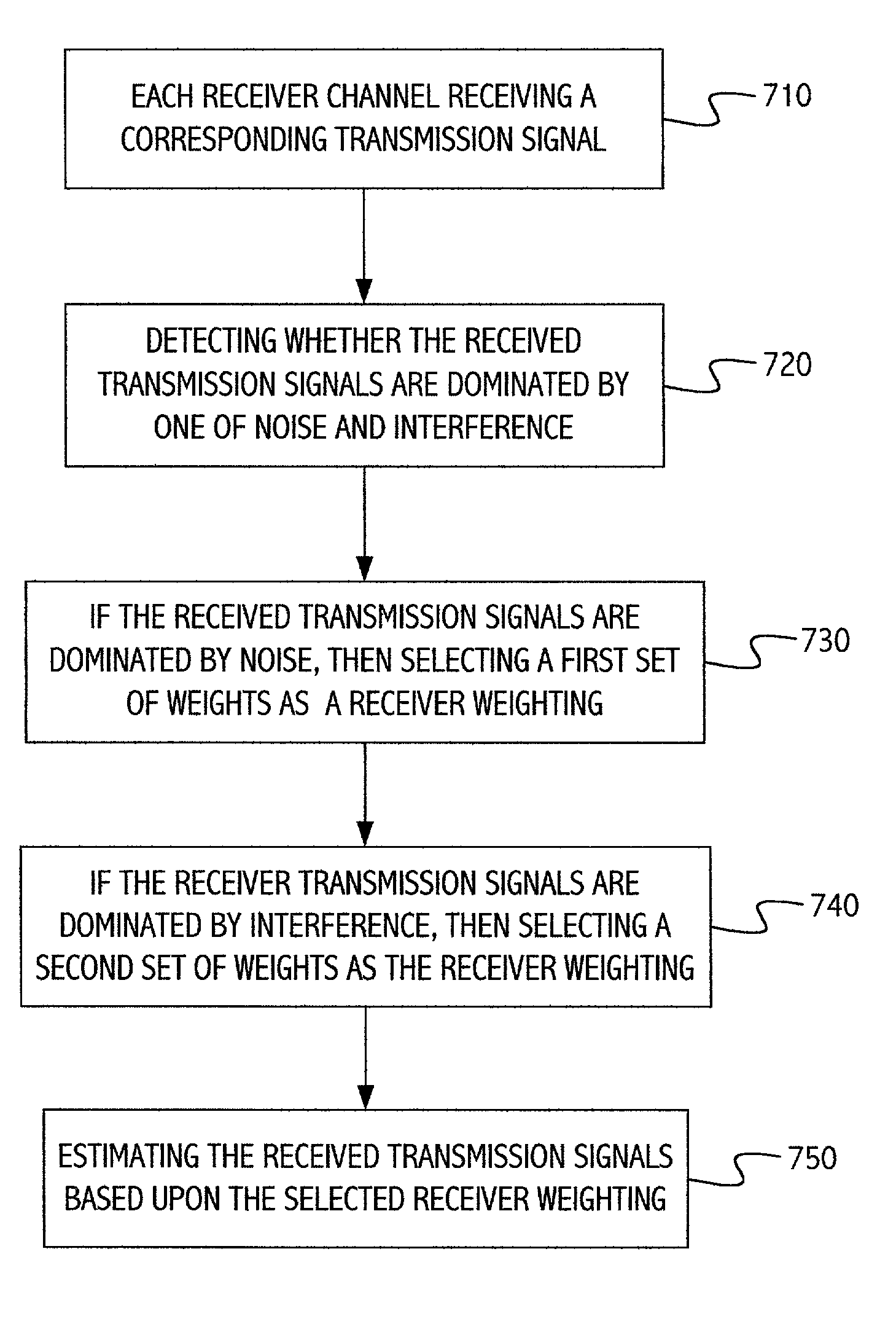
Robust multiple chain receiver
InactiveUS7012978B2Easy to implementEasy to receiveSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysCarrier signalTransmission channel
The present invention provides a method and system for receiving a plurality of transmission signals at a receiver, the transmission signals each traveling through a corresponding transmission channel. The receiver includes a plurality of receiver channels, a receiver channel corresponding to each transmission channel. Each receiver channel receives a corresponding transmission signal. The received transmission signals are detected to determine whether the received transmission signals are dominated by noise or interference. If the received transmission signals are dominated by noise, then a first set of weights are selected as a receiver weighting. If the received transmission signals are dominated by interference, then a second set of weights are selected as the receiver weighting. The received transmission signals are estimated based upon the receiver weighting. Detecting whether the received transmission signals are dominated by noise or interference includes determining a level of correlation between the received transmission signals. Detecting whether the received transmission signals are dominated by noise or interference can be determined during a time slot of nulled transmission signals. If the transmission signals are multiple carrier signals, then detecting whether the received transmission signals are dominated by noise or interference can be determined during a frequency and time slot of a nulled carrier of the transmission signals. The first set of weights can be based upon a first covariance matrix, wherein the first covariance matrix represents received noise and interference covariance. The second set of weights can be based upon the second covariance matrix, wherein the second covariance matrix represents interference covariance. The first set of weights and the second set of weights can also be used for transmission mode selection and receiver soft decoding.
Owner:INTEL CORP
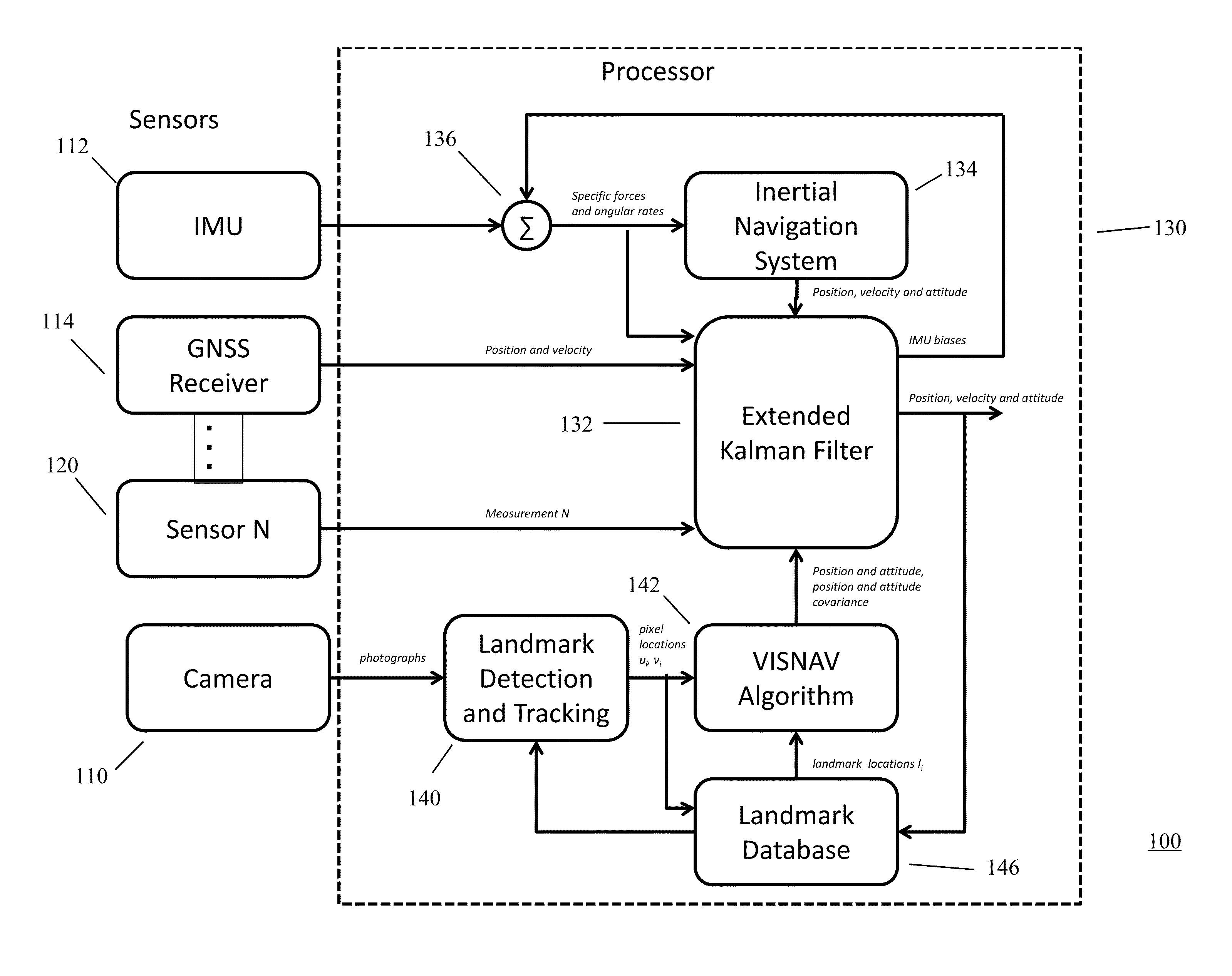
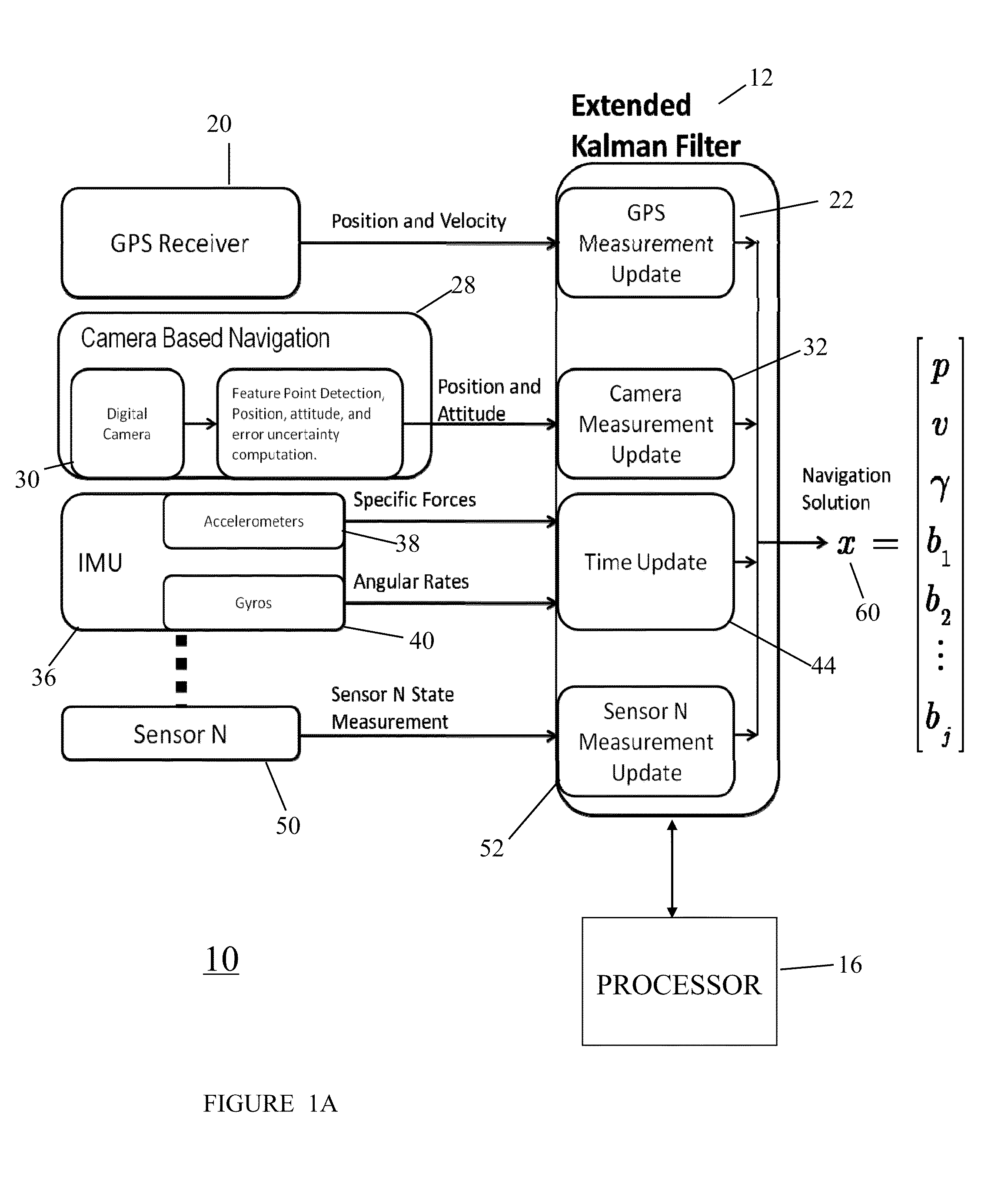
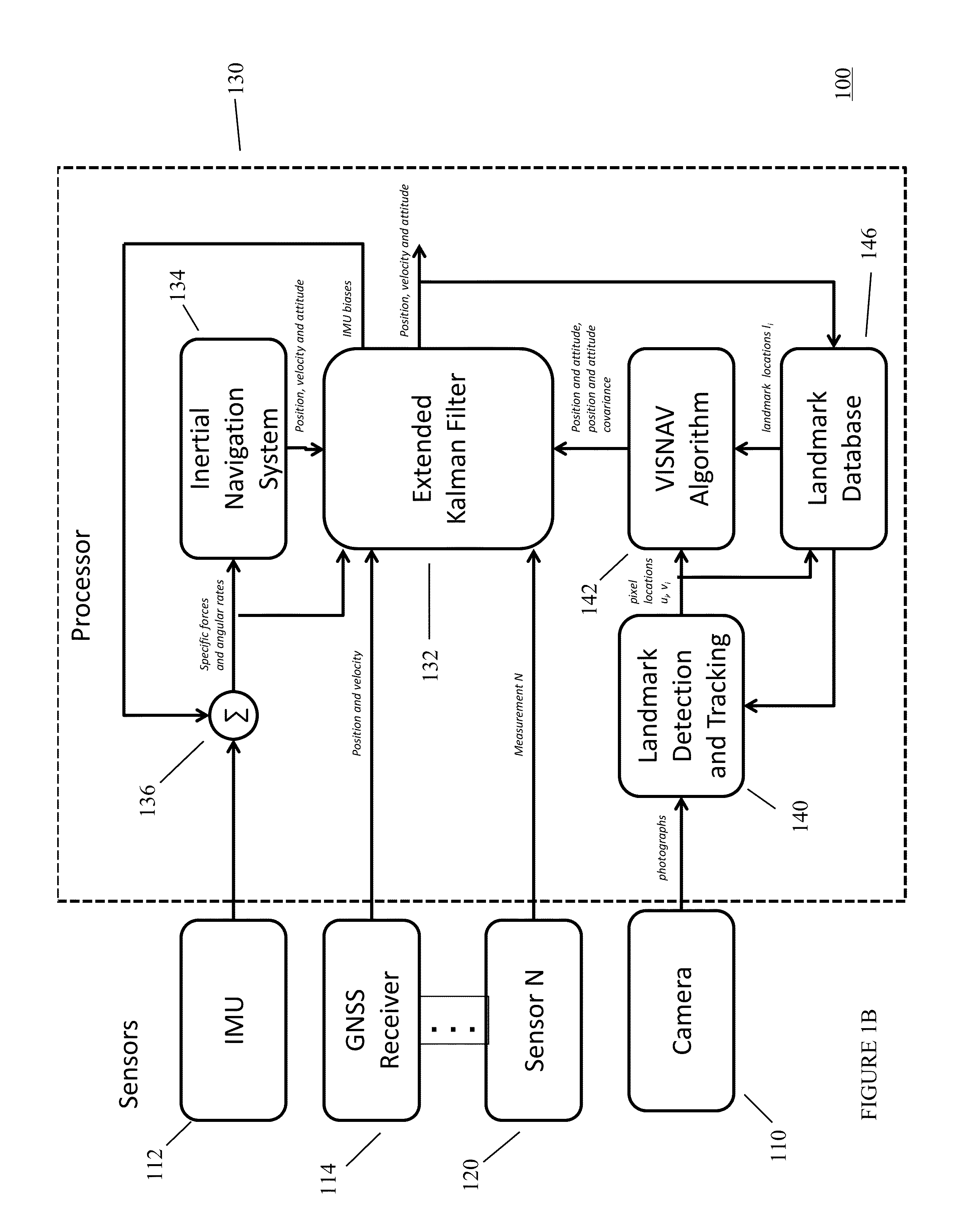
System to use digital cameras and other sensors in navigation
In one preferred embodiment, the present invention provide a navigation system for a movable platform comprising a GNSS receiver sensor for providing position signals representative of the estimated current position of the movable platform; a camera sensor for providing photographic images representative of the surroundings of the movable platform; and an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) sensor for providing specific force and angular rate signals representative of the current specific forces and rate of the movable platform. A processor is responsive to the camera photographic images to estimate the position and attitude of the movable platform, the covariance of the position and attitude estimates and the covariance of consecutive position and attitude estimates. The processor is responsive to the GNSS receiver's estimated position signal, the camera's estimated position and attitude signal, the camera's estimated position and attitude covariance, the camera's estimated correlation of the covariance of consecutive position and attitude estimates, and the specific force and angular rate signals, for providing a navigation solution representative of the estimated current position, velocity, and attitude of the movable platform.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Method of channel allocation
InactiveUS6041237APower managementTransmission control/equalisingTelecommunicationsDistribution method
A method of channel allocation for a communication connection to a radio interface in a mobile communication system with spatial subscriber separation. The method includes comparing the disclosed allocation method is to compare the theoretical minimum +E,otl P+EE (l) (given optimum spatial separability) to the anticipated downlink transmission power P(I) for each channel in the selection of a channel. In order to speed up the calculation, the factors allocated to the K communication connections are selected proportional to the dominant eigenvectors uk(Ck). A low value for the quotient in channel l allows one to conclude that the eigenvector uk for all K communication connections respectively fits well to the covariance matrices Ck of the other K-1 communication connections and, thus, a good spatial separability is established.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
Method for executing automatic evaluation of transmission quality of audio signals using source/received-signal spectral covariance
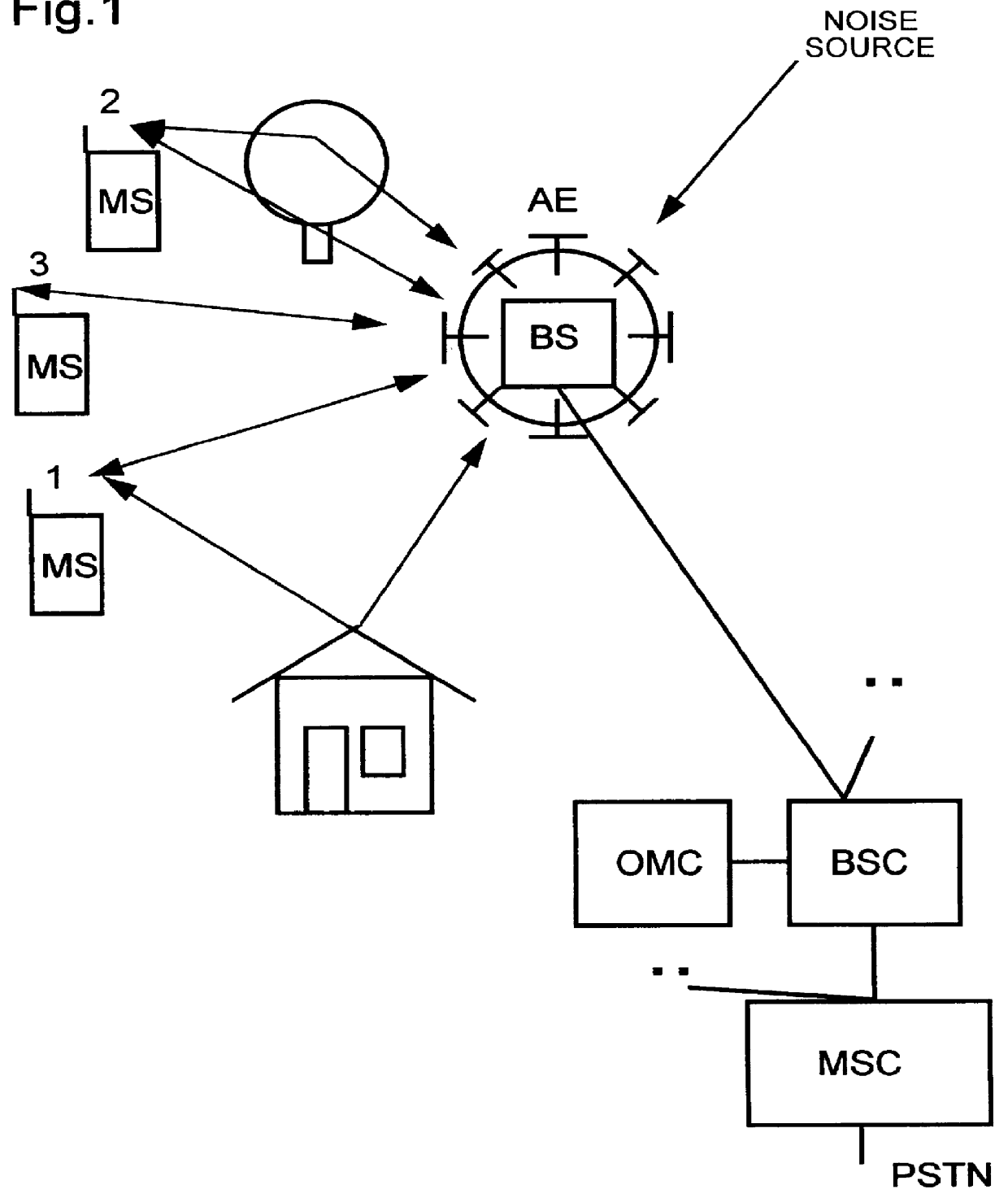
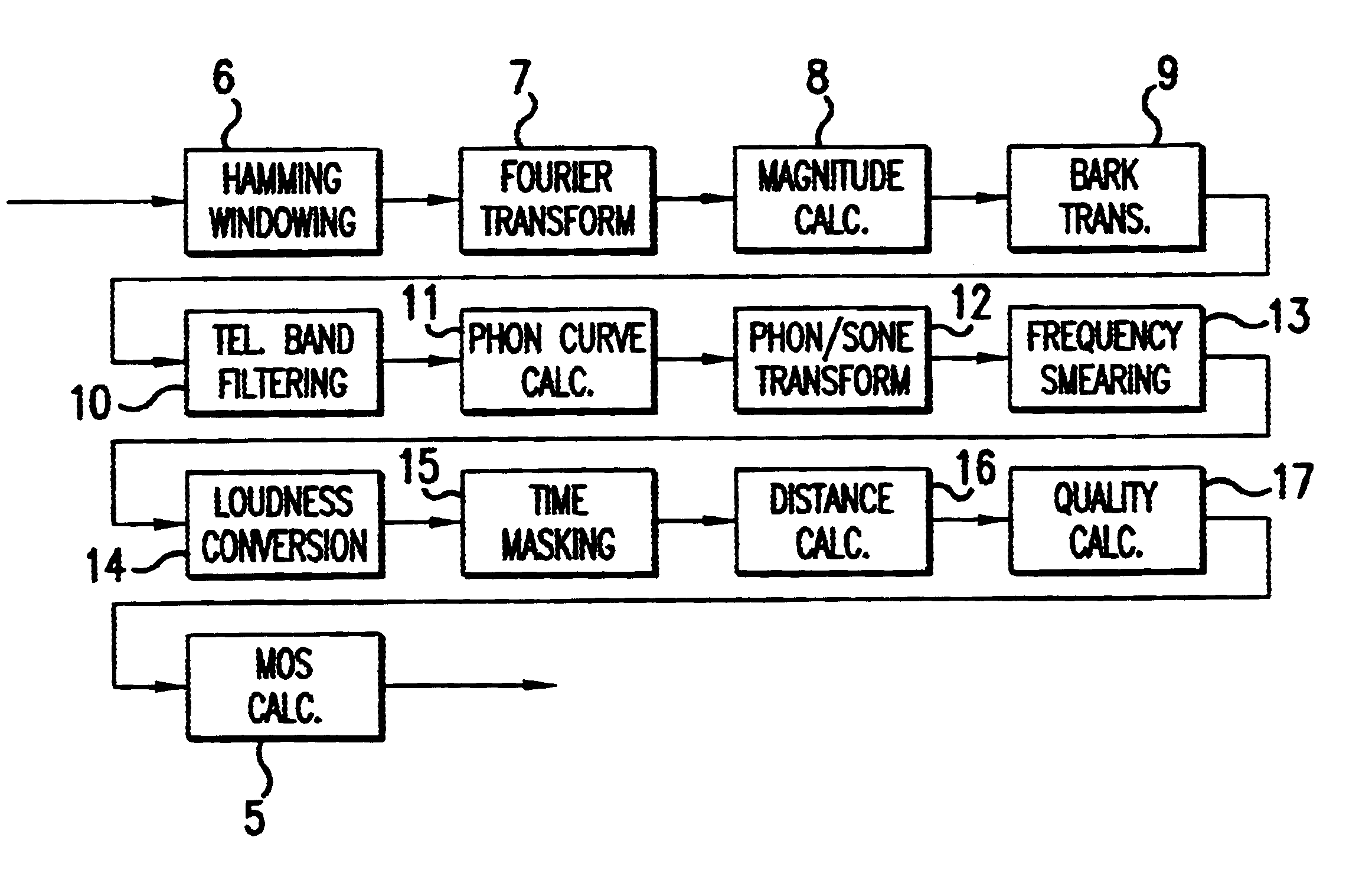
InactiveUS6651041B1Increase valueHigh signal energy of signalSpeech analysisWireless communicationObjective assessmentCovariance
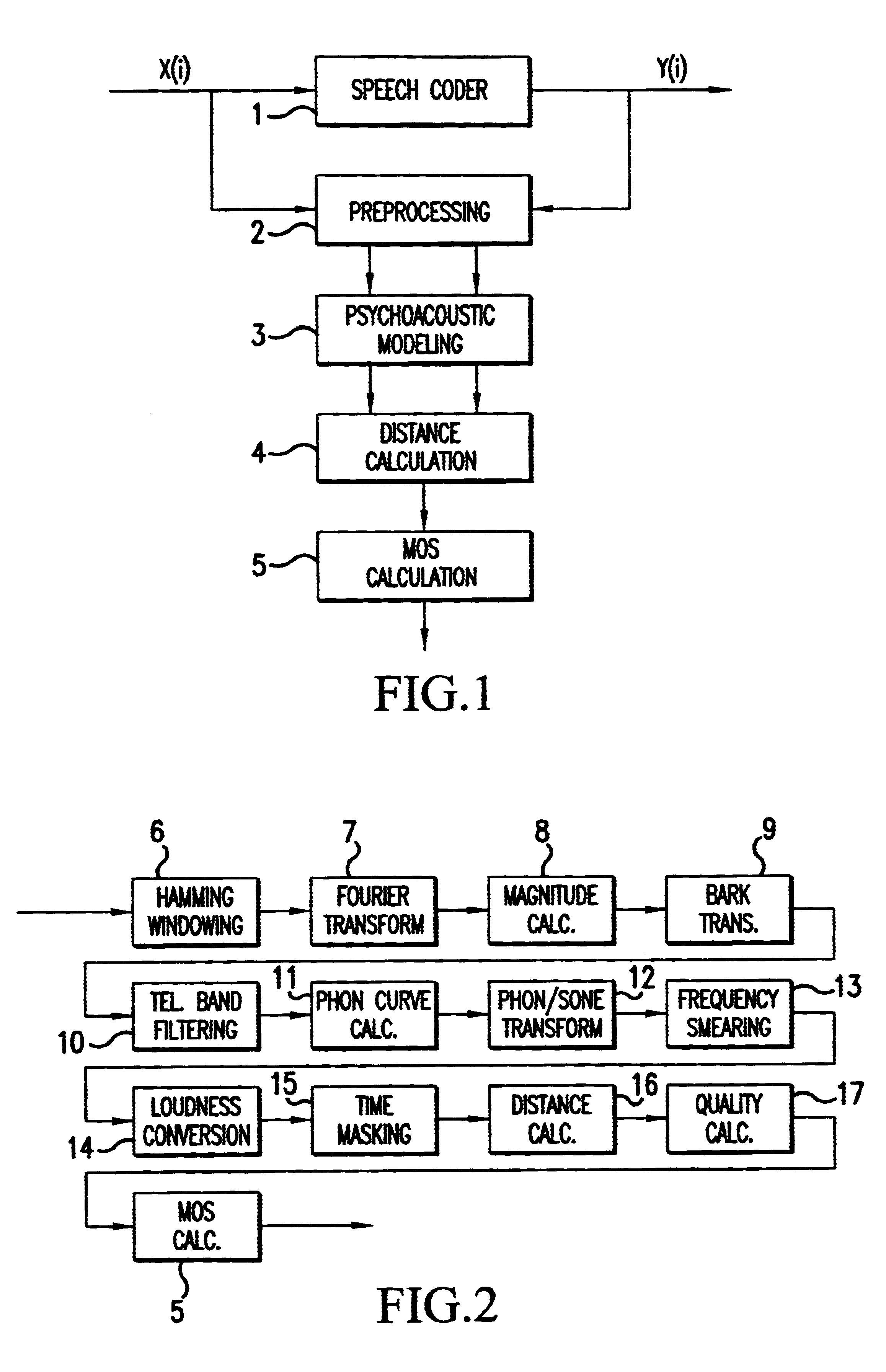
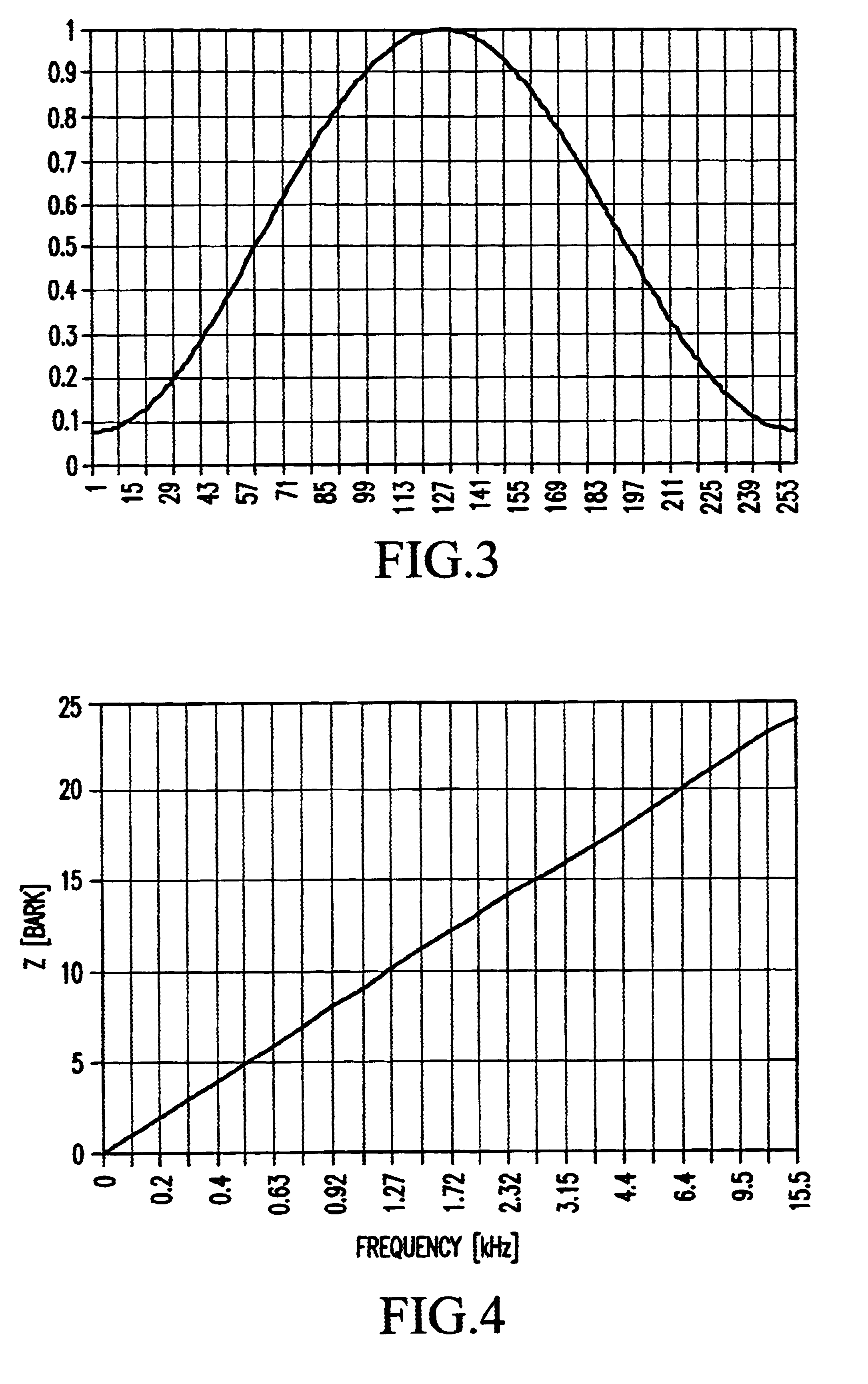
A source signal (e.g. a speech sample) is processed or transmitted by a speech coder 1 and converted into a reception signal (coded speech signal). The source and reception signals are separately subjected to preprocessing 2 and psychoacoustic modelling 3. This is followed by a distance calculation 4, which assesses the similarity of the signals. Lastly, an MOS calculation is carried out in order to obtain a result comparable with human evaluation. According to the invention, in order to assess the transmission quality a spectral similarity value is determined which is based on calculation of the covariance of the spectra of the source signal and reception signal and division of the covariance by the standard deviations of the two said spectra.The method makes it possible to obtain an objective assessment (speech quality prediction) while taking the human auditory process into account.
Owner:ASCOM
Hyperspectral remote sensing systems and methods using covariance equalization
InactiveUS7194111B1Reduce decreaseEasy to detectTelevision system detailsOptical detectionAlgorithmCovariance
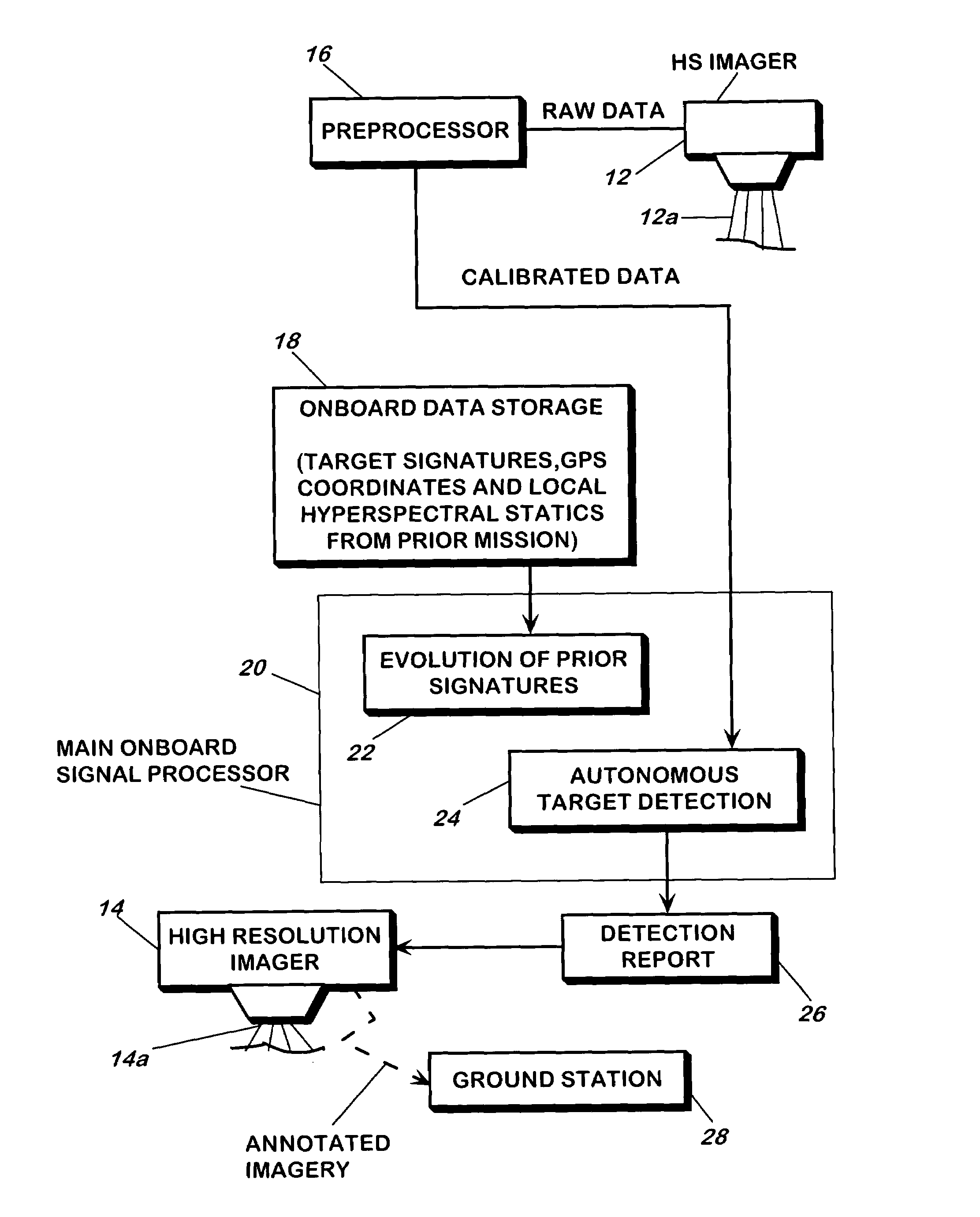
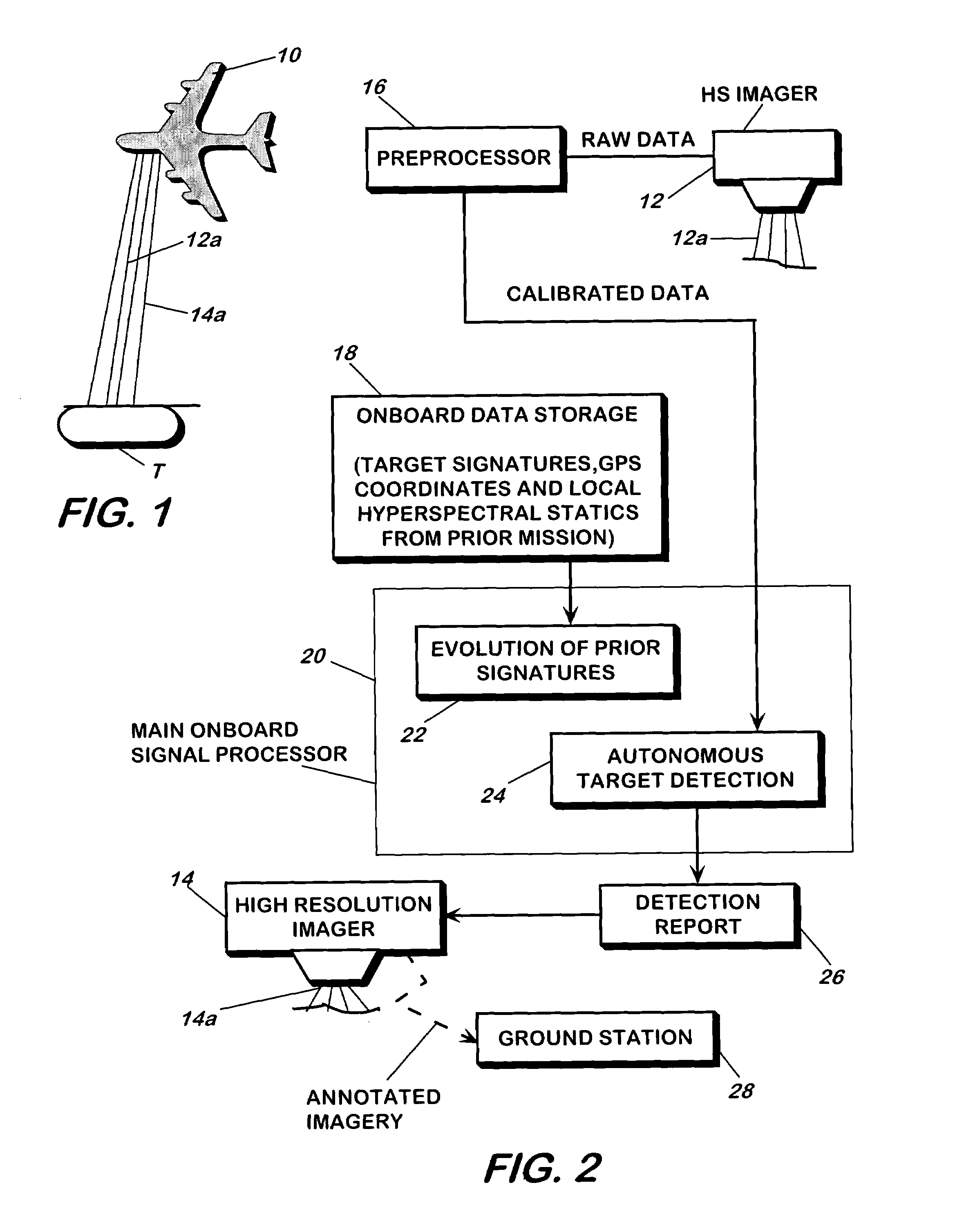
A method and apparatus for detecting a target or targets in a surrounding background locale based on target signatures obtained by a hyperspectral imaging sensor used the hyperspectral imaging sensor to collect raw target signature data and background locale data during a first data collection mission. The data is processed to generate a database including a plurality of target signatures and background data relating to the background locale. The hyperspectral imaging sensor is later used to collect further background data during a further, current data collecting mission so as to provide continuously updated background data, in real time. A covariance equalization algorithm is implemented with respect to the background data contained in the database and the updated background data collected during the current mission to effect transformation of each target signature of the database into a transformed target signature. A detection algorithm which employs the resultant transformed target signature is used to produce detection information related to the target or targets.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Optimization of channel equalizer
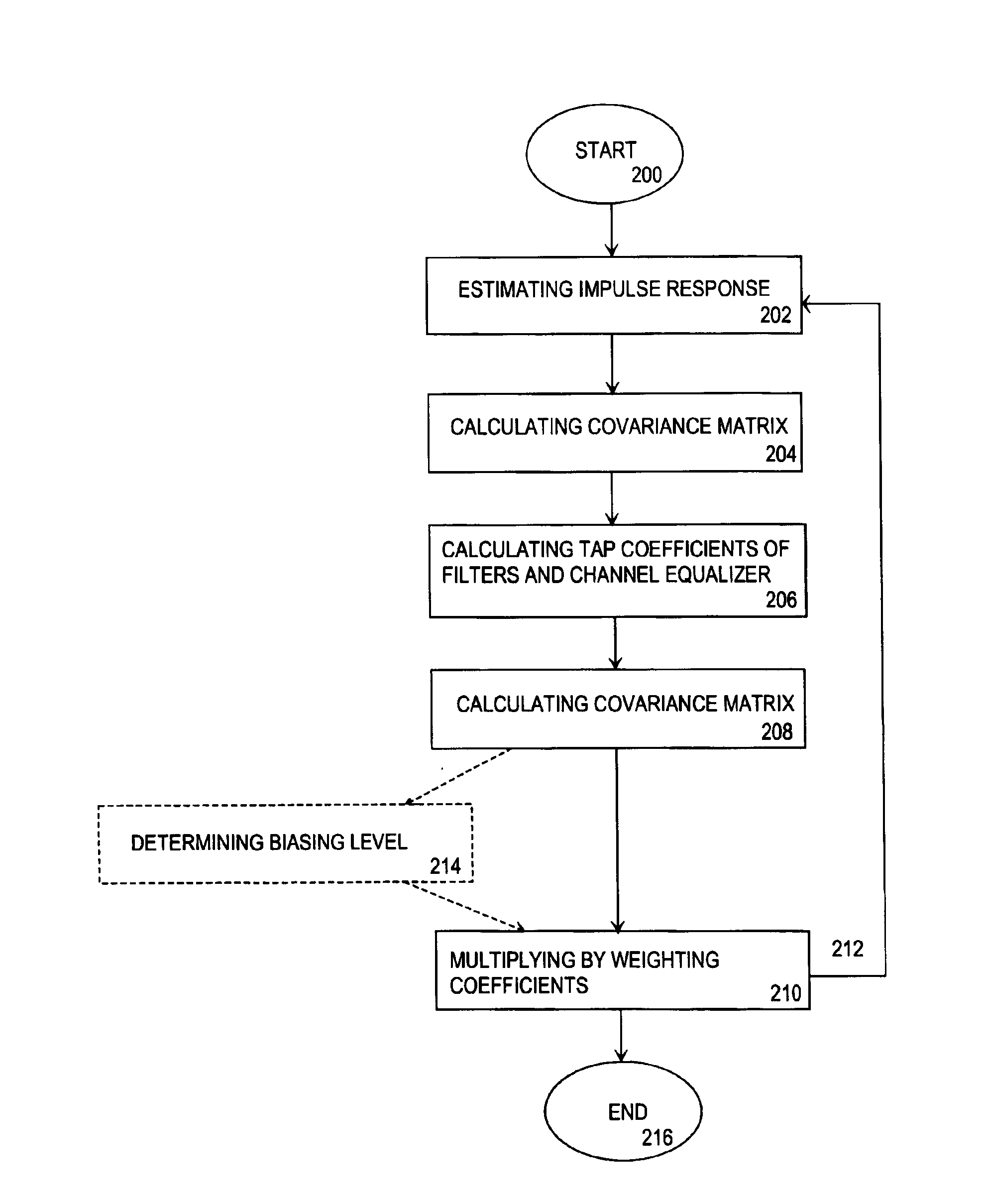
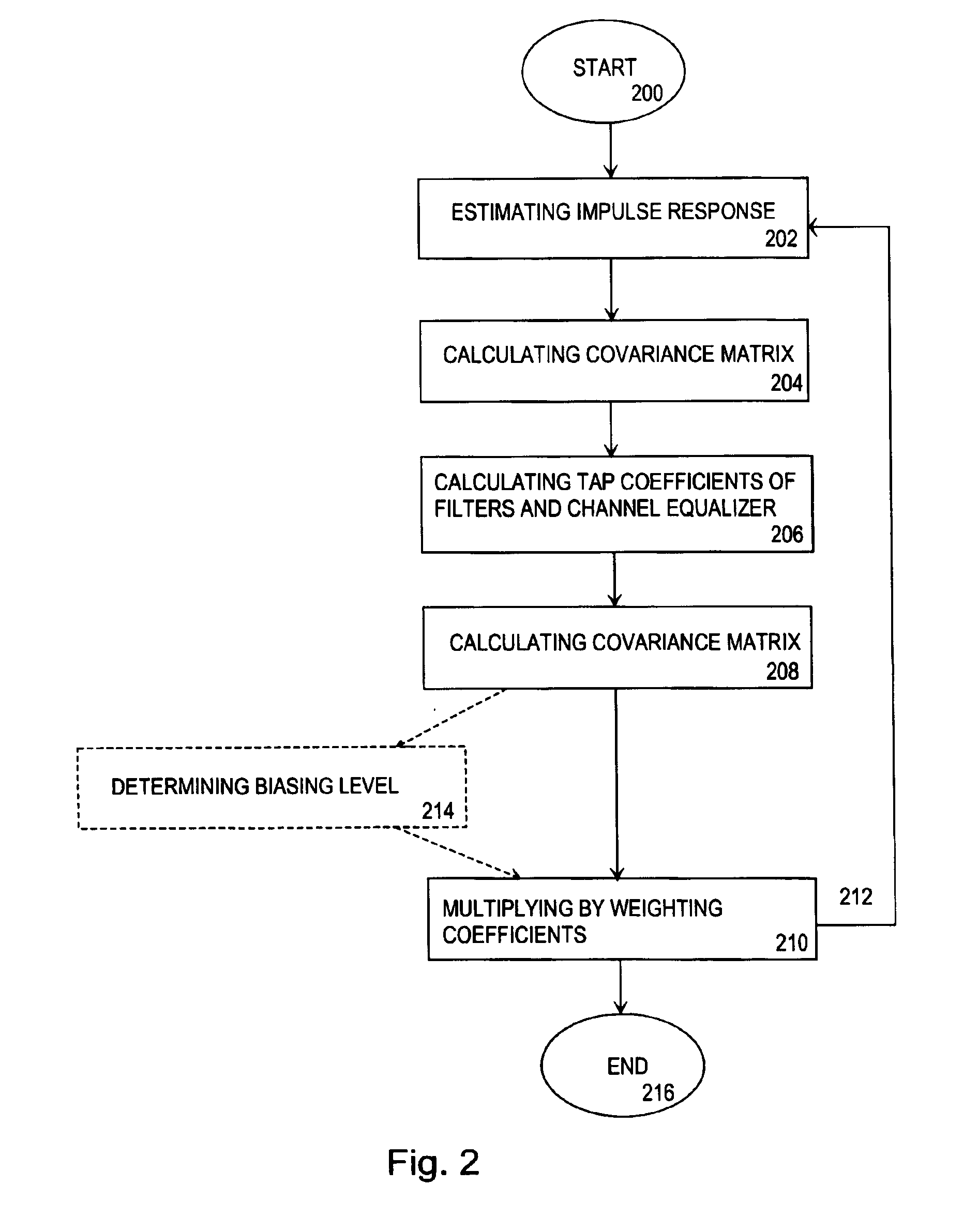
InactiveUS6954495B2Improve channel performanceImprove performanceMultiple-port networksError preventionWeight coefficientRadio receiver
A method for carrying out channel equalization in a radio receiver wherein an impulse response is estimated, noise power is determined by estimating a co-variance matrix of the noise contained in a received signal before prefiltering, and tap coefficients of prefilters and an equalizer are calculated. The method comprises determining the noise power after prefiltering by estimating a noise covariance matrix, after which input signals of the channel equalizer are weighted by weighting coefficients obtained from the noise covariance estimation.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Equalisation apparatus and methods
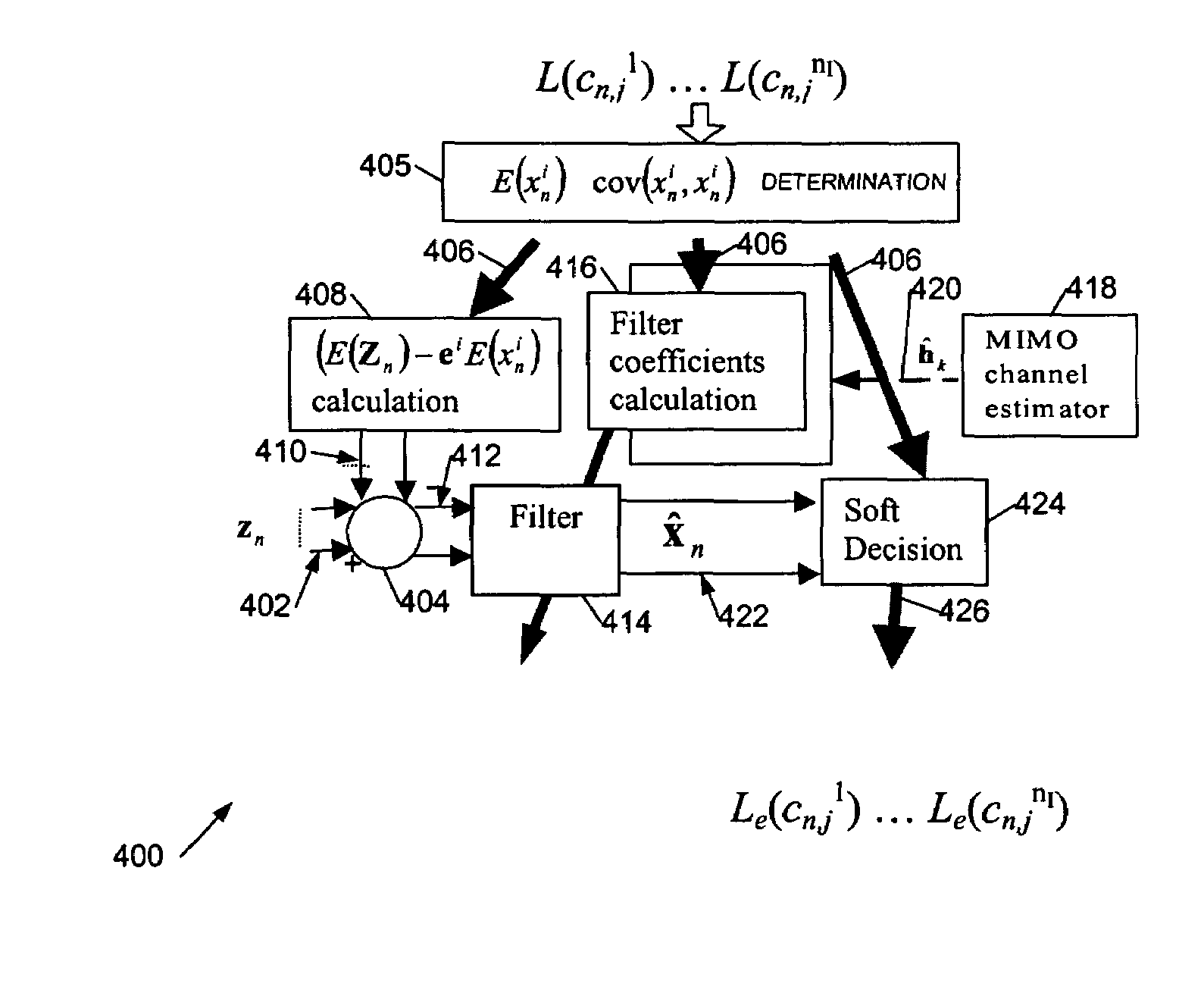
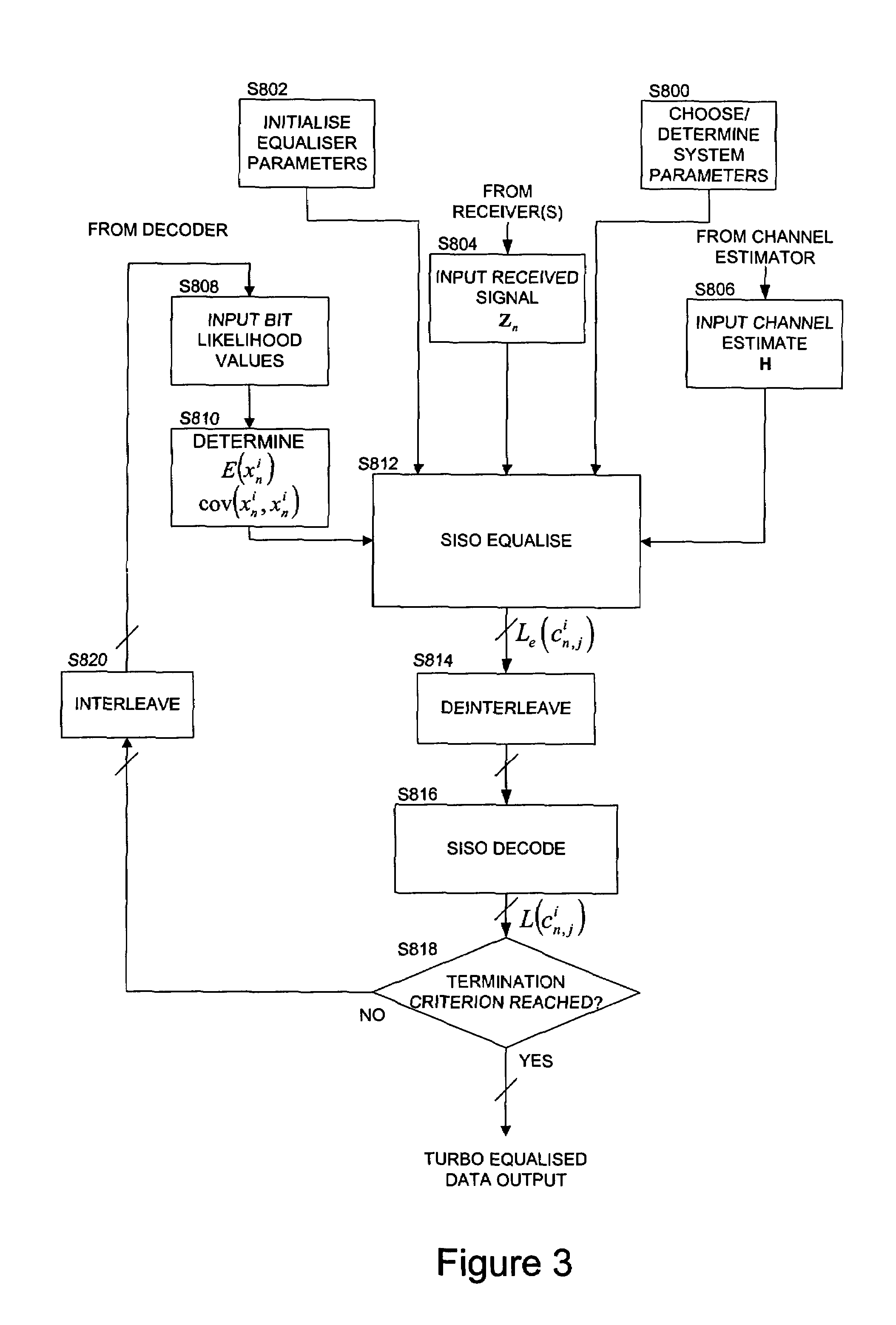
InactiveUS7333540B2Reduce ISIIncrease the lengthMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasCovarianceComputer science
The invention relates to apparatus, methods and computer program code for equalisation. A soft-in-soft-out (SISO) equaliser for use in a receiver for receiving data from a transmitter configured to transmit data from a plurality of transmit antennas simultaneously is described. The equaliser comprises at least one received signal input for inputting a received signal; a plurality of likelihood value inputs, one for each transmit antenna, for inputting a plurality of decoded signal likelihood values from a SISO decoder; a processor configured to determine from said plurality of signal likelihood values an estimated mean and covariance value for a signal from each of said transmit antennas; an expected signal determiner coupled to said processor to determine an expected received signal value using said mean values; a subtractor coupled to said received signal input to subtract said expected received signal value from said received signal to provide a compensated signal; a filter coupled to said subtractor to filter said compensated signal to provide a plurality of estimated transmitted signal values, one for each said transmit antenna; a filter coefficient determiner coupled to said processor to determine coefficients of said filter using said covariance values; and an output stage coupled to said filter to output a plurality of transmitted signal likelihood values, one for each said transmit antenna, for input to said SISO decoder.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Dynamic digital pre-distortion system
ActiveUS20080260066A1Simplify reduce numberImprove efficiencyTransmitters monitoringPower managementAudio power amplifierLinear filter
A Dynamic Digital Pre-Distortion (DDPD) system is disclosed to rapidly correct power amplifier (PA) non-linearity and memory effects. To perform pre-distortion, a DDPD engine predistorts an input signal in order to cancel PA nonlinearities as the signal is amplified by the PA. The DDPD engine is implemented as a composite of one linear filter and N-1 high order term linear filters. The bank of linear filters have programmable complex coefficients. To compute the coefficients, samples from the transmit path and a feedback path are captured, and covariance matrices A and B are computed using optimized hardware. After the covariance matrices are computed, Gaussian elimination processing may be employed to compute the coefficients. Mathematical and hardware optimizations may be employed to simplify and reduce the number of multiplication operands and other operations, which can enable the DDPD system to fit within a single chip.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS TECH INC
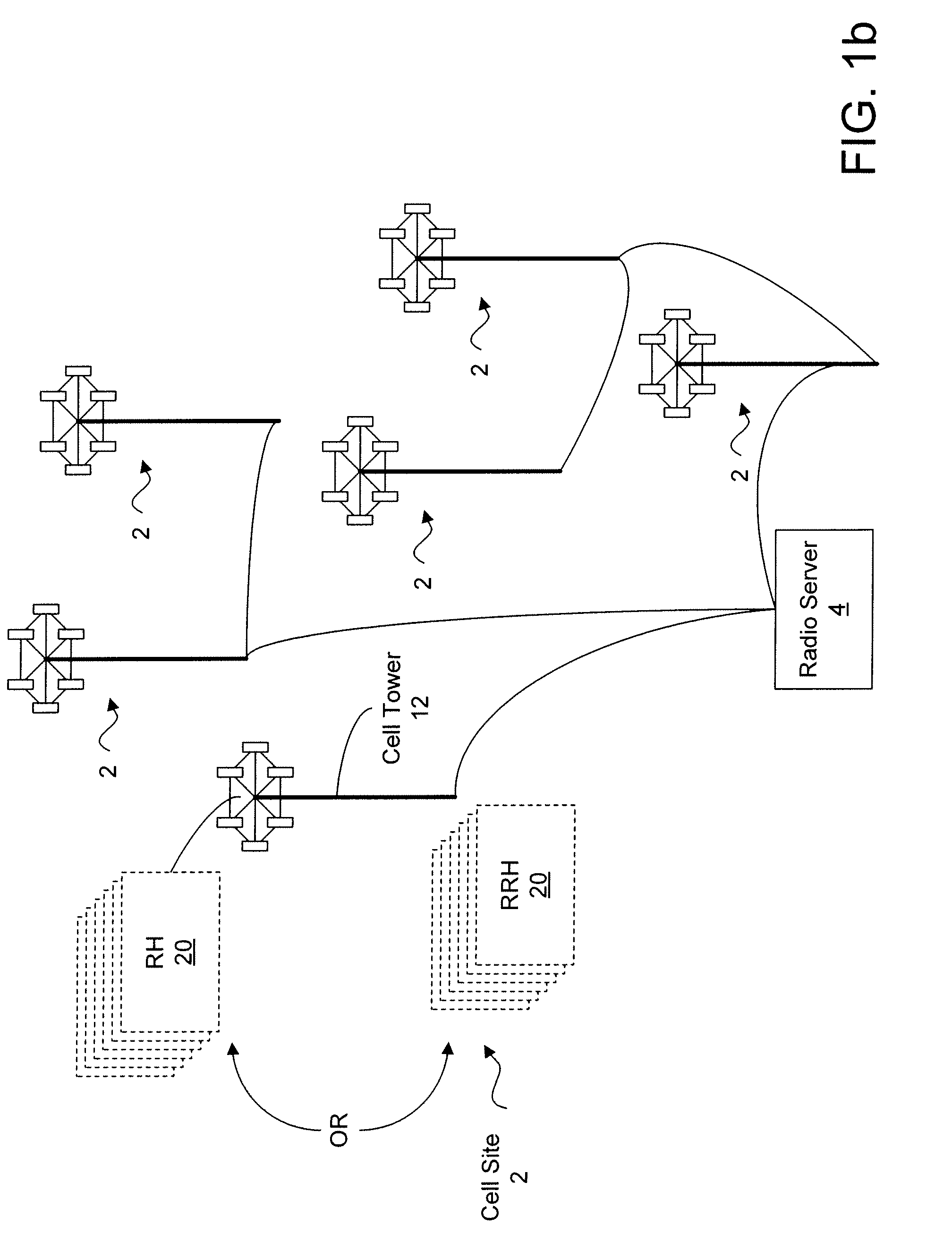
Method for altering link weights in a communication network within network parameters to provide traffic information for improved forecasting
InactiveUS7313629B1Improve forecastAdd modelDigital computer detailsTransmissionTraffic capacityLink weight
The present invention comprises methods for increasing the rank of the routing matrix of an IP network by systematically altering link weights in the IP network. A full rank routing matrix may be used with further methods in accordance with the present invention to estimate the mean traffic of the IP network based upon the full rank routing matrix and measured link utilization values. The mean traffic and the covariance of the traffic may be iteratively estimated until the estimates coverage. Example methods in accordance with the present invention for estimating mean traffic and covariance of traffic are described for both stationary and non-stationary link utilization data.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
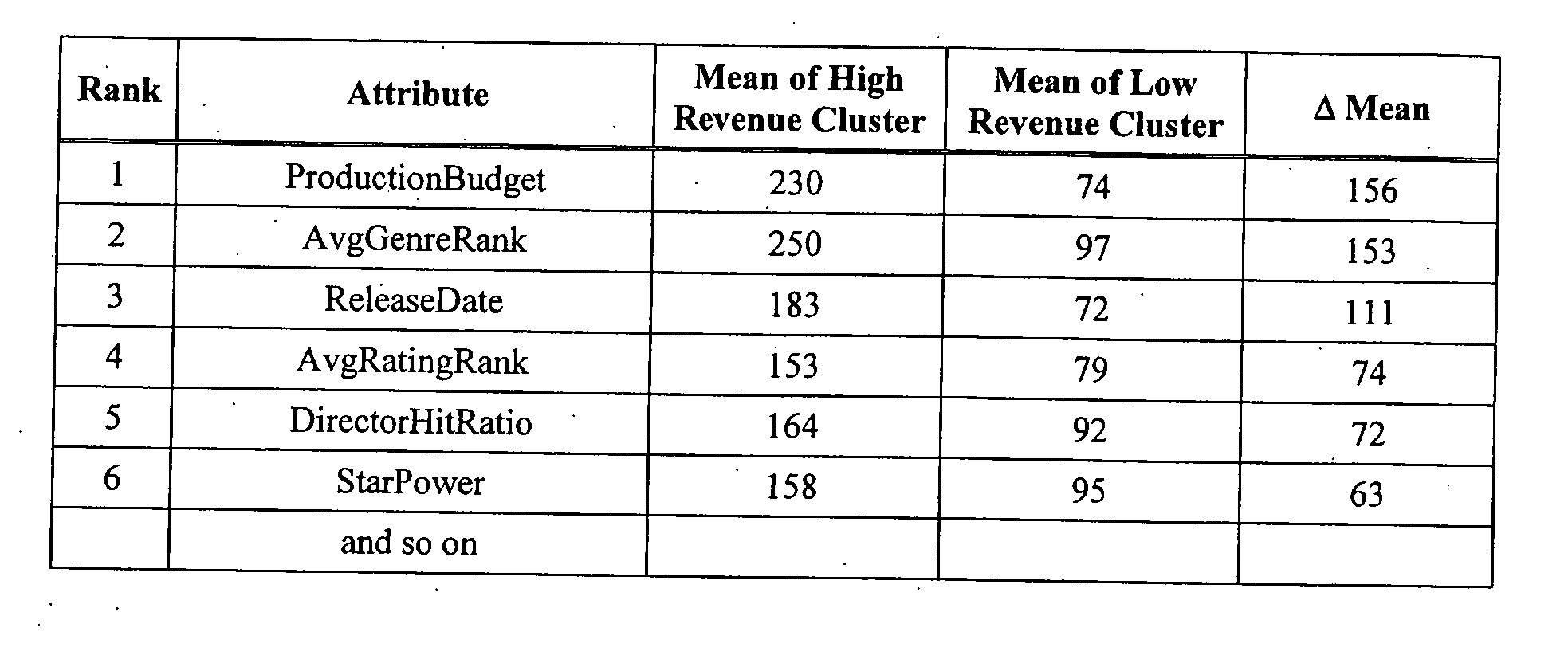
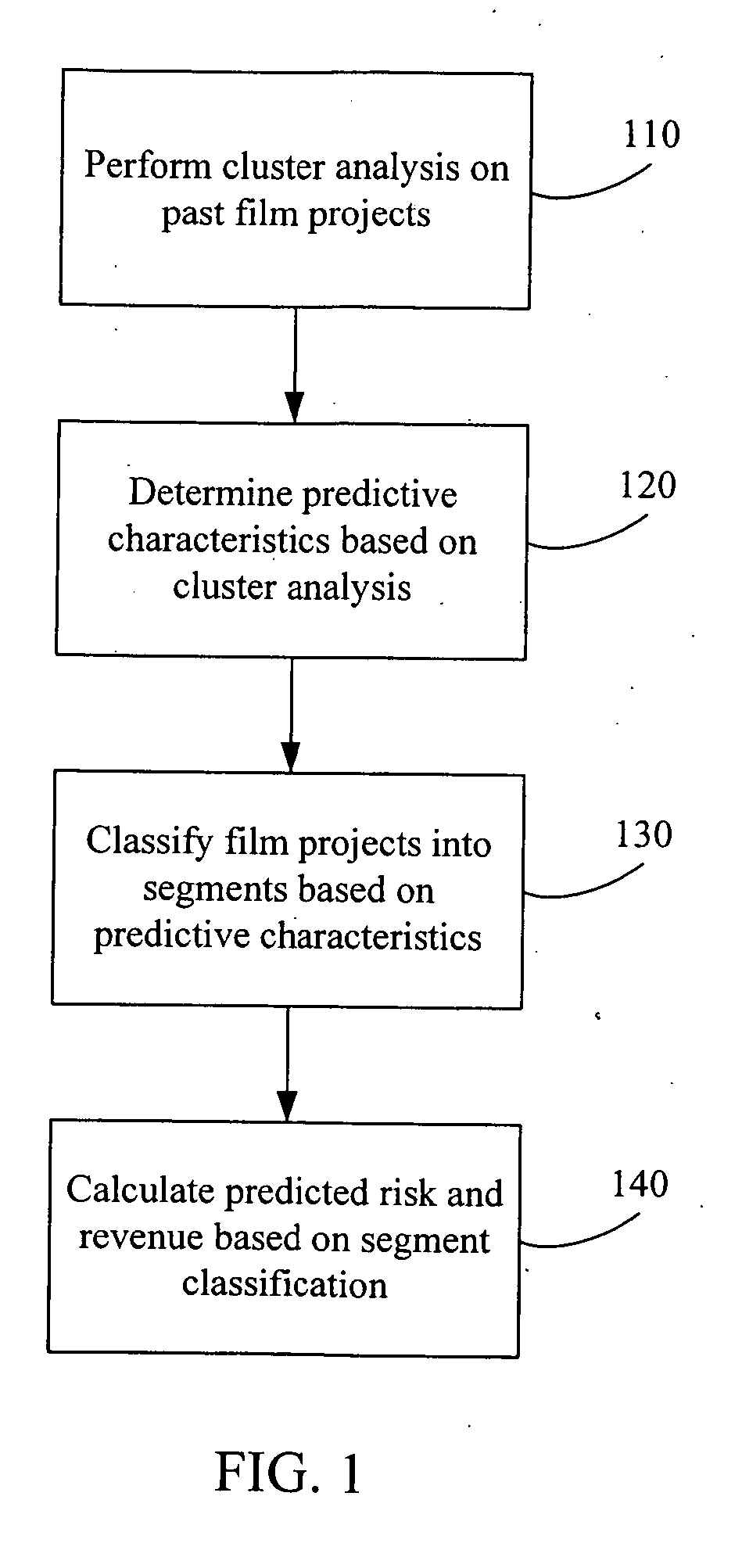
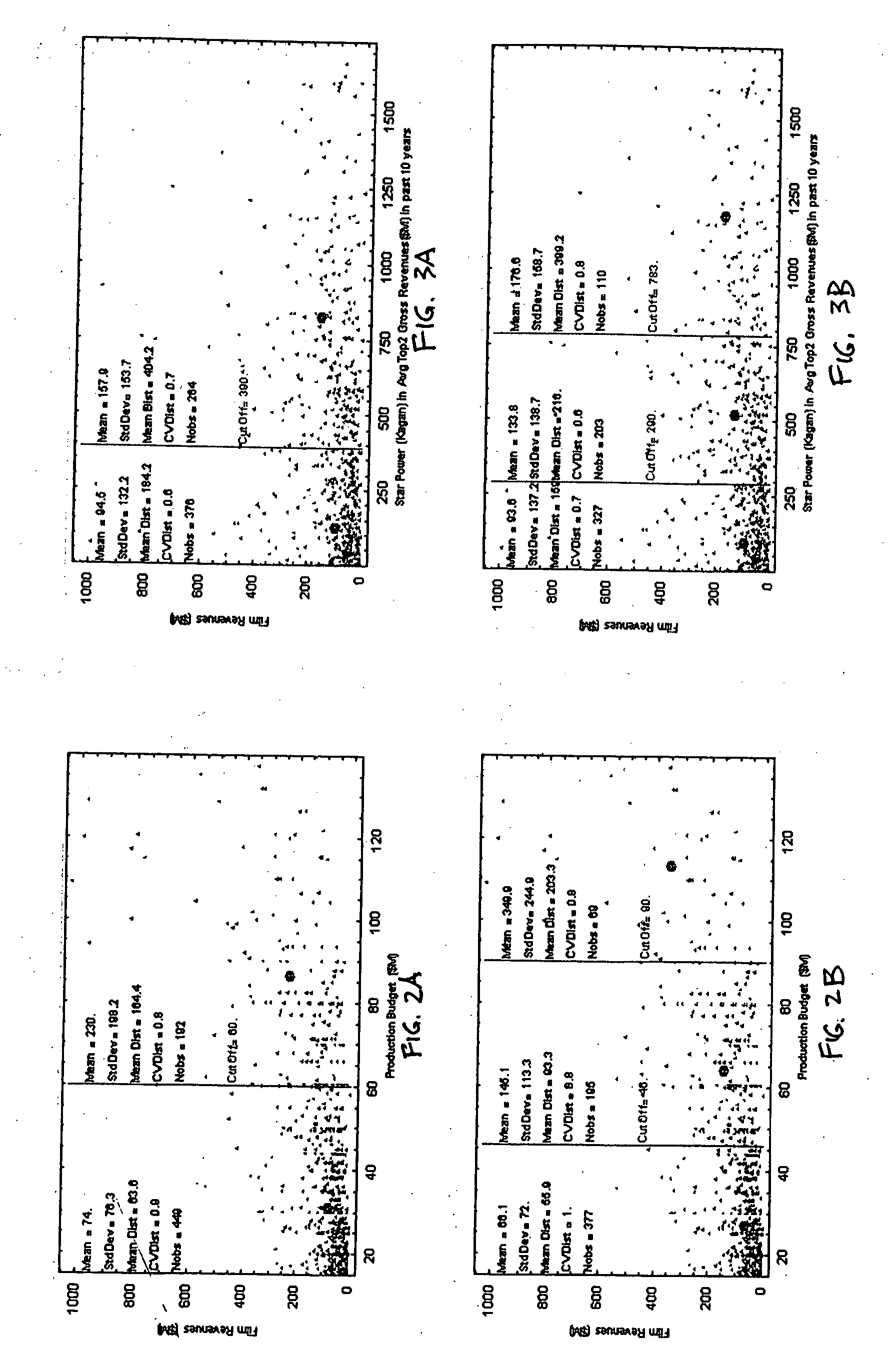
Predicting risk and return for a portfolio of entertainment projects
A portfolio of entertainment project such that the risk and return available to investors is attractive compared to other investments. Risk and return for a portfolio of entertainment projects is predicted based on historical performance of past “similar” projects. In one implementation, characteristics that are predictive of a project's revenue are determined by performing a cluster analysis of historical revenues from past projects. Projects in the portfolio are classified into various segments based on these predictive characteristics. Projects are selected to contruct a portfolio. The risk and return for the portfolio is calculated according to a risk-return model that is based on historical risk and revenues for past projects in the same segment and further based on historical covariance of revenue for past projects in different segments.
Owner:MCJB INVESTMENTS
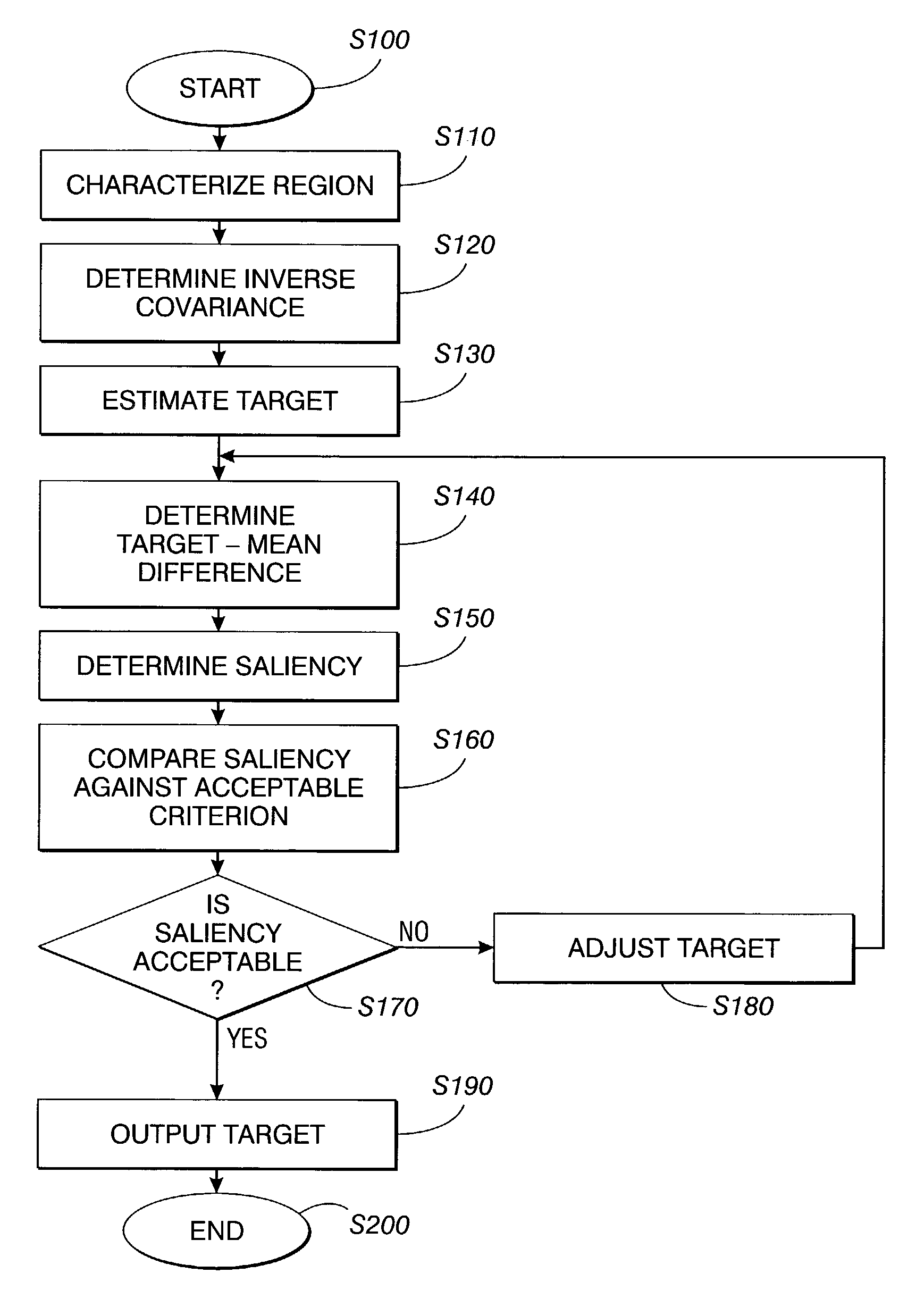
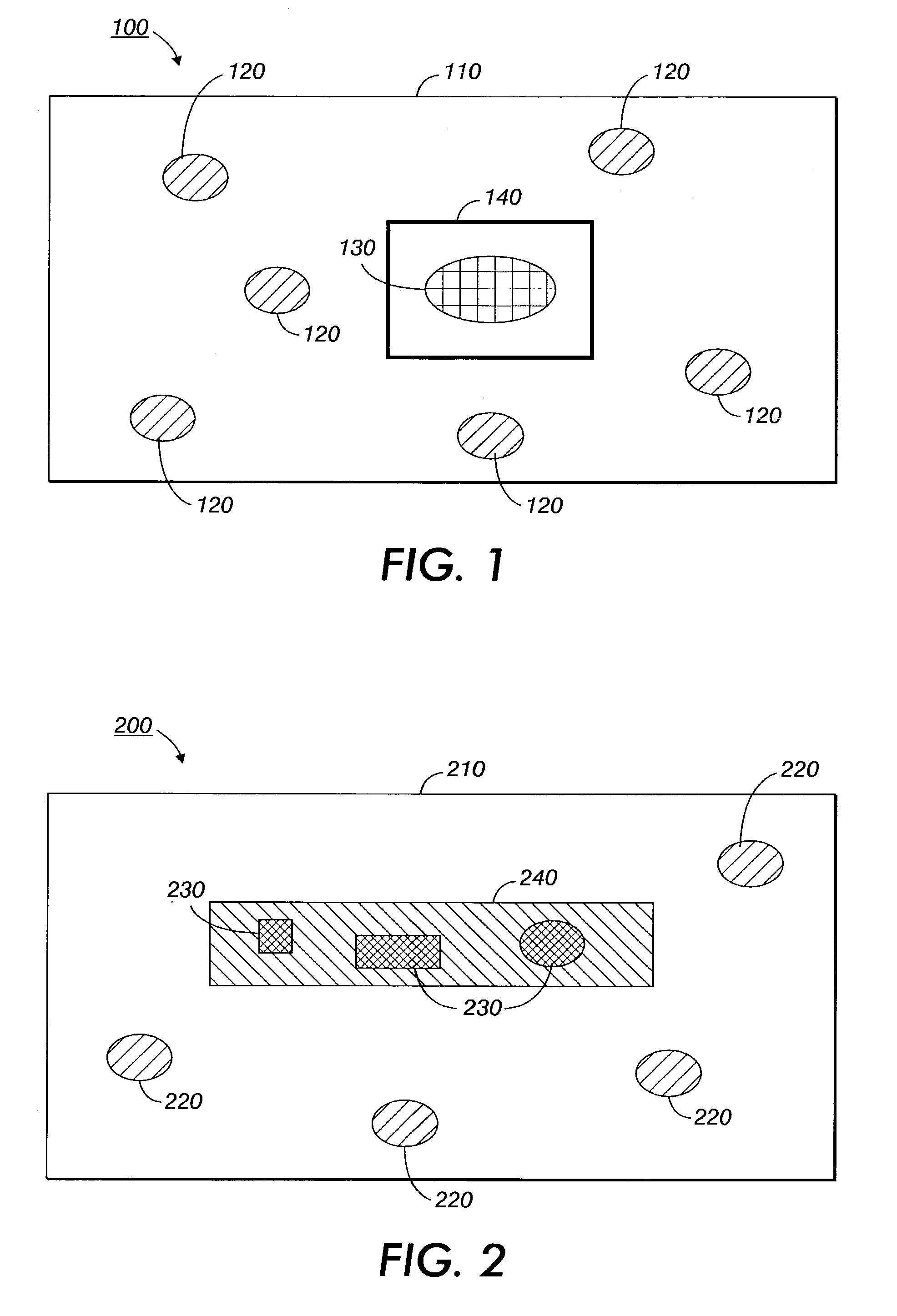
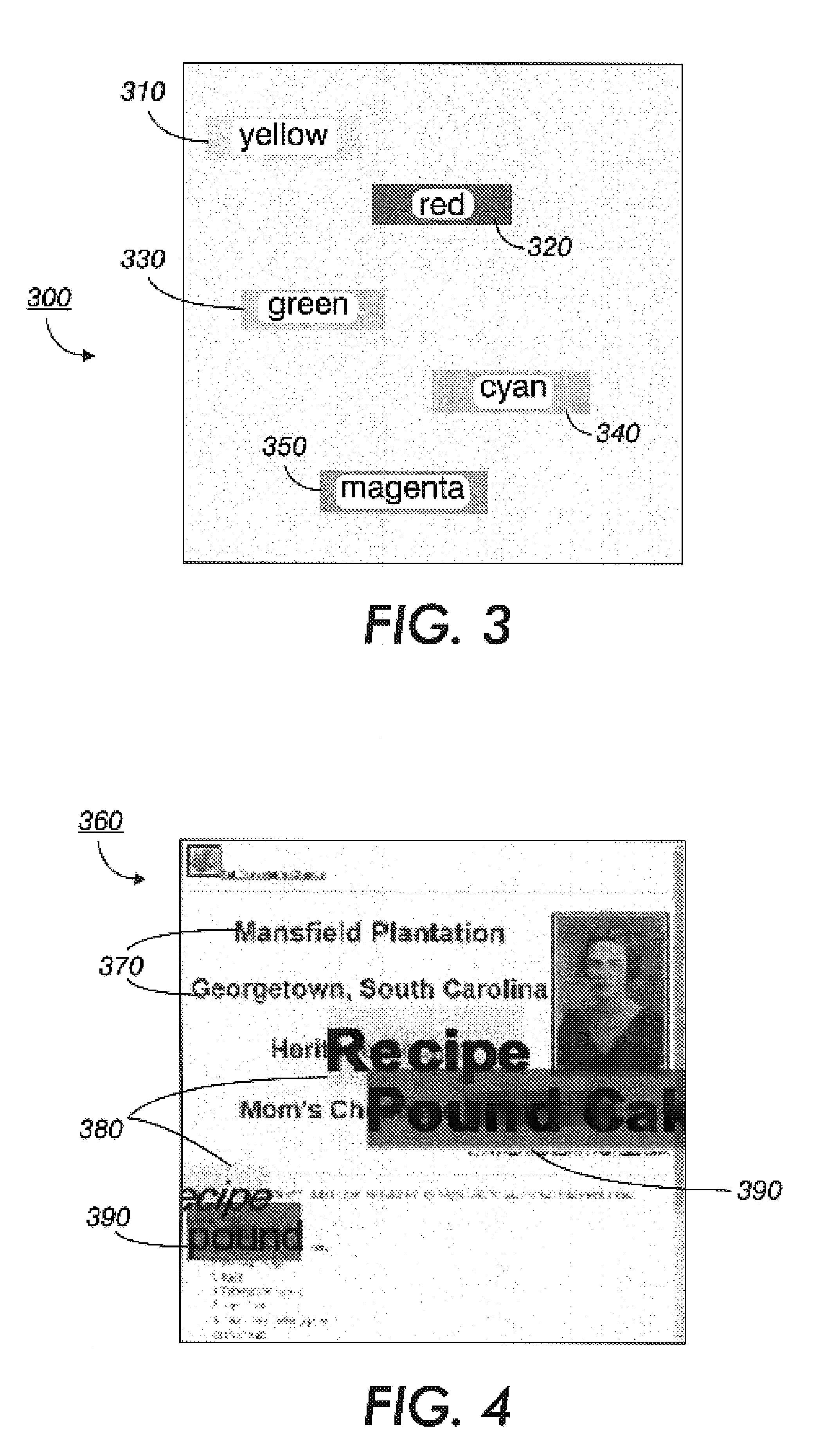
Systems and method for automatically choosing visual characteristics to highlight a target against a background
InactiveUS7130461B2Facilitate a viewer to distinguishMitigate attention-diverting influenceImage enhancementImage analysisCharacteristic spaceCovariance
A method for choosing visual characteristics of a characteristic space within a region includes calculating a mean characteristic of the region, determining a covariance of the region, inverting the covariance to produce an inverse covariance, estimating a target characteristic, determining a difference between the mean characteristic and the target characteristic transposing the difference to produce a difference transpose, determining a saliency from a product of the difference transpose multiplied by the inverse covariance multiplied by the difference, comparing the saliency to an acceptance criterion to yield one of an acceptance if the saliency satisfies the acceptance criterion and a rejection otherwise, adjusting the target characteristic and repeating the determining a difference, transposing the difference, determining a saliency and comparing the saliency steps if the comparing yields the rejection, and outputting the target characteristic if the comparing yields the acceptance.
Owner:XEROX CORP
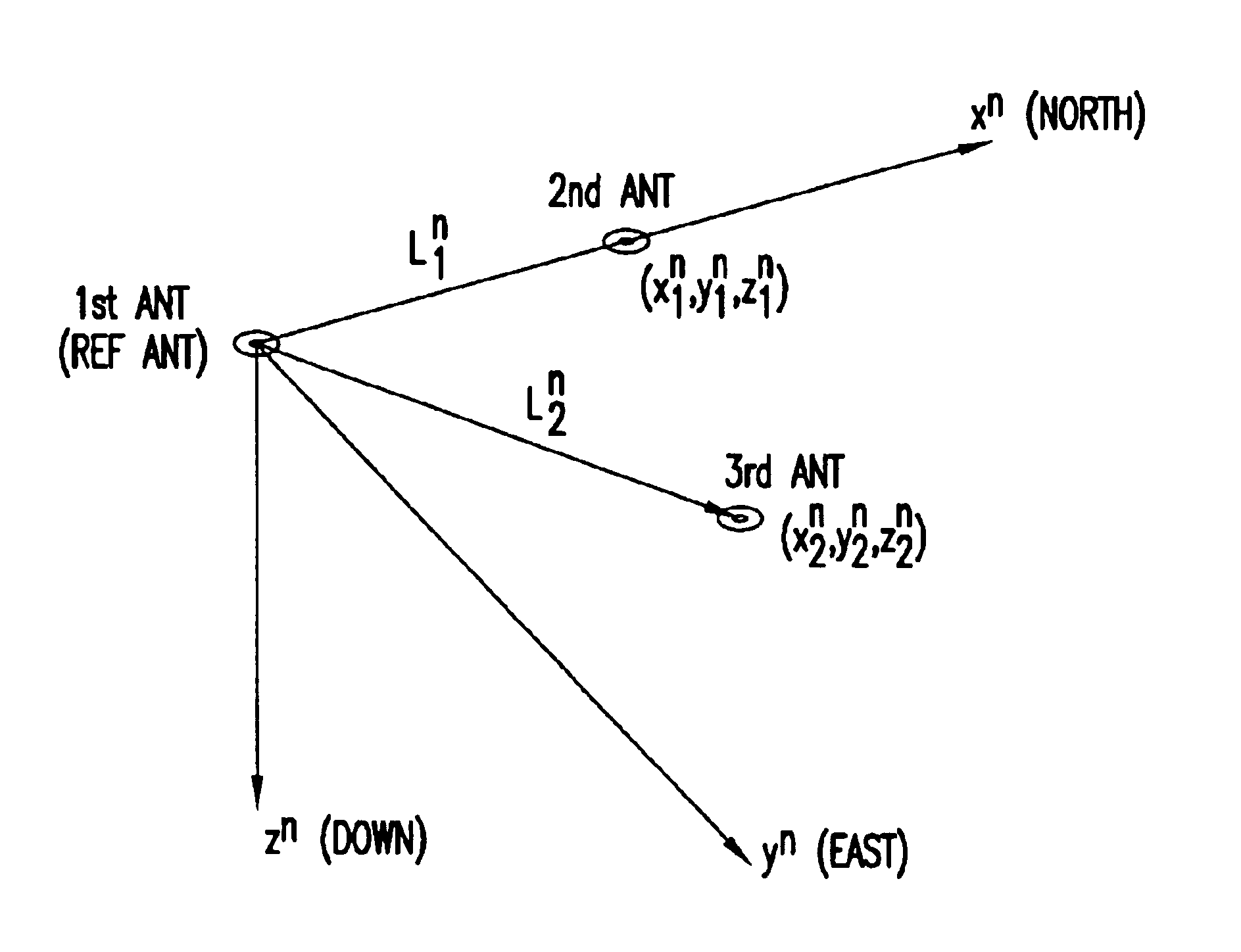
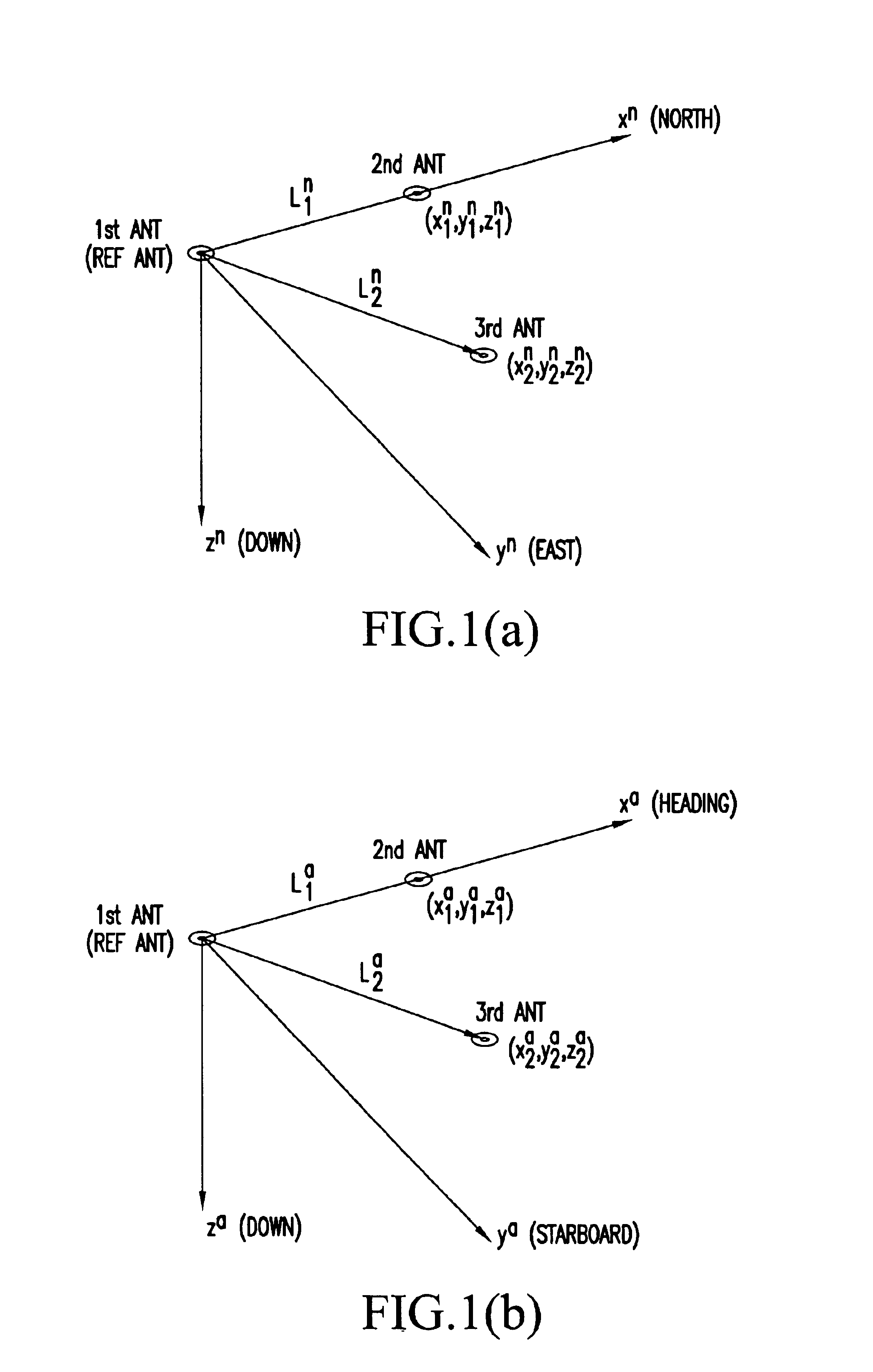
Attitude angle detecting apparatus
InactiveUS6792380B2Instantly calculateQuick checkDigital computer detailsPosition fixationAmbiguityInteger ambiguity
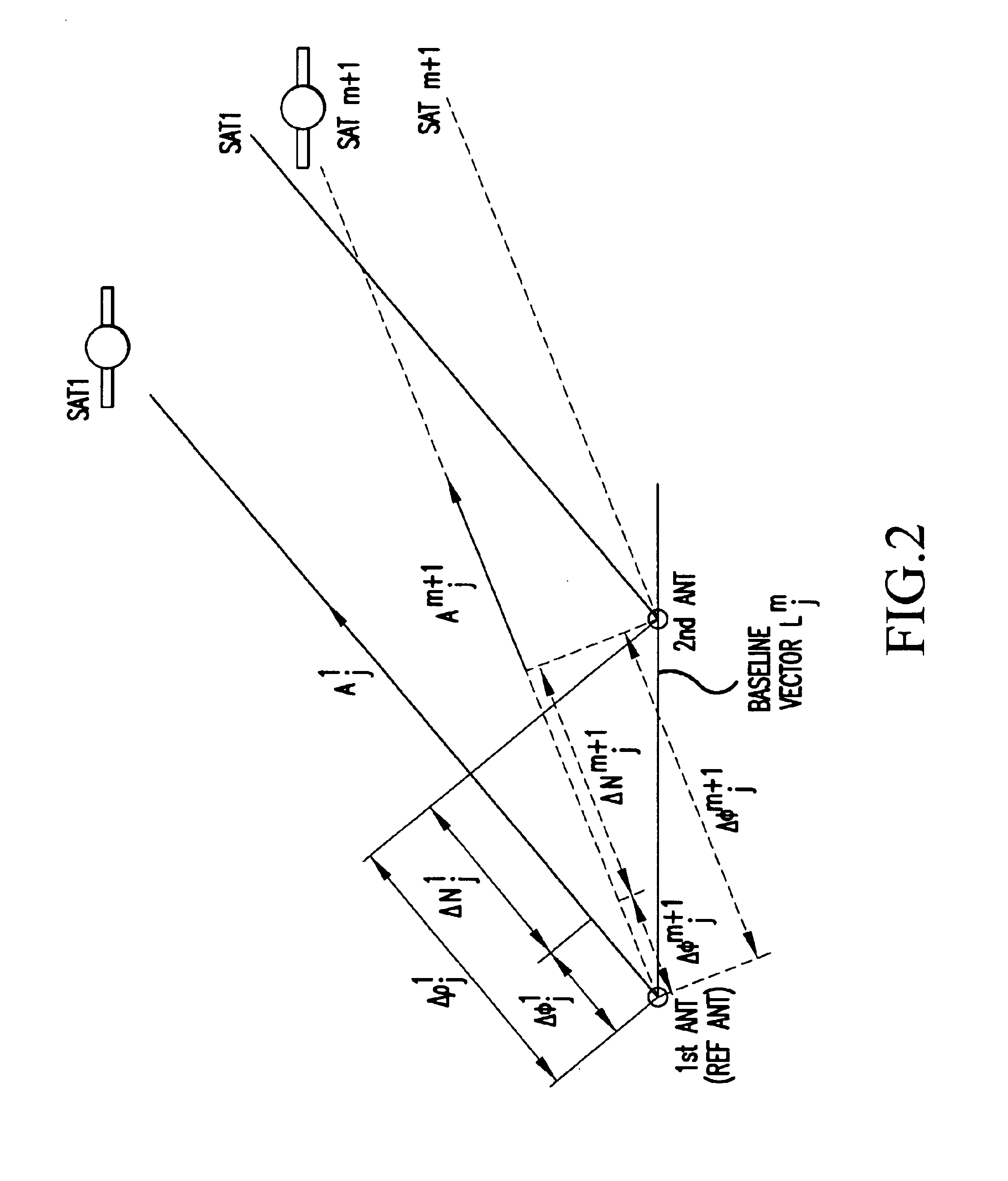
An attitude angle detecting apparatus receives radio waves transmitted from a plurality of position-fixing satellites with multiple antennas located at specific positions of a mobile unit, determines relative positions of the antennas and detects the heading and attitude of the mobile unit by determining carrier phase ambiguities quickly and accurately. When it is needed to redetermine integer ambiguities after recovery from an interruption of the radio waves from the position-fixing satellites or as a result of a change in combination of the position-fixing satellites, for example, the attitude angle detecting apparatus redetermines the integer ambiguities by using attitude angles and an attitude angle error covariance obtained from previous observation. This enables the attitude angle detecting apparatus to uninterruptedly obtain information on the heading and attitude of the mobile unit.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Online lithium ion battery SOC (state of charge) estimation method based on extended Kalman filter
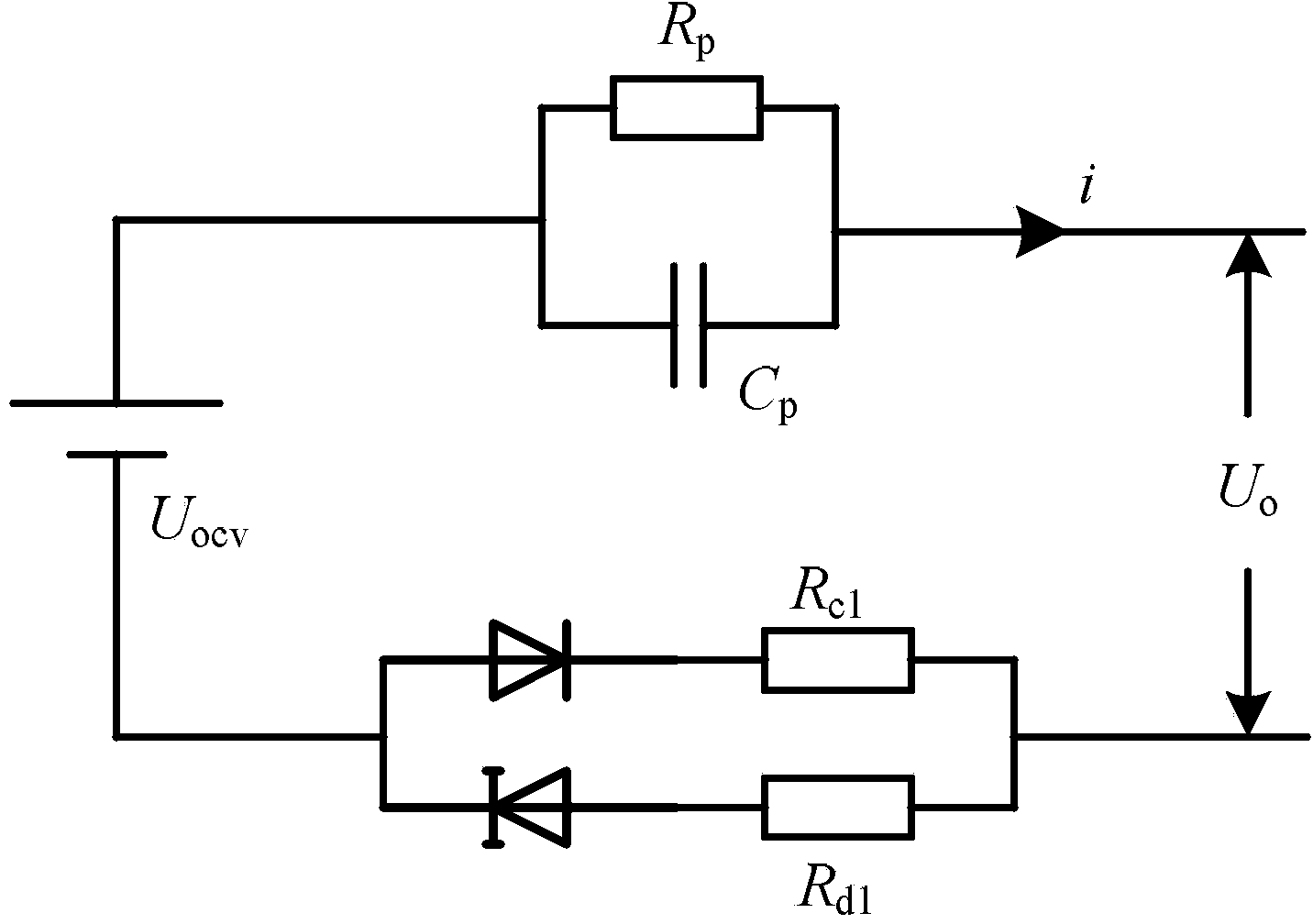
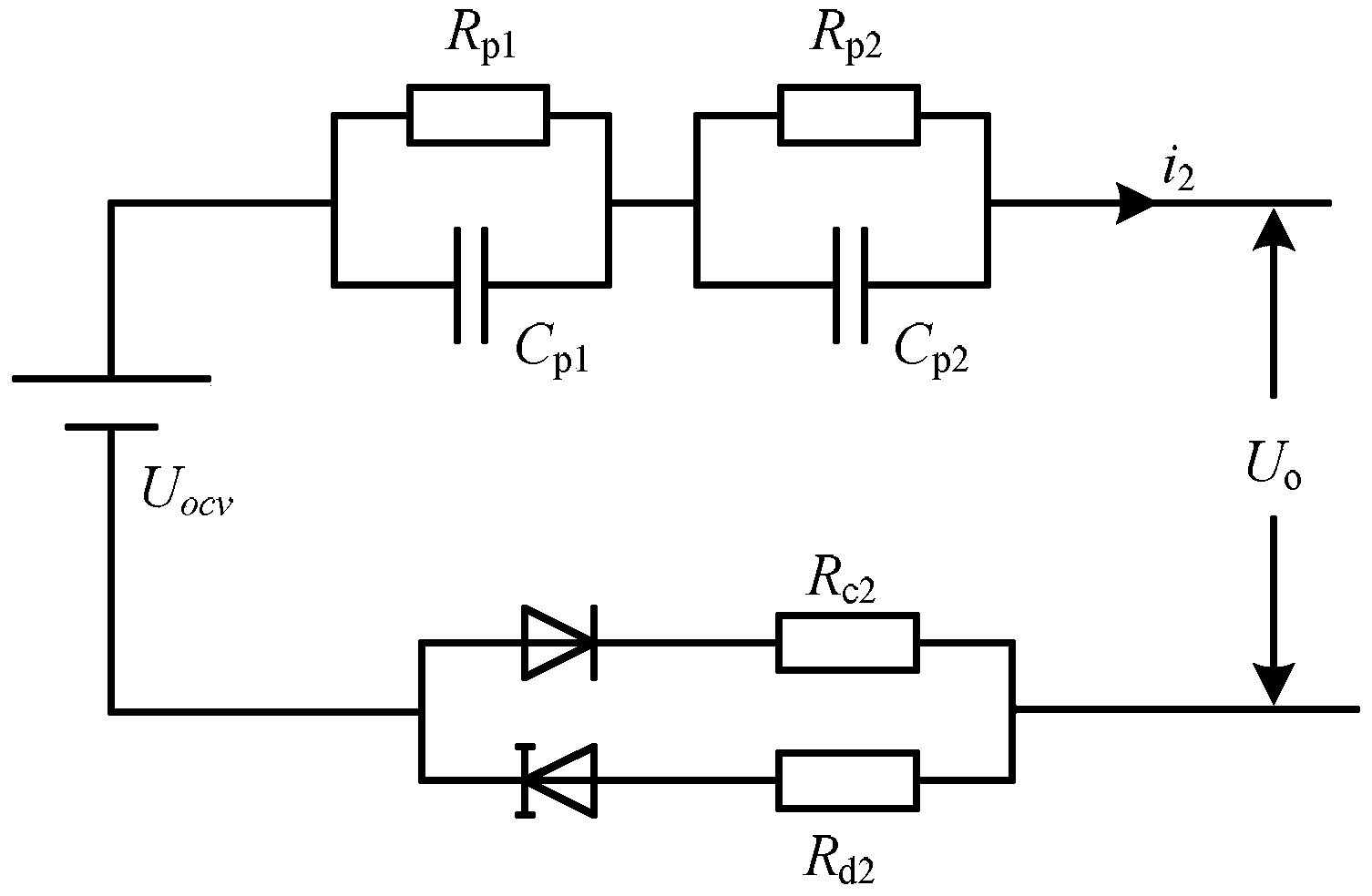
InactiveCN103529398AEstimates are accurate and reliableReliable convergenceElectrical testingCapacitanceEstimation methods
The invention discloses an online lithium ion battery SOC estimation method based on extended Kalman filter, belongs to the technical field of SOC prediction of a lithium ion battery, and aims to solve the problem that the reliability of the online estimation of a conventional lithium ion battery SOC is low due to influence of initial value selection. The method comprises the steps as follows: a voltage and current relation of a first-order RC (resistance / capacitance) equivalent circuit of a detected lithium ion battery and a voltage and current relation of a second-order RC equivalent circuit are established firstly; a charge-discharge experiment is performed on the detected lithium ion battery to establish a polynomial fitting function of a Kalman filter initial value SOC 0 of the detected lithium ion battery; a covariance P (0) of the Kalman filter initial value SOC 0 and a Kalman filter initial error of the detected lithium ion battery is obtained; and then, battery SOC estimation based on extended Kalman filter is performed, so that the online estimation of the lithium ion battery SOC is realized. The method is used for online estimation of the lithium ion battery SOC.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
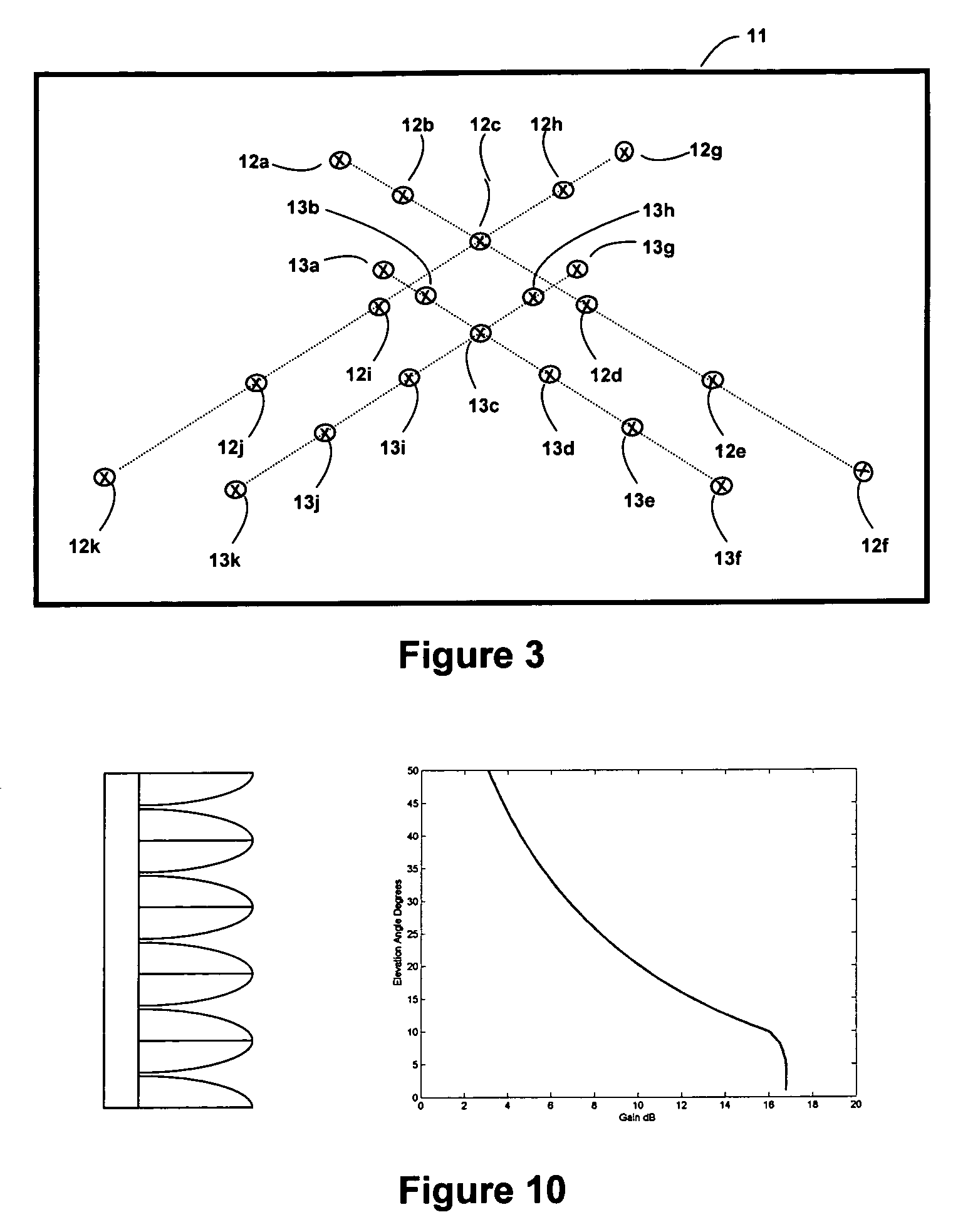
Multipath resolving correlation interferometer direction finding
ActiveUS20070273576A1Improve accuracyRobust and accurateMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWater useCovariance
Apparatus and a method utilizing correlation interferometer direction finding for determining the azimuth and elevation to an aircraft at long range and flying at low altitudes above water with a transmitting radar while resolving multipath signals. The signals from the radar are received both directly and reflected from the surface of the water using horizontally polarized and vertically polarized antenna arrays, are digitized and are stored in separate covariant matrices. Eigenvalues for the eigenvectors of the matrices processed on signal samples recorded on horizontally polarized X arrays are compared to the eigenvalues for the eigenvectors of the covariance matrices processed on signal samples recorded on vertically polarized X arrays. Incident field polarization is associated with the antenna array measurements that yield the strongest eigenvalue. The eigenvector and eigenvalues for the strongest signal are selected and used for subsequent signal processing. An initial global search assuming mirror sea-state reflection conditions using the signal eigenvector having the strongest eigenvalue is performed to yield an approximate elevation α and azimuth β to the aircraft. The approximate values are then used as the starting point for a subsequent conjugate gradient search to determine accurate elevation α and azimuth β to the aircraft.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
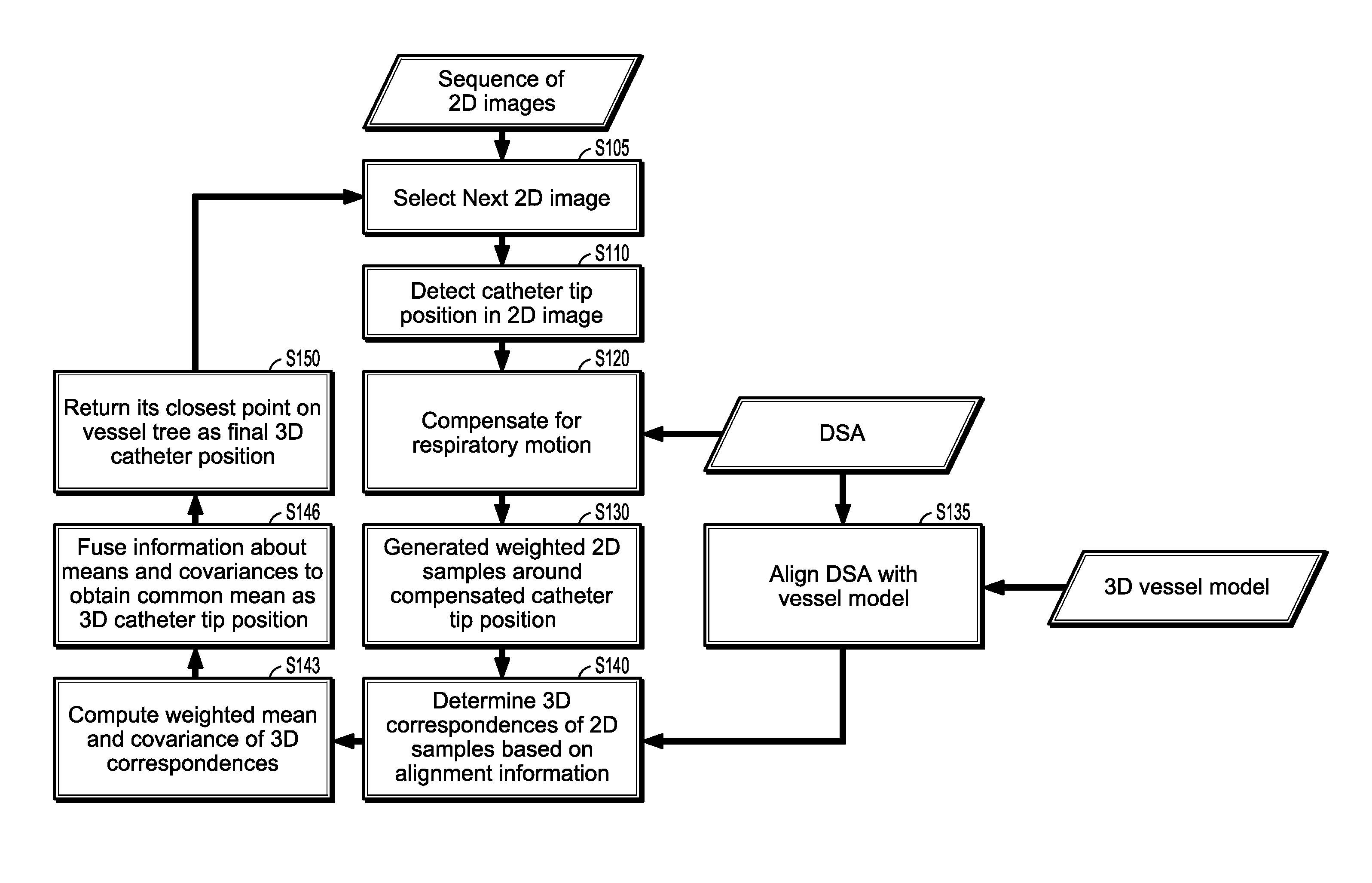
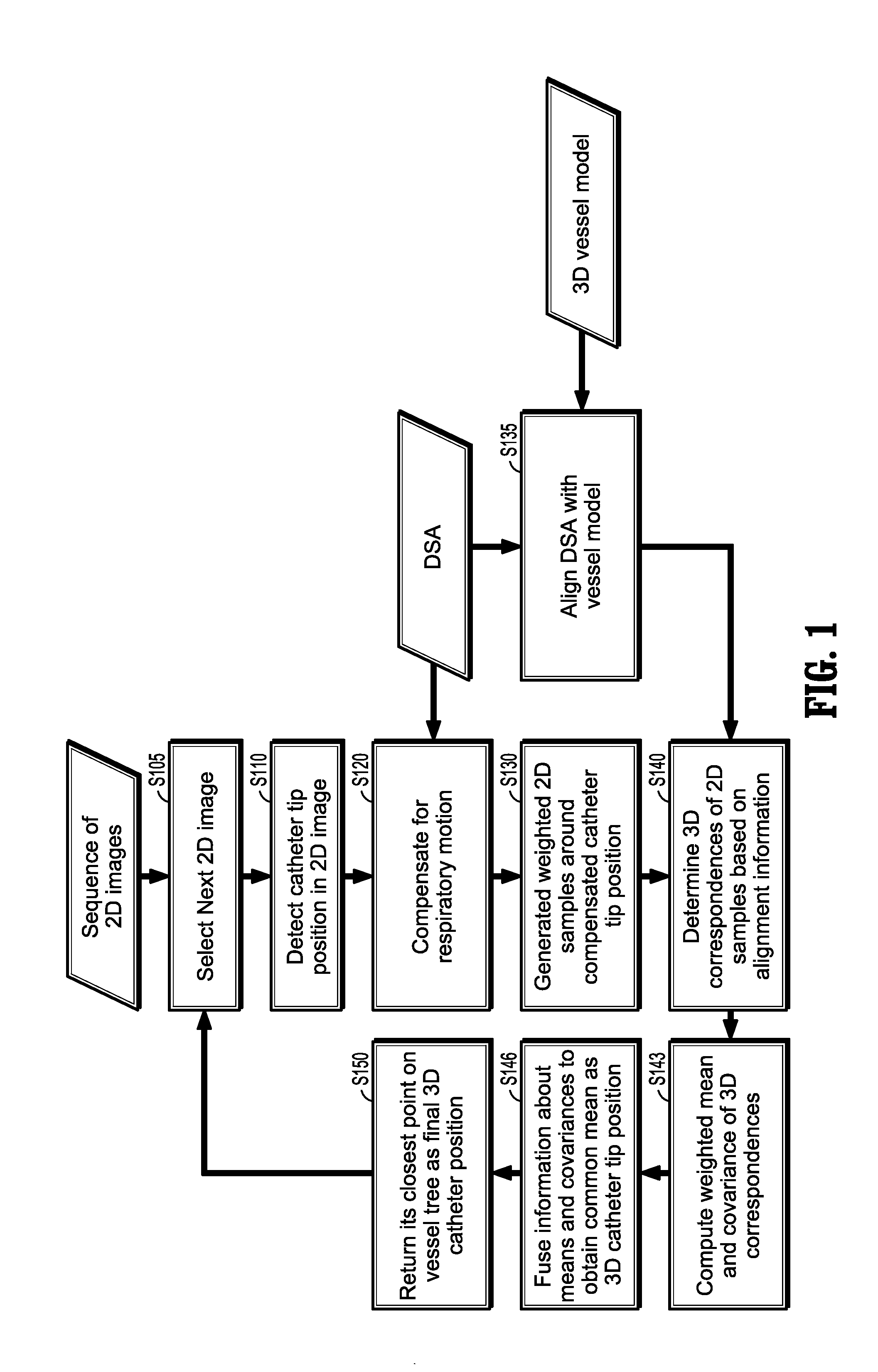
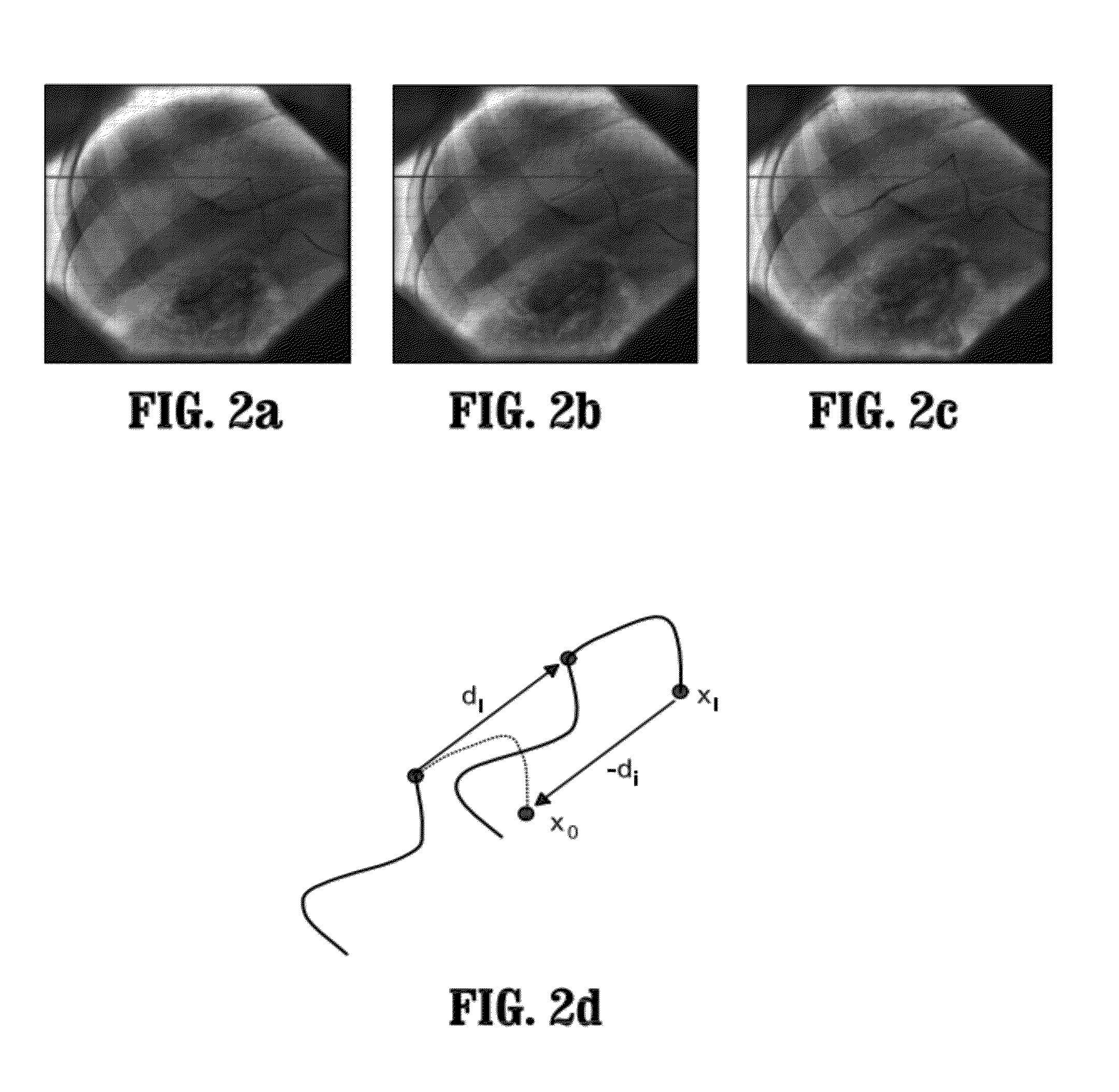
Method for dynamic road mapping
A method of determining a three-dimensional (3D) position of a catheter tip includes: compensating a 2D position of the tip of the catheter for respiratory motion to generate a compensated 2D catheter position, generating weighted sample points around the compensated 2D catheter position, determining correspondent points of the weighted sample points in a 3D image, computing a weighted mean and a weighted covariance of each correspondent point, and determining the 3D position of the catheter tip in the 3D image from a fusion of the weighted means and weighted covariances.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
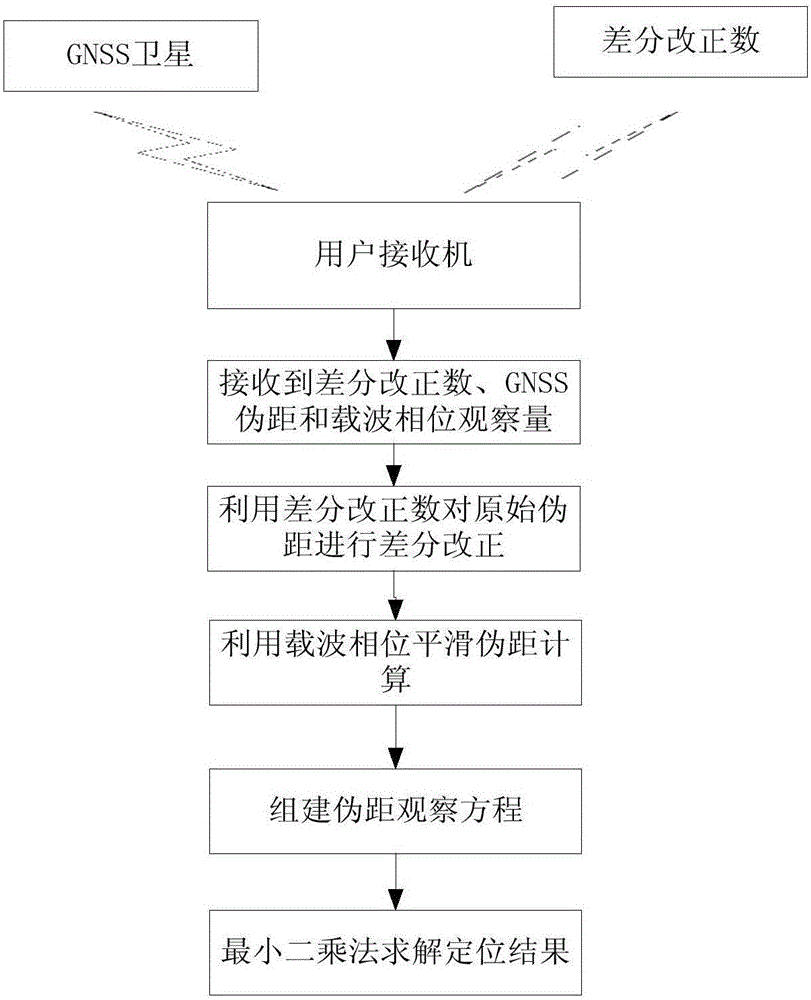
Autonomous integrated navigation system
InactiveCN103528587AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsSynthetic aperture radarCovariance
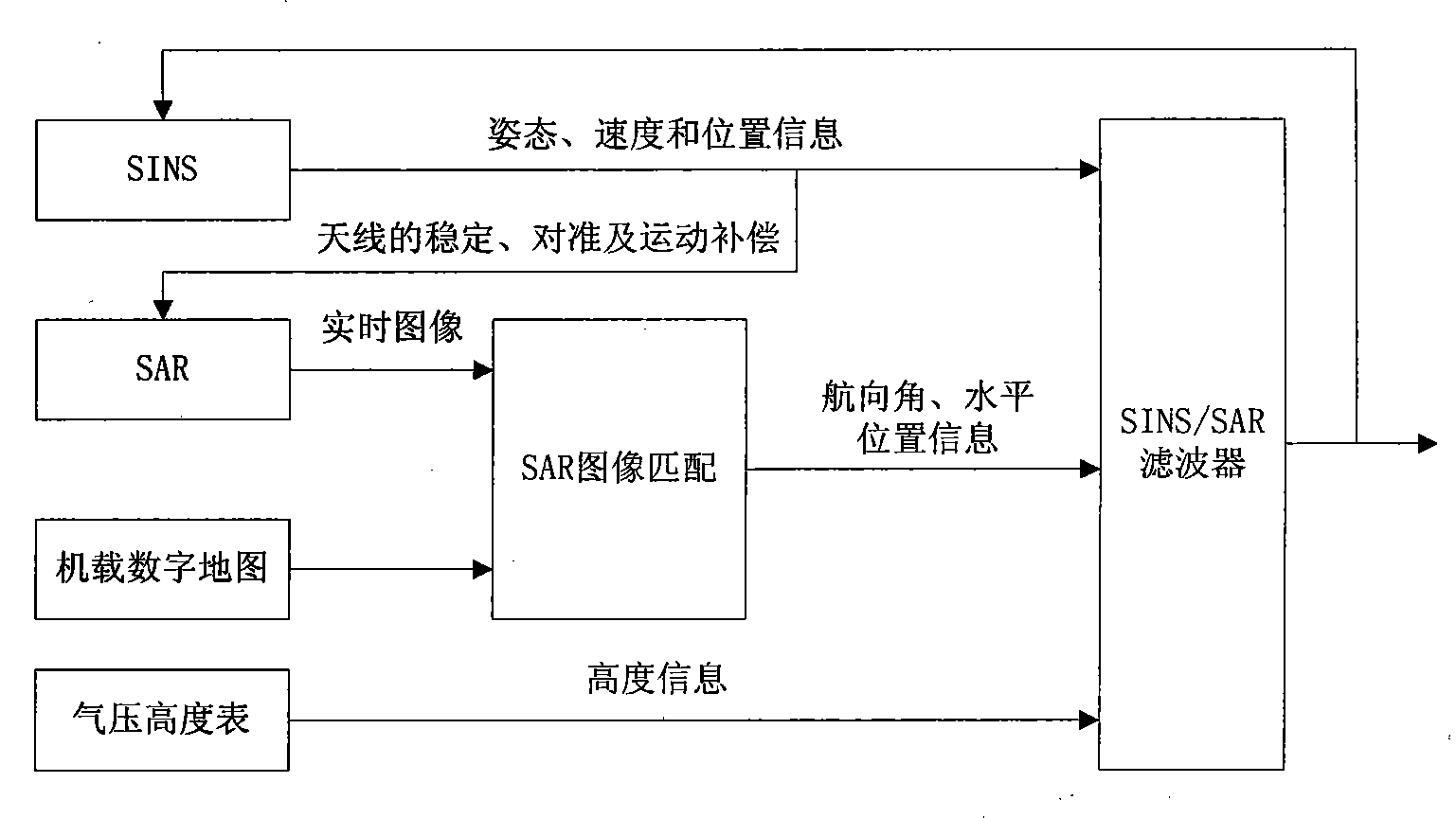
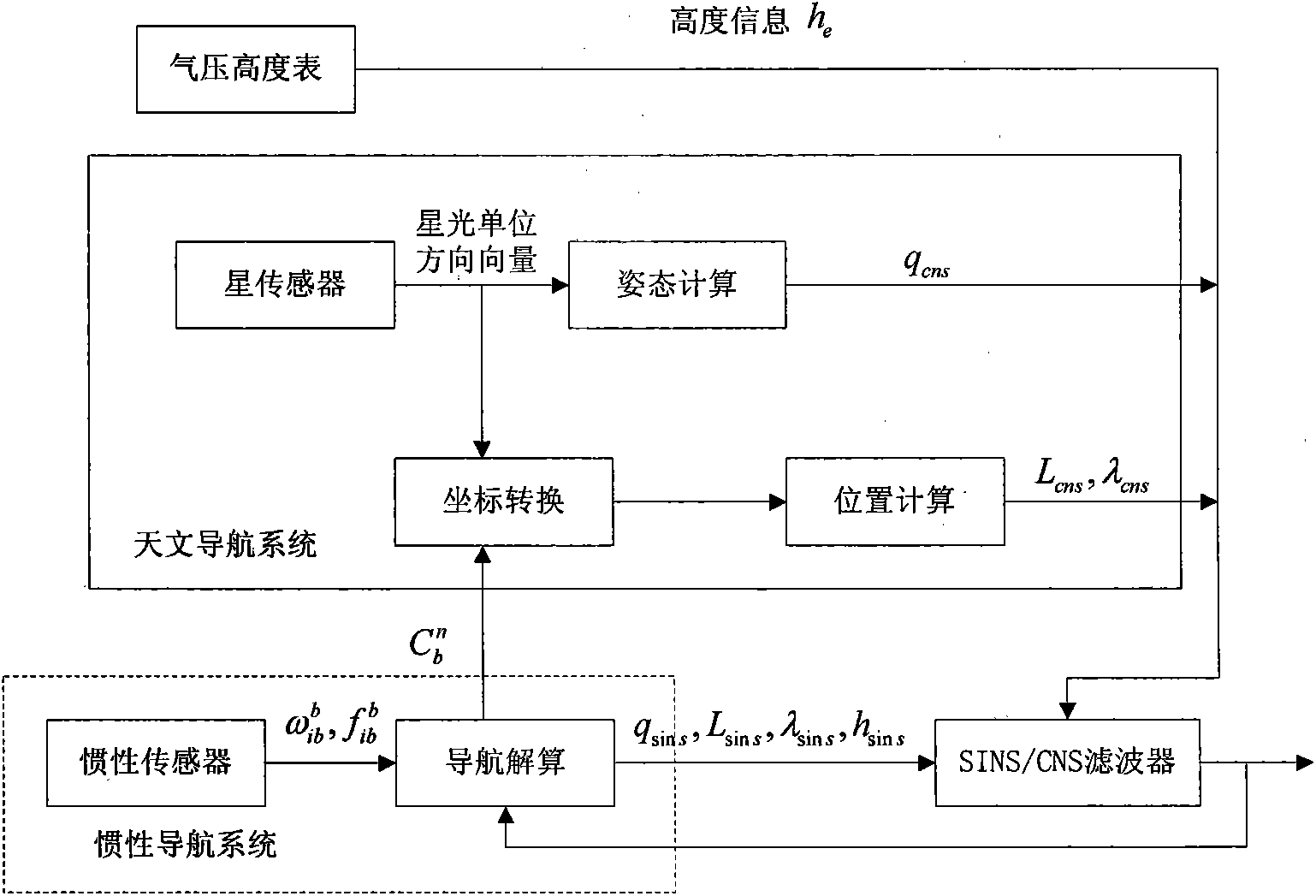
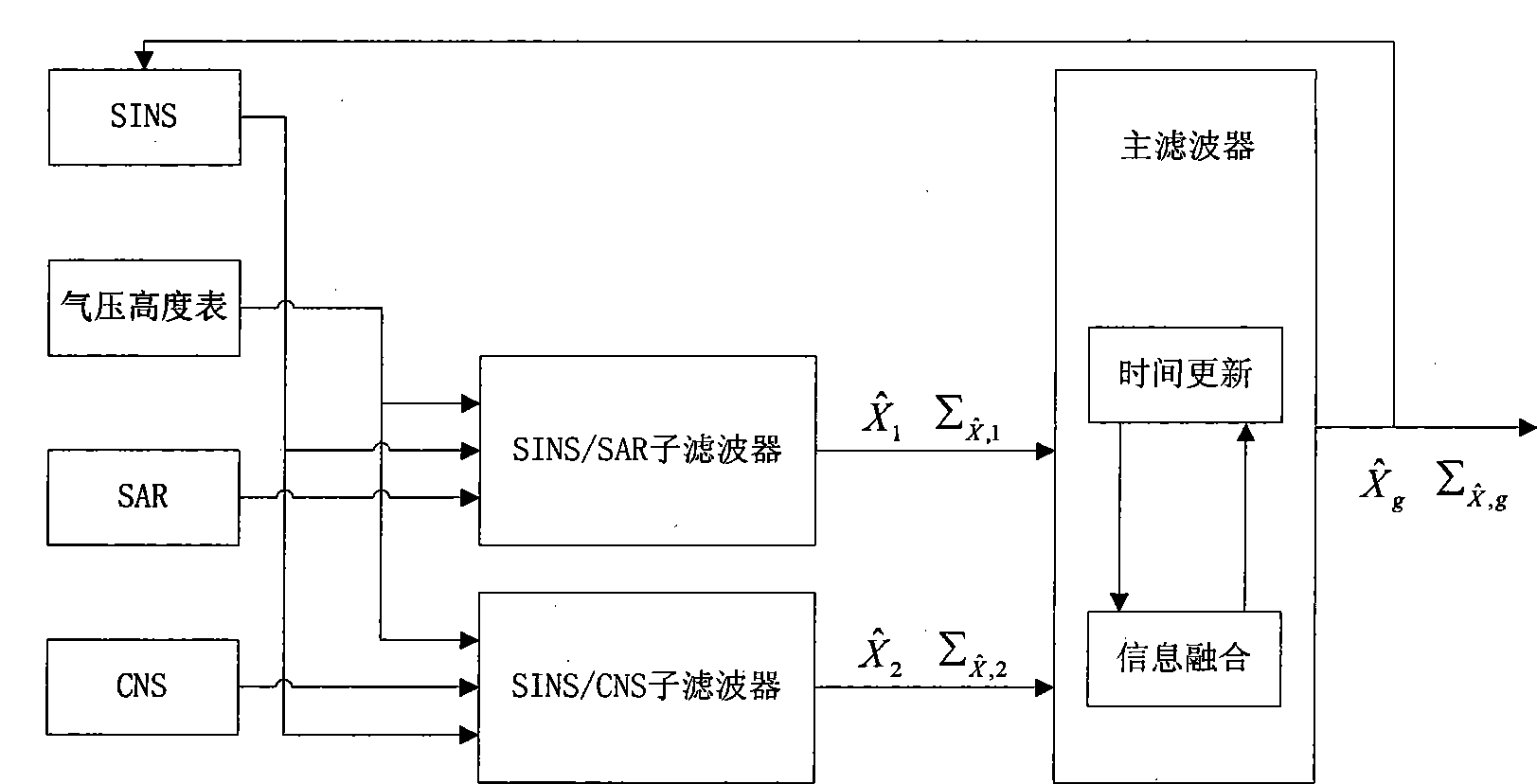
The invention relates to an autonomous integrated navigation system which belongs to the technical field of navigation systems. The SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) / SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) / CNS (Celestial Navigation System) integrated navigation system takes SINS as a main navigation system and SAR and CNS as aided navigation systems and is established by the following steps: firstly, designing SINS / SAR and SINS / CNS navigation sub-filters, calculating to obtain two groups of local optimal estimation values and local optimal error covariance matrixes of the integrated navigation system state, then transmitting the two groups of local optimal estimation values into a main filter by a federal filter technology for fusion to obtain an overall optimal estimation value and an overall optimal error covariance matrix, and finally, performing real-time correction on the error according to the overall optimal estimation value so as to obtain an optimal estimation fusion algorithm of the SINS / SAR / CNS integrated navigation system. The autonomous integrated navigation system, disclosed by the invention, is less in calculation amount and high in reliability, is applicable to aircrafts in near space, aircrafts flying back and forth in the aerospace, aircrafts for carrying ballistic missiles, orbit spacecrafts and the like, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
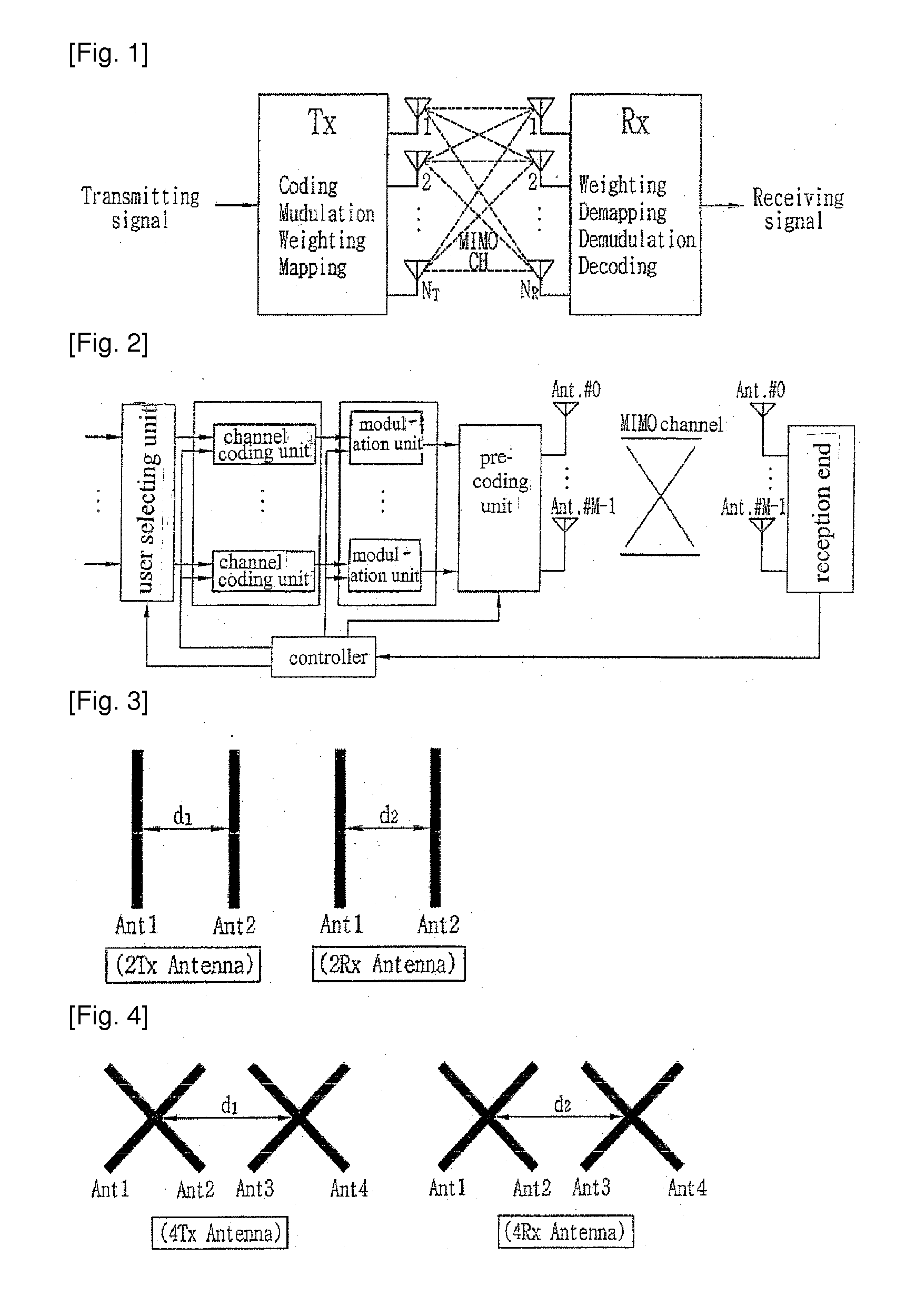
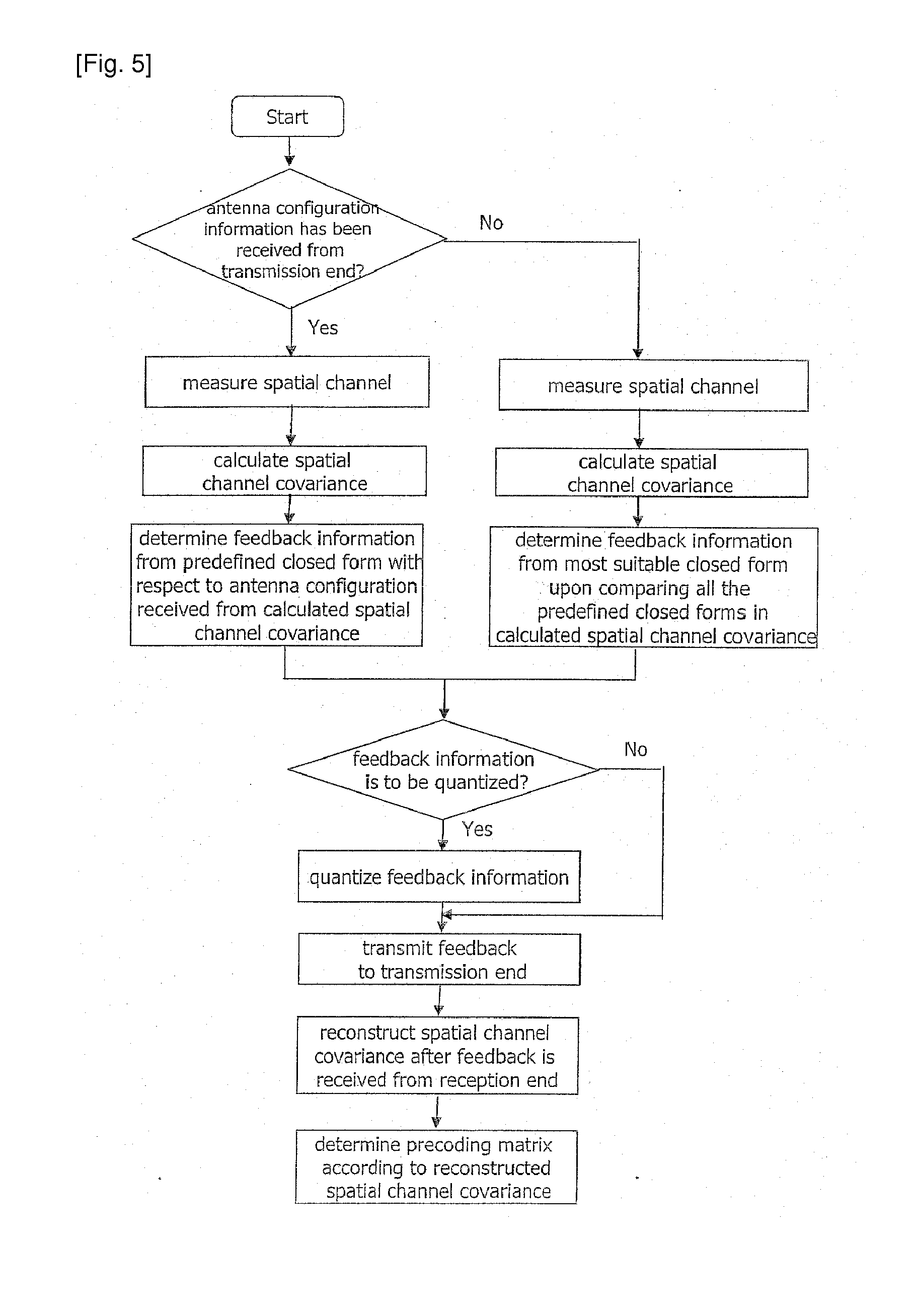
Method of Minimizing Feedback Overhead Using Spatial Channel Covariance in a Multi-Input Multi-Output System
InactiveUS20120069887A1Minimize feedback overheadLess consuming allocated radio resourceDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationMulti inputCommunications system
Disclosed is a method for minimizing feedback overhead in a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) communication method using multiple transmission and reception antennas. In particular, a method for minimizing feedback overhead in a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) communication system by using spatial channel covariance, as explicit channel status information (CSI) feedback method is disclosed.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
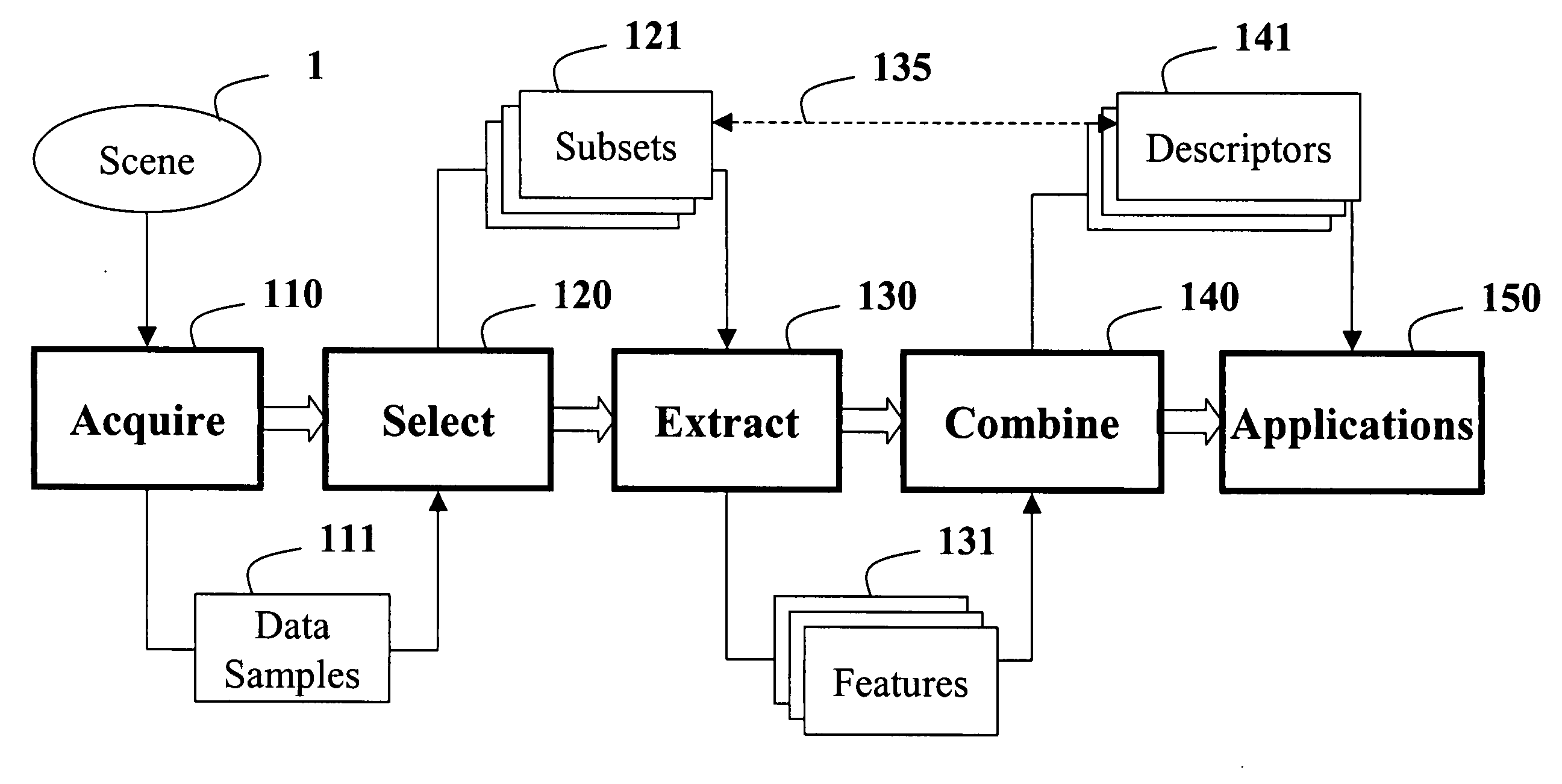
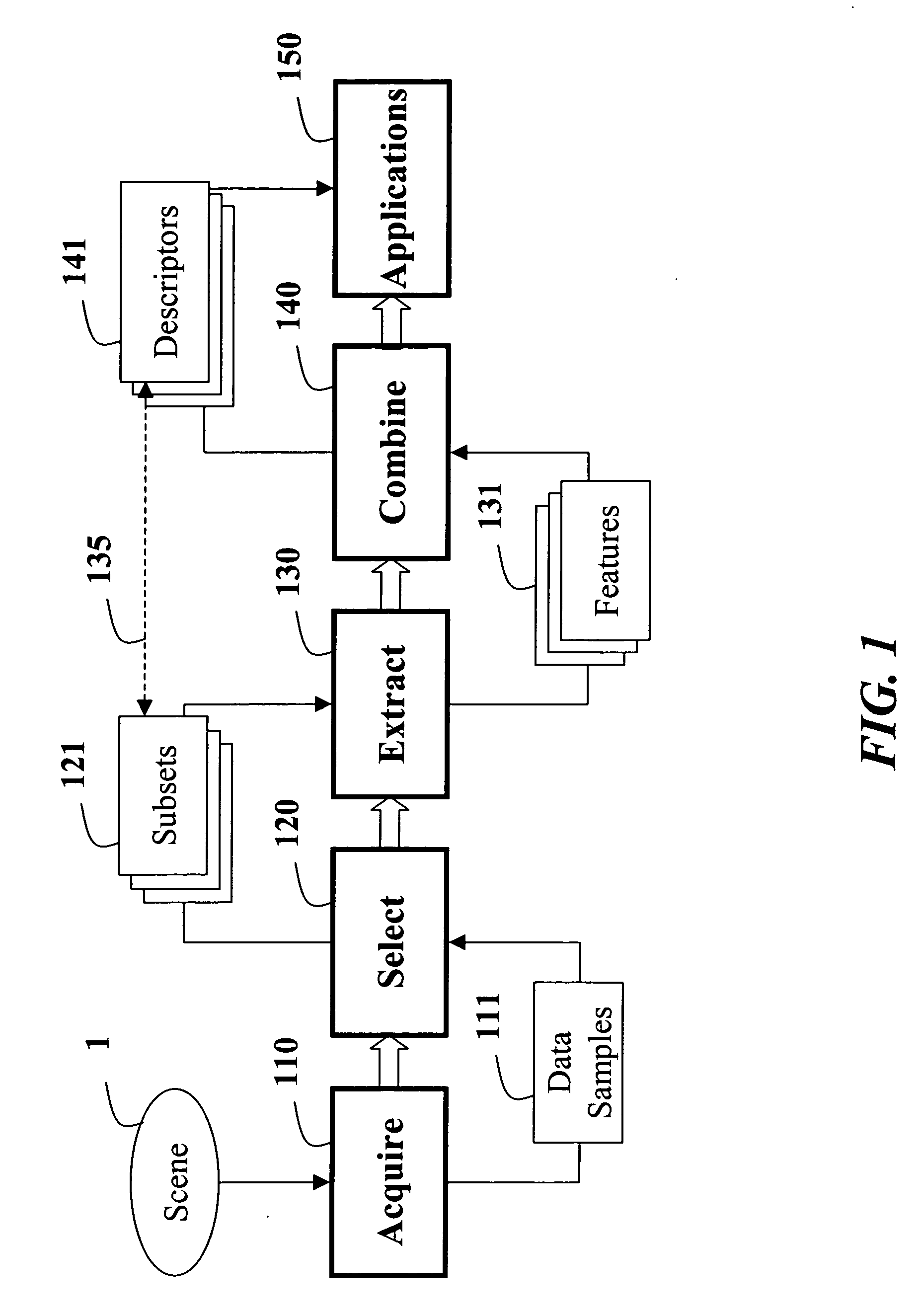
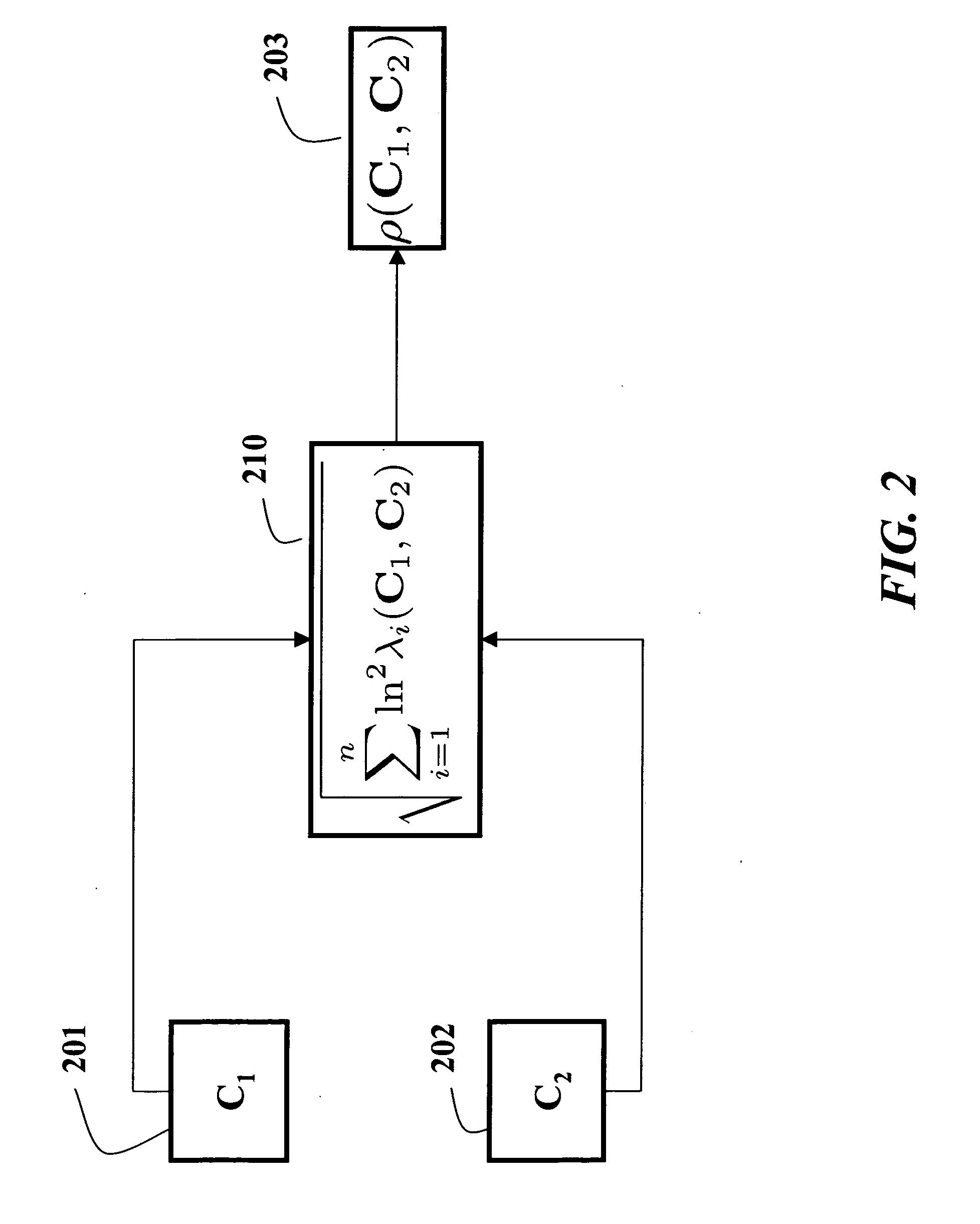
Method for constructing covariance matrices from data features
A method constructs descriptors for a set of data samples and determines a distance score between pairs of subsets selected from the set of data samples. A d-dimensional feature vector is extracted for each sample in each subset of samples. The feature vector includes indices to the corresponding sample and properties of the sample. The feature vectors of each subset of samples are combined into a d×d dimensional covariance matrix. The covariance matrix is a descriptor of the corresponding subset of samples. Then, a distance score is determined between the two subsets of samples using the descriptors to measure a similarity between the descriptors.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
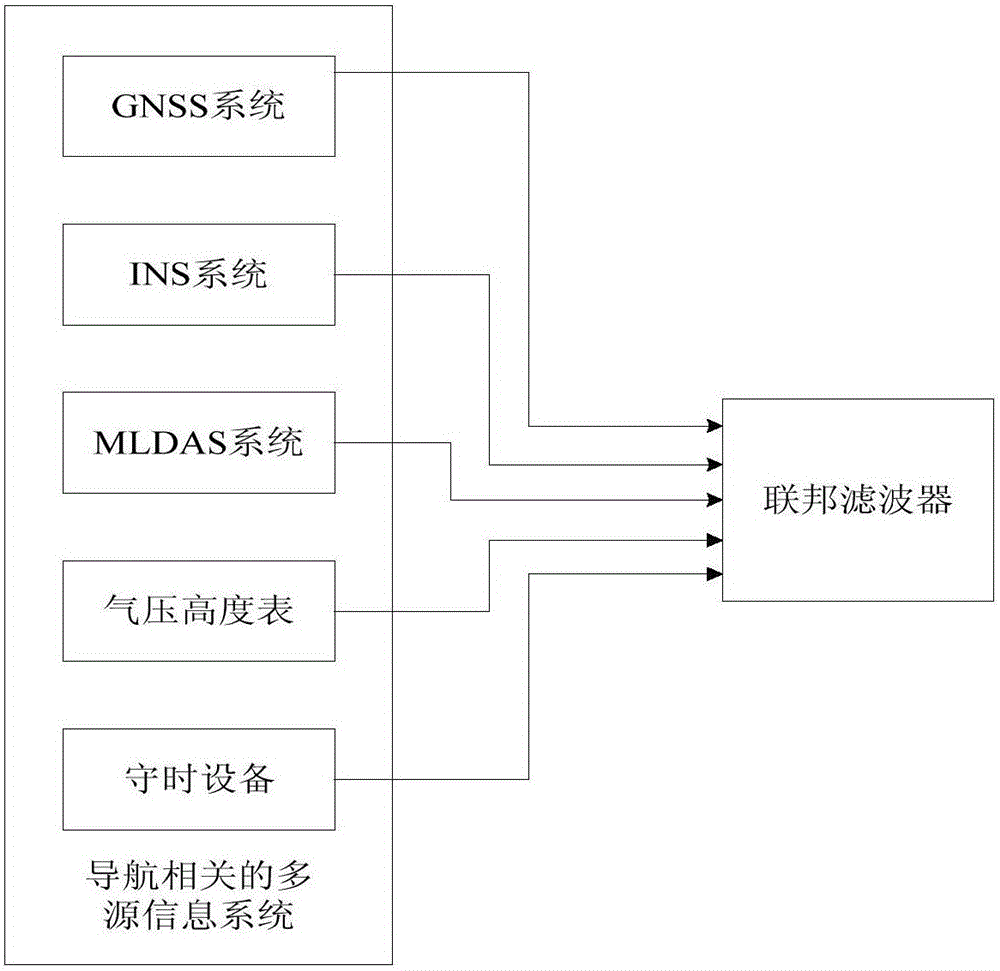
Integrated navigation method and equipment based on multisource information fusion
InactiveCN105758401ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingOn boardCovariance
The invention provides an integrated navigation method and equipment based on multisource information fusion. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining multisource navigation information, namely obtaining navigation related information from one or more of a global satellite navigation system GNSS, an inertial navigation system INS, a multimode region difference augmentation system MLDAS, a pressure altimeter and timekeeping equipment, which are arranged on an aircraft; performing fusion treatment on multisource information by using a federal wave filter, wherein the federal wave filter comprises a main wave filter and a plurality of local wave filters connected with the main wave filter, and each kind of the multisource navigation information and a reference signal are jointly input to one local wave filter; triggering the local wave filters to respectively calculate local estimation values and error covariance matrixes; triggering the main wave filter to perform wave filtering on the reference signal, and performing optimal infusion on the wave filtering results of the reference signal according to output results of the local wave filters and the local wave filters, so as to obtain a global optimum estimation value. Therefore, the availability and the integrity of on-board navigation equipment are improved.
Owner:ZHONGWEI IOT CHENGDU TECH CO LTD
Wireless communication system with interference compensation
InactiveUS7006795B2Reduce the amount of calculationMaximized through complex calculationsPower managementPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemData rate
A method and apparatus for assigning the data rate and / or power level to the mobile terminals without determining the highest theoretical system throughput, and without determining the highest weighted system throughput. An order is imposed on the terminals and the data rate and / or power covariance matrices are assigned such that the data rates of the terminals having a lower index in the order will not be decreased due to the presence of the terminals having a higher index in the order, and this is accomplished without changing the power covariance matrixes of the antennas involved in the communication with the lower index terminals. Thus, the assignment is made to the terminals based on the terminals requirements without regard to the interference introduced by the terminals with a higher index in the order since this interference will be compensated for by the compensation technique when the compensation technique process the terminals in accordance with the order. The invention reduces the amount of computation necessary to implement such compensation techniques on an ongoing, real-time basis in a real-world system.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
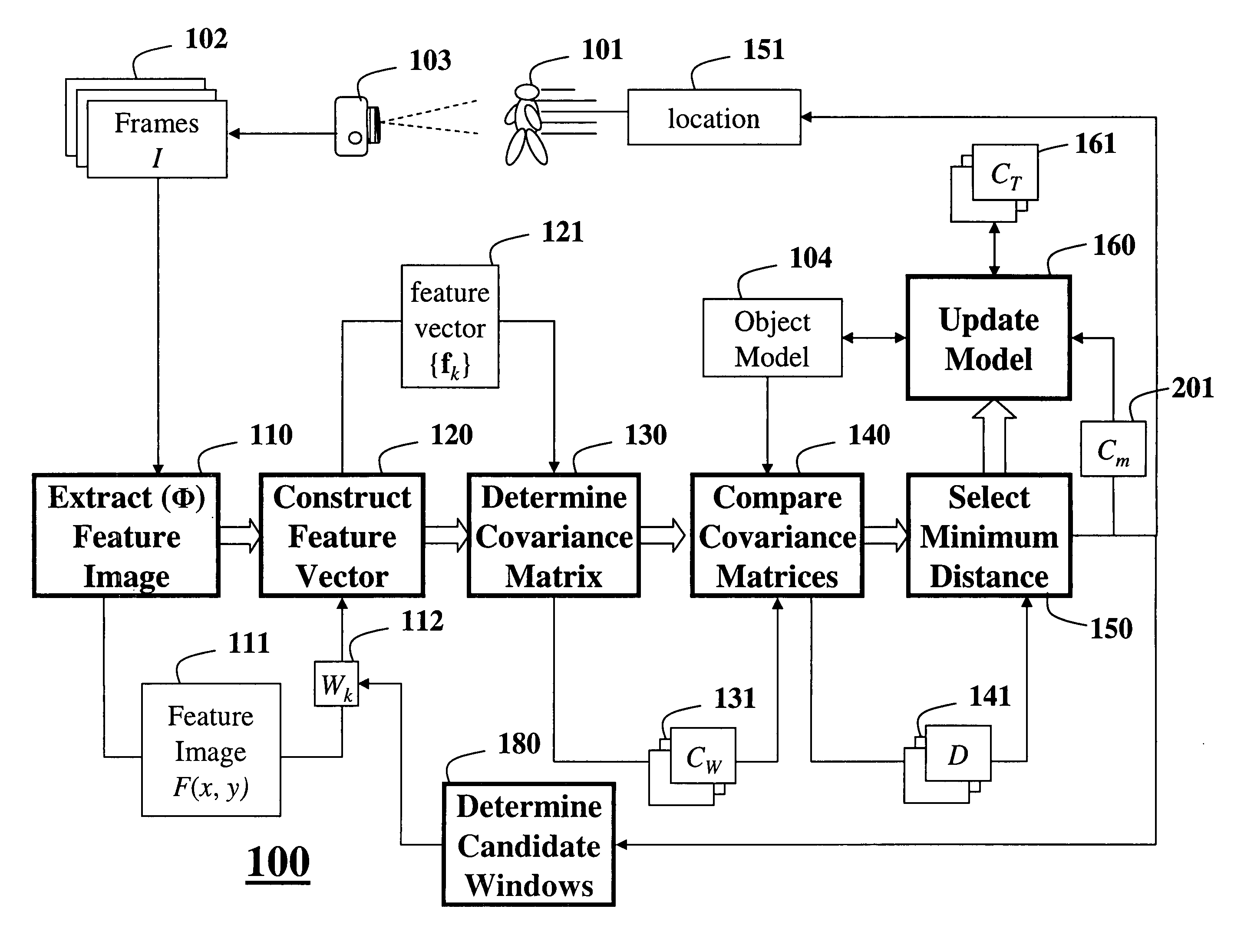
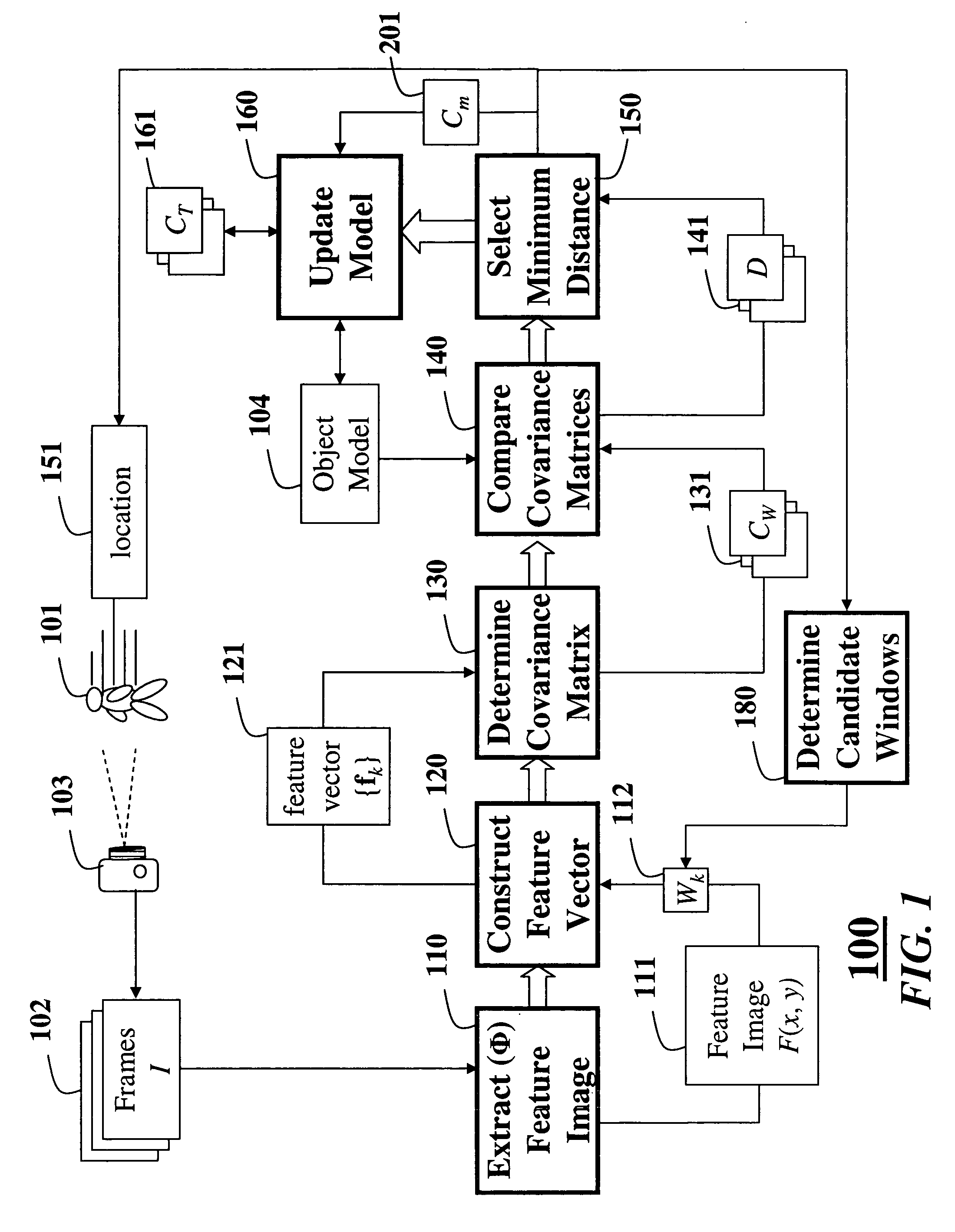
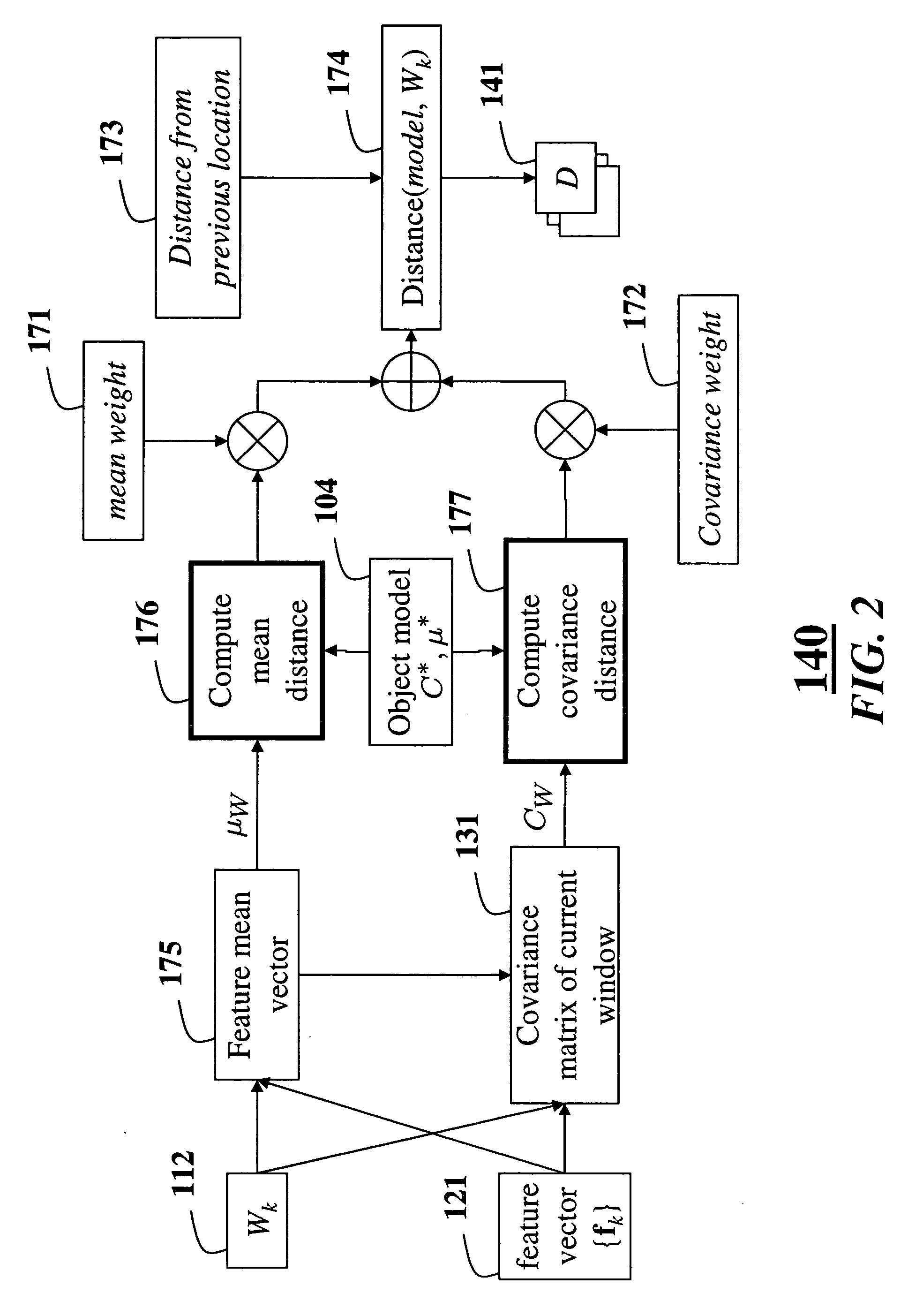
Method for tracking objects in videos using covariance matrices
ActiveUS20070183629A1Accurate detectionDimensionality is relatively smallImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCovariance
A method is provided for tracking a non-rigid object in a sequence of frames of a video. Features of an object are extracted from the video. The features include locations of pixels and properties of the pixels. The features are used to construct a covariance matrix. The covariance matrix is used as a descriptor of the object for tracking purposes. Object deformations and appearance changes are managed with an update mechanism that is based on Lie algebra averaging.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com