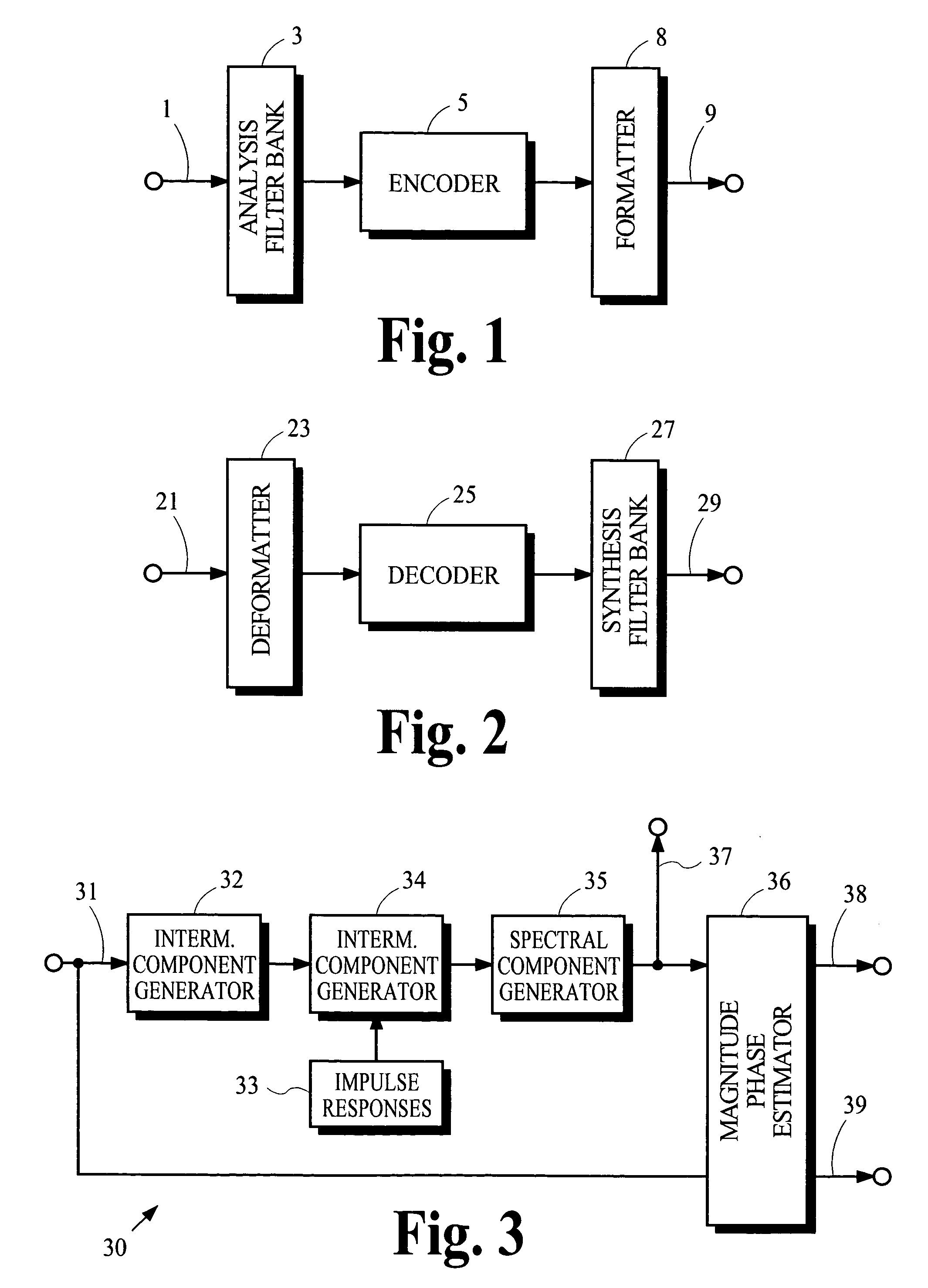
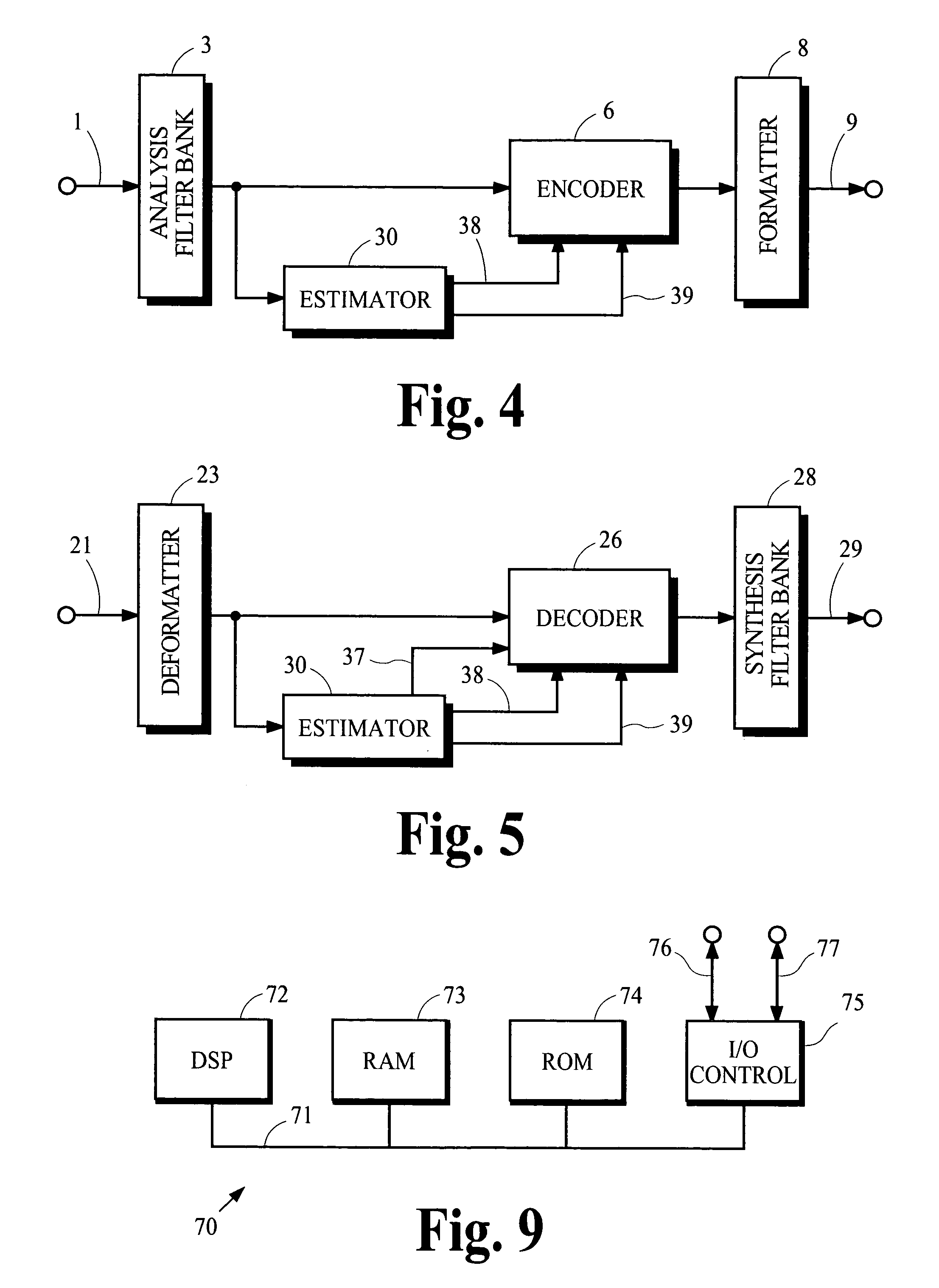
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
90 results about "Modified discrete cosine transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
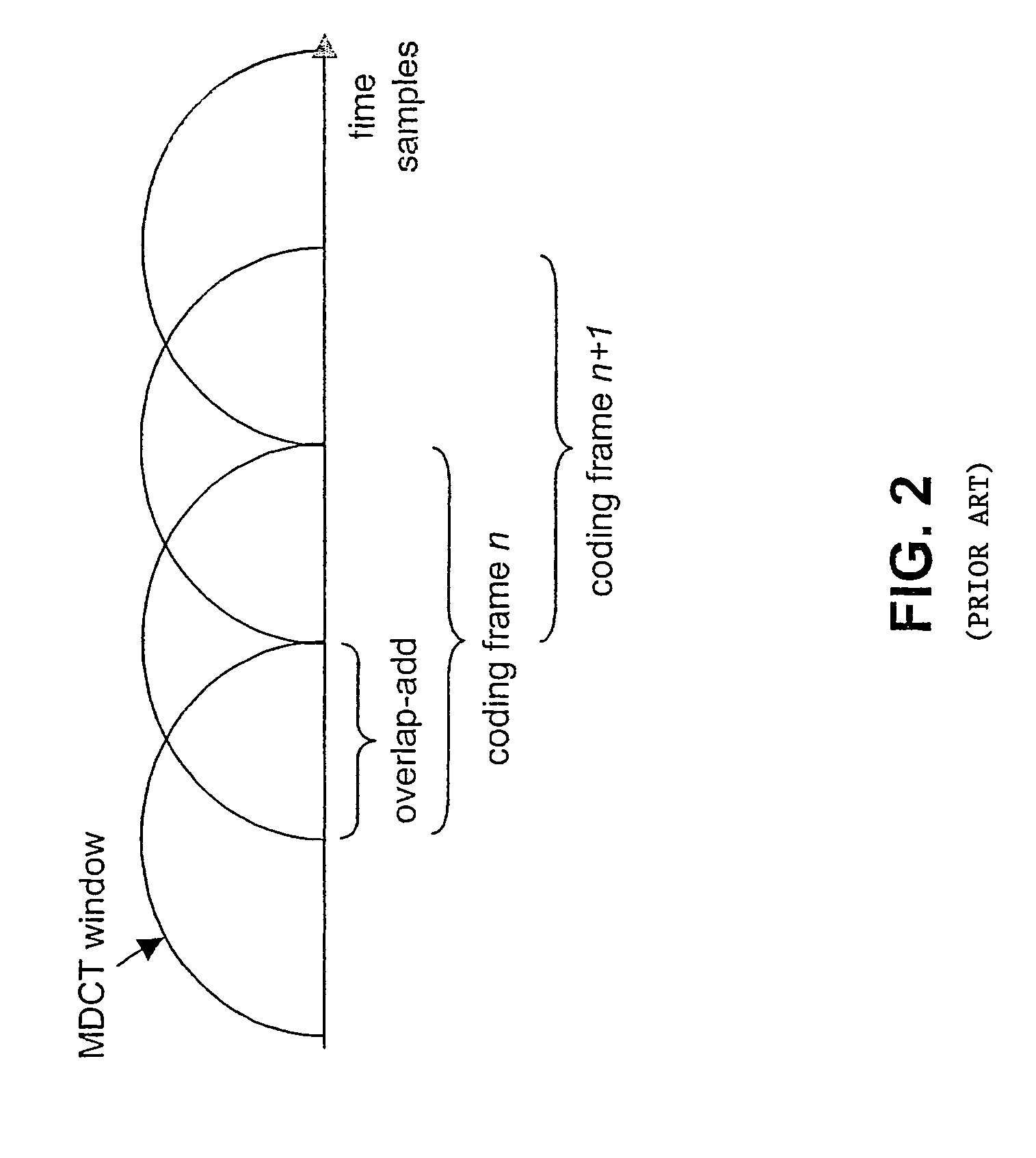
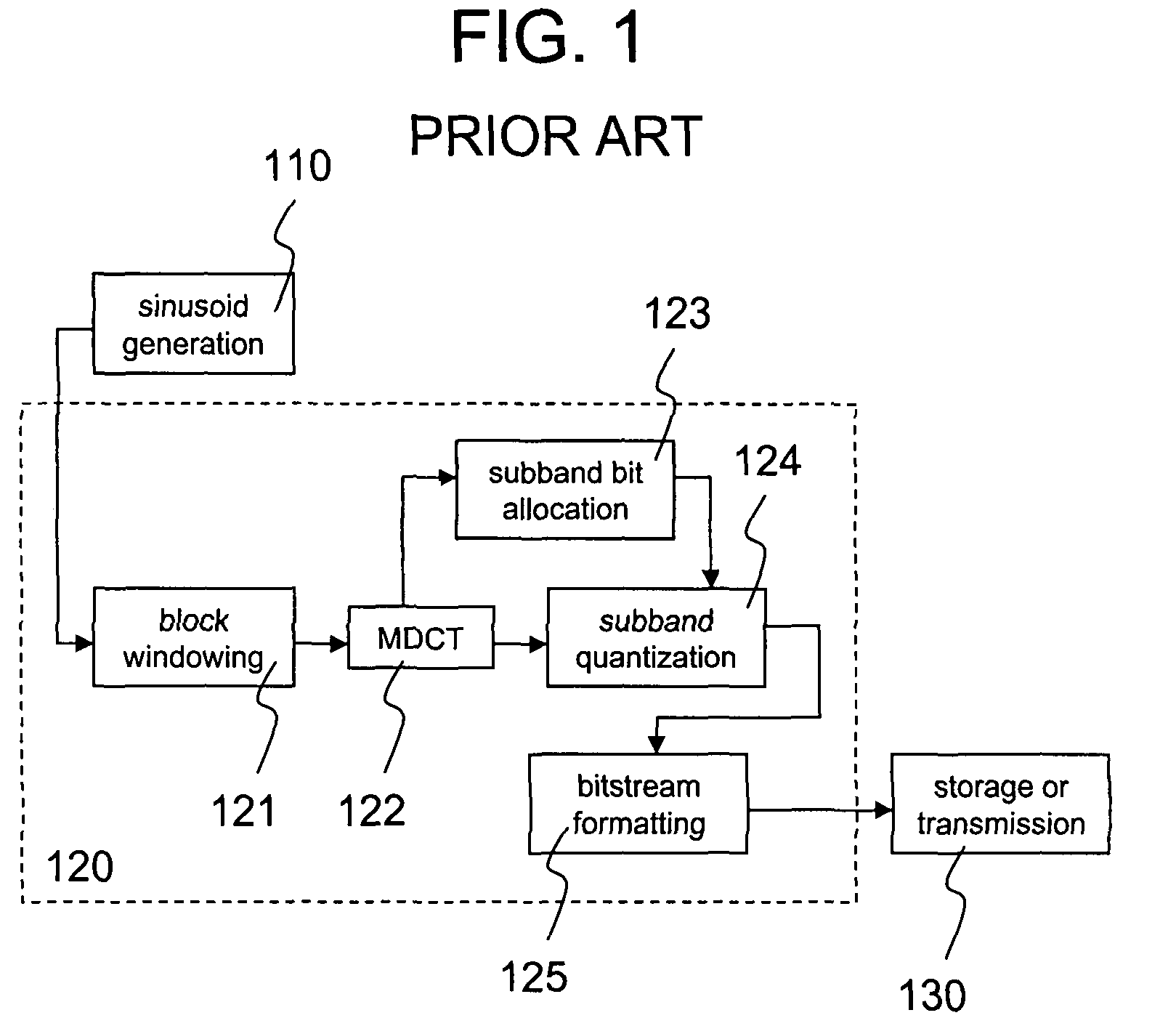
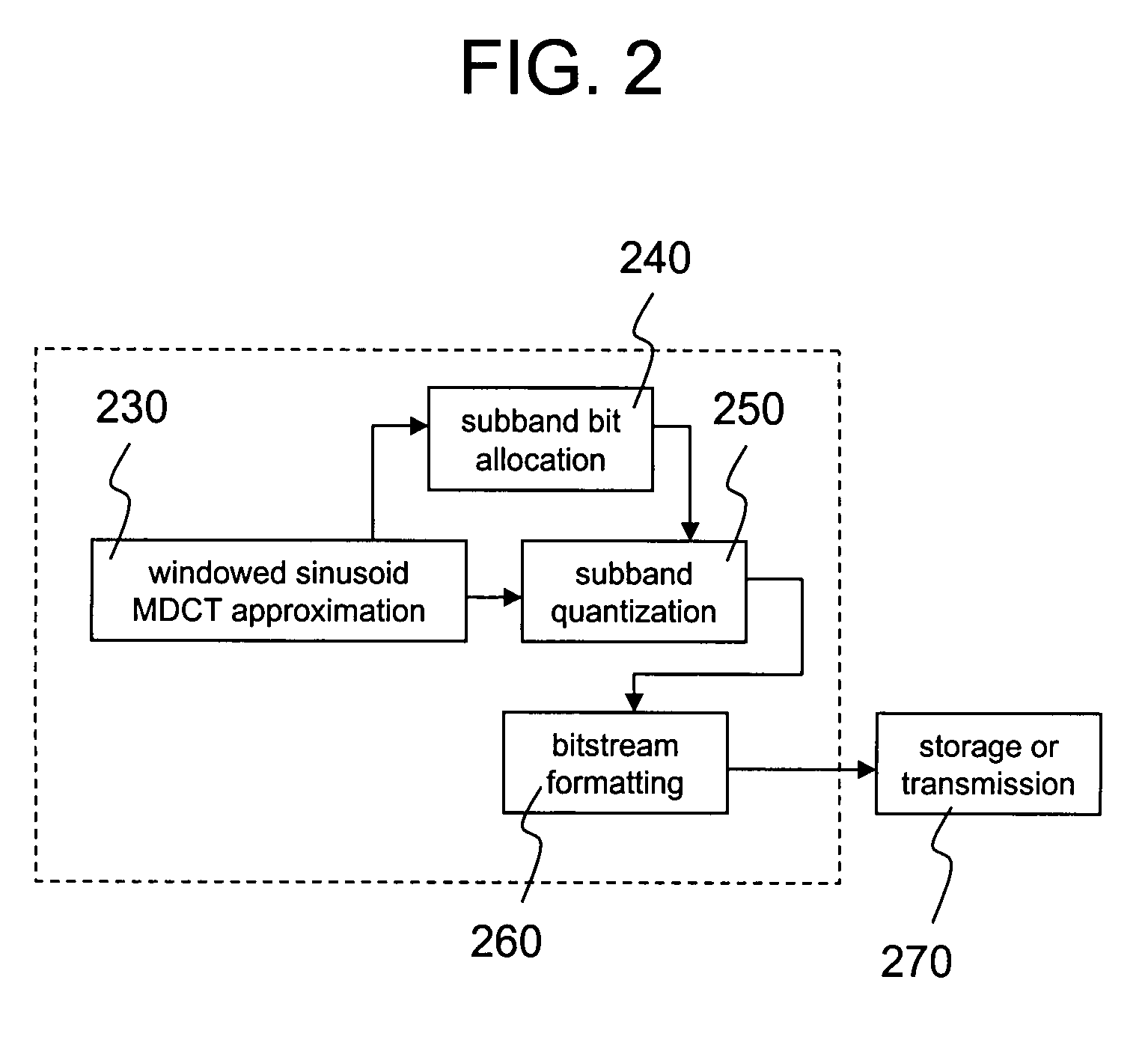
The modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) is a lapped transform based on the type-IV discrete cosine transform (DCT-IV), with the additional property of being lapped: it is designed to be performed on consecutive blocks of a larger dataset, where subsequent blocks are overlapped so that the last half of one block coincides with the first half of the next block. This overlapping, in addition to the energy-compaction qualities of the DCT, makes the MDCT especially attractive for signal compression applications, since it helps to avoid artifacts stemming from the block boundaries. As a result of these advantages, the MDCT is employed in most modern lossy audio formats, including MP3, AC-3, Vorbis, Windows Media Audio, ATRAC, Cook, AAC, Opus, and LDAC.
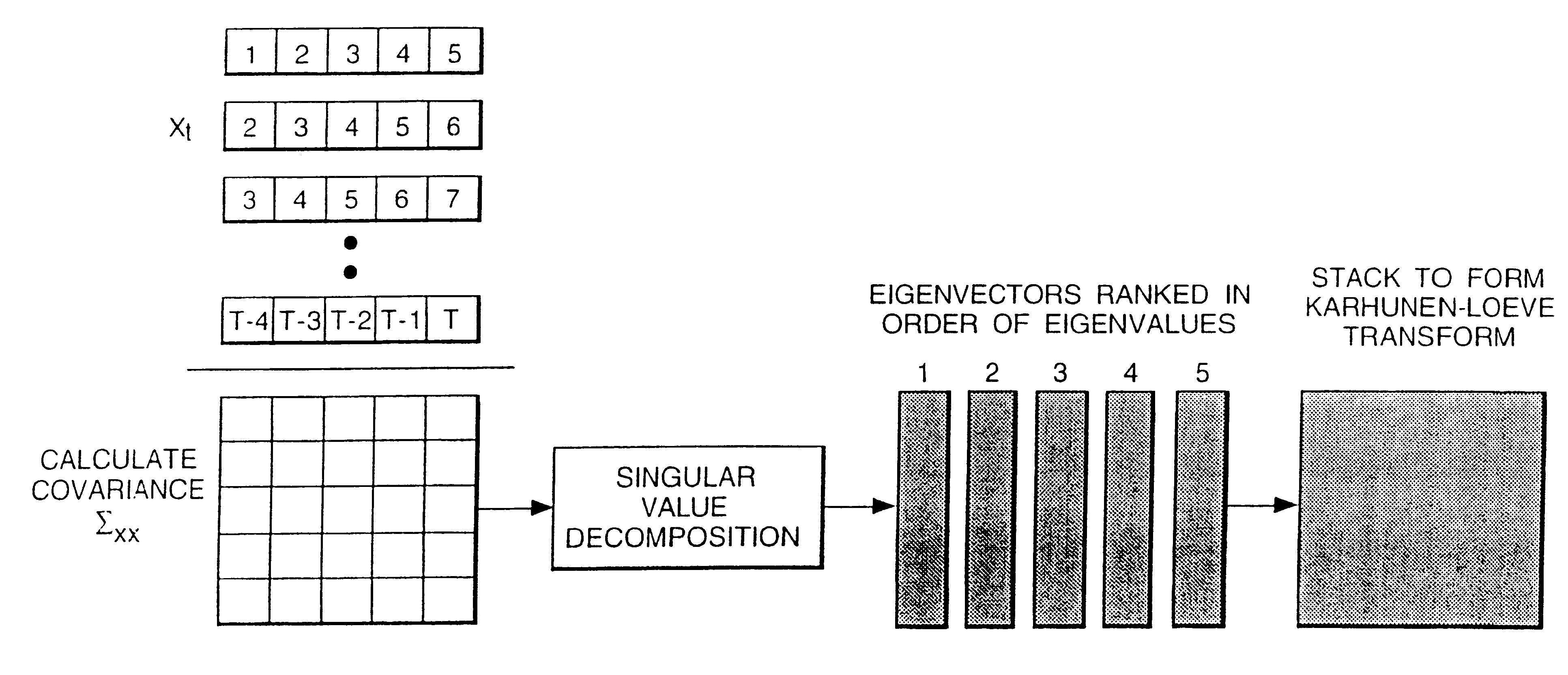
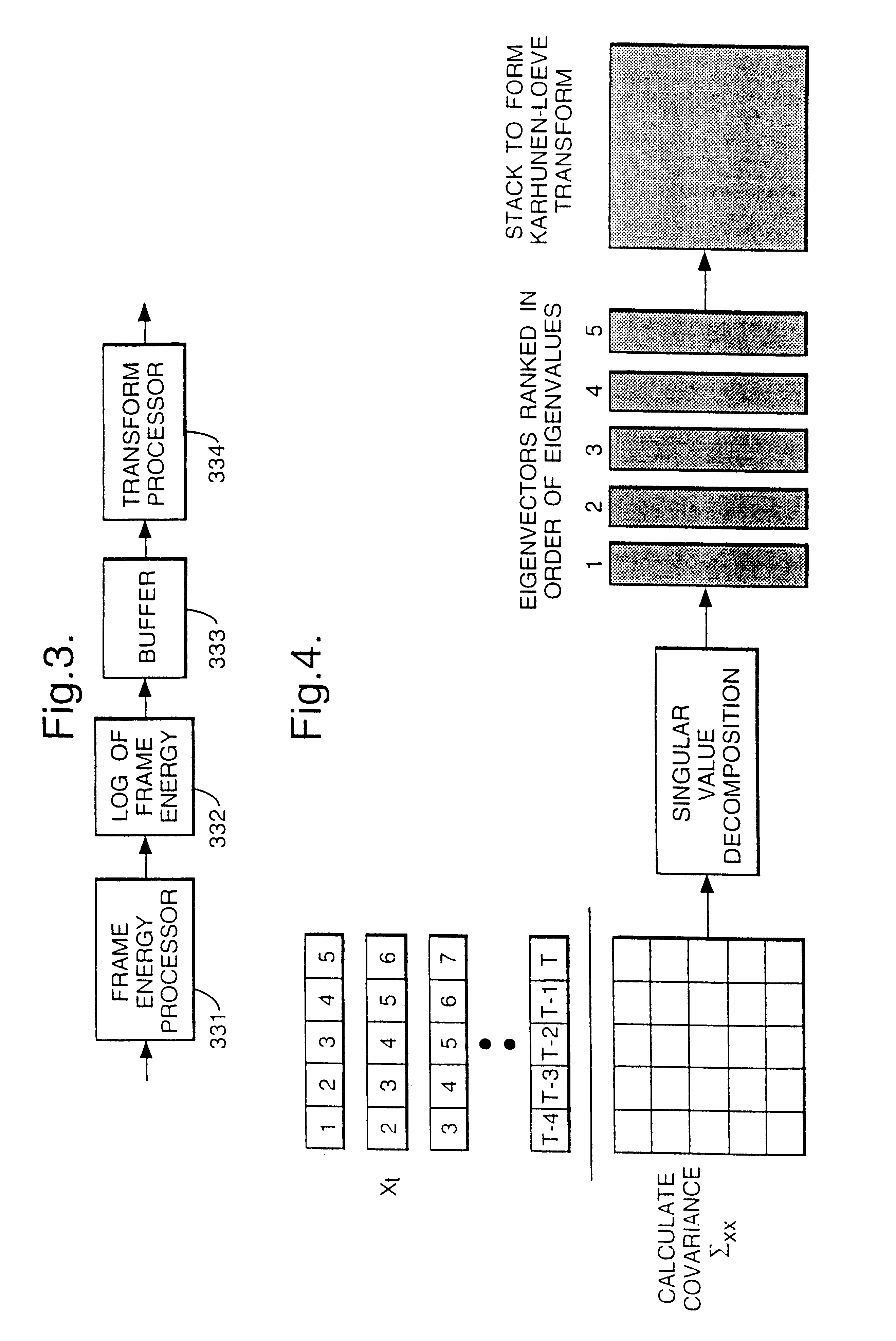
Speech transformation using log energy and orthogonal matrix
Calculate the log frame energy value of each of a pre-determined number n of frames of an input speech signal and apply a matrix transform to the n log frame energy values to form a temporal matrix representing the input speech signal. The matrix transform may be a discrete cosine transform.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
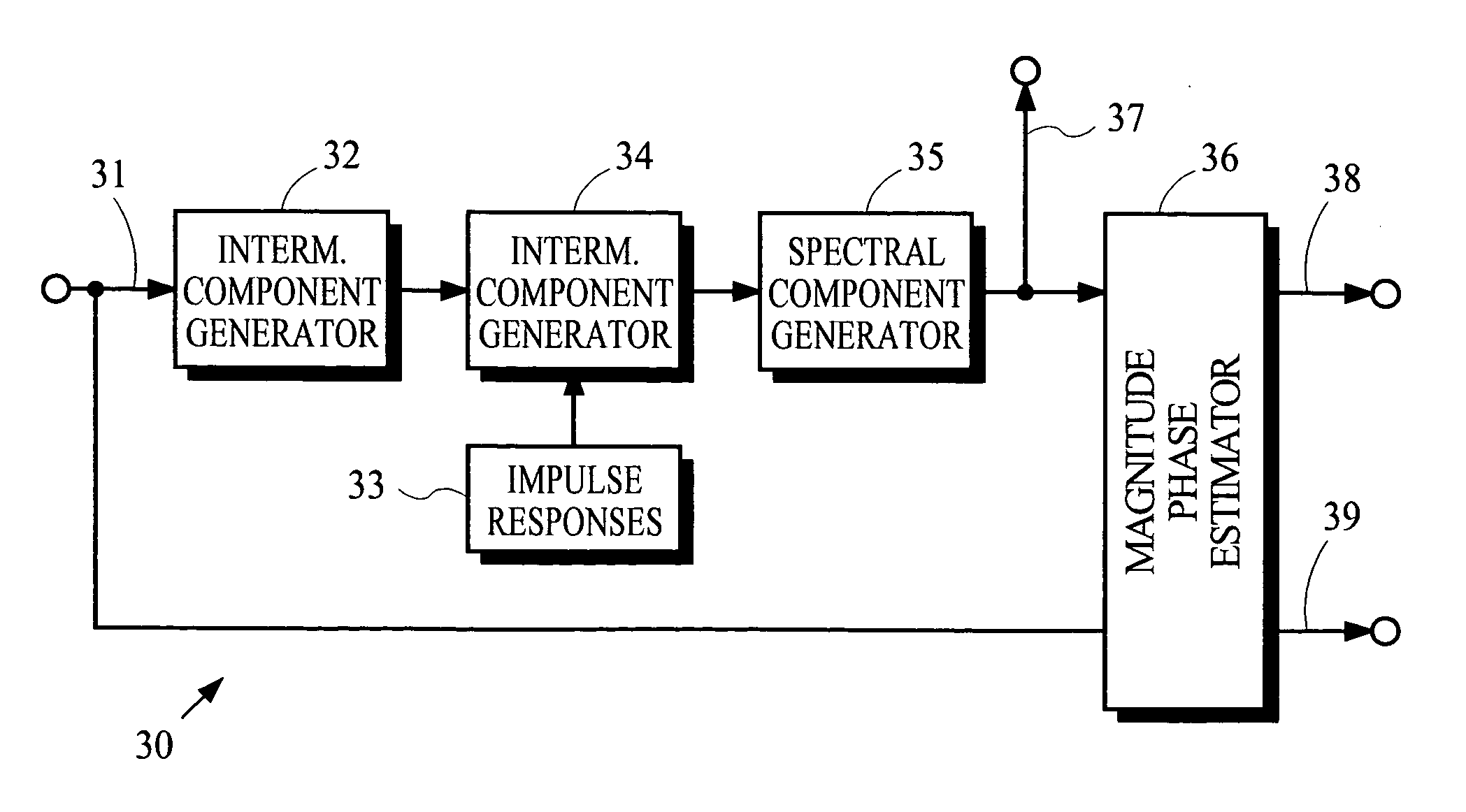
Coding techniques using estimated spectral magnitude and phase derived from MDCT coefficients
ActiveUS6980933B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpeech analysisComputation complexityFrequency spectrum
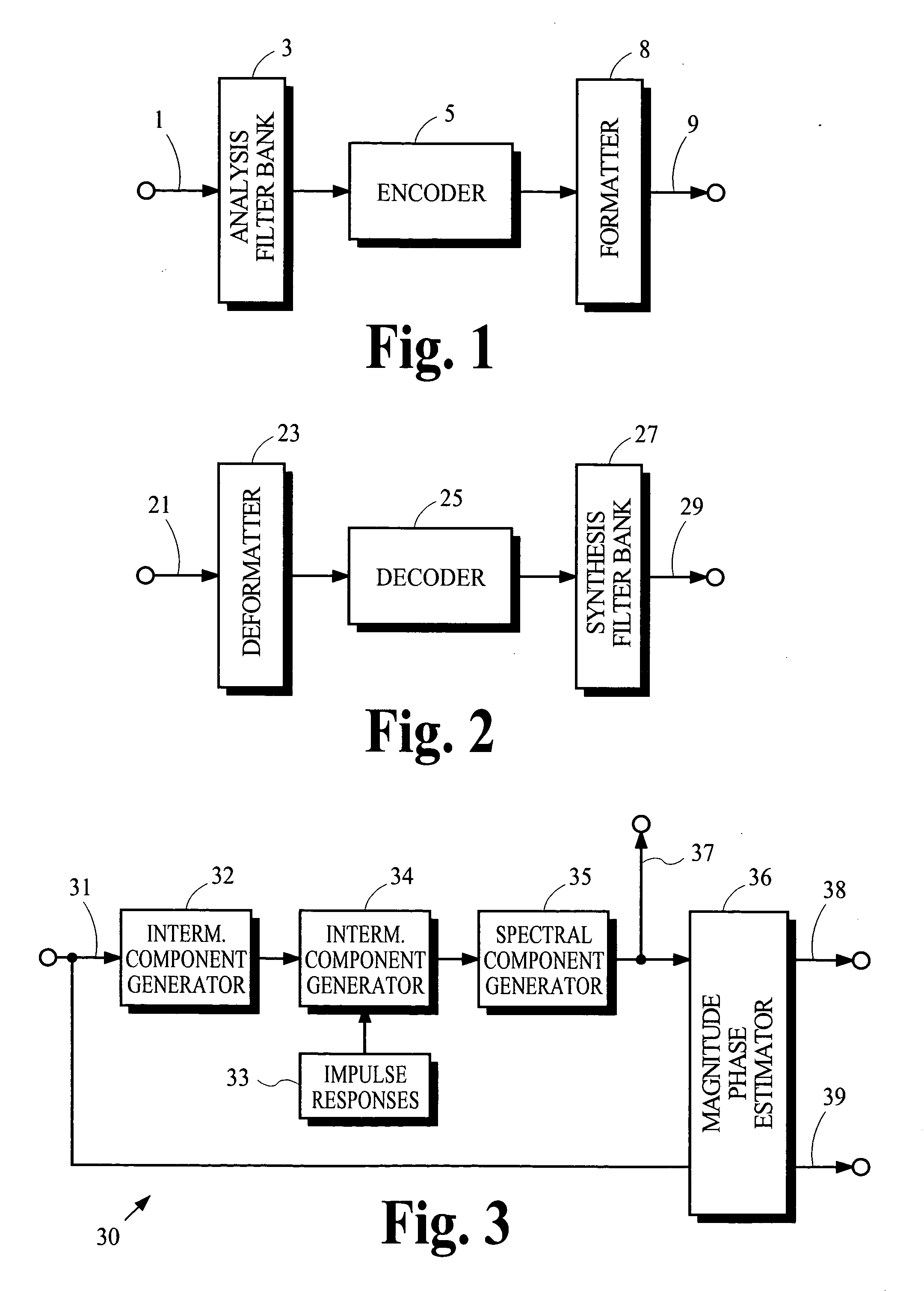
Estimates of spectral magnitude and phase are obtained by an estimation process using spectral information from analysis filter banks such as the Modified Discrete Cosine Transform. The estimation process may be implemented by convolution-like operations with impulse responses. Portions of the impulse responses may be selected for use in the convolution-like operations to trade off between computational complexity and estimation accuracy. Mathematical derivations of analytical expressions for filter structures and impulse responses are disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
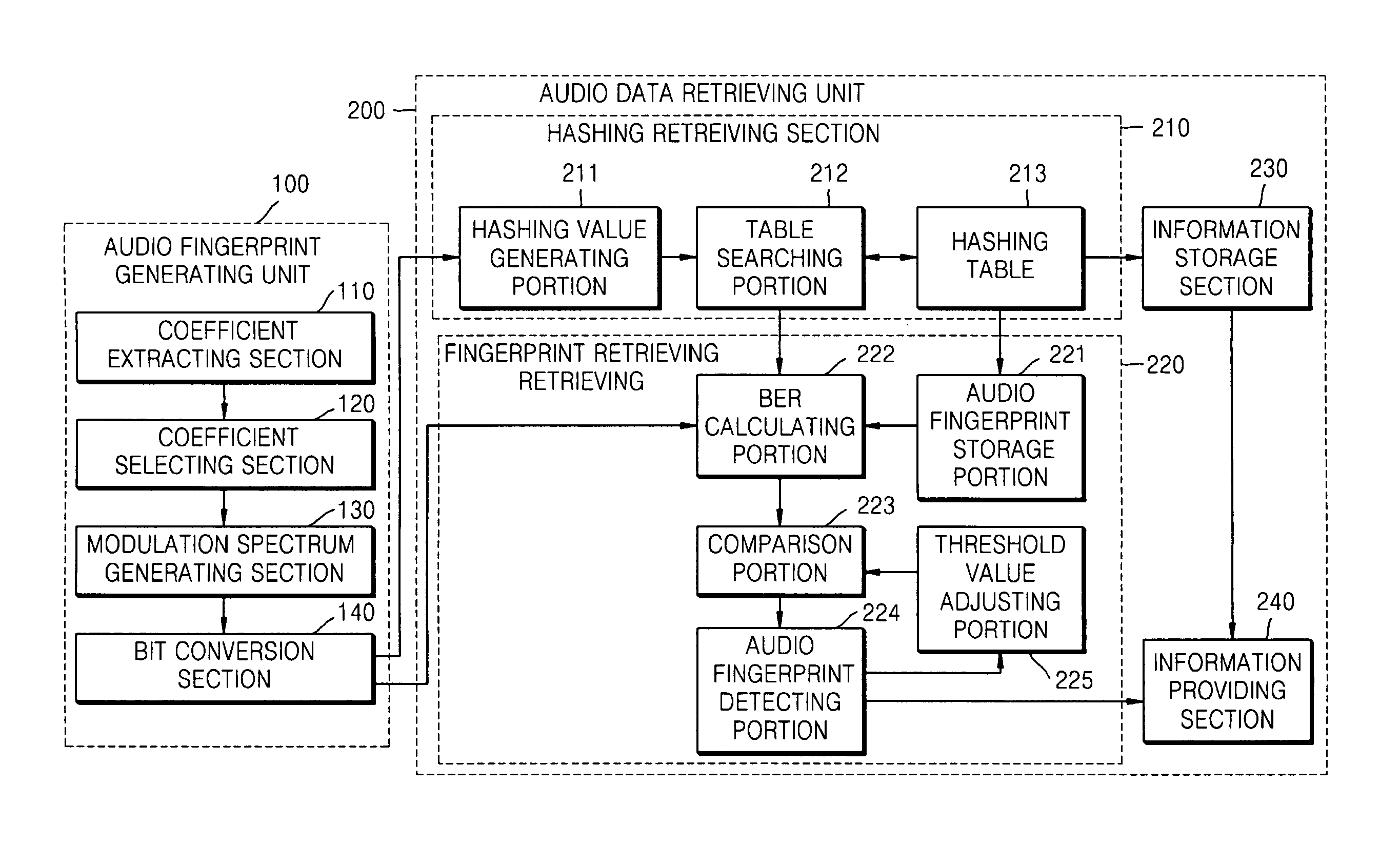
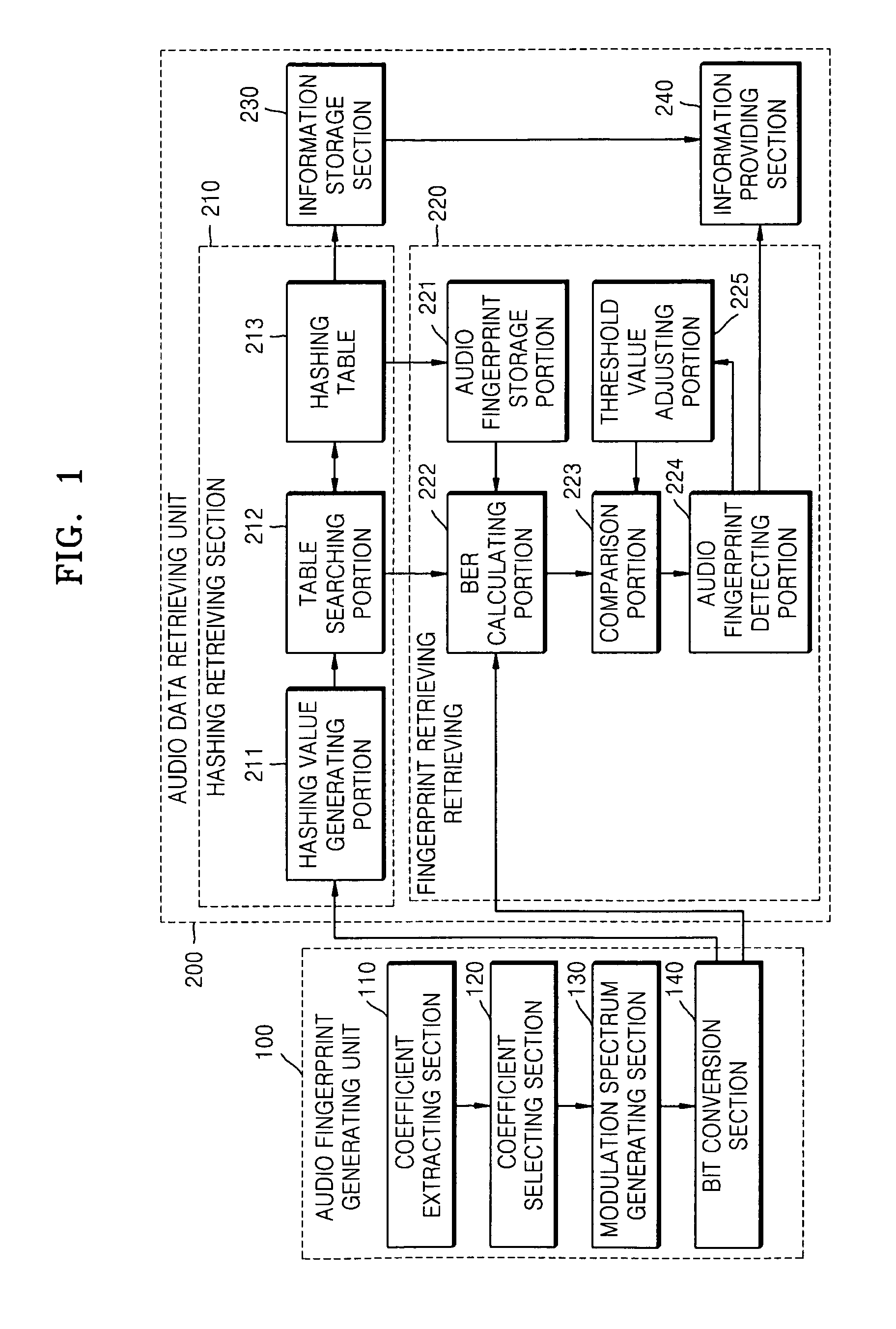
Device, method, and medium for generating audio fingerprint and retrieving audio data
Provided are device, method, and medium for generating an audio fingerprint and retrieving audio data. The device for generating an audio fingerprint includes: a coefficient extracting section partially decoding audio data in a compression area and extracting MDCT (Modified Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficients; a coefficient selecting section selecting an MDCT coefficient robust to noises from the extracted MDCT coefficients; a modulation spectrum generating section transforming the selected MDCT coefficient by the use of a Fourier transform method and generating a modulation spectrum; and a bit conversion section quantizing the generated modulation spectrum and generating an audio fingerprint. As a result, it is possible to accurately and rapidly retrieve the audio data recorded in a variety of environments. Since elements based on MP3 are used, it is possible to apply to MP3 applications in various manners. In addition, it is possible to apply to classification of audio data such as classification of music moods and classification of music genres and various other fields such as extraction of a specific event from moving images of sports.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adaptive quantization using code length in image compression
InactiveUS6882753B2Low memory and bus bandwidth requirementImprove processing efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionLandau quantization
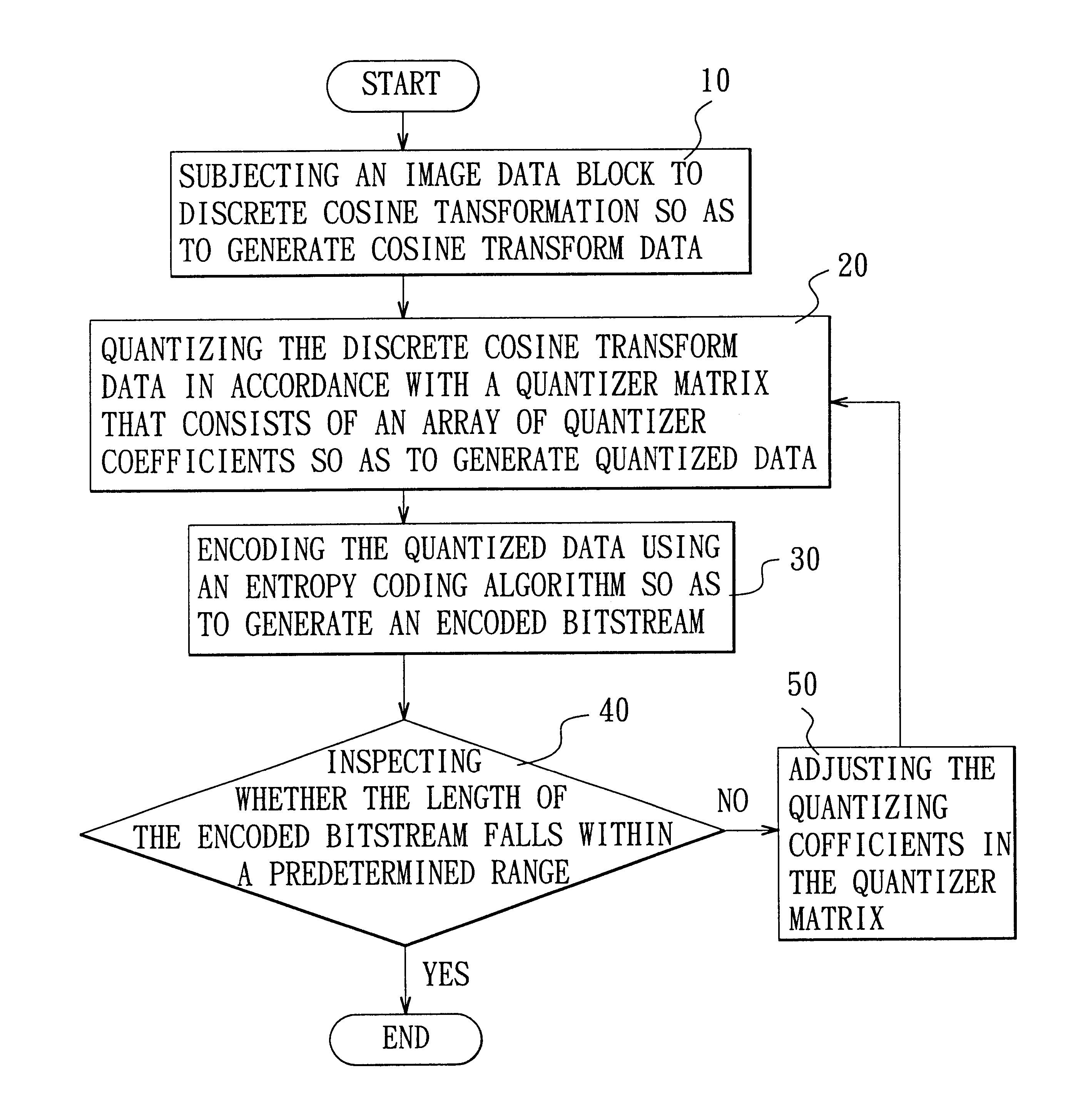
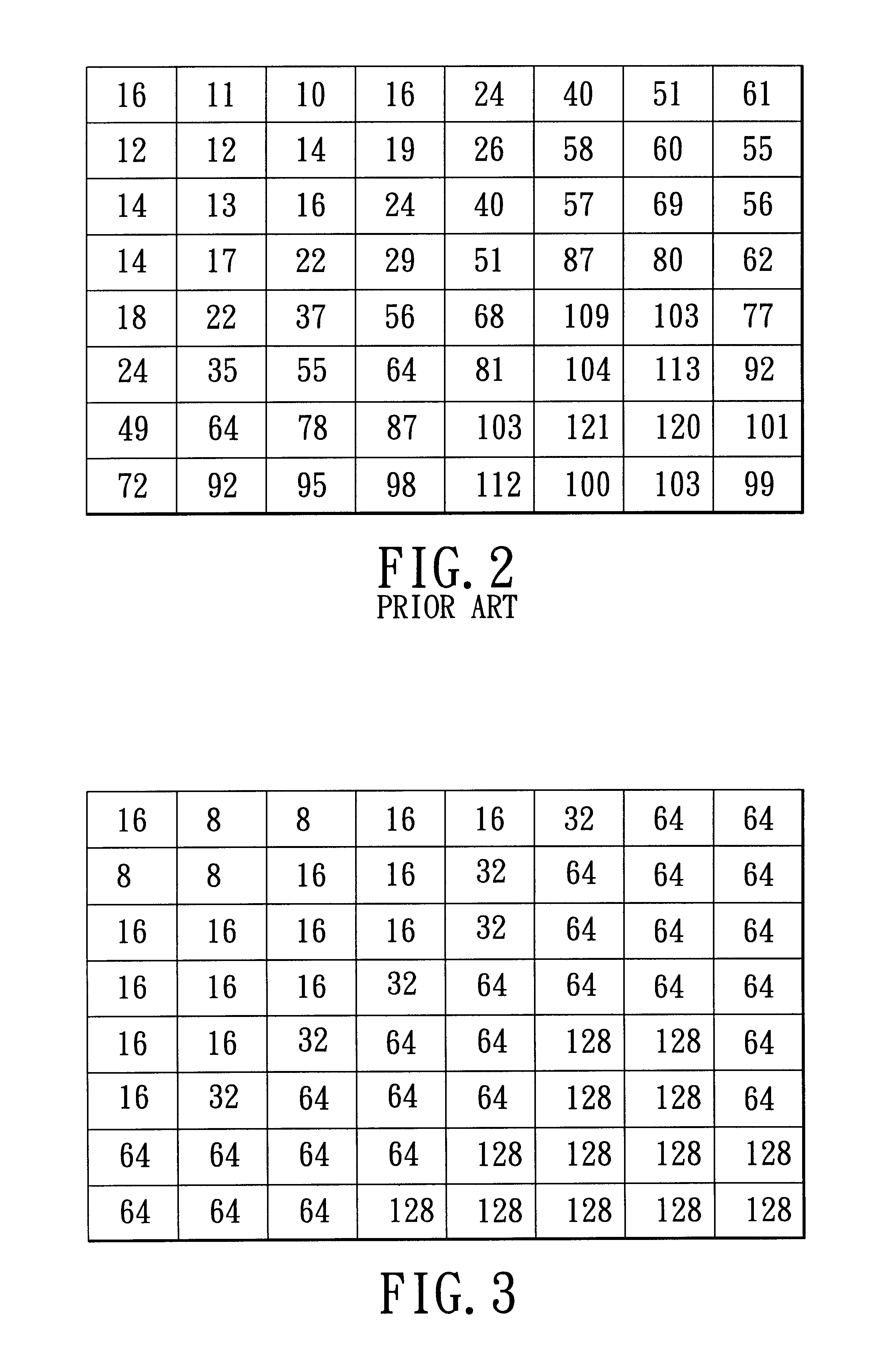
A method is adapted for compressing an image data block, and includes the steps of:(a) subjecting the image data block to discrete cosine transformation so as to generate discrete cosine transform data;(b) quantizing the discrete cosine transform data in accordance with a quantizer matrix that consists of an array of quantizing coefficients so as to generate quantized data;(c) encoding the quantized data using an entropy coding algorithm so as to generate an encoded bitstream; and(d) when the length of the encoded bitstream does not fall within a predetermined range, adjusting the quantizing coefficients in the quantizer matrix and repeating steps (b) and (c) until the length of the encoded bitstream falls within the predetermined range.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
Coding techniques using estimated spectral magnitude and phase derived from mdct coefficients
ActiveUS20050165587A1Overcome deficienciesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpeech analysisComputation complexityFrequency spectrum
Estimates of spectral magnitude and phase are obtained by an estimation process using spectral information from analysis filter banks such as the Modified Discrete Cosine Transform. The estimation process may be implemented by convolution-like operations with impulse responses. Portions of the impulse responses may be selected for use in the convolution-like operations to trade off between computational complexity and estimation accuracy. Mathematical derivations of analytical expressions for filter structures and impulse responses are disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
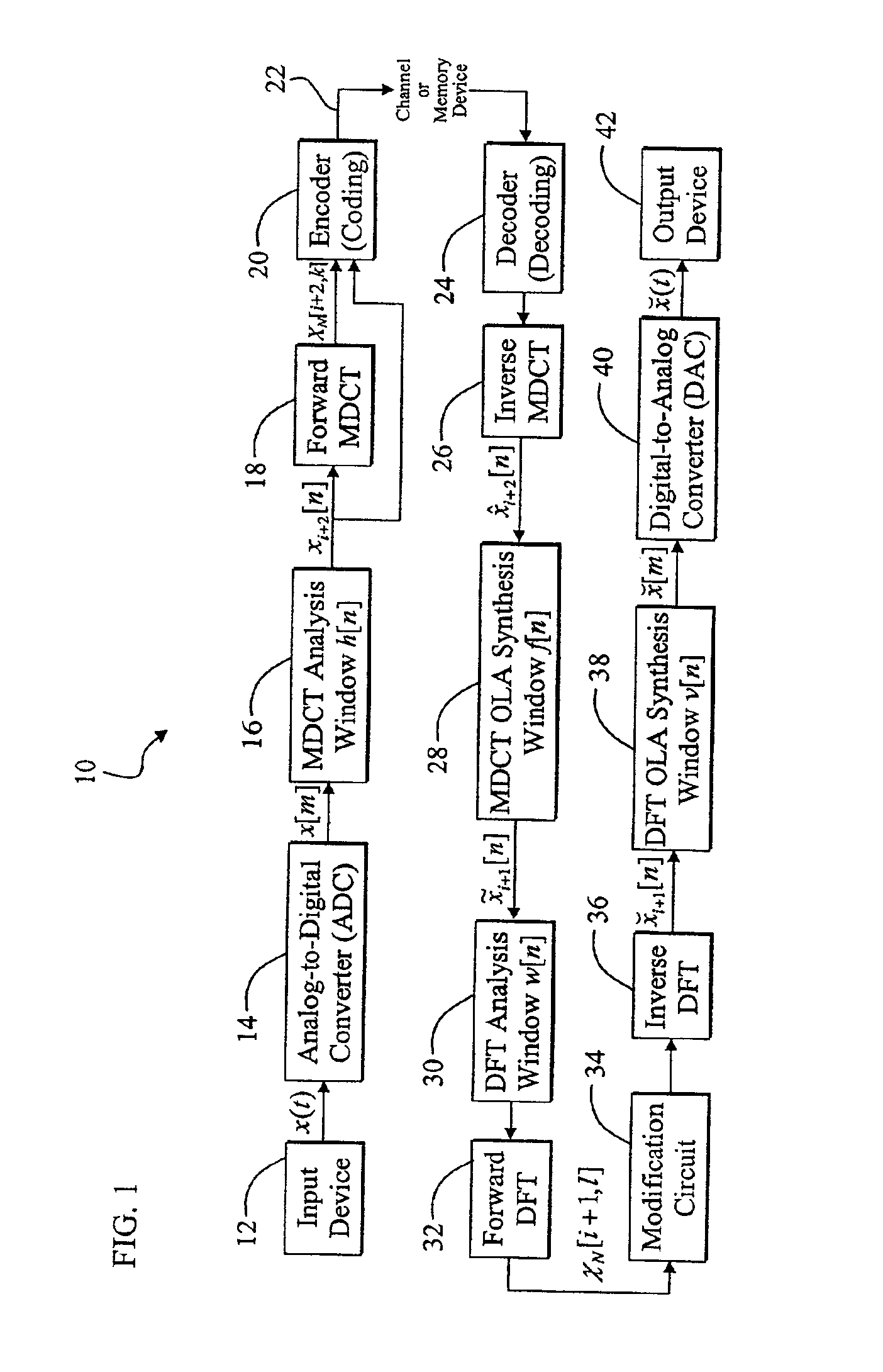
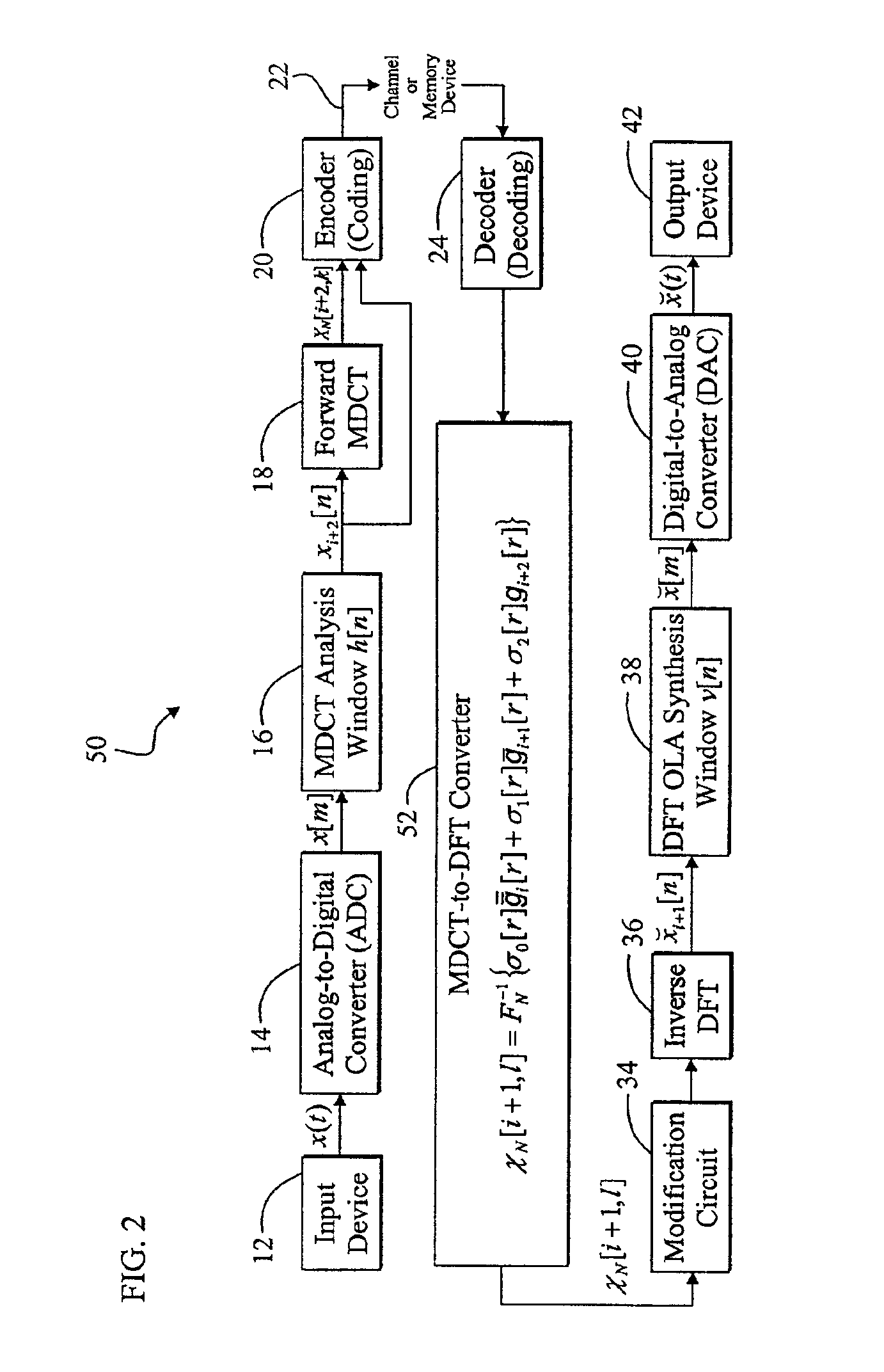
Efficient system and method for converting between different transform-domain signal representations
InactiveUS6963842B2Eliminating intermediate time-domain processingInnovative designCode conversionSpeech synthesisTime domainFourier transform on finite groups
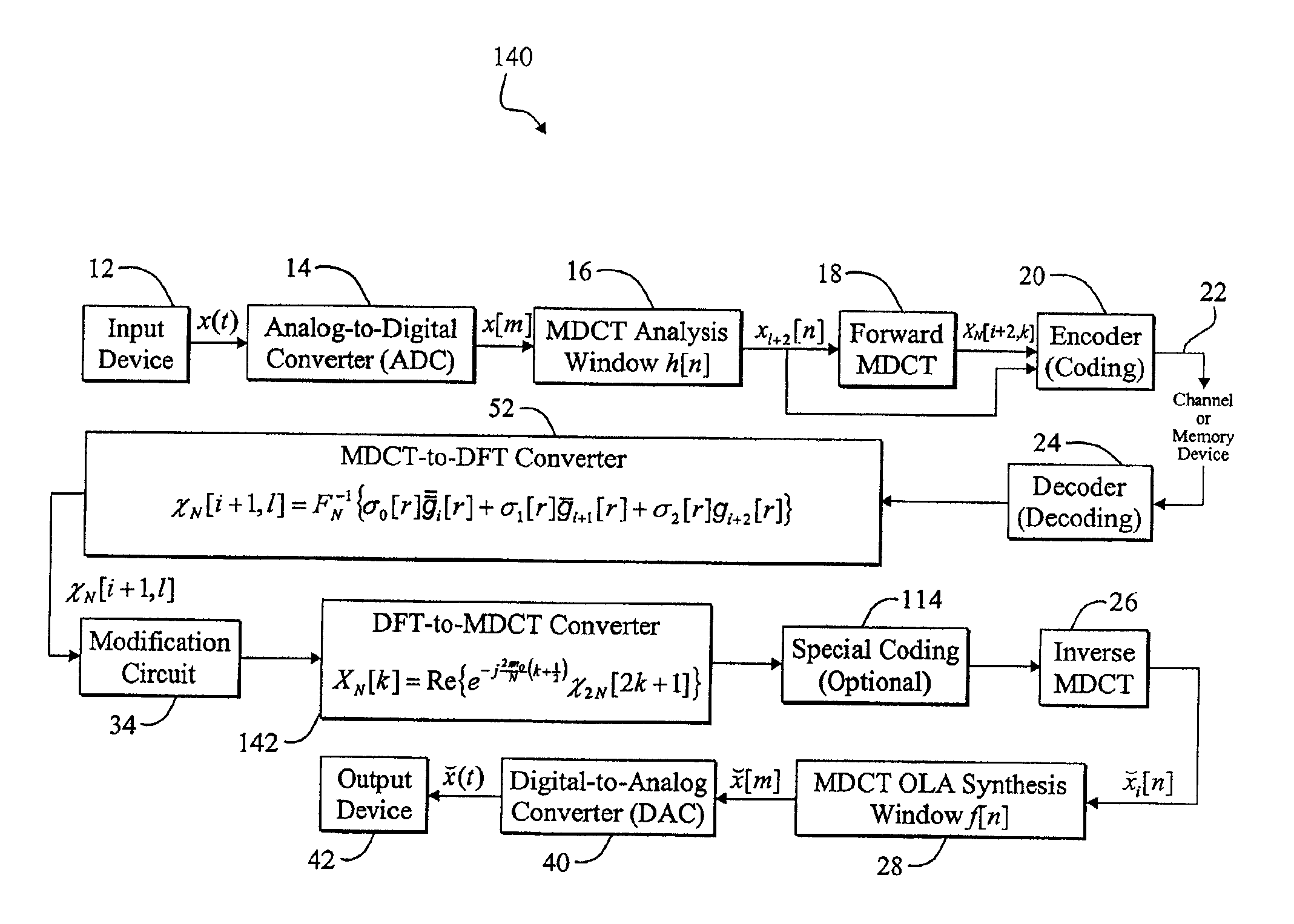
A memory-efficient system converting a signal from a first transform domain to a second transform domain. The system includes a first mechanism that obtains an input signal expressed via a first transform-domain signal representation. A second mechanism expresses the input signal via a second transform-domain signal representation without intermediate time-domain conversion. In the specific embodiment, the input signal is a Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT) signal. The second transform-domain signal representation is a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) signal. The second mechanism further includes a third mechanism that combines effects of an inverse MDCT, a synthesis window function, and an analysis window function, and provides a first signal in response thereto. A fourth mechanism converts the MDCT signal to the DFT signal based on the first signal. In a more specific embodiment, the synthesis window function is an MDCT synthesis window function, while the analysis window function is a DFT analysis window function. The fourth mechanism includes a mechanism for performing a fast transform on the MDCT signal and providing a first transformed signal in response thereto. The fourth mechanism further includes a mechanism for selectively delaying and updating the first transformed signal to yield second and third transformed signals, respectively, in response thereto. The fourth mechanism further includes a mechanism for operating on the first, second, and third transformed signals via third, second, and first combined window functions, respectively, and providing third, second, and first windowed signals, respectively, in response thereto. An adder adds the first, second, and third windowed functions to provide an added digital signal. An inverse DFT circuit performs an inverse DFT on the added digital signal to provide the DFT signal as output.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Scalable speech coding/decoding apparatus, method, and medium having mixed structure
InactiveUS20070033023A1Enhanced signalRestoration capability deterioratesSpeech analysisCode conversionSpeech inputLinearity
Provided are a scalable wide-band speech coding / decoding apparatus, method, and medium. An input wide-band speech input signal is first divided into a low-band signal and a high-band signal. The divided low-band signal is then coded using a code excited linear prediction (CELP) method. The divided high-band signal is coded using a harmonic method. A signal representing a difference between a synthetic signal obtained from the low-band and the high band, and a signal input to the low-band and the high-band is then coded using a modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) method. The coded signal is then multiplexed. The multiplexed signal is then output. Accordingly, high quality speech can be achieved for all layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
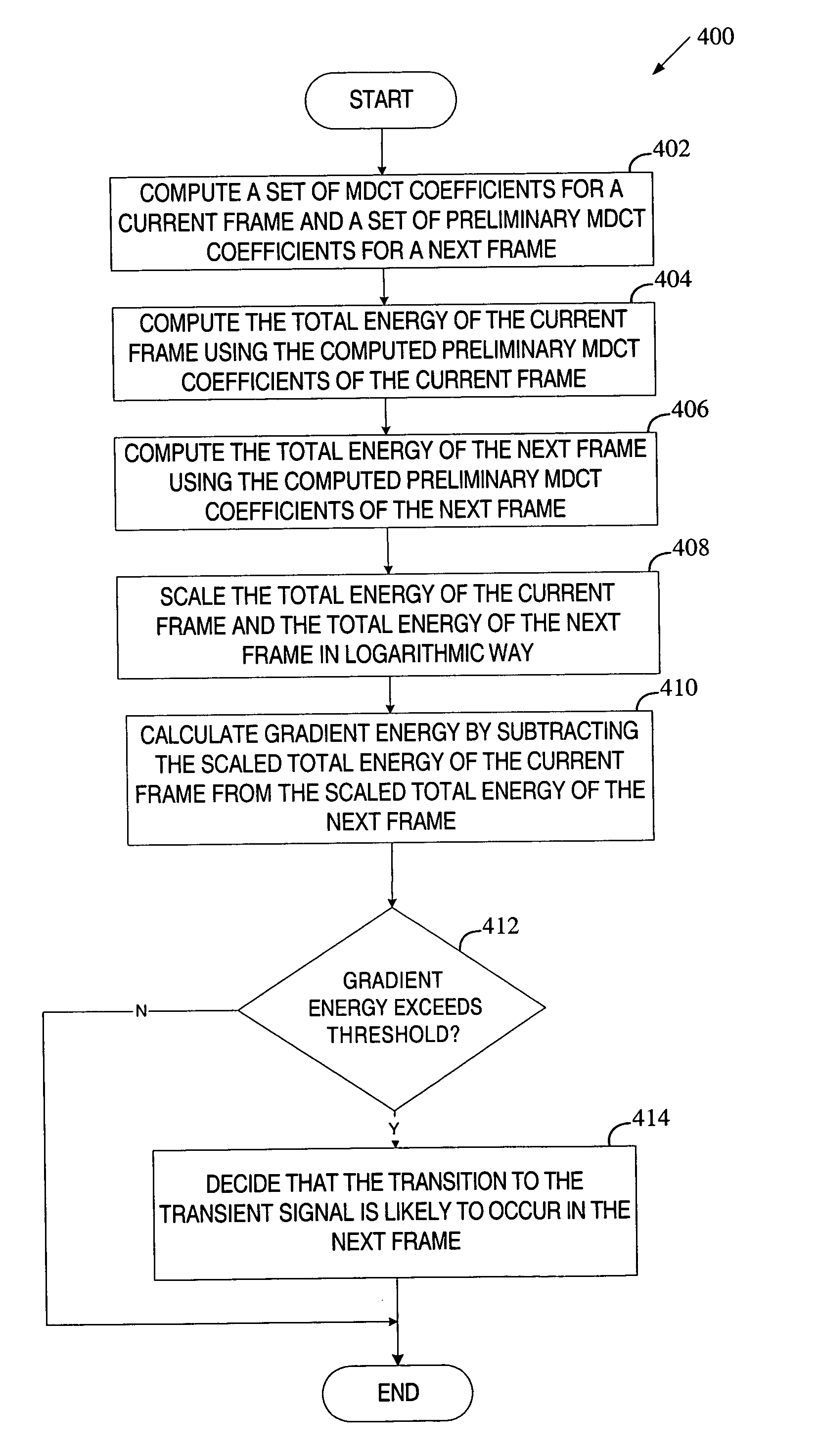
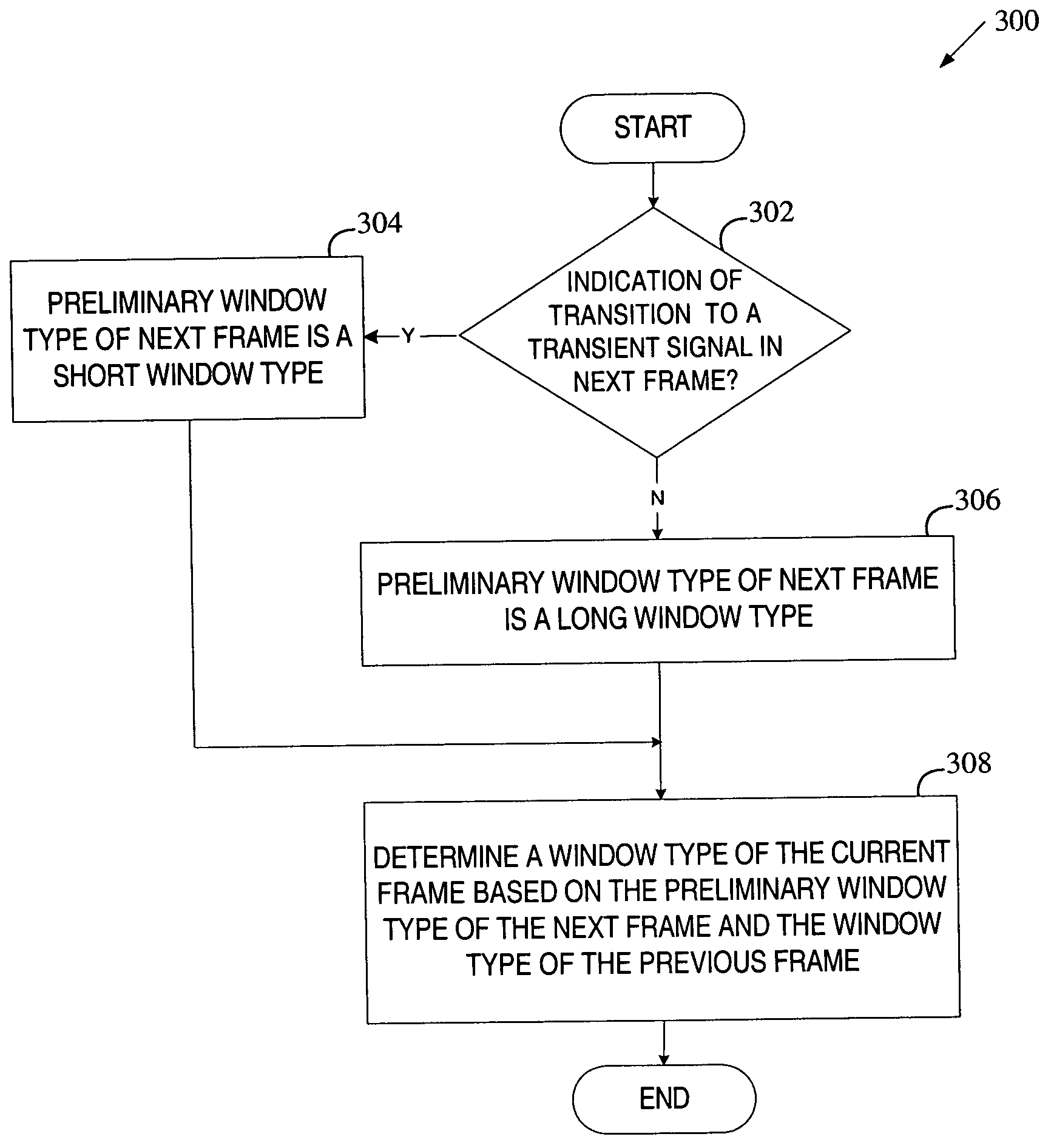
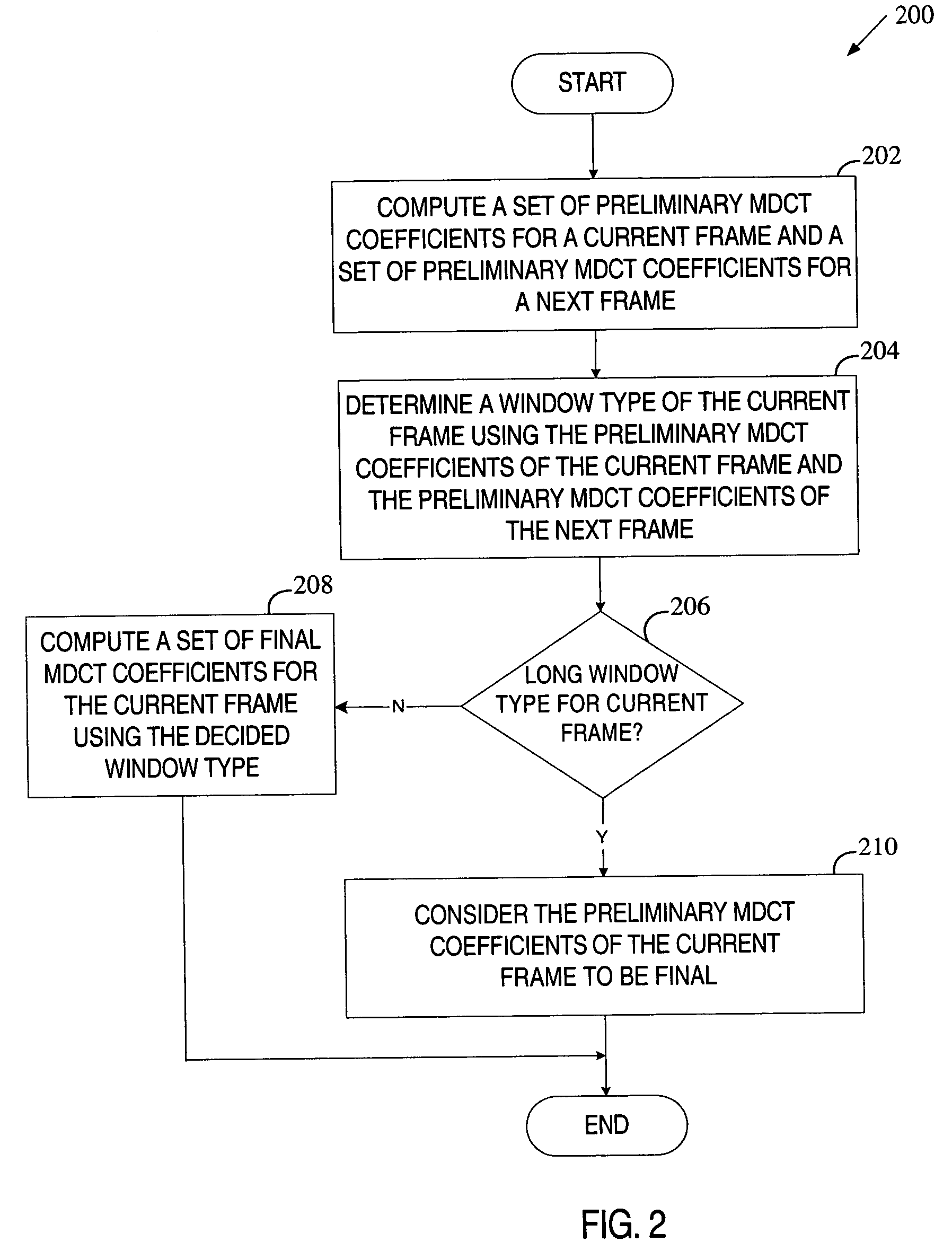
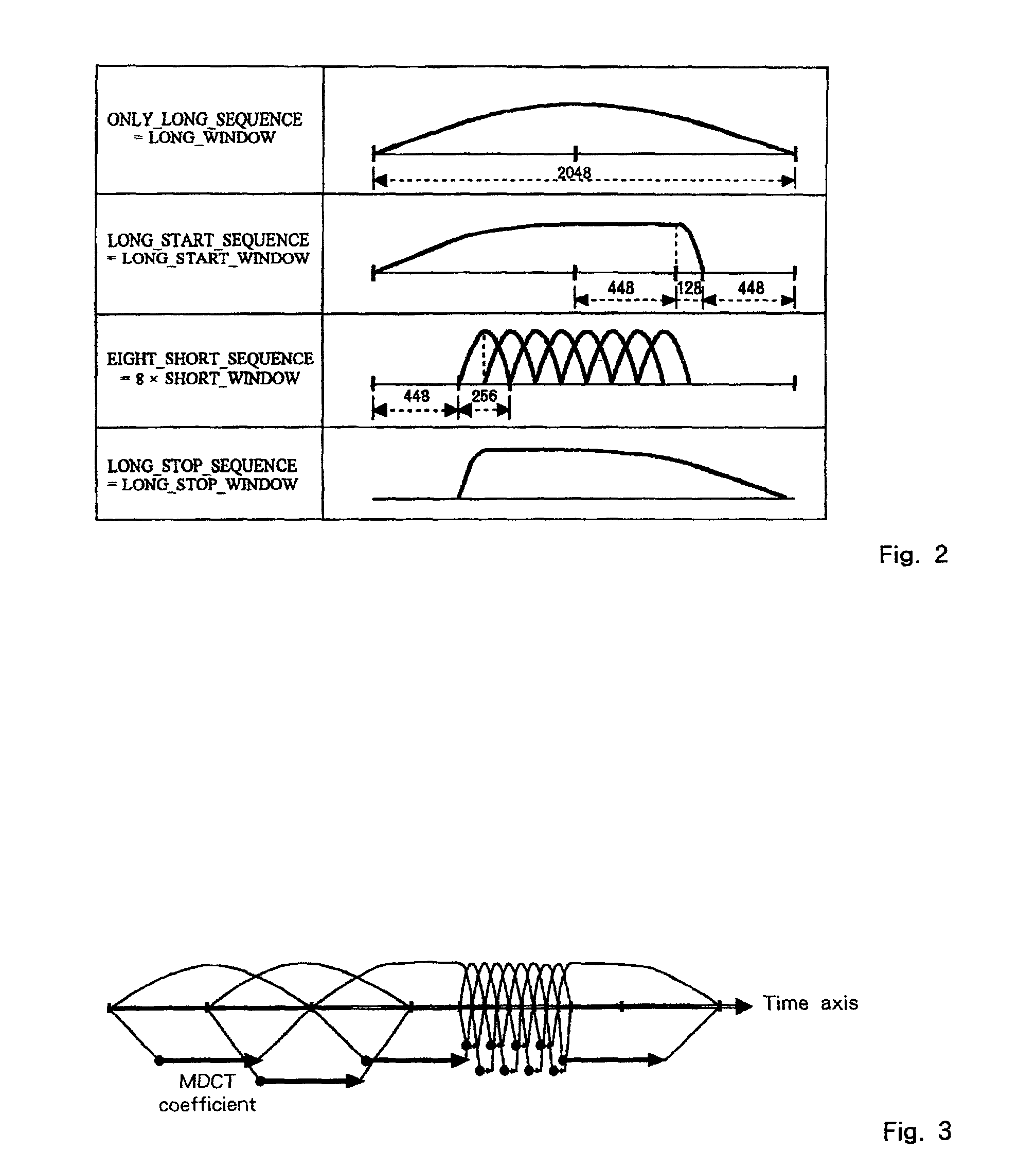
Method of making a window type decision based on MDCT data in audio encoding
ActiveUS20050071402A1Speech analysisComplex mathematical operationsPattern recognitionAudio frequency
Preliminary Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT) coefficients are computed for a current frame of data and a next frame of data using a long window type. The computed preliminary MDCT coefficients of the current and next frames are then used to determine the window type of the current frame. If the determined window type is not the long window type, final MDCT coefficients are computed for the current frame using the determined window type.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
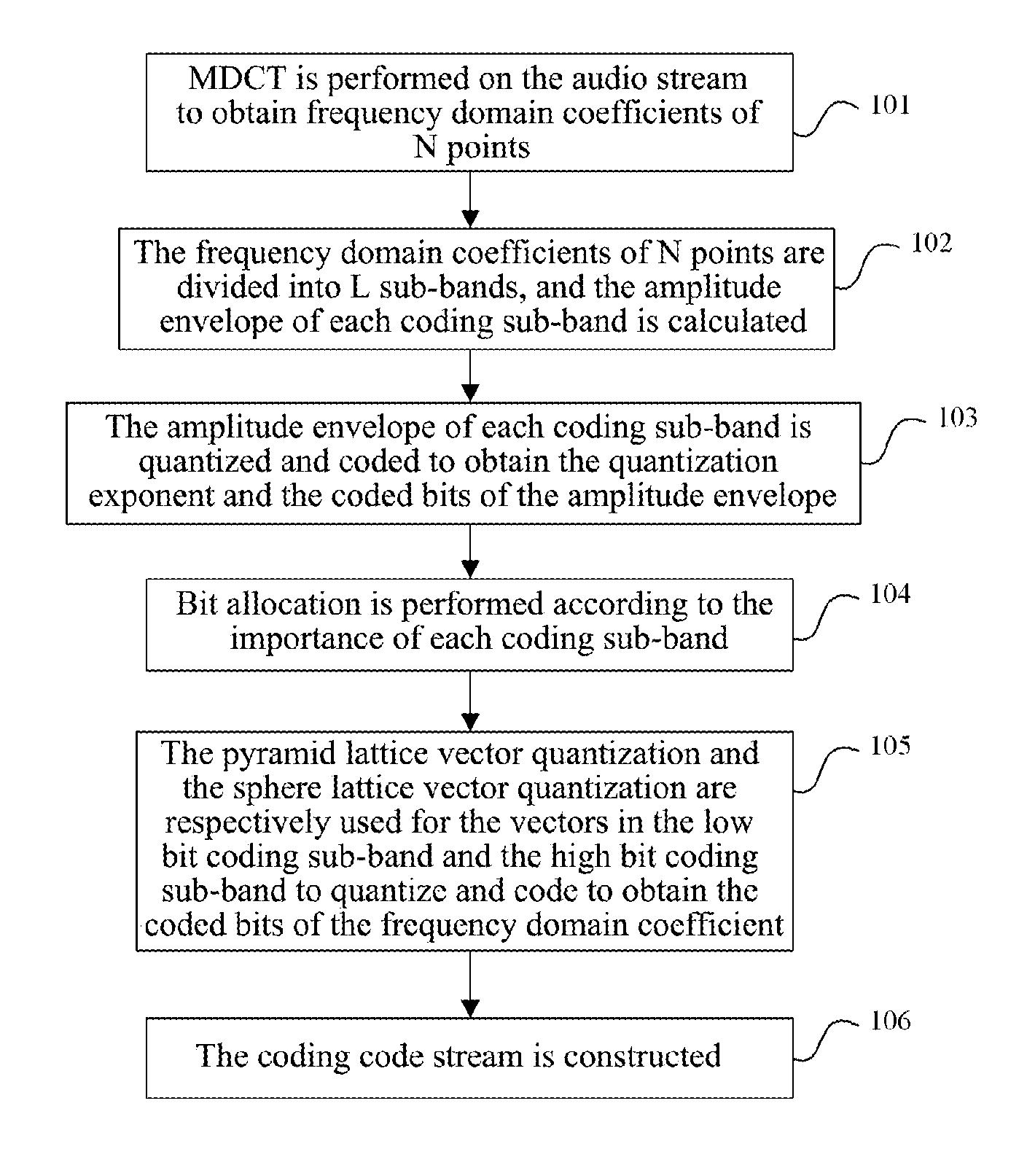
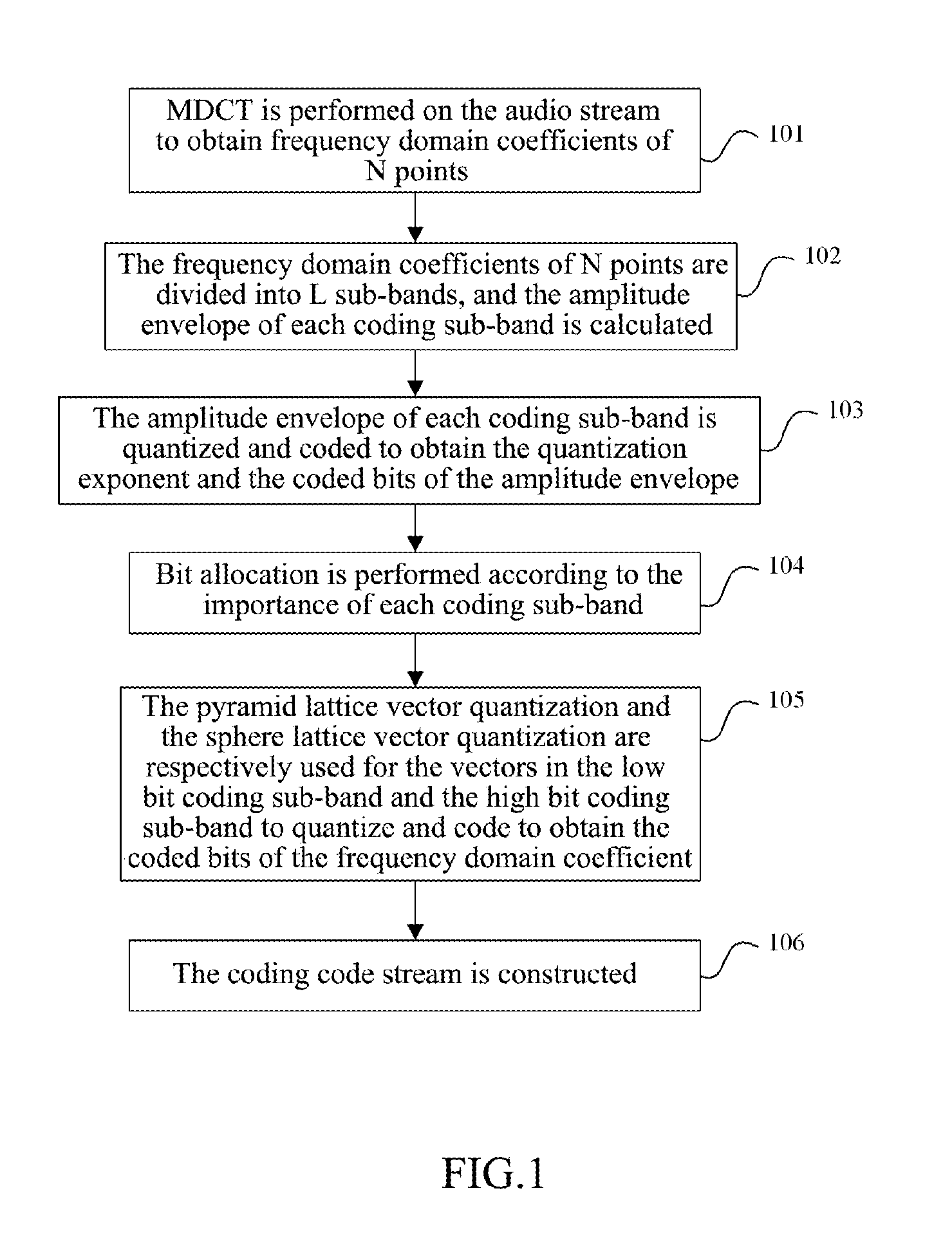
Audio-Encoding/Decoding Method and System of Lattice-Type Vector Quantizing
ActiveUS20120259644A1Increase the number ofDecrease the importance of the coding sub-bandSpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsComputer architecture
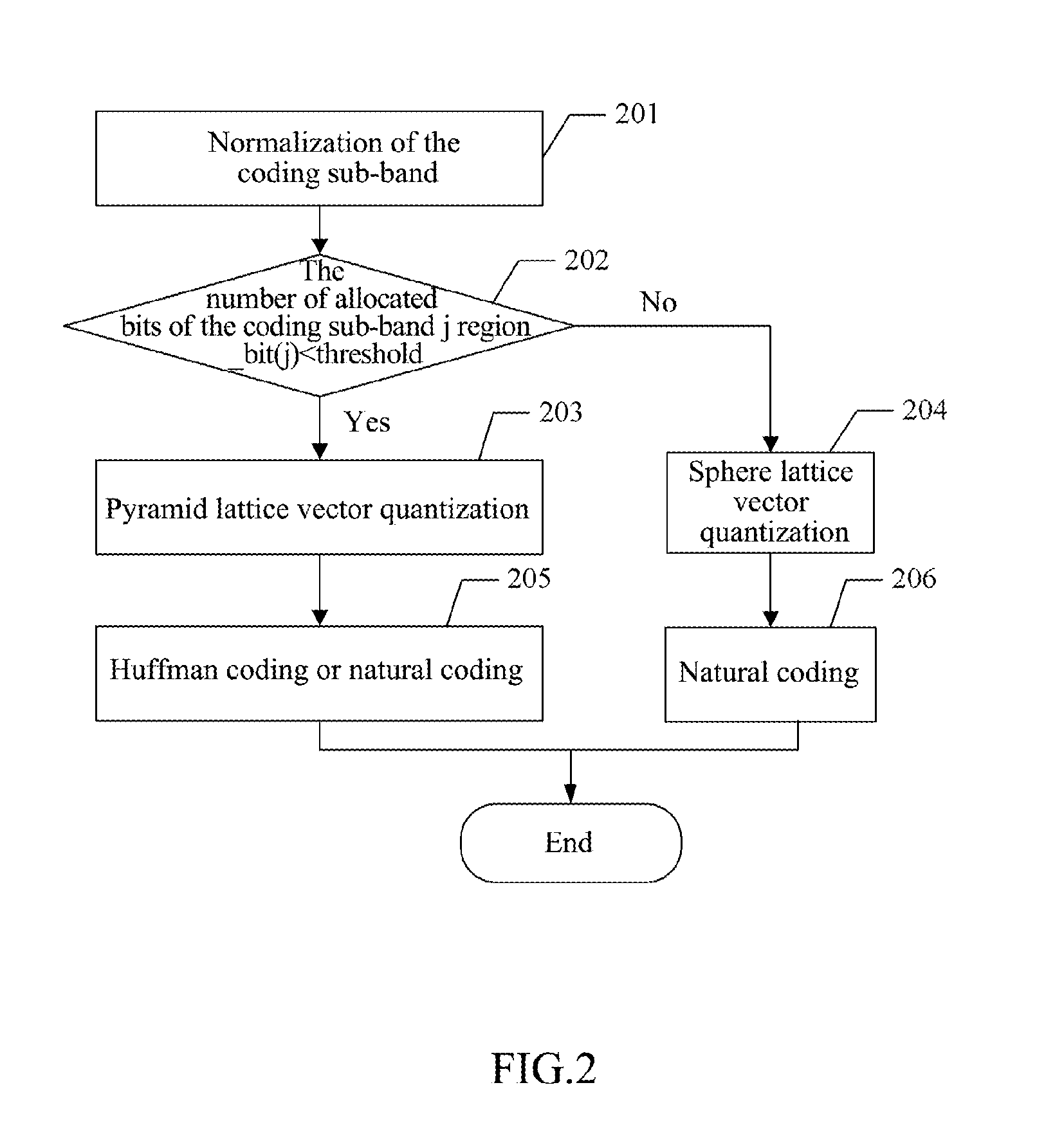
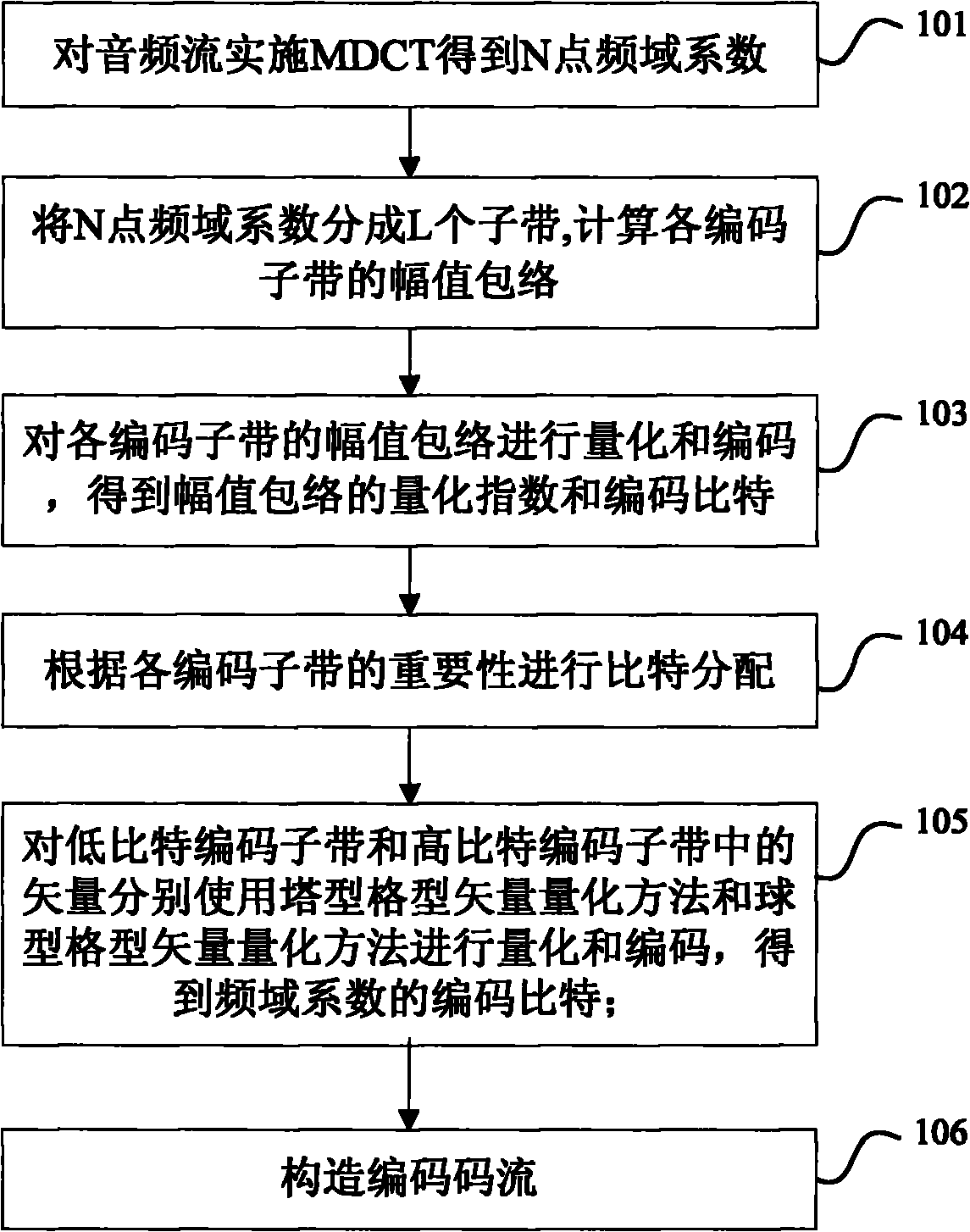
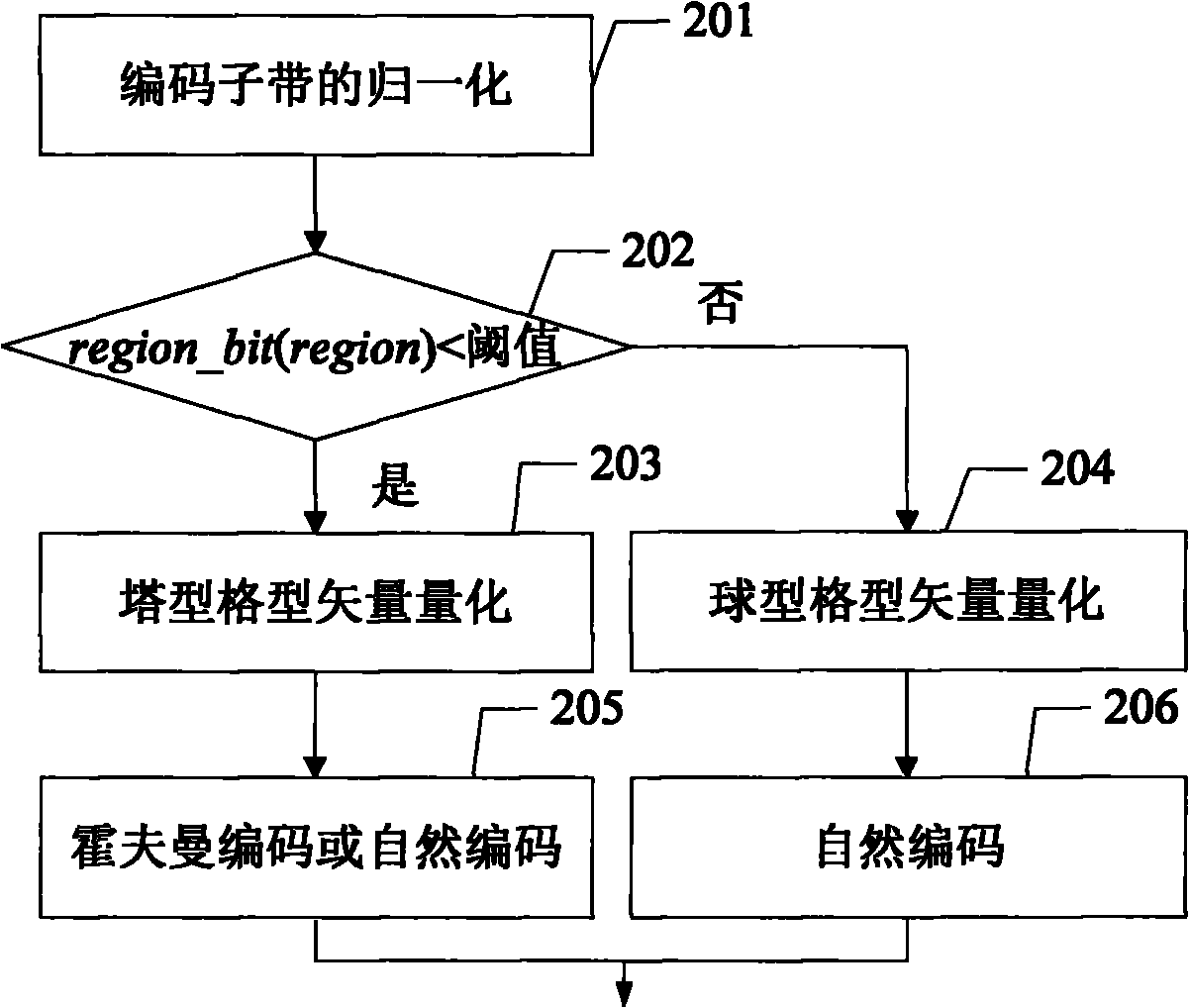
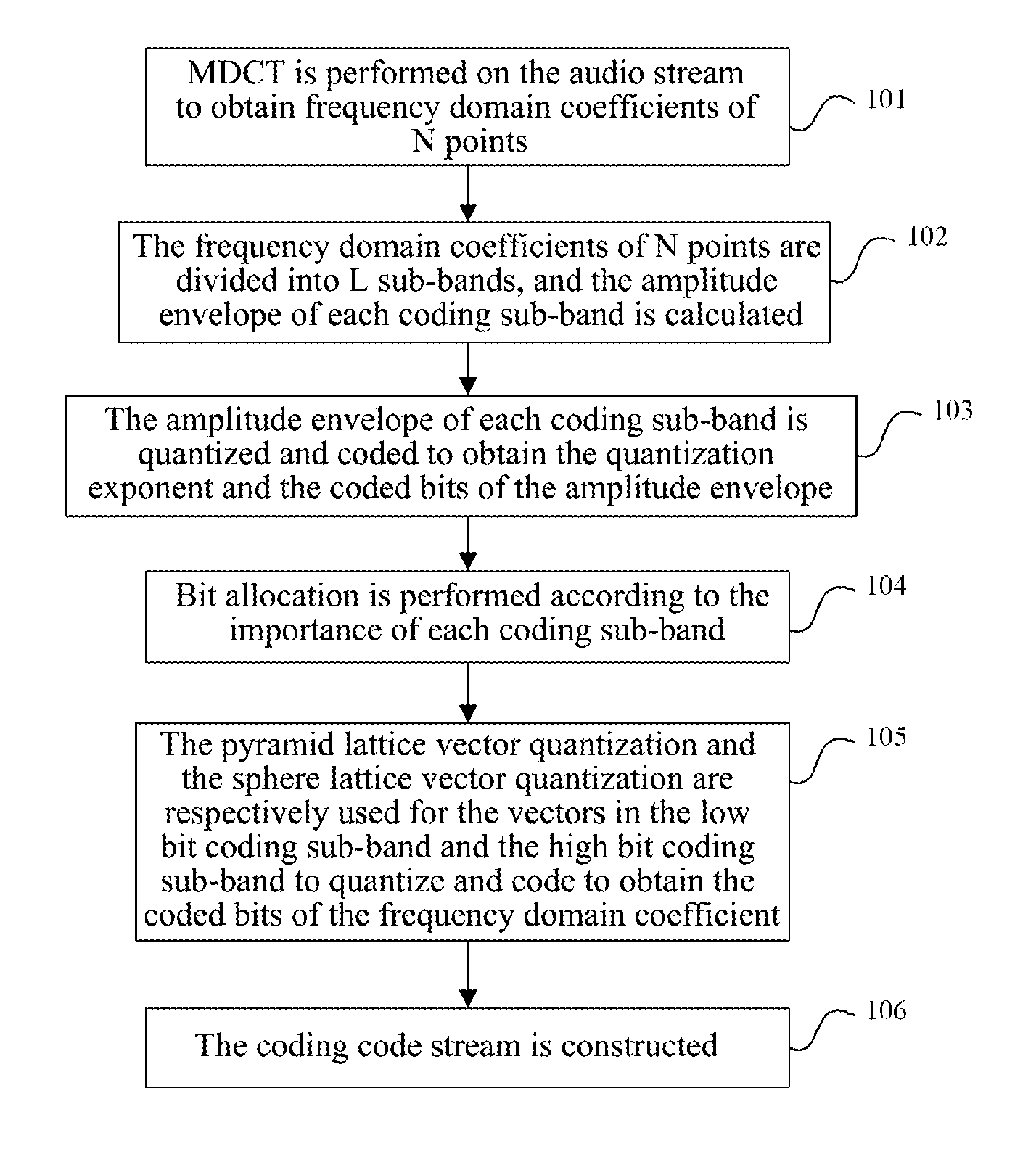
The audio coding method and system of lattice vector quantization is provided in the invention. The method comprises: dividing frequency domain coefficients of an audio signal for which a modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) has been performed into a plurality of coding sub-bands, and quantizing and coding an amplitude envelope value of each coding sub-band to obtain coded bits of amplitude envelopes; performing bit allocation on each coding sub-band, and performing normalization, quantization and coding respectively on vectors in a low bit coding sub-band with pyramid lattice vector quantization and on vectors in a high bit coding sub-band with sphere lattice vector quantization to obtain coded bits of the frequency domain coefficients; multiplexing and packing the coded bits of the amplitude envelope and the coded bits of the frequency domain coefficients of each coding sub-band, then sending them to a decoding side.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Switching between coding schemes
ActiveUS7876966B2Easy to operatePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesBase codeFrequency spectrum
Methods and units are shown for supporting a switching from a first coding scheme to a Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT) based coding scheme calculating a forward or inverse MDCT with a window (h(n)) of a first type for a respective coding frame, which satisfies constraints of perfect reconstruction. To avoid discontinuities during the switching, it is proposed that for a transient frame immediately after a switching, a sequence of windows (h0(n),h1(n),h2(n)) is provided for the forward and the inverse MDCTs. The windows of the window sequence are shorter than windows of the first type. The window sequence splits the spectrum of a respective first coding frame into nearly uncorrelated spectral components when used as basis for forward MDCTs, and the second half of the last window (h2(n)) of the sequence of windows is identical to the second half of a window of the first type.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
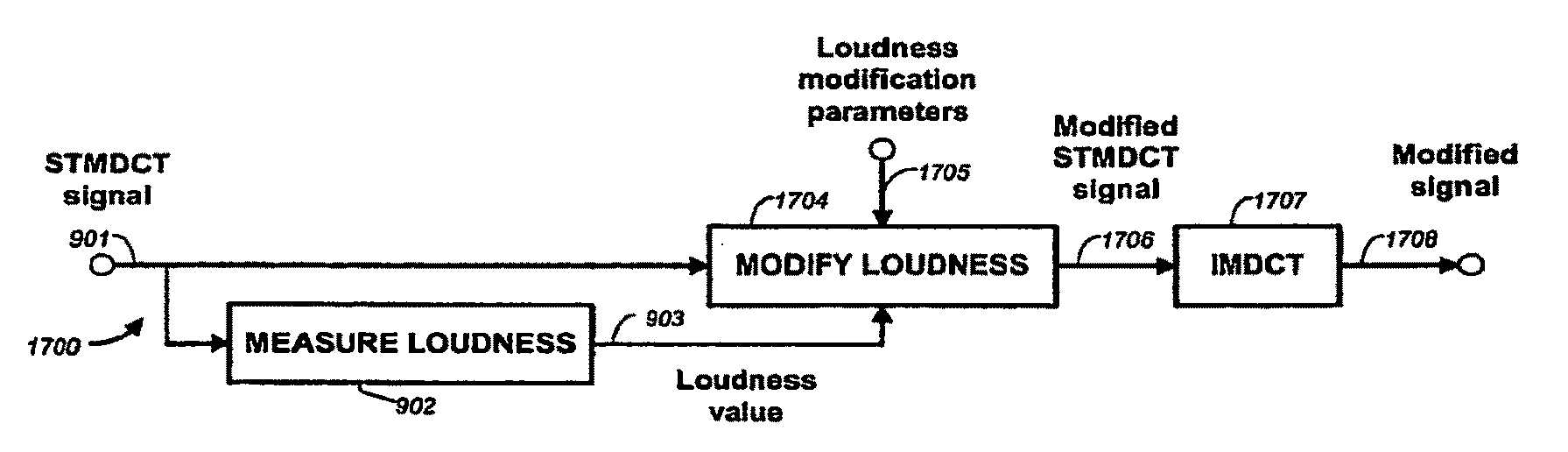
Audio Signal Loudness Measurement and Modification in the MDCT Domain
Processing an audio signal represented by the Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT) of a time-sampled real signal is disclosed in which the loudness of the transformed audio signal is measured, and at least in part in response to the measuring, the loudness of the transformed audio signal is modified. When gain modifying more than one frequency band, the variation or variations in gain from frequency band to frequency band, is smooth. The loudness measurement employs a smoothing time constant commensurate with the integration time of human loudness perception or slower.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and system for encoding and decoding lattice vector quantization audio
ActiveCN102081926AImprove efficiencyReduce complexitySpeech analysisCode conversionLattice vector quantizationVoice source
The invention provides a method for encoding and decoding lattice vector quantization audio. The method comprises the following steps: dividing a frequency domain coefficient of an audio signal which is subjected to modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) conversion into a plurality of encoding sub-bands, and quantizing and encoding amplitude enveloping value of each encoding sub-band to acquire encoding bit of amplitude envelope; performing bit distribution on each encoding sub-band, normalizing, quantizing and encoding vectors in low-bit encoding sub-bands and high-bit encoding sub-bands by using a tower lattice vector quantizing method and a spherical lattice vector quantizing method to acquire encoding bit of the frequency domain coefficient respectively; and complexly packaging theencoding bit of the amplitude envelope and the encoding bit of the frequency domain coefficient of each encoding sub-band, and transmitting the package to a decoding end. The method and the system for encoding and decoding the lattice vector quantizing audio can acquire better voice source encoding effect.
Owner:ZTE CORP
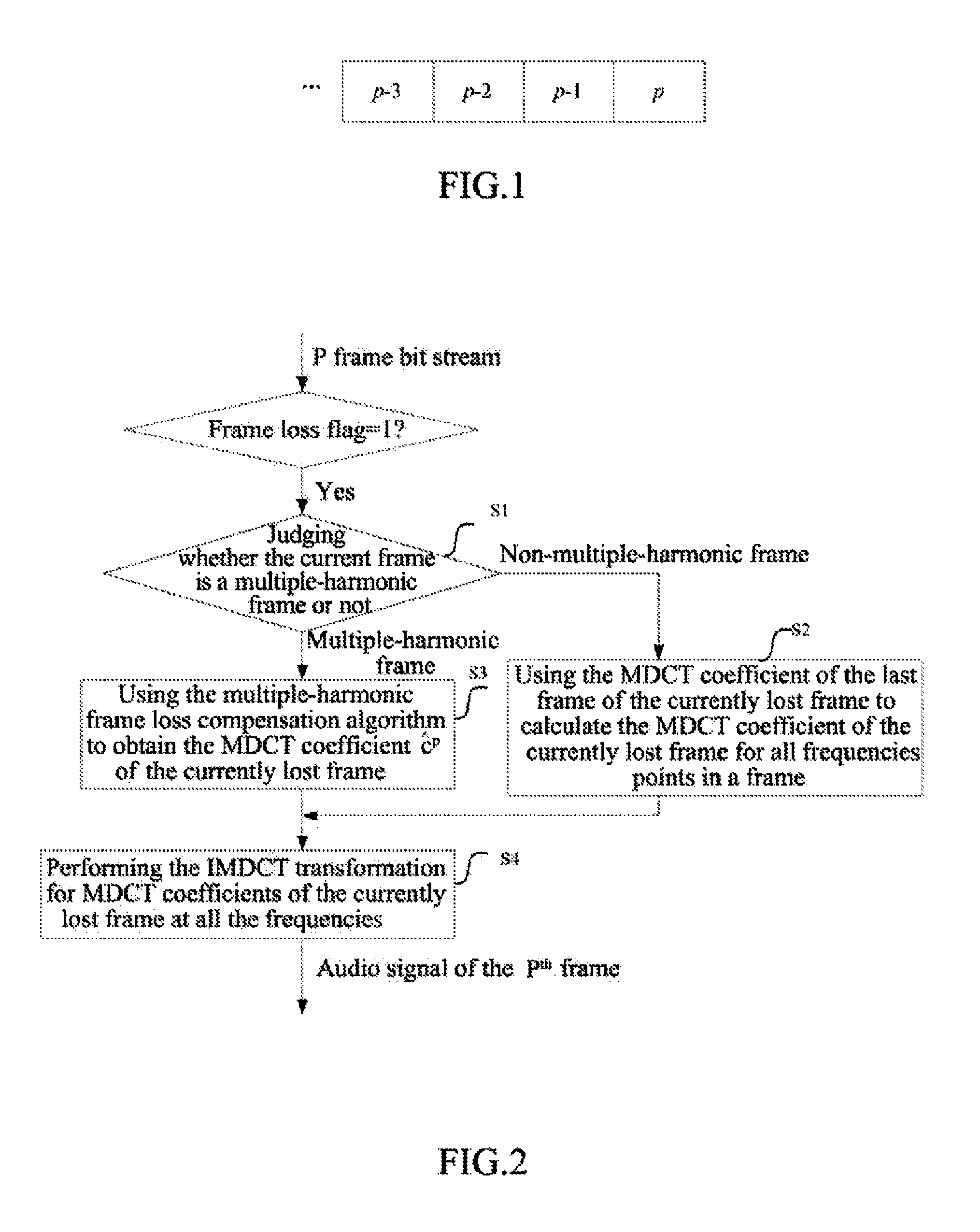
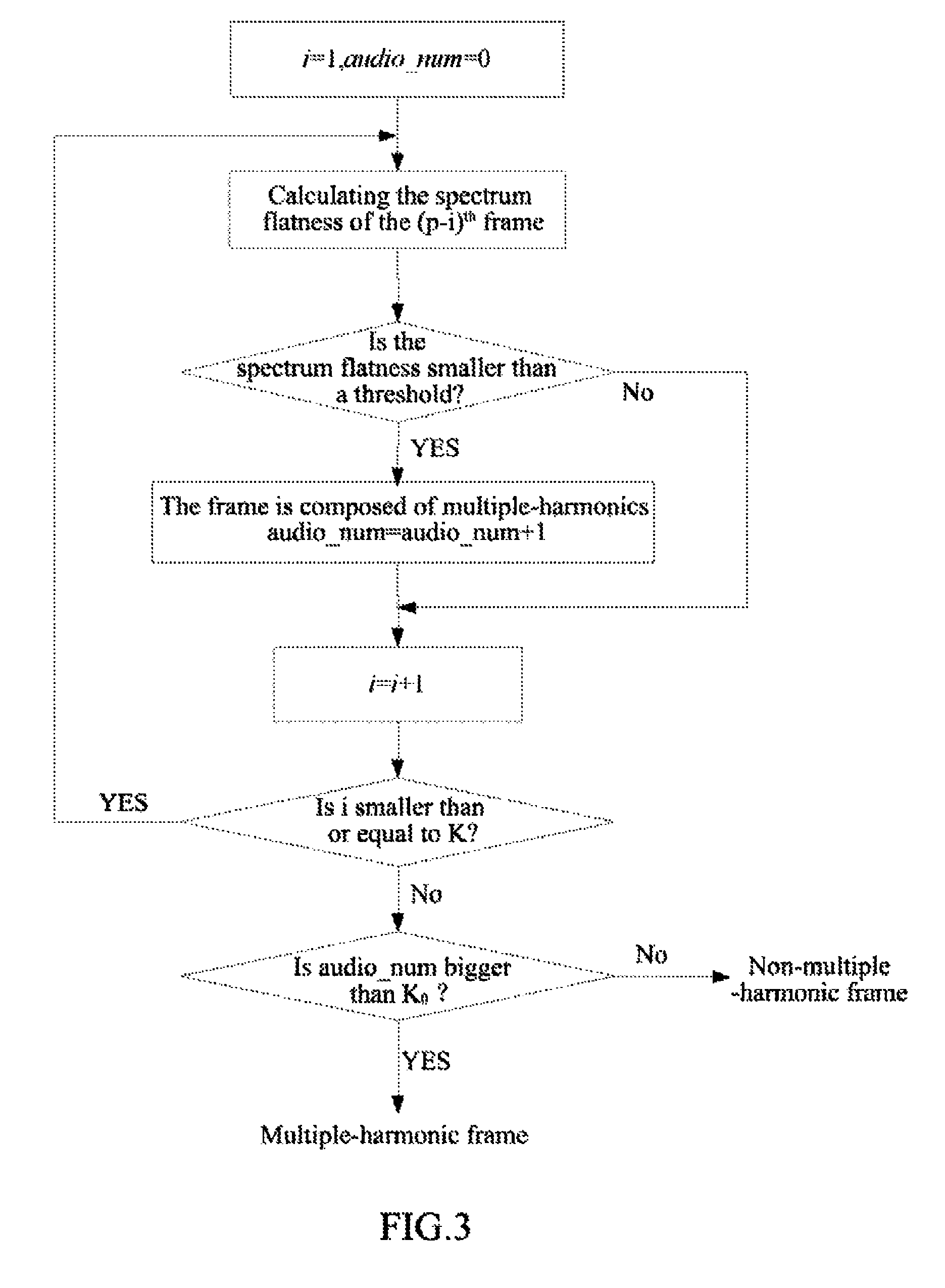
Compensator and Compensation Method for Audio Frame Loss in Modified Discrete Cosine Transform Domain
ActiveUS20120109659A1Small amount of calculationSmall volume of memory spaceSpeech analysisTransmissionTime domainComputer science
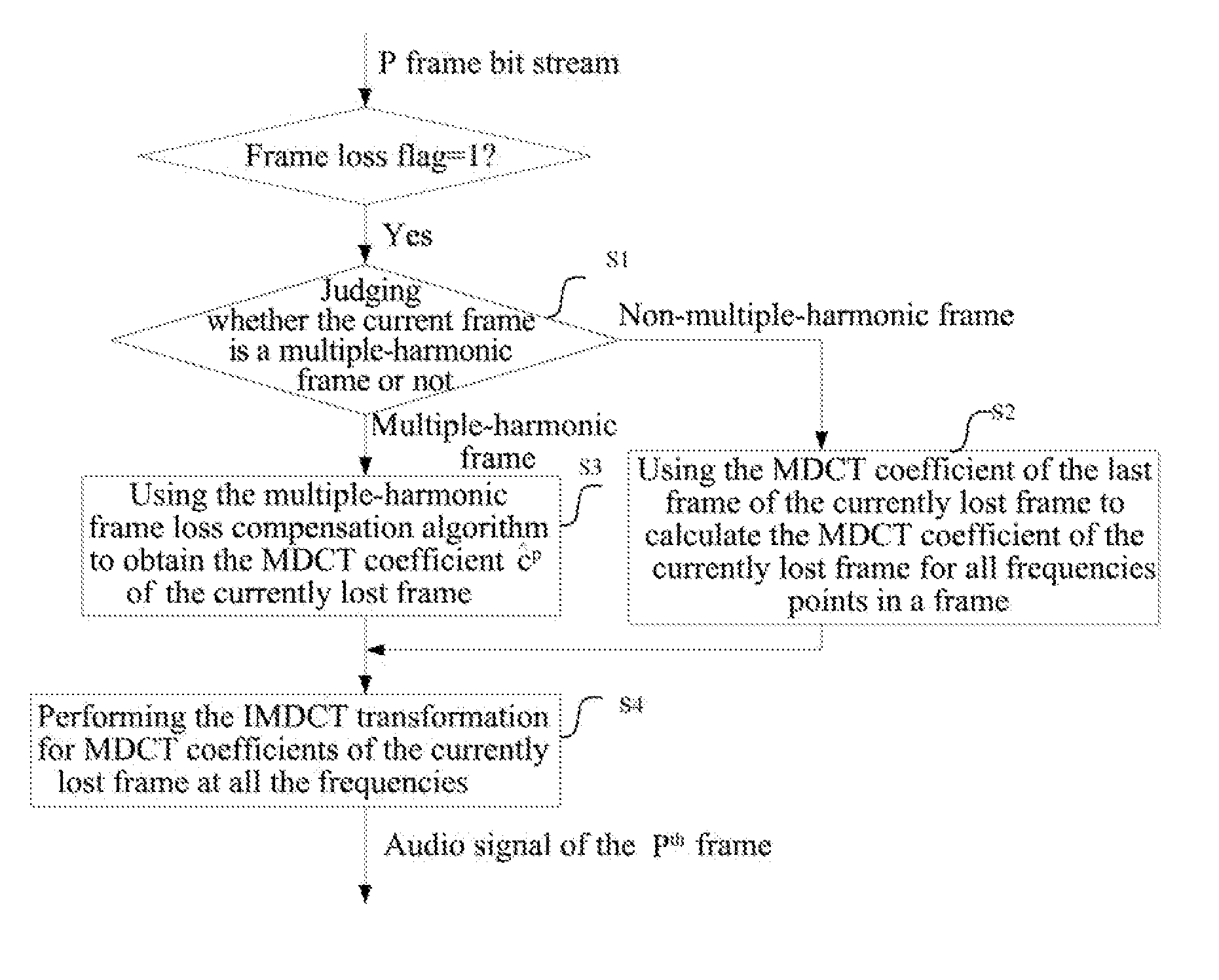
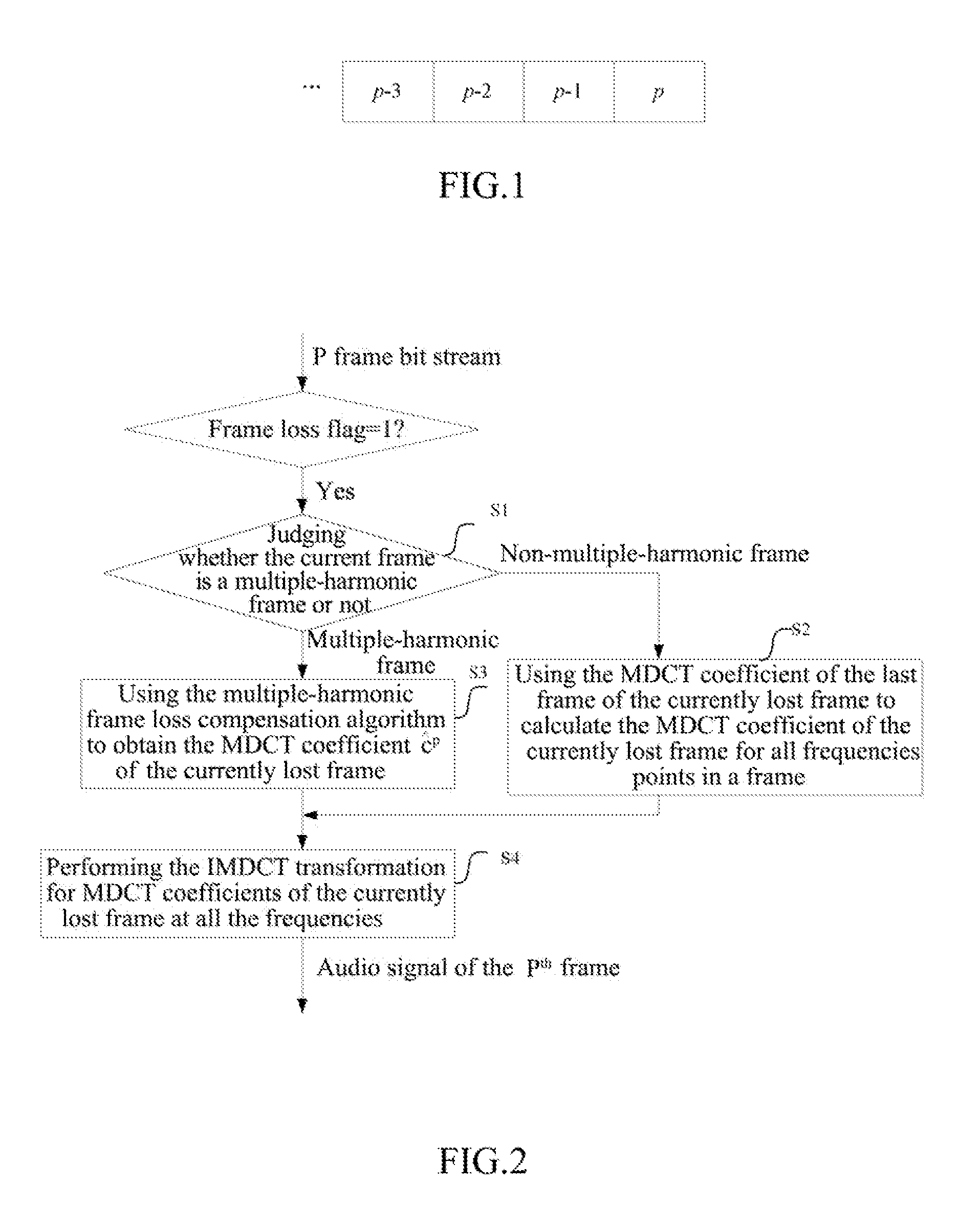
The invention provides a compensation method for audio frame loss in a MDCT domain, the method comprising: when a frame currently lost is a Pth frame, obtaining a set of frequencies to be predicted, and for each frequency in the set, using phases and amplitudes of a plurality of frames before a (P−1)th frame in a MDCT-MDST domain to predict a phase and an amplitude of the Pth frame, and using the predicted phase and amplitude to obtain a MDCT coefficient of the Pth frame at each corresponding frequency; for a frequency outside the set, using MDCT coefficients of a plurality of frames before the Pth frame to calculate a MDCT coefficient value of the Pth frame at the frequency; performing an IMDCT for the MDCT coefficients of the Pth frame to obtain a time domain signal of the Pth frame.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method of and apparatus to restore audio data
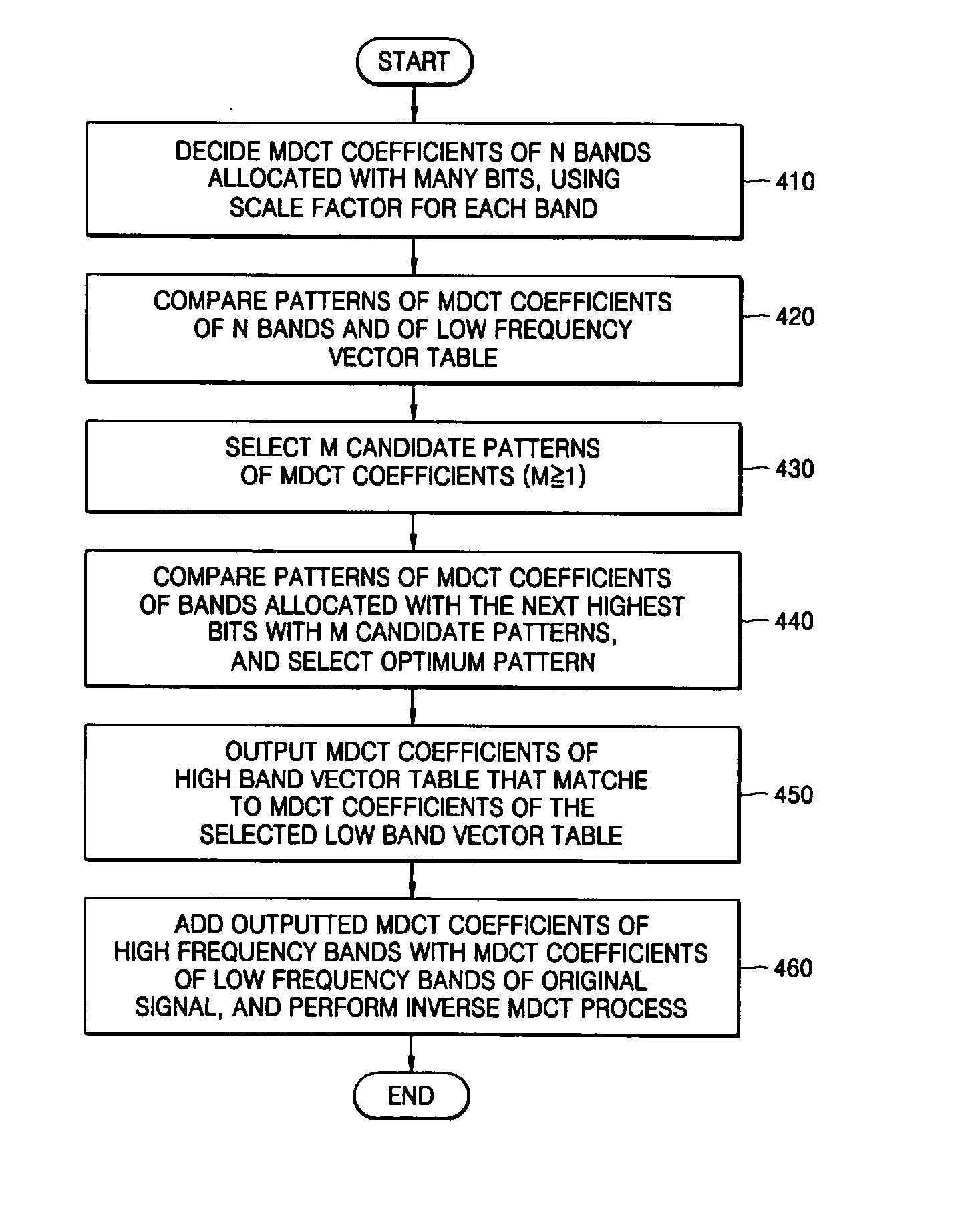
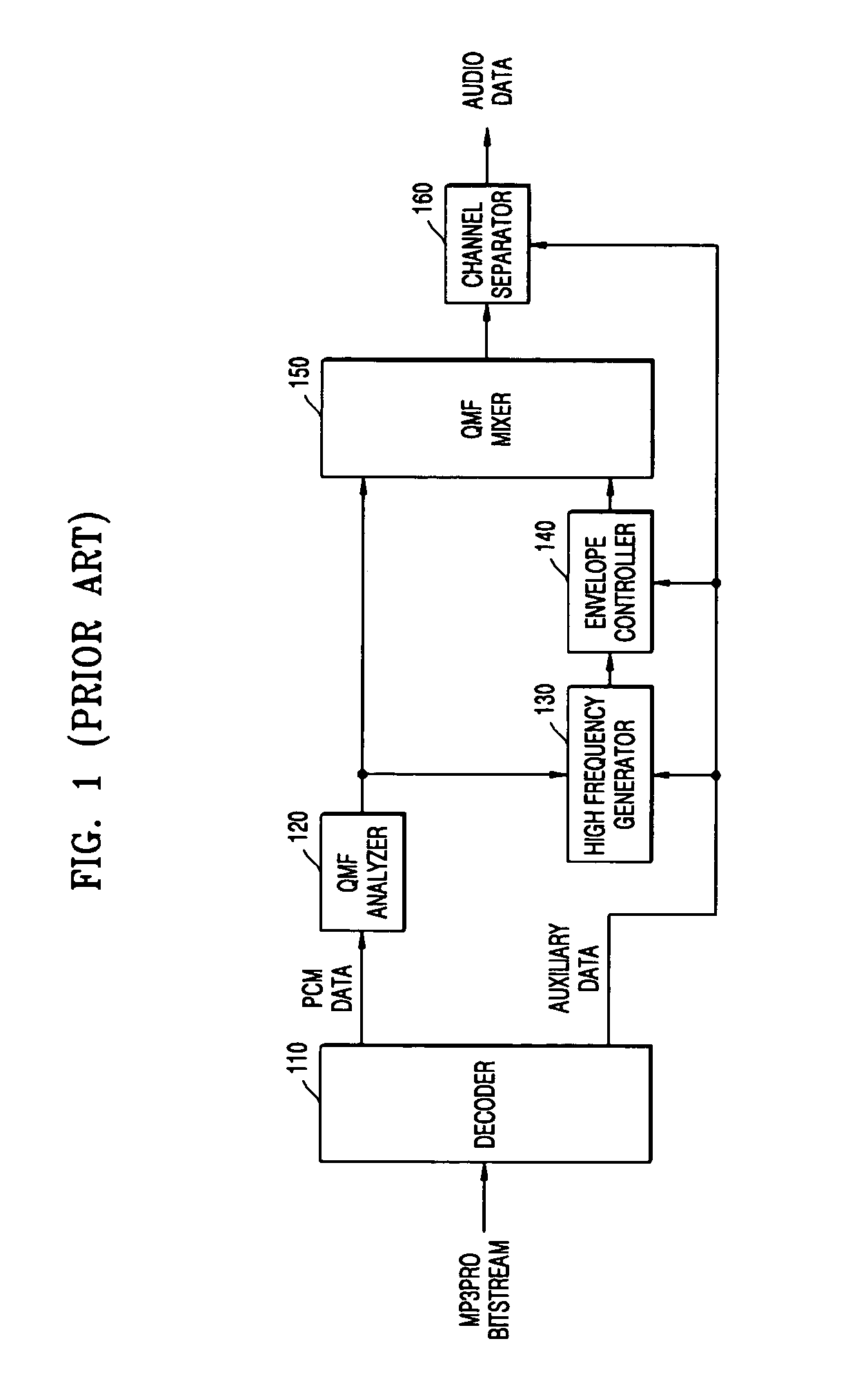
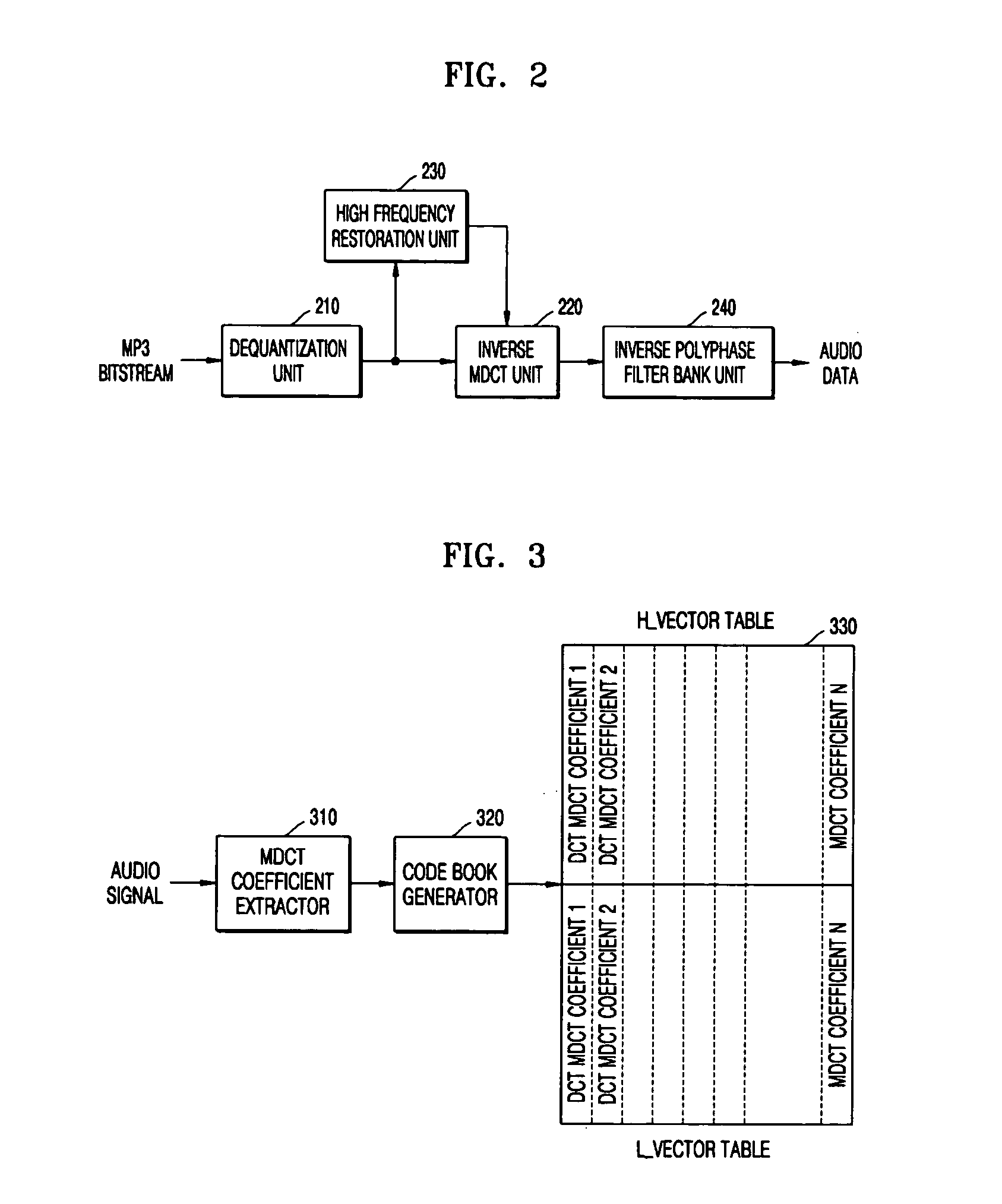
A method of and an apparatus to restore high frequency of a moving picture experts group audio layer 3 (MP3) audio signal within a decoder. The method includes: setting modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) coefficients of low bands and high bands of an audio signal, based on scale factor information of each band; extracting MDCT coefficients of low bands per band based on scale factors of each band after dequantizing inputted compressed audio bitstream; selecting the MDCT coefficients of the set low bands that corresponds to patterns of MDCT coefficients of low bands of the inputted compressed audio bitstream, and selecting the MDCT coefficients of the high bands that matches with the MDCT coefficients of the selected low bands; and performing an inverse MDCT by adding the MDCT coefficients of the selected high bands with the MDCT coefficients of the low bands.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
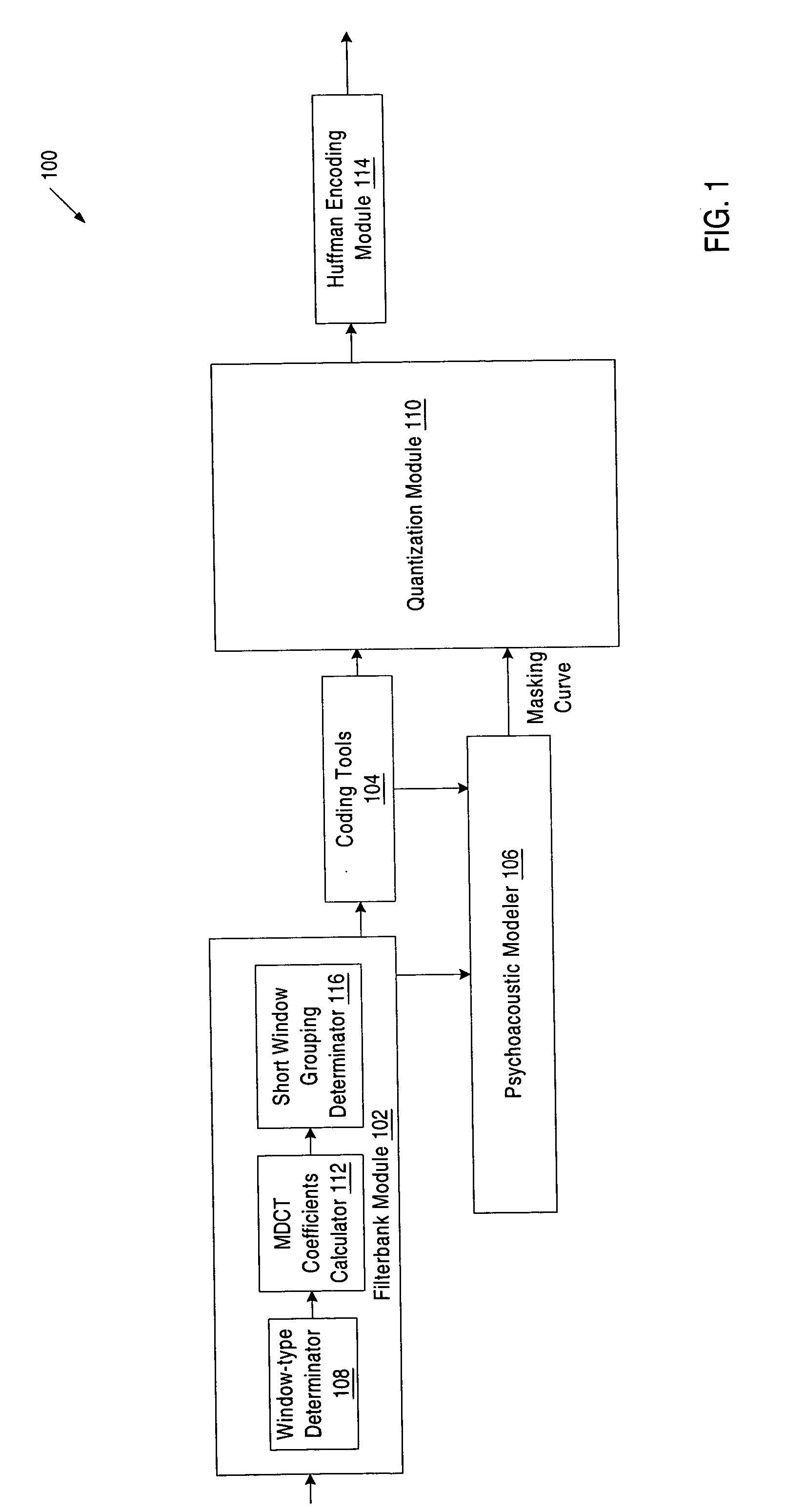
Audio encoding apparatus and audio encoding method
InactiveUS20130030796A1Improve sound qualitySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
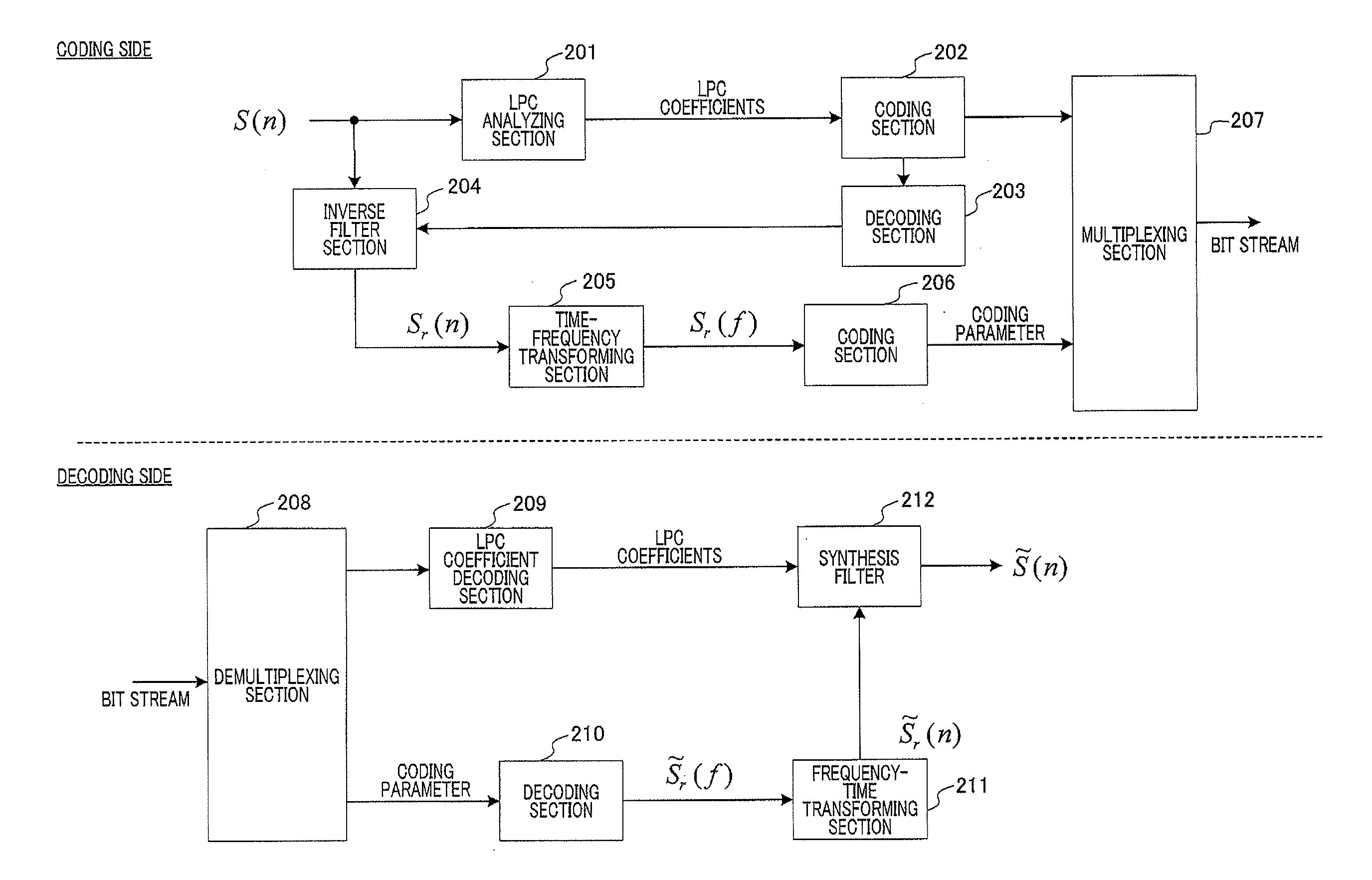
An audio encoding apparatus that allows a decoded signal exhibiting an excellent sound quality to be obtained on a decoding side. In the audio encoding apparatus (1000A), a time-frequency transform unit (1001) uses a time-frequency transform, such as a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) or a modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT), to transform a time domain signal (S(n)) to a frequency domain signal (spectrum factor) (S(f)). A psychoacoustic model analyzing unit (1002) performs a psychoacoustic model analysis of the frequency domain signal (S(f)), thereby obtaining a masking curve. An acoustic sense weighting unit (1003) estimates, based on the masking curve, an importance degree of acoustic sense, and determines and applies the weighting factors of respective spectrum factors to the respective spectrum factors. An encoding unit (1004) encodes the frequency domain signal (S(f)) as weighted in terms of the acoustic sense. A multiplexing unit (1005) multiplexes and transmits the encoded parameters.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Voice frequency signal frame loss compensation method and device
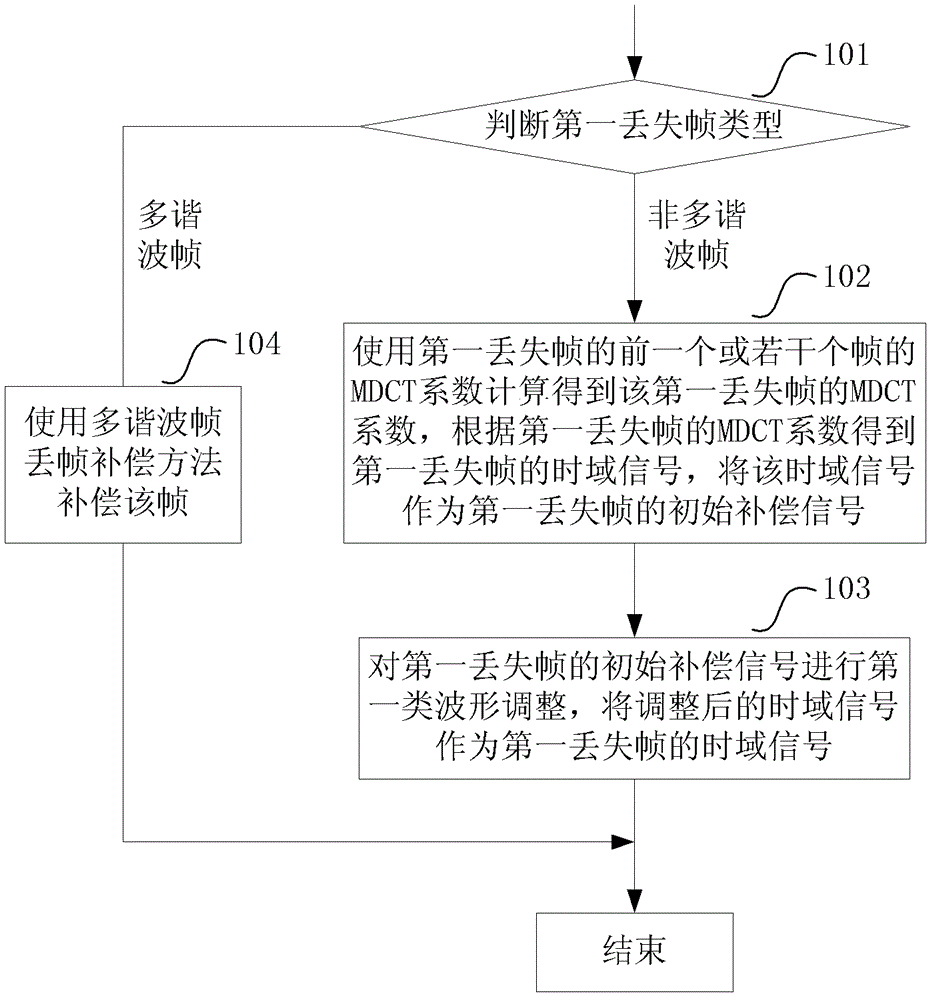
ActiveCN103065636AGuaranteed Compensation QualityImprove Compensation QualitySpeech analysisTime domainCompensation effect
The invention discloses a voice frequency signal frame loss compensation method and a voice frequency signal frame loss compensation device so as to obtain better compensation effects and at the same time guarantee zero time delay and low complexity. The method comprises the steps that when a following first frame is lost after frames are received correctly, the frame type of the first lost frame is judged, and when the first lost frame is a non-multiple-harmonic frame, a modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) coefficient of the first lost frame is worked out by using an MDCT coefficient of a prior frame or MDCT coefficients of a plurality of frames prior to the first lost frame; an original compensation signal of the first lost frame is obtained according to the MDCT coefficient of the first lost frame; the original compensation signal of the first lost frame undergoes a first type wave form adjustment, and a time domain signal obtained after the adjustment is used as the time domain signal for the first lost frame. The voice frequency signal frame loss compensation device comprises a frame type judging module, an MDCT coefficient obtaining module, an original compensation signal obtaining module and an adjustment module. Compared with the prior art, the voice frequency signal frame loss compensation method and the voice frequency signal frame loss compensation device have the advantages of being free of delay, small in computing quantity and storage quantity, easy to realize, good in compensation effect and the like.
Owner:ZTE CORP
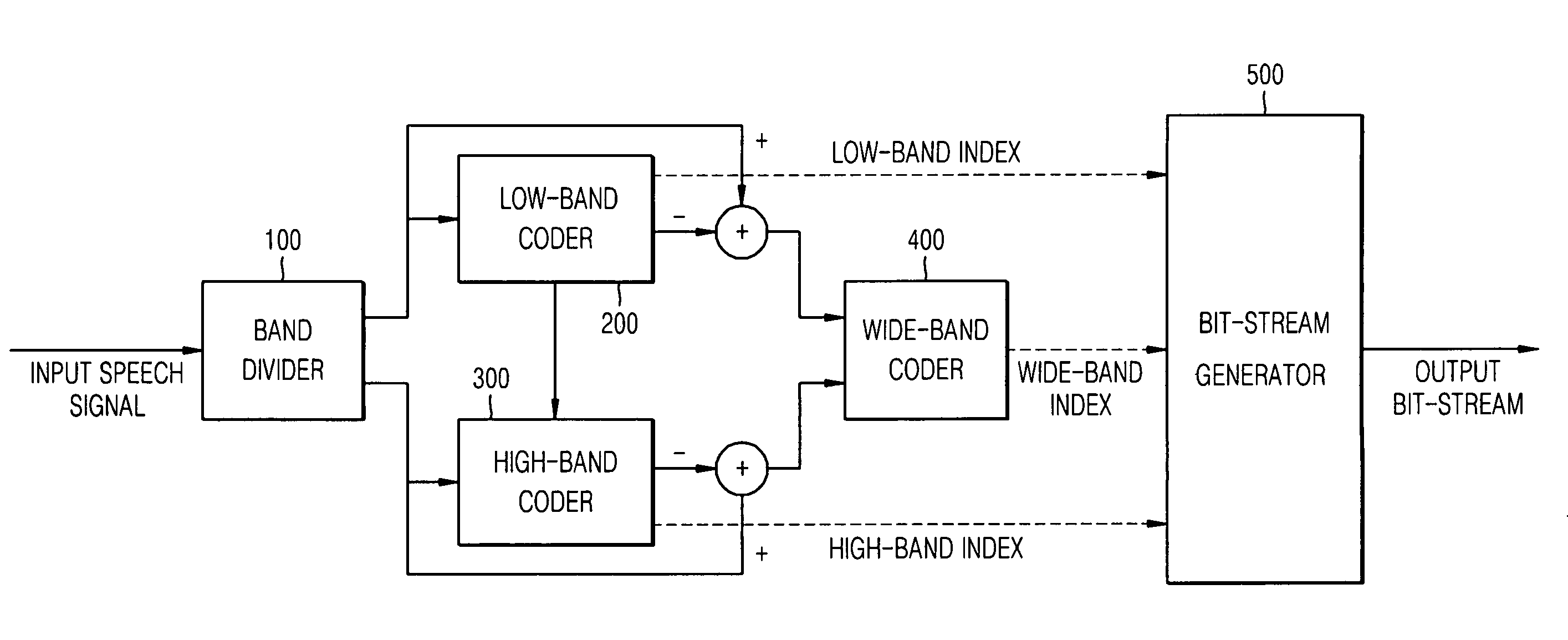
Speech coding apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080140393A1Reduce complexityMaintain consistencySpeech analysisCode-excited linear predictionSpeech code
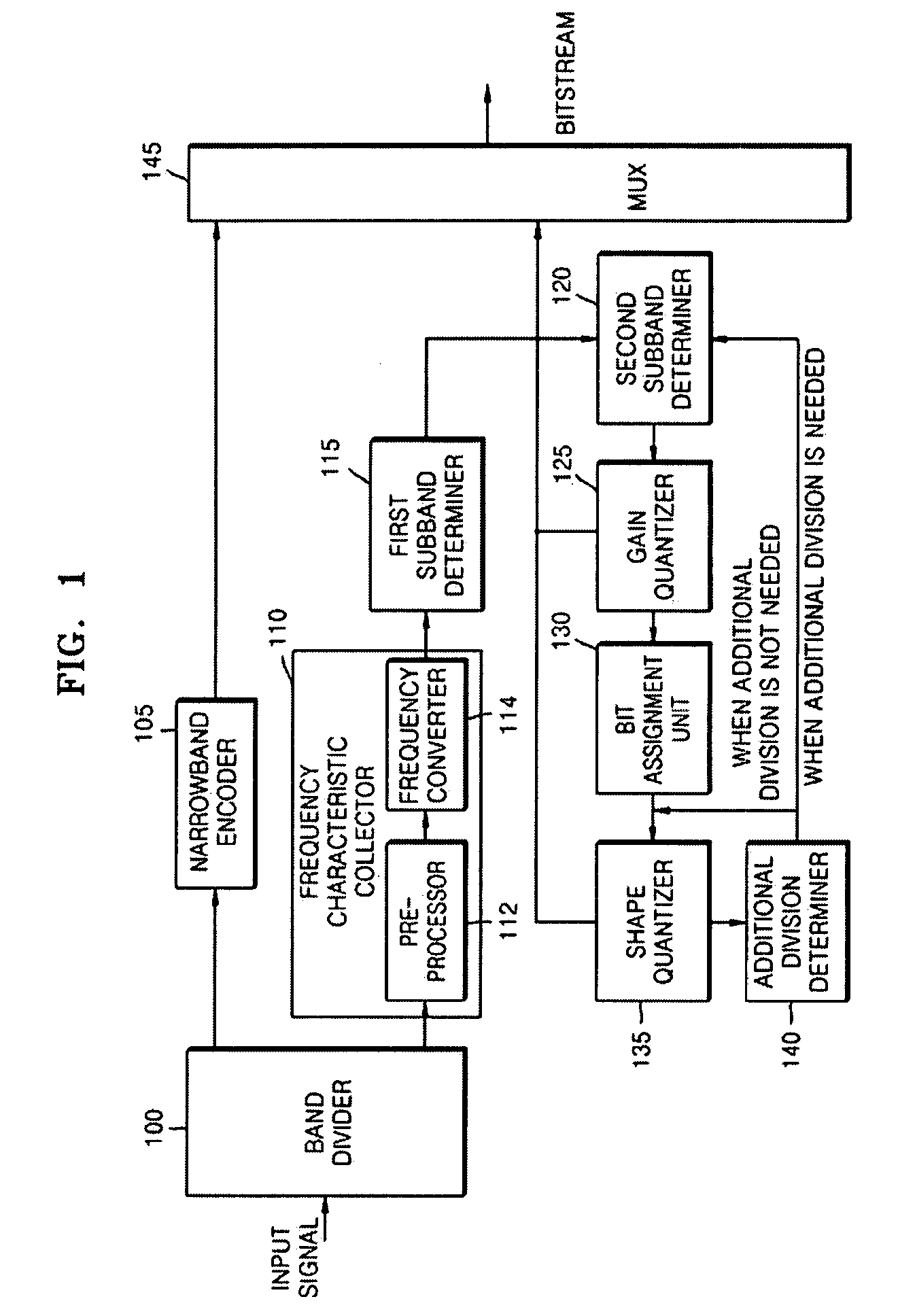
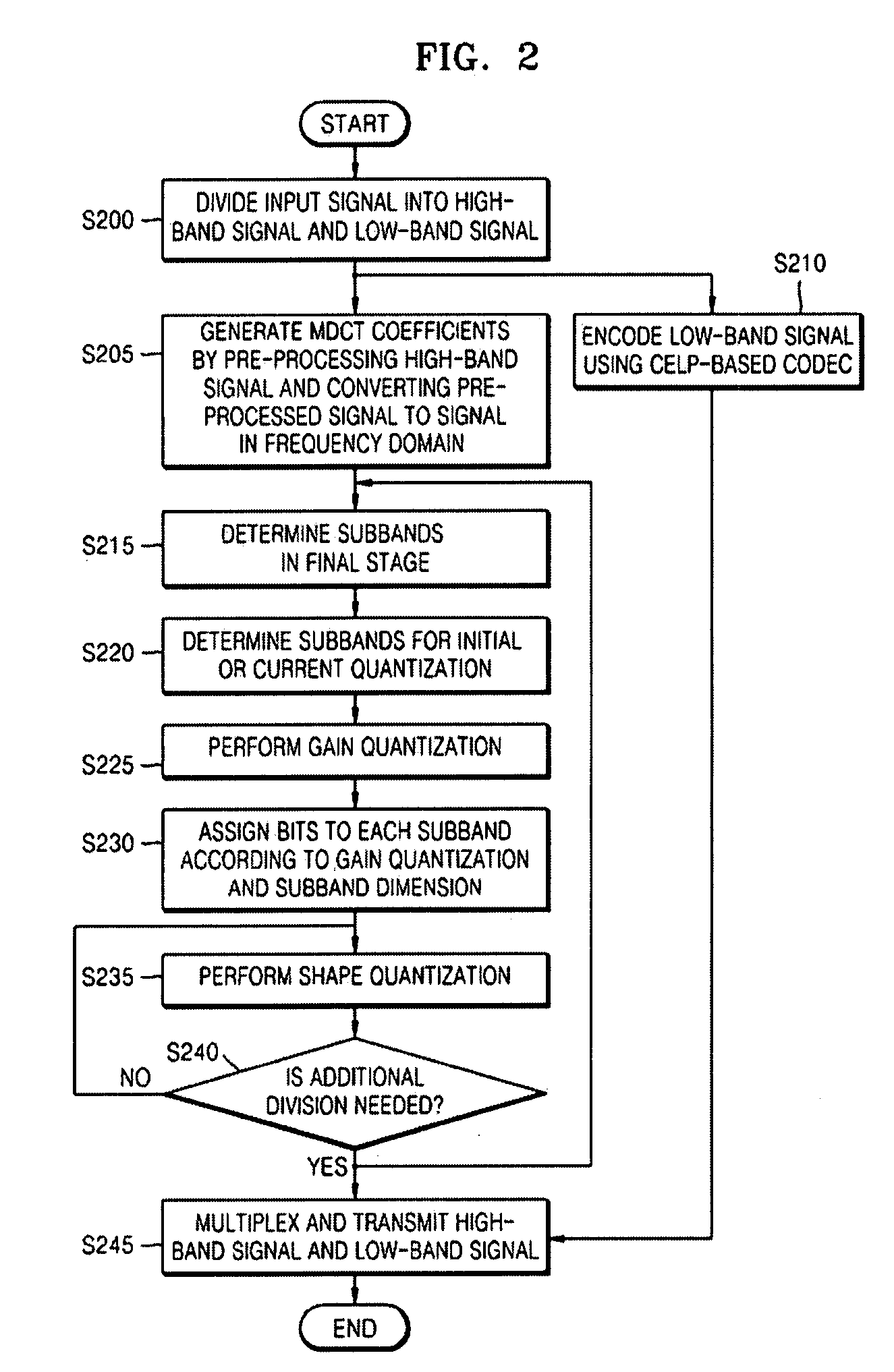
Provided is a speech coding apparatus and method. A band divider divides an input signal into a high-band signal and a low-band signal, a narrowband encoder encodes the low-band signal using a Code Excited Linear Prediction (CELP)-based narrowband speech codec, a frequency characteristic collector converts the high-band signal to a signal in a frequency domain and obtains Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT) coefficients, a subband determiner determines subbands in a final stage based on the MDCT coefficients and determines subbands for quantization based on the subbands in a final stage, a gain quantizer performs gain quantization of the subbands, a bit assignment unit assigns bits to the subbands according to the magnitude of the gain quantization, and a shape quantizer performs shape quantization of the subbands in an algebraic method. Accordingly, algorithm consistency can be maintained and a complexity can be reduced by extending a bandwidth with a small number of bits in a speech codec.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
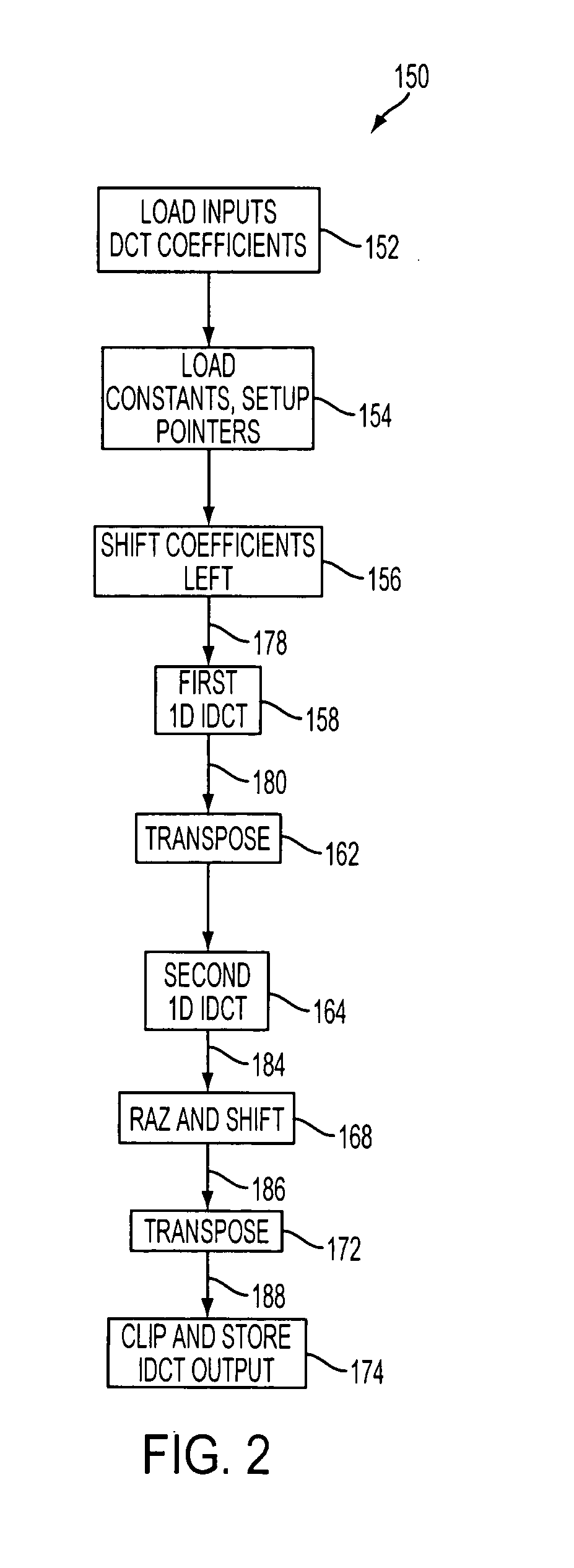
Implementation of an inverse discrete cosine transform using single instruction multiple data instructions
Compressed data are decompressed using an inverse discrete cosine transform (IDCT). A first one directional (1D) IDCT is performed resulting in a plurality of first 1D IDCT coefficients followed by a second 1D IDCT resulting in a plurality of second 1D IDCT coefficients. In performing the first 1D IDCT and the second 1D IDCT a first plurality of intermediate butterfly computations are performed which include performing a plurality of intermediate multiplications resulting in a plurality of initial products and performing a plurality of intermediate additions resulting in intermediate product which are maintained at no more than 16-bits utilizing a round near positive (RNP) rounding scheme. Following the second 1D IDCT a rounding and shifting of the plurality of second 1D IDCT coefficients is performed utilizing a round away from zero (RAZ) rounding scheme resulting in a plurality of output coefficients which comply with the IEEE 1180 standard.
Owner:HITACHI AMERICA
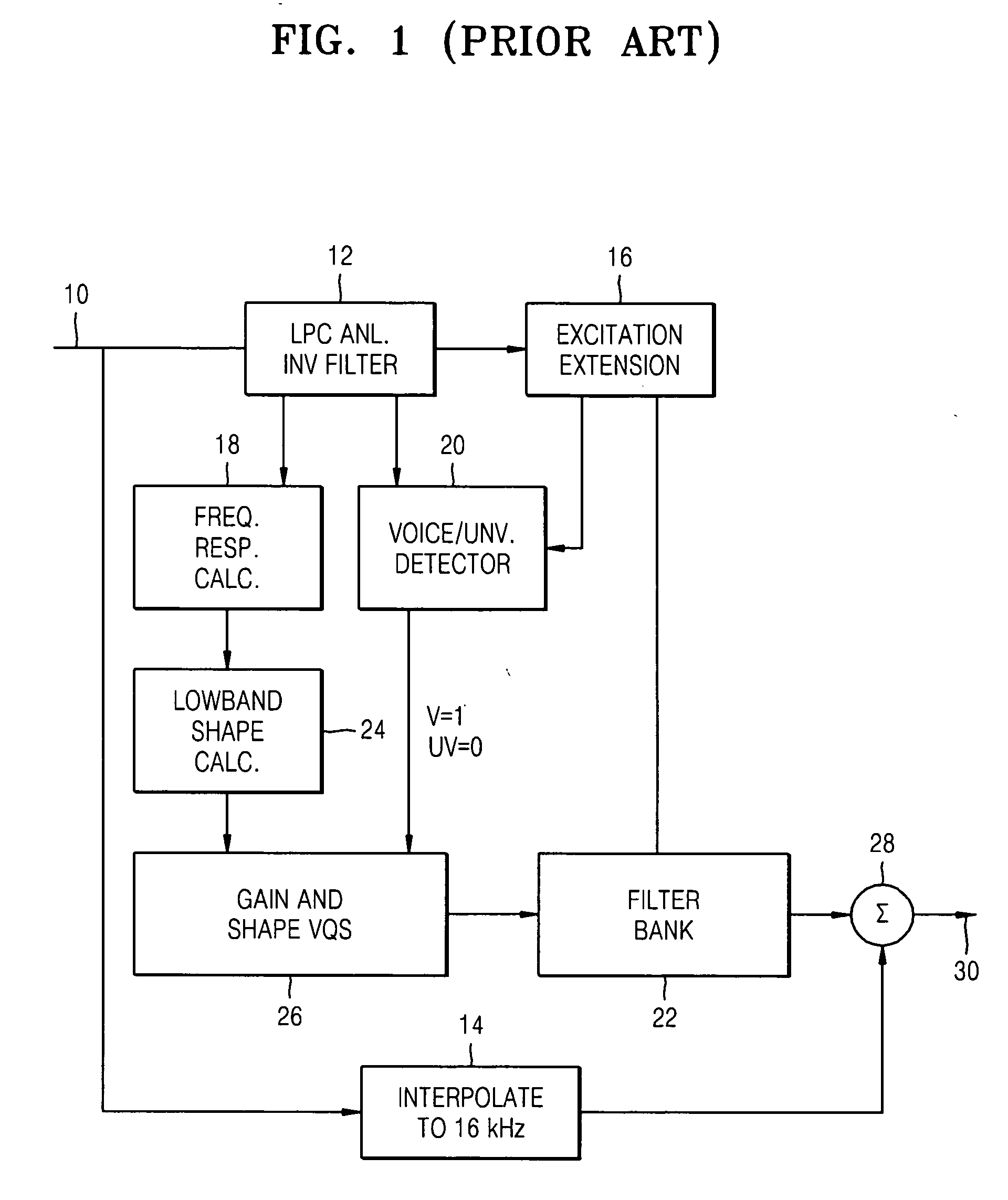
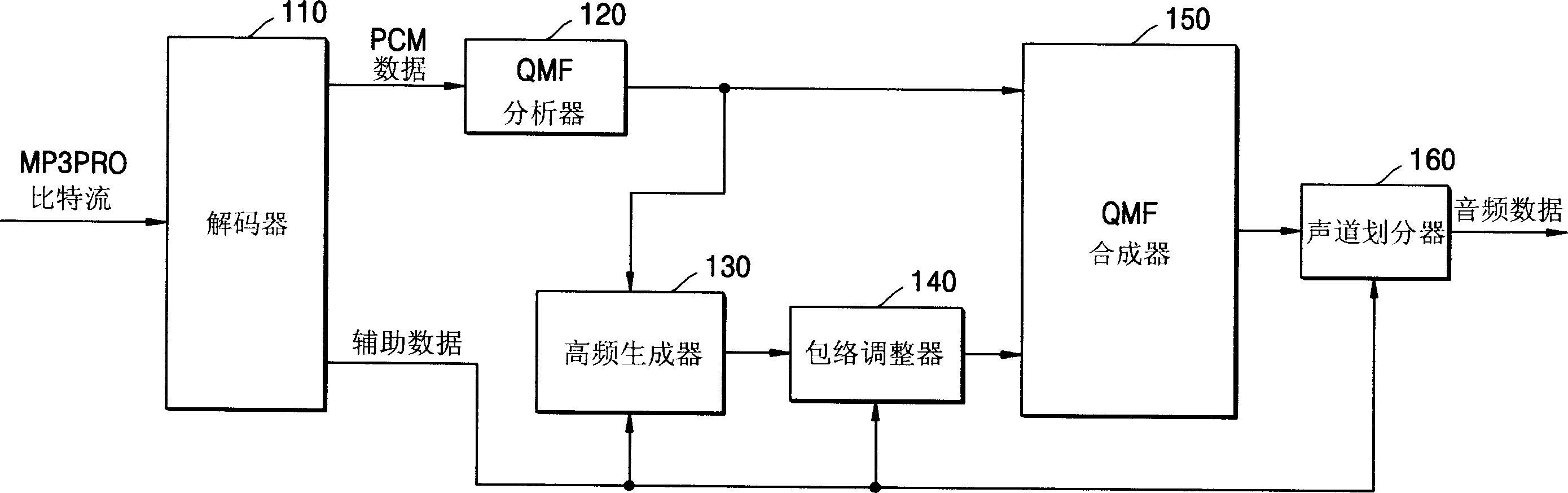
Method and apparatus to recover a high frequency component of audio data
InactiveCN1734555APulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisWeight coefficientLow frequency band
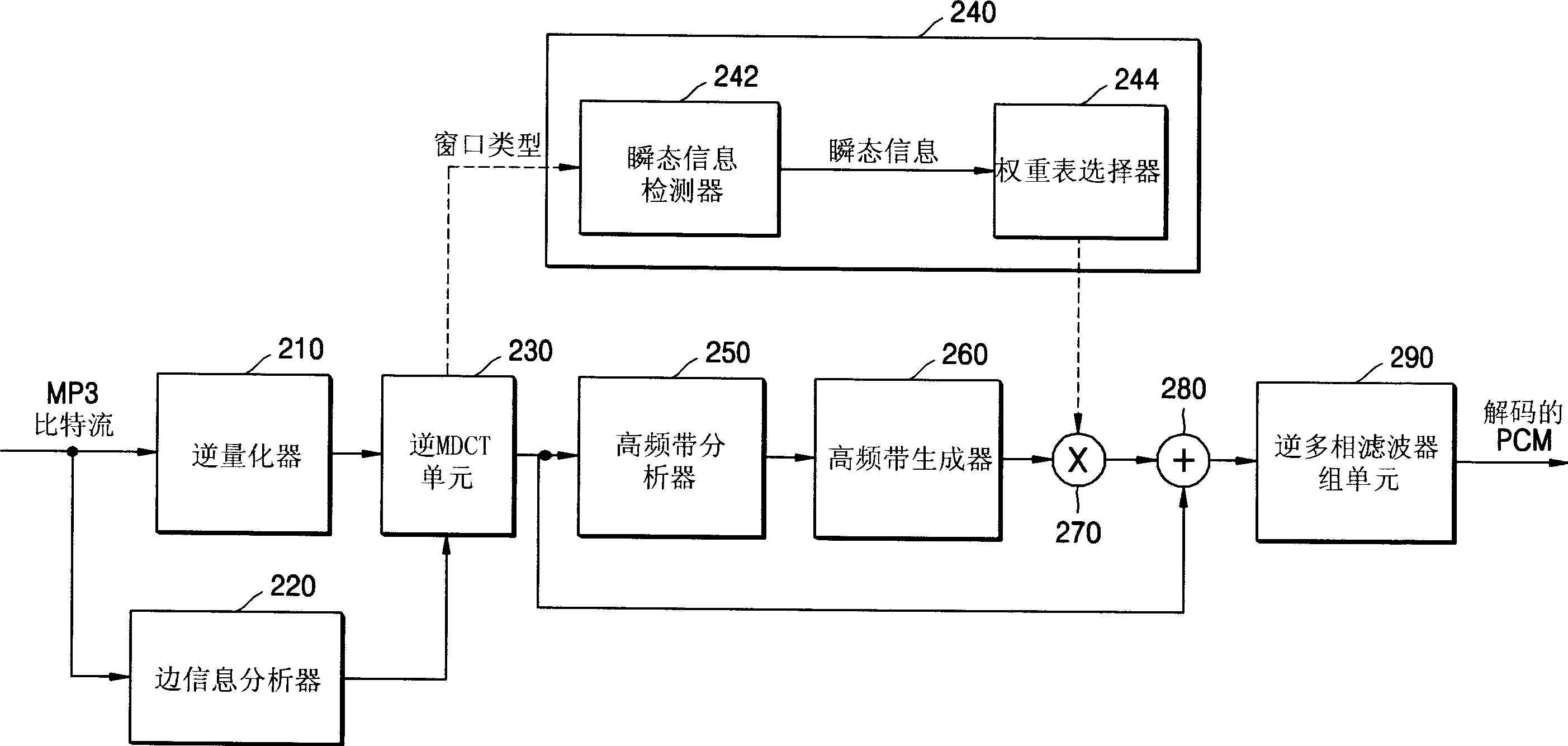
A method and an apparatus to recover a high frequency component of an MP3 encoded audio signal in an audio decoder. The method includes: generating a filter bank value of a low frequency band from a modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) coefficient, which is extracted from an input bitstream according to a window type, extracting transient information of a frame according to the window type and selecting a weight coefficient according to the extracted transient information, recovering a filter bank value of a lost high frequency band from the generated filter bank value of the low frequency band, and adjusting the recovered filter bank value of recovered high frequency components according to the weight coefficient.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electronic watermarking method and apparatus for compressed audio data, and system therefor
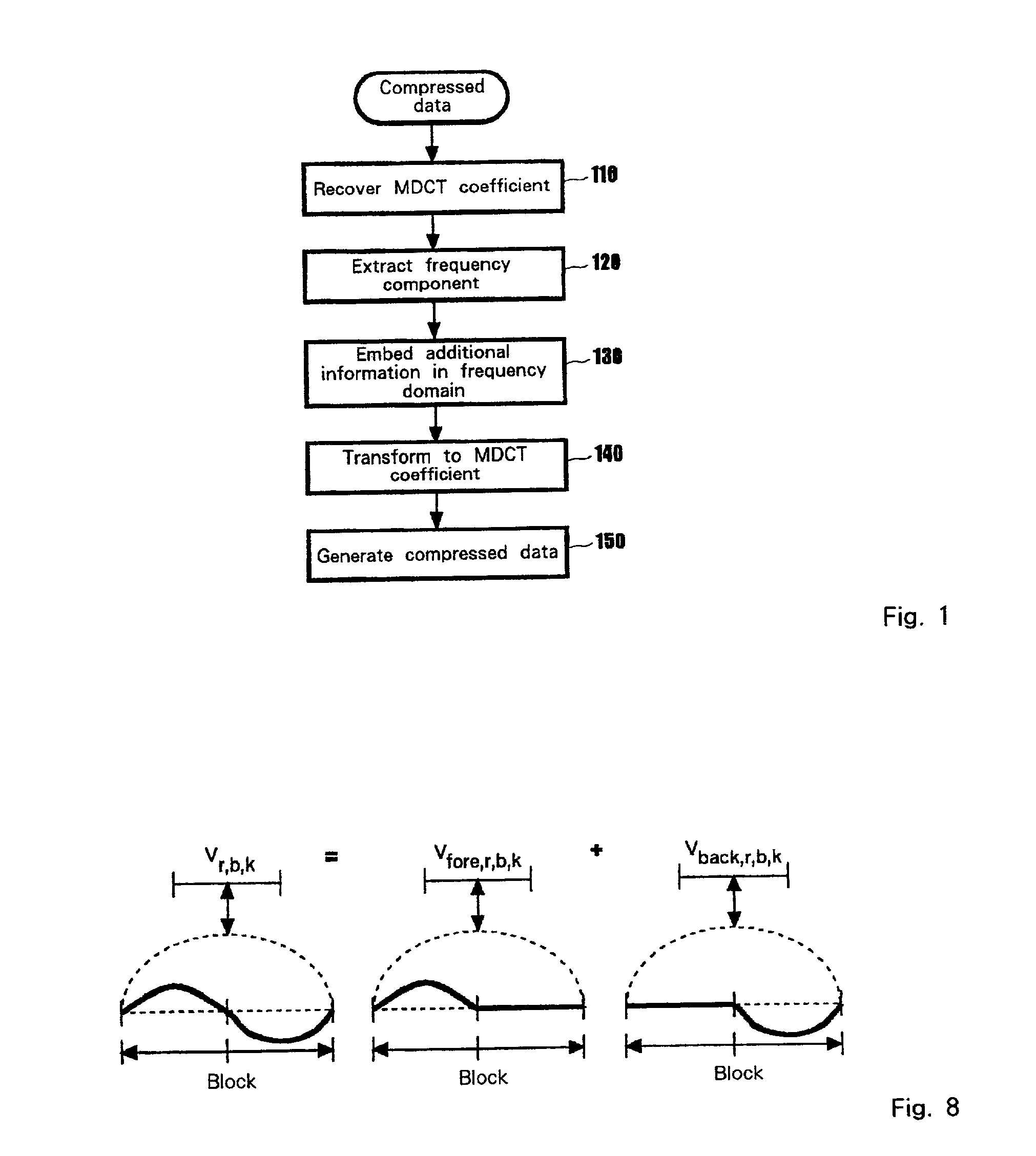
InactiveUS6985590B2Minimized additional informationSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAudio frequencyDigital audio
The present invention provides a method and a system with which information embedded in compressed digital audio data can be directly operated. An embodiment of the system for embedding additional information in compressed audio data includes: means for extracting MDCT (Modified Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficients from the compressed audio data; means for employing the MDCT coefficients to calculate a frequency component for the compressed audio data; means for embedding additional information in the frequency component obtained in a frequency domain; means for transforming into MDCT coefficients the frequency component in which the additional information is embedded; and means for using the MDCT coefficients, in which the additional information is embedded, to generate compressed audio data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Compensator and compensation method for audio frame loss in modified discrete cosine transform domain
The invention provides a compensation method for audio frame loss in a MDCT domain, the method comprising: when a frame currently lost is a Pth frame, obtaining a set of frequencies to be predicted, and for each frequency in the set, using phases and amplitudes of a plurality of frames before a (P−1)th frame in a MDCT-MDST domain to predict a phase and an amplitude of the Pth frame, and using the predicted phase and amplitude to obtain a MDCT coefficient of the Pth frame at each corresponding frequency; for a frequency outside the set, using MDCT coefficients of a plurality of frames before the Pth frame to calculate a MDCT coefficient value of the Pth frame at the frequency; performing an IMDCT for the MDCT coefficients of the Pth frame to obtain a time domain signal of the Pth frame.
Owner:ZTE CORP
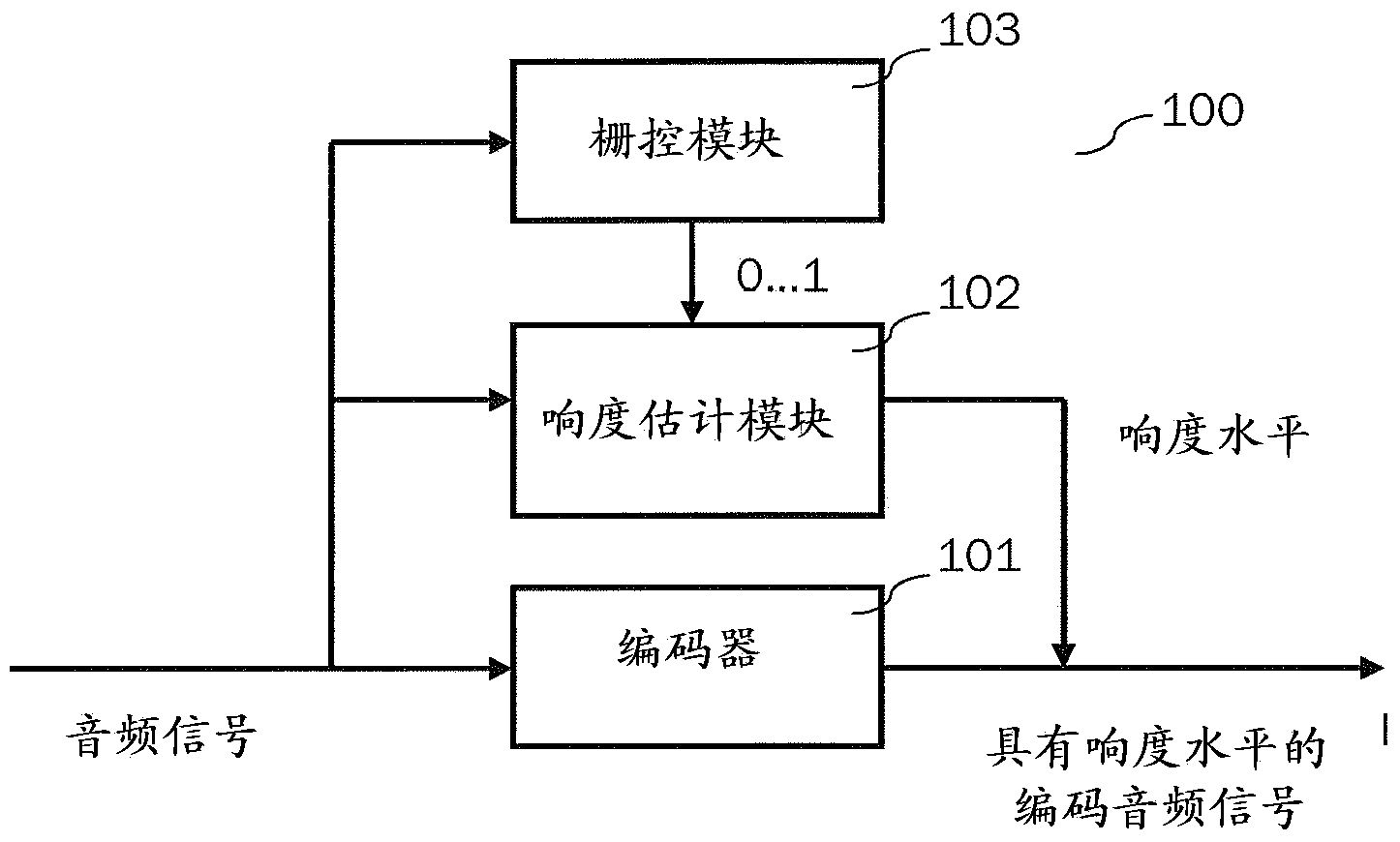
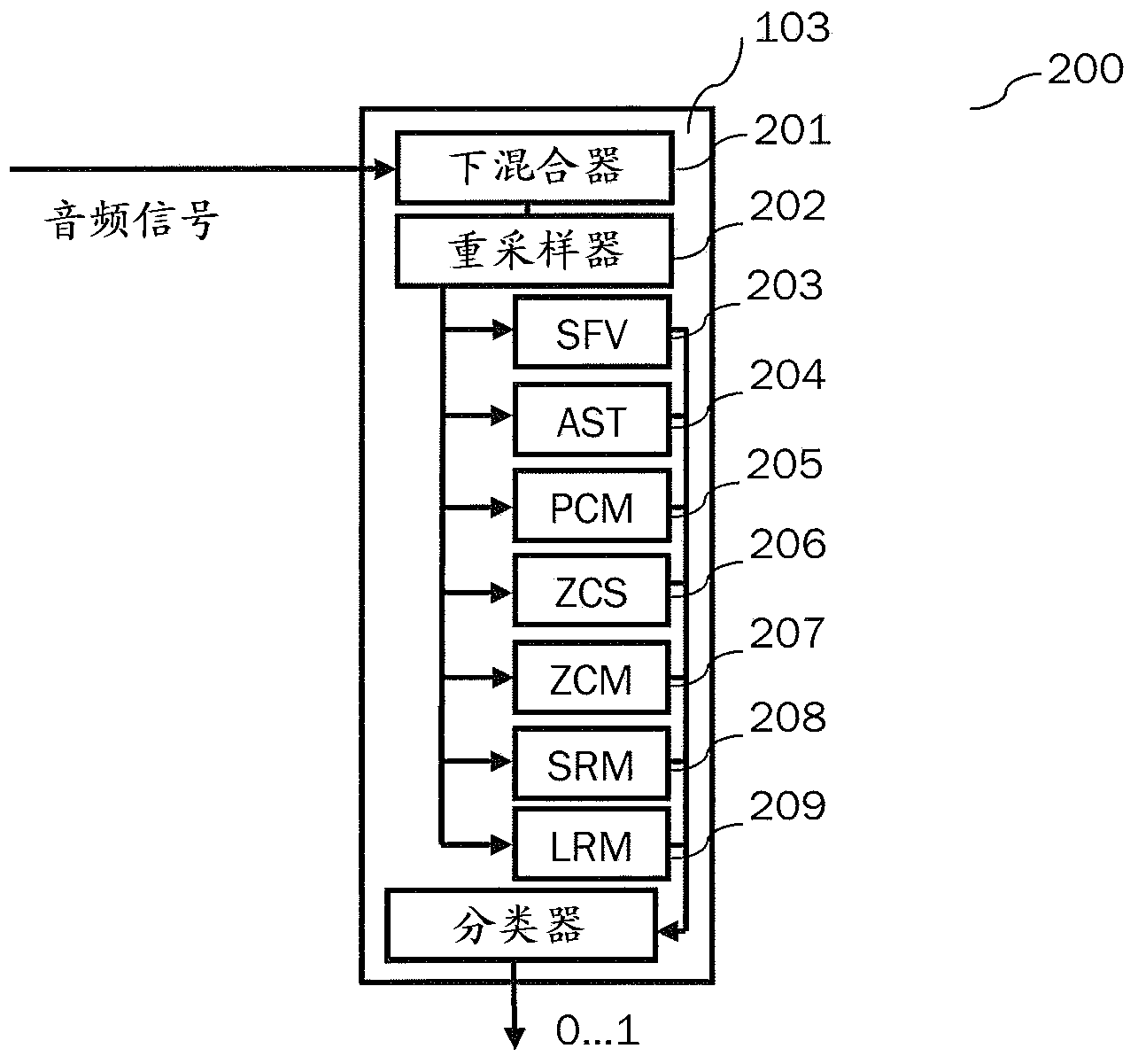
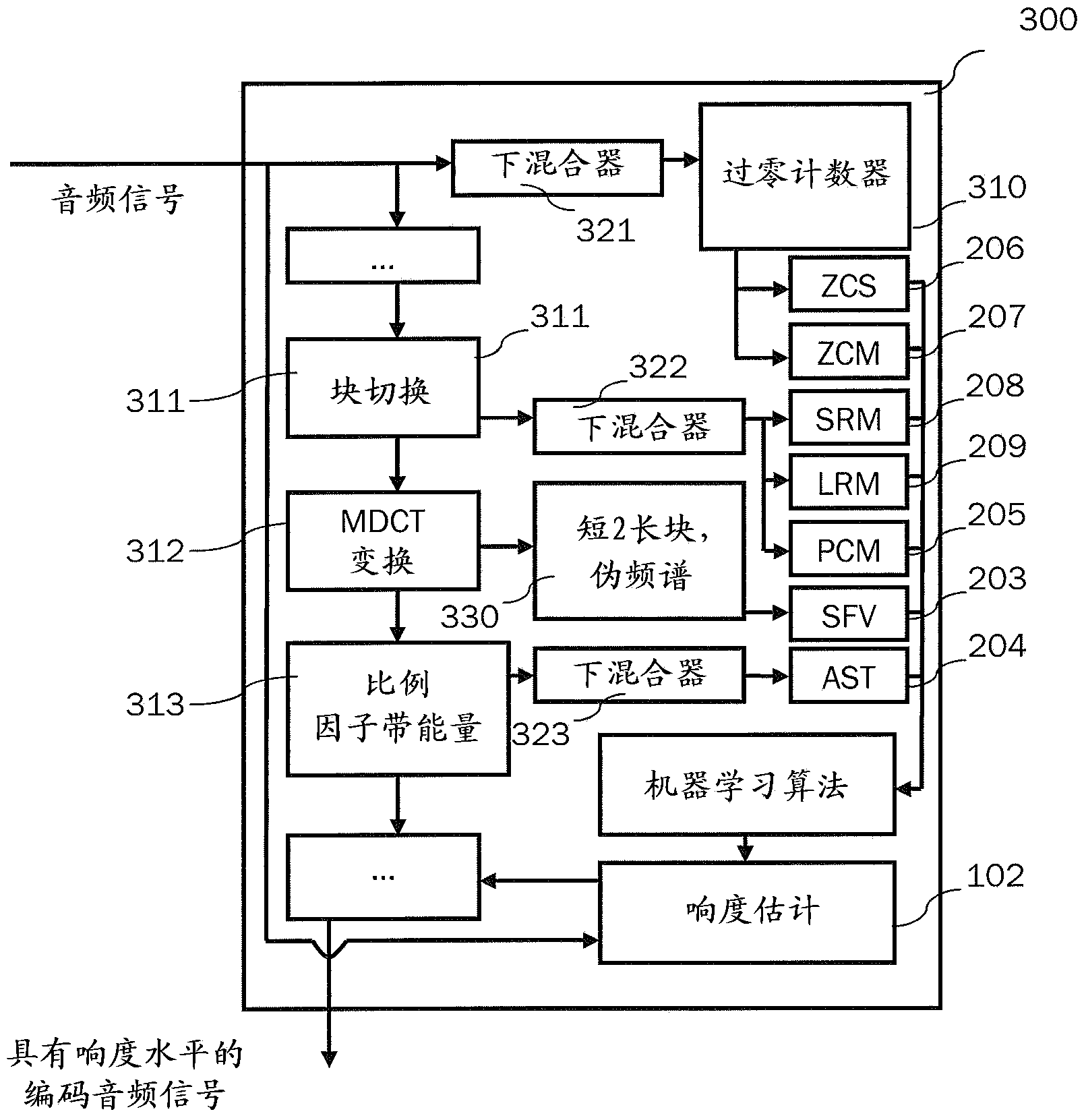
Efficient content classification and loudness estimation
The present document relates to methods and systems for encoding an audio signal. The method comprises determining a spectral representation of the audio signal. The determining a spectral representation step may comprise determining modified discrete cosine transform, MDCT, coefficients, or a Quadrature Mirror Filter, QMF, filter bank representation of the audio signal. The method further comprises encoding the audio signal using the determined spectral representation; and classifying parts of the audio signal to be speech or non-speech based on the determined spectral representation. Finally, a loudness measure for the audio signal based on the speech parts is determined.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
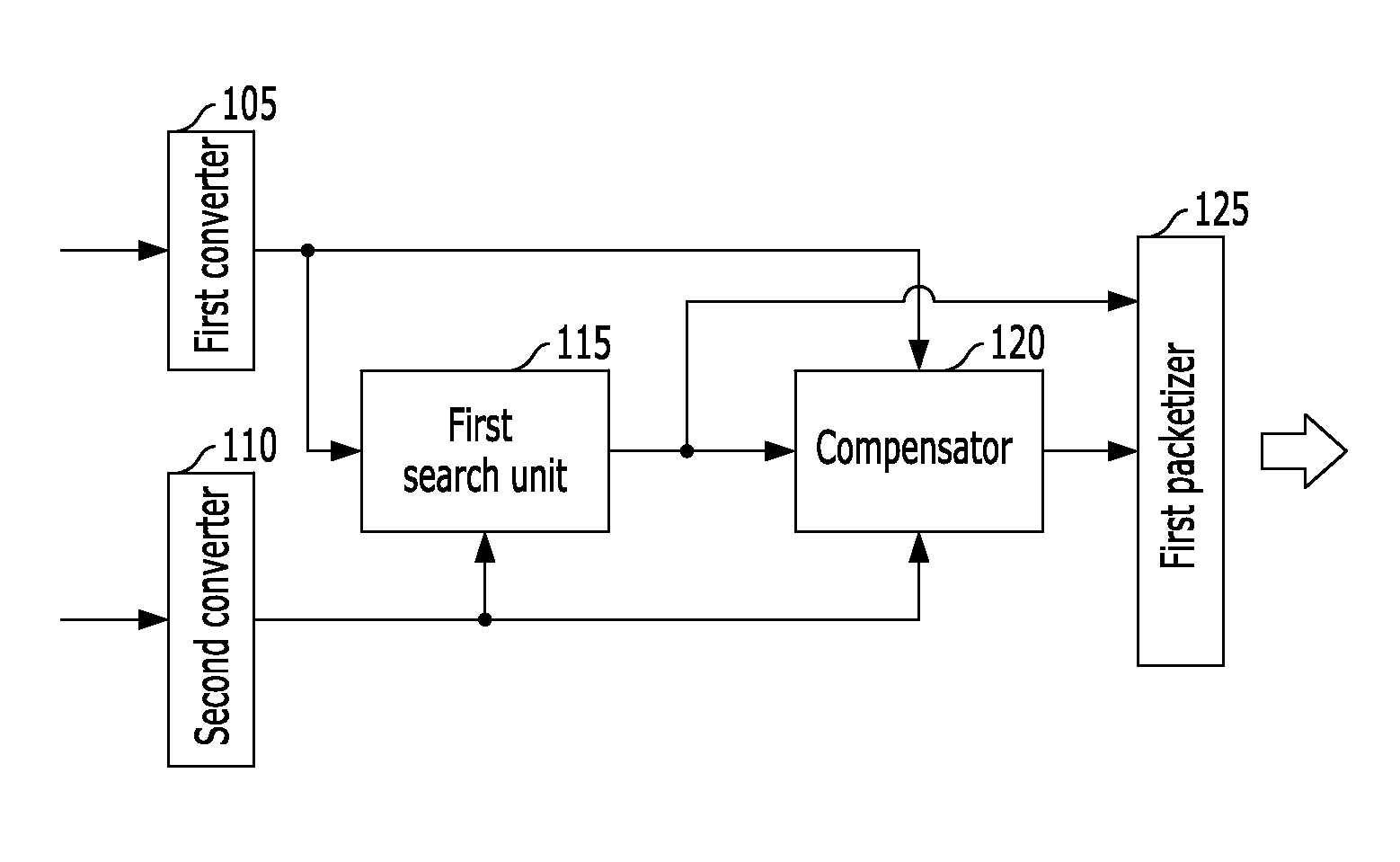
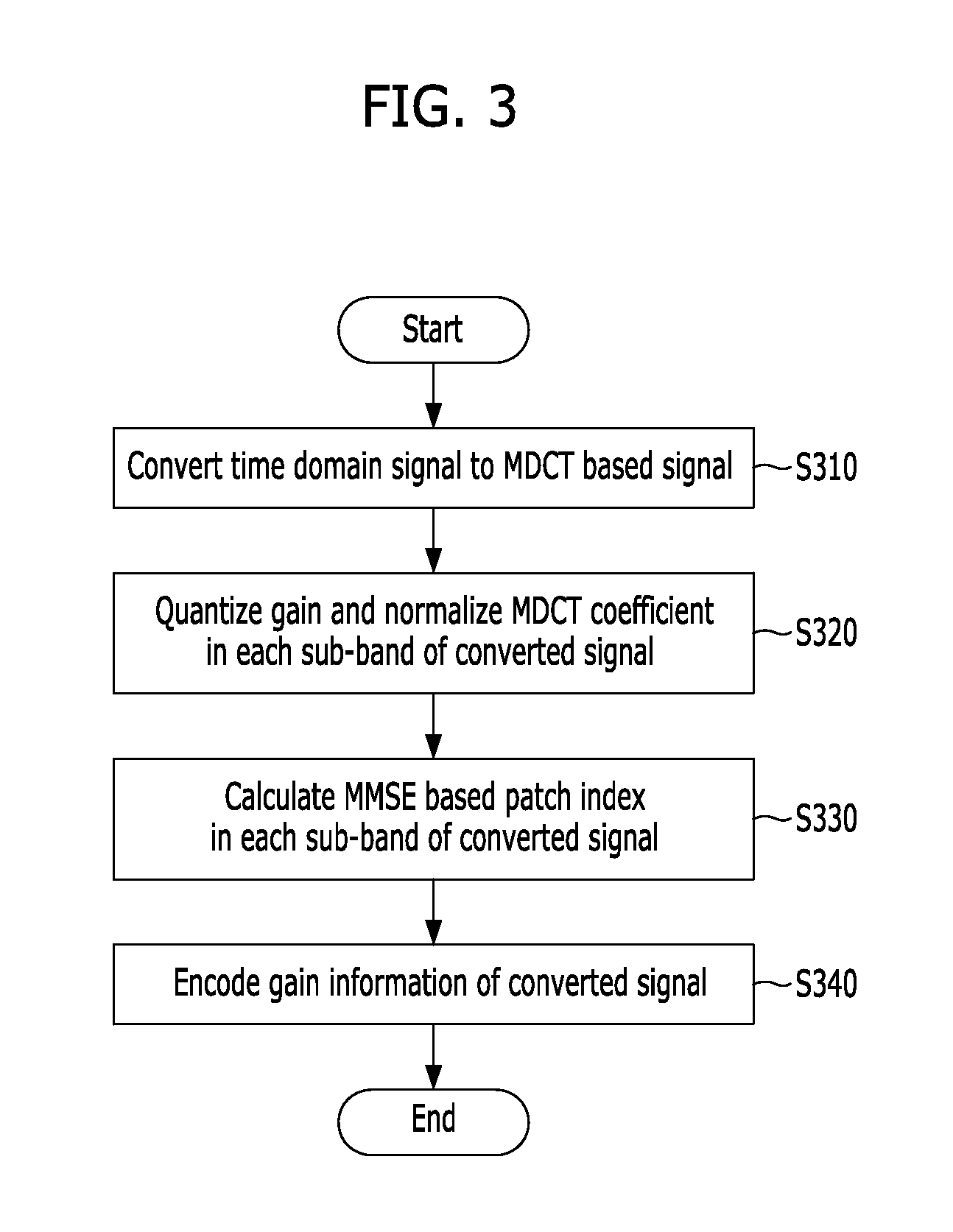
Apparatus and method for coding signal in a communication system
Provided is an apparatus and method for encoding a voice and audio signal by expanding a modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) based CODEC to a wideband and a super-wideband in a communication system. The apparatus for encoding a signal in a communication system, includes a converter configured to convert a time domain signal corresponding to a service to be provided to users to a frequency domain signal, a quantization and normalization unit configured to calculate and quantize gain of each subband in the converted frequency domain signal and normalize a frequency coefficient of the each subband, a search unit configured to search patch information of each subband in the converted frequency domain signal using the normalized frequency coefficient, and a packetizer configured to packetize the quantized gain and the searched patch information and encode gain information of each subband in the frequency domain signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Device, method, and medium for generating audio fingerprint and retrieving audio data
Provided are device, method, and medium for generating an audio fingerprint and retrieving audio data. The device for generating an audio fingerprint includes: a coefficient extracting section partially decoding audio data in a compression area and extracting MDCT (Modified Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficients; a coefficient selecting section selecting an MDCT coefficient robust to noises from the extracted MDCT coefficients; a modulation spectrum generating section transforming the selected MDCT coefficient by the use of a Fourier transform method and generating a modulation spectrum; and a bit conversion section quantizing the generated modulation spectrum and generating an audio fingerprint. As a result, it is possible to accurately and rapidly retrieve the audio data recorded in a variety of environments. Since elements based on MP3 are used, it is possible to apply to MP3 applications in various manners. In addition, it is possible to apply to classification of audio data such as classification of music moods and classification of music genres and various other fields such as extraction of a specific event from moving images of sports.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
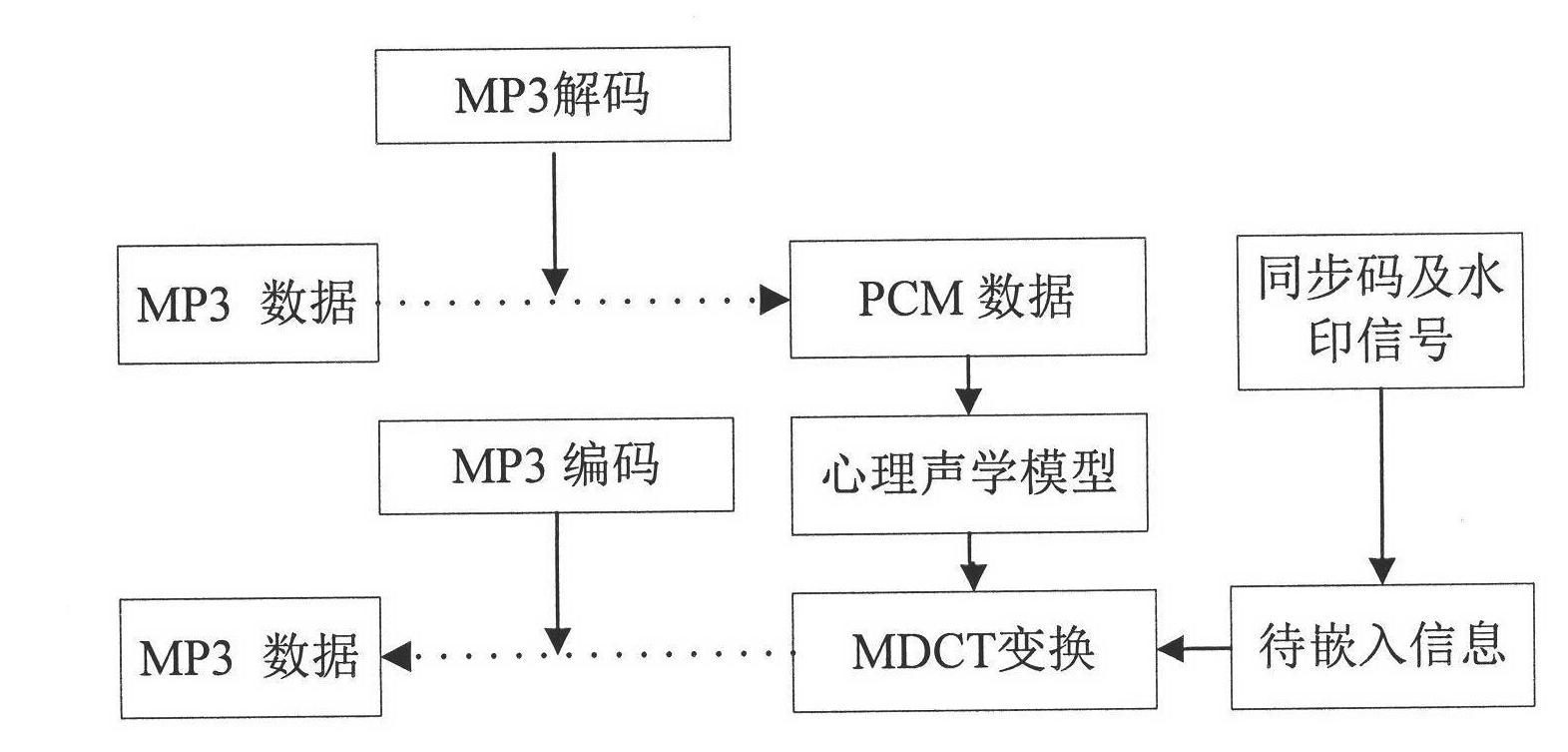
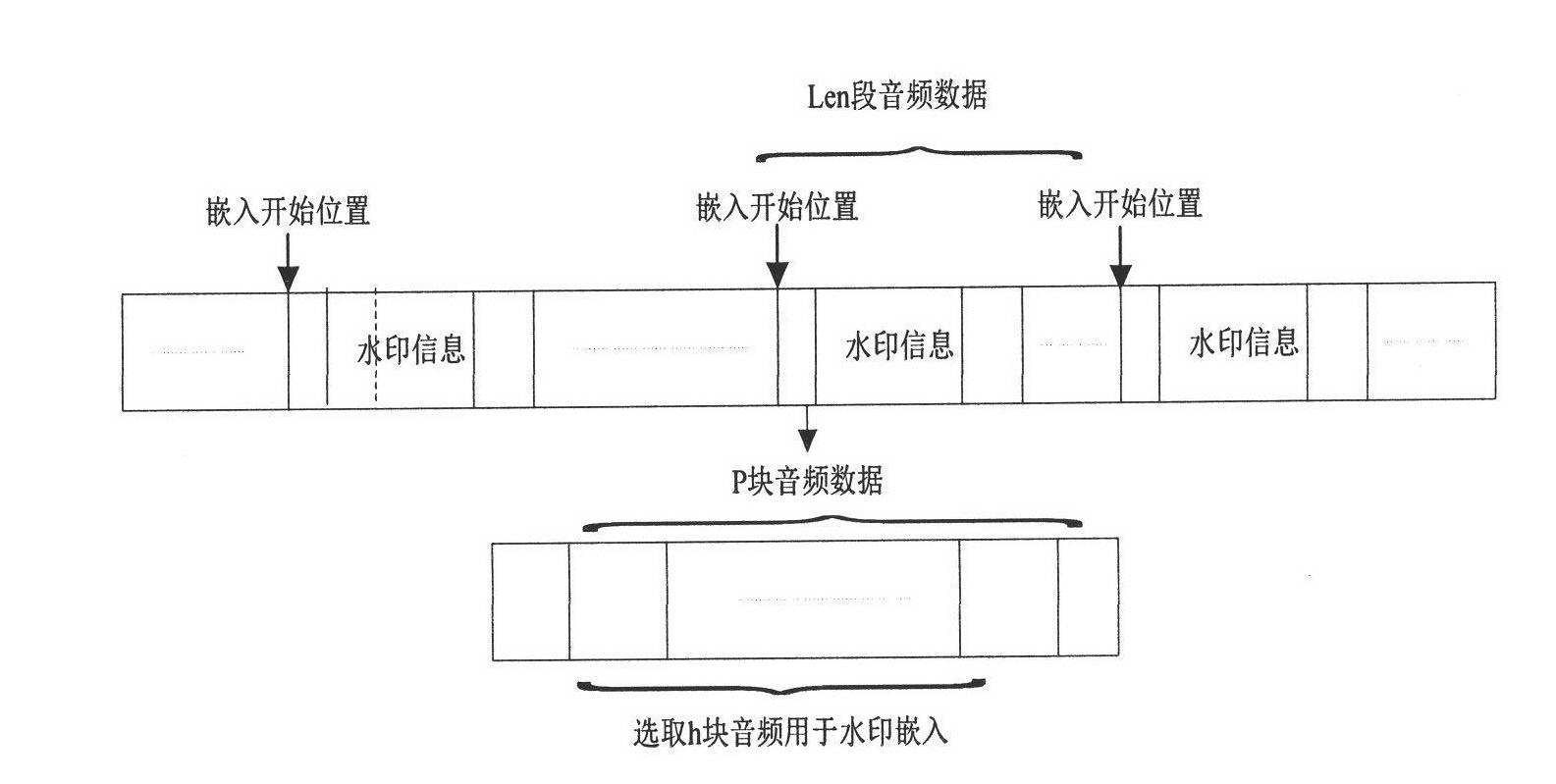
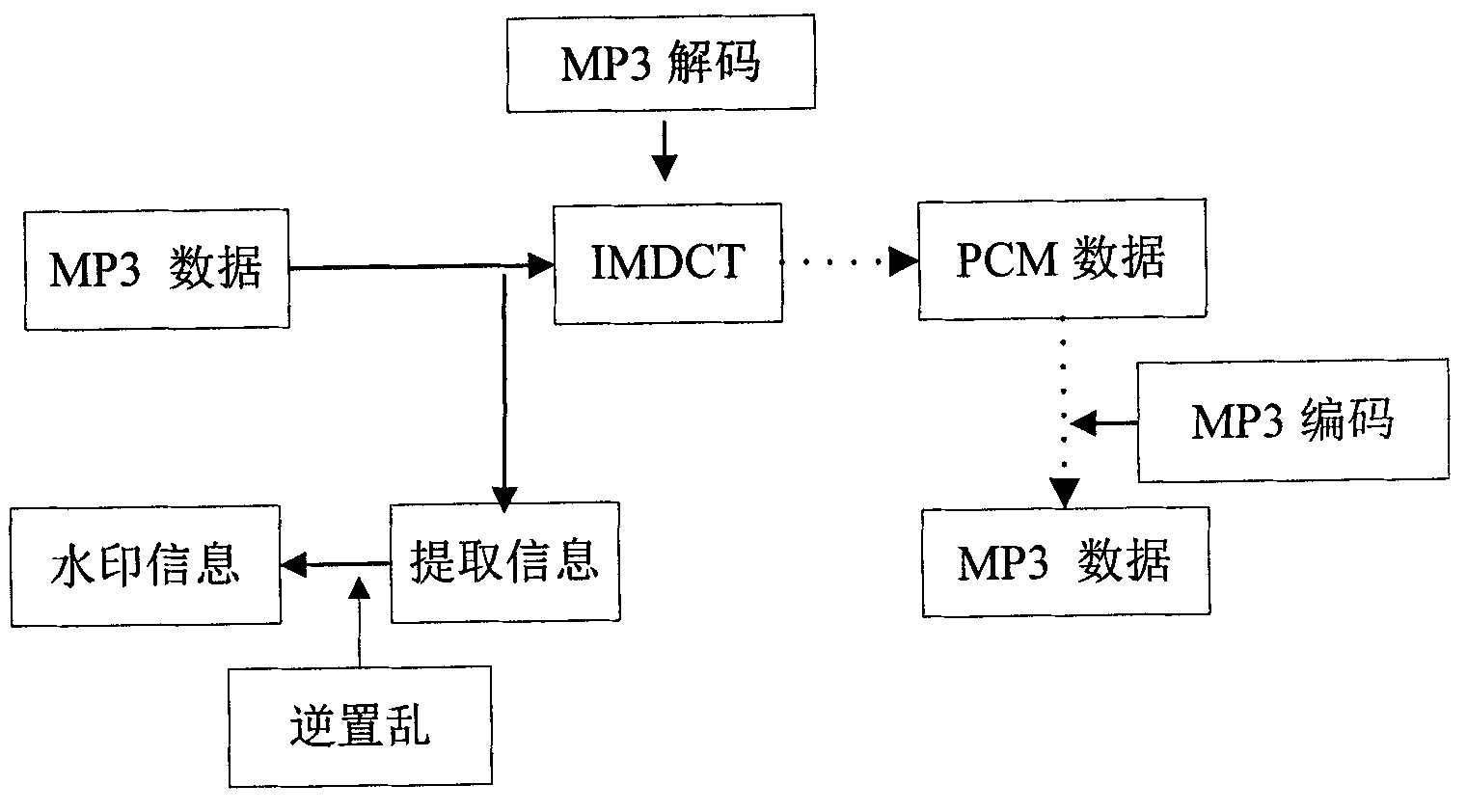
Audio watermarking method based on MP3 encoding principle
InactiveCN102324234AImprove robustnessMeet real-time requirementsSpeech analysisHuman auditory systemAudio watermark
The invention discloses an audio watermarking method based on the MP3 encoding principle, which belongs to the technical field of multimedia digital watermarks. The method includes two processes, i.e. watermark embedment and watermark extraction; a watermark is embedded into a low-frequency MDCT (Modified Discrete Cosine Transform) coefficient as an encoding process is carried out synchronously; in order to enhance the robustness of the watermark, an appropriate audio segment is chosen in combination with the frequency domain masking effect in a human auditory system to be embedded; and in order to resist desynchronization attacks, a synchronization mechanism is introduced. By processing the encoding process, the method fulfills the injection of the watermark, and the method can effectively resist common audio attacks, and also has good robustness on desynchronization attacks (such as shearing attacks, time scaling and the like). While taking audio watermark robustness into consideration, the method guarantees the auditory invisibility of audio contents, the computational complexity of the algorithm is low, and the method is easy to implement.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Audio-encoding/decoding method and system of lattice-type vector quantizing
ActiveUS9015052B2Increase the number ofDecrease the importance of the coding sub-bandSpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsComputer architecture
The audio coding method and system of lattice vector quantization is provided in the invention. The method comprises: dividing frequency domain coefficients of an audio signal for which a modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) has been performed into a plurality of coding sub-bands, and quantizing and coding an amplitude envelope value of each coding sub-band to obtain coded bits of amplitude envelopes; performing bit allocation on each coding sub-band, and performing normalization, quantization and coding respectively on vectors in a low bit coding sub-band with pyramid lattice vector quantization and on vectors in a high bit coding sub-band with sphere lattice vector quantization to obtain coded bits of the frequency domain coefficients; multiplexing and packing the coded bits of the amplitude envelope and the coded bits of the frequency domain coefficients of each coding sub-band, then sending them to a decoding side.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus for transforming between modified discrete cosine transform-based coder and hetero coder
ActiveUS20110137663A1Enhanced informationEliminate artifactsSpeech analysisComputer architectureDiscrete cosine transform
An encoding apparatus and a decoding apparatus in a transform between a Modified Discrete Cosine Transform (MDCT)-based coder and a hetero coder are provided. The encoding apparatus may encode additional information to restore an input signal encoded according to the MDCT-based coding scheme, when switching occurs between the MDCT-based coder and the hetero coder. Accordingly, an unnecessary bitstream may be prevented from being generated, and minimum additional information may be encoded.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Three-dimensional discrete cosine transform (DCT)-based geometric attack resistant volume data watermark realization method
InactiveCN102096896AStrong resistance to conventional attacksStrong ability to resist geometric attacksImage data processing detailsFeature vectorThird party
The invention discloses a three-dimensional discrete cosine transform (DCT)-based geometric attack resistant volume data watermark realization method, which belongs to the field of multimedia signal processing. The method comprises the steps of watermark embedding and watermark extraction. The watermark embedding step further comprises the following steps of: (1) performing global three-dimensional DCT on original volume data, and extracting a geometric attack resistant characteristic vector from a transform coefficient; and (2) obtaining a binary logic sequence through a Hash function by utilizing the characteristic vector and watermarks to be embedded, and storing the binary sequence to a third party. The watermark extraction step further comprises the following steps of: (3) performing the global three-dimensional DCT on tested volume data, and extracting the geometric attack resistant characteristic vector from the object; and (4) extracting the watermarks by utilizing the characteristics of the Hash function and the binary logic sequence stored in the third party. The method relates to a three-dimensional DCT-based volume data digital watermarking technology, is proved by experiments to have relatively higher geometric and conventional attach resistance, also relates to a zero-watermark technology, and avoids the watermark embedding changing the contents of the volume data.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com