Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8919results about "Image coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
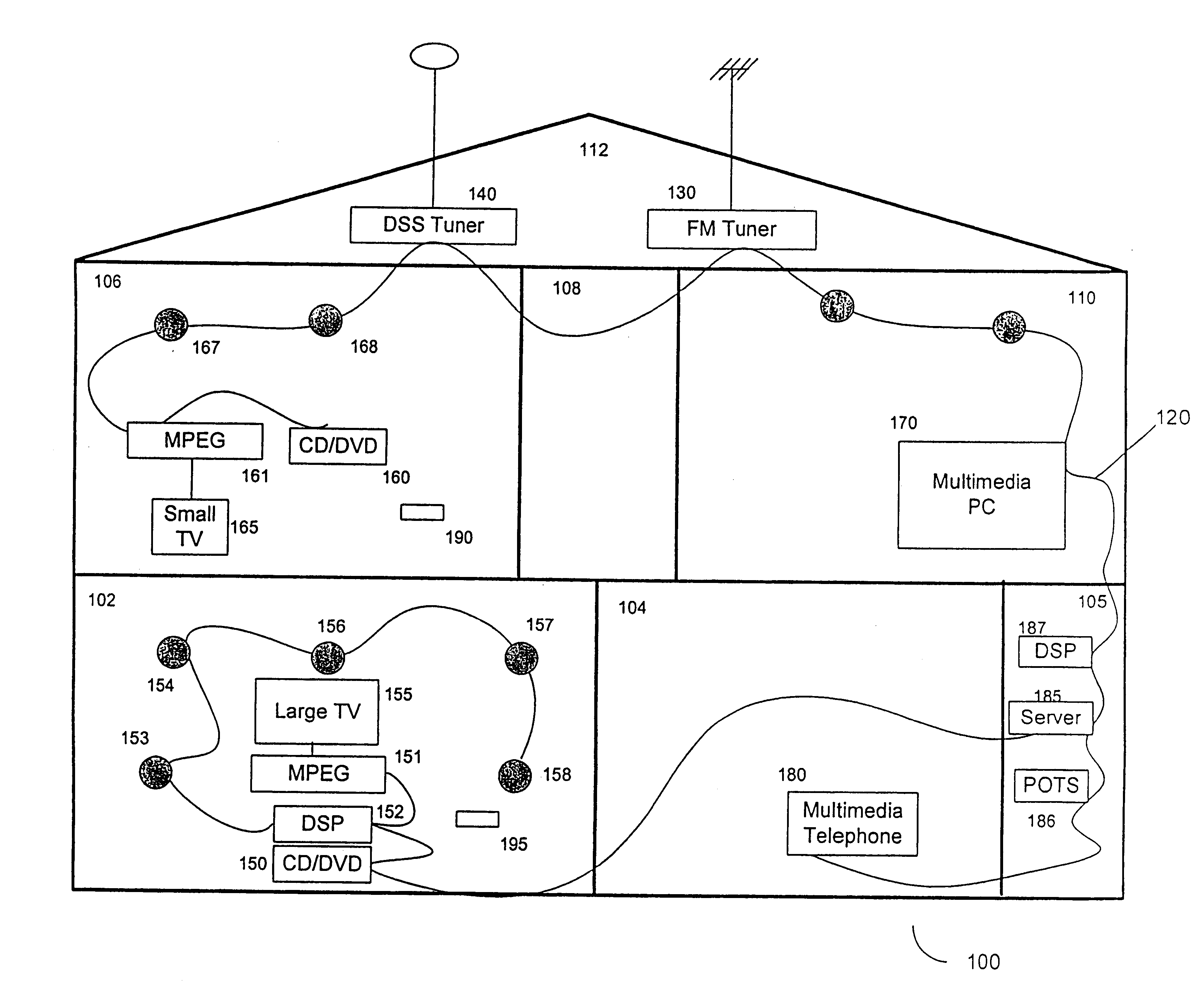
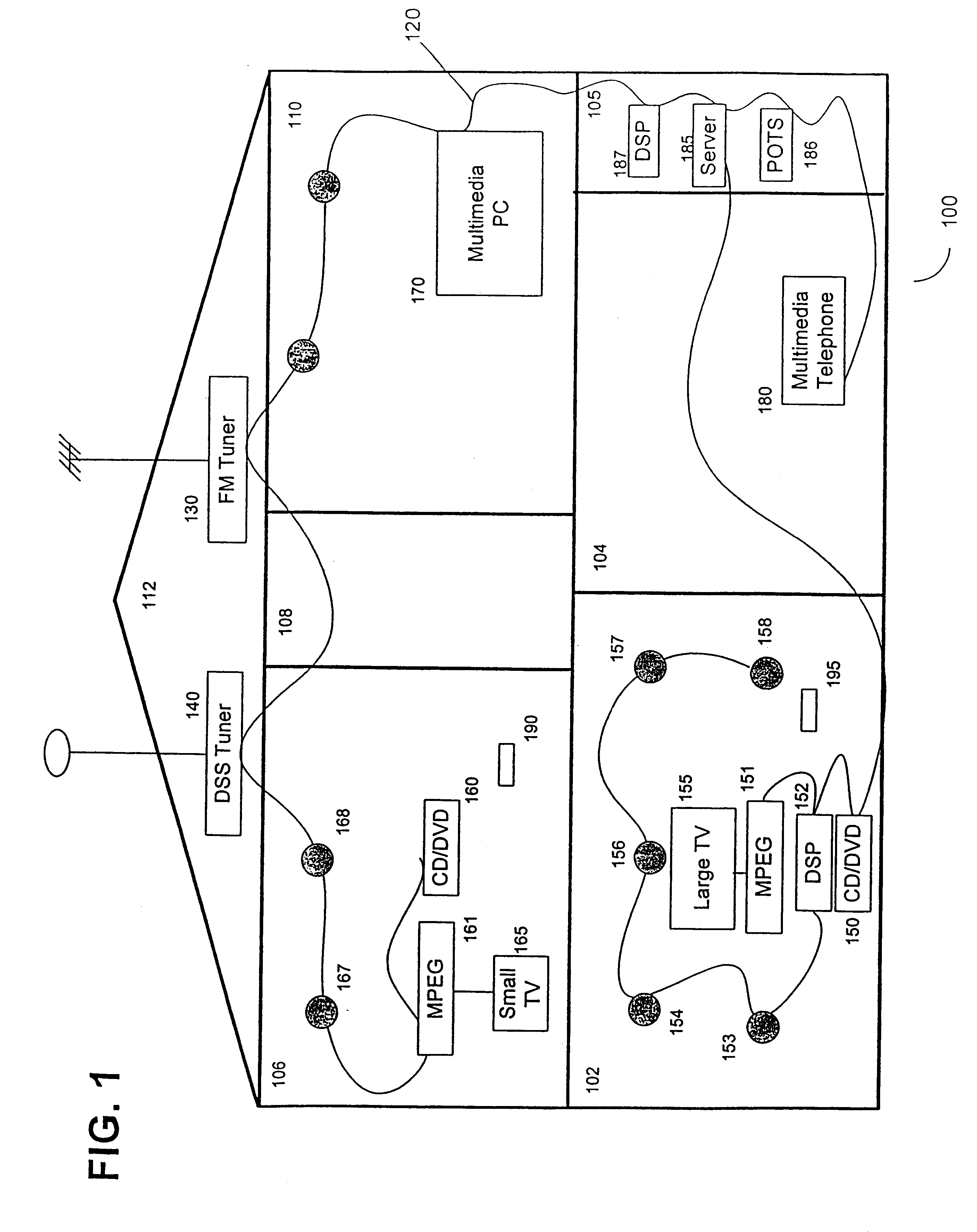
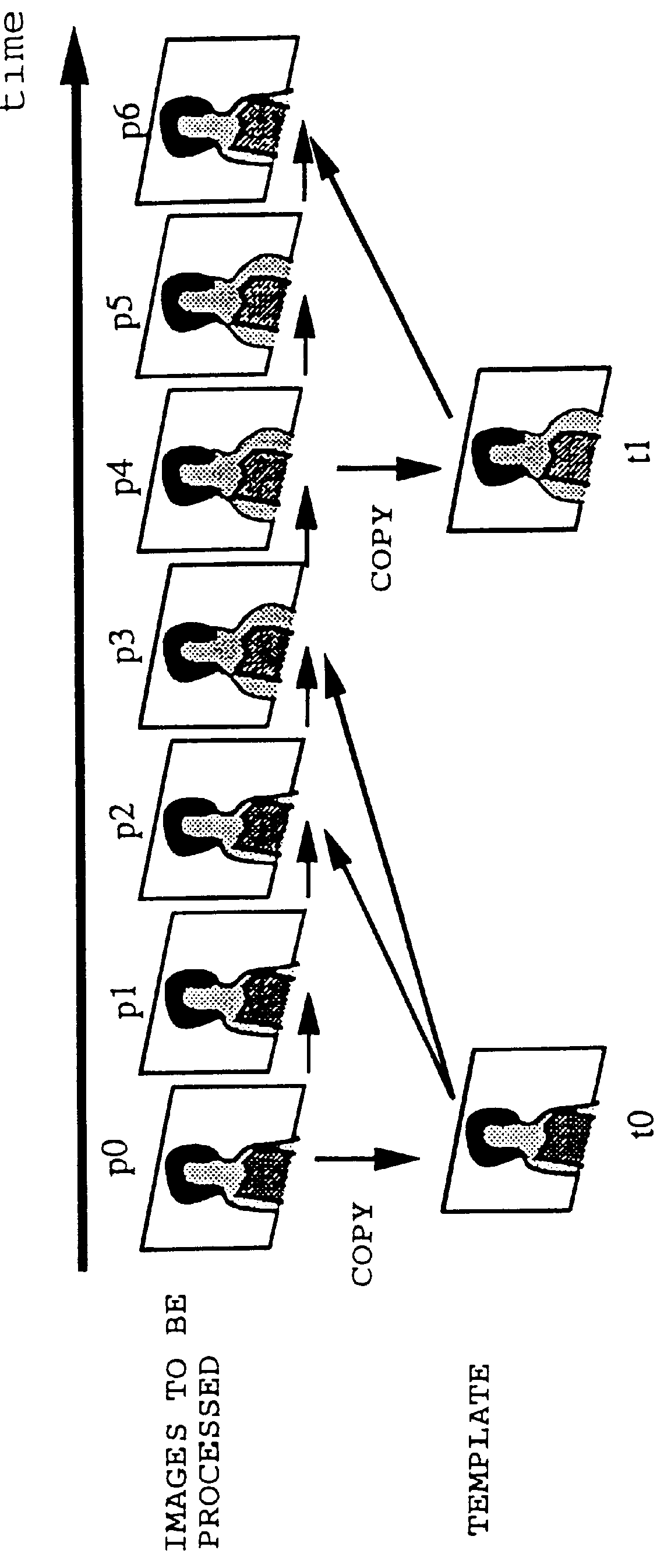
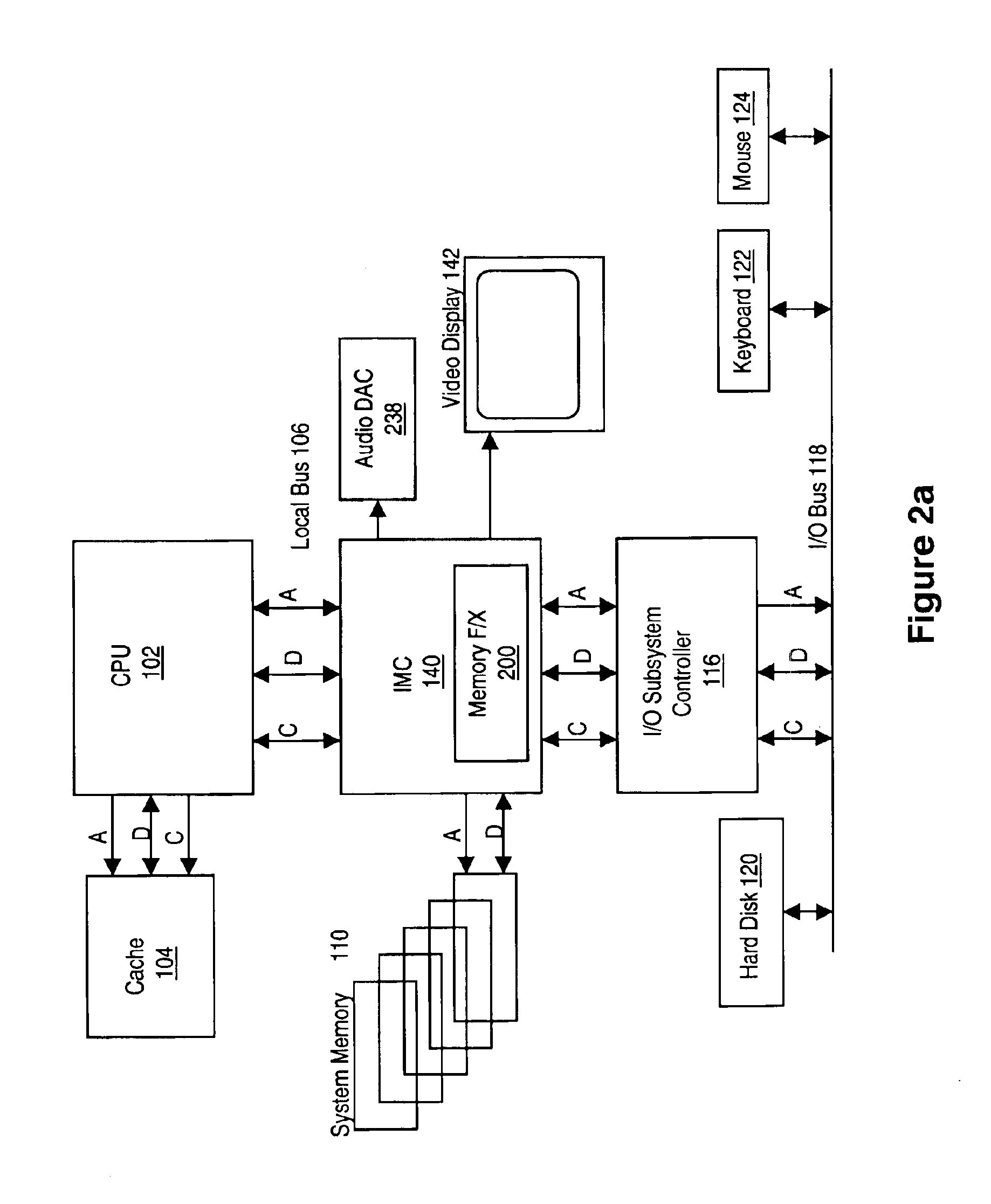
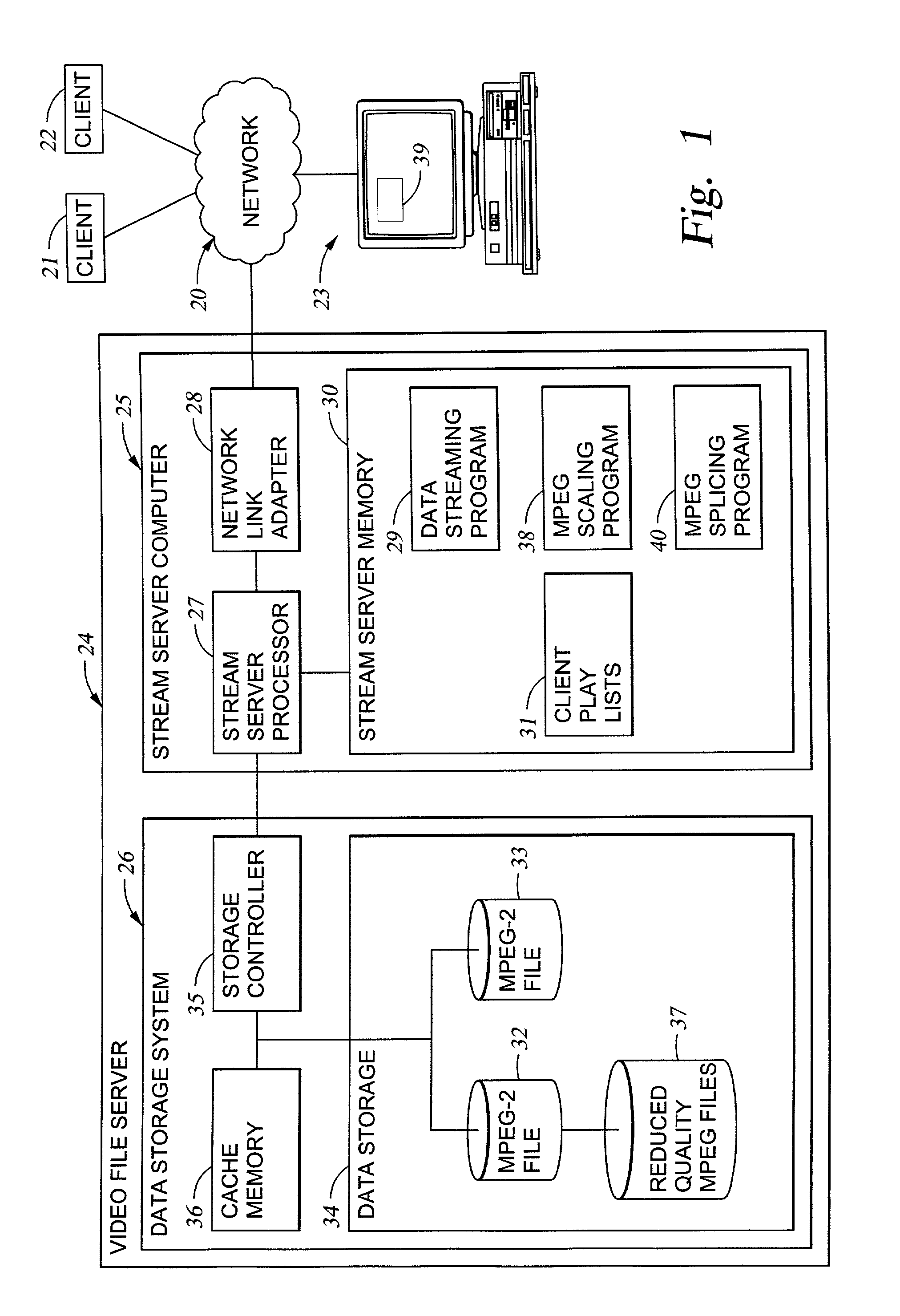
Synchronous network for digital media streams
InactiveUS6611537B1Avoid collisionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexData streamNetwork clock
A network adapter for a synchronous logical ring network operates on existing physical twisted-pair telephone topologies. Information propagates around the logical ring, reaching every device on each revolution around the network. Network devices are full-duplex, transmitting and receiving information on every clock cycle. Network devices arbitrate to be elected the network clock device. By synchronizing all network devices to a single reference clock, and providing fixed frames of information propagating around the network at consistent time intervals, the logical ring network ensures that information propagates from one device to another at consistent time intervals. The fixed-length frames are divided into two independent streams: a data stream for the distribution of real-time continuous digital media streams; and a system command stream for the distribution of system commands.
Owner:CENTILLIUM COMM
Apparatus and method for optimized compression of interlaced motion images
InactiveUS6289132B1Easy to compressAvoid inefficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImaging processingInterlaced video
Owner:QUVIS +1
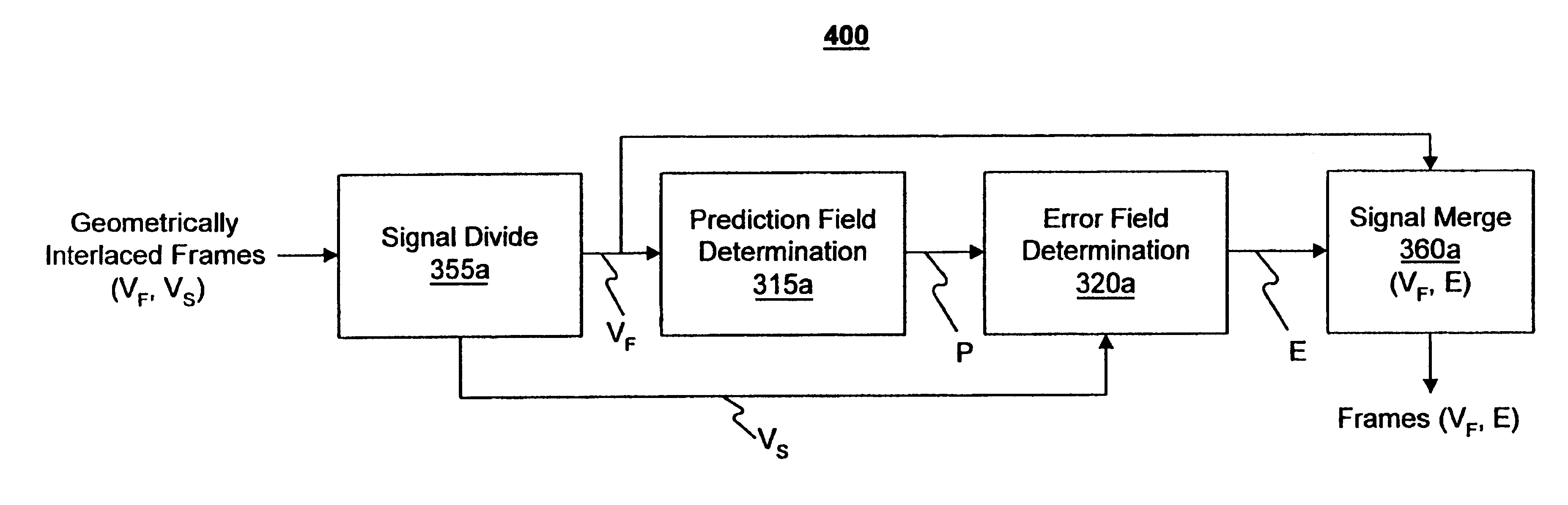
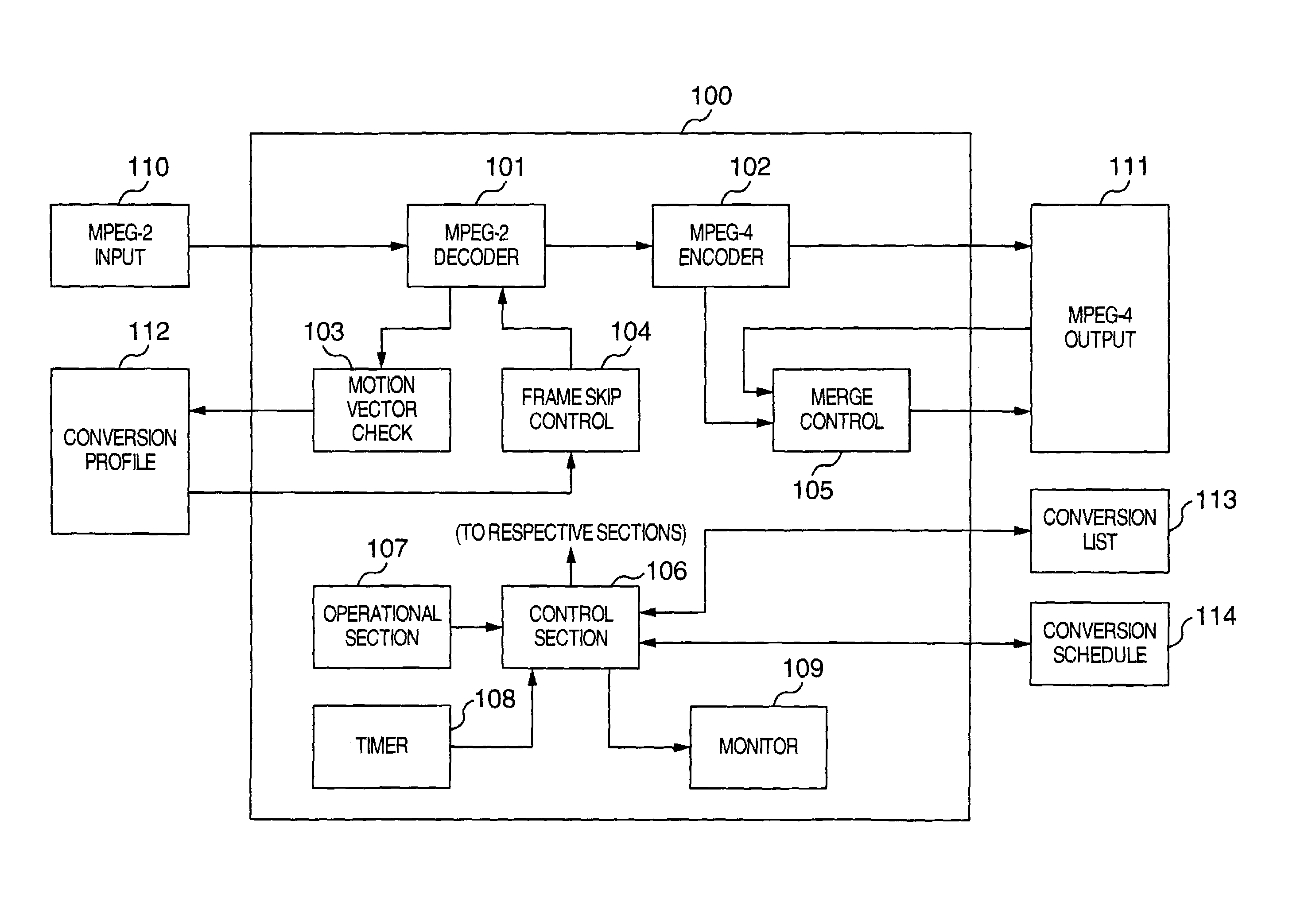
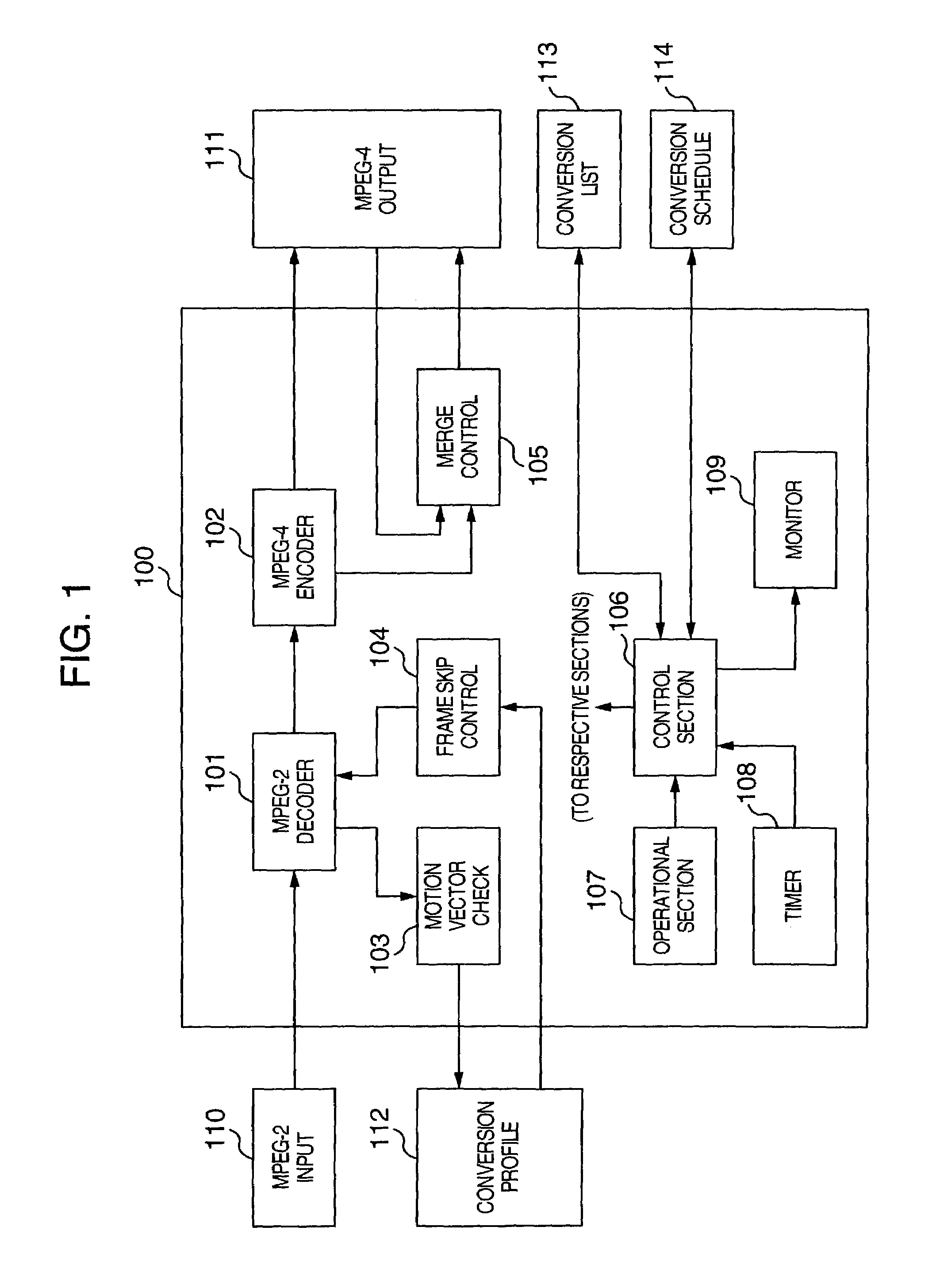
Image coding and decoding apparatus and methods thereof
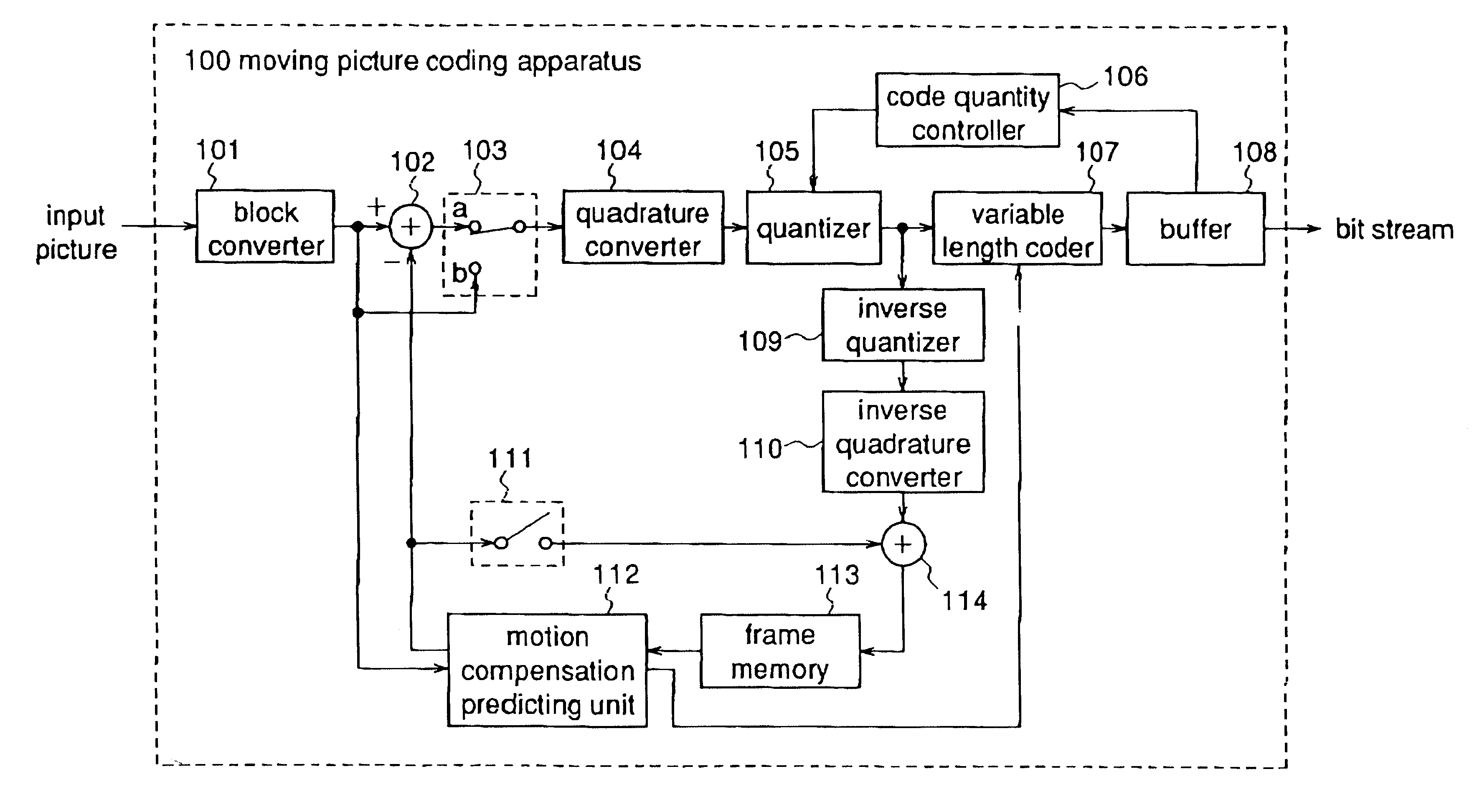
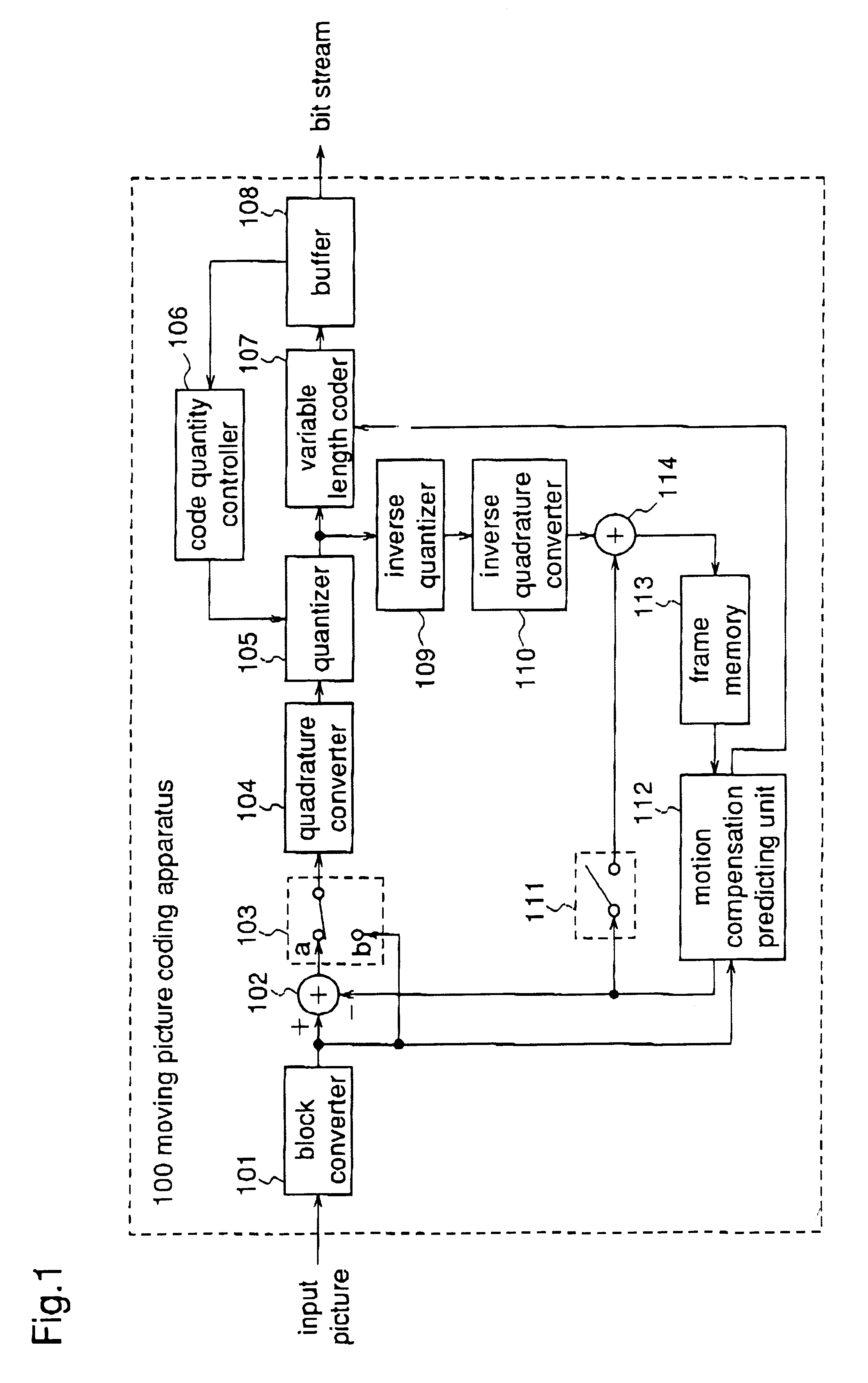
InactiveUS6081551APicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionExtensibilityMotion vector
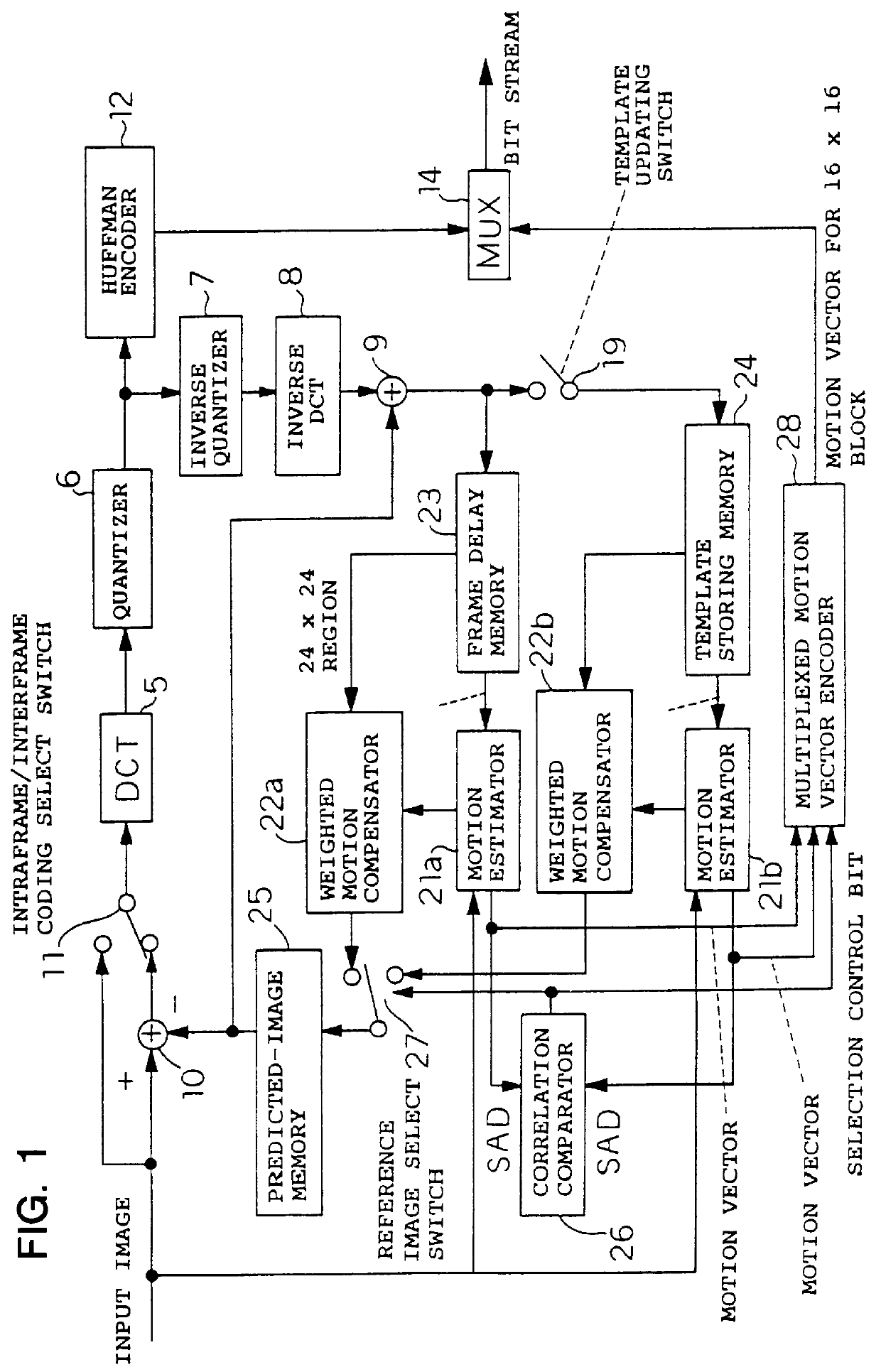
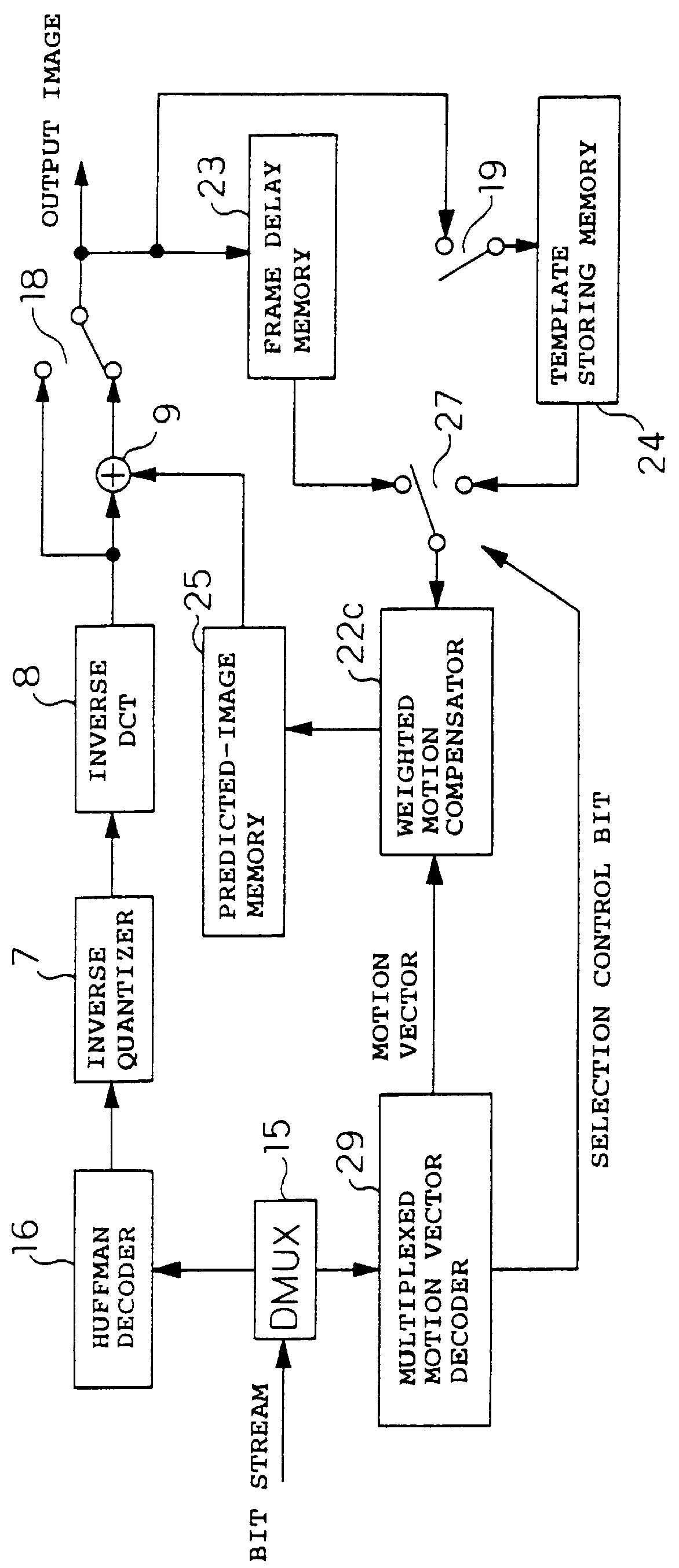
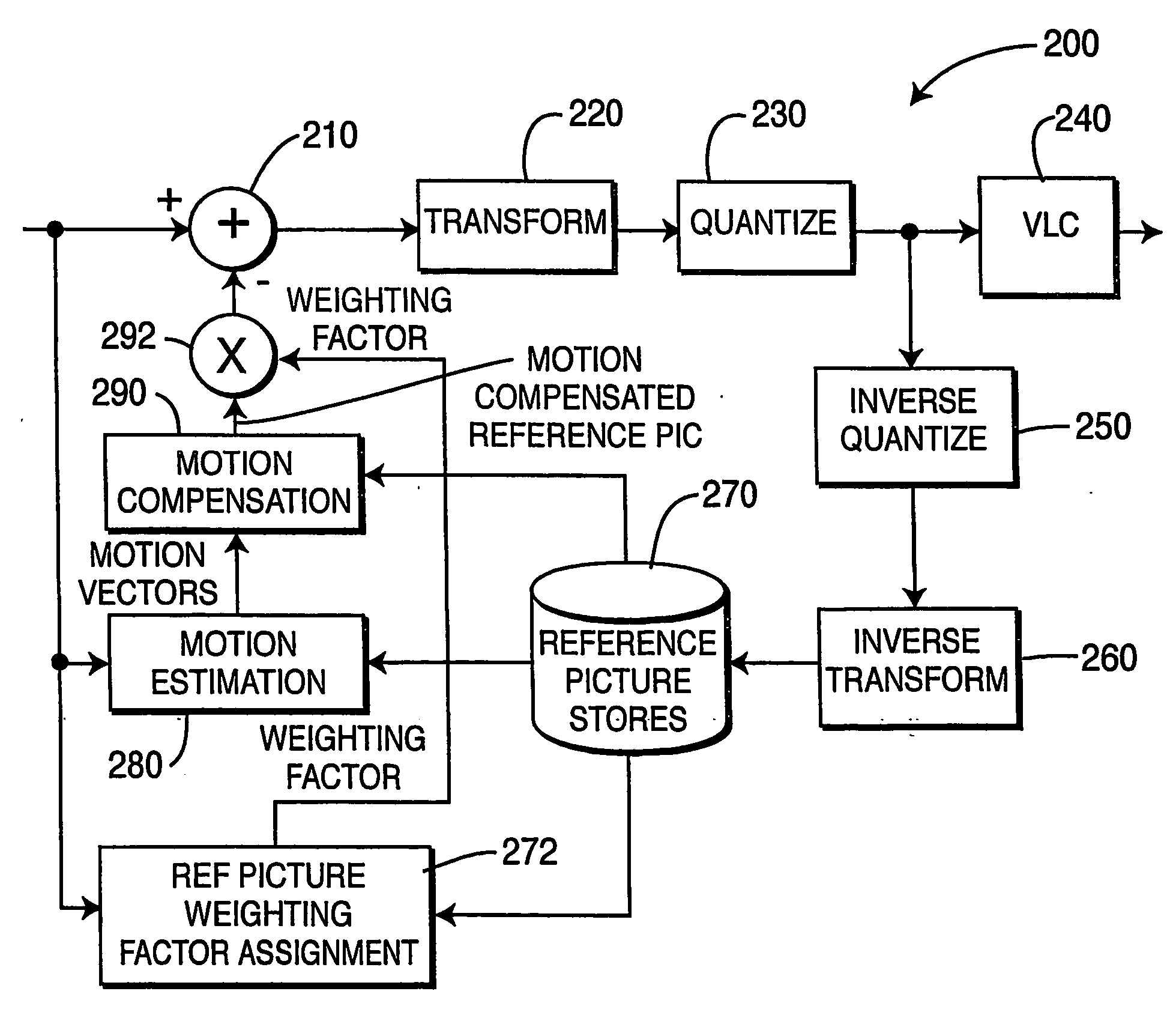
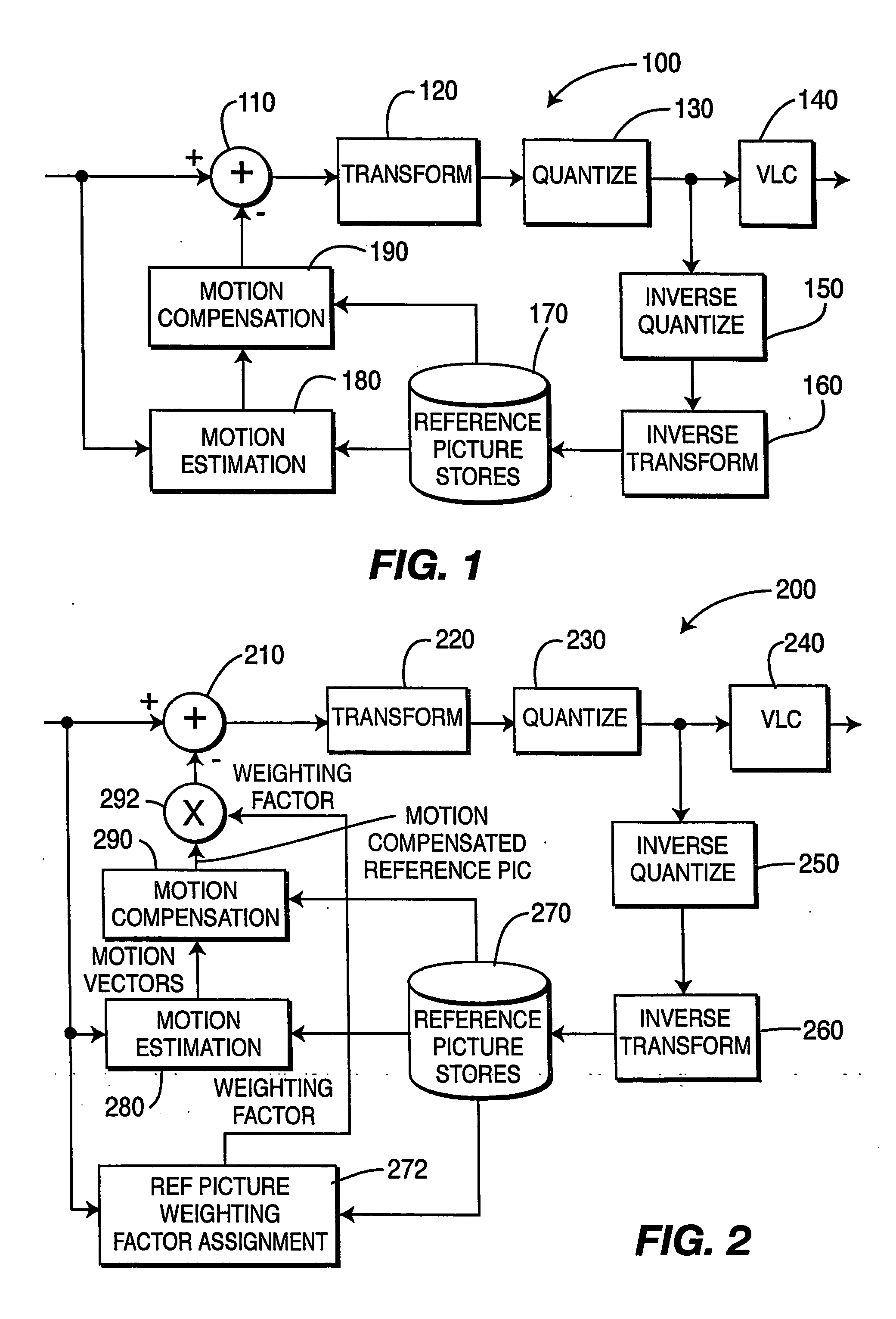
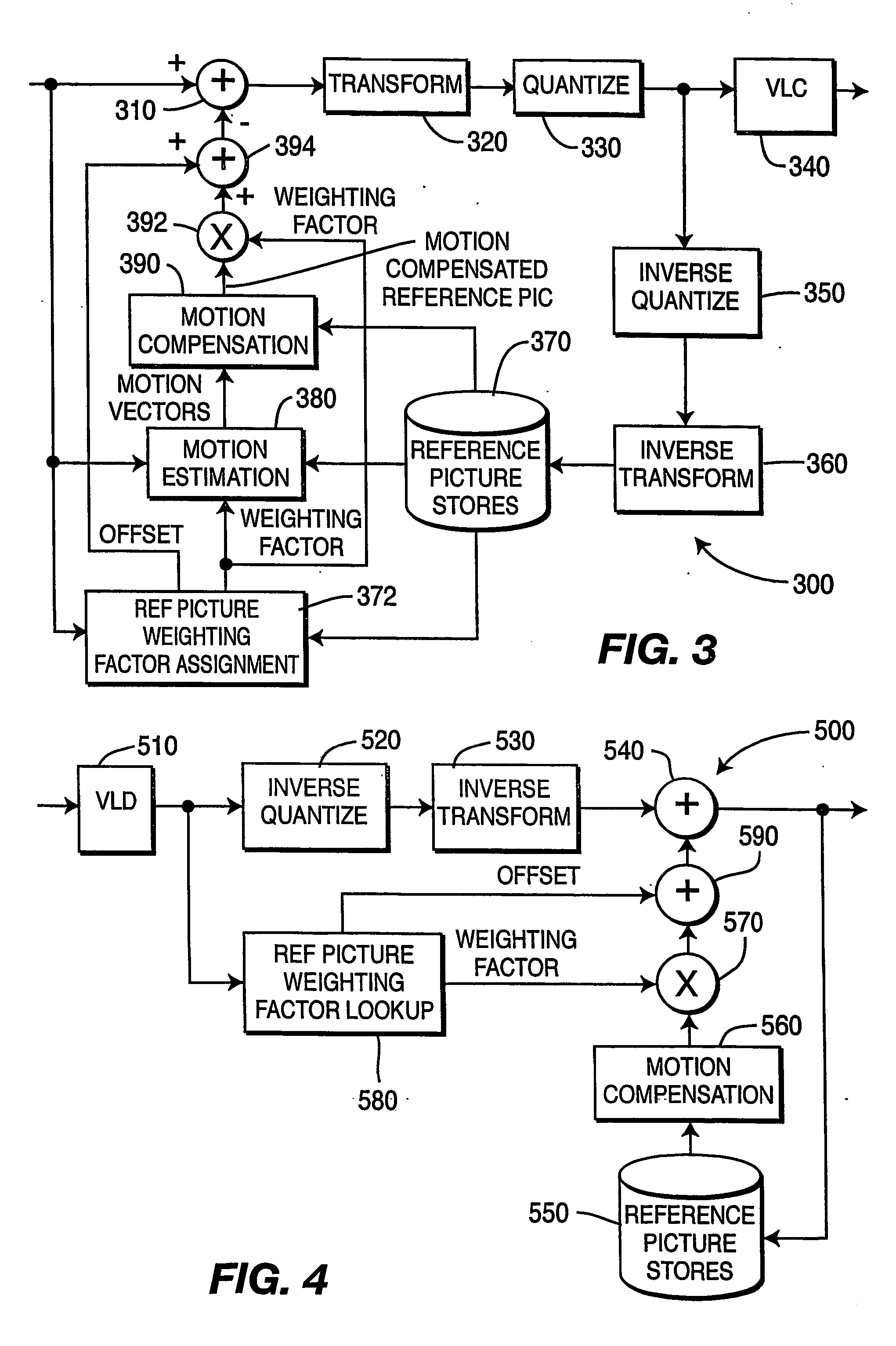
To achieve an image encoding apparatus that has extensibility by not limiting an image to be referenced, and that can reduce processing time satisfactorily if the processing of an ordinary frame is skipped, the apparatus of the present invention comprises: motion detecting means for detecting a motion vector for each block of a prescribed size from a reference image and an input image; weighted motion-compensation means for, based on the detected motion vector, extracting from the reference image an area of a prescribed size which is wider than the prescribed block size and which contains an area corresponding to each block of the input image, and for creating a predicted image for the input image by applying a predetermined weight to each of pixels in the wider area and by using the weighted pixels of the wider area; a predicted-image memory for storing the predicted image; encoding means for taking a residual between the stored predicted image and the input image, and for encoding the residual; and decoding means for decoding the encoded image data and thereby obtaining a reference image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
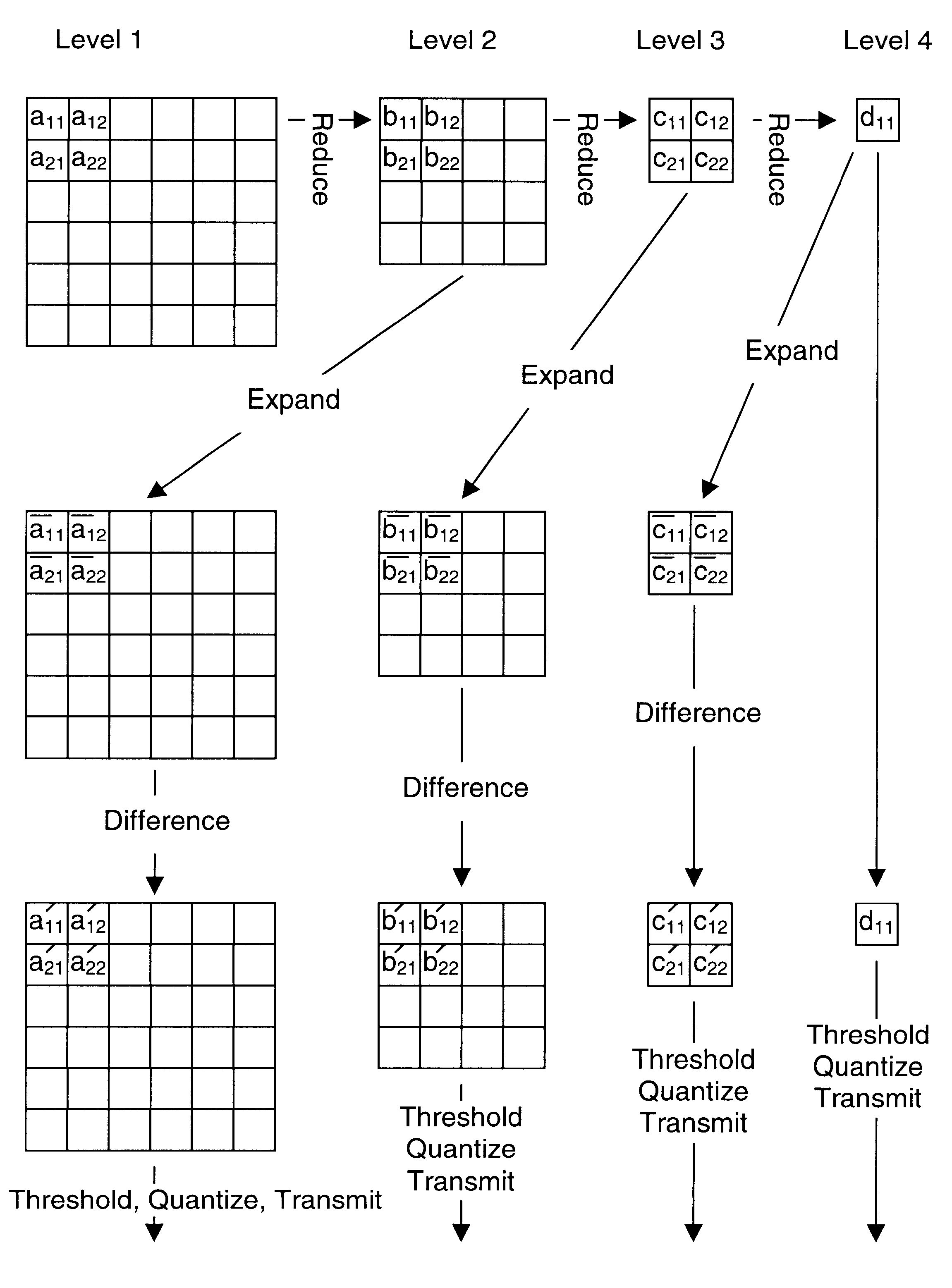
Foveated image coding system and method for image bandwidth reduction
InactiveUS6252989B1Increase in sizeQuick implementationDigitally marking record carriersPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData compressionImaging quality
A foveated imaging system, which can be implemented on a general purpose computer and greatly reduces the transmission bandwidth of images has been developed. This system has demonstrated that significant reductions in bandwidth can be achieved while still maintaining access to high detail at any point in an image. The system is implemented with conventional computer, display, and camera hardware. It utilizes novel algorithms for image coding and decoding that are superior both in degree of compression and in perceived image quality and is more flexible and adaptable to different bandwidth requirements and communications applications than previous systems. The system utilizes novel methods of incorporating human perceptual properties into the coding the decoding algorithms providing superior foveation. One version of the system includes a simple, inexpensive, parallel pipeline architecture, which enhances the capability for conventional and foveated data compression. Included are novel applications of foveated imaging in the transmission of pre-recorded video (without eye tracking), and in the use of alternate pointing devices for foveation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
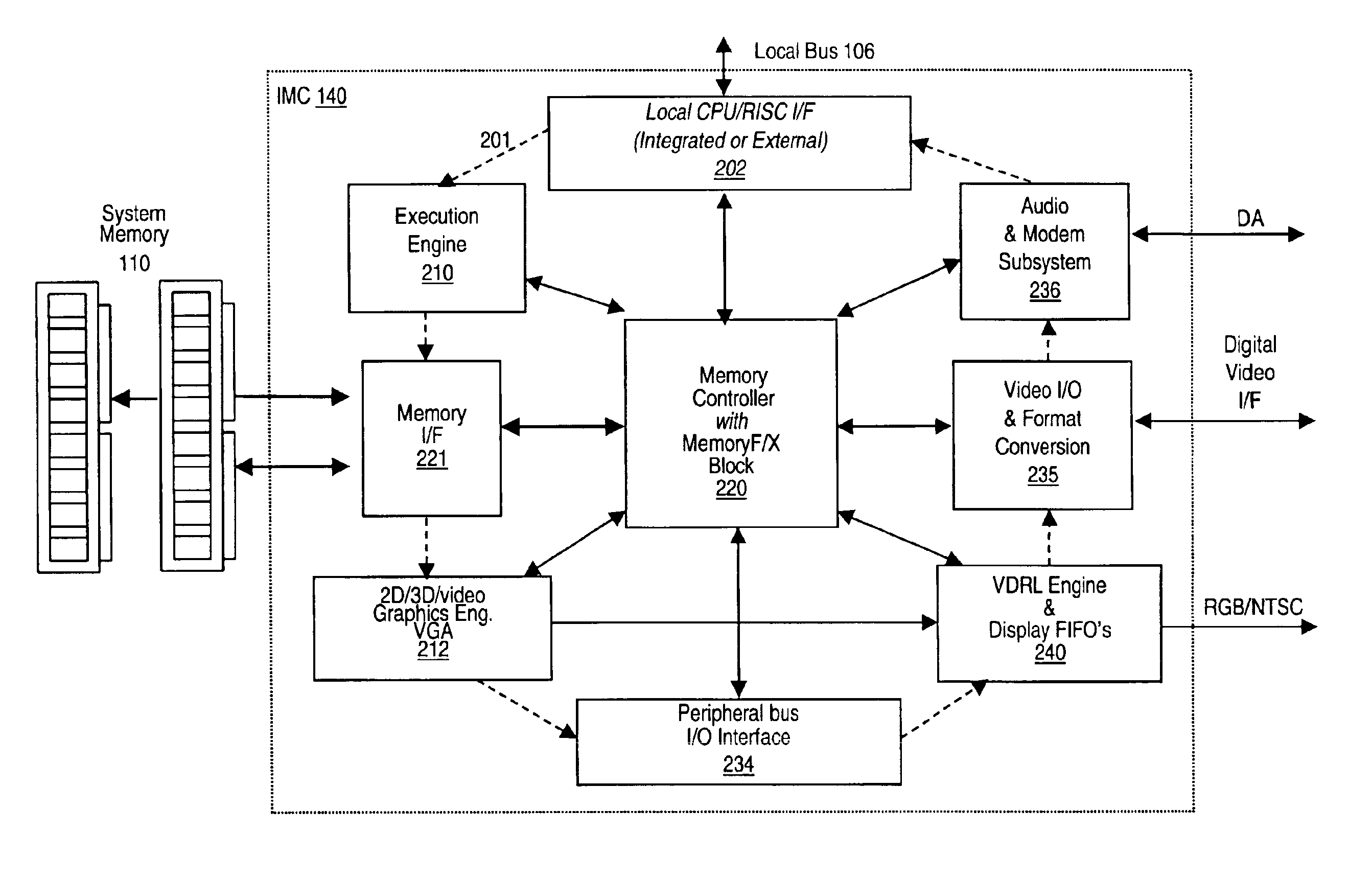
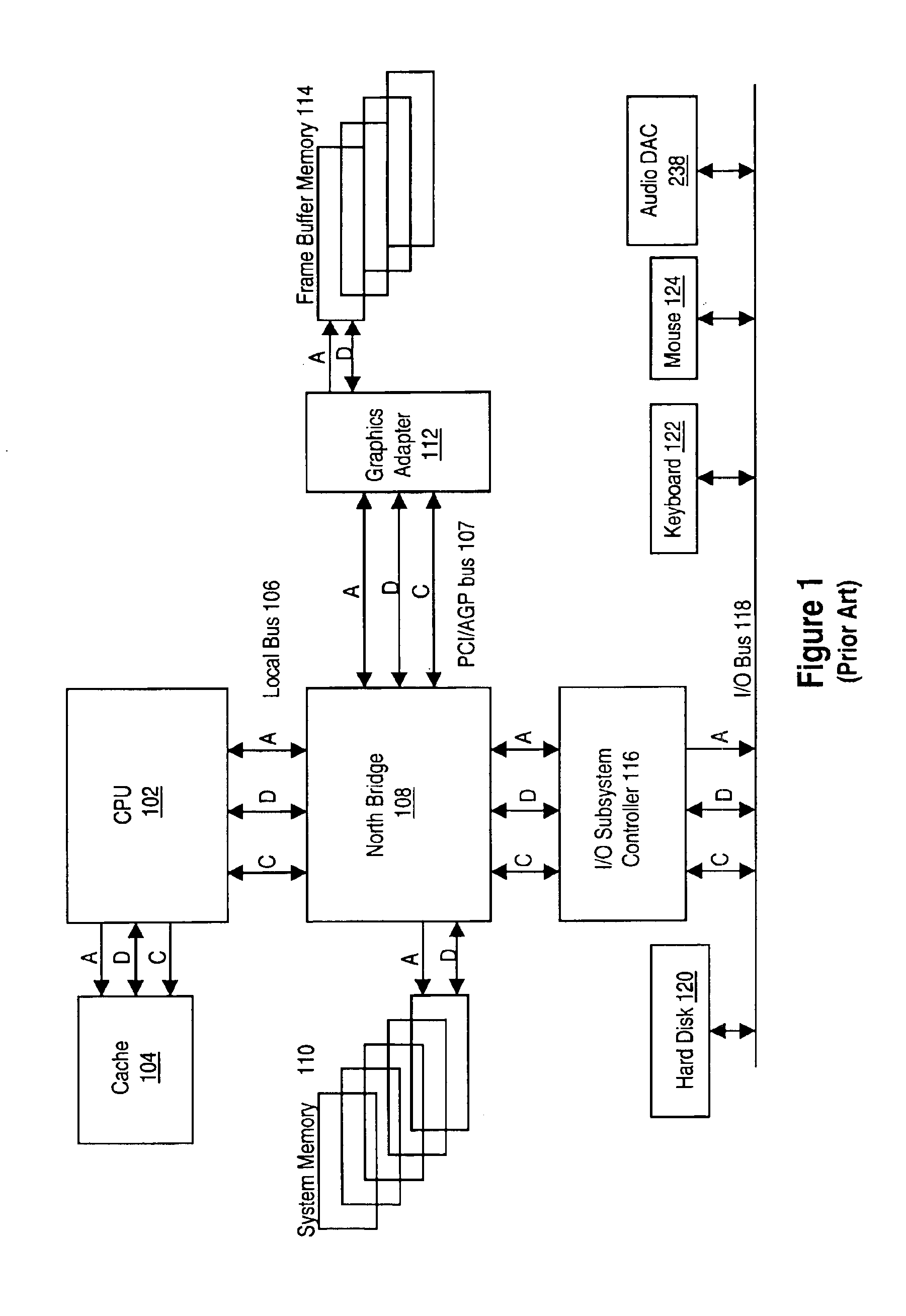
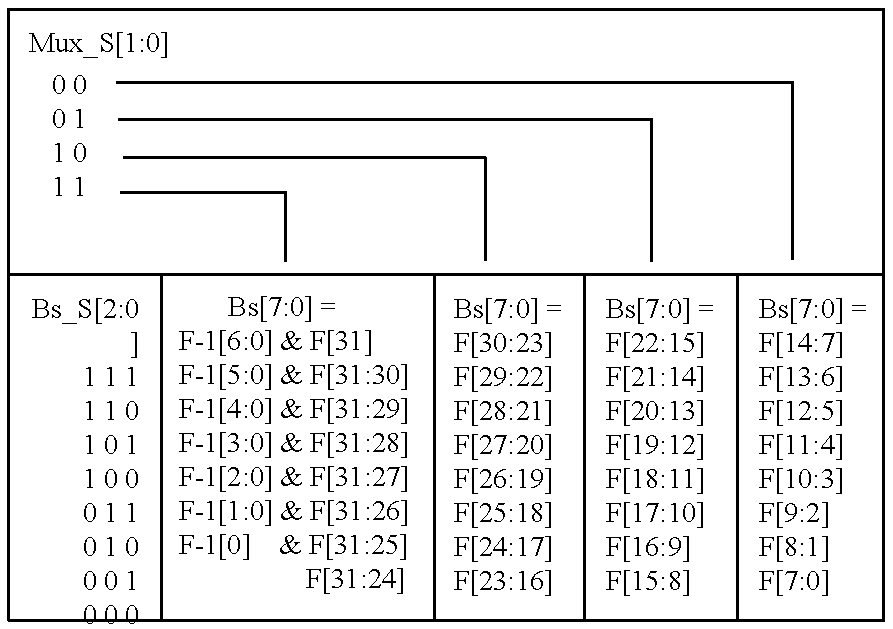
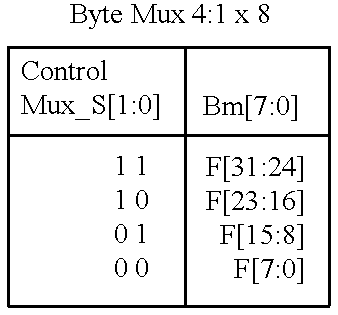
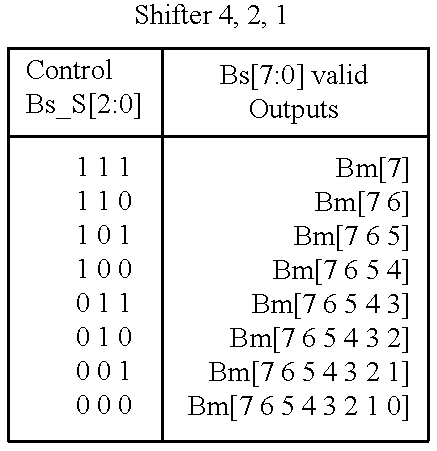
Memory module including scalable embedded parallel data compression and decompression engines
InactiveUS6879266B1Low costSmall data storage requirementMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel compressionParallel computing
An memory module including parallel data compression and decompression engines for improved performance. The memory module includes MemoryF / X Technology. To improve latency and reduce performance degradations normally associated with compression and decompression techniques, the MemoryF / X Technology encompasses multiple novel techniques such as: 1) parallel lossless compression / decompression; 2) selectable compression modes such as lossless, lossy or no compression; 3) priority compression mode; 4) data cache techniques; 5) variable compression block sizes; 6) compression reordering; and 7) unique address translation, attribute, and address caches. The parallel compression and decompression algorithm allows high-speed parallel compression and high-speed parallel decompression operation. The memory module-integrated data compression and decompression capabilities remove system bottlenecks and increase performance. This allows lower cost systems due to smaller data storage, reduced bandwidth requirements, reduced power and noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Audio and video decoder circuit and system
InactiveUS6369855B1Accelerates memory block moveAvoid confictTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionCoprocessorNetwork packet
An improved audio-visual circuit is provided that includes a transport packet parsing circuit for receiving a transport data packet stream, a CPU circuit for initializing said integrated circuit and for processing portions of said data packet stream, a ROM circuit for storing data, a RAM circuit for storing data, an audio decoder circuit for decoding audio portions of said data packet stream, a video decoder circuit for decoding video portions of said data packet stream, an NTSC / PAL encoding circuit for encoding video portions of said data packet stream, an OSD coprocessor circuit for processing OSD portions of said data packets, a traffic controller circuit moving portions of said data packet stream between portions of said integrated circuit, an extension bus interface circuit, a P1394 interface circuit, a communication coprocessors circuit, an address bus connected to said circuits, and a data bus connected to said circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Moving picture variable bit rate coding apparatus, moving picture variable bit rate coding method, and recording medium for moving picture variable bit rate coding program
InactiveUS6259739B1Improved coding resultIncrease the compression ratioTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer scienceTime processing
A moving picture variable bit rate coding apparatus receives digitized moving pictures and subjects them to coding according to a variable bit rate method using real time processing in response to the input of the pictures. The apparatus performs variable bit rate coding in real time by sequentially performing blocking, conversion processing, quantization processing, and generation of bit streams in response to the input of digitized moving picture data, and setting a quantization scale used for quantization corresponding to a quantity of generated bit streams to perform coding processing and control of quantization in parallel.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for representing real-time motion
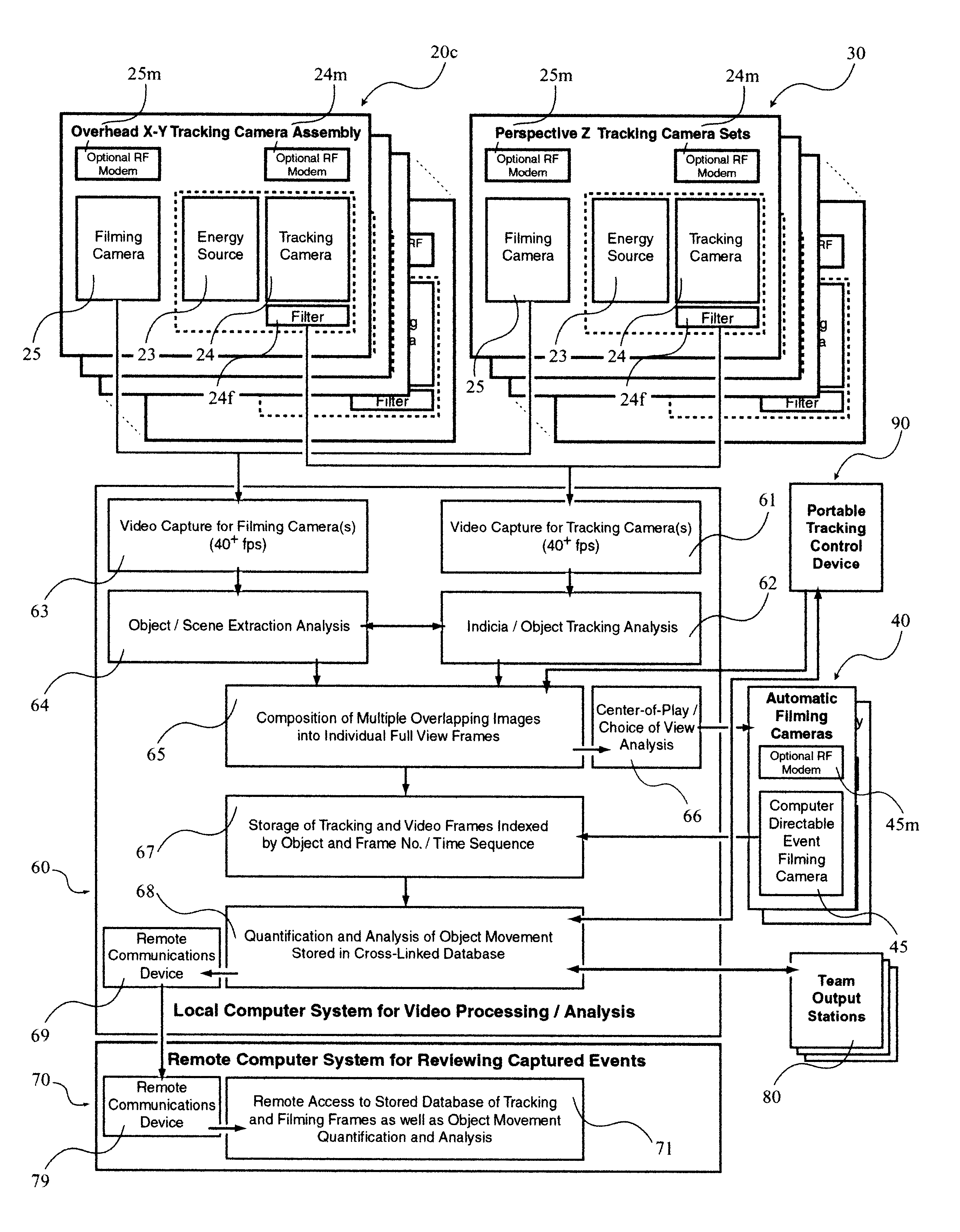
InactiveUS6707487B1Accurate game reconstructionReduce data flowImage enhancementTelevision system detailsGraphicsContinuation
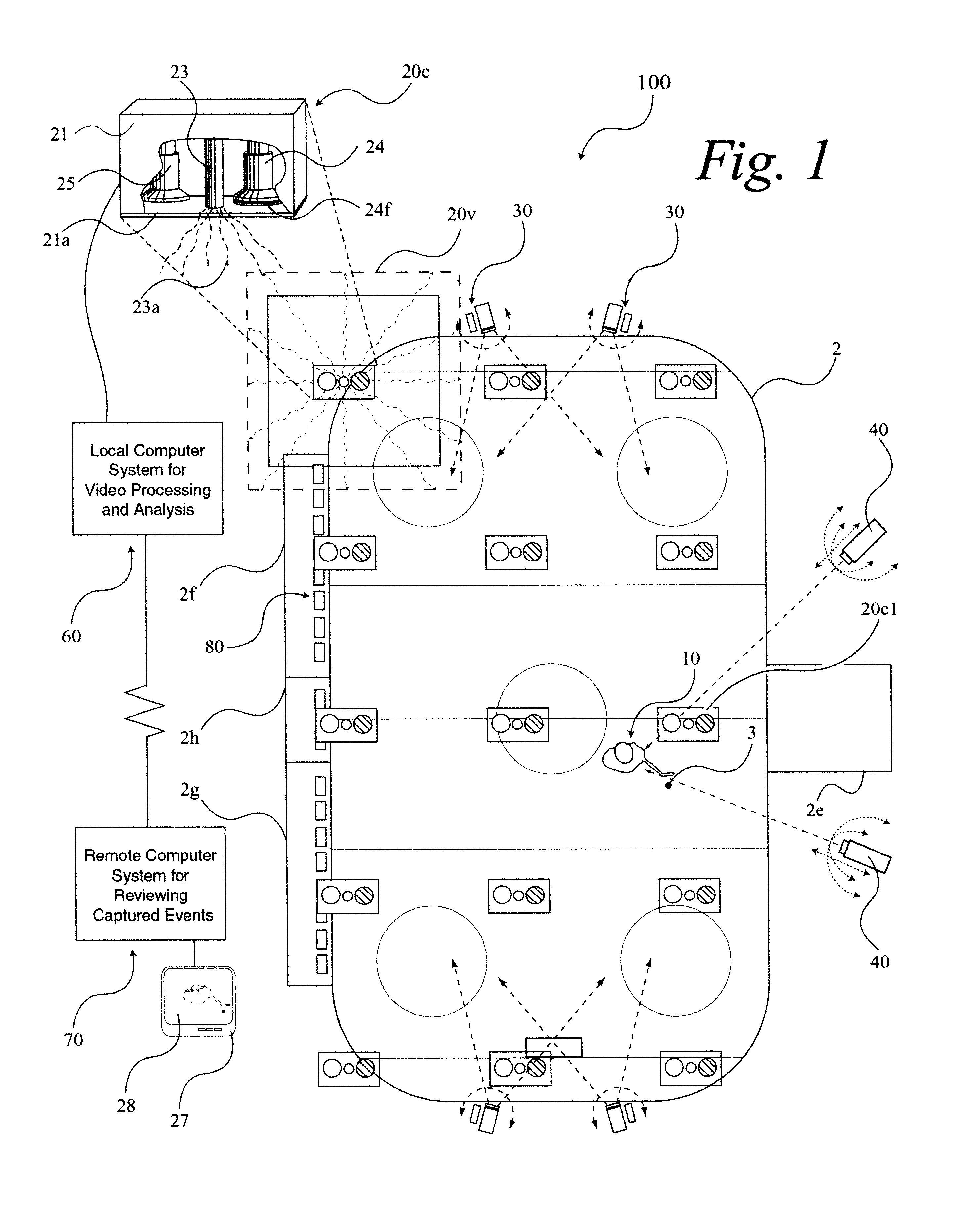
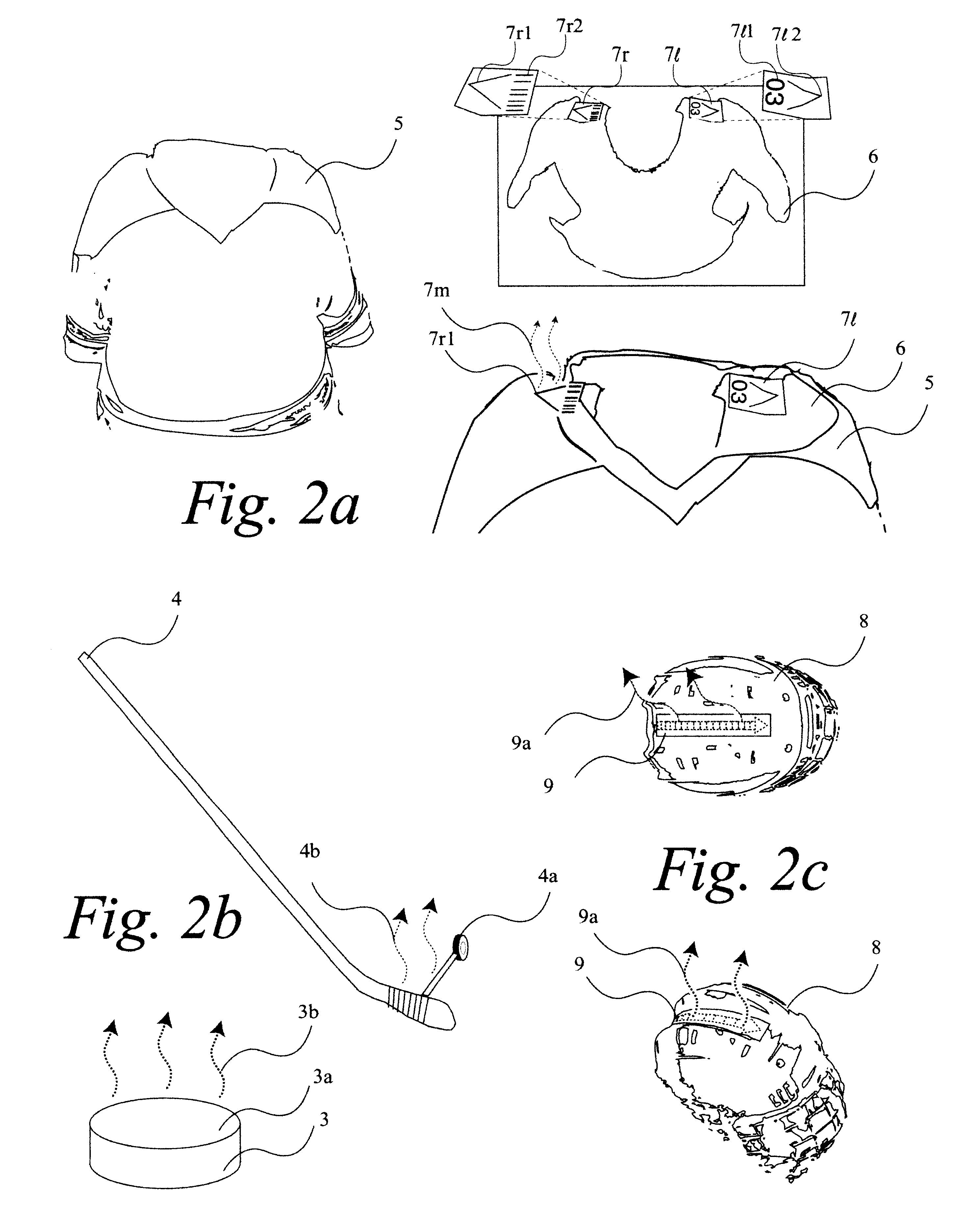
A system 100 for tracking the movement of multiple objects within a predefined area using a continuation of overhead X-Y tracking cameras 24 with attached frequency selective filter 24f. Also employed are perspective Z filming cameras sets 30. Objects to be tracked, such as player 17, have been marked to include some form of frequency selective reflective material such as an ink. Typical markers include patches 7r and 7l, sticker 9 and tape 4a as well as additional body joint markers 17af through 17l. System 100 radiates selected energy 23a throughout the predefined area of tracking that is specifically chosen to reflect off said reflective materials used to mark for instance player 17. The reflected energy is then received by tracking cameras 24 while all other ambient light is blocked by filter 24f. Local Computer System 60 continuously captures images from said tracking cameras 24 which include only the minimum information created by said reflected energy. System 60 efficiently locates said markings on said multiple objects and uses this location information to determine for each marking its angle of rotation, angle of azimuth and distance from a designated origin 17o local to player 17. Local origin 17o is then expressed as a three-dimensional coordinate with respect to the origin of the playing venue 2a. The continuous stream of tracked three-dimensional coordinates, defining the body joints on players such as 17, is then transmitted to a remote computer where it can be used to drive a graphic re-animation of the object movement. Along with this re-animation, additional performance measurements may be derived from the continuous stream and automatically made available in real-time.
Owner:MAXX HLDG
Moving picture encoding method and decoding method
ActiveUS20050152452A1Prediction efficiency can be improvedReduce data volumePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDecoding methodsTime information
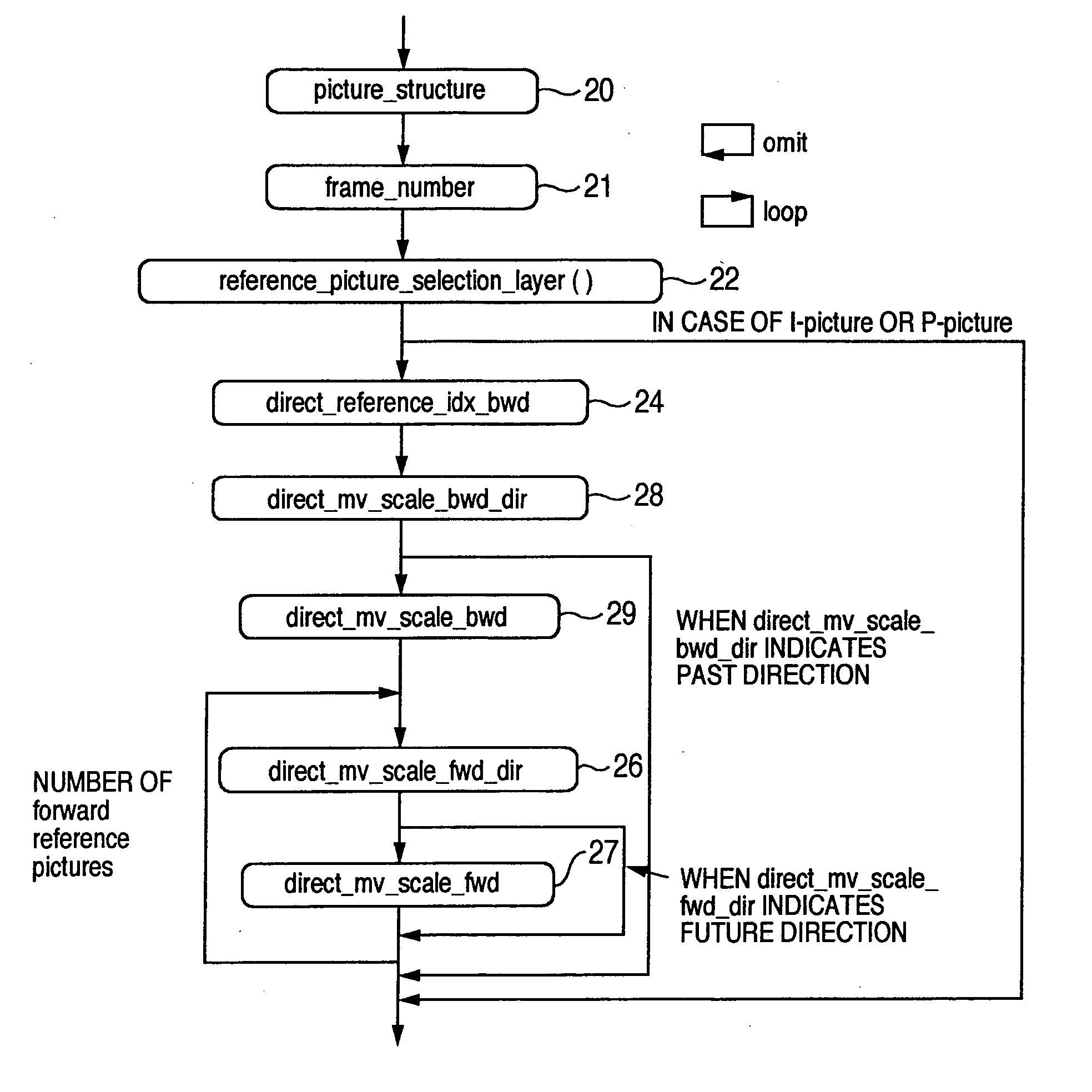
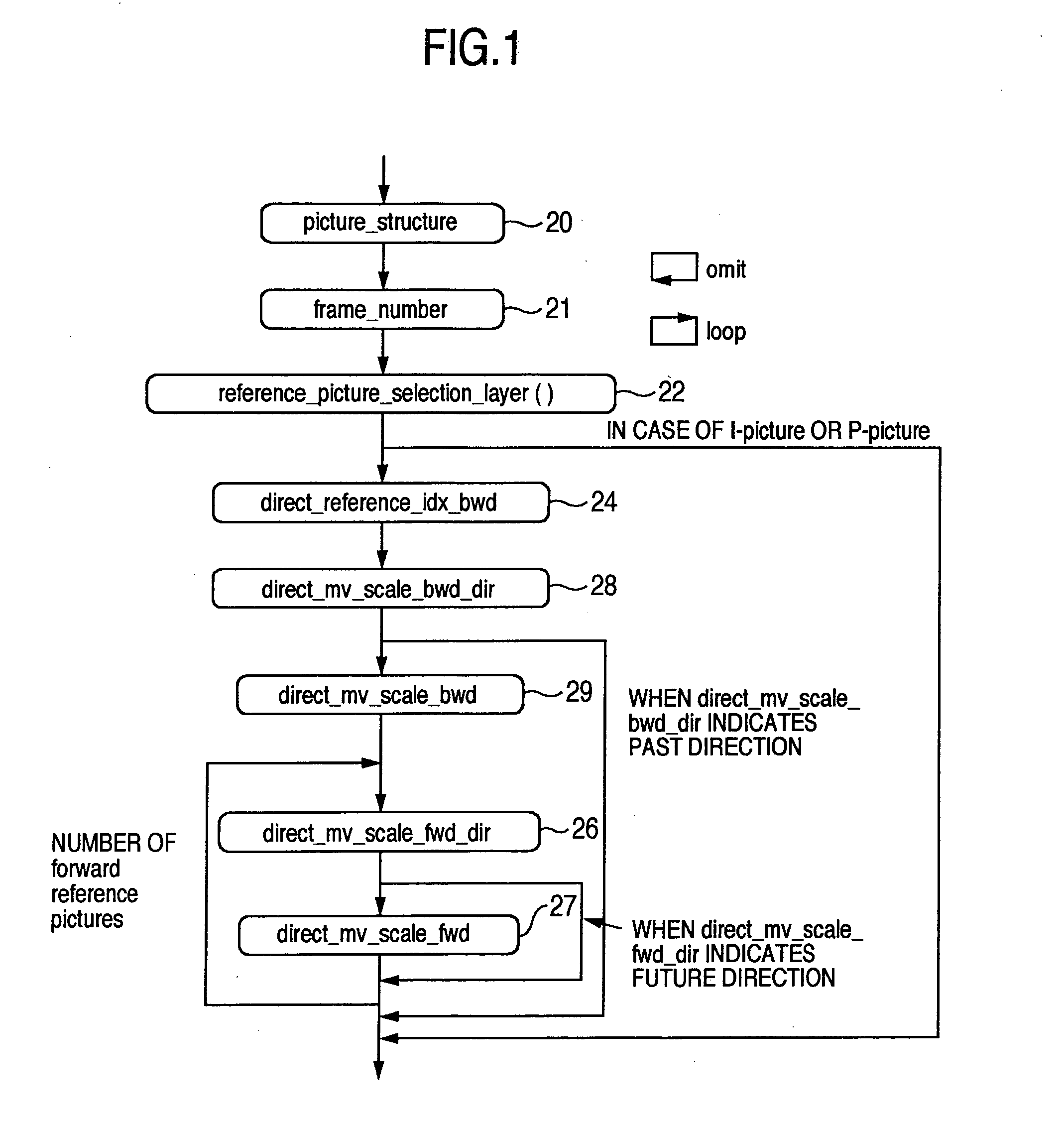
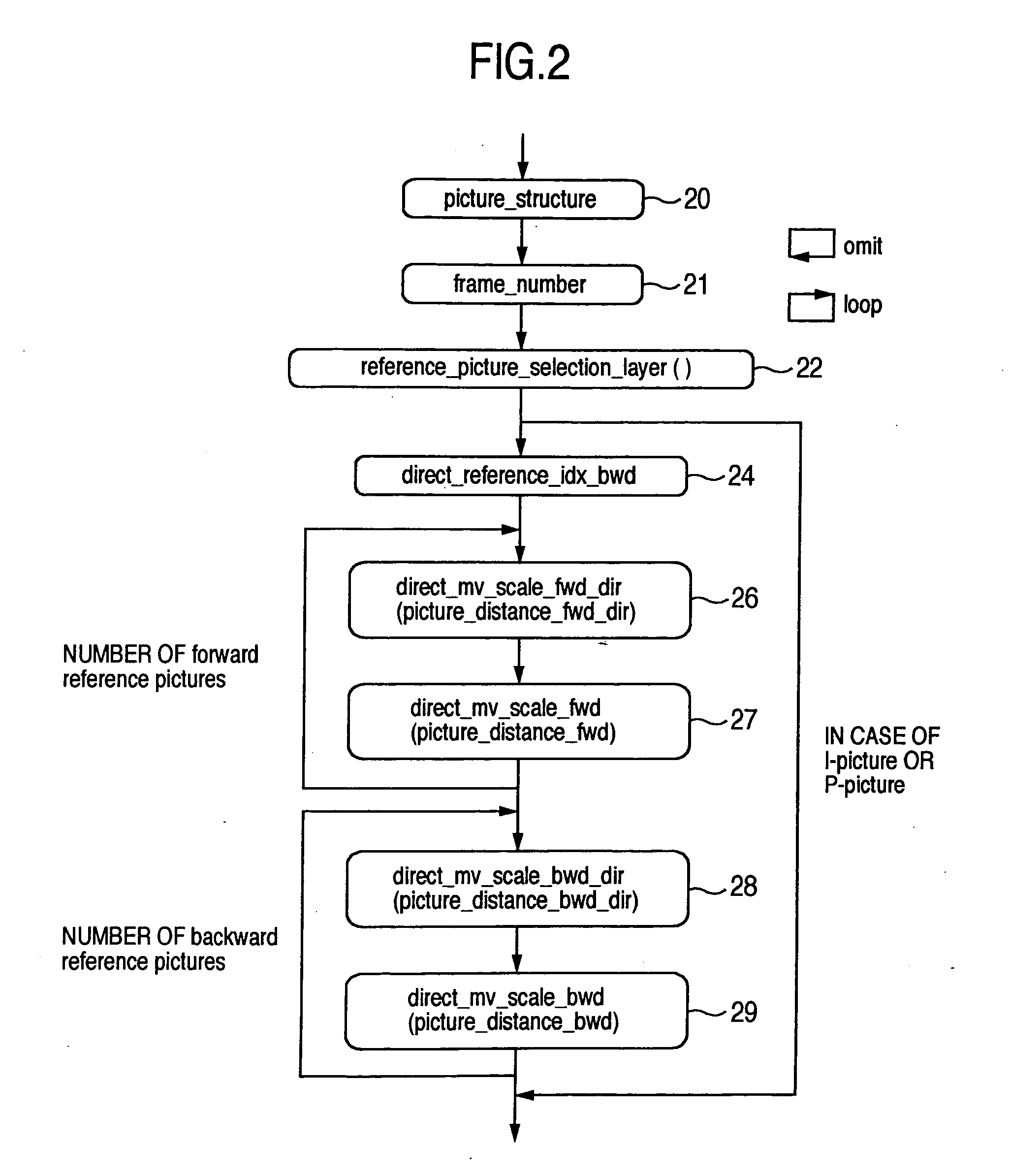
Conventionally there has been a case that the direct mode cannot be applied effectively depending on the block. With such being the case, information indicating whether a backward reference frame set by default can be utilized in the direct mode is provided to a decoder. A switching procedure to switch to a compensation method applicable when a collocated block has no forward motion vector for effective use, and the compensation method are also provided to the decoder. Thus, it is possible to clearly determine whether the reference frame can be used in the direct mode. Further, when the frame number has no time information, it is possible to effectively send information indicating the relationship between the reference frame and the current frame. Furthermore, the alternative mode and its switching procedure of the present invention make it possible to improve the prediction performance when the direct mode cannot be applied.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Removal of block encoding artifacts
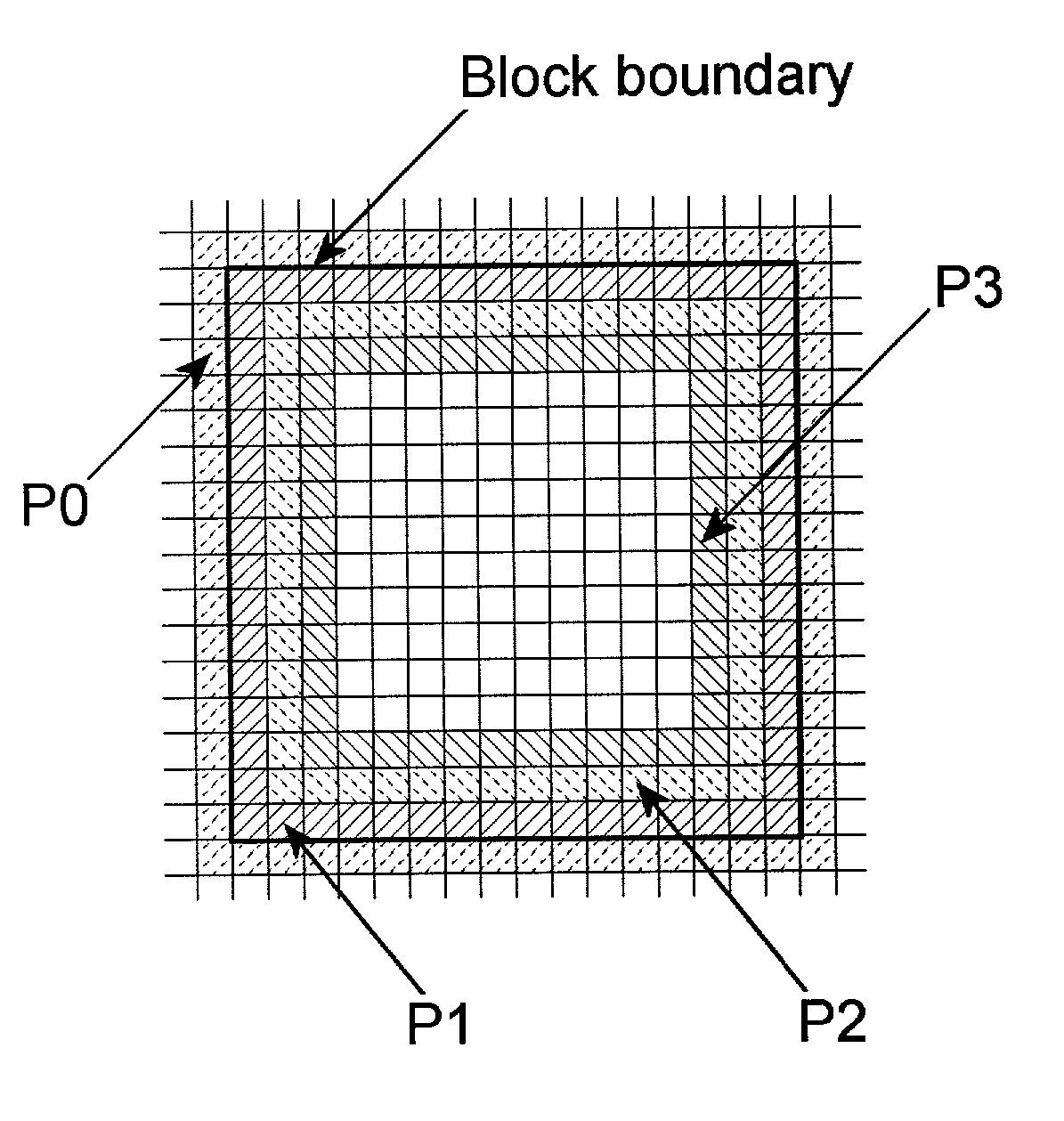
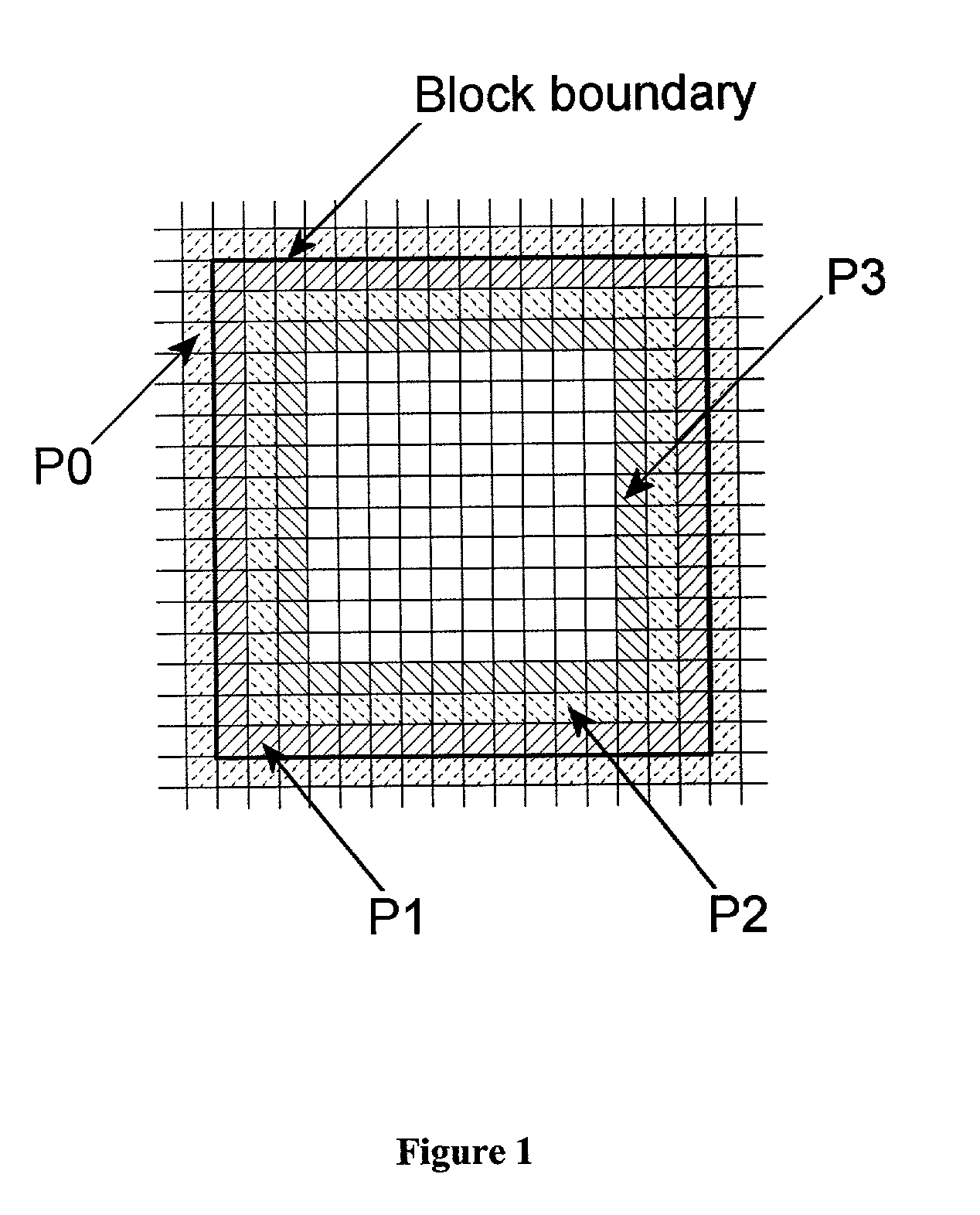
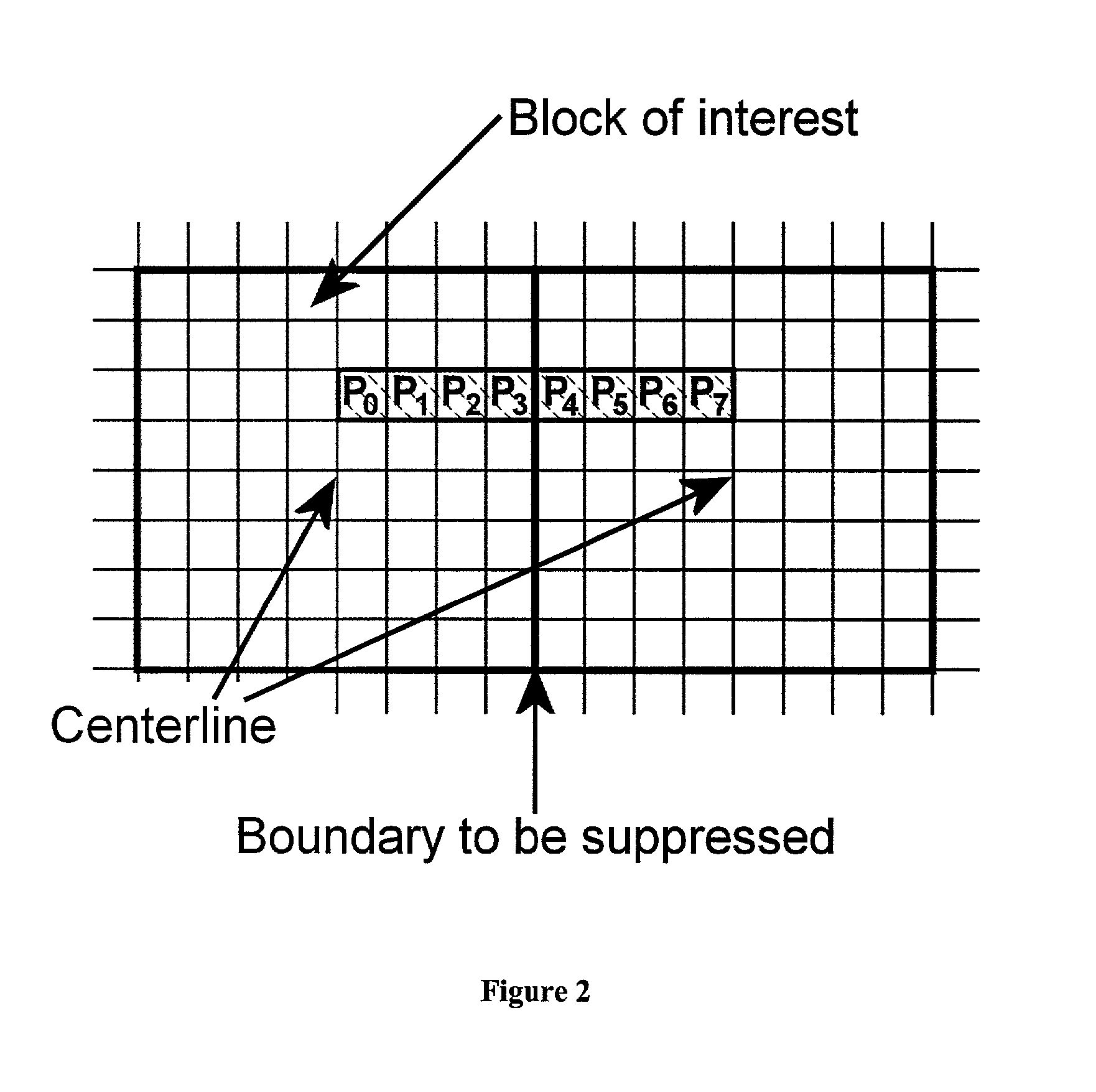
InactiveUS7003174B2Reduce artifactsAccessImage enhancementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVisibilityPattern recognition
A method of reducing artifacts in an image previously processed by block transform encoding may comprise the steps of:determining block boundaries;determining an approximate metric of artifact visibility;optionally interpolating across block boundaries;adaptively filtering luminance;optionally adaptively filtering chrominance;adaptively adjusting local saturation variation; andadaptively simulating high spatial frequency image detail;wherein the adaptive steps are executed to an extent or in an amount depending on the metric or standard or measurement of artifact visibility.
Owner:COREL CORP +1
Operating system independent method and apparatus for graphical remote access
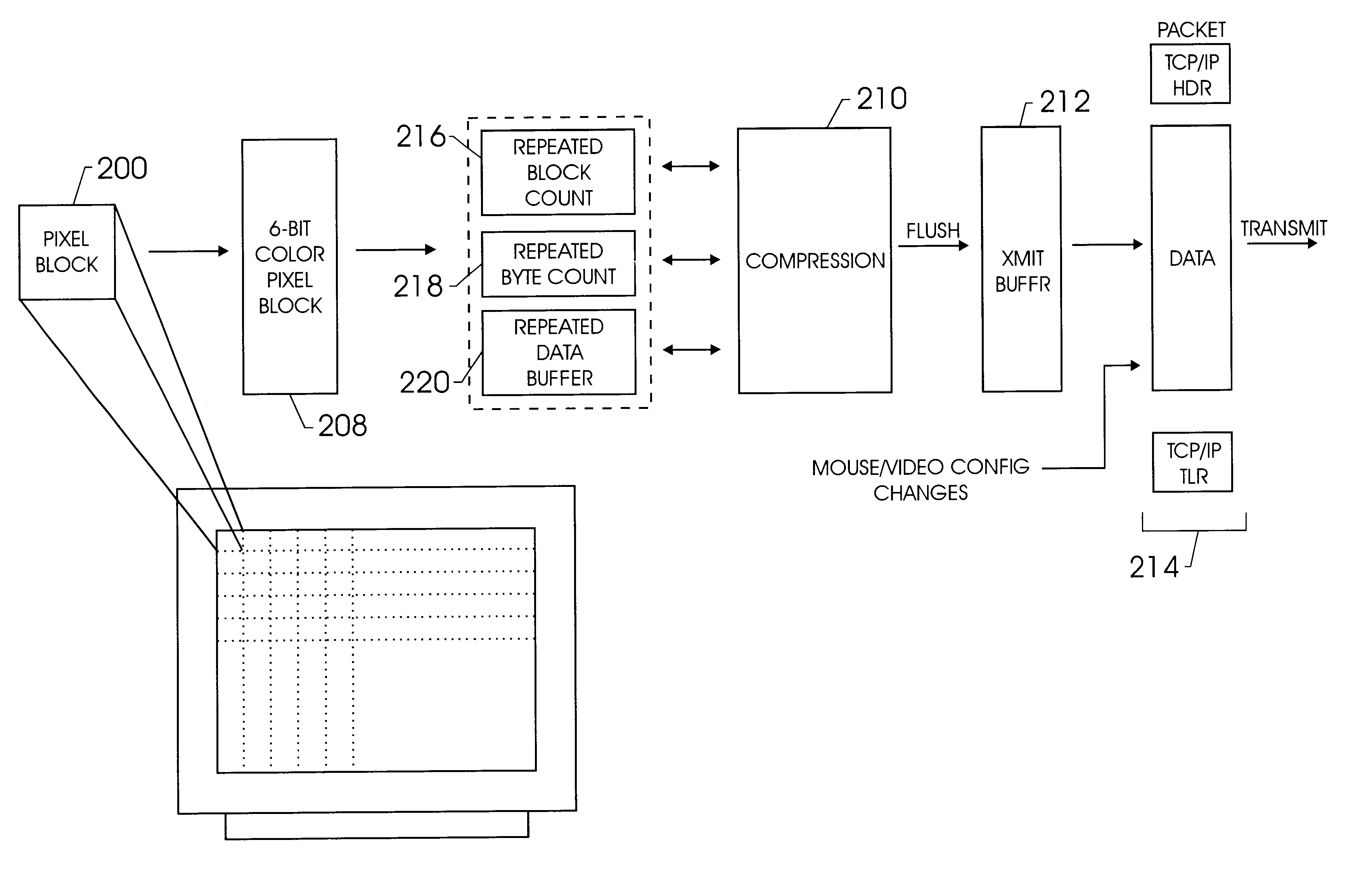
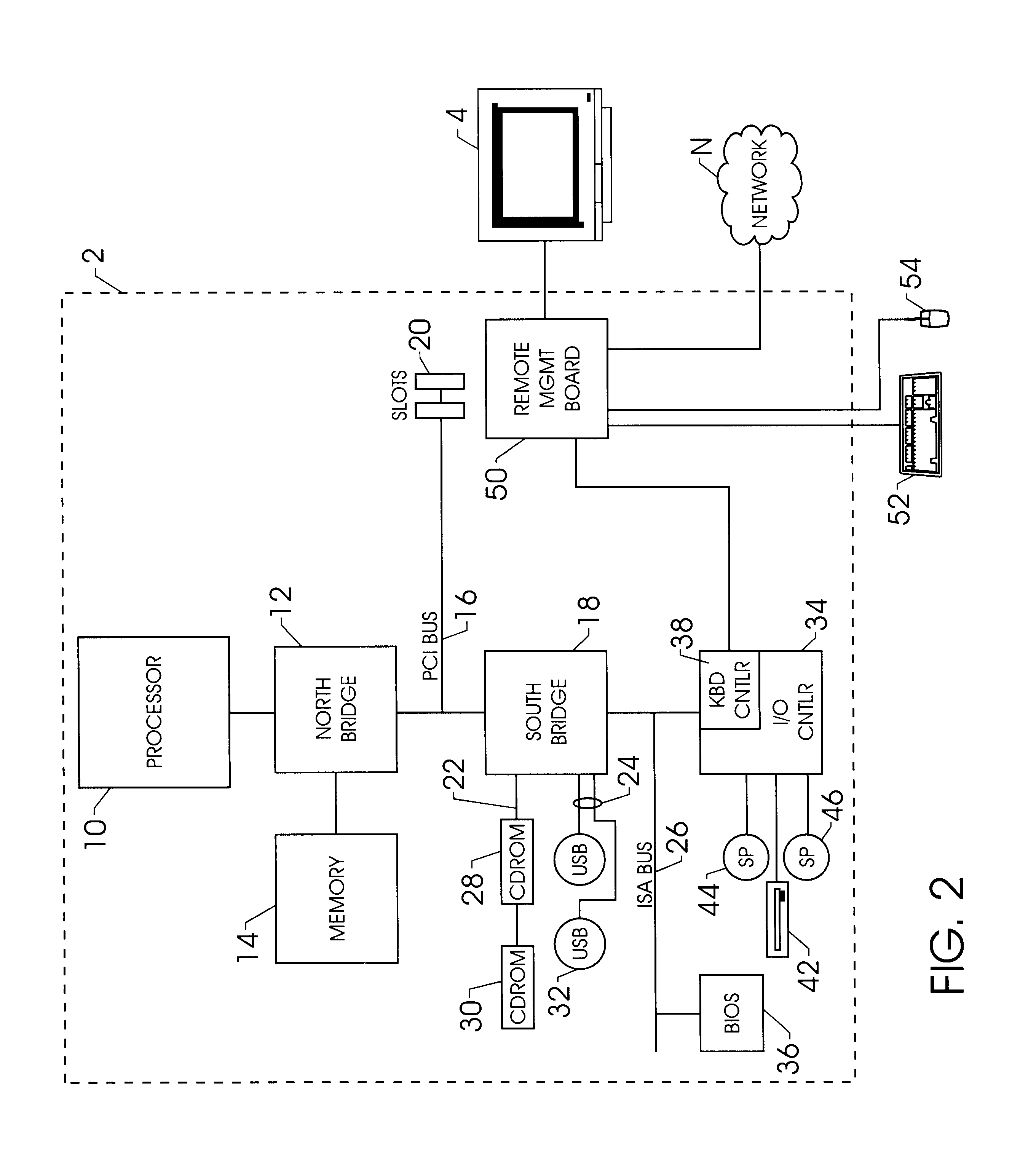
A method and apparatus for updating video graphics changes of a managed server to a remote console independent of an operating system. The screen (e.g. frame buffer) of the managed server is divided into a number of blocks. Each block is periodically monitored for changes by calculating a hash code and storing the code in a hash code table. When the hash code changes, the block is transmitted to the remote console. Color condensing may be performed on the color values of the block before the hash codes are calculated and before transmission. Compression is performed on each block and across blocks to reduce bandwidth requirements on transmission. Periodically, the configuration of a video graphics controller and a pointing device of the managed server are checked for changes, such as changes to resolution, color depth and cursor movement. If changes are found, the changes are transmitted to the remote console. The method and apparatus may be performed by a separate processor as part of a remote management board, a "virtual" processor by causing the processor of the managed server to enter a system management mode, or a combination of the two.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
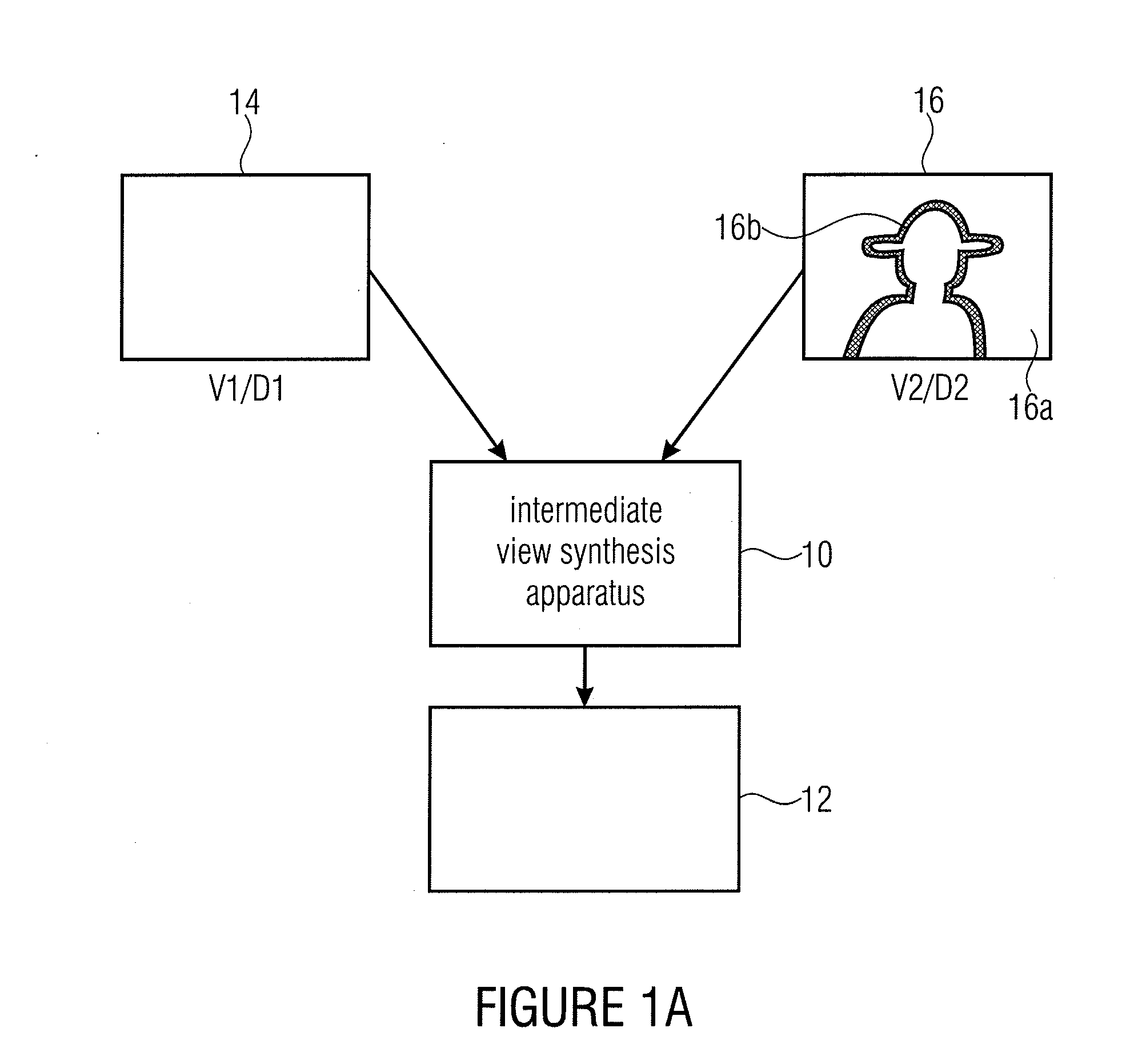
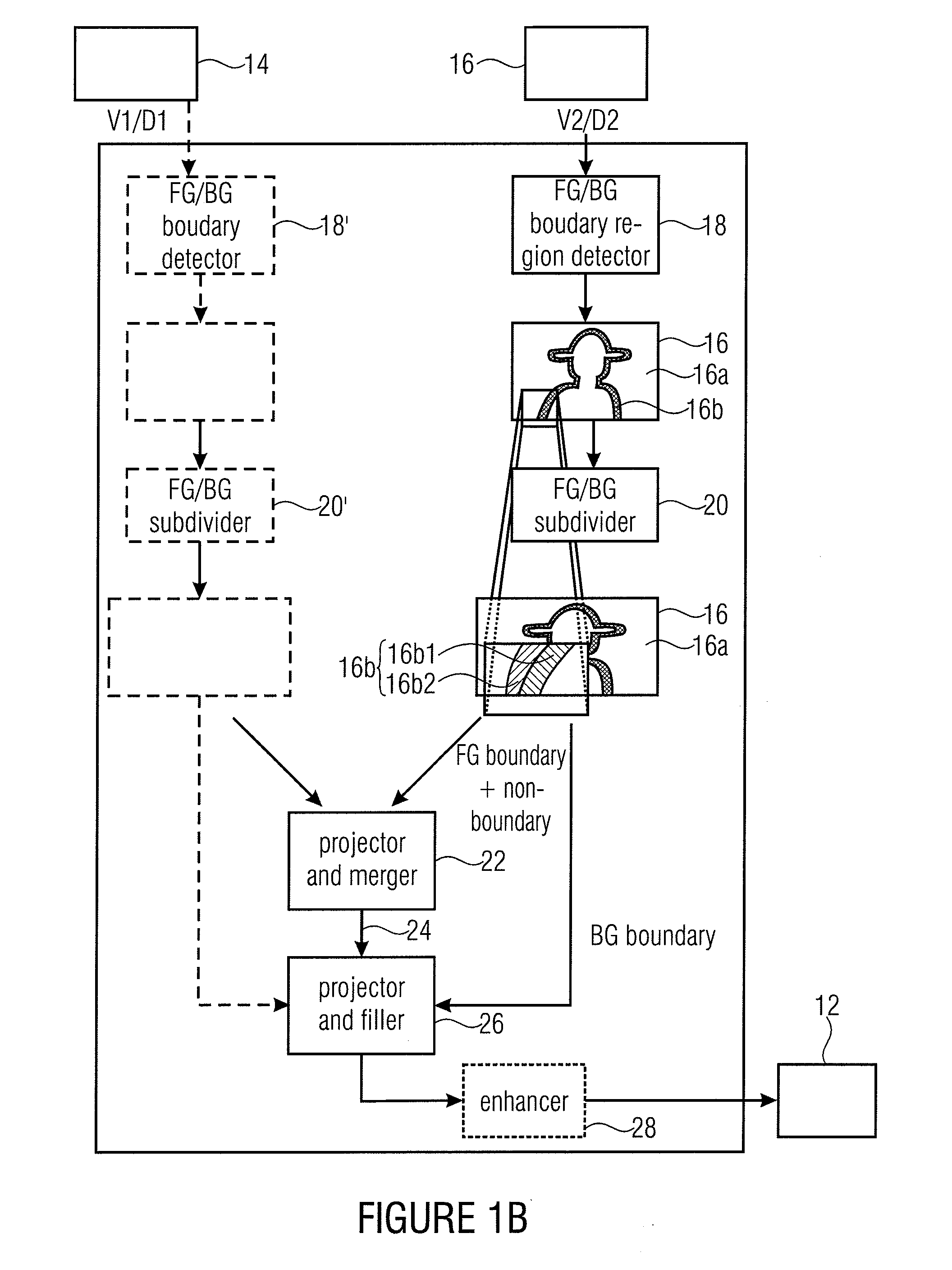
Intermediate View Synthesis and Multi-View Data Signal Extraction
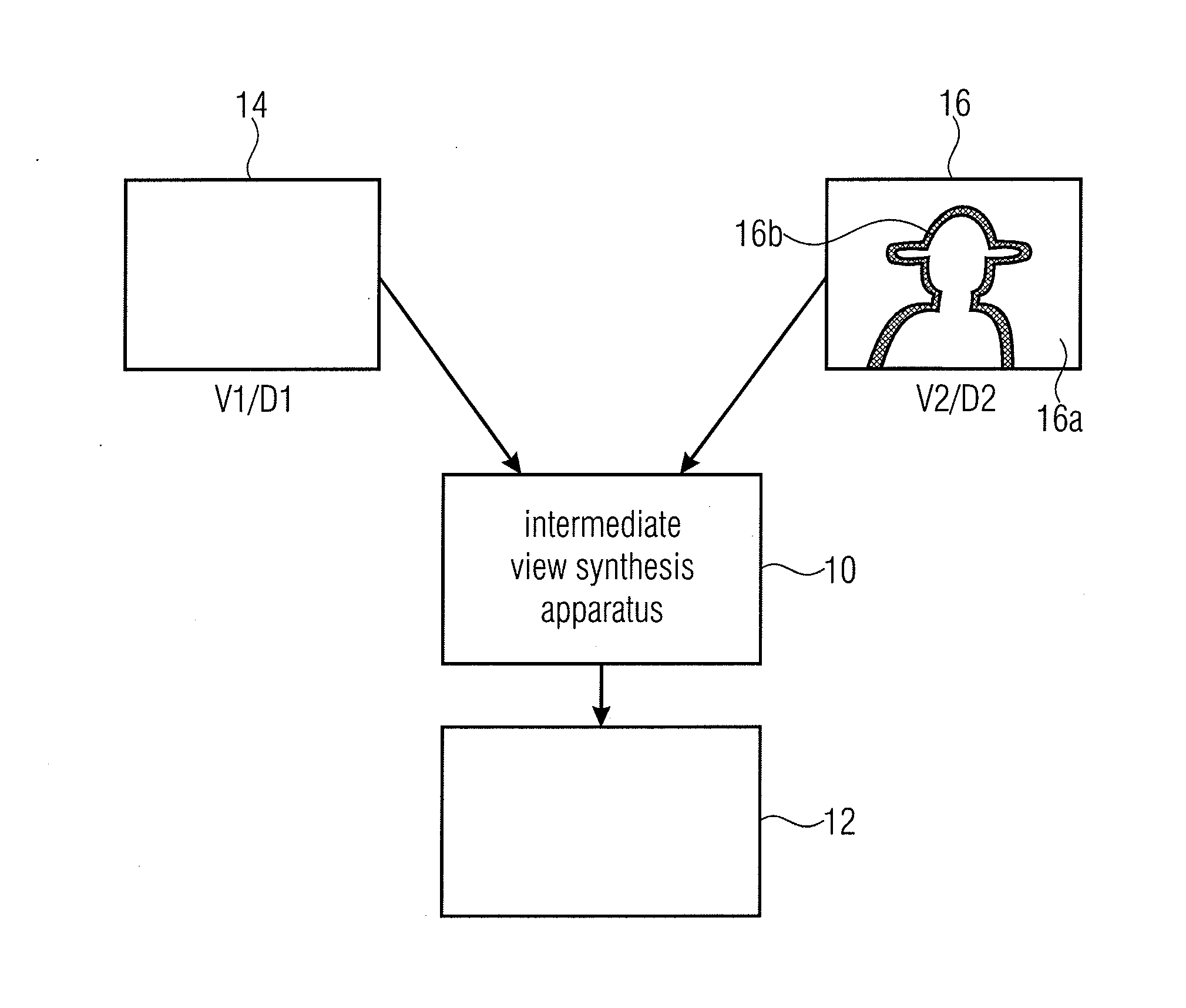
ActiveUS20110261050A1Avoid and reduce artifactImage codingCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer visionBoundary region
An intermediate view synthesis apparatus for synthesizing an intermediate view image from a first image corresponding to a first view and a second image corresponding to a second view different from the first view, the first and second images including depth information, wherein the second image being is divided-up into a non-boundary portion, and a foreground / background boundary region, wherein the intermediate view synthesis apparatus is configured to project and merge the first image and the second image into the intermediate view to obtain an intermediate view image, with treating the foreground / background boundary region subordinated relative to the non-boundary portion. A multi-view data signal extraction apparatus for extracting a multiview data signal from a multi-view representation including a first image corresponding to a first view and a second image corresponding to a second view being different from the first view is also described, the first and second images including depth information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Systems and methods for data compression such as content dependent data compression
Systems and methods for providing fast and efficient data compression using a combination of content independent data compression and content dependent data compression. In one aspect, a method for compressing data comprises the steps of: analyzing a data block of an input data stream to identify a data type of the data block, the input data stream comprising a plurality of disparate data types; performing content dependent data compression on the data block, if the data type of the data block is identified; performing content independent data compression on the data block, if the data type of the data block is not identified.
Owner:REALTIME DATA
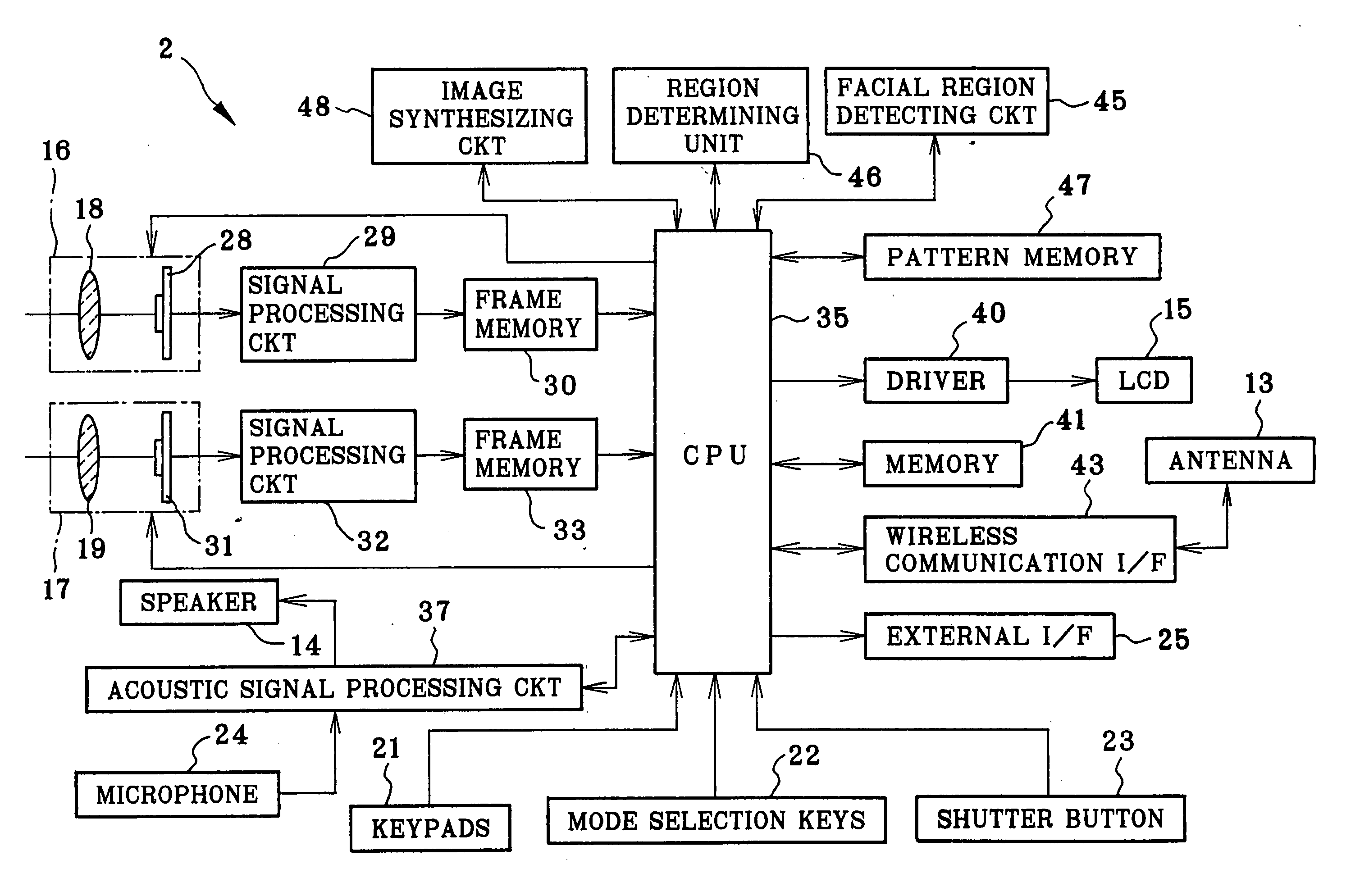
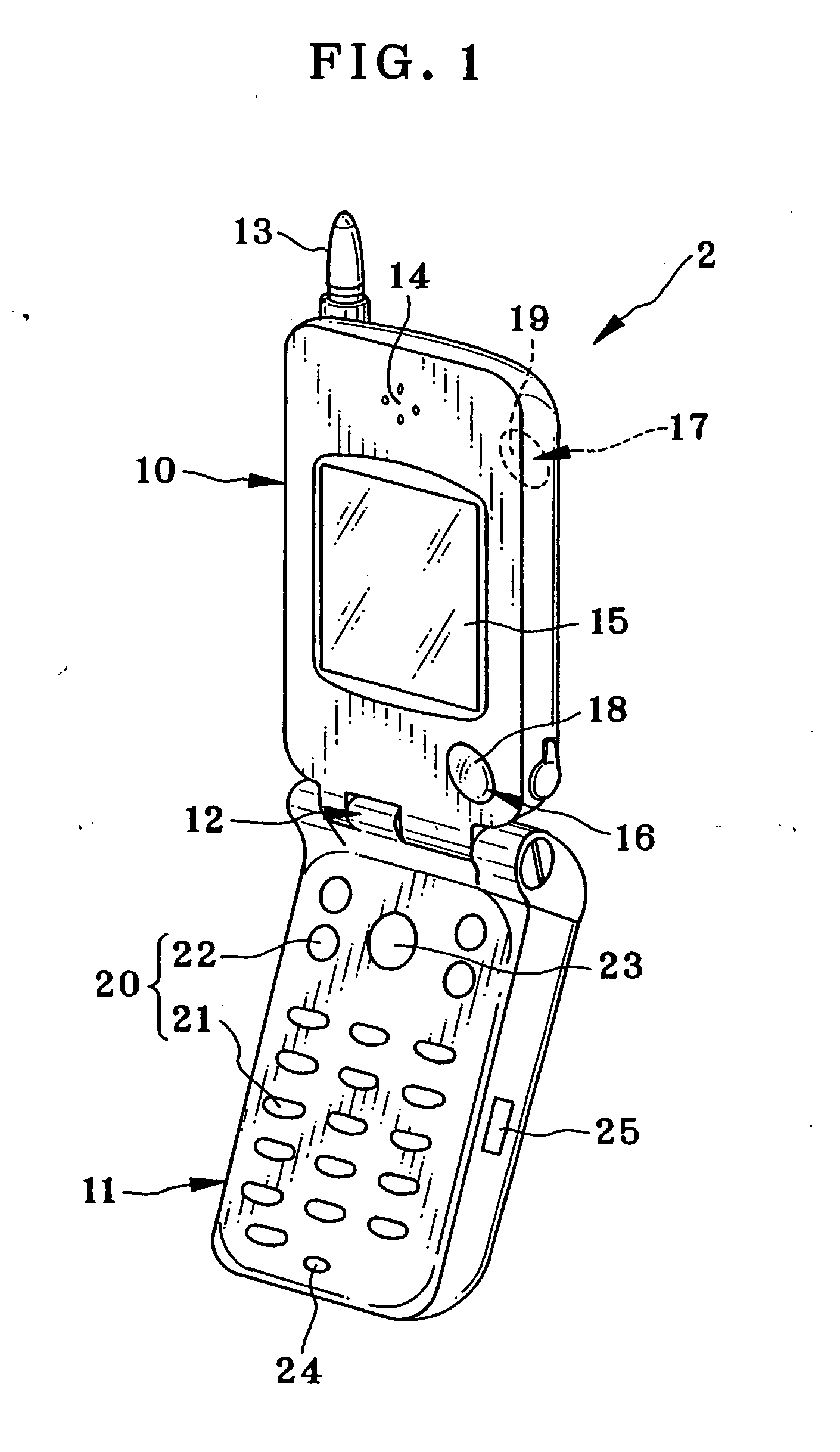
Image pickup device and image synthesizing method
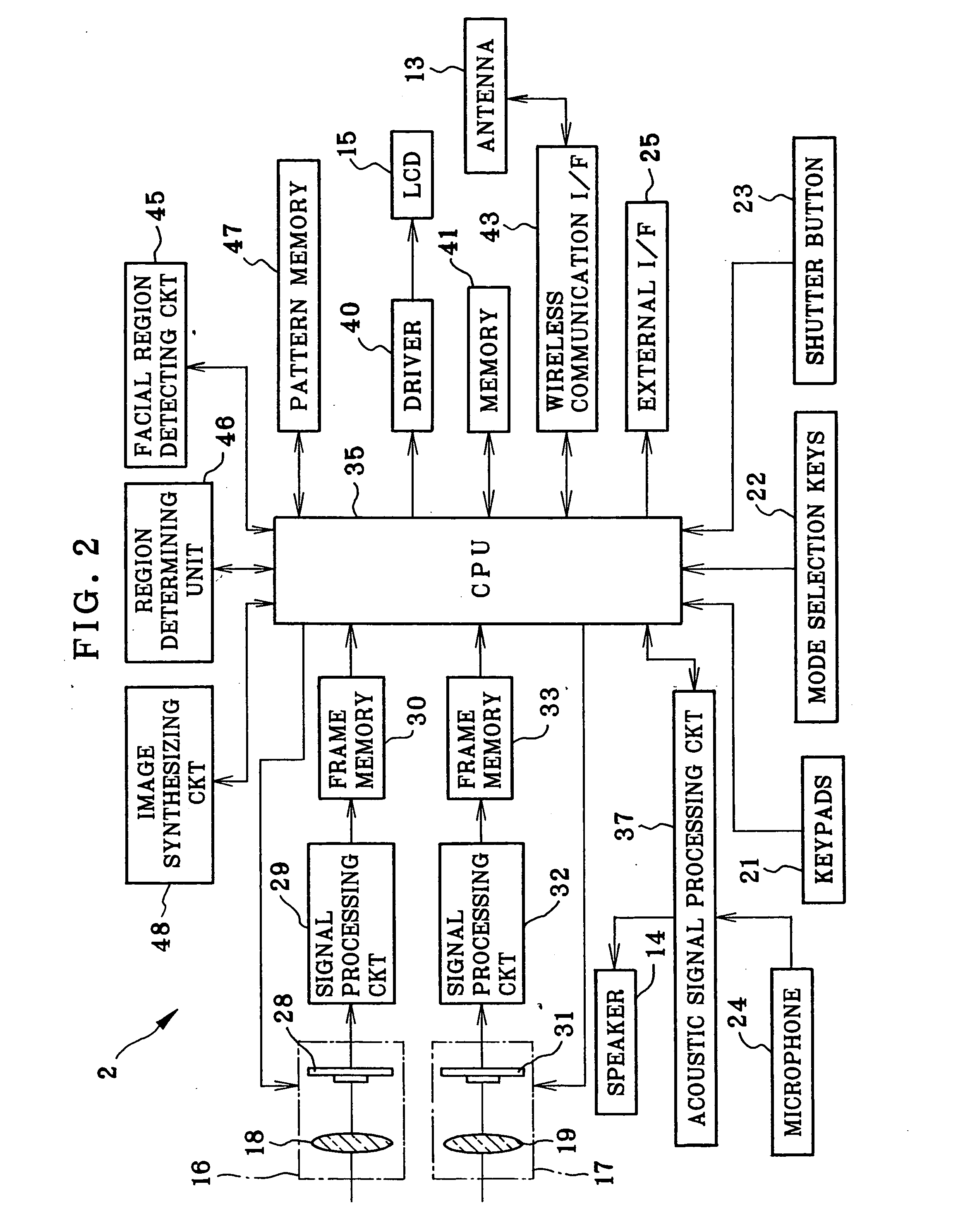
InactiveUS20050036044A1Easy to synthesizeEdited readily and easilyTelevision system detailsImage enhancementFacial regionImaging data
An image pickup device is constituted by a handset of cellular phone, wherein an image pickup unit photographs a user as first object, to output image data of a first image frame. A facial region detecting circuit retrieves a facial image portion of the user as first object according to image data of the first image frame. An image synthesizing circuit is supplied with image data of a second image frame including persons as second object. The facial image portion is synthesized in a background region being defined outside the persons as second object within the second image frame.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Efficient motion vector coding for video compression
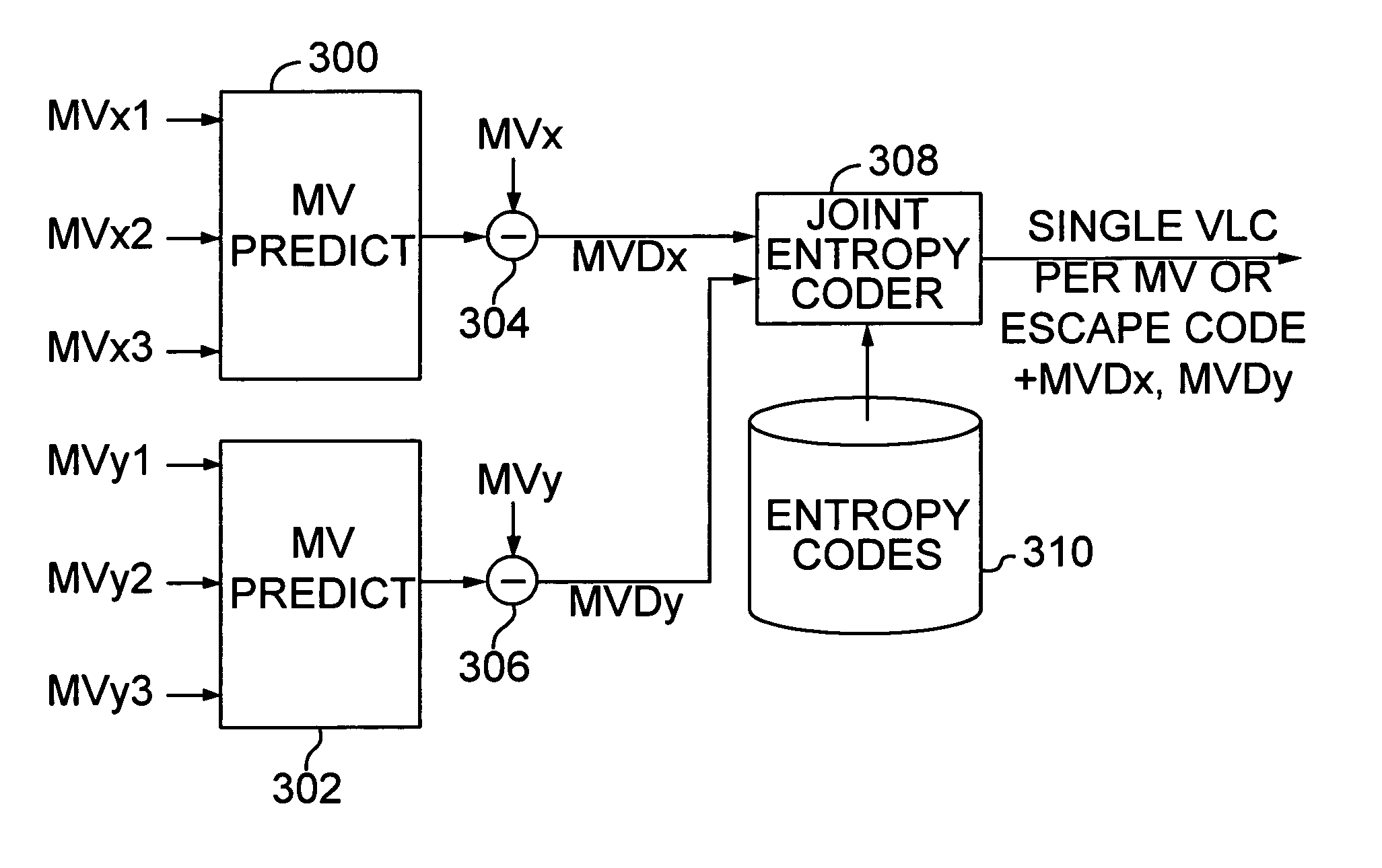
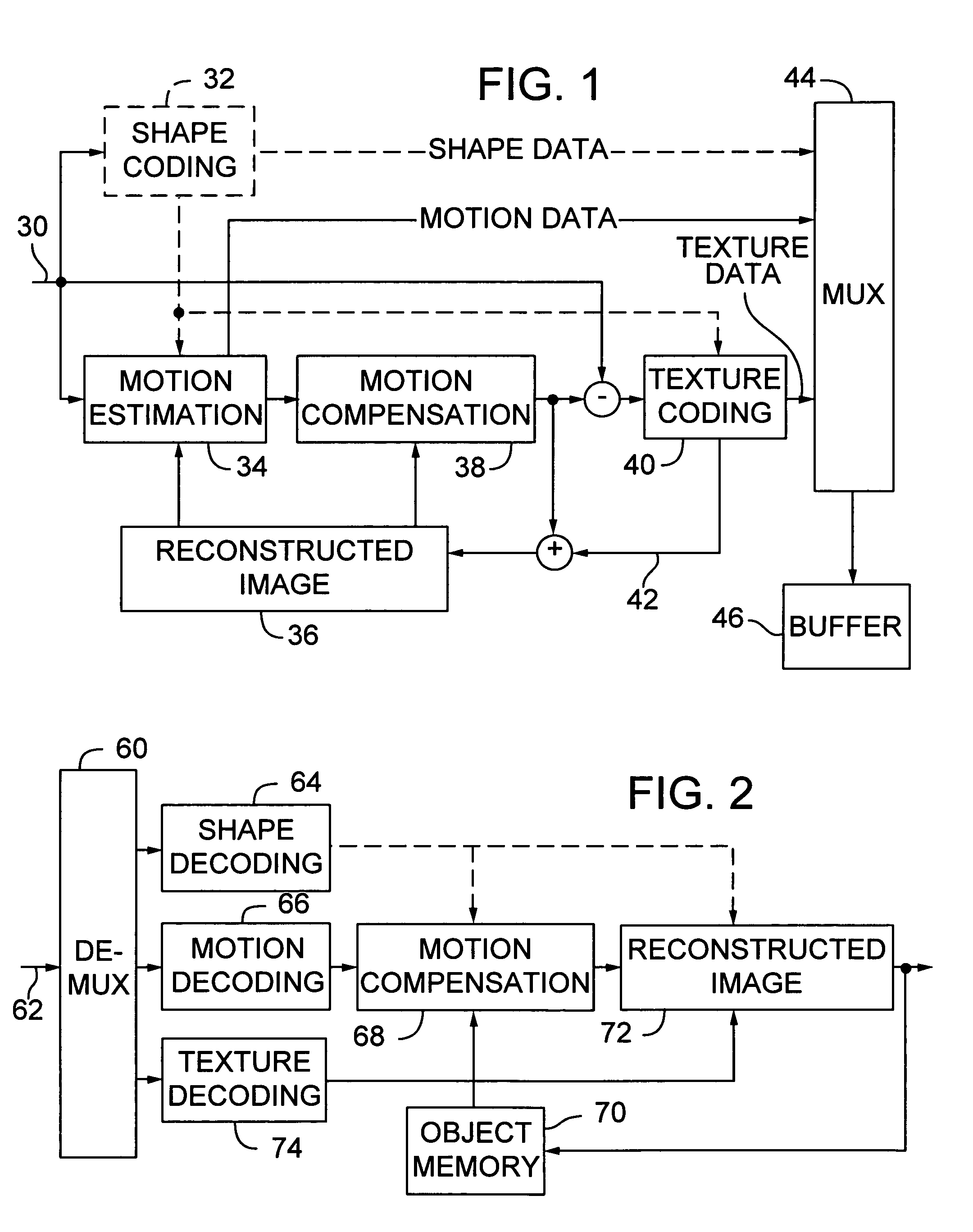
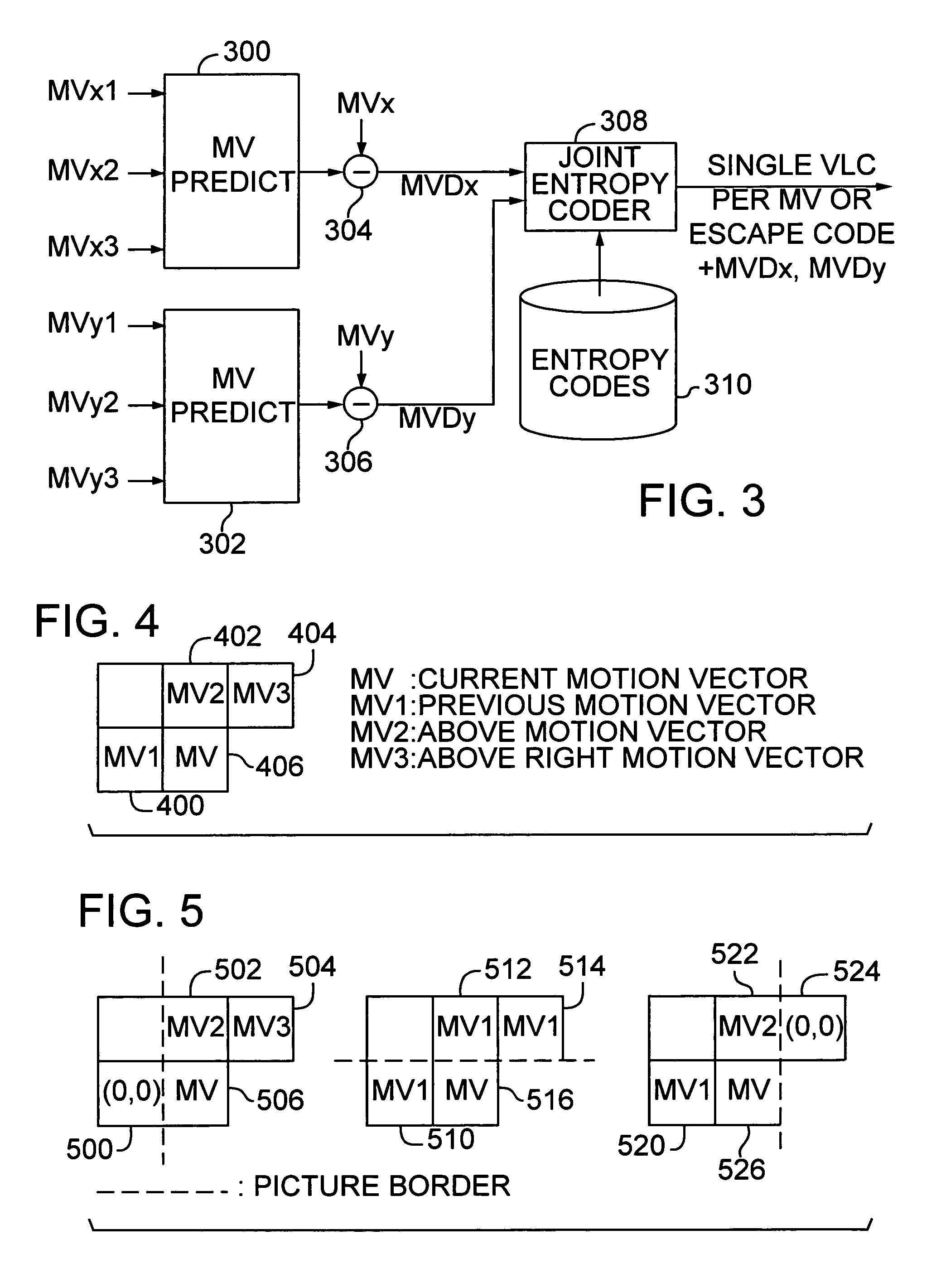
InactiveUS6983018B1Code motion vectors more efficientlyLengthen codePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionVariable-length codeVideo encoding
Video coding efficiency is improved by jointly coding the x and y components of motion vectors with a single variable length code. The motion vector components for a block of pixels are predicted based on motion vectors of neighboring blocks of pixels. The predicted x and y components are then jointly coded by assigning a single variable length code corresponding to the pair of components, rather than a separate code for each component. If the x and y components do not have a corresponding entry in the coding table, they are coded with an escape code followed by fixed length codes.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Video, audio and graphics decode, composite and display system
InactiveUS6853385B1Minimum total system costLow costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital videoDigital audio signals
A video, audio and graphics system uses multiple transport processors to receive in-band and out-of-band MPEG Transport streams, to perform PID and section filtering as well as DVB and DES decryption and to de-multiplex them. The system processes the PES into digital audio, MPEG video and message data. The system is capable of decoding multiple MPEG SLICEs concurrently. Graphics windows are blended in parallel, and blended with video using alpha blending. During graphics processing, a single-port SRAM is used equivalently as a dual-port SRAM. The video may include both analog video, e.g., NTSC / PAL / SECAM / S-video, and digital video, e.g., MPEG-2 video in SDTV or HDTV format. The system has a reduced memory mode in which video images are reduced in half in horizontal direction only during decoding. The system is capable of receiving and processing digital audio signals such as MPEG Layer 1 and Layer 2 audio and Dolby AC-3 audio, as well as PCM audio signals. The system includes a memory controller. The system includes a system bridge controller to interface a CPU with devices internal to the system as well as peripheral devices including PCI devices and I / O devices such as RAM, ROM and flash memory devices. The system is capable of displaying video and graphics in both the high definition (HD) mode and the standard definition (SD) mode. The system may output an HDTV video while converting the HDTV video and providing as another output having an SDTV format or another HDTV format.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
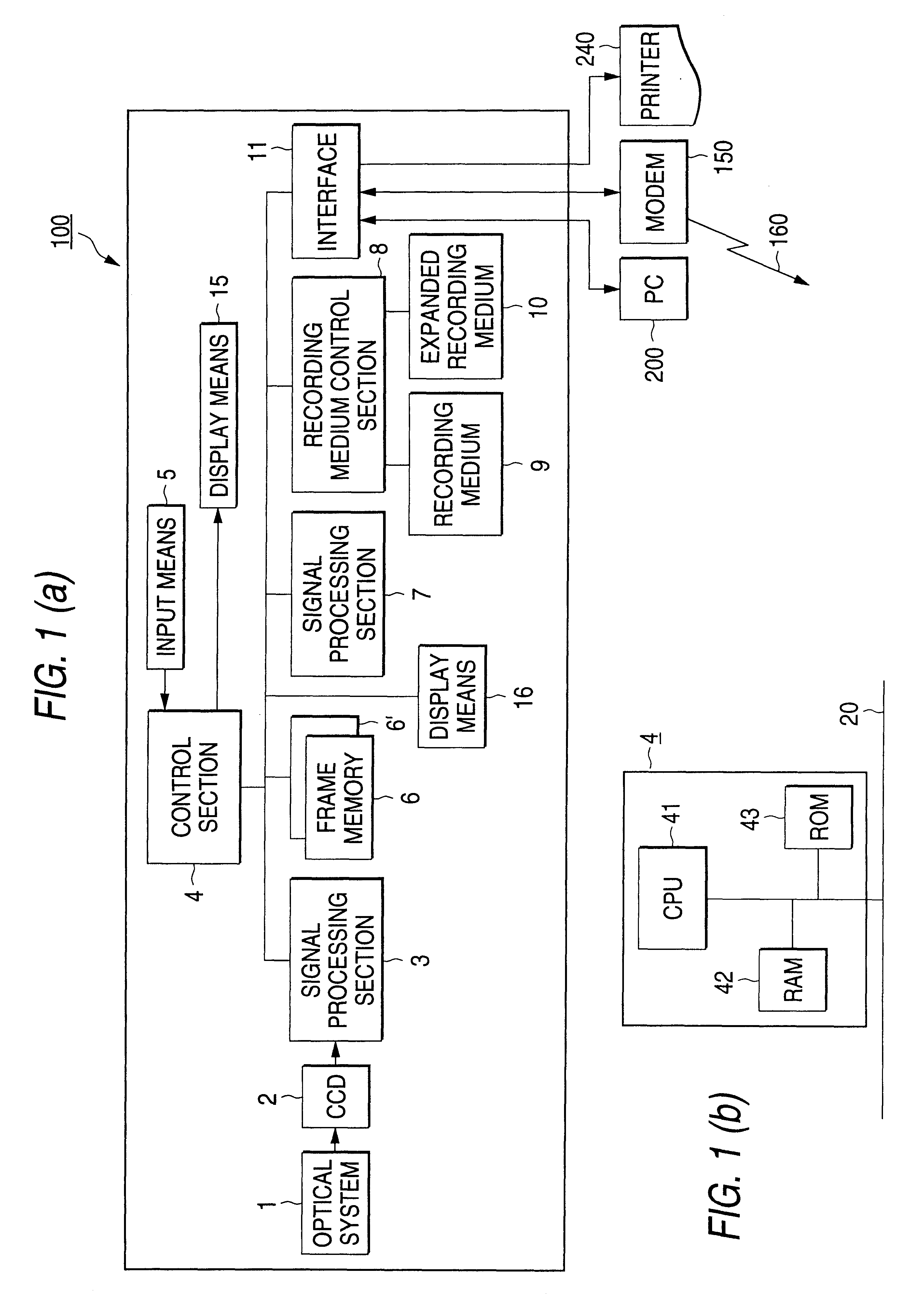
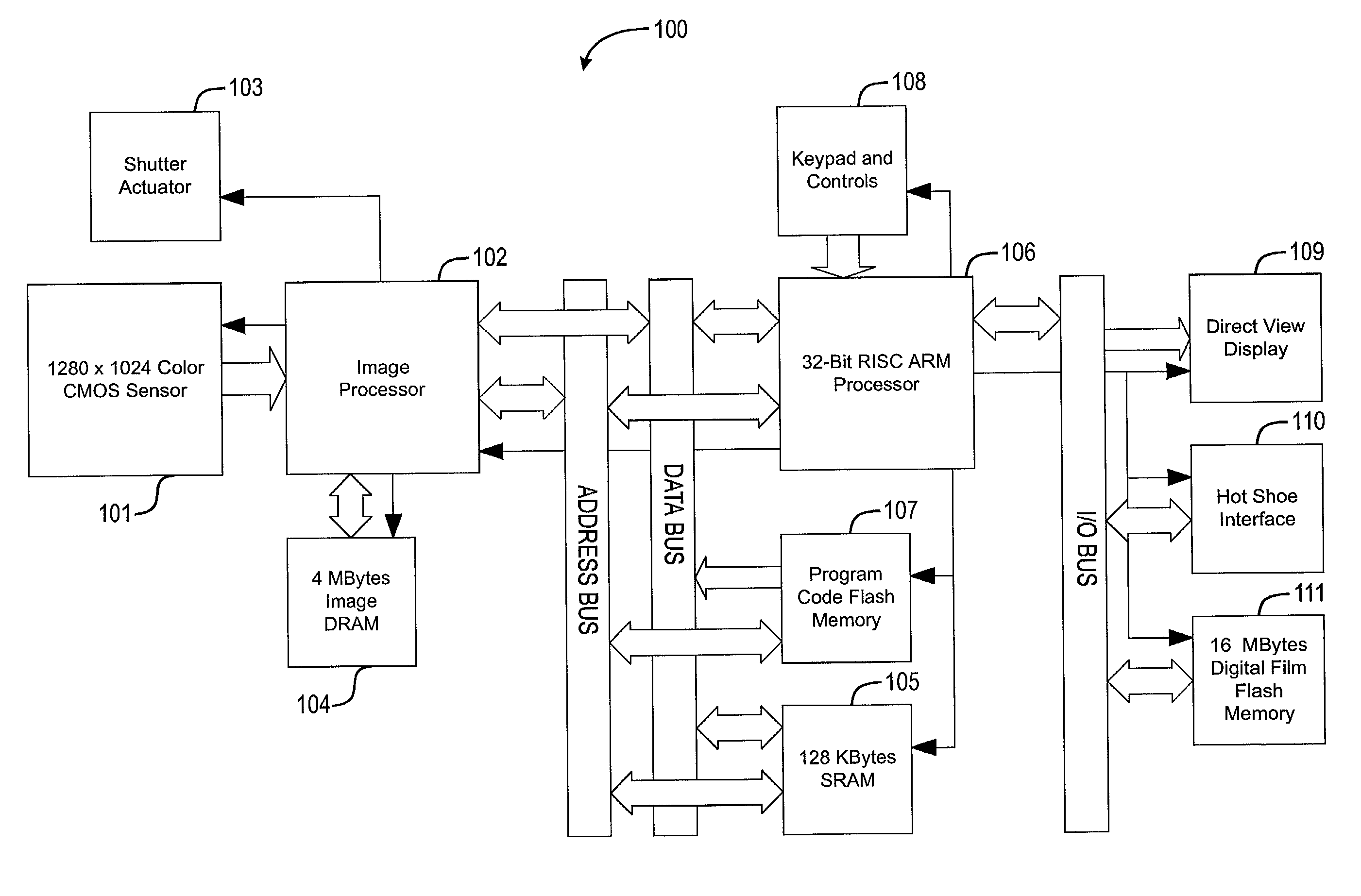
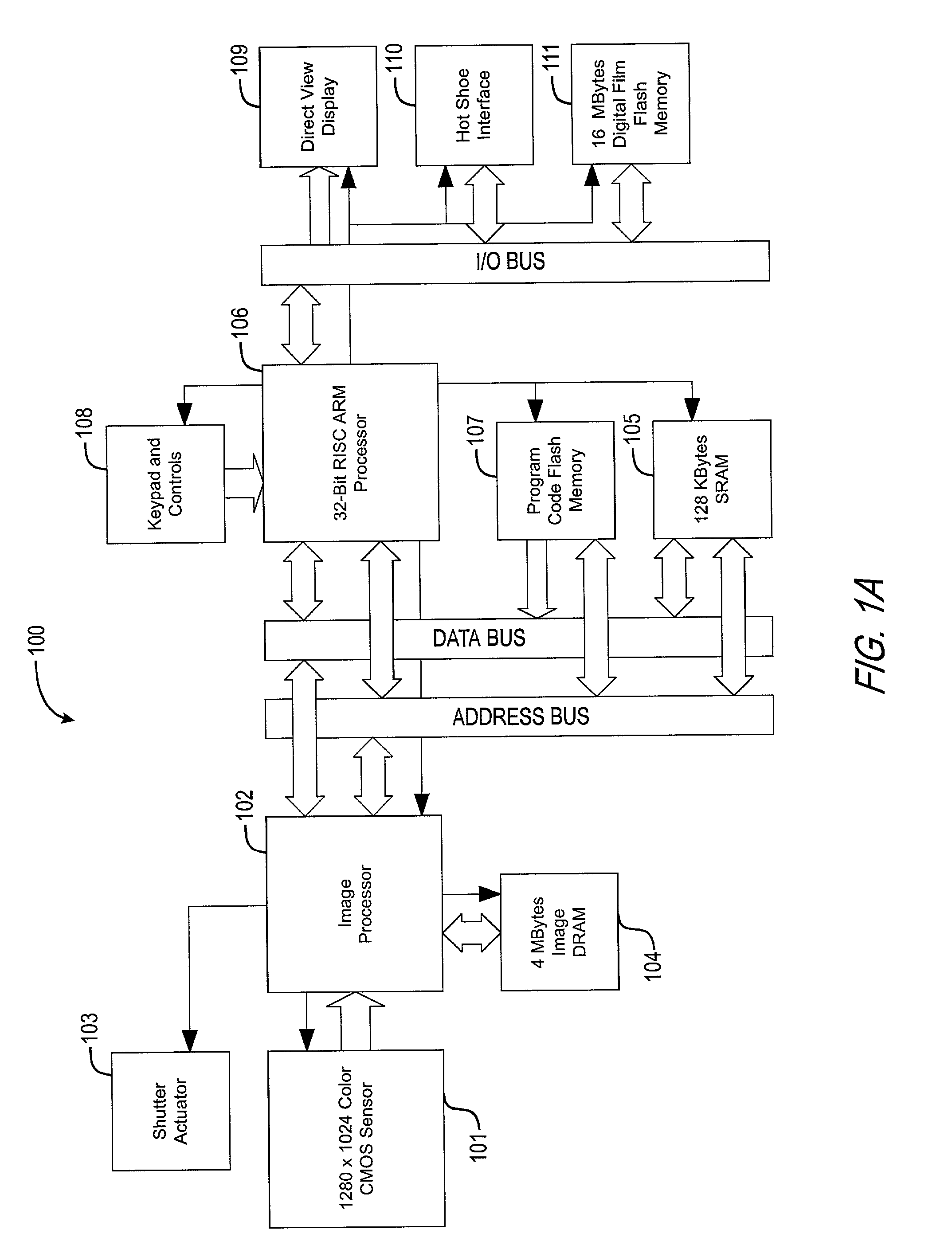
Digital camera and printing system
InactiveUS6618553B1Television system detailsColor television signals processingLiquid-crystal displayComputer graphics (images)
With a digital camera 100, a photographed image 31 is displayed on a liquid crystal display and the user selects a desired image and specifies print specifications of the number of print sheets, a print paper size, a print color mode, etc., then print image data is prepared. The prepared print image, data is transmitted from the digital camera 100 to a color printer of an output unit. An image is printed at the color printer in accordance with the print image data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
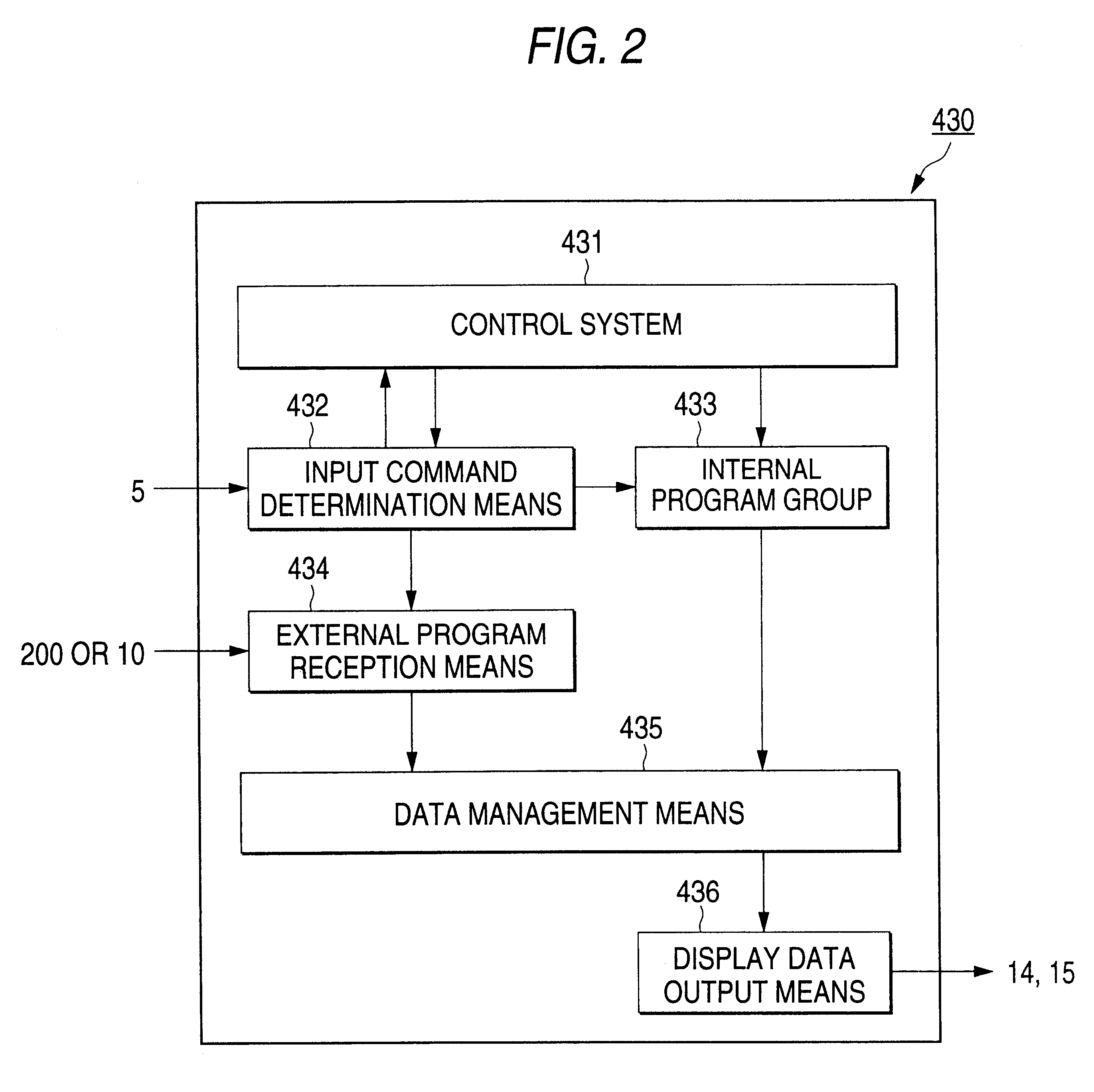
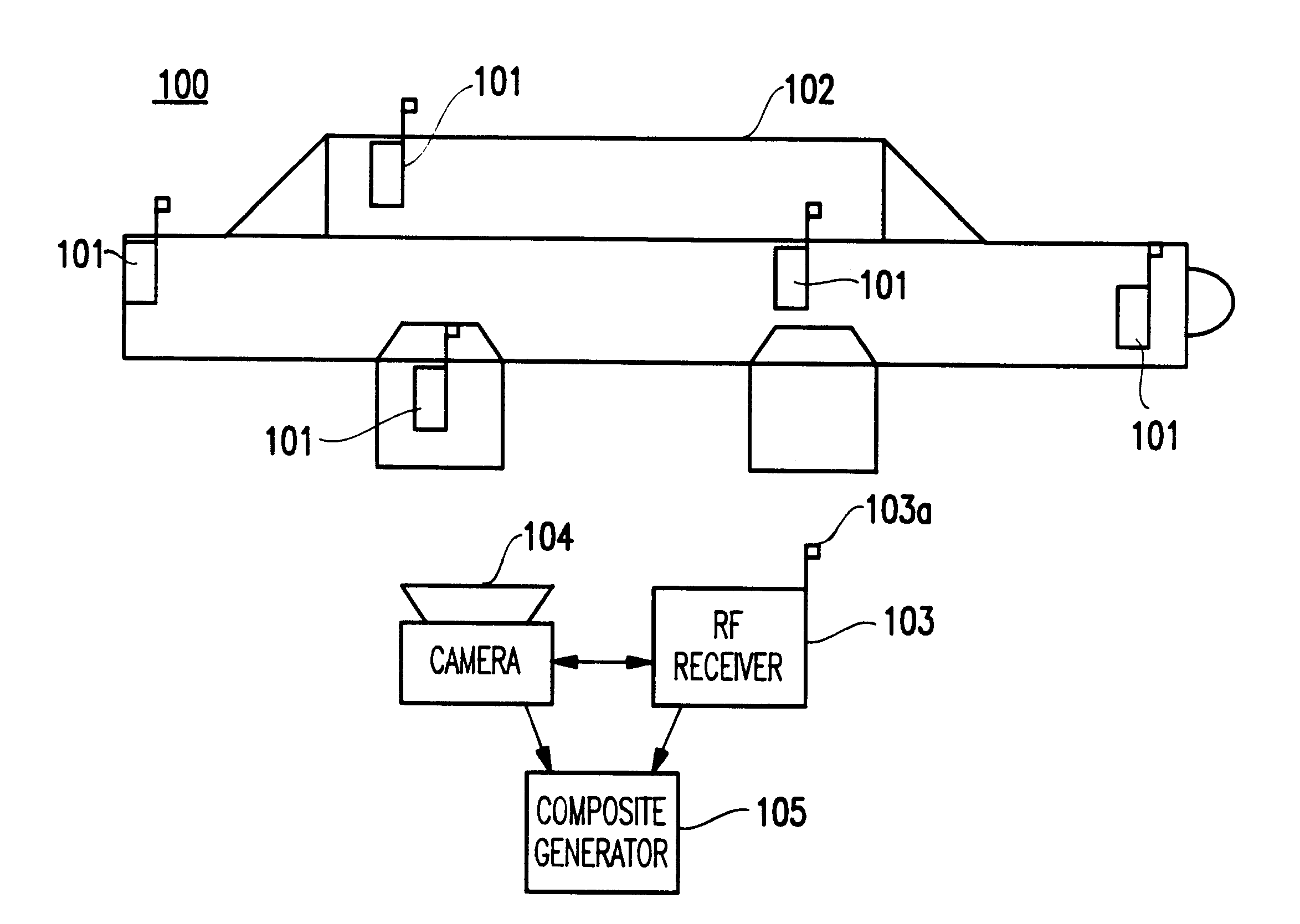
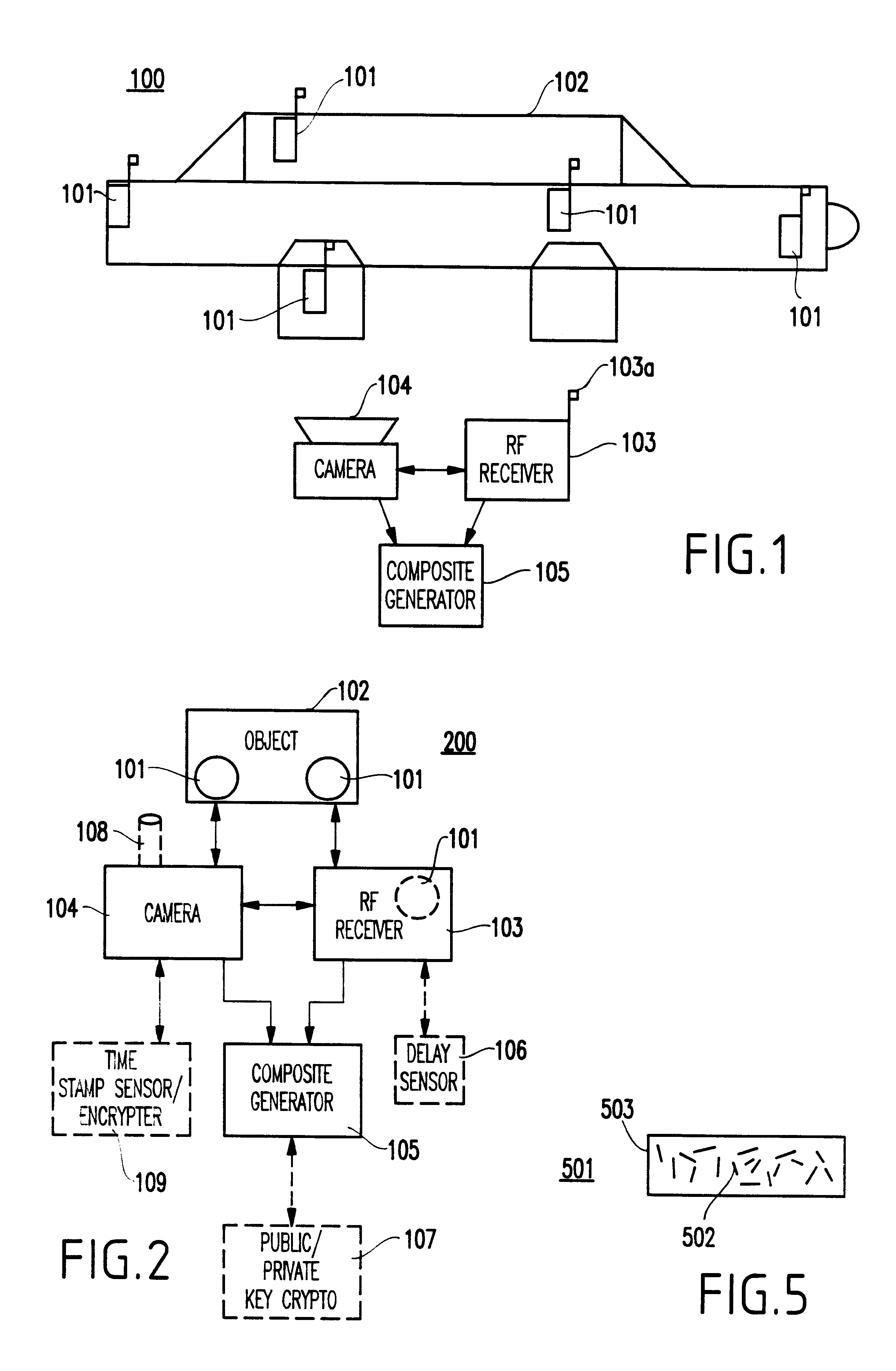
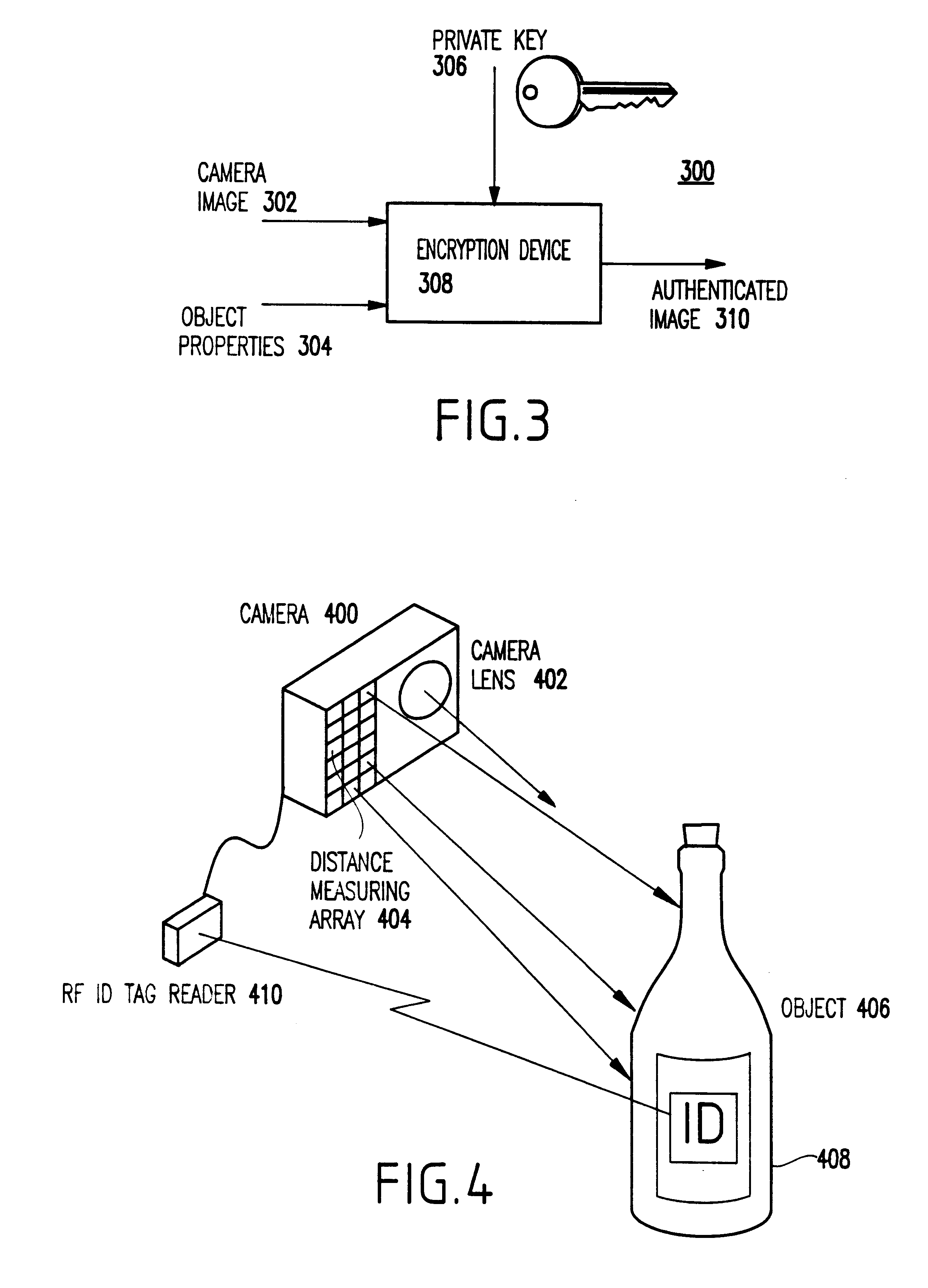
Method and system for authenticating objects and object data
InactiveUS6397334B1Improve reliabilityIncrease credibilityTelevision system detailsFinanceVideo camera
A system and method for authenticating an image of an object, include at least one identifier associated with the object, a receiver for interrogating the at least one identifier to produce identification information, a camera system for recording an image from the object including the at least one identifier, and a composite generator for encoding the identification information from the receiver along with the image acquired by the camera system, to produce composite data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Digital camera device providing improved methodology for rapidly taking successive pictures
InactiveUS7369161B2Extended latencyAvailable storageTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationLuminosityDigital image
An in-camera two-stage compression implementation is described that reduces the latency between snapshots to a fraction of that otherwise required by other systems that either process complete compression following each snapshot or that incorporate heavy, bulky, and expensive RAM hardware capable of maintaining several raw luminosity records (unprocessed file containing a digital image). In the 1st stage compression the raw luminosity record is quickly, yet partially, compressed to available RAM buffer space to allow a user to expeditiously capture a succeeding image. When the higher-priority processes, the user shooting pictures, and stage one compression subside, a 2nd stage compression, which is slower but more effective, decompresses the earlier partially-compressed images, and re-compresses them for saving in flash memory until they are distributed to a remote platform to be finally converted to the JPEG2000 format.
Owner:RPX CORP
System and method for generating and playback of three-dimensional movies
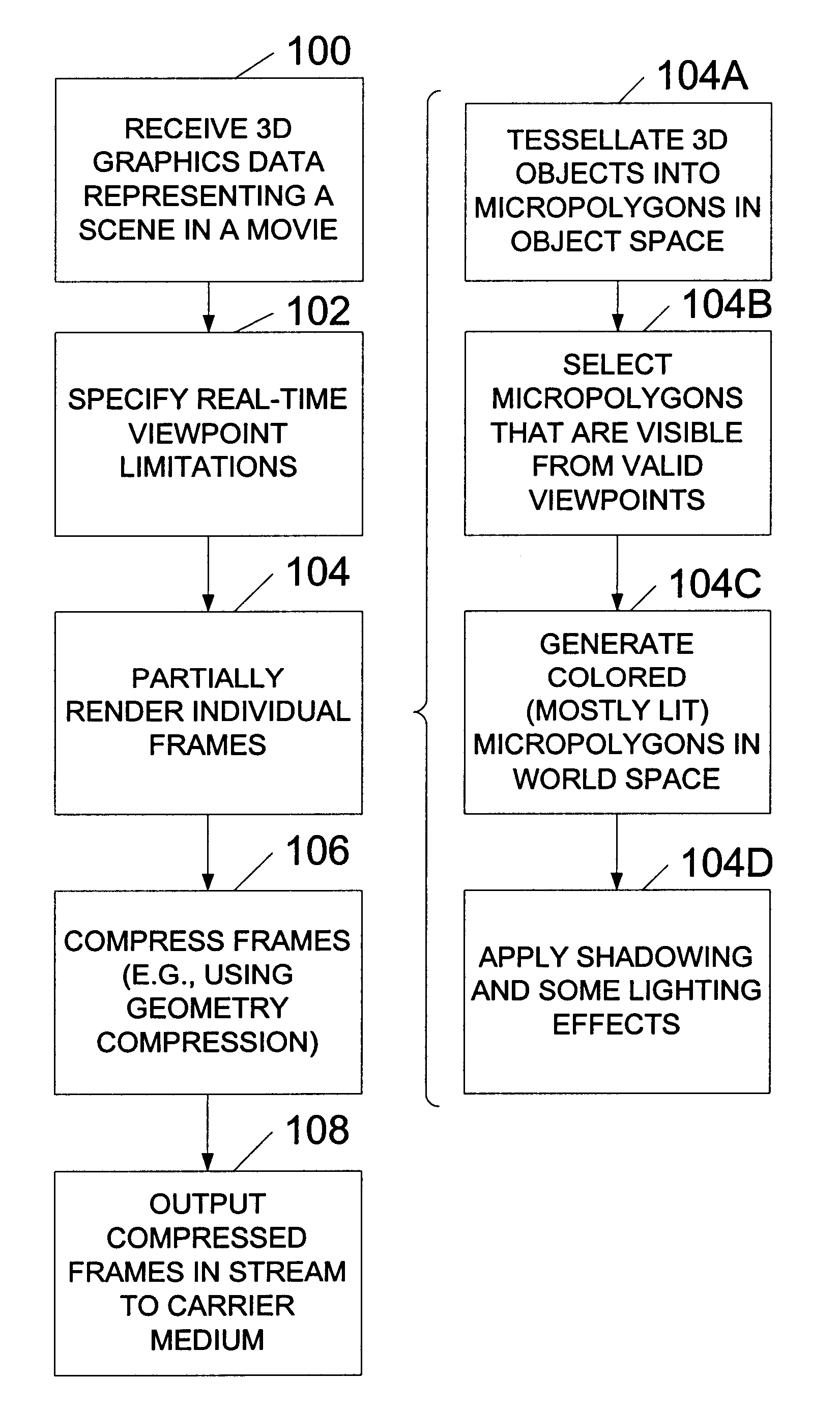
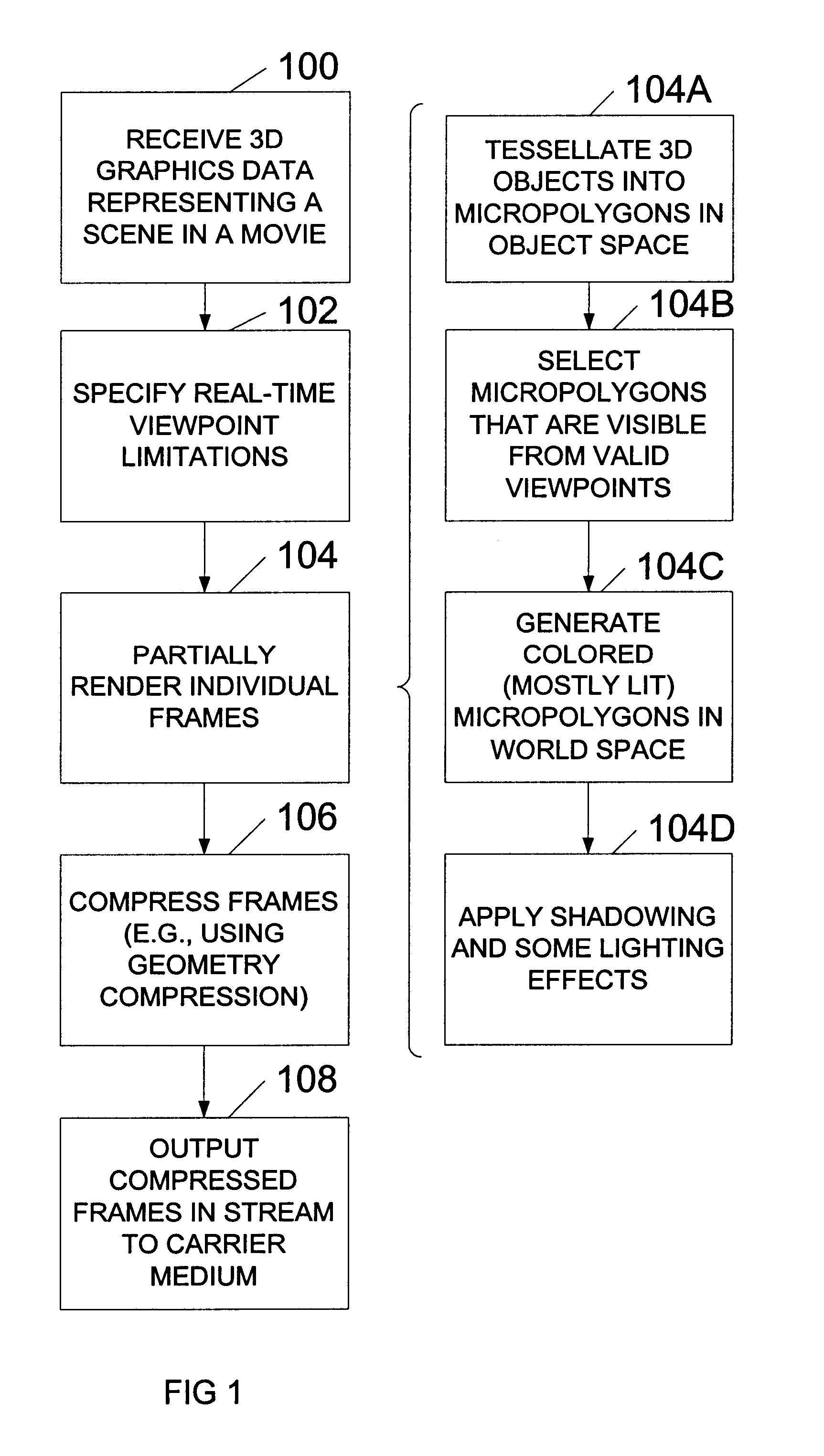
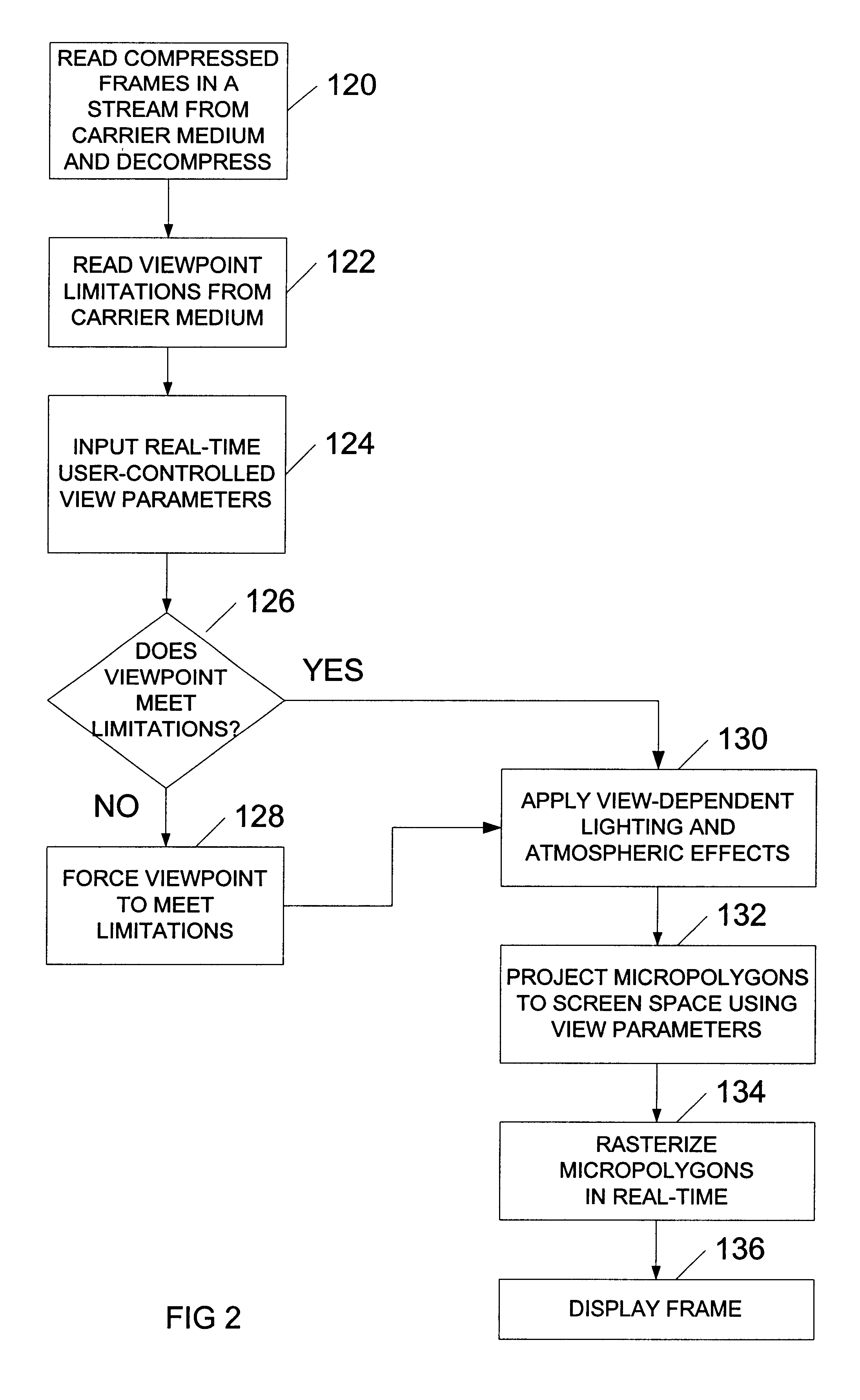
A system and method for generating and playing back three-dimensional (3D) movies are disclosed. The system is capable of partially rendering frames without relying upon exact viewpoint information. The partially rendered frames may be rendered to the extent possible without performing viewpoint-dependent processes, and then compressed and stored to a carrier medium. To reduce the amount of data to be stored, the viewer's possible viewpoints may be restricted (e.g., by defining a viewpoint-limiting volume or region). The resulting partially-rendered geometry data may be compressed using geometry compression. During playback, the compressed frames are read as a stream, and decompressed. Any final viewpoint-dependent rendering operations may then be performed (e.g., some lighting calculations and atmospheric effects, some fogging, specular highlighting, and reflections). A sensor such as a head-tracker may provide real-time viewpoint information that may be used by the playback system. After rendering, the frames are rasterized and then displayed in stereo.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and system for context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding
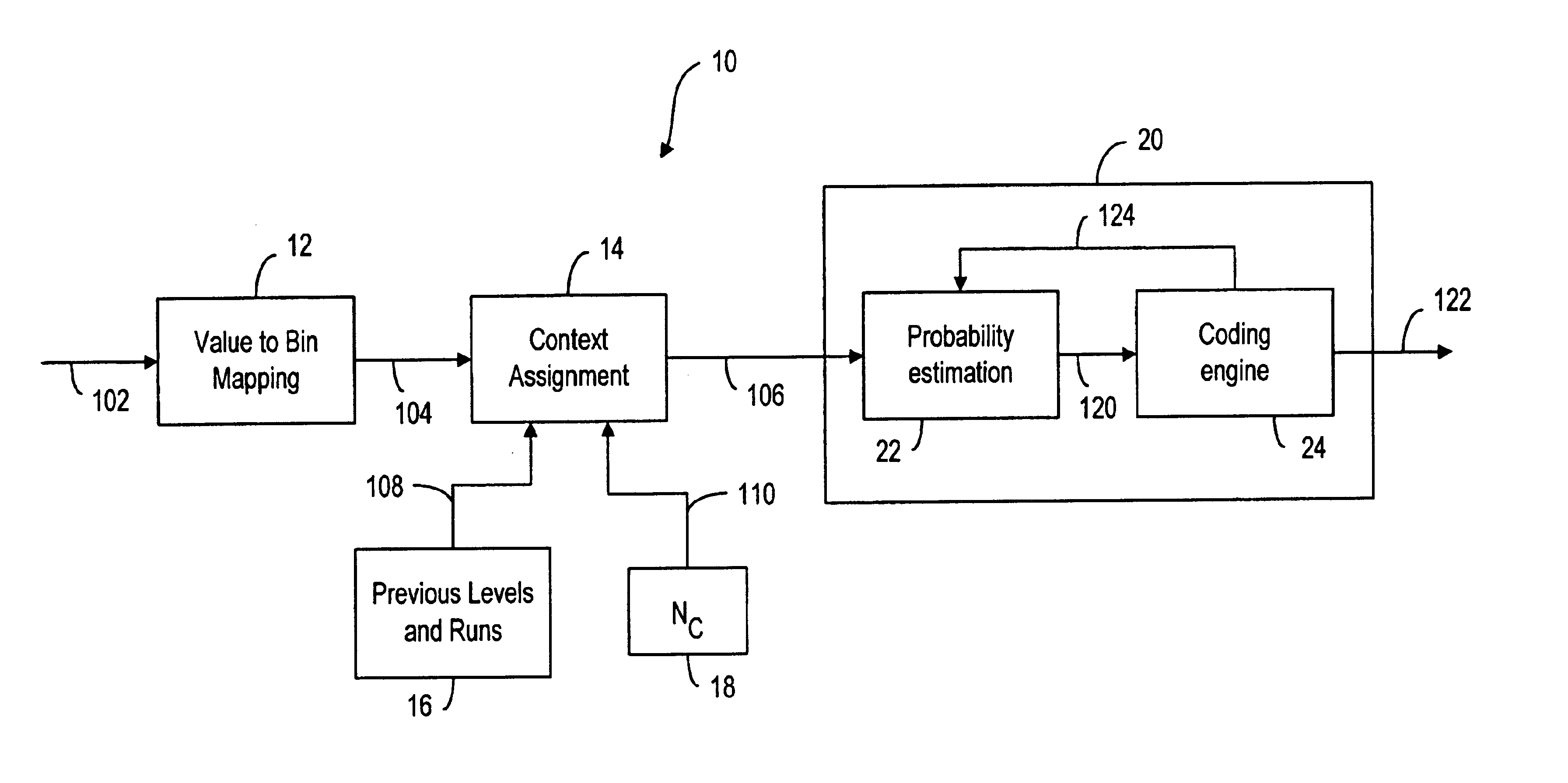
InactiveUS6856701B2Improve coding efficiencyCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionMultiple contextContext based
A method and system for image coding, wherein an image is divided into a plurality of blocks for scanning. The pixels values in the scanned block are represented by a plurality of level-run value pairs, wherein the level value is indicative of a non-zero pixel value and the run value is indicative of the number of consecutive zero pixel values preceding the non-zero pixel value. A plurality of contexts indicative of the level-run value pairs are conveyed to a decoder for allowing the decoder to reconstruct the image based on the contexts. The assignment of the contexts is also based on the level value of a preceding level-run pair. Additionally, instead of an end-of-block symbol, the number of non-zero coefficients is provided to the decoder prior to conveying the contexts thereto.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
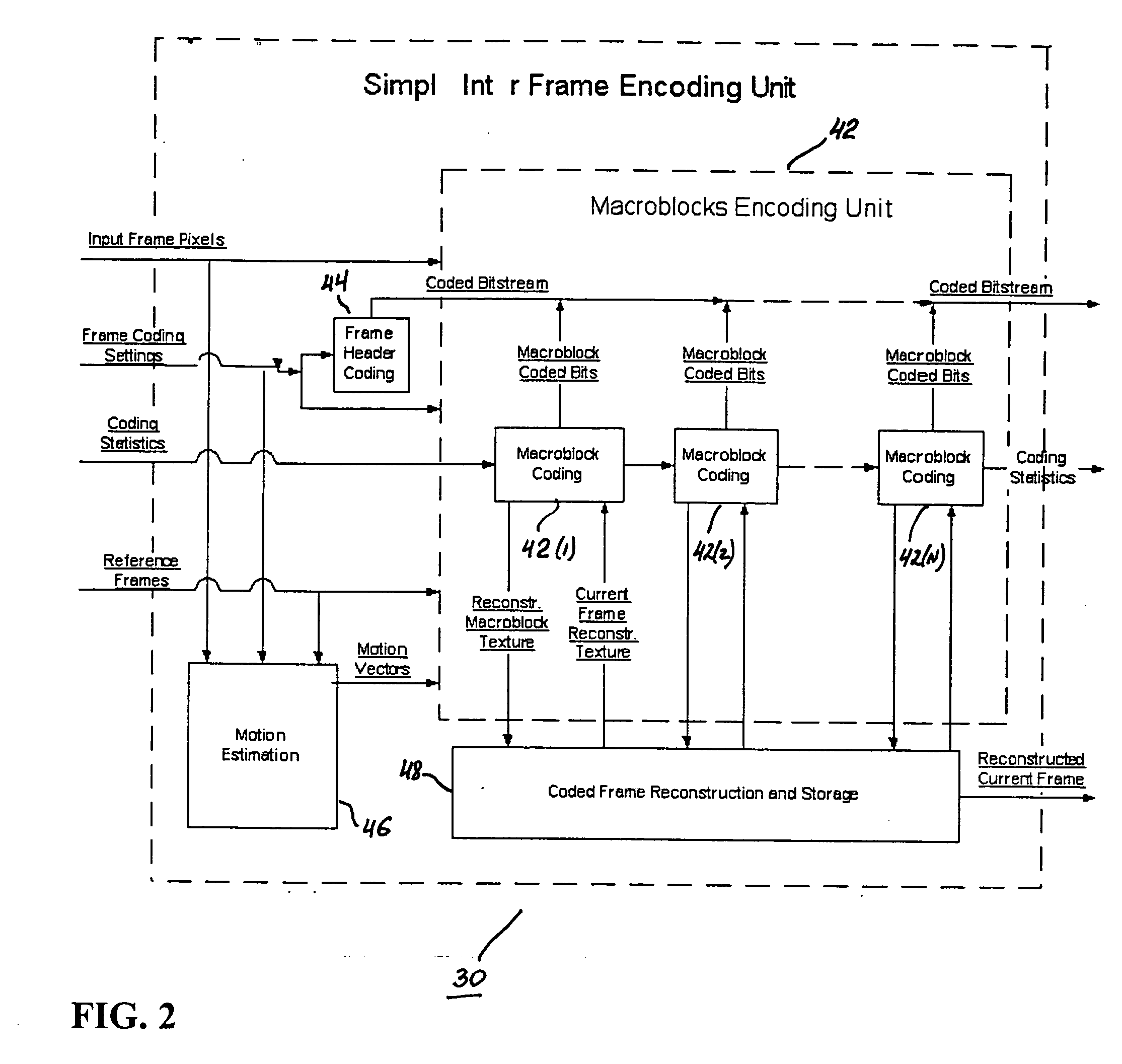
Real-time video coding/decoding
ActiveUS20050276323A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMotion vectorDownscaling
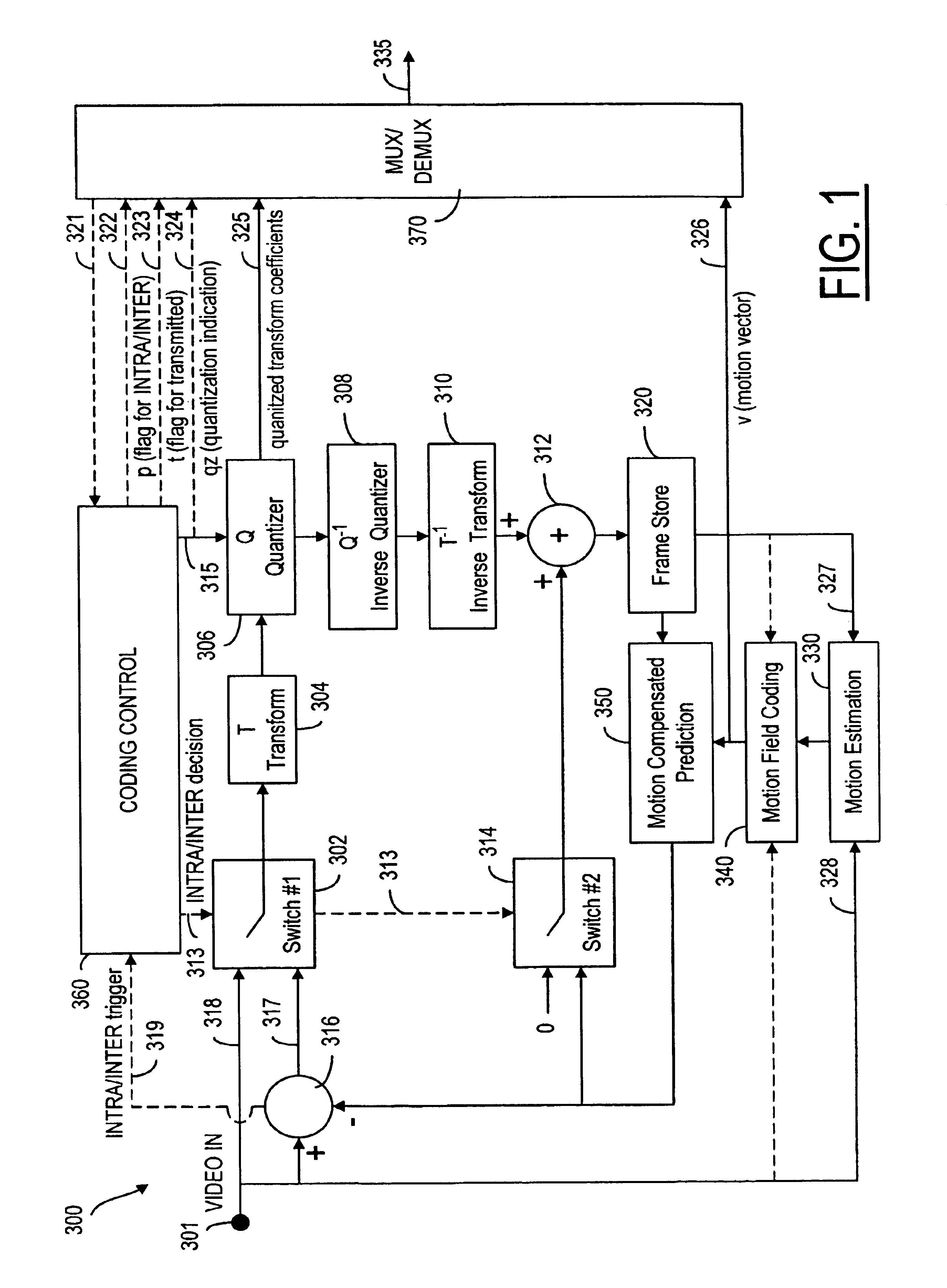
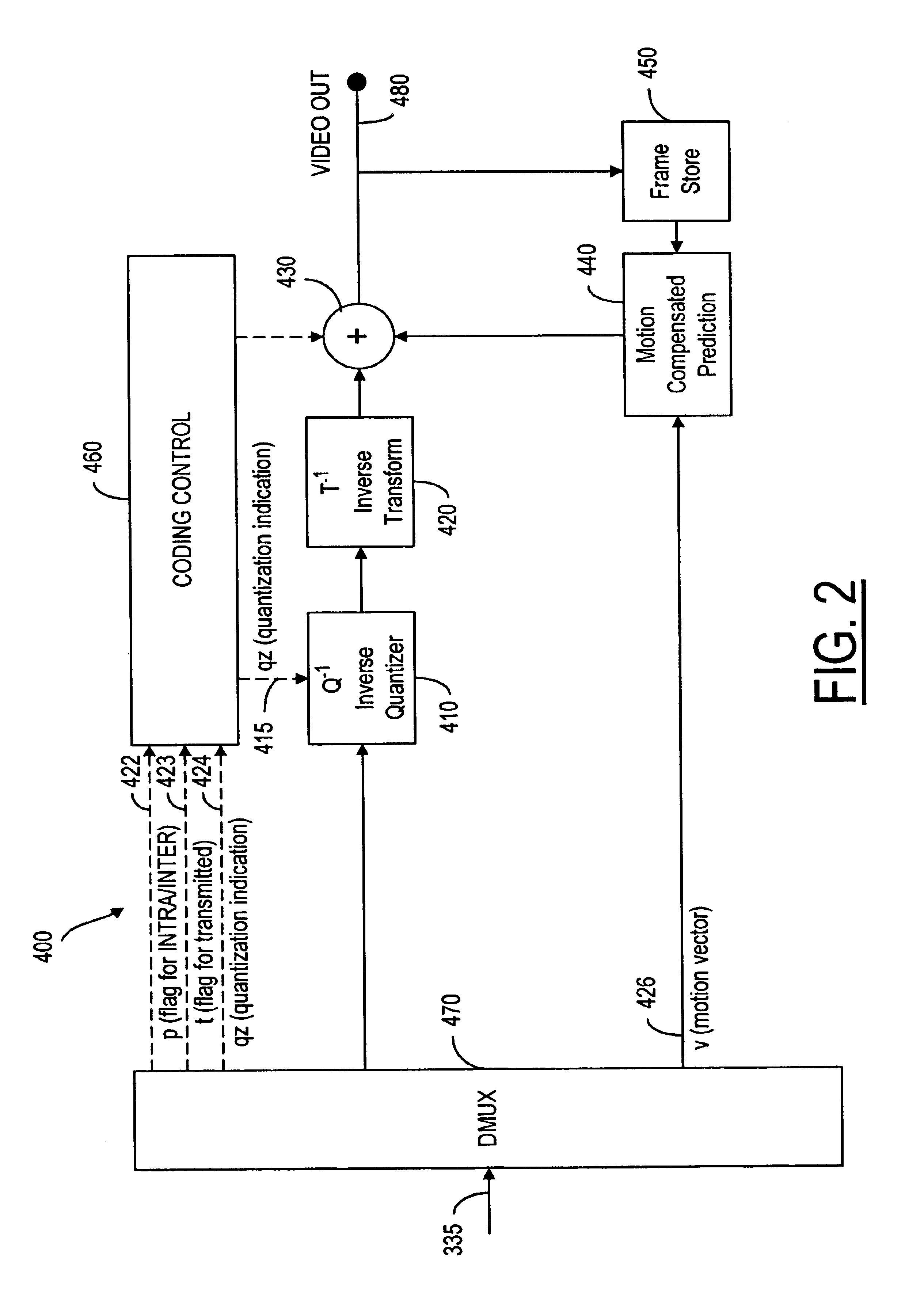
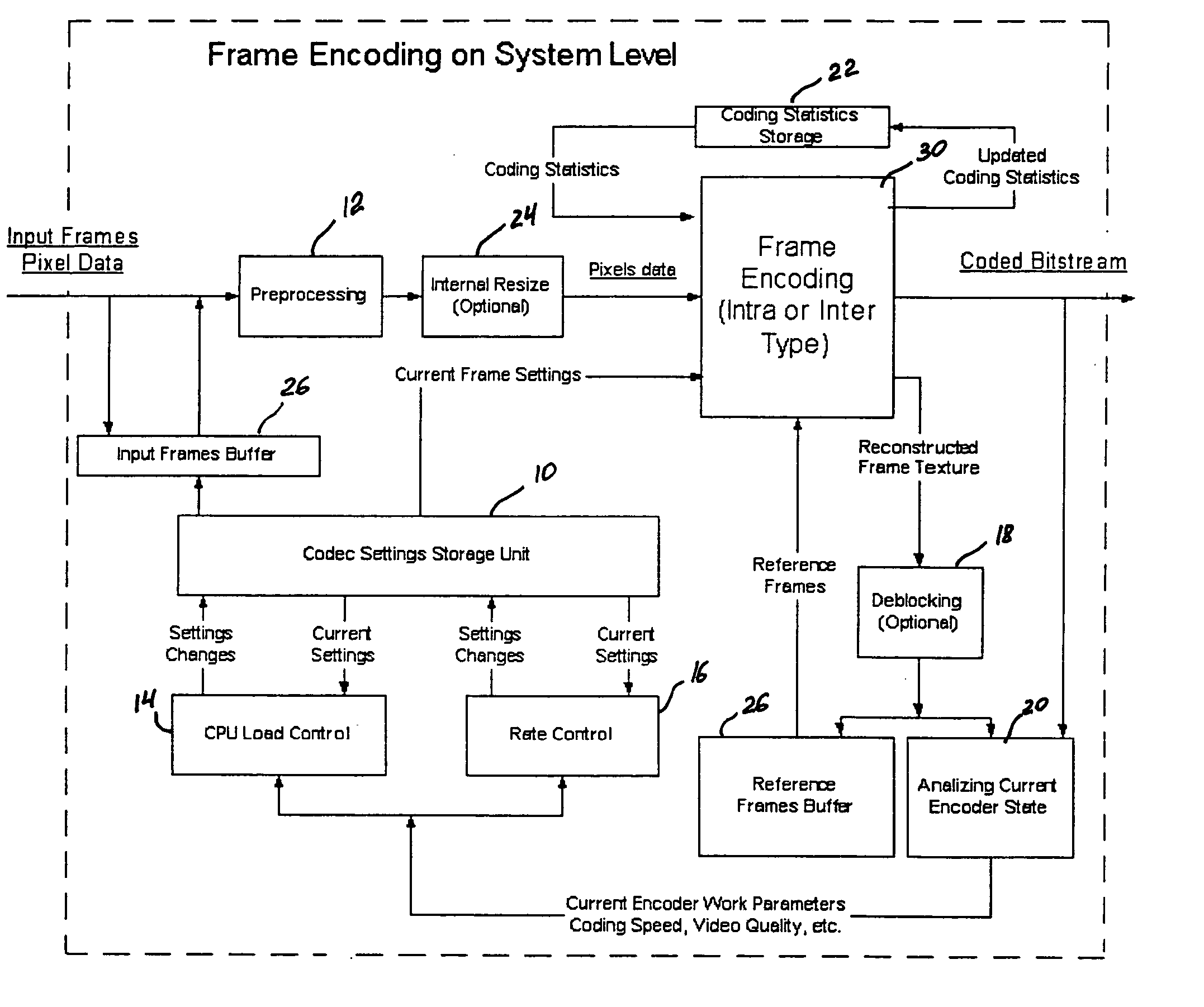
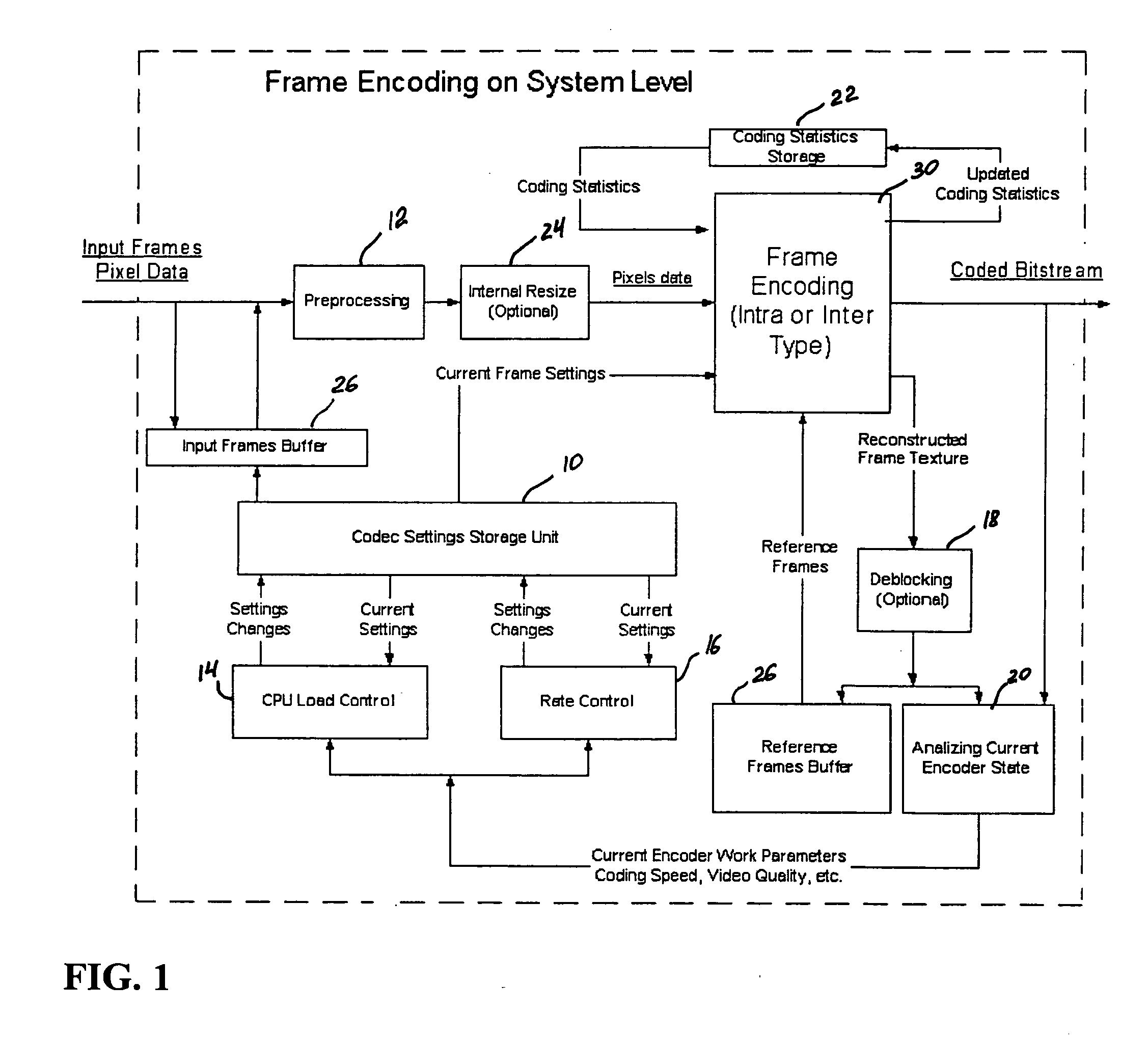
A video codec for real-time encoding / decoding of digitized video data with high compression efficiency, comprising a frame encoder receiving input frame pixels; a codec setting unit for setting and storing coding setting parameters; a CPU load controller for controlling desired frame encoding time and CPU loading; a rate controller for controlling frame size; a coding statistics memory for storing frequency tables for arithmetic coding of bitstream parameters and a reference frame buffer for storing reference frames. The frame encoder comprises a motion estimation unit, a frame head coding unit, a coded frame reconstruction and storage unit and a macroblock encoding unit. The macroblock encoding unit provides calculation of texture prediction and prediction error, transforming texture prediction error and quantization of transform coefficient, calculation of motion vector prediction and prediction error and arithmetic context modeling for motion vectors, header parameters and transform coefficients. The codec also includes a deblocking unit for processing video data to eliminate blocking effect from restored data encoded at high distortion level, which may be a part of encoder or decoder, an internal resize unit, providing matching downscaling of a frame before encoding and upscaling of decoded frame according to the coding setting parameters, and a noise suppression unit.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
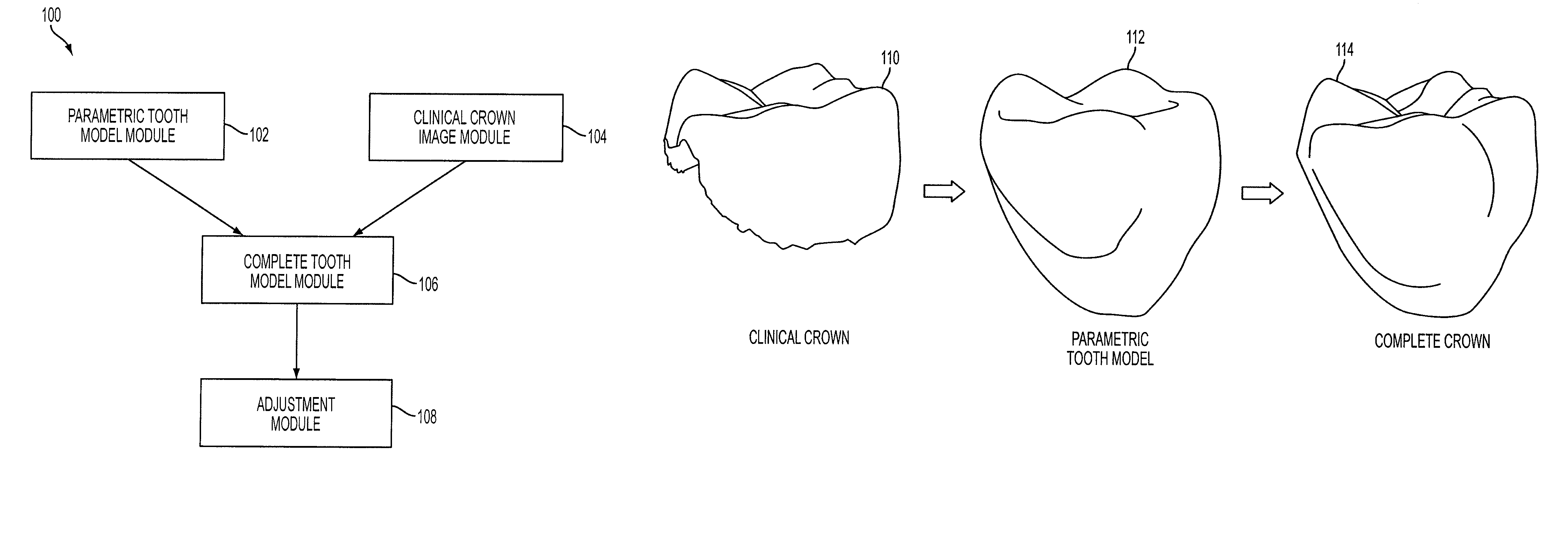
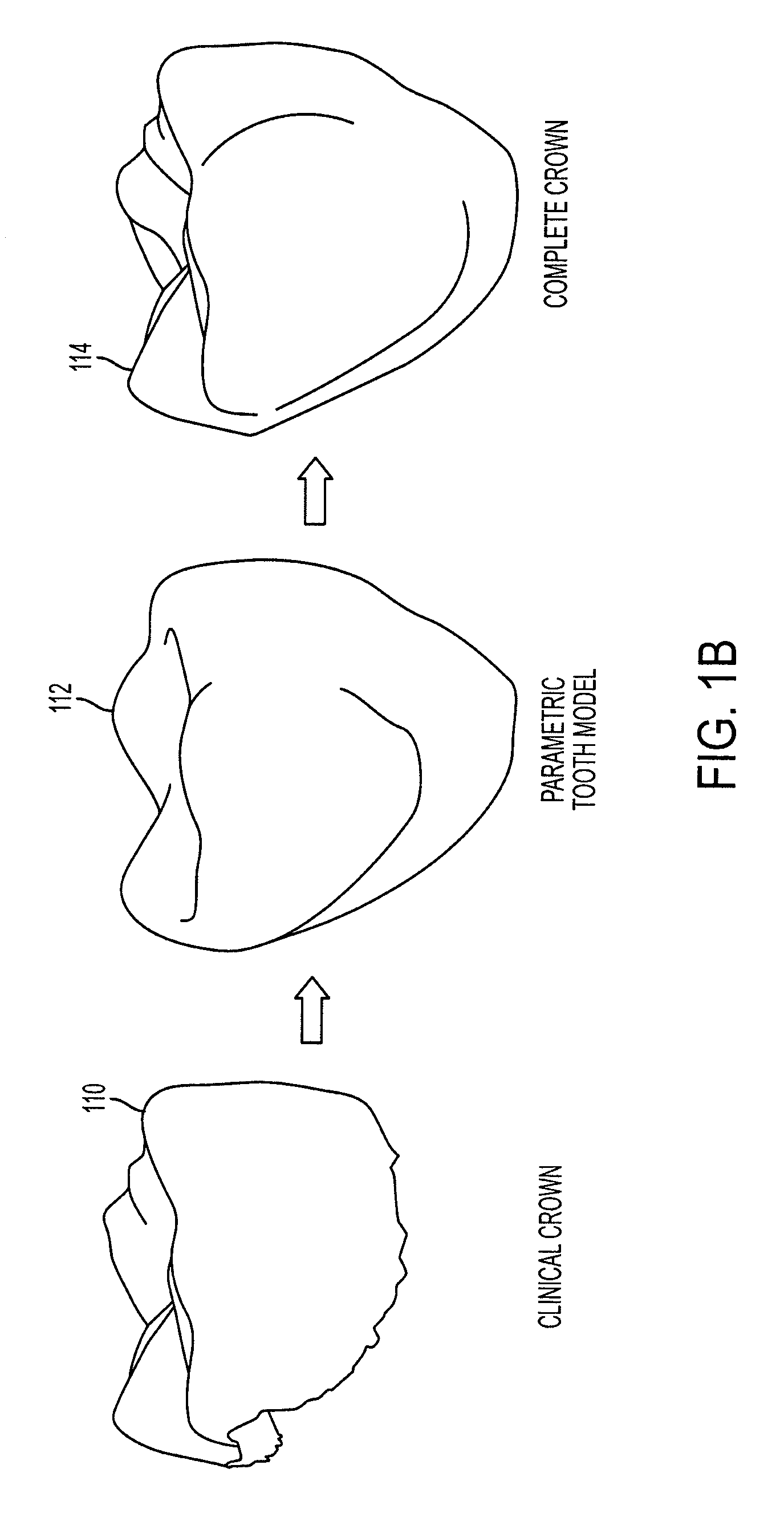
Reconstruction of non-visible part of tooth
Modeling a complete tooth of a patient to facilitate dental and / or orthodontic treatment includes generating a first set of digital data representing a clinical crown; generating a second set of digital data representing a plurality of digital tooth models of a particular tooth type each having a first parameterization; processing the second set of digital data to obtain a third set of digital data representing an average tooth model of the particular tooth type having a second parameterization which is less than the first parameterization; fitting the third set of digital data to the first set of digital data to create a set of digital data representing an interim tooth model; and morphing the set of digital data representing the interim tooth model to substantially mimic the anatomical shape of the clinical crown of the first set of digital data.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
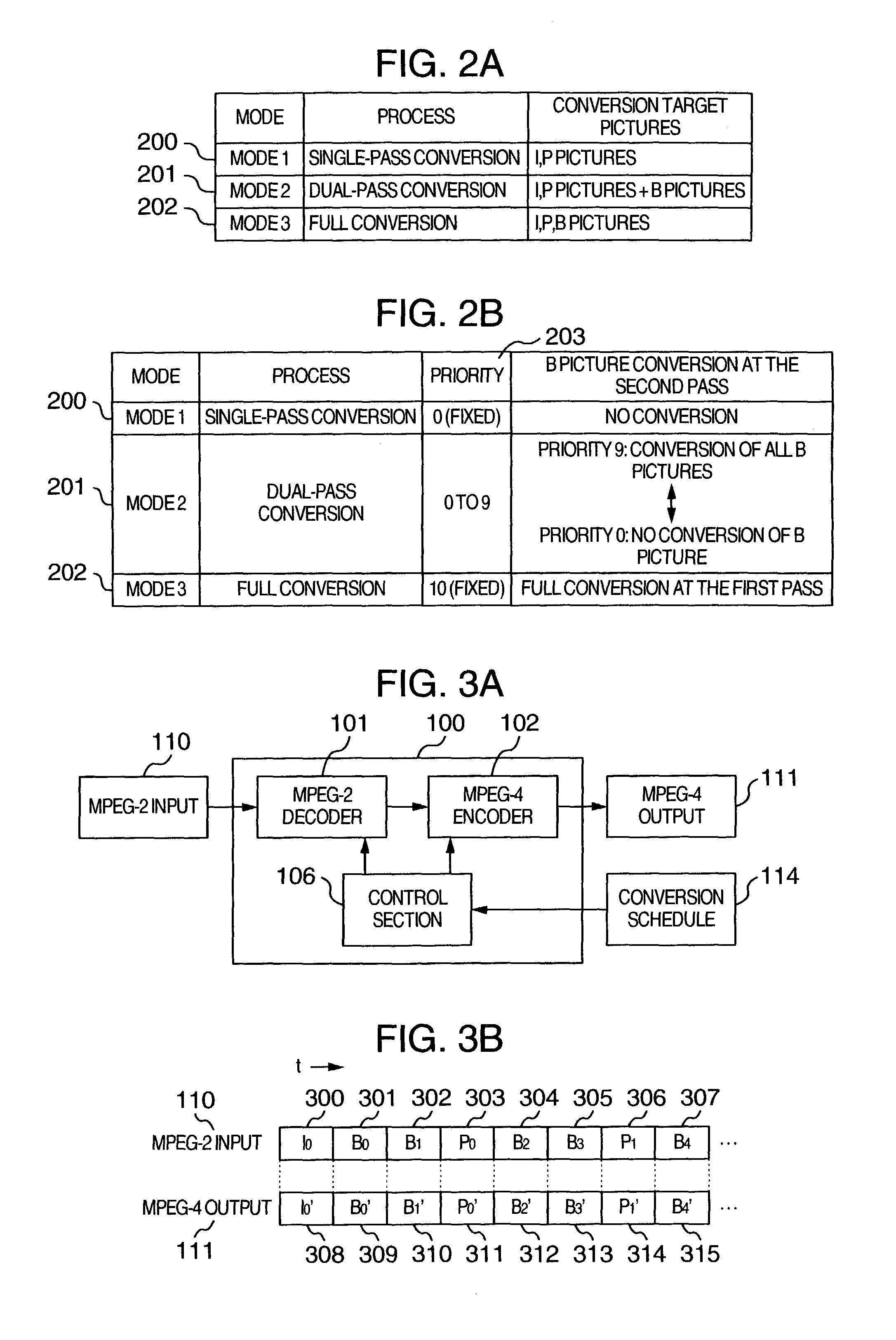
Video converter and computer program for executing said video converter
ActiveUS7212570B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer graphics (images)Two step
A video converter for converting a coding format of a great deal of video contents has three kinds of conversion modes including a conversion mode for performing conversion in two steps in accordance with the kinds of input pictures so that a converting operation can be completed within a limit time set in advance.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
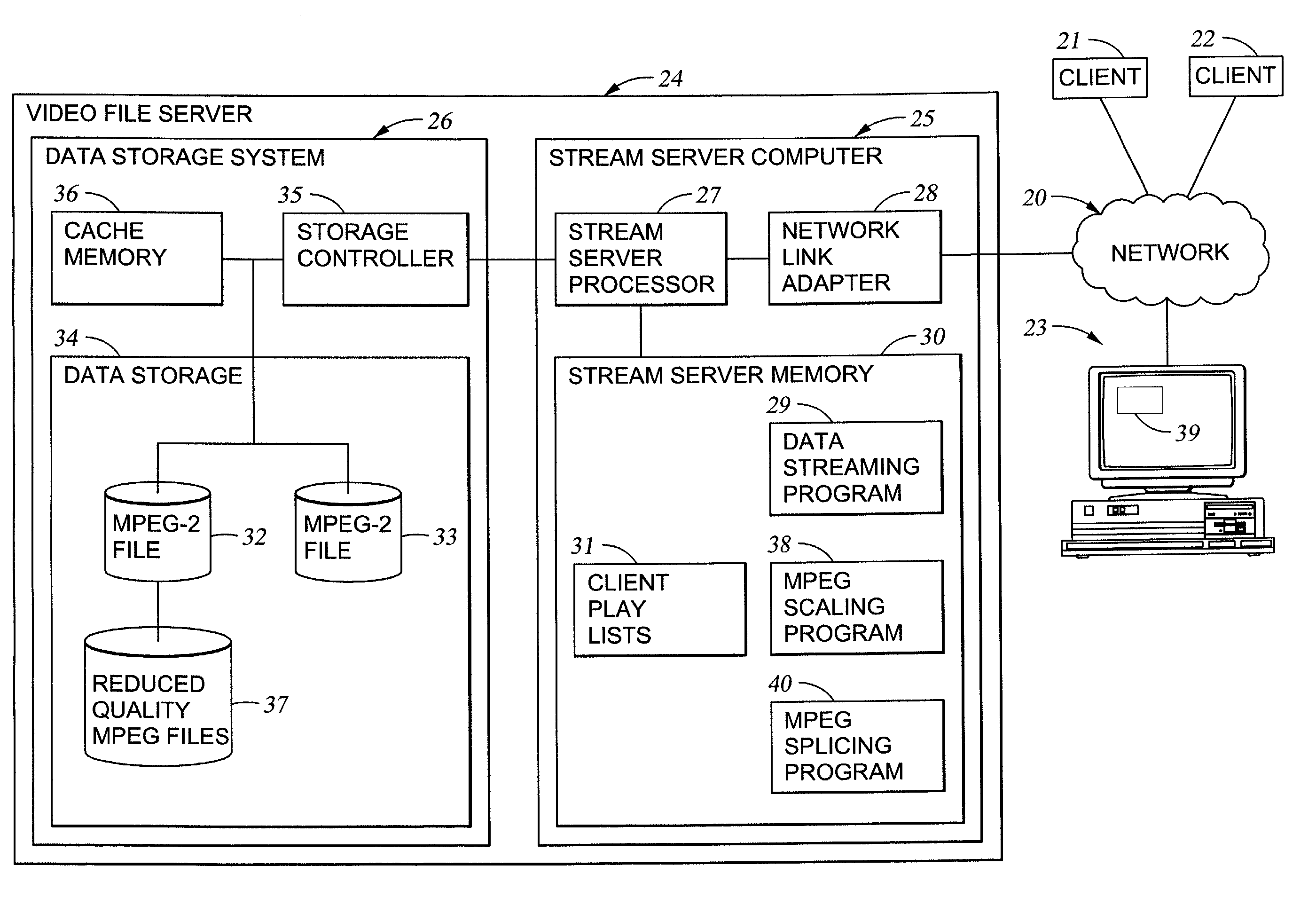
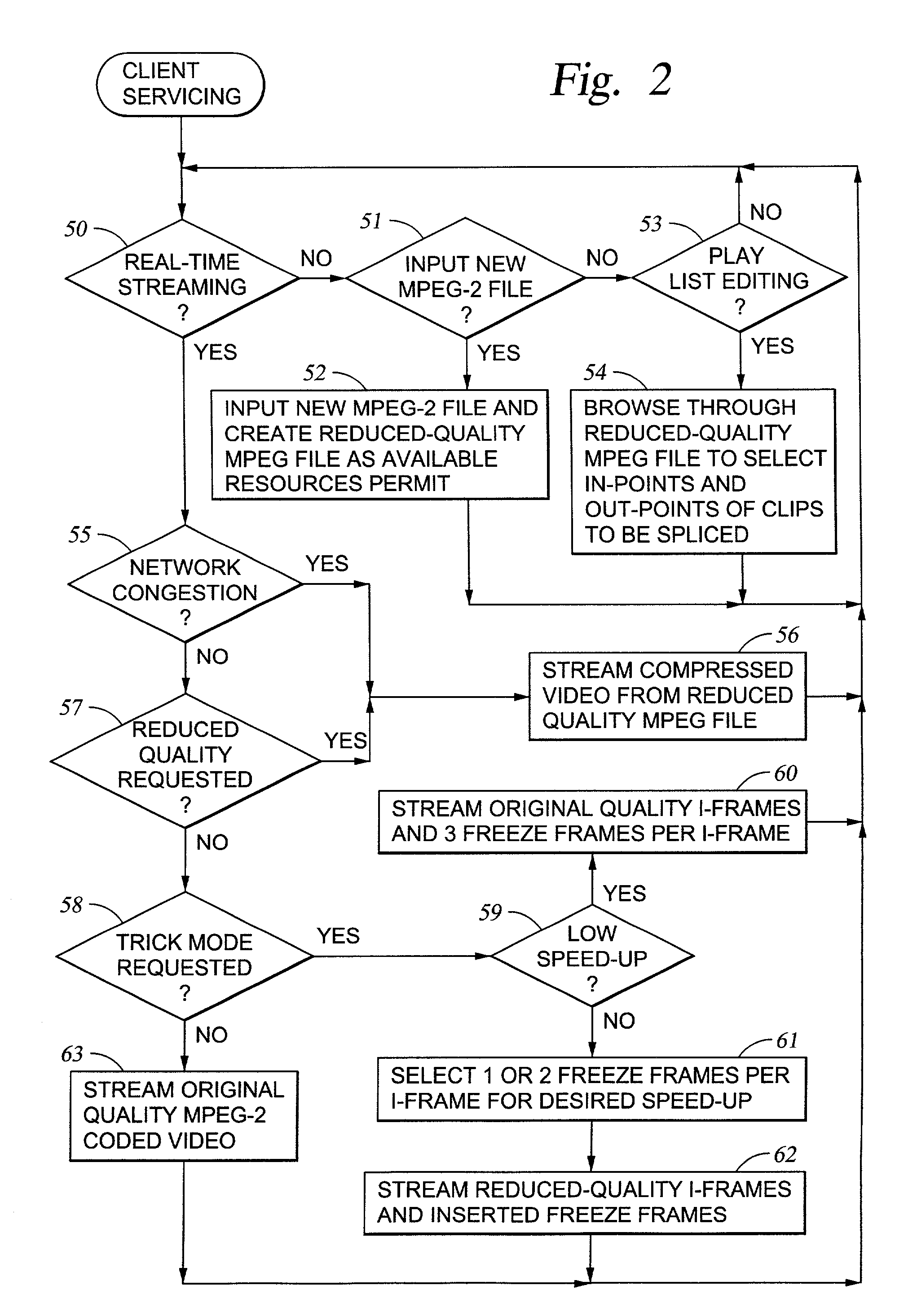
Largest magnitude indices selection for (run, level) encoding of a block coded picture
Transform coefficients for blocks of pixels in an original picture are quantized to produce respective sets of quantization indices for the blocks of pixels. The quantization indices for at least some of the blocks are produced by using a quantization step size that is not uniform within each block. Largest magnitude quantization indices are selected from the respective sets of quantization indices for (run, level) encoding to produce the (run, level) encoded picture. For example, MPEG-2 coded video includes a set of non-zero AC discrete cosine transform (DCT) coefficients for 8x8 blocks of pixels. For scaling the MPEG-2 coded video, non-zero AC DCT coefficients are removed from the MPEG-2 coded video to produce reduced-quality MPEG-2 coded video that includes no more than a selected number of largest magnitude quantization indices for the non-zero AC DCT coefficients for each 8x8 block.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
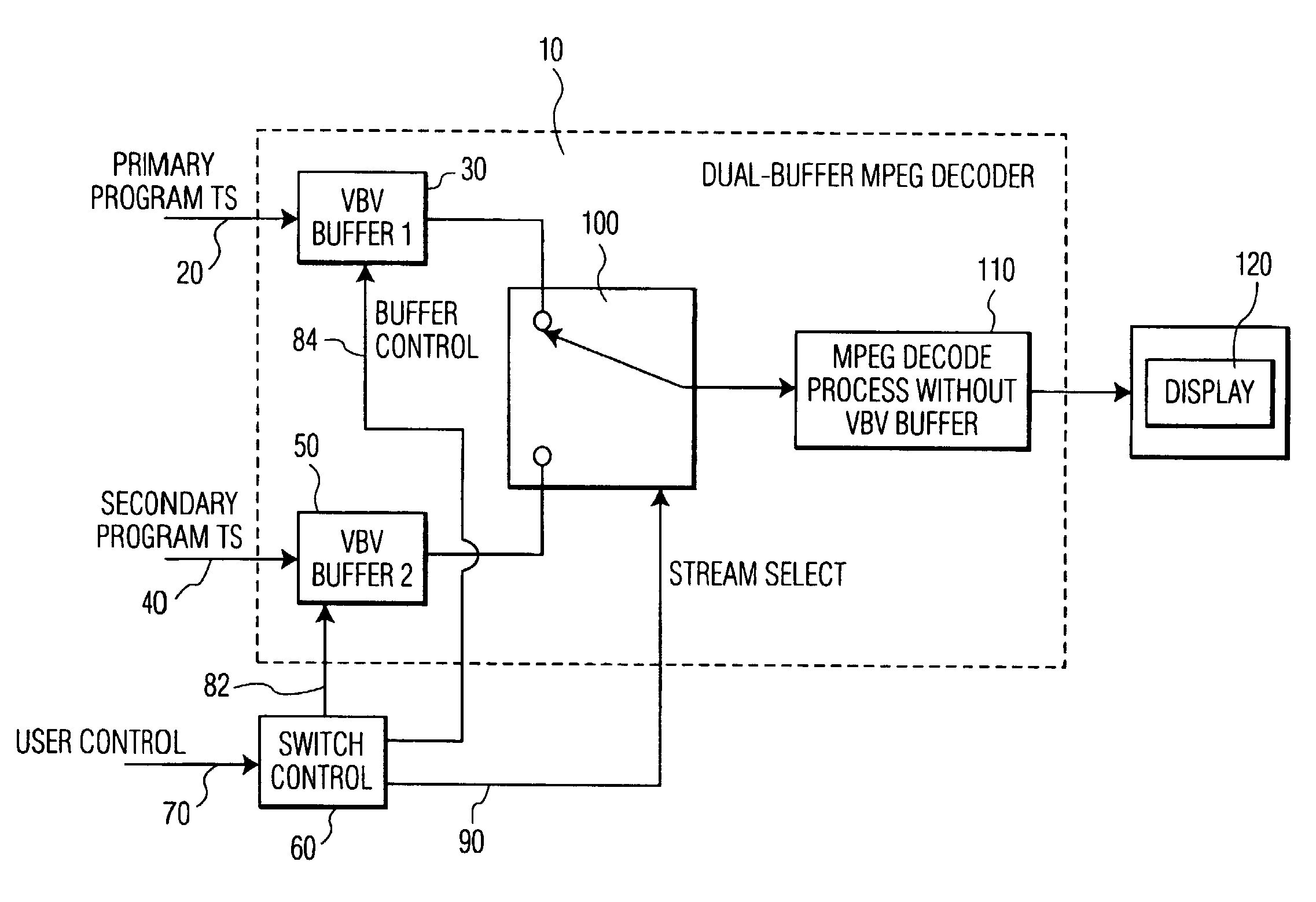
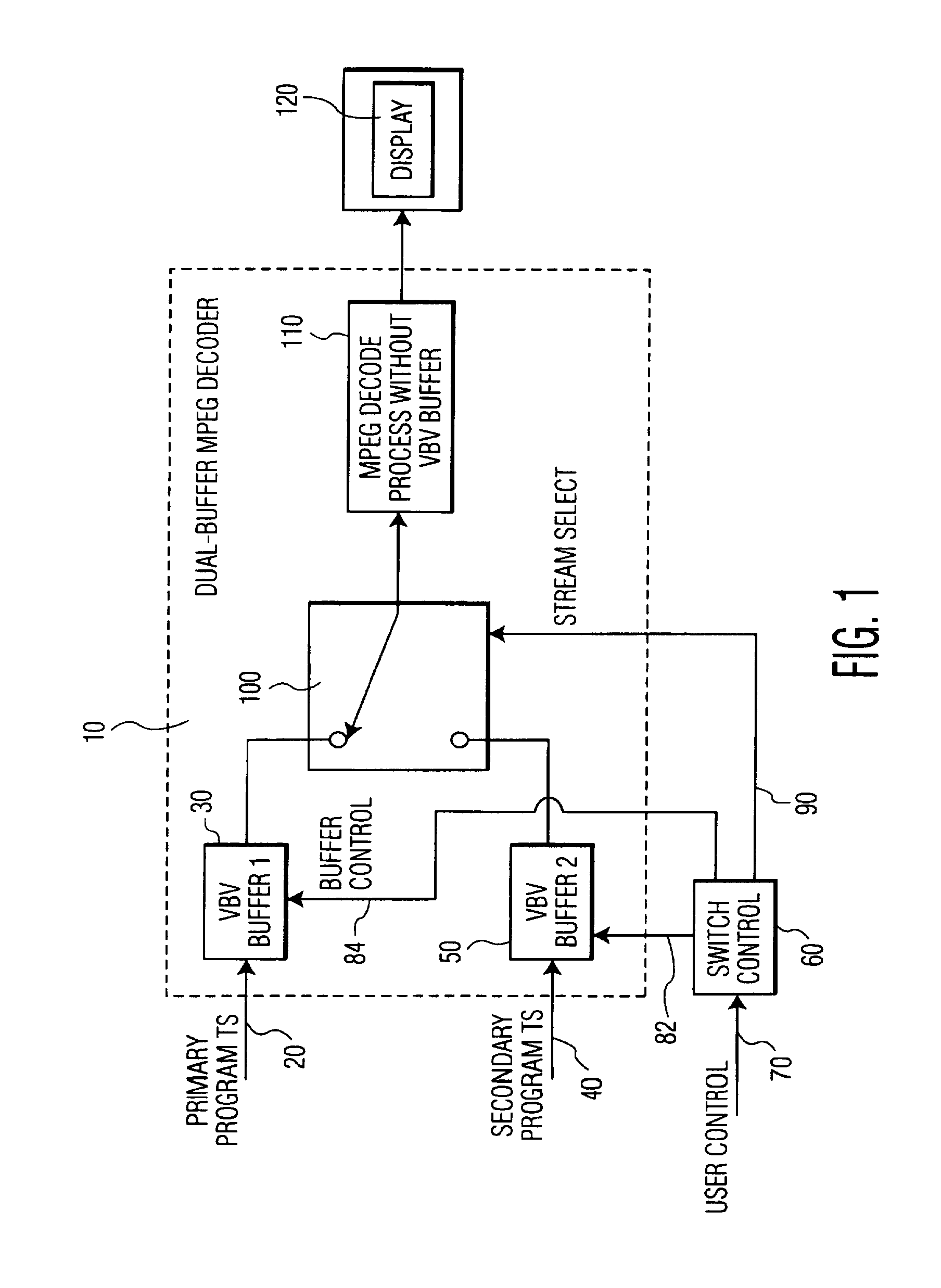
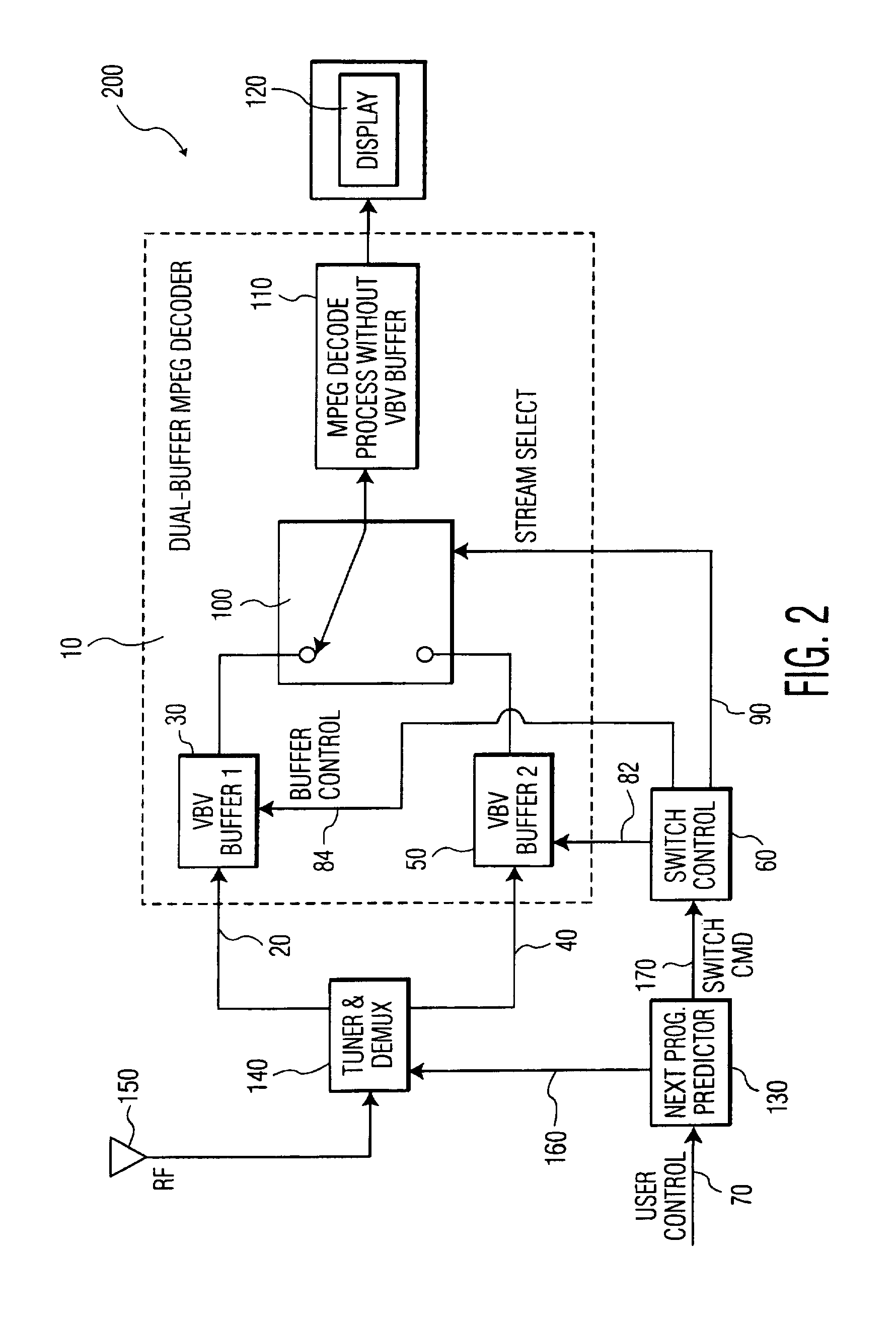
Video decoding and channel acquisition system
InactiveUS6985188B1Avoid adjustmentBroadcast with distributionTelevision system detailsDigital videoVideo decoding
A digital video decoding system receives packetized video data representing programs conveyed on a plurality of video channels. The system includes a plurality of buffers for storing encoded video data representing images of video programs conveyed on a corresponding plurality of video channels. An individual buffer, corresponding to an individual video channel, stores sufficient encoded video data to prevent an underflow condition following switching to decode a program conveyed on the individual video channel. A processor initiates switching to decode a program conveyed on a selected one of the plurality of video channels in response to a user channel selection input. A decoder decodes encoded video data received from one of the plurality of buffers corresponding to the program conveyed on the selected video channel as determined by switching initiated by the processor. The decoder also predicts a next channel to be selected by a user based on, (a) predetermined user channel and program preference criteria, (b) predetermined user channel navigation patterns, or (c) user data entry device sensory data.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
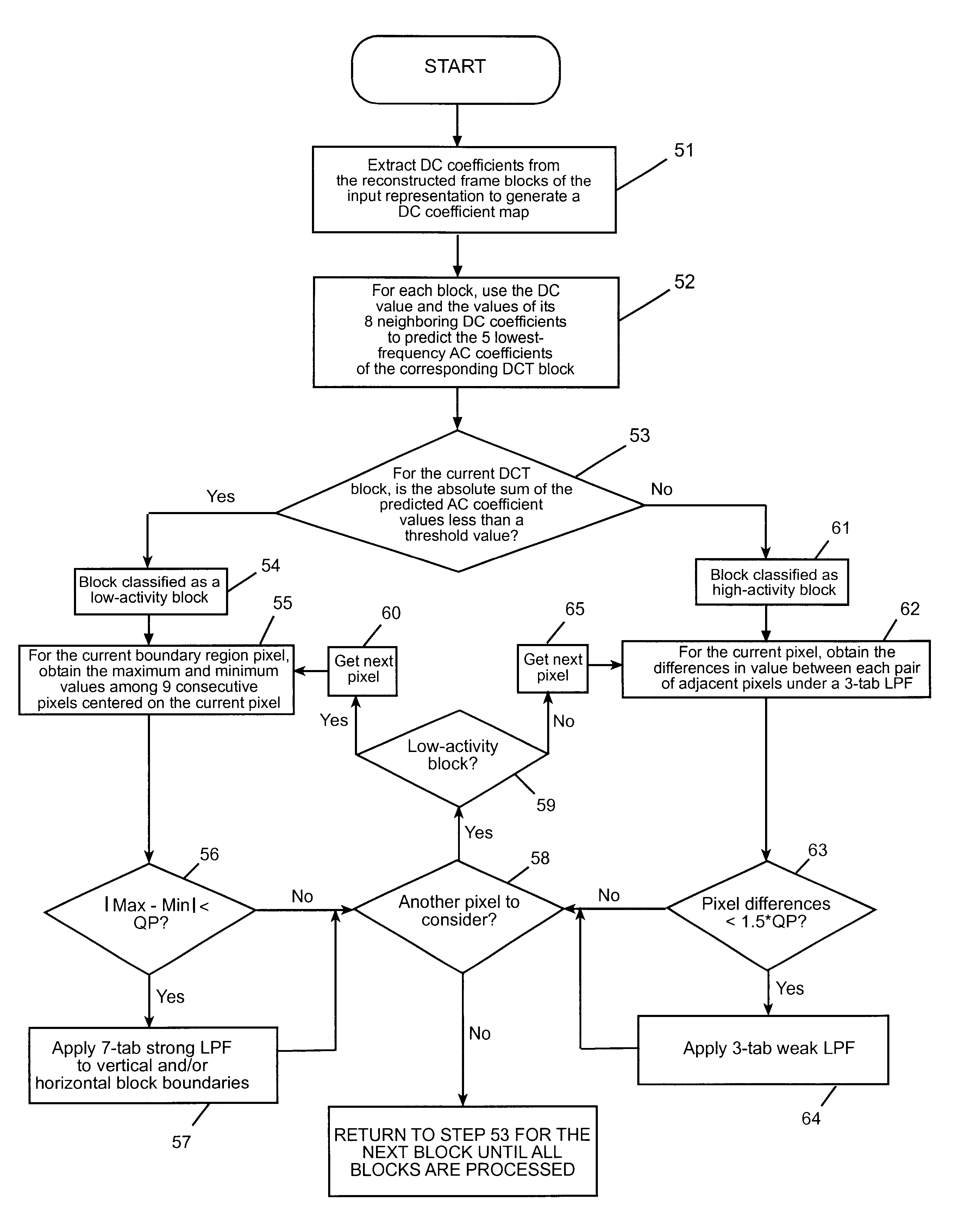
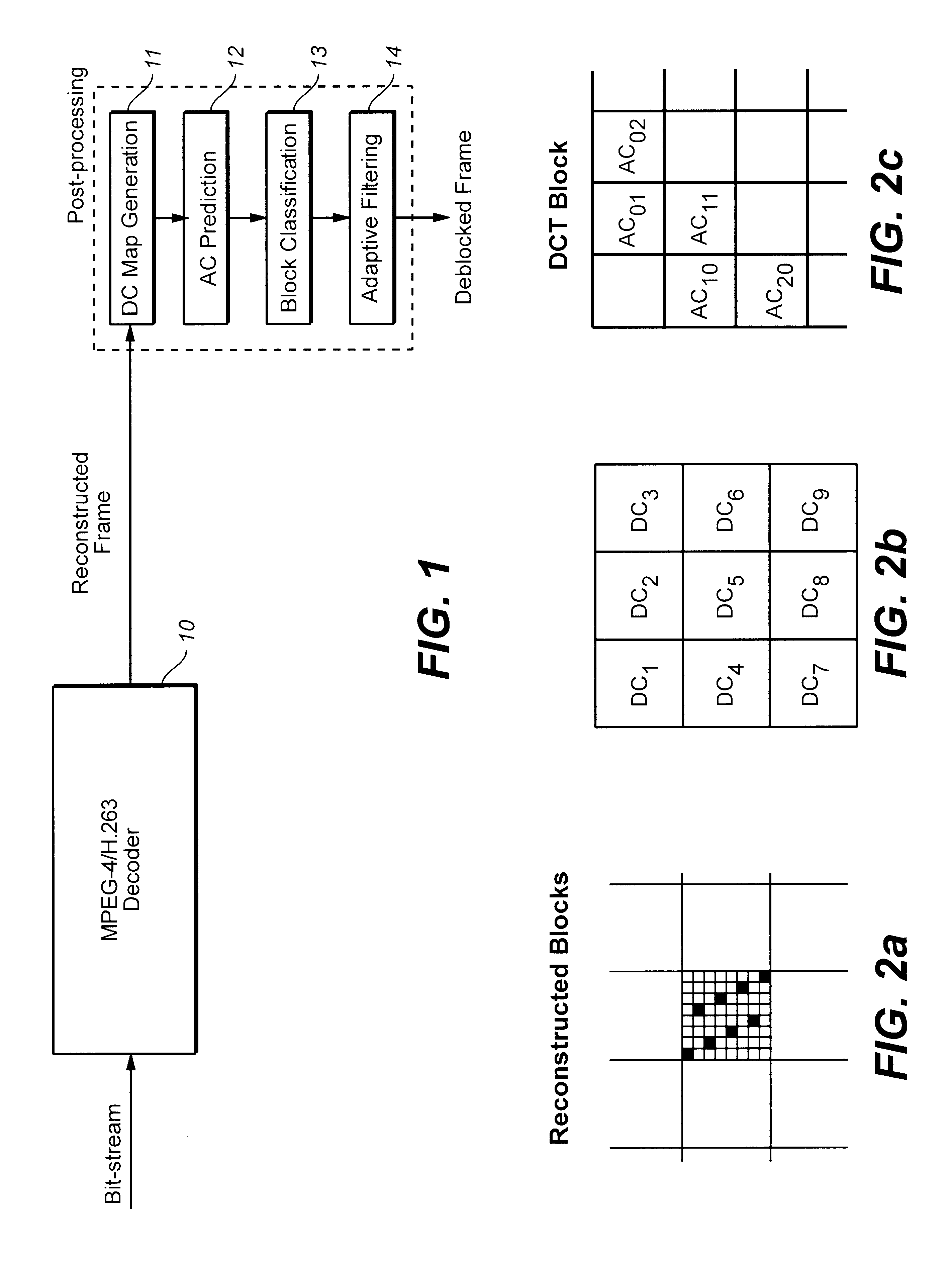
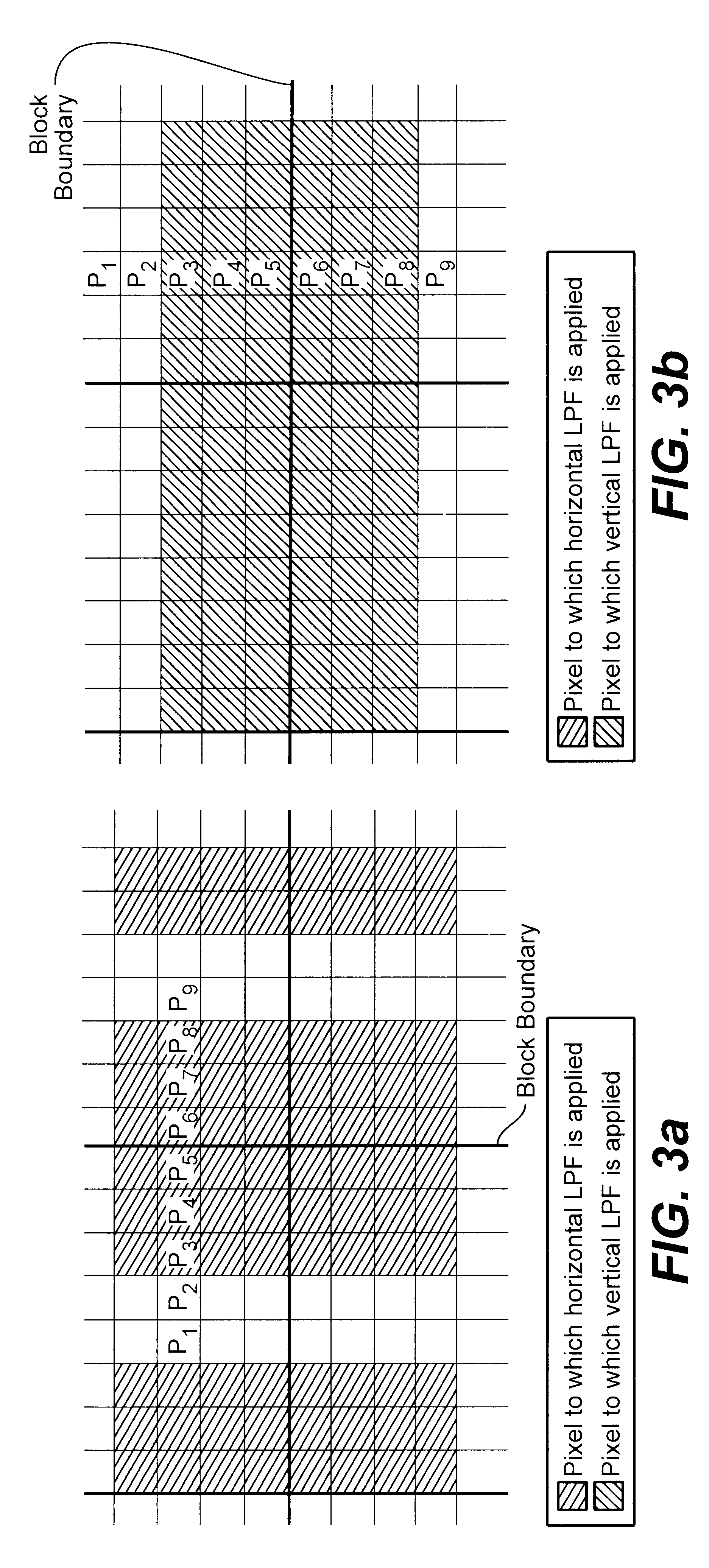
Reducing blocking and ringing artifacts in low-bit-rate coding
InactiveUS6983079B2Increase speedReducing blocking and artifactPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionLow activity
A technique to reduce blocking and ringing artifacts in low bit-rate block-based video coding is applied to each reconstructed frame output from the decoder. For each pixel block of a reconstructed frame, its DC value and DC values of the surrounding eight neighbor blocks are exploited to predict AC coefficients which might be lost in the quantization stage in the encoding process. The predicted AC coefficients are used to classify each reconstructed block as either a low-activity or a high-activity block. Low-pass filtering is then adaptively applied according to the classification of the block. Strong low-pass filtering is applied in low-activity blocks where the blocking artifacts are most noticeable, whereas weak low-pass filtering is applied in high-activity blocks where ringing noise as well as blocking artifacts may exist. The adaptive filtering reduces ringing noise as well as blocking artifacts without introducing undesired blur. In low activity blocks, the blocking artifacts are reduced by one dimensional horizontal and vertical low-pass filters which are selectively applied in either the horizontal and / or vertical direction depending on the locations and absolute values of the predicted AC coefficients. In high activity blocks, de-blocking and de-ringing is conducted by a single filter, applied horizontally and / or vertically, which makes the architecture simple.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Encoding of video cross-fades using weighted prediction
InactiveUS20060093038A1Efficient compressionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingArtificial intelligence
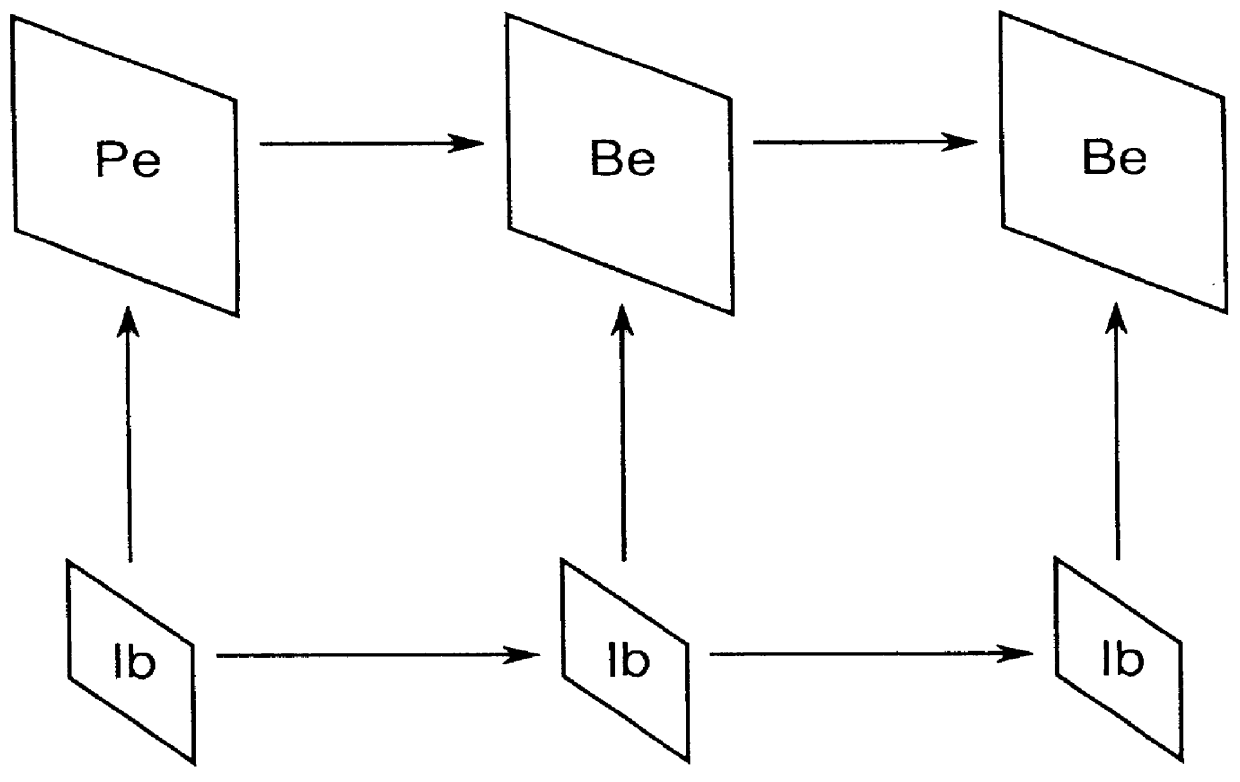
A video encoder and method are provided for encoding video signal data for at least one cross-fade picture disposed between a fade-out start picture and a fade-in end picture, where the encoder portion includes a reference picture weighting factor unit for assigning weighting factors corresponding to each of the fade-out start picture and the fade-in end picture, respectively, and the method for encoding cross-fades between pictures includes identifying pictures between which a cross-fade is desired, determining appropriate end-points for the cross-fade, and encoding the end-points prior to encoding the cross-fade picture.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Prediction apparatus and method for improving coding efficiency in scalable video coding
InactiveUS6043846ATelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer architectureSide information
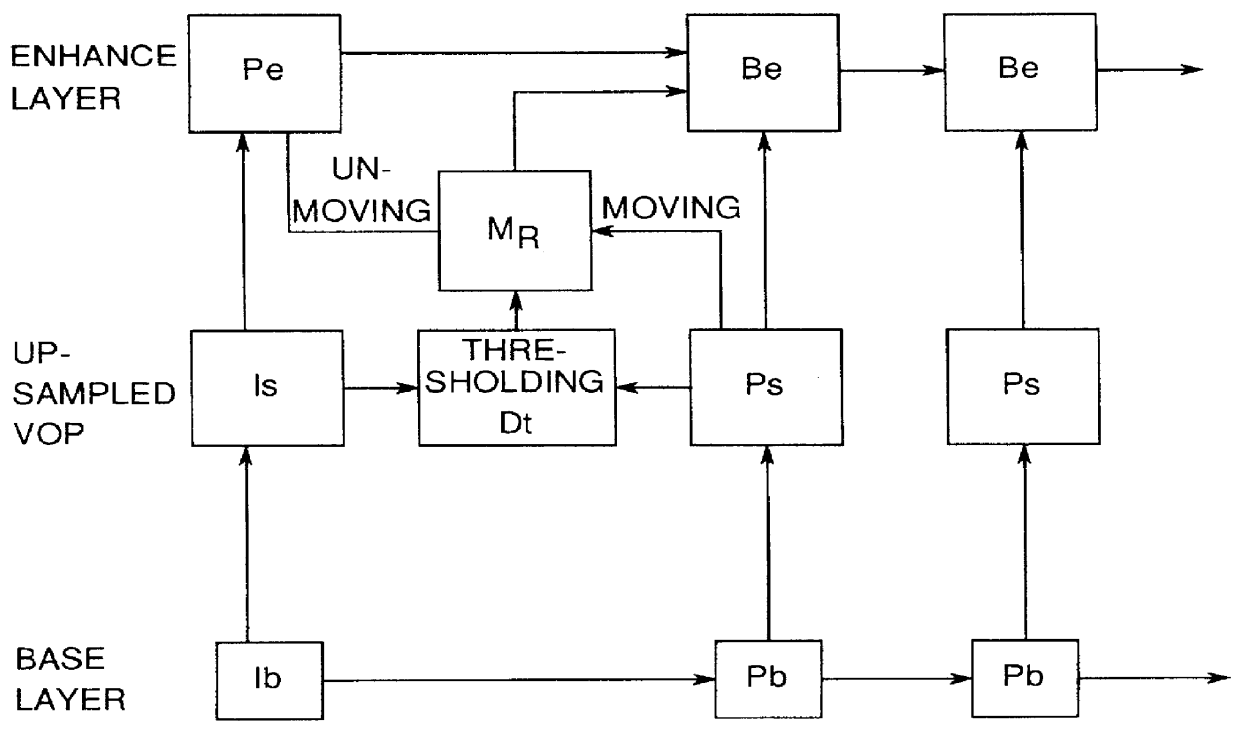
A prediction method, merged method, has been introduced in the enhancement layer of a multiple layer video coding. This merged method was designed to efficiently handle the prediction of the non moving parts in coding of the enhancement layer VOP or frame. All the information for this merged mode prediction is obtained from the base layer, and no additional side information is transmitted. This prediction mode when used together with combination of the existing forward mode, backward mode, and interpolated mode, can improve the coding efficiency for enhancement layer video coding, especially in low bit rate coding. The method can be used in most multiple layer video coding schemes, especially in spatial scalability video coding.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
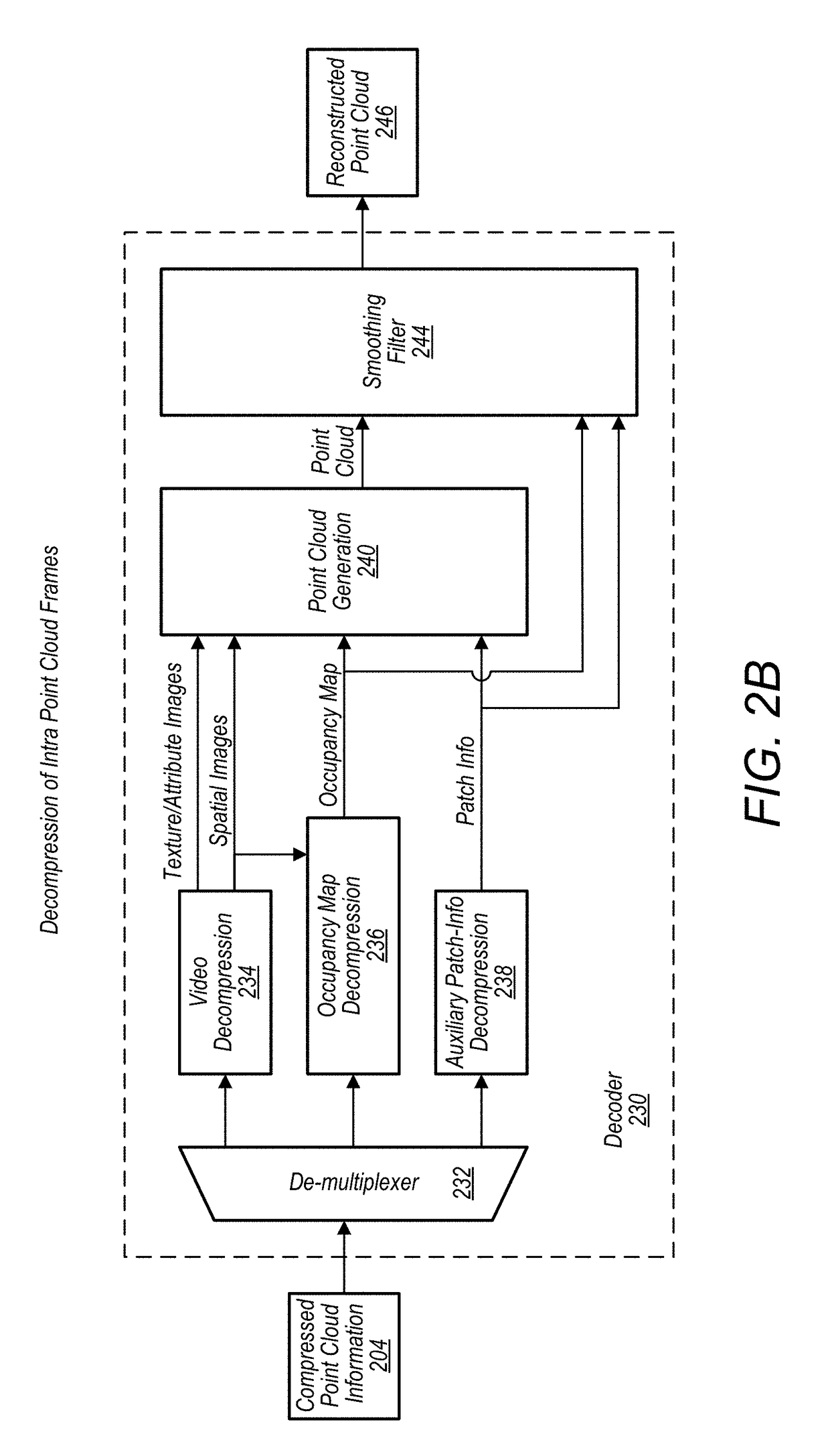
Point cloud compression
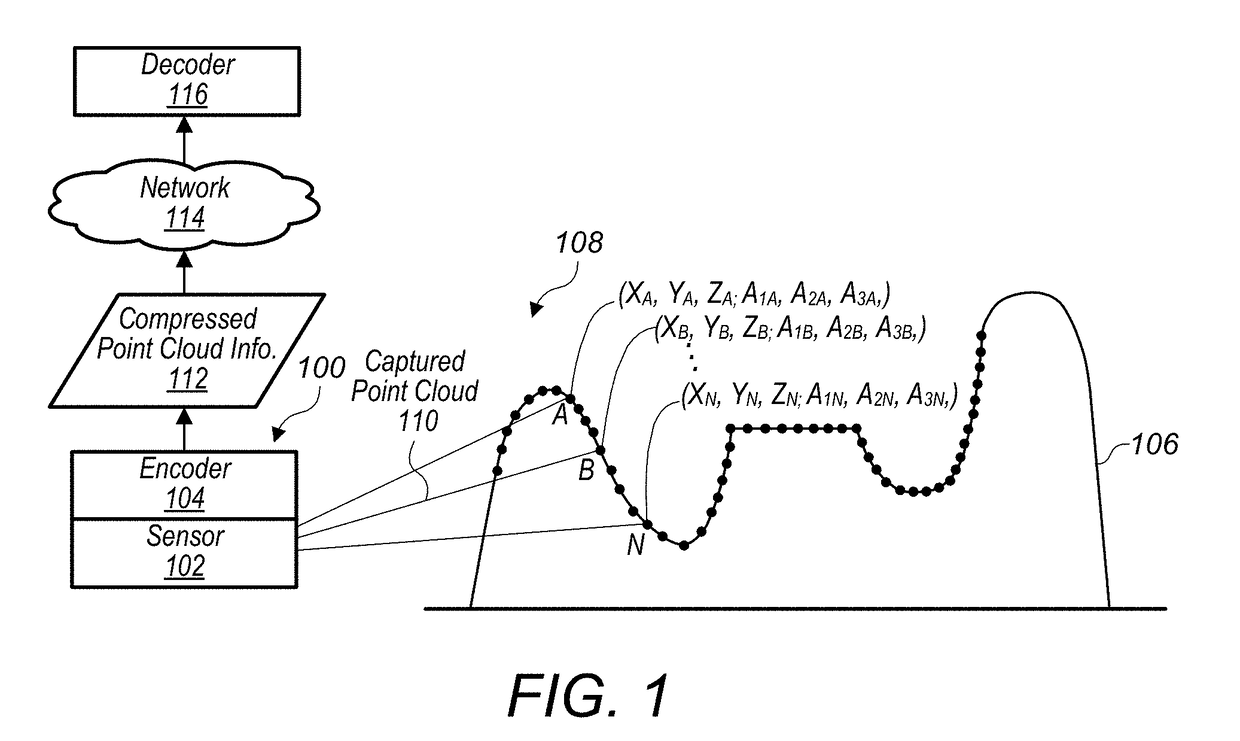
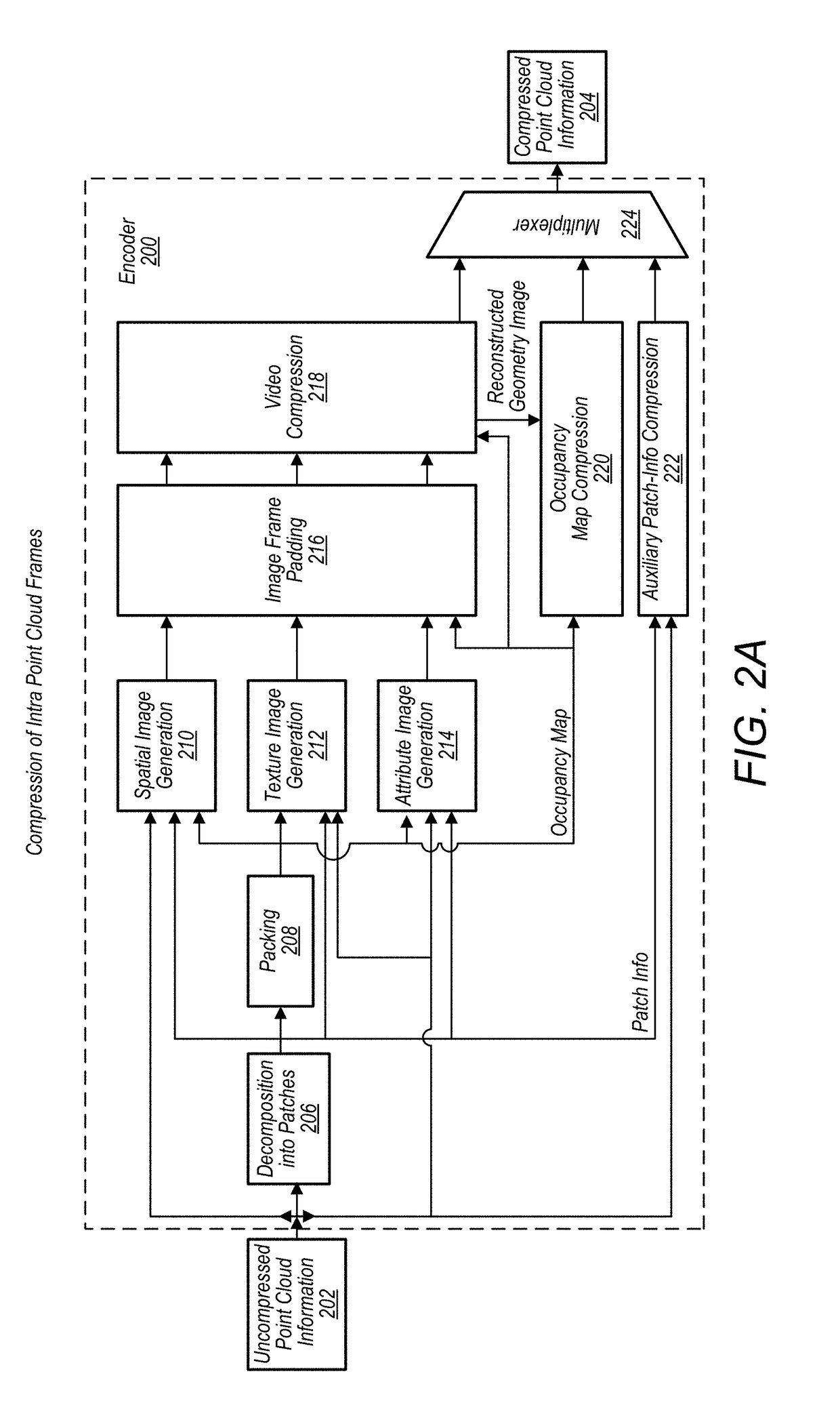
A system comprises an encoder configured to compress attribute information and / or spatial for a point cloud and / or a decoder configured to decompress compressed attribute and / or spatial information for the point cloud. To compress the attribute and / or spatial information, the encoder is configured to convert a point cloud into an image based representation. Also, the decoder is configured to generate a decompressed point cloud based on an image based representation of a point cloud.
Owner:APPLE INC
Popular searches
Digital video signal modification Selective content distribution Home automation networks Synchronous/start-stop systems Picture reproducers using projection devices Picture reproducers using solid-state color display Color motion picture films scanning Signal generator with optical-mechanical scanning Standards conversion Television signal transmission by single/parallel channels
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com