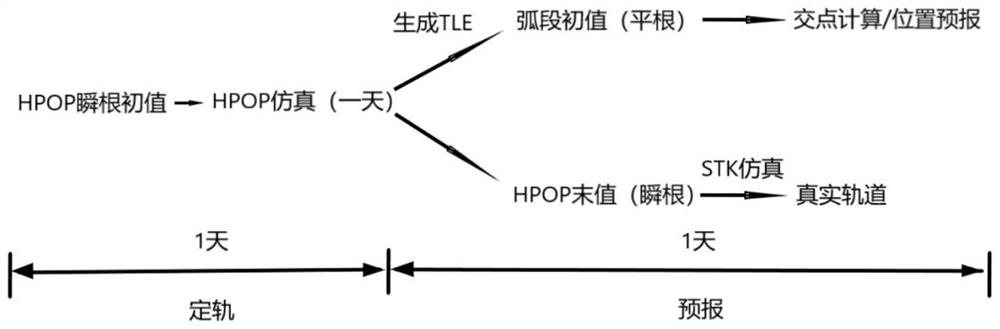
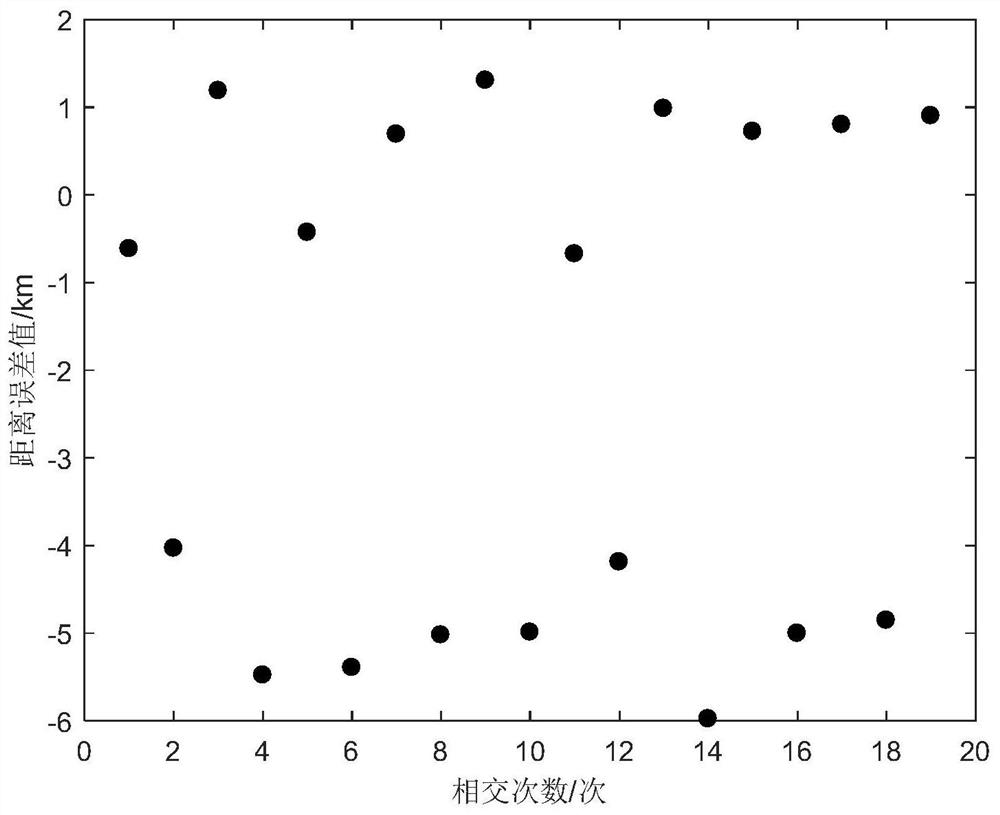
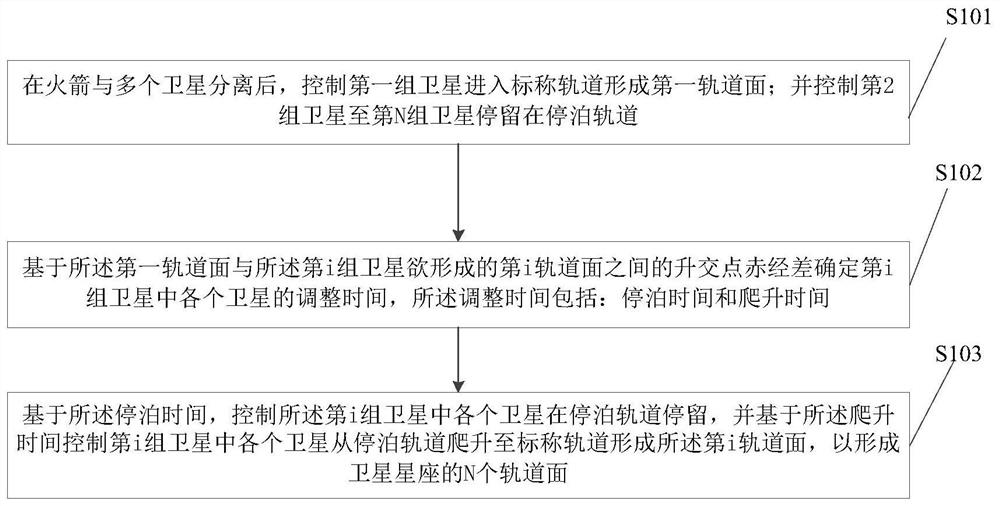
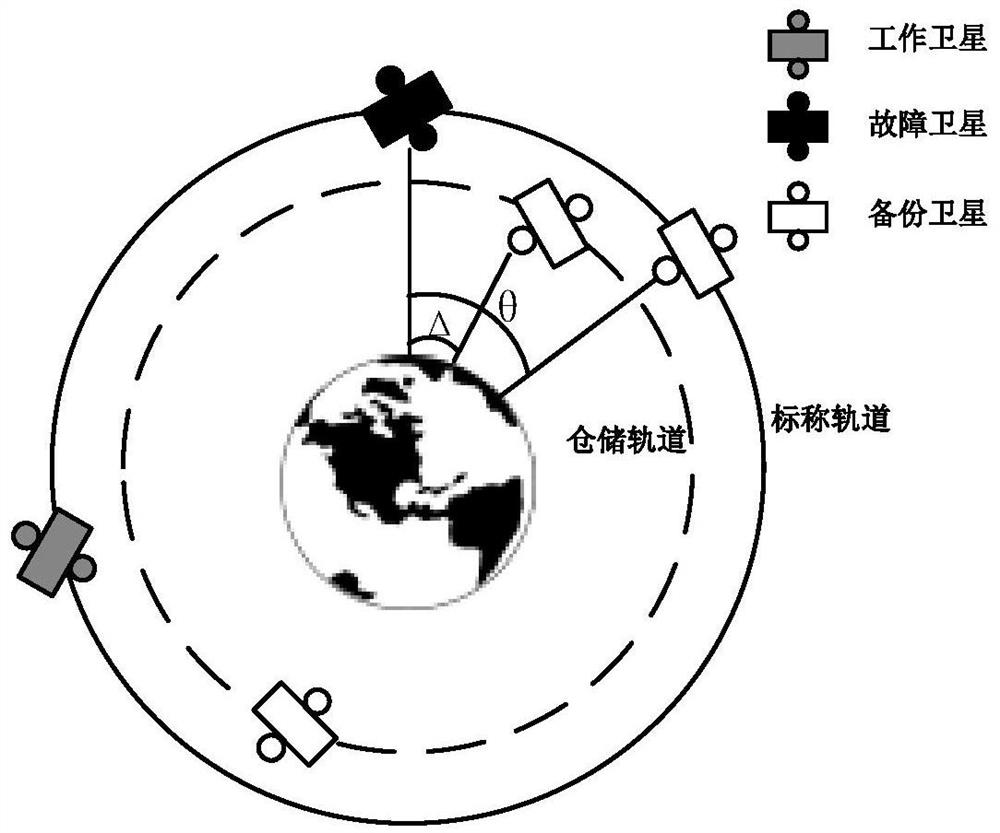
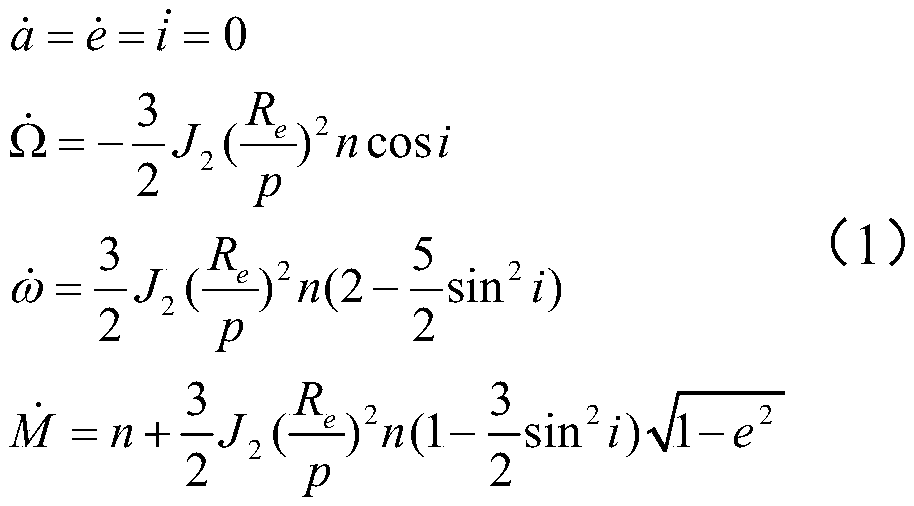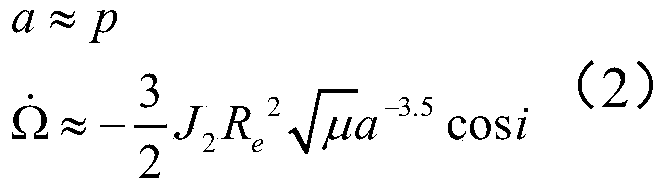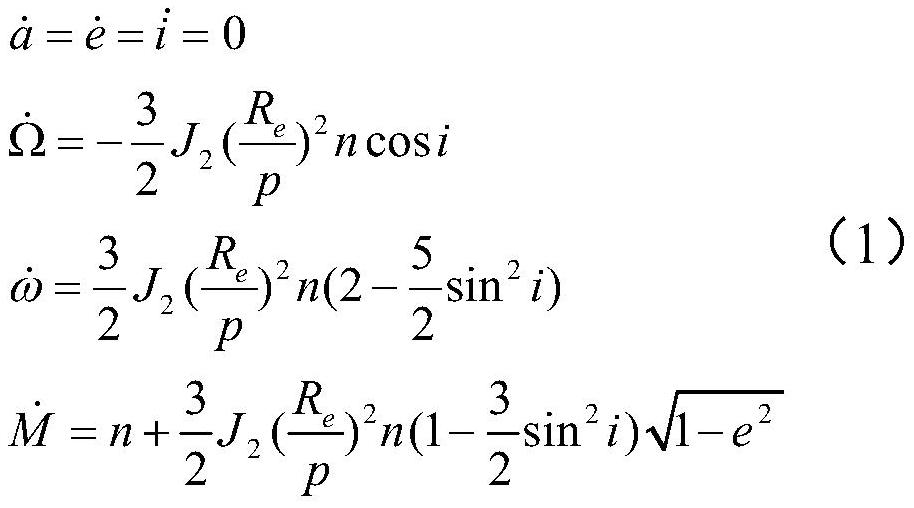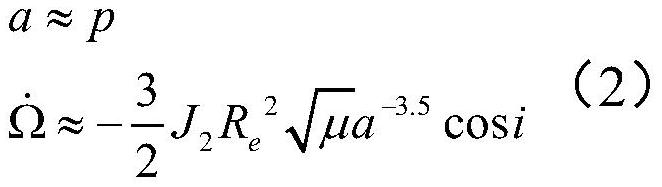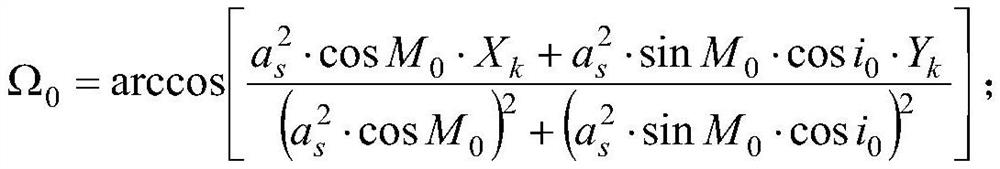Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Orbital plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
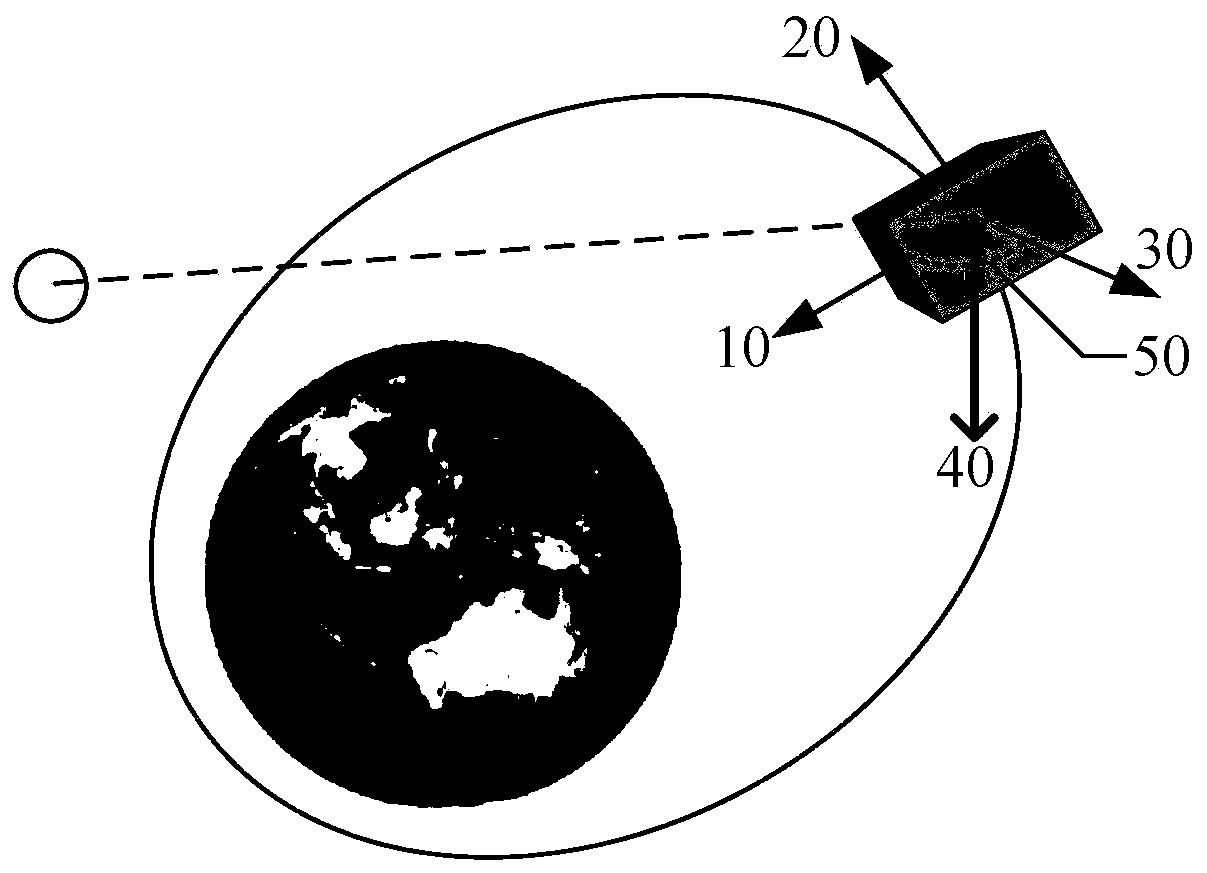
The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) and of an orbiting celestial body at two different times/points of its orbit.
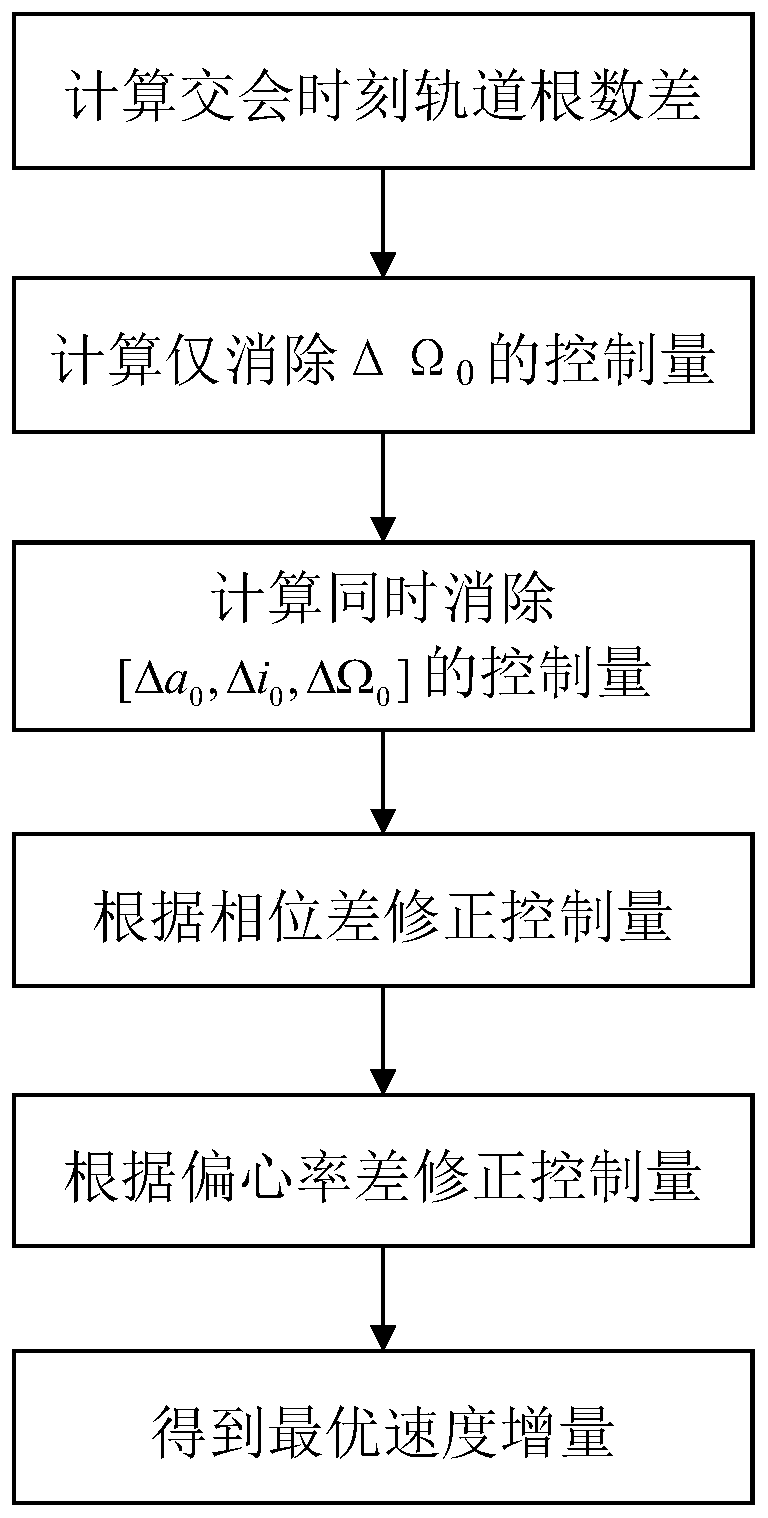
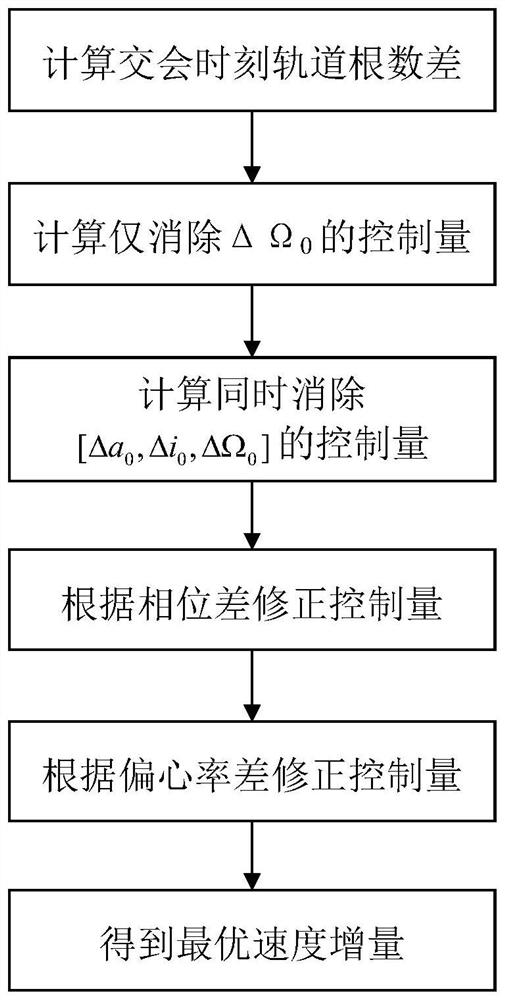
Method for rapidly estimating long-term orbital rendezvous optimal speed increment under J2 perturbation
ActiveCN110789739ADecrease speed incrementImprove optimization efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesLinear/angular speed measurementOrbital planeSimulation
The invention discloses a method for rapidly estimating a long-term orbital rendezvous optimal speed increment under J2 perturbation. The method includes the steps of calculating the orbital element difference of a non-maneuvering spacecraft and a target at the rendezvous moment, calculating an optimal control amount when only the ascending node ascensional difference is eliminated, substituting the optimal control amount as the initial value into a control amount optimizing model for eliminating the semi-major axis, dip angle and ascending node ascensional difference at the same time to obtain a new optimal control amount, modifying the control amount according to the phase difference in an orbital plane, modifying the control amount according to the eccentricity ratio vector difference,and finally obtaining the estimated optimal rendezvous speed increment. The method realizes the purpose of rapidly estimating the optimal rendezvous speed increment when precise solution is not neededand is high in estimating precision and suitable for the situations with large initial ascending node ascensional difference from a target orbit and small element differences from other orbits.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Calculation method of subsatellite points and photographic point trajectory self-intersection points of near-earth regression orbit satellite
ActiveCN111680354AQuality improvementEnhance the imageGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsOrbital planeOrbit perturbation
The invention discloses a calculation method of subsatellite points and photographic point trajectory self-intersection points of a near-earth regression orbit satellite. Based on an orbital perturbation model of the earth oblateness (J2), the mean influence of the earth oblateness on the long-term perturbation of the right ascension of the ascending node, the perigee argument and the aplanatic angle is utilized, so that the mean drift period and the orbital intersection period of the satellite orbital plane relative to the earth resonate, and revisit regression of the orbital relative to thesubsatellite point and the photographic point trajectory of the earth surface is formed. After the orbit inclination angle, the eccentricity ratio, the regression days and the period number are given,the orbit semi-major axis can be solved, then the longitude of the sub-satellite point trajectory self-intersection point is analyzed and solved, the latitude of the self-intersection point under thecorresponding precision is screened out through numerical screening, and the distribution situation of the sub-satellite point trajectory self-intersection point in one regression period can be obtained. The invention provides a practical near-earth regression orbit sub-satellite point trajectory self-intersection point calculation method, and the method has important application value in near-earth surveying and mapping, remote sensing, reconnaissance, InSAR and other regression orbit satellite measurement tasks.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
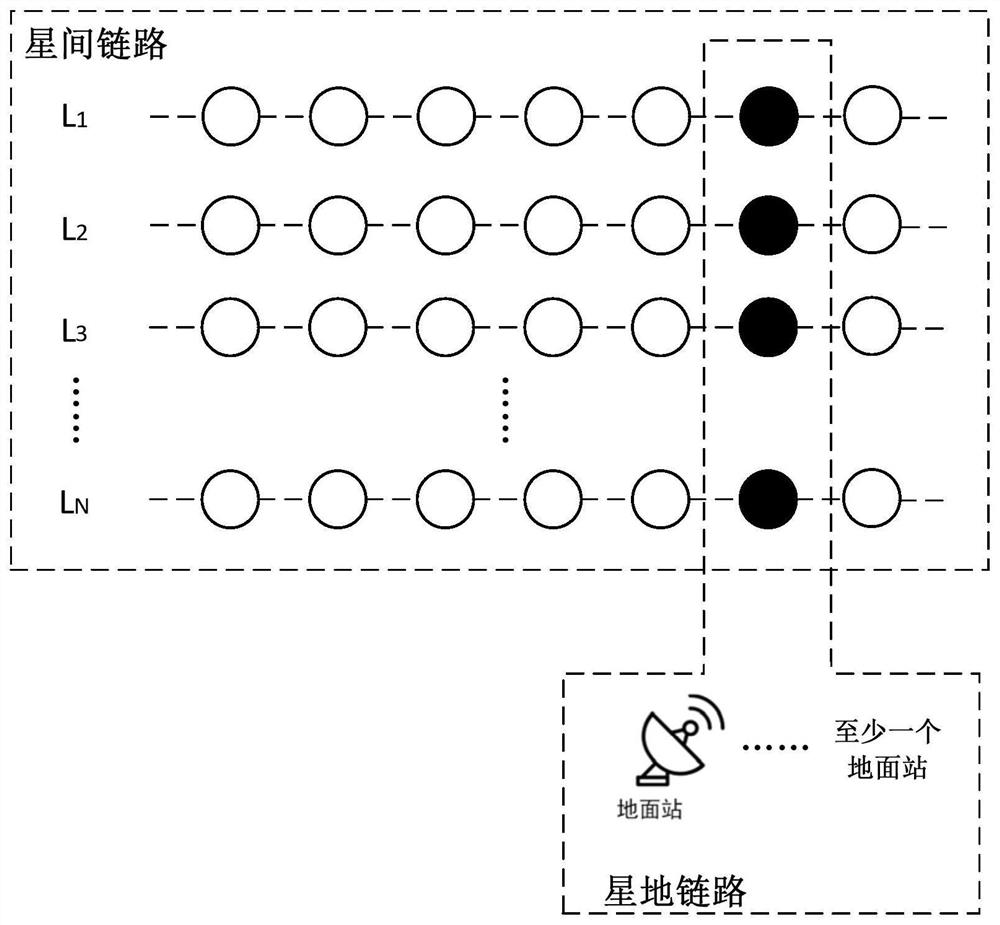
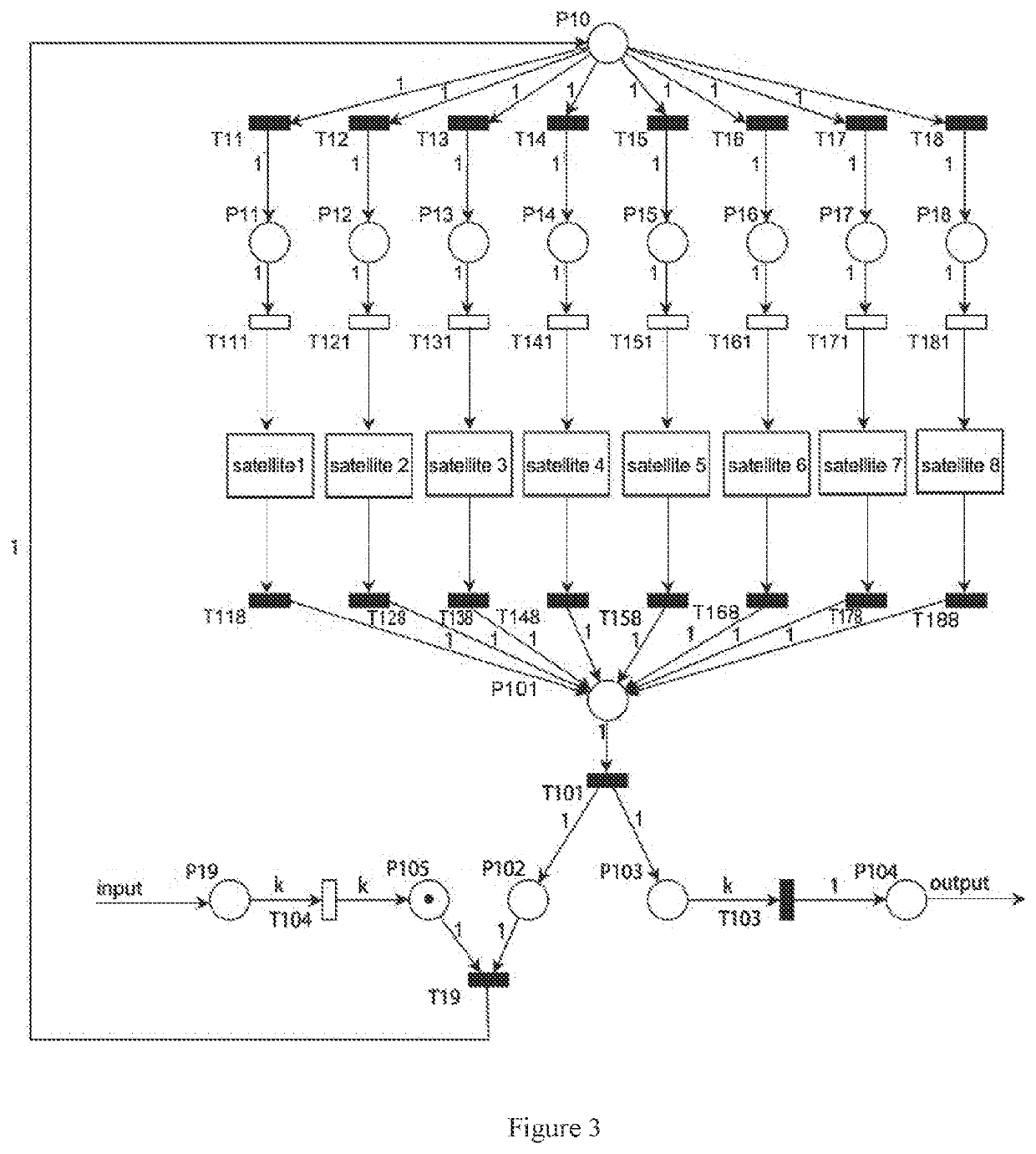
Measurement, operation and control system and method for low-orbit satellite constellation
The invention relates to a satellite positioning technology, and discloses a measurement, operation and control system and method for a low-orbit satellite constellation. The measurement, operation and control system comprises N common-orbit inter-satellite links corresponding to N orbital planes, each common-orbit inter-satellite link is used for data transmission between node satellites of the corresponding orbital plane, and N is larger than or equal to 2; and the system further comprises a satellite-ground link which is used for specifying the node satellites running to the intersection ofthe N orbital planes in each common-orbit inter-satellite link as hub satellites, and each common-orbit inter-satellite link performs data transmission with at least one ground station arranged nearthe latitude of the intersection of the N orbital planes through the hub satellites. According to the embodiment of the invention, while the low-orbit satellite constellation measurement, operation and control requirements are met, the technical complexity of the satellite is reduced, the cost of the satellite and the ground station is reduced, and the engineering feasibility of real-time measurement, operation and control of the low-orbit satellite constellation is improved.
Owner:QIANXUN SPATIAL INTELLIGENCE INC
Satellite steady sun-facing orientation method taking earth pointing deviation as constraint
ActiveCN110901956AOvercome the singularity of rapid flippingShorten speedCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital planeSpacecraft attitude control
The invention discloses a satellite steady sun-facing orientation method taking earth pointing deviation as constraint, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft attitude control. The stable sun-facing orientation method comprises the following two steps: establishing an expected attitude of a satellite by two steps: firstly, establishing an intermediate attitude of the satellite on the basis of a satellite-geocentric connecting line direction, a satellite orbital plane normal direction and a satellite advancing direction; and then rotating the middle attitude around an Euler axis for acertain angle to reduce the sun pointing deviation of the satellite and ensure that the included angle between the expected earth axis and the earth center direction is not greater than the constraint angle. The expected attitude of the satellite obtained according to the strategy can keep stable change, the singular phenomenon that the expected attitude of the satellite violently changes in a short time under the sun-earth-satellite collinear condition caused by a traditional strategy is avoided, and therefore peak energy consumption in the sun-oriented process of the satellite is greatly reduced.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
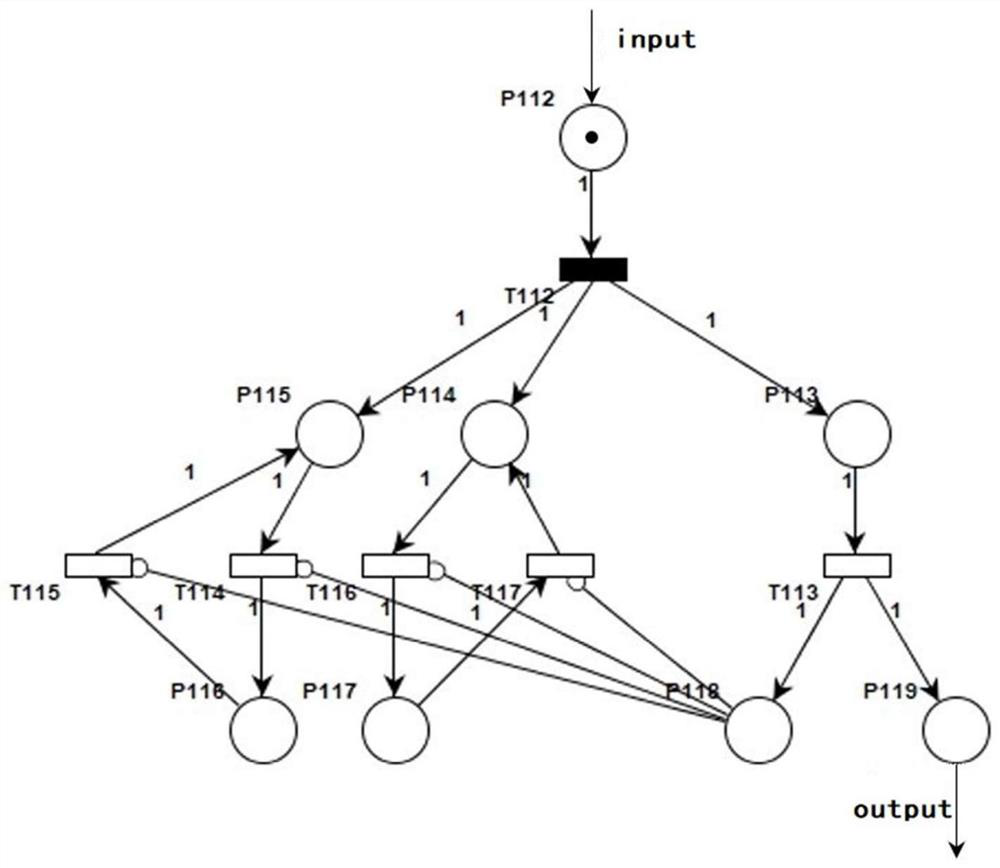
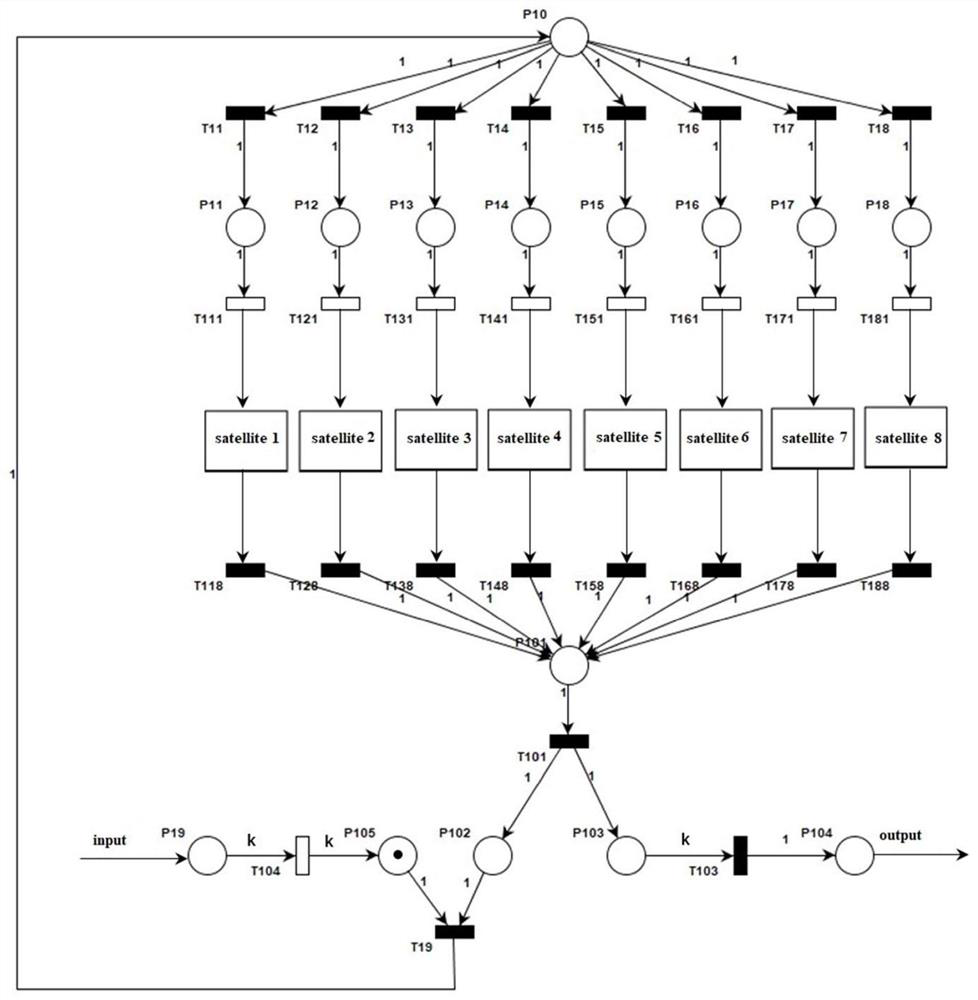
Method and system of evaluating a constellation spare strategy based on a stochastic time petri net
PendingUS20210389129A1Improve accuracyMore flexibleGeometric CADCosmonautic ground equipmentsConstellationReal-time computing
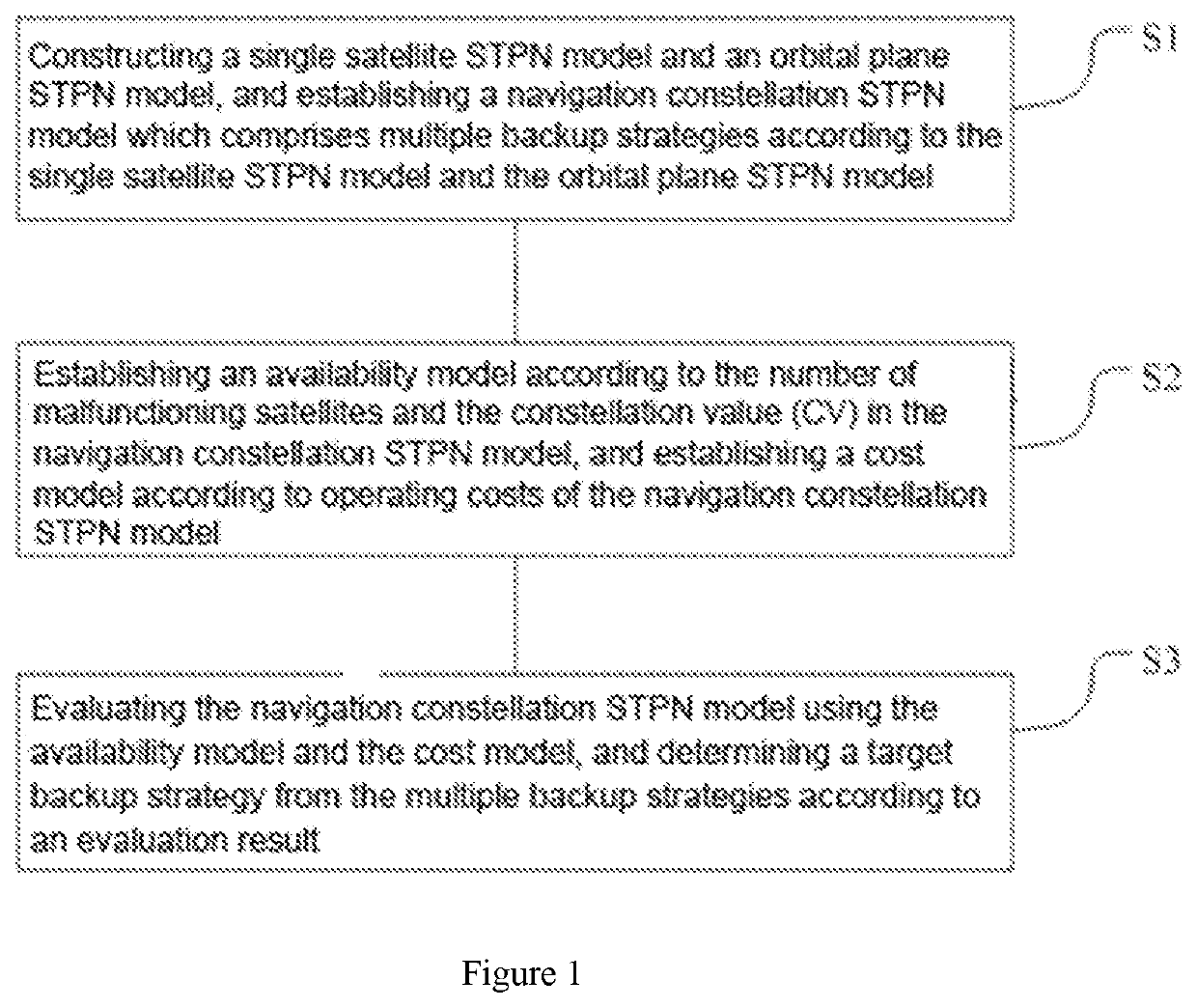
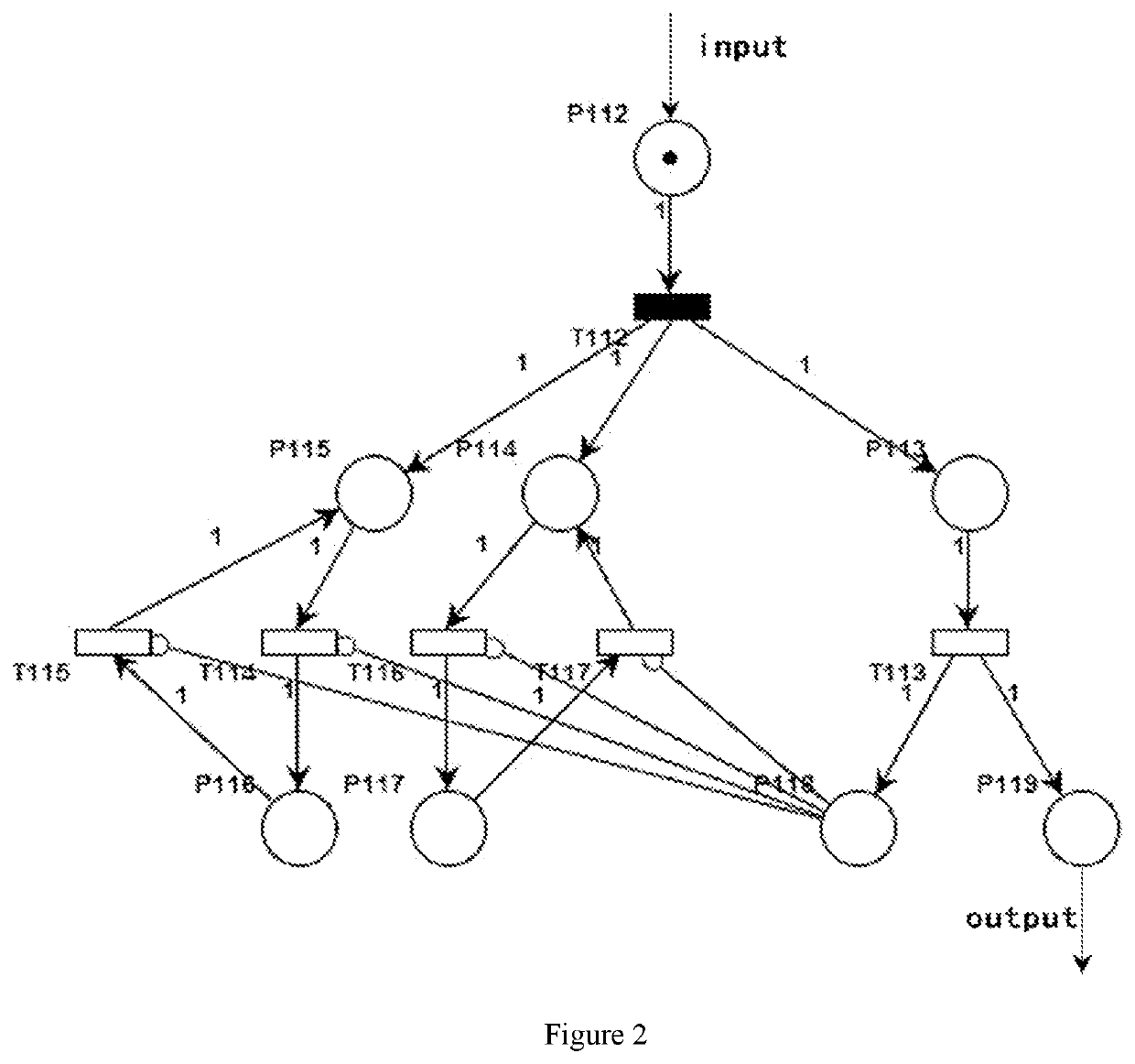
Provided is a method and system of evaluating a constellation spare strategy based on a stochastic time Petri net, which is applied in the technical field of constellation operation management. The method comprises: constructing a single satellite STPN model and an orbital plane STPN model, and establishing a navigation constellation STPN model that includes multiple spare strategies according to the single satellite STPN model and the orbital plane STPN model; establishing an availability model according to the number of malfunctioning satellites and the constellation value (CV) in the navigation constellation STPN model, and establishing a cost model according to operating costs of the navigation constellation STPN model; and evaluating the navigation constellation STPN model using the availability model and the cost model, and determining a target spare strategy from the multiple spare strategies according to an evaluation result.
Owner:SPACE ENG UNIV
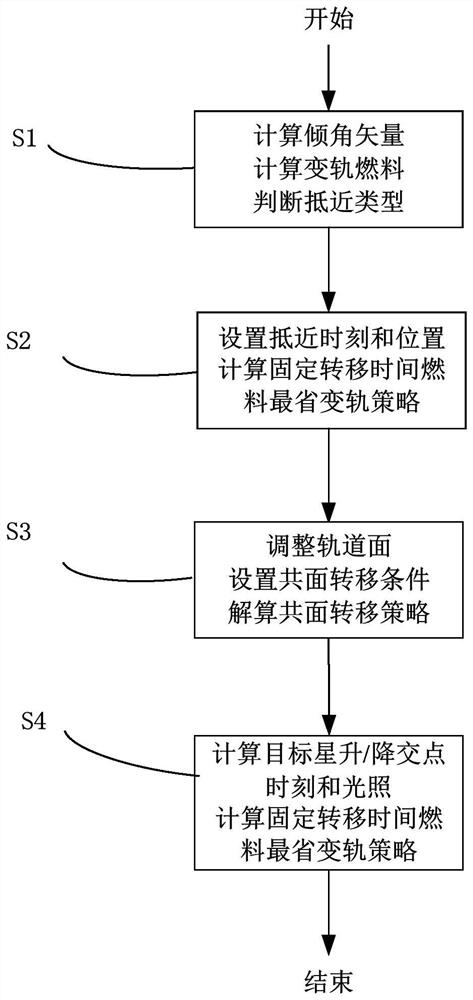
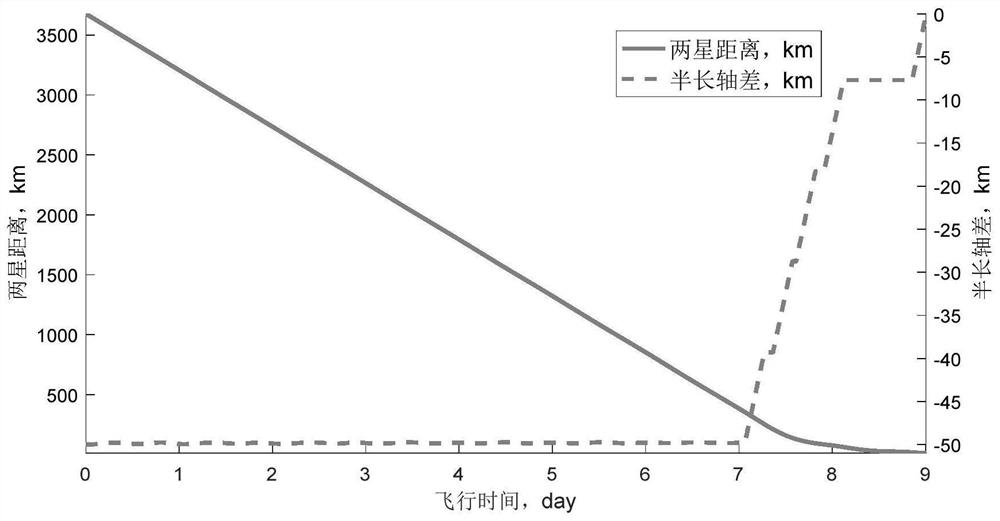
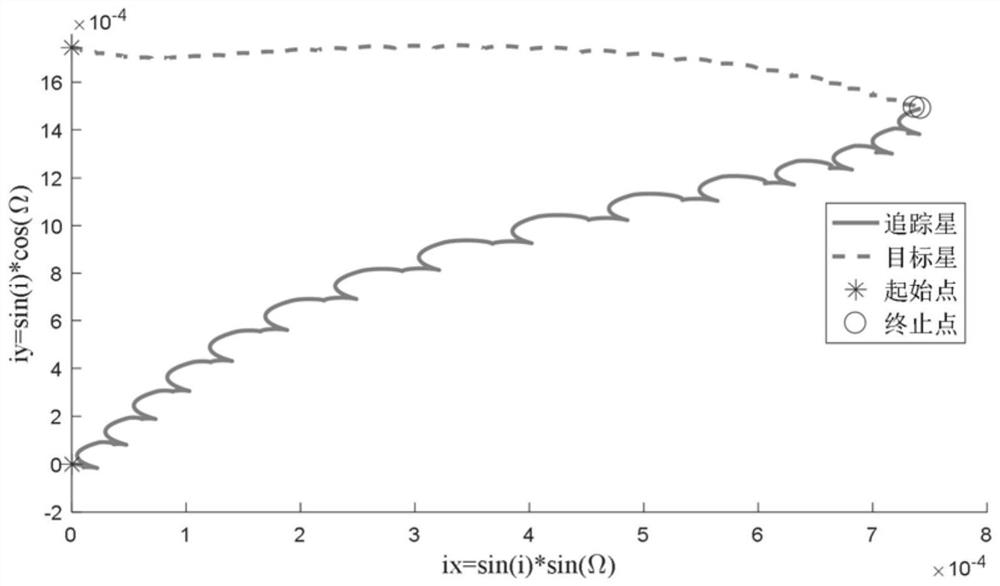
Continuous low-thrust high-orbit target orbital transfer approaching method and system
ActiveCN113636106ASolve the problem of continuous small thrust approachingPracticalCosmonautic vehiclesSustainable transportationOrbital planeEngineering
The invention provides a continuous low-thrust high-orbit target orbital transfer approaching method and system. The continuous low-thrust high-orbit target orbital transfer approaching method comprises the following steps that S1, calculating an inclination angle vector and adjusting the speed increment of the inclination angle vector to judge the approaching type; s2, solving a continuous low-thrust orbital transfer strategy by adopting an in-plane phase modulation mode for coplanar approaching; s3, for different-plane small-dip-angle approaching, calculating a low-thrust orbital transfer strategy in the mode that the orbital plane is adjusted firstly and then in-plane phase modulation is used; and S4, and calculating a low-thrust orbital transfer strategy by approaching a target at an ascending / descending intersection point for different-plane large-dip-angle approaching. According to the method, the problems of coplanar approaching, different-plane small-dip-angle approaching and different-plane large-dip-angle continuous low-thrust approaching of the high-orbit target are effectively solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
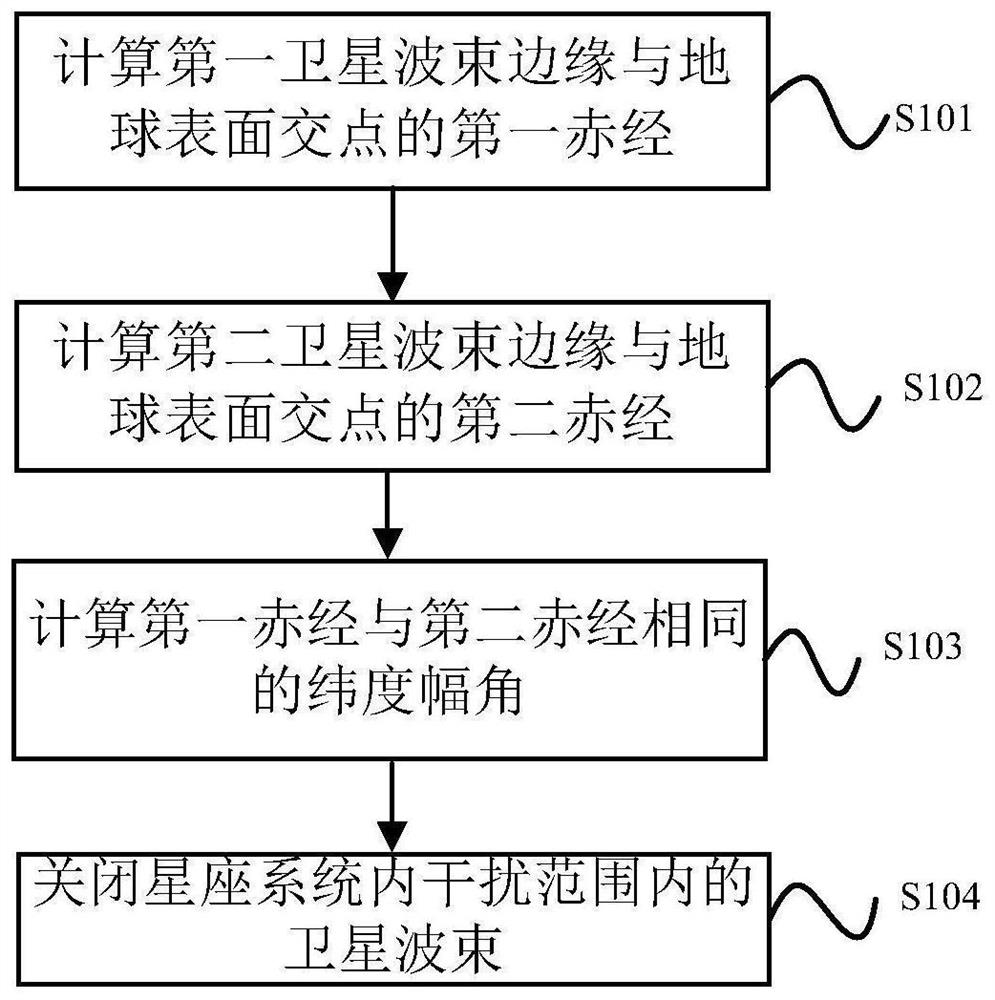
Internal frequency interference suppression method for a low-orbit constellation system
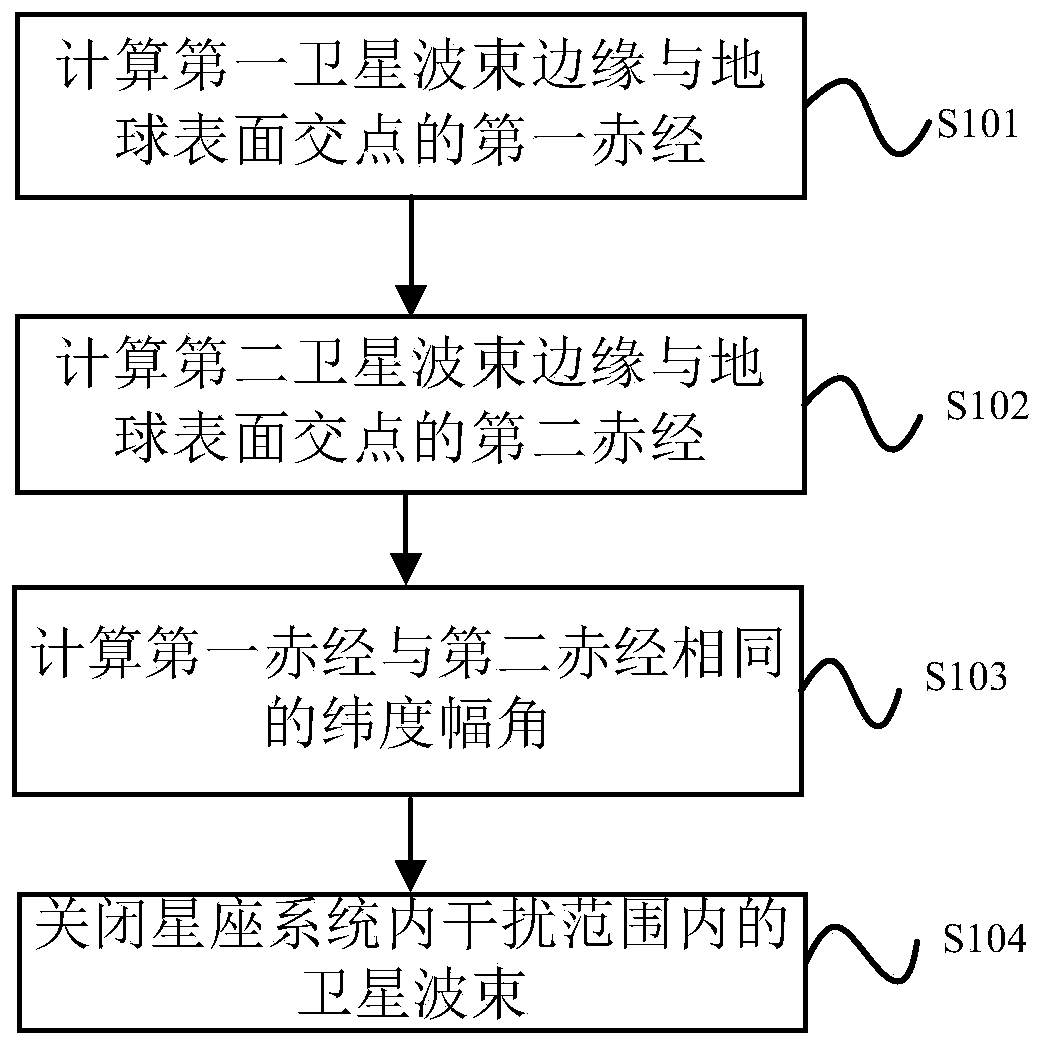
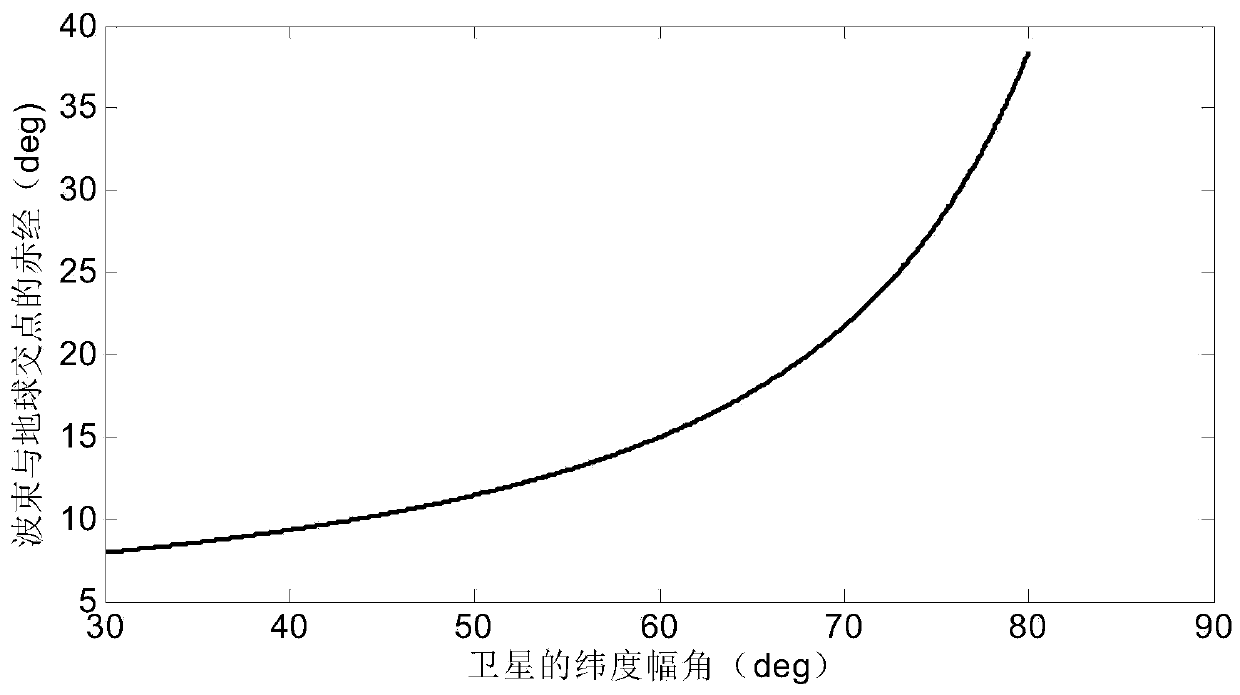
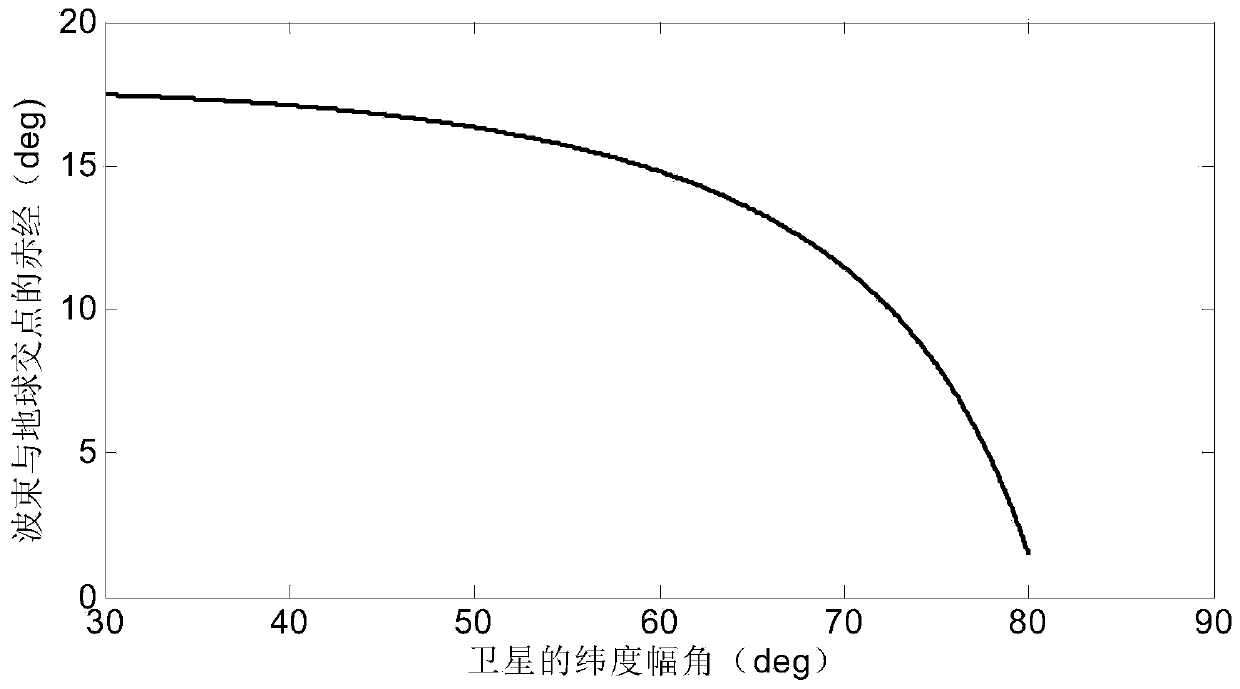
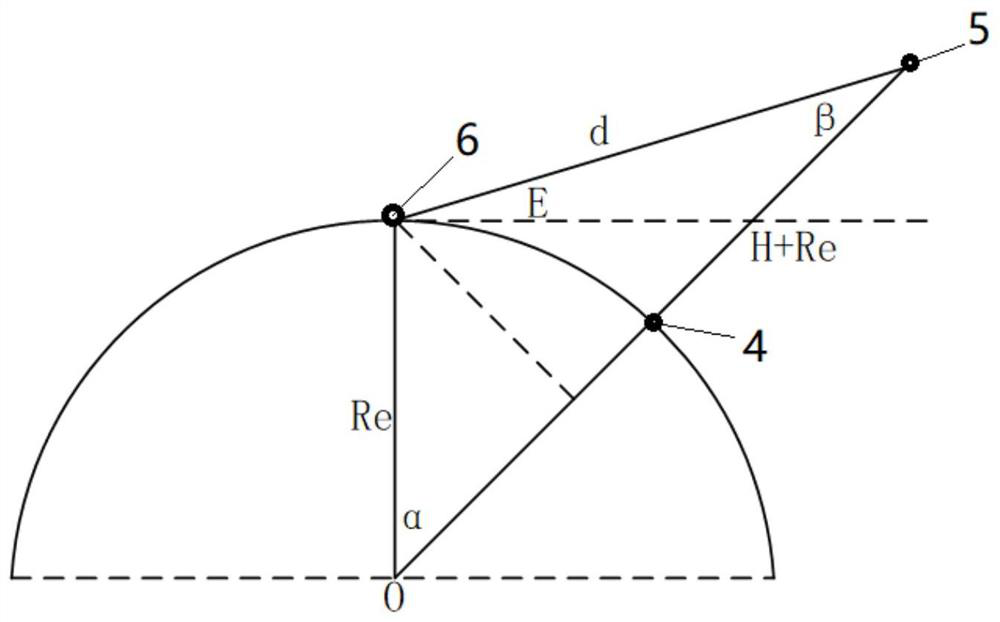
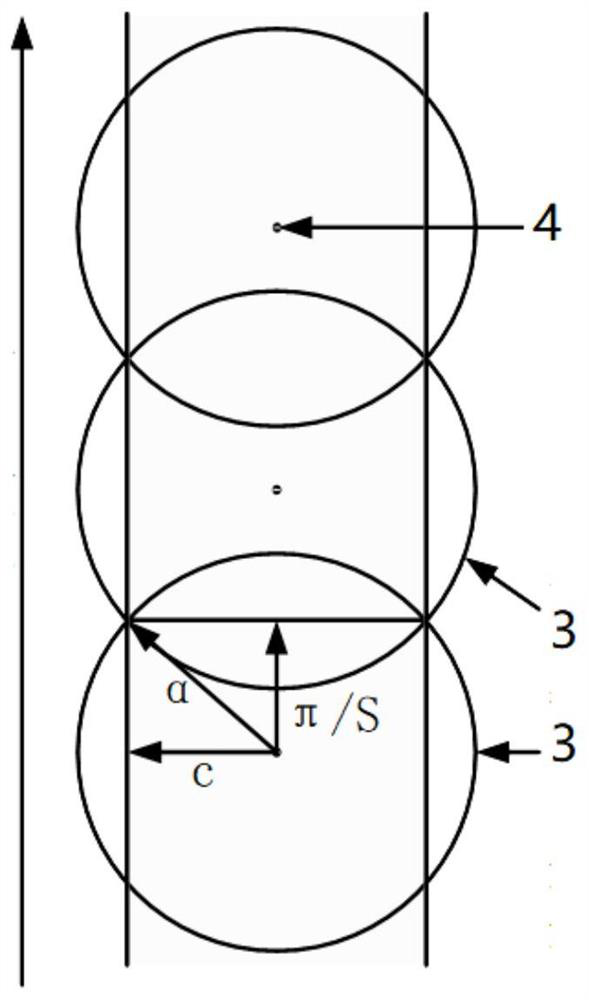
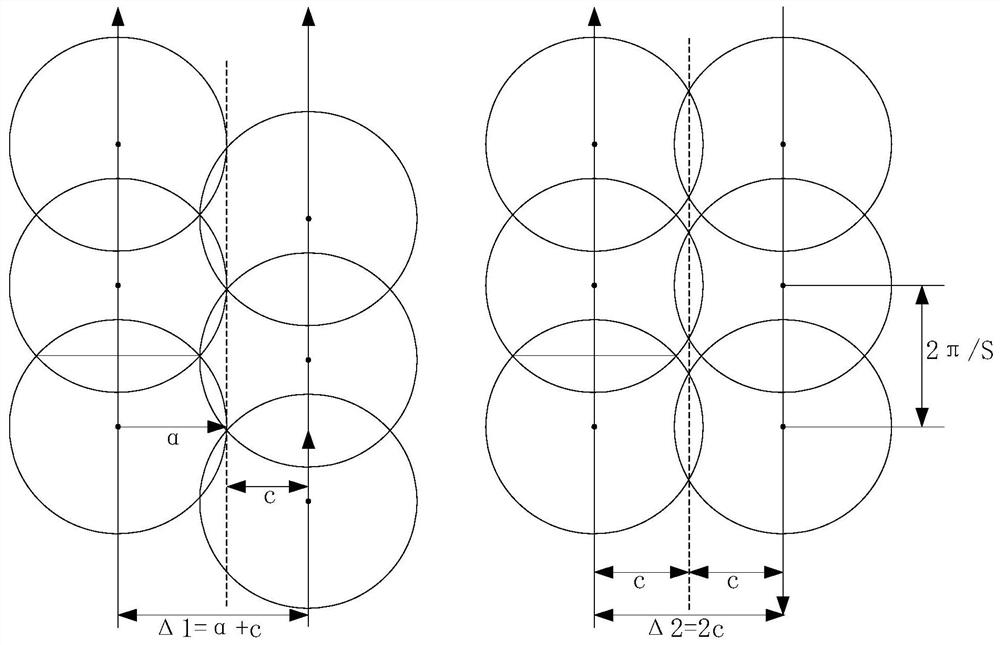
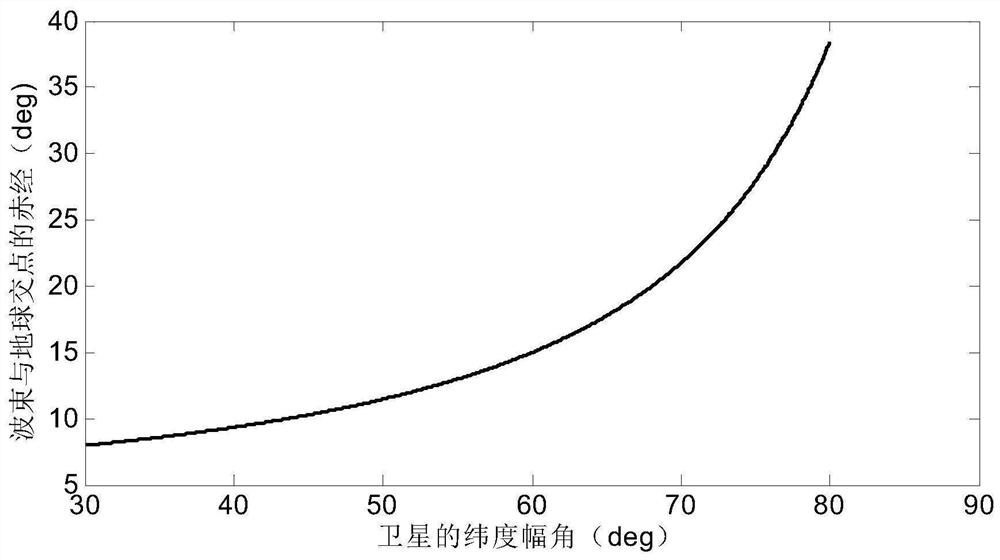
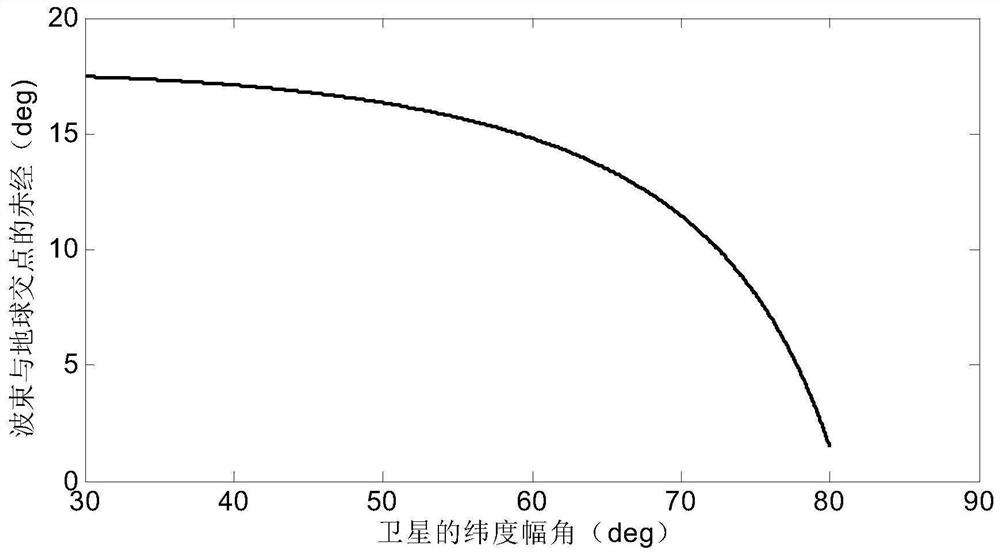
The invention discloses an internal frequency interference suppression method for a low-orbit constellation system. The low-orbit constellation system comprises satellites running on at least three orbital planes, each orbital plane comprises at least one satellite, and the method comprises the steps: calculating the first right ascension of the intersection point of the beam edge of a first satellite and the earth surface, wherein the first satellite is any satellite in any one of the at least three orbital planes; calculating a second right ascension of an intersection point of a beam edge of a second satellite and the earth surface, the second satellite being a satellite spaced apart from the first satellite by a distance of two orbital planes, and the second satellite and the first satellite having the same latitude argument; and calculating the same latitude argument uc of the first right ascension and the second right ascension, and determining the satellite beam shutdown range according to the calculated latitude argument uc. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the invention effectively suppresses the internal frequency interference of the low-orbitconstellation system on the premise of realizing the full coverage of the constellation system in the high-latitude area on the ground beams.
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
Construction method of multi-coverage reconfigurable constellation, and reconfigurable constellation
ActiveCN112073112AImprove reliabilityImprove service reliabilityRadio transmissionOrbital planeSingle star
The invention discloses a construction method of multi-coverage reconfigurable constellation, and the reconfigurable constellation. The method comprises the following steps: S1, enabling a preliminaryconfiguration to comprise a plurality of quasi-polar orbital planes which are distributed along different longitude lines and have the same orbit height, and enabling the quasi-polar orbital planes to be provided with a plurality of satellites; S2, obtaining a constellation longitude coverage band multiple number n according to the global continuous service reliability requirement R, the satellite design life T, the single-satellite reliability r and the single-satellite network compensation period t; S3, obtaining a single-satellite coverage geocentric angle alpha; and S4, obtaining a plurality of numerical combinations of the satellite number S' and the quasi-polar orbital plane number P' on the quasi-polar orbital planes meeting the constellation longitude coverage band multiple numbern according to a formula, and selecting one of the plurality of numerical combinations by a user to complete construction. The multi-coverage constellation design of the polar orbital low-orbit satellite is realized, the reliability requirement and cost of a single satellite are reduced, the bottleneck problems of over-design, high cost, high network repair period requirement and the like of theinternet satellite of the low-orbit satellite are solved, and a foundation is laid for providing carrier-grade reliable operation service of the internet of the low-orbit satellite.
Owner:中国星网网络应用有限公司
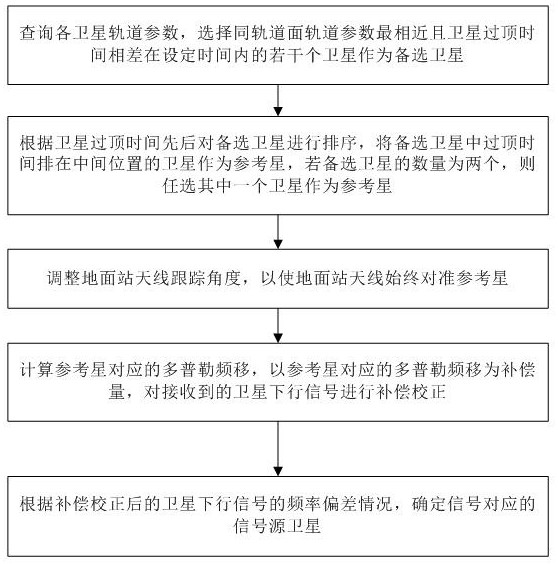
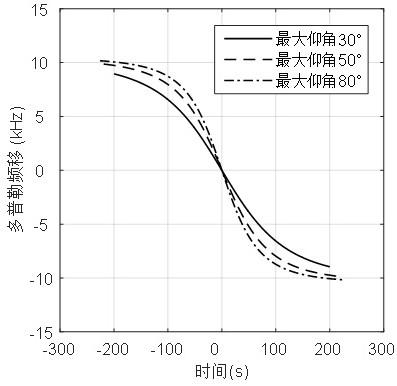
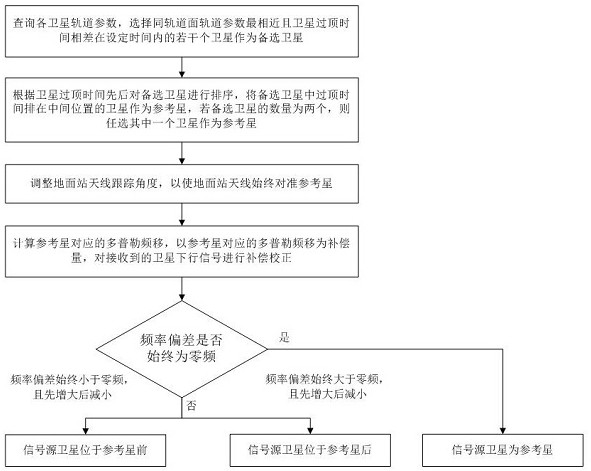
Satellite determination method and device based on Doppler effect
ActiveCN112269198AThe implementation process is simpleSimple calculationSatellite radio beaconingOrbital planeGround station
The invention discloses a satellite determination method and device based on a Doppler effect. The method comprises the steps of selecting a plurality of satellites which are most similar to orbital parameters of an orbital plane and have satellite topping time difference within set time as alternative satellites; sorting the alternative satellites according to the satellite topping time, and taking the satellite of which the topping time is ranked in the middle as a reference satellite; adjusting the tracking angle of a ground station antenna to always align the antenna with the reference satellite; calculating the Doppler frequency shift corresponding to the reference satellite, and carrying out compensation correction on the received satellite downlink signal by taking the Doppler frequency shift as a compensation amount; and determining a signal source satellite corresponding to the signal according to the frequency deviation condition of the compensated and corrected satellite downlink signal. According to the satellite determination method and device based on the Doppler effect, the signal source satellite corresponding to the signal can be determined when the received satellite signal cannot be analyzed on the ground or the satellite signal does not contain the real-time position information of the satellite, the implementation process is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
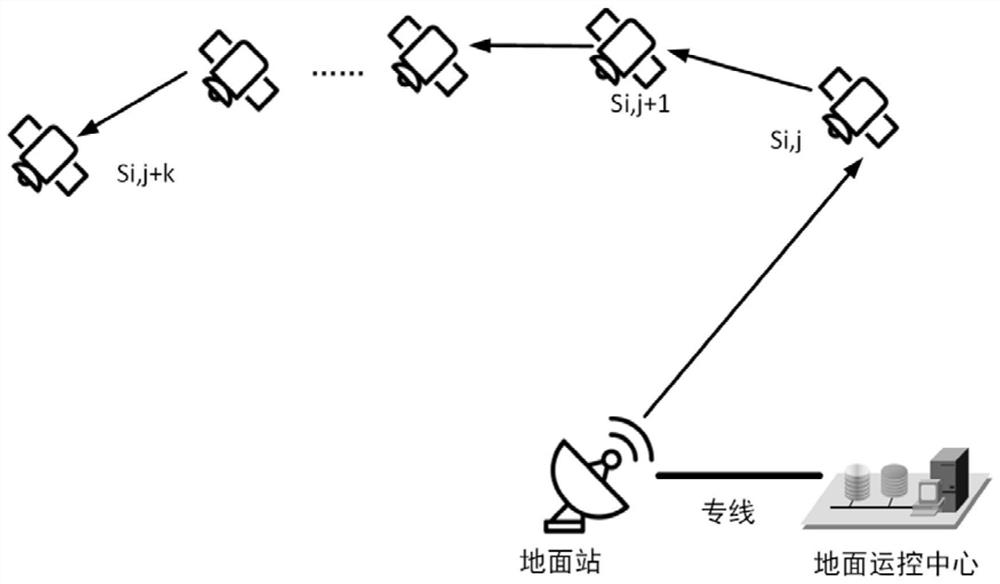
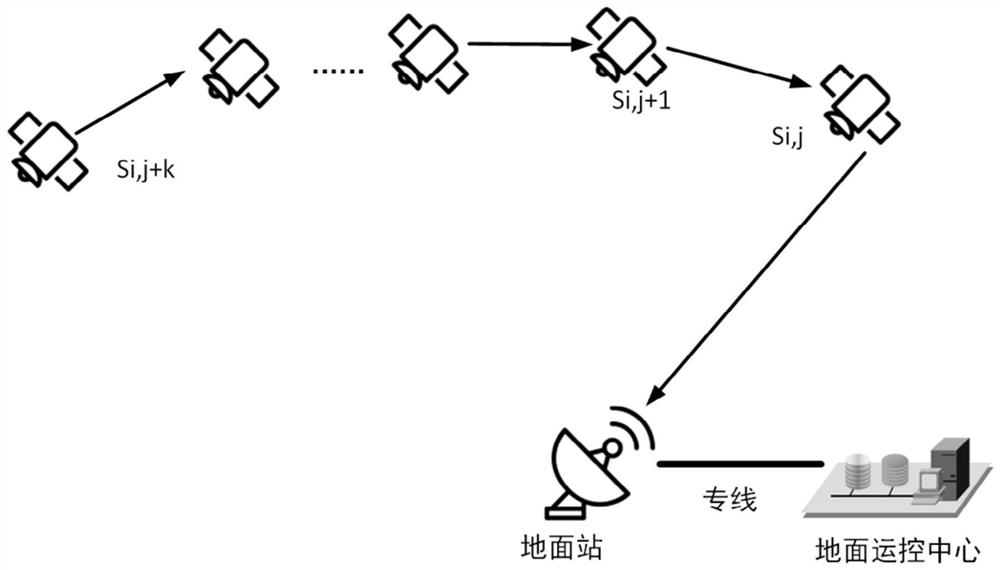
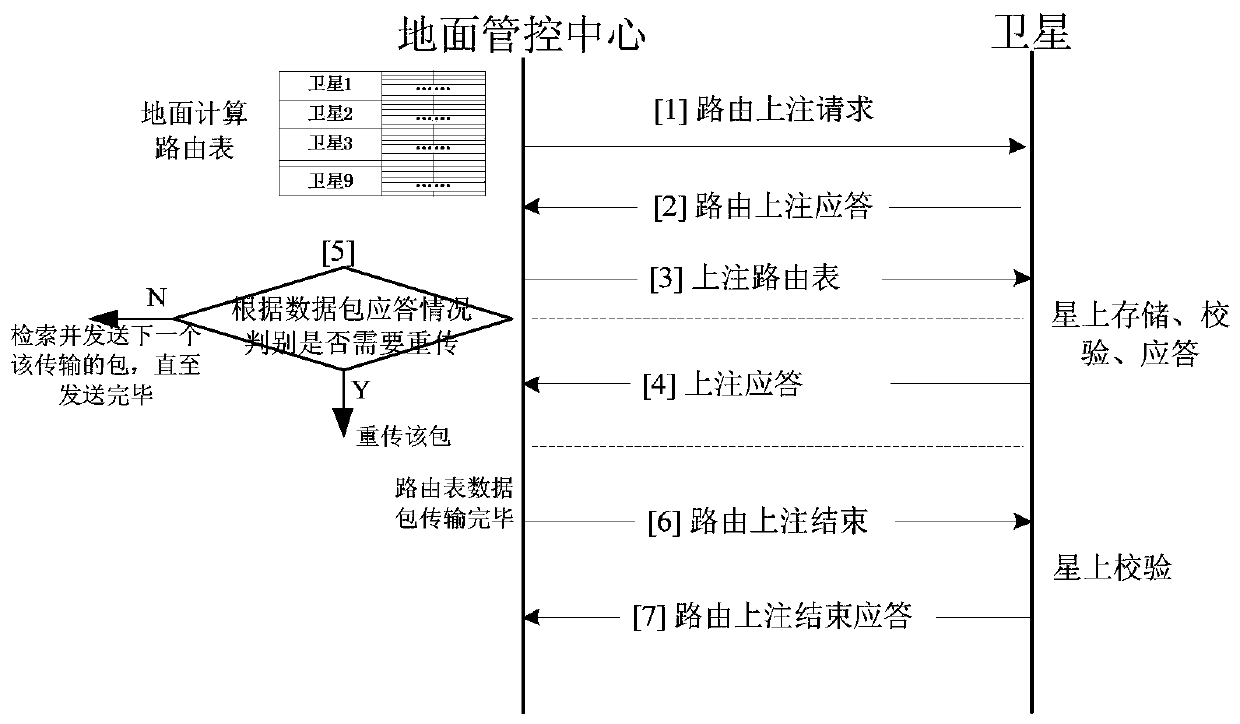
Routing table distribution method and device of low-orbit constellation system
ActiveCN111163010AImprove upload efficiencyEasy to operateRadio transmissionData switching networksOrbital planeTelecommunications
The invention provides a routing table distribution method and device of a low-orbit constellation system. The method comprises the steps of when a ground management and control center needs to updatea satellite routing table, obtaining routing tables of all satellites on an orbital plane where a transit satellite is located; splitting the routing table into a plurality of first routing table data packets through the ground management and control center; sequentially sending the plurality of first routing table data packets to the transit satellite; after the transit satellite receives all the first routing table data packets, integrating all the first routing table data packets into a routing table; splitting the routing table into a plurality of second routing table data packets throughthe transit satellite; and respectively distributing other second routing table data packets, except the second routing table data packet of the transit satellite, in the plurality of second routingtable data packets to all satellites on the orbital plane where the transit satellite is located through the transit satellite. According to the invention, the routing table uploading efficiency can be improved, the routing table is distributed by fully utilizing the fixed same-orbit inter-satellite link, the link is stable, and the operation is simple.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
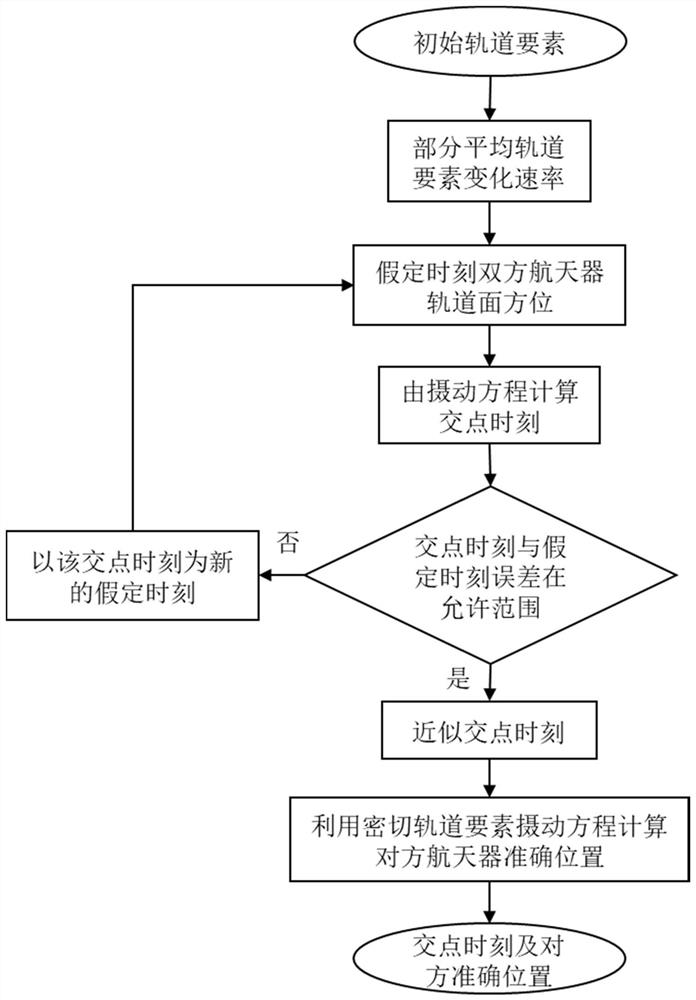
Intersection point moment and position solving algorithm based on orbit analysis perturbation solution
ActiveCN113128032AEasy to implementSmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOrbital planeGeometric relations
The invention discloses an intersection point moment and position solving algorithm based on an orbit analysis perturbation solution. A perturbation model which only considers the long-term item influence of the earth oblateness J2-J4 item is adopted for calculating the intersection point moment, the periodic item influence is ignored to reduce the calculation amount, and the orbital plane orientations of spacecrafts of both parties at the assumed moment are calculated by using a perturbation equation. An intersection point moment is calculated through the geometrical relationship, and the intersection point moment is compared with an assumed moment. If the error is large, the intersection point moment is taken as a new assumed moment to repeatedly calculate the intersection point moment until iteration convergence. Finally, the position of the spacecraft of the opposite party at the intersection point moment is solved by utilizing an osculating orbit element perturbation equation with long-term, long-period and short-period oscillation at the same time. The method not only can accurately calculate the moment and position of the intersection point, but also is simple and easy to implement, saves calculation time, calculation resources and memory, is especially suitable for spaceborne computers with shortage of calculation resources, and has good popularization prospects.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Large-scale low-orbit satellite constellation deployment method, device and equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN113525719AImplement the deployment methodShorten the durationArtificial satellitesHigh level techniquesOrbital planeSatellite constellation
The invention provides a large-scale low-orbit satellite constellation deployment method, device and equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of controlling a first group of satellites to enter a nominal orbit to form a first orbit surface after a rocket is separated from a plurality of satellites, controlling the second group of satellites to the Nth group of satellites to stay in a parking orbit, wherein the multiple satellites are divided into N groups, and the height of the nominal orbit is larger than that of the parking orbit, determining the adjustment time of each satellite in the ith group of satellites based on the right ascension difference of the ascending node between the first orbital plane and the ith orbital plane to be formed by the ith group of satellites, wherein the adjustment time comprises the parking time and the climbing time, and based on the parking time, controlling each satellite in the ith group of satellites to stay in a parking orbit, and based on the climbing time, controlling each satellite in the ith group of satellites to climb to a nominal orbit from the parking orbit to form the ith orbit surface so as to form a satellite constellation.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
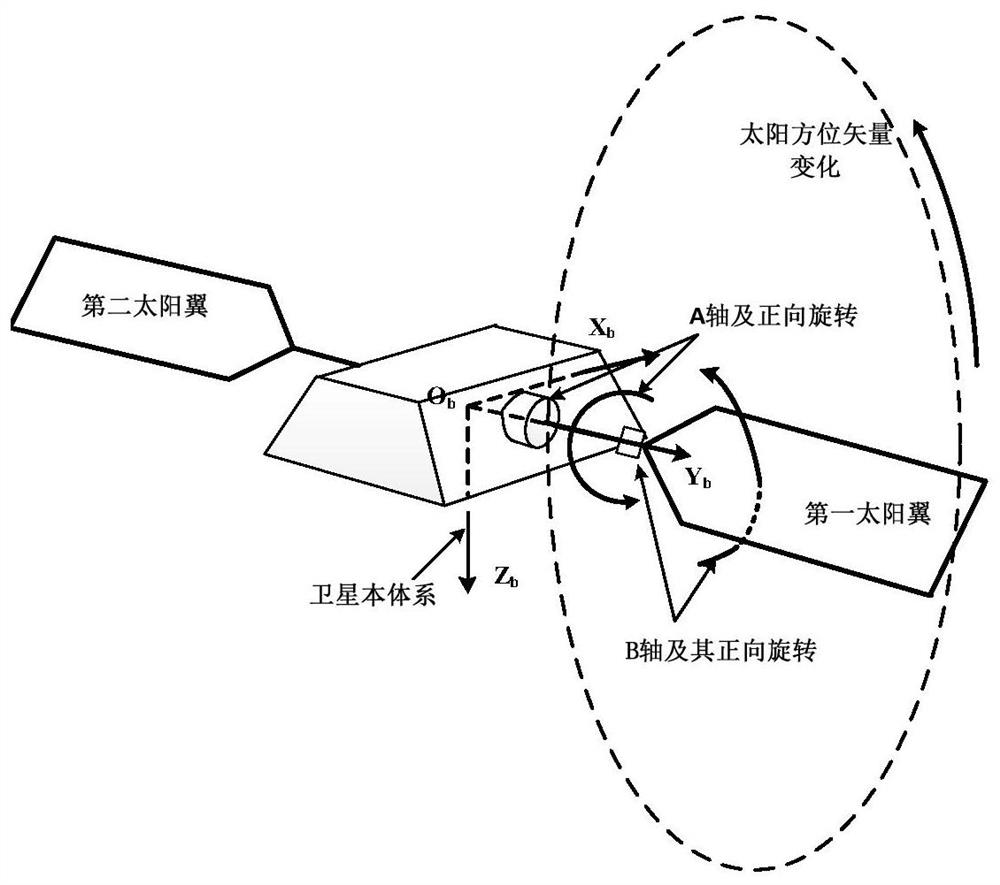
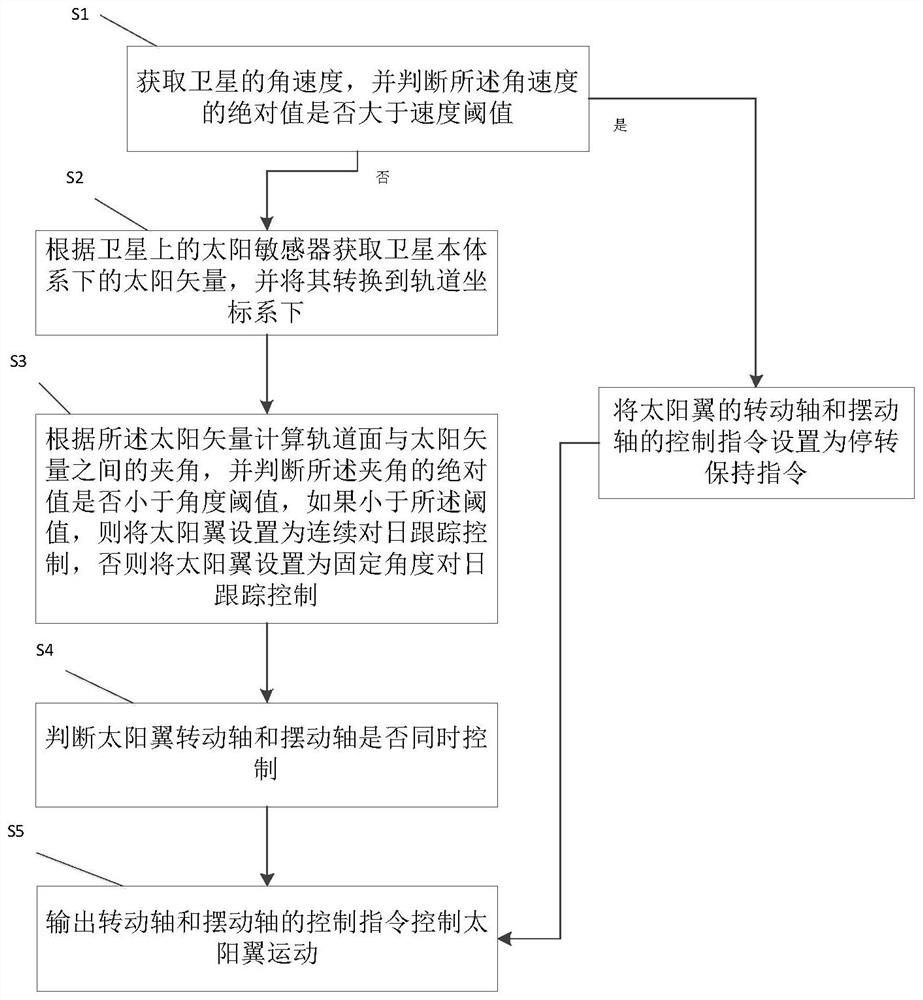
Low-orbit satellite two-degree-of-freedom solar wing control method
ActiveCN112937919AImprove work efficiencyReduce management costsCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsOrbital planeClassical mechanics
The embodiment of the invention discloses a low-orbit satellite two-degree-of-freedom solar wing control method, which comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring the angular velocity of a satellite, judging whether the absolute value of the angular velocity is greater than a velocity threshold value, if yes, setting a control instruction of a rotating shaft and a swinging shaft of a solar wing as a stalling keeping instruction, and then performing S5, otherwise, performing S2; S2, acquiring a sun vector in a satellite body system, and converting the sun vector into an orbital coordinate system; S3, calculating an included angle between the orbital plane and the sun vector, judging whether the absolute value of the included angle is smaller than an angle threshold value or not, if so, setting the solar wing as continuous sun tracking control, and otherwise, setting the solar wing as fixed-angle sun tracking control; S4, judging whether the rotating shaft and the swinging shaft of the solar wing are controlled at the same time, if yes, executing S5, and otherwise, adjusting the instruction of the rotating shaft; and S5, outputting control instructions of the rotating shaft and the swinging shaft to control the solar wing to move.
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
Task satellite scheduling method for infrared LEO constellation
ActiveCN112874814AImprove preferenceImprove timelinessArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital planeLongitude
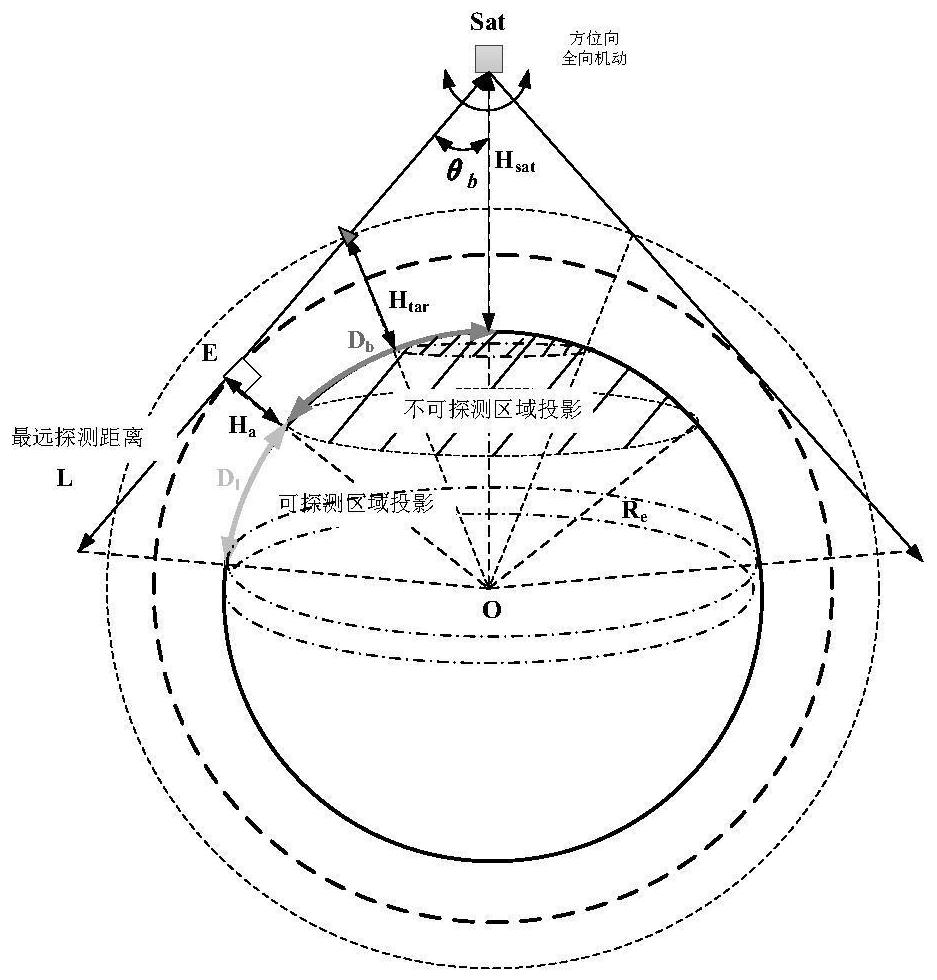
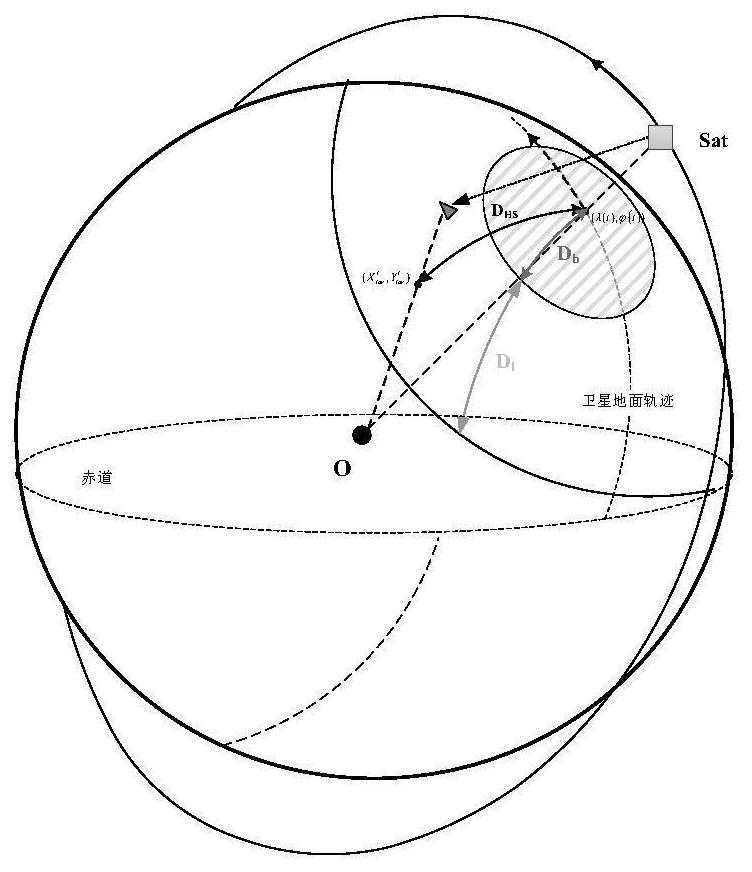
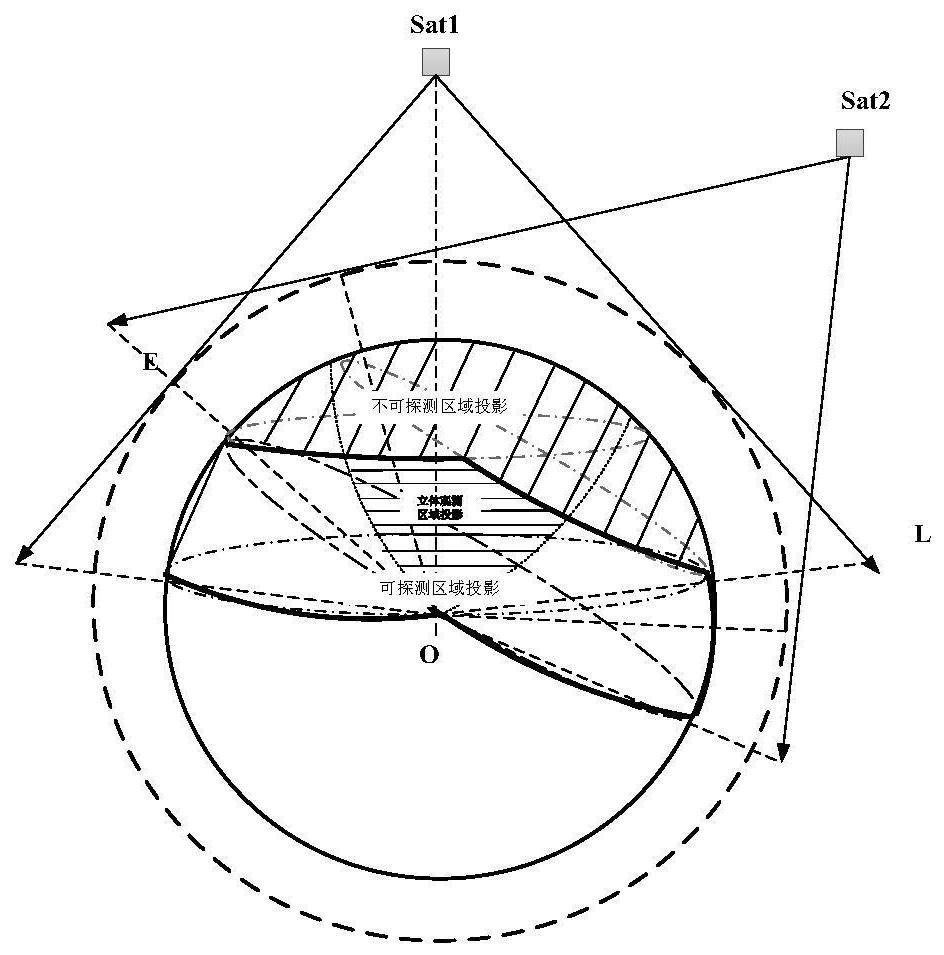
The invention relates to the technical field of aerospace, and provides a task satellite scheduling method for an infrared LEO constellation. The method comprises the following steps: projecting an invisible observation angle range of a satellite to a target to earth surface to obtain an undetectable range Db; projecting the maximum detection distance L of the satellite to the earth surface and removing the undetectable range Db to obtain a detectable range D1; projecting the target to the earth surface, and performing detectable analysis of the satellite and the target; screening orbital planes according to the longitude range of ascending nodes of the orbital planes and the geographic position of the target; and screening a task satellite from the screened orbital planes according to the relative motion relation between the satellite and the target and observable conditions. The problems that in the prior art, calculation is complex, on-satellite resource overhead is large and task planning timeliness is low in the task satellite scheduling process are at least partially solved, task satellite optimization efficiency and timeliness are improved, and the method has application value for task satellite scheduling of an infrared LEO constellation and design optimization of the constellation.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR MICROSATELLITES OF CAS +1
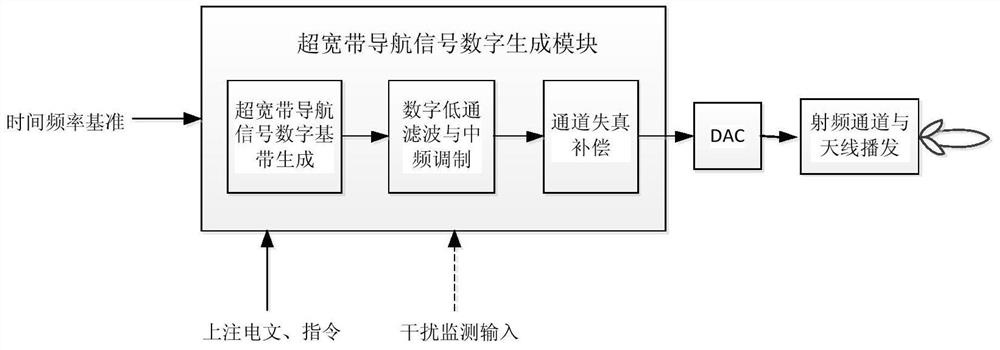
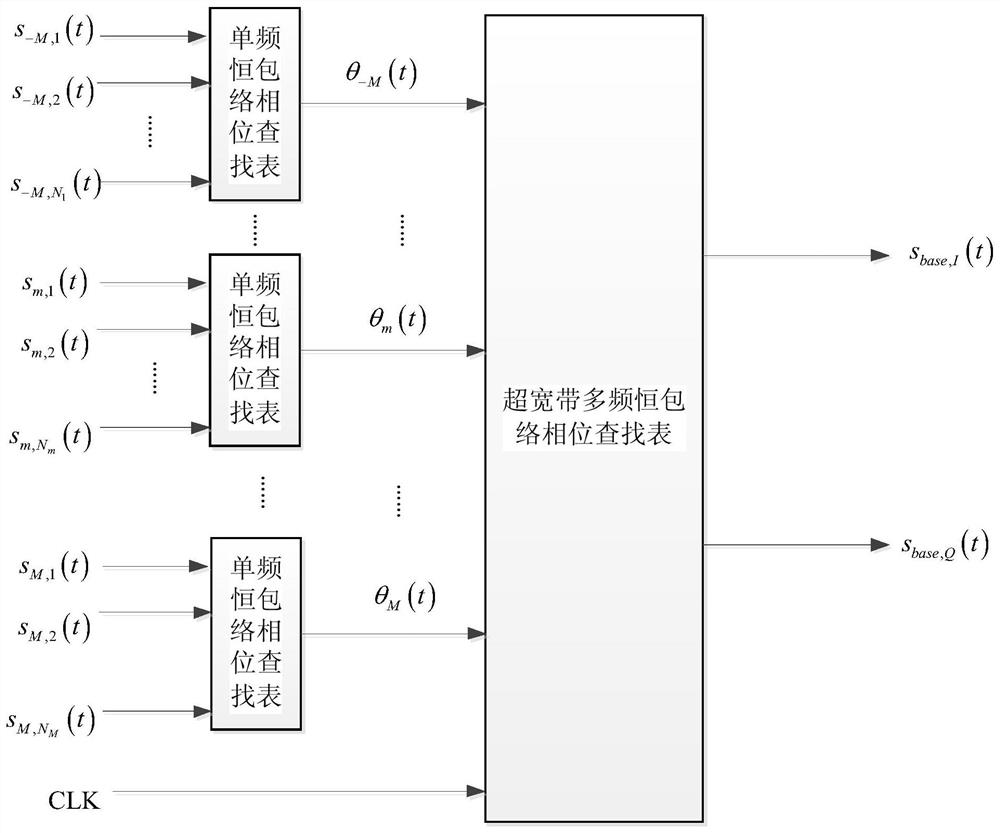
A system and method of generating and broadcasting ultra wide band navigation signals
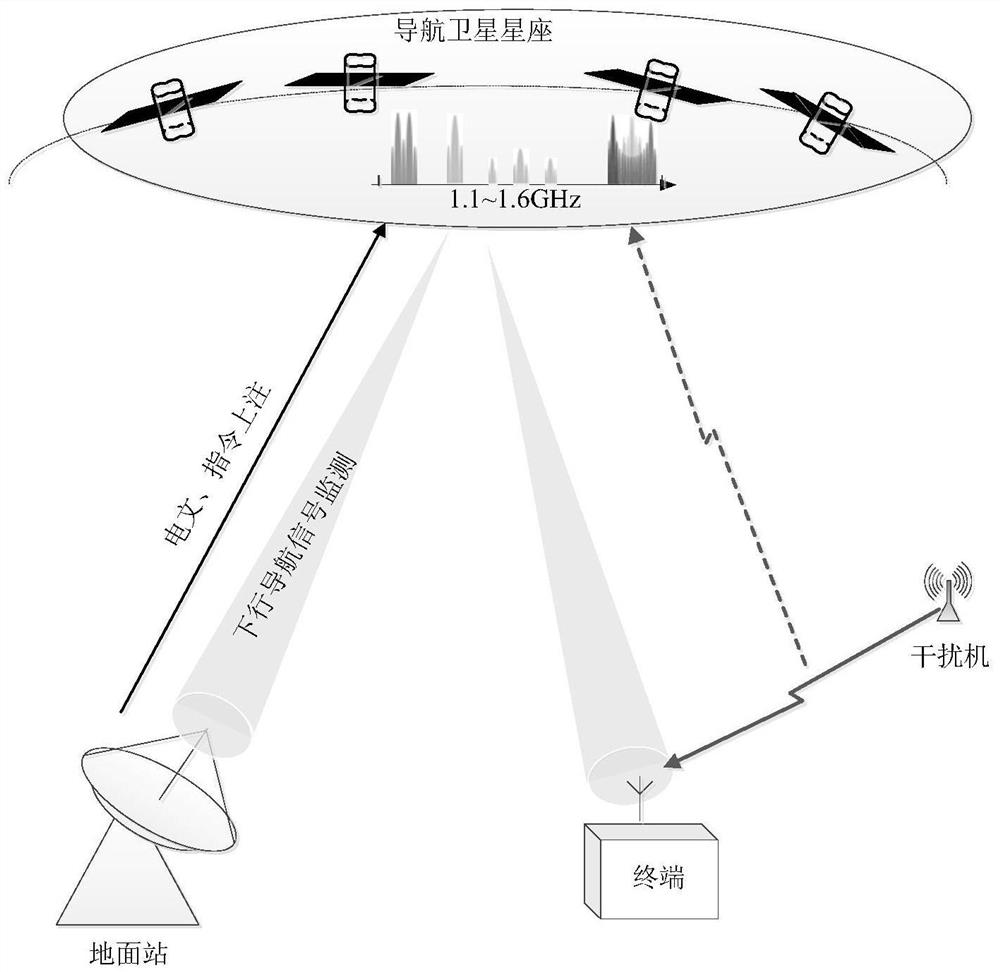
PendingCN111948681AImprove spectrum utilizationImprove anti-interference abilitySatellite radio beaconingHigh level techniquesUltra-widebandOrbital plane
The invention discloses a system and a method for generating and broadcasting ultra-wideband navigation signals. The system comprises a navigation satellite constellation, a ground station and a userterminal, the navigation satellite constellation is composed of a plurality of satellites with a plurality of orbital planes, and quadruple or more coverage of the navigation satellite constellation on the ground is achieved. Each navigation satellite in the navigation satellite constellation can establish connection with the ground station and receive navigation messages or instructions injectedto the ground station, the navigation satellites have ultra-wideband navigation signal generation and broadcast loads, and under the control of a frequency spectrum monitoring function, according to the time frequency reference and the navigation messages or instructions injected to the ground station, an ultra-wideband navigation signal is flexibly and quickly generated and broadcasted; under thecondition of ground instructions or autonomous interference monitoring, signal agility is carried out, active interference avoidance is realized, and the anti-interference capability is further improved.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
A Fast Estimation Method of Optimal Velocity Increment for Long-term Orbital Rendezvous under j2 Perturbation
ActiveCN110789739BDecrease speed incrementImprove optimization efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesLinear/angular speed measurementOrbital planeClassical mechanics
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Constellation backup strategy evaluation method and system based on random time Petri network
ActiveCN111795690AImprove accuracyIncrease flexibilityGeometric CADCosmonautic ground equipmentsOrbital planeEvaluation result
The invention relates to a constellation backup strategy evaluation method and system based on a random time Petri network, and belongs to the technical field of constellation operation management. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a single-satellite STPN model and an orbital plane STPN model, and establishing a navigation constellation STPN model containing various backup strategies according to the single-satellite STPN model and the orbital plane STPN model; establishing an availability model according to the number of fault satellites in the navigation constellation STPN model and the constellation CV value, and establishing a cost model according to the operation cost of the navigation constellation STPN model; and evaluating the navigation constellation STPN model by adopting the availability model and the cost model, and determining a target backup strategy from a plurality of backup strategies according to an evaluation result. According to the method, theimpact of random and determined events in the constellation on the system is fully evaluated, the influence of different backup strategies on constellation operation parameters can be effectively analyzed, and a quantitative basis can be provided for design optimization of navigation constellation backup strategies.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
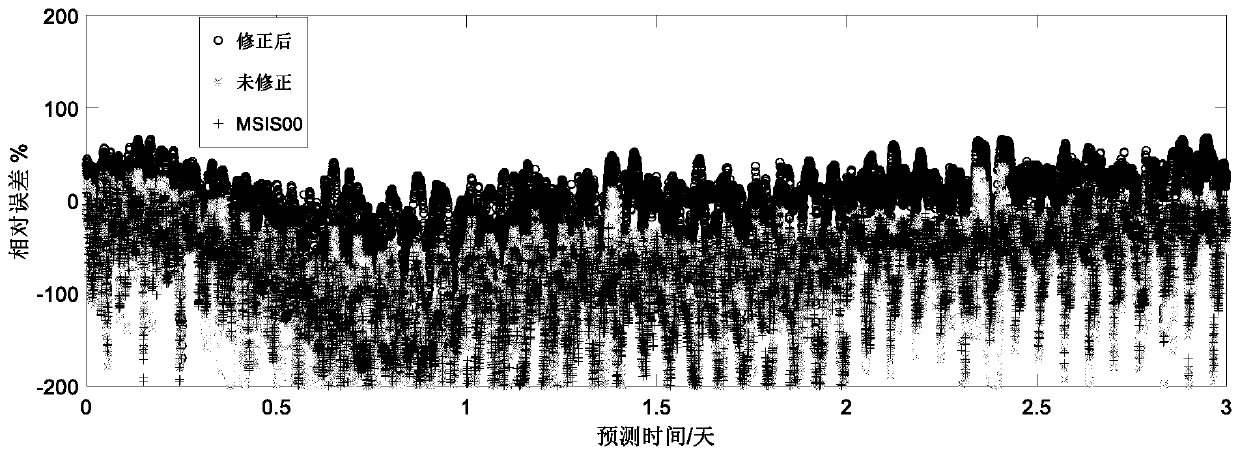
Thermal layer atmospheric density prediction method and system based on distributed sensing units
ActiveCN111259310AHigh precision requirementsBreak through the defect that the space cannot be expandedComplex mathematical operationsICT adaptationOrbital planeData set
The invention belongs to the technical field of atmospheric density sensing methods and space physics, and particularly relates to a hot layer atmospheric density prediction method based on distributed orbit atmospheric sensing units, which comprises the following steps: obtaining P distributed orbit atmospheric sensing units; in combination with an energy dissipation rate or semi-major axis attenuation, calculating an atmospheric density correction ratio of a track surface thermal layer where each distributed track atmospheric sensing unit is located; periodically and dynamically selecting the multiple space targets are uniformly distributed in the P distributed orbit atmosphere sensing units at different places; in all P distributed track atmosphere sensing units, calculating the atmospheric density of the space point of the space target on the corresponding orbital plane every 2-30 seconds; periodically acquiring a full-space atmospheric density data set {rhoO} within 3-24 hours; calculating a spherical harmonic coefficient, calculating the corrected inflection point temperature and escape layer temperature to form a thermal layer atmospheric density correction model, and obtaining the dynamically corrected thermal layer atmospheric density by using the correction model to predict the atmospheric density of any position in the future space.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
A constellation design method for spectrum coexistence between LEO constellation systems
ActiveCN110198184BSpectrum coexistenceNatural isolation angleRadio transmissionOrbital planeOrbital inclination
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
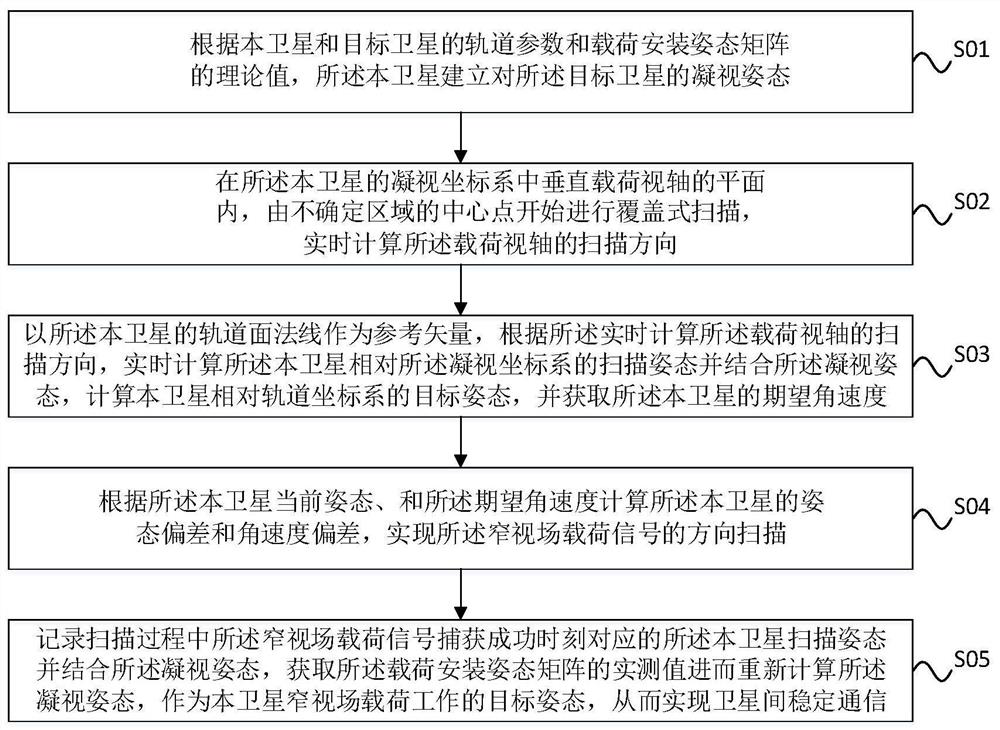
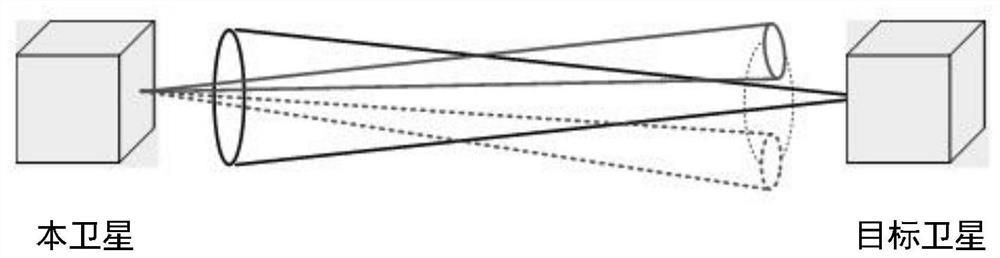
Method for realizing narrow-view-field load pointing calibration by satellite attitude maneuver assistance
The invention discloses a method for realizing narrow view field load pointing calibration by satellite attitude maneuver assistance. The method comprises the following steps that a target staring attitude is established according to orbit parameters of a local satellite and a target satellite and a theoretical value of a load installation matrix; in a vertical load visual axis plane in a satellite staring coordinate system, an Archimedes spiral is calculated from a central point, and the scanning direction of a load visual axis is planned in real time; a scanning attitude of a satellite relative to a staring coordinate system in real time is calculated according to a load visual axis direction planned by a spiral line by taking an orbital plane normal as a reference vector, a target attitude of the satellite relative to an orbital coordinate system is calculated in combination with the staring attitude, and an expected angular velocity of the satellite is obtained; the deviation of the attitude and the angular velocity is calculated according to the current attitude and the angular velocity of the satellite so as to realize spiral line scanning in the load signal direction; after the two parties capture the signals, the current attitude is recorded, the actual measurement value of the installation matrix corresponding to the load is calculated in combination with the theoretical attitude, and normal communication of the narrow-view-field load can be realized without spiral scanning again.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and device for suppressing internal frequency interference in low-orbit constellation system
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
A Method and Device for Optimizing the Orbit of a Variable-step Constellation Based on a Genetic Algorithm
ActiveCN109635332BImprove optimization time precisionReduce optimization timeGeometric CADMulti-objective optimisationOrbital planeAlgorithm
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Steady Sun Orientation Method for Satellites Constrained by Ground Pointing Bias
ActiveCN110901956BOvercome the singularity of rapid flippingShorten speedCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital planeSpacecraft attitude control
The invention discloses a satellite's stable sun-orientation method constrained by the ground pointing deviation, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft attitude control. The described steady-to-day orientation method establishes the desired attitude of the satellite in two steps: first establishes the intermediate attitude of the satellite based on the direction of the satellite-to-center line, the normal direction of the satellite orbital plane, and the forward direction of the satellite; The pulling axis is rotated by a certain angle to reduce the satellite's pointing deviation towards the sun, and ensure that the angle between the expected axis of the earth and the direction of the center of the earth is not greater than the constraint angle. The expected attitude of the satellite obtained according to the strategy can maintain a stable change, avoiding the strange phenomenon that the expected attitude of the satellite changes drastically in a short period of time when the sun-earth-satellite is collinear caused by the traditional strategy, thereby greatly reducing the process of satellite orientation to the sun. peak energy consumption in .
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
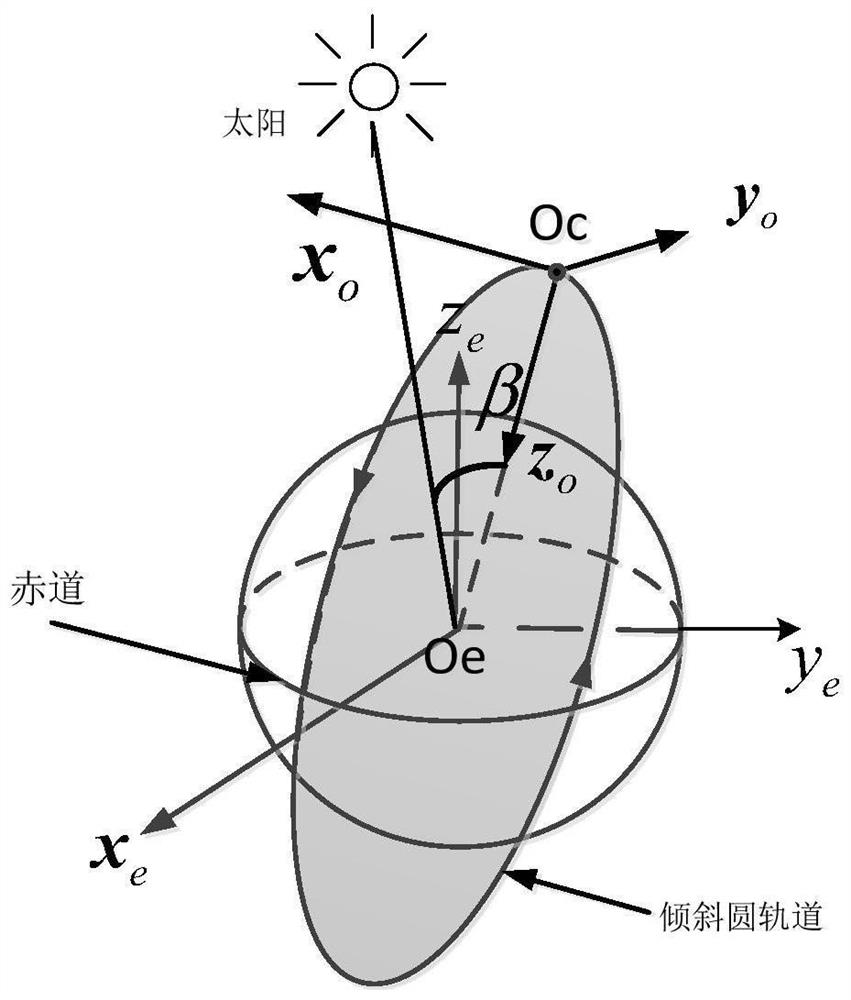
Design method for solar panel device of sun-synchronous orbit satellite and solar panel device designed by adopting method
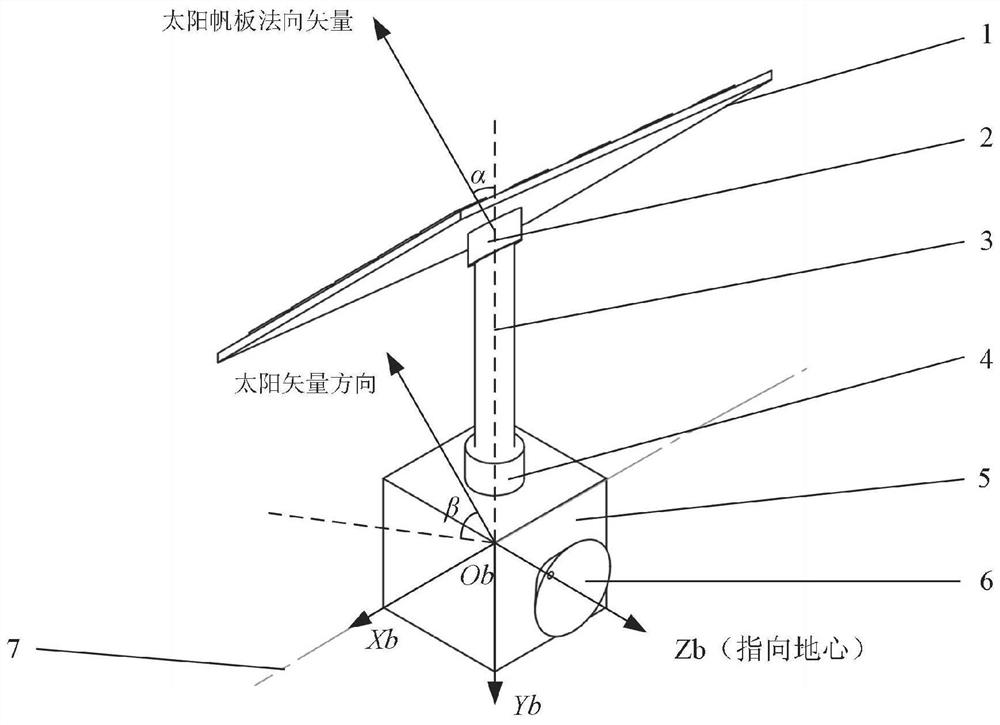
PendingCN114735232AEasy to driveLow costCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsOrbital planeSynchronous orbit
The invention discloses a design method of a solar panel device of a sun-synchronous orbit satellite and the solar panel device designed by adopting the method, belongs to the technical field of satellite solar panels, and solves the problems of difficulty in attitude adjustment, high manufacturing cost and long development period of an existing solar panel. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a satellite body coordinate system, wherein the satellite body coordinate system coincides with an orbital coordinate system; the rotating shaft of the solar panel coincides with the rotating axis of the sun vector; calculating an included angle beta between the sun vector and the orbital plane; according to the included angle beta, the included angle alpha between the normal of the solar panel and the rotating shaft of the solar panel is obtained, and the included angle alpha and the included angle beta are complementary angles; and designing the solar panel device according to the included angle alpha. The method is suitable for the design of the solar panel device of the remote sensing satellite with the unchanged attitude.
Owner:哈尔滨工大卫星技术有限公司
A Calculation Method Applicable to Pseudo-Lite Position
ActiveCN109932734BSolve the problem that the coordinates of stationary objects on the ground cannot be representedSimple algorithmSatellite radio beaconingOrbital planeAngular distance
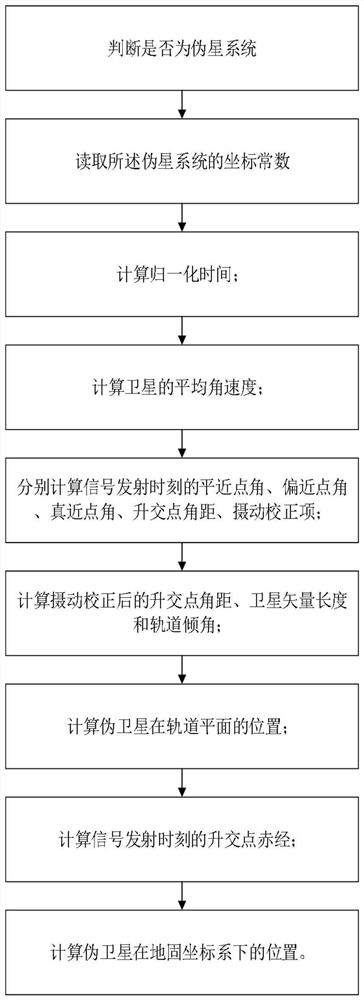
The present invention proposes a calculation method suitable for pseudolite positions, including: judging whether it is a pseudolite system; if so, reading the coordinate constant of the pseudolite system; calculating normalized time; calculating the average angular velocity of the satellite; calculating respectively Mean anomaly angle, deviating anomaly angle, true anomaly angle, ascending node angular distance, perturbation correction item at the time of signal transmission; calculate ascending node angular distance after perturbation correction, satellite vector length and orbit inclination angle; calculate pseudolites Position on the orbital plane; calculate the right ascension of the ascending node at the time of signal launch; calculate the position of the pseudolite in the ground-fixed coordinate system. The invention only modifies the basic earth parameters in the satellite position algorithm, so that the space position of the pseudolite can be calculated by using four ephemeris parameters, and solves the problem that the original broadcast ephemeris cannot represent the coordinates of ground stationary objects.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
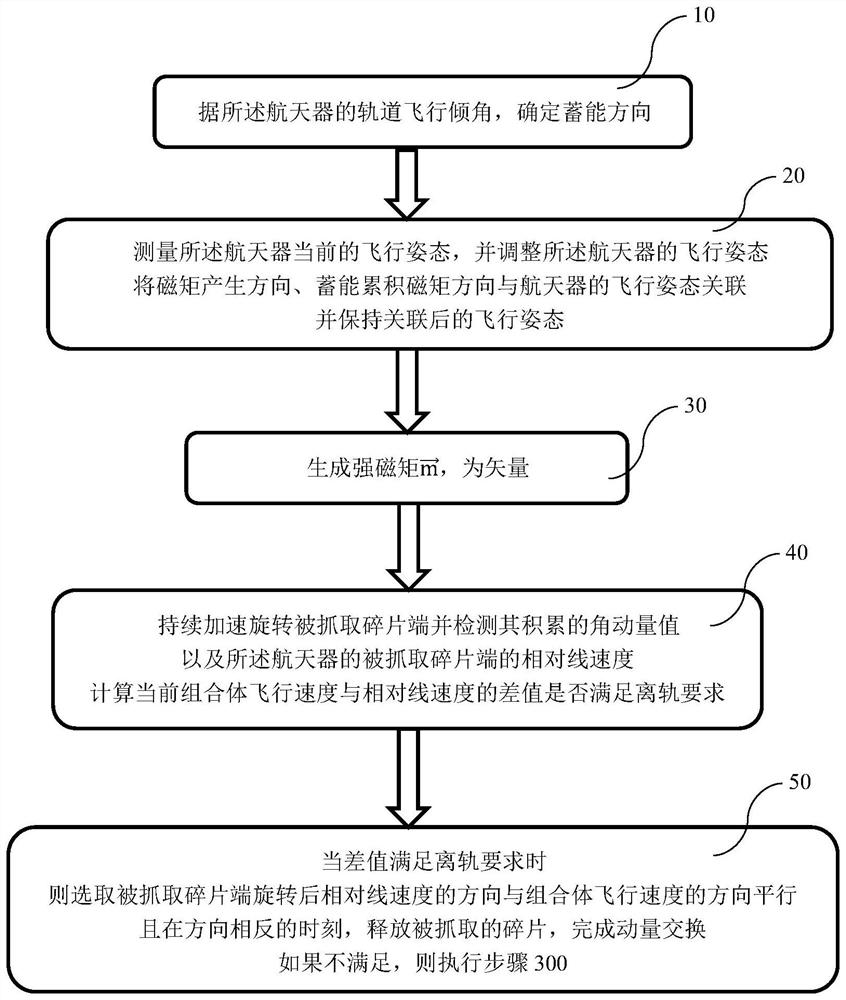
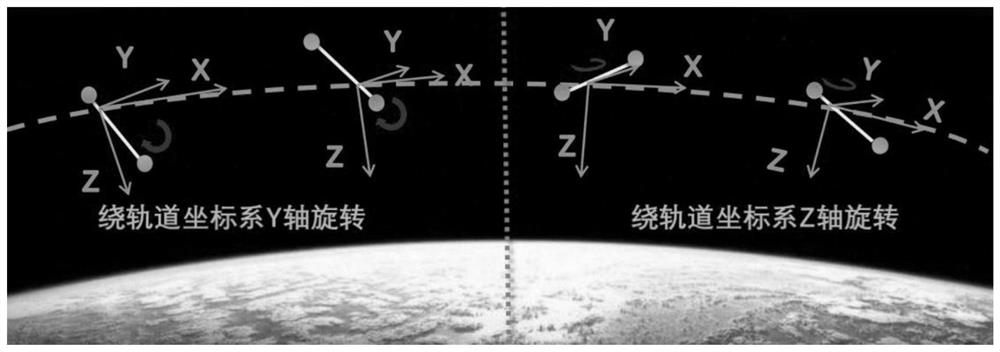
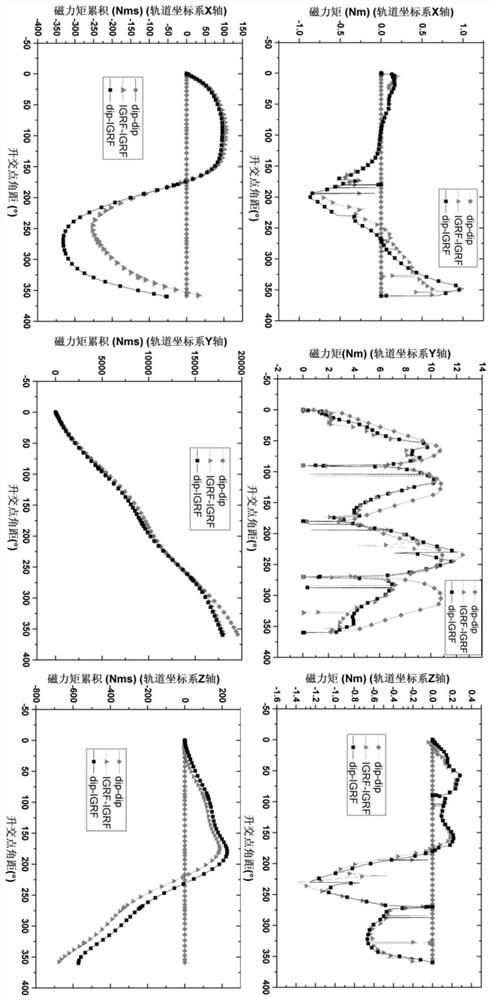
A method for adjusting orbit attitude coupling for deorbit delivery of low-orbit space debris with geomagnetic energy storage
ActiveCN110510154BImprove efficiencyImprove economyCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital planeOrbital period
The embodiment of the present invention discloses a geomagnetic energy storage low orbit space debris off-orbit delivery orbit attitude coupling adjustment method, which includes the following steps: Step 100, decomposing the entire geomagnetic energy storage low orbit period into energy gathering arcs and energy releasing arcs section, and configure the momentum wheel energy-absorbing device on the three axes of the spacecraft; step 200, respectively determine the energy-gathering arc section and the energy-discharging arc section when the spacecraft performs energy storage and accumulation around the y-axis of the orbital plane and the z-axis of the orbital plane; Step 300, after determining the energy-gathering arc segment, for the energy storage targets of different orbital coordinate systems Y-axis or Z-axis, complete the de-orbiting operation of space debris based on the geomagnetic energy storage low-orbit space debris de-orbiting control method; Step 400, After the energy release arc is determined, the three-axis momentum wheel energy absorbing device of the spacecraft is unloaded through the generated magnetic moment.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser link distribution method for optimizing network throughput
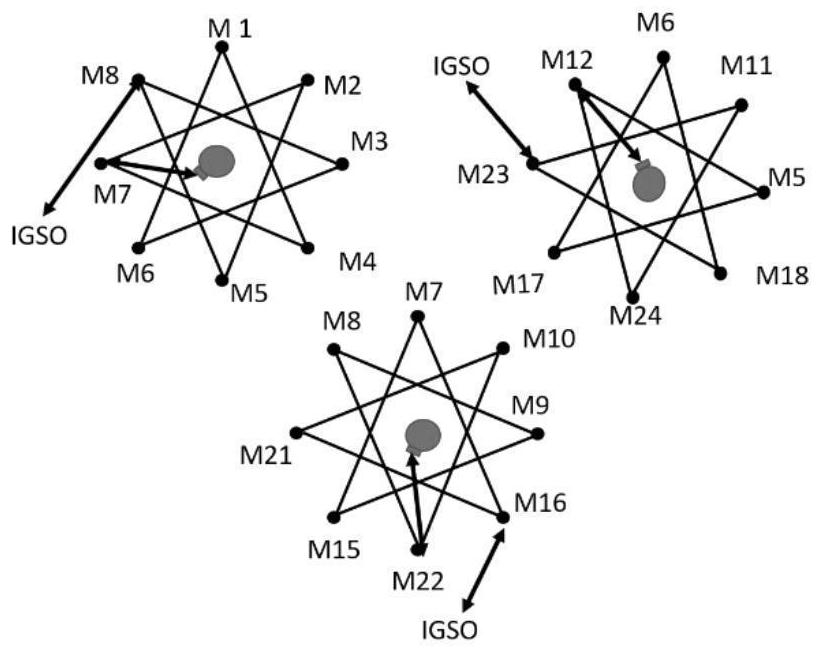
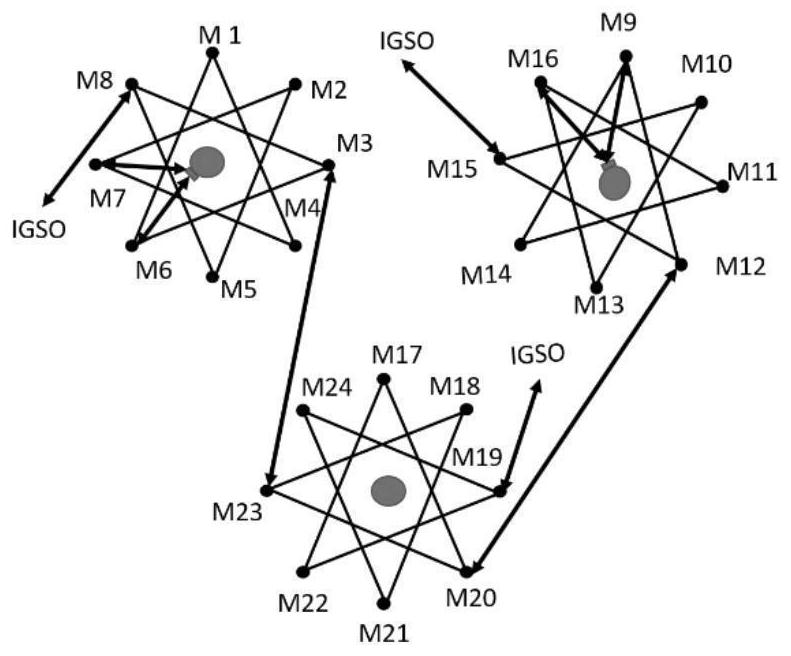
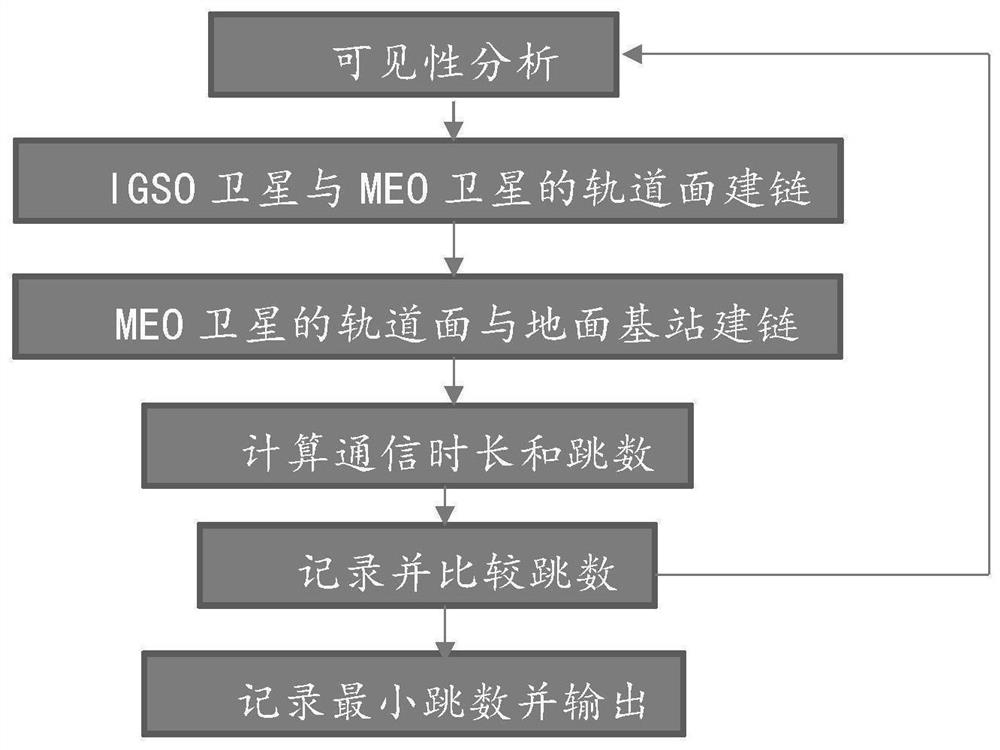
ActiveCN113037360ASolve the problem of small landing volumeImprove throughputRadio transmissionData switching networksSatellite dataOrbital plane
The invention relates to the technical field of spatial information networks, and provides a laser link distribution method for optimizing network throughput, which comprises the following steps: carrying out visibility analysis; selecting orbital planes of the IGSO satellite and the MEO satellite to establish a link; selecting an MEO satellite to establish a link with a ground base station and calculating communication overhead; recording a link establishment routing table; and circulating the steps and recording the link establishment routing table with the least output hops. According to the method, the balance between the on-satellite data and the landing data is completed through distribution of the laser links, the problem that the landing amount of the on-satellite data is small is solved, the inter-satellite network has good throughput, and reference is provided for networking of the next generation of Beidou navigation system.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR MICROSATELLITES OF CAS +1
Sun-synchronous circular orbit satellite sun exposure factor calculation method, device and electronic equipment
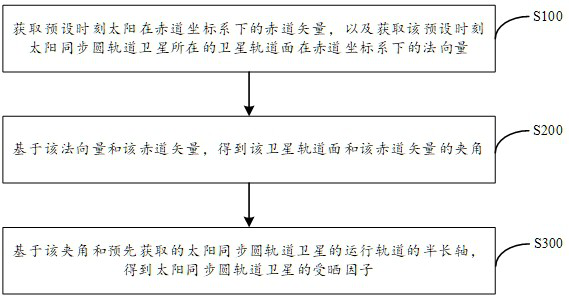
The application provides a sun-synchronous circular orbit satellite sun exposure factor calculation method, device and electronic equipment, which belong to the field of aerospace technology. The method includes: obtaining the equatorial vector of the sun in the equatorial coordinate system at a preset time, and obtaining the The normal vector of the satellite orbit plane where the sun-synchronous circular orbit satellite is located in the equatorial coordinate system, the equatorial vector is the unit vector pointing from the origin of the equatorial coordinate system to the center point of the sun at the preset moment; based on the normal vector and the equatorial vector, the satellite orbit is obtained The angle between the plane and the equator vector; based on the angle and the pre-acquired semi-major axis of the orbit of the sun-synchronous circular orbit satellite, the sun exposure factor of the sun-synchronous circular orbit satellite is obtained. This method does not need to calculate the orbit forecast of the sun and the satellite, nor does it need to calculate the time when the satellite enters and exits the earth's shadow, thereby simplifying the calculation process of the sun exposure factor of the sun-synchronous circular orbit satellite, shortening the calculation time, and reducing the requirements for designers.
Owner:成都国星宇航科技股份有限公司
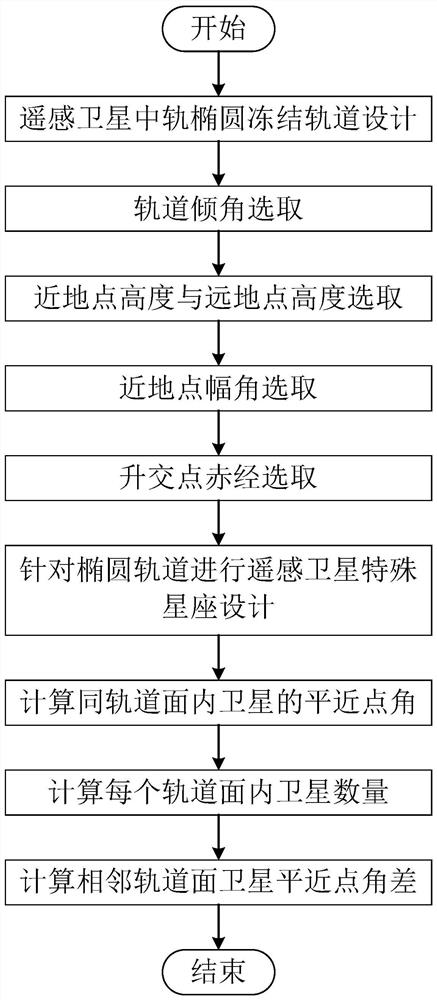
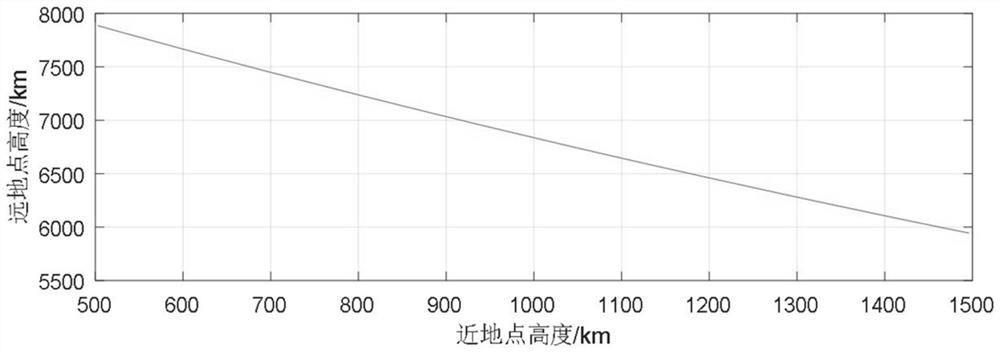
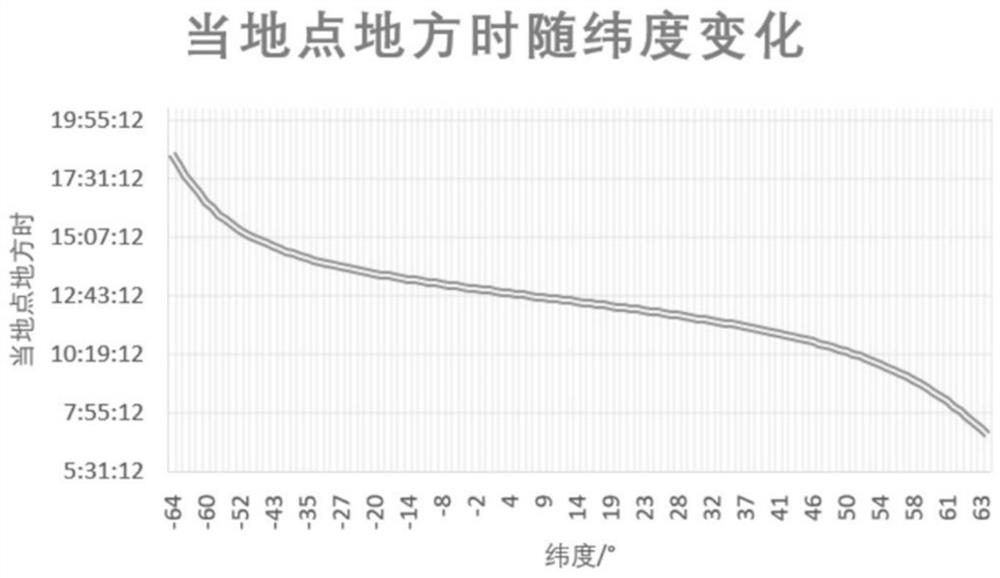
Medium-orbit elliptical orbit remote sensing satellite constellation design method
PendingCN114491999ASlow motionExpand coverage areaDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOrbital planeHigh spatial resolution
The invention relates to a method for designing a medium-orbit elliptical orbit remote sensing satellite constellation, which comprises the following steps of: S1, designing an elliptical frozen orbit of a medium-orbit elliptical orbit remote sensing satellite by utilizing the characteristic that the elliptical orbit of the medium-orbit elliptical orbit remote sensing satellite stays at an apogee for a long time; the method specifically comprises the following steps: S11, selecting an orbit inclination angle i; s12, selecting perigee height hp and apogee height ha; s13, selecting a perigee argument omega; s14, selecting the right ascension omega of the ascending node; s2, aiming at the characteristic that the elliptical orbit of the medium-orbit elliptical orbit remote sensing satellite is a non-uniform orbit with high perigee movement speed and low apogee movement speed, designing a special Walker constellation of the medium-orbit elliptical orbit remote sensing satellite; the method specifically comprises the following steps: S21, calculating a mean anomaly of a satellite in an orbital plane; s22, calculating the number s of satellites in each orbital plane; and S23, calculating the plane anomaly difference of the adjacent orbital planes. The method has the advantages that the method is oriented to optical remote sensing satellites, targets in key areas are highly revisited, and hotspot targets are monitored with high time resolution and high spatial resolution.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR MICROSATELLITES OF CAS +1
An autonomous security control method for space optical relative measurement equipment
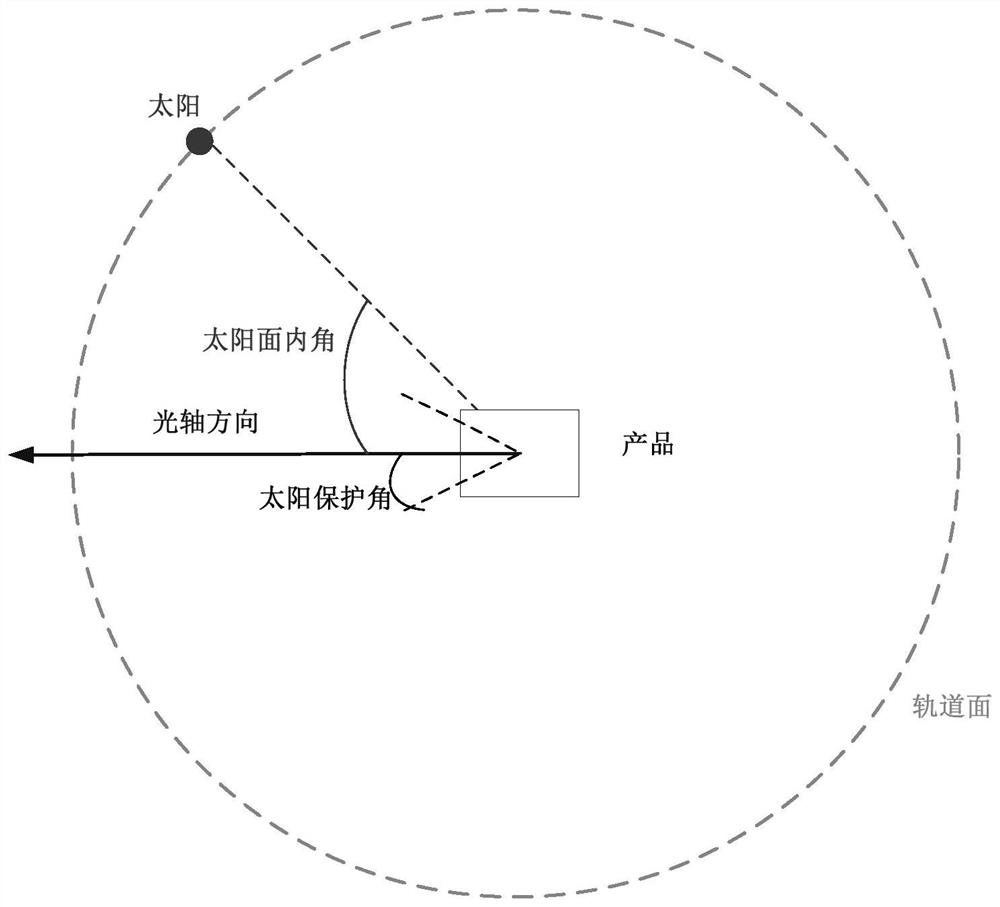
ActiveCN111988529BSatisfy the safety work requirements of on-orbit operationThe principle of the method is clearTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOrbital planeAngle of incidence
The invention discloses an autonomous safety control method for space optical relative measurement equipment, the method comprising: S1, determining the relative position of the sun on the orbital plane of the space optical relative measurement equipment, represented by the inner angle of the sun surface; S2, calculating the space optical relative measurement The included angle between the optical axis of the device and the inner angle of the solar surface in the step S1 is represented by the sun incidence angle; S3, according to the relationship between the sun incidence angle and the solar protection angle threshold of the space optics relative measurement device , execute the corresponding mode state. Its advantages are: the method rationally uses the relationship between the inner angle of the solar surface, the solar incident angle and the threshold value of the solar protection angle, and satisfies the requirements for the safe operation of the space relative measurement equipment in orbit. Rail work can ensure the safety of the space relative to the measuring equipment.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com