Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
659 results about "Image field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
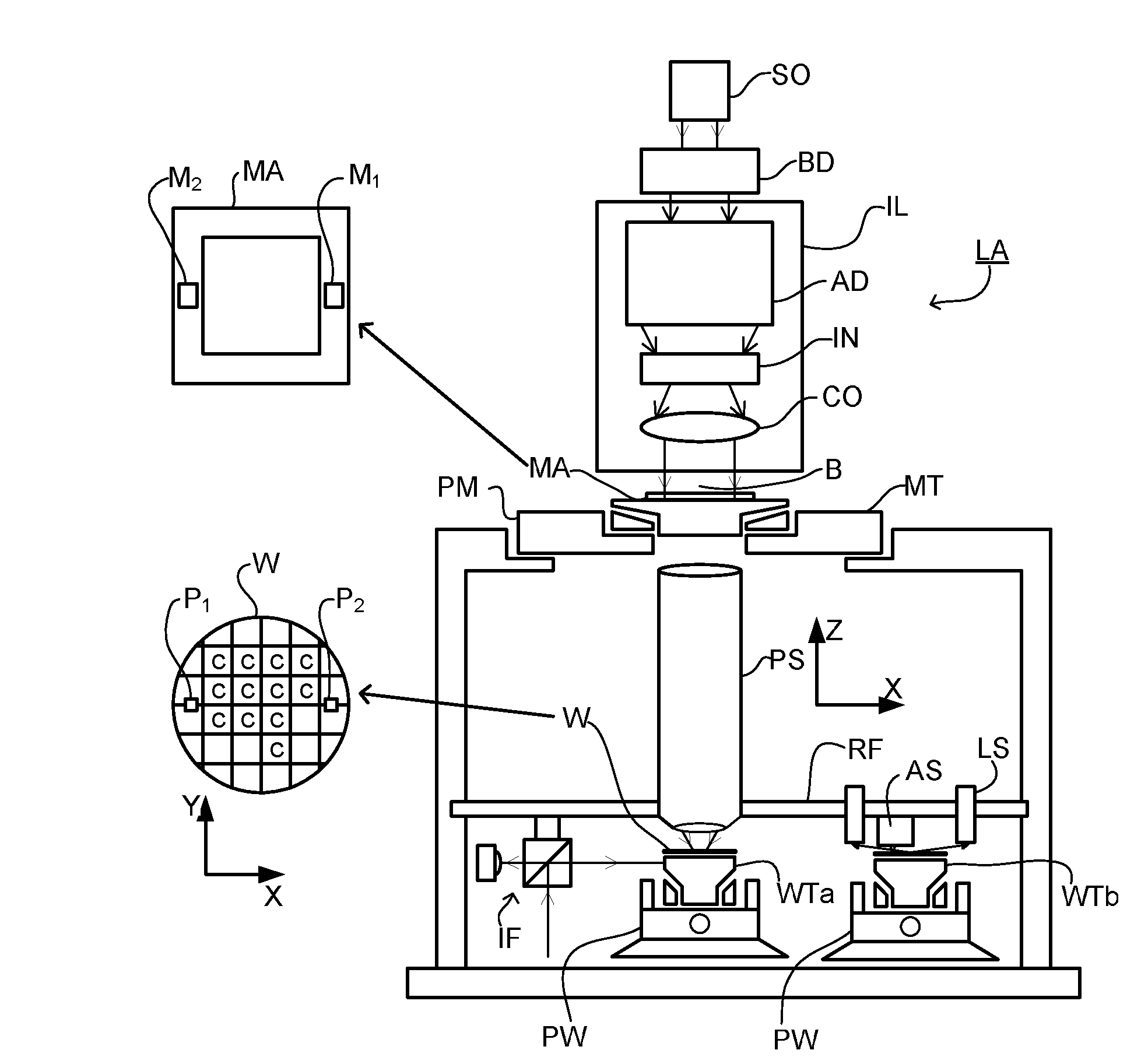
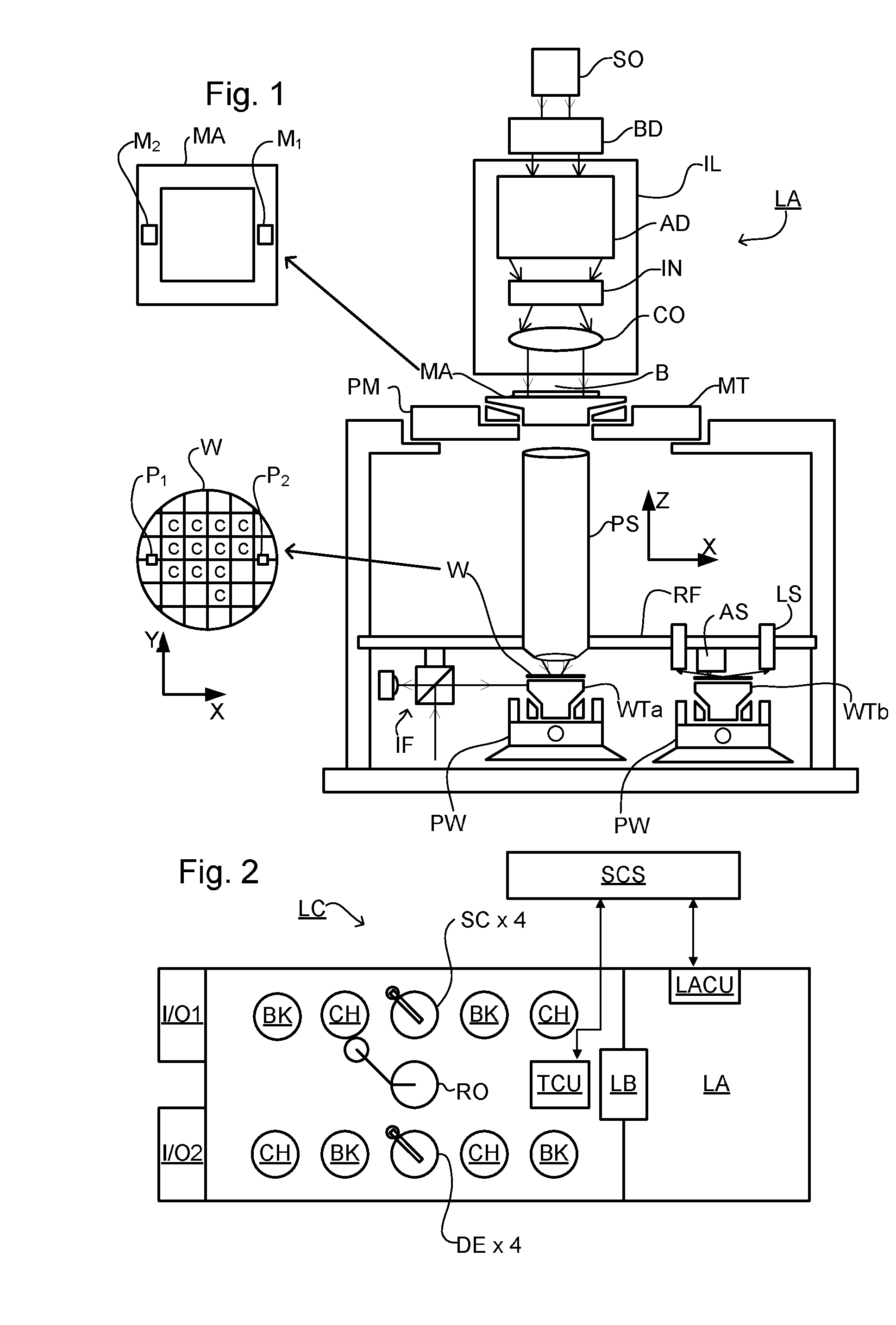
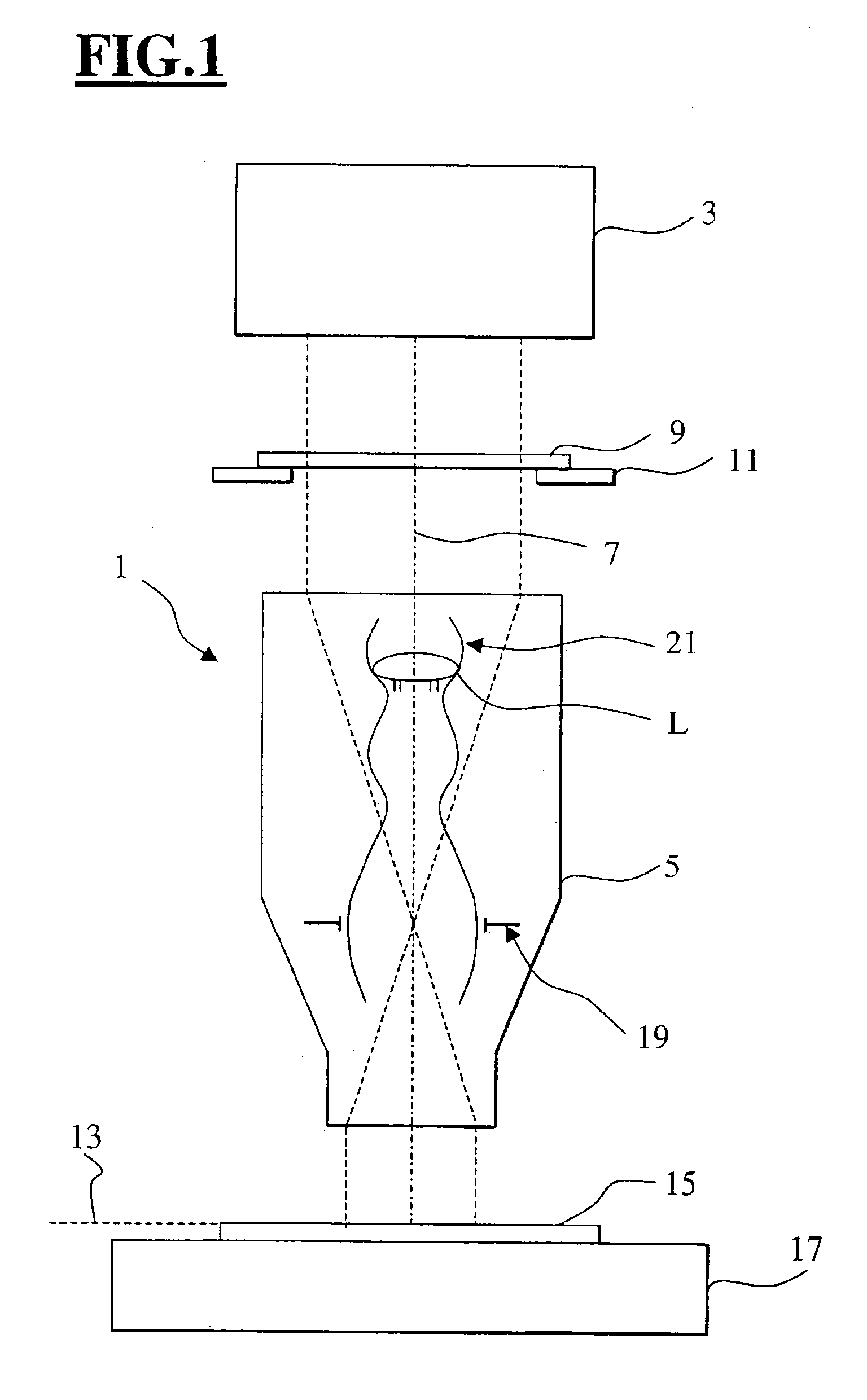
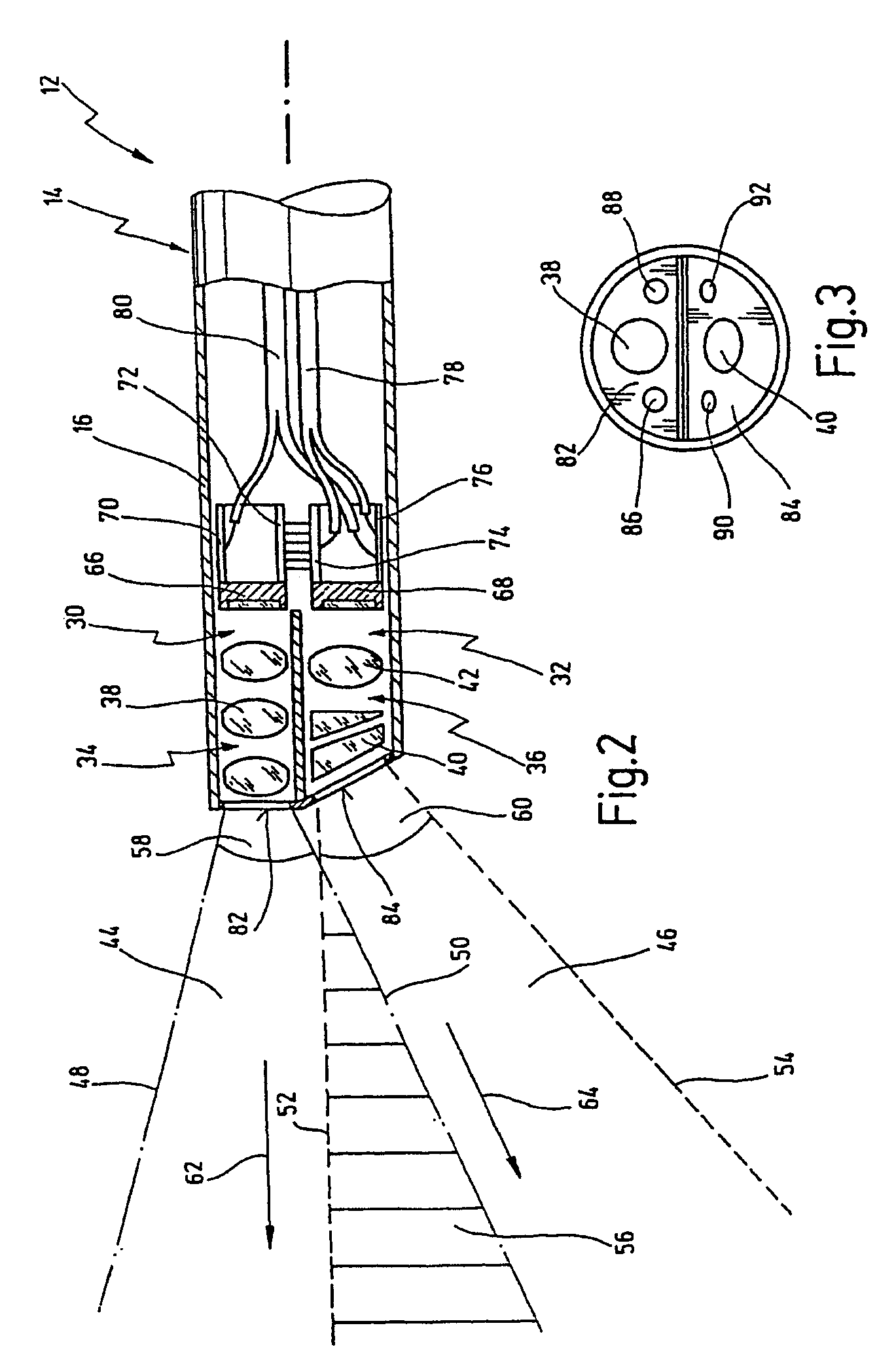
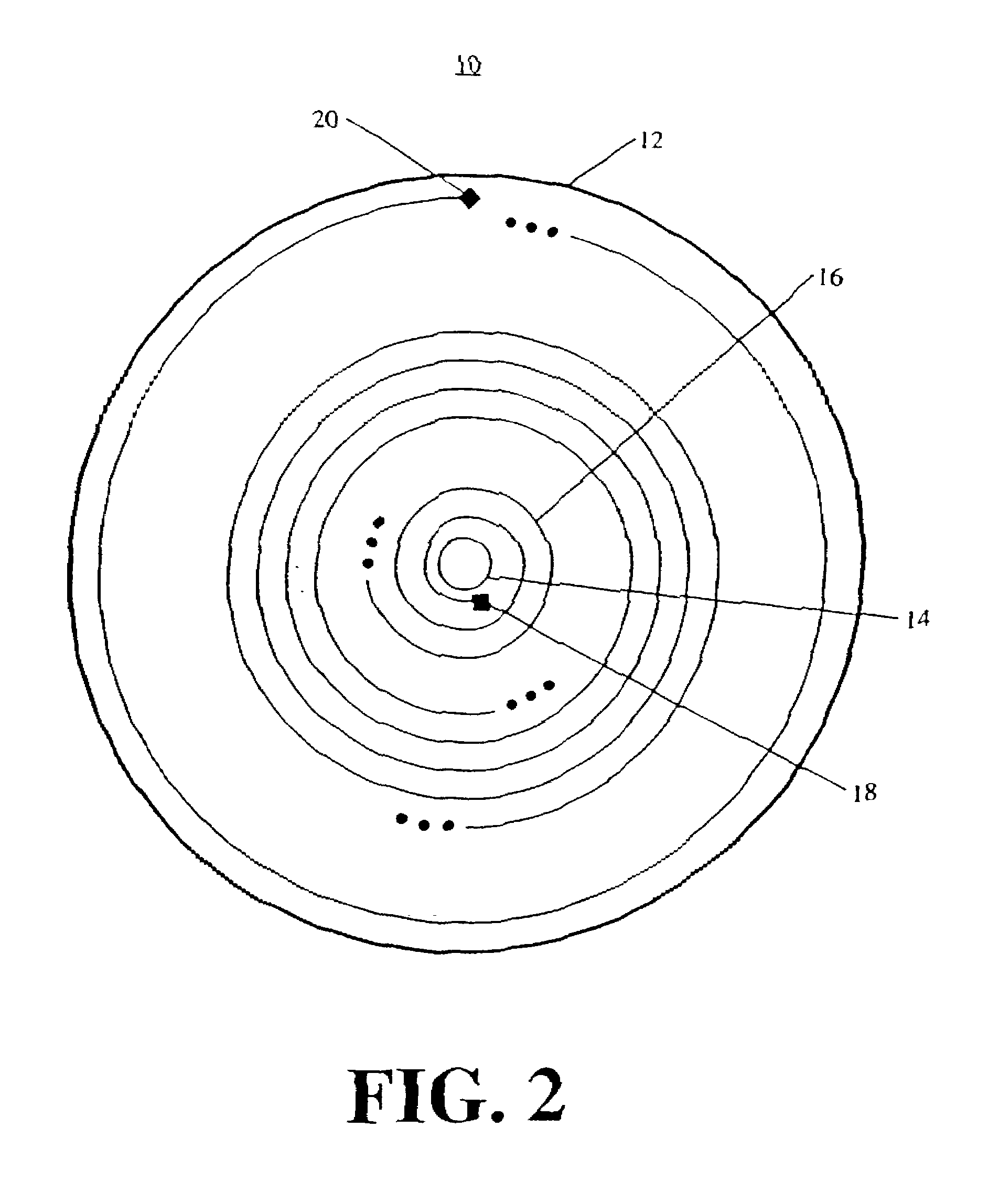
Metrology Method and Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus, Device Manufacturing Method and Substrate
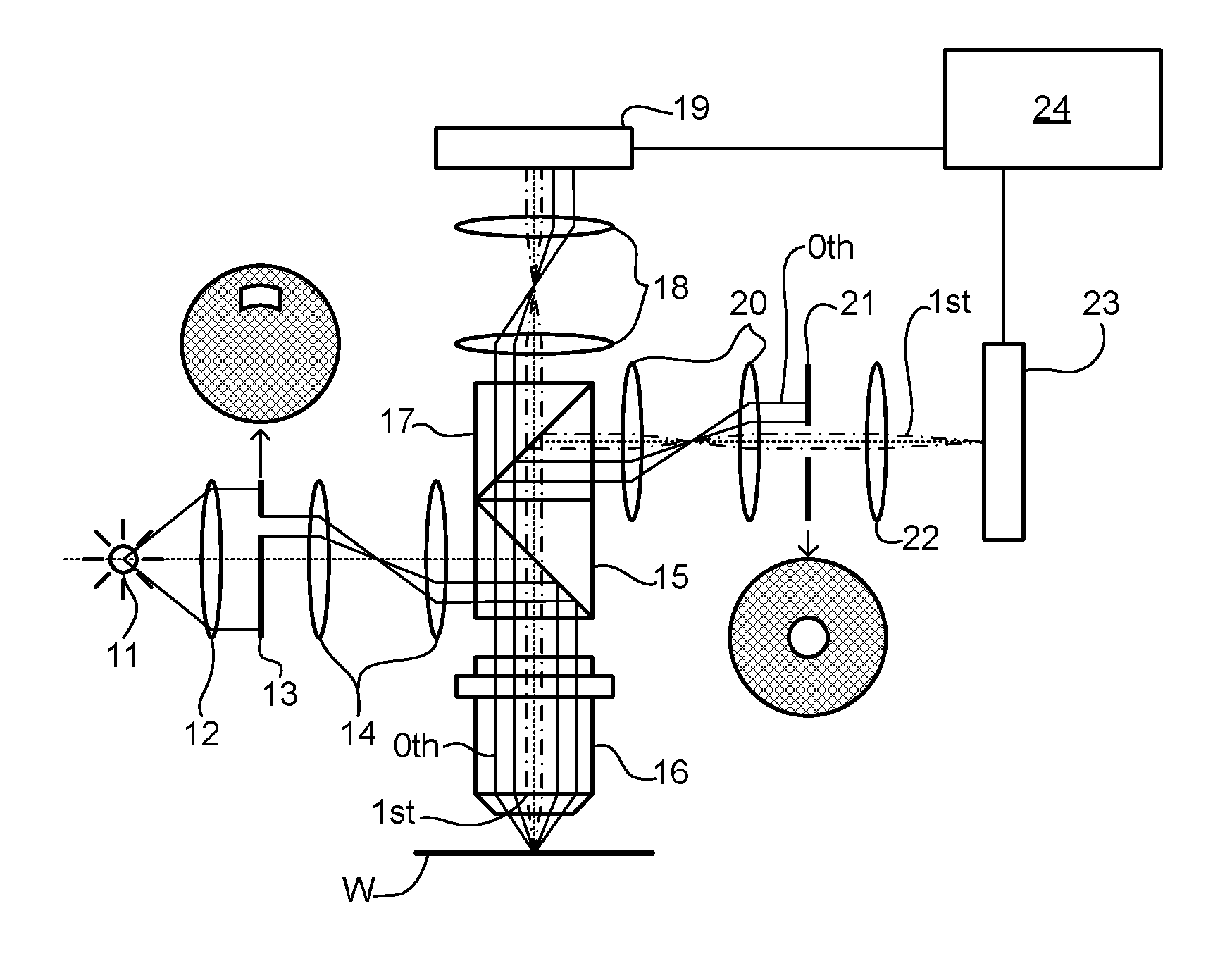
ActiveUS20110043791A1Made preciselySmall targetPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansMetrologyGrating
A metrology apparatus is arranged to illuminate a plurality of targets with an off-axis illumination mode. Images of the targets are obtained using only one first order diffracted beam. Where the target is a composite grating, overlay measurements can be obtained from the intensities of the images of the different gratings. Overlay measurements can be corrected for errors caused by variations in the position of the gratings in an image field.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
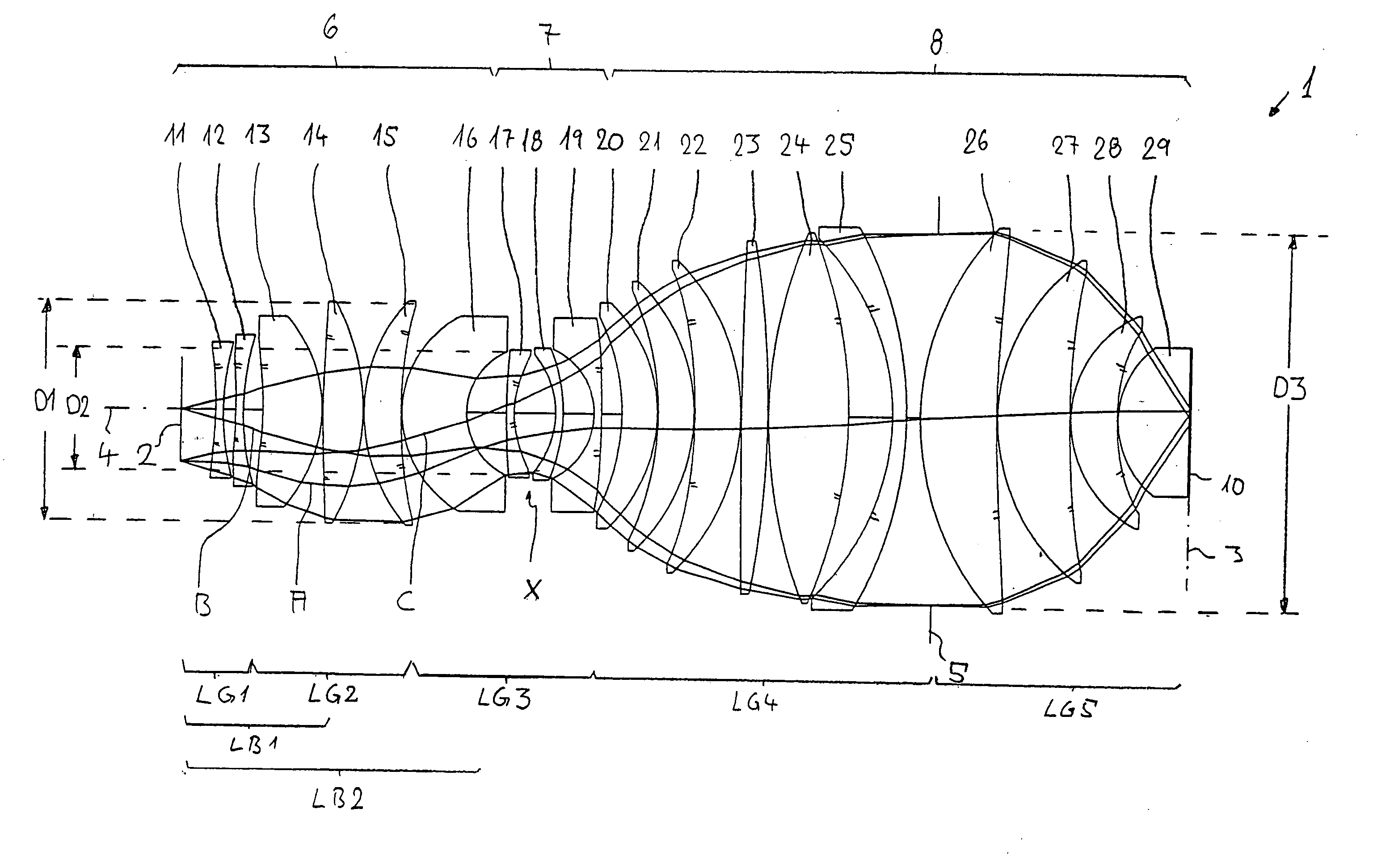
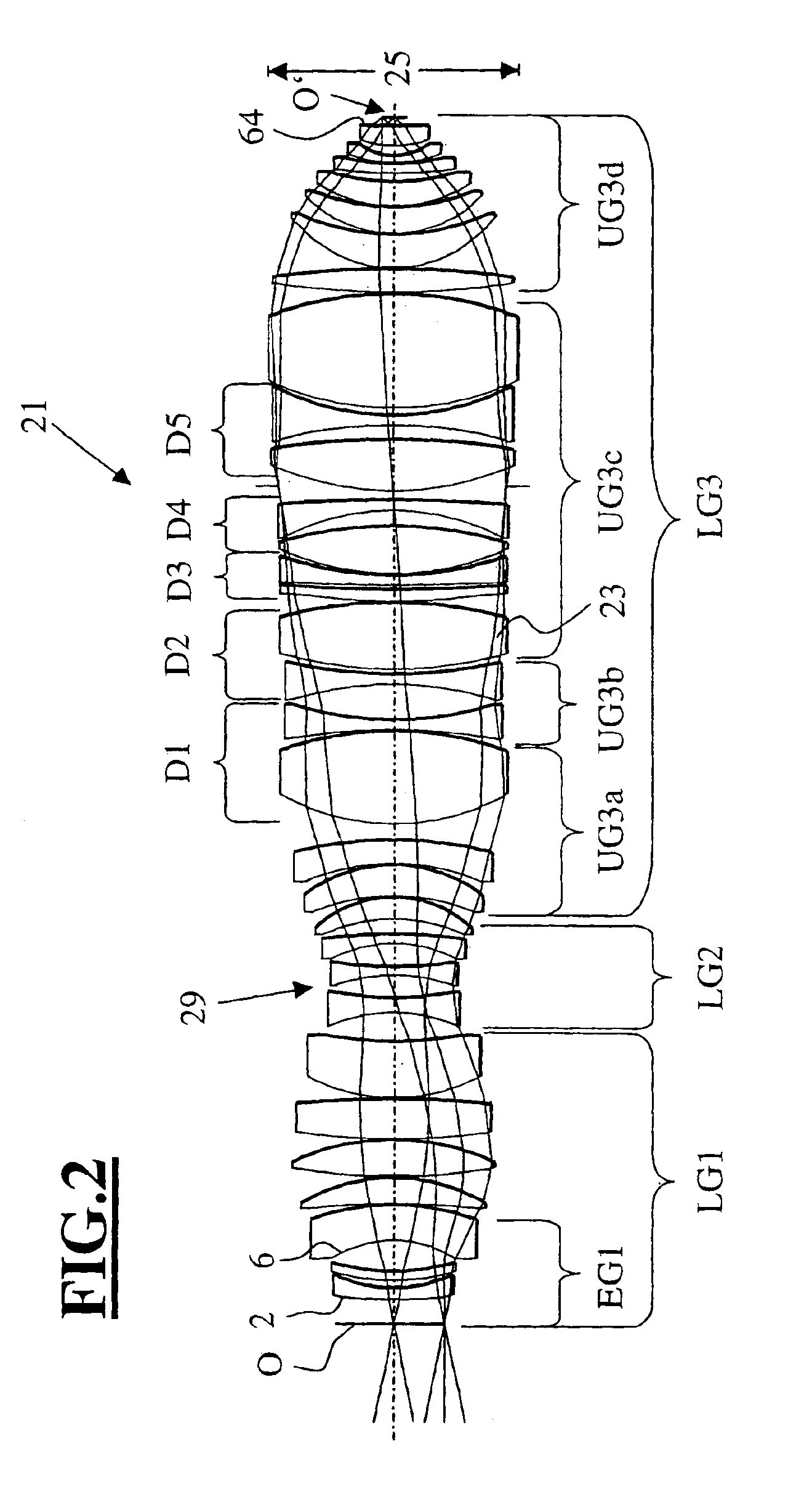
Refractive projection objective for immersion lithography
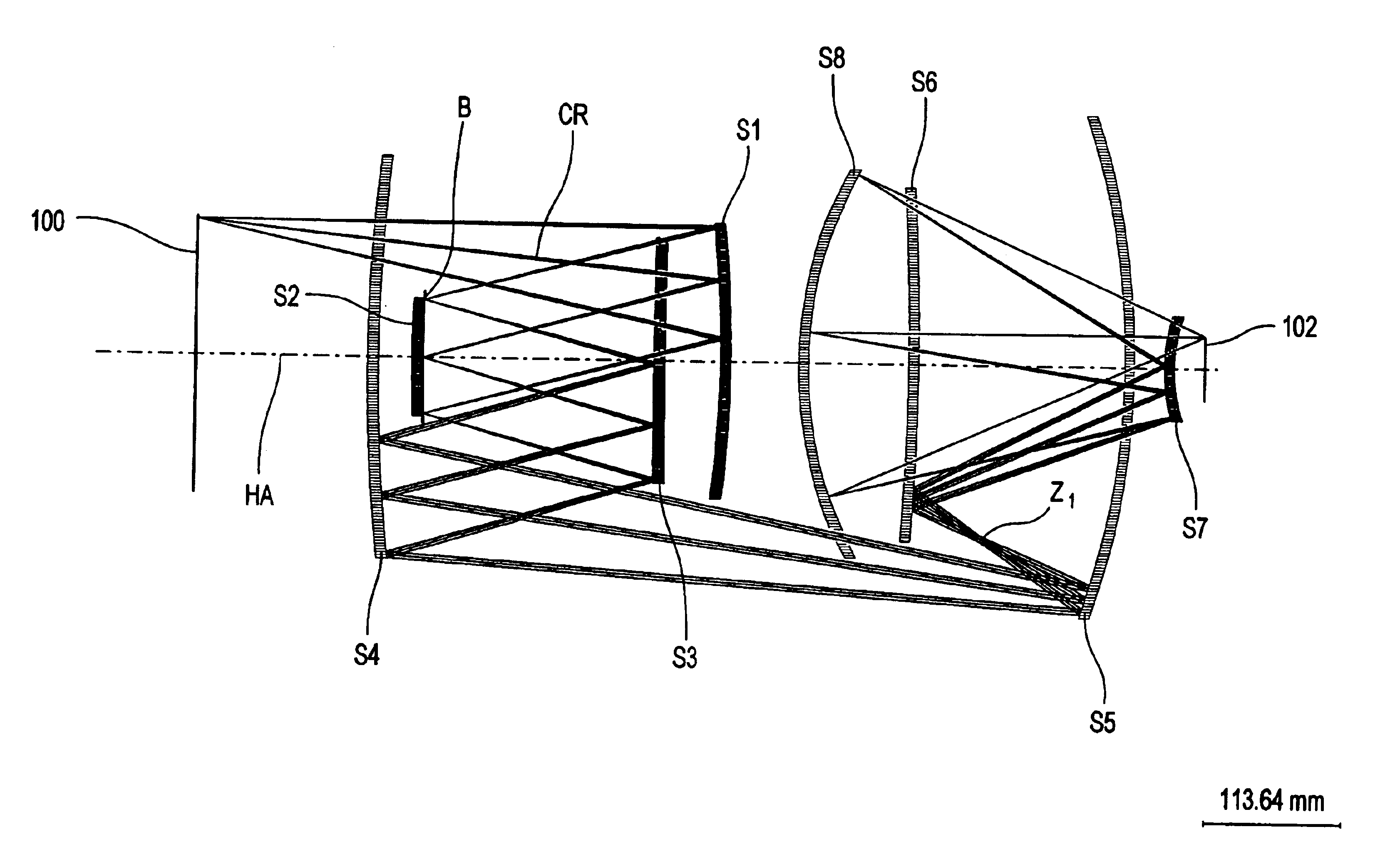
InactiveUS20050190455A1Small sizeGood correction stateMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHigh numerical apertureOptoelectronics
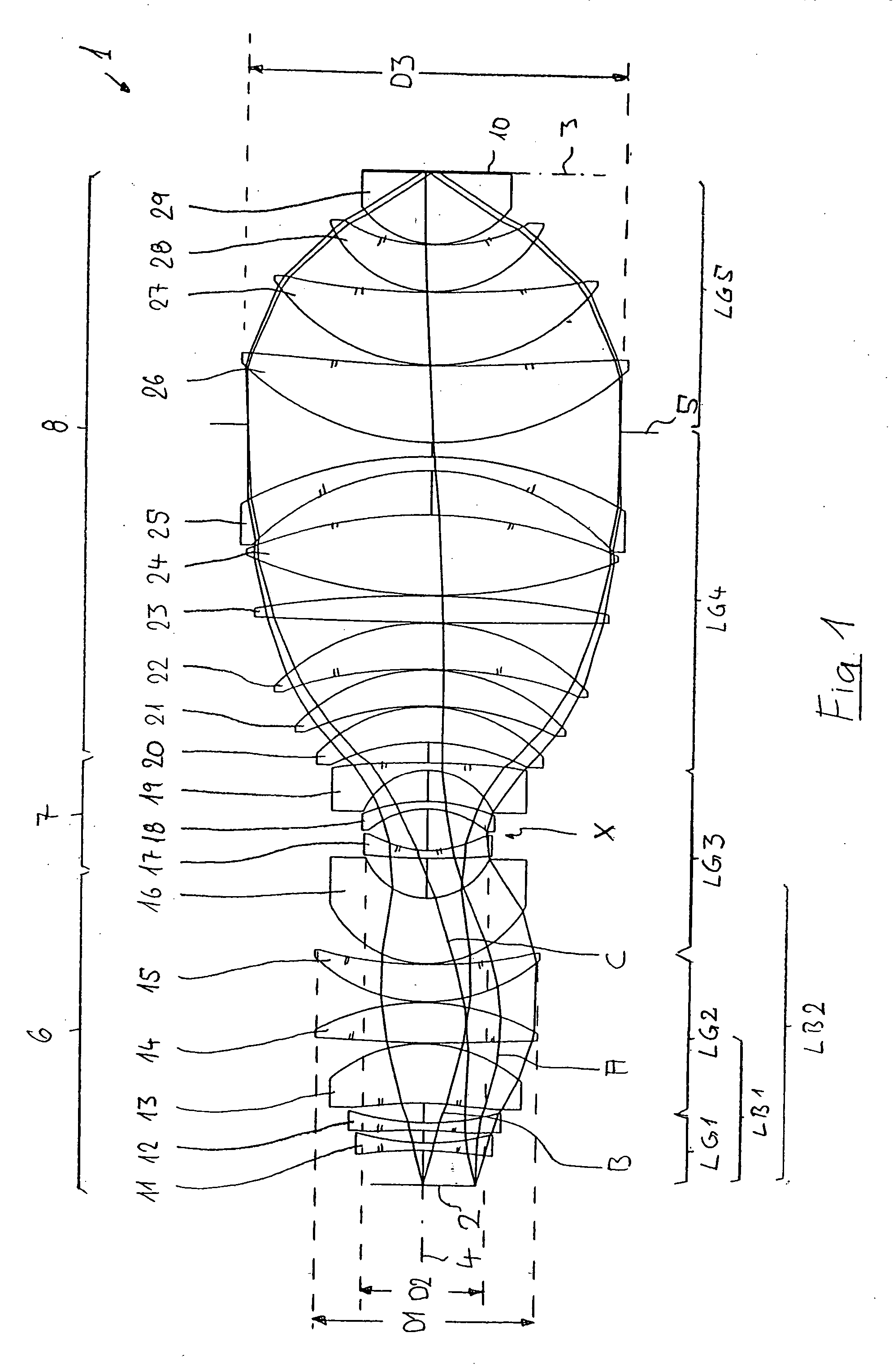
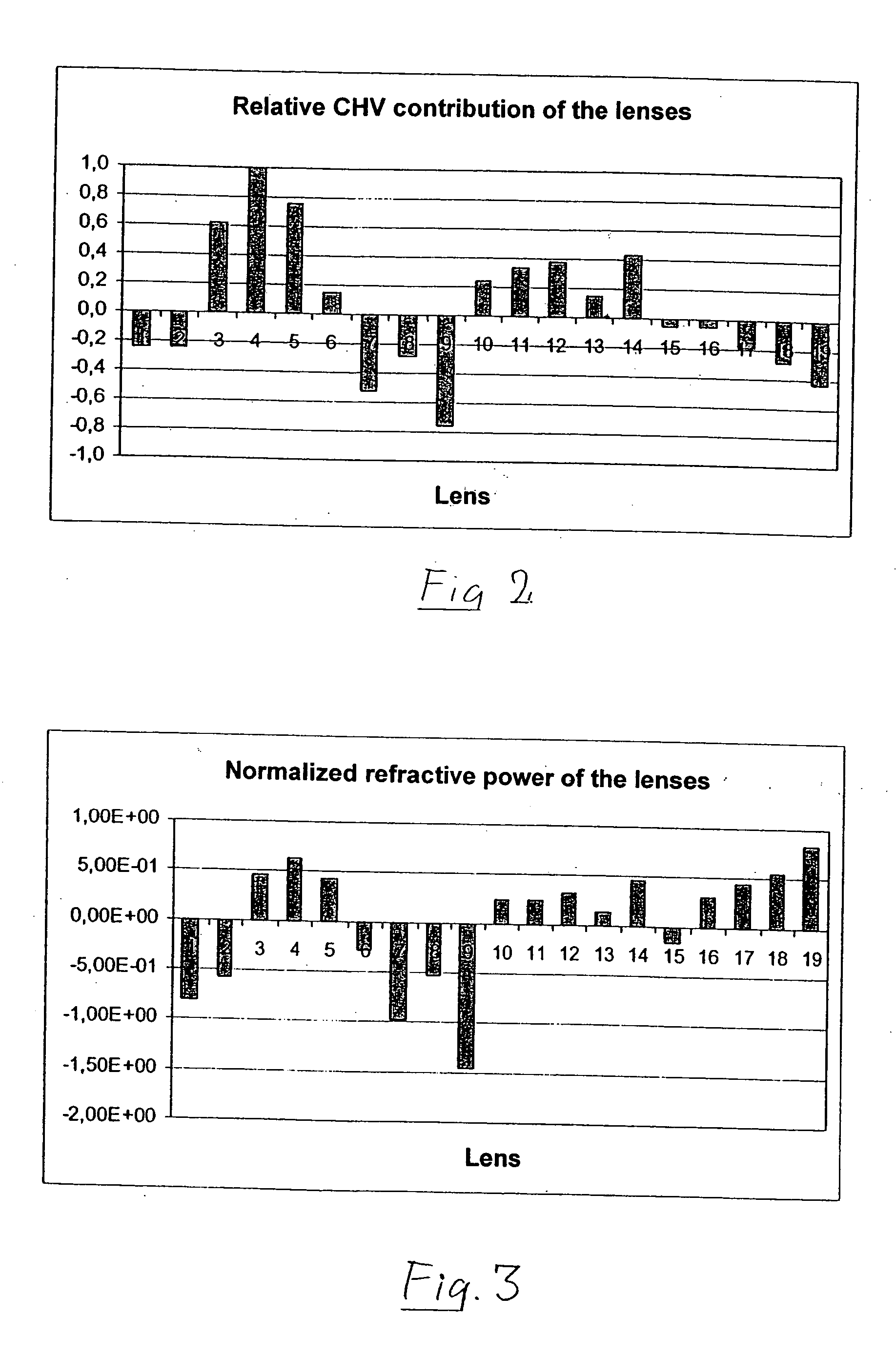
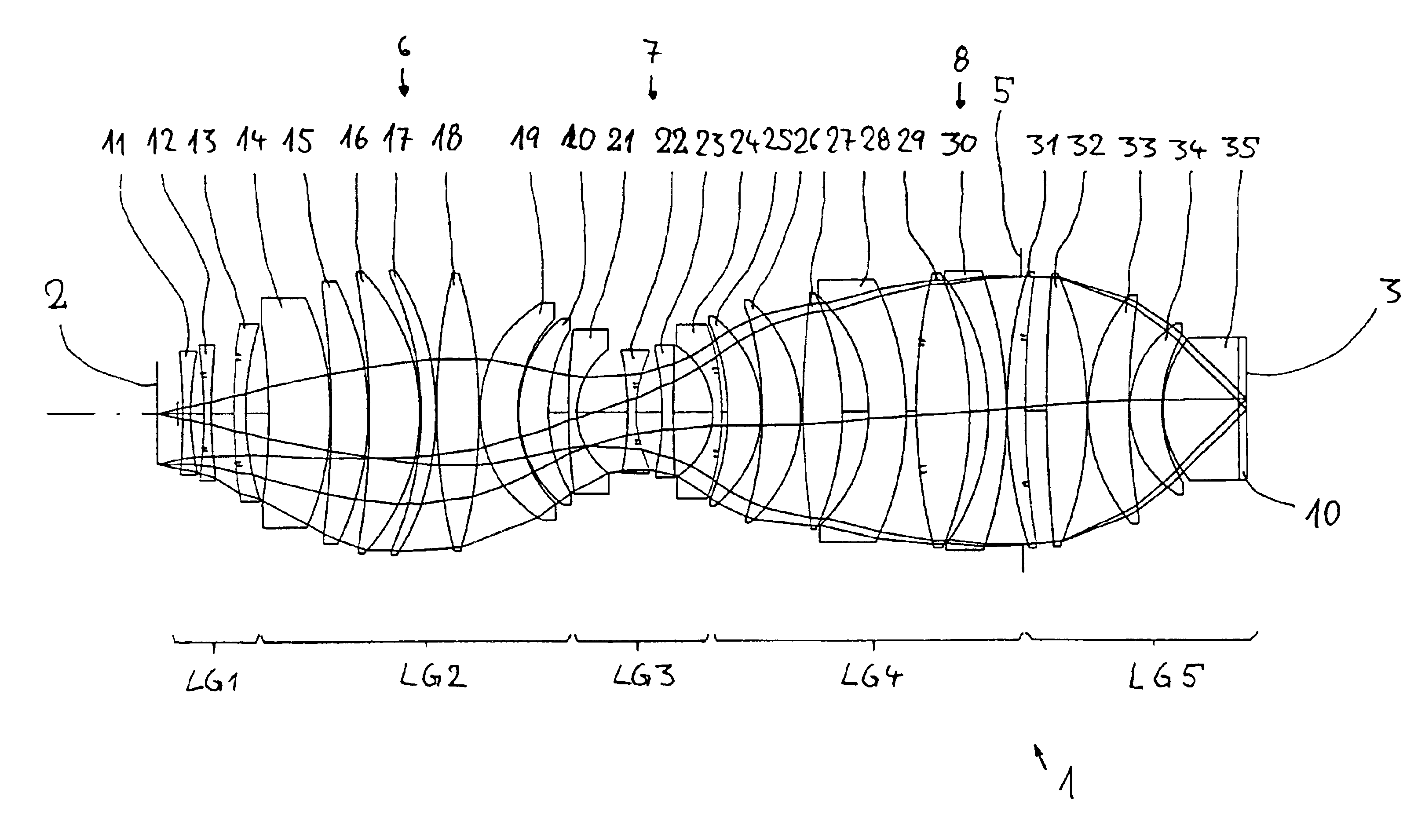
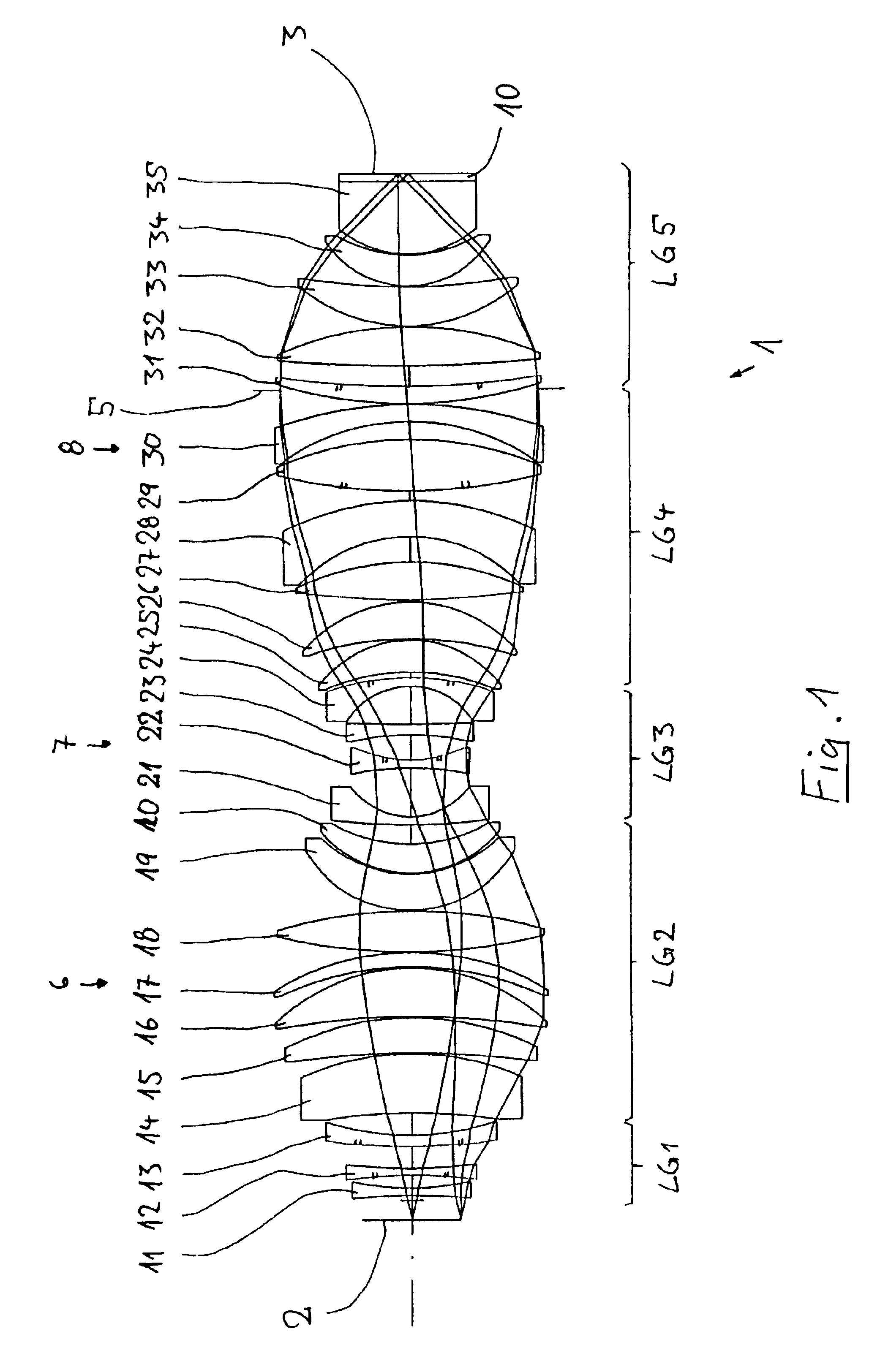
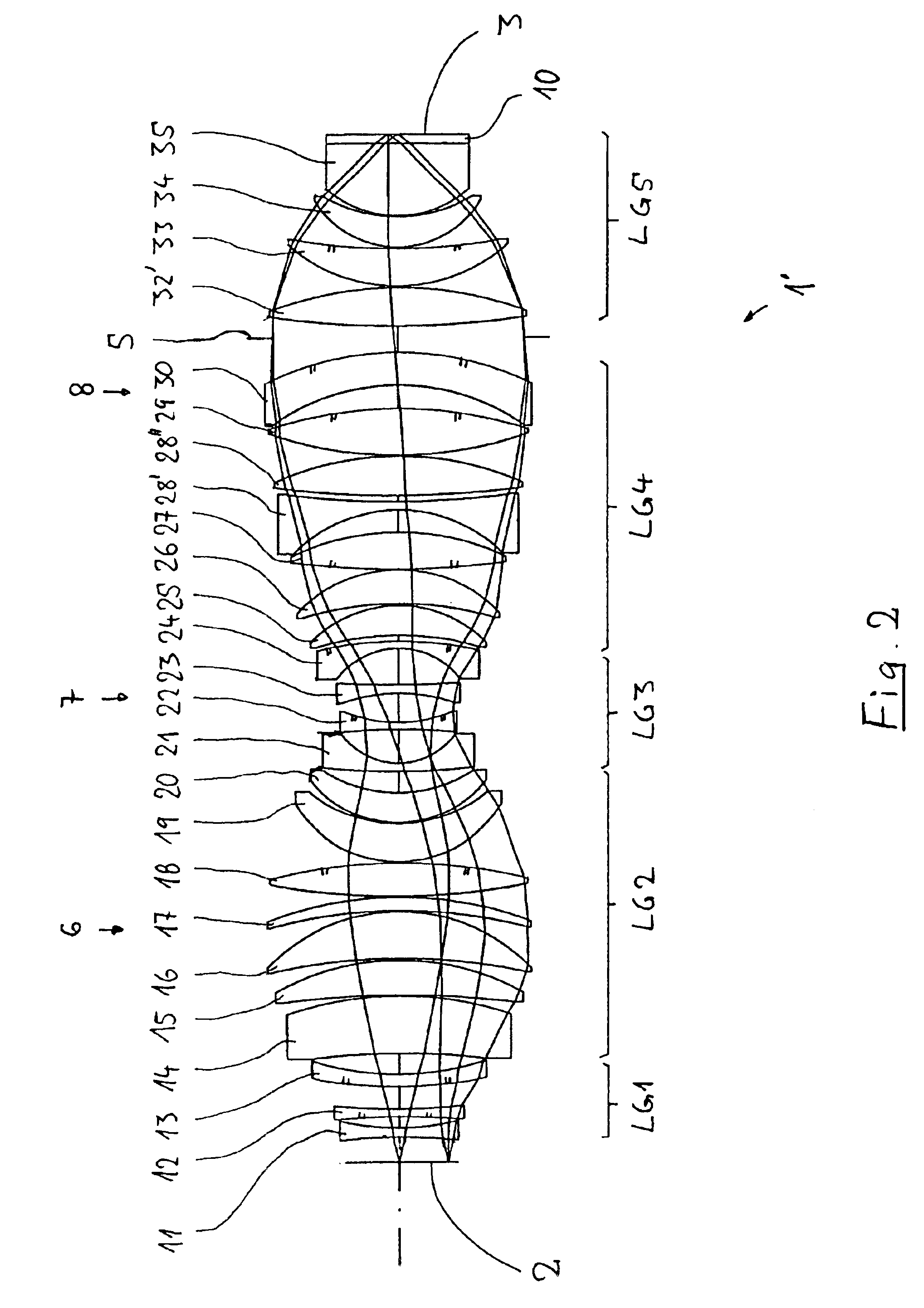
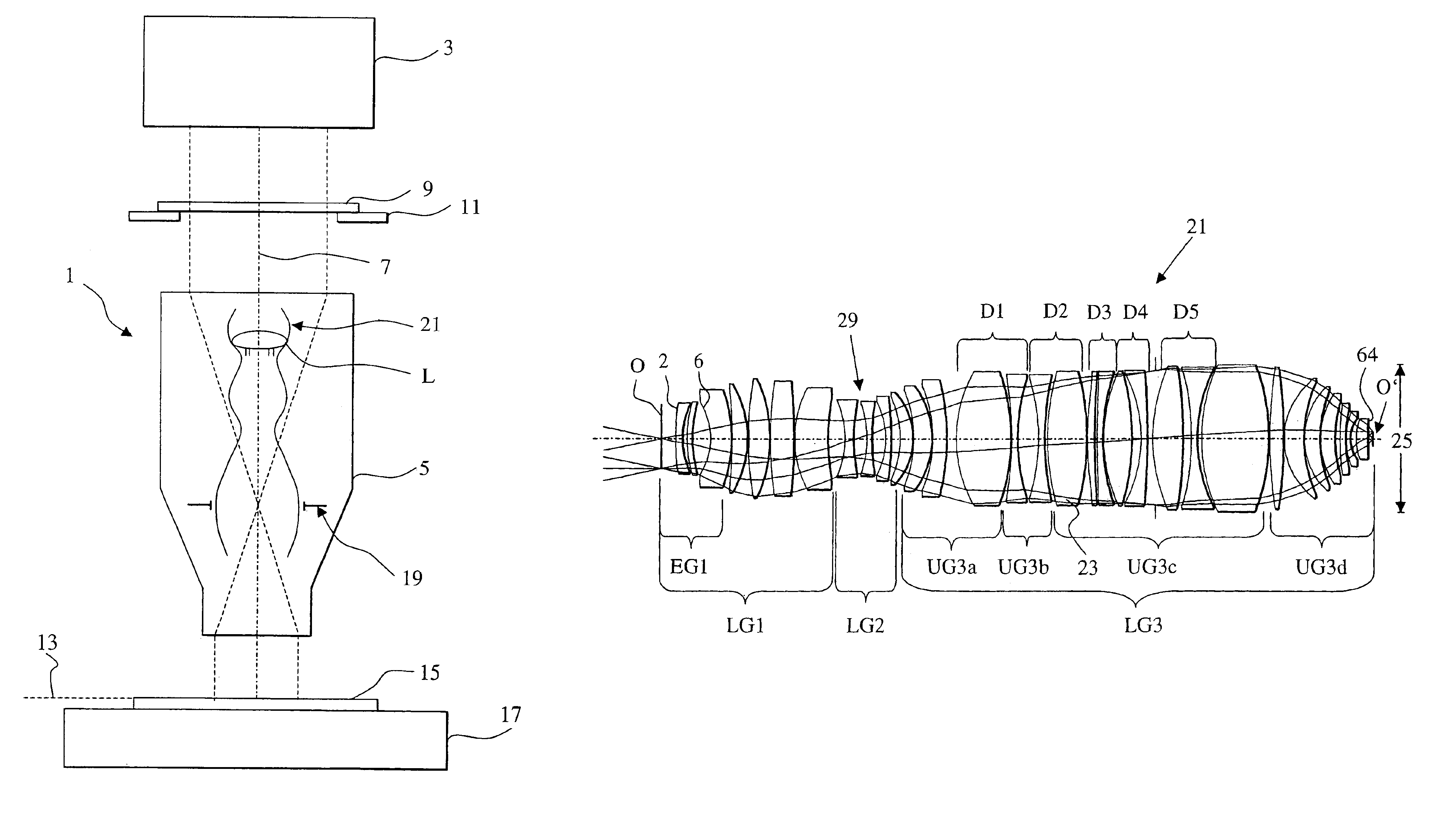
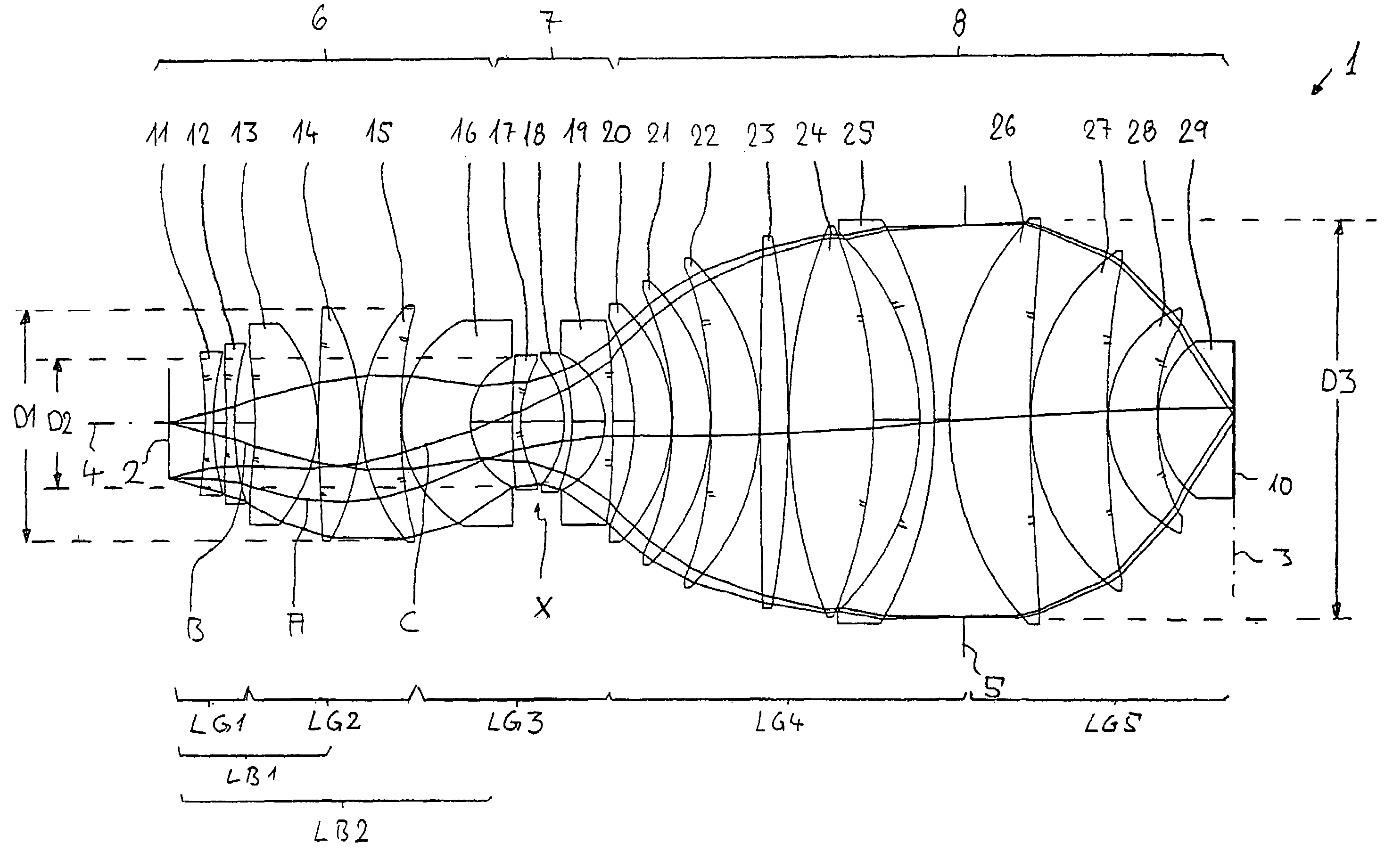
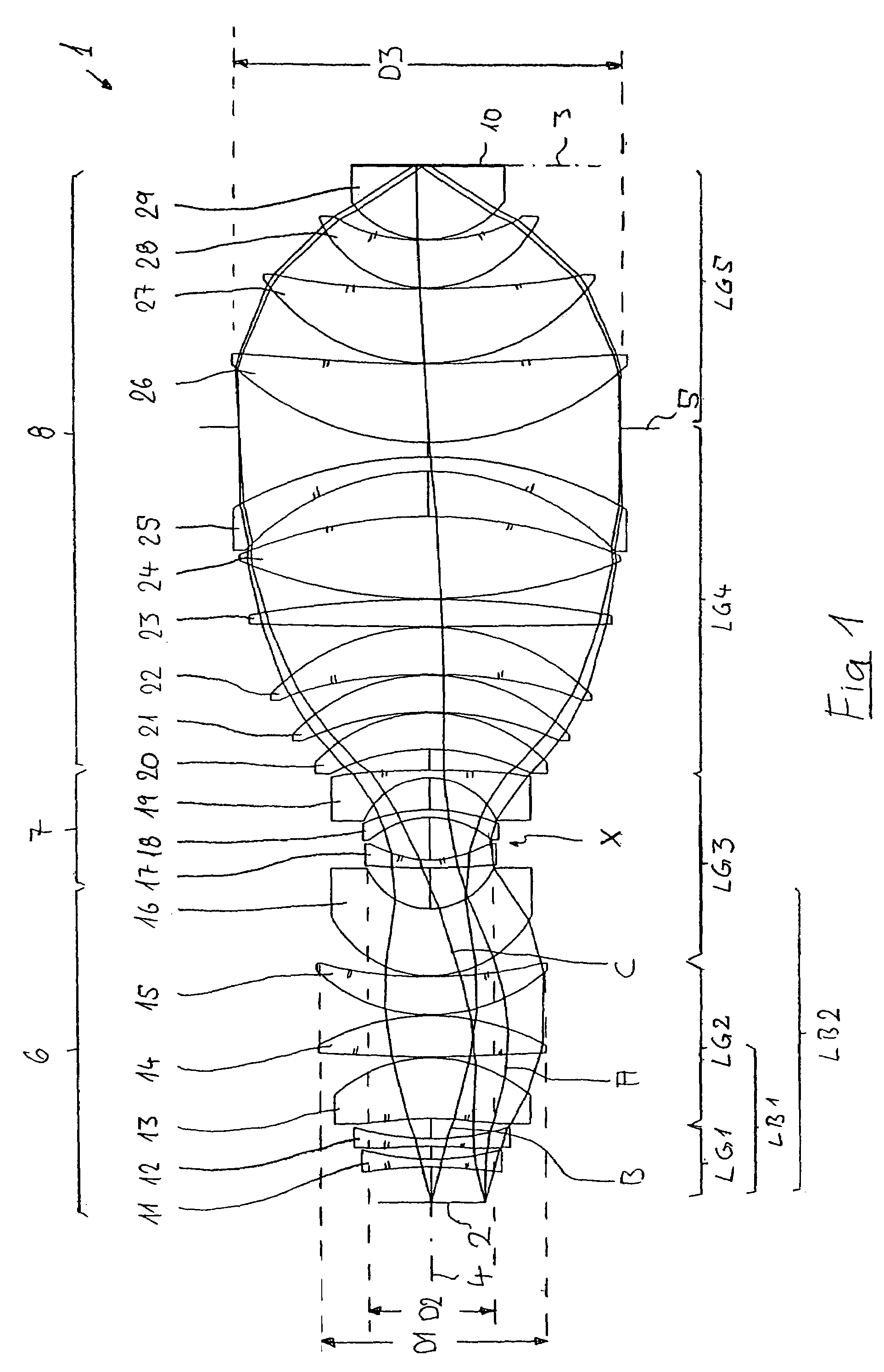
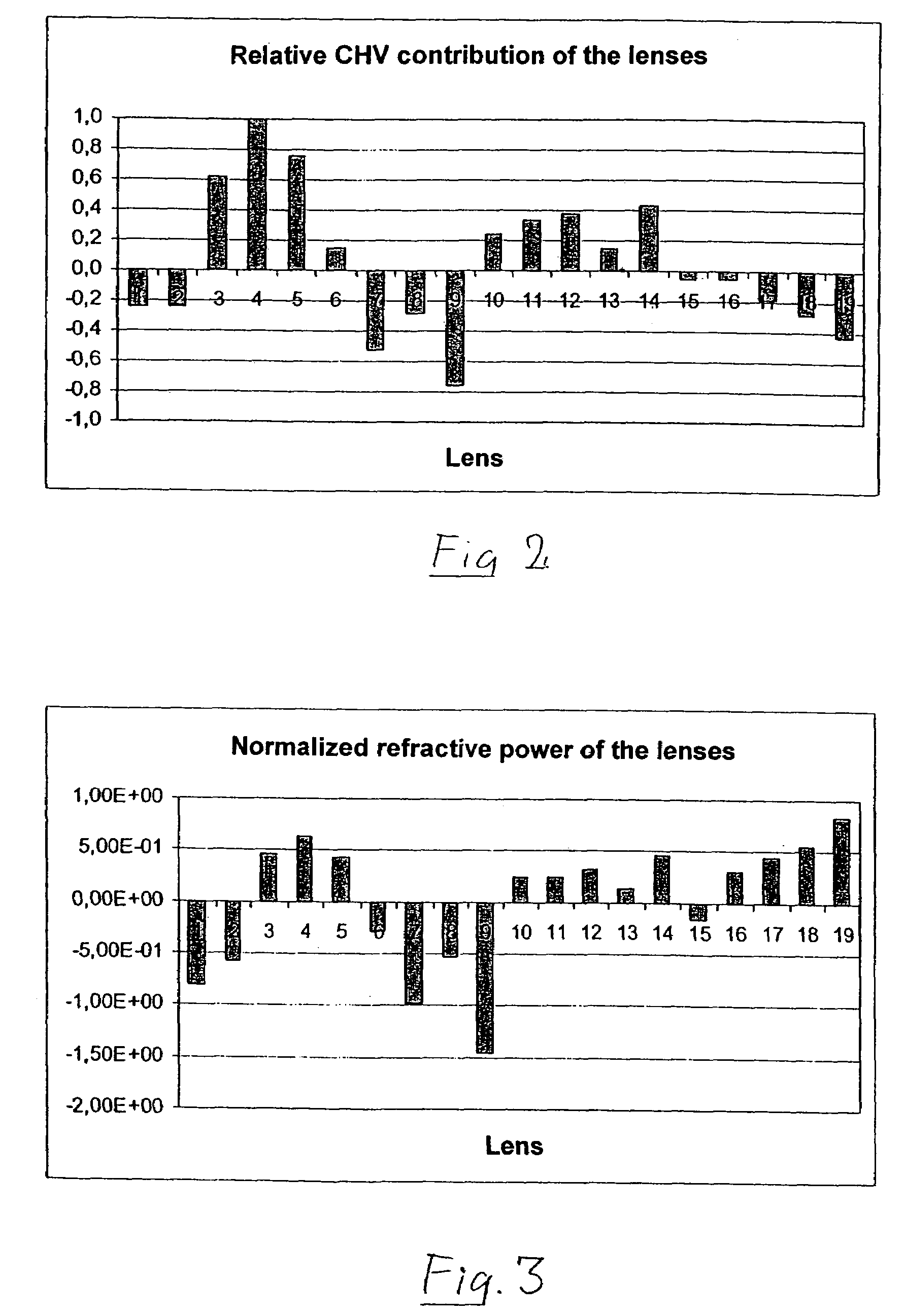
A purely refractive projection objective suitable for immersion microlithography is designed as a single-waist system with five lens groups, in the case of which a first lens group with negative refractive power, a second lens group with positive refractive power, a third lens group with negative refractive power, a fourth lens group with positive refractive power and a fifth lens group with positive refractive power are provided. A constriction site of narrowest constriction of the beam bundle lies in the region of the waist. A waist distance AT exists between the object plane and the constriction site X. The condition AT / L≦0.4 holds for a distance ratio AT / L between the waist distance AT and an object-image distance L of the projection objective. Embodiments of inventive projection objectives reach very high numerical apertures NA>1.1 in conjunction with a large image field and are distinguished by a compact overall size and good correction of the lateral chromatic aberration.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Refractive projection objective for immersion lithography
InactiveUS6891596B2Large numerical apertureGuaranteed true stateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLithographic artistBeam diameter
A purely refractive projection objective suitable for immersion micro-lithography is designed as a single-waist system with five lens groups, in the case of which a first lens group with a negative refracting power, a second lens group with a positive refracting power, a third lens group with a negative refracting power, a fourth lens group with a positive refracting power and a fifth lens group with a positive refracting power are provided. The system aperture is in the region of maximum beam diameter between the fourth and the fifth lens group. Embodiments of projection objectives according to the invention achieve a very high numerical aperture of NA>1 in conjunction with a large image field, and are distinguished by a good optical correction state and moderate overall size. Pattern widths substantially below 100 nm can be resolved when immersion fluids are used between the projection objective and substrate in the case of operating wavelengths below 200 nm.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Laser illuminating device and image display device
InactiveUS20100053565A1Remove speckle noiseUniform lightDiffusing elementsProjectorsDivergence angleLaser light
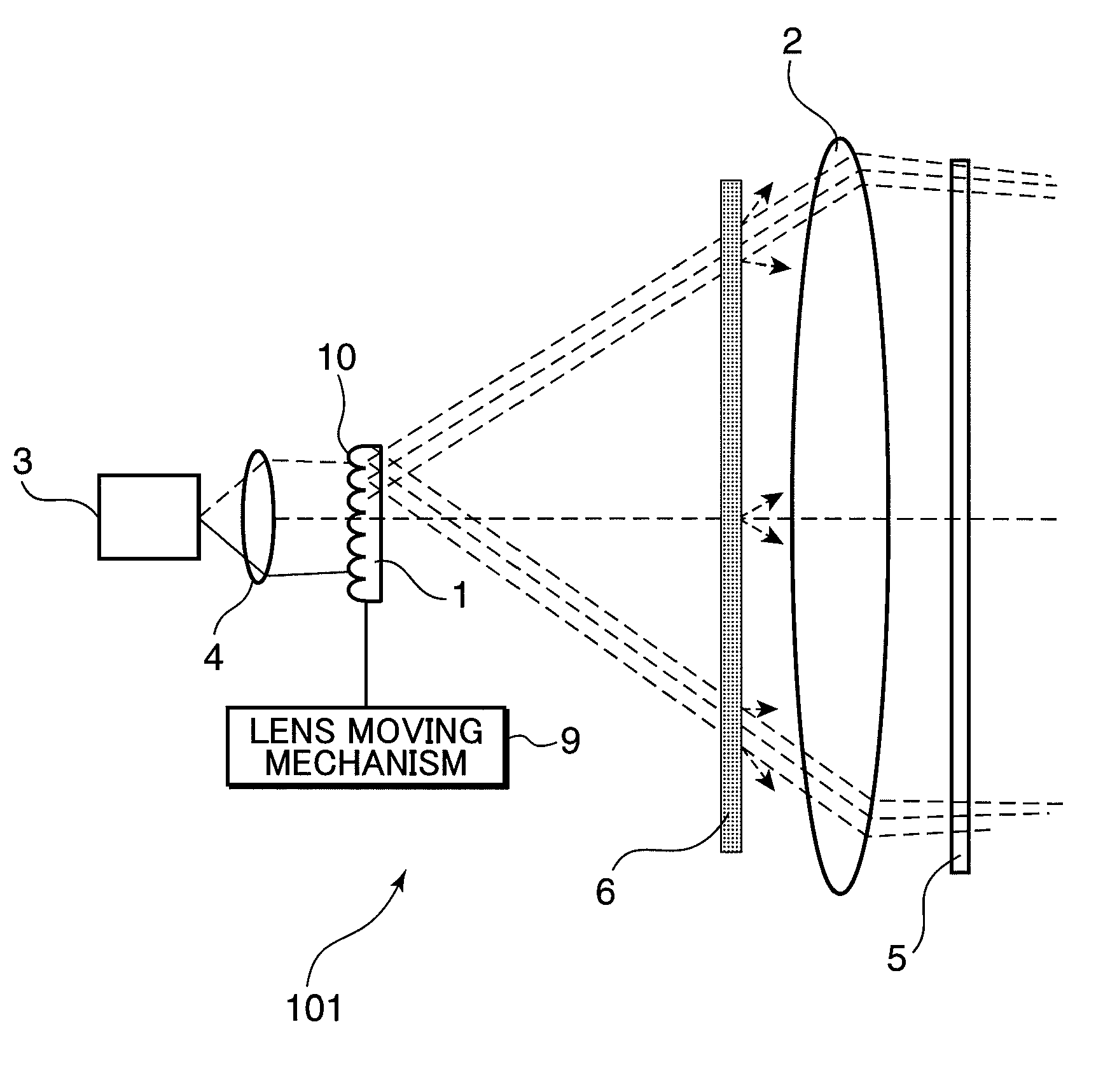
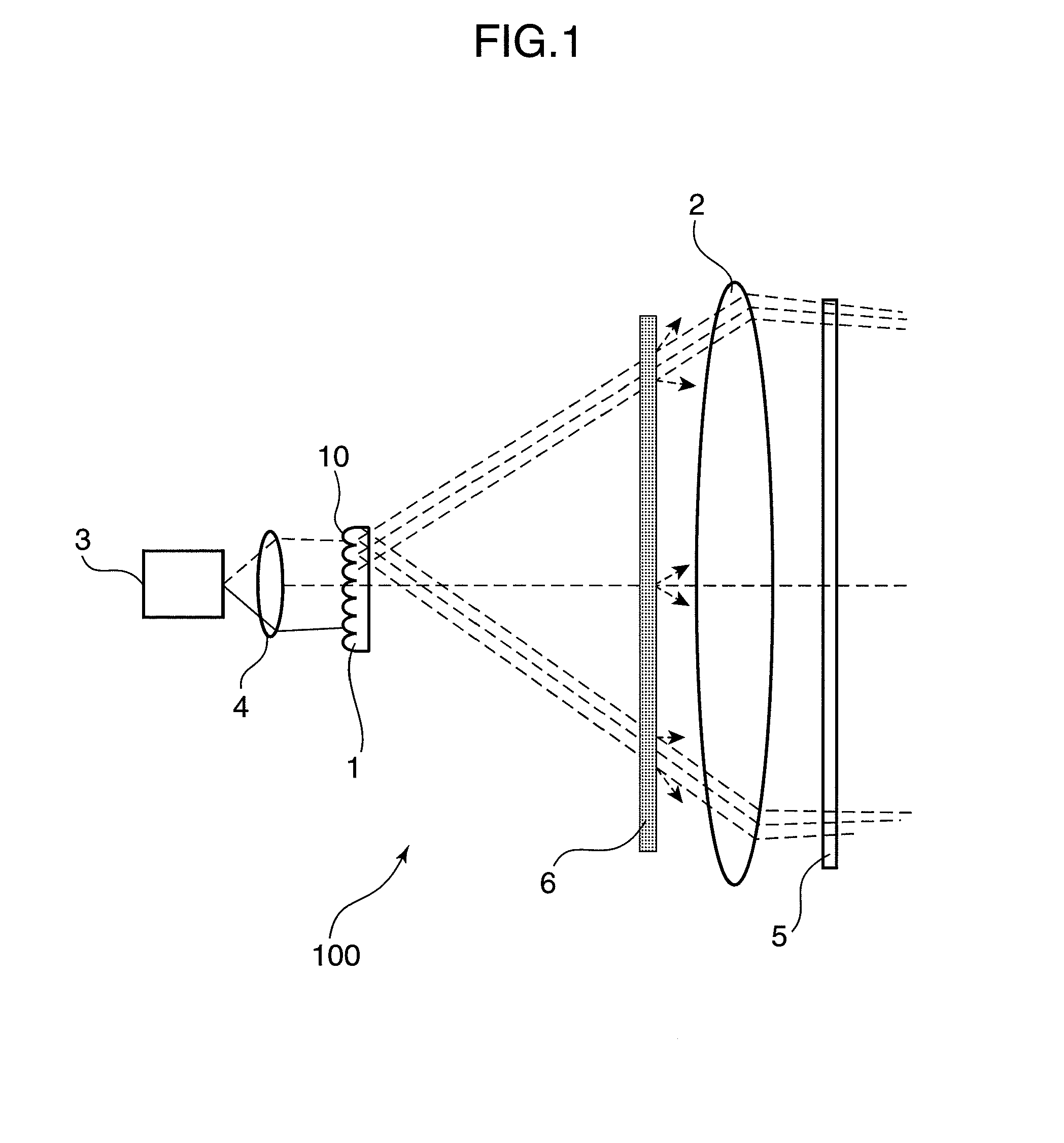
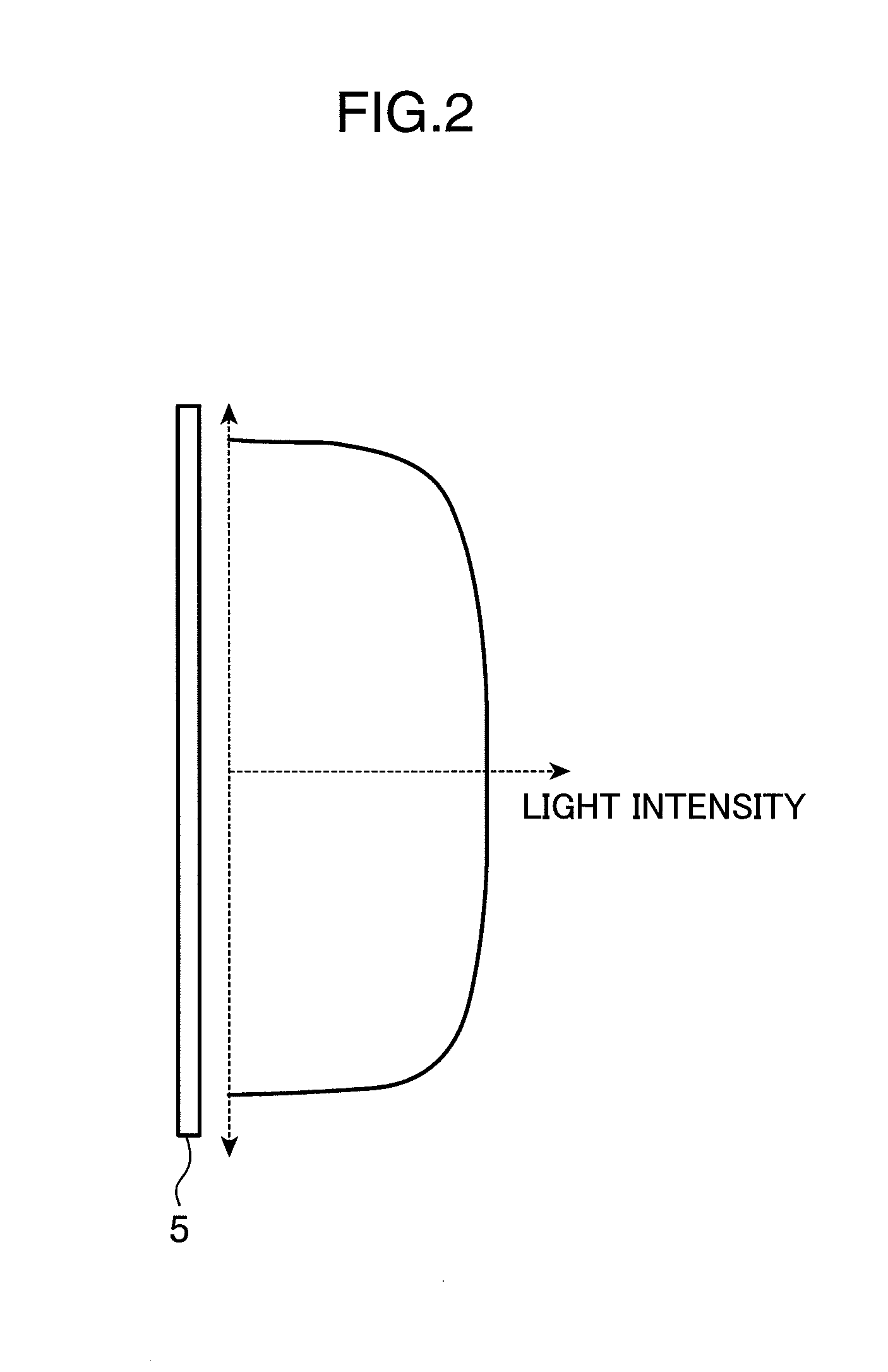
An object of the invention is to provide a laser illuminating device and an image display device that enable to remove speckle noises in a diffraction field and an image field, uniformly illuminate an illumination plane, and realize miniaturization. A laser illuminating device 100 includes a laser light source 3, a first lens 1 including a plurality of microlenses 10 each having a predetermined numerical aperture in an in-plane direction, each of the microlenses 10 being adapted to expand laser light emitted from the laser light source 3 to thereby superimpose the laser light transmitted through each of the microlenses 10; and a second lens 2 having an effective diameter larger than an effective diameter of the first lens 1, and for compensating for a divergence angle of the laser light expanded by each of the plurality of the microlenses 10.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Document scanner, system and method
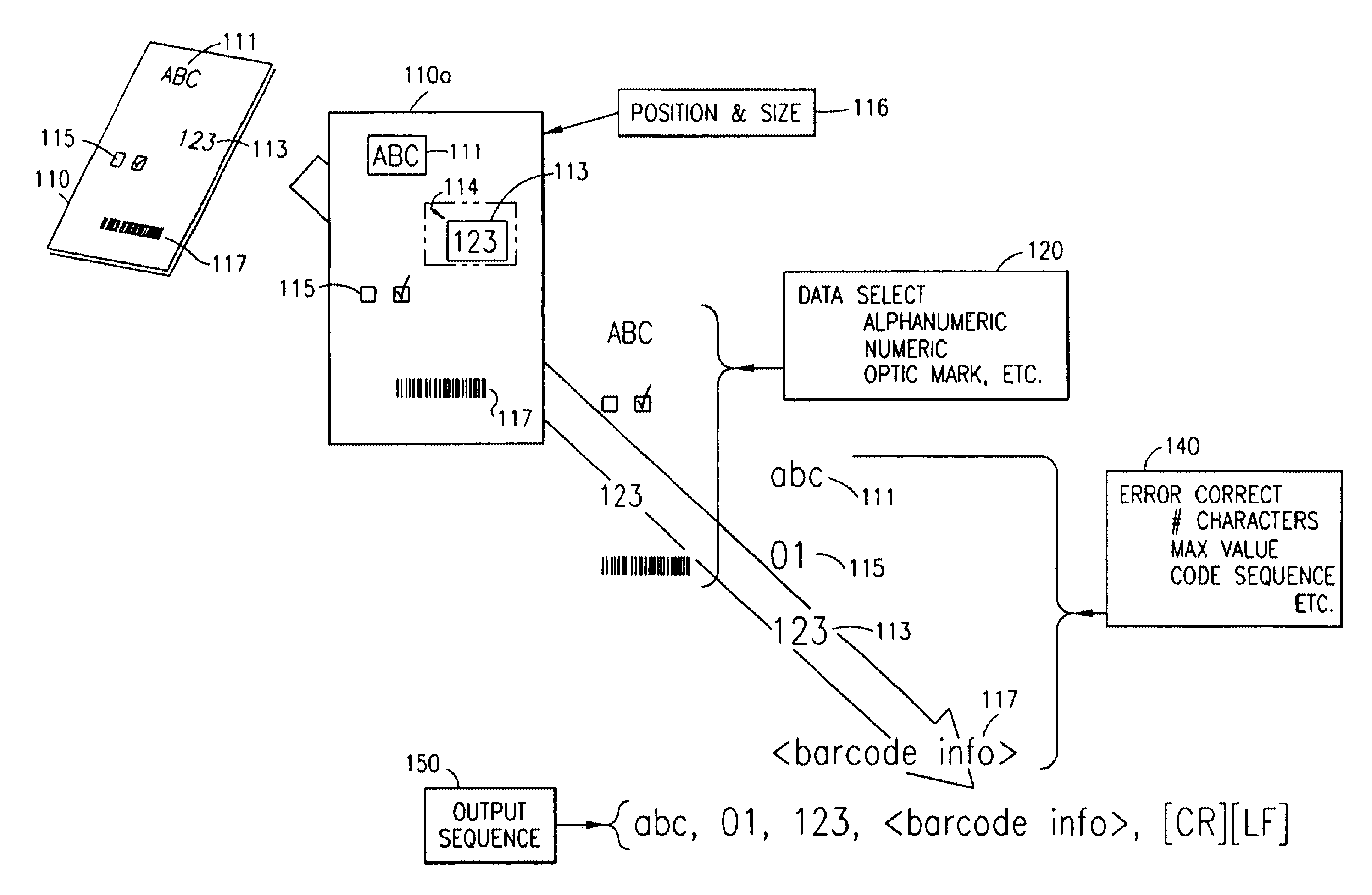
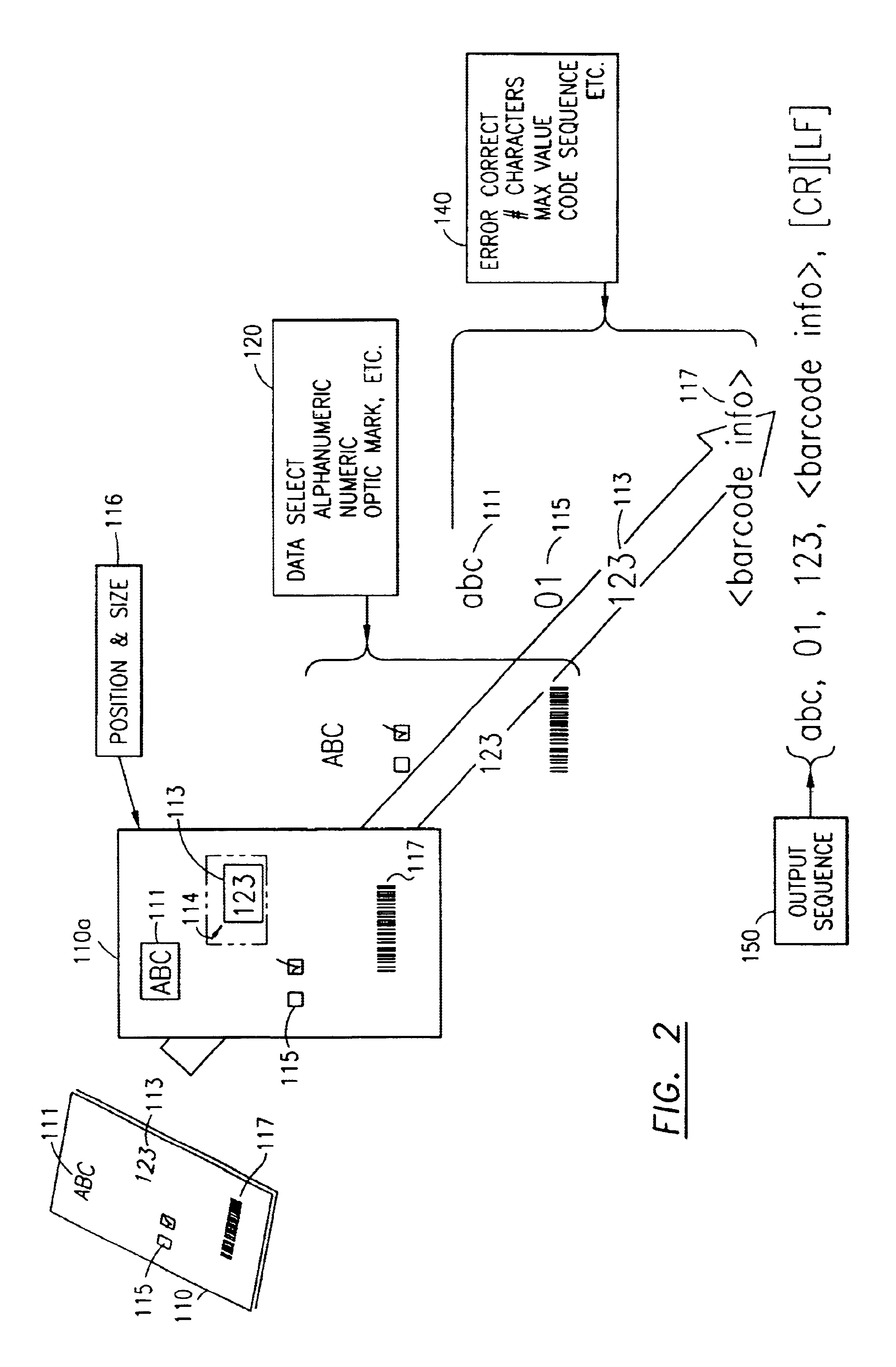
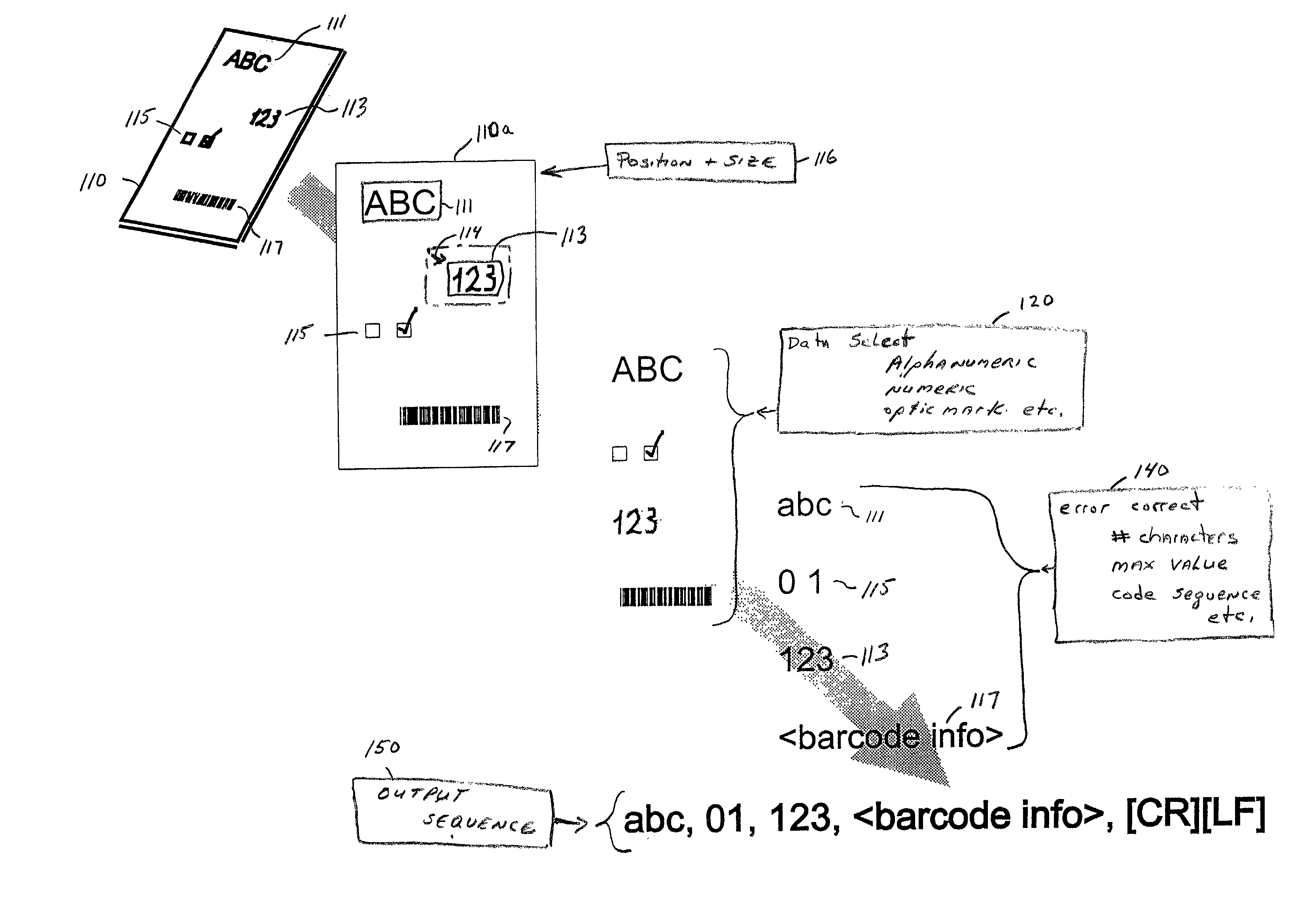
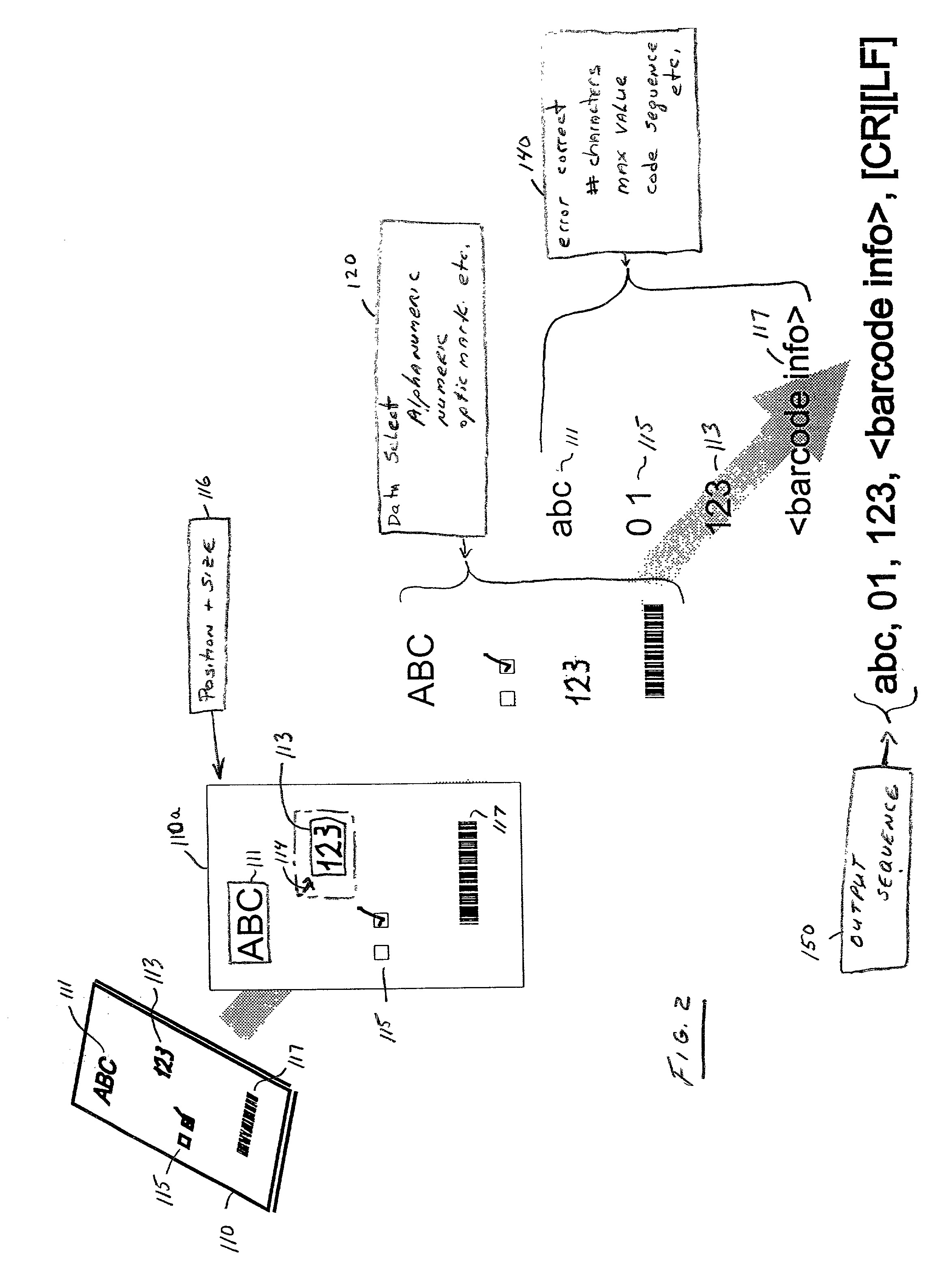
The document scanner system and method operates in conjunction with a document imprinted with data in a plurality of data image fields and a plurality of form documents adapted to have data imprinted thereon. The system output to a communications port is a delimited string of decoded characters. The method scans to obtain positional information of data fields or accepts topological form input by the operator. The operator identifies data descriptors, e.g. field size, data type, etc. The system and method scans the document imprinted with data and captures an image thereof. The scanned input document image is compared with the stored forms (particularly the stored data field descriptors, e.g., positional information, and data type). The system selects a stored form, extracts the data from each field, decodes or calculates the data, and validates the data and stores the decoded / calculated data in the output sequence.
Owner:MULTISCAN
Refractive projection objective with a waist
InactiveUS6891683B2Beneficial longitudinal chromatic aberrationIncrease the number ofMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical axisLight beam
A refractive projection objective for use in microlithography with lenses made exclusively of one and the same material has an image-side numerical aperture larger than 0.7. A light bundle defined by the image-side numerical aperture and by the image field has within the objective a variable light-bundle diameter smaller than or equal to a maximum light-bundle diameter. In a length interval measured on the optical axis from the system diaphragm towards the object field and at least equaling the maximum light-bundle diameter, the variable light-bundle diameter exceeds 85% of the maximum light-bundle diameter.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Endoscopic visualization apparatus with different imaging systems
InactiveUS7108657B2Precise positioningGood for observationSurgeryEndoscopesComputer scienceEndoscope
An endoscopic visualization apparatus has a first imaging system and at least one second imaging system, a first image field being covered by the first imaging system, and a second image field being covered by the second imaging system. The first imaging system and the second imaging system are arranged in a common housing. The first imaging system and the second imaging system are significantly different with regard to at least one optical parameter, and the first image field and the at least one second image field overlap one another only partially.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Display system having a three-dimensional convex display surface
ActiveUS20050017924A1Television system detailsBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsComputer graphics (images)Projection system
A display system has a display surface having a three-dimensional convex shape. A projection system projects an object field onto a continuous image field located on the interior of the display surface the display surface is extensive in its coverage, for example subtending an angle of at least 240 degrees to provide greater hemispherical coverage.
Owner:GLOBAL IMAGINATION
8-mirror microlithography projection objective
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Methods, apparatus and system to support large-scale micro- systems including embedded and distributed power supply, thermal regulation, multi-distributedsensors and electrical signal propagation
InactiveUS20130285739A1Improve production yieldReduce mechanical stressPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStructure of Management InformationEngineering
The present invention relates to technologies for integrated circuits and Large Area Integrated Circuits (LAICs), which are integrated circuits made from photo-repetition of one or several reticle image fields, stitched together on at least one lithographic process layer. It also relates to a specific class of LAIC that can connect to the contacts of other ICs placed on its surface, where specific contact detection algorithms means are disclosed. The innovations include means for defect tolerance of serial communication links, means for efficient diagnosis of short and stuck-at faults in regular reconfigurable network, means for a programmable interposer for rapid prototyping of 3D stacked chips, means to build efficient large area micro-system devices (LAMS), with distributed and configurable hierarchical structures for power supply, thermal regulation and signal propagation, means to reduce mechanical / thermal / thermo-mechanical issues in LAMS devices, means to propagate analog signal on a configurable digital network, means to predict thermo-mechanical stress peaks.
Owner:TRANSFERT PLUS S E C +2
Composite dual LCD panel display suitable for three dimensional imaging
InactiveUS20050146787A1Quality improvementHigh-quality imaging effectStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceEngineering
A three-dimensional imaging system and related methods is provided that utilizes a composite transmissive LCD panel. The composite LCD panel contains at least two layers of stacked liquid crystal cells positioned on top of one another relative to the imaging direction, is utilized to display at least two calculated images superimposed over one another at different distances within the panel from the viewer. Each layer of liquid crystal cells create multiple pixels from the cells, which pixels collectively can be operated to form independent images on each liquid crystal layer. The composite LCD panel can be used to create a continuous 3-D image field in a large viewing area or in multiple viewing areas in conjunction with a suitable 3-D image generation system.
Owner:VIRRILLI JAMES
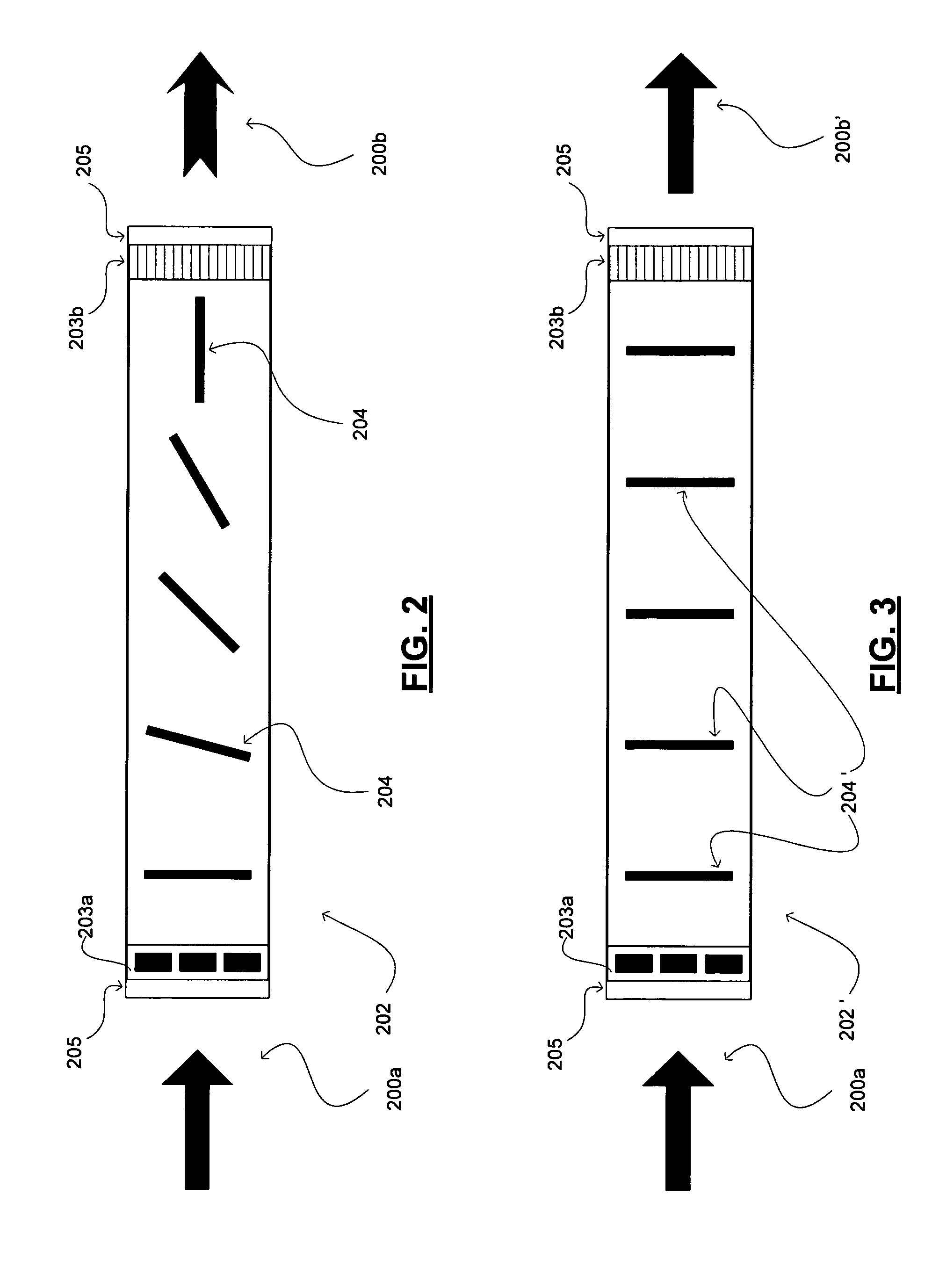
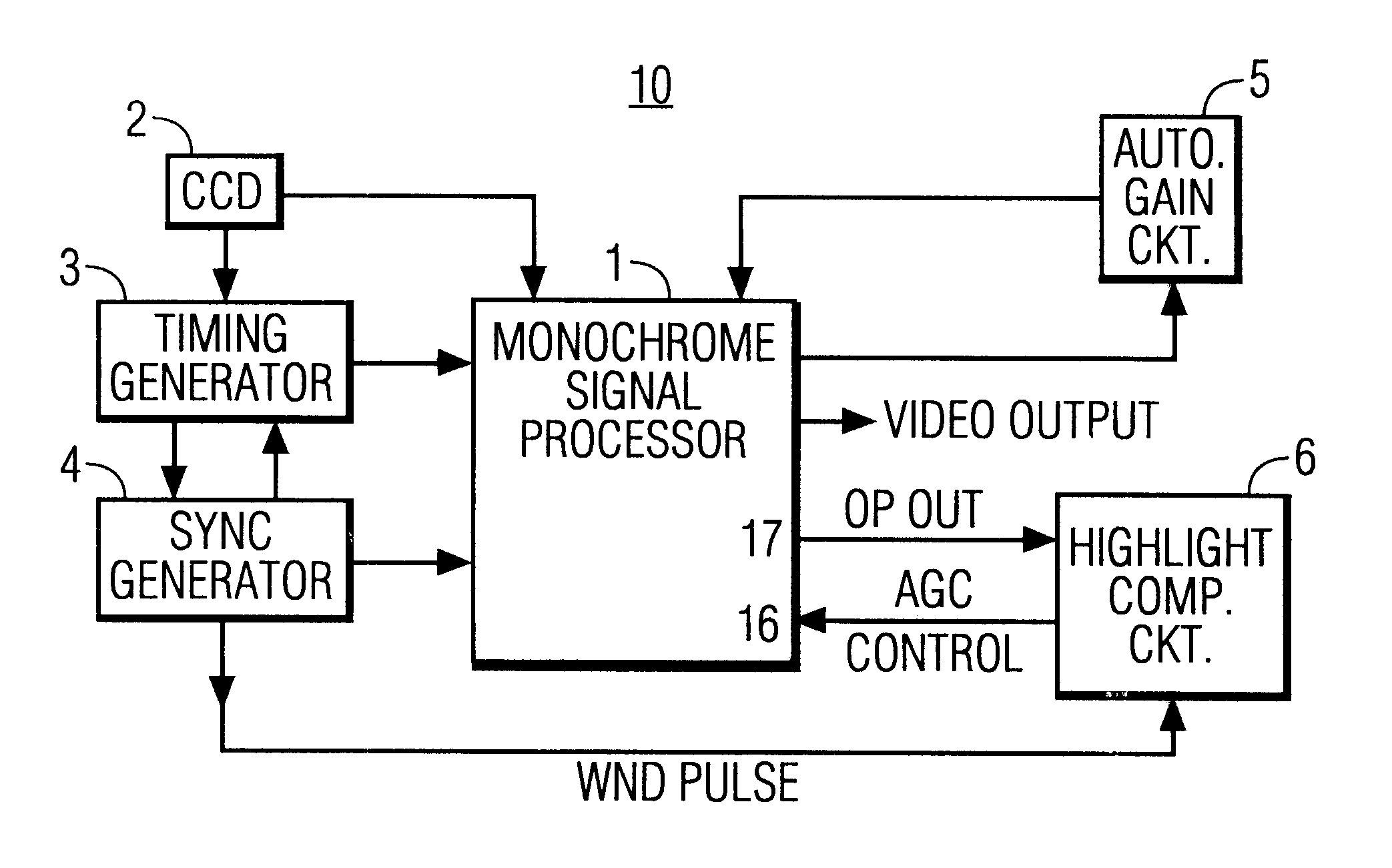
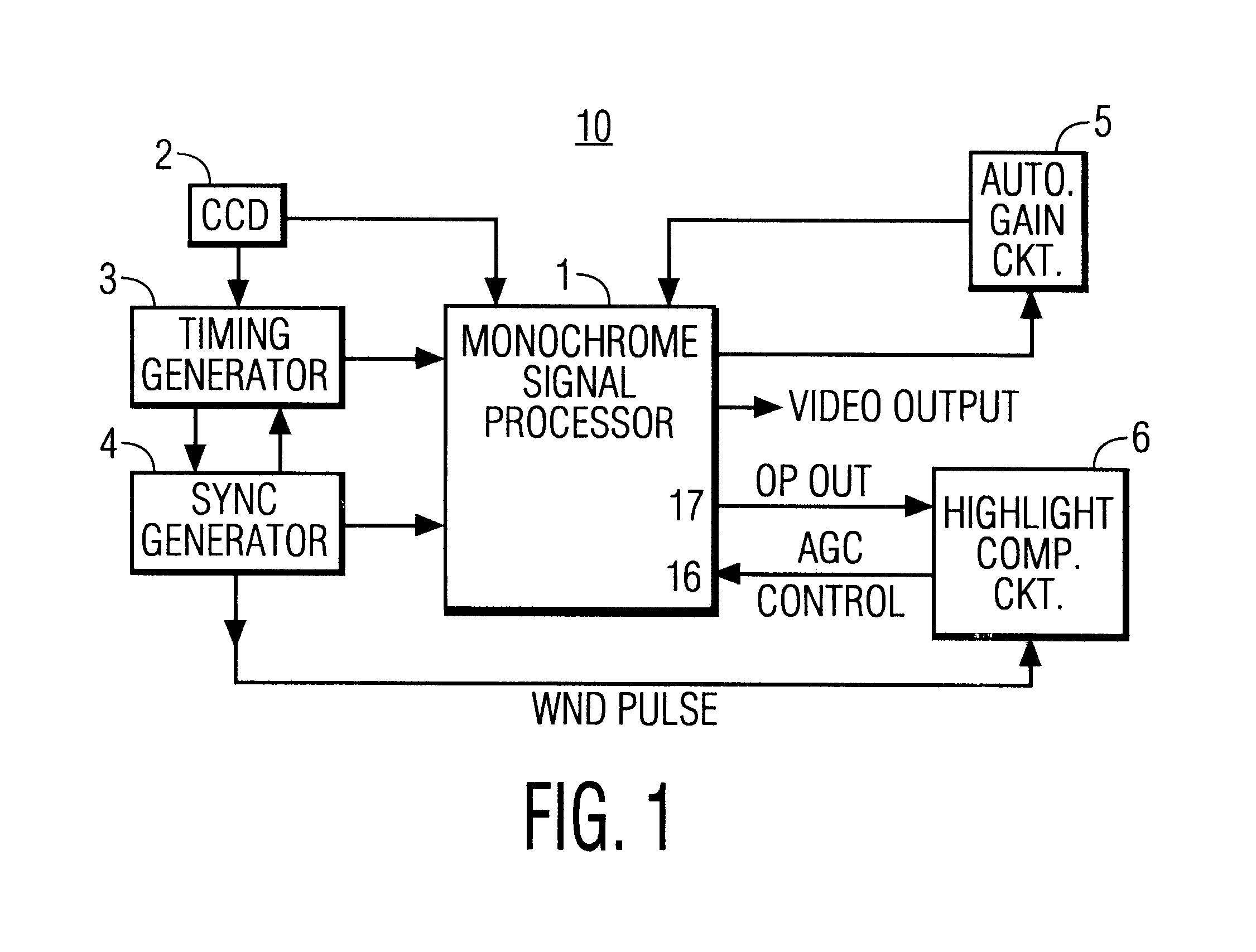
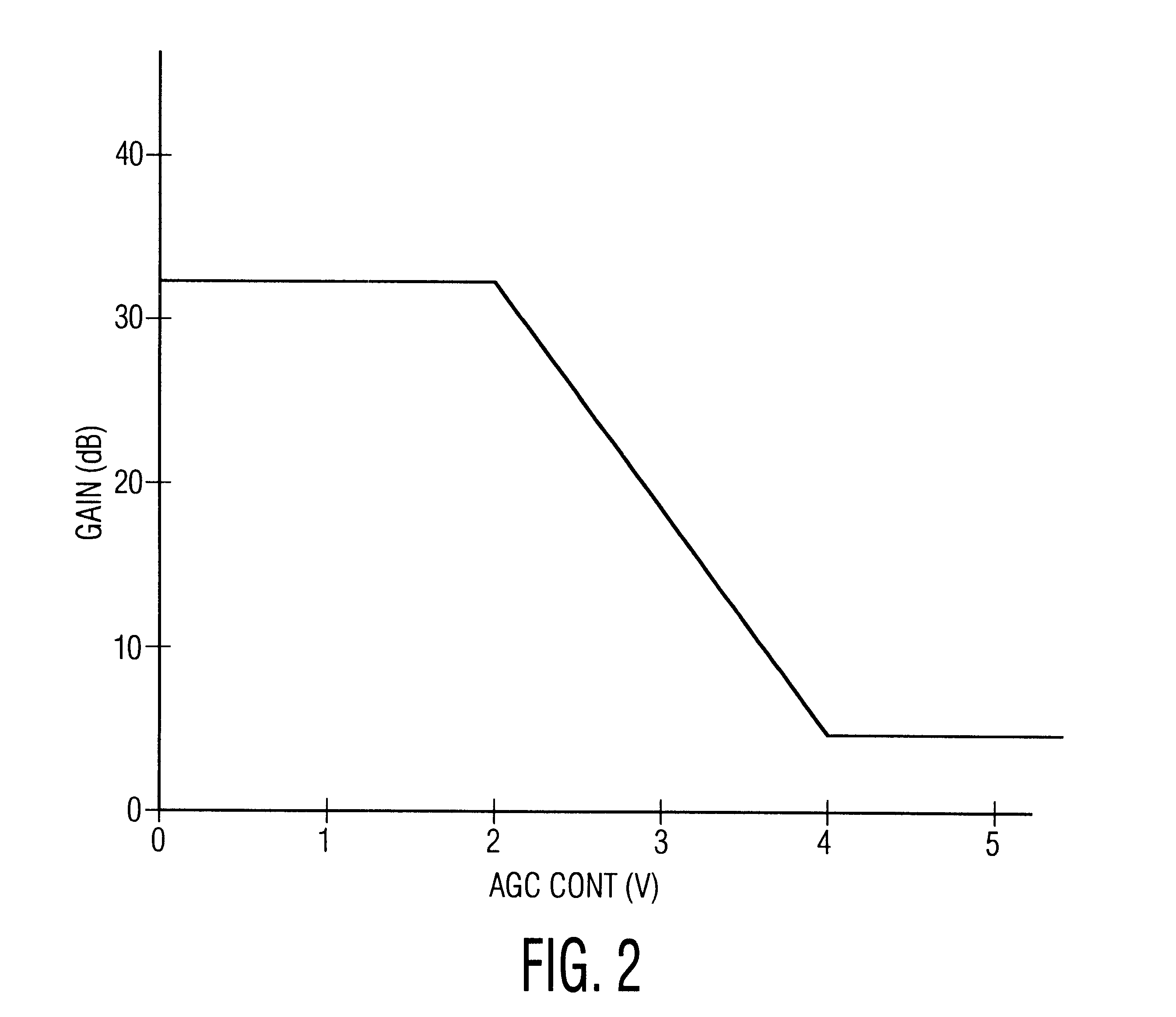
Highlight compensation apparatus for monochrome cameras
InactiveUS6489990B1Prevents white-washHigh gainTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer scienceImage signal
A monochrome camera system, includes a processor for producing an image signal, a first circuit for selectively adjusting an overall gain of the image signal produced by the processor, and a second circuit, coupled to the processor. The second circuit selectively adjusts a gain of a portion of the image signal within a predefined region of a field of the image without affecting an overall gain set by the first circuit of other portions of the image field.
Owner:PENDRAGON WIRELESS LLC
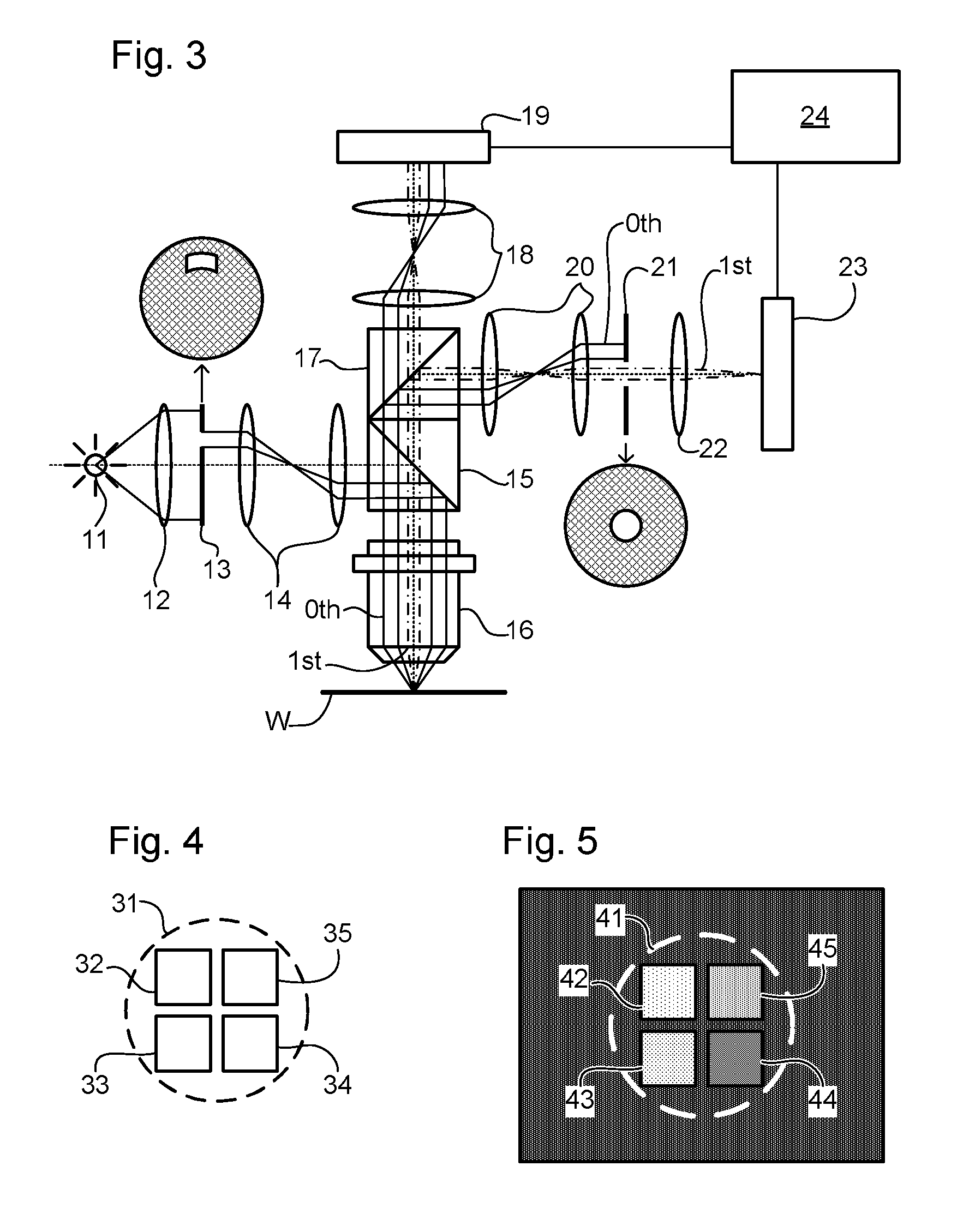
Metrology method and apparatus, lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method and substrate
ActiveUS8411287B2Made preciselyPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansGratingMetrology
A metrology apparatus is arranged to illuminate a plurality of targets with an off-axis illumination mode. Images of the targets are obtained using only one first order diffracted beam. Where the target is a composite grating, overlay measurements can be obtained from the intensities of the images of the different gratings. Overlay measurements can be corrected for errors caused by variations in the position of the gratings in an image field.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
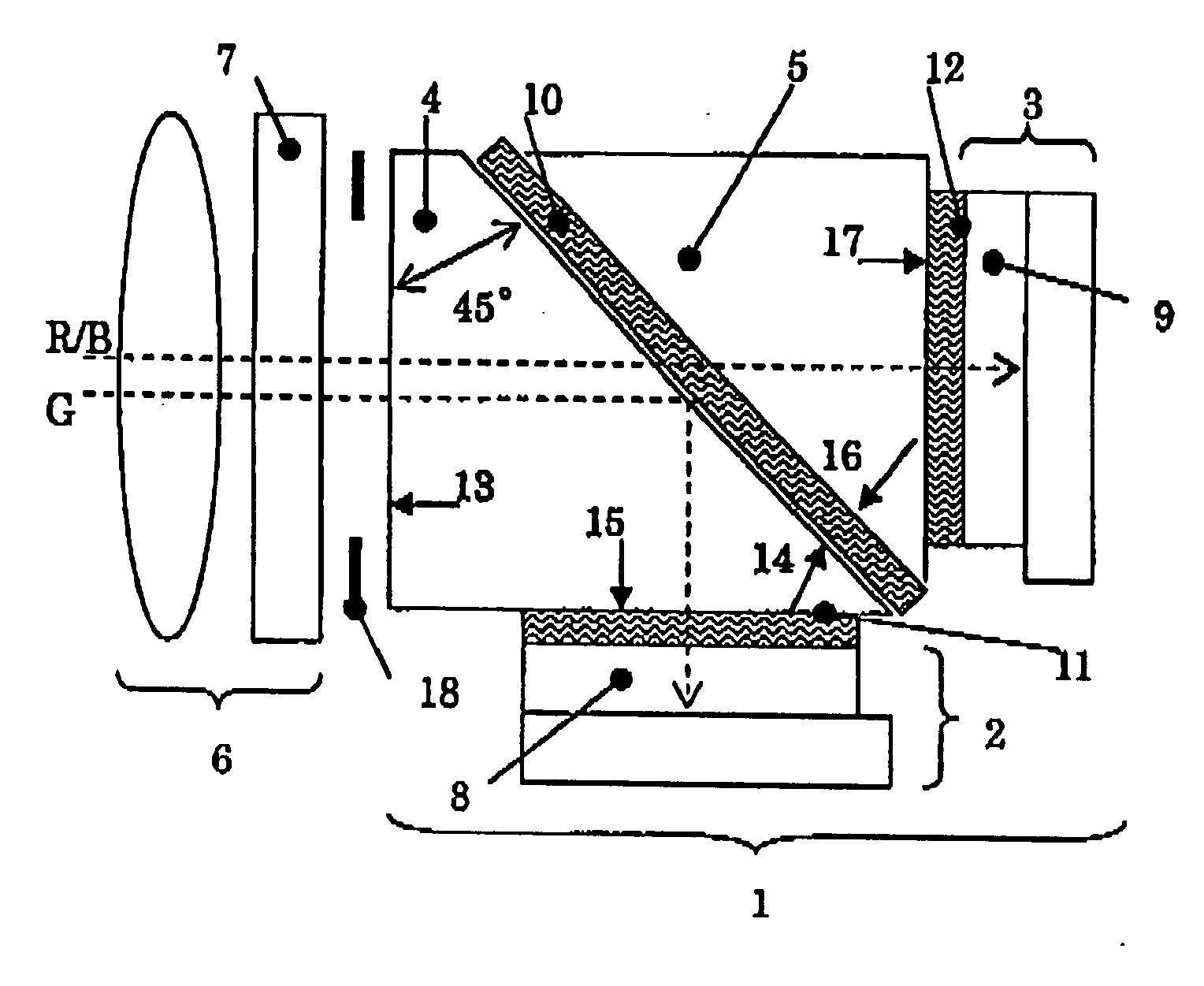
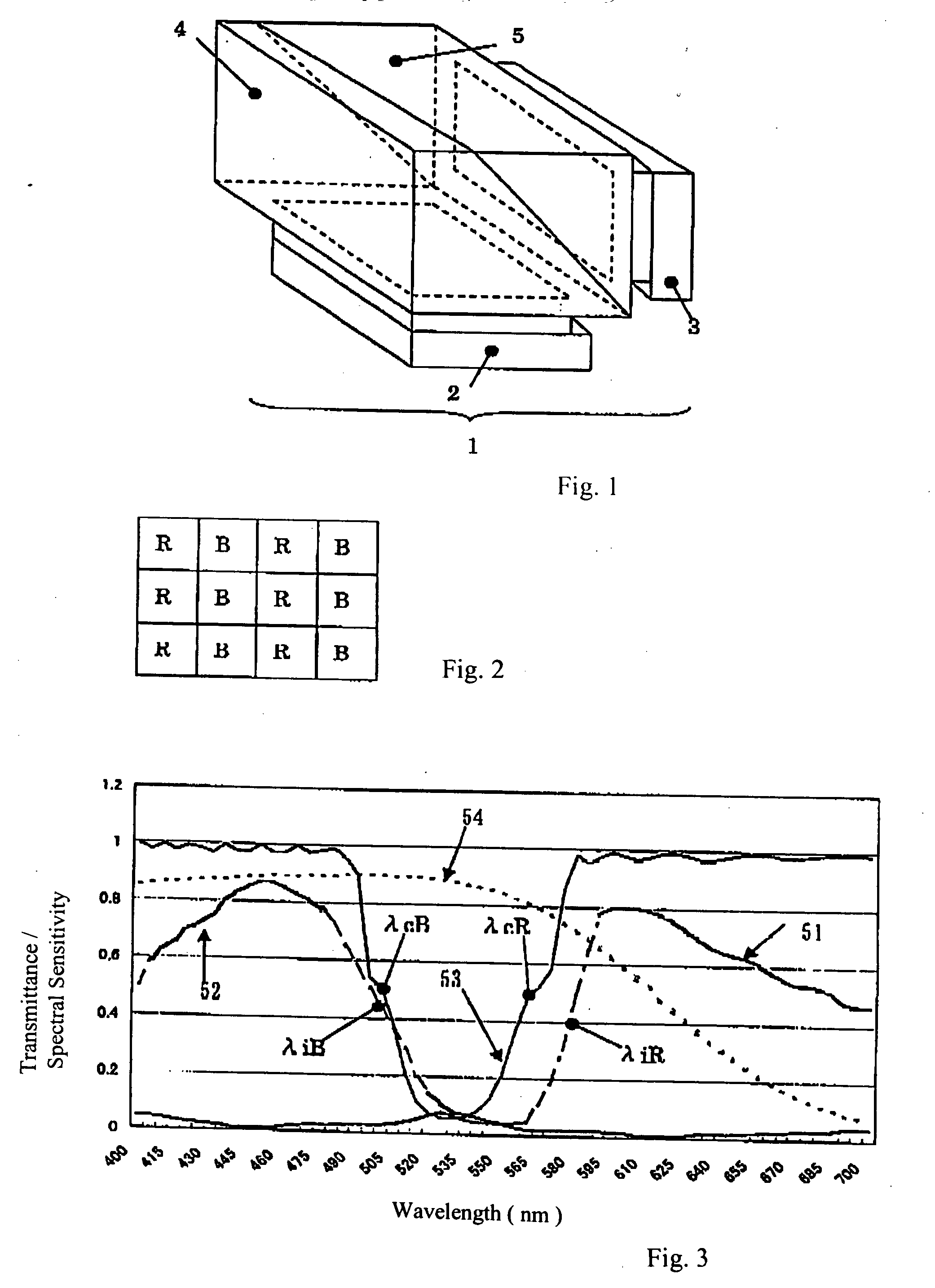
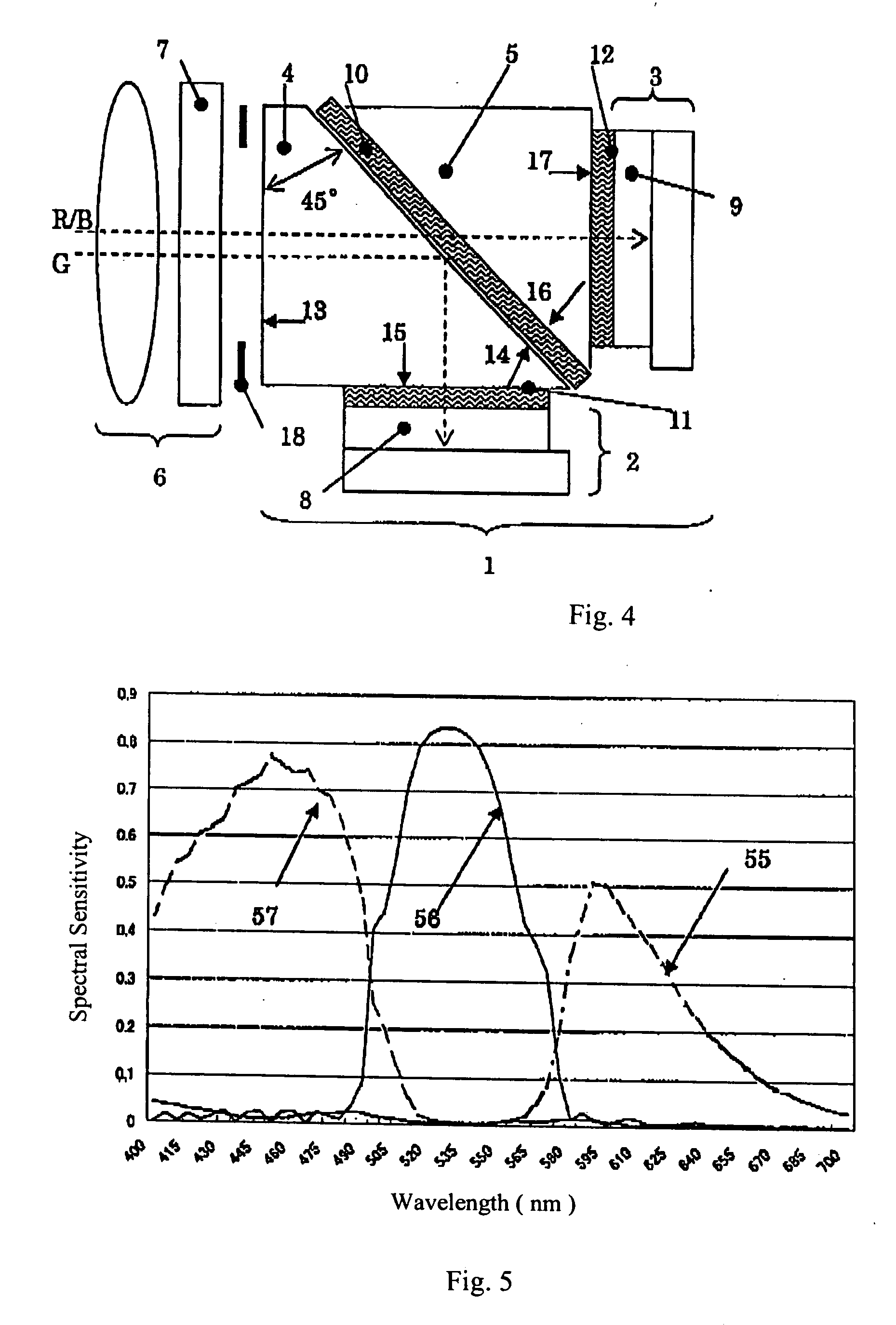
Image pickup apparatus having two image sensors
InactiveUS20070115376A1High return on investmentQuality improvementTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceSpectral transmissionPrism
An image pickup apparatus having two image sensors includes two solid state image pickup devices and a prism group that includes a color separation coating that reflects green light. Red and blue transmitting “on chip” color filters are supported on one of the two solid state image pickup devices. The image pickup apparatus has a spectral design to control color shading in changing environments, and is also designed for easy assembly. The spectral design requires that the spectral transmission characteristics of the color separation coating, the red and blue transmitting color filters, and the spectral sensitivity characteristics of pixels of the solid state image pickup devices satisfy certain conditions that pertain to boundaries between the red, blue, and green light. Image readout is provided by combining two adjacent pixels of the image field. A method of manufacturing such an image pickup apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Acoustic assessment of fluids in a plurality of reservoirs
InactiveUS6938995B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow propertiesAuditory radiationCoupling
The invention provides devices and methods for acoustically assessing the contents of a plurality of reservoirs that are typically provided as an array. An acoustic radiation generator is employed for generating acoustic radiation having an image field of a size sufficient to interrogate a plurality of selected reservoirs at one time. The generator is placed in acoustic coupling relationship via a fluid acoustic coupling medium to the selected reservoirs, and acoustic radiation generated by the generator is transmitted through the coupling medium, an exterior surface of the selected reservoirs, and the selected reservoirs. A characteristic of the transmitted acoustic radiation is analyzed so as to assess the contents of each of the selected reservoirs. Fluid may be ejected from the selected reservoirs according to the assessment. Optionally, a means is provided for removing fluid acoustic coupling medium from the exterior surface after acoustic assessment.
Owner:LABCYTE
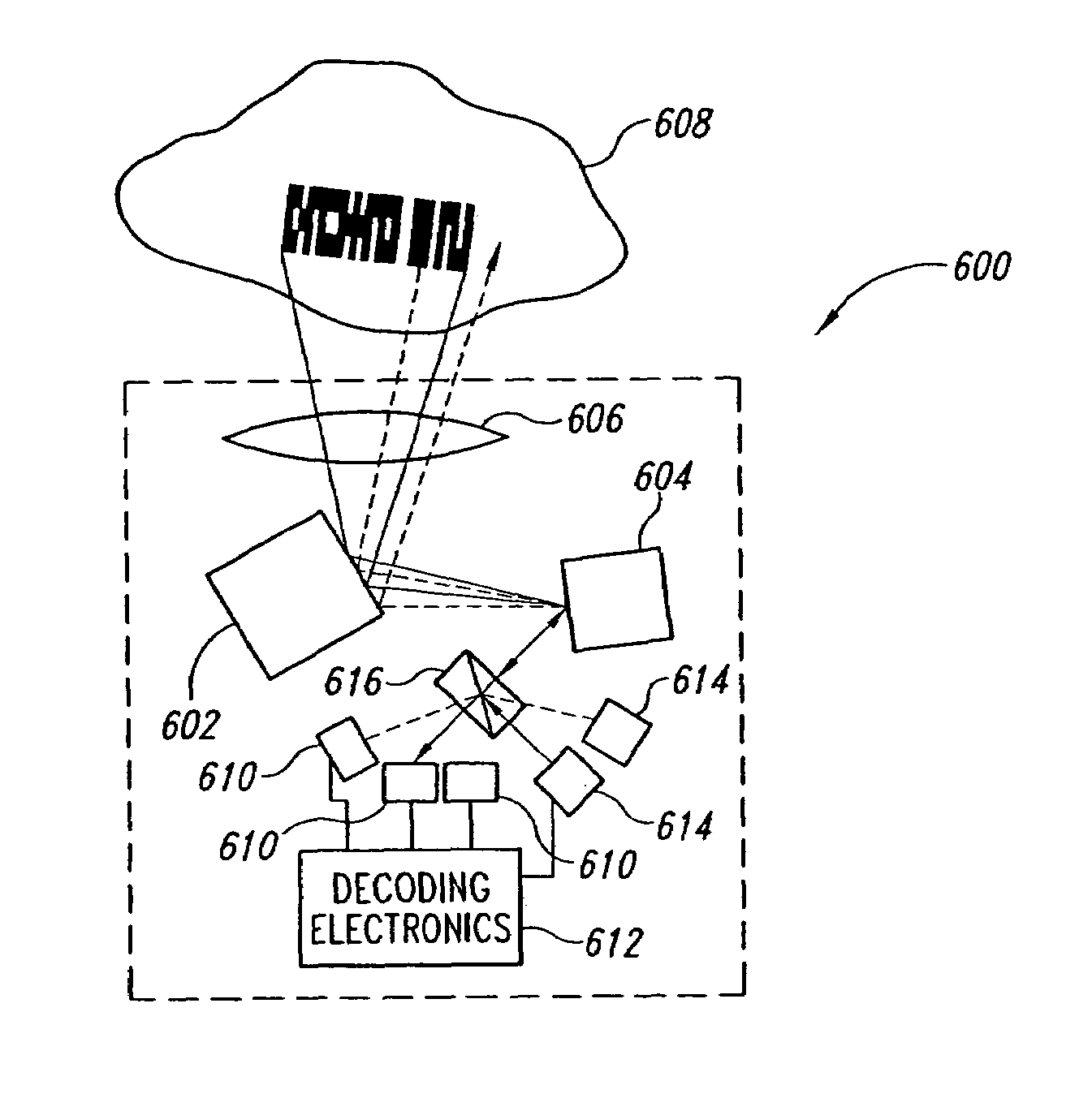
Image-based code reader for acquisition of multiple views of an object and methods for employing same
ActiveUS20100163627A1Visual representatino by photographic printingSensing by electromagnetic radiationDepth of fieldCard reader
Fold mirrors permit the imagers to be closer to each other and permit an optical code reader, such as a tunnel scanner, to confine them to a smaller housing volume or capacity. A plurality of sets of fold mirrors can also be employed to convey at least a portion of at least two different perspectives or two different depths of field of a composite view volume to different regions of an image field of a common imager. The sets of fold mirrors may also include split mirrors that have mirror components that reflect images from different view volumes to different imagers or different regions of an image field of a single imager.
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
Refractive projection objective for immersion lithography
InactiveUS7187503B2Small sizeGood correction stateMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHigh numerical apertureOptoelectronics
A purely refractive projection objective suitable for immersion microlithography is designed as a single-waist system with five lens groups, in the case of which a first lens group with negative refractive power, a second lens group with positive refractive power, a third lens group with negative refractive power, a fourth lens group with positive refractive power and a fifth lens group with positive refractive power are provided. A constriction site of narrowest constriction of the beam bundle lies in the region of the waist. A waist distance AT exists between the object plane and the constriction site X. The condition AT / L≦0.4 holds for a distance ratio AT / L between the waist distance AT and an object-image distance L of the projection objective. Embodiments of inventive projection objectives reach very high numerical apertures NA>1.1 in conjunction with a large image field and are distinguished by a compact overall size and good correction of the lateral chromatic aberration.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Projection apparatus
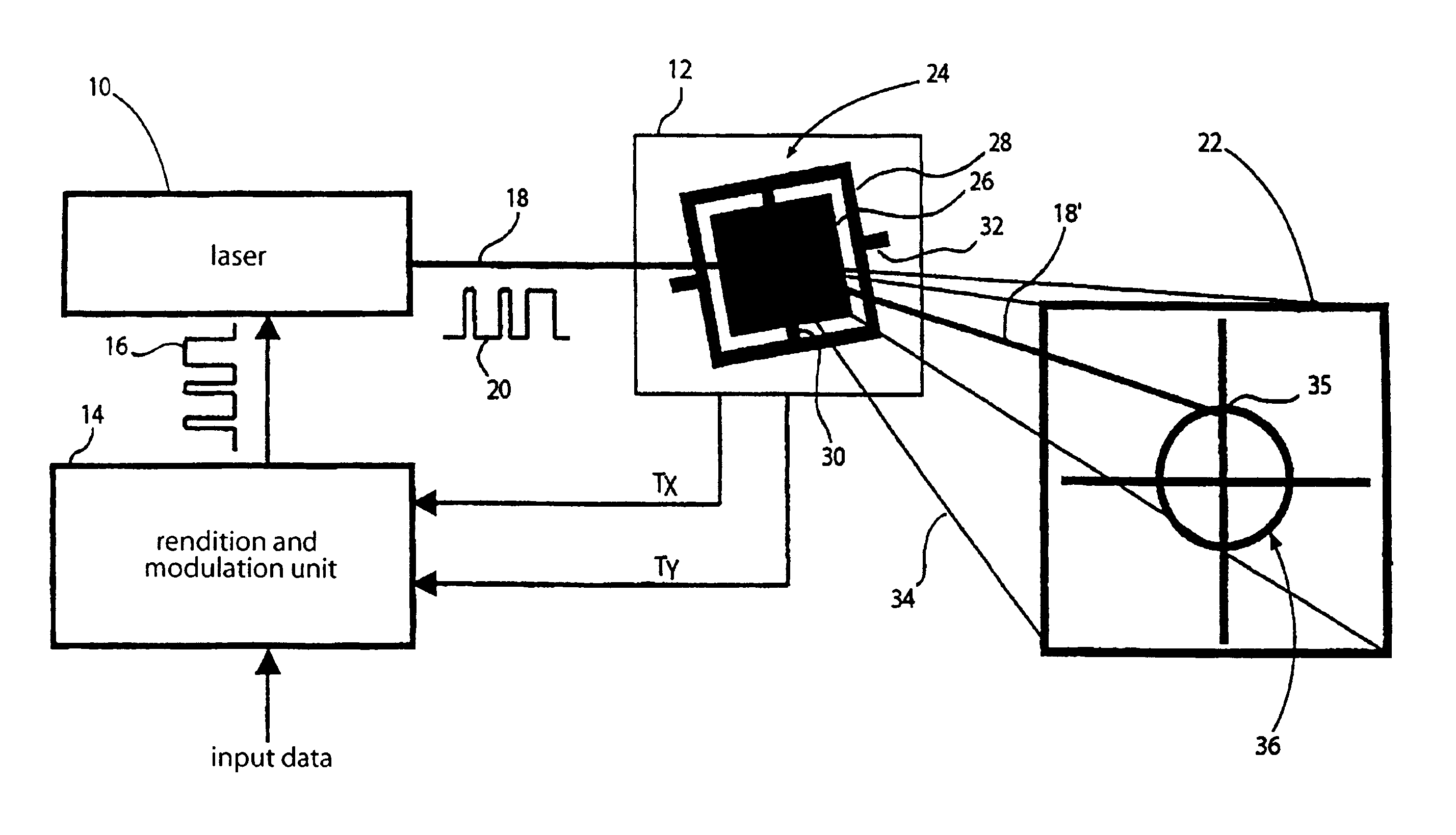
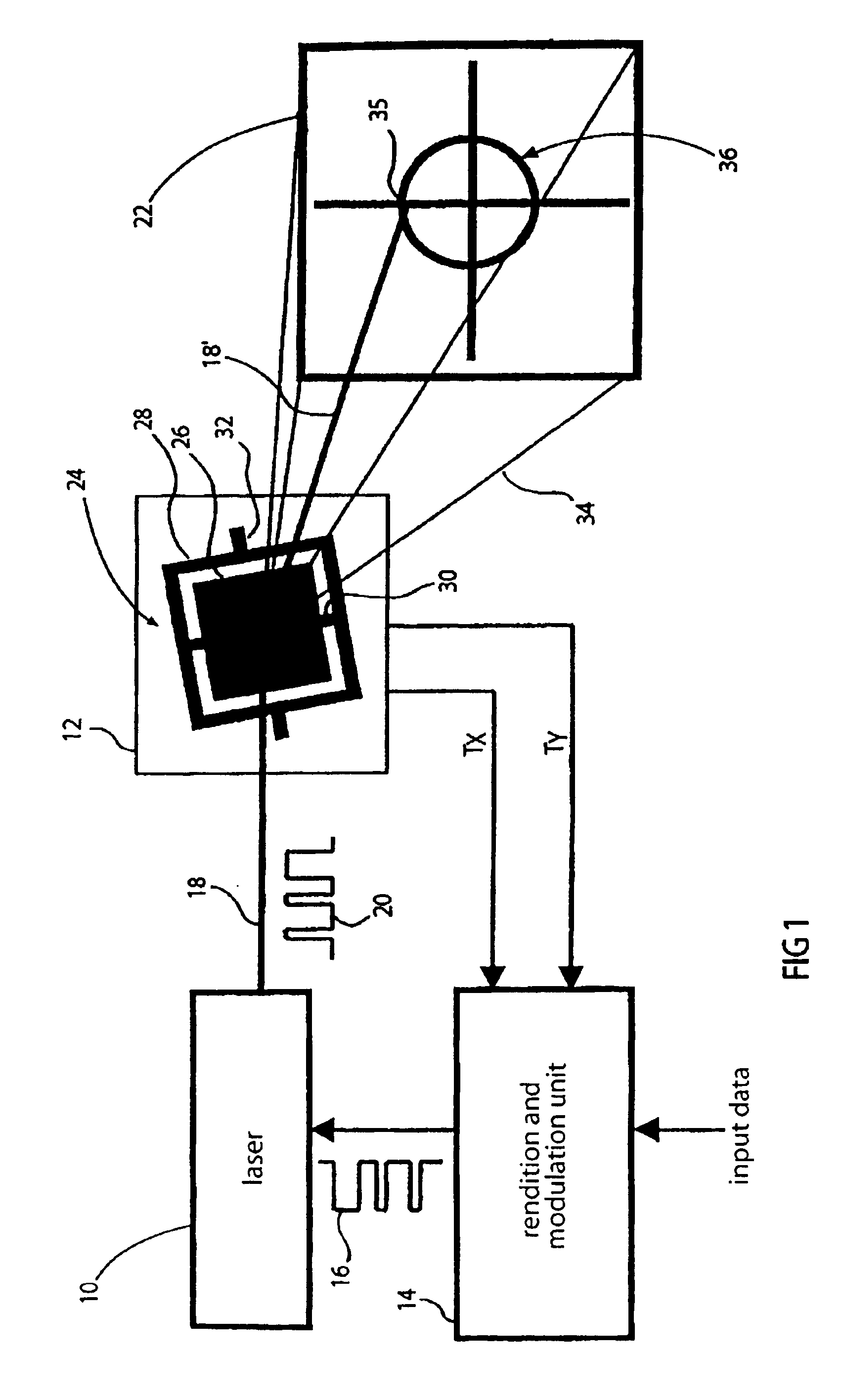
The present invention is based on the finding that the previous column and row representation in the scanning image projection has to be given up, in order to enable that the ratio between row and column frequency or vertical and horizontal deflection frequency is not critical and may be decreased. An inventive projection apparatus for projecting an image on an image field includes a deflection means for deflecting a light beam about a first deflection axis at a first deflection frequency and about a second deflection axis at a second deflection frequency different from the first, in order to move the light beam across the image field, as well as a modulation means for modulating an intensity of the light beam depending on the image to be projected. The first and second deflection frequencies differ by less than an order of magnitude.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Commercial skip and chapter delineation feature on recordable media
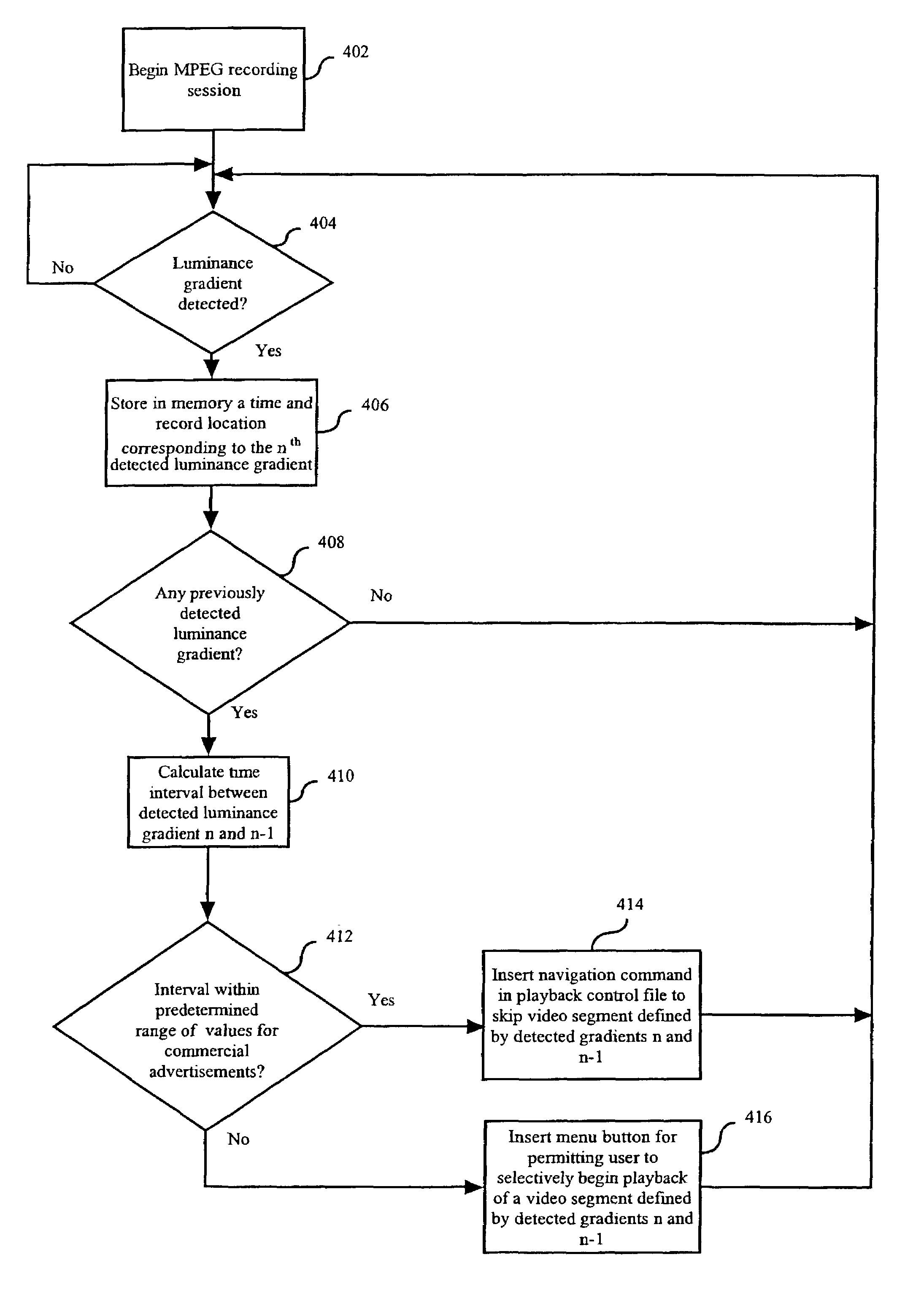
InactiveUS7272295B1Automatically identifyAutomatically selectively skipTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer graphics (images)Data recording
A method and apparatus for controlling an MPEG video media recording device to automatically identify and selectively skip segments of a video signal, such as commercial advertisements, during a recording session. During an MPEG video data recording session the system continuously monitors the video data being recorded to detect a scene change occurring over one or more image fields. In response to a detected scene change, the system stores in a file a time and record location on the media corresponding to the occurrence of the scene change. Depending upon the time interval between several of the detected scene changes, the system identifies a corresponding video segment as either a commercial advertisement or a chapter boundary. By identifying the segments in this way, the playback presentation can then be selectively controlled.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Techniques of modifying image field data by exprapolation
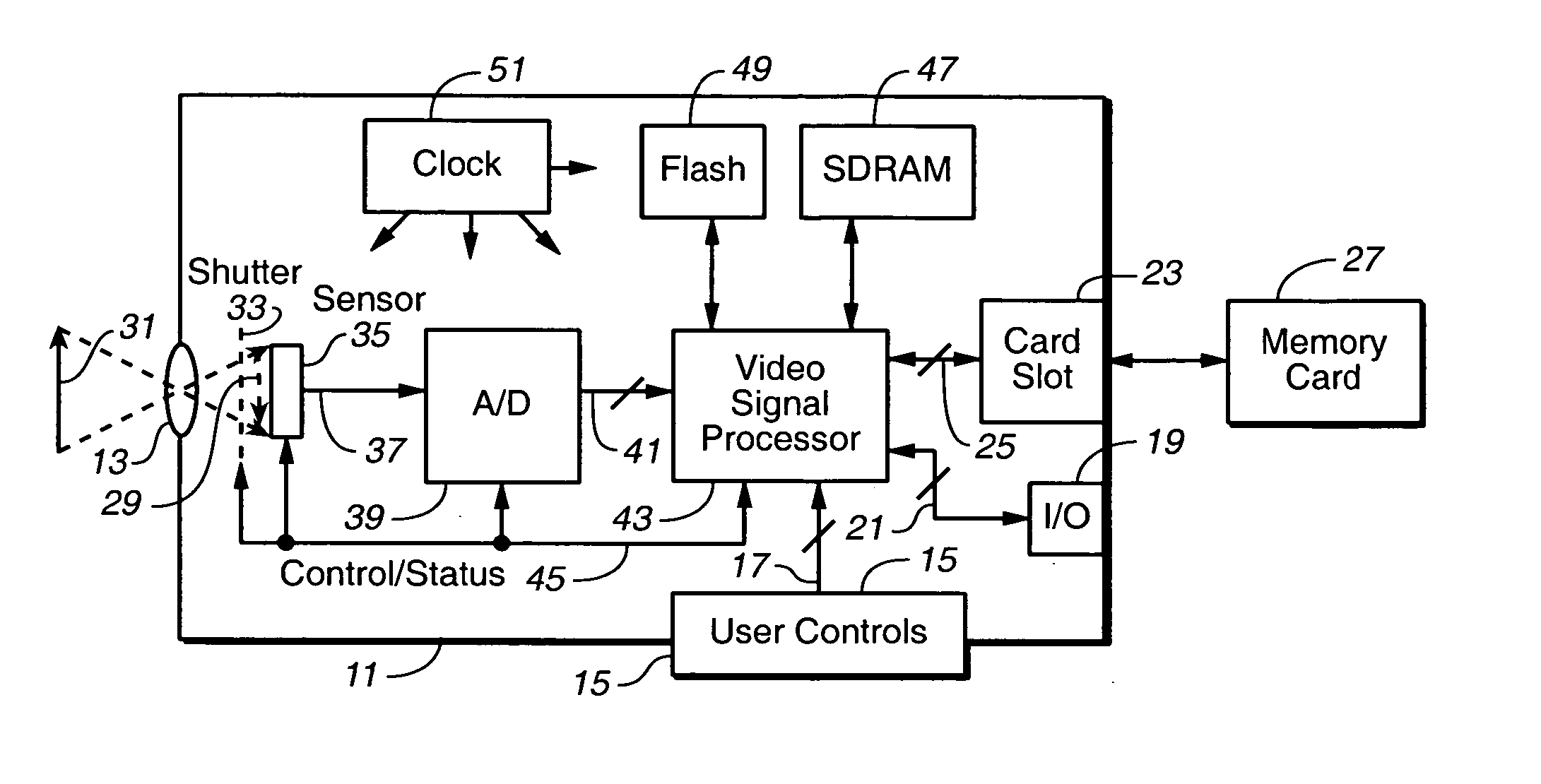
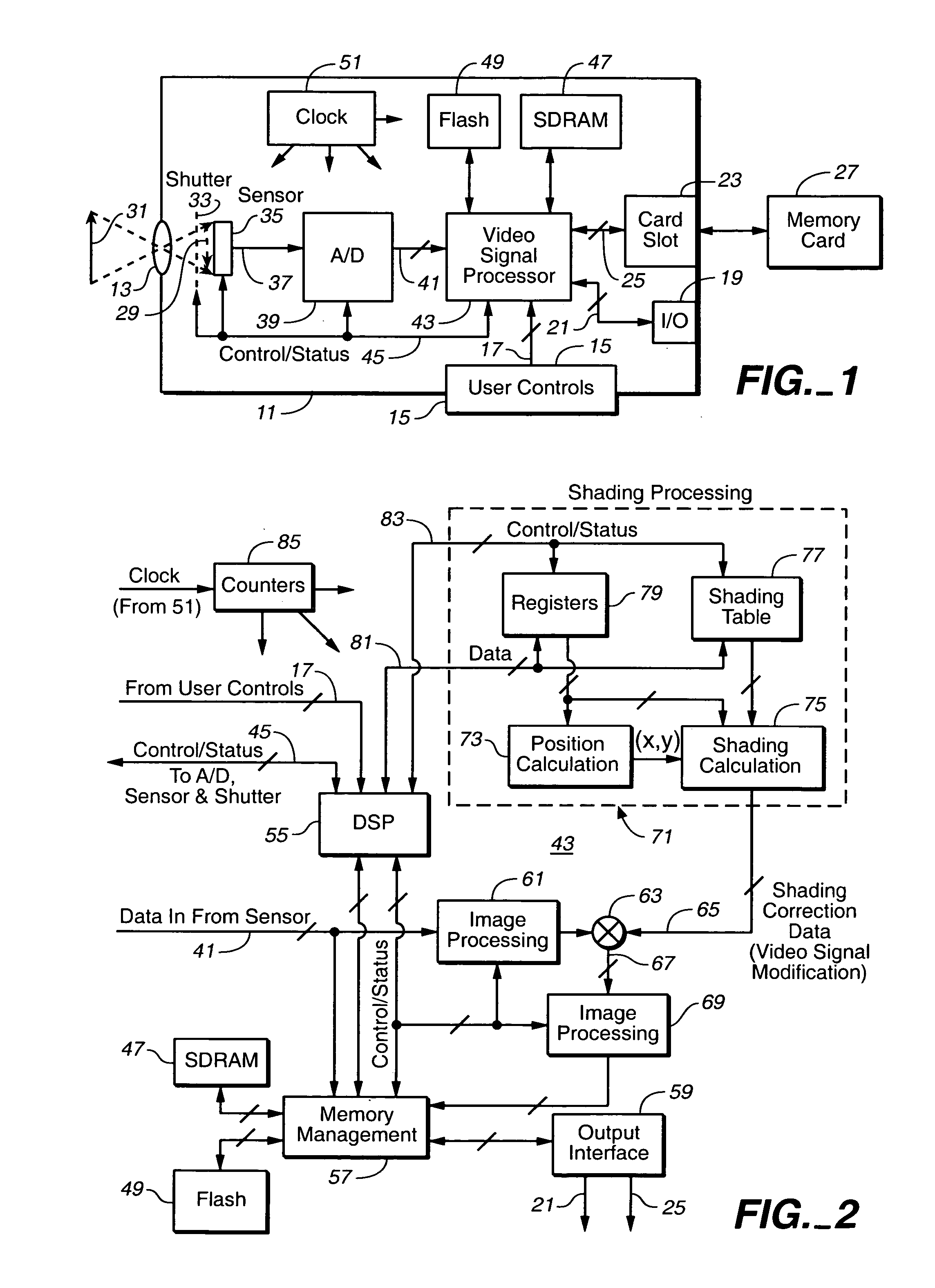
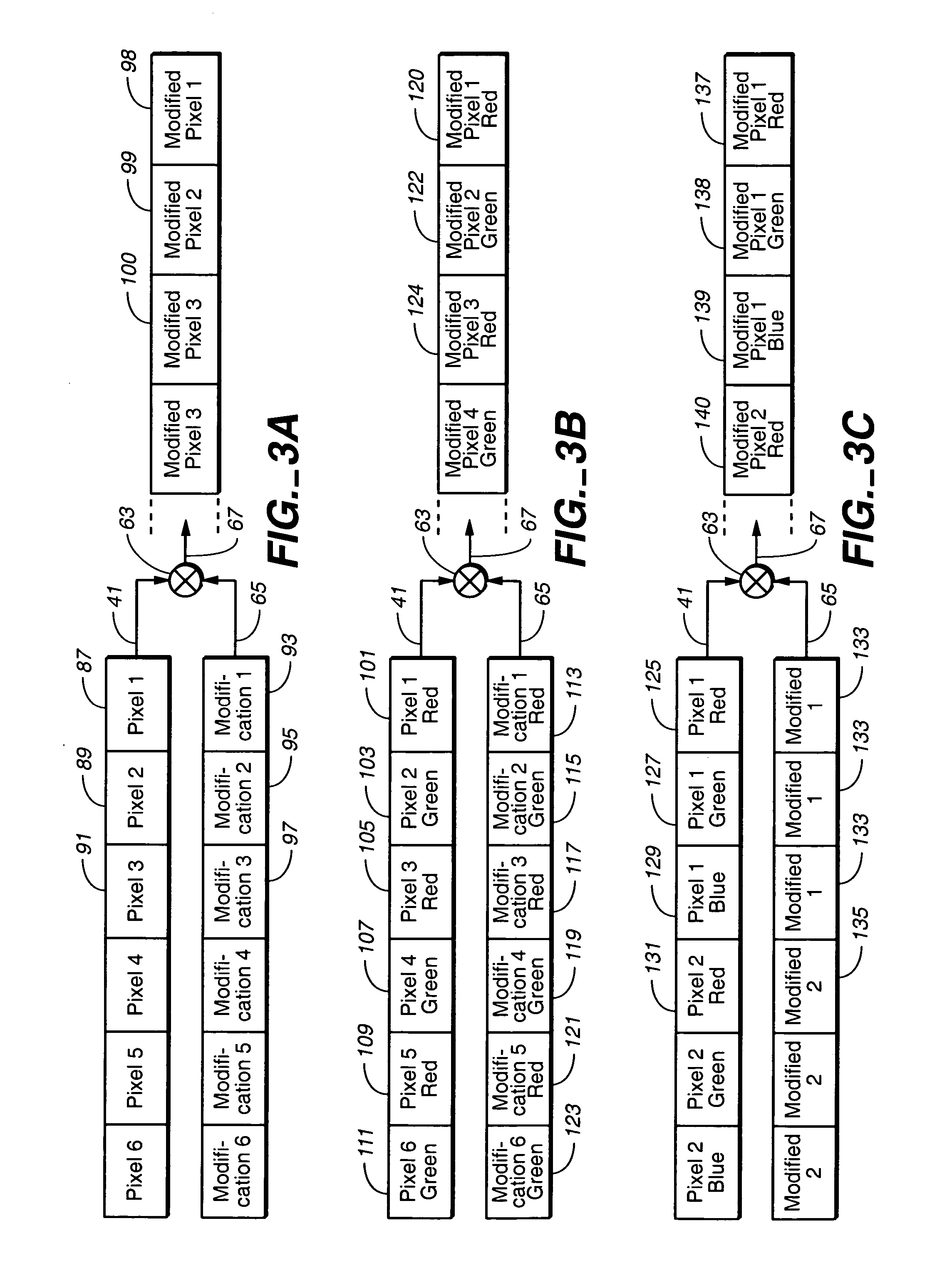
ActiveUS20050041806A1Low costNot adversely performanceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsVideo imageData transmission
Techniques for modifying data of an image that can be implemented in a digital camera, video image capturing device and other optical systems are provided to correct for Image image shading variations appearing in data from a two-dimensional photo-sensor. These variations can be caused by imperfect lenses, non-uniform sensitivity across the photo-sensor, and internal reflections within a housing of the optical system, for example. In order to correct for these variations, a small amount of modification data is stored in a small memory within the camera or other optical system, preferably separate correction data for each primary color. Image data from individual pixels are corrected on the fly by interpolating individual pixel corrections from the stored modification data, at the same rate as the image data is being acquired, so that the correction takes place without slowing down data transfer of picture data from the image sensor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Imaging system
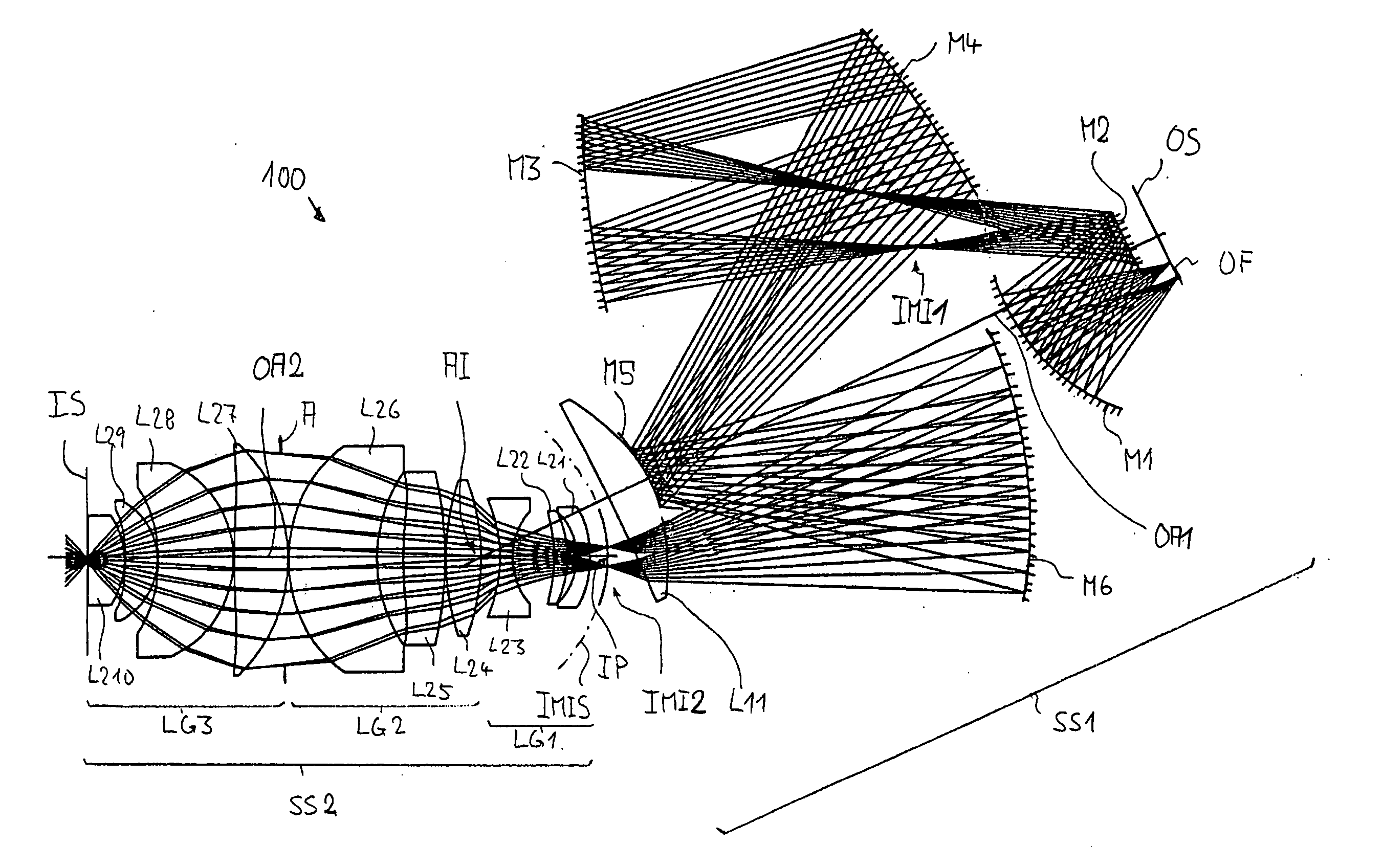
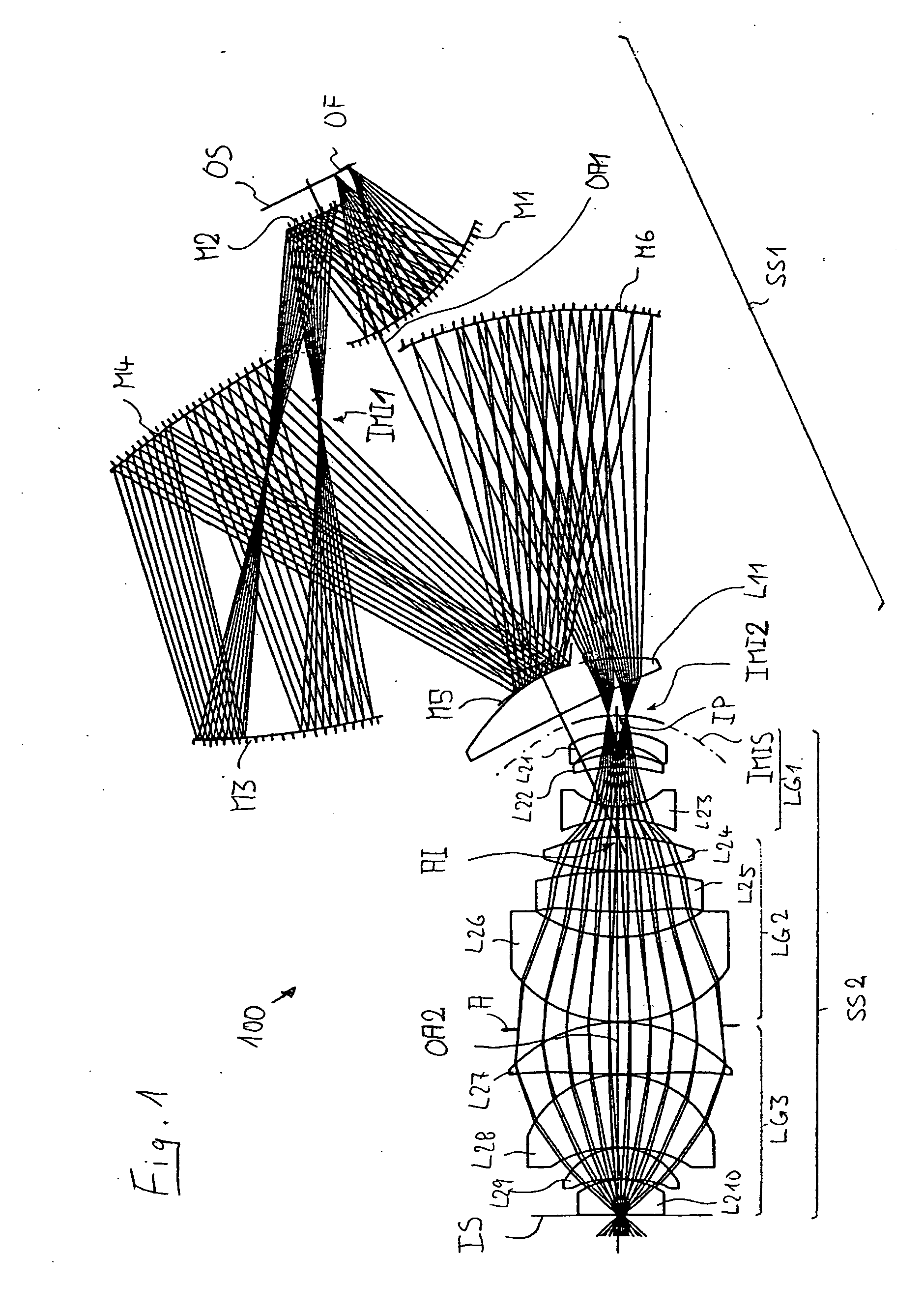
InactiveUS20060198018A1High image side numerical apertureSmall amountPhotomechanical apparatusMicroscopesIntermediate imageOptical axis
An imaging system for imaging an object field arranged in an object surface of the imaging system onto an image field arranged in an image surface of the optical system while creating at least one intermediate image including: a first imaging subsystem for creating the intermediate image from radiation coming from the object surface, the first imaging subsystem having a first optical axis; and a second imaging subsystem different in construction from the first imaging subsystem for imaging the intermediate image onto the image surface, the second imaging subsystem having a second optical axis; wherein the first optical axis is offset with respect to the second optical axis by an axis offset at the intermediate image and wherein the intermediate image has a correction status adapted to the axis-offset such that the correction status of the image field is essentially free from aberrations caused by the axis-offset.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Adaptive-scanning optical microscope
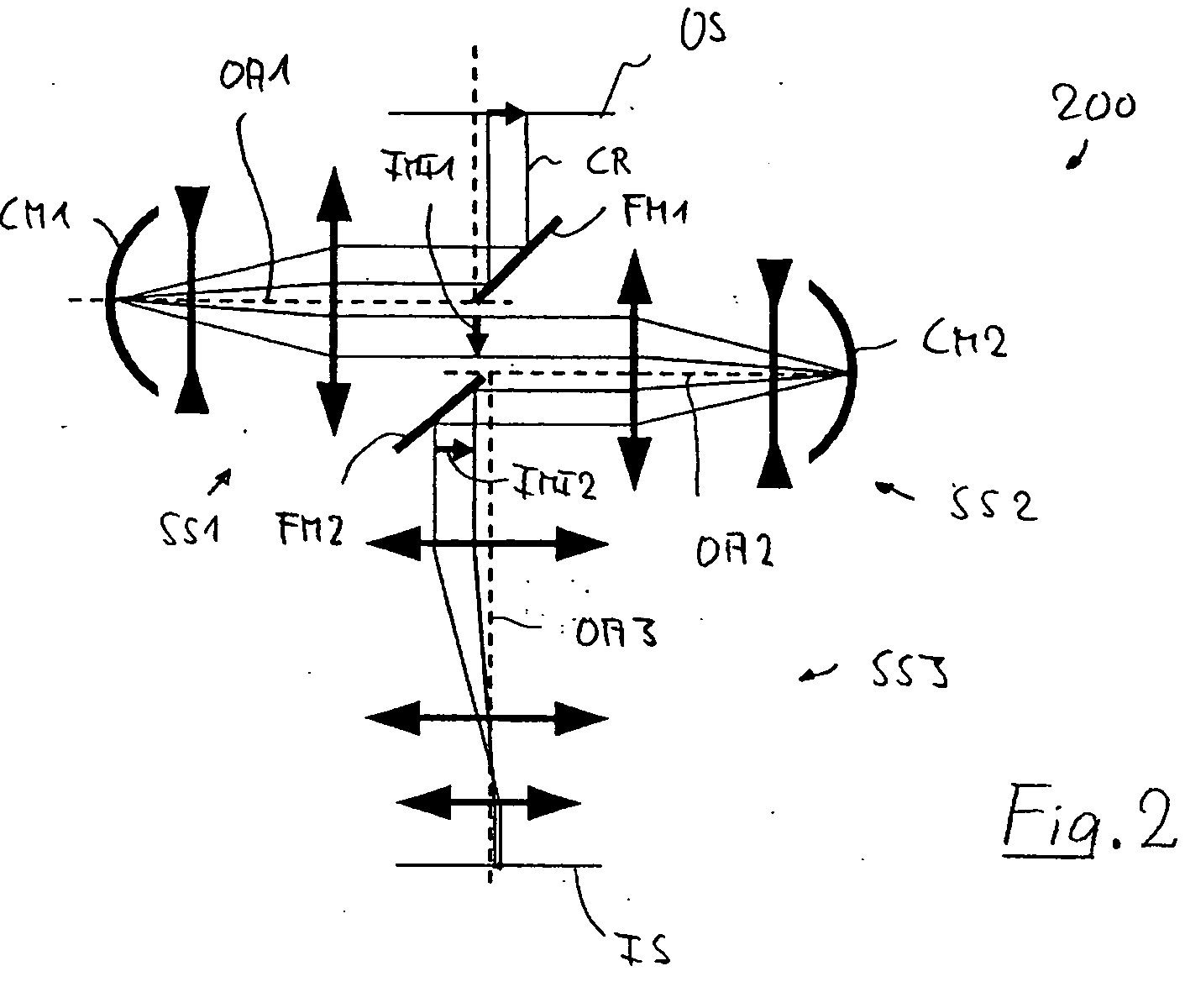
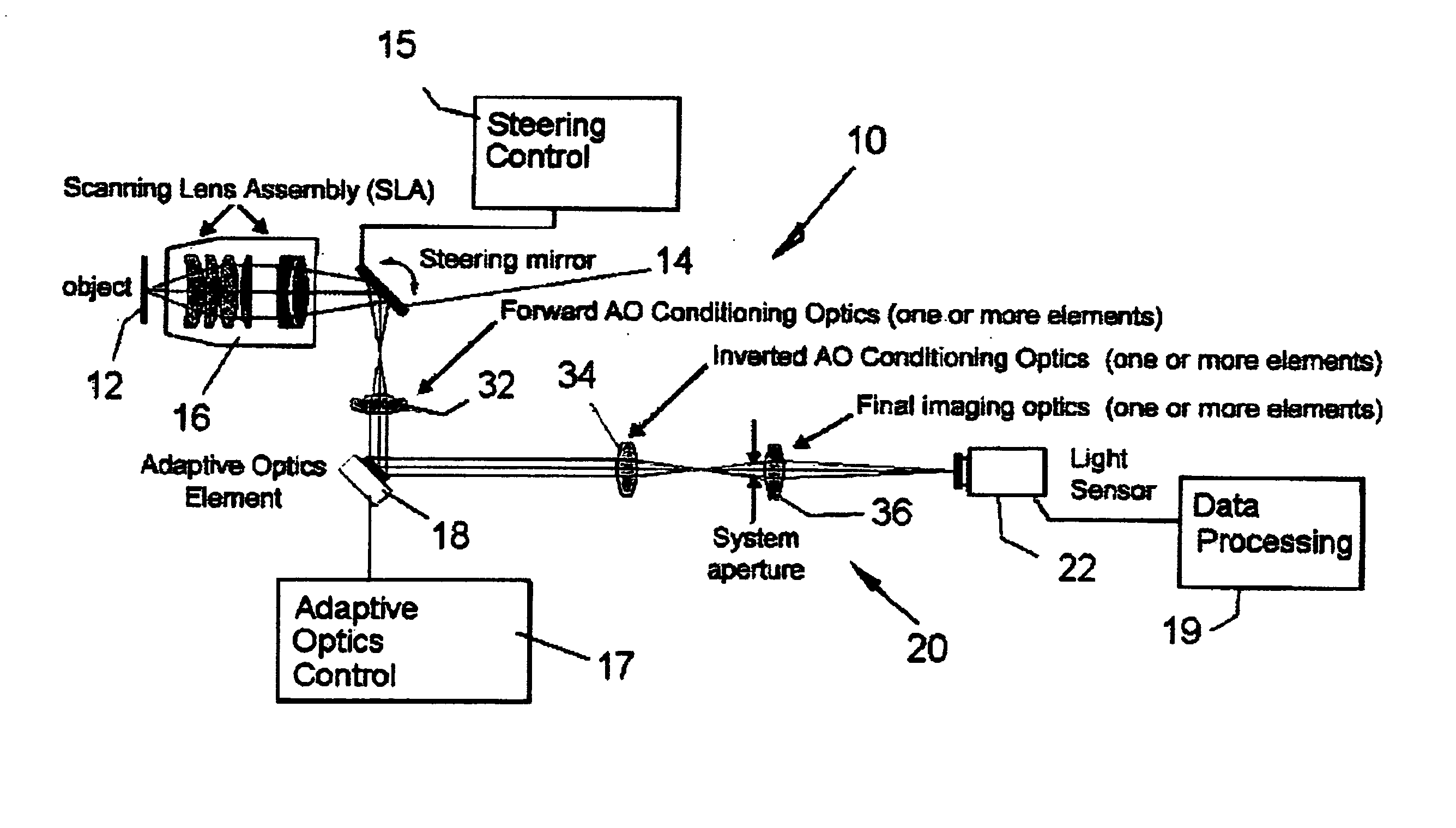
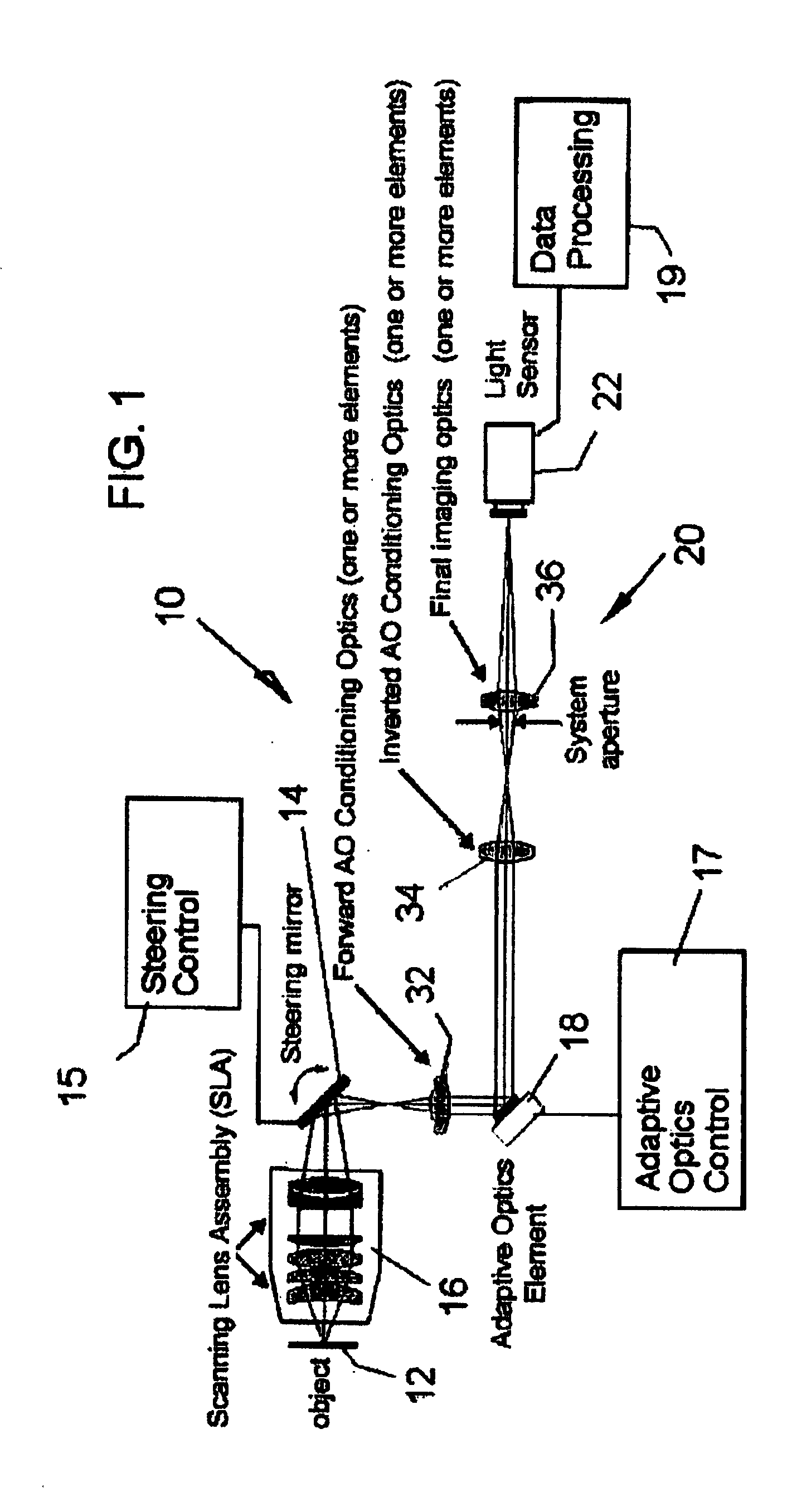
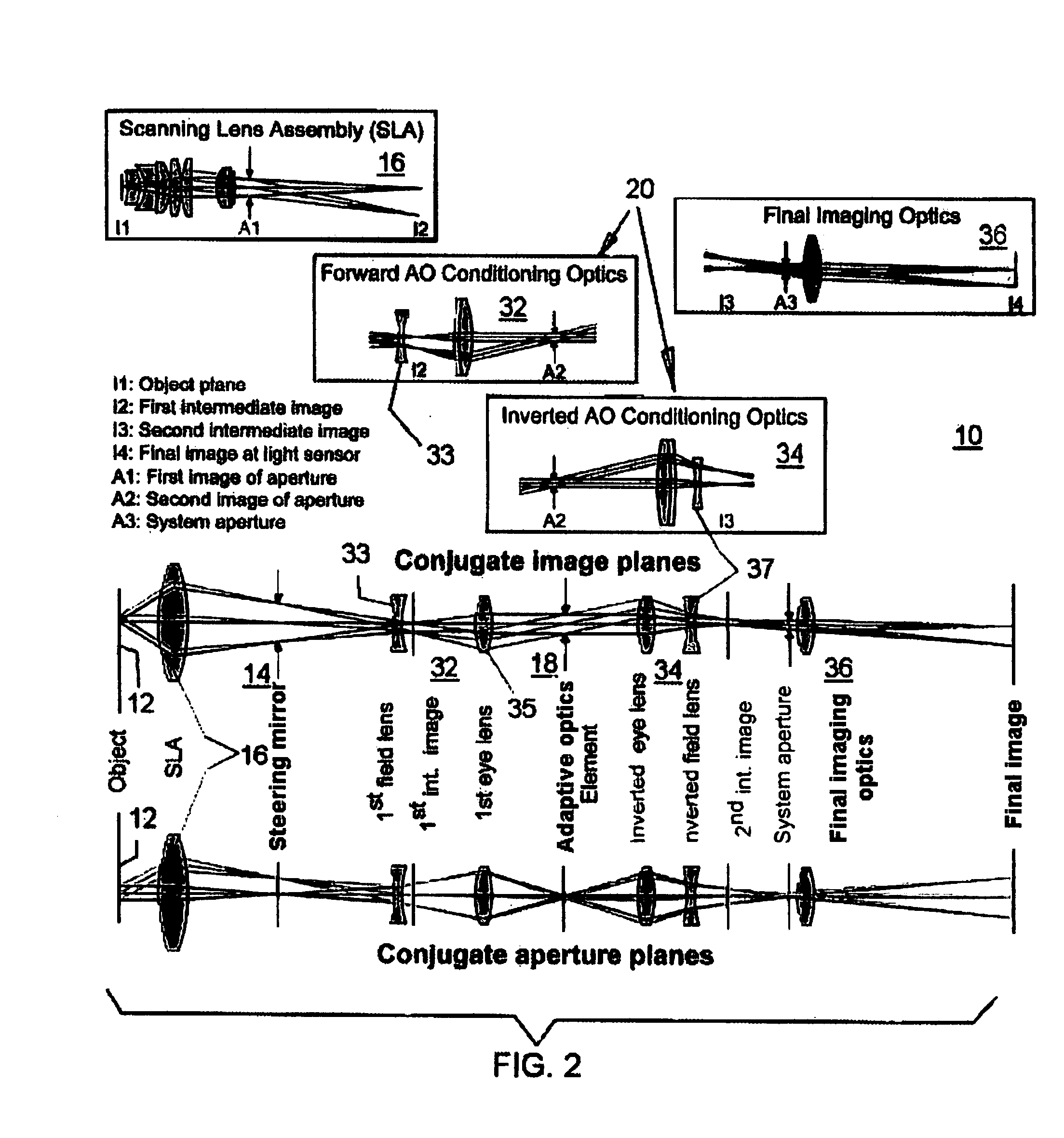
ActiveUS20070253057A1Improve performanceScanner lens is simplifiedMicroscopesPosition dependentOptical aberration
An adaptive scanning optical microscope has a scanner lens assembly for acquiring images from different parts of an object plane and for forming a preferably curved image field having at least some aberration which varies as a function of the part of the object plane from which the image is acquired. A steering mirror selects the field of view and steers light from the object and along a light path from the object plane to a final image plane. An adaptive optics element receives the steered light from the object and compensates for the field position dependent optical aberrations and additional optics are along at least part of the light path for conditioning and focusing the light as it moves from the steering mirror, past the adaptive optics element and to the final image plane.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
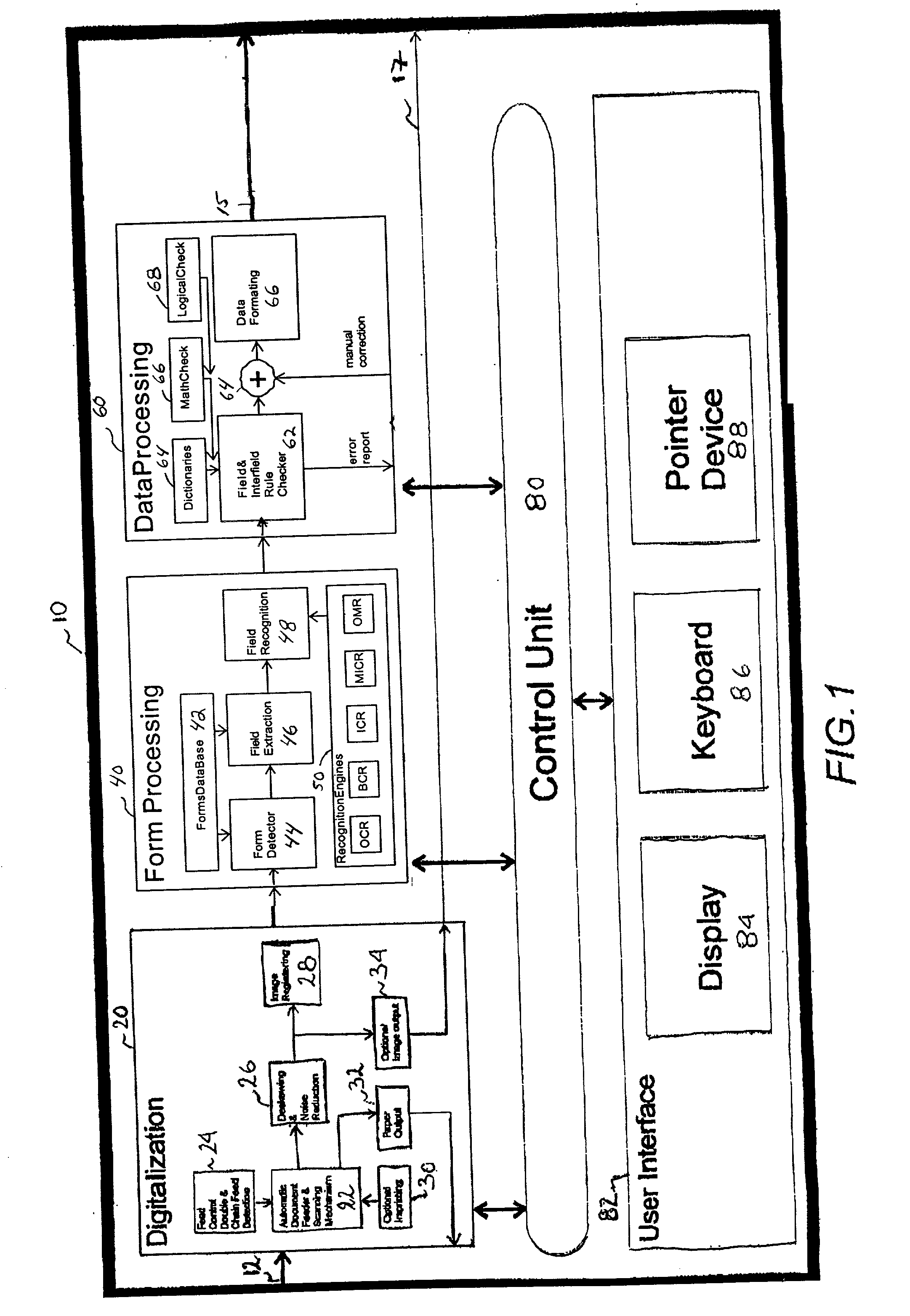
Document scanner, system and method
The document scanner, system and method operates in conjunction with a document imprinted with data and a plurality of form documents adapted to have data imprinted thereon. The documents have at least one and typically many data image fields. Ultimately, the document scanner, system and method outputs a delimited string of decoded characters to another computer system via a common computer communications port. The method includes either scanning a form document to obtain positional information of the data field or fields or inputting a topological description of the field. Typically, the operator identifies descriptors for each data field which include data field size information, data type information, the presence or absence of data validation parameters, the presence or absence of data error reporting and data correction routines or parameters, and data output destination information. The data output destination information locates the decoded data in a certain sequence or location in the delimited string of decoded characters output to the coupled computer system. The document scanner, system and method scans the document imprinted with data and captures an image thereof. The scanned input document image is compared with the stored forms, and particularly the stored data field descriptors utilizing positional, data field size and data type information. The system selects one of the stored forms, extracts the data from each data field, decodes or calculates the data, and validates the data (in the presence of data validation parameters) and stores the decoded / calculated data. A data error reporting and data correction system, activated in the presence of the data error reporting and correction descriptor, enables correction of errors.
Owner:MULTISCAN
Directed attention digital video recordation
ActiveUS20070035623A1Less contentMinimizing dataTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoConnection type
The present invention describes systems and methods of incorporating detailed snapshots of targeted areas of interest into a video or digitized recording of the overall scene including metadata to link the snapshots to the time and location in the overall scene from which the snapshot was acquired. A single fixed high-resolution scene camera or a fixed standard resolution scene camera of analog or IP connected type is used, co-located with at least one pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) camera or by using the same scene camera in a mode where less than full resolution of the scene camera is used for video but snapshots of areas are captured by the same camera where higher resolution thereof is used for snapshots than for video. The area of interest is selected by the object-tracking feature of an intelligent video system, operated without human intervention, by electronically-implemented identification of the existence of area-specific subjects or targets of interest in the scene image field.
Owner:CHECKVIDEO
Multiple beam scanning imager
InactiveUS7209271B2Light provideCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationLight beamGrating pattern
A display apparatus includes a scanning assembly that scans about two or more axes, typically in a raster pattern. A plurality of light sources emit light from spaced apart locations toward the scanning assembly such that the scanning assembly simultaneously scans more than one of the beams. The light sources are positioned such that their beams each illuminate discrete regions of the image field that are substantially non-overlapping with respect to the other discrete regions. The image is thus formed from a set of “tiles”. By activating a first light source during a forward sweep of the mirror and activating a second light source during a reverse sweep of the mirror, two halves a common line can be written during a single sweep of the mirror. Shifting the position of the sources such that the two halves are aligned reduces raster pinch. In alternative embodiments, the same approach is used for imaging. Also, various approaches to controlling the frequency responses of the various scanners are described, including active control of MEMs scanners and passive frequency tuning.
Owner:MICROVISION
Automatic detection of fluorescent flicker in video images
ActiveUS7502054B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsFrequency spectrumFluorescence
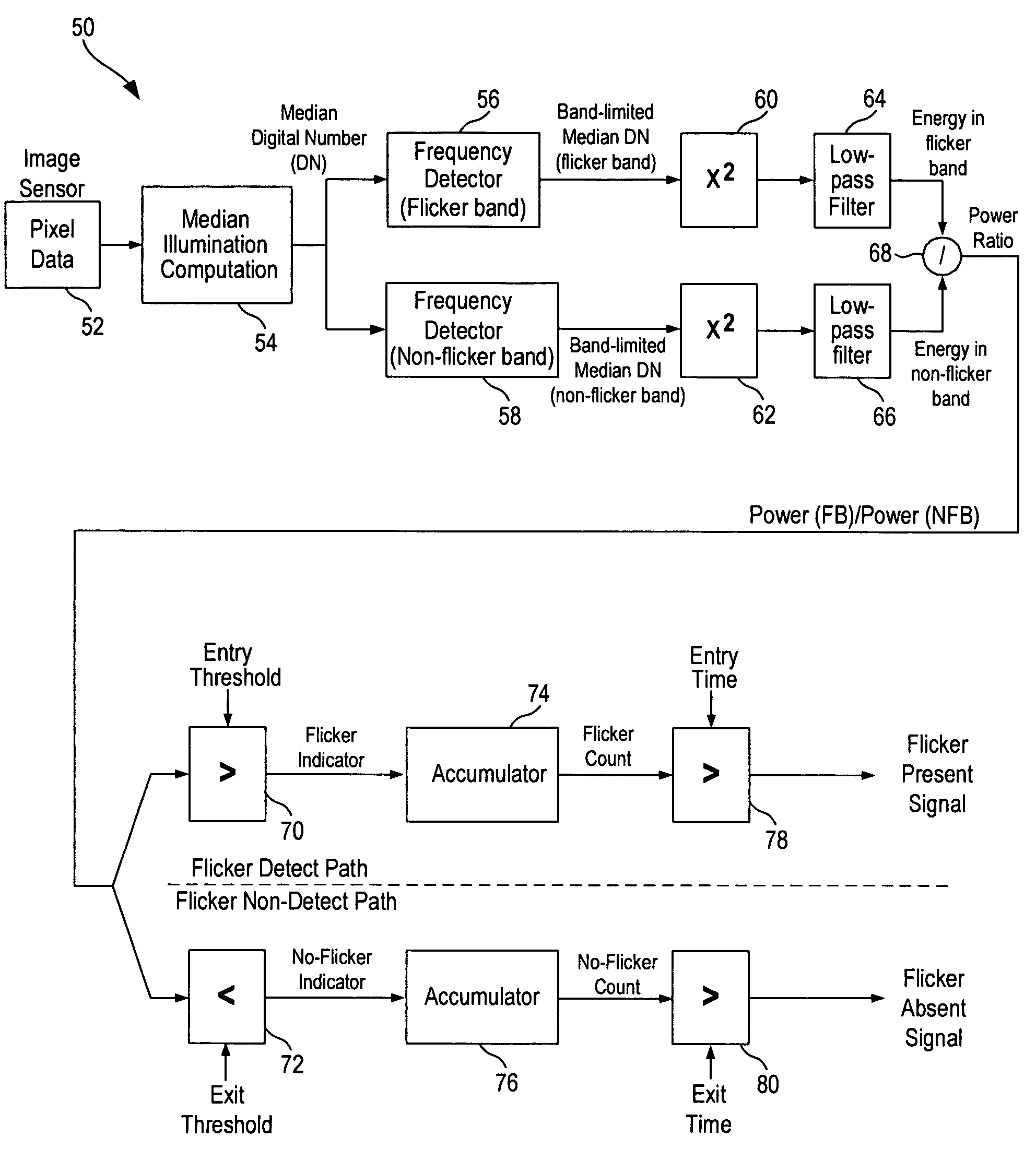
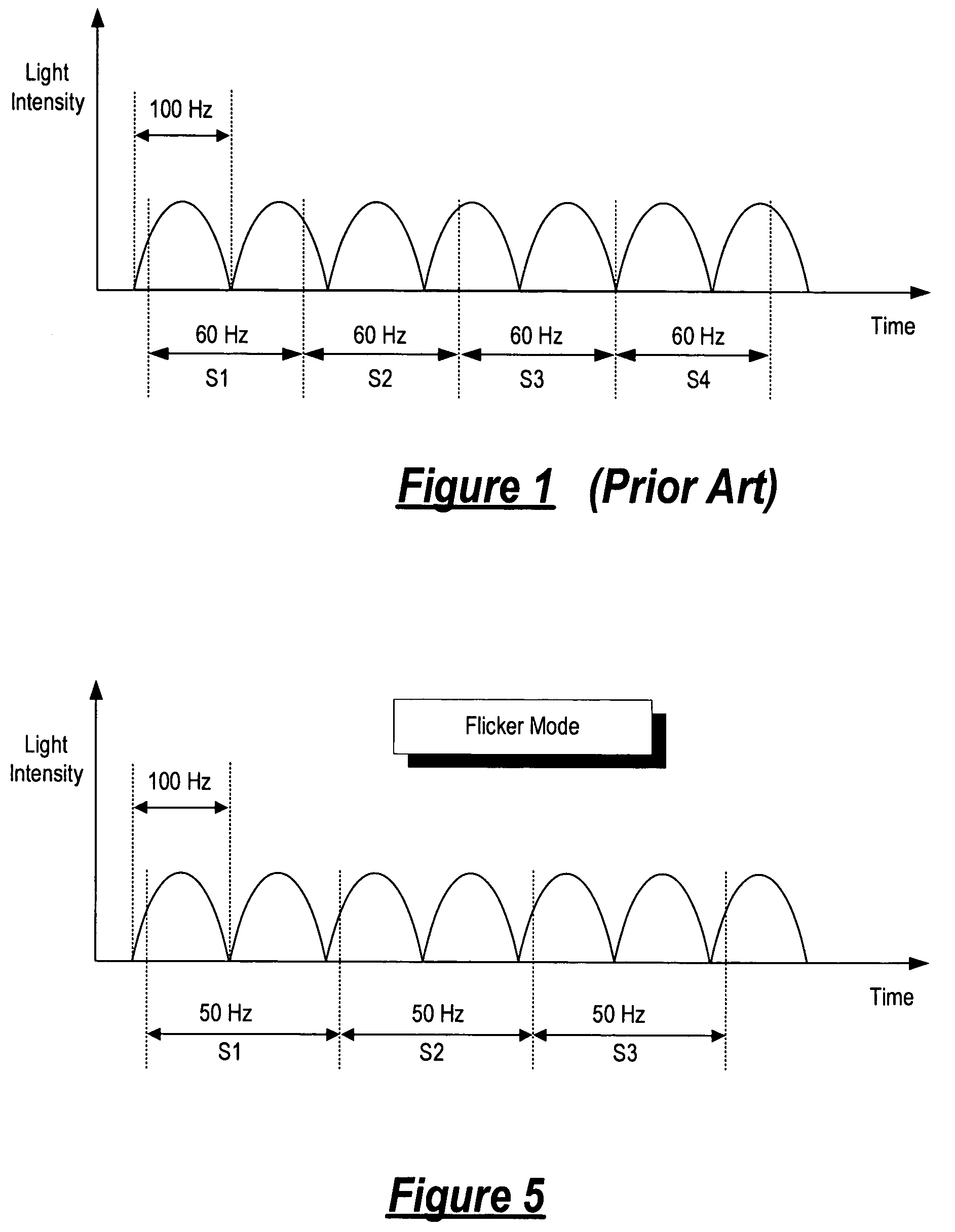
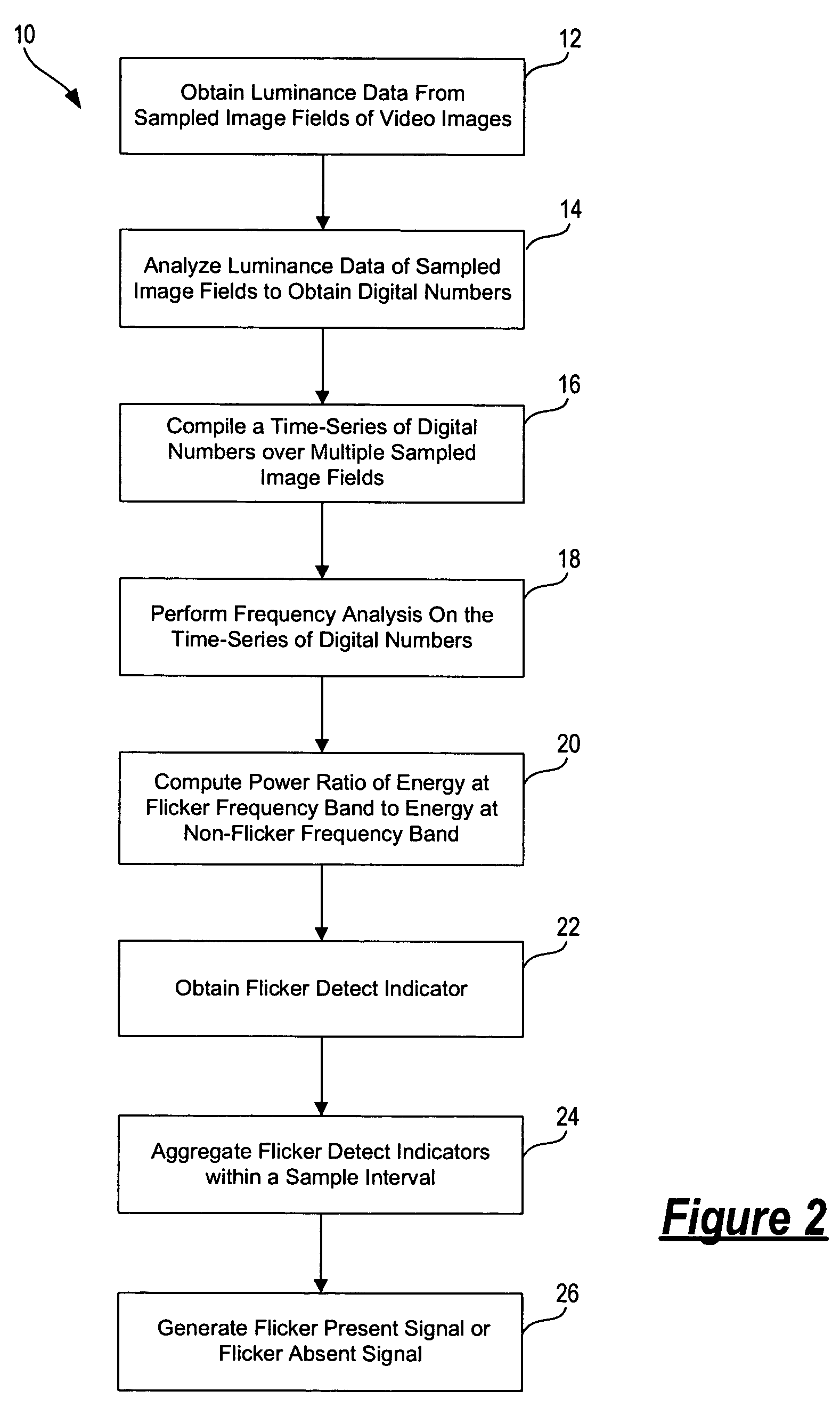
A method for detecting the presence of flicker in video images includes obtaining luminance data from sampled image fields and analyzing the luminance data to obtain a digital number characterizing the brightness of the luminance data. Frequency analysis is performed on a time-series of digital numbers collected over multiple sampled image fields to provide a signal indicative of the spectral energy at a flicker frequency band and a signal indicative of the spectral energy at a non-flicker frequency band. A ratio of the two spectral energy signals is computed as the flicker detect indicator. Multiple flicker detect indicators are accumulated to generate a flicker present signal. In one embodiment, the flicker detect indicator is accumulated only when the ratio has a value greater than a first threshold and the flicker present signal is asserted only when the number of flicker detect indicator signals accumulated exceeds an entry value.
Owner:PIXIM
Method for motion estimated and compensated field rate up-conversion (FRU) for video applications and device for actuating such method
InactiveUS6240211B1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh activationMostly True
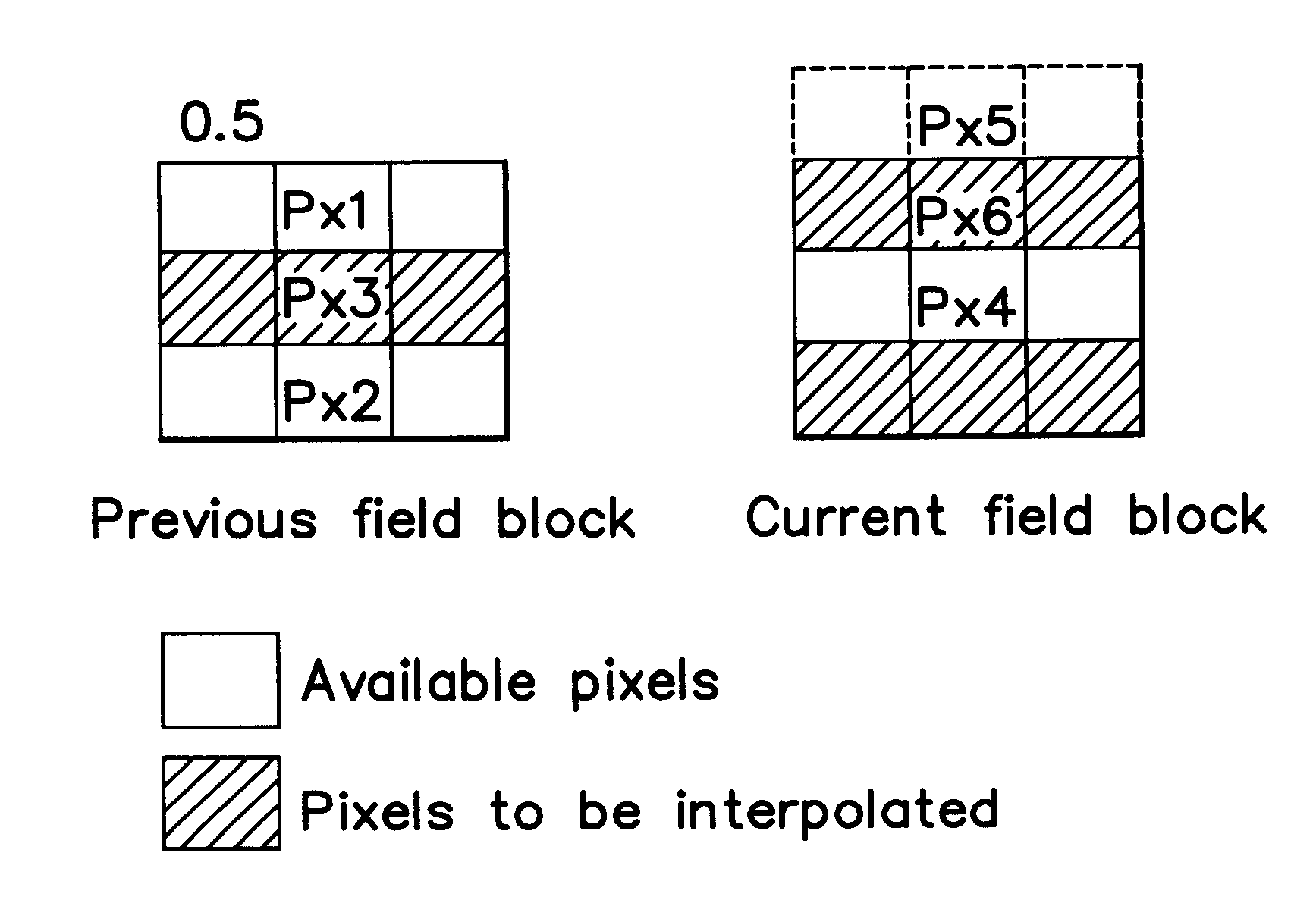
A method and a device for motion estimated and compensated Field Rate Up-conversion (FRU) for video applications is disclosed and claimed. The invention provides for dividing an image field to be interpolated into a plurality of image blocks, where each image block includes a respective set of image elements of the image field. In one embodiment, for each image block of a subset of image blocks, a group of neighboring image blocks is selected. A motion vector for the image block is estimated that describes the movement of the image block from a previous image field to a current image field on the basis of predictor motion vectors associated to the group of neighboring image blocks. Each image element of the image block is determined by interpolation of two corresponding image elements in the previous and current image fields related by the estimated motion vector. To estimate a motion vector, the invention provides for applying each of the predictor motion vectors to the image block to determine a respective pair of corresponding image blocks in the previous and current image fields. For each of the pairs of corresponding image blocks, an error function which is the Sum of luminance Absolute Difference (SAD) between corresponding image elements in the pair of corresponding image blocks is evaluated. For each pair of the predictor motion vectors, a degree of homogeneity is also evaluated, followed by the application of a fuzzy rule having an activation level that is proportional to the degree of homogeneity of the pair of predictor motion vectors and the error functions of the pair of predictor motion vectors. An optimum fuzzy rule having the highest activation level is selected, from which the best predictor motion vector is determined, having the smaller error function of the pair associated to the optimum fuzzy rule. In most cases, the motion vector for the image block is estimated on the basis of the best predictor motion vector.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Apparatus and Method for Analyzing a Bodily Sample
ActiveUS20160279633A1Diagnosis considerableExpense of considerableBiological particle analysisLaboratory glasswaresImaging processingDigital image
Apparatus and methods are described for use with a digital camera that is configured to acquire images of a bodily sample. Two or more stains are configured to stain the bodily sample. A computer processor drives the digital camera to acquire, for each of a plurality of imaging fields of the bodily sample, two or more digital images, at least one of the images being acquired under brightfield lighting conditions, and at least one of the images being acquired under fluorescent lighting conditions. The computer processor performs image processing on the digital images, by extracting visual classification features from the digital images and analyzing the extracted visual classification features. The computer processor outputs a result of the image processing that includes an indication of one or more entities that are contained within the sample. Other applications are also described.
Owner:S D SIGHT DIAGNOSTICS LTD
Projection Lens System of a Microlithographic Projection Exposure Installation
InactiveUS20080106711A1Improve image qualityReducing image fieldPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingProjection lensManipulator
A microlithographic projection exposure apparatus comprises a projection objective which images an object onto an image plane and has a lens with a curved surface. In the projection objective there is a liquid or solid medium which directly adjoins the curved surface over a region which is usable for imaging the object. The projection exposure apparatus also has an adjustable manipulator for reducing an image field curvature which is caused by heating of the medium during the projection operation.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Wide angle camera with prism array
InactiveUS20060215054A1Wide field of viewLight collection efficiency is improvedTelevision system detailsSignal generator with single pick-up deviceOptoelectronicsPrism
An imaging apparatus (40) has an optical sensor (14) with sensing elements (18). Each sensing element (18) has an array of sensing components (28). Each sensing component (28) provides a signal corresponding to a pixel for forming an image as an array of pixels. A lens array (76) has a number of lens elements (66). Each lens element (66) directs light to a corresponding sensing element (18) in the optical sensor (14). A prism array (60) has a number of prism elements (62), each prism element (62) directing incident light from the image field toward a corresponding lens element (66) in the lens array (76).
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com