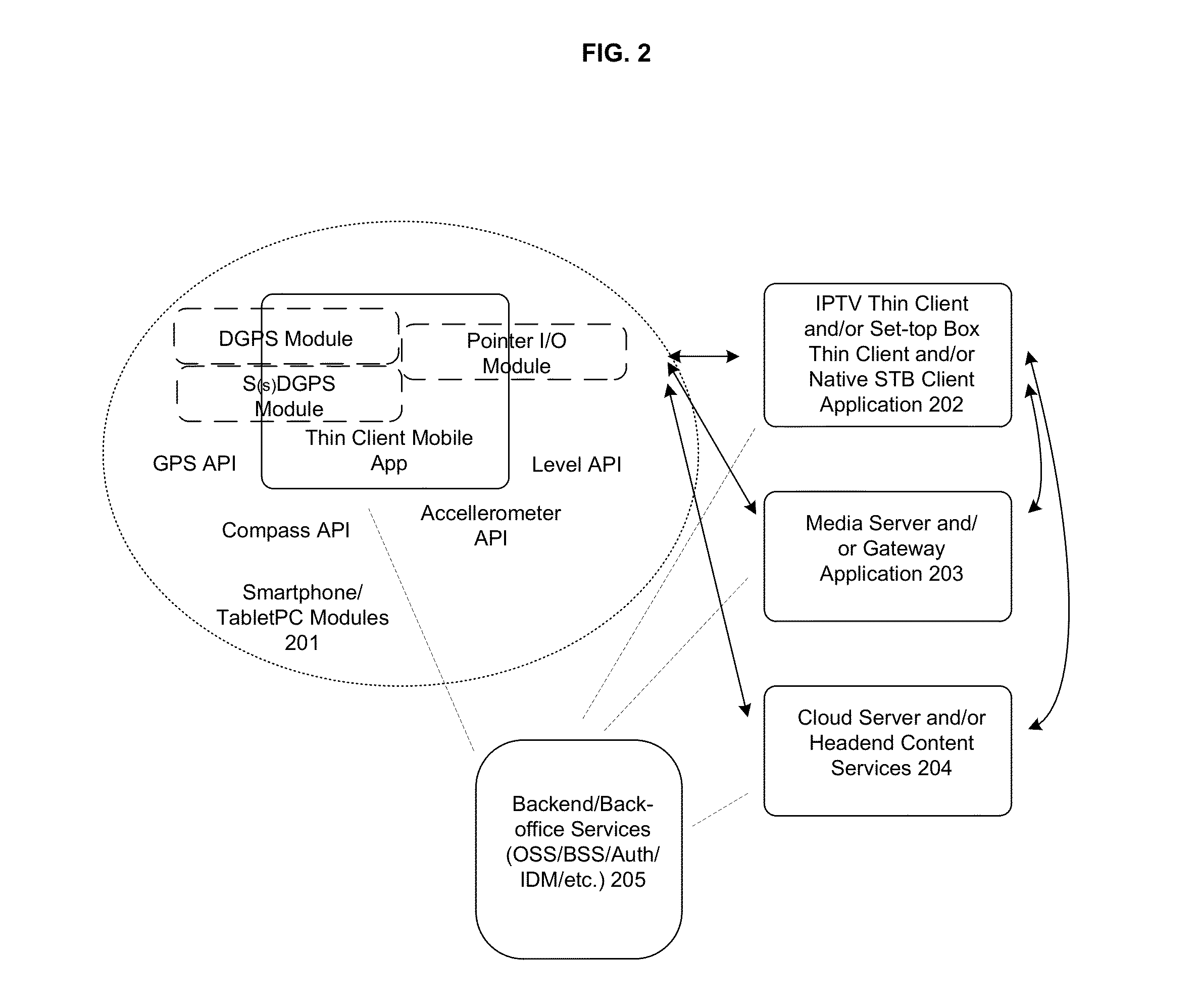
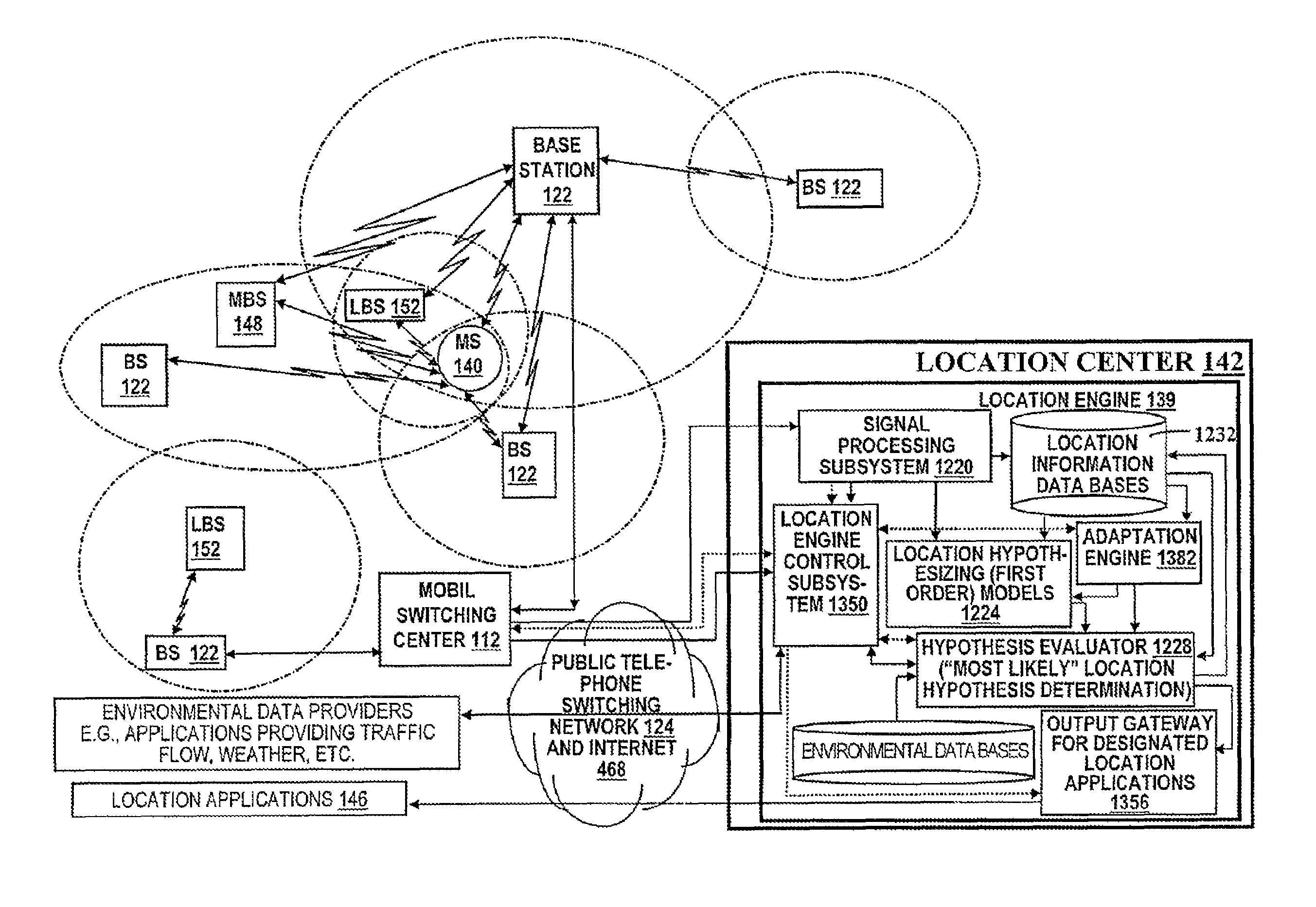
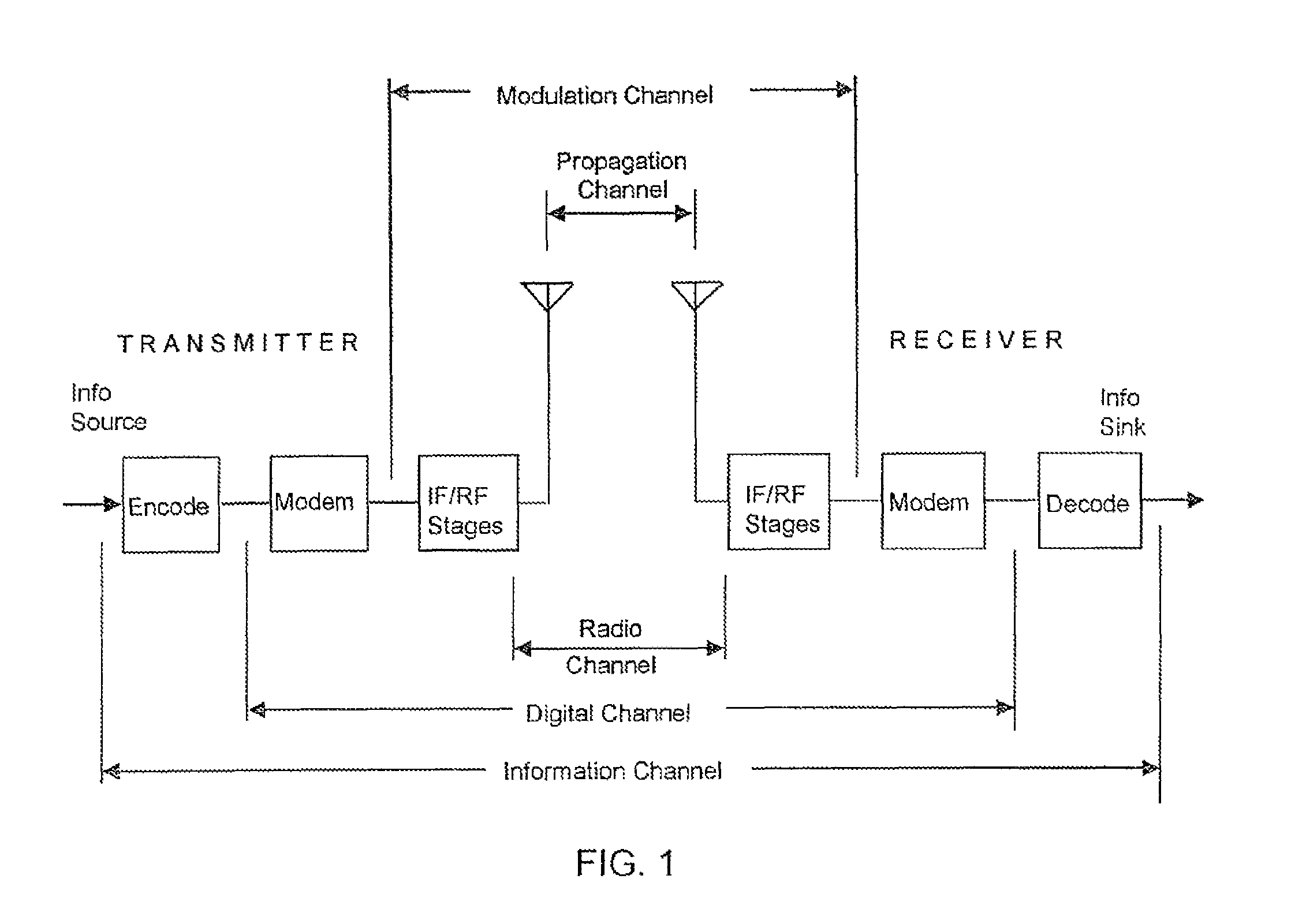
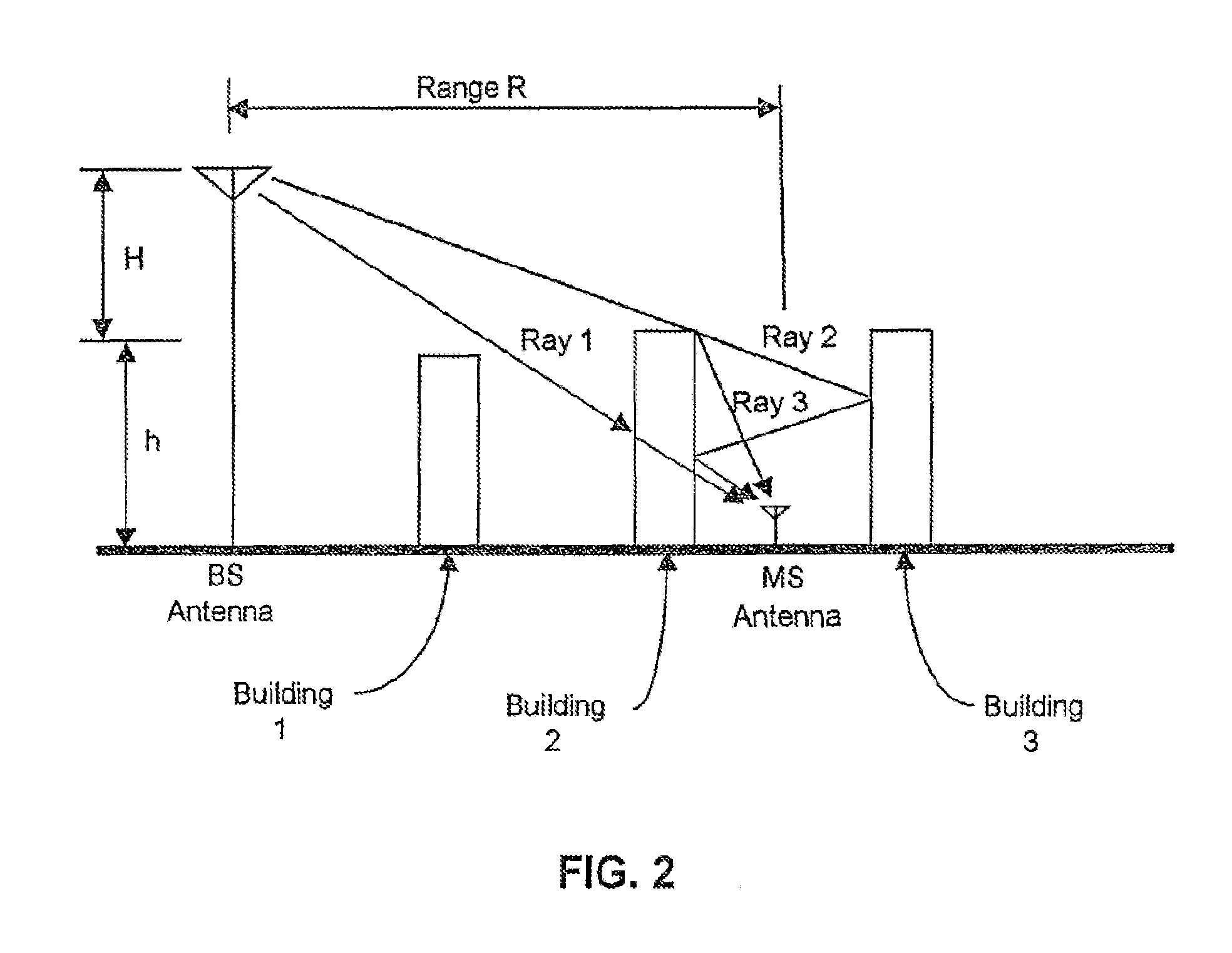
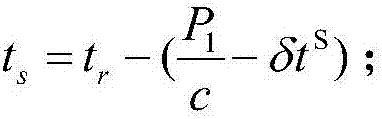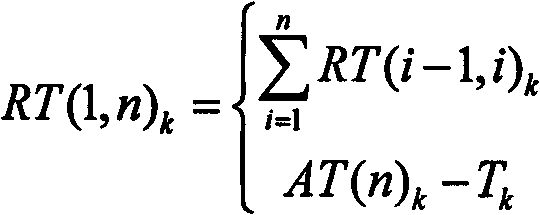Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4461 results about "Positioning technology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
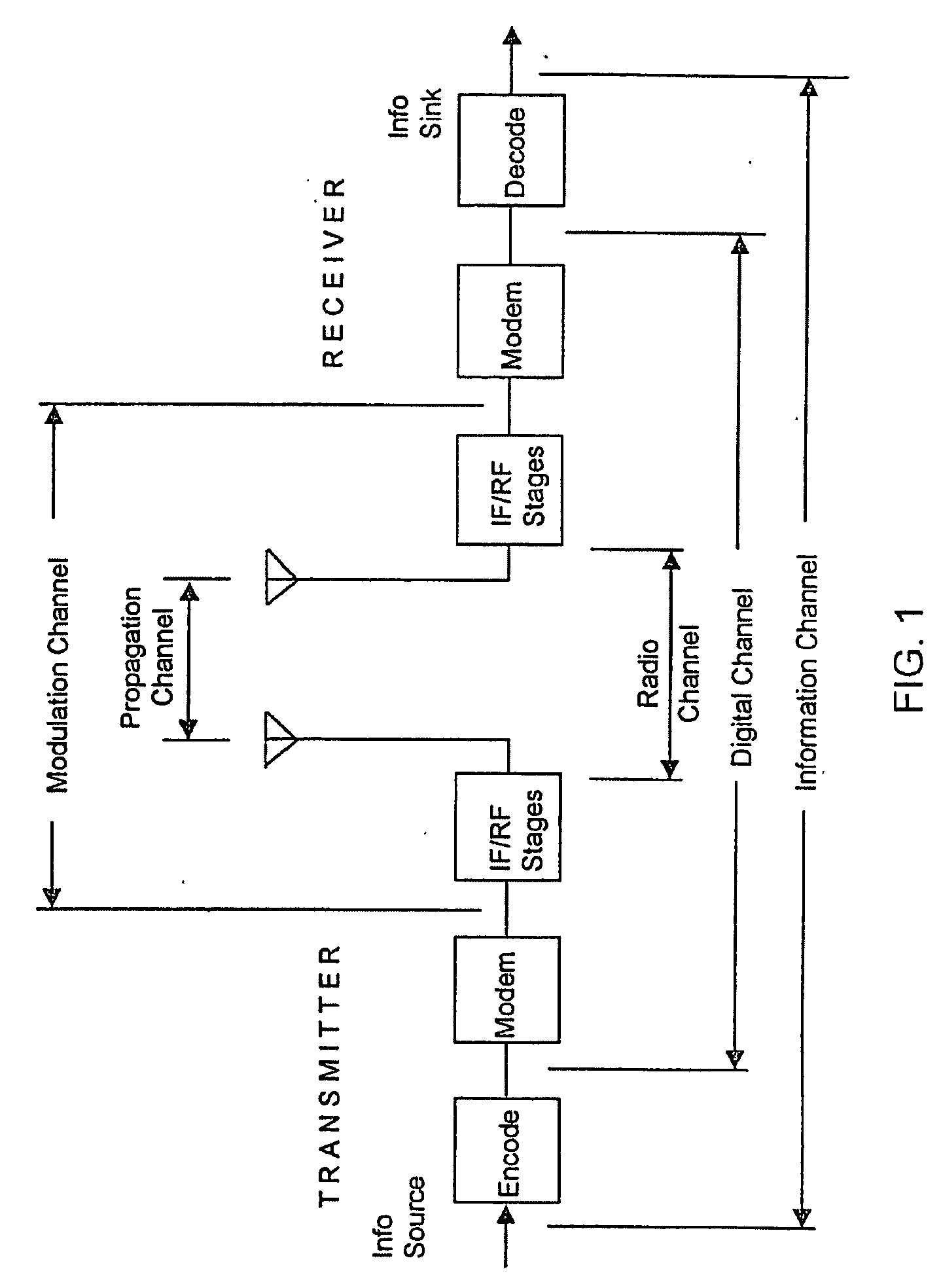
Positioning systems will use positioning technology to determine the position and orientation of an object or person in a room, building or in the world.
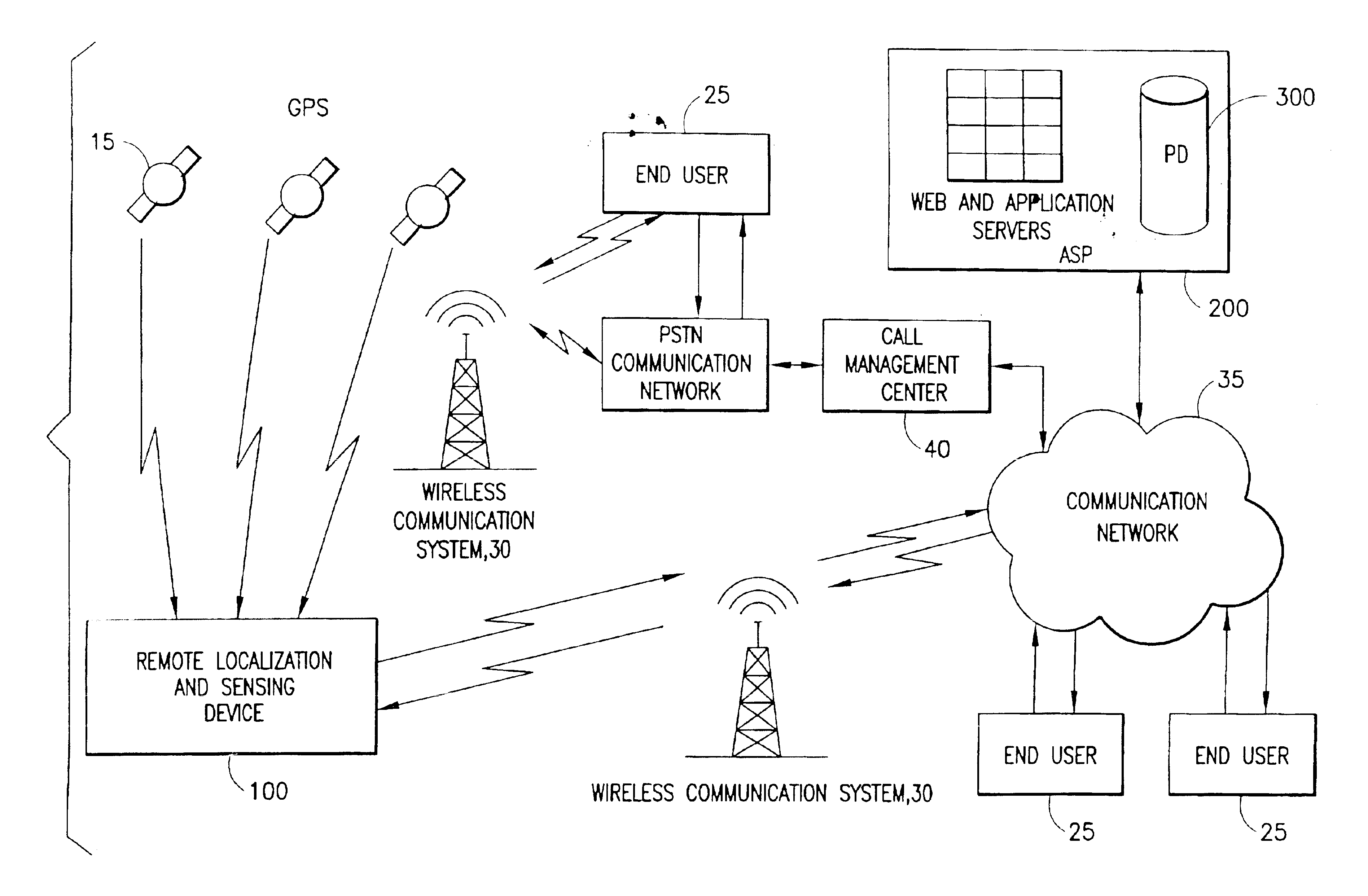
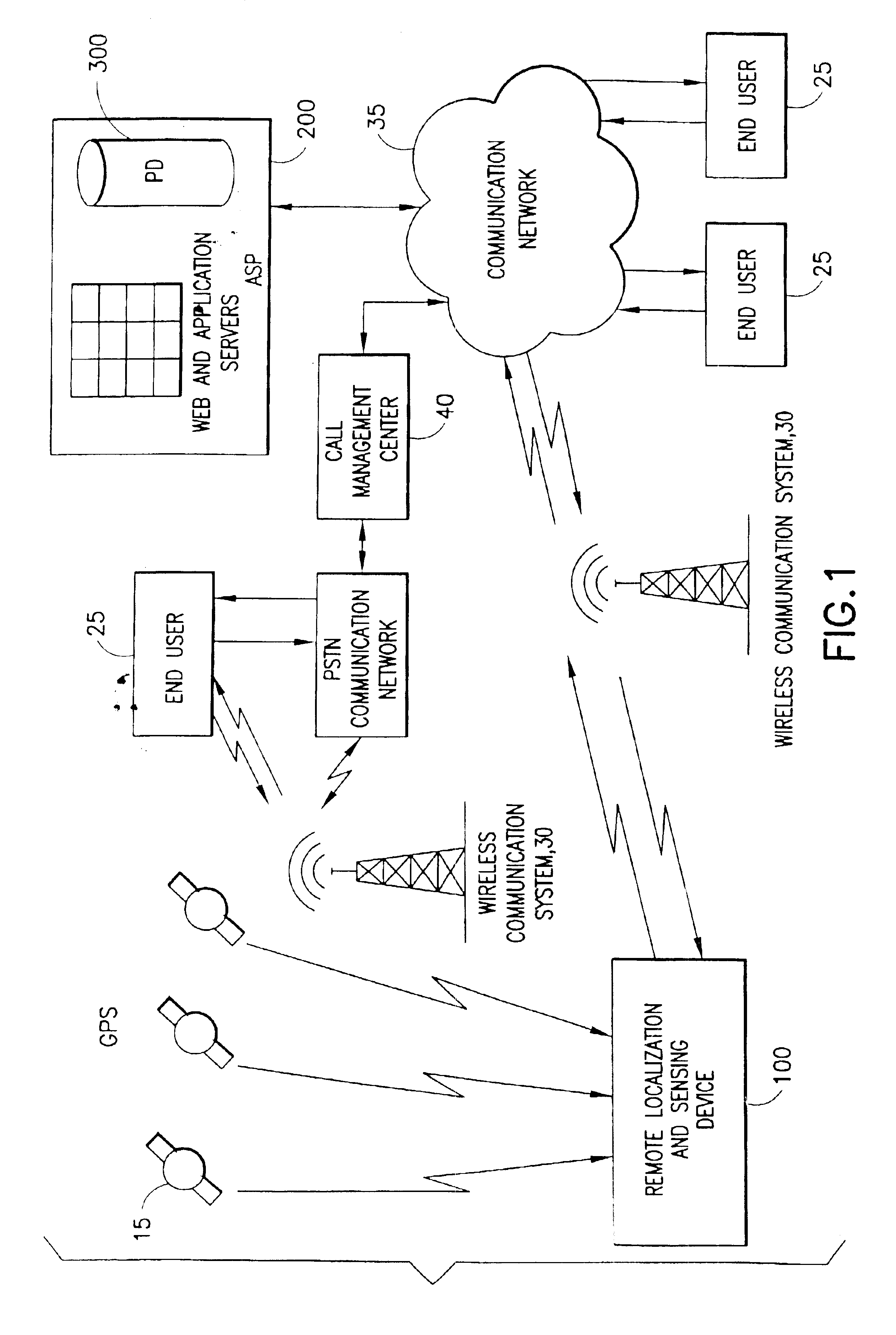
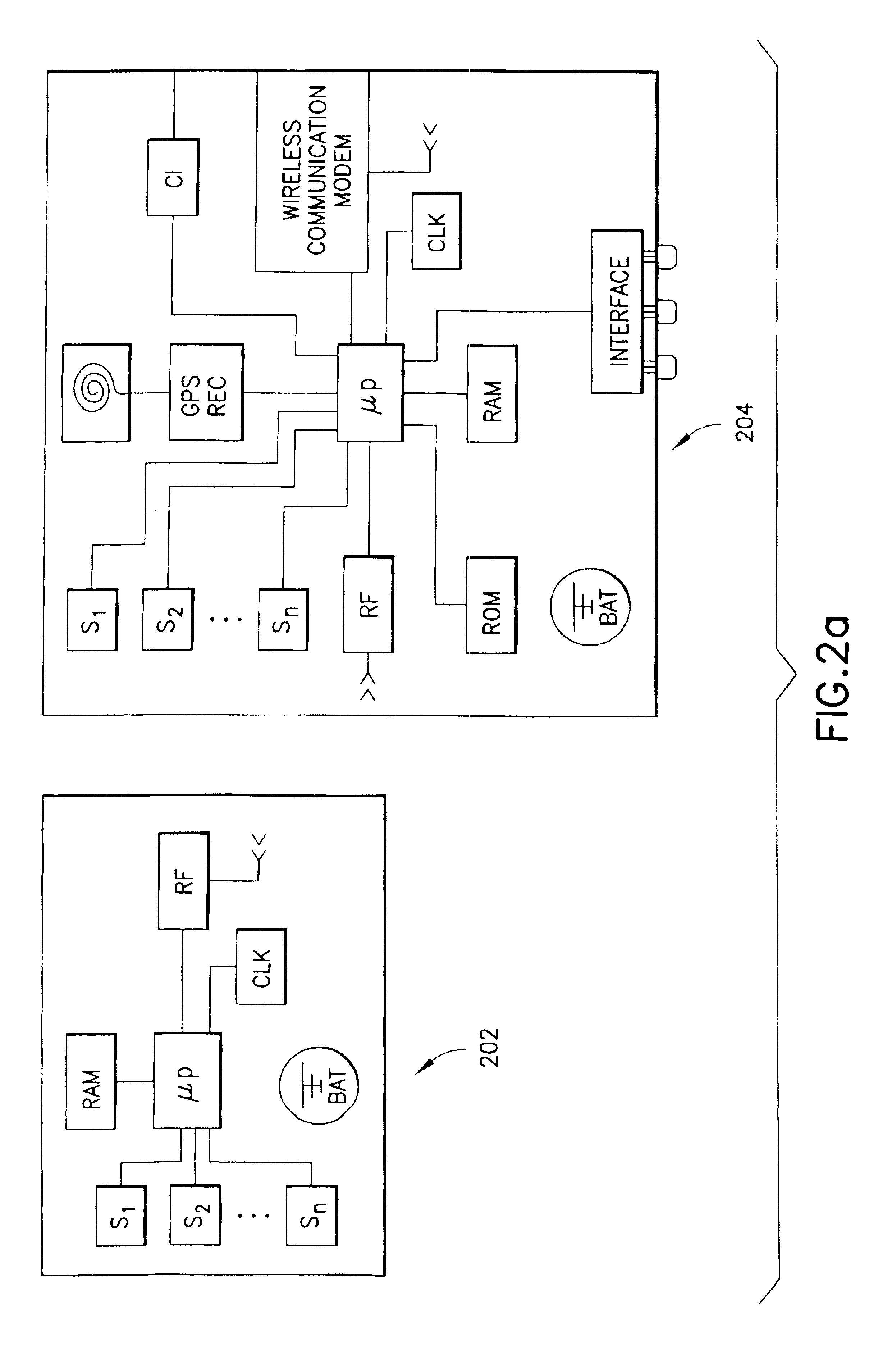
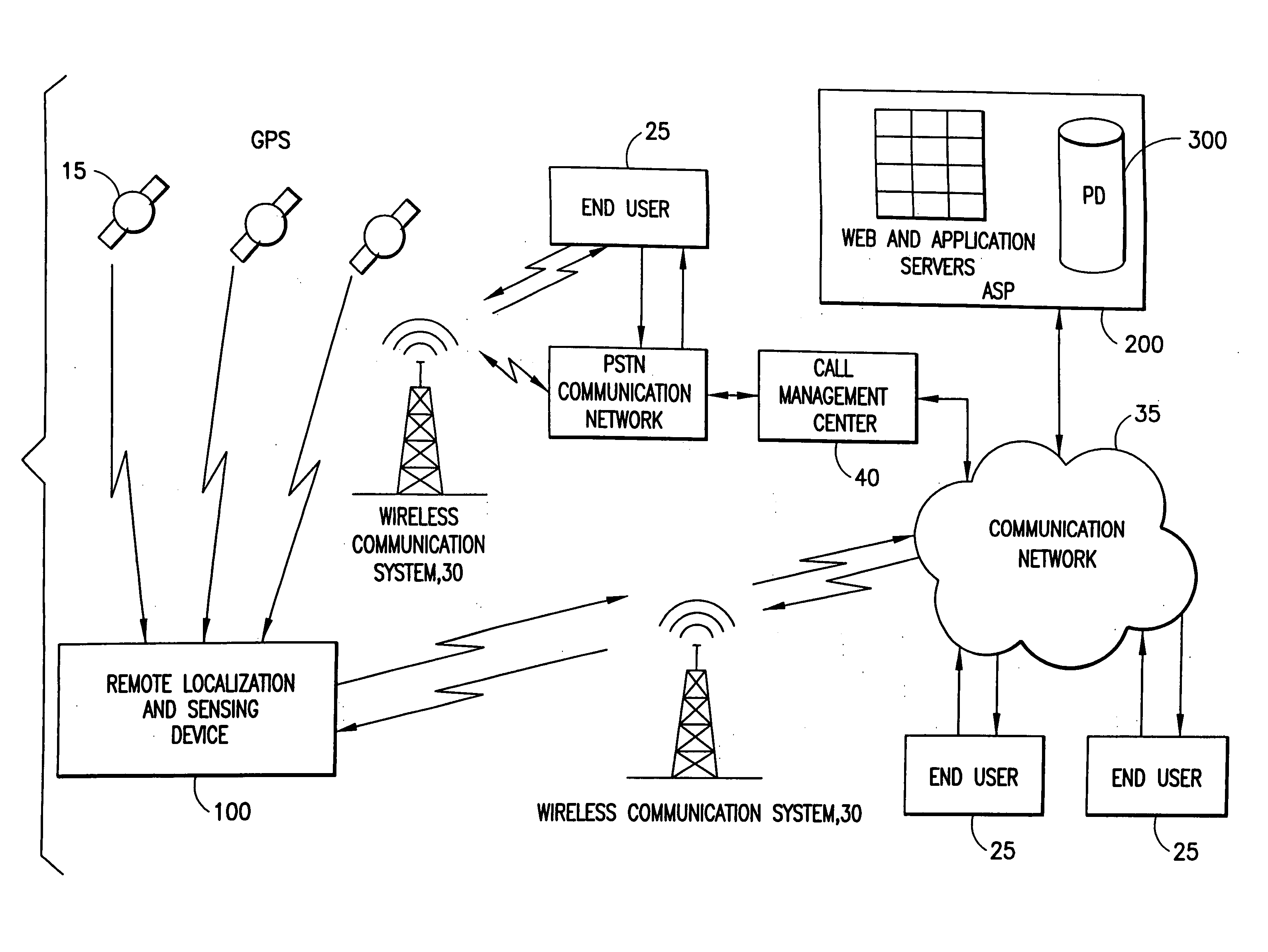
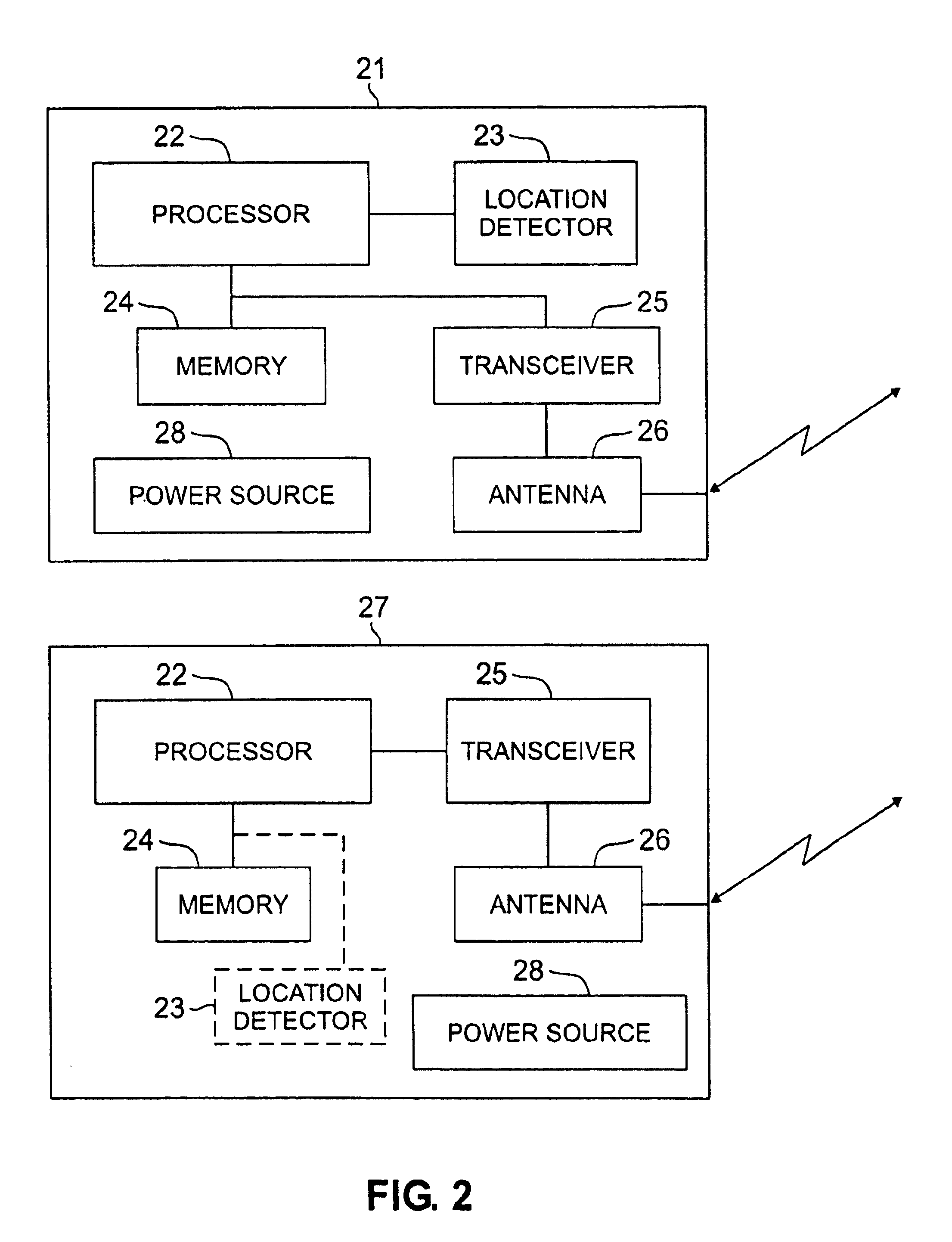
System for localizing and sensing objects and providing alerts
InactiveUS6847892B2Satisfies needTransmission systemsDigital data processing detailsTransceiverWireless transceiver
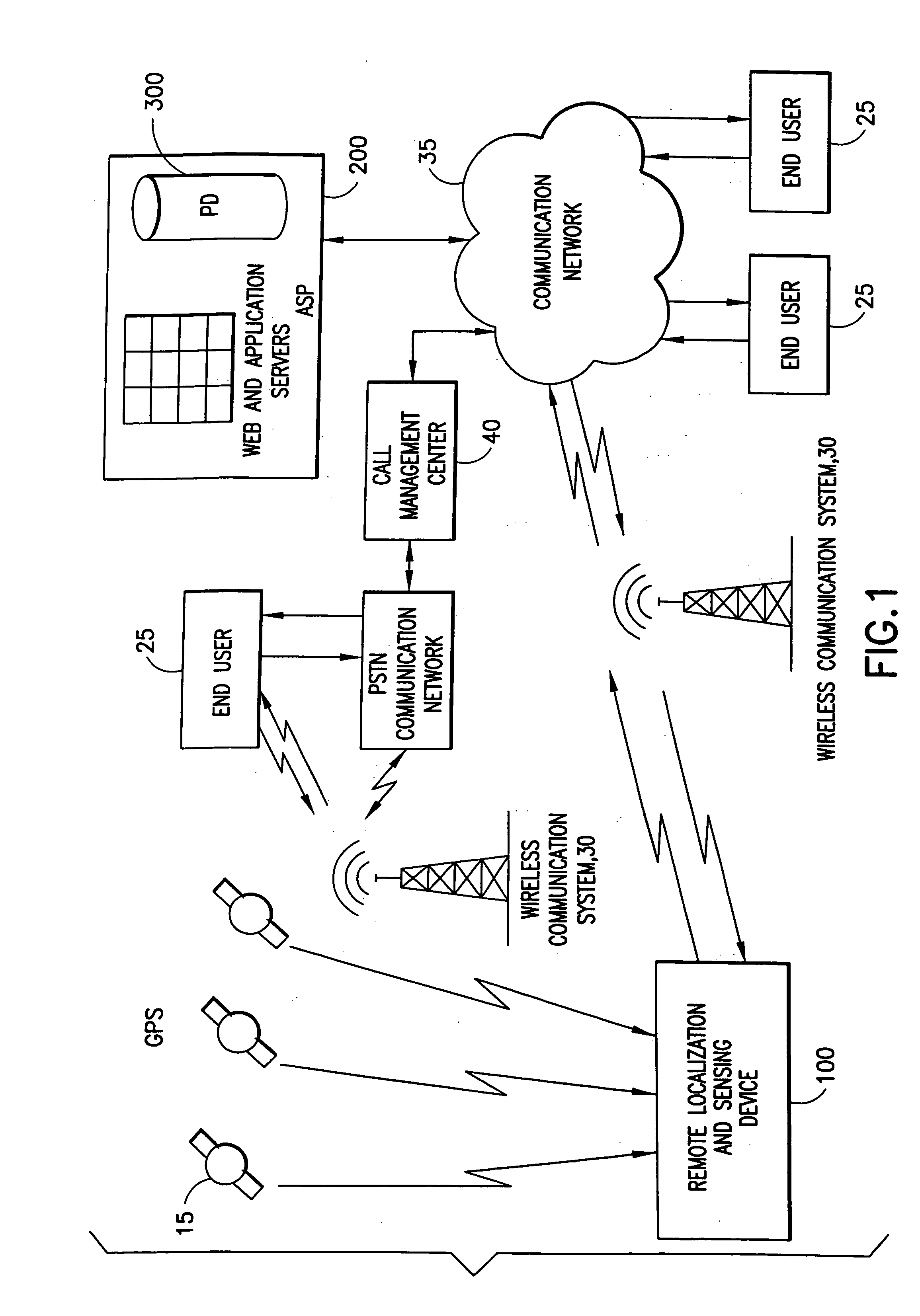
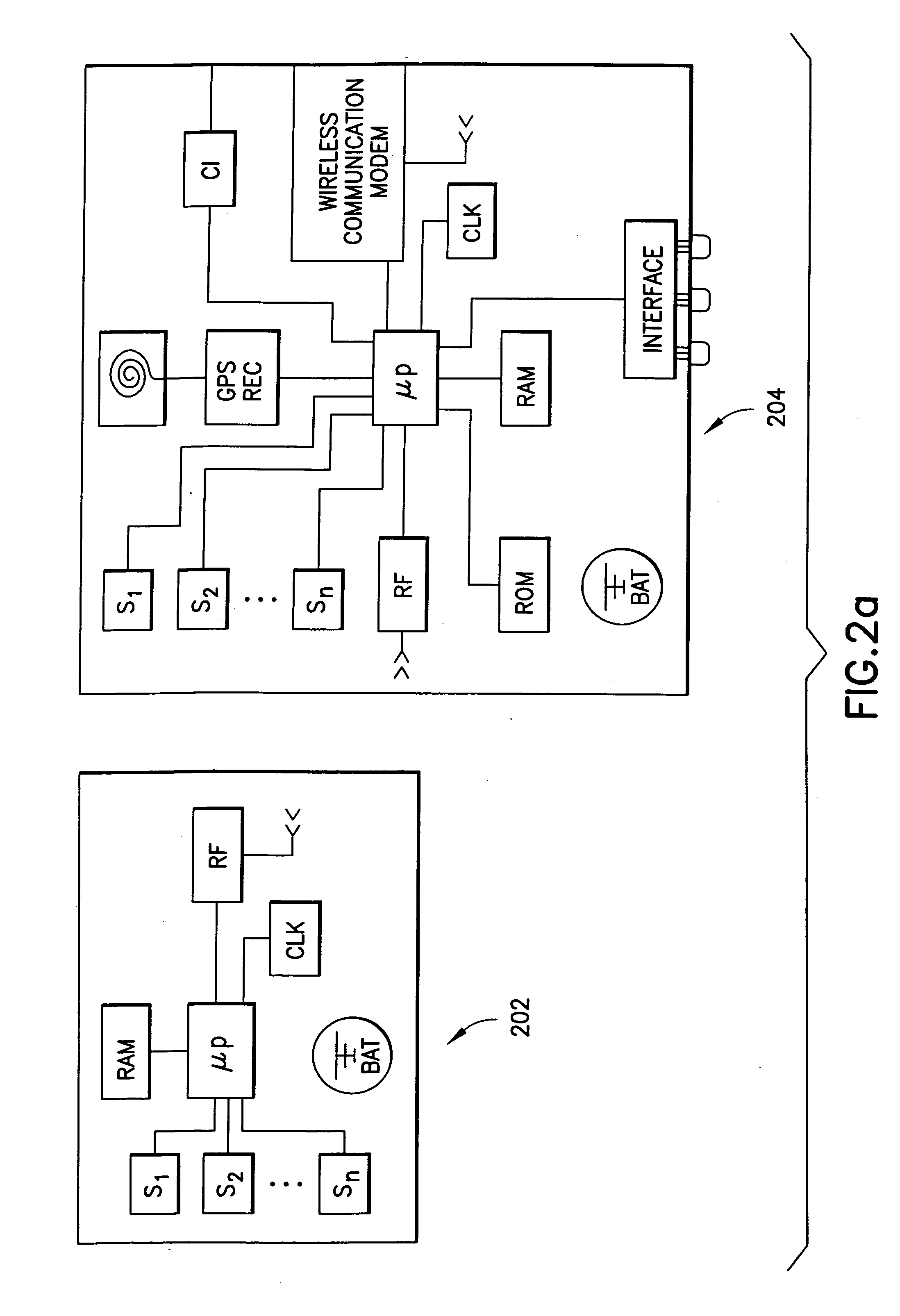
The present invention generally relates to systems, methods and applications utilizing the convergence of any combination of the following three technologies: wireless positioning or localization technology, wireless communications technology and sensor technology. In particular, certain embodiments of the present invention relate to a remote device that includes a sensor for determining or measuring a desired parameter, a receiver for receiving position data from the Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite system, a processor for determining whether or not alert conditions are present and a wireless transceiver for transmitting the measured parameter data and the position data to a central station, such as an application service provider (ASP). The ASP, in turn, may communicate the measured data, position data and notification of any alerts to an end user via an alert device. The present invention also relates to various applications and systems utilizing the capabilities of such a device.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC
Systems and methods for monitoring and tracking
InactiveUS20050250440A1Transmission systemsAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverWireless transceiver
Owner:KONSILLUS NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for synchronizing device information
InactiveUS6874037B1Enabling of informationMultiple digital computer combinationsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPositioning technologyComputer science
Two electronic devices automatically perform a synchronization session when one of the electronic devices is brought in proximity to the other electronic device. The synchronization session is initiated without user intervention based simply on the fact that the two devices have recently been brought within a predetermined distance of each other. The two electronic devices communicate in a wireless manner. The two devices may determine that they are within a predetermined distance of each other using global positioning technology, via which one of the devices determines its own position and compares it to a known position of the other electronic device. Alternatively, one of the electronic devices may output a low level signal that can be received by the other electronic device when within a certain range. Once the low level signal is received, the recipient of the low level signal outputs a stronger signal to ensure that it is received by the other electronic device requesting a synchronization session, which once established enables synchronization of information between the two devices.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC +2
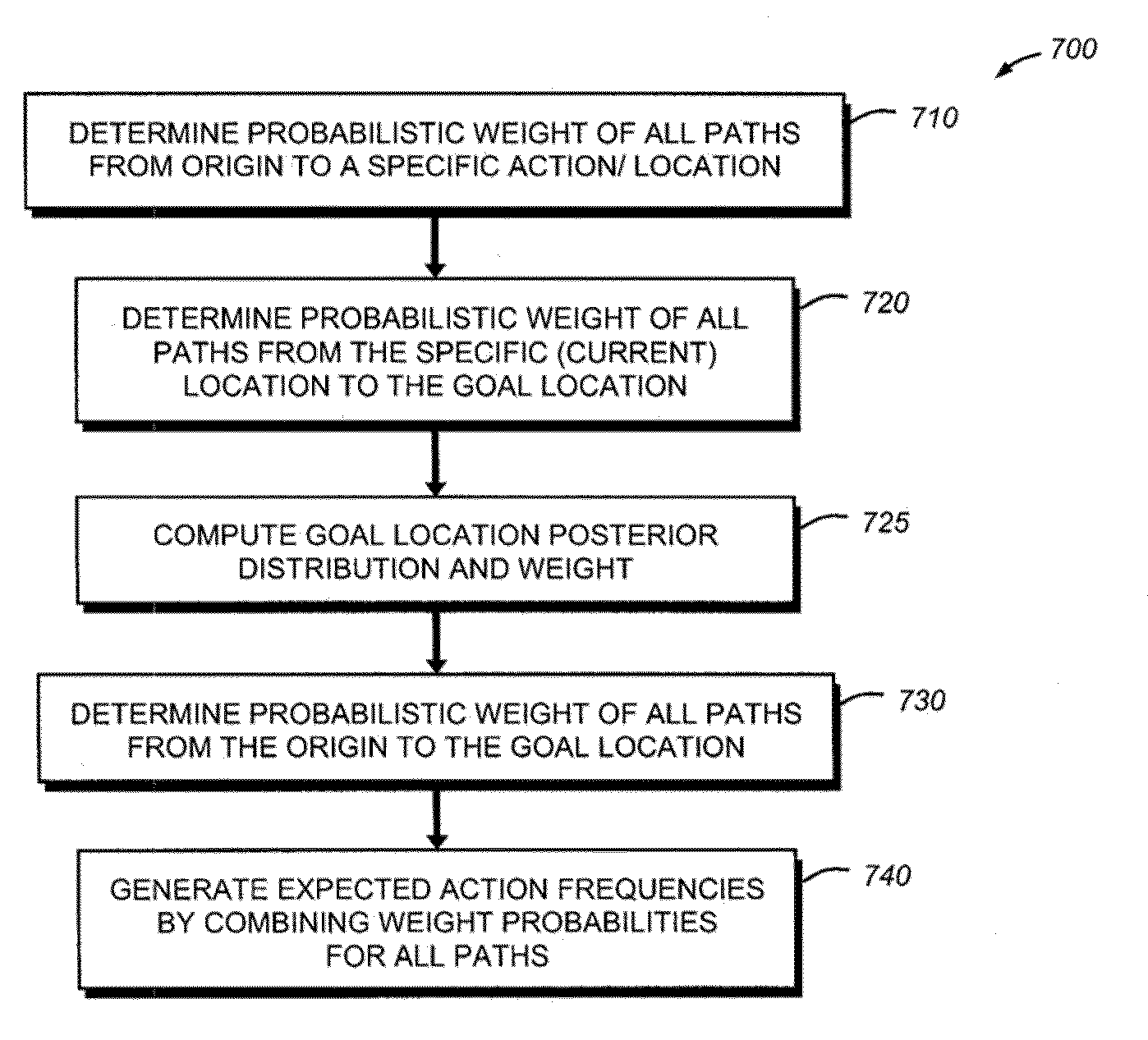
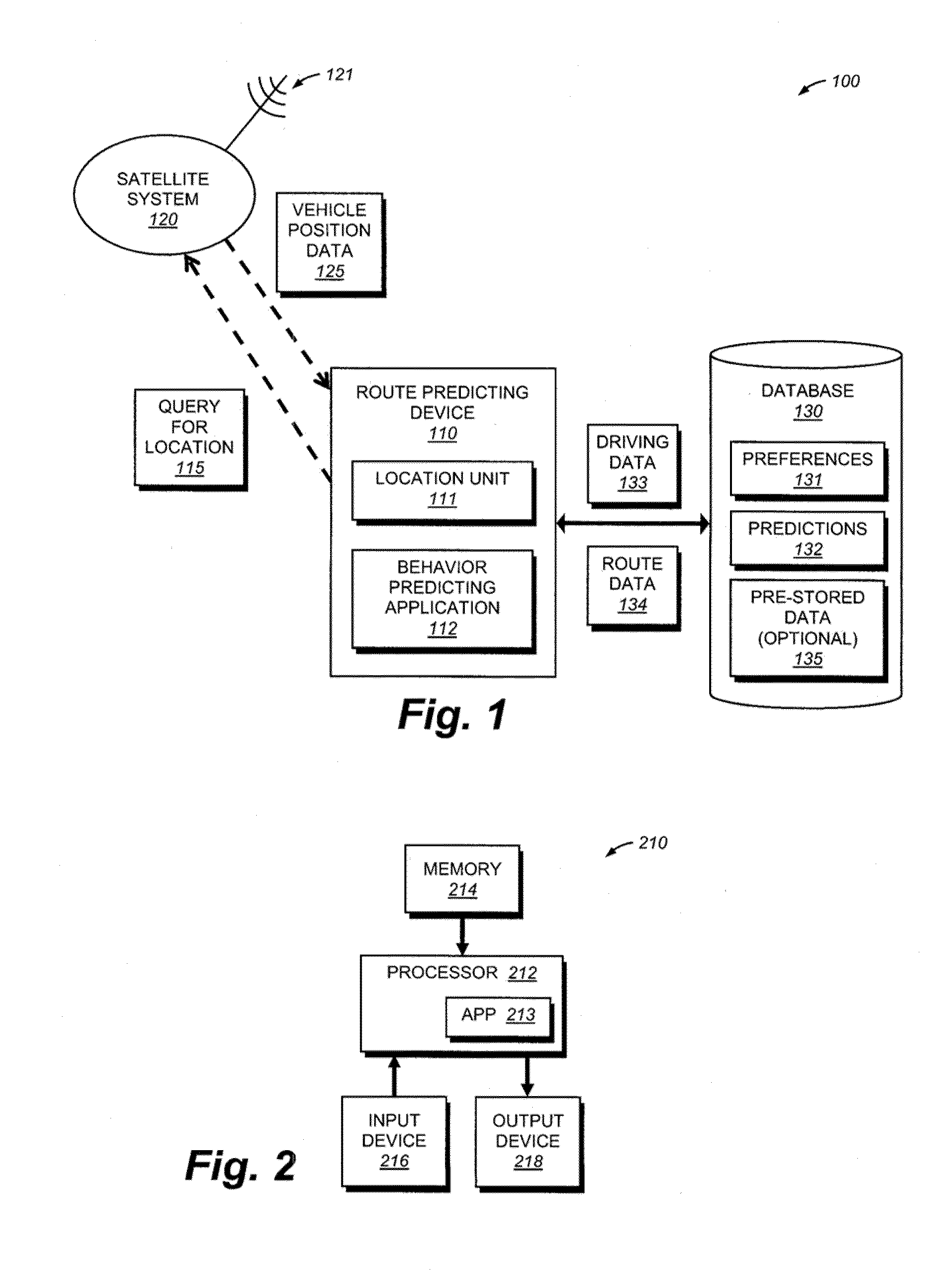
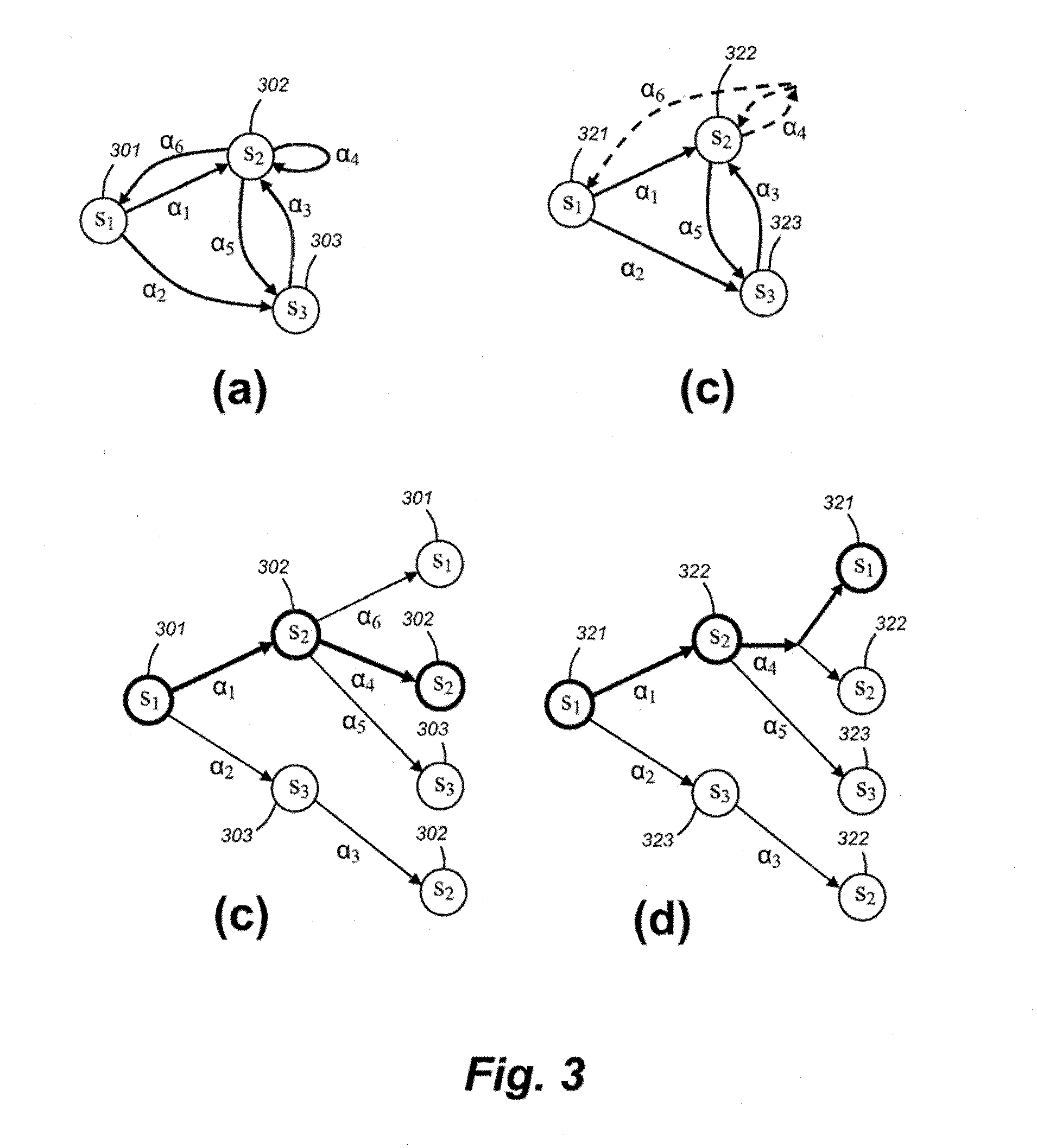
System, method and device for predicting navigational decision-making behavior
InactiveUS20100106603A1Overcome disadvantagesInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDriver/operatorSystems approaches
A system method and device for predicting navigational decision-making behavior is provided. The location of a device is used to generate the current location of the device, and a history of past locations of the device. A behavior predicting application predicts the route a drive is going to travel based on driver preferences, such as left-hand turns, avoidance of bridges, etc., as well as the preferred destinations and / or routes traveled in the past. The preferences of a particular driver can be learned by the system to be implemented in the behavior predicting application, or manually input by the driver. The system can employ GPS or other positioning technology to determine the location of the device. The device can be a standard GPS-enabled in-car device, or other portable device such as a cell phone or PDA.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
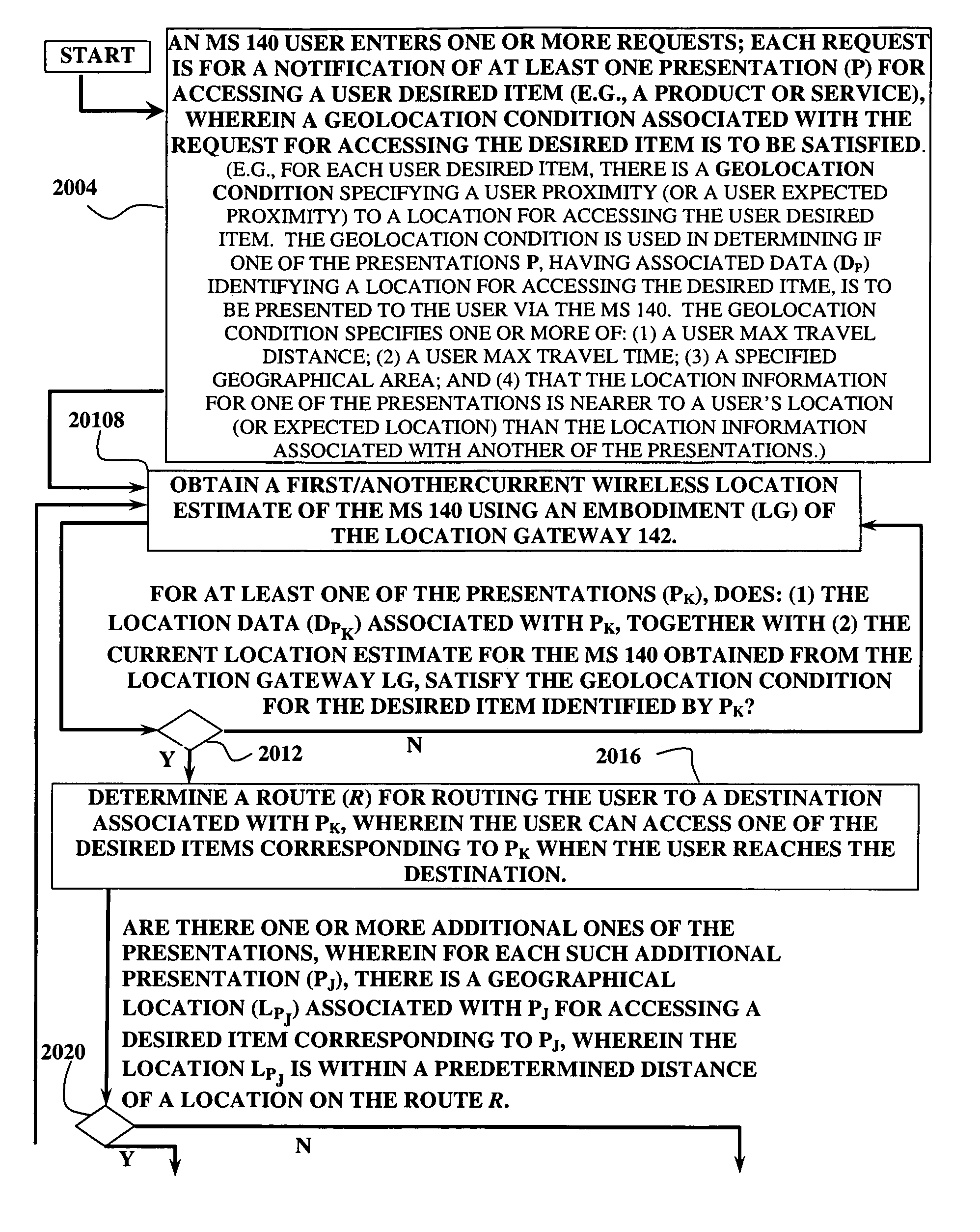
Wireless location gateway and applications therefor
InactiveUS7714778B2Accurate locationDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationInternet communicationModularity
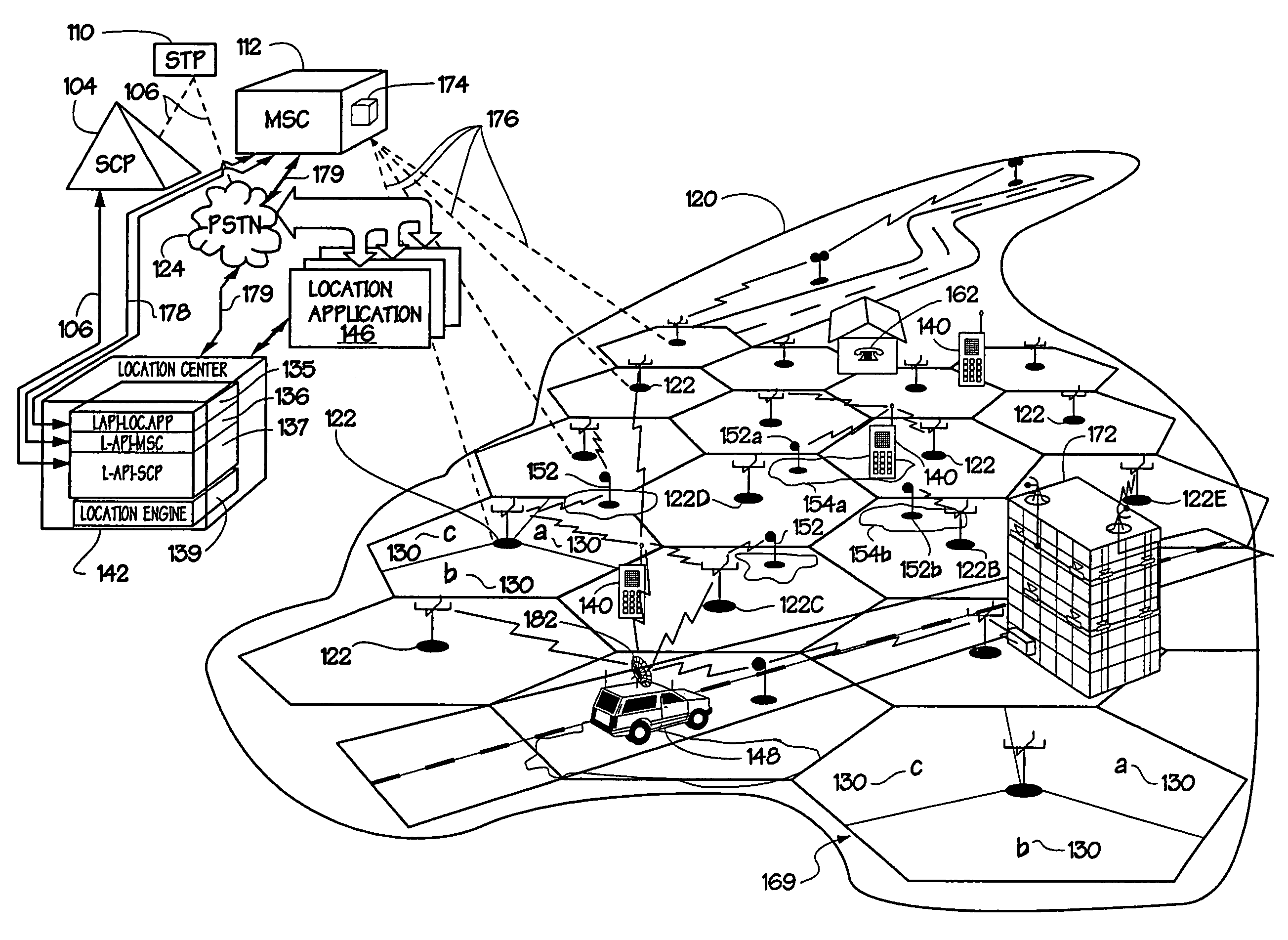
A system for wirelessly locating mobile station / units (MS) and using resulting location determinations for providing a product or service is disclosed. The system is useful for routing an MS user to a plurality of desired locations, alerting an MS user to a nearby desired product or service based on satisfaction of user criteria, and providing enhanced security and 911 response. In one embodiment, the system responds to MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location processing sites. A plurality of locating technologies including those based on: (1) TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) timing advance; (5) GPS and network assisted GPS, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from low cost base stations can be activated, in various combinations, by system embodiments. MS location difficulties resulting from poor location accuracy / reliability and / or poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:MOBILE MAVEN
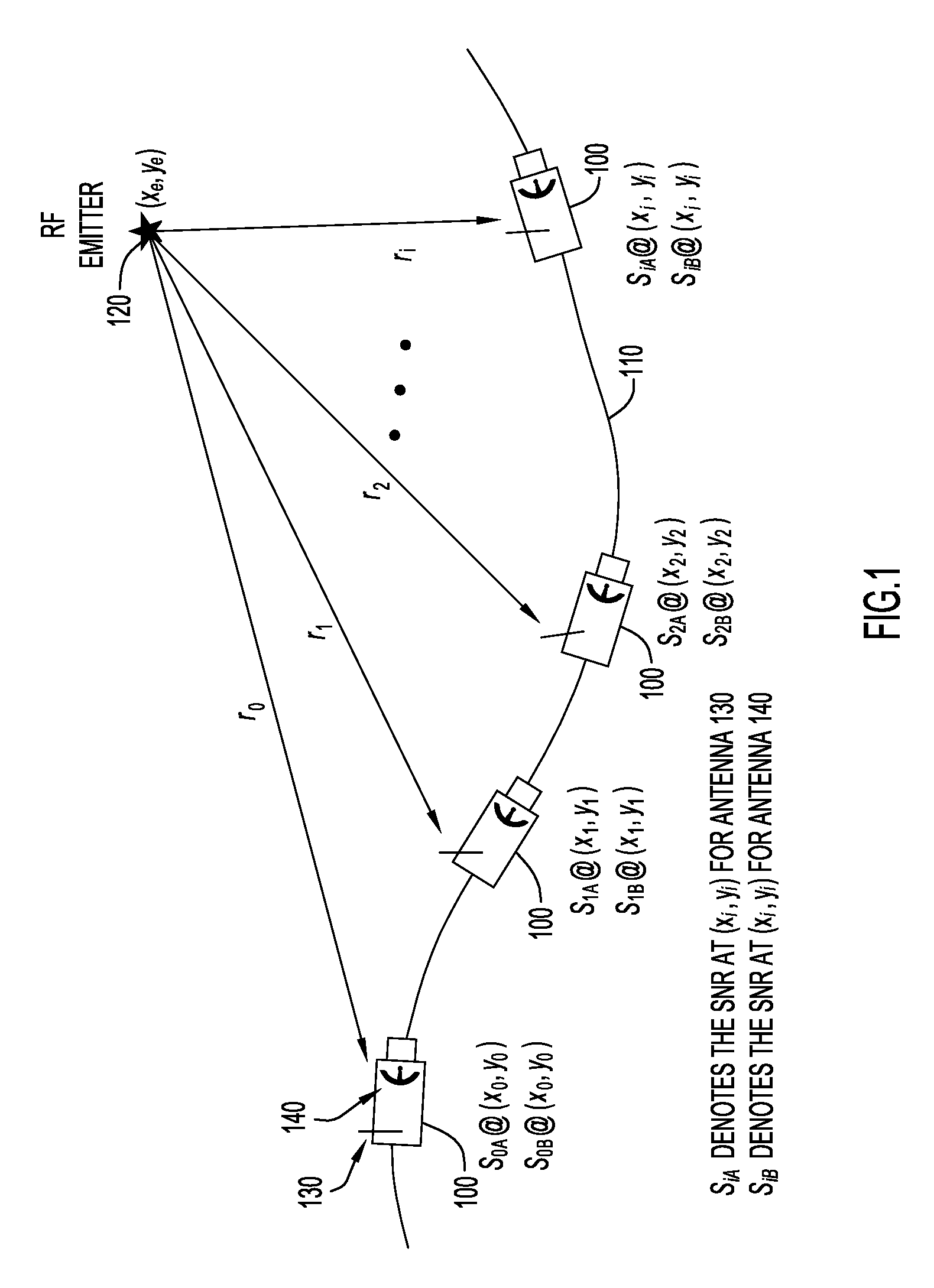
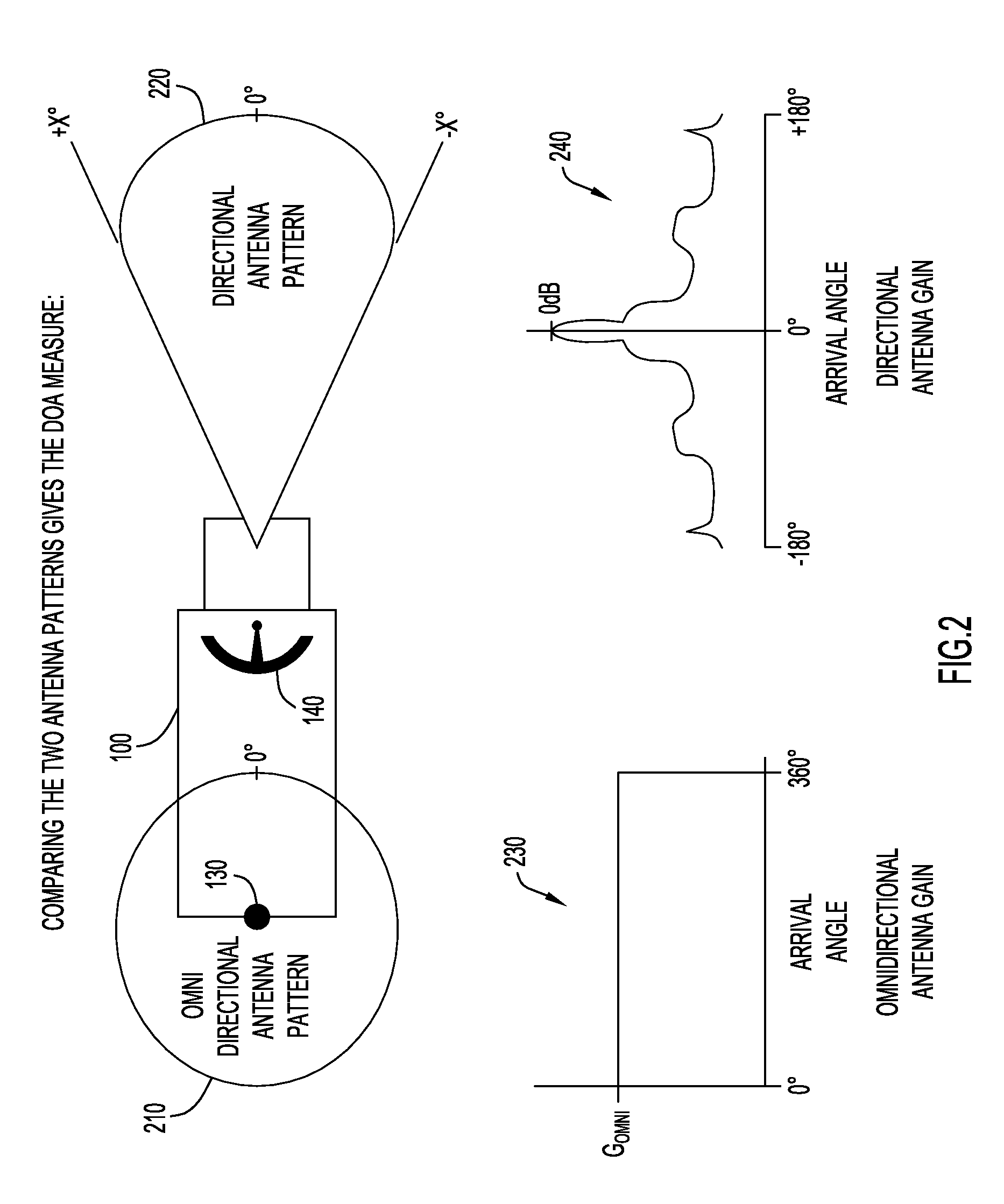
System and method for direction finding and geolocation of emitters based on line-of-bearing intersections
ActiveUS8723730B2Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Geolocation
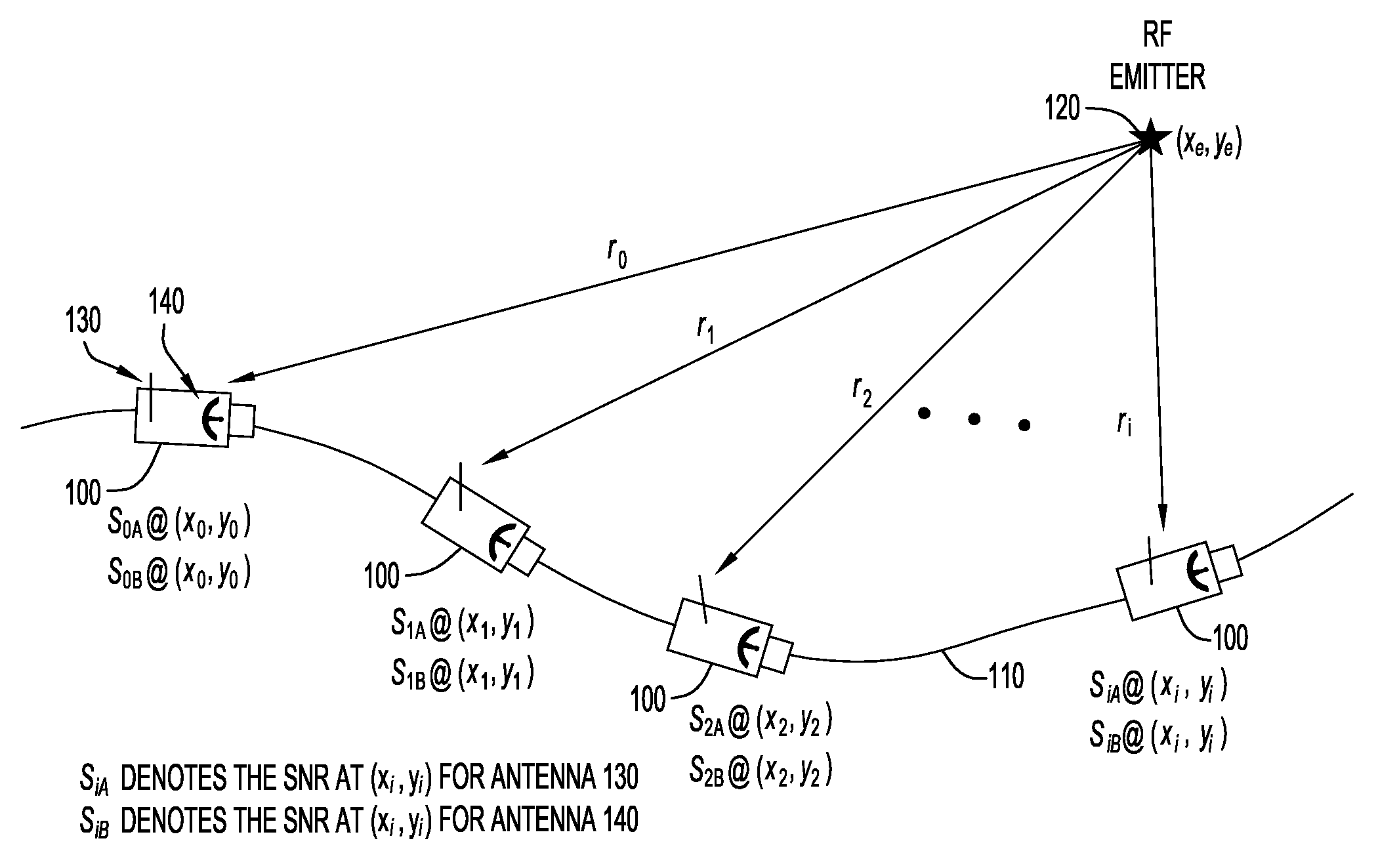
According to an embodiment of the present invention an emitter geolocation technique determines the geolocation of a radio frequency (RF) emitter using pair-wise line-of-bearing intersections that are derived from signal-to-noise ratios of transmitted signals received at a sensor. The technique may be employed with ground based vehicle or small unmanned air vehicles (UAV), and obtains reliable geolocation estimates of radio frequency (RF) emitters of interest.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Method and system for user interface for interactive devices using a mobile device
ActiveUS20130113993A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCloud baseTouchscreen
A software application and system that enables point-and-click interaction with a TV screen. The application determines geocode positioning information for a handheld device, and uses that data to create a virtual pointer for a television display or interactive device. Some embodiments utilize motion sensing and touchscreen input for gesture recognition interacting with video content or interactive device. Motion sensing can be coupled with positioning or localization techniques the user to calibrate the location of the interactive devices and the user location to establish and maintain virtual pointer connection relationships. The system may utilize wireless network infrastructure and cloud-based calculation and storage of position and orientation values to enable the handheld device in the TV viewing area to replace or surpass the functionality of the traditional TV remote control, and also interface directly with visual feedback on the TV screen.
Owner:REMOTE TELEPOINTER
Wireless location routing applications and architecture therefor
InactiveUS7903029B2Accurate locationInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesInternet communicationModularity
A system for wirelessly locating mobile station / units (MS) and using resulting location determinations for providing a product or service is disclosed. The system is useful for routing an MS user to a plurality of desired locations, alerting an MS user to a nearby desired product or service based on satisfaction of user criteria, and providing enhanced security and 911 response. In one embodiment, the system responds to MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location processing sites. A plurality of locating technologies including those based on: (1) TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) timing advance; (5) GPS and network assisted GPS, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from low cost base stations can be activated, in various combinations, by system embodiments. MS location difficulties resulting from poor location accuracy / reliability and / or poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:MOBILE MAVEN
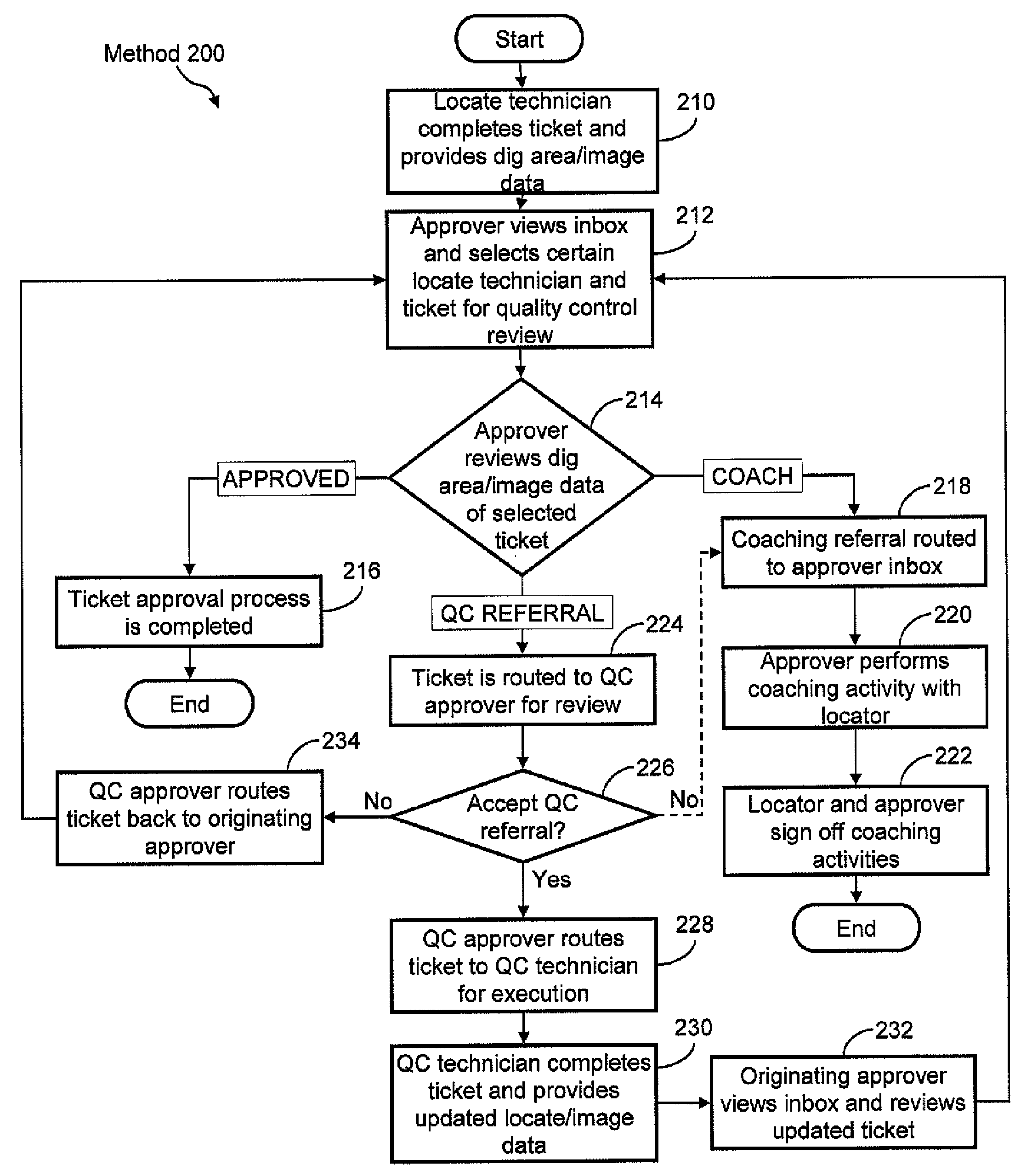
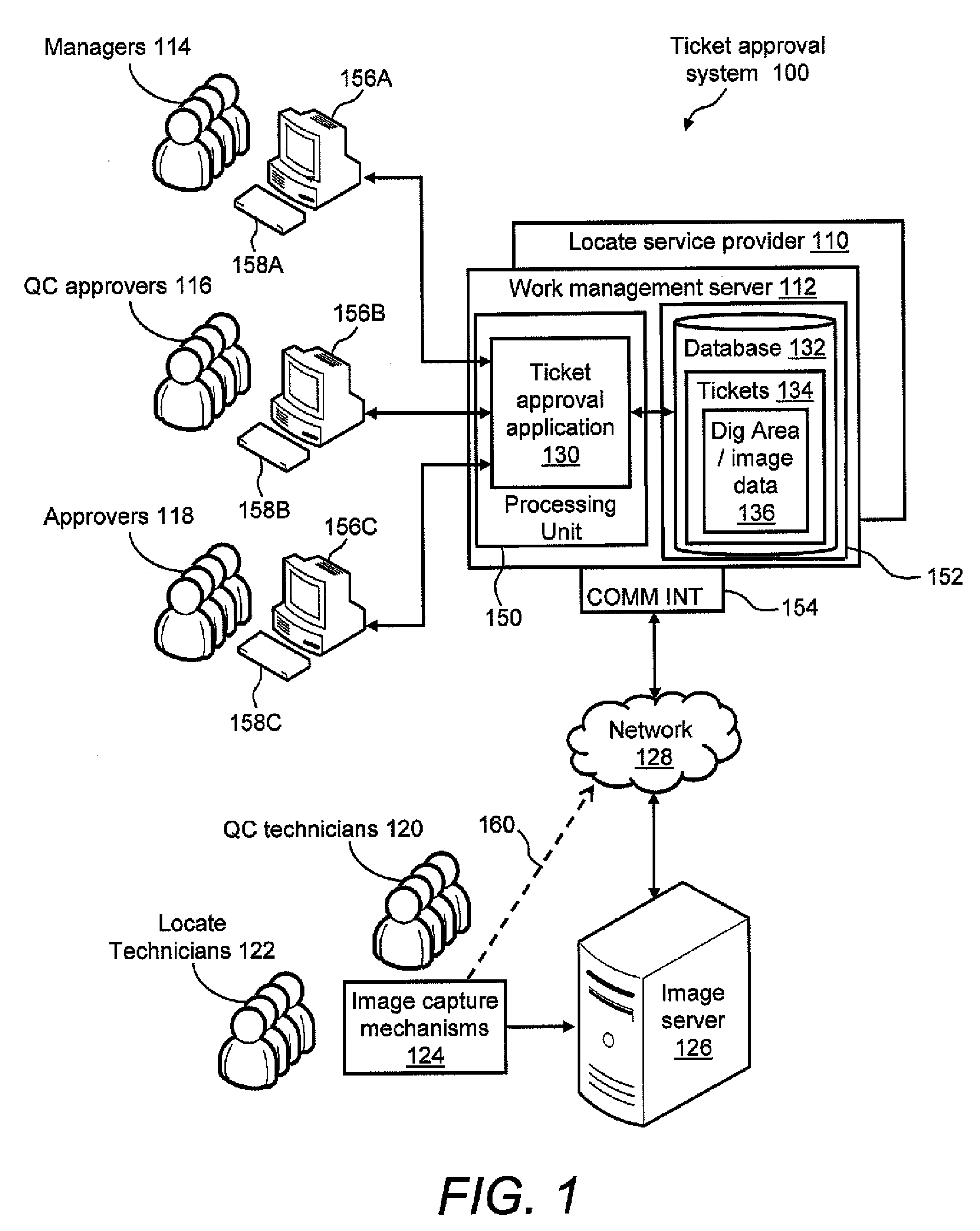
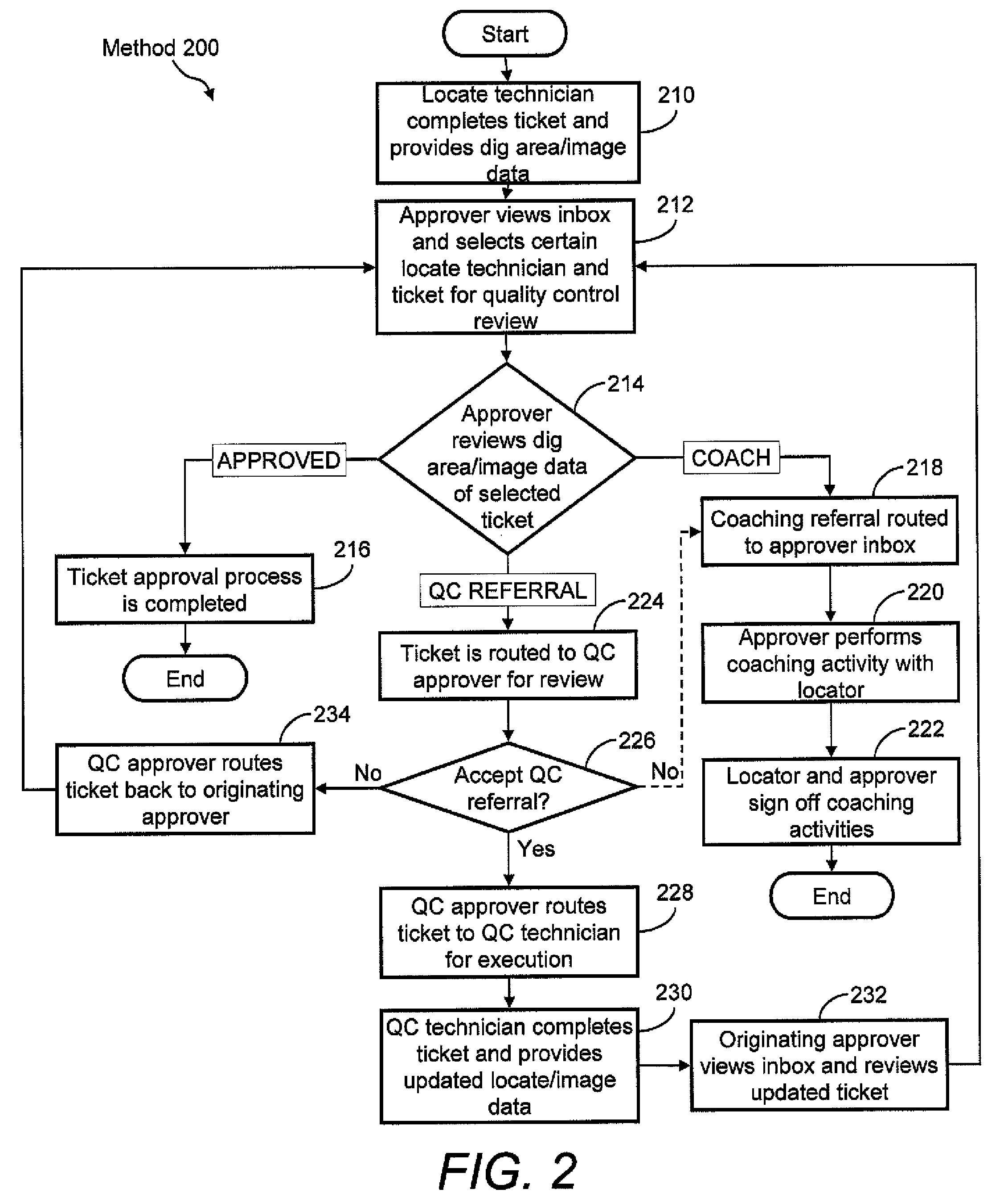
Ticket approval system for and method of performing quality control in field service applications
Methods for overseeing and assessing a locate and marking operation. A ticket is received including ticket information regarding the operation, and a first locate technician is dispatched to perform the operation pursuant to the ticket information. A locate manifest is received that includes at least one digital image associated with a dig area in which the locate technician performed the operation. The locate manifest is compared to the ticket information, and a determination is made if the operation is 1) satisfactory, 2) unsatisfactory and requires further quality control assessment and / or at least partial re-performance, or 3) satisfactory but the first locate technician requires coaching. One or more electronic indications of one of 1), 2) and 3) are provided so as to generate an electronic record of a quality assessment of the locate and marking operation.
Owner:CERTUSVIEW TECH LLC
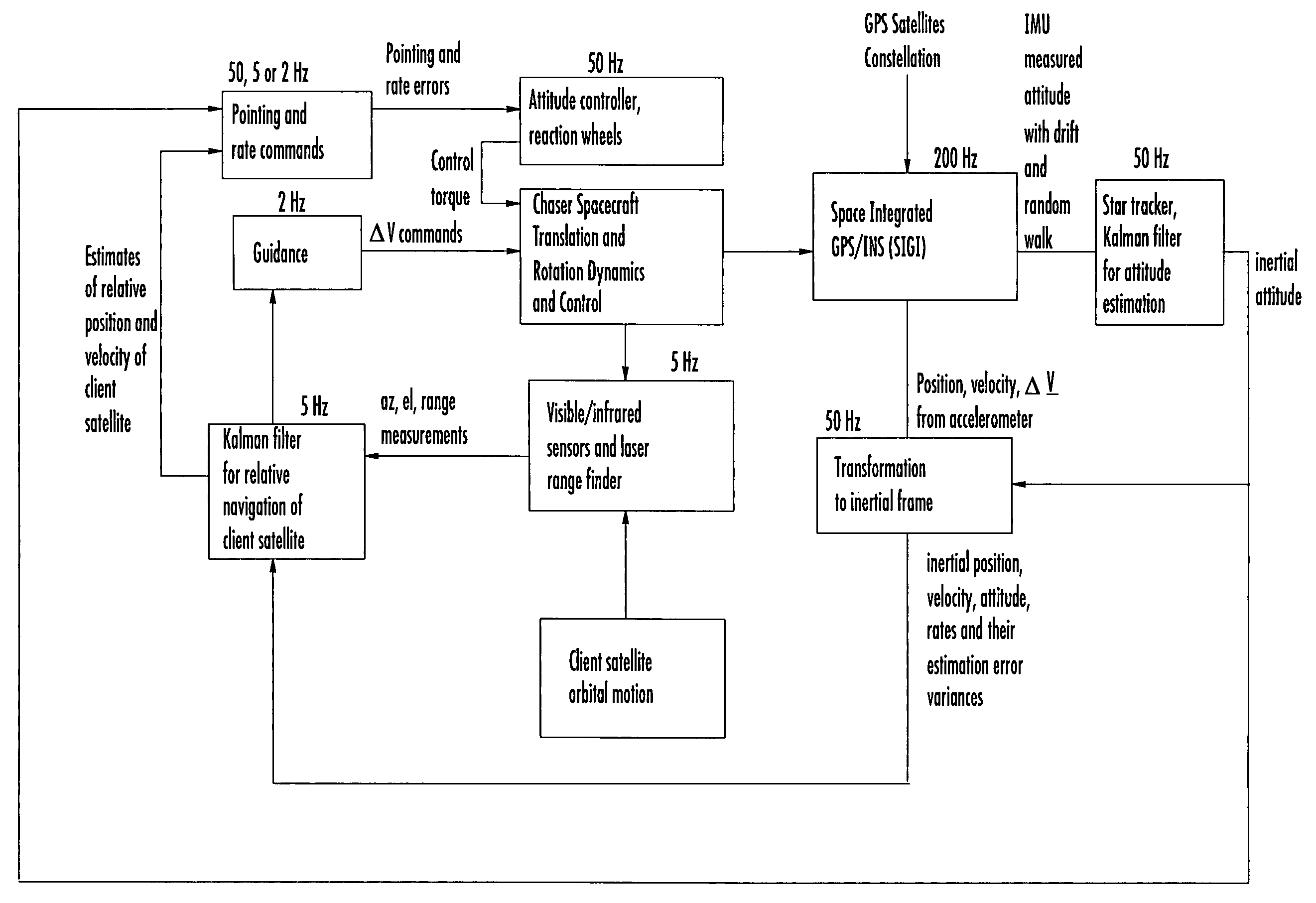
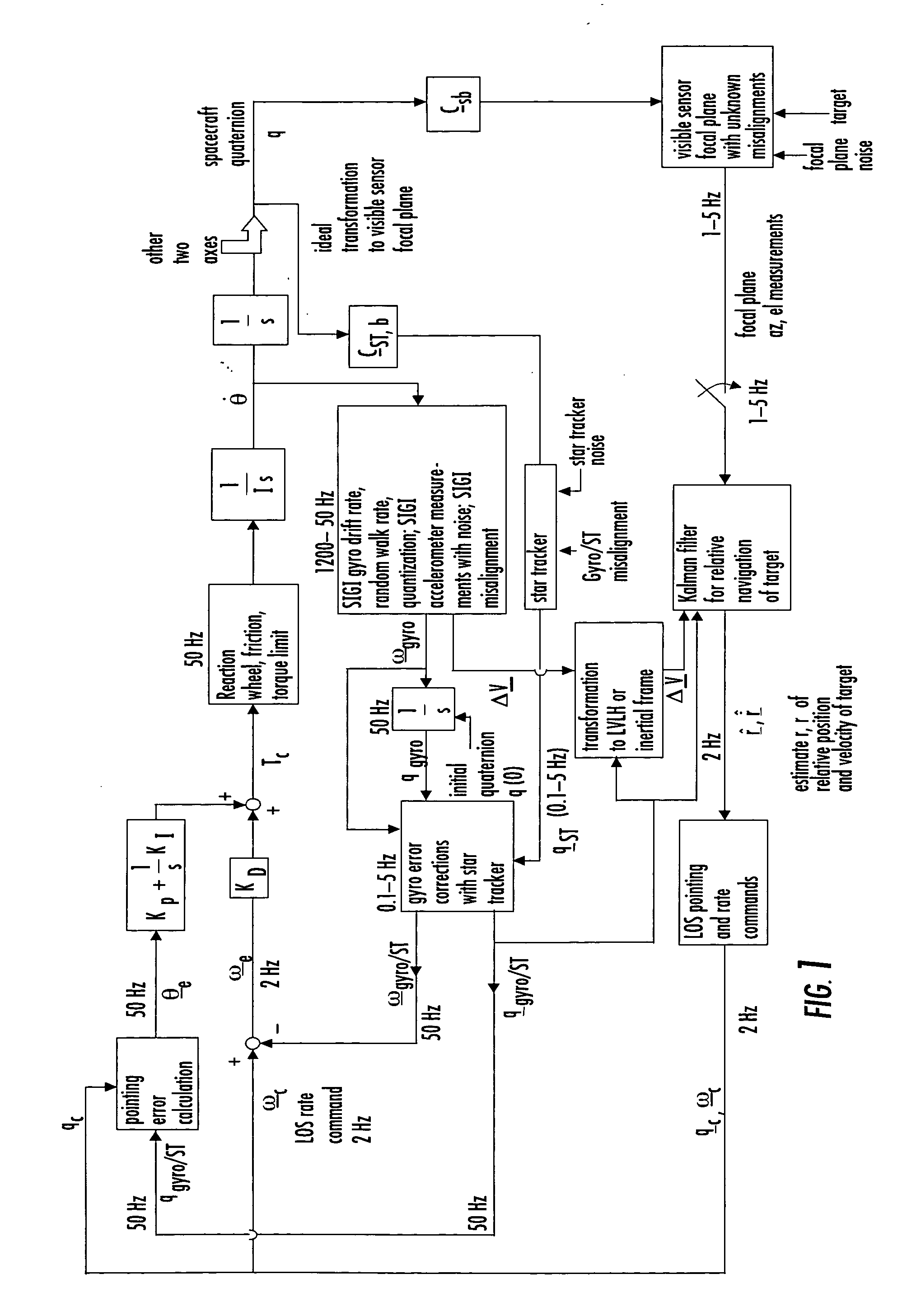
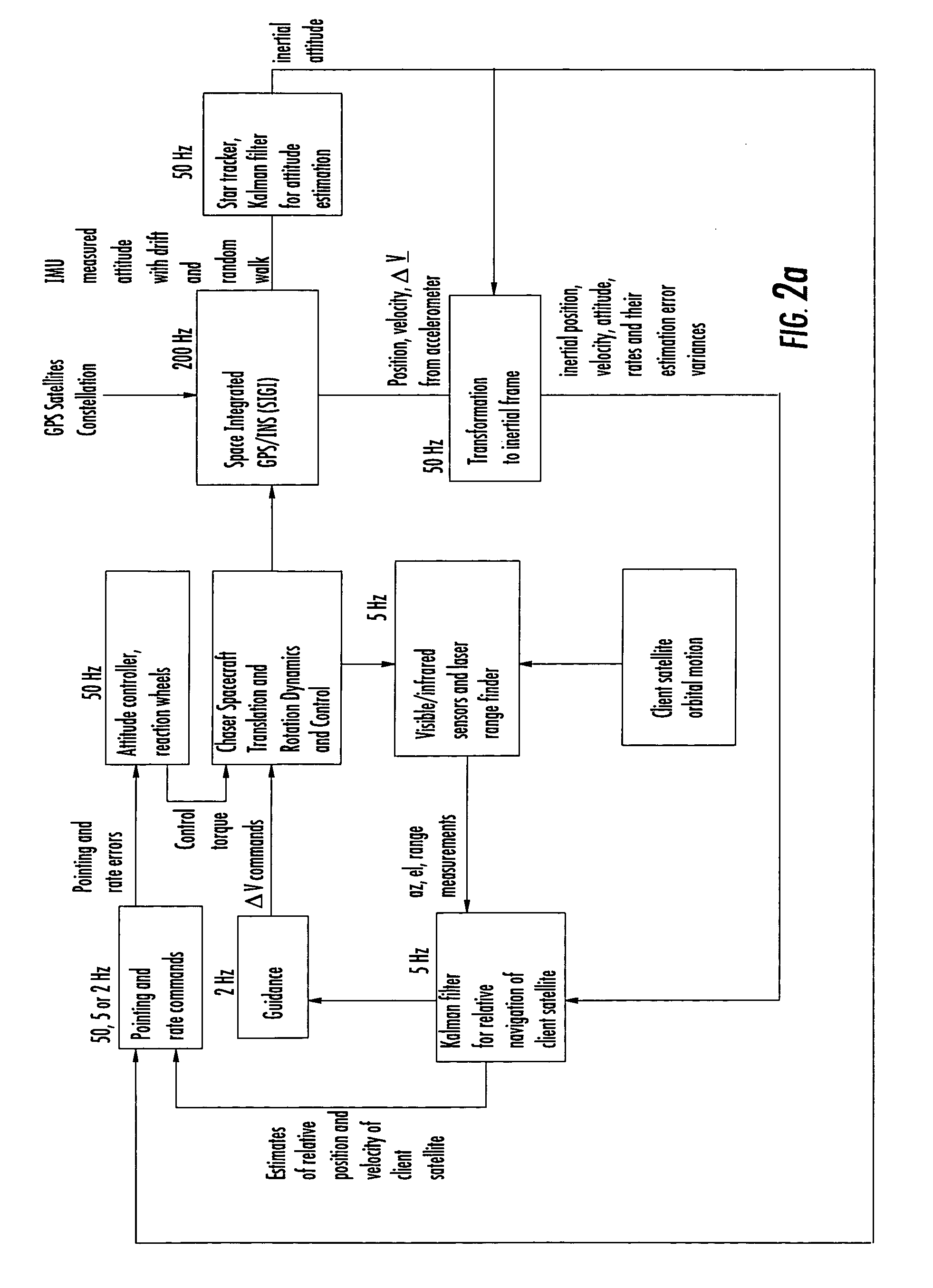
Laser range finder closed-loop pointing technology of relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing and tracking for spacecraft rendezvous
InactiveUS20050060092A1Improved functionality and precisionImprove ObservabilityInstruments for road network navigationCosmonautic vehiclesGyroscopeClosed loop
A closed-loop LRF pointing technology to measure the range of a target satellite from a chaser satellite for rendezvous is provided that includes several component technologies: LOS angle measurements of the target satellite on a visible sensor focal plane and the angles' relationships with the relative position of the target in inertial or LVLH frame, a relative navigation Kalman filter, attitude determination of the visible sensor with gyros, star trackers and a Kalman filter, pointing and rate commands for tracking the target, and an attitude controller. An analytical, steady-state, three-axis, six-state Kalman filter is provided for attitude determination. The system and its component technologies provide improved functionality and precision for relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing, and tracking for rendezvous. Kalman filters are designed specifically for the architecture of the closed-loop system to allow for pointing the laser rangefinder to a target even if a visible sensor, a laser rangefinder, gyros and a star tracker are misaligned and the LOS angle measurements from the visible sensor are interrupted.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
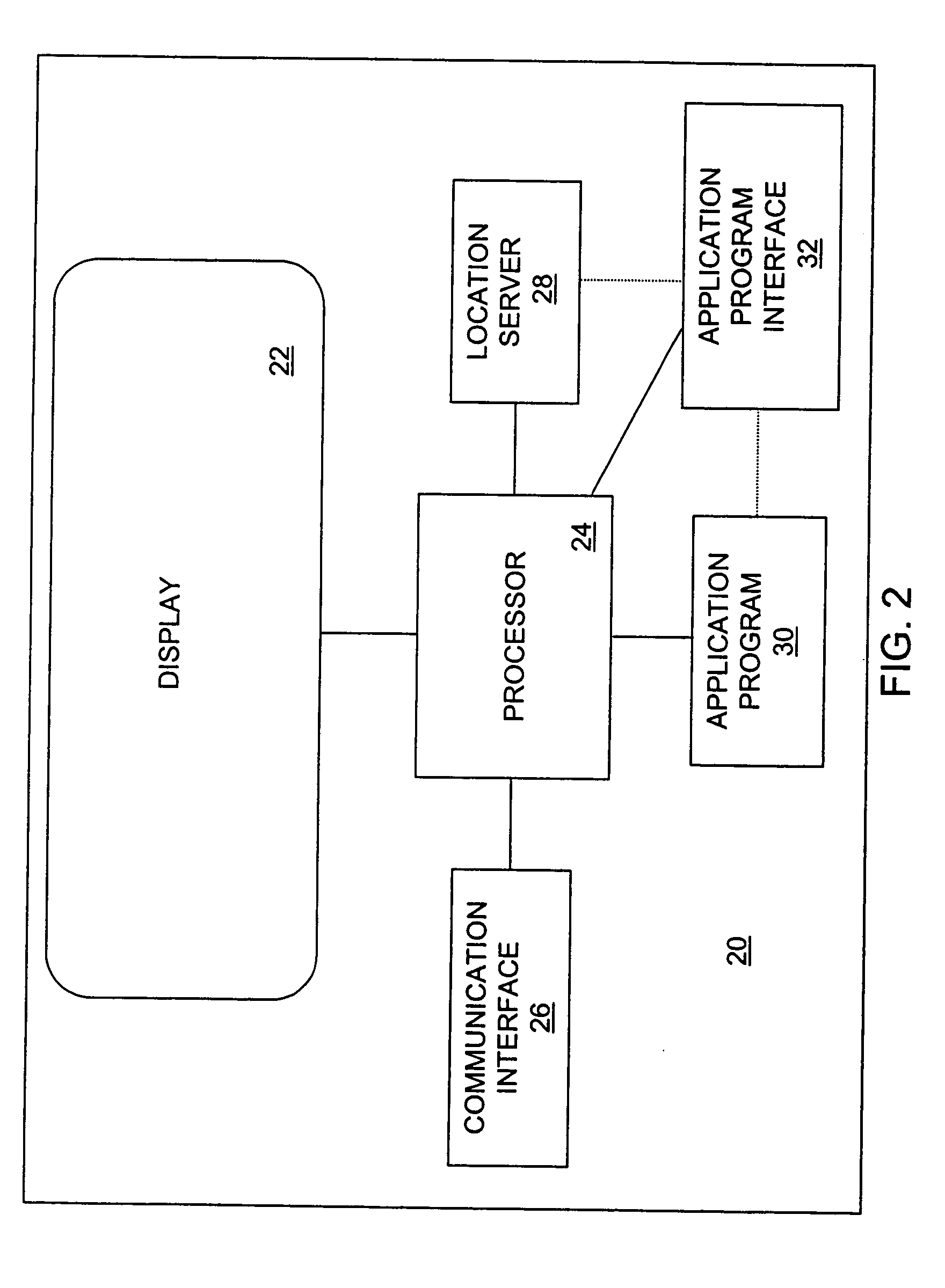
System and method for implementing a remote location acquisition application program interface
InactiveUS20050282557A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsLocation information based servicePublic interfacePositioning technology
An Application Program Interface (API) is defined at a requesting terminal. The API provides a common interface between an application program requesting a location for a target mobile terminal and a location server at the requesting terminal. The location server may be integrated into the API or may be a separate entity. The application program executing on the requesting terminal sends a request through the API for the location of the target mobile terminal. Thus, the API hides the positioning technology details and complexities from the requesting application program. The API communicates with a location determining source that determines the location of the target mobile terminal. The location determining source may be the target mobile terminal. Alternatively, the location determining source may be a network location server such as a Gateway Mobile Location Center or Mobile Positioning Center.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
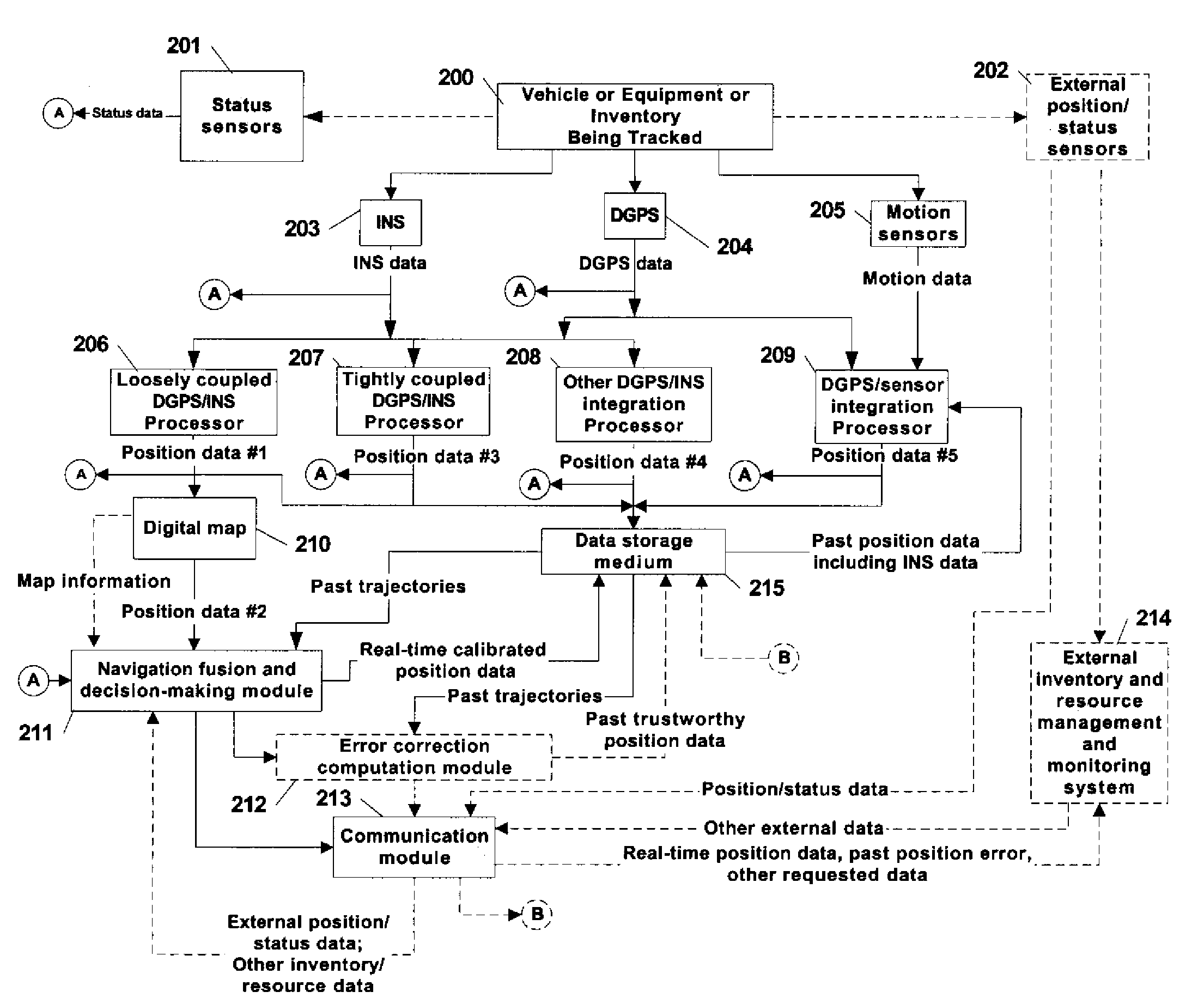
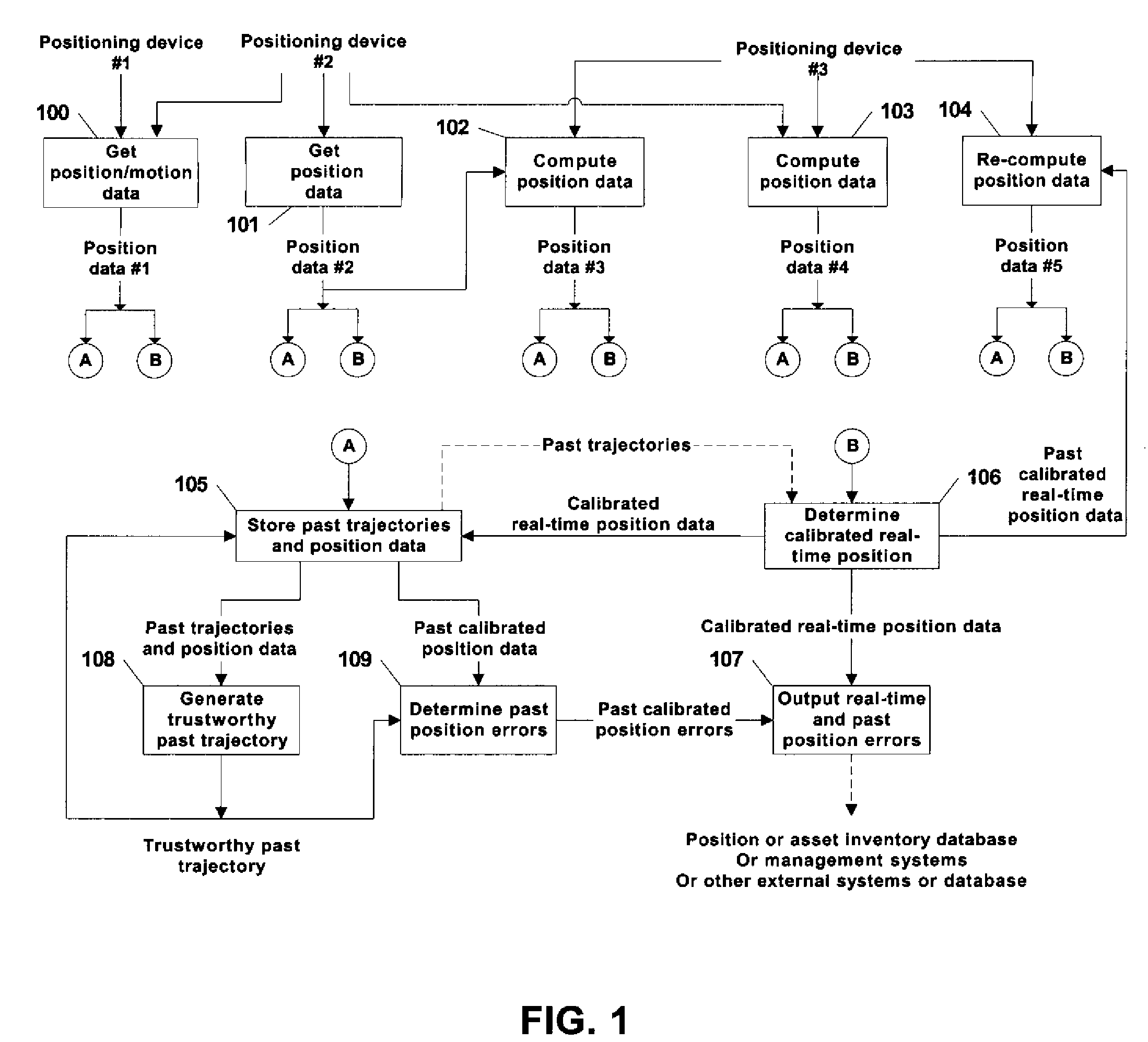
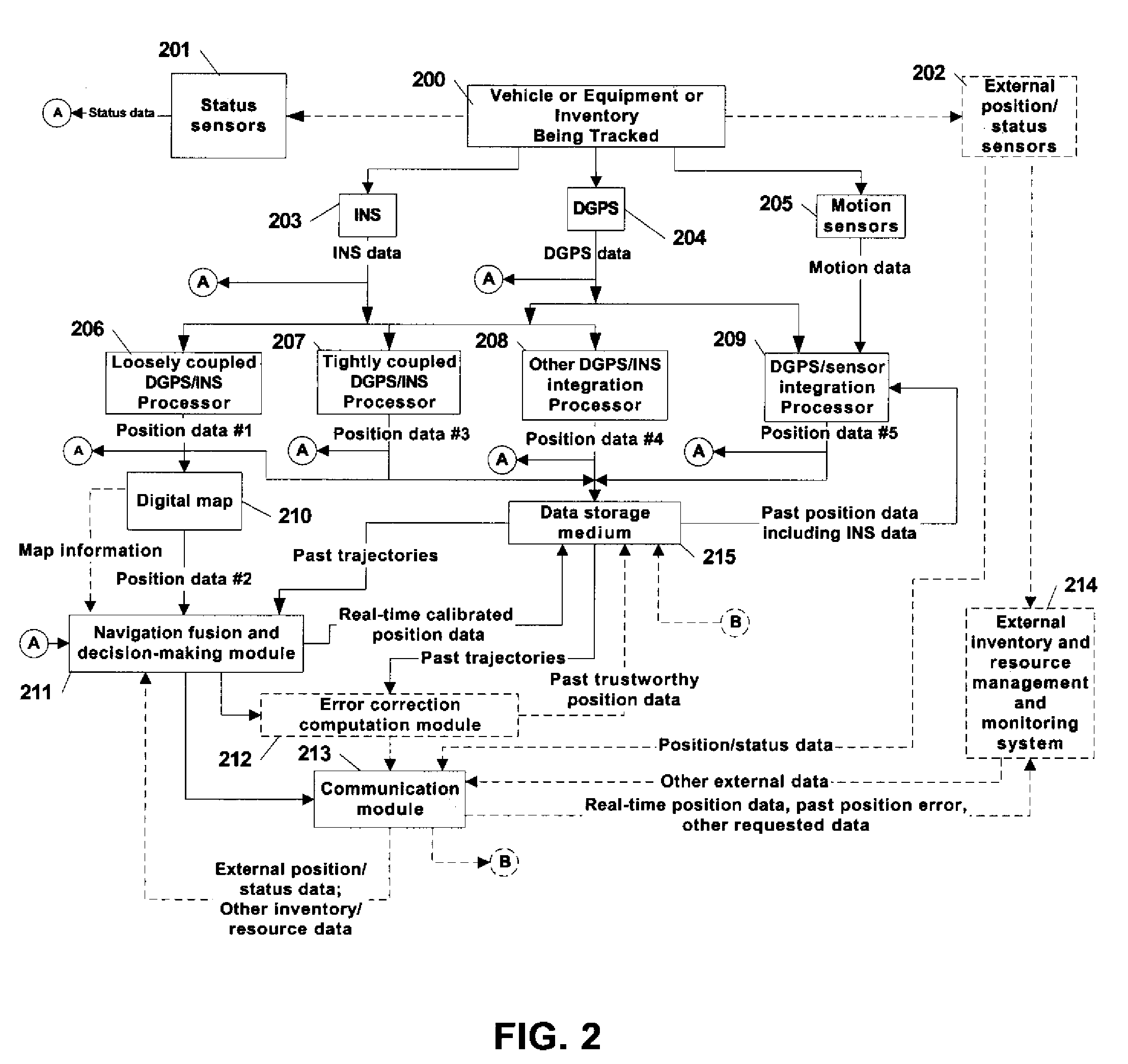
Automated asset positioning for location and inventory tracking using multiple positioning techniques
InactiveUS20070222674A1Accurate locationImprove accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationCorrection algorithmPosition error
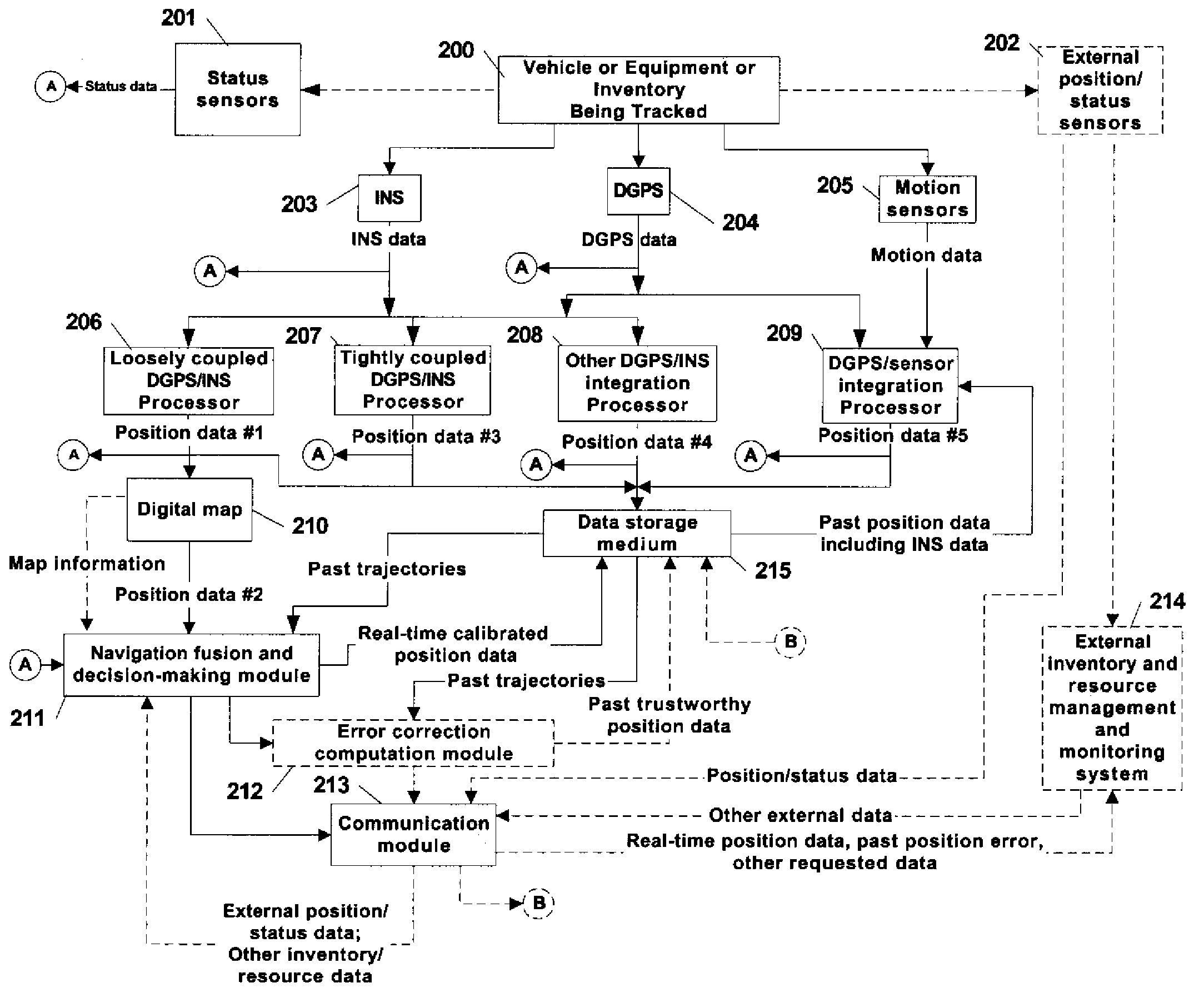
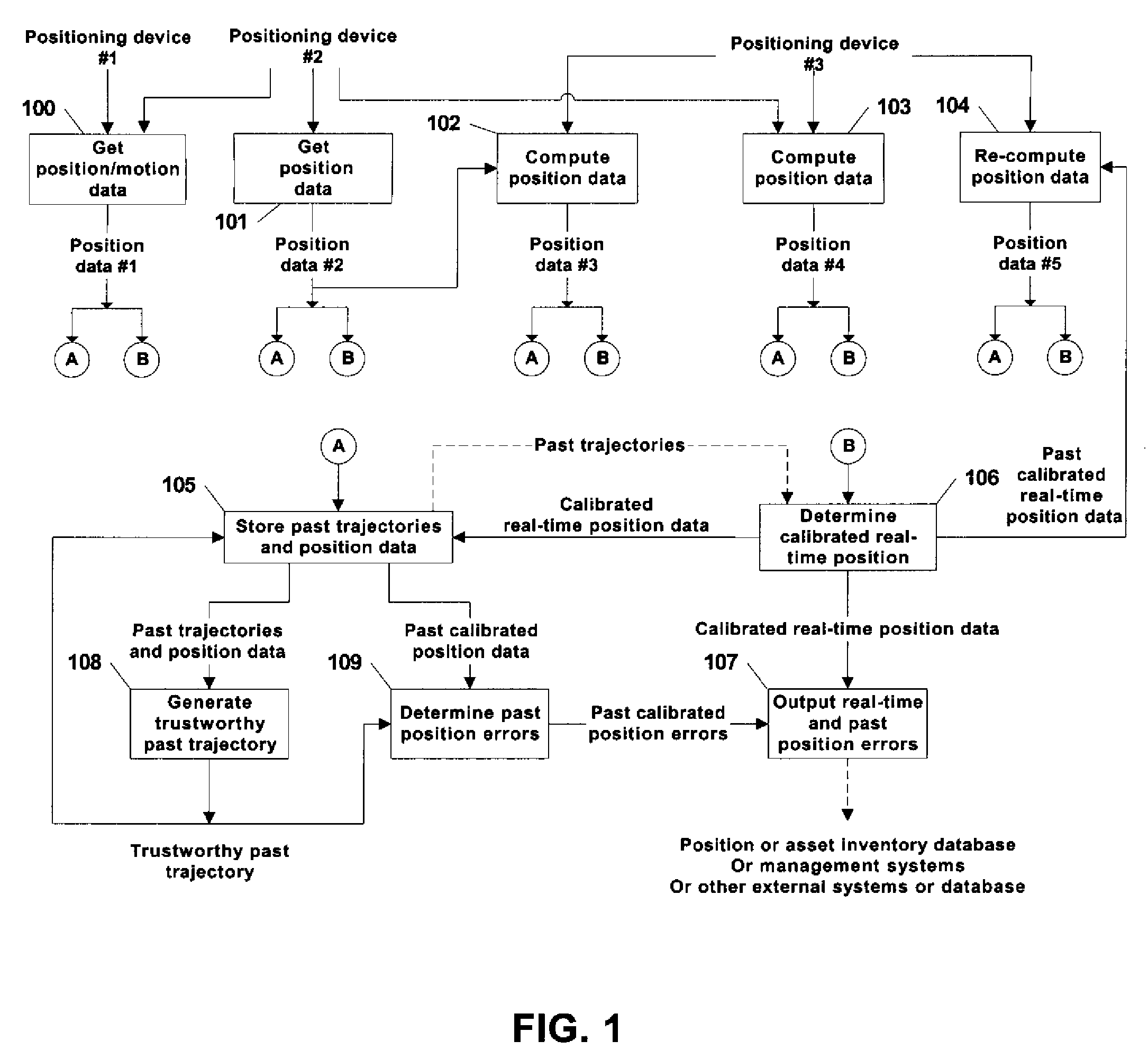
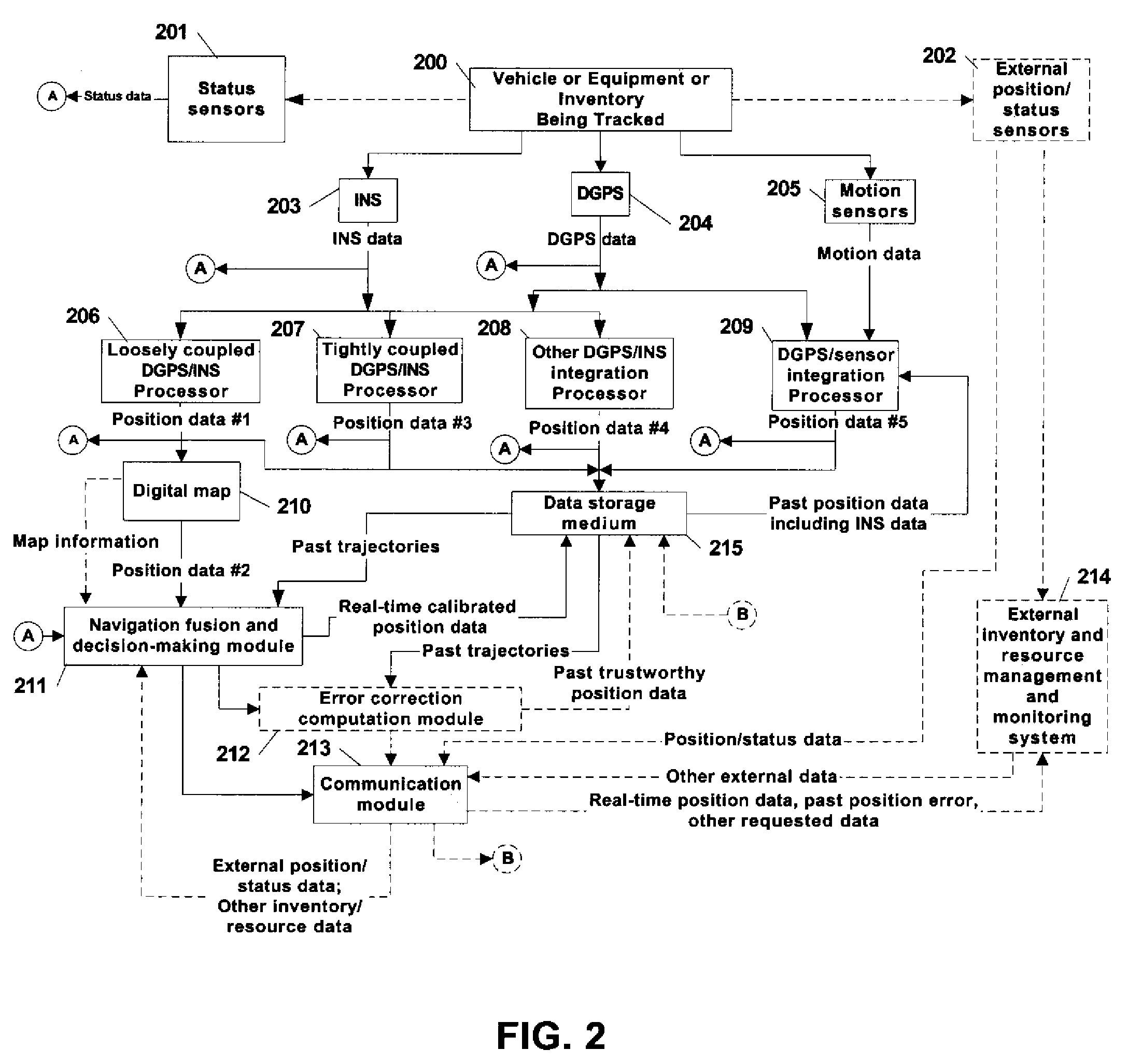
A system and method is provided for tracking and maintaining a highly accurate inventory of shipping containers that are stored within container storage facilities. The invention includes using multiple complementary real-time and post-processing positioning techniques associated with various positioning sensors that are associated with inventory pieces or equipment. Examples of such positioning techniques are DGPS, GPS with RTK, DGPS loosely-coupled with INS, DGPS tightly-coupled with INS, and DGPS deeply-coupled with INS. Data correction and fusion techniques are applied to these positioning stages to re-compute a calibrated position with an improved accuracy. An additional trajectory can be iteratively determined using the fusing technique until the position data becomes statistically trustworthy. Further, combinations of multiple real-time positioning techniques combined with past position error correction algorithms provide a high accuracy needed for inventory tracking.
Owner:MI JACK PRODS
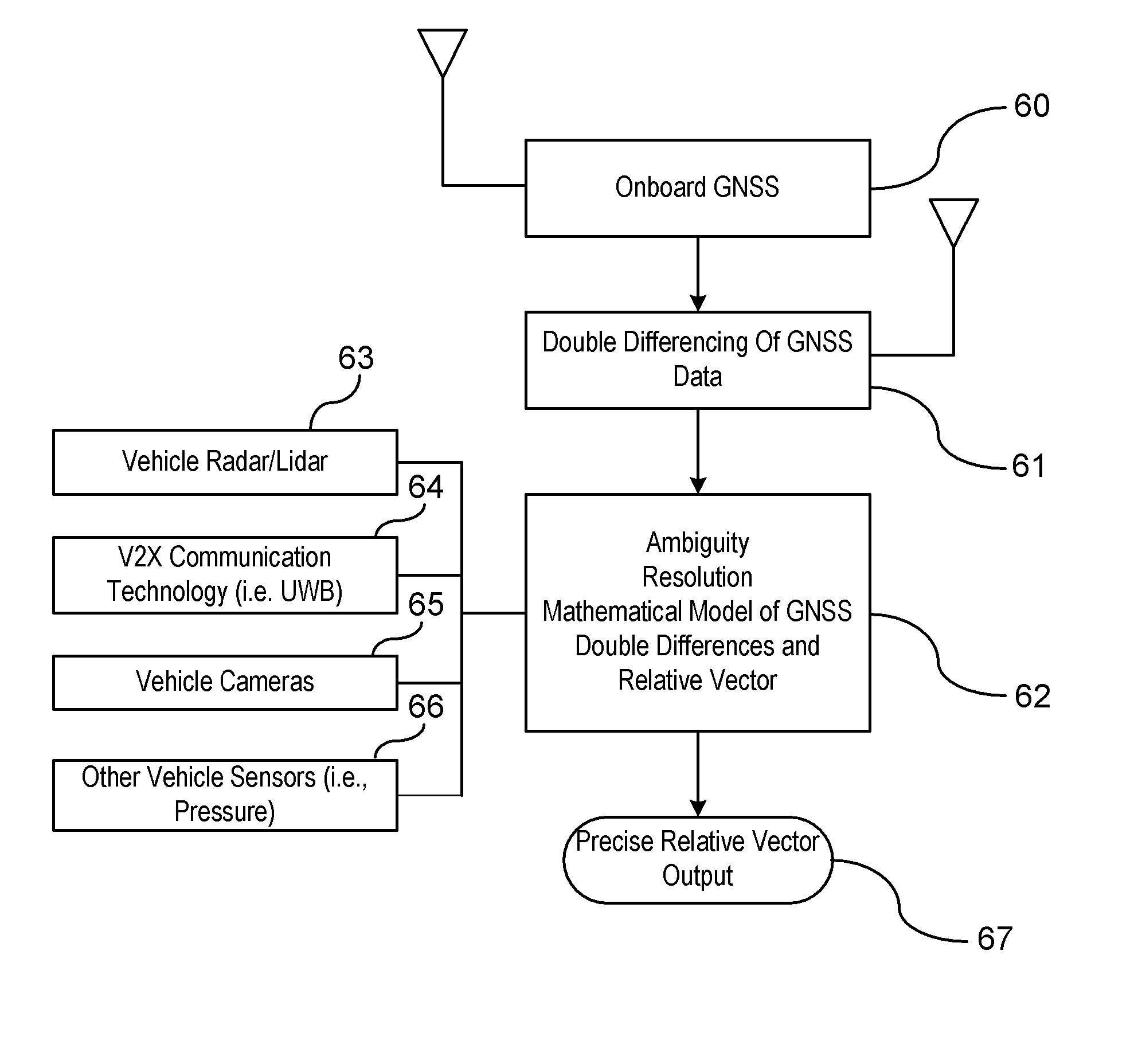
Measurement Level Integration of GPS and Other Range and Bearing Measurement-Capable Sensors for Ubiquitous Positioning Capability
A system and method are provided for determining a position of a host vehicle using a real time kinematics positioning technique when less than an optimal number of satellites are available for determining the position of the host vehicle. GPS data is retrieved from the host vehicle. GPS data is retrieved from vehicles remote from the host vehicle. Alternative vehicle position related data is retrieved. The position of the host vehicle is determined utilizing the real time kinematics positioning technique as a function of the retrieved GPS data of the host and remote vehicles and the alternative vehicle position data. The position of the host vehicle is utilized in a vehicle application.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
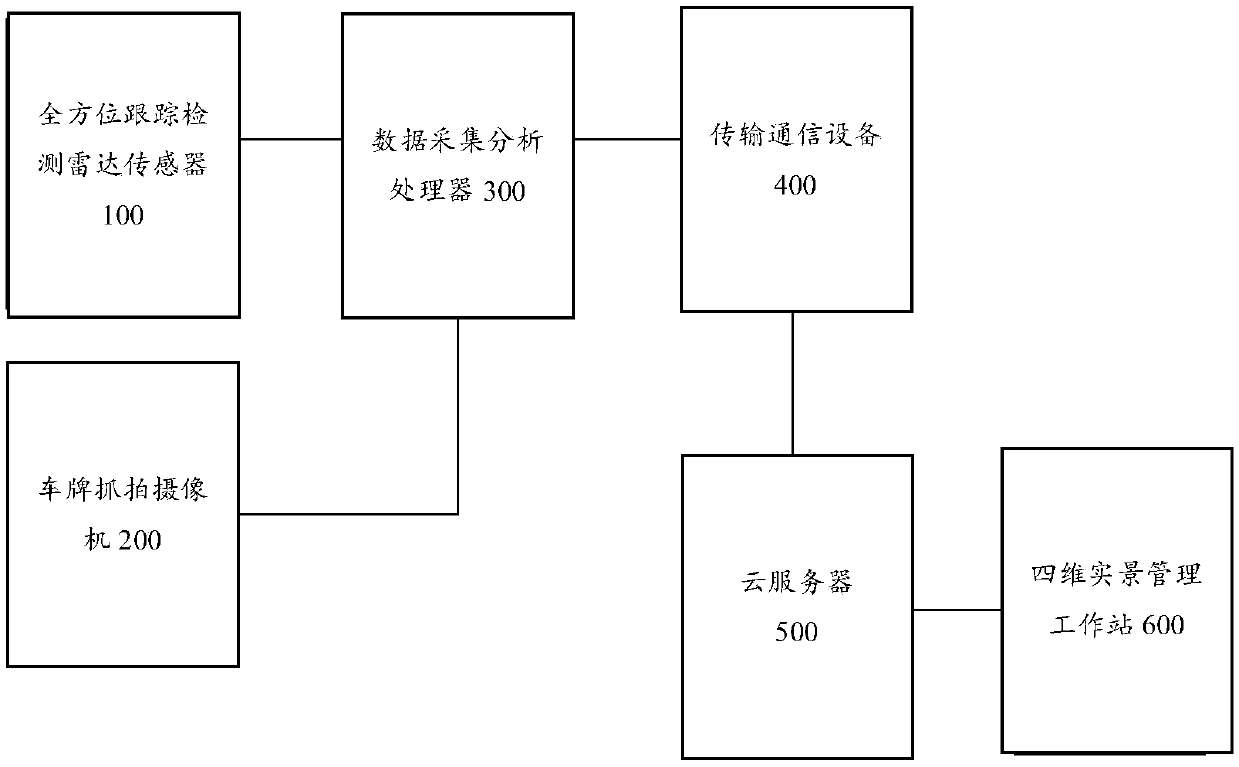
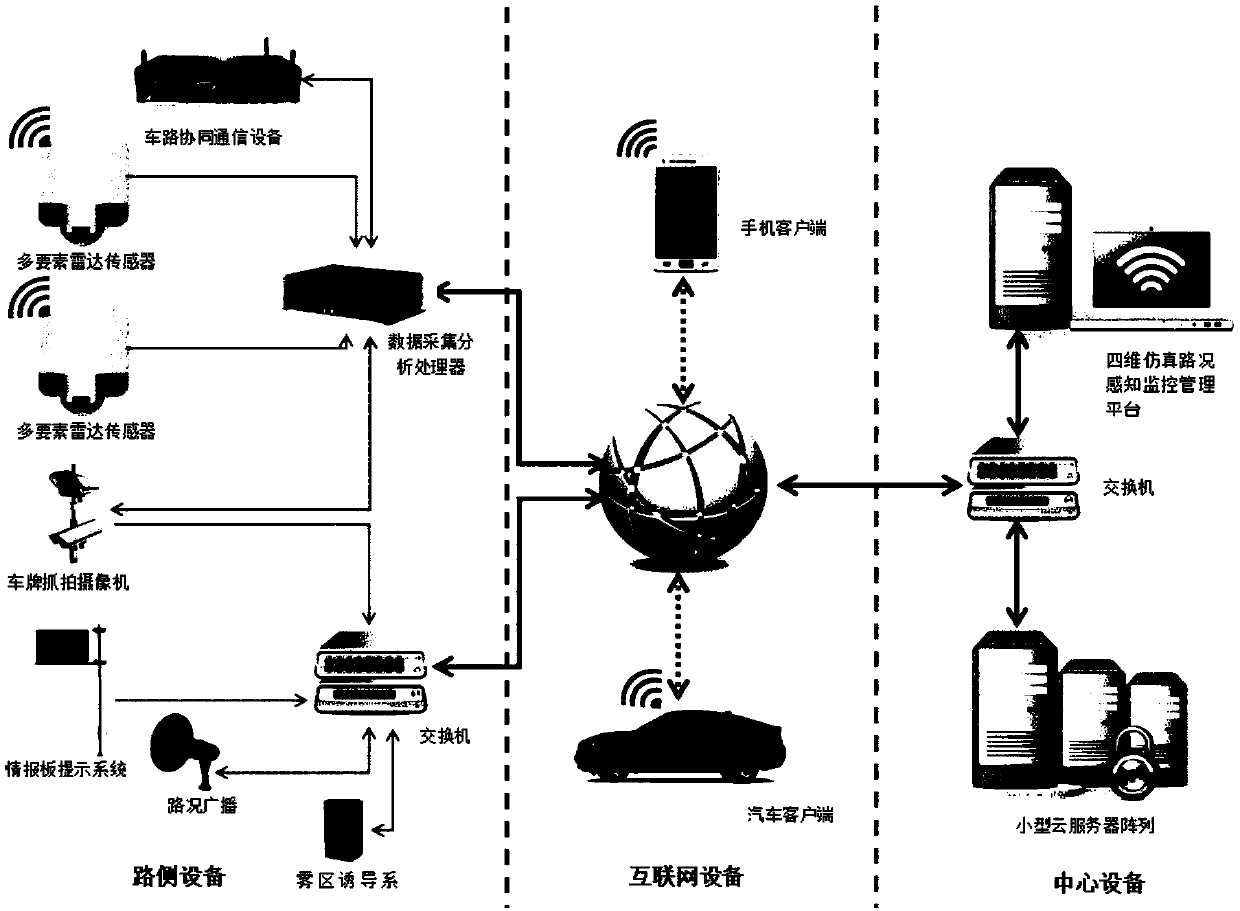
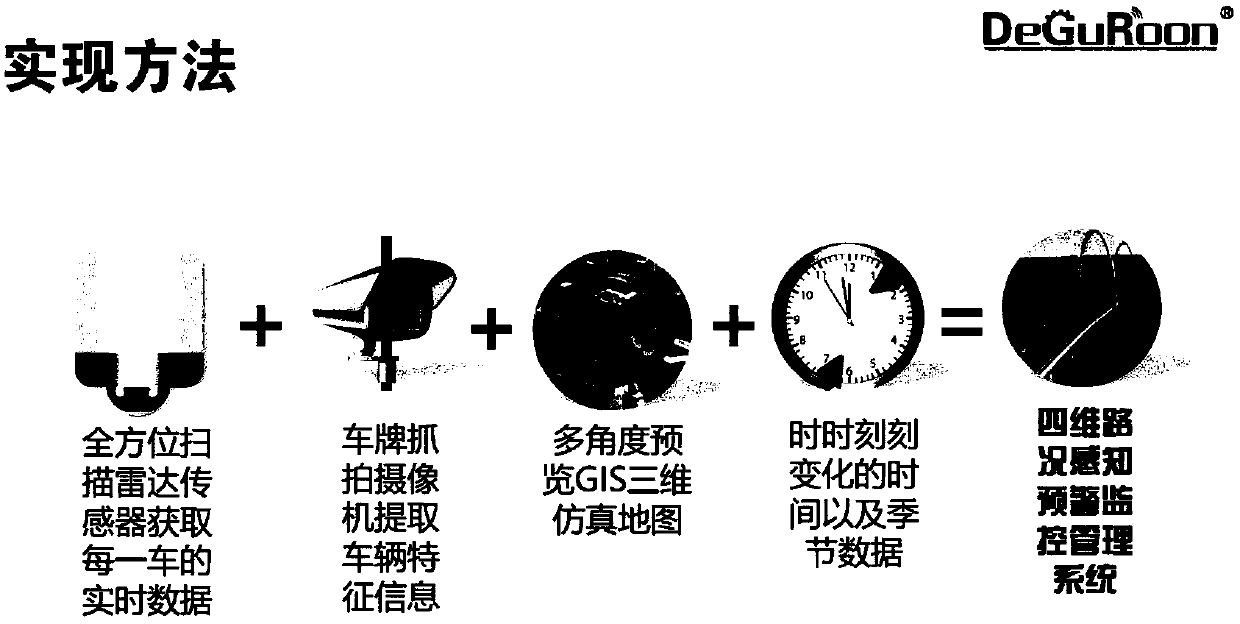
Four-dimensional live-action traffic road condition perceiving and early-warning monitoring management system based on radar tracking and positioning
ActiveCN108922188AEfficient Management ToolsDetection of traffic movementThree dimensional simulationLive action
The invention provides a four-dimensional live-action traffic road condition perceiving and early-warning monitoring management system based on radar tracking and positioning. According to the four-dimensional live-action traffic road condition perceiving and early-warning monitoring management system, a tracking and positioning technology, a license plate snapping technology, a vehicle and pedestrian three-dimensional simulation technology, a road monitoring technology, an early-warning and alarming technology, a traffic condition simulation technology, a network communication technology, a meteorological simulation technology, a computer graphic technology, a video rendering technology, a three-dimensional high-precision GIS map technology, a virtual reality fusion technology, a vehicle-road collaborative technology and a navigation technology are perfectly fused together; and through the system, the various demands of road traffic operation managers for road real-time monitoring orarea monitoring and the information demands of traveling of drivers and passengers for real-time and real traffic conditions are greatly met, and the various drawbacks which are imperfect and cannot be solved in an existing monitoring system are overcome, so that the management efficiency of the road managers is improved, the firm foundation is laid for automatic management of roads, and the important safety guarantee is also provided for traveling vehicles on the road.
Owner:河北德冠隆电子科技有限公司
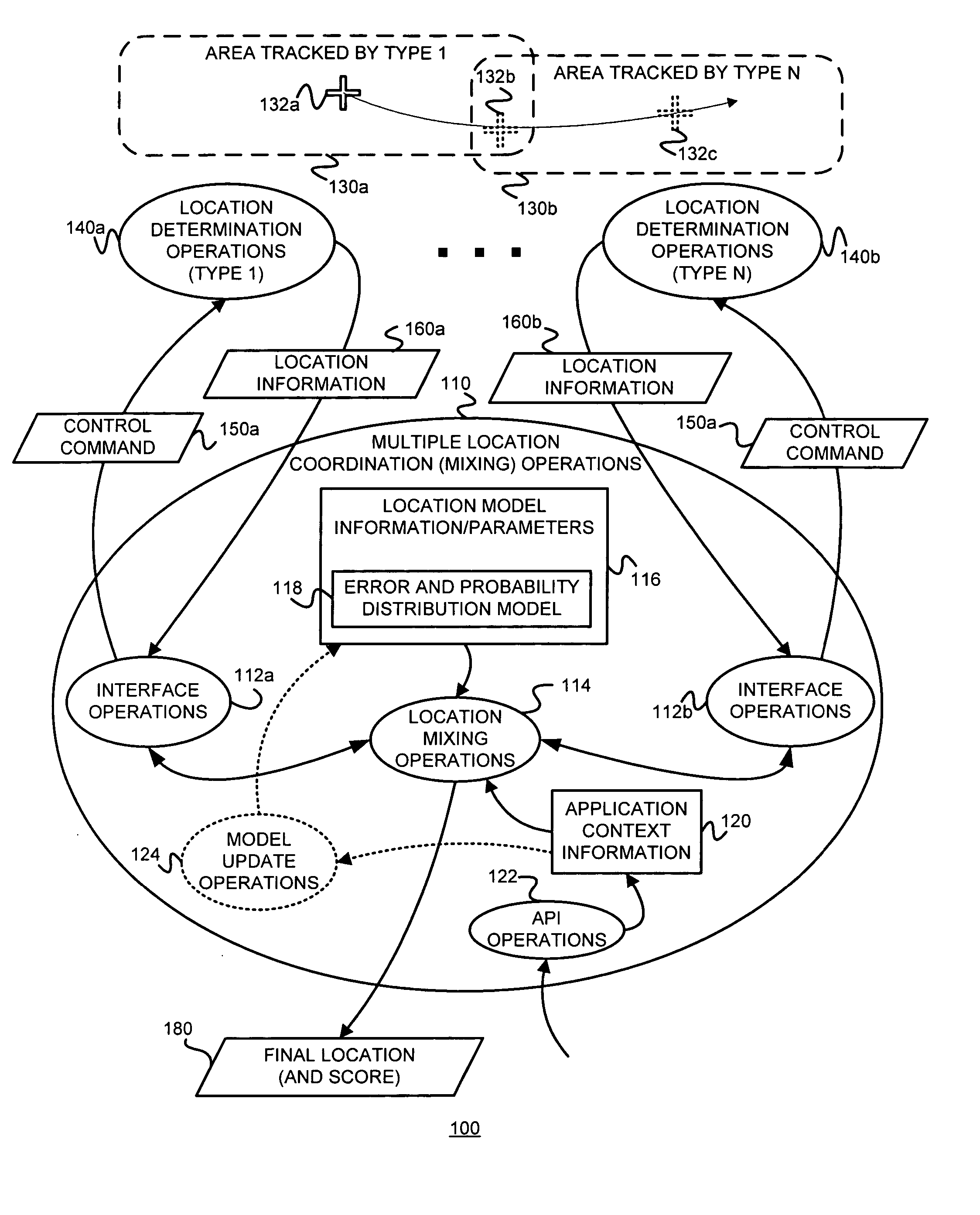
Determining a location or position using information from multiple location and positioning technologies and applications using such a determined location or position
InactiveUS20050107953A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlApplication specificPositioning technology
Owner:SARIMO TECH
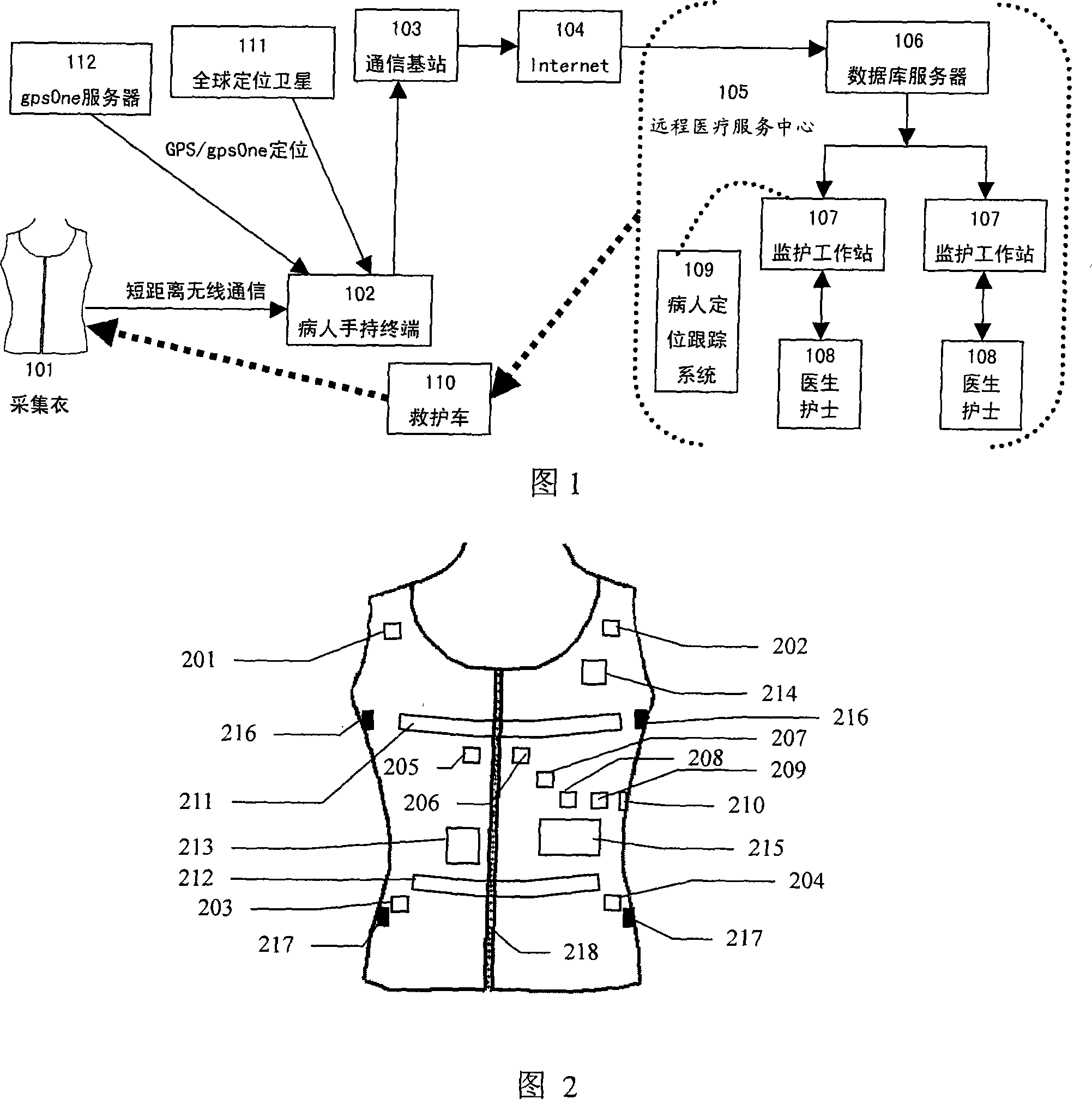
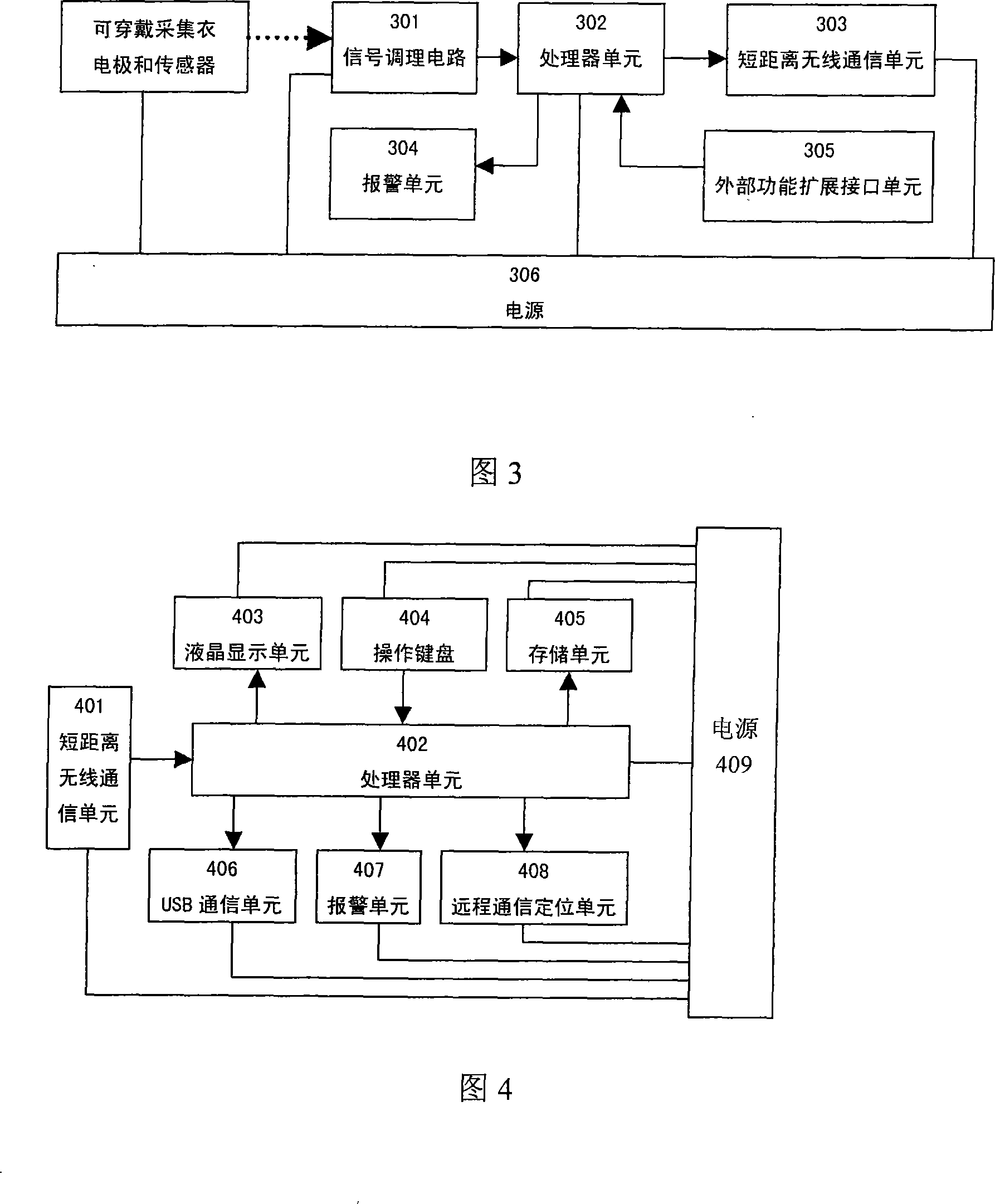
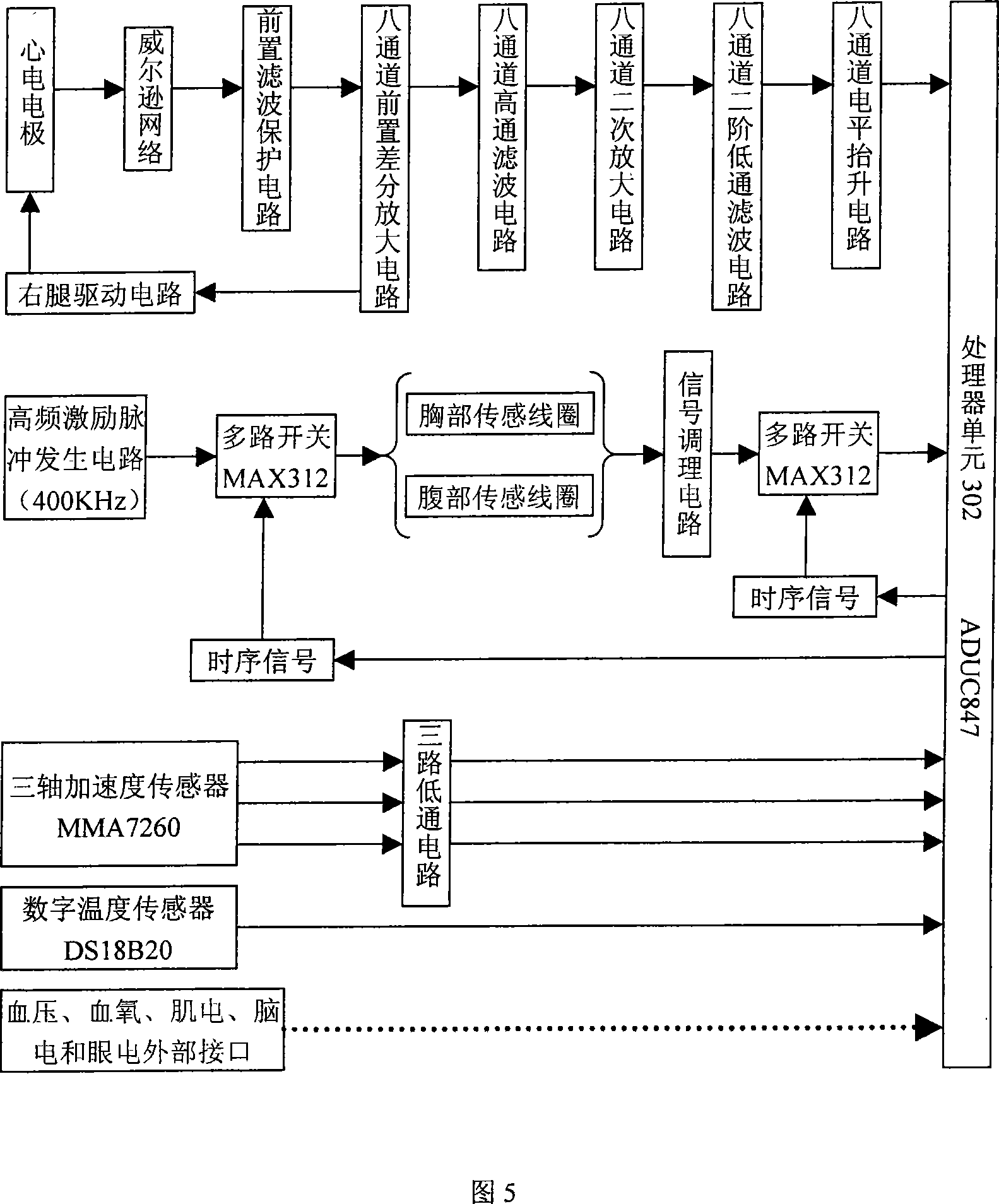
Wearable low-load physiological monitoring system
InactiveCN101019761ARealize mobile monitoringRealize remote dynamic monitoringTransmission systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringLow loadThe Internet
The present invention relates to physiological monitoring system, and is especially one kind of wearable low-load physiological monitoring system for multiparameter physiological signal acquisition. The physiological monitoring system consists of a wearable dynamic multiparameter acquisition coat, a patient's hand-held terminal and a remote medical service center. The wearable dynamic multiparameter acquisition coat communicates with the hand-held terminal in short radio communication mode, while the hand-held terminal communicates with the remote medical service center accessed to the Internet in remote radio communication mode. The present invention has the positive effect of realizing the movable monitoring, the remote dynamic monitoring and real-time tracking monitoring on low load physiological parameters of the patient.
Owner:SANITARY EQUIP INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI PLA
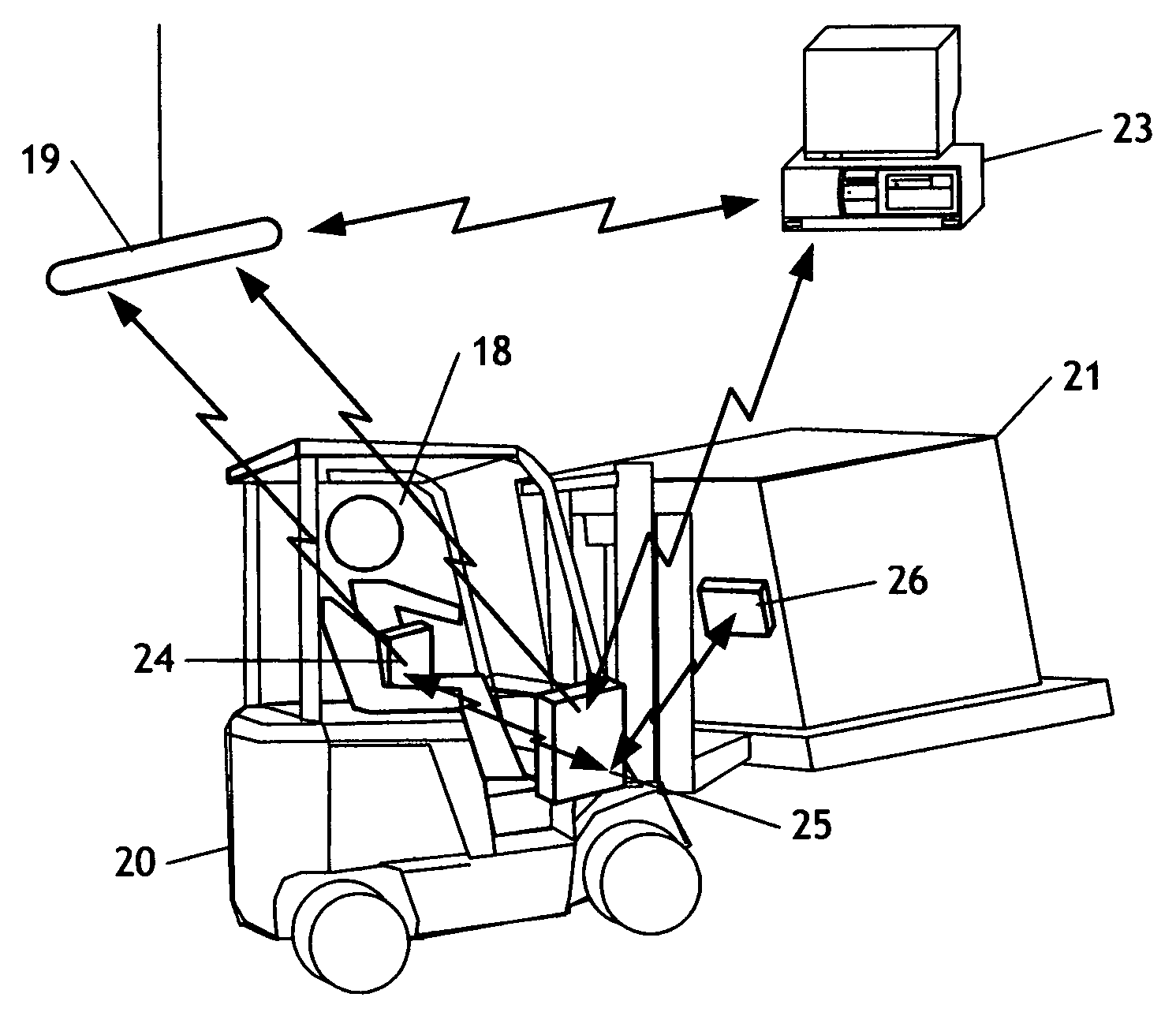
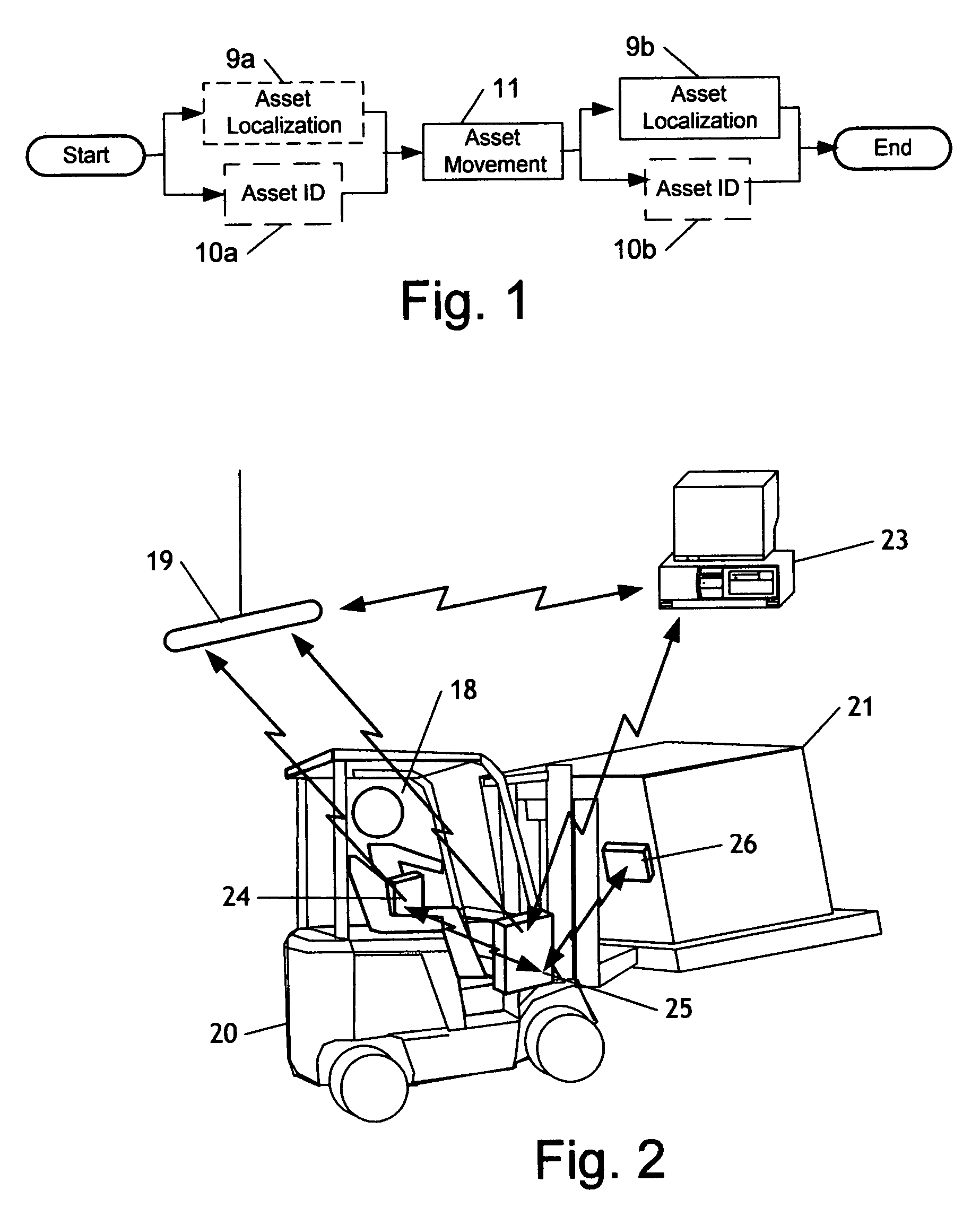
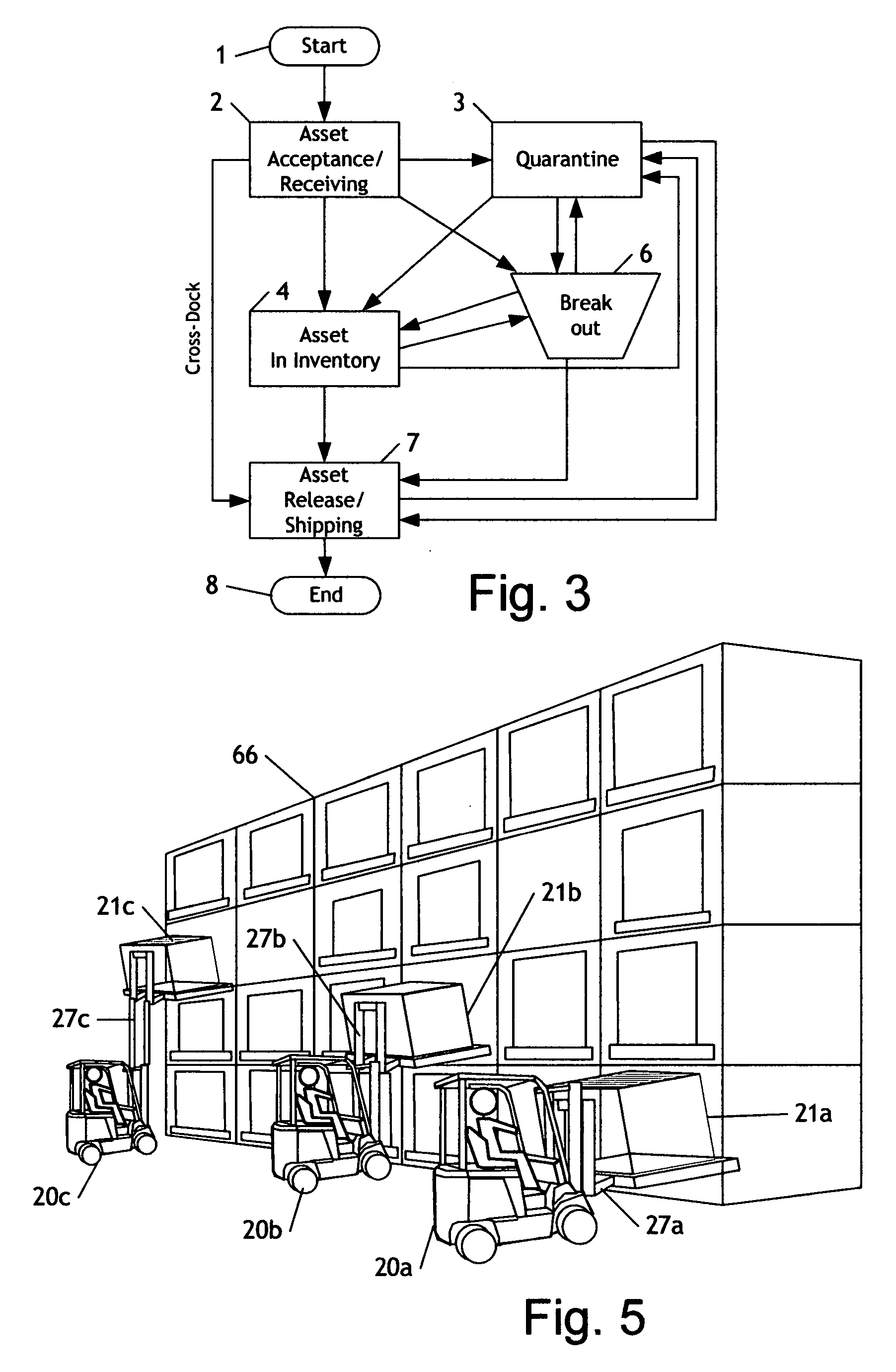
Asset localization identification and movement system and method
A system and method for identification and location of an asset by tracking the mover of the asset using a locating device associated with the mover and identifying the asset using an identification reader associated with the mover and a passive identification tag associated with the asset. A single mover may move many assets. An asset is identified; the mover then moves the asset to a destination location, whereupon the mover and asset position are determined. The asset location may then be recorded in memory. The measurement of the destination location may be extended from the location measured by the active location device by using additional measurement devices, for example a forklift height sensor. A further embodiment utilizes RFID or barcode technology for the passive tag and may utilize near field positioning technology for the active location device.
Owner:GAN CORP
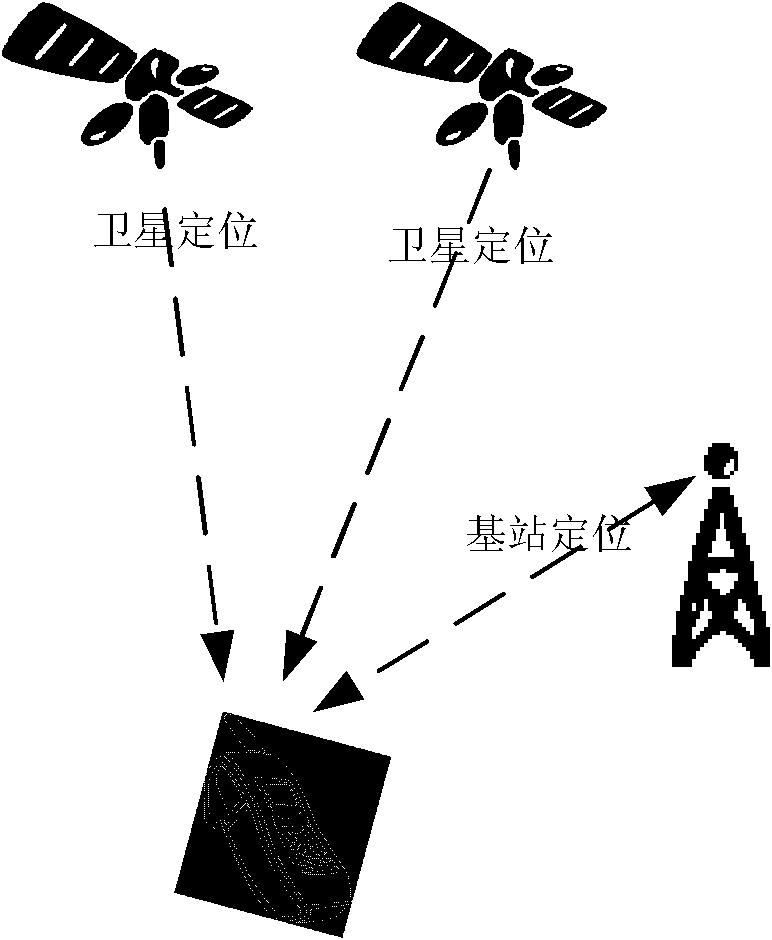
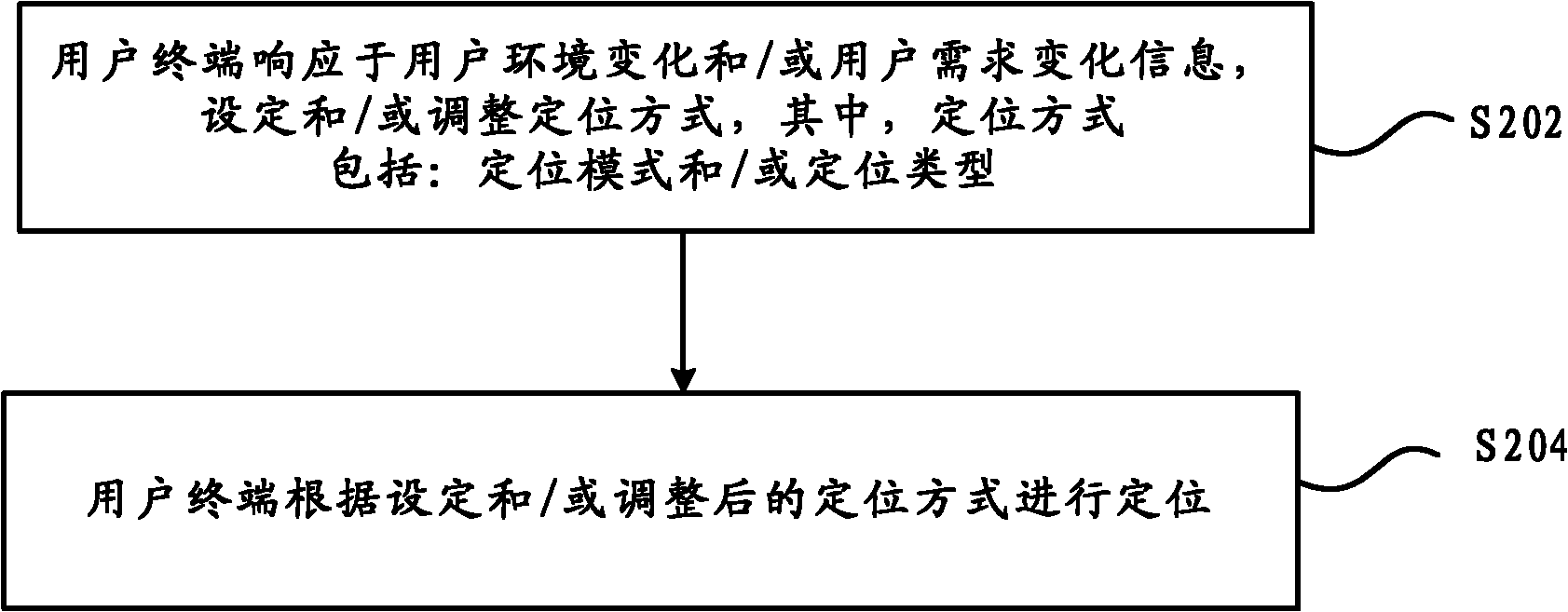
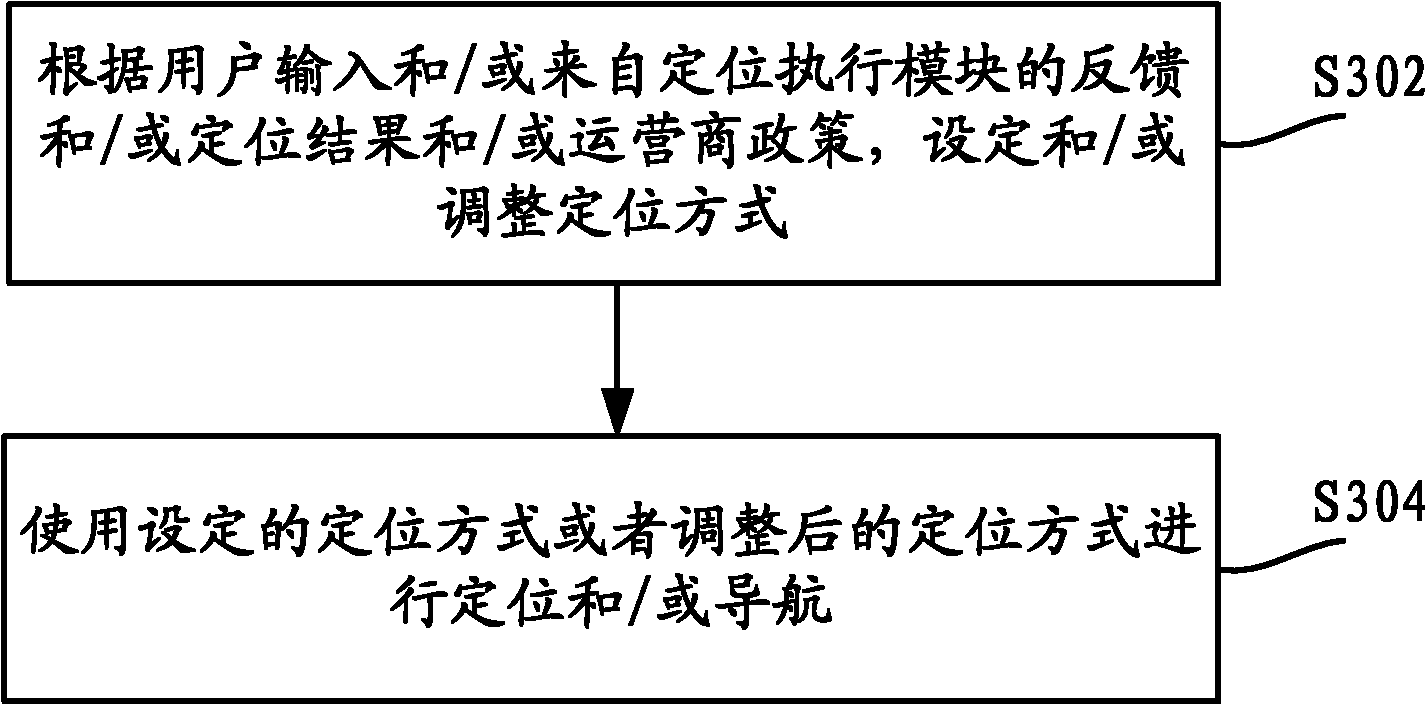
Positioning method and user terminal supporting multiple positioning modes
InactiveCN102036165AMeet needsMeet the needs of navigation and positioningSatellite radio beaconingLocation information based serviceUser environmentPositioning technology
The invention discloses a positioning method and user terminal supporting multiple positioning modes. The method comprises the following steps: the user terminal responds to user environment change and / or user requirement change information and sets and / or regulates a positioning mode, wherein the positioning mode comprises a positioning pattern and / or a positioning type; and the user terminal carries out a positioning operation in accordance with the set and / or regulated positioning mode. By using the technical scheme provided by the invention, the positioning or navigation precision can be improved, and the positioning technology can be adapted to the changes of user environments and user requirements, thereby achieving the purpose of meeting the positioning requirements of users under various conditions and the requirements for continuous navigation and positioning in the process of moving in a board space.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Automated asset positioning for location and inventory tracking using multiple positioning techniques
InactiveUS7646336B2Improve accuracyImprove data accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationCorrection algorithmPosition error
Owner:MI JACK PRODS
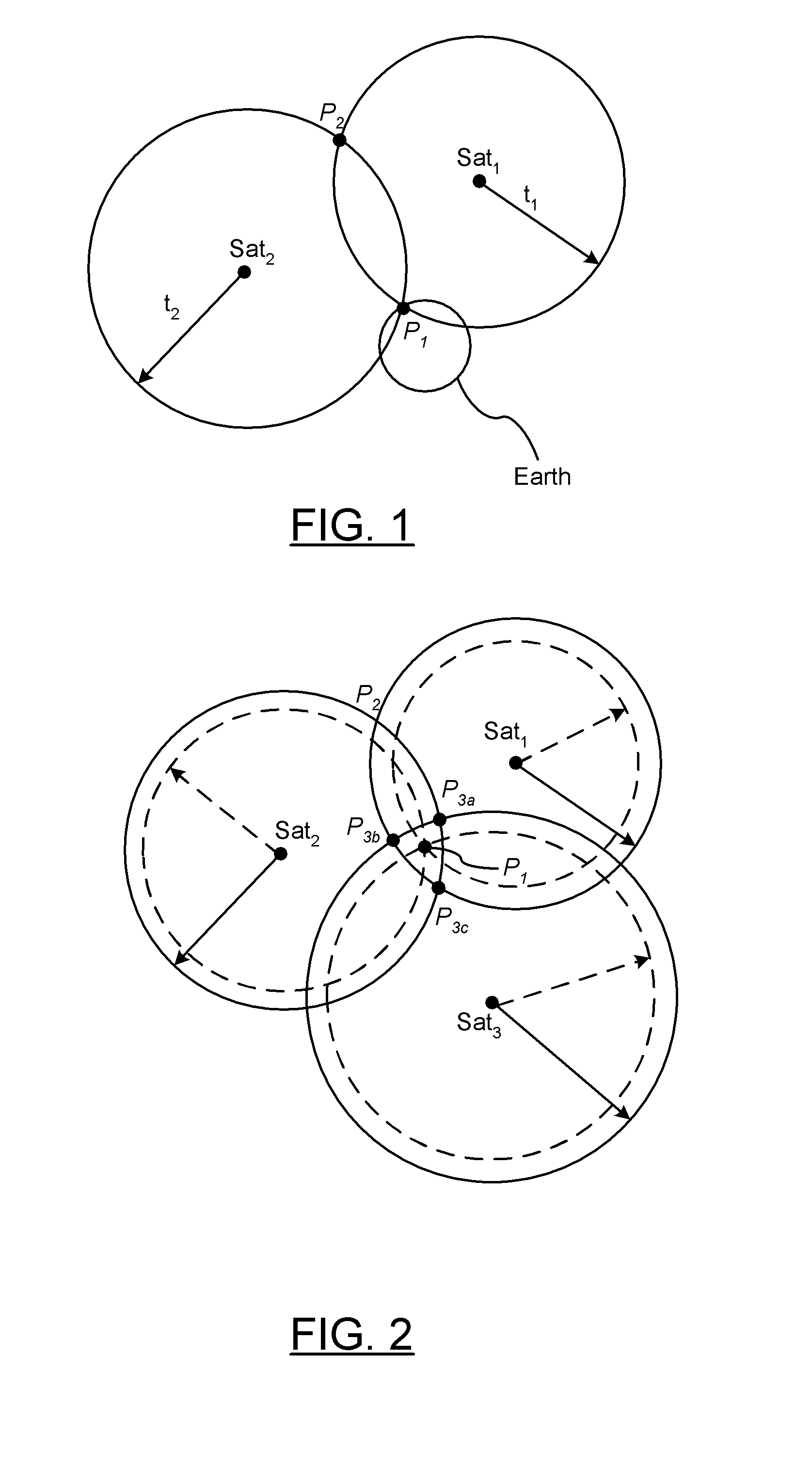
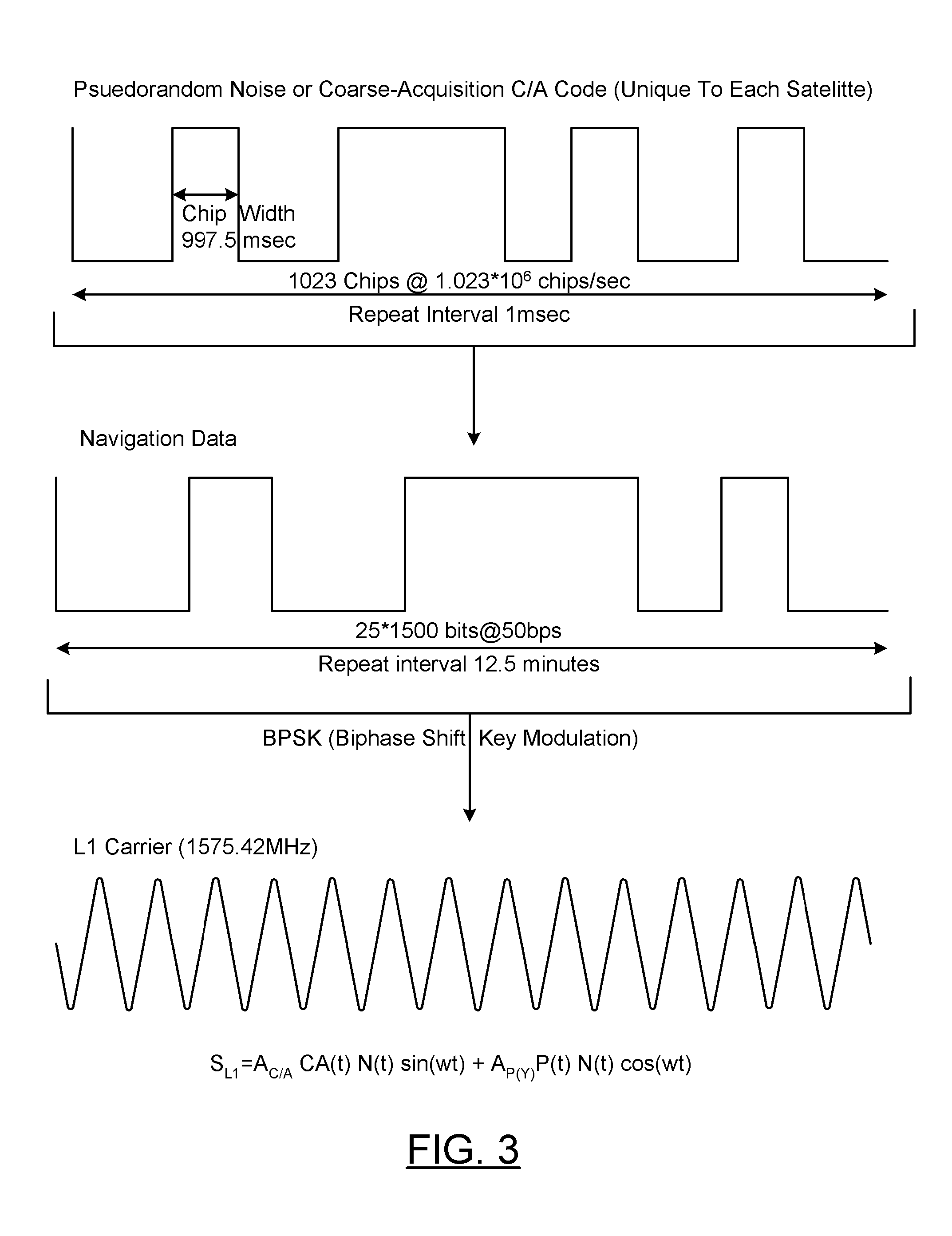
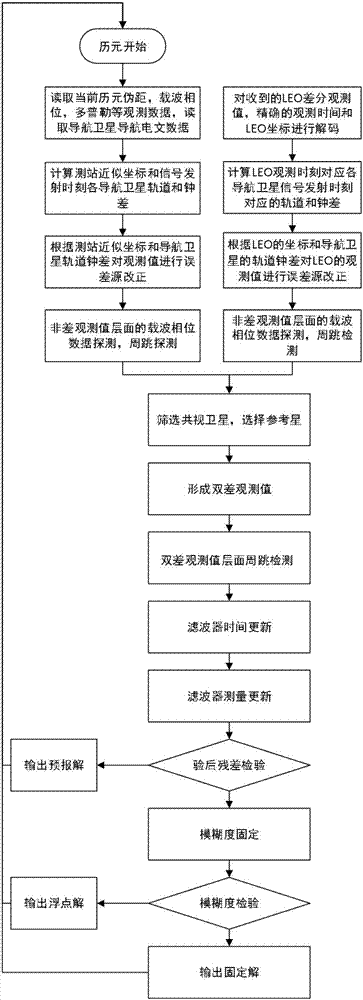
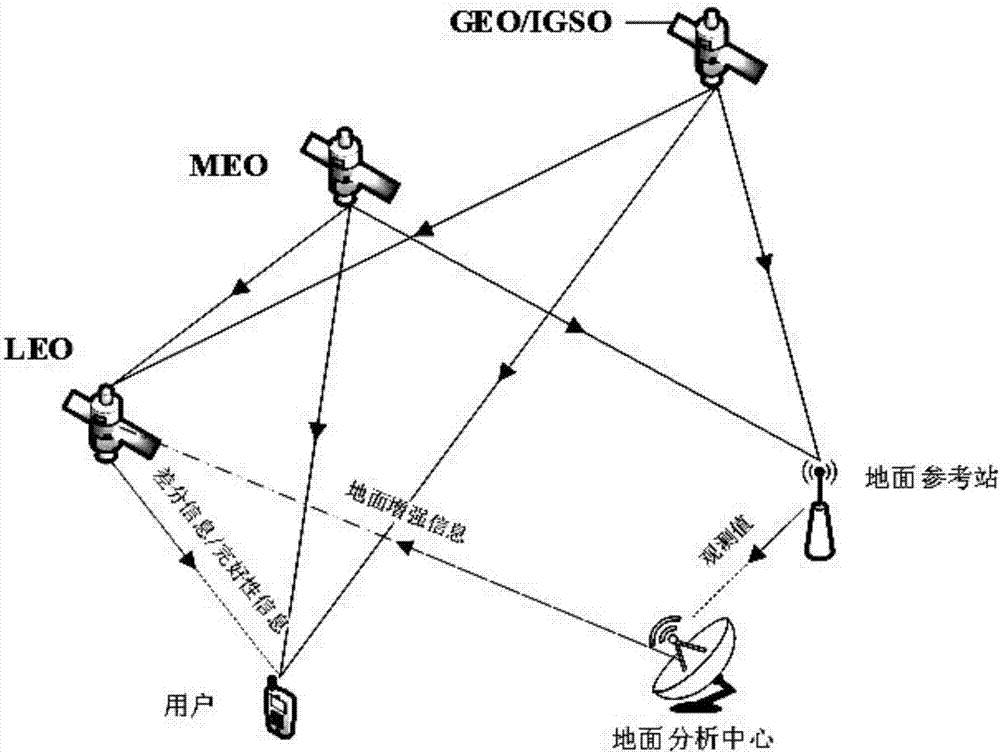
Low earth orbit satellite-based satellite-earth differential real-time precise positioning method
ActiveCN107229061ARapid positioningRealize Differential Positioning ServiceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceNatural satellite
The invention belongs to the satellite navigation and positioning technical field and discloses a low earth orbit satellite-based satellite-earth differential real-time precise positioning method. A low earth orbit satellite is utilized to broadcast the observation data and real-time orbit data of the satellite-borne GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver of the low earth orbit satellite to the ground; and after receiving the differential information broadcasted by the low earth orbit satellite, a ground receiver generates a double-difference observation value consisting of the differential information and a local GNSS observation value and performs pseudorange-based moving base station DGNSS (Differential Navigation Satellite System) positioning and carrier phase-based moving base station RTK (Rea-time kinematic) positioning. According to the positioning method of the invention, the global mobile low earth orbit satellite platform is adopted as a reference station, so that real-time precision differential positioning service in the whole world can be realized, and the method does not depend on the distribution of ground reference stations; and a user can realize differential real-time precise positioning just through using a single receiver, and therefore, the method is free of operating range restrictions, and data communication links are not required to be considered.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Wireless location routing applications and archectiture therefor
ActiveUS20080133126A1Accurate locationNavigational calculation instrumentsRoad vehicles traffic controlInternet communicationModularity
A system for wirelessly locating mobile station / units (MS) and using resulting location determinations for providing a product or service is disclosed. The system is useful for routing an MS user to a plurality of desired locations, alerting an MS user to a nearby desired product or service based on satisfaction of user criteria, and providing enhanced security and 911 response. In one embodiment, the system responds to MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location processing sites. A plurality of locating technologies including those based on: (1) TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) timing advance; (5) GPS and network assisted GPS, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from low cost base stations can be activated, in various combinations, by system embodiments. MS location difficulties resulting from poor location accuracy / reliability and / or poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:MOBILE MAVEN
Peer and composite localization for mobile applications
ActiveUS20100105409A1Improve accuracyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingSatellite radioLocalization system
A system and method for peer based localization system using radio technology, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi ad-hoc technology that enables mobile devices such as cell phones, smart phones, laptops, handheld communication devices, handheld computing devices, satellite radios, global positioning systems, PDAs, etc. to discover their physical location relative to one another. In addition, the peer based localization can use a plurality of radio technologies to increase the accuracy of the physical location estimates. Additionally or alternatively, the peer based localization technique can be combined with infrastructure based location techniques, such as triangulation, GPS, or infrastructure based Wi-Fi localization in order to transpose virtual coordinates into physical coordinates.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
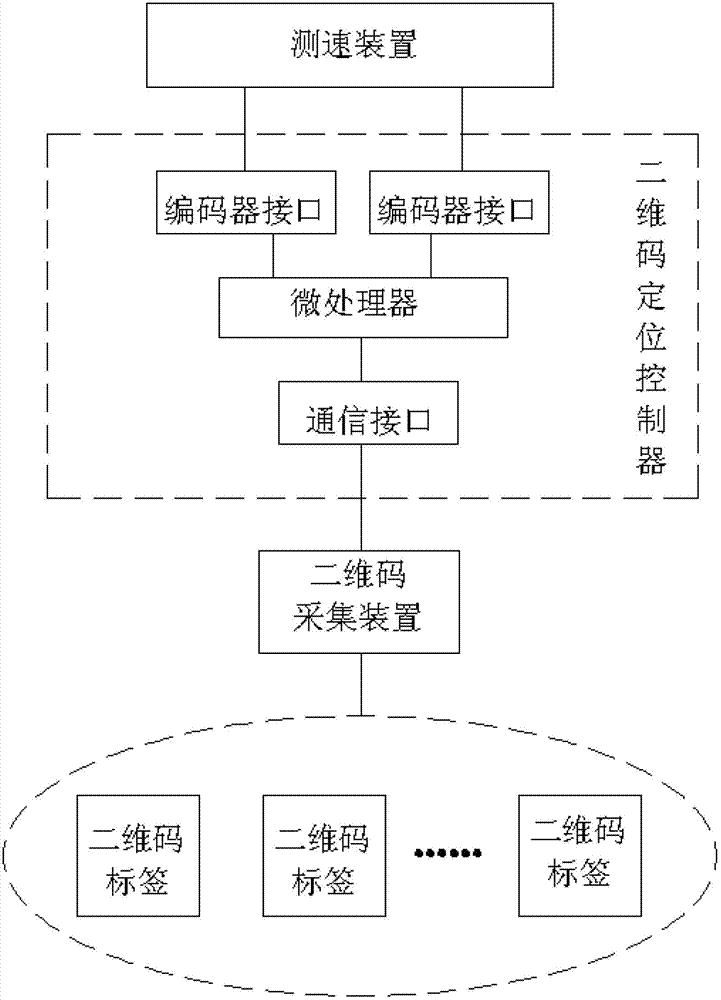
Indoor mobile robot positioning system and method based on two-dimensional code
ActiveCN102735235ASolve the speed problemFix the angle problemNavigation instrumentsCommunication interfaceImaging processing
The present invention relates to an indoor mobile robot positioning system and method based on two-dimensional code. The system includes a two-dimensional code positioning controller mounted on a mobile robot, a two-dimensional code acquisition device and a two-dimensional code label distributed in the indoor environment. The two-dimensional code positioning controller is composed of a microprocessor and a communication interface that are connected together. The microprocessor is connected with the two-dimensional code acquisition device through the communication interface and is used for controlling the two-dimensional code acquisition device to acquire two-dimensional code images, receive the two-dimensional code images acquired by the two-dimensional code image acquisition device and realize precise positioning function. The method acquires an actual position of the mobile robot through photographing the indoor two-dimensional code labels, transforming coordinates and mapping code values. The method of the invention organically combines visual positioning technique, two-dimensional code positioning technology and two degree of freedom measuring technology to realize the function of precise positioning of the mobile robot and solve problems of complex image processing and inaccurate positioning of a traditional vision positioning system.
Owner:爱泊科技(海南)有限公司
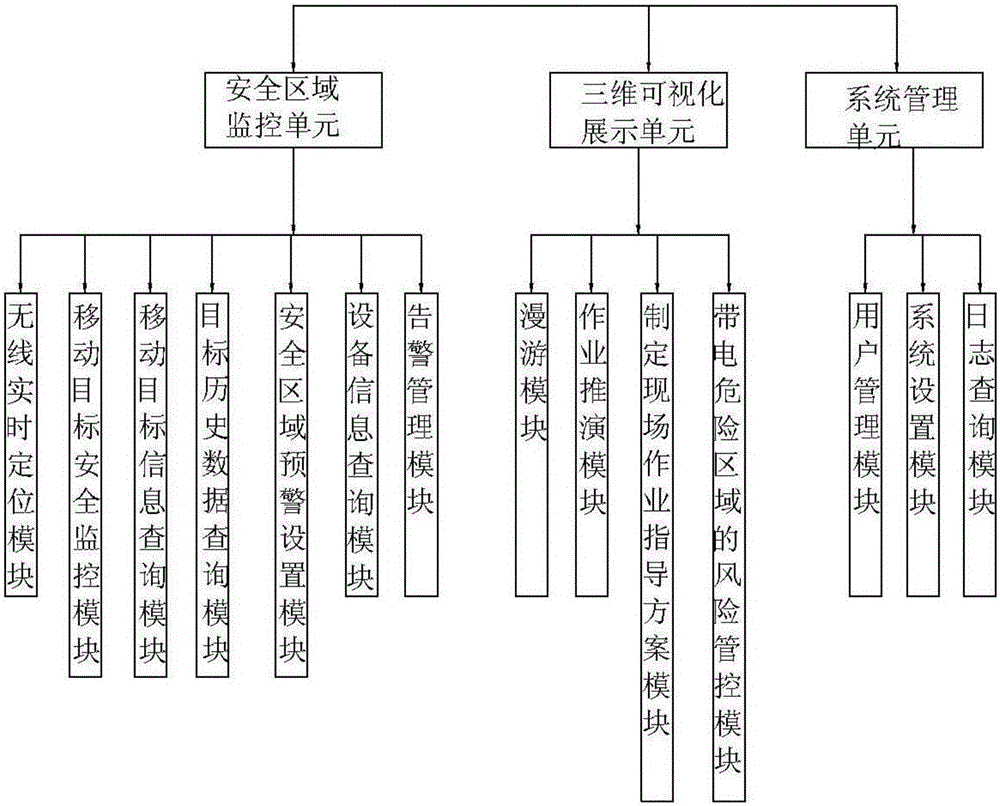
Transformer station three-dimensional real scene simulation system and implementation method
ActiveCN105956232ARealize 3D dynamic displayAvoid missingData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationSystems managementTransformer
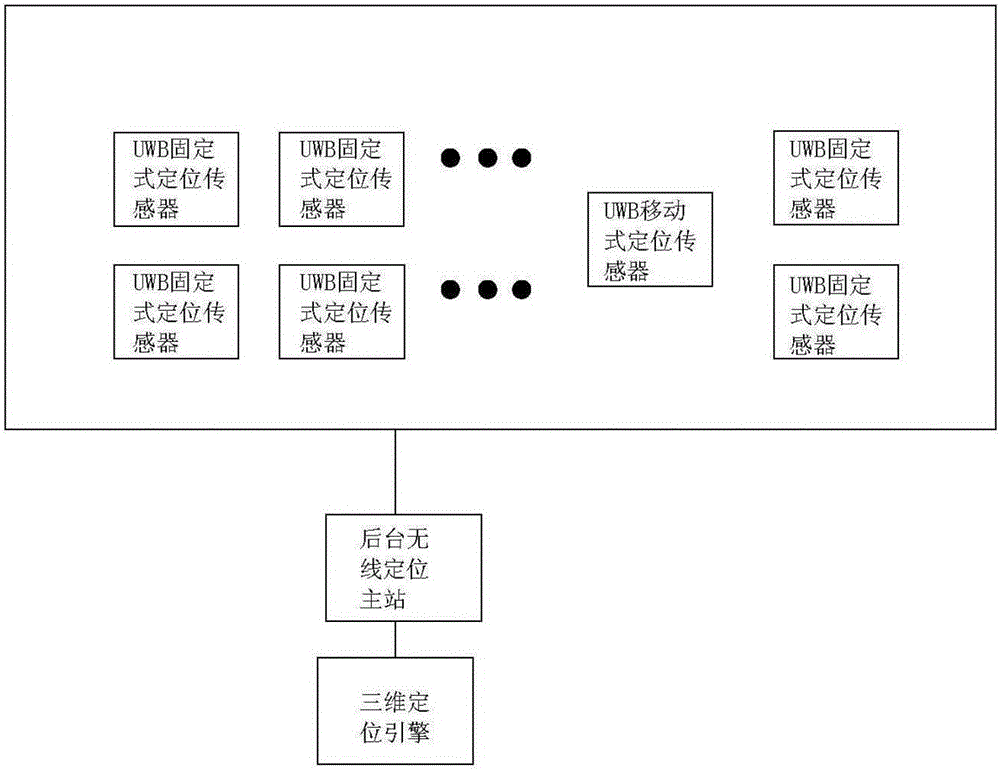
The invention relates to a transformer station three-dimensional real scene simulation system and an implementation method. The system comprises a safety region monitoring unit, a three-dimensional visualization display unit, and a system management unit. The safety region monitoring unit comprises a wireless real-time positioning module using a UWB positioning technology, a moving target security monitoring module, a moving target information query module, a target historical data query module, a safety region early warning setting module, an equipment information query module, and an alarm management module. The three-dimensional visualization display unit comprises a roaming module, an operation deduction module, a field operation instruction scheme making module, and a risk management and control module of an electrified dangerous region. The system management unit comprises a user management module, a system setting module, and a log query module. The system realizes functions of daily inspection and maintenance visual management of a transformer station, operating personnel daily inspection and maintenance process real-time tracking and monitoring, security alert alarm and intelligent recording management.
Owner:WUHAN NARI LIABILITY OF STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Method for handover of communication link using primary beam
InactiveCN105052199AHigh positioning accuracyRadio transmissionNetwork planningTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A method and apparatus for improving and performing mmW beam tracking is disclosed. Localization methods to improve prediction of the position of a WTRU are described, which may allow a millimeter wave base station (mB) to appropriately select a modified beam and to perform more efficient handover. WTRUs may report directional signal strength measurements to mBs, which may then be used to generate a directional radio environment map (DREM) for use in identifying secondary links to use when a primary link fails. Additional localization techniques using internal / external information for prediction are described. Historical data use and the use of data obtained from mB-mB cooperation including feedback information and reference signaling information are also described. Methods for beam tracking for directional relays and initial beam training optimization are described as well. Finally, WTRU localization precision improvement, beamwidth adaptation, and assisted beam tracking and handover methods are also described.
Owner:IDAC HLDG INC
Object tracking
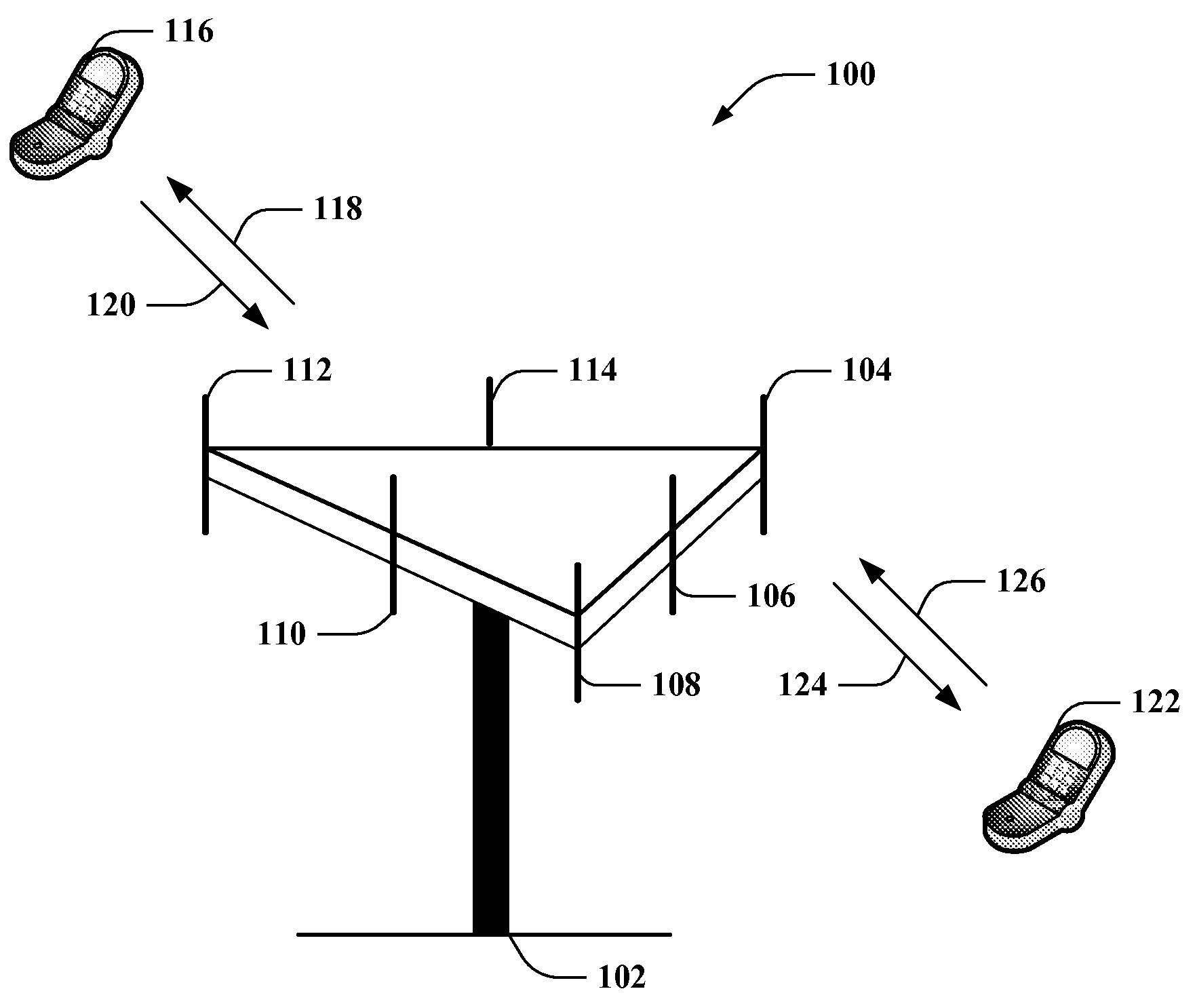
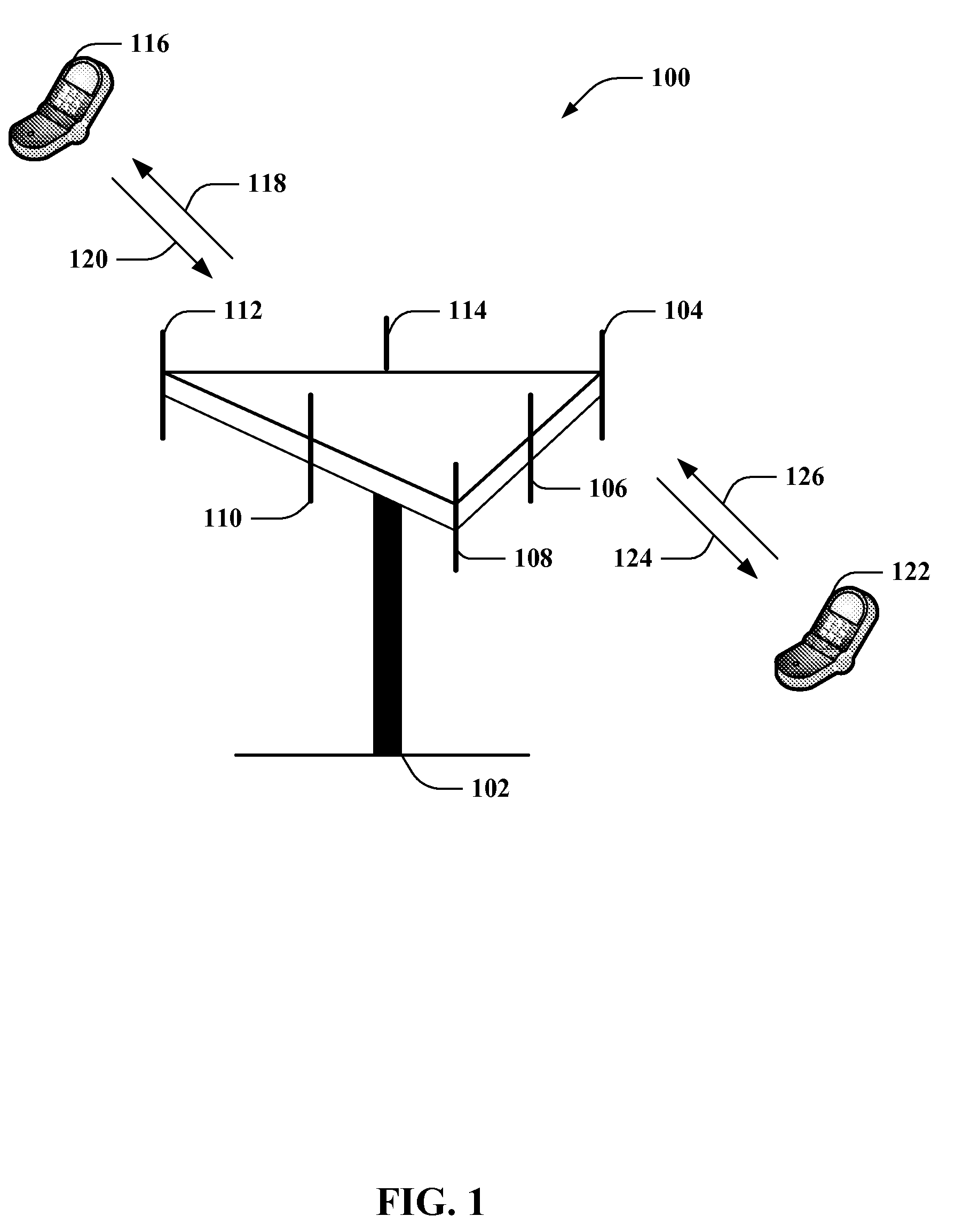
InactiveUS6989741B2Easy to appreciateElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingElectric signalling detailsElectronic taggingTriangulation
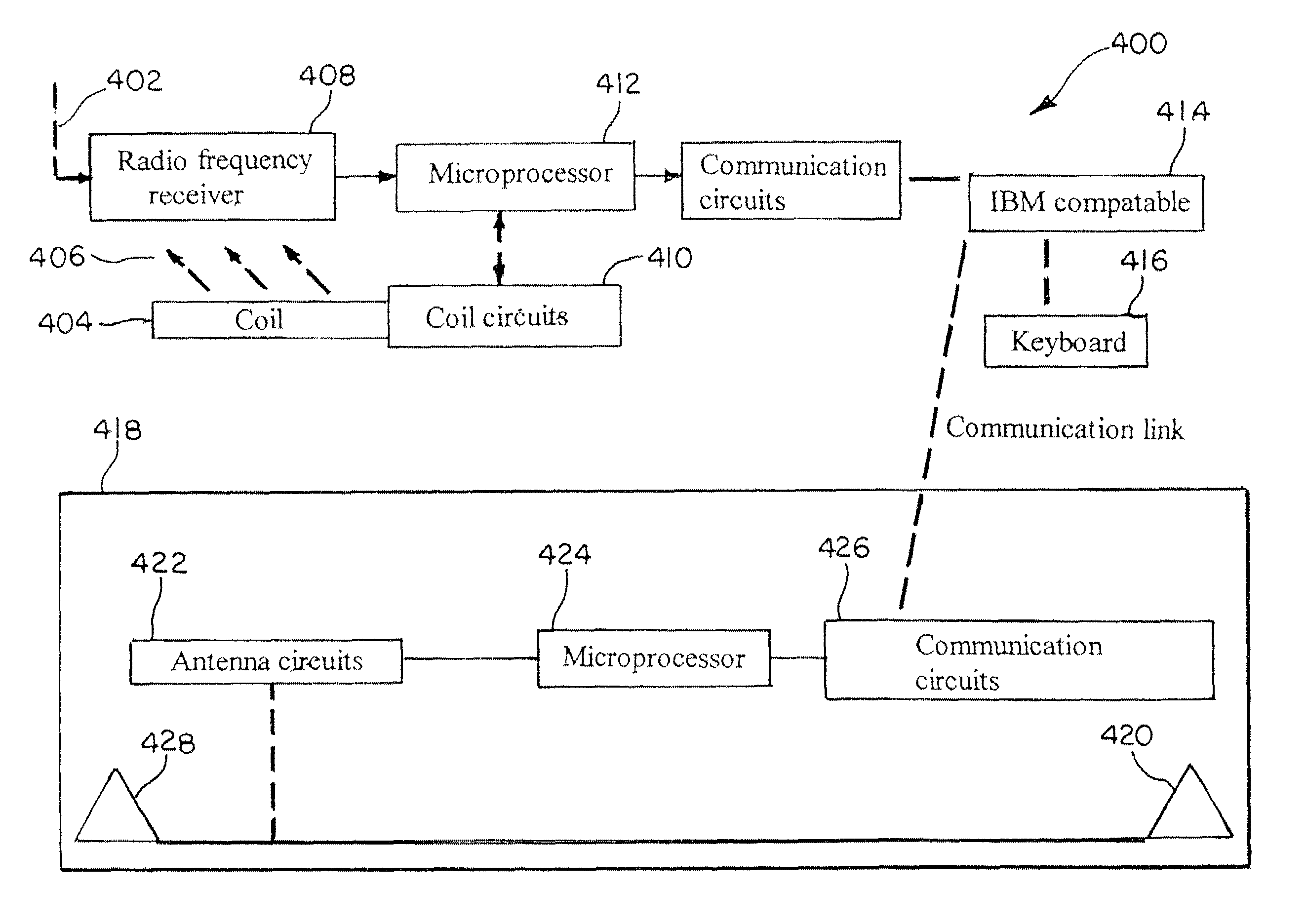
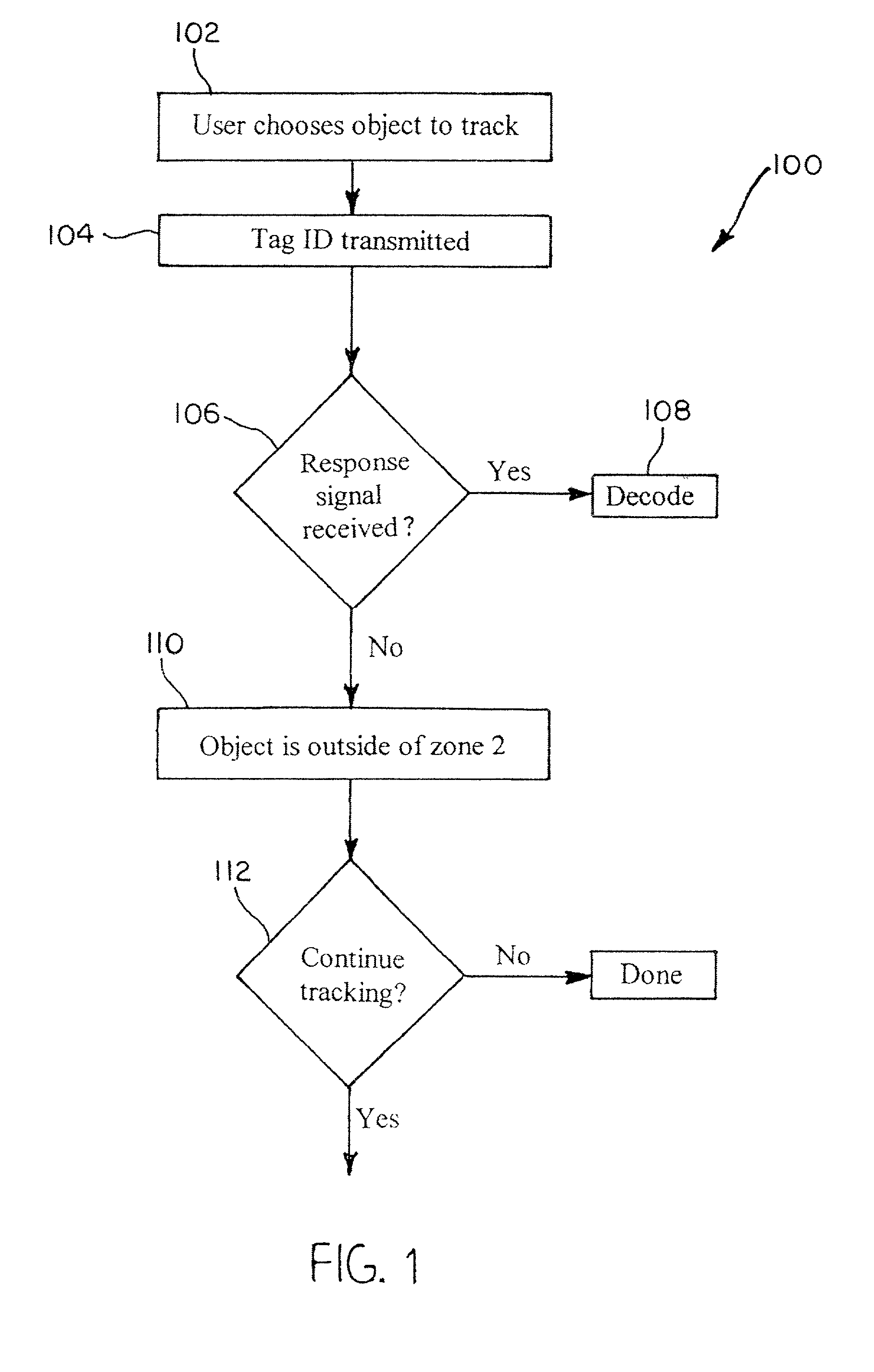
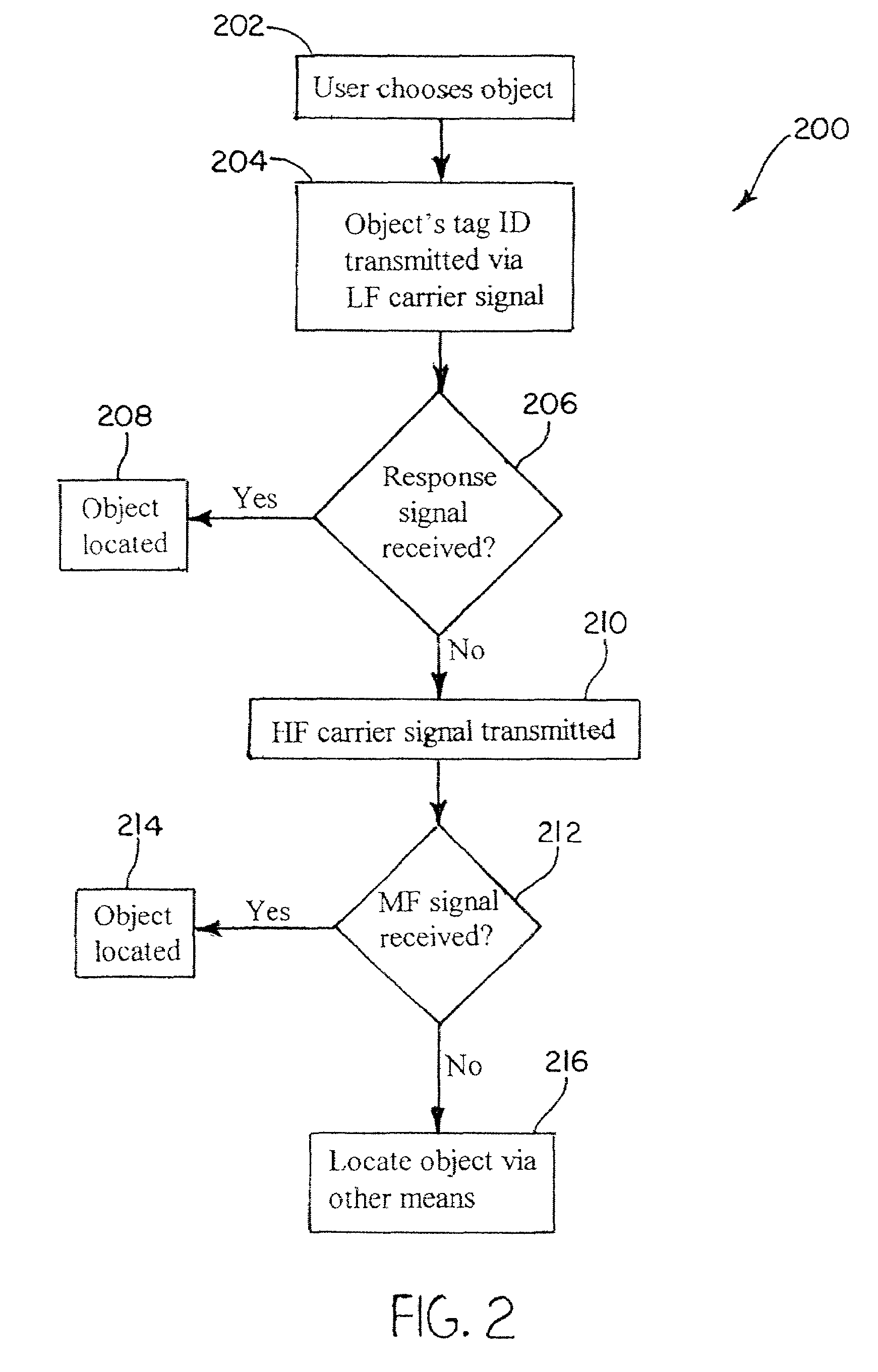
Methods and systems for tracking objects. Systems of the present invention include a base station capable of transmitting and receiving signals at multiple frequencies. Each object to be tracked has attached to it what for the purpose of the present specification is referred to as an electronic tag (“E-Tag”). Each E-Tag can transmit signals that can be received and interpreted by the base station and each E-Tag can receive and interpret signals transmitted by the base station. The transmitting (and receiving) of signals between the base station and an E-Tag allows the base station to track the E-Tag, and therefore, track the object to which the E-Tag is attached. Methods utilized to track objects in accordance with the present invention vary depending on the distance of the object from a base station (“range” of the object). The distances from the base station are divided into zones with the lowest numbered zone (that is, zone 1) being closest to the base station and the highest numbered zone being farthest away from the base station. Typically, embodiments of the present invention are adapted to track objects in four different zones. LF and HF communications can be utilized to track objects in zones 1 and 2, triangulation can be used to track objects in zone 3, and global location techniques can be utilized to track objects in zone 4. In a typical application, zone 1 covers a storage enclosure such as a desk drawer, a file cabinet, or a safe for example. Zone 2 frequently covers a room or a building, zone 3 covers up to the maximum distance for which triangulation technology can be used to track an object, and zone 4 covers the maximum distance for which global location techniques can be used to track an object.
Owner:FORWARD THINKING TRACKING LLC
Real-time information processing method in bus dynamic dispatching
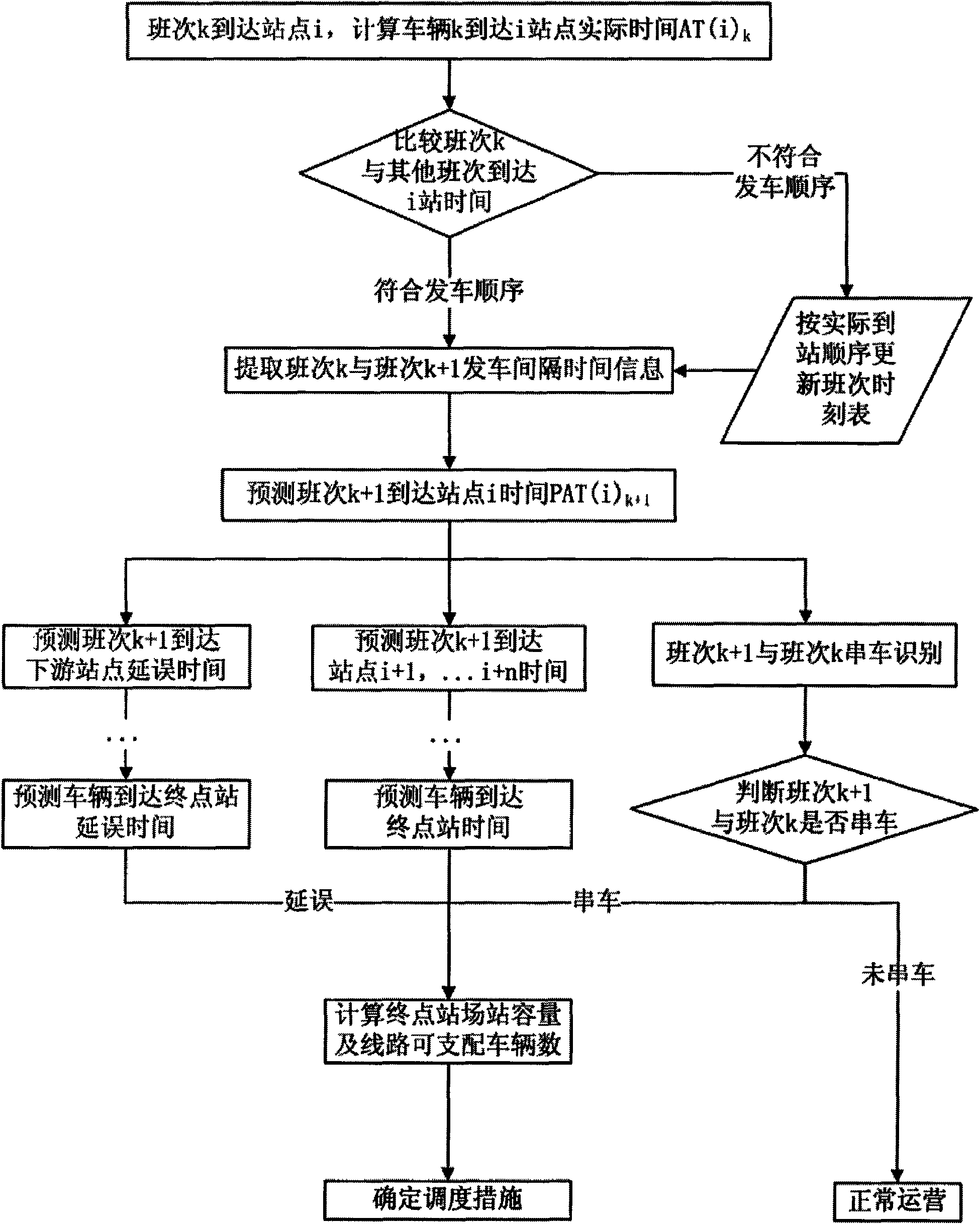
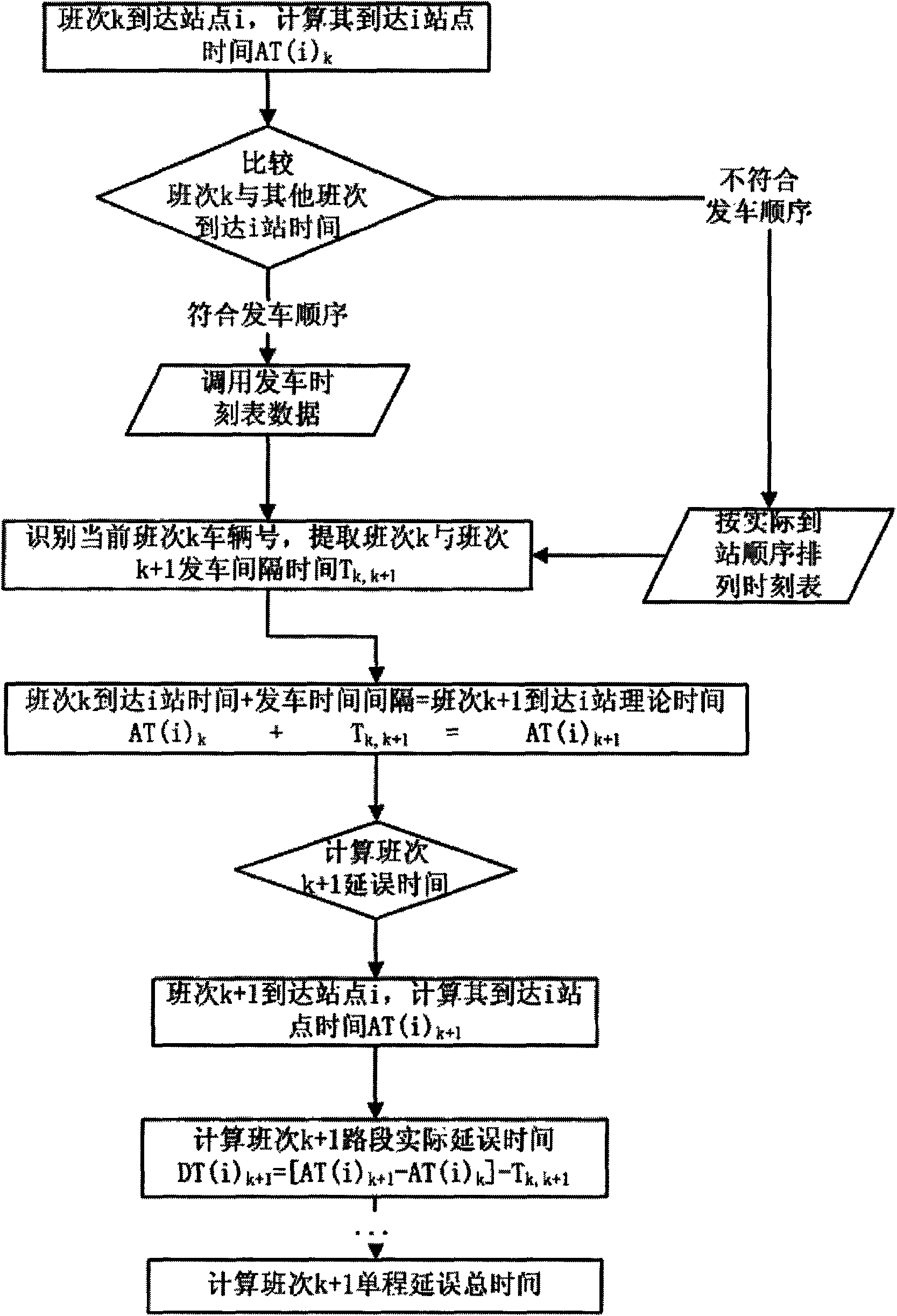
InactiveCN101615340AImprove dynamic scheduling efficiencyDetection of traffic movementTime informationReal time information processing
The invention relates to a real-time information processing method in bus dynamic dispatching, which is specially used for dynamic dispatching of bus single or area multi-line of the ground. The real-time information comprises vehicle positioning information and passenger flow information; acquiring equipment comprises a GPS vehicle-mounted terminal and an IC card POS machine terminal; a processing method comprises the following steps: acquiring and transmitting real-time information; processing and preprocessing real-time information; carrying out secondary processing to the acquired data; taking relevant technologies of ITS and the computer of the bus vehicle positioning technology, the bus passenger flow acquisition technology, the network communication technology, WebGIS and the like as support, acquiring real-time information of ground bus line operation, carrying out processing on the real-time information, calculating operating state of vehicle delay time, section passenger flow, load factor and the like, and carrying out vehicle bunching recognition; and using a Kalman filtering model to predict the arrival time and delay time of the bus vehicle, and providing decision basis for dynamic dispatching measures.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
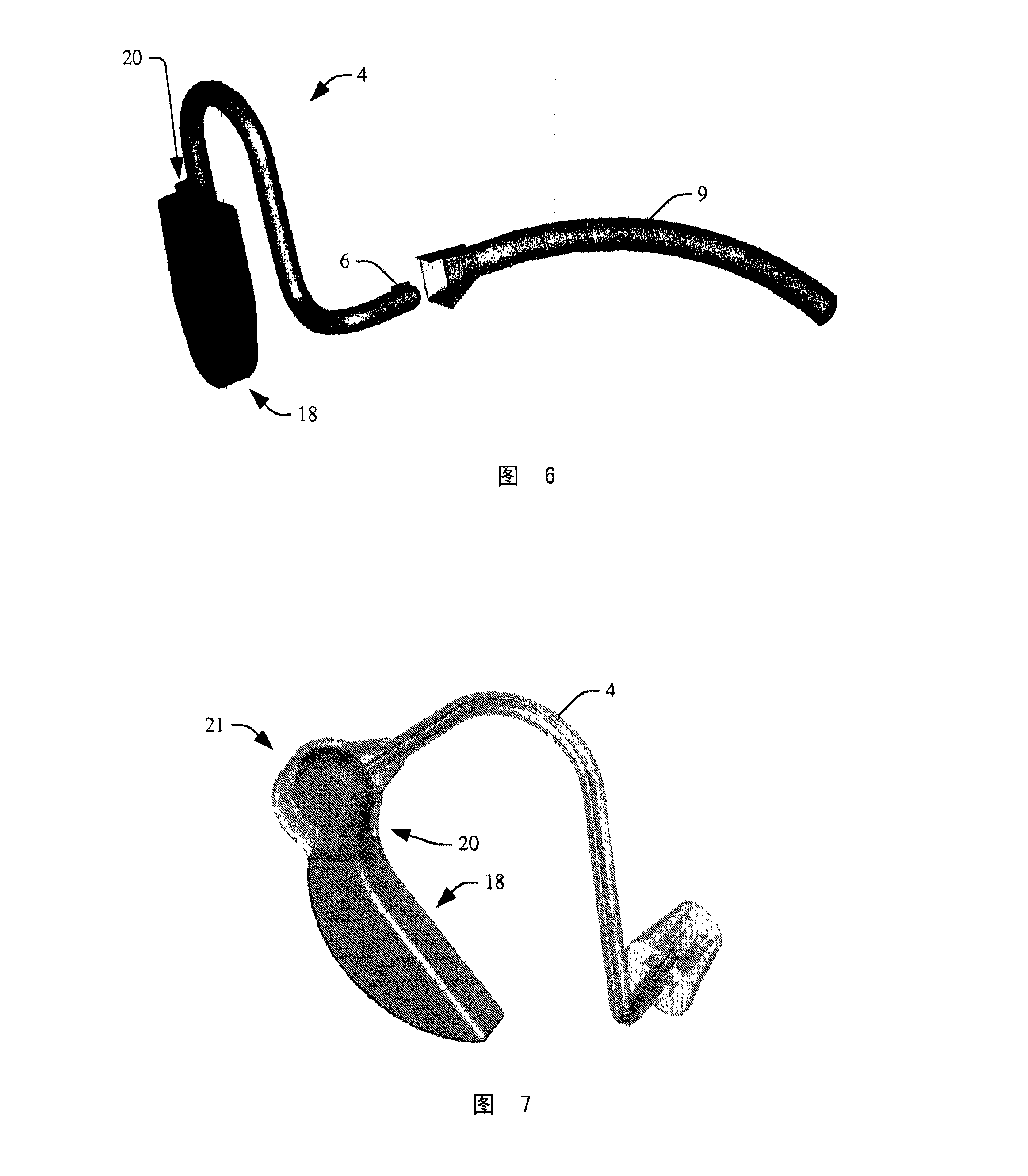
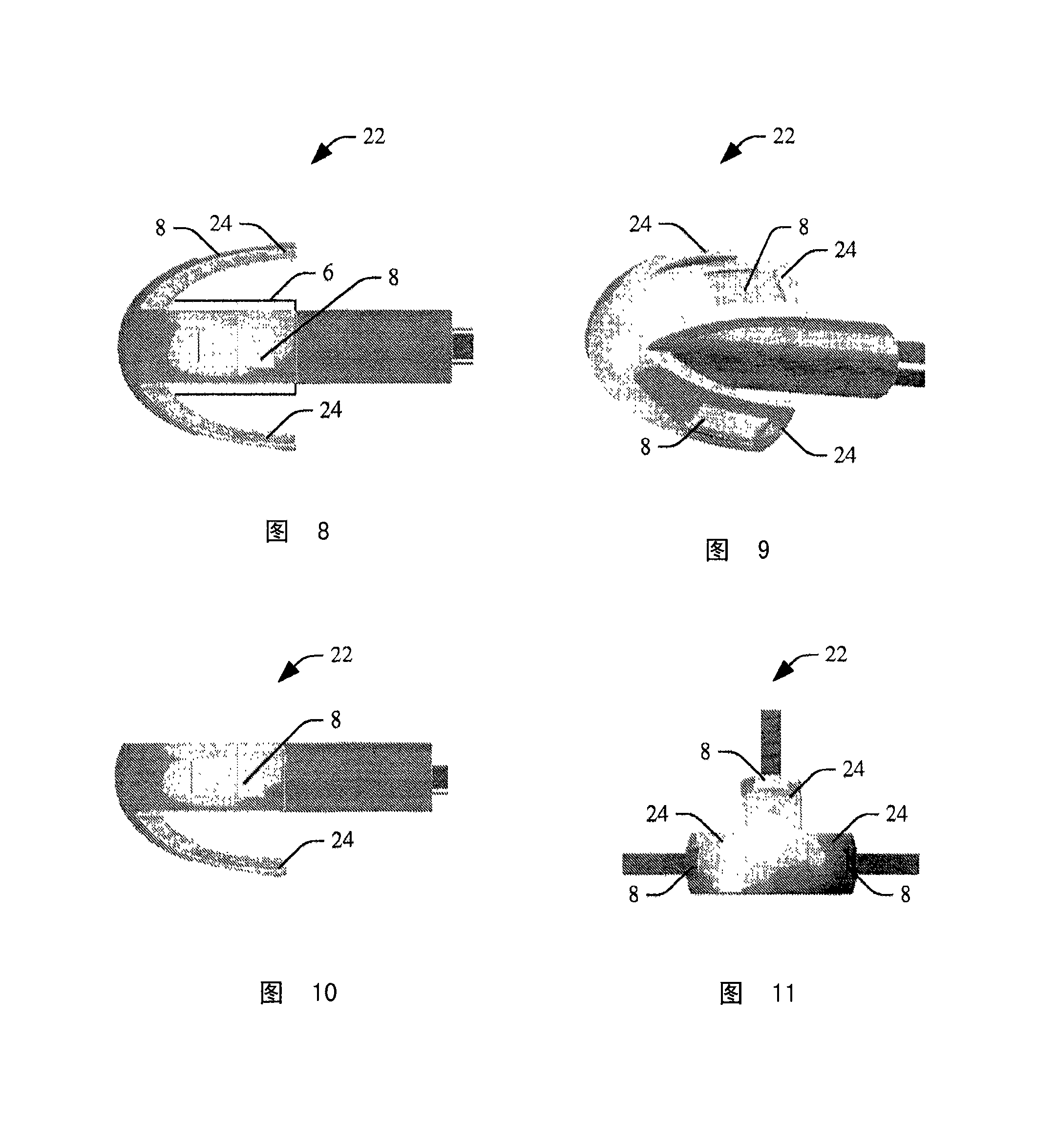
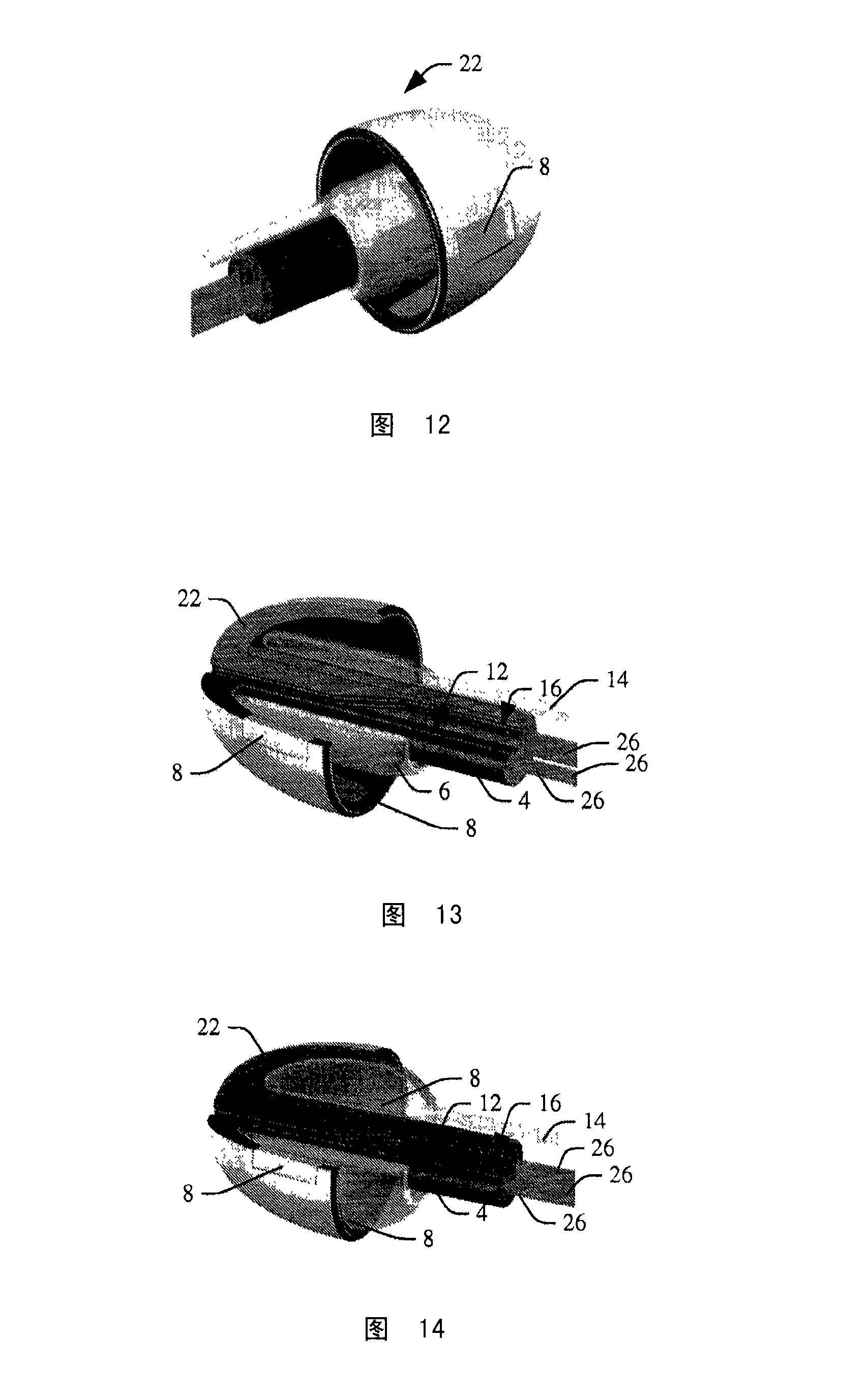
Sizing and positioning technology for an in-the-ear multi-measurement sensor to enable NIBP calculation
InactiveCN101212927ANon-invasive blood pressure measurementContinuous non-invasive measurementEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterMeasurement deviceProximate
An in-the-ear (ITE) physiological measurement device (2) includes a structure (4) formed to be easily inserted into ear canals of various shapes and sizes. An inflatable balloon (6) surrounds the end of the structure (4) to be placed in the ear. Optionally, a mushroom-shaped tip (22) is attached to the end of the structure (4) and carries a plurality of sensors (8). Inflation of the balloon (6) radially expands the tip (22) to place the sensor (8) adjacent to the vascular tissue in the ear canal. Once in place, one or more sensors (8) sense physiological signals from vascular tissue and bone structures.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
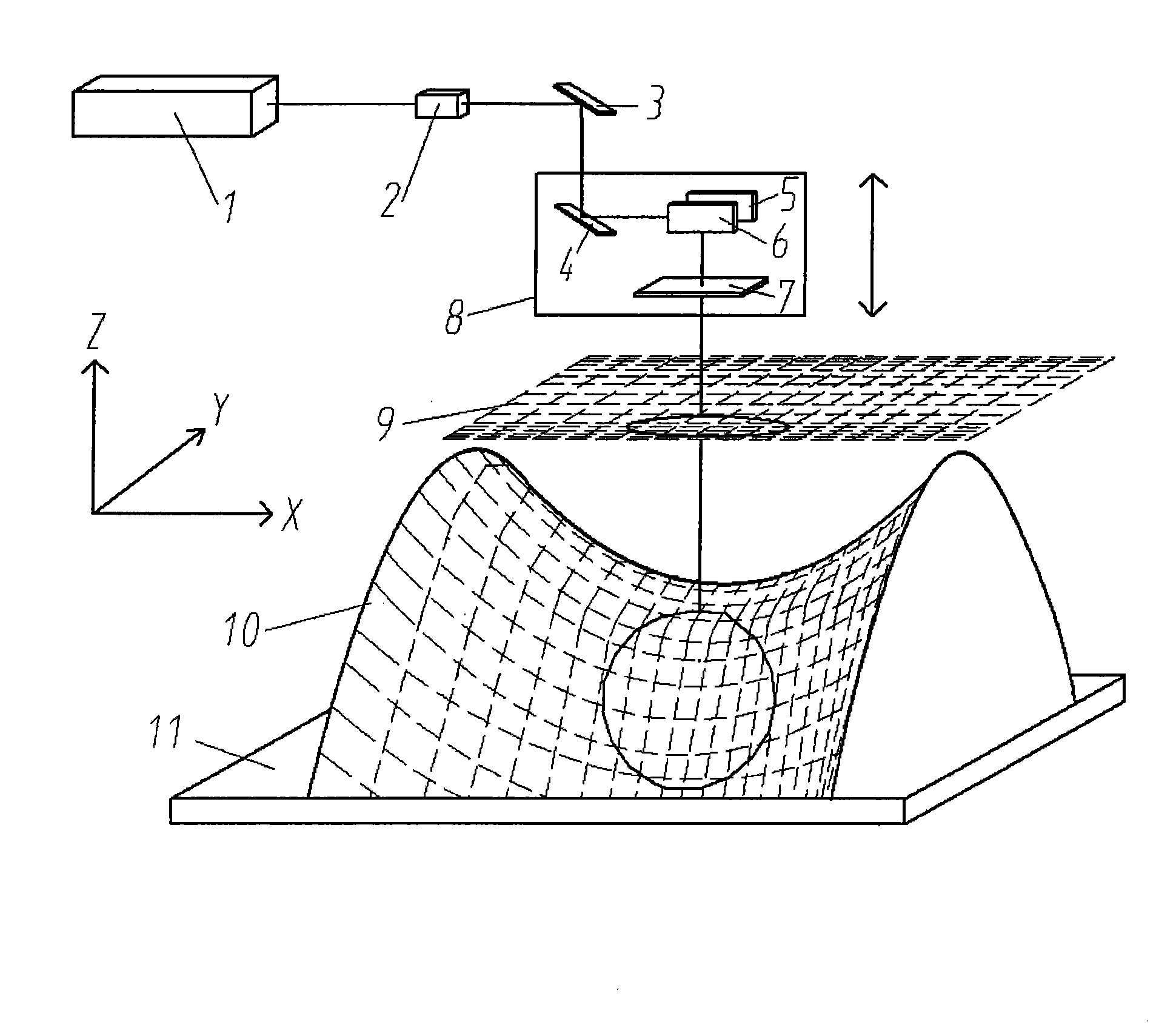
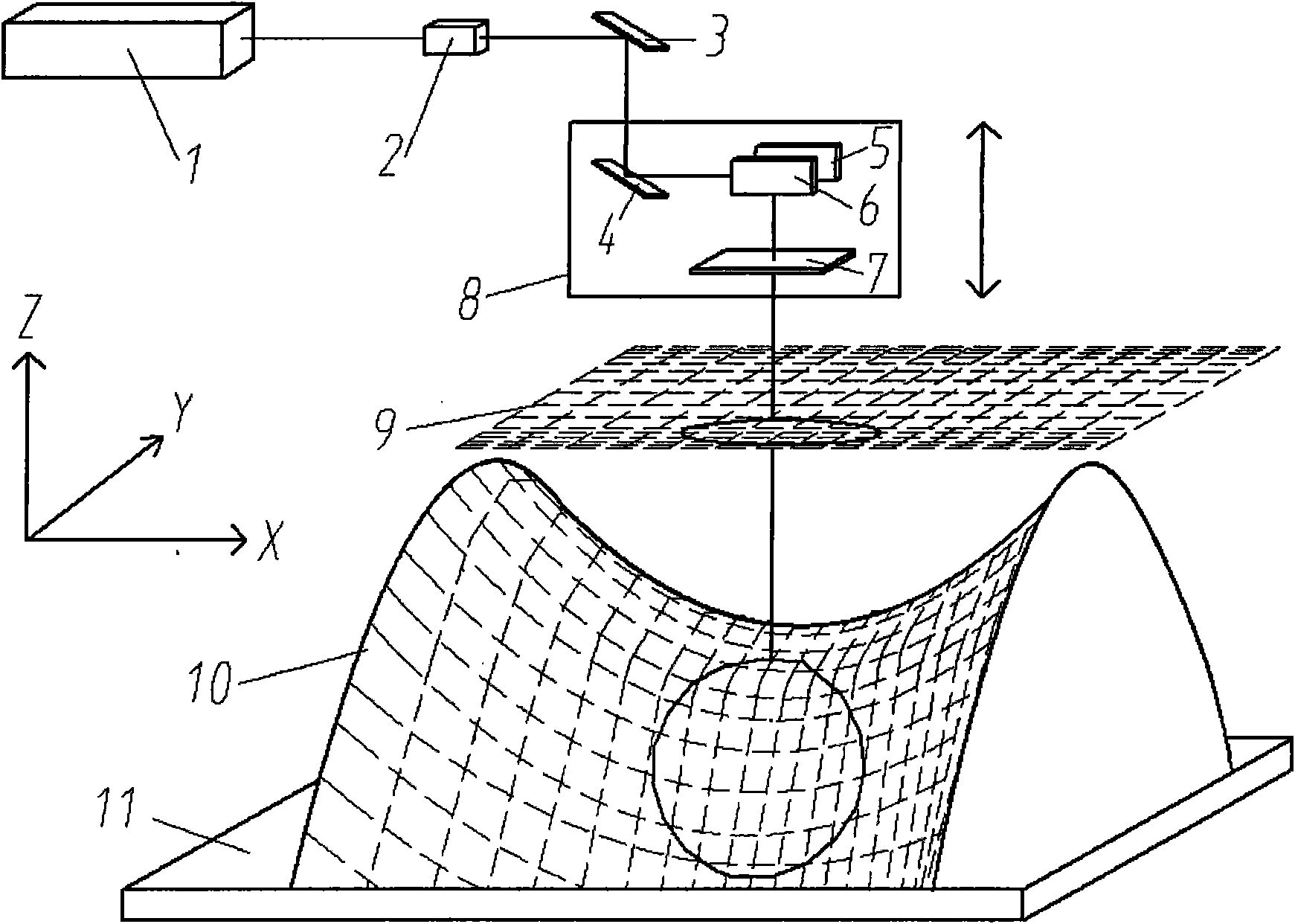
Method for projection-type laser etching on free curved surface
ActiveCN101786200AImprove efficiencySimple processLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingLaser processing
The invention discloses a method for projection-type laser etching on a free curved surface. By combining a laser galvanometer as well as a triaxial coordinate positioning technology and adopting the principles of partitioned parallel projection as well as height mapping, the invention directly conducts precise surface laser etching on the basis of a discrete point cloud model of a free curved surface part. The method has the characteristic that the laser etching properties such as the shape and size of a spot and the energy distribution remain unchanged within the focal depth range of a focusing lens, so that the free curved surface is converted into a plurality of plane subblocks for processing, and the high-precision processing efficiency of the free curved surface can be improved even by adopting the existing laser etching technology. The diameter of the focusing spot of a laser beam can reach tens of microns and is much smaller than the size of the part processed by a traditional knife tool; and the processing precision of nearly 10 microns can be realized by controlling the laser energy property. Under the premise of meeting the demands for high precision and high efficiency of pattern etching on the free curved surface, the method can realize high reliability and high flexibility in the processing of the free curved surface.
Owner:武汉飞能达激光技术有限公司
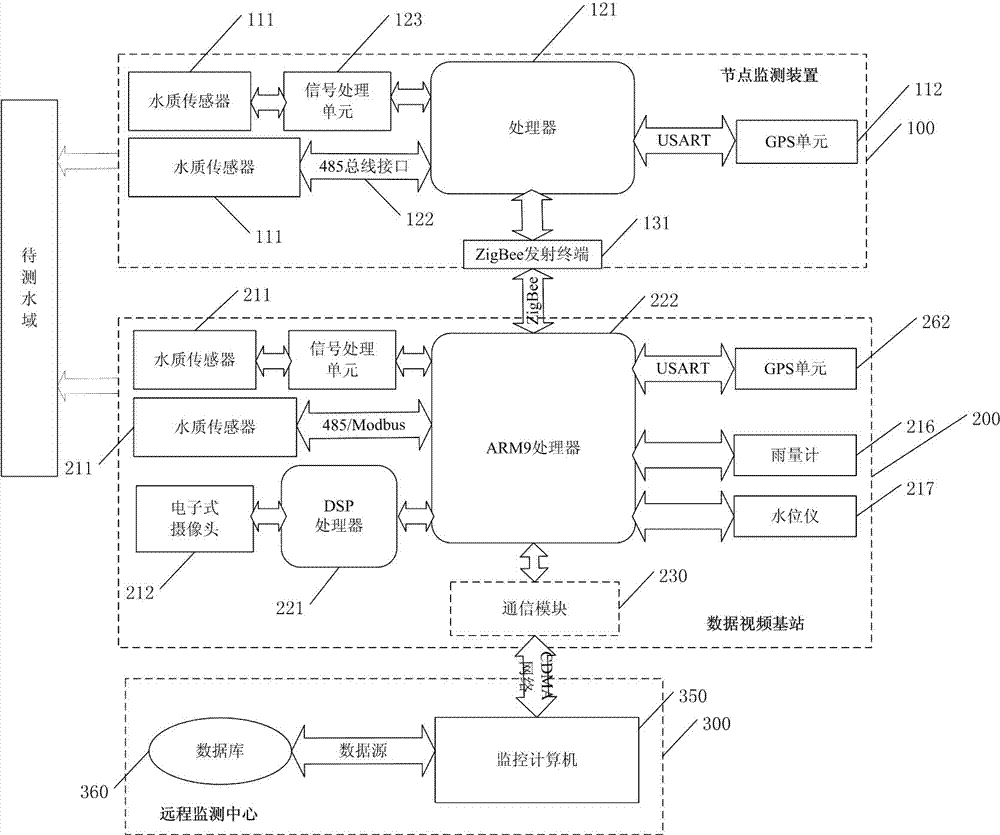
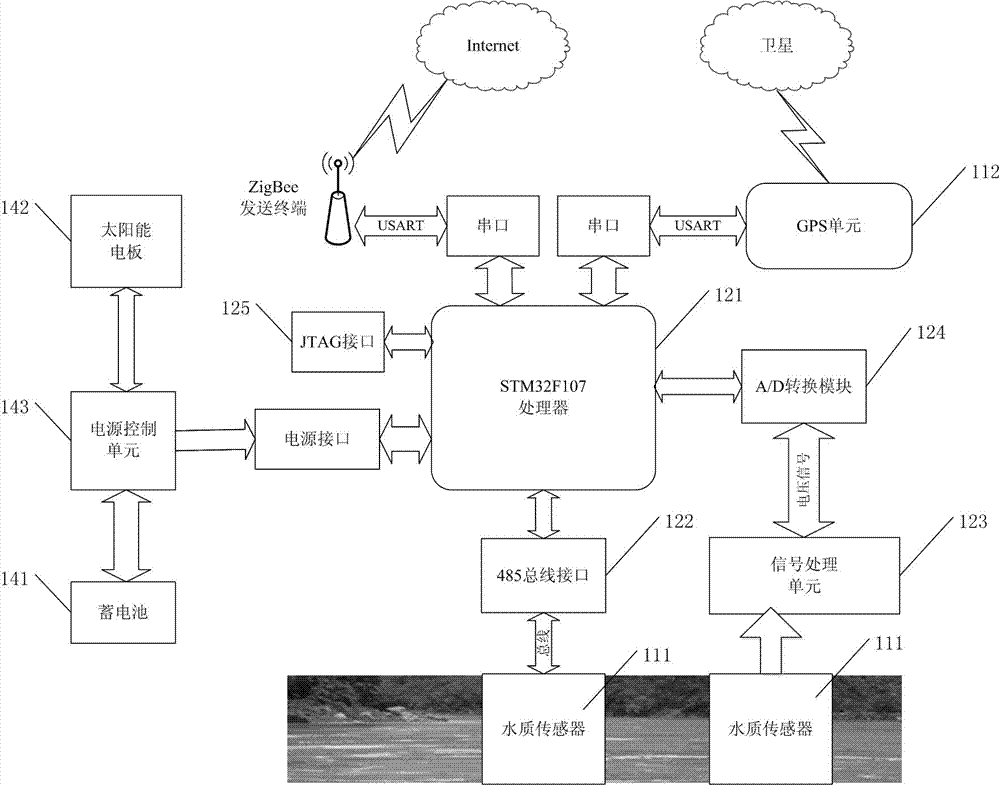
Online lake water quality monitoring system based on internet of things
InactiveCN102890142AExpand the scope of the fieldComprehensive scopeTesting waterWater qualityThe Internet
The invention relates to the fields of applications of the internet of things technology, the wireless sensor network technology, the global positioning system (GPS) positioning technology and the GIS electronic map technology, and discloses an online lake water quality monitoring system based on internet of things. The online lake water quality monitoring system comprises a node monitoring device, a data video base station and a remote monitoring center; the node monitoring device is arranged in a lake to be monitored, and is used for monitoring the lake water quality and transmitting the monitoring data obtained from the monitoring to the data video base station through an ZigBee network; the data video data base is arranged in the lake to be monitored for transmitting the received monitoring data, and water quality information and video information which are collected by the data video base station are transmitted to the remote monitoring center through a mobile communicating network; the remote monitoring center comprises a GIS module, and is used for controlling navigation of the data video base station by remote means depending on water quality map information which is provided by the GIS module after receiving the monitoring data and all information, and for assisting to treat water quality of the lake to be monitored.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com