Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3516 results about "Round complexity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
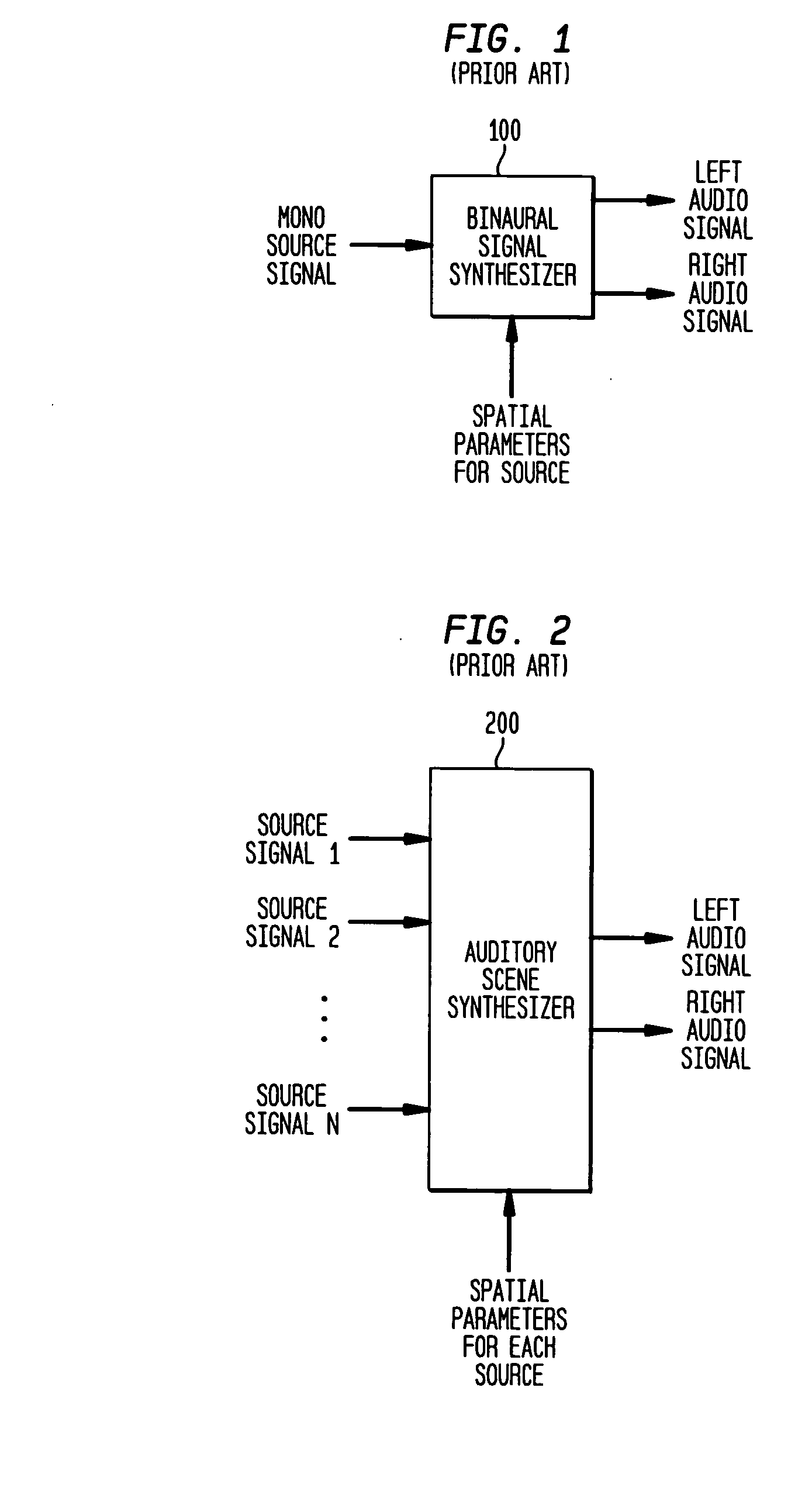
Round complexity is also a meaningful measure of complexity when constraints are placed on the allowed types of communication, particularly in the LOPC/LOCC frameworks where private/quantum communication is not allowed.
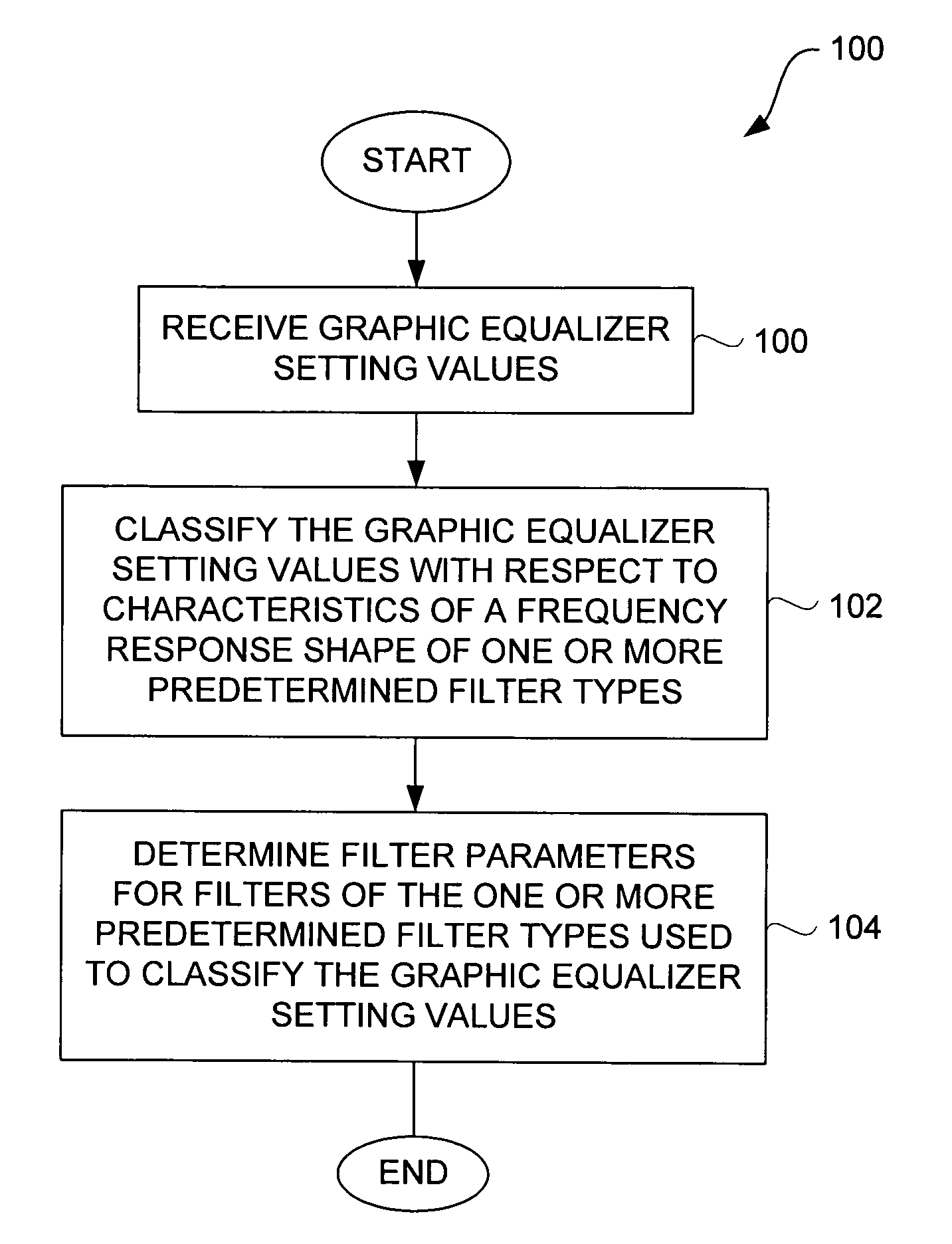
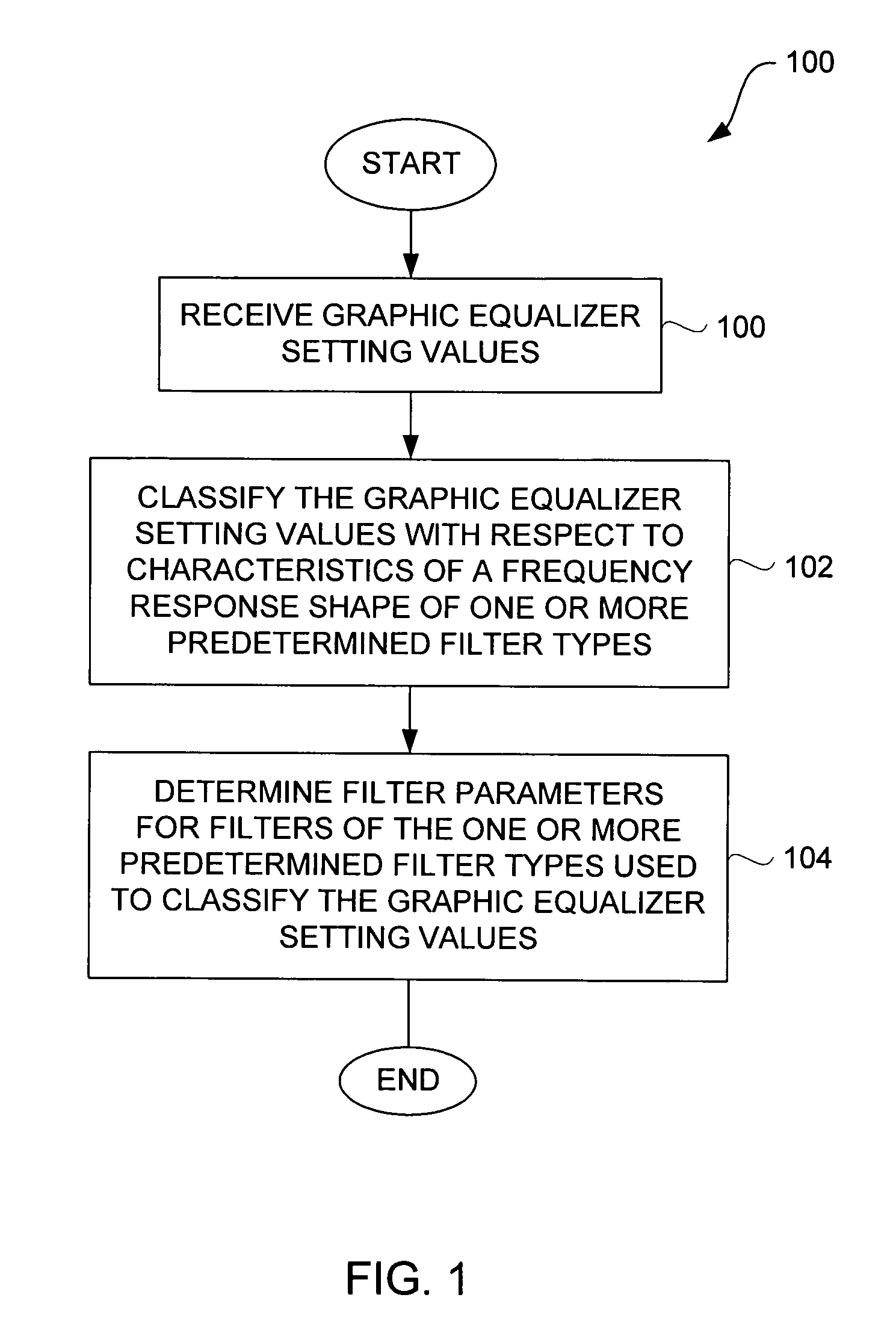
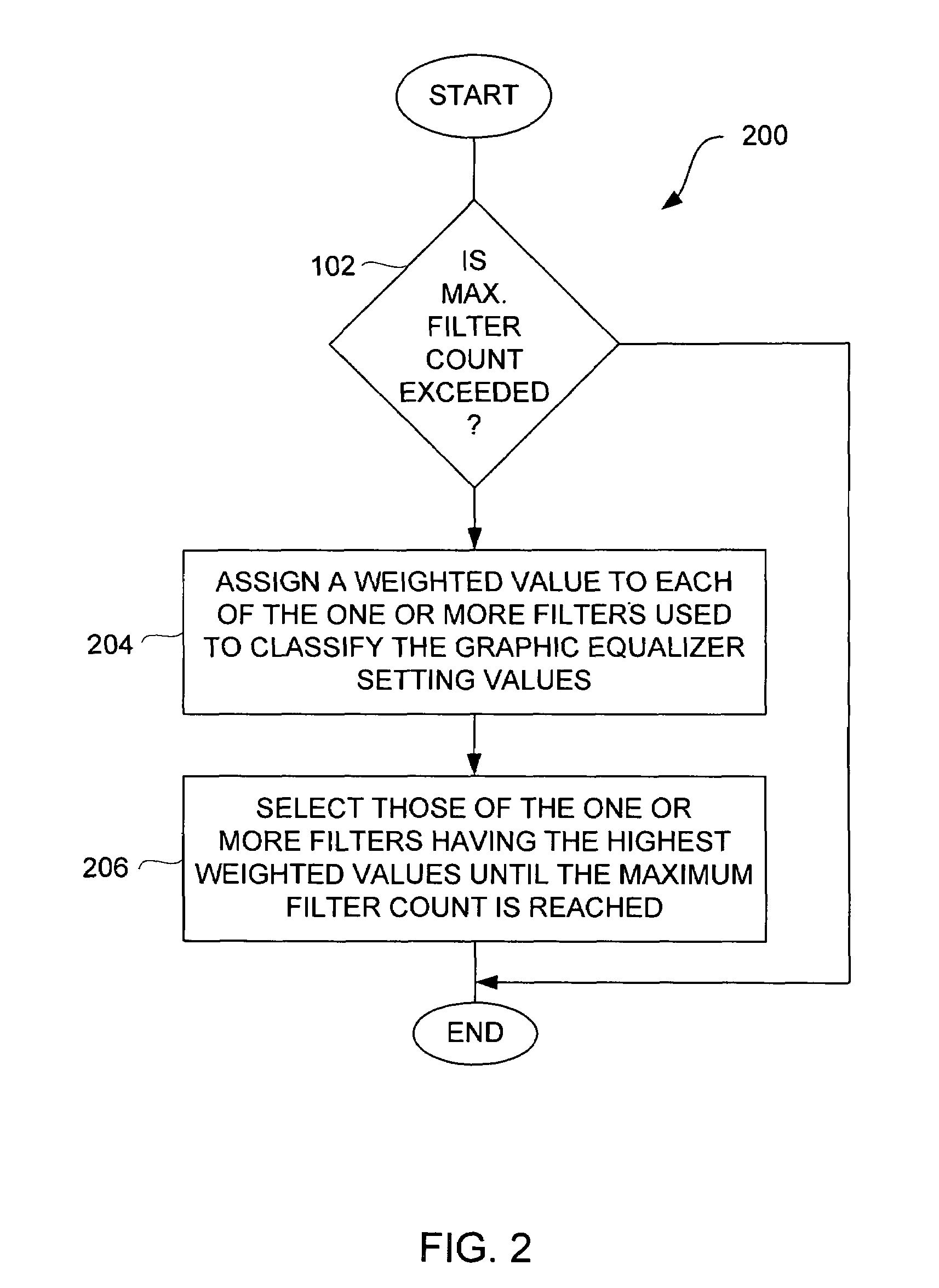
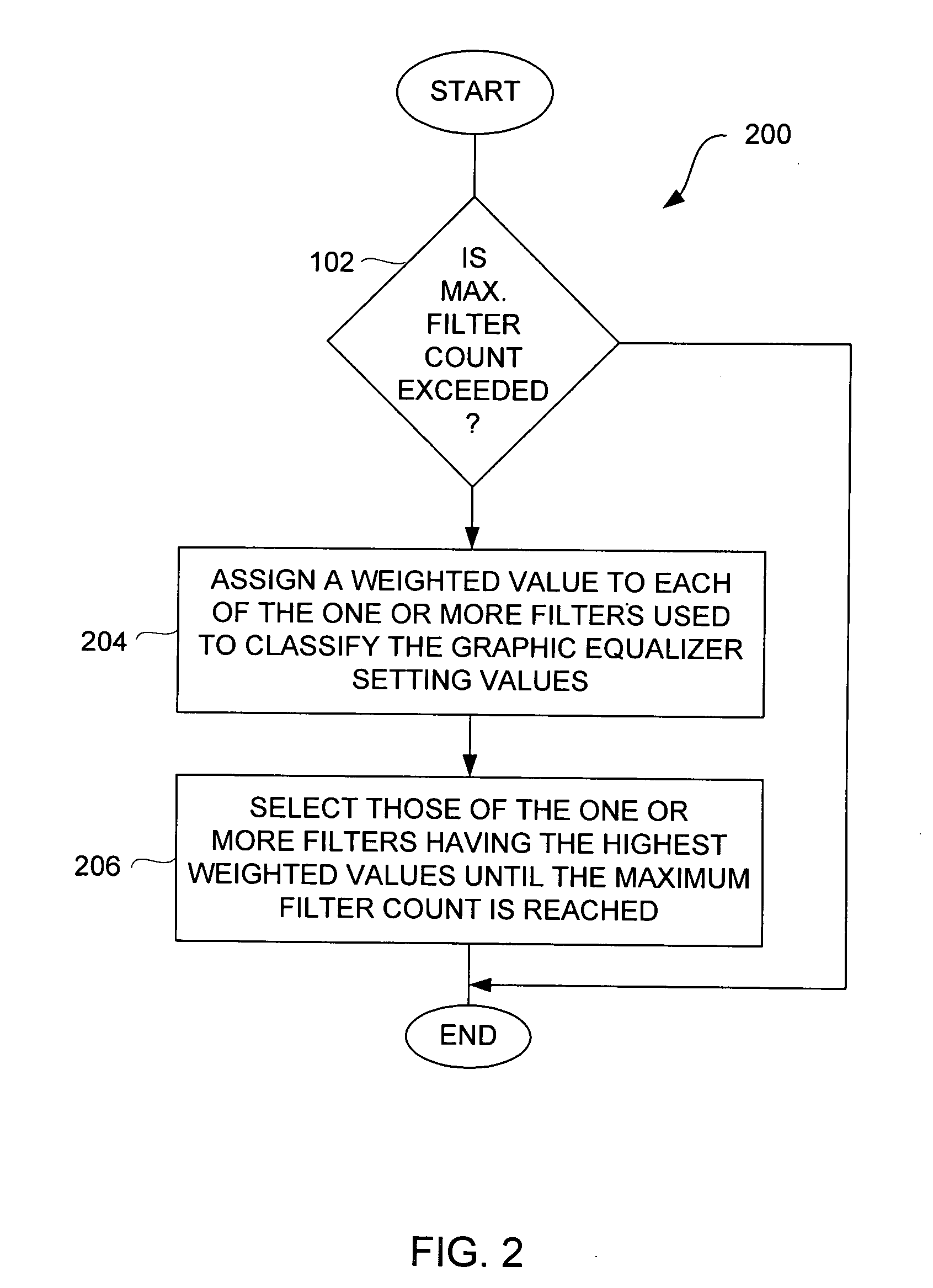
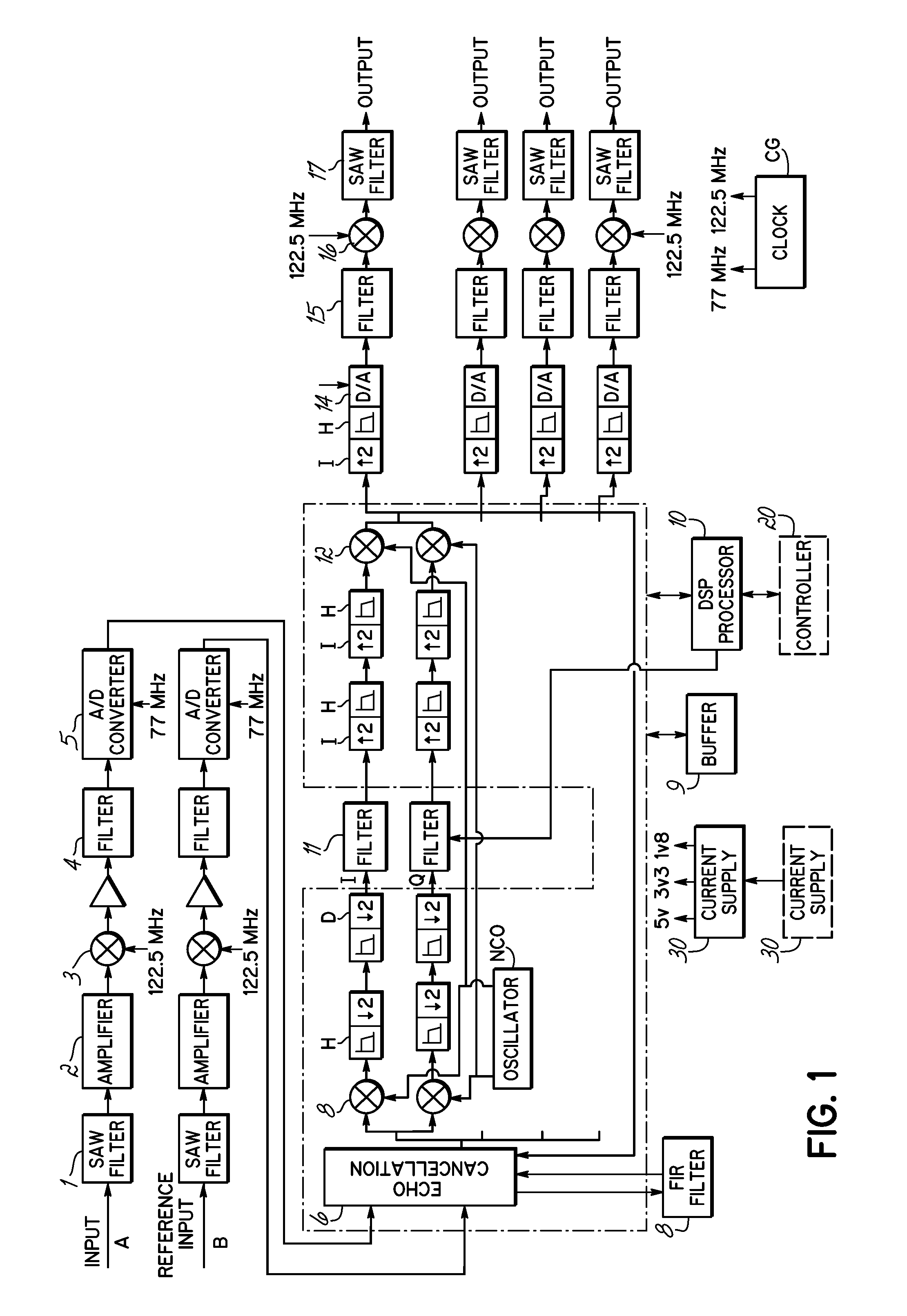
Method and system for approximating graphic equalizers using dynamic filter order reduction
InactiveUS7711129B2Limited computing resourceImprove approachSpecial data processing applicationsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsGraphicsMulti band
Improved approaches to flexibly implementing graphic equalizers on media players are disclosed. These approaches provide dynamic order reduction of a multi-band graphic equalizer so that equalizer effects can be timely performed with only limited computational resources. In one embodiment, a media player receives a media item and associated equalizer settings for a multi-band graphic equalizer. The media player can then automatically (i.e., without user action) approximate the multi-band graphic equalizer with the equalizer settings for the media item using a fewer number of filters. Fewer filters means order reduction, and thus reduction in computational requirements. After the multi-band graphic equalizer is approximated, the media player can present the media item to its user in accordance with the reduced complexity, approximated equalizer.
Owner:APPLE INC
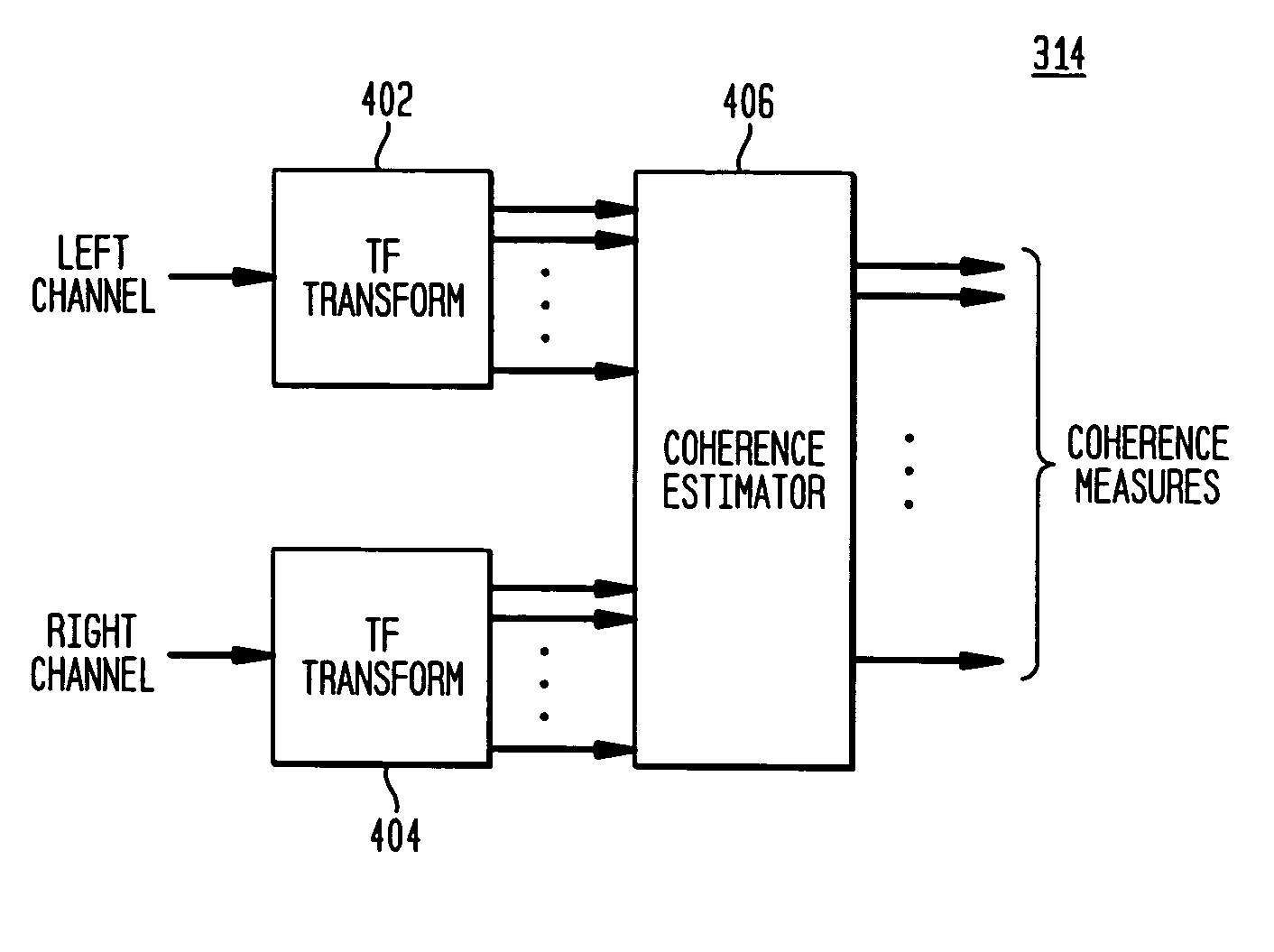
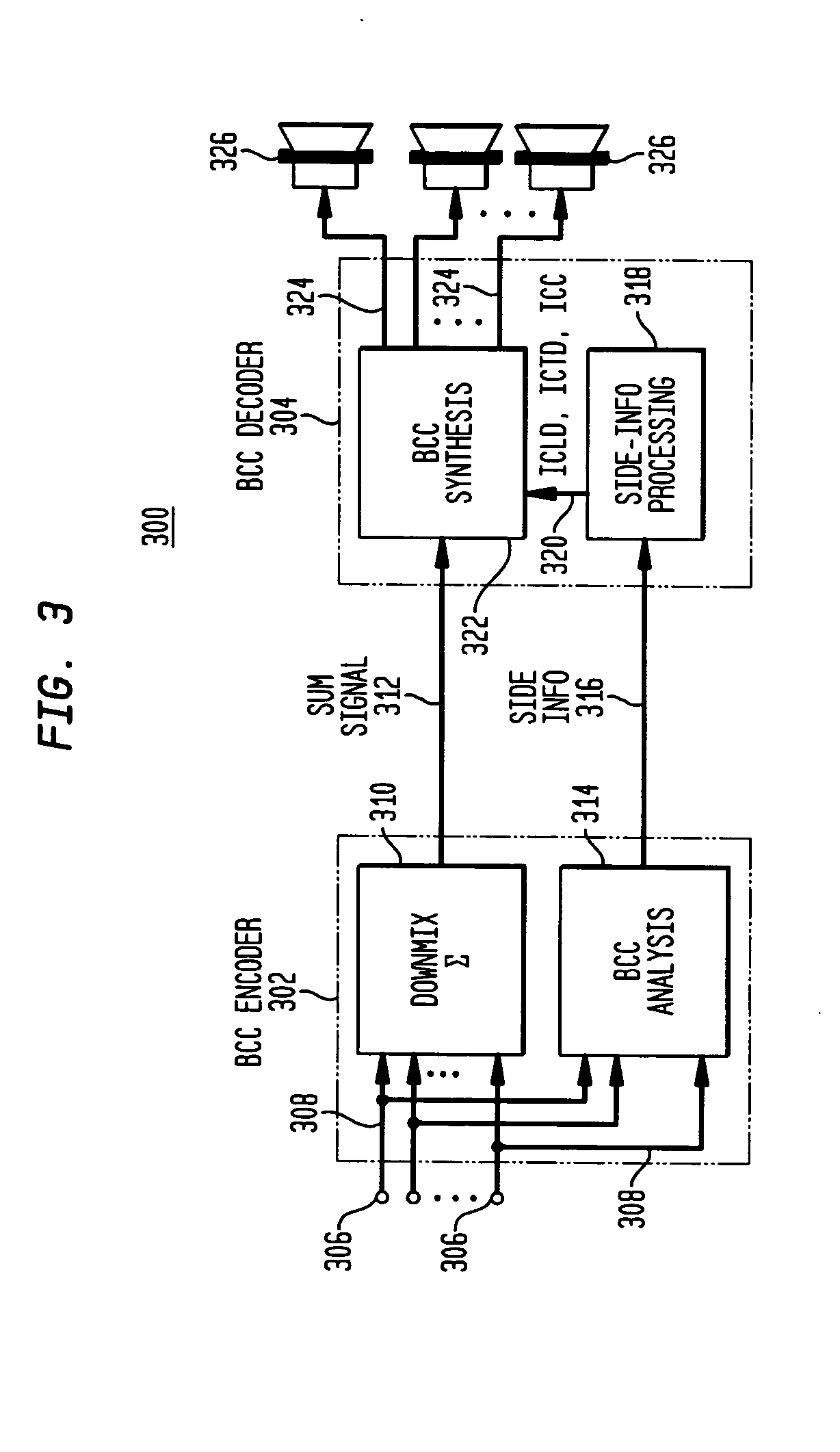
Late reverberation-based synthesis of auditory scenes
ActiveUS20050180579A1Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsGain controlSpeech analysisComputation complexityChannel correlation
A scheme for stereo and multi-channel synthesis of inter-channel correlation (ICC) (normalized cross-correlation) cues for parametric stereo and multi-channel coding. The scheme synthesizes ICC cues such that they approximate those of the original. For that purpose, diffuse audio channels are generated and mixed with the transmitted combined (e.g., sum) signal(s). The diffuse audio channels are preferably generated using relatively long filters with exponentially decaying Gaussian impulse responses. Such impulse responses generate diffuse sound similar to late reverberation. An alternative implementation for reduced computational complexity is proposed, where inter-channel level difference (ICLD), inter-channel time difference (ICTD), and ICC synthesis are all carried out in the domain of a single short-time Fourier transform (STFT), including the filtering for diffuse sound generation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
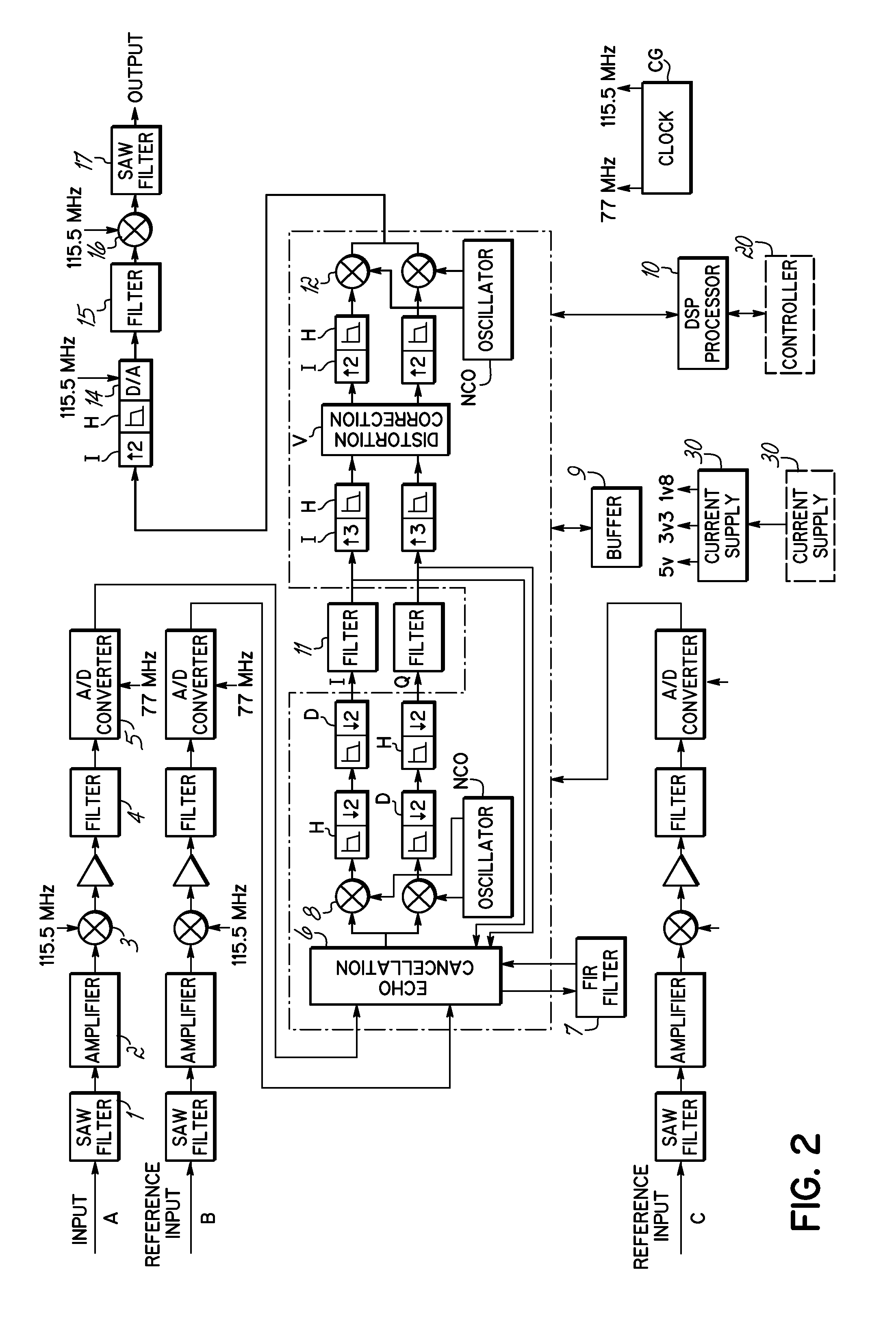
Method and system for approximating graphic equalizers using dynamic filter order reduction
InactiveUS20050201572A1Limited computing resourceImprove approachTransmission control/equlisationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMulti bandGraphics
Improved approaches to flexibly implementing graphic equalizers on media players are disclosed. These approaches provide dynamic order reduction of a multi-band graphic equalizer so that equalizer effects can be timely performed with only limited computational resources. In one embodiment, a media player receives a media item and associated equalizer settings for a multi-band graphic equalizer. The media player can then automatically (i.e., without user action) approximate the multi-band graphic equalizer with the equalizer settings for the media item using a fewer number of filters. Fewer filters means order reduction, and thus reduction in computational requirements. After the multi-band graphic equalizer is approximated, the media player can present the media item to its user in accordance with the reduced complexity, approximated equalizer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Efficient processing of XPath queries
InactiveUS7162485B2Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsRound complexityXSLT
The disclosed teachings provide methods and systems for efficient evaluation of XPath queries. In particular, the disclosed evaluation methods require only polynomial time with respect to the total size of an input XPath query and an input XML document. Crucial for the new methods is the notion of “context-value tables”. This idea can be further refined for queries in Core XPath and XSLT Patterns so as to yield even a linear time evaluation method. Moreover, the disclosed methods can be used for improving existing methods and systems for processing XPath expressions so to guarantee polynomial worst-case complexity.
Owner:GOTTLOB GEORG +2
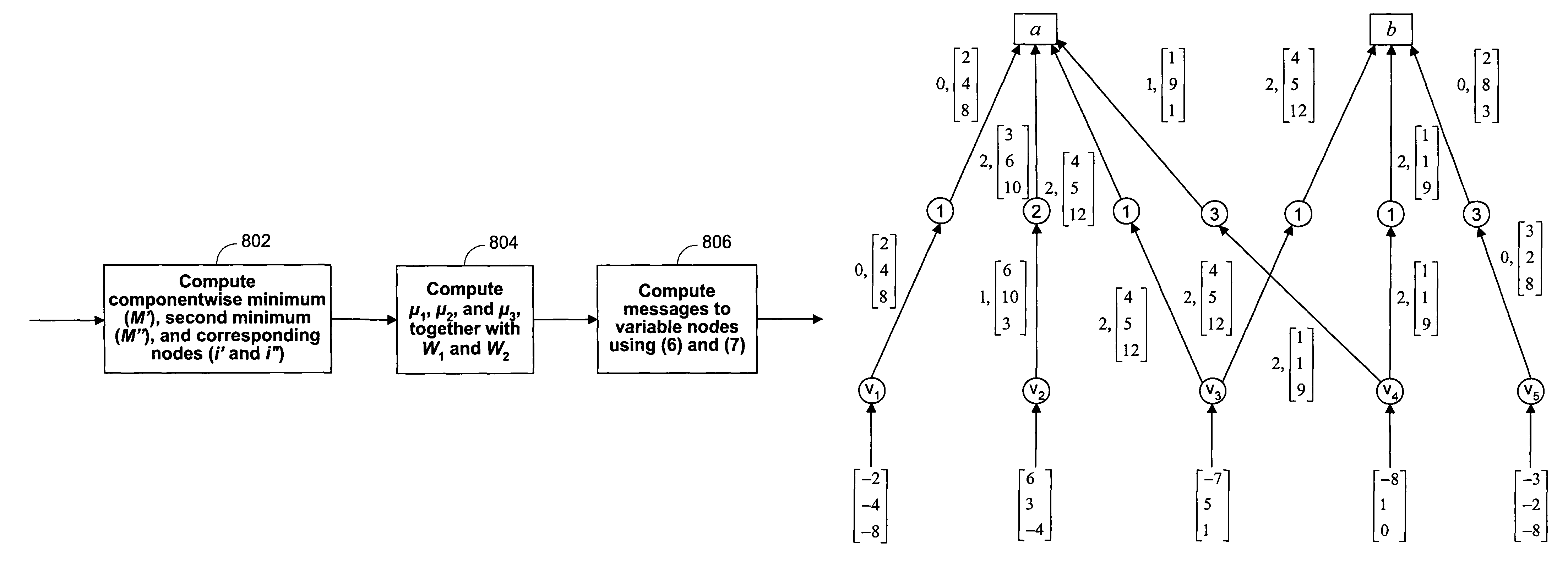
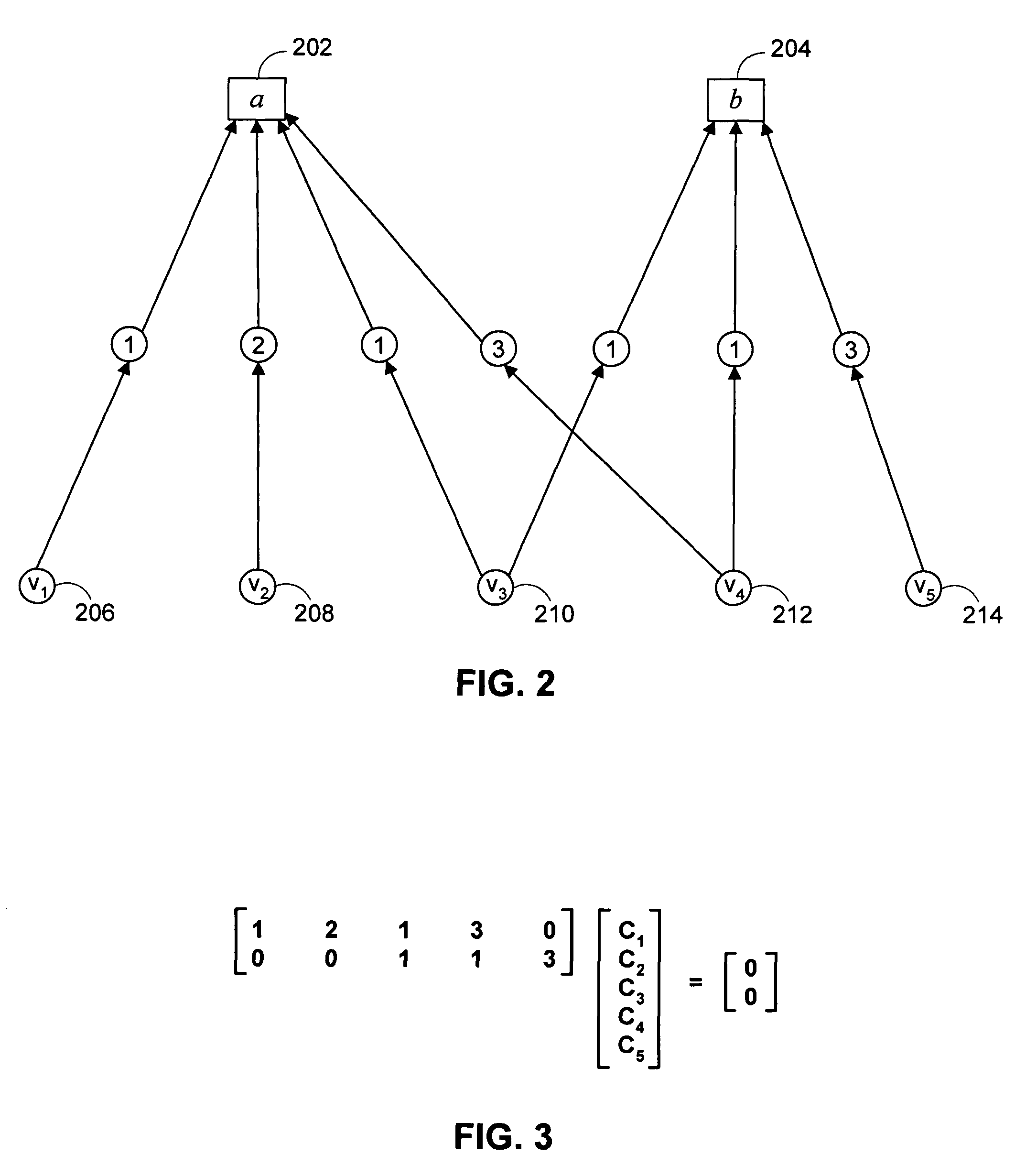
Reduced-complexity decoding of parity check codes
ActiveUS7752523B1Less resourcesData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionRound complexityTheoretical computer science
The disclosed technology provides a less resource intensive way to decode a parity check code using a modified min-sum algorithm. For a particular parity check constraint that includes n variable nodes, an LDPC decoder can compute soft information for one of the variable nodes based on combinations of soft information from other variable nodes, wherein each combination includes soft information from at most a number d of other variable nodes. In one embodiment, soft information from one of the other variable nodes is used in a combination only if it corresponds to a non-most-likely value for the other variable node.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
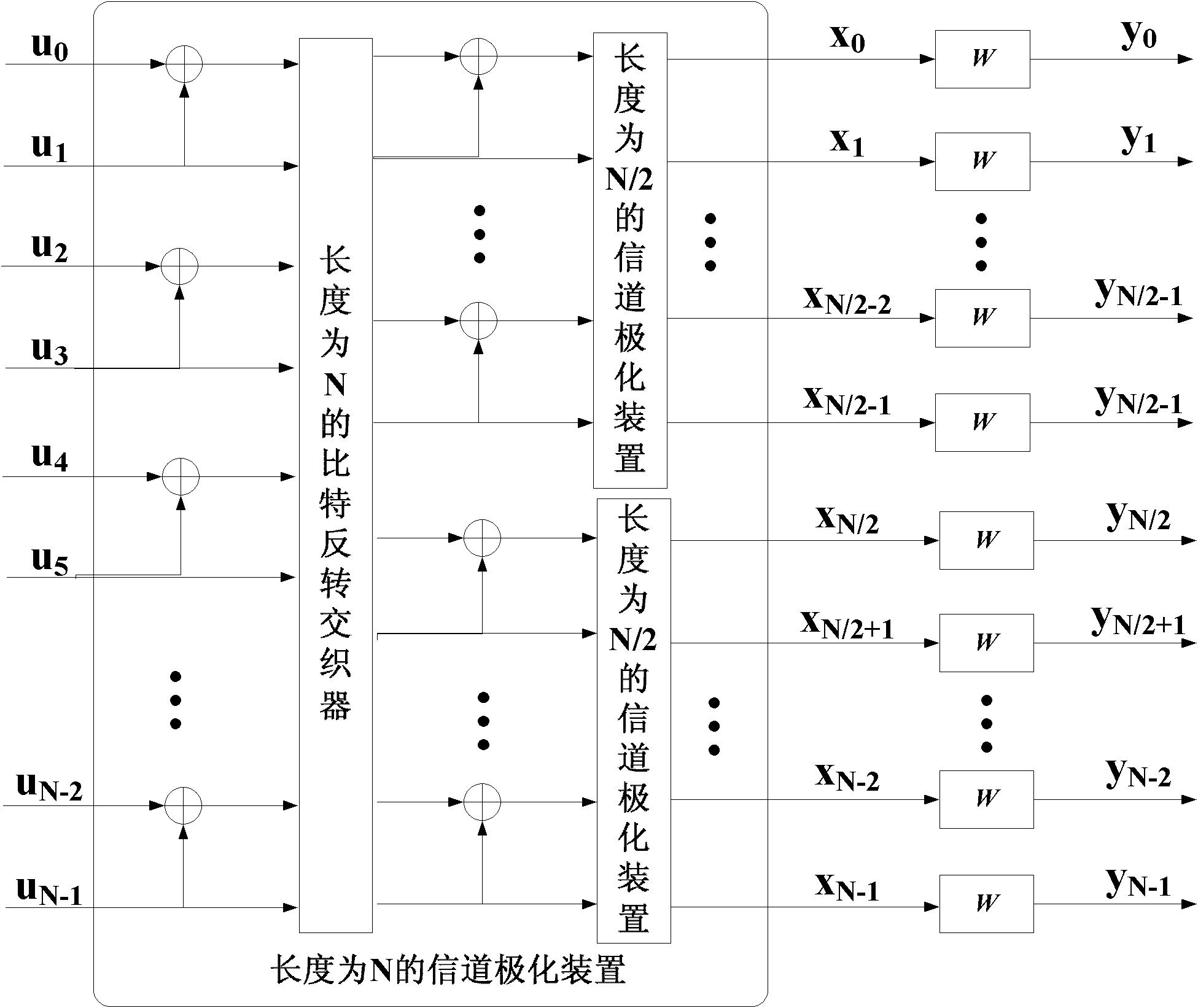
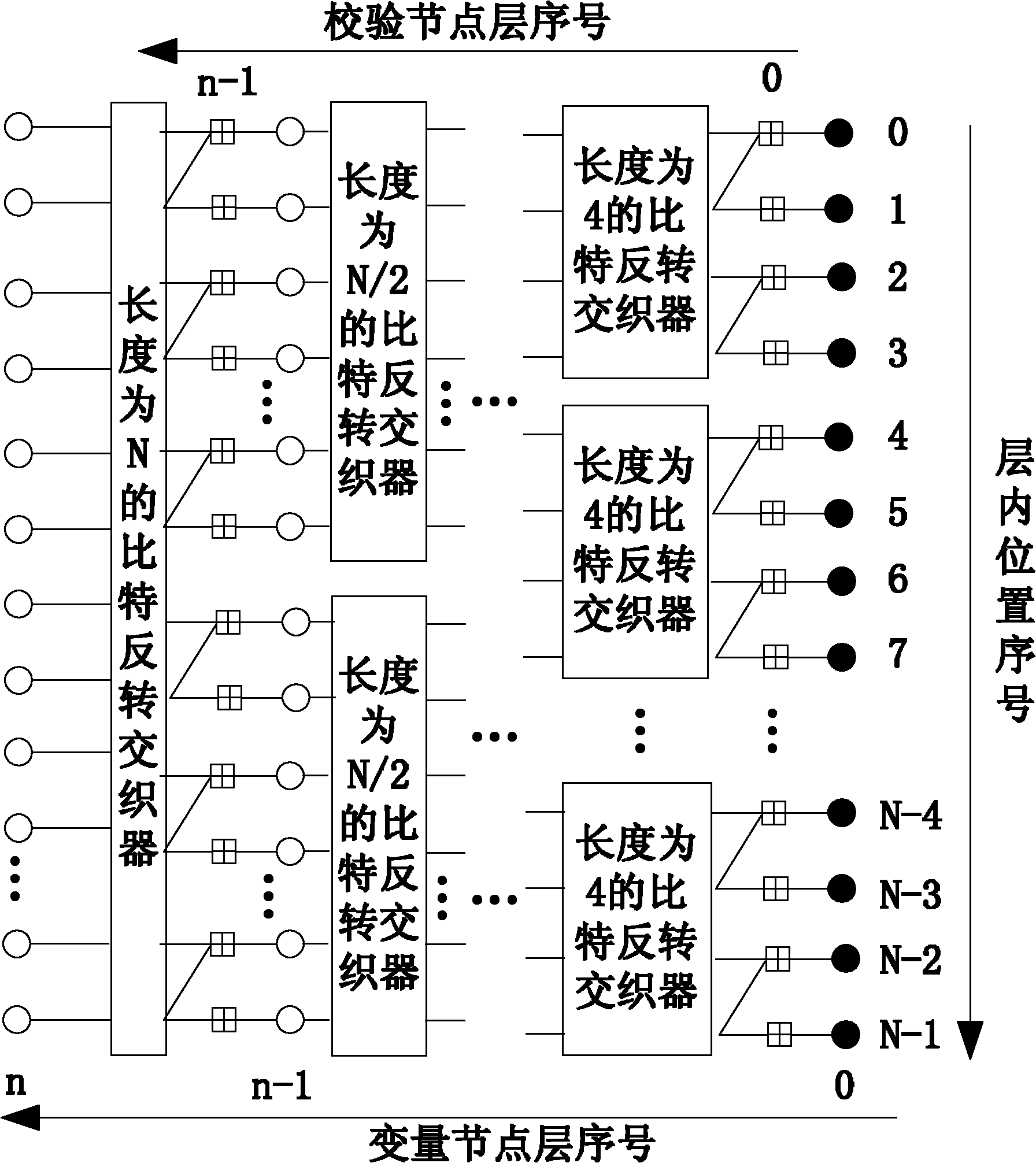
Channel-polarization-based encoder for staggered structure duplication code, and encoding and decoding methods thereof
InactiveCN102122966ASimple structureStrong error correction abilityCode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesTanner graphCoding block
The invention discloses a channel-polarization-based encoder for a staggered structure duplication code, and an encoding method and decoding methods thereof. The encoder consists of a duplication bit buffer with a storage capacity of L bits, a bit position mapper with a length N and a channel polarization device with the length N which are connected in sequence. The encoding method based on the encoder comprises the following steps of: embedding duplicated encoding into a channel polarization process, and introducing a duplicated relationship between parts of the bits of code blocks transmitted in sequence during the channel polarization for encoding. In addition, the invention further provides two decoding methods, which comprise the following steps of: decoding by using a simple and rapid successive cancellation (SC) algorithm, and performing iterative decoding by using a Tanner-graph-based belief propagation algorithm with excellent performance. On the basis of the innovative structure encoder, the encoding and decoding methods provided by the invention are stronger in error correction capability under the condition of not increasing the decoding complexity, and the transmission performance is obviously improved. The encoding and decoding methods are particularly applicable to an actual communication engineering system and have a good popularization and application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
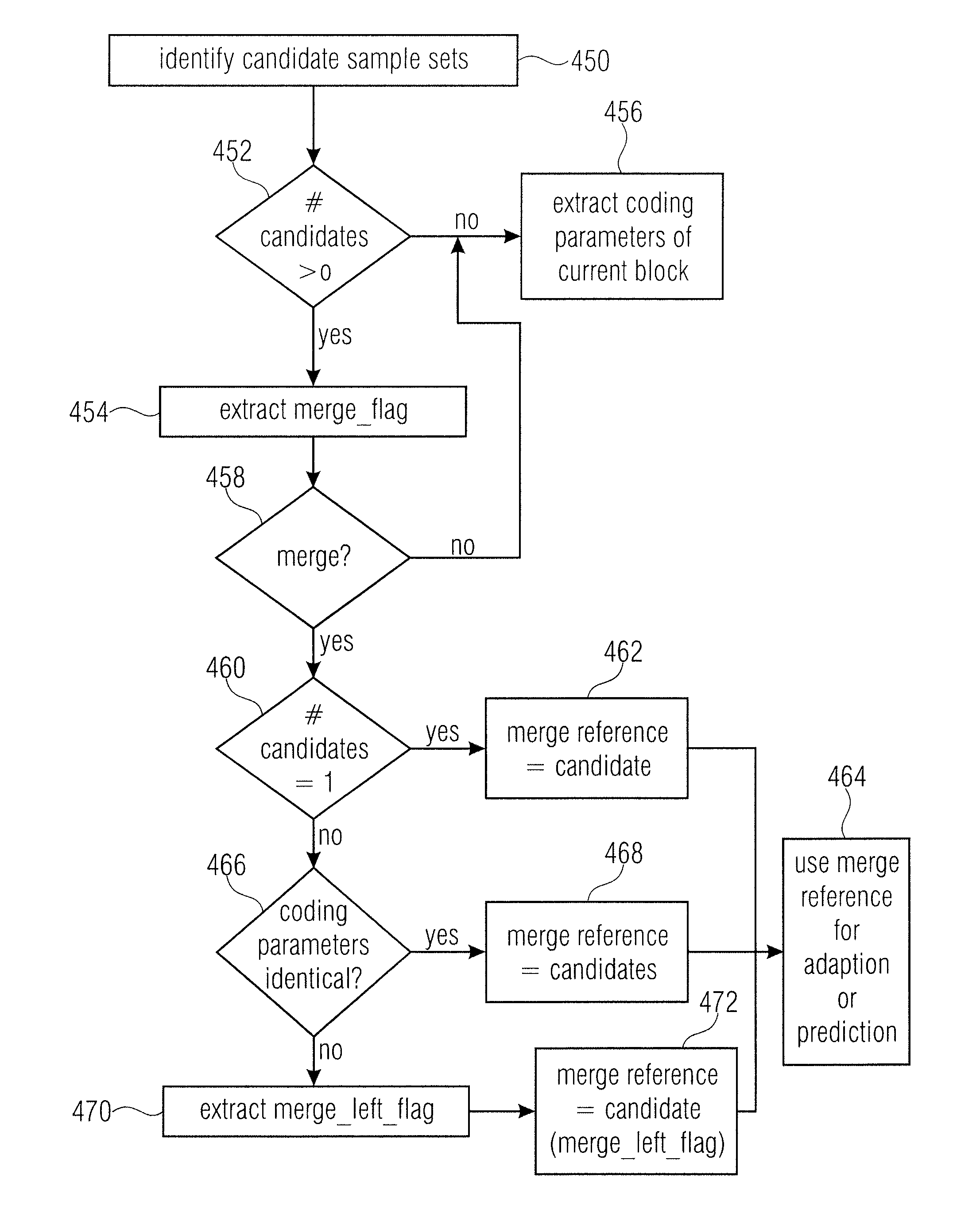
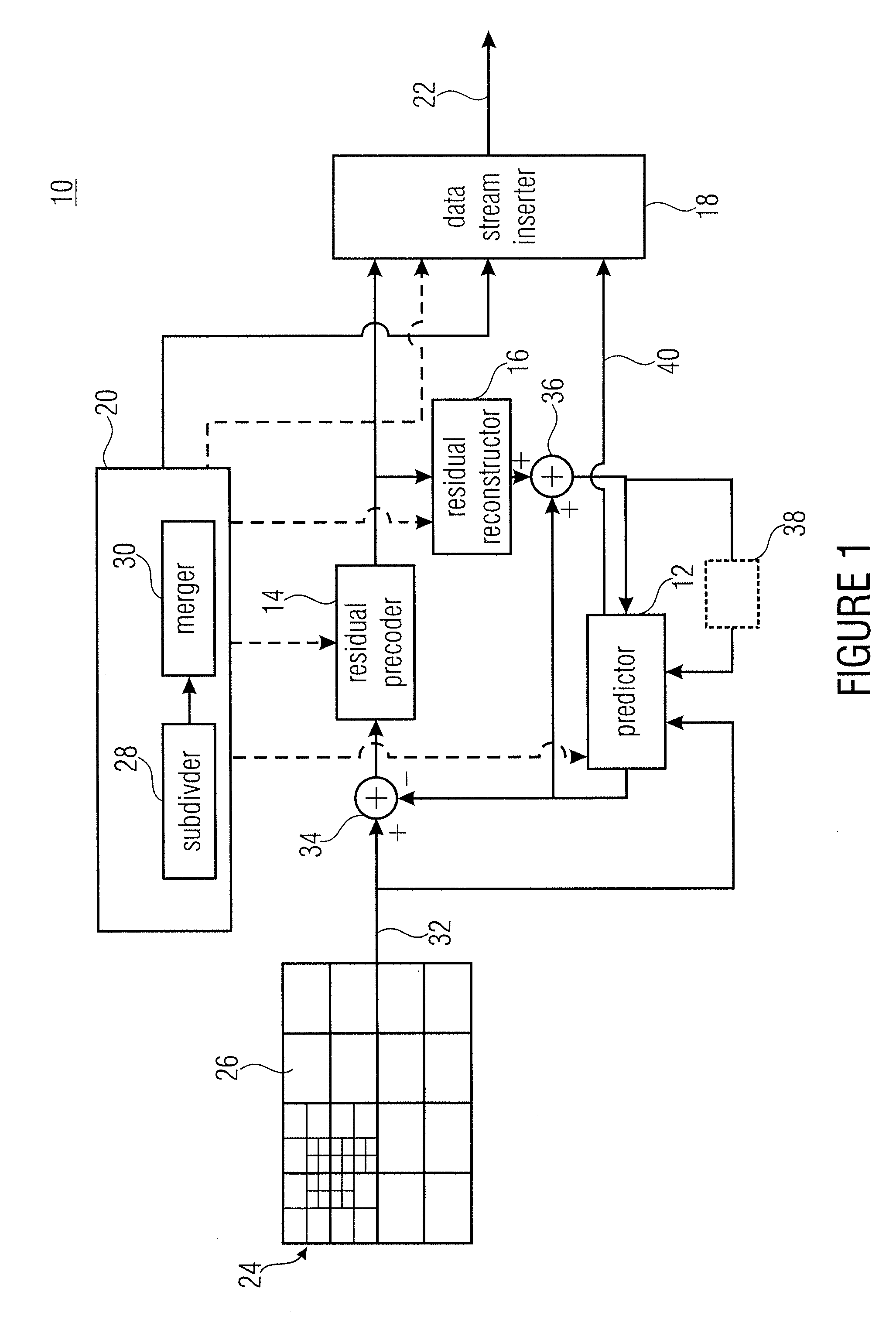
Inheritance in sample array multitree subdivision
ActiveUS20130034157A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureRound complexity
A better compromise between encoding complexity and achievable rate distortion ratio, and / or to achieve a better rate distortion ratio is achieved by using multitree sub-divisioning not only in order to subdivide a continuous area, namely the sample array, into leaf regions, but using the intermediate regions also to share coding parameters among the corresponding collocated leaf blocks. By this measure, coding procedures performed in tiles—leaf regions—locally, may be associated with coding parameters individually without having to, however, explicitly transmit the whole coding parameters for each leaf region separately. Rather, similarities may effectively exploited by using the multitree subdivision.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
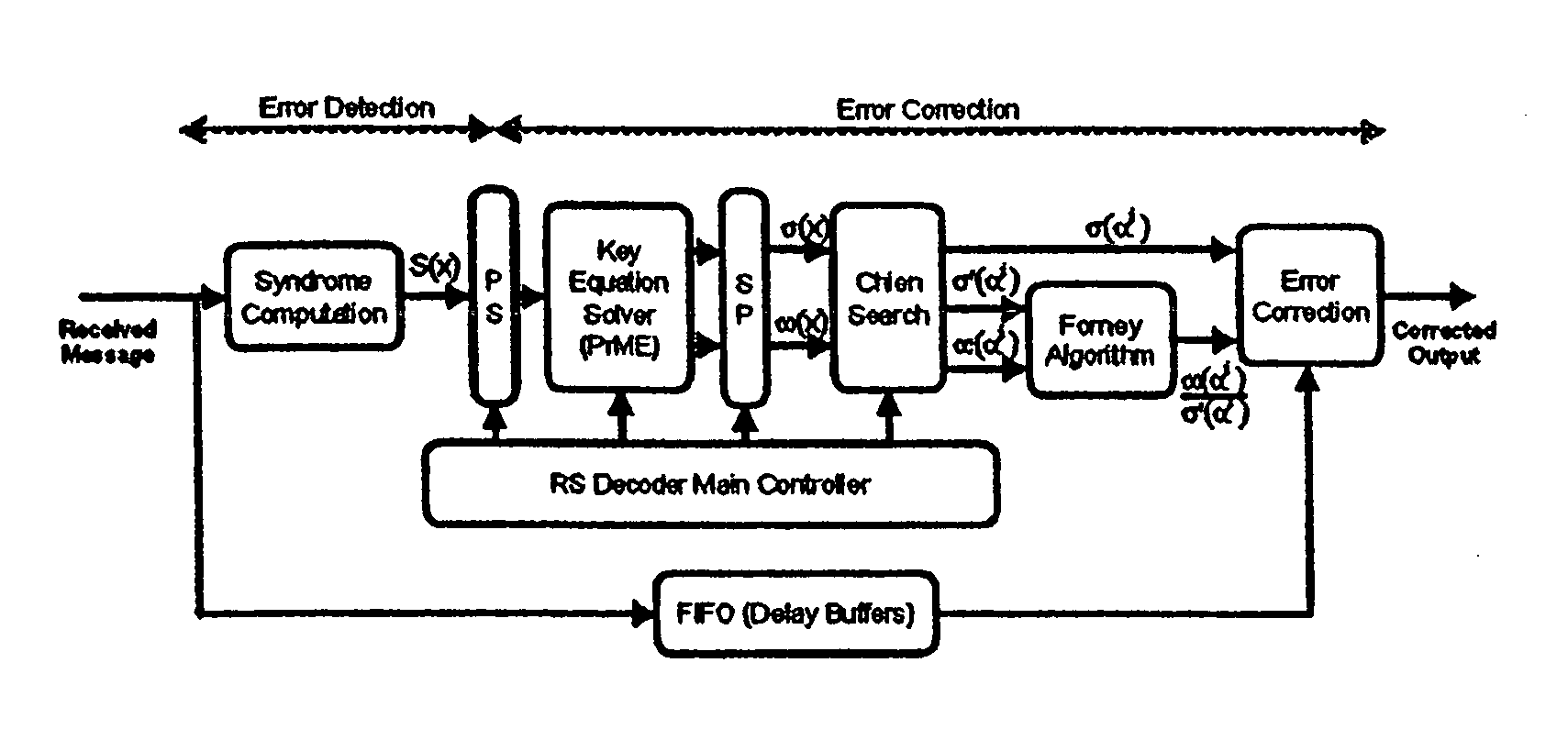
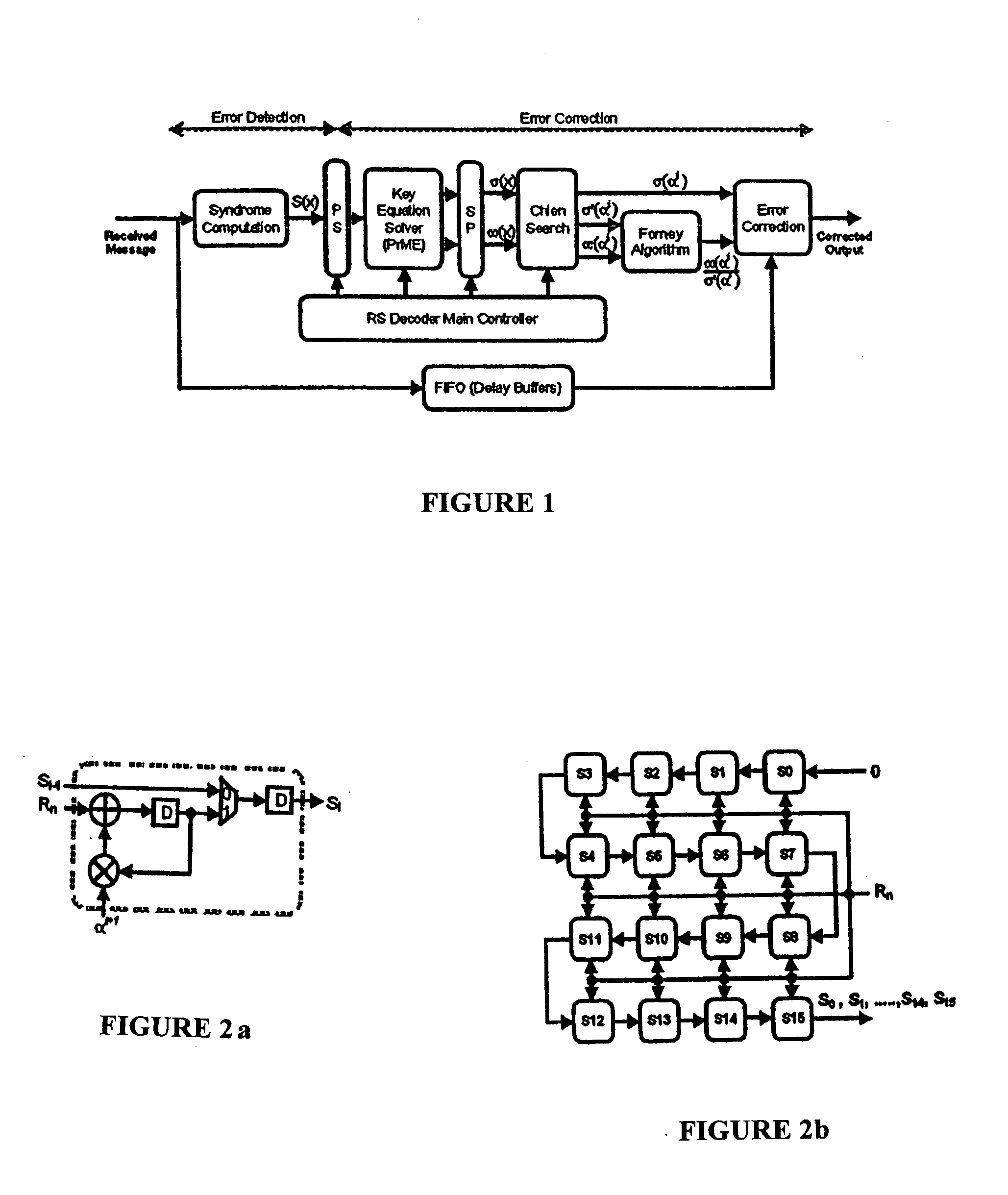
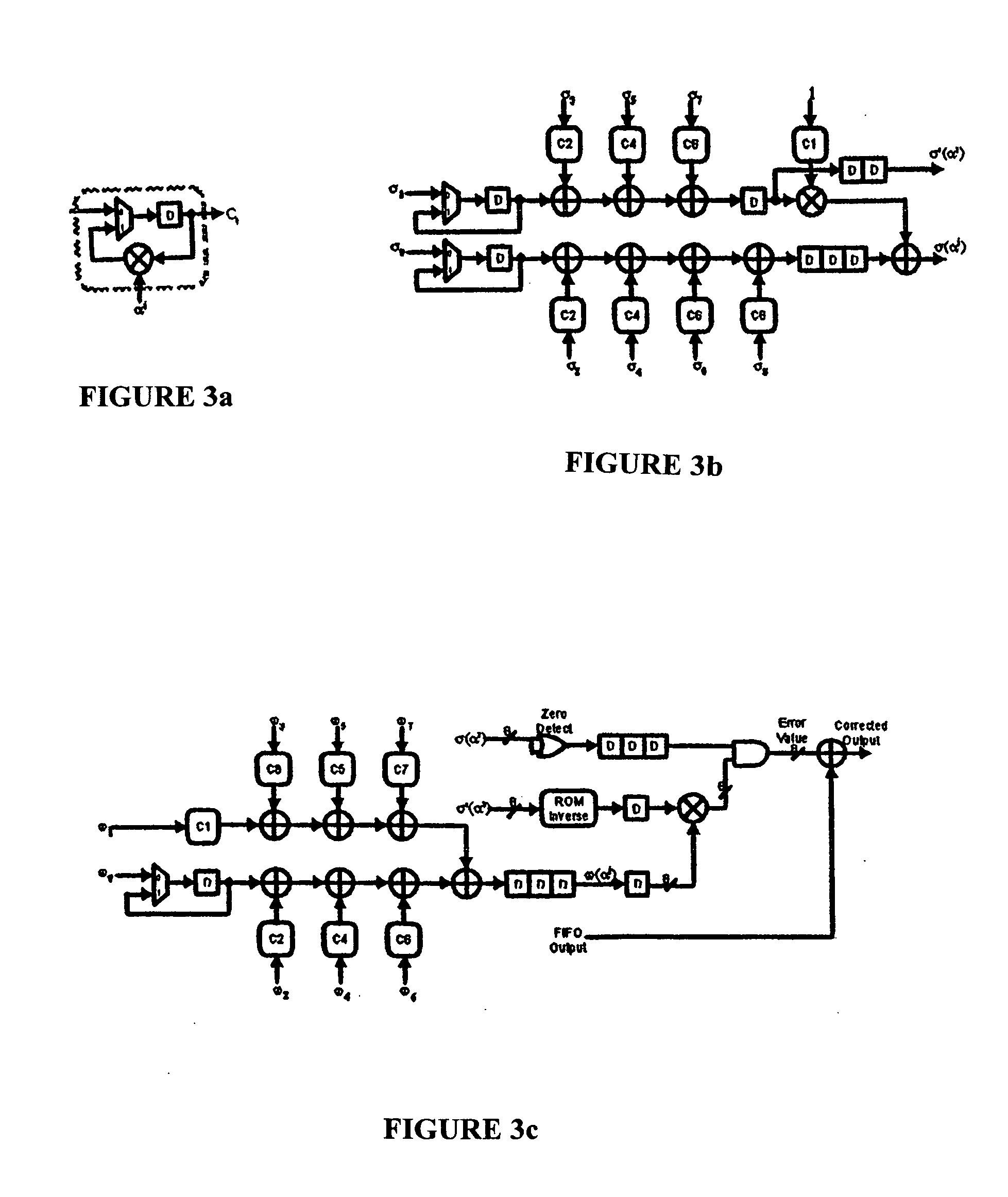
Reed-solomon decoder systems for high speed communication and data storage applications
InactiveUS20060059409A1Effective and reliable error correction functionalityReduce complexityCode conversionCoding detailsModem deviceHigh rate
A high-speed, low-complexity Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder architecture using a novel pipelined recursive Modified Euclidean (PrME) algorithm block for very high-speed optical communications is provided. The RS decoder features a low-complexity Key Equation Solver using a PrME algorithm block. The recursive structure enables the low-complexity PrME algorithm block to be implemented. Pipelining and parallelizing allow the inputs to be received at very high fiber optic rates, and outputs to be delivered at correspondingly high rates with minimum delay. An 80-Gb / s RS decoder architecture using 0.13-μm CMOS technology in a supply voltage of 1.2 V is disclosed that features a core gate count of 393 K and operates at a clock rate of 625 MHz. The RS decoder has a wide range of applications, including fiber optic telecommunication applications, hard drive or disk controller applications, computational storage system applications, CD or DVD controller applications, fiber optic systems, router systems, wireless communication systems, cellular telephone systems, microwave link systems, satellite communication systems, digital television systems, networking systems, high-speed modems and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
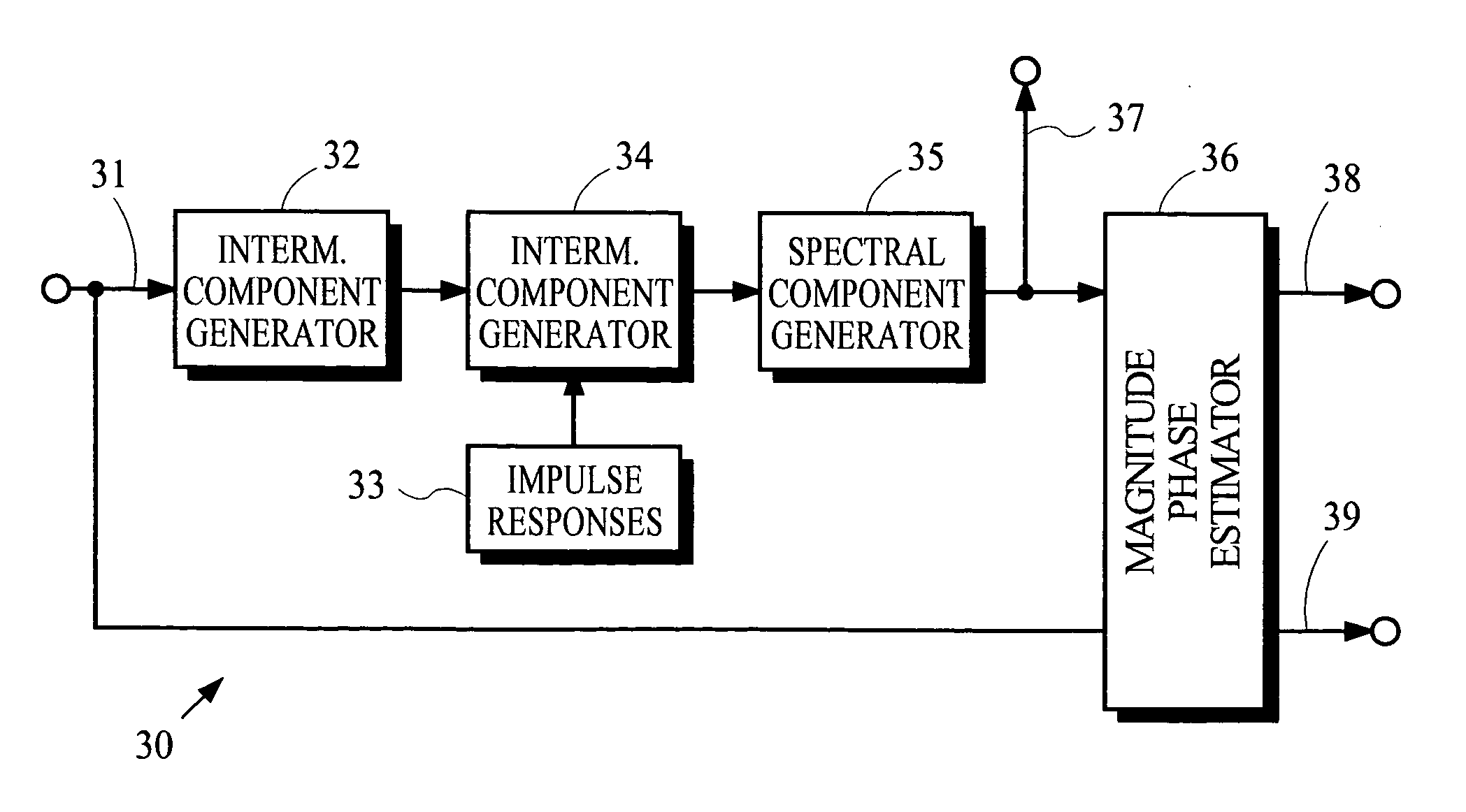
Coding techniques using estimated spectral magnitude and phase derived from MDCT coefficients
ActiveUS6980933B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpeech analysisComputation complexityFrequency spectrum
Estimates of spectral magnitude and phase are obtained by an estimation process using spectral information from analysis filter banks such as the Modified Discrete Cosine Transform. The estimation process may be implemented by convolution-like operations with impulse responses. Portions of the impulse responses may be selected for use in the convolution-like operations to trade off between computational complexity and estimation accuracy. Mathematical derivations of analytical expressions for filter structures and impulse responses are disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
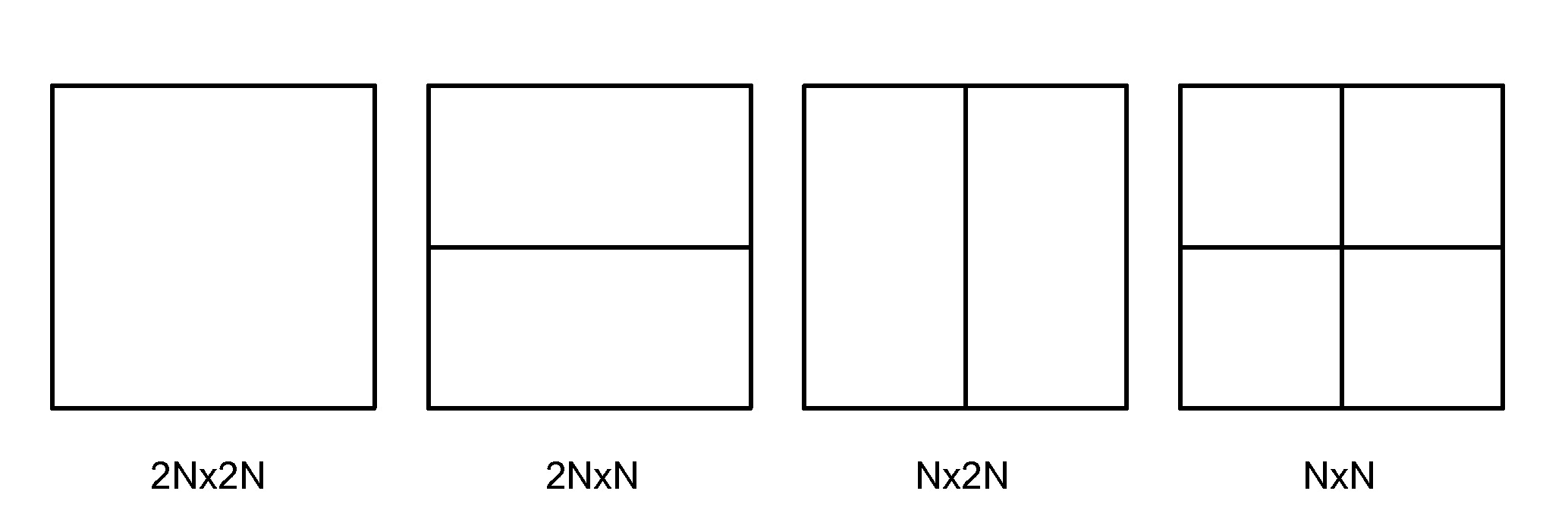
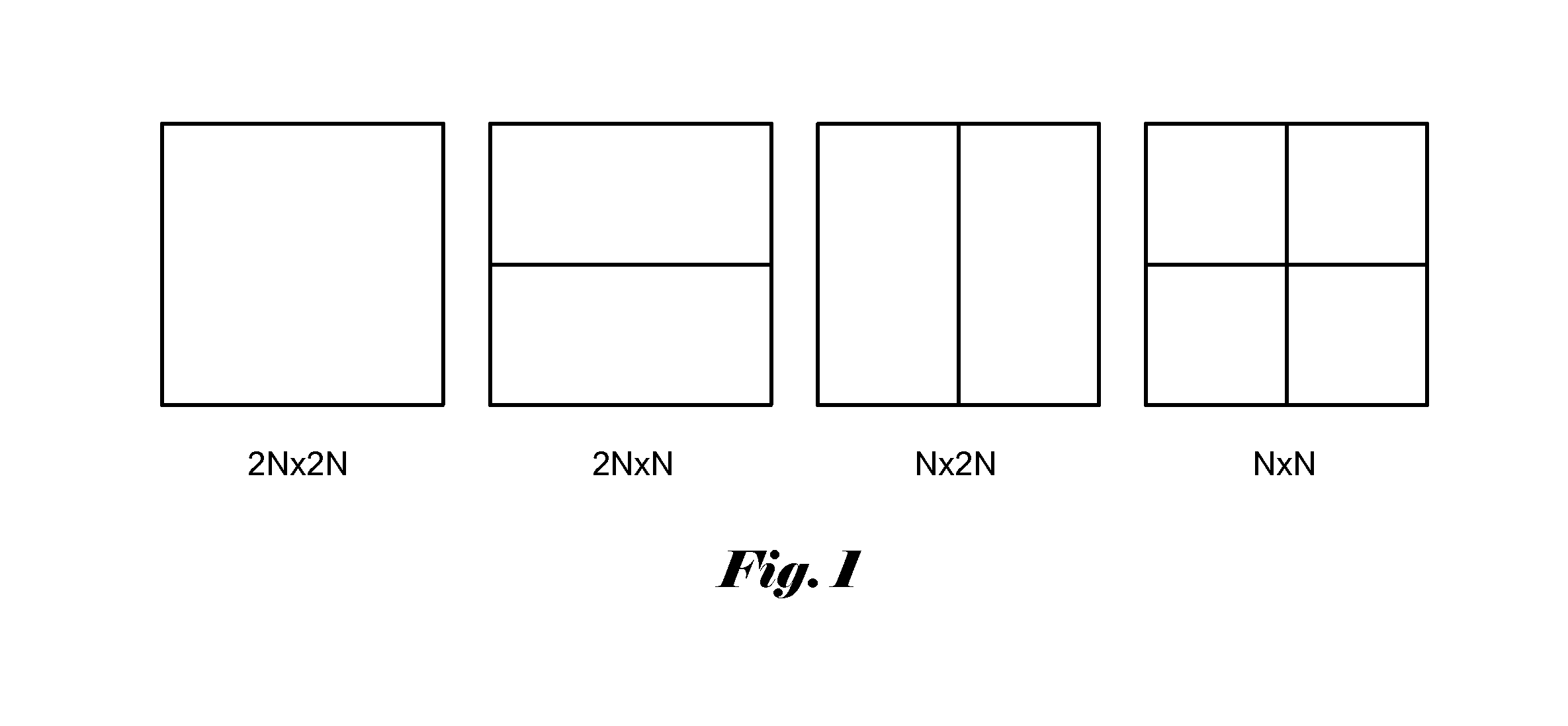
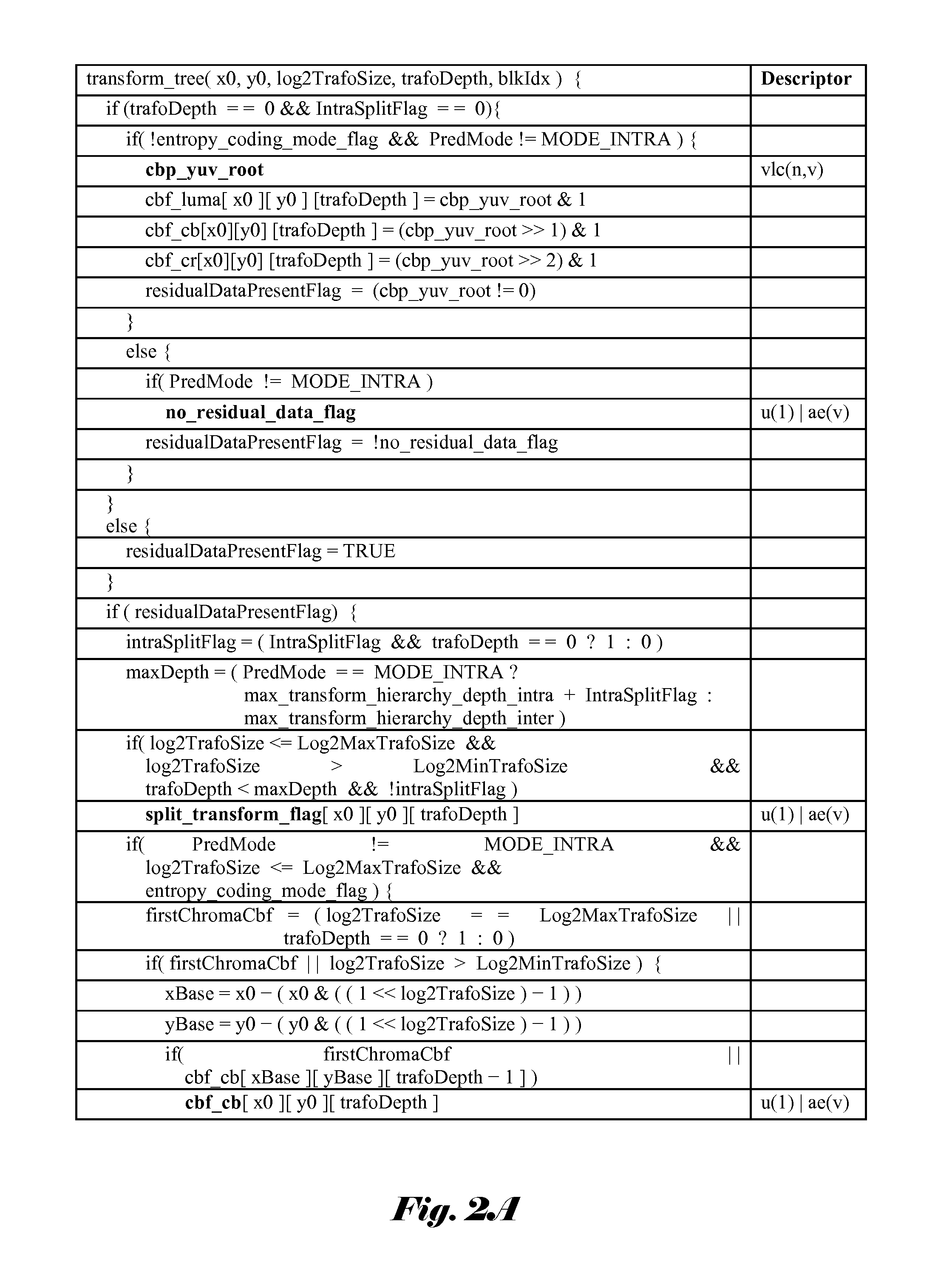
Method and Apparatus of Transform Unit Partition with Reduced Complexity
ActiveUS20120230411A1Reduced encoding computational complexitySmall motion estimation costColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRound complexityMotion vector
Three block concepts are introduced in HEVC: coding unit (CU), prediction unit (PU), and transform unit (TU). The overall coding structure is characterized by the various sizes of CU, PU and TU in a recursive fashion. For transform processing in current HEVC, a hierarchy RQT (Residual Quad Tree) is used and the TU size is related to the CU size, but independent of the PU size. This results in high encoding complexity and also causes increased processing time to process the syntax of residual quad tree. Accordingly a modified transform unit partition with reduced complexity is disclosed. According to an embodiment, the TU size may be restricted to the minimum of PU width and height, except for a 2N×2N coding unit with the 2N×2N partition type. In another embodiment, the maximum TU size equals to maximum of PU width and height, and the minimum TU size equals to minimum of the PU width and height, except for a 2N×2N coding unit with the 2N×2N partition type. In yet another embodiment, the TU size is selected between 2N×2N and N×N for the 2N×2N, 2N×N, N×2N and N×N partition types. The syntax element, split_transform_flag, is used to indicate the selection of 2N×2N or N×N TU size when needed. Furthermore, a method with reduced complexity of selecting the best merge candidate for the 2N×2N CU merge mode is disclosed. The method relies on R-D cost associated with the motion vector of merge candidate to reduce required computation.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
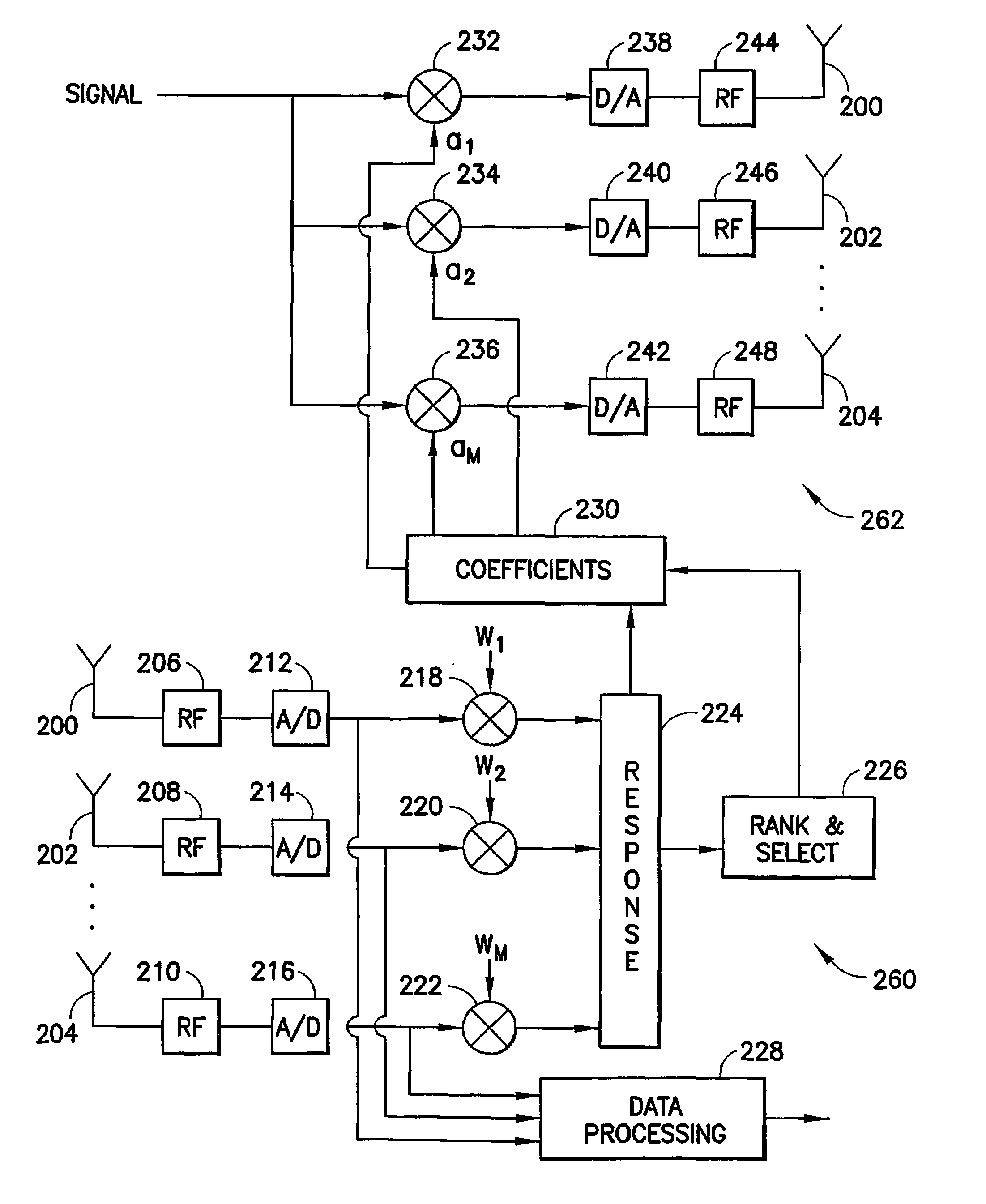
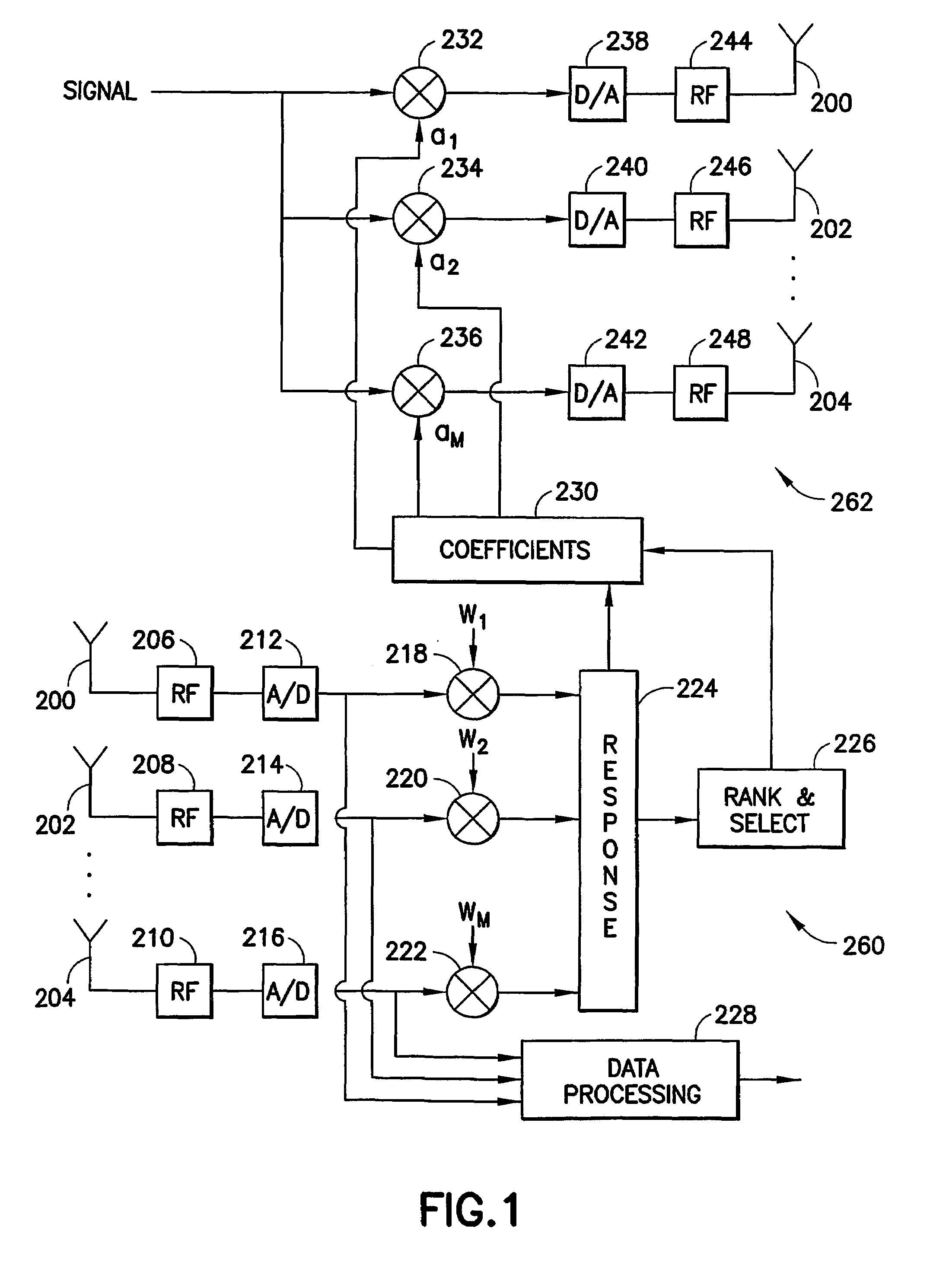
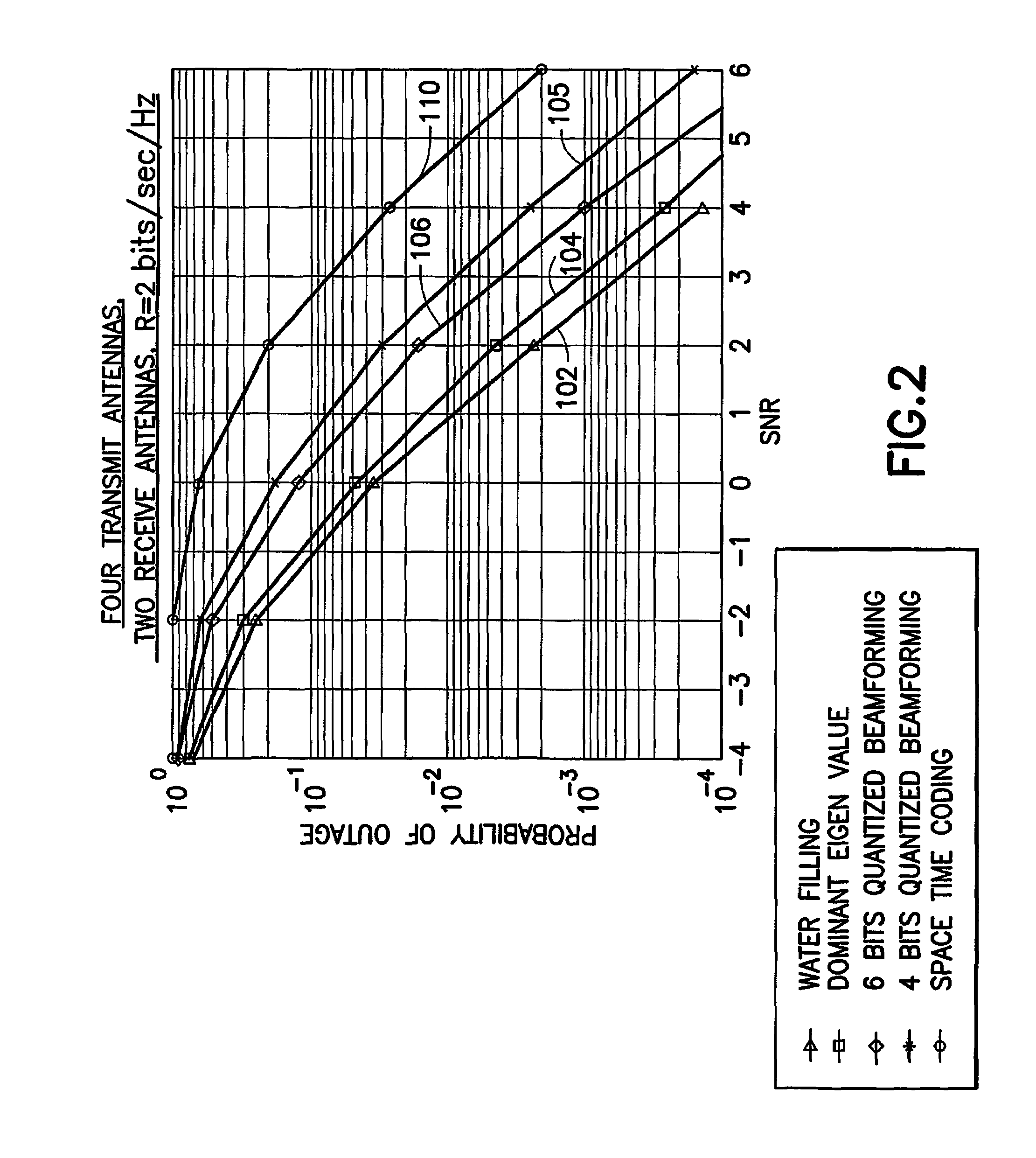
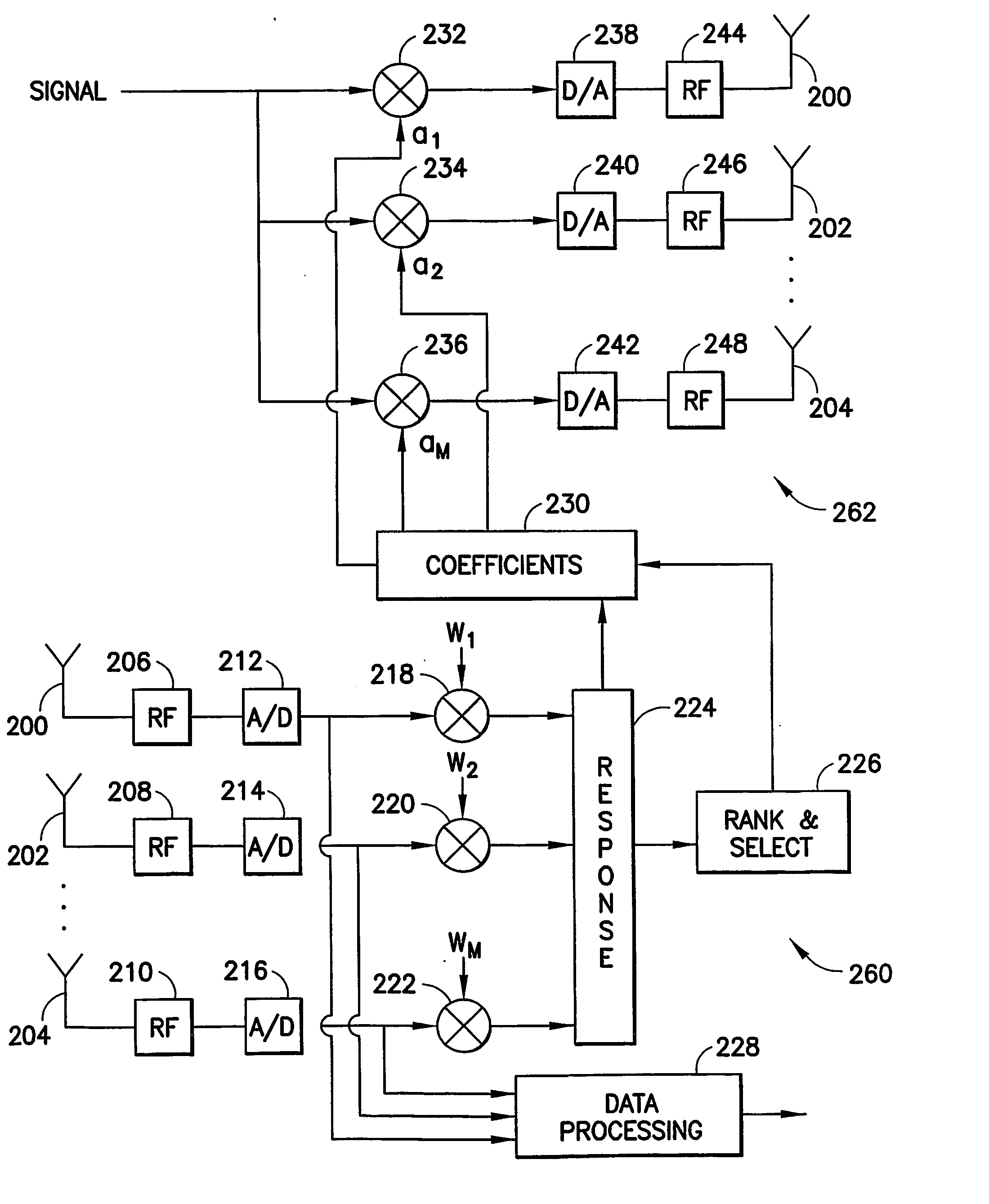
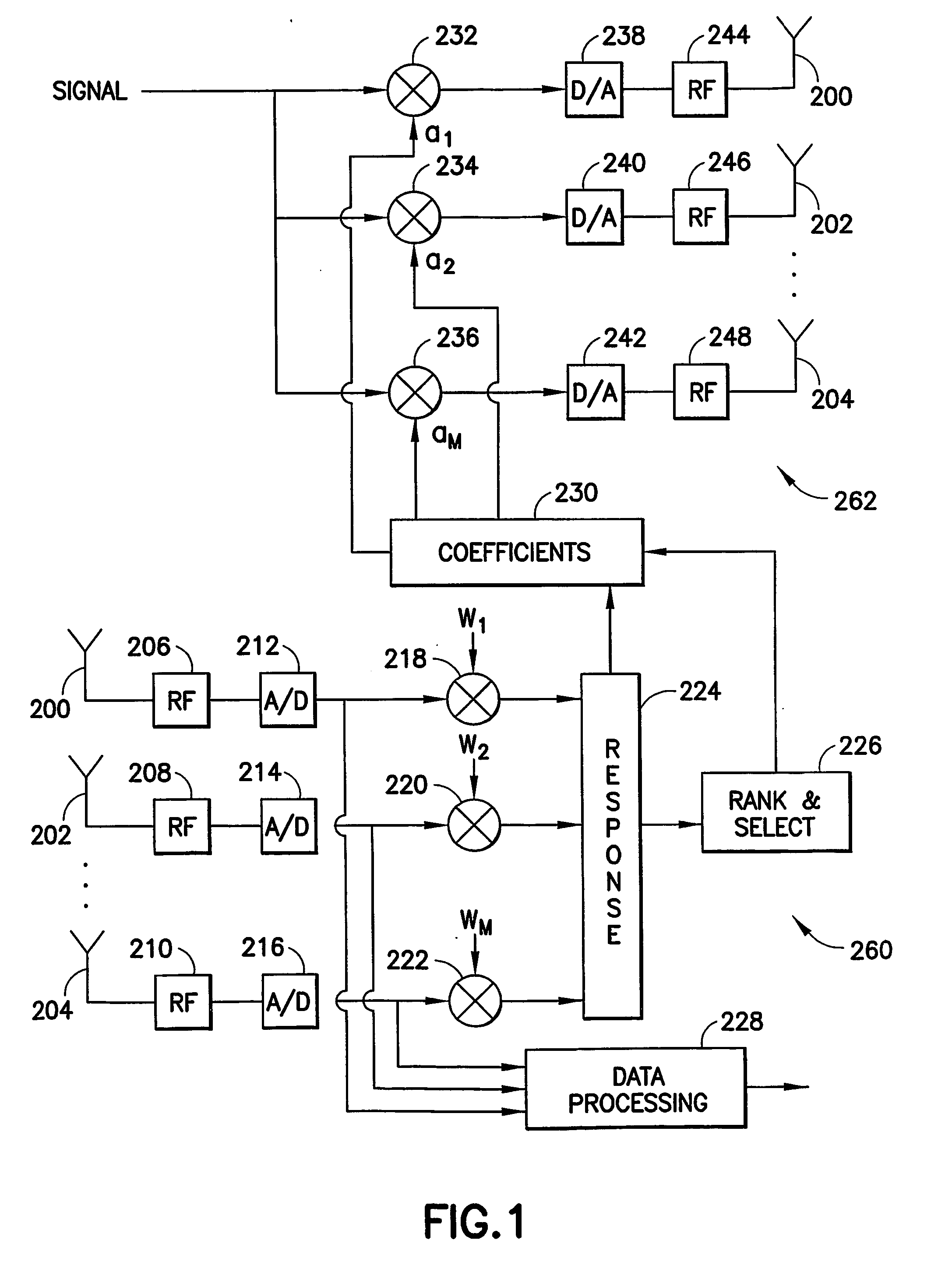
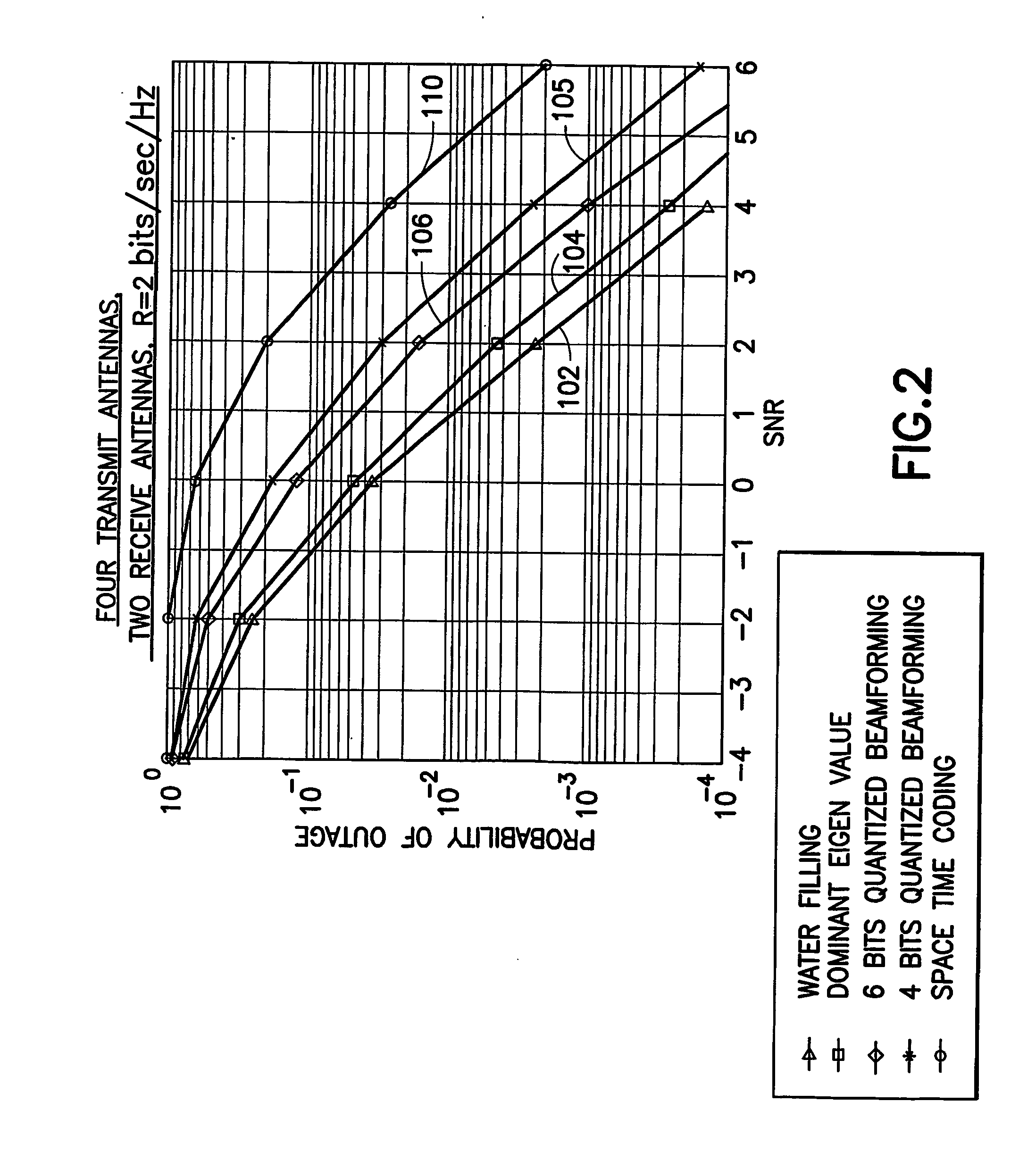
Low complexity beamformers for multiple transmit and receive antennas
InactiveUS7330701B2Power managementSpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationRound complexity
Beamforming systems having a few bits of channel state information fed back to the transmitter benefit from low complexity decoding structures and performances gains compared with systems that do not have channel state feedback. Both unit rank and higher rank systems are implemented. Substantial design effort may be avoided by following a method of using functions formulated for space-time systems with the change that the channel coherence time is equated to the number of transmit antennas and the number of antennas in the space-time formulation is fixed at one.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and apparatus for control and routing of wireless sensor networks
ActiveUS20060077918A1Efficient routingReliable data transmissionEnergy efficient ICTElectric signal transmission systemsLine sensorDirectional antenna
A scalable, minimum node complexity, energy efficient, and error-resilient routing method for wireless sensor networks is described. The network is partitioned into regions by power controlled base station scans using a directional antenna. Routing is performed using only local location information and instructions received from the base station at each sensor node with minimum processing and control overhead, thus allowing simple, low-cost sensor designs. Sensors in the network provide to a base station reports of the condition of the sensors themselves, and these reports are analyzed by the base station to determine improved routing instructions, which are then provided to the sensor nodes in control messages. Each data packet is relayed in an interleaved, loop-free mesh of sectors toward the base station, making data delivery robust to sensor failures and transmission errors. The disclosure also contains descriptions for simple edge-based tasking, query, code distribution, and network programming for sensor nodes. The method is suitable for large-scale, dense sensor networks for detection, alarming, and monitoring applications.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
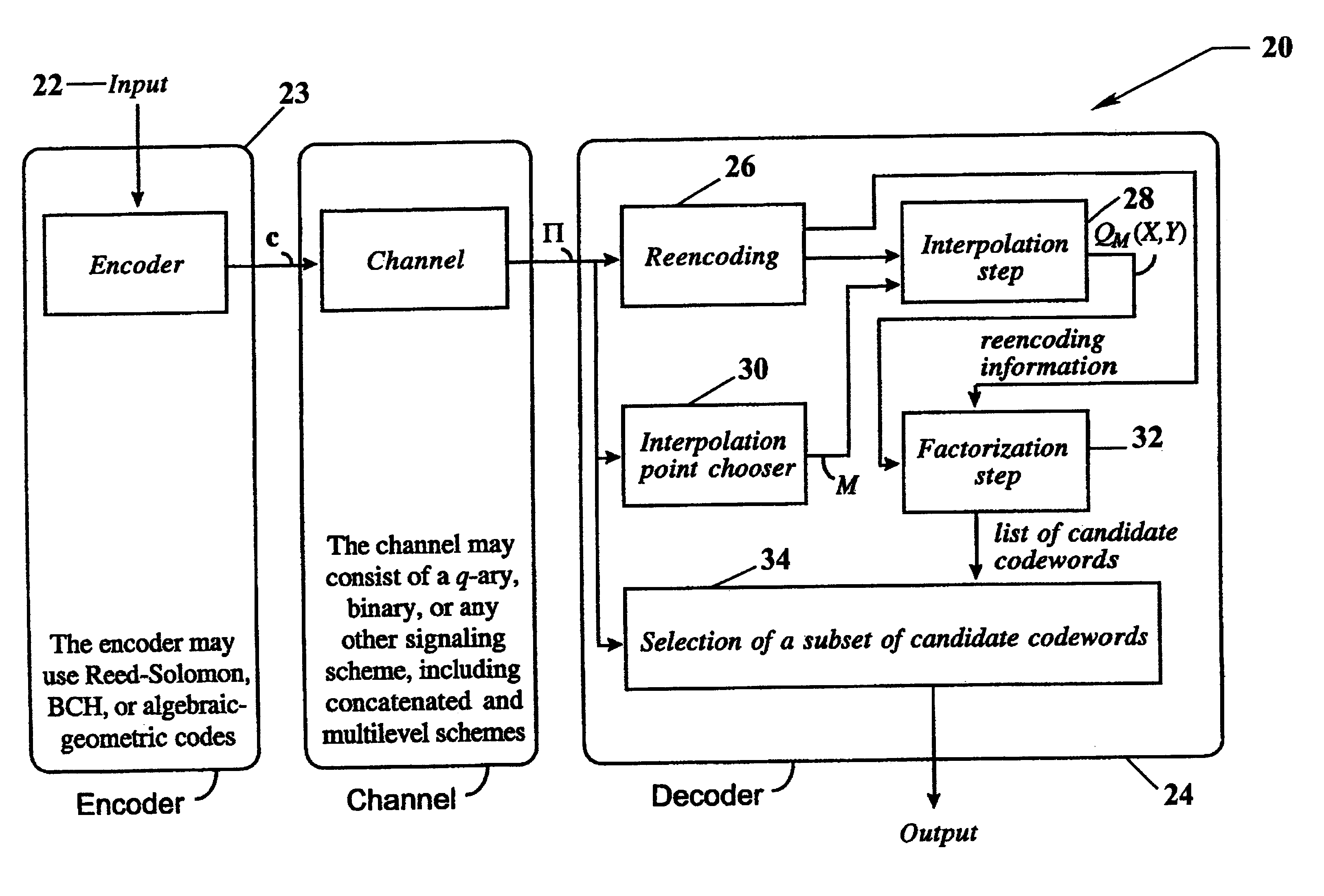
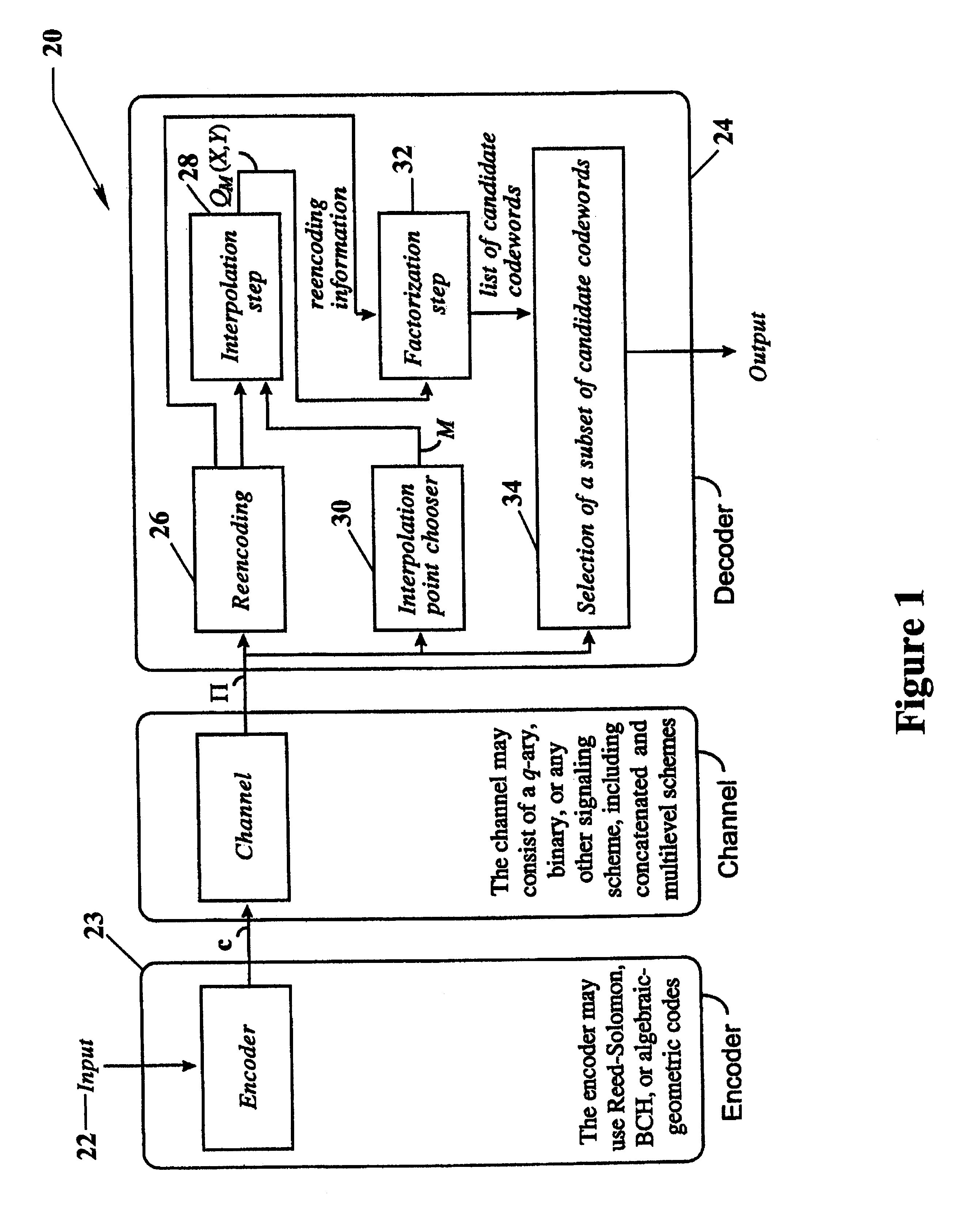
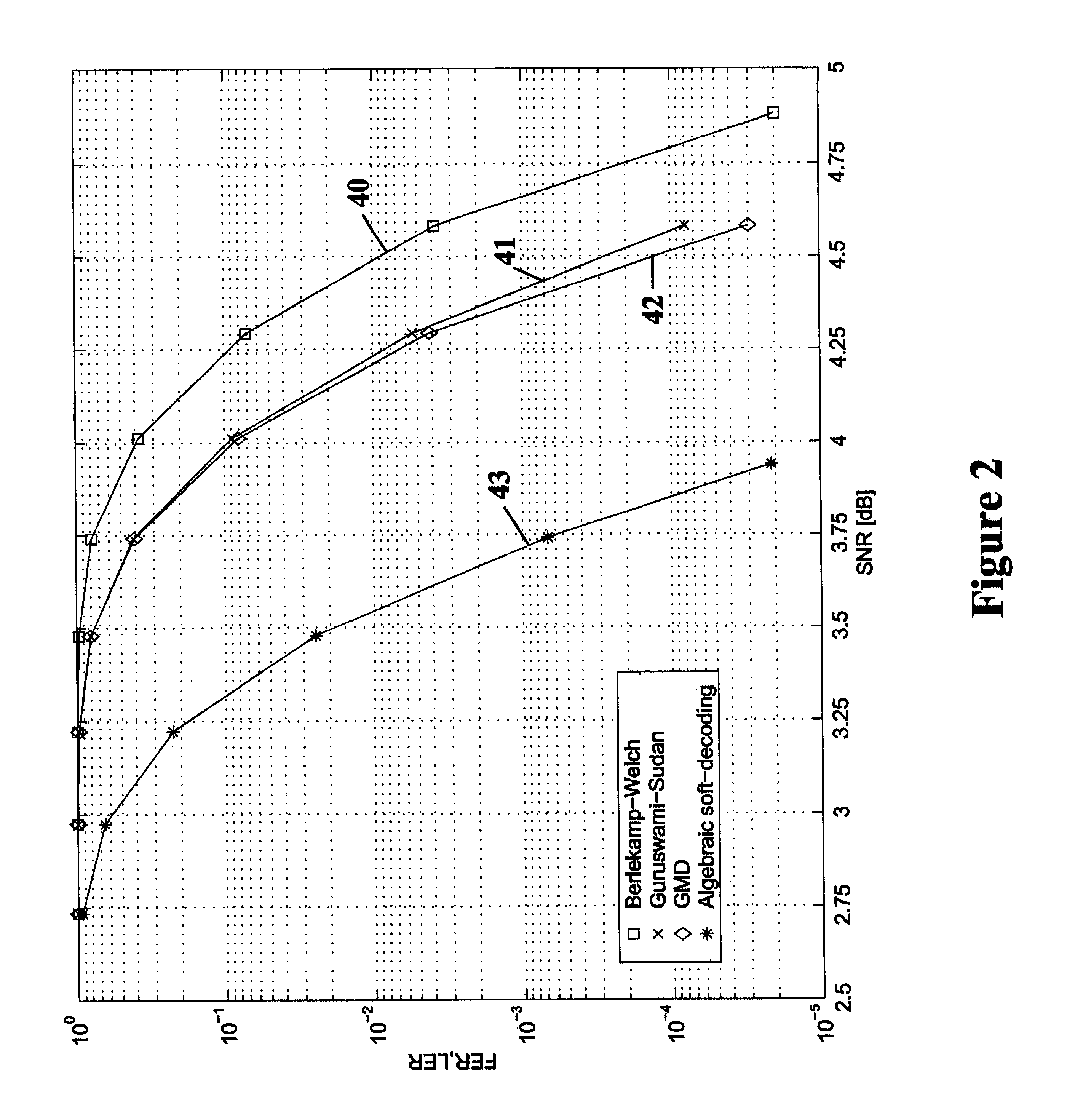
Algebraic soft decoding of reed-solomon codes
InactiveUS6634007B1Maximizes the expected scoreMaximizing the expected scoreOther decoding techniquesAlgebraic geometric codesDecoding methodsRound complexity
An algorithmic soft-decision decoding method for Reed-Solomon codes proceeds as follows. Given the reliability matrix Pi showing the probability that a code symbol of a particular value was transmitted at each position, computing a multiplicity matrix M which determines the interpolation points and their multiplicities. Given this multiplicity matrix M, soft interpolation is performed to find the non-trivial polynomial Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y) of the lowest (weighted) degree whose zeros and their multiplicities are as specified by the matrix M. Given this non-trivial polynomial Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y), all factors of Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y) of type Y-f(X) are found, where f(X) is a polynomial in X whose degree is less than the dimension k of the Reed-Solomon code. Given these polynomials f(X), a codeword is reconstructed from each of them, and the most likely of these codewords selected as the output of the algorithm. The algorithmic method is algebraic, operates in polynomial time, and significantly outperforms conventional hard-decision decoding, generalized minimum distance decoding, and Guruswami-Sudan decoding of Reed-Solomon codes. By varying the total number of interpolation points recorded in the multiplicity matrix M, the complexity of decoding can be adjusted in real time to any feasible level of performance. The algorithmic method extends to algebraic soft-decision decoding of Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem codes and algebraic-geometry codes.< / PTEXT>
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
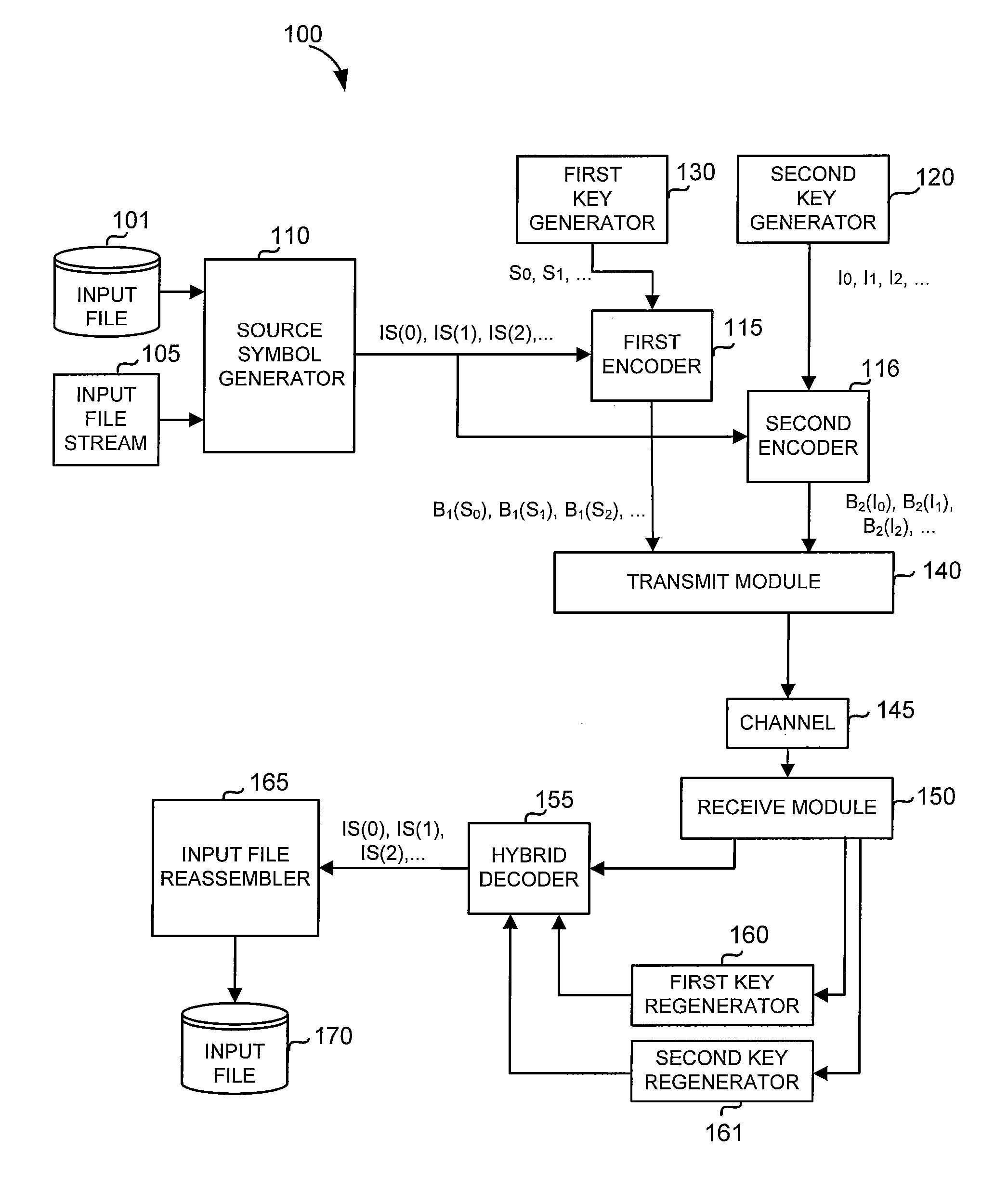
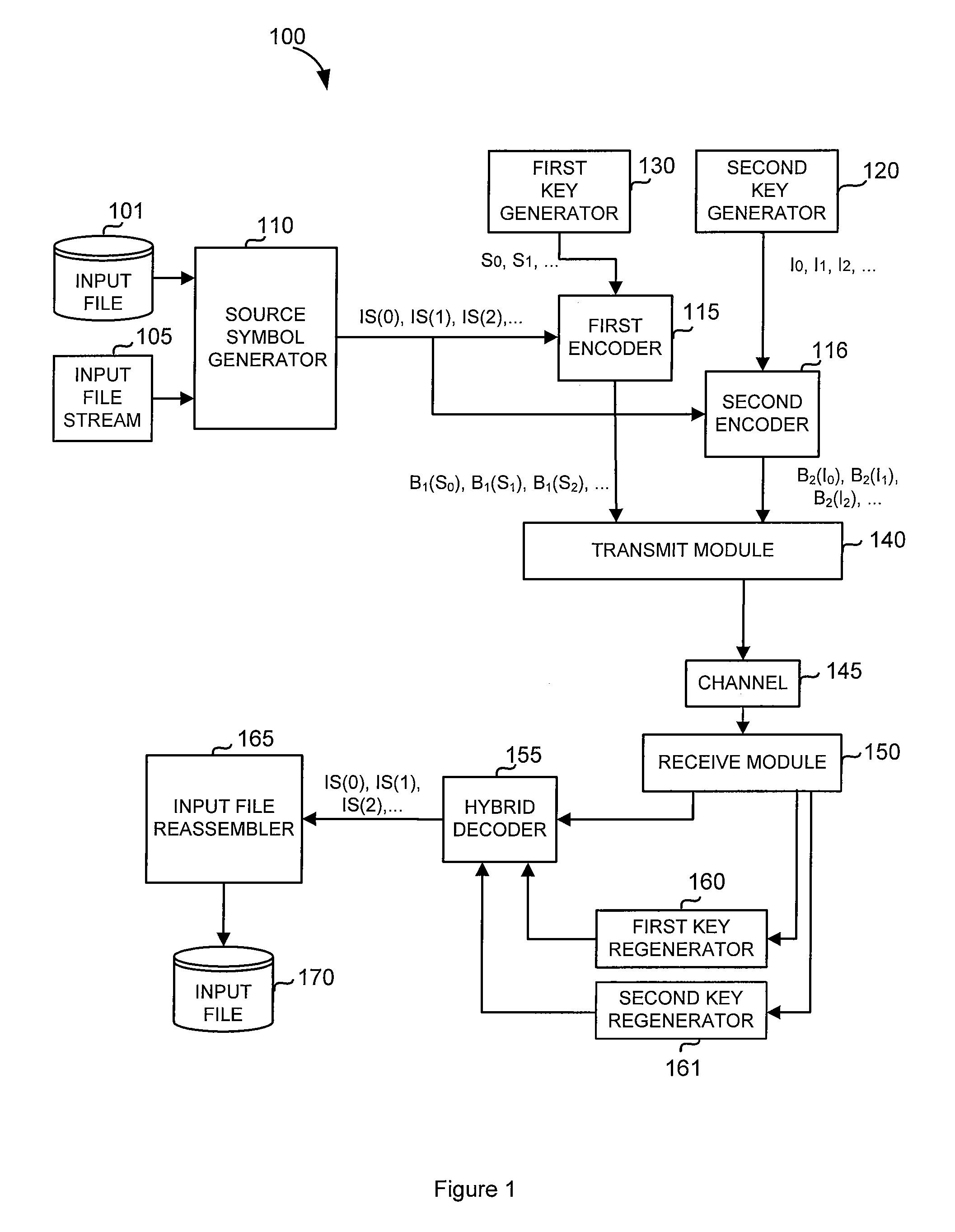
Code generator and decoder for communications systems operating using hybrid codes to allow for multiple efficient users of the communications systems
InactiveUS20070300127A1Error protectionImprove errorError preventionCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
A method of encoding data for transmissions from a source to a destination over a communications channel is provided. The method operates on an ordered set of source symbols and may generate zero or more redundant symbols from the source symbols, wherein data is encoded in a first step according to a simple FEC code and in a second step, data is encoded according to a second FEC code, more complex than the first FEC code. The first FEC code and / or the second FEC code might comprise coding known in the art. These steps result in two groups of encoded data in such a way that a low-complexity receiver may make use of one of the groups of encoded data while higher complexity receivers may make use of both groups of encoded data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
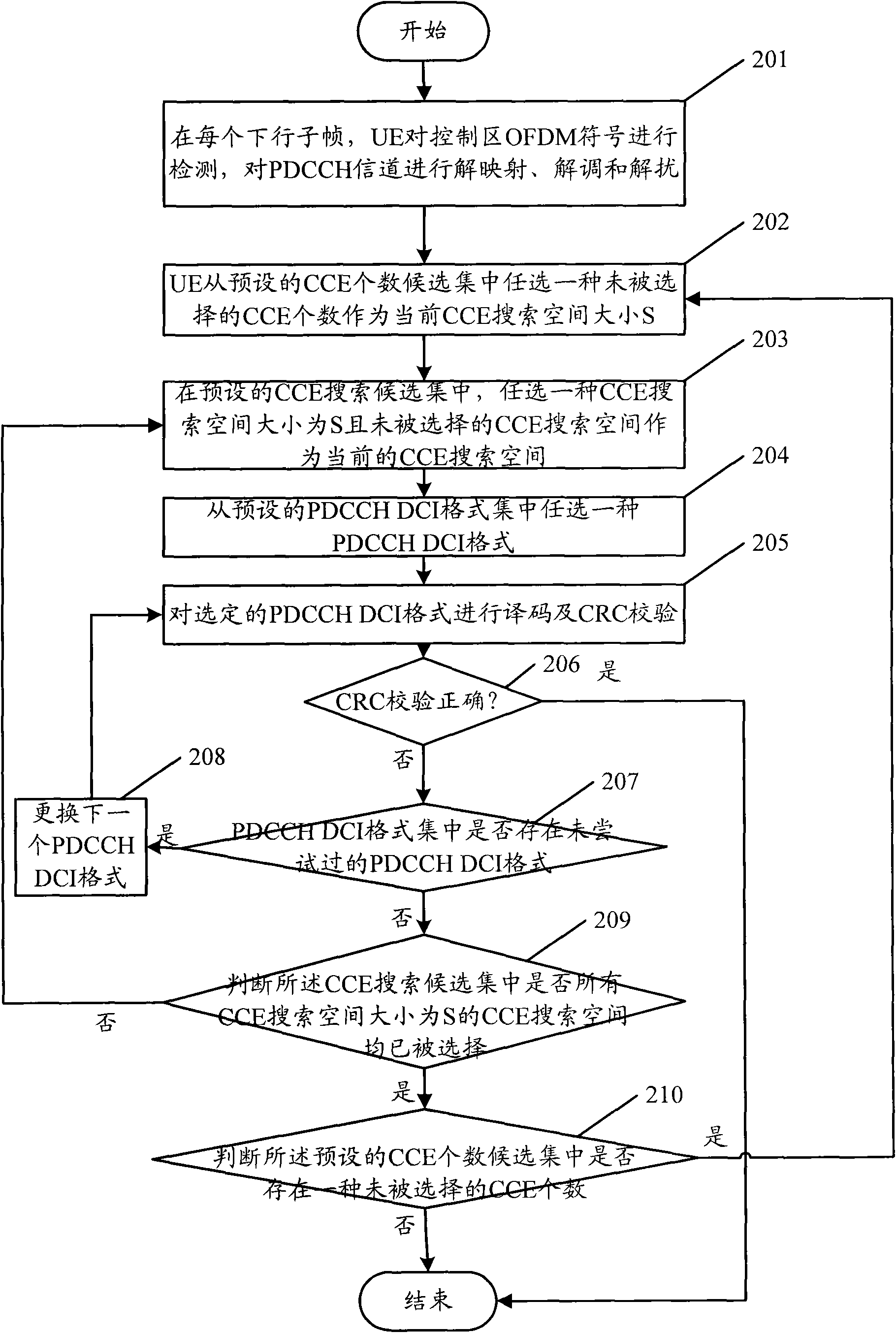
Blind detection method
ActiveCN101883369AReduce the amount of calculationReduce processing complexityEnergy efficient ICTError preventionRound complexitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
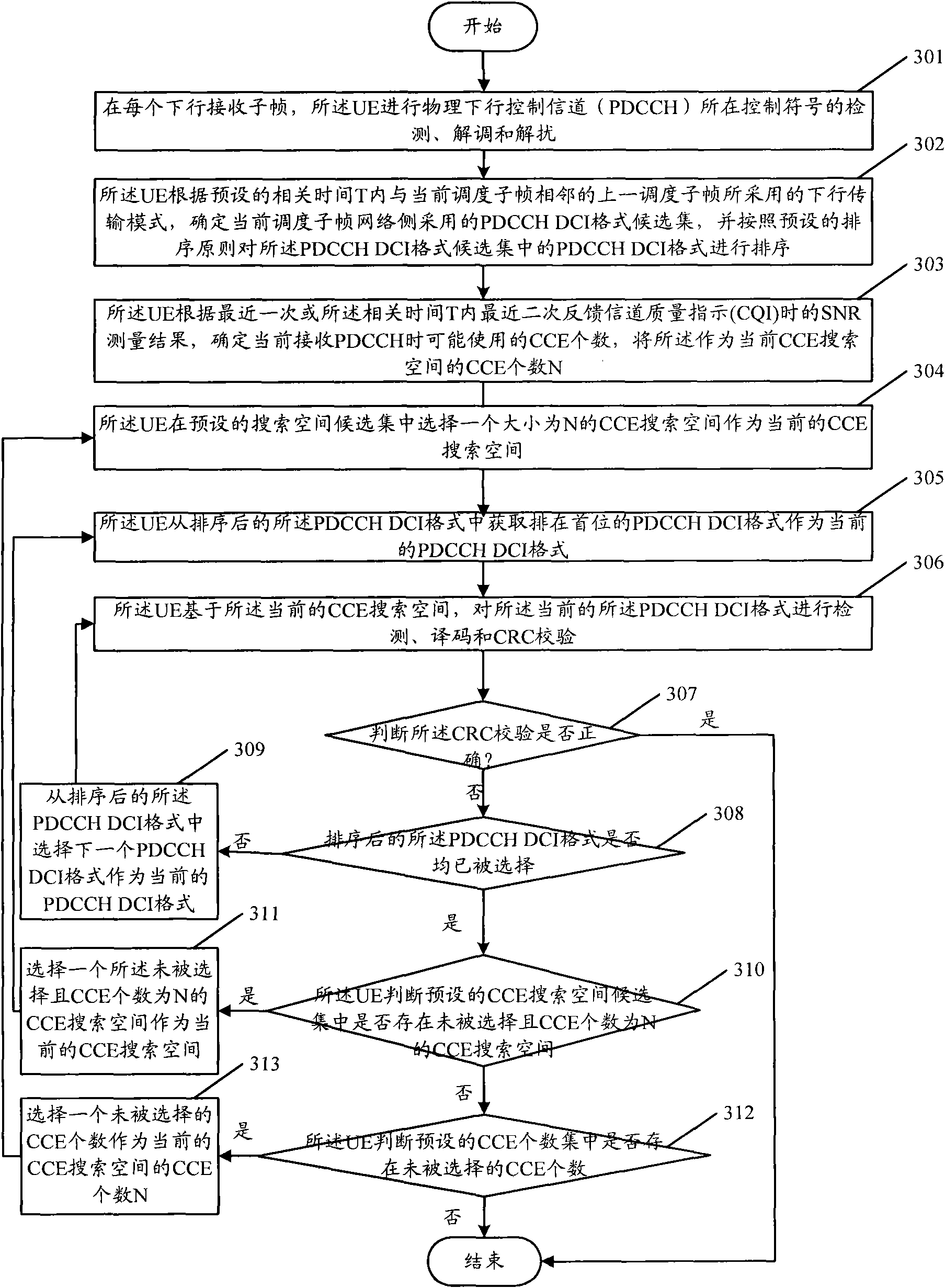
The invention provides a blind detection method. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a PDCCH DCI format candidate set for blind detection by using the transmission mode and historical dispatching information which are configured by a network for UE, and preliminarily determining the number of CCE resources for bearing a PDCCH by using signal-to-noise ratio measurement results of channels and channel changes of adjacent two-time scheduling so as to effectively reduce trying times of UE PDCCH blind detection. Therefore, the blind detection method can reduce calculated amount and processing complexity of the UE, reduces the power consumption of the UE and improves system performance.
Owner:北京万海云科技有限公司
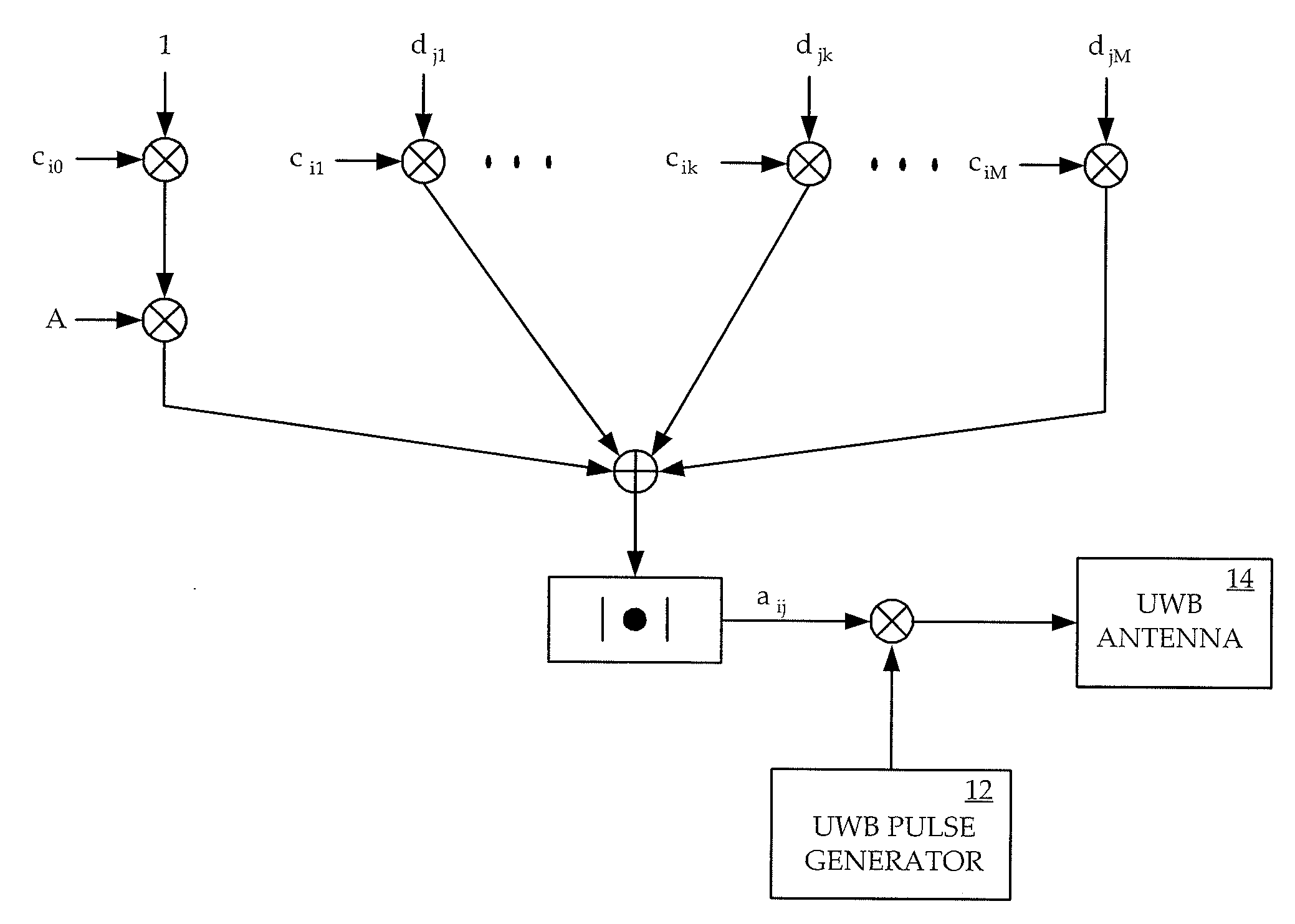
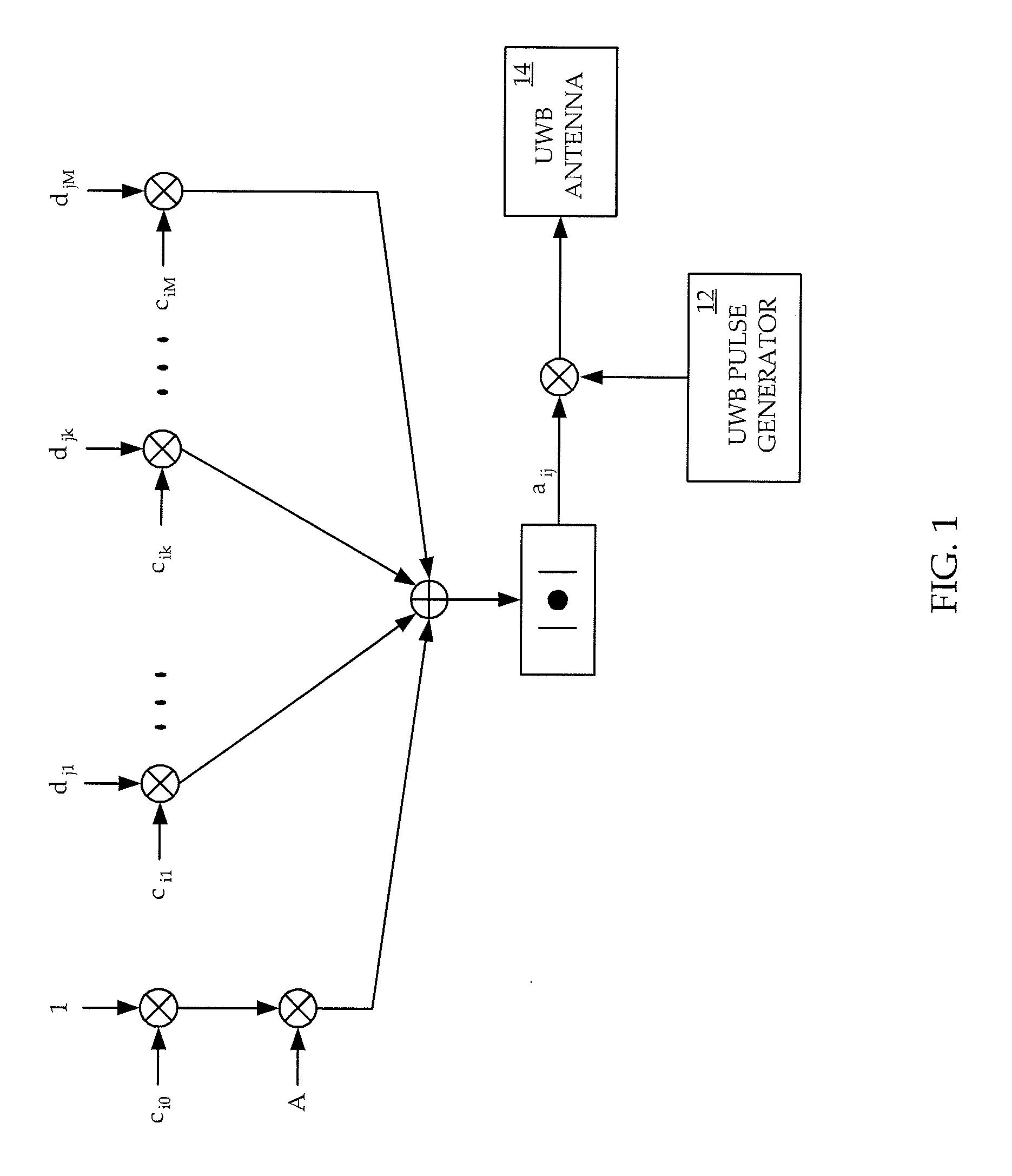
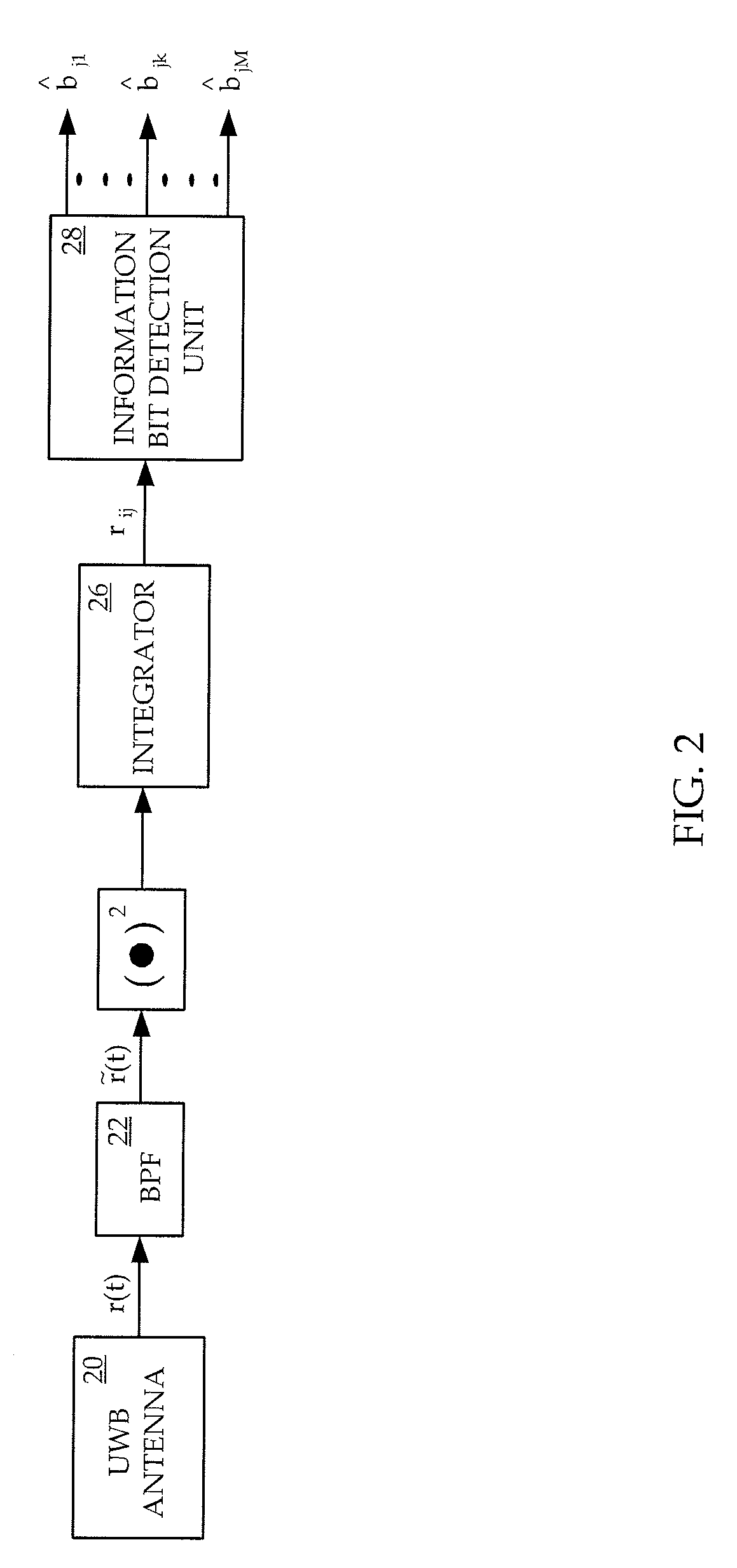
Impulse ultra-wideband radio communication system
ActiveUS20090258669A1Reduce complexityImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsSubstation equipmentRound complexityCarrier signal
A method and apparatus are provided for implementing an impulse ultra-wideband communications system which combines the technique of transmitted reference (TR) with a code-sifted reference scheme that separates the reference and the data pulses with a sequence of codes such as a subset of Walsh codes. The combination of the two techniques in ultra-wideband (UWB) radio systems removes the wideband delay elements required by conventional TR UWB systems. The invention provides a system with no analog carriers and lower complexities than other UWB systems, and which has better performances, higher tolerance to nonlinearity, and larger capacities
Owner:CHENGDU SPROUTING TECH CO LTD
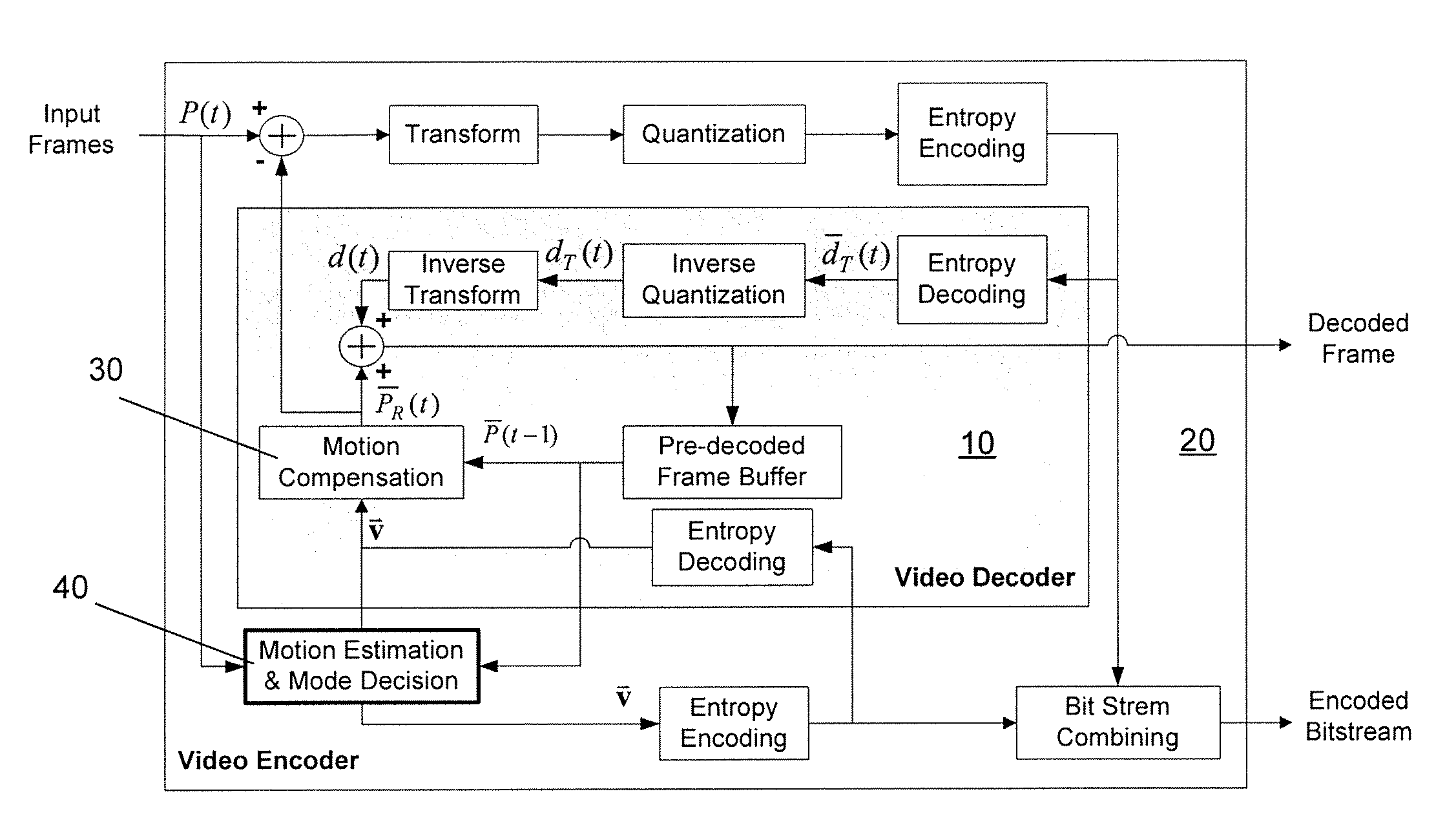
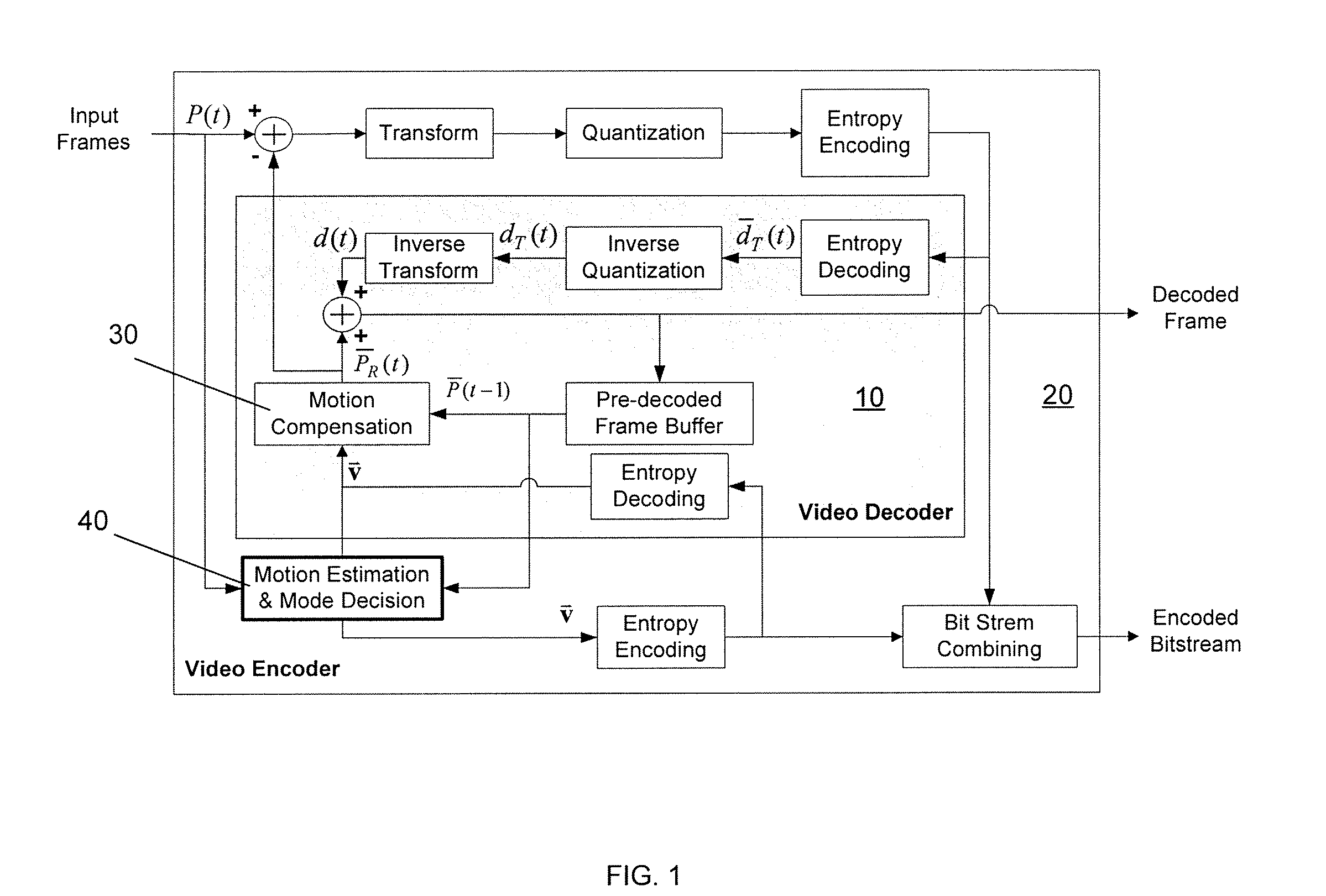
System and method for motion estimation and mode decision for low-complexity h.264 decoder
InactiveUS20080181308A1Reduce computing costMaintaining video qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRound complexityVideo encoding
The present invention relates to systems and methods for motion estimation and mode decision for low-complexity H.264 standard decoders. The present invention includes a method for optimizing the selection of motion vectors and motion compensation block modules in a video encoder in order to decrease the complexity of the video upon decoding. The novel method of the present invention may include novel steps for selecting motion vectors, block modes, and for applying a complexity-control algorithm to encode the received input video data sequence in accordance with the identified target complexity level. The present invention may be implemented in accordance with current and future video decoding standards to optimize decoding by reducing decoding complexity and thereby reducing required resources and power consumption.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
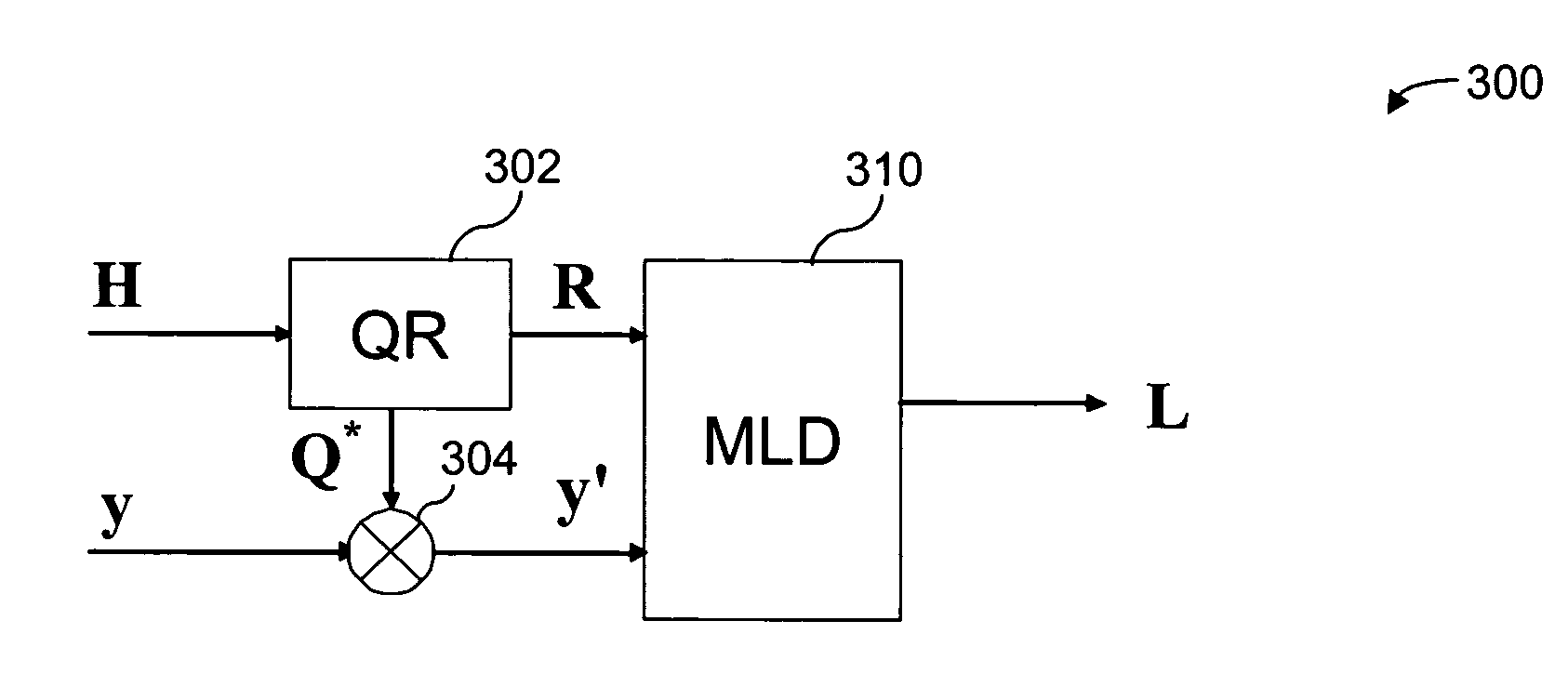
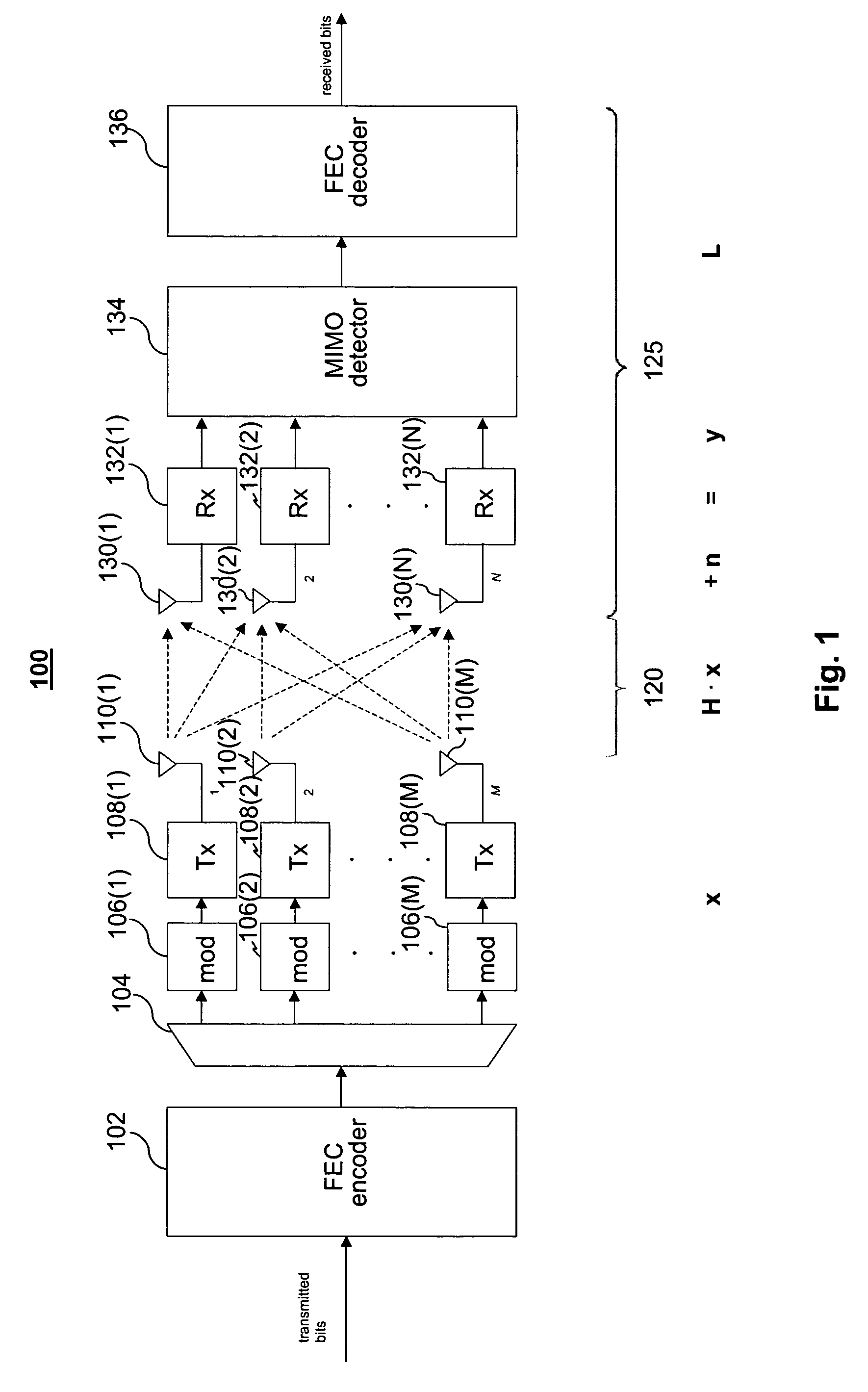
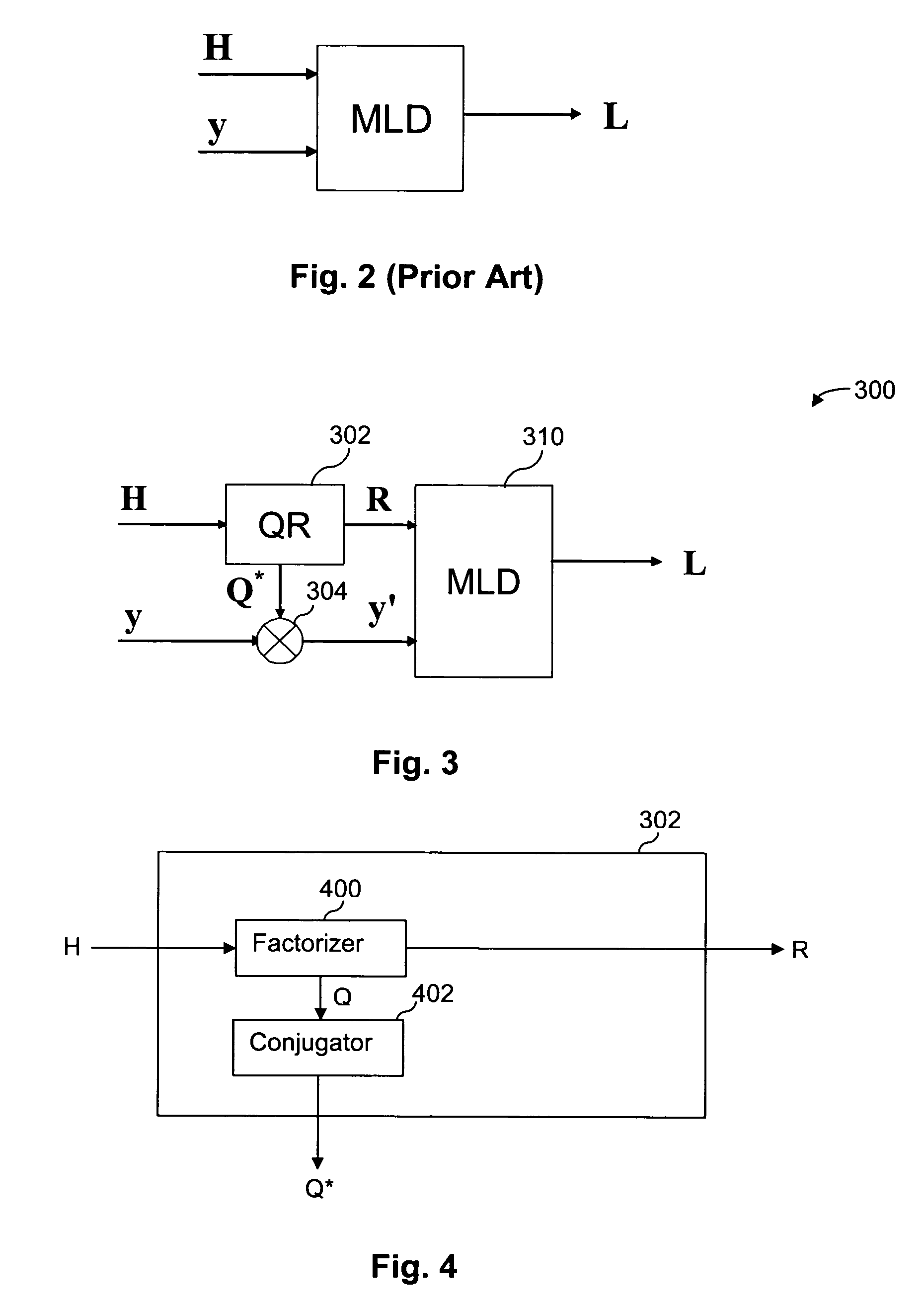
MIMO receiver using maximum likelihood detector in combination with QR decomposition
ActiveUS7489746B1Reduce computational complexityPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsQR decompositionRound complexity
A MIMO receiver is provided with a preprocessor for performing QR decomposition of a channel matrix H wherein the factored reduced matrix R is used in place of H and Q*y is used in place of the received vector y in a maximum likelihood detector (“MLD”). The maximum likelihood detector might be a hard-decision MLD or a soft-decision MLD. A savings of computational complexity can be used to provide comparable results more quickly, using less circuitry, and / or requiring less consumed energy, or performance can be improved for a fixed amount of time, circuitry and / or energy. Where the MLD uses approximations, such as finite resolution calculations (fixed point or the like) or L1 Norm approximations, the reduced number of operations resulting from using the reduced matrix results in improved approximations as a result of the finite resolution operations. Other methods of reducing the channel matrix might be used for suitable and / or cumulative advantages.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Universal error control coding system for digital communication and data storage systems
InactiveUS20080126908A1Reduce complexityReduce chip areaError detection/correctionCode conversionComputer architectureRound complexity
The universal forward error-correction coding system provides adjustable code rates and coding gains to greatly benefit the design of many modern digital communications (data storage) systems. The channel encoding and decoding methods are universal such that a single encoder and a single decoder can be used to implement all the forward error-correction codes of different code rates. This universal forward error-correction coding system also includes a novel systematic code generation procedure that has the capability of generating many classes of codes that provide the best balance between coding gain performance and implementation complexity.
Owner:COMM CODING
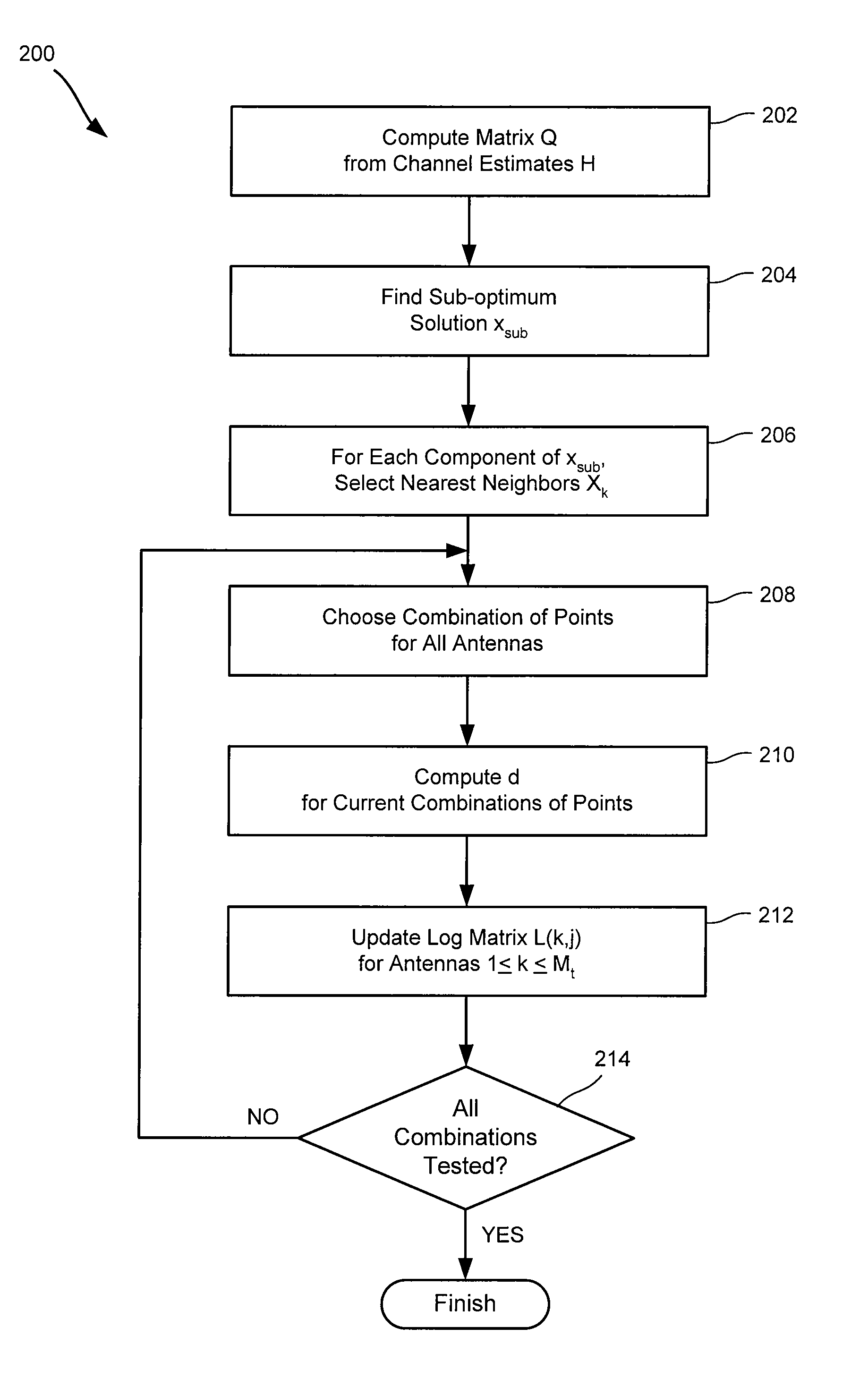
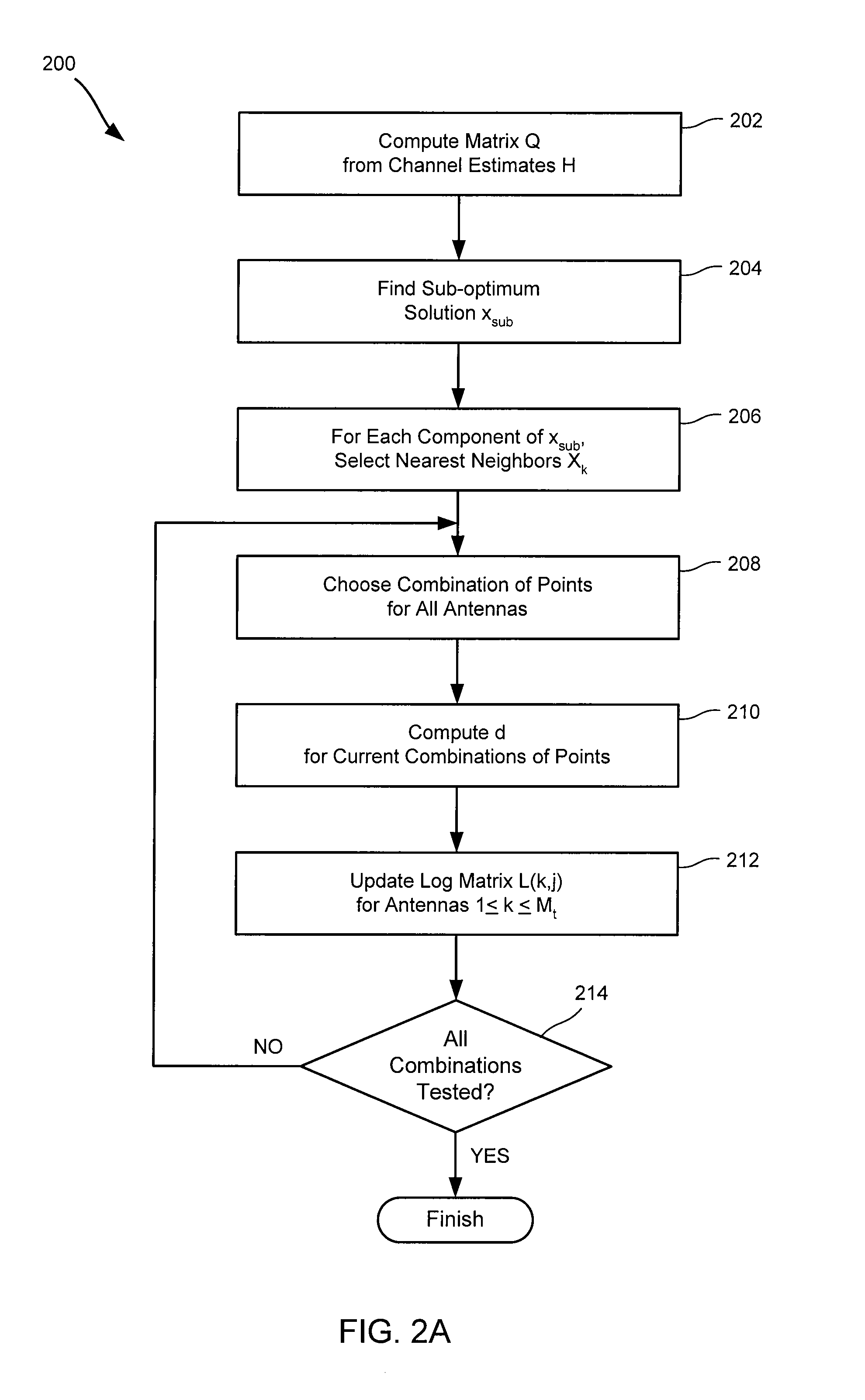
Soft symbol decoding for MIMO communication systems with reduced search complexity
InactiveUS7245666B1Reduce search complexityReduce in quantityPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRound complexitySymbol decoding
Soft symbol decoder algorithms for multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) receivers reduce the search complexity by searching over fewer than all possible combinations of transmitted symbols to compute log metrics for each transmitted bit from each transmit antenna. In one algorithm, a sub-optimal set of transmitted symbols is computed and the transmitted symbols are restricted to neighboring constellation points of the sub-optimal set. In another algorithm, all constellation points are searched for every antenna except one. In yet another algorithm, constellation points are searched excluding more than one antenna. The non-searched antenna(s) can be handled by either a bit stuffing or a soft slicing technique.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
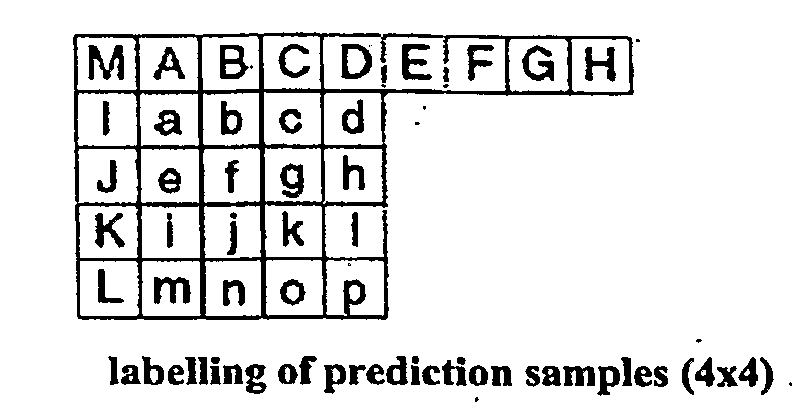
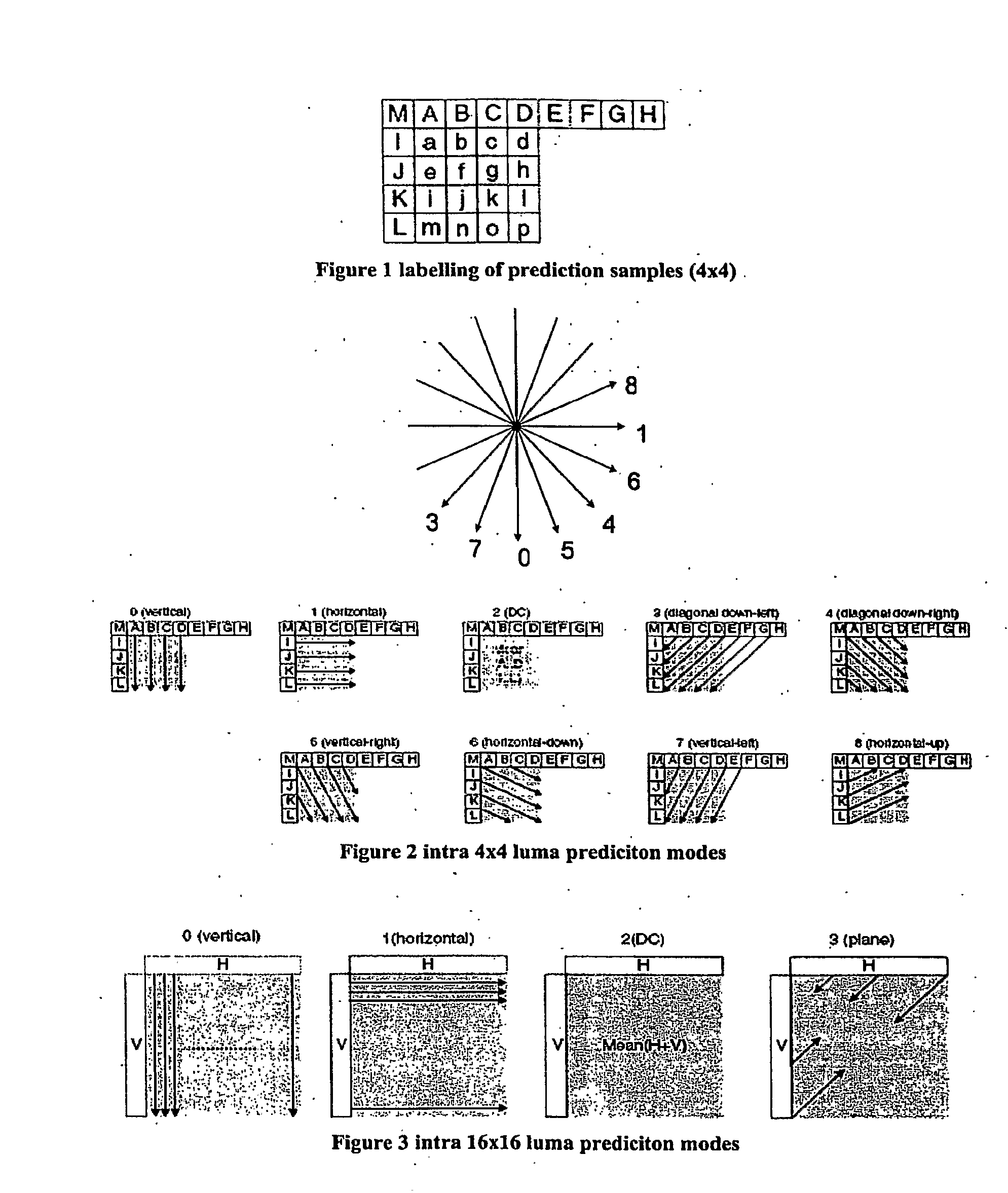
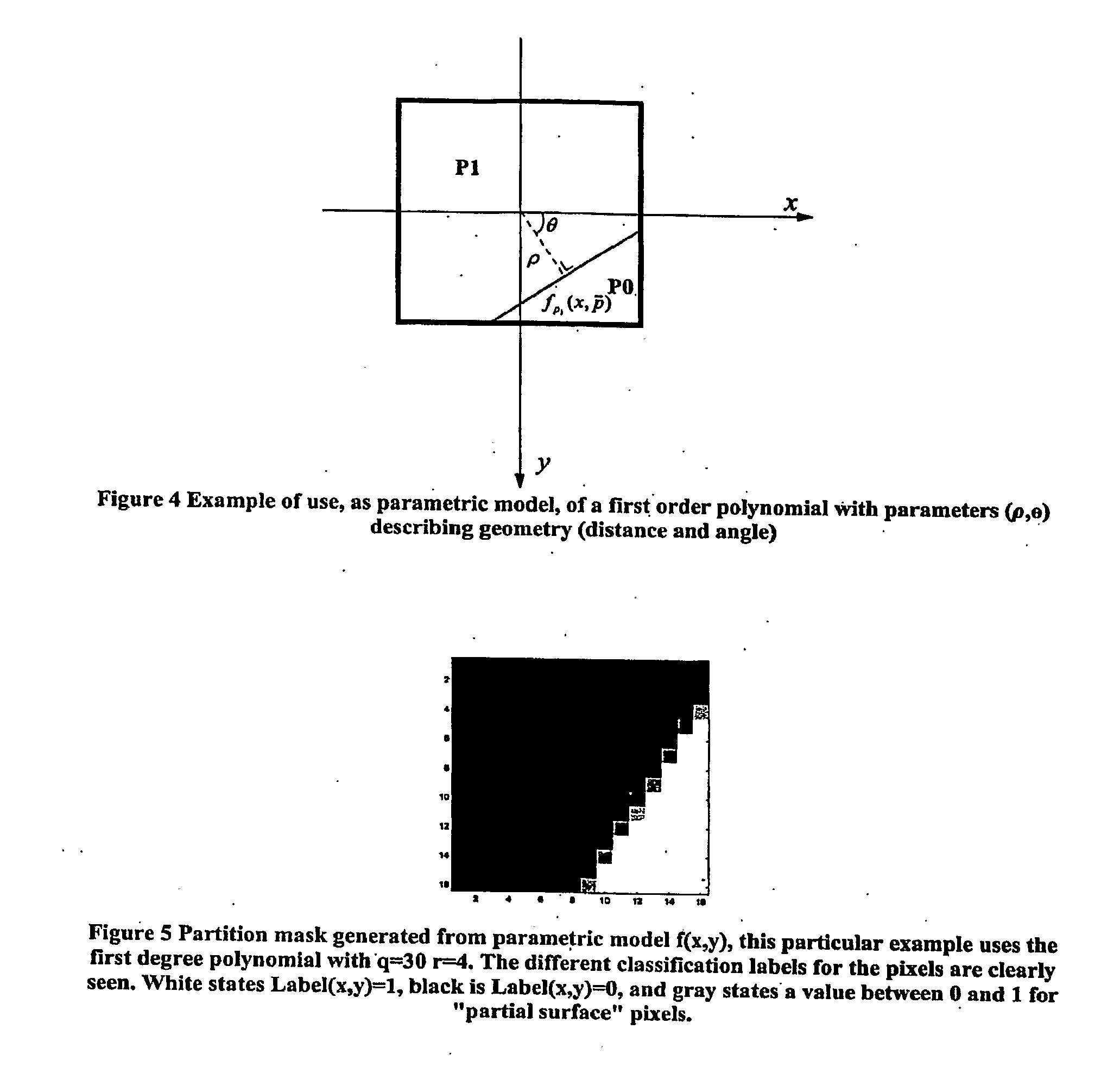
Geometric intra prediction
InactiveUS20090268810A1Efficient captureColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionComputation complexity
The use of parametric models to capture and represent local signal geometry allows a new geometric intra prediction scheme to better encode video images. The encoding scheme gives the video encoder the flexibility and scalability to match the video frame content with the desired computational complexity. It also allows the encoder to encode the images more efficiently using intra prediction because it reduces the artificial edges that occur during standard intra encoding.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Low complexity beamformers for multiple transmit and receive antennas
InactiveUS20060111148A1Power managementSpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationRound complexity
Beamforming systems having a few bits of channel state information fed back to the transmitter benefit from low complexity decoding structures and performances gains compared with systems that do not have channel state feedback. Both unit rank and higher rank systems are implemented. Substantial design effort may be avoided by following a method of using functions formulated for space-time systems with the change that the channel coherence time is equated to the number of transmit antennas and the number of antennas in the space-time formulation is fixed at one.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
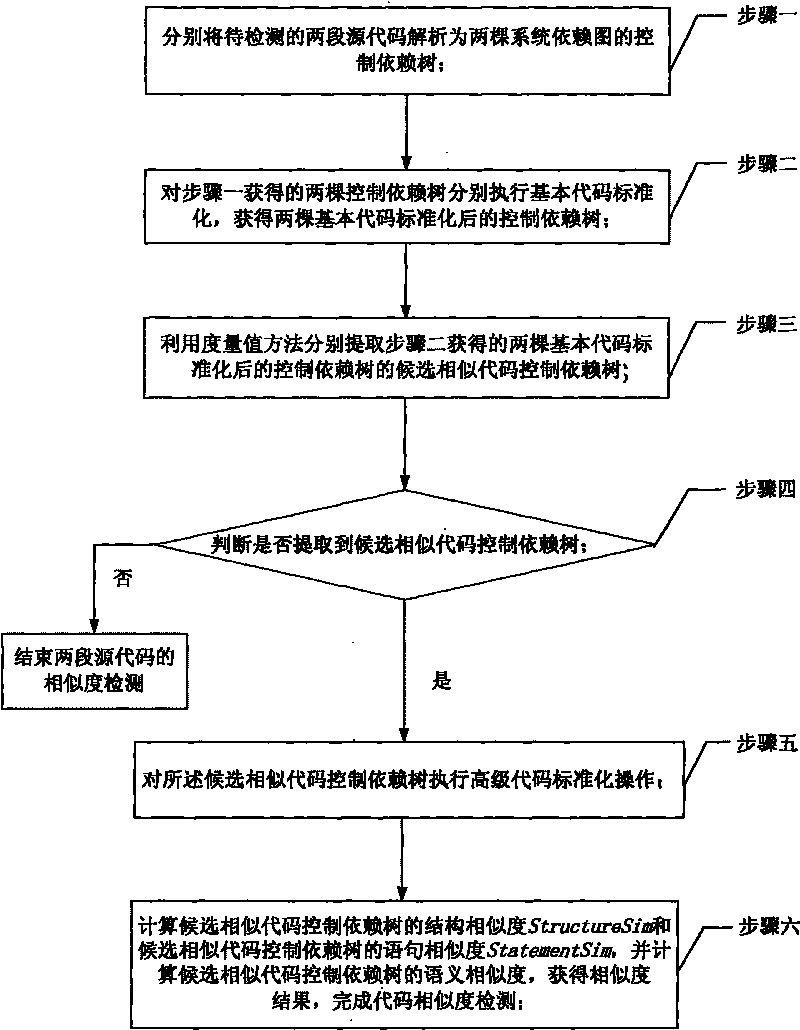
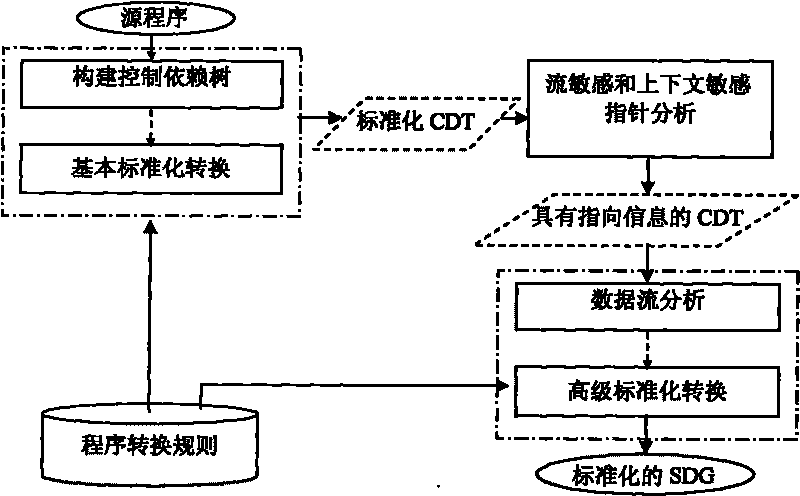
Method for detecting code similarity based on semantic analysis of program source code
InactiveCN101697121AEliminate diversificationImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsSpecific program execution arrangementsComputation complexityProgram code
The invention discloses a method for detecting code similarity based on semantic analysis of a program source code, which relates to computer program analyzing technology and a method for detecting complex codes of computer software. The method solves the prior problems of low similarity detection accuracy and high computing complexity on the codes of different syntactic representations and similar semantemes, and also solves the problem of incapability of realizing large-scale program code similarity detection. The method comprises the following steps: resolving two segments of source codes to be detected into two control dependence trees of a system dependence graph respectively and executing basic code standardization respectively; utilizing a measure method to extract candidate similar code control dependence trees of the control dependence trees which are subjected to the basic code standardization; executing an advanced code standardization operation on extracted candidate similar codes; and computing semantic similarity to obtain a similarity result so as to finish the code similarity detection. The method is applied to source code piracy detection, software component library query, software defect detection, program comprehension and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
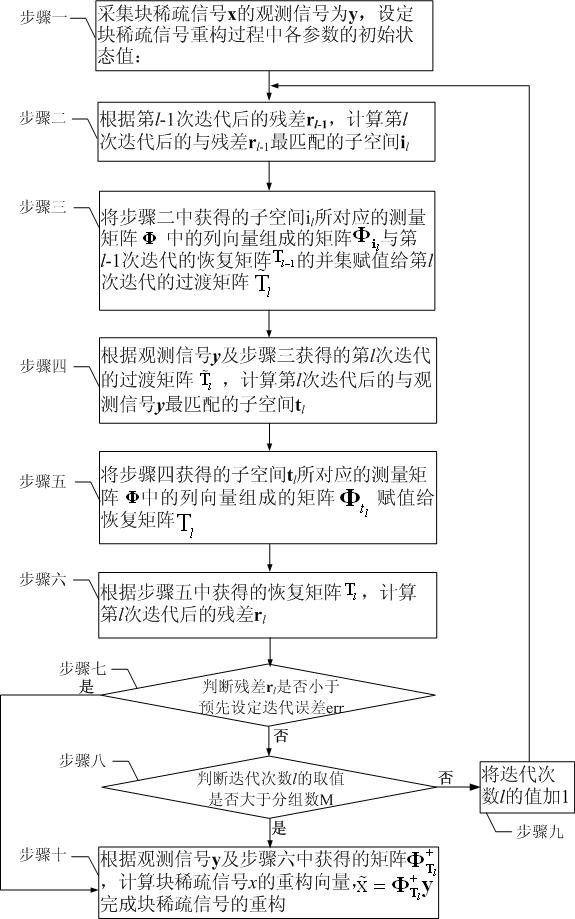
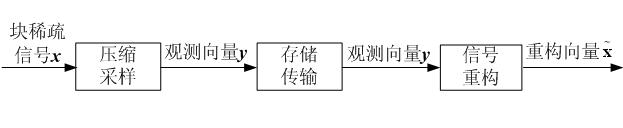
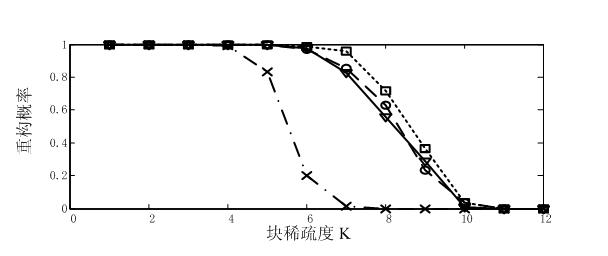
Compressed sensing-oriented block-sparse signal reconfiguring method
The invention discloses a compressed sensing-oriented block-sparse signal reconfiguring method, and particularly relates to a block-sparse signal reconfiguring algorithm, which aims to solve the problems that the optimization complexity of a mixed l2 / l1 optimization algorithm in the conventional block-sparse signal reconfiguring algorithm is relatively higher and that overmatching phenomenon is easily caused by a block-sparse matching pursuit algorithm or a block-sparse orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm. The method of the invention comprises the following steps of: correcting labels, in ameasurement matrix, of column vectors of a recovery matrix calculated in the iteration operation of the (l-1)th time by performing the iteration of the lth time, and for a block-sparse signal x with the block sparsity of K, reconfiguring the block-sparse signal x by performing the iteration for not more than K times. The method is applied to the reconfiguration of the block-sparse signal, particularly to the reconfiguration of a binary block-sparse signal.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
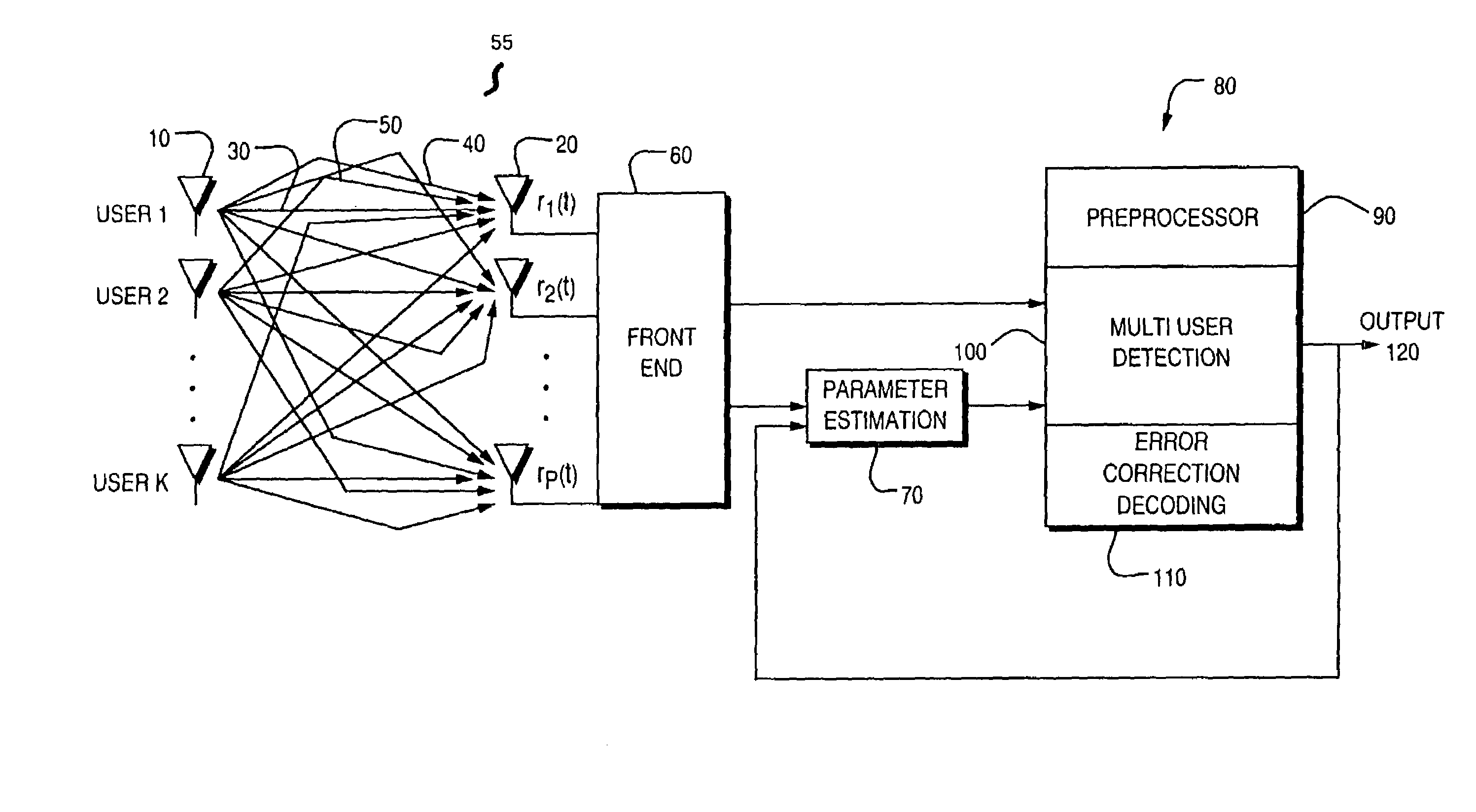
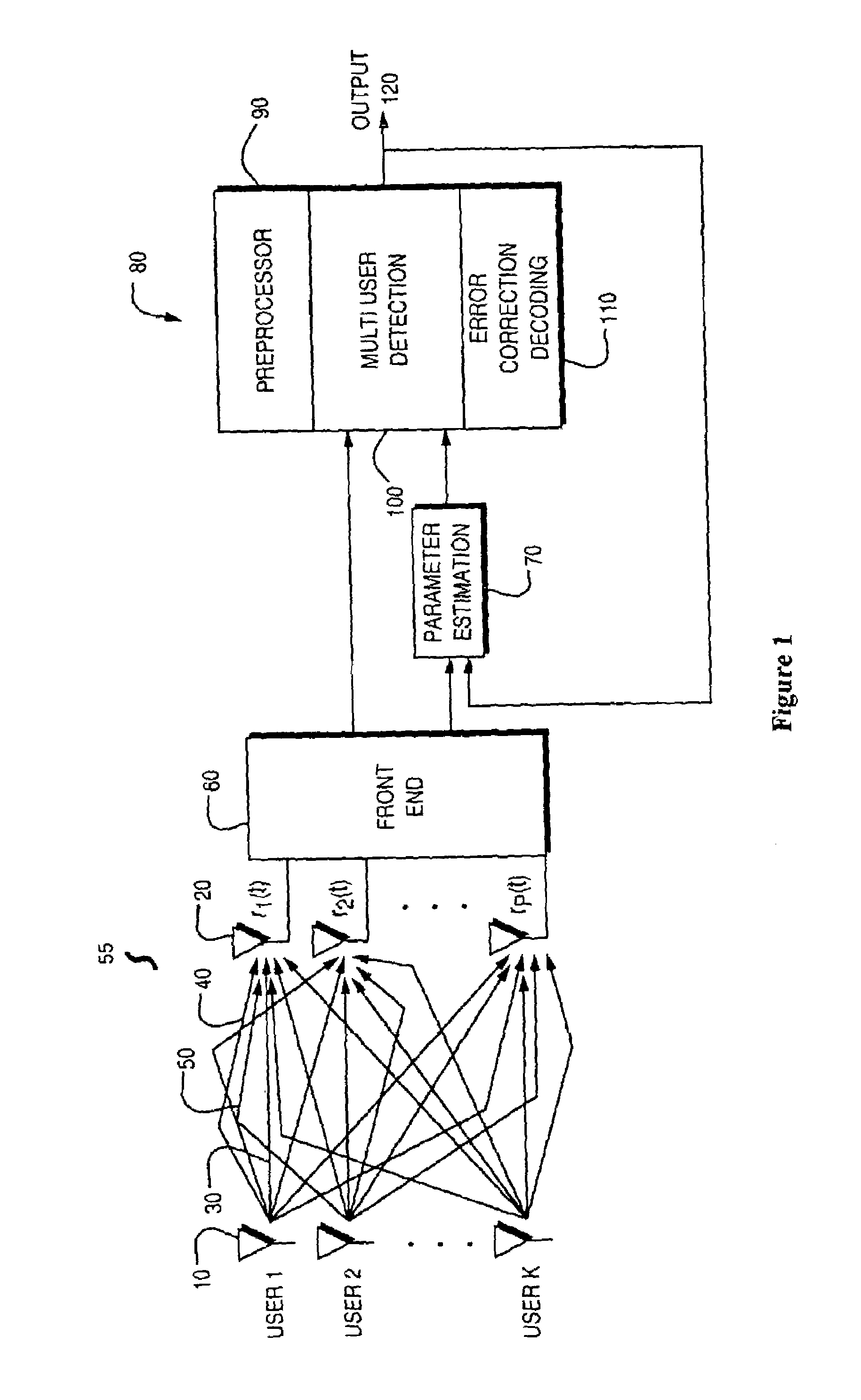
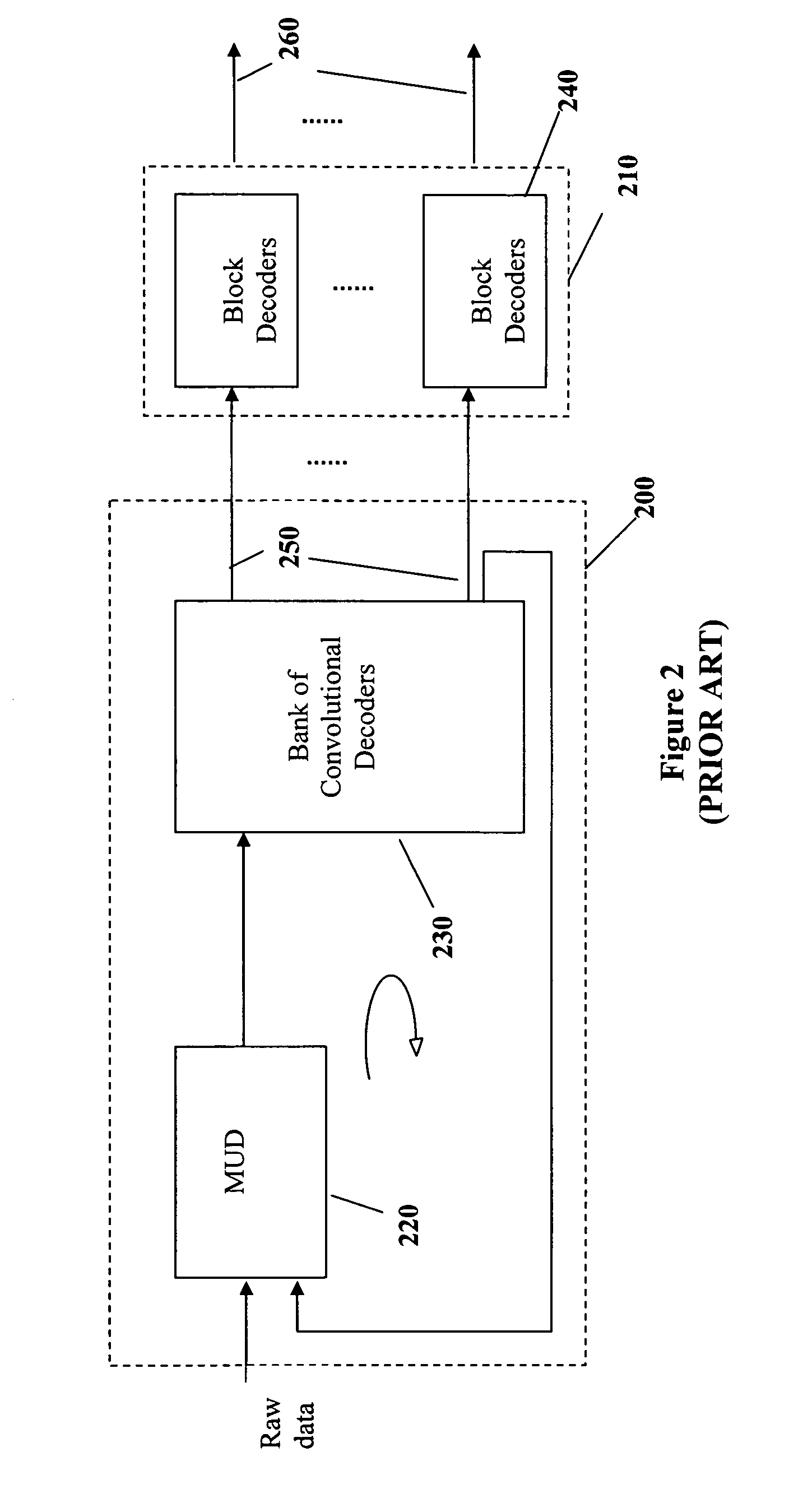
Reduced complexity multi-turbo multi-user detector
ActiveUS6967598B2Reduce the possibilityImprove performancePolarisation/directional diversityCode conversionPhase detectorRound complexity
A reduced complexity Turbo multi-user detector (MUD) processing system in multiple access communications channels that decreases the likelihood of improper decoding of the final values of interest and decreases the computation complexity for each iteration, thereby allowing for a reduction in the number of iterations performed and lowers the overall complexity without negatively impacting performance. In one form the present invention comprises a multi-user detector coupled to two or more decoder sections, two ore more recoders, and a compare and adjust section in such a manner that data flows iteratively to correct for errors in a computationally efficient manner.
Owner:COLLISION COMM INC
Digital repeater having bandpass filtering, adaptive pre-equalization and suppression of natural oscillation
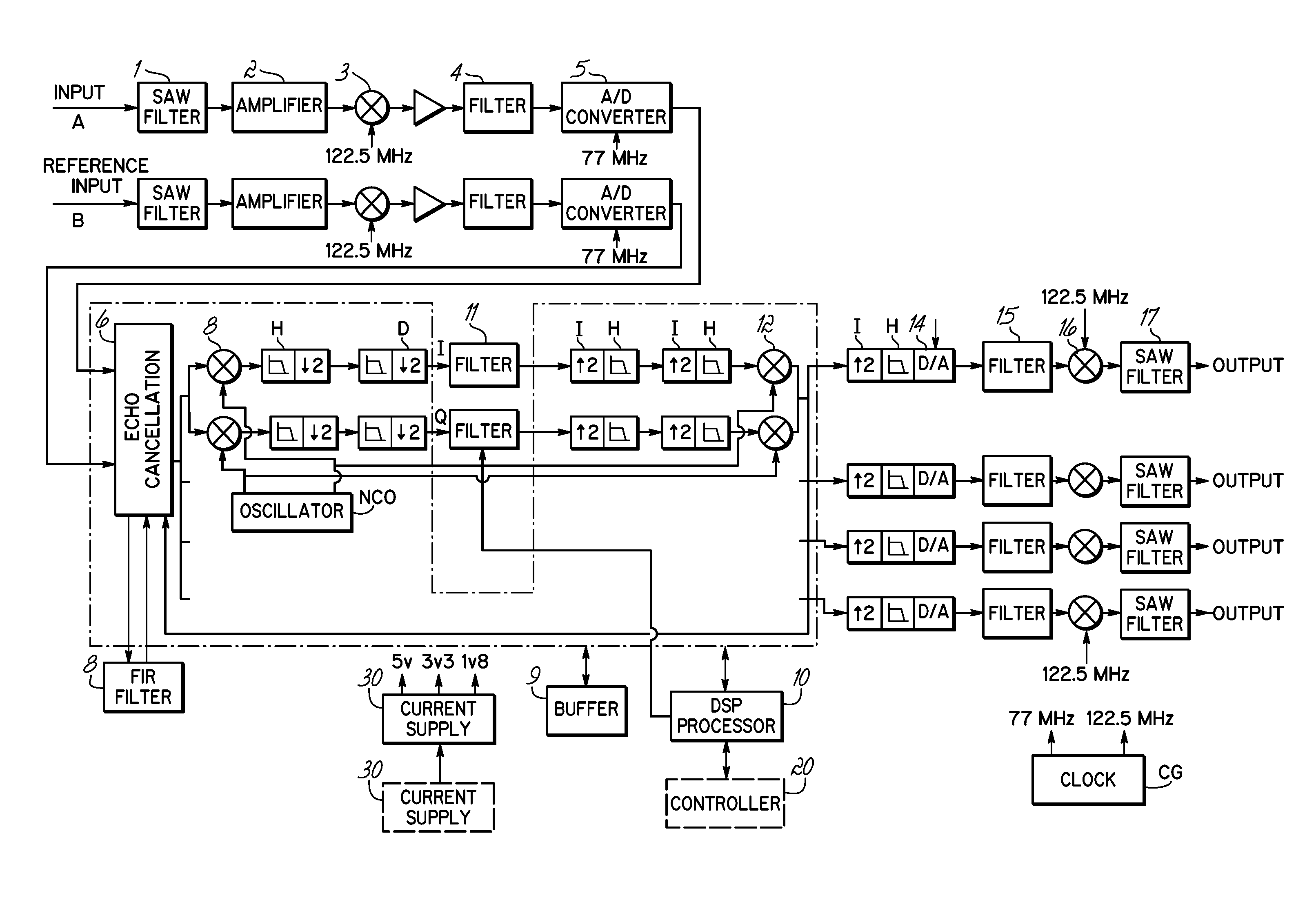
ActiveUS7809047B2Minimize complexityLow costModulated-carrier systemsRepeater/relay circuitsBandpass filteringComputation complexity
Repeaters, event those having digital processing, exist. The significant drawback of these digital repeaters is that the computational complexity or the processing speed has to be very high in order to guarantee, particularly when compensating for echo, that the necessary delay does not excessively impair the performance. The aim of the invention is to provide a structure of the repeater in which the computational complexity is reduced without this reduction having a negative effect on the performance during signal filtering and / or suppression of natural oscillation. To this end, the invention provides that in order to carry out bandpass filtering, adaptive pre-equalization and suppression of the natural oscillation, the components of the repeater in the uplink branch and downlink branch are arranged in a designated sequence, whereby duplex filters are used for coupling both repeater branches to the antennes. In addition, only one reconfiguration in the modules at the user is necessary in order to adapt to user-specific requirements. The invention is used in the field of digital repeaters for data systems technology and telecommunications technology.
Owner:STRONG FORCE IOT
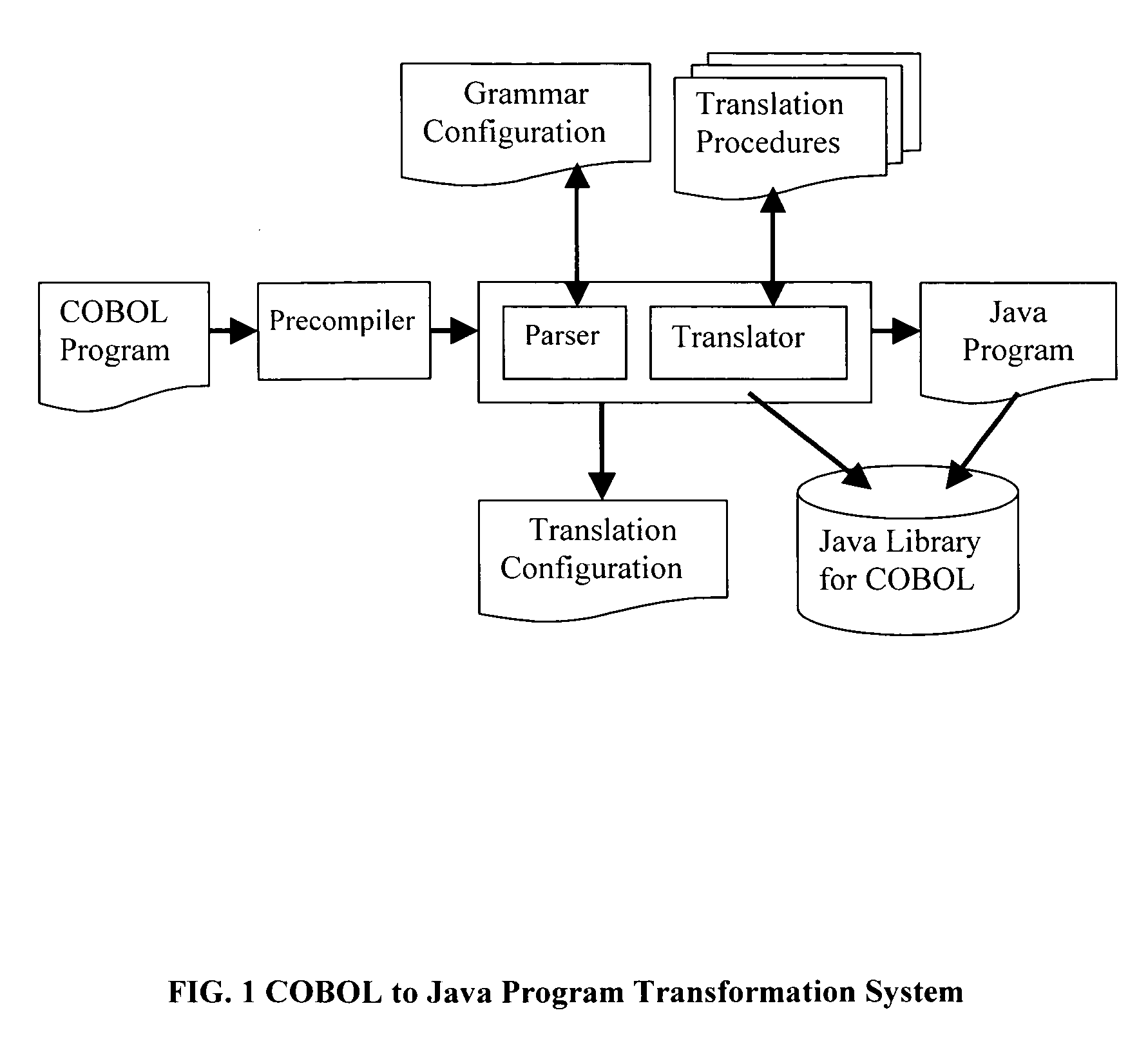
Method for program transformation and apparatus for COBOL to Java program transformation
InactiveUS20060031820A1Maintain maintainabilityImprove maintainabilityProgram controlMemory systemsTime complexityGoto
The present invention relates to a method for program transformation and an apparatus for COBOL to Java program transformation. The method consists of: (1) a new approach for statement-to-statement program transformation, facilitated by a predefined target language library, which keeps original comments, program control flow, functionality, and time complexity; (2) a new approach for goto statement elimination, which uses existing exception handling mechanism in target language and its implementation is hidden in a super class in a library; (3) a new extended BNF to distinguish different occurrences of the same term in a BNF production; (4) a new approach for embedded statement as a special marker statement and a comment, (5) in the description of the above, a program transformation specification language is defined to describe relationship between comments in two languages. (6) an apparatus, as the preferred embodiment of the method, is a COBOL to Java program transformation system Cobol2Java; a sample COBOL application and its Cobol2Java translation are given.
Owner:LI AIZHONG
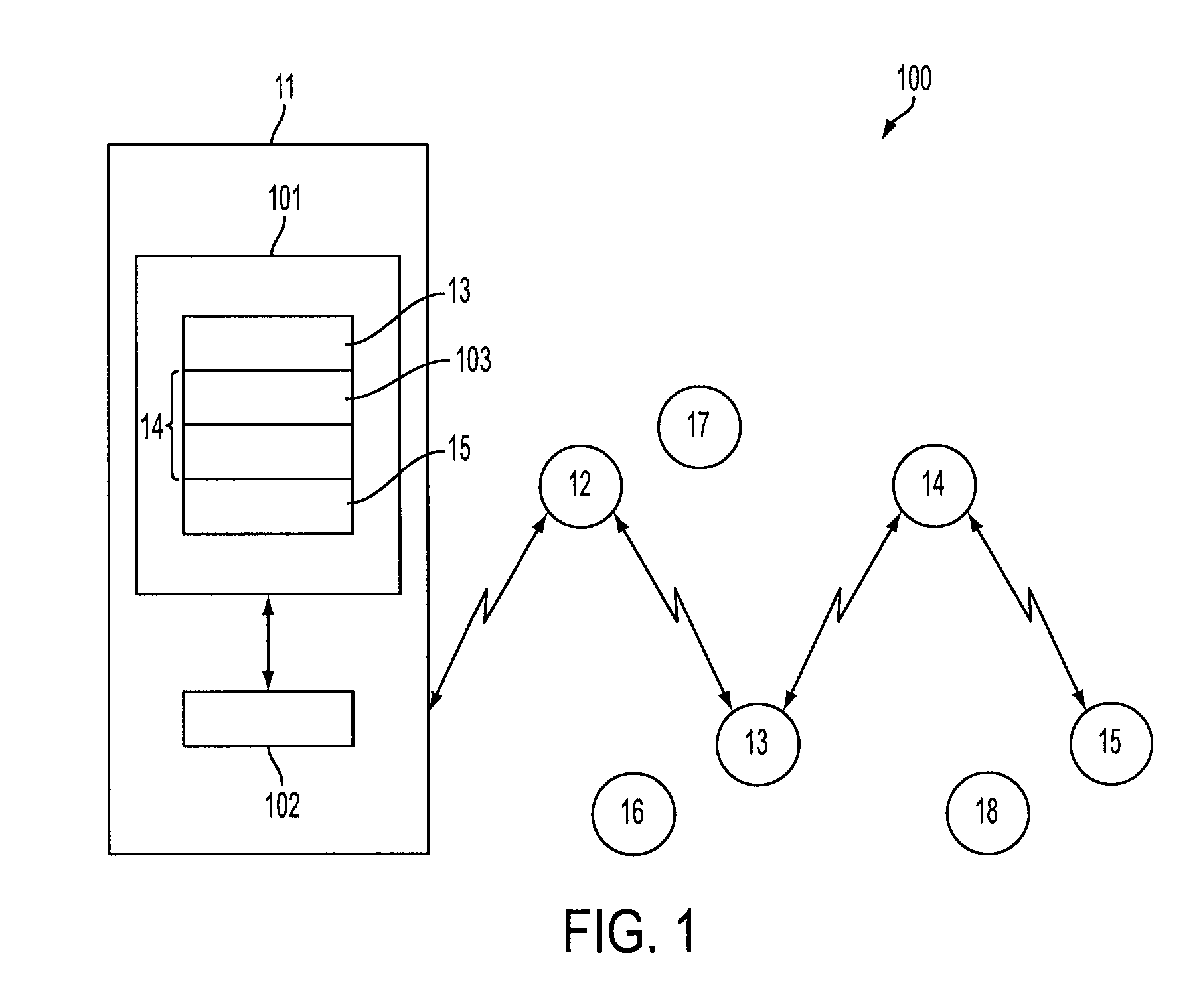
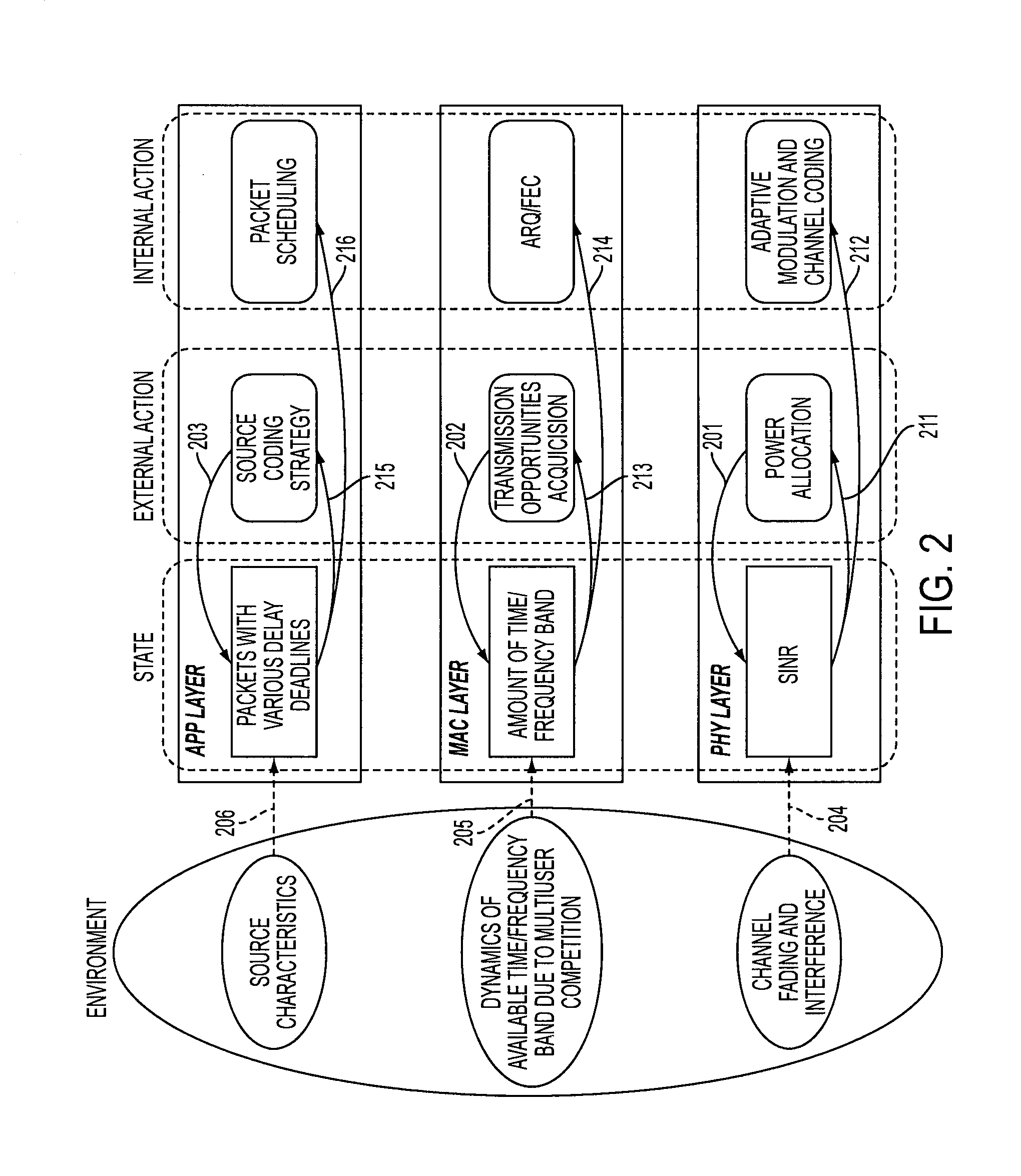
Adaptive network system with online learning and autonomous cross-layer optimization for delay-sensitive applications
InactiveUS20110019693A1Sub-optimal performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexReliable transmissionNetworked system
A network system providing highly reliable transmission quality for delay-sensitive applications with online learning and cross-layer optimization is disclosed. Each protocol layer is deployed to select its own optimization strategies, and cooperates with other layers to maximize the overall utility. This framework adheres to defined layered network architecture, allows layers to determine their own protocol parameters, and exchange only limited information with other layers. The network system considers heterogeneous and dynamically changing characteristics of delay-sensitive applications and the underlying time-varying network conditions, to perform cross-layer optimization. Data units (DUs), both independently decodable DUs and interdependent DUs, are considered. The optimization considers how the cross-layer strategies selected for one DU will impact its neighboring DUs and the DUs that depend on it. While attributes of future DU and network conditions may be unknown in real-time applications, the impact of current cross-layer actions on future DUs can be characterized by a state-value function in the Markov decision process (MDP) framework. Based on the dynamic programming solution to the MDP, the network system utilizes a low-complexity cross-layer optimization algorithm using online learning for each DU transmission.
Owner:SANYO NORTH AMERICA CORP +1
H.264/AVC frame inner prediction method based on edge characteristics
InactiveCN101494792AReduce complexityReduce the number of mode choicesTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPeak valueSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses an H.264 / AVC intra-prediction method based on edge characteristics, which includes: performing data block prejudging before intra-prediction based on principal edge intensity (DES) and the like edge direction characteristics calculated by the edge histogram description describing the image marginal distribution, selecting the mode subclass corresponding to the characteristics to perform RDO calculation, thereby reducing the mode selection number of the intra-prediction; at the same time directly determining the Intra_8*8 chrominance prediction mode from the Intra_16*16 brightness prediction mode according to the correlativity of the chrominance prediction mode and the brightness prediction mode, to further reduce the complexity of the algorithm. The method has six steps, and is convenient and facilitating. Practice shows that the method can obviously improve the encoding speed, and can ensure that the bit-rate encoding (an increase of 3%) and peak signal-noise ratio (reduced about 0.02dB) have little change compared with the full search method. The method has very good practical value and application prospects.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
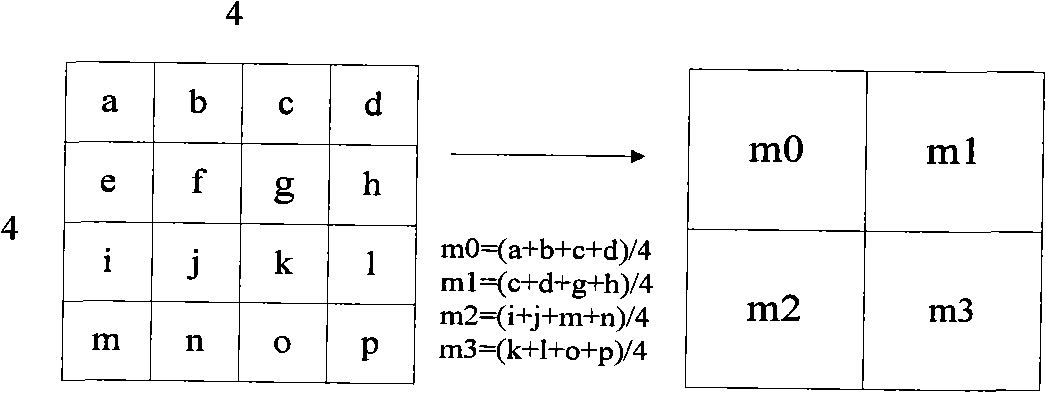
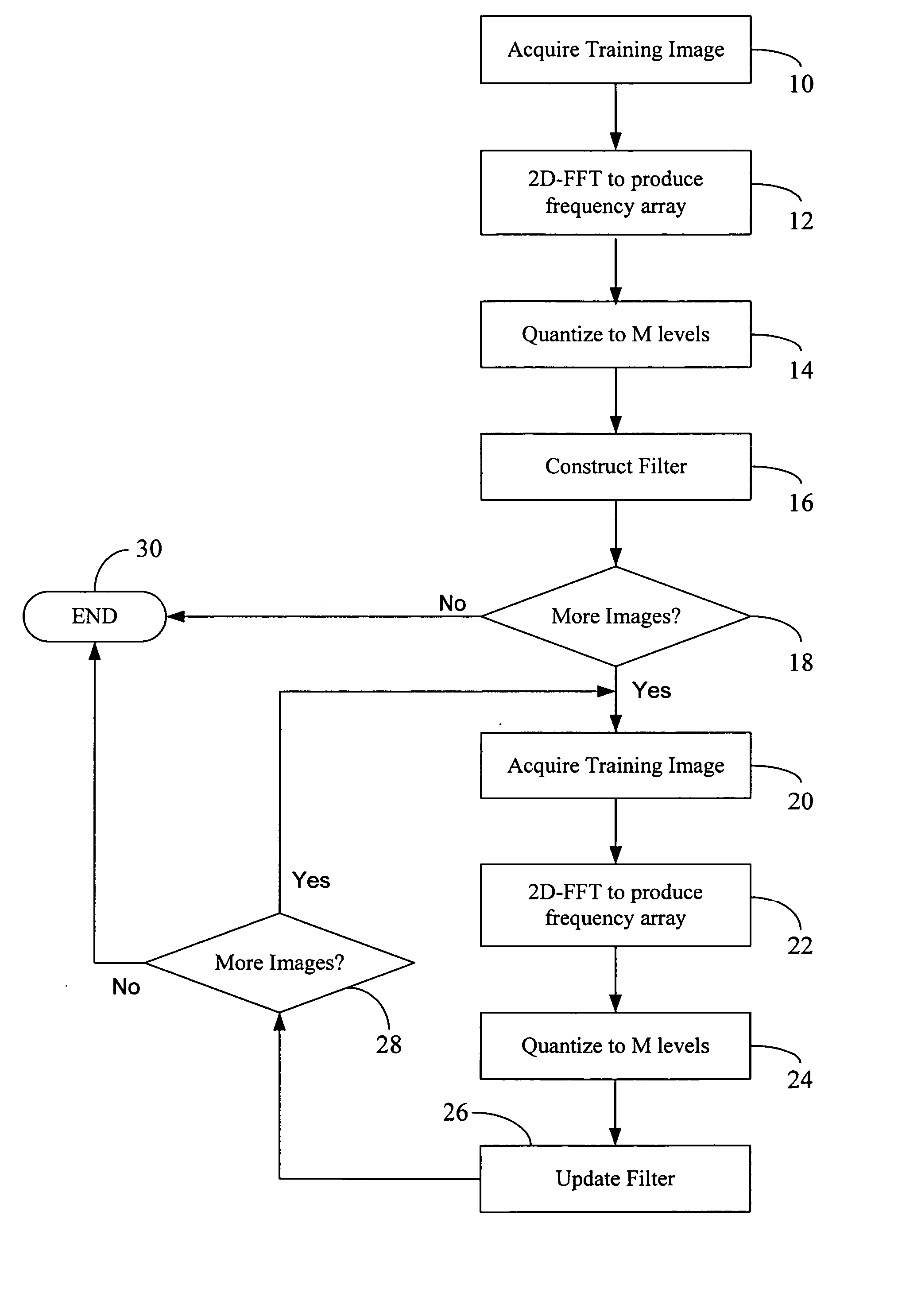
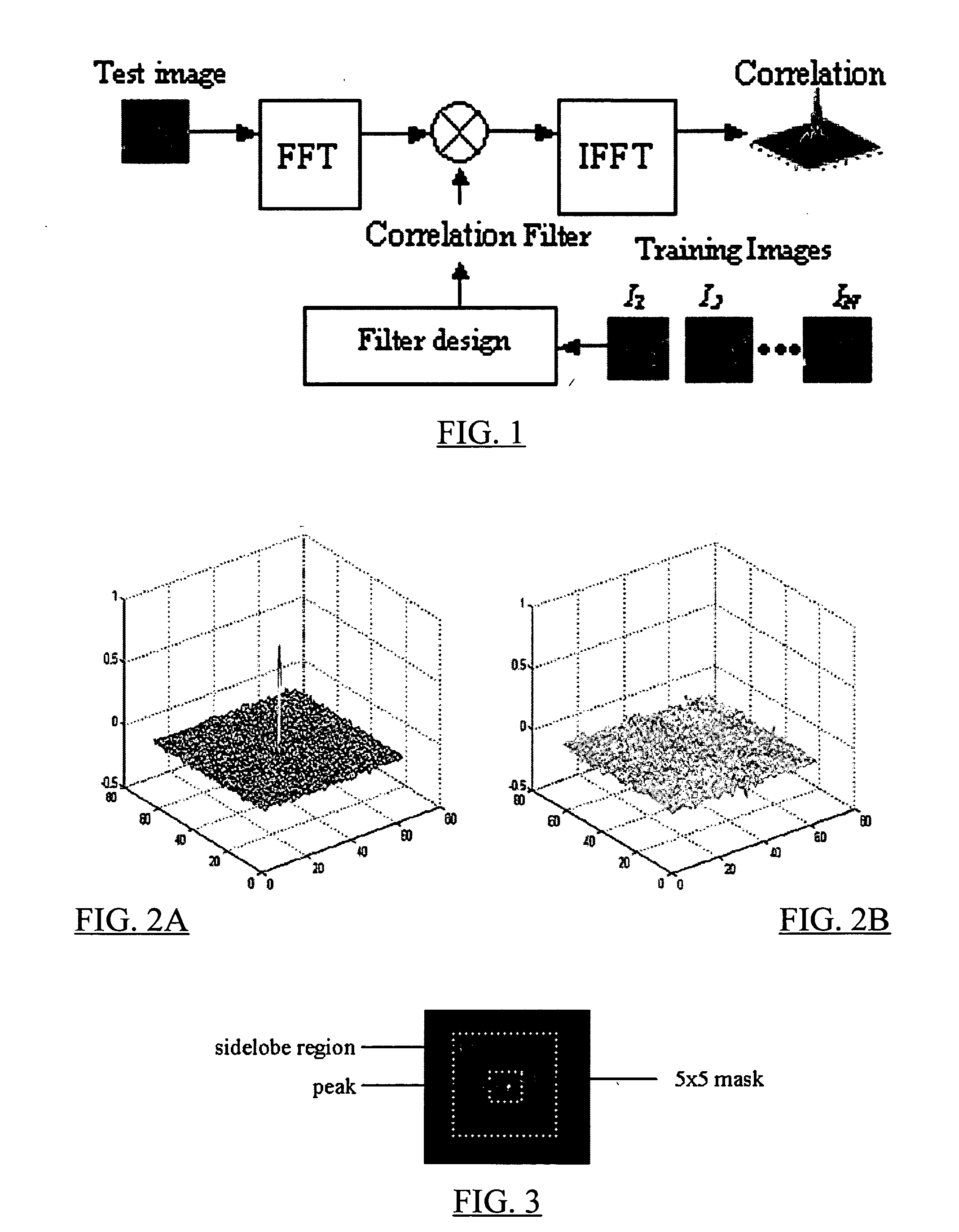
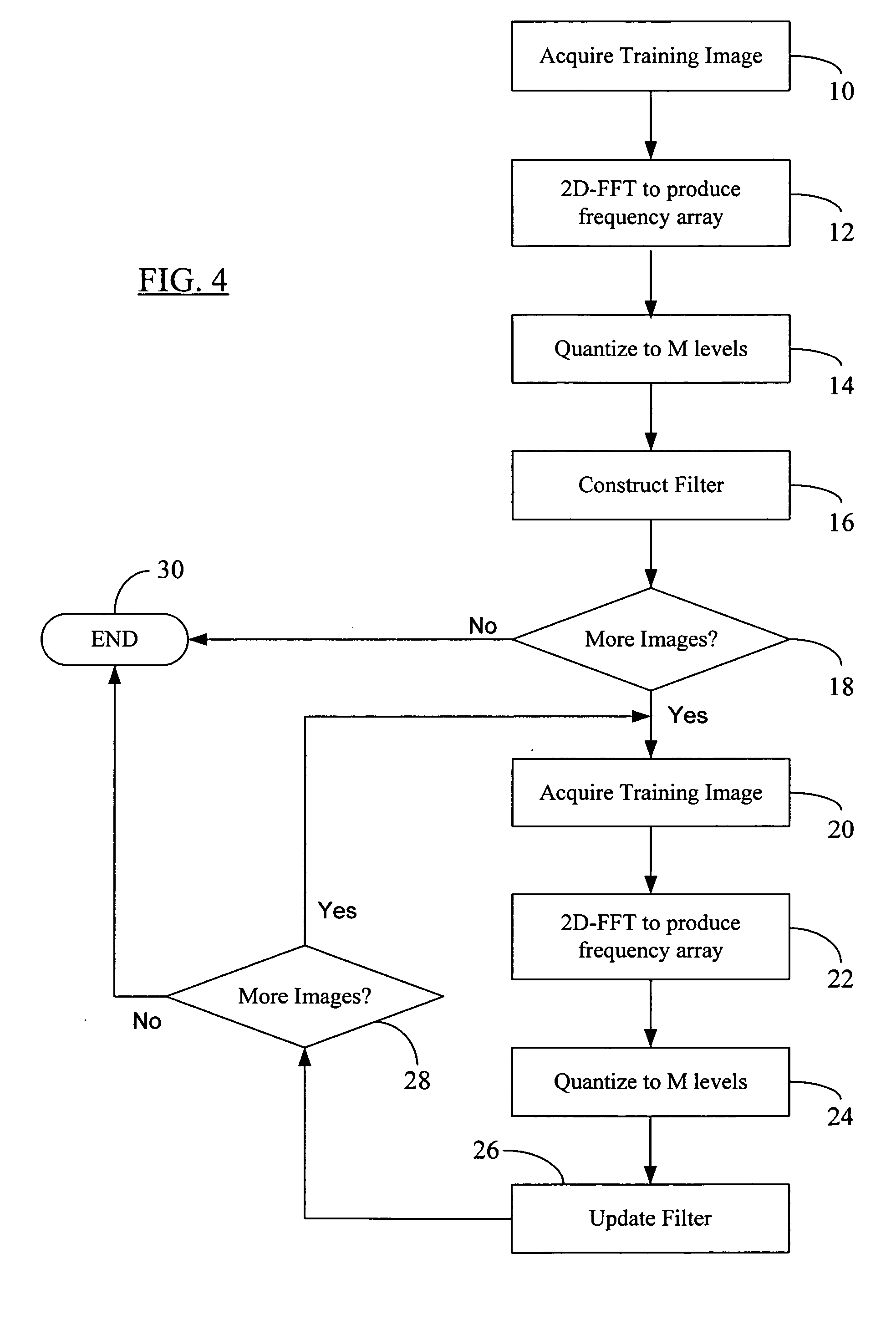
Reduced complexity correlation filters
InactiveUS20050018925A1Reduce storageReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionPhase correlationPattern recognition
A methodology is described to reduce the complexity of filters for face recognition by reducing the memory requirement to, for example, 2 bits / pixel in the frequency domain. Reduced-complexity correlations are achieved by having quantized MACE, UMACE, OTSDF, UOTSDF, MACH, and other filters, in conjunction with a quantized Fourier transform of the input image. This reduces complexity in comparison to the advanced correlation filters using full-phase correlation. However, the verification performance of the reduced complexity filters is comparable to that of full-complexity filters. A special case of using 4-phases to represent both the filter and training / test images in the Fourier domain leads to further reductions in the computational formulations. This also enables the storage and synthesis of filters in limited-memory and limited-computational power platforms such as PDAs, cell phones, etc. An online training algorithm implemented on a face verification system is described for synthesizing correlation filters to handle pose / scale variations. A way to perform efficient face localization is also discussed. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com