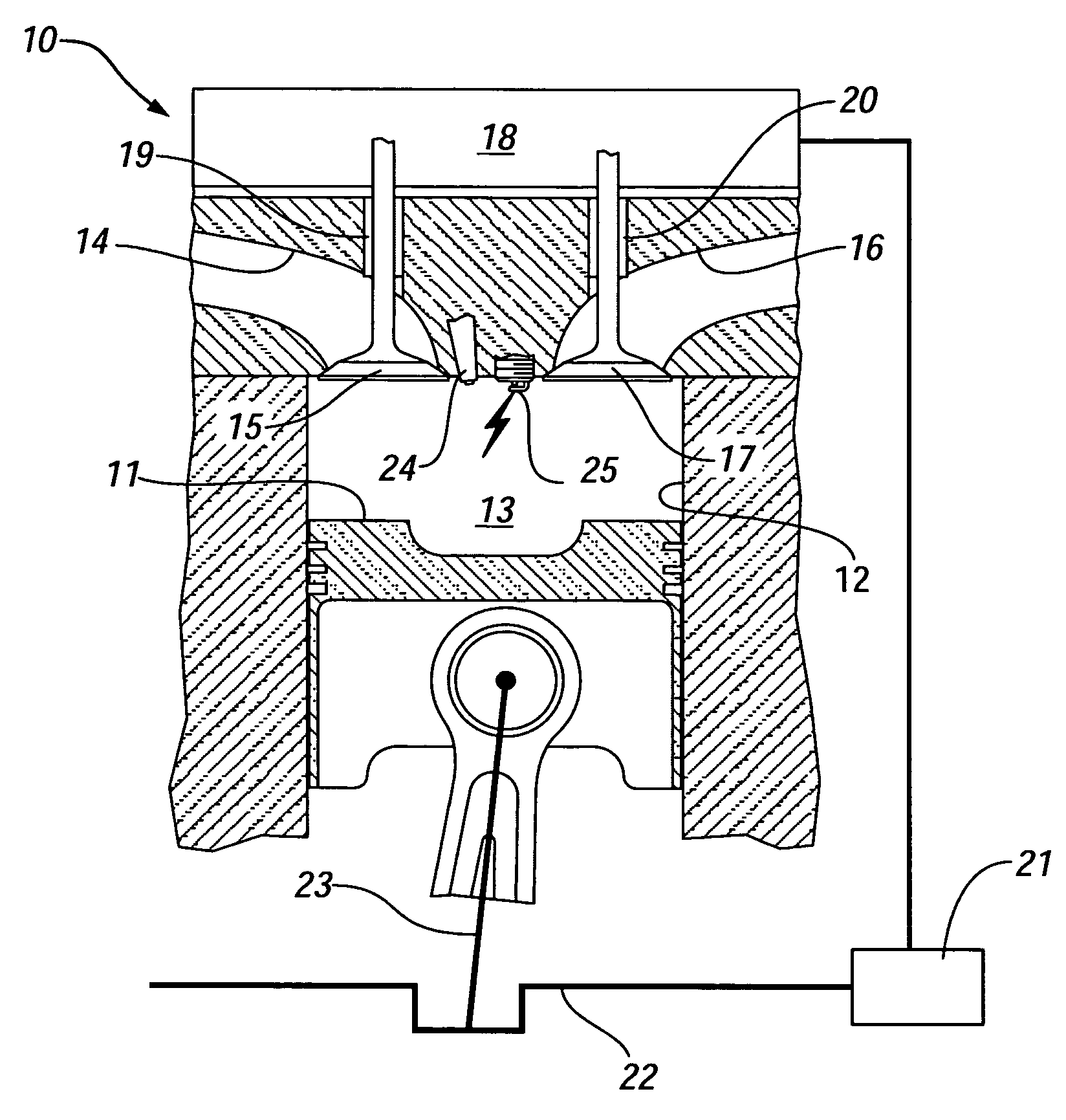
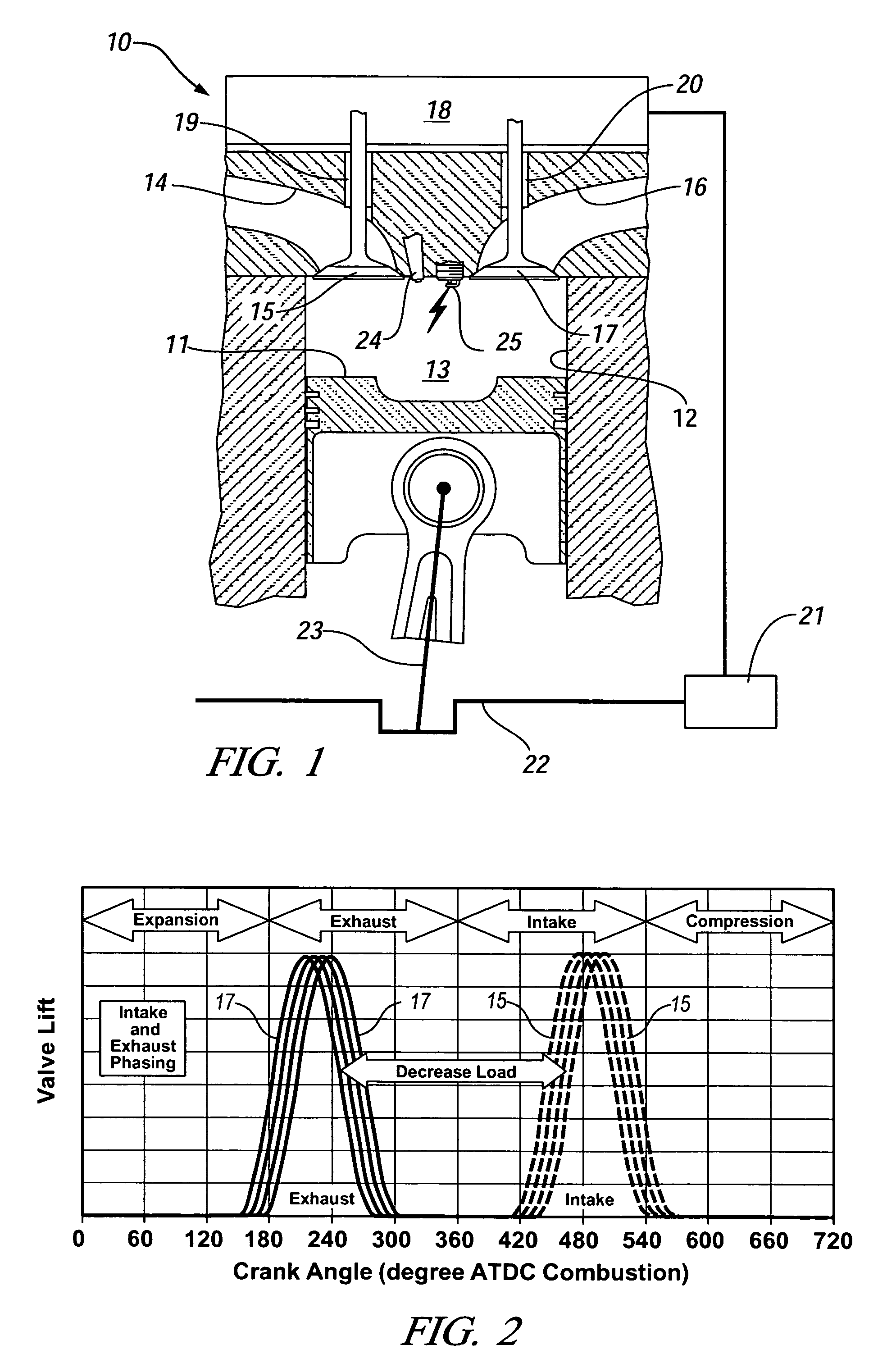
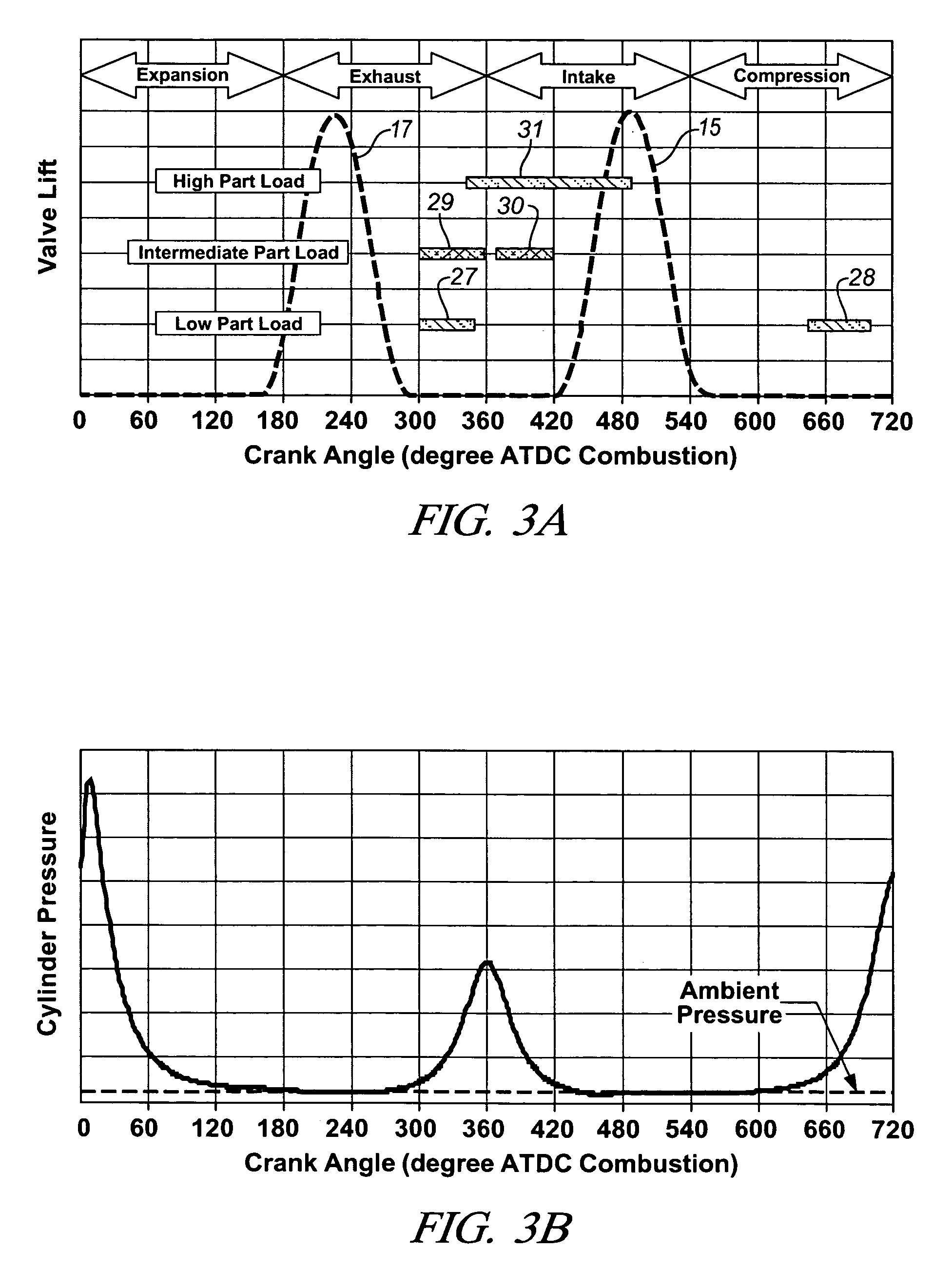
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2620 results about "Low load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
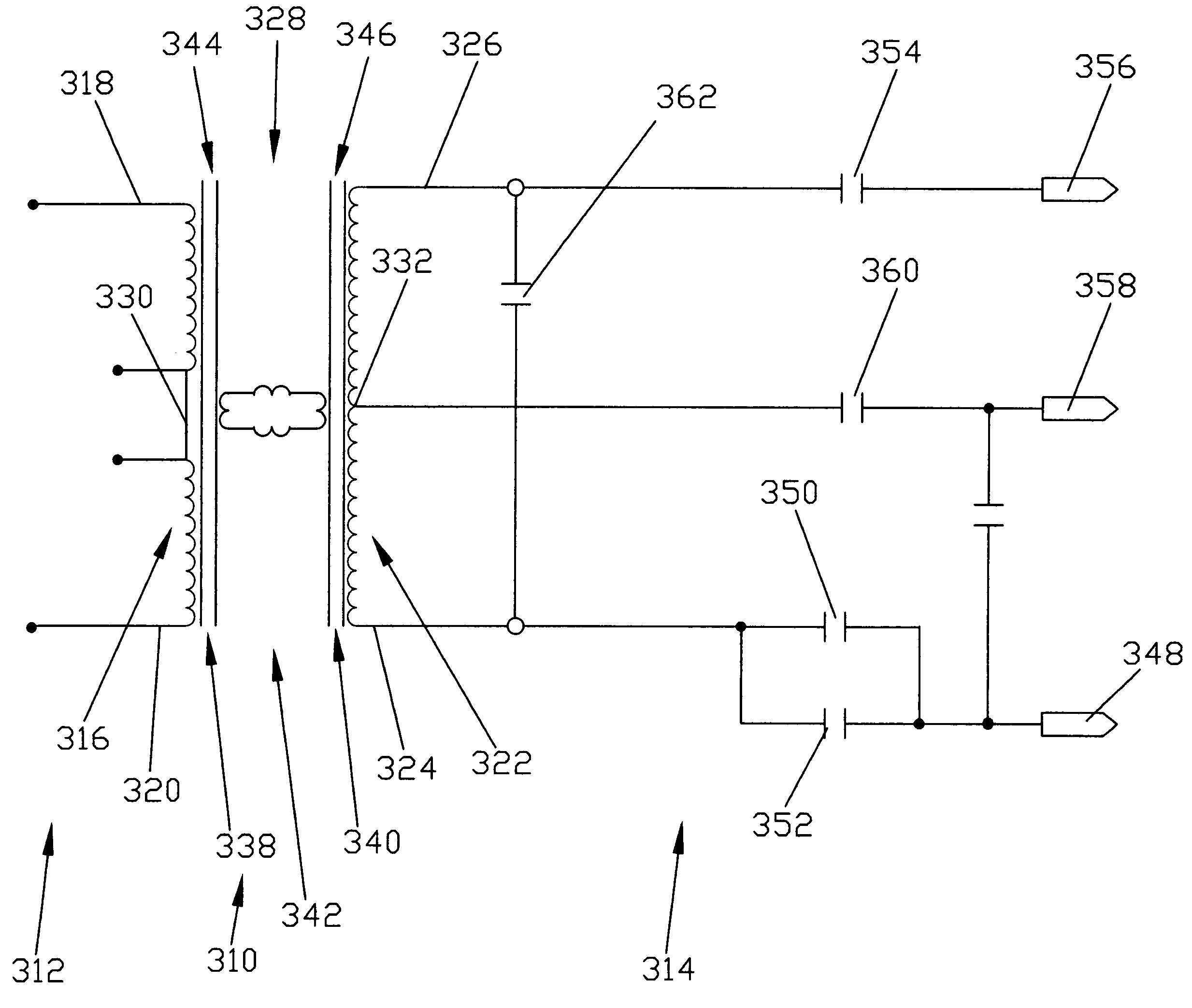
Planar transformer power supply
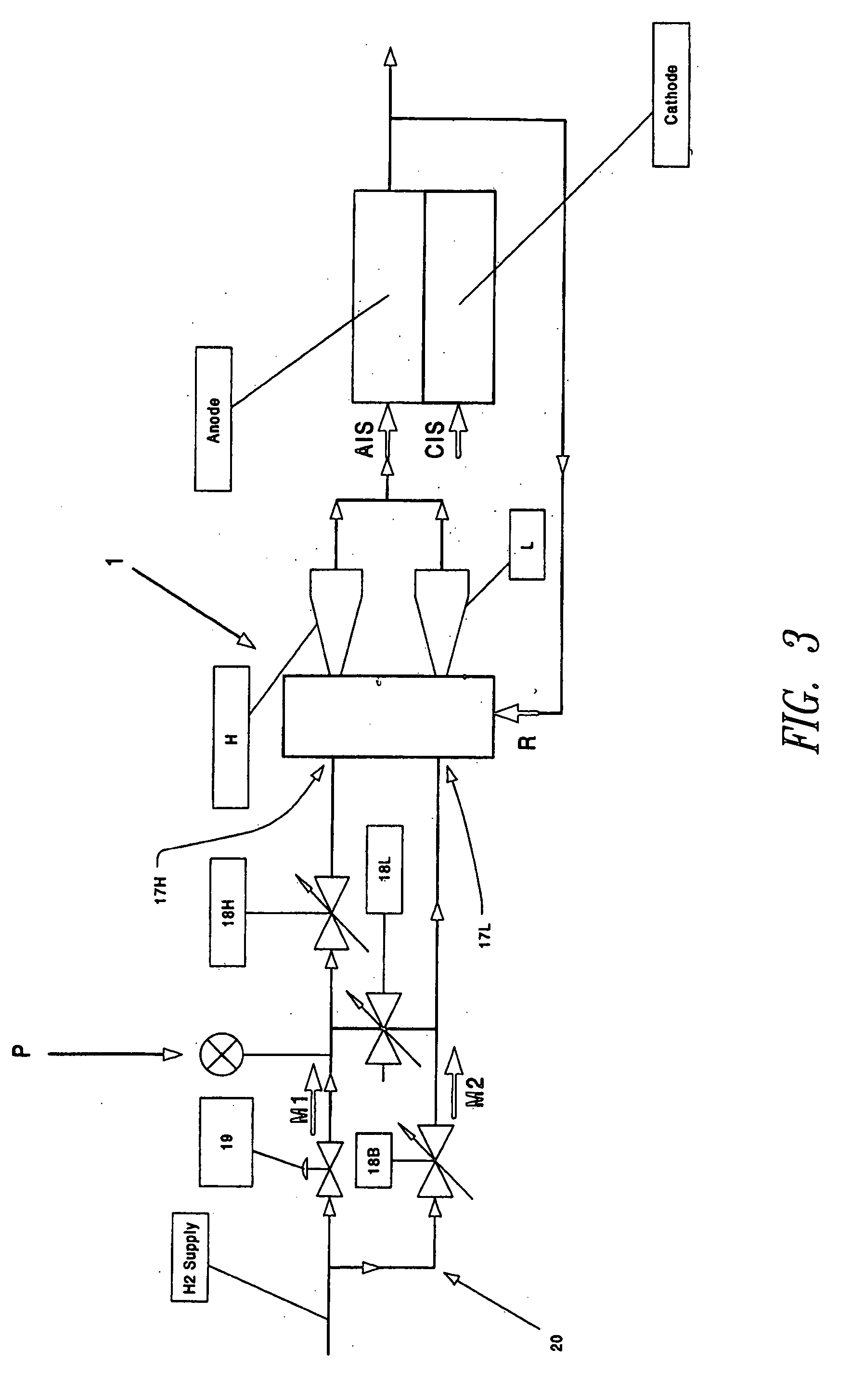
ActiveUS7502234B2Reduce negative impactMinimizing stray capacitanceDc-dc conversionConversion without intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceLow load
A planar transformer power supply for an electrosurgical device to minimize stray capacitance comprising a step down / step-up isolation transformer and circuitry to limit the effects of a short circuit in the output of the planar transformer power supply on the input to the planar transformer power supply to enhance power capacity at a low load impedance as low as from about 5 ohms to about 10 ohms and to operate at resonance at the output of the planar transformer power supply.
Owner:BOVIE MEDICAL CORP
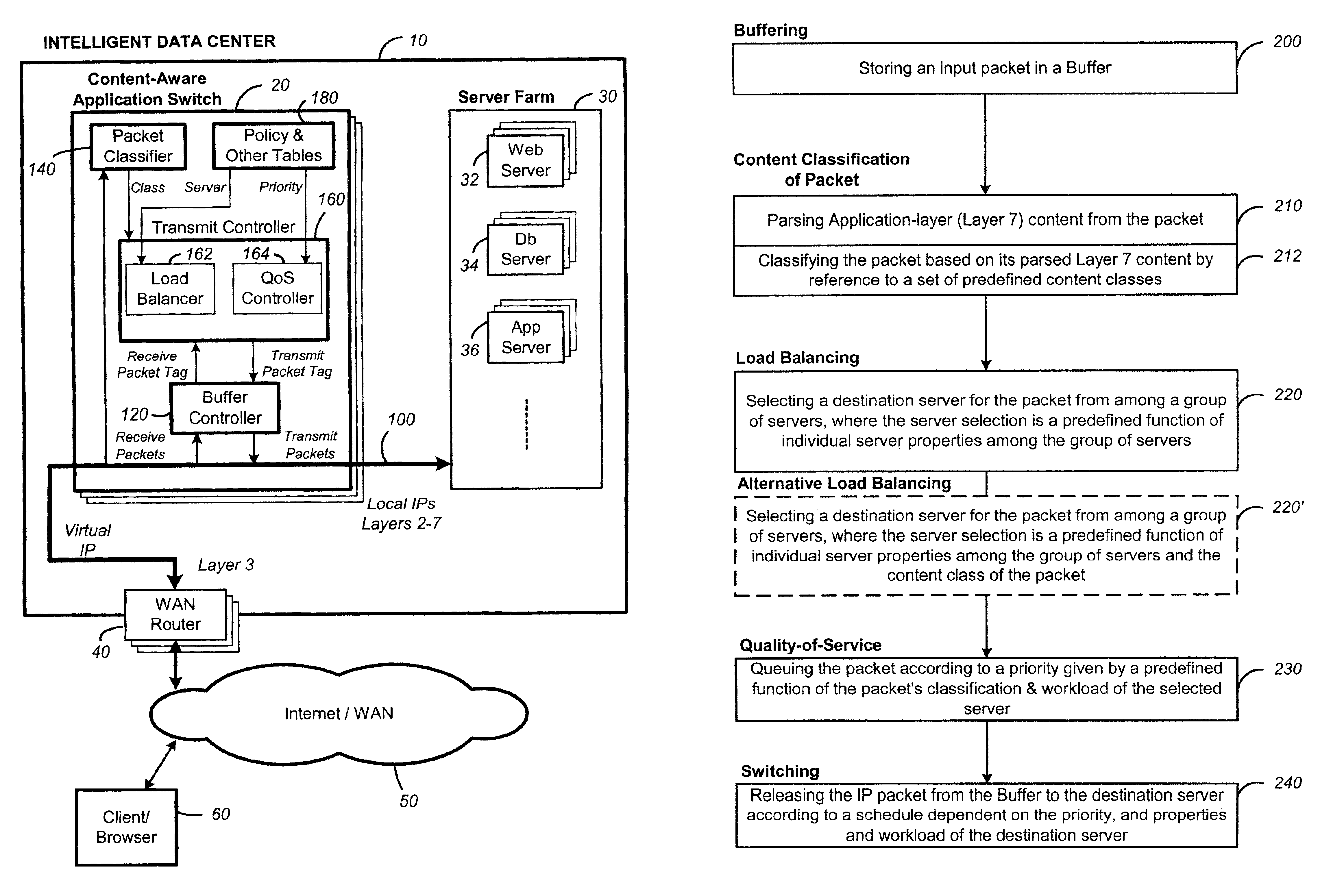
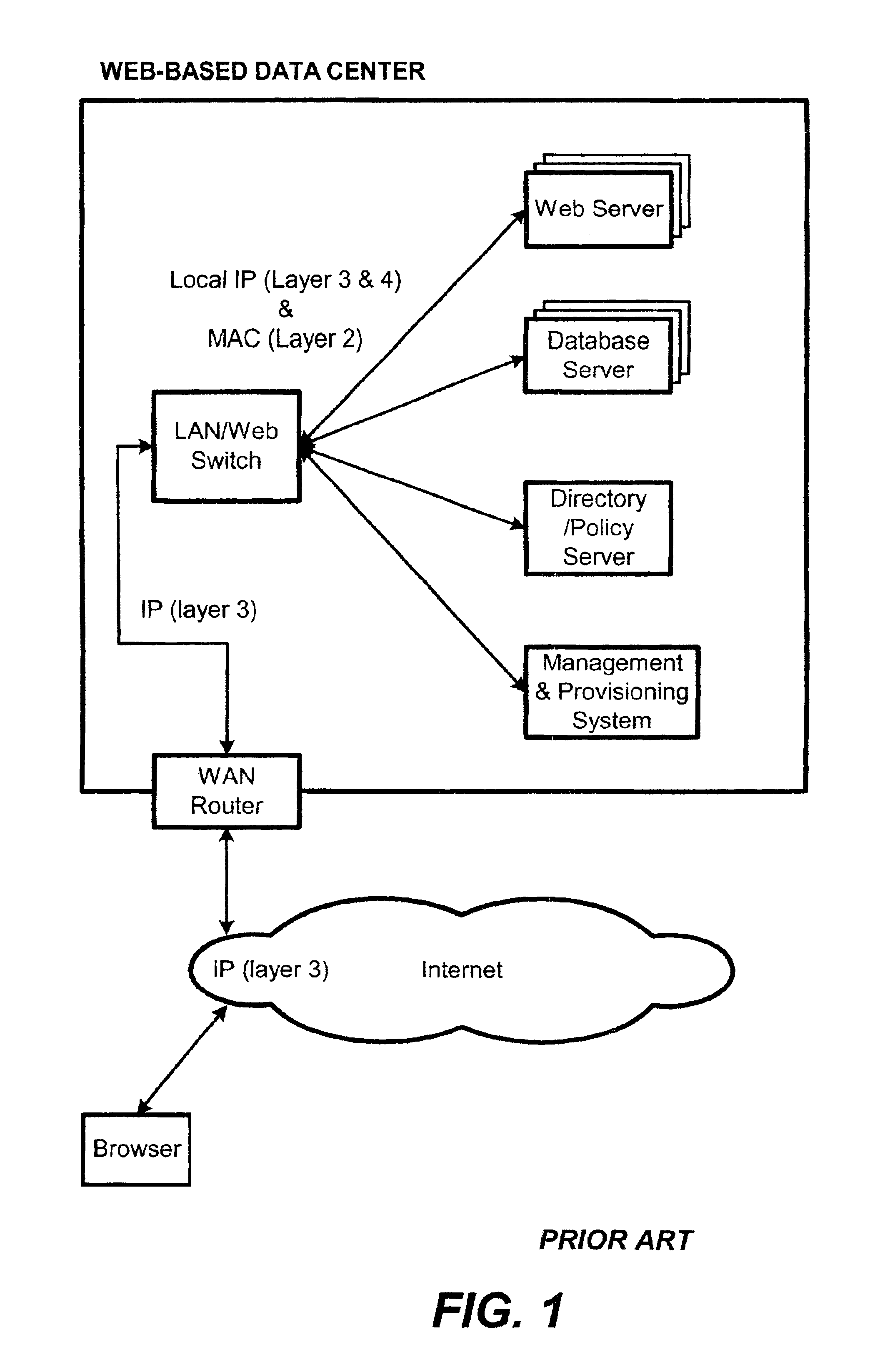
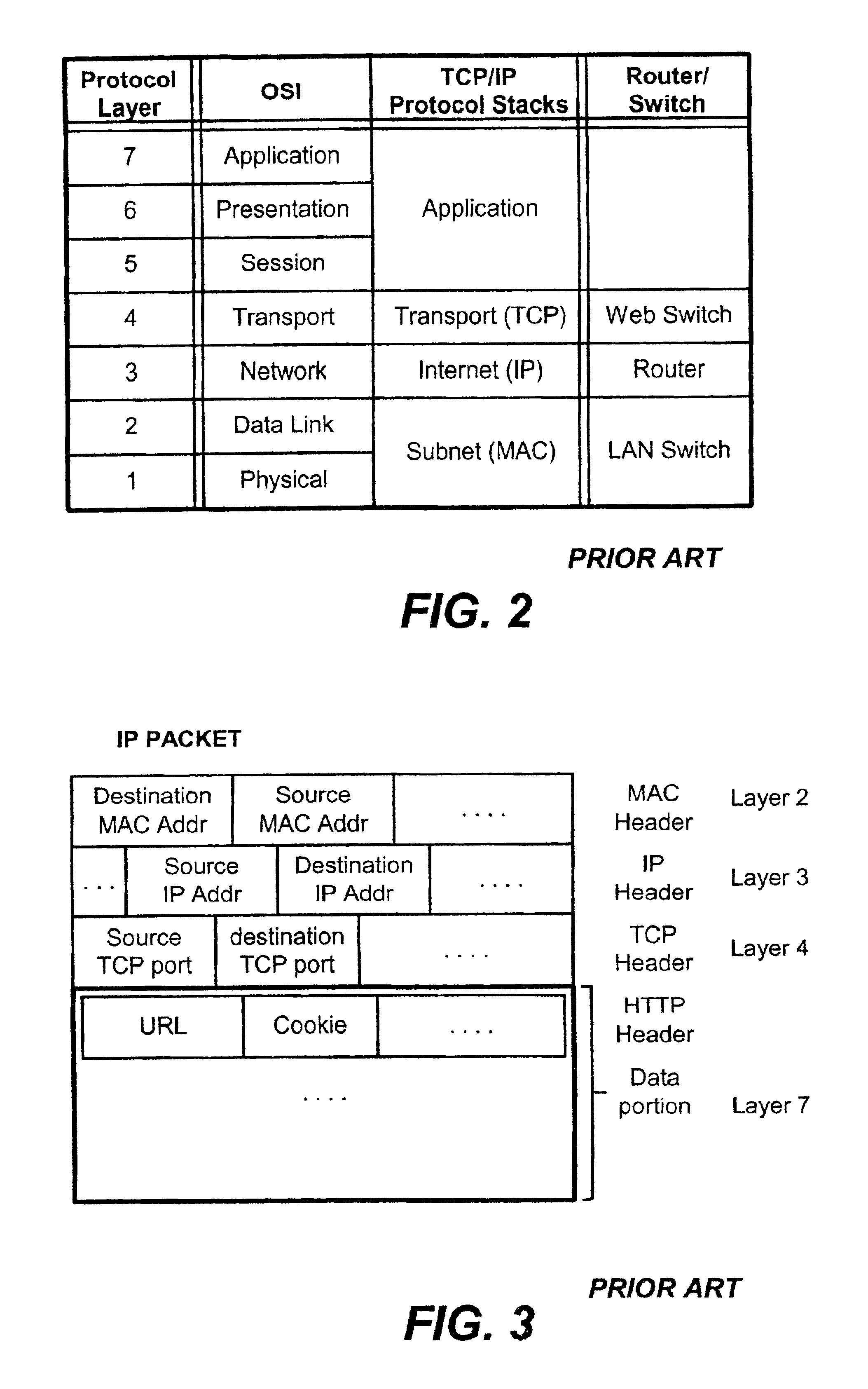
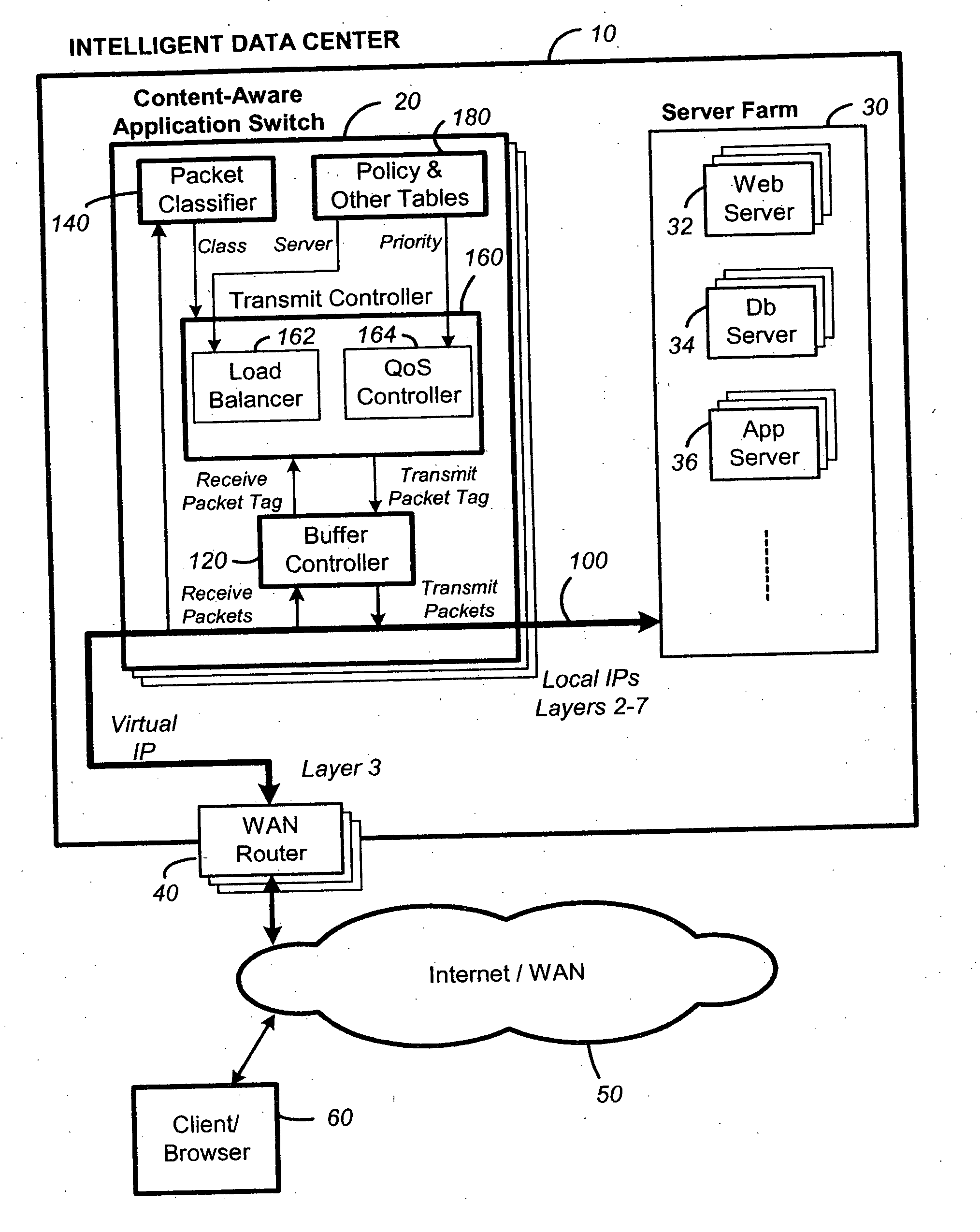
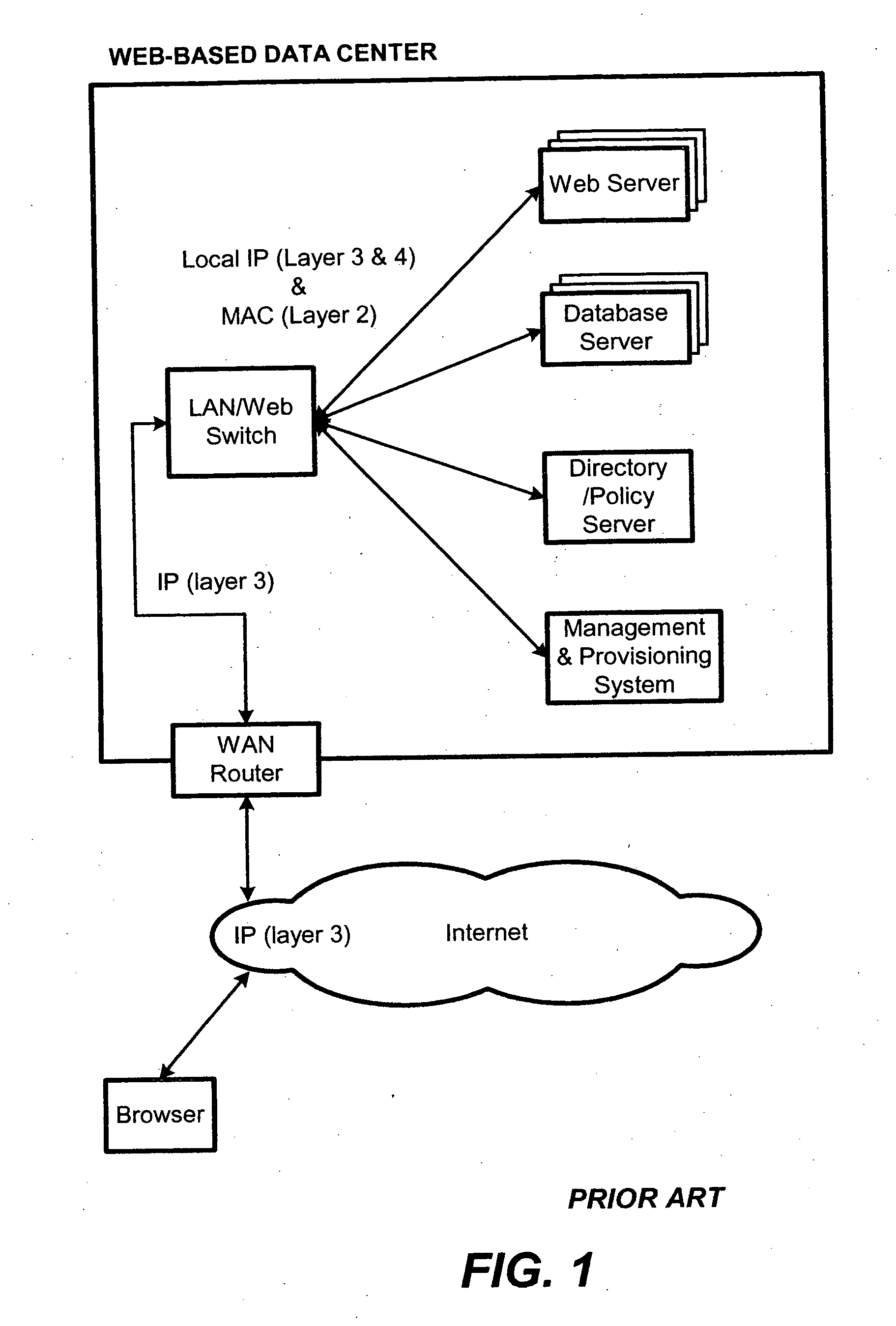
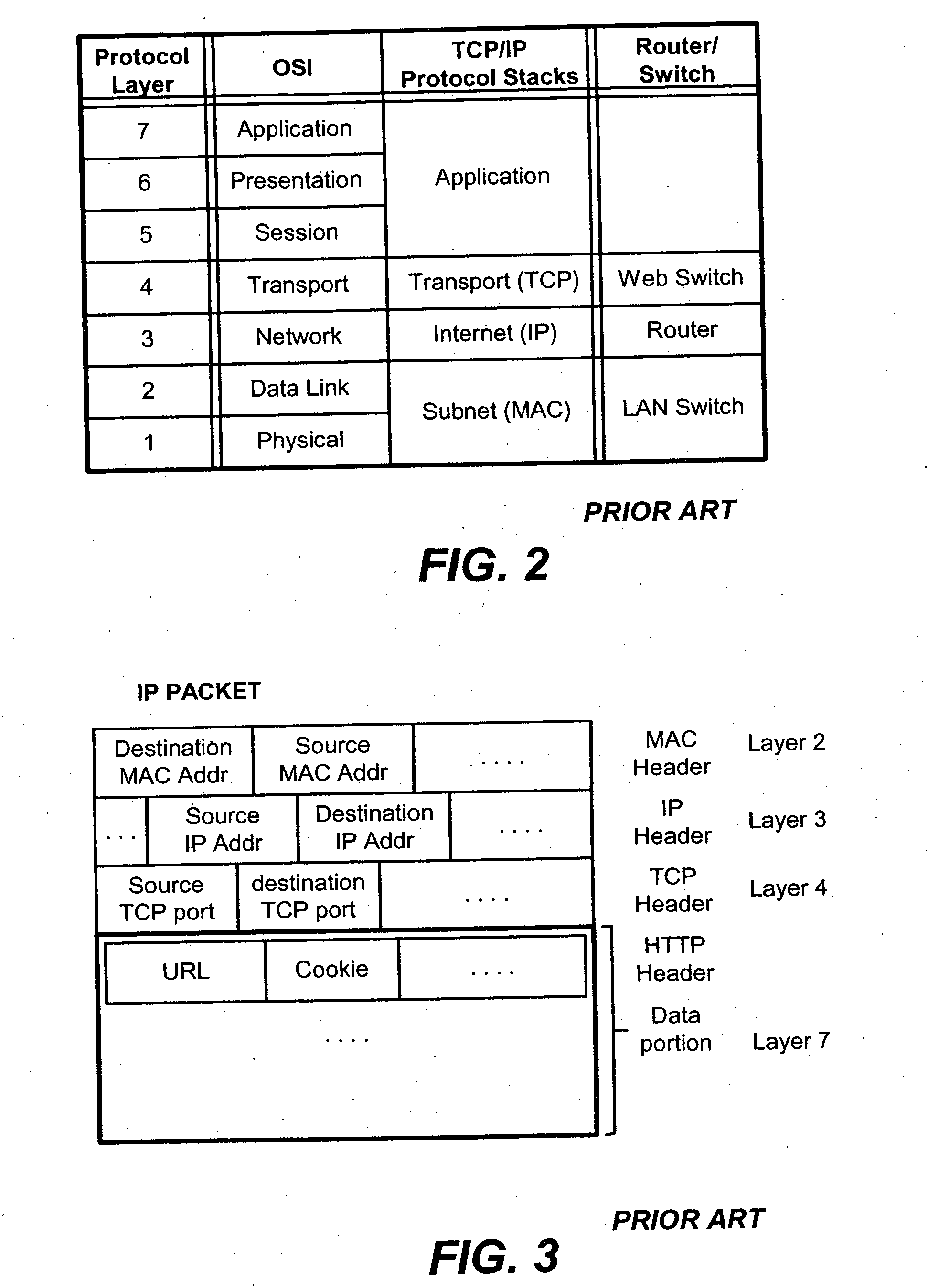
Content-aware application switch and methods thereof
InactiveUS6944678B2Easy to controlControl moreMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsQuality of serviceSlow-start
A content-aware application switch and methods thereof intelligently switch client packets to one server among a group of servers in a server farm. The switch uses Layer 7 or application content parsed from a packet to help select the server and to schedule the transmitting of the packet to the server. This enables refined load-balancing and Quality-of-Service control tailored to the application being switched. In another aspect of the invention, a slow-start server selection method assigned an initially boosted server load metric to a server newly added to the group of servers under load balancing. This alleviates the problem of the new server being swamped initially due to a very low load metric compared to that of others. In yet another aspect of the invention, a switching method dependent on Layer 7 content avoids delayed binding in a new TCP session. Layer 7 content is not available during the initial handshaking phase of a new TCP session. The method uses the Layer 7 content from a previous session as an estimate to help select the server and uses a default priority to scheduling the transmitting of the handshaking packets. Updated Layer 7 content available after the handshaking phase is then used to reset the priority for the transmit schedule and becomes available for use in load balancing of the next TCP session.
Owner:IBM CORP
Packet switch and method thereof dependent on application content
InactiveUS20060031374A1Easy to controlControl moreMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData packQuality of service
A content-aware application switch and methods thereof intelligently switch client packets to one server among a group of servers in a server farm. The switch uses Layer 7 or application content parsed from a packet to help select the server and to schedule the transmitting of the packet to the server. This enables refined load-balancing and Quality-of-Service control tailored to the application being switched. In another aspect of the invention, a slow-start server selection method assigned an initially boosted server load metric to a server newly added to the group of servers under load balancing. This alleviates the problem of the new server being swamped initially due to a very low load metric compared to that of others. In yet another aspect of the invention, a switching method dependent on Layer 7 content avoids delayed binding in a new TCP session. Layer 7 content is not available during the initial handshaking phase of a new TCP session. The method uses the Layer 7 content from a previous session as an estimate to help select the server and uses a default priority to scheduling the transmitting of the handshaking packets. Updated Layer 7 content available after the handshaking phase is then used to reset the priority for the transmit schedule and becomes available for use in load balancing of the next TCP session.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
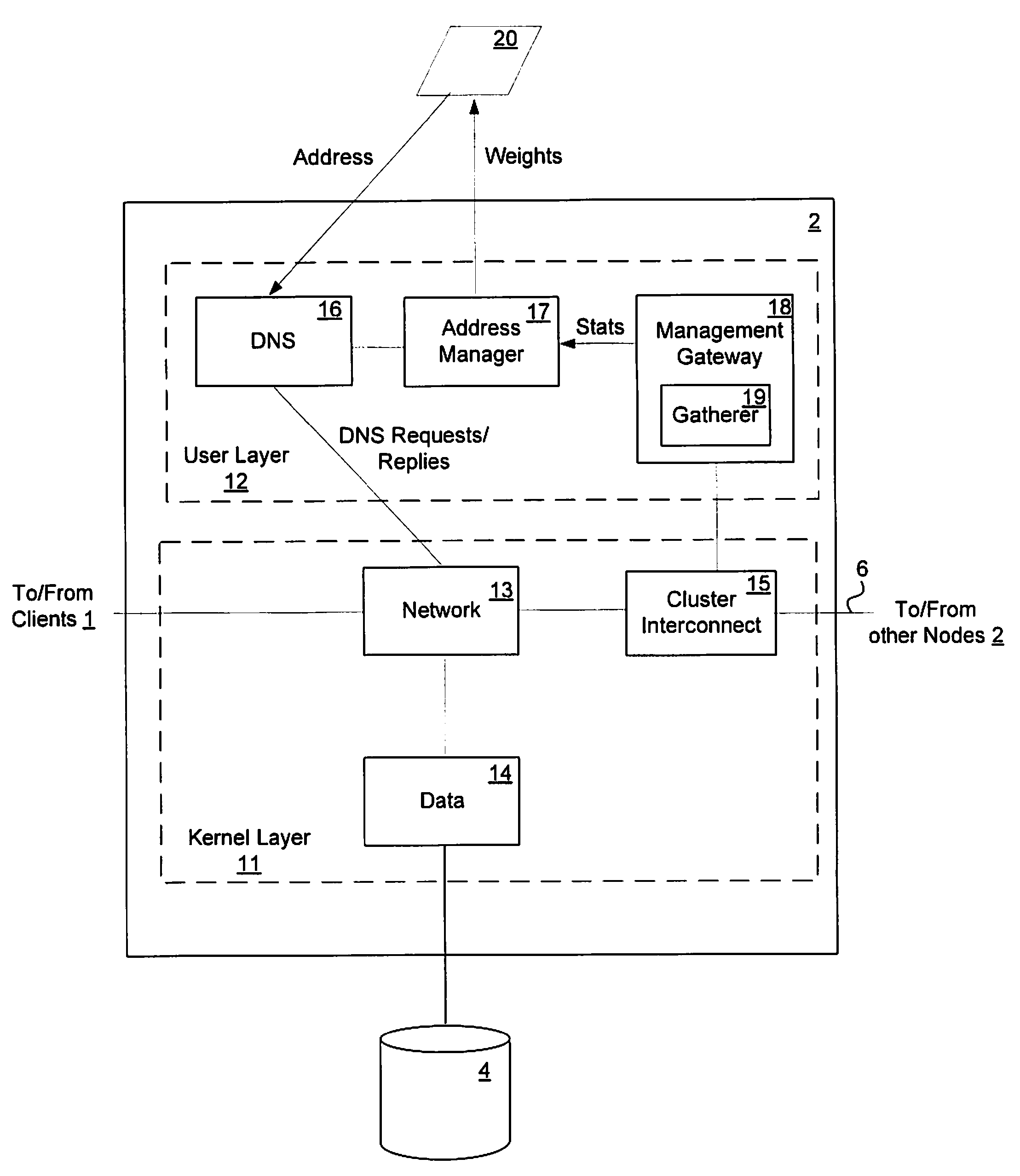
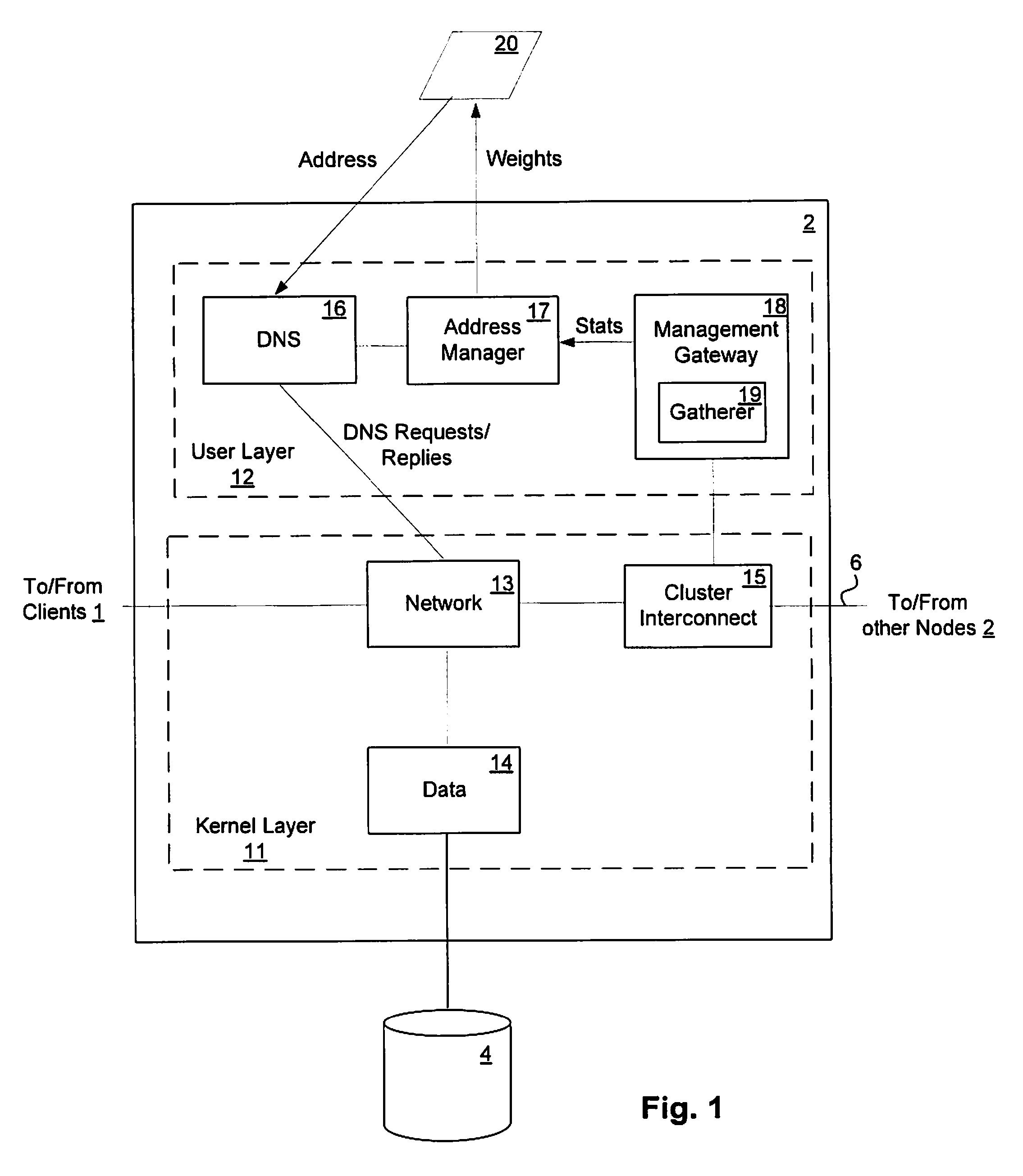
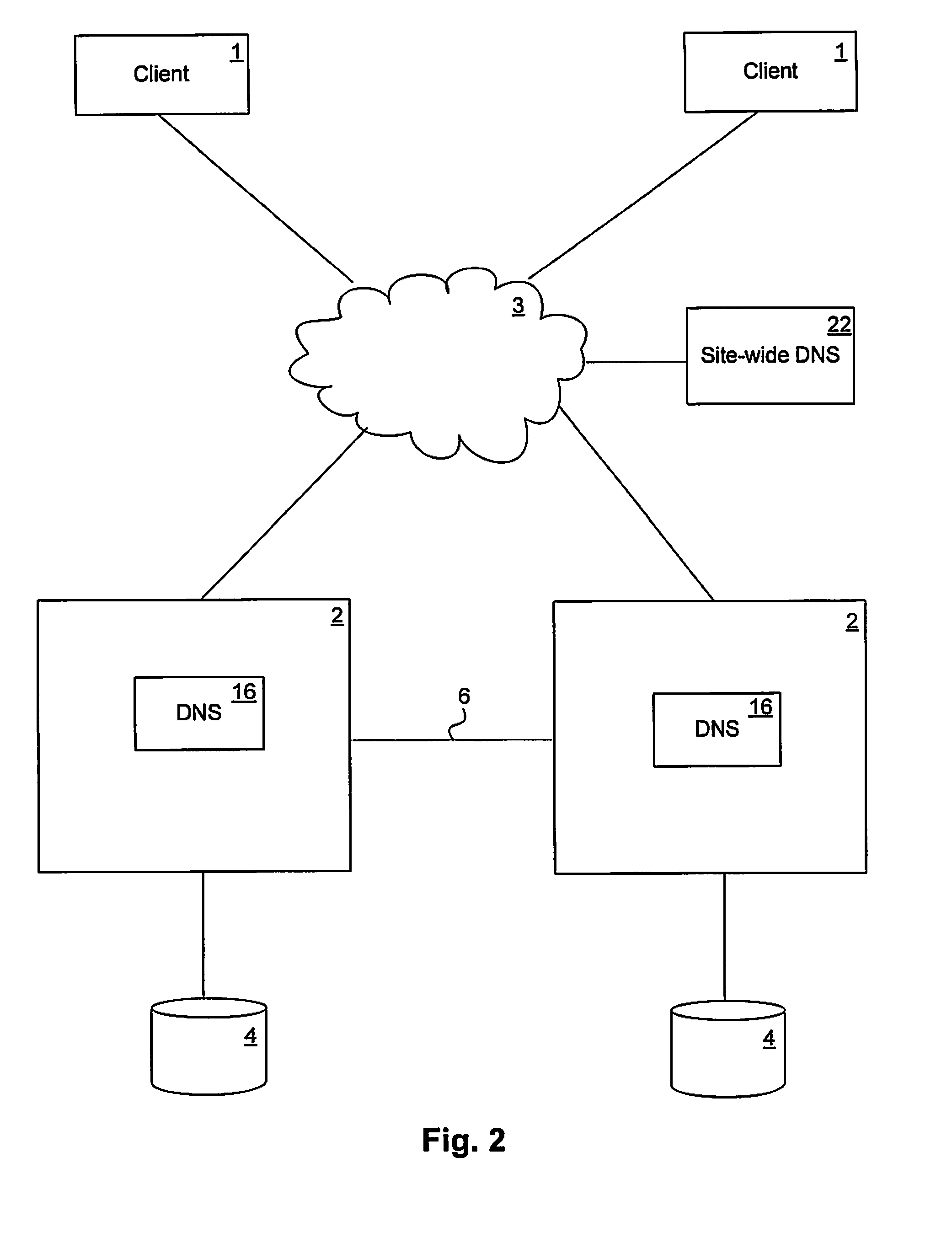
Load-derived probability-based domain name service in a network storage cluster
ActiveUS20100023621A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsDomain nameIp address
DNS name resolution is integrated into each node in a network storage cluster, to allow load balancing of network addresses, using a weighted random distribution to resolve DNS requests. A node in the cluster gathers statistics on utilization of resources, such as CPU utilization and throughput, on nodes in the cluster and distributes those statistics to all other nodes. Each node uses the same algorithm to generate weights for the various IP addresses of the cluster, based on the statistics distributed to it. The weights are used to generate a weighted list of available network addresses. In response to a DNS request, a DNS in a given node randomly indexes into the weighted address list to resolve requests to a network address. The weights are chosen so that the DNS is likely to pick an IP address which has a low load, to balance port and node usage over time.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method of operating a combustion system for increased turndown capability
ActiveUS7137256B1Emission reductionStable combustionContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion systemLow load
A method of operating a gas turbine engine combustion system at lower load conditions while maintaining required emissions levels is disclosed. The present invention includes multiple embodiments of axial, radial, and circumferential fuel staging within a can-type combustor having alternate ignition techniques of spark ignition or torch ignition.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
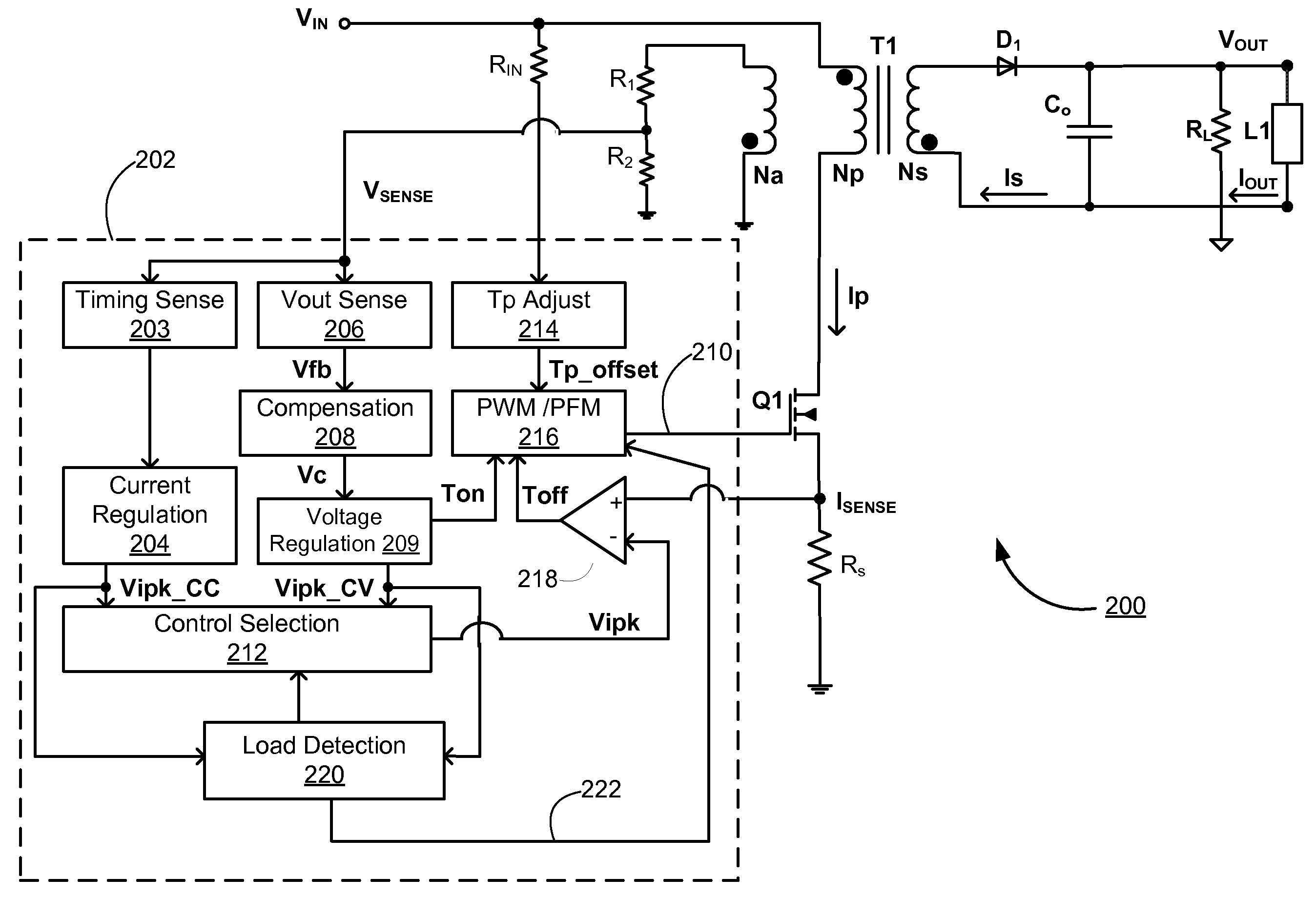
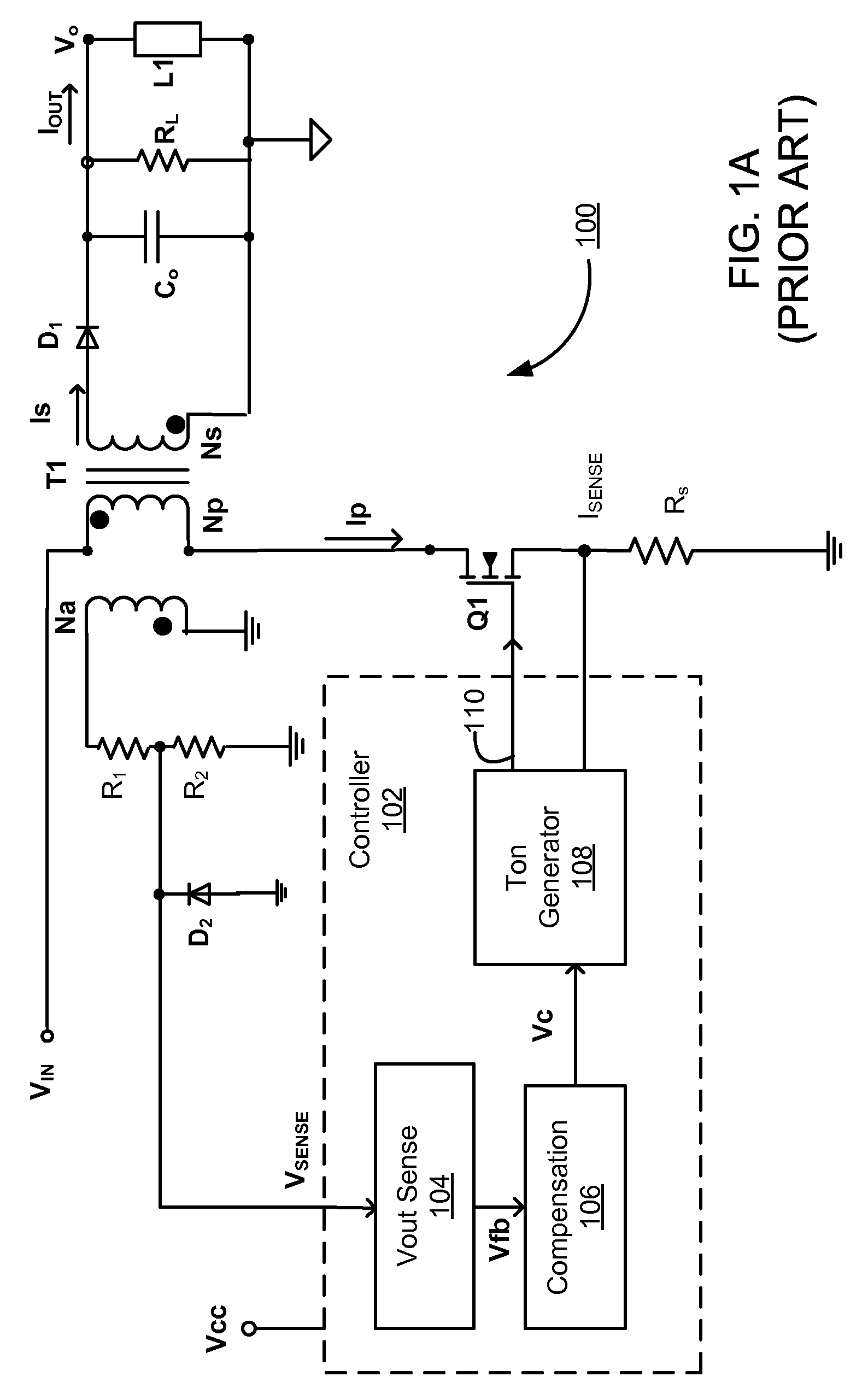
Detecting Light Load Conditions and Improving Light Load Efficiency in a Switching Power Converter
ActiveUS20100208500A1Minimize switching lossesReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLow loadVoltage regulation
A switching power converter detects low load conditions based on the ratio of a first peak current value for peak current switching in constant voltage regulation mode to a second peak current value for peak current switching in constant current regulation mode. The power supply load is considered to have a low load if the ratio is lower than a predetermined threshold. Once a low load condition is detected, the switching frequency of the switching power converter is reduced to a level that minimizes switching loss in the power converter. In addition, the switching power converter also adjusts the switching frequency according to the sensed input line voltage. An offset is added to the switching period to reduce the switching frequency of the switching power converter, as the input line voltage is increased.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
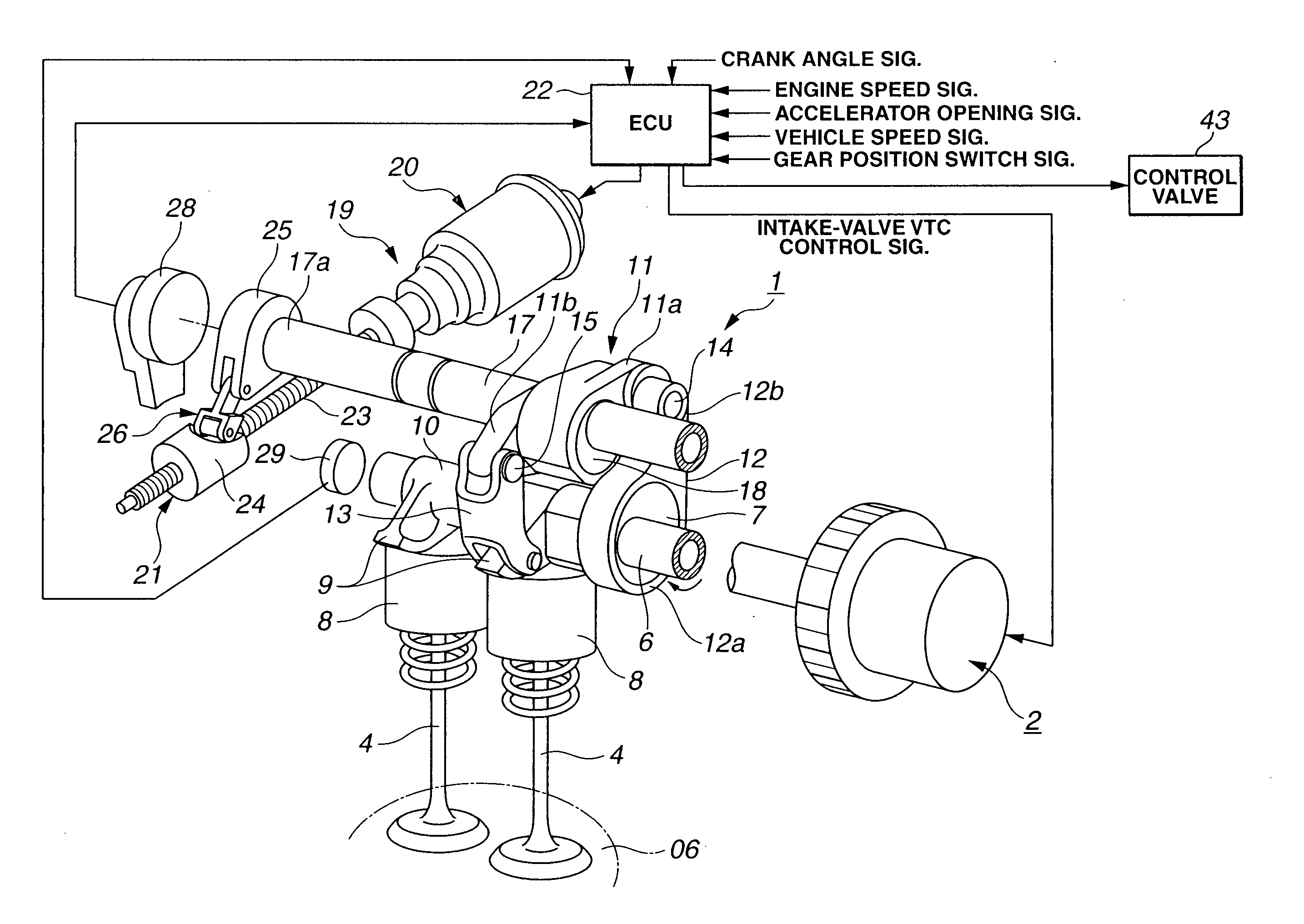
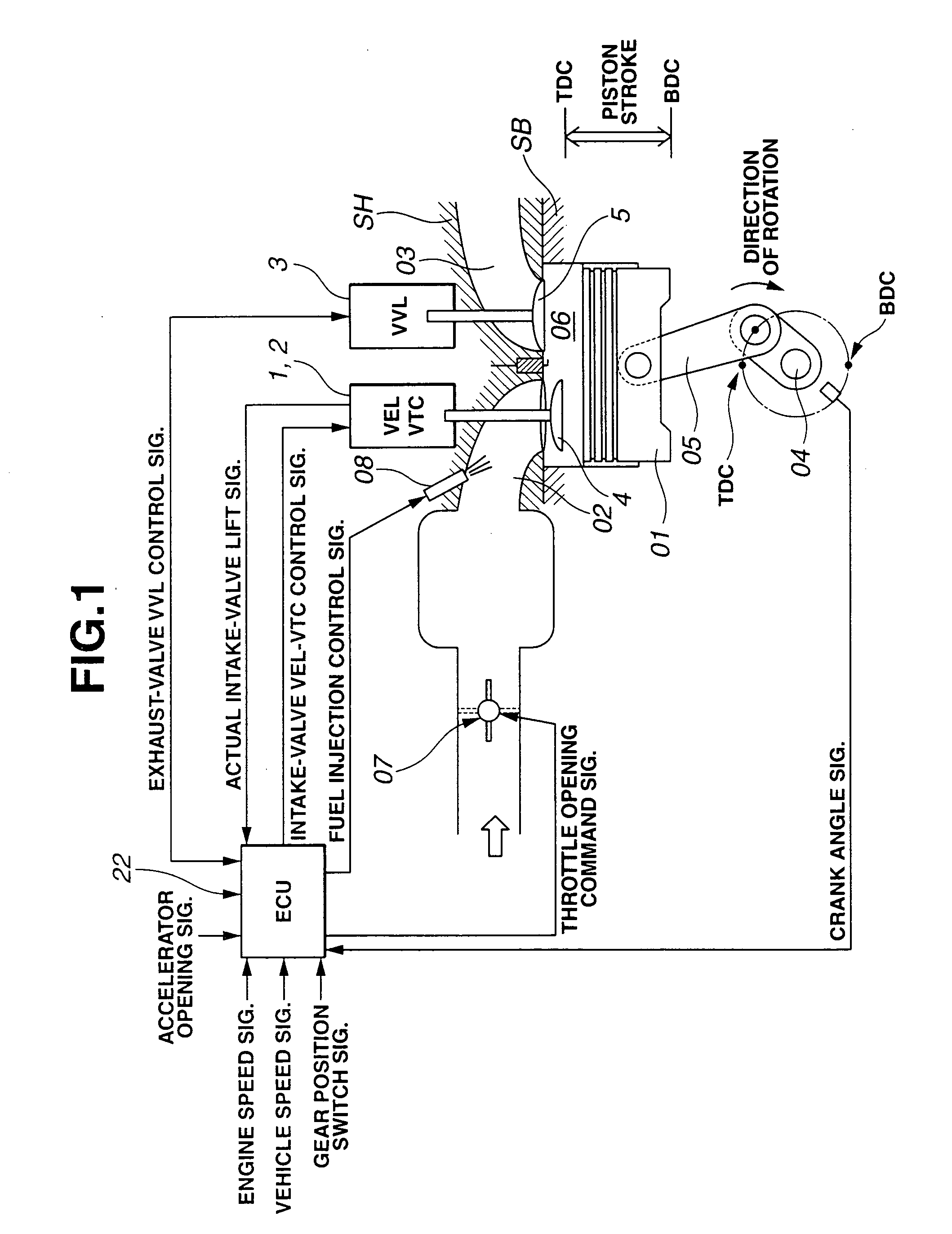
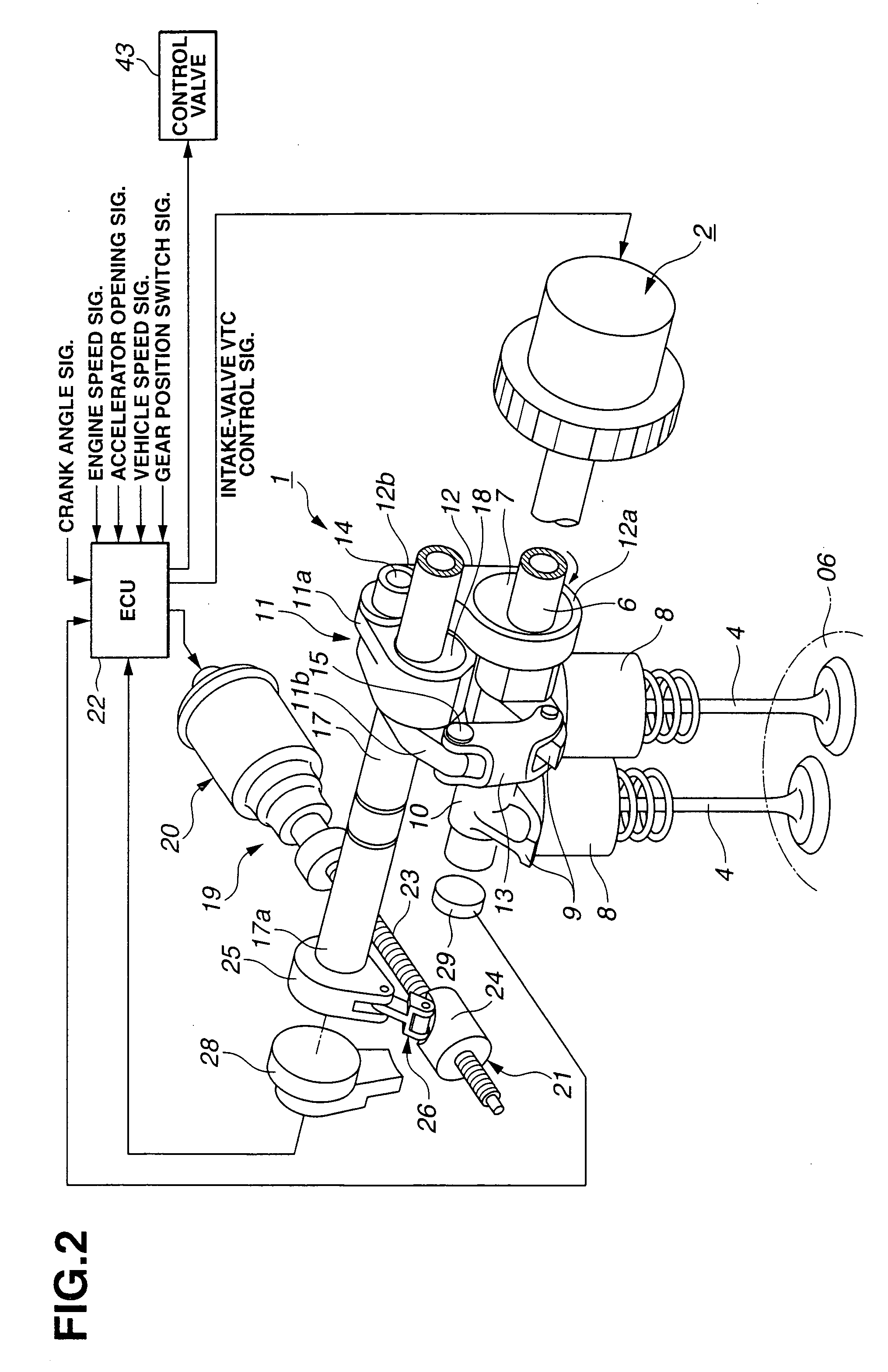
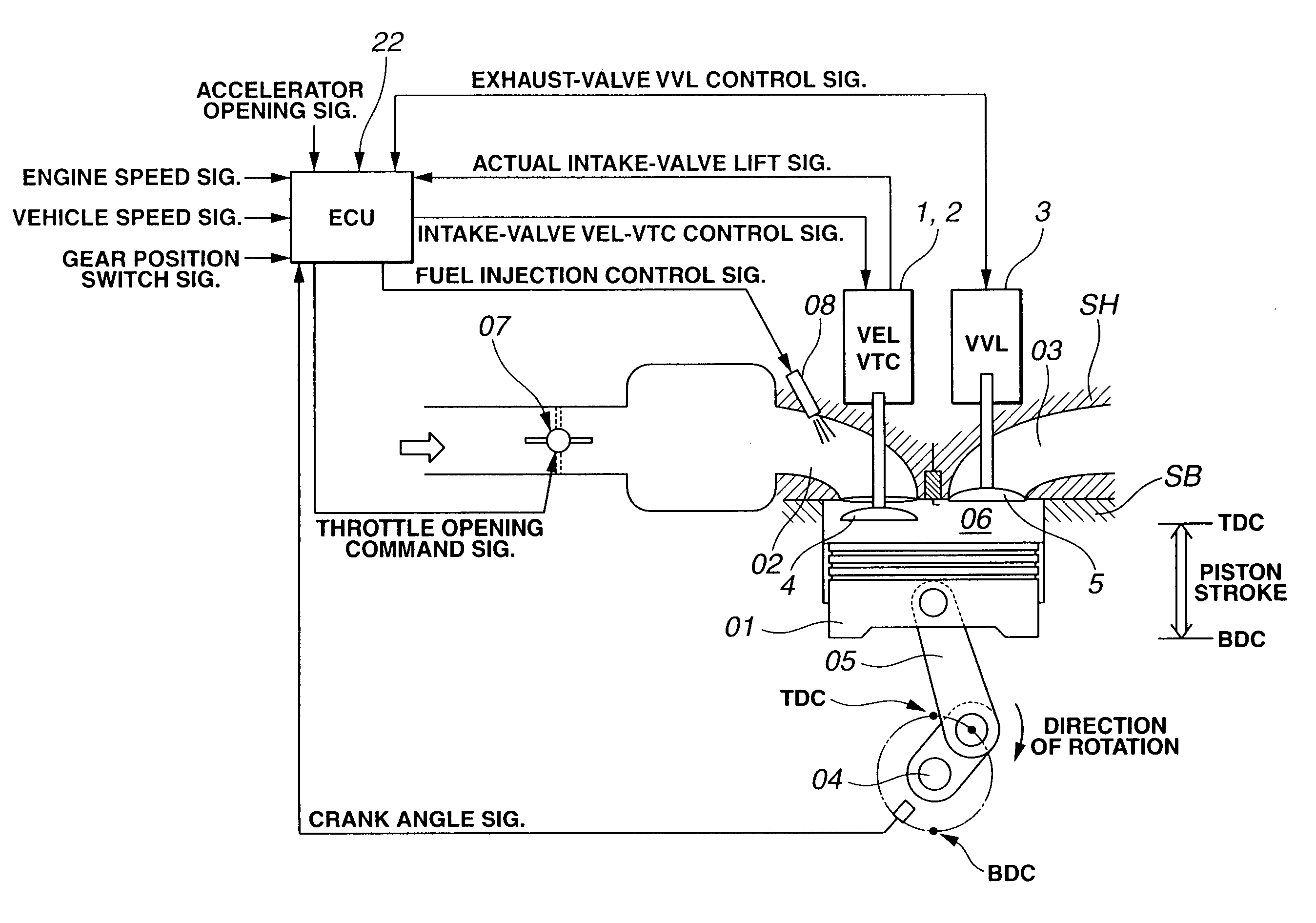
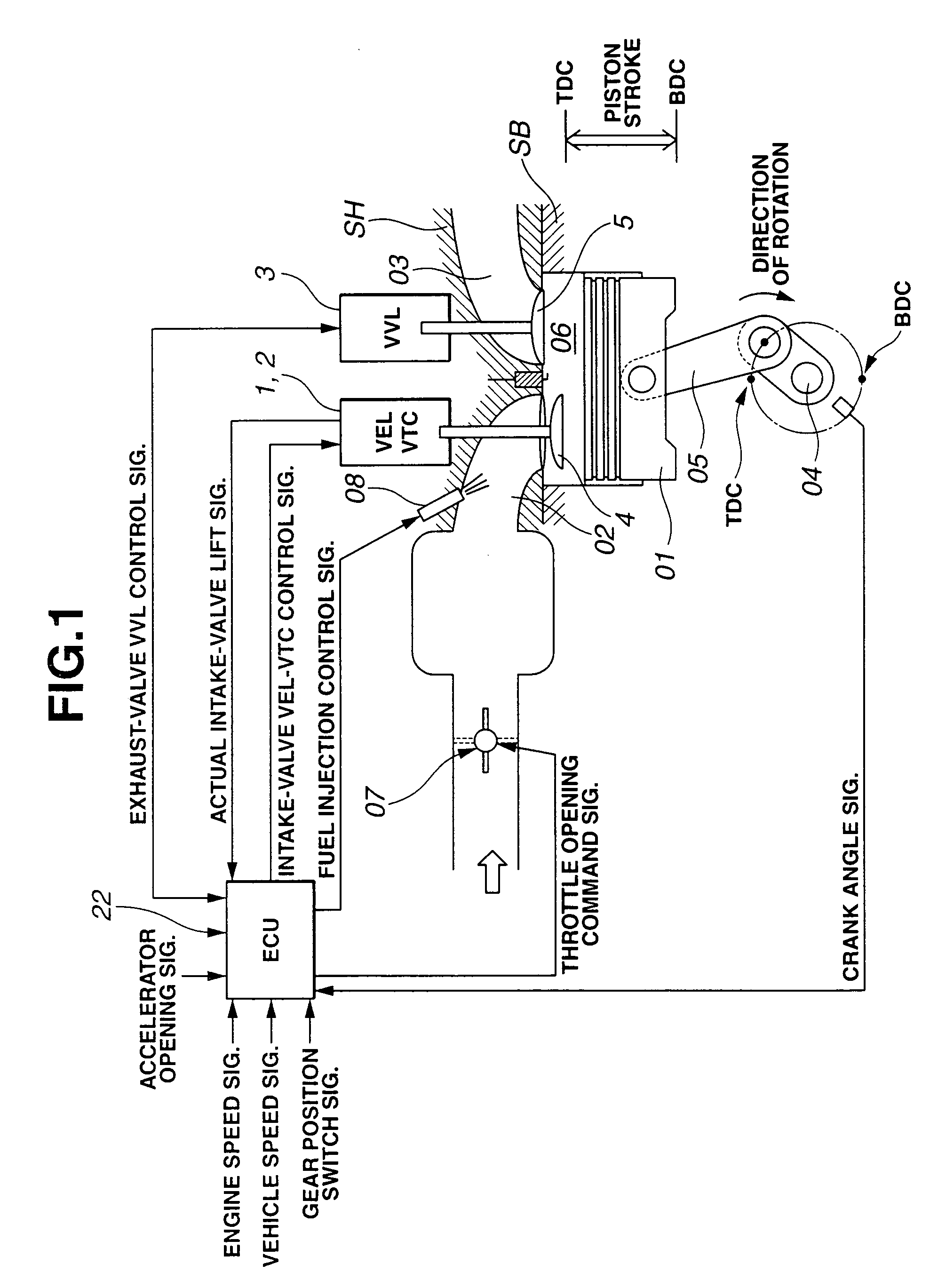
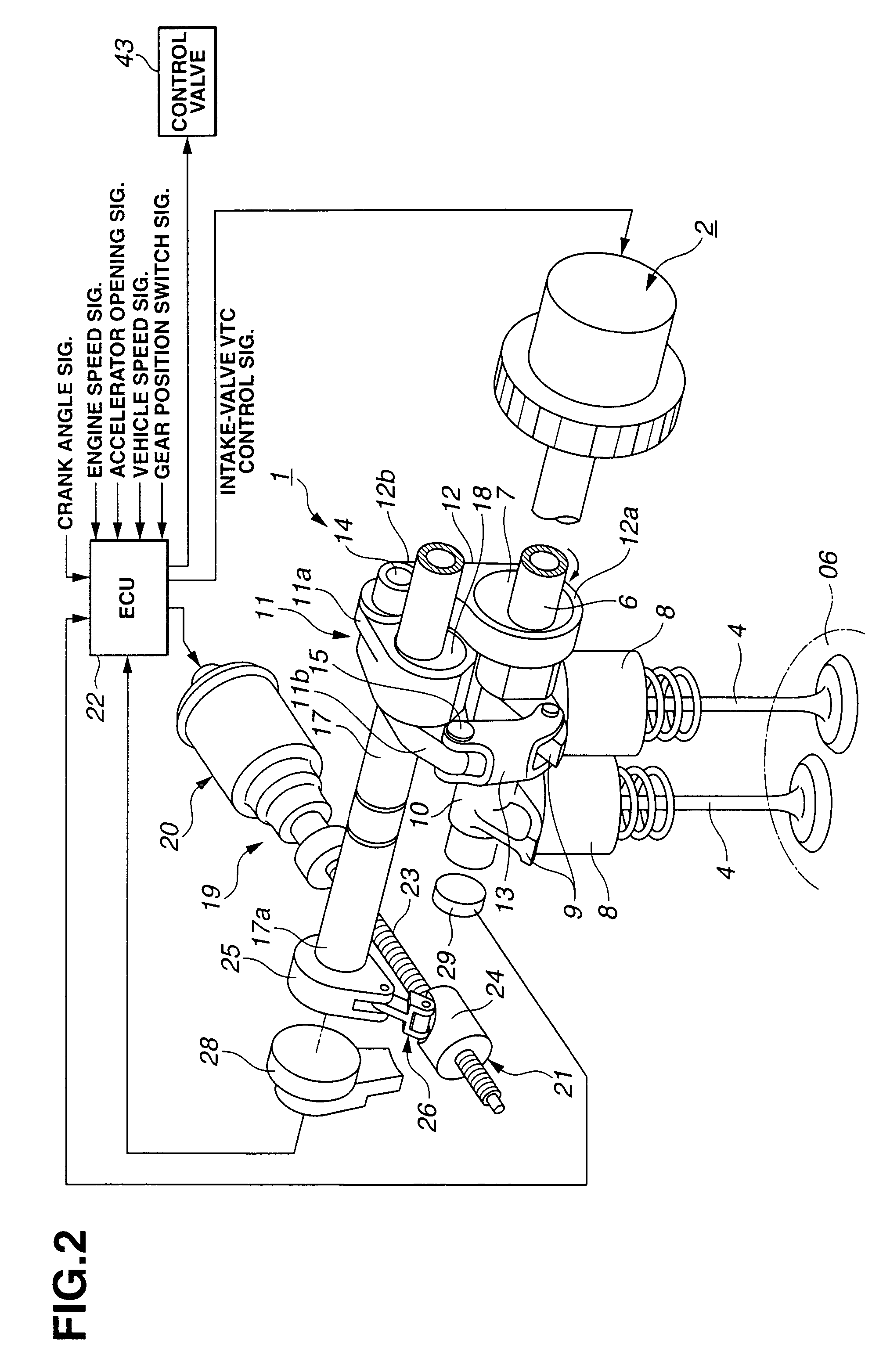
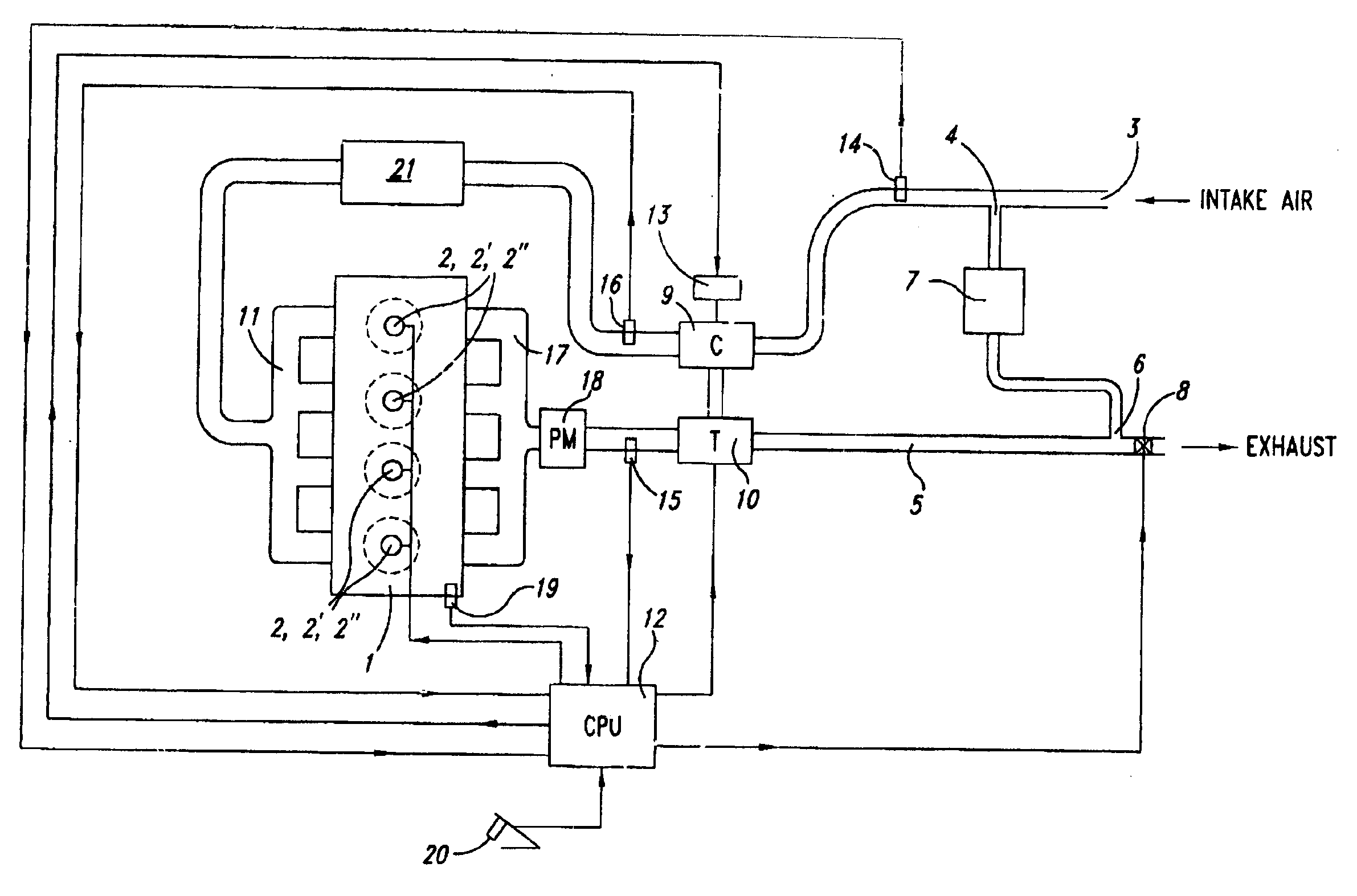
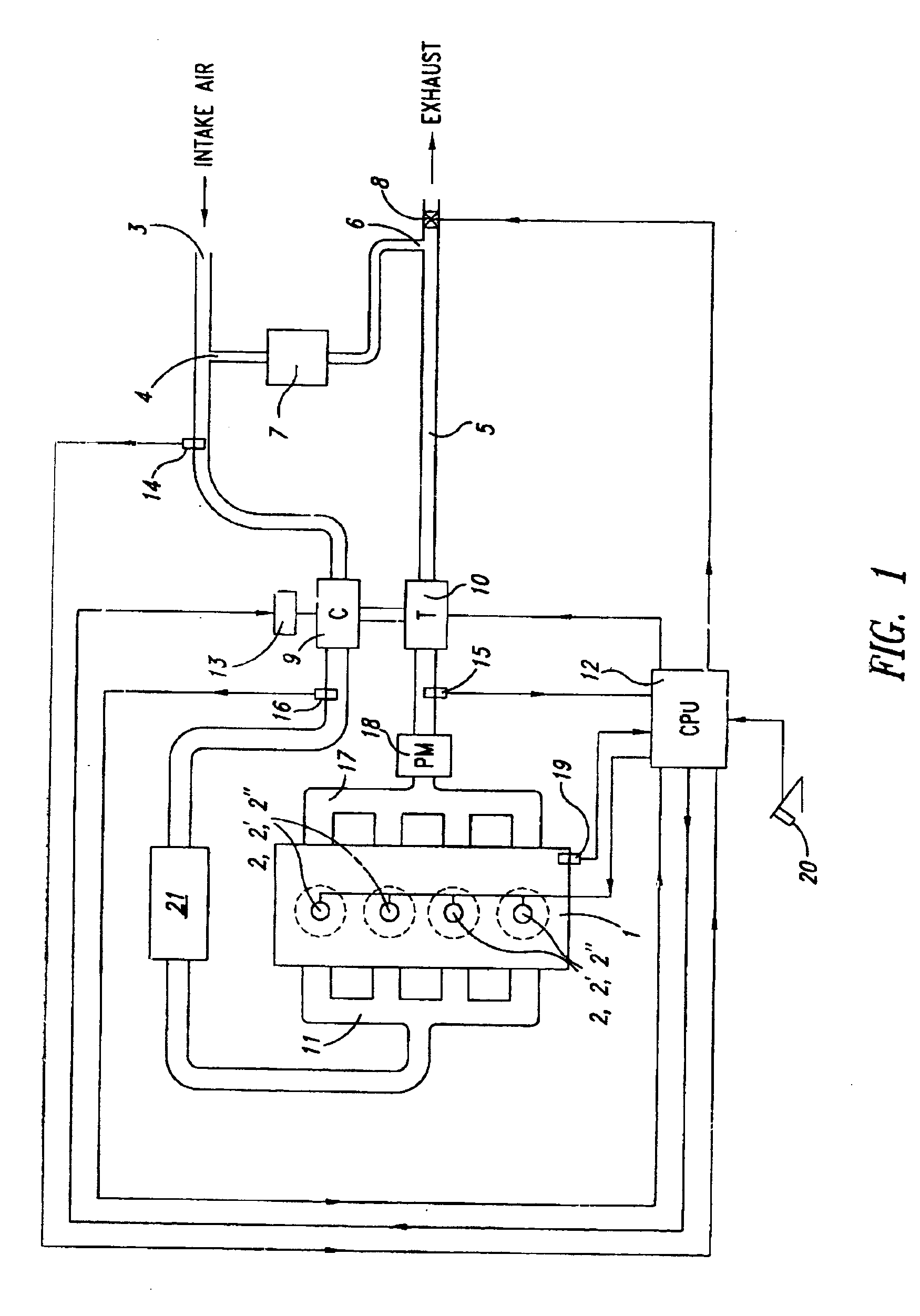
Cylinder cutoff control apparatus of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060037578A1Reduced engine braking effectTendency increaseValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
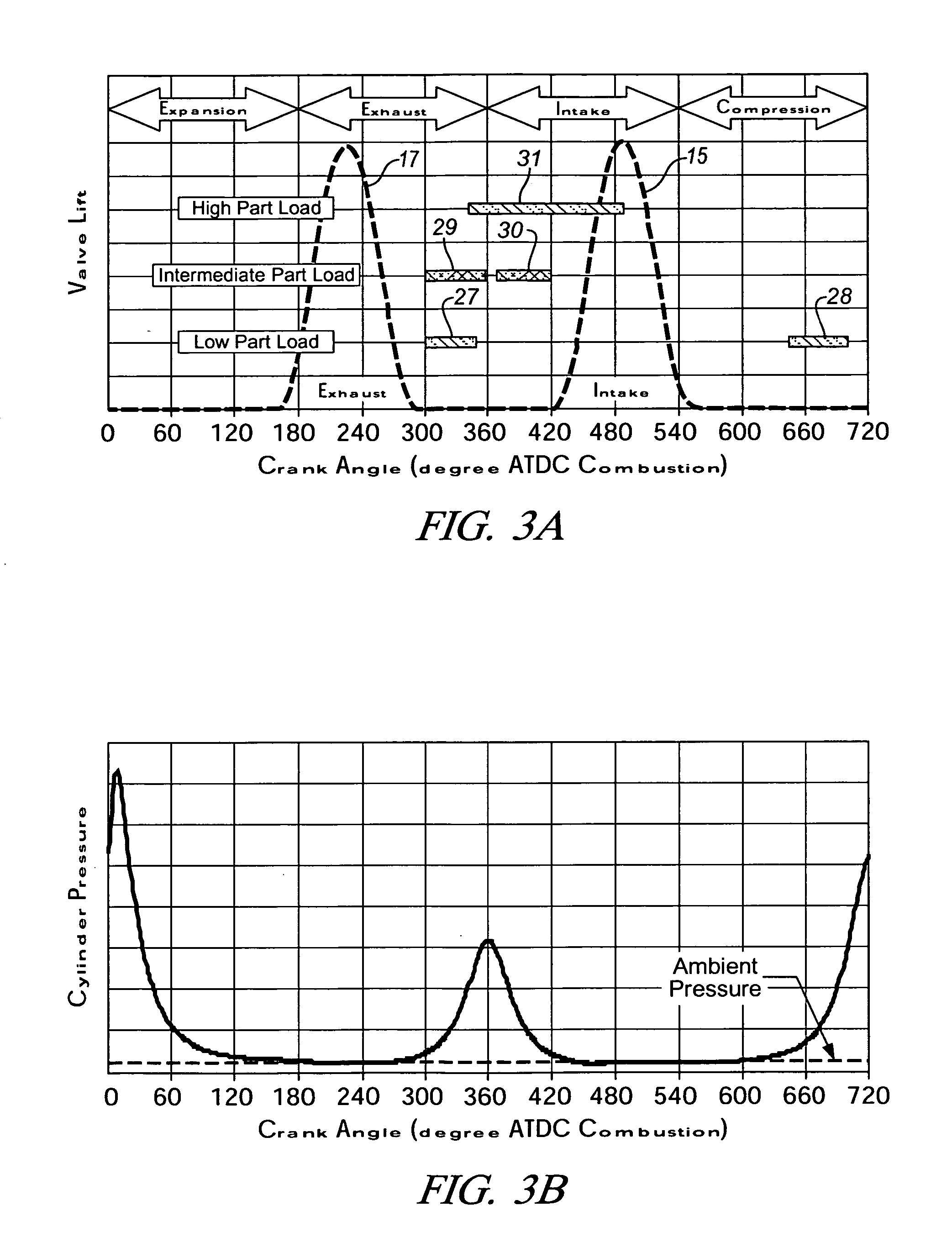
A cylinder cutoff control apparatus of an engine initiates a cylinder cutoff mode only when two conditions, namely a low load condition such as a vehicle cruising condition and an intake valve closure timing controlled to a given timing value before a bottom dead center, are both satisfied. A fuel cutoff mode is executed prior to the cylinder cutoff mode. During a transition to the cylinder cutoff mode, the control apparatus holds an intake valve open timing at a given timing value substantially corresponding to a top dead center, simultaneously with reducing an intake valve lift amount of each intake valve, subjected to cylinder cutoff control, to a zero lift. Immediately when the intake valve lift amount is reduced to below a lift threshold value, an exhaust valve lift amount of each exhaust valve, subjected to the cylinder cutoff control, is controlled to a zero lift.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Multi-cycle dump valve
InactiveUS20040084190A1Less timePrevent siphonFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsControl flowFree falling
A flow responsive dump valve mechanism for a straddle packer tool and has a valve controlled flow passage from which underflushed fluid, typically well treatment slurry, in a conveyance and fluid supplying tubing string can be dumped into a well casing. The dump valve mechanism incorporates a ratcheting power piston, an indexing mechanism and high and low load energy storage systems to accomplish open, closed and intermediate dump valve positions. The intermediate position increases the functionality of the tool by preventing accidental closure either due to the free fall of fluid through the coiled tubing or during flushing of the tool and permits the flow rate to be increased for thorough cleaning of the straddle tool and coiled tubing. For energy storage, a light compression spring provides power to cycle the indexing mechanism. Heavier load disc springs (Bellville Washers) are used to provide power for the ratcheting power piston to open the valve.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
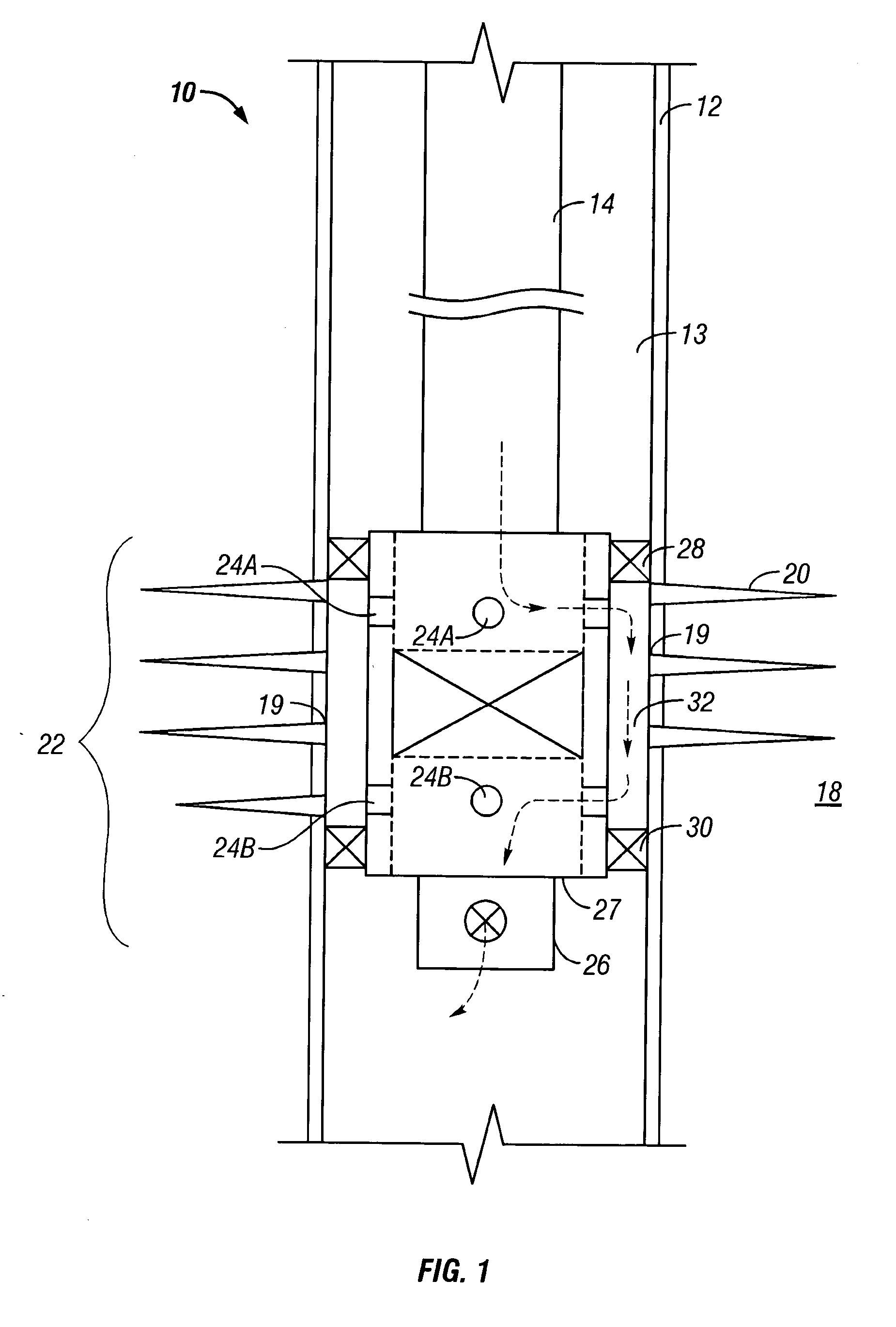
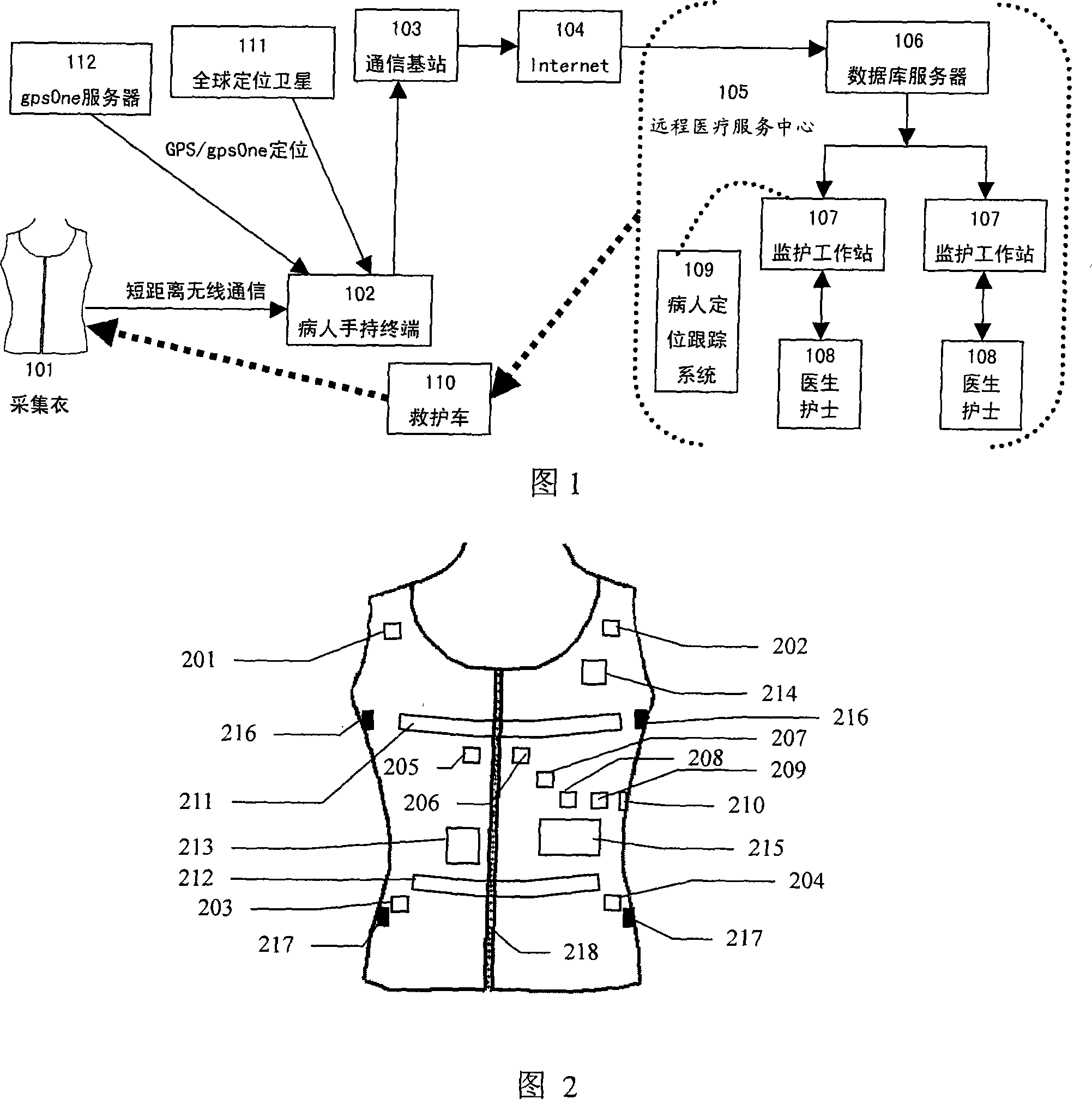
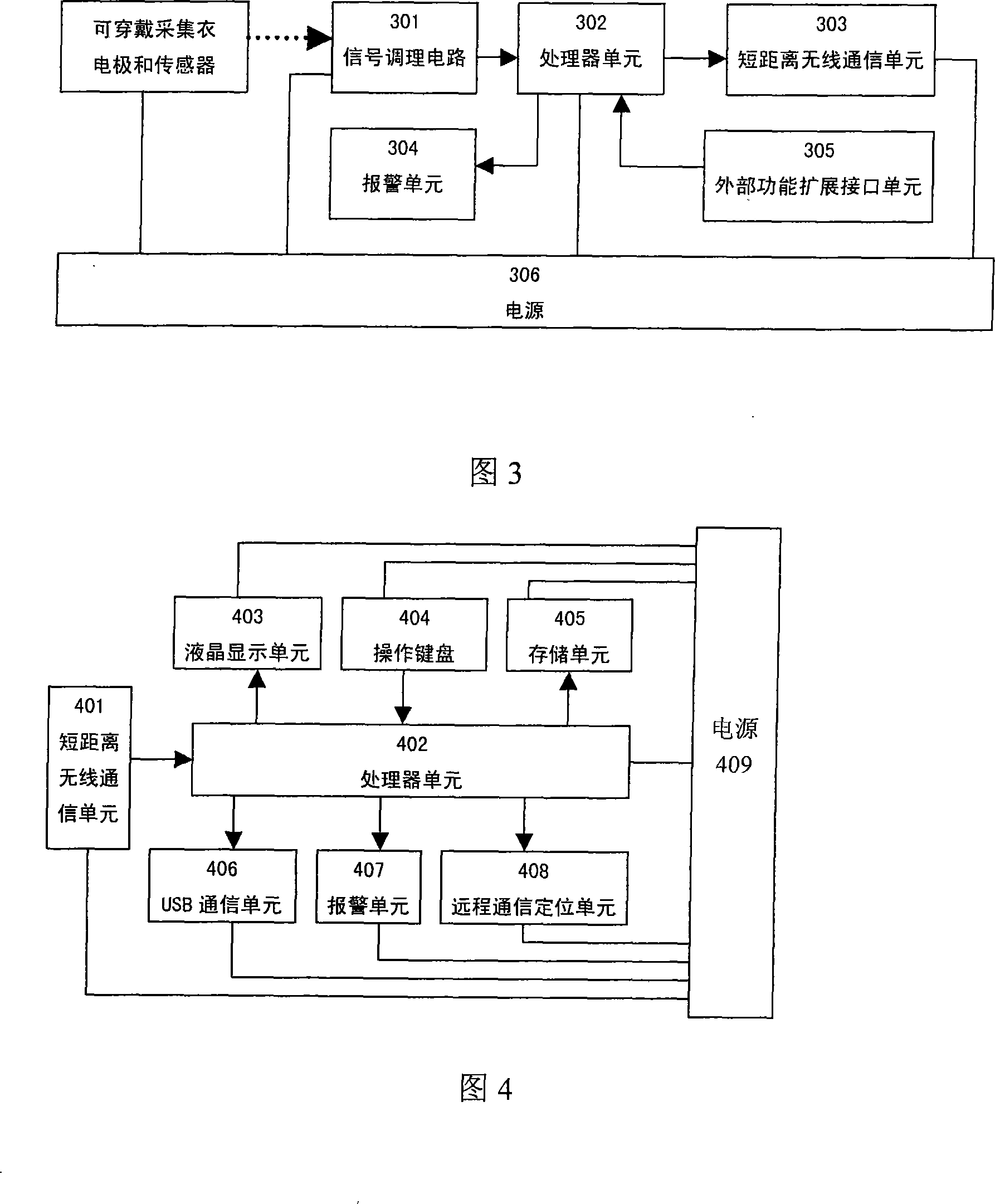
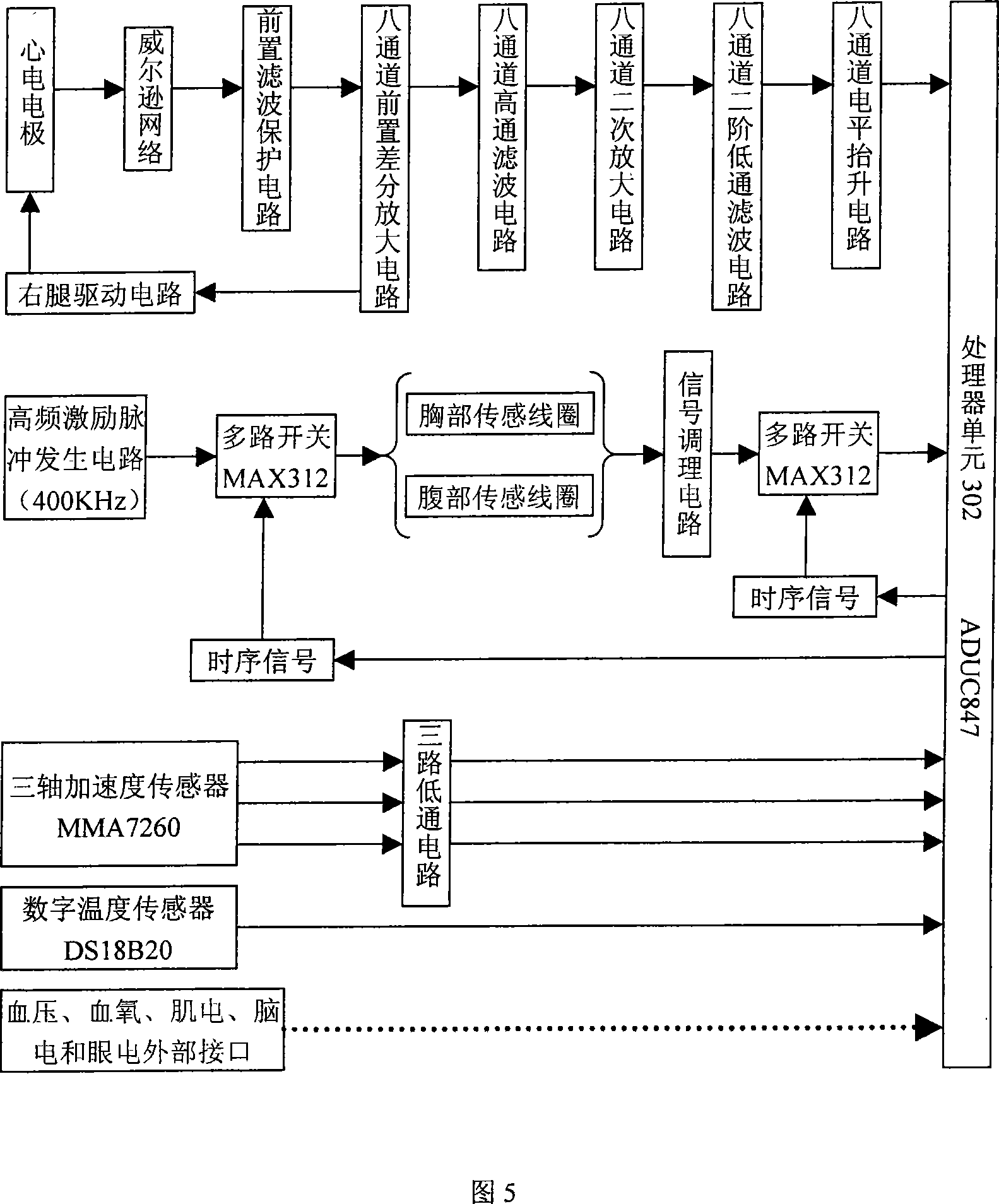
Wearable low-load physiological monitoring system
InactiveCN101019761ARealize mobile monitoringRealize remote dynamic monitoringTransmission systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringLow loadThe Internet
The present invention relates to physiological monitoring system, and is especially one kind of wearable low-load physiological monitoring system for multiparameter physiological signal acquisition. The physiological monitoring system consists of a wearable dynamic multiparameter acquisition coat, a patient's hand-held terminal and a remote medical service center. The wearable dynamic multiparameter acquisition coat communicates with the hand-held terminal in short radio communication mode, while the hand-held terminal communicates with the remote medical service center accessed to the Internet in remote radio communication mode. The present invention has the positive effect of realizing the movable monitoring, the remote dynamic monitoring and real-time tracking monitoring on low load physiological parameters of the patient.
Owner:SANITARY EQUIP INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI PLA
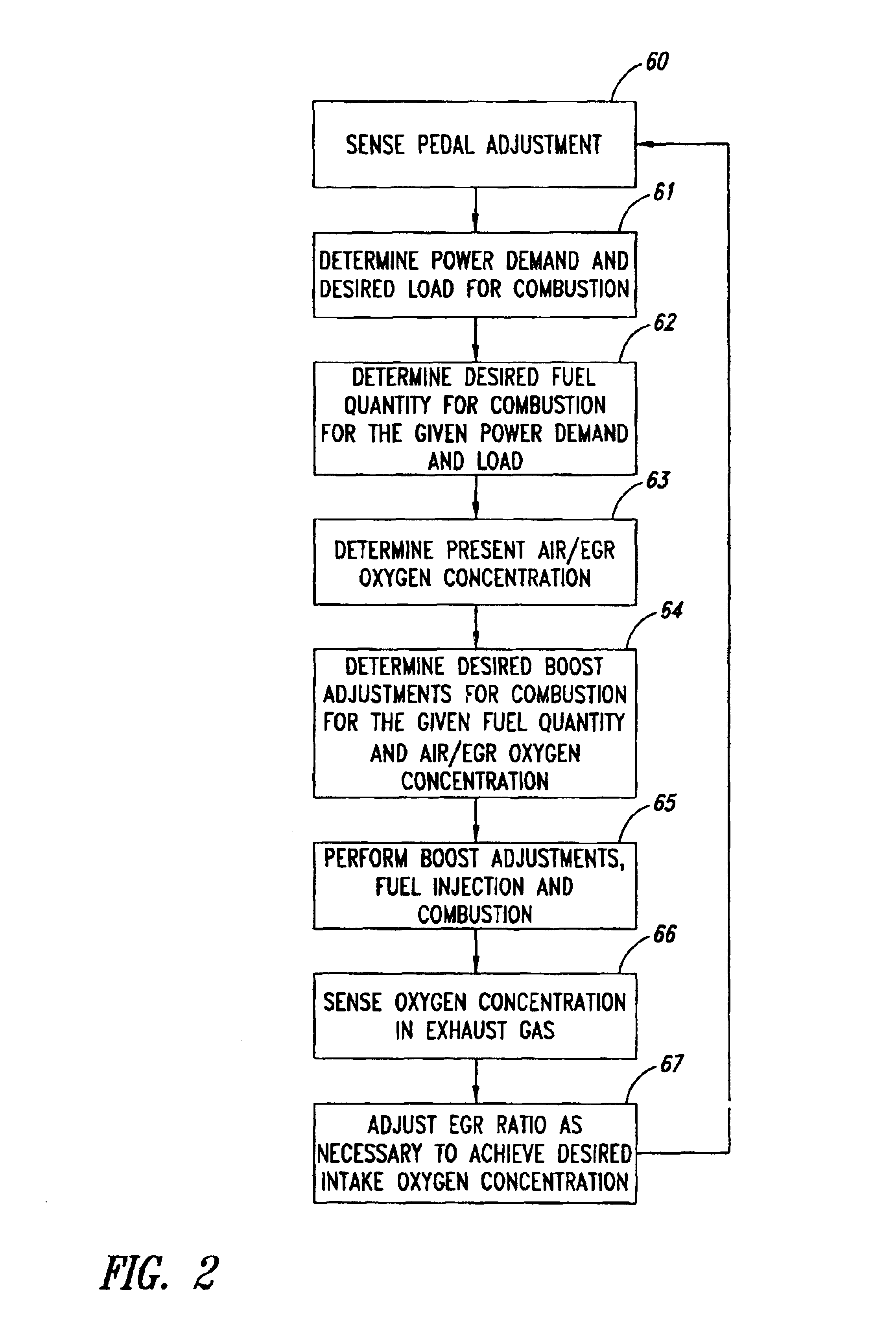
Method for load transient control between lean and stoichiometric combustion modes of direct-injection engines with controlled auto-ignition combustion
InactiveUS20060196469A1Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelStable stateHomogeneous charge compression ignition
A method is provided for control of a direct-injection engine operated with controlled auto-ignition (HCCI) during load transient operations between modes of lean combustion low load (HCCI / Lean) and stiochiometric combustion medium load (HCCI / Stoich.). The method includes 1) operating the engine at steady state, within a homogeneous charge compression-ignition (HCCI) load range, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during changes of operating mode between one to another of the HCCI / Stoich. medium load mode and the HCCI / Lean lower load mode by synchronizing change rates of predetermined controlled inputs to the current engine fueling change rate.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Control device for spark-ignition engine
InactiveUS20050016496A1Increase rangeEfficiently prevent knockingValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberLow speed
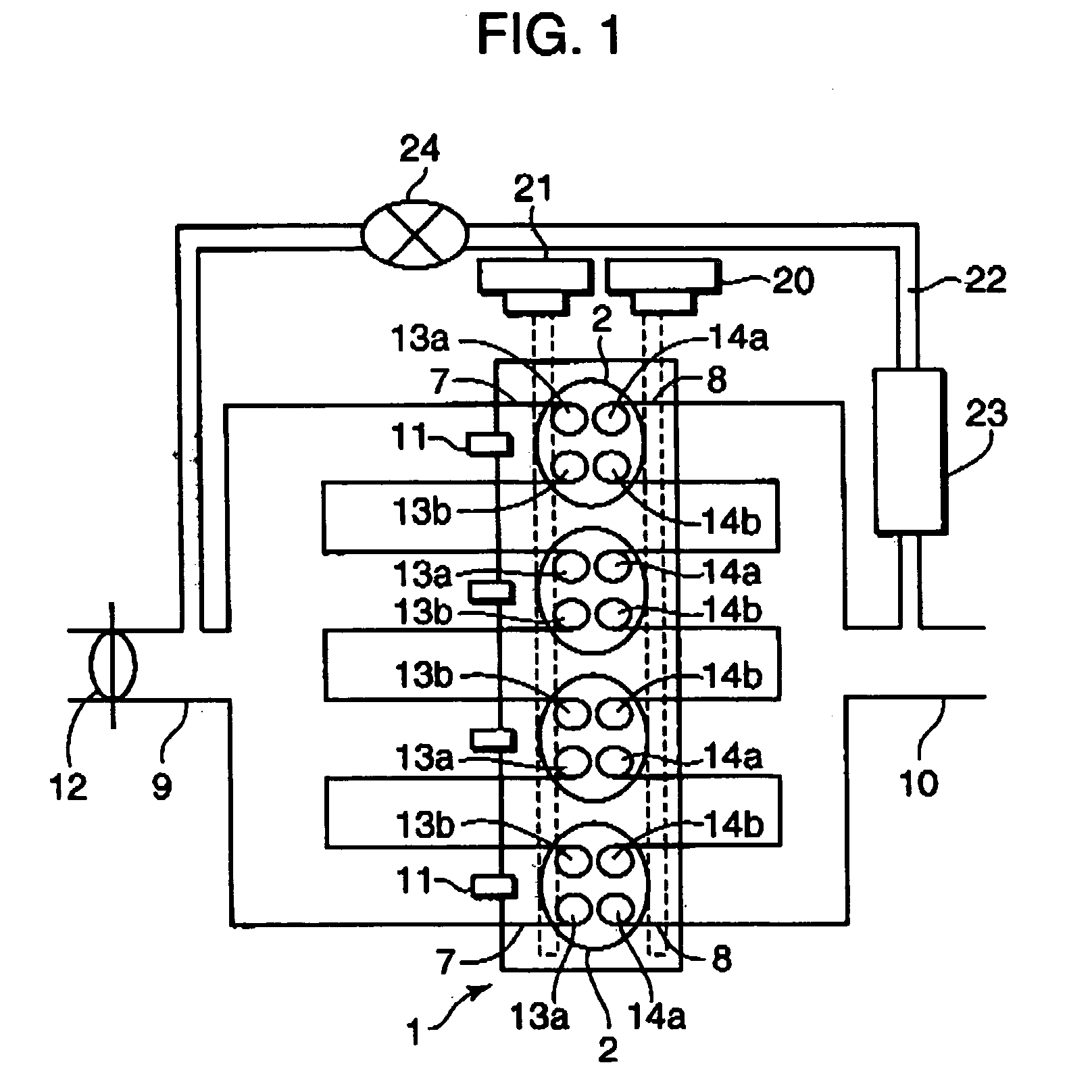
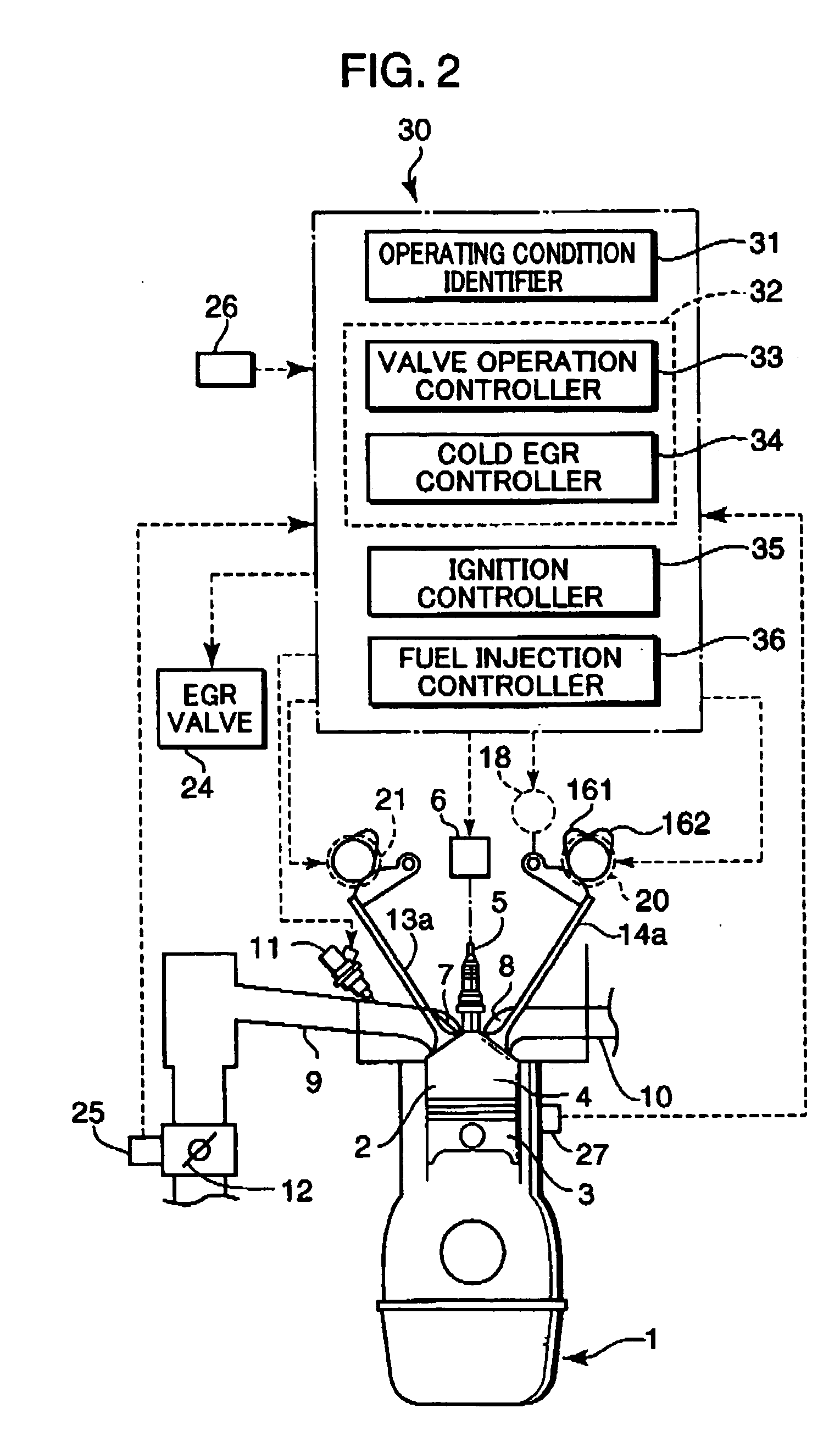
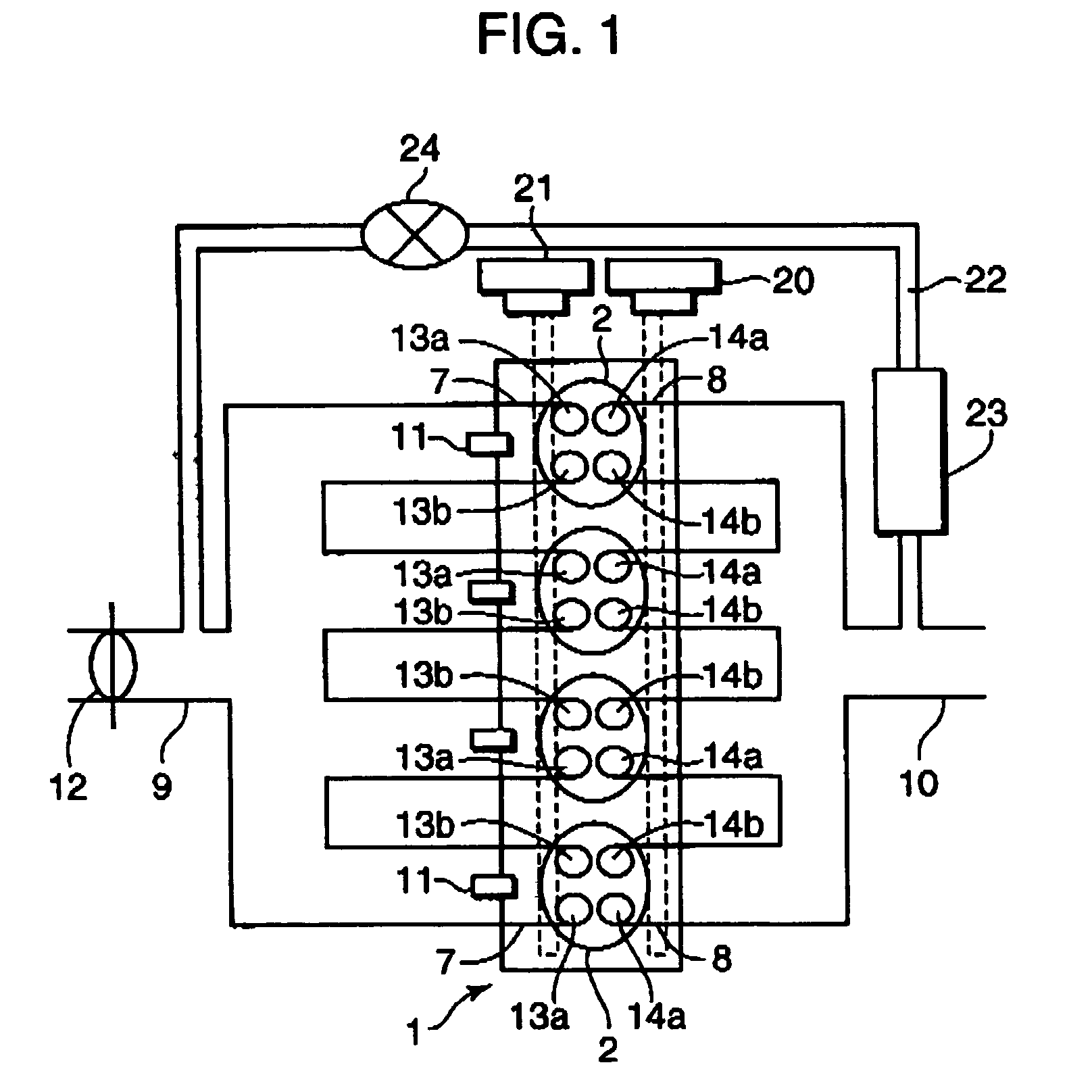
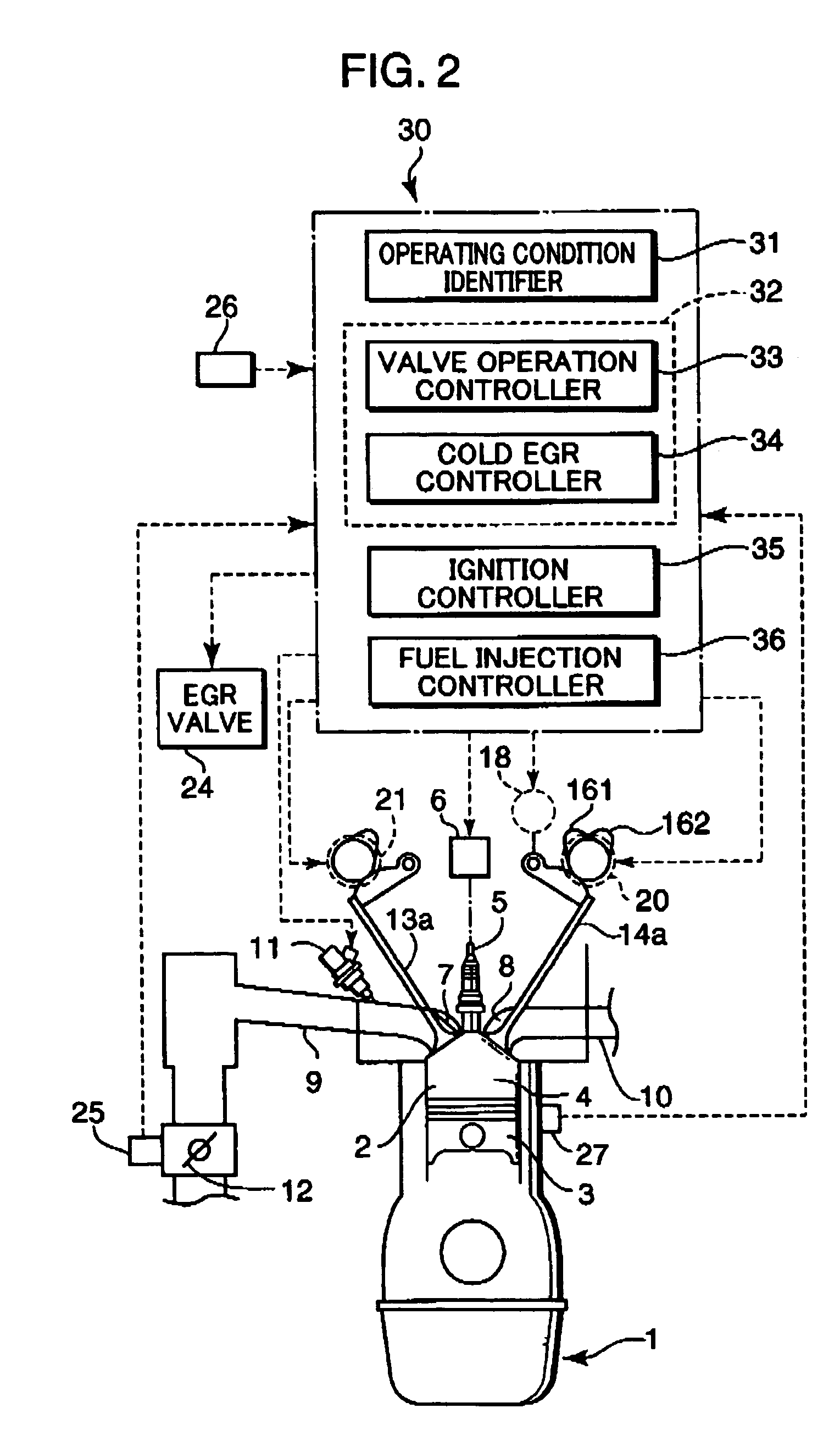
A control device for a spark-ignition engine, in which a mixture in a combustion chamber is fired by compression ignition in a part-load range under warm-running conditions, includes an EGR controller incorporating a valve operation controller for controlling internal EGR of hot burned gas and a cold EGR controller for controlling external EGR of cold burned gas. The EGR controller performs EGR control operation to leave the hot EGR gas in the combustion chamber in a lower-load, lower-speed region within a compression ignition combustion range and to introduce the cold EGR gas into the combustion chamber in a higher-load, higher-speed region within the compression ignition combustion range. The control device further includes a firing assist unit for inducing the compression ignition at least when ignitability of the mixture decreases due to introduction of the cold EGR gas in the compression ignition combustion range.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Method for transition between controlled auto-ignition and spark ignition modes in direct fuel injection engines
InactiveUS20060196466A1Eliminate misfiringEliminate partial burnValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExhaust valve
A method is provided for control of transition between combustion modes of a direct-injection engine operable in a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) mode at lower loads and a spark ignition flame propagation (SI) mode at higher loads. The engine includes a variable valve actuation system including two-step high and low lift valve actuation and separate cam phasing for both intake and exhaust valves. The method includes operating the engine at steady state, with fuel-air-exhaust gas mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, and controlling the engine during mode changes between the HCCI mode and the SI mode by switching the exhaust and intake valves between low lift for HCCI operation and high lift for SI operation. High load may be an SI throttled mode with an intermediate unthrottled mode (SI / NTLC} in which transition between HCCI and SI / NTLC modes requires switching only the exhaust valve lift and transition between SI / NTLC and SI throttled modes requires switching only the intake valve lift, with predetermined phase adjustments in the valve timing phasing.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Elasticated materials
This invention relates to an elasticated materials comprising a stiff carrier material that is satisfactorily elasticated with one or more elastic strands with a low load force, due to the use of a specific bonding pattern, with specific bonding areas. The bonding areas are typically separate bonding areas positioned on separate intervals along the length direction of the carrier material, whereby each bonding area comprises one or more separate bonding zones, extending in the width (X) direction. The invention also relates to absorbent articles comprising this elasticated material and processes for making the elasticated material.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Diesel engine system comprising a soot filter and low temperature NOx trap
The invention provides low temperature NO2 trap compositions useful for adsorbing NO2 from a gas stream at lower temperatures, and releasing the NO2 at higher temperatures. The low temperature trap compositions are useful for incorporation into a diesel exhaust system equipped with a soot filter. The NO2 from the diesel exhaust can be stored when the exhaust temperature is cool, e.g., during startup and at times of low load, and released when the exhaust is at higher temperatures. The released NO2 serves as an effective oxidant for the combustion of soot deposited on the soot filter. These temperatures are significantly lower than those required for the combustion of soot using O2 as an oxidant. The methods of the invention thereby provide a method for regenerating the soot filter within operating temperature ranges typical of diesel engine exhaust systems.
Owner:BBNT SOLUTIONS LLC +1
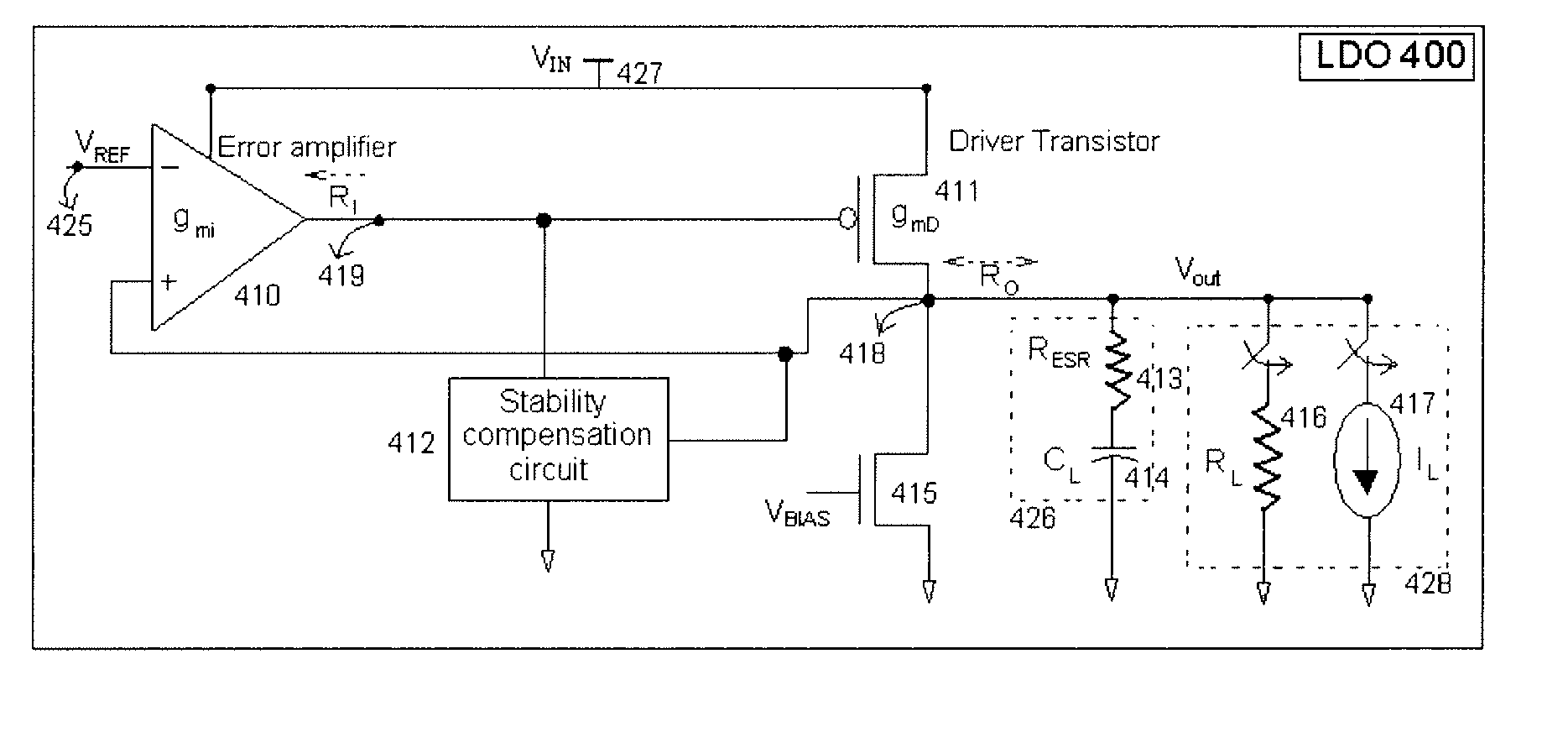
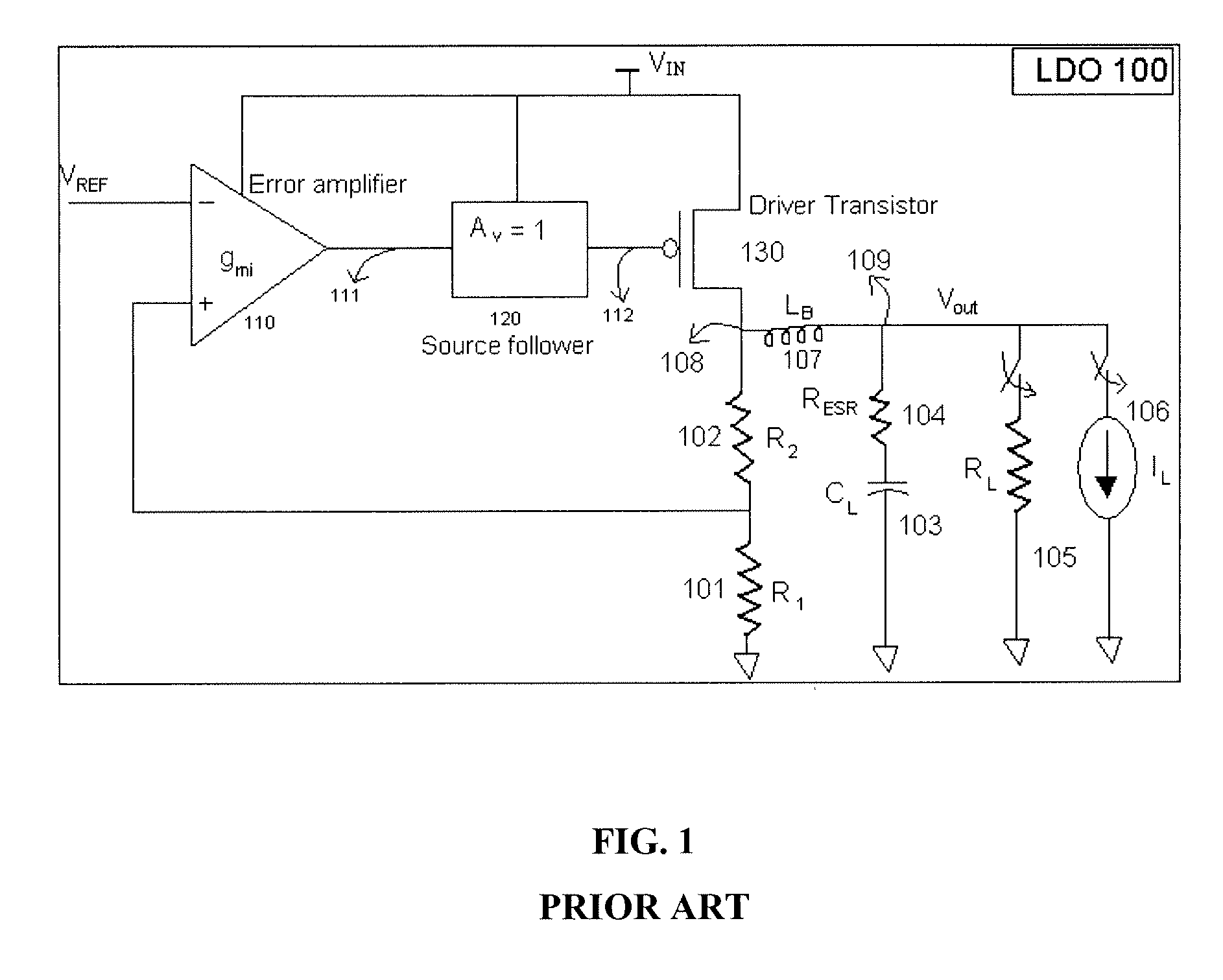
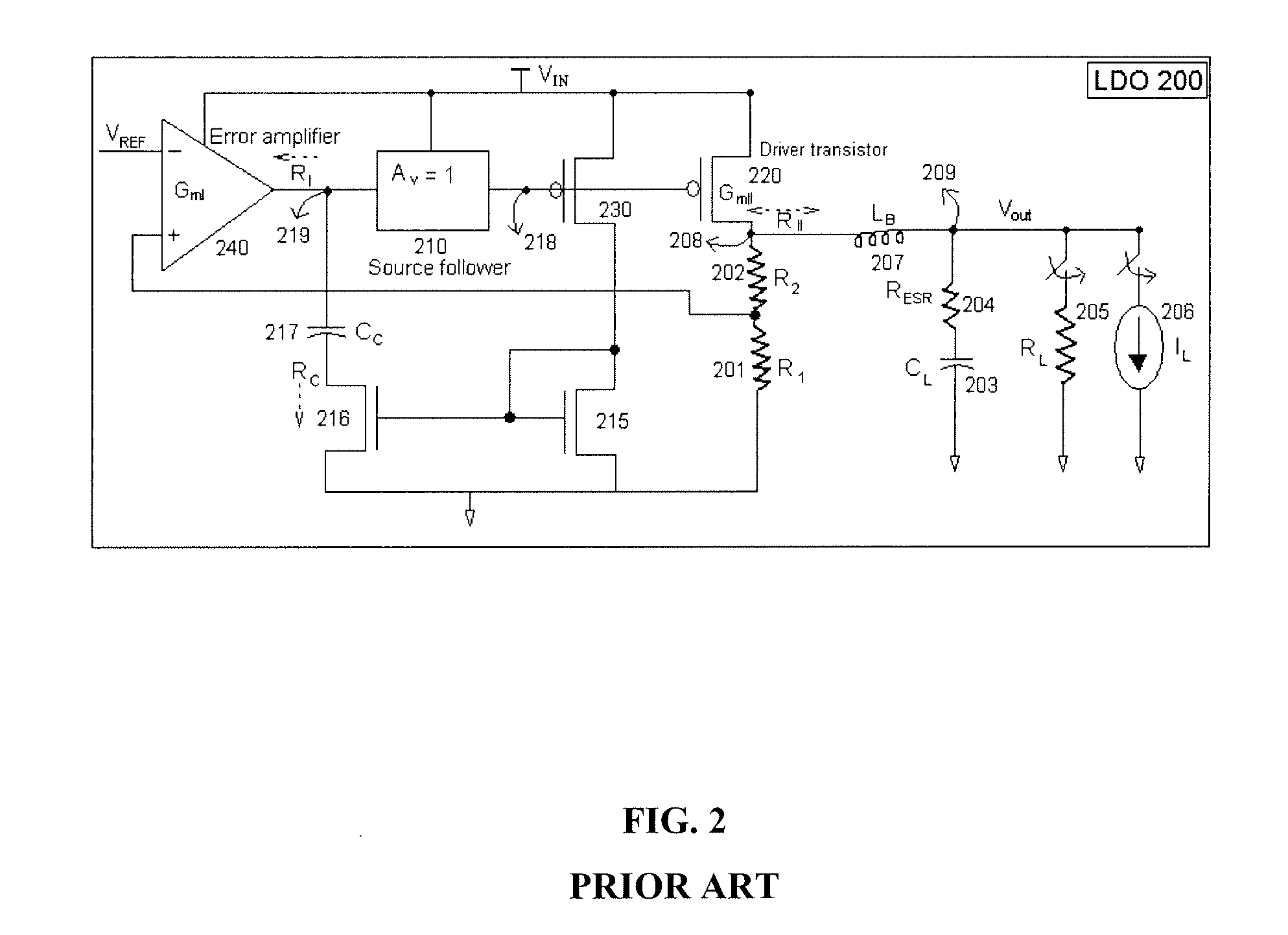
Low dropout regulator
InactiveUS20070159146A1Good phase marginMinimize power consumptionElectric variable regulationLow loadEngineering
The present invention provides a low dropout (LDO) regulator with a stability compensation circuit. A “zero frequency” tracking as well as “non-dominant parasitic poles' frequency reshaping” are performed to achieve a good phase margin for the LDO by means of the compensation circuit. In this compensation method neither a large load capacitor nor its equivalent series resistance is needed to stabilize a regulator. LDO regulators, in system on chip application, having load capacitors in the range of few nano-Farads to few hundreds of nano-Farads can be efficiently compensated with this compensation method. A dominant pole for the regulator is realized at an internal node and the second pole at an output node of the regulator is tracked with a variable capacitor generated zero over a range of load current to cancel the effect of each other. A third pole of the system is pushed out above the unity gain frequency of the open loop transfer function with the help of the frequency compensation circuit. The compensation technique is very effective in realizing a low power, low-load-capacitor LDO desirable for system on chip applications.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
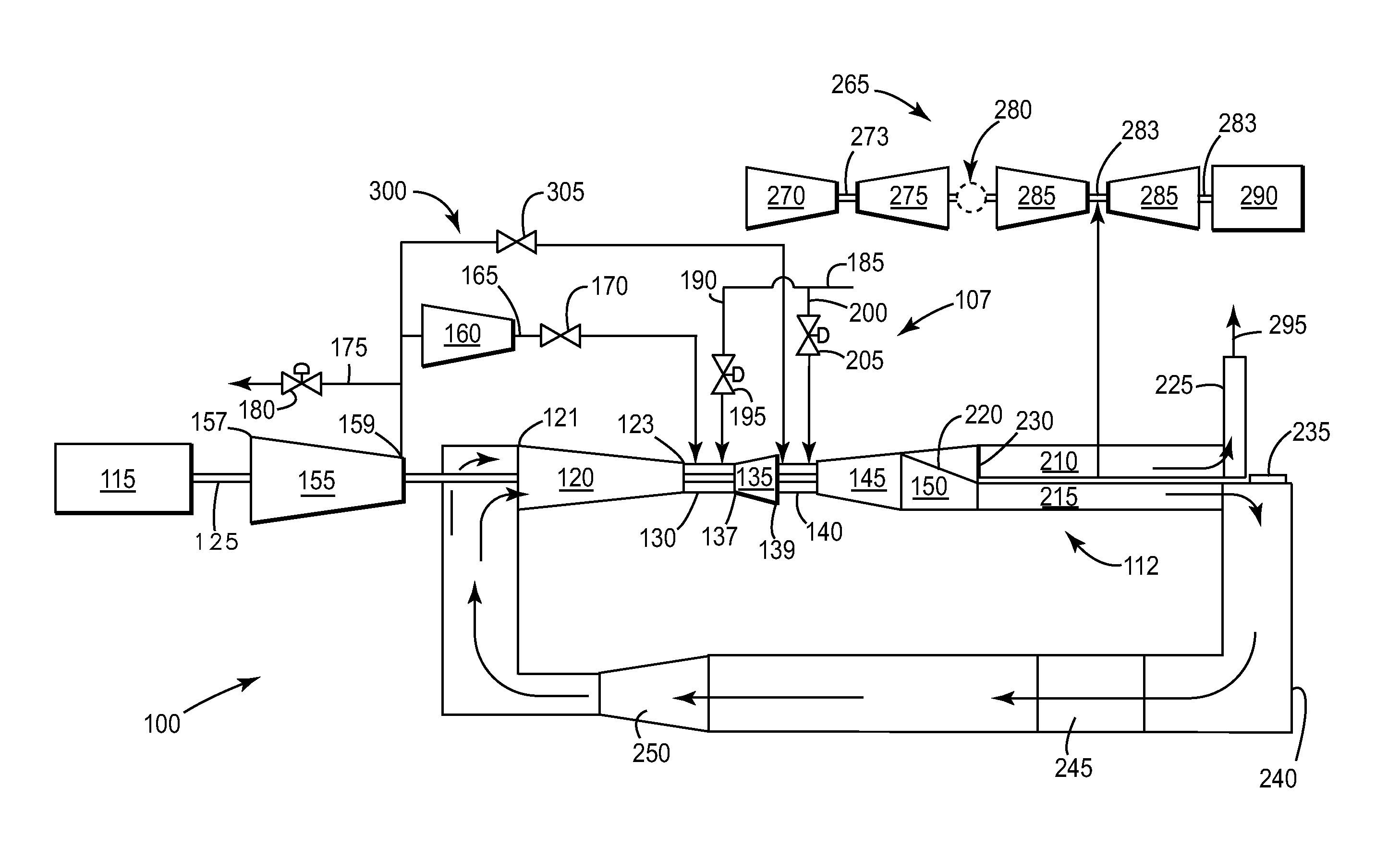
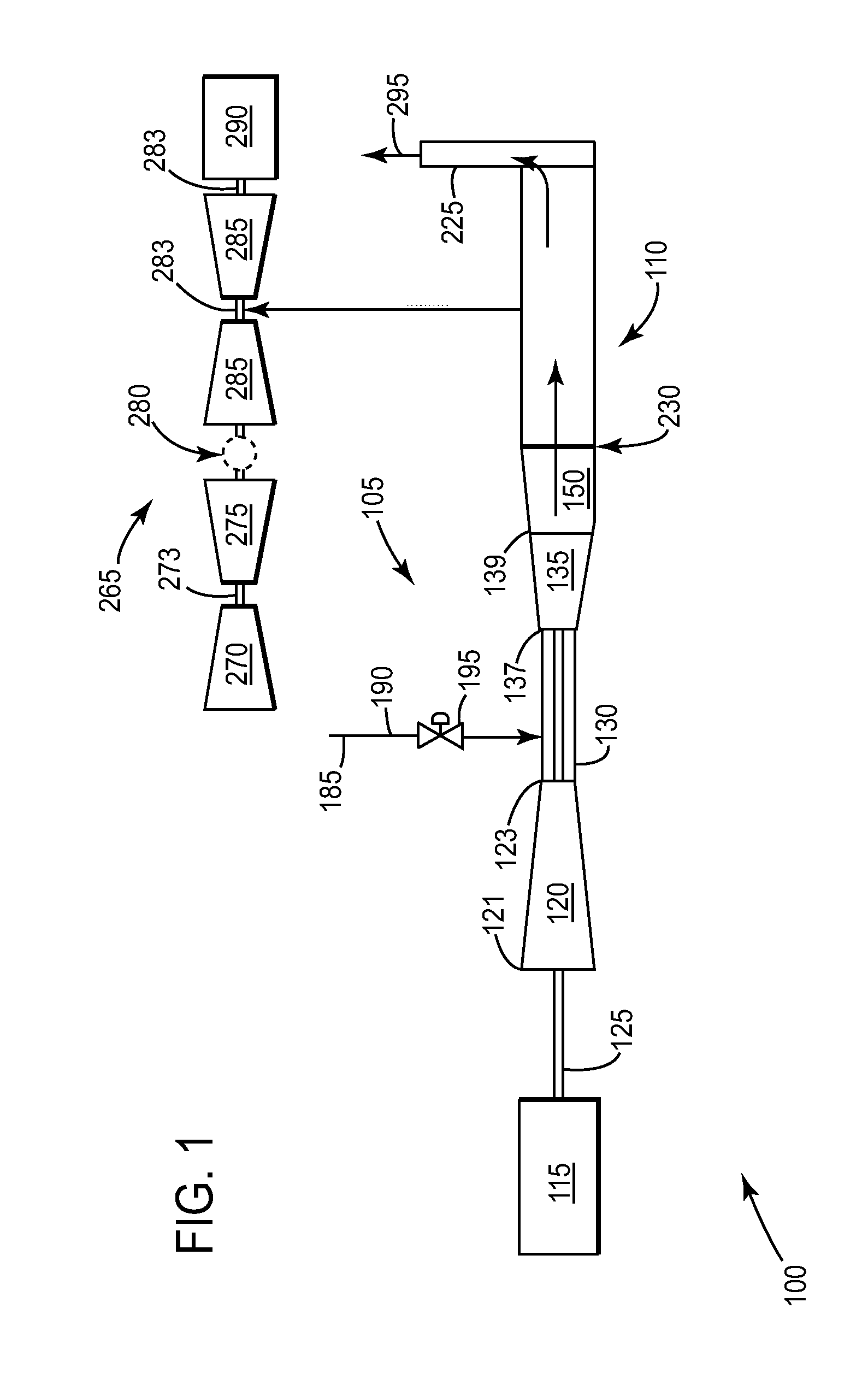
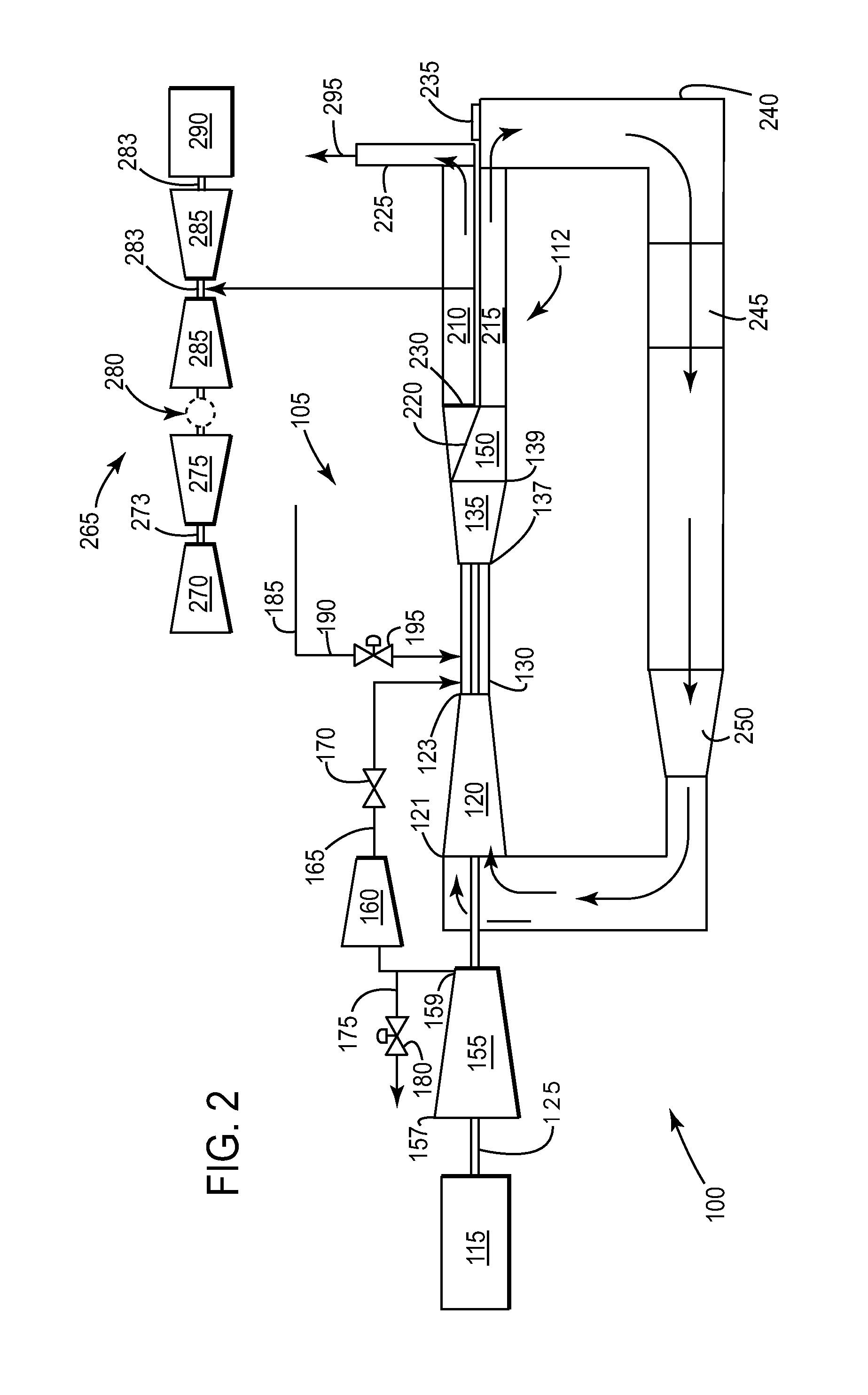
Method and system for controlling a powerplant during low-load operations
The present invention provides a system and method of operating a combined-cycle powerplant at part-load without shutting down an HRSG and steam turbine. The present invention may apply to a powerplant operating in an open-cycle mode. The present invention may also apply to a powerplant operating in a closed-cycle mode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
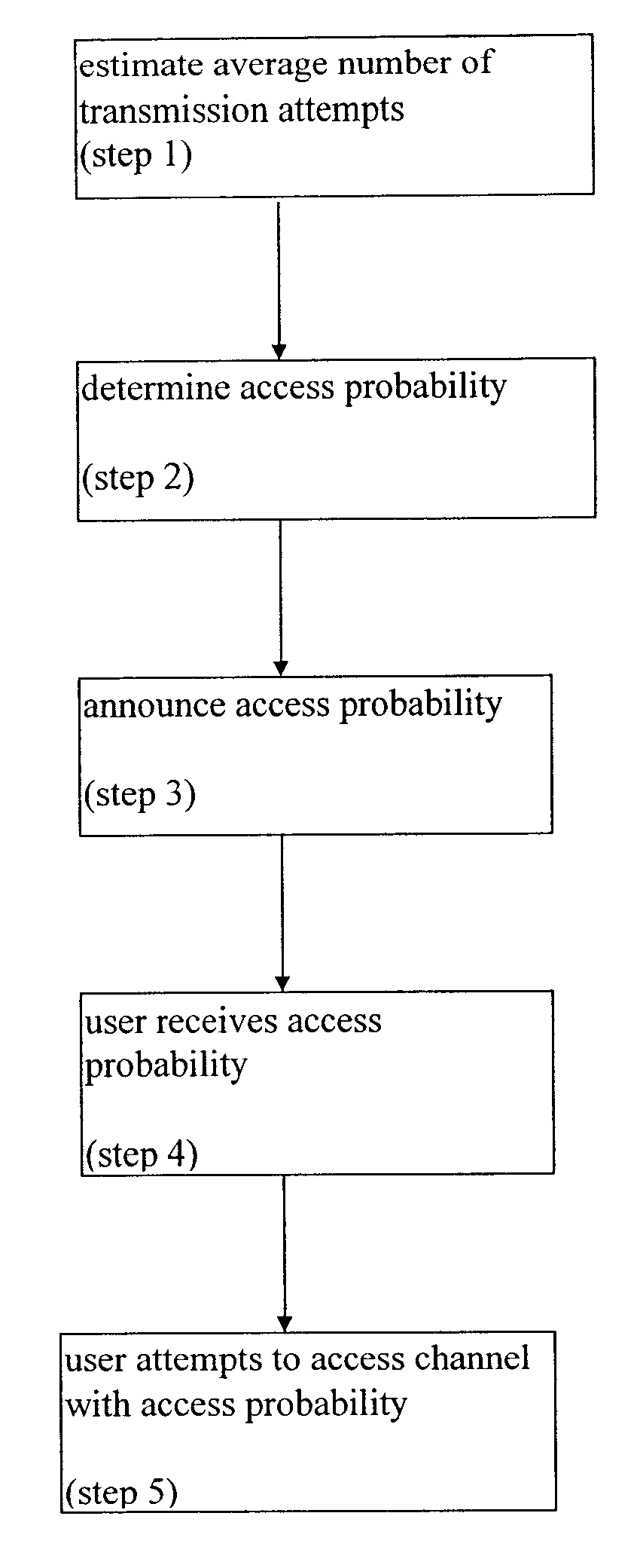
Announced dynamic access probability protocol for shared bandwidth networks
InactiveUS6418136B1Network traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionWireless mesh networkLow load
A system and a method for a dynamic probability access protocol for determining access to shared channels. Some networks have a common channel which is shared by many users. A key issue in such networks is the allocation of the shared channel among many competing users. The system and method of the present invention enable media access control in shared bandwidth networks. When the user wishes to send a message, the user transmits with a probability p, which depends on the load on the channel. The probability p is announced by the network, and transmitted to the users as a broadcast message. Under conditions of low load, the probability p approaches 1, while at high load p is relatively low. This media access control protocol guarantees high channel utilization at high load, as well as low delay at low load periods. The proposed method is applicable on wireless networks, such as cellular networks and satellite-based networks. In addition, the method and system of the present invention can be used in wired networks, for other applications such as local area networks (LAN), client / server networks, and accessing a Web site through the Internet. The method and system of the present invention are able to reduce the likelihood of collisions, without increasing the access delay at low load periods.
Owner:RAMOT UNIV AUTHORITY FOR APPLIED RES & INDAL DEVMENT
Cylinder cutoff control apparatus of internal combustion engine
A cylinder cutoff control apparatus of an engine initiates a cylinder cutoff mode only when two conditions, namely a low load condition such as a vehicle cruising condition and an intake valve closure timing controlled to a given timing value before a bottom dead center, are both satisfied. A fuel cutoff mode is executed prior to the cylinder cutoff mode. During a transition to the cylinder cutoff mode, the control apparatus holds an intake valve open timing at a given timing value substantially corresponding to a top dead center, simultaneously with reducing an intake valve lift amount of each intake valve, subjected to cylinder cutoff control, to a zero lift. Immediately when the intake valve lift amount is reduced to below a lift threshold value, an exhaust valve lift amount of each exhaust valve, subjected to the cylinder cutoff control, is controlled to a zero lift.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
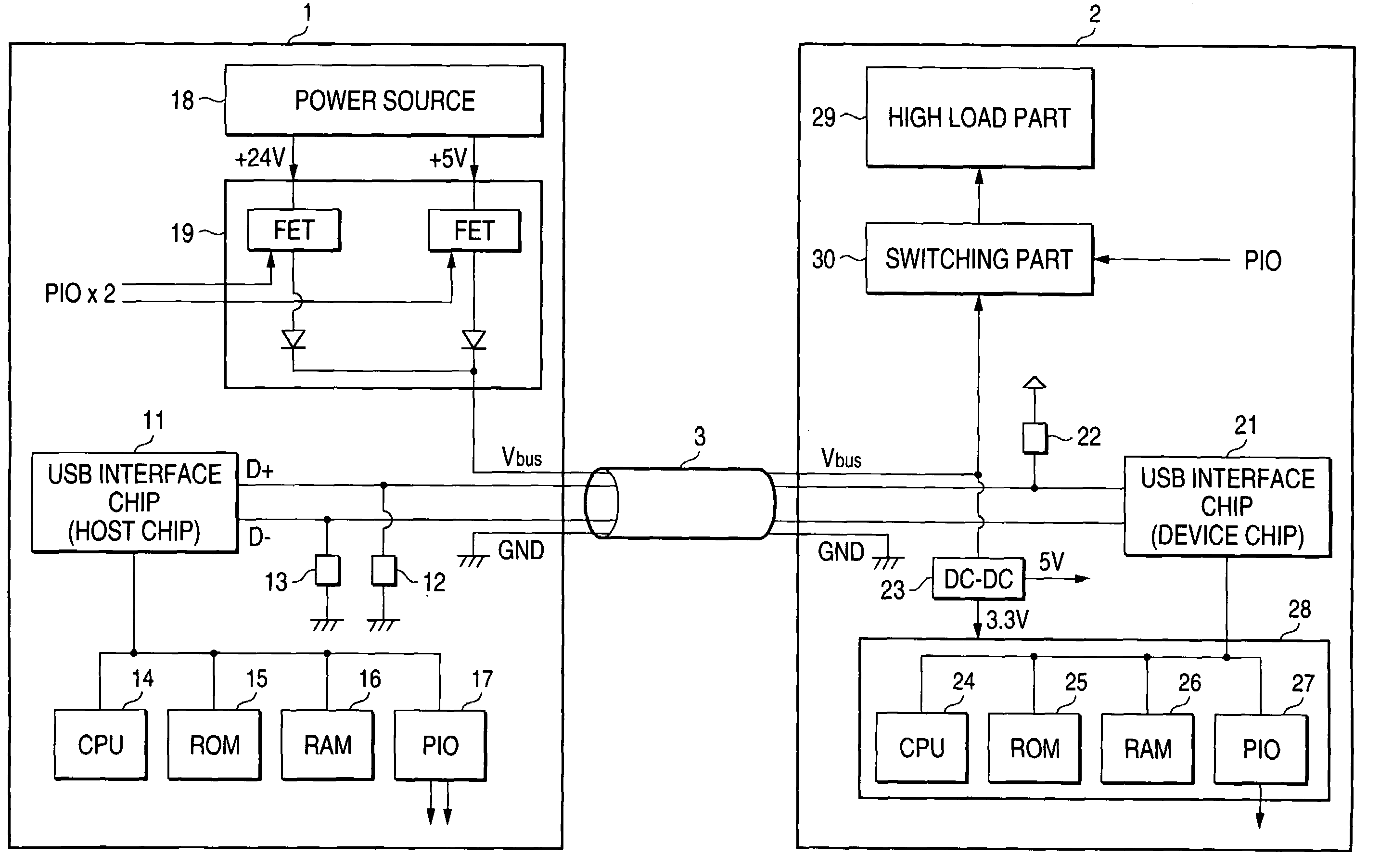
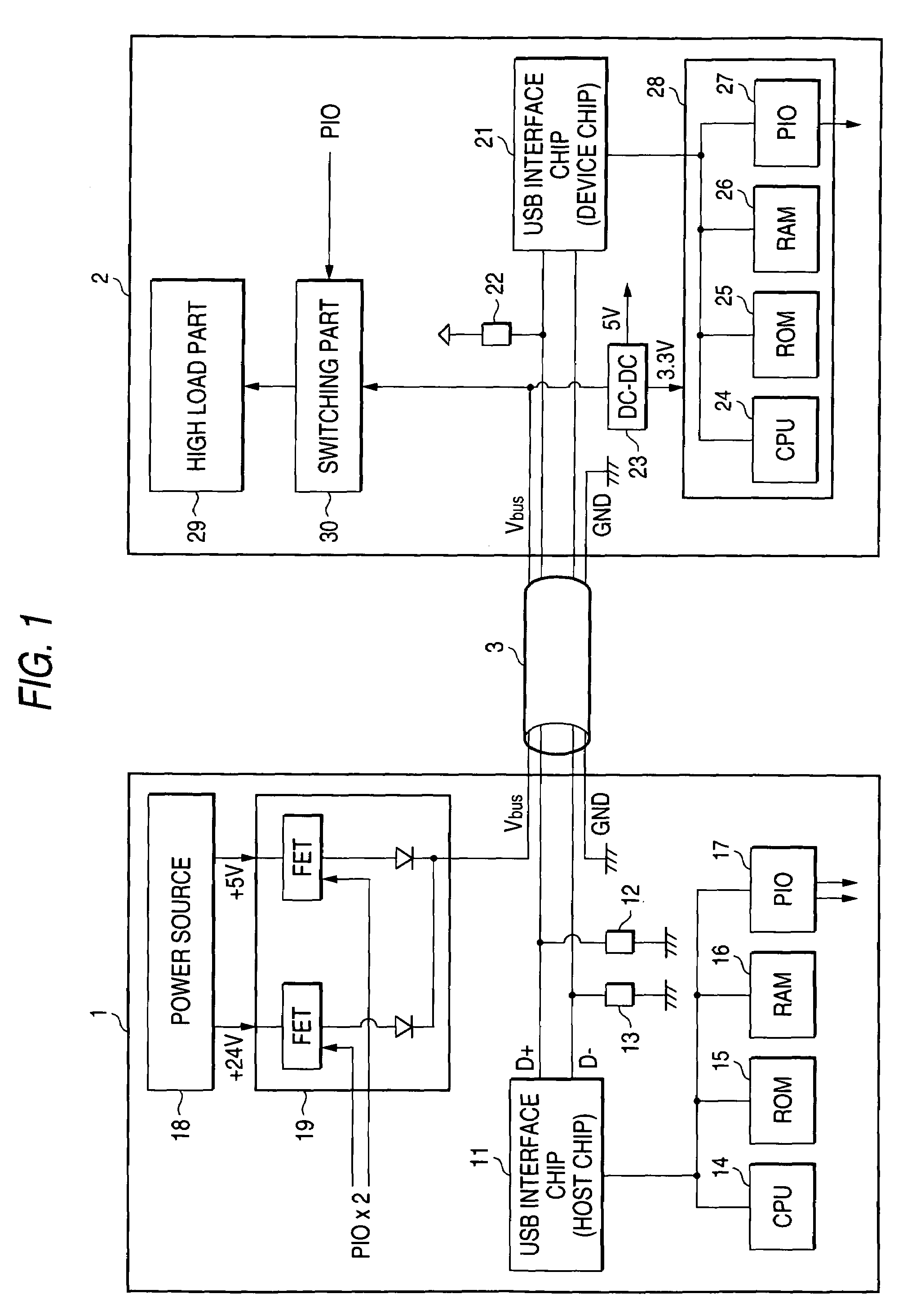
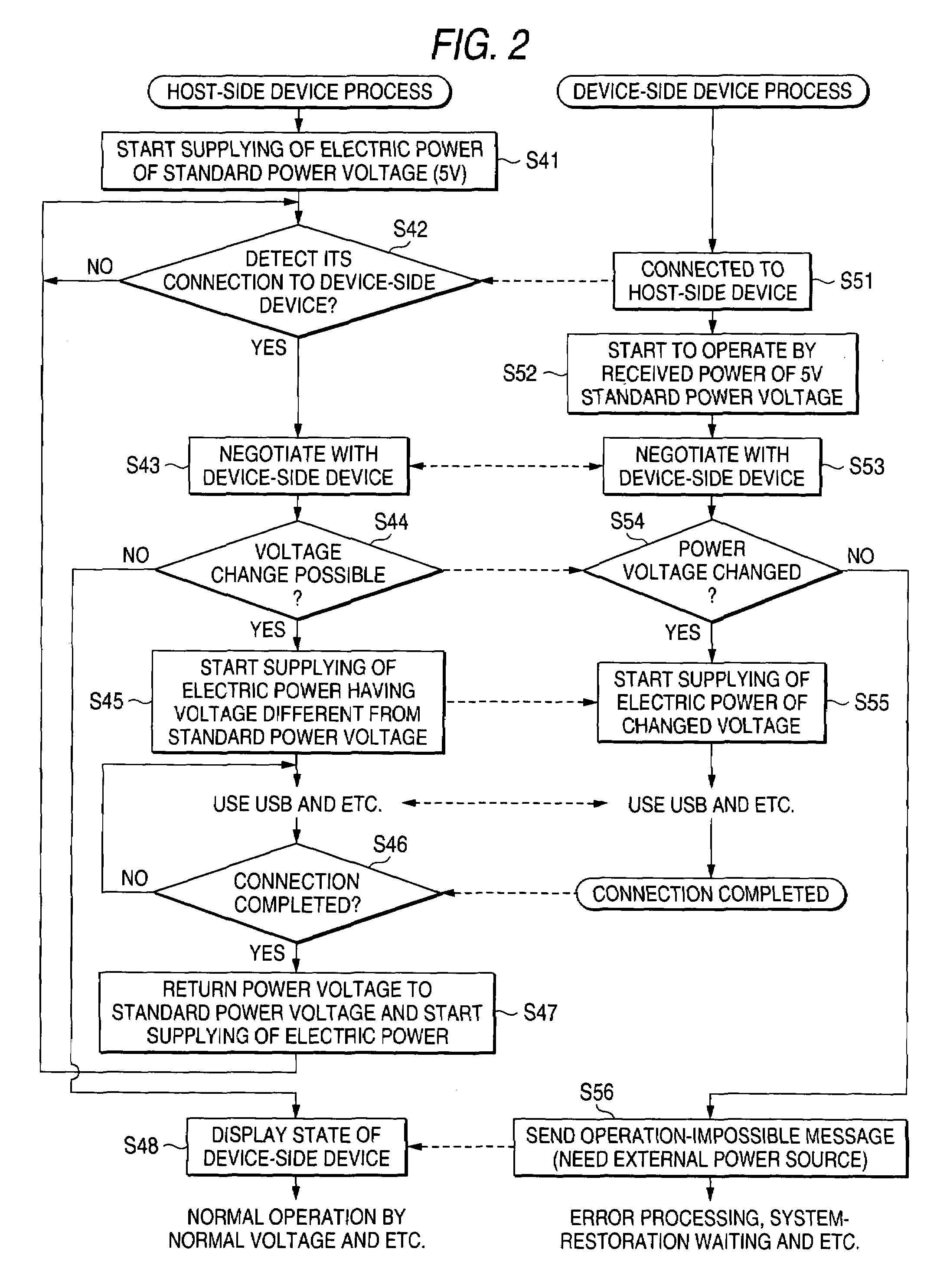
USB device that provides power that is different from power prescribed in the USB standard
InactiveUS7159132B2Minimal increase of costVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingCommunication unitLow load
A USB device for performing communications with a second device through a USB interface while supplying electric power to the second device through a power-source supplying line in the USB interface. The USB device includes a communication unit for communicating with the second device, a power source capable of outputting electric power of a voltage being different from a standard power voltage prescribed in the standards of the USB interface. The power source supplies the electric power to the second device through the power-source supplying line. The second device includes a low load unit and a high load unit The power source supplies the electric power having a power voltage higher than the standard power voltage to the high load unit through the power-source supplying line.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Combustor of gas turbine and combustion control method for gas turbine
ActiveUS7673454B2Improve performanceOccurrence of unburned fuel between the first group and the second groupGas turbine plantsHot gas positive displacement engine plantsCombustorLow load
In a combustor, divisional fluid passages of a first group, and divisional fluid passages of a second group are present on an inner peripheral side, and divisional fluid passages are also present on an outer peripheral side, and swirl air flows are gushed from the divisional fluid passages. When the total amount of fuel supplied to the combustor is small as in a speed increasing state or in a low load state, fuel is injected only into the divisional fluid passages of the first group. Since a fuel injection region is limited to a position on the inner peripheral side, particularly, a specific position, the concentration of a fuel gas comprising a mixture of fuel and air is lean, but is higher than a flammability limit concentration, even when the total amount of fuel is small.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Compression-ignited IC engine and method of operation
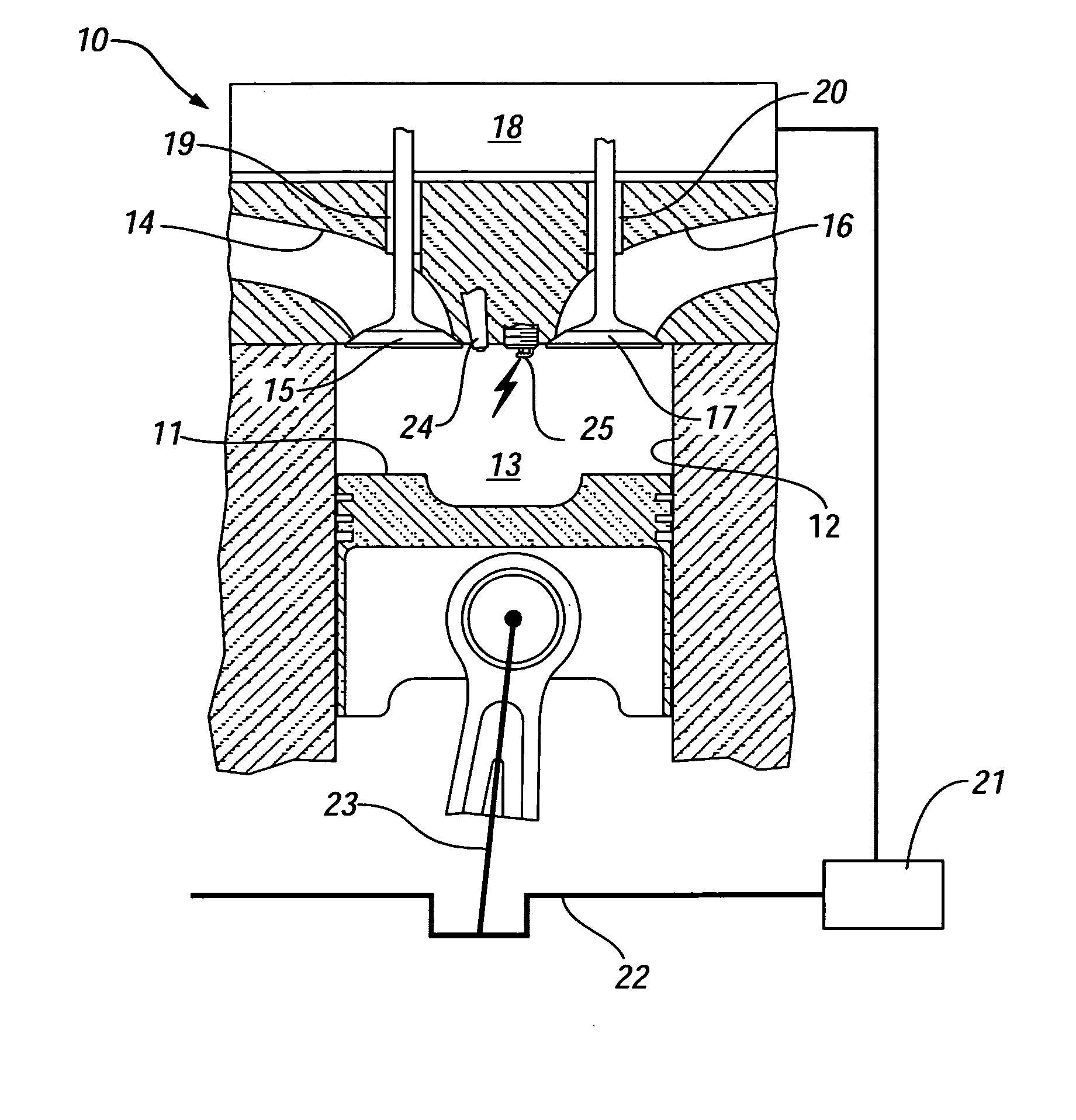
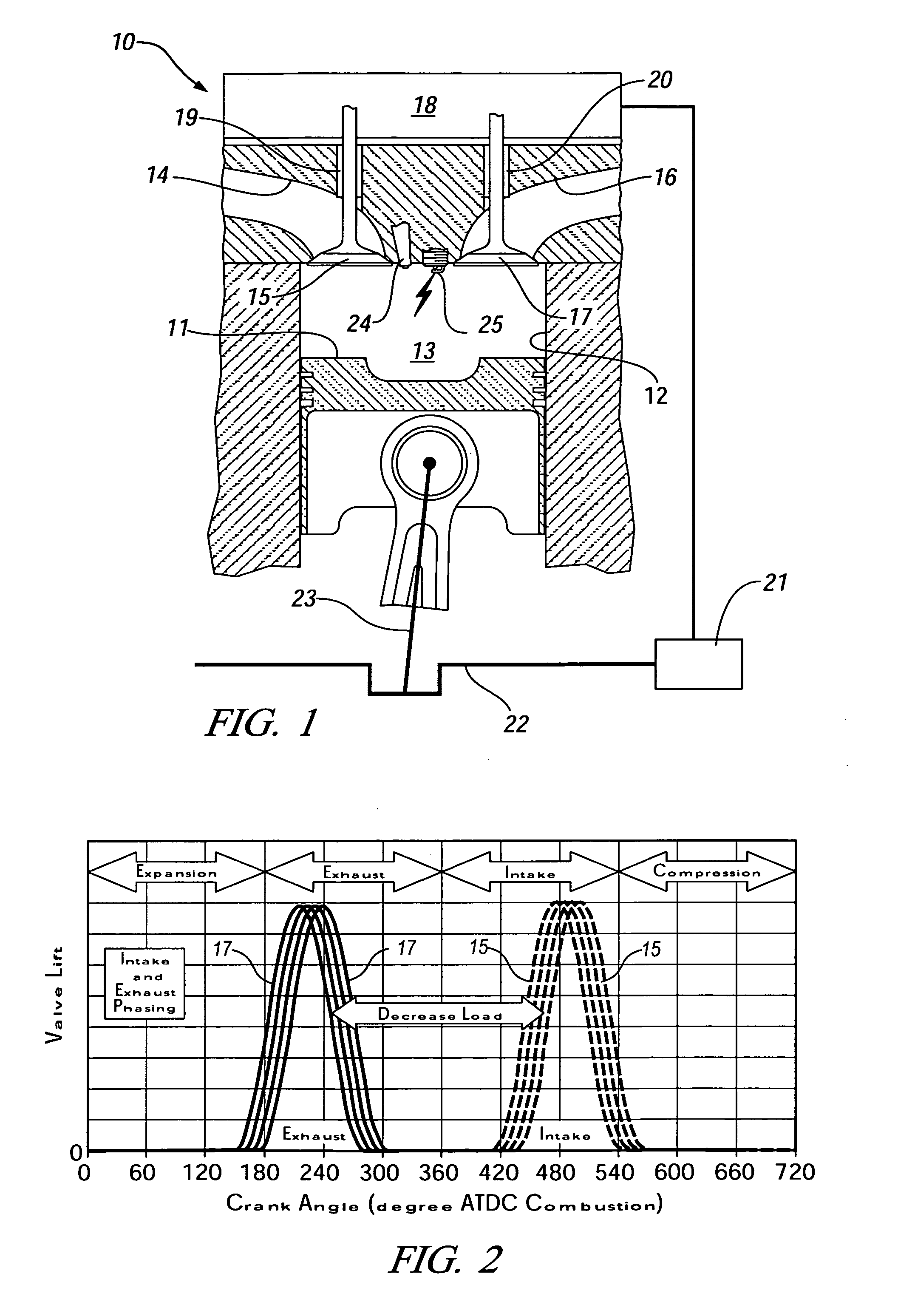
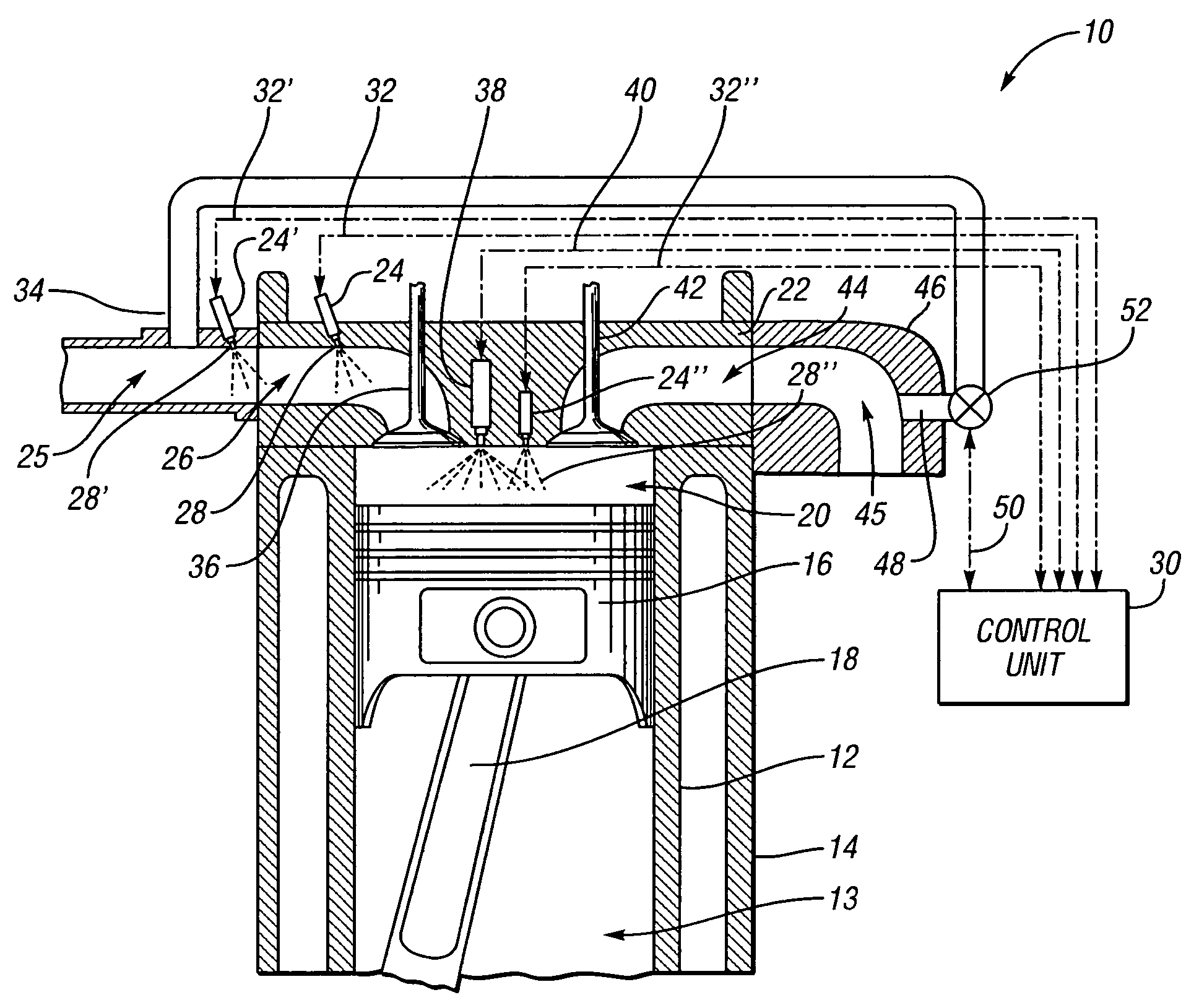
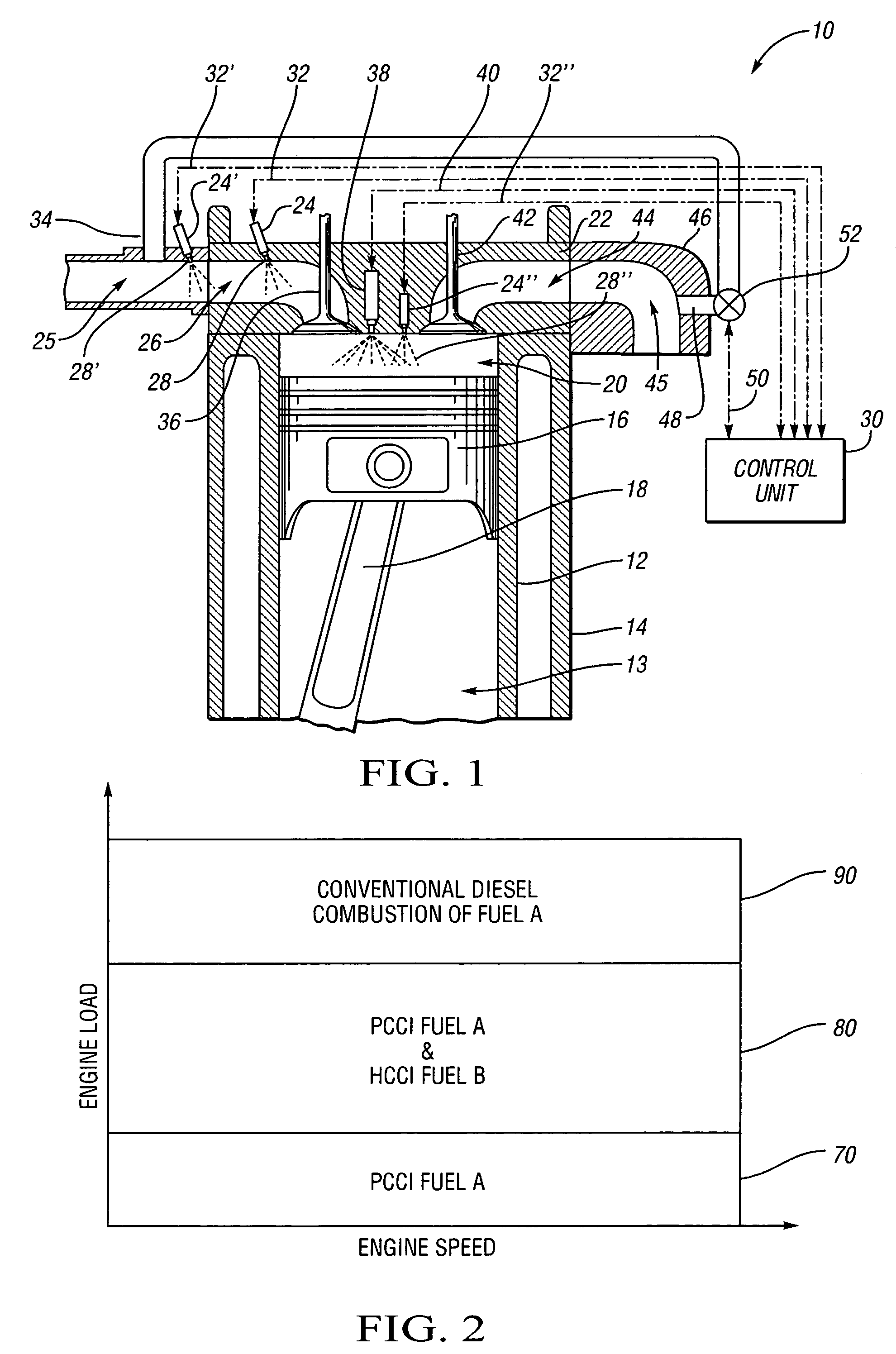
InactiveUS20060180121A1Emission reductionImprove efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionTop dead center
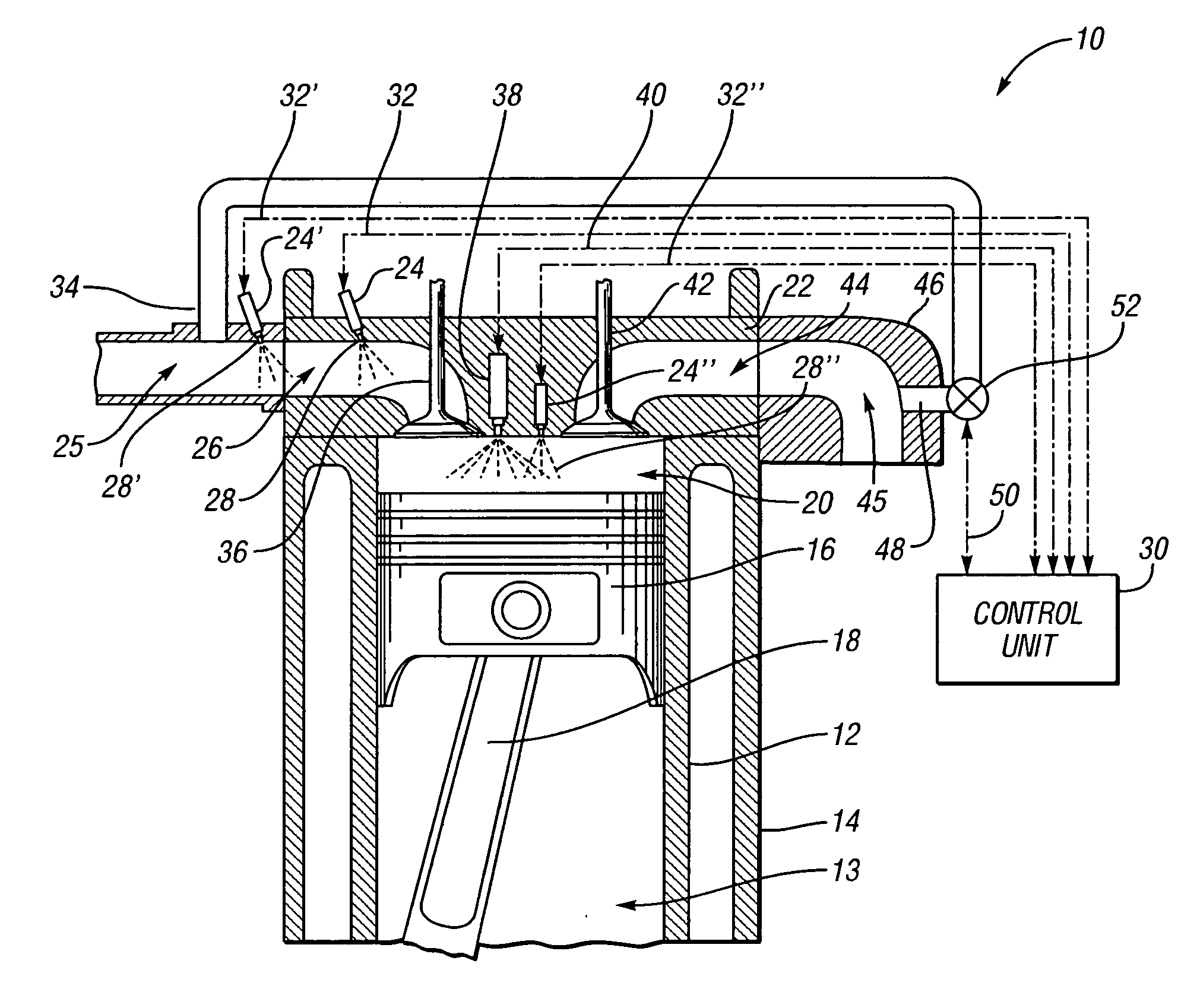
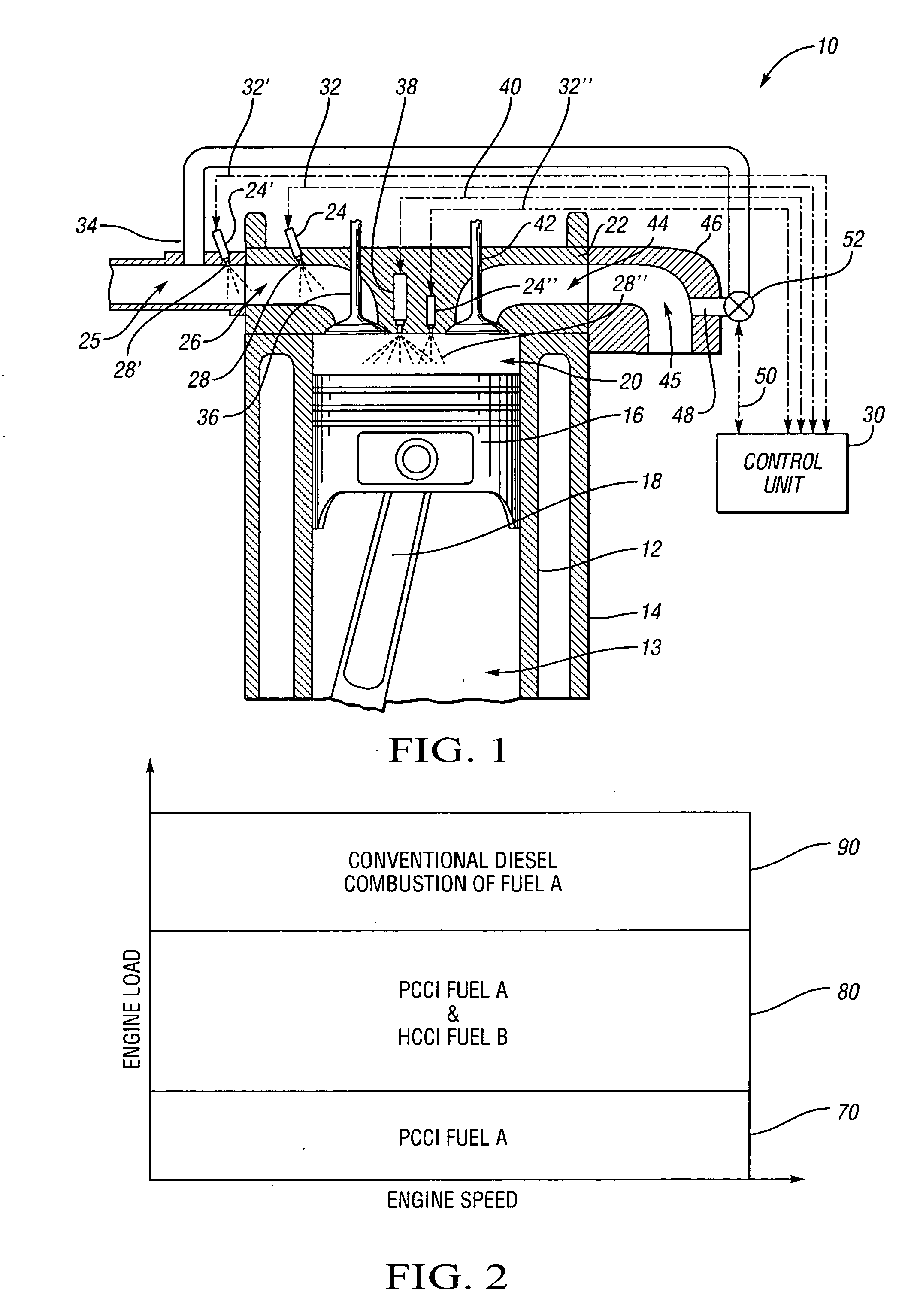
The present invention is a compression ignition internal combustion engine and method of operation which expands the load limit of quietly operating a premixed charge compression ignition (PCCI) engine by injecting a secondary fuel B, in ratios lean of stoichiometric, either into the intake air stream or directly into the cylinder to form a homogeneous fuel B and air mixture. Near top dead center of the compression stroke, a PCCI-type direct injection of fuel A event is used to initiate combustion of both fuel A and B at the proper time. At low loads the combustion mode is characterized a PCCI-type with high EGR rates. At medium loads the combustion mode is that of homogeneous combustion of fuel B coupled with PCCI combustion of fuel A. At the highest loads the engine will revert to a conventional diesel combustion mode of fuel A to maintain power density.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
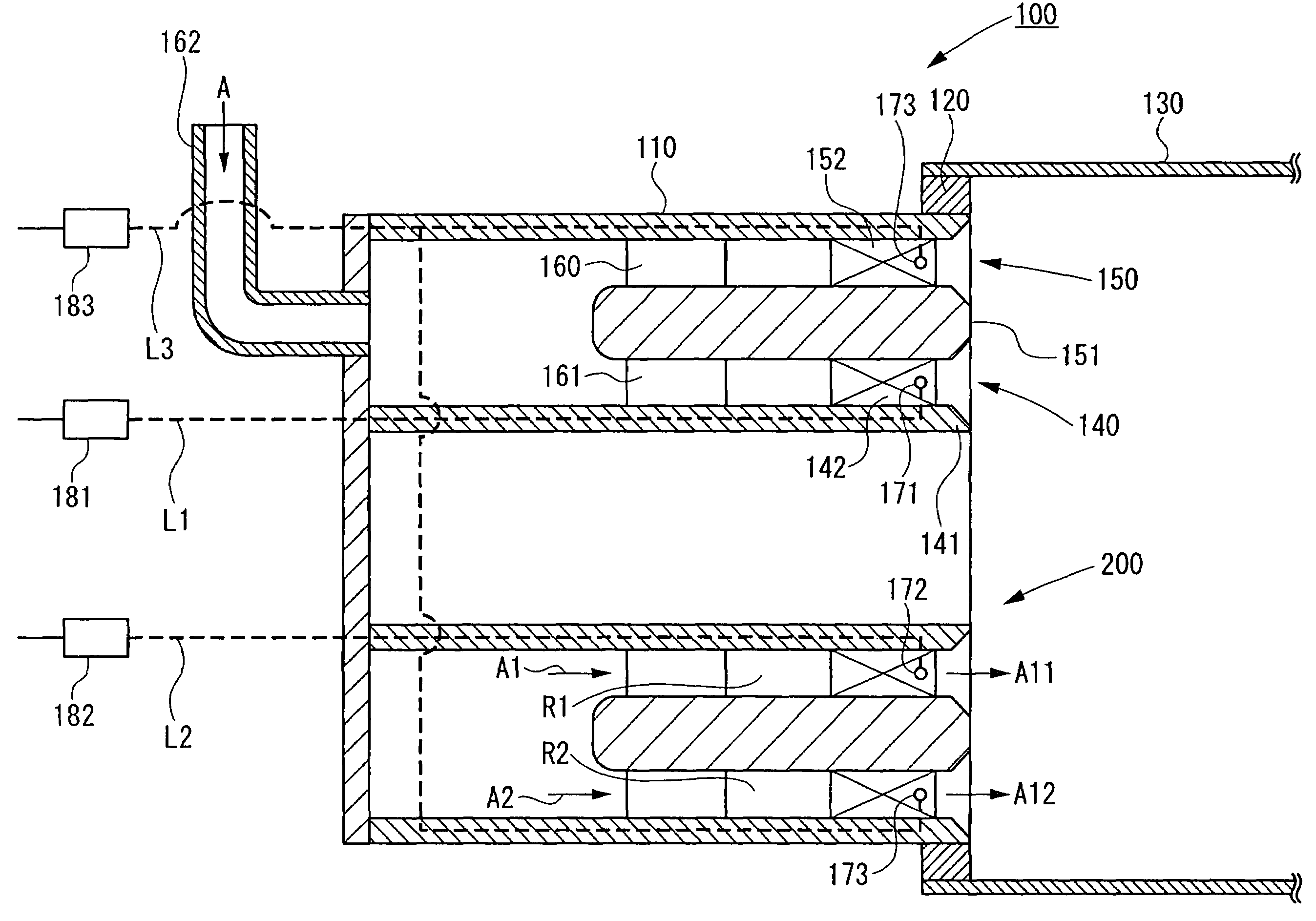
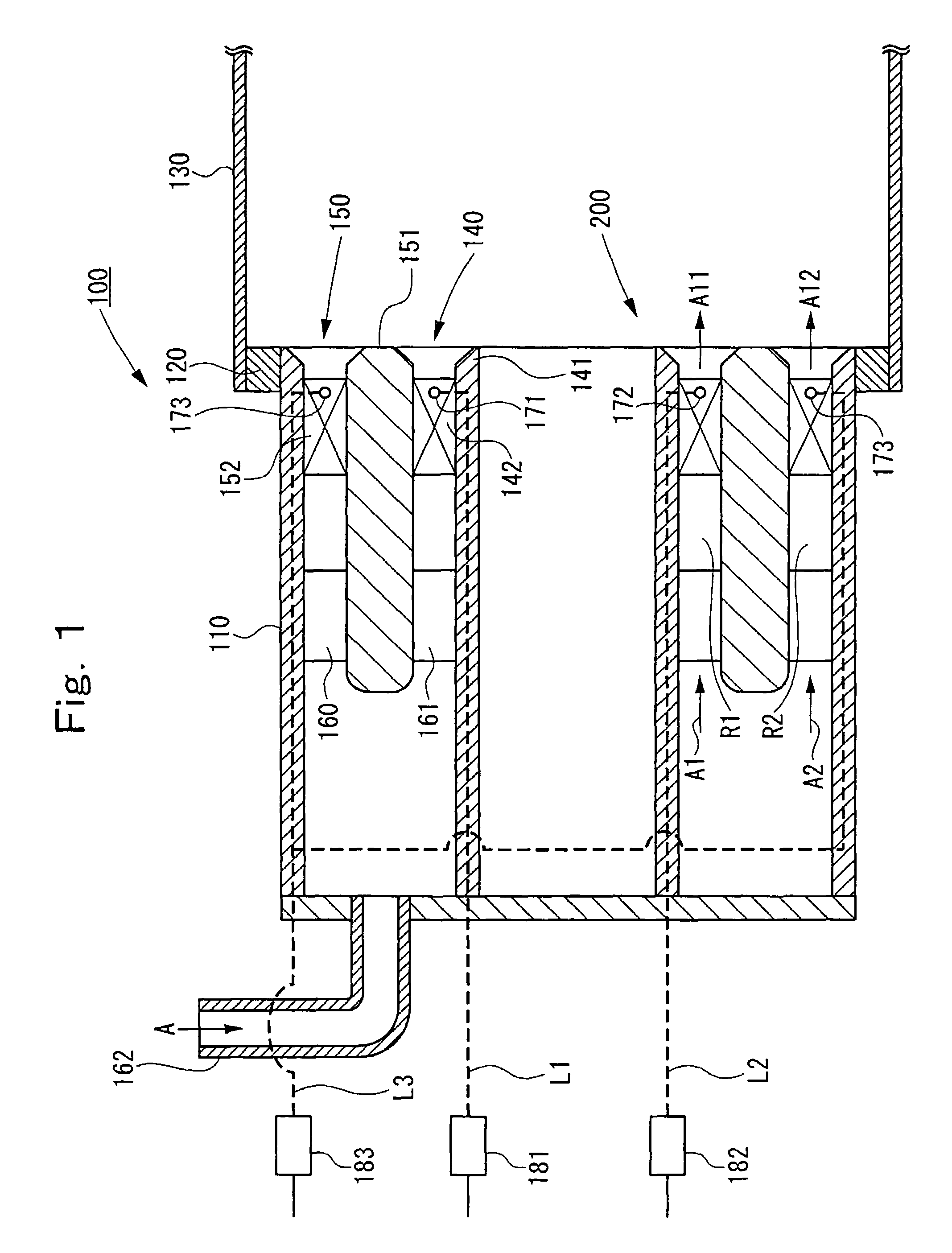
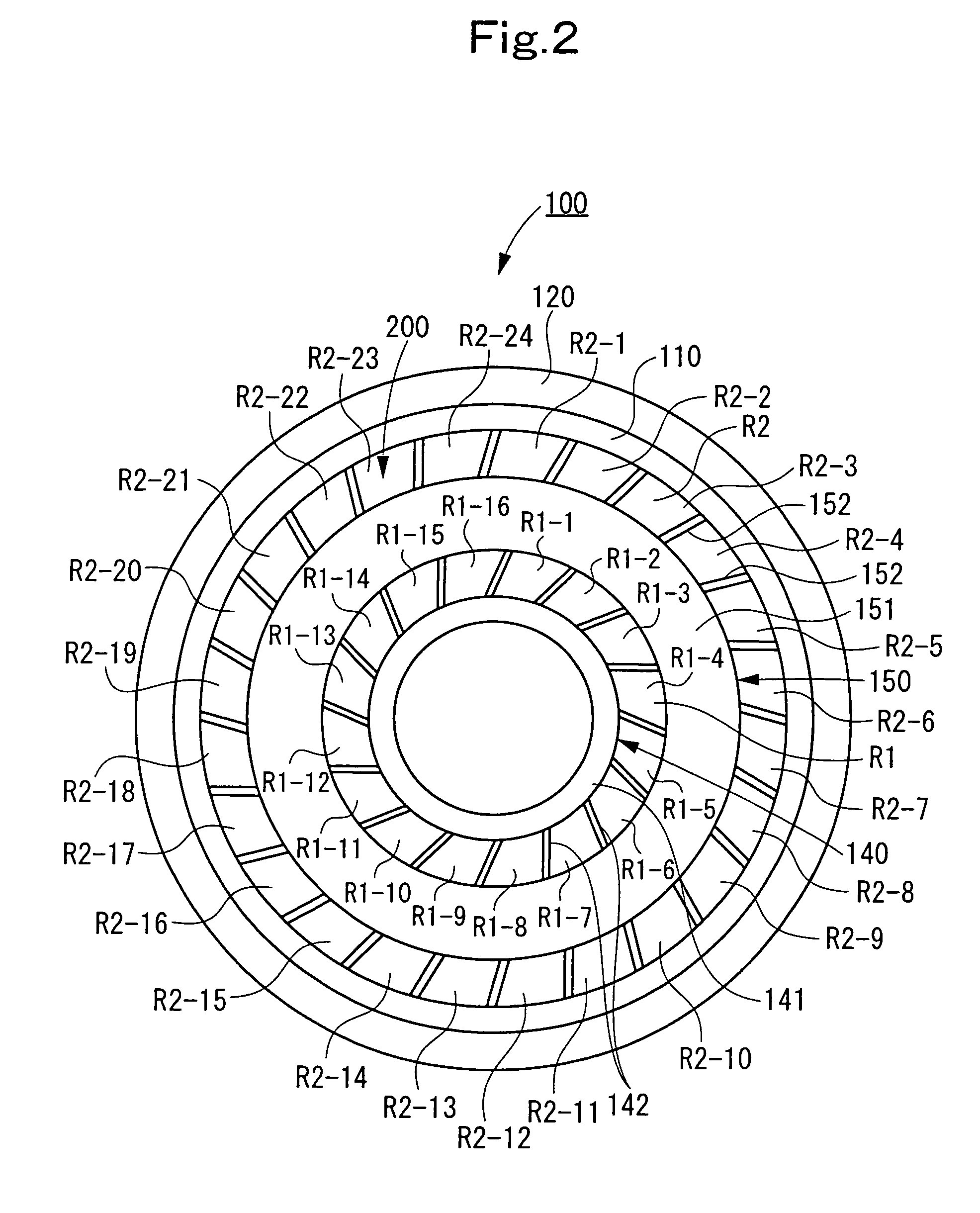
Compliant hybrid gas journal bearing using integral wire mesh dampers
A compliant hybrid gas journal bearing includes compliant hybrid bearing pads having a hydrostatic recess and a capillary restrictor for providing a flow of pressurized gas to the bearing. The bearing also includes an inner rim adjacent the bearing pads, an outer rim and a damper bridge between the inner and outer rims. The damper bridge has an axial length that is less than an axial length of the bearing pads and the outer rim to form a damper cavity on each side of the damper bridge. An integral wire mesh damper is situated within the damper cavity on each side of the damper bridge. Integral centering springs are located between the inner and outer rims to provide radial and rotational compliance to the bearing pads. The oil-free bearing design addresses the low damping and low load capacity characteristics that are inherent in present day compliant air foil bearing designs, while retaining the compliance to changes in rotor geometry.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Exhaust compound internal combustion engine with controlled expansion
A piston compound internal combustion engine is disclosed with an expander piston deactivation feature. A piston internal combustion engine is compounded with a secondary expander piston, where the expander piston extracts energy from the exhaust gases being expelled from the primary power pistons. The secondary expander piston can be deactivated and immobilized, or its stroke can be reduced, under low load conditions in order to reduce parasitic losses and over-expansion. Two mechanizations are disclosed for the secondary expander piston's coupling with the power pistons and crankshaft. Control strategies for activation and deactivation of the secondary expander piston are also disclosed. In addition, six-cylinder engine configurations are defined by replicating groups of two power pistons and one expander piston.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Control device for spark-ignition engine
InactiveUS6968825B2Increase rangeEfficiently prevent knockingValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberLow speed
A control device for a spark-ignition engine, in which a mixture in a combustion chamber is fired by compression ignition in a part-load range under warm-running conditions, includes an EGR controller incorporating a valve operation controller for controlling internal EGR of hot burned gas and a cold EGR controller for controlling external EGR of cold burned gas. The EGR controller performs EGR control operation to leave the hot EGR gas in the combustion chamber in a lower-load, lower-speed region within a compression ignition combustion range and to introduce the cold EGR gas into the combustion chamber in a higher-load, higher-speed region within the compression ignition combustion range. The control device further includes a firing assist unit for inducing the compression ignition at least when ignitability of the mixture decreases due to introduction of the cold EGR gas in the compression ignition combustion range.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Fuel cell system with fluid stream recirculation
An electric power generation system has a multiple jet ejector assembly for recirculating an exhaust stream. The system includes a fuel cell stack having a reactant stream inlet, a reactant stream outlet and at least one fuel cell. A pressurized reactant supply provides a reactant to the multiple jet ejector assembly. The multiple jet ejector assembly includes two motive flow inlets, one suction inlet, fluidly connected to the reactant stream outlet to receive a recirculated flow from the fuel cell stack, and one discharge outlet, fluidly connected to the reactant stream inlet to provide an inlet stream to the fuel cell stack. A pressure regulator is interposed between the pressurized reactant supply and the two motive flow inlets of the multiple jet ejector assembly. A first solenoid valve is interposed between the first motive flow inlet and the regulator. A second solenoid valve is interposed between the second motive flow inlet and the regulator. A by-pass line connects the pressurized reactant supply to the second motive flow inlet. A by-pass solenoid valve is interposed in the bypass line between the pressurized reactant supply and the second motive flow inlet. During low-load operating conditions, the second solenoid valve is open and the first and by-pass solenoid valves are closed, so that pressurized reactant, controlled by the regulator, is directed to the second motive flow inlet. During high-load operating conditions, the second solenoid valve is closed and the first and by-pass solenoid valves are open, so that pressurized reactant, controlled by the regulator, is directed to the first motive flow inlet and pressurized reactant, not controlled by the regulator, is directed to the second motive flow inlet.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO +1
Low emission diesel combustion system with low charge-air oxygen concentration levels and high fuel injection pressures
InactiveUS6857263B2Cost effectiveLower Level RequirementsLiquid coolingEngine sealsLow loadMass ratio
This invention sets forth a commercially viable diesel combustion system that meets environmentally acceptable levels of NOx emissions (i.e. 0.2 g / bhp-hr or lower across a full map of engine speeds and loads) without the need for use of NOx aftertreatments, and simultaneously maintains engine-out PM emissions relatively close (e.g. with smoke levels at or below 3 BSN) to environmentally acceptable PM post-aftertreatment levels. The invention achieves these results by operating within a unique combination of parameters. These parameters comprise: (1) charge-air oxygen concentration below 16%, preferably between 10% and 15%, more preferably between 11% and 14%, and most preferably between 12% and 13.5% for virtually all engine operating conditions (but not necessarily at no-load or low load conditions), (2) fuel injection pressures at or exceeding 1800 bar, preferably exceeding 2100 bar, more preferably exceeding 2300 bar, and most preferably exceeding 2500 bar, at most engine speeds and loads, and (3) charge-air mass / fuel mass ratio between 25:1 and 45:1 for medium and high loads. Furthermore, the system is preferably run continuously slightly lean of stoichiometry, providing just enough excess oxygen to facilitate completeness of combustion and to maintain an exhaust oxygen level sufficient for continuous trap regeneration at a balance point in operation.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
Compression-ignited IC engine and method of operation
InactiveUS7121254B2Improve efficiencyEmission reductionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustionTop dead center
The present invention is a compression ignition internal combustion engine and method of operation which expands the load limit of quietly operating a premixed charge compression ignition (PCCI) engine by injecting a secondary fuel B, in ratios lean of stoichiometric, either into the intake air stream or directly into the cylinder to form a homogeneous fuel B and air mixture. Near top dead center of the compression stroke, a PCCI-type direct injection of fuel A event is used to initiate combustion of both fuel A and B at the proper time. At low loads the combustion mode is characterized a PCCI-type with high EGR rates. At medium loads the combustion mode is that of homogeneous combustion of fuel B coupled with PCCI combustion of fuel A. At the highest loads the engine will revert to a conventional diesel combustion mode of fuel A to maintain power density.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Wireless communication system, wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method, and computer program
ActiveUS20050276243A1Avoid confictAvoid the conflict of reservation useNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemLow load
In the case where there is a conflict over a band between communication stations that have reserved the band, the communication stations mediate and avoid the conflict of reservation use with low-load processing. In a wireless communication system, band reservation use is permitted, and a plurality of reservation types are provided according to priority of communication. A communication station that performs reservation use describes a reservation type and a rock-paper-scissors value in a beacon. When there occurs a conflict of reservation use at some area, reservation use having higher priority remains, and a communication station that has performed reservation use having a lower priority moves it to another area. In the case where there is a conflict between reservations having the same priority, the communication apparatuses that have performed reservation use perform control by rock-paper-scissors between themselves, and move the reservation of the apparatus that has lost by the judgment.
Owner:SONY CORP
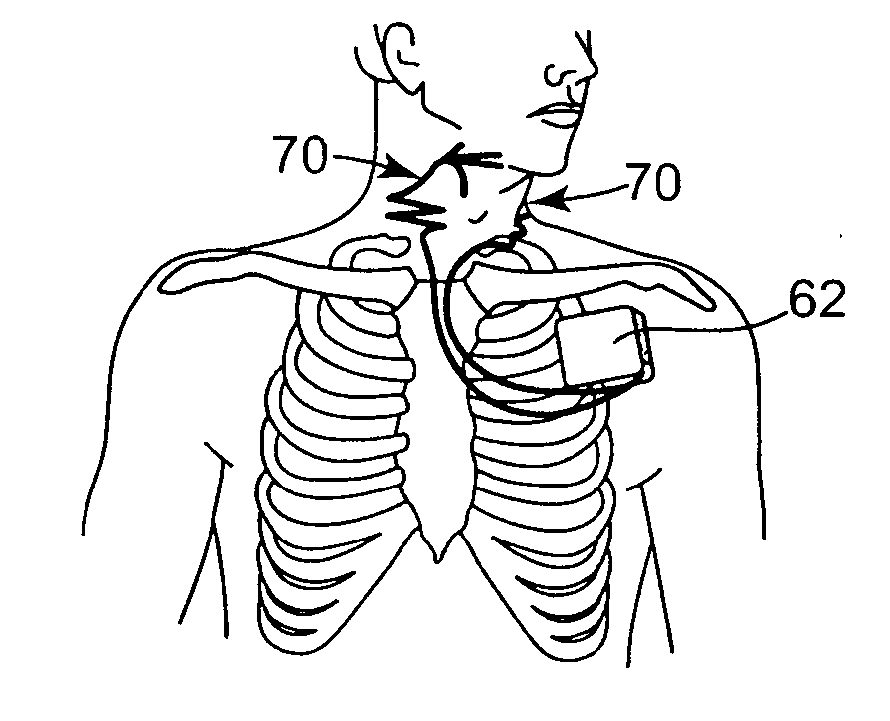
Implantable medical lead assemblies with improved flexibility and extensibility and having a substantially two-dimensional nature
Implantable medical leads assemblies that are flexible and extensible in a controllable manner with a substantially two-dimensional profile to fit between adjacent tissue layers and to facilitate subject body movements. In particular, implantable medical leads advantageously are able to permit and withstand multiple degree of freedom that are useful for use in the neck region of a subject body and other regions of any subject's body that may benefit from increased flexibility and extensibility. Preferably, features of medical leads are utilized to permit extensibility and are based upon the provision of shaped features that controllably permit lead extension under low load, but that maintain a desired shape under no load. The shaped lead portions provide extensibility to the lead as the shapes elastically deform under load.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Load transient control methods for direct-injection engines with controlled auto-ignition combustion
InactiveUS20060196467A1Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHomogeneous charge compression ignitionLow load
A direct injection controlled auto-ignition engine is operated at steady state, within a homogeneous charge compression-ignition (HCCI) load range and with fuel-air-diluent mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, of engine control inputs, including at least fueling mass flow rate, injection timing (FI), spark timing (SI) and exhaust recompression obtained by negative valve overlap (NVO). During load change rates below a predetermined threshold, SI, FI and NVO change rates are synchronized to current changes in the fueling mass flow rate. For fast load increases above the threshold, the cylinder charge is temporarily enriched by increasing the percentage of residual gas or reducing the percentage of fresh air mass in the charge sufficiently to maintain auto-ignition temperature during the load change. This may be done by delaying NVO action for a predetermined speed-dependent number of engine cycles. At very low loads, stable fuel rate reduction may require an alternate method involving deceleration fuel cut-off followed by a step change during refire.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com