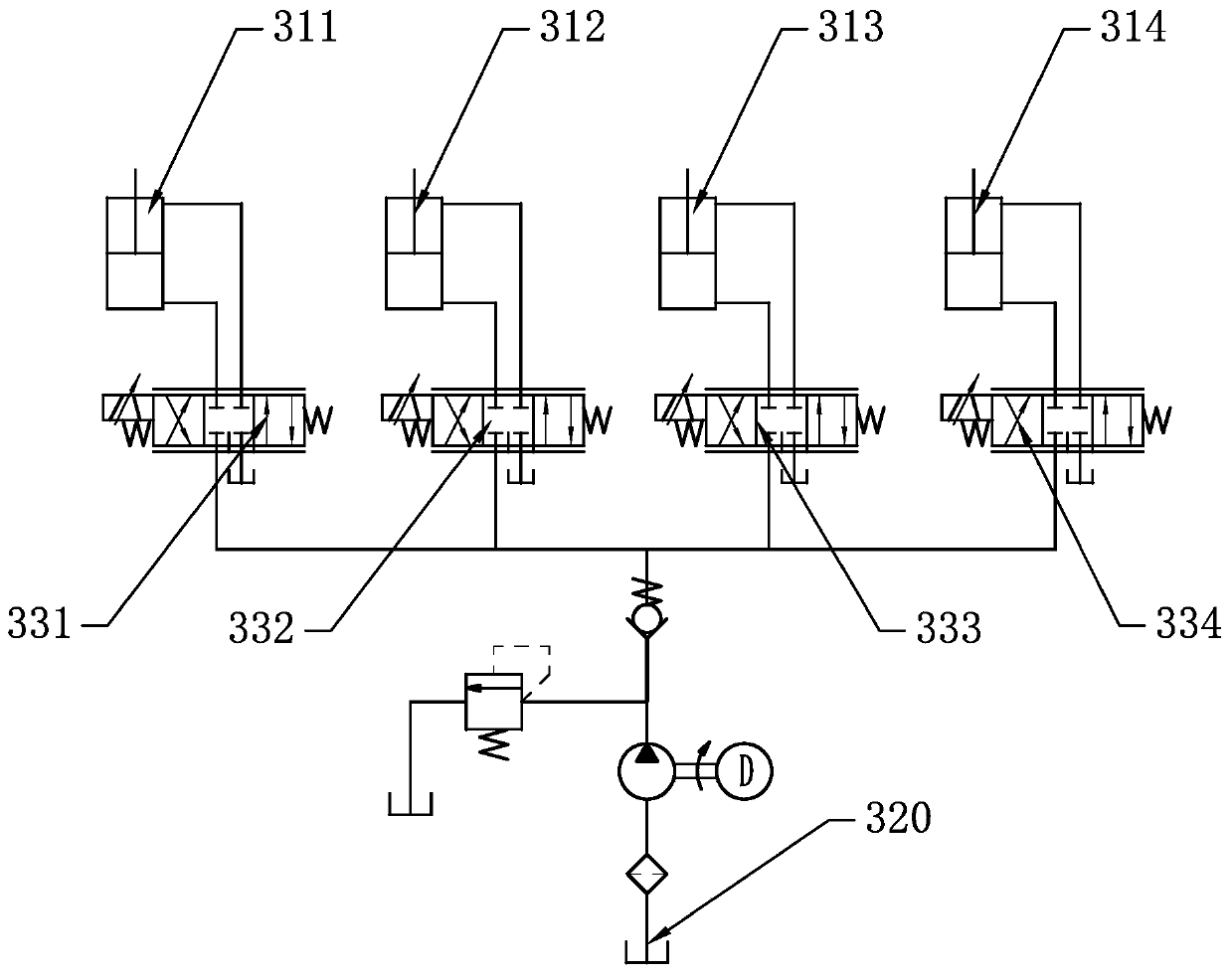
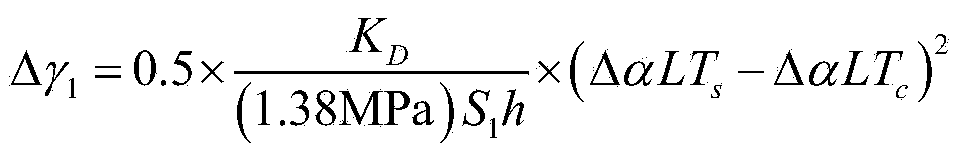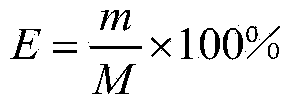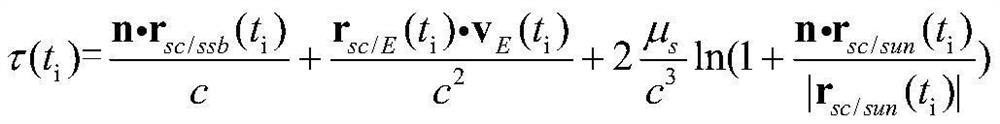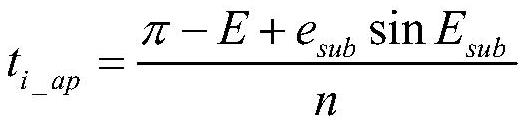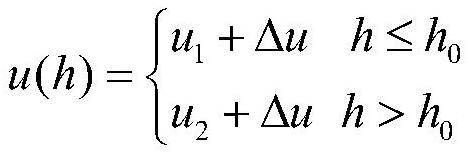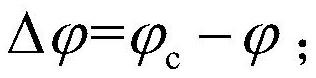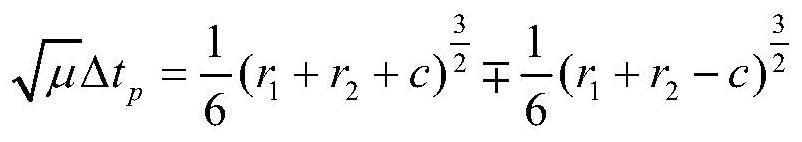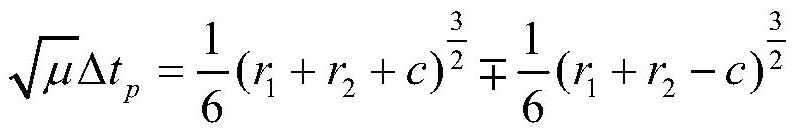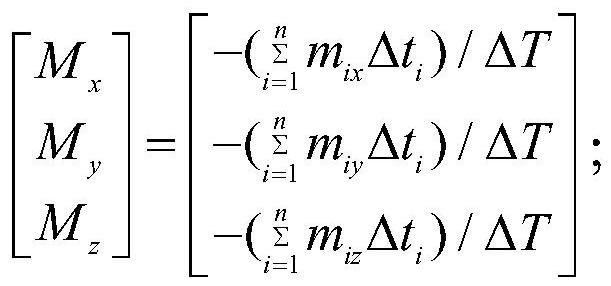Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "Delta" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Delta is an American versatile family of expendable launch systems that has provided space launch capability in the United States since 1960. More than 300 Delta rockets have been launched with a 95% success rate. Only the Delta IV Heavy rocket remains in use as of August 22, 2019. Delta rockets are currently manufactured and launched by the United Launch Alliance.
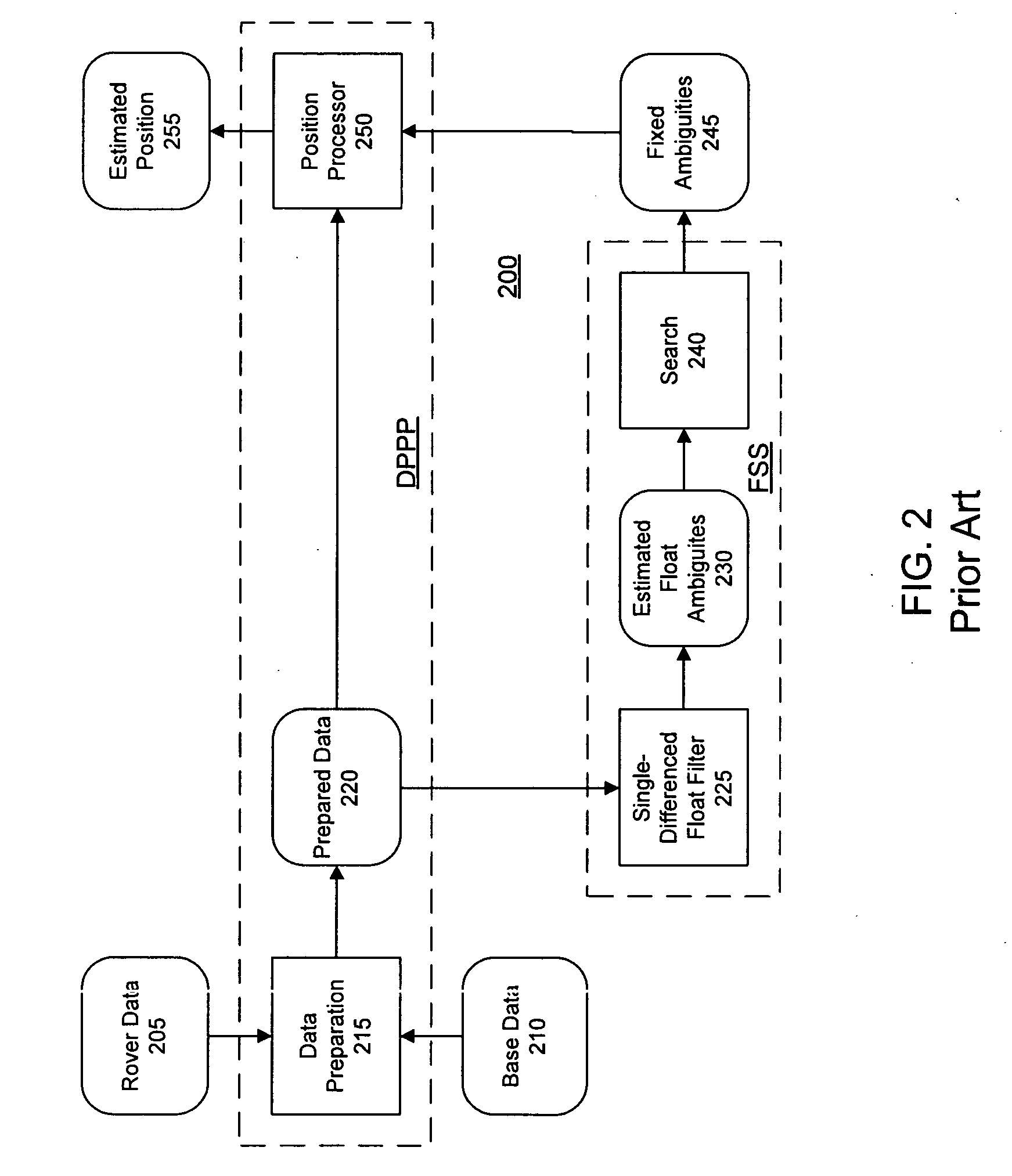
GNSS position coasting
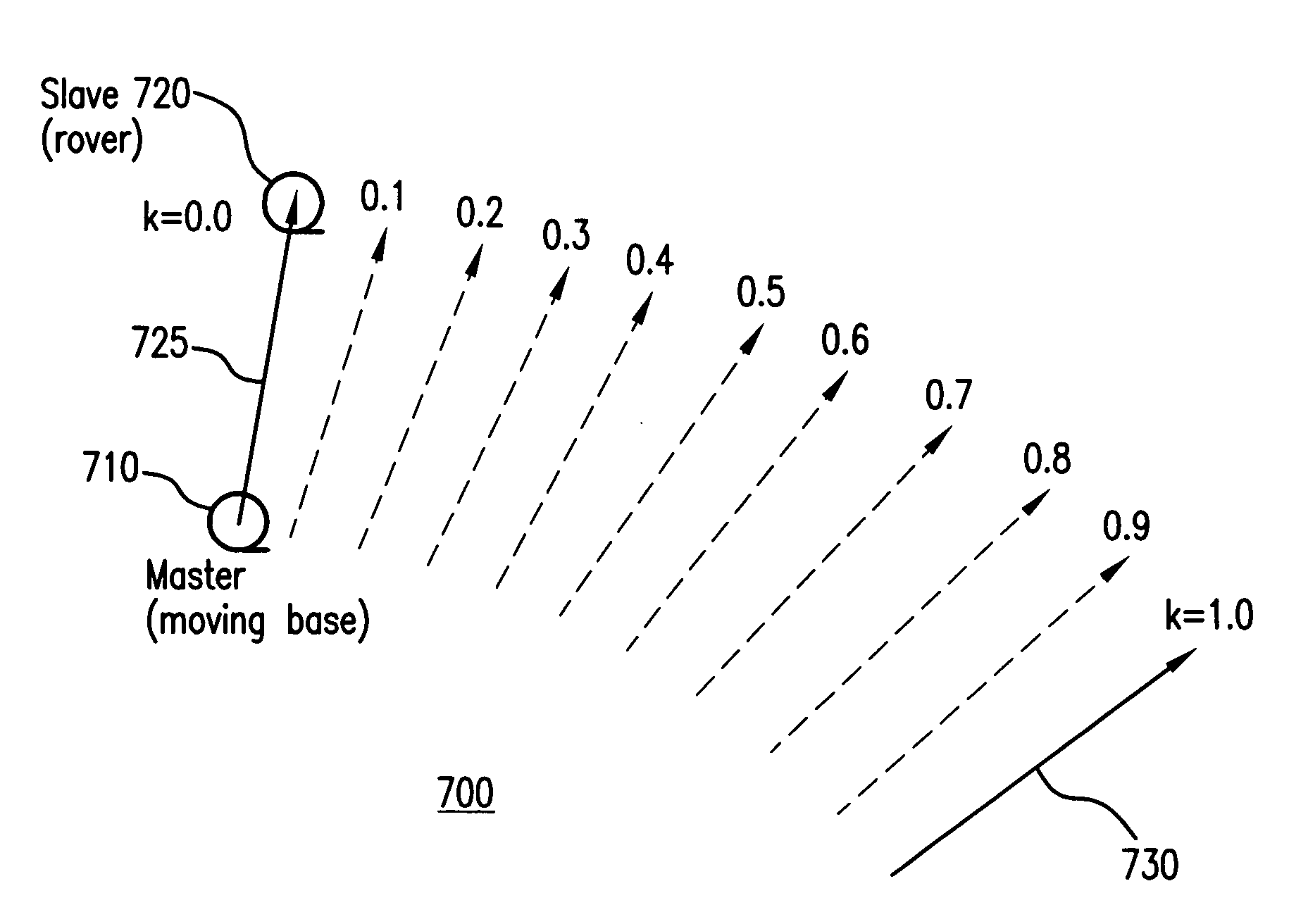
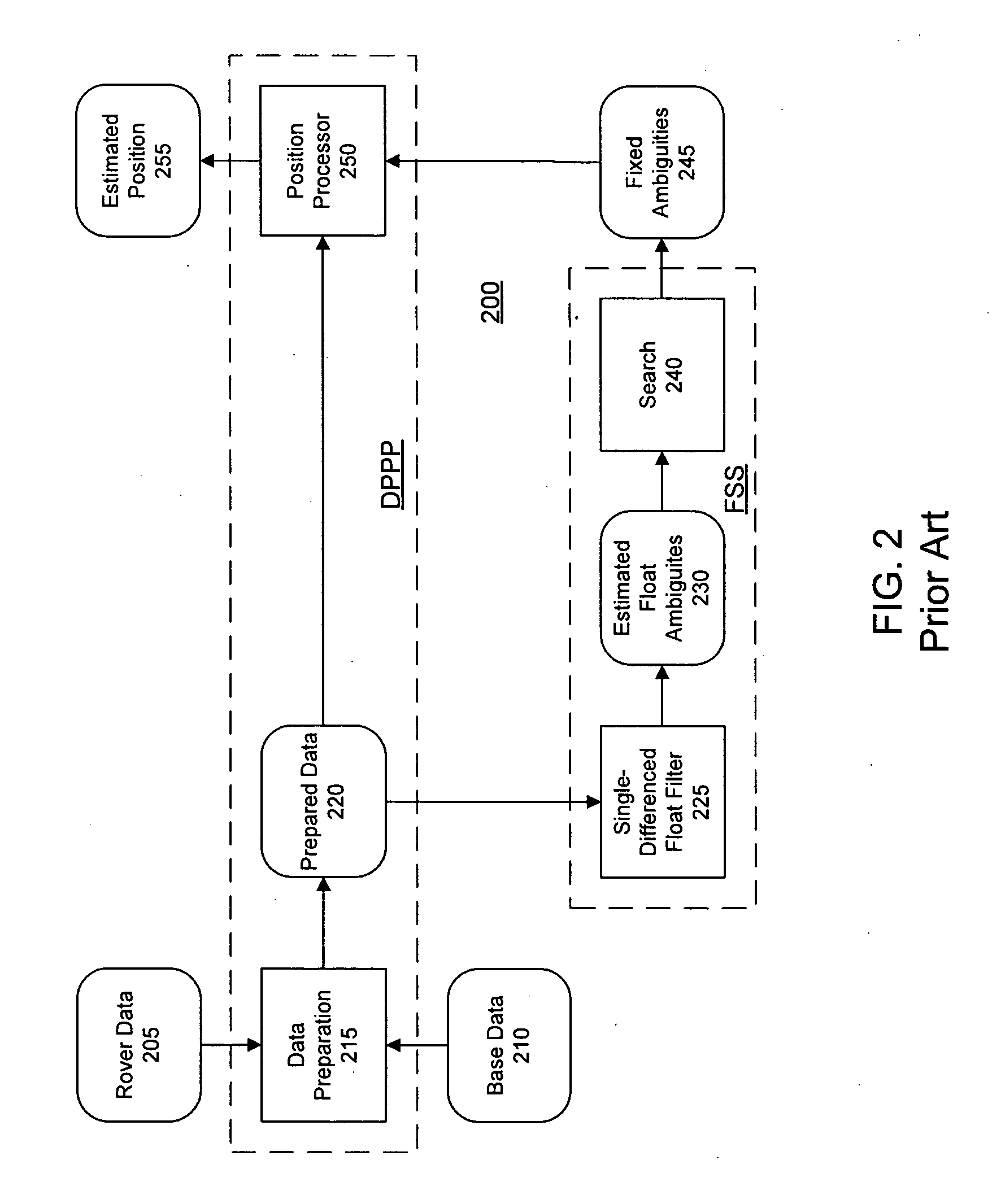
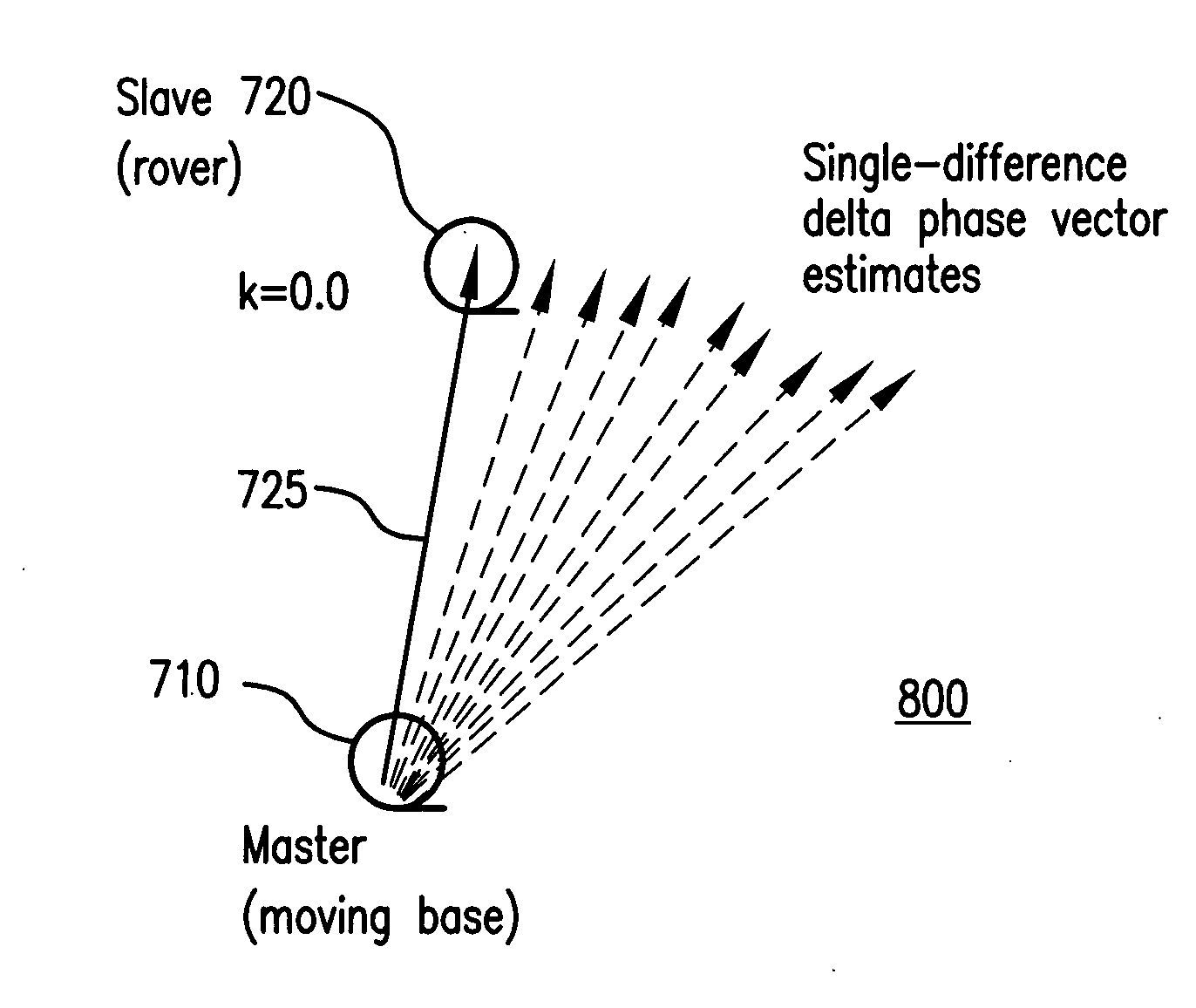
Methods and apparatus are presented for determining a position of an antenna of a GNSS rover from observations of GNSS signals collected at the antenna over multiple epochs and from correction data for at least one of the epochs. A first-epoch rover position relative to a base location is determined for a first epoch using a single-differencing process based on one of (i) fixed carrier-phase ambiguities and (ii) a weighted average of carrier-phase ambiguity candidates which is converged to a predetermined threshold. A second-epoch rover position relative to a base location is determined for a second epoch using a single-differencing process. A second-epoch update of the first-epoch rover position relative to the base location is determined for the second epoch using a single-differenced delta phase process and the first-epoch rover position is combined with the second-epoch update to obtain a second-epoch delta phase rover position relative to a moving base location of the second epoch. The second-epoch delta phase rover position is selected as reliable if the second-epoch rover position is not based on one of (i) fixed carrier-phase ambiguities and (ii) a weighted average of carrier-phase ambiguity candidates which is converged to a predetermined threshold.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
GNSS moving base positioning
Methods and apparatus are presented for determining a position of an antenna of a GNSS rover from observations of GNSS signals collected at the antenna over multiple epochs and from correction data for at least one of the epochs. A first-epoch rover position relative to a moving base location is determined, a second-epoch update of the first-epoch rover position relative to the moving base location for a second epoch is determined using a single-differenced delta phase process, and the first-epoch position and the second-epoch update are combined to obtain a second-epoch rover position relative to a moving base location of the second epoch.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
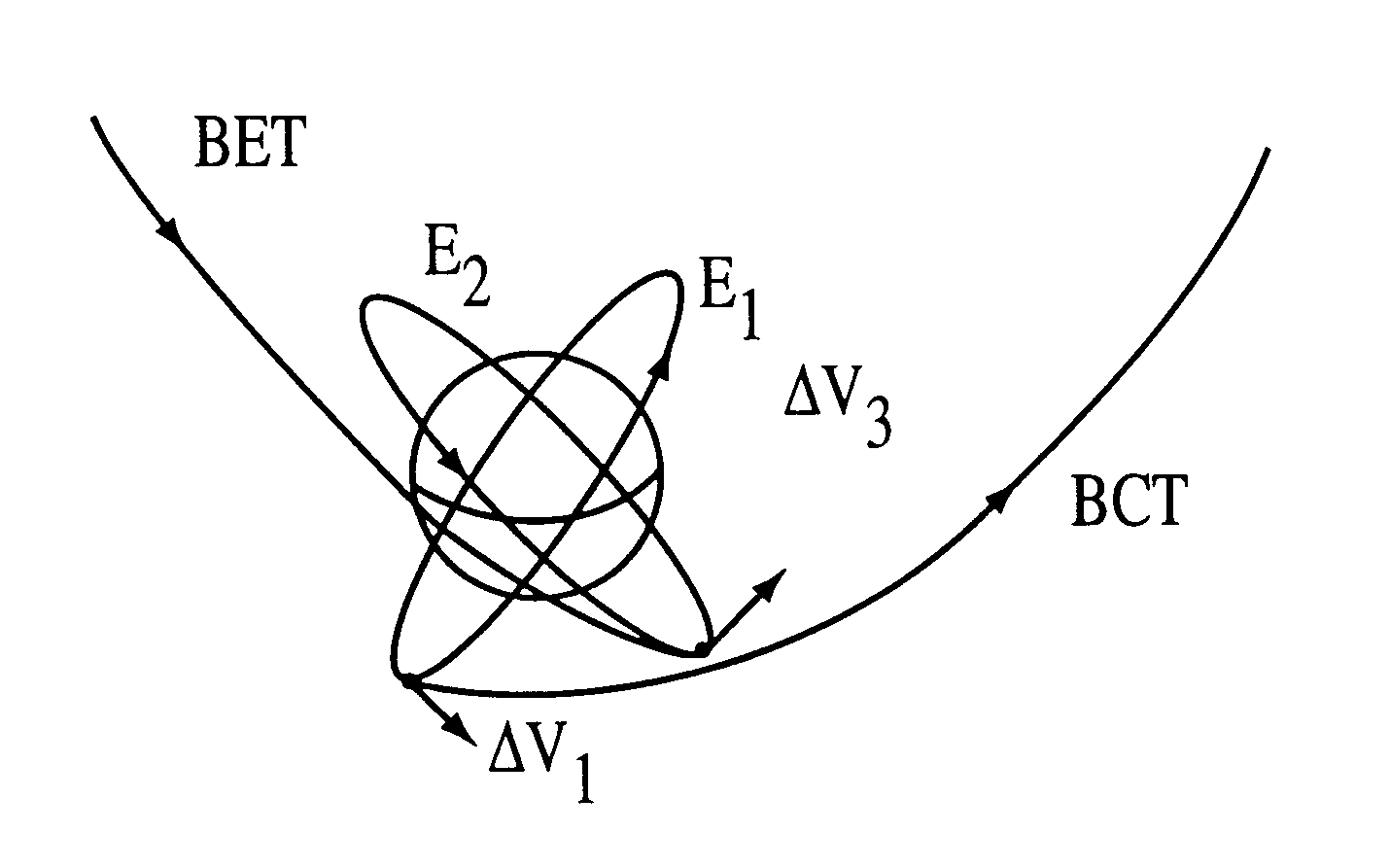
Low energy method for changing the inclinations of orbiting satellites using weak stability boundaries and a computer process for implementing same
InactiveUS6097997ARequirement become largeReduces propellant requirementLaunch systemsInstruments for comonautical navigationEllipseCircular orbit
When a satellite is orbiting the earth in an elliptic orbit, it has a certain inclination with respect to the earth's equator. The usual way to change the inclination is perform a maneuver by firing the rocket engines at the periapsis of the ellipse. This then forces the satellite into the desired inclination. There is a substantially more fuel efficient way to change the inclination. This is done by an indirect route by first doing a maneuver to bring the satellite to the moon on a BCT (Ballistic Capture Transfer). At the moon, the satellite is in the so called fuzzy boundary or weak stability boundary. A negligibly small maneuver can then bring it back to the earth on a reverse BCT to the desired earth inclination. Another maneuver puts it into the new ellipse at the earth. In the case of satellites launched from Vandenberg AFB into LEO in a circular orbit of an altitude of 700 km with an inclination of 34 DEG , approximately 6 km / s is required to change the inclination to 90 DEG . This yields a savings of approximately 13% in Delta-V as compared to the standard approach which could translate into a significant increase of payload or perhaps a smaller launch vehicle. This may have applications to commercial satellite launches for the Iridium or Teledesic networks and others.
Owner:GALAXY DEVMENT
Low energy method for changing the inclinations of orbiting satellites using weak stability boundaries and a computer process for implementing same
InactiveUS6341250B1Velocity becomes largerReduces propellant requirementLaunch systemsInstruments for comonautical navigationDelta-vEllipse
When a satellite is orbiting the earth in an elliptic orbit, it has a certain inclination with respect to the earth's equator. The usual way to change the inclination is perform a maneuver by firing the rocket engines at the periapsis of the ellipse. This then forces the satellite into the desired inclination. There is a substantially more fuel efficient way to change the inclination. This is done by an indirect route by first doing a maneuver to bring the satellite to the moon on a BCT (Ballistic Capture Transfer). At the moon, the satellite is in the so called fuzzy boundary or weak stability boundary. A negligibly small maneuver can then bring it back to the earth on a reverse BCT to the desired earth inclination. Another maneuver puts it into the new ellipse at the earth. In the case of satellites launched from Vandenberg AFB into LEO in a circular orbit of an altitude of 700 km with an inclination of 34°, approximately 6 km / s is required to change the inclination to 90°. This yields a savings of approximately 13% in Delta-V as compared to the standard approach which could translate into a significant increase of payload or perhaps a smaller launch vehicle. This may have applications to commercial satellite launches for the Iridium or Teledesic networks and others.
Owner:GALAXY DEVMENT
Multipurpose pneumatic type launch airborne landing flight training device
The invention provides a multipurpose pneumatic type ejection airborne landing flight training device, and an ejection method is utilized to eject training personnel to a high altitude, the training personnel utilize the airborne landing flight training devices equipped for the training personnel to perform airborne landing or air the training personnel flight training, or the trainers without any device are ejected to safety protection equipment in a fixed-point mode to perform parachuting basic training. The training device comprises a base seat, a pneumatic ejection device, a saddle-shaped ejection seat, an elevation angle adjuster and safe landing protection facilities, wherein the elevation angle adjuster and the ejection device are arranged on the base seat, the ejection seat is arranged on the ejection device, and the safe landing protection facilities are arranged on a landing point. The airborne landing flight training device comprises a parachute, a delta wing aircraft, a wing outfit aircraft, a fixed wing aircraft or other single pawn airborne landing flight devices, when the airborne landing flight training device is used, geographical environment limitation does not exist, parachuting, delta wing flight, wing outfit flight, fixed flight or pneumatic parachute flight motions can be popularized quickly, and meanwhile, the research and development of the sports equipment can further be driven.
Owner:奚金明
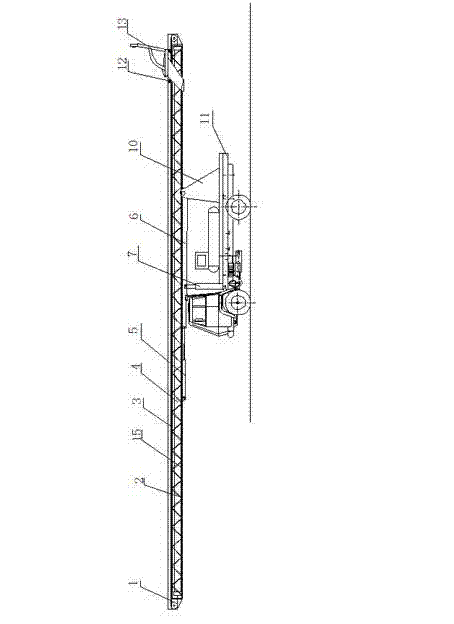
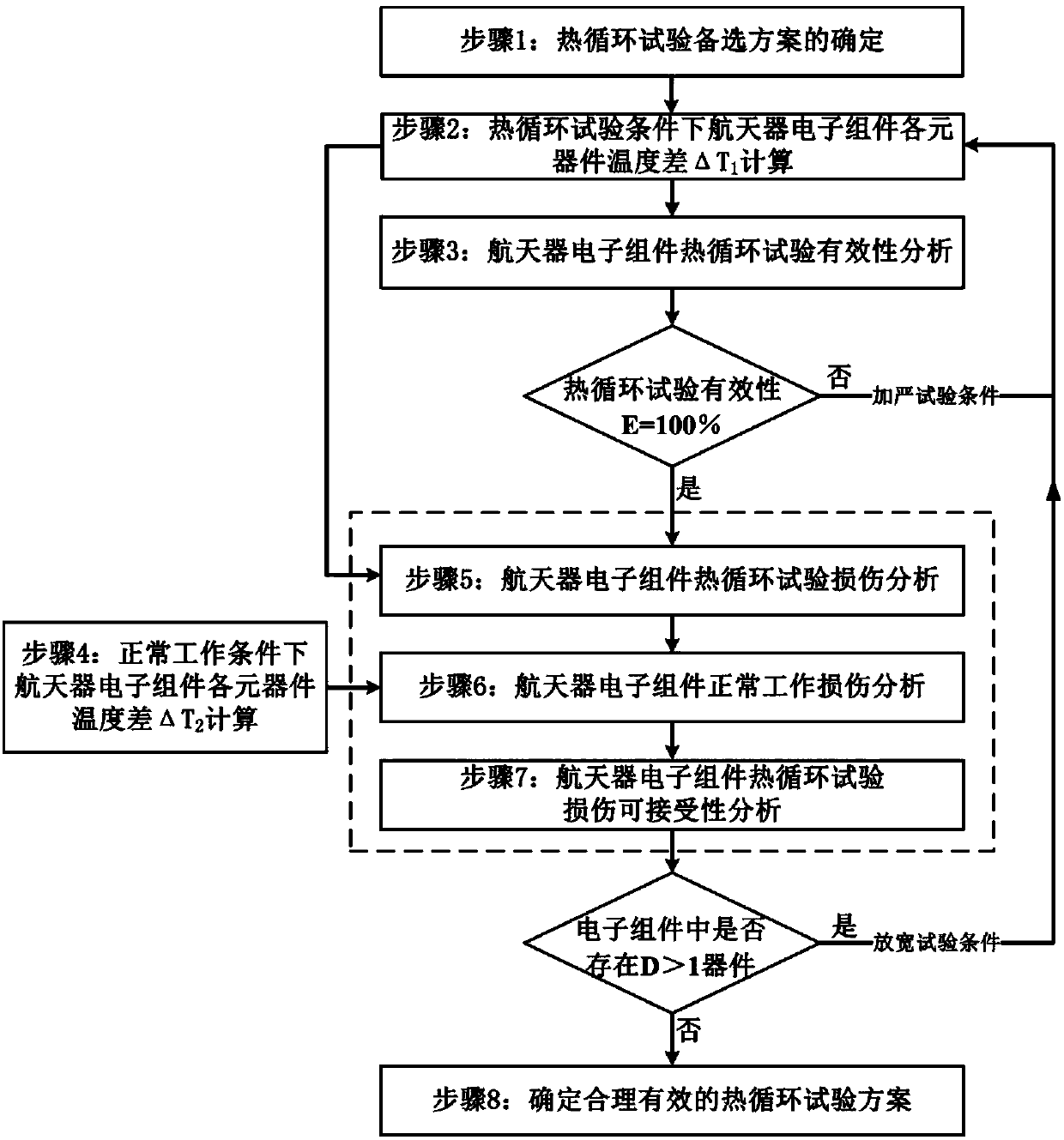
Method for determining spacecraft electronic assembly heat cycle test scheme
InactiveCN104007351AEasy to determineEasy to operateElectrical testingEngineeringTemperature difference
A method for determining a spacecraft electronic assembly heat cycle test scheme comprises the first step of determining a heat cycle test alternative scheme, the second step of calculating the temperature difference delta T1 of all components of a spacecraft electronic assembly under the heat cycle test condition, the third step of analyzing the heat cycle test validity of the spacecraft electronic assembly, the fourth step of calculating the temperature difference delta T2 of all the components of the spacecraft electronic assembly under the normal work condition, the fifth step of analyzing heat cycle test damage of the spacecraft electronic assembly, the sixth step of analyzing normal work damage of the spacecraft electronic assembly, the seventh step of analyzing heat cycle test acceptability of the spacecraft electronic assembly and the eighth step of finally determining the heat cycle test scheme. According to the method, the heat cycle test scheme can be prevented from causing over-tests and under-tests on the spacecraft electronic assembly, and the application risk of the spacecraft electronic assembly in the astronavigation project is lowered.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Spacecraft low-thrust perturbation rendezvous trajectory optimization method and system
ActiveCN112084581AImprove computing efficiencyGeometric CADSustainable transportationClassical mechanicsTrajectory optimization
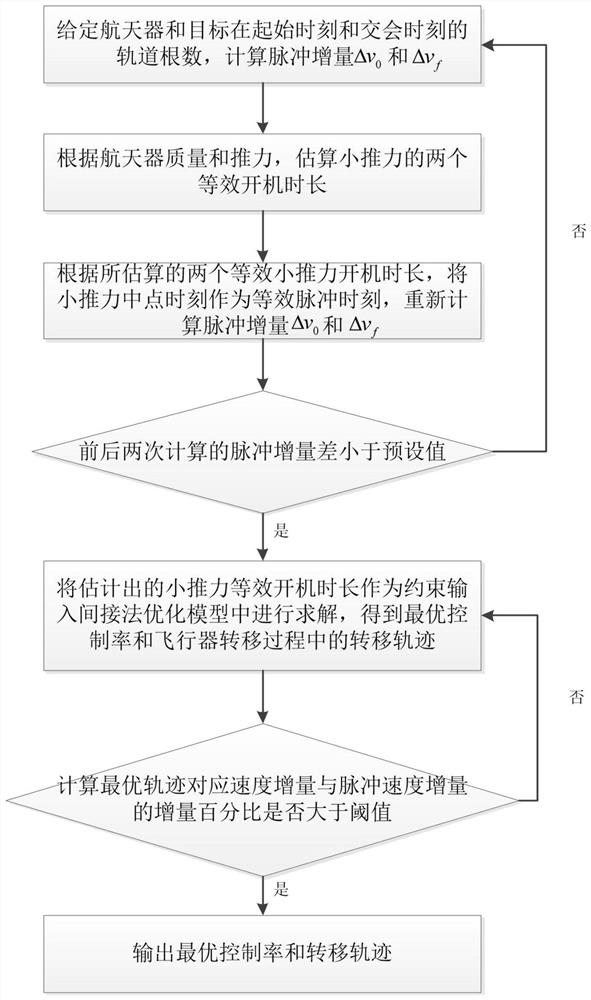
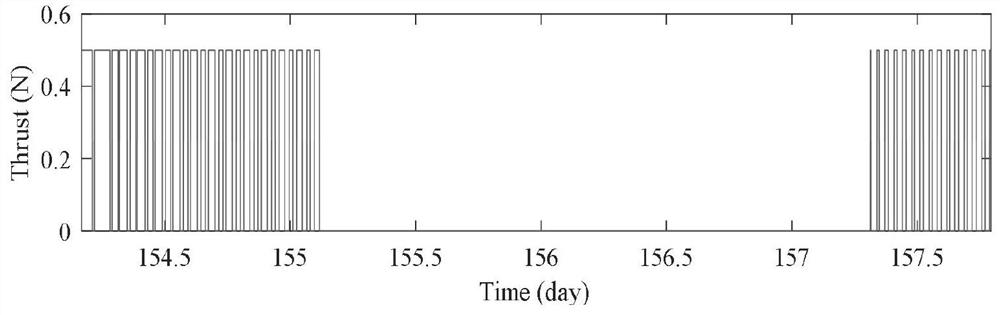
The invention discloses a low-thrust perturbation rendezvous trajectory optimization method and system. The method comprises the steps: giving the number of orbits of a spacecraft and a target at thestart and rendezvous moments, and calculating a four-pulse speed increment; supposing that the low-thrust switching strategy is an on-off-on mode, and estimating two startup durations of low thrust; recalculating a new four-pulse speed increment by taking a small-thrust midpoint moment as an equivalent pulse moment according to the two small-thrust startup durations; until the change of the pulseincrement calculated in the previous and later times is smaller than a preset value, outputting a small-thrust startup time length; inputting the estimated low-thrust startup time length as a constraint into an indirect method optimization model for solving to obtain an optimal control rate, an optimal transfer track and an optimal mass variation; and calculating the increment percentage delta ofthe speed increment and the pulse speed increment corresponding to the optimal control rate, if delta is greater than a threshold value, solving the step 5 again, and if delta is less than the threshold value, outputting the optimal control rate and the transfer track.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
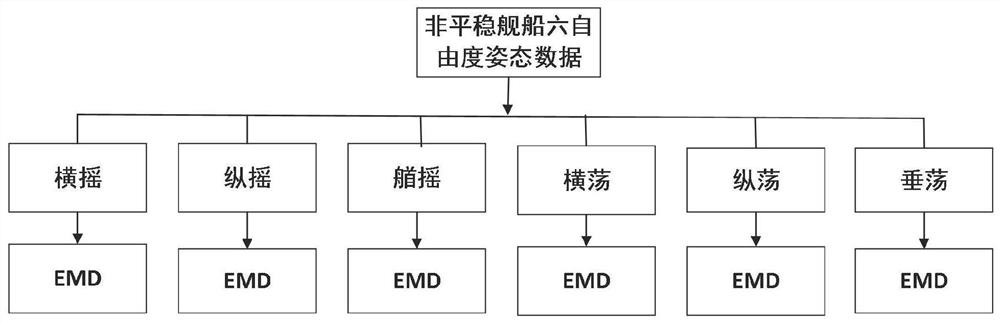
Short-term ship attitude prediction method based on empirical mode decomposition and support vector regression
PendingCN112052623AImprove boundary effectEasy to handleKernel methodsCharacter and pattern recognitionMaritime navigationAlgorithm
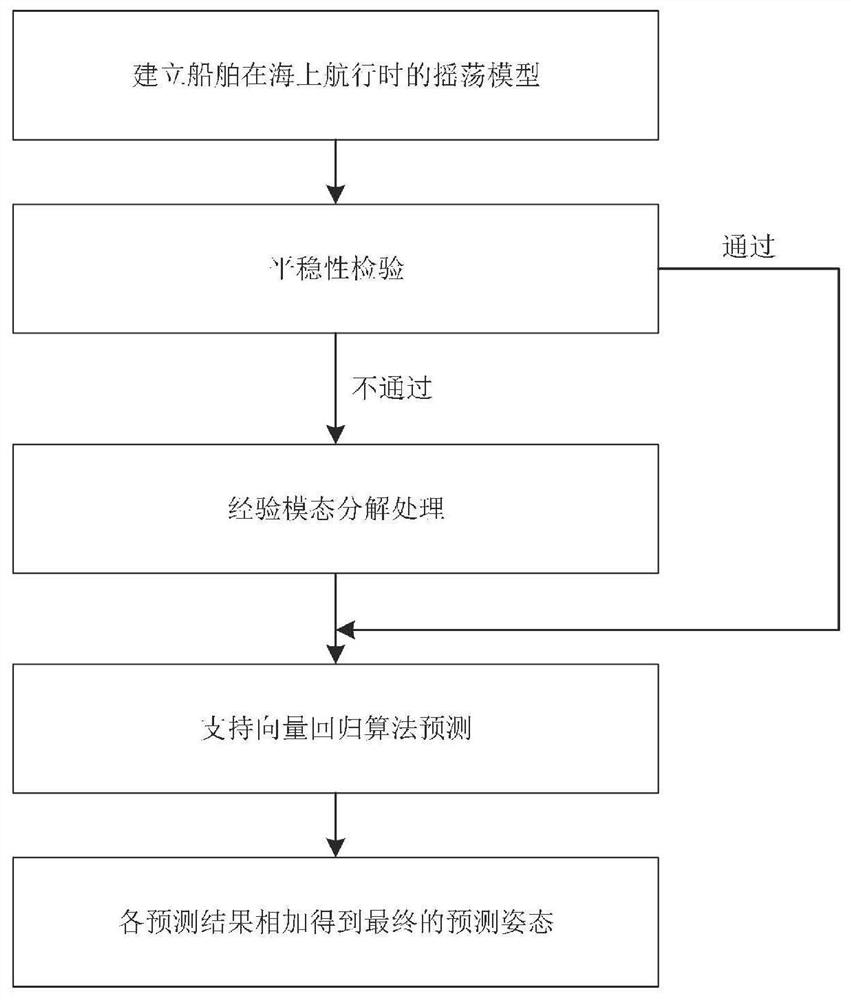
The invention discloses a short-term ship attitude prediction method based on empirical mode decomposition and support vector regression. The method comprises the steps that 1, when guidance instruction calculation is conducted for the first time, a convex optimization planning method is applied to conduct guidance instruction calculation, and a calculation result is stored; 2, after first onlinetrajectory planning is completed, in the same planning period, an online trajectory planning method based on convex optimization and a polynomial guidance method are applied in parallel, and guidanceinstructions uCVX and uIGM are obtained respectively; 3, when uCVX-uIGM is smaller than delta and the polynomial guidance planning precision meets the requirement, a polynomial guidance method is switched for guidance calculation, and otherwise, a guidance instruction calculated by a planning method based on convex optimization is adopted for flight; and 4, after switching to the polynomial guidance calculation guidance instruction, guidance instruction and the shutdown time are directly calculated by applying the polynomial guidance until landing. Through empirical mode decomposition and a support vector regression algorithm, the method can be effectively suitable for ship attitude prediction of marine navigation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
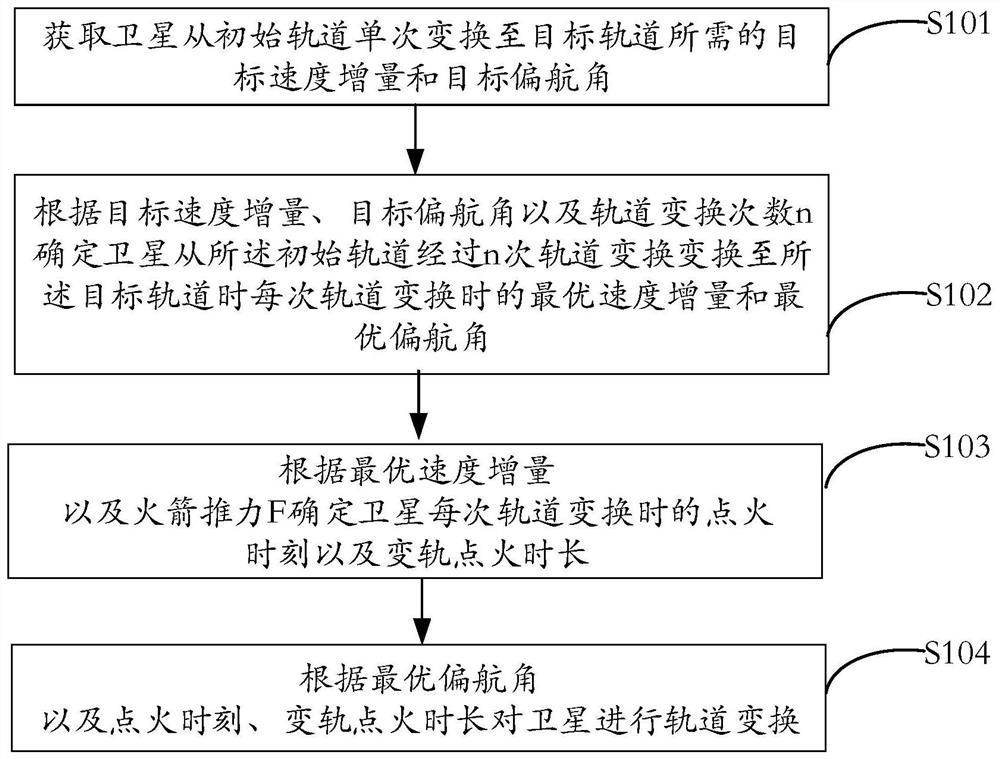
Satellite orbit transformation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113525721ACosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusClassical mechanicsSatellite orbit
The invention provides a satellite orbit transformation method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium, relates to the field of aerospace, and can solve the problems that the satellite orbit transformation method is relatively complex and low in solving efficiency. According to the satellite orbit transformation method, the method comprises the steps of obtaining a target speed increment and a target yaw angle required by a satellite for single transformation from an initial orbit to a target orbit; according to the target speed increment, the target yaw angle and the orbital transformation frequency n, determining the optimal speed increment delta vi and the optimal yaw angle beta i of the satellite in each orbital transformation from the initial orbit to the target orbit through n times of orbital transformation, n is an integer larger than 1, and i is an integer larger than 0 and smaller than or equal to n; according to the delta vi and the rocket thrust F, determining the ignition moment tidev and the orbital transfer ignition duration delta ti of the satellite during orbital transfer each time; and performing orbit transformation on the satellite according to the beta i, the tidev and the delta ti. According to the method, the satellite orbit transformation strategy can be obtained through optimization and accurate calculation, and the solving efficiency is improved.
Owner:陕西星邑空间技术有限公司
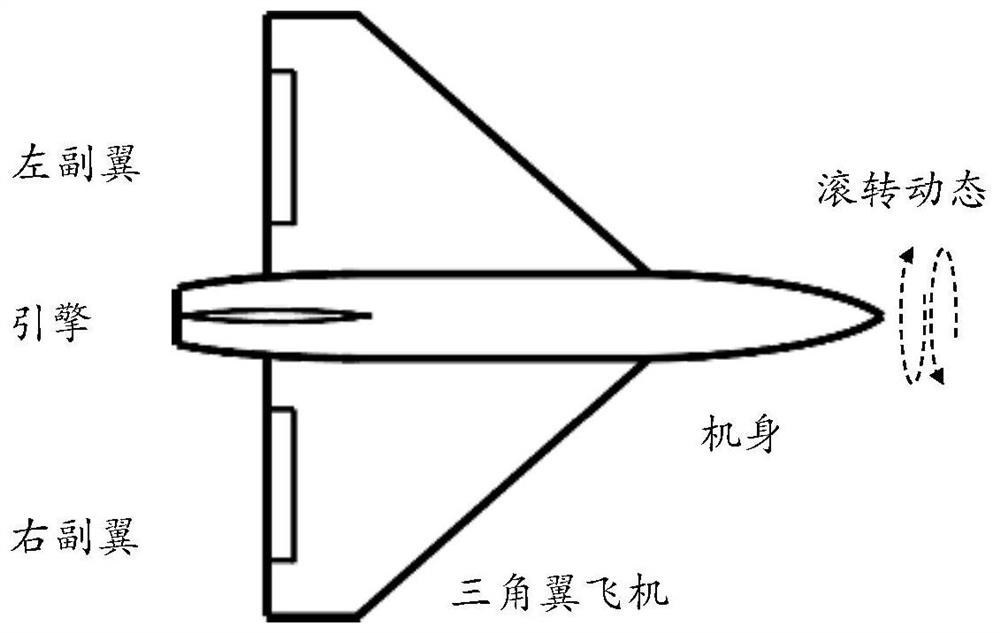
Nonlinear system output feedback self-adaptive control system and method adopting HOSM observer
The embodiment of the invention provides a nonlinear system output feedback self-adaptive control system and method adopting an HOSM observer, which relate to the technical field of self-adaptive control. For a single-input single-output uncertain nonlinear system with actuator limitation, particularly under the condition of control gain uncertainty and actuator speed limitation, the characteristics of an HOSM observer are utilized, and the unmeasured state of the system can be accurately estimated under the condition that only the output quantity of the observed system is needed. The design of the relatively independent observer enables the design of the controller to be easier, and when the method is applied to the rolling dynamic control of the delta wing aircraft, the self-adaptive adjustment capability of the delta wing aircraft to the external environment and the robustness of the self-adaptive control system are also improved.
Owner:中国空气动力研究与发展中心设备设计与测试技术研究所
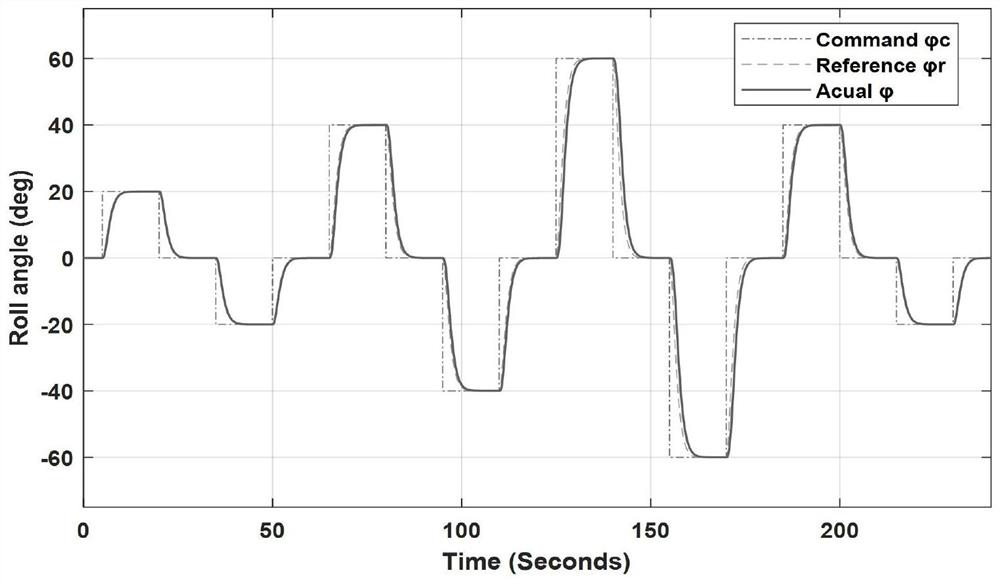
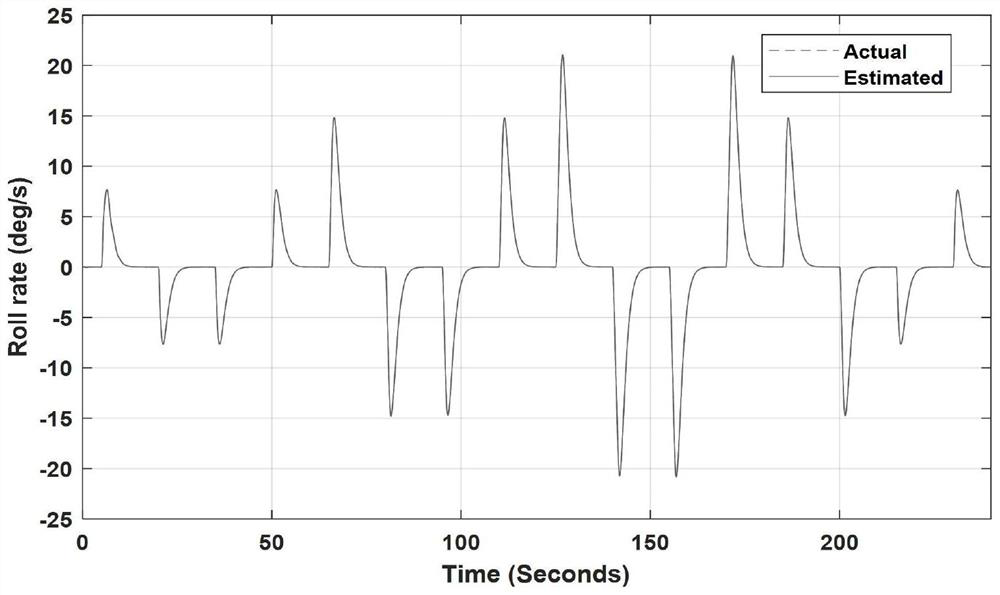
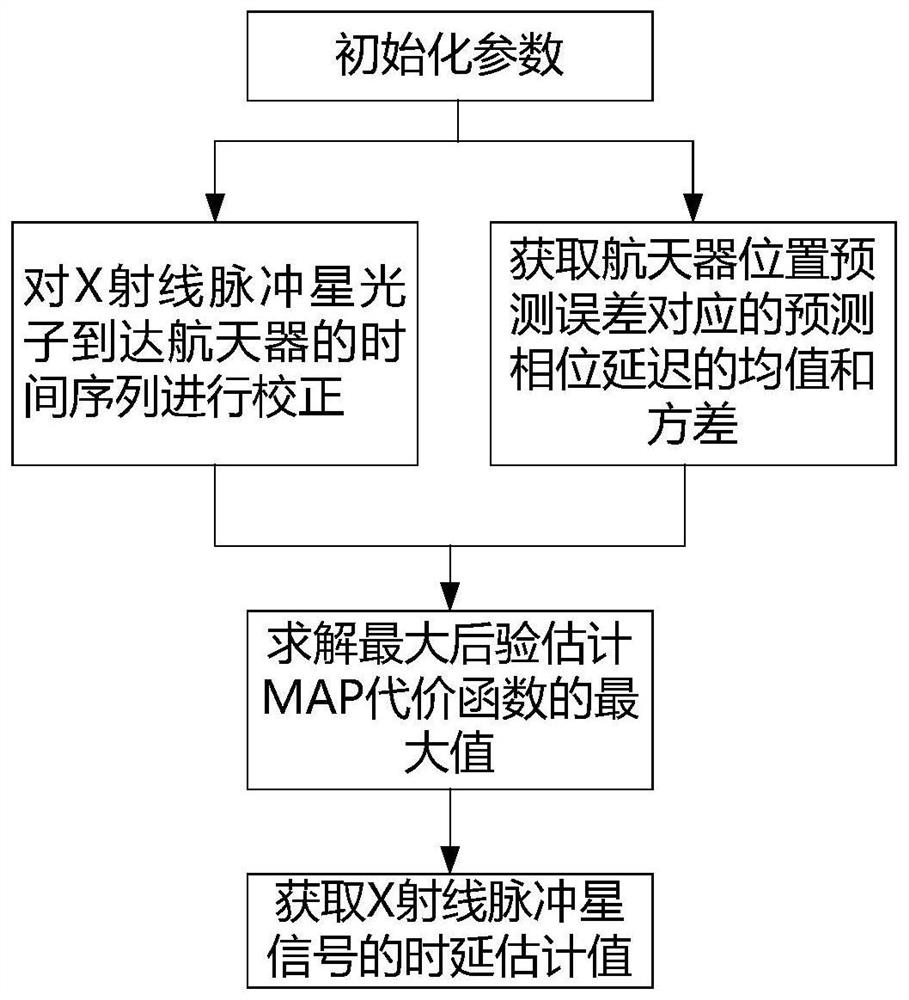
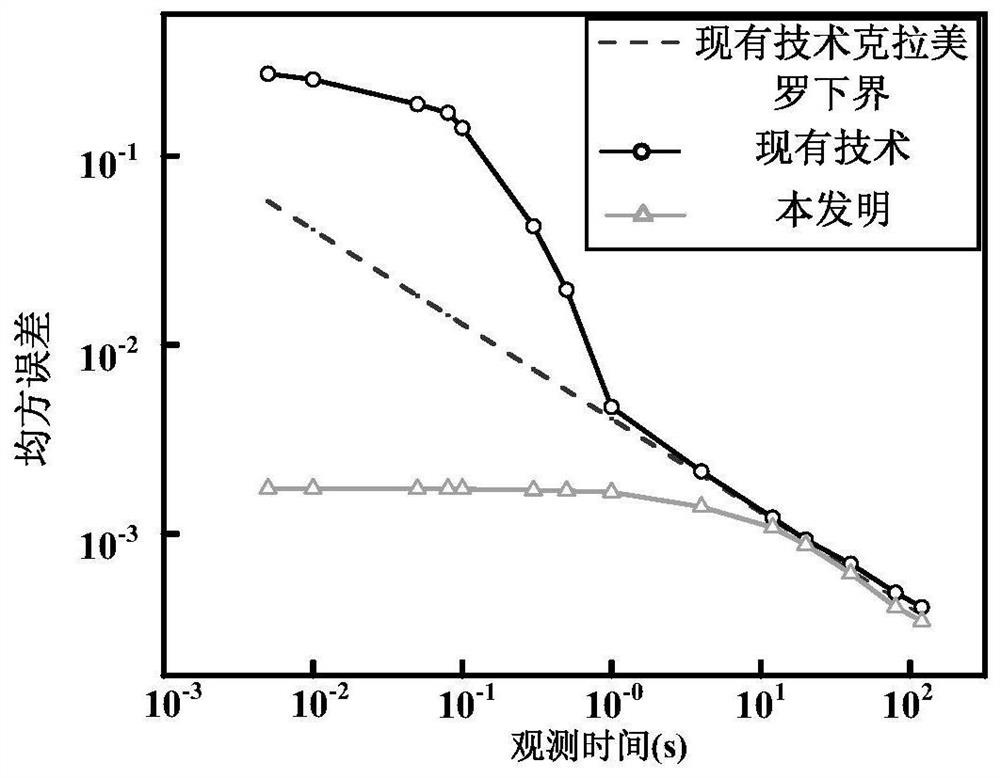
X-ray pulsar signal time delay estimation method based on maximum posteriori estimation
ActiveCN113375697AAvoid the impact of estimation accuracyHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationPulsarTime delays
The invention provides an X-ray pulsar signal time delay estimation method based on maximum posteriori estimation. The method comprises the following implementation steps: (1) initializing parameters; (2) correcting the time sequence of the X-ray pulsar photons reaching the spacecraft; (3) obtaining a mean value and a variance of prediction phase delay corresponding to a spacecraft position prediction error delta r; (4) solving a maximum value of a maximum posteriori estimation MAP cost function; and (5) obtaining the time delay estimation value of the X-ray pulsar signal. The maximum value of the maximum posteriori estimation MAP cost function is solved through the corrected time sequence and the mean value and variance of the prediction phase delay corresponding to the spacecraft position prediction error, and the time delay estimation value of the X-ray pulsar signal is obtained through the maximum value of the maximum posteriori estimation MAP cost function and the rotation frequency of the X-ray pulsar, so that the influence on the estimation precision due to the fact that only the photon arrival time sequence is considered and the spacecraft position prediction error is not considered in the prior art is avoided, and the time delay estimation precision is improved under the same observation time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Precise low-latency GNSS satellite clock estimation
A wide-lane ambiguity and a respective satellite wide-lane bias are determined for the collected phase measurements for each satellite (S804) for assistance in narrow-lane ambiguity resolution. Satellite correction data is determined for each satellite in an orbit solution based on the collected raw phase and code measurements and determined orbital narrow-lane ambiguity and respective orbital satellite narrow-lane bias (S808). A slow satellite clock correction is determined based on the satellite orbital correction data, the collected raw phase and code measurements, and clock narrow-lane ambiguity and respective satellite narrow-lane bias (S812). A low latency clock module or data processor determines lower-latency satellite clock correction data or delta clock adjustment to the slow satellite clock based on freshly or recently updated measurements of the collected raw phase measurements that are more current than a plurality of previous measurements of the collected raw phase measurements used for the slow satellite clock correction to provide lower-latency clock correction data (S814).
Owner:DEERE & CO
Aircraft rapid trajectory optimization method meeting strict time and position constraints
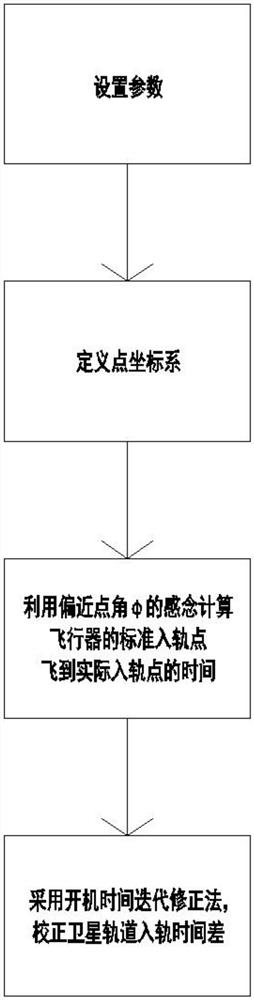
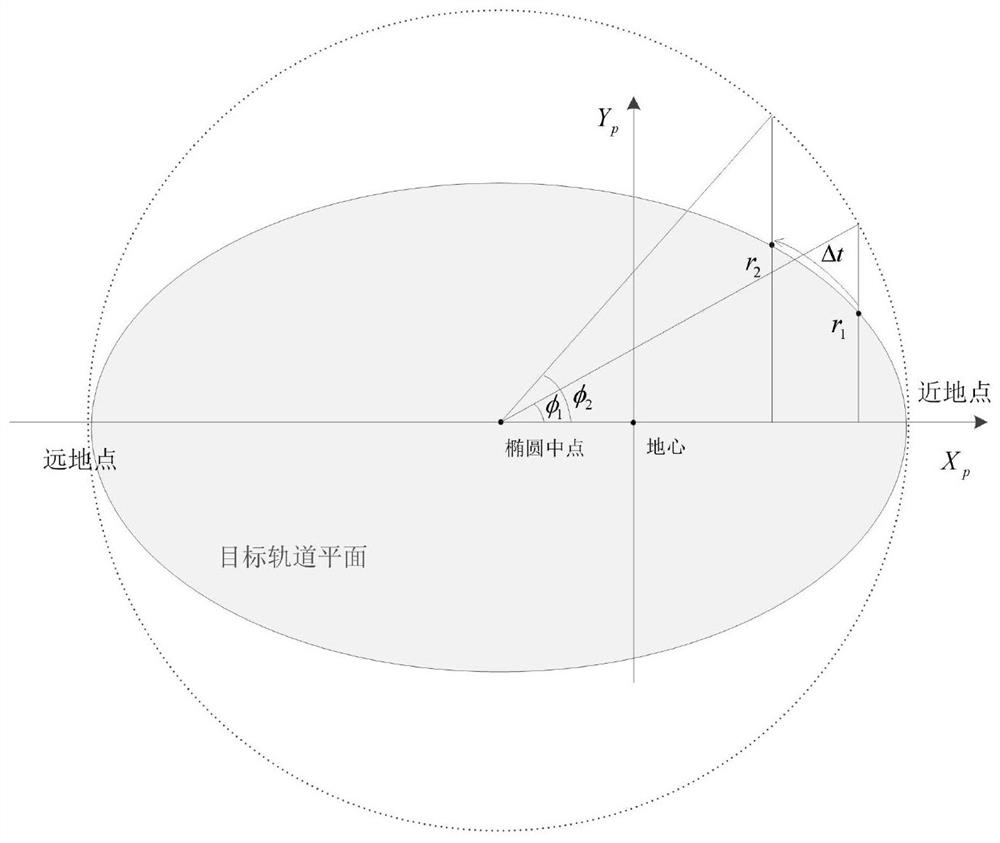
ActiveCN112486196AGuaranteed Constraint AccuracyGuaranteed timing and fixed-point entry into orbitAttitude controlFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
The invention discloses an aircraft rapid trajectory optimization method meeting strict time and position constraints. The aircraft rapid trajectory optimization method comprises the steps of: step 1,setting parameters, wherein the parameters in a quasi-state comprise that the load is injected into a track at time t1, and a standard injection point is r1; supposing that through track online replanning and self-adaptive guidance, the load is injected into the track at time t2, and an actual injection point is r2; step 2, defining a point coordinate system, wherein an origin OP of the coordinate system is the geocenter, and an xp axis is on a connecting line of the geocenter and a target track perigee and points to the perigee; step 3, based on the parameters and the point coordinate systems in the step 1 and the step 2, calculating time delta t of an aircraft flying from r1 to r2 by utilizing the concept of an approximate point angle phi; and step 4, correcting the orbit injection timedeviation of a satellite by using the steps 1-3 and a core secondary secondary startup time iterative correction method. The problems that the thrust of a high-thrust liquid rocket engine applied toa carrier rocket cannot be adjusted, the orbit injection point cannot be accurately controlled, and in other words, the orbit injection position cannot be restrained are solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
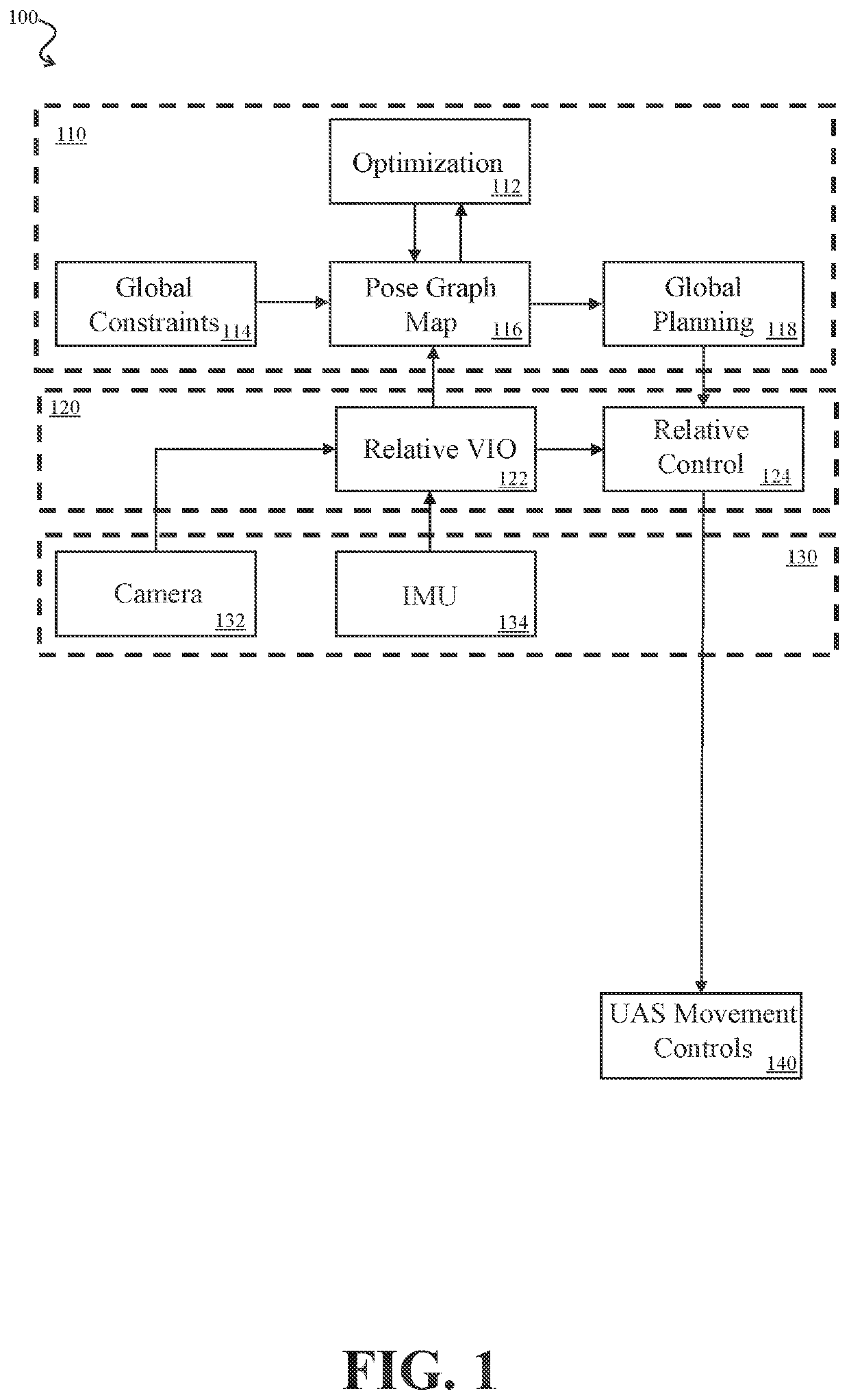
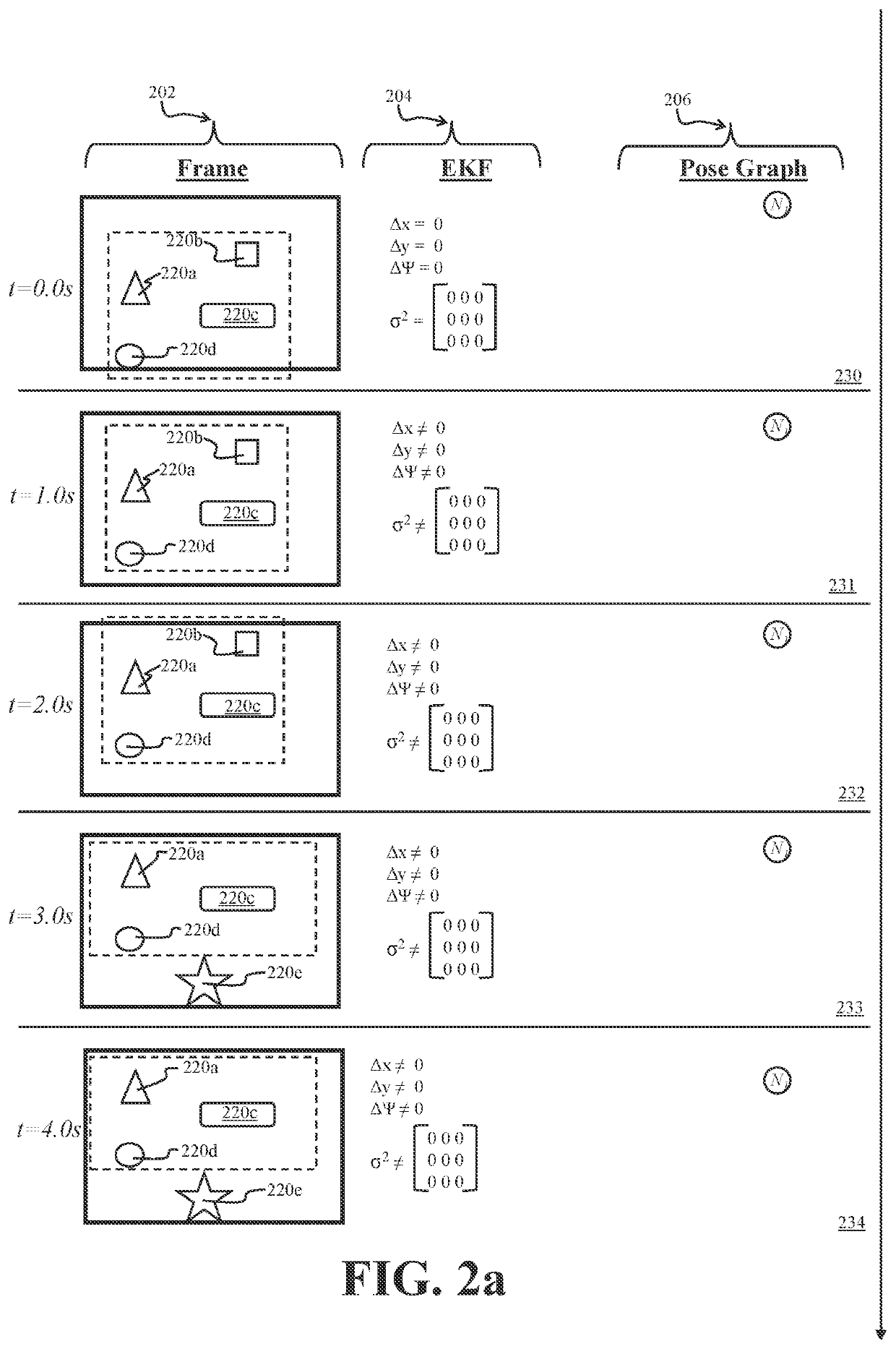
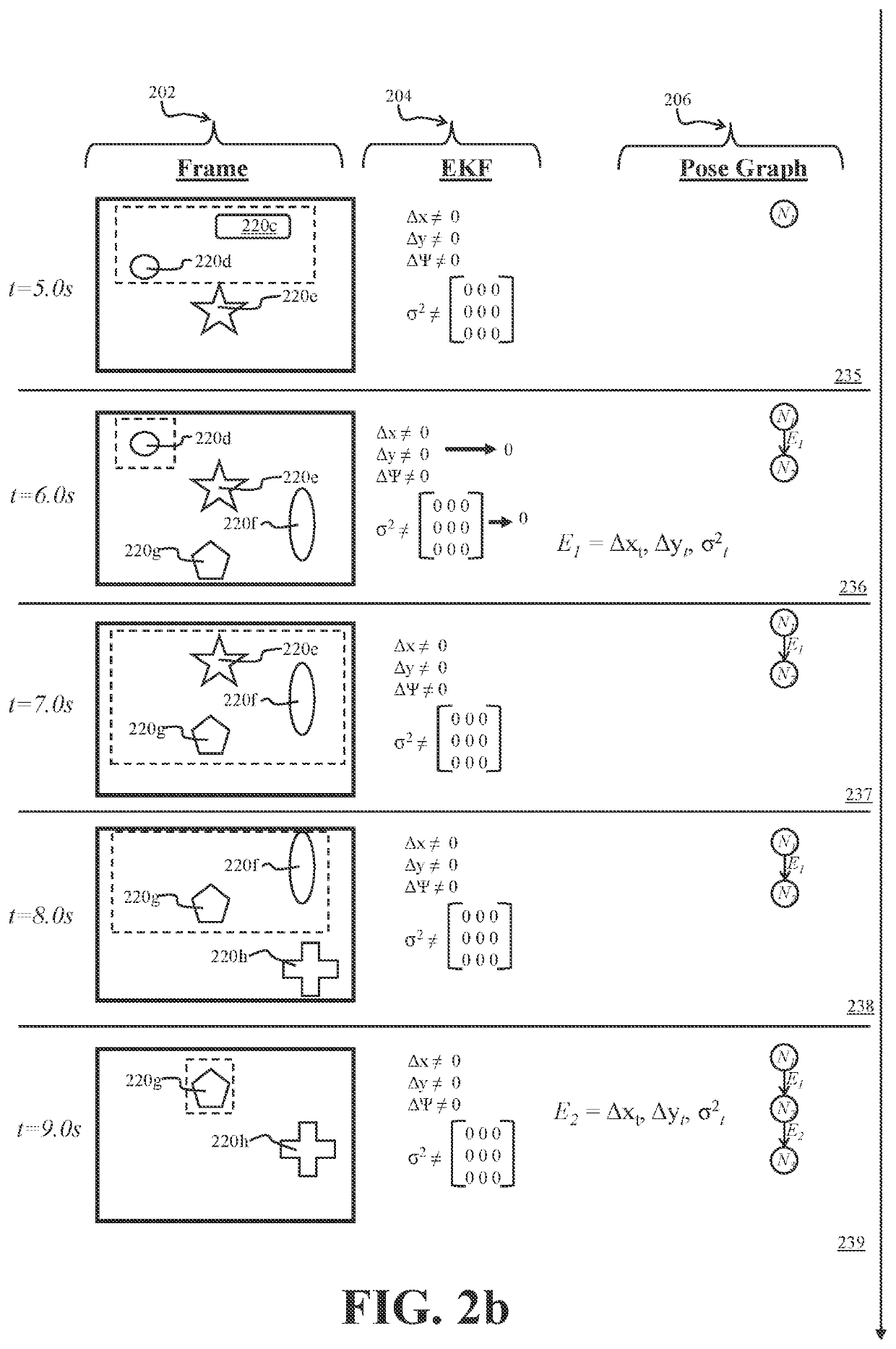
Cooperative Aircraft Navigation
A UAS may use camera-captured ground feature data to iteratively estimate pose change through a Kalman filter. To avoid excessive drift, the UAS may periodically perform a reset by publishing delta pose and covariance as an edge in a global pose graph, by zeroing out the delta pose and covariance. To further improve global pose estimation, two UASs may share range information and associated pose graph information, thereby providing an additional constraint for each UAS to use in its pose graph optimization.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
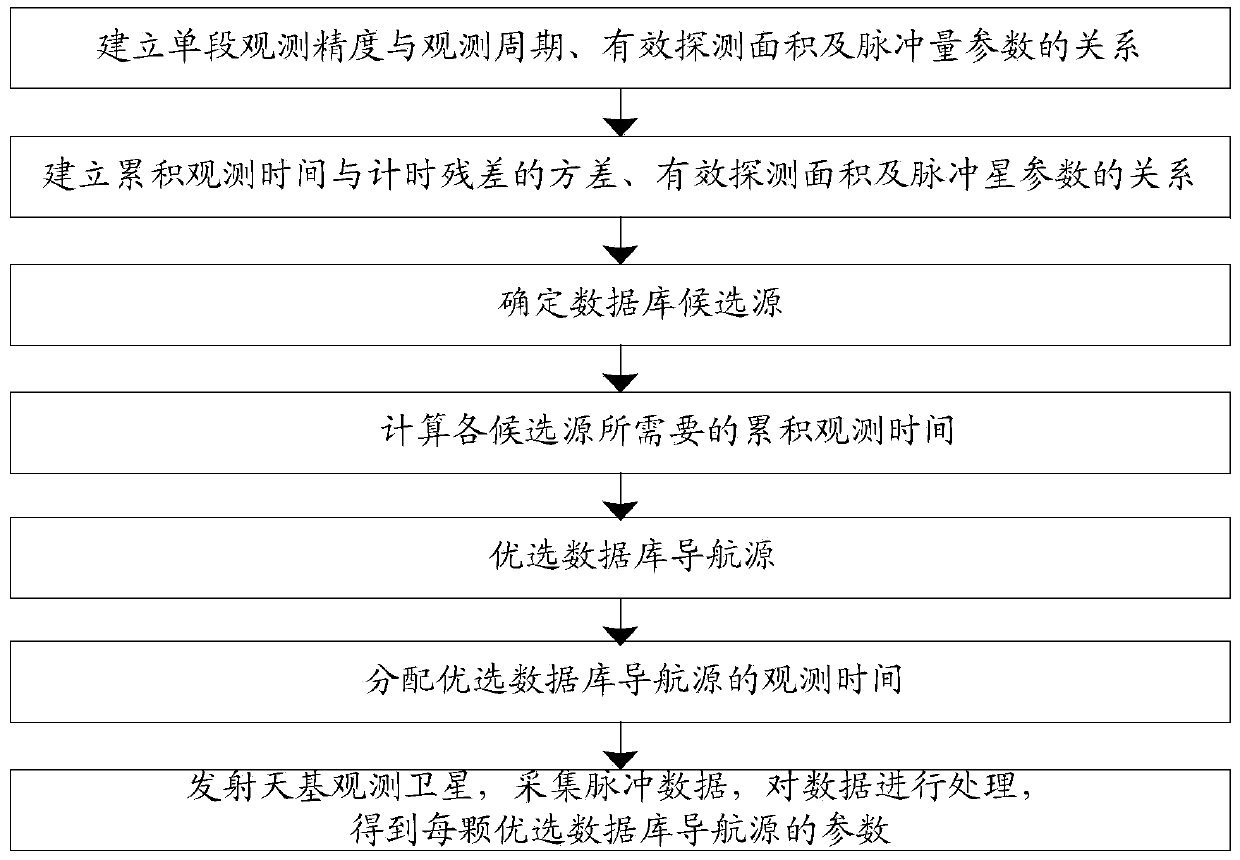
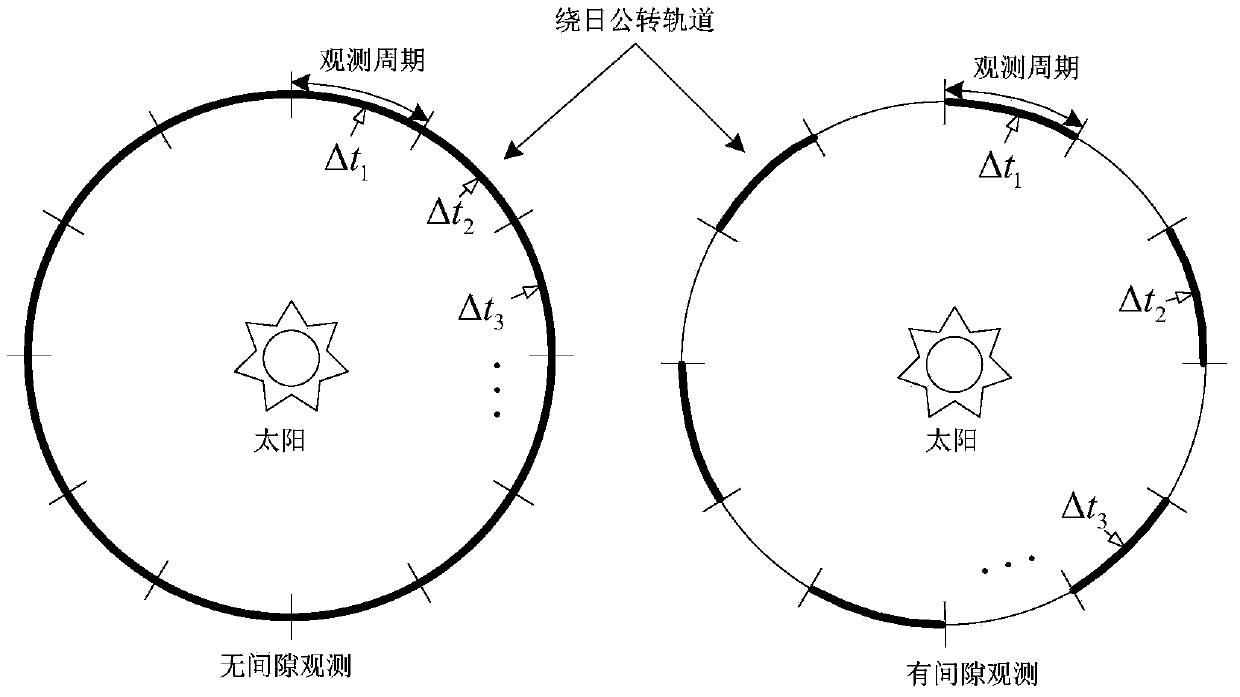
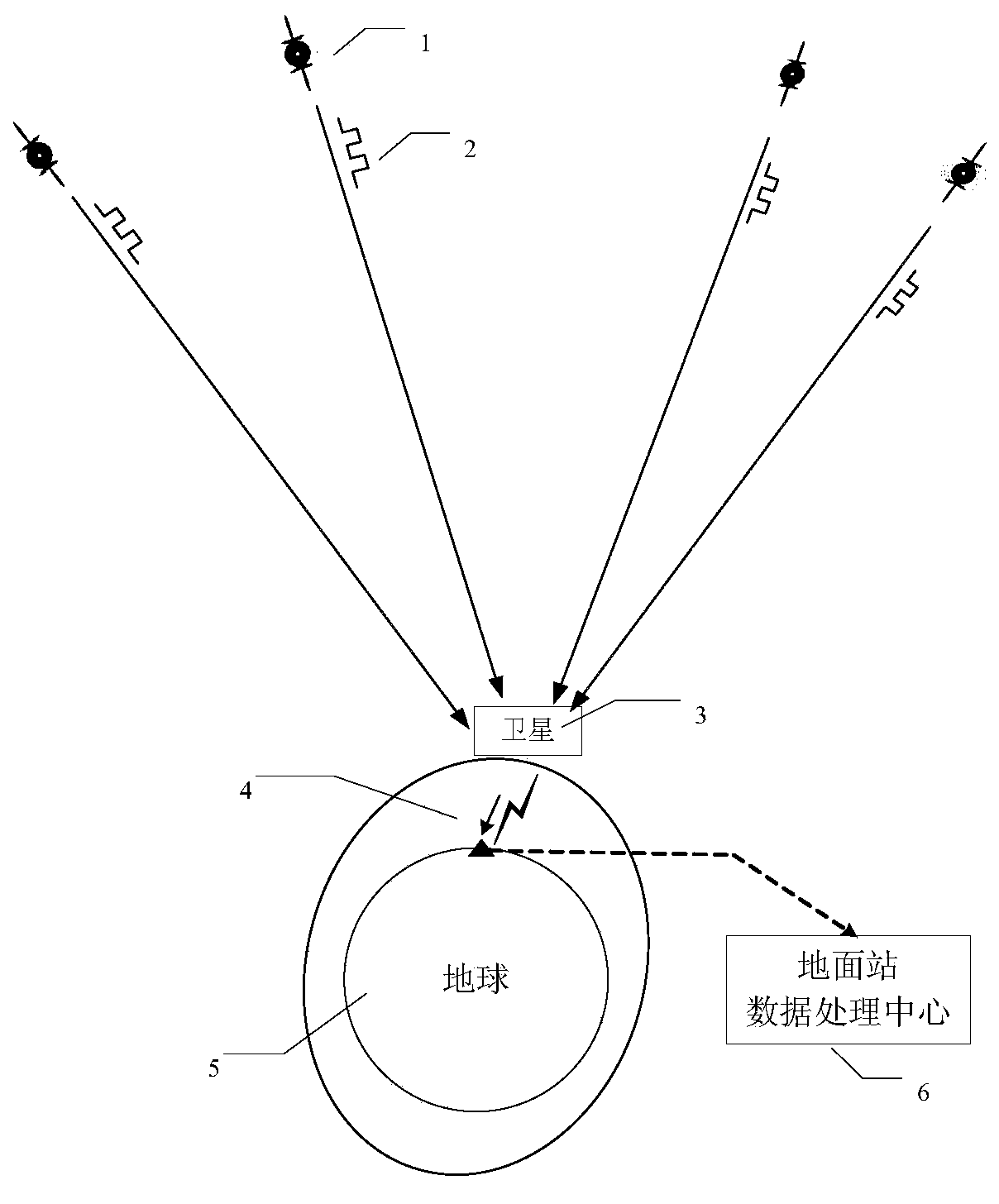
Method for building space-based pulsar navigation database
InactiveCN103471585ARealize high-precision measurementIncrease the lengthNavigation by astronomical meansSpecial data processing applicationsObservation dataData mining
The invention discloses a method for building a space-based pulsar navigation database. The method comprises the following steps: (1) building a relation among one-section observation precision, observation cycle, effective detection areas and pulsar parameters; (2) building a relation among accumulated observation time, variances of timing residual errors, the effective detection areas and the pulsar parameters; (3) selecting database candidate sources; (4) calculating the accumulated observation time required by the candidate sources in the different effective detection areas within the given var (delta t); (5) selecting optimal database navigation sources; (6) selecting the effective detection areas and distributing the observation time of the optimal database navigation sources; (7) launching a space-based observation satellite which runs around the earth and is used for observing the different optimal database navigation sources according to the distributed observation time and downloading observation data to the ground; (8) fitting the downloaded data to obtain the parameters of each optimal database navigation source, which are mainly used for pulsar navigation calculation of a spacecraft.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
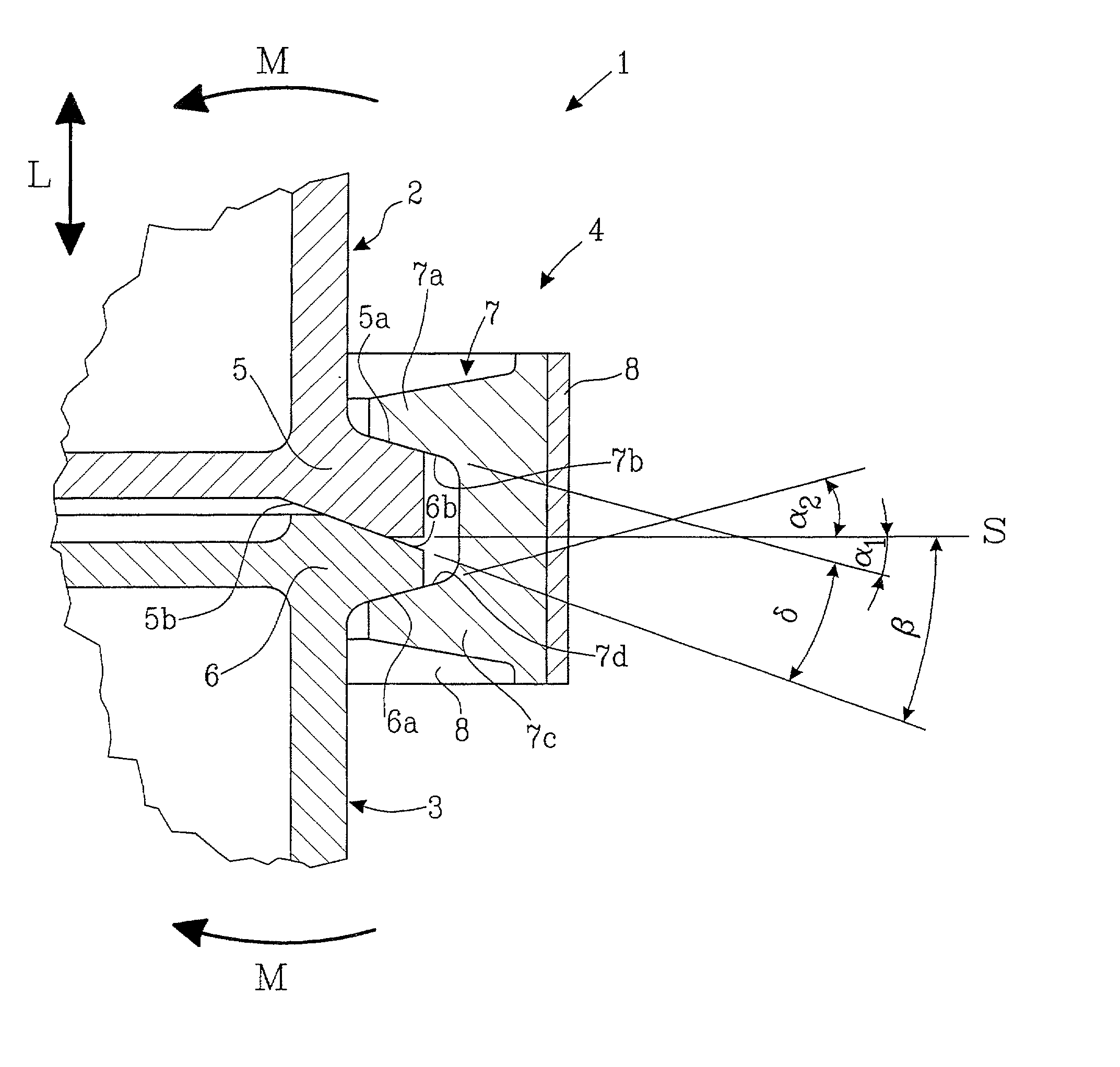
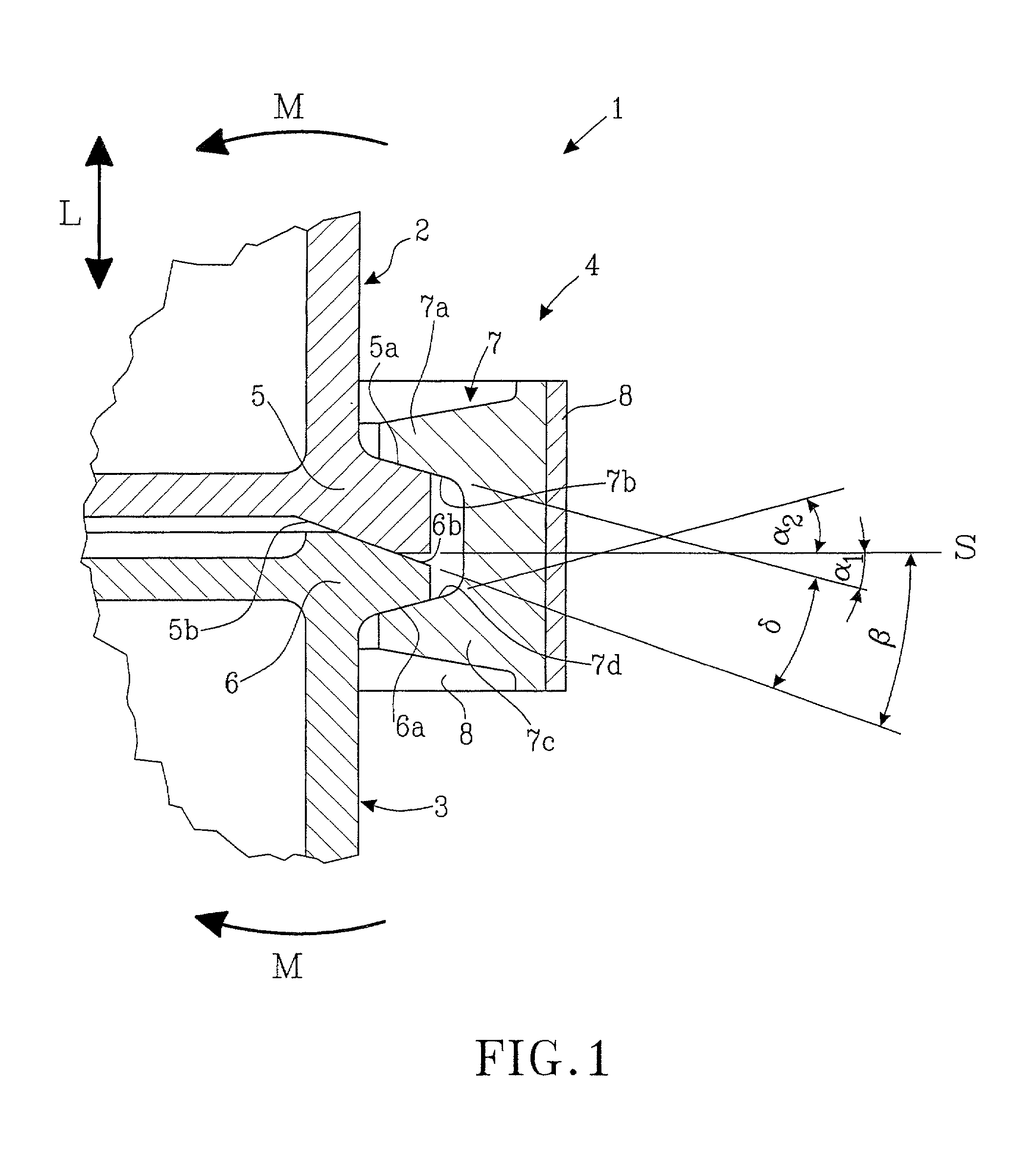
Joint on a spacecraft
A joint (4) on a spacecraft (1) for holding together a first craft part (2) and a second craft part, (3) detachable from the first craft part (2). The joint (4) comprises a first flange (5) fixed on the first craft part (2), and a second flange (6) fixed on the second craft part (3), and a number of clamps (7) having a first (7a) and a second (7c) clamp lip, the said clamps being distributed about the periphery of the flanges (5, 6). The clamps transfer radial forces from a tightening device (8), fitted to the clamps (7), so as to fasten the two flanges (5, 6) together. The first flange (5) is clamped between a first clamp surface (7b) on the first clamp lip (7a), and a separation surface (6b) on the second flange (6). These surfaces (7b, 6b) form an acute angle delta, the apex of which is directed in towards the spacecraft (1).
Owner:SAAB ERICSON SPACE
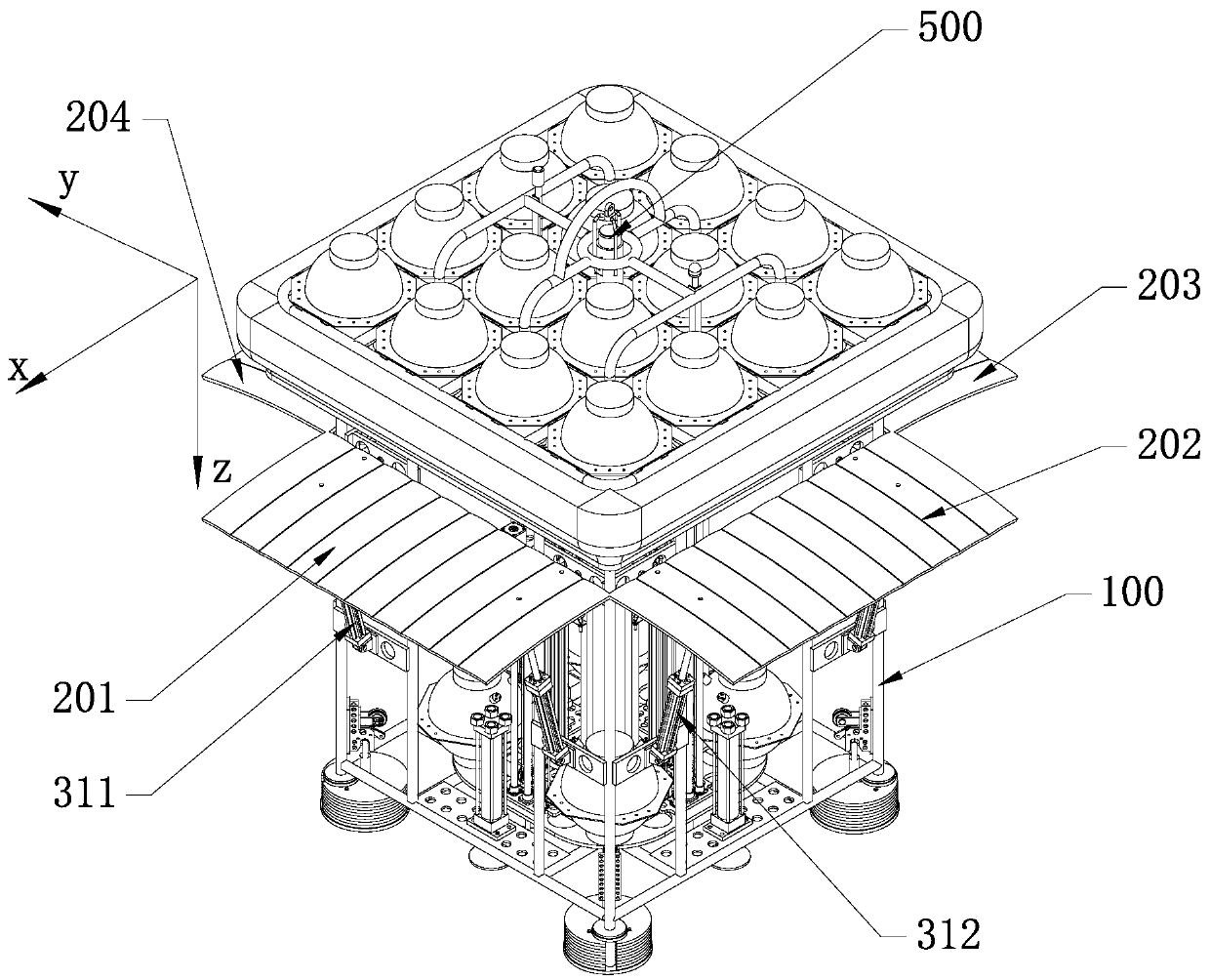
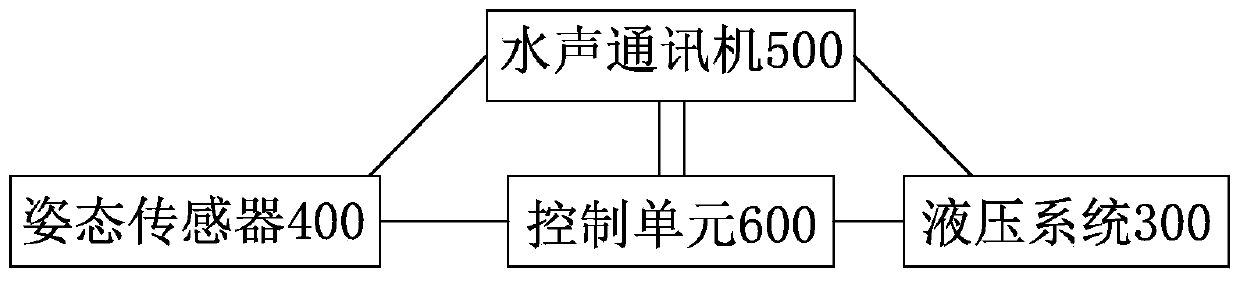
Control device and method for landing point area and speed of deep sea lander
PendingCN110844028AReduce disturbanceReduce shockUnderwater equipmentAltitude or depth controlControl cellMachine
The invention discloses a control device and method for the landing point area and the speed of a deep-sea lander. The device comprises a carrying platform, wing plates, a hydraulic system, an attitude sensor, an underwater sound communication machine and a control unit. The method comprises the steps of first, building a fixed coordinate system O2-xyz; second, building a follow-up coordinate system O1-xyz on the carrying platform; third, calculating a coordinate value of the center of the carrying platform in the fixed coordinate system; fourth, calculating a coordinate value of the central point of the landing area in the follow-up coordinate system, and marking the direction nt of a connection line from the central point of the landing area to the central point of the carrying platform;and fifth, enabling the direction of the resultant force of the thrust of one wing plate and the thrust of the other wing plate to be the same as the direction nt. According to the control device andmethod for the landing point area and the speed of the deep-sea lander, after the lander is affected by sea current in the diving process, adjustment can be carried out with the control method to make the lander get close to a target area continuously, the accuracy and energy consumption of landing can be adjusted by changing the control interval time delta t, and it is guaranteed that the landing point is within the expected detection area range.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
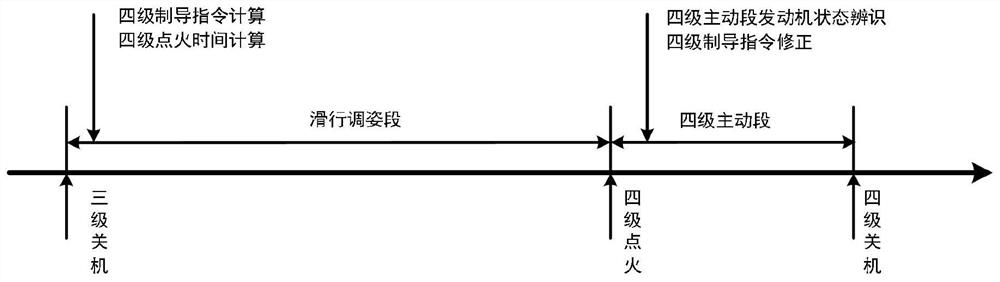
Solid carrier rocket injection correction method
ActiveCN113602532AEliminate energy biasOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to shut down precisely like a liquid engineCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusClassical mechanicsControl theory
The invention discloses a solid carrier rocket injection correction method which comprises the following steps: when a three-stage engine is shut down, acquiring the speed position state quantity of the rocket body; determining a sliding attitude instruction and fourth-stage ignition time according to the speed position state quantity and the orbit parameter information; adjusting the attitude of the rocket according to the sliding attitude instruction in the sliding attitude adjusting section until the rocket is adjusted to the four-stage fixed-axis attitude; when the fourth-stage ignition time is up, sending out a fourth-stage ignition instruction so that the rocket enters a fourth-stage active section; calculating the number of predicted injection orbits in the whole process of the four-stage active section at intervals of delta t4 according to an inner ballistic curve of an engine and engine state parameters; calculating to obtain a compensation value of the four-stage attitude angle instruction by predicting the number of injection orbits and the number of target orbits; and updating the fourth-stage attitude angle instruction according to the compensation value until the fourth-stage engine is used up and shut down. According to the method, the solid rocket engine is accurately shut down, and the injection cost is reduced due to the fact that the thrust terminating device does not need to be arranged.
Owner:BEIJING ONESPACE TECH CO LTD +4
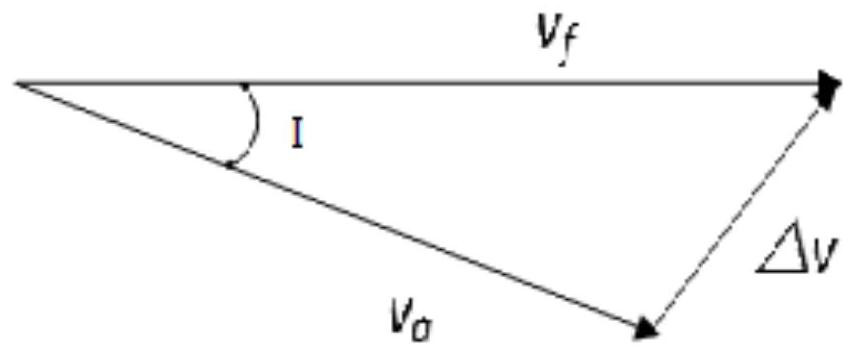
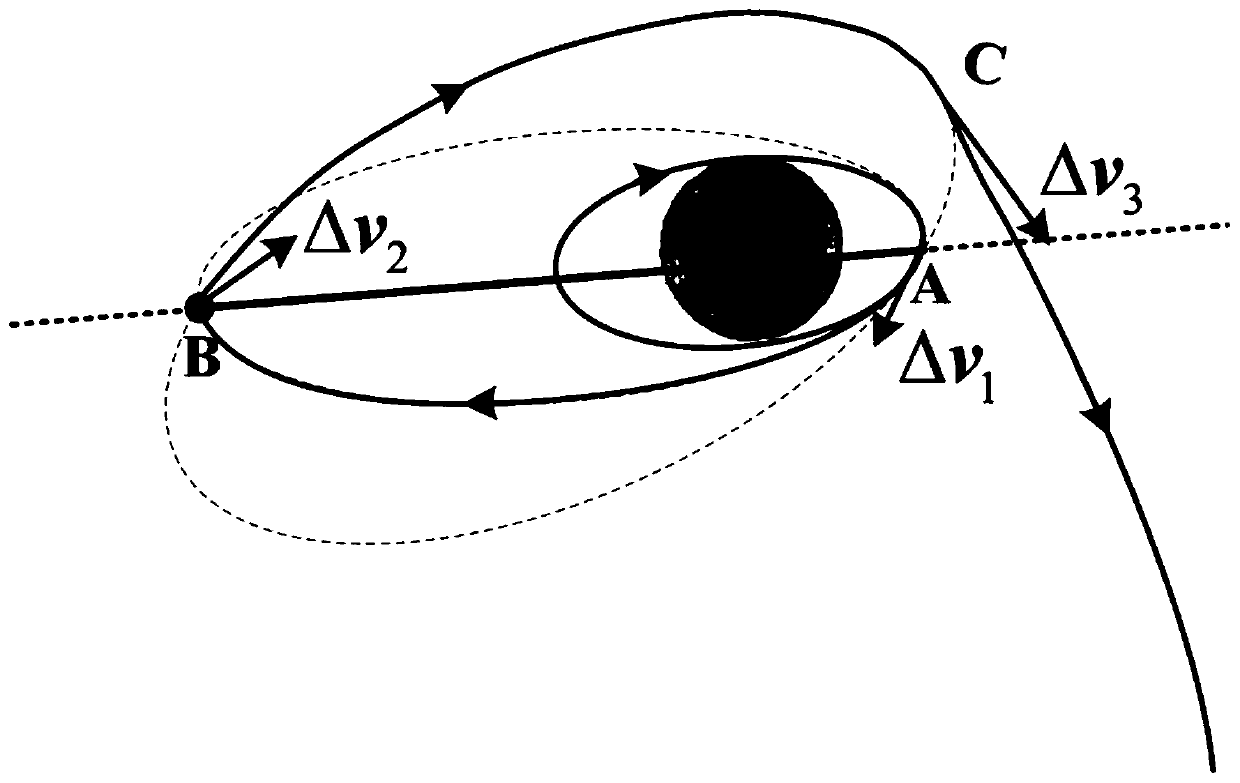
Month-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method
ActiveCN110704952AFast and efficient preliminary approximation analysisIntuitive and concise preliminary approximate analysisGeometric CADDelta-vEngineering
The invention discloses a moon-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method, which comprises the following steps: A, obtaining a normal unit vector h1 of a lunar orbit plane, a normal unit vector h2 of a lunar escape orbit plane and positions rA, rB and rC for applying three pulses by taking a moon center as an original point; B, obtaining a conical surface S1 with the lunar escape orbit aiming v infinity out as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S1 is eta; C, enabling the plane where v infinity out and h1 are located to serve as the datum plane, setting the rotating angle sigma of rC around the straight line where v infinity out is located, and determining rC and a lunar escape orbit plane; D, obtaining a conical surface S2 with the straight line where rC is located as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S2 is alpha; E, obtaining the included angle beta between h1 and v infinity out and the different-plane differencexi between the lunar orbit and the lunar escape orbit; F, solving the sizes delta v1, delta v2 and delta v3 of the three pulses; G, solving a total speed increment delta v; and H, changing the independent variable influencing the delta v to obtain a change rule of the delta v. According to the method, the spatial geometrical relationship is utilized, and preliminary approximate analysis can be rapidly, effectively, visually and simply carried out on the speed increment required by the three-pulse maneuvering process.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Standard trajectory tracking guidance method based on height-range ratio
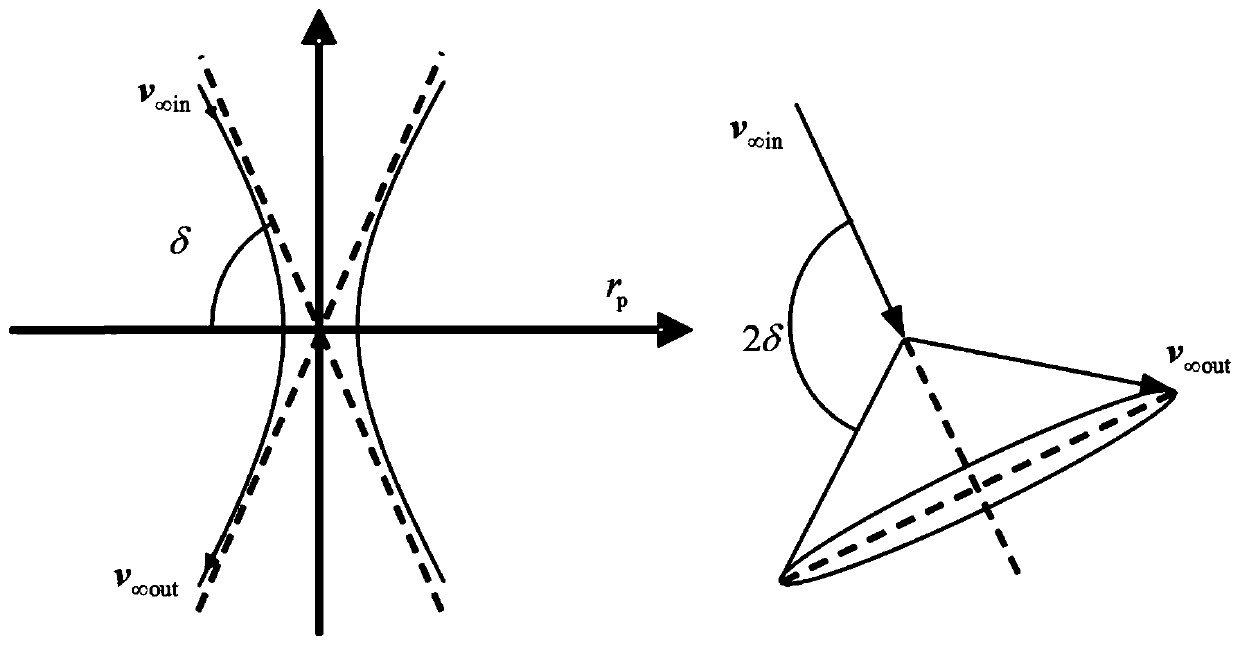
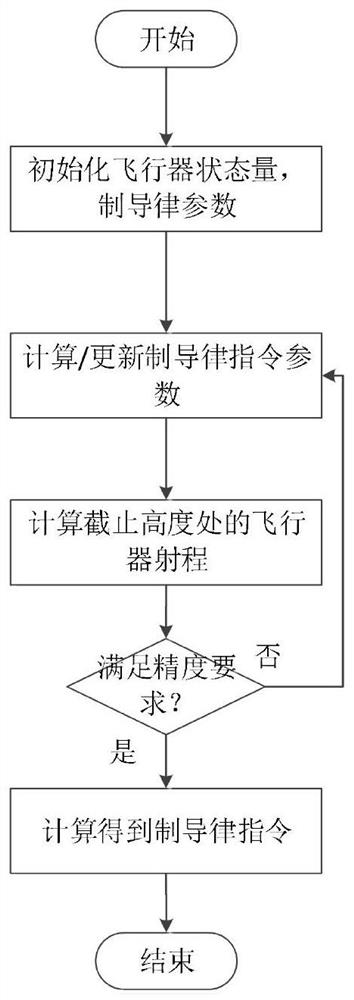
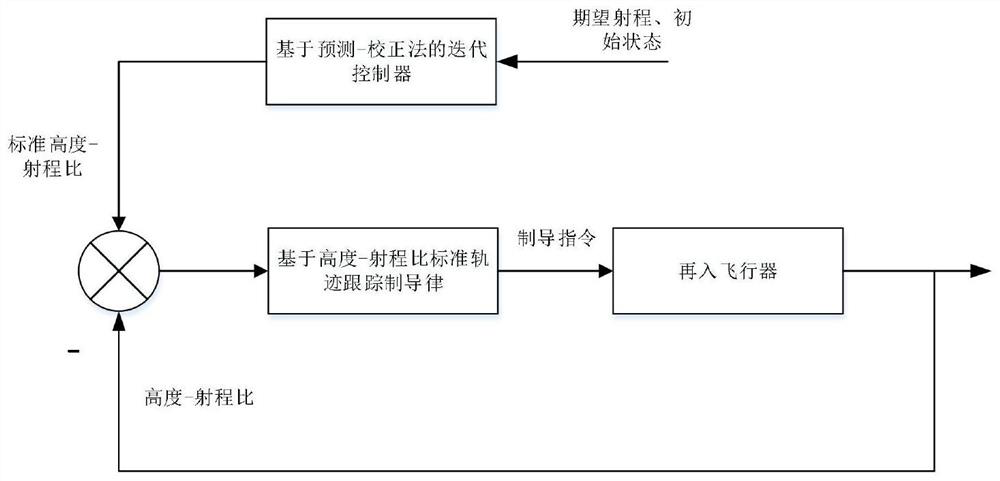
ActiveCN112034879AImprove Guidance AccuracyWell formedPosition/course control in three dimensionsFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a standard trajectory tracking guidance method based on a height-range ratio. The method comprises the steps of 1, determining the total range of an aircraft and an aircraft height and speed corridor under constraint conditions; 2, designing a guidance law instruction of a segmentation constant value, and recording the guidance law instruction as u (h); 3, obtaining terminal ranges f1 and f2 in a prediction correction method formula; 4, calculating a gain k, a parameter h *, a range f *, and an updating parameter tau on the premise of an approximate linearization hypothesis, ; 5, carrying out n times of iterative computation to obtain a time sequence of theheight-range ratio; 6, when the reentry vehicle is subjected to external interference in the flight process, and the initial condition is uncertain, improving the guidance precision through the correction value delta u of the control quantity; and 7, forming a guidance law instruction form when the reentry vehicle is subjected to external interference and initial conditions are uncertain. In order to solve the problem of standard trajectory tracking of an under-actuated reentry vehicle system, longitudinaland lateral planes are combined, and the concept of height-range ratio is introduced to solve the problem.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
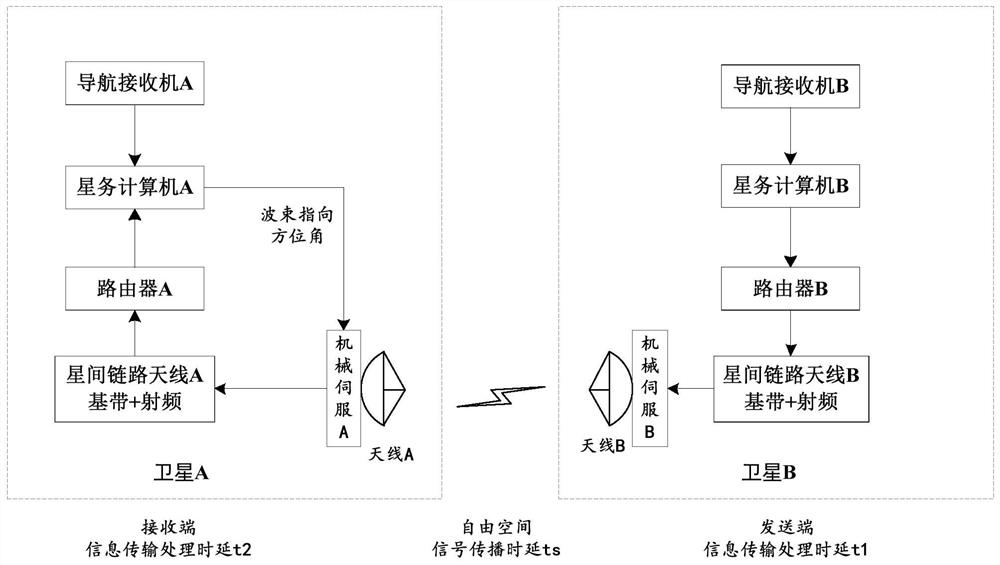
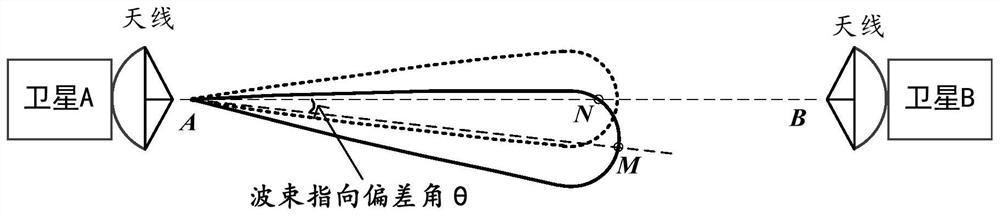
Different-orbit inter-satellite communication link beam pointing error calculation method and module
ActiveCN112039576AGuaranteed accuracyRadio transmissionInformation transmissionTelecommunications link
The embodiment of the invention discloses a different-orbit inter-satellite communication link beam pointing error calculation method and module, a storage medium and computer equipment, and the method comprises the steps of: S10, determining error source parameters of antenna beam pointing, including antenna self-pointing angle precision a1 and a2, antenna installation reference angle deviation b1 and b2, satellite attitude pointing precision c1 and c2, the satellite attitude stabilization precision omega s1 and omega s2, the satellite orbit data updating period t0, the maximum value omega 1of the relative pitch angle speed of two satellites, the maximum value omega 2 of the relative yaw angle speed of the two satellites, and the total orbit information transmission and processing time delay delta t; S30, calculating the component of the antenna beam pointing deviation angle in the pitching direction according to the formula theta 1=a1+b1+c1+omega s1.t0+omega 1.delta t; S50, calculating a component theta 2 of the antenna beam pointing deviation angle in the yaw direction according to a formula theta 2=a2+b2+c2+omega s2.t0+omega 2.delta t; and S70, substituting the theta 1 and thetheta 2 into a formula theta=(theta 12+theta 22)1 / 2, and calculating the antenna beam pointing deviation angle theta.
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
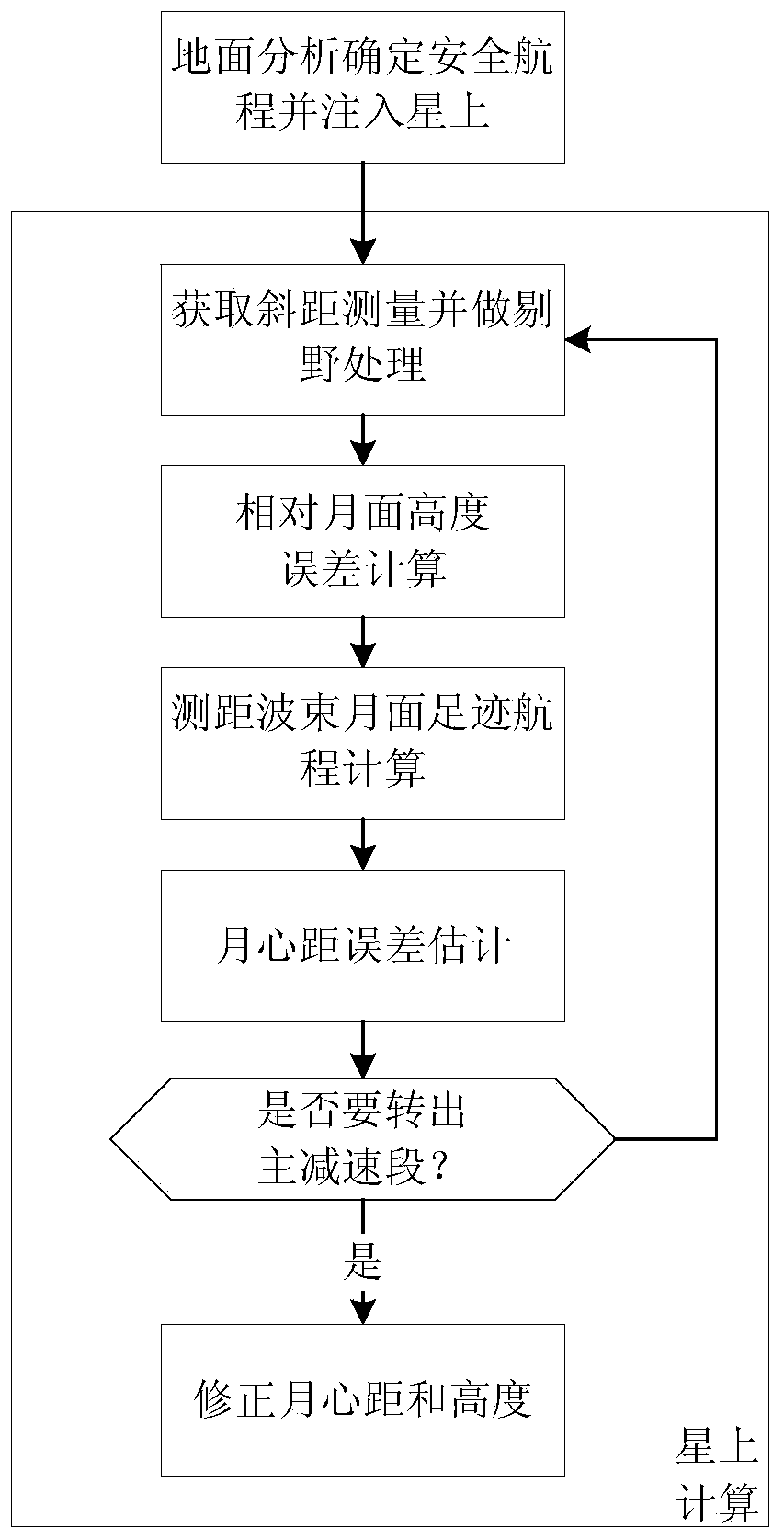
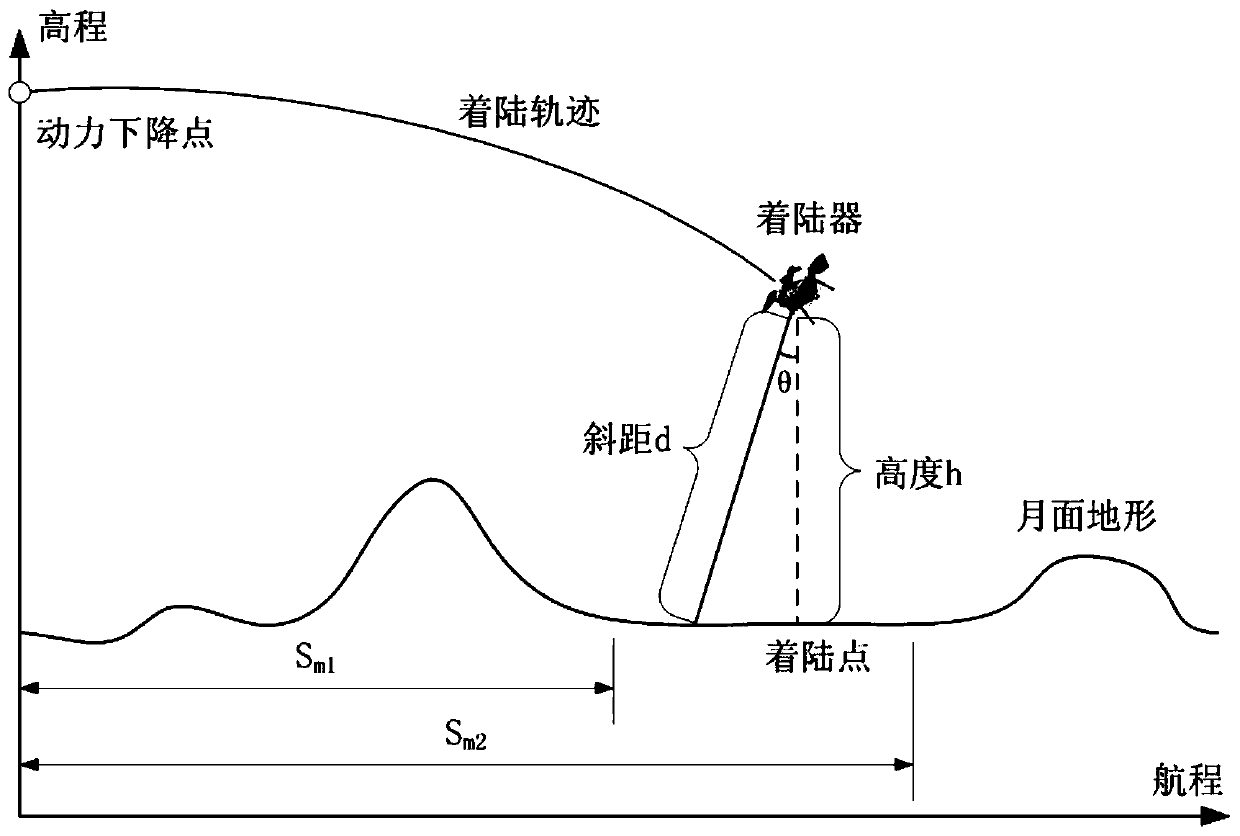
Terrain estimation method for lunar soft lander
ActiveCN111443710AGuaranteed validityStable flightPosition/course control in two dimensionsProfile tracingTerrainAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to a terrain estimation method for a lunar soft lander: (1) two ranging sensors are used to measure the slant distance between the lunar lander and the lunar surface; (2) the first relative lunar surface height error delta qL and the second relative lunar surface height error delta qR are calculated according to the slant distance measured respectively by the first ranging sensor and the second ranging sensor; (3) respectively according to the installation direction of the first ranging sensor and the second ranging sensor, as well as the current position and attitude ofthe lander, the first ranging beam lunar footprint range SmL and the second ranging beam lunar footprint range SmR are calculated; (4) the lunar center distance error is calculated according to the above parameters, otherwise, the calculation times of the lunar center distance error are changed and back to step (1), and the lunar center distance error is recalculated; (5) When the lander will turn out of the main deceleration section, the lunar center distance of the landing site and the height of the lunar lander shall be corrected according to the lunar center distance error.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Minimum energy trajectory strict construction method considering influence of earth rotation
ActiveCN111475767AFull and precise descriptionUniversalComplex mathematical operationsEarth's rotationDelta
The invention discloses a minimum energy trajectory strict construction method considering influence of earth rotation, which adopts an accurate geophysical model (considering earth oblateness and rotation) and can accurately construct a minimum energy trajectory between two three-dimensional geodetic points under a two-body motion model. Besides, the influence of earth rotation on the trajectorystructure is deeply excavated; the strict analytical solution of the minimum energy trajectory is found theoretically, and two small quantities of the difference value epsilon between the ratio of thegeocentric distance of the target point to the geocentric distance of the launching point and 1 and the perigee amplitude angle offset delta omega of the elliptical orbit are introduced, so that themethod has universality and a simple formula, and is a minimum energy free trajectory strict construction method suitable for any two space points.
Owner:ZIJINSHAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
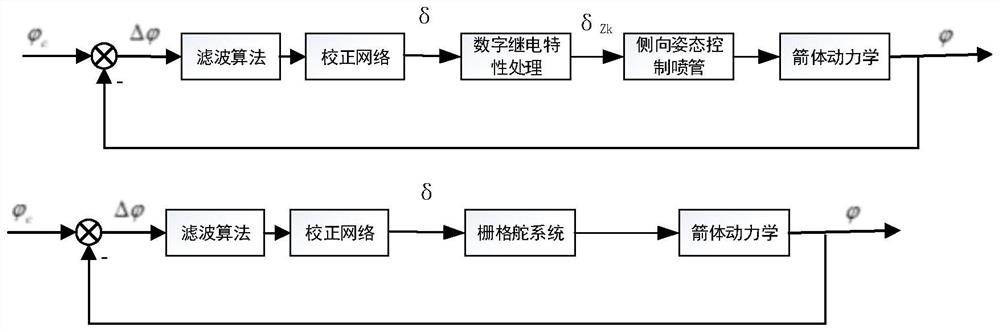
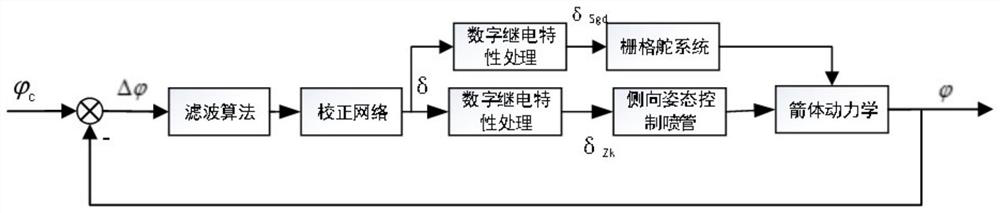
Carrier rocket attitude control method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114265419AImprove performanceImprove robustnessAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsRocket launchControl signal
The invention relates to a carrier rocket attitude control method, which comprises the following steps of solving a control angle deviation, filtering a program angle deviation according to a filtering algorithm, calculating a filtered control signal according to a designed correction network, obtaining a control instruction delta of a lateral attitude control nozzle, carrying out digital relay characteristic processing on the control instruction, and carrying out digital relay characteristic processing on the control instruction. And meanwhile, on-off control is carried out on the lateral attitude control spray pipe and the grid rudder system. Aiming at a carrier rocket adopting a control scheme of a grid rudder and a lateral attitude control spray pipe, the invention provides an attitude control system design method adopting grid rudder and lateral attitude control spray pipe compound control in an initial rocket launching section, so that the requirement on attitude control torque can be effectively reduced, the rocket attitude fuel consumption is reduced, the carrier rocket performance is improved, and the carrier rocket performance is improved. And the method has high engineering application value.
Owner:AEROSPACE SCI & IND KET TECH CO LTD
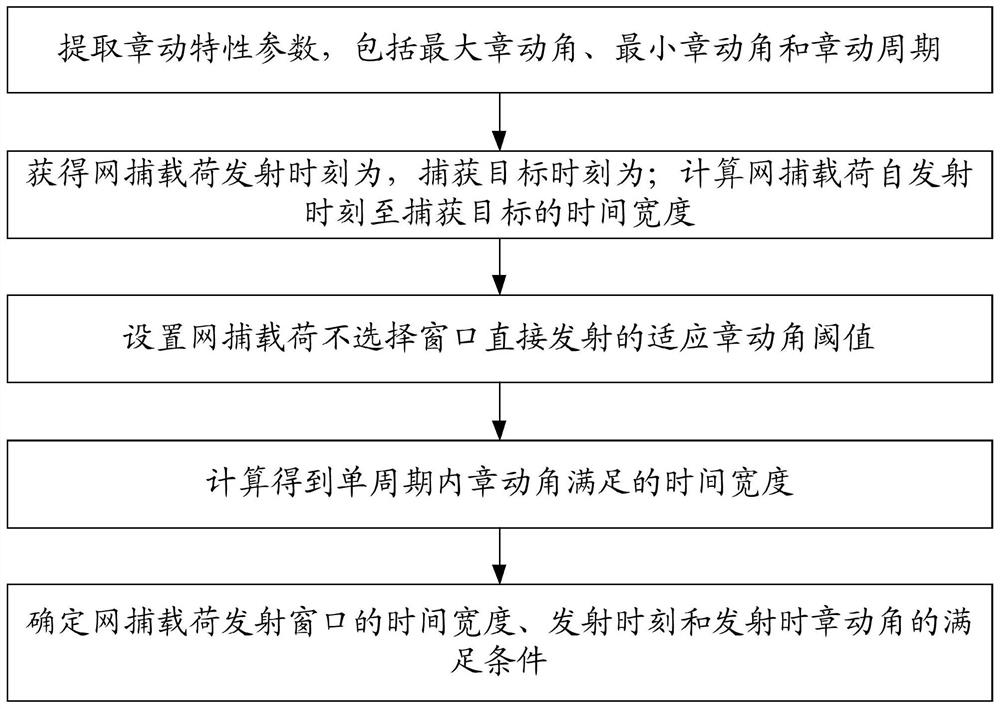
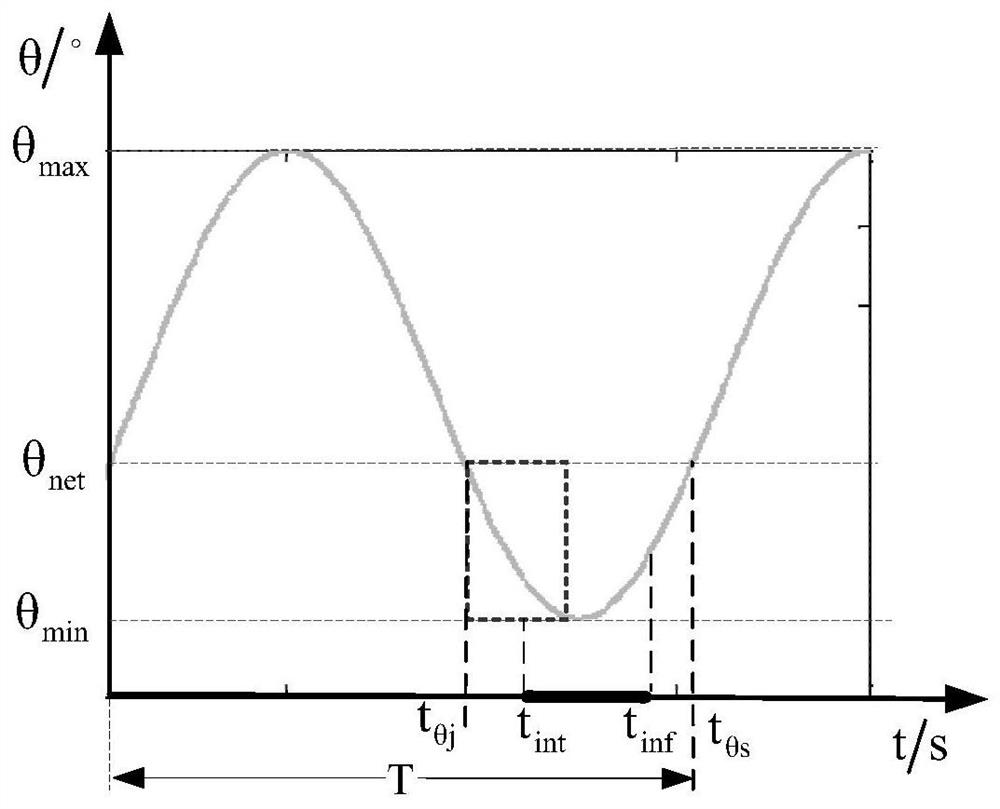
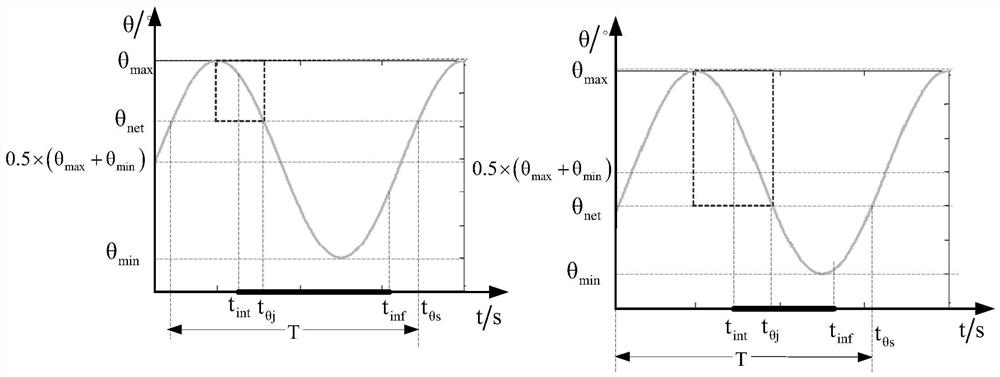
Method for selecting net capture load launching window based on waste satellite attitude nutation characteristics
ActiveCN112572836ASolving the Reliable Capture ProblemCosmonautic vehiclesToolsSatellite technologyAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to a method for selecting a net capture load launching window based on waste satellite attitude nutation characteristics, and belongs to the technical field of satellite net capture of waste satellites. The method comprises the steps of: 1, extracting a maximum nutation angle theta max, a minimum nutation angle theta min and a nutation period T; 2, acquiring a net capture load launching moment tint and a capture target moment tinf; calculating the time width Tnet according to the formula that Tnet=tinf-tint; 3, setting an adaptive nutation angle threshold theta net directly launched by a net capture load non-selection window; 4, calculating the time width T theta=t theta s-t theta j when the nutation angle theta is less than or equal to theta net in a single period; and 5, determining the satisfactory conditions of time width delta T of a net capturing load launching window, the launching moment tint and the nutation angle theta during launching; according to thewaste satellite attitude nutation rule, the net capture load nutation angle adaptive capacity and the time width of the net capturing load from the launching moment to capturing, the invention provides a launching window selection method, and reliable capturing of the large-attitude nutation waste satellite is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
Spacecraft formation flight method on small-thrust suspension orbit
ActiveCN108614578ALarge space spanStable formation configurationPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitDeep space exploration
The invention discloses a spacecraft formation flight method on a small-thrust suspension orbit. Mapping of orbital parameters (hz, k, alpha, delta E, delta r) of a bounded suspension orbit to formation parameters (delta T, delta omega) is established, wherein the following formula is met: f:(hz, k, alpha, delta E, delta r) to (delta T, delta omega); formation conditions of three kinds of formation types are determined; and then suspension orbits of main satellites and salve satellites meeting all formation conditions are searched in a two-dimensional(delta T, delta omega) plane to realize bounded formation flight of the main satellites and salve satellites. Therefore, three different kinds of bounded relative orbits are obtained and the orbit precision is high. The method is suitable forlong-period large-scale formation flight; and implementation of a near-surface mission or a deep-space exploration formation mission is ensured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
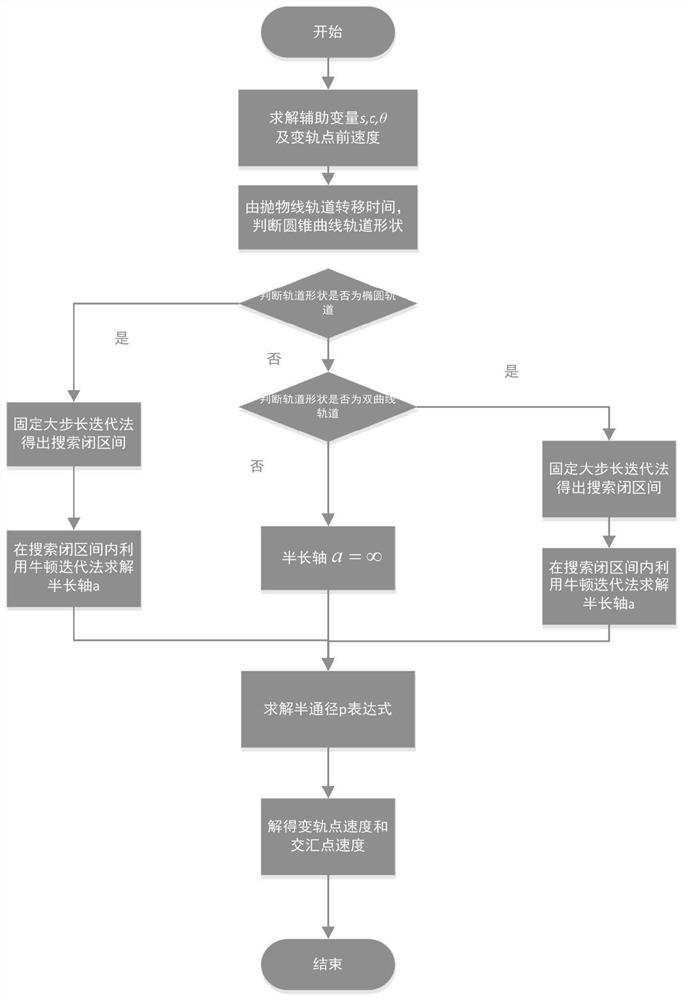
semi-major axis iteration space transfer orbit calculation method for Lambert orbital transfer problem based on Newton iteration
PendingCN111753244AImprove solution efficiencySolve the problem of solving space transfer orbitComplex mathematical operationsAnalytical equationsComputational physics
The invention discloses an improved solving method for a Lambert orbital transfer problem based on a Newton iteration thought. The method comprises the steps of 1, calculating a transfer angle theta,an auxiliary variable c and an auxiliary variable s; 2, determining the shape of the track according to the transfer angle and the auxiliary variable in the step 1; 3, when delta t is larger than delta tp, determining that the transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit, and carrying out solving; 4, when delta t is smaller than delta tp, determining that the transfer orbit is a hyperbolic orbit, and carrying out solving; 5, when delta t is equal to delta tp, determining that the transfer orbit is a parabola orbit, and carrying out solving; 6, expressing the Lambert orbital transfer problem analytical equation in the steps 3-5 as a function of a conic curve semi-major axis, and calculating a conic curve semi-drift diameter; 7, calculating orbital transfer point speed and intersection speed; and 8, proving the high efficiency and accuracy of the improved solving method for the Lambert orbital transfer problem based on the Newton iteration thought. The invention aims to improve the solving speed of the Lambert orbital transfer problem in spacecraft rendezvous.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fiber-fed advanced pulsed plasma thruster (FPPT)
ActiveUS10570892B2Reduce the total massMinimize safety concernMultiple fixed capacitorsCosmonautic vehiclesRange safetyCeramic capacitor
A Fiber-fed Pulsed Plasma Thruster (FPPT) will enable enhanced low Earth orbit, cis-lunar, and deep space missions for small satellites. FPPT technology utilizes an electric motor to feed PTFE fiber to its discharge region, enabling high PPT propellant throughput and variable exposed fuel area. An innovative, parallel ceramic capacitor bank dramatically lowers system specific mass. FPPT minimizes range safety concerns by the use of non-pressurized, non-toxic, inert propellant and construction materials. Estimates are that a 1U (10 cm×10 cm×10 cm, or 1 liter) volume FPPT thruster package may provide more than 10,000 N-s total impulse and a delta-V of 1.4 km / s delta-V for an 8 kg CubeSat.
Owner:CU AEROSPACE
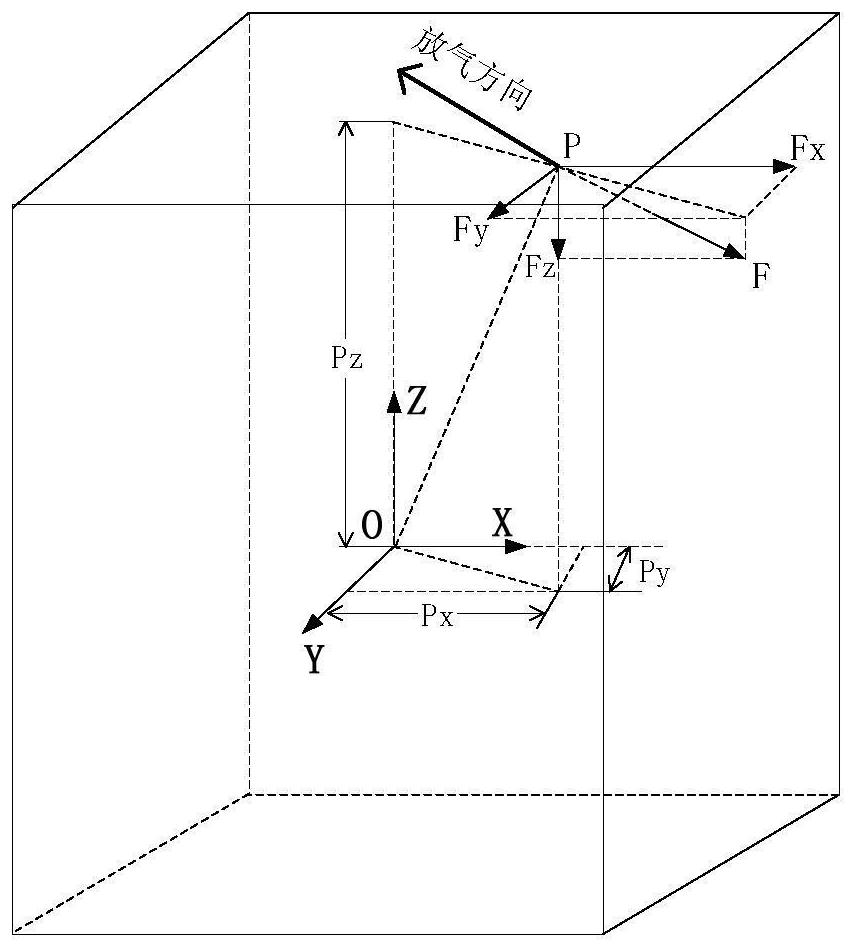
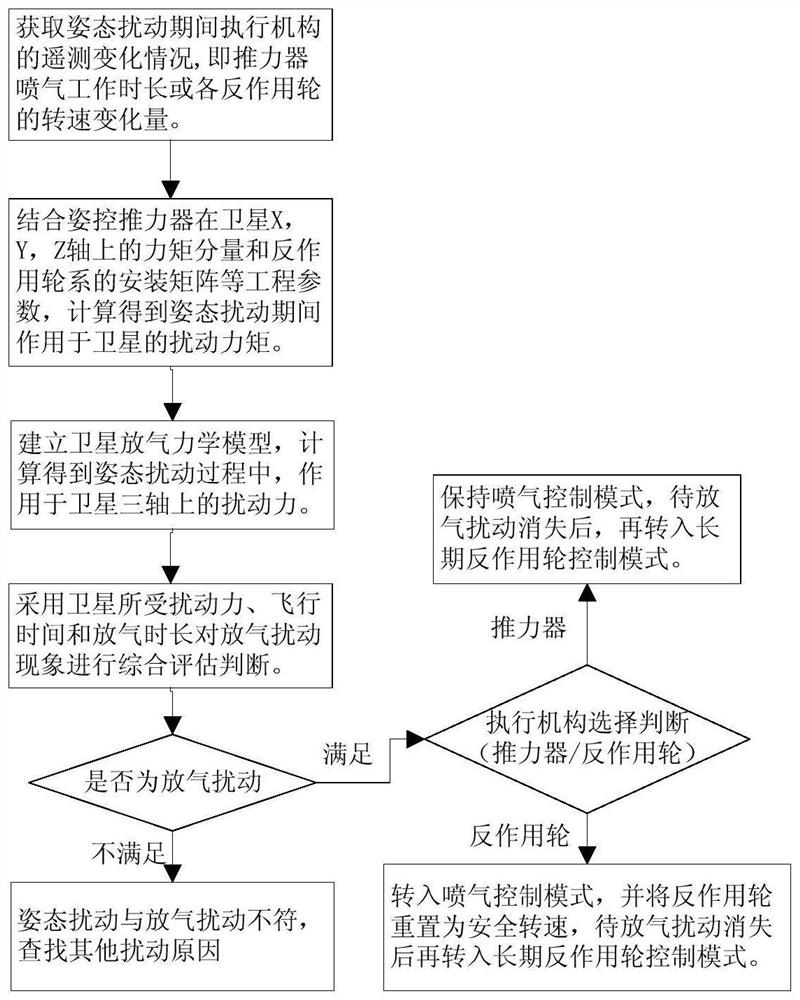
Evaluation system and evaluation method for deflation disturbance at initial satellite orbit injection stage
ActiveCN112193438ACosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusMechanical modelsClassical mechanics
The invention relates to an evaluation method for deflation disturbance at an initial satellite orbit injection stage, which comprises the following steps: (1) at the initial satellite orbit injectionstage, for a satellite suspected to have a satellite deflation disturbance phenomenon, obtaining the telemetry data variation of an execution mechanism during attitude disturbance through satellite telemetry; (2) calculating to obtain disturbance torque acting on three axes of a satellite body coordinate system in an attitude disturbance period; (3) establishing a satellite deflation mechanical model based on the satellite configuration layout design and possible mechanical parameters of deflation sites, and obtaining the relationship between the disturbance force and the disturbance torque of each axis of the satellite in the deflation disturbance process; (4) obtaining a criterion condition that the attitude disturbance phenomenon is satellite deflation disturbance according to the satellite flight time T, the disturbance force action duration delta T, the magnitude of the disturbance force F and the attitude disturbance phenomenon; and (5) judging the attitude disturbance phenomenon at the initial satellite orbit injection stage according to criterion conditions. The method and the model provided by the invention provide a basis for on-orbit disposal of deflation disturbance.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
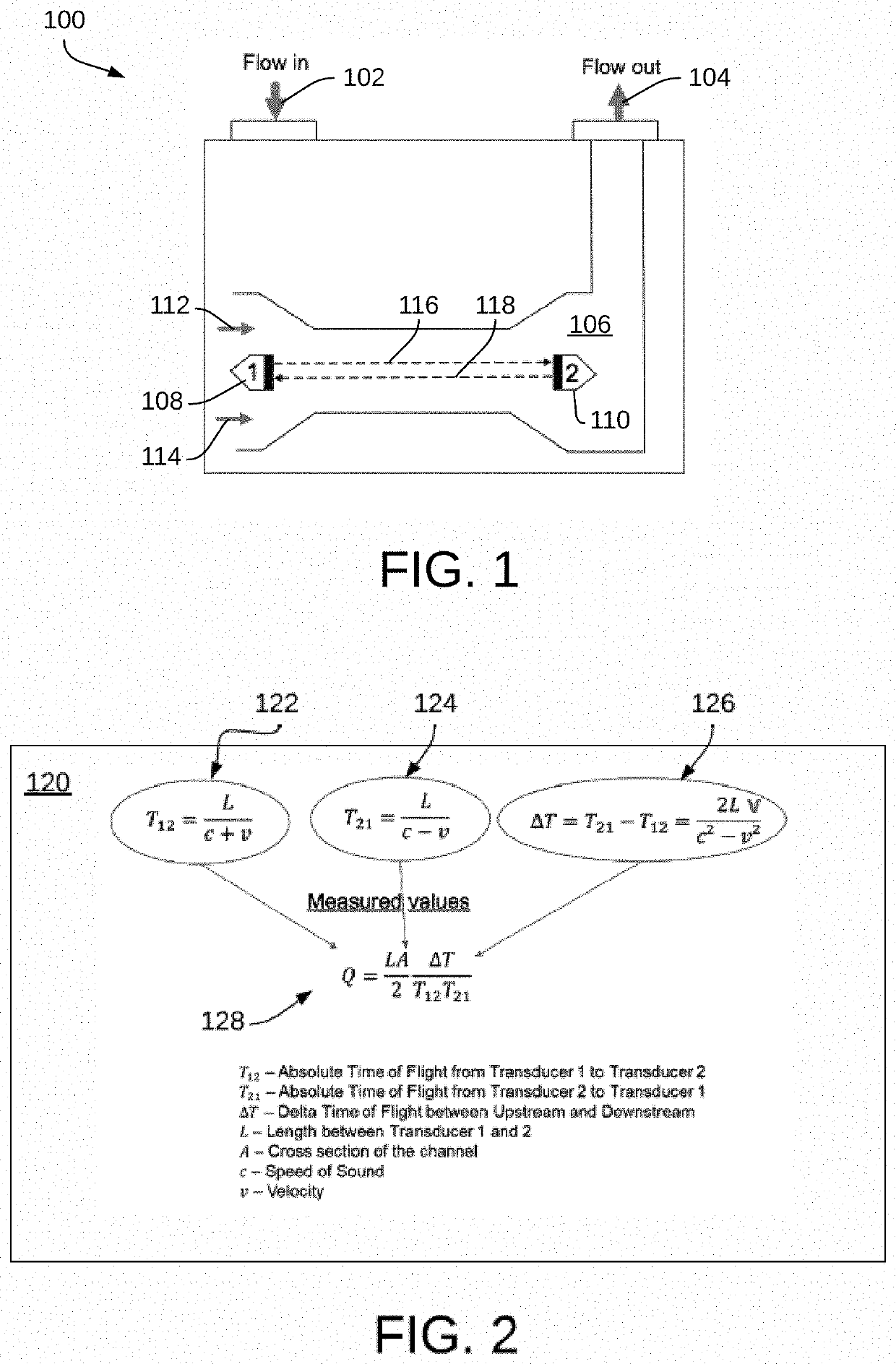
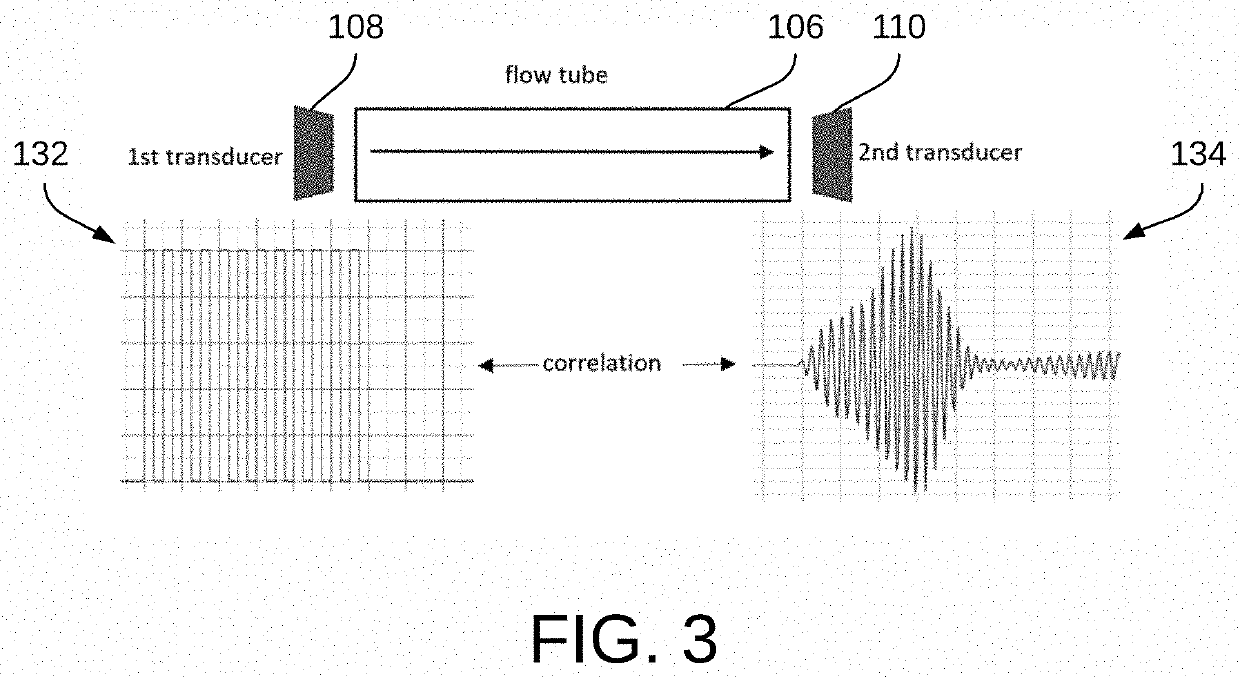
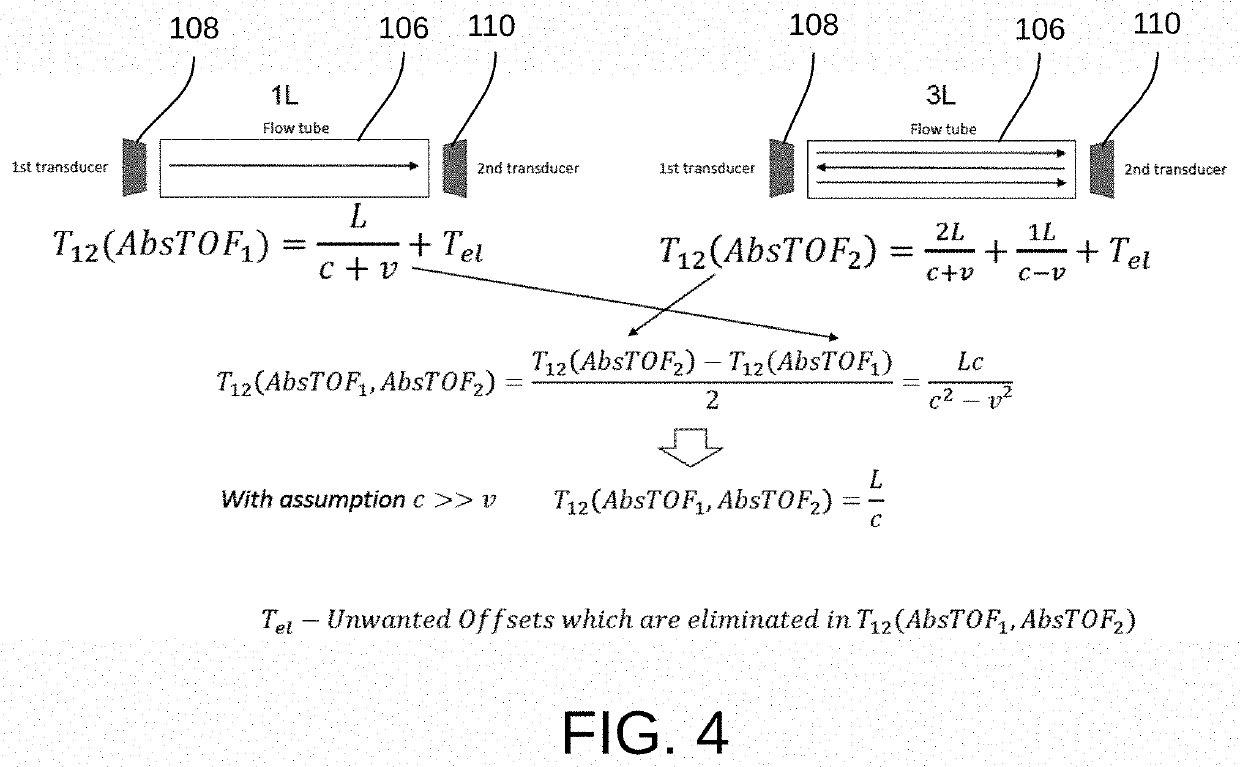
Flow measurement by combining 3l echo with delta time-of-flight cross correlation
PendingUS20210381863A1Improve accuracyVolume/mass flow measurementPulse sequenceMechanical engineering
Methods and systems for flow measurement can involve calculating an absolute-time-of-flight with respect to a flow of a fluid in a flow channel by reflected signals, reflected and unreflected signals, or a pulse train, determining a delta-time-of-flight with a cross correlation of two signals with respect to the flow of the fluid in the flow channel, and calculating the flow rate of the flow of the fluid in the flow channel based on the absolute-time-of-flight and the cross correlation of the delta-time-of-flight.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com