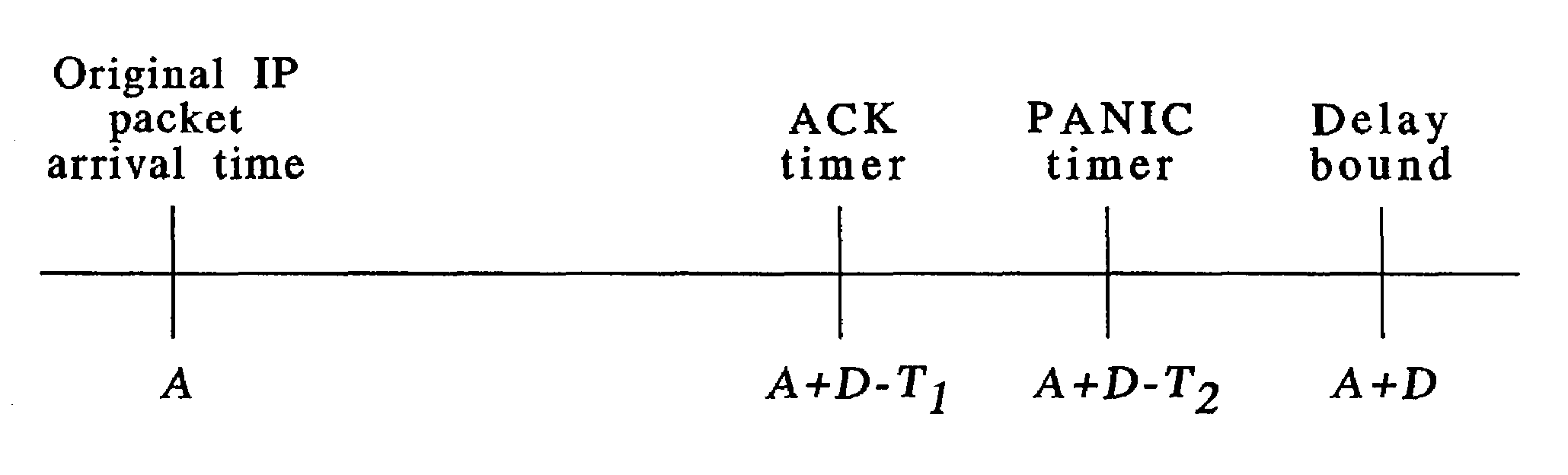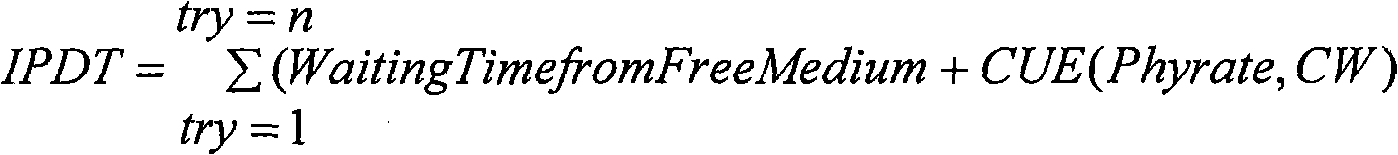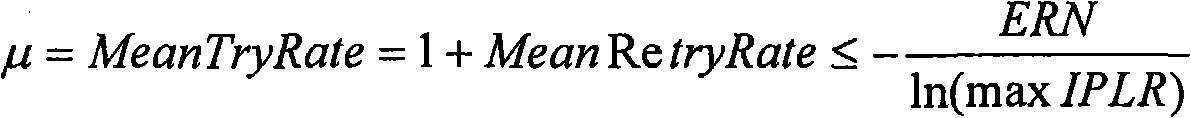Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Delayed binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
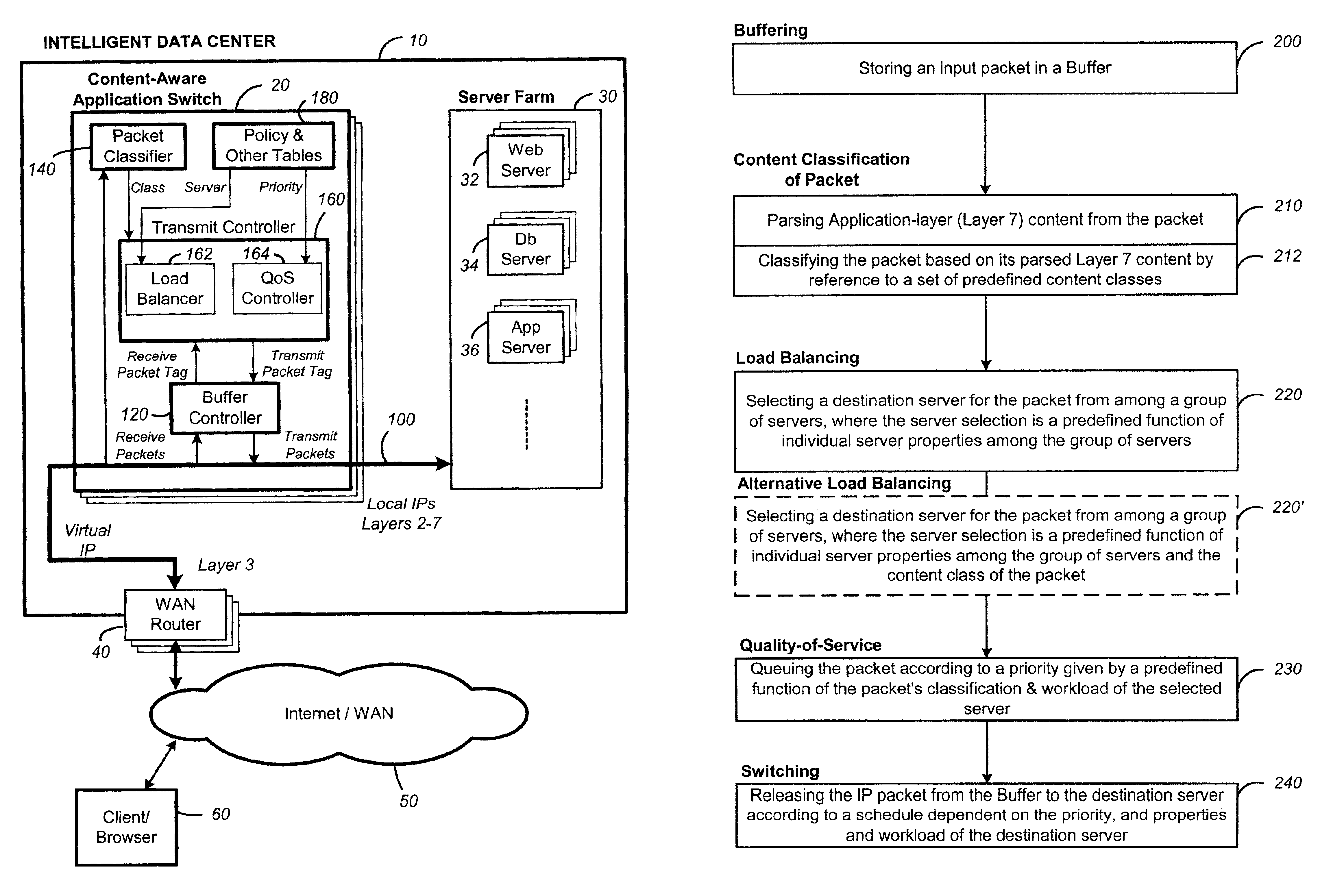
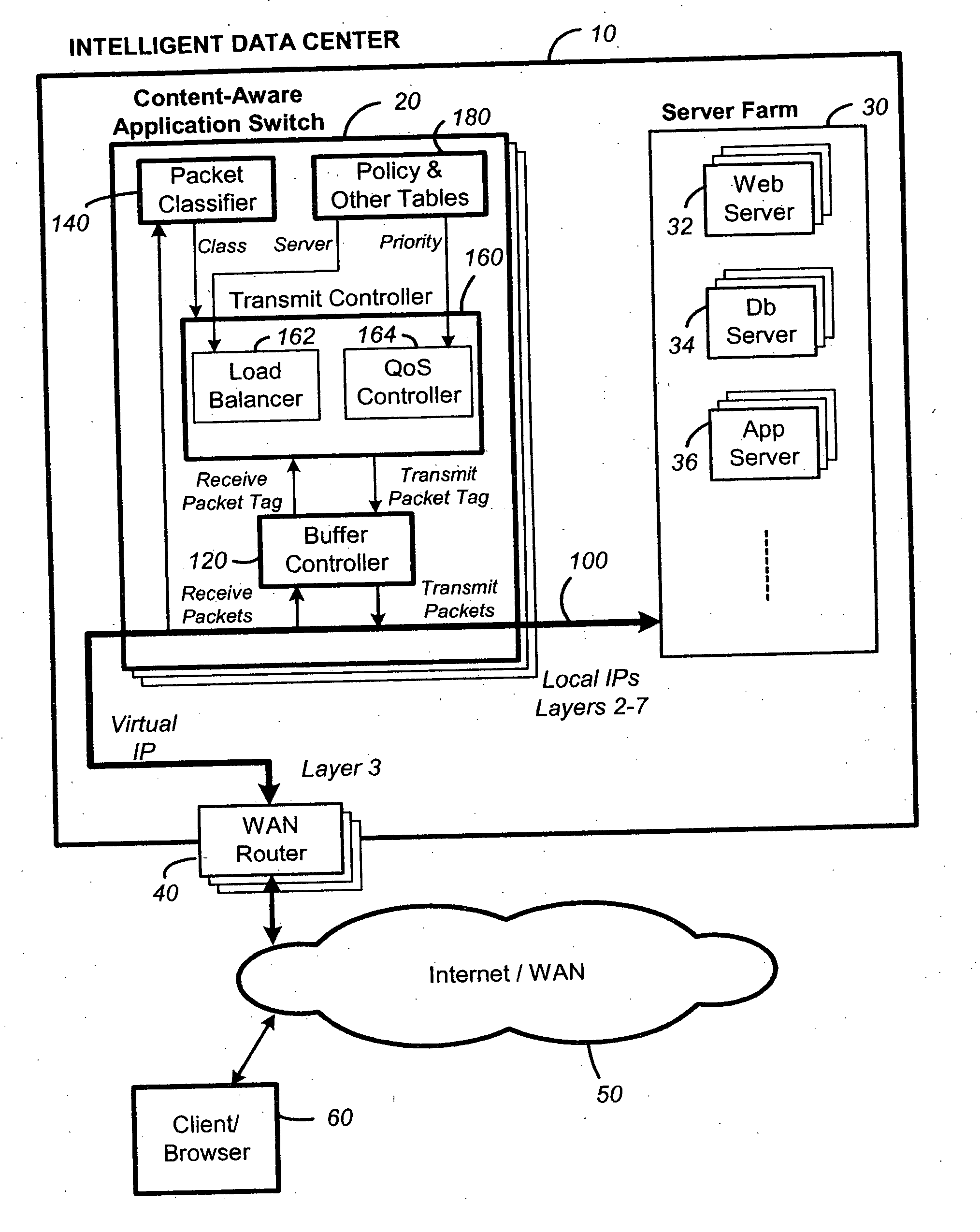
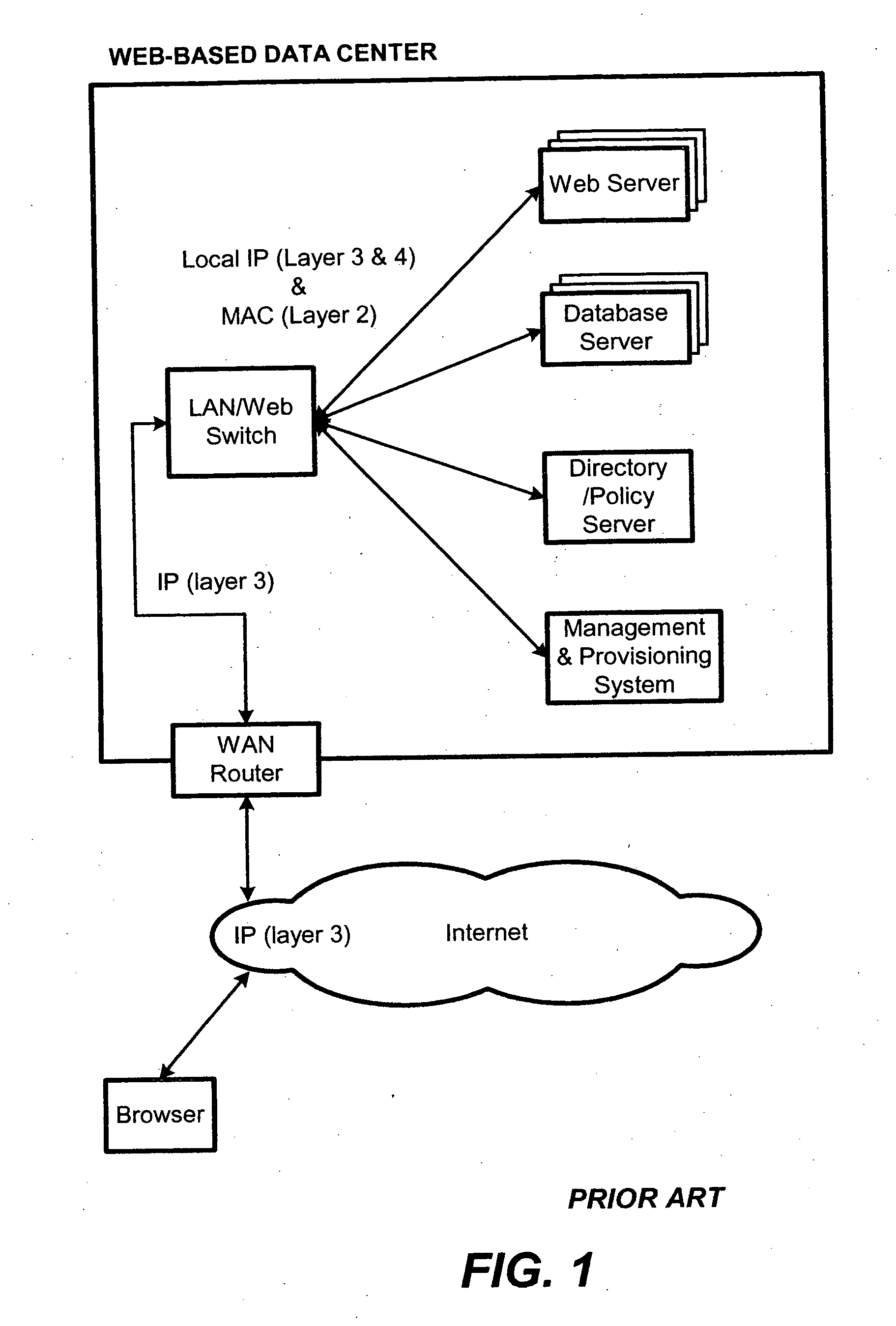
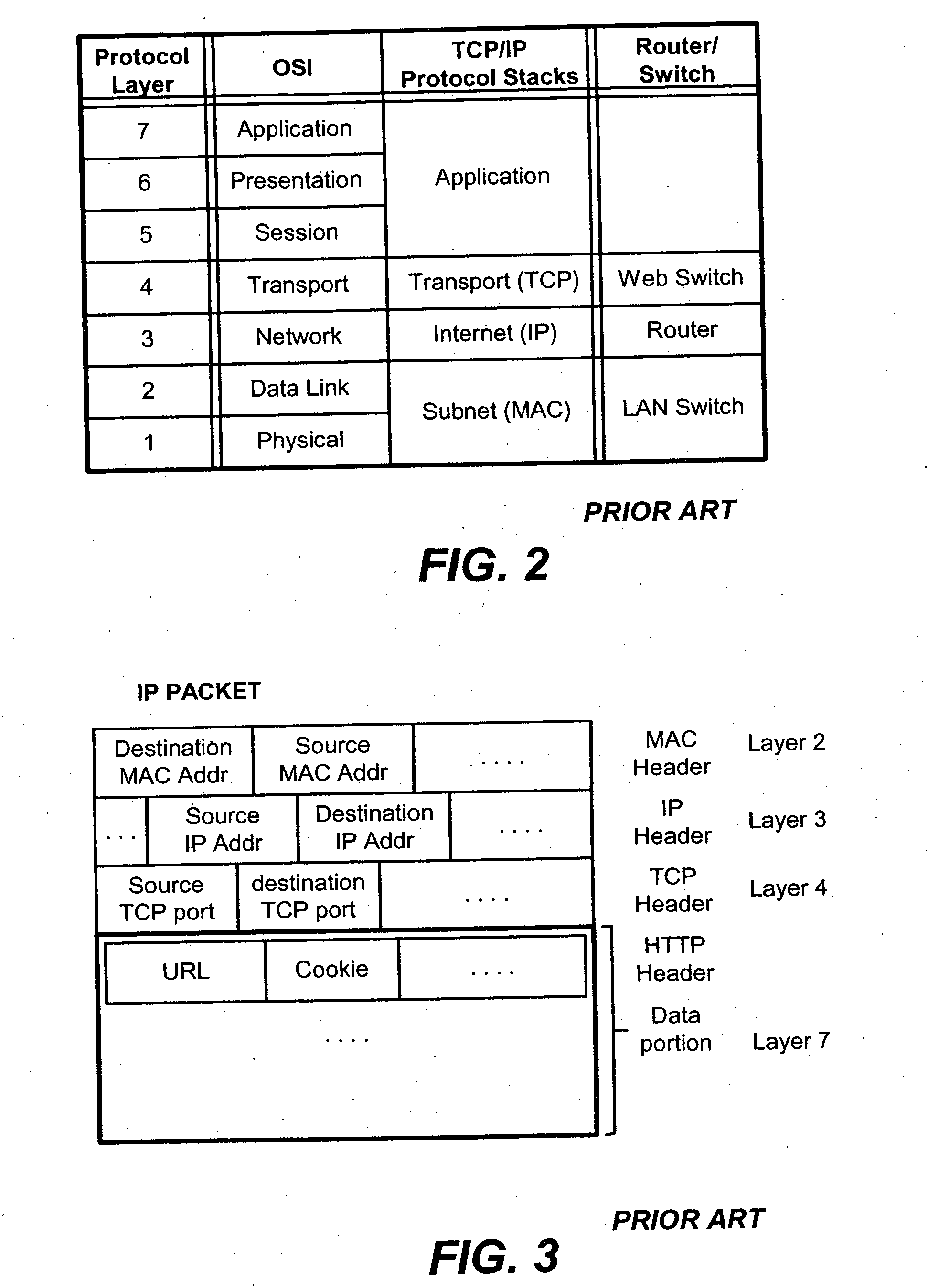
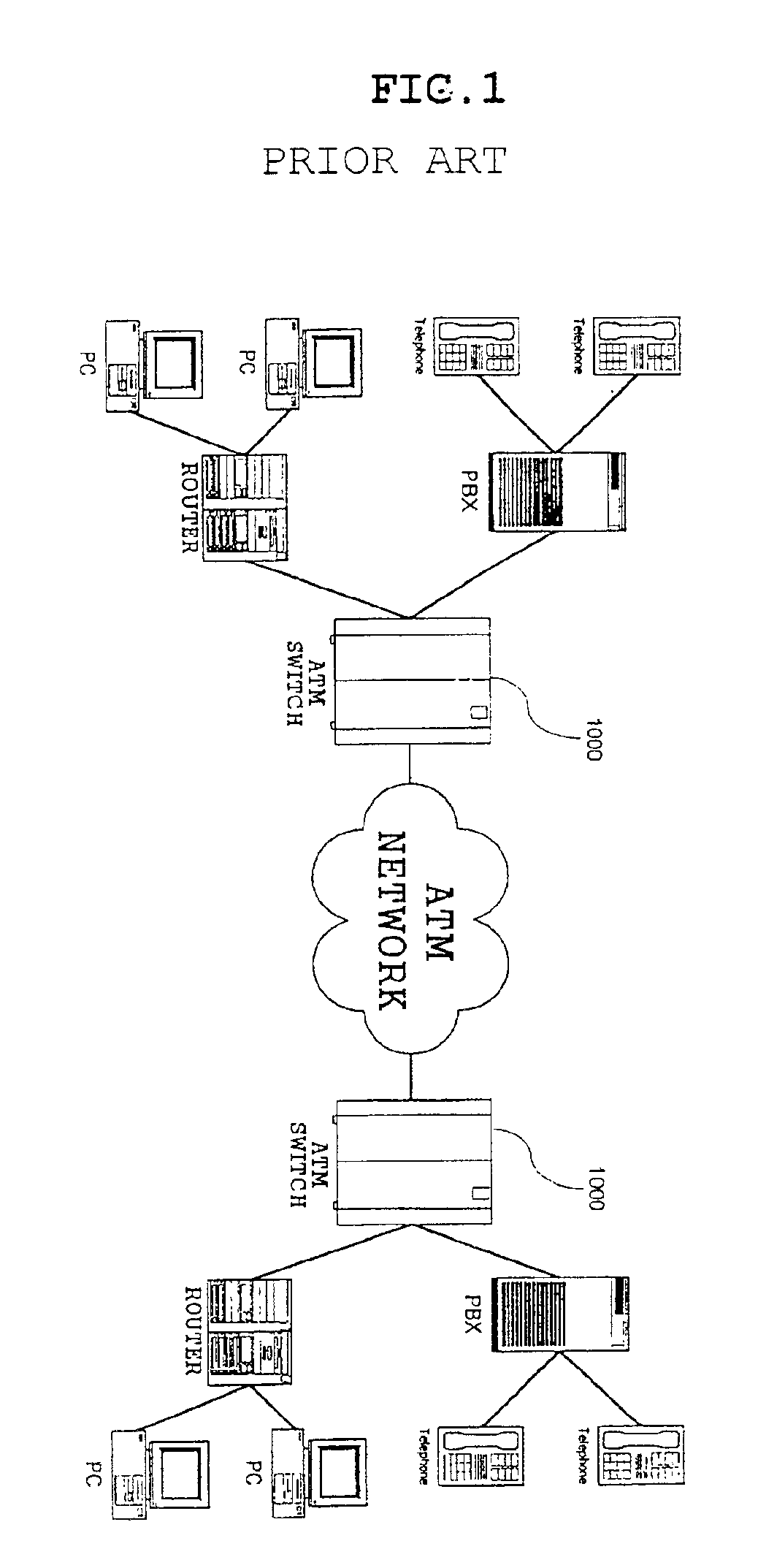
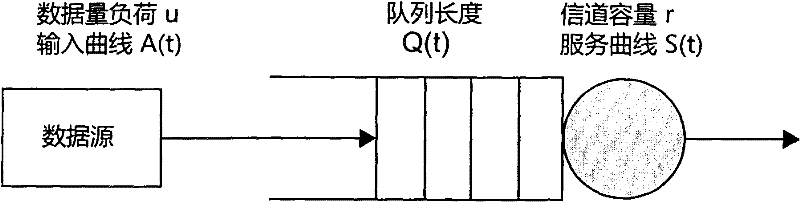
Delayed binding, also called TCP connection splicing, is the postponement of the connection between the client and the server in order to obtain sufficient information to make a routing decision. Some application switches and routers delay binding the client session to the server until the proper handshakes are complete so as to prevent denial-of-service attacks.
Content-aware application switch and methods thereof
InactiveUS6944678B2Easy to controlControl moreMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsQuality of serviceSlow-start
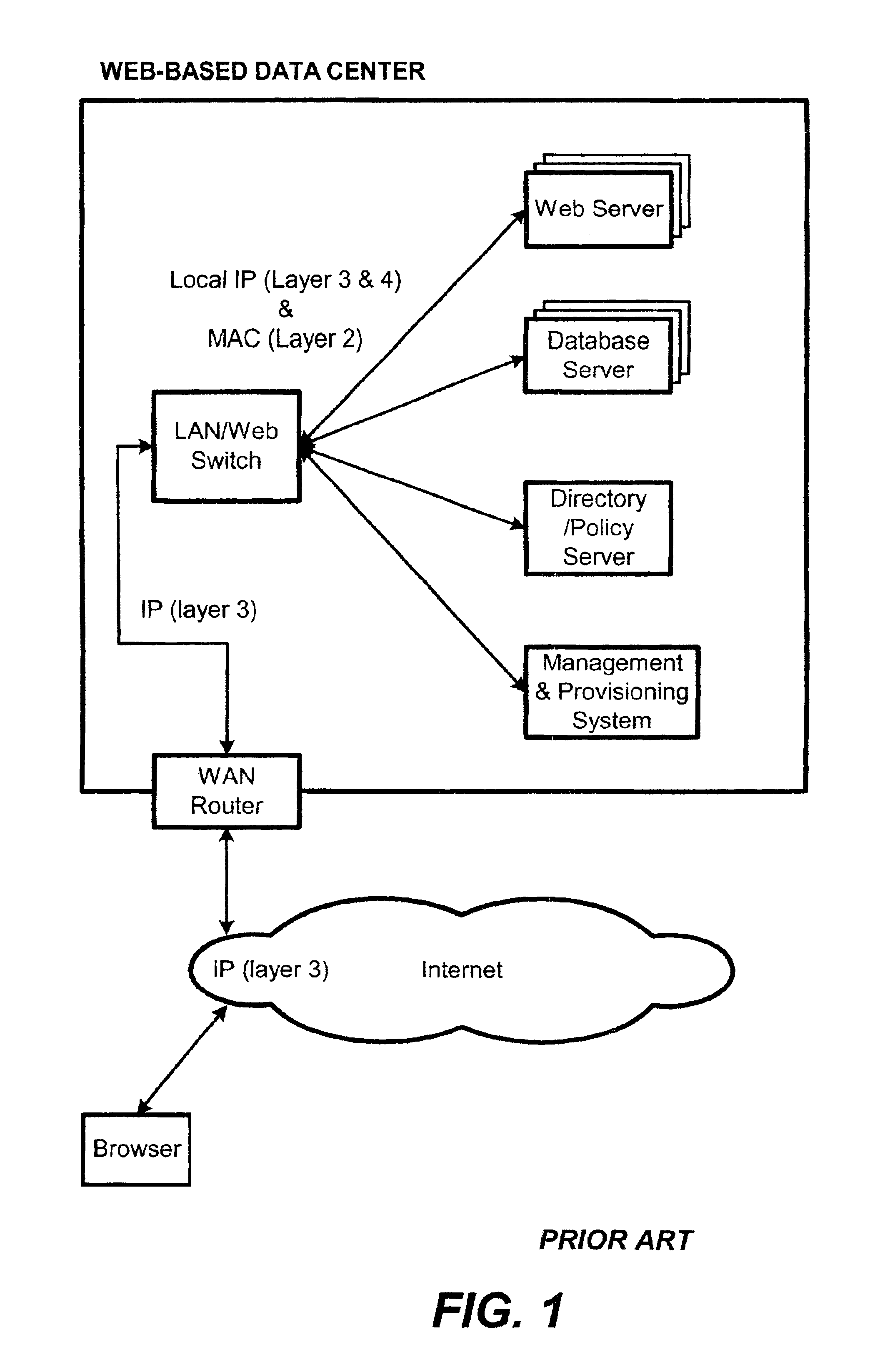
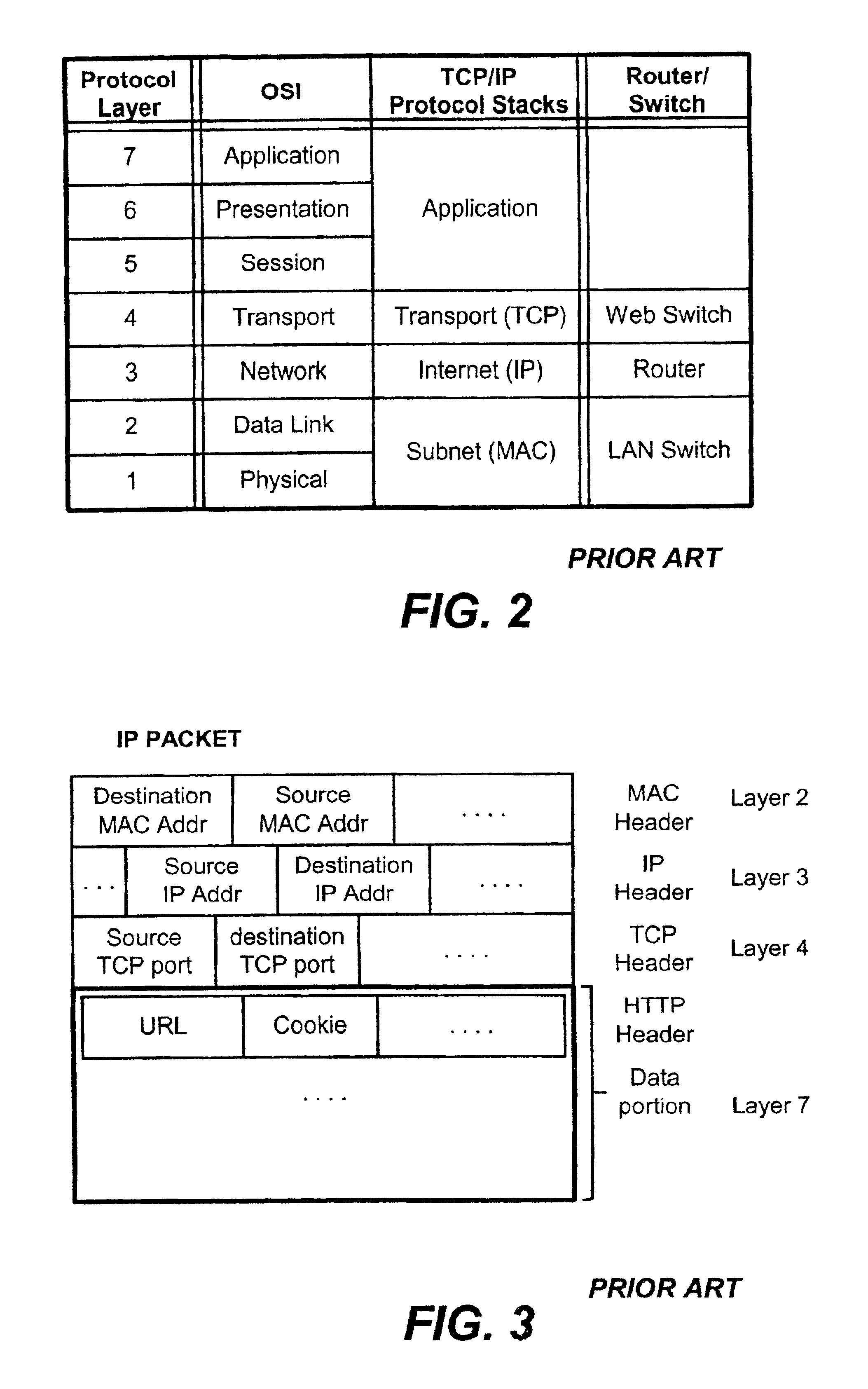
A content-aware application switch and methods thereof intelligently switch client packets to one server among a group of servers in a server farm. The switch uses Layer 7 or application content parsed from a packet to help select the server and to schedule the transmitting of the packet to the server. This enables refined load-balancing and Quality-of-Service control tailored to the application being switched. In another aspect of the invention, a slow-start server selection method assigned an initially boosted server load metric to a server newly added to the group of servers under load balancing. This alleviates the problem of the new server being swamped initially due to a very low load metric compared to that of others. In yet another aspect of the invention, a switching method dependent on Layer 7 content avoids delayed binding in a new TCP session. Layer 7 content is not available during the initial handshaking phase of a new TCP session. The method uses the Layer 7 content from a previous session as an estimate to help select the server and uses a default priority to scheduling the transmitting of the handshaking packets. Updated Layer 7 content available after the handshaking phase is then used to reset the priority for the transmit schedule and becomes available for use in load balancing of the next TCP session.
Owner:IBM CORP
Packet switch and method thereof dependent on application content
InactiveUS20060031374A1Easy to controlControl moreMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData packQuality of service
A content-aware application switch and methods thereof intelligently switch client packets to one server among a group of servers in a server farm. The switch uses Layer 7 or application content parsed from a packet to help select the server and to schedule the transmitting of the packet to the server. This enables refined load-balancing and Quality-of-Service control tailored to the application being switched. In another aspect of the invention, a slow-start server selection method assigned an initially boosted server load metric to a server newly added to the group of servers under load balancing. This alleviates the problem of the new server being swamped initially due to a very low load metric compared to that of others. In yet another aspect of the invention, a switching method dependent on Layer 7 content avoids delayed binding in a new TCP session. Layer 7 content is not available during the initial handshaking phase of a new TCP session. The method uses the Layer 7 content from a previous session as an estimate to help select the server and uses a default priority to scheduling the transmitting of the handshaking packets. Updated Layer 7 content available after the handshaking phase is then used to reset the priority for the transmit schedule and becomes available for use in load balancing of the next TCP session.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
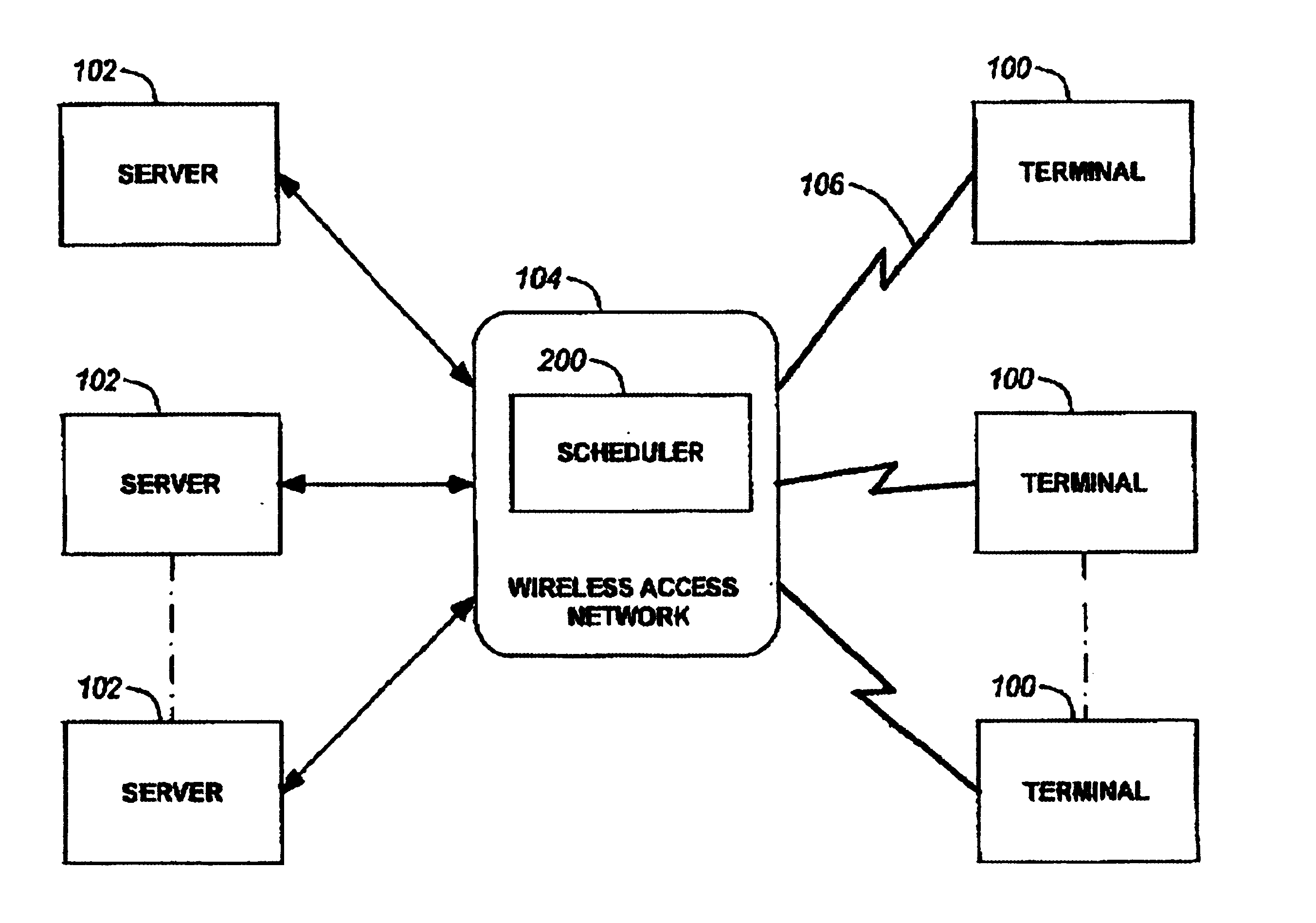
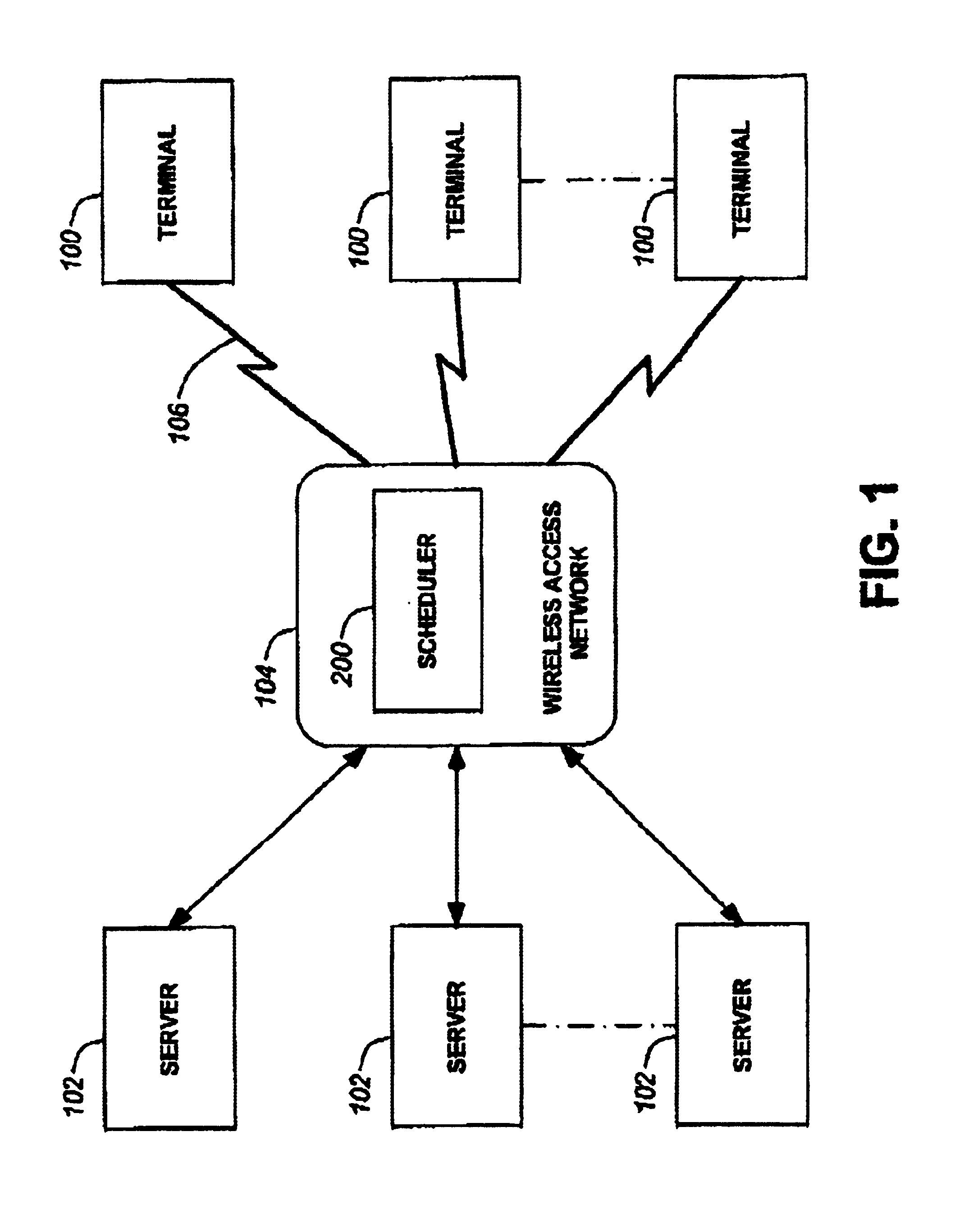
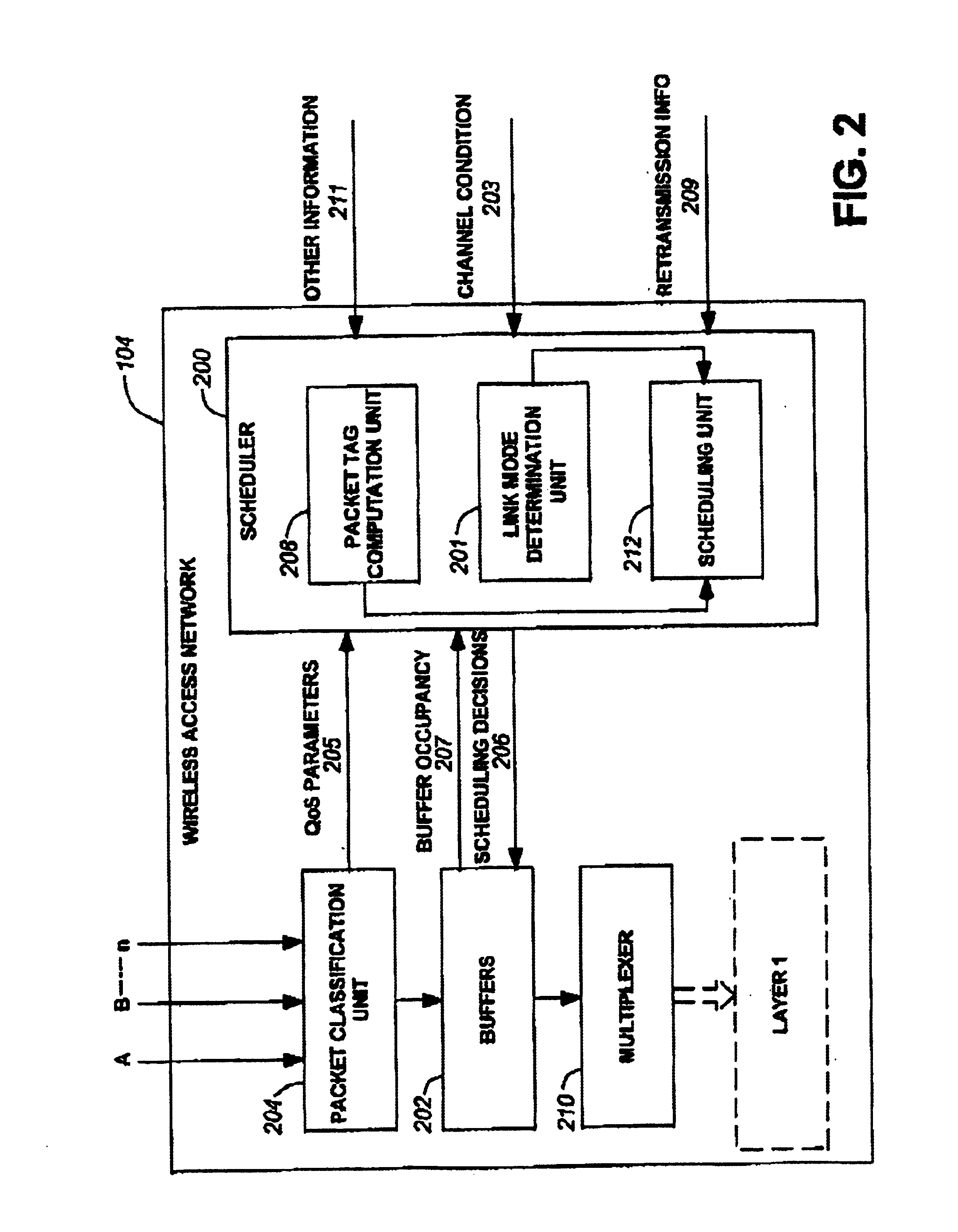
Method and system for wireless packet scheduling with per packet QoS support and link adaptation
InactiveUS6879561B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsTelecommunications networkPacket scheduling
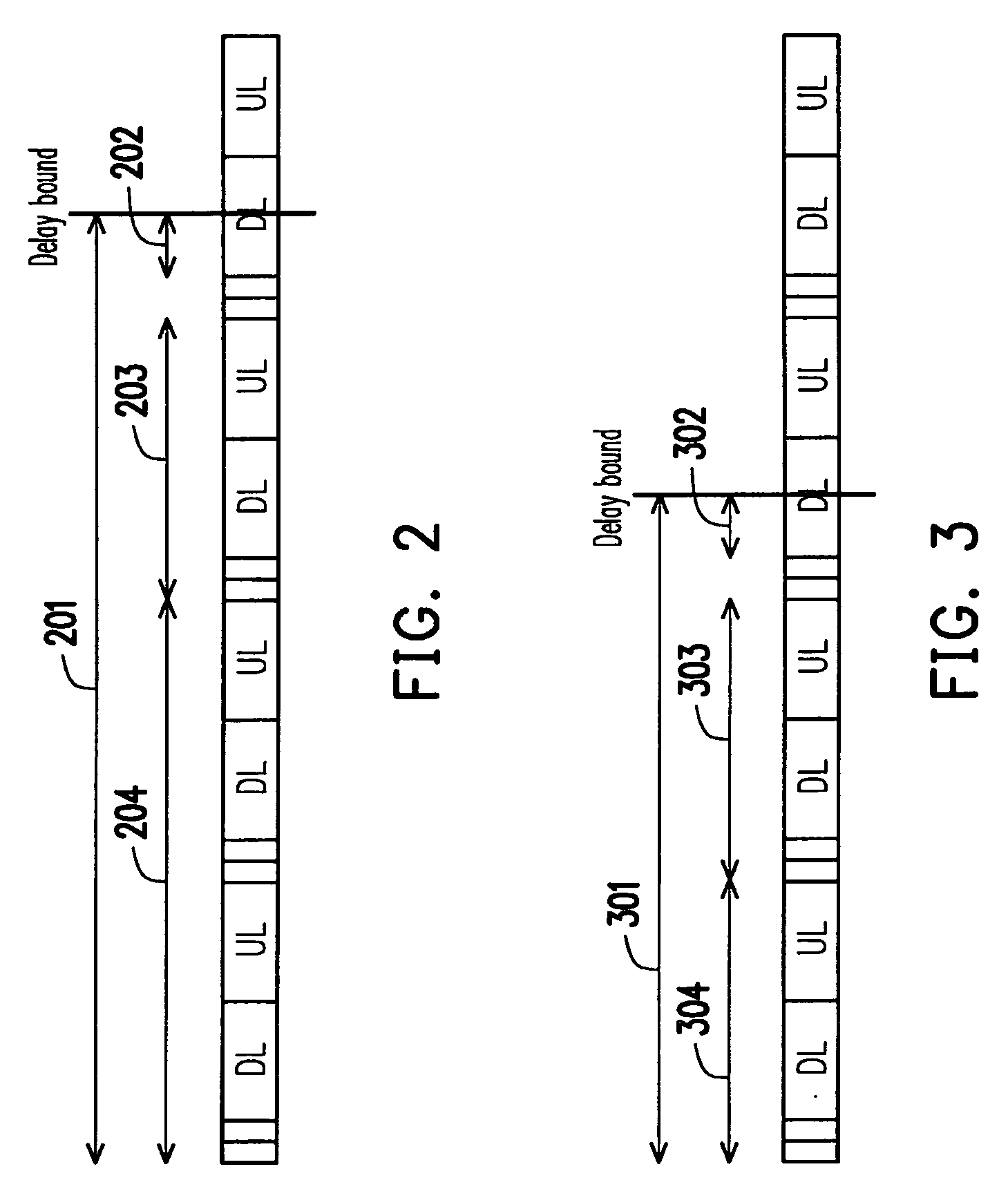
A method and system for scheduling data in the down, or forward, link, on a per packet basis in a wireless telecommunications network. The scheduler determines the order of packets to be sent from multiple queues based on per IP QoS, real time channel condition and real time buffer occupancy. The scheduler determines the necessary support link adaptation on a per packet basis based on per packet QoS and the channel condition. The scheduling system and method take into consideration both upper layer per packet QoS, for example packet delay bound, and the real time channel condition (C / I) for each mobile terminal. The method of the present invention also determines the layer 2 frame length for each scheduled packet.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for quality of service (QoS) support in a packet-switched network
InactiveUS7075927B2Reduce in quantityNetwork degradationError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceDelayed binding
A method and system for transporting traffic having disparate qualities of service classes across a packet-switched network includes receiving at an ingress node of a network a plurality of packets each comprising a quality of service (QoS) class defined externally to the network. Packets having a QoS class comprising delay bound guarantees and a low drop priority are combined into a first internal QoS class. Packets having a QoS class comprising a flexible drop priority and no delay bound guarantees are combined into a second internal QoS class. Packets having a QoS class including no delivery guarantees are combined into a third internal QoS class. The packets are transmitted in the network based on their internal QoS class.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting data over a network within a specified time limit
ActiveUS7058085B2Facilitate communicationAvoid lostError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
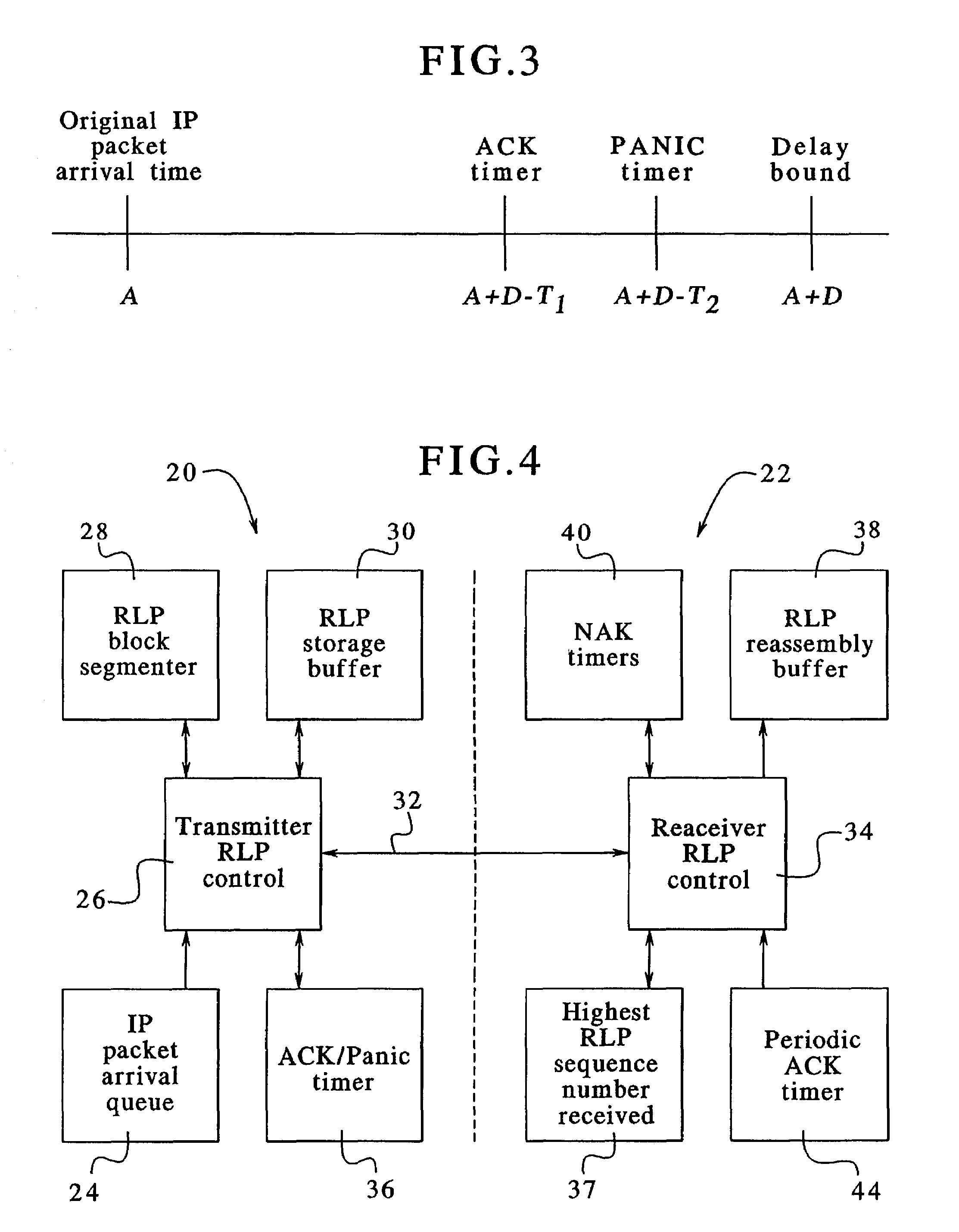
A radio link protocol for a communications system ensures that delivery of Internet protocol data packets occurs within a set delay bound for the packets, in order to satisfy specified quality of service levels. Data packets arriving at a transmitter are subdivided into data blocks. As each block is transmitted, the transmitter starts an associated acknowledgement timer. The timer is turned off, before it expires, if the transmitter timely receives from a receiver a message informing the transmitter that the associated block was successfully received. If such message is not received, the timer expires and the transmitter sends an acknowledgement request signal to the receiver and starts an associated panic timer. The panic timer is turned off, before it expires, if the transmitter subsequently timely receives a message that the associated block was successfully received. If such message not received, the panic timer expires and the transmitter sends one of more copies of the corresponding block to the receiver before occurrence of the delay bound. If the transmitter receives a negative acknowledgement message from the receiver, that a block is missing or corrupted, the transmitter retransmits a copy of the block to the receiver. To reduce messaging traffic, the transmitter cancels acknowledgement and panic timers based upon information contained in negative acknowledgement messages, and the receiver can periodically send acknowledgement messages to inform the transmitter of successfully received blocks.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic automatic retransmission request in wireless access networks
InactiveUS7032153B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSignalling characterisationAccess networkWireless mesh network
A method and system for providing dynamic ARQ, on a per packet basis, in a wireless telecommunications access network. By taking into consideration both per packet QoS based on, for example, packet delay bound, and potential delays caused by retransmission, a dynamic NAK-based ARQ scheme is presented that dynamically adapts the retransmission parameters to the per packet QoS to provide improved radio link quality, particularly for non-delay sensitive services and applications. The ARQ parameters that are dynamically adjusted can include the number of retransmission rounds, and the number of retransmissions in each round.
Owner:APPLE INC
Real-time messaging method and apparatus
ActiveUS9178916B2Lower capability requirementsMultiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationReal-time Transport ProtocolMessage passing
A system and method for the late-biding of time-based media in real-time With late binding, the sender may create time-based media before or at the same time an active delivery route to the recipient is discovered. As soon as the route becomes available, the media is transmitted. The existing DNS and email infrastructure is possibly used for route discovery, while any real-time transmission protocol may be used for the actual delivery of the media. “Progressive” emails may also be used for the real-time delivery of time-based media.
Owner:VOXER IP
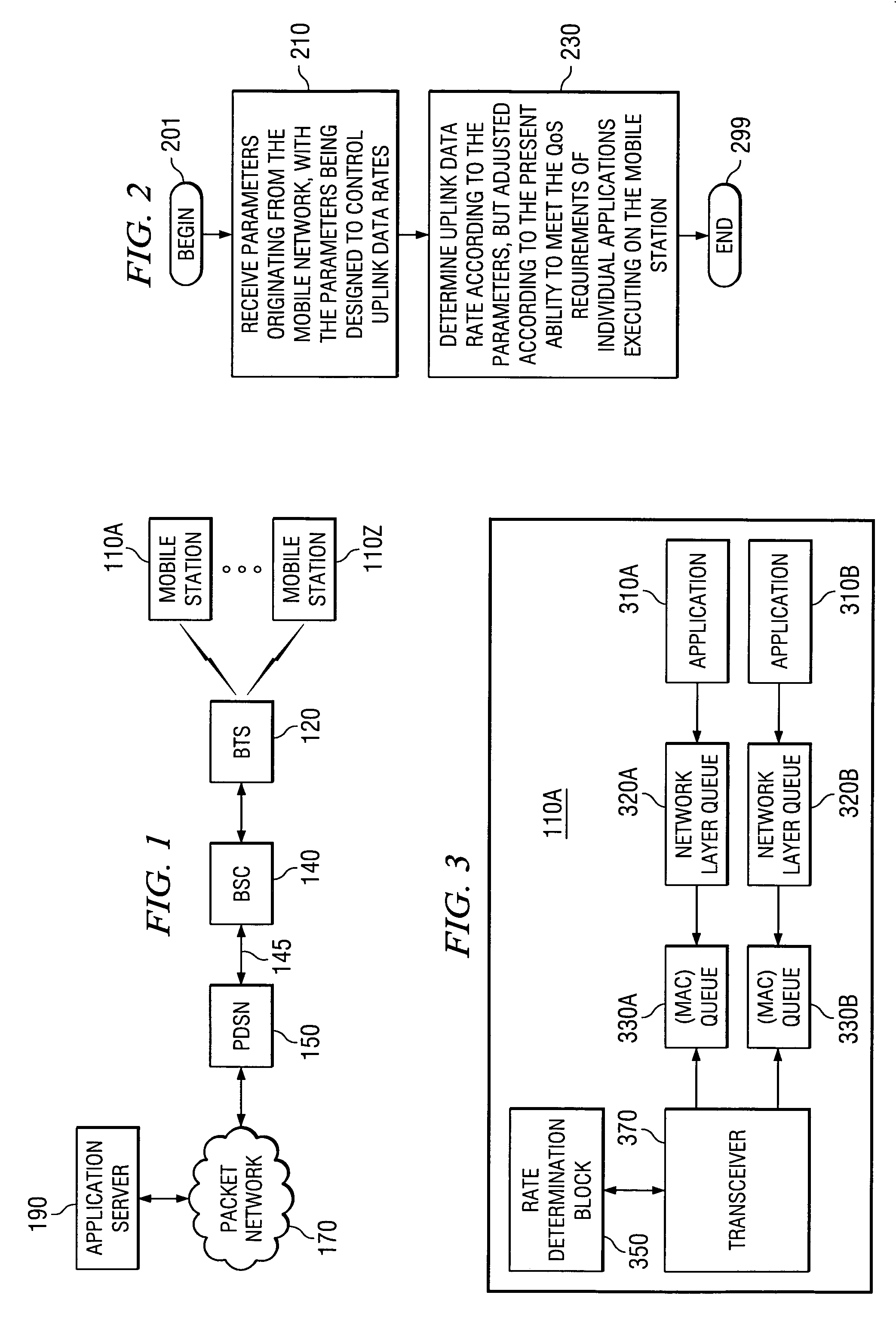
Providing optimal uplink data rates to mobile stations when mobile networks send parameters controlling the data rates
ActiveUS20070032200A1Transmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceData rate
The uplink data rate is dynamically adjusted in a mobile station according to the mobile station's ability to meet QoS (quality of service) requirements of applications executing on the mobile station. In an embodiment, the transition probabilities received from a mobile network are first compensated according to the ability to meet QoS requirements, and the uplink data rate is then computed based on the compensated transition probabilities. According to another aspect of the present invention, the base station dynamically adjusts the transition probabilities based on delay bound requirement of packets and / or average delay or data flow rate requirement.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Tracking area management method and apparatus for long term evolution telecommunication systems
ActiveUS20110294524A1Minimize total traffic cost functionWireless commuication servicesNetwork data managementTraffic capacityTransition probability matrix
An MME keeps track of network tracking mobility characteristics by periodically updating a TA transition probability matrix derived from a global table that maintains UE movement data in the network by noting current TA and most recently known previous TA of each EU for every TAU event and paging event. The MME also maintains data of the number of paging events and TAUs performed by each UE and stores a paging ratio versus TAU for each UE. The UE characteristics, UE paging ratio, and network mobility characteristic are utilized in an algorithm that constructs a TA list for each UE designed to minimize the overall traffic cost function for paging events and TAU events for that UE and the overall network. Optionally, the TA list for each EU is constrained to meet certain minimum performance characteristics such as a predetermined paging success rate target and / or a predetermined delay bound target.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
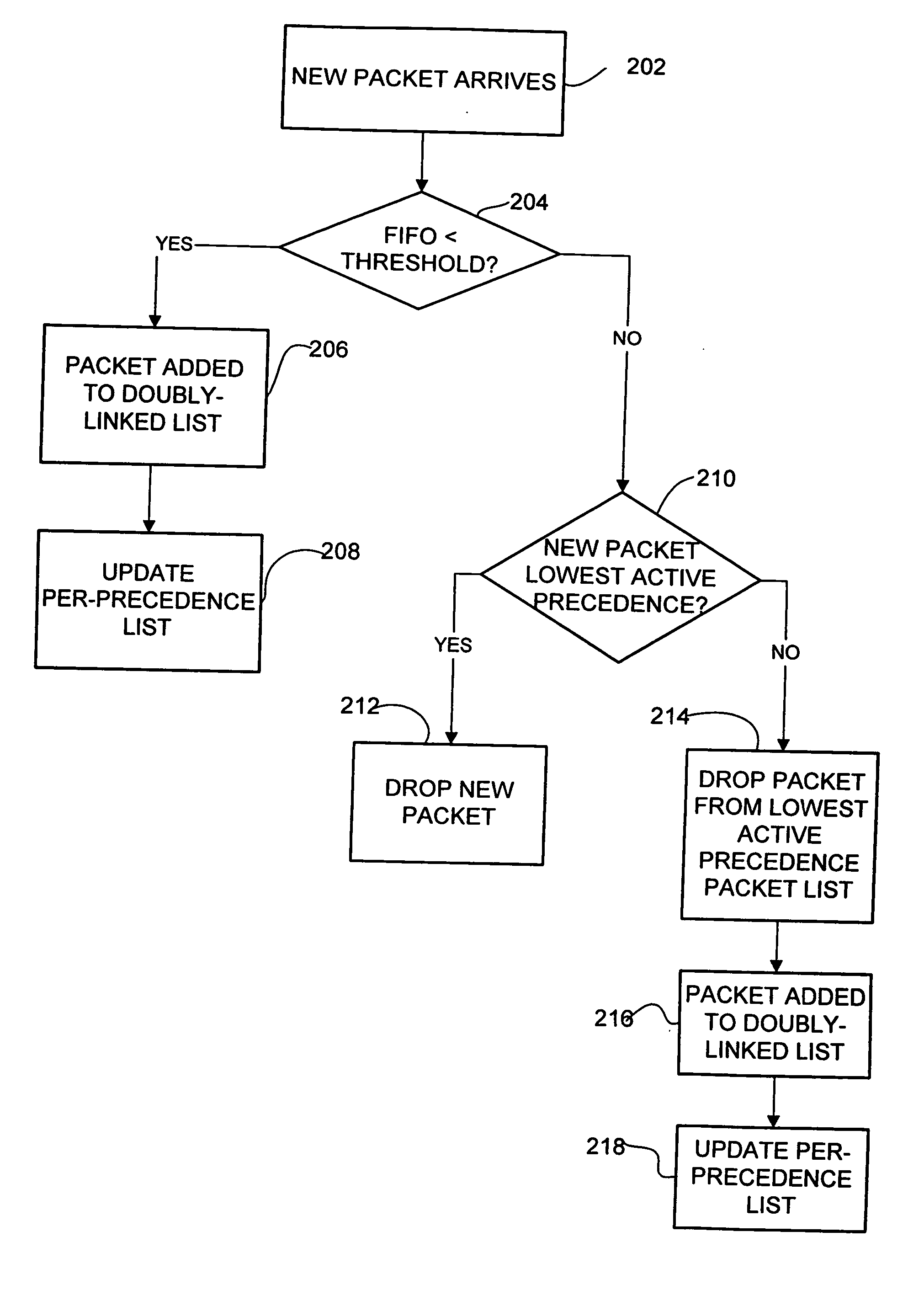
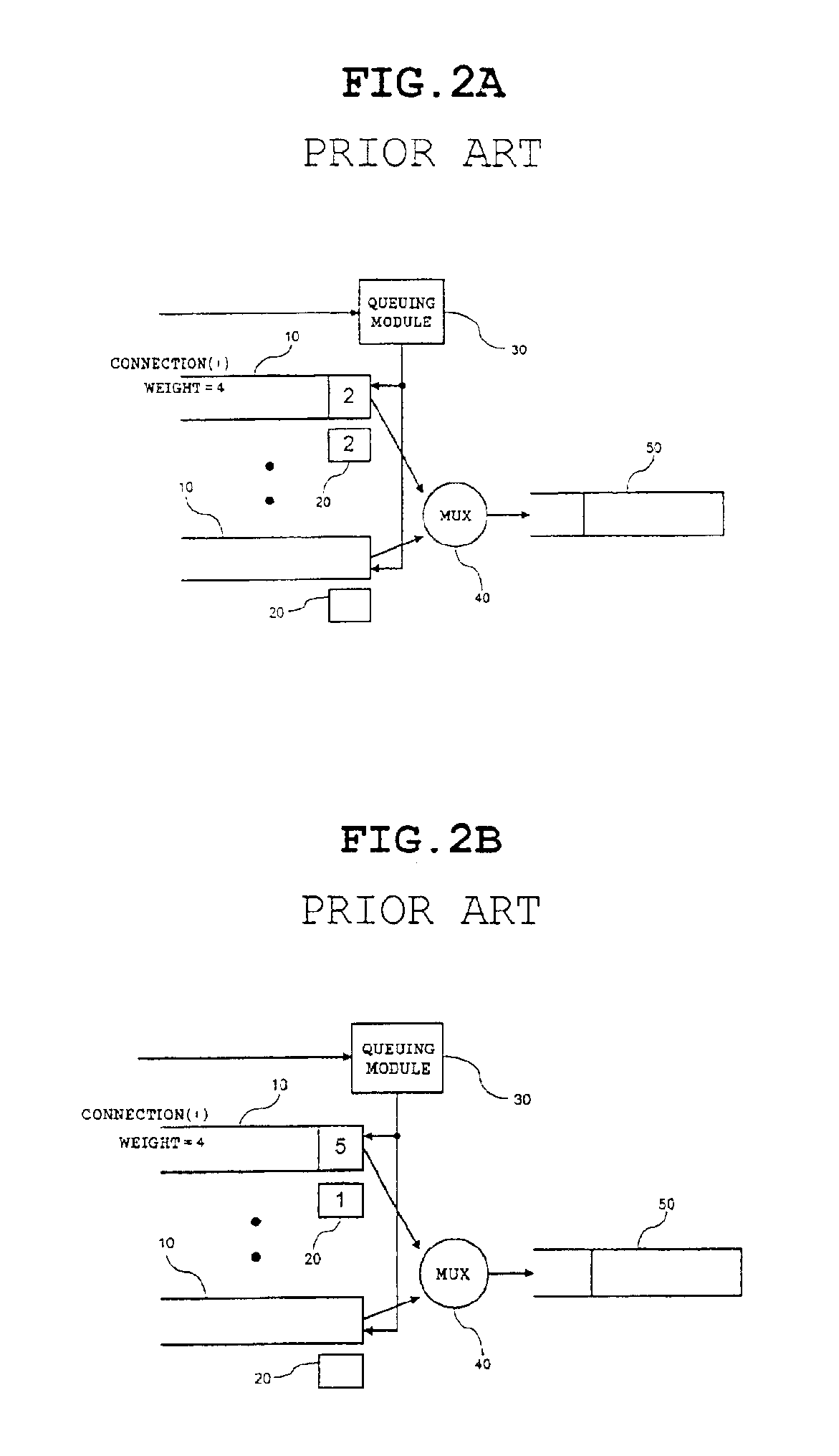
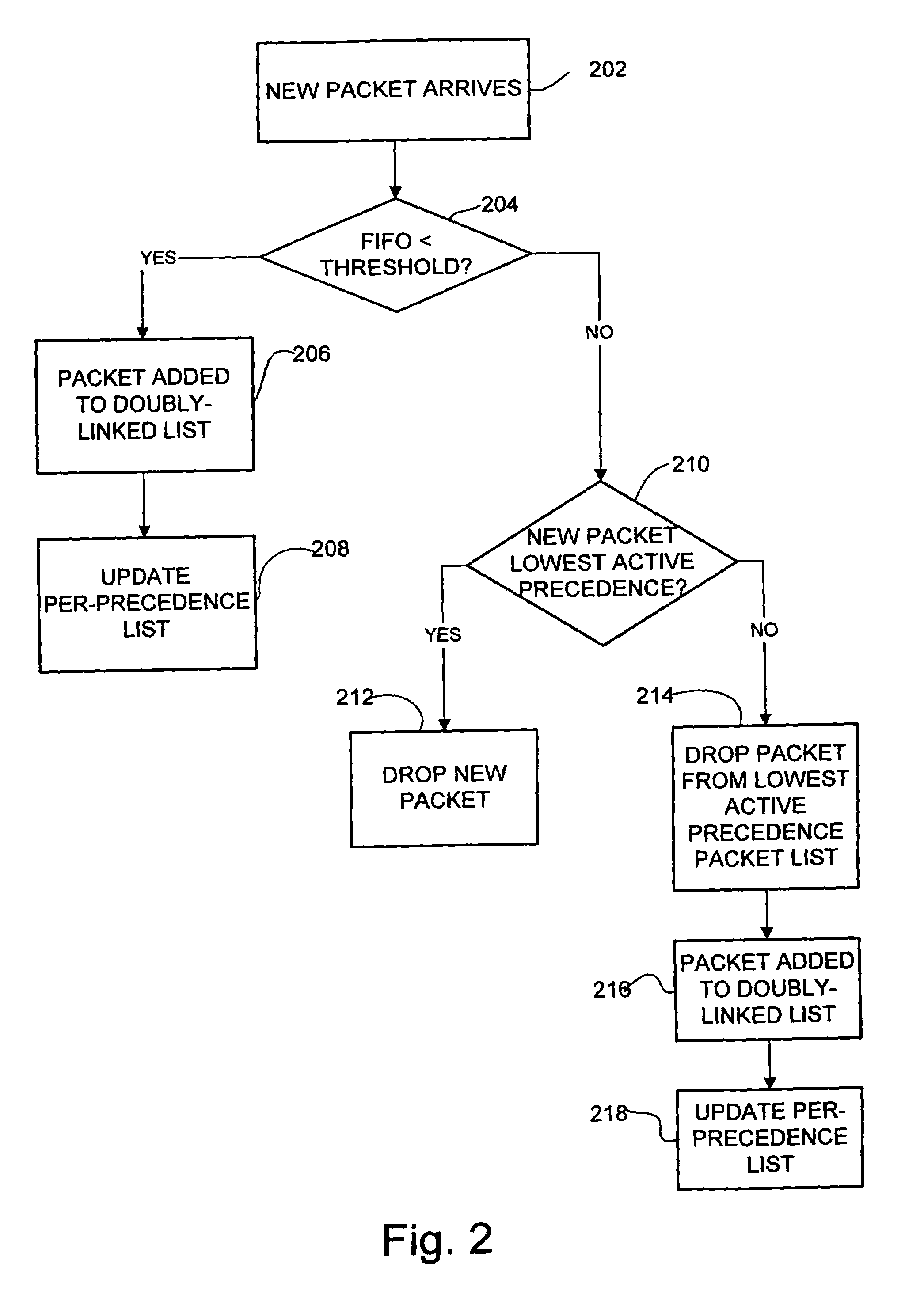
Method and system for providing delay bound and prioritized packet dropping
A method and system for providing delay bound and prioritized packet dropping are disclosed. The system limits the size of a queue configured to deliver packets in FIFO order by a threshold based on a specified delay bound. Received packets are queued if the threshold is not exceeded. If the threshold is exceeded, a packet having a precedence level less than that of the precedence level of the received packet is dropped. If all packets in the queue have a precedence level greater than that of the packet received, then the received packet is dropped if the threshold is exceeded.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
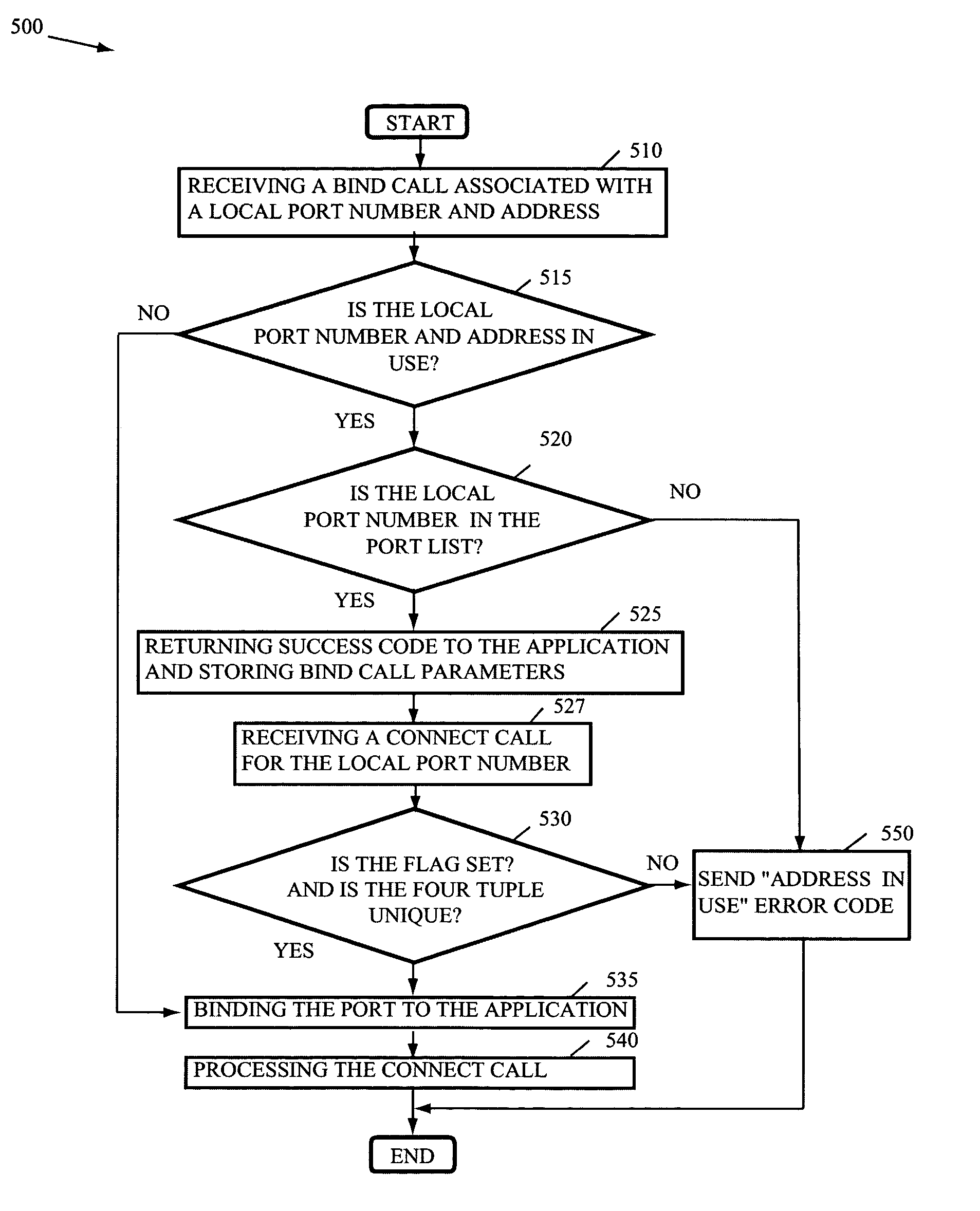
Reducing delays associated with port binding
InactiveUS20060050717A1Reduce delaysError preventionTransmission systemsComputerized systemDelayed binding
Owner:IBM CORP
Wireless transmission rate control method
InactiveCN101855873ANetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksWireless transmissionDelayed binding
The purpose of this invention is a method to provide a specific physical rate adapted to 802.11 WMM in EDCA mode which may be integrated as well in an Access Point as in a Station. The objective of this method is to select the 802.11 phyrate (physical rate) the most adapted for each WMM AC (Access category) of traffic requirements: For each AC it guaranties an IPLR (IP packet Lost ratio) specific physical rate and adapted to nature of the transported content. For BK (Background) and BE (Best Effort) it optimizes the used CUE (Channel Usage Estimation) in order to provide maximum bandwidth, For VI (Video) and VO (Voice) AC to guaranty first the delay bound (i.e. max IP Delay transmission (IPDT) ) and when this condition is met it optimizes the used CUE.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
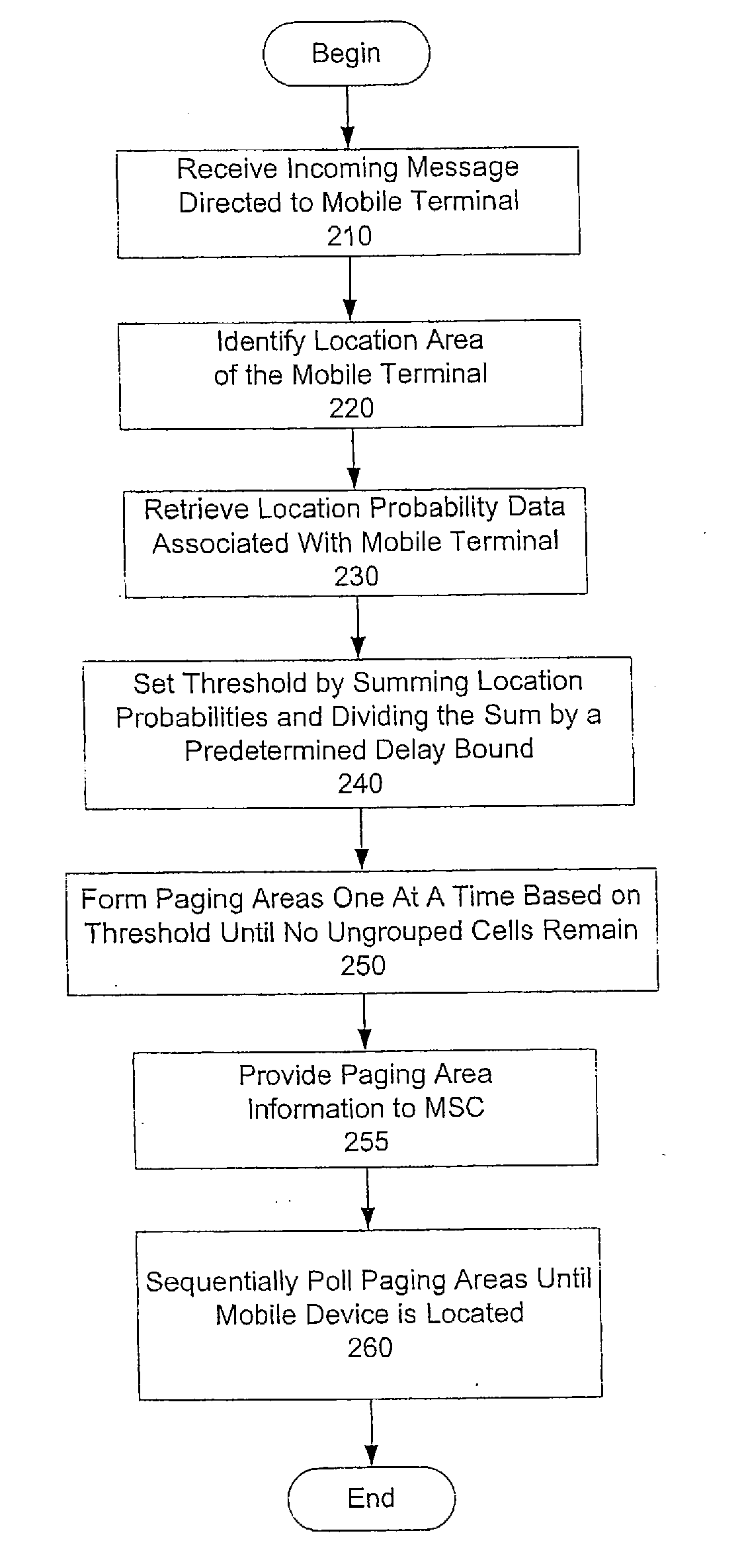
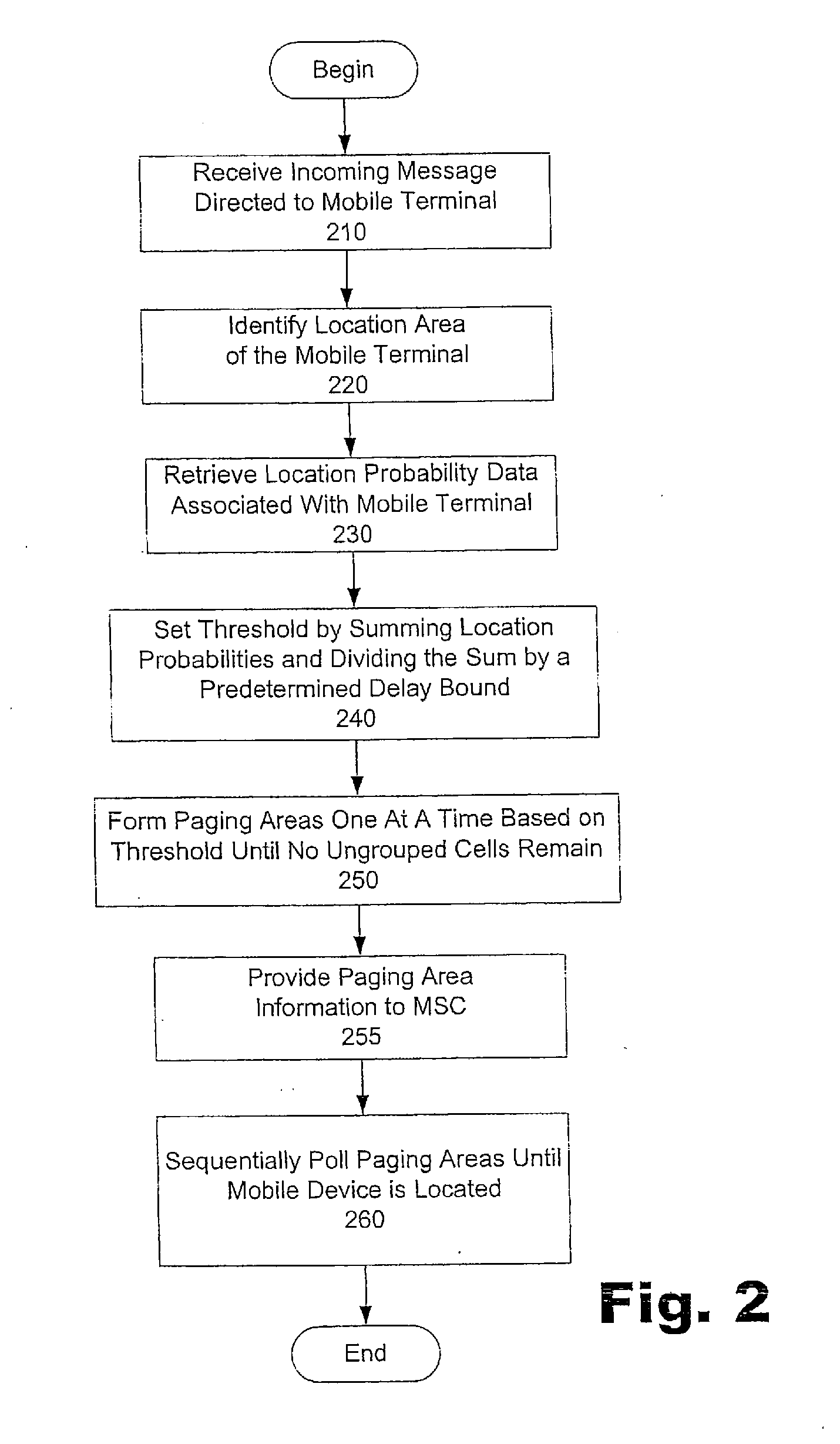
System and method for location area planning in mobile communication networks under delay bound
In one of many possible embodiments, a method of locating a mobile terminal within a location area of a mobile communication network is provided. In the method, a threshold is set by calculating a sum of all location probabilities in the location area and dividing the sum by a maximum number of polling cycles allowed before the mobile terminal is located. Cells in the location area are arranged in non-ascending order according to their location probabilities. Multiple paging areas are formed one at a time by starting with a first cell not used in a previous paging area, grouping cells in order, and stopping when the total of location probabilities reaches the threshold or when no more ungrouped cells exist within the location area.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Apparatus and method for delay bound weighted round robin cell scheduling in asynchronous transfer mode switch
InactiveUS6937601B2Minimize overheadMeet the requirementsData switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionCell schedulingDelayed binding
An apparatus and method for DBWRR (Delay Bound Weighted Round Robin) cell scheduling in an ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) switch. More particularly, the present invention provides an apparatus and method for DBWRR cell scheduling in a high-speed ATM switch which can meet requirements for a cell transfer delay of real-time traffic in the ATM switch and minimize a processing overhead of the switch.
Owner:USRCOM KOREA
Apparatus and method for performing congestion control in a communication system
ActiveUS20110170414A1Performance advantageError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemDelayed binding
A method for performing congestion control in a communication system. The method includes transmitting a request message to a node using a first packet with a highest priority and receiving a response message corresponding to the request message using the first packet and at least one of a plurality of second packets, estimating a one-way delay of the first packet according to a round trip time for the first packet, converting one of the one-way delay of the first packet and the one-way delay of at least one of the plurality of second packets into a quality of service (QoS) level using a predetermined upper delay bound for a corresponding packet, and converting the converted QoS level into an effective congestion level representing a congestion degree in a network and performing congestion control using the effective congestion level.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for providing delay bound and prioritized packet dropping
A method and system for providing delay bound and prioritized packet dropping are disclosed. The system limits the size of a queue configured to deliver packets in FIFO order by a threshold based on a specified delay bound. Received packets are queued if the threshold is not exceeded. If the threshold is exceeded, a packet having a precedence level less than that of the precedence level of the received packet is dropped. If all packets in the queue have a precedence level greater than that of the packet received, then the received packet is dropped if the threshold is exceeded.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Providing optimal uplink data rates to mobile stations when mobile networks send parameters controlling the data rates
ActiveUS7480488B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceControl data
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Tracking area management method and apparatus for long term evolution telecommunication systems
ActiveUS8571583B2Minimize total traffic cost functionWireless commuication servicesNetwork data managementTransition probability matrixNetwork mobility
An MME keeps track of network tracking mobility characteristics by periodically updating a TA transition probability matrix derived from a global table that maintains UE movement data in the network by noting current TA and most recently known previous TA of each EU for every TAU event and paging event. The MME also maintains data of the number of paging events and TAUs performed by each UE and stores a paging ratio versus TAU for each UE. The UE characteristics, UE paging ratio, and network mobility characteristic are utilized in an algorithm that constructs a TA list for each UE designed to minimize the overall traffic cost function for paging events and TAU events for that UE and the overall network. Optionally, the TA list for each EU is constrained to meet certain minimum performance characteristics such as a predetermined paging success rate target and / or a predetermined delay bound target.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
Method for wireless device to estimate end-to-end delay probability characteristic in multi-hop wireless network
InactiveCN102244876AEfficient calculation of end-to-end delay probabilityError preventionWireless communicationNetwork packetDelayed binding
The invention discloses a method for a wireless device to estimate an end-to-end delay probability characteristic in a multi-hop wireless network, which comprises the following steps that: each wireless device in the multi-hop wireless network monitors the performance of a local link to obtain own probability parameter gamma indicating that a data packet of the wireless device is directly served so that the wait delay of the wireless device is 0, and a descent speed parameter theta in an exponential distribution; secondly, each wireless device broadcasts the own probability parameter gamma and the descent speed parameter theta in the multi-hop wireless network so that each wireless device establishes a parameter comparison table of every wireless device in the multi-hop wireless network to the probability parameter gamma and the descent speed parameter theta of the wireless device; and finally, each wireless device calculates the end-to-end exceeding delay bound probability of a data packet of the wireless device to be transmitted according to the own established parameter comparison table and a route of the own data packet to be transmitted to another wireless device. Through simulation comparison, the method disclosed by the invention is well fitted with theoretical analysis results, and a completely perfect explanation can be given to the end-to-end delay probability characteristic in the multi-hop wireless network.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
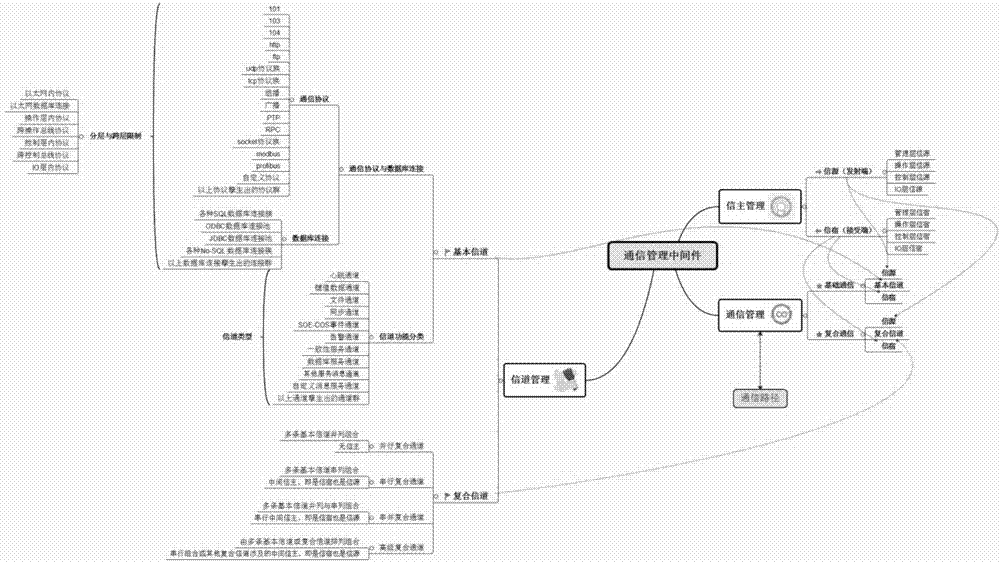
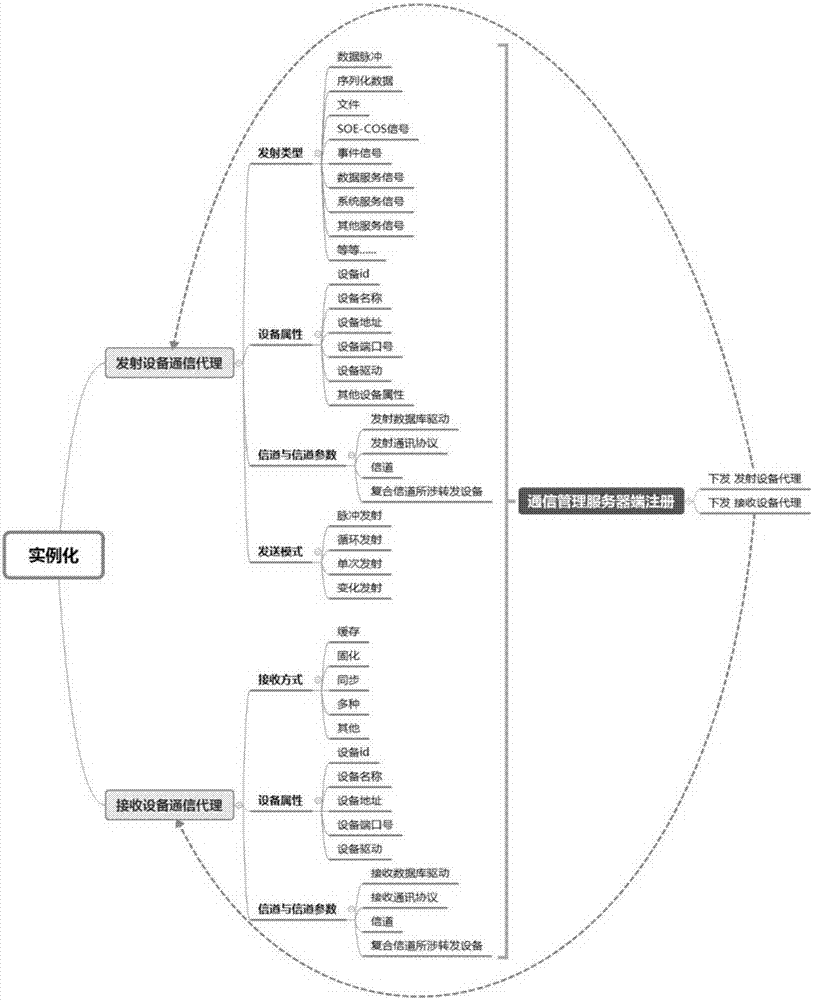
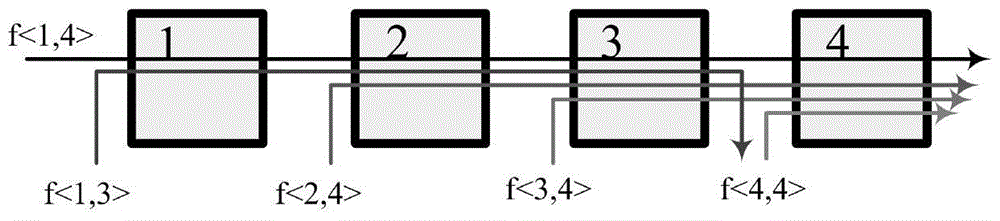
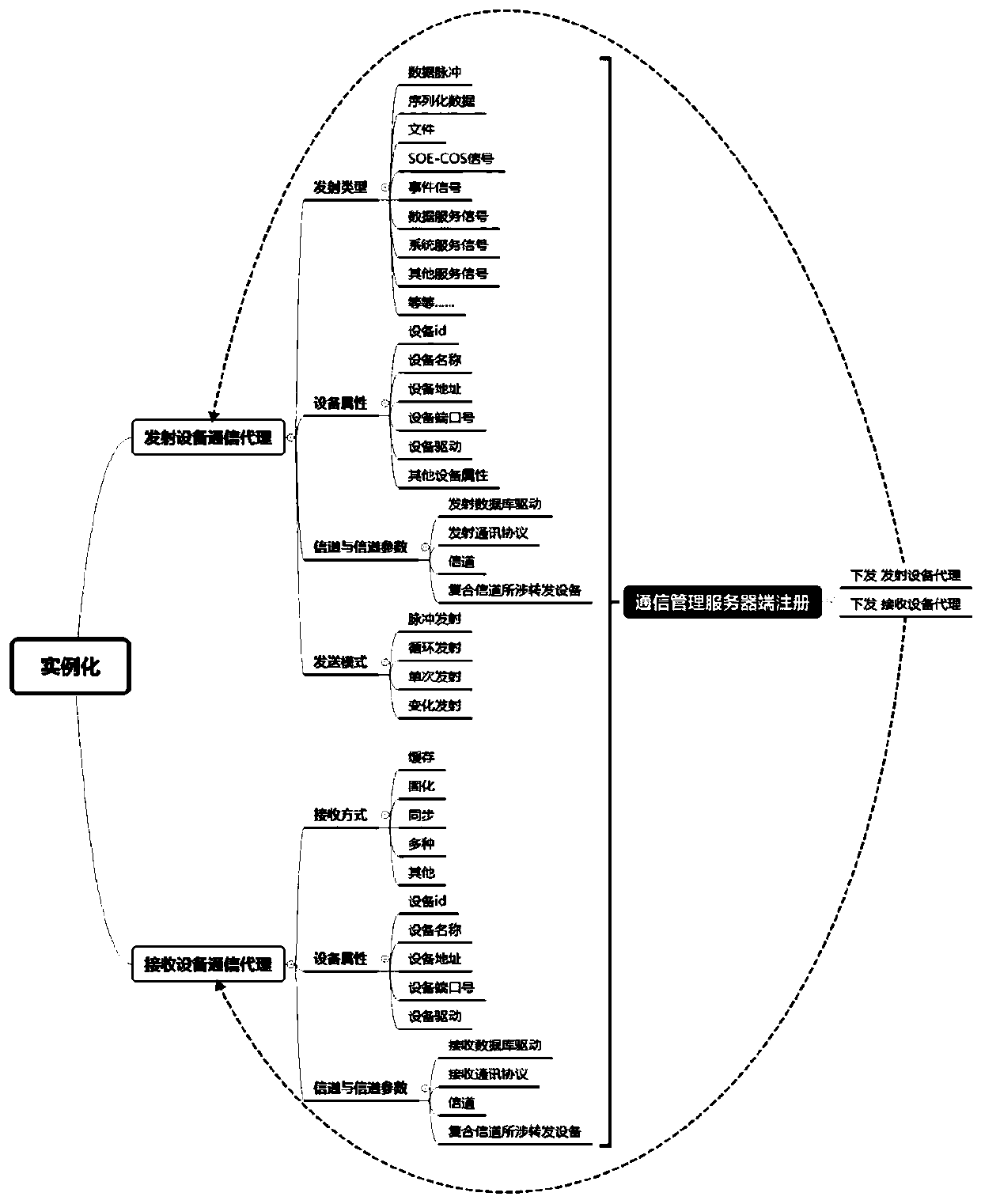
DCS communication loose coupling management method
ActiveCN107231433AReduce complexityMaintain and increase opennessTransmissionCommunications systemTelecommunications link
The invention discloses a DCS communication loose coupling management method. A communication management server builds a DCS communication management middleware and re-defines a communication path; a communication management server side registers the communication path; receiving-transmitting equipment receives registration information via a communication proxy to perform instantiation; when starting, the receiving-transmitting equipment firstly inquiries whether a remote communication management server has update content via the communication proxy of the equipment, if the update content exists, a library update process is performed, delayed binding initialization is performed after instantiation again, if the update content does not exist, delayed binding initialization; an instance which has completed delayed binding is activated; a communication link is built for transmitting or receiving communication information. According to the method provided by the invention, resetting and debugging complexity degrees caused by modification and upgrade of the system are reduced, so that the communication process of the DCS is automatic, openness of the DCS system is kept and improved, and complexity of a heterogonous software and hardware platform of the distributed system is reduced.
Owner:NANJING GUODIAN NANZI WEIMEIDE AUTOMATION CO LTD
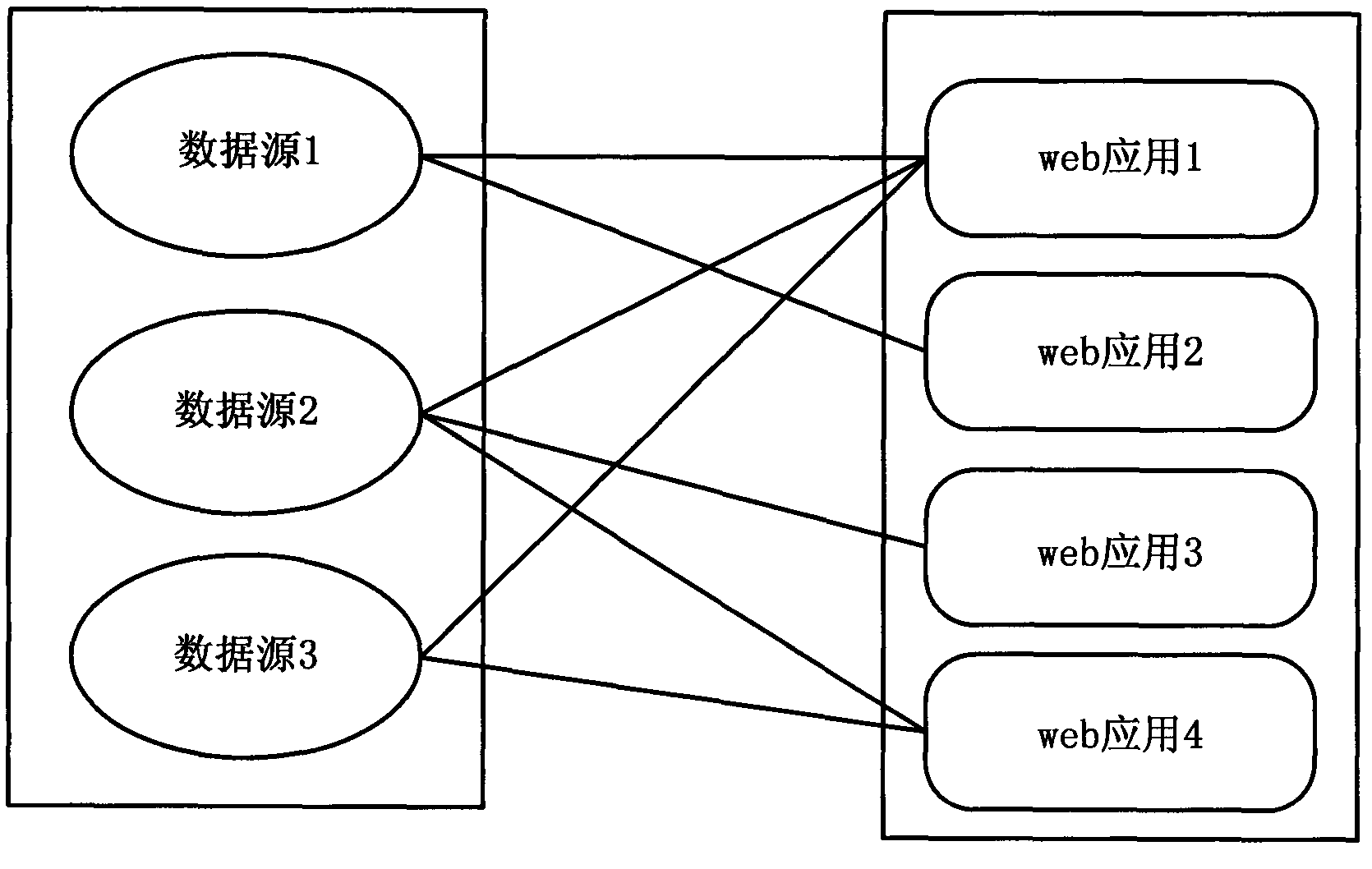
Realization of web application data source delay binding
InactiveCN103019660AReduce the disadvantages of configuration in practical applicationsSpecific program execution arrangementsWeb applicationDelayed binding
The invention discloses a realization of web application data source delay binding, and belongs to the technical field of the web application management. The invention aims to solve the technical problem that a specific data source can be determined to use only in the implementation process. The realization of the web application data source delay binding comprises data source management and web application management, wherein the data source management is used for configuring data source information and testing whether data sources can be correctly connected to uniformly manage the data sources; the web application management is used for dynamically binding the data sources and a web application, backuping the web application of each edition and managing the web application of a historical edition and has the functions of regressing the edition and reloading the edition.
Owner:PCI TECH GRP CO LTD
System, method, and recording medium for scheduling packets to be transmitted
ActiveUS8340080B2Improve performance and capacityData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsNon real timeNetwork packet
A system for scheduling packets to be transmitted is provided. The system includes a soft delay bound calculator module and a frame determination module. The soft delay bound calculator module calculates a soft delay bound for a non-real-time packet based on a packet size of the non-real-time packet and a minimum reserved traffic rate of a channel. The frame determination module determines whether a real-time packet must be transmitted at a current frame according to a delay bound, a transmission time, and a possible retransmission time thereof, and whether a non-real-time packet must be transmitted at a current frame according to a soft delay bound, a transmission time, and a possible retransmission time thereof. Thus, it is possible to improve the performance of the system while keeping the QoS thereof in a mixed service environment.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
System, method, and recording medium for scheduling packets to be transmitted
ActiveUS20090161660A1Improve performanceIncrease capacityData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsNon real timeDelayed binding
A system for scheduling packets to be transmitted is provided. The system includes a soft delay bound calculator module and a frame determination module. The soft delay bound calculator module calculates a soft delay bound for a non-real-time packet based on a packet size of the non-real-time packet and a minimum reserved traffic rate of a channel. The frame determination module determines whether a real-time packet must be transmitted at a current frame according to a delay bound, a transmission time, and a possible retransmission time thereof, and whether a non-real-time packet must be transmitted at a current frame according to a soft delay bound, a transmission time, and a possible retransmission time thereof. Thus, it is possible to improve the performance of the system while keeping the QoS thereof in a mixed service environment.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Apparatus and method for writing curve servo sector image
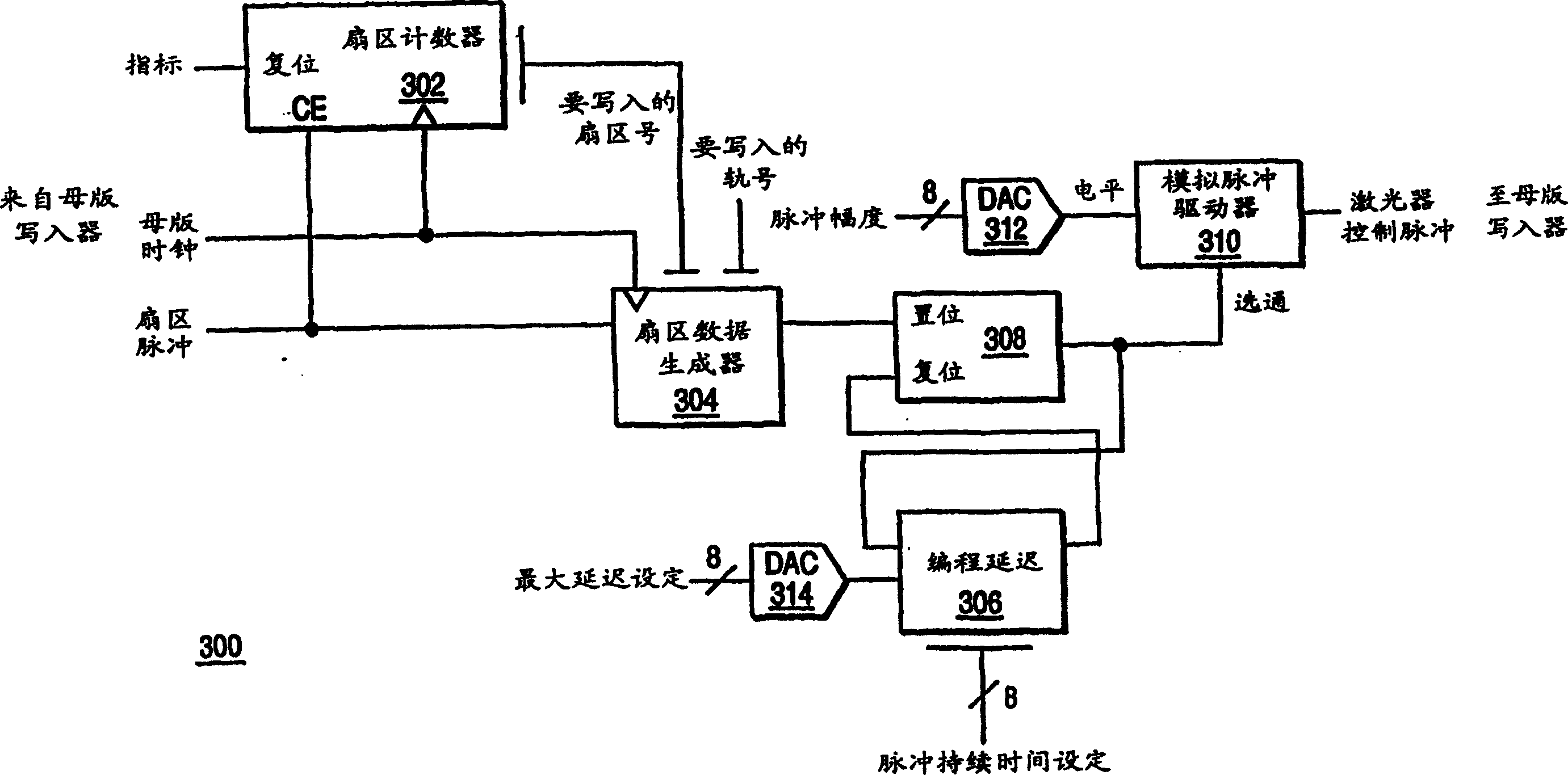
Curve servo is generated on a master medium by determining a series of offsets between the radial alignment reference and the desired curve servo sector, and expressing each offset as a set delay for master writer control sector chart. Incorporating delays into the master writer allows data mapping to be employed to generate curved servo sector patterns. In this way, a curved servo sector pattern with desired resolution is produced without increasing computational overhead or increasing memory requirements, or reducing yield. The delay may be transformed into control settings such as sector delay, clock cycle delay, and residual fractional delay settings each representing a fraction of the delay. In some embodiments, a piecewise linear approximation of the curve shape can be implemented to reduce the amount of control data required, and a master write controller that generates multiple laser pulses can be implemented.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
A wireless device, its packet scheduling method, and a wireless system transmission method
InactiveCN102469518BGood delay effectSuppress the problem of inconsistent delayNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksRound complexityPacket scheduling
The invention discloses a wireless device, a packet scheduling method thereof, and a transmission method of a wireless system. The packet scheduling method of the wireless device comprises the following steps: Step 1: N data packets carrying delay boundaries and destinations are waiting in a buffer server service; step 2, the server calculates the number of data packets M that can be served in the next time period; step 3, when M≥N>0, the server serves all the data packets in the buffer; when N>M>0, the server Select the top M packets with the largest probability of exceeding the delay bound for service. The invention is not only suitable for multi-hop network, but also for single-hop network; it can provide better end-to-end data packet delay performance, and at the same time can better ensure fairness; there is no dependency relationship between wireless devices, and can be distributed independently. Compared with the centralized distribution, it has better scalability and is also suitable for non-centralized mesh networks; it has low complexity and is easy to implement.
Owner:BEIJING RED SEA TECH
Method for Estimating End-to-End Delay Probability Characteristics for Wireless Devices in Multi-Hop Wireless Networks
InactiveCN102244876BEfficient calculation of end-to-end delay probabilityError preventionWireless communicationNetwork packetDelayed binding
The invention discloses a method for a wireless device to estimate an end-to-end delay probability characteristic in a multi-hop wireless network, which comprises the following steps that: each wireless device in the multi-hop wireless network monitors the performance of a local link to obtain own probability parameter gamma indicating that a data packet of the wireless device is directly served so that the wait delay of the wireless device is 0, and a descent speed parameter theta in an exponential distribution; secondly, each wireless device broadcasts the own probability parameter gamma and the descent speed parameter theta in the multi-hop wireless network so that each wireless device establishes a parameter comparison table of every wireless device in the multi-hop wireless network to the probability parameter gamma and the descent speed parameter theta of the wireless device; and finally, each wireless device calculates the end-to-end exceeding delay bound probability of a data packet of the wireless device to be transmitted according to the own established parameter comparison table and a route of the own data packet to be transmitted to another wireless device. Through simulation comparison, the method disclosed by the invention is well fitted with theoretical analysis results, and a completely perfect explanation can be given to the end-to-end delay probability characteristic in the multi-hop wireless network.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
An anti-interference channel switching method suitable for wireless sensor networks
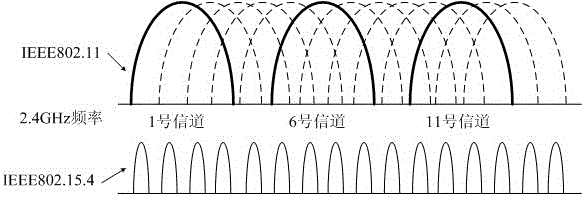
InactiveCN103546971BAvoid interferenceReduce distractionsNetwork topologiesTransmissionWireless sensor networkingRadio channel
The invention discloses an anti-jamming channel switching method suitable for a wireless sensor network. Firstly, according to IEEE802.11 wireless channel distribution and IEEE802.15.4 wireless channel distribution, IEEE802.15.4-based wireless sensor network channels are classified. According to the classification results, different types of channel sets are reorganized. The wireless sensor network nodes are classified by the minimum repeated node negotiation method, and correspond to the above-mentioned different types of channel sets. The temporal superframe is divided into multiple time slots, and each time slot is divided into multiple sub-time slots. Network nodes perform wake-up monitoring in corresponding sub-time slots through pseudo-random algorithm or query schedule method. Finally, network nodes perform channel switching according to their own Latin square algorithm and initial channel in each time slot. The method of the invention is improved in end-to-end data average delay, data delay upper limit and delay jitter performance index.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A multi-egress aggregation flow analysis method with an upper bound on the delay of on-chip network
The invention relates to a multi-exit gather stream analyzing method for a network on chip delay bound. The multi-exit gather stream analyzing method is realized through the following steps: step a, confirming a target stream, to be more specific, selecting one stream to serve as the target stream, and enabling the other streams to serve as conflict streams; step b, searching the conflict streams and cutting into standard streams, finding all the conflict streams in a target stream route and cutting into I-type standard streams and II-type standard streams; step c, calculating a standard stream arrival curve so as to obtain the arrival curve of each type of standard streams; step d, calculating the bottleneck node of each sub-stream of each II-type standard stream; step e, calculating the target stream delay bound according to a formula. The multi-exit gather stream analyzing method for the network on chip delay bound is more precise to calculate the target stream delay at the analysis level, the analysis result is closer to the maximum delay obtained in performing practical simulation, and accordingly the network performance analysis is greatly facilitated.
Owner:黄山市开发投资集团有限公司
A distributed control system dcs communication loose coupling management method
ActiveCN107231433BReduce complexityMaintain and increase opennessTransmissionTelecommunications linkEngineering
The invention discloses a DCS communication loose coupling management method. A communication management server builds a DCS communication management middleware and re-defines a communication path; a communication management server side registers the communication path; receiving-transmitting equipment receives registration information via a communication proxy to perform instantiation; when starting, the receiving-transmitting equipment firstly inquiries whether a remote communication management server has update content via the communication proxy of the equipment, if the update content exists, a library update process is performed, delayed binding initialization is performed after instantiation again, if the update content does not exist, delayed binding initialization; an instance which has completed delayed binding is activated; a communication link is built for transmitting or receiving communication information. According to the method provided by the invention, resetting and debugging complexity degrees caused by modification and upgrade of the system are reduced, so that the communication process of the DCS is automatic, openness of the DCS system is kept and improved, and complexity of a heterogonous software and hardware platform of the distributed system is reduced.
Owner:NANJING GUODIAN NANZI WEIMEIDE AUTOMATION CO LTD
Wireless transmission rate control method
InactiveCN101855873BNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksWireless transmissionDelayed binding
The purpose of this invention is a method to provide a specific physical rate adapted to 802.11 WMM in EDCA mode which may be integrated as well in an Access Point as in a Station. The objective of this method is to select the 802.11 phyrate (physical rate) the most adapted for each WMM AC (Access category) of traffic requirements: For each AC it guaranties an IPLR (IP packet Lost ratio) specific physical rate and adapted to nature of the transported content. For BK (Background) and BE (Best Effort) it optimizes the used CUE (Channel Usage Estimation) in order to provide maximum bandwidth, For VI (Video) and VO (Voice) AC to guaranty first the delay bound (i.e. max IP Delay transmission (IPDT) ) and when this condition is met it optimizes the used CUE.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com