Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8304results about "Non-redundant fault processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Debugging site errors by an admin as a guest user in a multi-tenant database environment
An approach for debugging site errors in a multi-tenant database system is disclosed. An example method can include receiving a request from a site administrator to access an enhanced error message and determining if the site administrator is approved for viewing the enhanced error message by evaluating exceptions associated with the enhanced error message, the request, and the site administrator. The example method further includes modifying a detailed error message related to the request for generating the enhanced error message, and providing the enhanced error message to the site administrator based on the approval determination.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
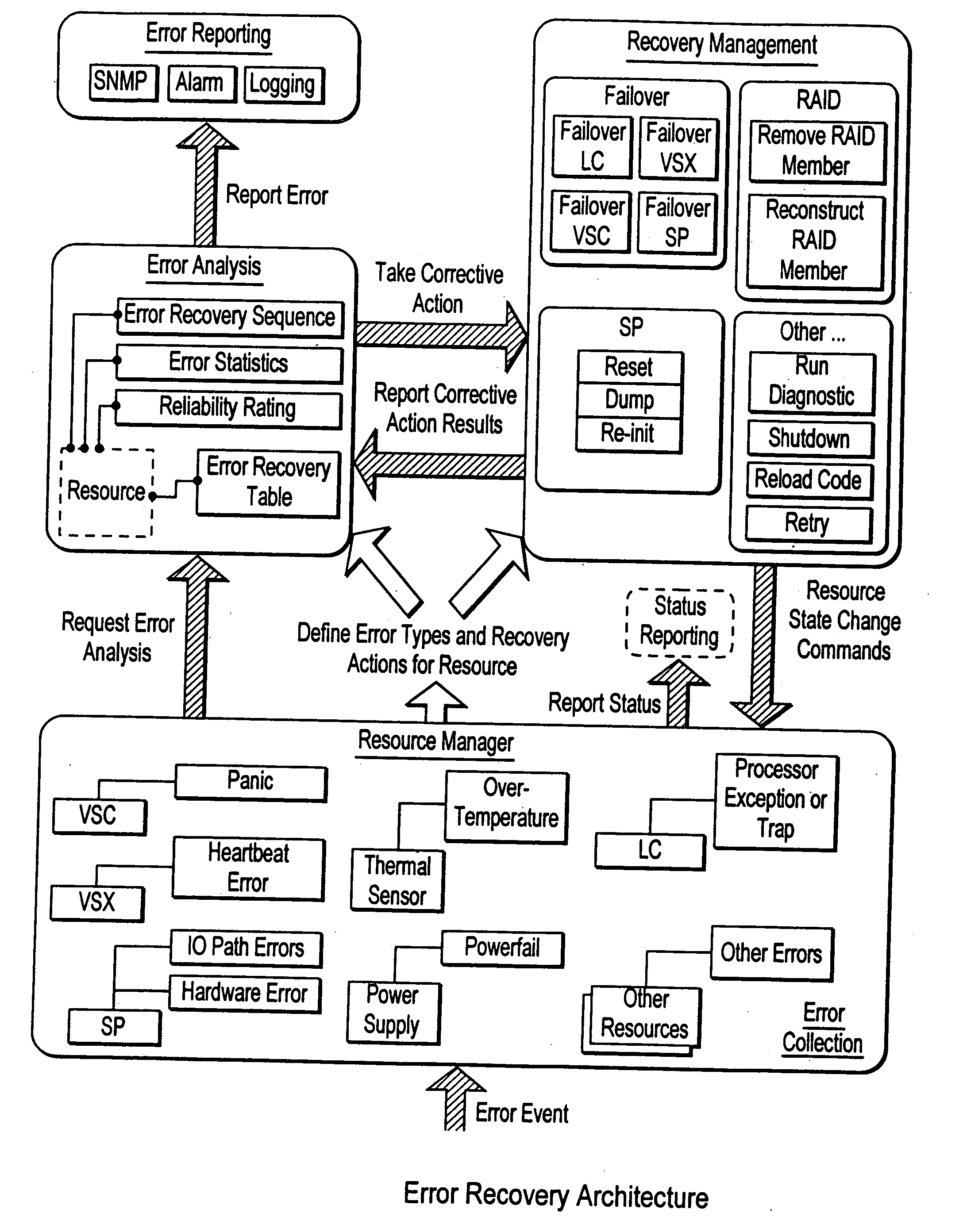
Software fault management system
InactiveUS6012152ASupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInformation repositoryManagement information systems
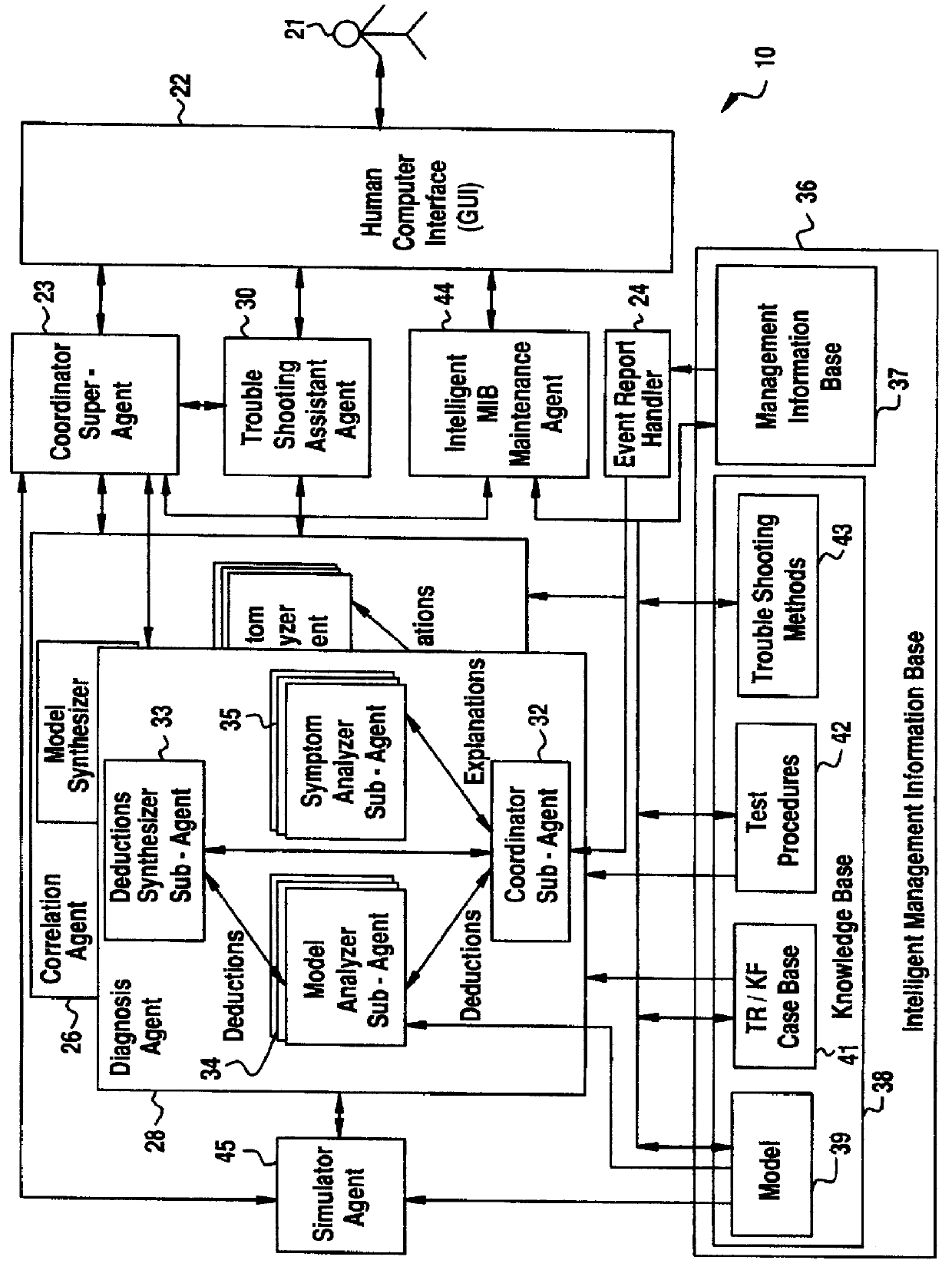
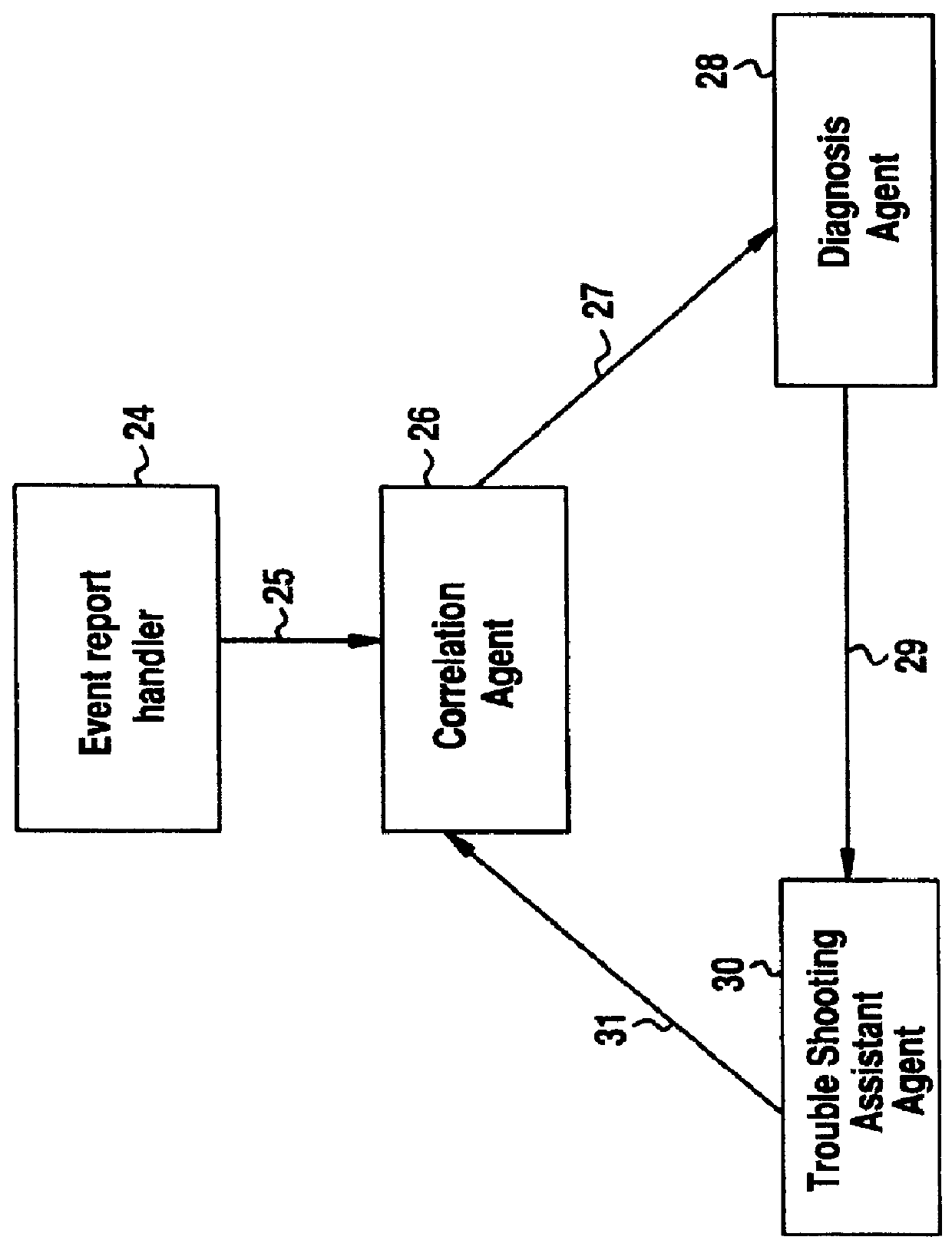
A Software Fault Management (SFM) system for managing software faults in a managed mobile telecommunications network. The SFM system includes an Intelligent Management Information Base (I-MIB) comprising a Management Information Base (MIB) and a Knowledge Base (KB) having a functional model of the managed network and a trouble report / known faults (TR / KF) case base. The SFM system also includes an intelligent multi-agent portion having a plurality of agents which process the software faults utilizing the functional model from the I-MIB, case-based information, and other management information. The I-MIB and the intelligent multi-agent portion are compliant with Telecomunications Management Network (TMN) principles and framework. Fault management is both proactive and reactive. The SFM system is made independent of technology-specific implementations by representing the underlying switch design knowledge in a modular and changeable form which is then interpreted by the intelligent multi-agent portion. A clear separation is maintained between the generic procedural inference mechanisms and agents, and the specific and explicit models of the different network elements of a mobile telecommunications network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
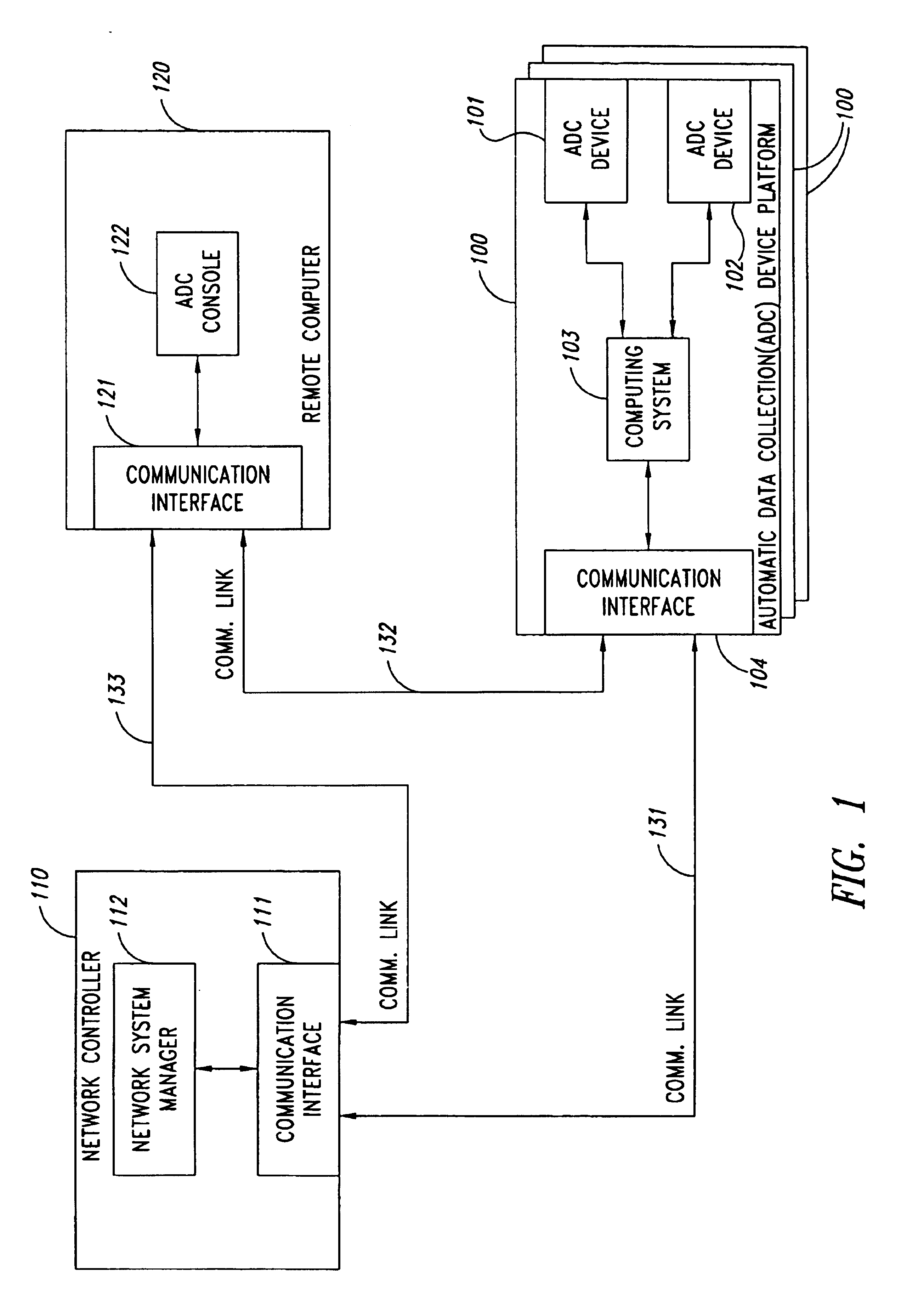
Testing automatic data collection devices, such as barcode, RFID and/or magnetic stripe readers
ActiveUS8944332B2Conveying record carriersTesting sensing arrangementsData acquisitionBarcode reader
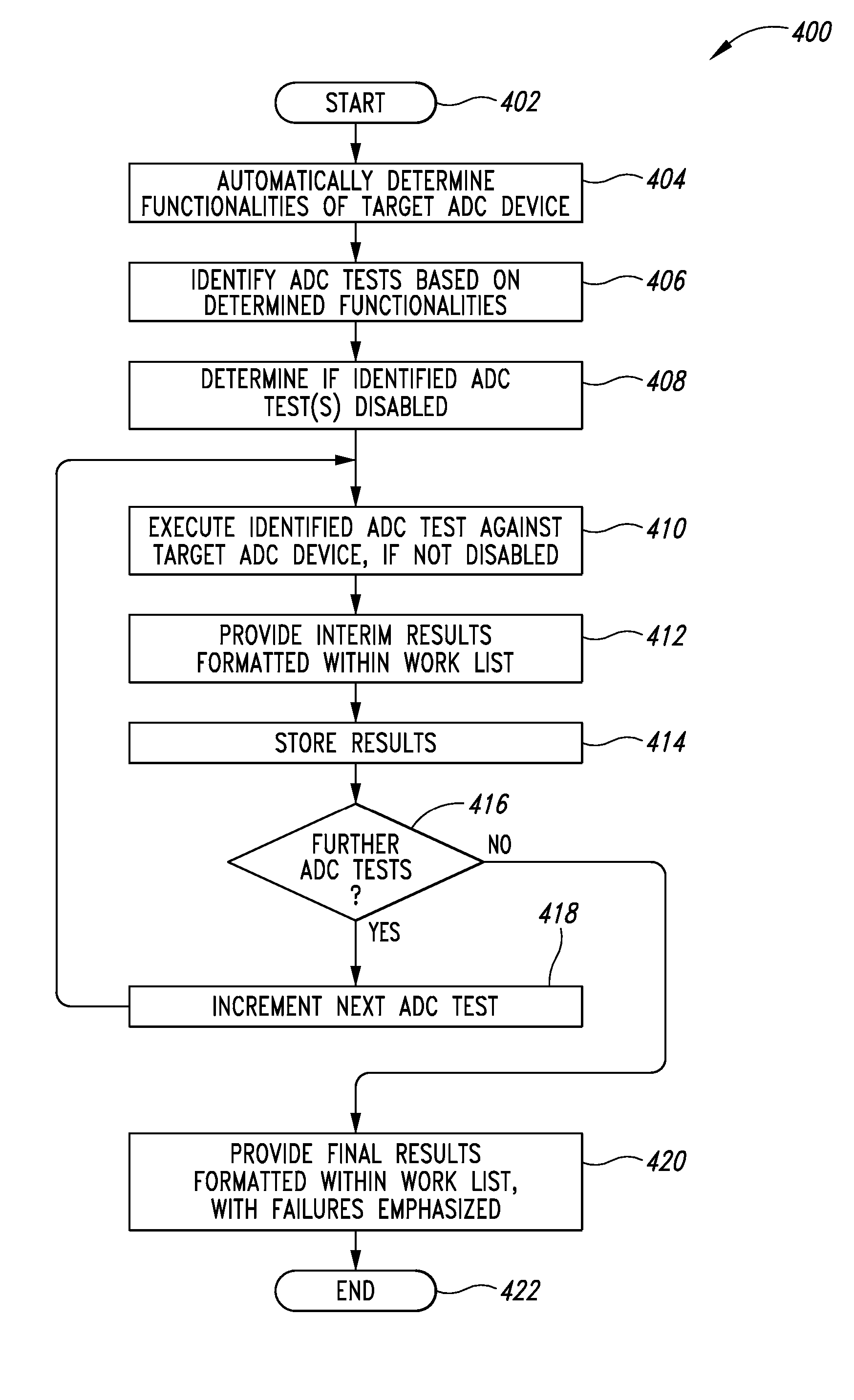
Automatic data collection devices such as barcode readers, RFID readers, magnetic stripe readers and the like may be tested using ADC device test executables, modules or processes stored at a variety of network locations. One or more sets of tests or work lists may be defined to facilitate testing. Tests may be identified by name and / or keyword. Keywords may be indicative one or more functionalities tested by the respective ADC device test module.
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
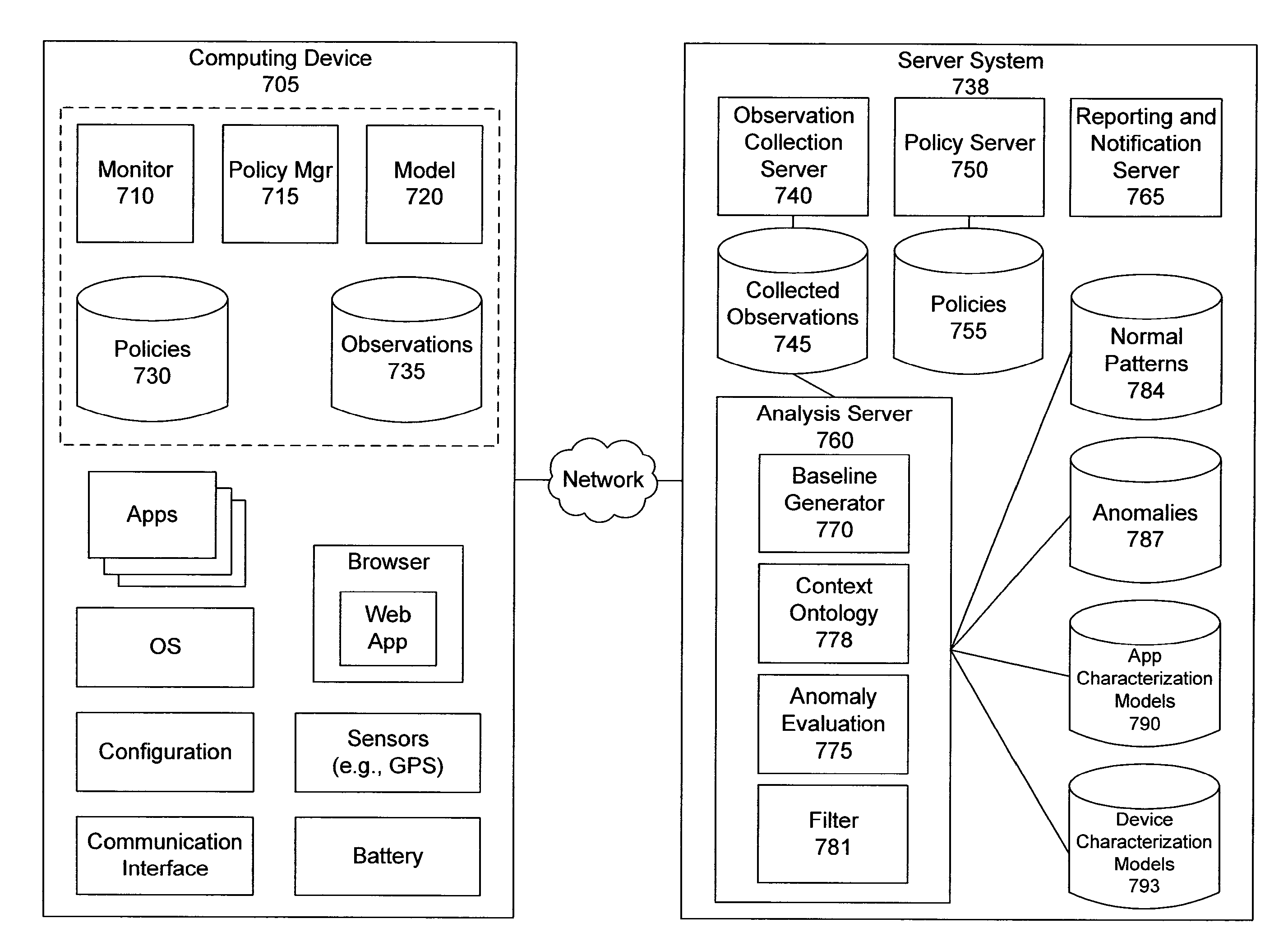
Distributed monitoring, evaluation, and response for multiple devices
ActiveUS20150163121A1Easy to monitorReduce monitoringDigital data processing detailsNon-redundant fault processingWeb applicationMultiple device
Owner:LOOKOUT MOBILE SECURITY
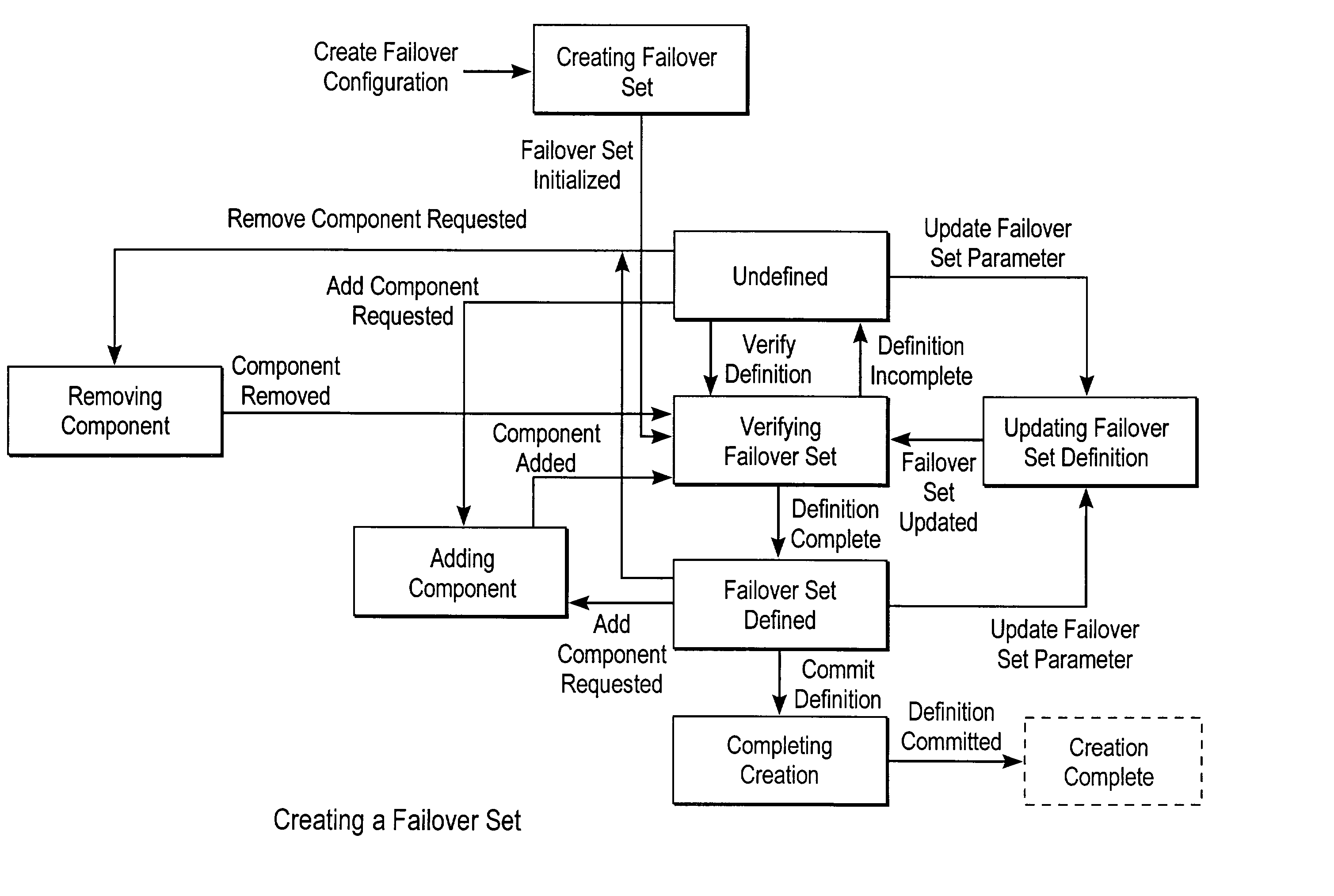
Failover processing in a storage system
InactiveUS7039827B2Improve usabilityInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsFault toleranceFailover
Failover processing in storage server system utilizes policies for managing fault tolerance (FT) and high availability (HA) configurations. The approach encapsulates the knowledge of failover recovery between components within a storage server and between storage server systems. This knowledge includes information about what components are participating in a Failover Set, how they are configured for failover, what is the Fail-Stop policy, and what are the steps to perform when “failing-over” a component.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
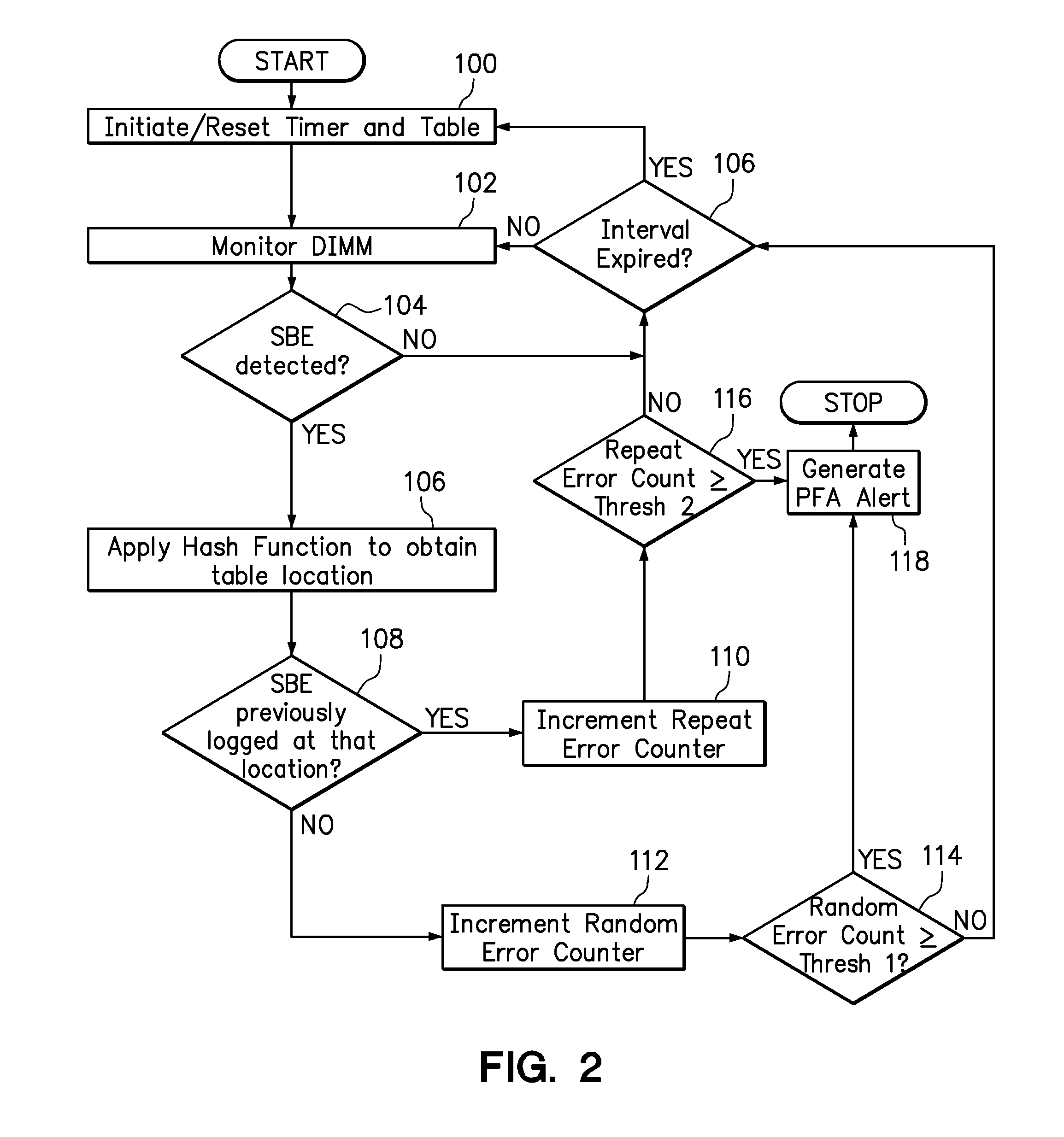
Use of hashing function to distinguish random and repeat errors in a memory system
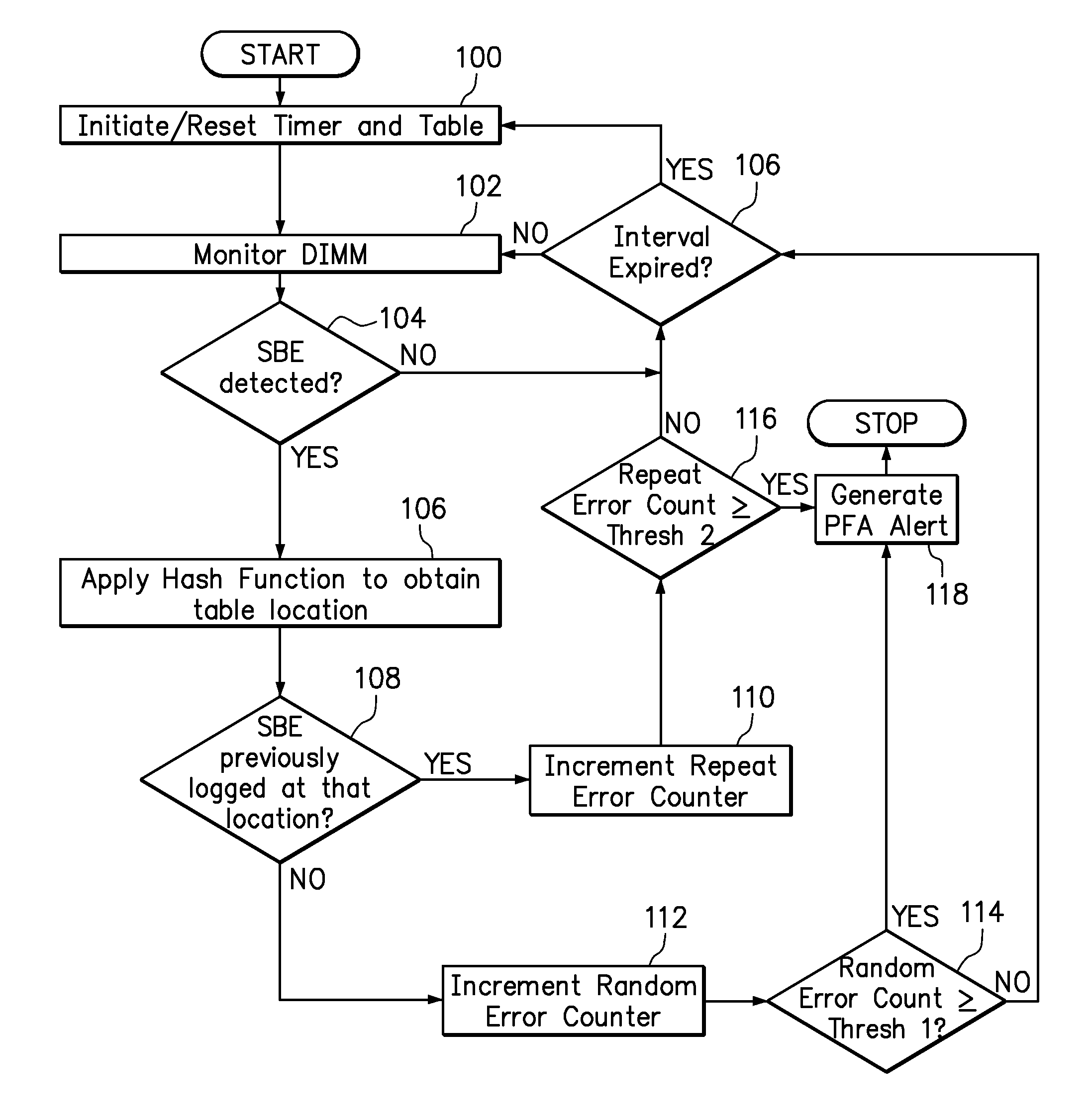
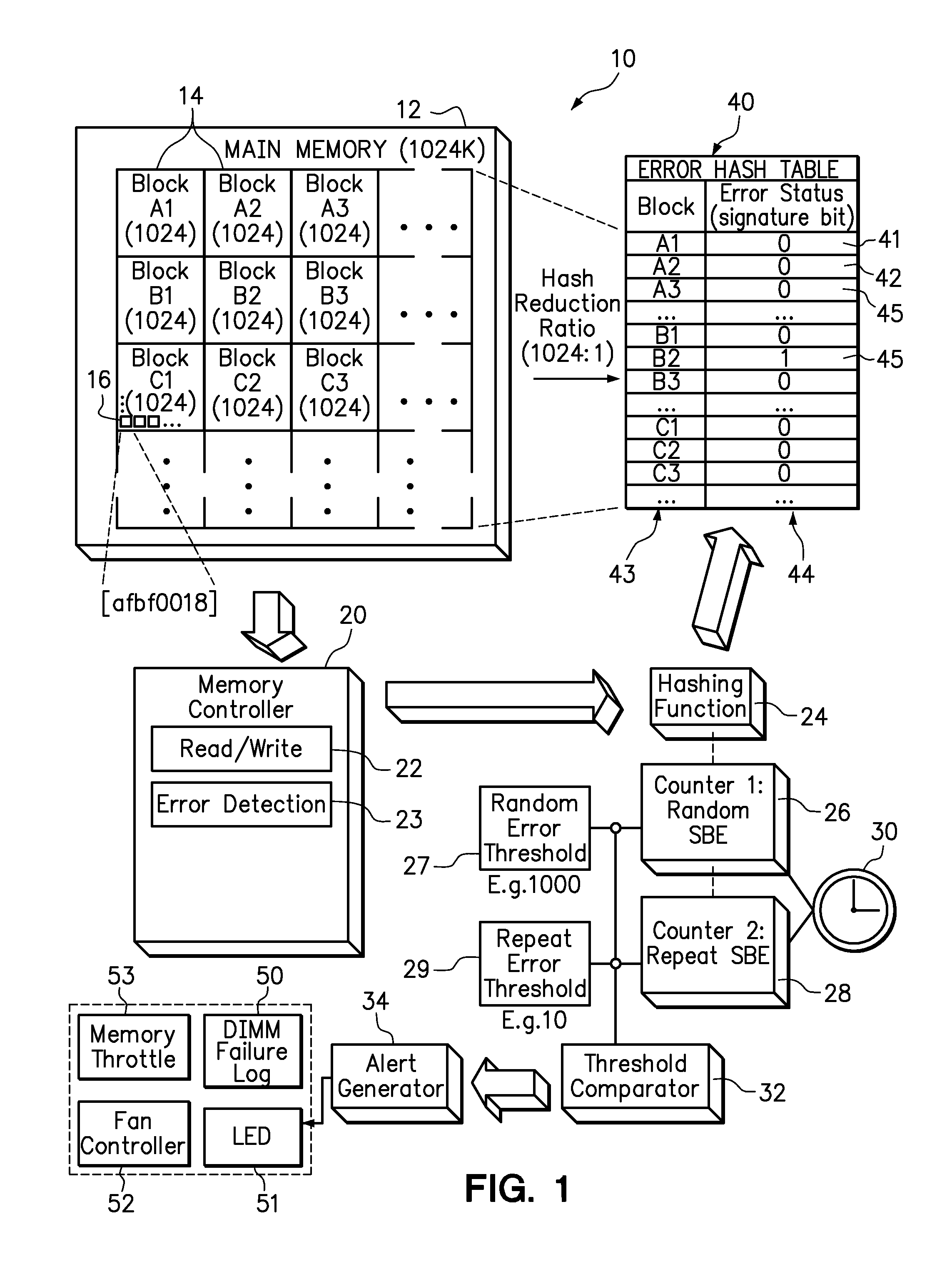
One embodiment provides an error detection method wherein single-bit errors in a memory module are detected and identified as being a random error or a repeat error. Each identified random error and each identified repeat error occurring in a time interval is counted. An alert is generated in response to a number of identified random errors reaching a random-error threshold or a number of identified repeat errors reaching a repeat-error threshold during the predefined interval. The repeat-error threshold is set lower than the random-error threshold. A hashing process may be applied to the memory address of each detected error to map the location of the error in the memory system to a corresponding location in an electronic table.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
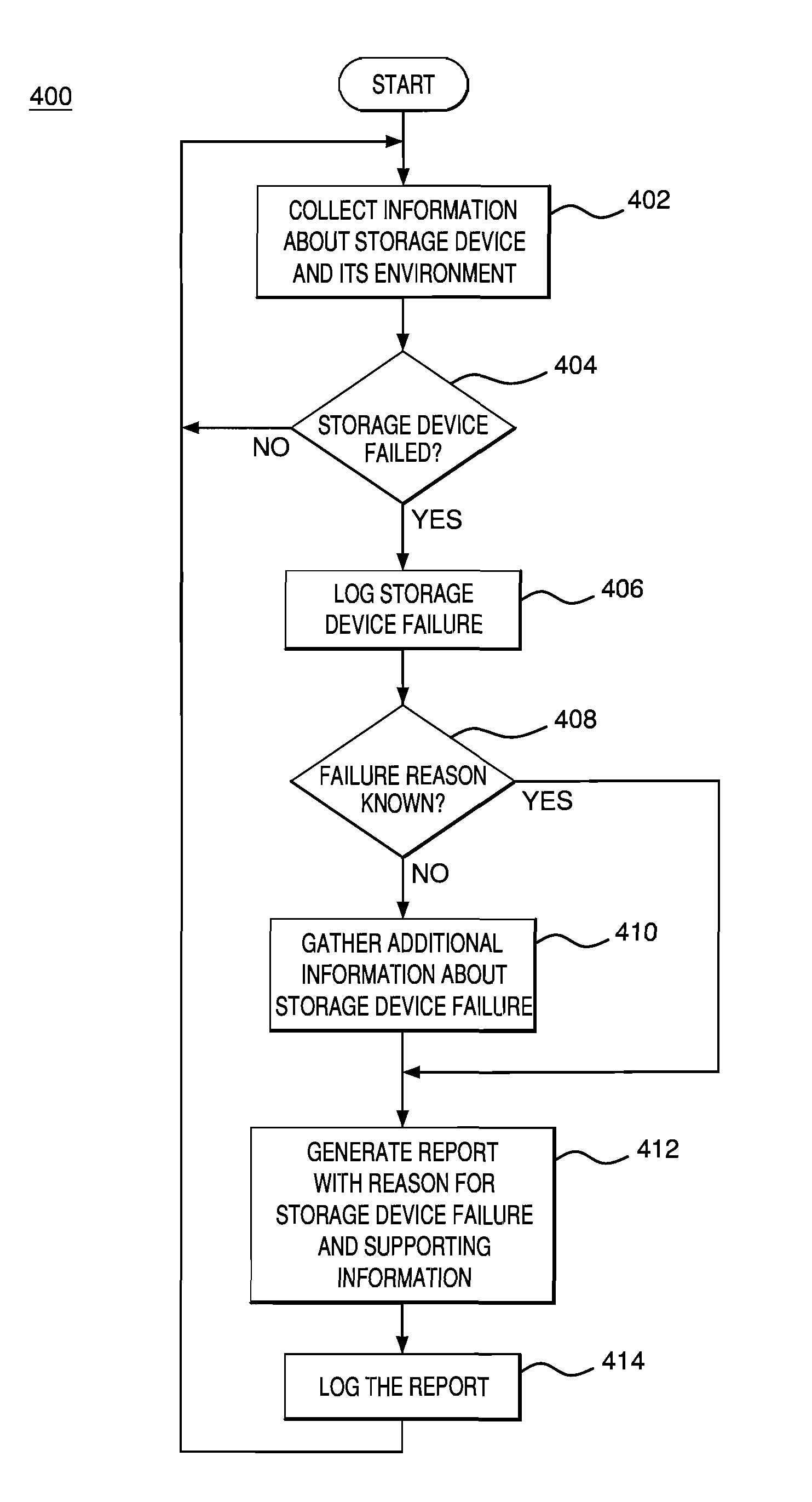
Creating environmental snapshots of storage device failure events
InactiveUS8949863B1Interprogram communicationNon-redundant fault processingRelevant informationDevice failure
A storage device failure in a computer storage system can be analyzed by the storage system by examining relevant information about the storage device and its environment. Information about the storage device is collected in real-time and stored; this is an on-going process such that some information is continuously available. The information can include information relating to the storage device, such as input / output related information, and information relating to a storage shelf where the storage device is located, such as a status of adjacent storage devices on the shelf. All of the relevant information is analyzed to determine a reason for the storage device failure. Optionally, additional information may be collected and analyzed by the storage system to help determine the reason for the storage device failure. The analysis and supporting information can be stored in a log and / or presented to a storage system administrator to view.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Emerging bad block detection
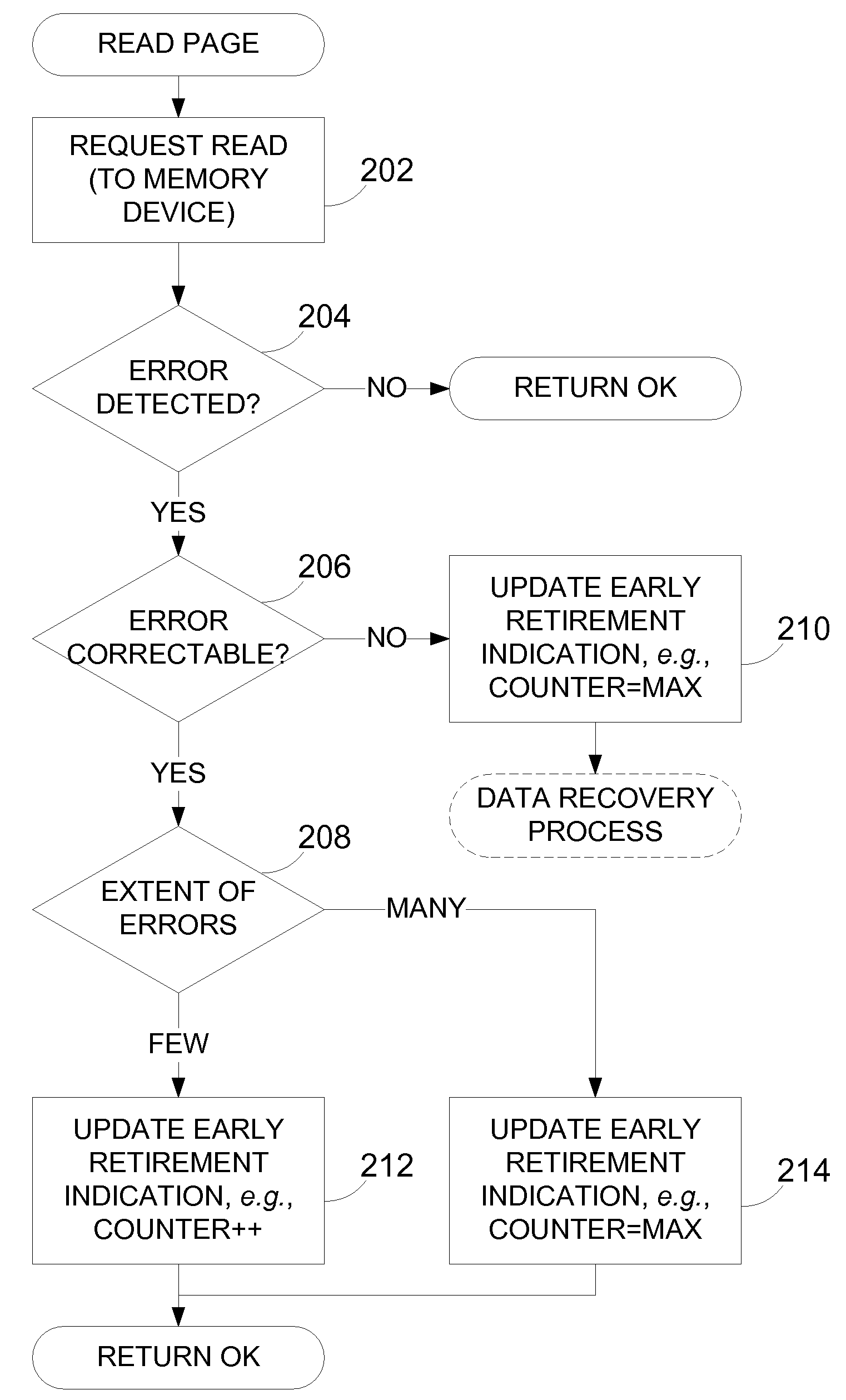
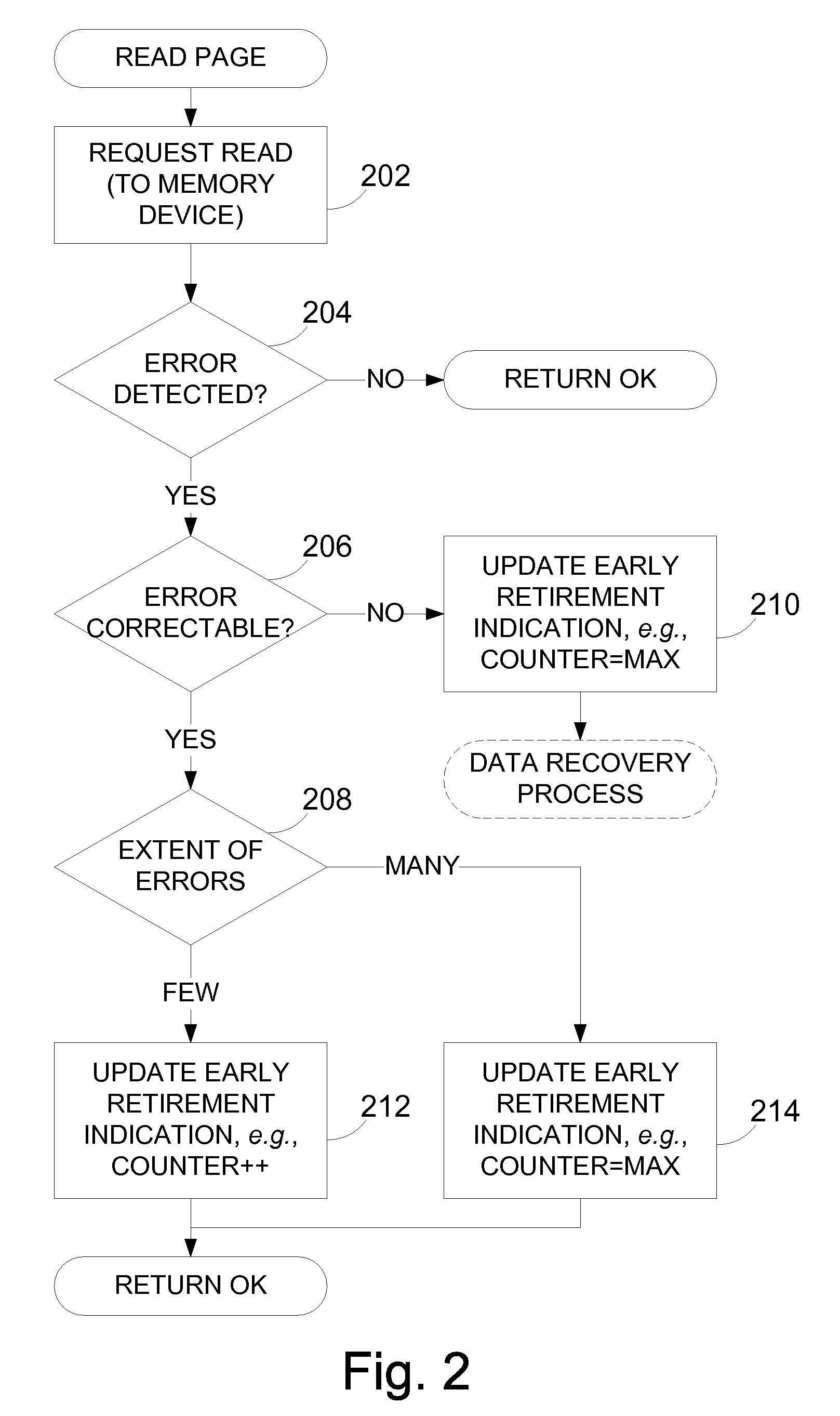
Apparatus and methods, such as those that read data from non-volatile integrated circuit memory devices, such as NAND flash. For example, disclosed techniques can be embodied in a device driver of an operating system. Errors are tracked during read operations. If sufficient errors are observed during read operations, the block is then retired when it is requested to be erased or a page of the block is to be written. One embodiment is a technique to recover data from uncorrectable errors. For example, a read mode can be changed to a more reliable read mode to attempt to recover data. One embodiment further returns data from the memory device regardless of whether the data was correctable by decoding of error correction code data or not.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Duration of alerts and scanning of large data stores
InactiveUS20070050777A1Multiprogramming arrangementsNon-redundant fault processingThermostatEmbodied agent
Described are techniques used in monitoring the performance, security and health of a system used in an industrial application. Agents included in the industrial network report data to an appliance or server. The appliance stores the data and determines when an alarm condition has occurred. Notifications are sent upon detecting an alarm condition. The alarm thresholds may be user defined. A threat thermostat controller determines a threat level used to control the connectivity of a network used in the industrial application.
Owner:IND DEFENDER
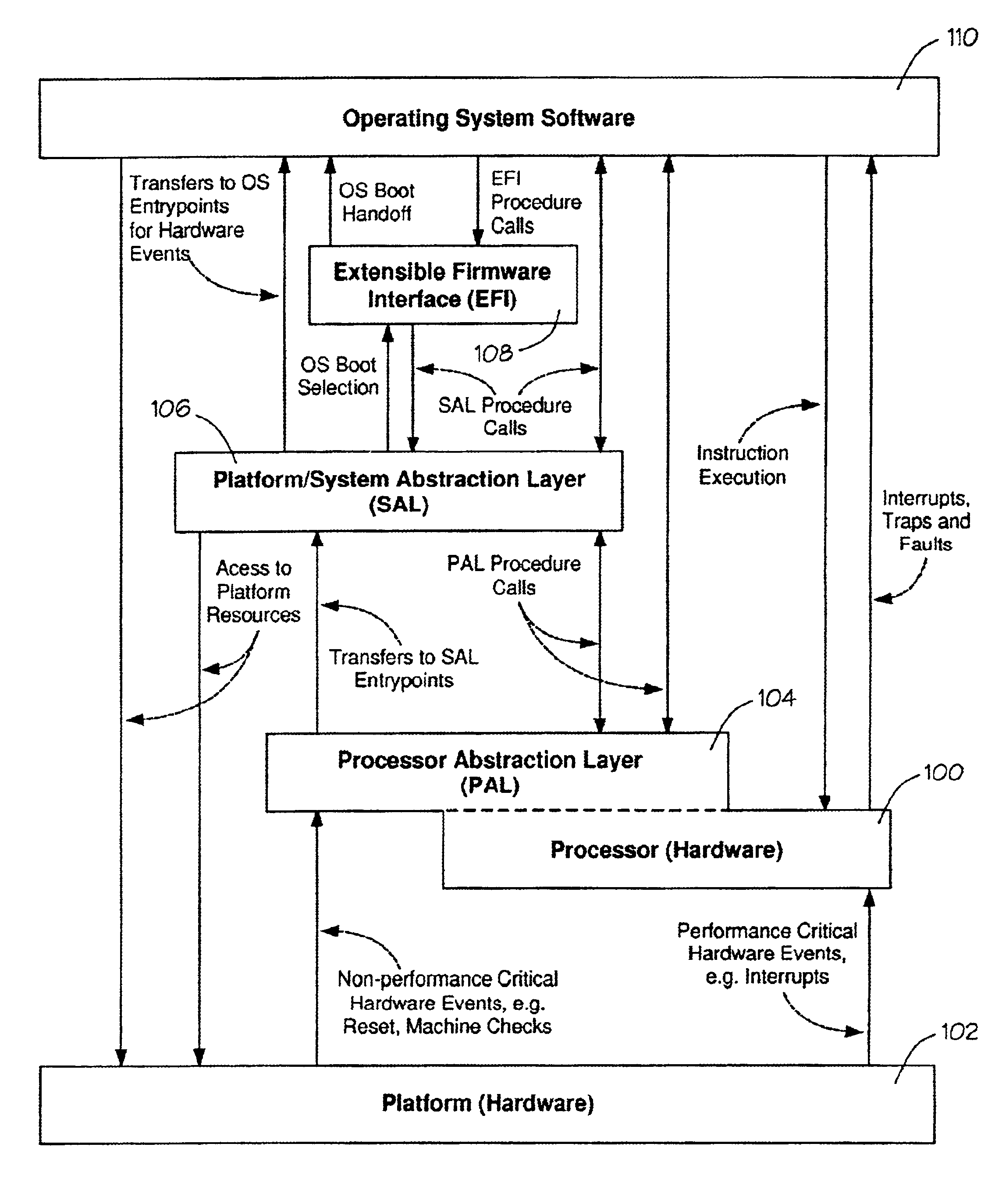
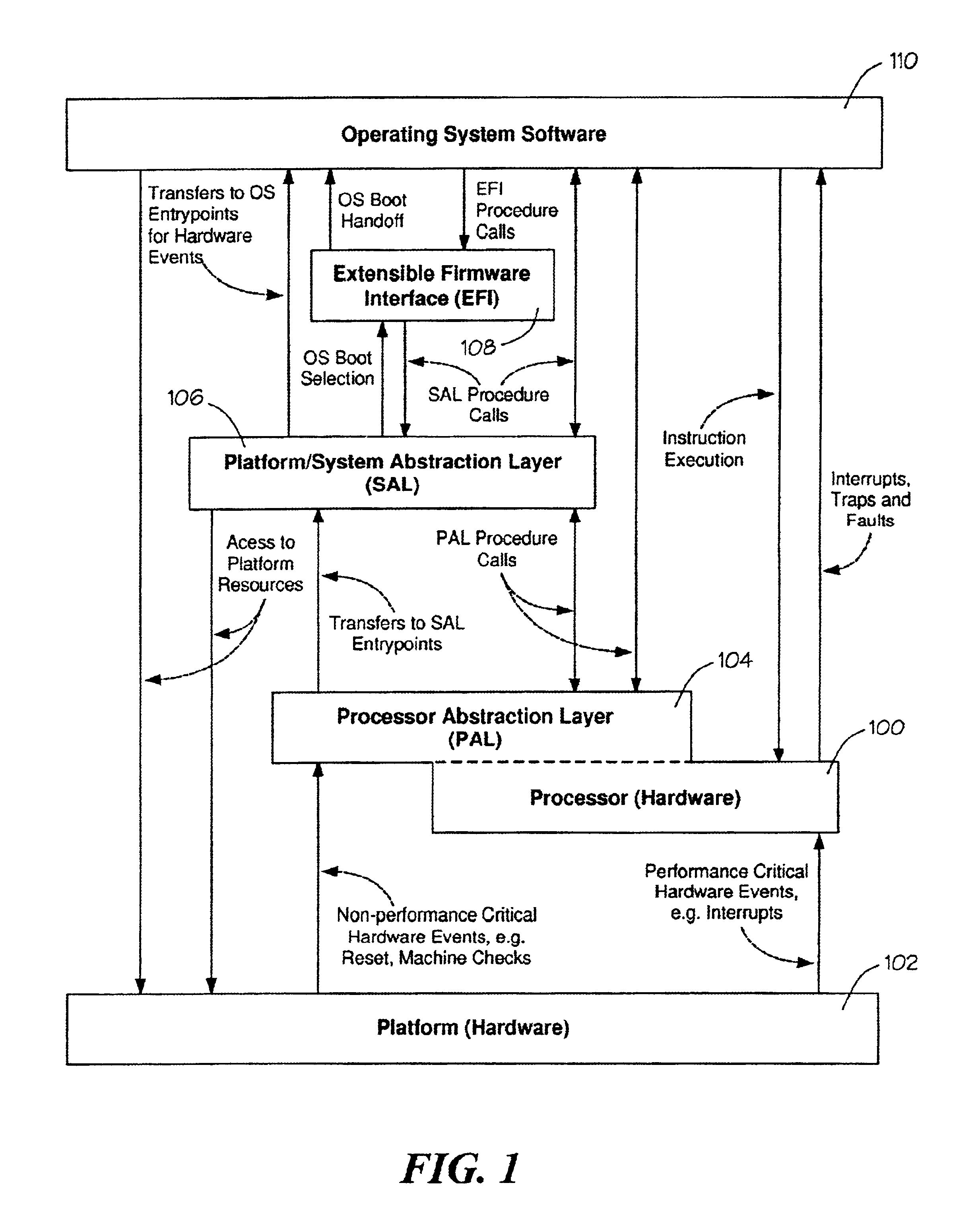
Method of correcting a machine check error
Processor implementation-specific instructions save a processor state in a system memory and attempt to correct the error. Control is then transferred to processor-independent instructions. Control is returned to the processor implementation-specific instructions which then return to an interrupted context of the processor by restoring the processor state.
Owner:INTEL CORP
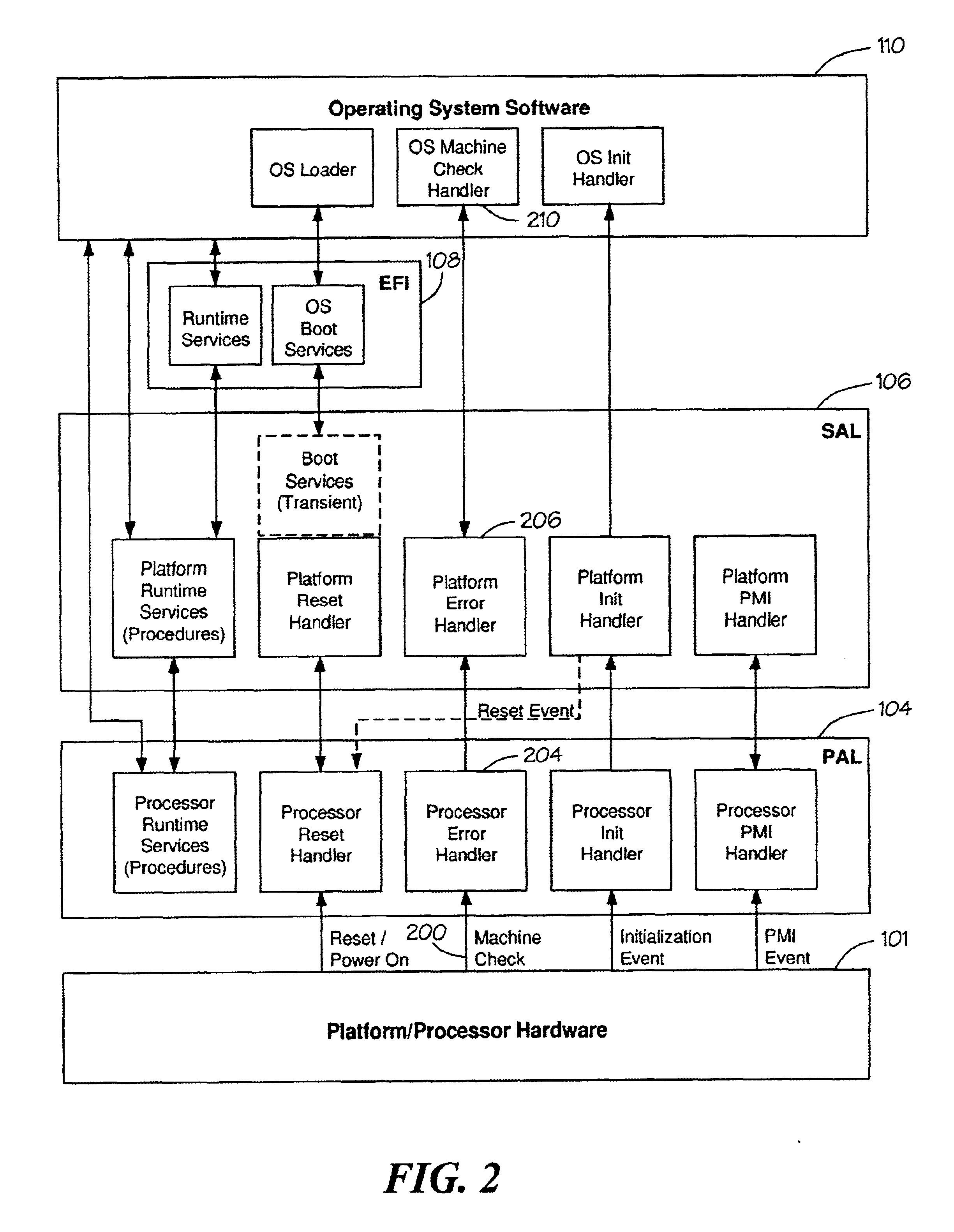
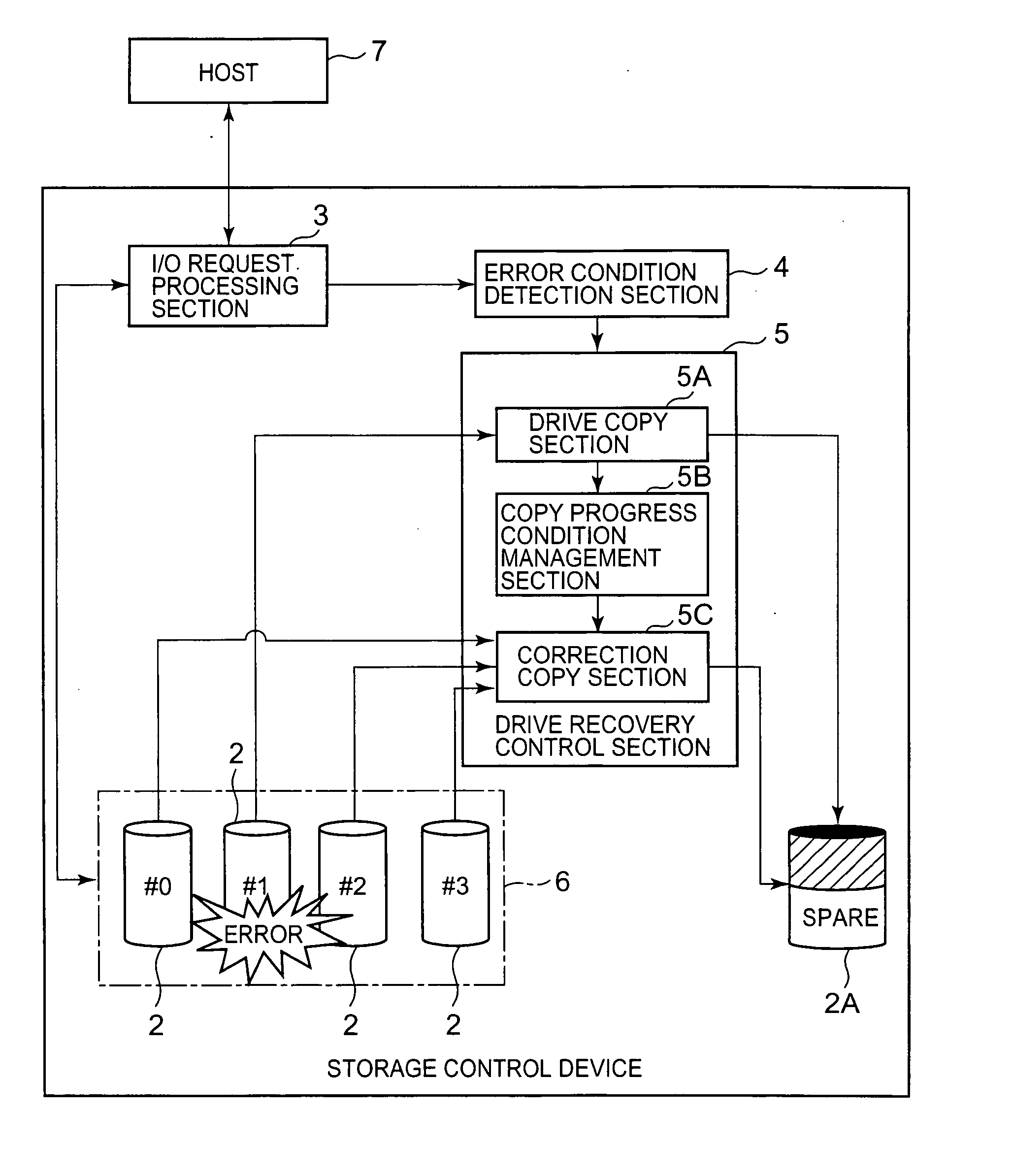
Storage control device and data recovery method for storage control device
The present invention efficiently recovers an error drive by suppressing futile copying. When the number of errors of the disk drive is equal to or more than a first threshold, data stored in the disk drive is copied to a spare drive by a drive copy section. When the number of errors of the disk drive is equal to or more than a second threshold prior to completion of the drive copy, the disk drive is closed, and a correction copy by a correction copy section is started in place of the drive copy. The correction copy section starts the correction copy from the position where the drive copy is interrupted by taking over the drive copy completion position (copy interrupt position) managed by a copy progress condition management section.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
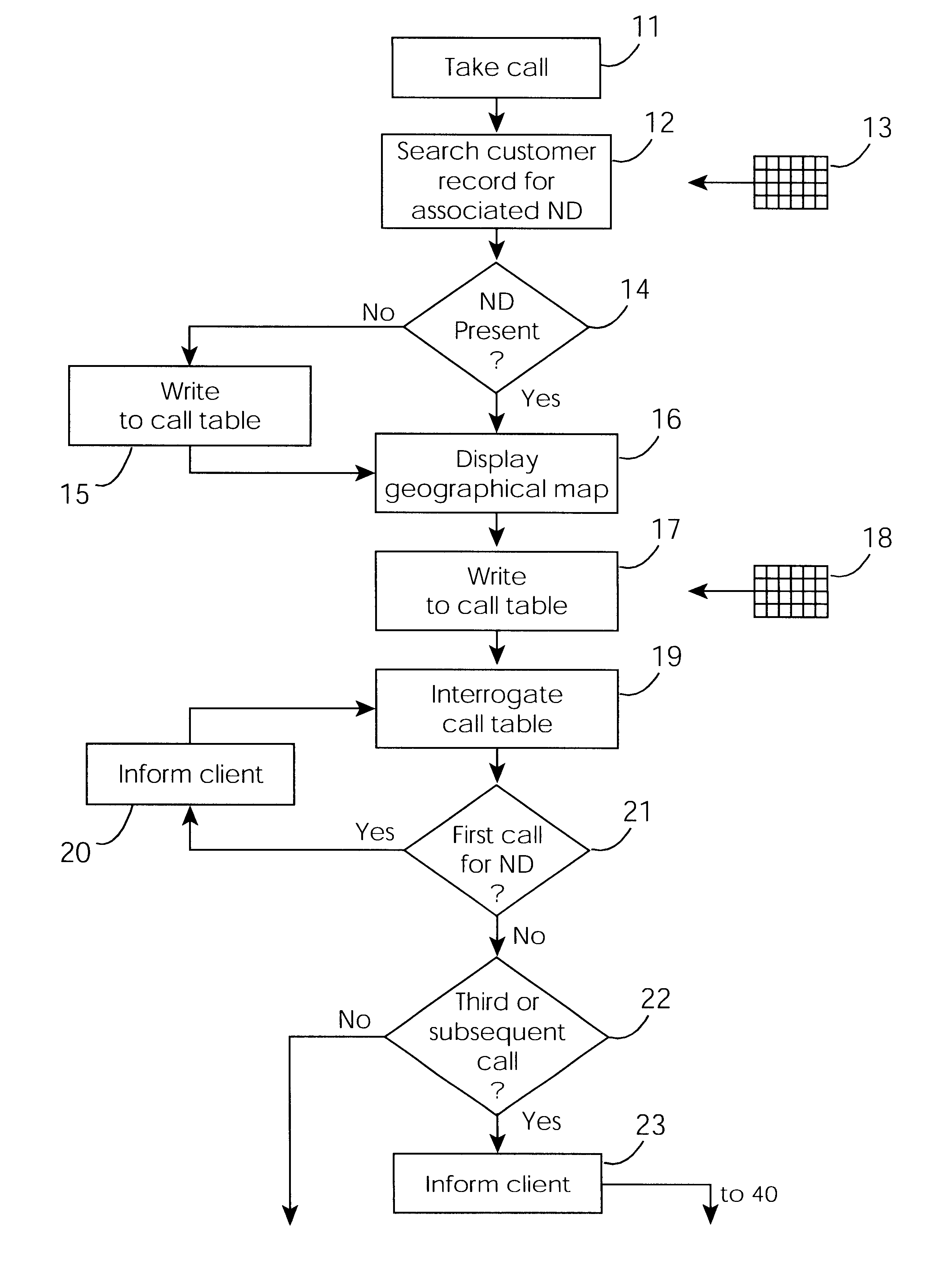
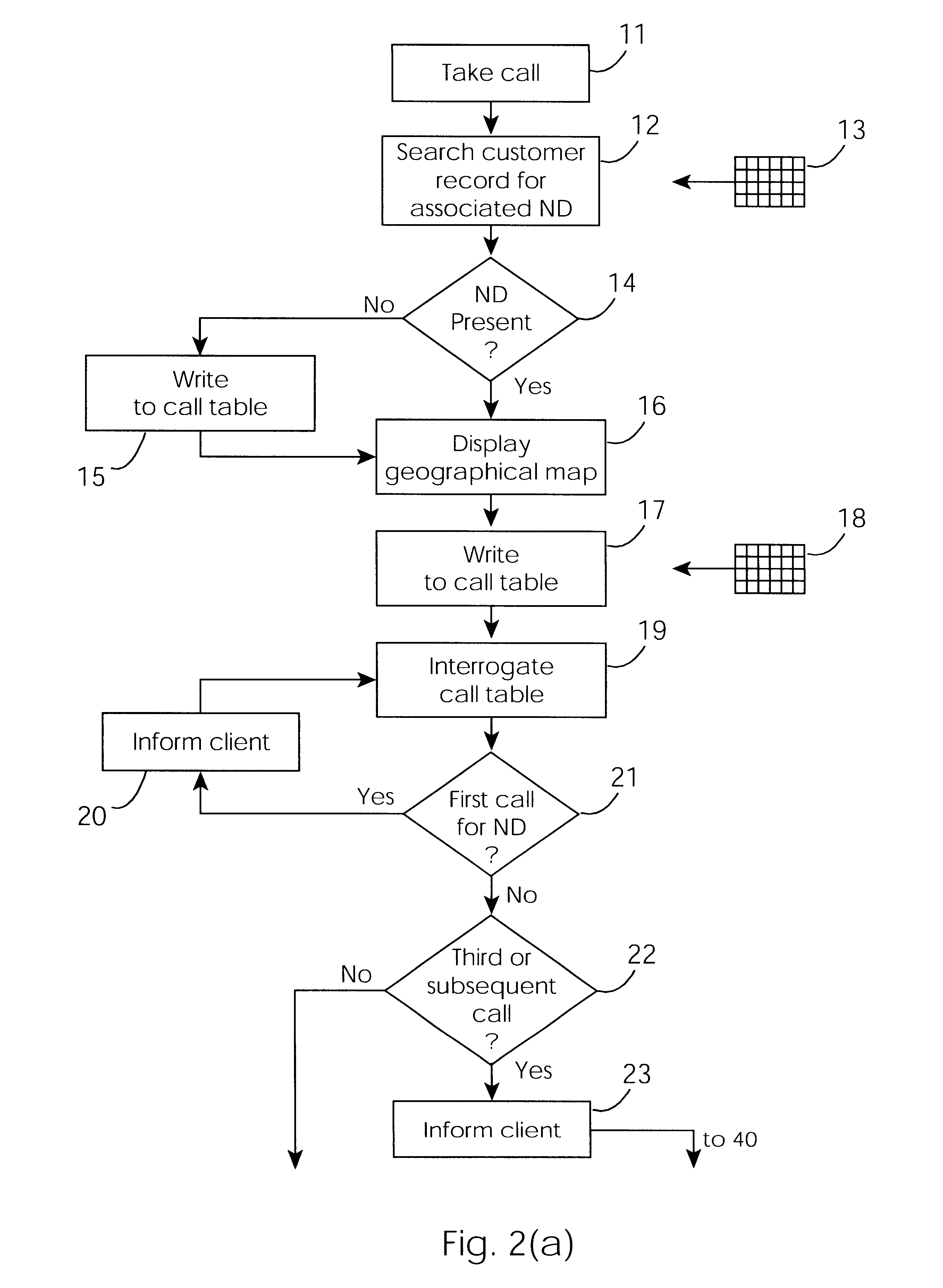
Cable network repair control system
InactiveUS6671824B1Shorten the timeSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentControl systemEngineering
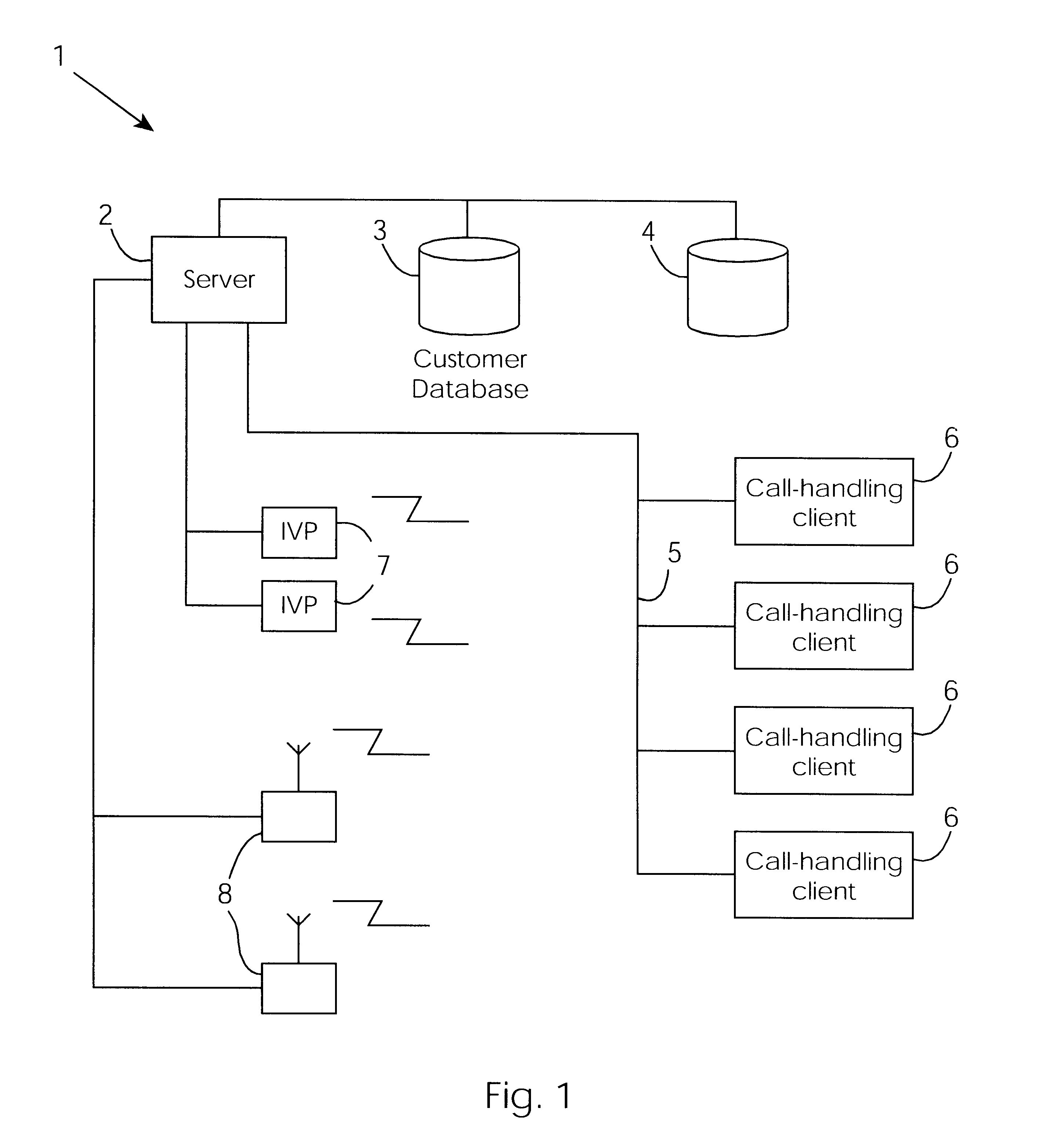
A cable network repair control system including a server communicating with multiple call-handling clients in a trouble call center. The databases are used to automatically determine an associated network device for the customer who makes a trouble call. When a second call is received for a particular network device, an inferencing engine automatically operates to identify potential repairs crews and to control communication with them to ensure that optimum use of the repair crew time and quick repair. Various tables are generated dynamically and are used to update management status tables for reviewing of network repair status.
Owner:LAKEFIELD ETECH GROUP
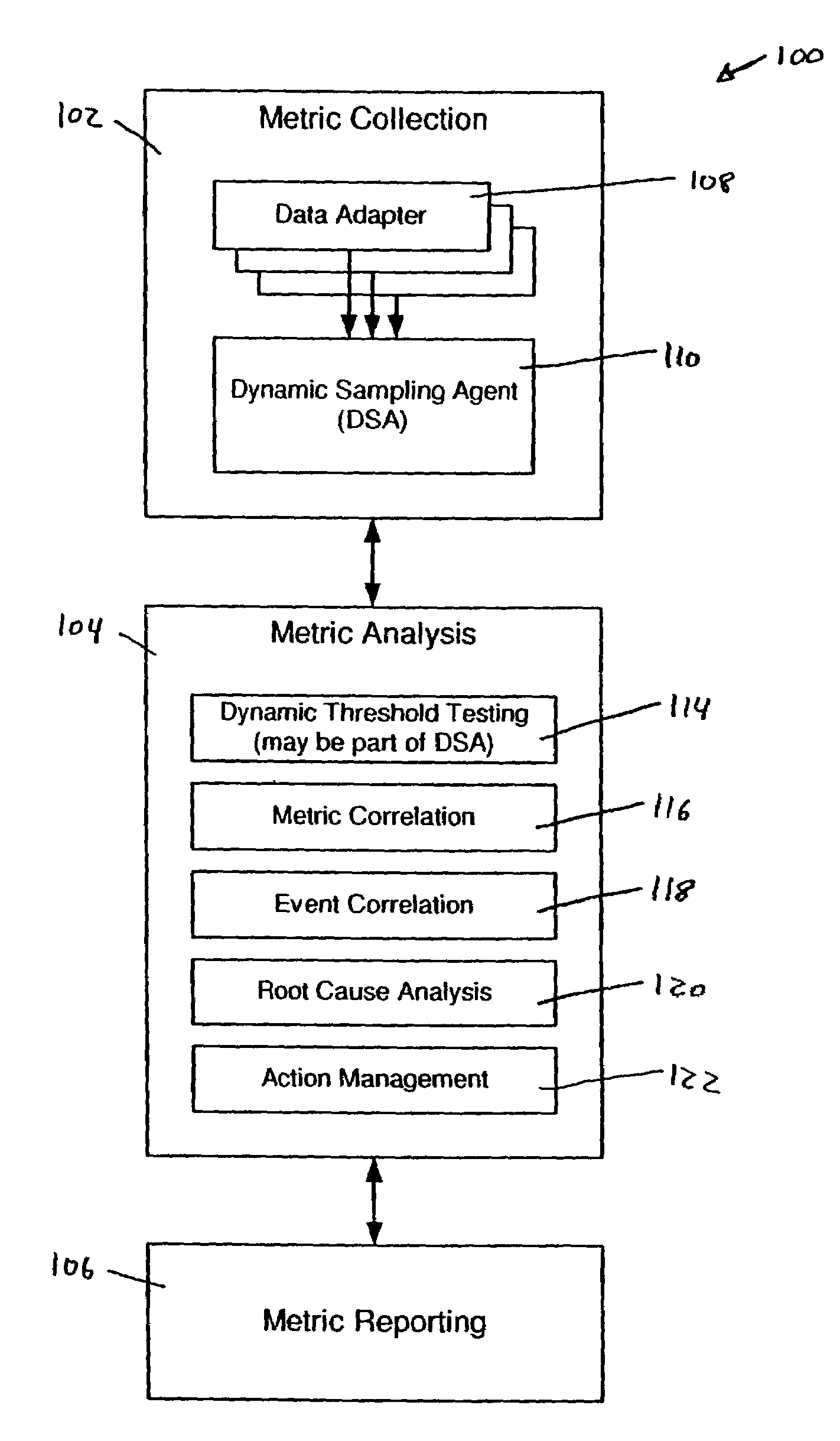
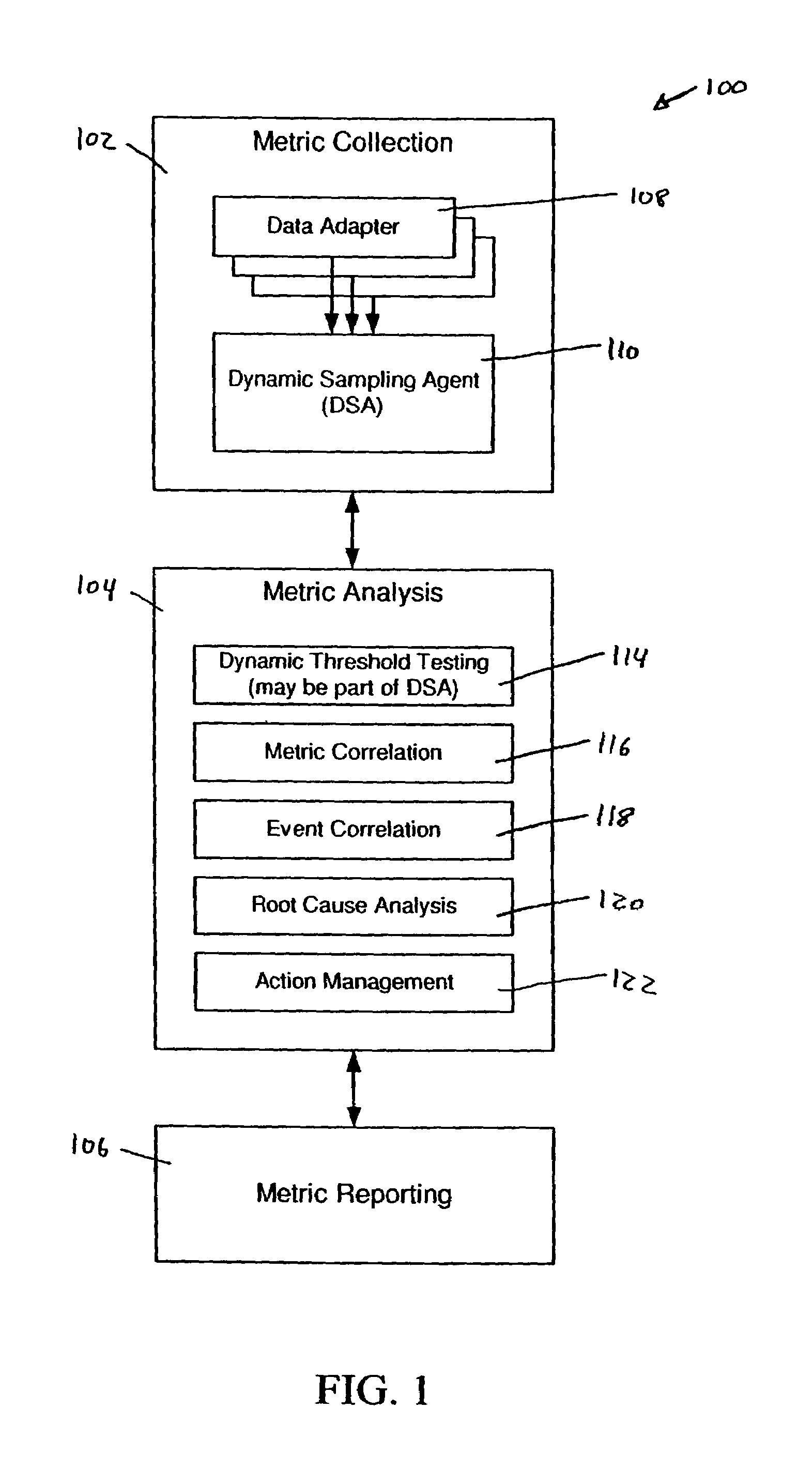
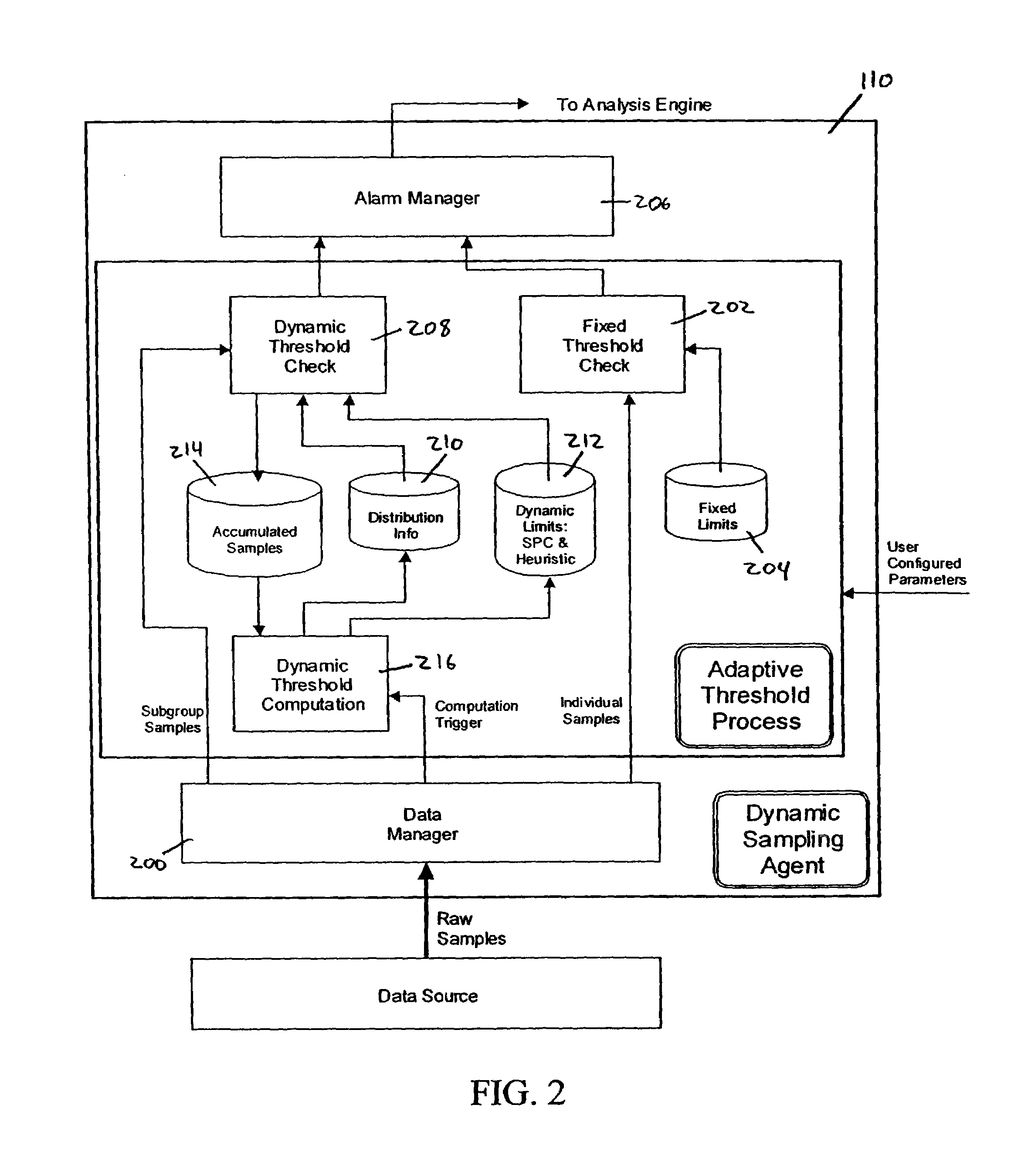
System and methods for adaptive threshold determination for performance metrics
A system and method for dynamically generating alarm thresholds for performance metrics, and for applying those thresholds to generate alarms is described. Statistical methods are used to generate one or more thresholds for metrics that may not fit a Gaussian or normal distribution, or that may exhibit cyclic behavior or persistent shifts in the values of the metrics. The statistical methods used to generate the thresholds may include statistical process control (SPC) methods, normalization methods, and heuristics.
Owner:ATERNITY LLC
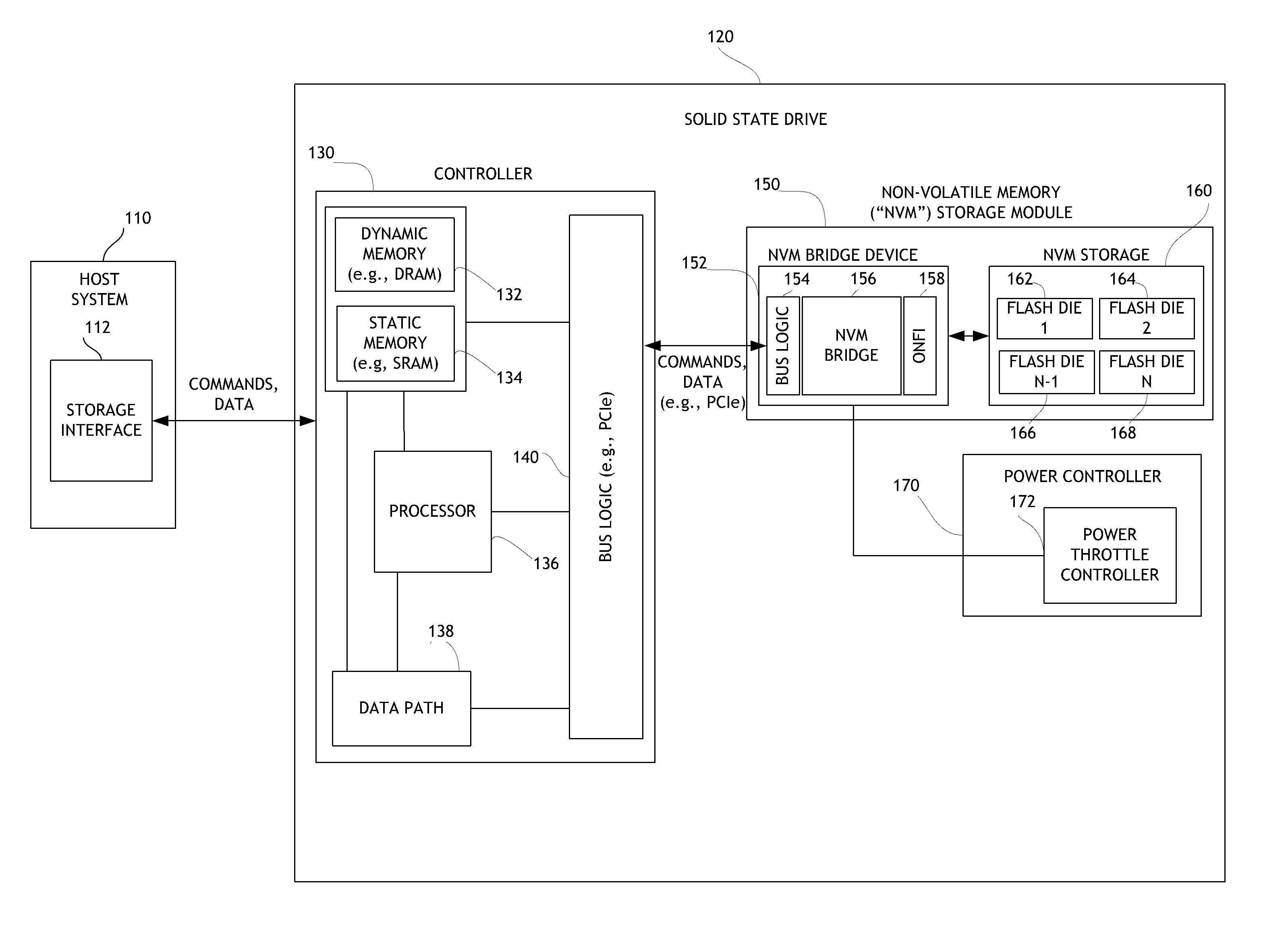
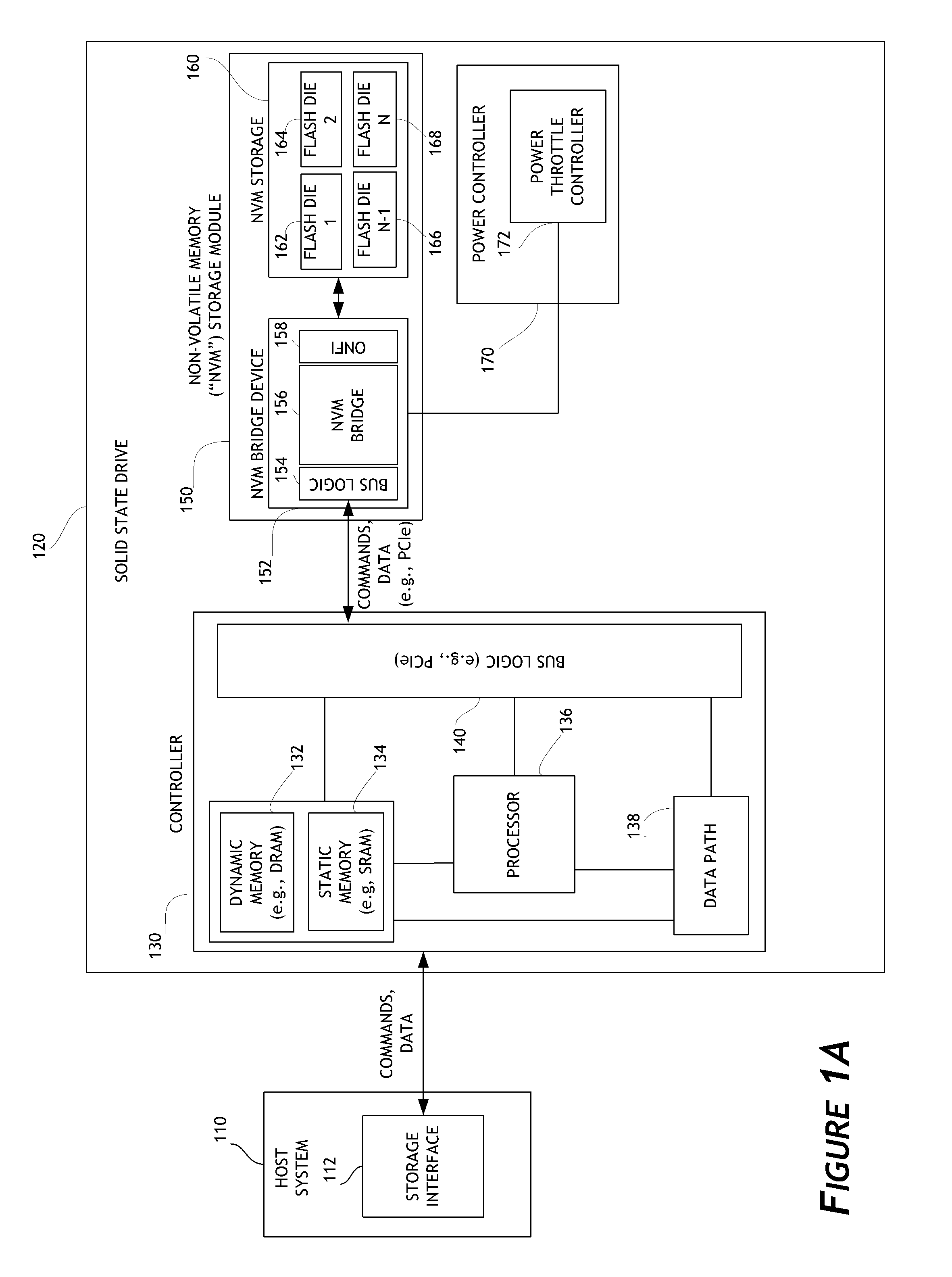
Systems and methods for error injection in data storage systems
ActiveUS8707104B1Solving precise measurementsTested and reliableDetecting faulty computer hardwareRead-only memoriesSolid-state storageHybrid storage system
Embodiments of the solid-state storage system provided herein are configured to perform improved mechanisms for testing of error recovery of solid state storage devices. In some embodiments, the system is configured to introduce or inject errors into data storage commands or operations performed in the non-volatile memory. Injected errors include corruption of data stored in the non-volatile memory, deliberate failure to execute storage operations, and errors injected into communication protocols used between various elements of the device. In some embodiments, injected errors can include direct errors that trigger an immediate execution of error recovery mechanisms and delayed errors that trigger execution of error recovery mechanisms at a later time. Error recovery mechanisms can be tested in an efficient, reliable, and deterministic manner to help ensure effective operation of storage devices. The integrity of non-volatile memory can also be tested.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
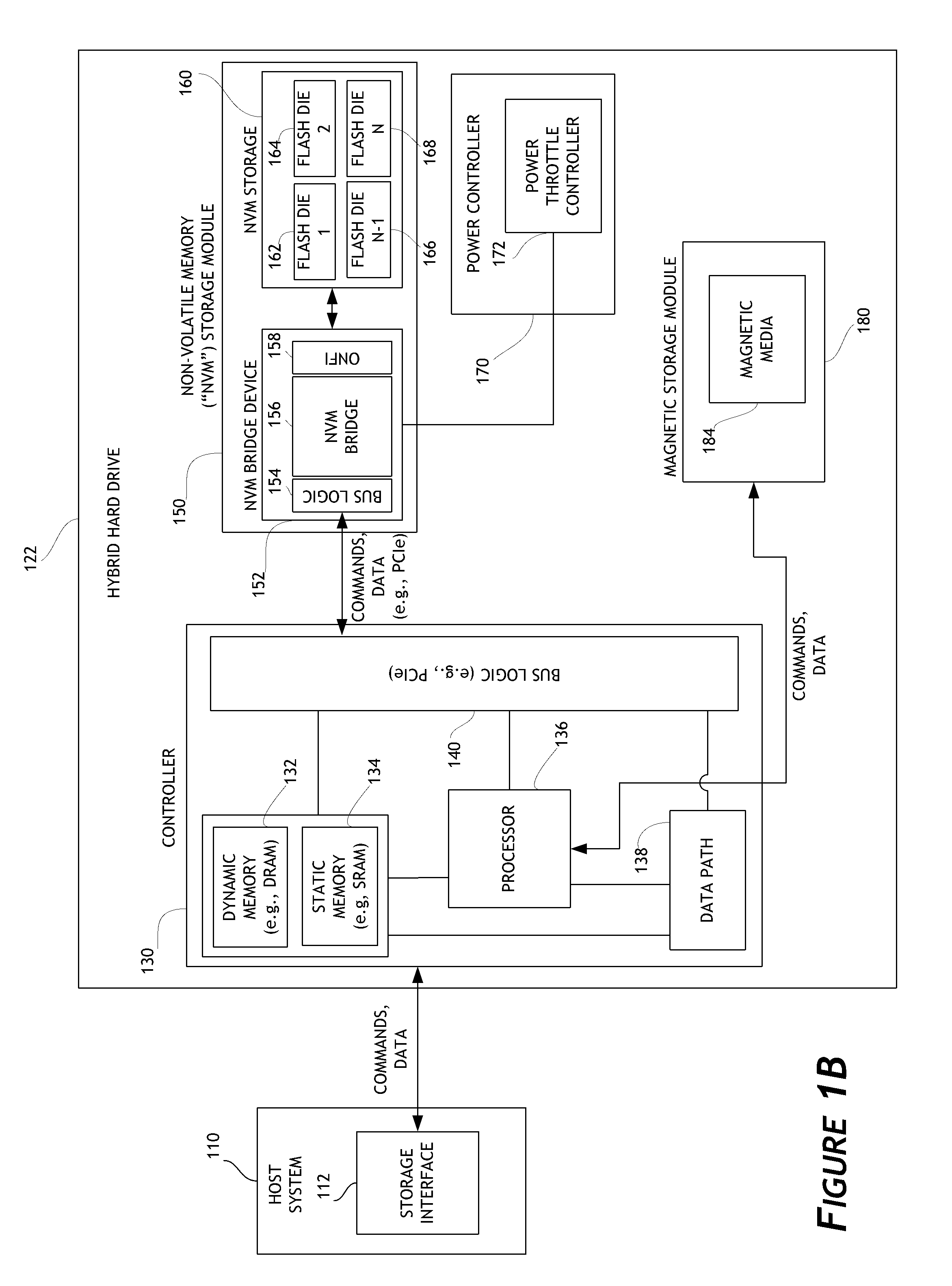
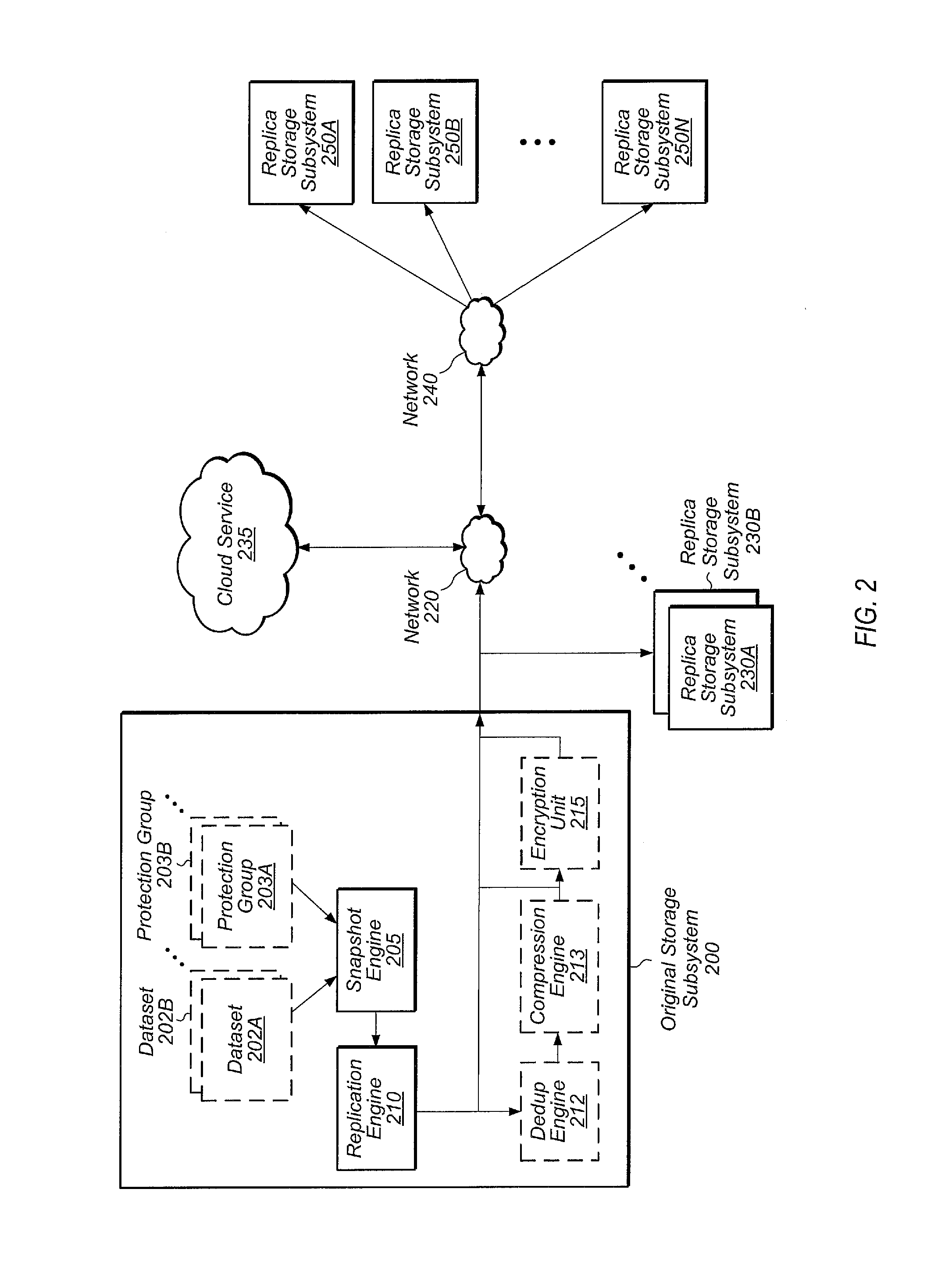
Cloud alert to replica
InactiveUS9552248B2Non-redundant fault processingRedundant operation error correctionComputer hardwareData set
Systems, methods, and computer readable storage mediums for generating an alert on a failure of a storage subsystem to phone home to the cloud in a replication environment. A dataset is replicated from a first storage subsystem to a second storage subsystem. The first and second storage subsystems also phone home log data to the cloud on a periodic basis. In response to detecting a failure of the first storage subsystem to phone home, the cloud generates and sends an alert to the second storage subsystem. In response to receiving this alert, the second storage subsystem starts disaster recovery operations for the dataset.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
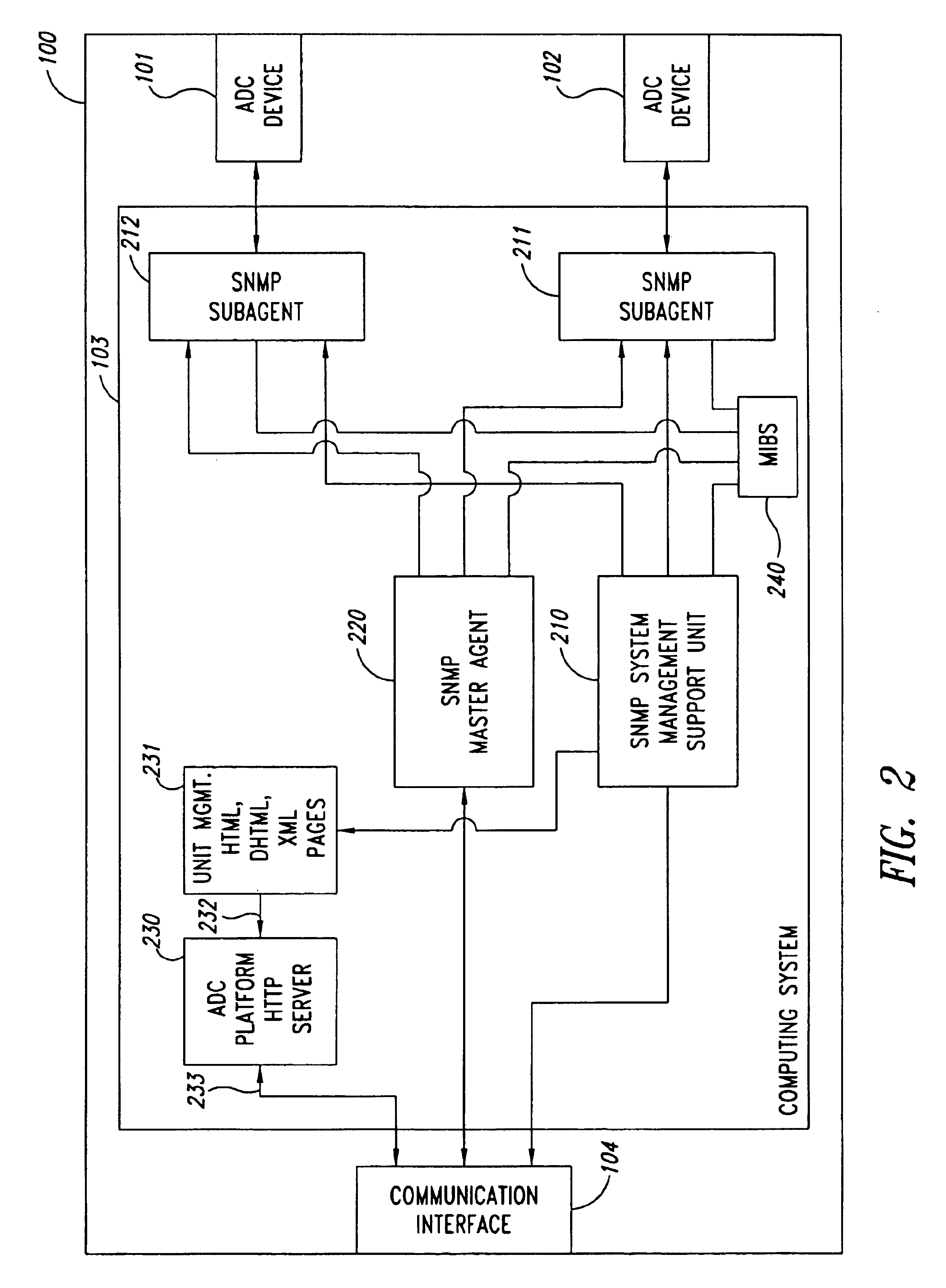
Remote anomaly diagnosis and reconfiguration of an automatic data collection device platform over a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6857013B2Detecting faulty hardware by remote testDigital computer detailsTelecommunications linkExtensible markup
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
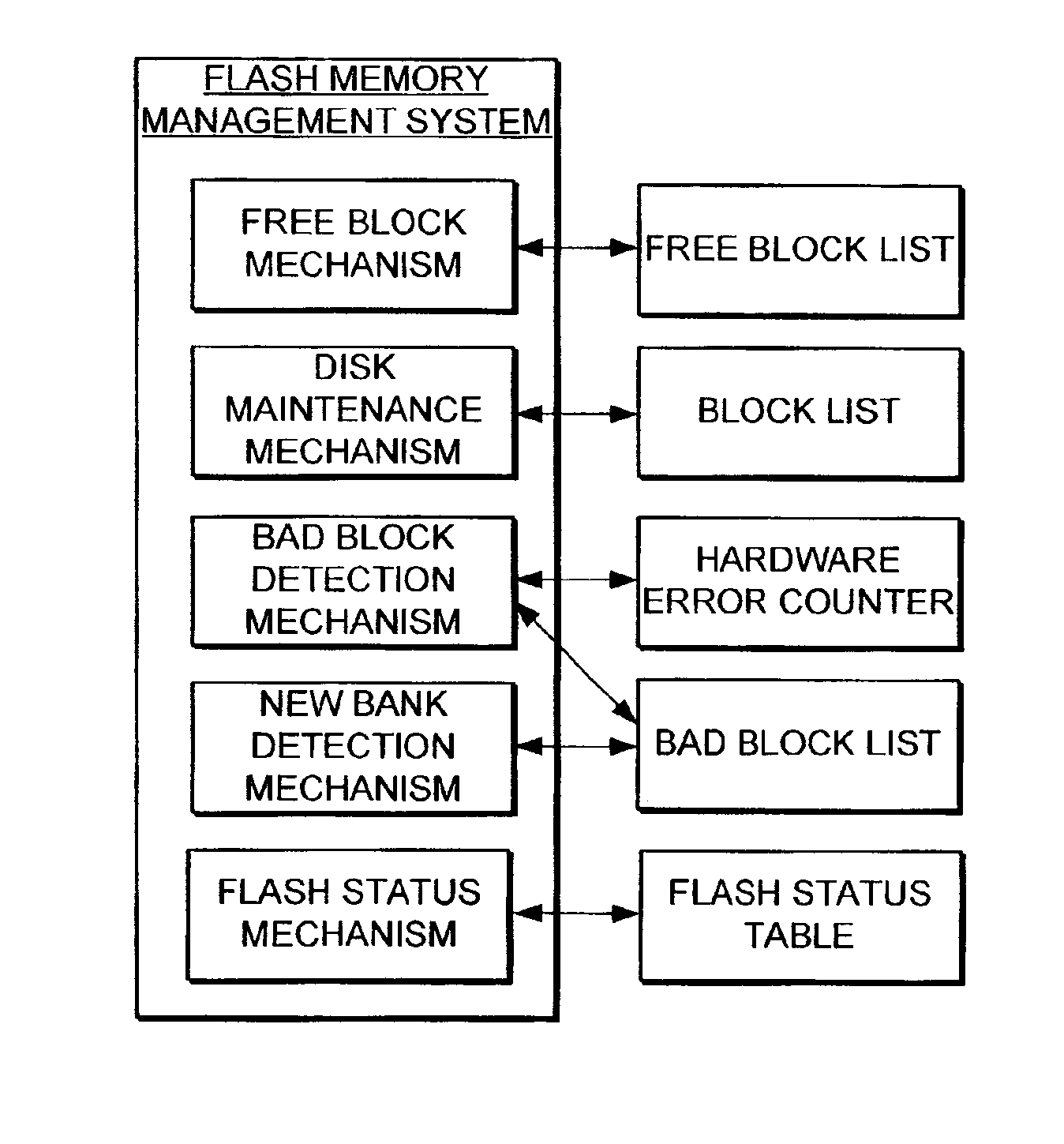
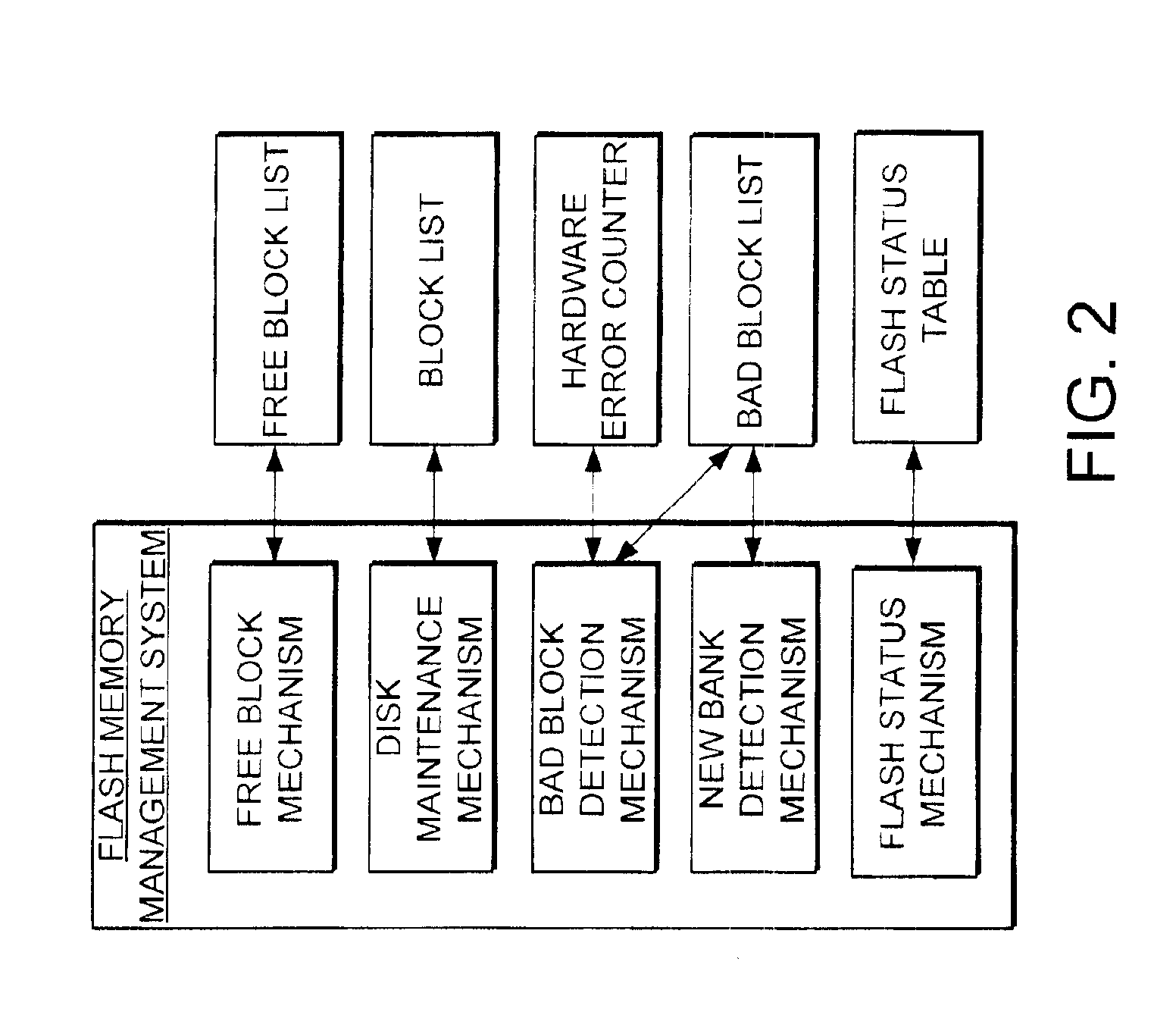
Flash memory management system and method utilizing multiple block list windows
InactiveUS6895464B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilityInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionRapid accessBlock detection
The present invention provides a flash memory management system and method with increased performance. The flash memory management system provides the ability to efficiently manage and allocate flash memory use in a way that improves reliability and longevity, while maintaining good performance levels. The flash memory management system includes a free block mechanism, a disk maintenance mechanism, and a bad block detection mechanism. The free block mechanism provides efficient sorting of free blocks to facilitate selecting low use blocks for writing. The disk maintenance mechanism provides for the ability to efficiently clean flash memory blocks during processor idle times. The bad block detection mechanism provides the ability to better detect when a block of flash memory is likely to go bad. The flash status mechanism stores information in fast access memory that describes the content and status of the data in the flash disk. The new bank detection mechanism provides the ability to automatically detect when new banks of flash memory are added to the system. Together, these mechanisms provide a flash memory management system that can improve the operational efficiency of systems that utilize flash memory.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
Web controls validation
InactiveUS6915454B1Receipt is inhibitedNon-redundant fault processingSpecific program execution arrangementsError processingFile comparison
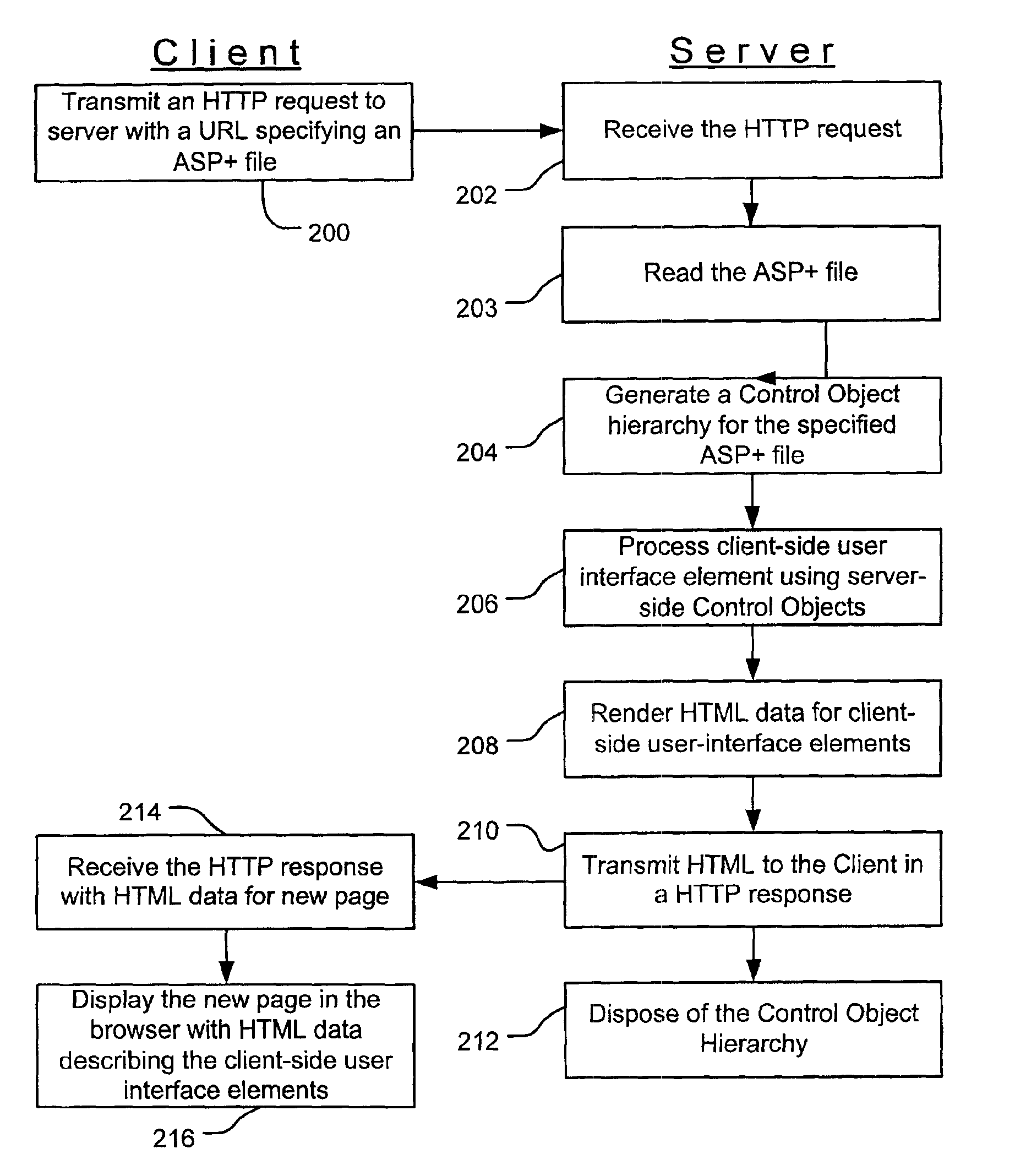
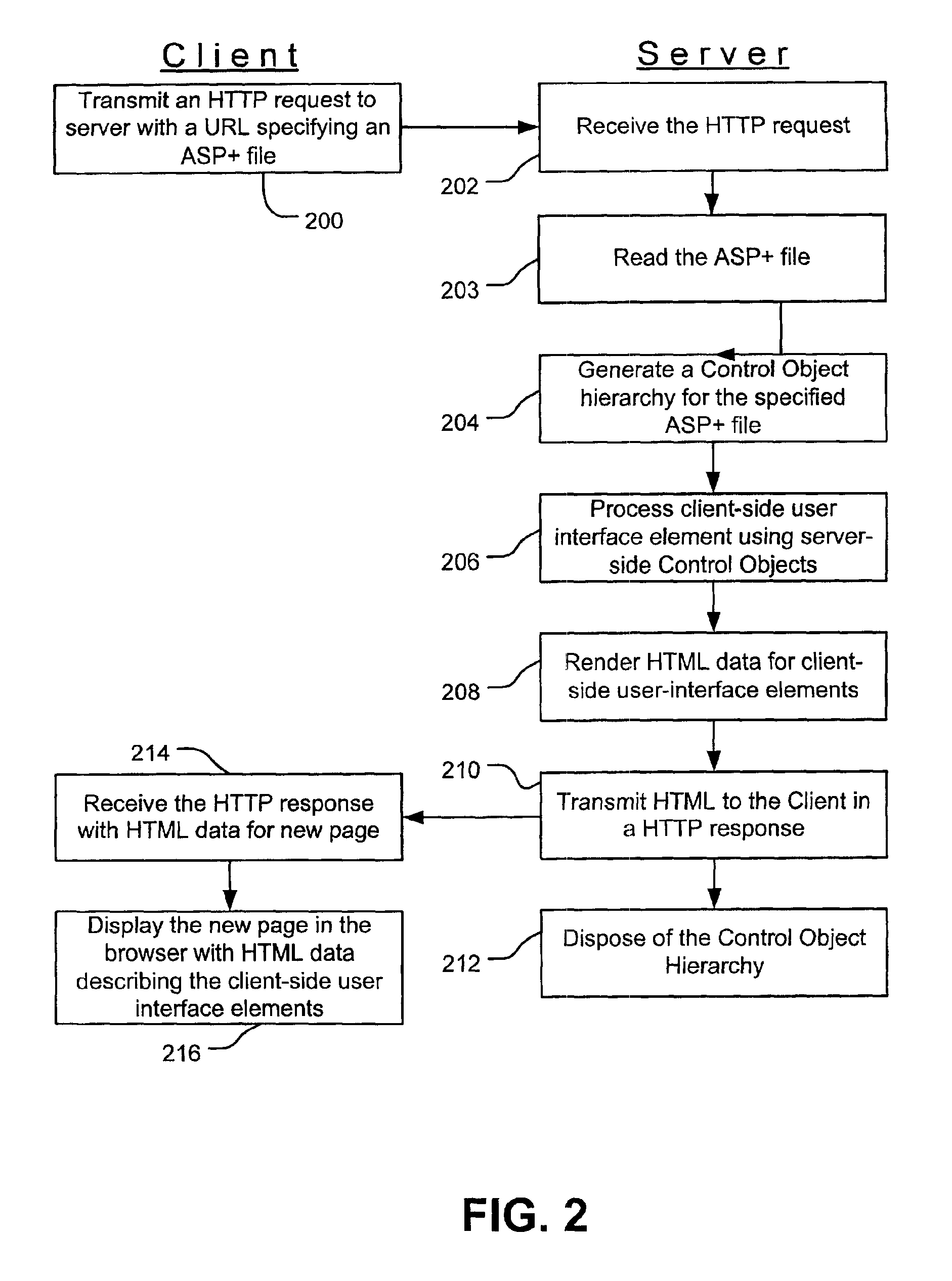
Web control validation may be defined using one or more declarations that are included in an ASP+ file by the web page author. The declarations specify server-side objects that validate the input data received in the web page and provide error handling in the event of a validation failure error. Validation declaration parameters specify the validation criteria against which the input data is validated. Example validation operations involve regular expressions, required fields, data comparison, range comparison and custom validation. Validation parameters can also specify- either server-side validation or client-side validation, depending on the client browser's capabilities. In a server-side scenario, a server-side validation object processes the input data received in an HTTP request from the client. In a client-side scenario, a server-side validation object renders the appropriate client-side code to validate the input data without a round trip between the client and the server.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Failover processing in a storage system
InactiveUS20060117212A1Improve usabilityInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsFault toleranceFailover
Failover processing in storage server system utilizes policies for managing fault tolerance (FT) and high availability (HA) configurations. The approach encapsulates the knowledge of failover recovery between components within a storage server and between storage server systems. This knowledge includes information about what components are participating in a Failover Set, how they are configured for failover, what is the Fail-Stop policy, and what are the steps to perform when “failing-over” a component.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
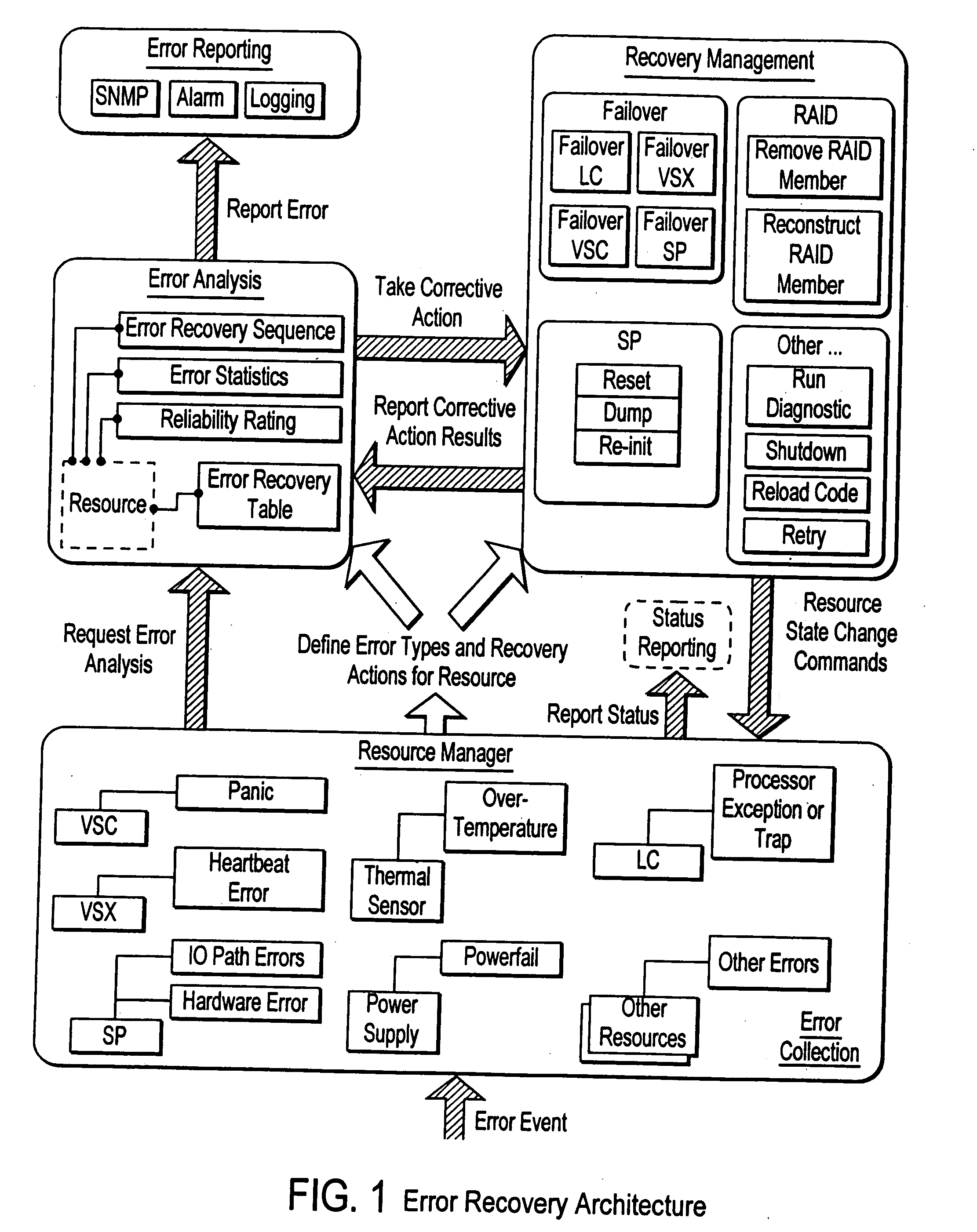
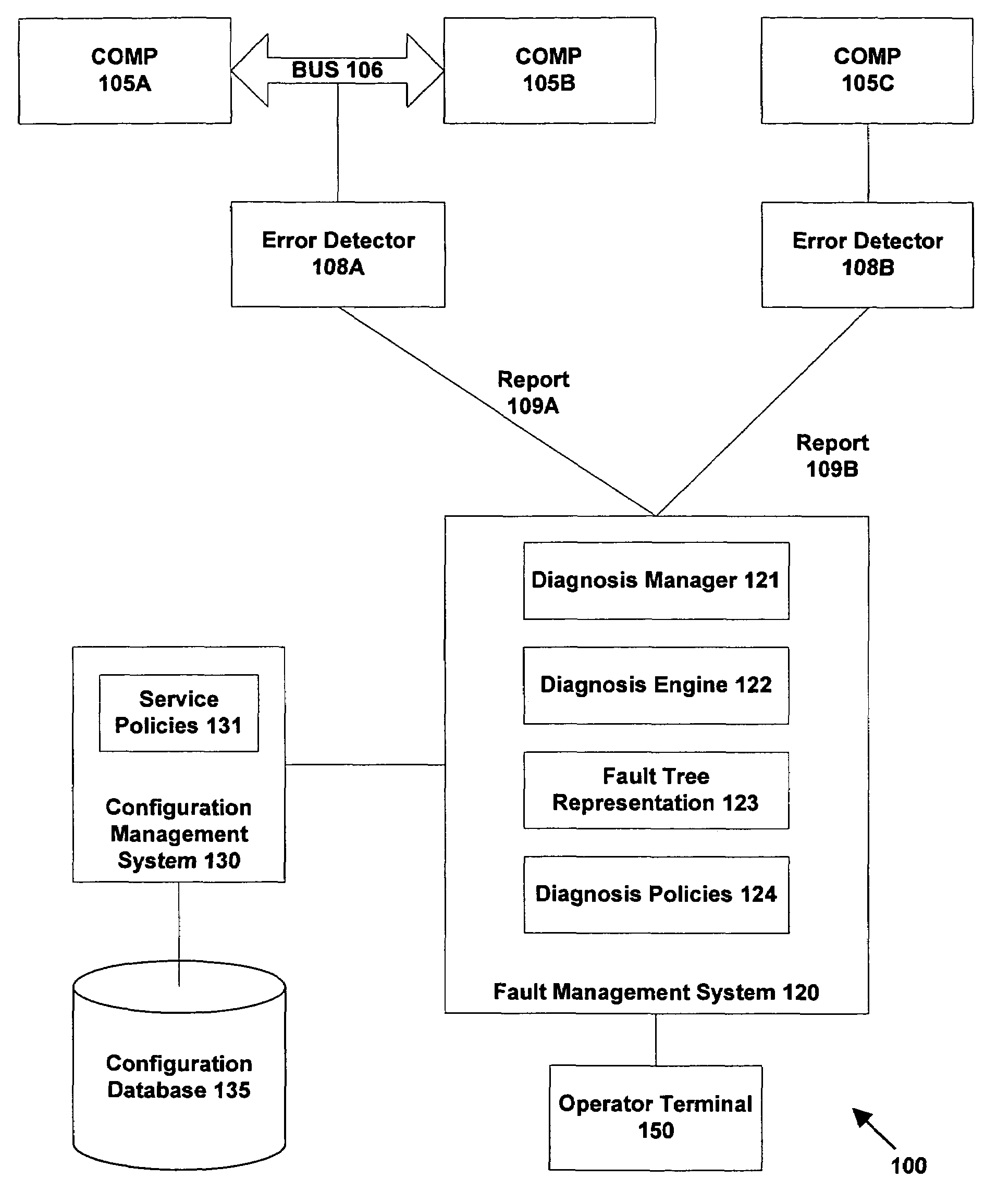
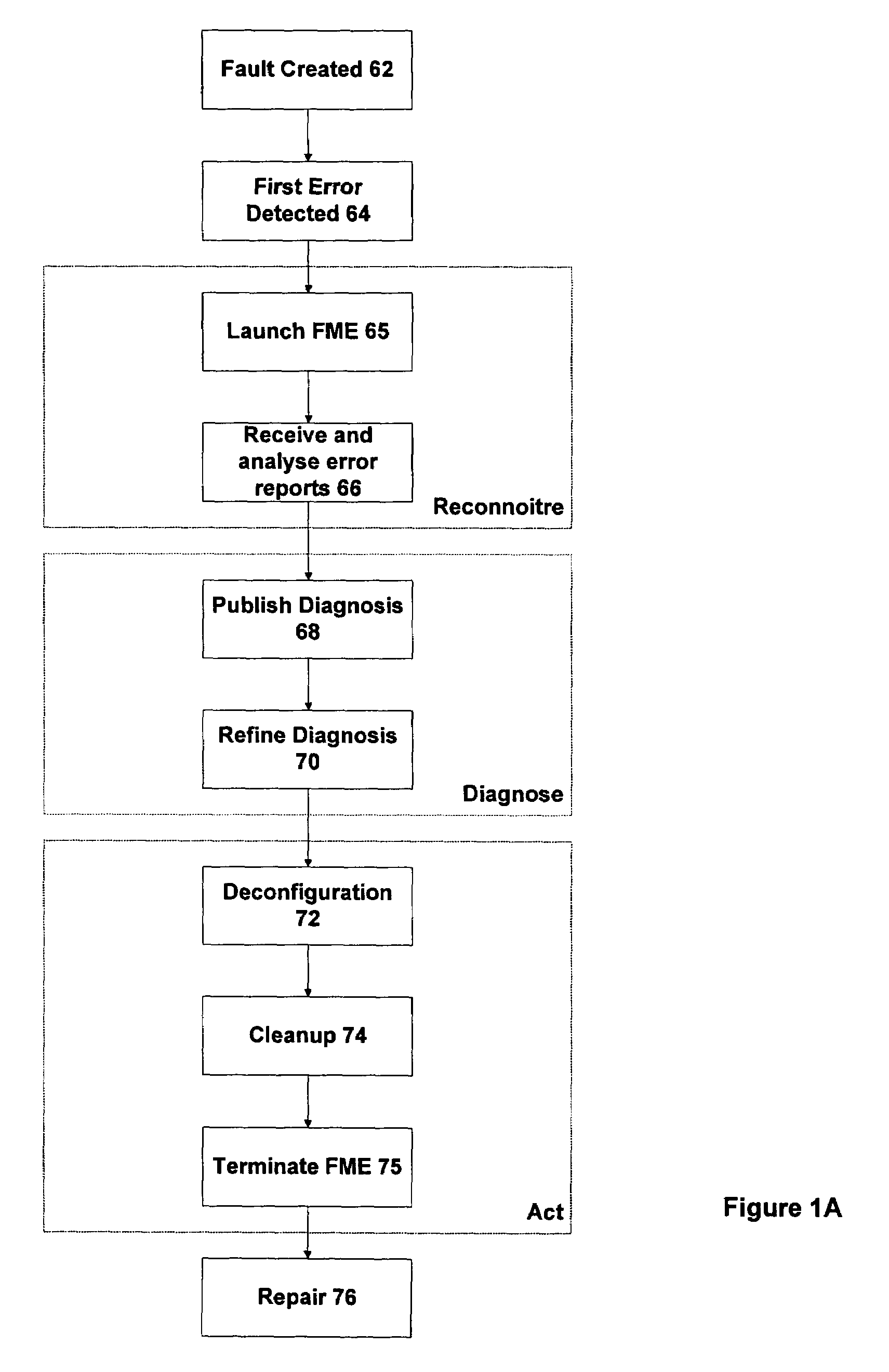
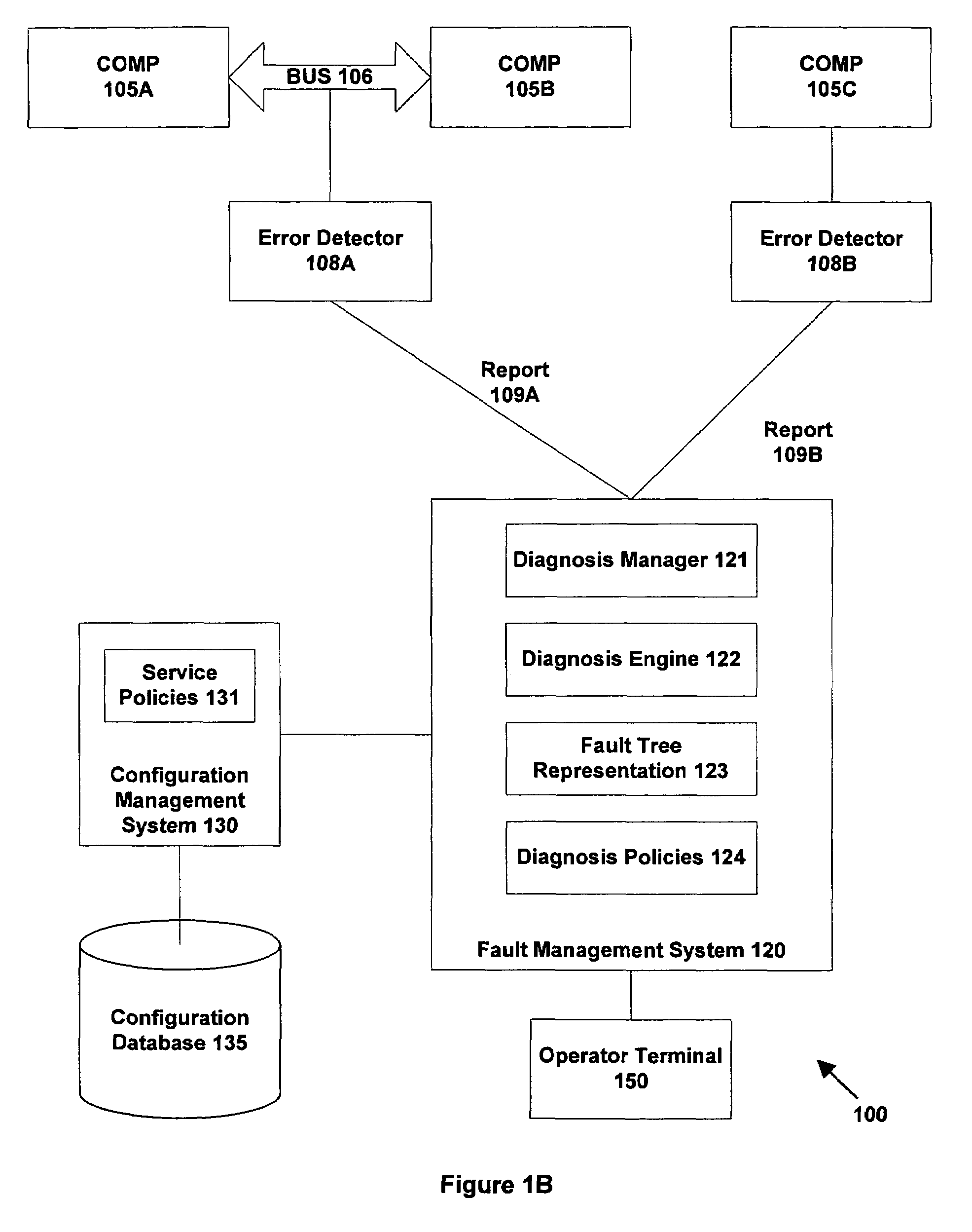
System and method for automated problem diagnosis
ActiveUS7379846B1Assisted identificationAssist in locationDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringTime informationError reporting
A method and system are provided for automated diagnosis for a system. In one embodiment, the method includes providing a fault tree representation of the system, the fault tree specifying propagations of errors generated in the system by problems to produce error reports. At least some of the propagations have timing information associated therewith. One or more error reports having timing information associated therewith are received and analysed using the fault tree representation to determine a suspect list of problems. The suspect list contains those problems that could have generated errors to produce the received error reports compatible with the propagations in the fault tree, and consistent with the timing information associated with the propagations and the received error reports.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
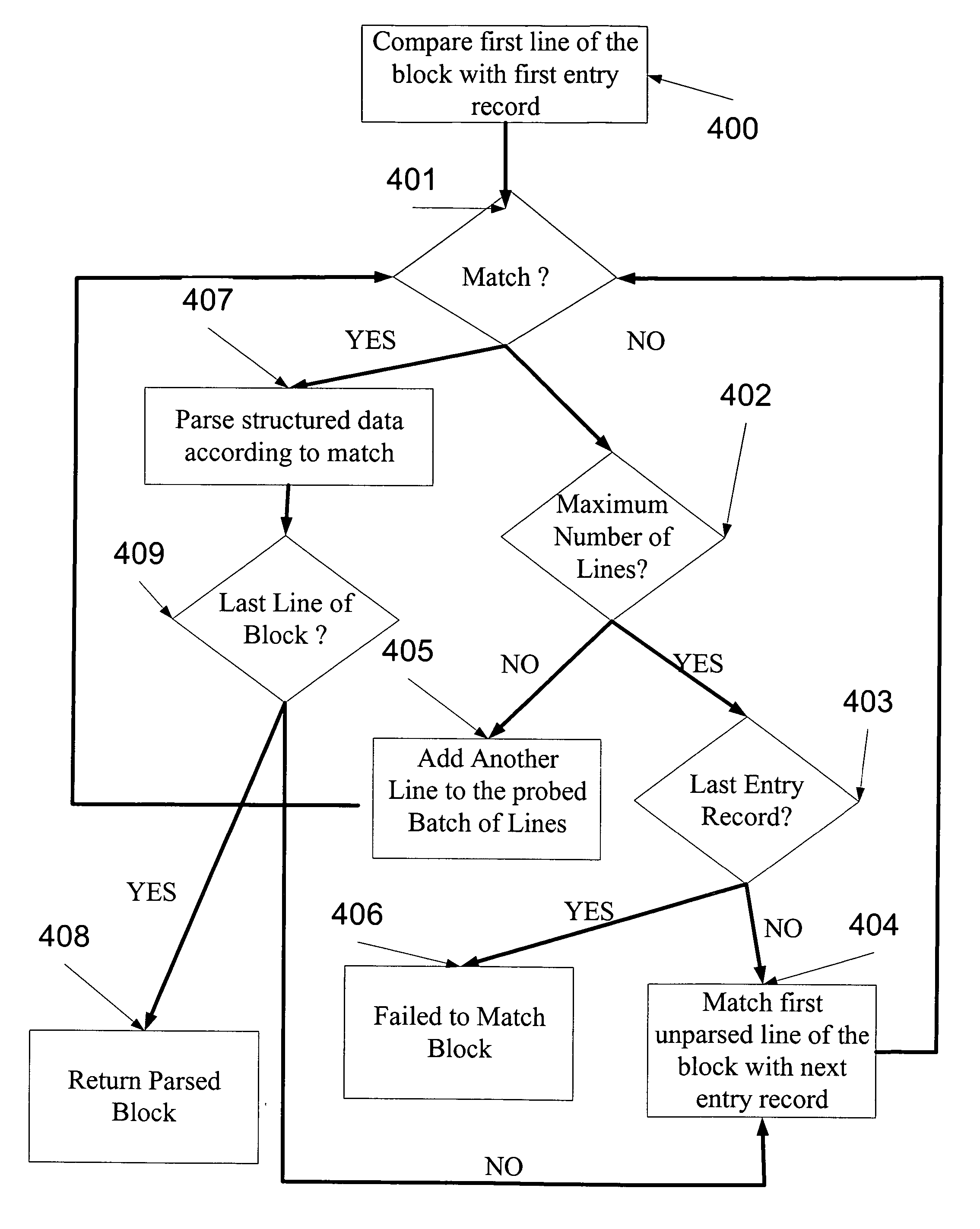
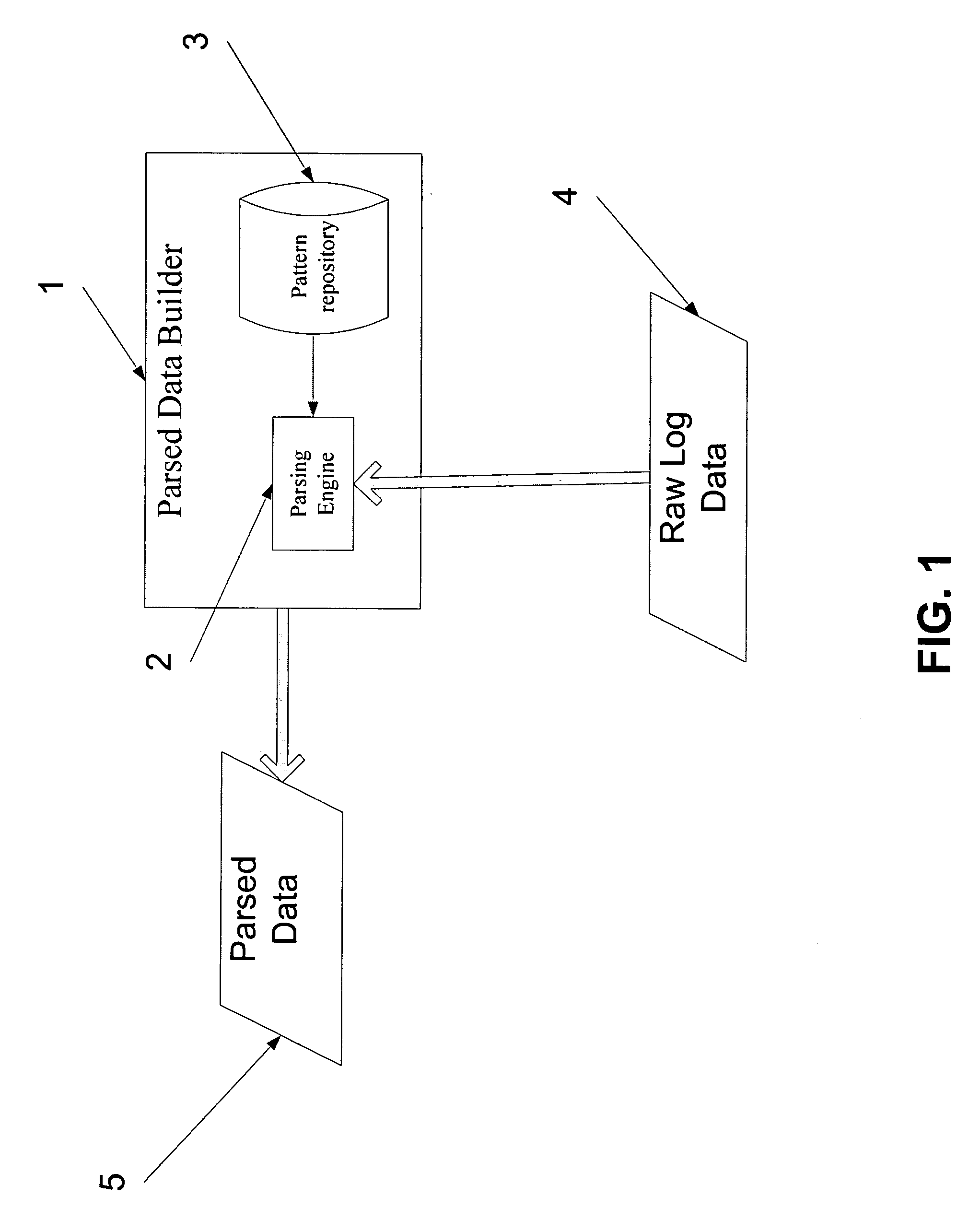
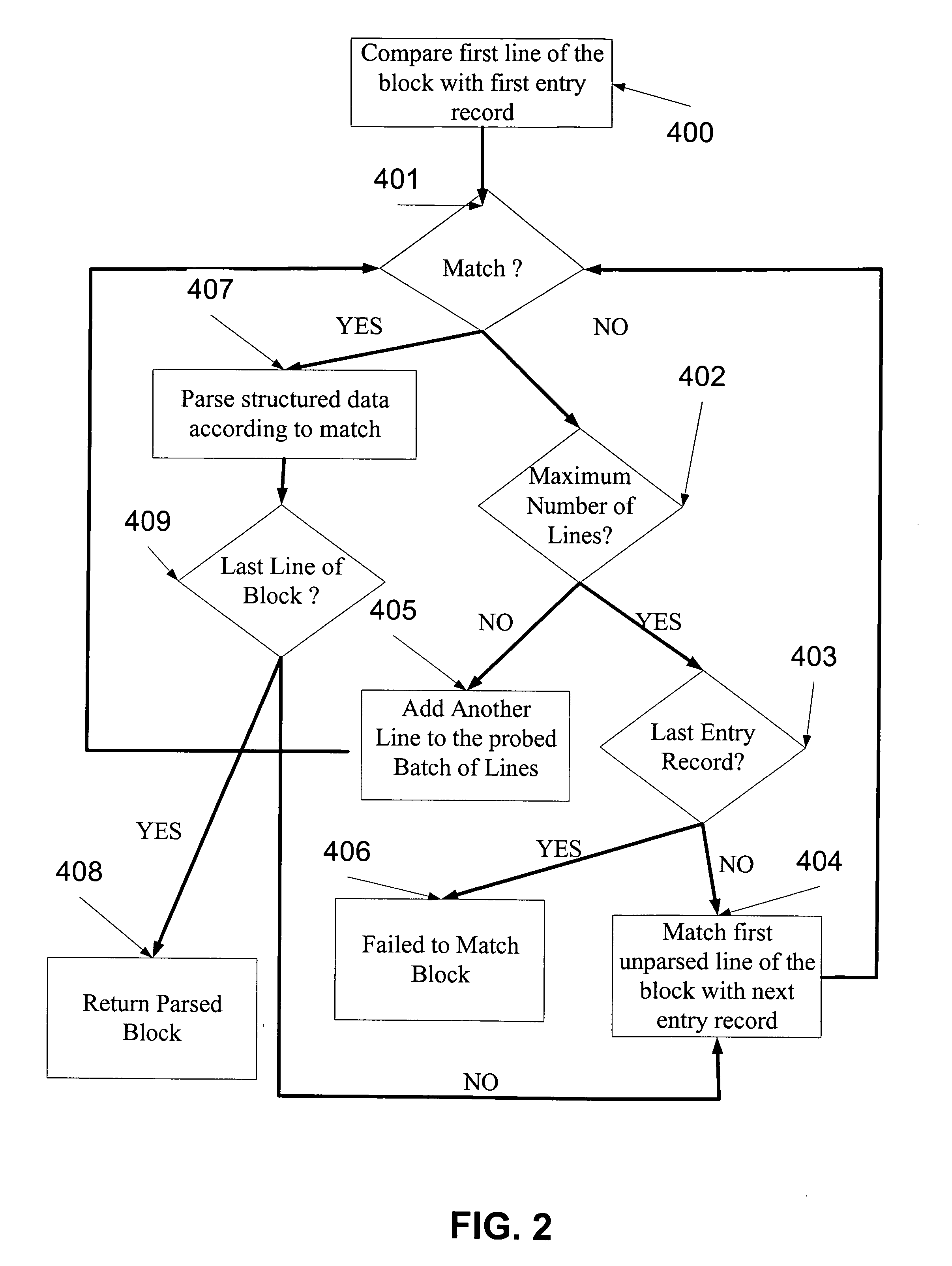
System and method for analysis and management of logs and events
ActiveUS20060184529A1Digital data processing detailsNon-redundant fault processingComputerized systemData mining
A log record analyzing system for monitoring log records from at least one computerized system. The log record analyzing system comprises a pattern repository that stores a plurality of pattern object records of different grammar types and a parsing engine which is adapted to receive a raw log data input. The parsing engine facilitates the matching between the raw log data input and at least one of the pattern object records. The parsing engine outputs parsed data according to the matching.
Owner:XPOLOG
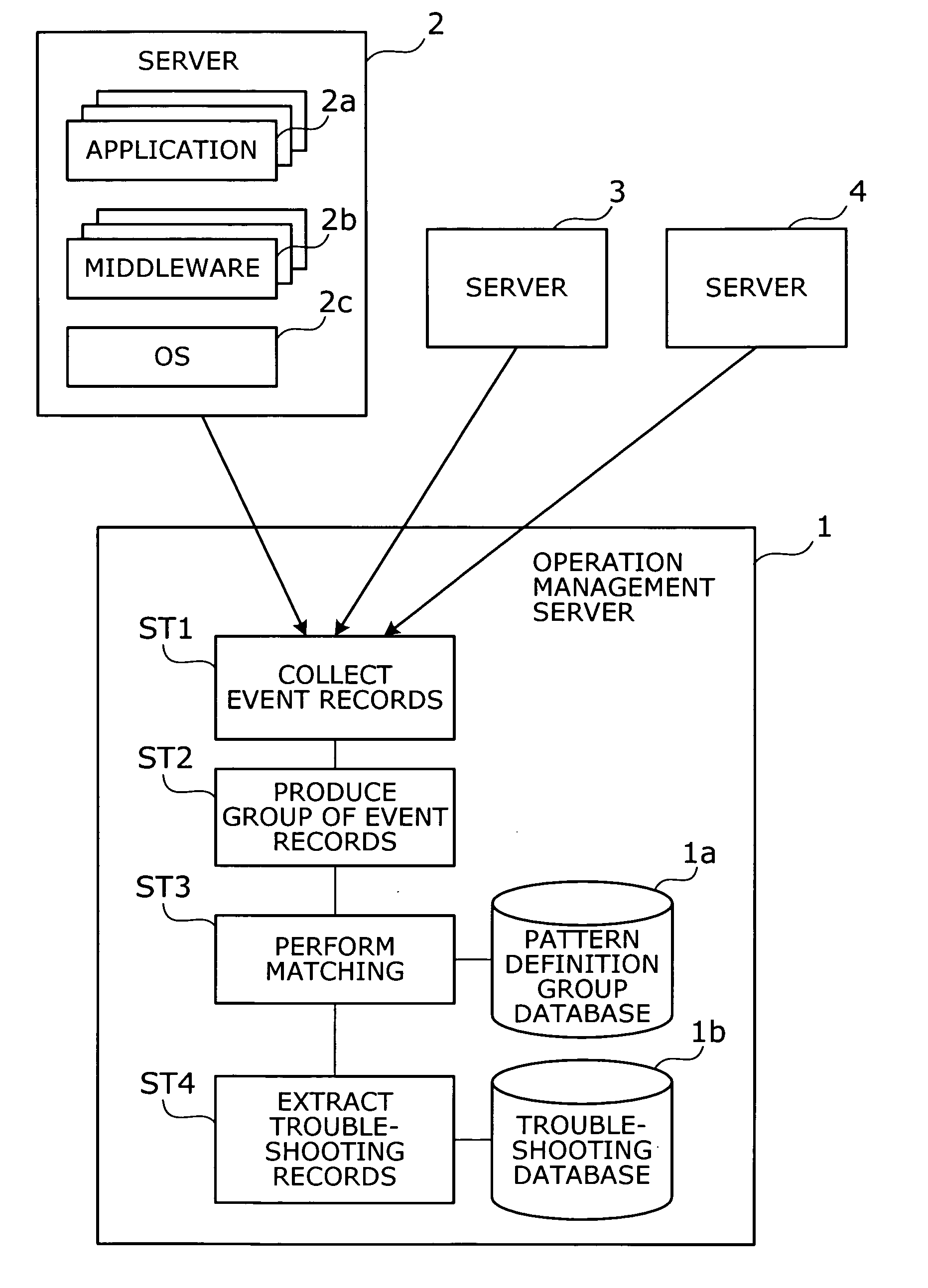
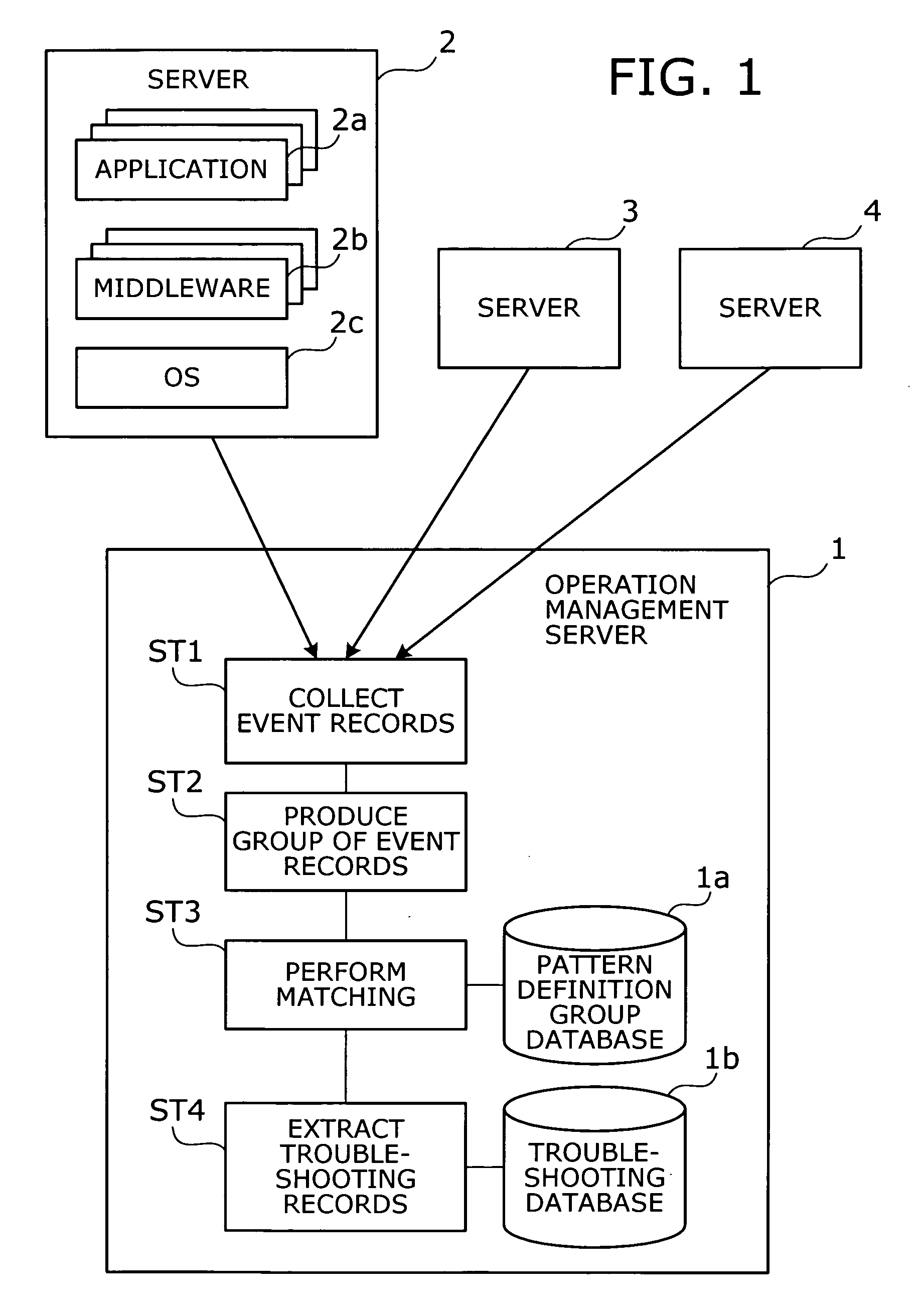
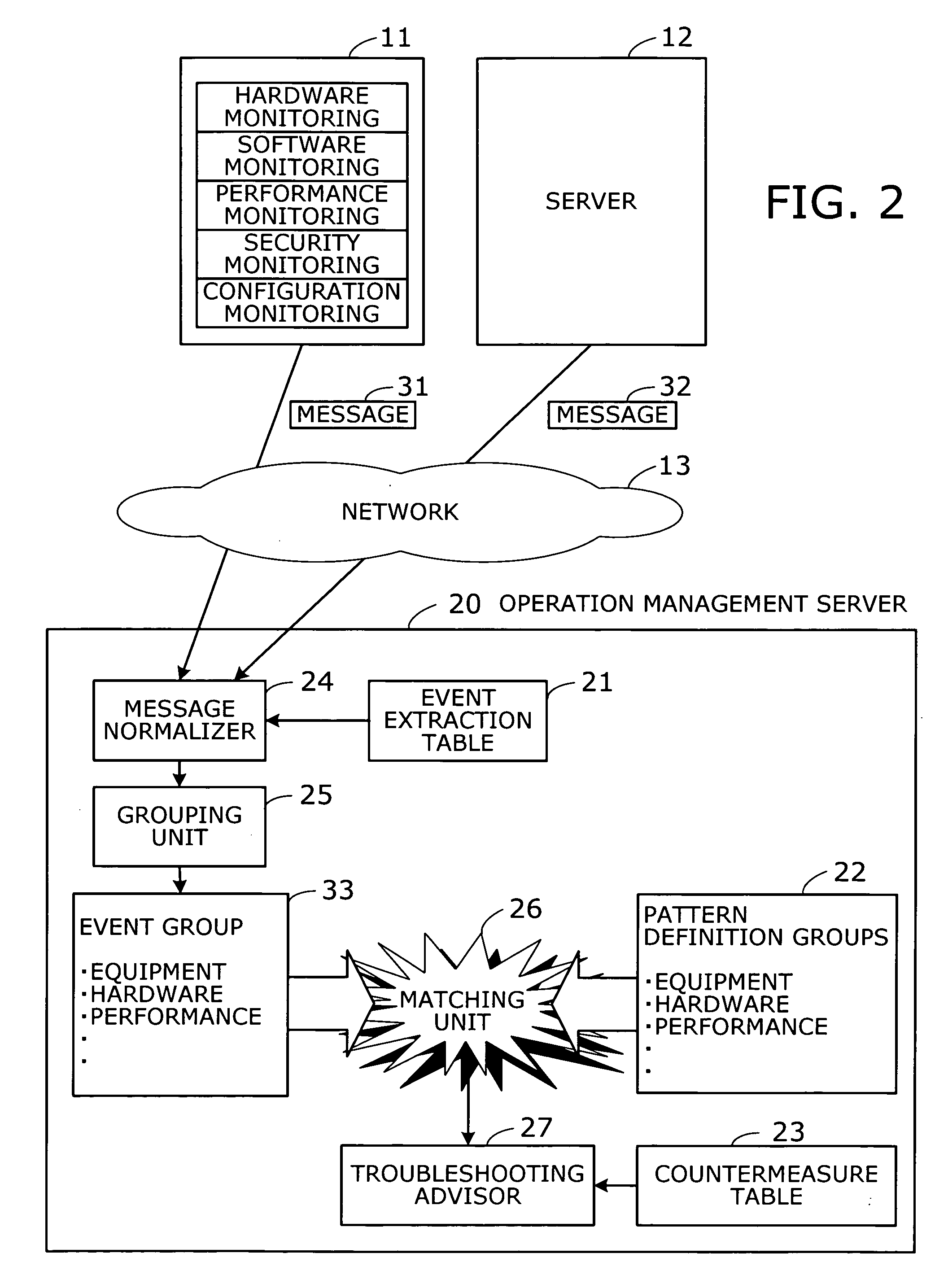
Operation management method and operation management server
InactiveUS20050172162A1Data processing applicationsDetecting faulty computer hardwareSoftwareReal-time computing
A method is provided to point out which software program is causing a problem. Event records are collected from target objects being monitored. An event group is then produced by grouping the collected event records. The event group is compared with a plurality of pattern definition groups in terms of occurrence patterns of event records, where each pattern definition group defines a pattern of event records that would be produced upon occurrence of a particular problem. Subsequently a troubleshooting record is extracted. This troubleshooting record has previously been associated with a pattern definition group resembling the event group in terms of occurrence patterns of event records.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
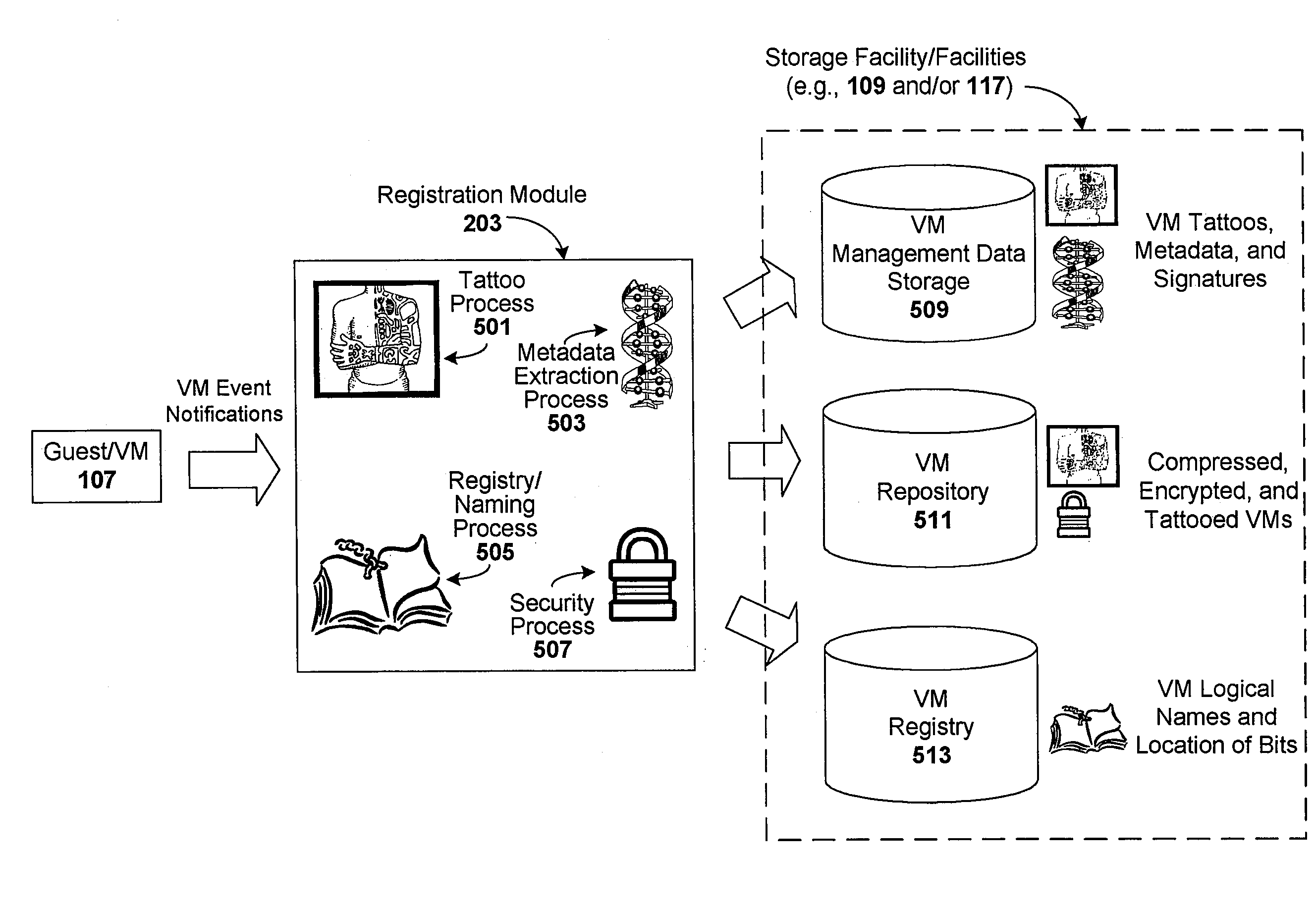
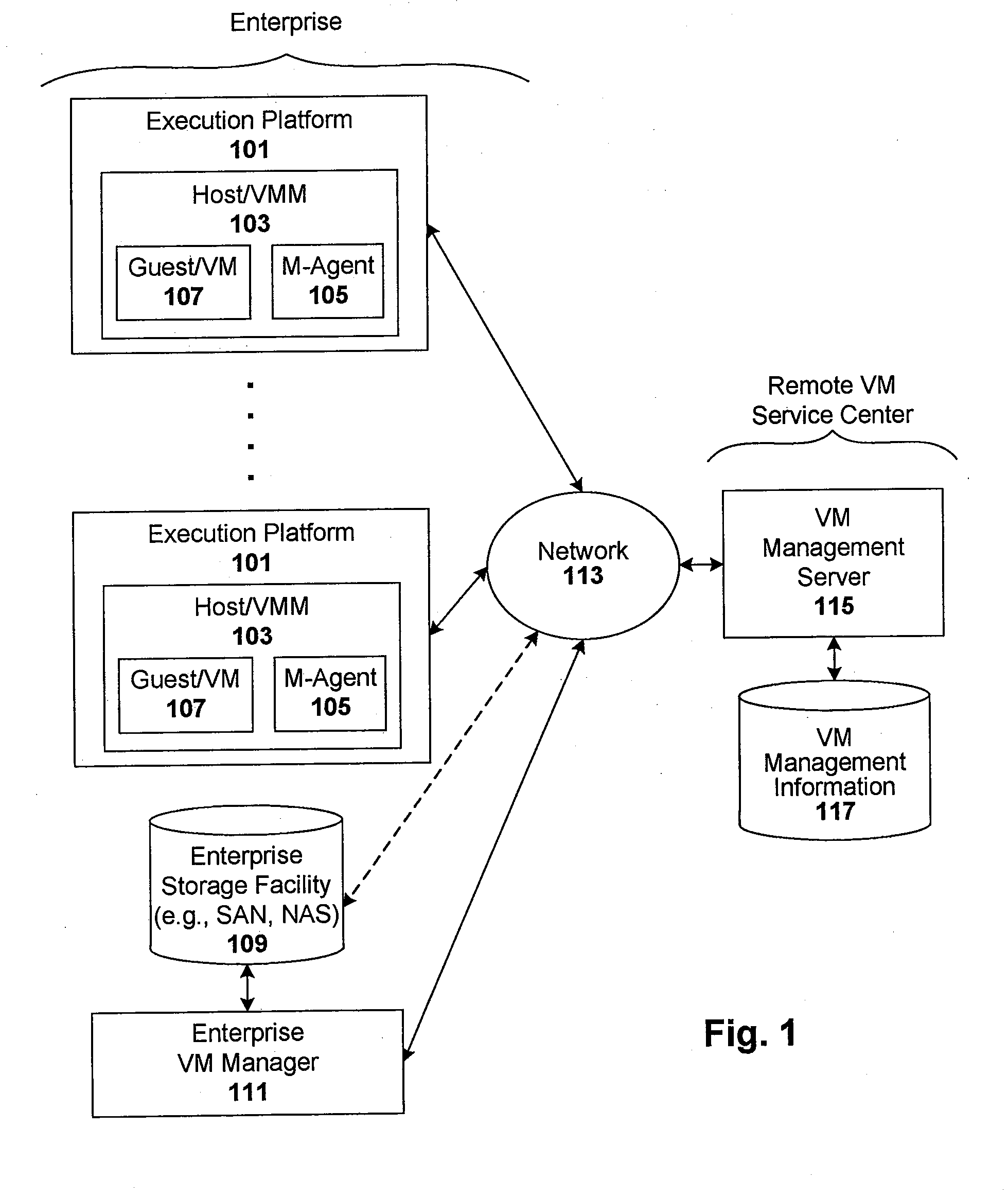
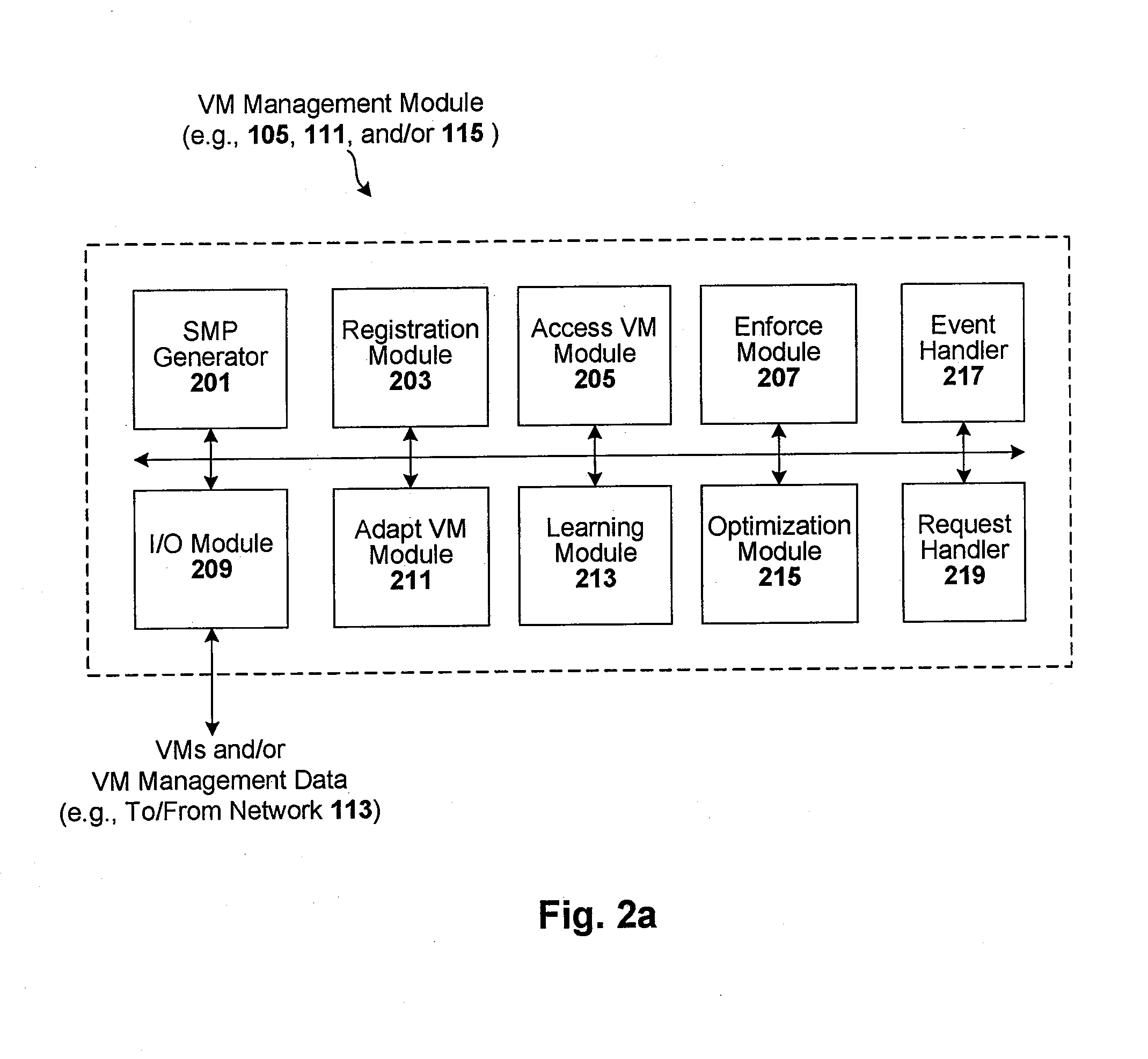
Enforcement of compliance policies in managed virtual systems
ActiveUS20080134176A1Preventing executionNon-redundant fault processingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSystems managementMetadata
Techniques are disclosed for controlling and managing virtual machines and other such virtual systems. VM execution approval is based on compliance with policies controlling various aspects of VM. The techniques can be employed to benefit all virtual environments, such as virtual machines, virtual appliances, and virtual applications. For ease of discussion herein, assume that a virtual machine (VM) represents each of these environments. In one particular embodiment, a systems management partition (SMP) is created inside the VM to provide a persistent and resilient storage for management information (e.g., logical and physical VM metadata). The SMP can also be used as a staging area for installing additional content or agentry on the VM when the VM is executed. Remote storage of management information can also be used. The VM management information can then be made available for pre-execution processing, including policy-based compliance testing.
Owner:RED HAT
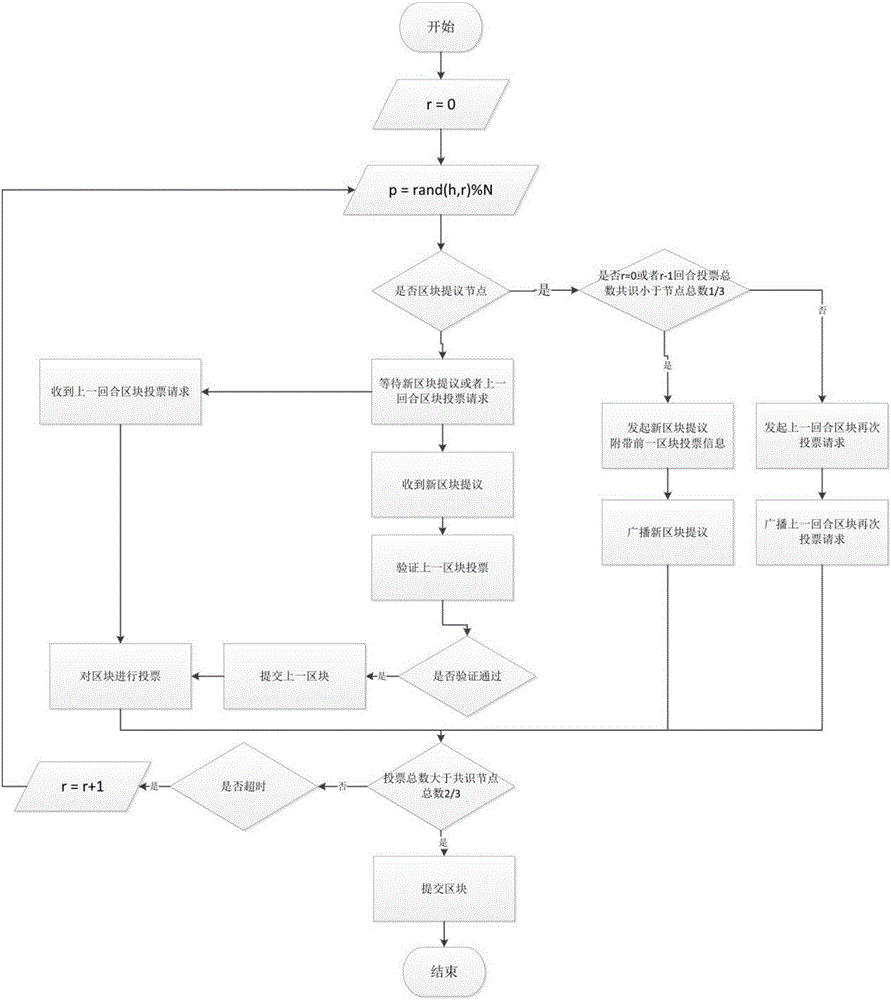
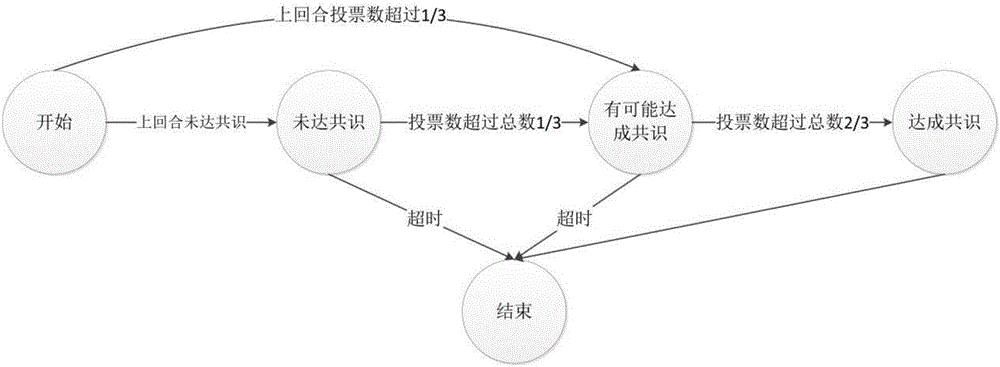
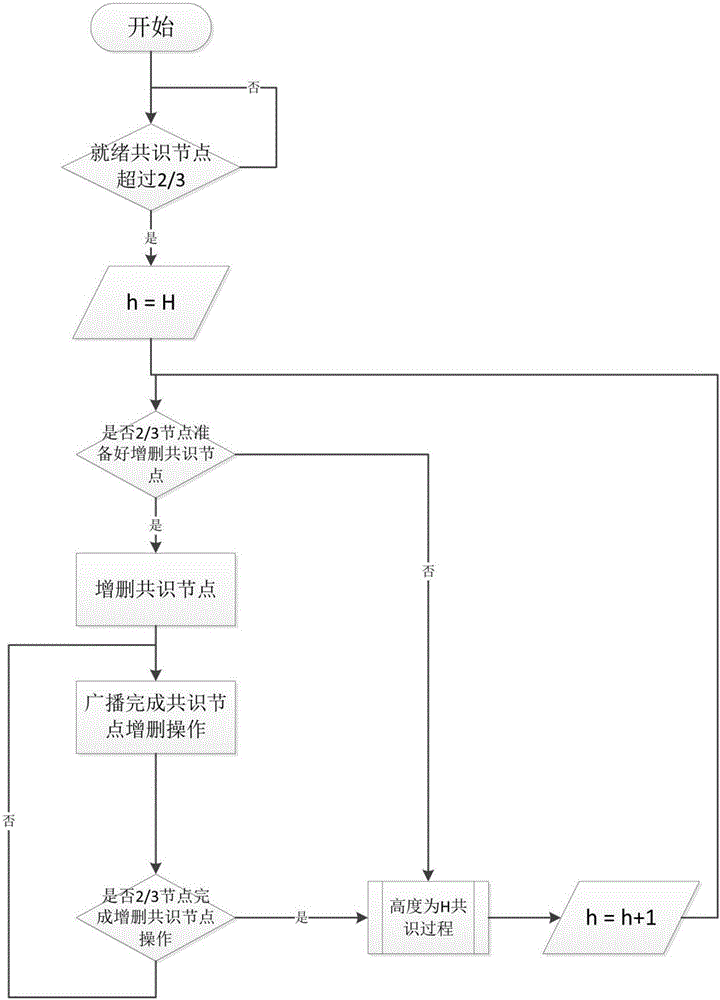
Byzantine-fault-tolerant consensus method applied to block chain
ActiveCN106445711ASave computing resourcesAvoid computing power competitionNon-redundant fault processingByzantine fault toleranceStochastic algorithms
The invention discloses a byzantine-fault-tolerant consensus method applied to a block chain. The method comprises the steps of specifying a certain number of right and interest accounts and initial consensus accounts in an initiated block of the block chain; after a consensus process is started, for the height h of a current block, selecting a consensus account to initiate a proposal of a new block according to a fixed random algorithm in a consensus account list; receiving the proposal and voting a block with the height of h by other consensus nodes; within a period of time, if the number of votes exceeds eta 1, representing that a consensus is formed, and starting the consensus of a block with the height of h+1 in the next round; if the number of votes does not exceed eta 1 but exceeds eta 2, representing that the consensus is possibly formed, broadcasting a voting request of the block in the previous round, and continuing to wait for a period of time; and if the number of votes does not exceed eta 2, cancelling the proposal in the round and re-performing the proposal of the new block. Therefore, computing resources can be saved; a large amount of blocks can be continuously generated; and computing power competition is avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUNXIANG NETWORK TECH
Efficient reduction of read disturb errors in NAND FLASH memory
InactiveUS7818525B1Disturb errorEfficient reduction of Read Disturb errorMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesPhysical addressTranslation table
Methods and apparatuses for reduction of Read Disturb errors in a NAND FLASH memory system comprise a controller configured to organize FLASH memory devices into blocks, each block having a plurality of pages, and each page defining an individually addressable physical memory location. The controller is further configured to accumulate a Block READ Count corresponding to the number of times any pages in a first block of pages have been read since the first block was last erased. Once the READ count reaches a predetermined number, the controller responds to subsequent READ requests for pages within the first block by moving data associated with a requested page to a page in a second, different block without moving data associated with other pages in the first block, and modifying a logical-to-physical translation table to associate the moved data with the physical address of the page in the second block.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fault diagnosis, repair and upgrades using the acoustic channel
InactiveUS20050028034A1Need be addressBroadcast information characterisationNon-redundant fault processingVocal tractEngineering
An acoustic channel is used for fault diagnosis, repair, and upgrades. Remote diagnosis uses self-test data encoded into sound waves. Repair data and upgrades are also encoded and transmitted as sound waves.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
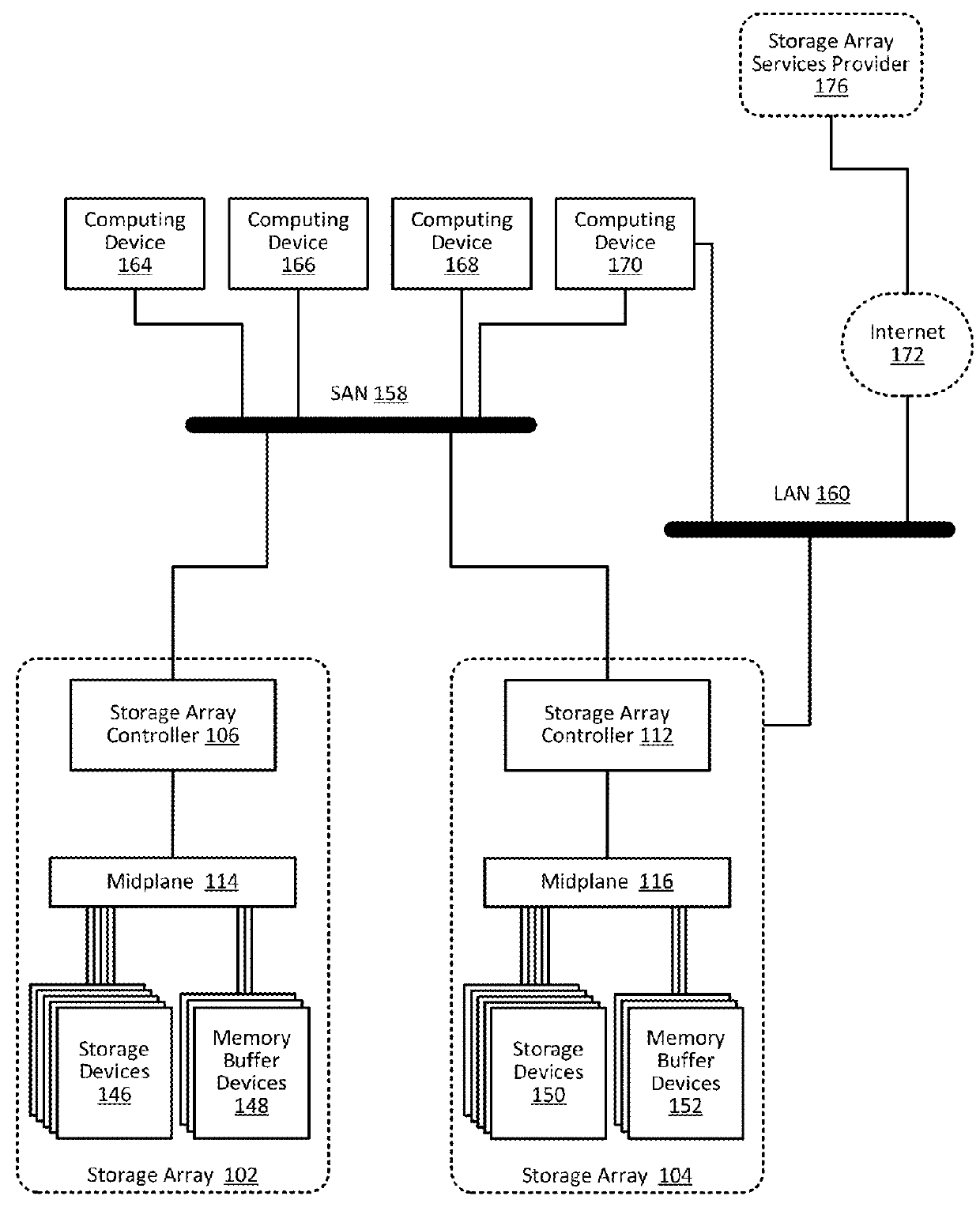
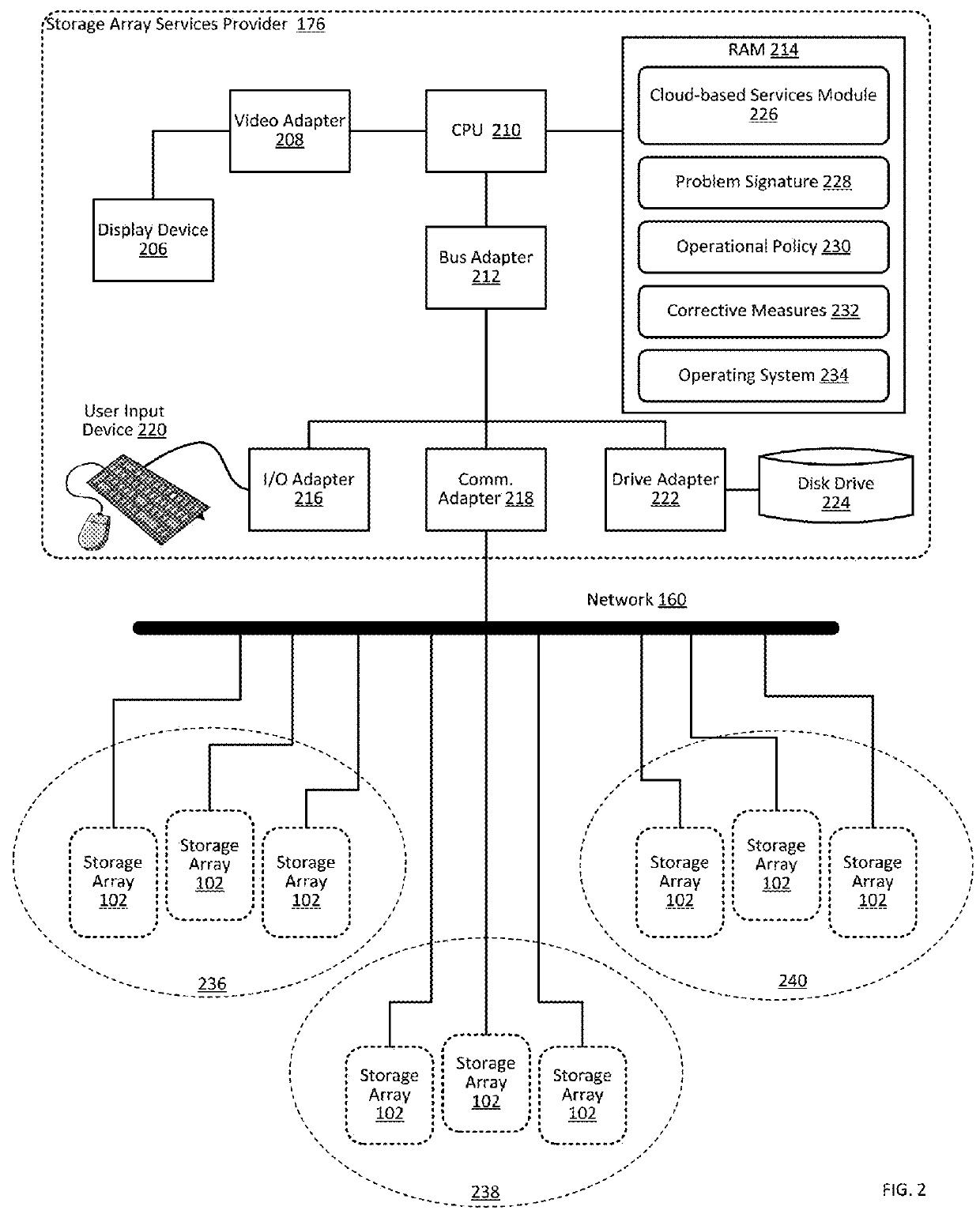
Proactively providing corrective measures for storage arrays
ActiveUS9384082B1Particular problemHardware monitoringReliability/availability analysisReal-time computingOperational policies
Owner:PURE STORAGE
System and method for evaluating monitored computer systems
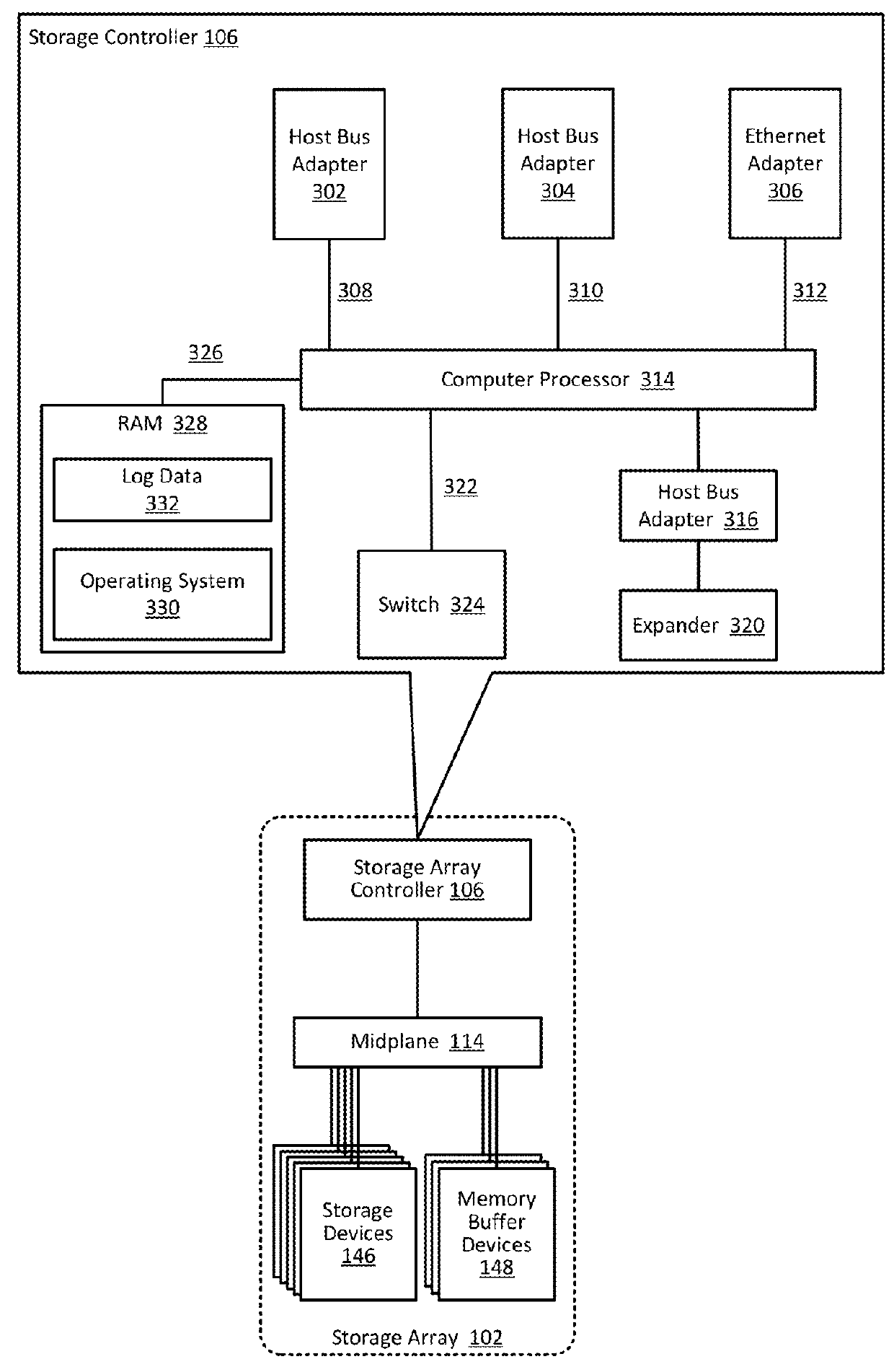
InactiveUS6237114B1Hardware monitoringEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionImage resolutionComputerized system
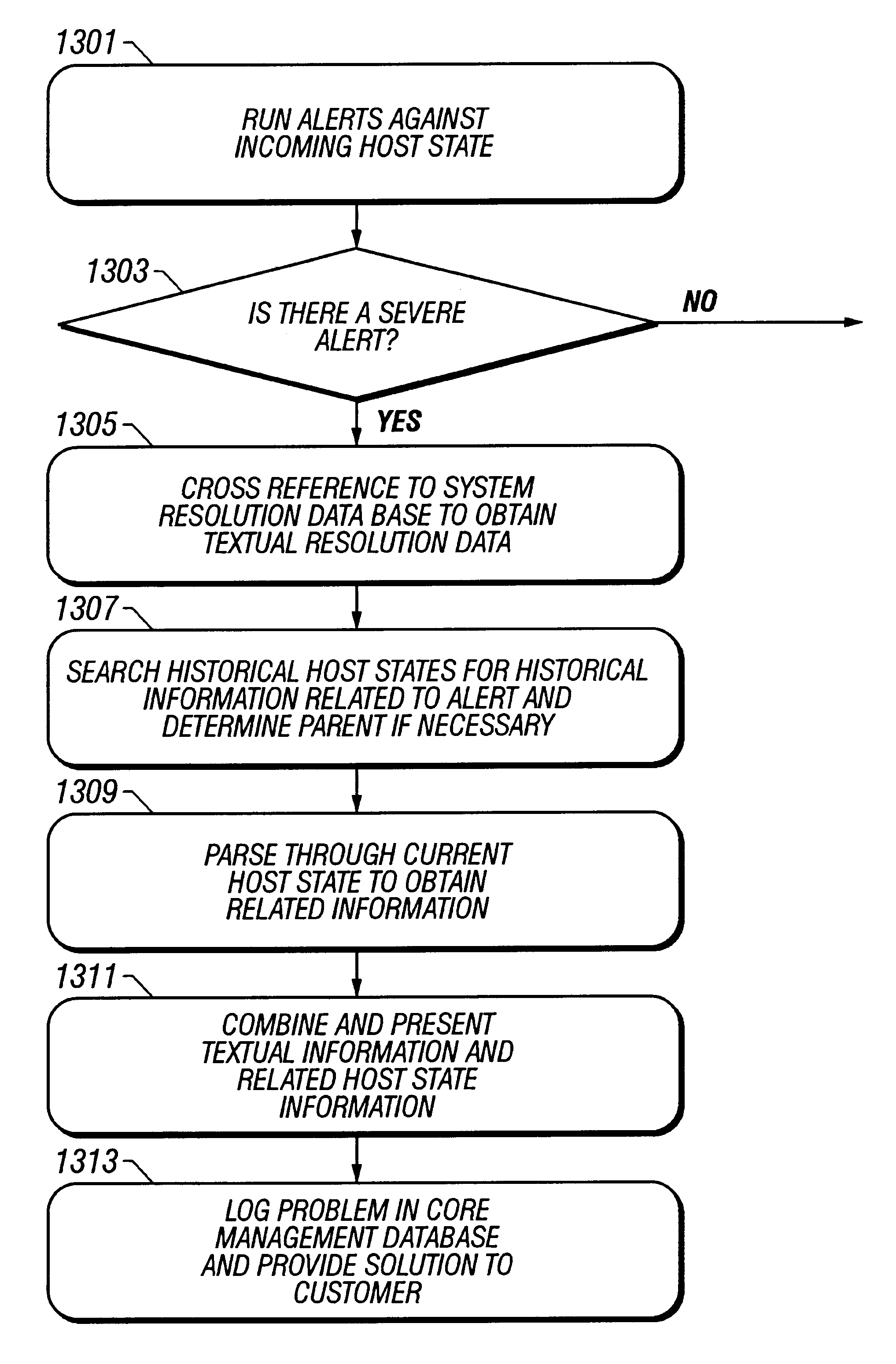
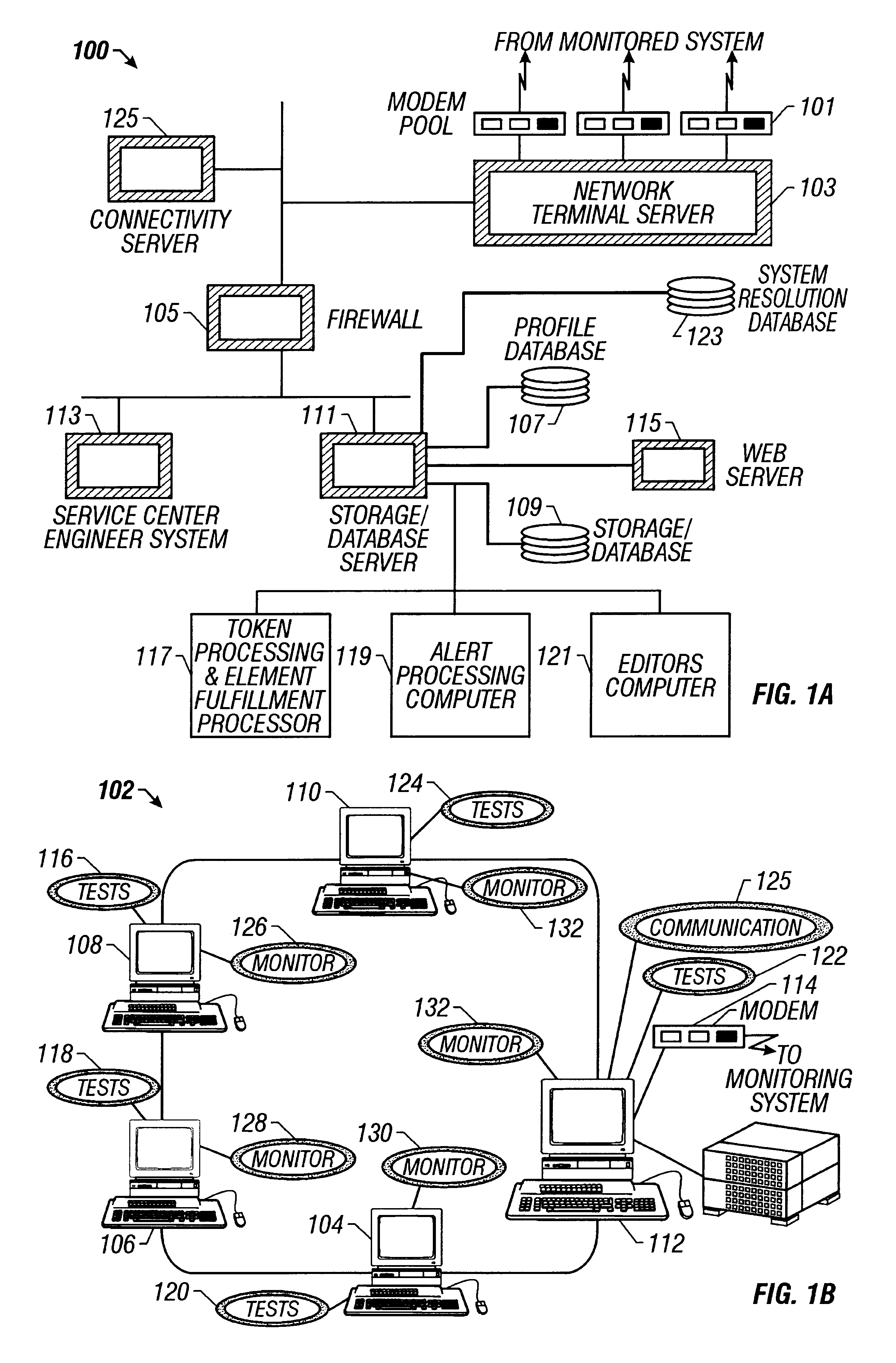
A computer system used in monitoring another computer system provides both textual resolution information describing a likely solution for a problem encountered in the monitored computer system as well as component information that relates to the particular problem. The component information includes the various hardware, software and operating conditions found in the monitored computer system. The monitoring computer system determines if a condition of a predetermined severity exists in the monitored computer system according to diagnostic information provided from the monitored computer system. The diagnostic information is represented in the monitoring computer system as a hierarchical representation of the monitored computer system. The hierarchical representation provides present state information indicating the state of hardware and software components and operating conditions of the monitored computer system. The resolution information relating to the condition is retrieved from a resolution database and relevant component information is retrieved from the hierarchical representation of the computer system and presented to a support engineer to assist them in diagnosing the problem in the monitored computer system.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
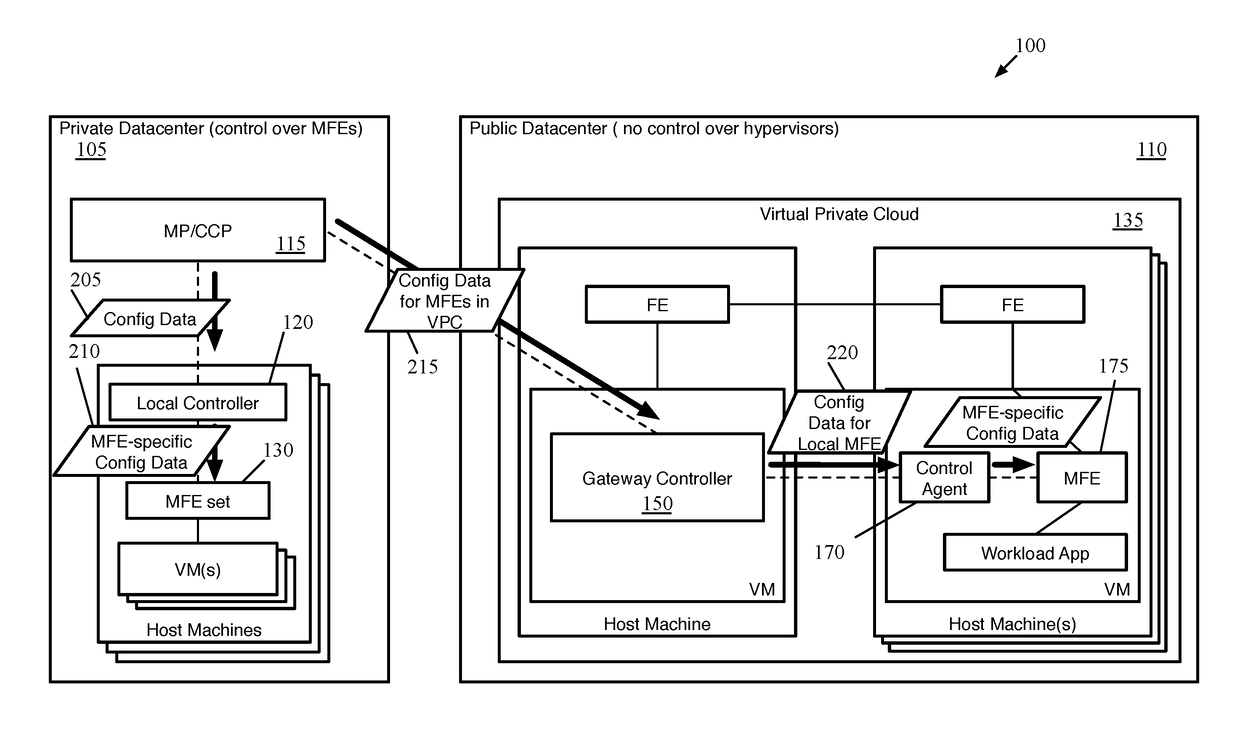
Distributed Network Encryption for Logical Network Implemented in Public Cloud
ActiveUS20180063193A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey distributionKey storage
Some embodiments provide a method for a first data compute node (DCN) operating in a public datacenter. The method receives an encryption rule from a centralized network controller. The method determines that the network encryption rule requires encryption of packets between second and third DCNs operating in the public datacenter. The method requests a first key from a secure key storage. Upon receipt of the first key, the method uses the first key and additional parameters to generate second and third keys. The method distributes the second key to the second DCN and the third key to the third DCN in the public datacenter.
Owner:NICIRA
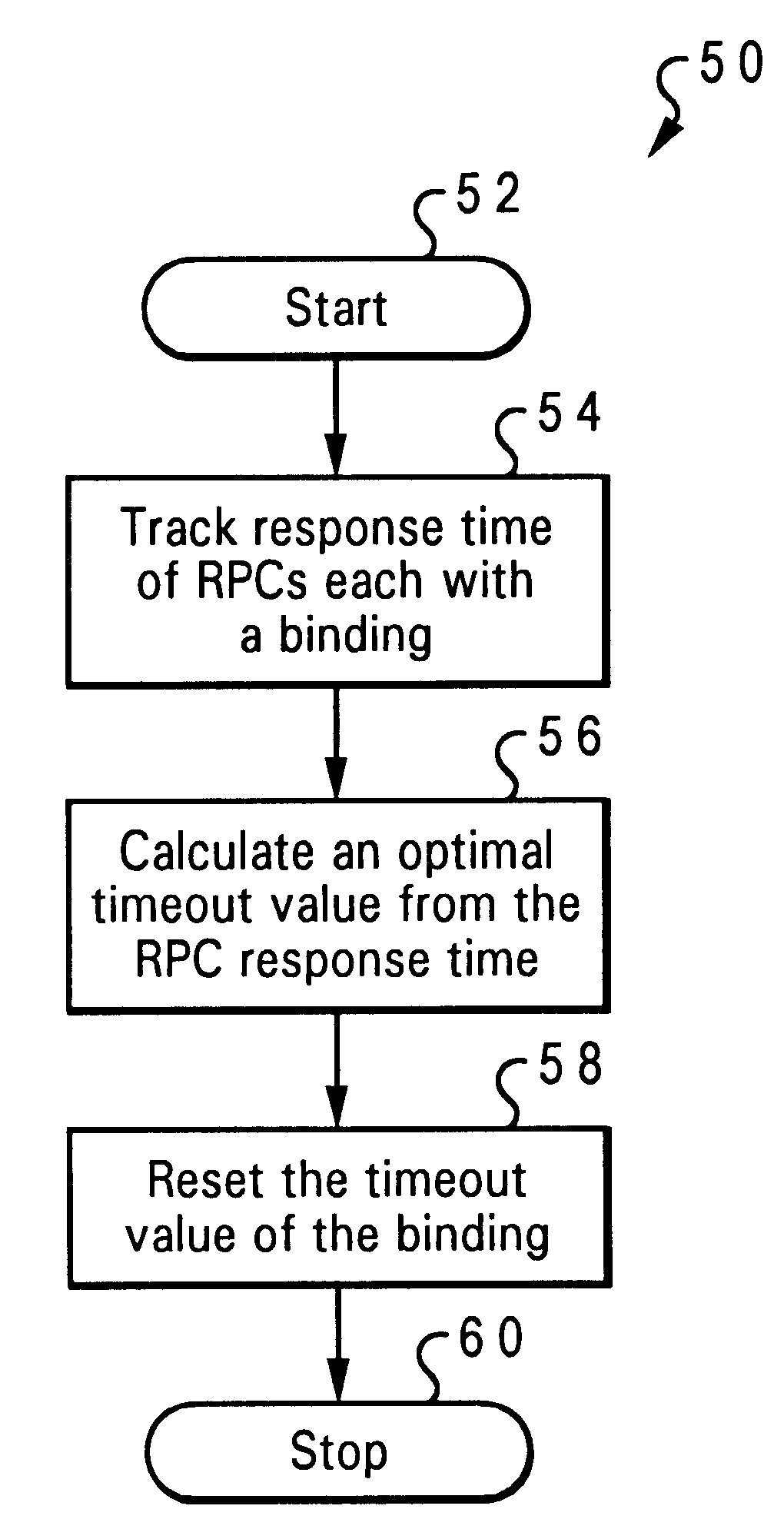
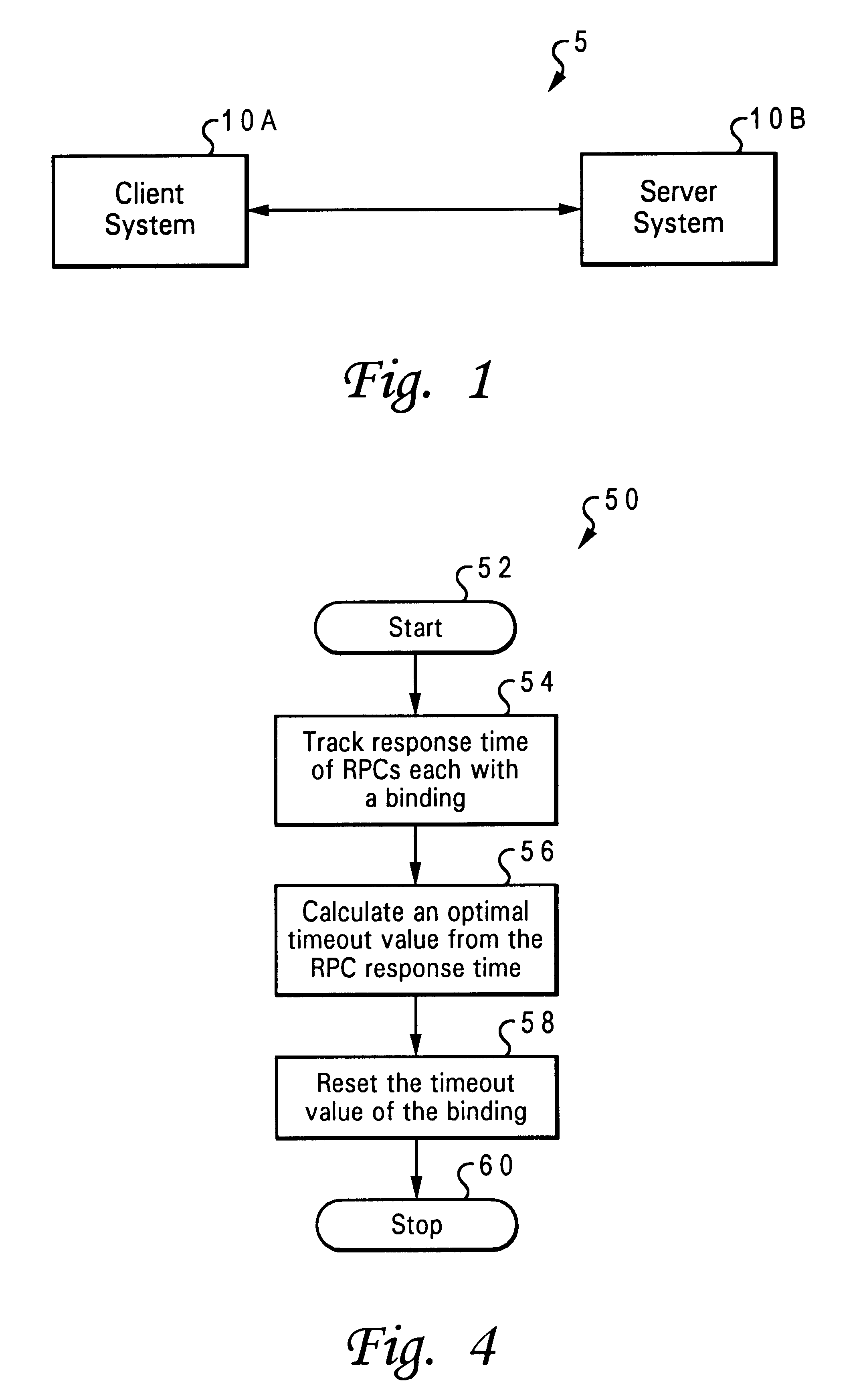
Adaptive timeout value setting for distributed computing environment (DCE) applications
InactiveUS6526433B1Hardware monitoringMultiple digital computer combinationsValue setDistributed Computing Environment
An adaptive timeout value setting is determined for DCE applications, wherein the timeout value setting is adapted and adjusted according to environmental factors and communication conditions between a client / server pair. The adaptive timeout value setting takes into consideration the communication time between a client and a server in each client / server pair in determining and setting a timeout value for each pair. The timeout value for a client / server pair is adjusted in a dynamic fashion so that the client is able to be more adaptive to real environment changes and so that the server's performance is not degraded due to ineffective timeouts. The system and method determines an adaptive timeout value setting in distributed computing environment (DCE) applications for a client / server pair wherein each pair has a client system and a server system. A server response time of the server system is tracked to a remote procedure call from the client system. The remote procedure call includes a binding handle, and the server response time is based on a time of the server system responding to the remote procedure. An optimal timeout value is calculated from the response time, and a timeout value of the binding handle is reset as the optimal timeout value.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com