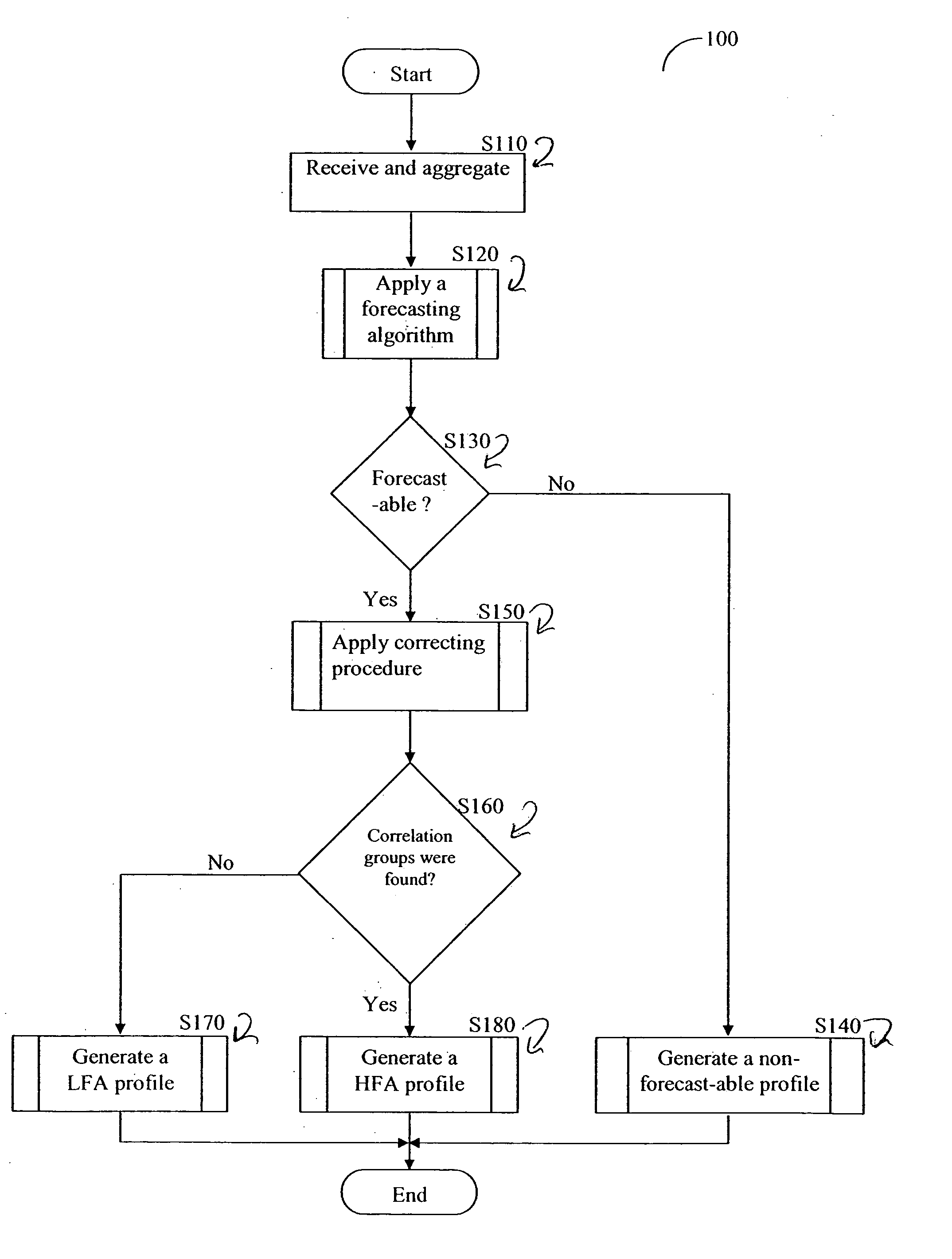
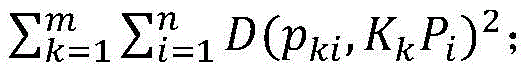Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
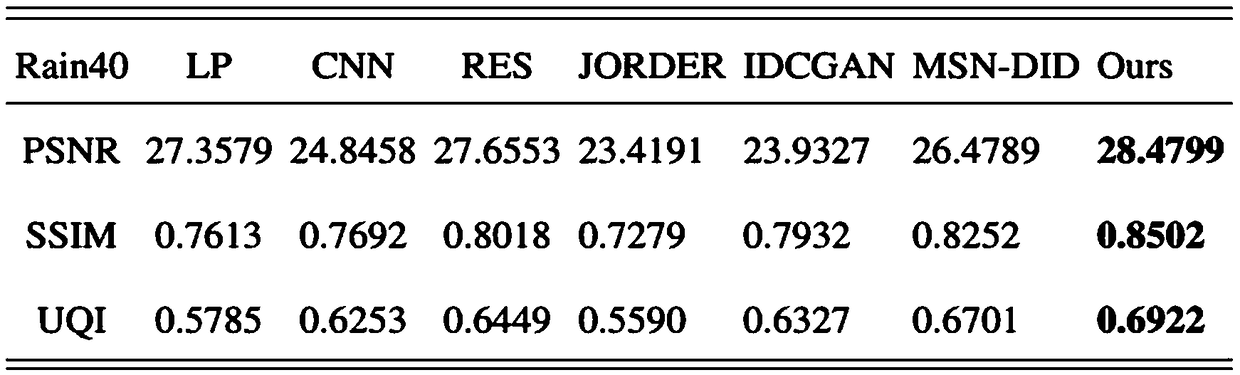
733 results about "Error function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the error function (also called the Gauss error function) is a special function (non-elementary) of sigmoid shape that occurs in probability, statistics, and partial differential equations describing diffusion.
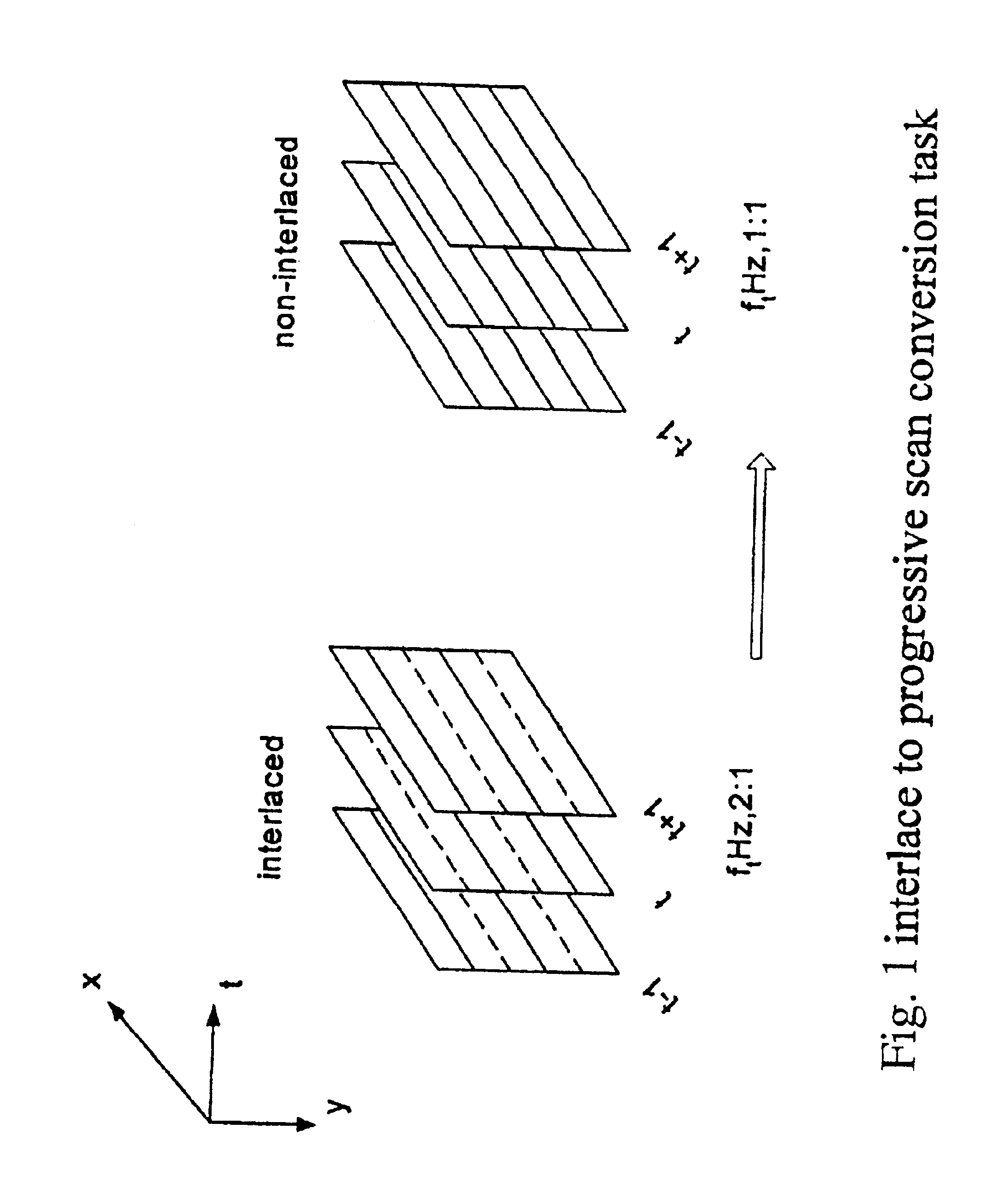
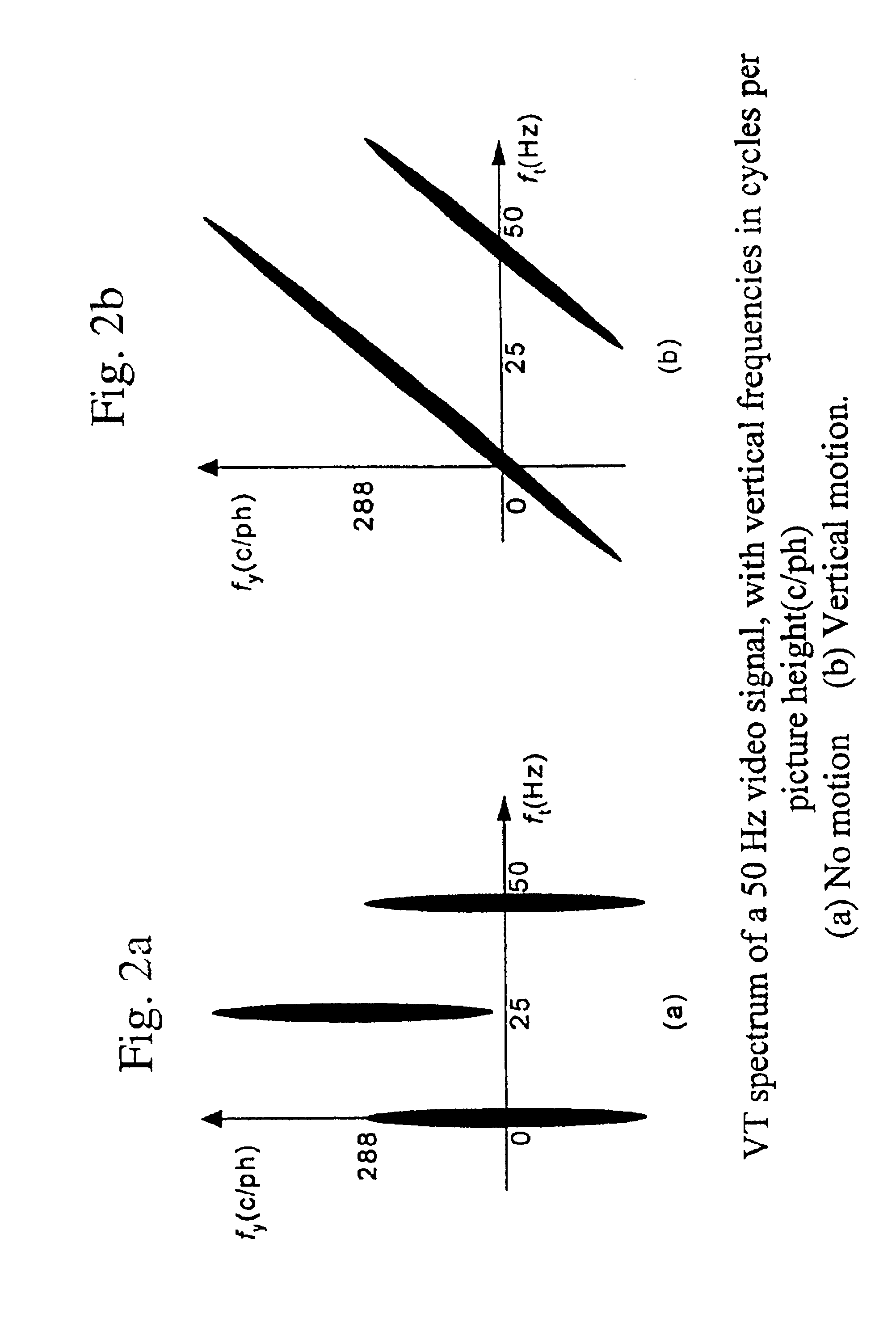
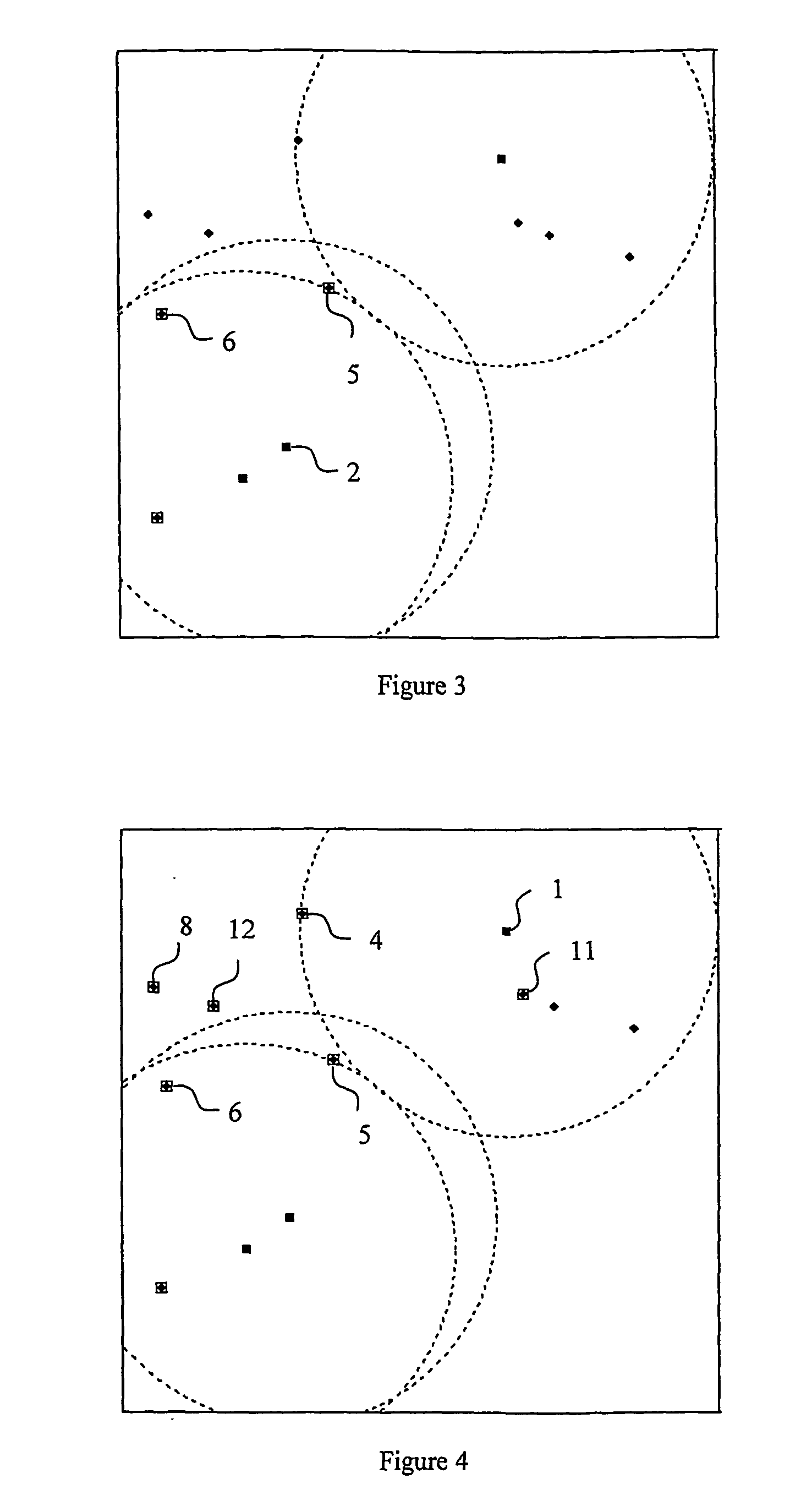
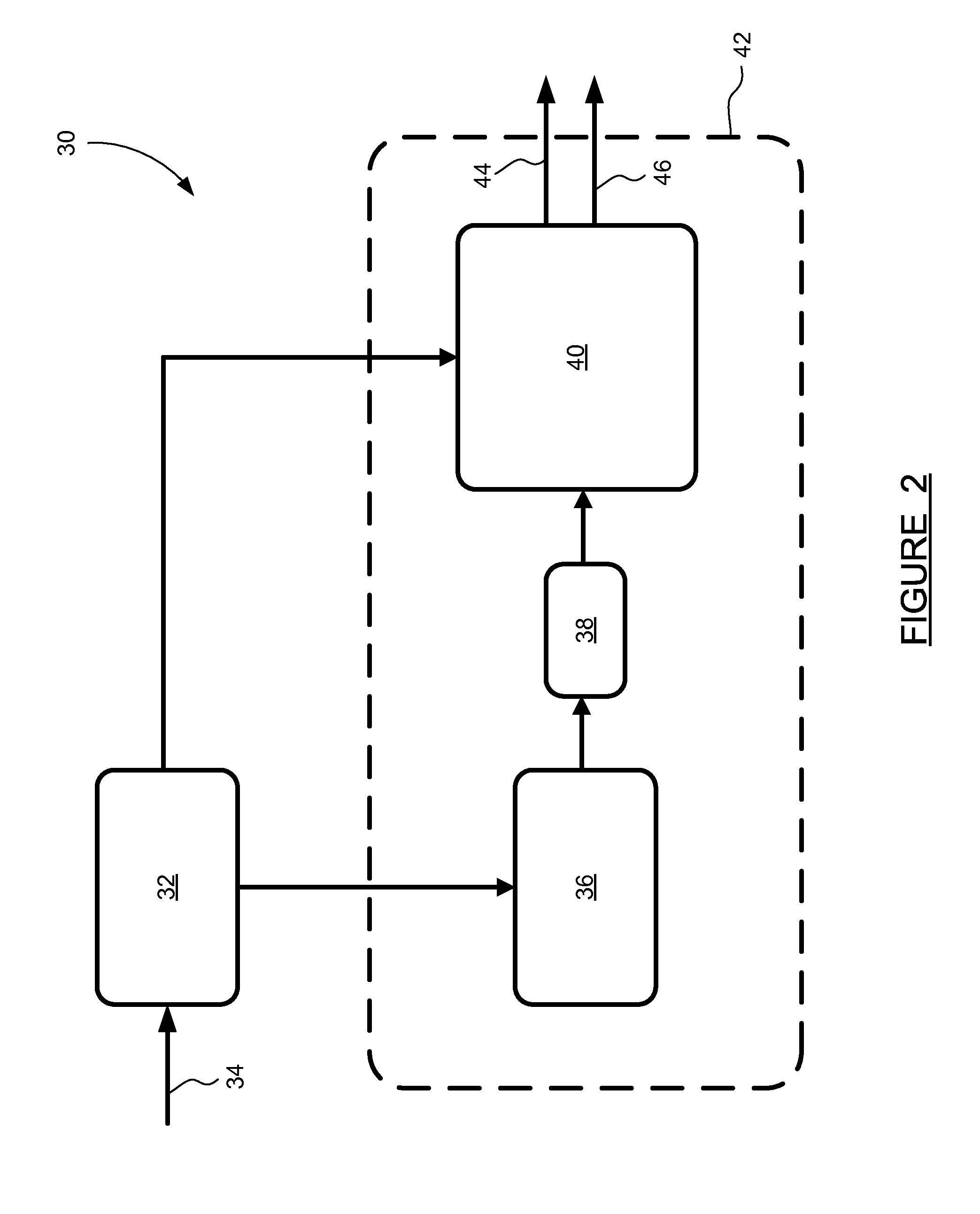
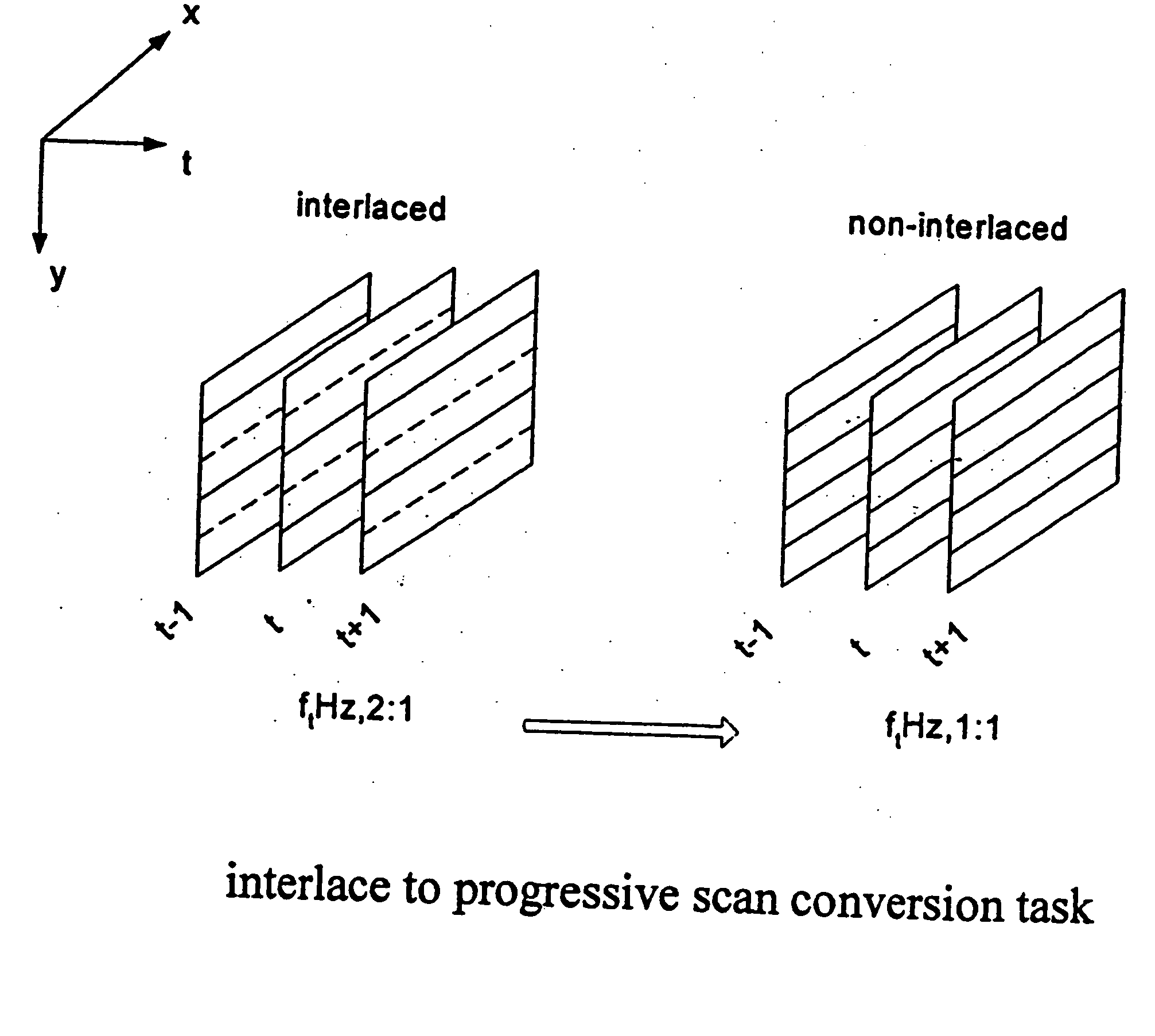
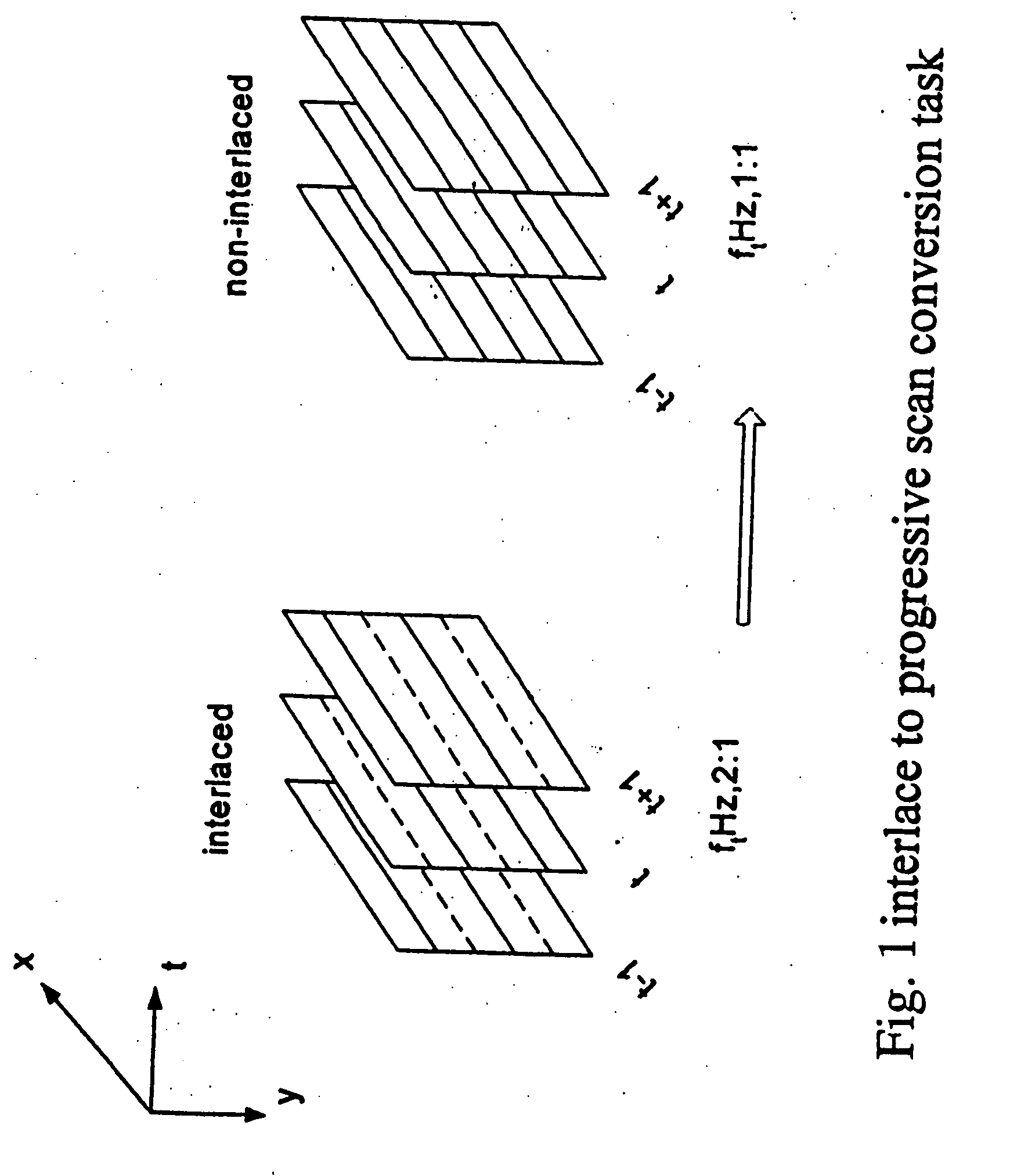
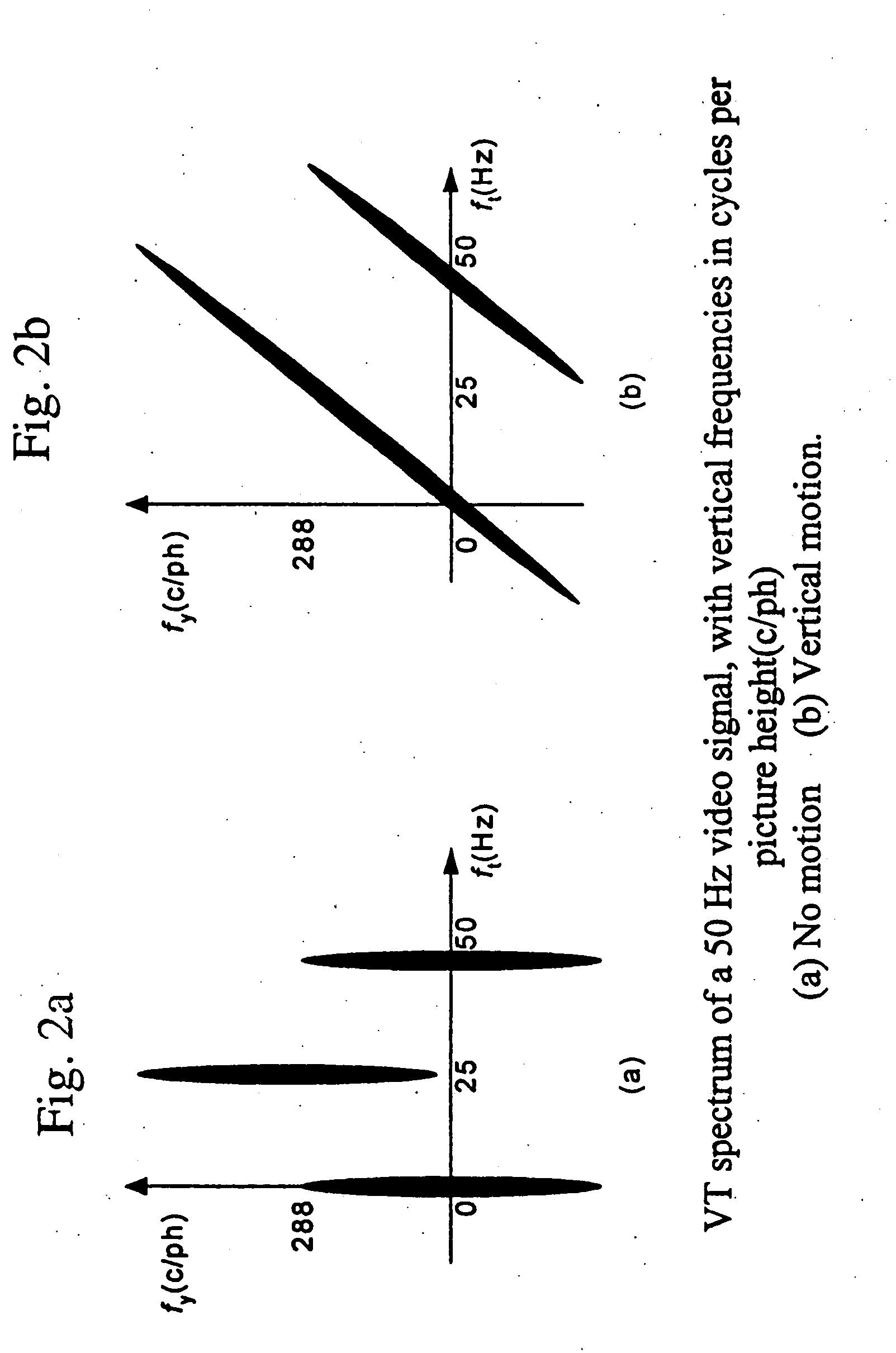
Adaptive interlace-to-progressive scan conversion algorithm
InactiveUS6940557B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsProgressive scanData set
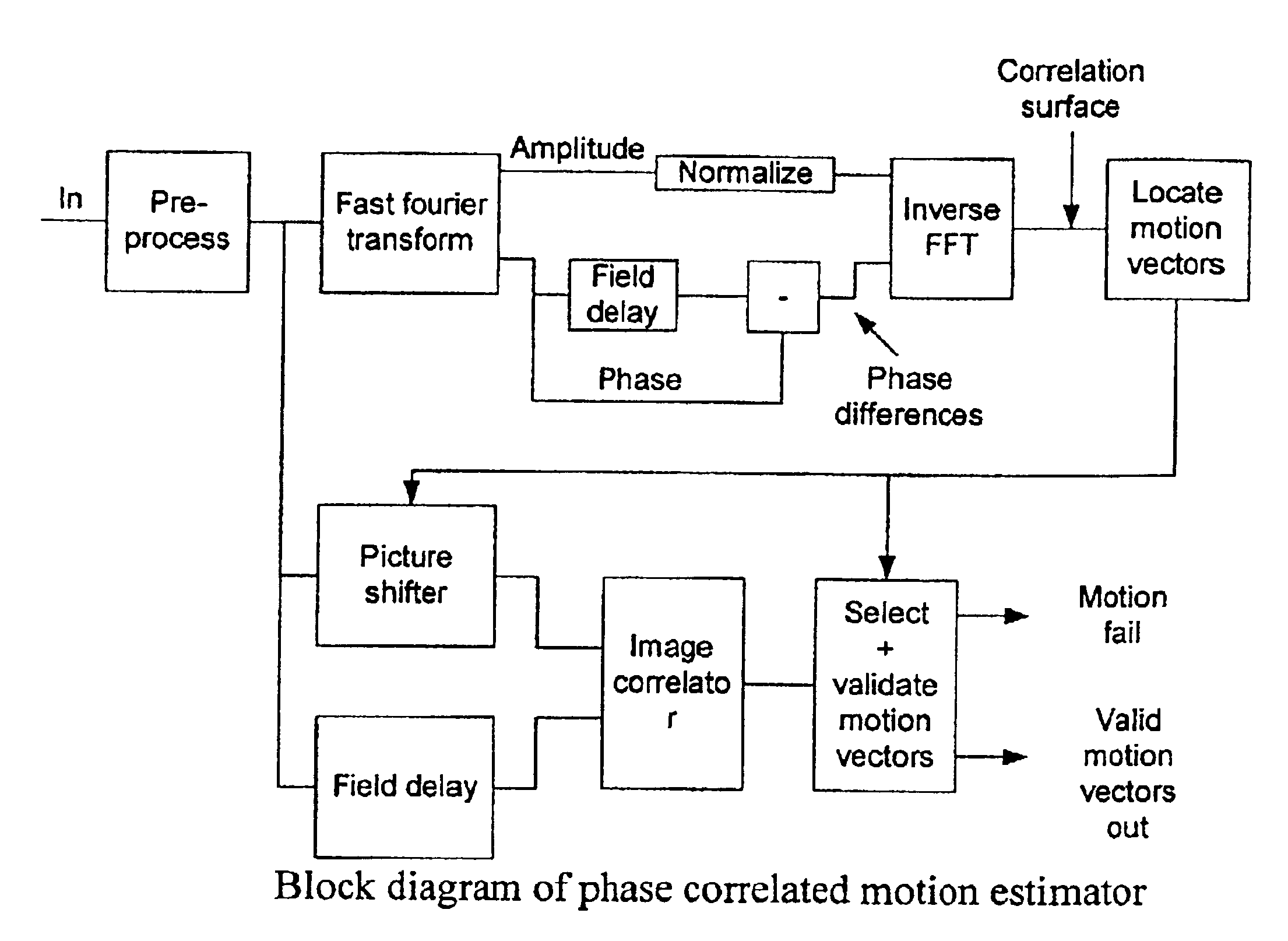
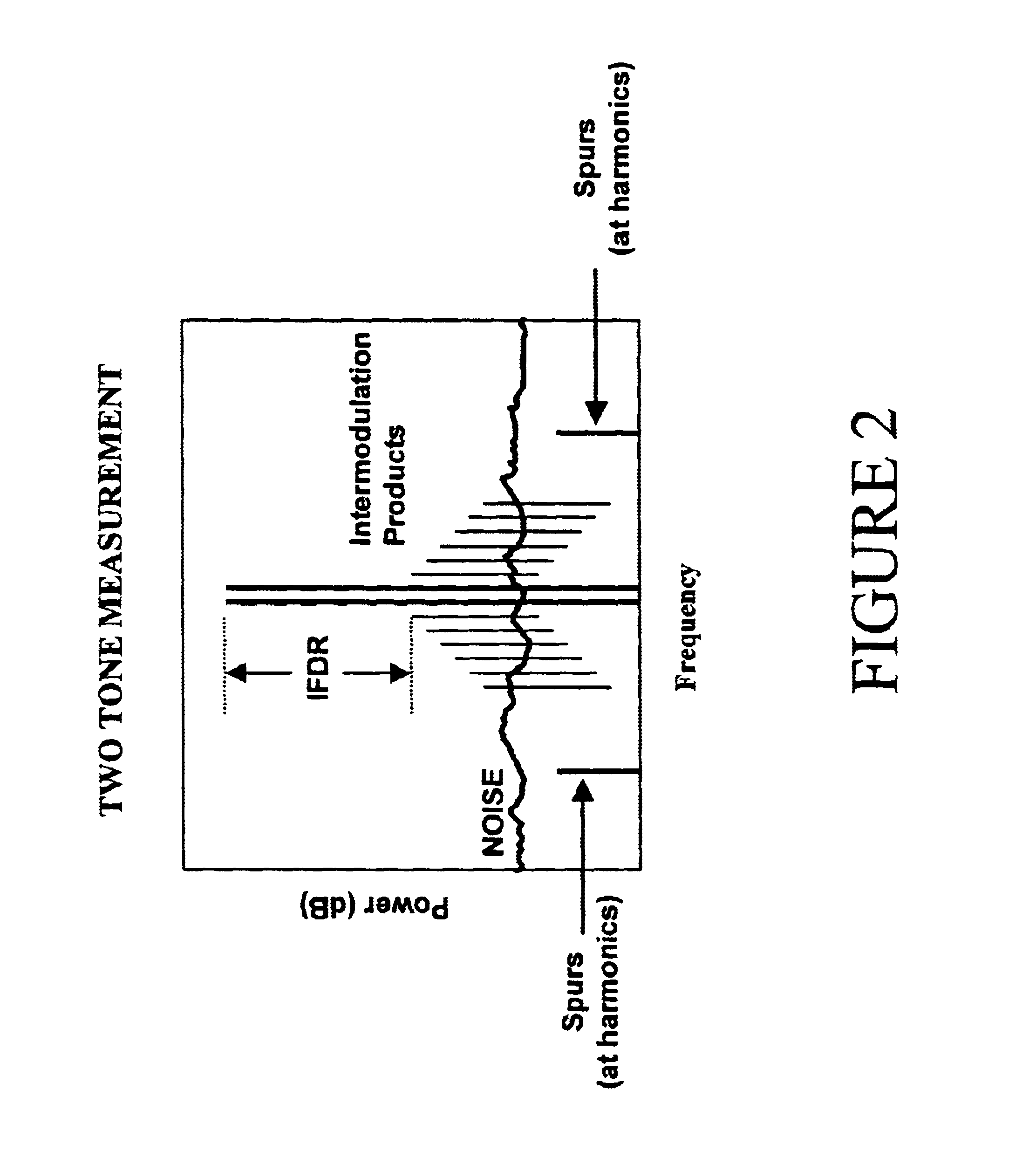
An interlace-to-progressive scan conversion system comprises: a spatial line averaging prefilter; a motion estimator; a three-stage adaptive recursive filter. The motion estimator comprises: a 3-D recursive search sub-component having a bilinear interpolator; a motion correction sub-component having an error-function including penalties related to the difference between a given candidate vector and a plurality of neighboring vectors; a block erosion sub-component. The motion estimator assumes that motion is constant between fields. The three-stage adaptive recursive filter comprises: a first stage that selects between using static pixels data and moving pixels data from a next field; a second stage that selects a more valid set of data between motion compensated data from a previous field and the pixels selected by the first stage; a third stage that combines an intra-field interpolation with the more valid set of data selected by the second stage.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
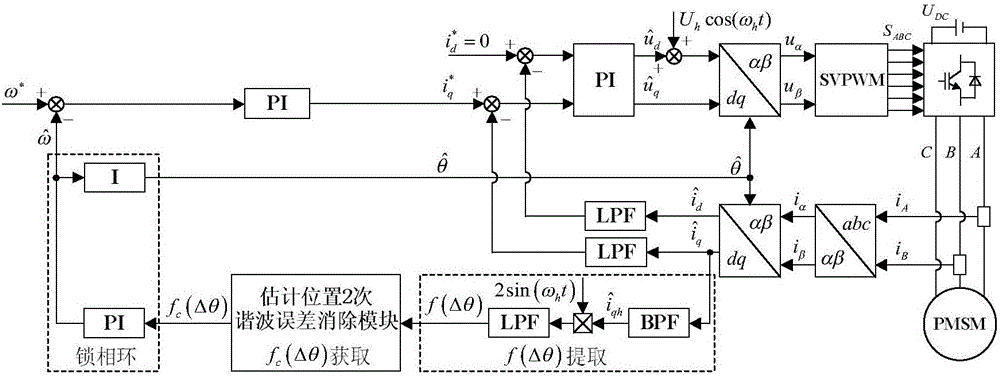
Method for improving estimation accuracy of rotor position of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN106788071AEasy to implementReduce computing burdenElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlControl systemHarmonic
The invention discloses a method for improving the estimation accuracy of the rotor position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of realizing estimation of the rotor position of the permanent magnet synchronous motor by utilizing a pulse-shake high frequency voltage injection method, processing the extracted position estimation error function, eliminating a second harmonic component introduced due to asymmetric motor parameters, so as to obtain a processed position estimation error function, then establishing a phase-locked loop, and adjusting the phase-locked loop to be 0, thus obtaining estimated rotor speed and estimated rotor position. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively inhibit position estimation second harmonic error caused by the asymmetric motor parameters, and the performance of a control system without a position sensor can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
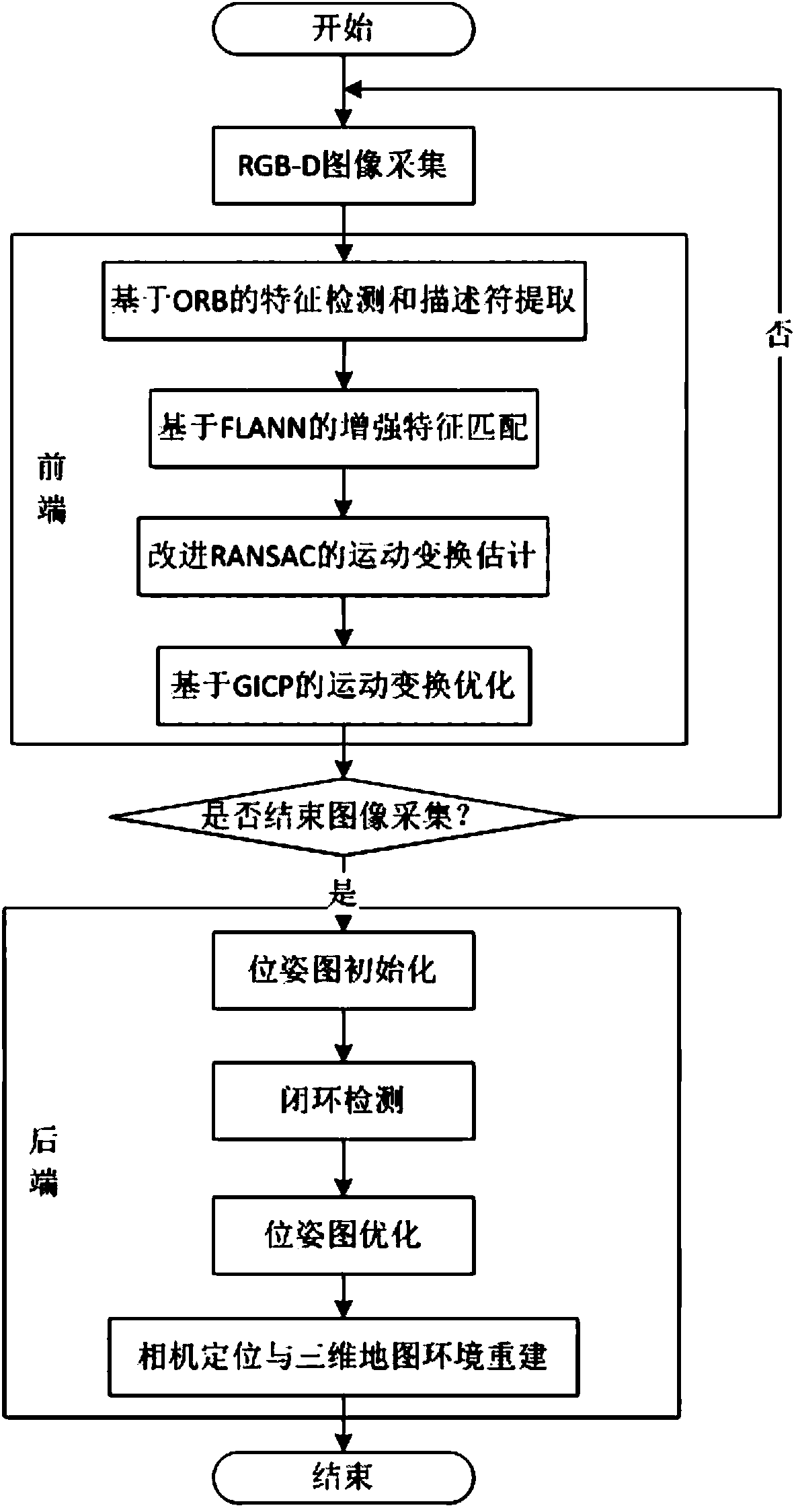
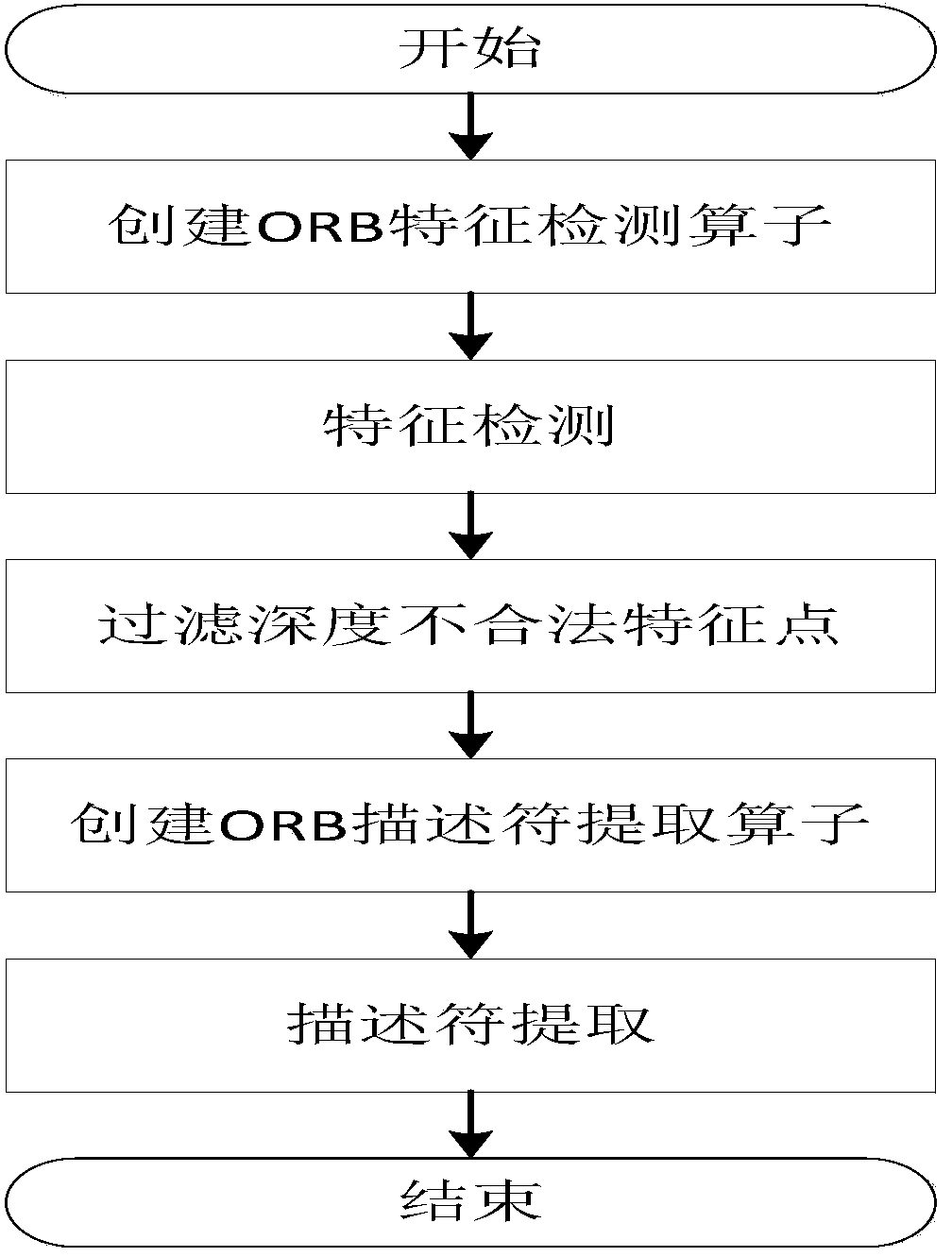
Improved method of RGB-D-based SLAM algorithm
InactiveCN104851094AMatching result optimizationHigh speedImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudEstimation methods
Disclosed in the invention is an improved method of a RGB-D-based simultaneously localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm. The method comprises two parts: a front-end part and a rear-end part. The front-end part is as follows: feature detection and descriptor extraction, feature matching, motion conversion estimation, and motion conversion optimization. And the rear-end part is as follows: a 6-D motion conversion relation initialization pose graph obtained by the front-end part is used for carrying out closed-loop detection to add a closed-loop constraint condition; a non-linear error function optimization method is used for carrying out pose graph optimization to obtain a global optimal camera pose and a camera motion track; and three-dimensional environment reconstruction is carried out. According to the invention, the feature detection and descriptor extraction are carried out by using an ORB method and feature points with illegal depth information are filtered; bidirectional feature matching is carried out by using a FLANN-based KNN method and a matching result is optimized by using homography matrix conversion; a precise inliners matching point pair is obtained by using an improved RANSAC motion conversion estimation method; and the speed and precision of point cloud registration are improved by using a GICP-based motion conversion optimization method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and arrangement for detecting a watermark using statistical characteristics of the information signal in which the watermark is embedded
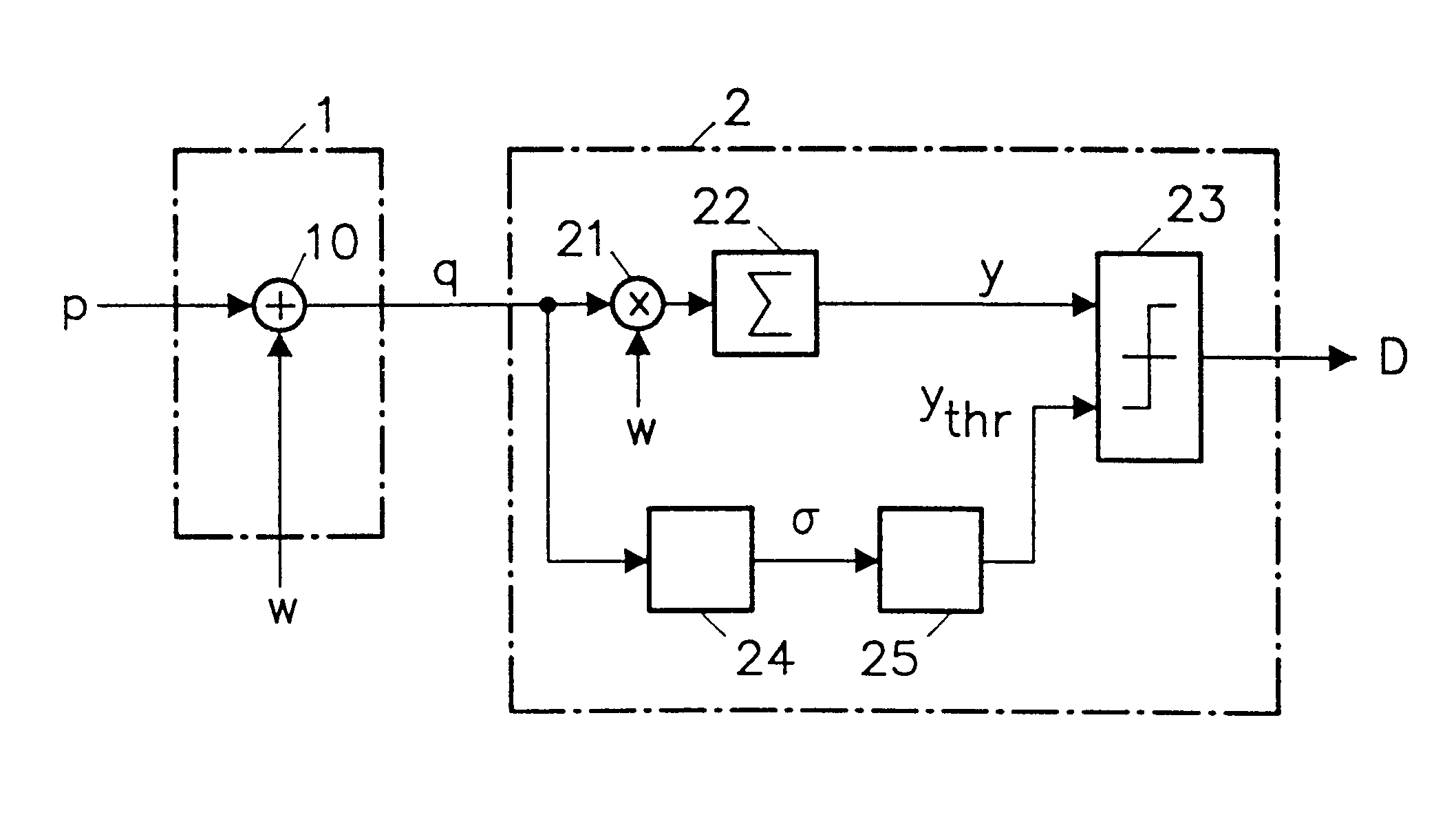
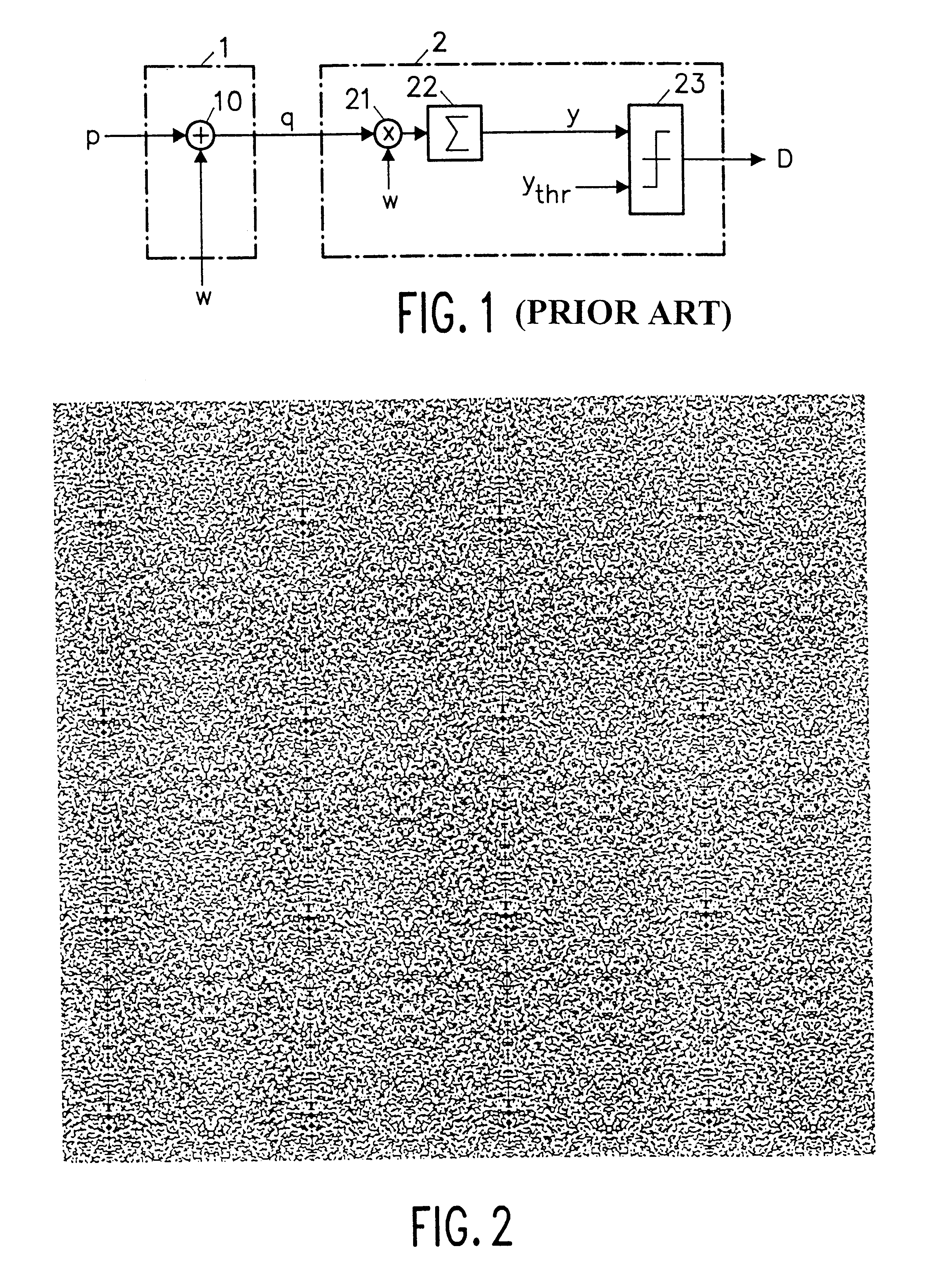
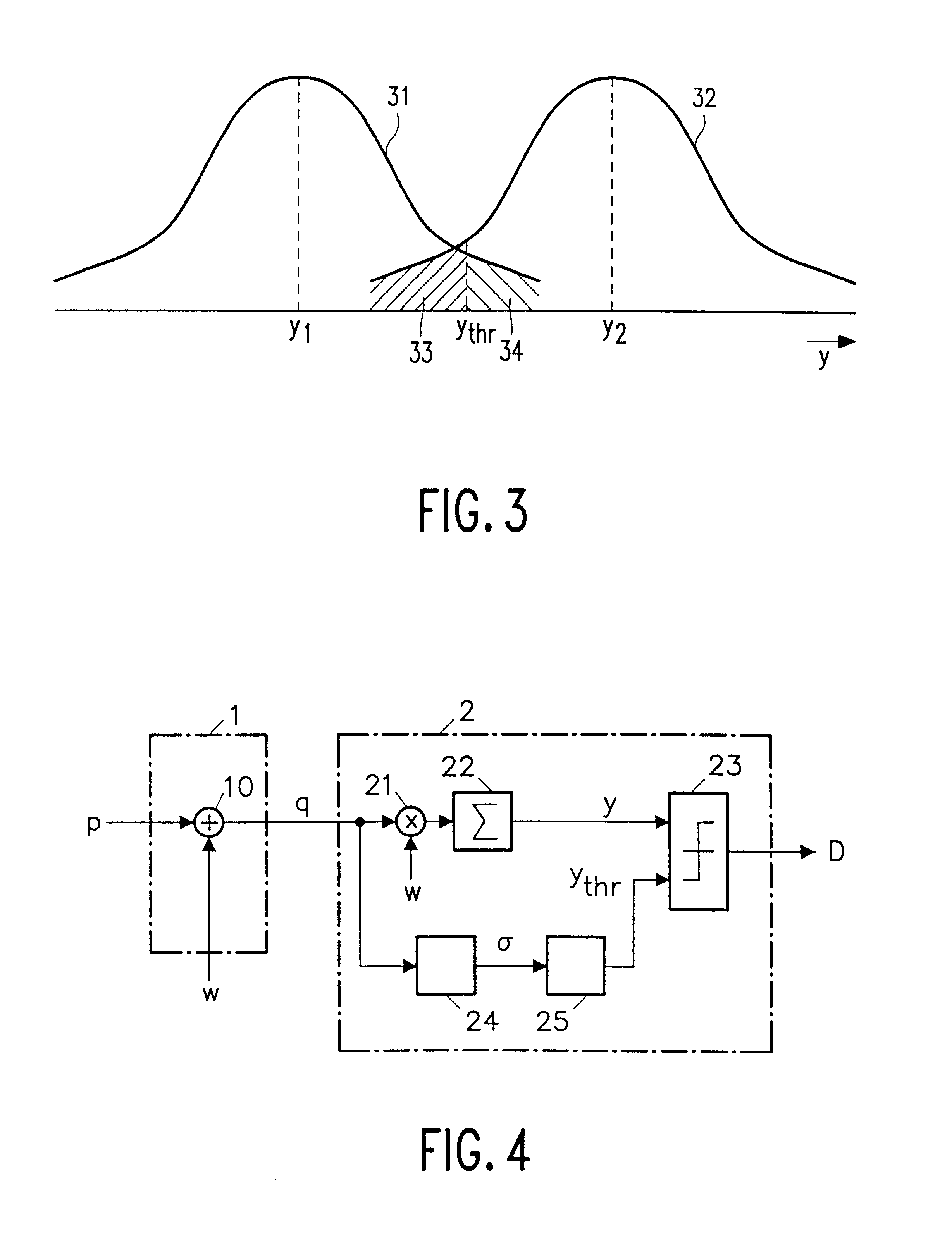
Recently developed methods for copy protection rely on a watermark detector to judge whether multimedia content can be copied or not. In such copy protection schemes, a watermark detector examines the multimedia content and outputs a signal (D) indicating whether a watermark is present or not. Known watermark detectors determine a decision variable (y) indicating to which extent the watermark is present, for example, the amount of correlation between input signal and a reference copy of the watermark to be detected. The watermark is detected if the decision variable exceeds a predetermined threshold (ythr)In accordance with the invention, the threshold value (ythr) is adaptively controlled in dependence upon statistical characteristics of the information signal and a desired probability of false alarms (watermark detected whereas the signal is not watermarked). In an embodiment, the watermark detector determines the standard deviation (sigma) of the pixel values threshold level and calculates the threshold value in accordance with the relationin which erfc is the error function and sigma is said standard deviation of the information signal values.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP +1
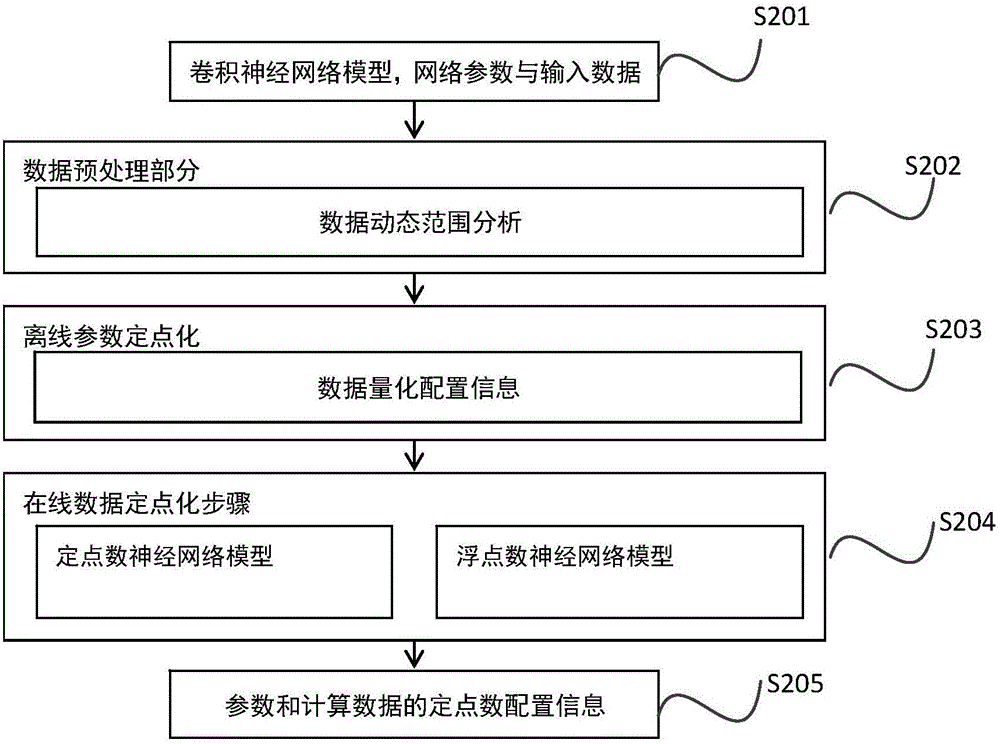
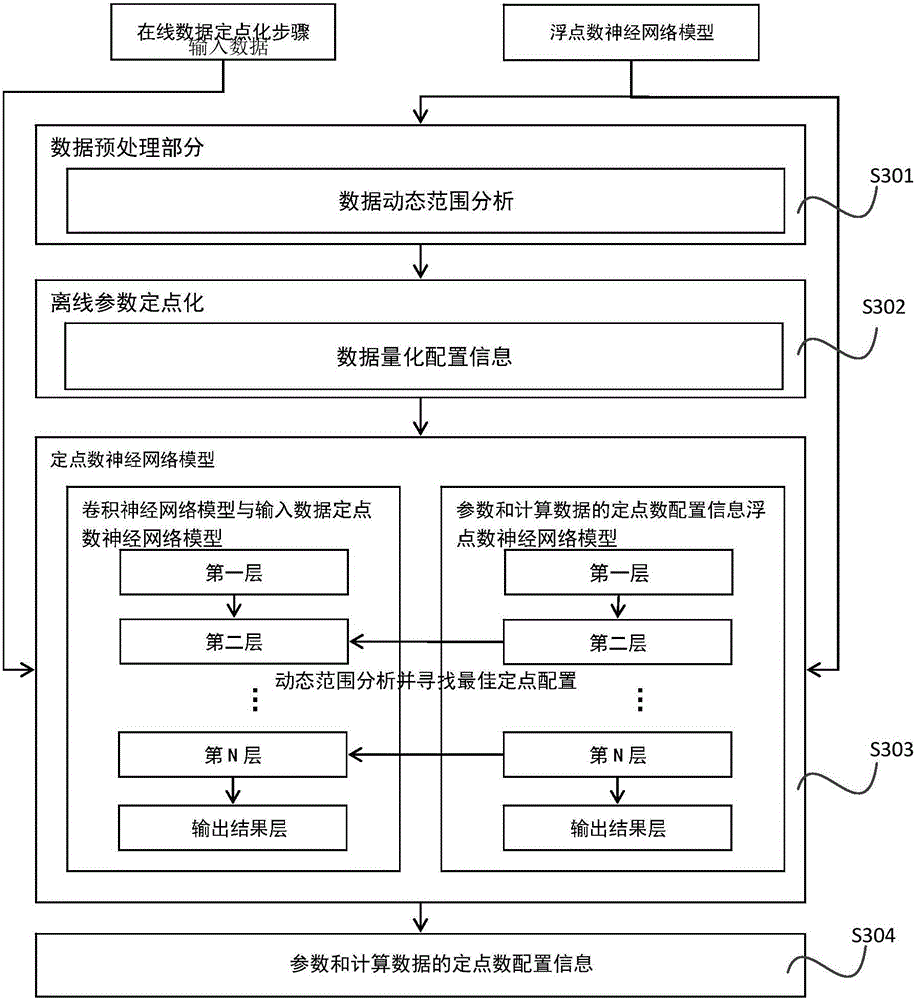
Method and apparatus for fixed-pointing layer-wise variable precision in convolutional neural network
InactiveCN105760933AReduce precision lossFast transmissionNeural learning methodsFloating pointNetwork data
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for fixed-pointing the layer-wise variable precision in a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: estimating fixed-pointing configuration input to various layers in the convolutional neural network model respectively in accordance with input network parameters and a value range of input data; based on the acquired fixed-point configuration estimation and the optimal error function, determining the best fixed-point configuration points of the input data and network parameters of various layers and outputting the best fixed-point configuration points; inputting respectively the input data which is subject to fixed-pointing and an input data of an original floating-point number as a first layer in the convolutional neural network and computing the optimal fixed-point configuration point of the output data of the layer, and inputting the output result and an output result of the original first layer floating-point number as a second layer. The rest of the steps can be done in the aforementioned manner until the last layer completes the whole fixed-pointing. The method of the invention guarantees the minimum precision loss of each layer subject to fixed-pointing of the convolutional neural network, can explicitly lower space required by storing network data, and can increase transmitting velocity of network parameters.
Owner:BEIJING DEEPHI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
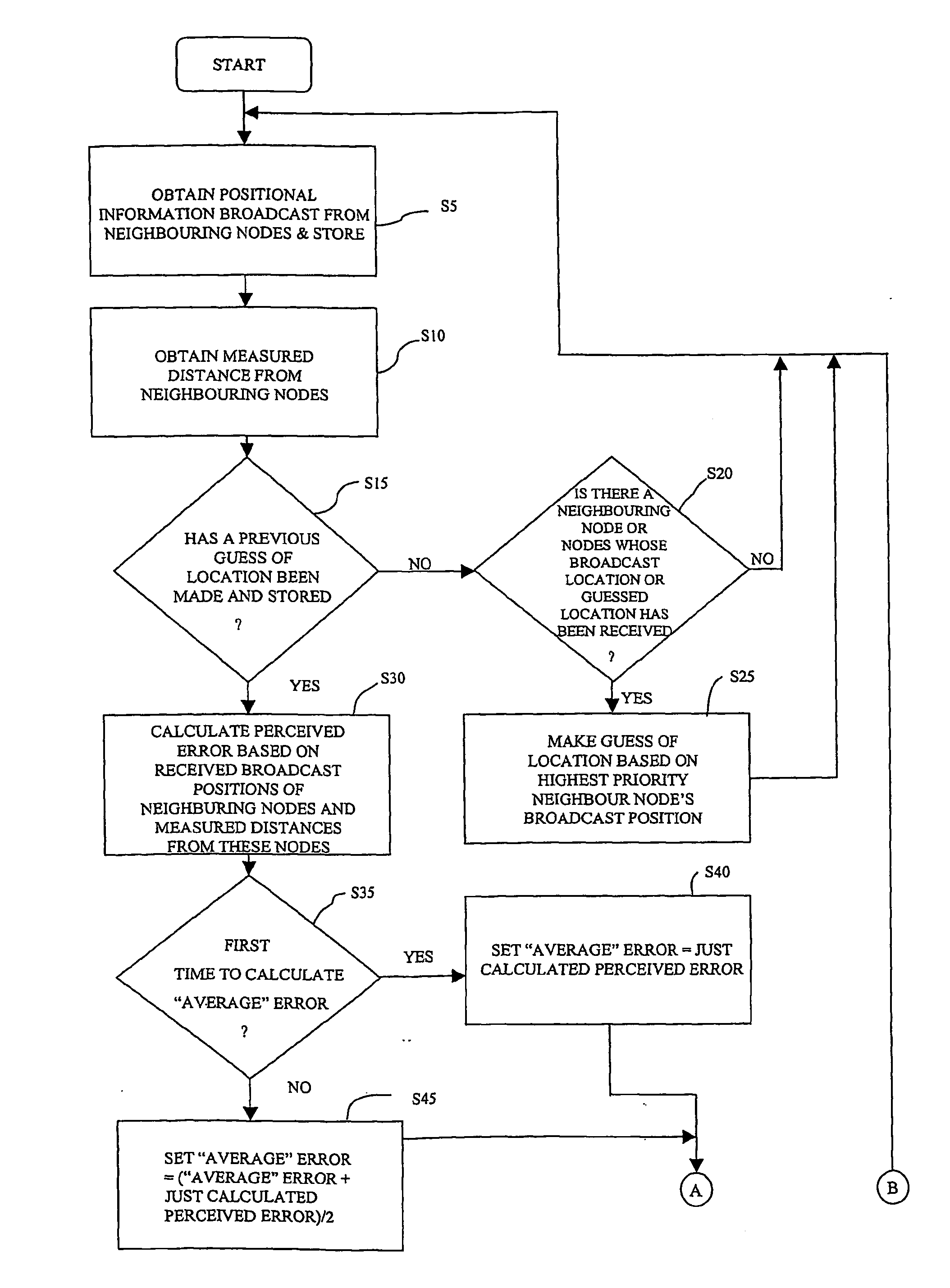
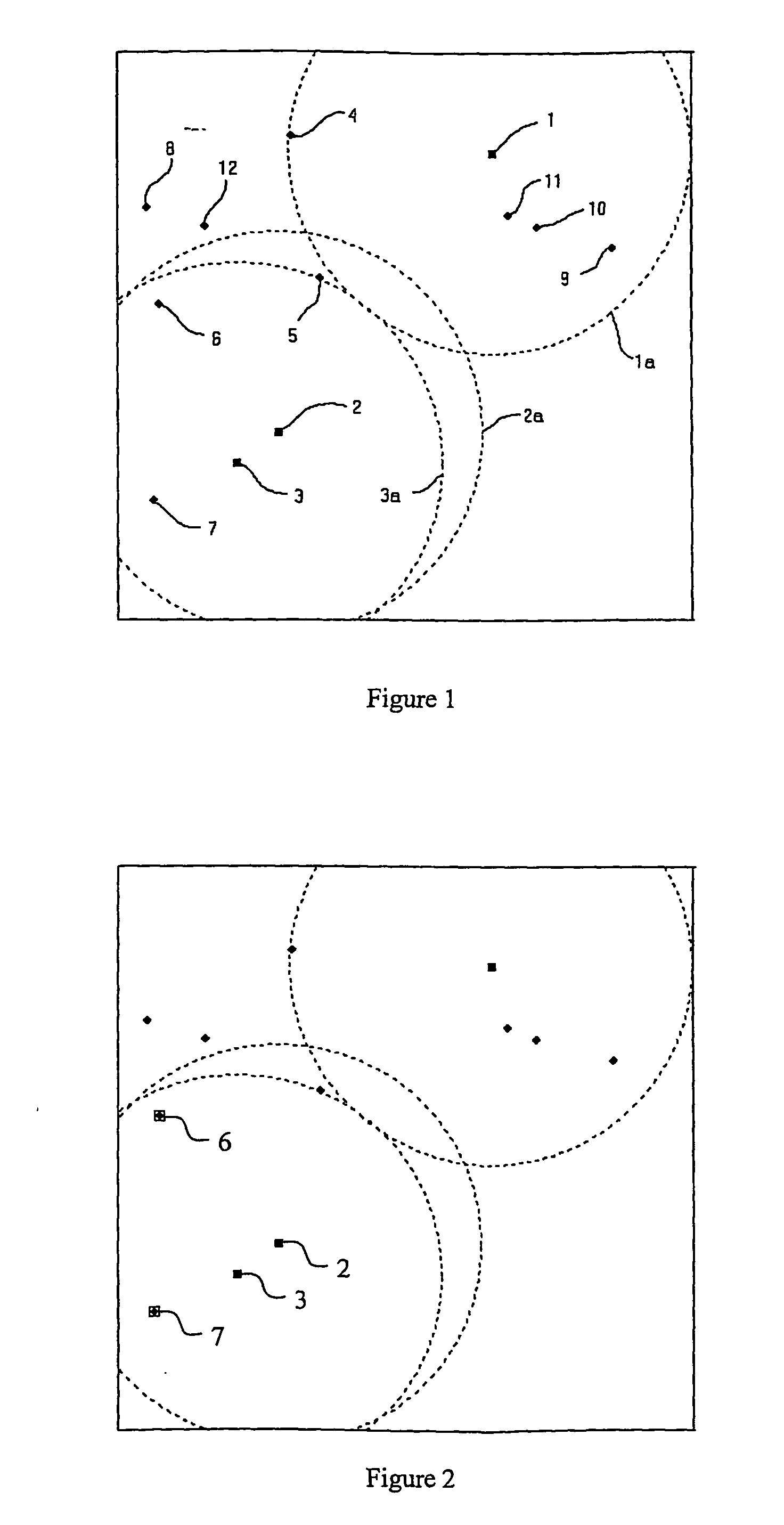
Method and apparatus for locating devices
InactiveUS20050233748A1Low costEffective positioningPosition fixationData switching by path configurationWireless ad hoc networkError function
A method of obtaining positional information about individual wireless devices a1-a16, r1-r125 within a wireless ad-hoc network including a plurality of position determining devices r1-r125 which include means for estimating the distance between themselves and other similar devices which are within range. The method includes the steps of: calculating the hypothetical distance between a respective node's estimated position and the estimated position of each of its neighbouring devices whose broadcast estimated position has been received and whose distance from the respective node has been measured comparing the calculated hypothetical distance with the measured distance; modifying the respective node's estimated position so as to reduce an error function dependent upon the difference between the hypothetical and measured distances and periodically resetting the respective node's estimated location to a new position in a manner which does not seek to reduce the error function within a single iteration so as to avoid the location from getting stuck in a local minimum value of the error function.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
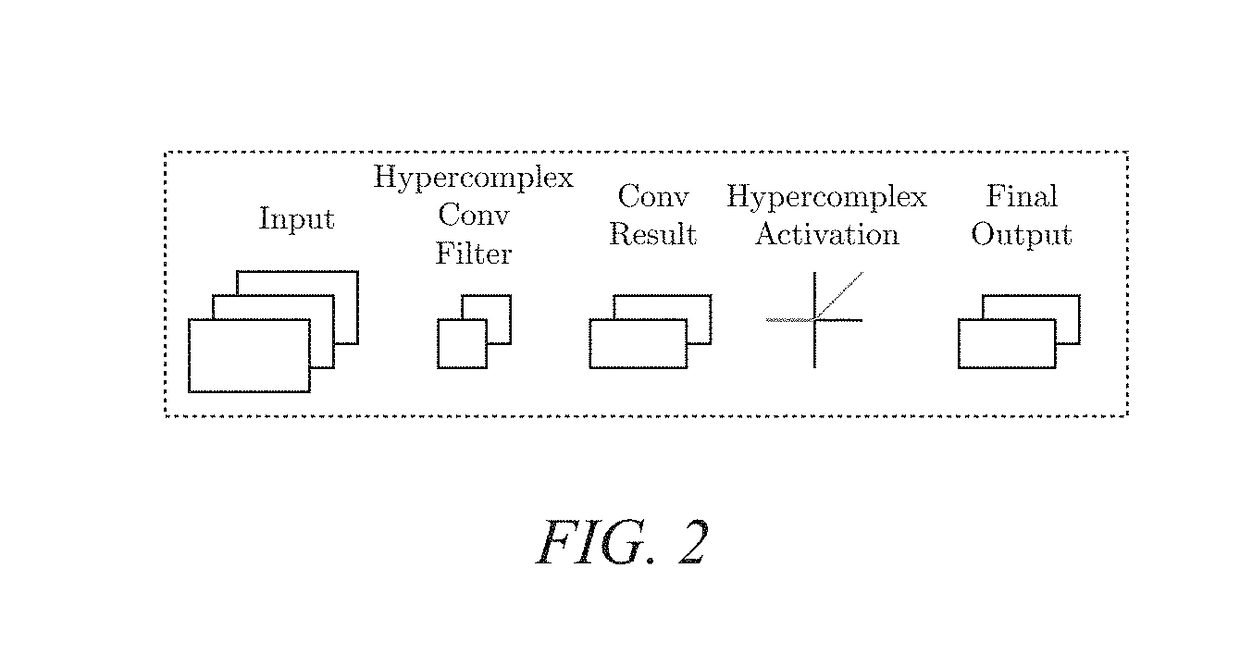
Hypercomplex deep learning methods, architectures, and apparatus for multimodal small, medium, and large-scale data representation, analysis, and applications
A method and system for creating hypercomplex representations of data includes, in one exemplary embodiment, at least one set of training data with associated labels or desired response values, transforming the data and labels into hypercomplex values, methods for defining hypercomplex graphs of functions, training algorithms to minimize the cost of an error function over the parameters in the graph, and methods for reading hierarchical data representations from the resulting graph. Another exemplary embodiment learns hierarchical representations from unlabeled data. The method and system, in another exemplary embodiment, may be employed for biometric identity verification by combining multimodal data collected using many sensors, including, data, for example, such as anatomical characteristics, behavioral characteristics, demographic indicators, artificial characteristics. In other exemplary embodiments, the system and method may learn hypercomplex function approximations in one environment and transfer the learning to other target environments. Other exemplary applications of the hypercomplex deep learning framework include: image segmentation; image quality evaluation; image steganalysis; face recognition; event embedding in natural language processing; machine translation between languages; object recognition; medical applications such as breast cancer mass classification; multispectral imaging; audio processing; color image filtering; and clothing identification.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
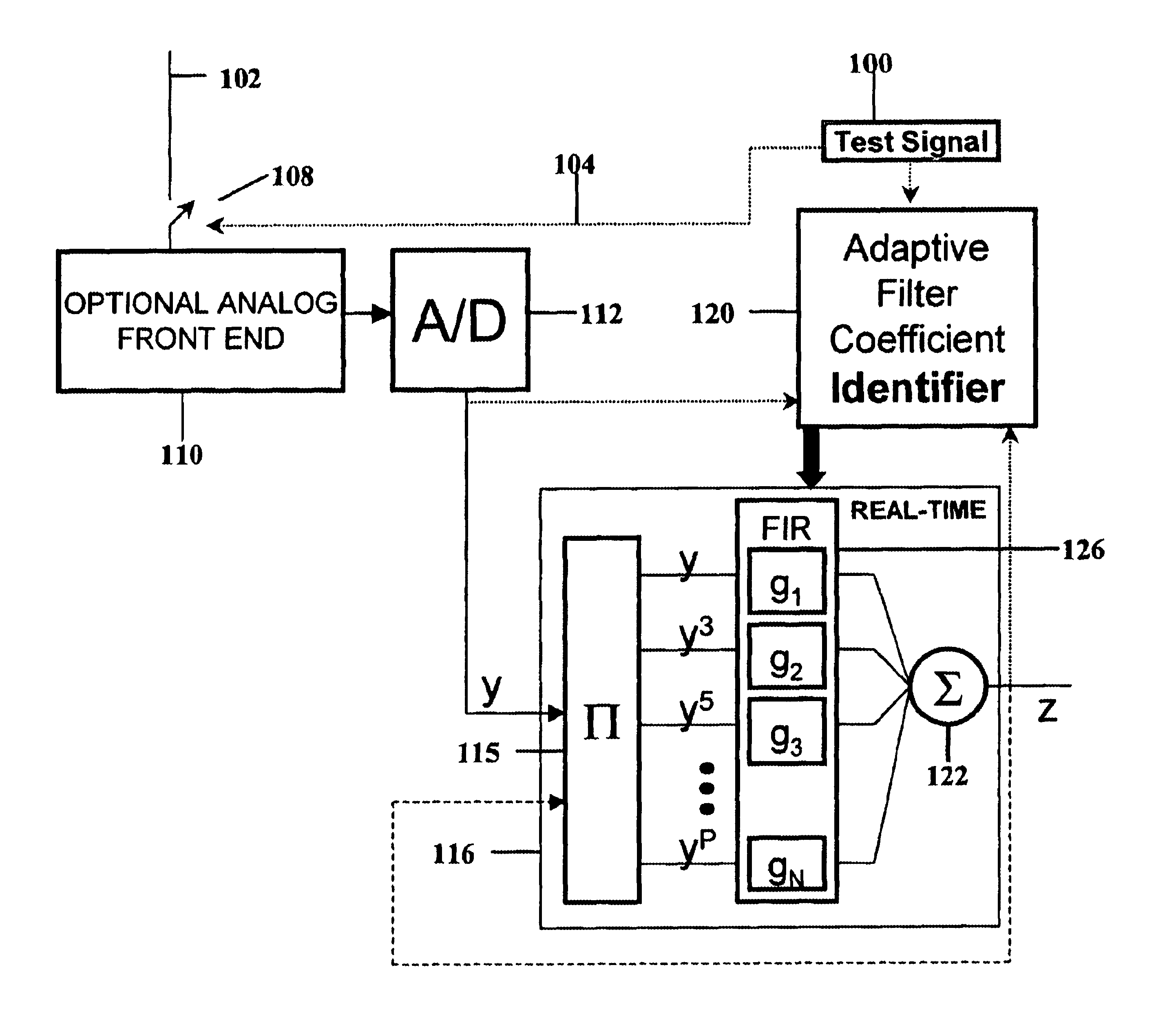
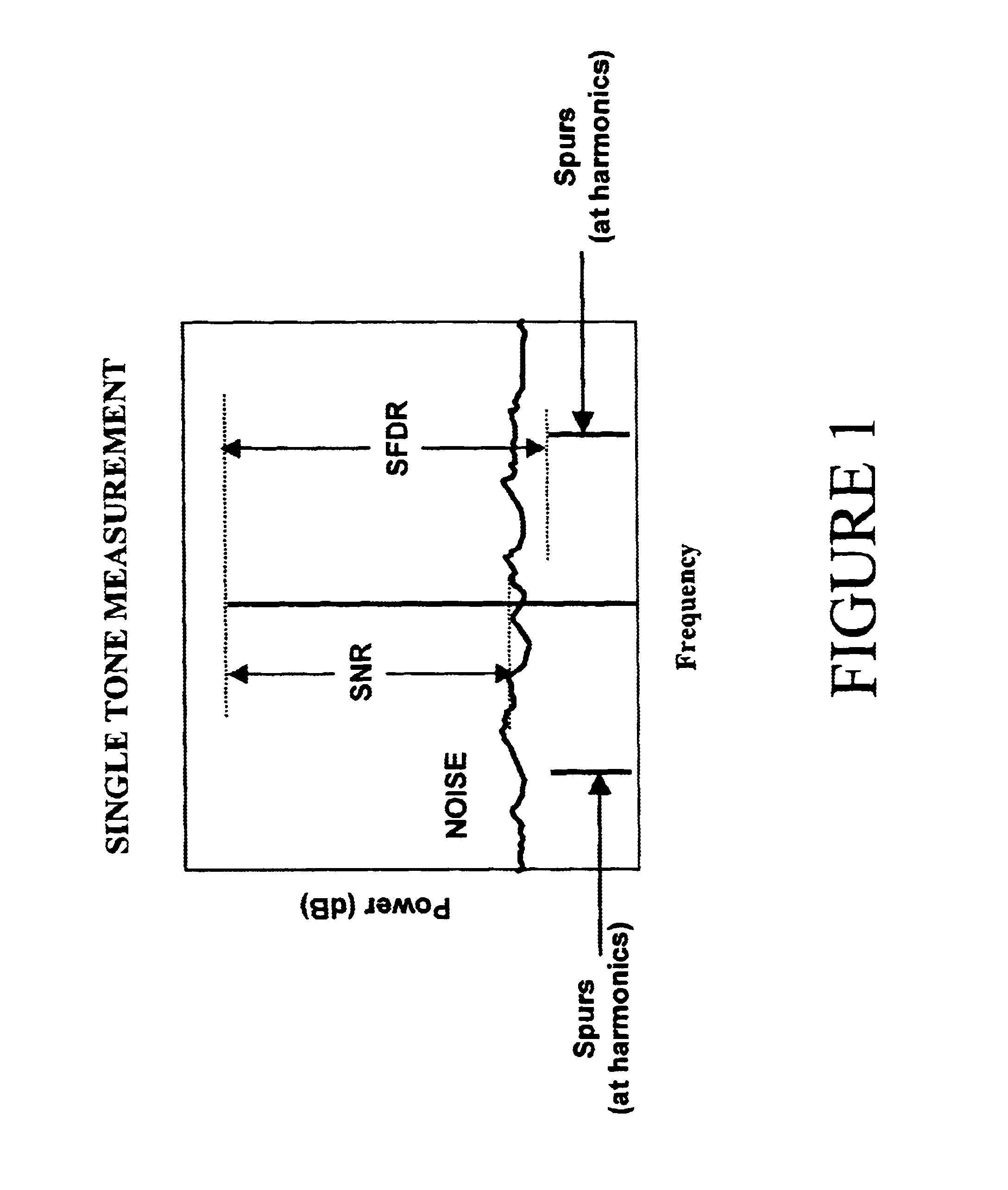
Highly linear analog-to-digital conversion system and method thereof
InactiveUS6639537B1Reduce nonlinear distortionMinimizes non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFinite impulse responseNonlinear distortion
A highly linear analog-to-digital (ADC) conversion system has an analog front-end device in cascade with a standard ADC converter, and a tunable digital non-linear equalizer. The equalizer corrects the quantization distortion, deviations from ideal response, and additive noises generated by the analog front-end device and ADC converter. The equalizer is formed by three main parts: Generate Function Streams Unit, Finite Impulse Response FIR filters and a summer. The equalizer receives the unequalized output from the ADC converter and generates a plurality of monomial streams in a systolic fashion. Each of the monomial streams is passed through a corresponding linear finite impulse response FIR filter. A convolution sum of all outputs from the FIR filters produces a unique equalized output with the non-linear distortion reduced to a satisfactory level. The FIR filter coefficients are determined by an Identity Equalizer Coefficient Unit, and a Test Signal Generator with different types of test signals. The FIR filter coefficients are set to minimize an error function.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
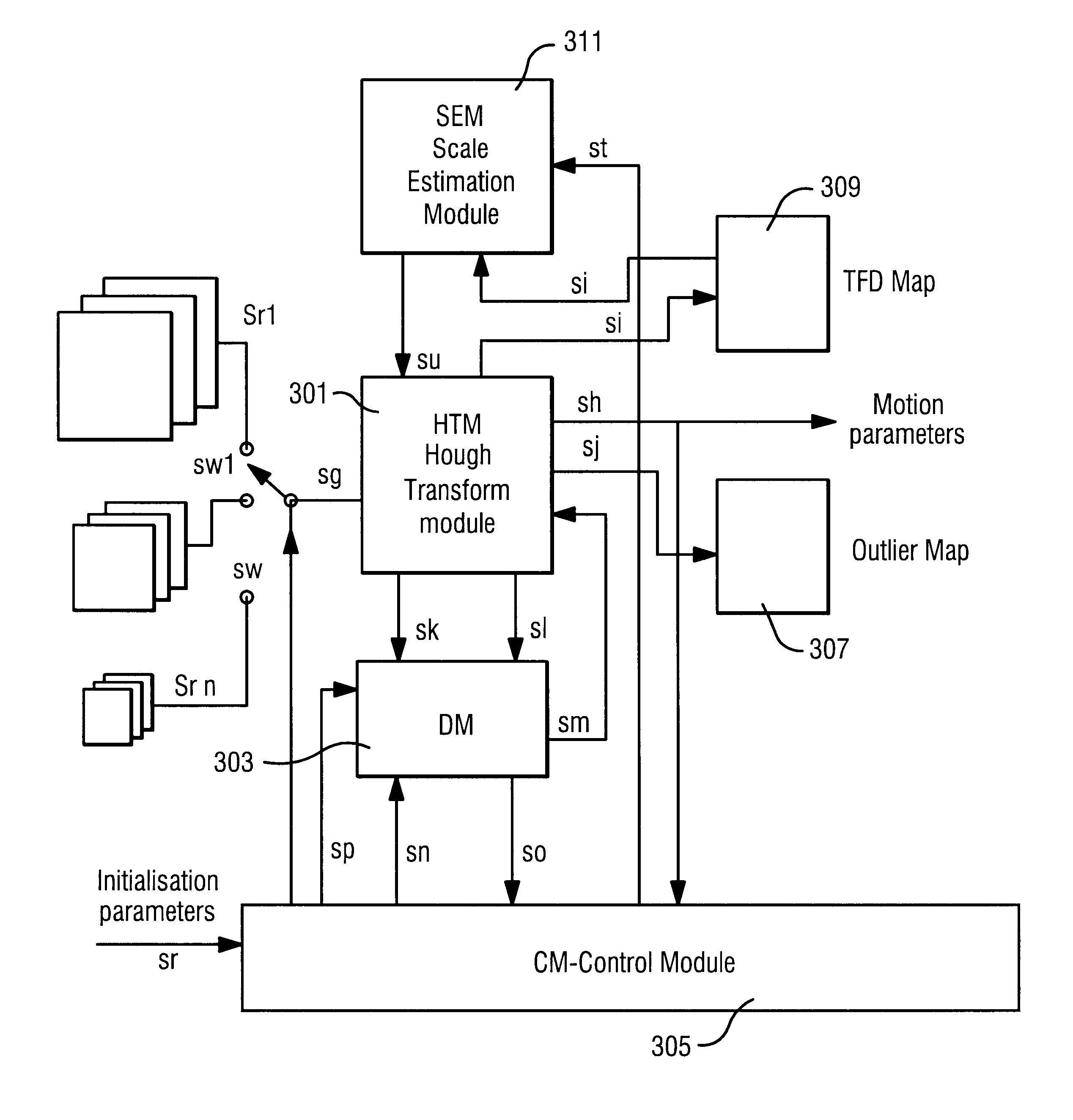
Hough transform based method of estimating parameters
A Hough transform based method of estimating N parameters a=(a1, . . . , aN) of motion of a region Y in a first image to a following image, the first and following images represented, in a first spatial resolution, by intensities at pixels having coordinates in a coordinate system, the method including: determining the total support H(Y,a) as a sum of the values of an error function for the intensities at pixels in the region Y; determining the motion parameters a that give the total support a minimum value; the determining being made in steps of an iterative process moving along a series of parameter estimates a1, a2, . . . by calculating partial derivatives dHi=MH(Y,an) / Man,i of the total support for a parameter estimate an with respect to each of the parameters ai and evaluating the calculated partial derivatives for taking a new an+1; and wherein, in the evaluating of the partial derivatives, the partial derivatives dHi are first scaled by multiplying by scaling factors dependent on the spatial extension of the region to produce scaled partial derivatives dHNi.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
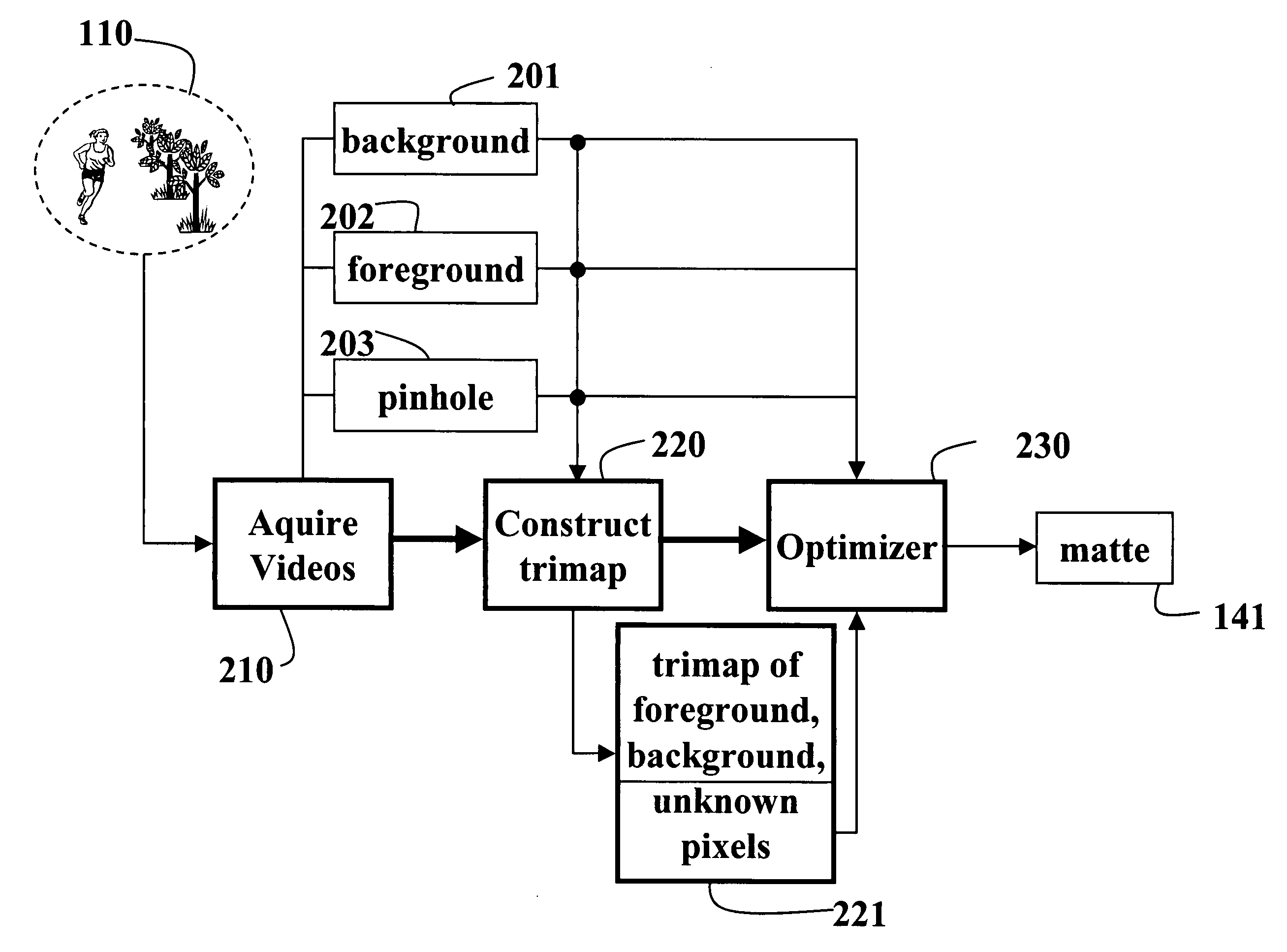
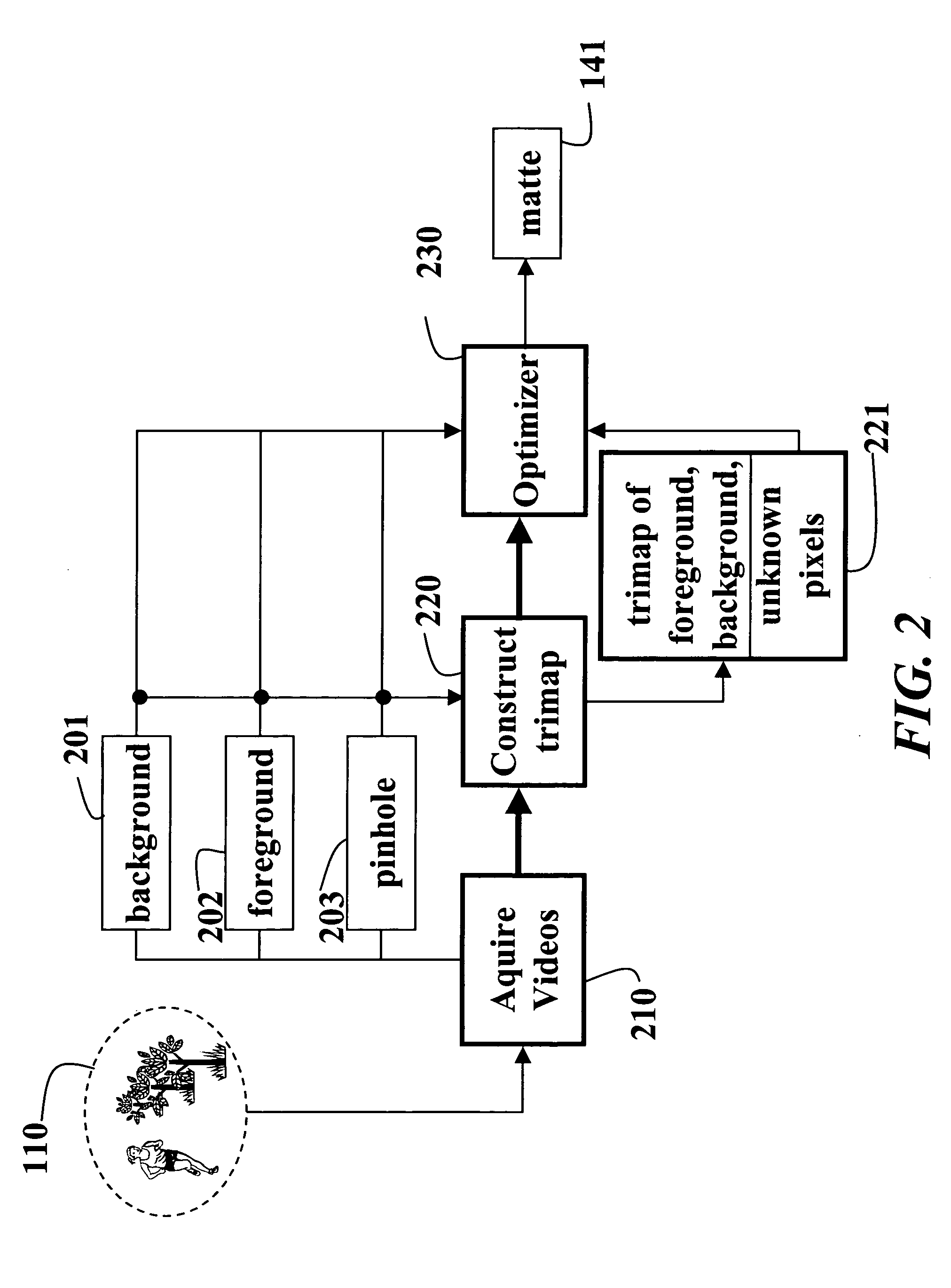
System and method for image matting
InactiveUS20060221248A1High-frequency componentSolve the real problemTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsError functionBackground image
A method and system extracts a matte from images acquired of a scene. A foreground image focused at a foreground in a scene, a background image focused at a background in the scene, and a pinhole image focused on the entire scene are acquired. These three images can be acquired sequentially by a single camera, or simultaneous by three cameras. In the later case, foreground, background and pinhole sequences of images can be acquired. The pinhole image is compared to the foreground image and the background image to extract a matte representing the scene. The comparison classifies pixels in the images as foreground, background, or unknown pixels. An optimizer minimizes an error function in the form of Fourier image equations using a gradient descent method. The error function expresses pixel intensity differences.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Training convolutional neural networks on graphics processing units
InactiveCN101253493ADigital computer detailsImage data processing detailsComputational scienceError function
A convolutional neural network is implemented on a graphics processing unit. The network is then trained through a series of forward and backward passes, with convolutional kernels and bias matrices modified on each backward pass according to a gradient of an error function. The implementation takes advantage of parallel processing capabilities of pixel shader units on a GPU, and utilizes a set of start-to-finish formulas to program the computations on the pixel shaders. Input and output to the program is done through textures, and a multi-pass summation process is used when sums are needed across pixel shader unit registers.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for indoor geolocation using an impulse response fingerprinting technique
ActiveUS20070010956A1Minimize error functionPolarisation/directional diversityDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionData setIndoor geolocation
A system and method for predicting the location of a transmitter in an indoor zone of interest, including fixed receiver for receiving a signal from the transmitter, the receiver deriving a fingerprint from the received signal, and a trained neural network. The trained neural network predicts the transmitter location from the fingerprint. The method includes receiving a signal transmitted from the transmitter at a fixed-location receiver, deriving a fingerprint from the received signal, supplying the fingerprint to a trained neural network, and reading the predicted location from the neural network. The artificial neural network may further be trained and include a plurality of weights and biases is also shown. The method may include collecting a training data set of fingerprints and corresponding locations, inputting the training data set to the neural network, and adjusting the weights and biases by minimising a sum of squares error function.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE +1
Modeling changes in the state-of-charge open circuit voltage curve by using regressed parameters in a reduced order physics based model
A method for modeling changes in the state of charge vs. open circuit voltage (SOC-OCV) curve for a lithium-ion battery cell as it ages. During battery pack charging, voltage and current data are gathered for a battery cell. A set of state equations are used to determine the stoichiometry and state of charge of the cathode half-cell based on the charging current profile over time. The voltage and current data, along with the stoichiometry and state of charge of the cathode half-cell, are then used to estimate maximum and minimum solid concentration values at the anode, using an error function parameter regression / optimization. With stoichiometric conditions at both the cathode and anode calculated, the cell's capacity and a new SOC-OCV curve can be determined.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
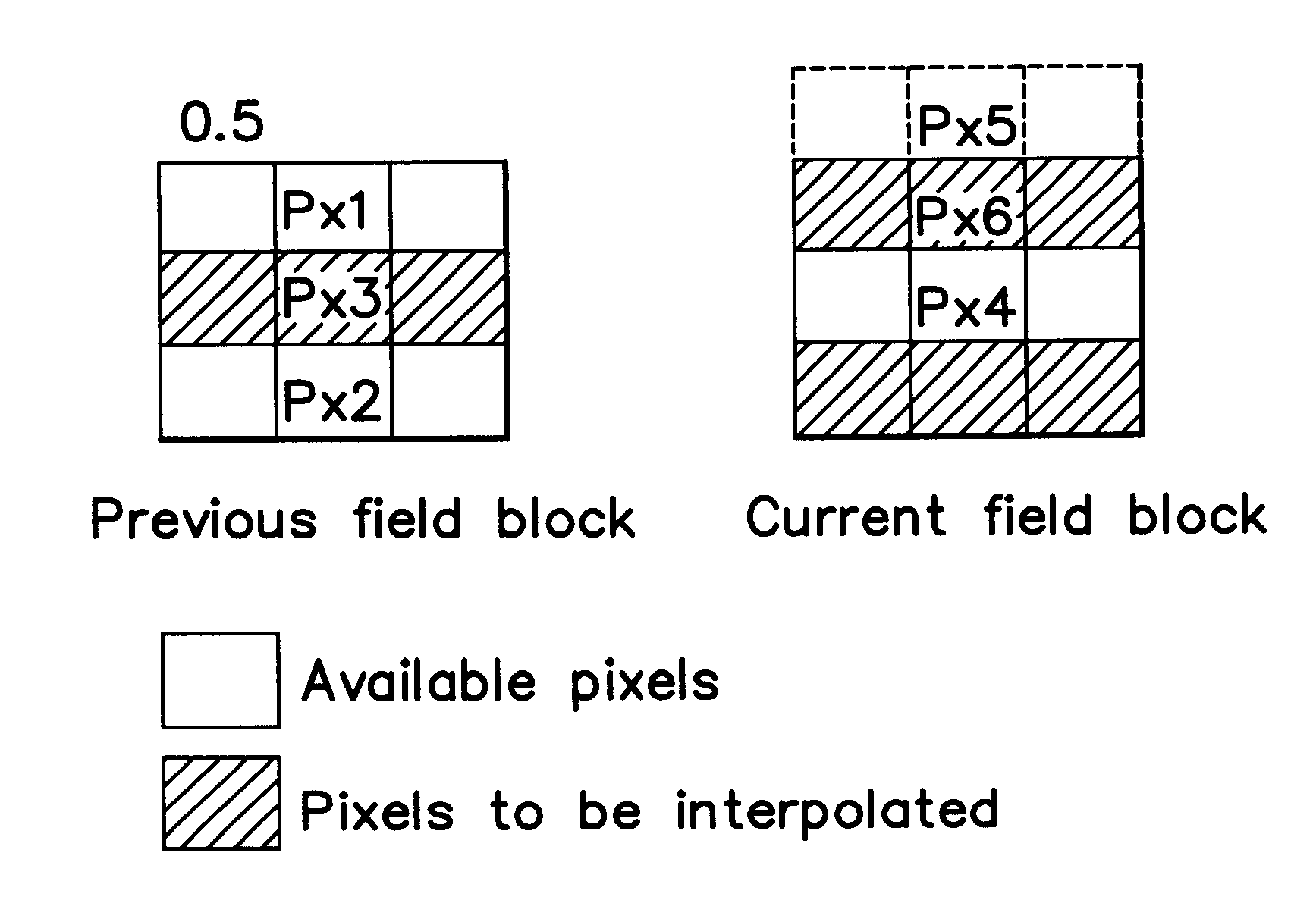
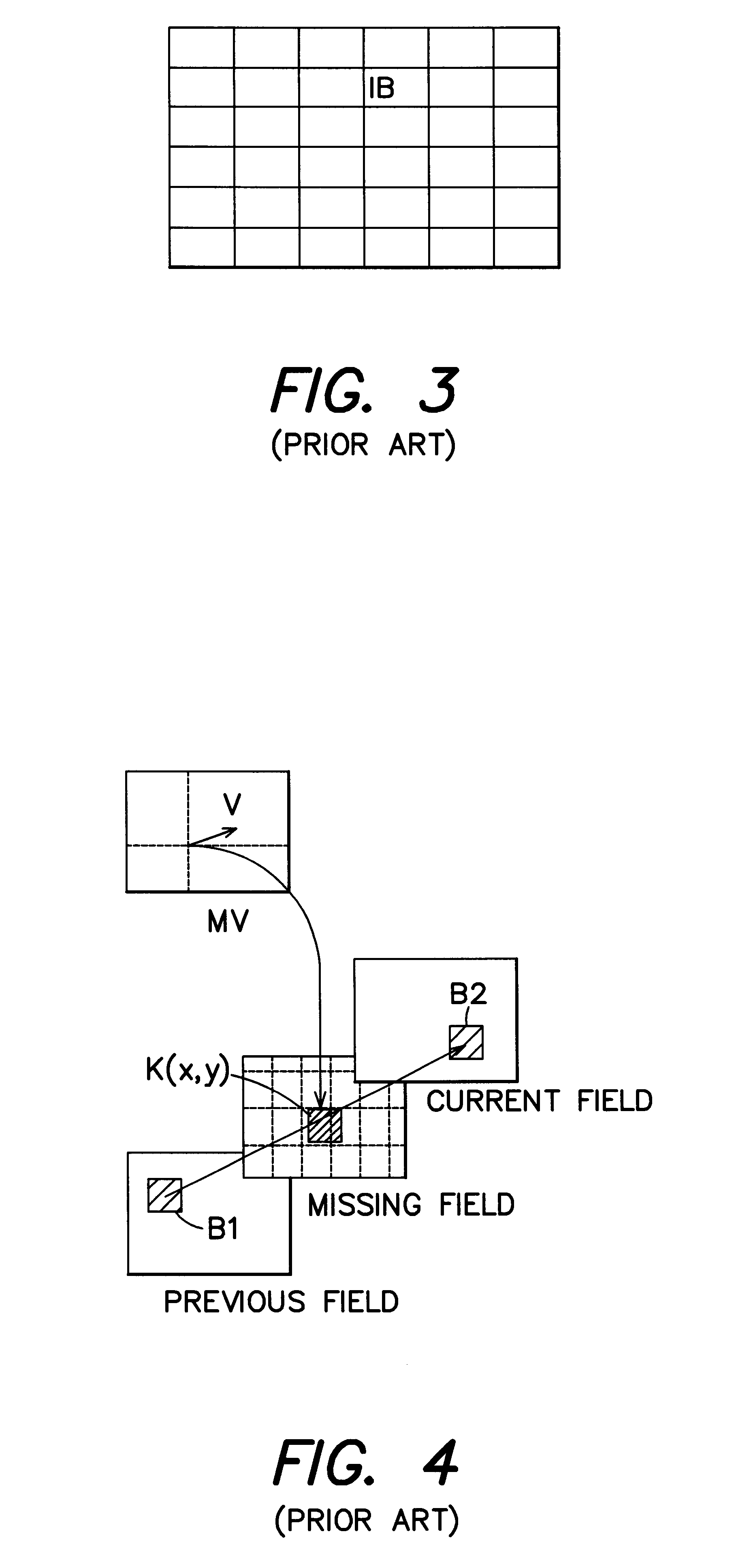
Method for motion estimated and compensated field rate up-conversion (FRU) for video applications and device for actuating such method
InactiveUS6240211B1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh activationMostly True
A method and a device for motion estimated and compensated Field Rate Up-conversion (FRU) for video applications is disclosed and claimed. The invention provides for dividing an image field to be interpolated into a plurality of image blocks, where each image block includes a respective set of image elements of the image field. In one embodiment, for each image block of a subset of image blocks, a group of neighboring image blocks is selected. A motion vector for the image block is estimated that describes the movement of the image block from a previous image field to a current image field on the basis of predictor motion vectors associated to the group of neighboring image blocks. Each image element of the image block is determined by interpolation of two corresponding image elements in the previous and current image fields related by the estimated motion vector. To estimate a motion vector, the invention provides for applying each of the predictor motion vectors to the image block to determine a respective pair of corresponding image blocks in the previous and current image fields. For each of the pairs of corresponding image blocks, an error function which is the Sum of luminance Absolute Difference (SAD) between corresponding image elements in the pair of corresponding image blocks is evaluated. For each pair of the predictor motion vectors, a degree of homogeneity is also evaluated, followed by the application of a fuzzy rule having an activation level that is proportional to the degree of homogeneity of the pair of predictor motion vectors and the error functions of the pair of predictor motion vectors. An optimum fuzzy rule having the highest activation level is selected, from which the best predictor motion vector is determined, having the smaller error function of the pair associated to the optimum fuzzy rule. In most cases, the motion vector for the image block is estimated on the basis of the best predictor motion vector.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Method and apparatus for detecting abnormal behavior of enterprise software applications
A method and apparatus for detecting abnormal behavior of enterprise software applications is disclosed. A profile that represents the behavior of the function is created for each service and error function integrated in an enterprise software application. This profile is based on input measurements, such as response time, throughput, and non-availability. For each such input measurement, the expected behavior is determined, as well as the upper and lower bounds on that expected behavior. The invention further monitors the behavior of service and error functions and produces an exception if at least one of the upper or lower bounds is violated. The detection scheme disclosed is dynamic, adaptive, and has self-learning capabilities.
Owner:CERTAGON
Neural network equalization method used for indoor visible light communication system
ActiveCN105007118AReduce Intersymbol InterferenceReduce bit error rateClose-range type systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError functionVisible light communication
The invention provides a neural network equalization method used for an indoor visible light communication system, and belongs to the visible light wireless communication technology field. The method includes the steps: utilizing a ceiling bounce model to calculate a VLC channel impulse response, carrying out photoelectric conversion for a visible light power signal received by a receiving end, and sending a sequence to a neutral network channel equalizer after amplification sampling; utilizing a heredity algorithm to optimize initialization weights and thresholds among neurons, establishing a neural network for training, and minimizing an error function; and judging an output, restoring the sent sequence, and finally achieving an equalization purpose. According to the scheme, interference among codes is obvious minimized, an error rate is reduced, the communication quality is further improved, a transmission rate that the system can reach is increased, the training time is shortened, and the system complexity is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
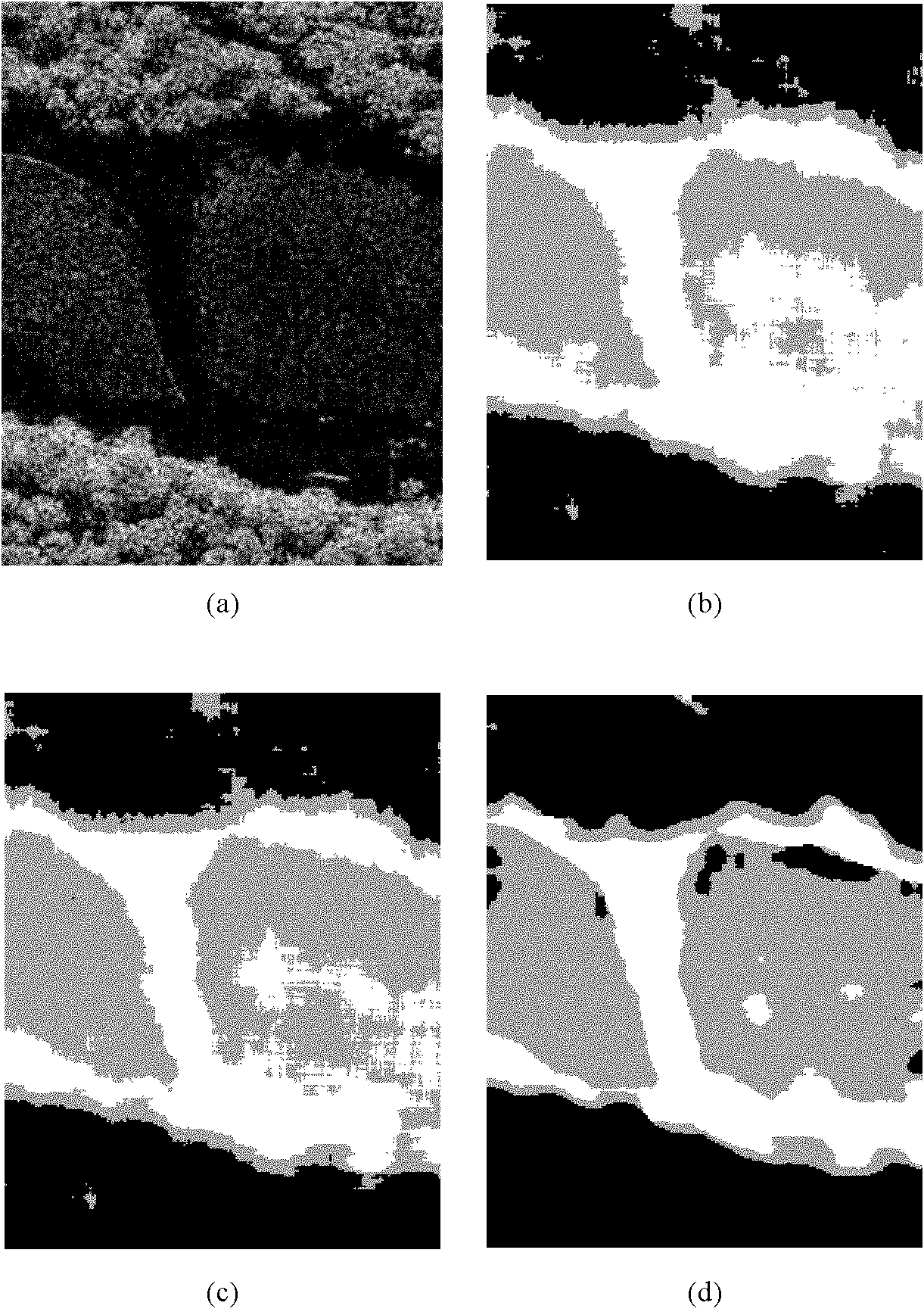
SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image segmentation method based on dictionary learning and sparse representation
InactiveCN102129573AShorten the timeImage segmentation results are goodCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionInverse synthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image segmentation technique based on dictionary learning and sparse representation, and mainly solves the problems that the existing feature extraction needs a lot of time and some defects exist in the distance measurement. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting an image to be segmented, and determining a segmentation class number k; (2) extracting a p*p window for each pixel point of the image to be segmented so as to obtain a test sample set, and randomly selecting a small amount of samples from the test sample set to obtain a training sample set; (3) extracting wavelet features of the training sample set; (4) dividing the training sample set by using a spectral clustering algorithm; (5) training a dictionary by using a K-SVD (Kernel Singular Value Decomposition) algorithm for each class of training samples; (6) solving sparse representation vectors of the test sample on the dictionary; (7) calculating a reconstructed error function of the test sample; and (8) calculating a test sample label according to the reconstructed error function to obtain the image segmentation result. The invention has the advantages of high segmentation speed and favorable effect; and the technique can be further used for automatic target identification of SAR images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
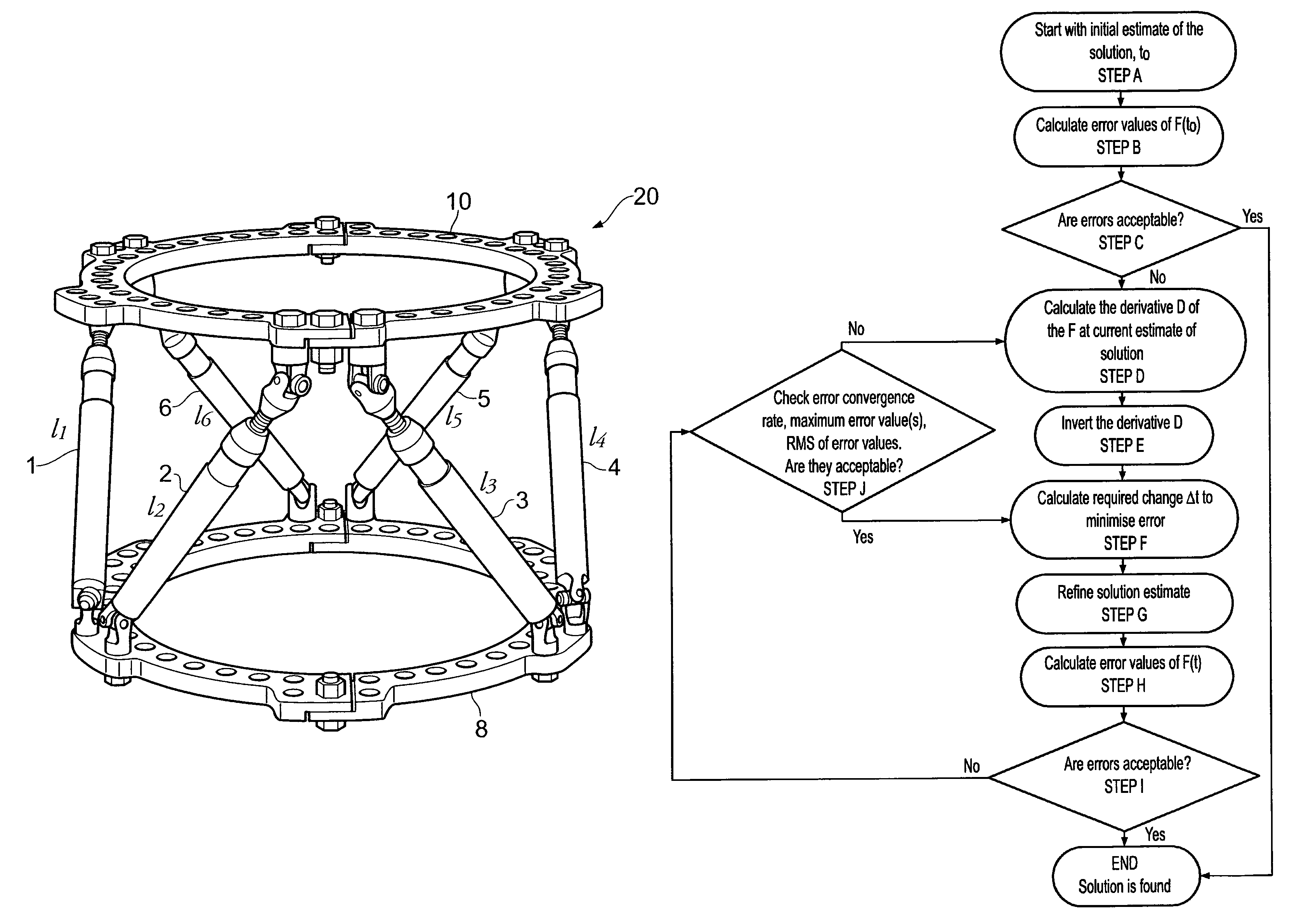
Analysis of parallel manipulators
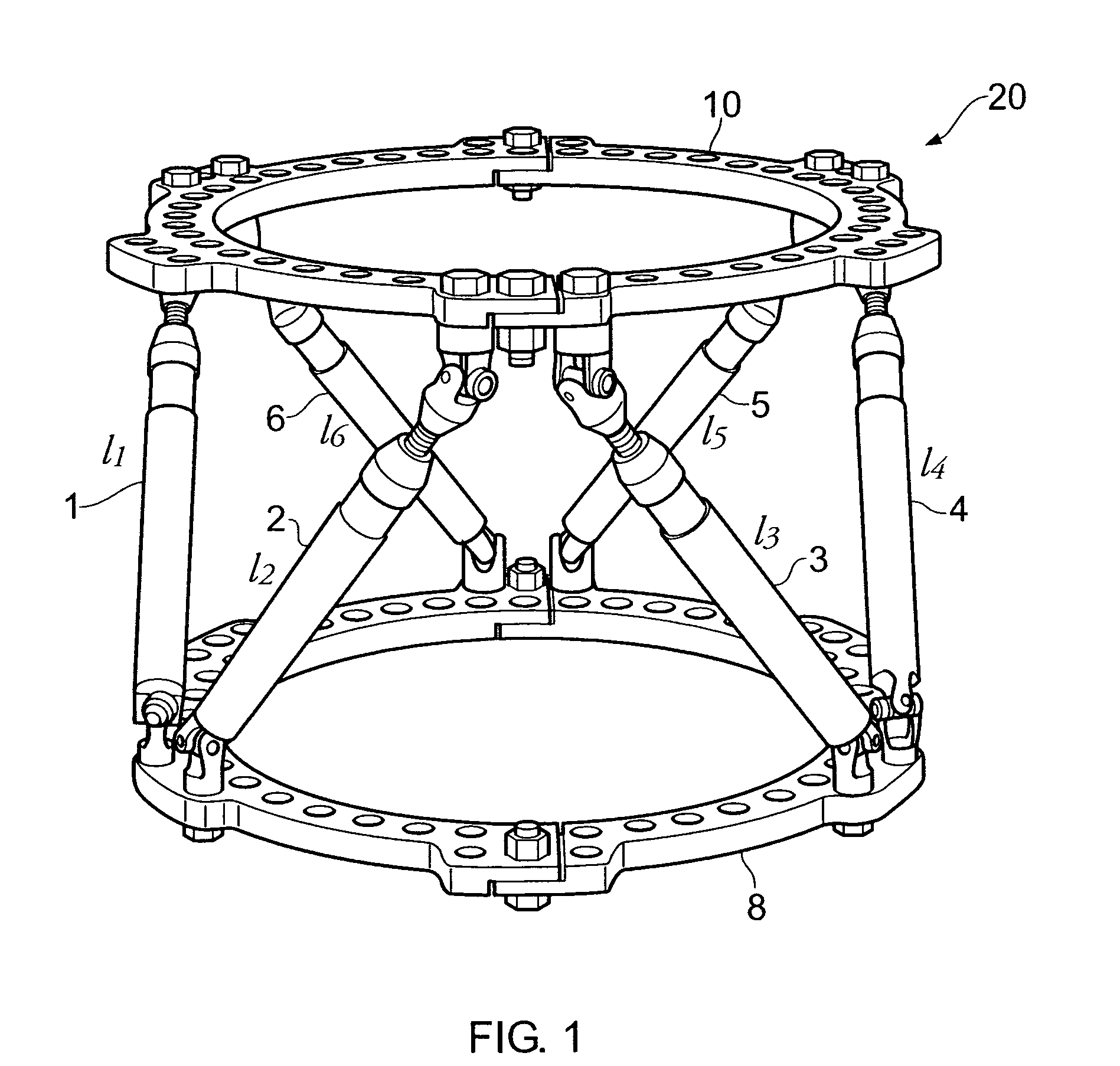
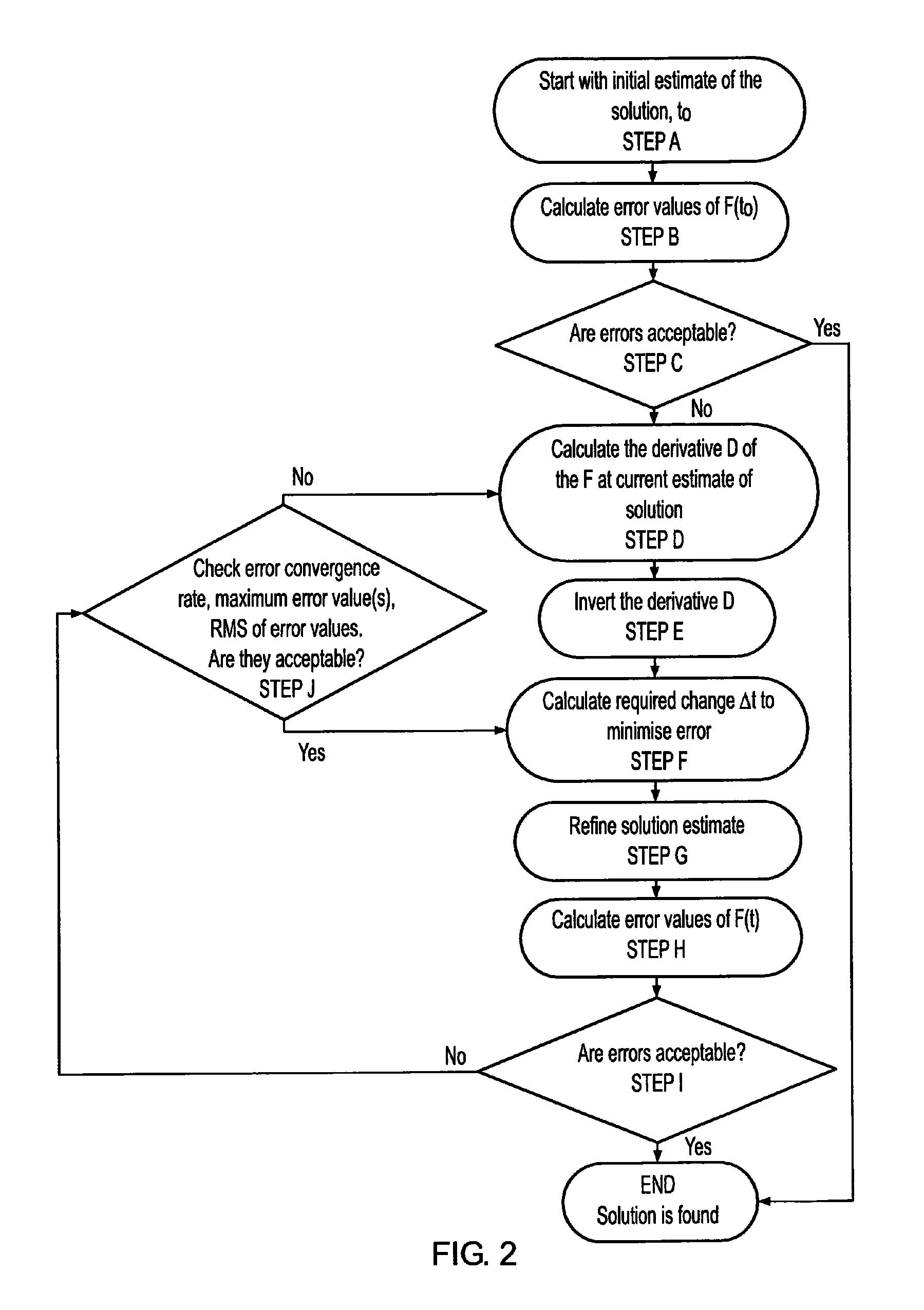
ActiveUS8296094B2Easy to operateSufficient level of accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital computer detailsError functionParallel manipulator
A method of determining the positions and orientations of the base (8) and platform (10) of a parallel manipulator using an iterative calculation in which successive iterations calculate estimates of said positions and orientations, each estimate being determined from the previous estimate using an inverse of a derivative of an error function (F), that function also being used to determine error values for each estimate, wherein if the error values are deemed unacceptable a new derivative is calculated and the iteration is repeated, whereas if the error values are deemed acceptable the same derivative is used in a subsequent iteration. Thus the derivative need not be re-calculate for each iteration, whereby the process can operate more rapidly, e.g. in real time.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
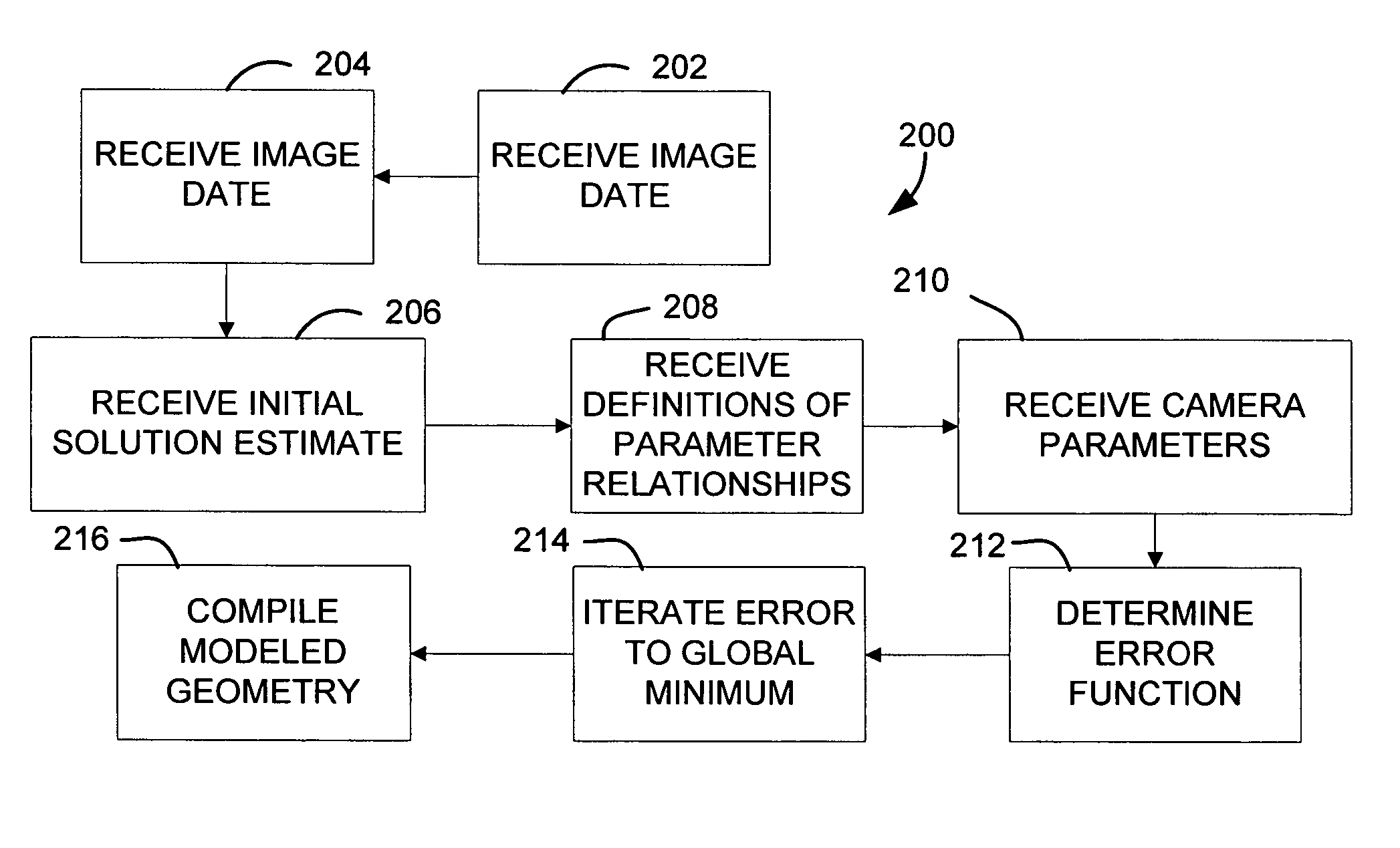
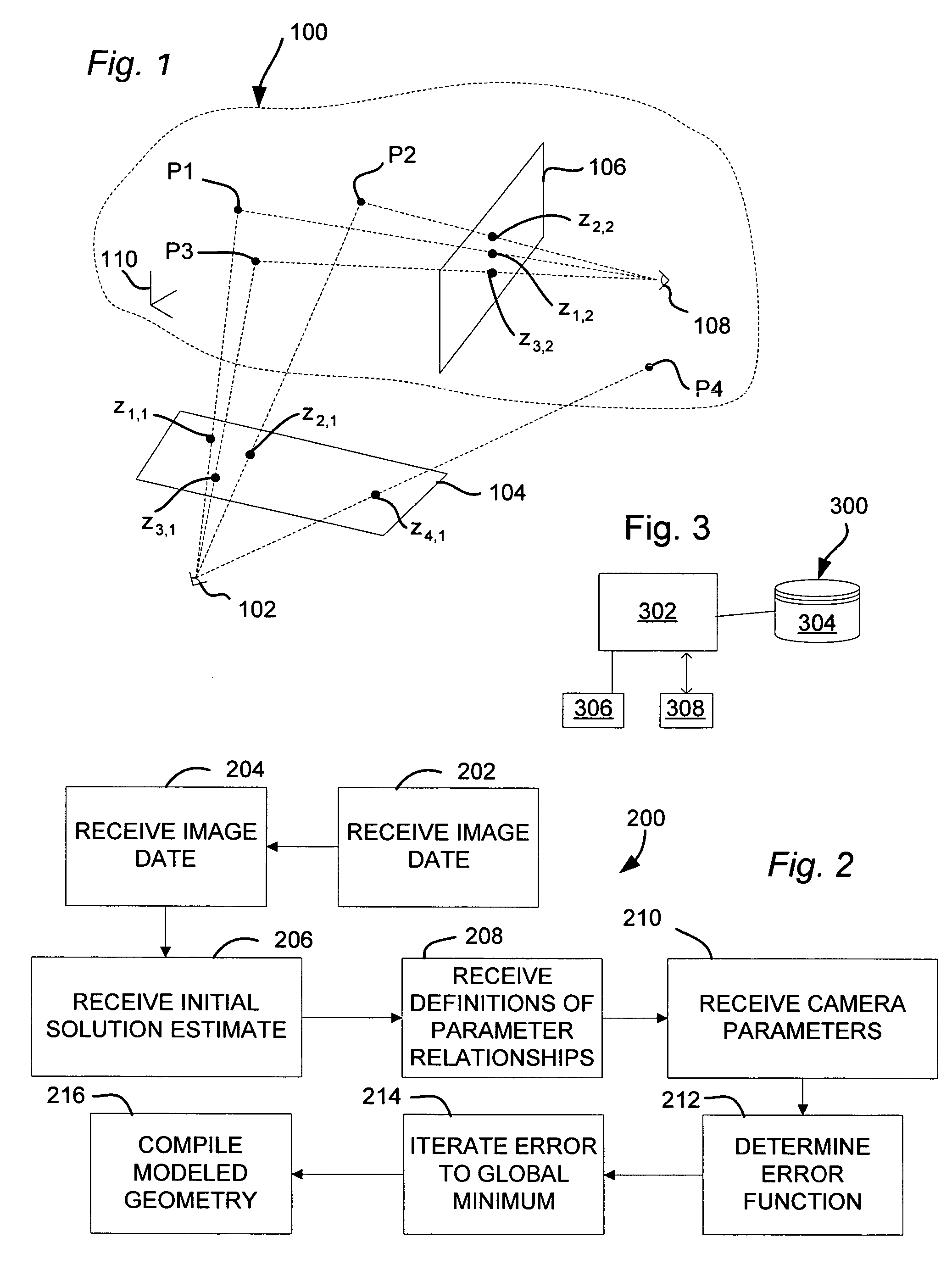
Reverse-rendering method for digital modeling
ActiveUS6990230B2Accurate reconstructionSimple calculationDetails involving processing stepsTelevision system detailsComputer graphics (images)Error function
A method for automatically or semi-automatically constructing a digital 3D model of a scene from photographic data and photogrammetry data includes defining an initial rough model as a solution estimate. A reverse rendering step includes a second-order solution method that employs automatic differentiation techniques to accurately compute derivatives of an error function. In an embodiment of the method, at least one camera is placed within the scene being constructed, and photographic data from this camera is used in the solution process.
Owner:WARNER BROS ENTERTAINMENT INC
Method for locating mobile terminals, system and components therefor
InactiveUS20050208951A1Position fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCo ordinateError function
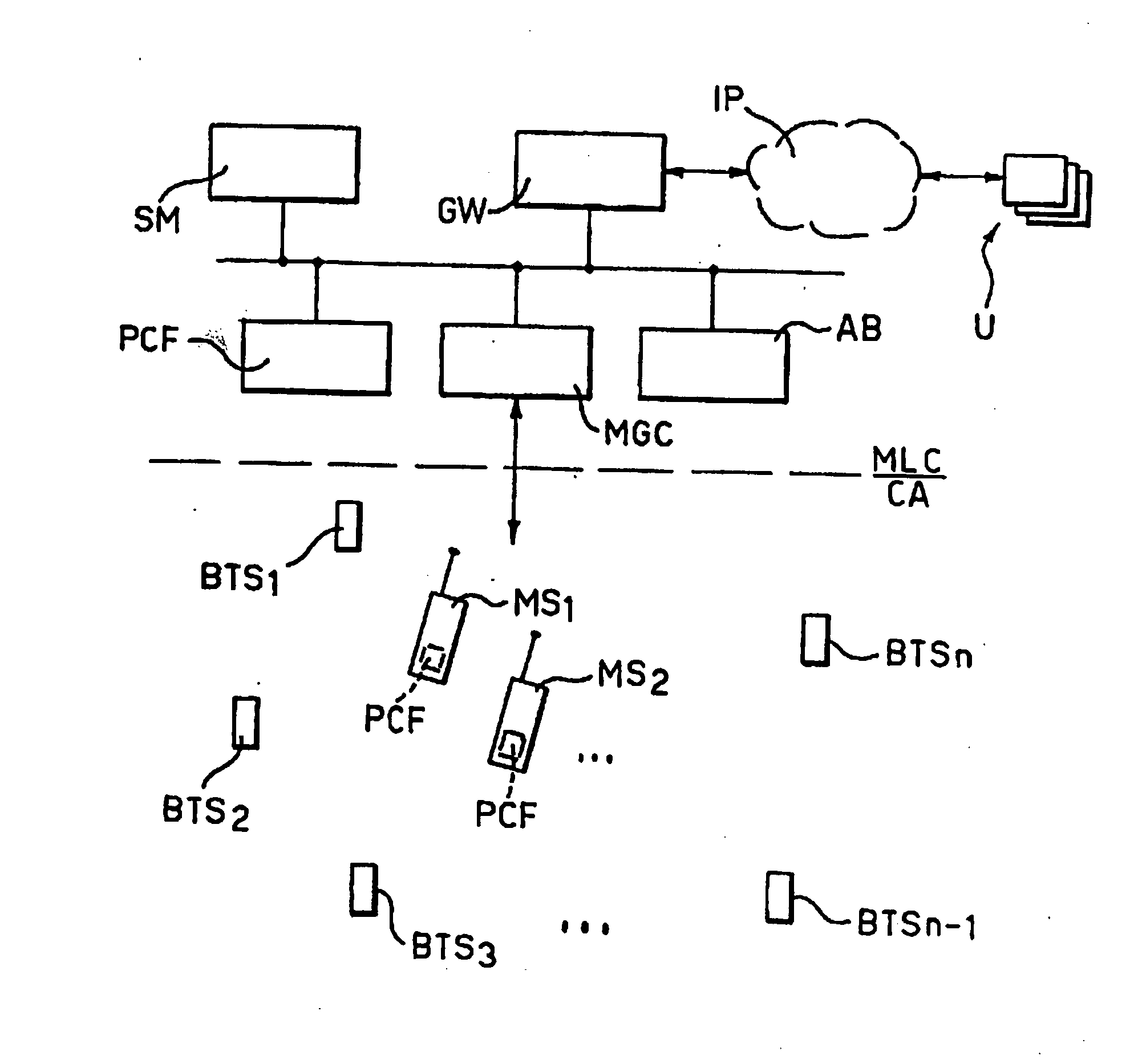
To locate a mobile terminal (MS1, MS2, . . . ) within a mobile communication network comprising at least a radio base station (BTS1, BTS2, . . . , BTSn), a set of physical dimensions are measured, which identify, according to respective functions, the location coordinates (x, y, z) of the mobile terminal. The method comprises the steps of: generating, starting from said set of physical dimensions and respective functions, a global locating error function (φ) which has a minimum for values of said locating co-ordinates (x, y, z) corresponding with the position occupied by said mobile terminal, seeking the minimum of said error function (φ) by varying at least one of said locating co-ordinates (x, y, z), and locating said mobile terminal in correspondence with the value of said at least one locating co-ordinate corresponding to said minimum.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for X-ray image
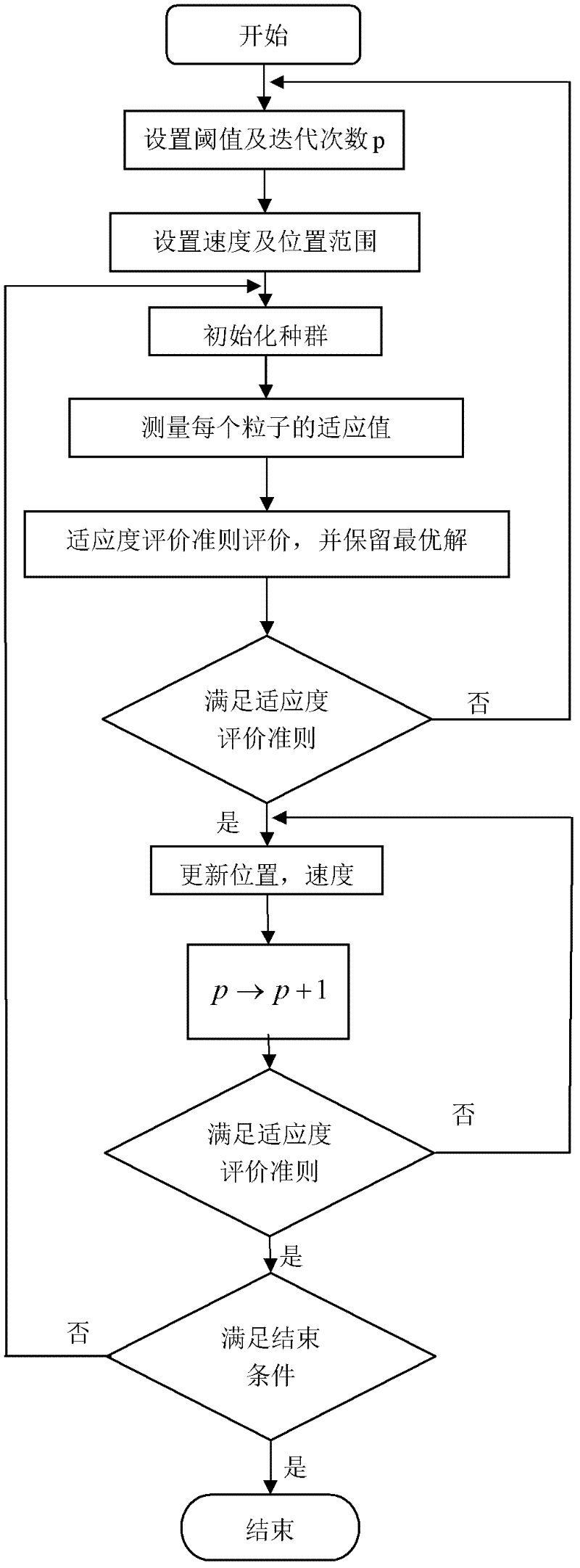
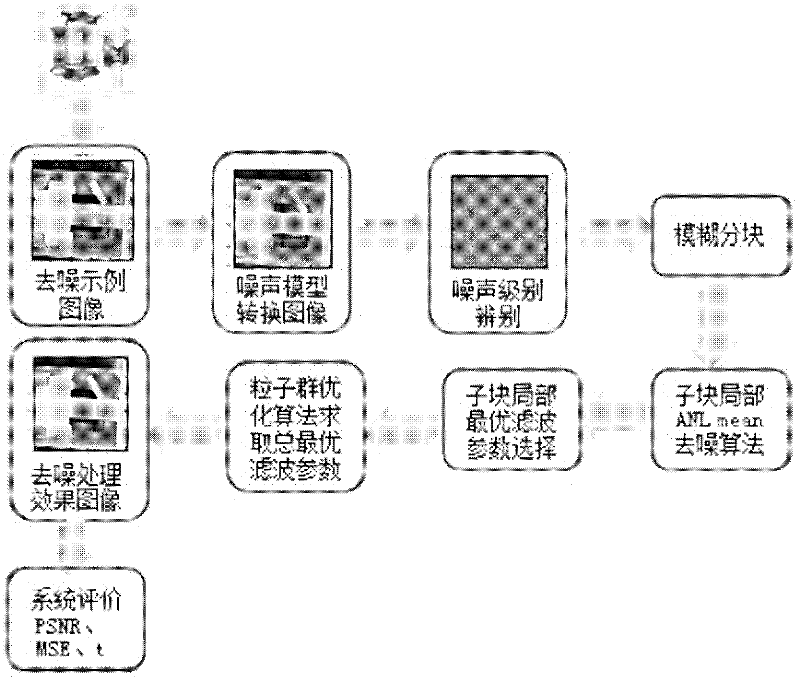
The invention provides a bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for an X-ray image. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) a selecting method of a fuzzy de-noising window; and 2) a bivariate fuzzy adaptive nonlocal average filtering algorithm. The method has the beneficial effects that in order to preferably remove the influence caused by the unknown quantum noise existing in an industrial X-ray scan image, the invention provides the bivariate nonlocal fuzzy adaptive non-linear average filtering de-noising method for the X-ray image, in the method, a quantum noise model which is hard to process is converted into a common white gaussian noise model, the size of a window of a filter is selected by virtue of fuzzy computation, and a relevant weight matrix enabling an error function to be minimum is searched. A particle swarm optimization filtering parameter is introduced in the method, so that the weight matrix can be locally rebuilt, the influence of the local relevancy on the sample data can be reduced, the algorithm convergence rate can be improved, and the de-noising speed and precision for the industrial X-ray scan image can be improved, so that the method is suitable for processing the X-ray scan image with an uncertain noise model.
Owner:YUN NAN ELECTRIC TEST & RES INST GRP CO LTD ELECTRIC INST +1
Systems and methods for reducing position errors in image correlation systems during intra-reference-image displacements
InactiveUS20030090681A1Reduce accumulated errorsImprove accuracyImage analysisGeometric image transformationReference imageError function
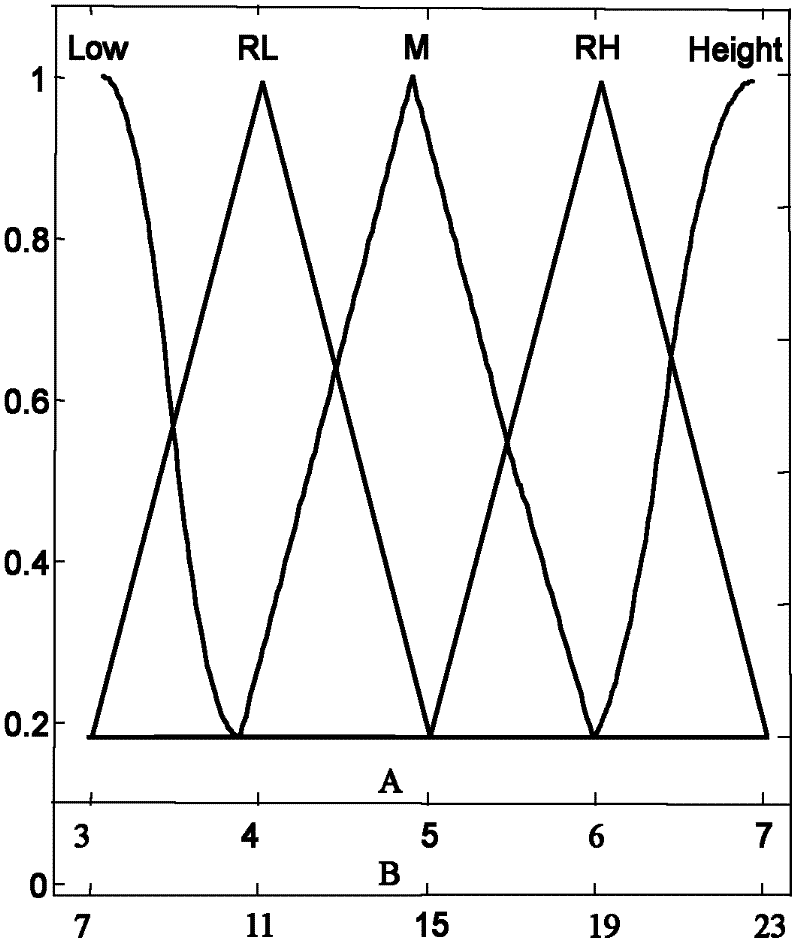
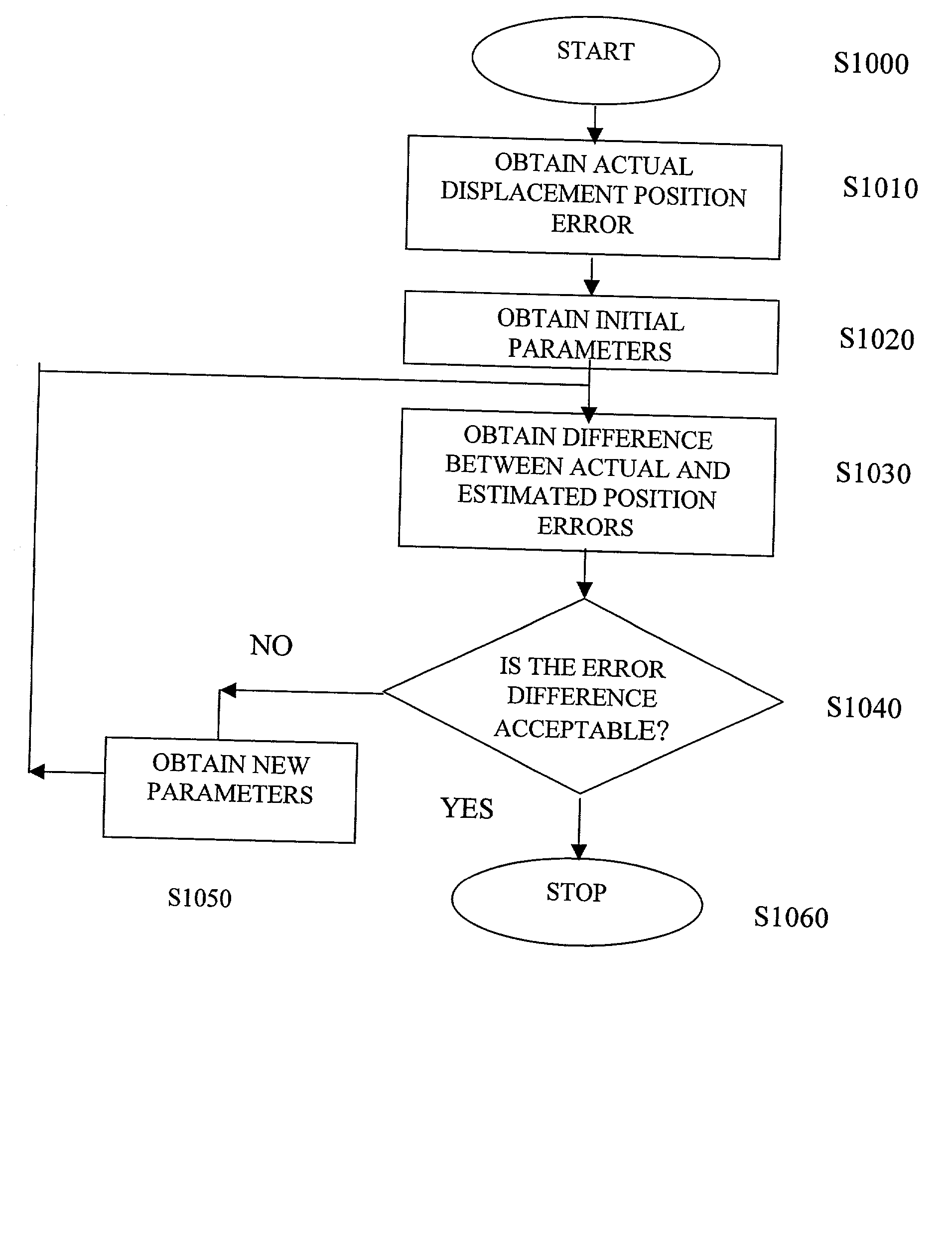
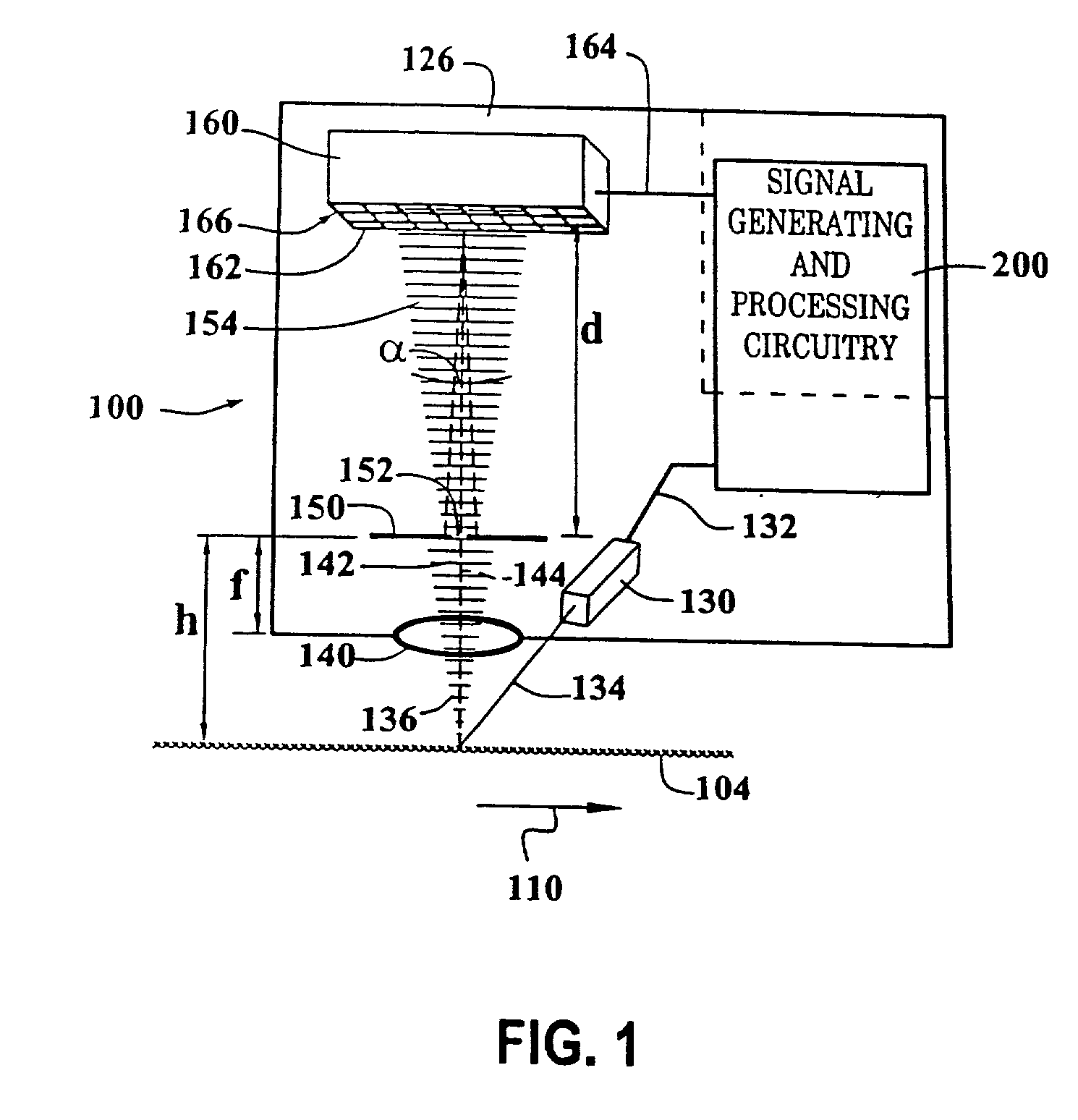
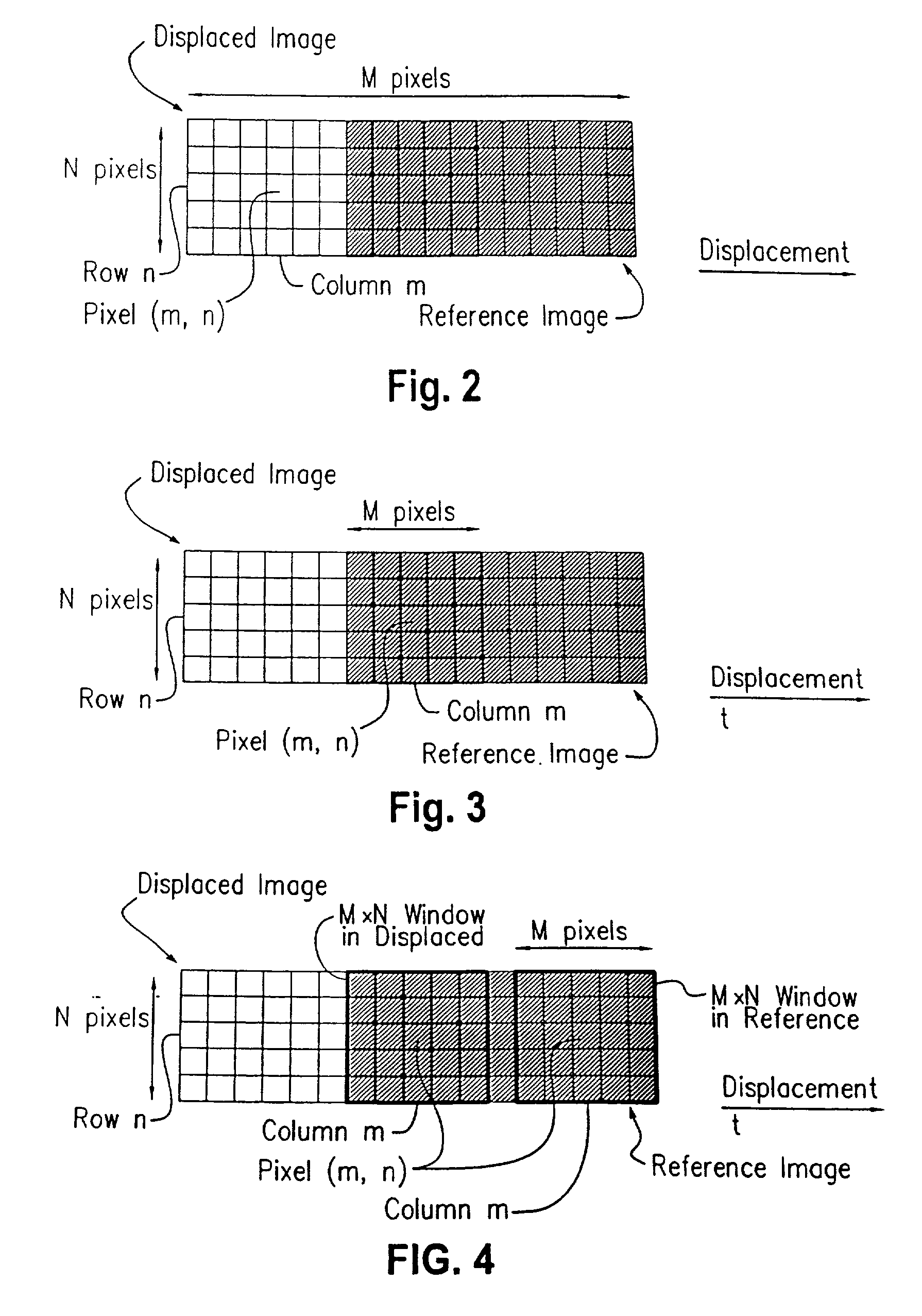
A position error correcting, or reducing, method and system used in an image-correlation system which obtains an error function generally reflecting an error occurring over a nominal reference image update length and an error occurring at a first frequency and various other system errors. The error can be compared to a first reference to fit the position error. In various embodiments, parameters of an error function can be varied in fitting the error function to the first reference. The obtained error function can then be used to determine the position error and render more accurate the image correlation system. In one exemplary implementation, the first frequency is related to a pixel pitch and the nominal reference image update length related to the distance between reference image changes is the maximum usable reference image update length.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Equipment and method for tracking face
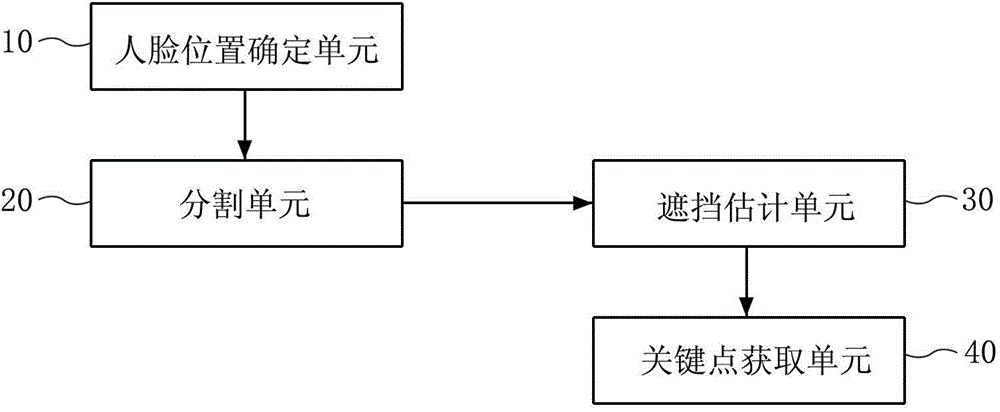
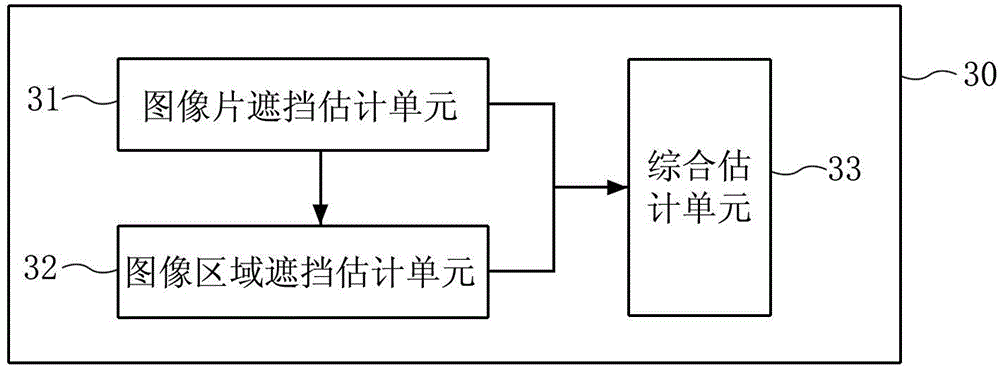
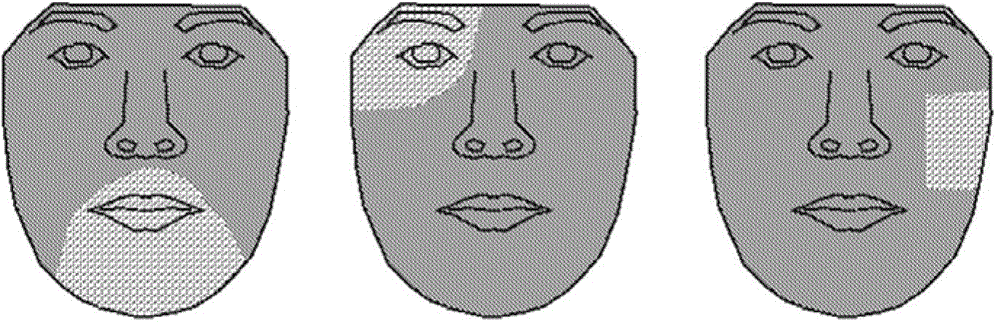
ActiveCN104573614AImprove tracking performanceEffective trackingImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCrucial point
The invention provides equipment and a method for tracking a face. The equipment comprises a face position determining unit, a segmenting unit, a blocking estimating unit and a key point acquisition unit, wherein the face position determining unit is used for determining the face position from the current fame image; the segmenting unit is used for segmenting the image of the face position into each part image of the face; the blocking estimating unit is used for estimating the blocking probability of each part image segmented based on a blocking probability model, and estimating the blocking probability of each pixel in the image of the face position based on the blocking probability of each part image; the key point acquisition unit is used for matching the two-dimensional shape model of the face with a face shape through minimizing a matching error function related to the blocking probability of each pixel, so that the positions of face key points on the current frame image are obtained, and the tracking of the face is finished.
Owner:BEIJING SAMSUNG TELECOM R&D CENT +1
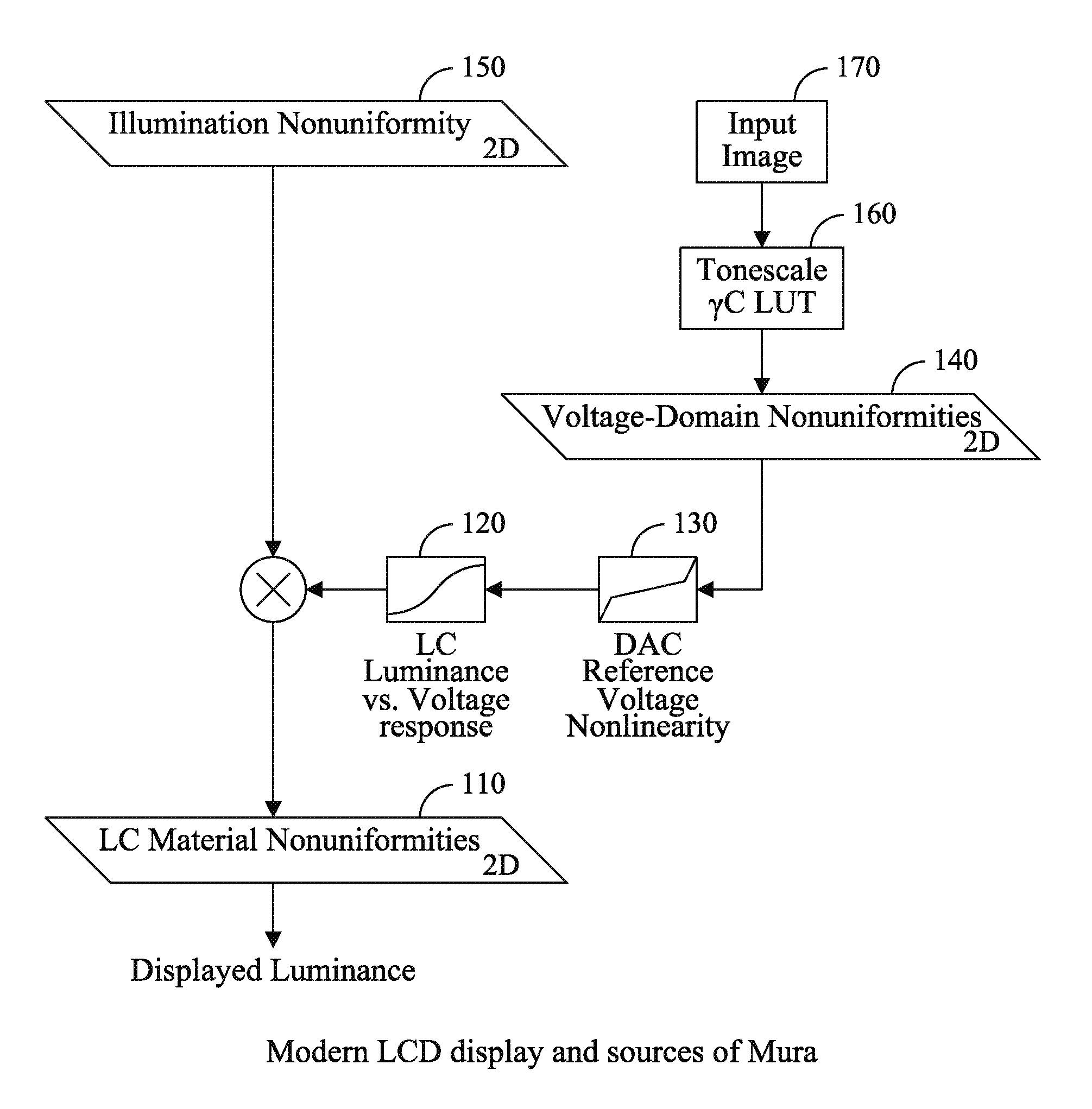
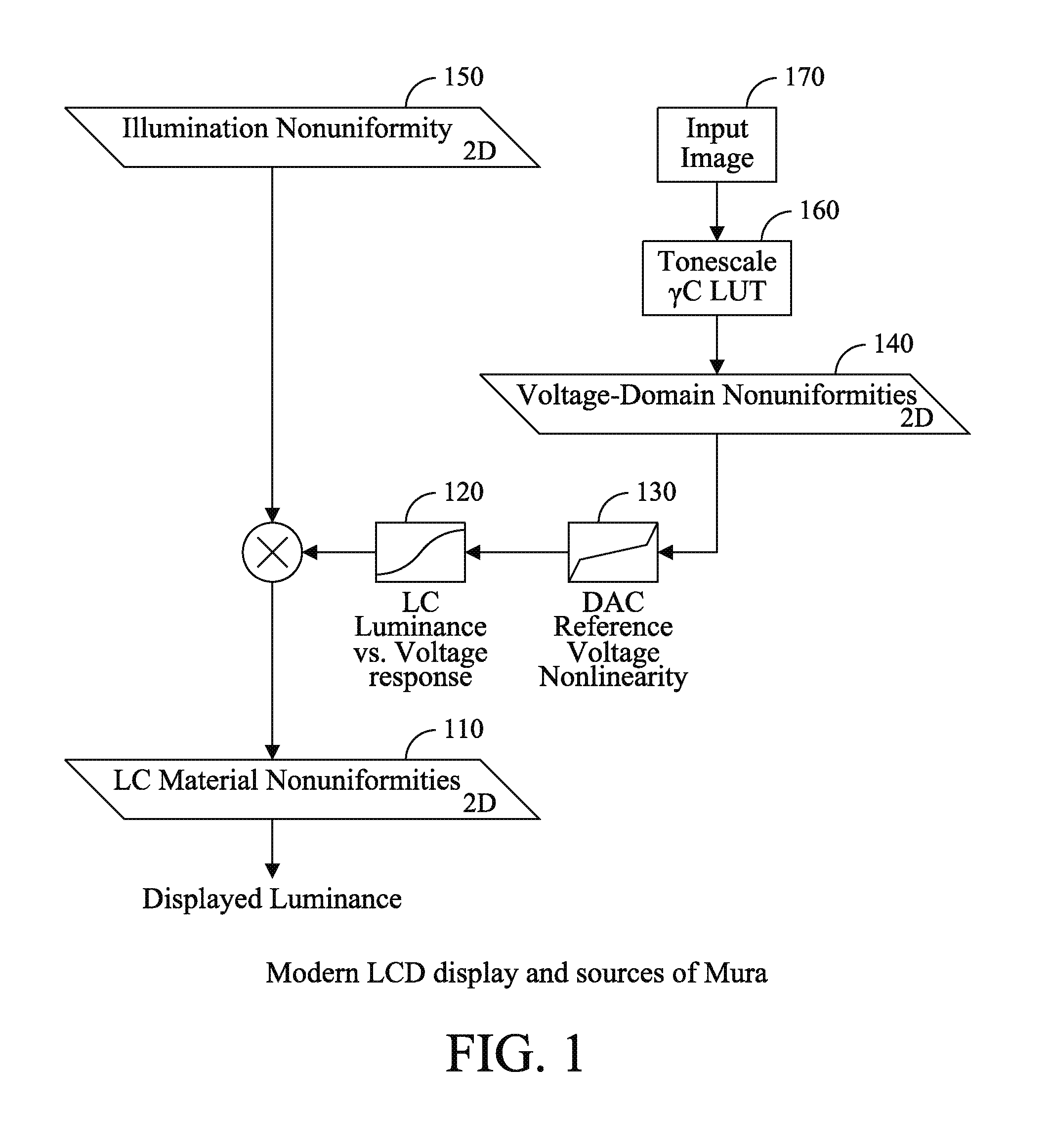
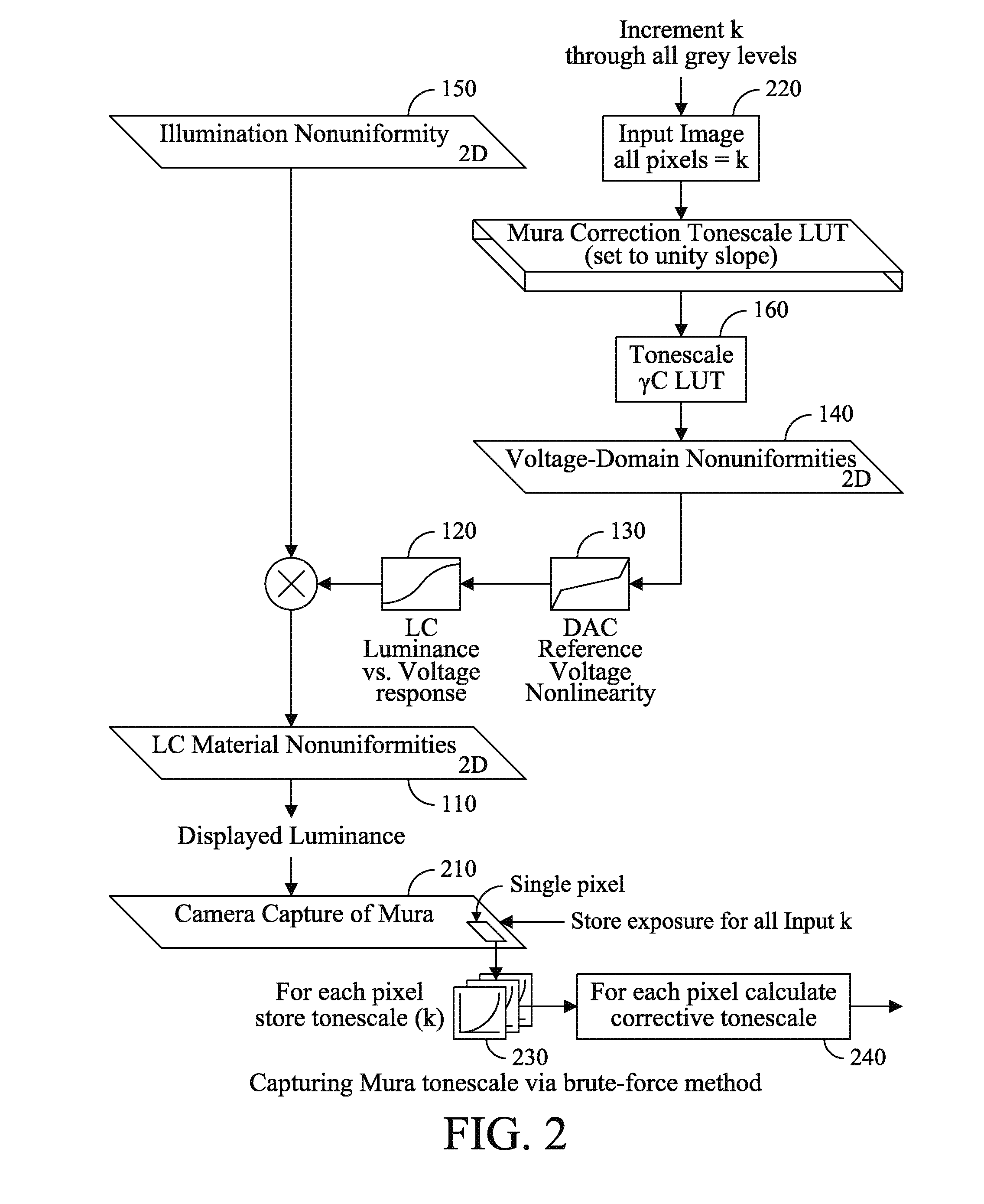
Capture time reduction for correction of display non-uniformities
InactiveUS20120075354A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
A display includes a plurality of gray levels being provided to a plurality of pixels of the display and illuminating each of the pixels with the plurality of gray levels. The display applying corrective data for the pixels so as to reduce the mura effects of the display for the plurality of gray levels, wherein a selection of code values for the corrective data is determined based upon a minimization of an error function.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
Inference engine for discovering features and making predictions using generalized incremental singular value decomposition
InactiveUS20070150428A1Knowledge representationInference methodsPattern recognitionSingular value decomposition method
Method of automated inference using generalized incremental singular value decomposition by following the gradient of a cost function incorporating an error function of the implicit matrix defined by a current estimate of a partial SVD and the observed values. Accommodates sparse or overfilled matrices and correction for nonlinearities. Any number of observed values can be supplemented or updated, and predictions made at at any time. Any number of features can be used. Useful wherever there are two classes of objects (or the same class twice) for which there is a particular value implicitly associated with each pairing of such objects, for example including preference, filtering, rating, and recommender systems, image and other data recognition, compression, and restoration systems, warning systems, autonomous navigation, expert systems, machine learning, language processing, semantic analysis, artificial intelligence, knowledge systems, behavior prediction, economic and financial modeling, and modeling of natural systems.
Owner:WEBB BRANDYN
Adaptive interlace-to-progressive scan conversion algorithm
InactiveUS20060146187A1Improve performanceImprove forecast accuracyTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesProgressive scanData set
Owner:MICRONAS SEMICON
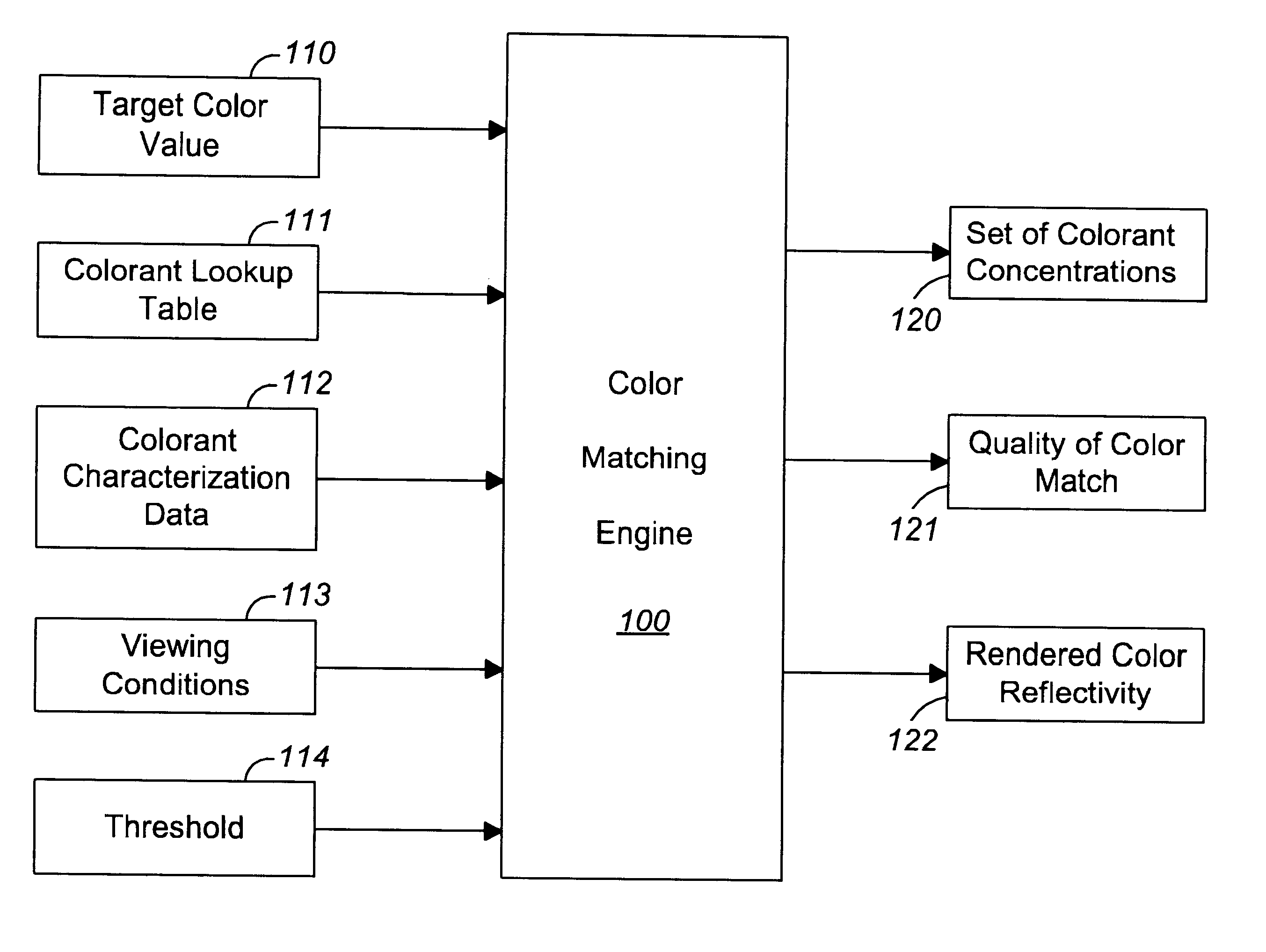
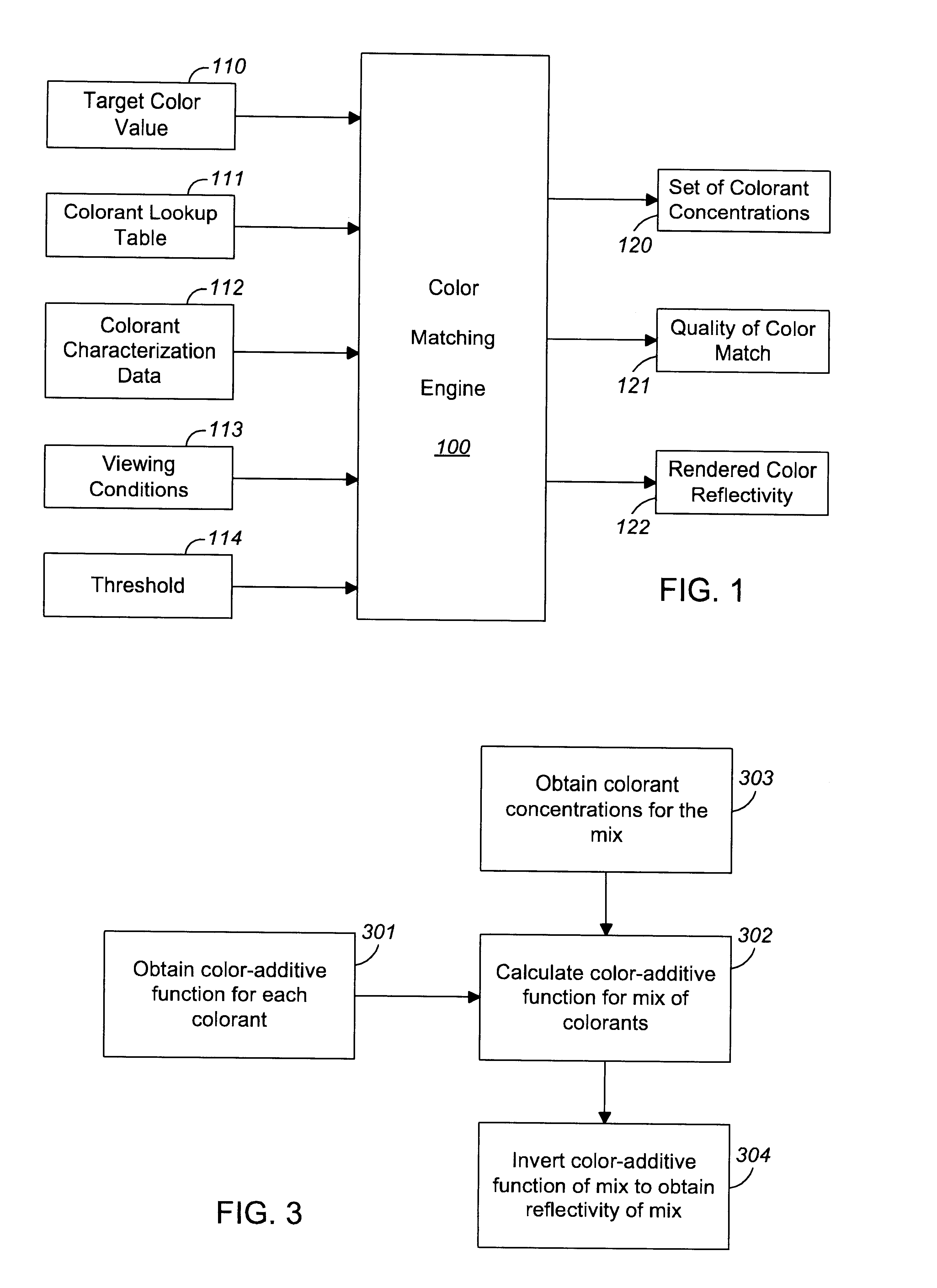
Spectral color matching to a device-independent color value
InactiveUS6646763B1Digitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersPattern recognitionTwo grid
Methods, systems, and apparatus for mapping a nonspectral representation of a target color, such as an input color tuple, to a set of concentration values for a set of device-specific colorants. The invention includes using the input color tuple to derive a first set of colorant concentration values from a color lookup table; and refining the first set of colorant concentration values by an iterative non-linear process to generate a final set of colorant concentration values. The first set of colorant concentration values can derived by using an input color tuple as an index to obtain grid-point concentration values at two grid points of the color lookup table and calculating the first set of colorant concentration values as a linear interpolation of the grid-point concentration values. In an implementation that provides a color function table of color-additive function values, the iterative non-linear process can include iteratively (a) calculating an interim color tuple from an interim set of colorant concentration values and the color function table, the initial interim set of colorant concentration values being the first set of colorant concentration values, and (b) deriving an interim set of colorant concentration values from a difference between the input color tuple and the interim color tuple. The calculations can include calculating a partial derivative of an error function from the difference between the input color tuple and the interim color tuple; and using the partial derivative to derive a successor interim set of colorant concentration values from a current interim set of colorant concentration values.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
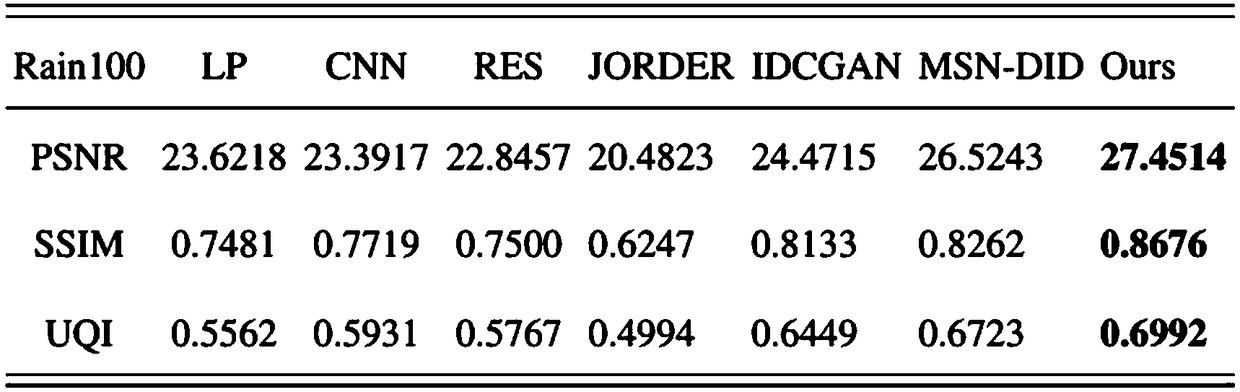
Single-frame rainfall removing method based on multi-scale feature fusion
ActiveCN109360155AGood effect in removing rainUniversalImage enhancementNeural architecturesPeak valueError function
The invention provides a single frame image rain removing method based on multi-scale feature fusion, Feature extraction of rainless images with different scale receptive fields, then deconvolution operation to get the result of rainless images, using the combination of coarse-scale features and fine-scale features, to promote the rainless images generated by fine-scale to achieve the best effectof rainless. By removing rainlines on multiple scales, the algorithm can be used in a variety of rainwater situations, and the rainout algorithm is more universal. The invention cites the antagonisticerror and the perceptual error to construct a new error function, and trains the rain removing model without any prior knowledge, and does not need to preprocess and post-process the image, thus ensuring the integrity of the whole structure. The results on a plurality of test sets show that the invention can improve the peak signal-to-noise ratio on the luminance signal channel by 2-5dB.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
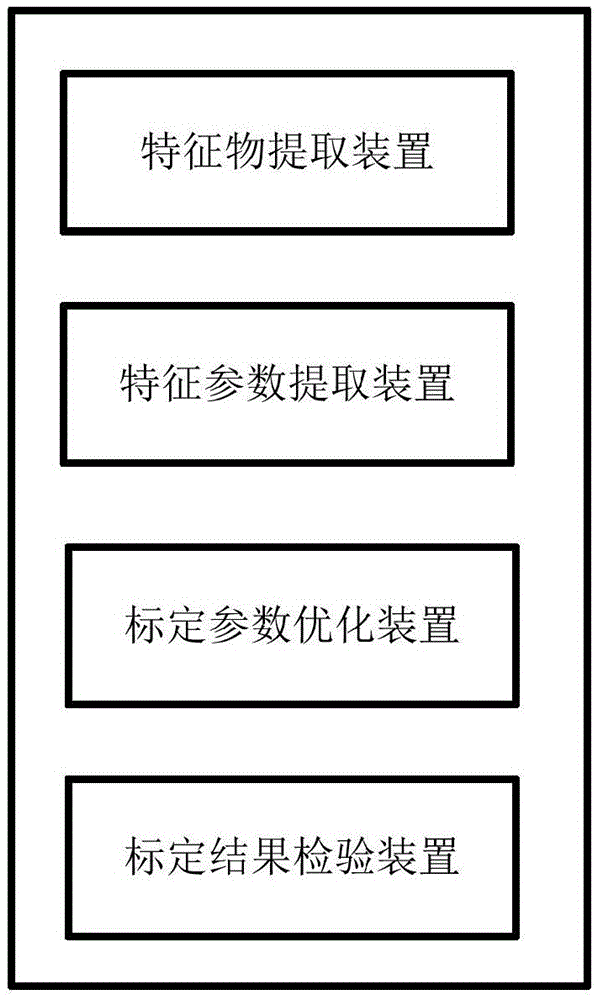
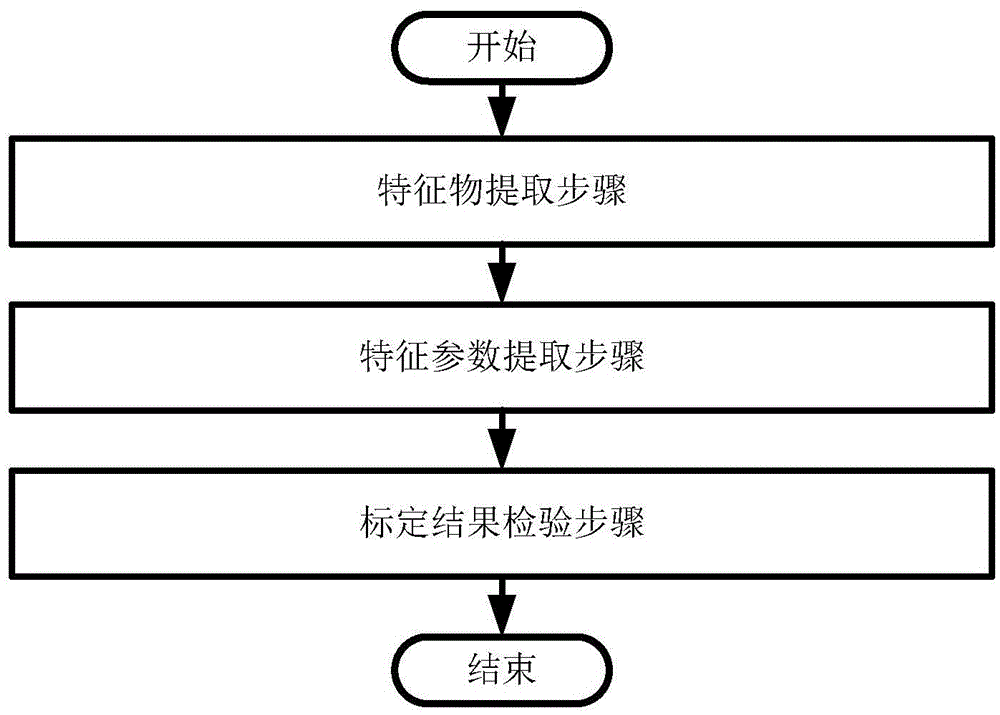
Vehicle-mounted panoramic around view calibration system and method
ActiveCN105608693AImprove calibration accuracyAccurate CalibrationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMulti camera
The present invention provides a vehicle-mounted panoramic around view calibration system and method. The method comprises: extracting an image containing a feature object from images acquired by a panoramic around view system, and marking the image as a feature object image; extracting feature object useful information from the feature object image; according to the feature object useful information, optimizing a calibration parameter; and verifying accuracy of a calibration result, wherein the calibration result refers to a calibration parameter obtained by optimization. According to the system and method provide by the present invention, optimization of the calibration parameter is taken as an optimization problem, and an error function based on a multi-camera feature projection error, so as to indicate a calibration error under a current optimization result, so that calibration is more accurate and rapider, and calibration precision of the panoramic around view system is improved; and calibration can be optimized and corrected by using an artificial marker or a non-artificial marker, so that calibration efficiency and applicability of the panoramic around view system are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OUFEI INTELLIGNET VEHICLE INTERNET TECH CO LTD
A six-degree-of-freedom attitude estimation method based on Tag
ActiveCN109345588AImprove robustnessImprove pose estimation accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisEstimation methodsImaging quality
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom attitude estimation method based on Tag, By adding a tag to the object to aid detection, the Tag on the object is identified by the camera, Help SLAM complete initialization, After initialization, A feature point is continuously extracted from each frame of the image, and according to whether the speed matrix corresponding to the previous frame is empty, Camera pose estimation is carried out, and the initial value of camera pose estimation is taken as the initial value, and the re-projection error function of map points corresponding to feature points is adopted as the objective function to optimize camera pose, so as to obtain the optimized camera pose and map points corresponding to feature points, and then the camera pose is converted intothe pose of the object. The method of the invention has good robustness when the imaging quality is poor and the object moves at high speed, and has very high attitude estimation accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com