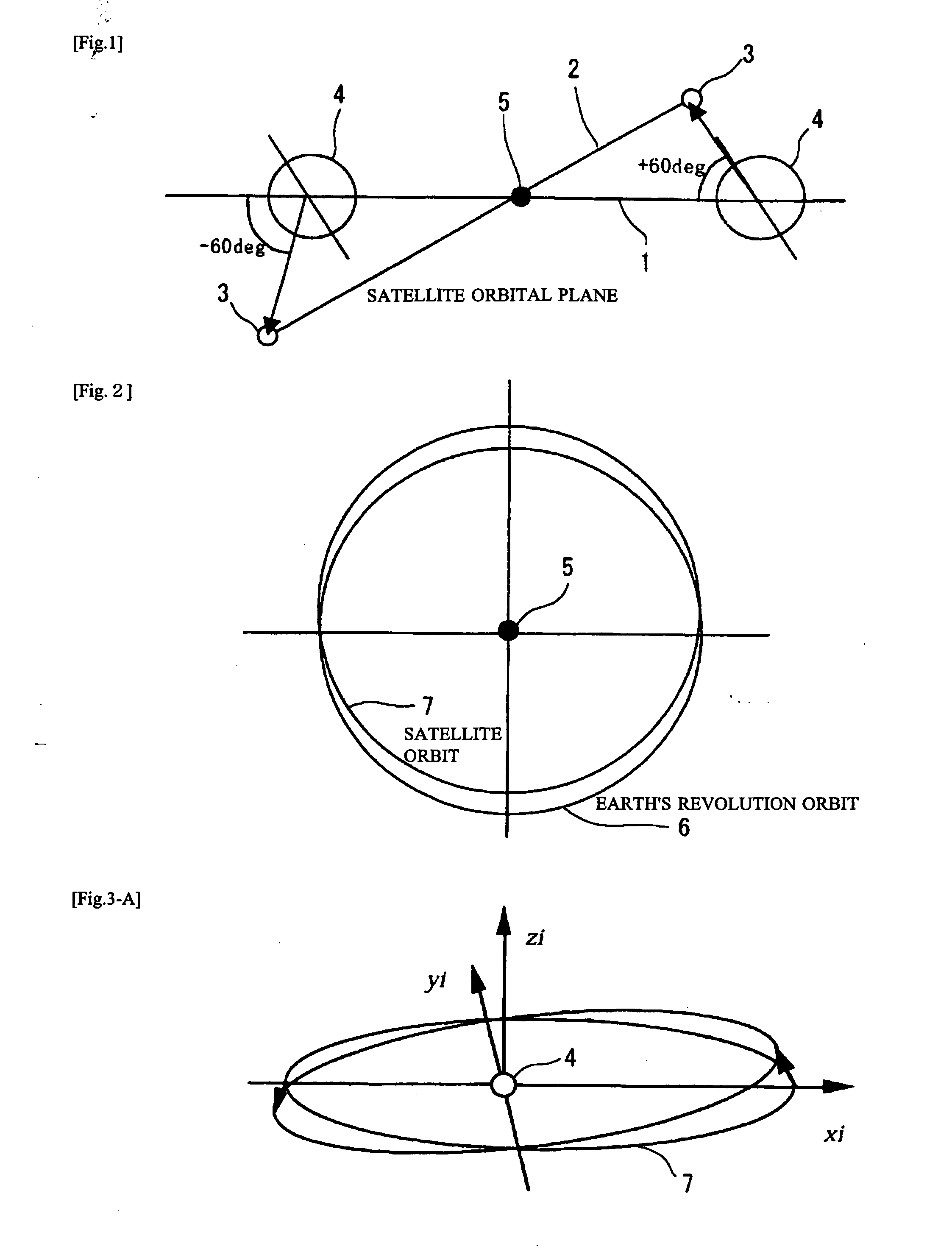
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
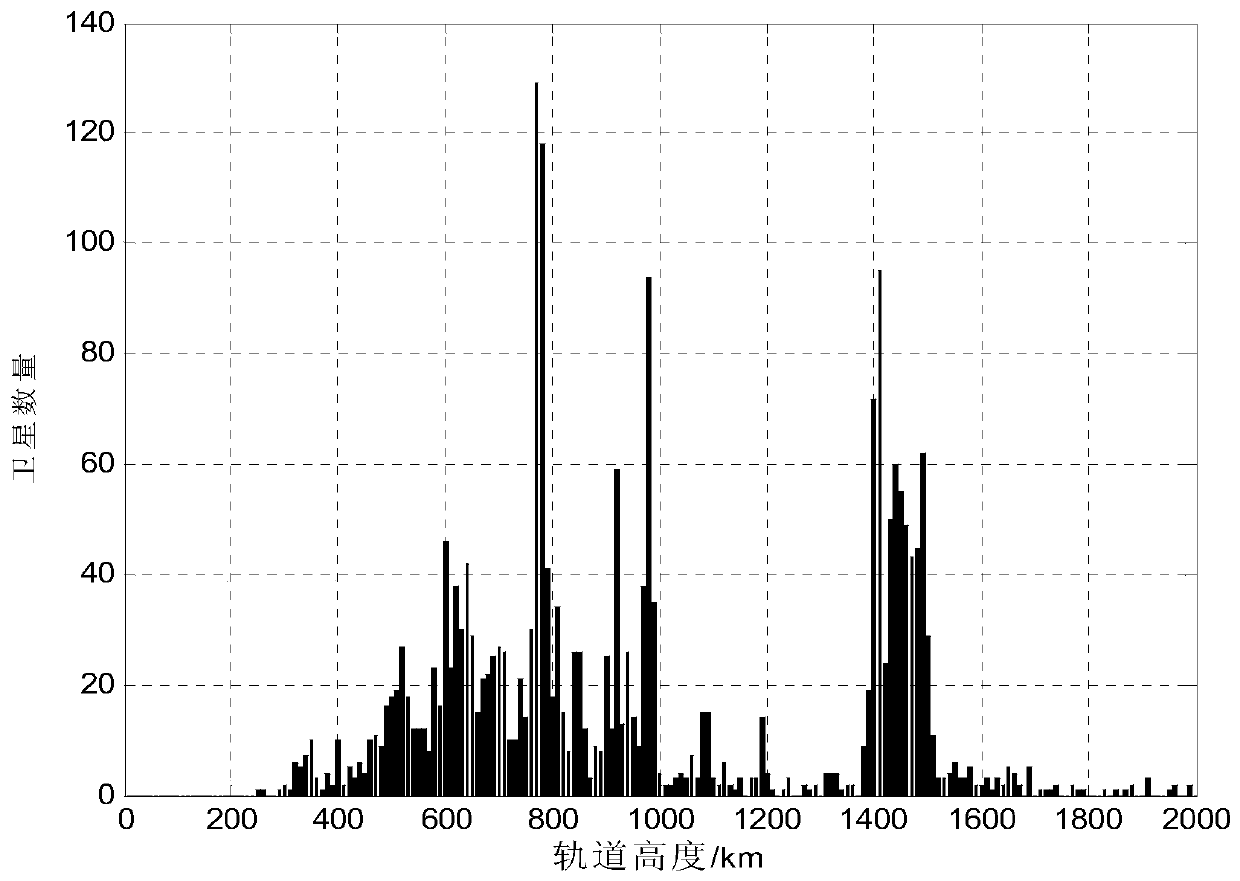
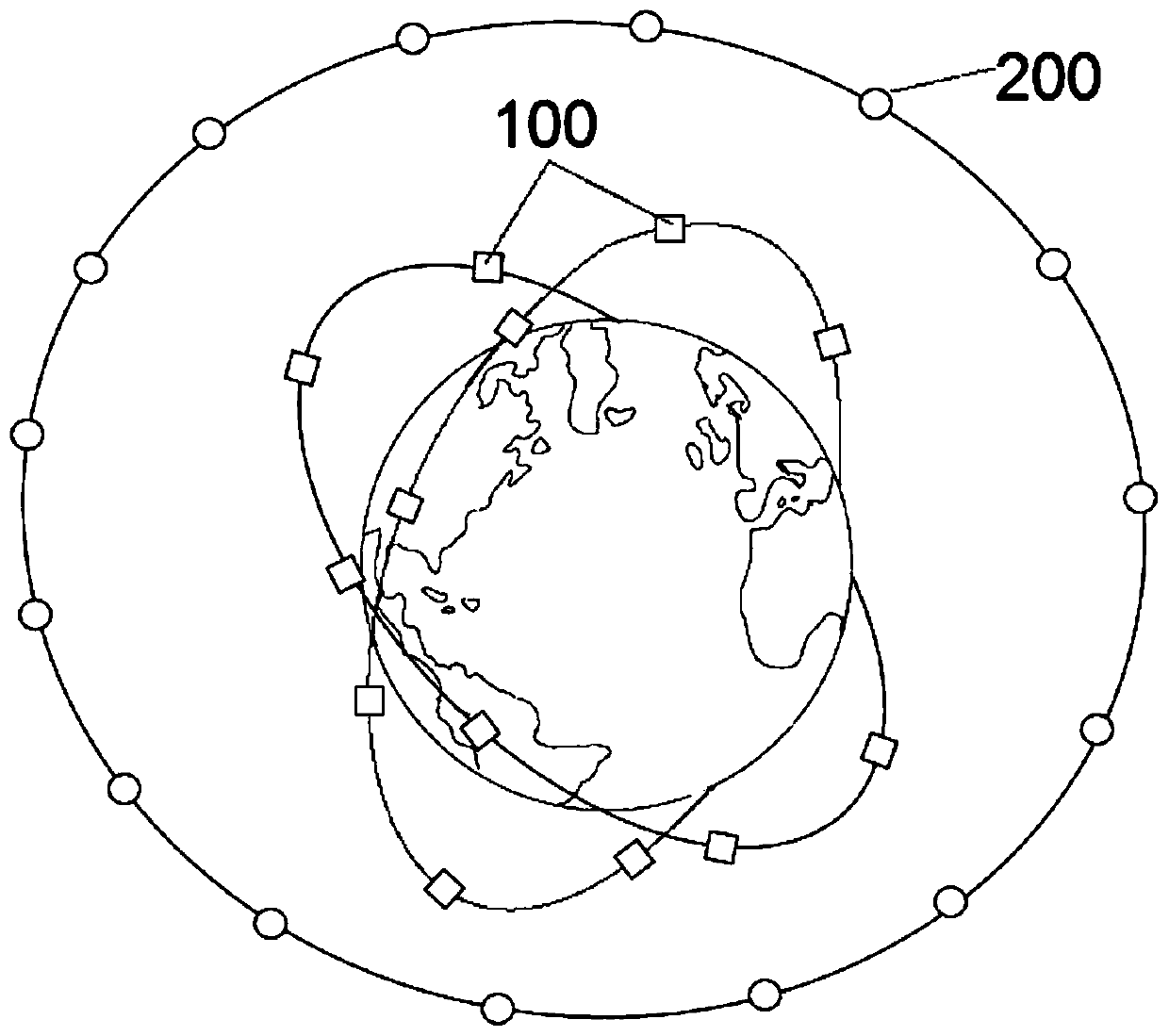
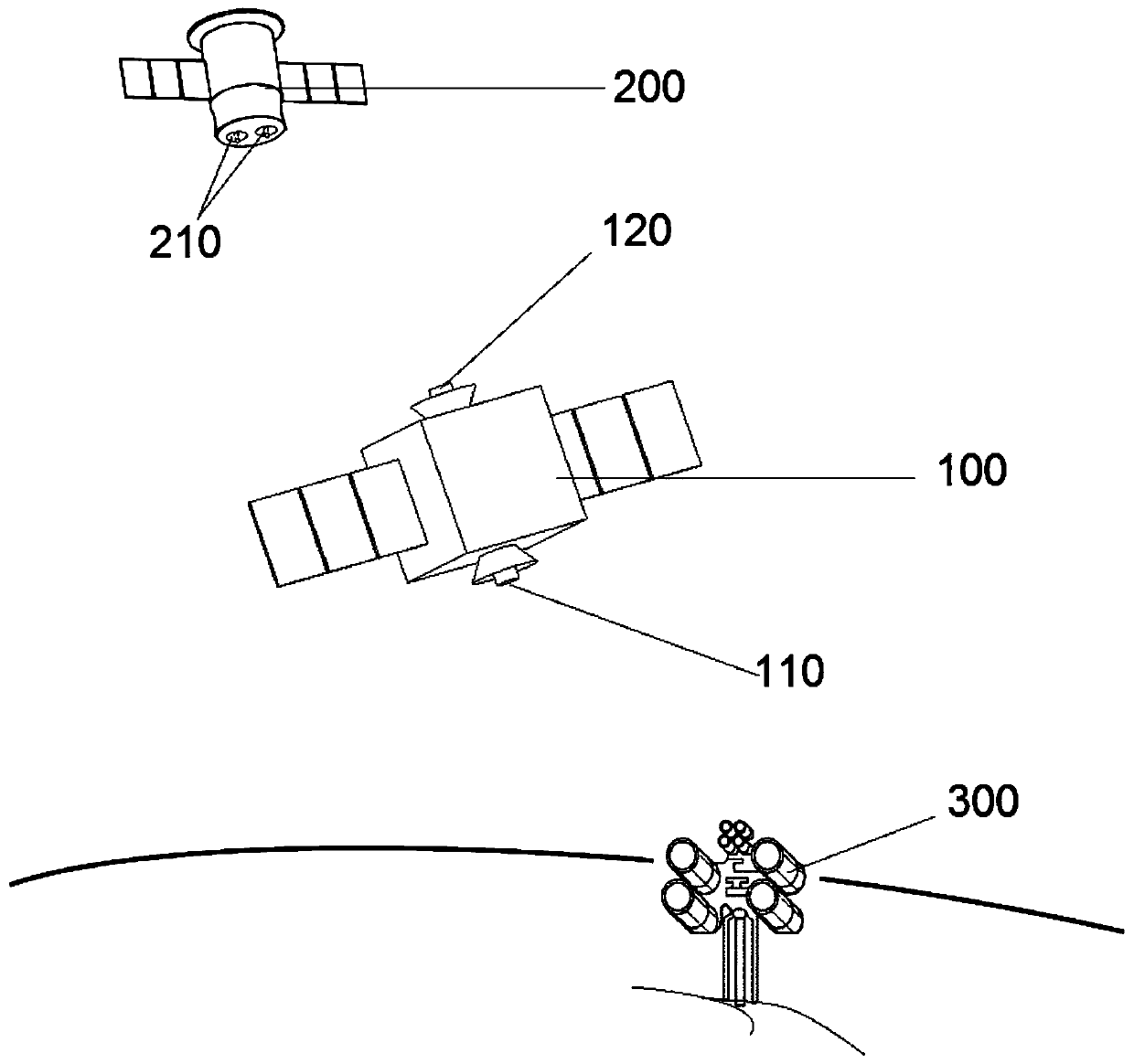
107 results about "Orbit plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Time slot optimization-based double-layer satellite network routing method
ActiveCN104821844AReduce overheadImprove reliabilityRadio transmissionData switching networksNatural satelliteRouting table
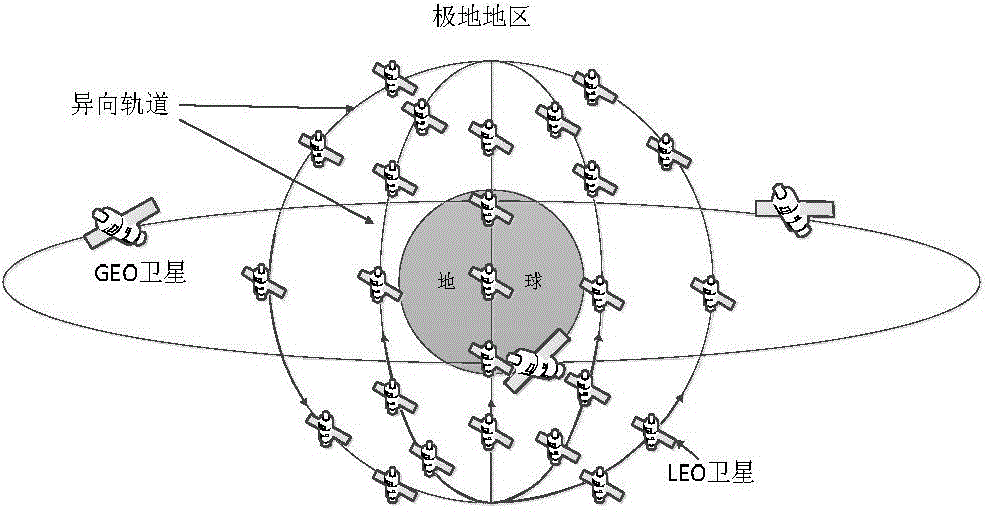
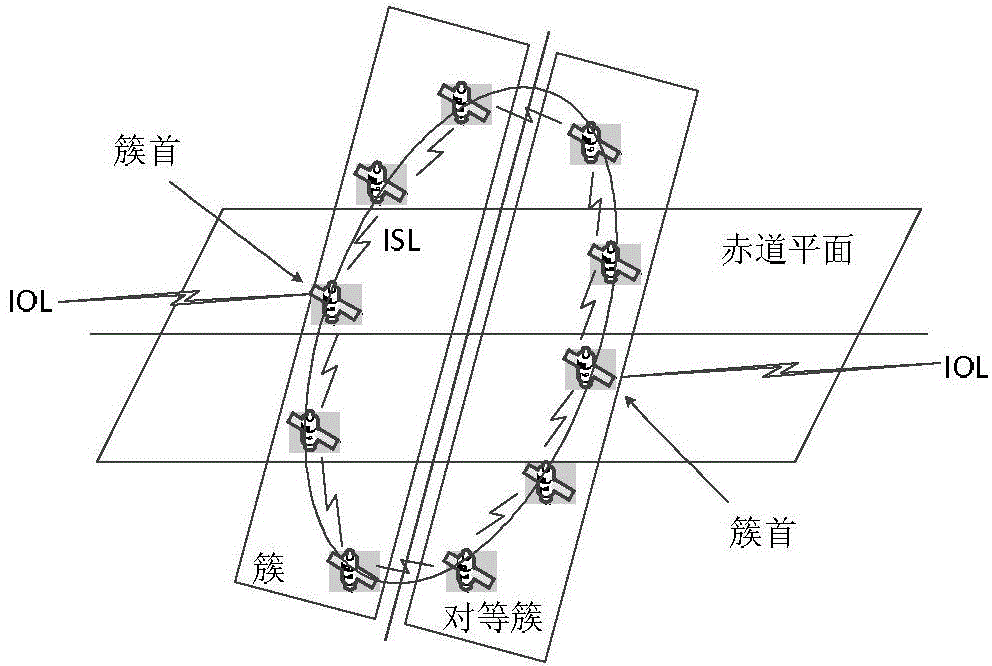
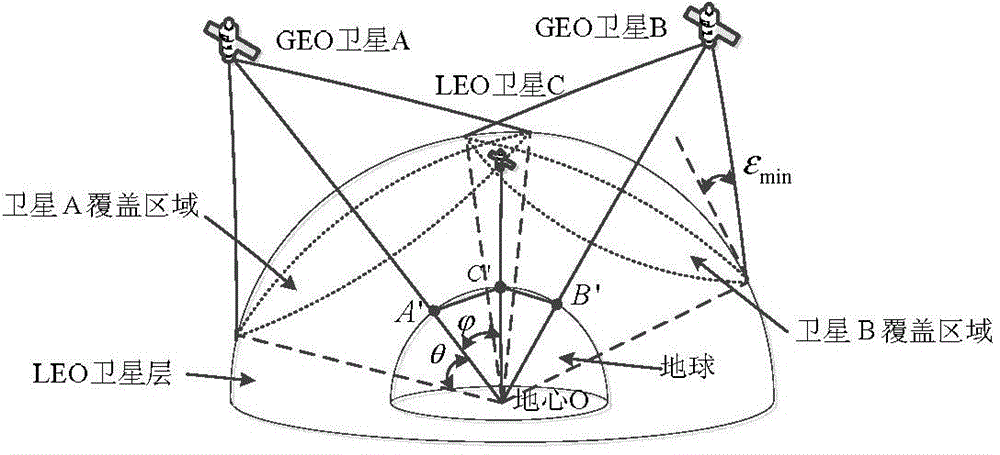
The invention relates to a time slot optimization-based double-layer satellite network routing method, so as to solve the problems that routing protocol overhead in the traditional method is large, an LEO satellite is hard to be connected with a GEO satellite in a polar region, and temporary link breaking of a polar orbit satellite between polar region orbits is not considered. The method comprises steps: (1) a 3GEO+66LEO double-layer satellite network model is built; (2) a covering domain grouping + orbit plane clustering-based satellite grouping management method is applied to determine a control relationship between an upper layer of satellites and a lower layer of satellites; (3) according to the control relationship between the upper layer of satellites and the lower layer of satellites, time slot division and optimization are carried out on a satellite operation cycle; (4) on the basis of location prediction routing algorithm, the GEO satellites calculate a routing table for the LEO satellites; and (5) the first step to the fourth step are combined, and routing updating is carried out when each time slice starts. The method belongs to the field of satellite communication.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
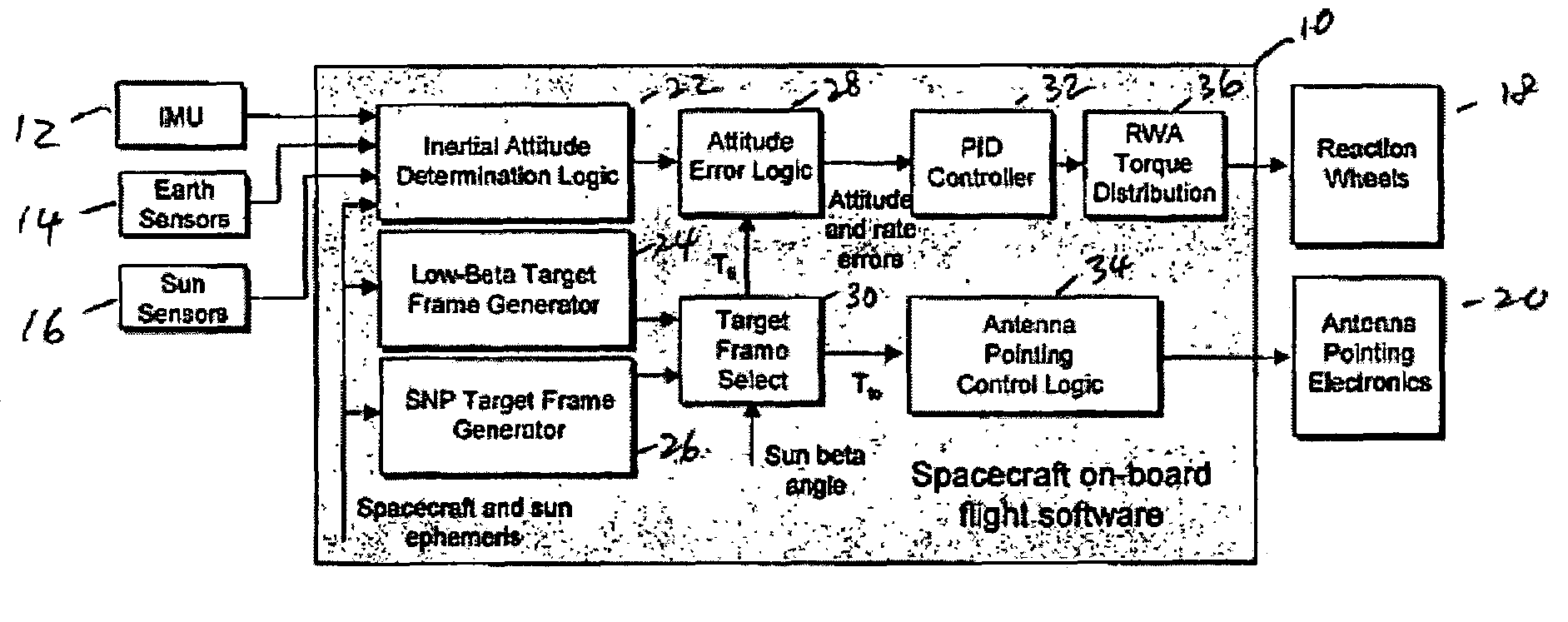
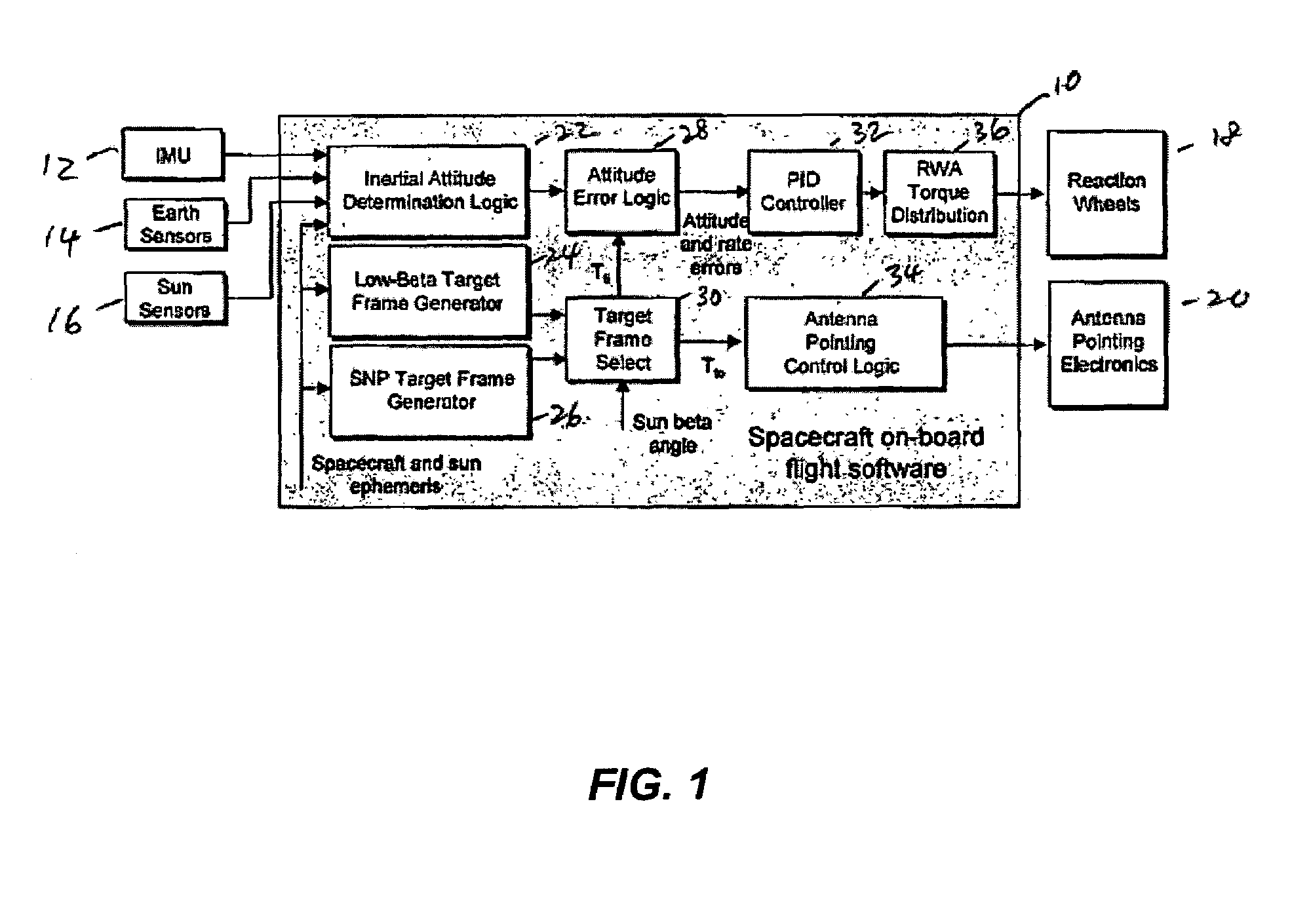
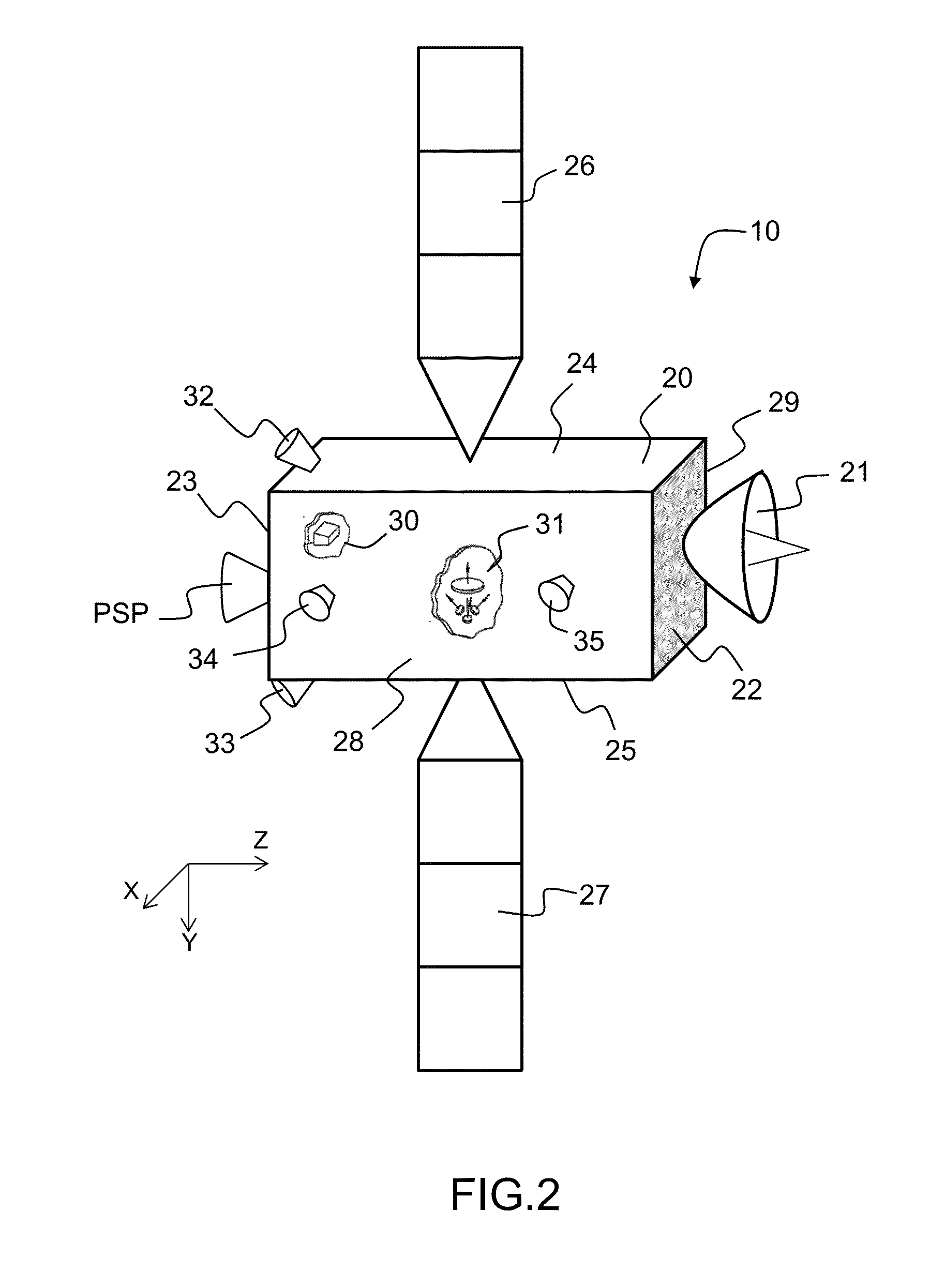
Attitude and antenna steering system for geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) spacecraft
ActiveUS7357356B1High rateLarge rotation angleCosmonautic vehiclesRadio transmissionBeta angleGeosynchronous orbit
A system for providing attitude and antenna steering for a spacecraft is disclosed. The spacecraft has a number of reaction wheels and a number of antennas. The system includes control logic configured to: determine a beta angle, the beta angle being the angle between a sun vector and an orbit plane of the spacecraft, and alternately engage either a first mode or a second mode to provide attitude and antenna steering based on the beta angle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Propulsion system in two modules for satellite orbit control and attitude control
ActiveUS20140361123A1Cosmonautic propulsion system apparatusArtificial satellitesAttitude controlSatellite orbit
A propulsion system for the orbit control of a satellite in Earth orbit driven at a rate of displacement along an axis V tangential to the orbit comprises two propulsion modules, fixed to the satellite, and facing one another relative to the plane of the orbit, each of the propulsion modules comprising, in succession: a motorized rotation link about an axis parallel to the axis V; an offset arm; and a plate supporting two thrusters, suitable for delivering a thrust on an axis, arranged on the plate on either side of a plane P at right angles to the axis V passing through a centre of mass of the satellite; each of the two thrusters being oriented in such a way that the thrust axes of the two thrusters are parallel to one another and at right angles to the axis V.
Owner:THALES SA
Complimentary retrograde/prograde satellite constellation
InactiveUS20070284482A1Defence devicesCosmonautic partsSatellite constellationIntercontinental ballistic missile
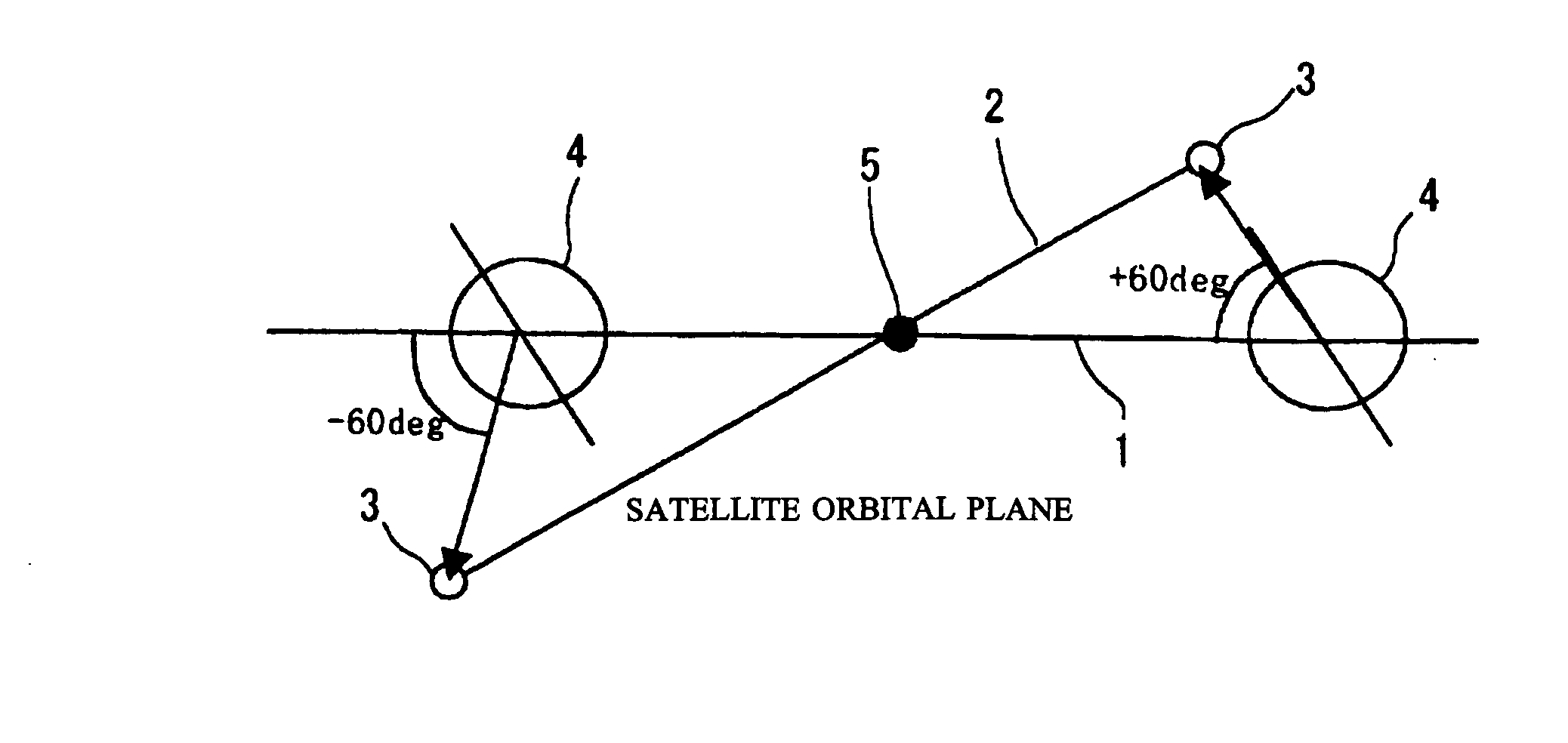
A method for sensing and monitoring ICBM threats using a constellation of earth orbiting satellites. The method includes arranging a first and a second plurality of threat sensing satellites in earth orbit. The first plurality is selected to have a first prograde orbit plane with a first inclination angle between about 30° to 70° with respect to the earth's equator and an Argument of Perigee equal to about 270°. The second plurality is selected to have a first retrograde orbit plane with a second inclination angle between about 110° to 150° with respect to the earth's equator and an Argument of Perigee equal to about 270°. The second inclination angle is selected to be a symmetric conjugate of the first inclination angle. The first and second plurality of threat sensing satellites are distributed respectively within the first prograde and first retrograde orbits with a Walker distribution of T / P / 1. Synchronization of a plurality of epochs of the first plurality of satellites with a plurality of epochs of the second plurality of satellites is performed to provide uniform inter-plane satellite spacing for improved monitoring of an ICBM threat.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
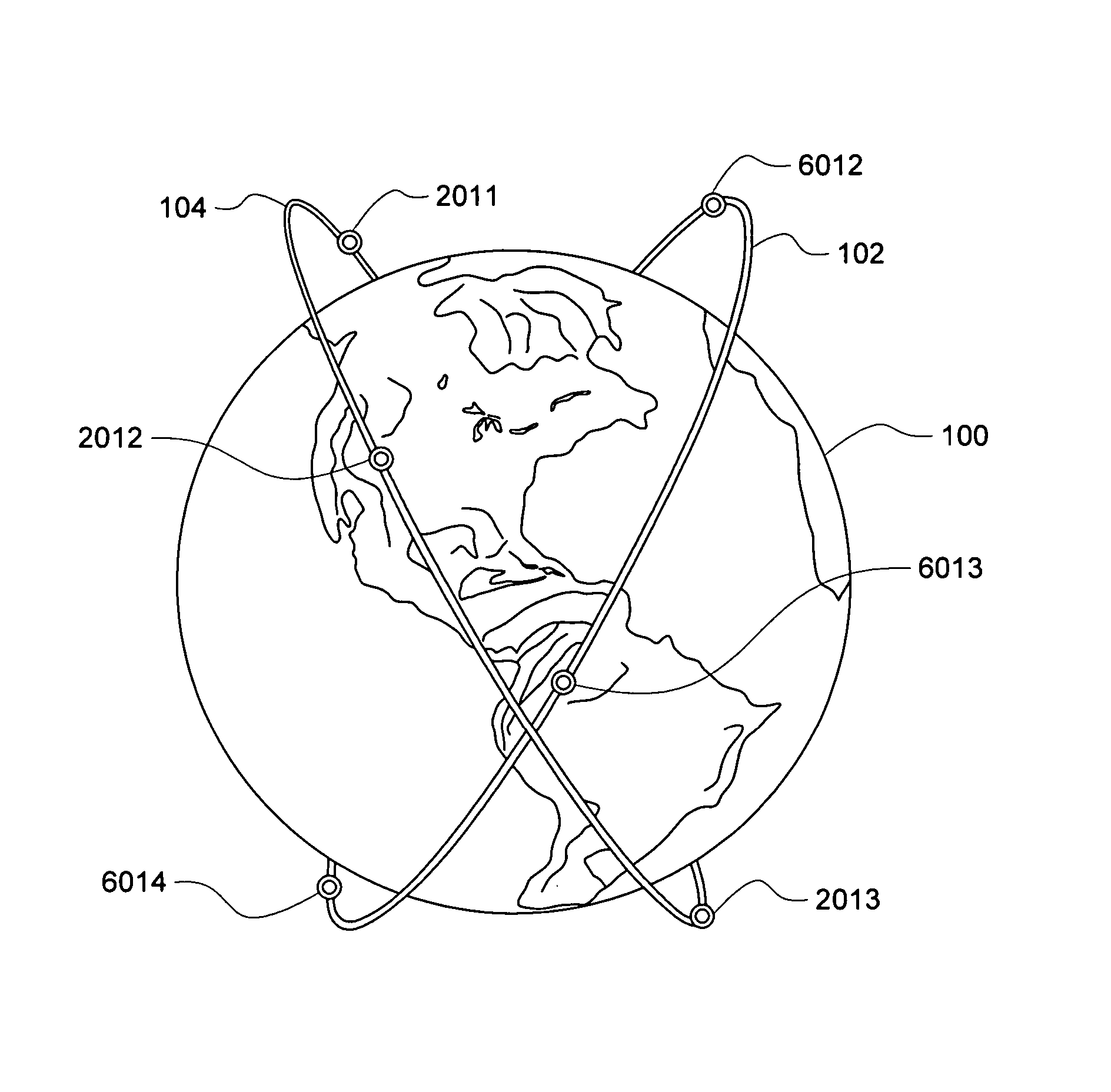
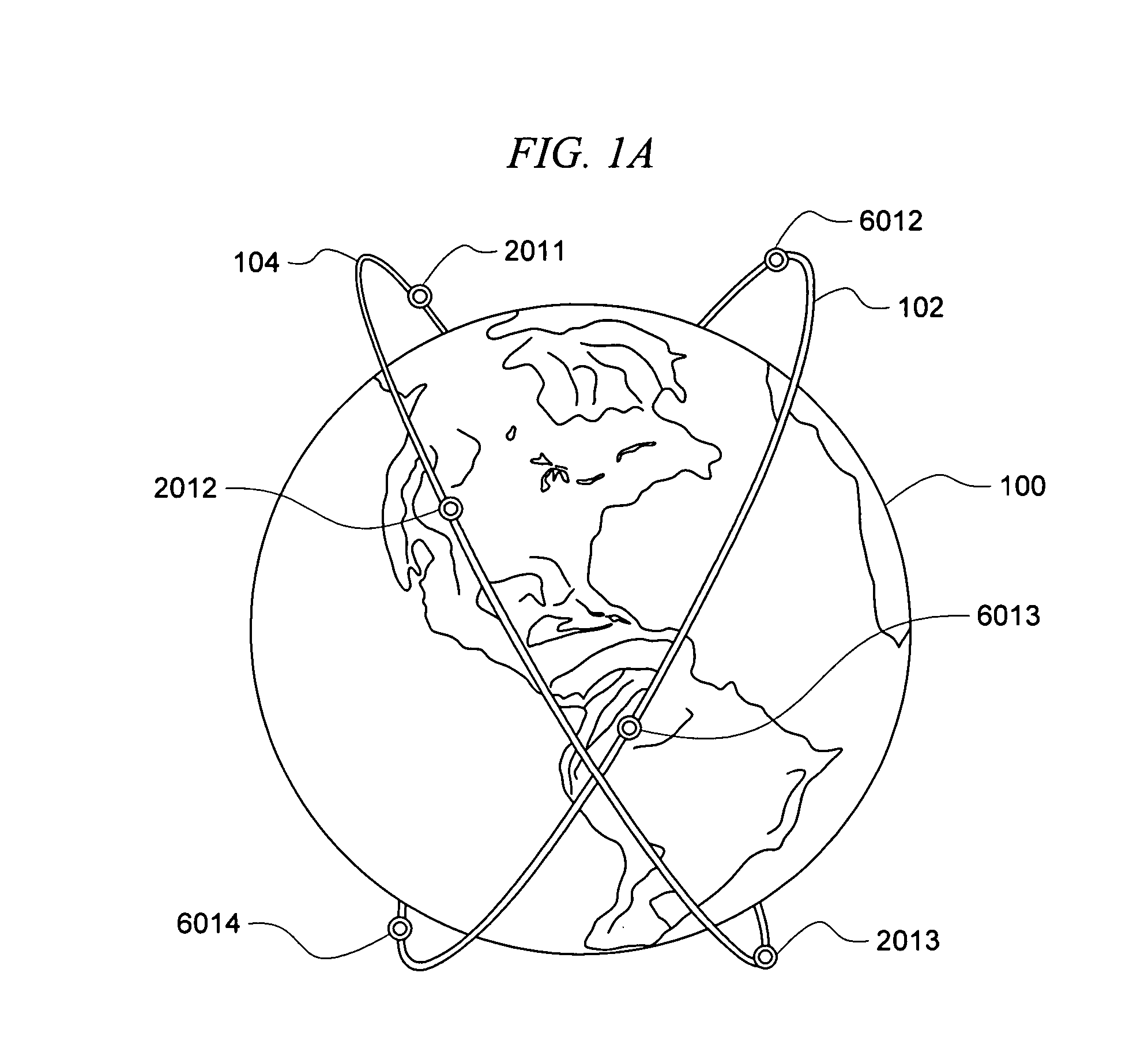
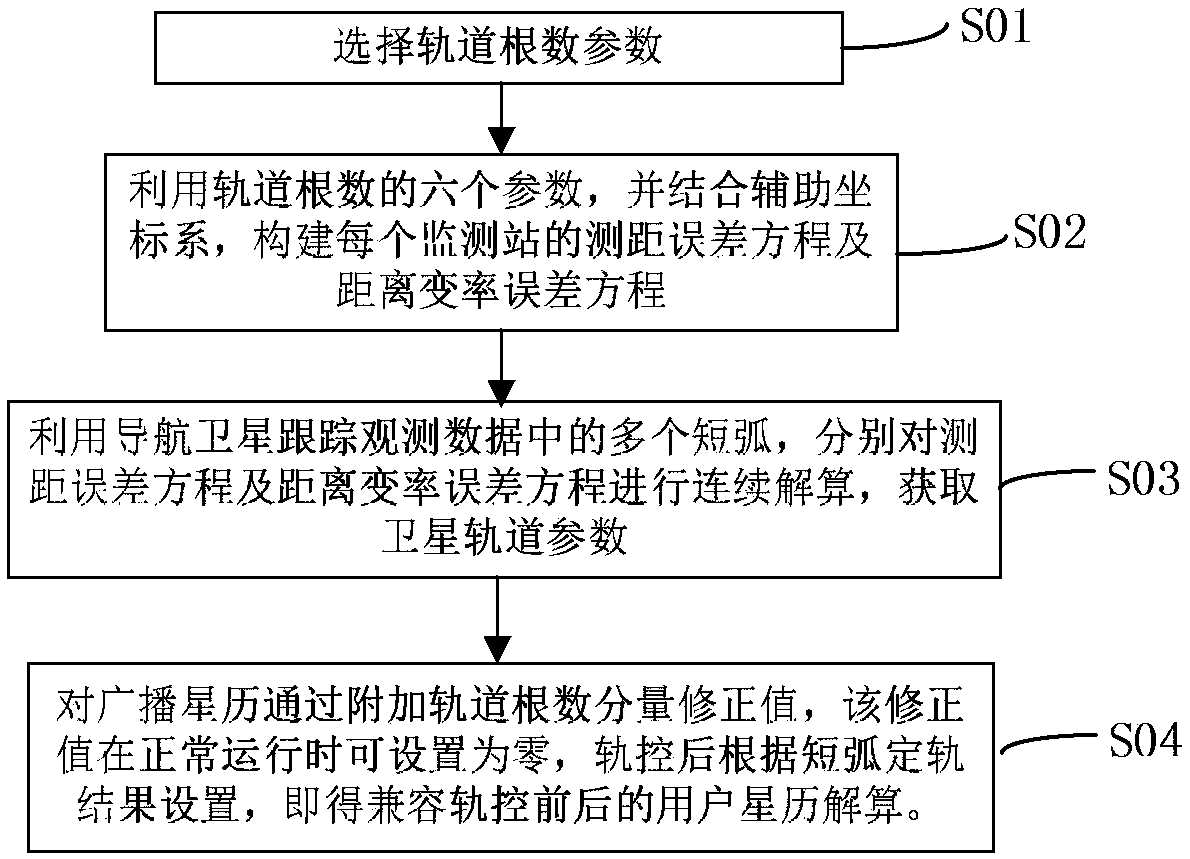
Navigation satellite orbit rapid recovery method based on short arc orbit determination and forecast
ActiveCN108761507AFast track back to normal useConvenient and seamless dockingSatellite radio beaconingRecovery methodRight-hand rule
The invention belongs to the technical field of navigation satellite precision orbit determination, and specifically relates to a navigation satellite orbit rapid recovery method based on short arc orbit determination and forecast. The navigation satellite orbit rapid recovery method based on short arc orbit determination and forecast includes the steps: through short arc orbit determination and short arc forecast, taking the distance from of the satellite at a reference epoch to the geocenter as the radial component, taking the distance from the satellite to the initial orbit plane as the secondary normal component, taking the third component defined according to the right hand rule of the coordinate system as the tangential component, taking the time rate of change of the radial component, the secondary normal component and the tangential component, and performing rapid recovery of the navigation satellite orbit through compatible user ephemeris calculation with an additional component correction value. The navigation satellite orbit rapid recovery method based on short arc orbit determination and forecast can realize seamless docking of the ephemeris solution method of the userbefore and after orbit control, can improve the accuracy of satellite orbit determination and forecast, can obtain the satellite precise orbit of the user application demand in a relatively short timeafter orbit control, and can make accurate forecast so as to enable the satellite to resume normal use and guarantee normal operation of the satellite system, and has important guiding significance for the technical field of navigation satellite orbit determination.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Pulse and pneumatic assistance combination-based low-orbit orbit plane transfer method
InactiveCN106383994AGreat changeabilityIncrease flexibilitySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsAviationDynamic equation
The invention discloses a pulse and pneumatic assistance combination-based low-orbit orbit plane transfer method, relates to a large-range orbit plane transfer method for an earth low-orbit spacecraft, and belongs to the field of aerospace. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing the number of orbits and a dynamic equation of a flight process in atmosphere; changing an orbit of the spacecraft to a highly elliptic orbit in a maneuvering manner by applying a pulse, and enabling the spacecraft to enter the atmosphere by applying an de-orbit pulse at an apogee; selecting an optimization target as a maximum change amount of an orbit plane, giving constraints and obtaining an optimal control rate and a terminal state variable meeting aerodynamic requirements, thereby finishing pneumatic assisted orbit plane transfer; and enabling the spacecraft to fly out of the atmosphere and run to a target orbit height along a transfer orbit, and enabling the spacecraft to enter a target orbit by applying an orbit determination pulse. According to the method, the orbit plane transfer of the low-orbit spacecraft can be finished with relatively low fuel consumption; and the method is good in robustness, high in repeatability, small in influence of spacecraft orbit orientation, high in flexibility of a pneumatic assistance process, and wide in application range for the target orbit.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Medium and low orbit constellation satellite beam frequency resource allocation method
The invention provides a medium and low orbit constellation satellite beam frequency resource allocation method. The medium and low orbit constellation satellite beam frequency resource allocation method comprises the steps of: performing initial sub-band allocation on each beam, and taking a certain fixed carrier in the sub-band allocated by each beam as the carrier of a broadcasting channel, wherein the initial sub-band of each beam is at least a sub-band; according to the odd number or even number of the orbit planes of the satellite constellation, determining a main orbit plane and a supplementary orbit plane; realizing coverage of partial areas to the ground including the two poles through single coverage composed of a satellite in the main orbit plane, and performing beam opening orclosing on the satellite in the supplementary orbit plane, so that the coverage of a blank area to the ground at the medium and low latitudes is completed; performing frequency resource allocation oneach terminal by taking the carrier as the unit, and, if the number of access terminals under a certain beam is beyond the user number born by the initial sub-band, increasing available sub-bands or carriers for the satellite beam; and realizing complete coverage. By means of the medium and low orbit constellation satellite beam frequency resource allocation method in the invention, constellationbeam frequency resource allocation can be realized better; and the method has the characteristics of being simple, high-efficiency and high in engineering practicability.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE INFORMATION ENG RES INST
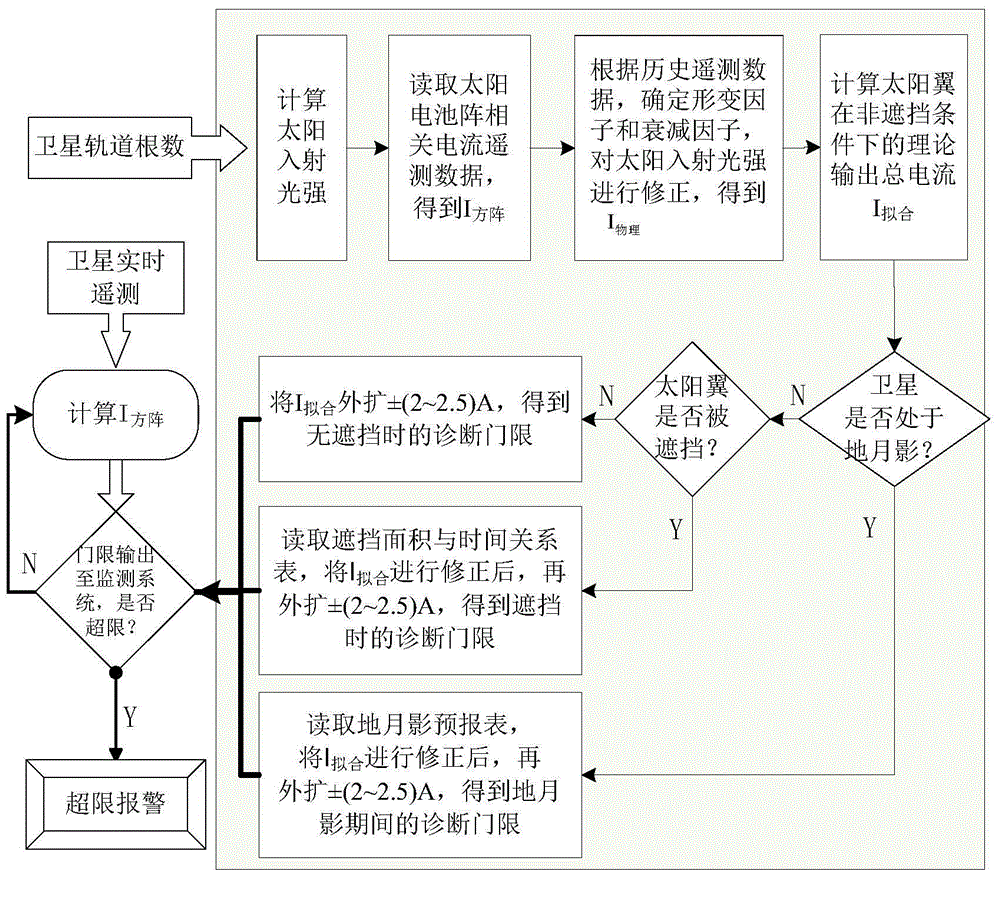
Fault diagnosis method for output current of on-orbit satellite solar cell array
ActiveCN104836529ASimple modelEasy to implementPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationUltrasound attenuationDiagnosis methods
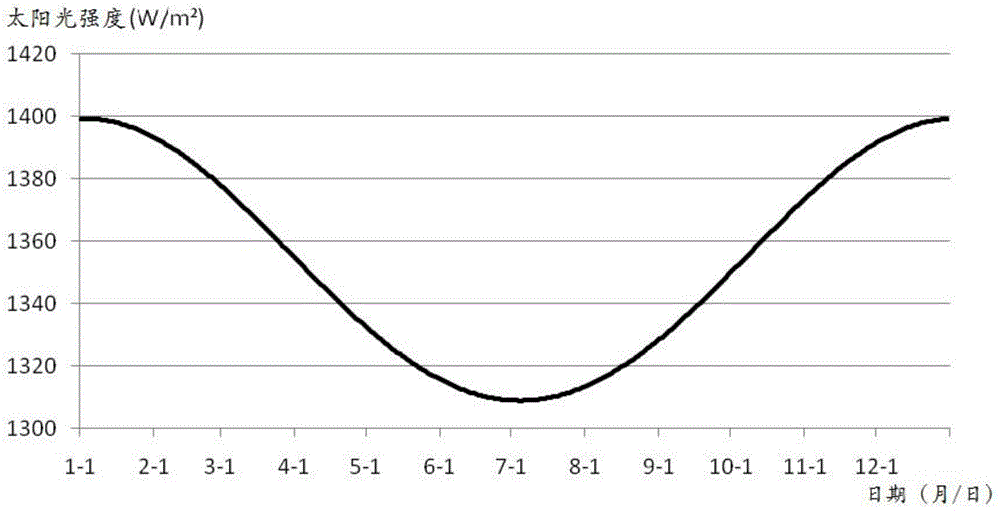
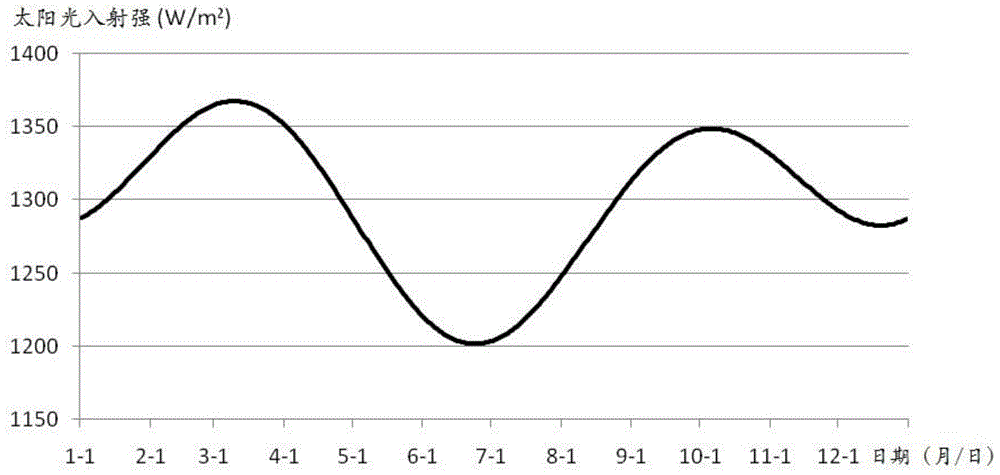
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method for output current of on-orbit satellite solar cell array. A simplified semi-physical model of the output current of the solar cell array is provided by being combined with actual on-orbit satellite telemetering historical data, on-orbit attenuation conditions of the on-orbit satellite solar cell array, the solar incident light intensity, an included angle between a sunlight vector and an orbit plane and the like, the physical model of the output current of the solar cell array is optimized by using epsilon.(cosbeta)<n>, and a dynamic alarm threshold of the output current of the solar cell array is acquired on the basis, thereby carrying out fault diagnosis on the solar cell array more accurately and more reasonably, and greatly reducing the risk of missing alarm while improving the fault diagnosis accuracy. In addition, the fault diagnosis method is moderate in calculation amount of the model, thereby being convenient for project implementation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Complimentary retrograde/prograde satellite constellation
A method for sensing and monitoring ICBM threats using a constellation of earth orbiting satellites. The method includes arranging a first and a second plurality of threat sensing satellites in earth orbit. The first plurality is selected to have a first prograde orbit plane with a first inclination angle between about 30° to 70° with respect to the earth's equator and an Argument of Perigee equal to about 270°. The second plurality is selected to have a first retrograde orbit plane with a second inclination angle between about 110° to 150° with respect to the earth's equator and an Argument of Perigee equal to about 270°. The second inclination angle is selected to be a symmetric conjugate of the first inclination angle. The first and second plurality of threat sensing satellites are distributed respectively within the first prograde and first retrograde orbits with a Walker distribution of T / P / 1. Synchronization of a plurality of epochs of the first plurality of satellites with a plurality of epochs of the second plurality of satellites is performed to provide uniform inter-plane satellite spacing for improved monitoring of an ICBM threat.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
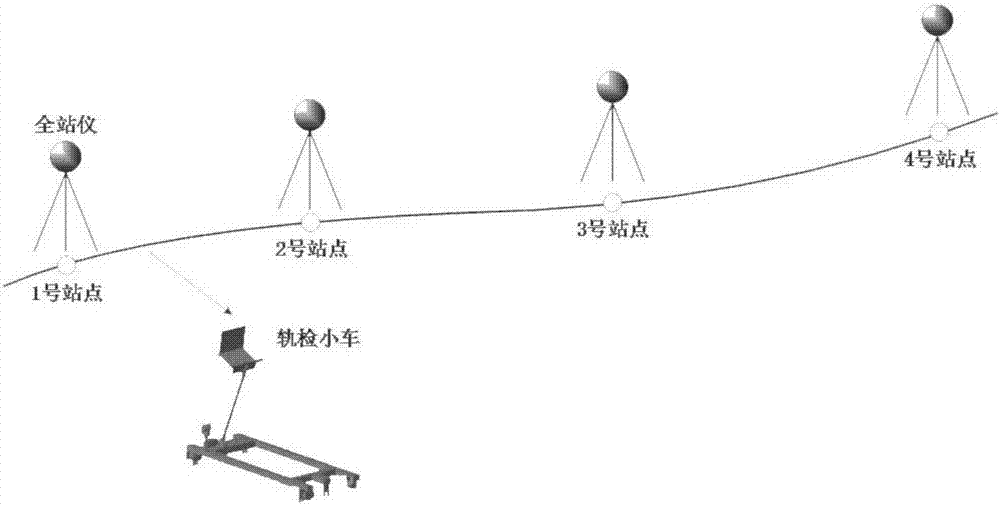
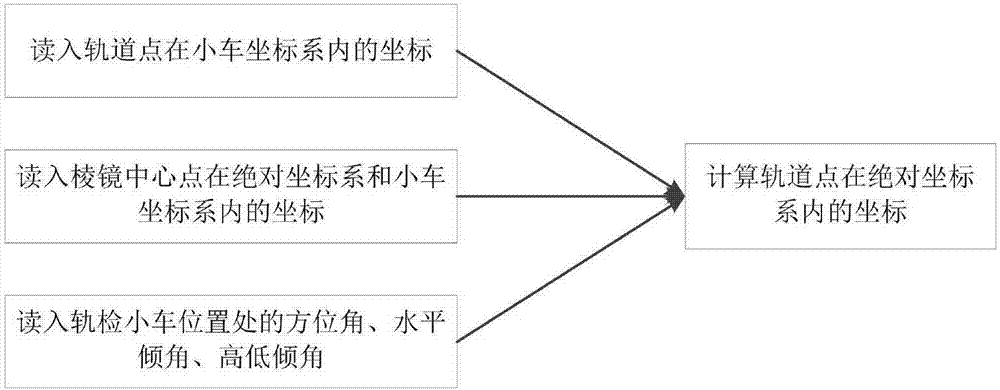
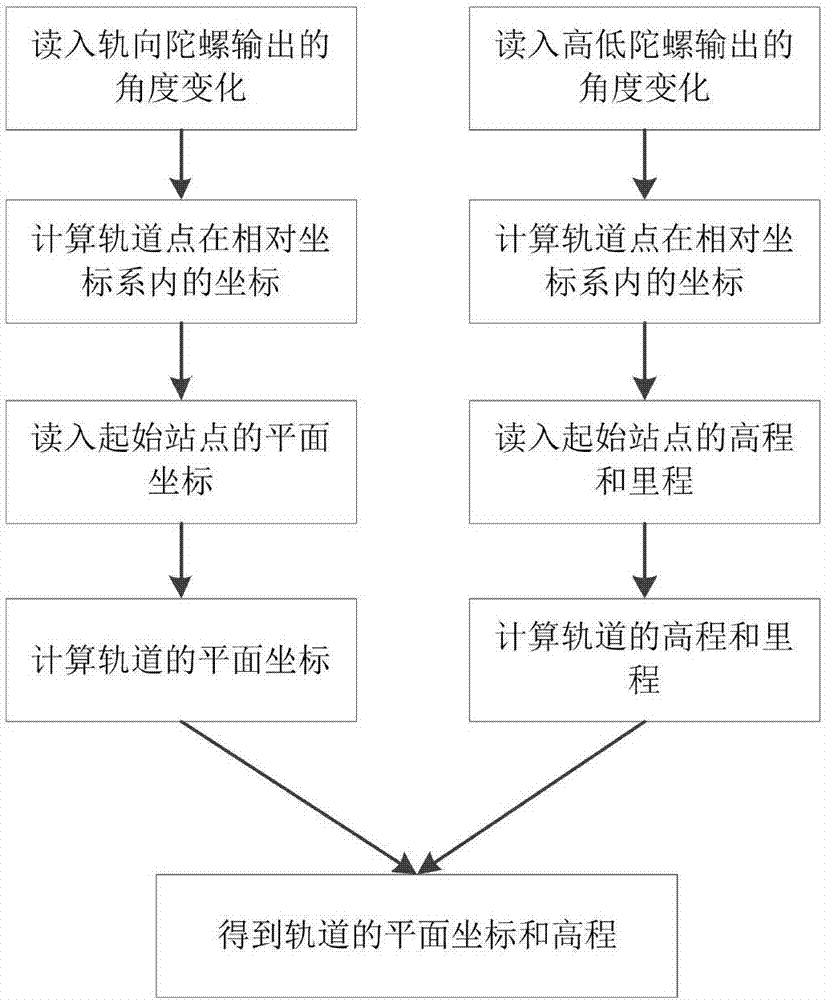
Method for detecting geometric states of tracks on basis of combined measurement
InactiveCN107128328AImprove detection efficiencySave manpower and material resourcesHeight/levelling measurementRailway auxillary equipmentPrismAbsolute measurement
The invention discloses a track geometric state detection method based on combined measurement, which comprises the following steps: setting stations at regular intervals on a complete detection line; The coordinates of the center point of the prism on the track inspection trolley in the absolute coordinate system when it is at the position of each station, according to the installation position of the center point of the prism on the track inspection trolley, the coordinates of the center point of the prism in the coordinate system of the track inspection trolley when it is at each station position ; Obtain the coordinates of the track points in the absolute coordinate system according to the azimuth, horizontal inclination, and high and low inclination angles of the track inspection trolley at each station; when performing relative measurements between stations, use the track inspection trolley to sample at equal intervals to obtain the geometric state of the track Relative information, the planar coordinates and elevations of all inter-site tracks are calculated. The invention combines the advantages of relative measurement and absolute measurement, and can realize rapid and high-precision measurement of track plane coordinates and elevation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Novel rotating miller
InactiveCN101648287AEasy to locate and installLow costLarge fixed membersMilling equipment detailsEngineeringOrbit plane
The invention discloses a novel rotating miller which comprises a main beam that is connected with an electric appliance cabinet; a drag link mechanism is arranged above the main beam, a workbench isarranged below the main beam, a rotating mechanism is arranged at the lower end of the workbench, and a left beam and a right beam are arranged at the left end and the right end of the main beam, wherein the right beam is connected with a longitudinal beam, the left beam and the right beam are connected to a power cutting head, a support structure is arranged at the side of the connection part ofthe main beam and the right beam, and alarm lamps are arranged at two ends of the main beam. The invention has good security, small volume, convenient installation and gas milling speed and can achieve the advantages that two annular orbit planes are processed simultaneously after once positioning, and the parallelism degree is high after being processed.
Owner:NANTONG ZHENHUA HEAVY EQUIP MFG
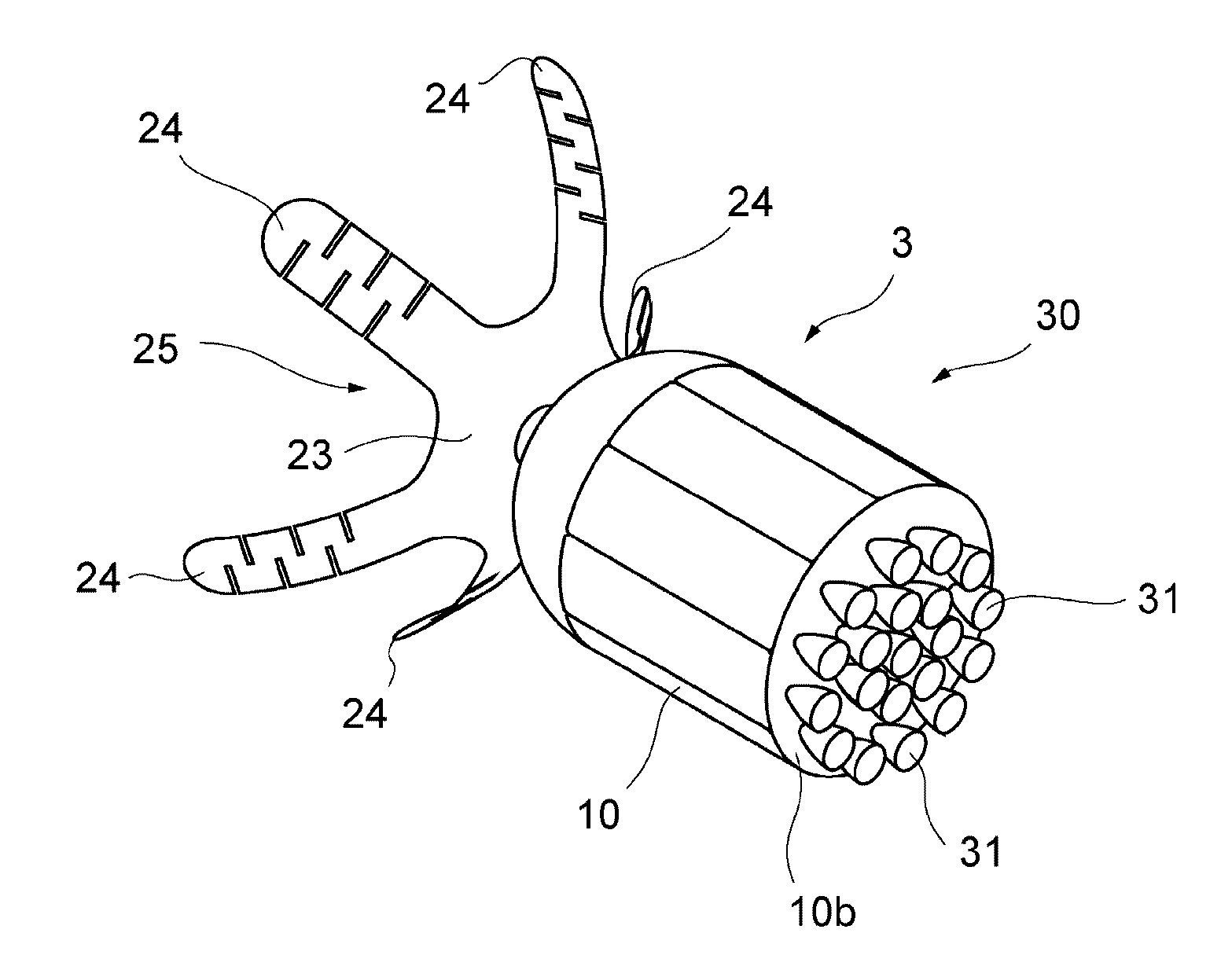
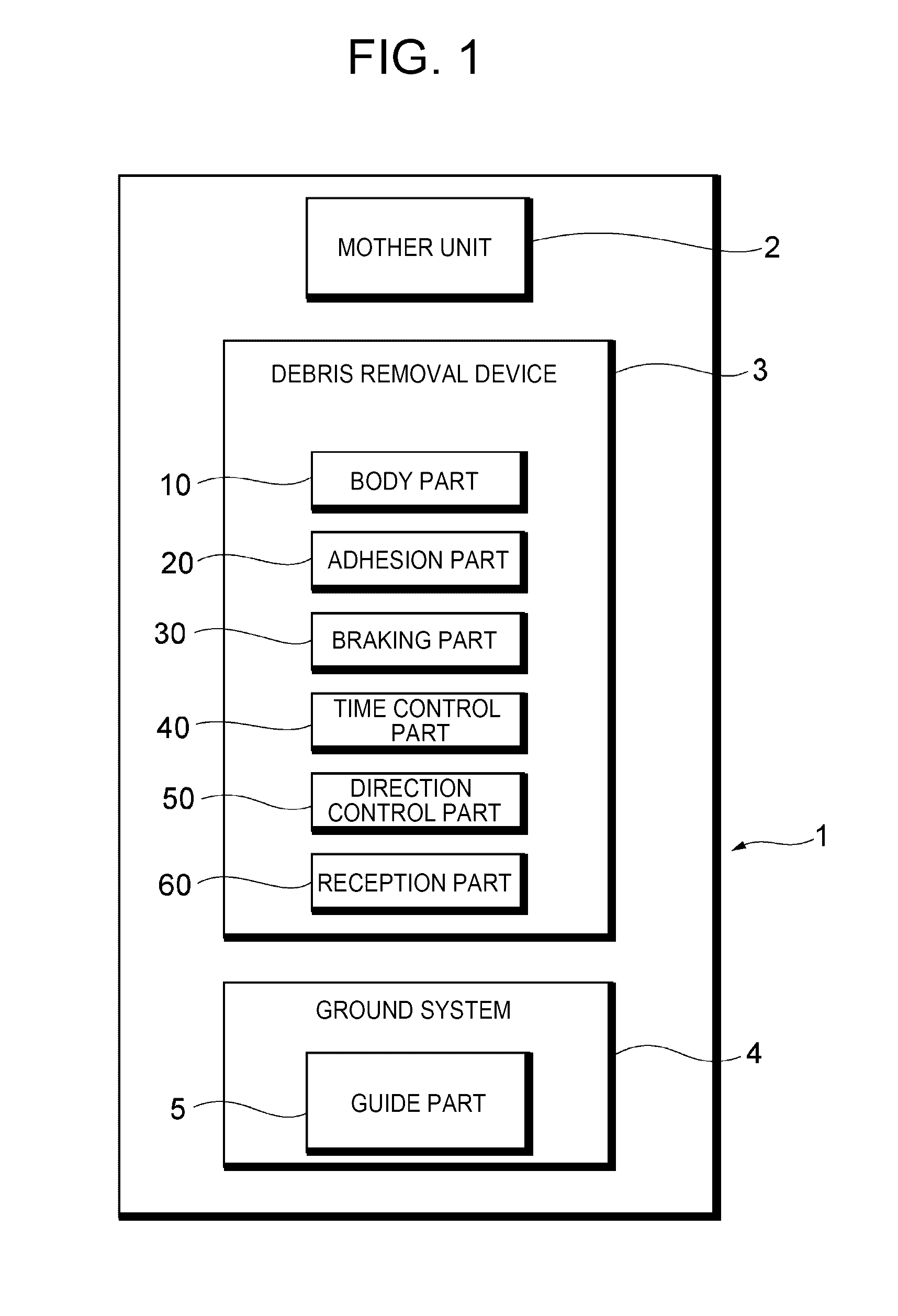
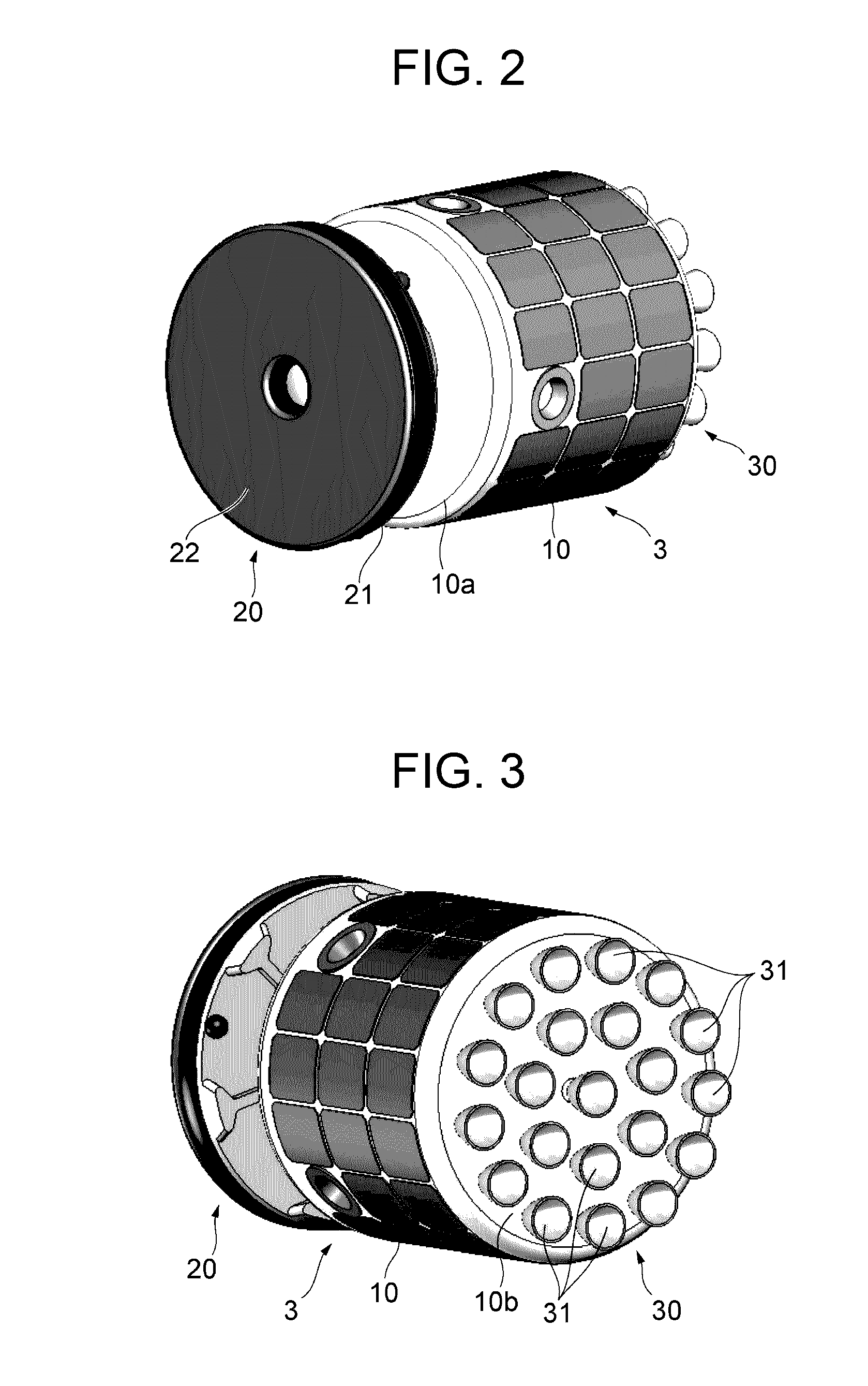
Debris removal device and debris removal system
InactiveUS20170015444A1Save spaceEfficient removalCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusEngineeringBrake force
A debris removal device includes: a body part; an adhesion part to let the space debris adhere to the body part; a braking part to generate braking force in a specific direction, to act on the space debris adhering to the body part via the adhesion part during circling of the body part around the orbit together with the space debris; and a timing control part to control generation timing of the braking force. The timing control part generates the braking force, during circling of the body part together with the space debris around the orbit, when the body part is located at a specific region on the orbit where a direction of the braking force is substantially parallel to an orbit plane including the orbit and substantially parallel to a tangential line of the orbit, and in substantially an opposite direction of a circling direction of the space debris.
Owner:ASTROSCALE JAPAN
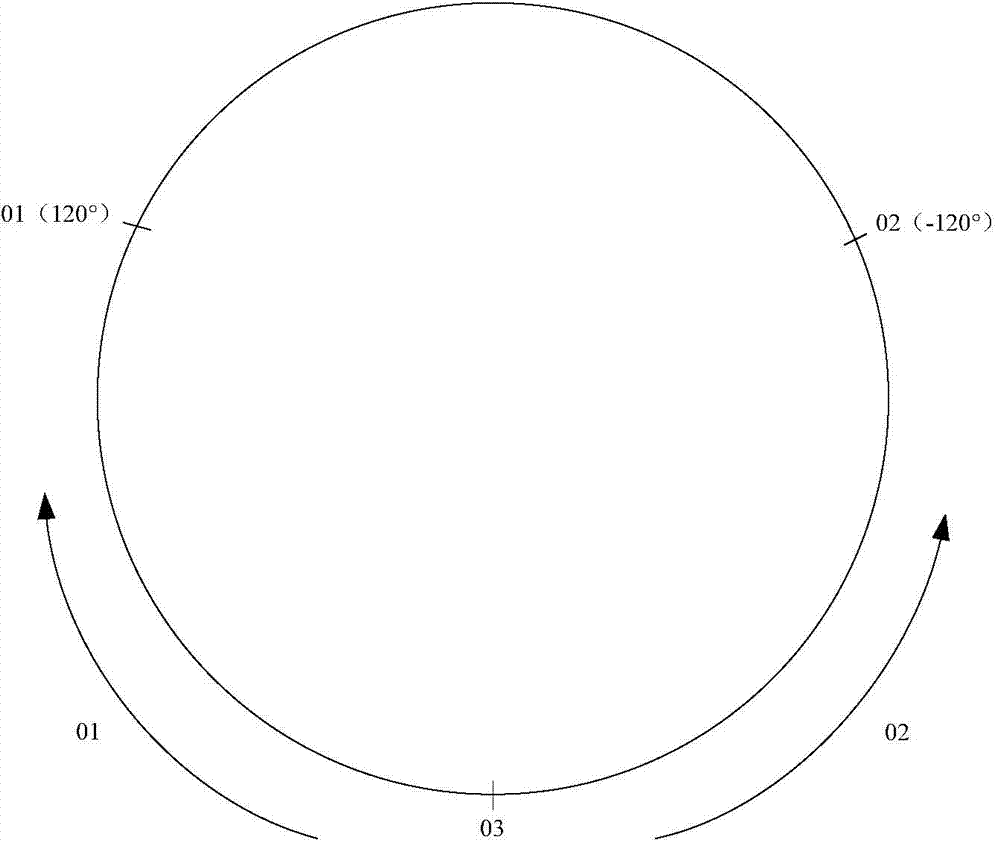
Structure variable mixed-orbit satellite constellation
ActiveCN106788671AIncreased global coverage multiplicityImprove self-management abilityNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionNatural satelliteLow latitude
The invention discloses a structure variable mixed-orbit satellite constellation, comprising a GEO (Geosynchronous Orbit) sub constellation, an IGSO (Inclined Geo Stationary Earth Orbit) sub constellation and an MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) sub constellation. The GEO sub constellation comprises n GEO satellites distributed on n orbit positions of a geosynchronous orbit, and coverage areas between the adjacent satellites are connected and cover medium and low latitude areas in a full longitude manner. The IGSO sub constellation comprises five IGSO satellites, wherein the IGSO1, IGSO2 and IGSO3 satellites are located in the same orbit plane, and the phase difference between the adjacent satellites is 120 degrees; and simultaneously, the IGSO3, IGSO4 and IGSO5 satellites have the same ground track. The MEO sub constellation comprises m*k satellites distributed on k orbit planes, m satellites are on each orbit plane, and the MEO sub constellation has global coverage capability. When the structure of the constellation is reconstructed, the IGSO4 and IGSO5 satellites flexibly enter an HEO (High-altitude Earth Orbit) and run. The constellation has excellent global coverage capability, self management capability and flexible and variable structure.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
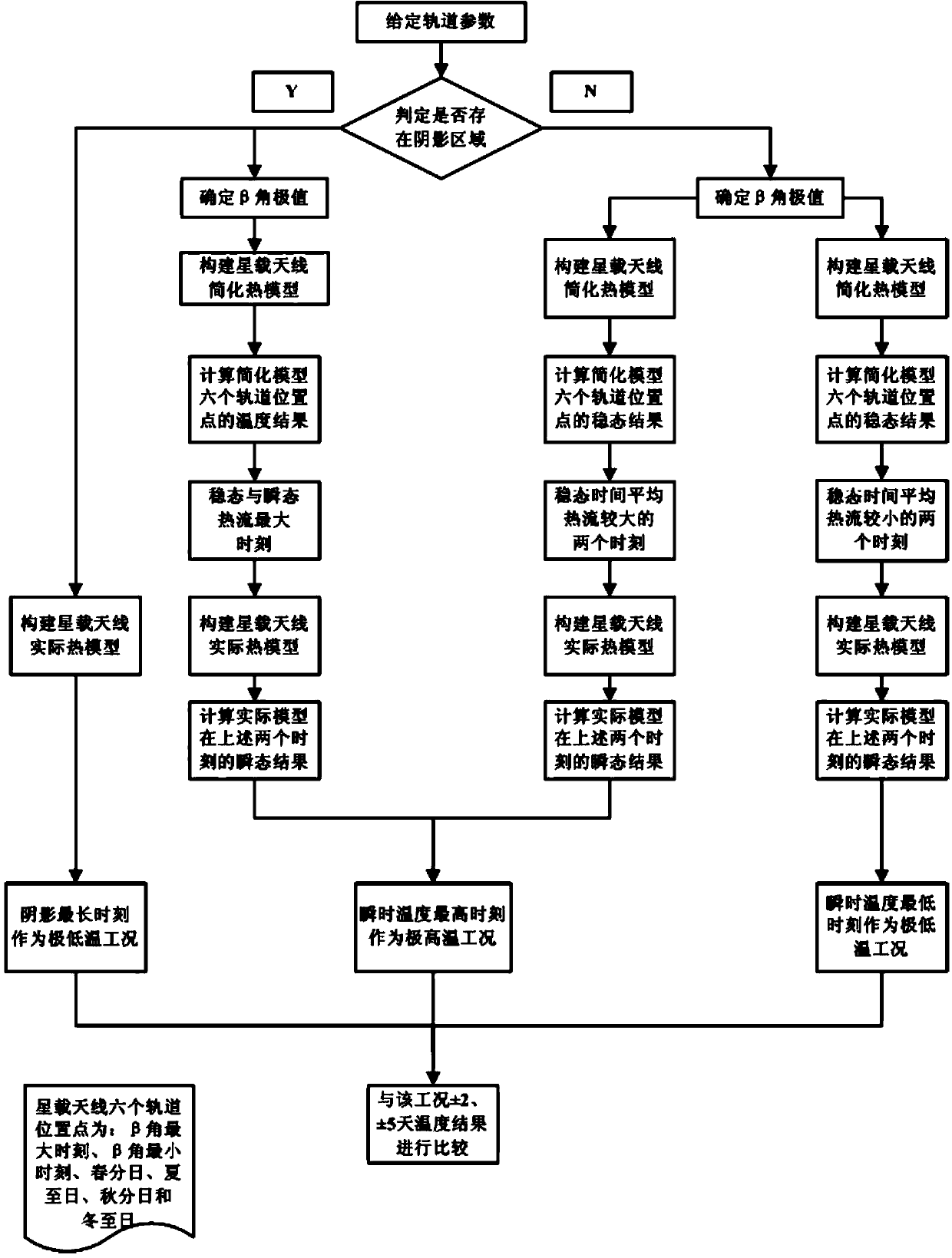
Method for forecasting extreme working conditions of in-orbit temperatures of spaceborne antenna
InactiveCN103778348ATo achieve the purpose of extreme working conditionsSpecial data processing applicationsHeat flowPredictive methods
The invention discloses a method for forecasting extreme working conditions of in-orbit temperatures of a spaceborne antenna. The method comprises the steps of (1) calculating the change rule of the incident angles beta of the sun relative to an orbit plane within one year through given orbit parameters, (2) calculating a shined factor through the change rule of the angles beta within the year according to the parameters given in the step (1) and then determining whether a shadow moment exists within one period, (3) forecasting the extreme low-temperature working condition of the spaceborne antenna according to the existence of the shadow moment or not determined in the step (2), (4) forecasting the extreme high-temperature working condition of the spaceborne antenna according to the existence of the shadow moment or not determined in the step (2), (5) comparing each extreme temperature working condition with temperatures of 2 days and 5 days before and after the data of the working condition, and taking the temperature in the temperature working condition TMax as the extreme high-temperature working condition and the temperature in the temperature working condition TMin as the extreme low-temperature working condition. The method targets at the spaceborne antenna, and is capable of determining the shined factor of the orbit within the year by calculating the change rule of the incident angles beta of the sun relative to the orbit plane and then determining the dates of the extreme working conditions of the orbit; as a result, the extreme temperatures of the spaceborne antenna are calculated by loading an extremum heat flow by an envelope method, and then the purpose of forecasting the extreme working conditions of the spaceborne antenna is achieved.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD +1
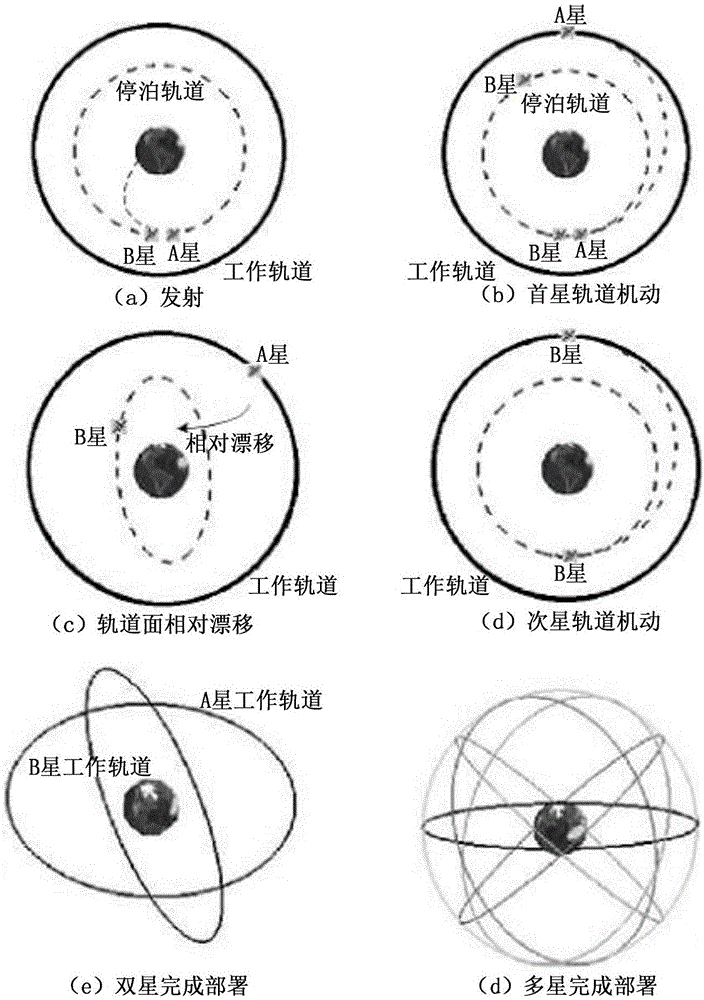
Walker constellation deployment method based on double berthing orbits
ActiveCN106802667ASolve the shortcomings of the long deployment cycle of different planesOptimizing Deployment Accuracy AnglePosition/course control in three dimensionsDeployment timeEngineering
The invention provides a Walker constellation deployment method based on double berthing orbits. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, delivering satellites for deploying a Walker constellation to a first berthing orbit and the second berthing orbit respectively; S2, enabling the first satellite to enter a working orbit through orbital maneuver and enabling the remaining satellites to remain in the first berthing orbit and the second berthing orbit; S3, waiting for the precessional motion of the orbital surface of the current berthing orbit relative to the orbital surface of a working orbit of an adjacent satellite until an ascending node of orbital surface and the right ascension have a preset angle, and then enabling the next satellite to enter the working orbit through orbital maneuver, and in the same way, enabling all the satellites for deploying the Walker constellation to enter the working orbits successively. The method can solve the limitation of a single-orbit plane deployment using one rocket with multi satellites, and solve the long single-berthing-orbit different-surface deployment period of the one rocket with multi satellites, and optimizes constellation deployment time and satellite deployment precision angle of the satellite relative position.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
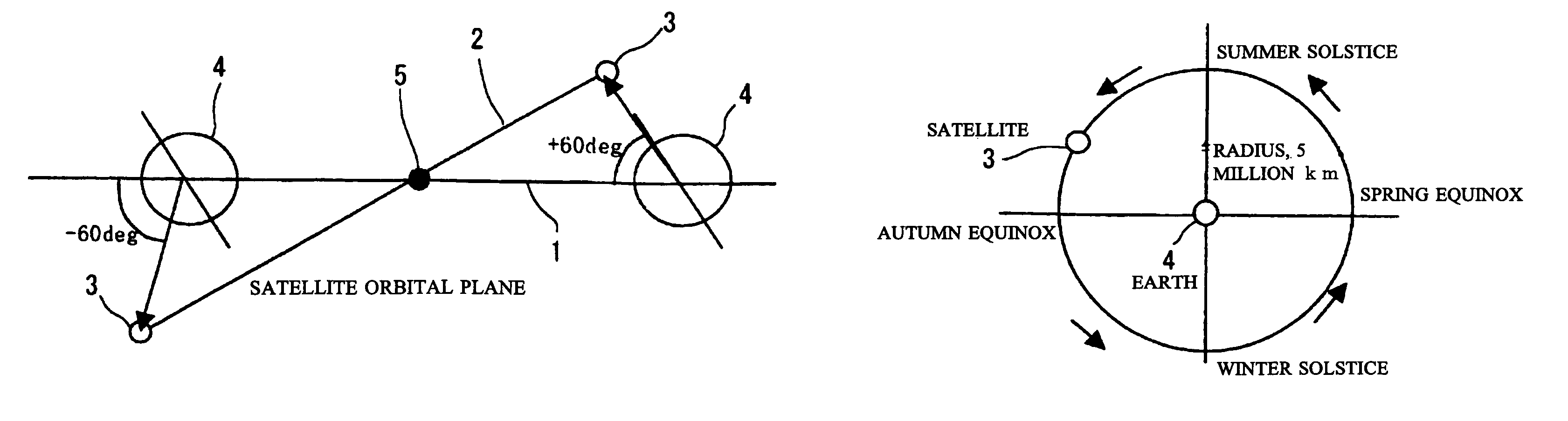
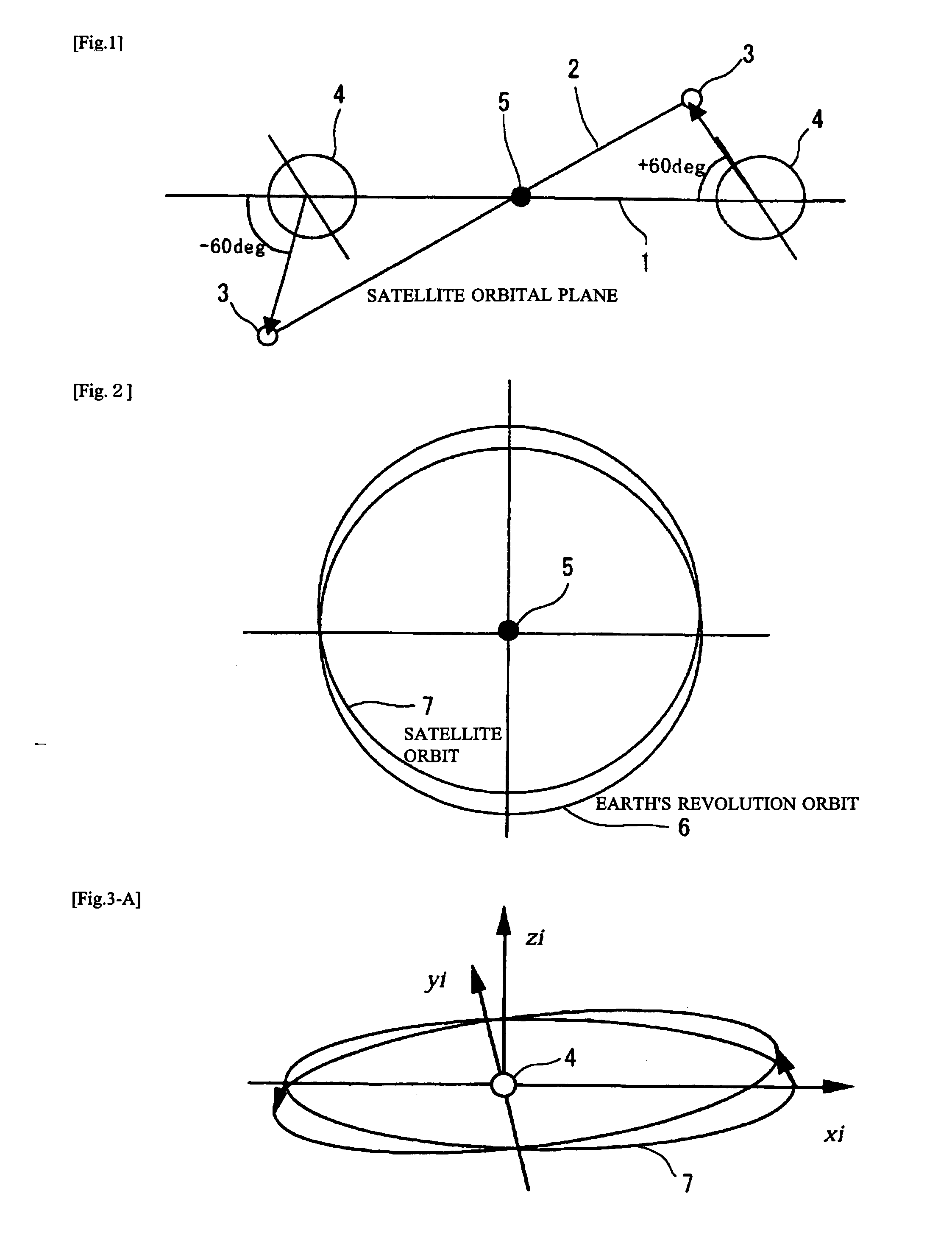
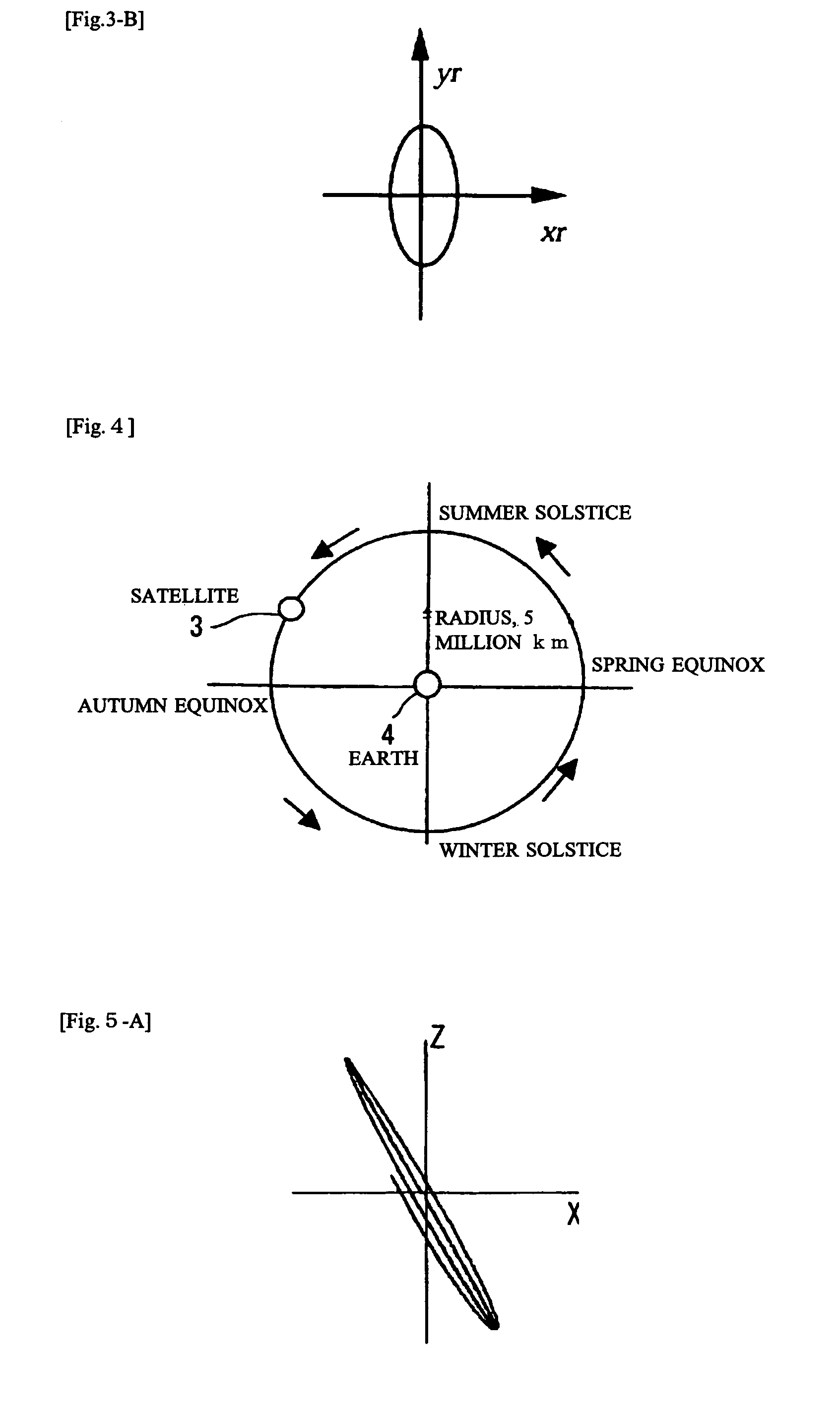
Ultrahigh altitude sun-synchronous orbit satellite system
InactiveUS7806369B2Increase distanceImprove accuracyArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusNatural satelliteElliptic motion
An ultrahigh altitude sun-synchronous orbit satellite system having one or plural satellites orbiting the sun such that the satellites revolve around the earth in a substantially circular or elliptic motion at an altitude of several million kilometers from the earth, beyond the sphere of earth gravity influence. The satellites are placed on an orbital plane relative to both the sun and the earth and keep a distance and geometry between the satellites, sun and earth substantially constant. The satellite system performs any one of the services of space observation, global observation, and satellite communication. The satellites orbit the sun with both inclination and eccentricity distinct from those of the revolution of the earth and revolve around the earth with a sun synchronous property in which the local solar time is kept constant at a point on the surface of the earth directly beneath the satellite.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
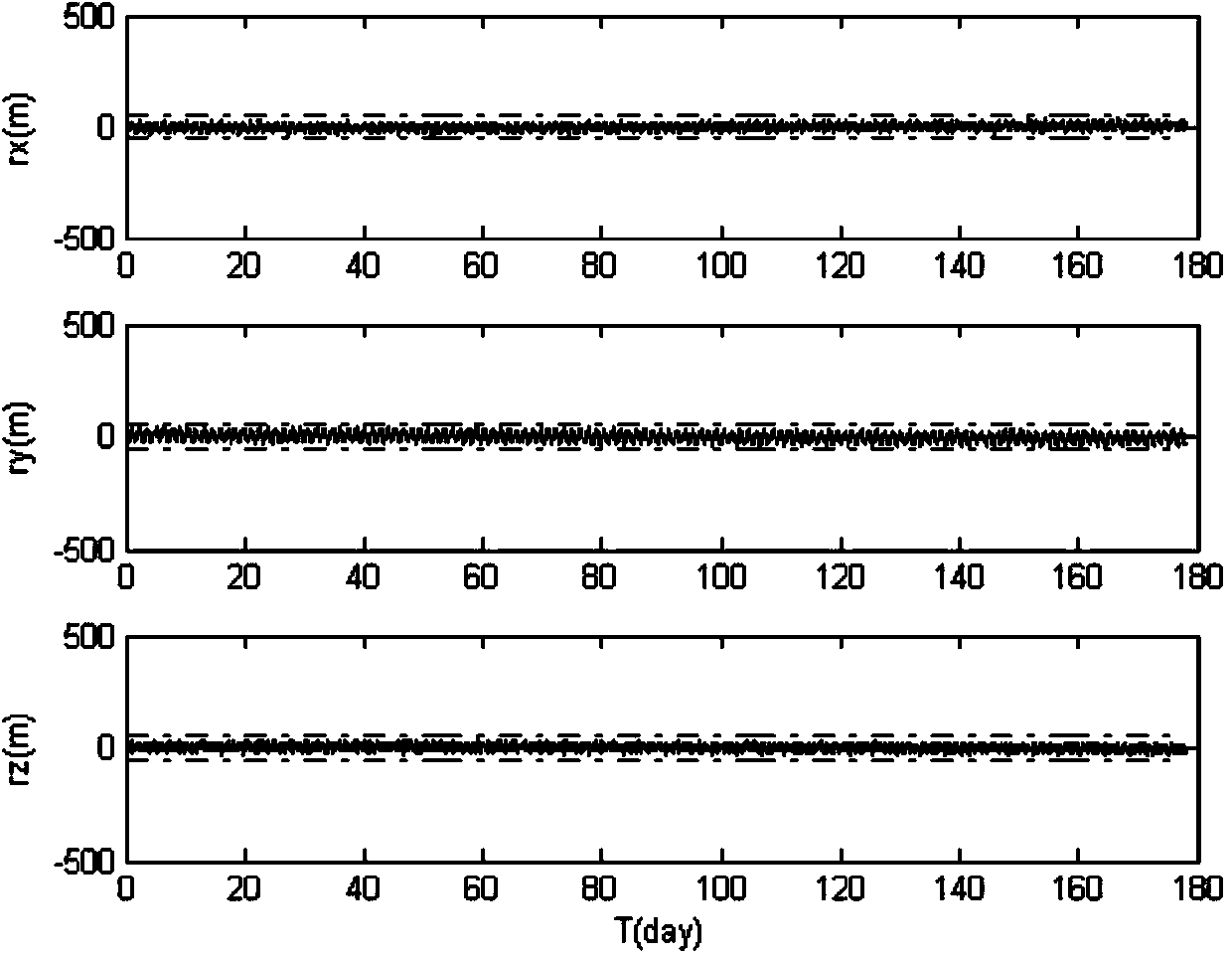
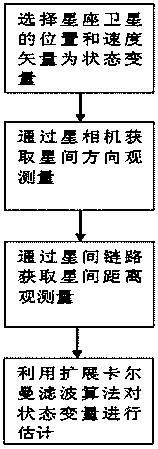
Constellation navigation method based on coplanar inter-satellite direction measurement and different-plane inter-satellite distance measurement
InactiveCN103954281AImprove ranging accuracyNavigation by astronomical meansSurvivabilityDynamic equation
The invention discloses a constellation navigation method based on coplanar inter-satellite direction measurement and different-plane inter-satellite distance measurement. The method comprises the following steps: performing inter-satellite direction measurement between adjacent satellites on the same orbit plane through a satellite camera photographic observation mode aiming at a constellation consisting of multiple satellites, performing inter-satellite distance measurement through an inter-satellite link, establishing the inter-satellite link among satellite constellations on different orbit planes, and performing inter-satellite distance measurement; fusing the measurement information of relative positions between the satellites on the same orbit plane and inter-satellite distance measurement information on different orbit planes by adopting an extended Kalman filter (EKF) algorithm, and estimating the position vectors and speed vectors of satellites taking participate in navigation by combining with an orbital dynamics equation. The method can be used for realizing a constellation satellite autonomous navigation task with high precision requirement and contributes to reducing the dependence degree of satellites on ground control and enhancing the independent survival capacity of a satellite system in the case of emergency.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method for determining intersection coordinates of satellite wave beam and earth
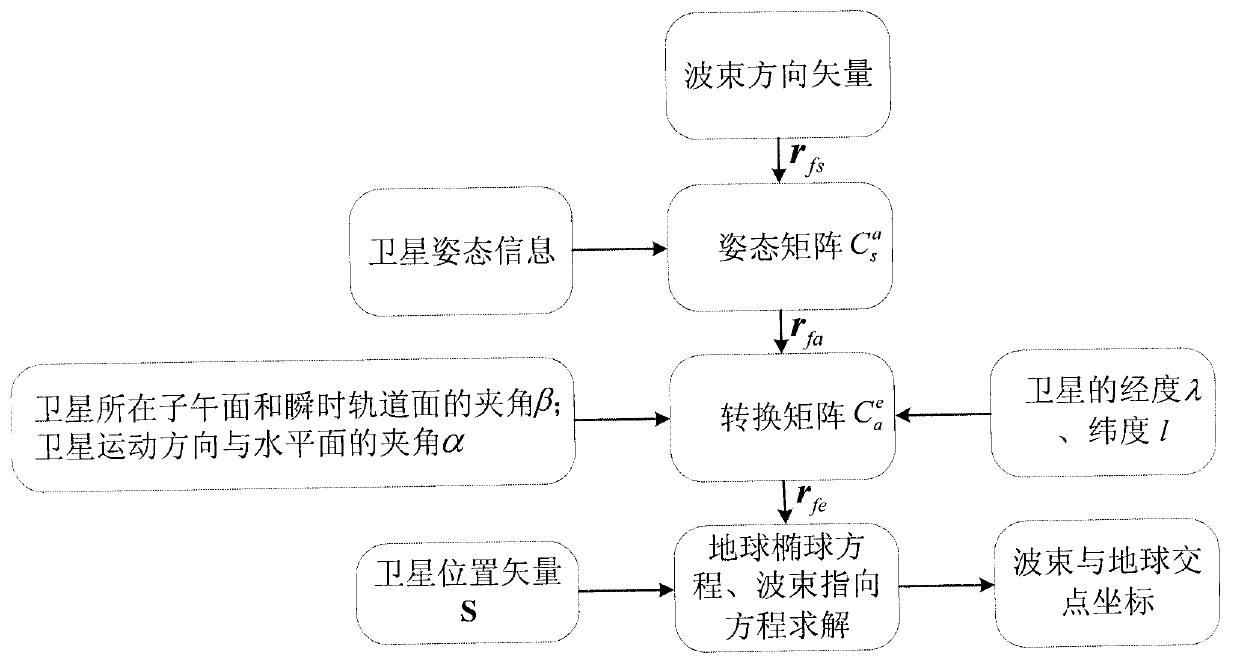
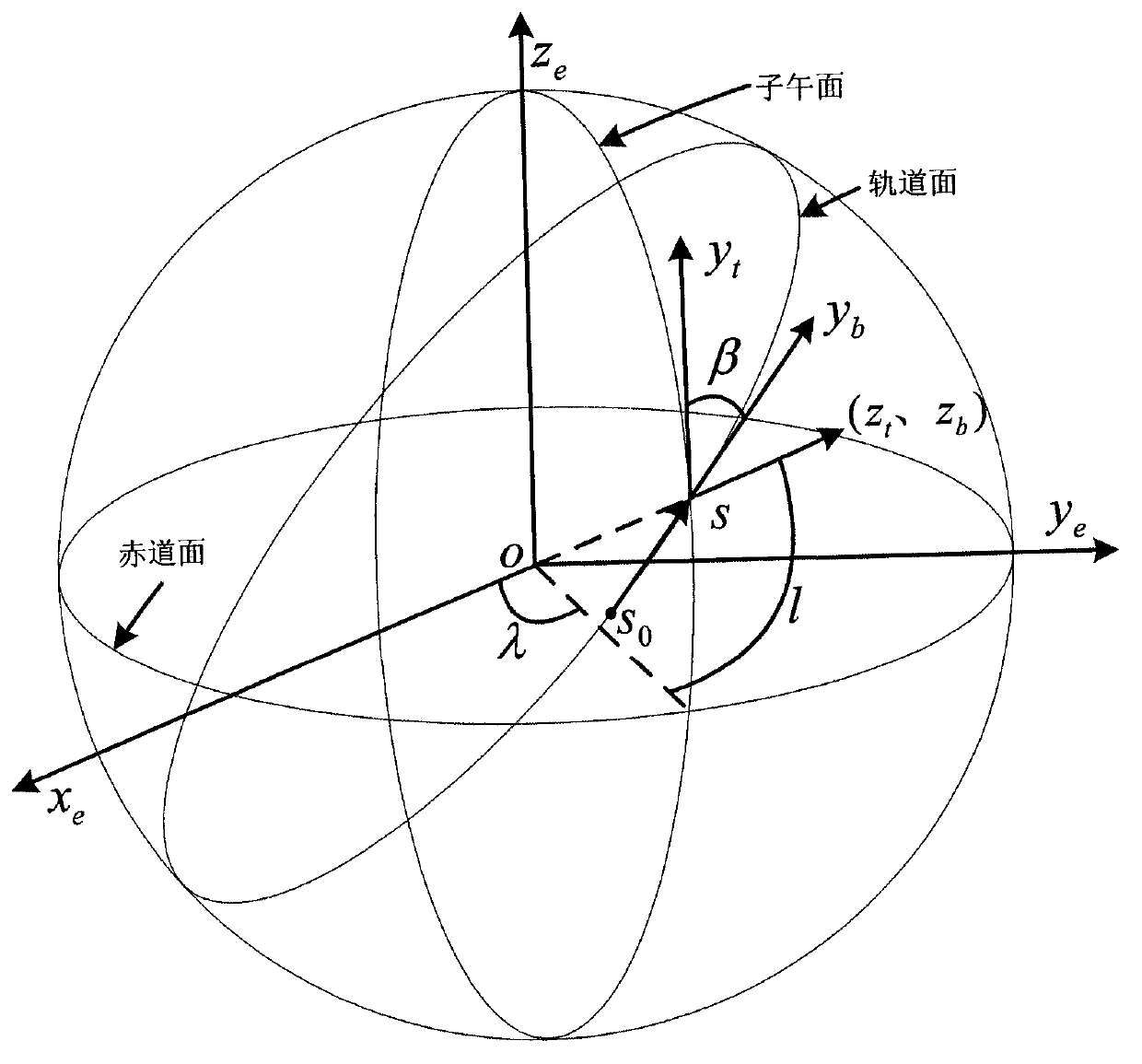
ActiveCN102819019AEasy accessImprove reliabilityIndication/recording movementFluid speed measurementLongitudeGeographic coordinate system
The invention discloses a method for determining intersection coordinates of a satellite wave beam and the earth. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) seeking a unit vector rfs of the satellite wave beam in a satellite body coordinate system; (2) calculating a conversion matrix of the satellite body coordinate system and a satellite track coordinate system by a yaw angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle of a satellite; (3) calculating the conversion matrix of a geographic coordinate system and an earth coordinate system by longitude lambda and latitude I of the satellite; (4) calculating the conversion matrix of an auxiliary coordinate system and the geographic coordinate system by an included angle beta of a meridian plane on which the satellite is and an instantaneous orbit plane of the satellite and an included angle alpha between a movement direction of the satellite and a geographic horizontal plane; (5) converting the unit vector rfs into the earth coordinate system to obtain rfe by coordinate system conversion; (6) associating a linear parameter equation of satellite beam incidence with an earth ellipsoid equation, and calculating two groups of coordinates [xje, yje and zje]T, wherein a group of coordinates near the satellite are coordinates of an intersection point of the satellite wave beam and the earth.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Full-simulating sun-moon-earth instrument
The invention relates to a full-simulating sun-moon-earth instrument which comprises a sun rotation and lighting device, an earth rotation device, an earth revolution device, a moon rotation device, a moon revolution device, an earth-moon rising and dropping device, and speed regulating and control circuits, wherein the earth-moon rising and dropping device is arranged at the external end of a long arm of the earth revolution device; the earth rotation device, the moon revolution device, the moon rotation device and the moon rising and dropping device are arranged on the earth-moon rising and dropping device; all the devices above run around the sun at the centre; and the full-simulating sun-moon-earth instrument is characterized in that the earth synchronously rises and drops during performing the revolution around the sun, and the moon synchronously rises and drops during performing the revolution around the earth; with the adoption of the composite motion, the due intersect angles can be formed between an earth revolution orbit plane and the sun equator plane and between a moon revolution orbit plane and the earth equator plane; the speed ratio of the sun to the moon to the earth under the rotation and the revolution can be similar to the actual speed ratio by carrying out electronic speed regulating; and the star image drawn on a transparent celestial sphere is similar to the actual star image, therefore, the running of the three balls can be comprehensively and really displayed in a three-dimensional and vivid way, and the running rules and resulting astronomical phenomena and the natural phenomena can be popularly and quickly indicated; and the practical significance is brought to popularization of the astronomical knowledge.
Owner:万林
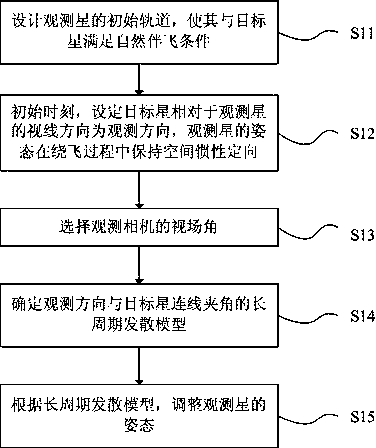
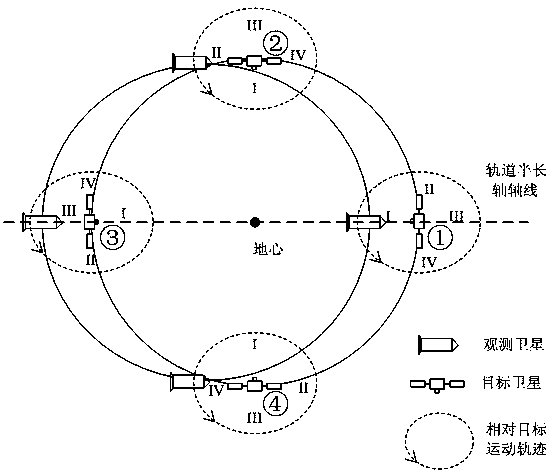
Same orbit plane satellite observation orbit design method under nature accompanying condition
ActiveCN105512374AReduce maneuvering requirementsLow costSpecial data processing applicationsTime cyclesSatellite observation
The invention discloses a same orbit plane satellite observation orbit design method under a nature accompanying condition; the method comprises the following steps: designing an observation satellite initial orbit satisfying the nature accompanying condition with a target satellite; setting a visual direction, relative to the observation satellite, of the target satellite as the observation direction, and keeping space inertia orientation of the observation satellite in a flying process; selecting a visual angle of an observation camera; determining an observation direction and target satellite connecting line angle long-time cycle radiate model; adjusting the observation satellite gesture according to the long-time cycle radiate model. The satellite observation orbit design method can reduce the observation satellite space flying orbit gesture orbit coupling maneuvering requirement; a control system and an execution mechanism are simple, and cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
Ultrahigh Altitude Sun-Synchronous Orbit Satellite System
InactiveUS20080029650A1Increase distanceImprove accuracyArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSynchronous orbitCelestial sphere
A system which comprises a sun-synchronous orbit satellite (3) revolving around the sun (5) and apparently revolving around the earth at a period of approximately one year while keeping the direction and the geometry to the sun and the earth (4) constant at an ultrahigh altitude of several millions km keeping clear of the influence zone of the earth, and which provides any of astronomical or global observation service and communication service. An observation satellite, which meets such conditions that a vector normal to a virtual orbital plane centering around the earth is substantially fixed regardless of revolution, can sweep the substantially entire celestial sphere during a single revolution while avoiding the effect of light and heat from the earth, and can keep a local solar time at a sub-satellite point on the surface of the earth constant, can be attained. A communication satellite, where the substantially hemisphere of the earth can be covered at a time simultaneously with one satellite and the substantially entire region of the earth can be covered with a small number or three satellites, is attained. Geometrical relations with the sun and the earth can be frozen approximately by the adjustment of the i / e ratio or by the use of perturbation by the attraction of the earth gravity. Operation from launch to insertion into an intended orbit can be achieved with significantly low fuel consumption by utilizing the perturbation owing to the attraction of the earth gravity.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Method and system for driving solar wing to face the sun through low-inclination-angle orbit single-shaft SADA
InactiveCN111792058AOrientation towards the sunLow costCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsSolar sailEngineering
The invention provides a method for driving a solar wing to face the sun through a low-inclination-angle orbit uniaxial SADA. The method comprises the following steps: S1, determining coordinates of asolar vector in an orbit system by an on-board sensor; S2, calculating a satellite yaw angle according to the projection of the sun vector on the XoOYo plane of the orbit; S3, calculating expected yaw angle and angular velocity information in satellite attitude motion; S4, calculating the rotation angle of a solar wing driving device according to an included angle between the normal coordinate ofthe solar panel and the solar vector when the solar wing driving device is in a zero position; and S5, controlling the satellite to maneuver by the on-board actuating mechanism, and rotating the solar wing driving device in a matching mode to ensure that the solar wing points to the sun. The invention further provides a system for driving the solar wing to face the sun through the low-inclination-angle orbit single-shaft SADA. The method has the advantages that the single-axis SADA is used for replacing the double-axis SADA in the low-inclination-angle orbit to achieve sun orientation of thesolar wing, cost is reduced, reliability is improved, and control is easy.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
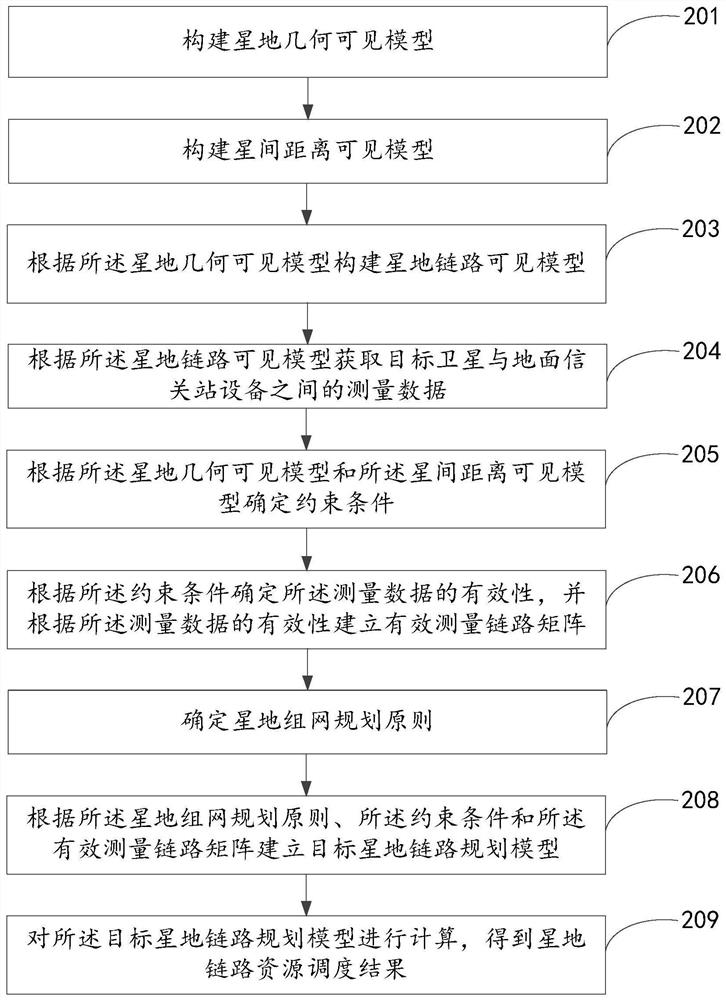
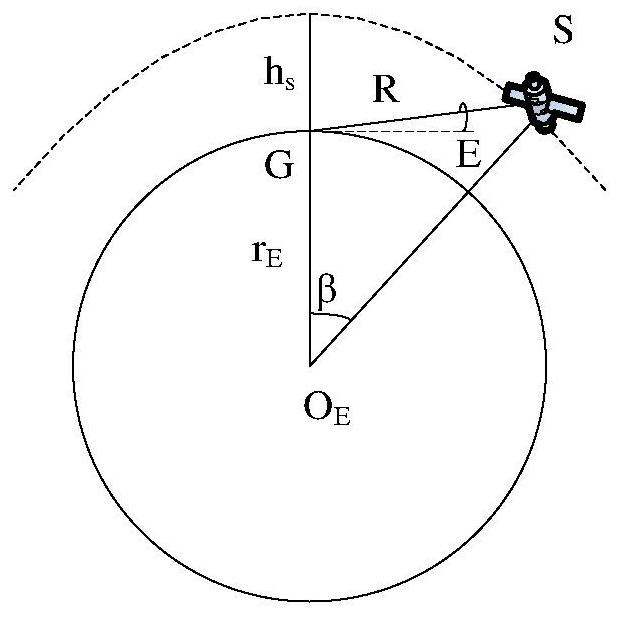
Low-orbit Internet constellation satellite-ground link planning method based on constraint satisfaction
The invention provides a low-orbit internet constellation satellite-ground link planning method based on constraint satisfaction, and relates to the technical field of satellites, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a satellite-ground geometric visible model; constructing an inter-satellite distance visible model; constructing a satellite-ground link visible model according to the satellite-ground geometric visible model; acquiring measurement data between the target satellite and ground gateway station equipment according to the satellite-ground link visible model; determining constraint conditions; determining the validity of the measurement data according to the constraint condition, and establishing an effective measurement link matrix according to the validity of the measurement data; determining a satellite-ground networking planning principle; establishing a target satellite-ground link planning model according to a satellite-ground networking planning principle, constraint conditions and the effective measurement link matrix; and calculating the target satellite-ground link planning model to obtain a satellite-ground link resource scheduling result. According to the method, the planning constraint problems of neglecting constellation configuration, constellation orbit plane balanced use and the like during multi-task scheduling of a low-orbit constellation without an inter-satellite link are solved.
Owner:陕西星邑空间技术有限公司
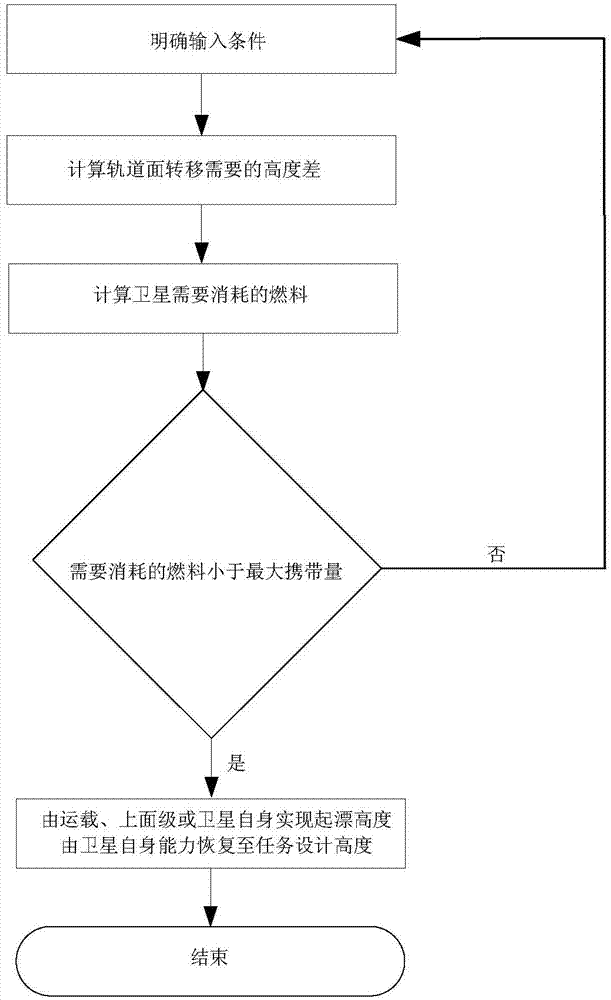
Method for distributing and transferring multiple satellites launched by one rocket to different orbit planes
ActiveCN103885456AReduce consumptionImprove performancePosition/course control in three dimensionsNatural satelliteHeight difference
The invention discloses a method for distributing and transferring multiple satellites launched by one rocket to different orbit planes. Firstly, orbit injection dip angles i, target heights Hf, time T for completing deployment of tasks and orbit plane drifting distances delta omega needed by all the satellites need to be determined, and critical height differences delta a for transferring the satellites to the target obit planes in the assigned time T are calculated according to the input conditions. Satellite drifting starting heights are provided through a piggybacking separation mode or an upper-level orbital transferring mode, or when the quantity of fuel carried by the satellites enables corresponding orbit transferring capability to be achieved, drifting is begun by directly transferring to the drifting starting heights from the orbit injection height. The different drifting starting heights corresponding to all the satellite are set under the premise that the satellites can arrive in the assigned time T, and the satellites are restored to designed heights respectively after arriving at the target orbit planes. Selection of obits and piggybacking is carried out on piggybacking satellites or multiple constellation satellites according to given drifting time in tasks and existing orbit injection conditions, different fuel demands of all the satellites are deployed when piggybacking conditions exist or constellation tasks meet requirements, and different orbit distributing and transferring are completed after obit injection according to designed drifting modes.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
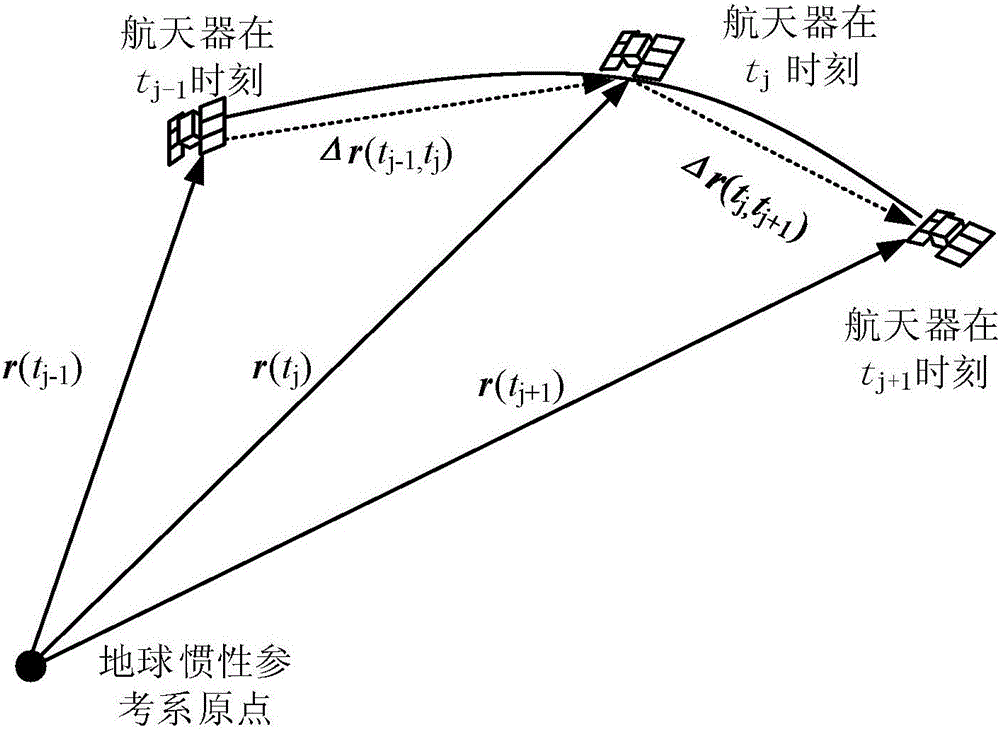
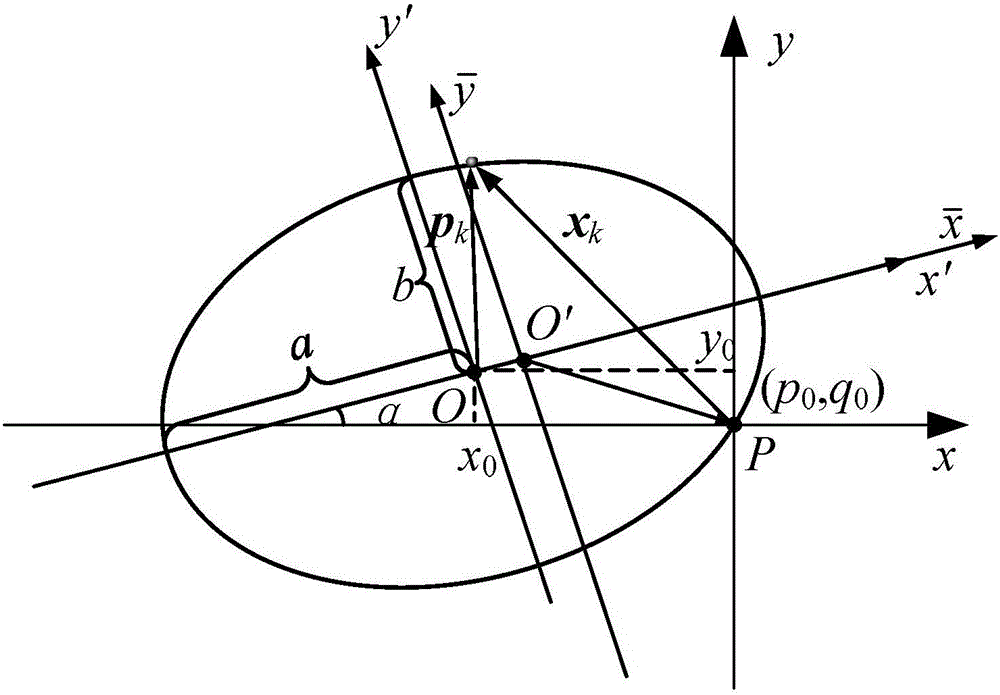
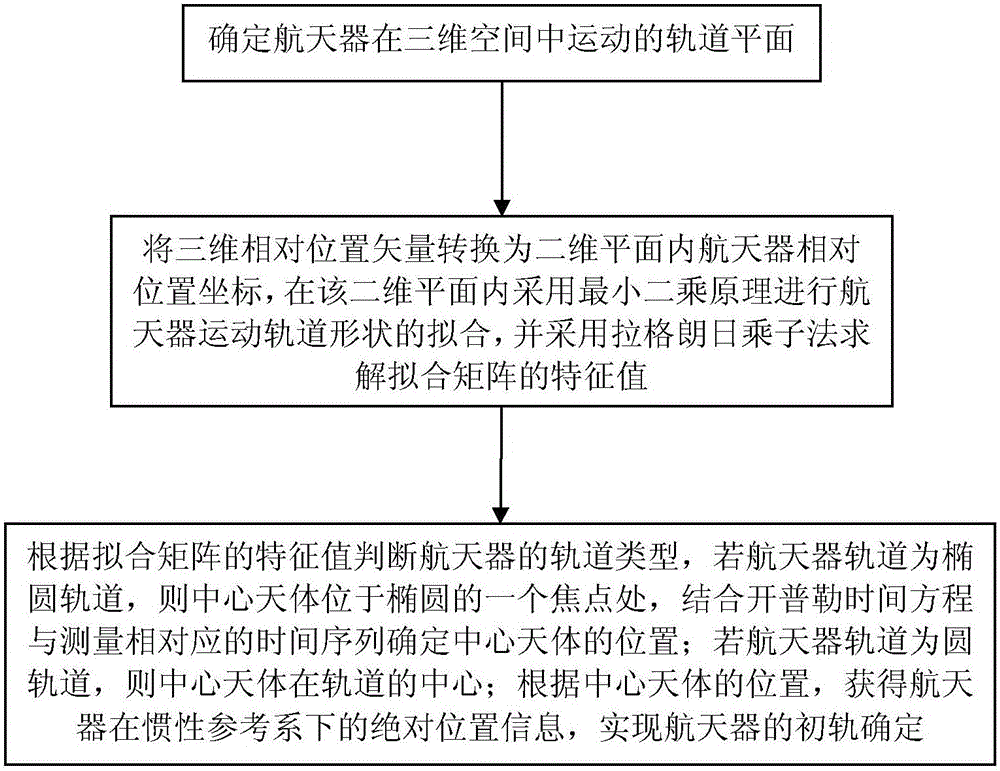
Method for determining orbit of spacecraft by using relative position increment
ActiveCN106092099AIncrease autonomyOrbit determination method is simpleNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationCelestial bodyThree-dimensional space
A method for determining orbit of a spacecraft by using relative position increment belongs to the technical field of determination of spacecraft orbit, and aims at solving the problem that a conventional orbit determination method based on measured epoch difference needs to employ other orbit determination method for obtaining initial position information. The method for determining orbit of the spacecraft by using relative position increment comprises: firstly, determining the motional orbit plane of the spacecraft in a three-dimensional space; then, converting the three-dimensional relative position vector into a spacecraft relative position coordinate in a two-dimensional plane, fitting the spacecraft motion orbit shape in the two-dimensional plane by employing a least square method, and determining eigenvalue of the fit matrix by employing lagrangian multiplier; and finally, determining the spacecraft orbit type according to the eigenvalue of the fit matrix, and obtaining the absolute position information of the spacecraft in an inertia reference system according to the position of a central celestial body, so as to determine the initial orbit of the spacecraft. The method is applicable to orbit determination of spacecraft.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
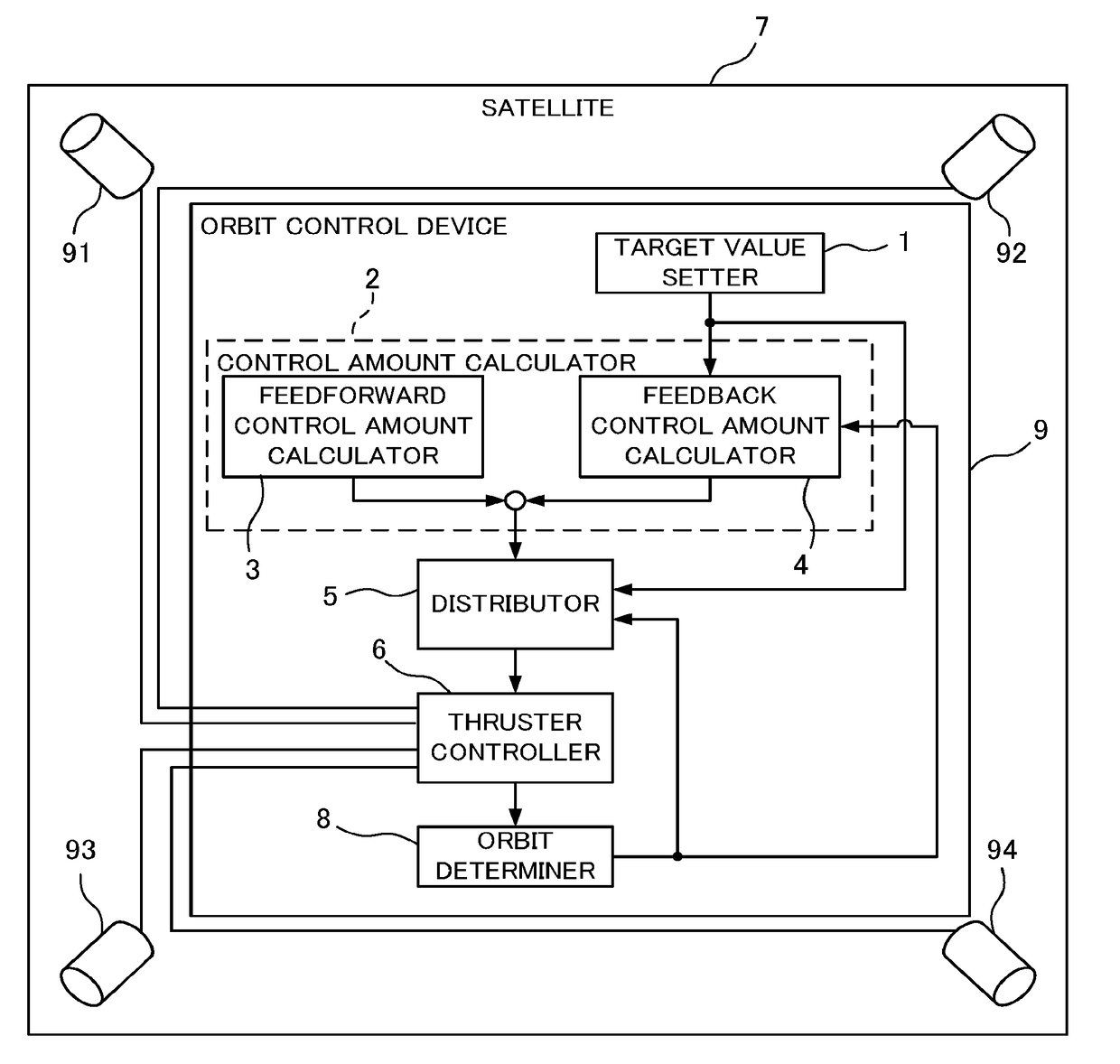
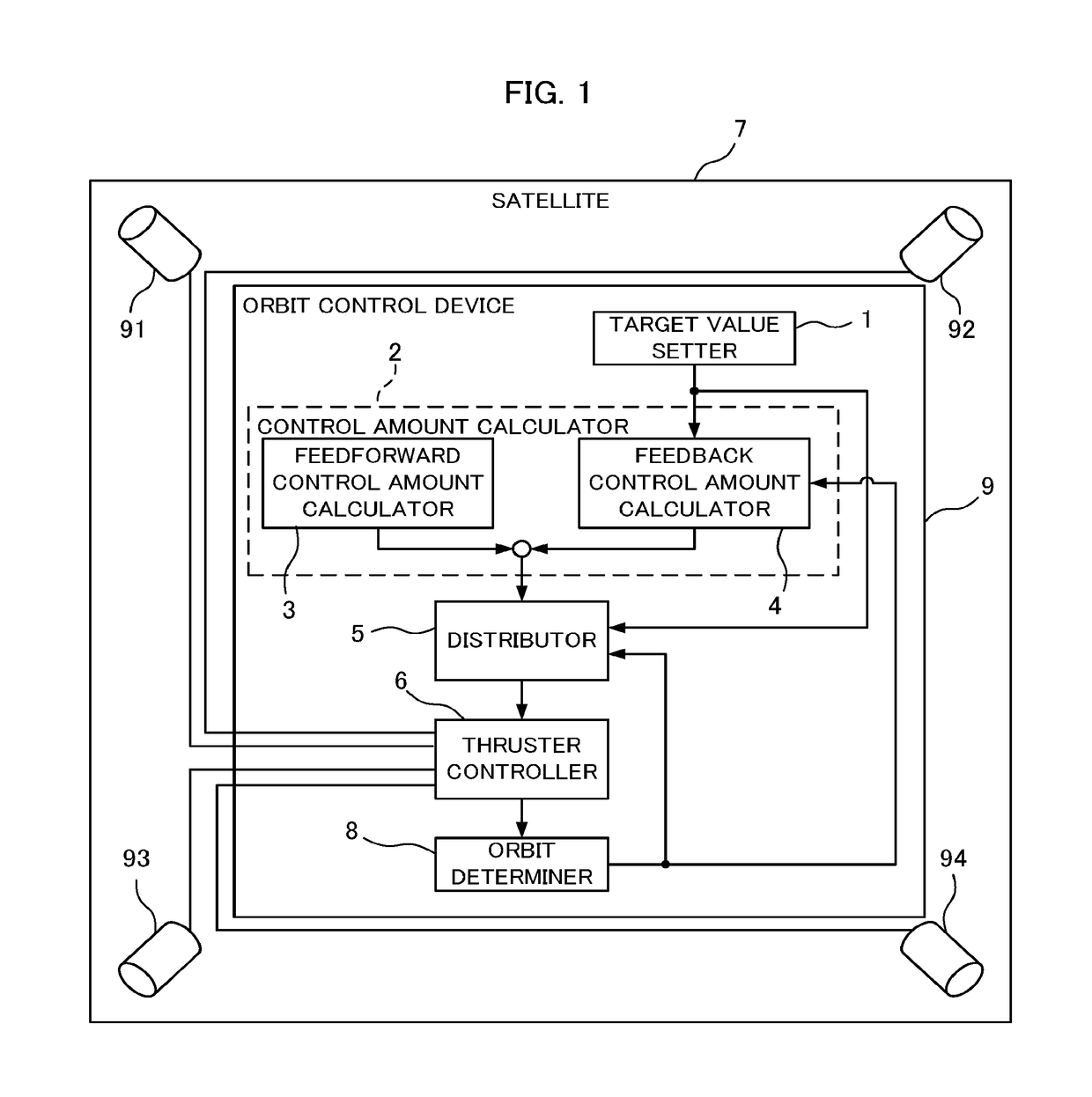
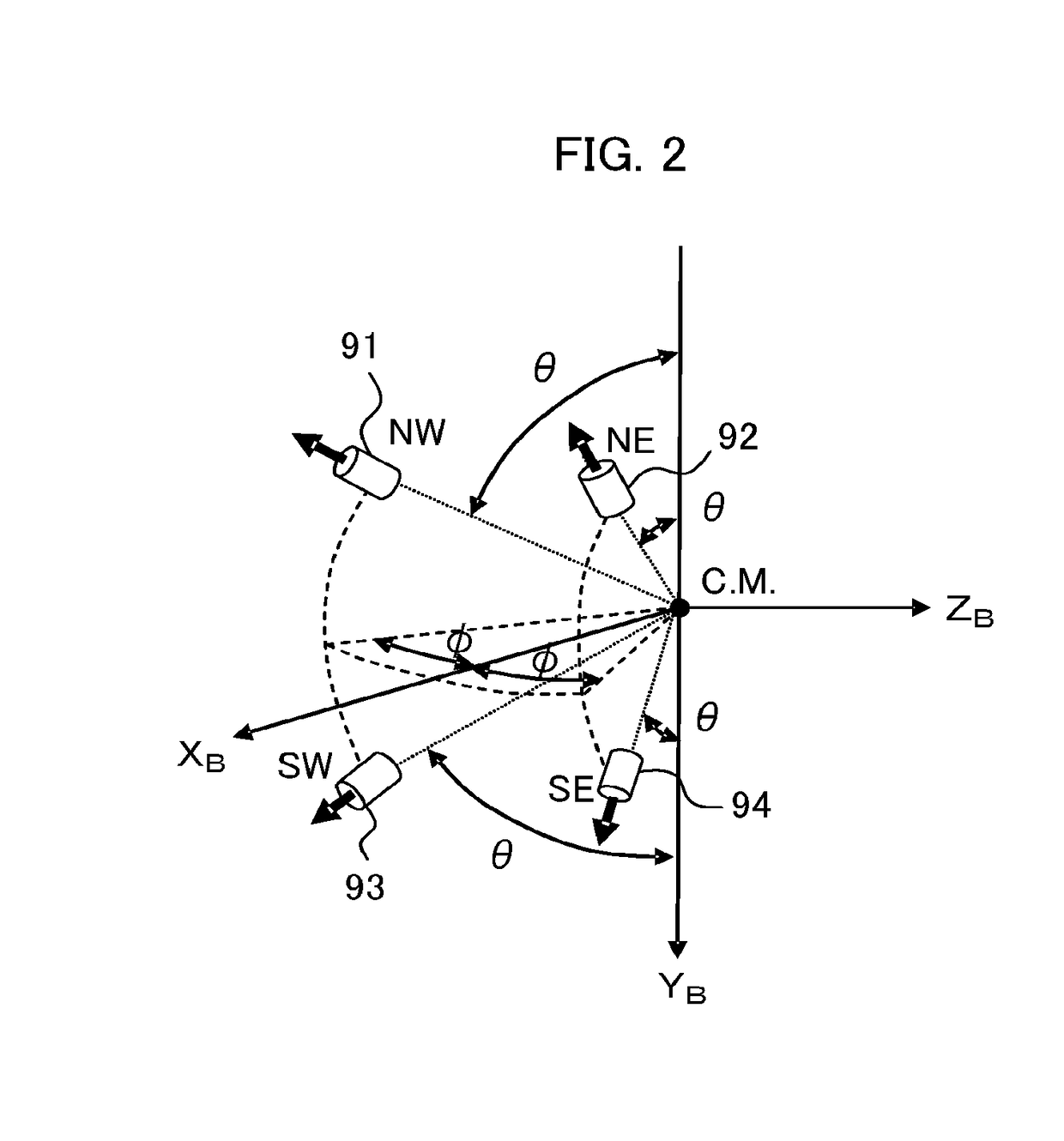
Orbit control device and satellite
A satellite comprises thrusters disposed with the firing directions each facing away from the mass center of satellite and different from each other. A control amount calculator calculates control amounts of the mean orbital elements from the mean orbital elements and the temporal change rates of the mean orbital elements set by an orbit determiner, and the target values. A distributor calculates firing timings and firing amounts of the thrusters for realizing the control amounts of the mean orbital elements by expressing a motion of satellite with orbital elements, solving an equation taking into account coupling of an out-of-plane motion and an in-plane motion due to thruster disposition angles and thruster firing amounts at multiple times, and combining one or more thruster firings controlling mainly an out-of-the-orbit-plane direction and one or more thruster firings controlling mainly an in-the-orbit-plane direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for obtaining high-resolution and large-breadth remote sensing images by utilizing small satellite group
InactiveCN107194875AReduce widthIncrease redundancyGeometric image transformationCosmonautic partsEarth observationImage resolution
Under the existing technical conditions, the high resolutions and large breadths of images obtained by remote sensing satellites are mutually contradictory. The invention discloses a method for obtaining high-resolution and large-breadth remote sensing images by utilizing a small satellite group. According to the method, multiple satellites are grouped to be operated, so that high-resolution and large-breadth earth observation images can be obtained. By adoption of the method, each small satellite has a strict requirement for resolutions of observation instruments and the breadth requirement can be properly broadened; and after orbit injection, all the small satellites can be uniformly distributed on a same orbit plane, and also can be operated in a relatively concentrated way. When an observation task is carried out for each time, a large area is segmented, on and off moments of reasonable observation instruments are distributed for each satellite, lateral tilt angle and pitch angles of satellite attitudes are set, finally, images obtained by all the small satellites are spliced to realize one-time transition of the satellites and obtain high-resolution and large-breadth earth observation images, and if the quantity of the small satellites in the satellite group is more, the breadths of the images are larger. Moreover, by adoption of a satellite group design, the risk of causing the whole satellite task to lose efficacy due to the failure of individual satellites is reduced.
Owner:北京宇航智科科技有限公司
Construction method of space-based space target monitoring photoelectric fence system
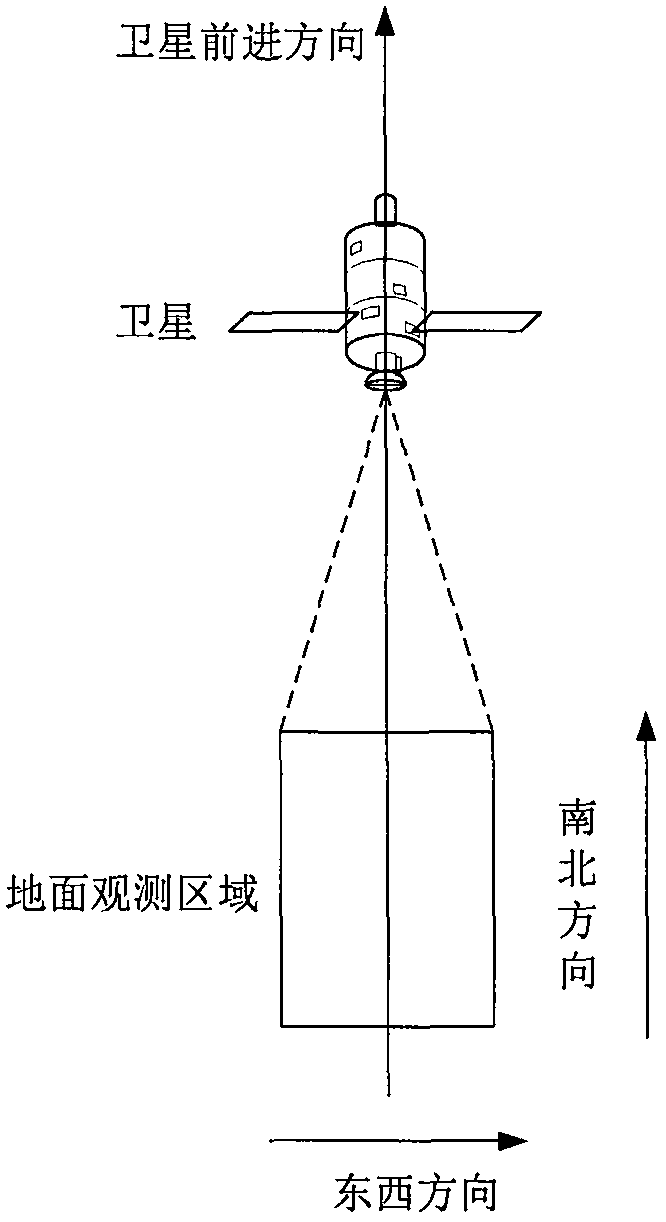
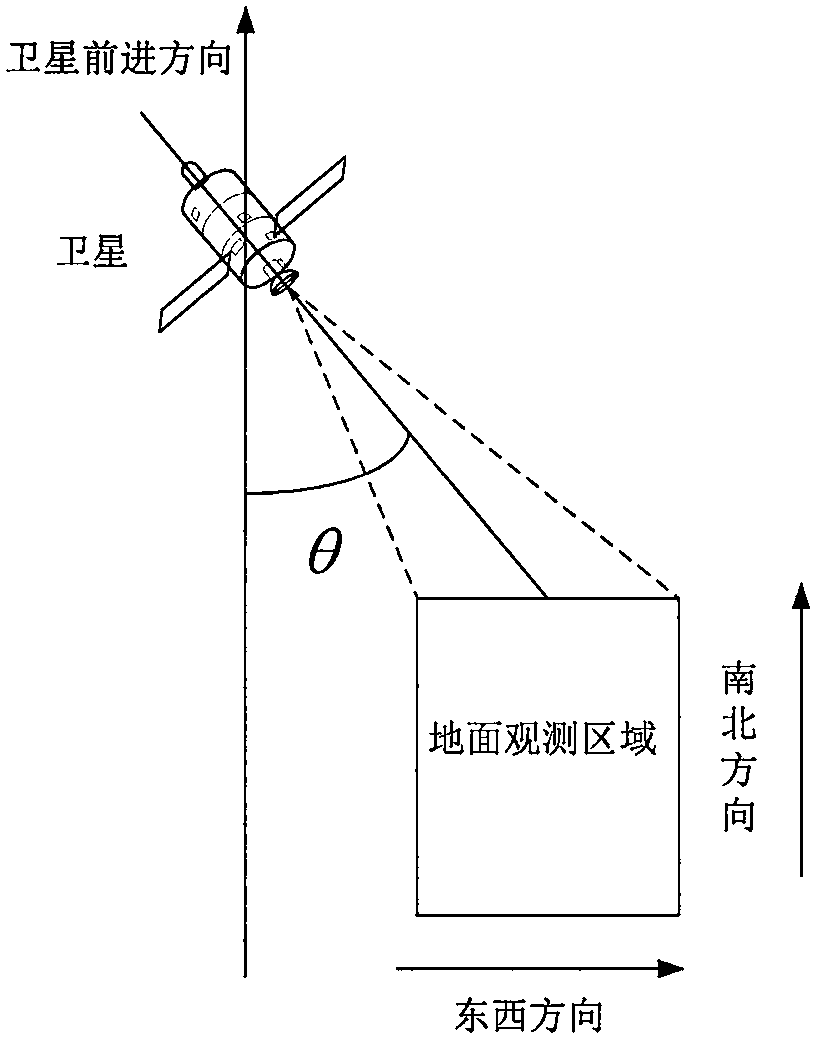
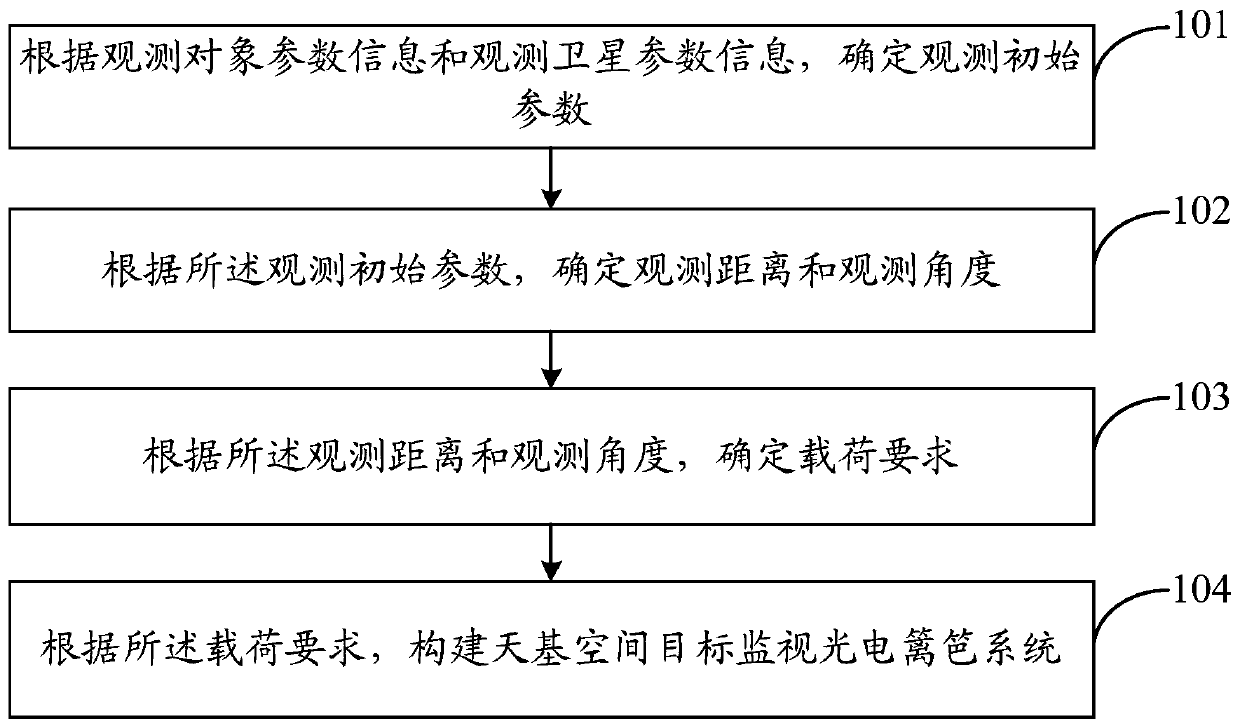
ActiveCN110017815AHigh target coverageIncrease coveragePhotogrammetry/videogrammetryPhotoelectric effectOrbit plane
The invention discloses a construction method of a space-based space target monitoring photoelectric fence system. The method comprises the steps of: determining observation initial parameters according to parameter information of an observation object and parameter information of observation satellites; determining an observation distance and an observation angle according to the observation initial parameters; determining a load requirement according to the observation distance and the observation angle; and constructing the space-based space target monitoring photoelectric fence system according to the load requirement. Through the constructed space-based space target monitoring photoelectric fence system, multiple observation satellites are arranged on a same orbit plane, and the observation range of each observation satellite is intersected with that of the adjacent observation satellites to form an observation loop, so that the space targets running on low orbits can pass throughthe observation loop in each circle and then high-aging observation can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
High-orbit target approaching observation method based on finite time constraint
ActiveCN111367167AClear stagesSimple and fast operationAdaptive controlComplex mathematical operationsObservational methodEngineering
The invention discloses a high-orbit target approaching observation method based on finite time constraint. The method comprises: determining the relative position relation between a high-orbit service spacecraft and a target spacecraft; determining an approaching mode, an observation moment and an observation position; calculating the relative longitude drift rate, the orbital transfer amount andthe orbital transfer moment; the high-orbit service spacecraft realizing the rounding and floating of the orbit through twice orbital transfer; calculating a traversing moment set of the high-orbit service spacecraft traversing the target orbit plane; calculating an included angle between the orbit plane of the high-orbit service spacecraft and the target orbit plane; selecting an intermediate moment of the crossing moment set to carry out orbital transfer on the high-orbit service spacecraft, so that an orbital plane of the high-orbit service spacecraft coincides with a target orbital plane;and the high-orbit service spacecraft running on the new orbit after orbital transfer for 12 hours before a preset observation moment; and the high-orbit service spacecraft reaching a predetermined observation position through one-time orbital transfer. According to the method, the problems of non-standardization and complex illumination condition constraints of the current approach process method are solved, and the development of subsequent high-orbit observation tasks is supported.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Distributed remote sensing satellite system
ActiveCN109781635AImprove and ensure transmission efficiencyScene recognitionColor/spectral properties measurementsSensing dataSynchronous orbit
The invention relates to a distributed remote sensing satellite system. The system comprises a plurality of first satellites and a plurality of second satellites, the plurality of first satellites arelow-orbit remote sensing satellites and are distributed on at least two orbit planes; wherein each of the at least two orbit planes is provided with at least three first satellites, the second satellite is a geosynchronous orbit satellite, and remote sensing data collected by the first satellite can be directly transmitted to a ground station or indirectly transmitted to the ground station through the corresponding second satellite. High-definition remote sensing images are collected through the low-orbit remote sensing satellites, remote sensing data can be transmitted to the ground stationby means of the synchronous orbit satellites, and the transmission efficiency of the remote sensing data is greatly improved and guaranteed.
Owner:SPACETY CO LTD (CHANGSHA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com