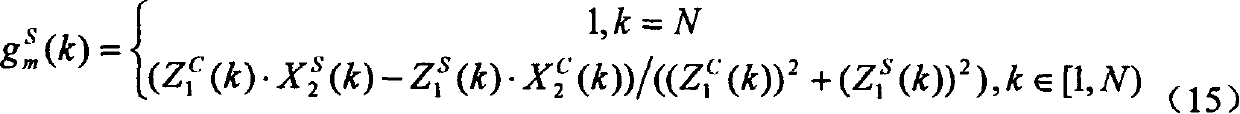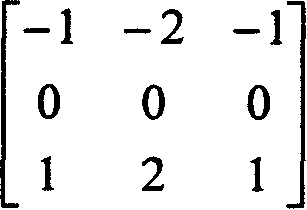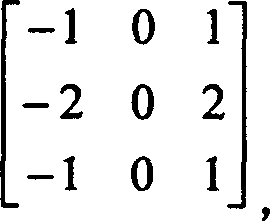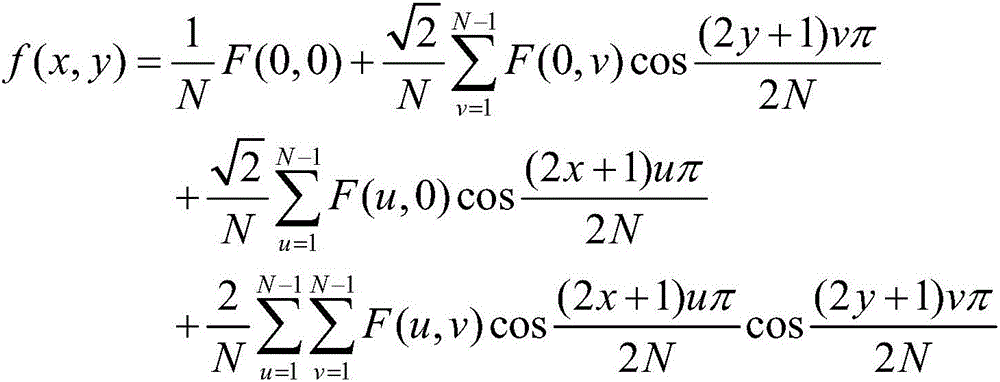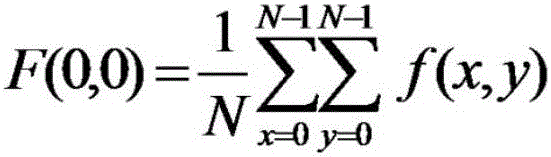Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
899 results about "Discrete cosine transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
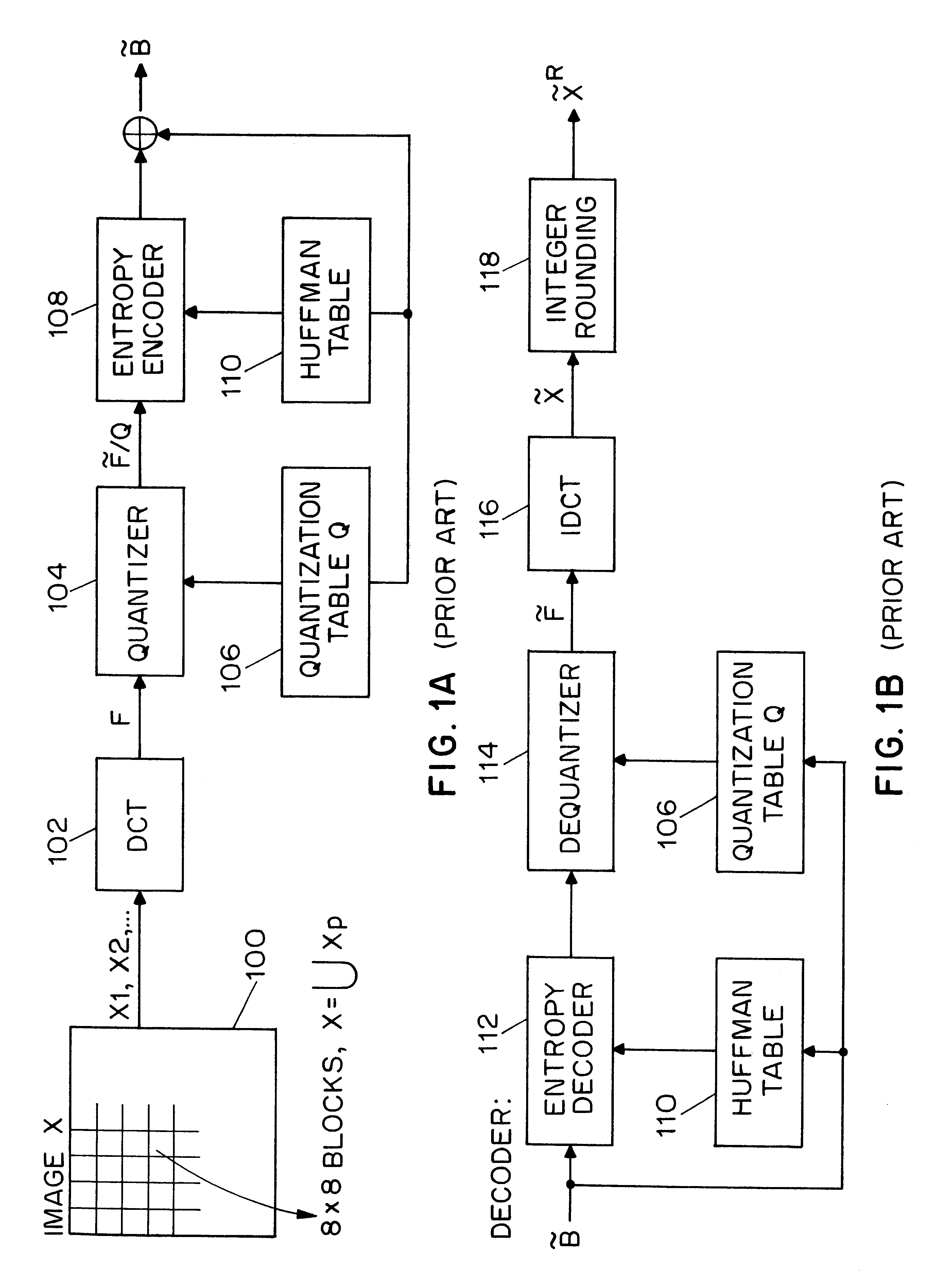
A discrete cosine transform (DCT) expresses a finite sequence of data points in terms of a sum of cosine functions oscillating at different frequencies. This is the standard data compression technique widely used by most digital media standards, for image compression (e.g. JPEG and HEIF, where small high-frequency components can be discarded), video coding (e.g. MPEG and H.26x), digital audio (e.g. MP3 and AAC) and digital television (e.g. SDTV and HDTV). DCTs are also important to numerous applications in science and engineering, such as spectral methods for the numerical solution of partial differential equations.
Method and apparatus for image authentication
InactiveUS6532541B1User identity/authority verificationImage watermarkingDigital signatureDiscrete cosine transform
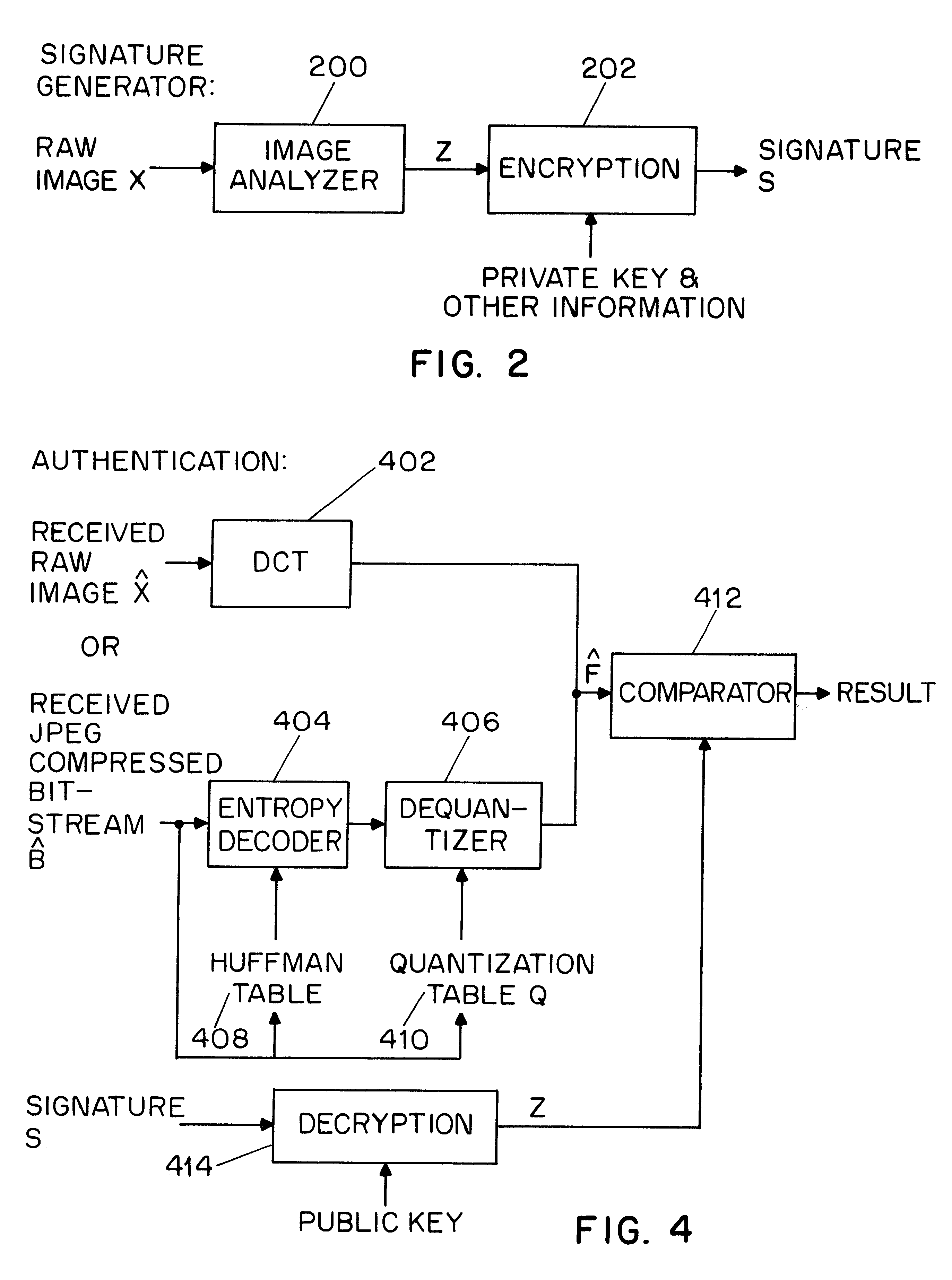
A system for authentication of a digital image includes a signature generator for creating a robust digital signature for an original image based on instrument features of the image. An authentication processor extracts a set of invariant features for the original image from the digital signature, generates a corresponding set of invariant features for the present image to be authenticated and compares the two sets of invariant features to determine whether the image has been subjected to malicious manipulation. The invariant features include the polarity and magnitude of the difference between discrete cosine transform coefficients at corresponding coefficient locations in selected image block pairs. The intensity of the original image is also authenticated by comparing a mean value of coefficient of the original image to the mean value of the coefficient of the present image.
Owner:NAT SCI FOUND NSF
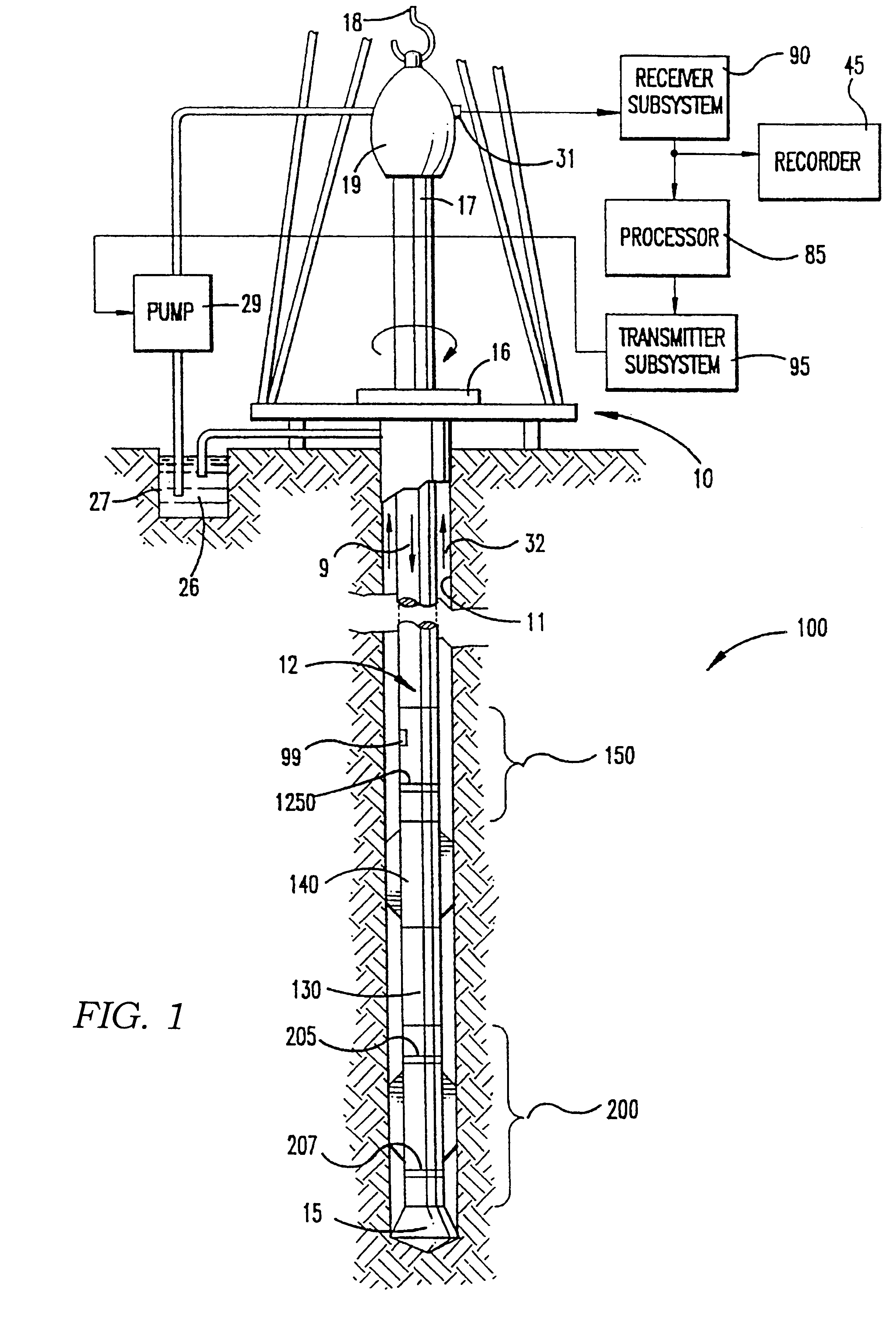
Data compression method for use in wellbore and formation characterization
A method is disclosed for compressing a frame of data representing parameter values, a time at which each parameter value was recorded, and an orientation of a sensor at the time each parameter value was recorded. Generally the method includes performing a two-dimensional transform on the data in the orientation domain and in a domain related to the recording time. In one embodiment, the method includes calculating a logarithm of each parameter value. In one embodiment, the 2-D transform includes generating a Fourier transform of the logarithm of the parameter values in the azimuthal domain, generating a discrete cosine transform of the transform coefficients in the time domain. This embodiment includes quantizing the coefficients of the Fourier transform and the discrete cosine transform. One embodiment of the method is adapted to transmit resistivity measurements made by an LWD instrument in pressure modulation telemetry so that while-drilling images of a wellbore can be generated. The one embodiment includes encoding the quantized coefficients, error encoding the encoded coefficients, and applying the error encoded coefficients to the pressure modulation telemetry.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
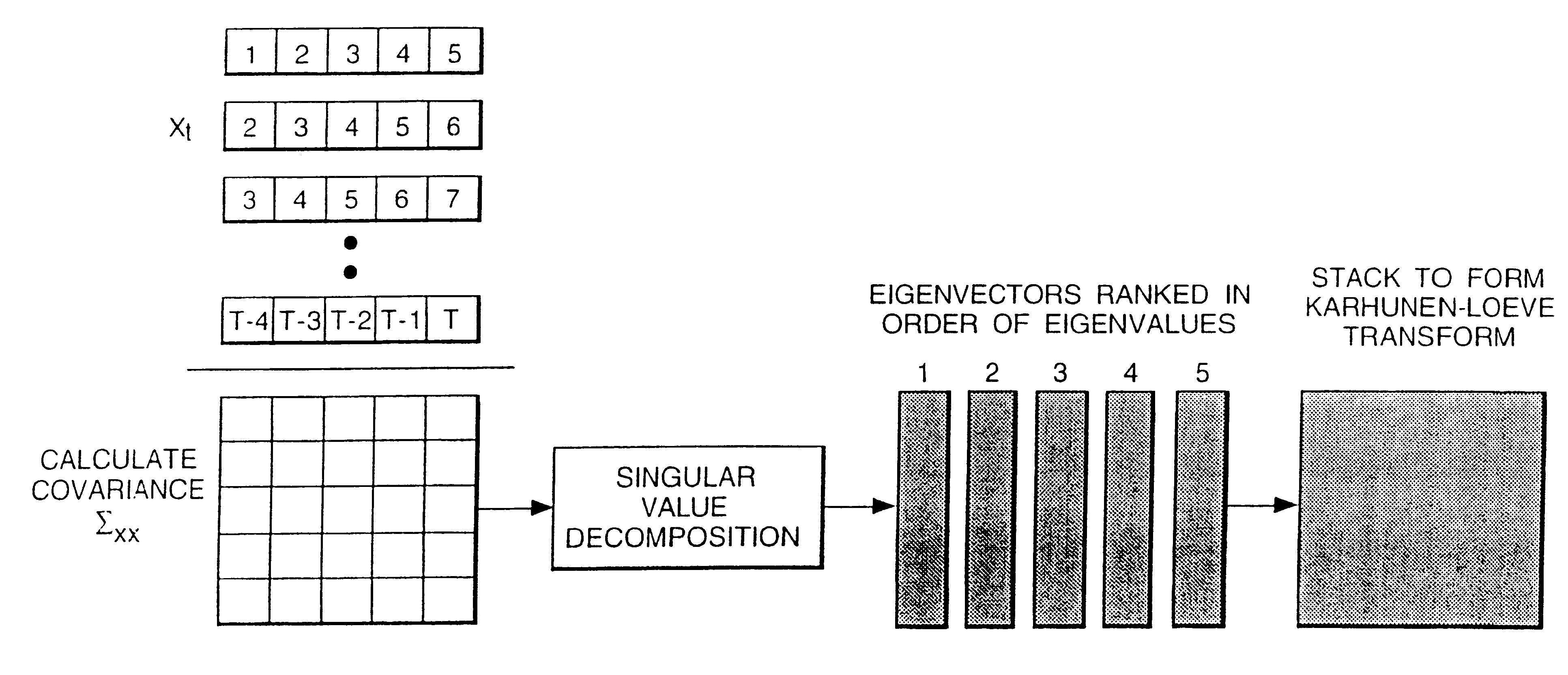
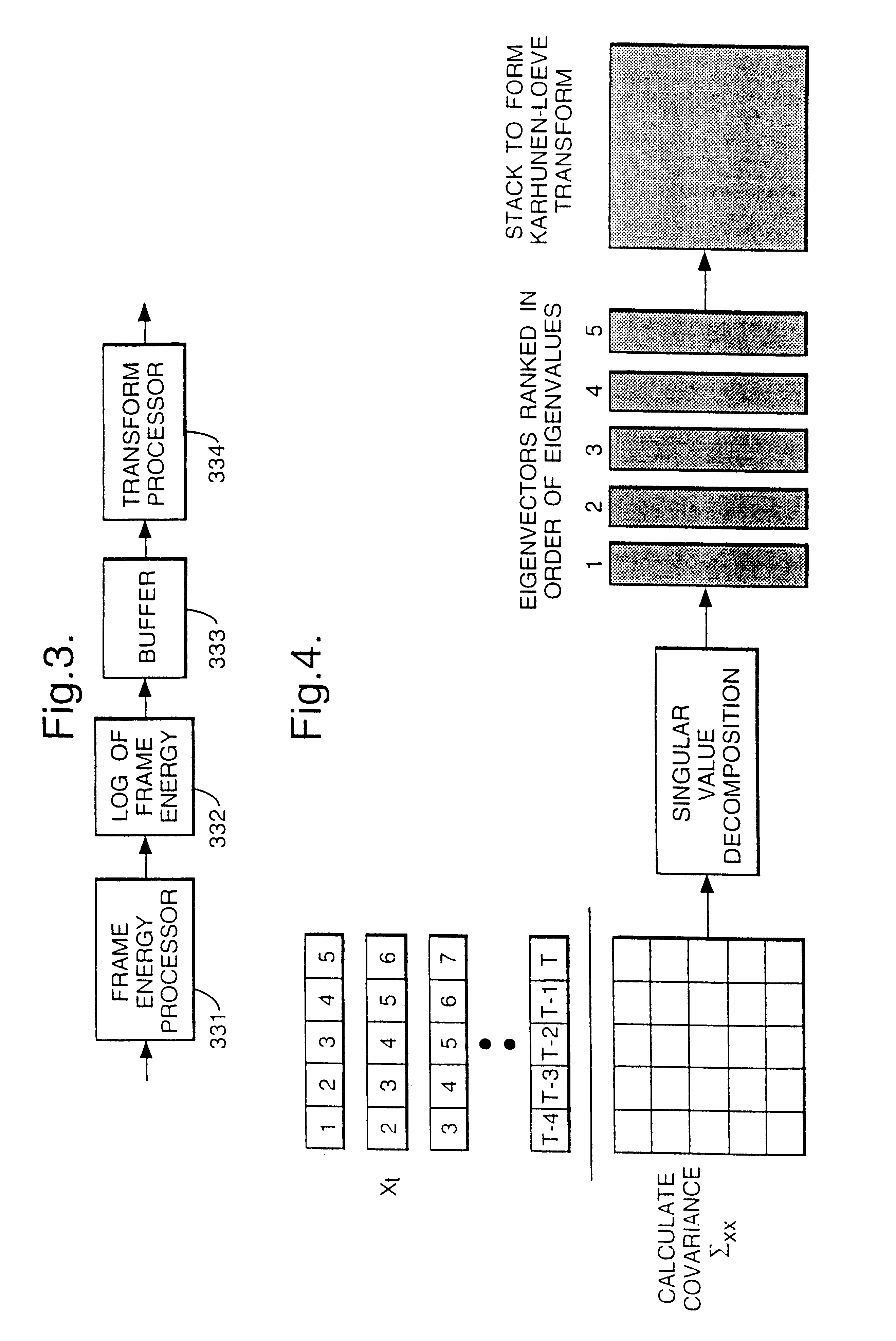
Speech transformation using log energy and orthogonal matrix
Calculate the log frame energy value of each of a pre-determined number n of frames of an input speech signal and apply a matrix transform to the n log frame energy values to form a temporal matrix representing the input speech signal. The matrix transform may be a discrete cosine transform.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative converter accoding to the correlation of residual signal
InactiveUS20090238271A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareRate distortion
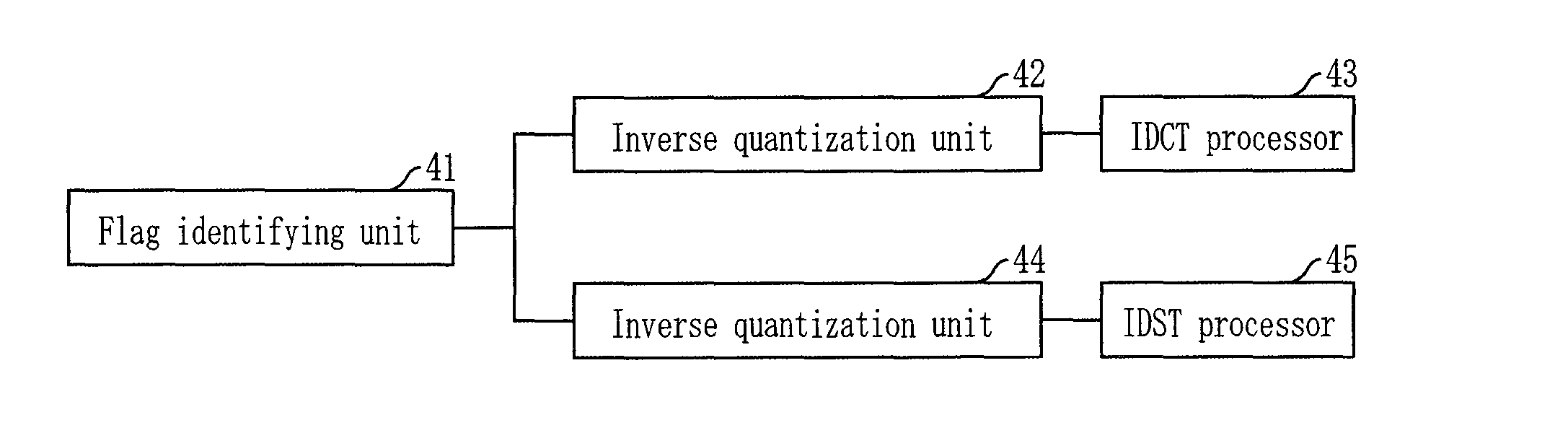
Provided is an apparatus and method for encoding and decoding using alternative transform units according to the correlation of residual signals. The video encoding apparatus includes a first transforming unit for performing discrete cosine transform (DCT), first quantization, first inverse quantization, and inverse DCT on a block basis onto residual coefficients generated after intra frame prediction or inter frame prediction; a second transforming unit for performing discrete sine transform (DST), second quantization, second inverse quantization, and inverse DST on a block basis onto the residual coefficients; a selecting unit for selecting one having a high compression rate between the first and second transforming units for each block through performing rate-distortion optimization; and a flag marking unit for recording information about the selected transforming unit at a flag bit provided on a macroblock basis.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +2
Electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system
InactiveUS20130243105A1Improve quality scoreLow distortion rateCode conversionComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionEcg signalFrequency spectrum
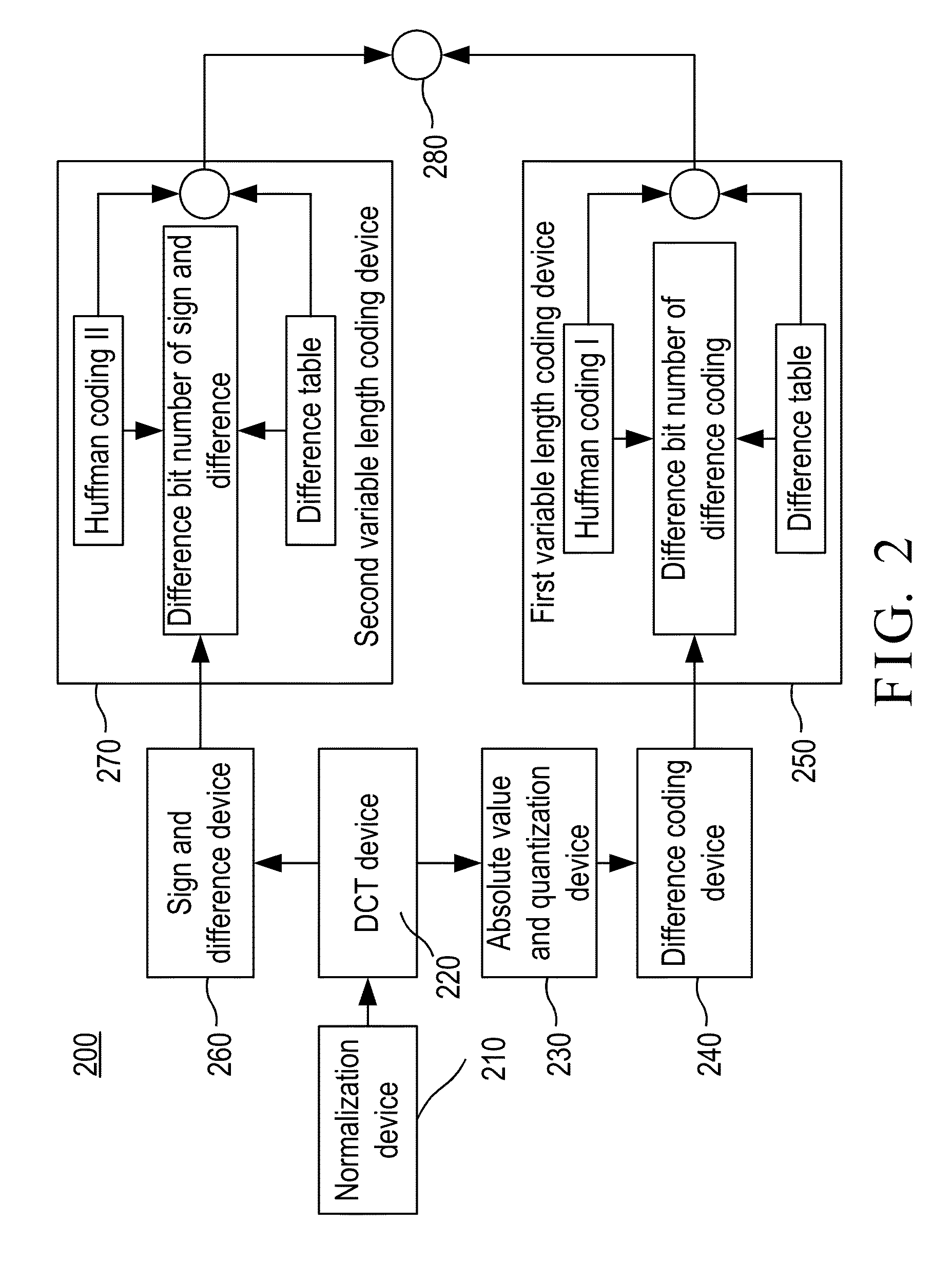
The invention provides an electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system. The invention uses the sign characteristics of the coefficients of the discrete cosine transform type IV and the characteristics of quantization of spectrum to perform the differential pulse code modulation of the spectrum for preserving the high frequency characteristics of the spectrum of the discrete Fourier transform. The invention also uses the Huffman coding to increase the compression ratio. Different from the conventional compression technology, the invention uses the fact that the quantization values of the spectrum in the high frequency are almost the same to increase the compression ratio and preserve the characteristics of high frequency components of the spectrum.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Image processing system, image processing method, and image processing program
ActiveUS7054503B2Easy to processReducing mosquito noiseImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingDiscrete cosine transform
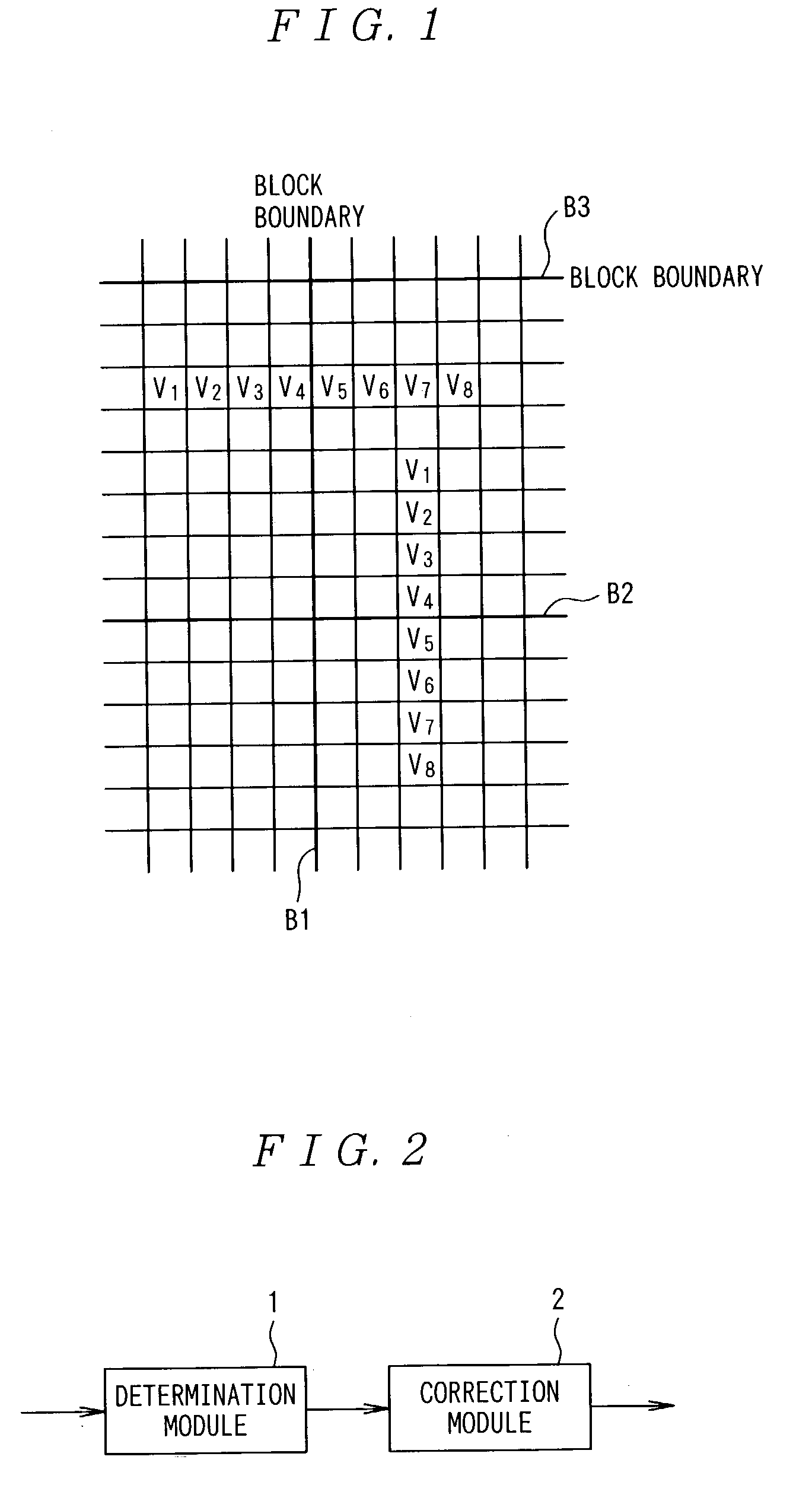
In the present invention, 2N pixels (having signal levels V1 through V8), including a boundary pixel, that consist of N pixels on each side of a boundary and run orthogonally to the boundary are referenced to determine whether correction should be performed or not. If it is determined that the correction should be performed, the boundary pixel and M pixels on each side of the boundary pixel are used to perform the correction. In an image processing system for performing filtering on pixels belonging to a block, which is a unit of discrete cosine transform in image compression, the maximum value of differences between neighboring pixels in at least half, including a pixel of interest, of all the pixels composing a block to be processed is obtained. Differences between neighboring pixels in 2N pixels, including the pixel of interest, that run orthogonally to the boundary between blocks and consist of N pixels on each side of the boundary are calculated. The differences calculated are compared with a threshold corresponding to the maximum value to determine whether filtering should be performed. If it is determined that filtering should be performed, the pixel of interest and M pixels on each side of the pixel of interest are used to perform filtering. N is a positive integer and M is a positive integer smaller than N.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
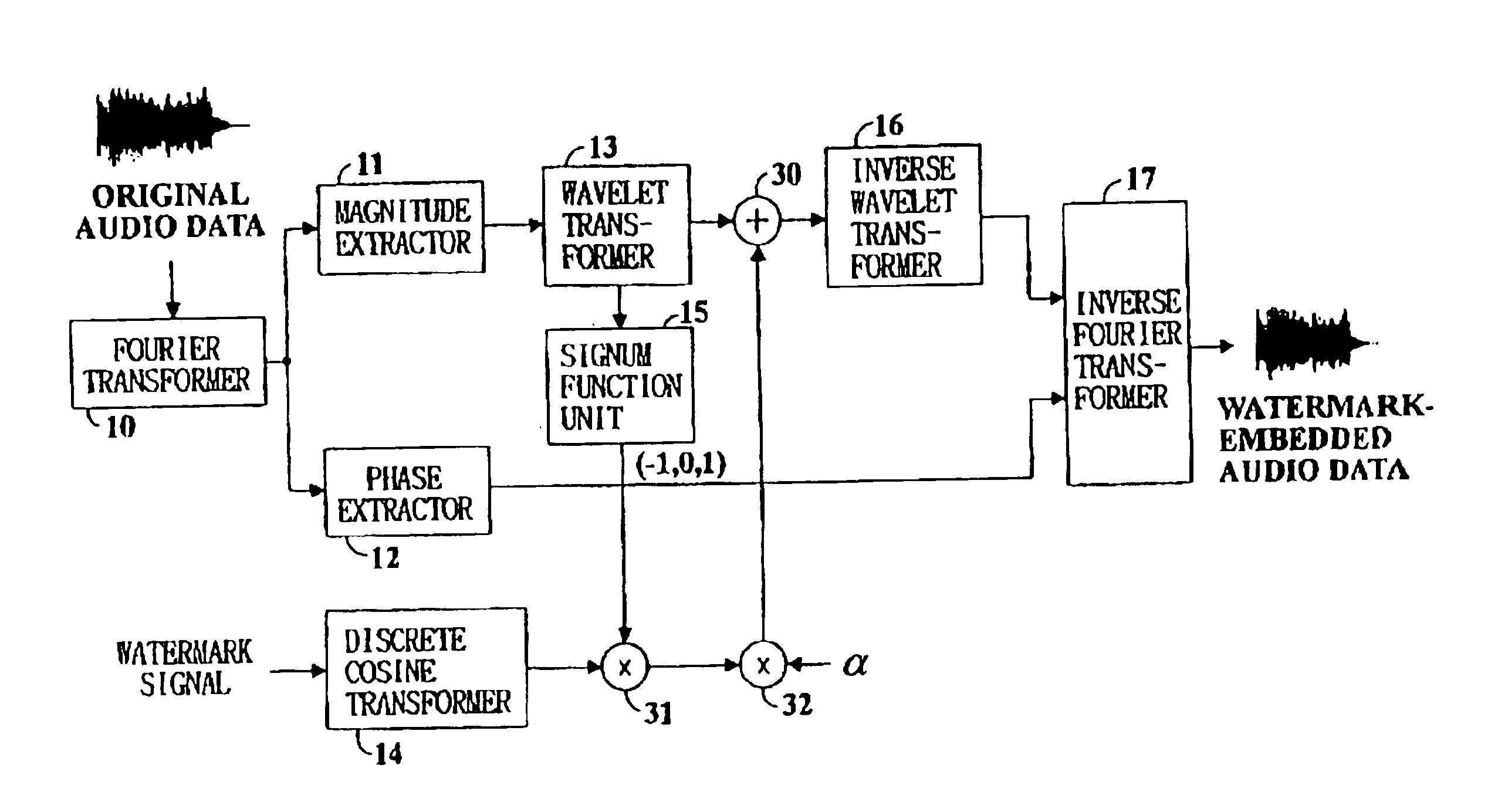
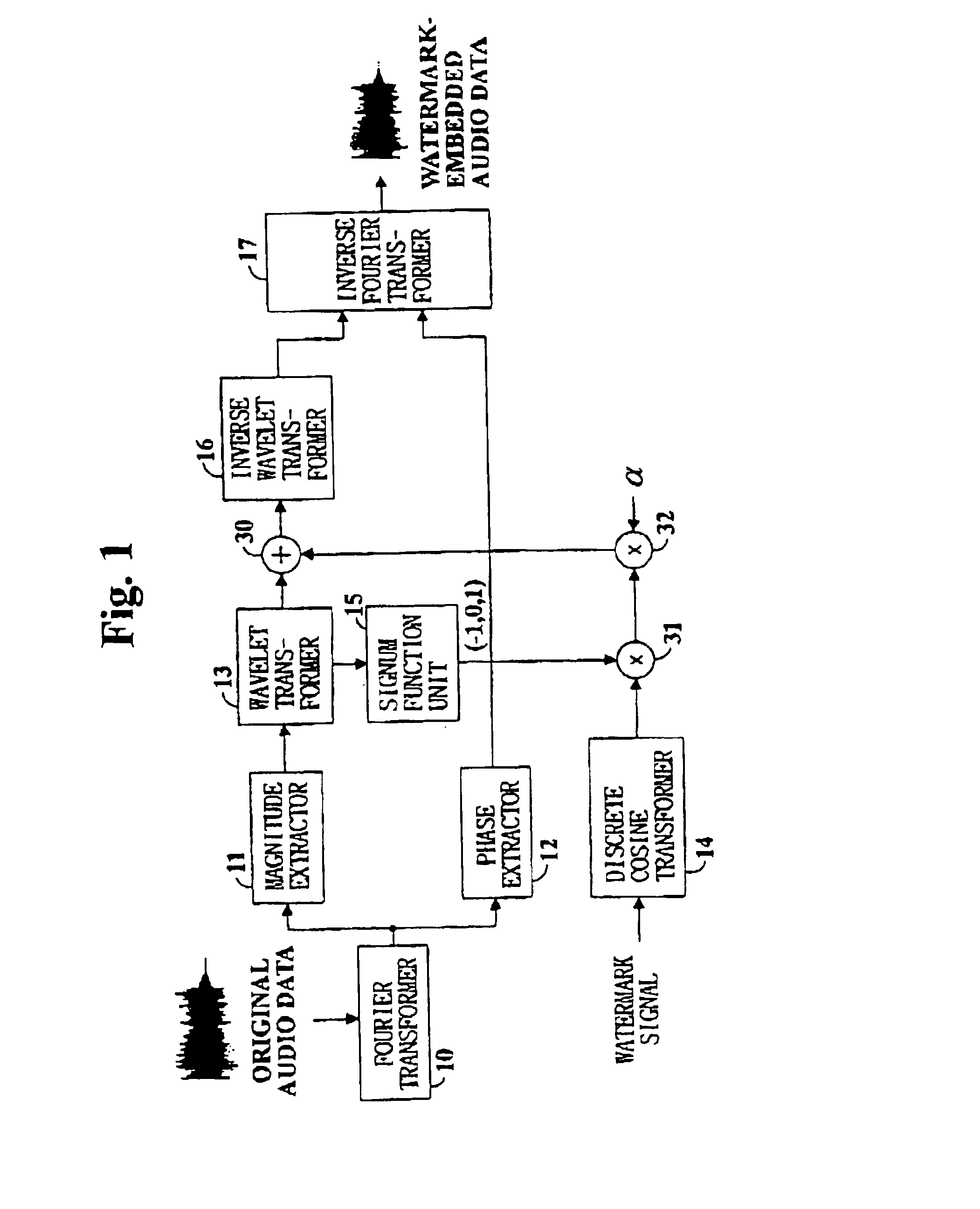
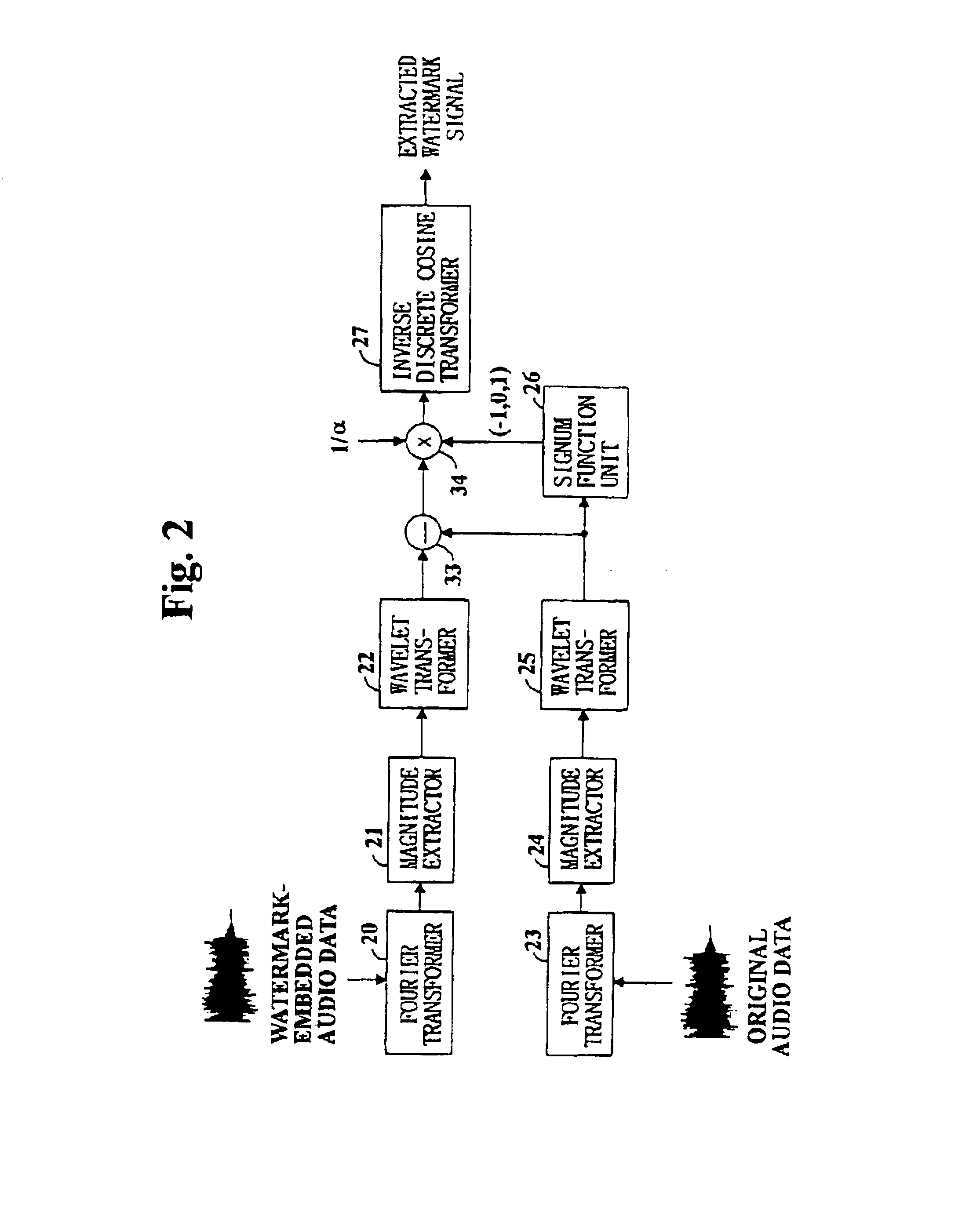
Digital watermarking method and apparatus for audio data
InactiveUS6839673B1Minimize distortionElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisComputer hardwareFourier transform on finite groups
Digital watermarking of digital audio is performed by Fourier transforming digital audio data, wavelet transforming the magnitude components of the Fourier transform coefficients of the digital audio data, discrete cosine transforming a watermark signal, multiplying the sign of the wavelet transform coefficients of the magnitude components to the coefficients of the discrete cosine transformed watermark signal, adding the coefficients of the Fourier transformed digital audio data and the adjusted discrete cosine transformed watermark signal, and inverse wavelet transforming the audio signal's coefficients before inverse Fourier transformation to finally generate watermark-embedded audio signal data.
Owner:MARKANY
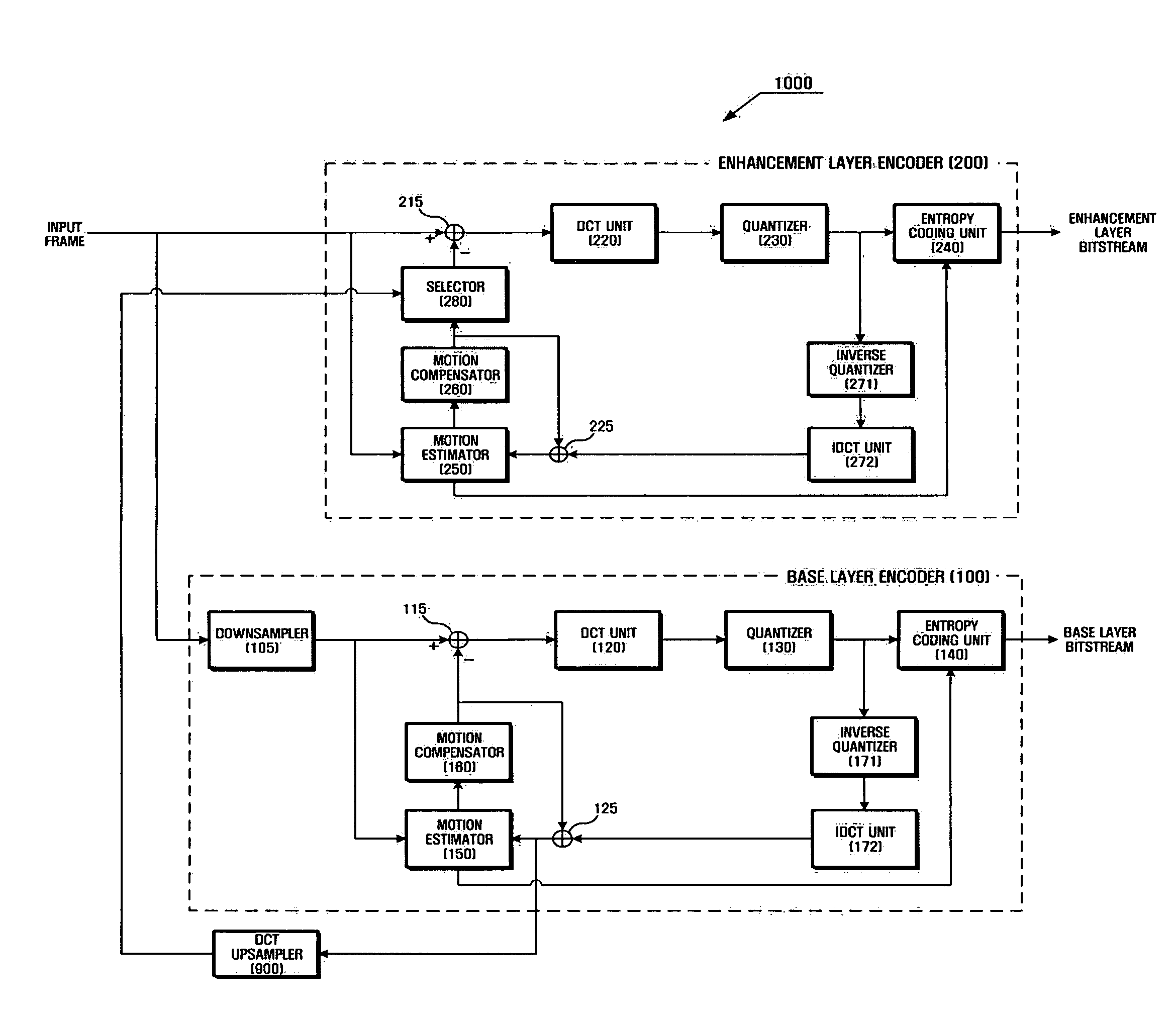
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding multi-layer video using DCT upsampling
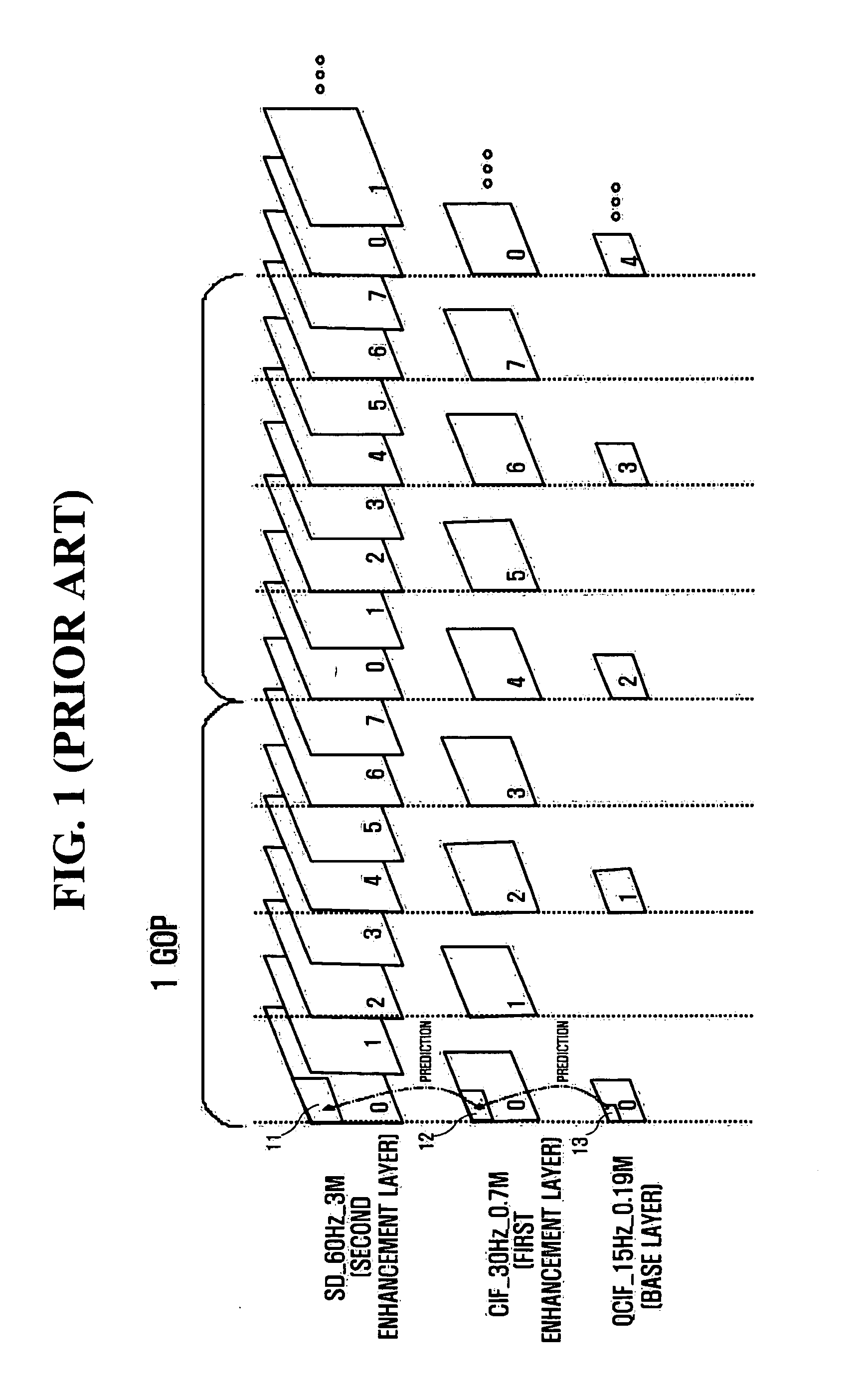
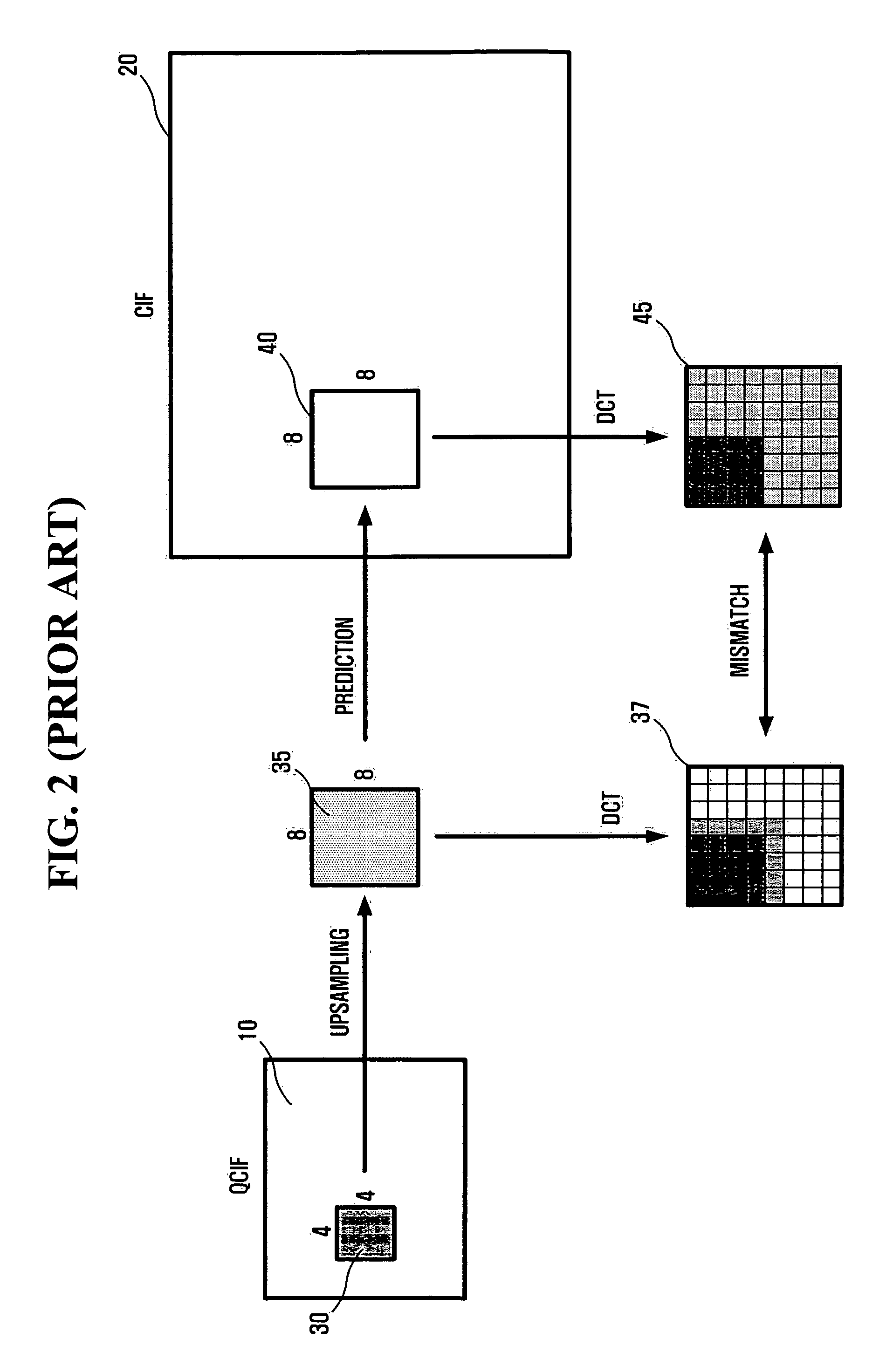
InactiveUS20060120448A1Reduce mismatchRotating vibration suppressionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCoding decodingDiscrete cosine transform
A method and apparatus for more efficiently upsampling a base layer to perform interlayer prediction during multi-layer video coding are provided. The method includes encoding and reconstructing a base layer frame, performing discrete cosine transform (DCT) upsampling on a second block of a predetermined size in the reconstructed frame corresponding to a first block in an enhancement layer frame, calculating a difference between the first block and a third block generated by the DCT upsampling, and encoding the difference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Efficient implementation of block-based transform on graphics processing unit
ActiveUS20060204119A1Improve processing speedPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputational scienceGraphics
Implementations of transforms, such as a discrete cosine transform (DCT) and inverse DCT on a graphics processing unit (GPU), use direct matrix multiplication. GPU features such as parallel graphics pipelines, multi-channel capability, and multiple render targets are used to obtain significantly faster processing speeds than on a conventional central processing unit (CPU). Various rendering modes may be used, such as point rendering mode, line rendering mode, and triangle or quadrilateral rendering mode.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
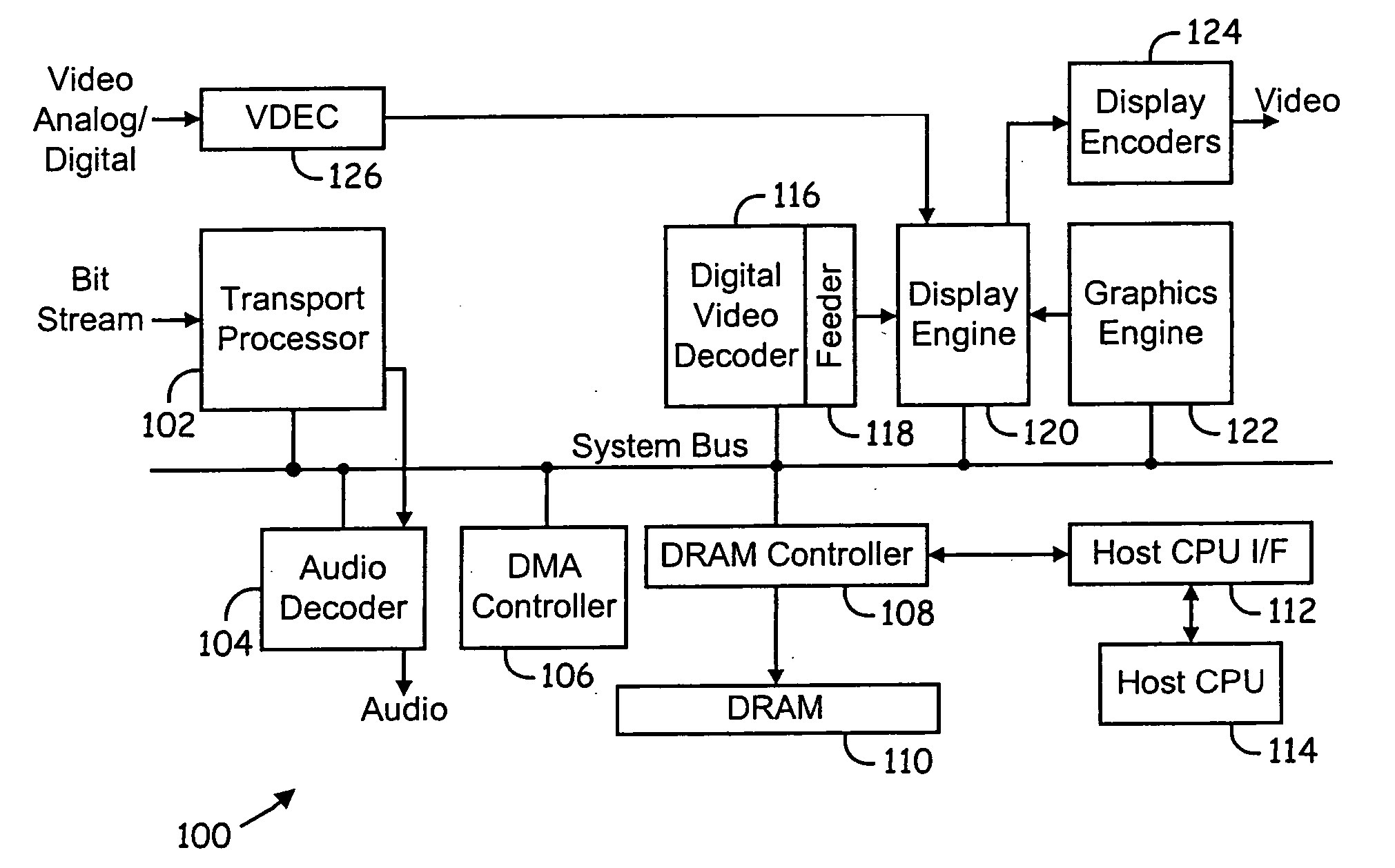
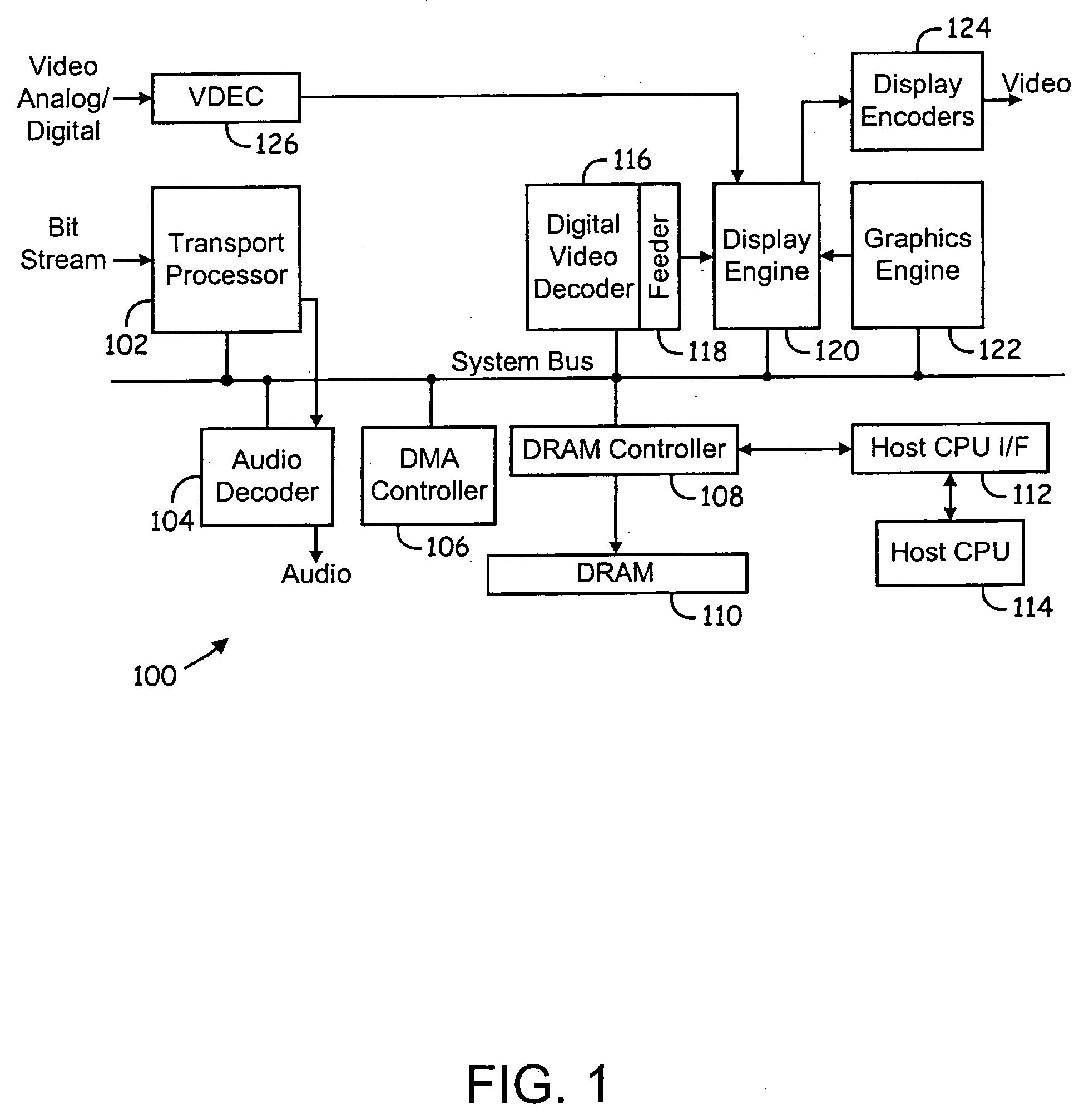
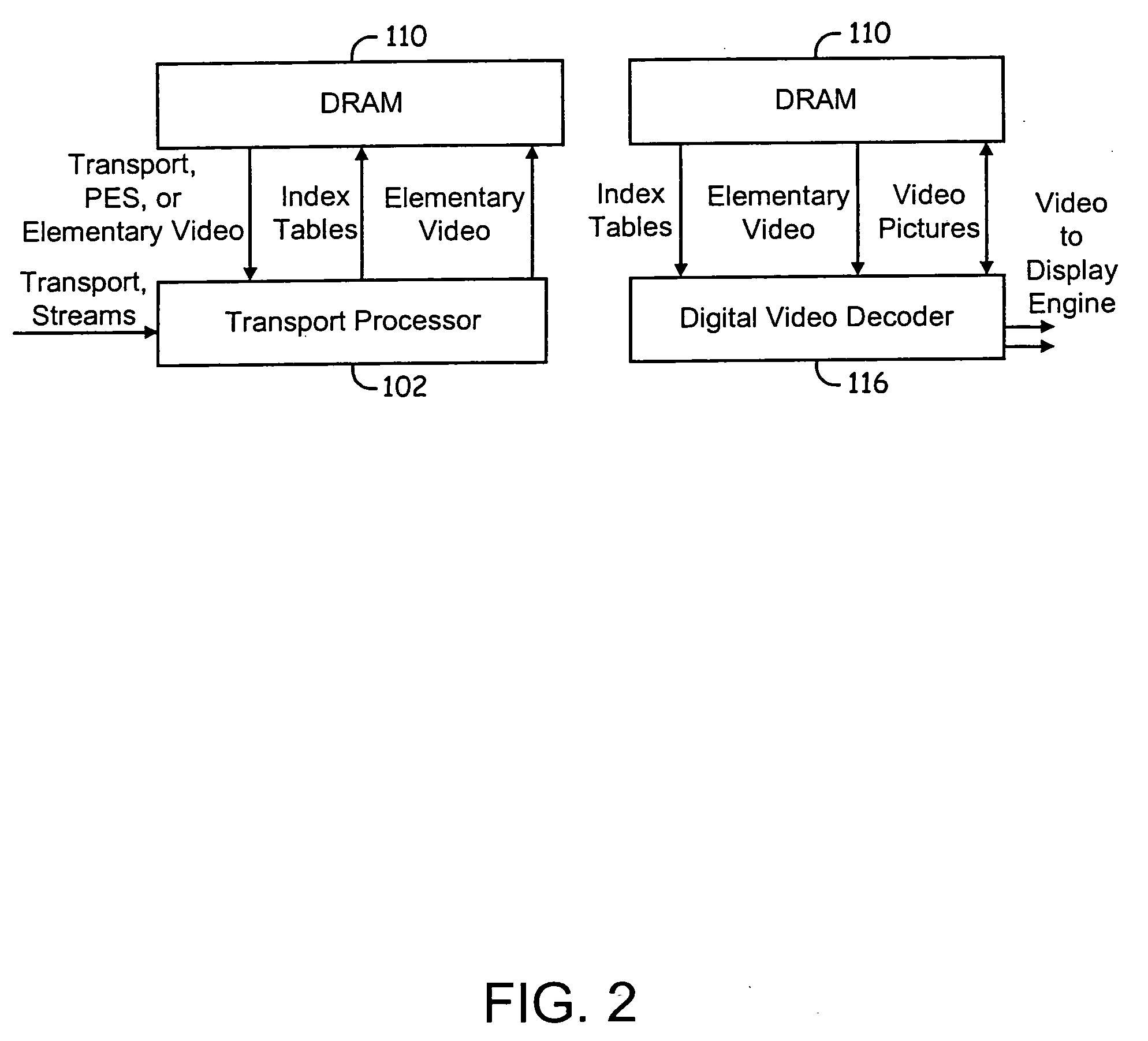
Video decoding system supporting multiple standards
ActiveUS20050123057A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDigital videoData stream
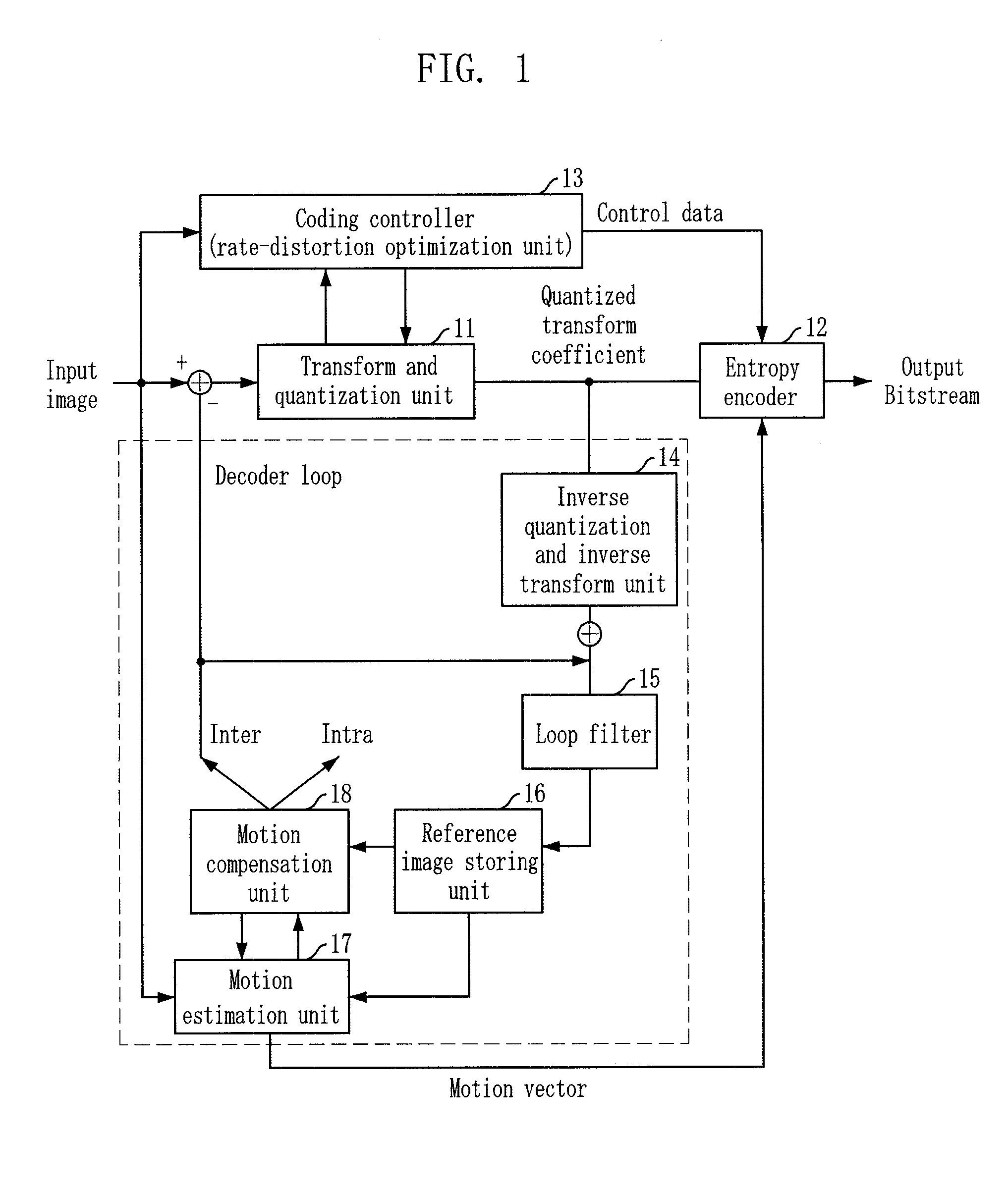
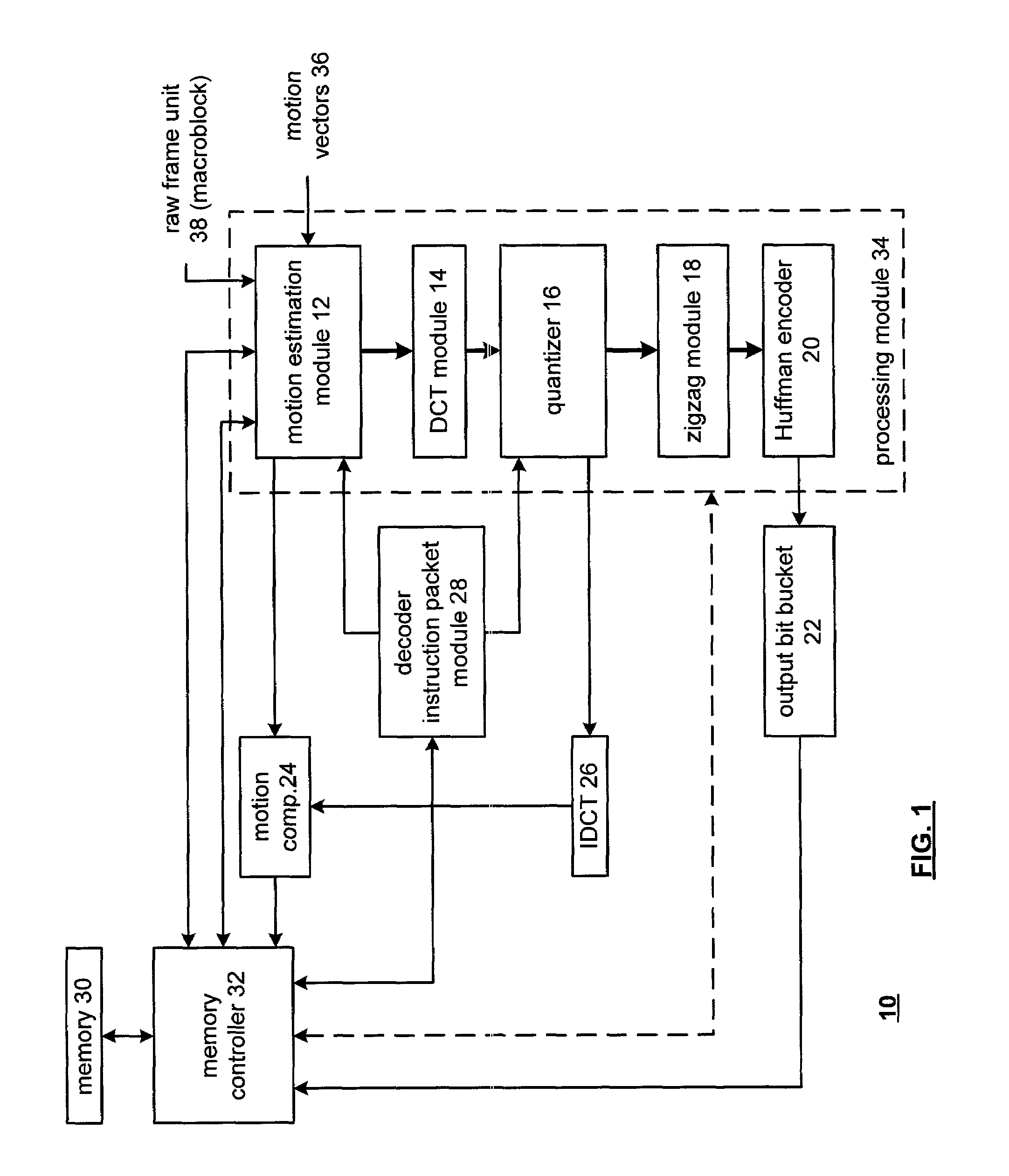
System and method for decoding digital video data. The decoding system employs hardware accelerators that assist a core processor in performing selected decoding tasks. The hardware accelerators are configurable to support a plurality of existing and future encoding / decoding formats. The accelerators are configurable to support substantially any existing or future encoding / decoding formats that fall into the general class of DCT-based, entropy decoded, block-motion-compensated compression algorithms. The hardware accelerators illustratively comprise a programmable entropy decoder, an inverse quantization module, a inverse discrete cosine transform module, a pixel filter, a motion compensation module and a de-blocking filter. The hardware accelerators function in a decoding pipeline wherein at any given stage in the pipeline, while a given function is being performed on a given macroblock, the next macroblock in the data stream is being worked on by the previous function in the pipeline.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
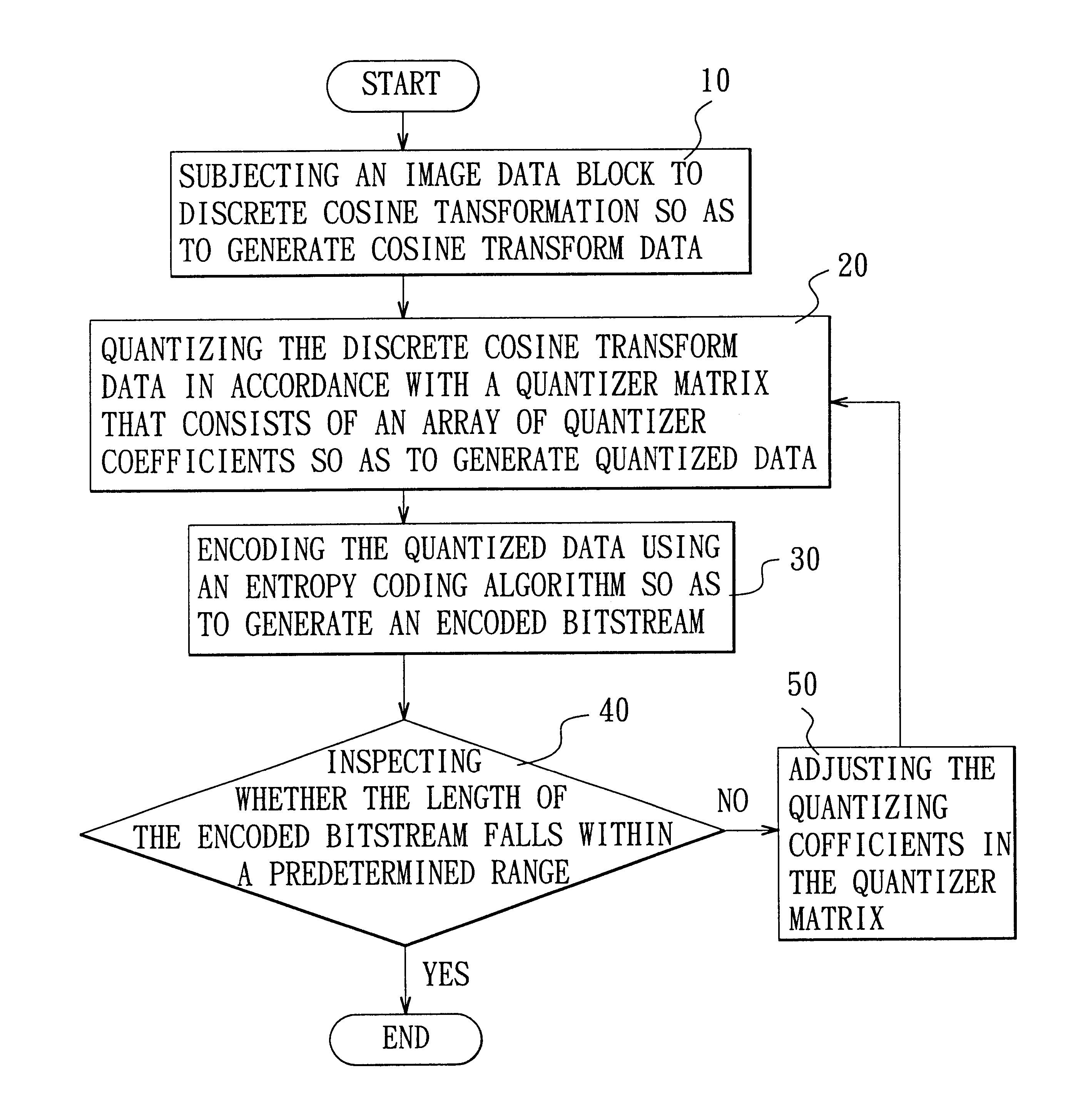
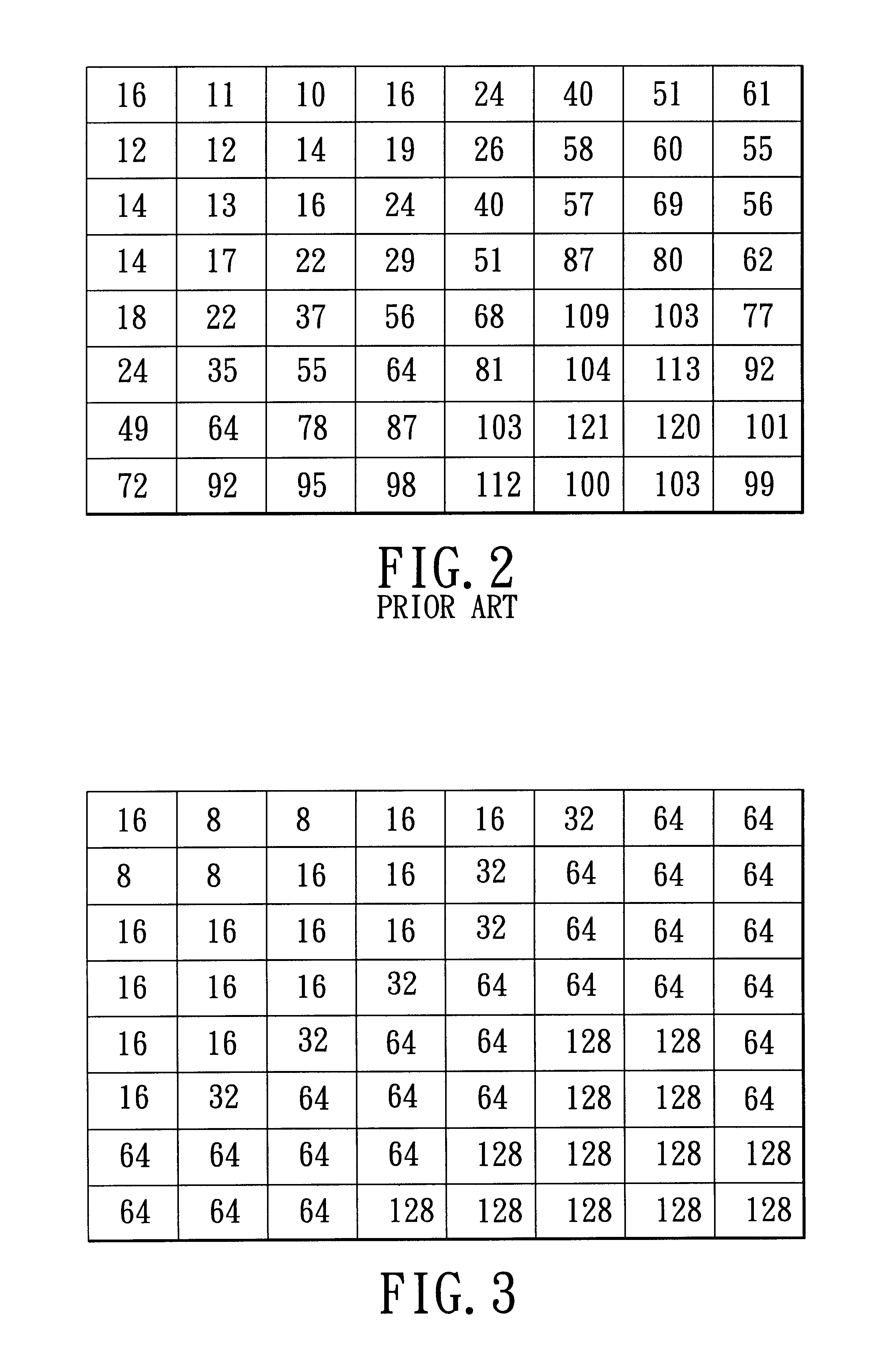
Adaptive quantization using code length in image compression
InactiveUS6882753B2Low memory and bus bandwidth requirementImprove processing efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionLandau quantization
A method is adapted for compressing an image data block, and includes the steps of:(a) subjecting the image data block to discrete cosine transformation so as to generate discrete cosine transform data;(b) quantizing the discrete cosine transform data in accordance with a quantizer matrix that consists of an array of quantizing coefficients so as to generate quantized data;(c) encoding the quantized data using an entropy coding algorithm so as to generate an encoded bitstream; and(d) when the length of the encoded bitstream does not fall within a predetermined range, adjusting the quantizing coefficients in the quantizer matrix and repeating steps (b) and (c) until the length of the encoded bitstream falls within the predetermined range.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
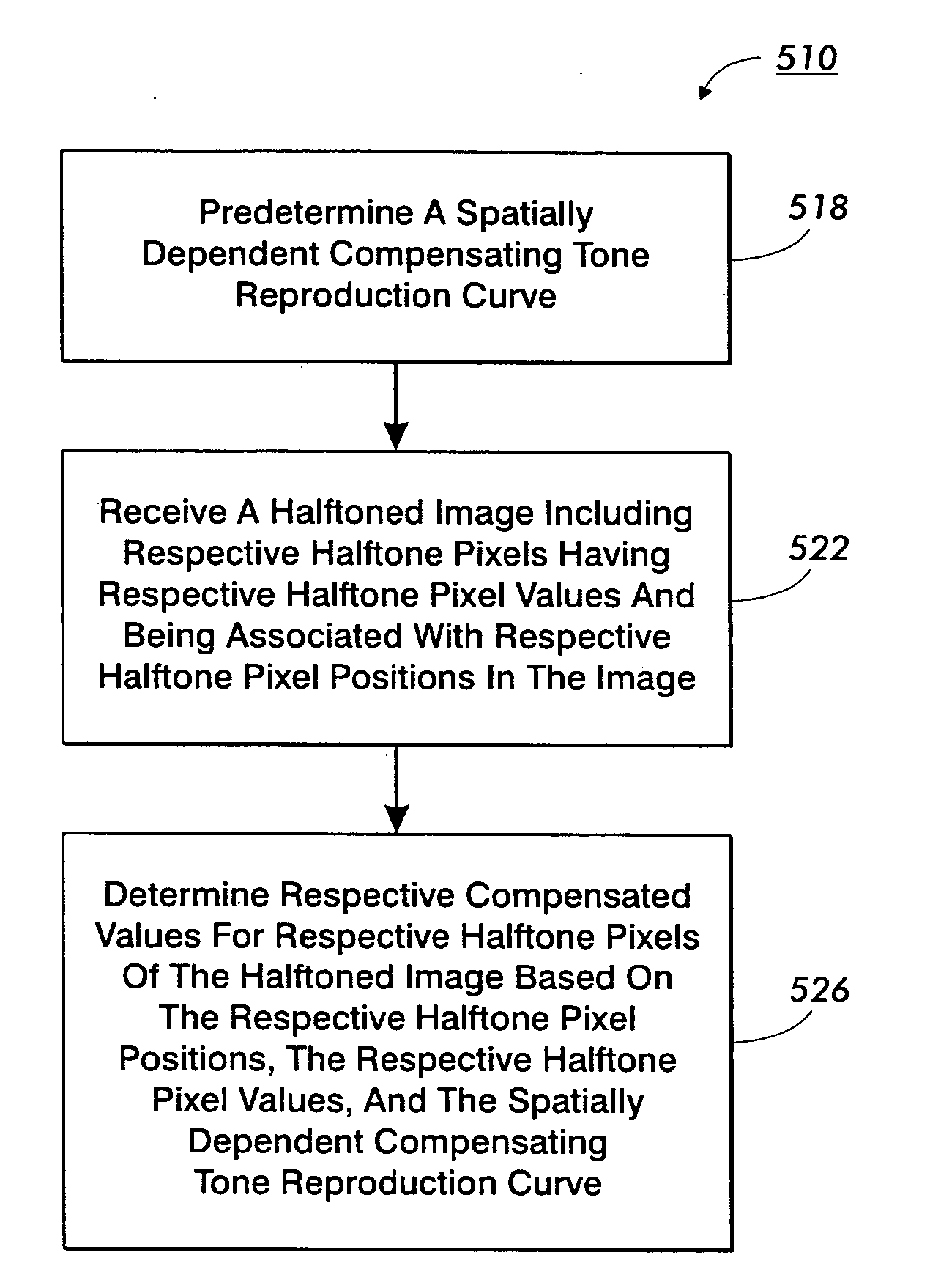
Uniformity compensation in halftoned images
ActiveUS20060077489A1Image enhancementDigitally marking record carriersSingular value decompositionTone reproduction
Compensation for rendering device non-uniformities is provided for halftoned images. A spatially dependent tone reproduction curve (TRC) provides compensation values. Pixel location information is used to access TRC values. For example, the values are modification values. The modification values are added to the pixel values to generate combined values. Quantization is applied to the combined values to prepare compensated image data for rendering. For example, Rank Ordered Error Diffusion is applied to the combined values. The combined values may include diffused error from previously processed pixels. Gray values may be estimated for the respective pixels. The estimated gray values may be used to access compensation information from a TRC that is both spatially and gray value dependent. Mathematical basis decomposition is used to reduce TRC memory requirements. For example, Discrete Cosine Transformation, Singular Value Decomposition or Principal Component Analysis is used to determine a compact form for the TRC.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Apparatus and Method For Encoding and Decoding Moving Picture Using Adaptive Scanning
ActiveUS20080285644A1Increase the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
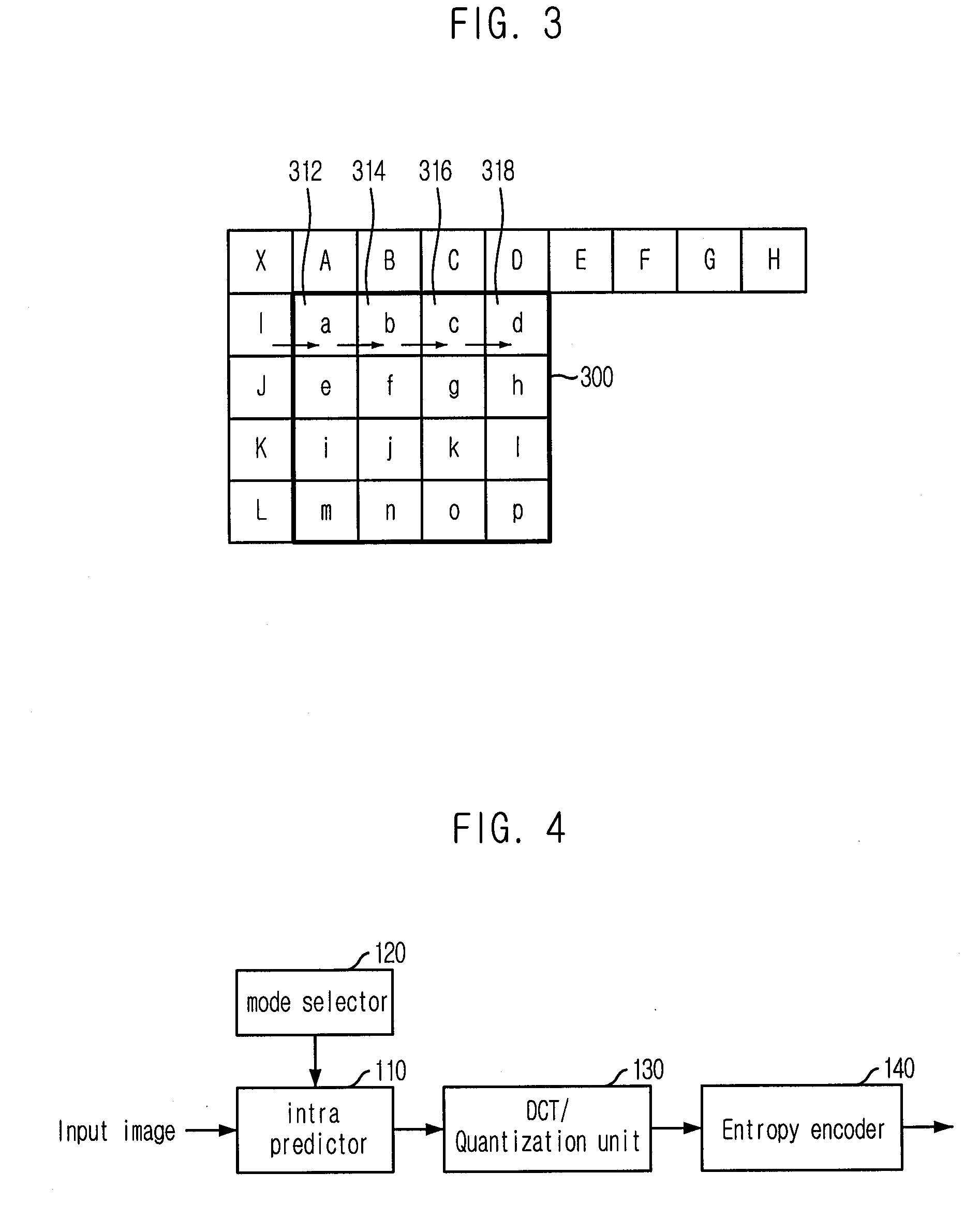
Provided is an apparatus and method for encoding / decoding moving pictures based on adaptive scanning. The moving picture apparatus and method can increase a compression rate based on adaptive scanning by performing intra prediction onto blocks of a predetermined size, and scanning coefficients acquired from Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) of a residue signal and quantization differently according to the intra prediction mode. The moving picture encoding apparatus includes: a mode selector for selecting and outputting a prediction mode; a predictor for predicting pixel values of pixels to be encoded of an input video based on the prediction mode to thereby output a residue signal block; a transform / quantization unit for performing DCT onto the residue signal block and quantizing the transformed residue signal block; and an encoder for adaptively scanning and encoding the quantized residue signal block based on the prediction mode.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Channel quality index feedback reduction for broadband systems
ActiveUS20080229177A1Network traffic/resource managementError detection/correctionCommunications systemCarrier signal
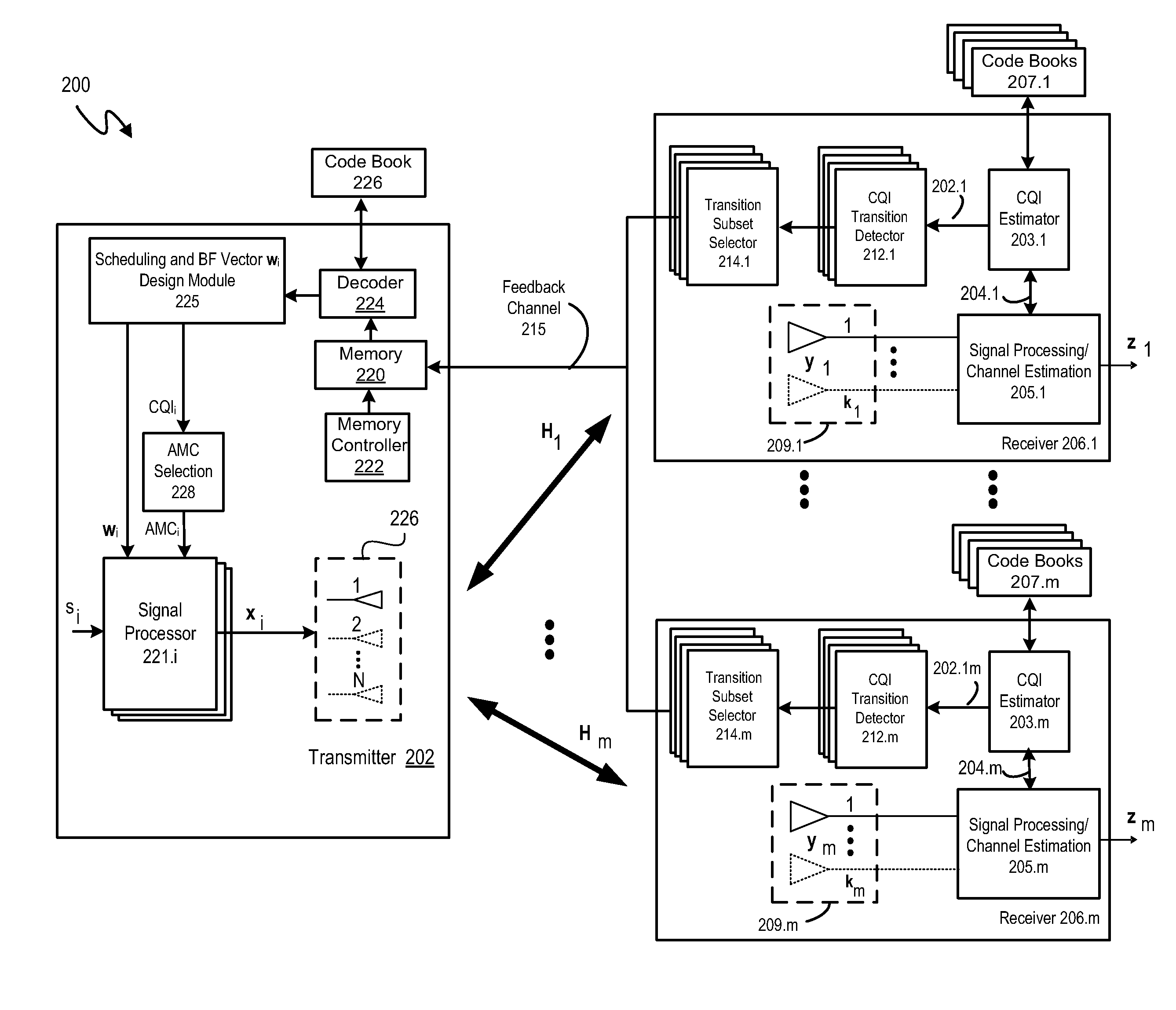
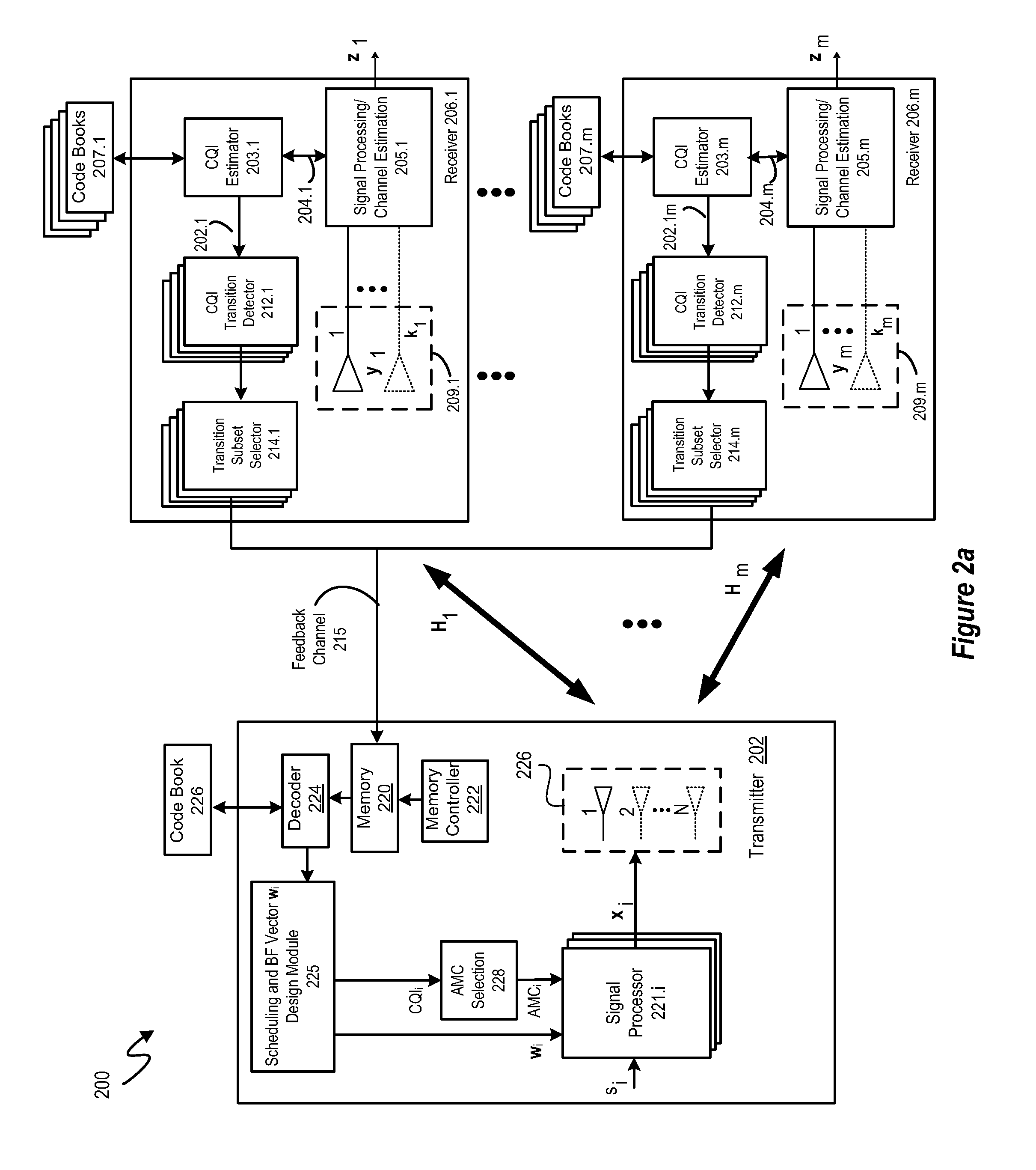
A system and methodology are disclosed for exploiting channel correlation in time and / or frequency to reduce CQI feedback in wireless communications systems. By compressing CQI feedback at the receiver to reduce redundancy in CQI feedback information that results from the channel correlation, the average feedback rate is reduced. In various embodiments, redundancy in time may be removed from the CQI feedback by monitoring variations of the CQI information in time at the receiver so that CQI information for a given CQI reporting instance is communicated to the transmitter only if it differs from the CQI information for the previous CQI reporting instance. Otherwise, no feedback is performed. In other embodiments, CQI feedback is compressed by performing a discrete cosine transform (DCT) on the CQI data. The compressed CQI feedback information is then communicated to the transmitter through the feedback control channel where it is decoded into the original CQI information and used to generate signal processing information for various sub-carriers.
Owner:APPLE INC
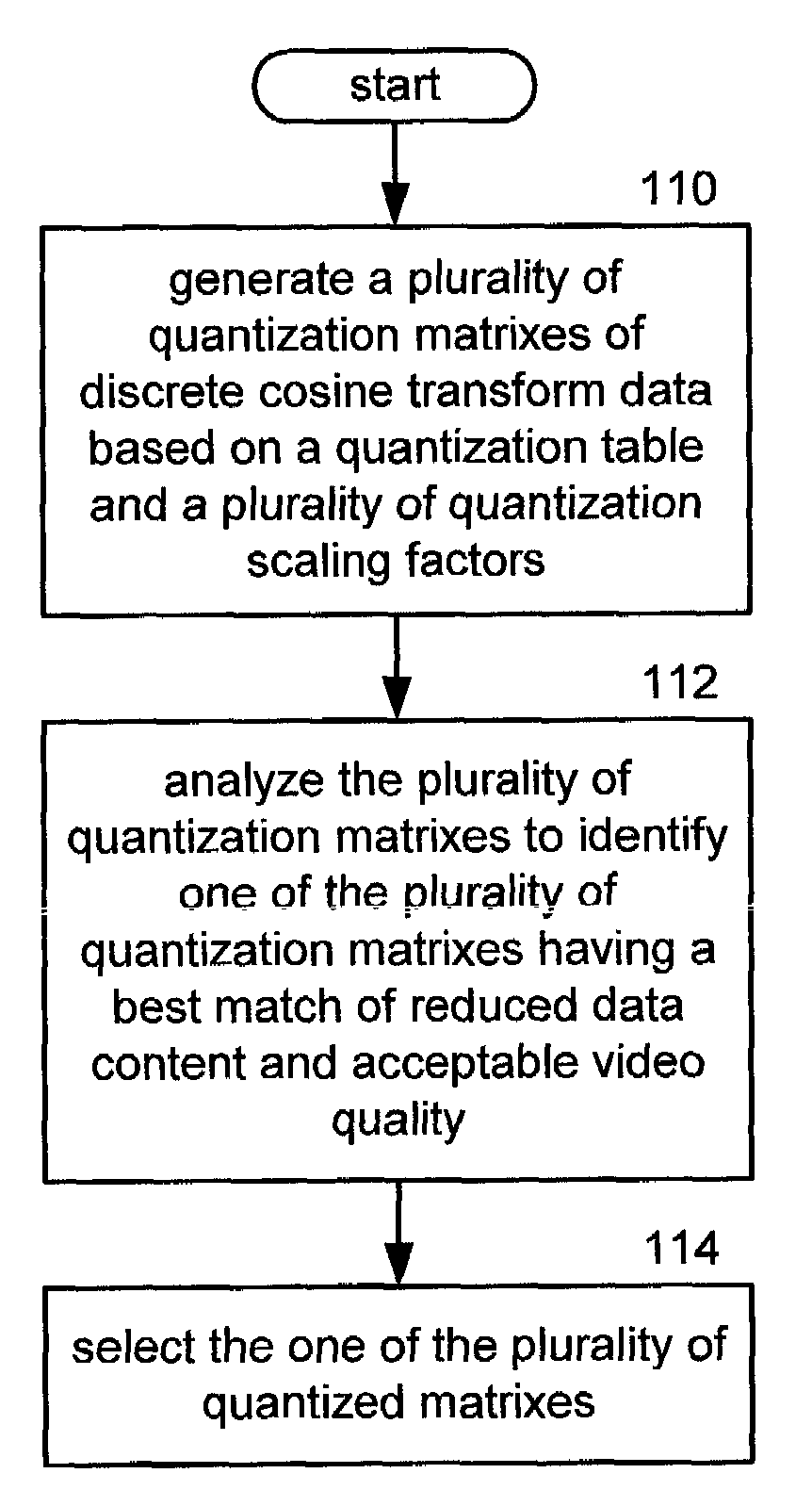
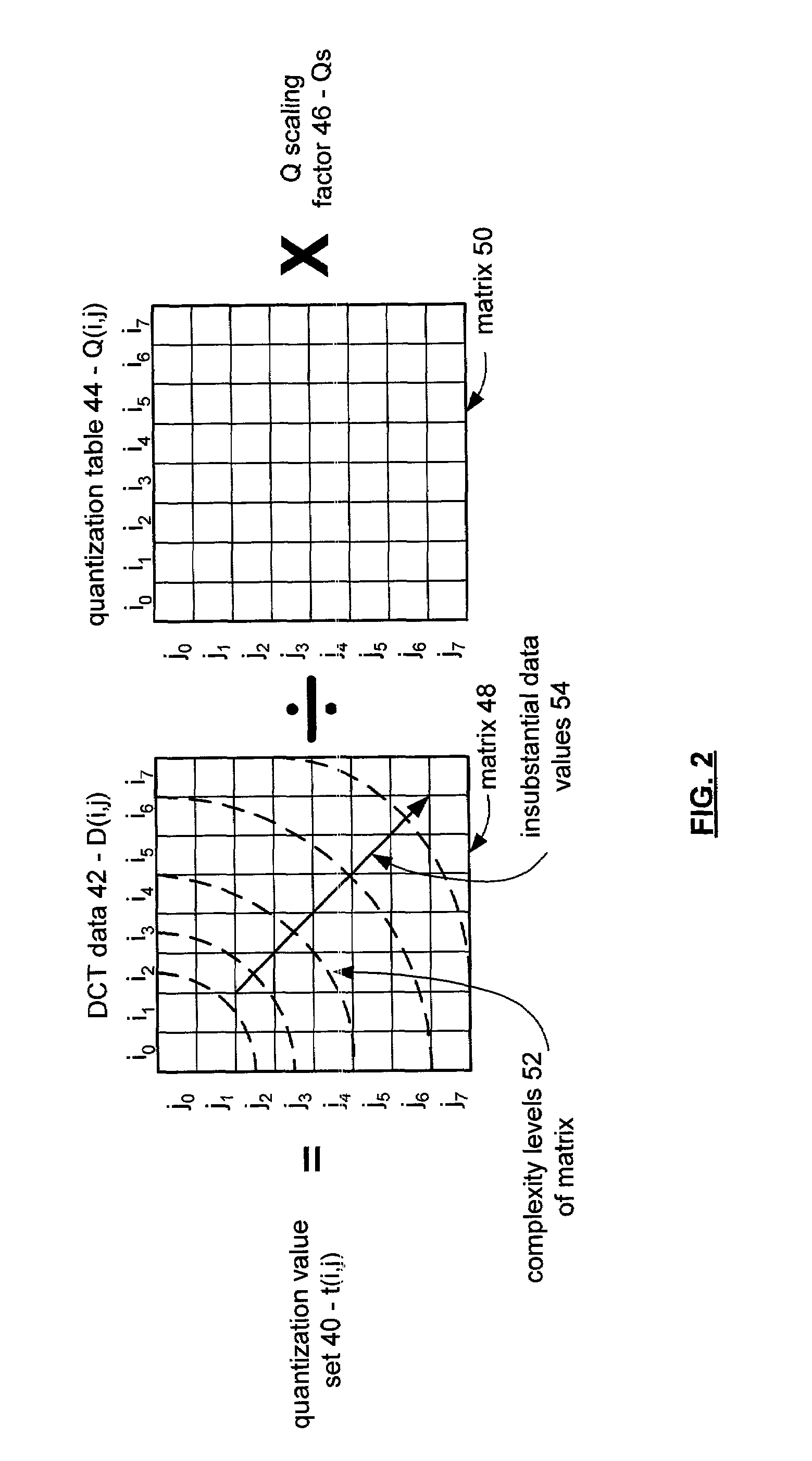
Method and apparatus for controlling amount of quantization processing in an encoder
InactiveUS7042941B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareDiscrete cosine transform
A method and apparatus for controlling the amount of quantization processing used within an encoder that compresses video and / or audio data include processing that begins by receiving discrete cosine transform data of a block of a frame of data. The process then proceeds by obtaining a quantization table related to the frame of data. The processing then continues by obtaining a quantization scaling factor related to the frame. The processing then continues by determining whether quantization processing limits have been exceeded for quantization of preceding blocks of the frame of data. If the number of bits processed for the preceding blocks exceeds a certain desired level, the processing increases the quantization scaling factor. The processing then continues by generating quantization data from the discrete cosine transform data, the quantization table and the increased quantization scaling factor.
Owner:VIXS SYSTEMS INC
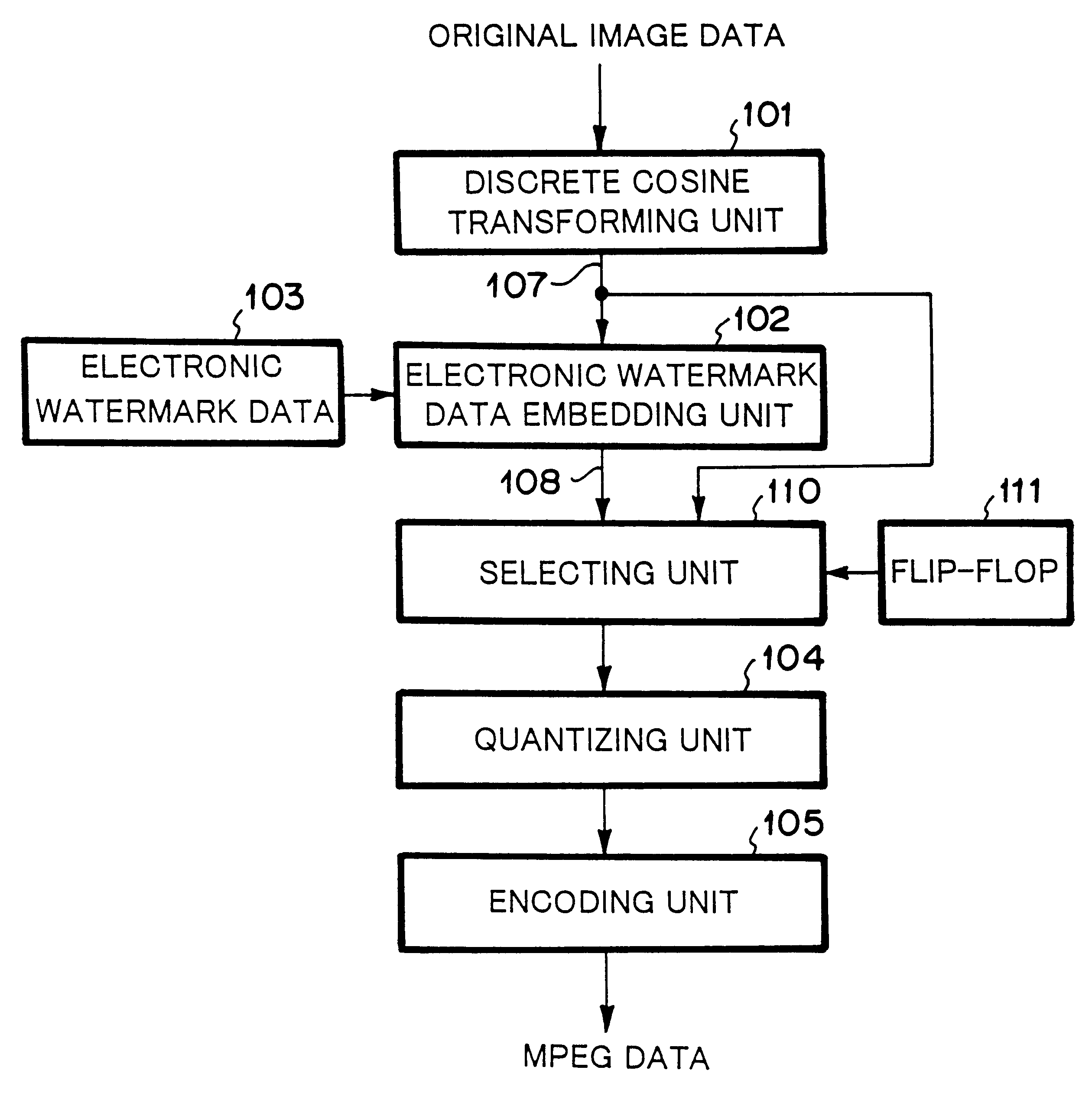
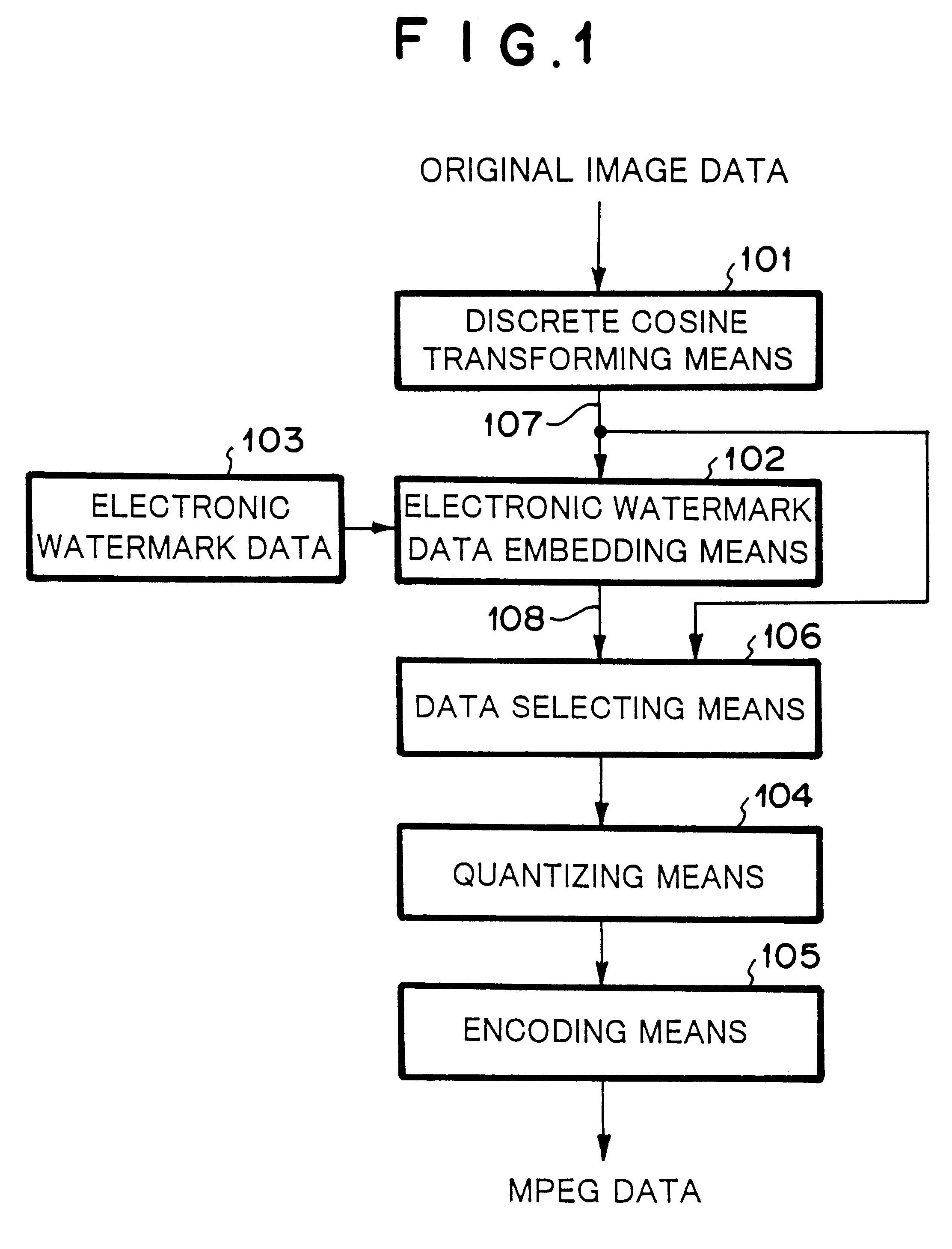
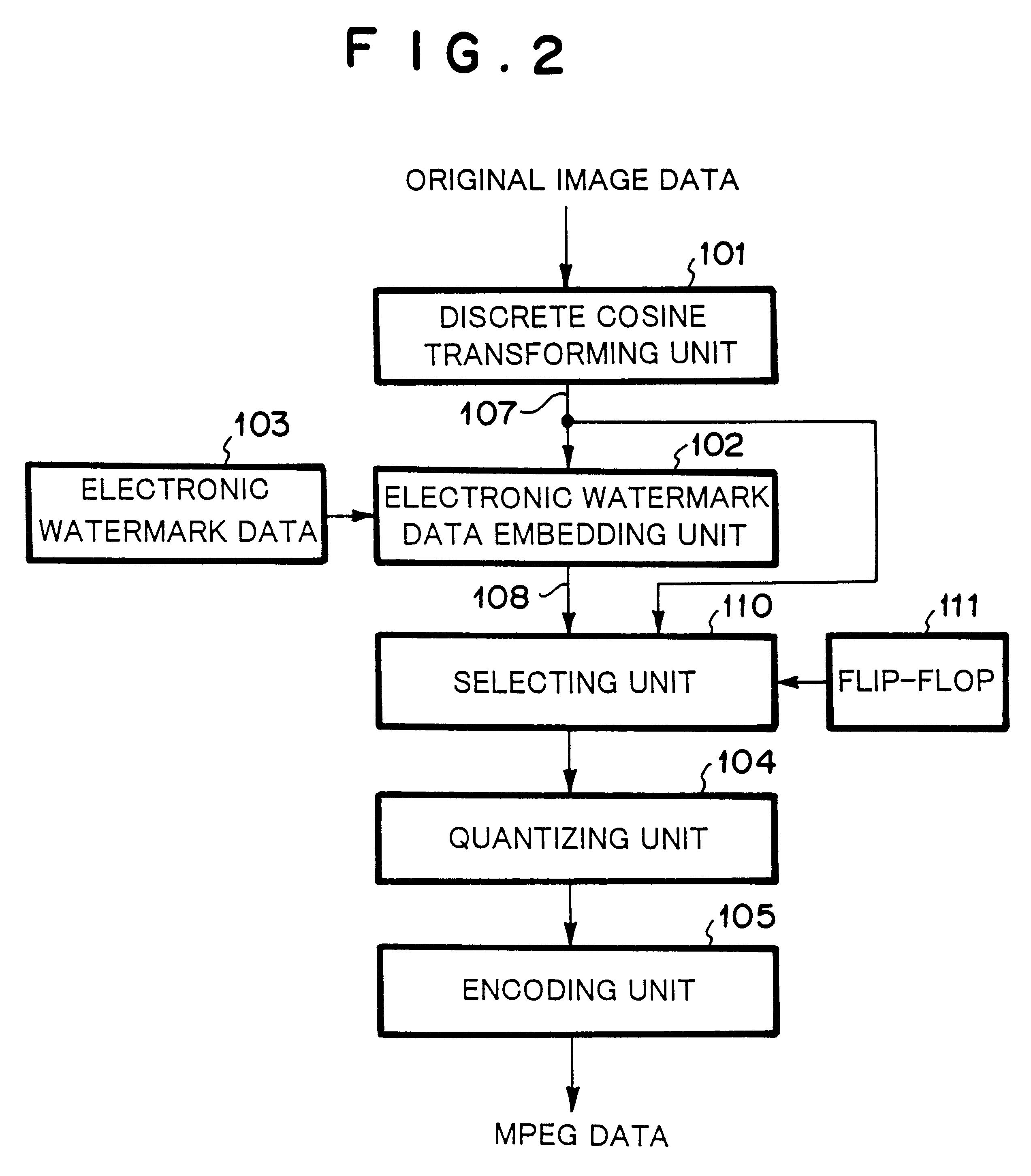
Image data encoding system and image inputting apparatus
InactiveUS6298142B1Character and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsPattern recognitionTransformer
An image data encoding system has a discrete cosine transformer for discrete cosine transforming the original image, an electronic watermark data embedding circuit for embedding the electronic watermark data in the data that has been transformed by the discrete cosine transformer, and a data selector for selecting the output signal of the discrete cosine transformer or the output signal of the electronic watermark data embedding circuit. Another image data encoding system has an electronic watermark embedding circuit for embedding electronic watermark data selected from a plurality of types of electronic watermark data to the digital image data, wherein at least one of the plurality of types of electronic watermark data is predetermined electronic watermark data that does not affect the digital image data even if the electronic watermark data is embedded in the digital image data.
Owner:NEC PERSONAL COMPUTERS LTD
Methods circuits and systems for transmission and reconstruction of a video block
InactiveUS20100014584A1Improve robustnessAvoid large deviationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Discrete cosine transform
Disclosed is a method, circuit and system for transmission and reconstruction of a video block. A video stream may be composed of sequential video frames, and each video frame may be composed of one or more video blocks including a set of pixels. Prior to transmission of the data associated with a video block, the video block data may be transformed into a set of transform (e.g. frequency) coefficients using a spatial to frequency transform such as a two dimensional discrete cosine transform. Selection of the subset of transform coefficients to be transmitted may be based on a characteristic of the video block.
Owner:AMIMON
JPEG packed block structure
InactiveUS20020076115A1Not impose processing costSpeedCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionENCODEDiscrete cosine transform
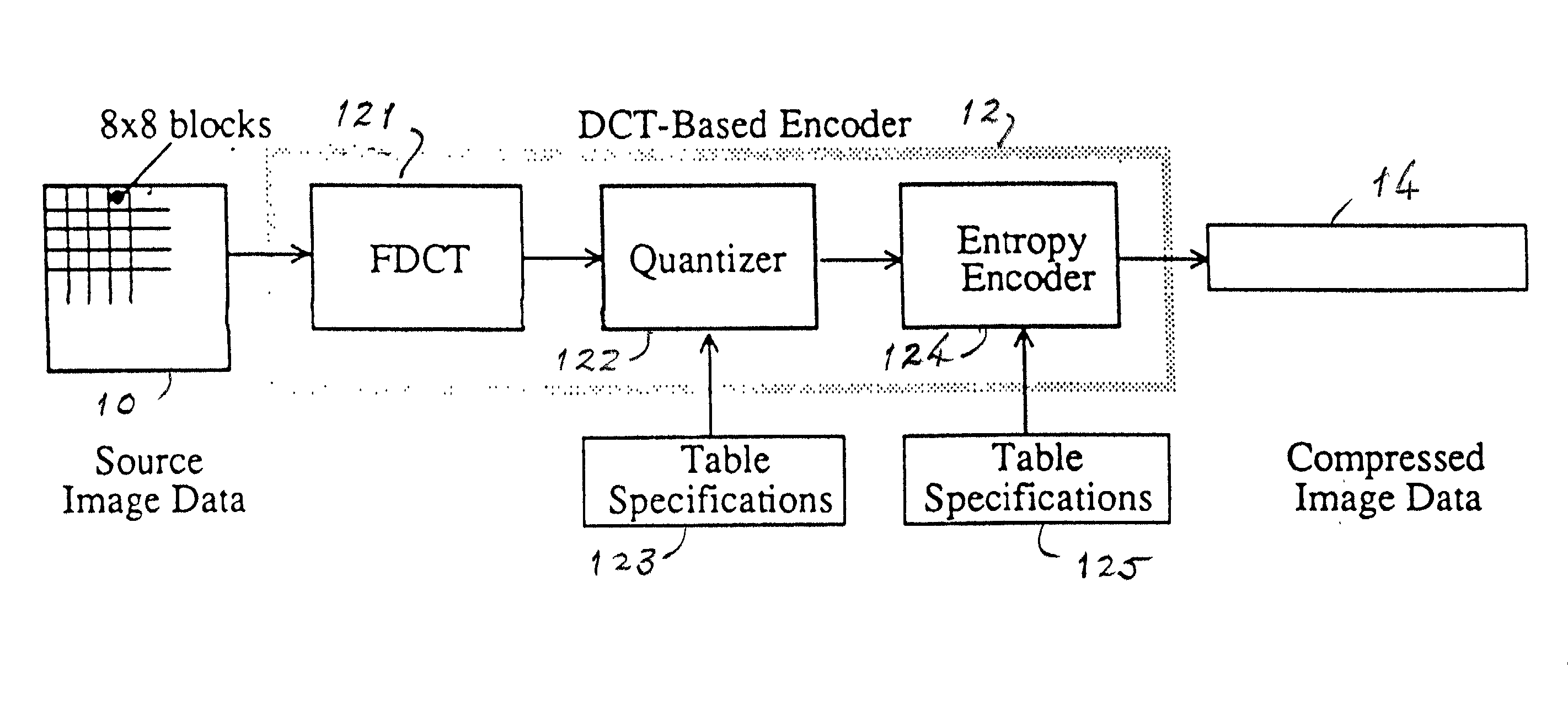
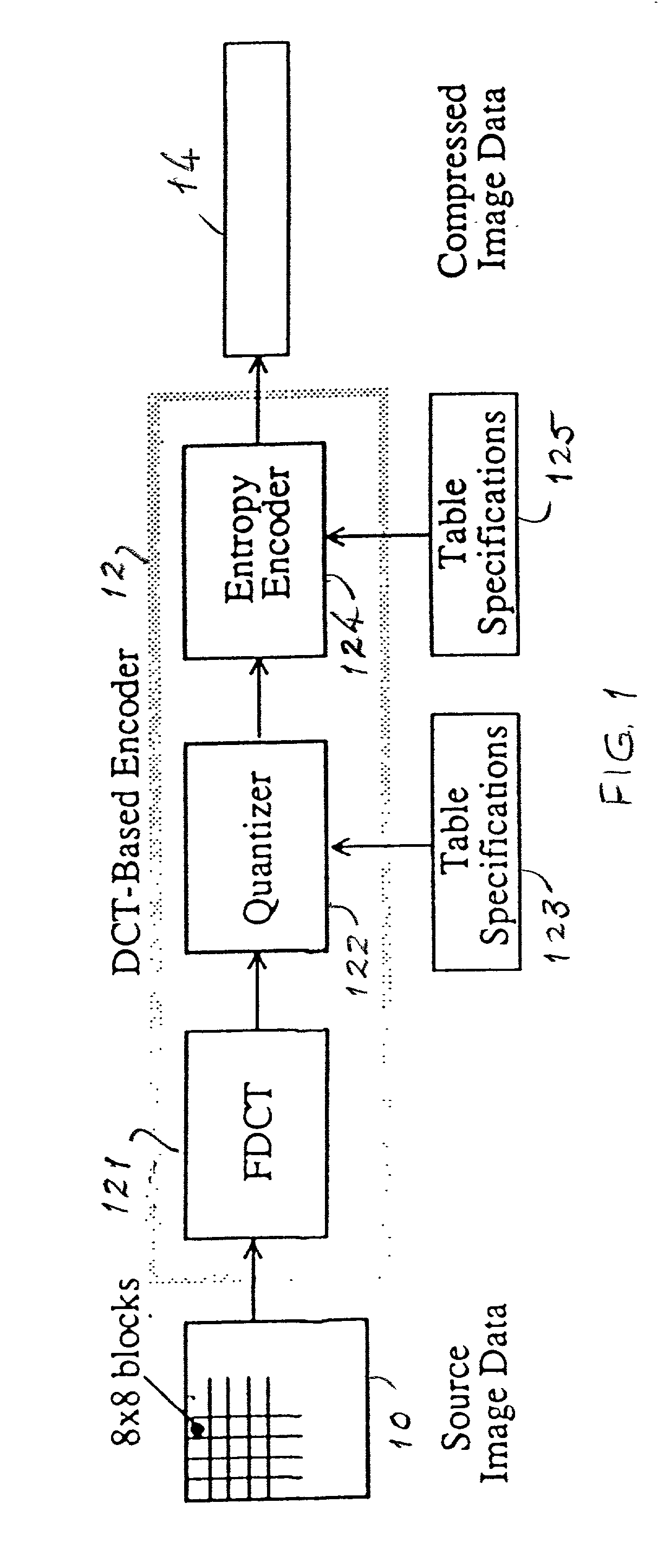
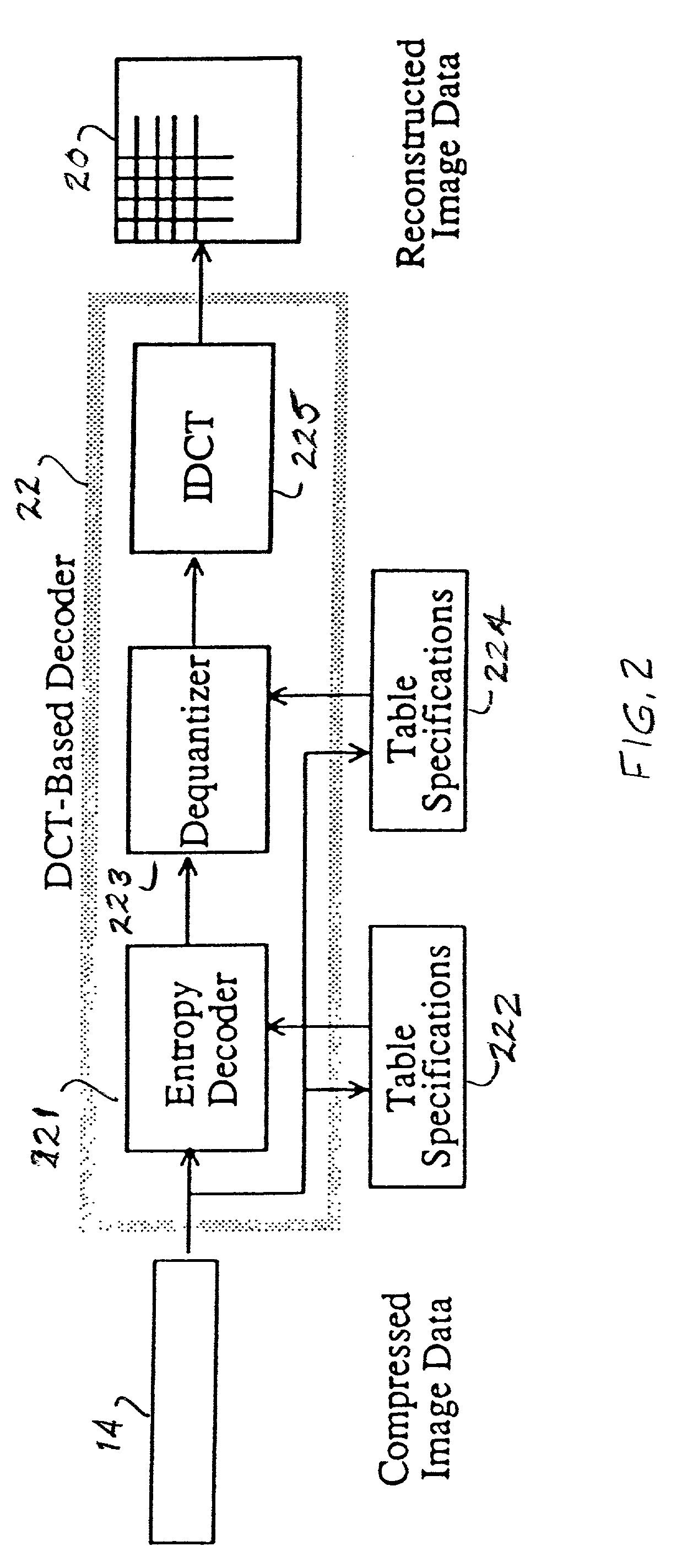
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) images are encoded and decoded as fast as possible for a variety of disparate applications. A novel structure stores the 8x8 Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) blocks after entropy decoding in a JPEG decoder or after the Forward Discrete Cosine Transform (FDCT) in the JPEG encoder to use as an intermediate format between transform processes. The format was chosen to speed up the entropy decode and encode processes and is based on the information needed for the JPEG Huffman entropy coding, but lends itself to fast execution of other DCT based transforms, including arithmetic entropy coding.
Owner:RICOH KK
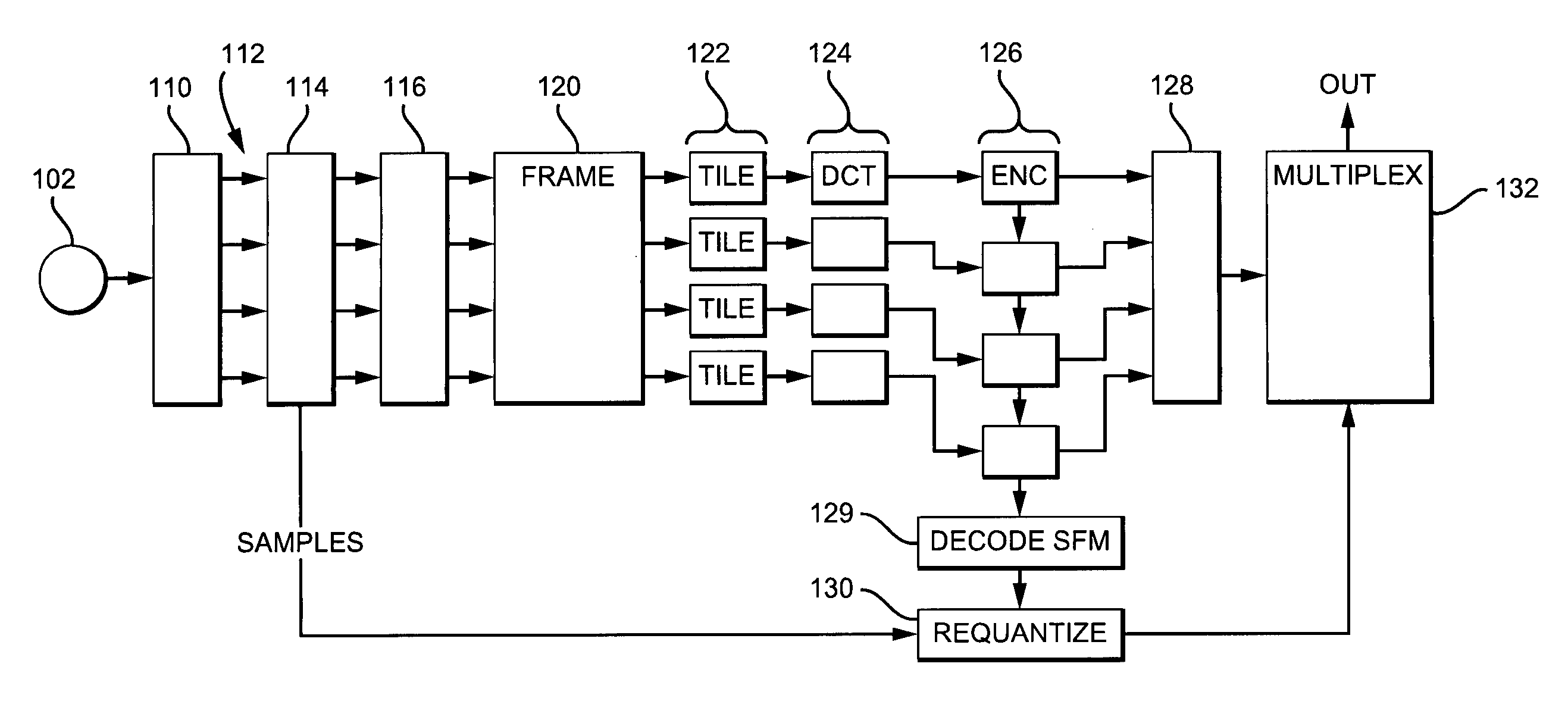
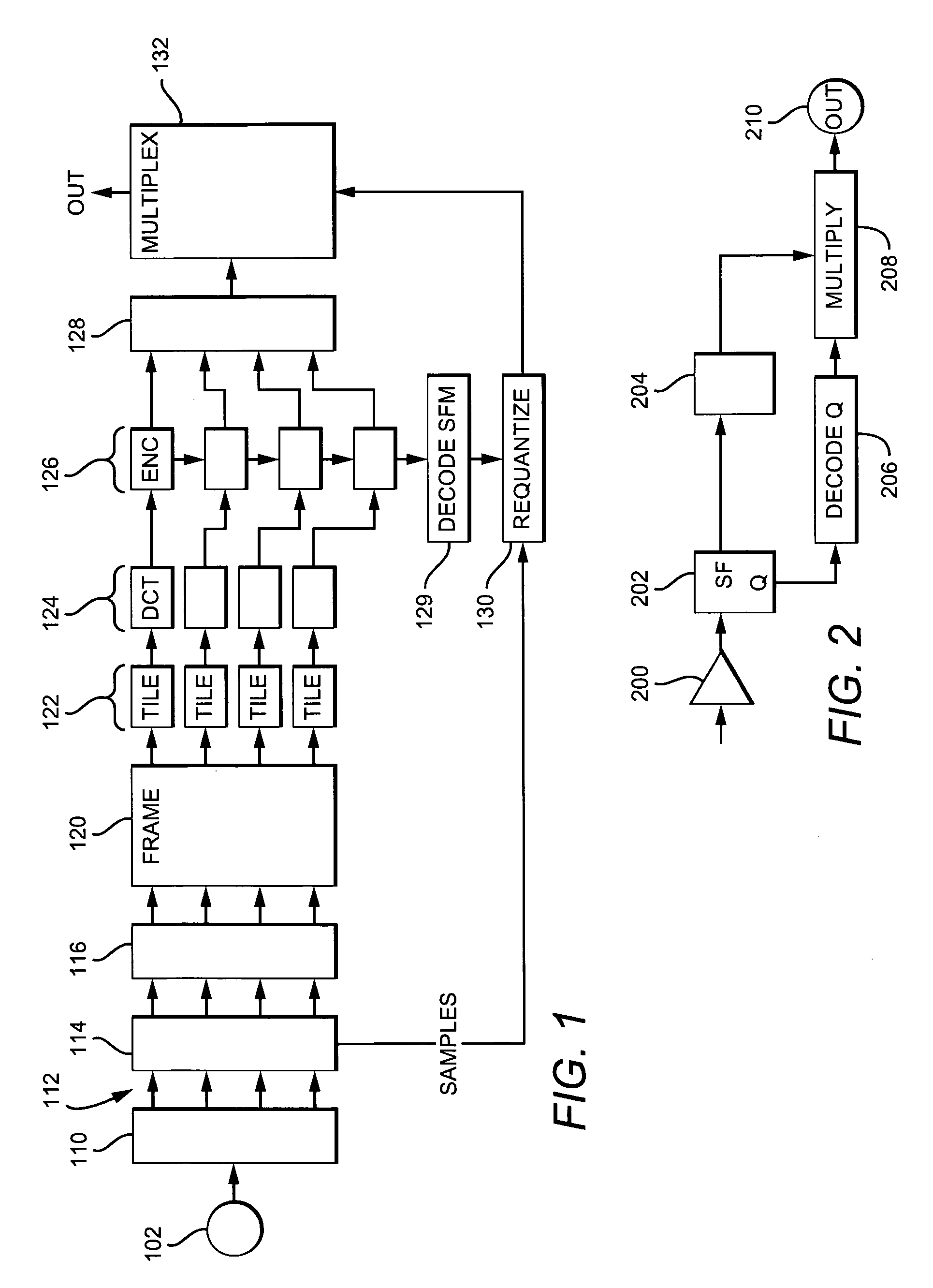
Compression of audio scale-factors by two-dimensional transformation
Digital audio samples are represented as a product of scale factors codes and corresponding quantity codes, sometimes referred to as exponent / mantissa format. To compress audio data, scale factors are organized by sample time and frequency either by filtering or frequency transformation, into a two-dimensional frame. The frame may be decomposed into “tiles” by partition. One or more such scale factor tiles are compressed by transformation by a two-dimensional, orthogonal transformation such as a two dimensional discrete cosine transform. Optional further encoding is applied to reduce redundancy. A decoding method and an encoded machine readable medium complement the method of encoding.
Owner:DTS
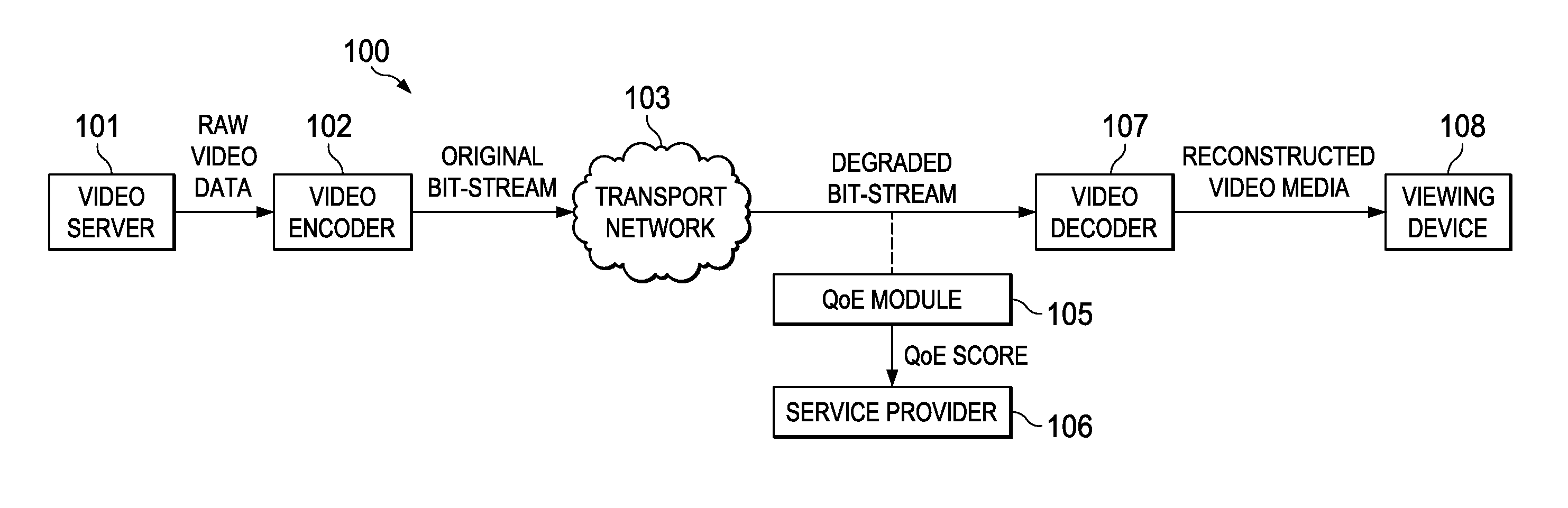
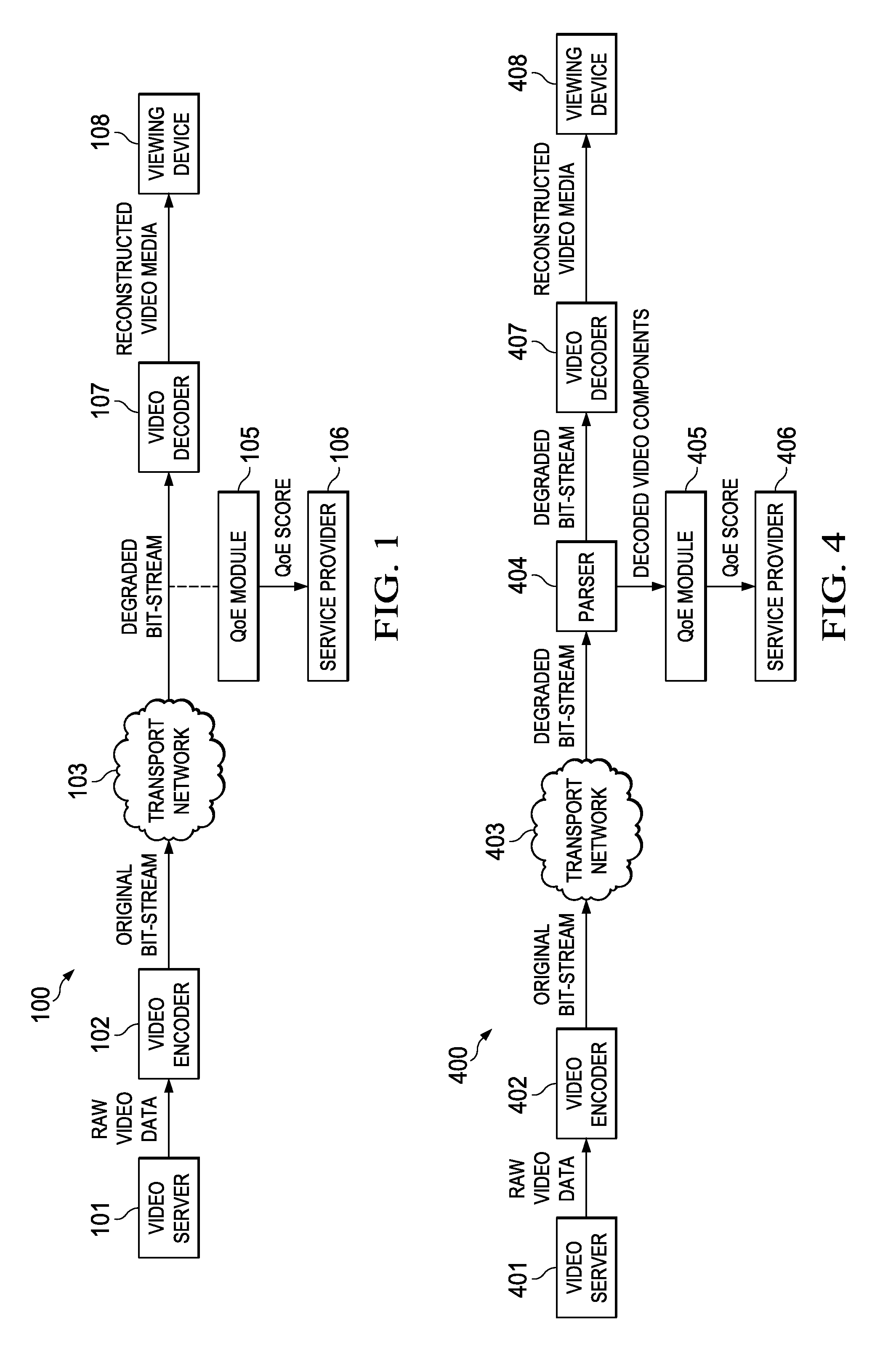
No-Reference Video/Image Quality Measurement with Compressed Domain Features
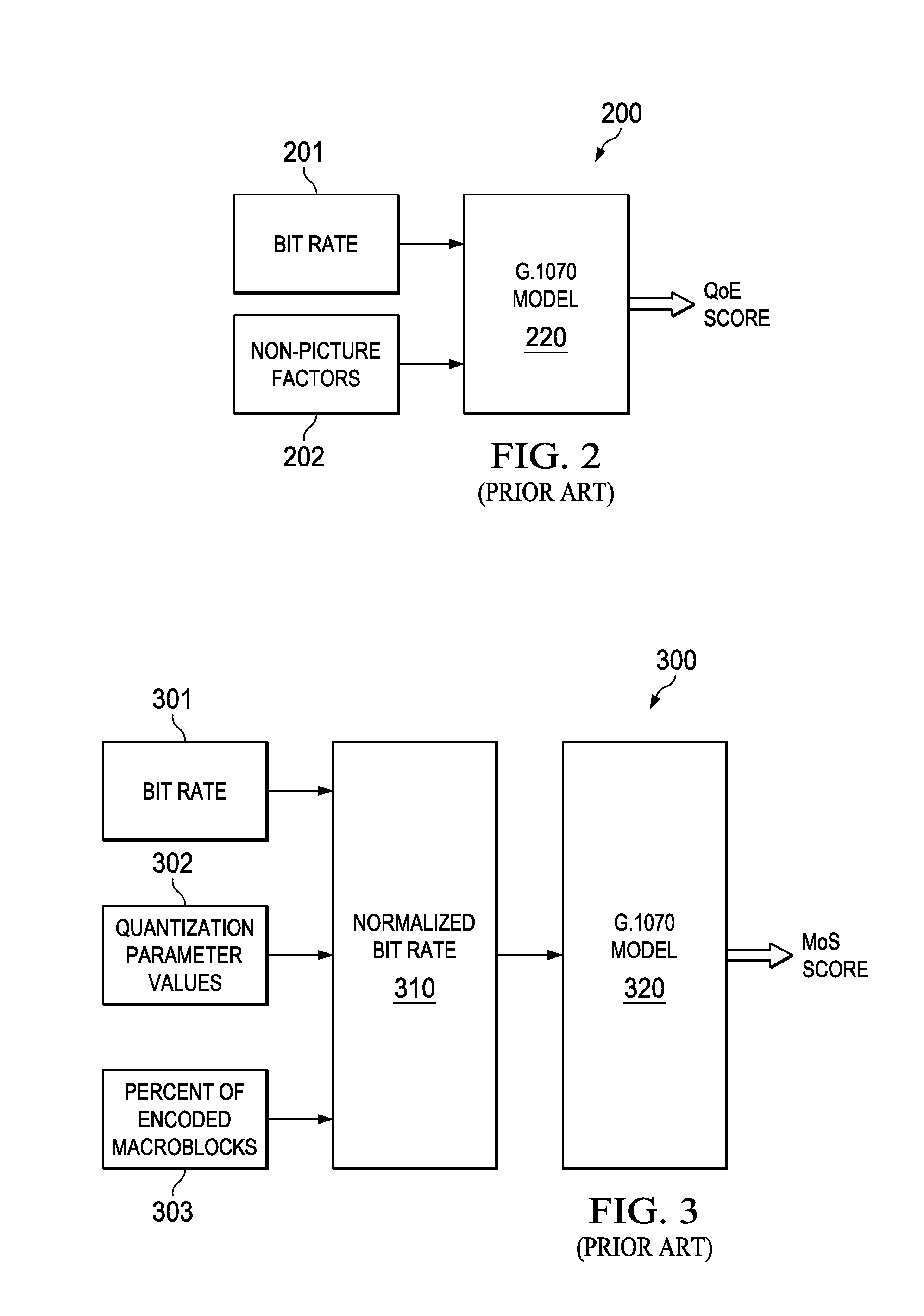
Techniques for objectively determining perceived video / image quality, the techniques including receiving a degraded bit-stream comprising encoded video / image data, and subsequently parsing the bit-stream to extract one or more video / image coding components. The video coding components may include intra-prediction modes, discrete cosine transform (DCT) coefficients, motion information, or combinations thereof, and may be used as a basis for objectively predicting a Quality of Experience (QoE) or Motion Opinion Score (MOS) score of the degraded bit-stream.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Video compression coding-decoding method
InactiveCN1658673ALess importantRaise the importanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationMotion vectorVideo encoding
A compressing encoding and decoding method which includes the following: encode the video compressed signals with the programs, discrete cosine transform DCT; transform and quantitate; set the channel buffer storage before the encoding bit flow gets into the channel; the buffer storage must have a control mechanism; movement estimate; the position excursion is described by the movement vector, and a movement vector represents the displacement in the two actinic and vertical directions; as movement estimating, the P frame image uses the former most recent decoded I frame or P frame as the referenced image called the forward forecast; the movement compensation; the movement vector calculated by the movement estimate moves the macro piece in the referenced image to the corresponding position in the actinic and vertical direction, then namely produce the forecast to the compressed image; and search and calculate the subpels; the quantitation, storage and movement search after the sampling signals are made the discrete cosine transform DCT transform are all completed in the frequency field. The video encoder finishes all the calculation in the frequency field. The compressed rate is high, and the calculating quantity is small.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
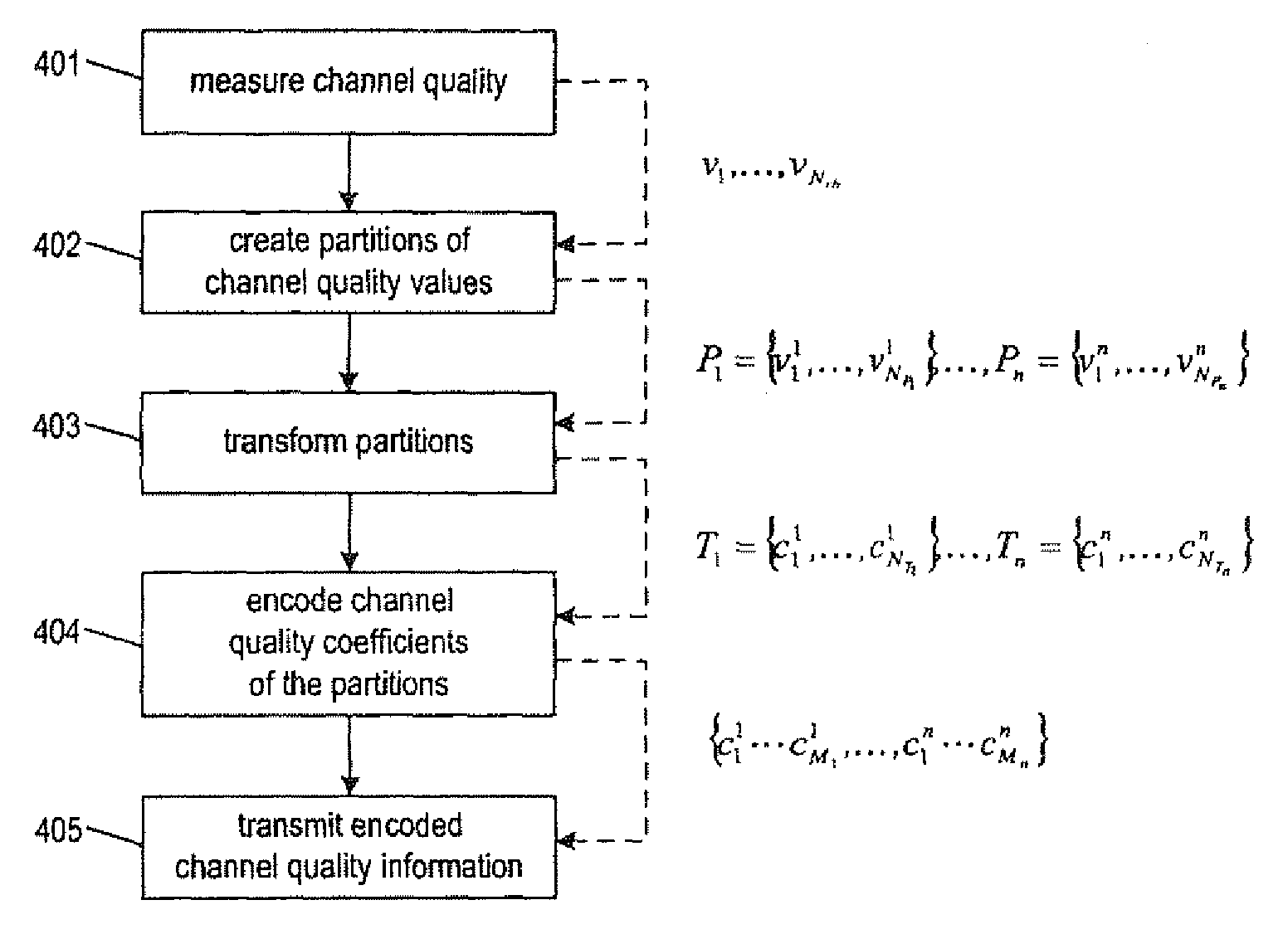
Communication scheme for channel quality information
ActiveUS20100015923A1Reduce overheadAccurate reconstructionTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel state informationCommunications system
The invention relates to a method for transmitting and a method for reconstructing channel quality information in a communication system. Further, the invention also provides a transmitter and receiver performing these methods, respectively. The invention suggests a scheme for communicating channel quality measures that on the one hand allows for an accurate reconstruction of the channel quality measures at the receiver and on the other hand requires an acceptable transmission overhead. This is achieved by partitioning channel quality measures into at least two partitions and to compress the values partition-wise, for example by means of a discrete cosine transform and the transmission of only a subset of the resulting coefficients.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
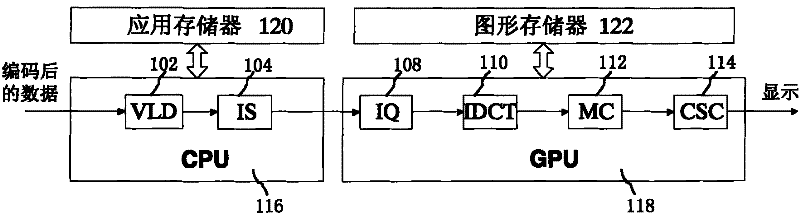
Video decoding method and system
InactiveCN102223525AProcessing speedTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDiscrete cosine transformResidual value
The invention discloses a video decoding method and a video decoding system. The method comprises the following steps of: performing variable length decoding and reverse scanning on coded video data of a picture by utilizing a central processing unit to acquire the video data of the picture subjected to variable length decoding and reverse scanning; performing reverse quantization, reverse discrete cosine transform, motion compensation and color space transform on the video data of the picture subjected to variable length decoding and reverse scanning by utilizing a programmable graphic processing unit to acquire the video data of the picture subjected to the decoding, wherein the video data of the picture subjected to variable length decoding, reverse quantization and reverse discrete cosine transform comprises a brightness residual value and a chromaticity residual value of each pixel in the picture. The brightness residual value and the chromaticity residual value of any pixel in the picture are subjected to motion compensation according to an equality 1 to acquire a brightness value and a chromaticity value of the pixel, namely the equality 1 as follows: sum=residual + (1.0-MC_flag)*128.0 + MC_flag*prediction (1).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
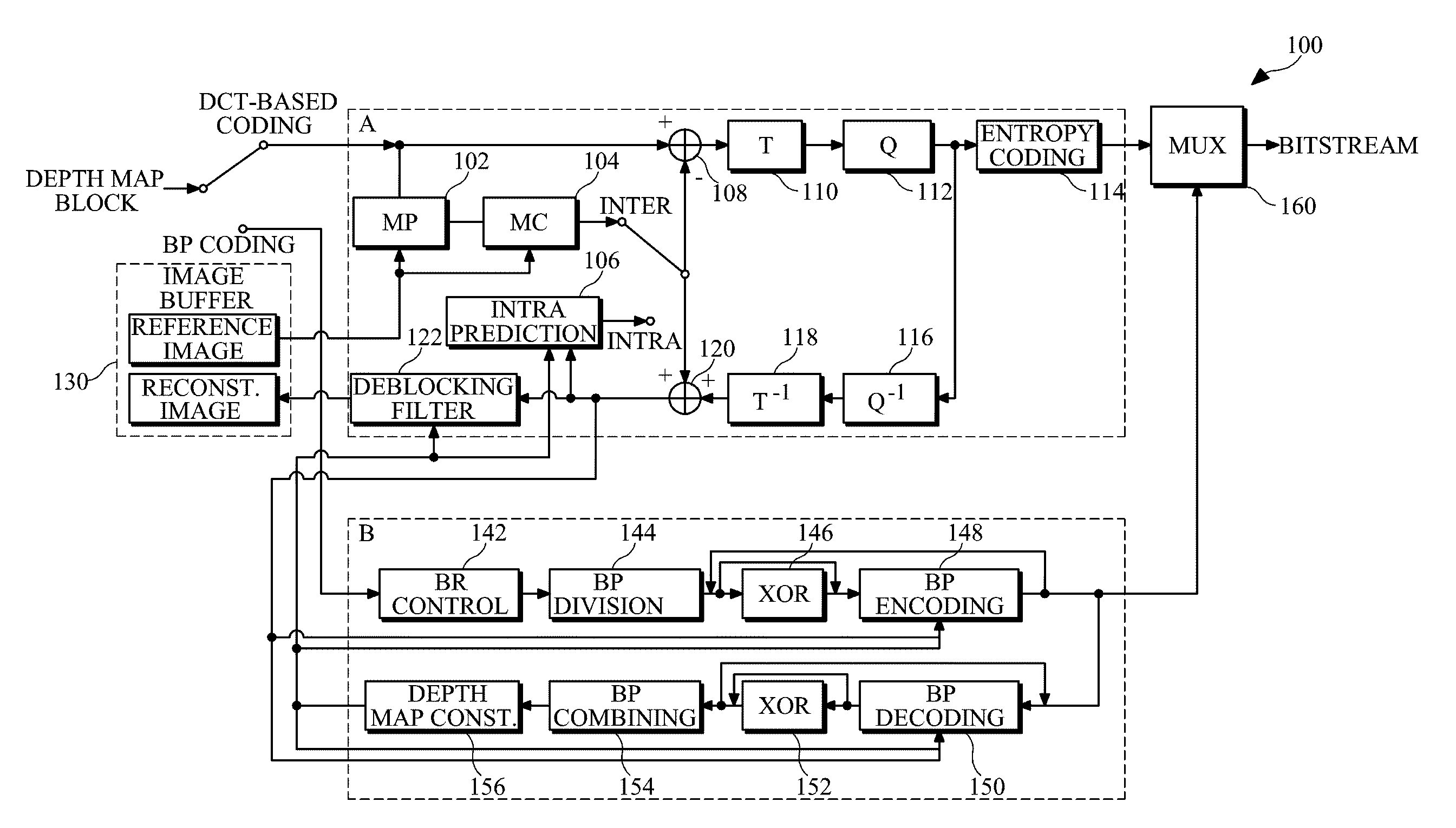
Method and apparatus for block-based depth map coding and 3D video coding method using the same
ActiveUS20100231688A1Maximize advantageEfficient compressionPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer architectureDepth map coding
Provided are a block-based depth map coding method and apparatus and a 3D video coding method using the same. The depth map coding method decodes a received bitstream in units of blocks of a predetermined size using a bitplane decoding method to reconstruct a depth map. For example, the depth map coding method may decode the bitstream in units of blocks using the bitplane decoding method or an existing Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)-based decoding method adaptively according to decoded coding mode information. The bitplane decoding method may include adaptively performing XOR operation in units of bitplane blocks. For example, a determination on whether or not to perform XOR operation may be done in units of bitplane blocks according to the decoded value of XOR operation information contained in the bitstream.
Owner:UNIV IND COOP GRP OF KYUNG HEE UNIV
Method for providing variable bit rate in streaming service
InactiveUS7054365B2Minimize timeEasy to handlePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo bitstreamCommunications system
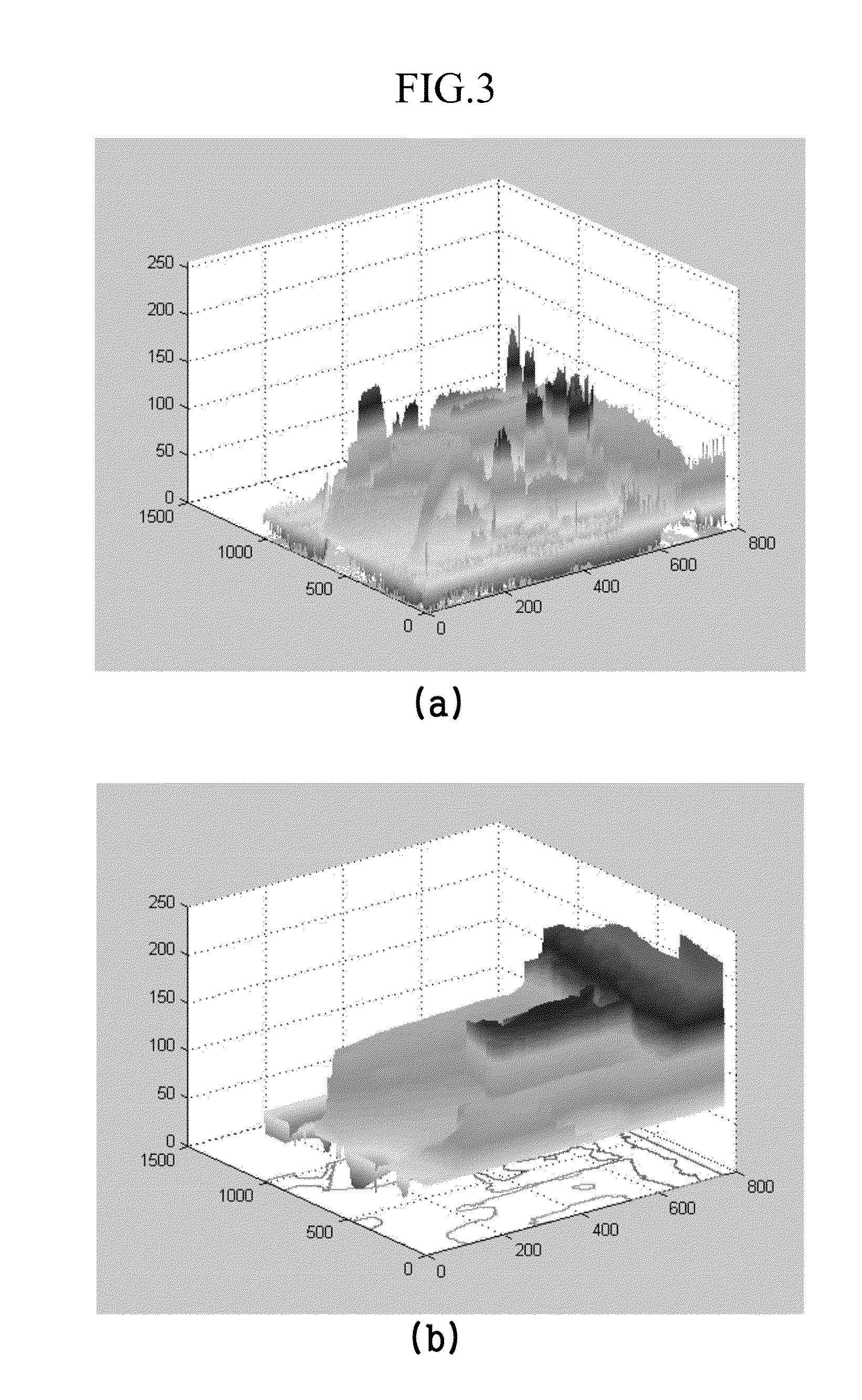
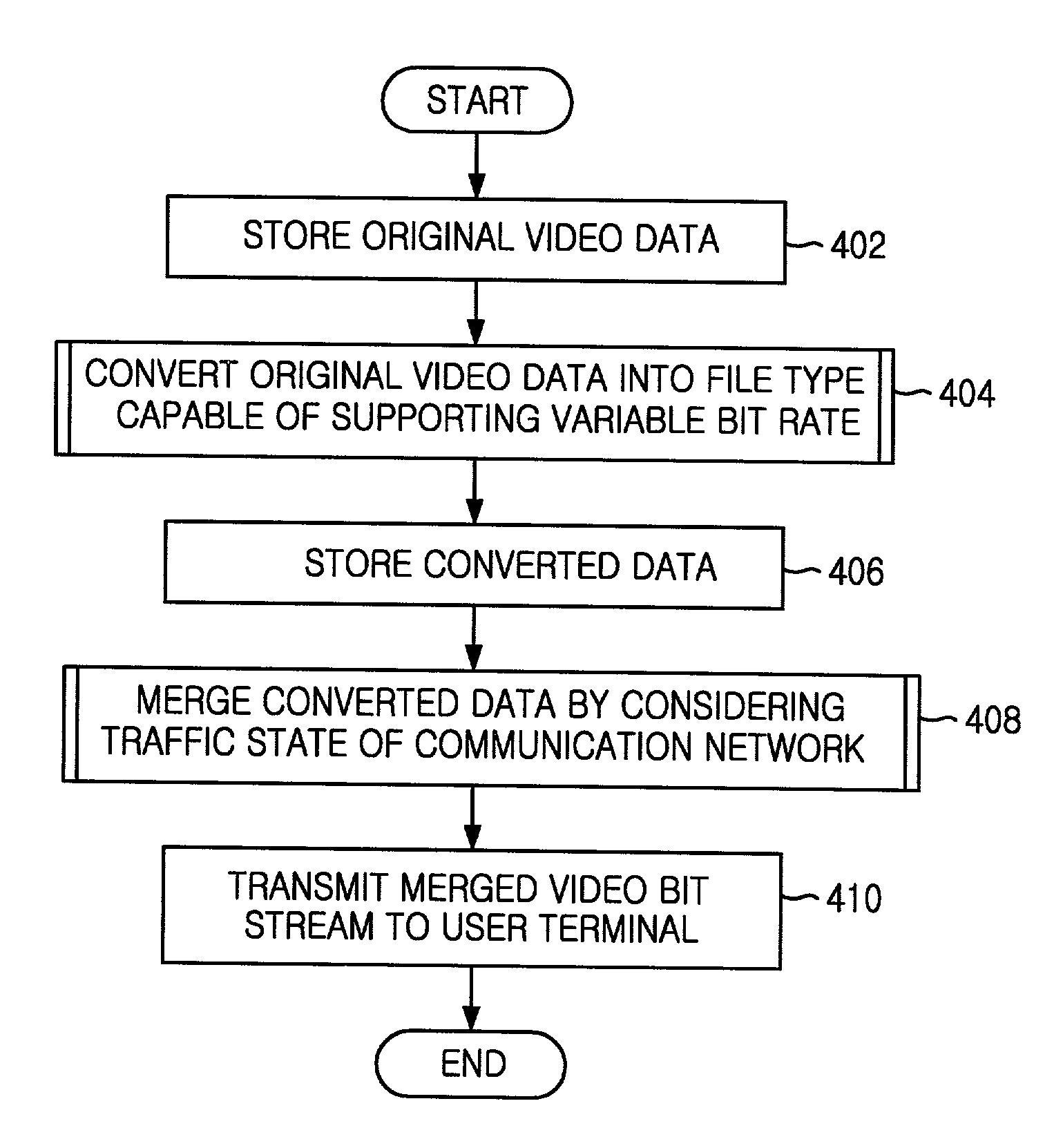
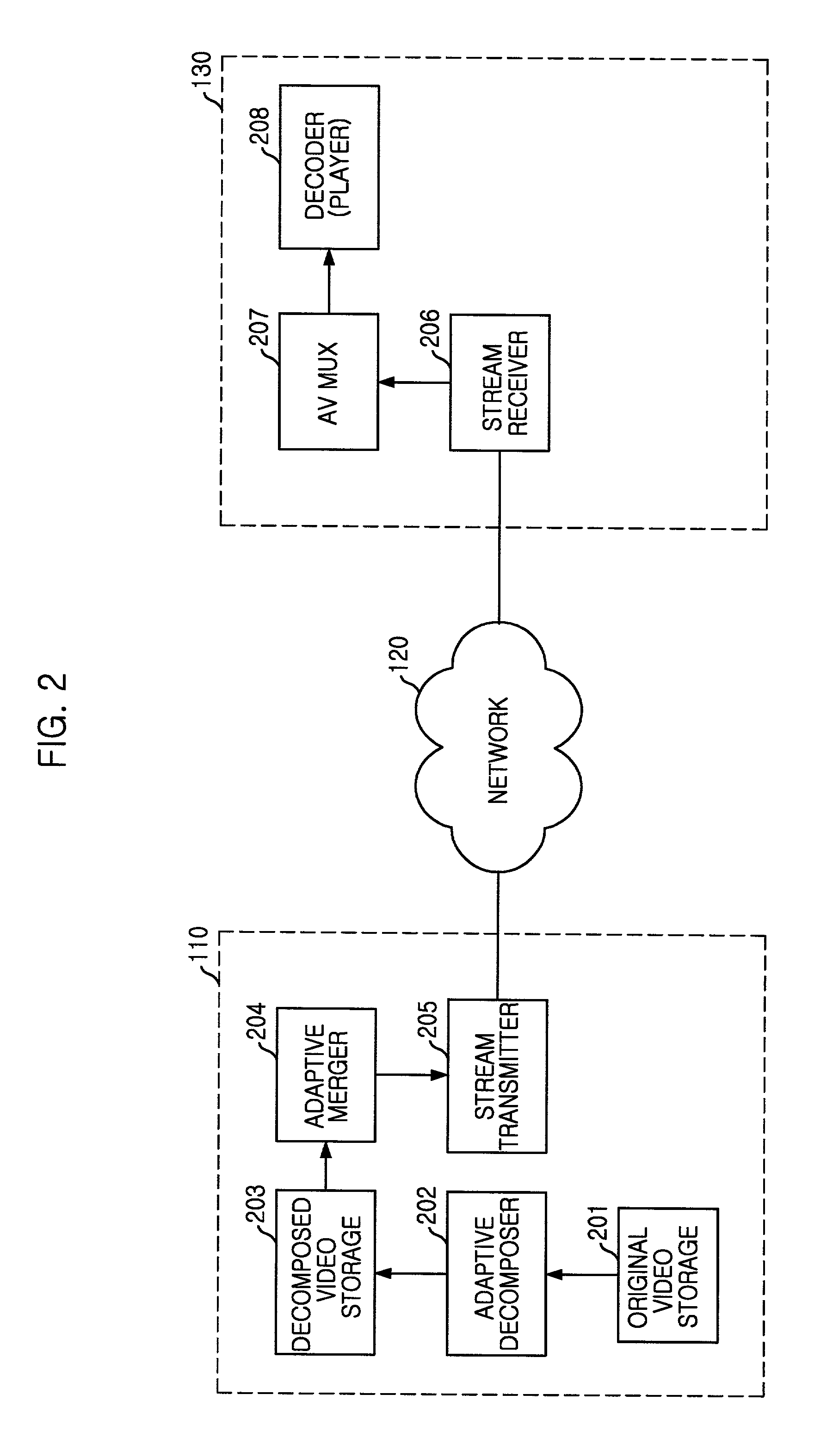
In the method for managing a variable bit rate so as to provide a streaming service and in the record medium capable of being read through a computer having a record of a program to realize the inventive method, a frame rate controlling system through a removal of a frame and a fidelity controlling system are used to change a bit rate of multimedia video data and thereby provide a multimedia streaming service based on the various bit rates according to a bandwidth change of a communication network, the fidelity controlling system being gotten by differently providing selection ranges for discrete cosine transform (DCT) coefficients in a unit of a block within a frame. This inventive method comprises a first step of decomposing an original video bit stream stored already, into a file type capable of supporting the variable bit rate, and then storing it; a second step of merging data based on the decomposed type by considering a traffic state of a communication network; and a third step of providing the streaming service by using the video bit stream merged, whereby effectuating in a use of an information communication system etc.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Optimal scanning method for transform coefficients in coding/decoding of image and video
InactiveUS7215707B2Improve compression efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision system scanning detailsNonzero coefficientsVideo encoding
An optimal scanning method for coding / decoding an image signal is provided. In a method of coding an image signal through a discrete cosine transform, at least one is selected among a plurality of reference blocks. A scanning order in which to scan blocks to be coded of the reference blocks is generated and the blocks to be coded are scanned in the order of the generated scanning order. The at least one selected reference block is temporally or spatially adjacent to the block to be coded. When the blocks to be coded are scanned, probabilities that non-zero coefficients occur are obtained from the at least one selected reference block, and the scanning order is determined in descending order starting from the highest probability. Here, the scanning order is generated to be a zigzag scanning order if the probabilities are identical. The optimal scanning method increases signal compression efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
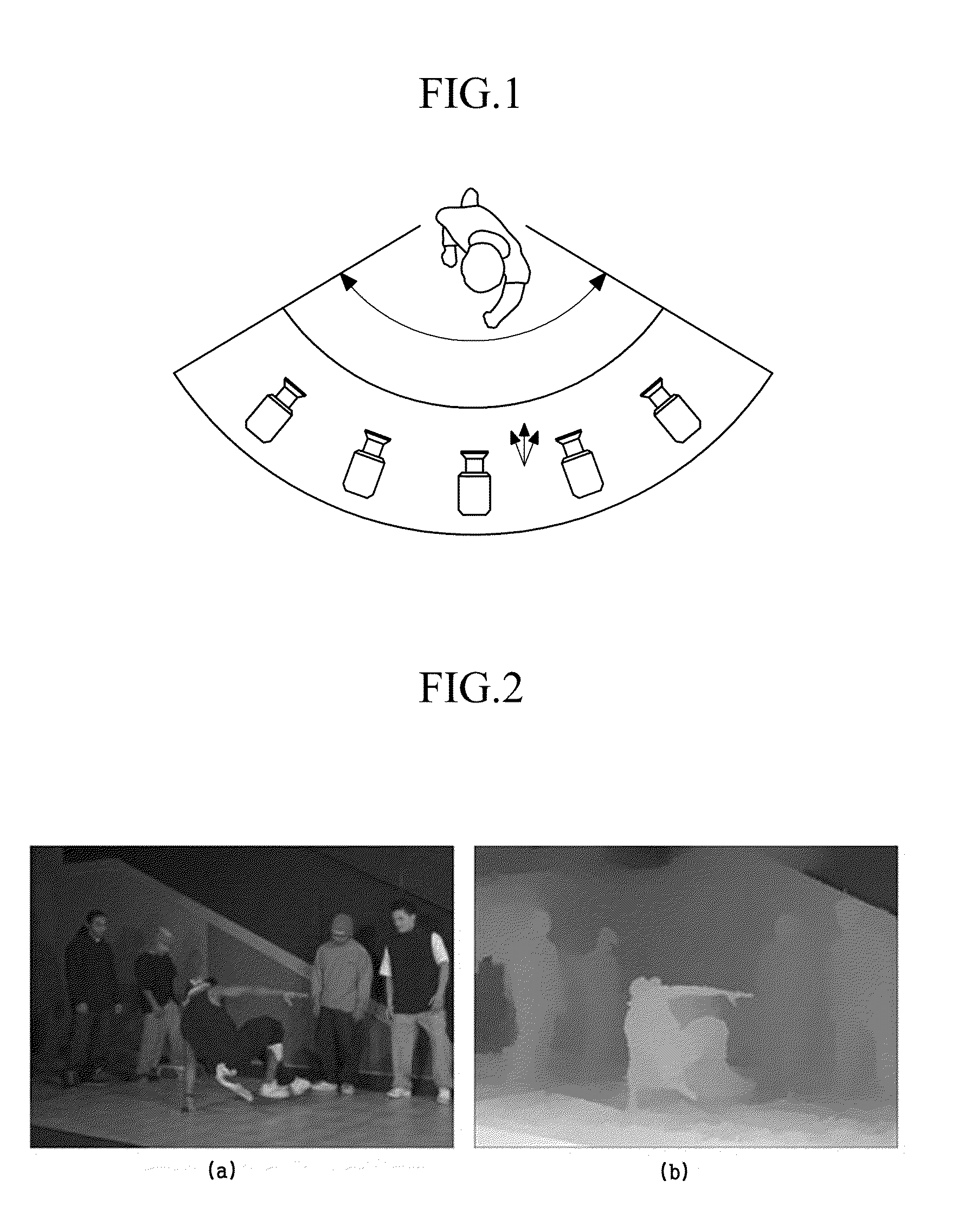
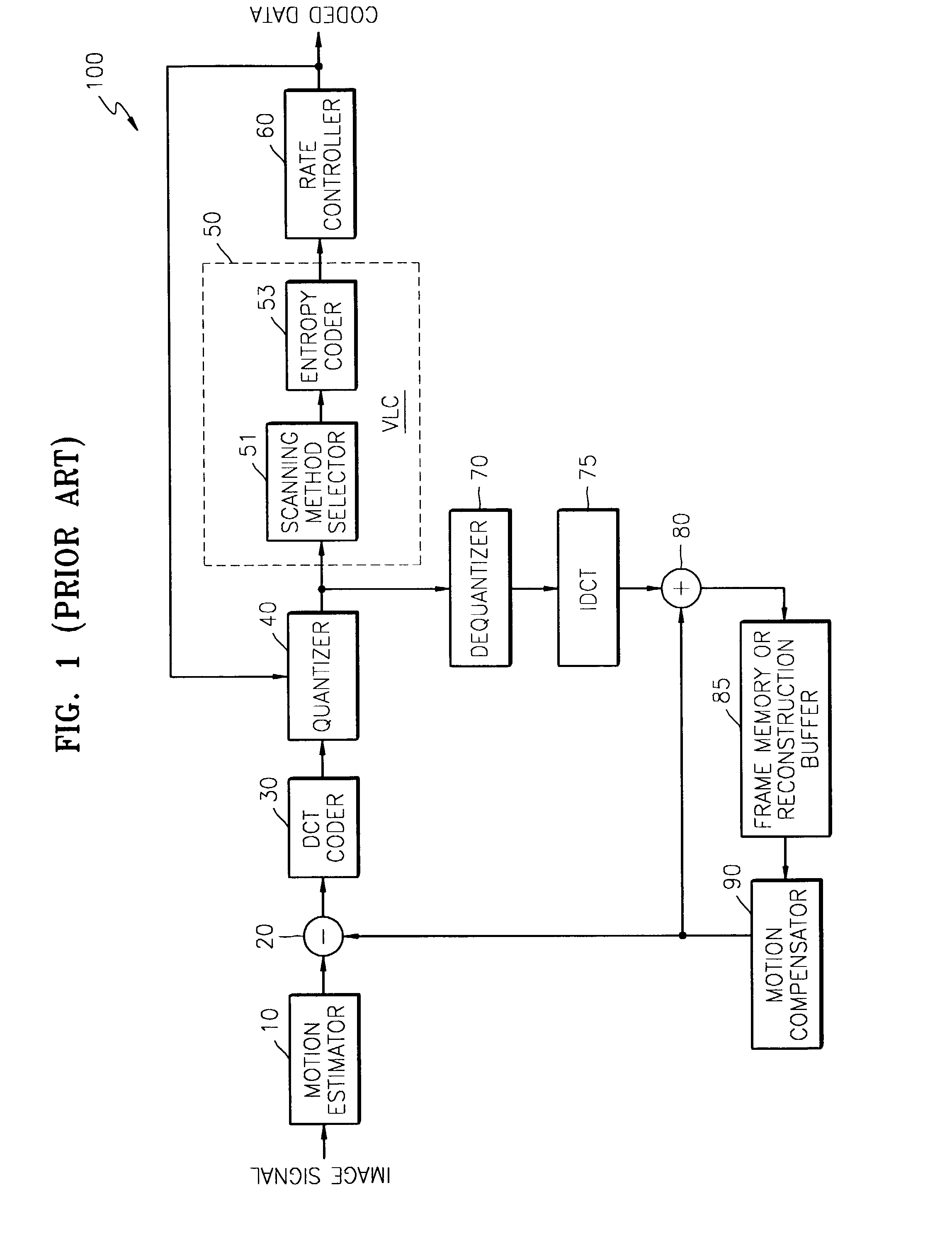
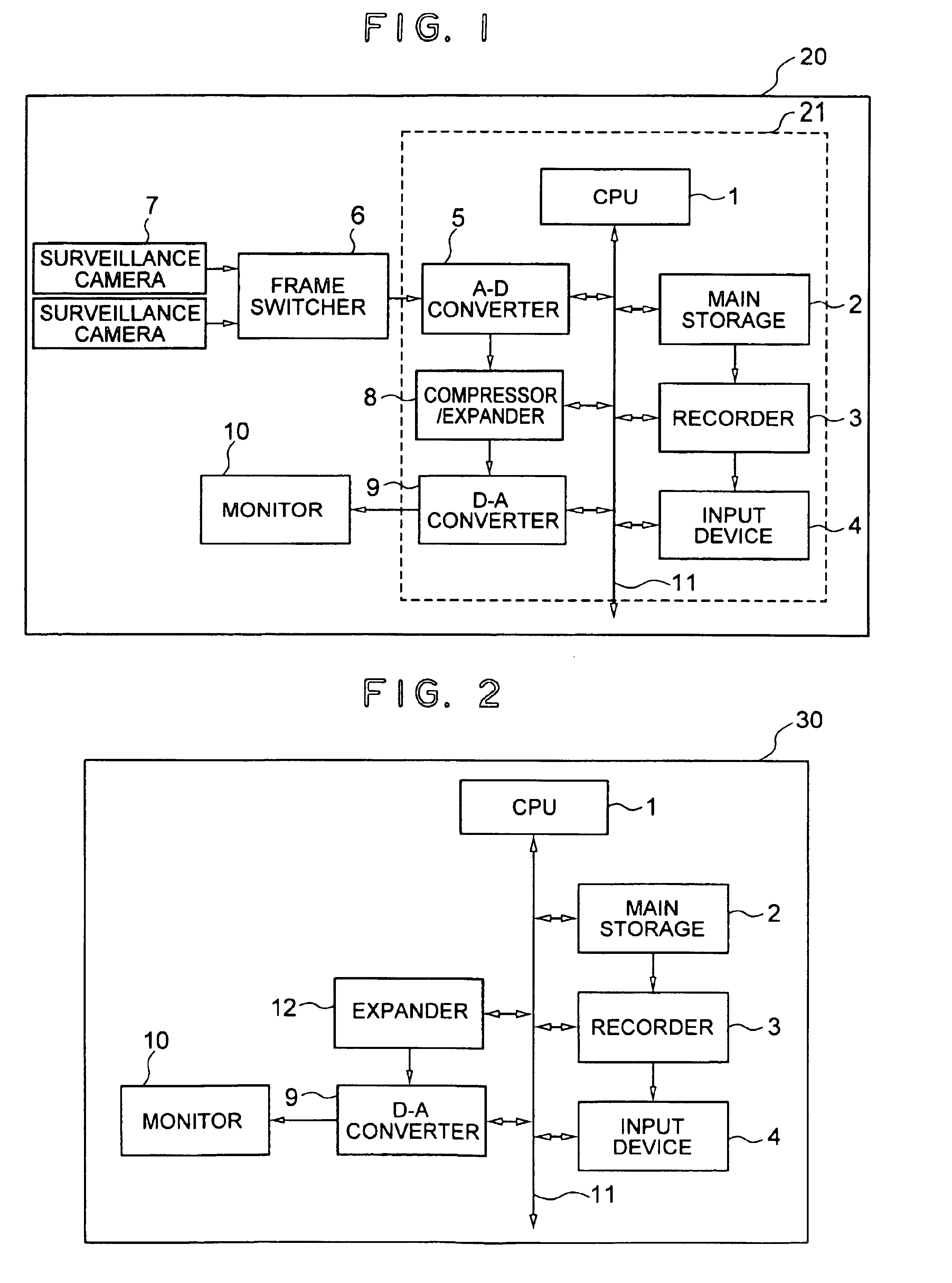
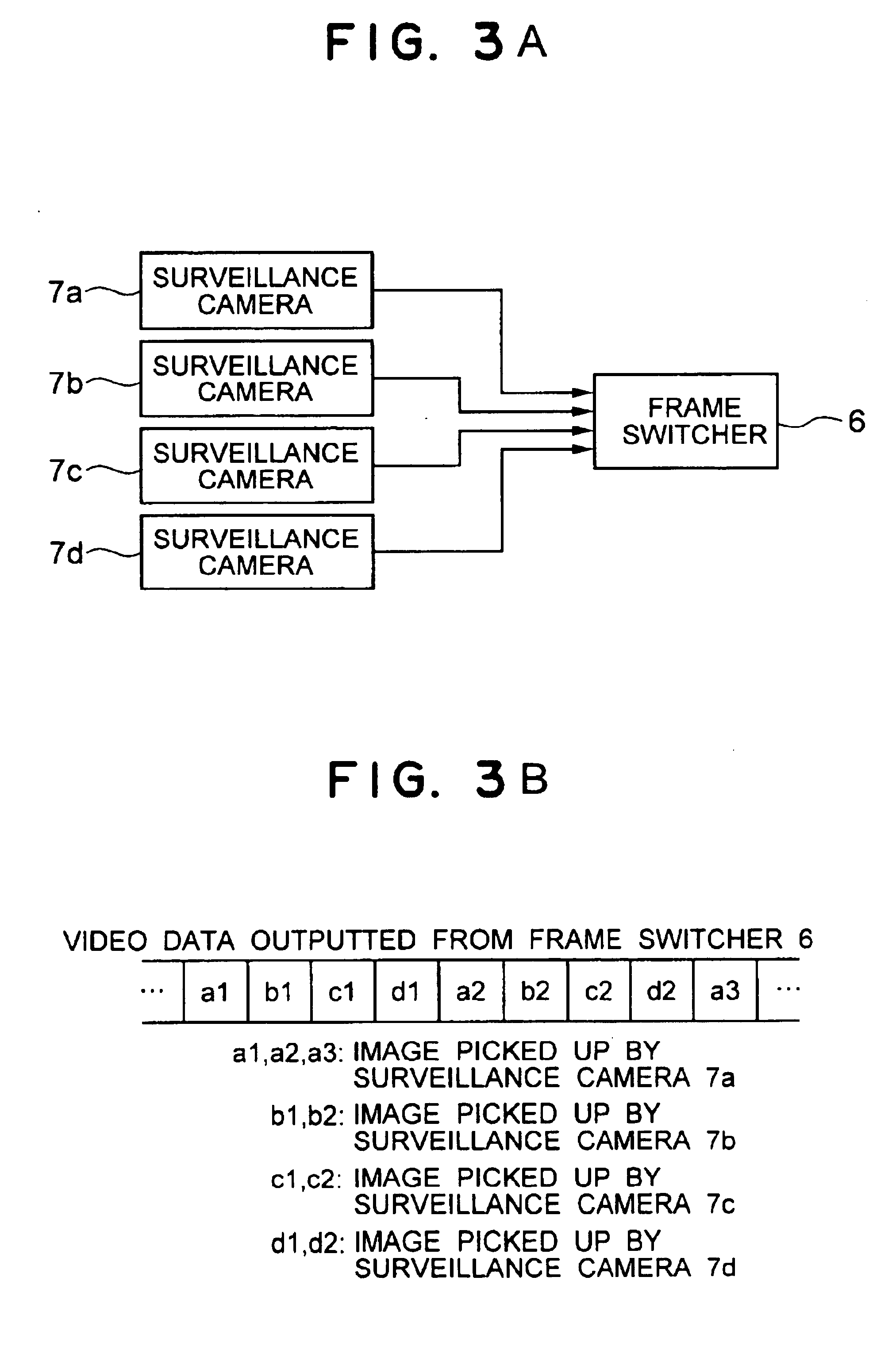
Surveillance system
InactiveUS6842540B1Increased evidenceEasy to separateTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSurveillance cameraDiscrete cosine transform
A surveillance image is acquired from a surveillance camera. Supplement information (such as date and time, and surveillance camera number) relating to the surveillance image is acquired. By imaging the supplement information, supplement information image data is generated. A quantized discrete cosine transform coefficient block obtained by conducting discrete cosine transform and then quantization on surveillance image data of the surveillance image is added to a quantized discrete cosine transform coefficient block obtained by conducting discrete cosine transform and then quantization on the supplement information image data. A resultant sum is subjected to Huffman encoding. The result is recorded.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
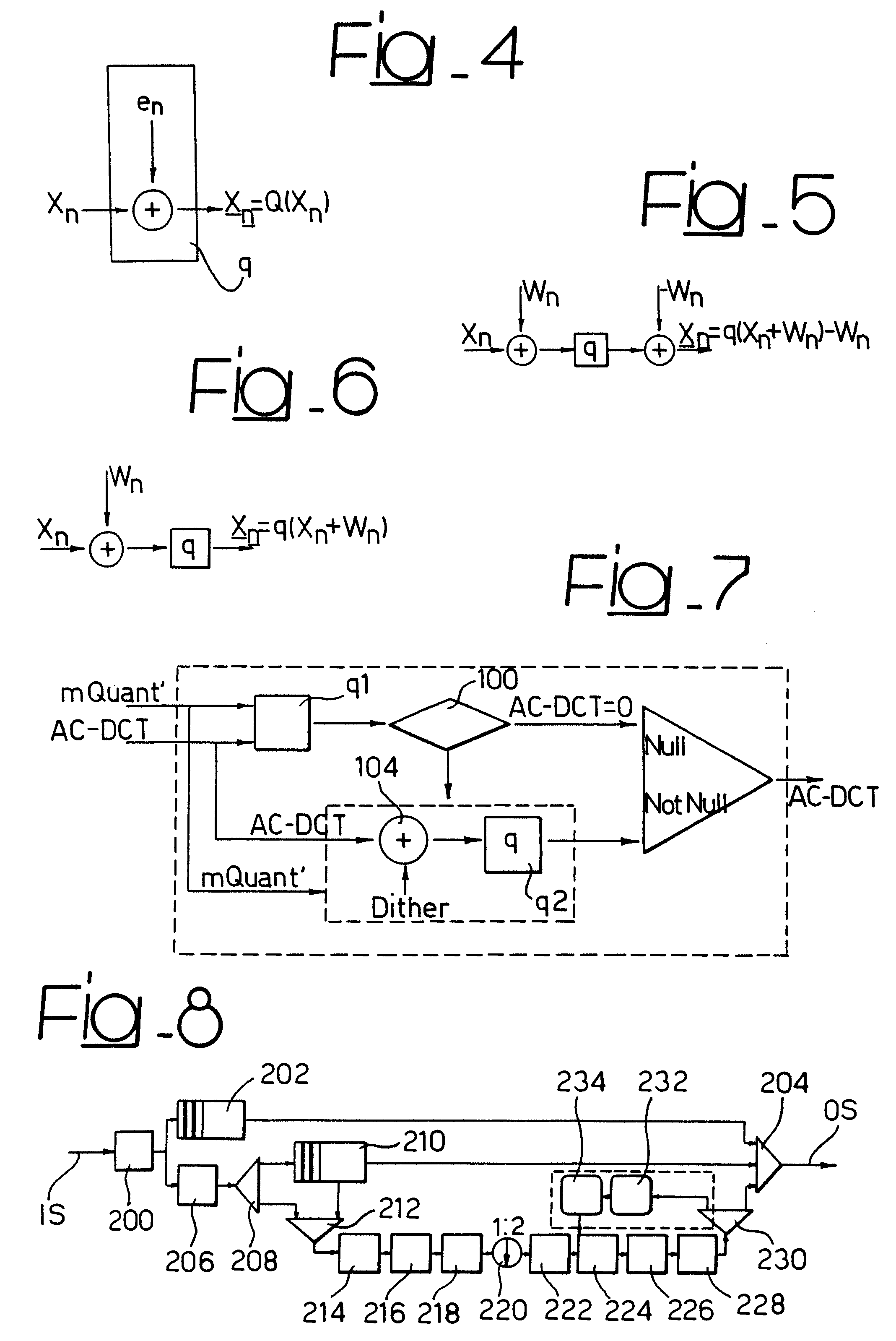
Quantization method and system for video MPEG applications and computer program product therefor
ActiveUS7301999B2Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationTranscodingDiscrete cosine transform
Digital signals are converted between a first and second format by a conversion process including generating coefficients representing the digital signals. The coefficients may be discrete cosine transform coefficient generated during encoding / transcoding of MPEG signals. The coefficients are subject to quantization by generating a dither signal that is added to the coefficients before quantization to generate a quantized signal. Preferably, each coefficient is first subject to a first quantization in the absence of any dither signal added to generate an undithered quantized coefficient. If the undithered quantized signal is equal to zero the undithered quantized coefficient is taken as the output quantized signal. If the undithered quantized coefficient is different from zero, the dither signal is added and the dithered coefficient thus obtained is subject to quantization to generate the output quantized signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Digital watermarking embedding, extracting and quantizing step size coordinating factor optimizing method and device
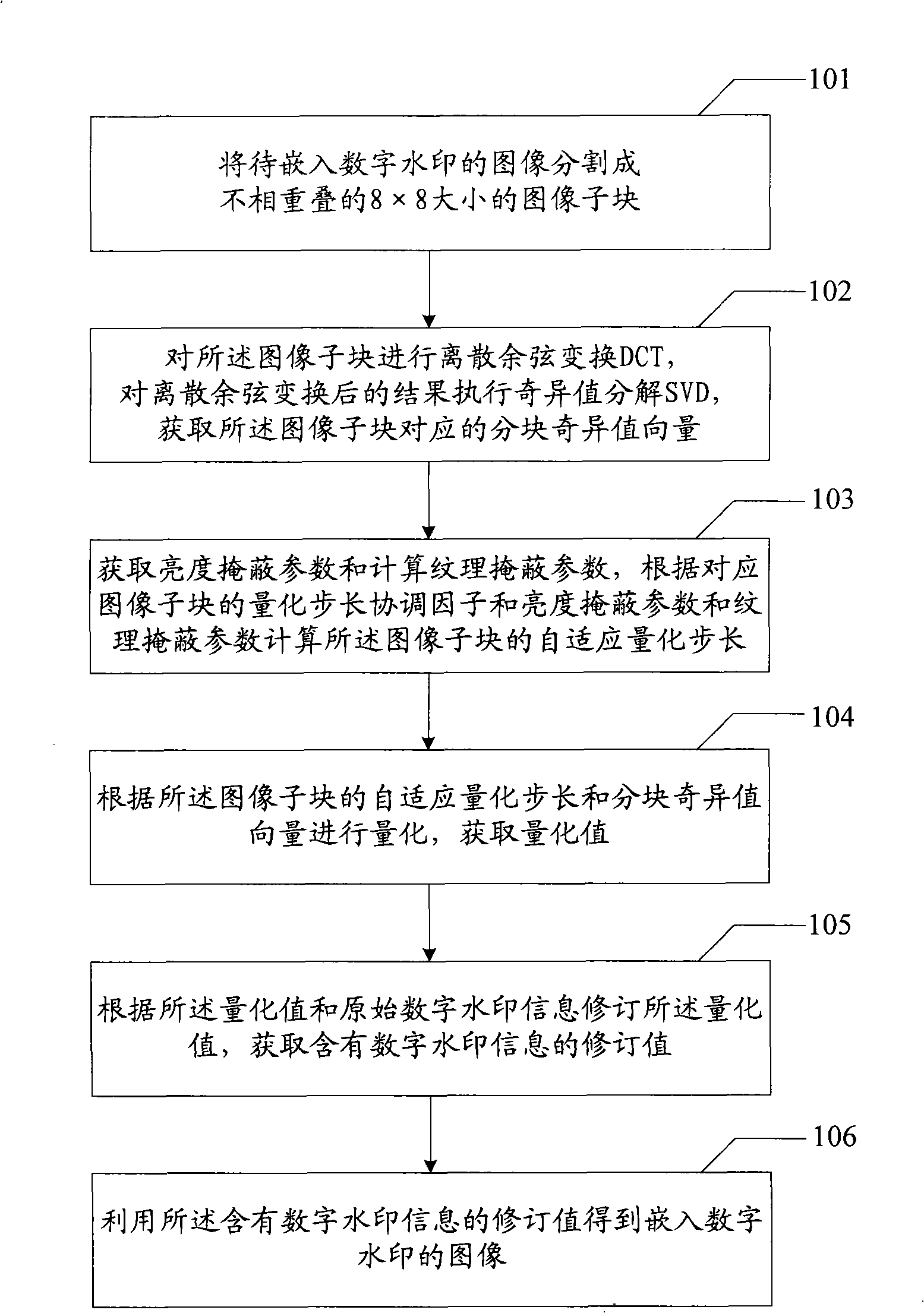
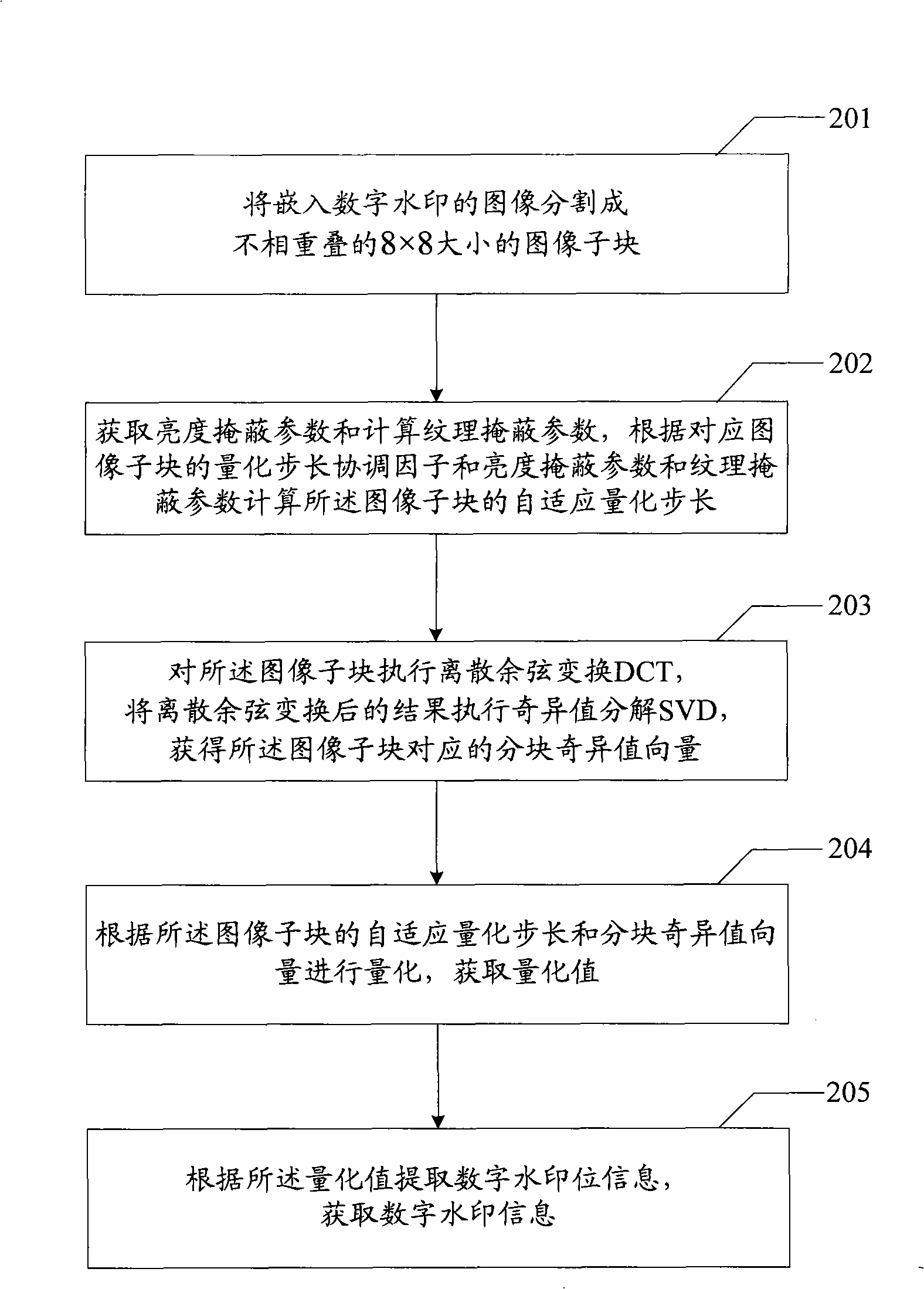
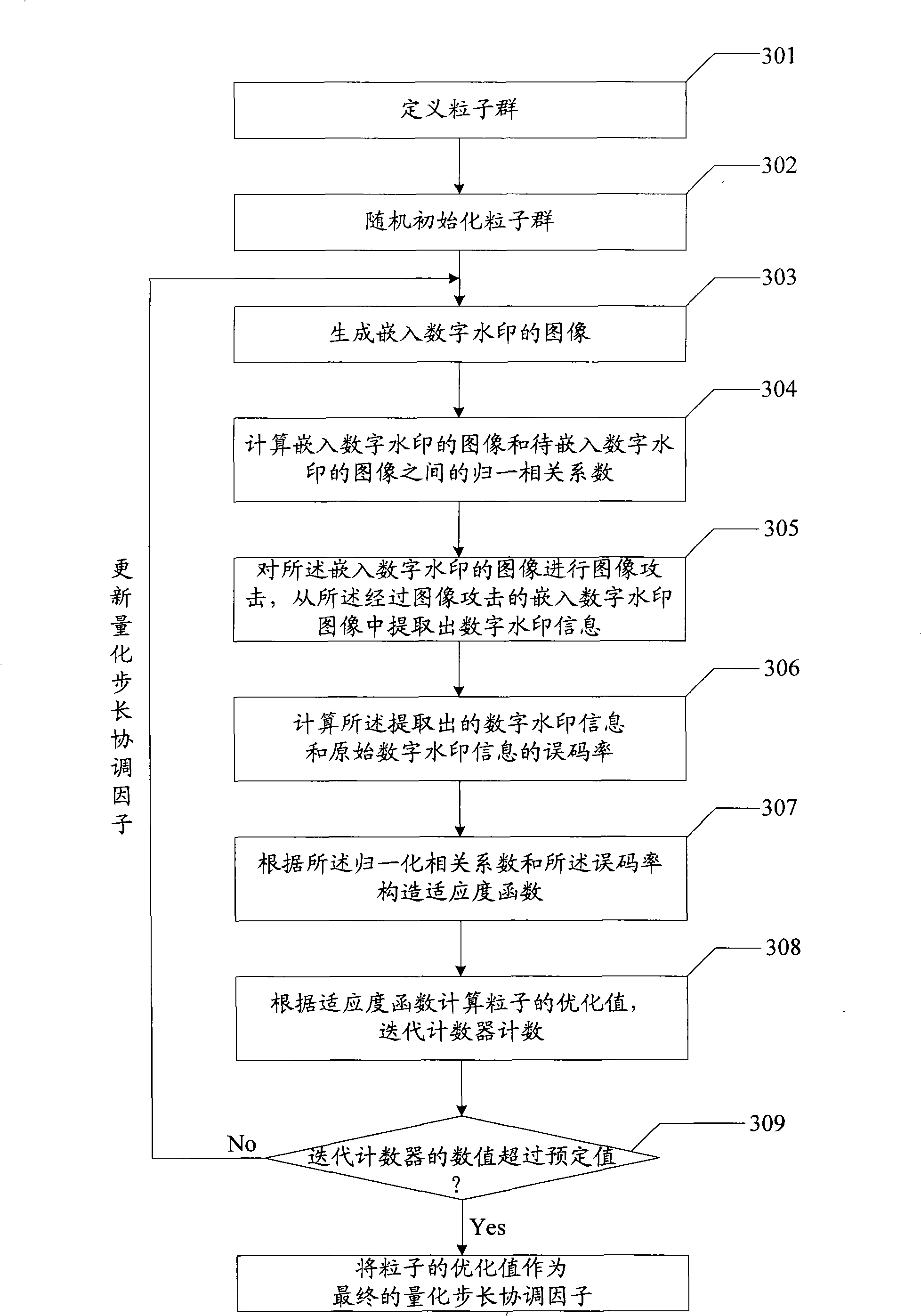
The invention relates to an embedding, extracting and quantization step size coordination factor optimizing method of a digital watermark and a device thereof. The embodiment of an embedding method of the digital watermark comprises the steps that: an image to be embedded with the digital watermark is divided into image subblocks with preset size; DCT (discrete cosine transform) is executed to the image subblocks; SVD (singular value transform) is executed to the result after DCT so as to obtain a blocking singular value vector of the image subblocks; a texture masking parameter is calculated to obtain a brightness masking parameter; according to a quantization step size coordination factor, the brightness marking parameter and the texture masking parameter of the image subblocks, a self-adaptive quantization step size of the image subblocks is obtained; the self-adaptive quantization step size of the image subblocks and the blocking singular value vector are quantized to obtain a quantization value; amendment is carried out according to the quantization value and the information of the digital watermark to obtain an amendment value of the information of the digital watermark; and the amendment value containing the information of the digital watermark is utilized to obtain the image embedded with the digital watermark. The embodiment of the invention realizes the balance of the invisibility and the robustness of a digital watermarking method.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Image retrieval method based on content improved Average Hash
InactiveCN105912643AReduce frequencyReduce computing timeSpecial data processing applicationsImage retrievalDiscrete cosine transform
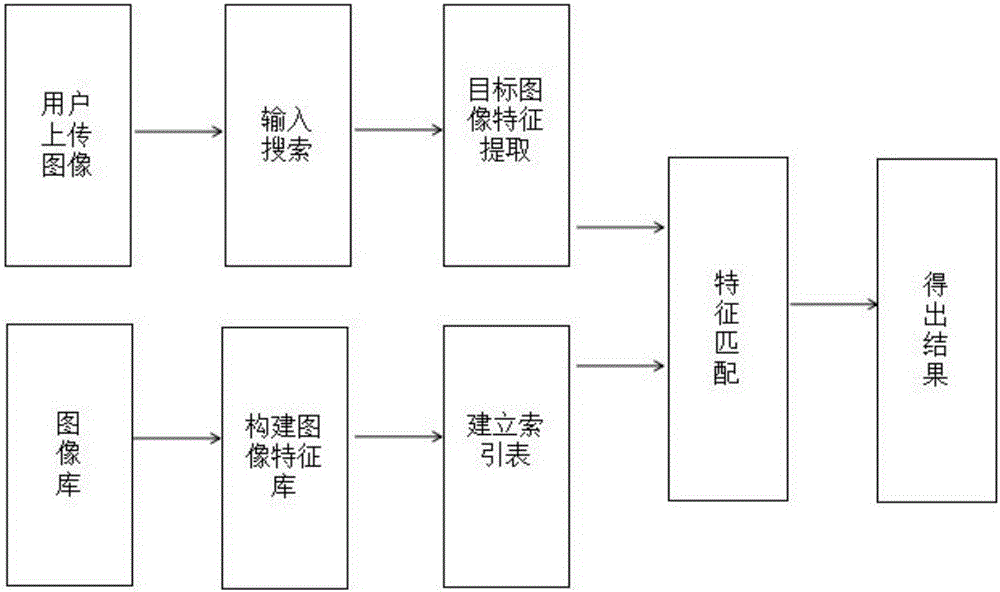
The present invention discloses an image retrieval method based on content improved Average Hash. According to the method, the size of an image is reduced, grey-scale map processing is performed on the image, characteristics of a target image are obtained through repeated discrete cosine transform and Hash calculation processing; and matching operation is performed on the obtained characteristics and characteristics in an image characteristic library through similarity detection, and a retrieval result is obtained. By adoption of the method, a general image library can be effectively retrieved, and the detection effect is good; and certain deformed images can also be well tolerated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com