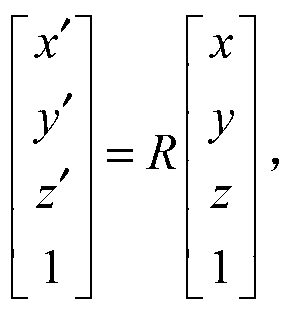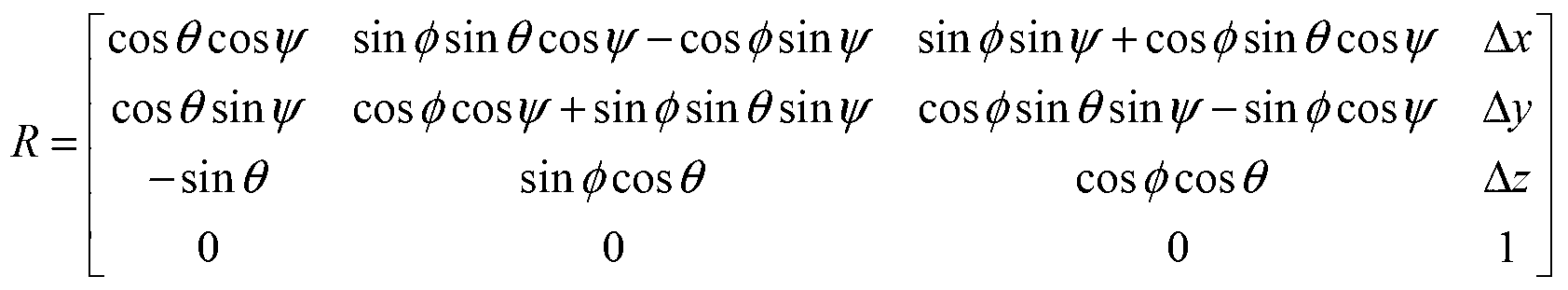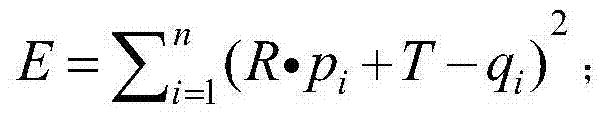Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
566 results about "Color depth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Color depth or colour depth (see spelling differences), also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, in a bitmapped image or video framebuffer, or the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel. For consumer video standards, such as High Efficiency Video Coding (H.265), the bit depth specifies the number of bits used for each color component. When referring to a pixel, the concept can be defined as bits per pixel (bpp), which specifies the number of bits used. When referring to a color component, the concept can be defined as bits per component, bits per channel, bits per color (all three abbreviated bpc), and also bits per pixel component, bits per color channel or bits per sample (bps). Color depth is only one aspect of color representation, expressing the precision with which colors can be expressed; the other aspect is how broad a range of colors can be expressed (the gamut). The definition of both color precision and gamut is accomplished with a color encoding specification which assigns a digital code value to a location in a color space.
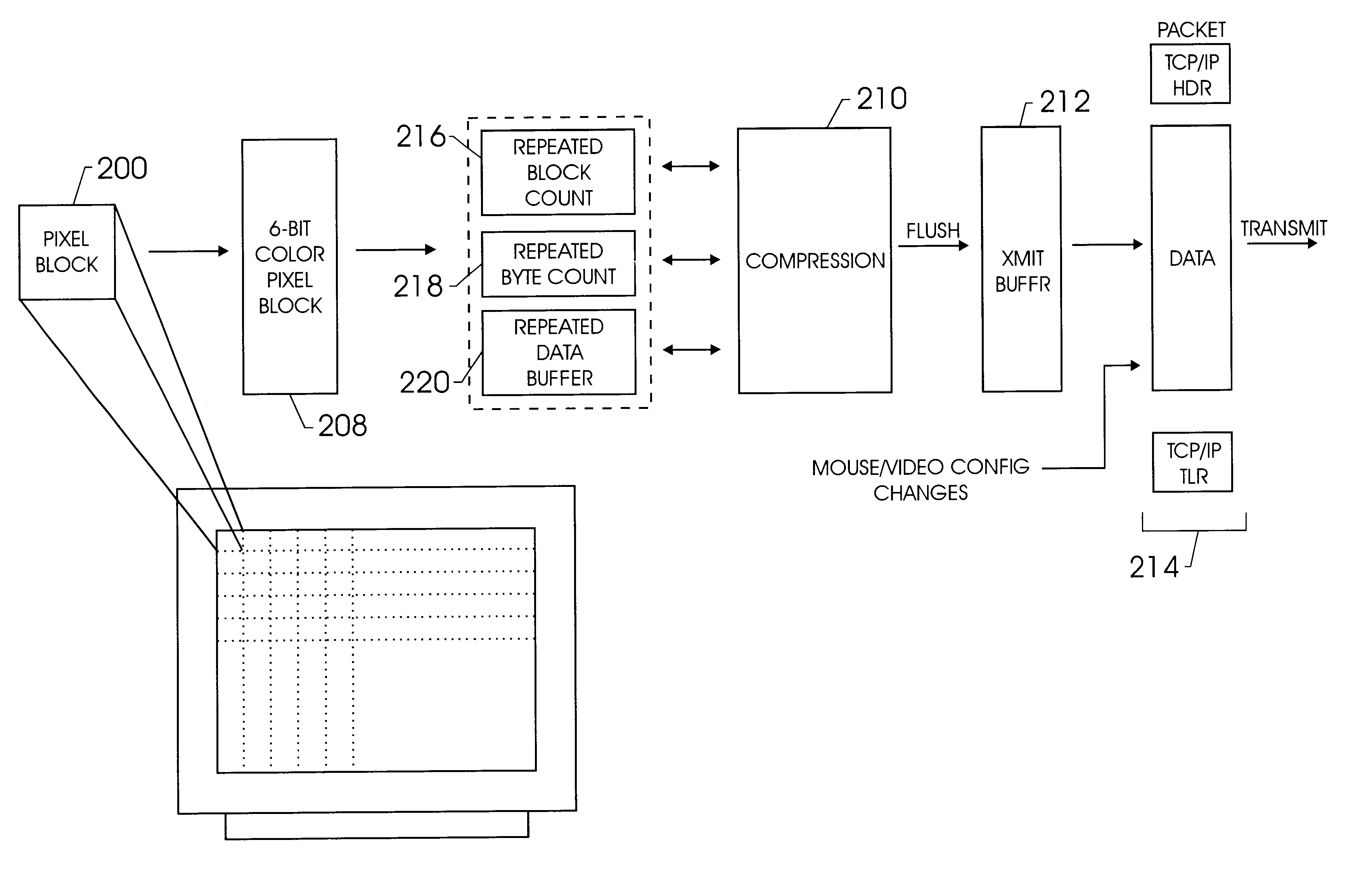
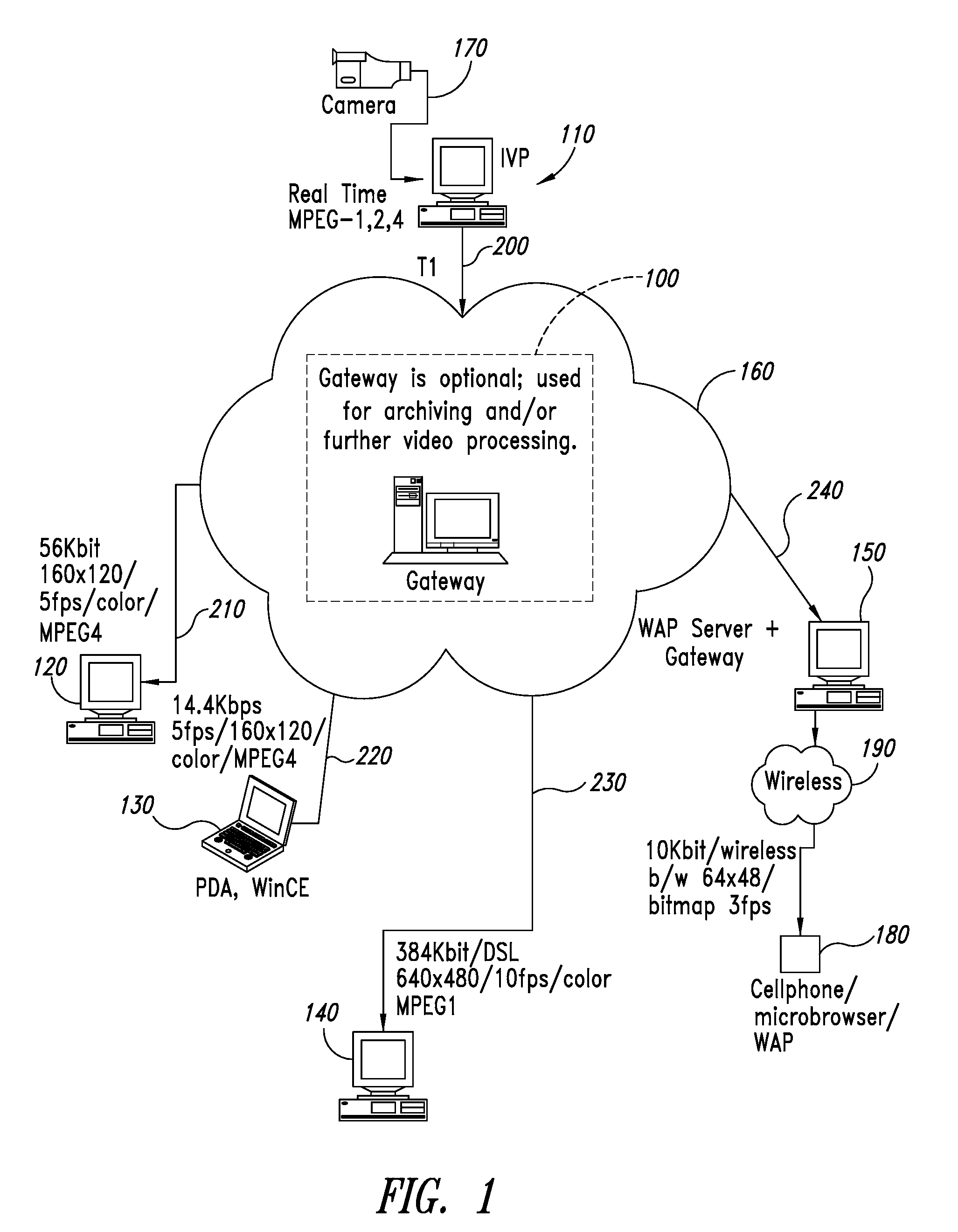
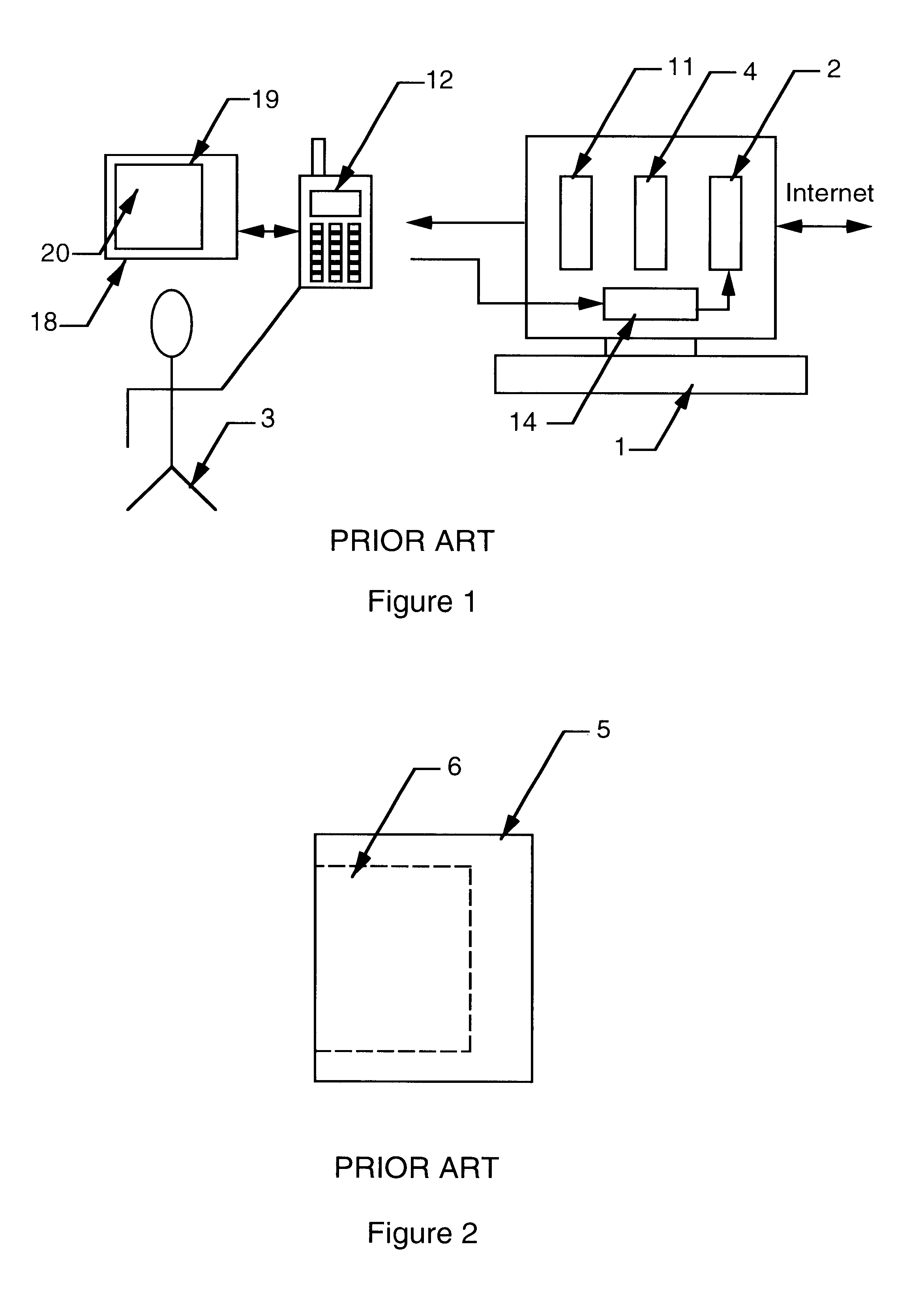
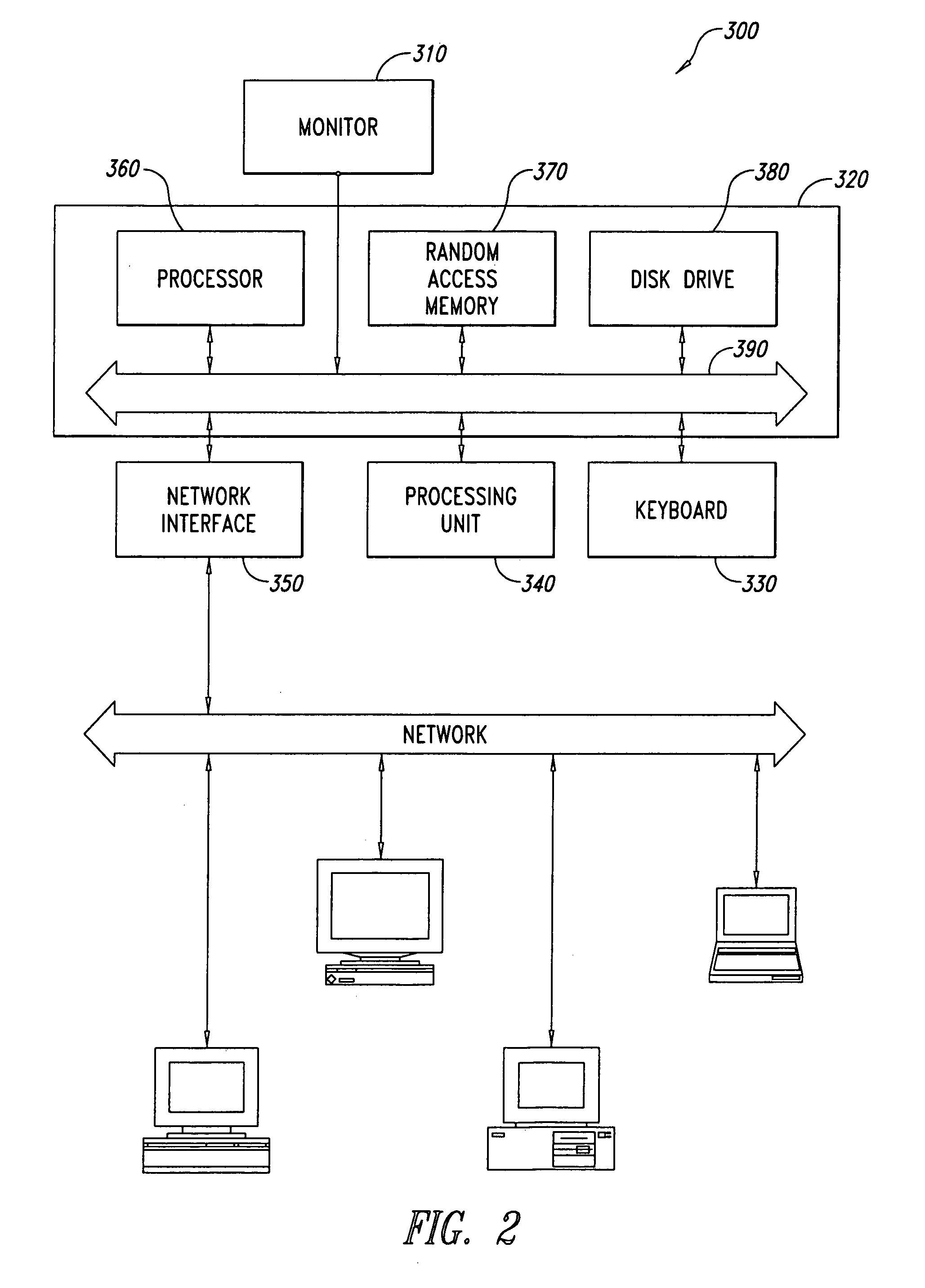
Operating system independent method and apparatus for graphical remote access
A method and apparatus for updating video graphics changes of a managed server to a remote console independent of an operating system. The screen (e.g. frame buffer) of the managed server is divided into a number of blocks. Each block is periodically monitored for changes by calculating a hash code and storing the code in a hash code table. When the hash code changes, the block is transmitted to the remote console. Color condensing may be performed on the color values of the block before the hash codes are calculated and before transmission. Compression is performed on each block and across blocks to reduce bandwidth requirements on transmission. Periodically, the configuration of a video graphics controller and a pointing device of the managed server are checked for changes, such as changes to resolution, color depth and cursor movement. If changes are found, the changes are transmitted to the remote console. The method and apparatus may be performed by a separate processor as part of a remote management board, a "virtual" processor by causing the processor of the managed server to enter a system management mode, or a combination of the two.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
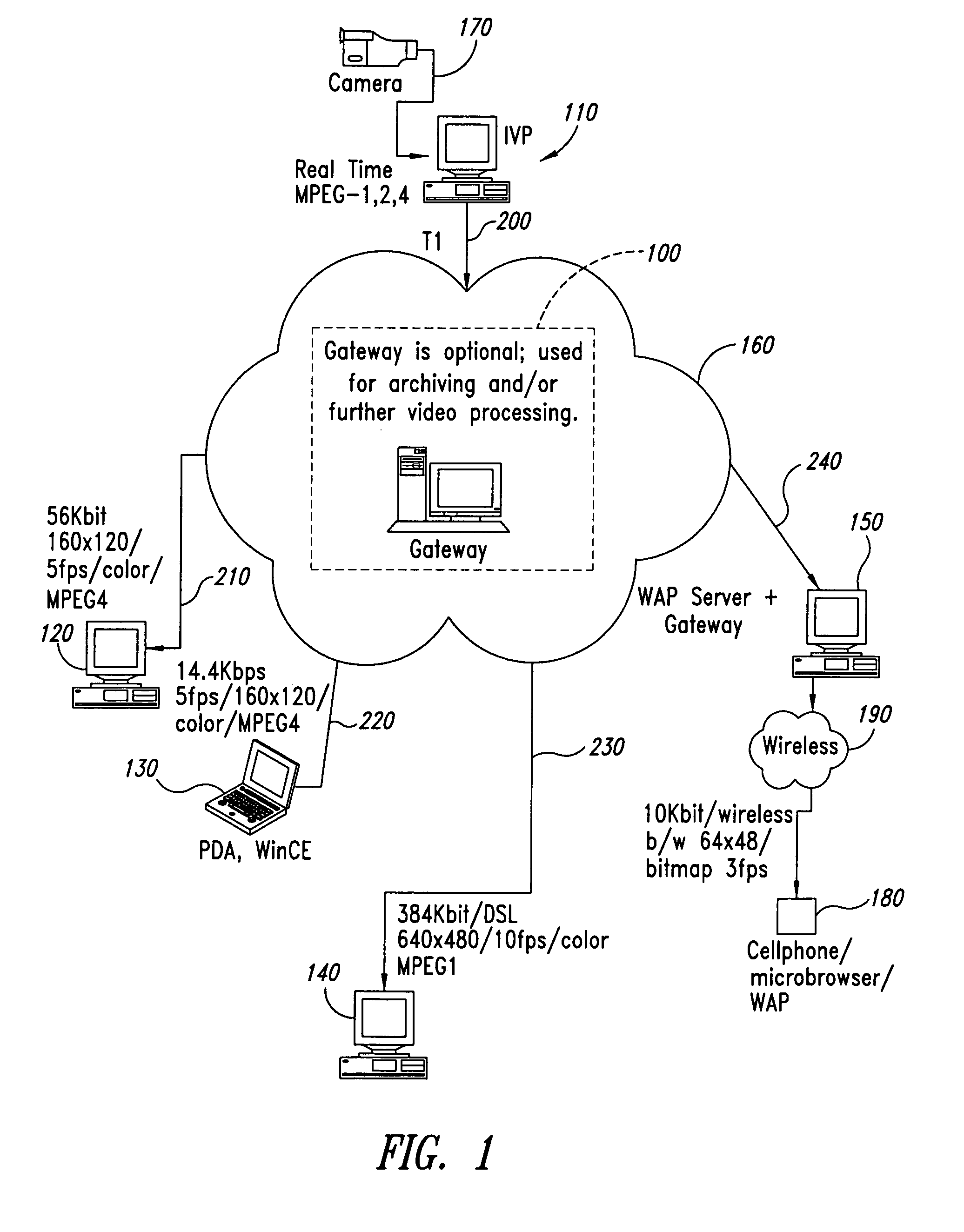
Methods for transforming streaming video data
InactiveUS7339993B1Reduces input bandwidthReduce bandwidth usagePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningData streamImage resolution
A method for forming an output stream of data includes determining an output resolution for the output stream of data, determining an output frame rate for the output stream of data, determining an output color depth for the output stream of data, retrieving a first frame of data, a second frame of data, and a third frame of data from an input stream of data, the input stream of data having an input resolution, an input frame rate, and an input color depth, subsampling the first frame of data, the second frame of data, and the third frame of data to respectively form a first subsampled frame of data, a second subsampled frame of data, and a third subsampled frame of data, when the output resolution is lower than the input resolution, dropping the second subsampled frame of data, when the output frame rate is lower than the input frame rate, reducing color depth for the first subsampled frame of data and the second subsampled frame of data to respectively form a first reduced frame of data and a second reduced frame of data, when the output color depth is smaller than the input color depth, and converting the first reduced frame of data and the second reduced frame of data into the output stream of data.
Owner:ADAPTIVE STREAMING INC
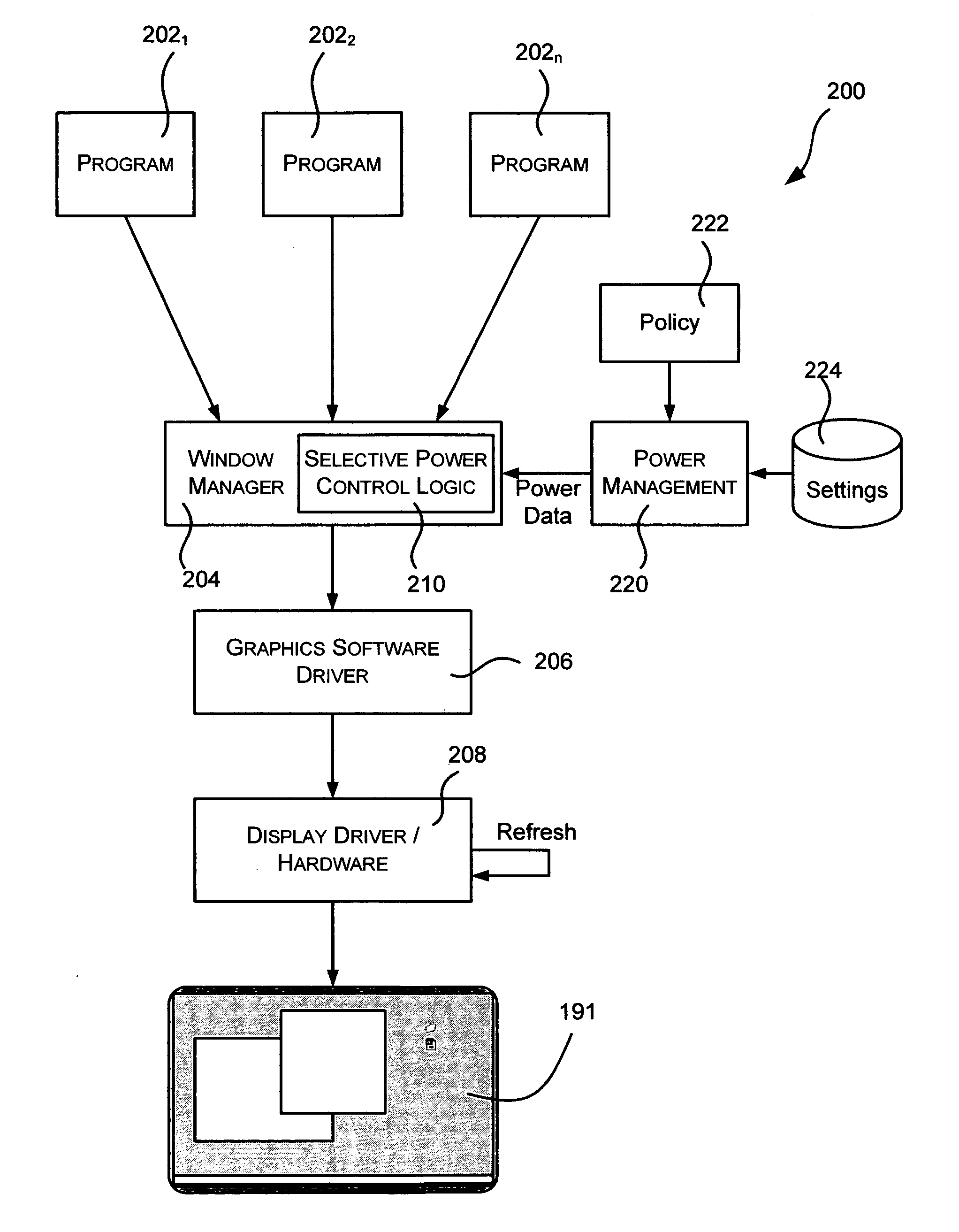
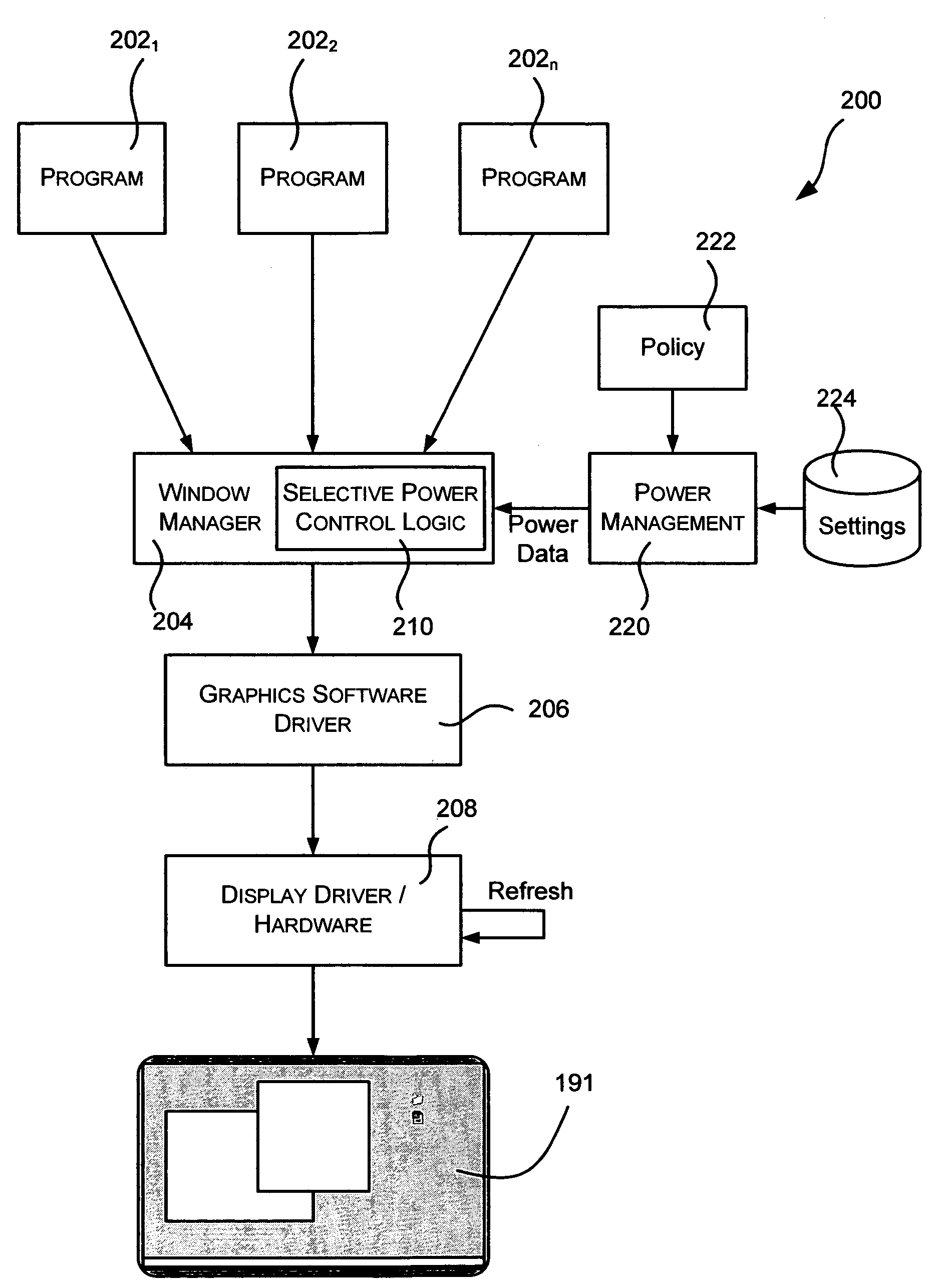
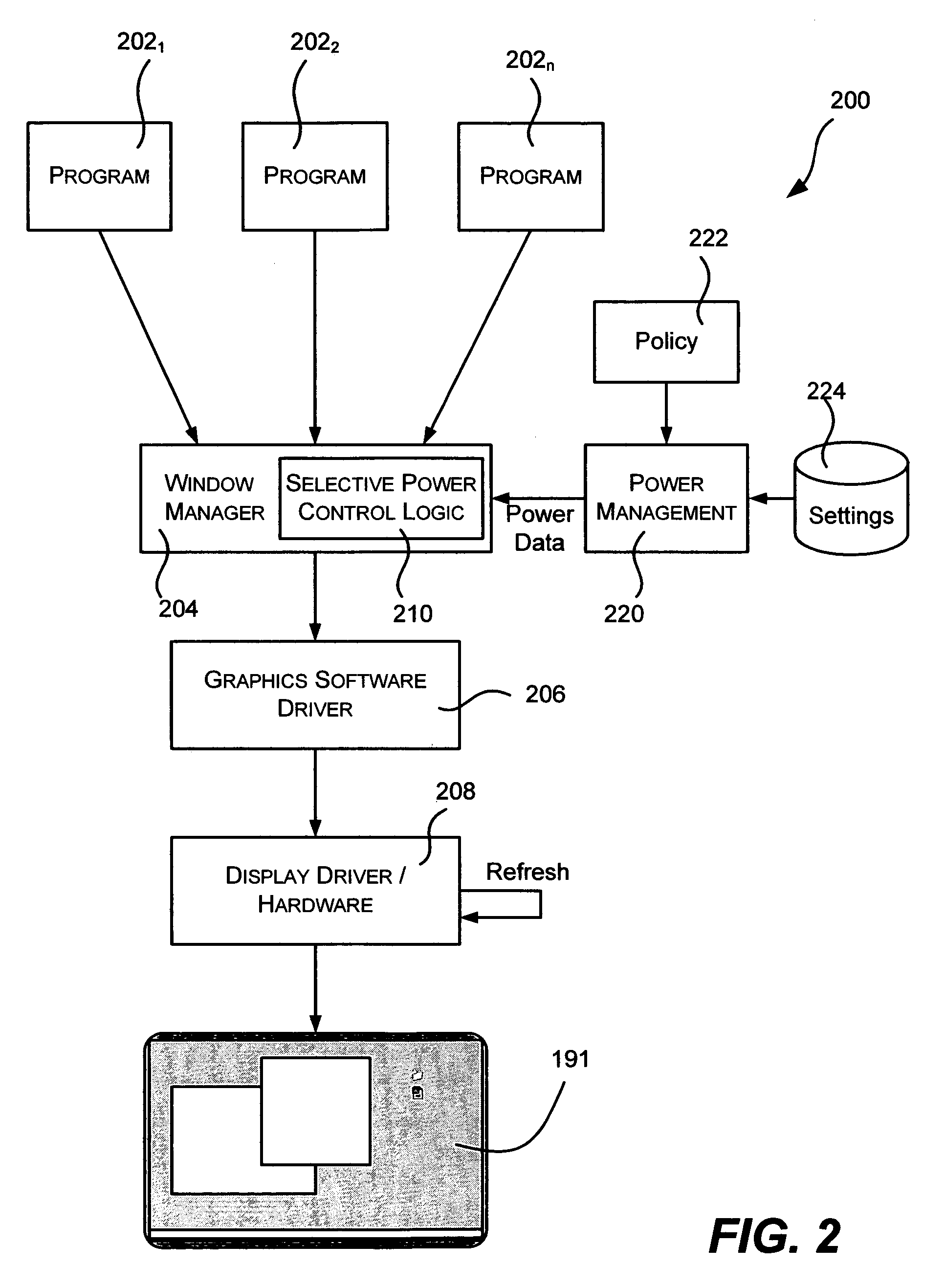
Advanced power management for computer displays
ActiveUS20060101293A1Reduced color levelDisplay is darkenedEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDisplay deviceColor depth
Described is a method and system for power management of mobile computer displays, in which areas of the screen are selectively controlled to consume less power than other areas. For example, a foreground window having focus may receive normal brightness, while background areas are dimmed. To this end, the pixels of selected areas are controlled to vary color depth, resolution, refresh rate, brightness and / or the on / off state for any part of the display. Power settings for parts of the display not corresponding to a focused window can be gradually reduced over time. Power policy may determine which areas are given reduced power, and external mechanisms provide information useful in the determination, such as when the user last interacted with a window, where the mouse is hovering, explicit user instructions as to how to power manage a window, and sensors that detect where the user is likely to want more power.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Portable high speed internet access device with encryption
InactiveUS6928461B2Low costSecure deliveryDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsThe InternetSound file
Owner:TULI RAJA SINGH MR
Computer program product for transforming streaming video data
InactiveUS7114174B1Reduce colorReduces input bandwidthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningData streamImage resolution
Owner:ADAPTIVE STREAMING INC
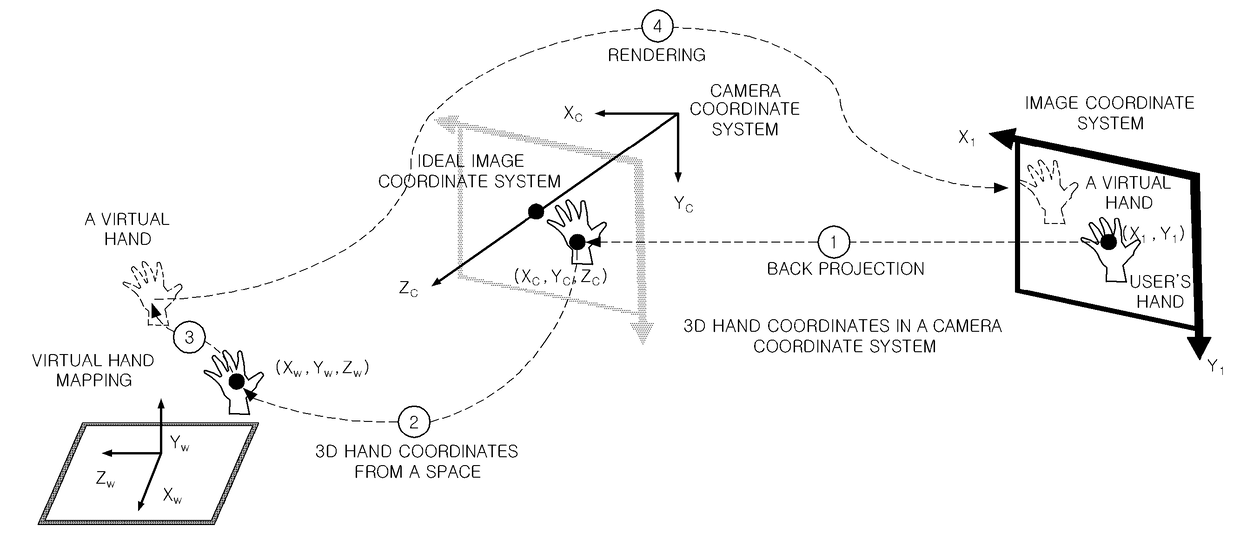
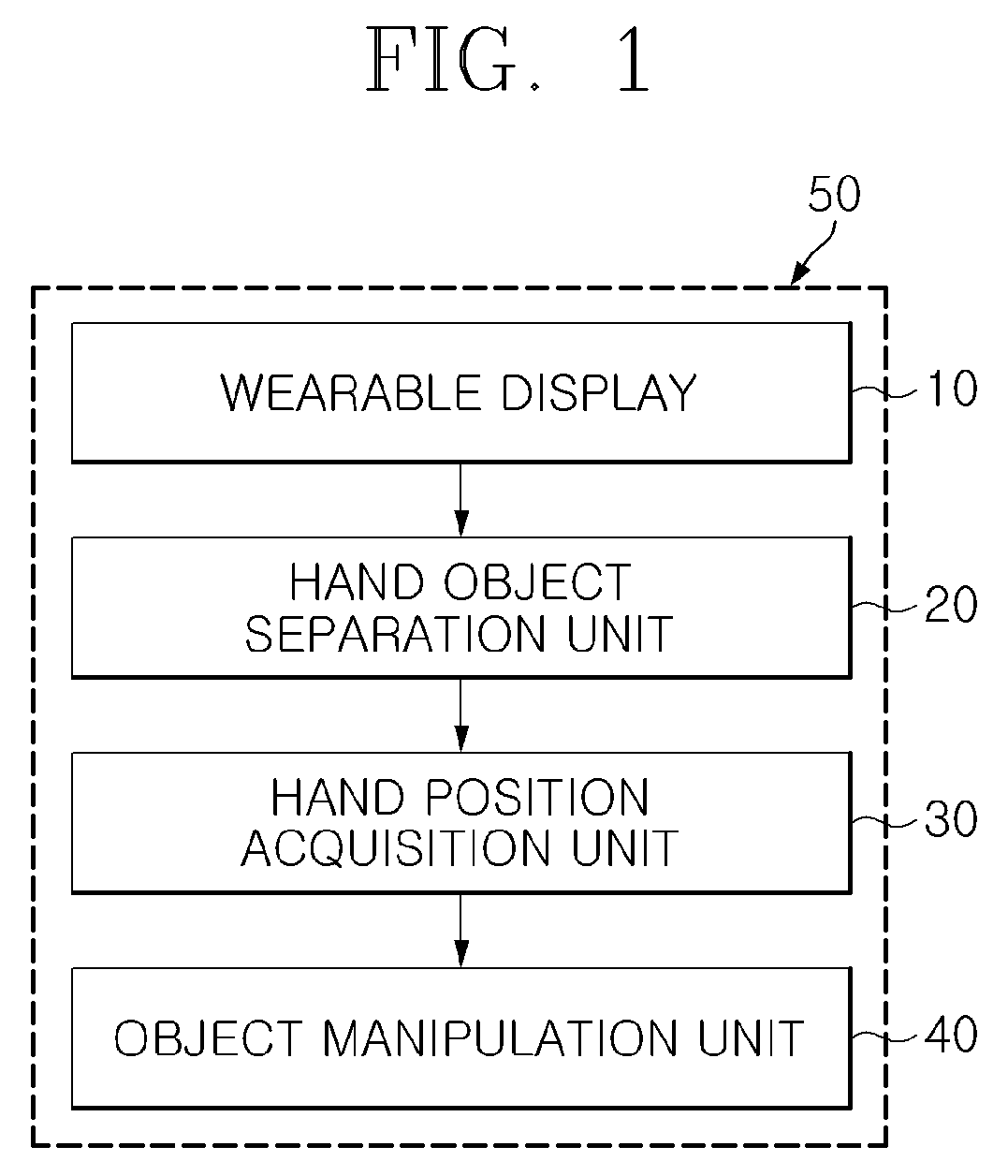
Apparatus and method for estimating hand position utilizing head mounted color depth camera, and bare hand interaction system using same
InactiveUS20170140552A1Increase distanceRecognition distanceInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementInteraction systemsColor depth
The present invention relates to a technology that allows a user to manipulate a virtual three-dimensional (3D) object with his or her bare hand in a wearable augmented reality (AR) environment, and more particularly, to a technology that is capable of detecting 3D positions of a pair of cameras mounted on a wearable display and a 3D position of a user's hand in a space by using distance input data of an RGB-Depth (RGB-D) camera, without separate hand and camera tracking devices installed in the space (environment) and enabling a user's bare hand interaction based on the detected 3D positions.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Portable high speed internet access device with encryption
InactiveUS20020099766A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsSound fileColor depth
The invention discloses a portable remote device that allows the user to access the Internet and World Wide Web. The portable device connects to a cellular telephone, thus providing wireless connection to the internet via a host computer which runs a browser, that takes information received from the Internet or other sources and renders it onto a virtual display in its memory. This information is directed to software, which reduces the color depth of the information to a lower depth color image. This reduced image is then compressed and encrypted by another software and sent to the portable device of the invention, which decrypts and decompresses it for displaying to the user. The browser may also reduces the color depth and compress the image without need for further software. Thus, the user views a bit map or raster image of a Web page, which is stored into memory. The portable device further comprises methods of pointing and clicking on text and images which represent links to other pages. Web pages with links may also be sent to the portable device, which stores them into memory to facilitate off-line viewing from the memory of the device. The user may also select desired links to each web page. Email messages may be retrieved manually or automatically at programmed times. Video frames and sound files may also be displayed on the portable device, with the aid of a buffer memory to facilitate uninterrupted playback.
Owner:TULI RAJA SINGH MR
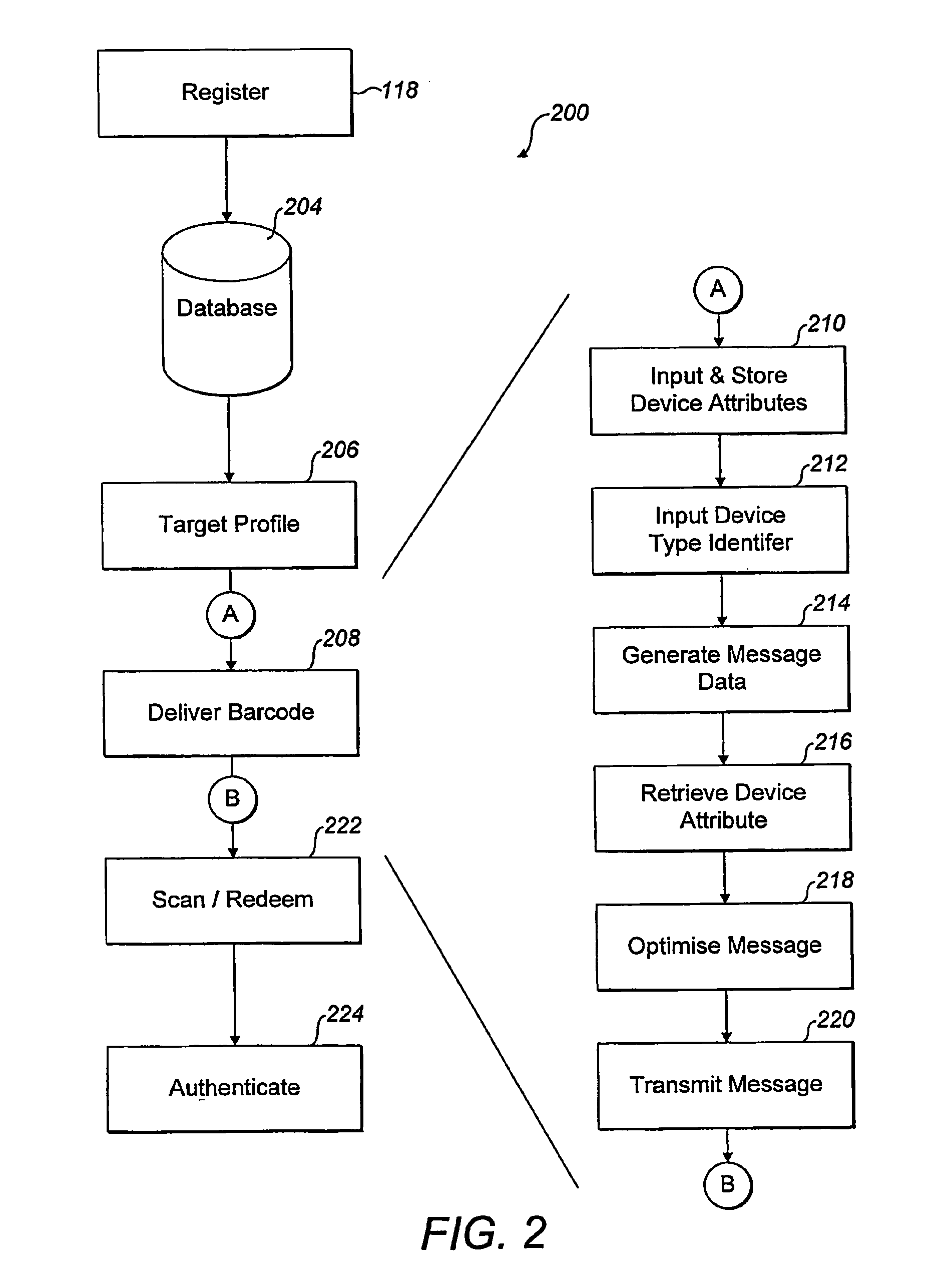
Optimised messages containing barcode information for mobile receiving devices
ActiveUS7693744B2Easy to operateAdvertisementsSubstation equipmentComputer hardwareDevice Properties
A system for delivering coupons containing barcodes to a mobile device such as a mobile phone is disclosed. A message processor means (106) generates message data comprising a coupon. A message optimizer means (116) generates an optimized message responsive to the message data and the capabilities of the mobile device (124). Preferably the capabilities of the mobile device comprise device attribute associated with a mobile device type, and are stored in a database means (110). The optimized message is transmitted to the mobile device. For basic mobile devices, simple text message including barcode number and associated text will be delivered. Otherwise, subject to the mobile device supporting the required display dimensions and color depth, a barcode image, picture, and / or multimedia content will be delivered.
Owner:NCR FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS GRP LTD
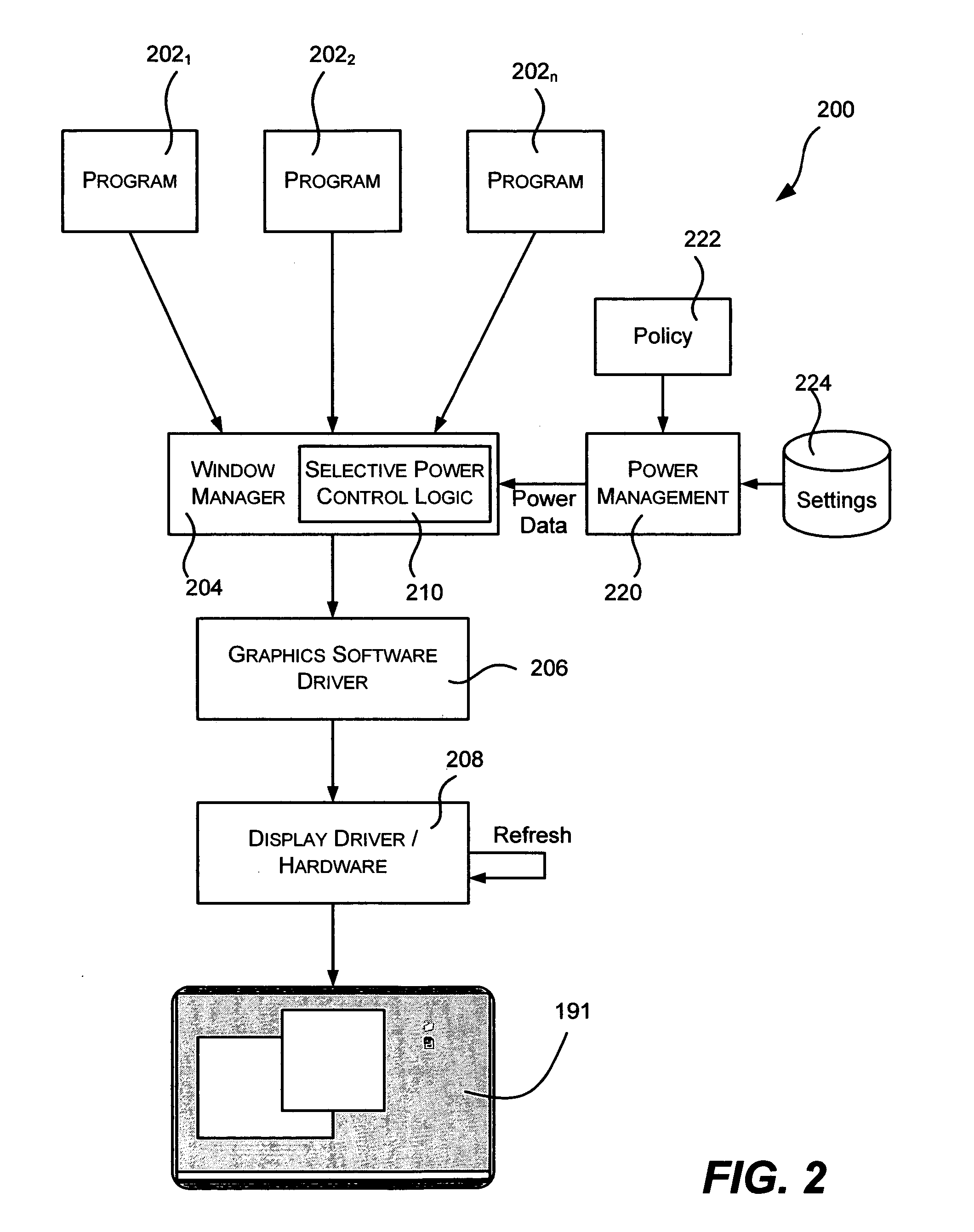
Advanced power management for computer displays
ActiveUS7389432B2More display capabilityLess powerEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementMouseoverDisplay device
Described is a method and system for power management of mobile computer displays, in which areas of the screen are selectively controlled to consume less power than other areas. For example, a foreground window having focus may receive normal brightness, while background areas are dimmed. To this end, the pixels of selected areas are controlled to vary color depth, resolution, refresh rate, brightness and / or the on / off state for any part of the display. Power settings for parts of the display not corresponding to a focused window can be gradually reduced over time. Power policy may determine which areas are given reduced power, and external mechanisms provide information useful in the determination, such as when the user last interacted with a window, where the mouse is hovering, explicit user instructions as to how to power manage a window, and sensors that detect where the user is likely to want more power.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
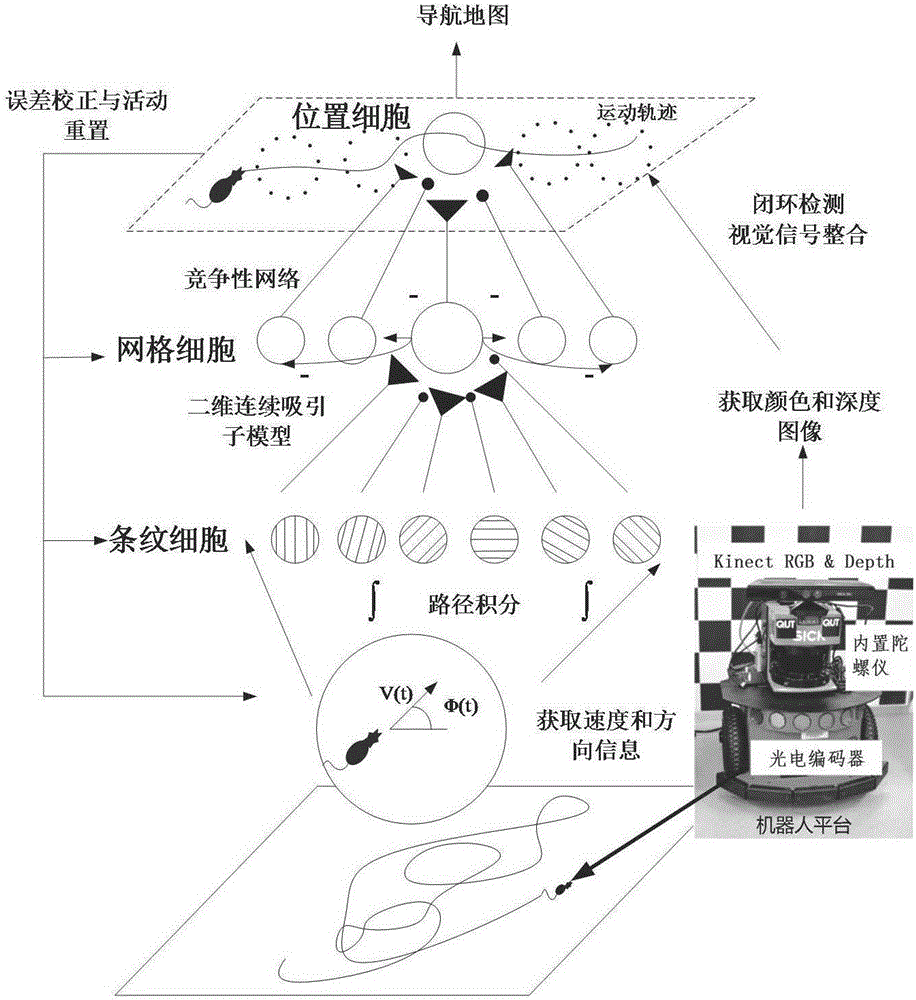
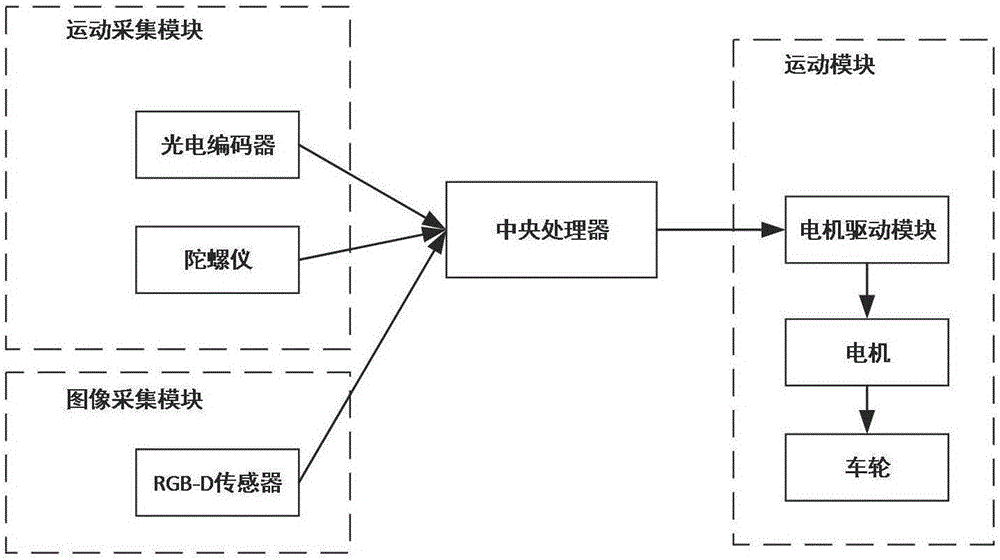
Robot navigation map construction method based on rat brain hippocampus spatial cells
The invention provides a robot navigation map construction method based on rat brain hippocampus spatial cells. According to an information transfer loop of spatial navigation related cells in a hippocampus structure of a mammal, a robot acquires a current autonomic movement clue and color depth image information through environment exploration. The autonomic movement clue progressively forms coding to the spatial environment through path integration and characteristic extraction of the spatial cells in the hippocampus structure. The place field of place cells is gradually formed in an exploration process and furthermore covers the whole spatial environment, thereby forming a cognitive map. Meanwhile, Kinect acquires color depth image information of a view scene right in front of the current position as an absolute reference for performing closed-loop detection on the path and correcting a path integration error. At a closed-loop point, a system resets spatial cell discharging activity and performs correction on the path integration error. Nodes on a final navigation map comprise place cell mass coding information, corresponding visual cues and place topological relationships.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
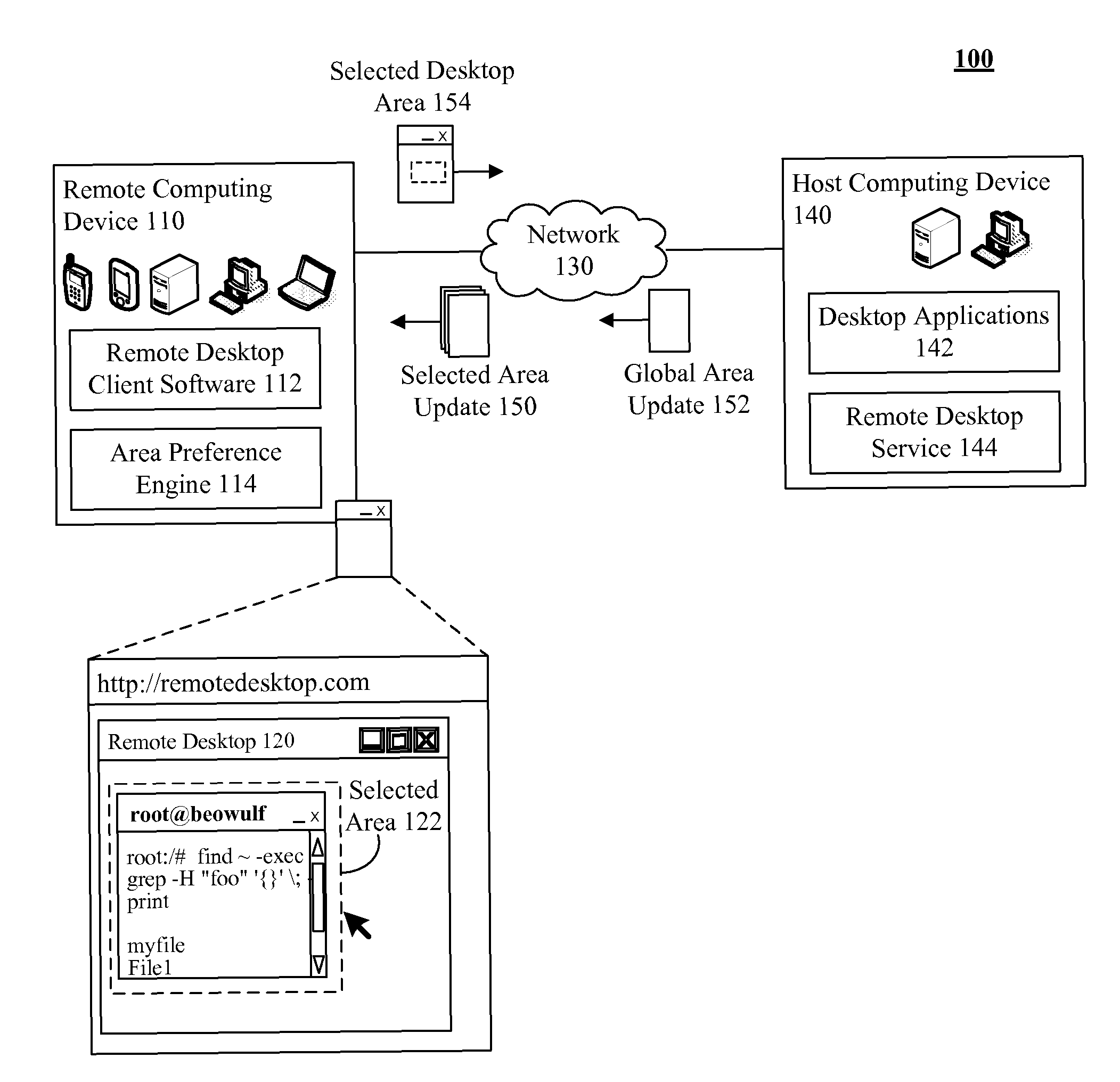
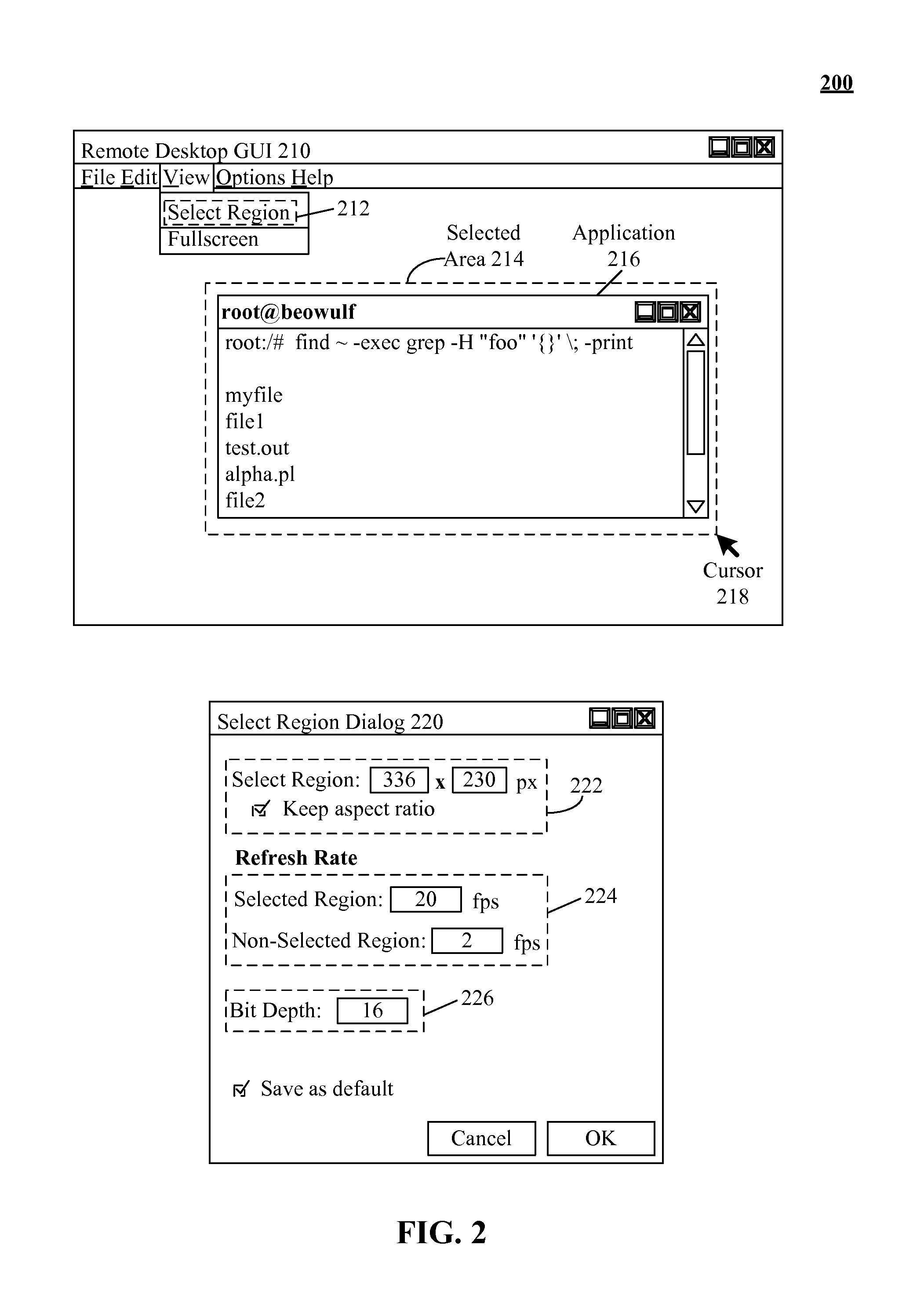
Bandwidth usage and latency reduction of remote desktop software based on preferred rendering of a user selected area
ActiveUS7895521B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionRemote desktopComputer graphics (images)
The present invention discloses a solution for bandwidth usage reduction of remote desktop software based on preferred rendering of a user selected area. The solution can allow a user to select a specified region of a remote desktop to gain precedence over non-selected regions. An area preference engine can be configured to convey user preference, settings, and selection areas. Selected regions can be user configured to render with different settings than non-selected regions such as resolution, color depth, frame rate, update frequency, and the like. Non-selected regions can be configured to receive lower priority updates than selected regions.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Motor vehicle filter structure having visual indicator of useful life
InactiveUS6875249B2Low efficiencyIncrease pressure dropCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesMobile vehicle
Filter media and filter structure or media pack can be engineered to exhibit high initial efficiency and to surface load particulate removed from a gaseous stream. The filter technology protects engine operation from ingested particulate and accumulates the particulate as a surface loaded layer visible on the surface of the structure. The particulate accumulates as a surface loaded layer until it achieves a certain depth of particulate or gray scale characteristic or color depth indicative of the end of the useful life of the filter prompting a change of the filter structure. The filter structure is characterized by its ability to surface load particulate, avoid accumulation of particulate in the depth media and enhance the characteristics of the material through surface loading. Such technology is particularly useful in light duty vehicle maintenance technology.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
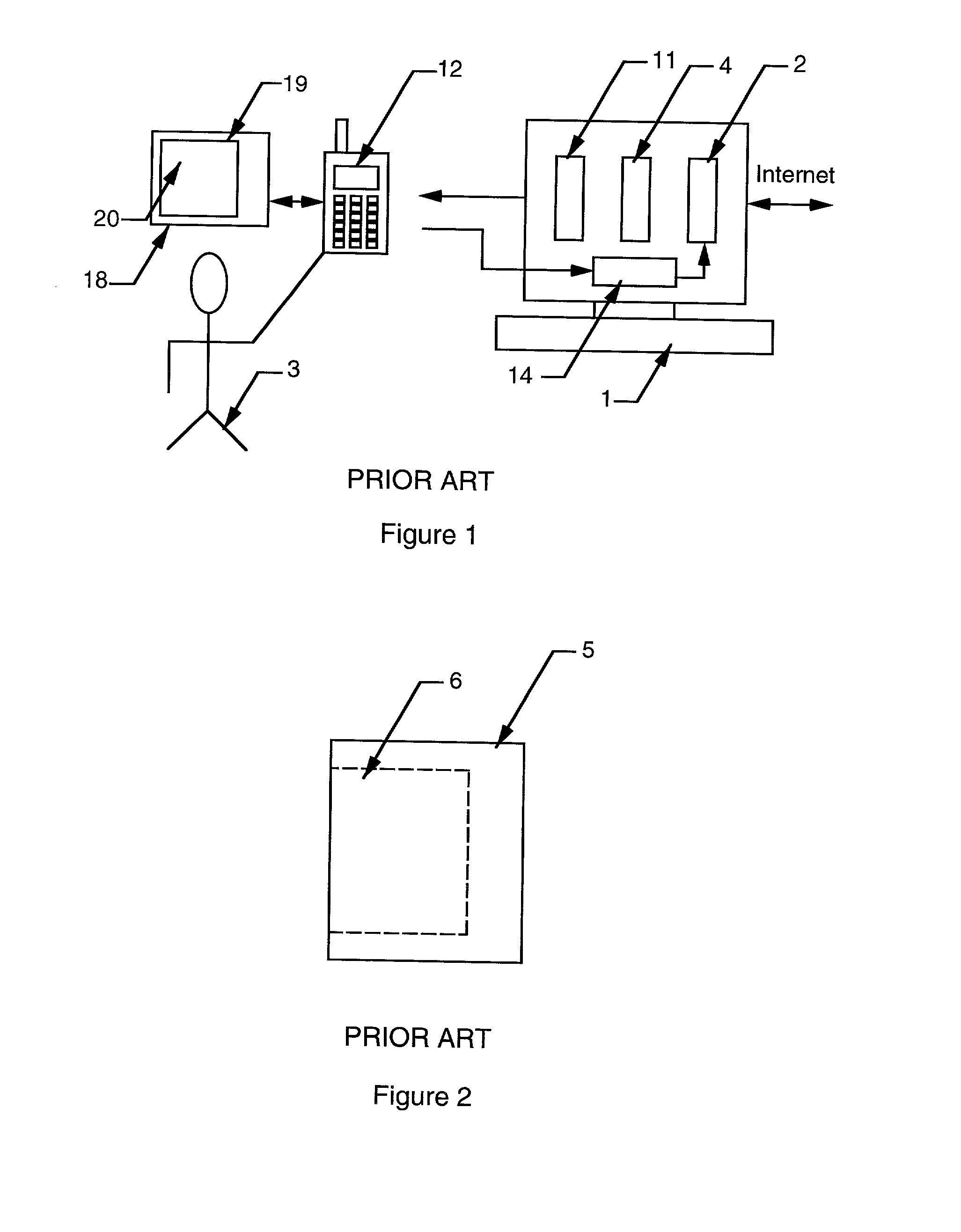
Portable high speed internet access device
InactiveUS20020030844A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital data information retrievalThe InternetHigh speed internet access
The invention discloses a portable device providing access to the Internet. A host computer runs a browser taking information received from the Internet, renders it onto a virtual display in memory, reduces the color depth, compress and sends it to the device. Thus, the user views a bit map or raster image of a Web page on the device, which also contains a browser software program, that runs on the device containing its own window. This window contains buttons or icons providing web functions and implements scrolling on the web page received with respect to the window. The windows of the browsers in the host computer and device are adjustable in size and may be set to match for text formatting. The size of the web page received from the Internet is the size sent to the device when converted to an image, which varies with each web page received.
Owner:TULI RAJA SINGH MR
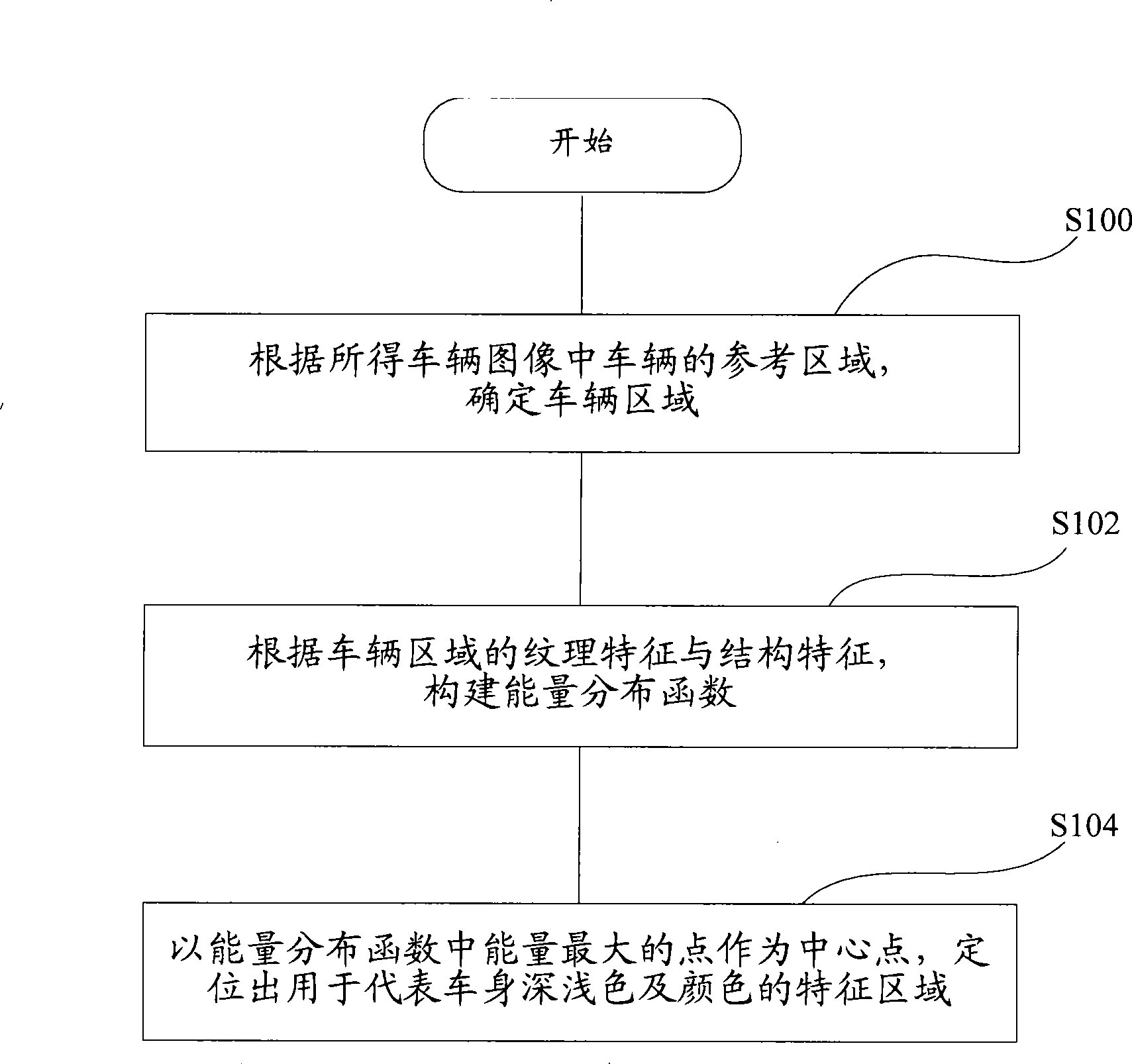
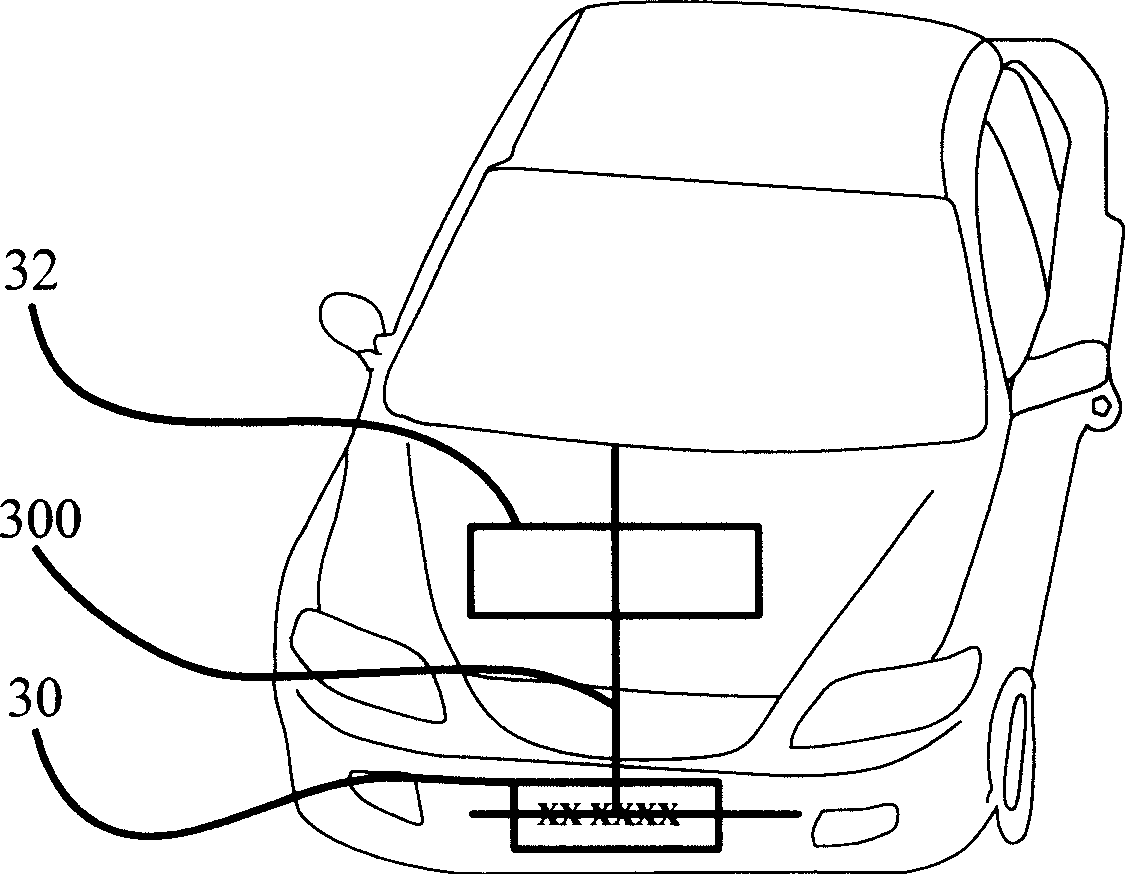
Characteristic area positioning method, car body color depth and color recognition method
ActiveCN101504717ASmall amount of calculationImprove recognition accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryReference RegionColor recognition
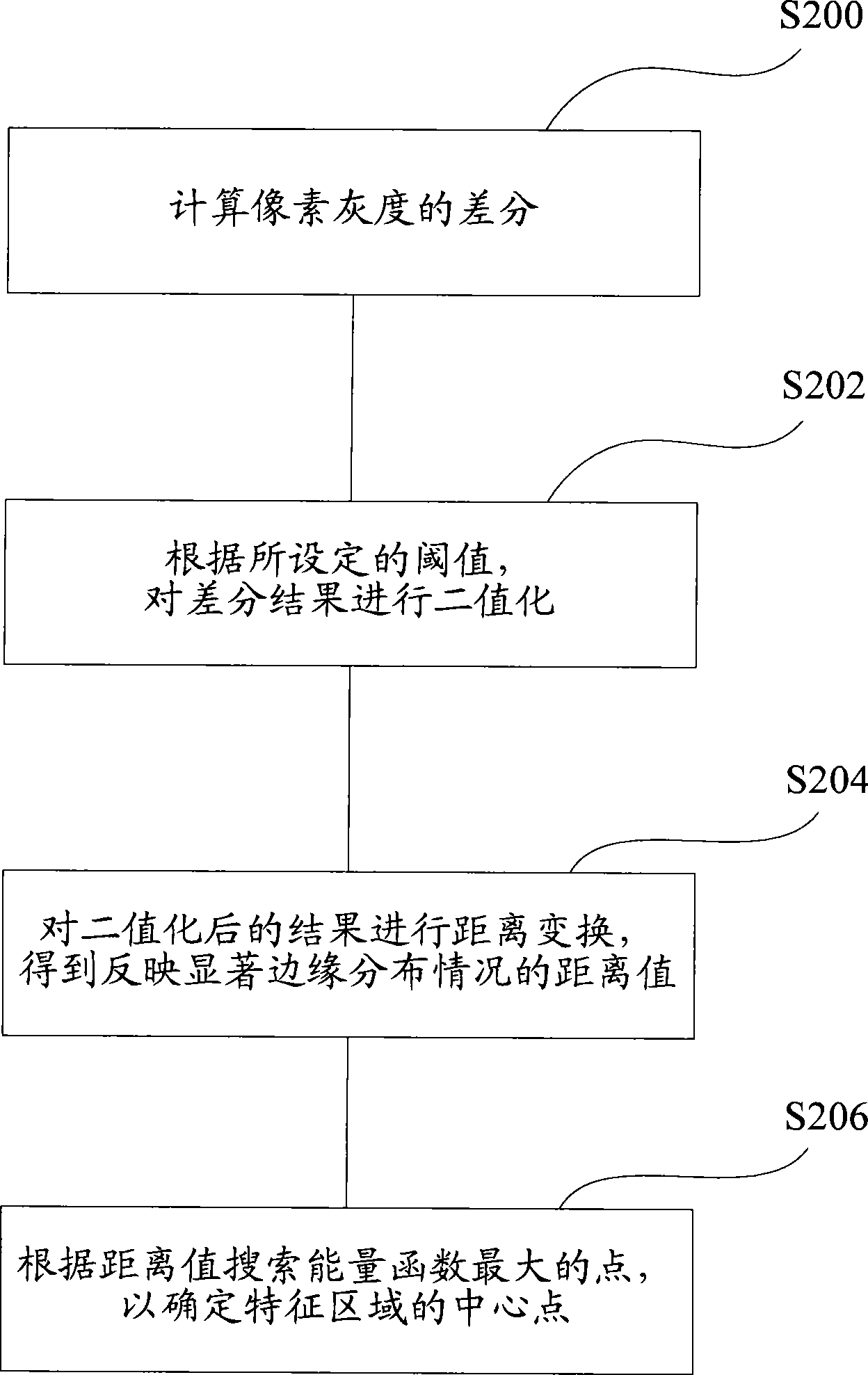
The invention discloses a method for positioning a characteristic region representing a dark and light color and a color of a vehicle body, which comprises the steps of: determining a vehicle region according to a reference region of a vehicle in an acquired vehicle image; constructing an energy distribution function according to texture characteristics and structural characteristics of the vehicle region; and positioning the characteristic region used for representing the dark and light color and the color of the vehicle body by taking a point with maximum energy in the energy distribution function as a central point. The invention also provides a method for identifying the dark and light color of the vehicle body and a method for identifying the color of the vehicle body. The application of the method can reduce computation amount, quicken computation speed, and improve identification accuracy rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI GOLDWAY INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYST CO LTD
Method and system for digital image management
InactiveUS20020180764A1Web data retrievalCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Digital rights management
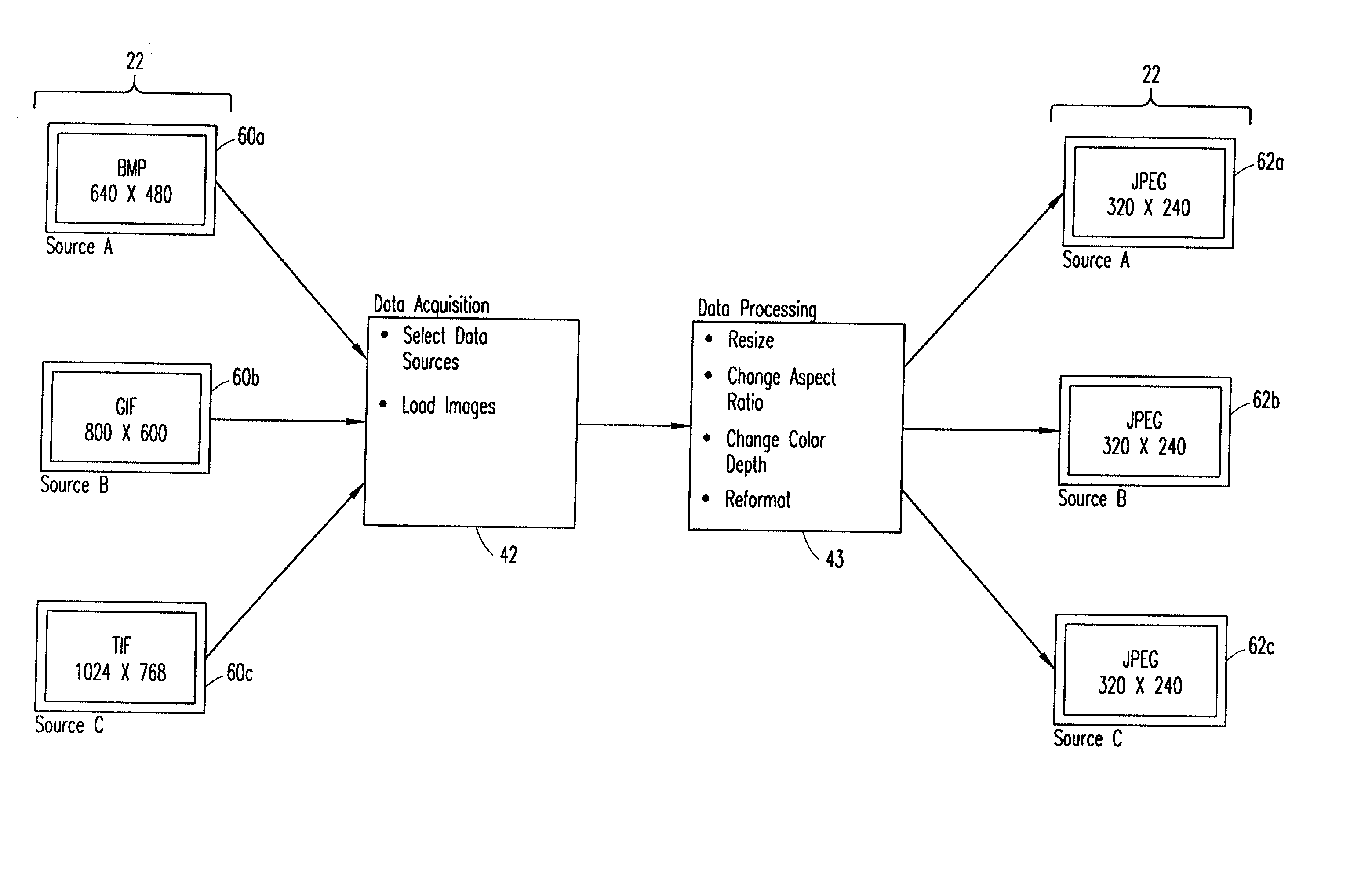
Method and system for converting a plurality of digital images having different attributes to a common, selected / preset set of attributes, and for transferring them to a centralized storage unit are disclosed. Initially, the source locations of the digital images are identified. Next, the desired image attributes such as size, aspect ratio, color depth, and compression format for the digital images are selected. The digital images are then converted from their original attributes to the selected / preset attributes. The converted images are thereafter uploaded to the centralized storage unit where they may be stored and subsequently downloaded to one or more different users.
Owner:GILBERT JOHN +1
Near-eye light-field display system
InactiveUS20160313558A1Increase and reduce distanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectrostatic motorsImage resolutionDisplay device
A near-eye light field display for use with a head mounted display unit with enhanced resolution and color depth. A display for each eye is connected to one or more actuators to scan each display, increasing the resolution of each display by a factor proportional to the number of scan points utilized. In this way, the resolution of near-eye light field displays is enhanced without increasing the size of the displays.
Owner:GUTIERREZ ROMAN
Stain detection and classification method and device for sensor of digital camera
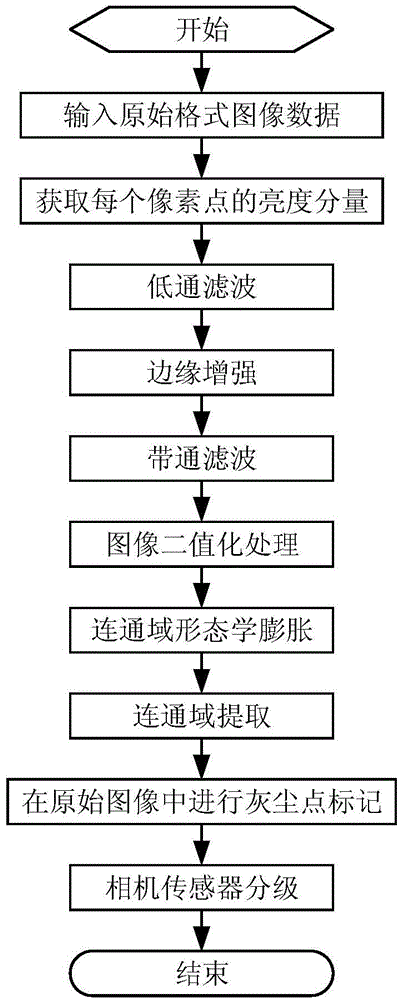
ActiveCN104867159AMeet needsGood effectImage enhancementImage analysisClassification methodsCurrent sensor
The invention discloses a stain detection method for a sensor of a digital camera, and a method and a device for classifying the sensor of the camera based on the detection method, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting original image data and obtaining luminance component via interpolation, (2) low-pass filtering, (3) edge enhancement, (4) band-pass filtering, (5) image binaryzation operation and morphological dilation, (6) connectivity area abstraction, (7) marking stain in an original image, (8) classifying the sensor and outputting image level. The invention is divided as two function modules which are used for detecting the stain and classifying the sensor. A contiguous item of a classification decision function is from features such as quantity, area, and color depth of the stain detected in a shooting image. The method and the device of the invention is simple and efficient and can be used for fast detecting stain position on the sensor and carrying out accurate level evaluation to current sensor according to the feature of theses stains.
Owner:BEIJING DAHENG IMAGE VISION +1
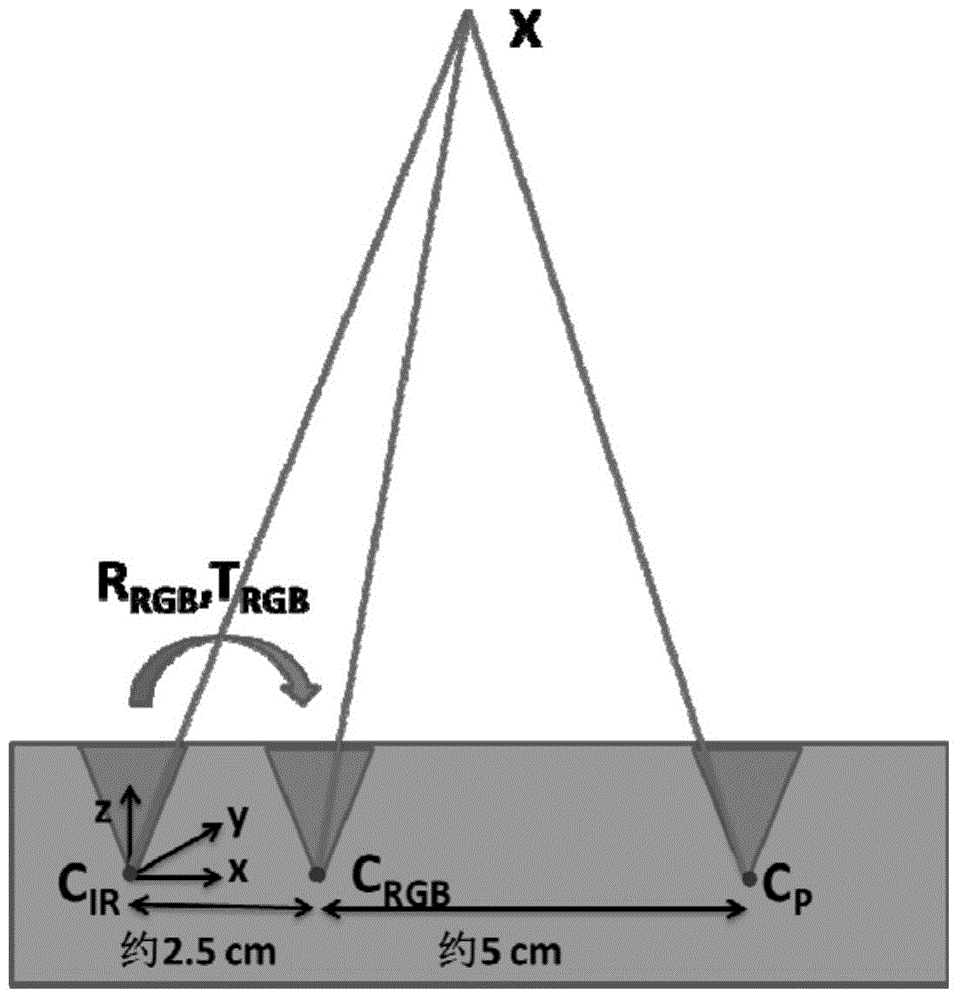
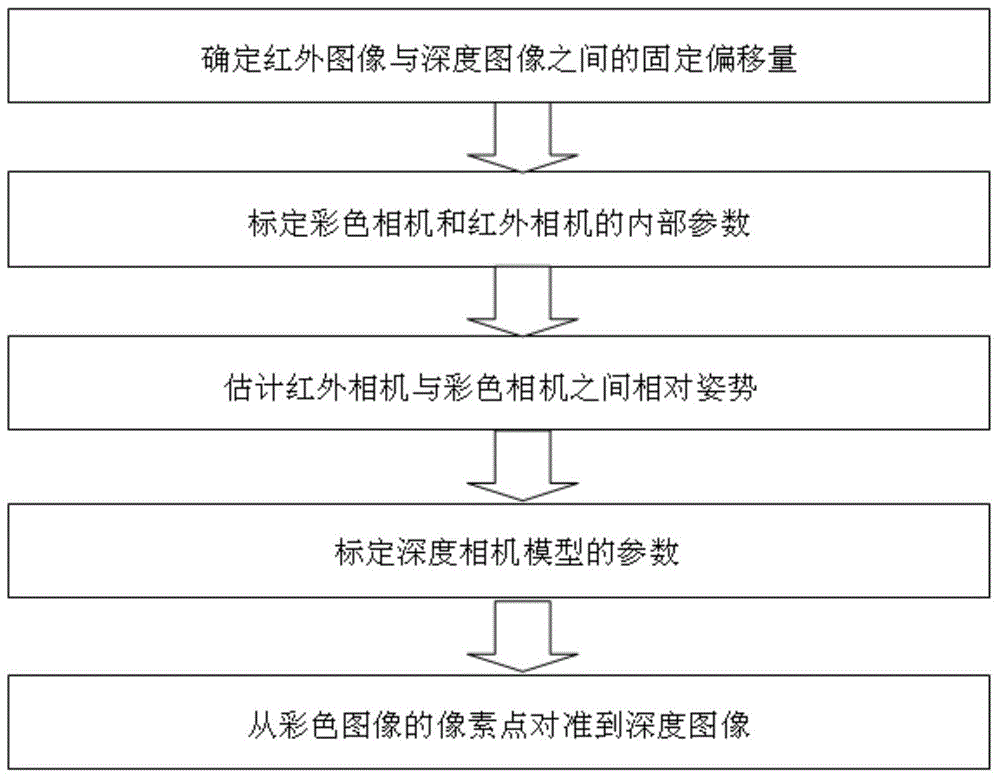
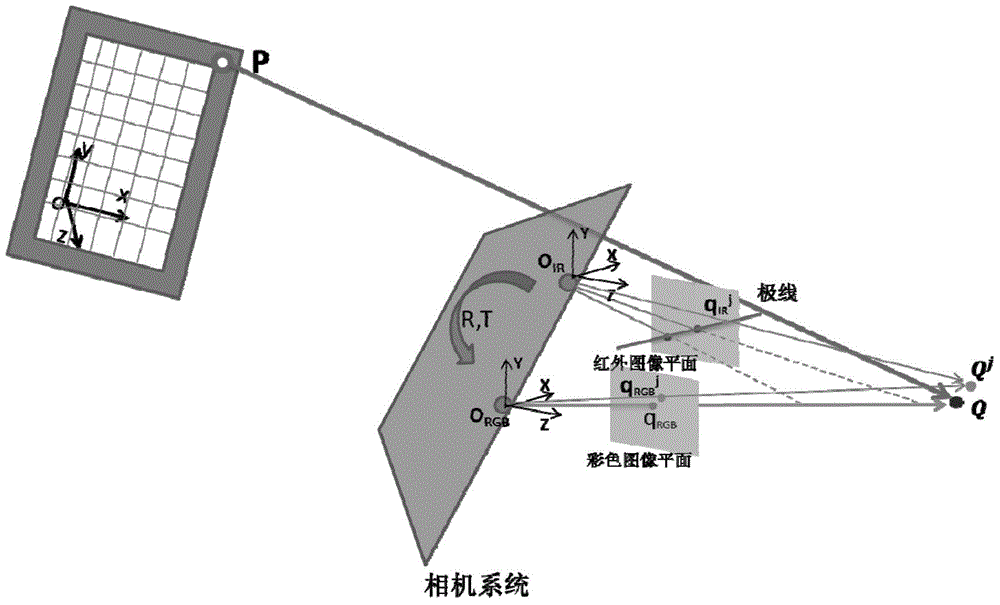
Pixel-level alignment algorithm for color images to depth images of color depth camera
ActiveCN104616284AAchieve direct alignmentImprove fusion efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionLarge size
The invention discloses a pixel-level alignment algorithm for color images to depth images of a color depth camera. The pixel-level alignment algorithm comprises the steps of 1) determining an offset between an infrared image and a depth image, 2) calibrating the internal parameters of an infrared camera and a color camera, respectively, 3) calibrating relative postures between the infrared camera and the color camera, 4) calibrating the parameters of a depth camera model, 5) starting from one pixel point of the color image, finding out corresponding pixel points on the depth image by use of the internal and external parameters of an infrared image and a color image, thereby determining the depth of the pixel points of the color image. According to the pixel-level alignment algorithm, the corresponding depth information is directly obtained from the color image, the alignment of the color information to the depth information can be realized, a fusion image of a larger size can be obtained, and the information is richer.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
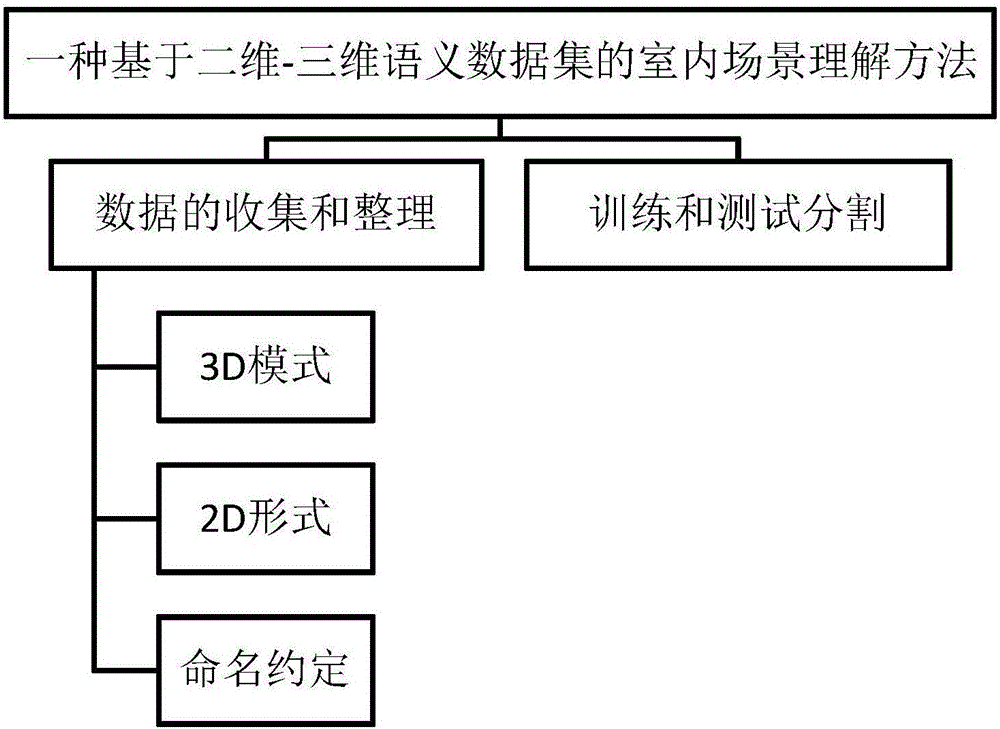
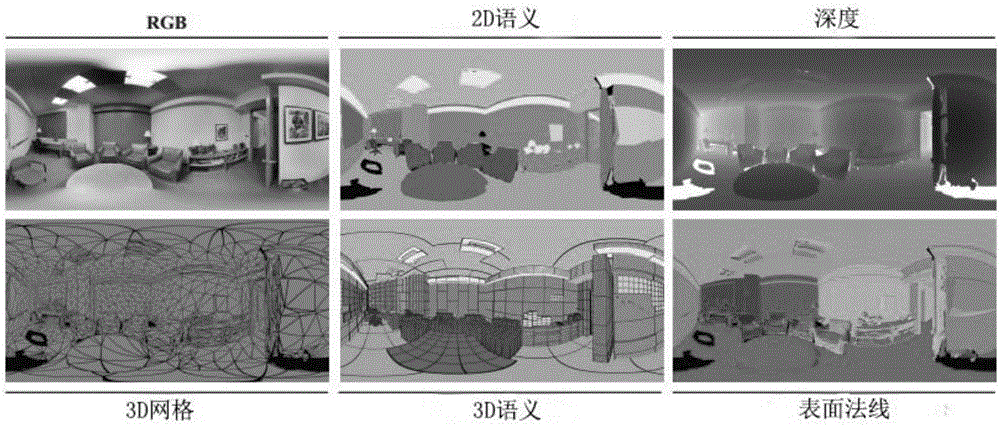
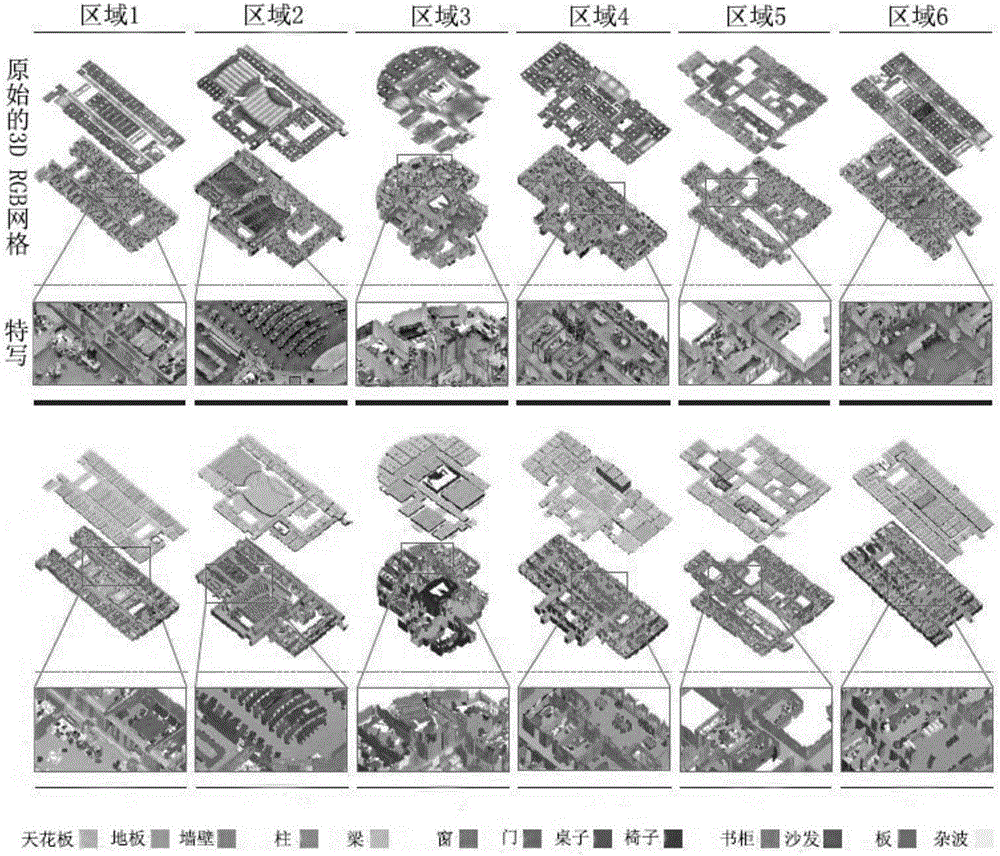
Indoor scene understanding method based on 2D-3D semantic data set
InactiveCN106709481AReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionPoint cloud
The invention discloses an indoor scene understanding method based on a 2D-3D semantic data set. The indoor scene understanding method comprises the main content of collection, arrangement, training and test division of data and comprises the following steps: firstly capturing an image, outputting a scanning region, an original color depth image (RGB-D) and a 3D texture grid, sampling the grid to generate point clouds, carrying out semantic annotation on the data, projecting each point label to a 3D grid and an image field, and representing certain regions with concentrated data to parts with similar buildings in aspects of appearances and architectural features, so as to define standard training and test division. According to the semantic data set disclosed by the invention, cross-modal study models and non-supervision methods can be developed and united by virtue of rules existing in large-scale indoor spaces; powerful prompts are provided for the detection of semanteme, layout, shields, shapes and modes; and the indoor scene understanding method is not limited by scale, diversity and number.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
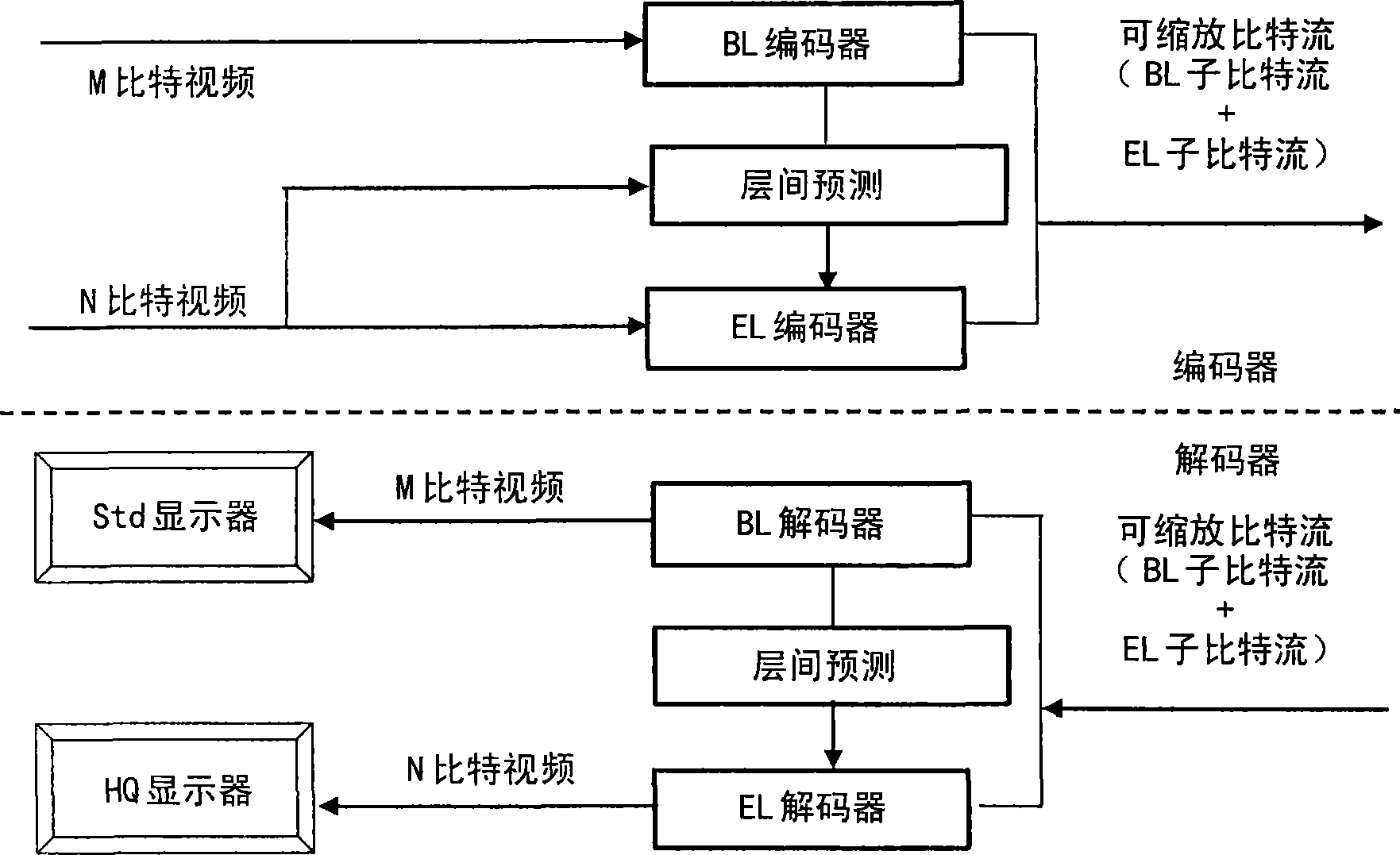
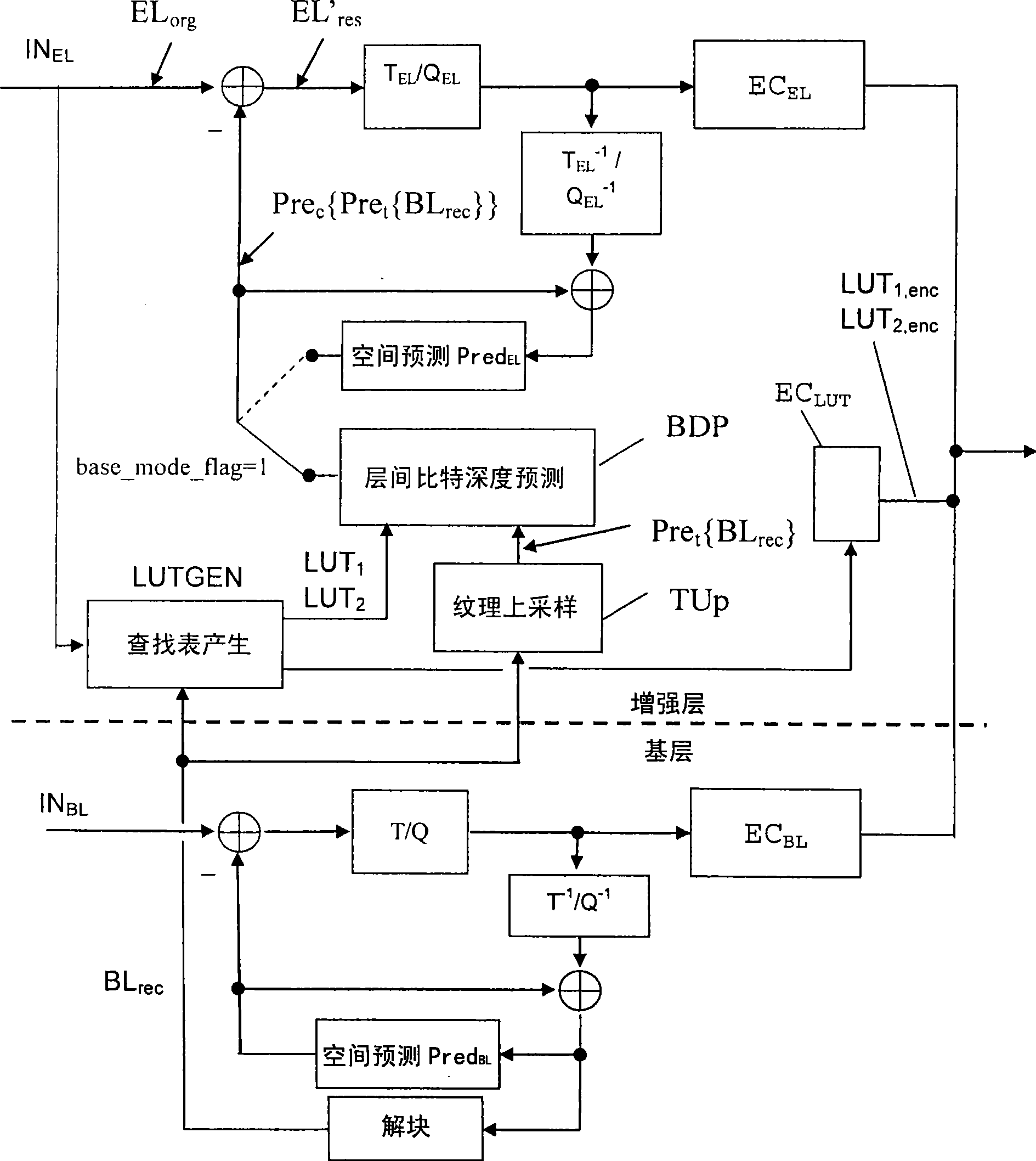
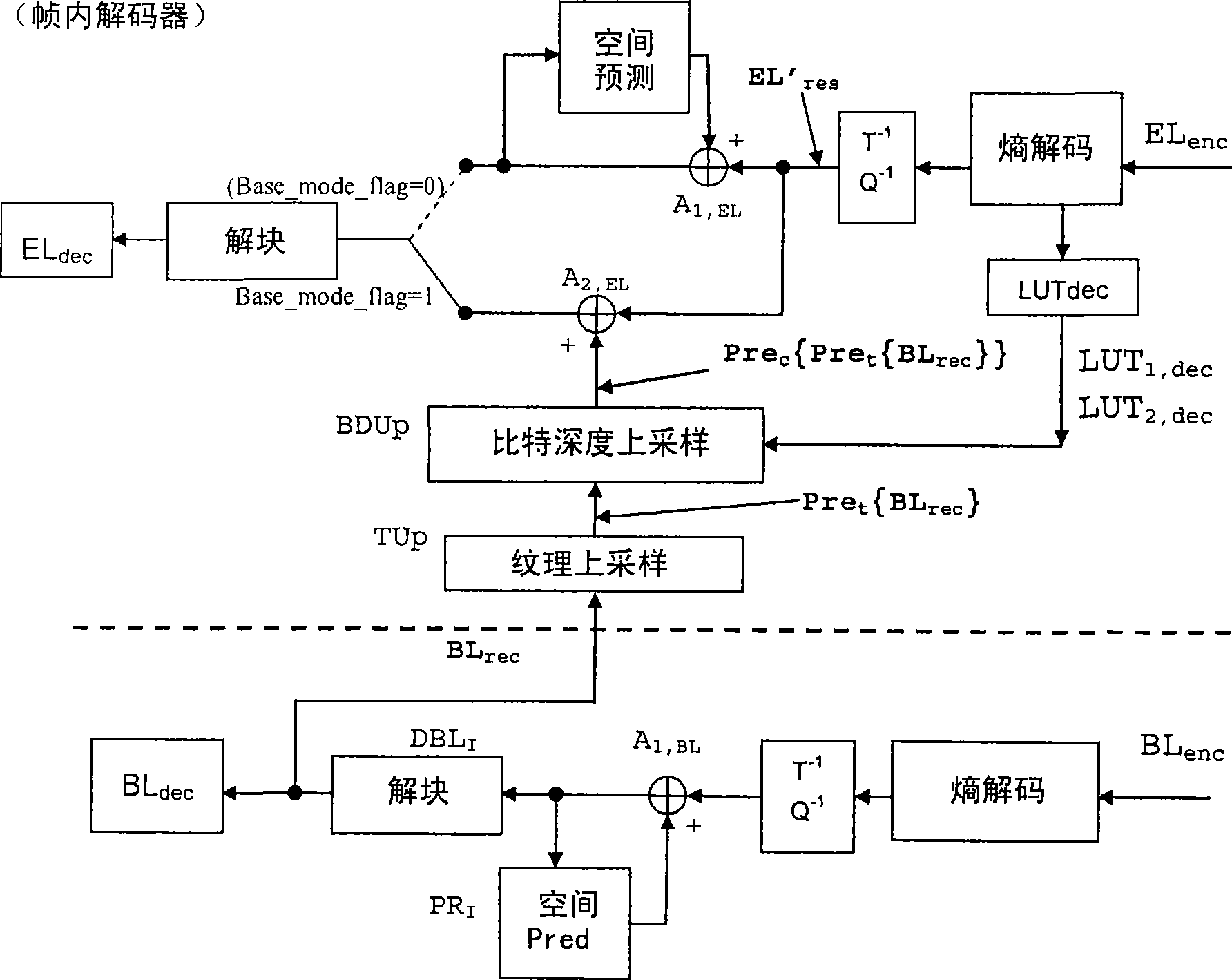
Enhancement layer residual prediction for bit depth scalability using hierarchical luts
ActiveCN101415120AColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideo bitstreamTone mapping
The invention discloses a method for the predication of residual error of classified-LUT-used and bit-depth-scalable enhanced layer. The scalable video bit stream may have H264 / AVC compatible basic layer and scalable enhanced layer, wherein the scalability relates to the color bit depth. According to the invention, BL information carries out bit depth up-sampling using single search table mapped by reverse tone on two or more levels which are image level, image bar level and MB level. The search table is carried out differential coding and contained in the head information. The process of the bit depth up-sampling (BDUp) is as follows: the process enhances the number of the value of each pixel and relative to the colour intensity of the pixel. Based on the search table, the data of the basic layer after the up-sampling is used for predicting the enhance layer in the relative position. The up-sampling is finished at a coder, and a decoder by the same mode, wherein the up-sampling relates to time, space and bit depth. Therefore, the bit depth up-sampling (BDUp) is compatible with the texture up-sampling (TUp).
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
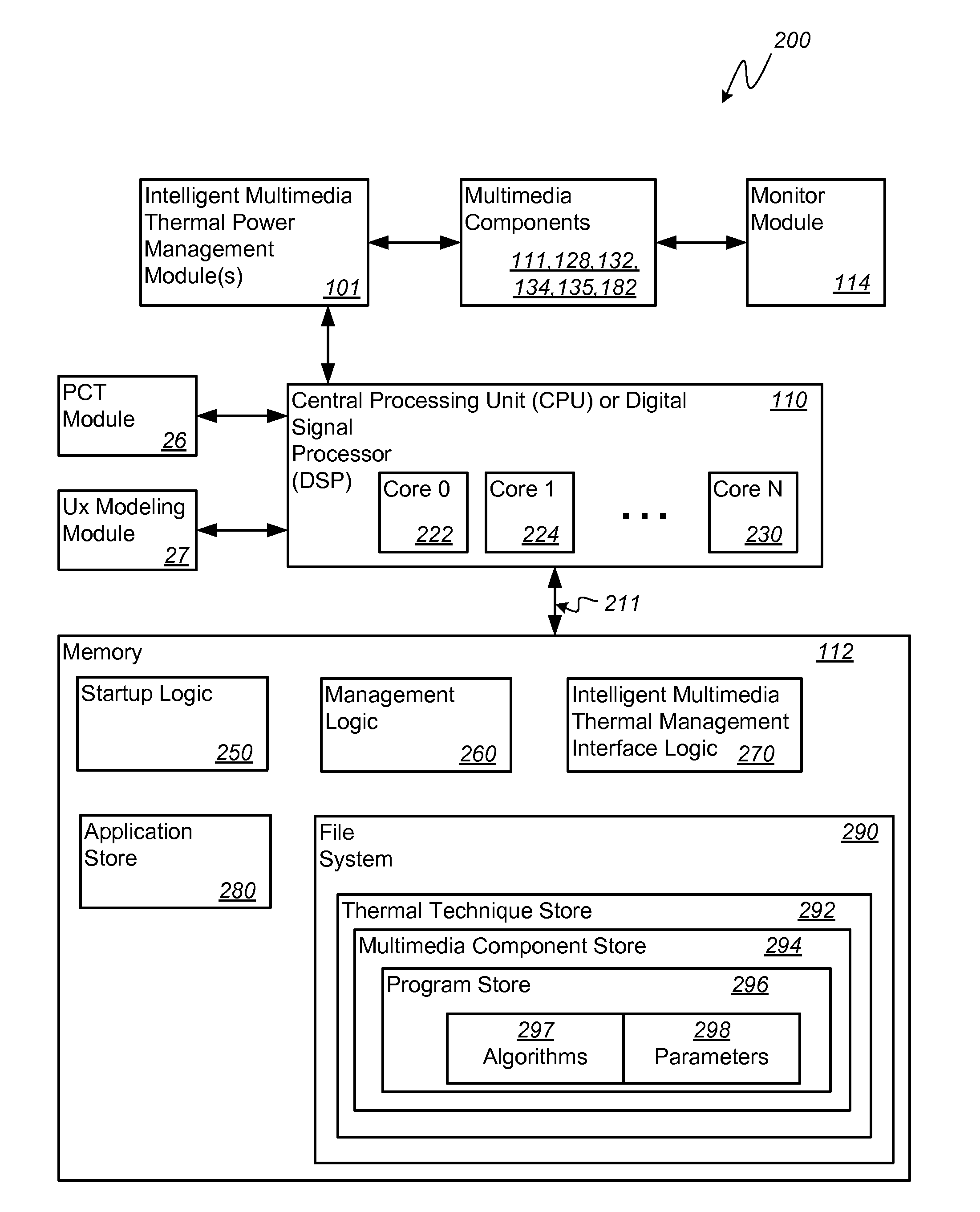
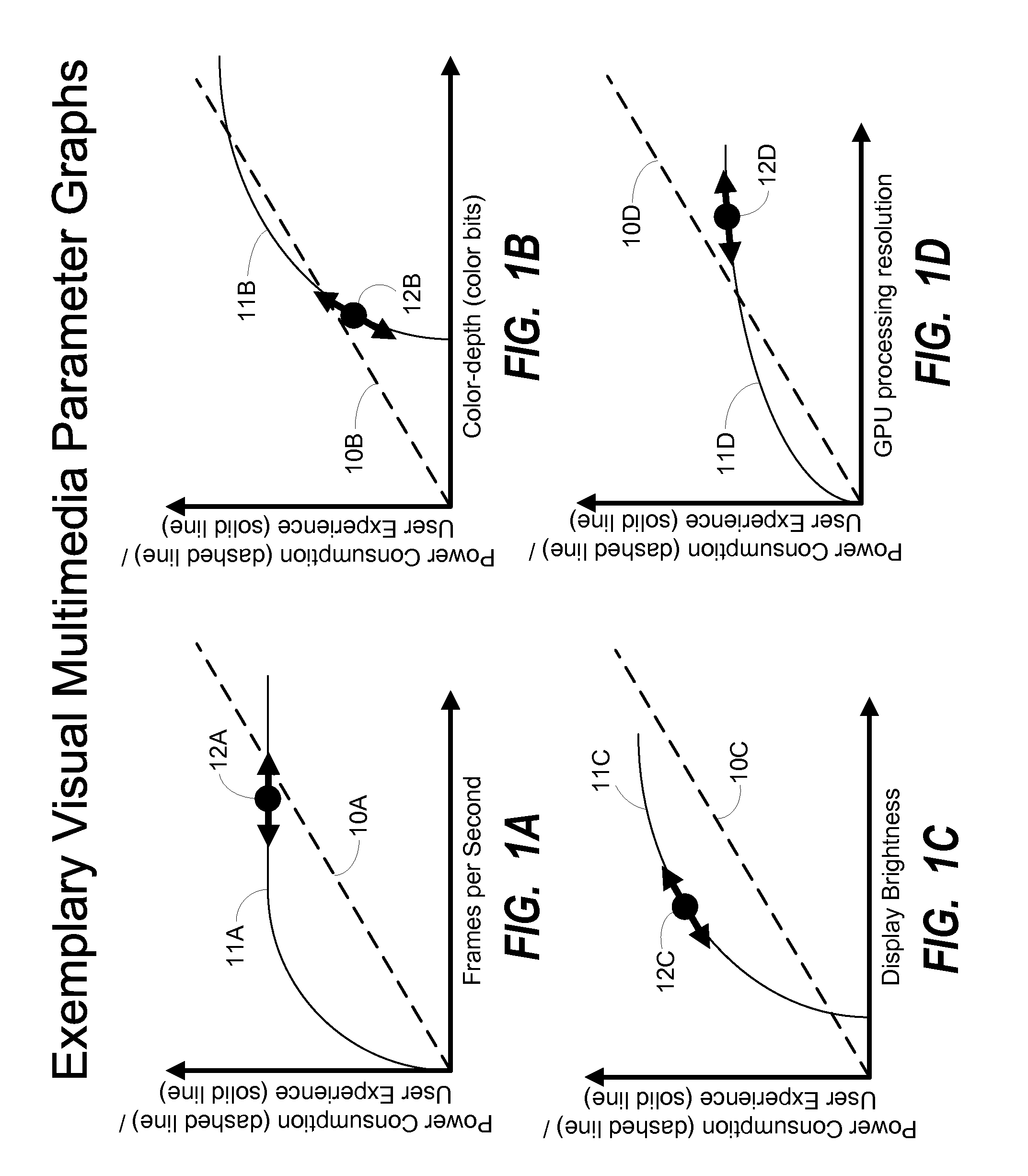
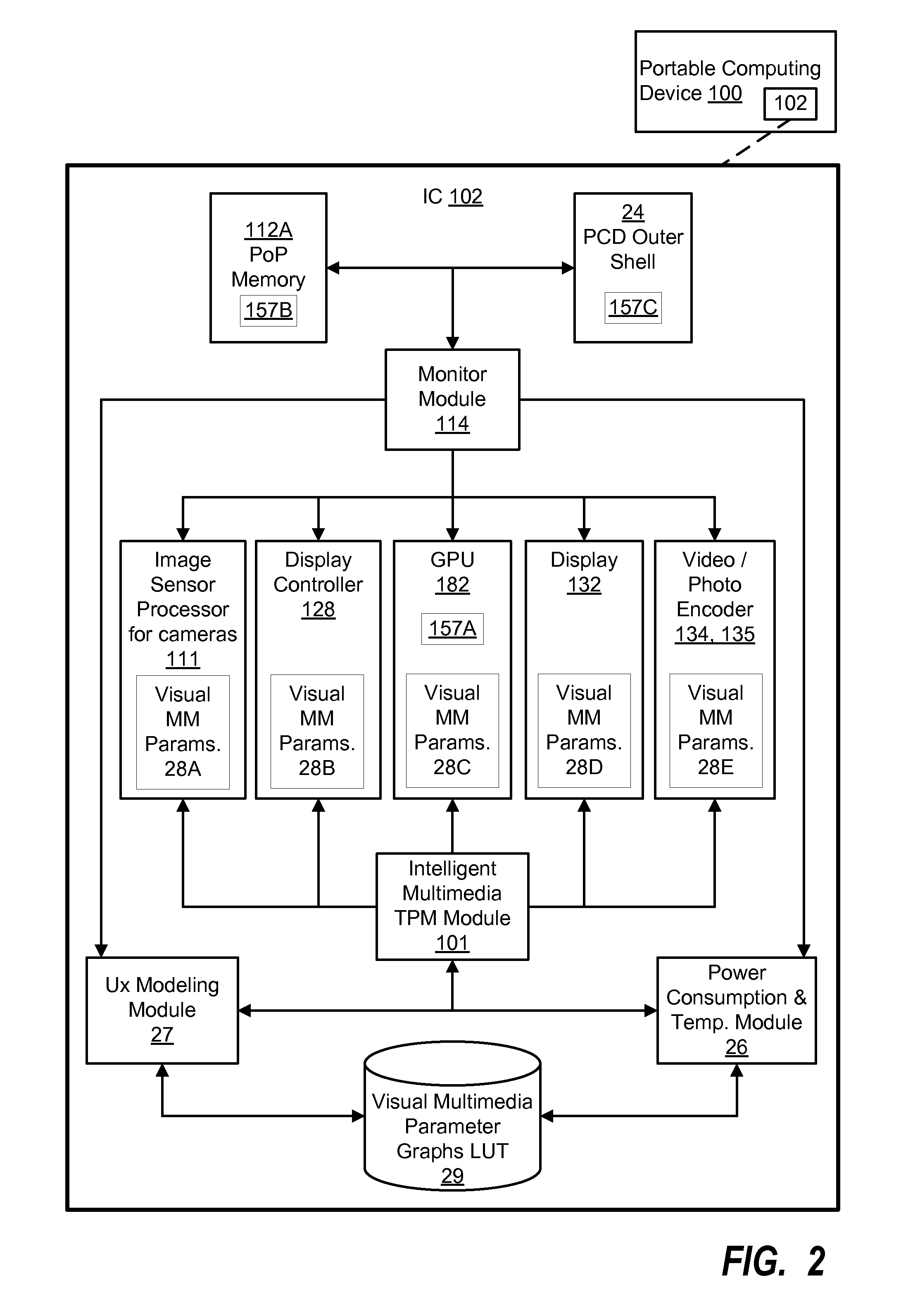
System and method for intelligent multimedia-based thermal power management in a portable computing device
ActiveUS20140359324A1Positive impact on user experienceReduce power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage resolutionAlgorithm Selection
Various embodiments of methods and systems for intelligent multimedia-based thermal power management implemented in a portable computing device (“PCD”) are disclosed. To reduce or increase power consumption in the PCD, embodiments adjust one or more visual multimedia parameters, the settings of which contribute to power consumption associated with an overall multimedia workload. The selection of visual multimedia parameters for setting adjustment is a function of the change in user experience versus the change in power consumption that will likely result from the setting adjustment. Exemplary visual multimedia parameters for which settings may be adjusted by certain embodiments include, but are not limited to, color depth, display brightness, GPU processing resolution, image dynamics algorithm selection, resolution scaling ratios and frames per second processing rates.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Picture processing method and terminal
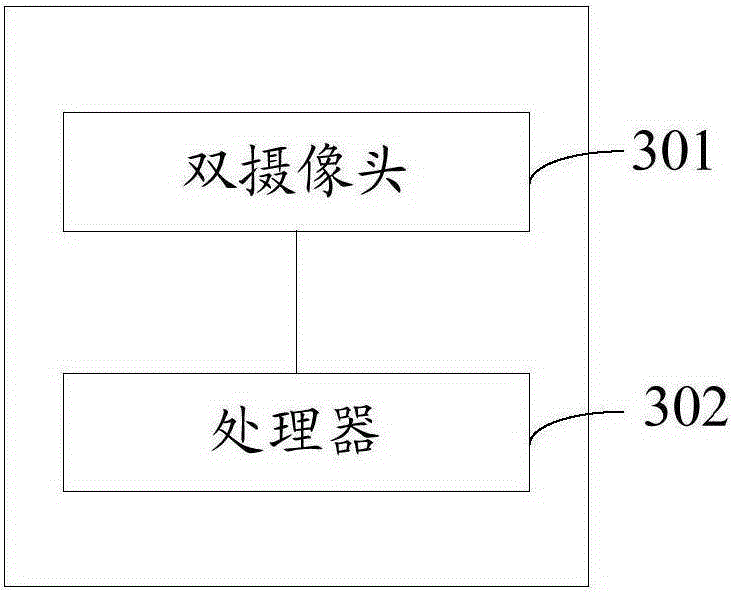
ActiveCN105245774AAchieve three-dimensional card effectFun to shootTelevision system detailsImage analysisComputer terminalColor depth
The embodiment of the invention discloses a terminal. The terminal comprises: a two-camera unit used for taking a picture and obtaining first depth information and first color information of the picture, a processor used for dividing the picture into a background region and a foreground region according to the first depth information of the picture obtained by the two-camera unit, and extracting second depth information and second color information of the edge of the foreground region, and performing stroke processing on the edge of the foreground region according to the direct proportion relationship of a depth value in the second color information and color depth in stroke processing and based on the second depth information and the second color information of the edge of the foreground region. The embodiment of the invention discloses a picture processing method.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Integral three-dimensional color laser radar data point cloud generating method and device thereof
InactiveCN103308925APrecise distance informationRich environmental informationElectromagnetic wave reradiationDrive motorLaser data
The invention solves the problems such as feature extraction, asynchronization and synchronization, feature relevance and data difference value to fuse visual data and laser radar data so as to generate three-dimensional color depth image data, namely a three-dimensional color laser data point cloud, thereby providing precise distance information and rich environment information, effectively overcoming the defects of the traditional laser radar and the visual sensor in the aspects of robustness, information amount, precision and cost. The invention integrates a two-dimensional laser radar, a monocular vision sensor, an inertial navigation data measuring unit, a driving motor and the like into an information fusion-based three-dimensional color laser radar integral unit with universal applicability and high precision, and utilizes inertial navigation data and visual data to perform secondary alignment on laser radar data, the structure is simple, equipment does not need to be subjected to precise calibration, the performance is reliable and stable, the practicability is strong, and the method and the device can be widely used in various indoor and outdoor environments under the motion condition, and have certain universal applicability.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-dimensional reconstruction method of single object, based on color depth camera
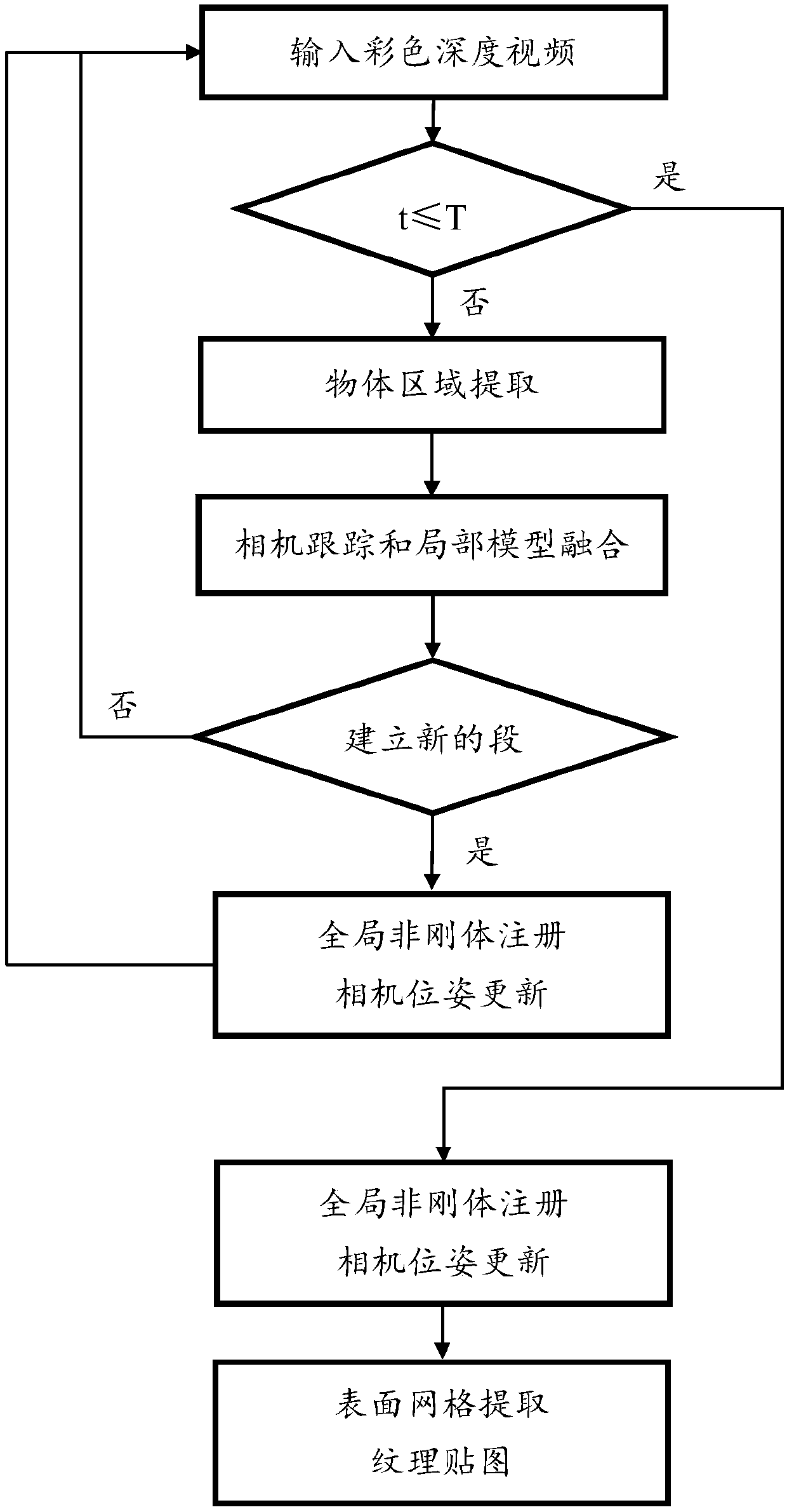
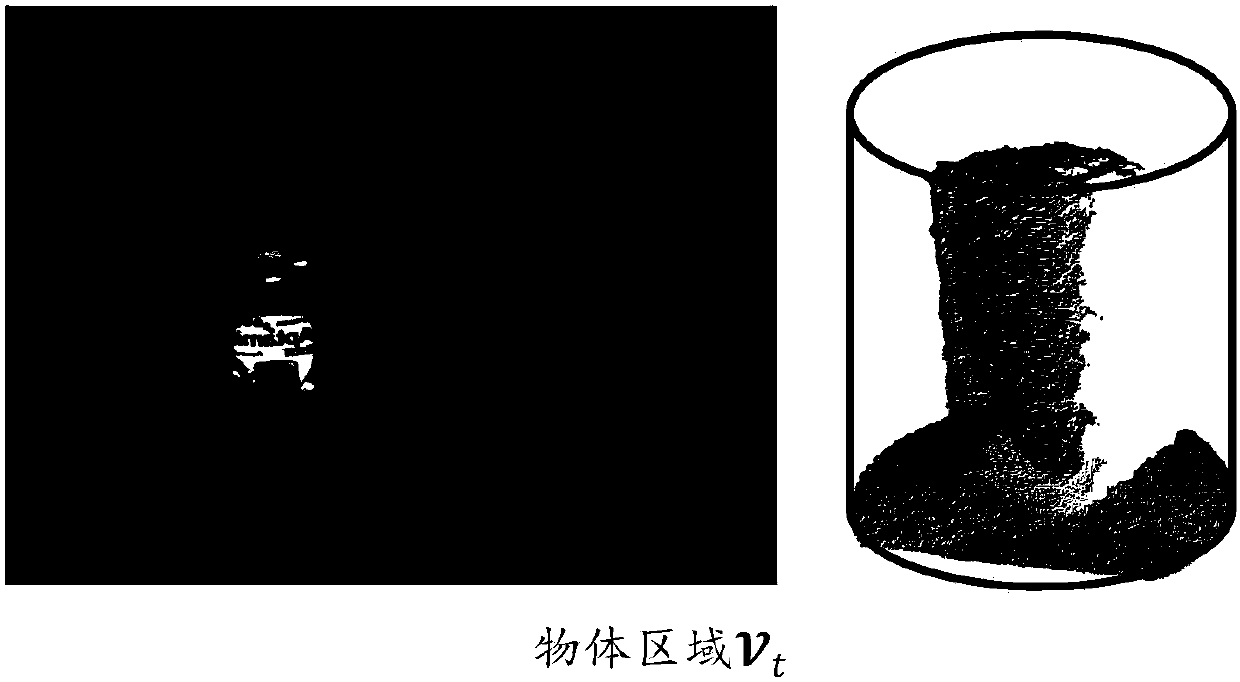
ActiveCN107845134AShorten the trackImage enhancementImage analysisReconstruction methodDimensional modeling
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method of single object, based on a color depth camera. The three-dimensional reconstruction method of single object, based on a color depthcamera includes the three steps: 1) during the scanning process, extracting the scanned object area; 2) according to the color depth data, performing camera tracking and local fusion of the depth data, and performing global non rigid body registration on the locally fused data, and gradually constructing an overall three-dimensional model and the accurate key frame camera position; and 3) performing grid extraction on the fusion model, according to the obtained key frame camera position and the key frame color image, calculating the texture map of the three-dimensional grid model. The method framework of the three-dimensional reconstruction method of single object, based on the color depth camera can guarantee that even if the proportion of the object in the image is relatively smaller, geometrical reconstruction and texture mapping with high quality can still be performed when single object is reconstructed. The three-dimensional reconstruction method of single object, based on a color depth camera has the advantages of being clear, being high in speed, being robust in the result, and being able to be applied to the virtual reality scene construction field and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for improving color depth of LCD device
InactiveCN101256751AHigh color depth bit countCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayVoltage reference
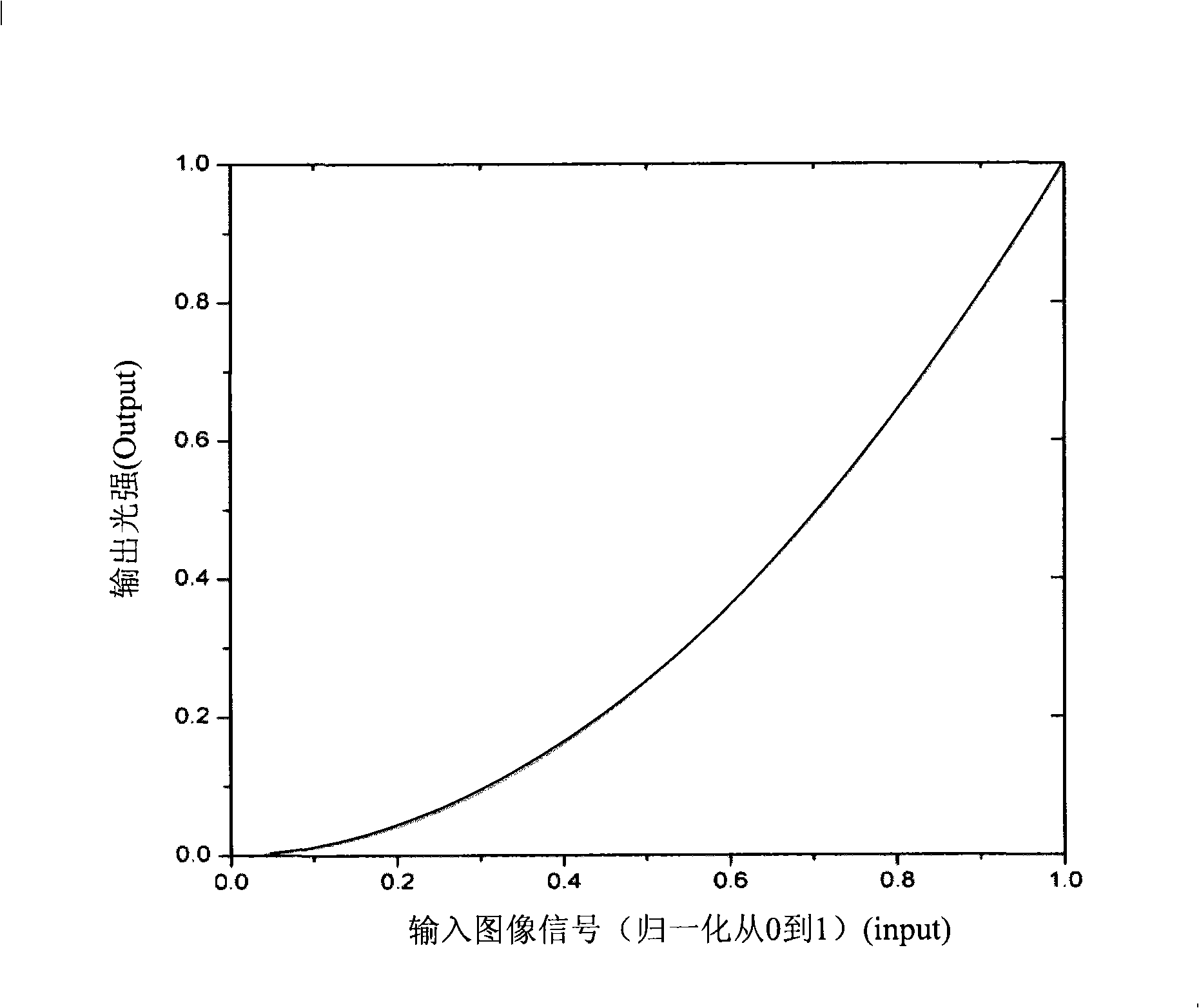
The invention relates to a method improving color depth for a liquid crystal display device, comprising the steps of: firstly, obtaining input image data; then undergoing dynamic Gamma Correction for the image signal; then dividing gray scale number corresponding to a reference display precision bit value into a plurality of gray scale intervals; after that, determining the display precision bit value according to intensity of the gray scale distribution data in the plurality of gray scale intervals; in addition, re-allocating Gamma reference voltage to the each gray scale interval according to the display precision bit value of each gray scale interval; and finding the corresponding LUT table according to the Gamma reference voltage re-allocated for each gray scale interval so as to obtain the corresponding output data value.
Owner:NANJING CEC PANDA LCD TECH
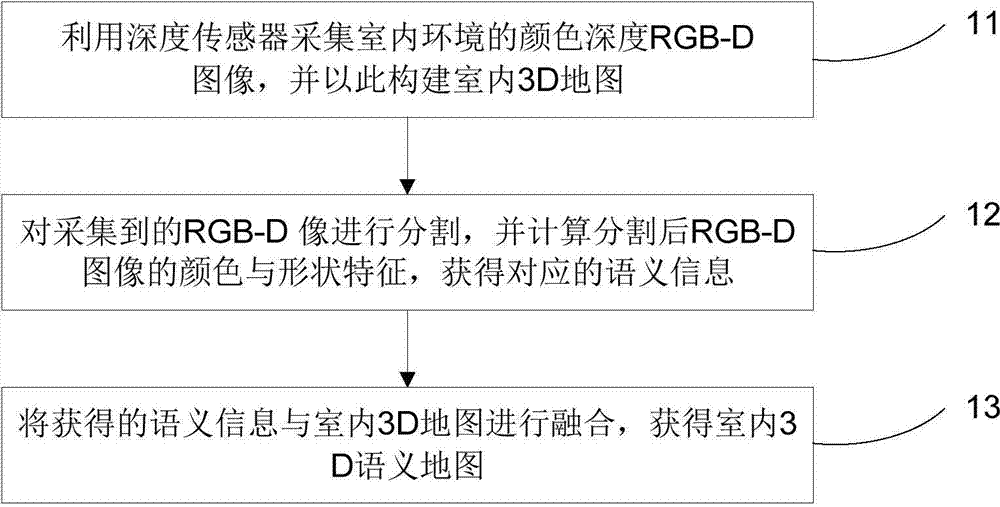
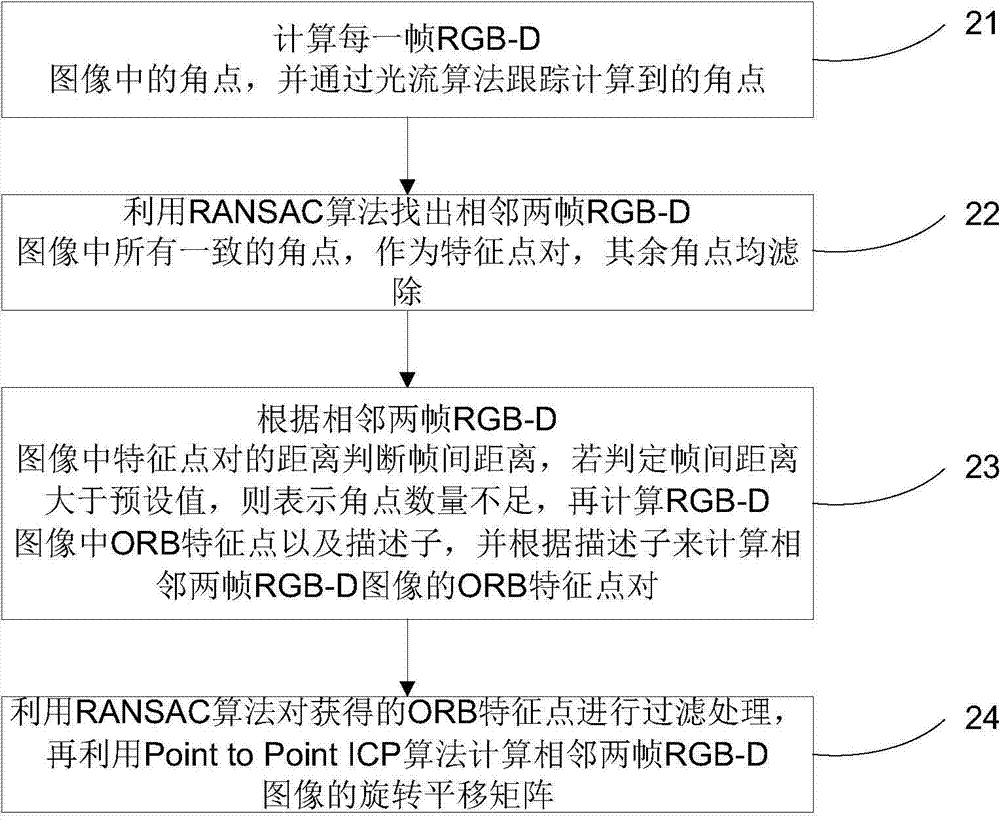
Depth sensor-based method of establishing indoor 3D (three-dimensional) semantic map
ActiveCN104732587ARealize the real purpose of intelligent semantic perception3D modellingStructural semanticsColor depth
The invention discloses a depth sensor-based method of establishing an indoor 3D (three-dimensional) semantic map. The method includes: using a depth sensor to acquire a color depth RGB-D image of an indoor environment to establish an indoor 3D map thereby; segmenting the acquired RGB-D image, and calculating color and shape features of the segmented RGB-D image to acquire corresponding semantic information; fusing the acquired semantic information and the indoor 3D map to obtain the indoor 3D semantic map. The method has the advantage that the method is suitable for establishing semantic information, such as structural semantic information and furniture semantic information, so as to facilitate a robot executing high-level intelligent operations.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for converting depth image in high resolution
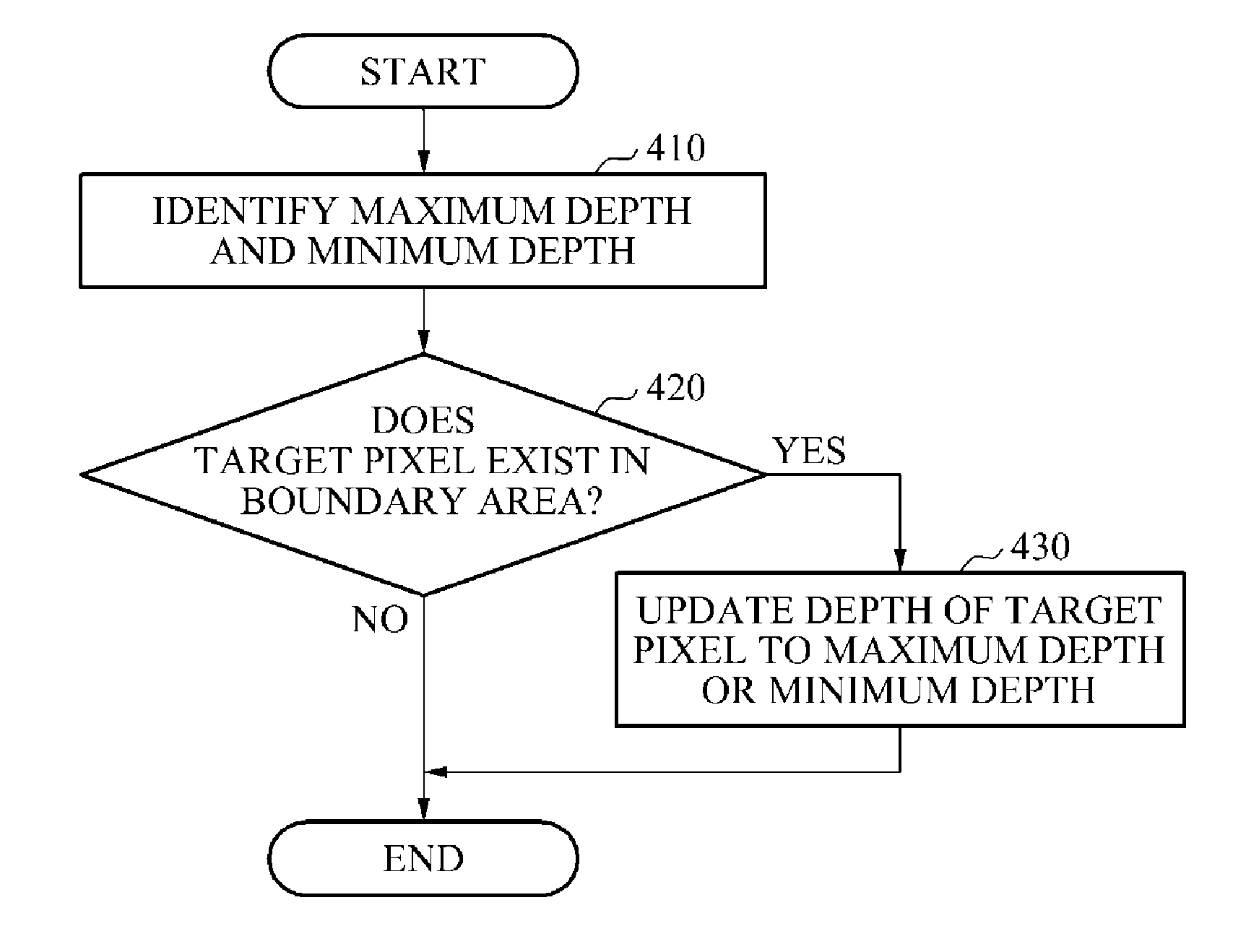
ActiveUS20150036926A1Cancel noiseImprove imaging resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingAudio power amplifier
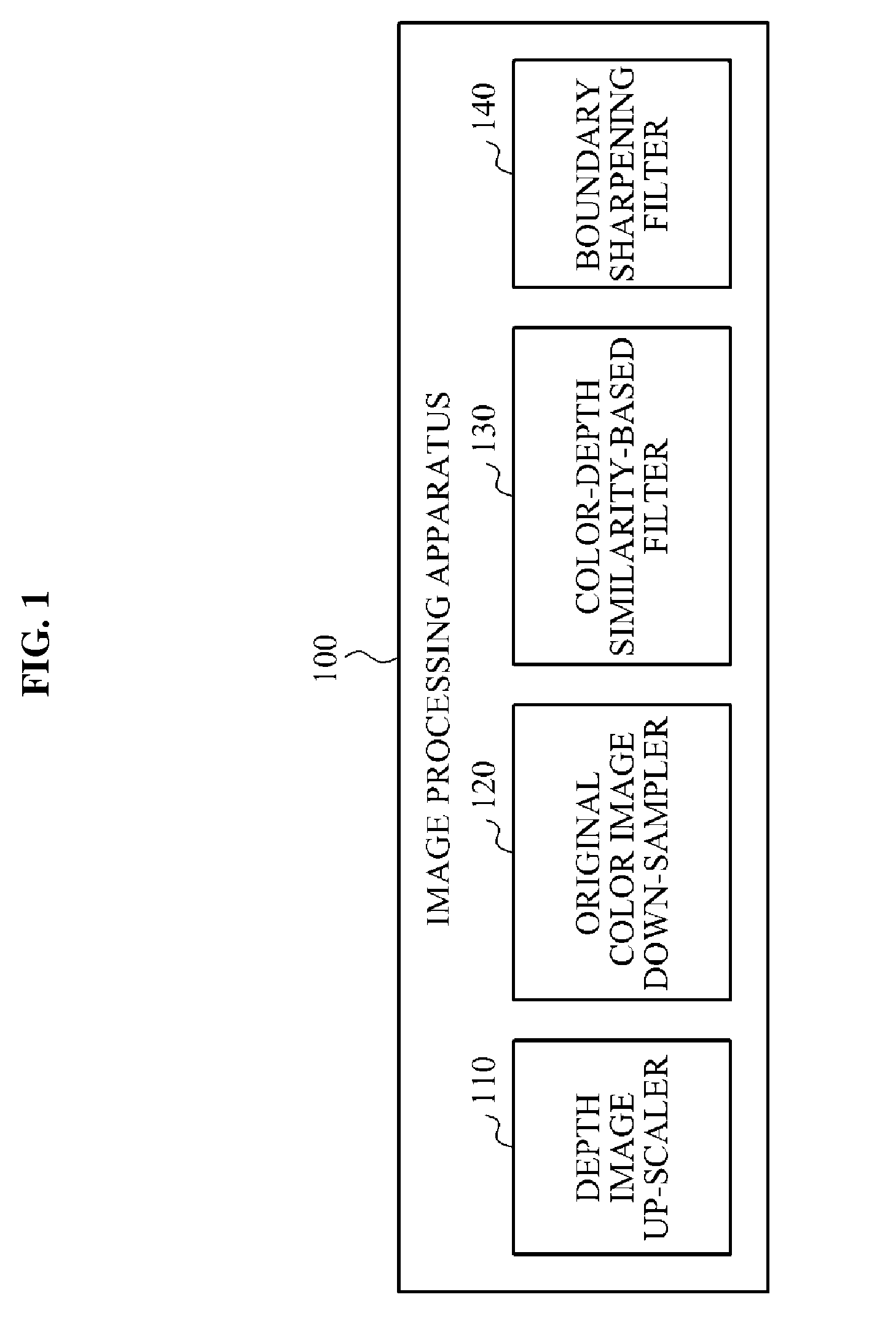
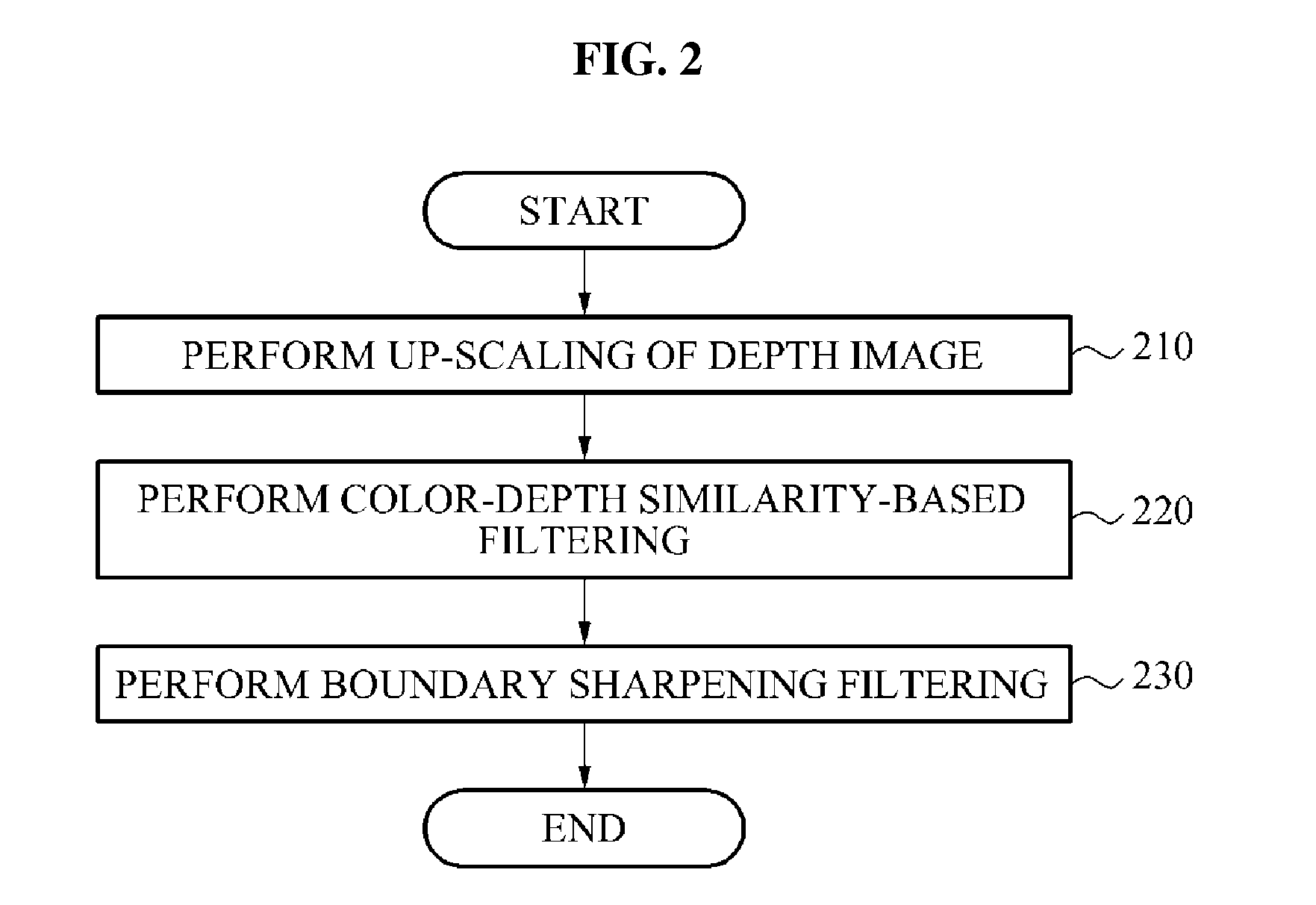
Provided are a method and an apparatus for image processing. A scene includes a low resolution depth image and a high resolution color image. A depth image up-scaler up-scales the depth image using an interpolation so as to improve the resolution of the depth image. A color-depth similarity based filter removes noise from the up-scaled depth image using the color image and the up-scaled depth image. A boundary sharpening filter converts a boundary between objects in the up-scaled depth image into a clearer boundary. The resolution of the depth image may increase to the level of the resolution of the color image by means of the depth image up-scaler, the color-depth similarity based filter and the boundary sharpening filter, and the depth of each pixel in the depth image may be adjusted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Manufacturing technique of stereoscopic underglaze multicolor ceramic
The invention relates to a manufacturing technique of stereoscopic underglaze multicolor ceramic, which comprises the following steps: carrying out ball milling on a selected ceramic raw material, screening, slurrying, carrying out injection forming on a mold to obtain a required shape, preparing a blank, and carrying out bisque firing to obtain a biscuit; carving out a stereoscopic multilayer plain color picture on the biscuit with a carving tool; dipping a drawing tool into underglaze multicolor pigments, and drawing and decorating on the stereoscopic picture of the biscuit to obtain a colored biscuit; carrying out color depth gradation treatment on the picture of the colored biscuit by using a special brush; and covering a glaze layer on the surface of the colored biscuit subjected to color treatment; and firing the glaze-covered colored biscuit in a kiln again to obtain the finished product. The technique adopts the two modes of biscuit carving and mold carving. The ceramic article prepared by the technique has the advantages of strong stereoscopic effect, abundant colors, high color layering effect and glossy and bright glaze.
Owner:HUNAN NEW CENTURY CERAMICS
Halftone edge enhancement for production by an image forming device
ActiveUS20070223044A1Increase productionReduce the impactImage enhancementVisual presentation using printersImage formationMorphological filter
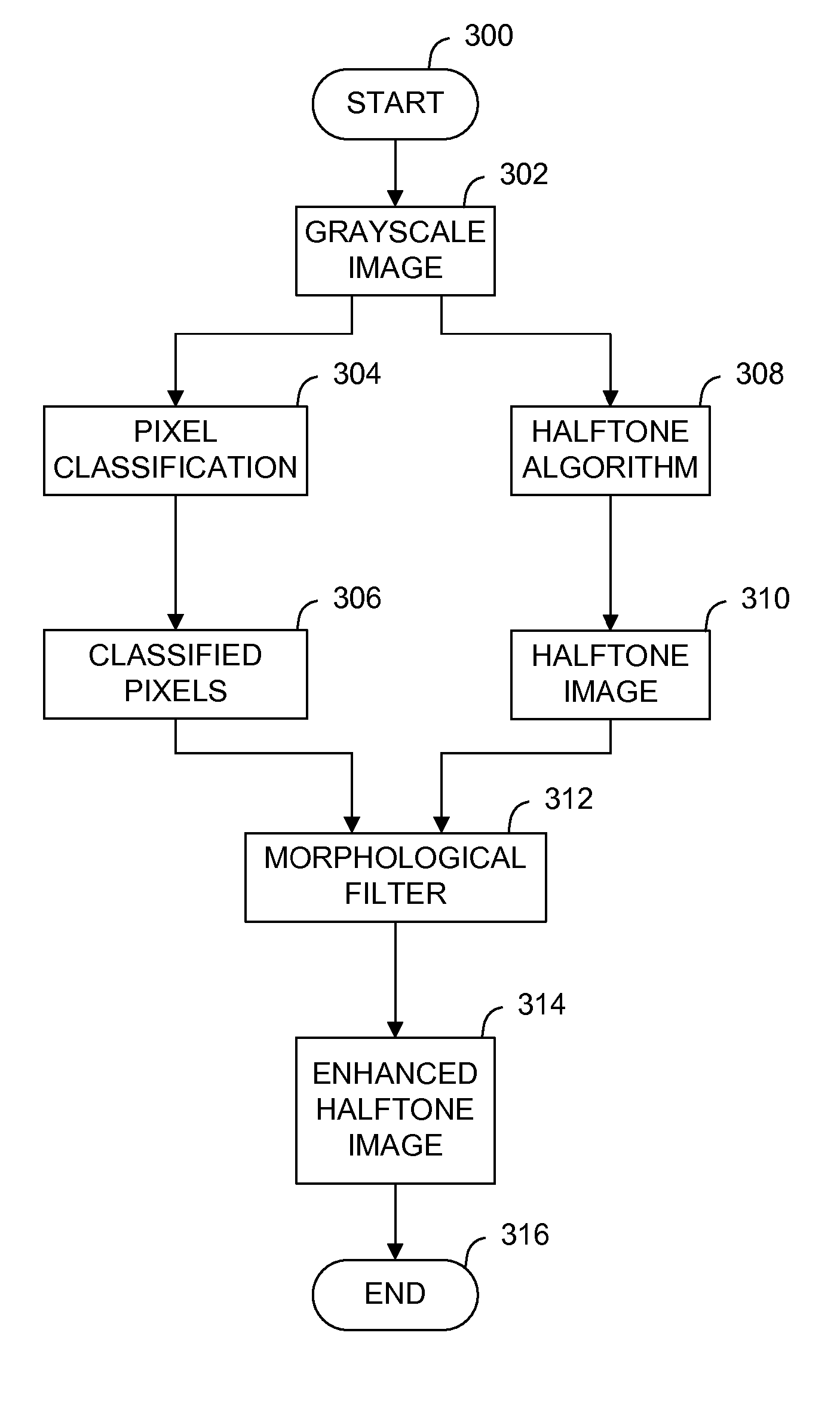
Digital images that are produced by an image forming device may be processed using an edge enhancement technique to reduce the effects of halftone color depth reductions. For each element in the original image, certain detail elements are classified by examining the magnitude of pixel intensity gradients between elements of interest in a first window applied at each element and other elements in the first window. If a first predetermined condition is satisfied, those elements locations are stored. After halftoning, a morphological filter may be applied to the same element locations in the halftone image to enhance the halftone image.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Portable high speed internet access device with scrolling
InactiveUS20020115477A1Reduce color depthReduce displaySubstation equipmentTwo-way working systemsCredit cardComputer hardware
The invention discloses a portable remote device that connects wirelessly to the internet or other sources via a host computer which runs a browser, taking information received and renders it onto a virtual display in memory. This information is directed to software which reduces the color depth, compresses and sends it to the portable device, which decompresses and stores it into memory for displaying. The information captured and sent to the remote device is limited to the size of the browser's window, which may be considerably smaller than the image in the virtual display. The browser automatically scrolls to other parts of the image to capture it entirely, sending segments simultaneously to other software responsible for color depth reduction and compression, whilst it scrolls to other segments. The host computer keeps a record of credit card details for each user on file, hence there is no encryption required between the host and remote device, as the host automatically inserts credit card details from its database in the appropriate location for each credit card purchase over the Internet.
Owner:SINGH RAJA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com