Method for distributing and transferring multiple satellites launched by one rocket to different orbit planes
A transfer method and surface distribution technology, applied in three-dimensional position/course control and other directions, can solve problems such as separate launches, and achieve the effects of reducing fuel consumption, improving constellation system efficiency, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
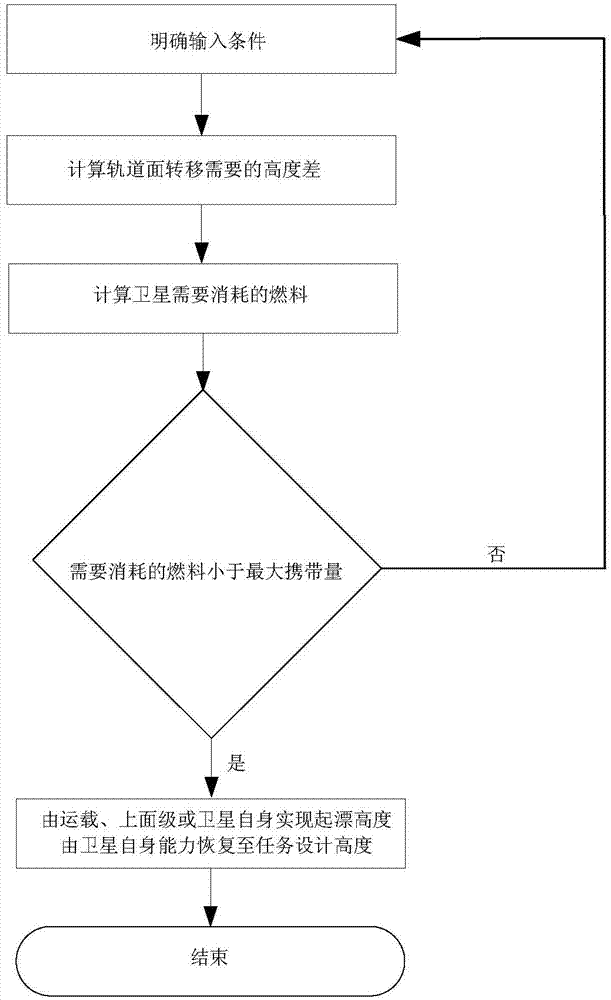
[0025] Take the uniform transfer of the orbital plane launched by a three-star rocket as an example.
[0026] (1) Orbital inclination i=25°, orbital height H f =700km, the deployment time of the constellation is required to be no more than half a year, and the total fuel consumption shall not exceed 30kg.
[0027] (2) According to the uniform distribution requirements of the given orbital planes, the drift rates of the orbital planes of the two stars are respectively and Marked by numbers 01 and 02, the orbital height of the drift relative to the reference star 03 is H f . According to the formulas (1) and (2), it can be known that the altitudes of the stars 01 and 02 are relative to H f The maximum difference is -212km and 212km respectively, that is, the highest altitude of 01 star is 488km, and the lowest altitude of 02 star is 912km.
[0028] (3) Assuming that the weight of the whole star is 500kg, and the rated vacuum ratio of the engine is 200s, it can be calculat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com