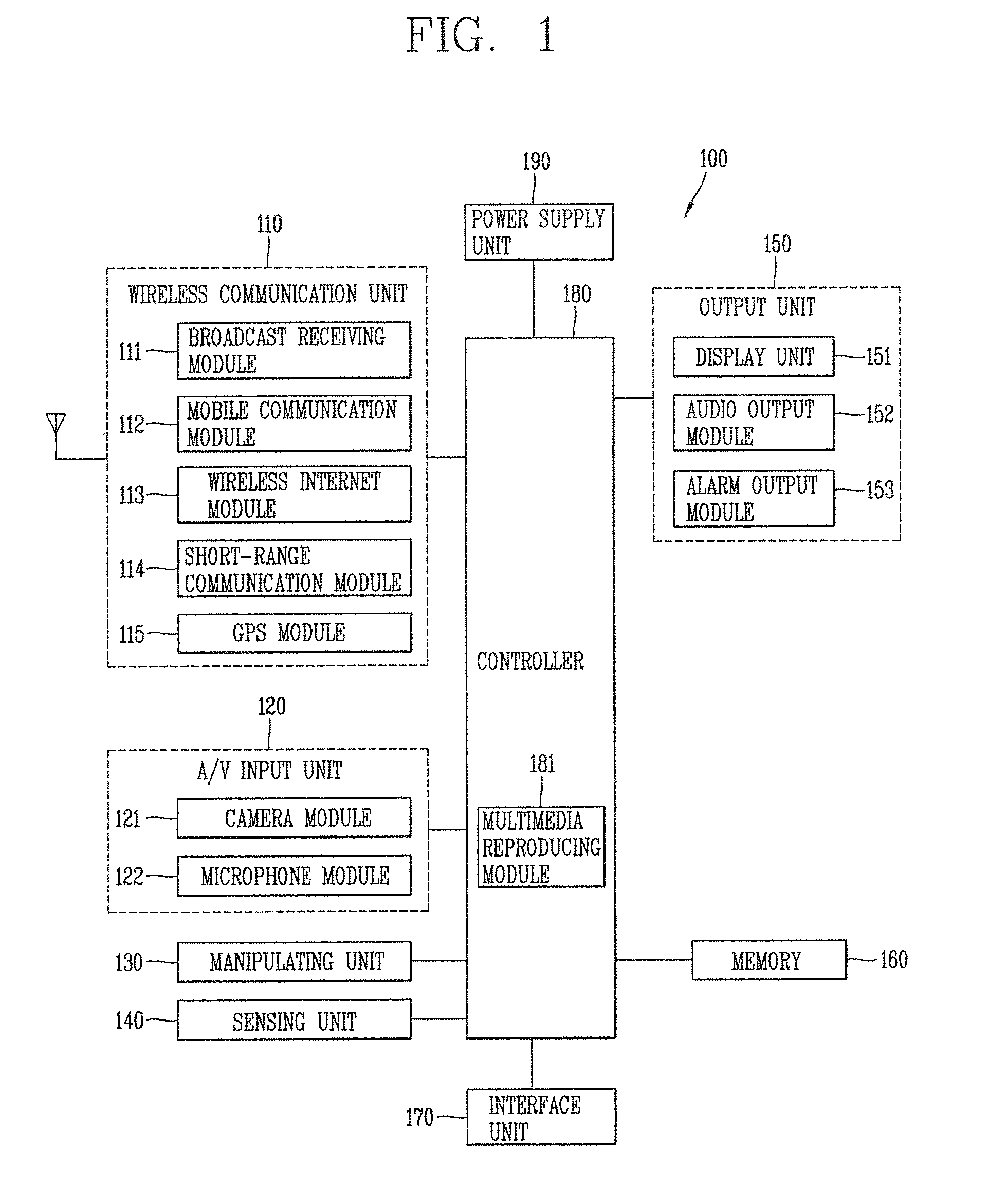
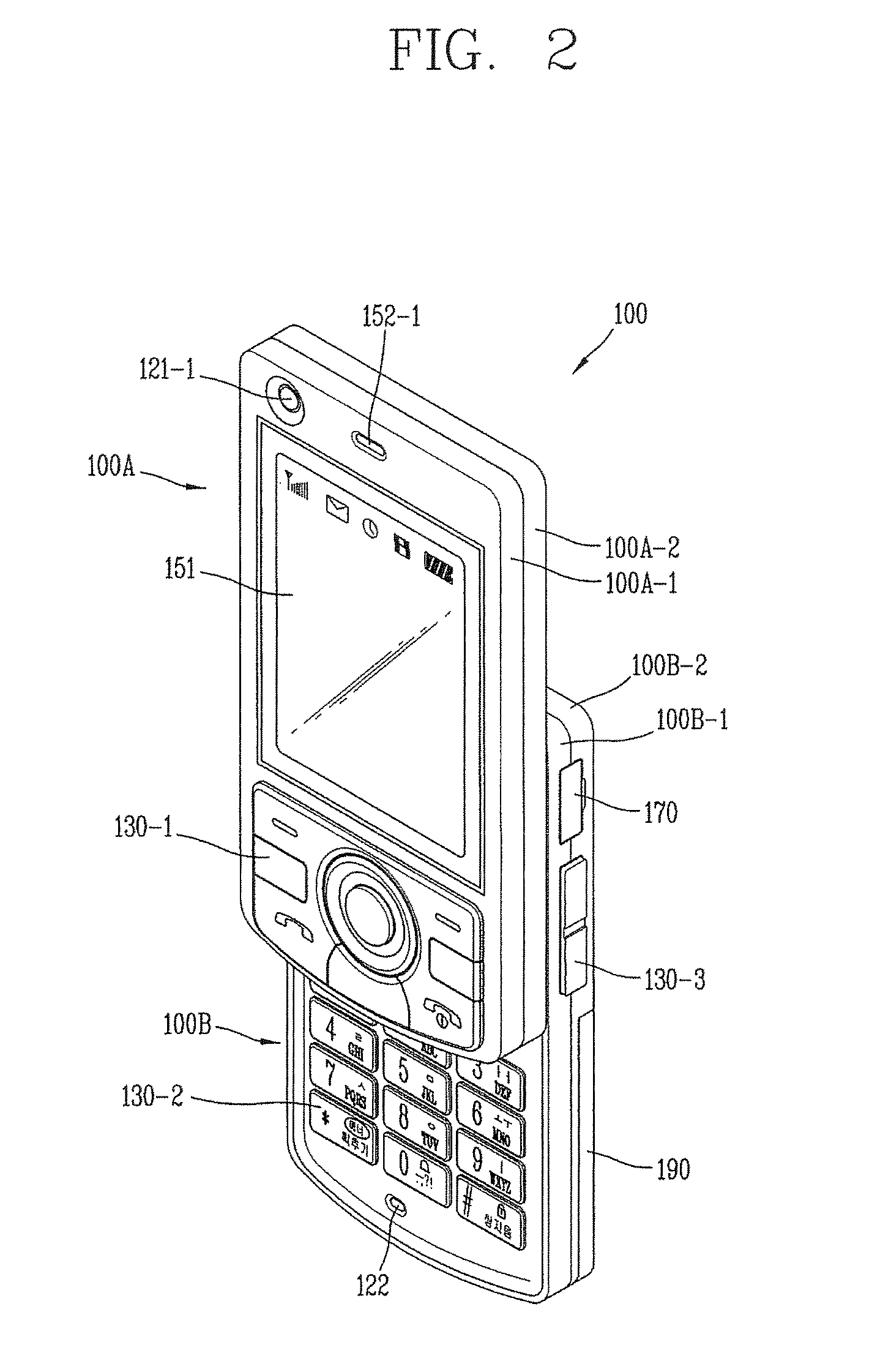
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5576 results about "Background image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
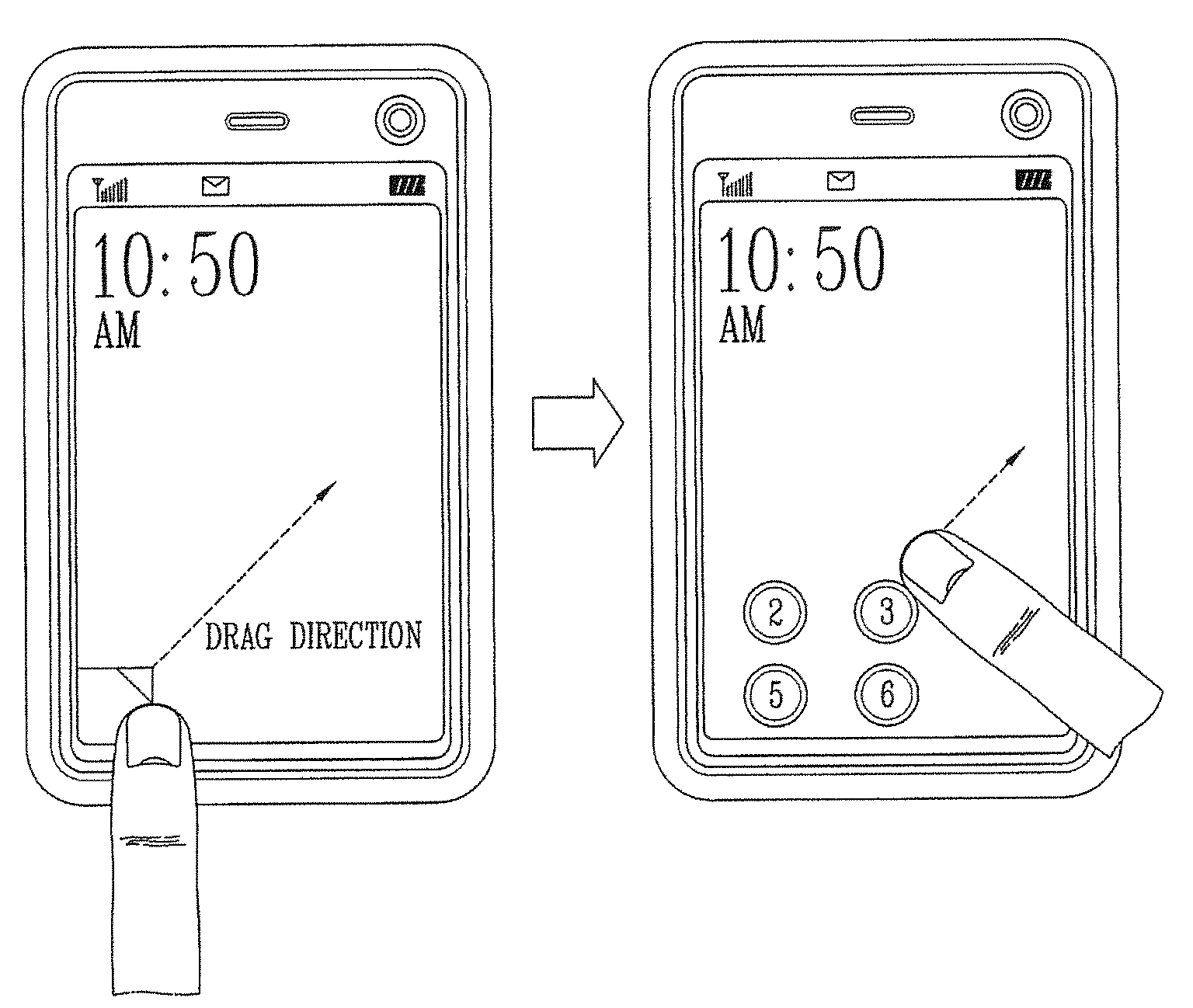
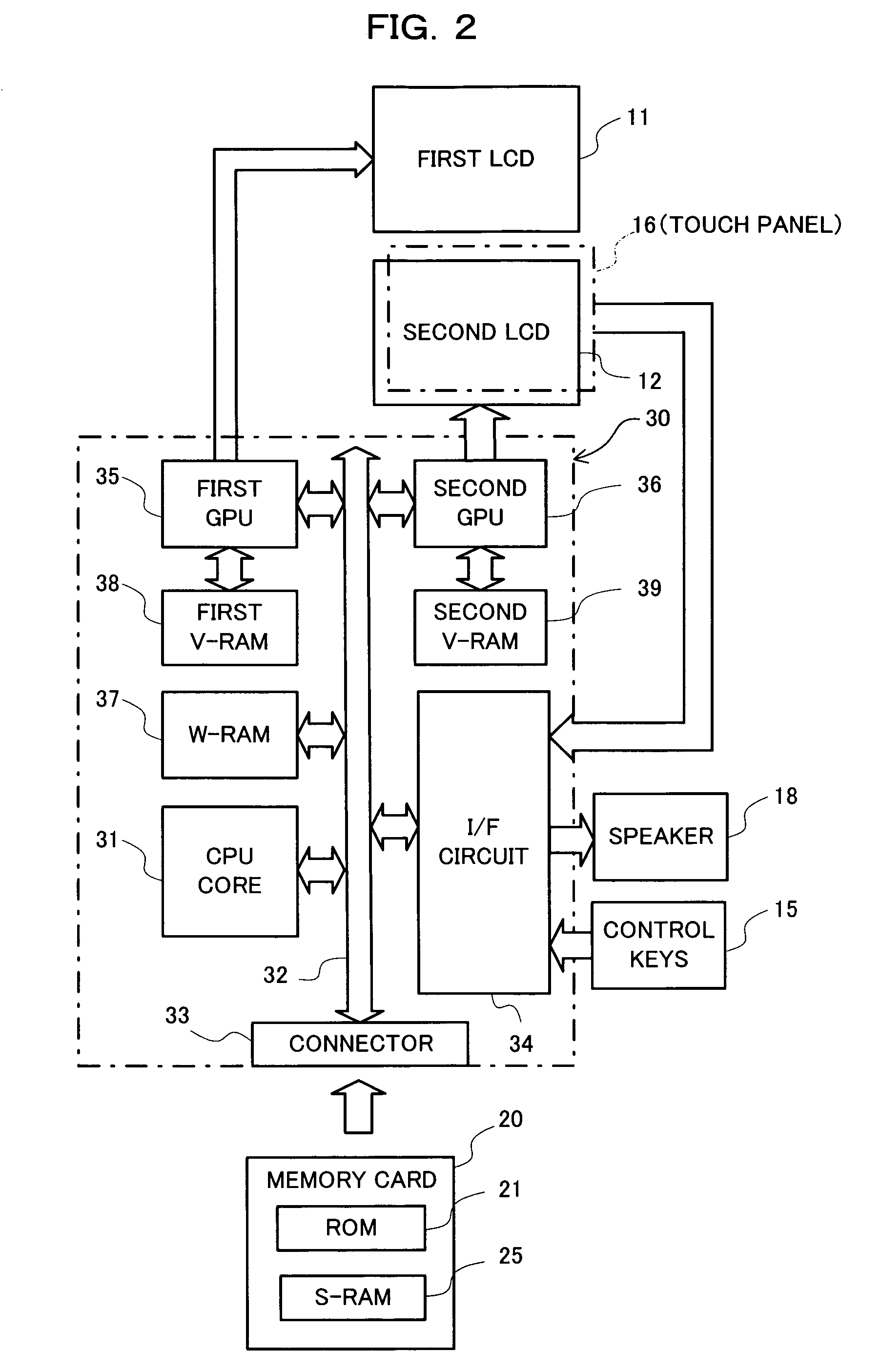
Menu display method for a mobile communication terminal
InactiveUS20090094562A1Substation equipmentInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Background image
A mobile terminal comprising a display module to display a tag and to display a menu screen image related to the tag at one portion of a background image as the tag is dragged, the menu screen image being displayed according to a dragging direction and a dragging distance; an input unit to detect a touch input with respect to the display module or the tag to determine the dragging direction and the dragging distance; and a controller to expose or hide the menu screen image according to the dragging direction the dragging distance of the inputted touch.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
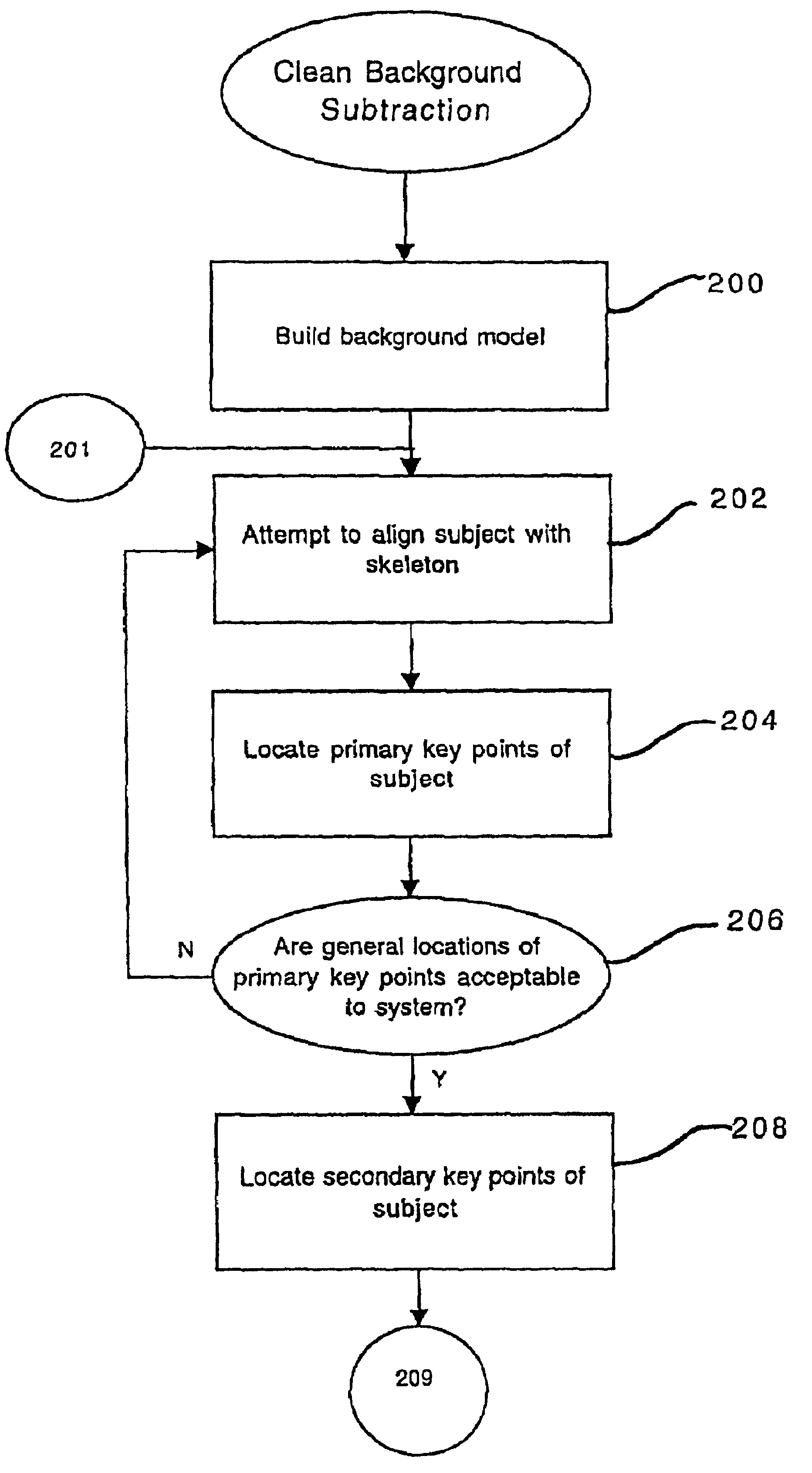
Method and apparatus for performing a clean background subtraction
InactiveUSRE42256E1Easy to determineReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisEdge extractionBackground image
A background subtraction apparatus of the present invention includes a key point locator for locating key points on a known object type, a boundary point locator for locating boundary points of the known object that make up the edges of the known object, and an edge processor for processing the edges to provide a clean-edged extraction of the known object from a background image. Preferably, the key point locator includes an alignment detector for detecting alignment of an image of the known object type with a skeleton image. Still more preferably, the skeleton image is an exoskeleton image and the known object type is a human being.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Virtual desktop manager system and method
The present invention comprises a method and computer implemented system for presenting multiple virtual desktops on a display of a computer system. A “pager” window is displayed on a desktop (either real or virtual) which comprises multiple subpanes, each of which contains a scaled virtual desktop having dimensions that are proportional to, but less than the dimensions of a corresponding virtual desktop. Each scaled virtual desktop provides a representation of the corresponding full-size virtual desktop that would display one or more application windows whose content may optionally be replaced by the icon designating the application program or data file displayed therein, for sake of visual clarity. The present invention also provides a mechanism for varying the background image of virtual desktop, and thus, of each scaled virtual desktop pane, in addition to a number of enhancements to the user interface for controlling the virtual desktop environment including transparency hiding of the pager window, constant aspect ratio scaling of the pager window, mouse desktop changing with corner exclusion, display and interaction with window lists, individual pop up menus for windows, starting desktop selection, a method for moving windows between virtual desktops, a method to override virtual desktop behaviors, a method for placing child windows on the same desktop as the parent window, notification of desktop changes, tracking topmost application on other desktops, sticky monitors, and API remote control.
Owner:THOMPSON JEFFREY W +4
Video game device and video game program
ActiveUS20060094502A1Video gamesSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Face sheet
A moving character and a background image are displayed on a display screen with a touch panel thereon. When the player operates the touch panel to draw a line in an intended path extending between a start point and an end point along which the player wishes to guide the moving character, an operation trace image having the shape of the line drawn is displayed on the display screen. Then, the moving character moves along or in parallel to the operation trace image. The operation trace image is gradually erased after a predetermined amount of time elapses. Thus, it is possible to provide a video game device and a video game program in which the player can influence the moving path or the moving direction of the player (moving) character based on the shape and / or the direction of the line drawn by the player.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD +1
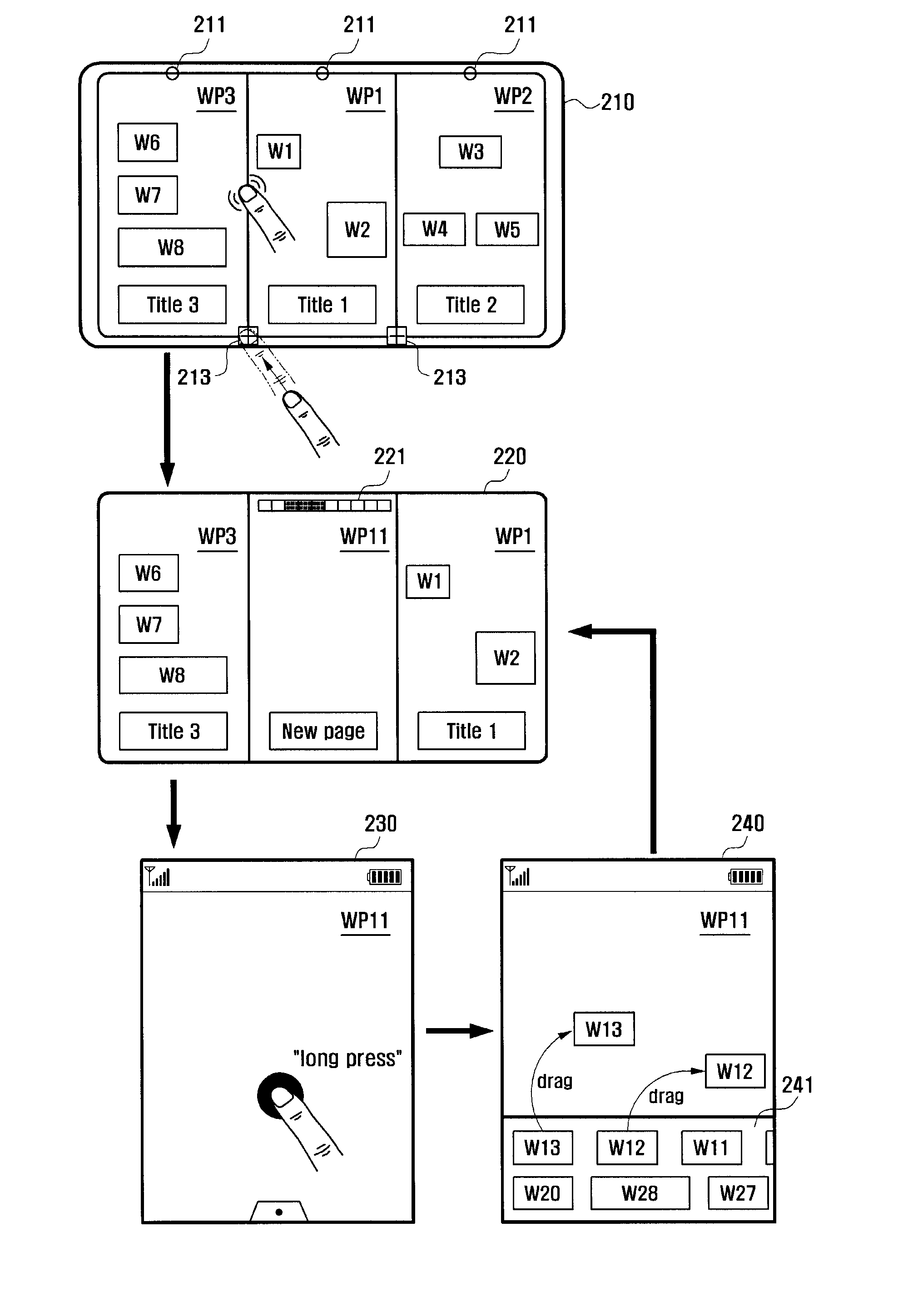
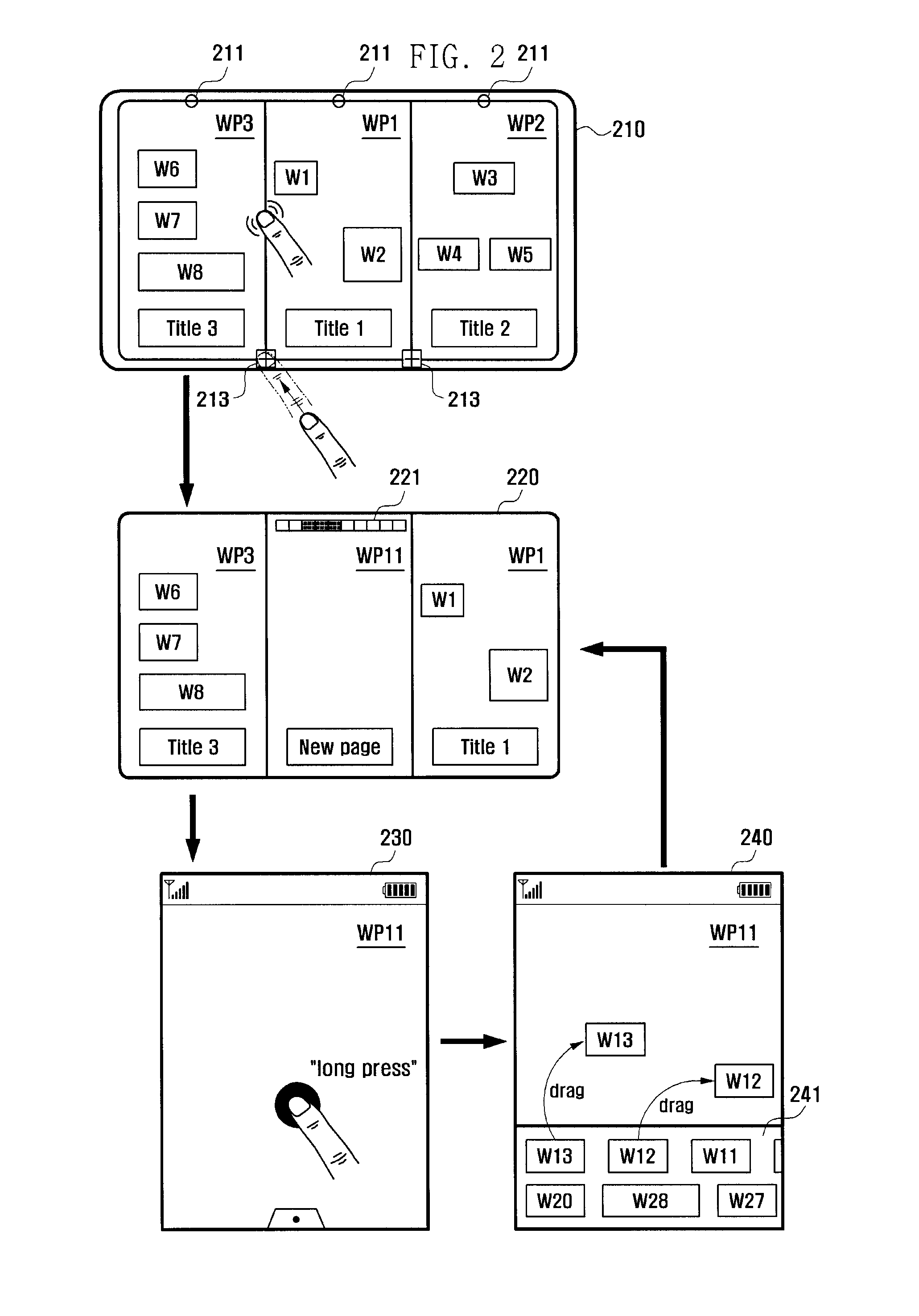
Mobile device and method for editing pages used for a home screen
ActiveUS20100295789A1Quickly and conveniently editingSimply and easily editInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsHome screenMobile device
Provided are a method and related mobile device for editing, in an integrated, convenient and quick manner, various menu pages selectively used for a home screen. In response to a given input signal, the mobile device outputs a page edit screen including a specific page displayed on the home screen. Then, in response to subsequent input signals, the mobile device may add a new page, delete a selected page, change a title of a selected page, move or remove a selected icon in a page, change a background image of a selected page, or change a positional order of pages.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and Method for Producting Multi-View Contents
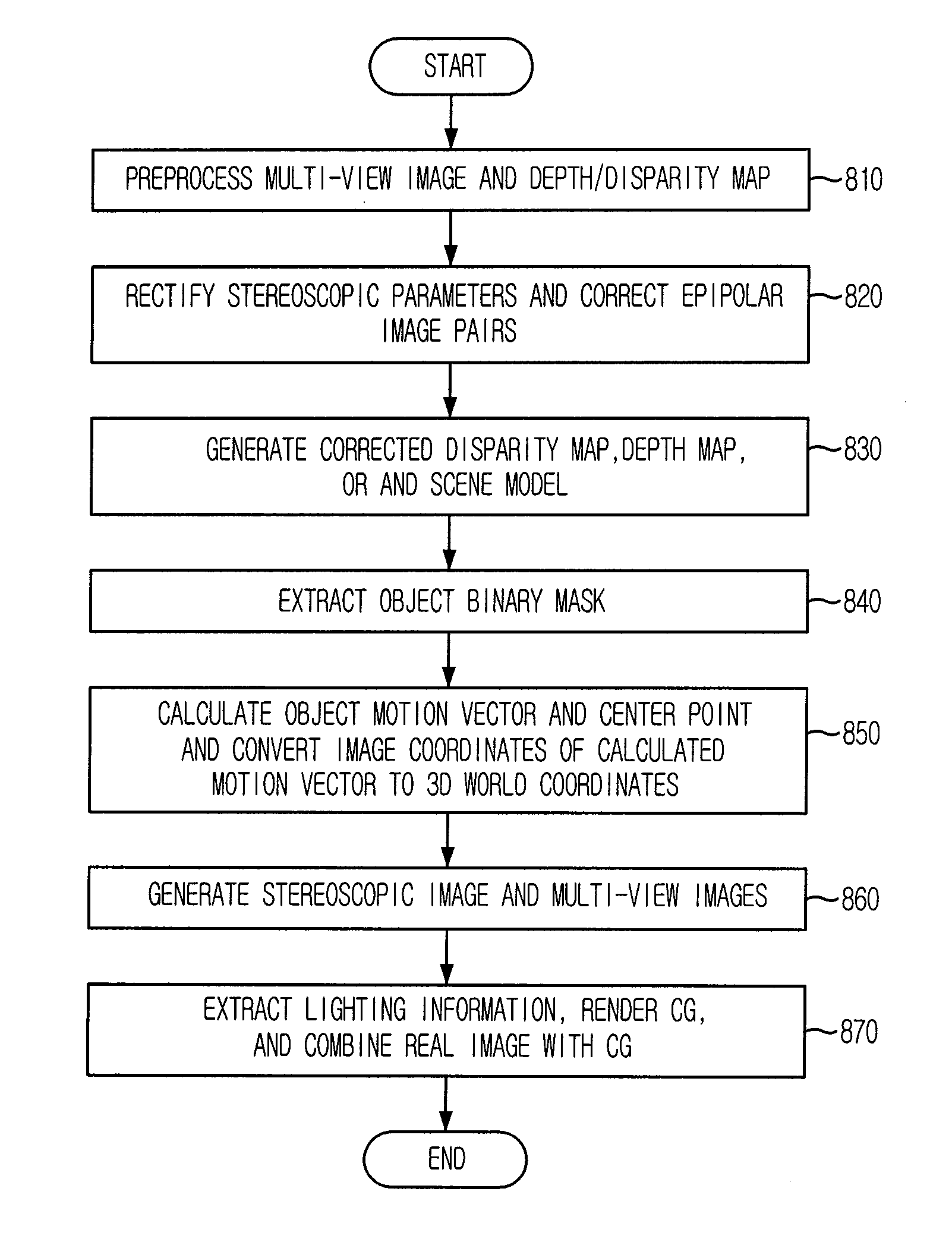
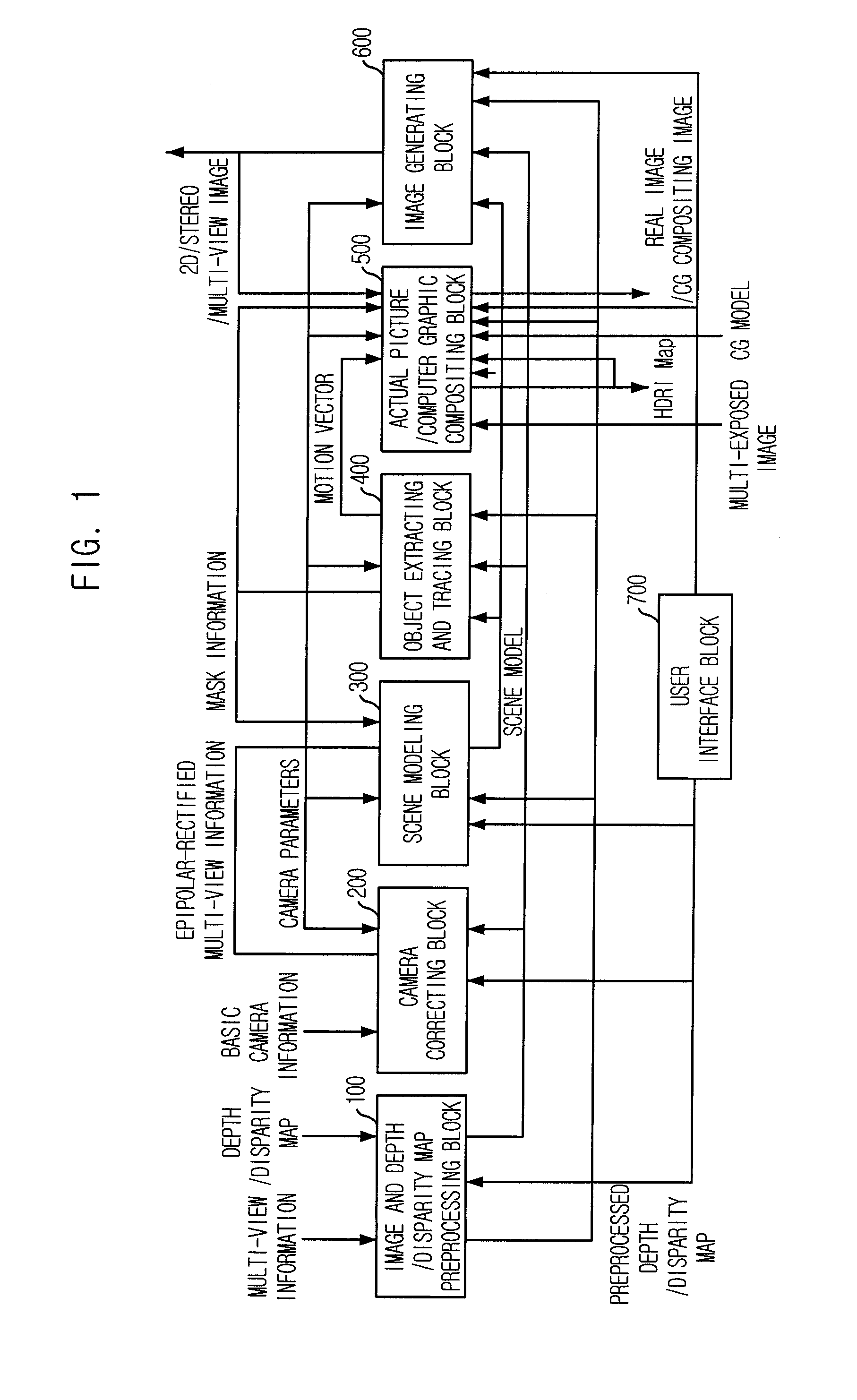
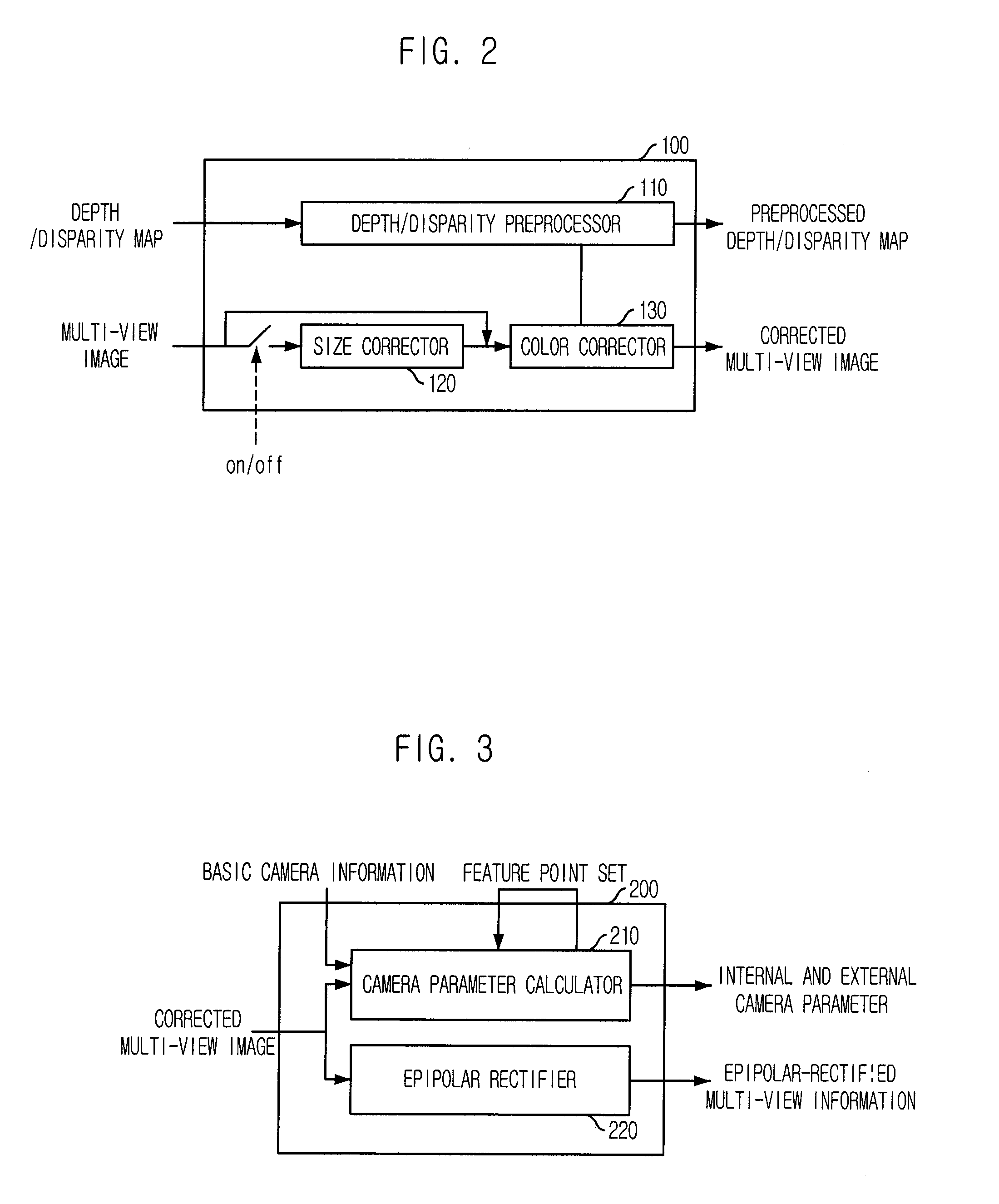
Provided are a contents generating apparatus that can support functions of moving object substitution, depth-based object insertion, background image substitution, and view offering upon a user request and provide realistic image by applying lighting information applied to a real image to computer graphics object when a real image is composited with computer graphics object, and a contents generating method thereof. The apparatus includes: a preprocessing block, a camera calibration block, a scene model generating block, an object extracting / tracing block, a real image / computer graphics object compositing block, an image generating block, and the user interface block. The present invention can provide diverse production methods such as testing for the optimal camera viewpoint and scenic structure before contents are actually authored and compositing two different scenes taken in different places into one scene based on a concept of a three-dimensional virtual studio in the respect of a contents producer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
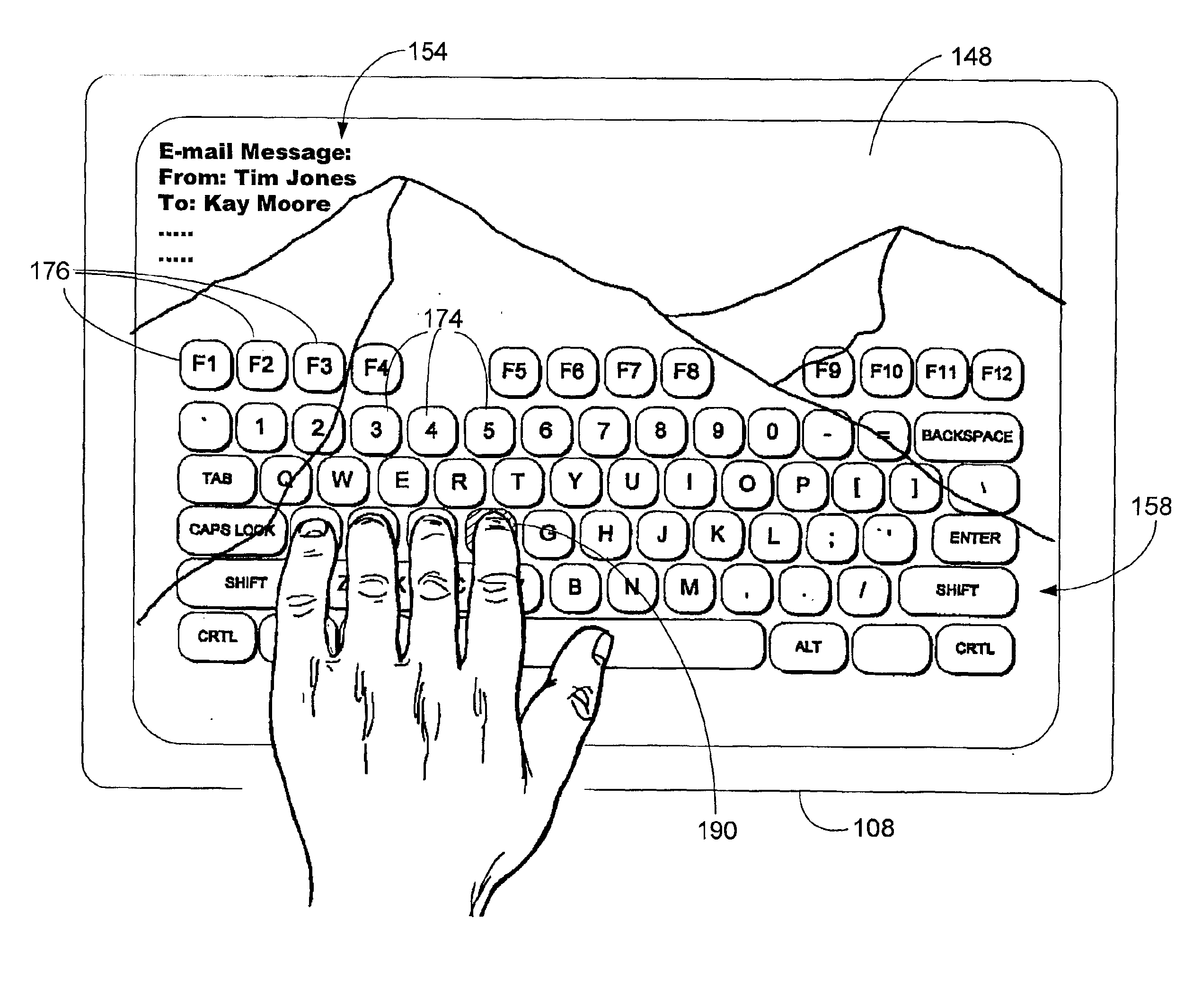
Virtual keyboard for touch-typing using audio feedback
InactiveUS6882337B2Increase awarenessPrecise alignmentInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsBackground imageData input
A virtual keyboard displayed on a touch sensitive screen allows a user to do touch-typing thereon to enter textual data into a computer. The keyboard image has a standard key layout for typewriting, and the keys are sized to allow the fingers of the user to take the positions necessary for “ten-finger” touch-typing in the standard fashion. The virtual keyboard image is semi-transparently displayed over on a background image, with the individual keys shown with shaded edges so that they can be easily distinguished from features in the background image. When a key is touched, a sound is generated. The sound generated when the touch is away from a target portion of the key is different from the sound generated when the touch is on or adjacent to the target portion of the key, thereby providing audio feedback to enable the user to adjust finger positions to maintain proper alignment with the virtual keys.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
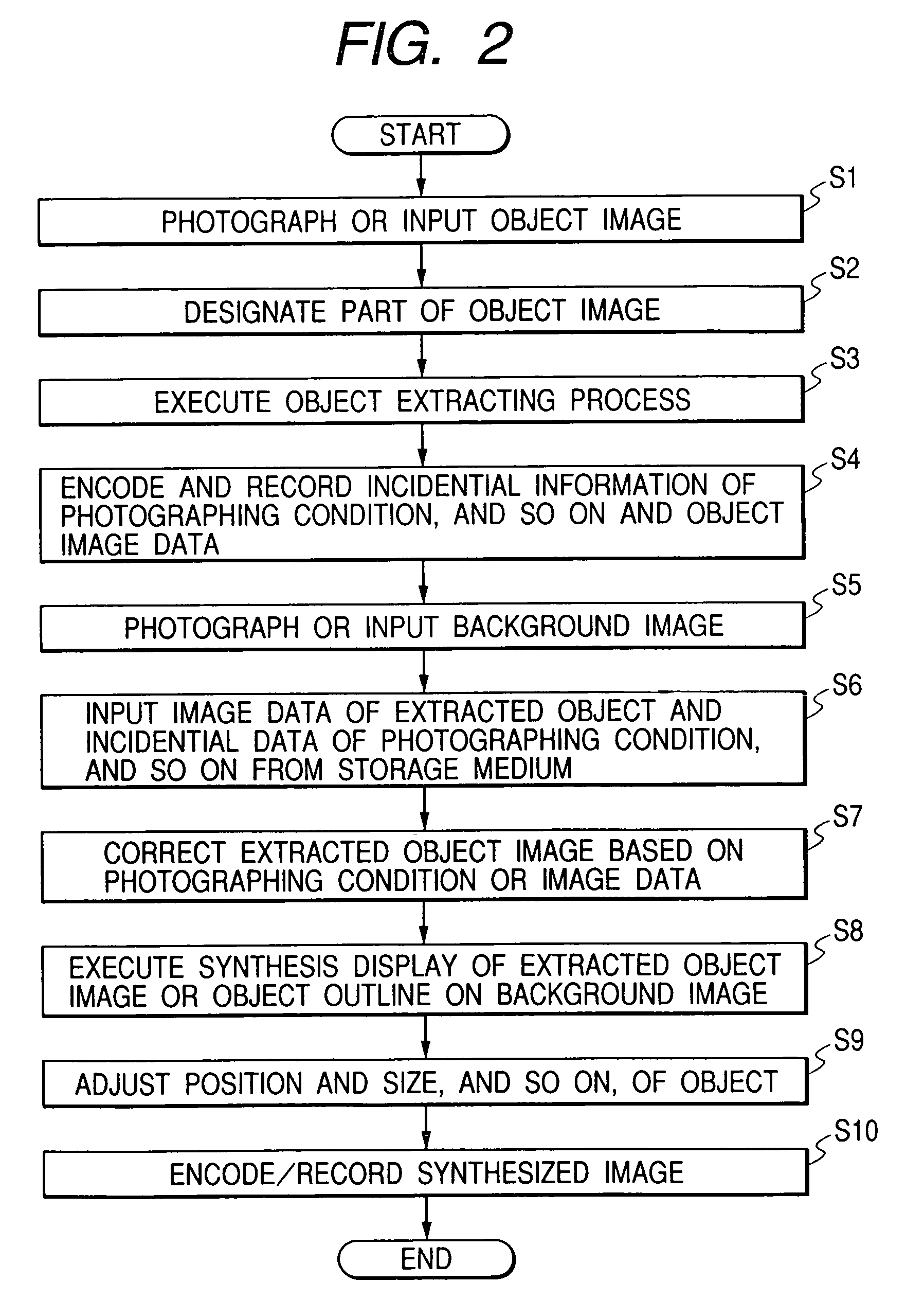
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and storage medium
InactiveUS6987535B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
A user photographs an image including an object to be extracted, uses an instruction selection unit or the like to designate an extraction range, and an object extraction circuit performs extraction. The image data of an extracted object area is compressed / encoded, and stored together with photographing conditions into a storage unit. Subsequently, a background image is photographed or inputted. While the background image is displayed, the previously extracted object image is read from the storage unit. To suppress a difference in gradation and hue between the background image and the object image, the gradation and hue of the object image are adjusted, mixing and smoothing with the background image are performed in the vicinity of an object outline, and the object image is overwritten, synthesized, and displayed on the background image. The position and size of the object image are adjusted according to a user's instruction. Synthesized image data is recorded in a recording medium.
Owner:CANON KK
Systems and methods for night time surveillance
InactiveUS20060238617A1Reduce field of regardTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMonitoring systemBackground image
Methods and systems for surveillance are described. One described method for use in a surveillance system having a camera, comprises generating a background image of the camera's field of regard, receiving a live video image of the camera's current field of view, wherein the field of view is within the field of regard, and correlating a position of the live video image within the background image.
Owner:OPSIGAL CONTROL SYST
Three-dimensional display system
InactiveUS7016116B2Low costEasy to useStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Background image
An image display system provides a viewer with an experience of three dimensional images by presenting a composite image source. The system includes first and second image sources, a beamcombiner, a lens and a reflective element. The reflective elements reflects the image of the second image source to the beamcombiner. The first and second image sources, the beamcombiner, and the single lens present a foreground image and a background image, with the background image presented at a greater distance from the viewer than the foreground image. The viewer perceives the foreground image and the background image as part of a scene having depth.
Owner:DOLGOFF EUGENE
Gallery Application For Content Viewing
ActiveUS20110126148A1Geometric image transformationStill image data indexingGraphicsGraphical user interface
A gallery software application enables a user to browse, view, and interact with various content items, such as still images and videos. The gallery includes a graphical user interface that displays multiple images in the foreground and one image in the background. The foreground images represent content items. The background image is generated based on one of the foreground images. As the foreground images are scrolled, the background image changes.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Predicting inventory events using semantic diffing
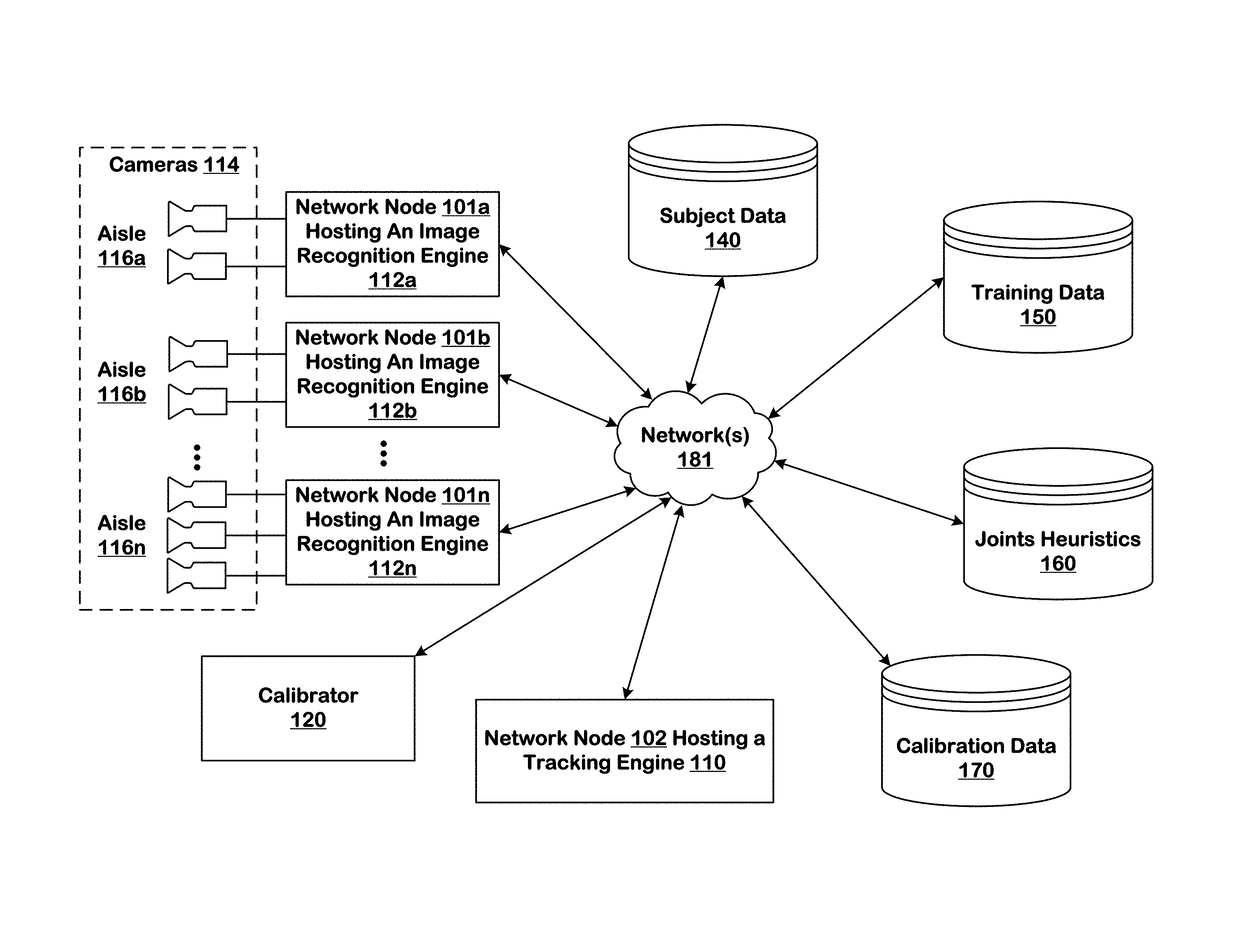
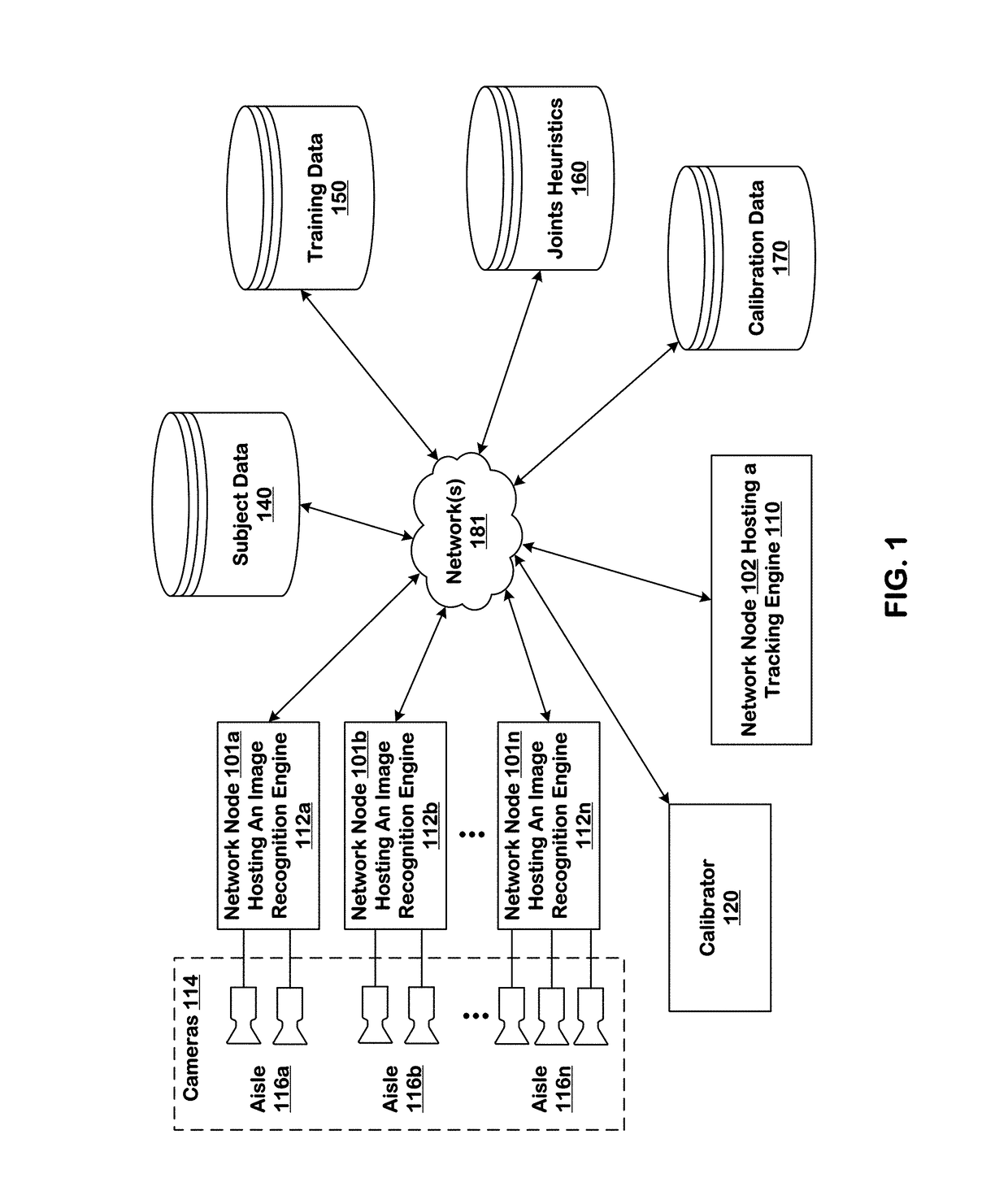
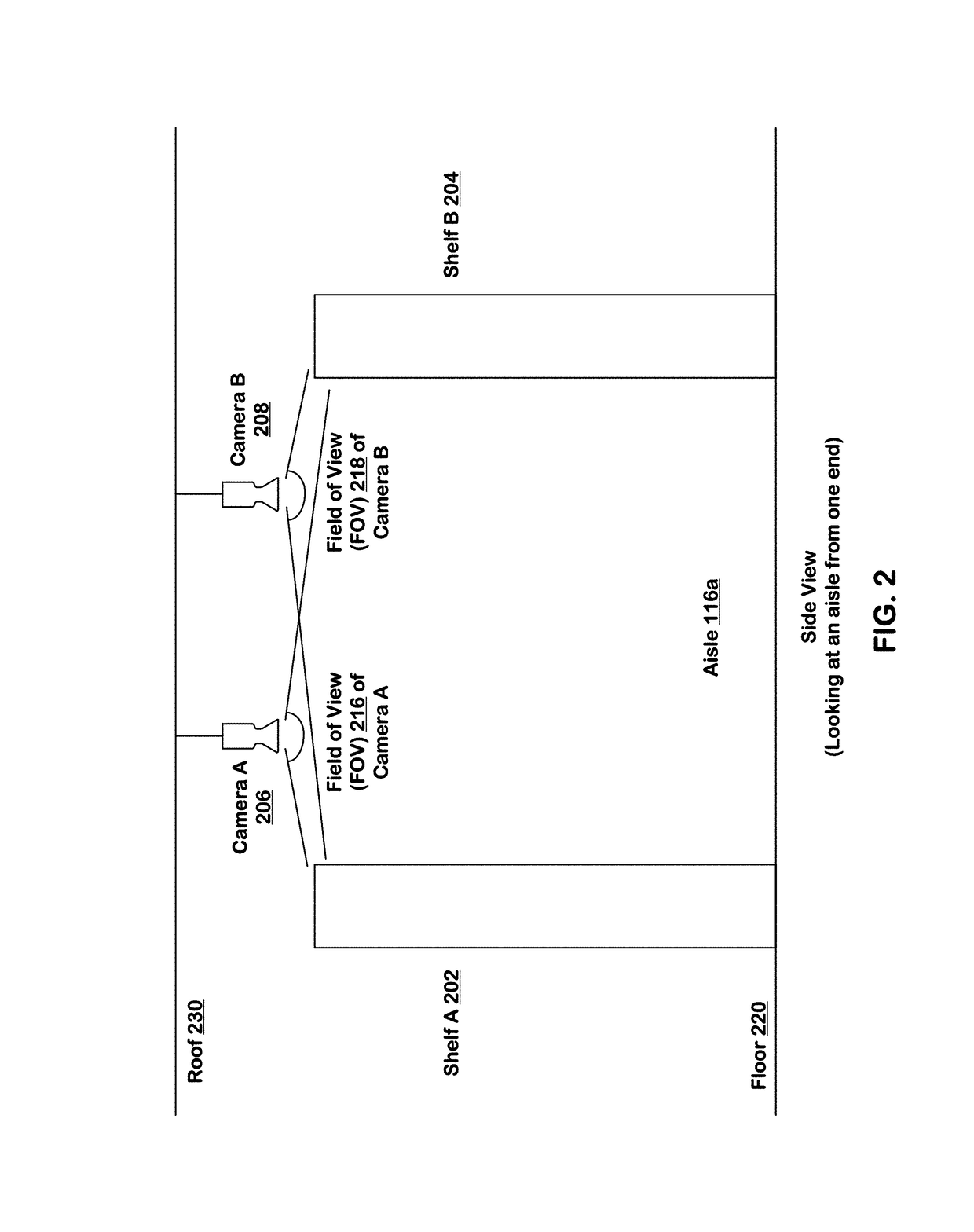
ActiveUS10127438B1ConfidenceImprove accuracyImage enhancementMathematical modelsInventory managementBackground image
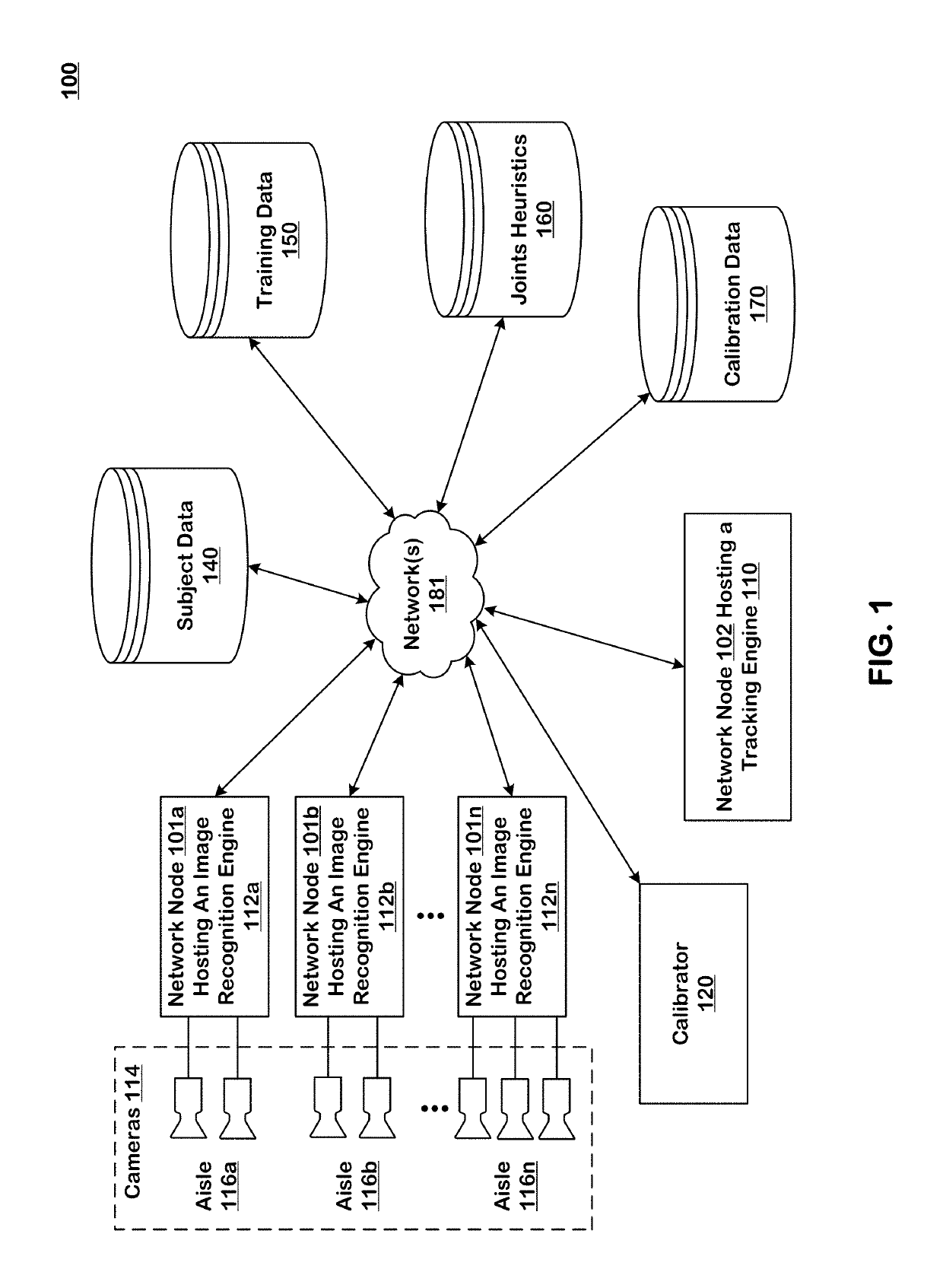
Systems and techniques are provided for tracking puts and takes of inventory items by subjects in an area of real space. A plurality of cameras with overlapping fields of view produce respective sequences of images of corresponding fields of view in the real space. In one embodiment, the system includes first image processors, including subject image recognition engines, receiving corresponding sequences of images from the plurality of cameras. The first image processors process images to identify subjects represented in the images in the corresponding sequences of images. The system includes second image processors, including background image recognition engines, receiving corresponding sequences of images from the plurality of cameras. The second image processors mask the identified subjects to generate masked images. Following this, the second image processors process the masked images to identify and classify background changes represented in the images in the corresponding sequences of images.
Owner:STANDARD COGNITION CORP
Image processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS7162101B2Accurate extractionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage extractionImaging processing
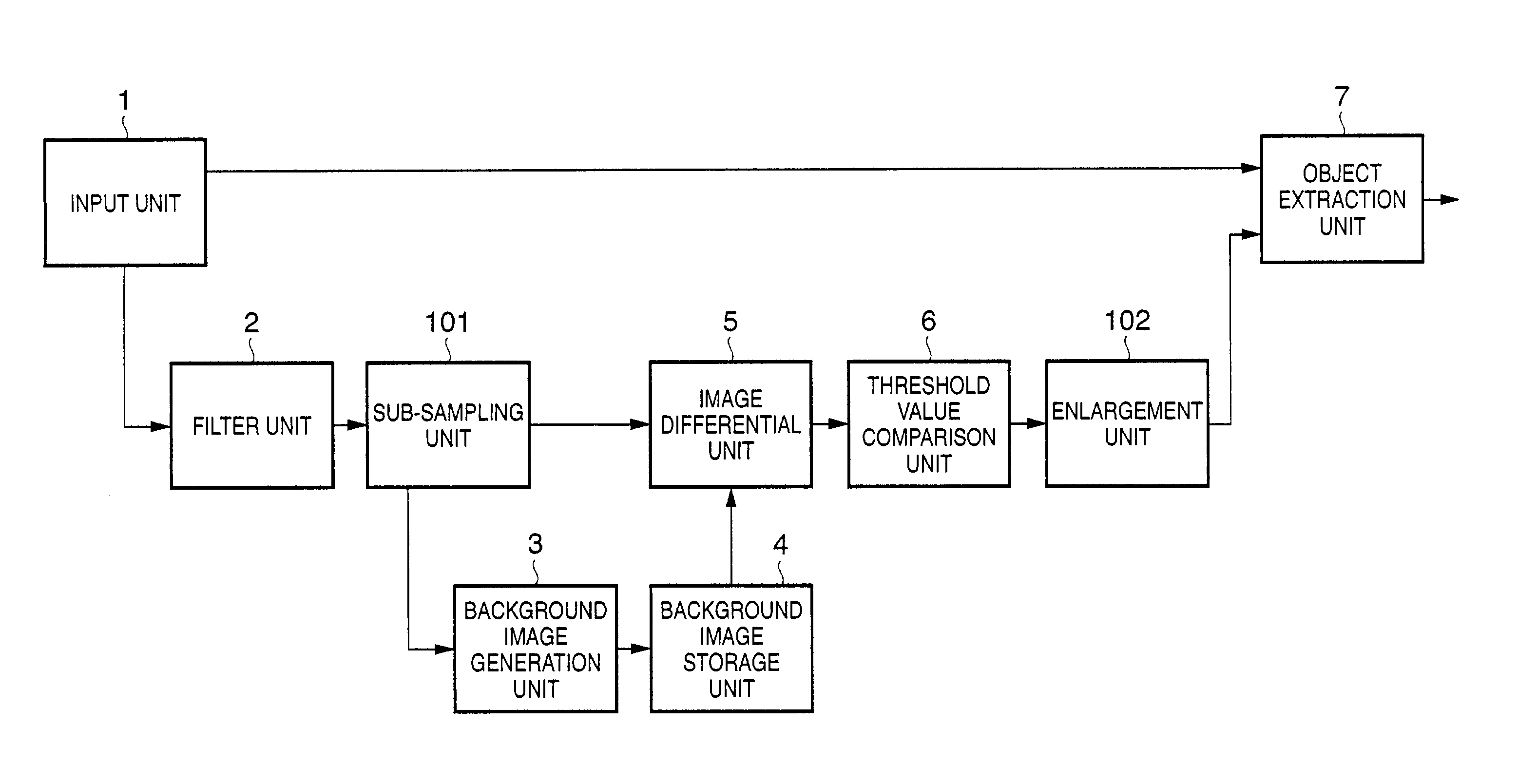
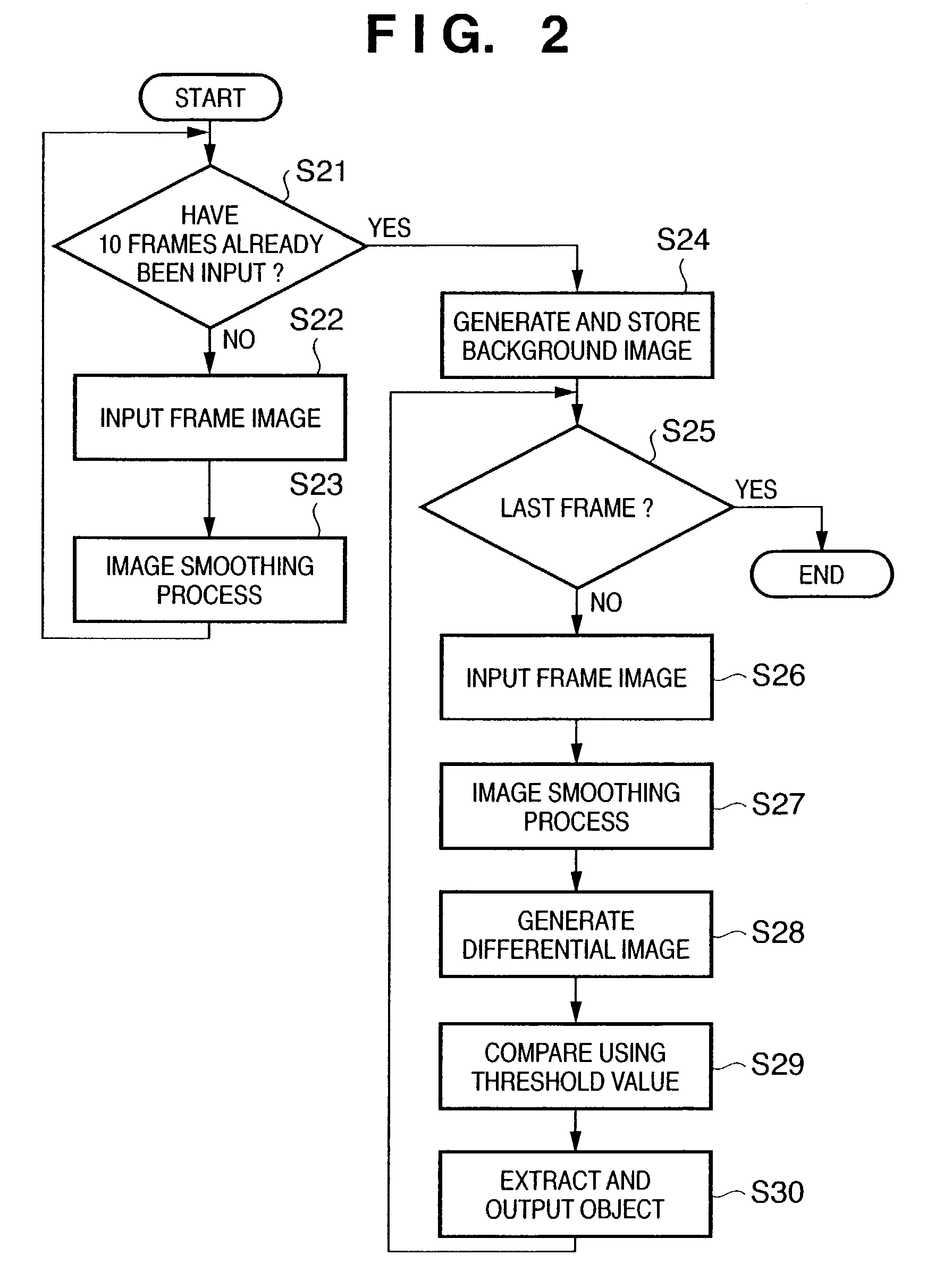
An image processing apparatus and method, which can appropriately extract an object even when the focus of a camera having an automatic focus adjustment function shifts from the background to the object. To this end, frame images which are sensed by an image sensing unit and are sequential in the time axis direction are input from an input unit. The input frame images are smoothed by a filter unit. A background image generation unit generates an average image of a predetermined number of smoothed frame images as a background image. An image differential unit generates a differential image between the predetermined smoothed frame image and the background image. An object extraction unit extracts an object region where a predetermined object is sensed, on the basis of the differential image.
Owner:CANON KK
Recording medium storing 3D image processing program, the program, 3D image processing method and video game apparatus
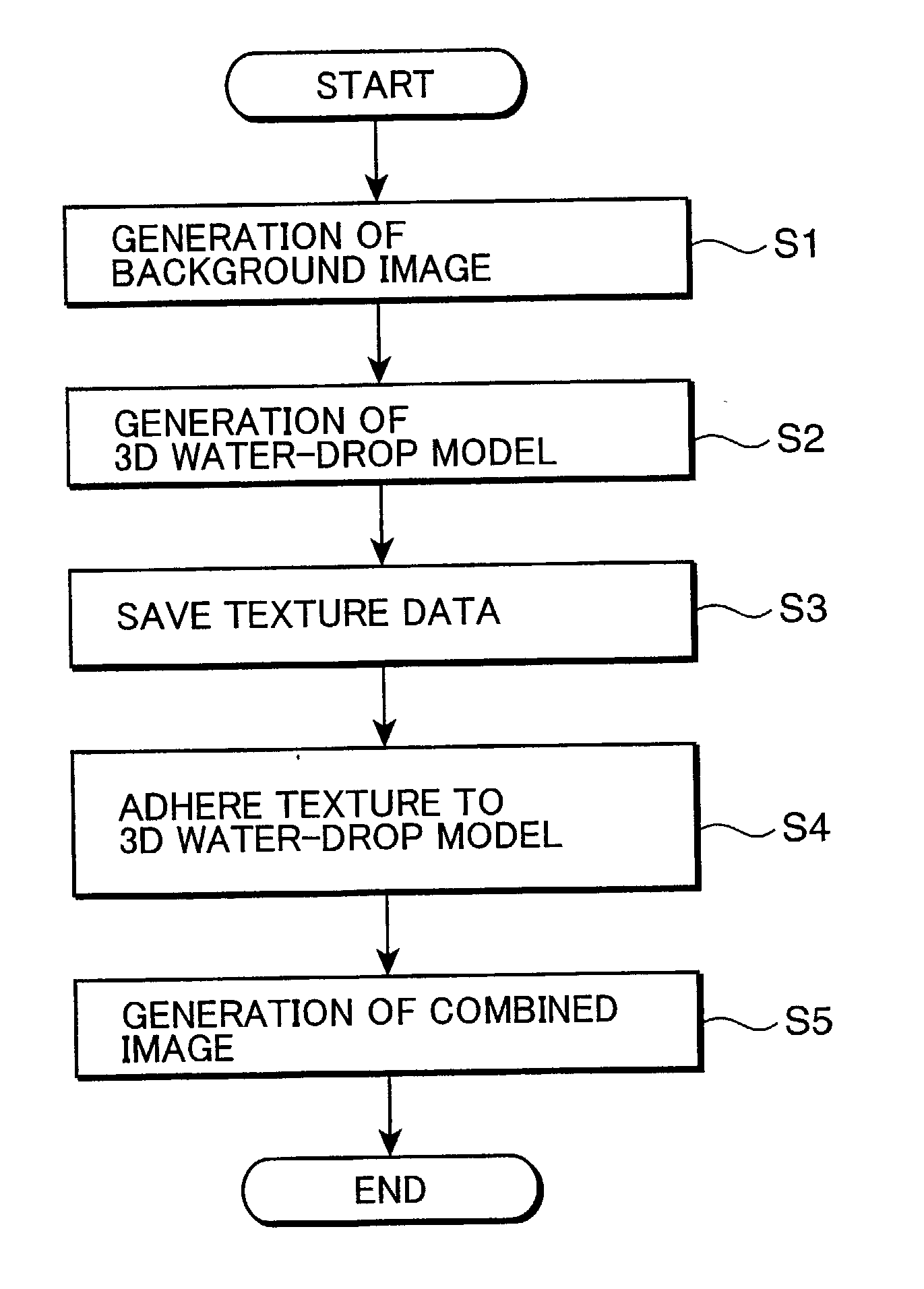
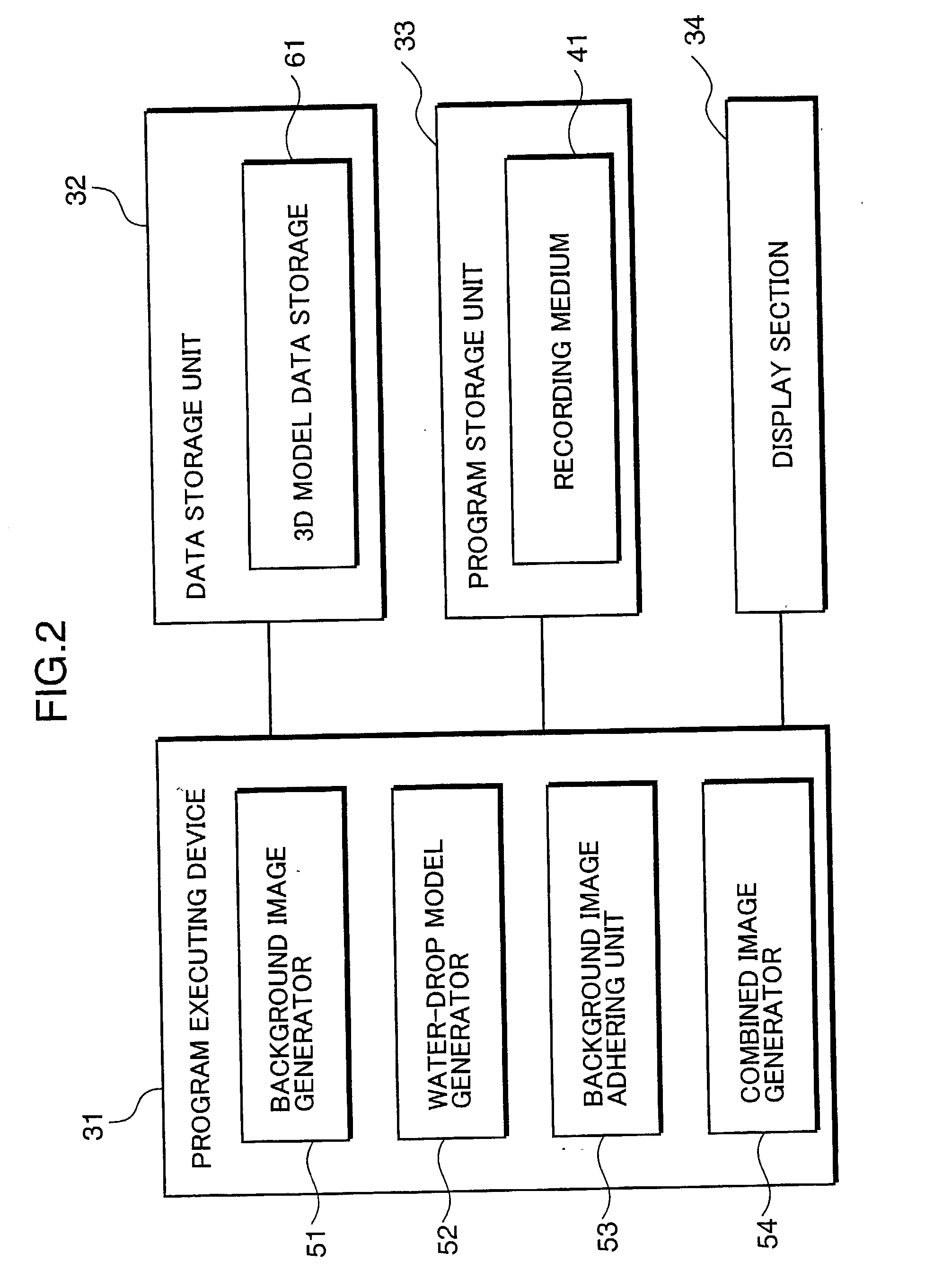
A background image generator 51 renders a first 3D model representing a landscape to generate a background image, an image generator 52 generates a second 3D model to be located between a camera viewpoint and the first 3D model, an image adhering unit 53 selects a specified range of the background image and adheres the background image within the selected range as a texture to the second 3D model, and a combined image generator 54 renders the second 3D model having the background image within the specified range adhered thereto and combines the rendered model with the background image to generate a combined image.
Owner:KONAMI DIGITAL ENTERTAINMENT CO LTD
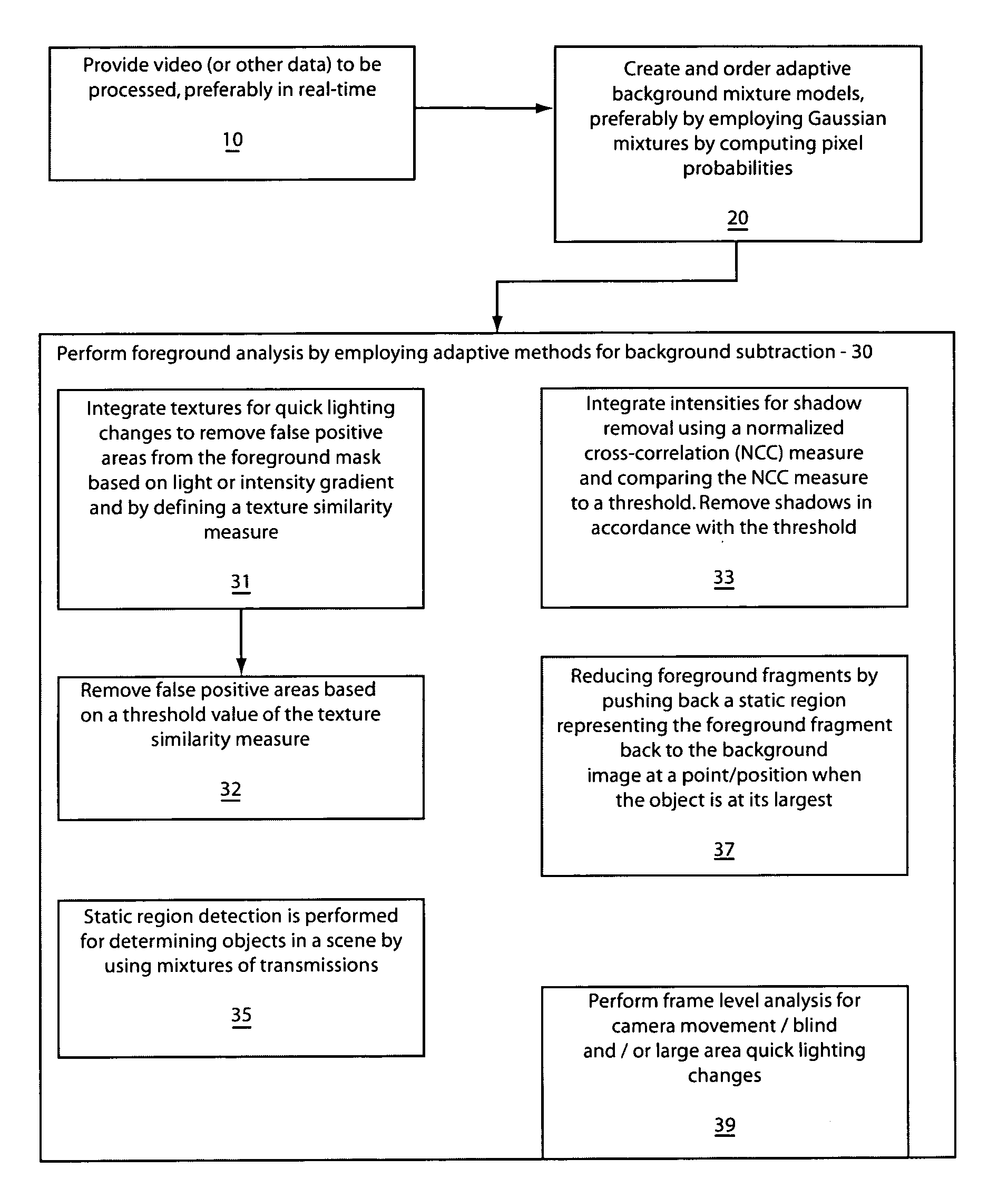
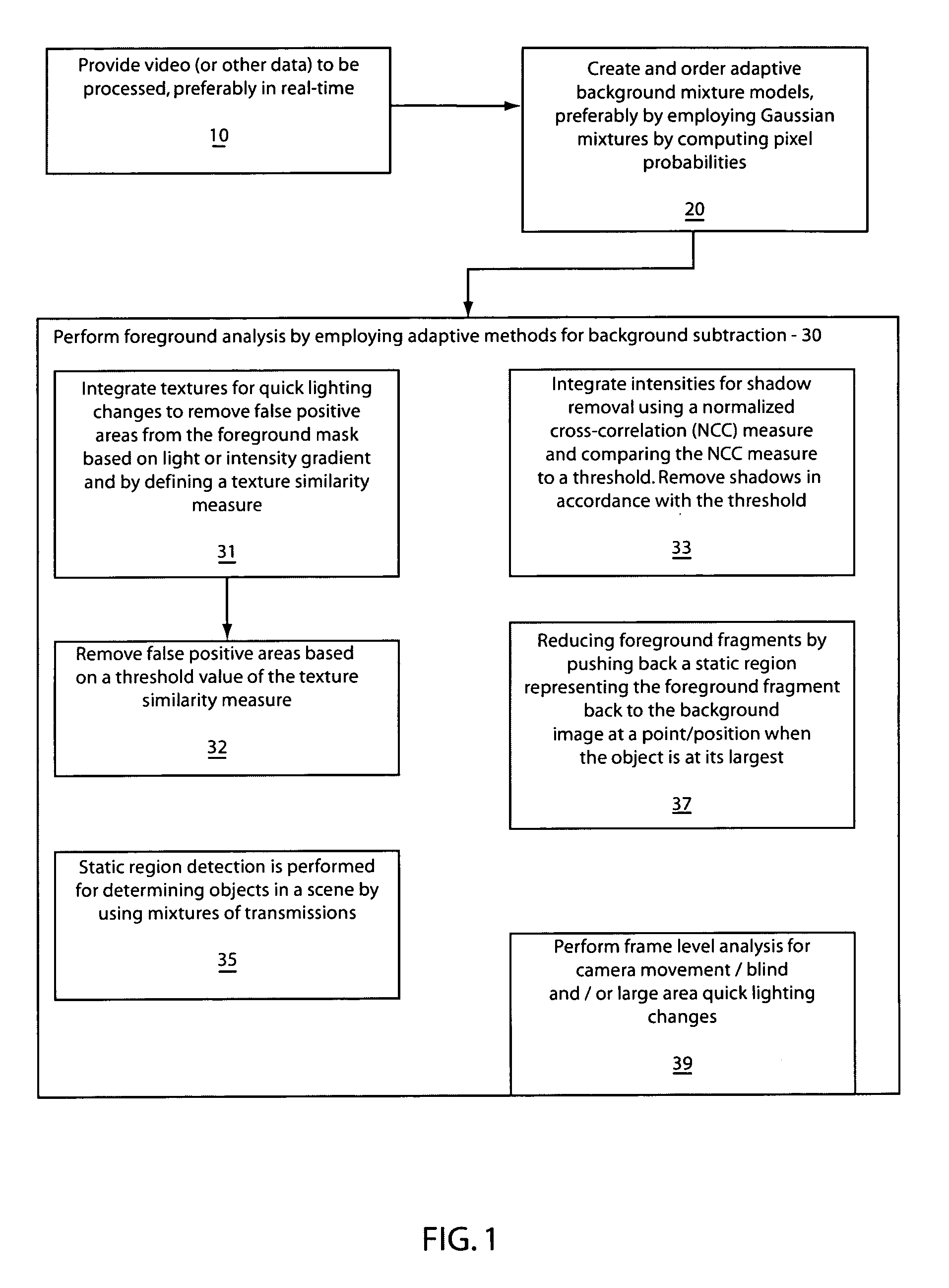
Robust and efficient foreground analysis for real-time video surveillance
Systems and methods for foreground analysis in real-time video include background subtraction and foreground detection, shadow removal, quick lighting change adaptation, static foreground region detection, foreground fragment reduction, and frame level change detection. Processes include background image extraction and foreground detection, integrating texture information of the background image and a current frame to remove false positive foreground areas resulting from lighting changes, integrating pixel intensity information by determining a cross-correlation of intensities between a current frame and the background image for each pixel in a foreground mask to remove image shadows. Static foreground region detection and fragment reduction are also included.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for recognizing objects in radar imagery
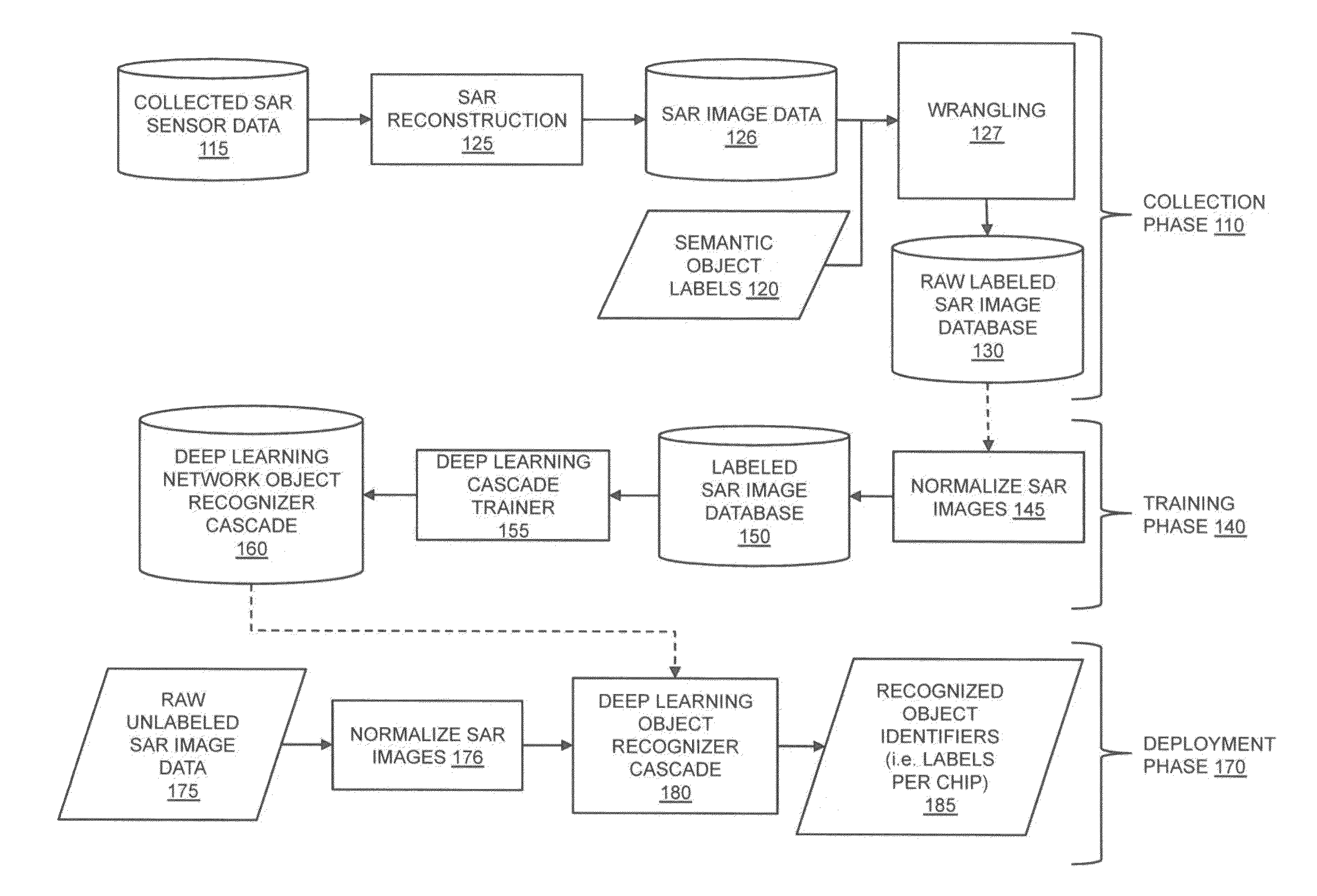
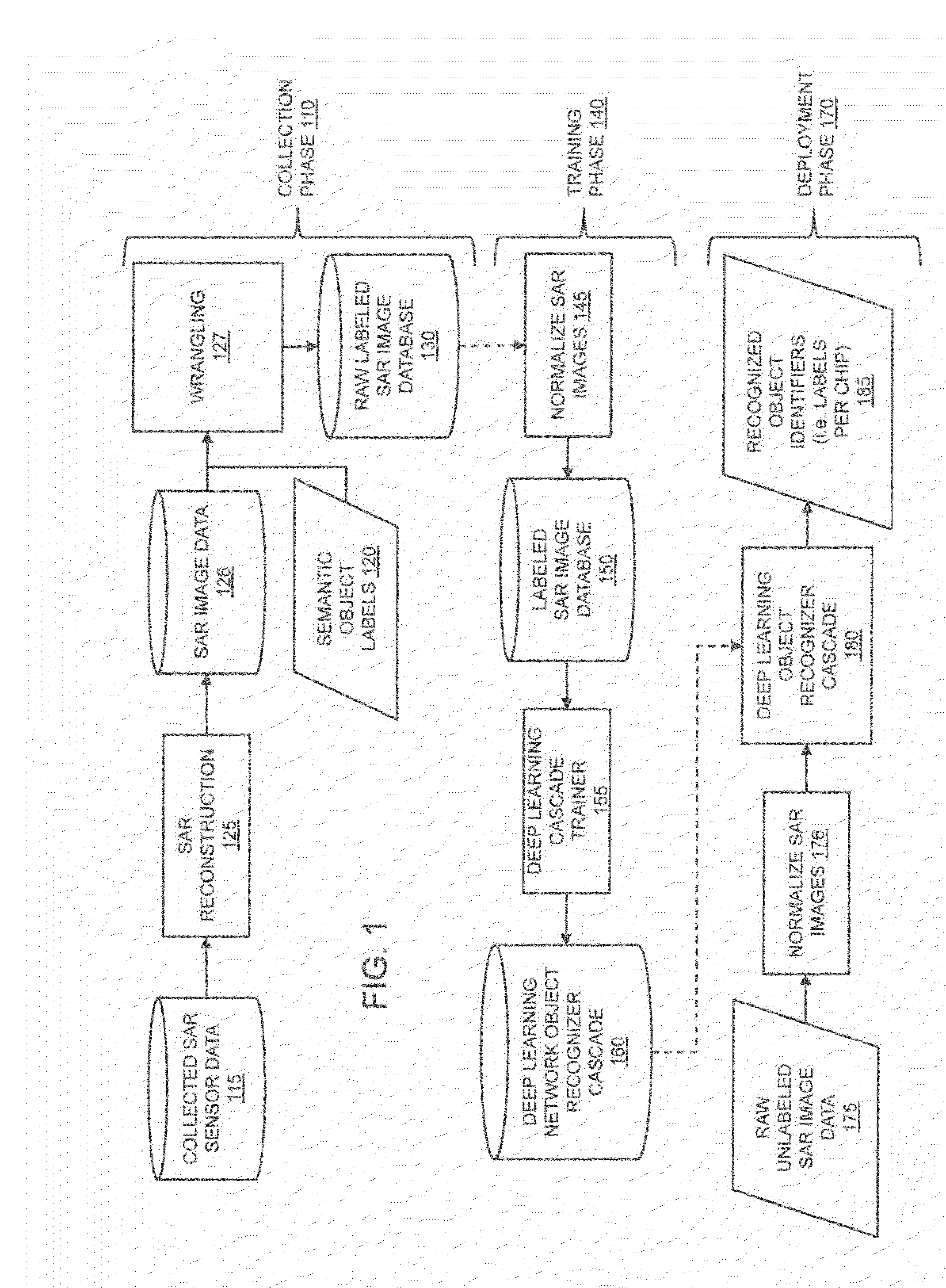
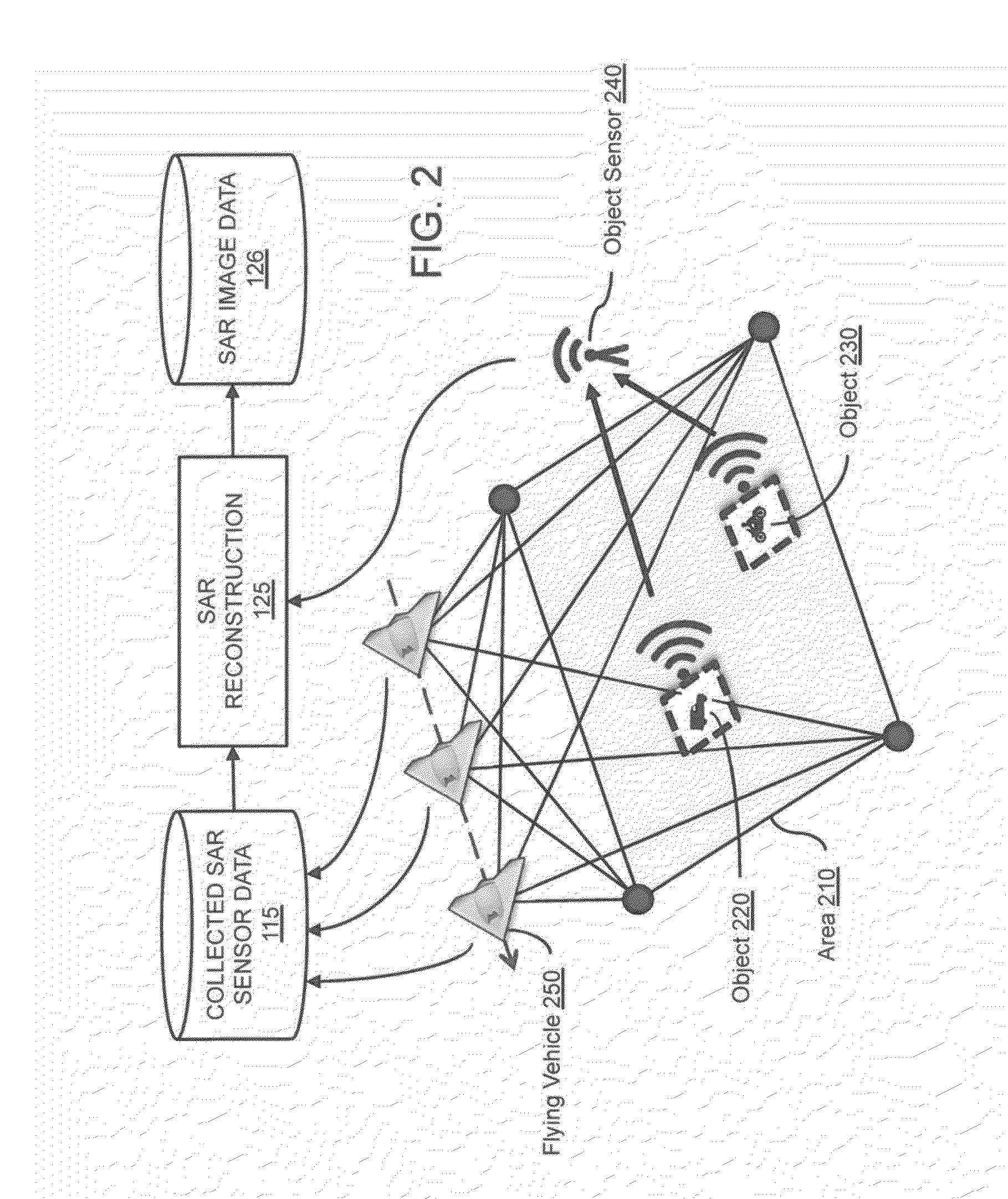
ActiveUS20160019458A1Low in size and weight and power requirementImprove historical speed and accuracy performance limitationDigital computer detailsDigital dataPattern recognitionGraphics
The present invention is directed to systems and methods for detecting objects in a radar image stream. Embodiments of the invention can receive a data stream from radar sensors and use a deep neural network to convert the received data stream into a set of semantic labels, where each semantic label corresponds to an object in the radar data stream that the deep neural network has identified. Processing units running the deep neural network may be collocated onboard an airborne vehicle along with the radar sensor(s). The processing units can be configured with powerful, high-speed graphics processing units or field-programmable gate arrays that are low in size, weight, and power requirements. Embodiments of the invention are also directed to providing innovative advances to object recognition training systems that utilize a detector and an object recognition cascade to analyze radar image streams in real time. The object recognition cascade can comprise at least one recognizer that receives a non-background stream of image patches from a detector and automatically assigns one or more semantic labels to each non-background image patch. In some embodiments, a separate recognizer for the background analysis of patches may also be incorporated. There may be multiple detectors and multiple recognizers, depending on the design of the cascade. Embodiments of the invention also include novel methods to tailor deep neural network algorithms to successfully process radar imagery, utilizing techniques such as normalization, sampling, data augmentation, foveation, cascade architectures, and label harmonization.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
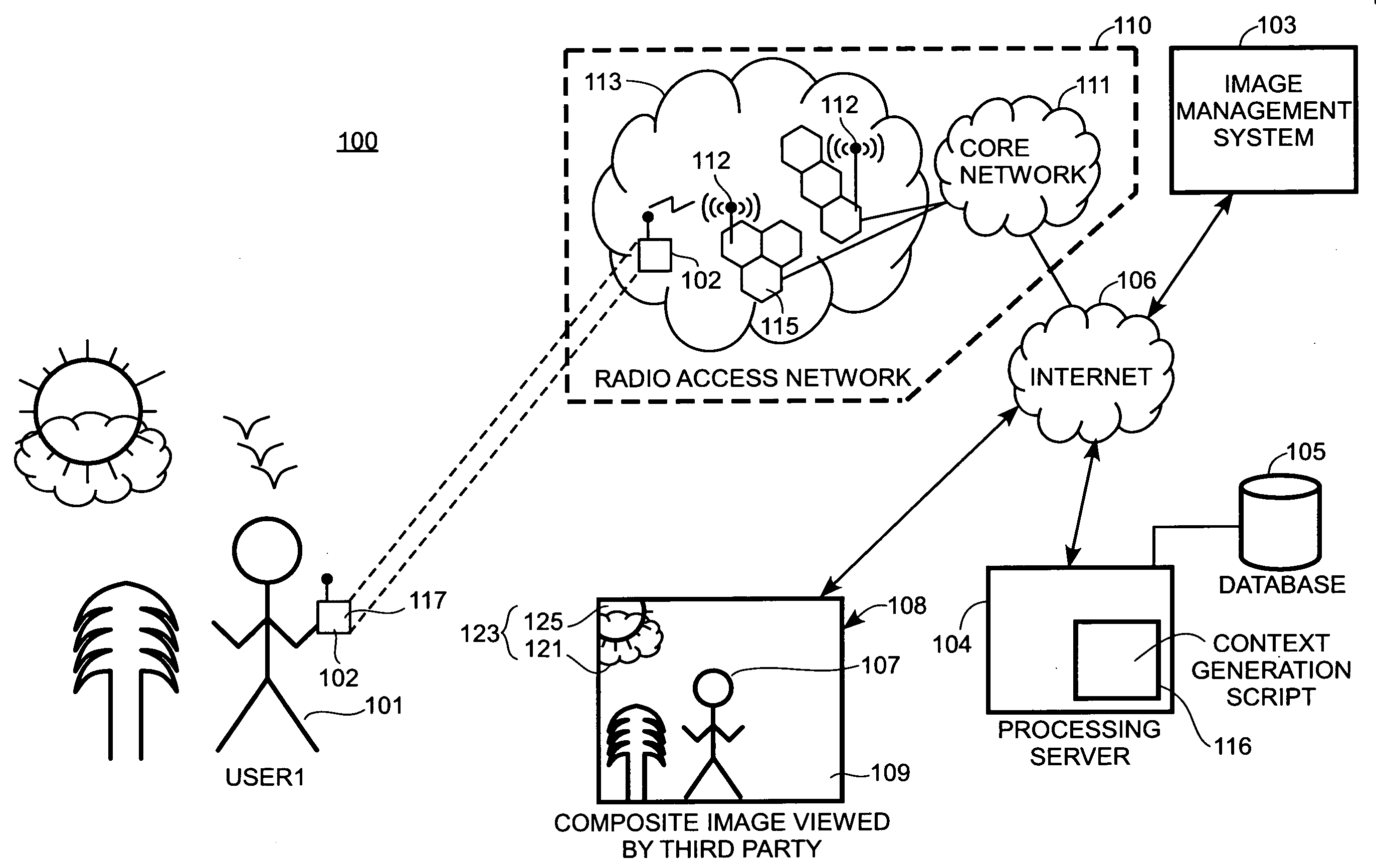
Context avatar
Methods and systems for generating information about a physical context of a user are provided. These methods and systems provide the capability to render a context avatar associated with the user as a composite image that can be broadcast in virtual environments to provide information about the physical context of the user. The composite image can be automatically updated without user intervention to include, among other things, a virtual person image of the user and a background image defined by encoded image data associated with the current geographic location of the user.
Owner:STARBOARD VALUE INTERMEDIATE FUND LP AS COLLATERAL AGENT
Example-Based Two-Dimensional to Three-Dimensional Image Conversion Method, Computer Readable Medium Therefor, and System
ActiveUS20100014781A1Character and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsGraphics3d image
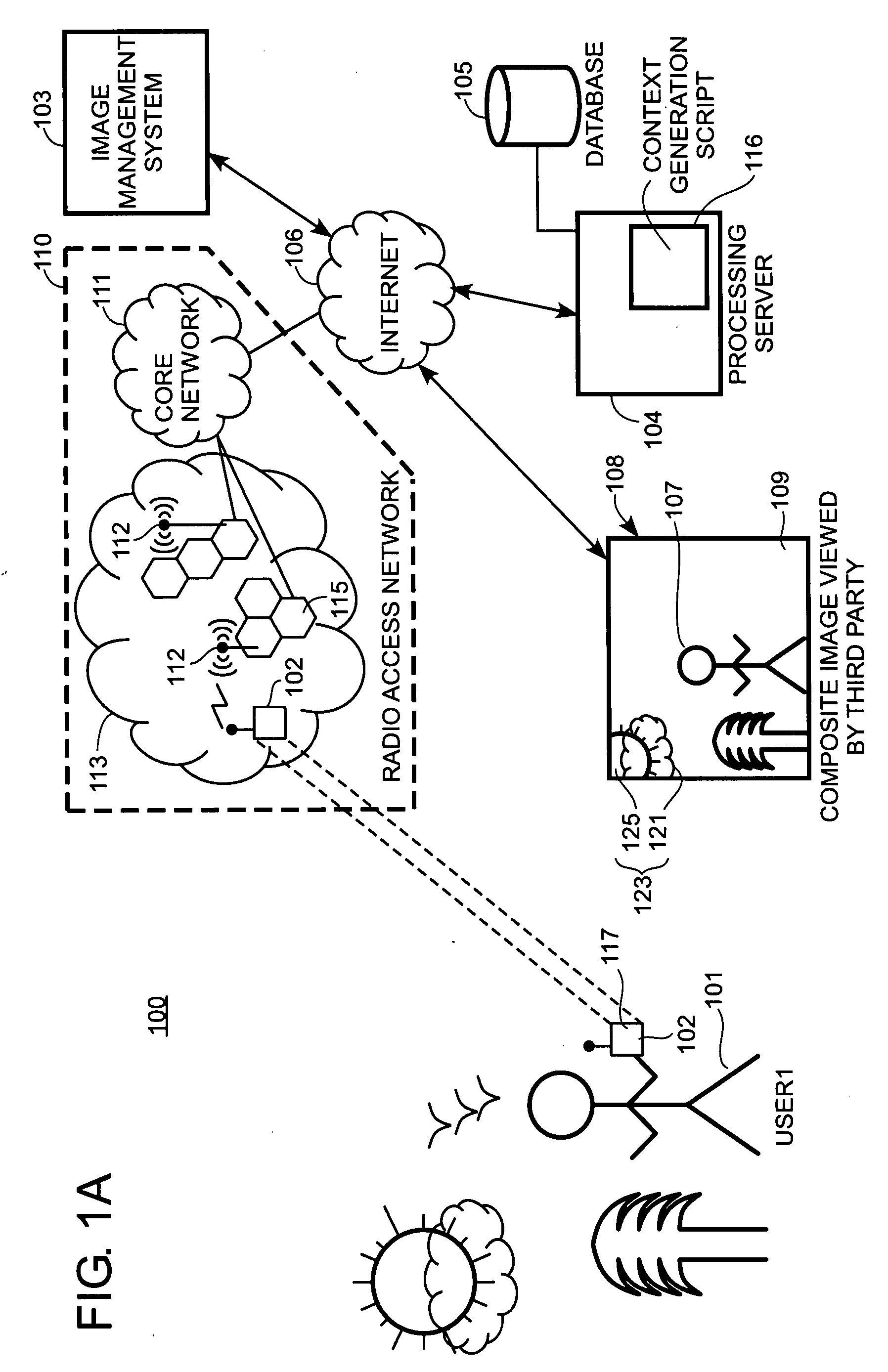
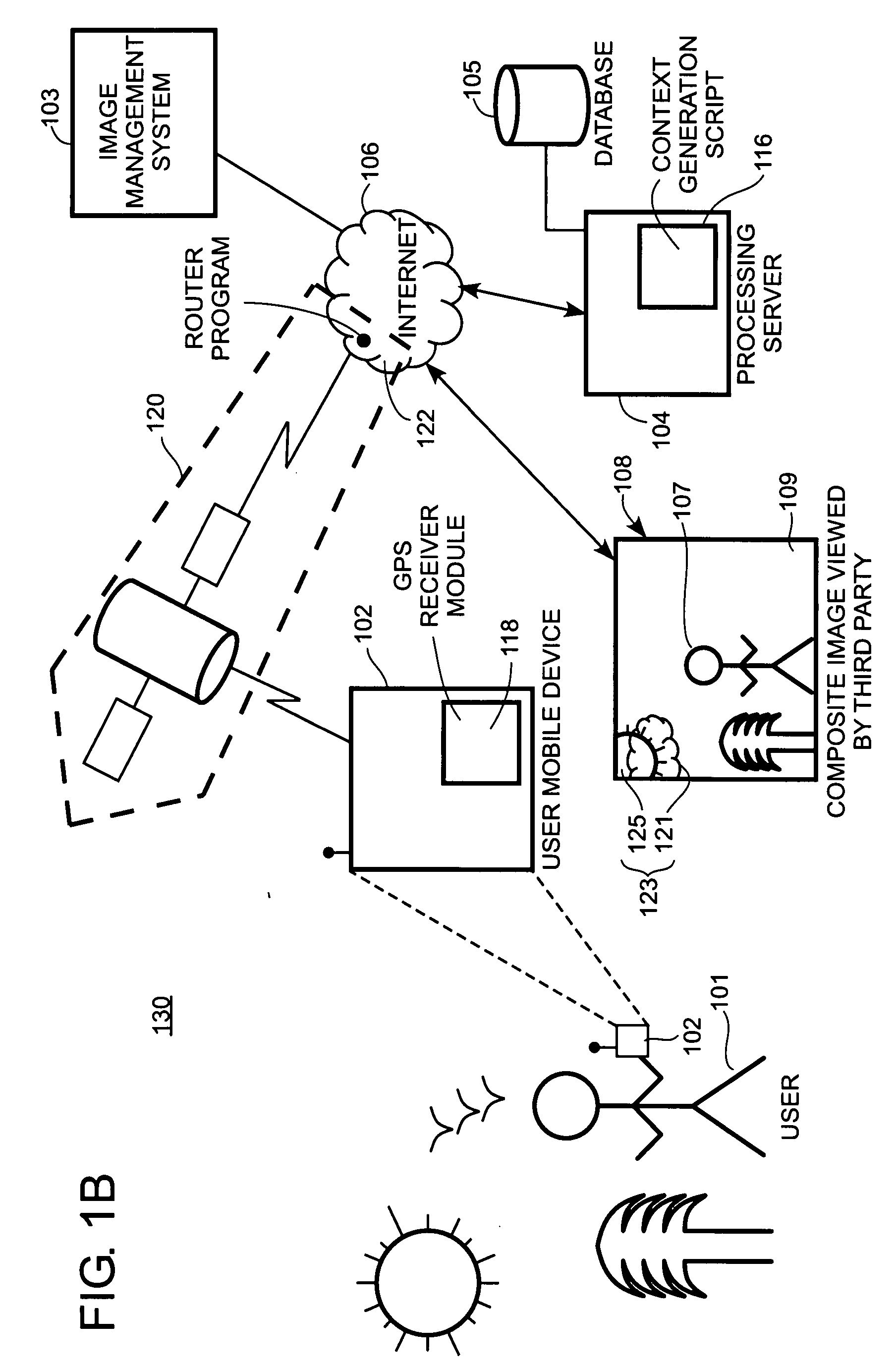
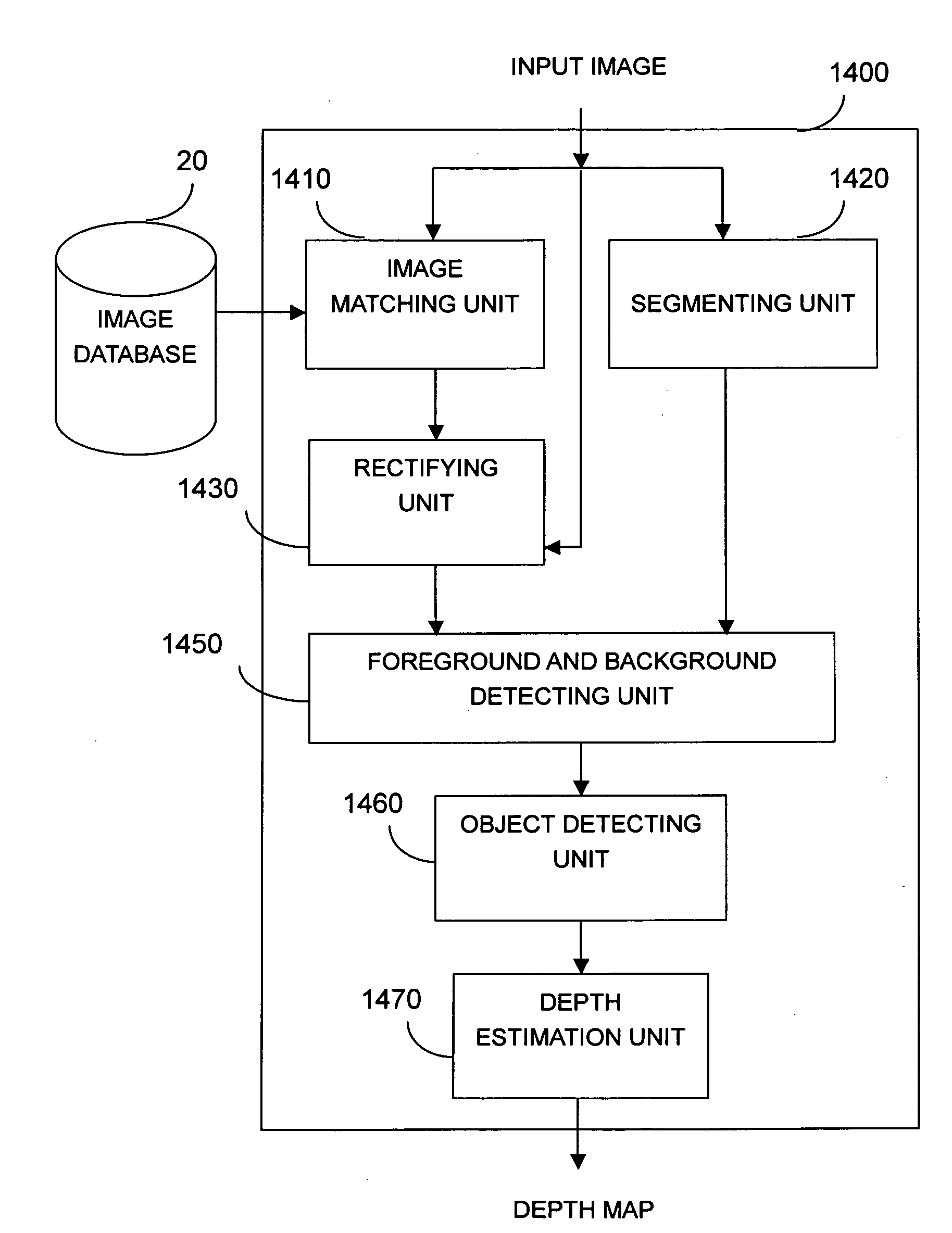
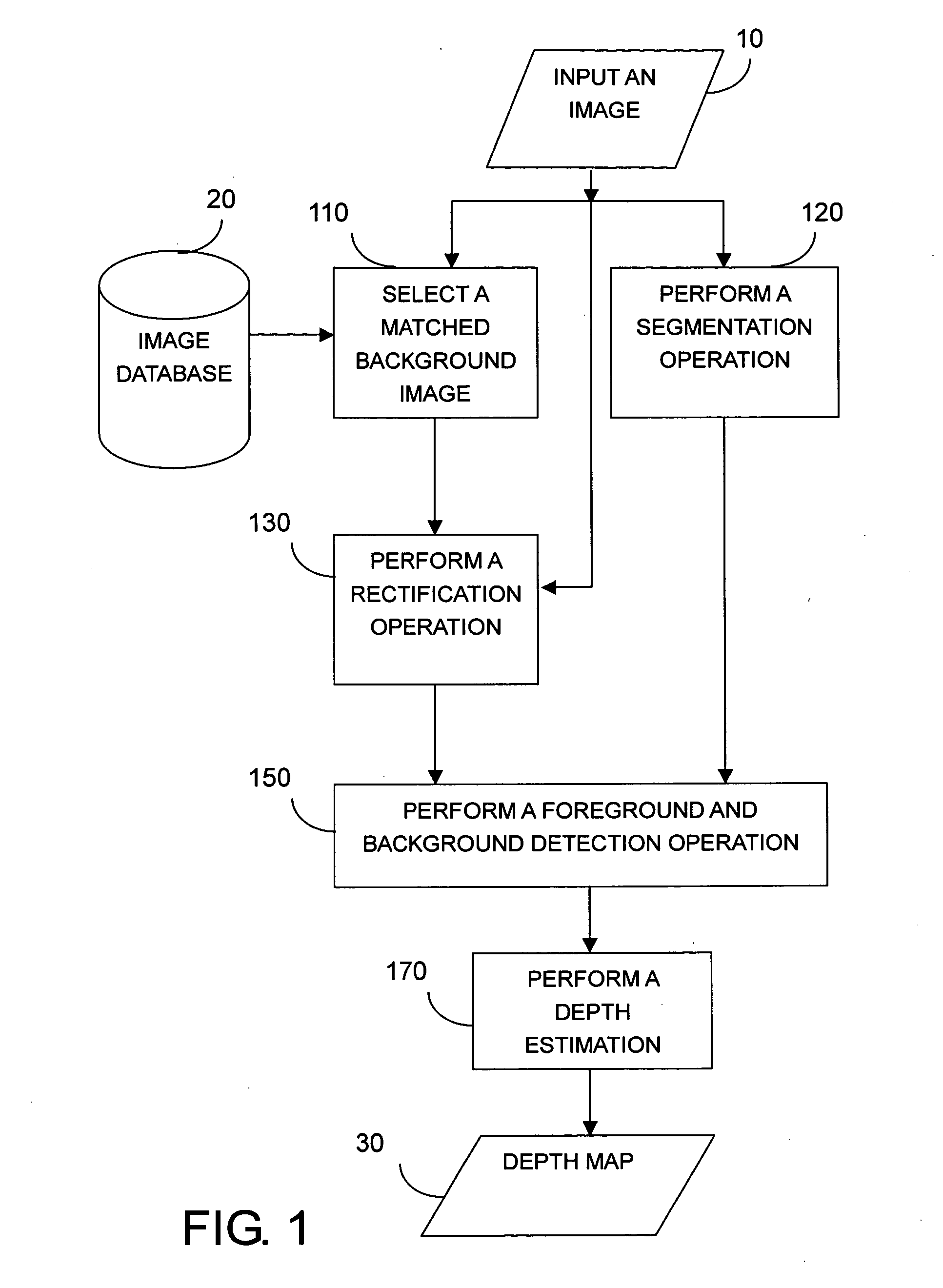
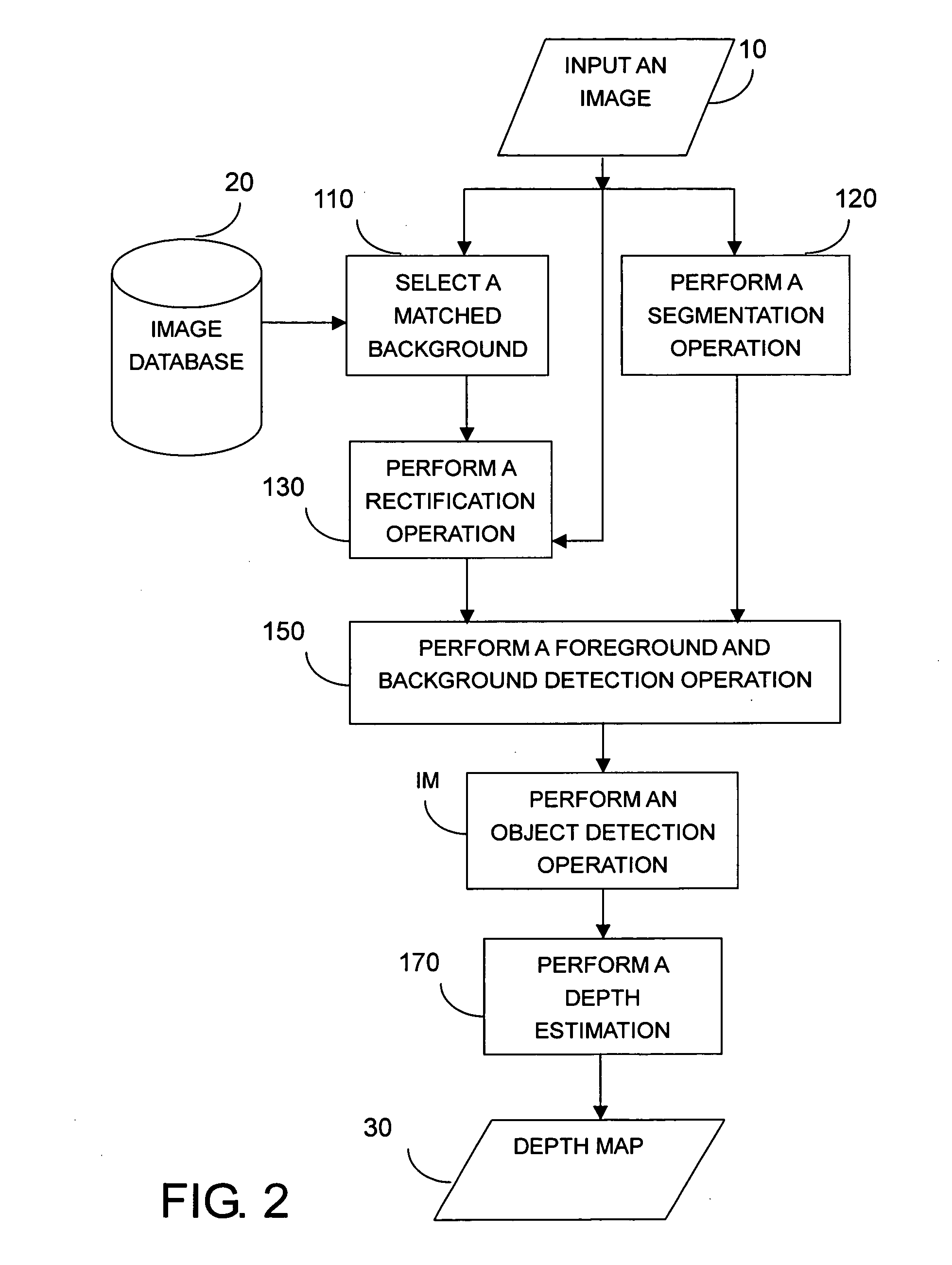
An example-based 2D to 3D image conversion method, a computer readable medium therefor, and a system are provided. The embodiments are based on an image database with depth information or with which depth information can be generated. With respect to a 2D image to be converted into 3D content, a matched background image is found from the database. In addition, graph-based segmentation and comparison techniques are employed to detect the foreground of the 2D image so that the relative depth map can be generated from the foreground and background information. Therefore, the 3D content can be provided with the 2D image plus the depth information. Thus, users can rapidly obtain the 3D content from the 2D image automatically and the rendering of the 3D content can be achieved.
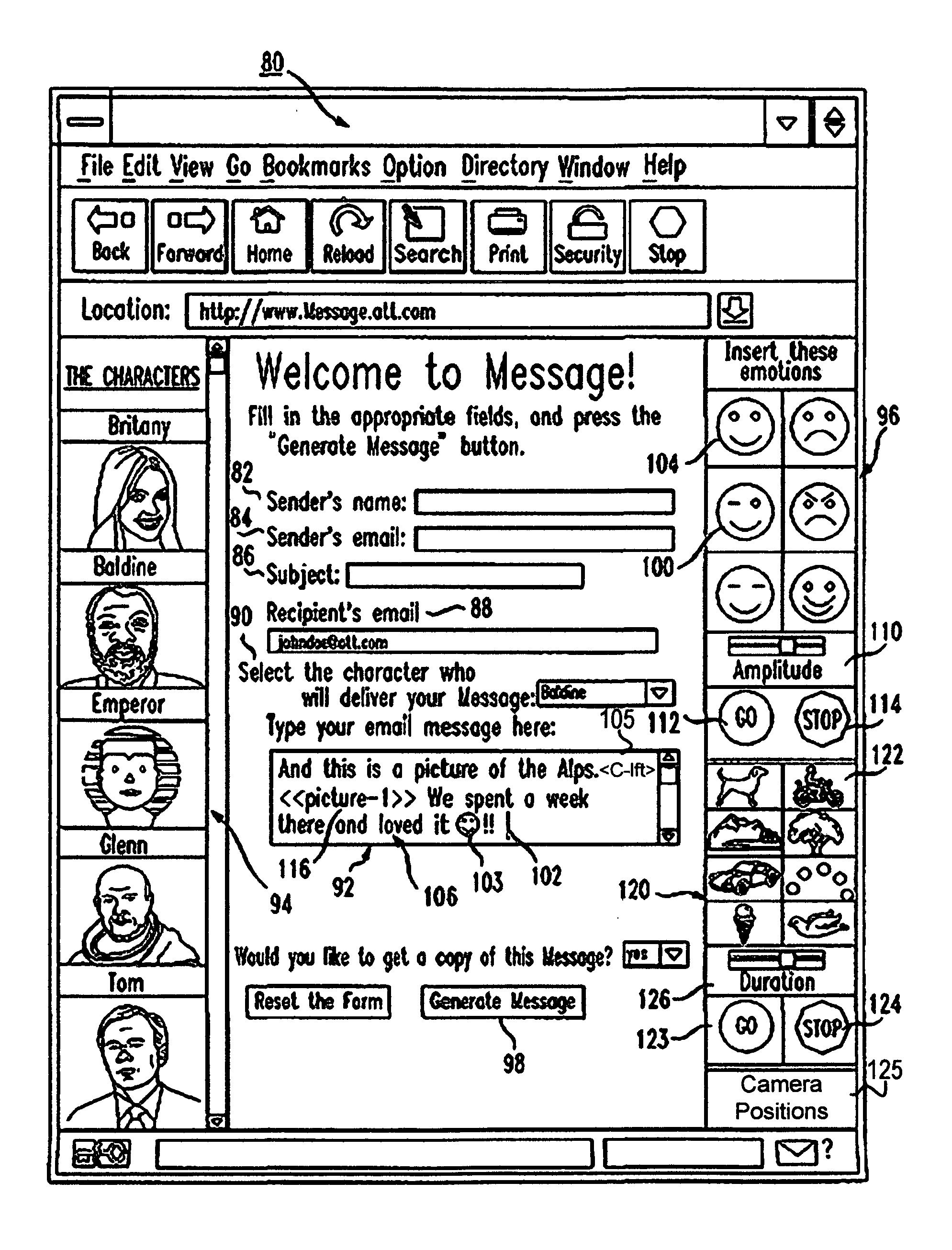
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Segmenting images and simulating motion blur using an image sequence
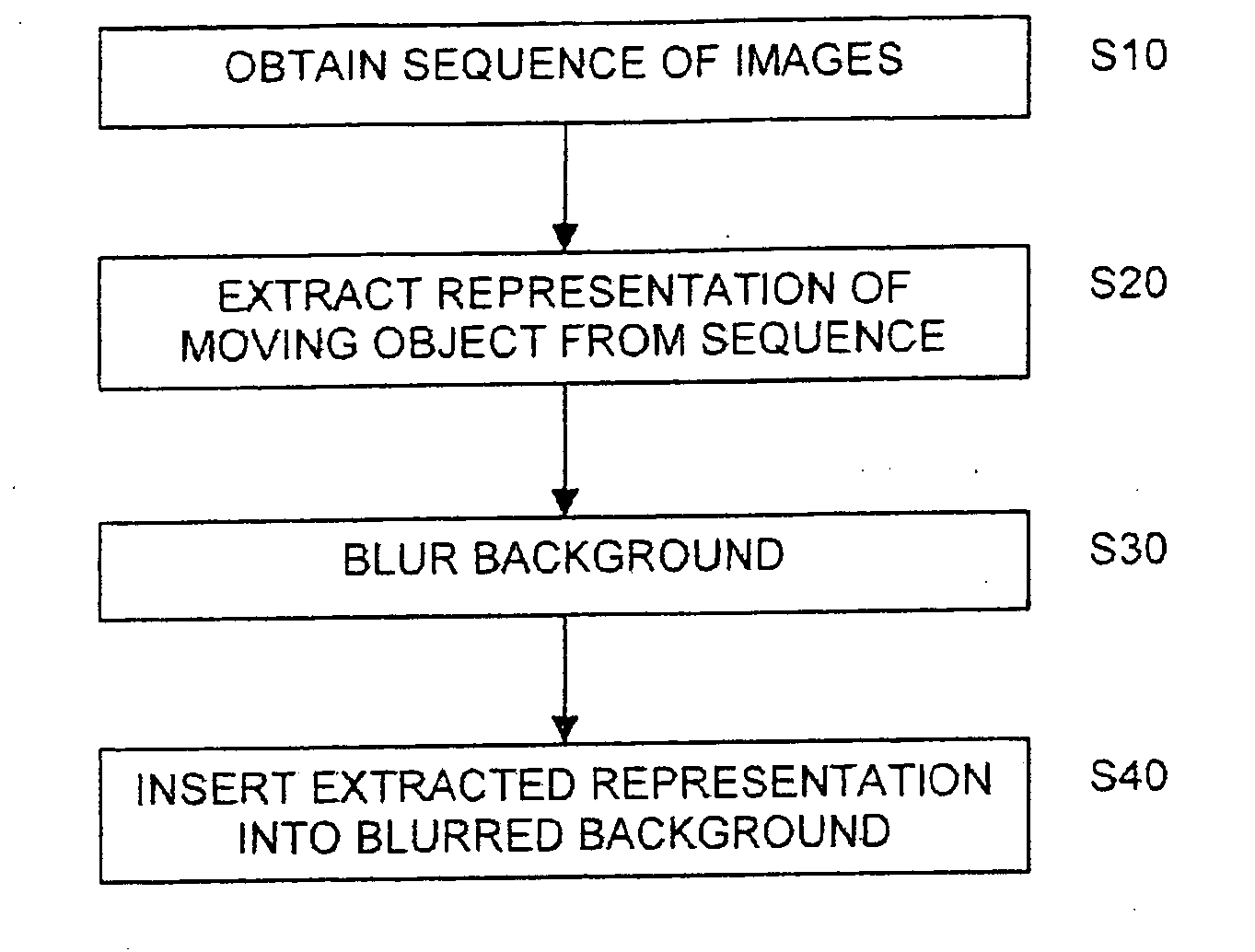
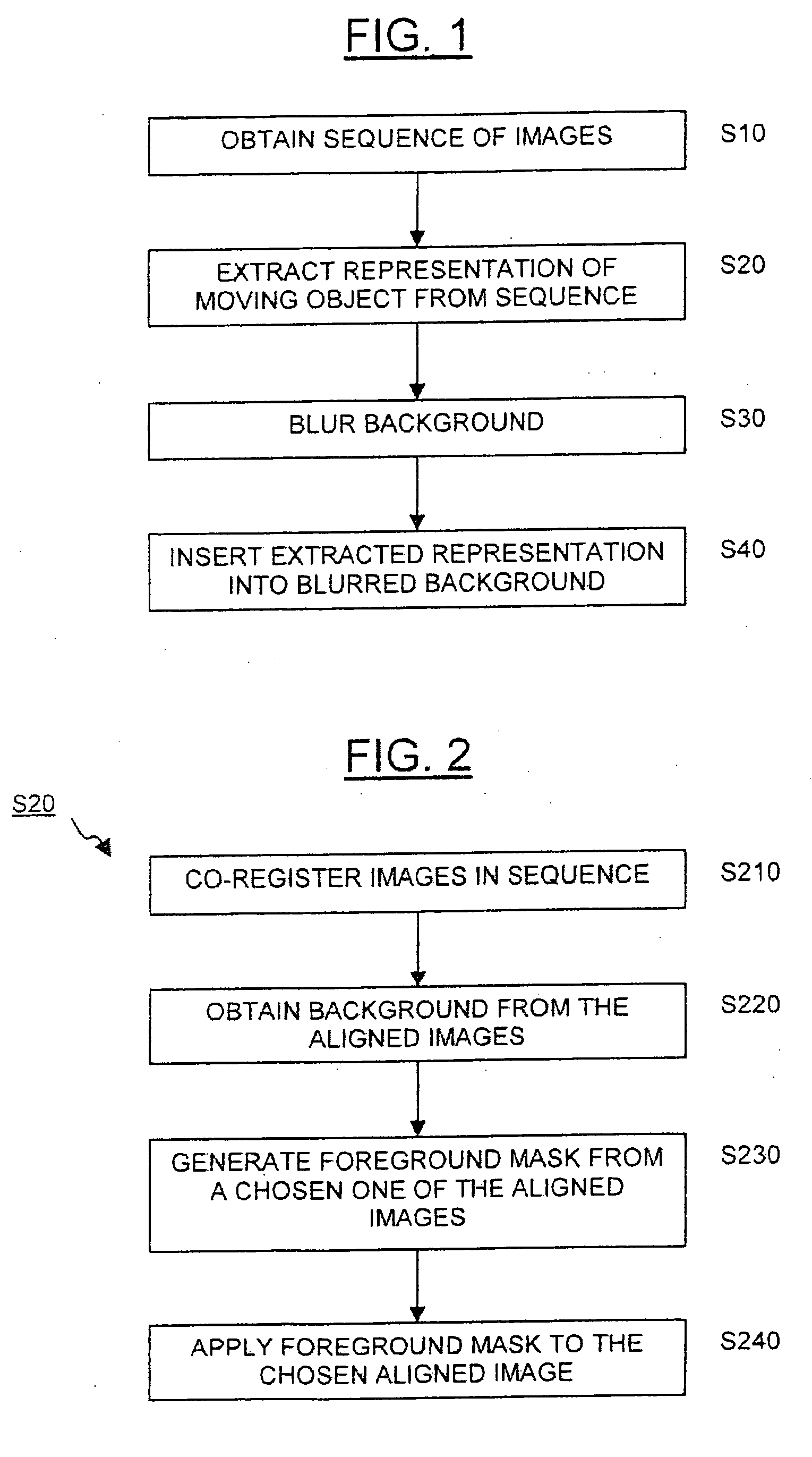
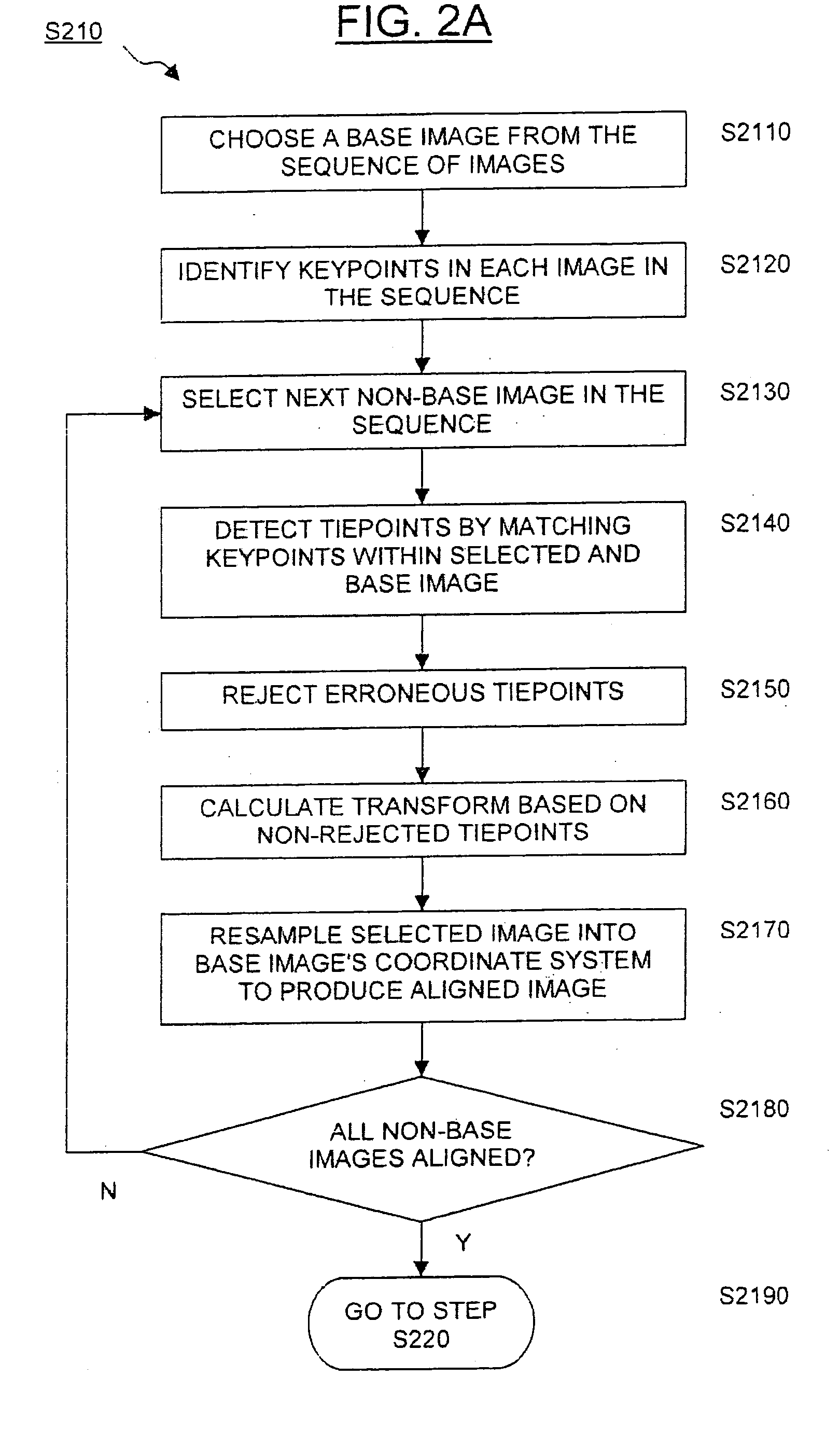
A sequence of images depicts a foreground object in motion. A base image is selected, and the other images in the sequence are co-registered with the base image in order to align the images to a common coordinate system. A background image and a binary foreground mask are generated from the sequence of aligned images. By applying the foreground mask to a chosen one of the aligned images, a representation of the moving object is extracted. After blurring the background image, the extracted representation may be superimposed onto the blurred background image to produce a new image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
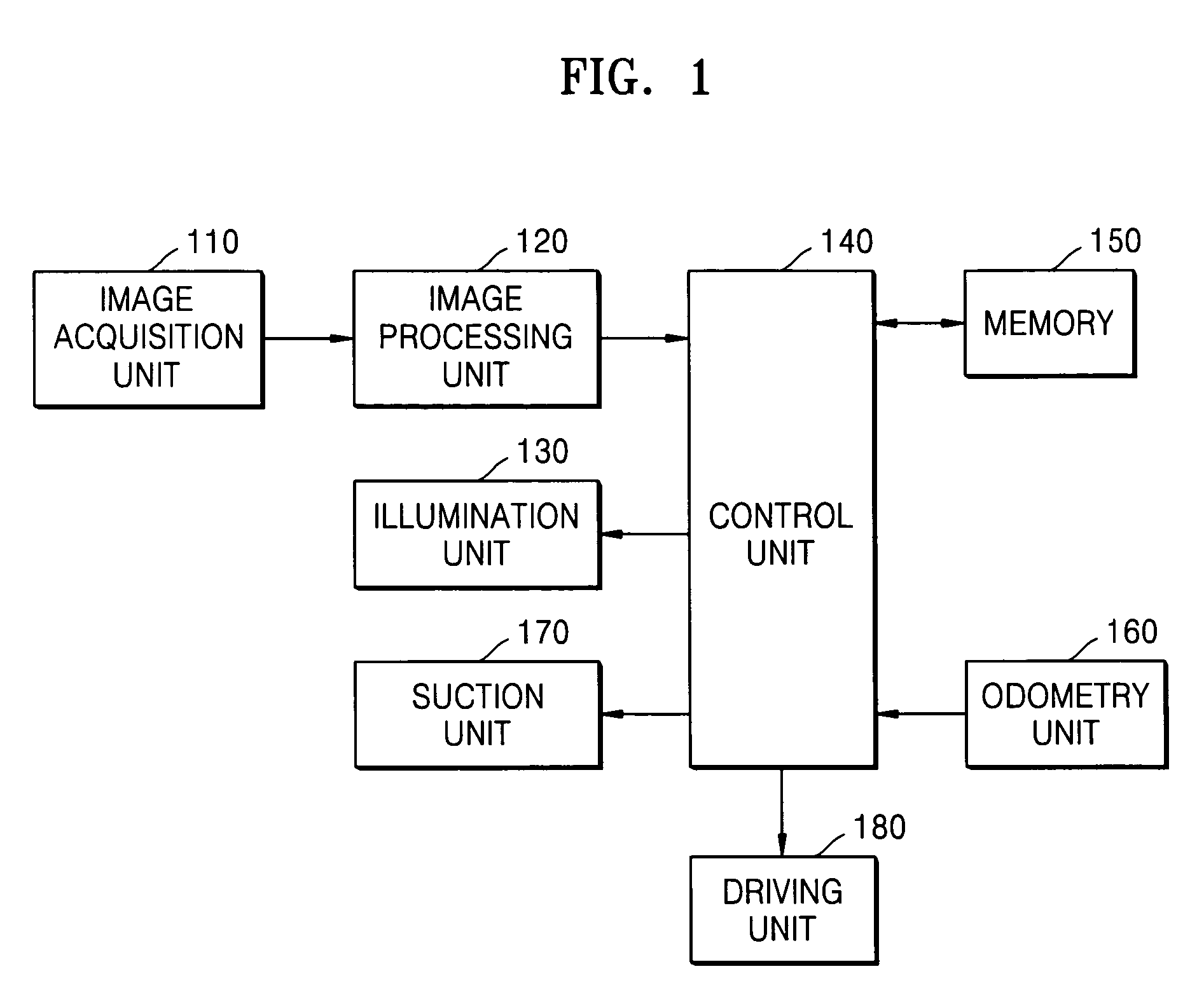
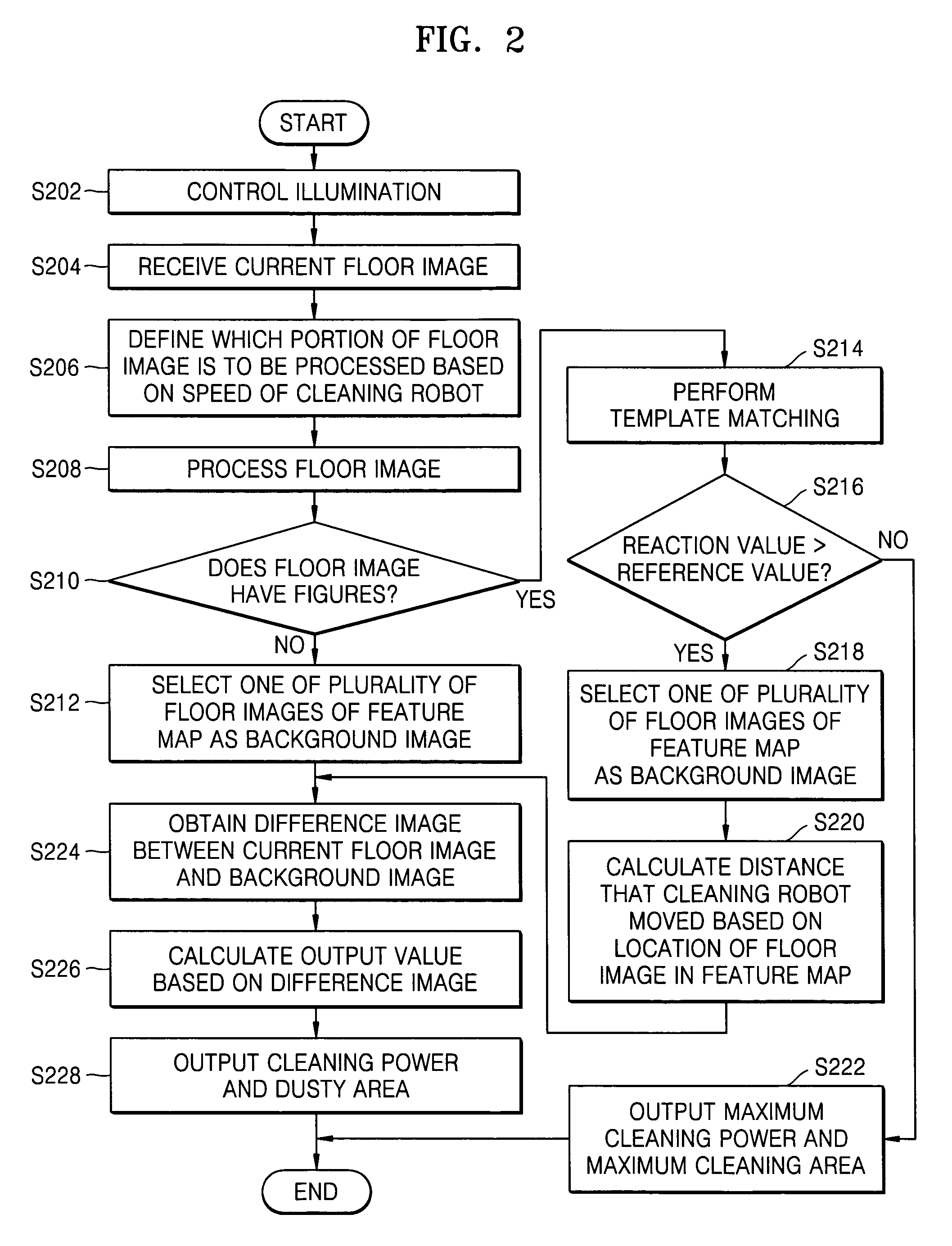
Dust detection method and apparatus for cleaning robot
A dust detection method and apparatus of a cleaning robot. The dust detection method involves acquiring a floor image as a current floor image of a predetermined place at a current location of the cleaning robot in the predetermined place; obtaining a difference image between the current floor image and a background image selected from a feature map consisting of a plurality of floor images of the predetermined place; and detecting a dusty area based on the difference image and adjusting a cleaning power of the cleaning robot.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
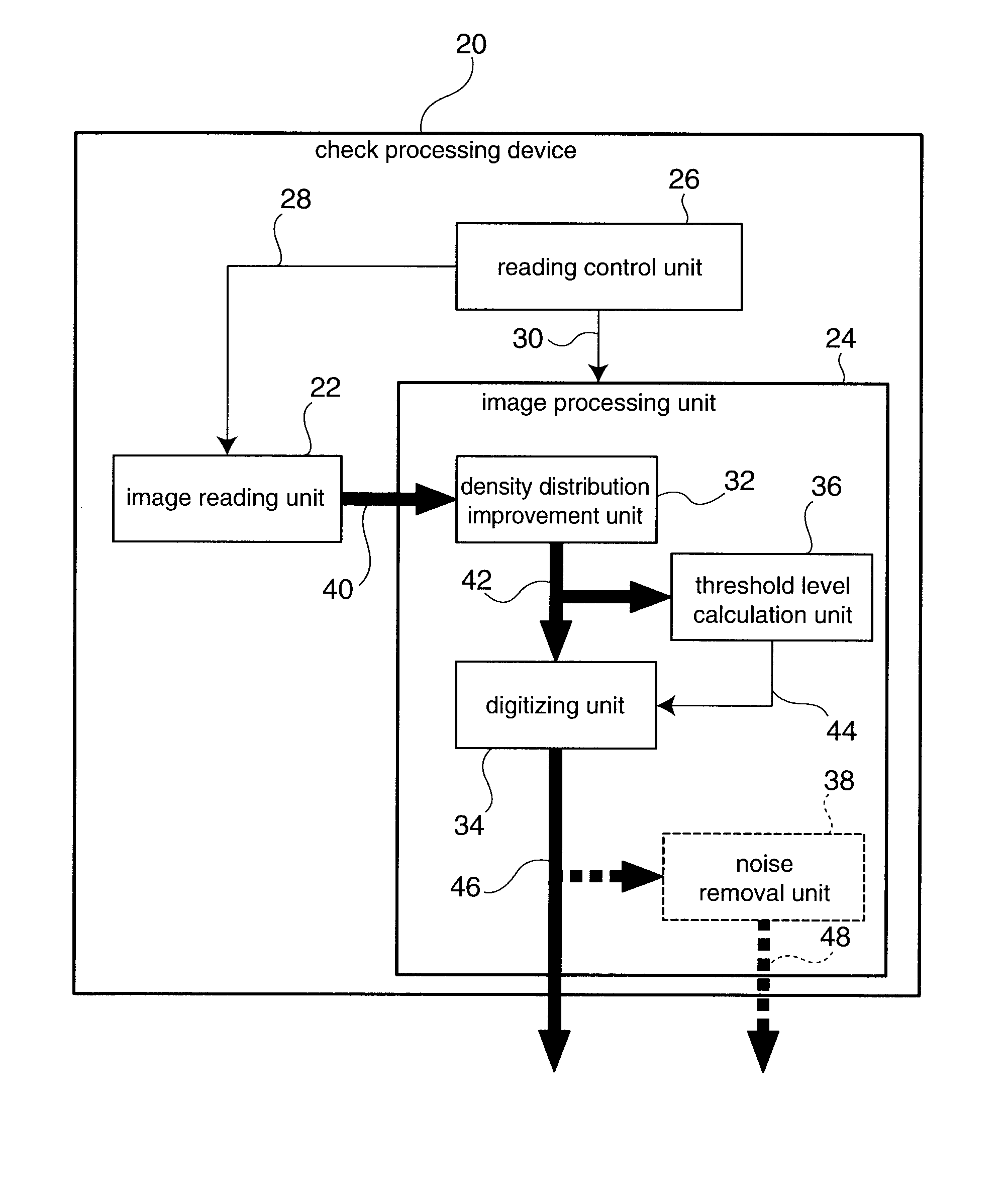
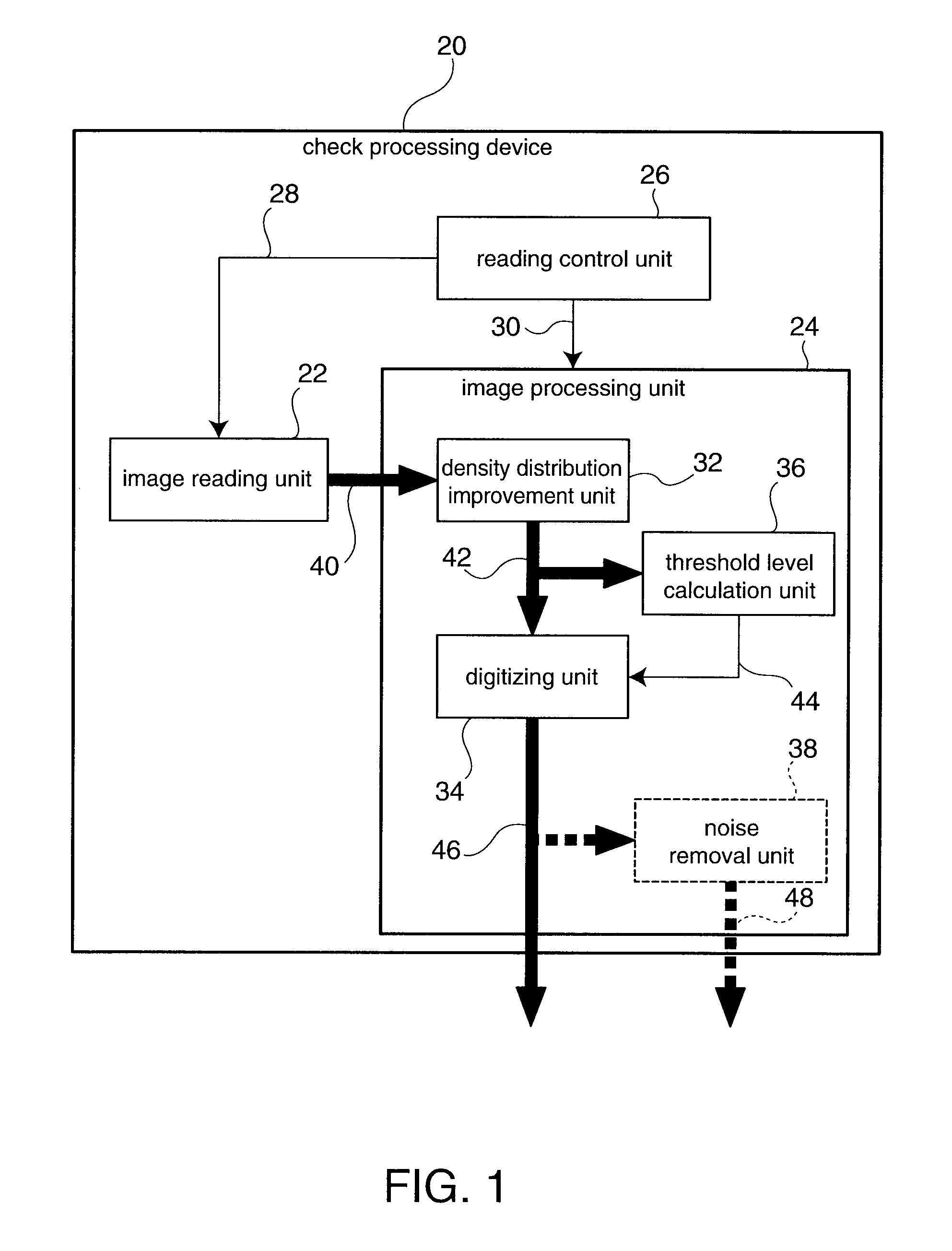
Image Processing Apparatus And Image Processing Method
InactiveUS20070019243A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingDensity distribution
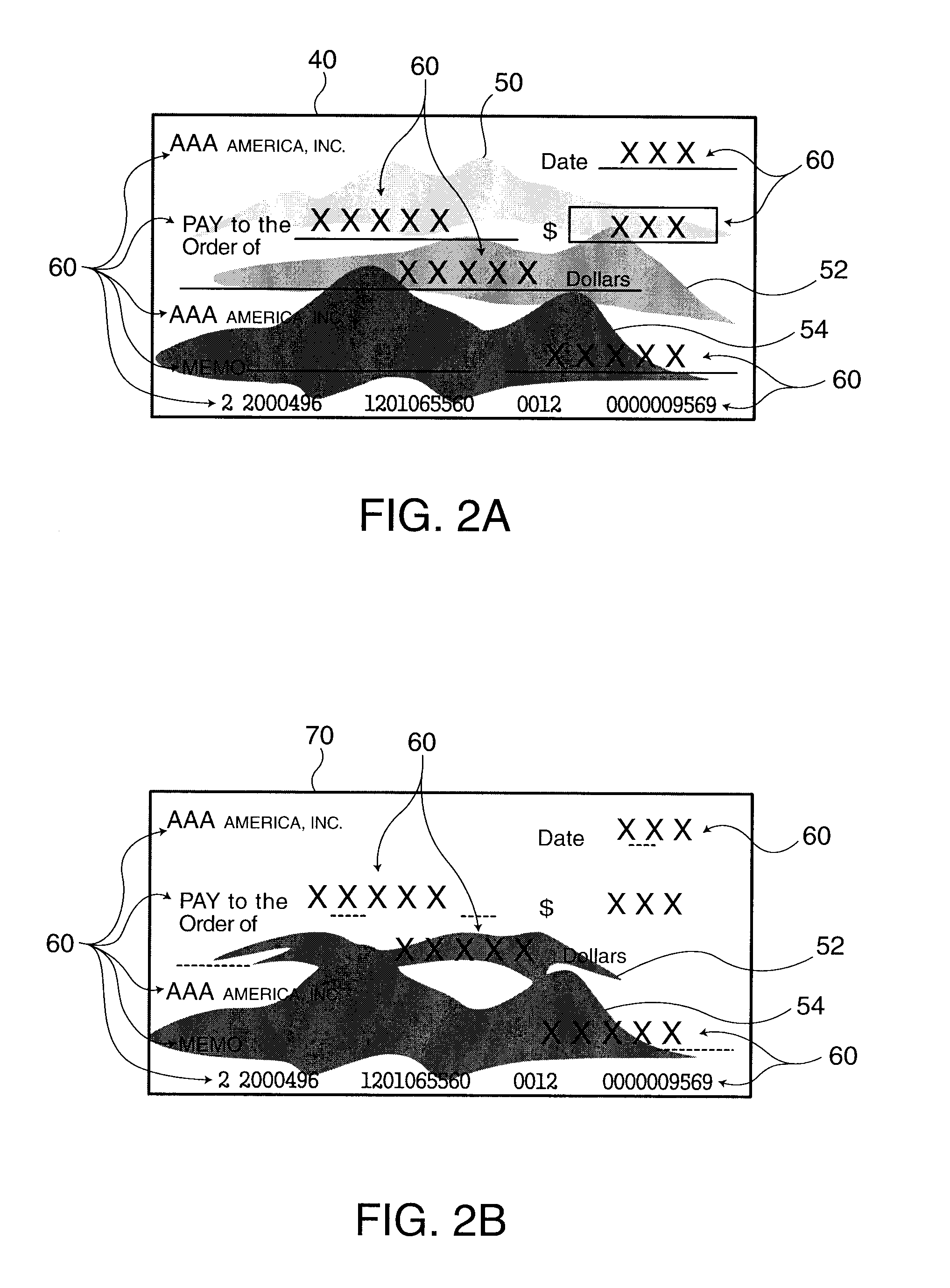
Background images are removed and only the desired payment information is extracted from a grayscale image of a check or similar financial instrument. A density distribution improvement process applied to grayscale raw image data 40 acquired by scanning a check corrects the density distribution of the raw image data 40 to separate the density range of the desired payment information from the density range of the background image. Image sharpening or contrast enhancement can be used as the density distribution improvement method. A threshold level 44 for clearly separating the payment information from the background image is then calculated from the characteristics of the density distribution of the grayscale improved image data 42 acquired by the density distribution improvement process. Histograms of the density distributions are used to determine the characteristics of the density distribution. The improved image data 42 is then converted to binary image data 46 using the threshold level 44. Most of the background image is white and most of the desired payment information is black in the binary image data 46.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Automated multiplayer game table with unique image feed of dealer
ActiveUS20050164762A1Unique and more realistic gaming environmentImprove the environmentApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesComputer graphics (images)Video production
A method and apparatus are used to simultaneously display a virtual dealer and a dynamic visual background image in connection with a multi-player video platform simulating and effecting play of a casino table card game. The dealer imagery is in the foreground and the background is behind the dealer. The background is either a live video feed from the casino, live feed from another location or event or pre-recorded image sequences. The various videos are keyed or masked and layered together using known video production technology.
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
Super light-field lens
Light field imaging systems, and in particular light field lenses that can be mated with a variety of conventional cameras (e.g., digital or photographic / film, image and video / movie cameras) to create light field imaging systems. Light field data collected by these light field imaging systems can then be used to produce 2D images, right eye / left eye 3D images, to refocus foreground images and / or background images together or separately (depth of field adjustments), and to move the camera angle, as well as to render and manipulate images using a computer graphics rendering engine and compositing tools.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
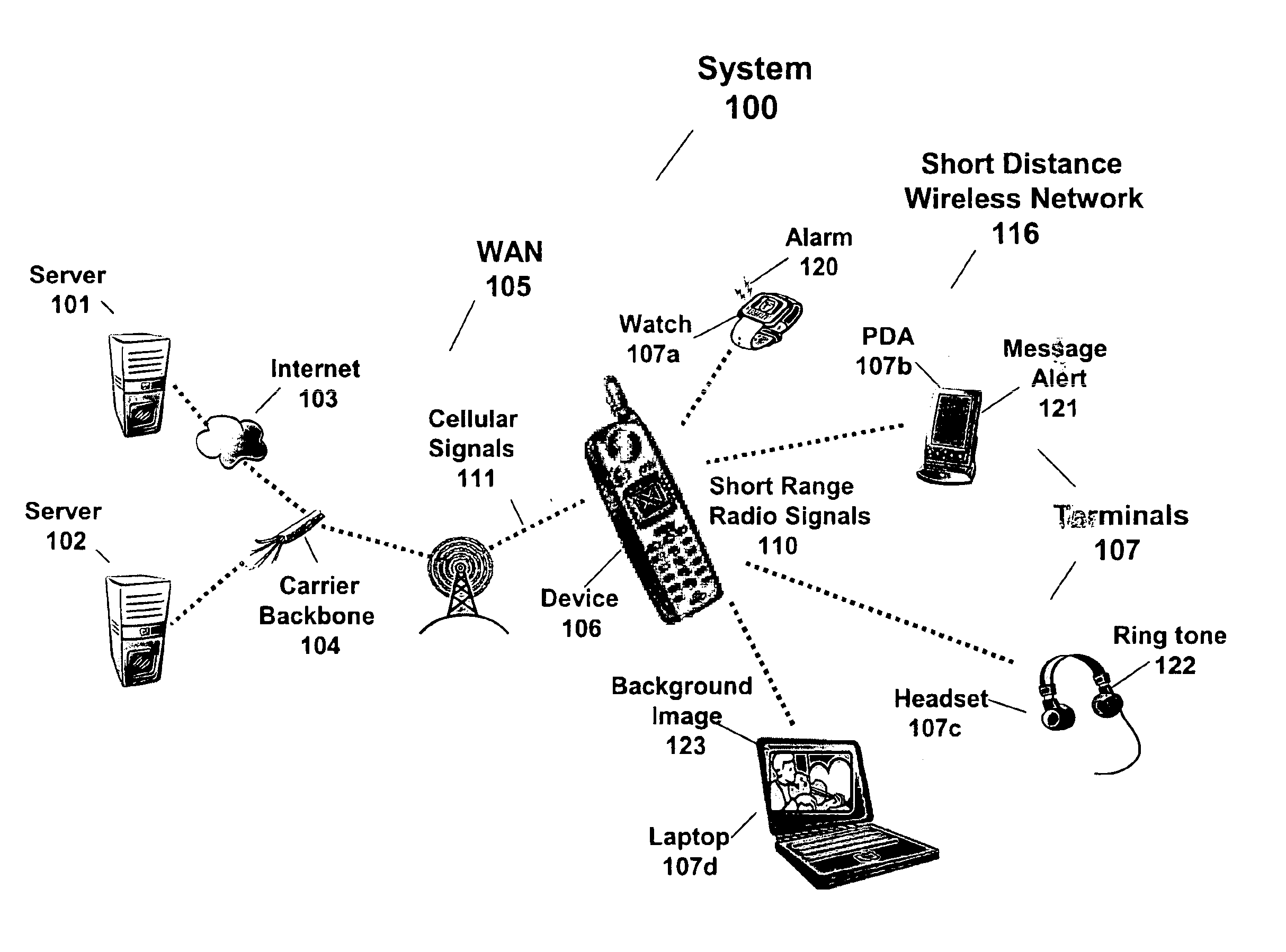
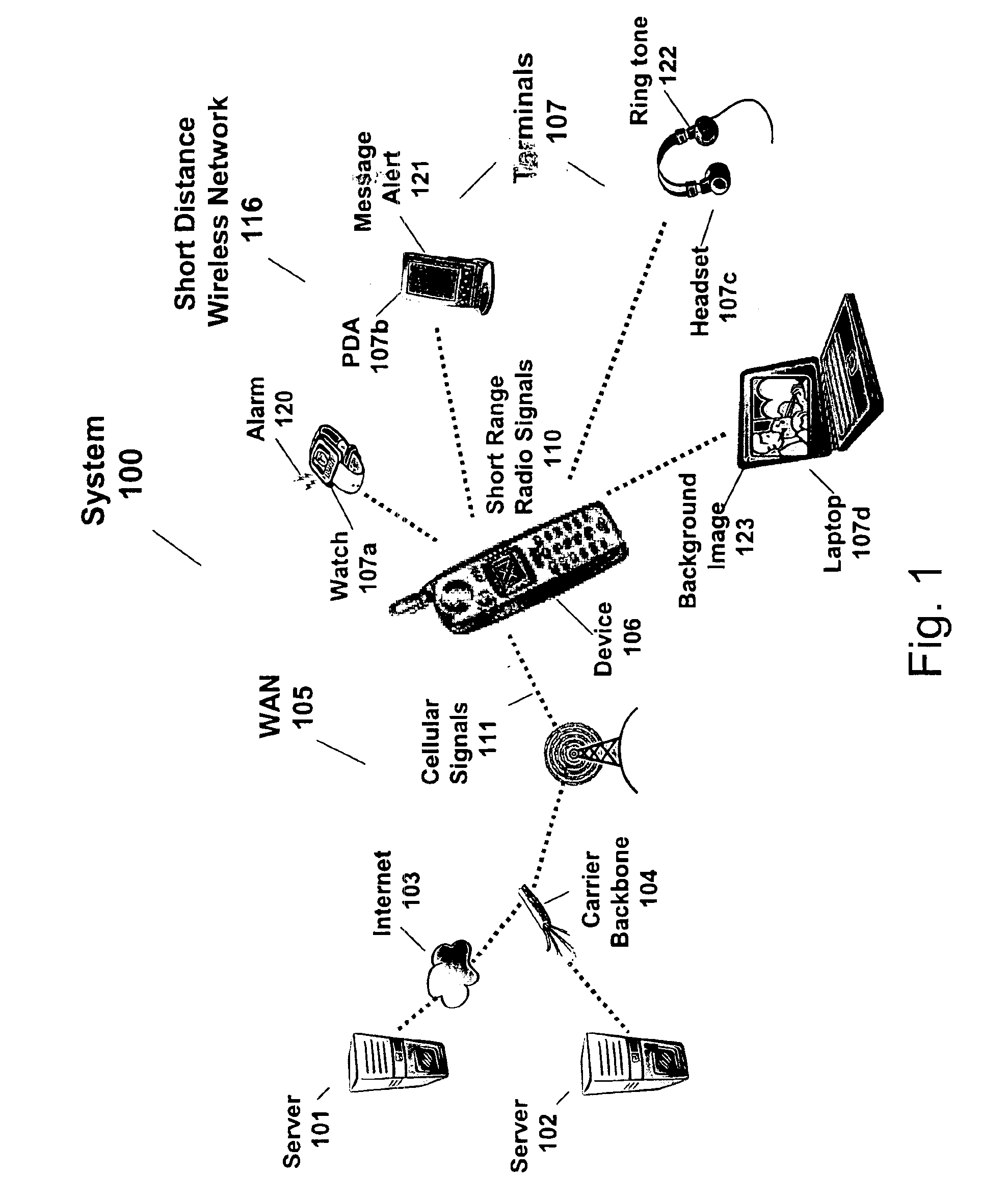
Method, system and computer readable medium for providing an output signal having a theme to a device in a short distance wireless network
InactiveUS6909878B2Safely output signalCordless telephonesNear-field transmissionWeb siteTelecommunications network
A method, system, and computer readable medium allows a user to select an output signal for device / terminal in short distance wireless network. In embodiments of the present invention, the output signal is a ring tone, alarm, background image, vibration signal, font type, or portion of a motion picture. In embodiments of the present invention, a system comprises a first and second device, in a short distance wireless network, generating a first and second output signal. A cellular device generates a first and a second short-range radio signals responsive to a cellular signal from a cellular network. The cellular signal includes a first multimedia file for the first device and a second multimedia file for the second device. In an embodiment of the present invention, the first multimedia file and second multimedia file are thematically related. In an embodiment of the present invention, a processing device is coupled to the cellular network and stores the first and second multimedia files. In an embodiment of the present invention, a user selects a theme on a device or at a web site in order to change the output signals in the short distance wireless network. In an embodiment of the present invention, the output signals are changed periodically without user intervention. In still a further embodiment of the present invention, promoters or users pay a telecommunication network provider for conveniently and safely changing the output signals.
Owner:IXI MOBILE R&D
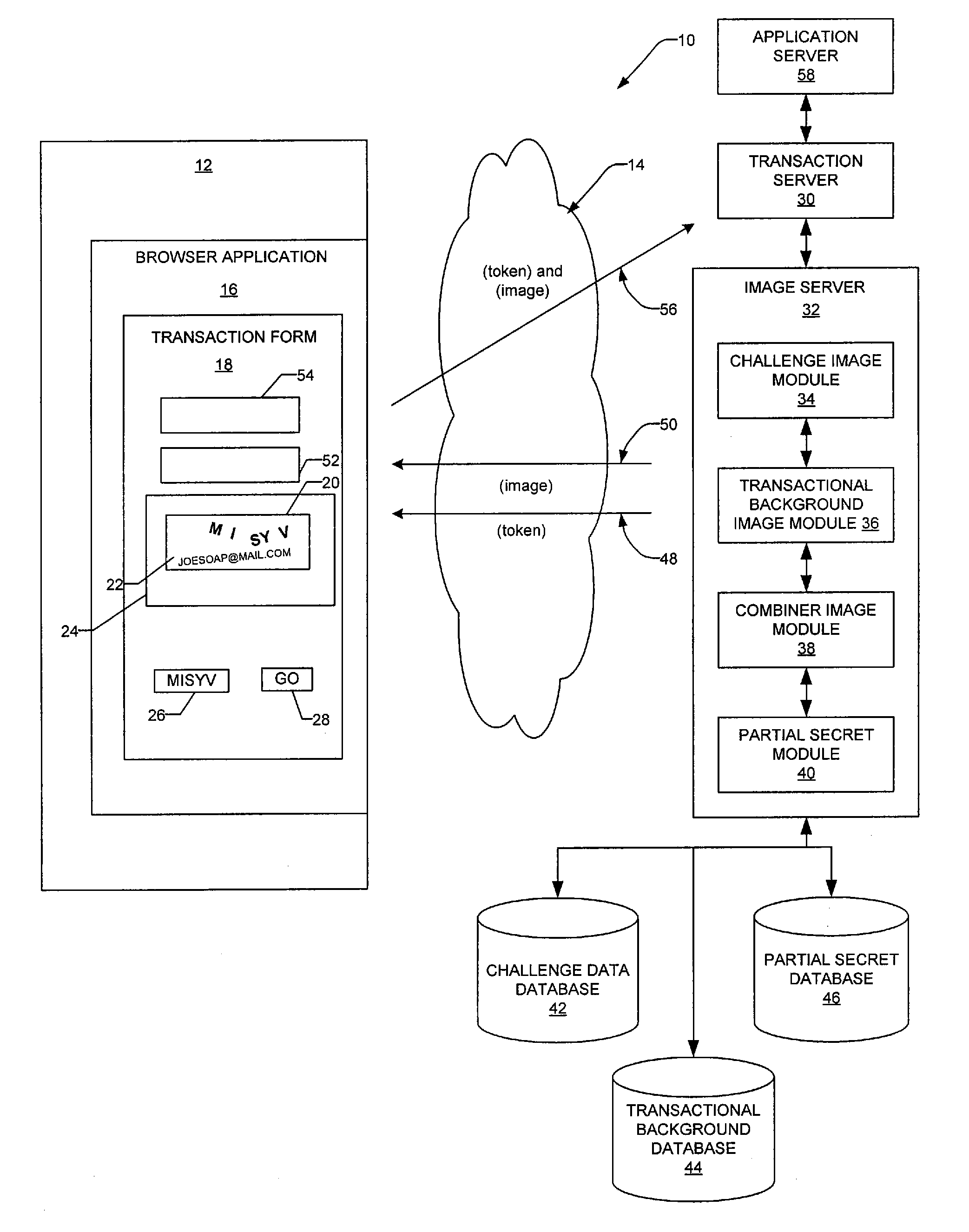
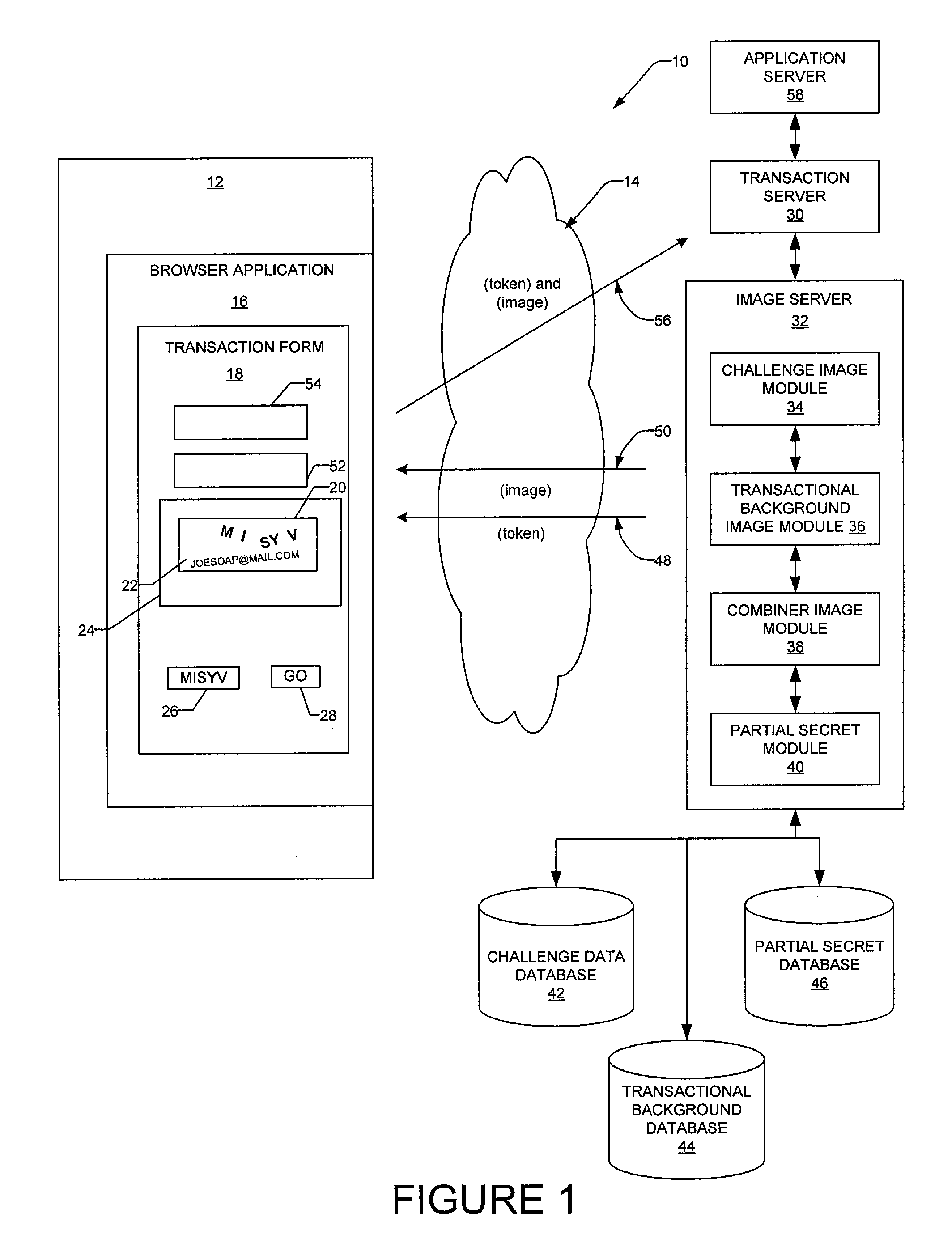
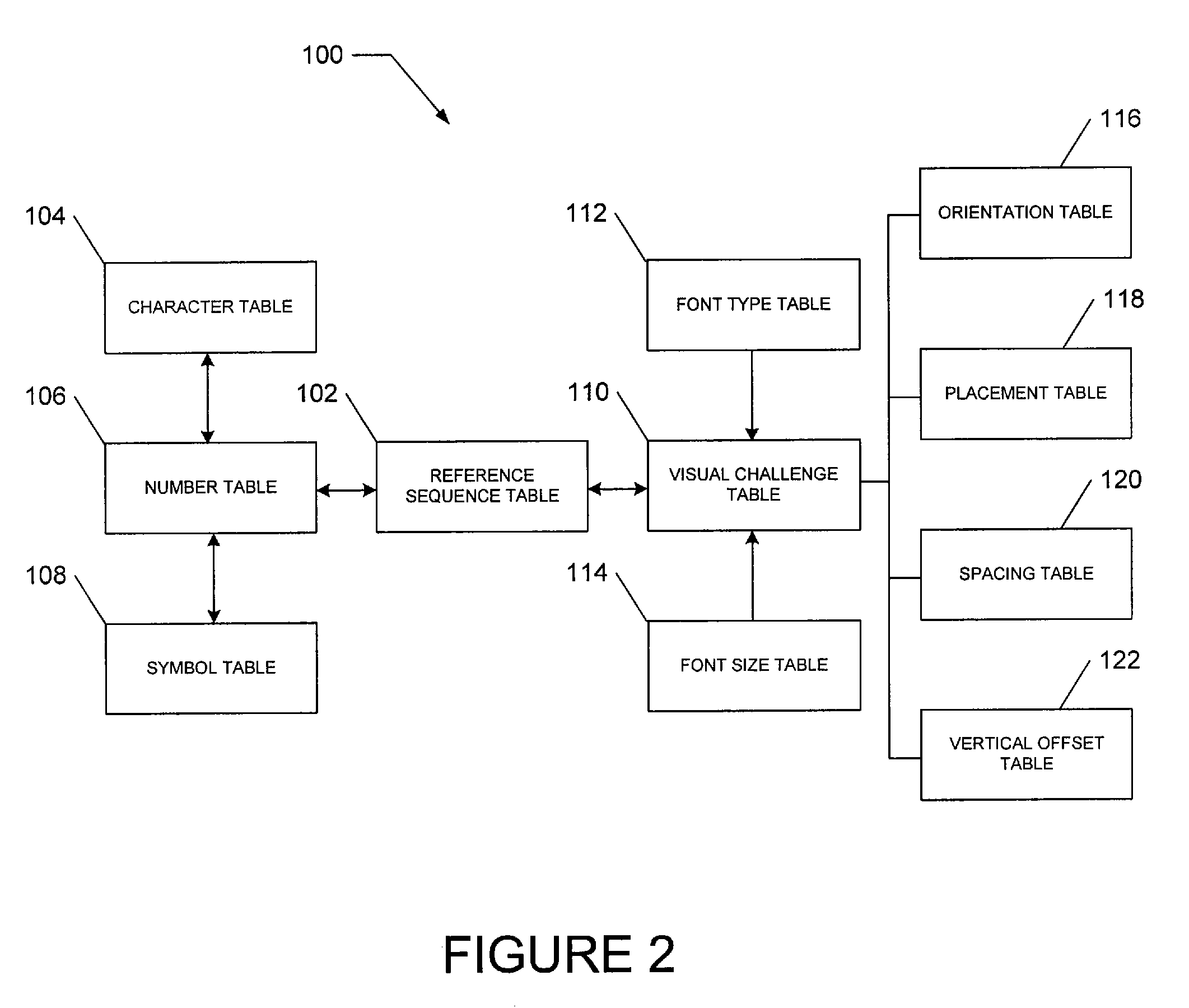
Transactional visual challenge image for user verification
InactiveUS20080209223A1User identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationUser verificationInternet privacy
A method and a system generate a transactional visual challenge image to be presented to a user thereby to verify that the user is human. For example, an image module generates a visual challenge to be presented to a user as part of a challenge-response to verify that the user is human. A transactional background image module identifies a transactional background that is associated with a specific transaction and a combiner image module combines the visual challenge and the transactional background into an image which is to be presented to the user during transaction authorization, the transactional background associating the visual challenge with the particular transaction.
Owner:EBAY INC
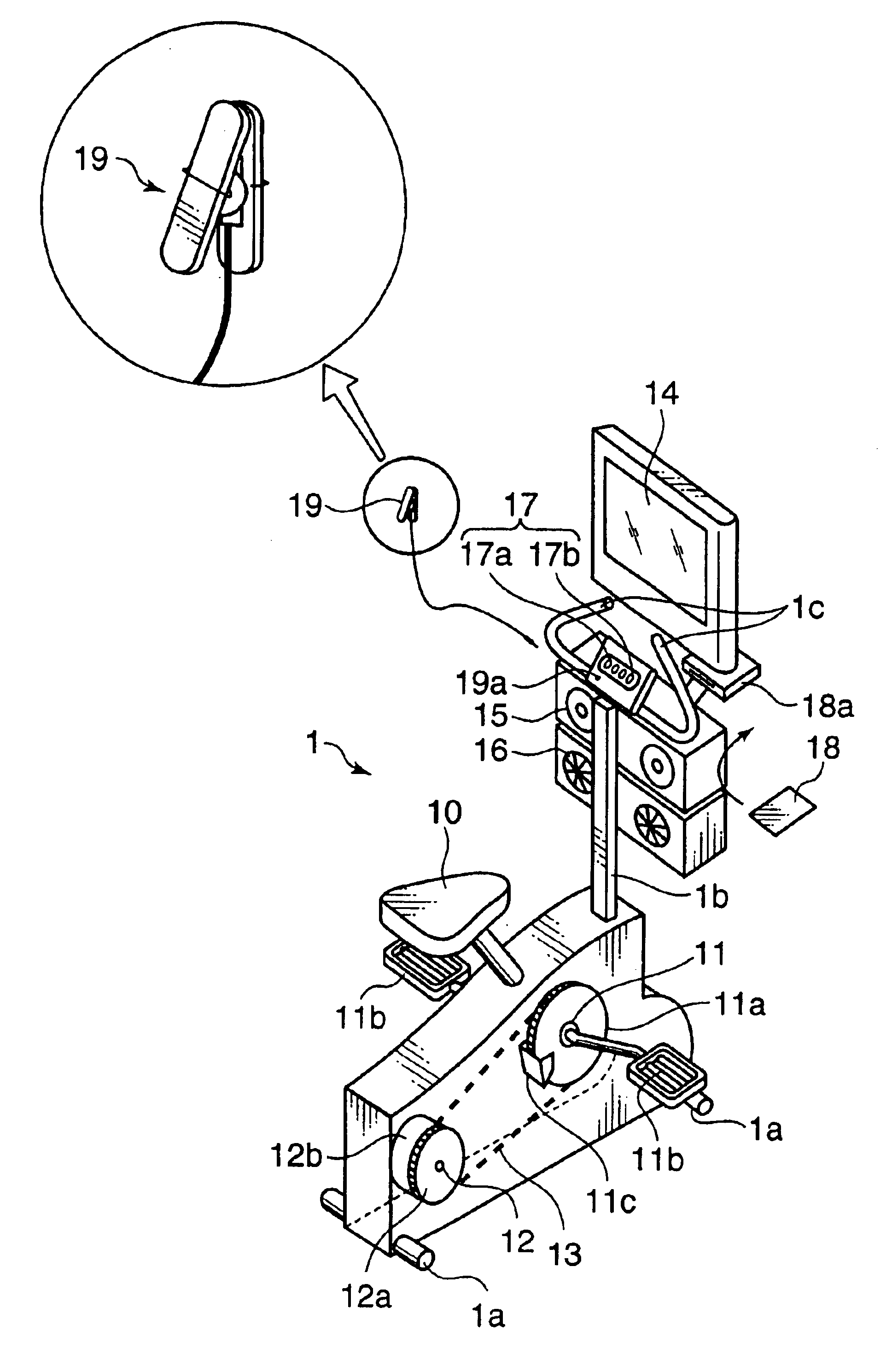
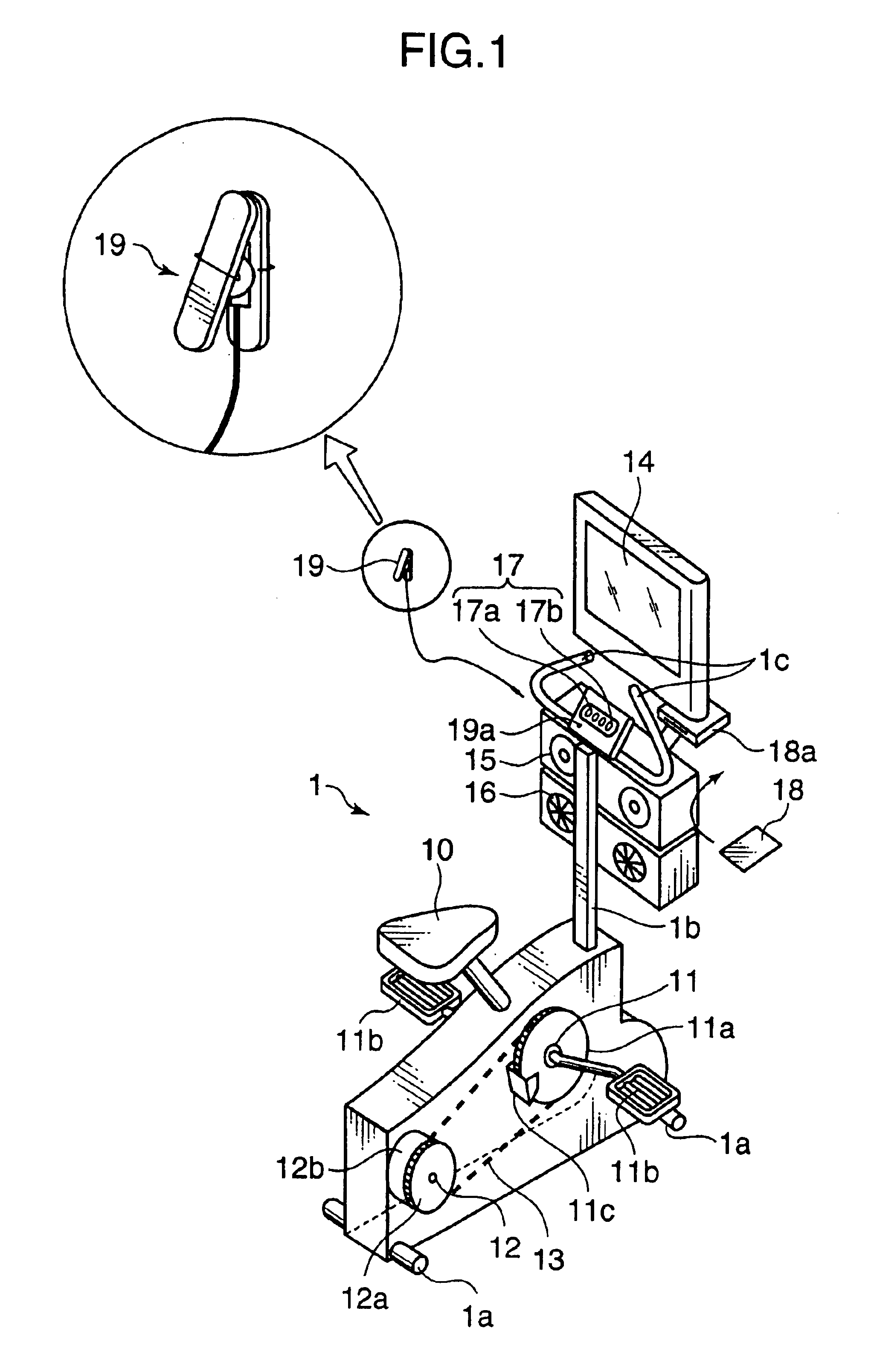
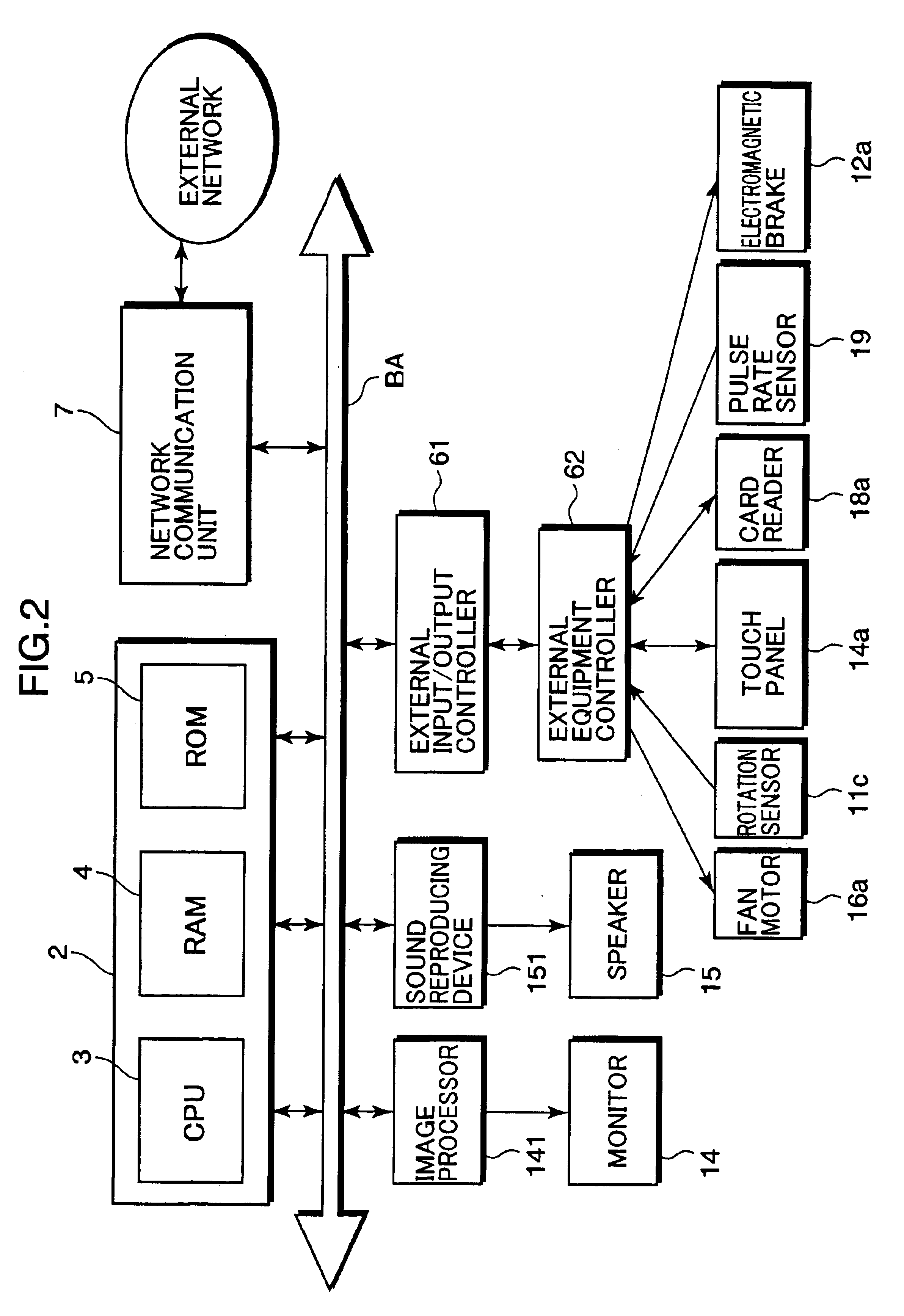
Exercise assisting method and apparatus implementing such method
Owner:KONAMI SPORTS & LIFE
Method for sending multi-media messages using customizable background images
A system and method of providing sender customization of multi-media messages through the use of inserted images or video. The images or video may be sender-created or predefined and available to the sender via a web server. The method relates to customizing a multi-media message created by a sender for a recipient, the multi-media message having an animated entity audibly presenting speech converted from text created by the sender. The method comprises receiving at least one image from the sender, associating each at least one image with a tag, presenting the sender with options to insert the tag associated with one of the at least one image into the sender text, and after the sender inserts the tag associated with one of the at least one images into the sender text, delivering the multi-media message with the at least one image presented as background to the animated entity according to a position of the tag associated with the at least one image in the sender text. In another embodiment of the invention, a template is provided to the sender to create multi-media messages using predefined static images or video clips. The method comprises providing the sender with a group of customizable multi-media message templates, each template of the groups of templates including predefined parameters comprising a predefined text message, a predefined animated entity, a predefined background, predefined background music, and a predefined set of emoticons within the text of the message. The sender is further provided with options to accessorize the animated entity with various additional features such as glasses and the like for more creative presentation of the multi-media message.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
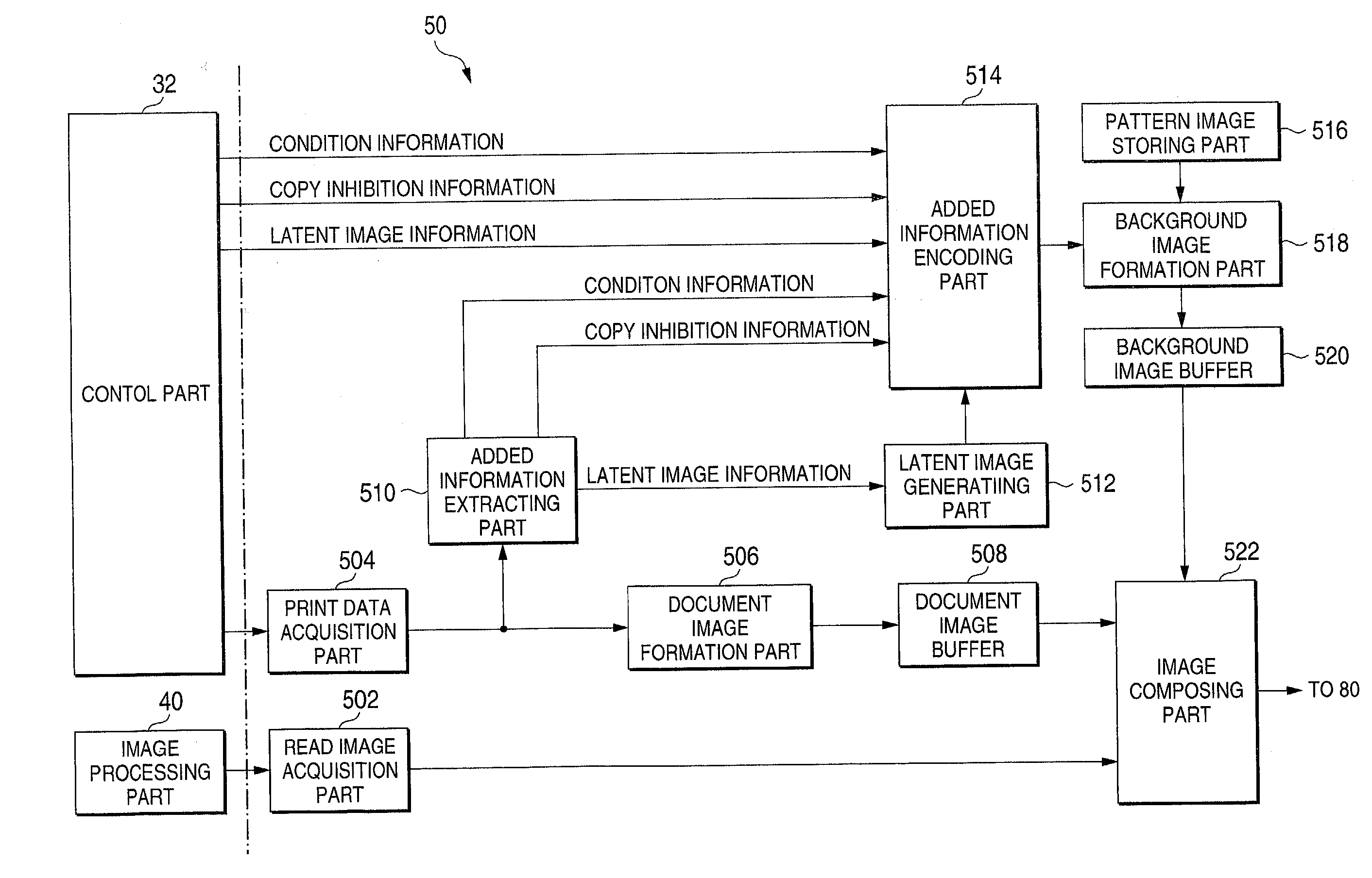
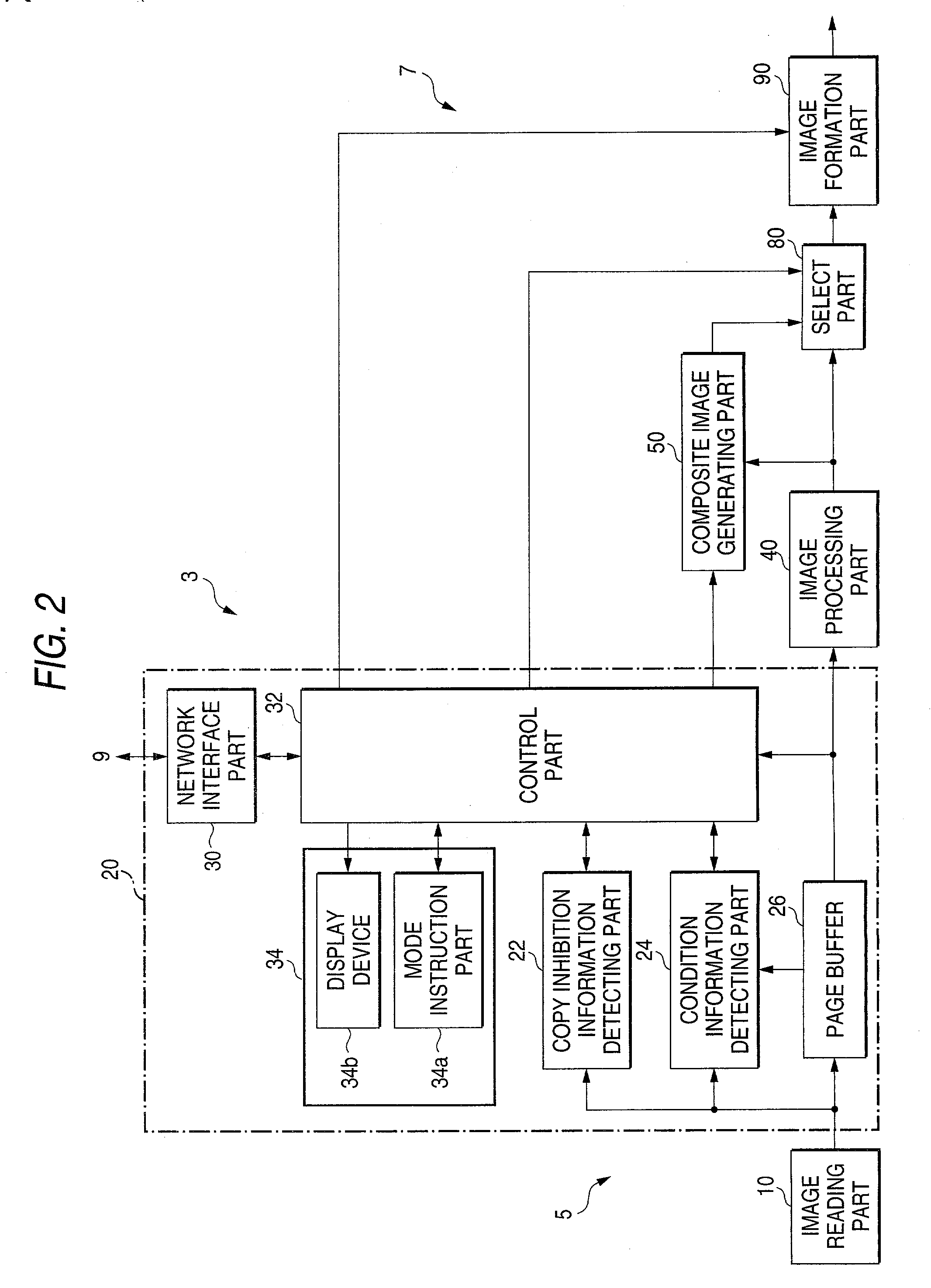
Image generating method, device and program, and illicit copying prevention system
InactiveUS20030179412A1User identity/authority verificationVisual presentation using printersComputer graphics (images)Paper document
An added information encoding part repeatedly arranges two kinds of copy inhibition code arrays of the unit two-dimensional arrays to which copy inhibition codes are assigned, and condition code arrays of the unit two-dimensional arrays to which codes for removing the copy inhibition are assigned, into a two-dimensional array according to given rules. A background image formation part generates a background image in which copy inhibition pattern image areas and condition pattern image areas are repeatedly and two-dimensionally arranged according to given rules, while referring to this array, and the pattern images corresponding to respective codes stored in the background image formation part, and stores the generated background image into a background image buffer. An image composing part reads out document images from a document image buffer, and the background image from the background image buffer, and superimposes them into a composite image.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
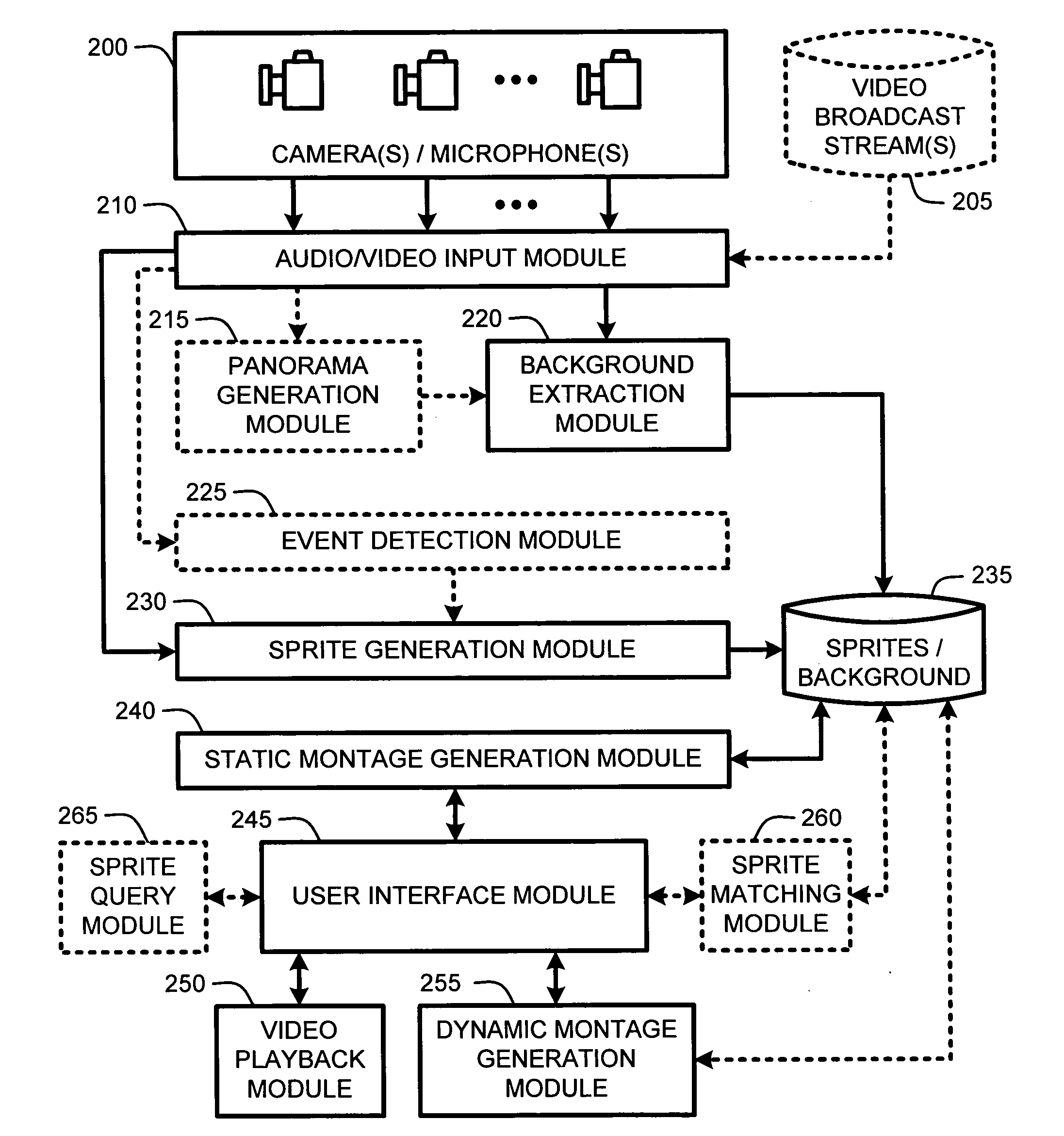
Interactive montages of sprites for indexing and summarizing video
ActiveUS20060117356A1Quick reviewAvoid normal displayDigital data information retrievalElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsEvent typeInteractive video
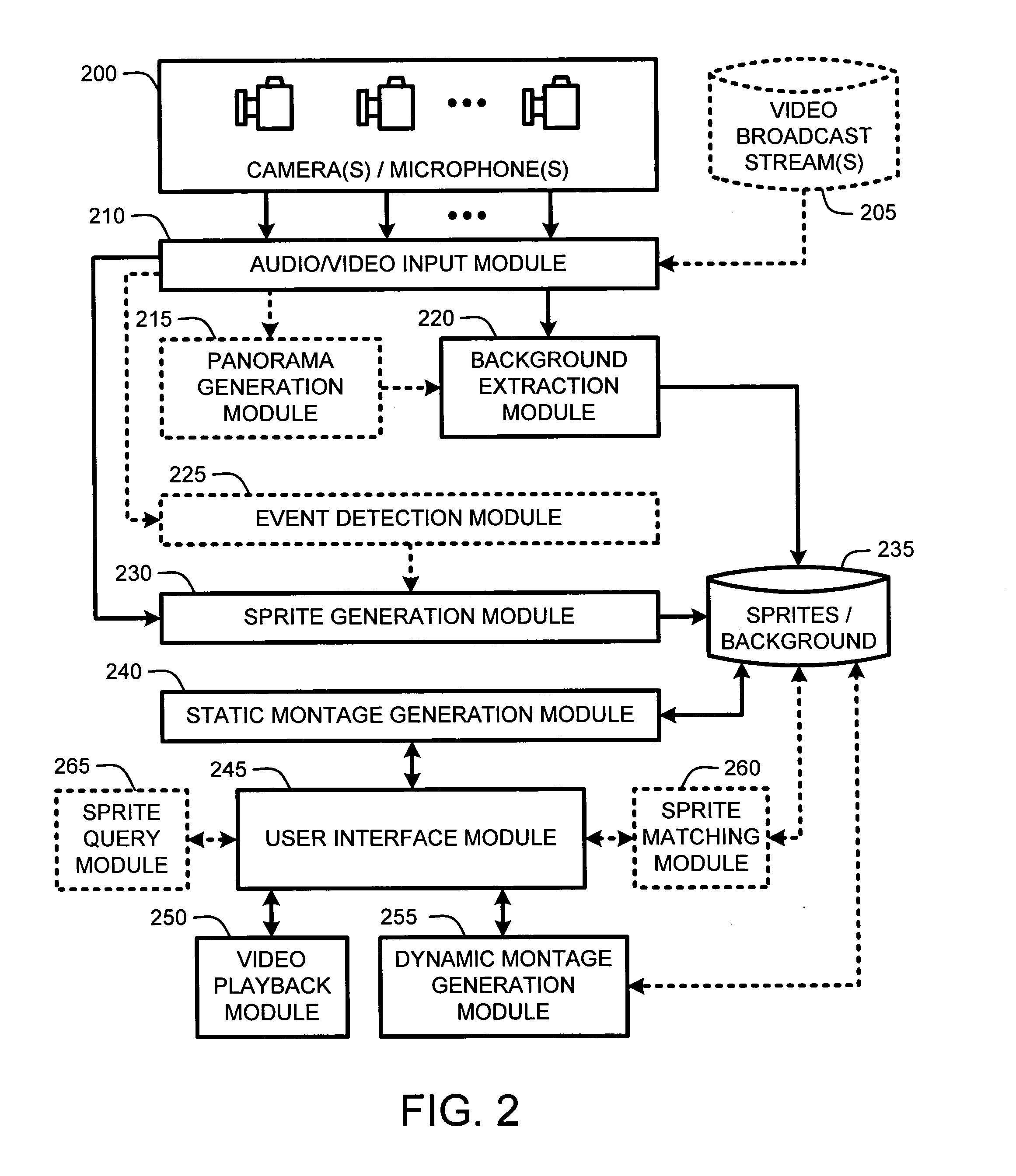
A “Video Browser” provides interactive browsing of unique events occurring within an overall video recording. In particular, the Video Browser processes the video to generate a set of video sprites representing unique events occurring within the overall period of the video. These unique events include, for example, motion events, security events, or other predefined event types, occurring within all or part of the total period covered by the video. Once the video has been processed to identify the sprites, the sprites are then arranged over a background image extracted from the video to create an interactive static video montage. The interactive video montage illustrates all events occurring within the video in a single static frame. User selection of sprites within the montage causes either playback of a portion of the video in which the selected sprites were identified, or concurrent playback of the selected sprites within a dynamic video montage.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Machine learning-based subject tracking
ActiveUS10474992B2ConfidenceImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisLearning basedBackground image
Systems and techniques are provided for tracking puts and takes of inventory items by subjects in an area of real space. A plurality of cameras with overlapping fields of view produce respective sequences of images of corresponding fields of view in the real space. In one embodiment, the system includes first image processors, including subject image recognition engines, receiving corresponding sequences of images from the plurality of cameras. The first image processors process images to identify subjects represented in the images in the corresponding sequences of images. The system includes second image processors, including background image recognition engines, receiving corresponding sequences of images from the plurality of cameras. The second image processors mask the identified subjects to generate masked images. Following this, the second image processors process the masked images to identify and classify background changes represented in the images in the corresponding sequences of images.
Owner:STANDARD COGNITION CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com