Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1792 results about "Key distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
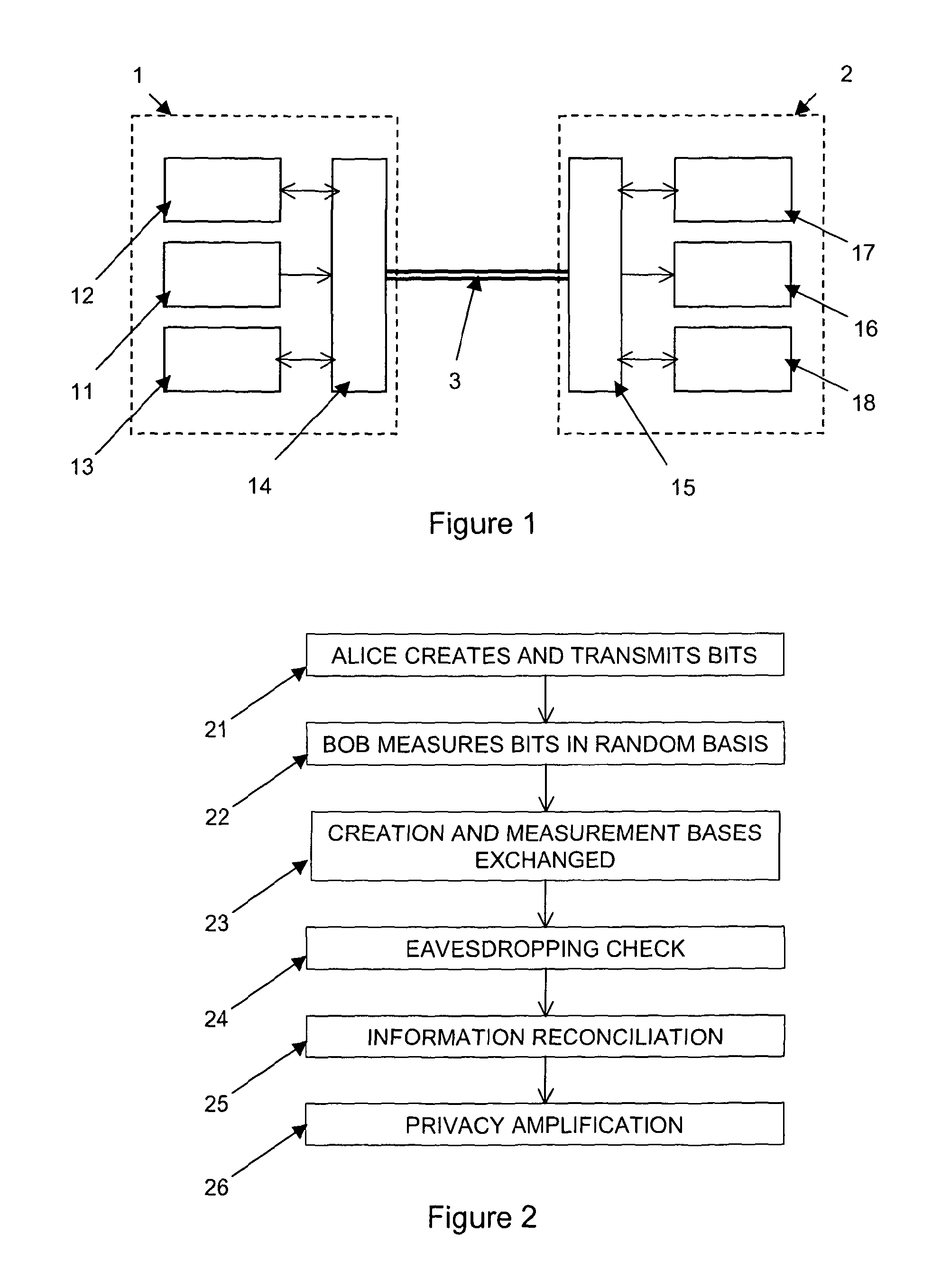
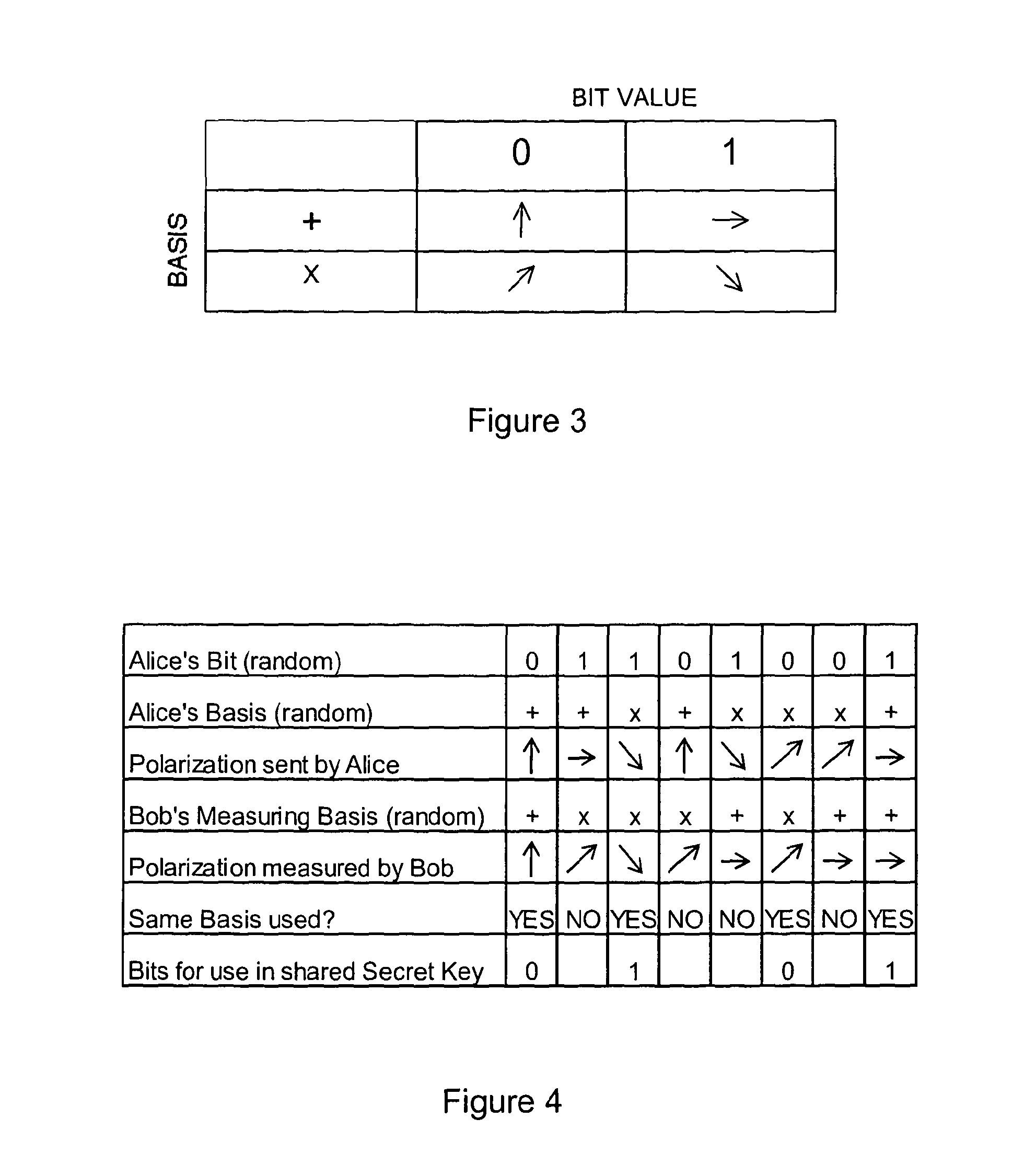
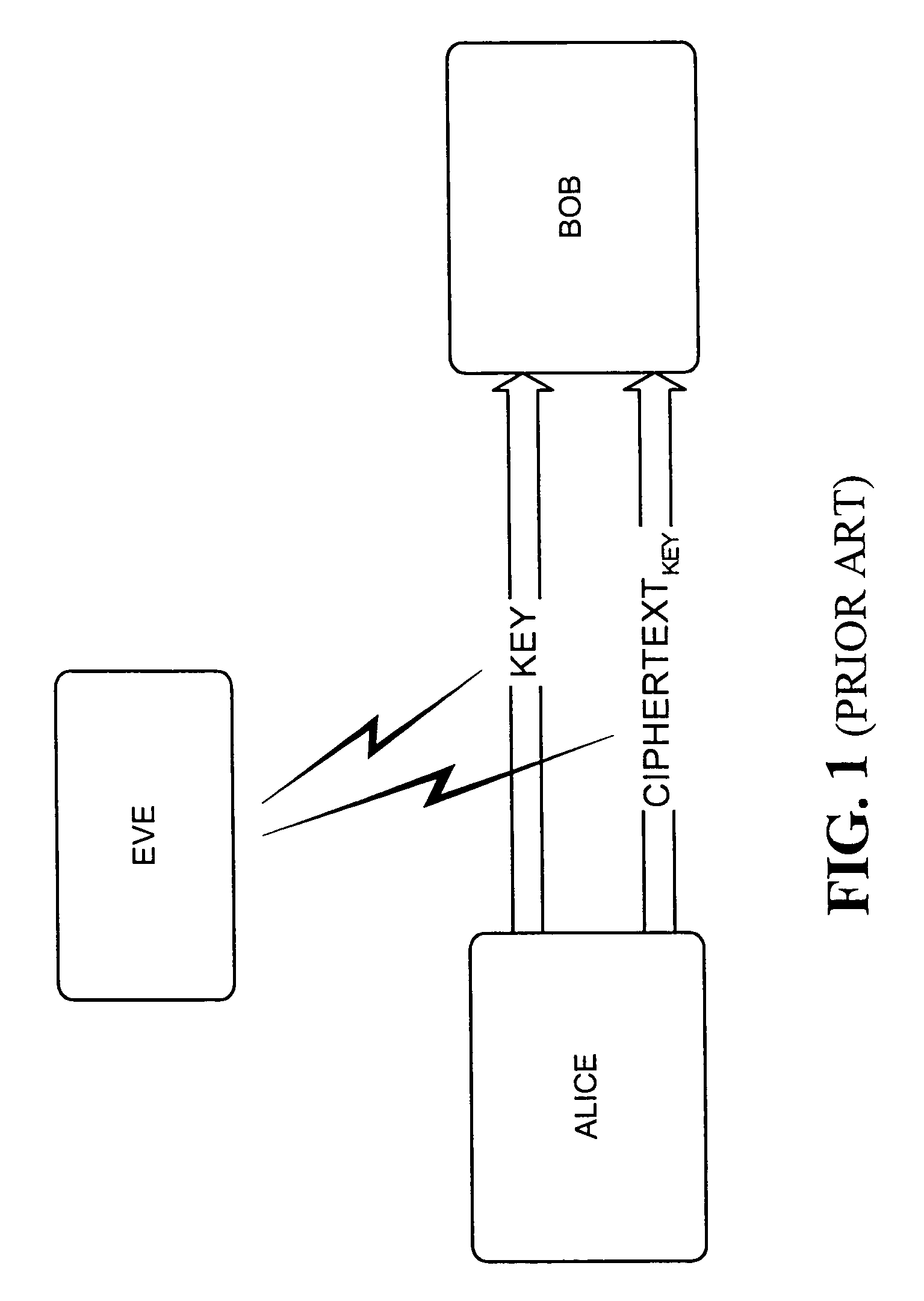
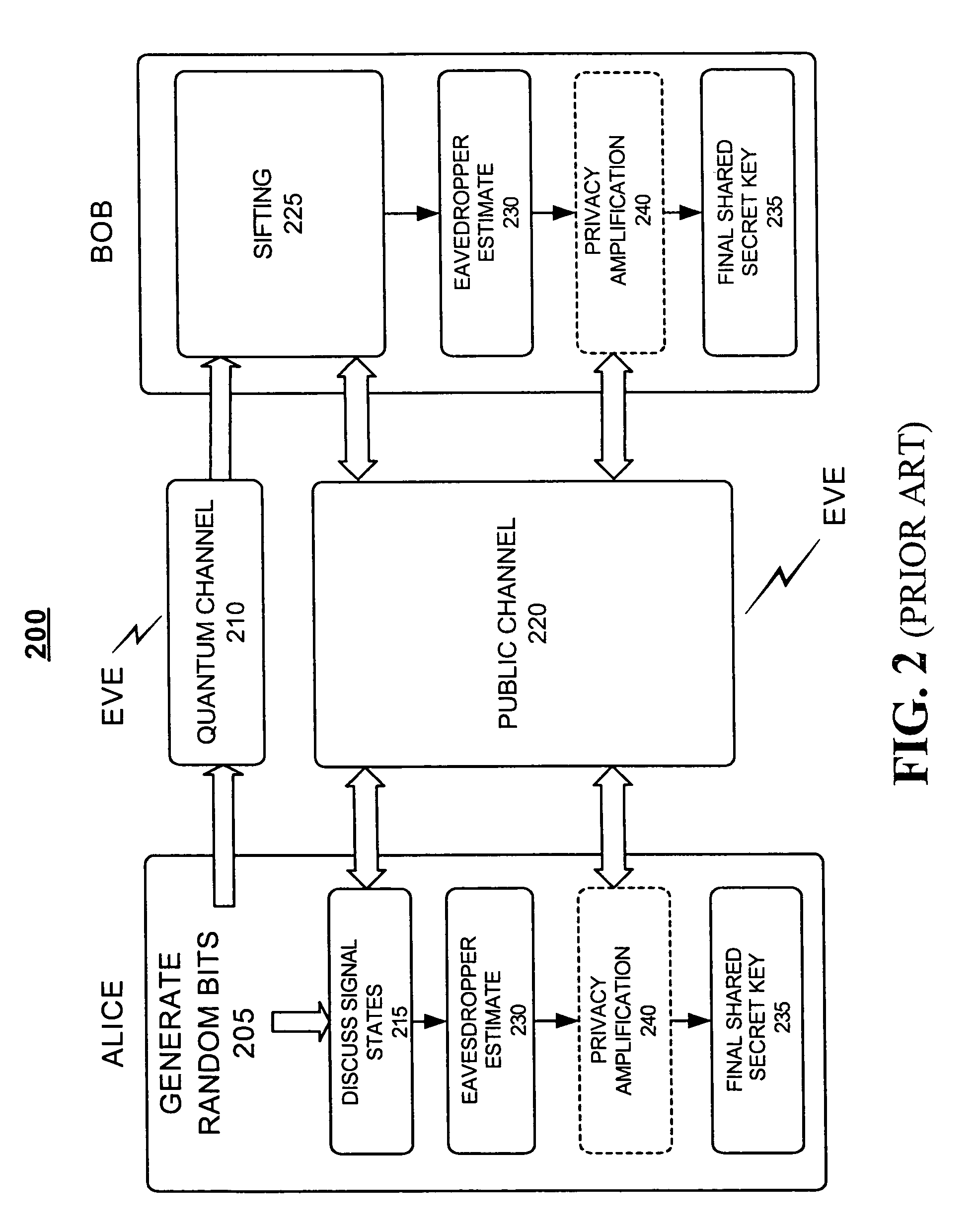
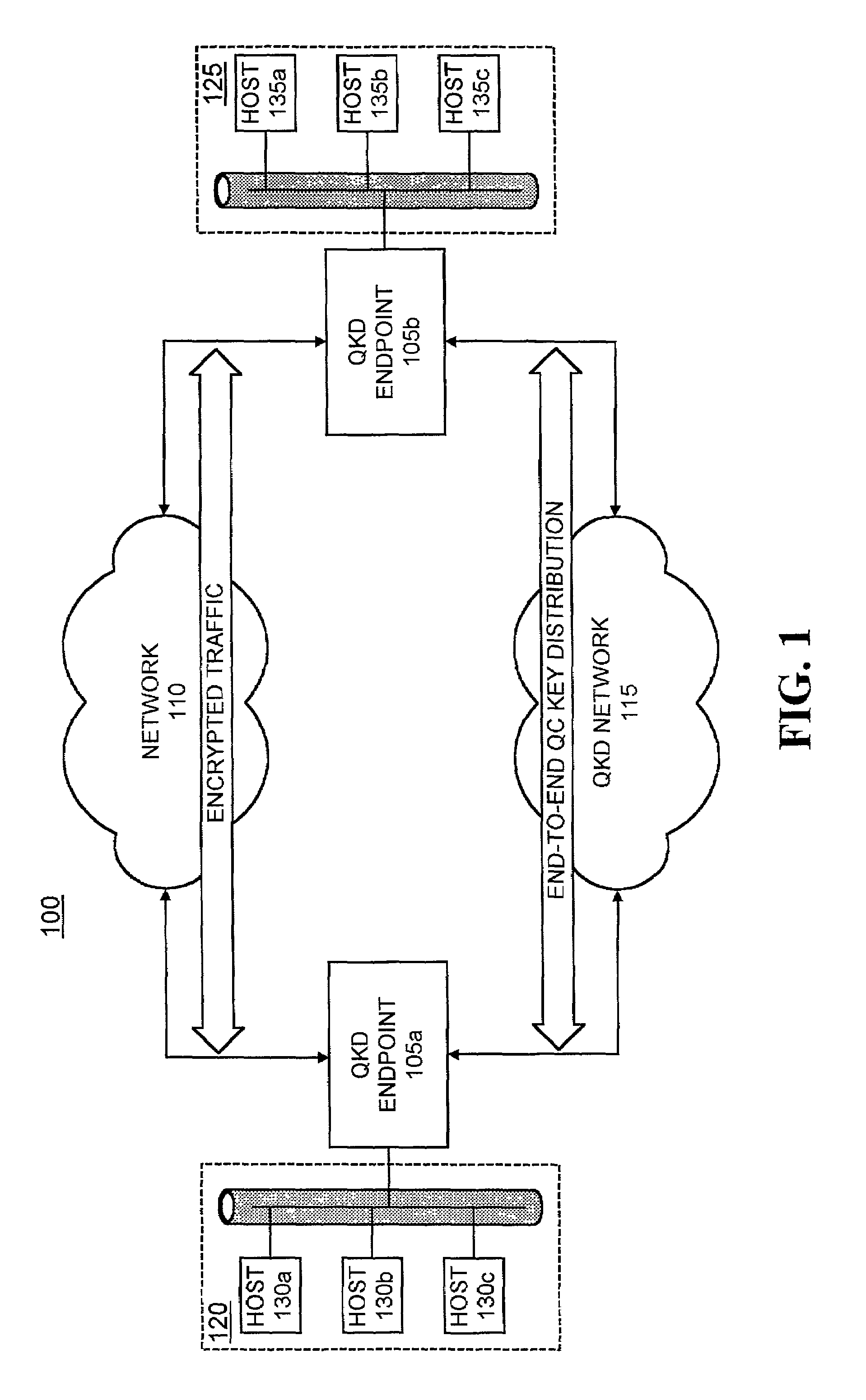
In symmetric key cryptography, both parties must possess a secret key which they must exchange prior to using any encryption. Distribution of secret keys has been problematic until recently, because it involved face-to-face meeting, use of a trusted courier, or sending the key through an existing encryption channel. The first two are often impractical and always unsafe, while the third depends on the security of a previous key exchange.
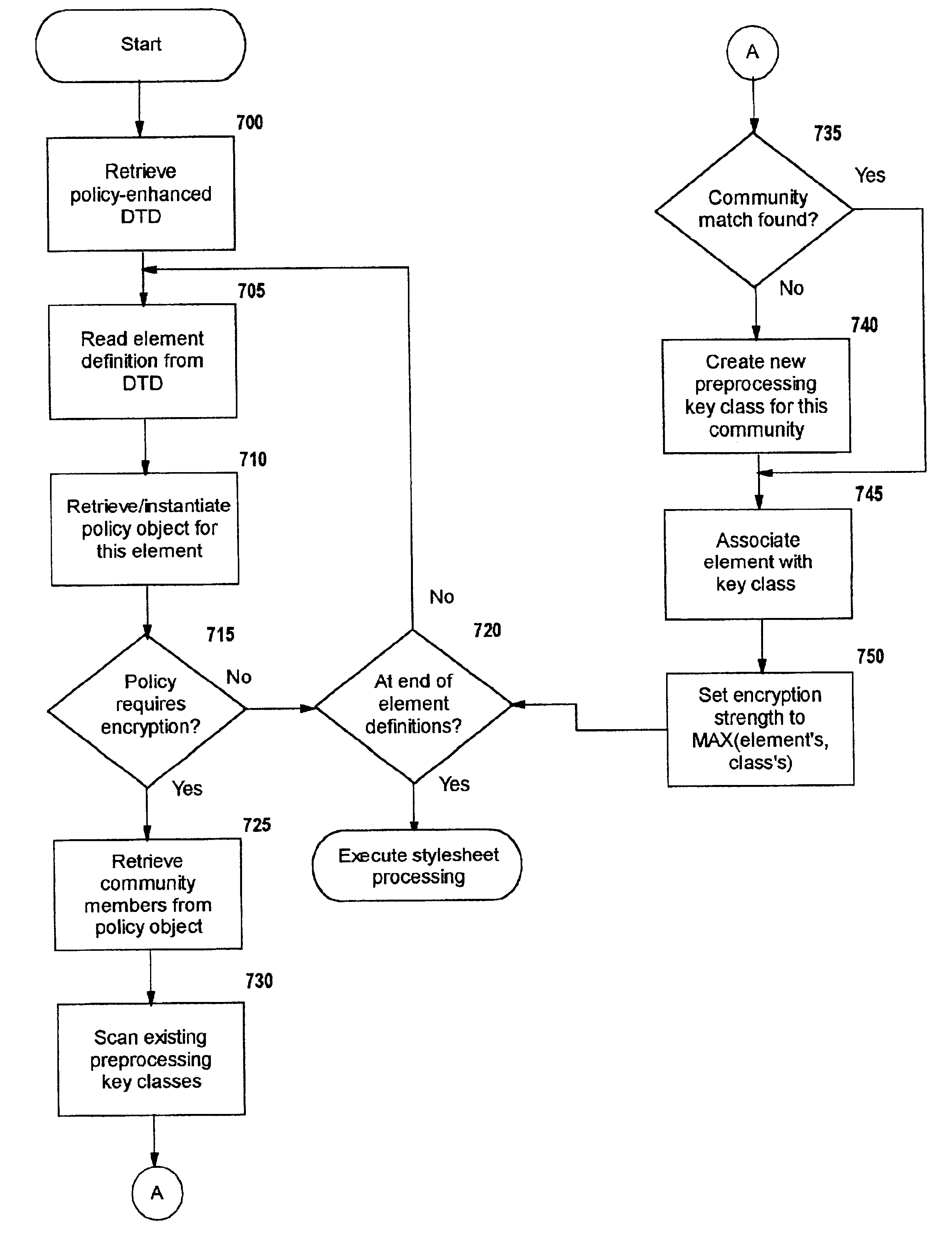
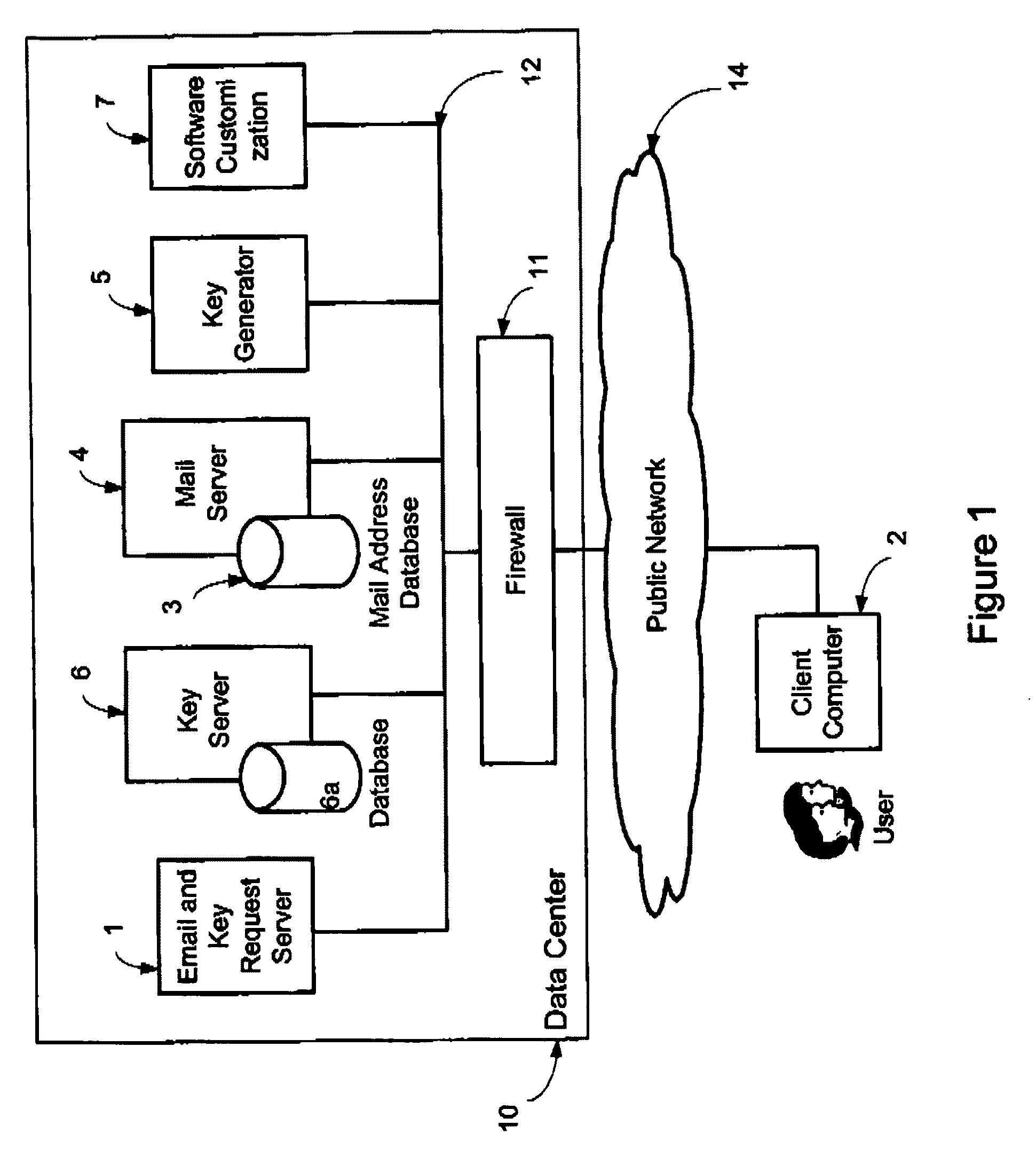
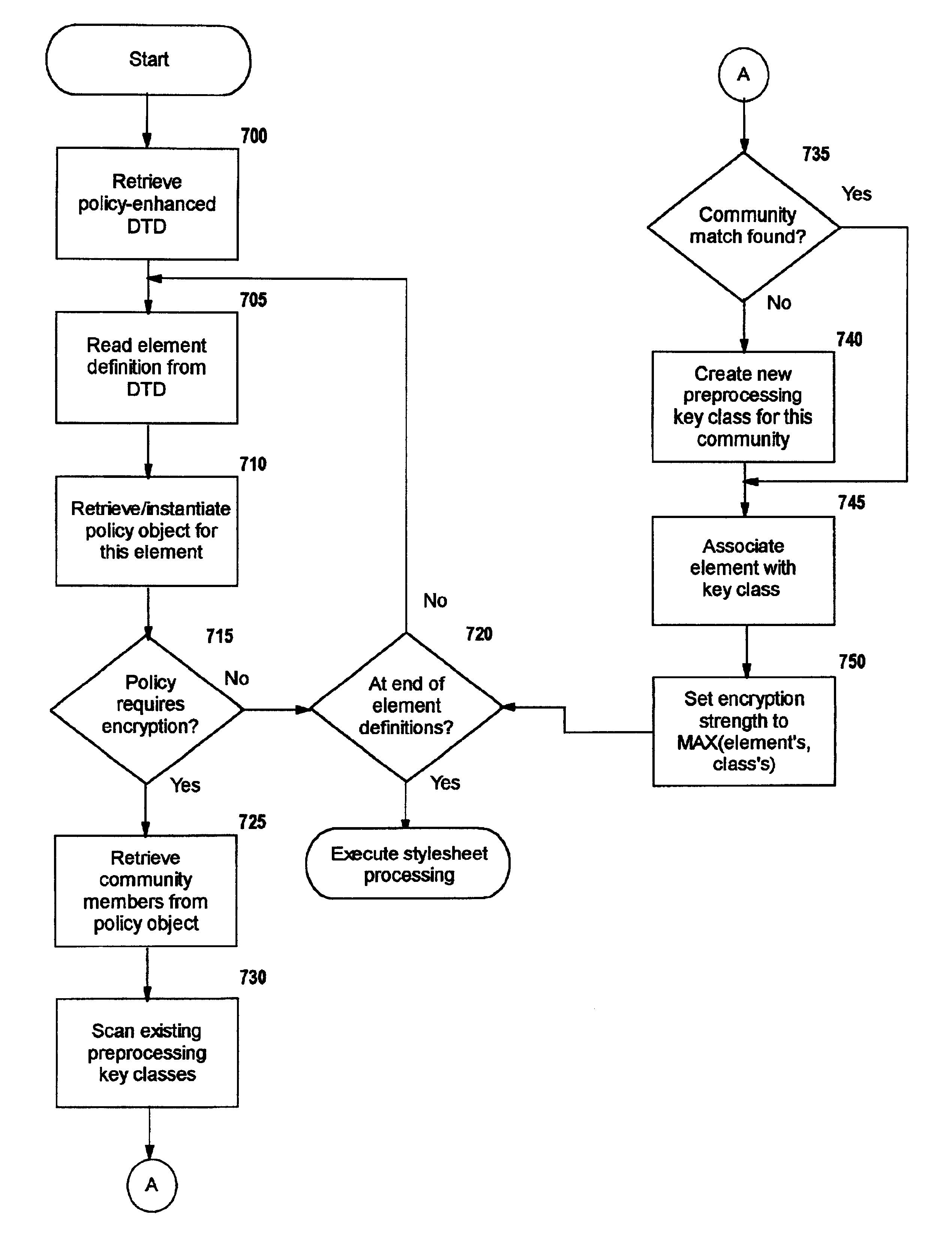
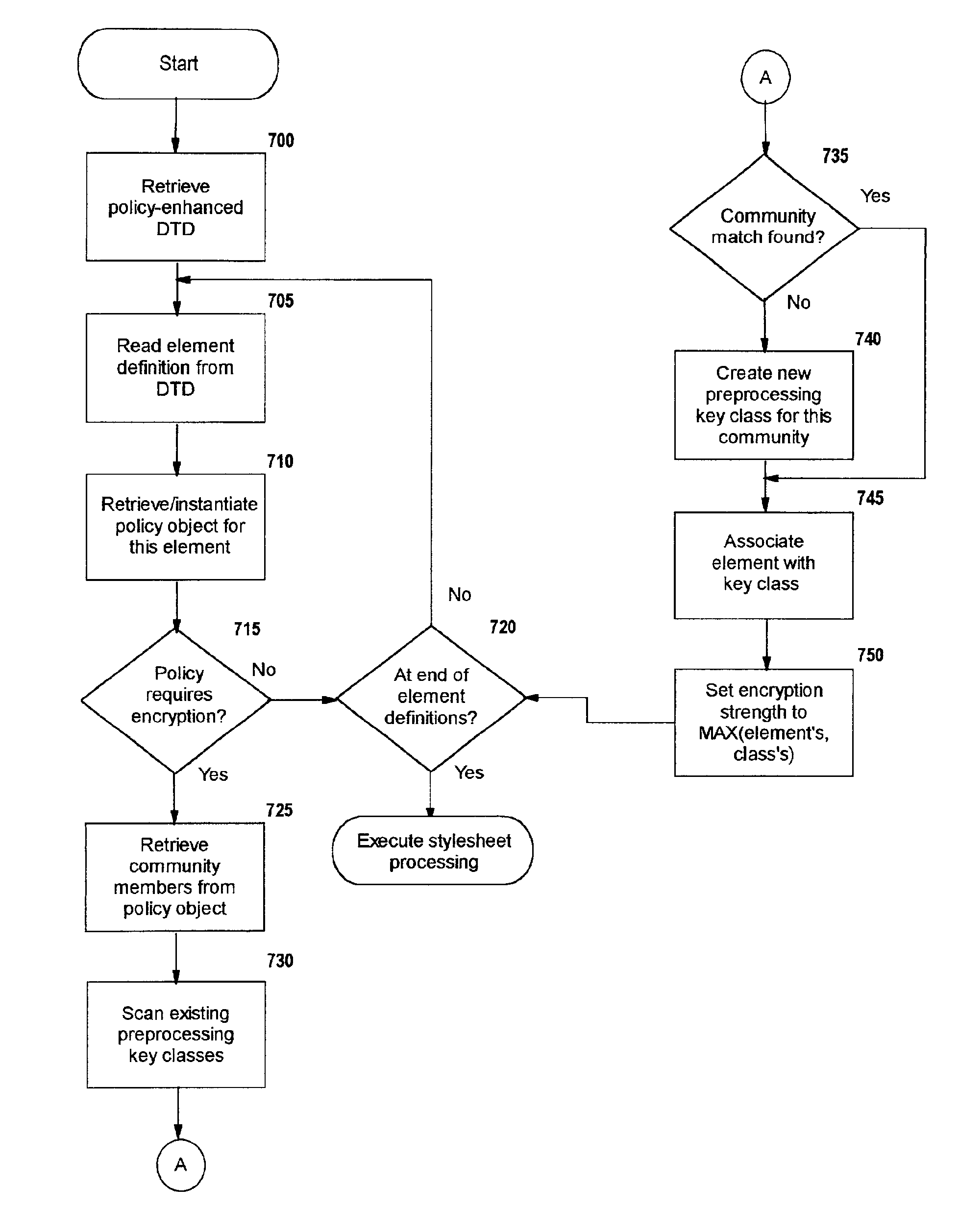
Selective data encryption using style sheet processing
InactiveUS6931532B1Security policy efficientlyEfficiently enforcedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEngineeringExtensible markup
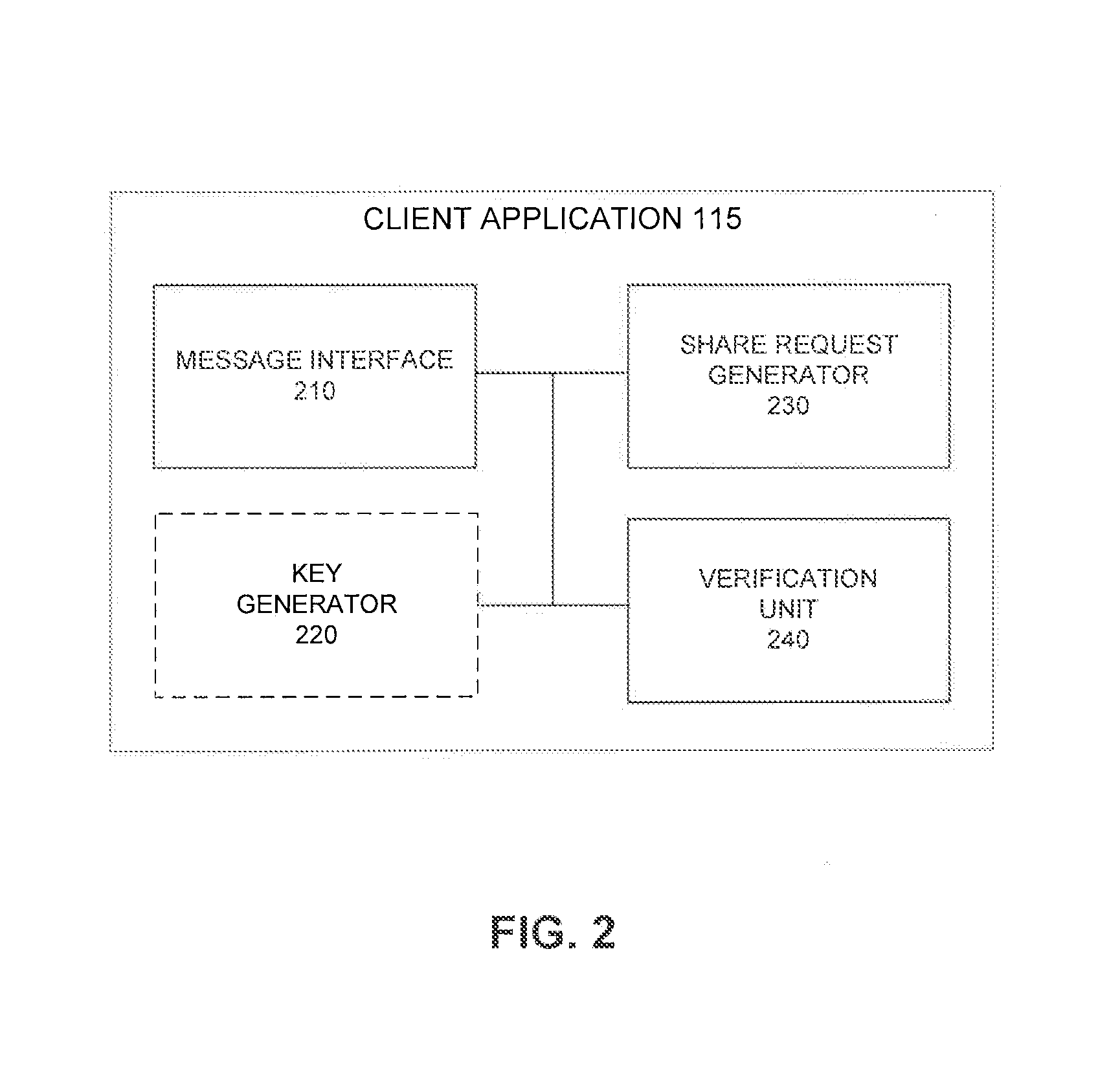
A method, system, and computer program product for selectively encrypting one or more elements of a document using style sheet processing. Disclosed is a policy-driven augmented style sheet processor (e.g. an Extensible Stylesheet Language, or “XSL”, processor) that creates a selectively-encrypted document (e.g. an Extensible Markup Language, or “XML”, document) carrying key-distribution material, such that by using an augmented document processor (e.g. an augmented XML processing engine), an agent can recover only the information elements for which it is authorized. The Document Type Definition (DTD) or schema associated with a document is modified, such that the DTD or schema specifies a reference to stored security policy to be applied to document elements. Each document element may specify a different security policy, such that the different elements of a single document can be encrypted differently (and, some elements may remain unencrypted). The key distribution material enables a document to be encrypted for decryption by an audience that is unknown at the time of document creation, and enables access to the distinct elements of a single encrypted document to be controlled for multiple users and / or groups of users. In this manner, group collaboration is improved by giving more people easier access to information for which they are authorized, while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized agents. A key recovery technique is also defined, whereby the entire document can be decrypted by an authorized agent regardless of how the different elements were originally encrypted and the access protections which were applied to those elements.
Owner:IBM CORP
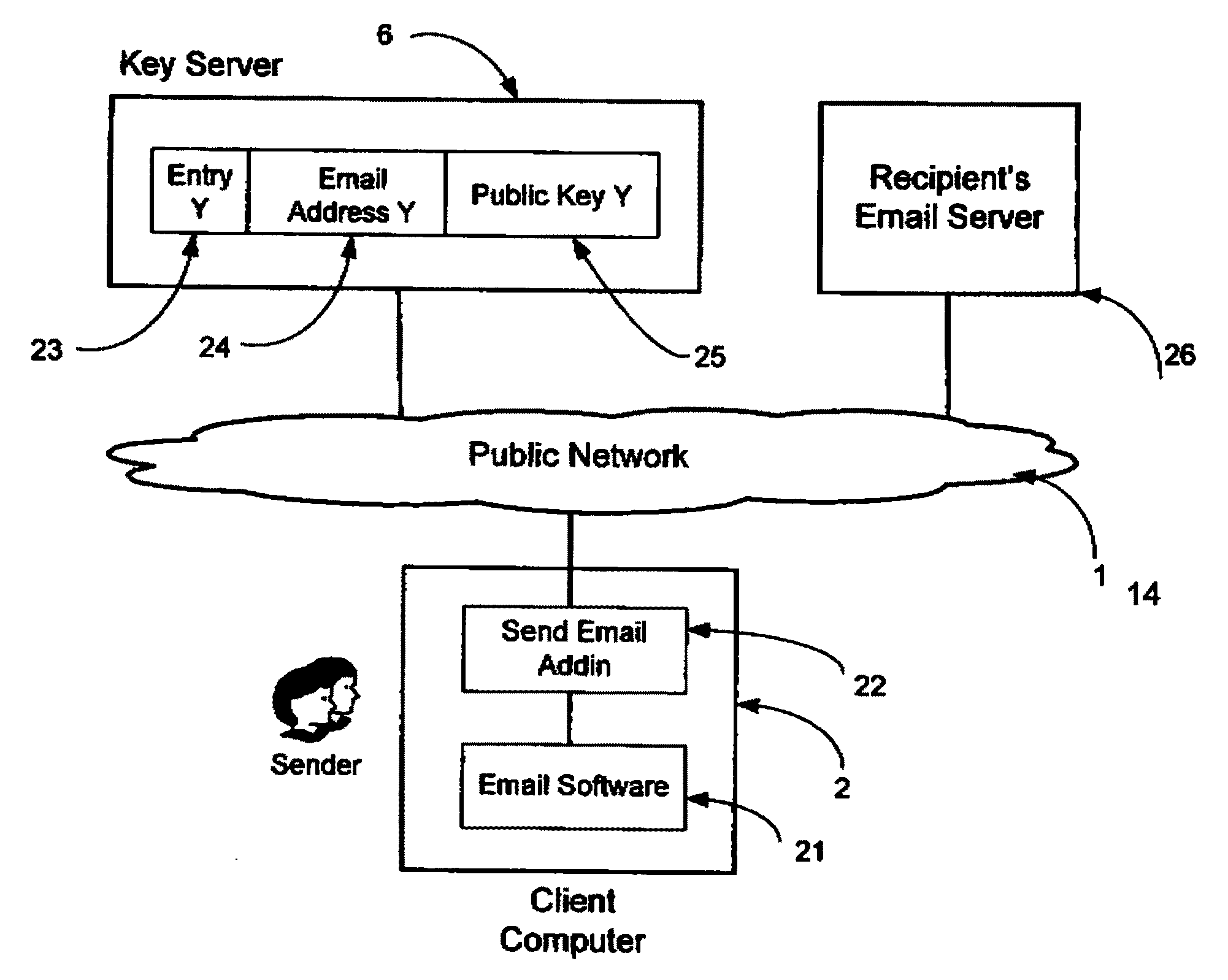
System and method for secure electronic communication services
InactiveUS20090198997A1Easy accessSecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageScalable systemEmail address
A system, method and software module for secure electronic communication services, wherein a public key (25) of private-public-key pair (30,25) is associated with an email address (24), internet name or other registered unique identifier; the registered user of the unique identifier holds the private-key (30) securely, and the respective public-key (25) is made accessible on a key server (6) for look-up and retrieval by other users, for encryption of communications to be sent to the holder of the private-key, and optionally for message confidentiality, message integrity and authentication of sender and recipient, without requiring certificates. A distributed and scalable system is provided by a server network (600; 401, 501) for registration, key distribution and management preferably using a kDNS server hierarchy (601,602,603) or a key-DNS server hierarchy (701,702,) and associated protocols so that public-keys of recipients can be searched and retrieved over the internet based on the recipients email address or other unique identifier, thus facilitating secure communication between users in different network domains and organizations.
Owner:TOPOSIS CORP
Selective data encryption using style sheet processing for decryption by a client proxy
InactiveUS6978367B1Security policy efficientlyEfficiently enforcedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDocumentation procedureDocument preparation
A method, system, and computer program product for selectively encrypting one or more elements of a document using style sheet processing. Disclosed is a policy-driven augmented style sheet processor (e.g. an Extensible Stylesheet Language, or “XSL”, processor) that creates a selectively-encrypted document (e.g. an Extensible Markup Language, or “XML”, document) carrying key-distribution material, such that by using an augmented document processor (e.g. an augmented XML processing engine), an agent can recover only the information elements for which it is authorized. The Document Type Definition (DTD) or schema associated with a document is modified, such that the DTD or schema specifies a reference to stored security policy to be applied to document elements. Each document element may specify a different security policy, such that the different elements of a single document can be encrypted differently (and, some elements may remain unencrypted). The key distribution material enables a document to be encrypted for decryption by an audience that is unknown at the time of document creation, and enables access to the distinct elements of a single encrypted document to be controlled for multiple users and / or groups of users. In this manner, group collaboration is improved by giving more people easier access to information for which they are authorized, while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized agents. A key recovery technique is also defined, whereby the entire document can be decrypted by an authorized agent regardless of how the different elements were originally encrypted and the access protections which were applied to those elements.
Owner:IBM CORP
Selective data encryption using style sheet processing for decryption by a key recovery agent
InactiveUS6941459B1Security policy efficientlyEfficiently enforcedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDocumentation procedureExtensible markup
A method, system, and computer program product for selectively encrypting one or more elements of a document using style sheet processing. Disclosed is a policy-driven augmented style sheet processor (e.g. an Extensible Stylesheet Language, or “XSL”, processor) that creates a selectively-encrypted document (e.g. an Extensible Markup Language, or “XML”, document) carrying key-distribution material, such that by using an augmented document processor (e.g. an augmented XML processing engine), an agent can recover only the information elements for which it is authorized. The Document Type Definition (DTD) or schema associated with a document is modified, such that the DTD or schema specifies a reference to stored security policy to be applied to document elements. Each document element may specify a different security policy, such that the different elements of a single document can be encrypted differently (and, some elements may remain unencrypted). The key distribution material enables a document to be encrypted for decryption by an audience that is unknown at the time of document creation, and enables access to the distinct elements of a single encrypted document to be controlled for multiple users and / or groups of users. In this manner, group collaboration is improved by giving more people easier access to information for which they are authorized, while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized agents. A key recovery technique is also defined, whereby the entire document can be decrypted by an authorized agent regardless of how the different elements were originally encrypted and the access protections which were applied to those elements.
Owner:PHONENICIA INNOVATIONS LLC SUBSIDIARY OF PENDRELL TECH
Secure Management of Operations on Protected Virtual Machines
ActiveUS20150319160A1Well formedMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsKey distributionVirtual machine
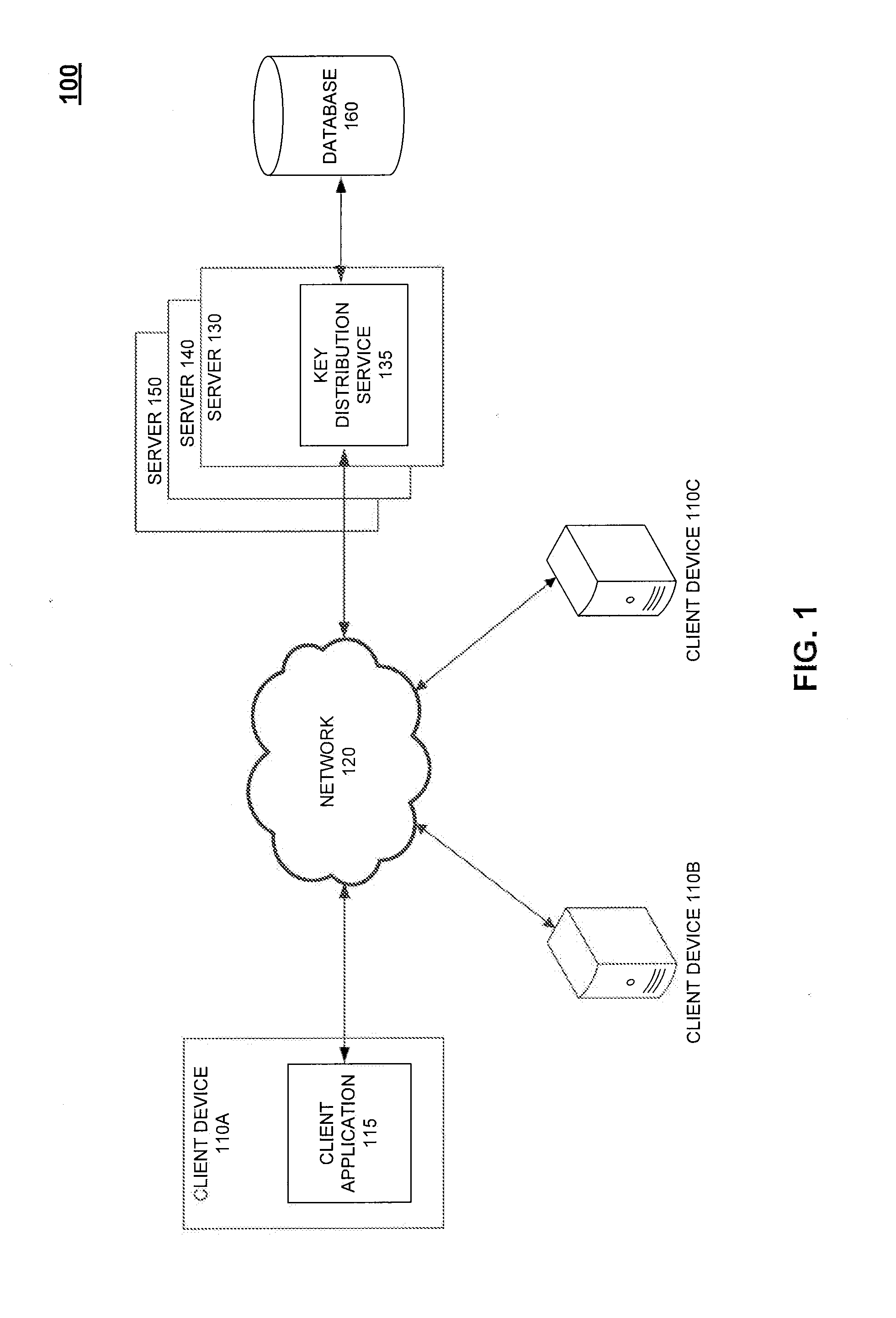
Deploying an encrypted entity on a trusted entity is illustrated herein. A method includes, at a trusted entity, wherein the trusted entity is trusted by an authority as a result of providing a verifiable indication of certain characteristics of the trusted entity meeting certain requirements, receiving an encrypted entity from an untrusted entity. The untrusted entity is not trusted by the authority. At the trusted entity, a trust credential from the authority is used to obtain a key from a key distribution service. The key distribution service is trusted by the authority. The key is used to decrypt the encrypted entity to allow the encrypted entity to be deployed at the trusted entity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
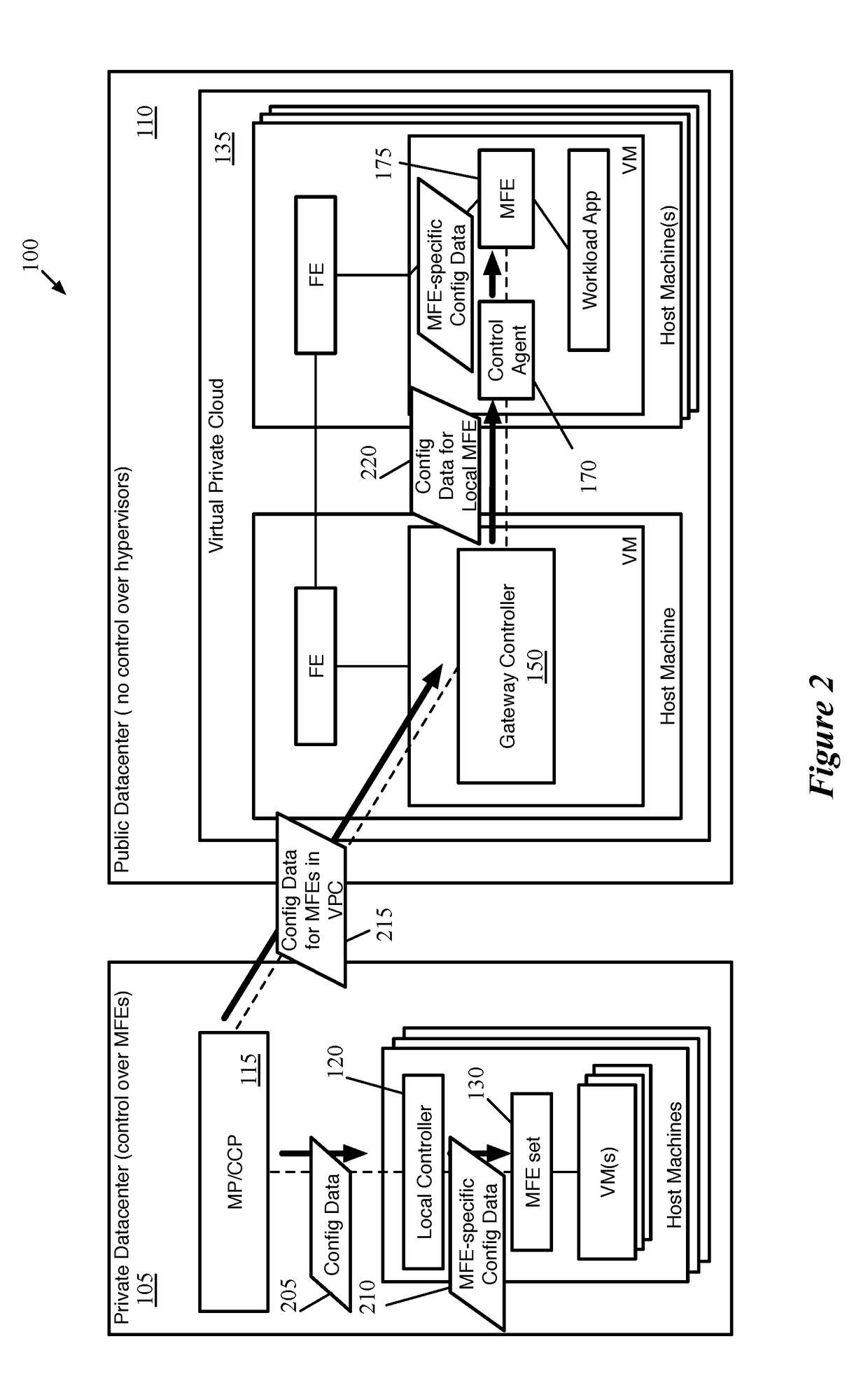
Distributed Network Encryption for Logical Network Implemented in Public Cloud
ActiveUS20180063193A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey distributionKey storage
Some embodiments provide a method for a first data compute node (DCN) operating in a public datacenter. The method receives an encryption rule from a centralized network controller. The method determines that the network encryption rule requires encryption of packets between second and third DCNs operating in the public datacenter. The method requests a first key from a secure key storage. Upon receipt of the first key, the method uses the first key and additional parameters to generate second and third keys. The method distributes the second key to the second DCN and the third key to the third DCN in the public datacenter.
Owner:NICIRA
Selective data encryption using style sheet processing for decryption by a group clerk
InactiveUS6961849B1Security policy efficientlyEfficiently enforcedKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEngineeringExtensible markup
A method, system, and computer program product for selectively encrypting one or more elements of a document using style sheet processing. Disclosed is a policy-driven augmented style sheet processor (e.g. an Extensible Stylesheet Language, or “XSL”, processor) that creates a selectively-encrypted document (e.g. an Extensible Markup Language, or “XML”, document) carrying key-distribution material, such that by using an augmented document processor (e.g., an augmented XML processing engine), an agent can recover only the information elements for which it is authorized. The Document Type Definition (DTD) or schema associated with a document is modified, such that the DTD or schema specifies a reference to stored security policy to be applied to document elements. Each document element may specify a different security policy, such that the different elements of a single document can be encrypted differently (and, some elements may remain unencrypted). The key distribution material enables a document to be encrypted for decryption by an audience that is unknown at the time of document creation, and enables access to the distinct elements of a single encrypted document to be controlled for multiple users and / or groups of users. In this manner, group collaboration is improved by giving more people easier access to information for which they are authorized, while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized agents. A key recovery technique is also defined, whereby the entire document can be decrypted by an authorized agent regardless of how the different elements were originally encrypted and the access protections which were applied to those elements.
Owner:IBM CORP
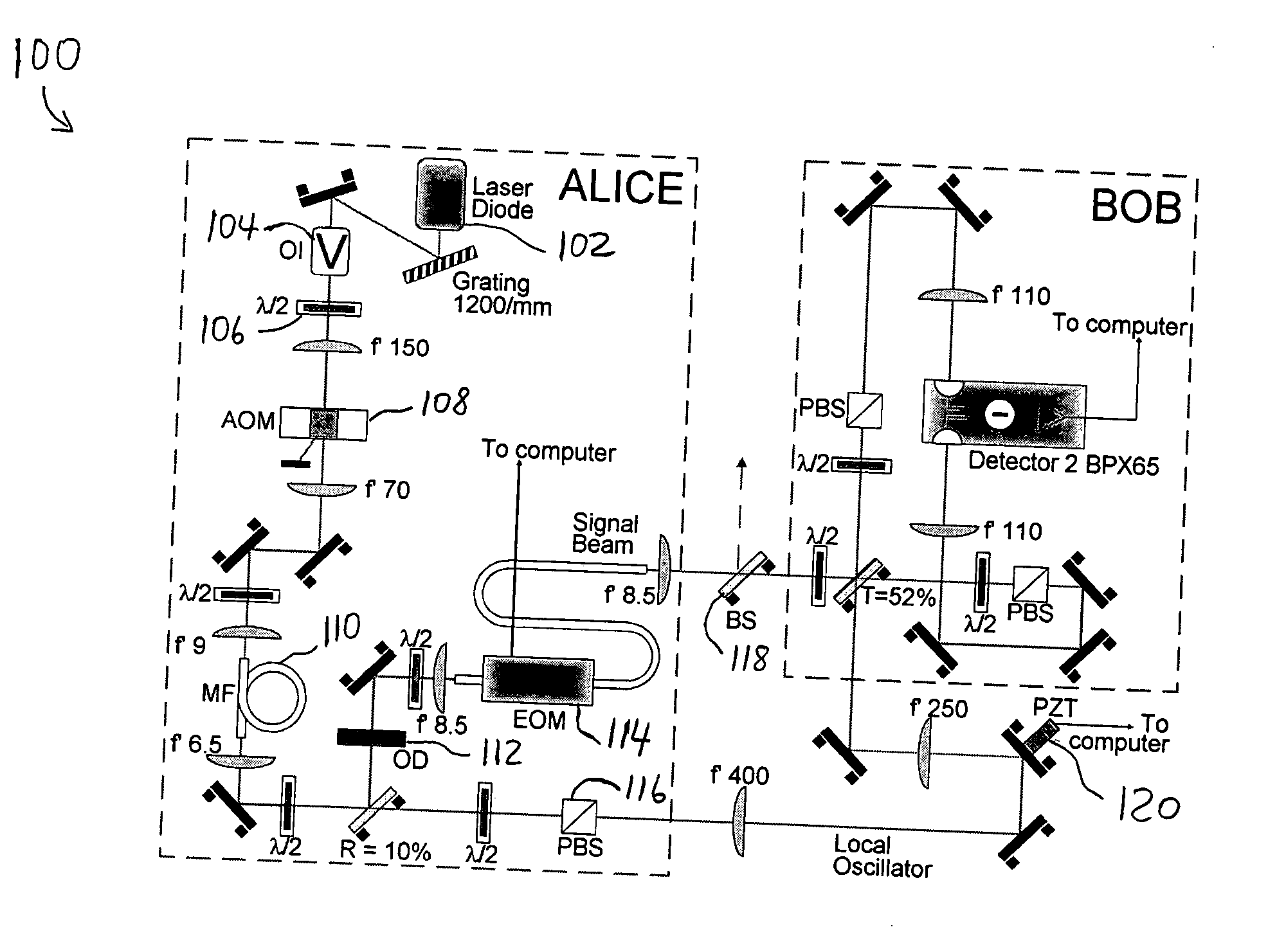
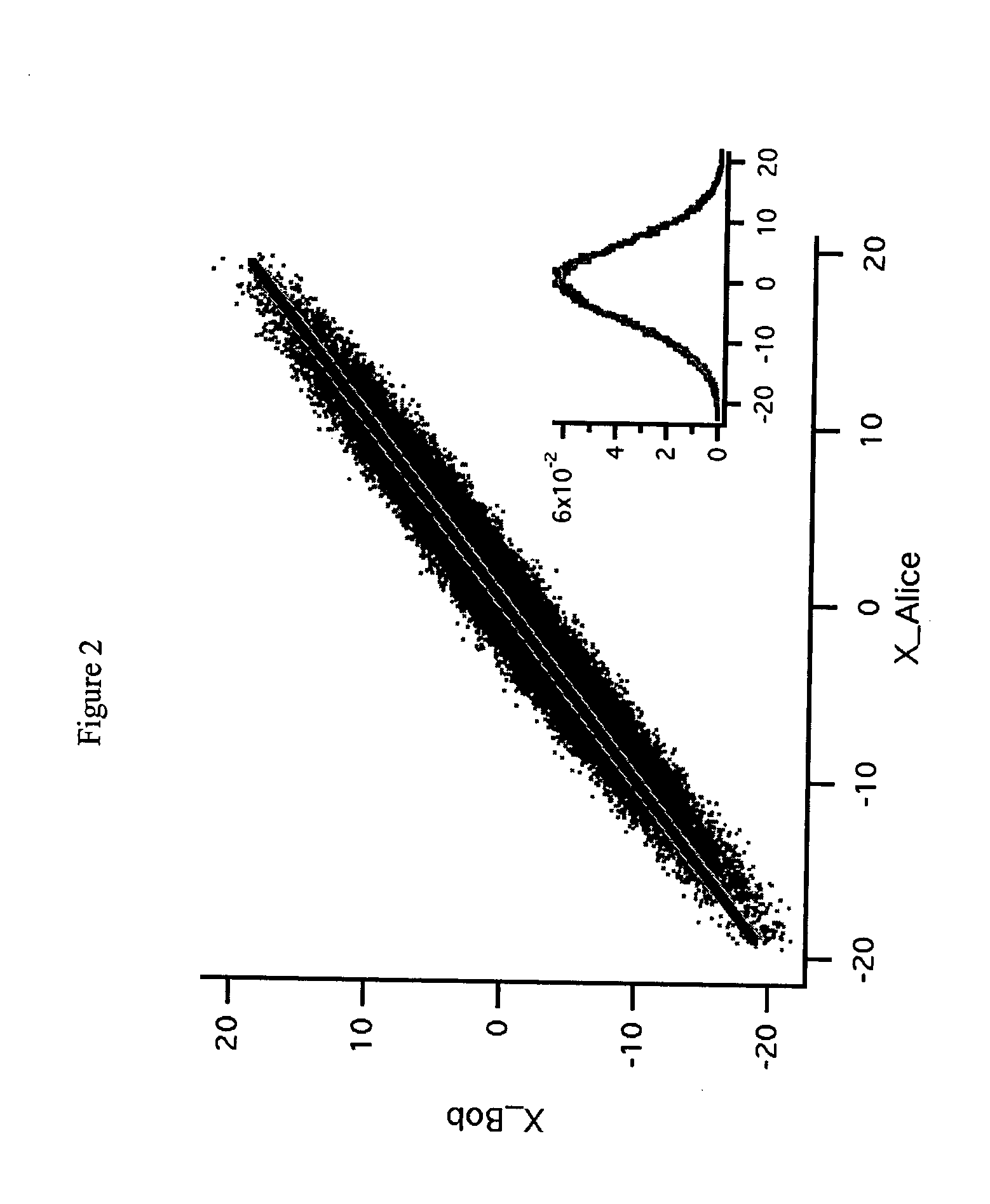
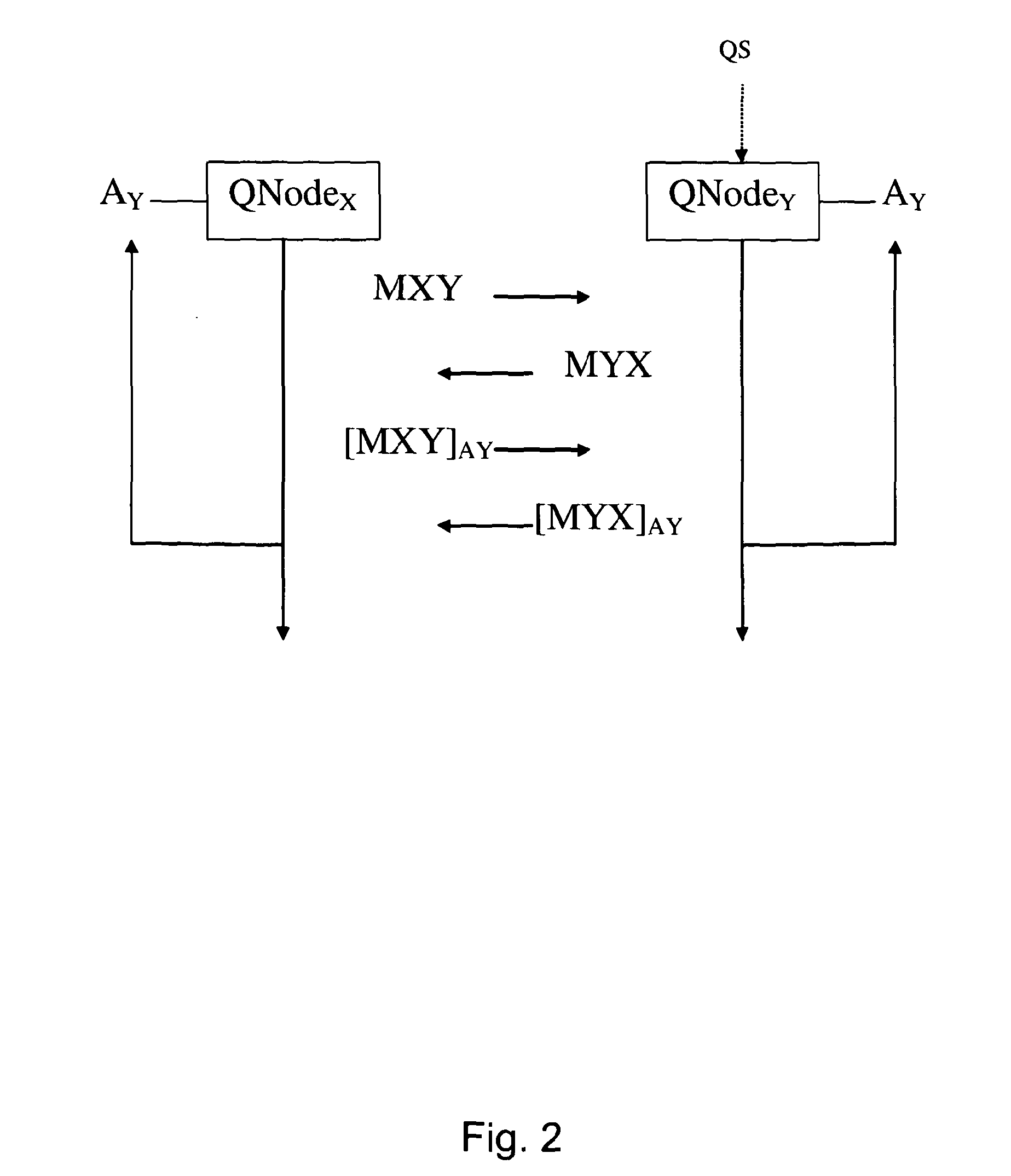
High-rate quantum key distribution scheme relying on continuously phase and amplitude-modulated coherent light pulses
InactiveUS20040109564A1Level of securityIncrease chanceKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationHigh rateCoherent states
One aspect of the present invention is related to a quantum cryptographic scheme comprising at least one sending unit including a physical means of encoding and distributing a raw key in the quadrature components of quantum coherent states that are continuously modulated in phase and amplitude, at least one receiving unit containing a physical means of performing homodyne detection of the quantum coherent states in order to measure the quadrature components of the states, a quantum channel for connecting the sending unit to the receiving unit, a two-way authenticated public channel for transmitting non-secret messages between the sending unit and the receiving unit, a quantum key distribution protocol ensuring that the information tapped by a potential eavesdropper can be estimated from the quantum channel parameters, and a direct or reverse reconciliation protocol that converts the raw continuous data into a common binary key.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
Secure, efficient, and mutually authenticated cryptographic key distribution
ActiveUS7418596B1Easy to useIncreased speed mobilityKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionPasswordKey distribution
Systems and methods disclosed herein provide secure, efficient, and mutually authenticated cryptographic key distribution. A client or client manufacturer may pre-generate and pre-encrypt the cryptographic keys, store the encrypted keys within the client, and deliver such keys to the serving network's access server via the client, while also relying upon, if available, the authentication performed by a trusted access server of an intermediate network which the client must traverse in order to obtain access the serving network. If not available, a client password stored within the client may be used to enable client authentication by the serving network prior to acceptance of the delivered cryptographic keys.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
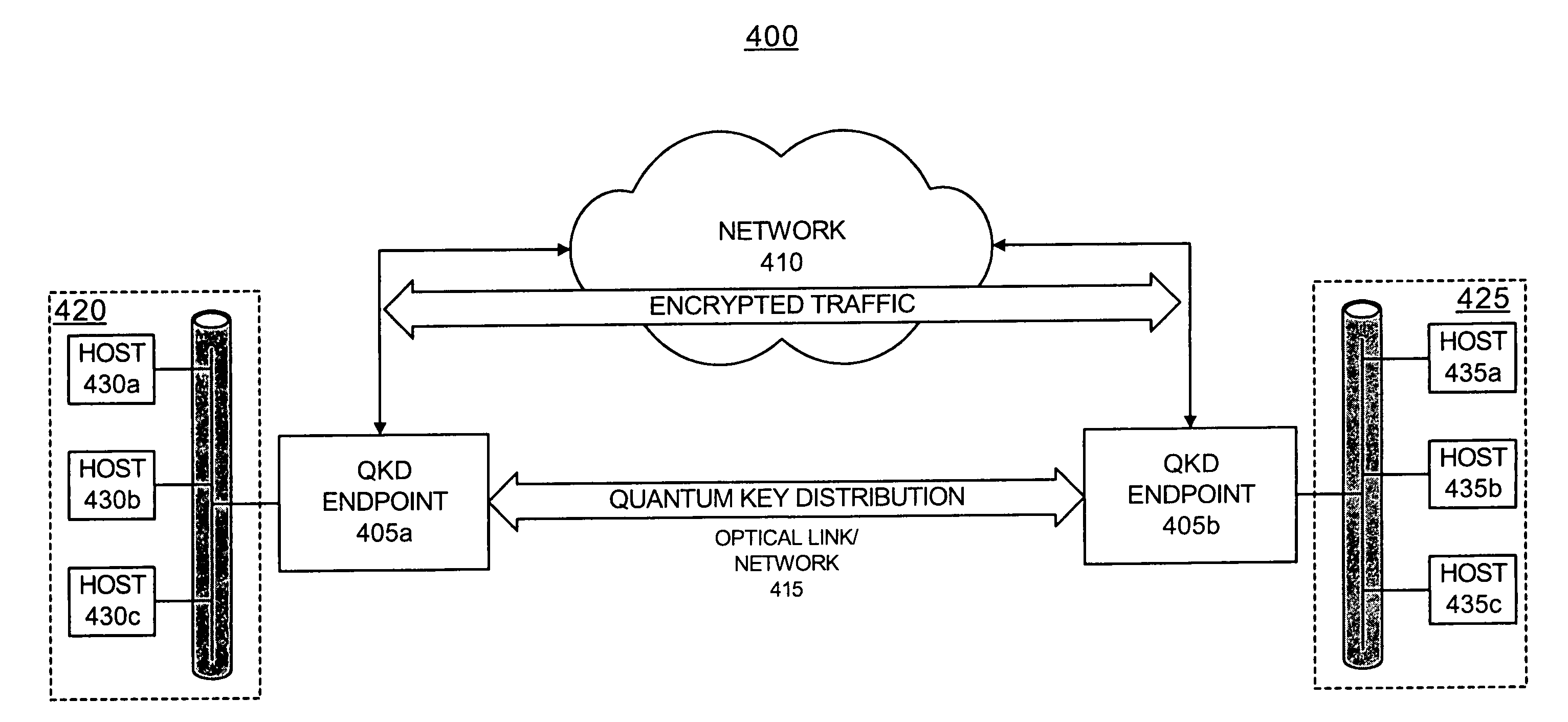
Methods and apparatus for use in quantum key distribution
ActiveUS20120177201A1Without prohibitive costEfficient executionKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationComputer hardwareFiber
Methods and apparatus for use in quantum key distribution (QKD) are described. A quantum QKD signal is generated at a source and transmitted through a fibre optic network to an endpoint, a key being agreed with communication over a classical QKD channel. The classical QKD channel contains additional information relevant to a network over which keys are distributed, and may be processed at nodes intermediate between the source and the endpoint.
Owner:QUBITEKK
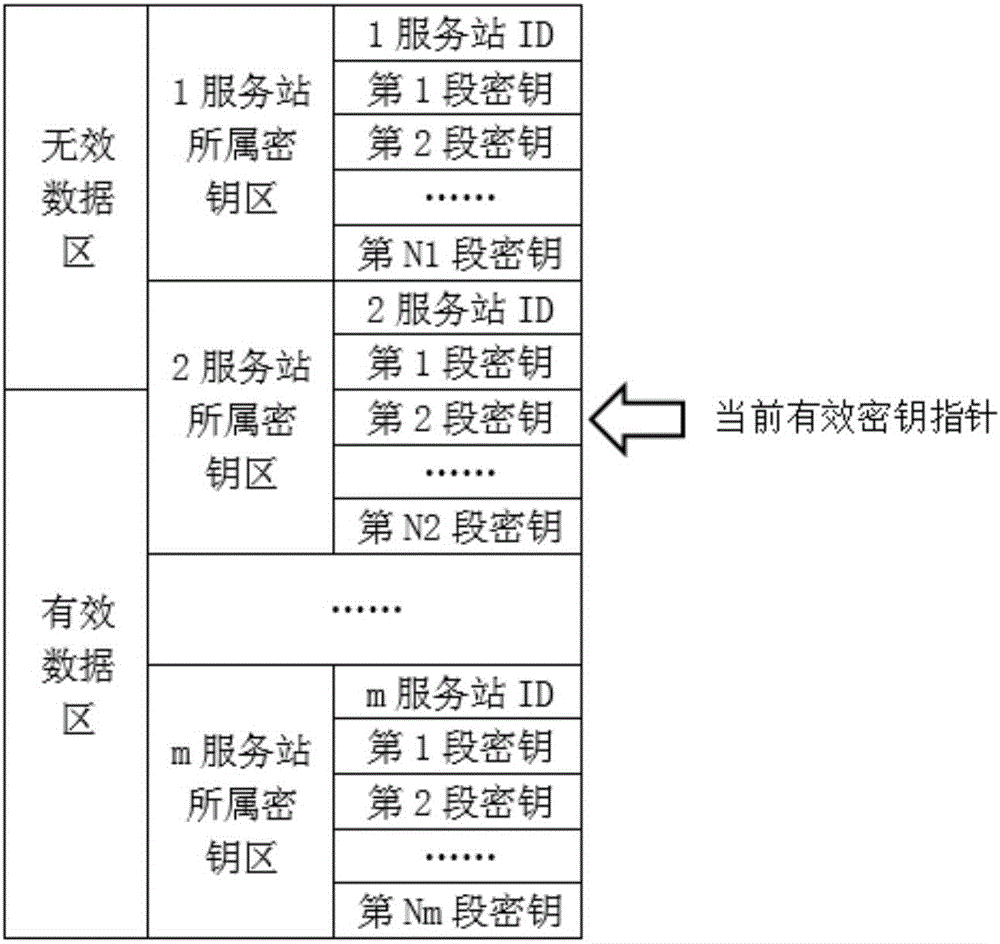
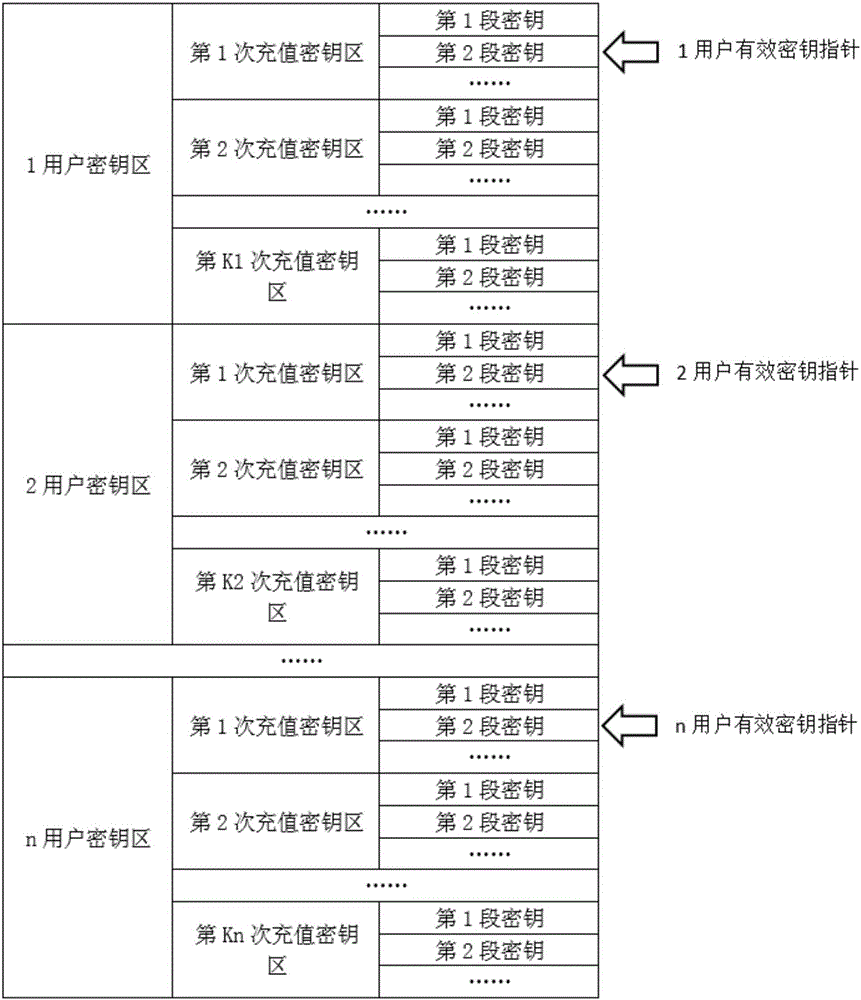
Key distribution method and system
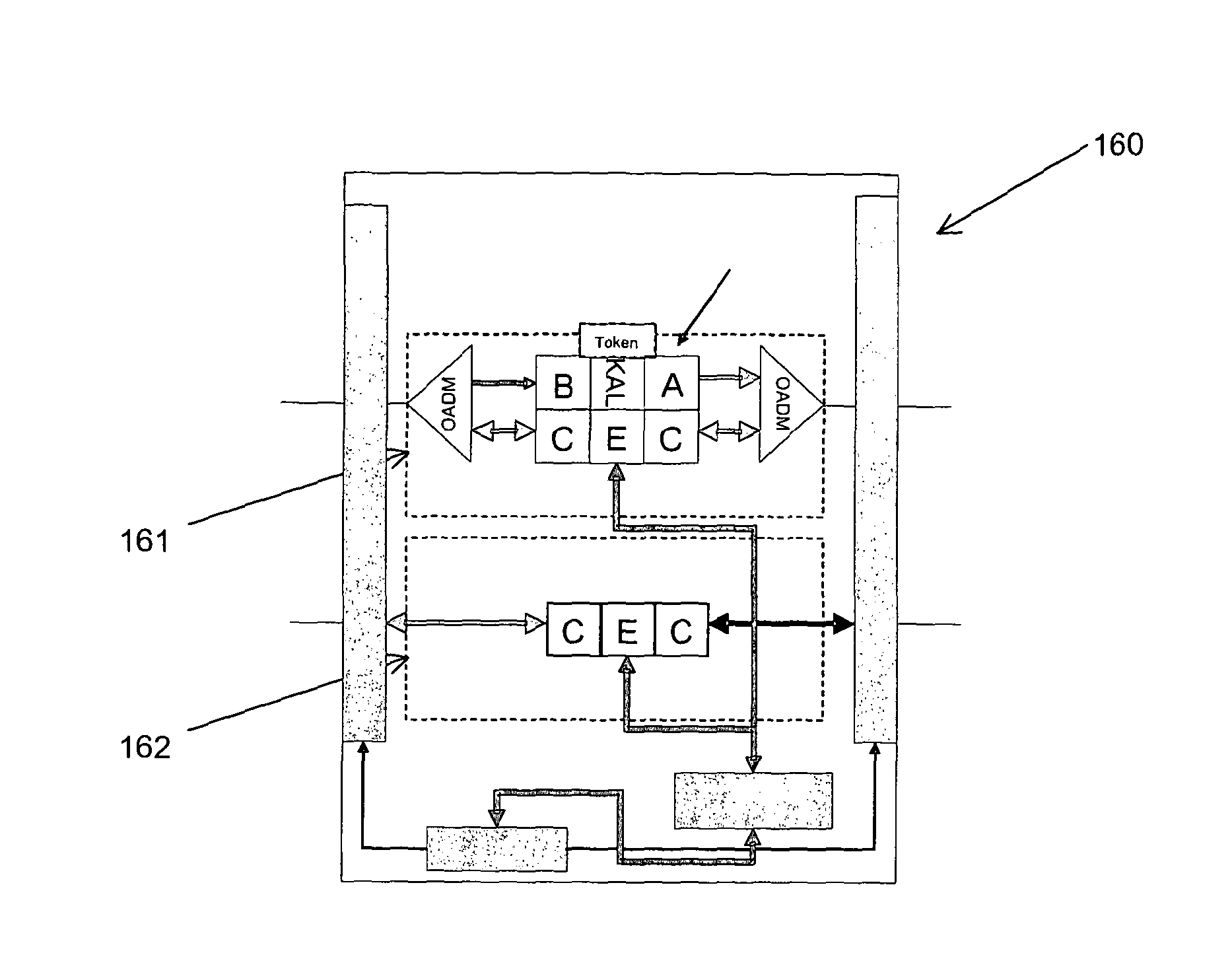
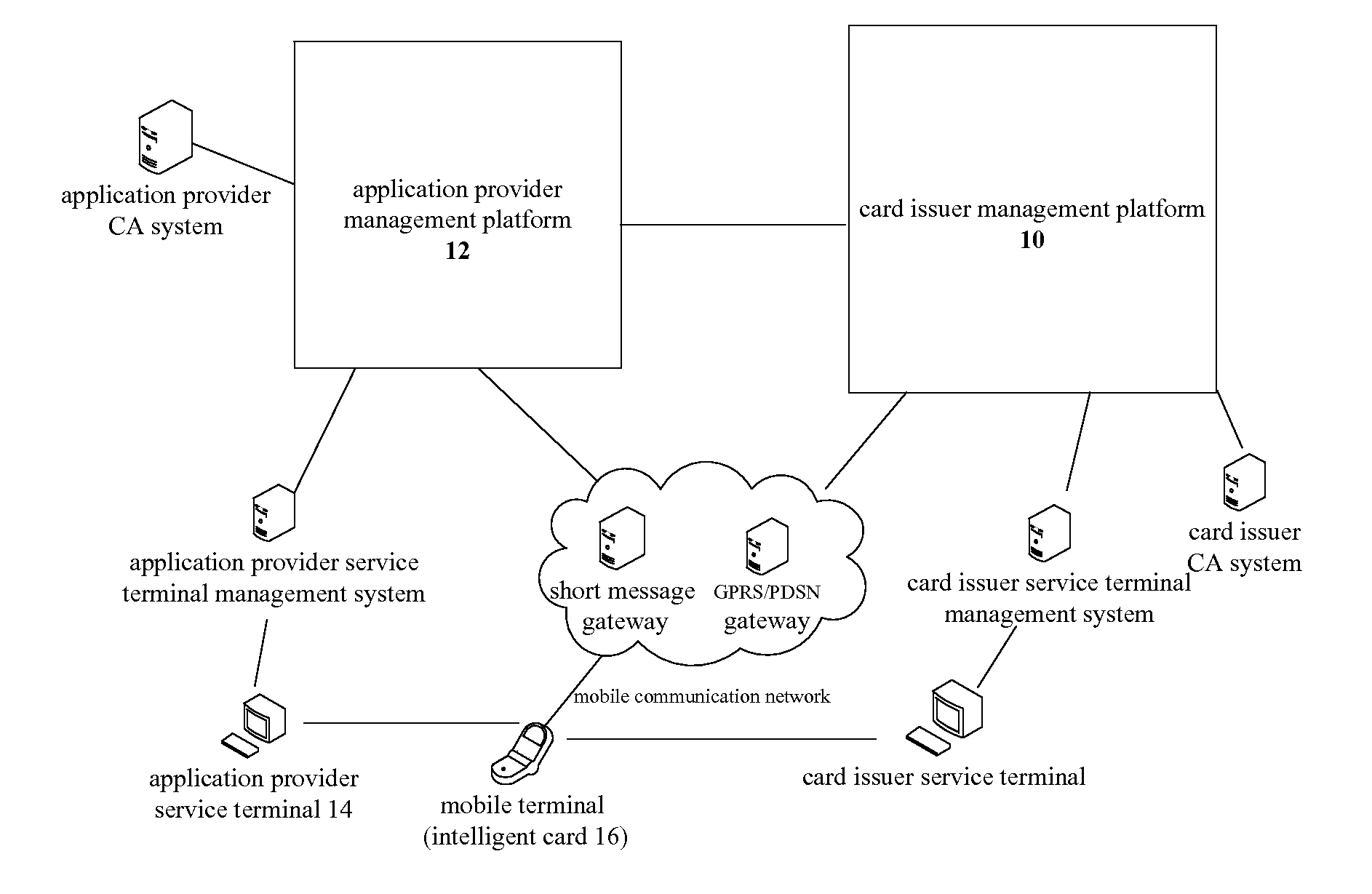
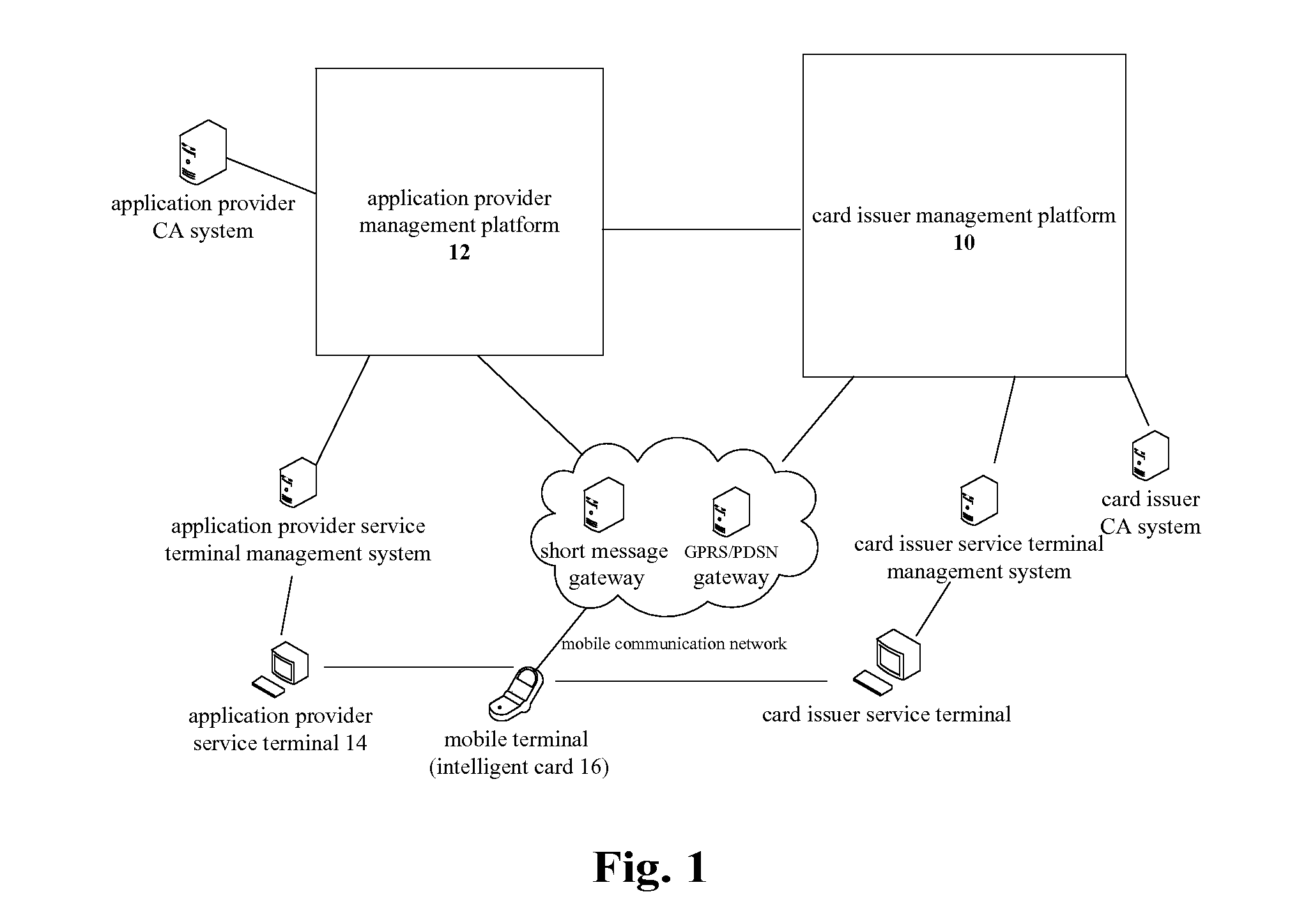
InactiveUS20110280406A1Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationNear-field systems using receiversSecurity domainSmart card
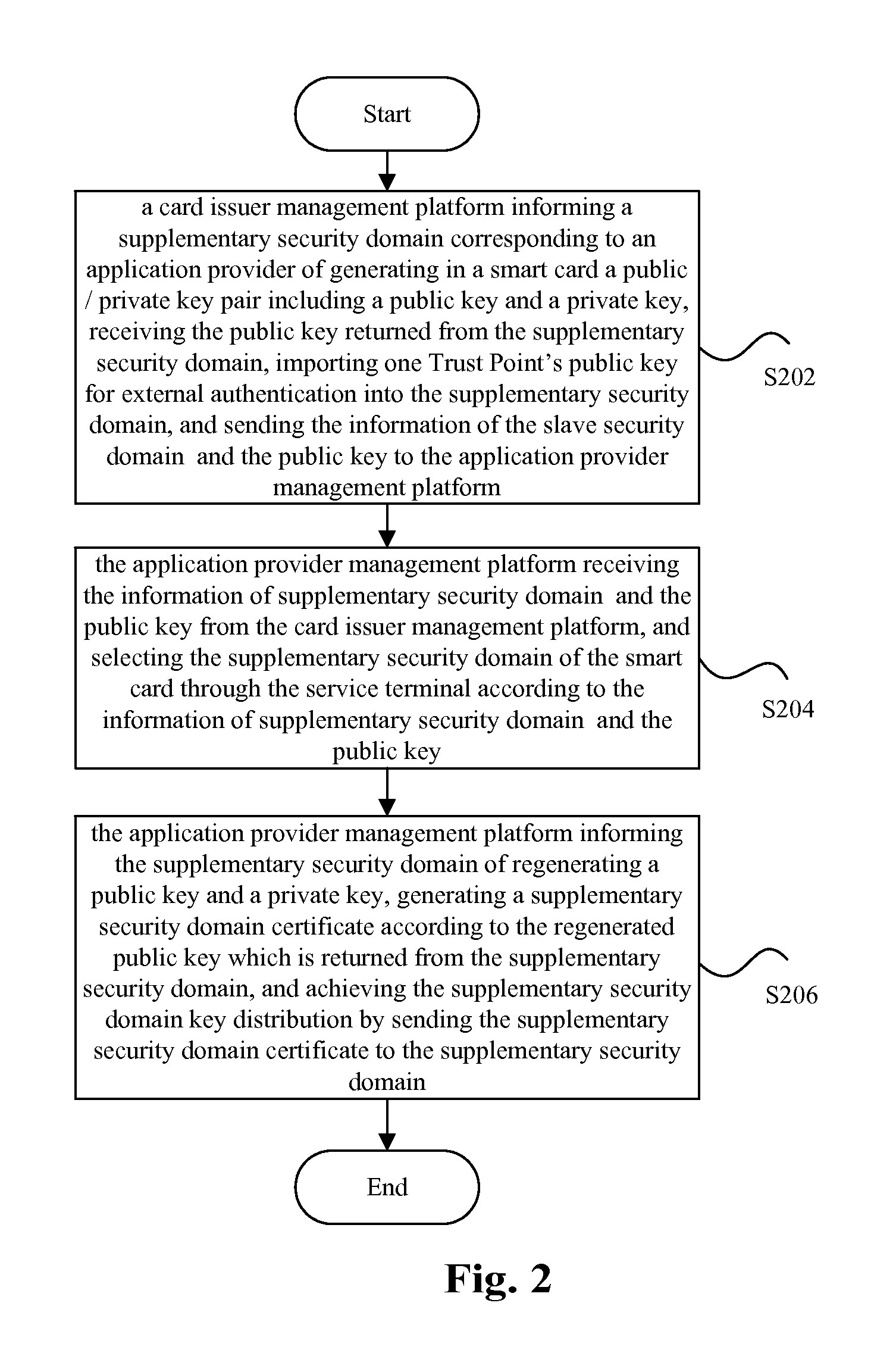
The present invention discloses a key distribution method and system, the method includes: a card issuer management platform informing a supplementary security domain corresponding to an application provider of generating in a smart card a public / private key pair including a public key and a private key, receiving the public key returned from the supplementary security domain, importing a public key for trust point for external authentication into the supplementary security domain, and transmitting the information of the supplementary security domain and the public key to the application provider management platform; the application provider management platform receiving the information of the supplementary security domain and the public key from the card issuer management platform, and selecting the supplementary security domain of the smart card by a service terminal according to the information of the supplementary security domain and the public key; the application provider management platform informing the supplementary security domain of regenerating a public key and a private key, generating a supplementary security domain certificate according to the regenerated public key which is returned from the supplementary security domain, and achieving the supplementary security domain key distribution by transmitting the supplementary security domain certificate to the supplementary security domain. The present invention can improve the security of the supplementary security domain key distribution.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and system for encrypting and decrypting data using an external agent
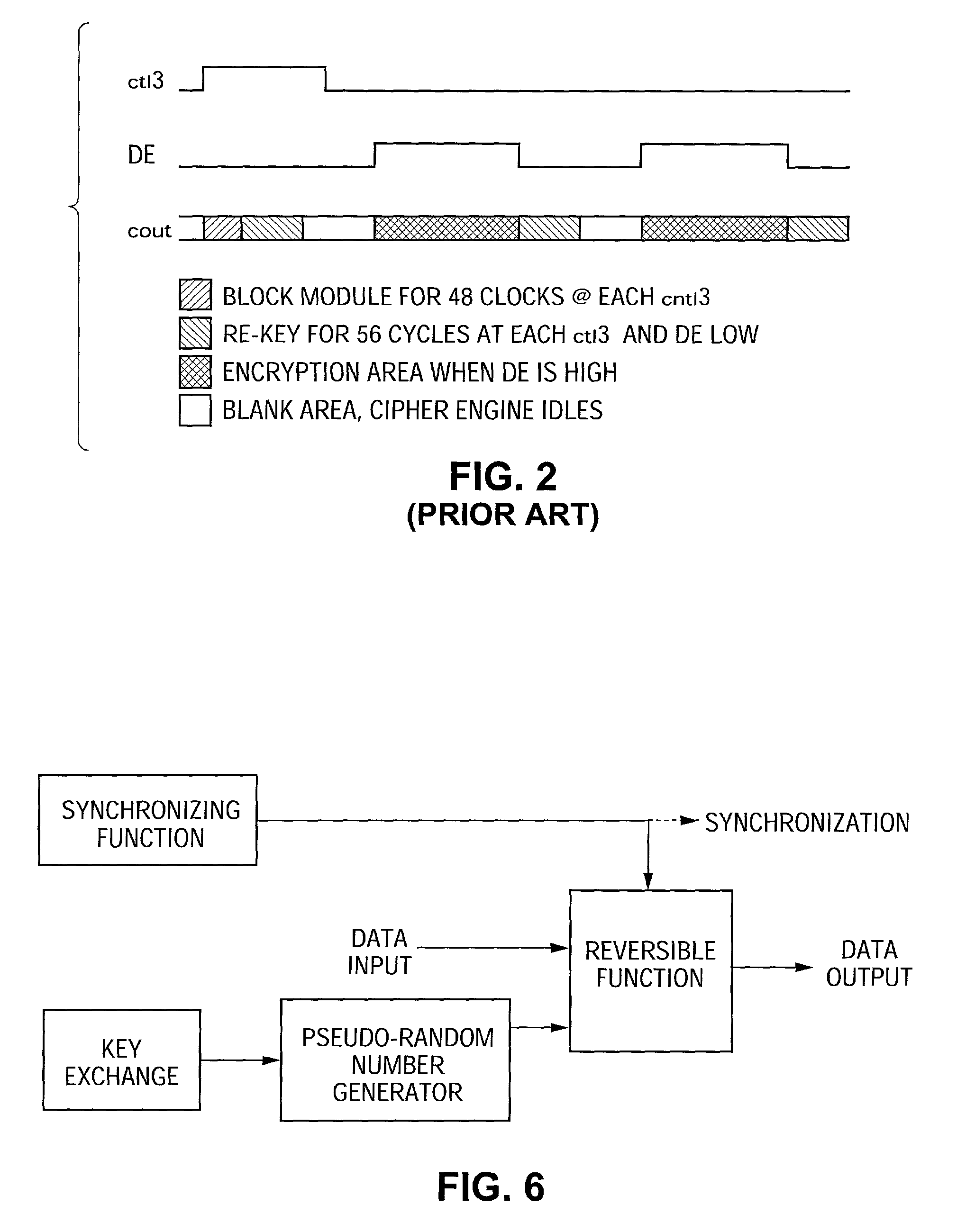
ActiveUS7242766B1Improve securitySynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesSecret communicationResponse processTelecommunications link
A communication system including a transmitter, a receiver, a communication link (for example, a TMDS-like link), and preferably also an external agent with which the transmitter and receiver can communicate, in which video data (or other data) are encrypted, the encrypted data are transmitted from the transmitter to the receiver, and the transmitted data are decrypted in the receiver, a transmitter and a receiver for use in such a system, a cipher engine for use in such a transmitter or receiver, a method for operating such a transmitter or receiver to encrypt or decrypt data, and a method for distributing keys to the transmitter and receiver. The receiver can be a player coupled to a downstream receiver by a TMDS-like link, and configured to re-encrypt the decrypted data (for example, using an AES or HDCP protocol) and send re-encrypted data over the link to the receiver. Optionally, the player is a repeater which translates the decrypted data from the transmitter, and then re-encrypts the translated data for transmission to the downstream receiver. The transmitter can itself be a player that receives and decrypts encrypted data from an upstream source. In preferred embodiments, the system implements a content protection protocol including a challenge-response procedure. After a new key is supplied to the receiver (and the same new key should have been supplied to the transmitter) and before the receiver can use the new key, the challenge-response procedure requires that the receiver validate the transmitter by verifying that the transmitter has proper knowledge of the new key.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Autocompensating quantum cryptographic key distribution system based on polarization splitting of light
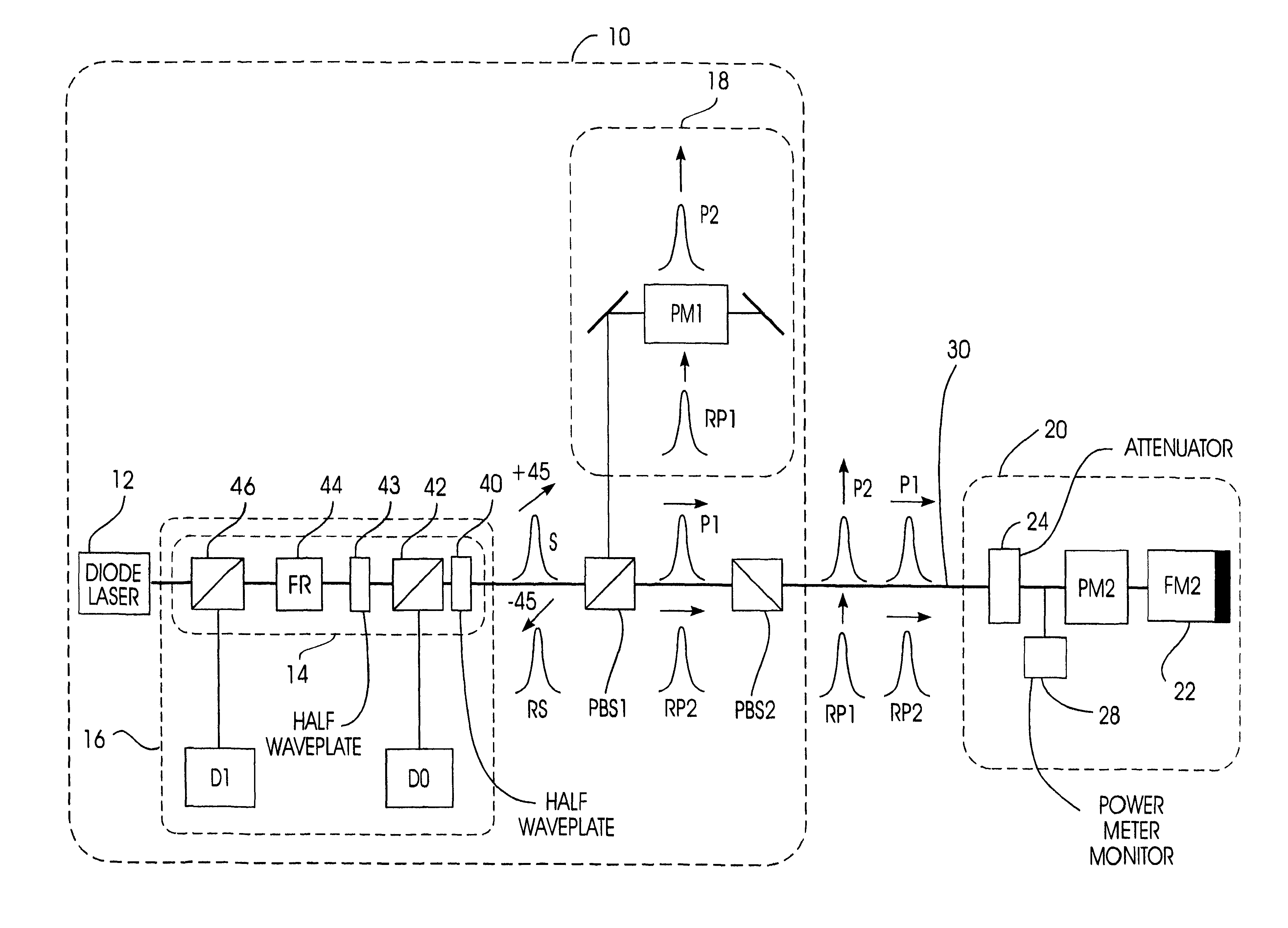
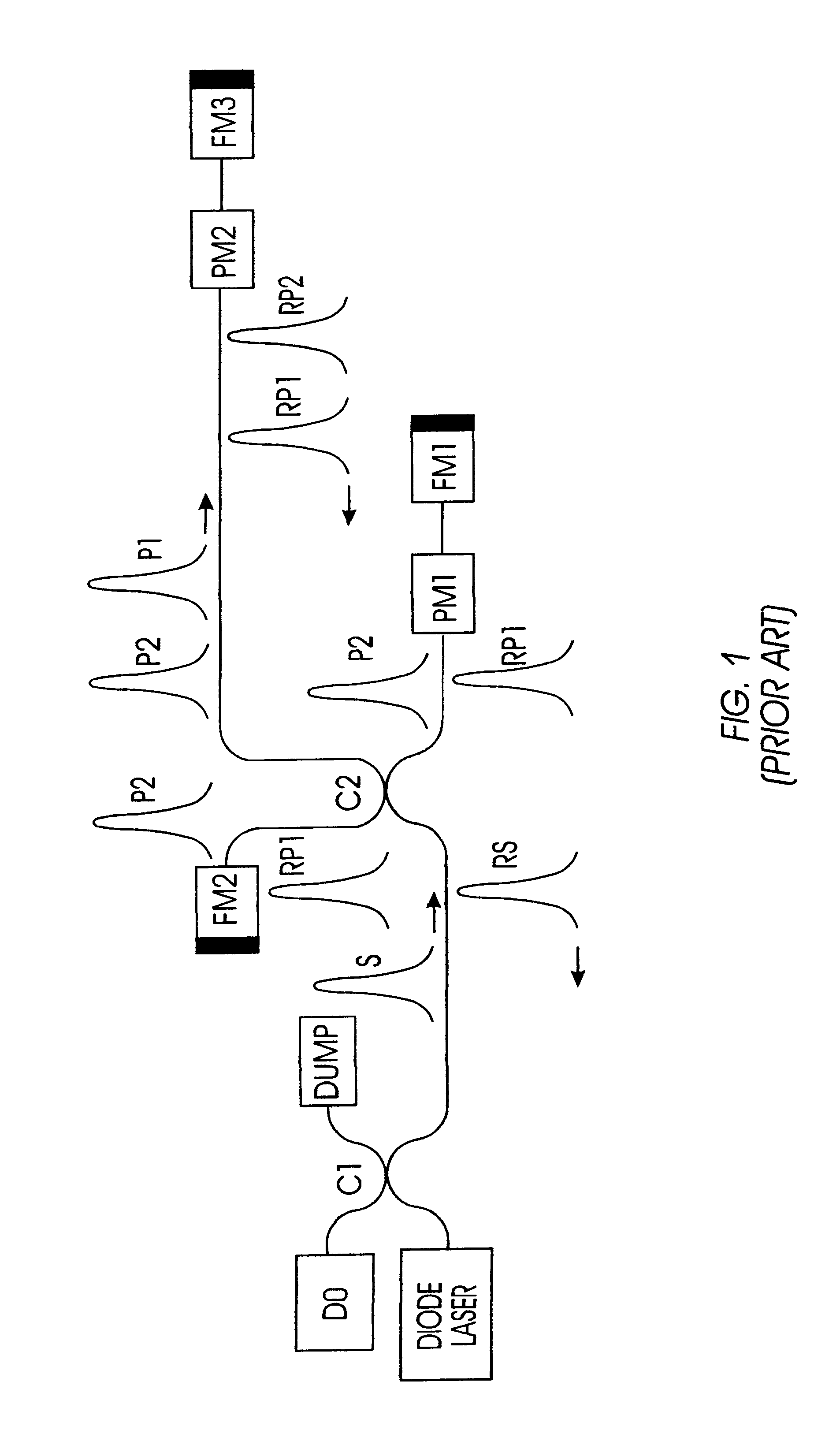
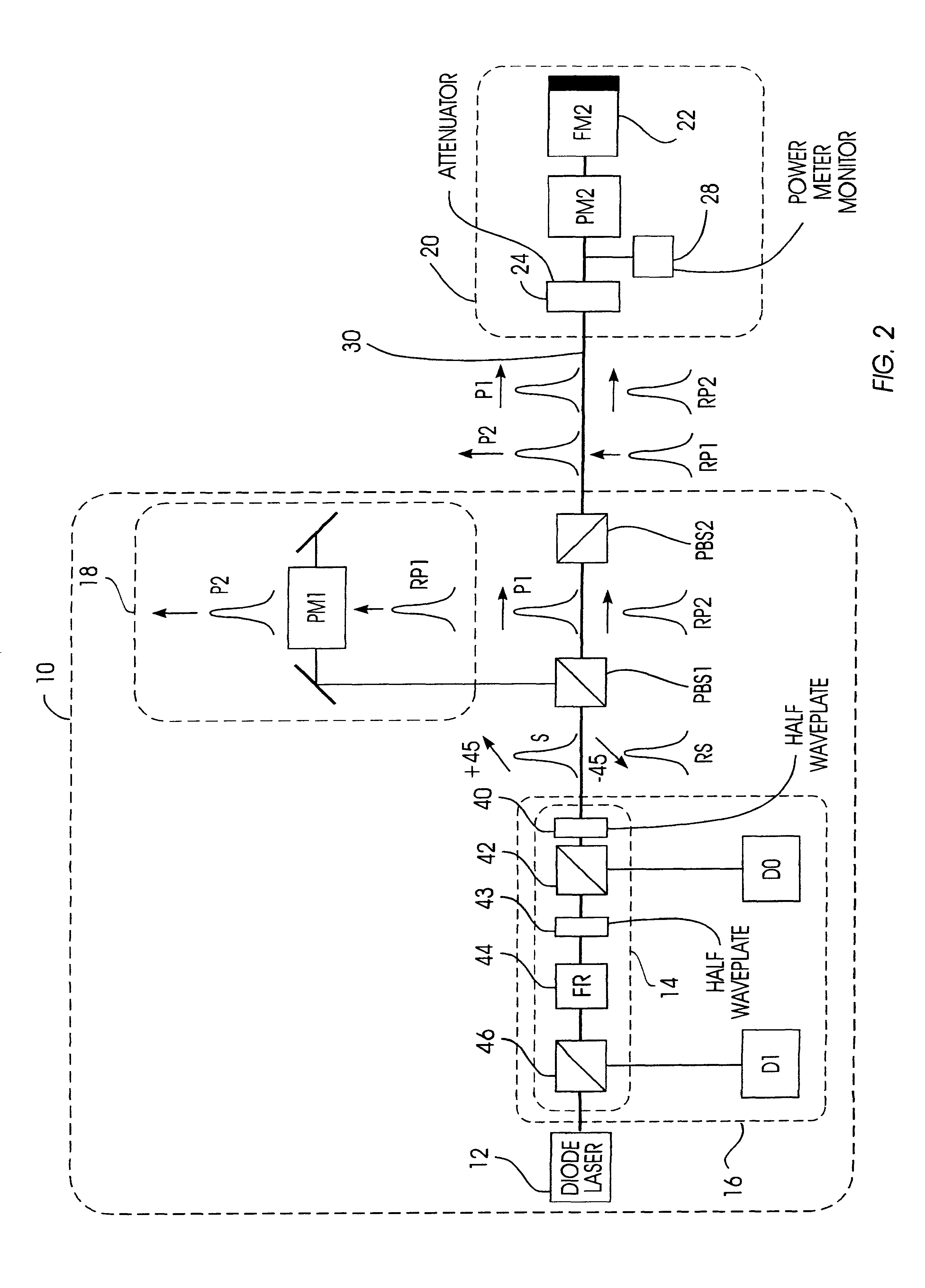
A quantum cryptographic key distribution (QKD) system splits discrete light signals from a laser source into a pair of light pulses that are orthogonally polarized with respect to each other, imparts a phase shift to one or both of these separate pulses during their round trip from the sender to the receiver and back, assures that the return pulses from the receiver are attenuated to single-photon pulses, recombines the phase-shifted pulses at the sender, and then detects from the recombined signal its polarization state, which is representative of the net phase shift imparted by the sender and receiver. The phase modulator at the receiver transmits only one polarization (e.g., vertical), but is used in a manner that permits it to equally modulate both polarization components of an arriving pulse. In this arrangement, when both components of a pulse reach the phase modulator at the receiver, they are both entirely vertically polarized and a phase shift is imparted at that time. This has the advantage that the effect of any time variation or phase errors in the phase modulator will be the same on both components. The key information is decoded at a detection stage at the sender that uses two detectors, one of which detects a first polarization state corresponding to the phase difference between the two phase shifts being 0 and the other of which detects a second polarization state corresponding to the phase difference between the two phase shifts being pi.
Owner:IBM CORP
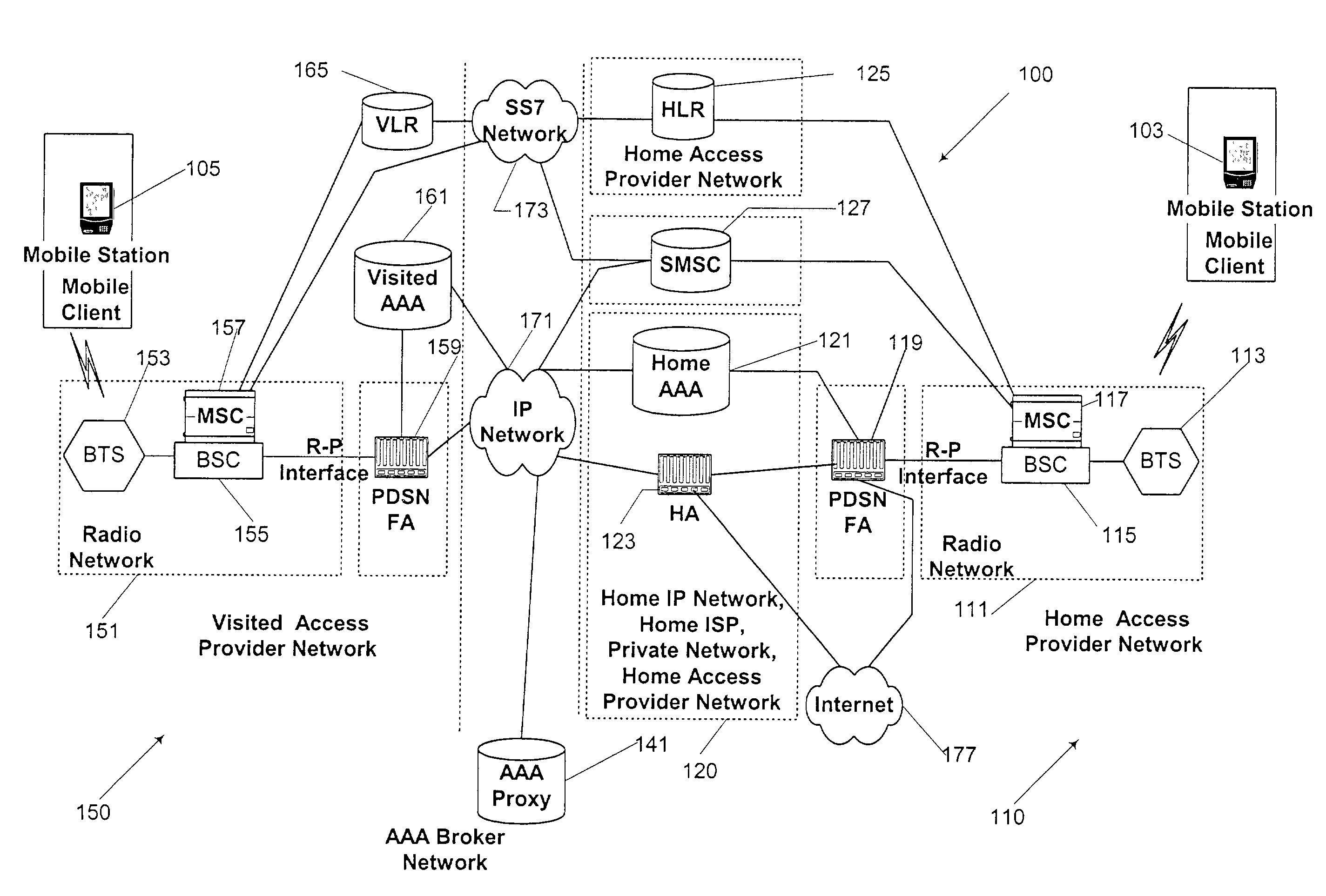
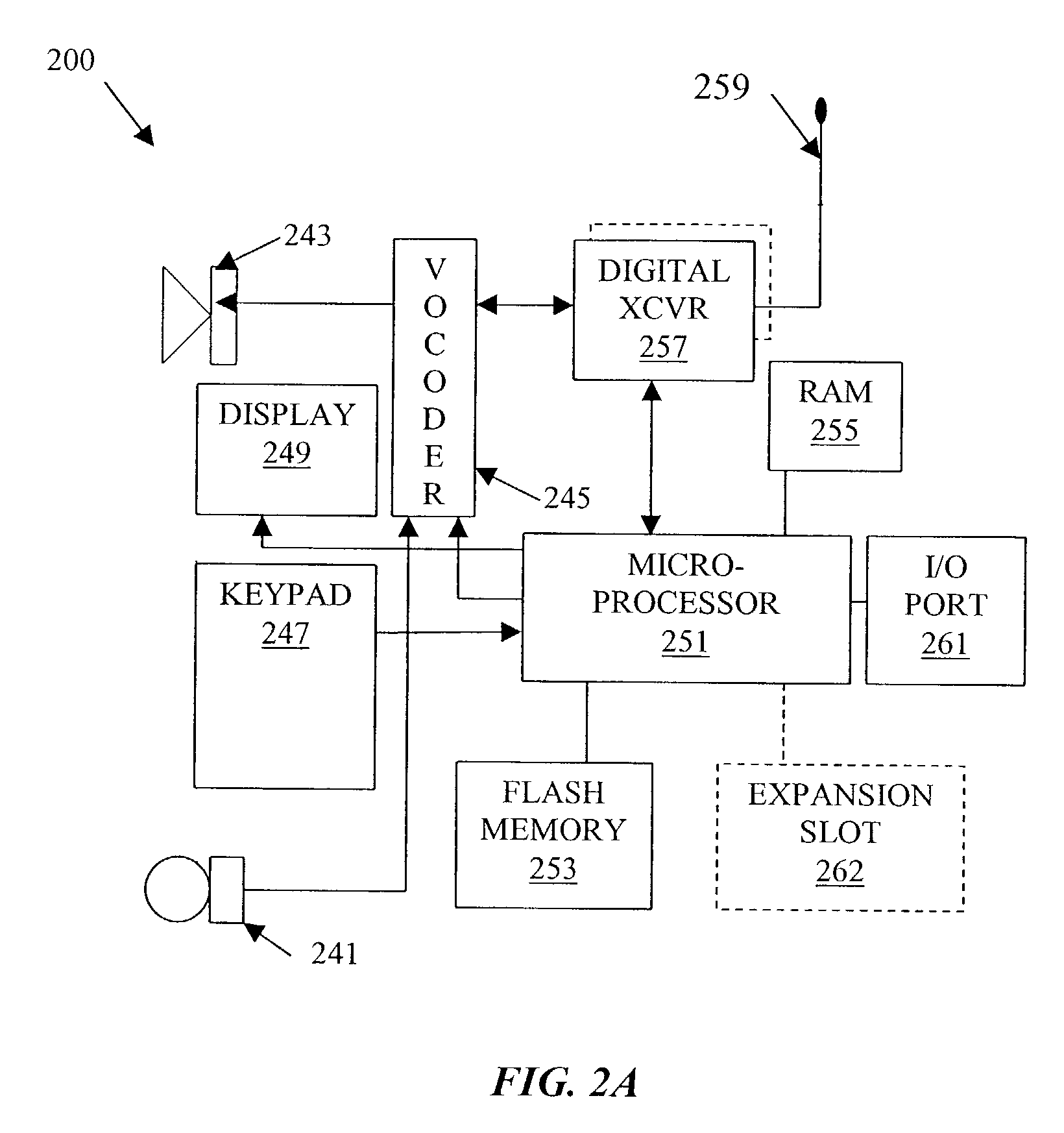
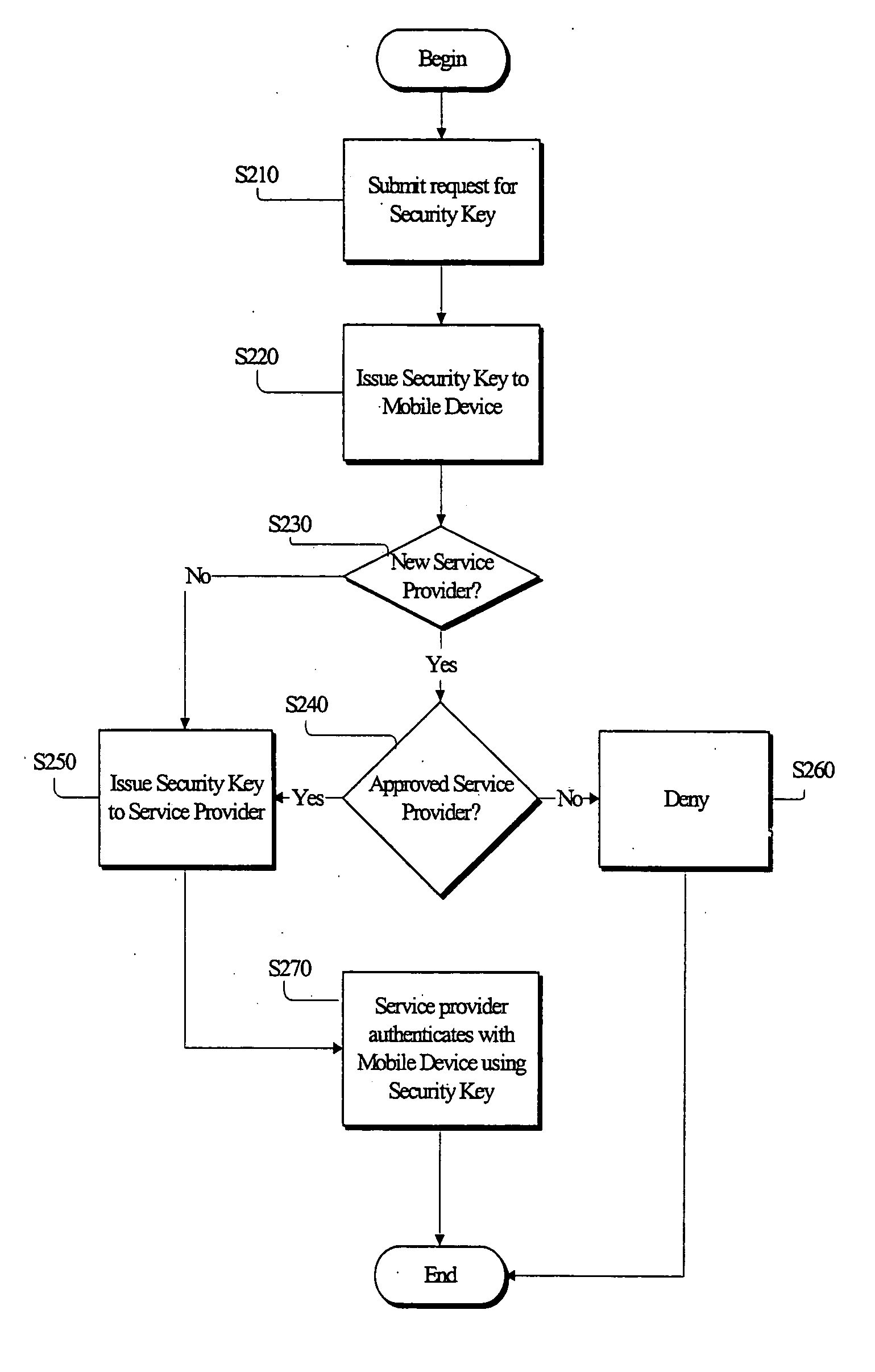
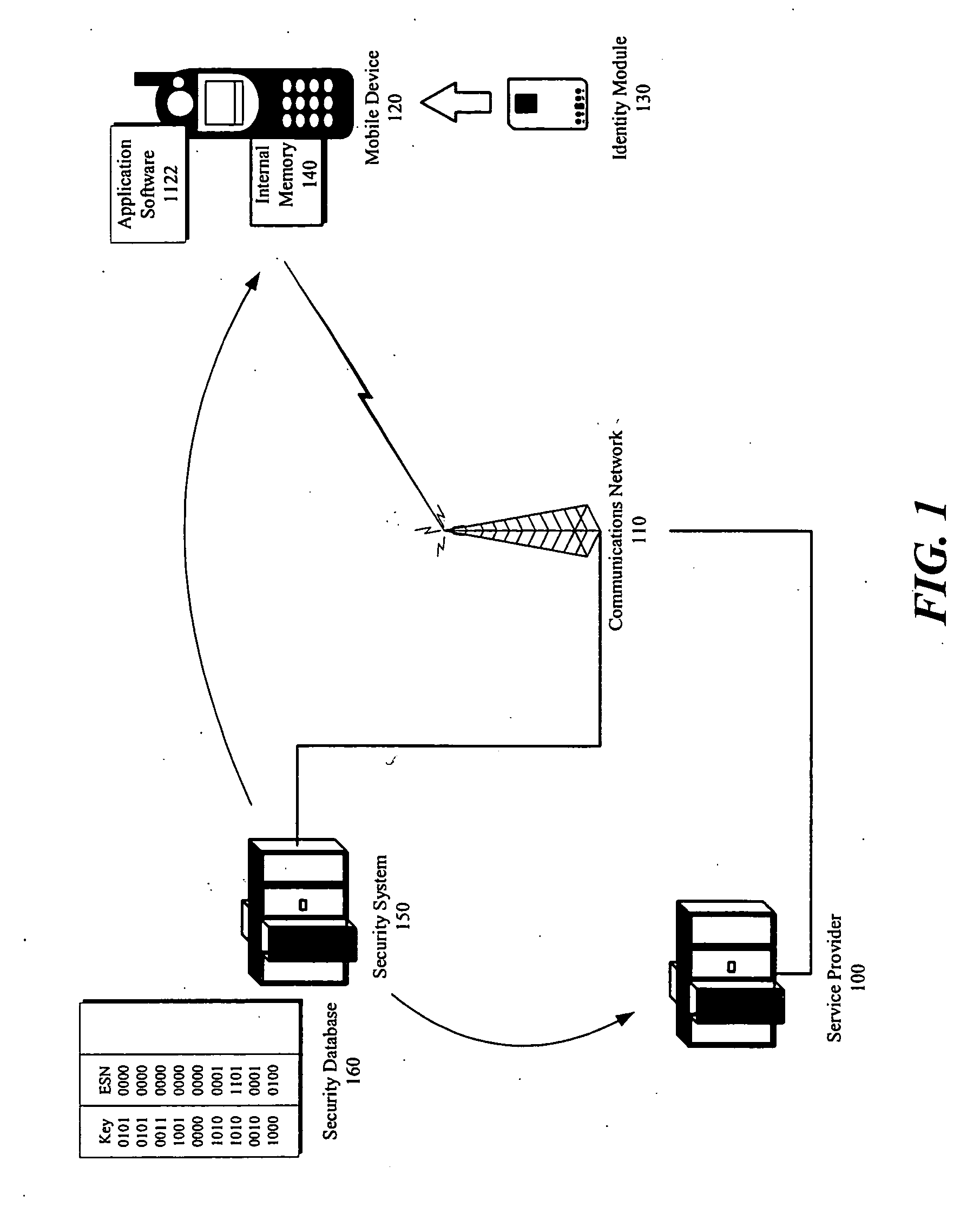
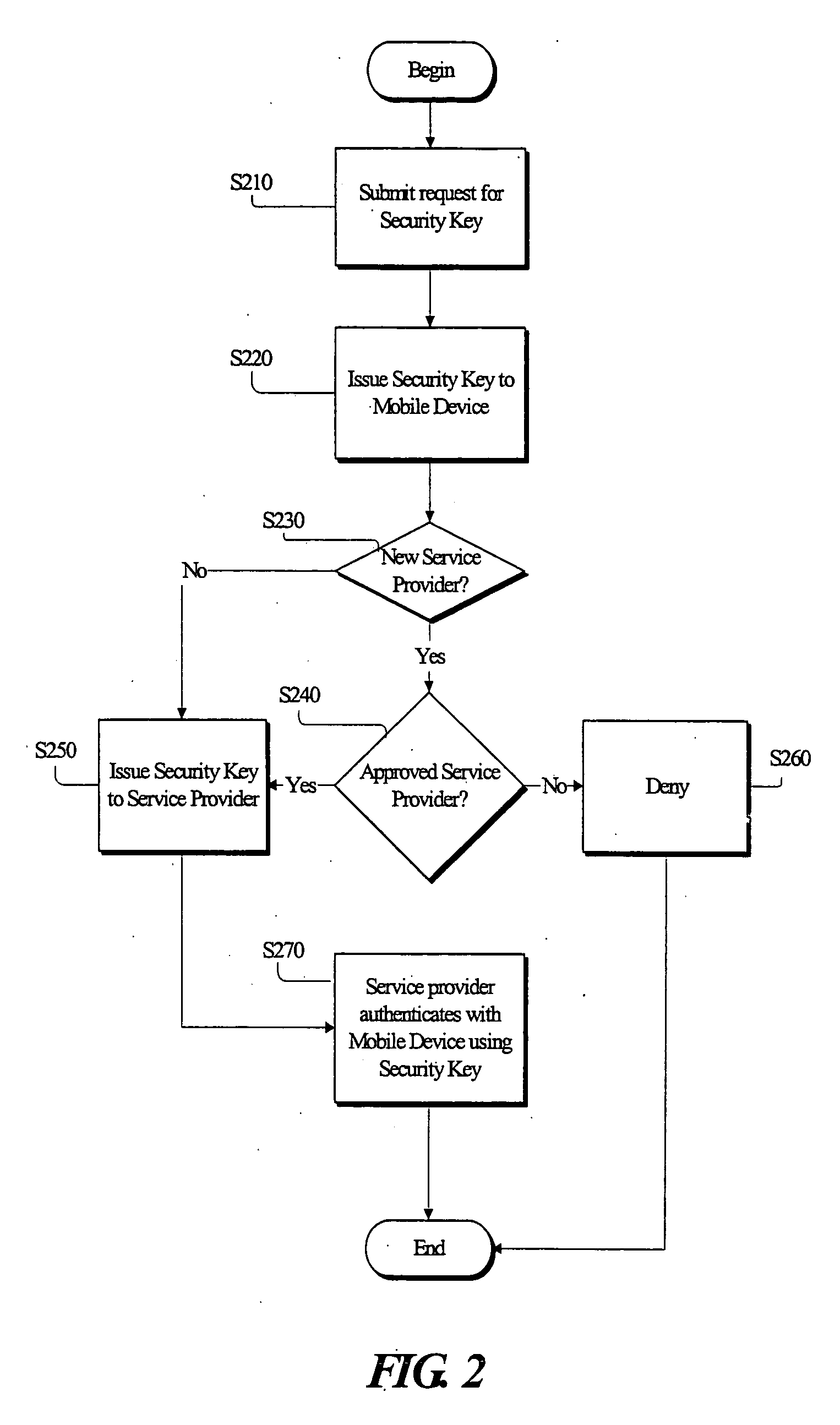
Security key management system and method in a mobile communication network
InactiveUS20050227669A1Request can be deniedUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsService provisionKey assignment
A security system for managing security key assignment in a mobile communications terminal, the security system comprising a key generating mechanism for generating a unique security key for a mobile device, in response to a request received by the security system from the mobile device; a transmission mechanism for transmitting the unique security key to the mobile device; and a data storage mechanism for storing the unique security key for the mobile device in association with an identifier identifying the mobile device, wherein the unique security key is transmitted to a service provider, in response to a request submitted by the service provider to the security system.
Owner:IXI MOBILE R&D
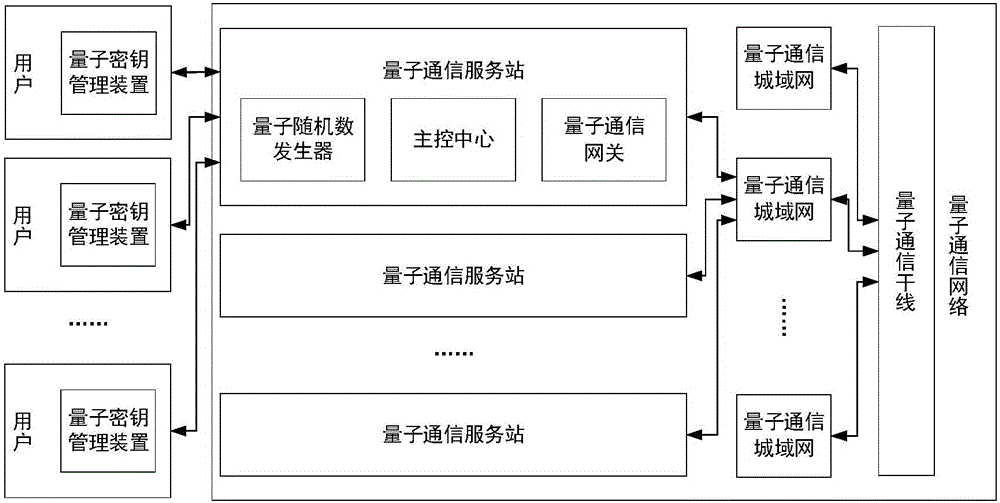
Quantum communication service station, quantum key management device, key configuration network, and key configuration method
ActiveCN106452740AAddress access security issuesAchieve coverageKey distribution for secure communicationSecurity questionKey distribution
The invention discloses a quantum communication service station, a quantum key management device, a key configuration network, and a key configuration method. The key configuration method comprises the following steps: responding to a key distribution request; authenticating a user of the key distribution request; writing a key generated with a true random number into a quantum key management device of the authenticated user. The key configuration method is different from the existing quantum key distribution QKD method in that key distribution of ultra high security is realized by pairing quantum key management devices and service stations at the end of a quantum communication network, the problem about access security at the end of a quantum communication network is solved, and terminal access is not a weak link of a quantum communication scheme. The quantum communication network can completely cover and replace the classic communication network in service.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENZHOU QUANTUM NETWORK TECH CO LTD
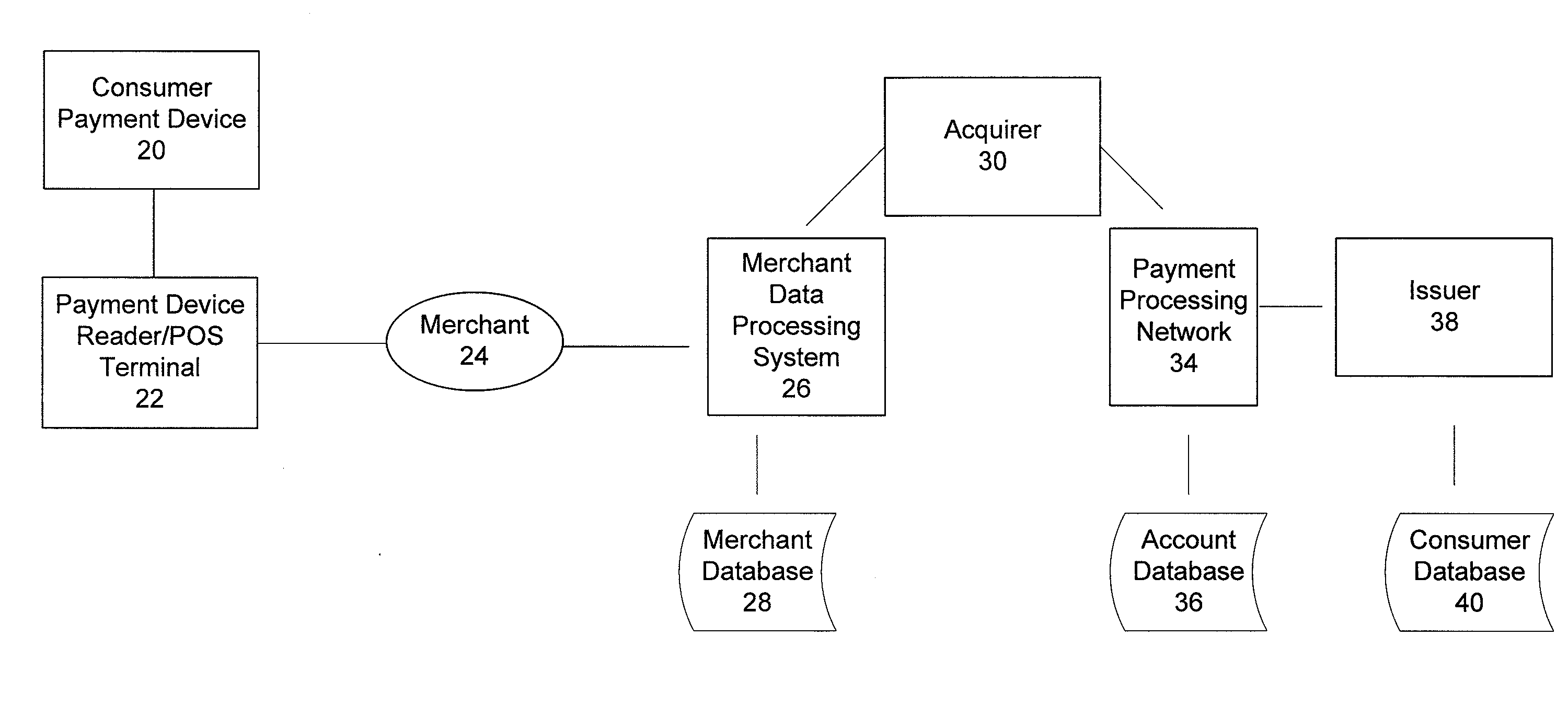
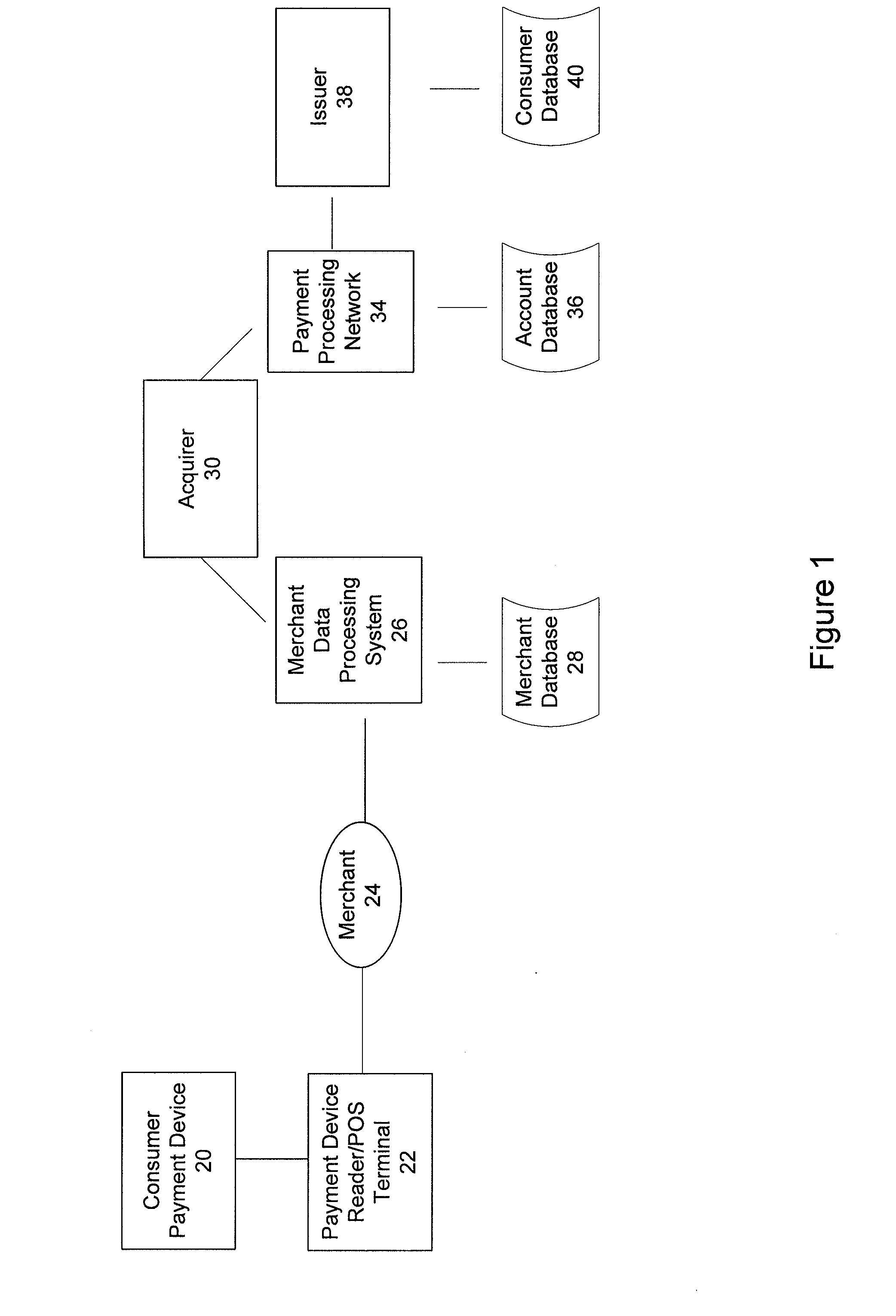
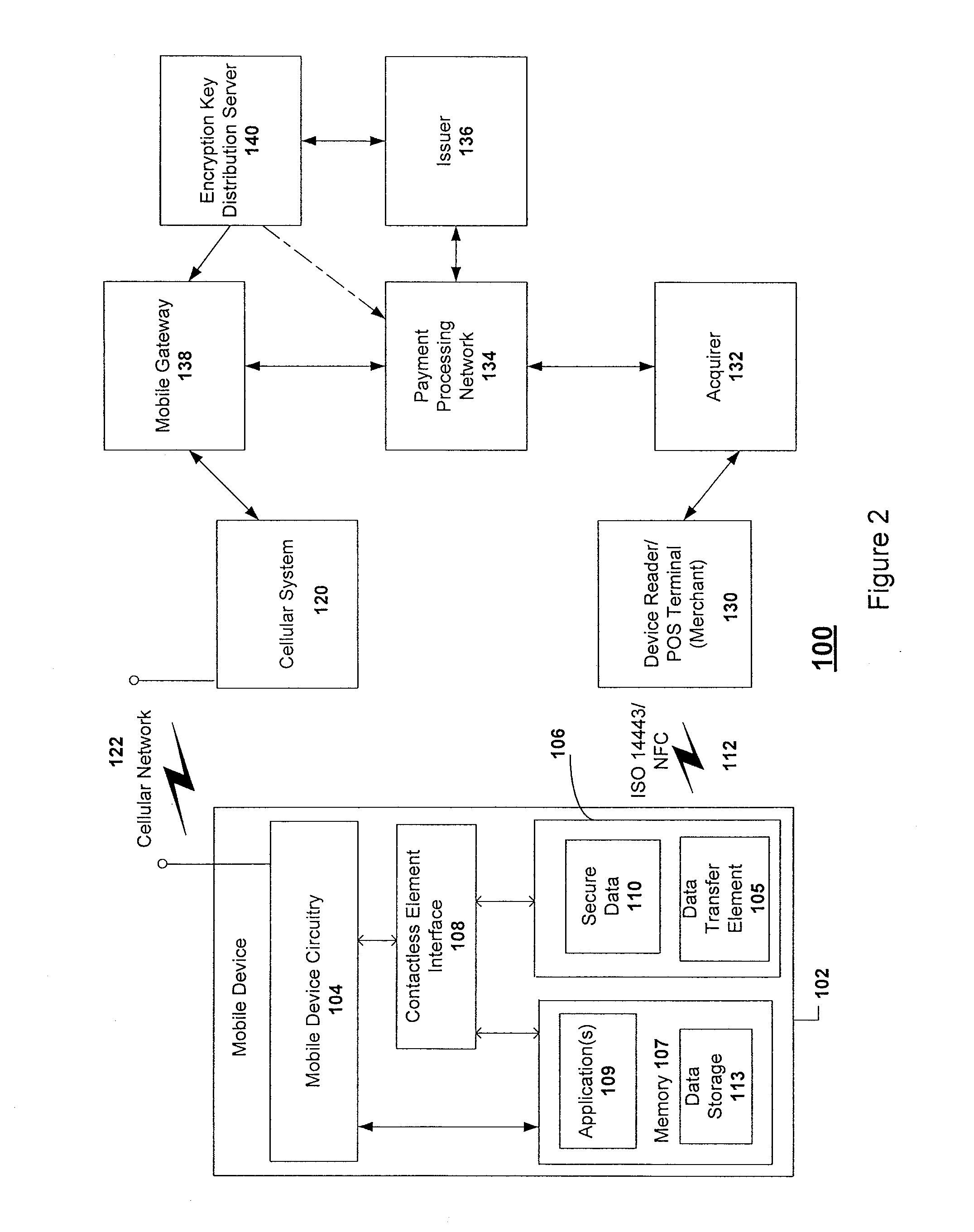
Over the air update of payment transaction data stored in secure memory
ActiveUS20100211507A1Easy to updateGood synchronizationFinanceMultiple keys/algorithms usagePayment transactionApplication software
A system, apparatus, and method for processing payment transactions that are conducted using a mobile device that includes a contactless element, such as an integrated circuit chip. The invention enables the updating, correction or synchronization of transaction data maintained by an Issuer with that stored on the device. This is accomplished by using a wireless (cellular) network as a data communication channel for data provided by an Issuer to the mobile device, and is particularly advantageous in circumstances in which the contactless element is not presently capable of communication with a device reader or point of sale terminal that uses a near field communications mechanism. Data transferred between the mobile device and Issuer may be encrypted and decrypted to provide additional security and protect the data from being accessed by other users or applications. If encryption keys are used for the encryption and decryption processes, they may be distributed by a key distribution server or other suitable entity to a mobile gateway which participates in the data encryption and decryption operations.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
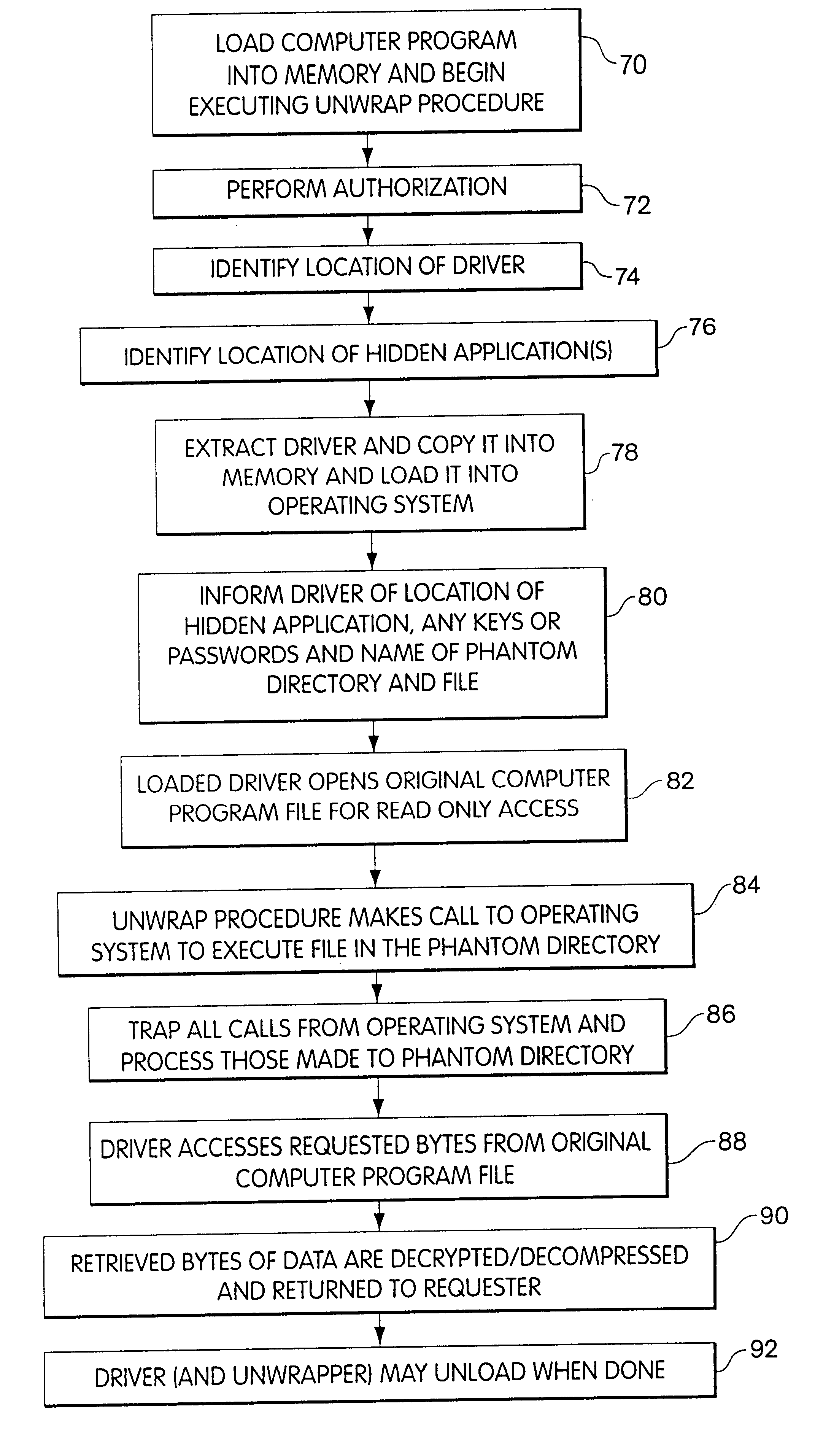
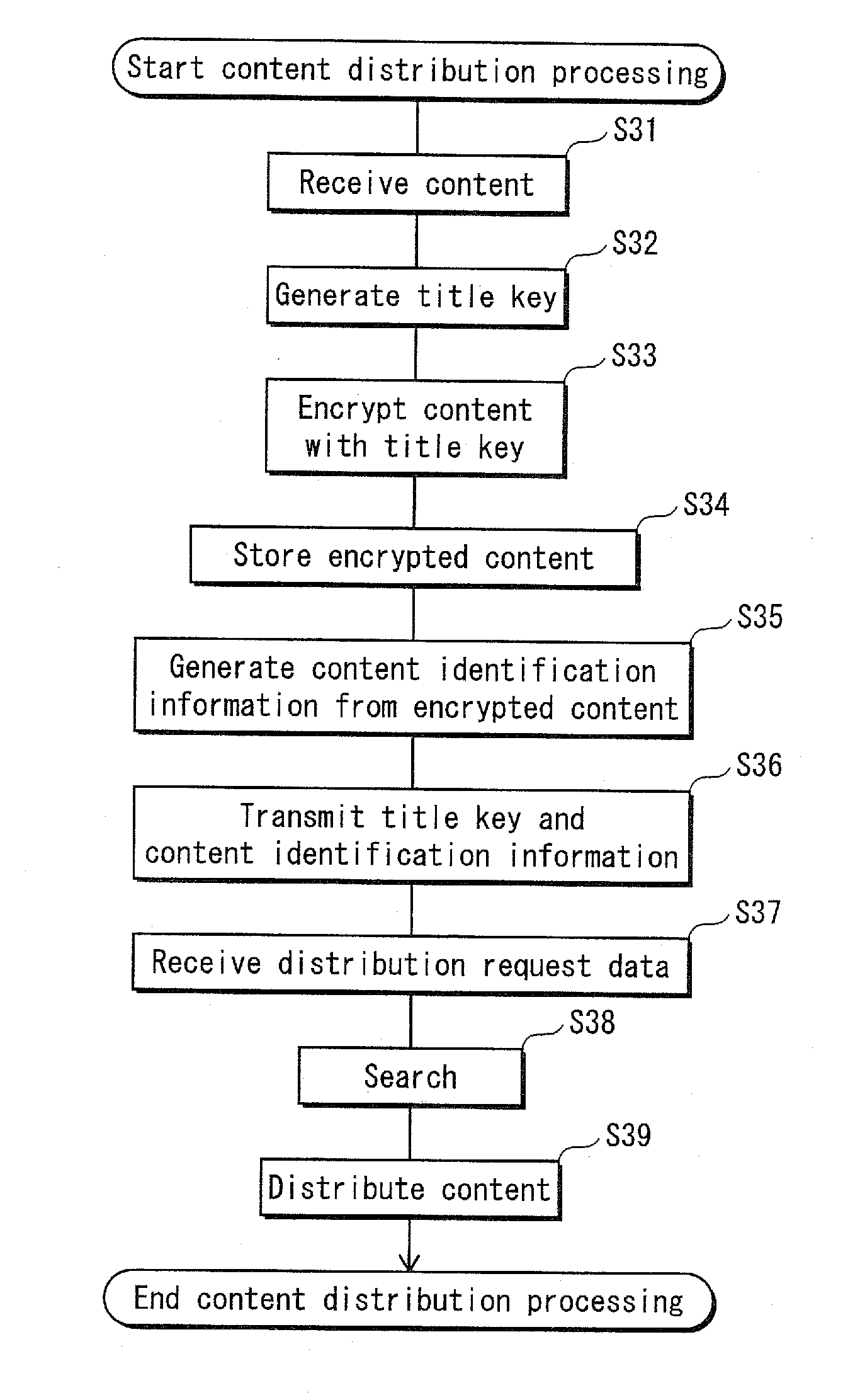
One-time pad Encryption key Distribution
InactiveUS6868495B1Ability can be reducedReduce attackKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPaymentSuccessful completion
Some of these problems with digital information protection systems may be overcome by providing a mechanism which allows a content provider to encrypt digital information without requiring either a hardware or platform manufacturer or a content consumer to provide support for the specific form of corresponding decryption. This mechanism can be provided in a manner which allows the digital information to be copied easily for back-up purposes and to be transferred easily for distribution, but which should not permit copying of the digital information in decrypted form. In particular, the encrypted digital information is stored as an executable computer program which includes a decryption program that decrypts the encrypted information to provide the desired digital information, upon successful completion of an authorization procedure by the user. In combination with other mechanisms that track distribution, enforce royalty payments and control access to decryption keys, the present invention provides an improved method for identifying and detecting sources of unauthorized copies. Suitable authorization procedures also enable the digital information to be distributed for a limited number of uses and / or users, thus enabling per-use fees to be charged for the digital information.
Owner:RPX CORP
Systems and methods for implementing path length control for quantum cryptographic systems
ActiveUS7627126B1Reduce impactReduce QBERKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPath lengthKey distribution
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
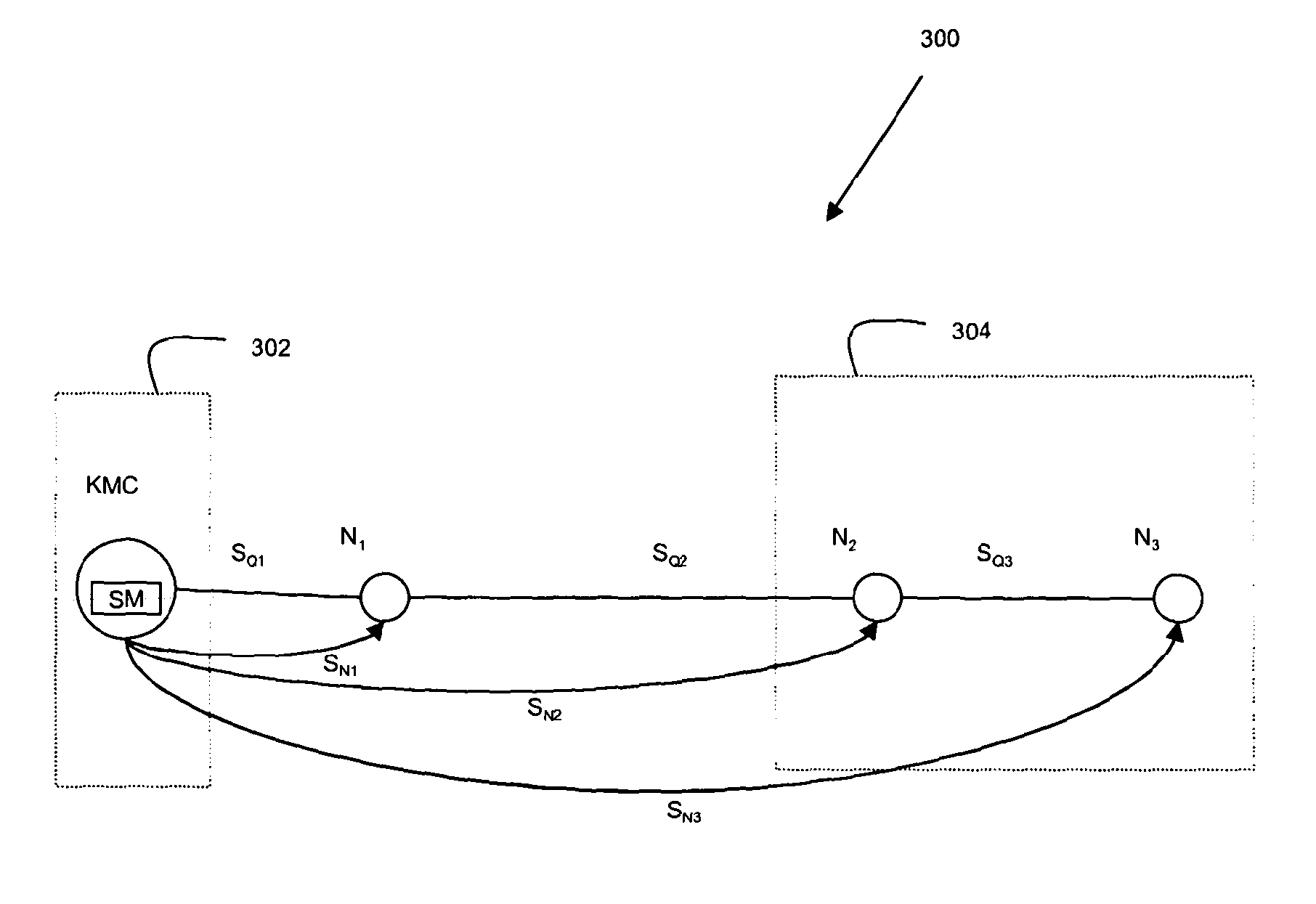
Quantum key distribution
ActiveUS20130251145A1Improve network securityIncrease ratingsKey distribution for secure communicationKey distributionQuantum key distribution
Methods and apparatus for quantum key distribution are described, in particular including methods and networks 300 arranged to improve and / or ensure the security of data transmitted thereby by (i) ensuring a certain level of loss within at least part of the network, (ii) placing a penultimate and an endpoint nodes in situated in a secure second enclave, (iii) analysing a transmitted bit stream to ensure that it does not provide an unacceptable amount of information about the key that may be generated therefrom, and / or (iv) varying the order in which bits are used to generate a key.
Owner:QUBITEKK
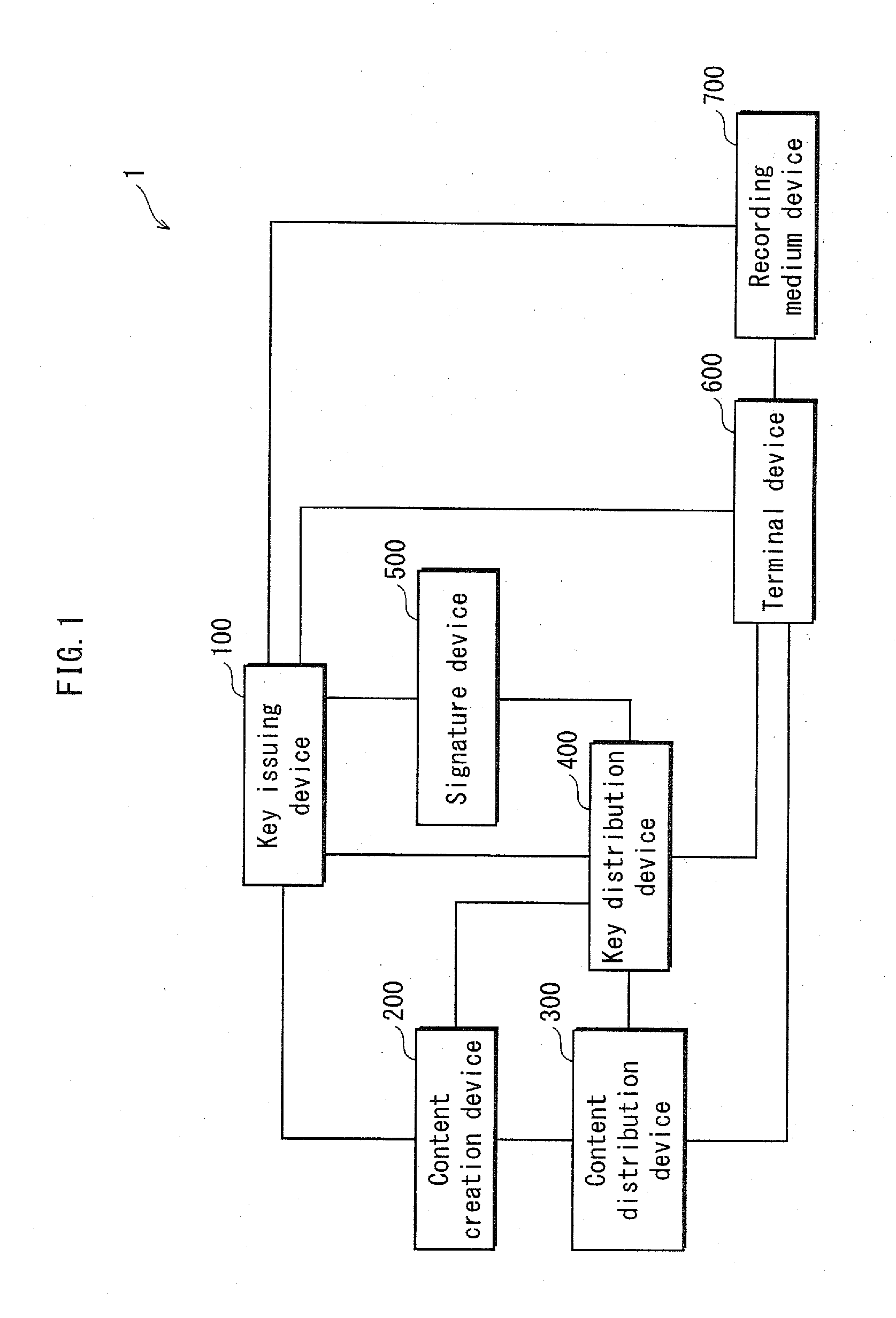
Terminal device, verification device, key distribution device, content playback method, key distribution method, and computer program
ActiveUS20130054971A1Prevent Malicious UseIncreased riskKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareTerminal equipment
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
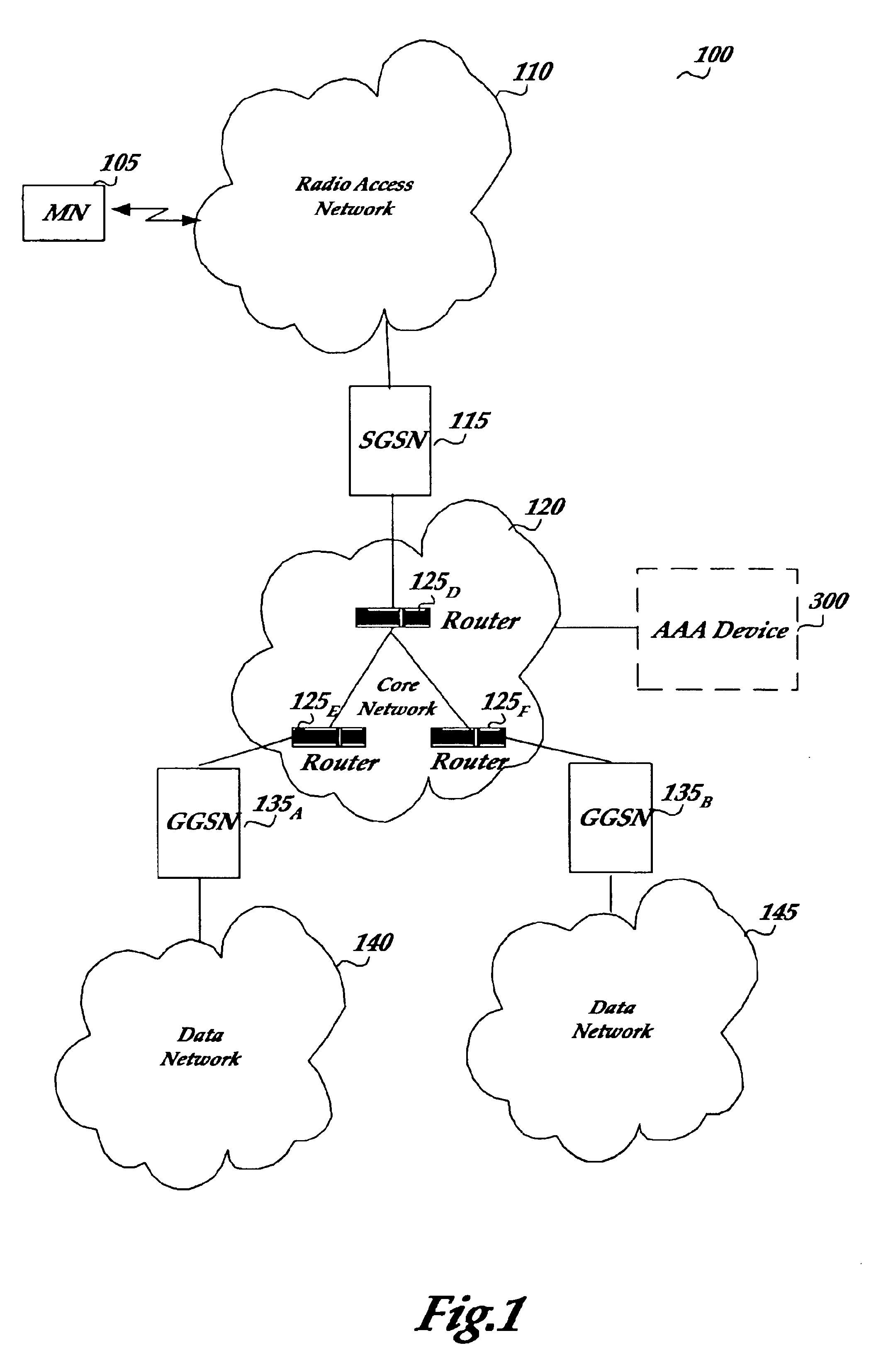
Scheme for device and user authentication with key distribution in a wireless network
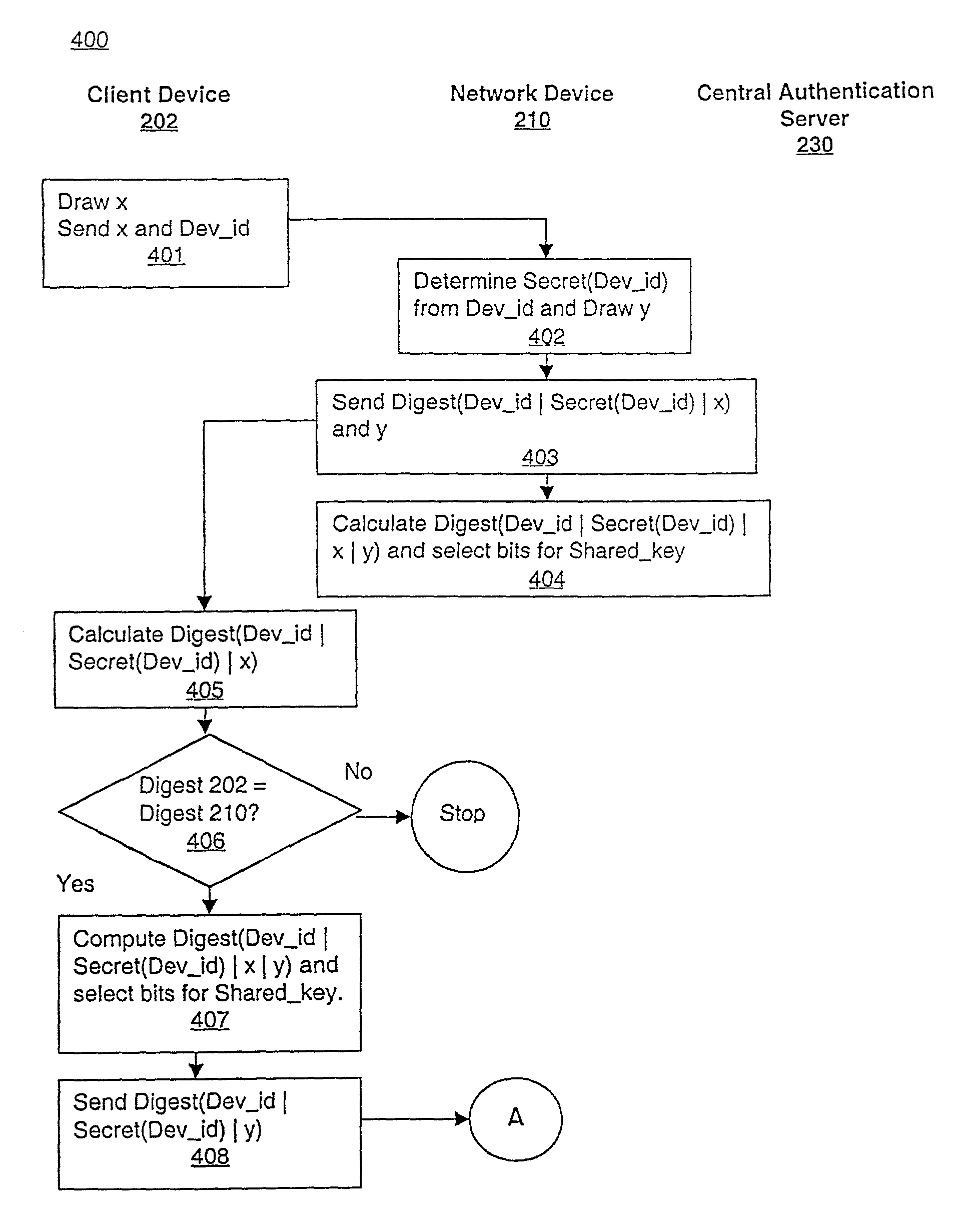
ActiveUS7350076B1Reduction in marketLarge processing capabilityRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationWeb authenticationSecret share
In a computer network, a method of mutually authenticating a client device and a network interface, authenticating a user to the network and exchanging encryption keys. In one embodiment, the method comprises authenticating the client device at the local network device point, with which the client device exchanges an encryption key and then the user is authenticated by a central authentication server. In another embodiment, the method comprises authenticating the client device at the central authentication server, with which the client device exchanges a key which is passed to the network device with a secret shared between the central authentication server and the network device. In this embodiment, the user is also authenticated at the central authentication server.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Method and system for secure over-the-top live video delivery
ActiveUS20120331293A1Cryptographic strength can be increasedHigh strengthMultiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationKey distributionLive video
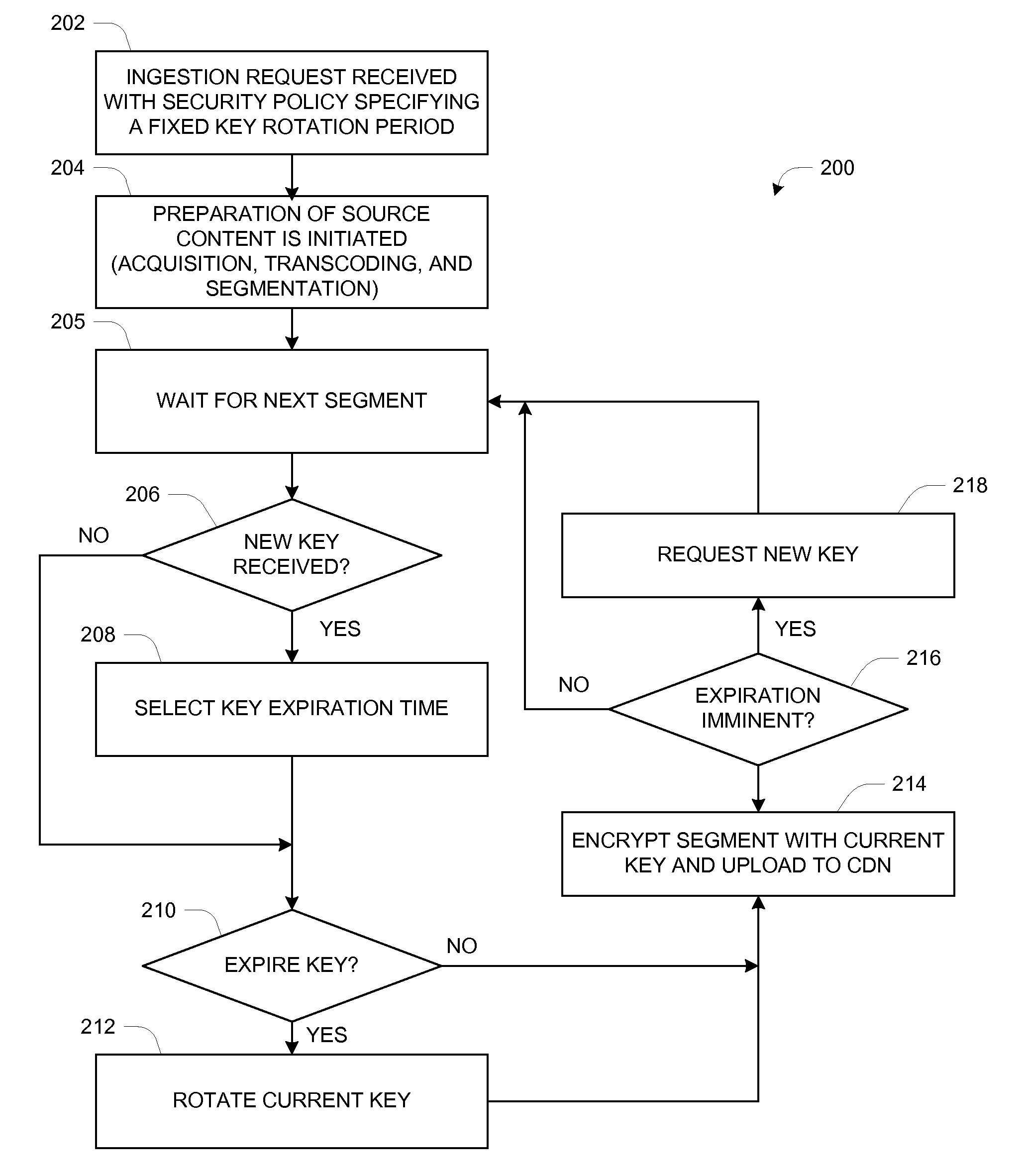
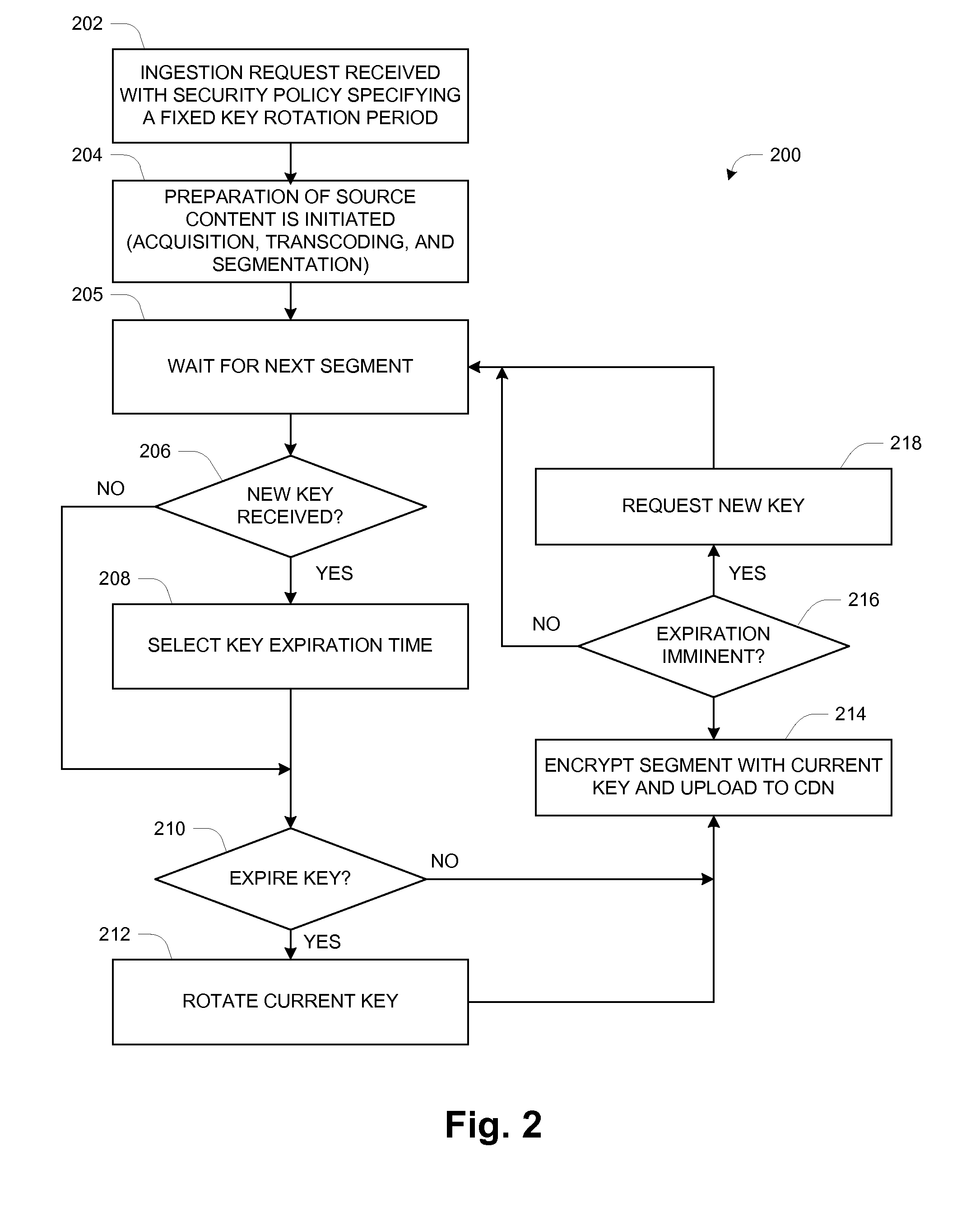
A method is provided for managing key rotation (use of series of keys) and secure key distribution in over-the-top content delivery. The method provided supports supplying a first content encryption key to a content packaging engine for encryption of a first portion of a video stream. Once the first content encryption key has expired, a second content encryption key is provided to the content packaging engine for encryption of a second portion of a video stream. The method further provides for notification of client devices of imminent key changes, as well as support for secure retrieval of new keys by client devices. A system is also specified for implementing a client and server infrastructure in accordance with the provisions of the method.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
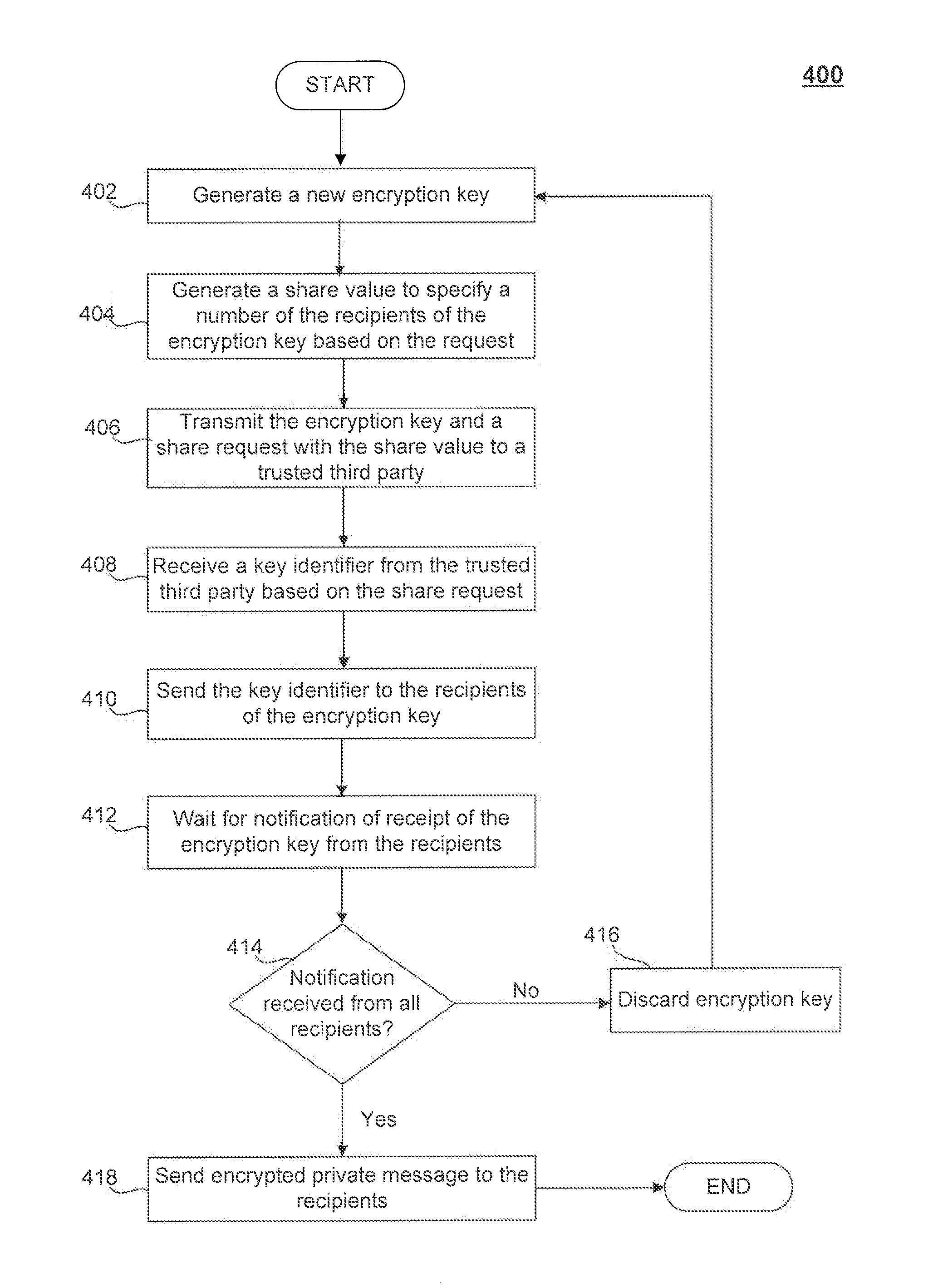
Secure key distribution for private communication in an unsecured communication channel
ActiveUS8379857B1Secure distributionMitigate or preclude any loss of confidential information during communicationKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationSecure communicationPrivate communication
A method to enable the secure distribution of encryption keys so as to facilitate private communication between users in an unsecured communication network is provided. Such a method may also provide a way to detect an unauthorized access of an encryption key so as to mitigate or prevent any loss of confidential information during communication.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and method for key distribution in a hierarchical tree
InactiveUS7043024B1Key distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsTheoretical computer scienceKey distribution
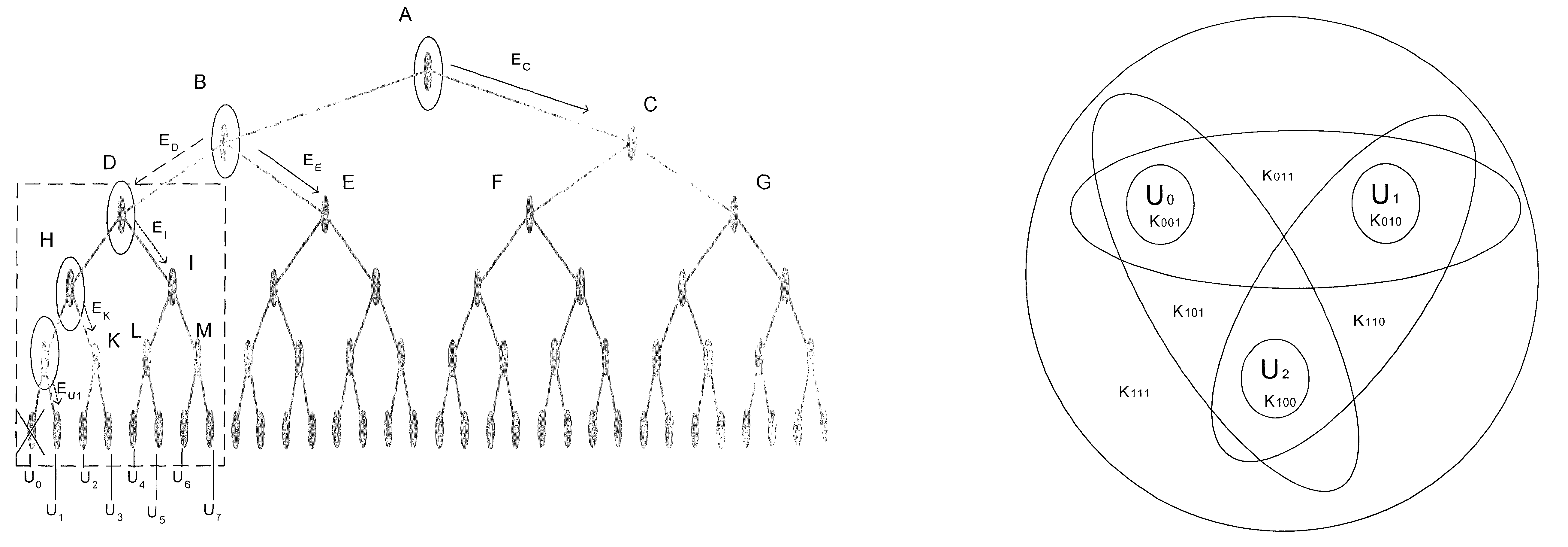
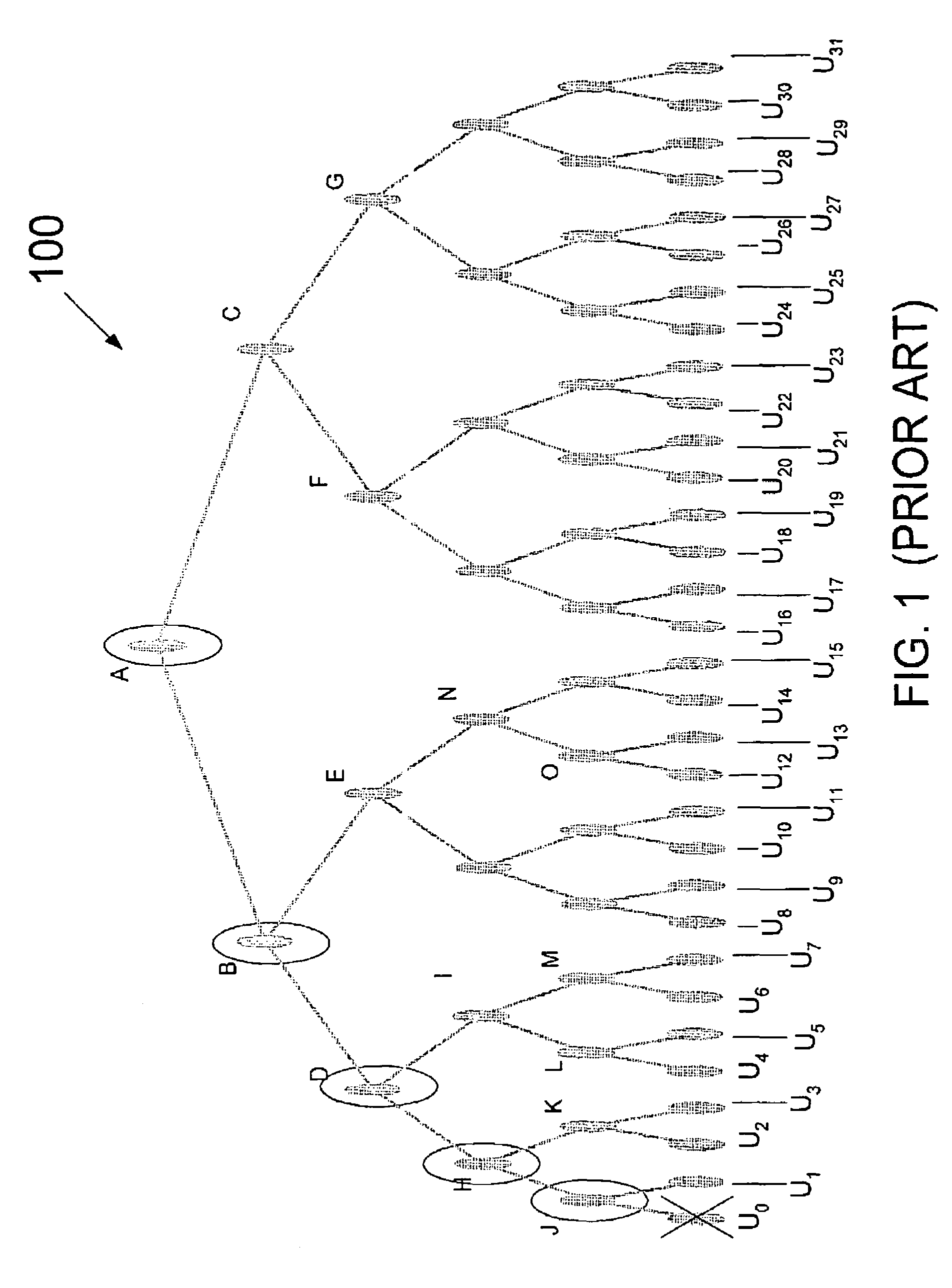
A system and method for reusable efficient key distribution is disclosed. Key distribution is effected through the application of self-repairing groups that obviate the need for key distribution messages in portions of a hierarchical tree. In one embodiment, the self-repairing group is based on a reusable power set.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
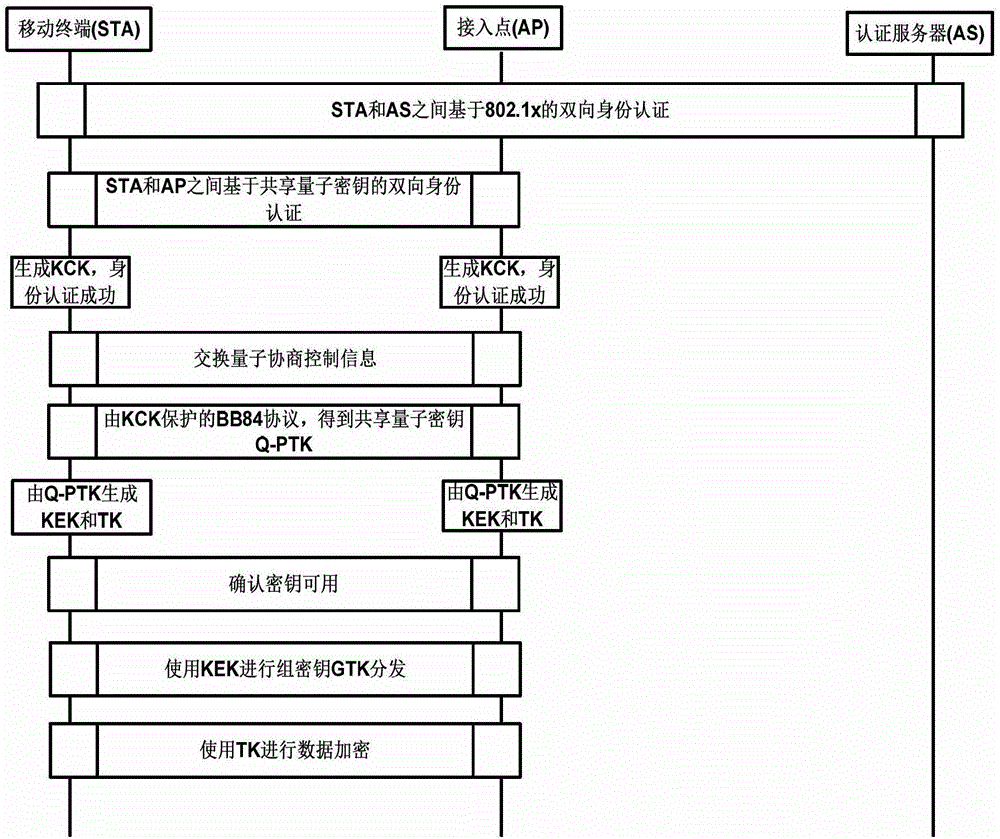
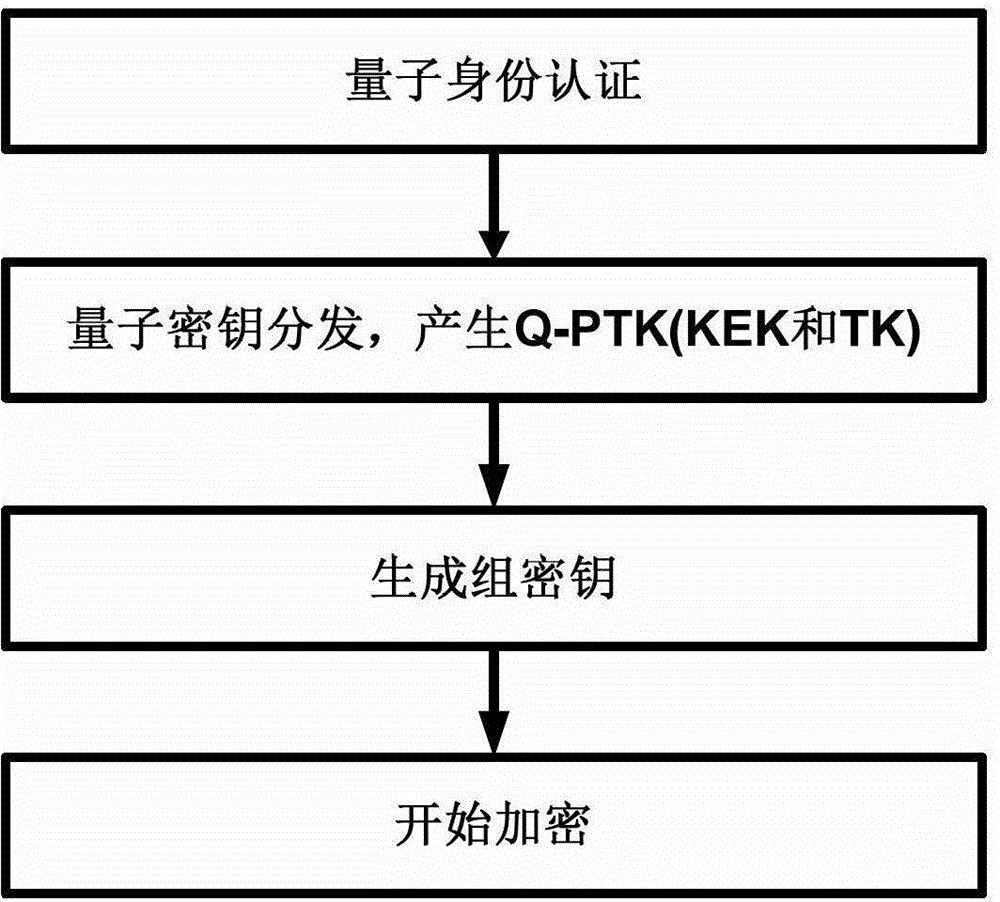
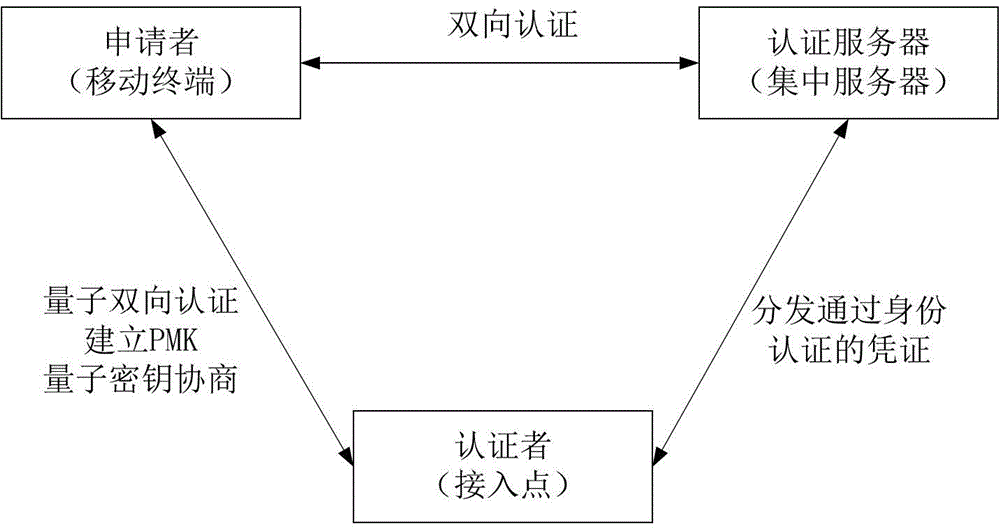
Wireless local area network security communication method based on quantum key distribution
InactiveCN103338448AImprove securityTamper-proofKey distribution for secure communicationSecurity arrangementQuantum technologyAuthentication server
The invention provides a wireless local area network security communication method based on quantum key distribution. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) identity authentication based on quantum keys is carried out; (2) quantum key negotiation is carried out; and (3) encryption is started. With the method of the invention adopted, information exchange between a faked access point and an applicant, the waste of system resources or a caused denial of service attack can be can avoided; bidirectional authentication between the applicant and an authentication server as well as between the applicant and an authenticator can be realized, and therefore, the security of the identity authentication is greatly improved; keys produced in the identity authentication can be adopted to protect message authentication in key negotiation, and therefore, attacks such as the tamper of a intermediary can be prevented; the security of key negotiation based on quantum technology is guaranteed by physical laws, and therefore, the key negotiation based on quantum technology has undecodability, and can withstand the decoding of a quantum computer with strong computational ability, and therefore, the security of a whole system can be enhanced.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Systems and methods for path set-up in a quantum key distribution network
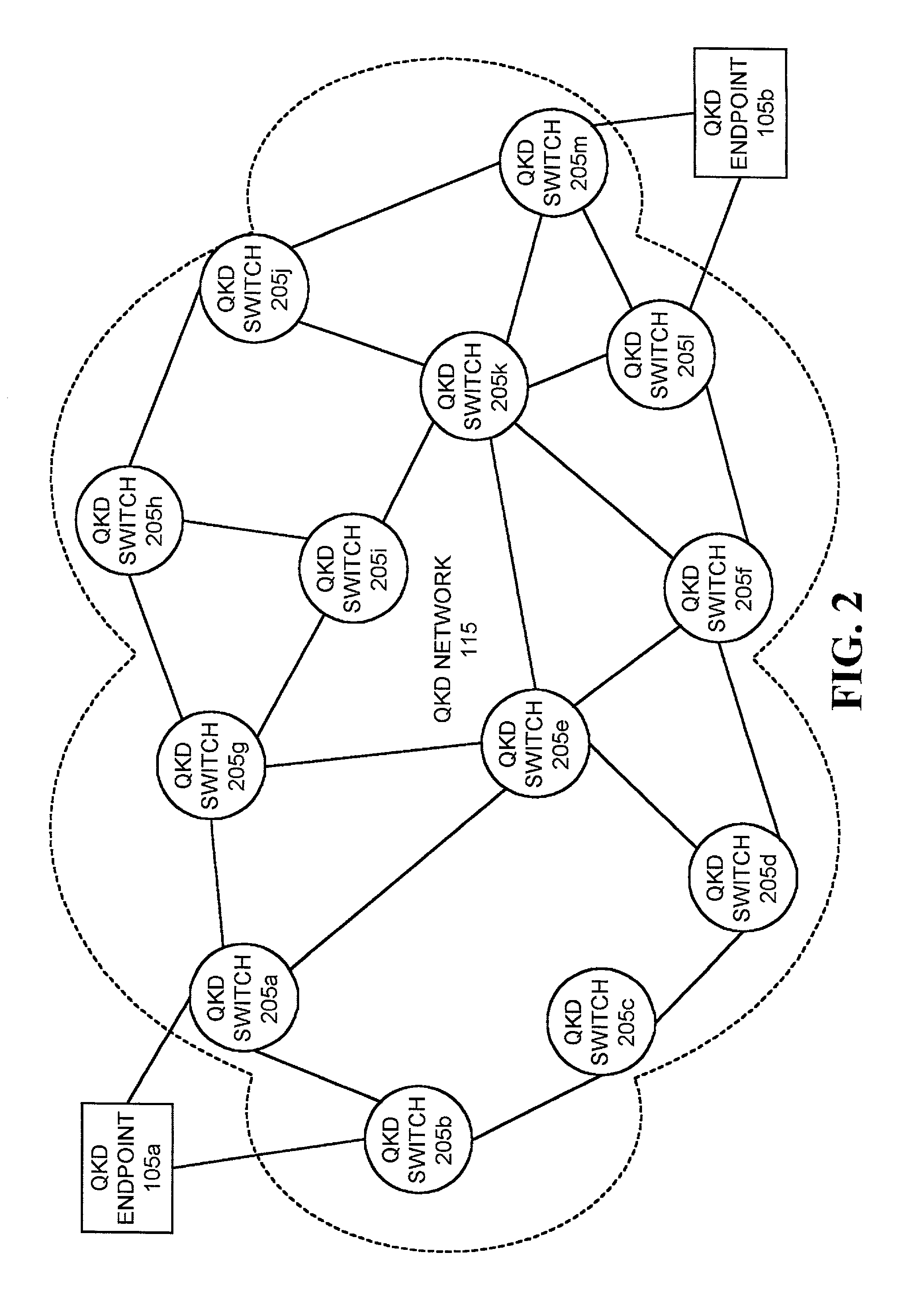
InactiveUS7068790B1Low costReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsKey distributionEavesdropping
A system establishes a path for distributing data through an optical network (115). The system includes an optical switch (205a) and a data distribution endpoint (105a). The optical switch (205a) establishes a first encryption key distribution path through the optical network (115), the first encryption key distribution path including multiple optical switches and optical links. The data distribution endpoint (105a) determines whether eavesdropping has occurred on the first encryption key distribution path using quantum cryptography. The optical switch (205a) further establishes a second data distribution path through the optical network (115) responsive to the eavesdropping determination. The second encryption key distribution path includes multiple optical switches and optical links.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
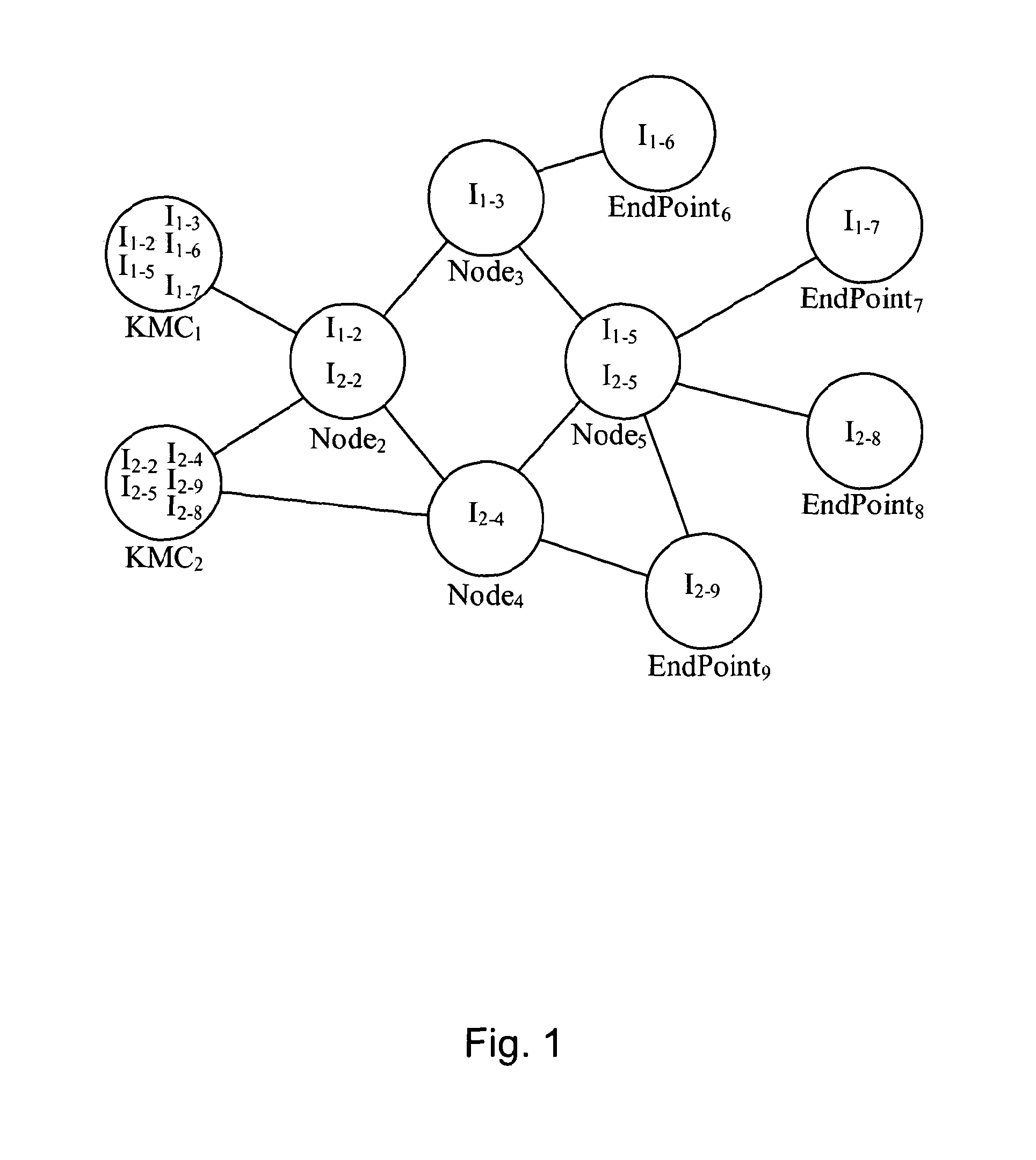
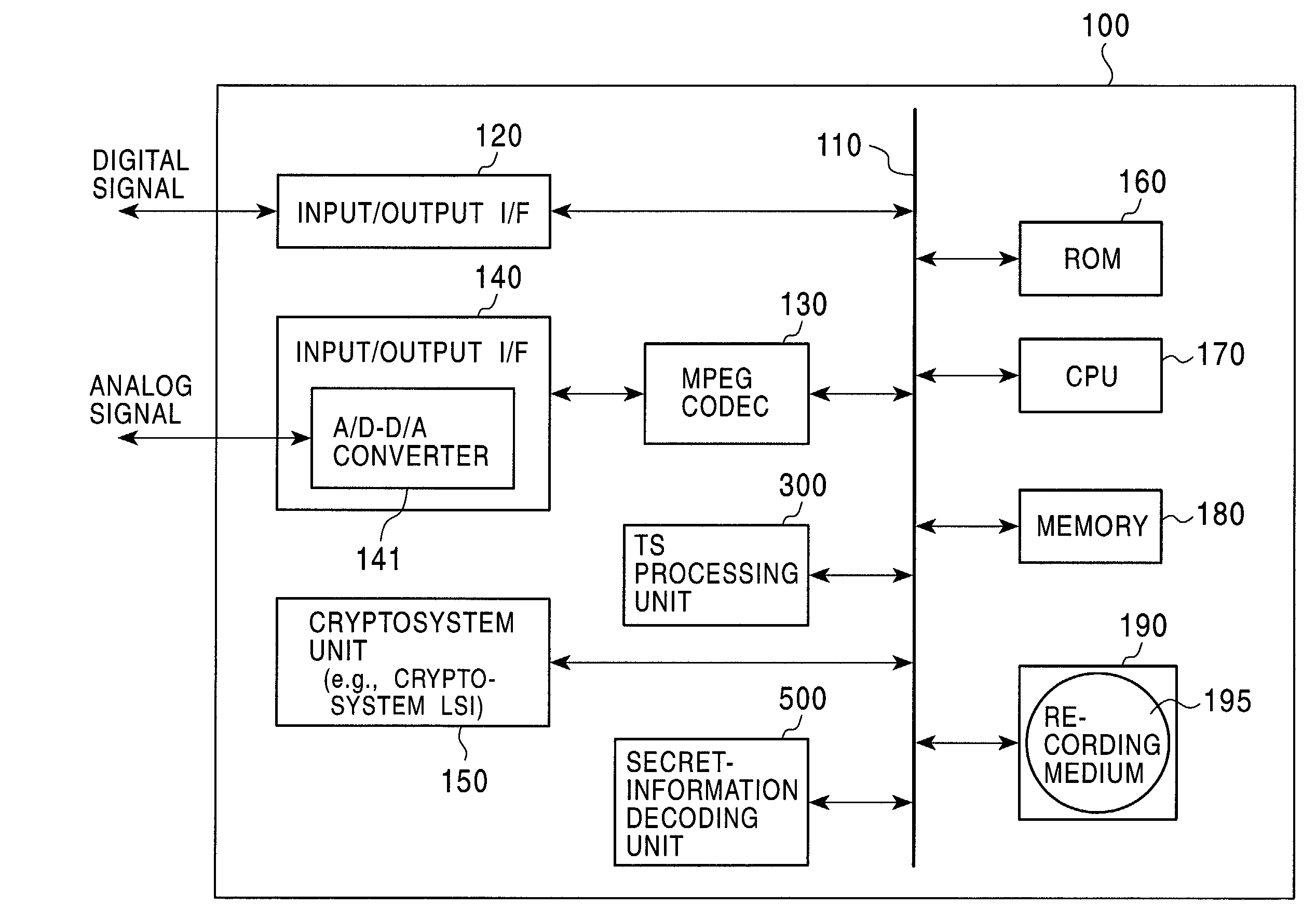
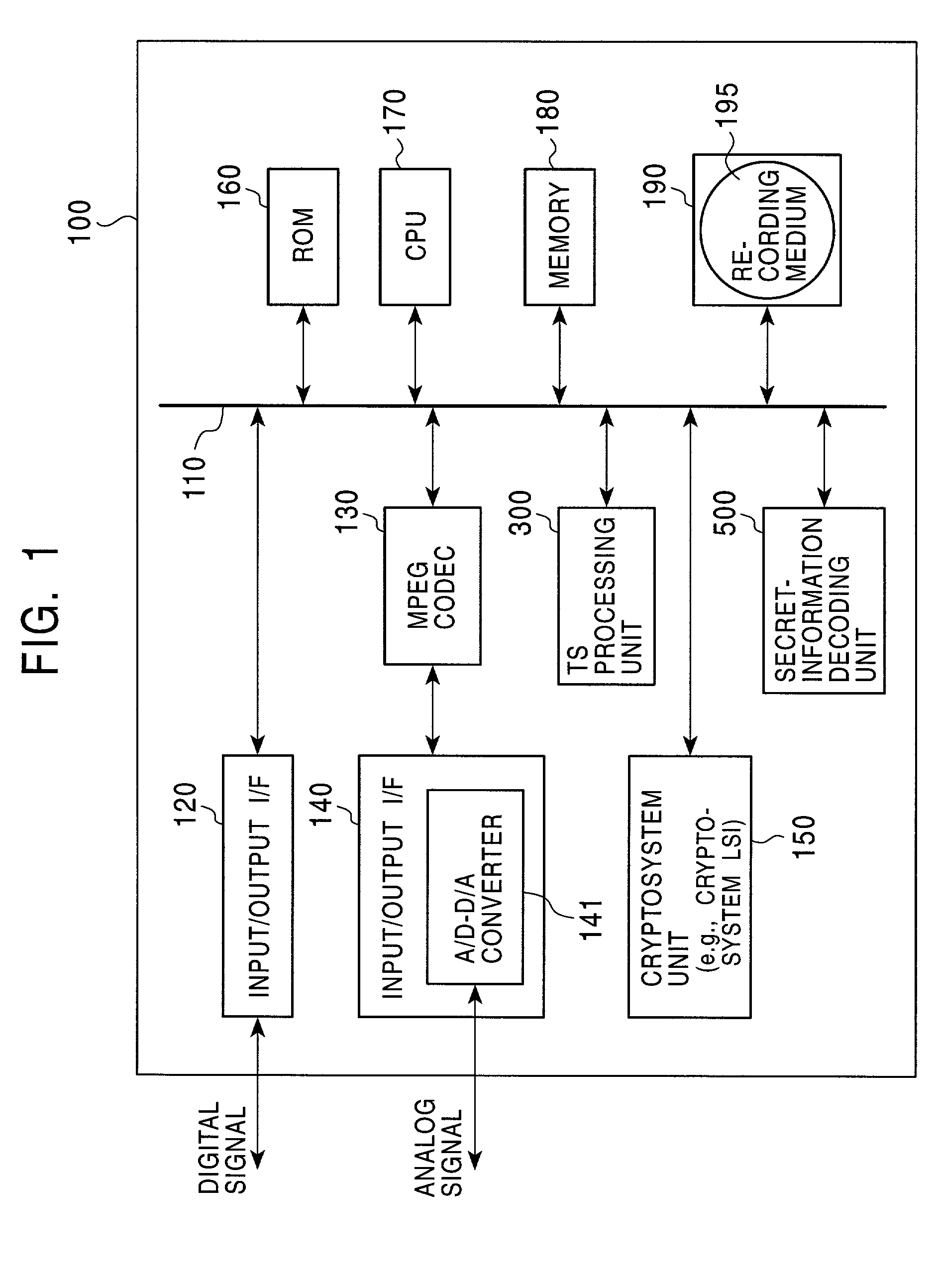
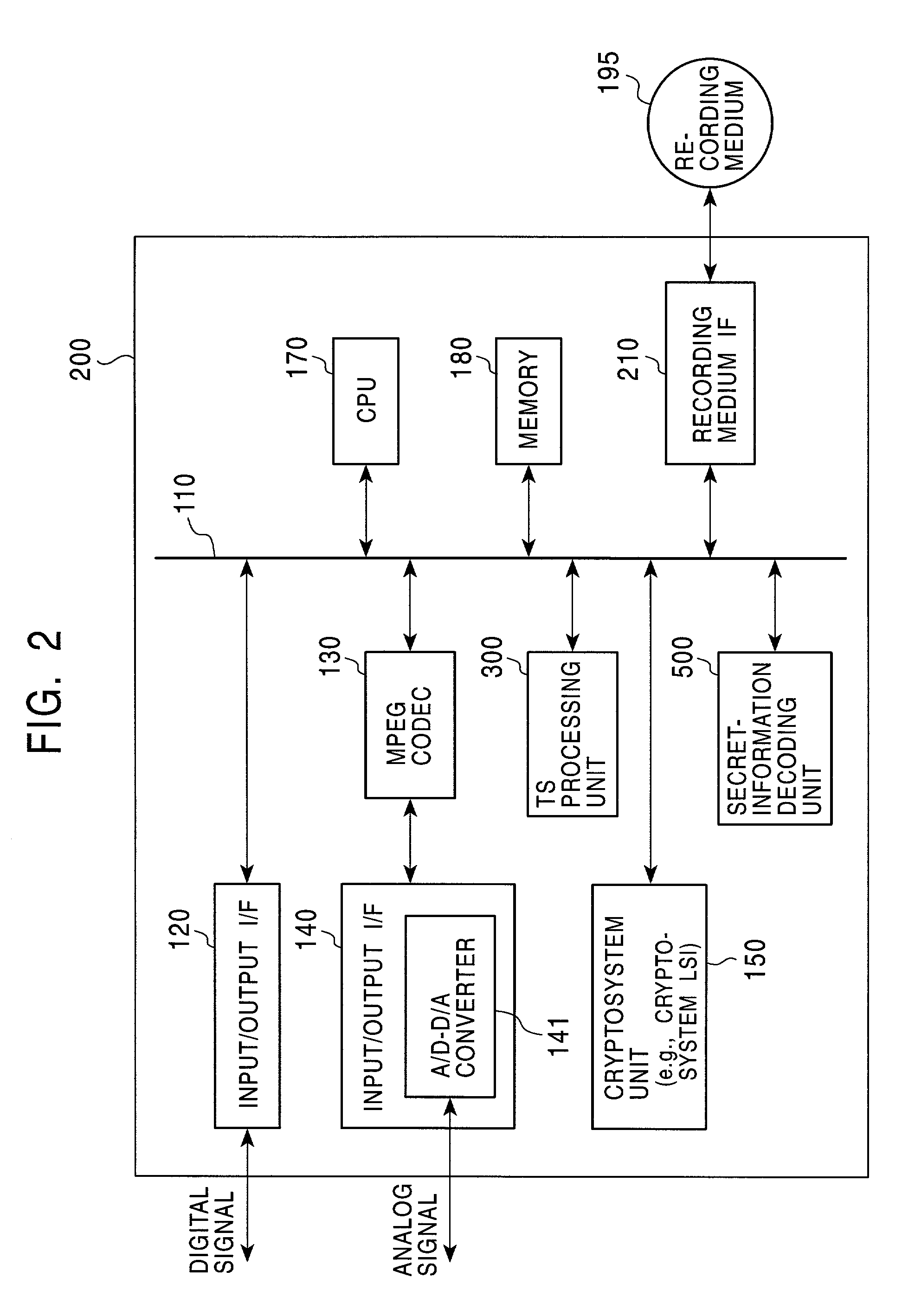
Information recording device, information playback device, information recording method, information playback method, and information recording medium and program providing medium used therewith
InactiveUS7319752B2Raise security concernsUnauthorized useTelevision system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareCryptosystem
An information recording / playback device stores beforehand, on a recording medium, secret information in which a writing / reading method thereof cannot be analyzed and which can be read only by a special reading method. The secret information is applied to a key for content encryption or decryption when performing recording or playback of contents on the recording medium, such as music data and image data. The secret information is, for example, a stamper ID. By using the stamper ID as secret information, and a master key and a media key which are distributed in a tree-structure key-distribution system, a content-cryptosystem key is generated. Accordingly, each content is allowed to be used in only an appropriate device in which the special reading method for the secret information can be executed and to which the key is distributed by the tree-structure key-distribution system.
Owner:SONY CORP
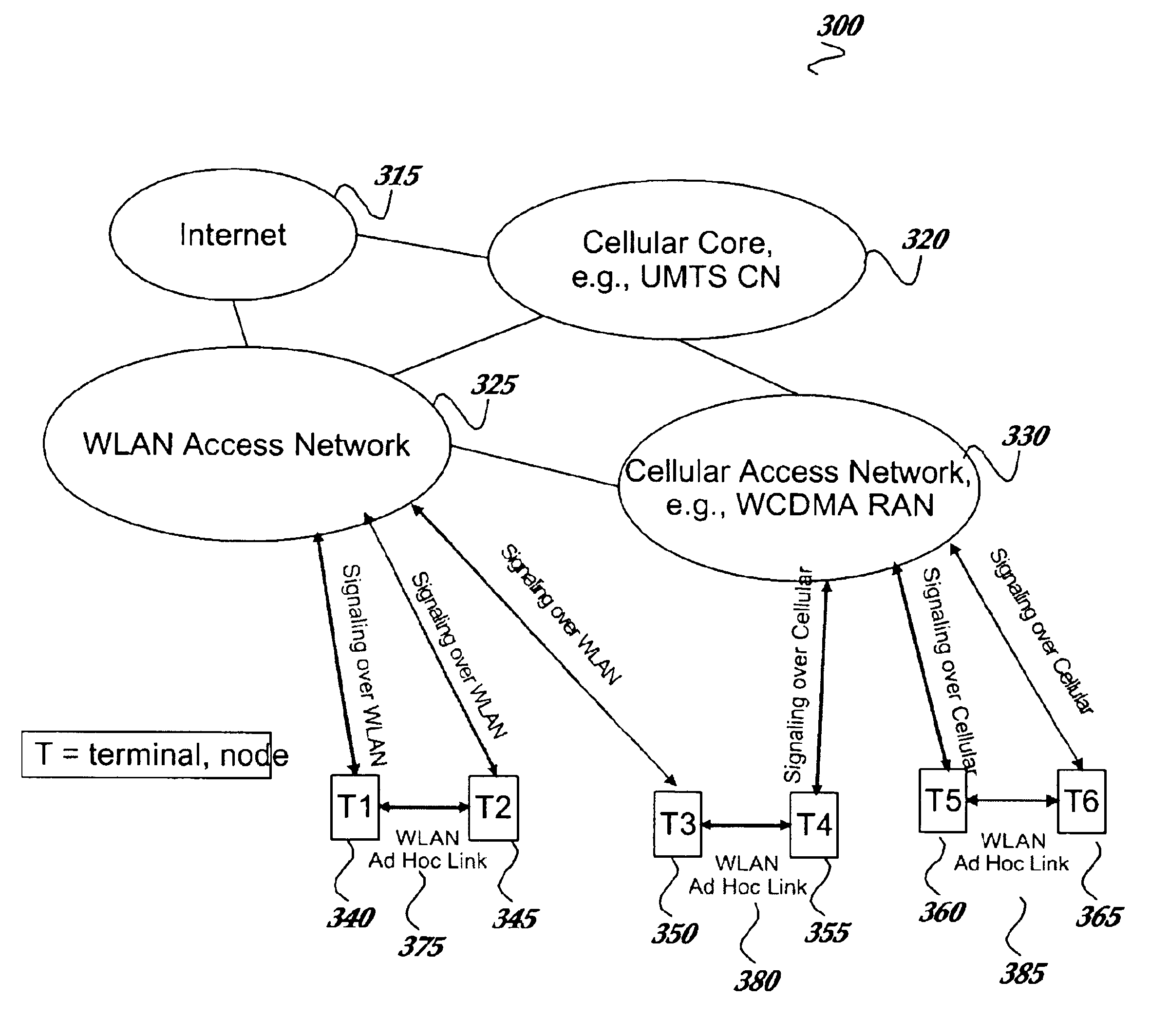
Ad hoc networking of terminals aided by a cellular network
InactiveUS6904055B2Increase incomeEasy to processNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexDual modeUser authentication
A fast and secure ad hoc communication system is established between terminals with the aid of a network. Terminals equipped with a non-cellular interface may establish a high data rate peer-to-peer or multi-hop ad hoc connection with the support of a cellular network. The cellular network may provide signaling for user authentication, peer identification, key distribution for a secure non-cellular connection set-up, radio resources management messages, routing assistance information, as well as charging and billing for the service. A non-cellular link may be used for fast and secure ad hoc communication between the terminals. Signaling may be transported either over a non-cellular access network or, using dual-mode terminals, over the cellular RAN. A combination of the signaling transports is also possible.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method for distributes the encrypted key in wireless lan
InactiveUS20050226423A1Simplifies AP structureLow costKey distribution for secure communicationNetwork topologiesComputer hardwareAir interface
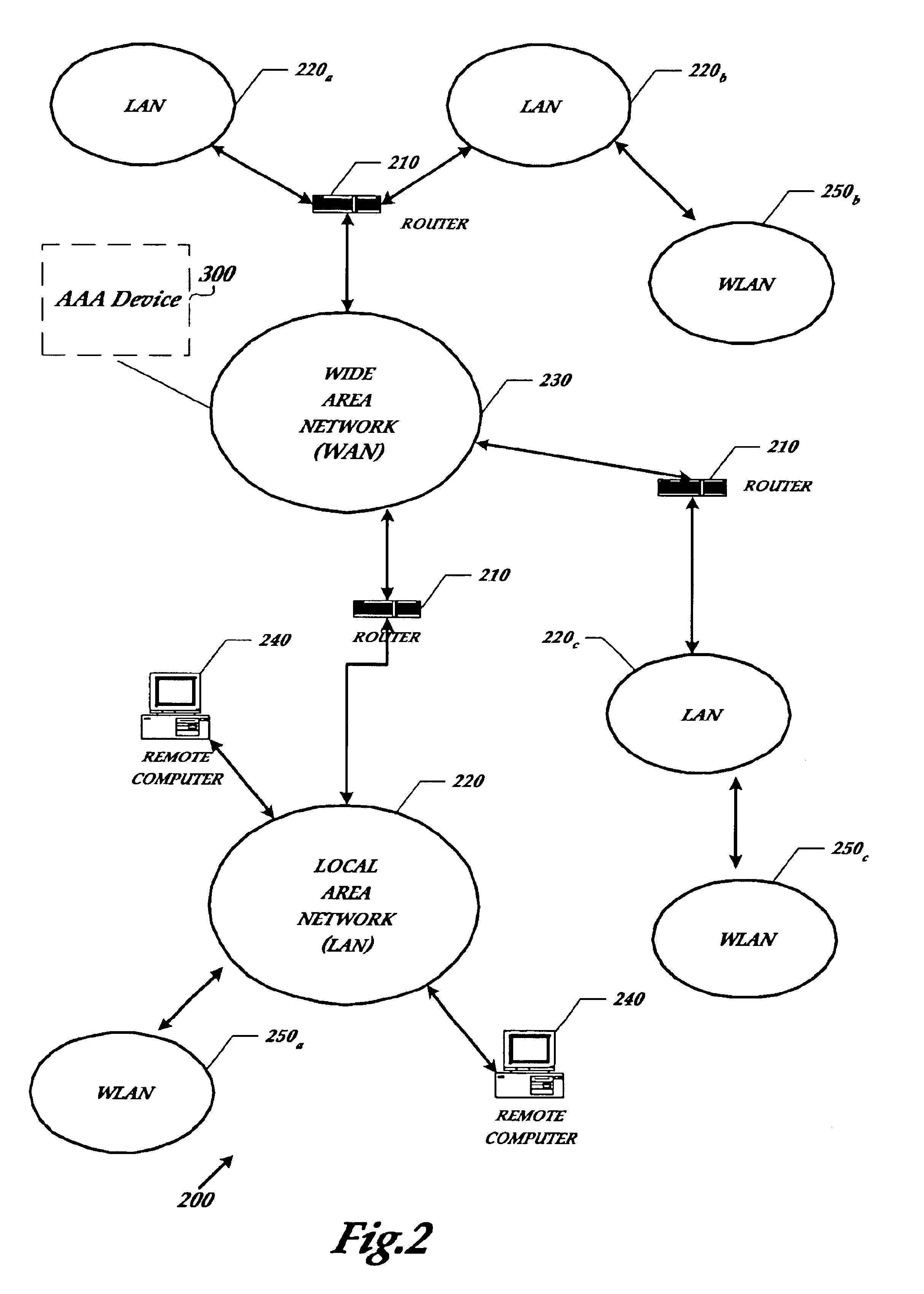
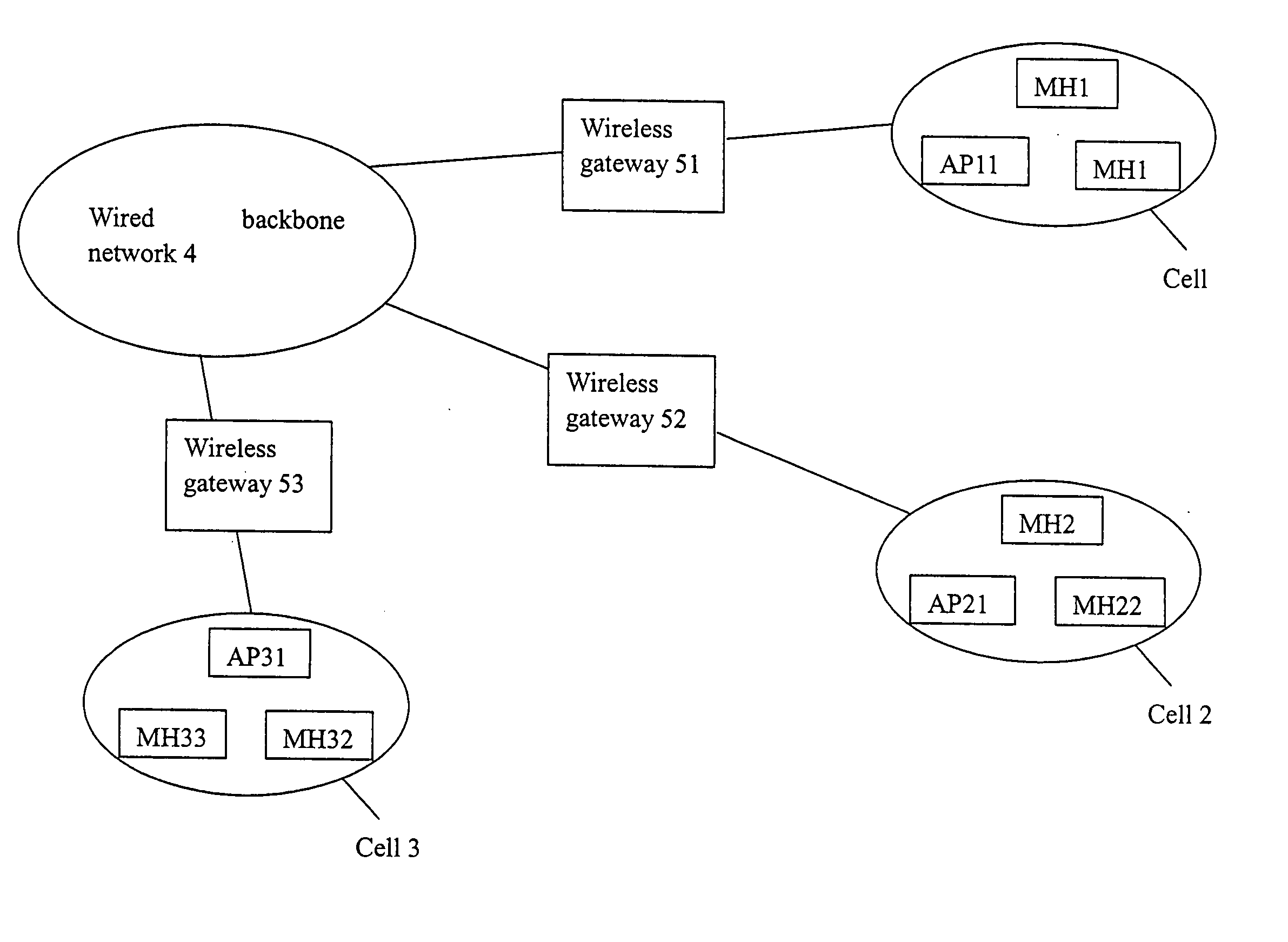
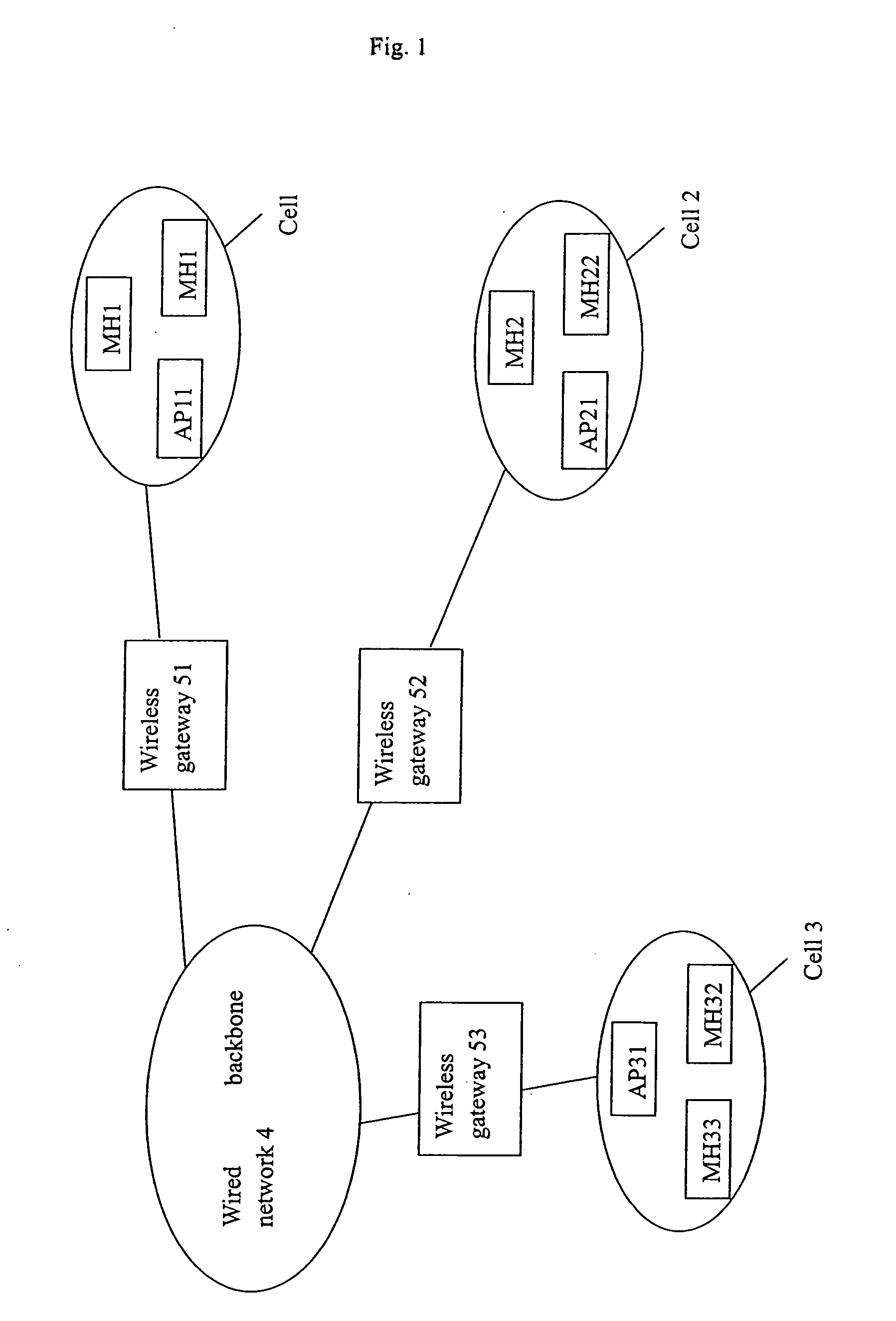
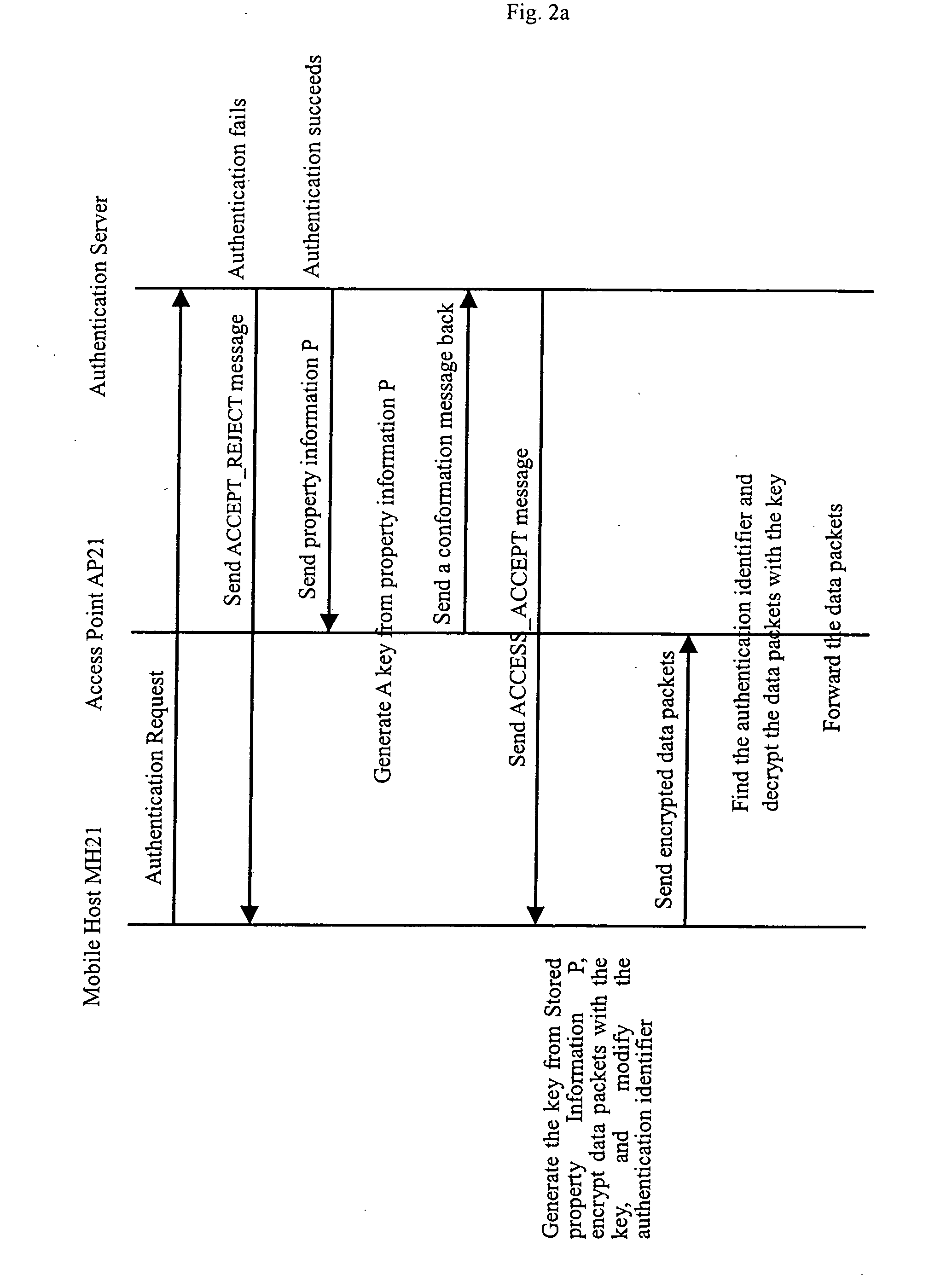
A method for distributing encryption keys in WLAN that combines a key distribution process with an authentication process of mobile hosts and utilizes an authentication server or a wireless gateway to manage key distribution so that mobile hosts can roam in a scope larger than the coverage area of the key management server. Because the key distribution does not transmit the key, which is not encrypted via the air interface, the method ensures the key is safe. In addition, the method can be used under different WLAN protocols. Because the AP does not need to manage user information, the method simplifies AP structure, and thus lowers the cost.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Quantum-key-distribution-network-based mobile encryption system and communication method thereof
ActiveCN102196425AReduce computationGuaranteed distribution securitySecurity arrangementPlaintextTelecommunications
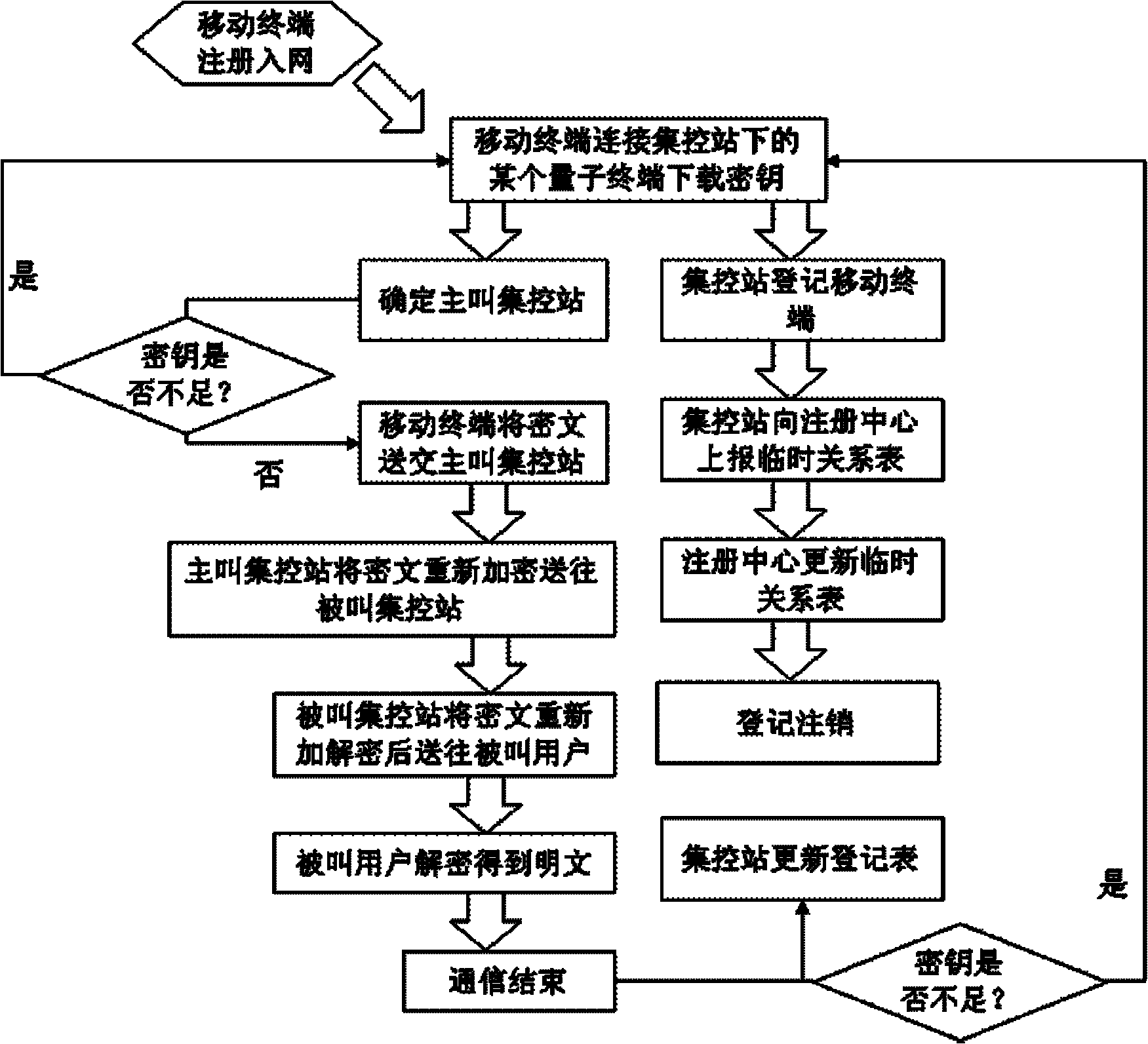
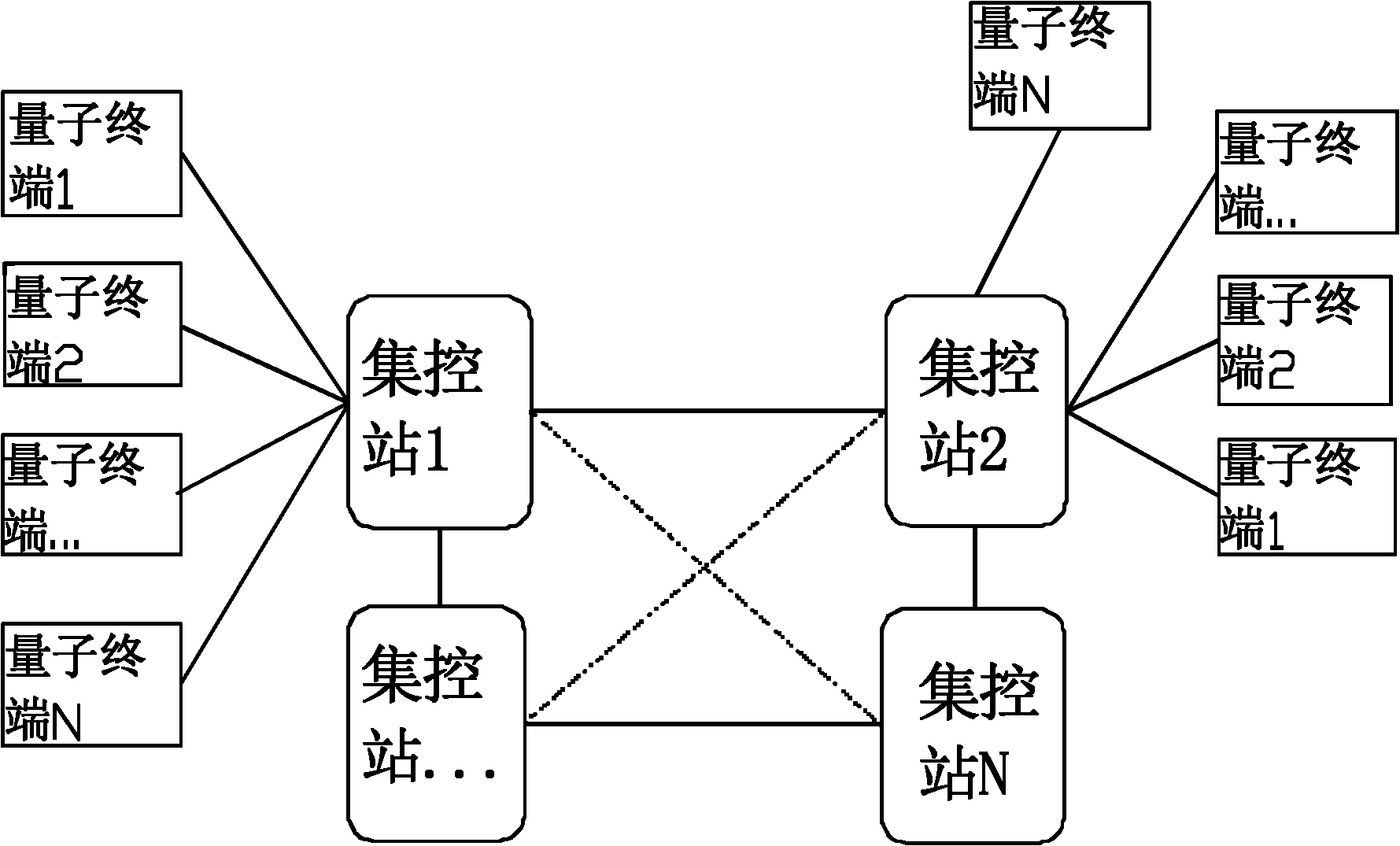
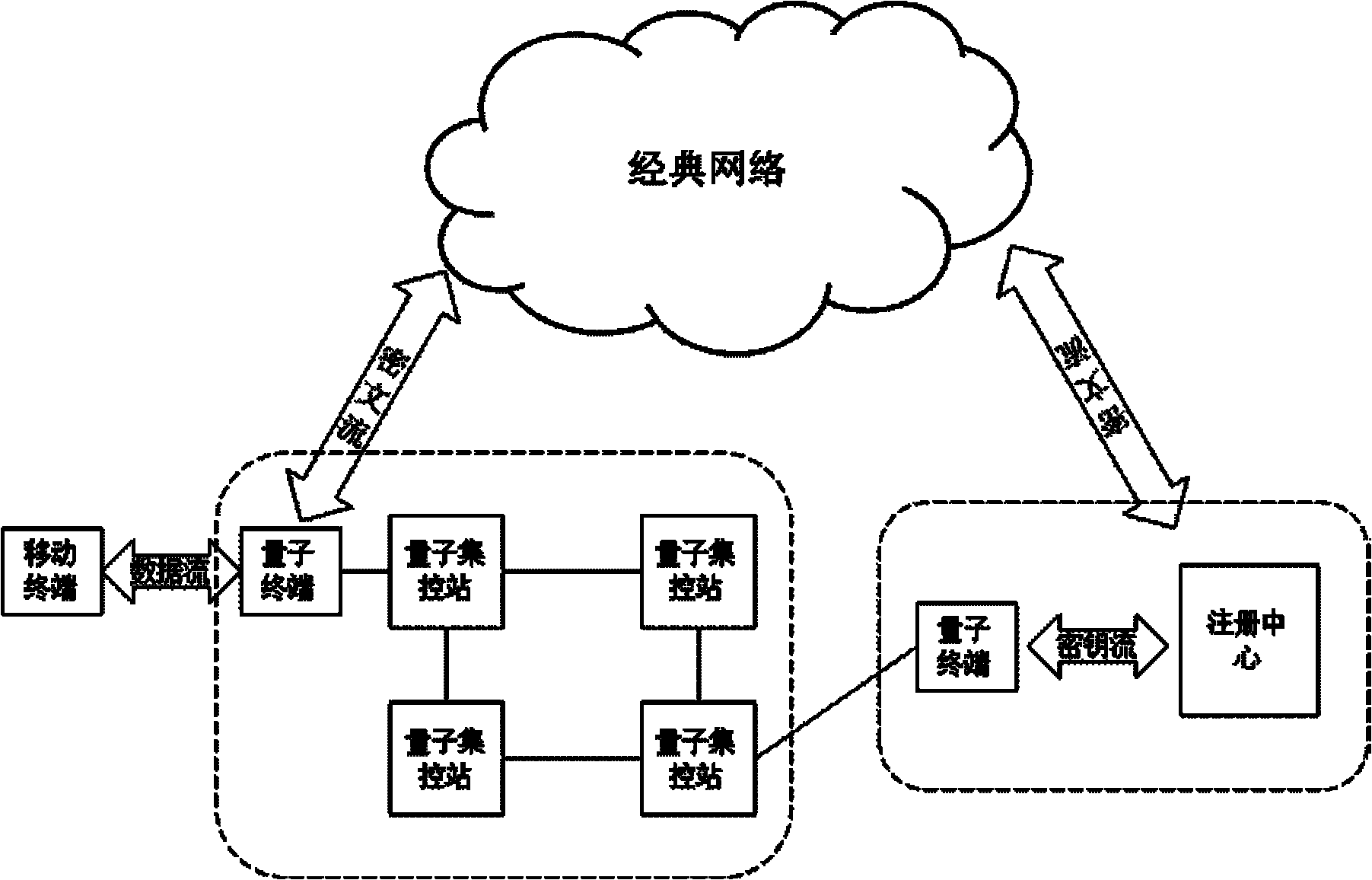
The invention discloses a quantum-key-distribution-network-based mobile encryption system and a communication method thereof. The method comprises that: a mobile terminal is registered in a network; the registered mobile terminal is connected with any quantum terminal by a key updating interface, and applies for the downloading of shared keys in a certain data volume to the quantum terminal; after the mobile terminal downloads the keys, the quantum terminal transmits a quantum centralized control station address to the mobile terminal for updating, and the mobile terminal takes a centralized control station on the quantum centralized control station address as a calling centralized control station; after the calling centralized control station is determined, the mobile terminal submits a cipher text to the calling centralized control station; the calling centralized control station re-encrypts the cipher text, and transmits the re-encrypted cipher text to a called centralized control station; the called centralized control station re-encrypts the cipher text, and transmits the re-encrypted cipher text to a called user; and after the called user decrypts the re-encrypted cipher text to obtain a plaintext, the communication is finished. In the method, the encryption does not require multiple matrix multiplication operations, so the computational load of the encryption is greatlyreduced; and simultaneously, the key distribution security of the highest level can be ensured in the key distribution of a quantum key distribution network.
Owner:QUANTUMCTEK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com