Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
319results about How to "Improve network security" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Remote computer virus scanning
InactiveUS20010005889A1Improve network securityLower the volumeMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsRemote computerVirus
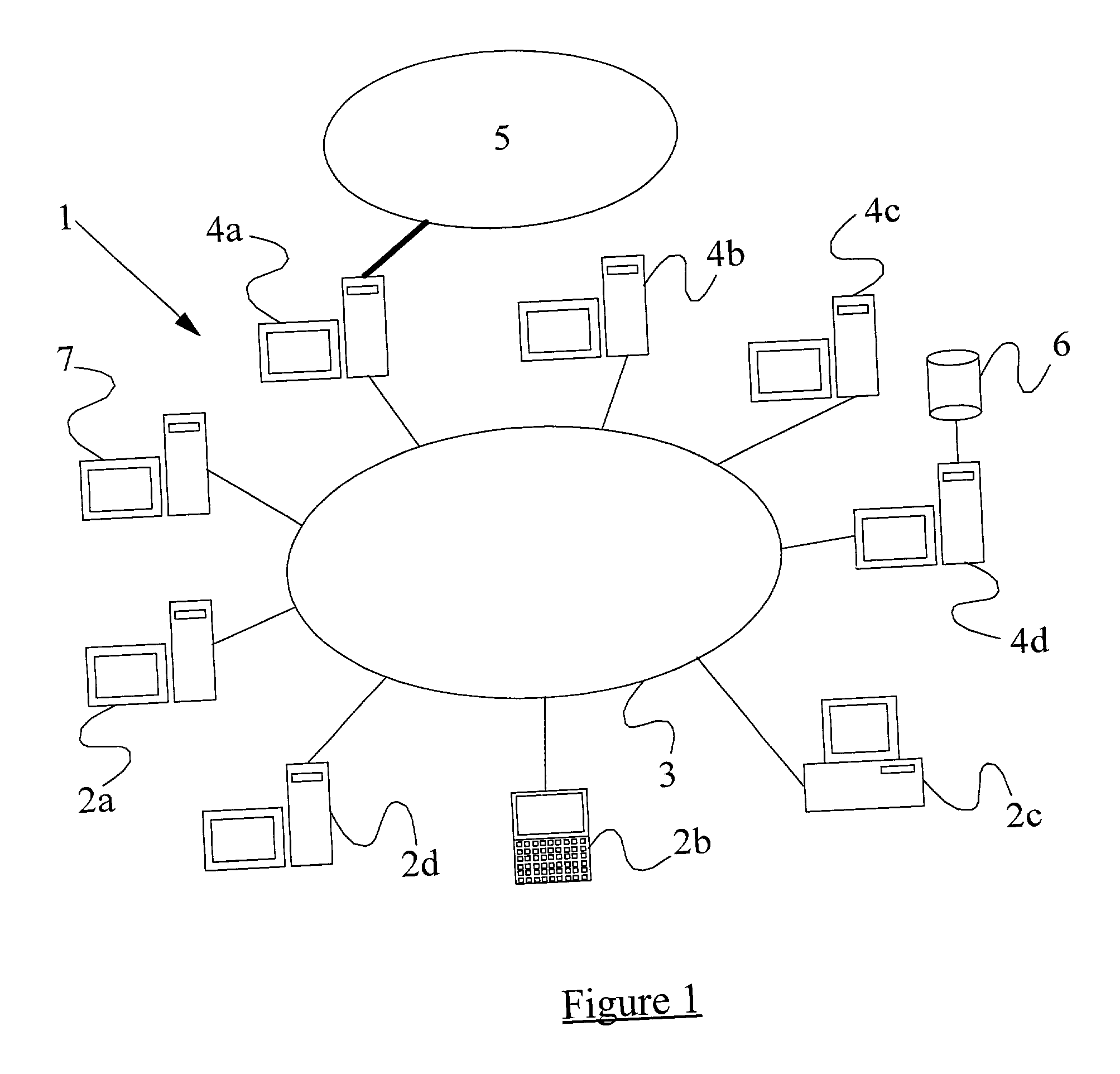
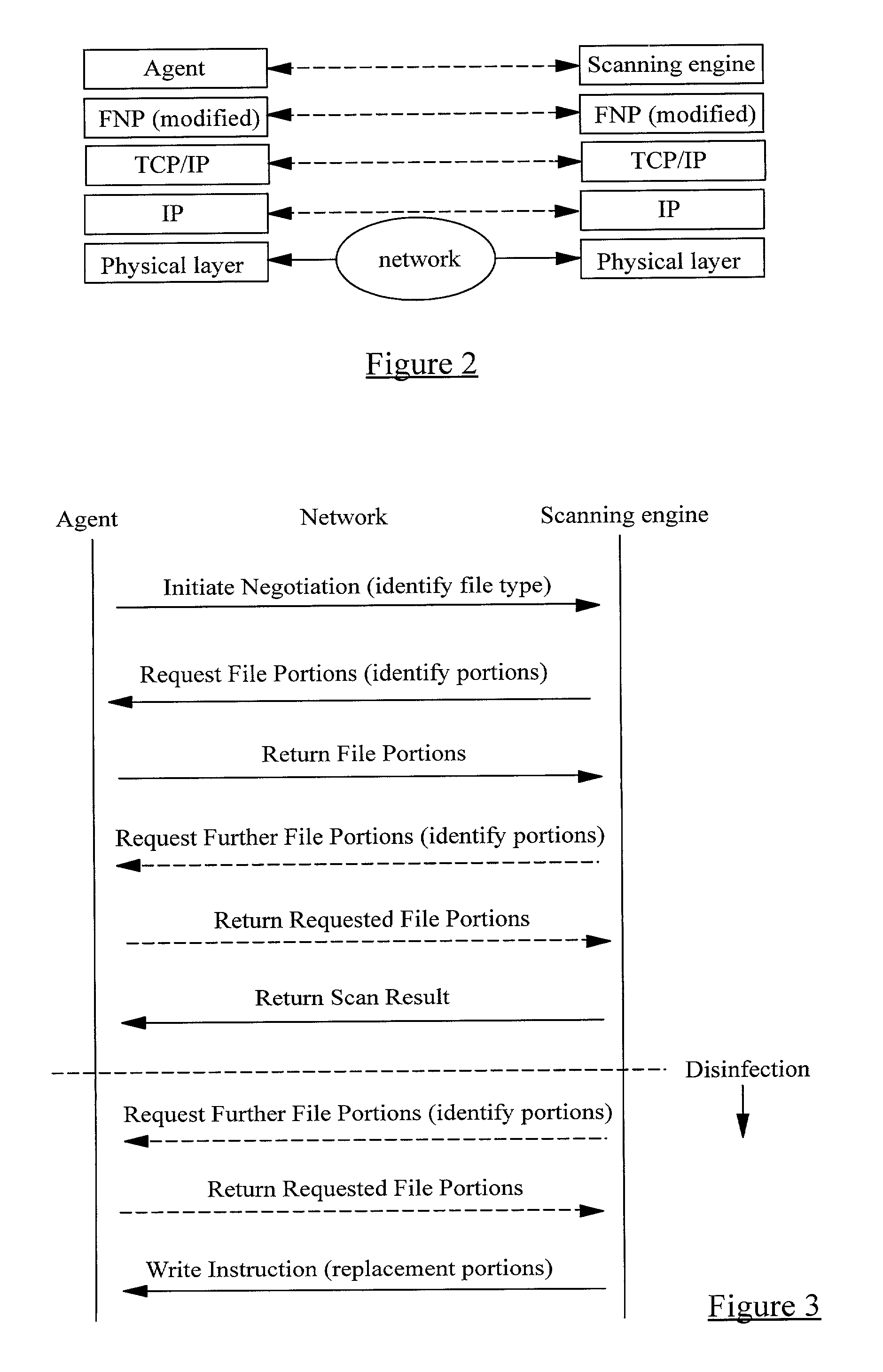
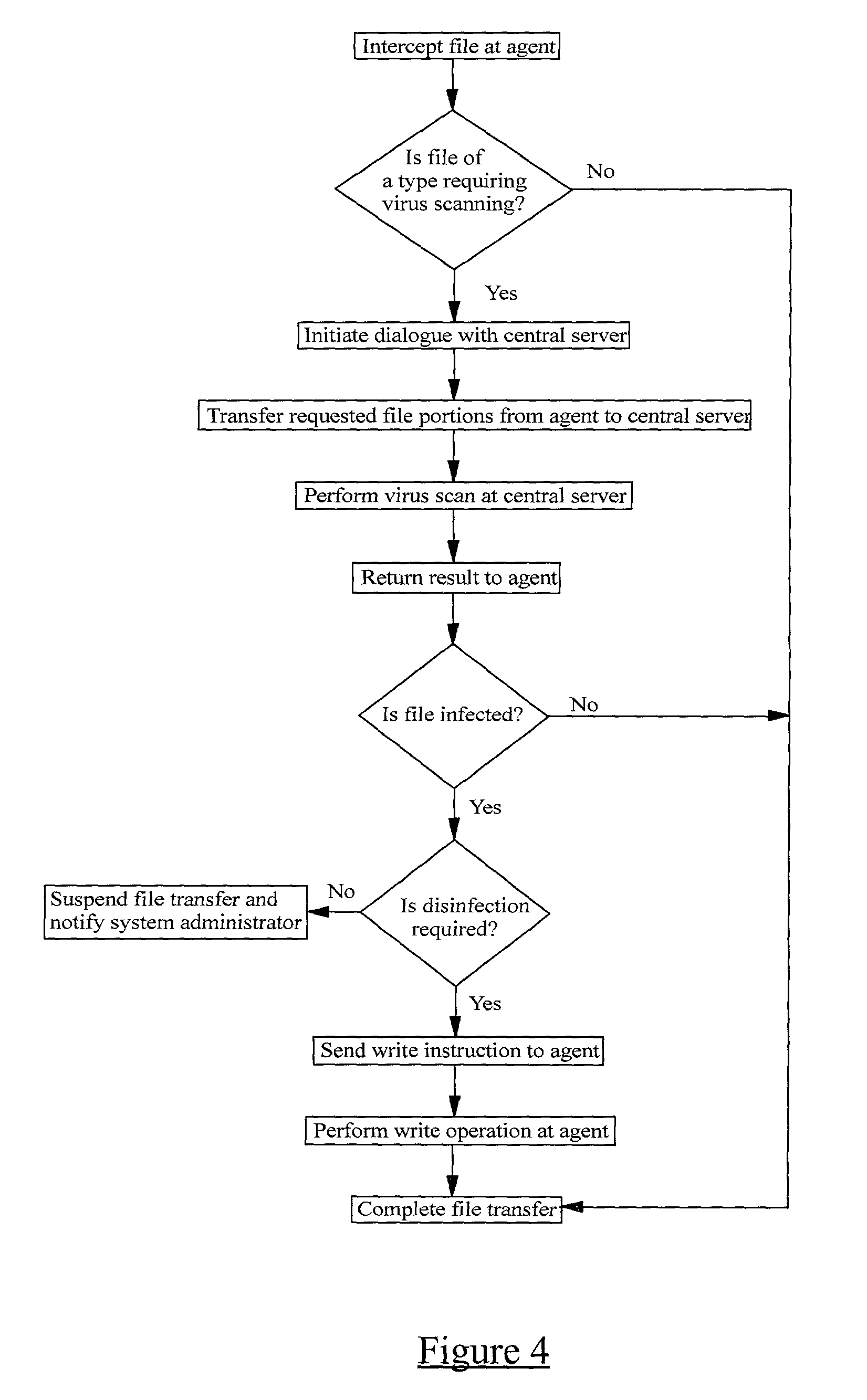
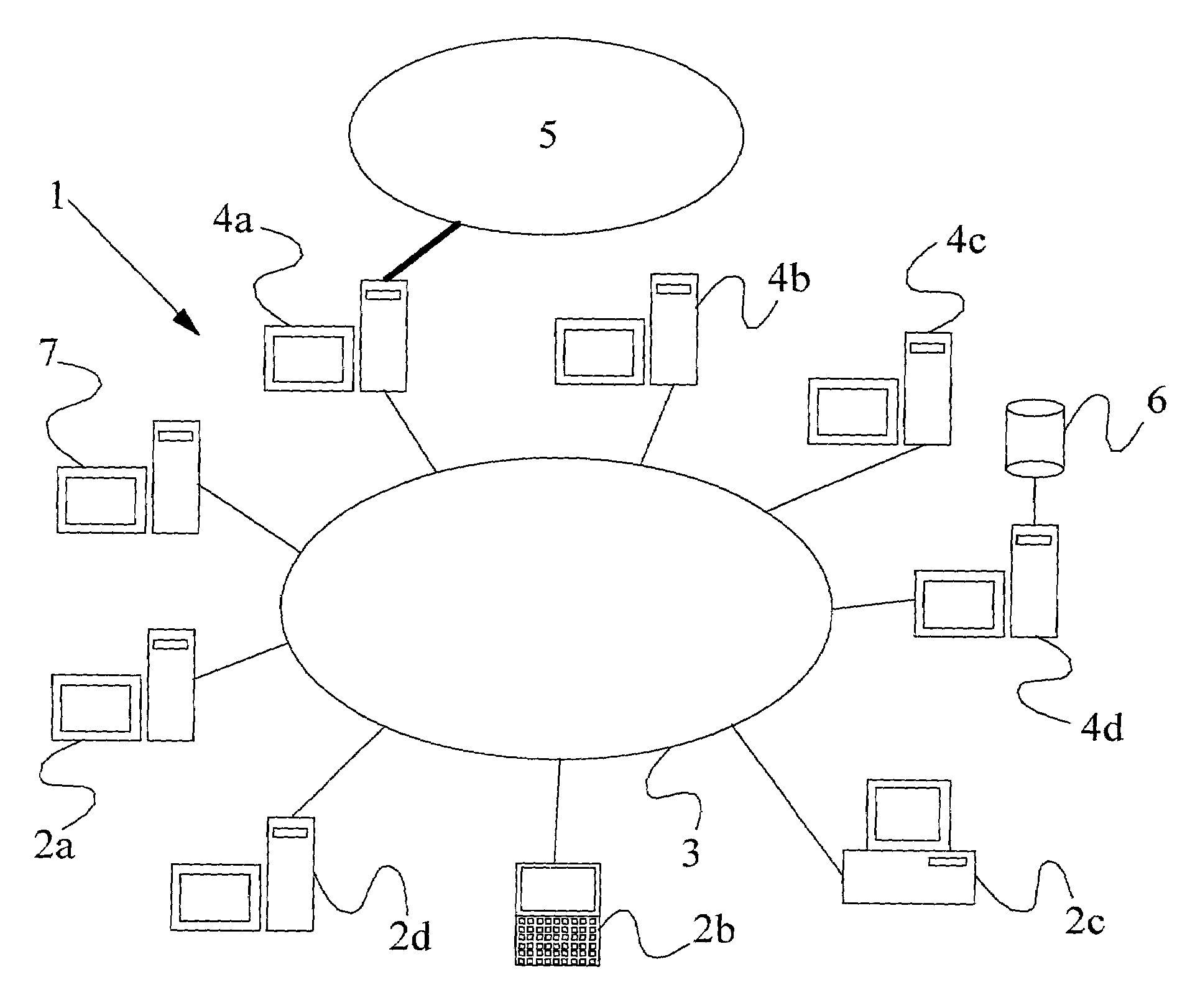
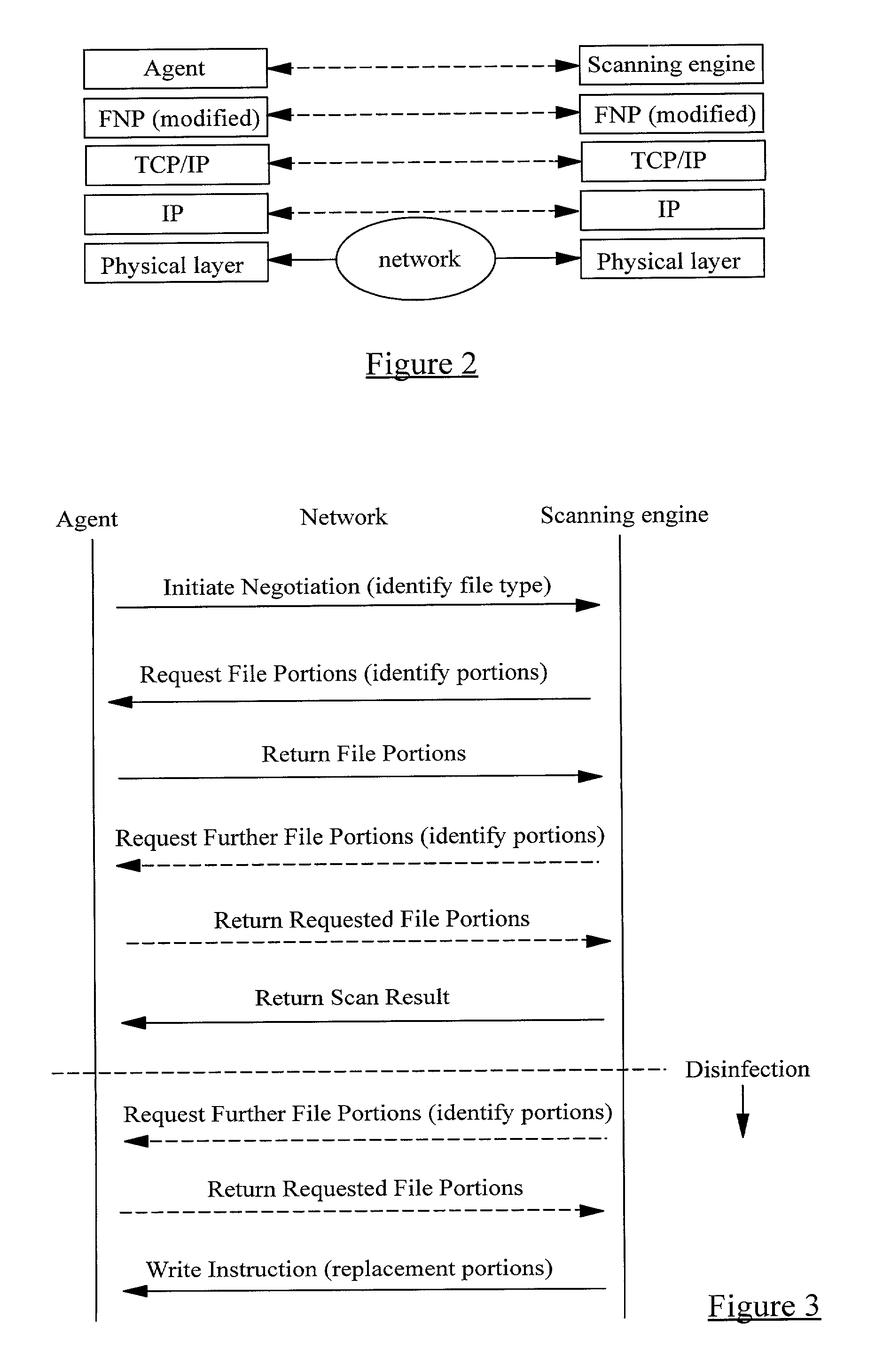
A method of scanning electronic files for computer viruses comprises identifying at a first node 4 of a computer network 1, electronic files which require to be scanned for computer viruses. The first node 4 initiates a dialogue with a second node 7 of the network 1, the second node comprising a virus scanning application. During the dialogue, the second node 7 identifies to the first node 4 one or more portions of the electronic file required by the virus scanning application. The first node 4 transfers the identified portions to the second node 7 which then carries out a virus scanning operation. The result of this operation is then returned to the first node 4.
Owner:F SECURE CORP
Method and apparatus for capturing and filtering datagrams for network security monitoring
ActiveUS7467408B1Improve network securityReduce network trafficMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionTraffic capacitySecurity monitoring
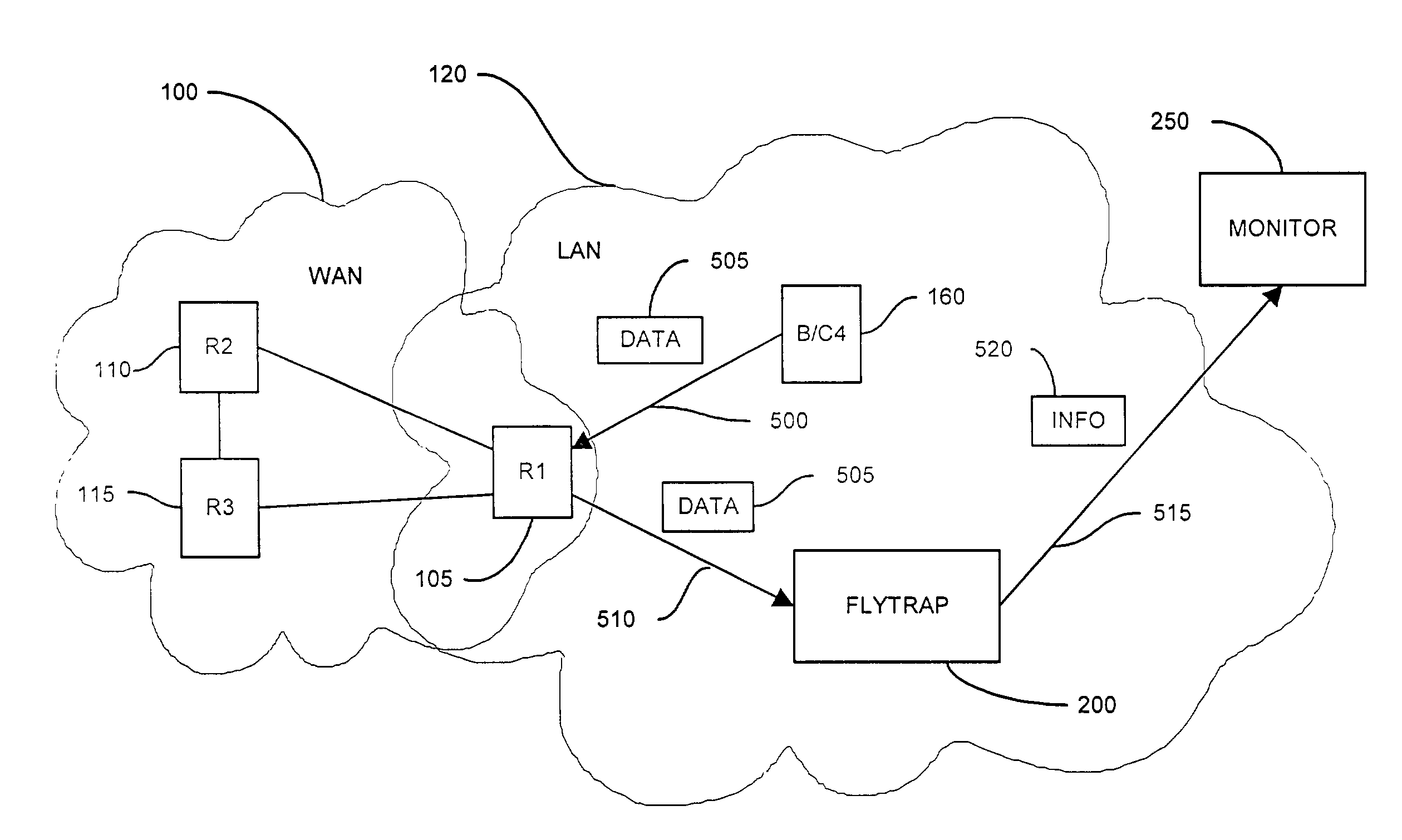
A method and system for security monitoring in a computer network has a packet sink with filtering and data analysis capabilities. The packet sink is a default destination for data packets having an address unrecognized by the network routers. At the packet sink, the packets are filtered and statistical summaries about the data traffic are created. The packet sink then forwards the data to a monitor, the information content depending on the level of traffic in the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and node for acquiring content and content network
InactiveUS20130041982A1Reduce wasteImprove network securityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionWorld Wide WebName resolution
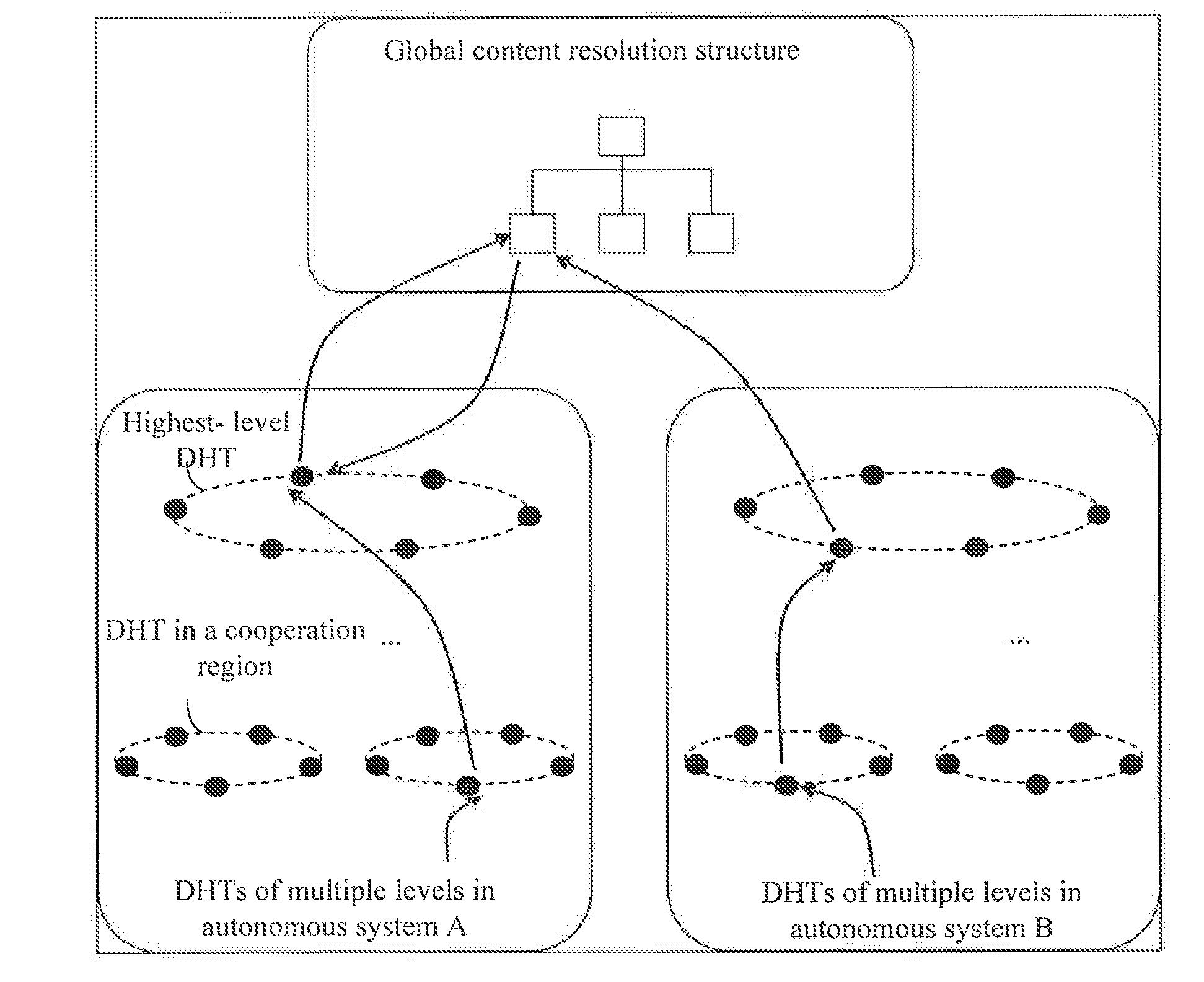
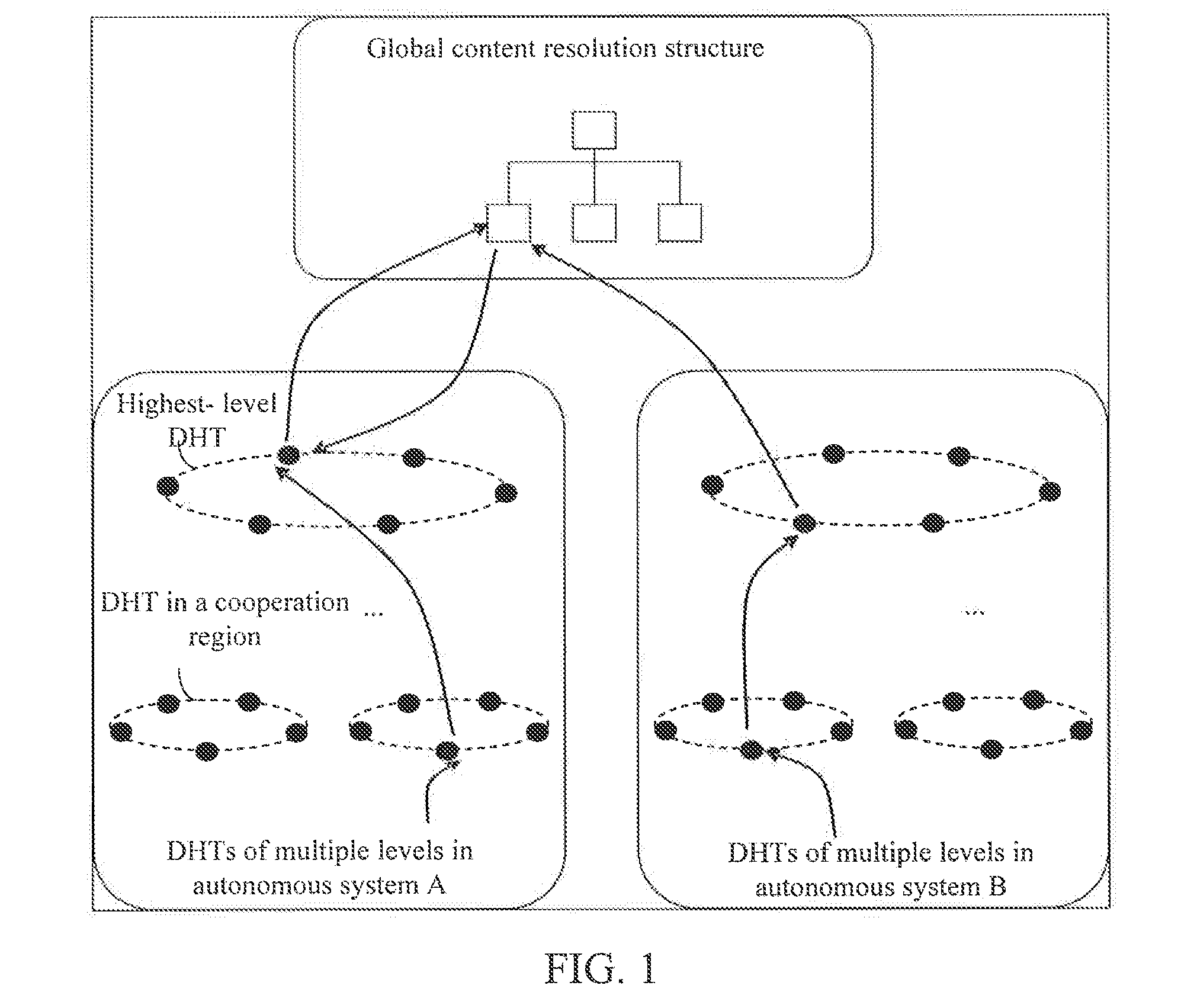
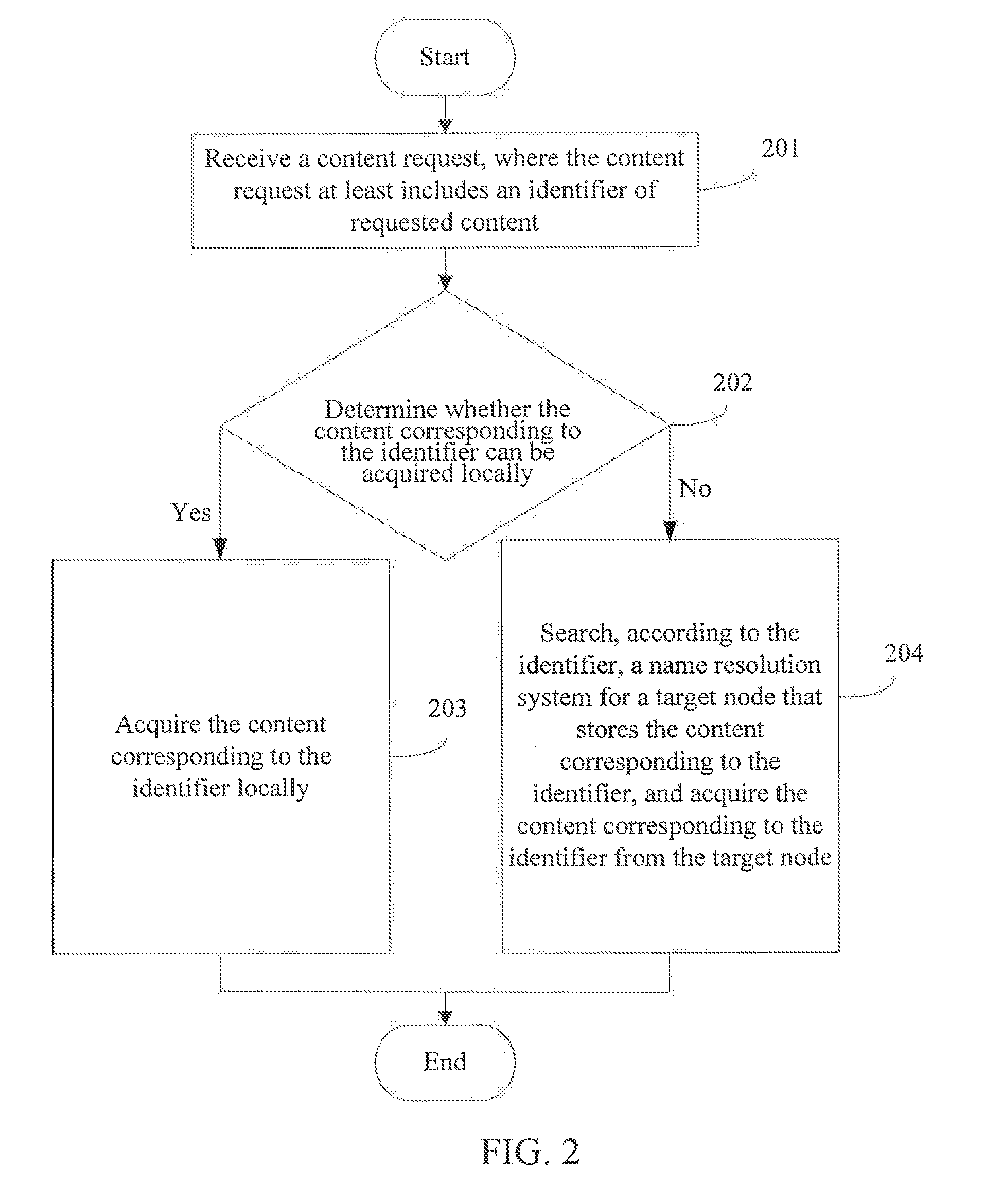
The present invention discloses a method and node for acquiring content and a content network, and is related to the field of communications. The method includes: receiving a content request, where the content request at least includes an identifier of requested content; determining whether the content corresponding to the identifier can be acquired locally; if yes, acquired the content corresponding to the identifier locally; otherwise, searching, according to the identifier, a name resolution system for a target node that stores the identifier, and acquiring the content corresponding to the identifier from the target node; where the name resolution system comprises a multilevel DHT and a global content resolution structure, and the global content resolution structure supports name aggregation and longest matching search.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Remote computer virus scanning
InactiveUS7020895B2Lower the volumeImprove network securityMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsRemote computerVirus
A method of scanning electronic files for computer viruses comprises identifying at a first node 4 of a computer network 1, electronic files which require to be scanned for computer viruses. The first node 4 initiates a dialogue with a second node 7 of the network 1, the second node comprising a virus scanning application. During the dialogue, the second node 7 identifies to the first node 4 one or more portions of the electronic file required by the virus scanning application. The first node 4 transfers the identified portions to the second node 7 which then carries out a virus scanning operation. The result of this operation is then returned to the first node 4.
Owner:F SECURE CORP
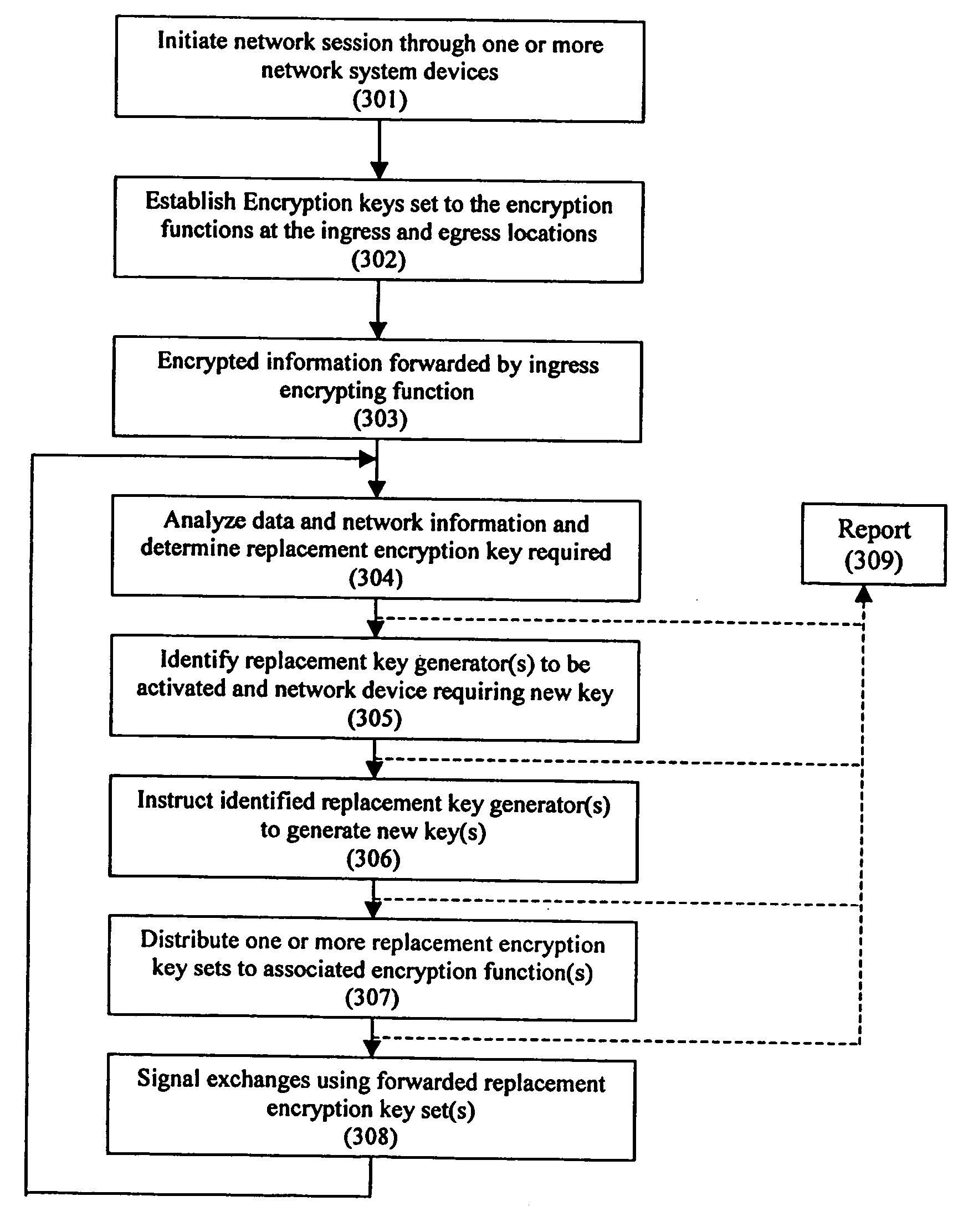
Encryption security in a network system
InactiveUS20060031936A1Improve network securityImprove securityMultiple keys/algorithms usageMemory loss protectionTransmission protocolTraffic capacity
A system and method for enhancing the security of signal exchanges in a network system. The system and method include a process and means for generating one or more replacement encryption key sets based on information and events. The information that may cause the generation of a replacement encryption key set includes, but is not limited to, a specified period of time, the level and / or type of signal traffic, and the signal transmission protocol and the amount of data sent. A key manager function initiates the replacement encryption key process based on the information. The replacement encryption key set may be randomly or pseudo-randomly generated. Functions attached to the network system required to employ encryption key sets may have encryption key sets unique to them or shared with one or more other attached functions. The system and method may be employed in a wireless, wired, or mixed transmission medium environment.
Owner:ENTERASYS NETWORKS
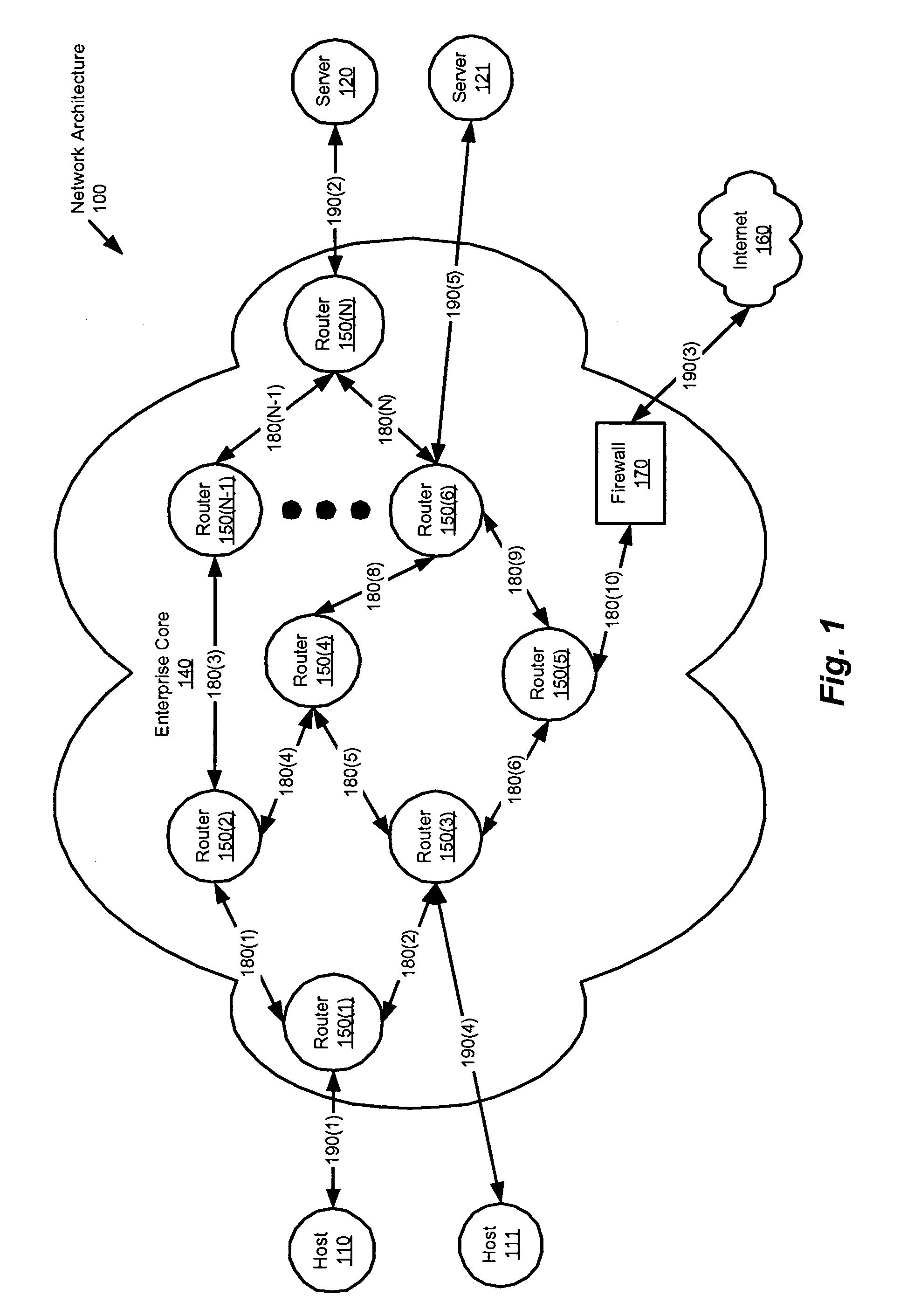
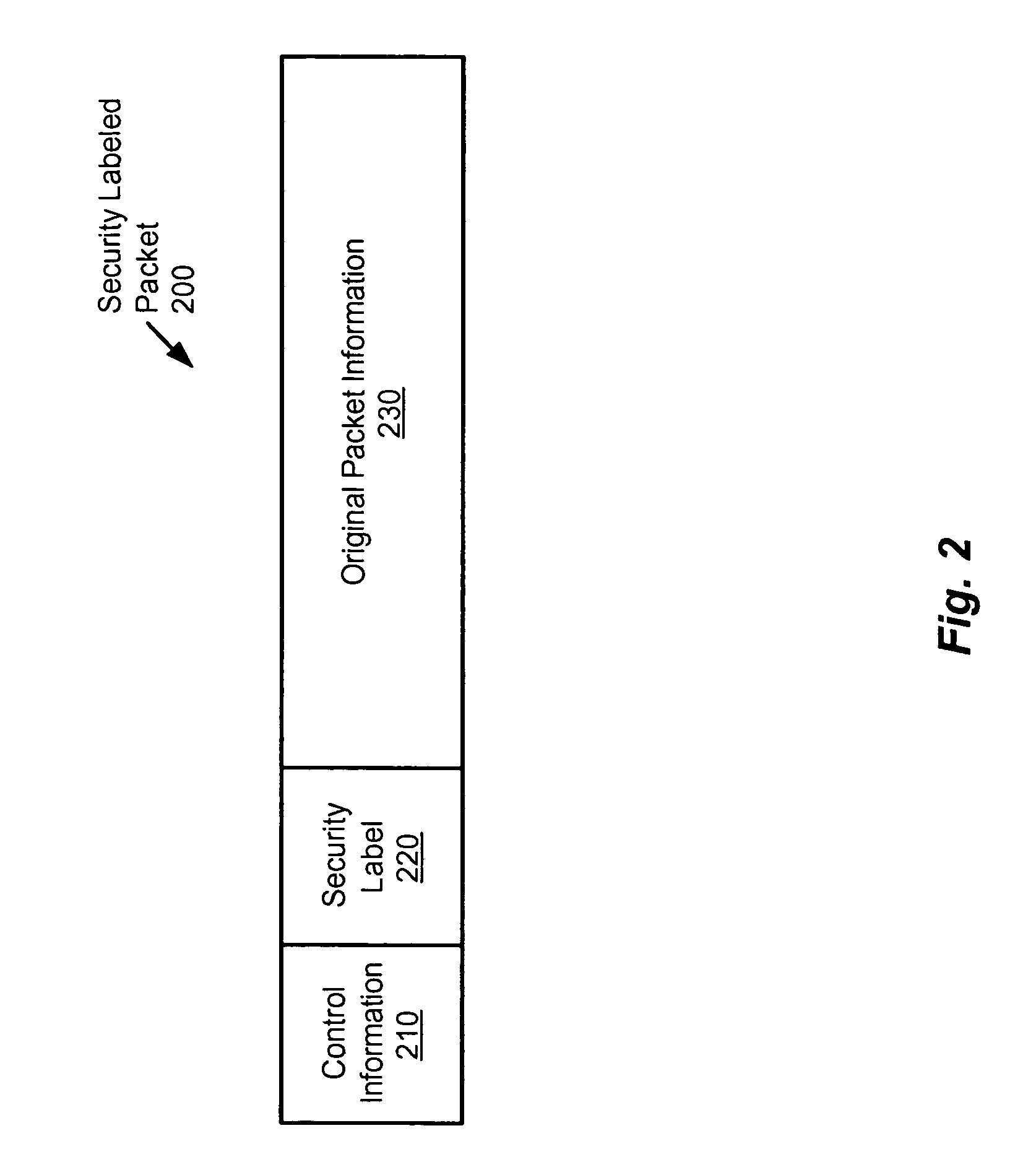
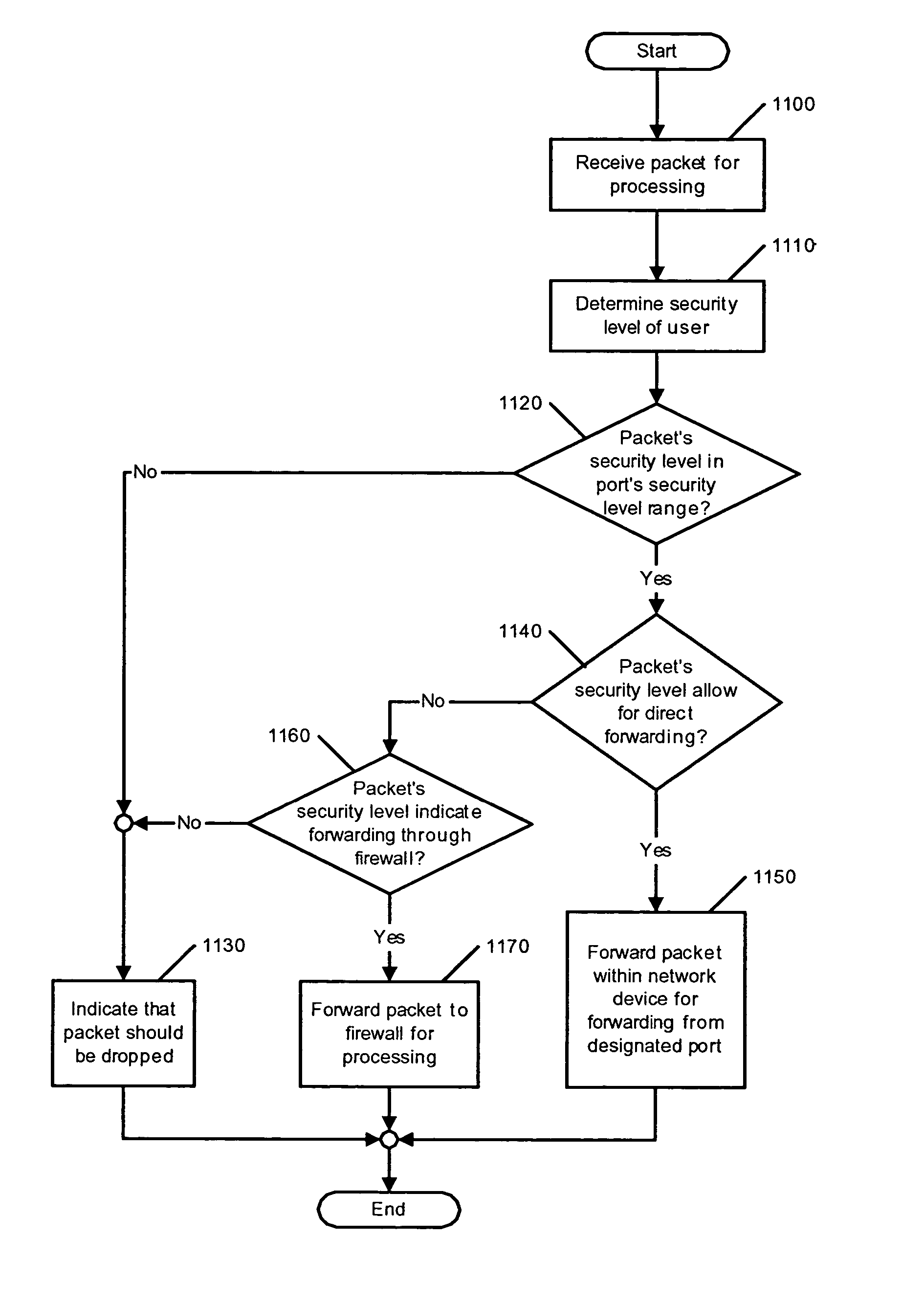
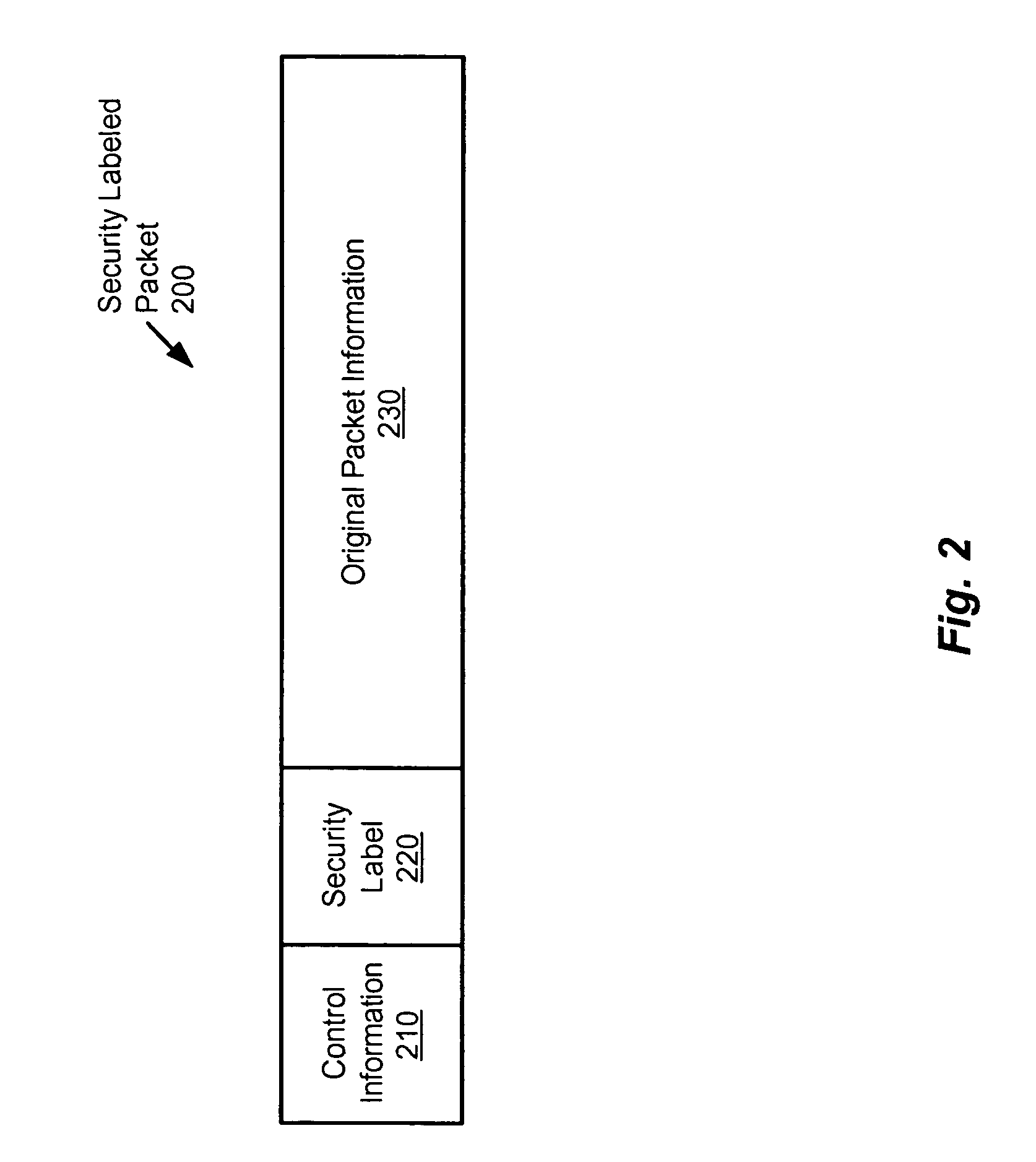
Method and apparatus for providing network security using security labeling
ActiveUS20050097357A1Reduces potential leakageImprove network securityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork security policySecurity level
A method and apparatus for providing network security using security labeling is disclosed. The method includes comparing first security level information and second security level information, and indicating processing to be performed on the packet based on the comparing. The first security level information is stored in a security label of a packet received at a network node, while the second security level information is stored at the network node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
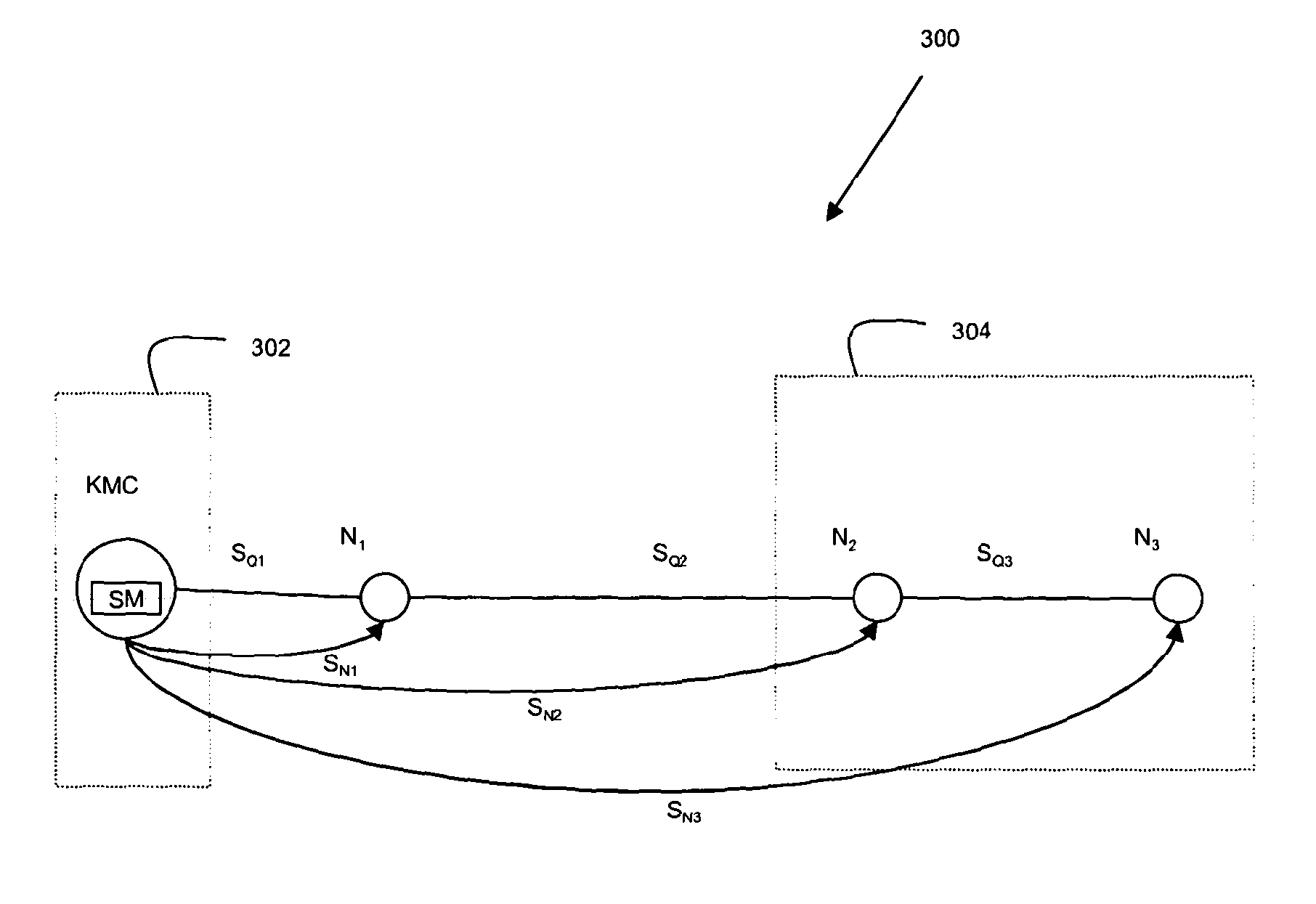
Quantum key distribution
ActiveUS20130251145A1Improve network securityIncrease ratingsKey distribution for secure communicationKey distributionQuantum key distribution
Methods and apparatus for quantum key distribution are described, in particular including methods and networks 300 arranged to improve and / or ensure the security of data transmitted thereby by (i) ensuring a certain level of loss within at least part of the network, (ii) placing a penultimate and an endpoint nodes in situated in a secure second enclave, (iii) analysing a transmitted bit stream to ensure that it does not provide an unacceptable amount of information about the key that may be generated therefrom, and / or (iv) varying the order in which bits are used to generate a key.
Owner:QUBITEKK
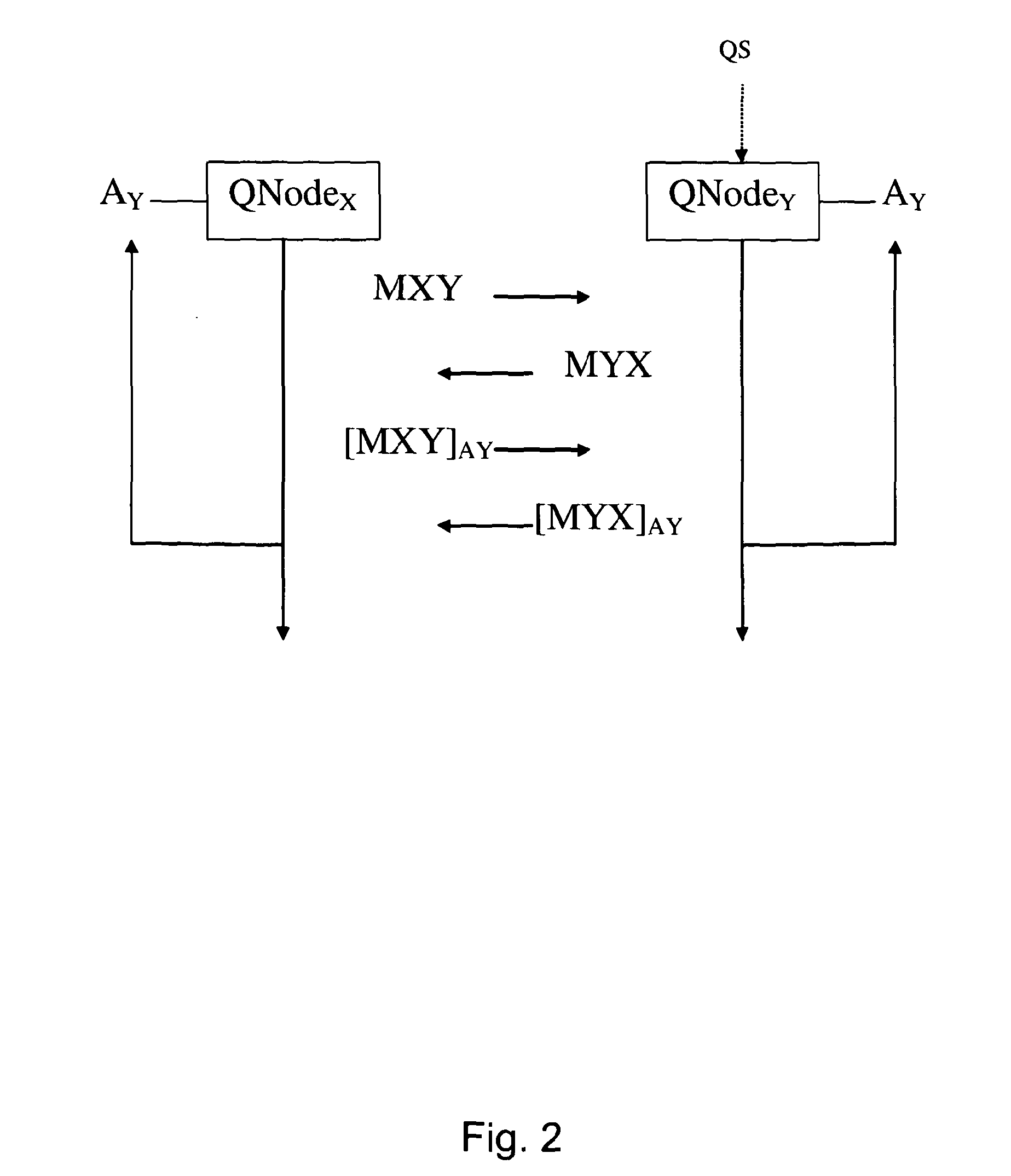
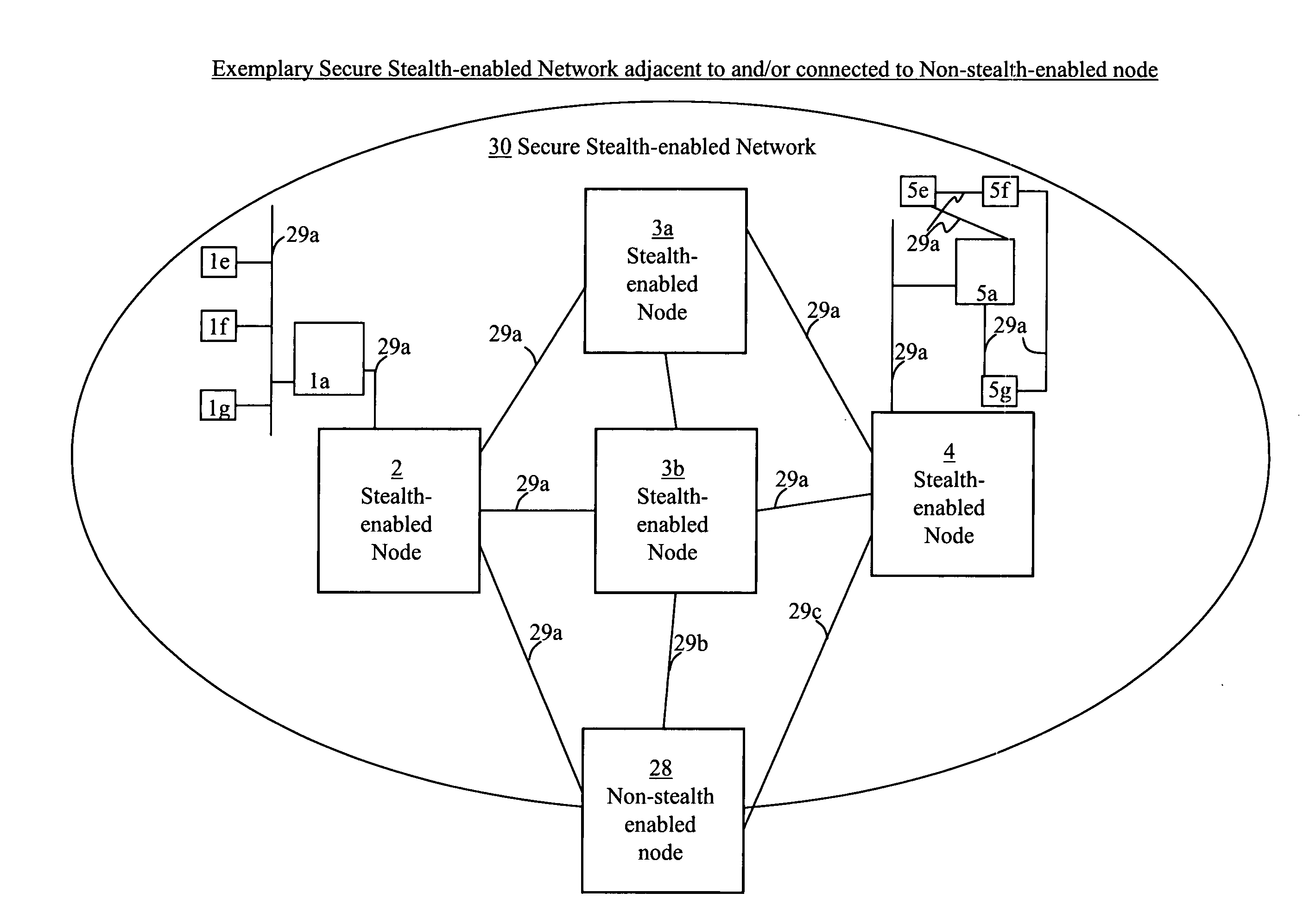
Stealth packet switching
InactiveUS20050094640A1Low probability of interceptReduce probabilityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationHidden dataNetwork architecture
Systems, methods, devices, and network architectures are disclosed for creating and implementing secure wireless, wired, and / or optical stealth-enabled networks using specially modified packets, cells, frames, and / or other “stealth” information structures. This enables stealth packets to have a low probability of detection, a low probability of interception, and a low probability of interpretation. Stealth packets are only detected, intercepted, and correctly interpreted by stealth-enabled network equipment. In its simplest form, stealth packet switching modifies the packet structure, protocols, timing, synchronization, and other elements through various rule-violations. This creates stealth packets, which normal equipment cannot receive correctly, and hence normal equipment discards the stealth packets. Stealth packets may be further enhanced with encryption techniques which focus on encrypting the packet structure itself, as opposed to merely encrypting the data. Using encryption to modify the packet structure itself adds an entirely new level of encryption complexity, thus making the stealth communications orders of magnitude more difficult to decrypt than standard decryption techniques. Combining stealth packets with time-based reservation packet switching enables total encryption of the packet (including header and preamble encryption) capable of routing through multiple hops without decryption of headers and preamble at each hop. Time-based reservation packet switching can also guarantee real-time stealth packet delivery through a network that is totally congested from data storms, virus caused congestion, and / or denial of service attacks.
Owner:HOWE WAYNE RICHARD
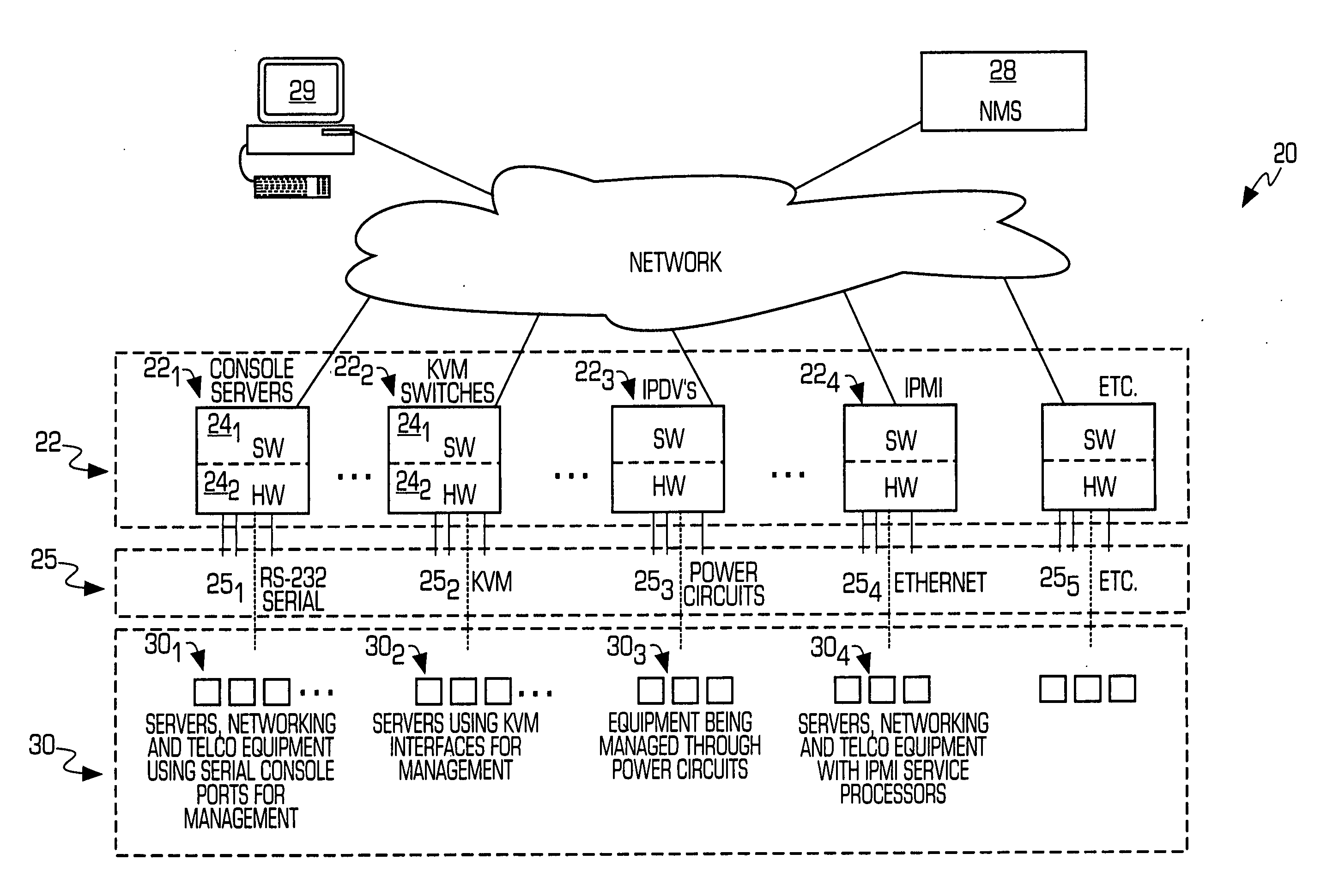
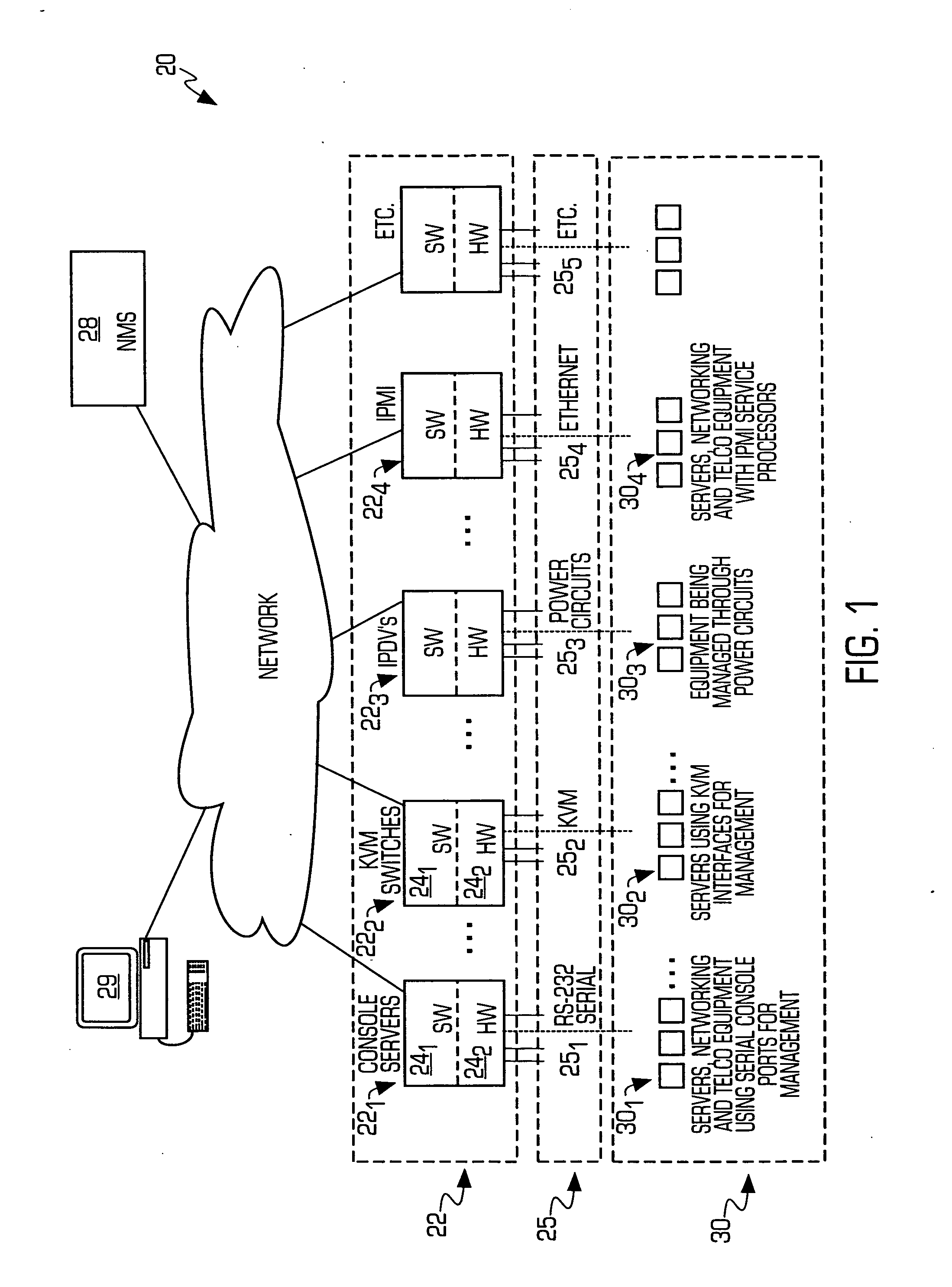
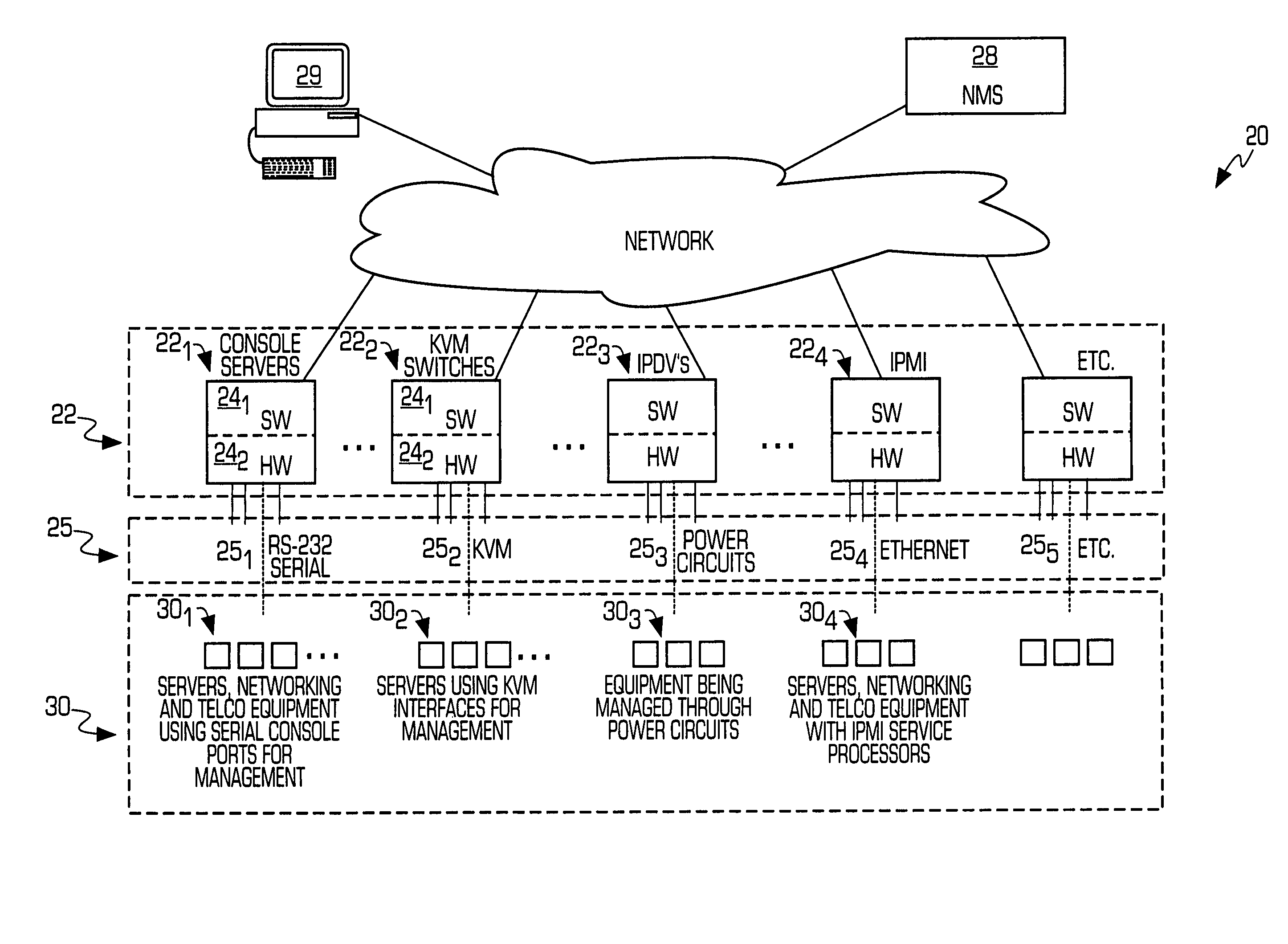
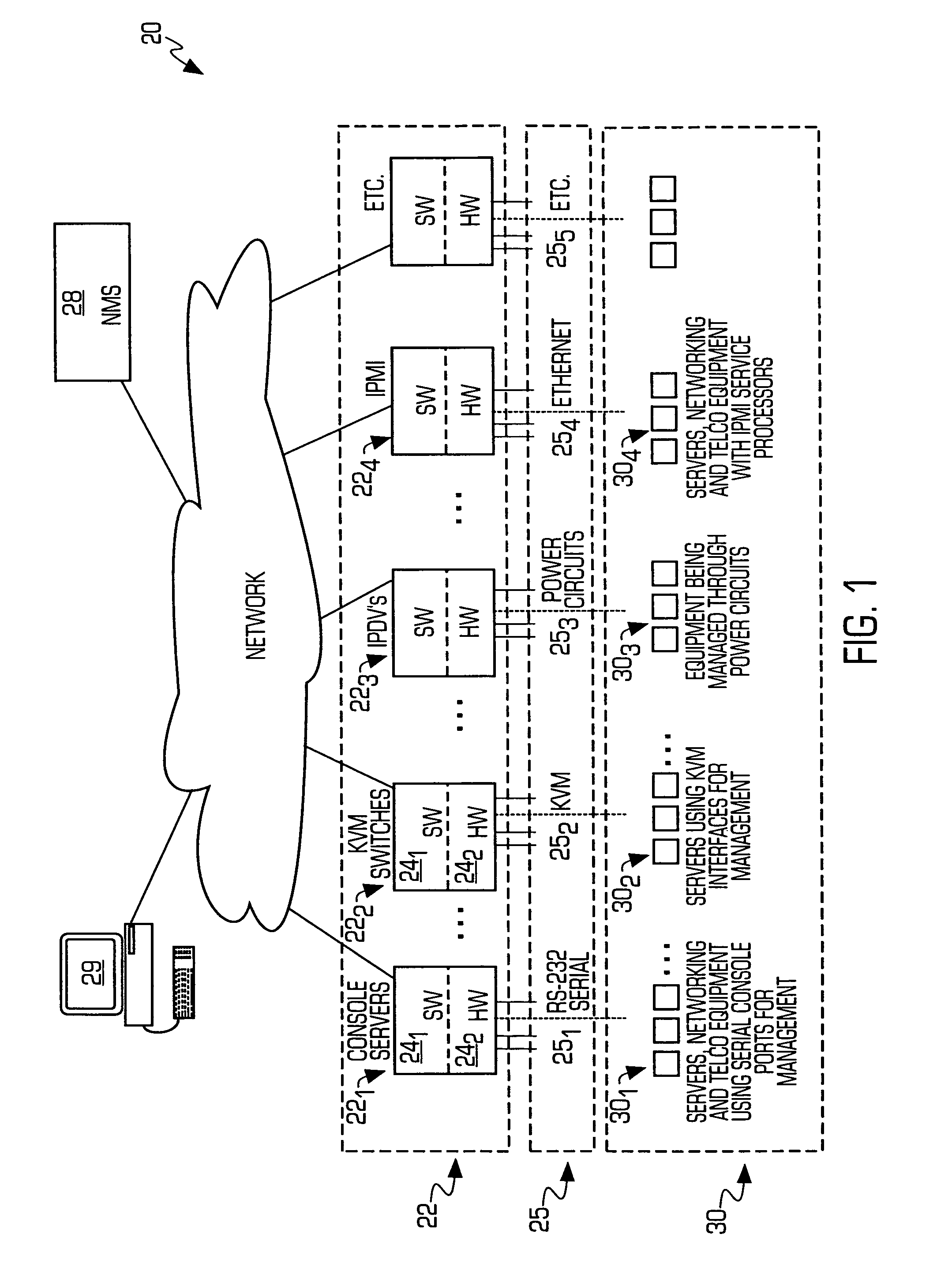
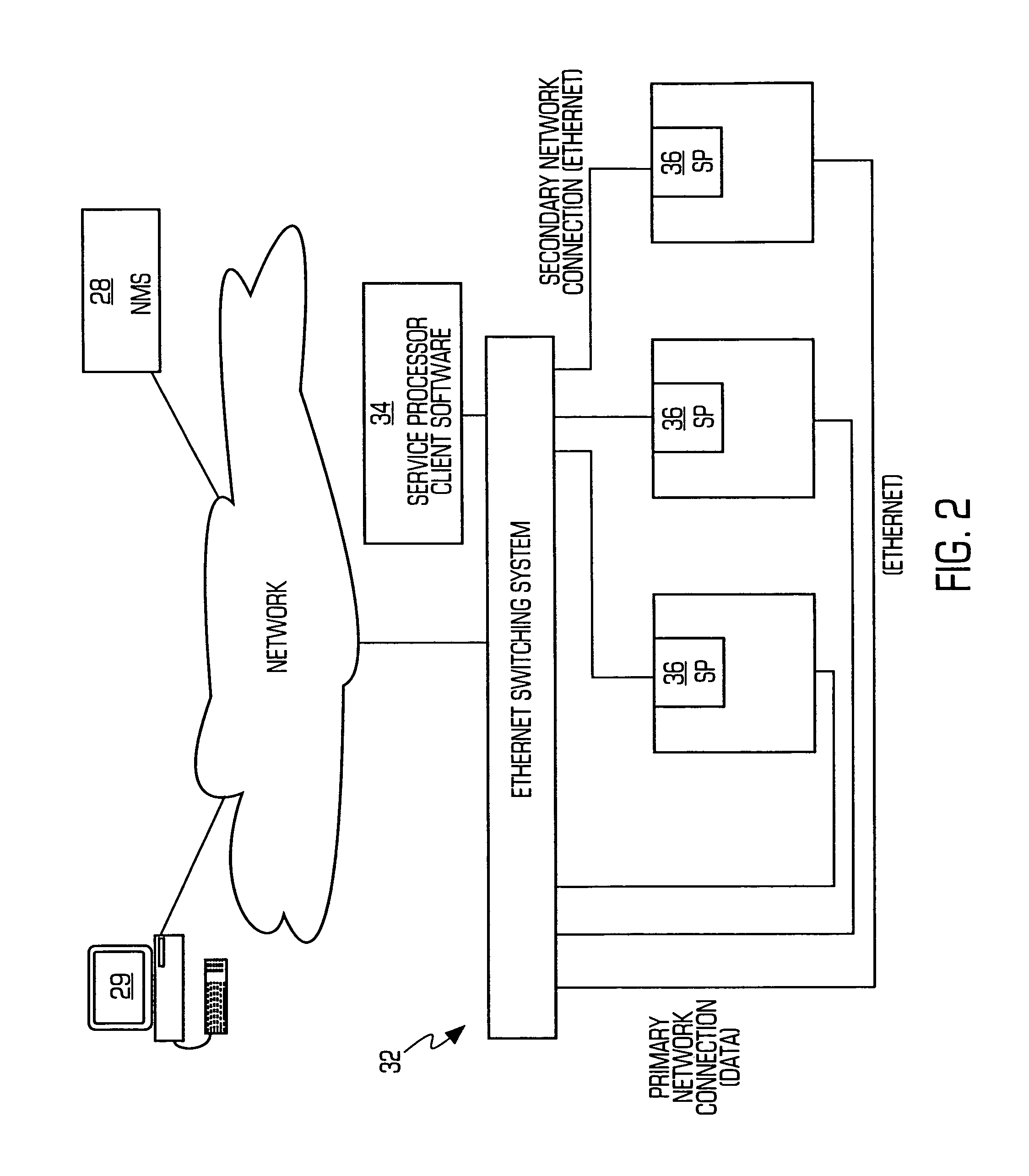
Service processor gateway system and appliance
ActiveUS20050129035A1Low costReduce complexityData switching by path configurationNetworking protocolSecure transmission
A system for physically consolidating and securing access to service processors and management modules in computer, telecommunication and networking equipment is provided that isolates the management ports from the data network. The system converts low-level management protocols into higher-level network protocols suitable for secure transport over the data network. The system may encrypt the common format management data. The system may also authenticate each user that attempts to access the management interfaces.
Owner:VERTIV IT SYST INC
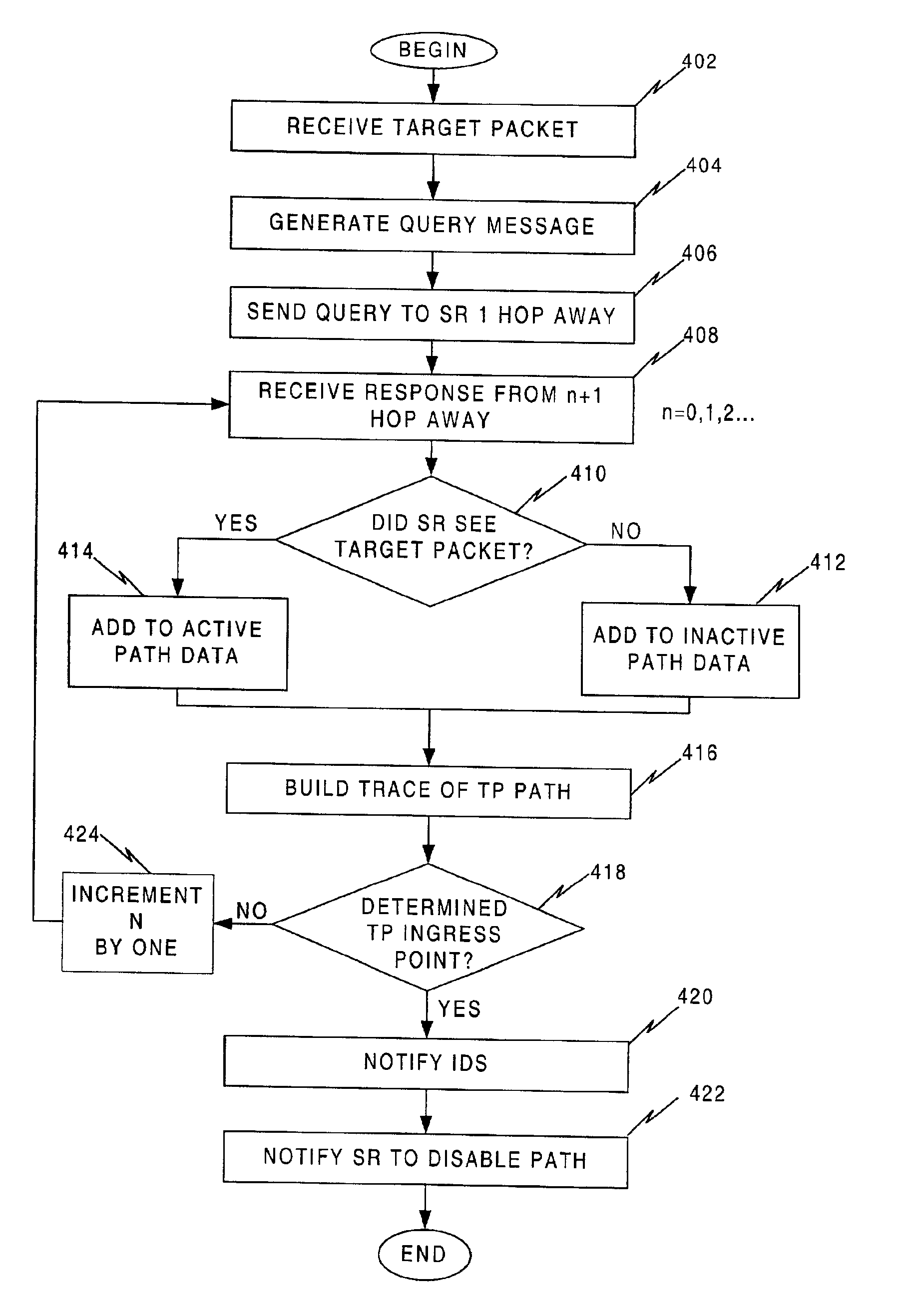
Method and apparatus for tracing packets
InactiveUS6981158B1Easy to optimizeEliminate problem causedMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsNetwork packetDistributed computing
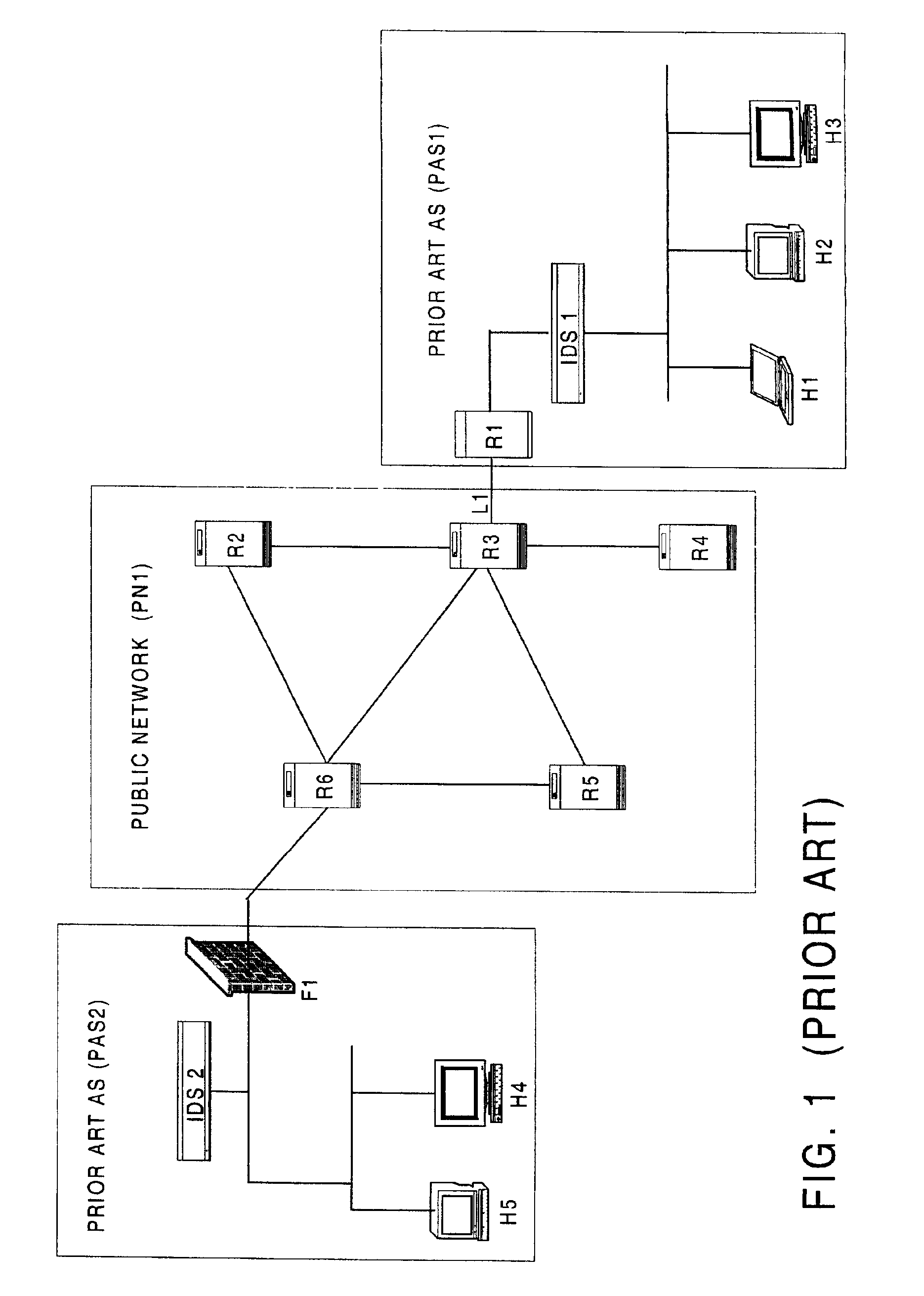
A system and method for performing source path isolation in a network. The system comprises an intrusion detection system (IDS), a source path isolation server (SS1) and at least one router configured to operate as a source path isolation router (SR1) operating within an autonomous system. When IDS detects a malicious packet, a message is sent to SS1. SS1 in turn generates a query message (QM) containing at least a portion of the malicious packet. Then, QM is sent to participating routers located one hop away. SR1 uses the query message to determine if it has observed the malicious packet by comparing it with locally stored information about packets having passed through SR1. SR1 sends a reply to SS1, and SS1 uses the reply to identify the ingress point into the network of the malicious packet.
Owner:STRAGENT
Active intrusion resistant environment of layered object and compartment keys (AIRELOCK)
InactiveUS20020066035A1Improve network securityAccurate and rapid fault or attack isolationMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSecurity domainManaged object
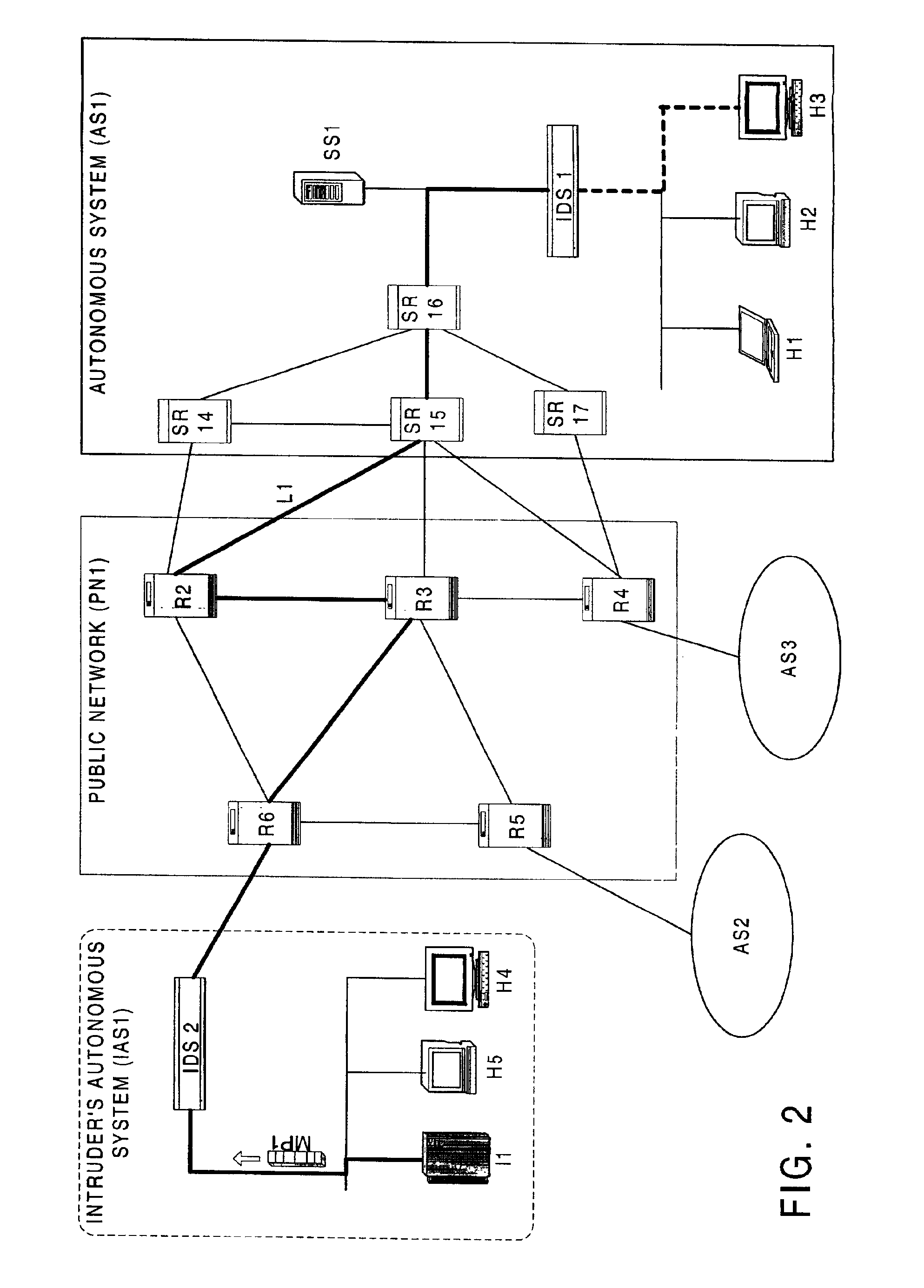
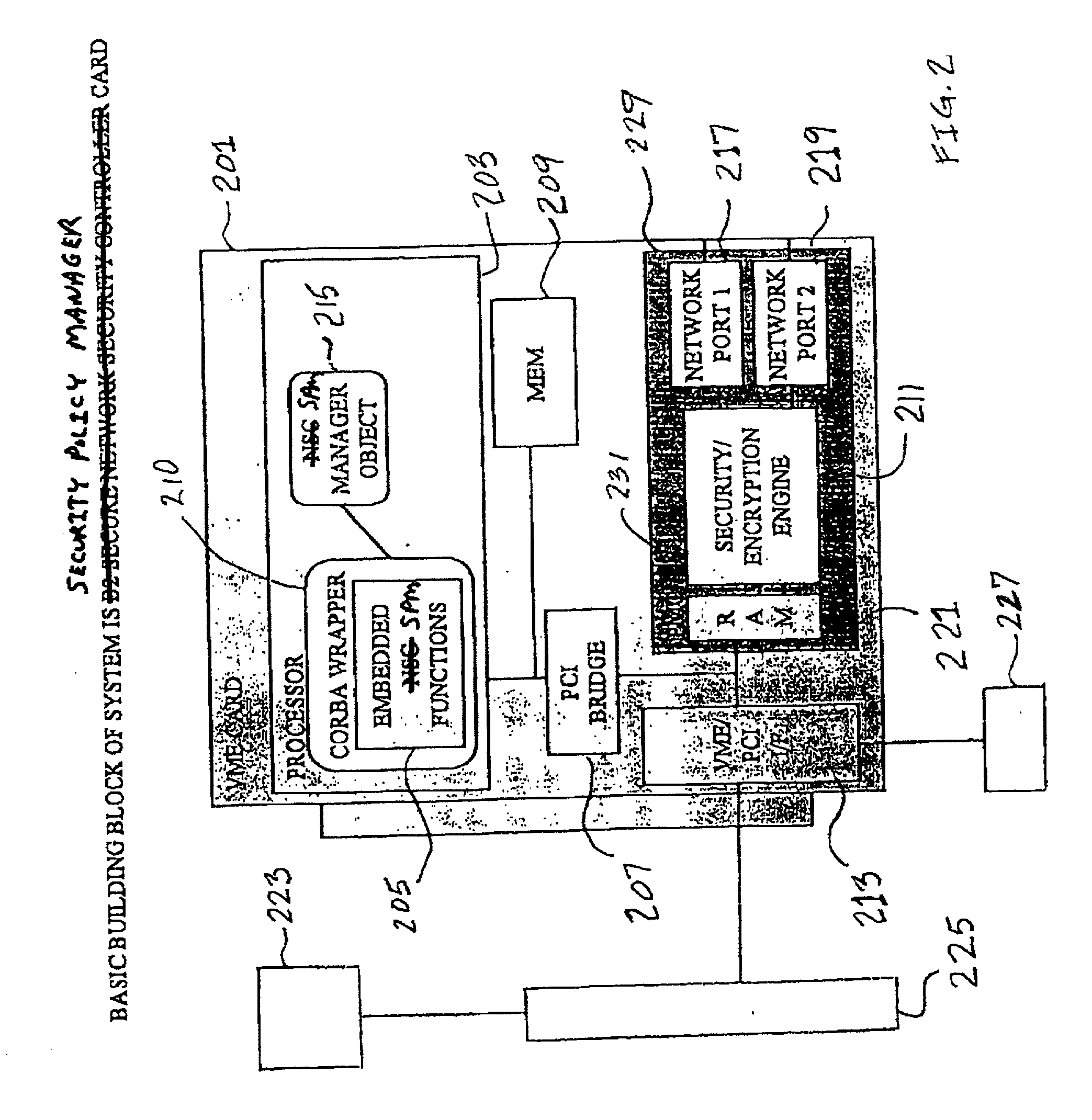
A high level of security and fault tolerance is provided in a digital network by use of highly secure infrastructure of user transparent signalling for communicating detection of signals at a network node having characteristics of a potential attack to another node and controlling communications at routers at the node from another node in response to the user transparent signals. A processor is connected to the routers and the network through an encryption engine and includes a manager object to issue control commands to nodes of a locally lower hierarchy tier and managed objects to detect potential attacks and exercise control over the routers responsive to signals from a node of a locally higher hierarchy tier. Identifications are provided for communications between nodes regardless of whether or not a corresponding user is identified and communications are logged. Thus any network session comprises one or more secure sessions in a plurality of security domains and any fault or potential attack can be compartmentalized to a node or sector of the network and isolated while normal communications are continued over redundant network links.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
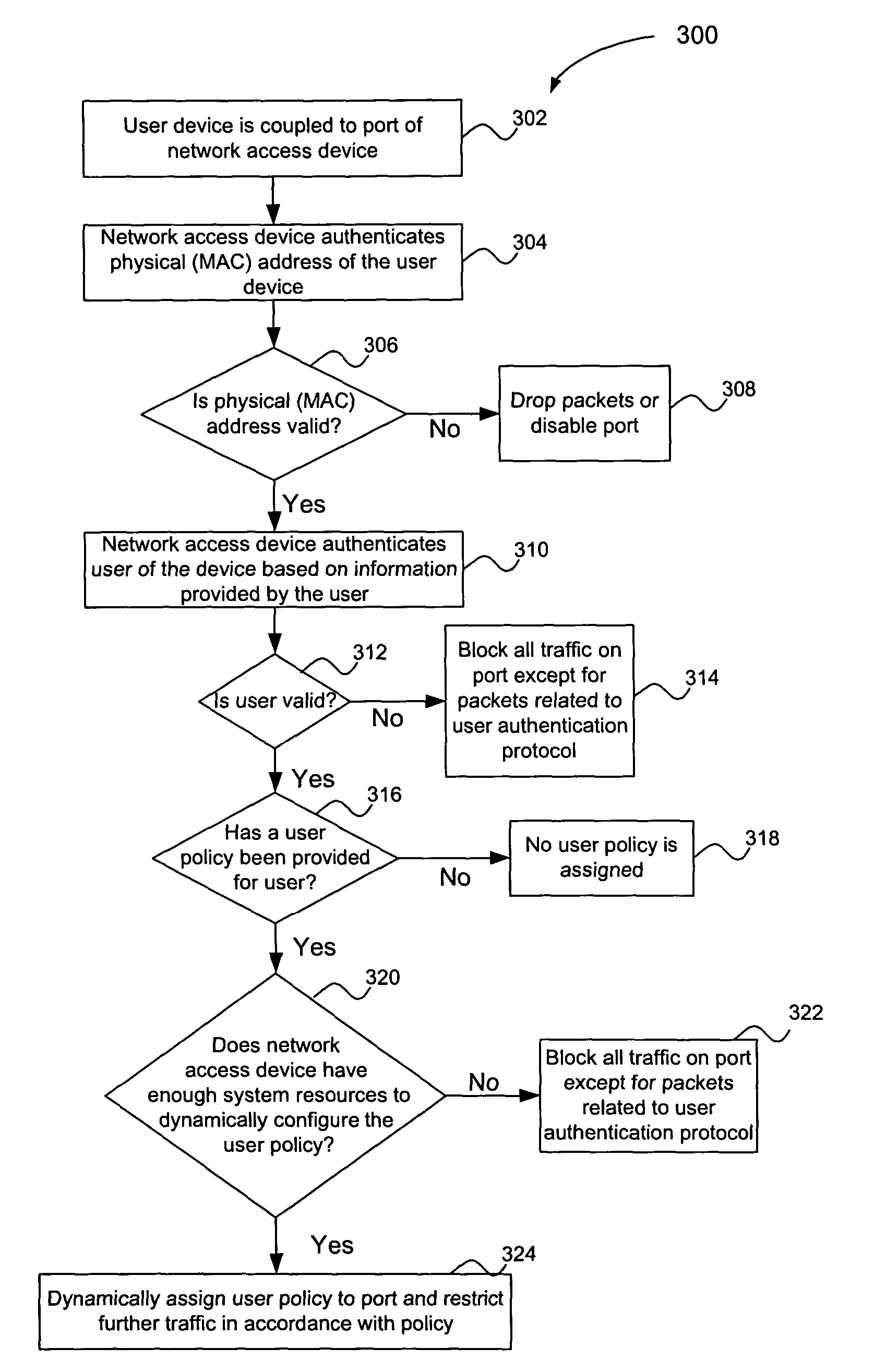
Multiple tiered network security system, method and apparatus using dynamic user policy assignment
InactiveUS7735114B2Improve network securityEfficiently provideUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsThree levelUser authentication
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
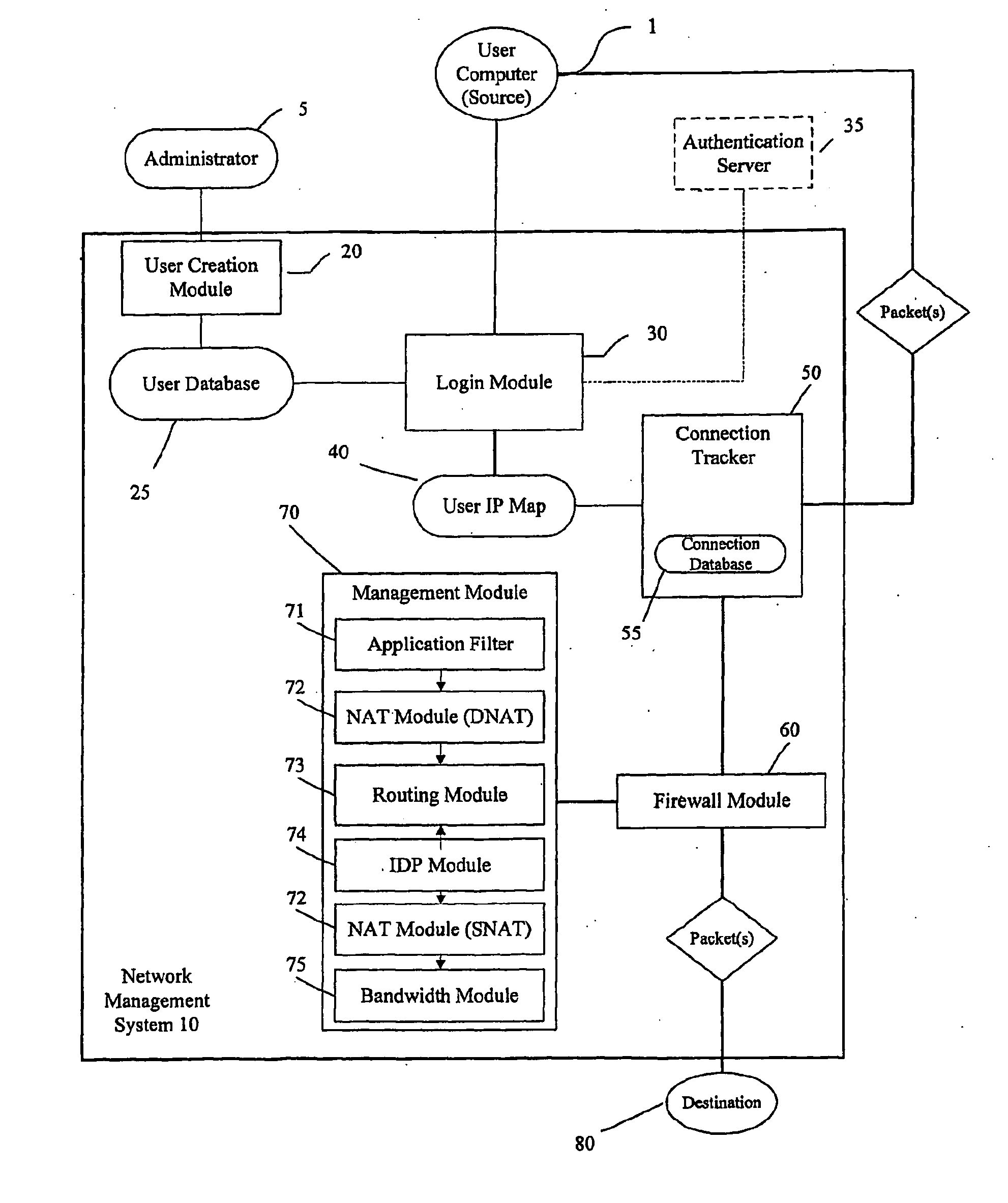
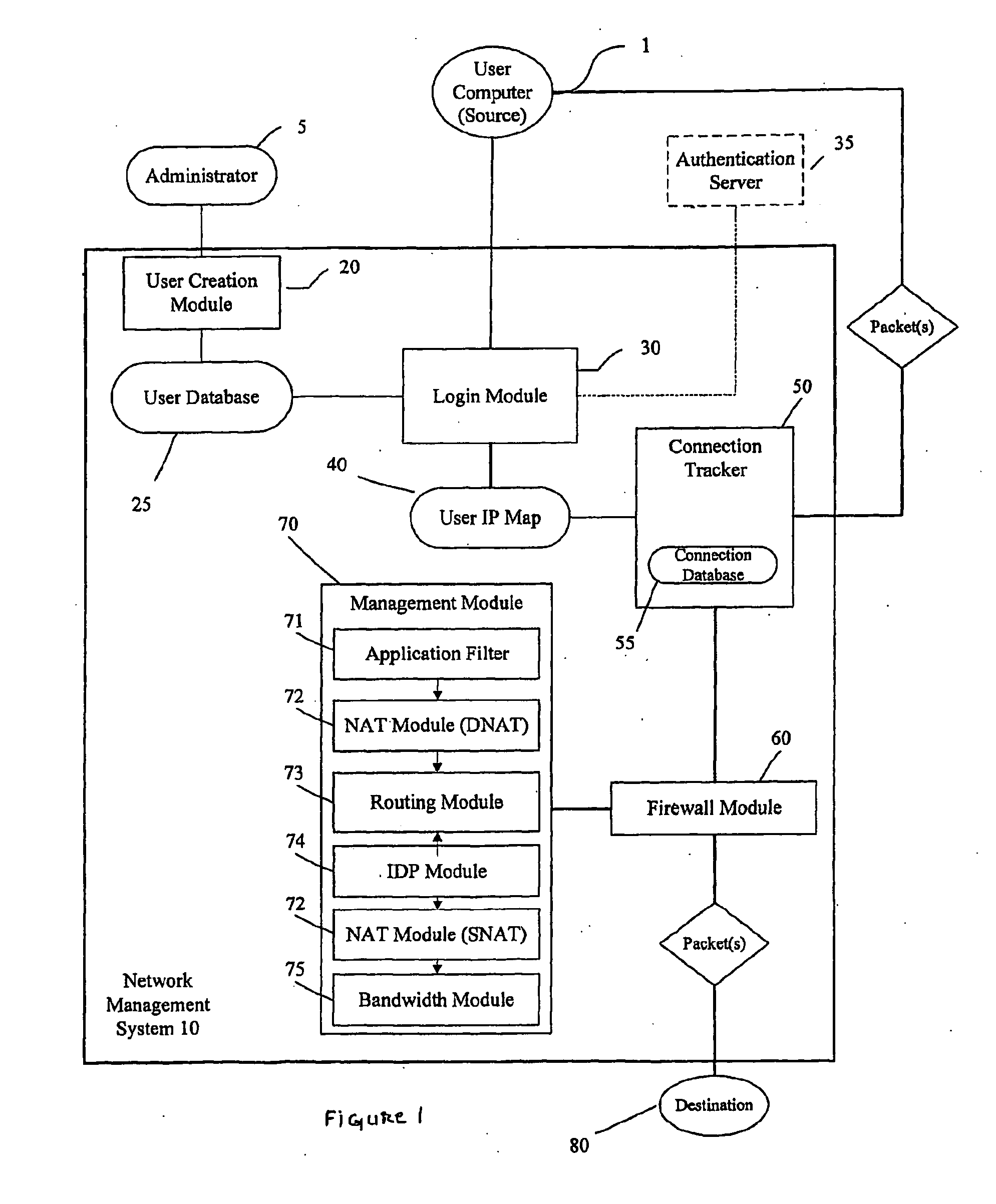
Identity and policy-based network security and management system and method
ActiveUS20100100949A1Improve network securityEnhanced resource optimizationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationNetwork security policyManagement system
A system and method for providing security for a network connecting a source and a destination. The system and method provide a security and management system between the source and the destination which is configured to apply rules and policies which are specific to the user to the connection between the source and the destination. The user-specific policies are used to govern.
Owner:SOPHOS
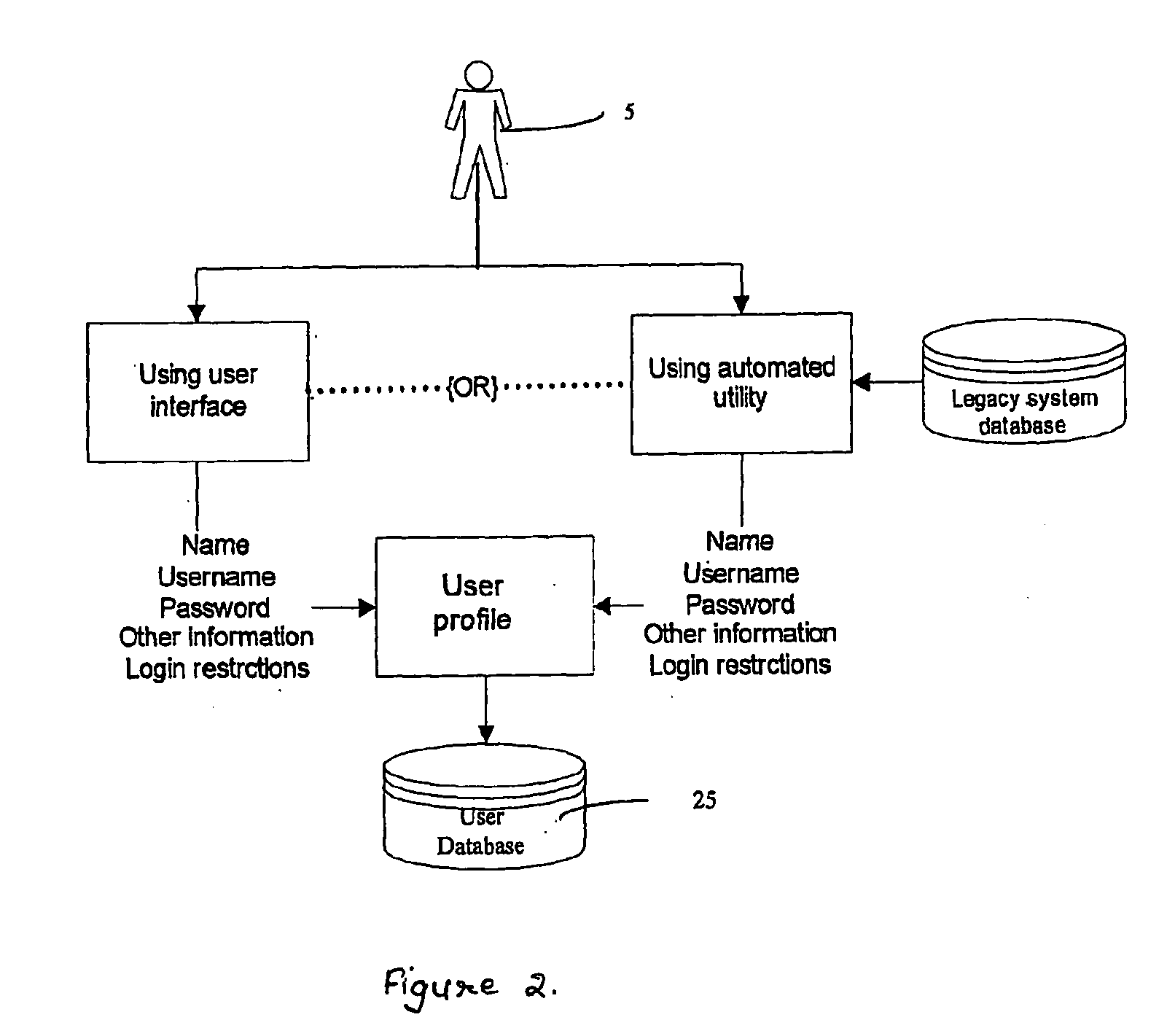
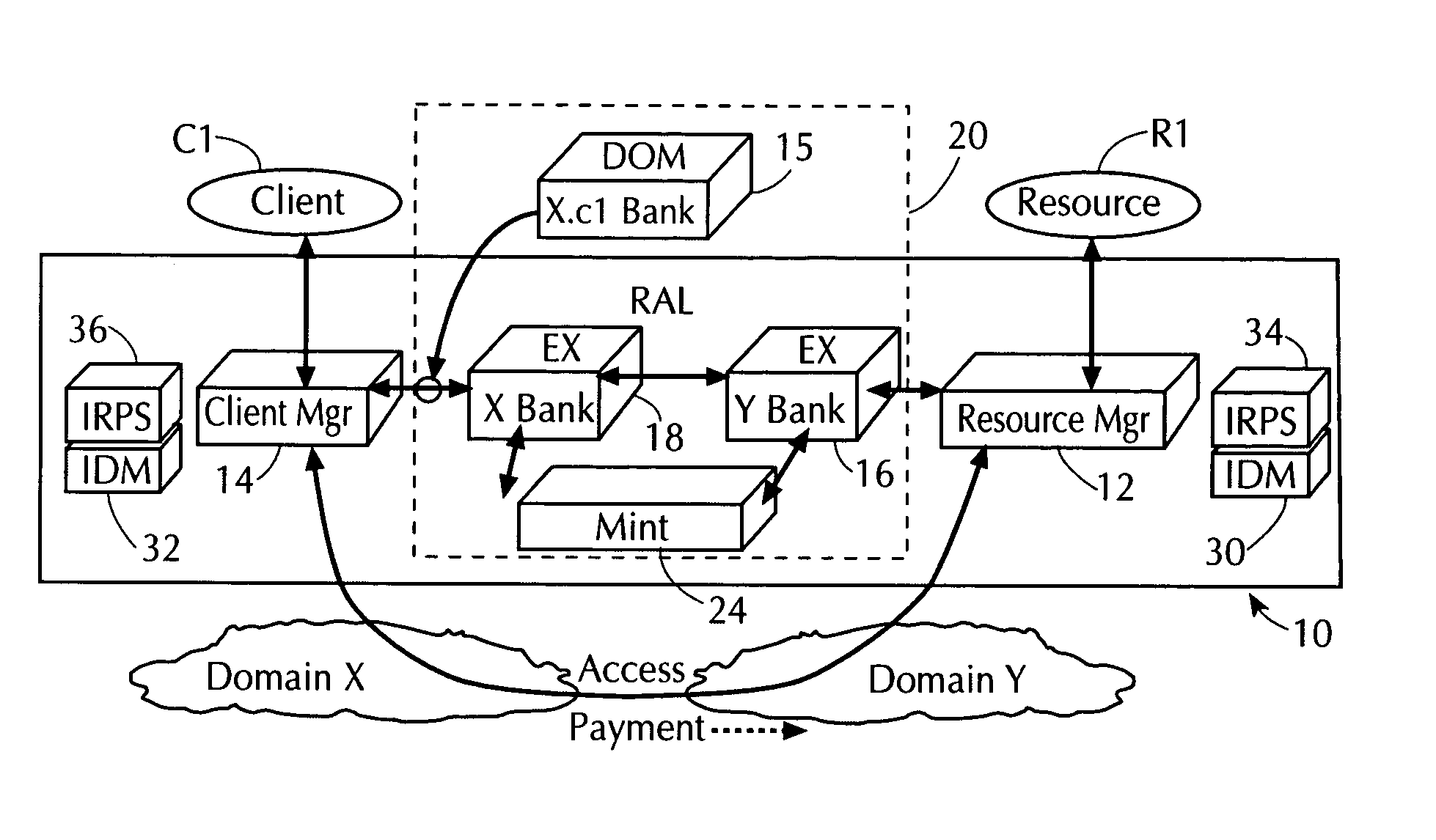
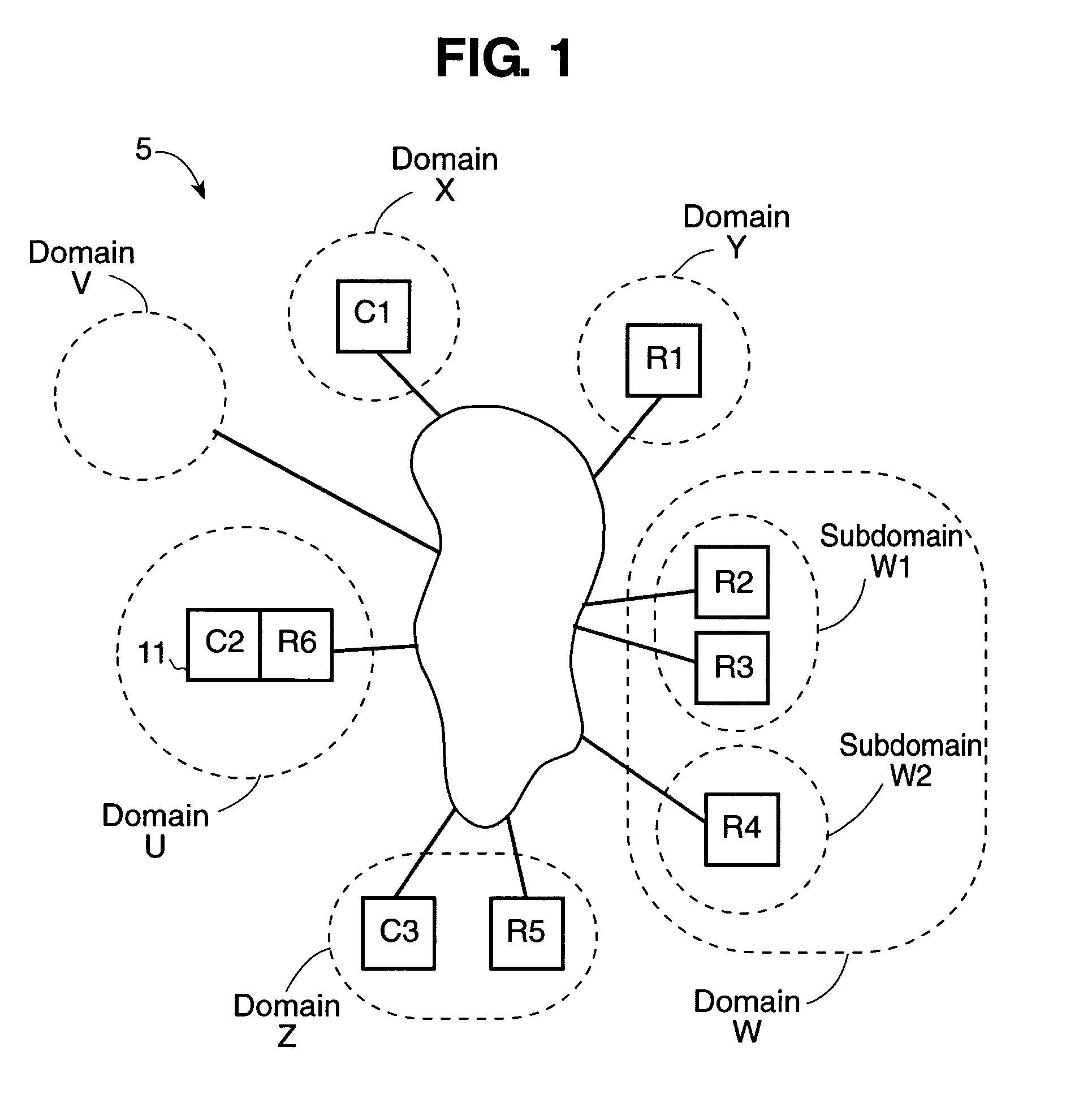
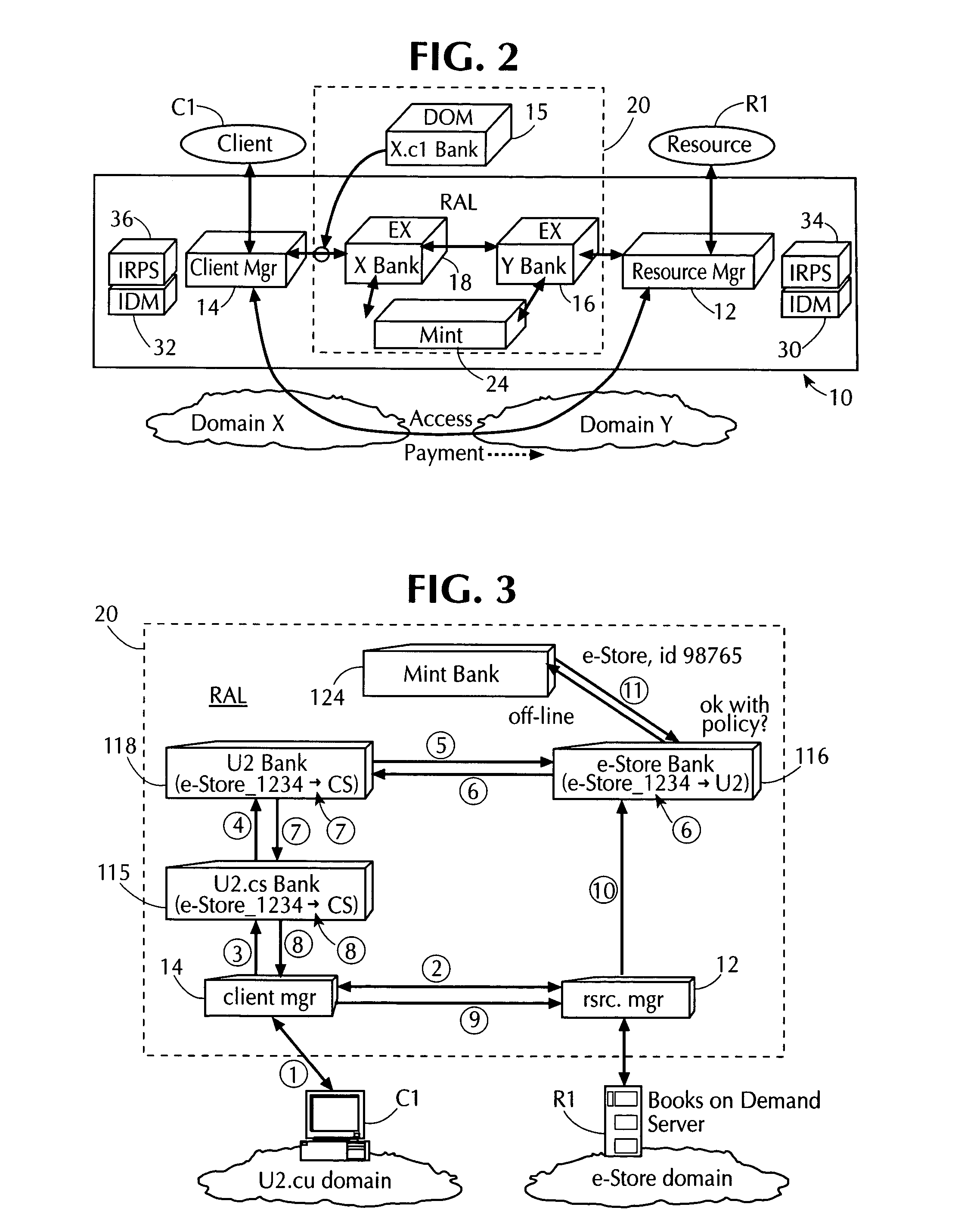
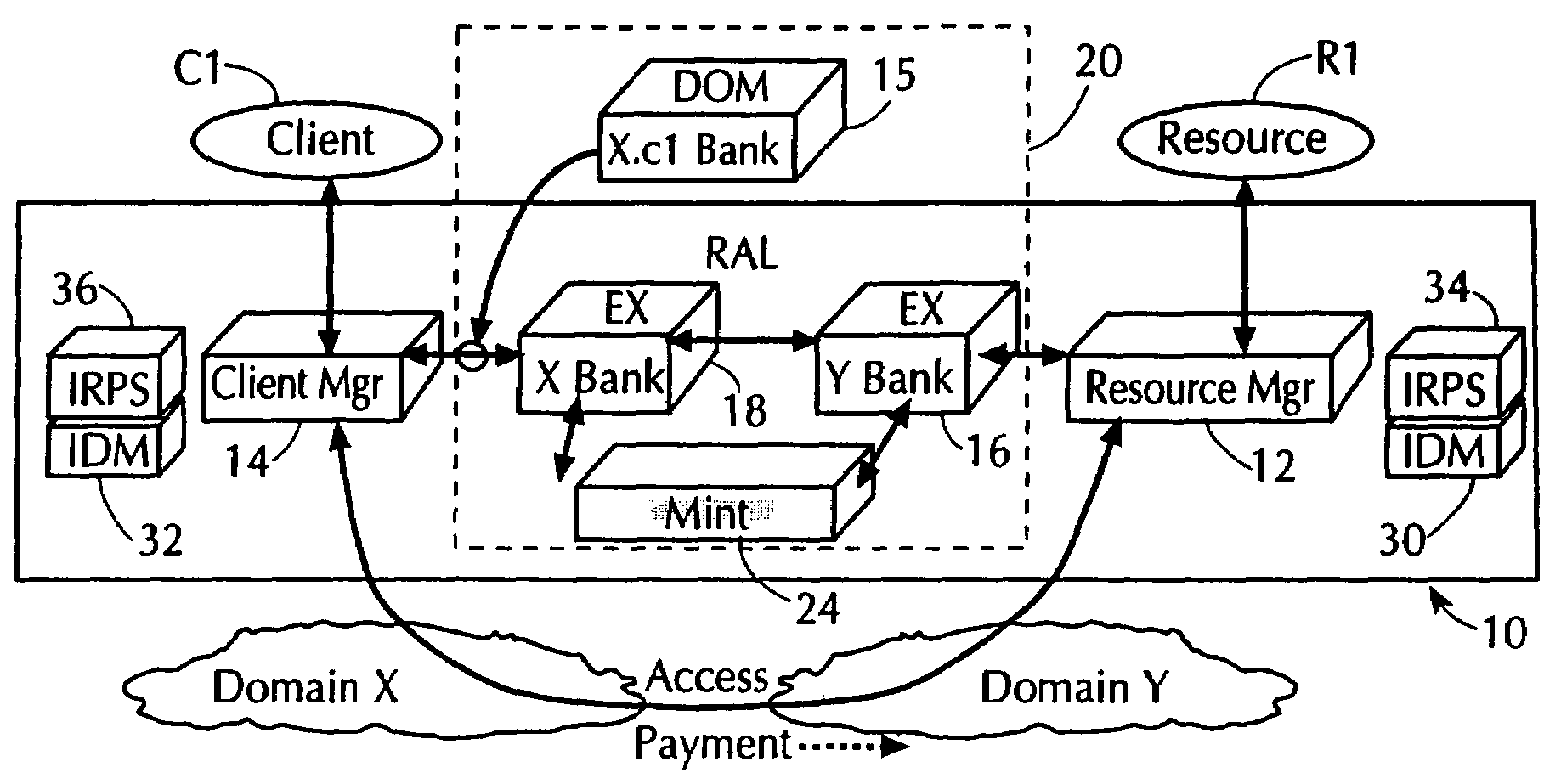
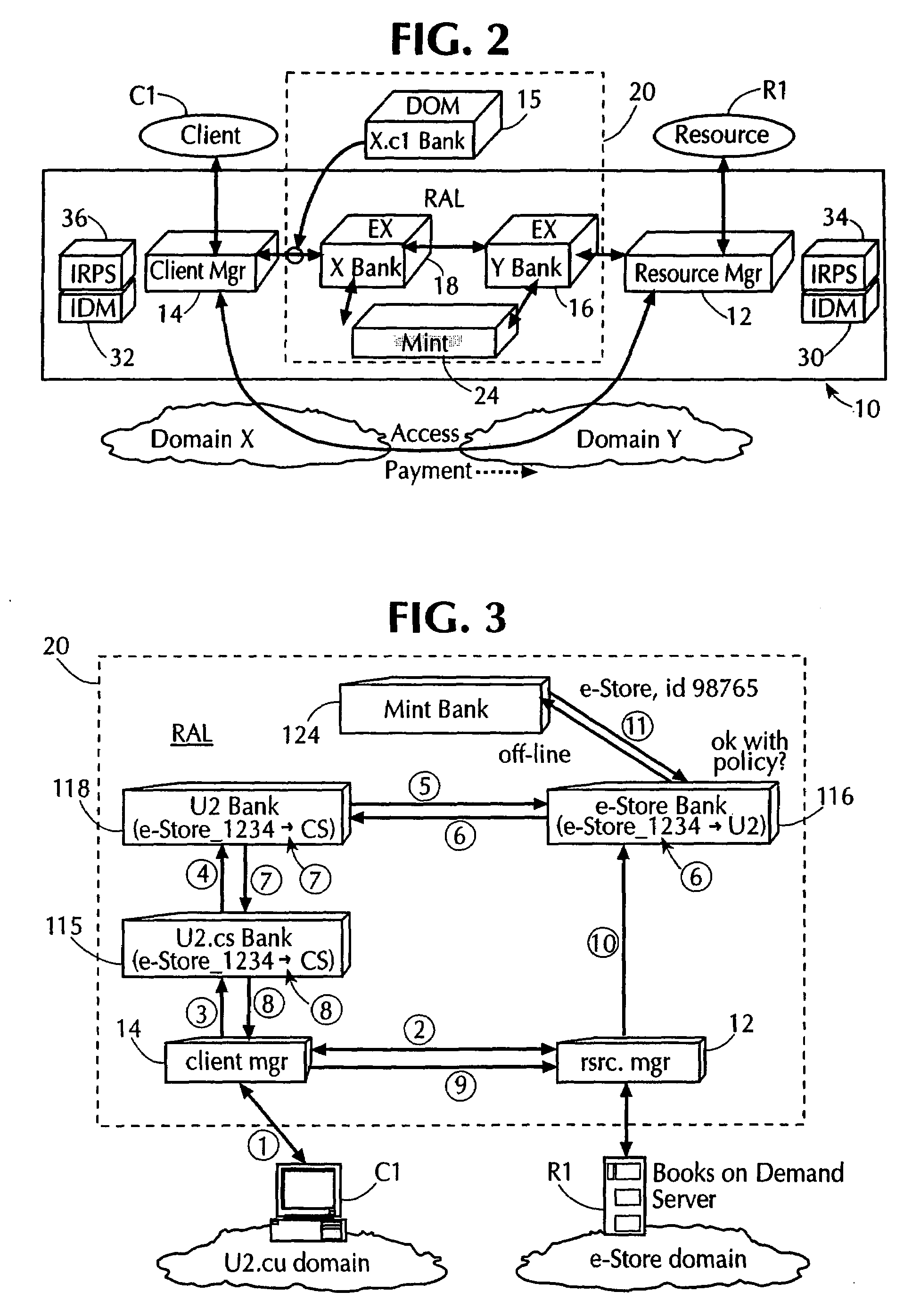
Using electronic security value units to control access to a resource
InactiveUS7013296B1Improve network securityLimited accessDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsClient-sideResource management
A network utilizes electronic security value units to prevent unauthorized access to resources in the network. The network includes at least a resource manager and an electronic bank server (e.g., the local resource bank). The resource manager determine a pricing strategy in electronic security value units for a group of one or more resources in the network. The electronic bank server selectively distributing electronic security value units to a client in the network, where the electronic security value units are unique to a group of one or more resources. Accordingly, access to a resource in the group, by the client, is determined by at least the above pricing strategy and by an amount of electronic security value units distributed to the client.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
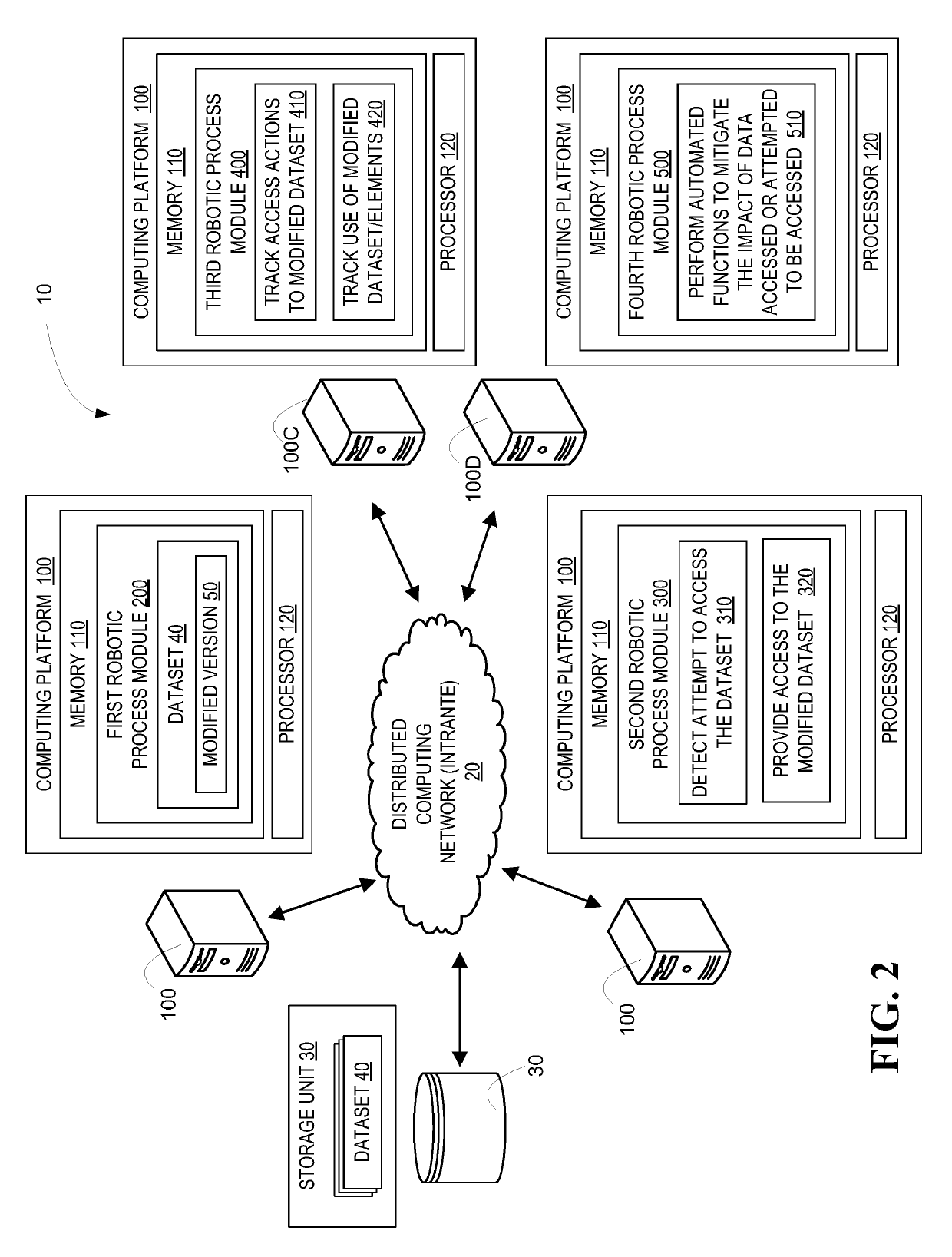
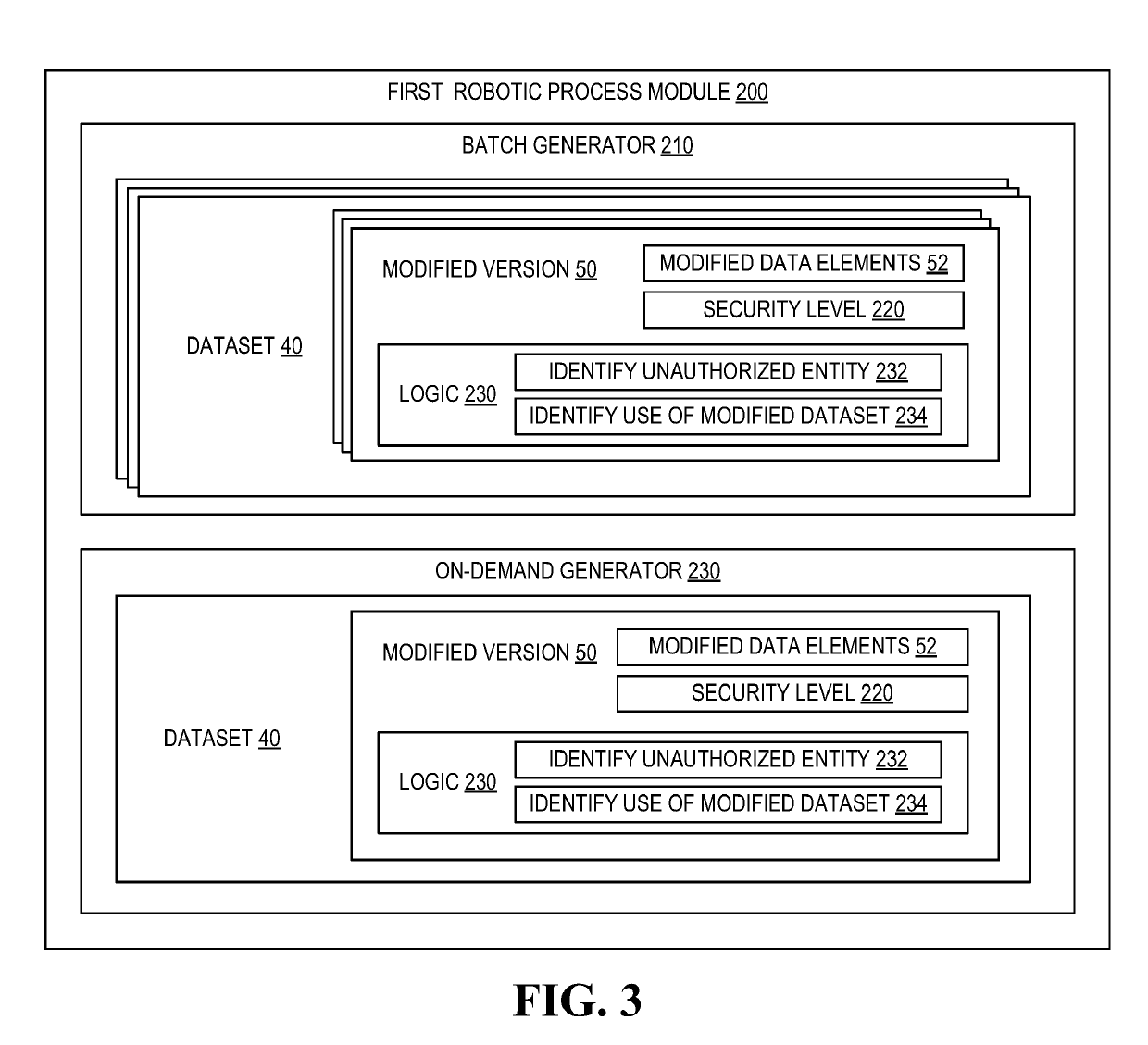
Robotic process automation resource insulation system
ActiveUS20190124100A1Enhance computer network securityReduce harmDigital data protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceData setEngineering
A system for implementing robotic process automation (RPA) to enhance computer network security. Specifically, RPA is used to detect an unauthorized attempt to access a dataset and, in response, the unauthorized entity is provided access to a bot-generated modified dataset that includes modified data elements that are reasonable facsimiles of the actual data elements and do not expose confidential data. Once access to the modified data set is provided, RPA is implemented to track actions by the unauthorized entity accessing the modified data set and, once copied, RPA is implemented to track usage of the data by the unauthorized entity. Additionally, RPA may be implemented to mitigate damages caused by attempts or actual accessing of the actual datasets by performing actions that prevent further damages, such as deactivating / activating resource storage and authorizing previously configured resource events.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
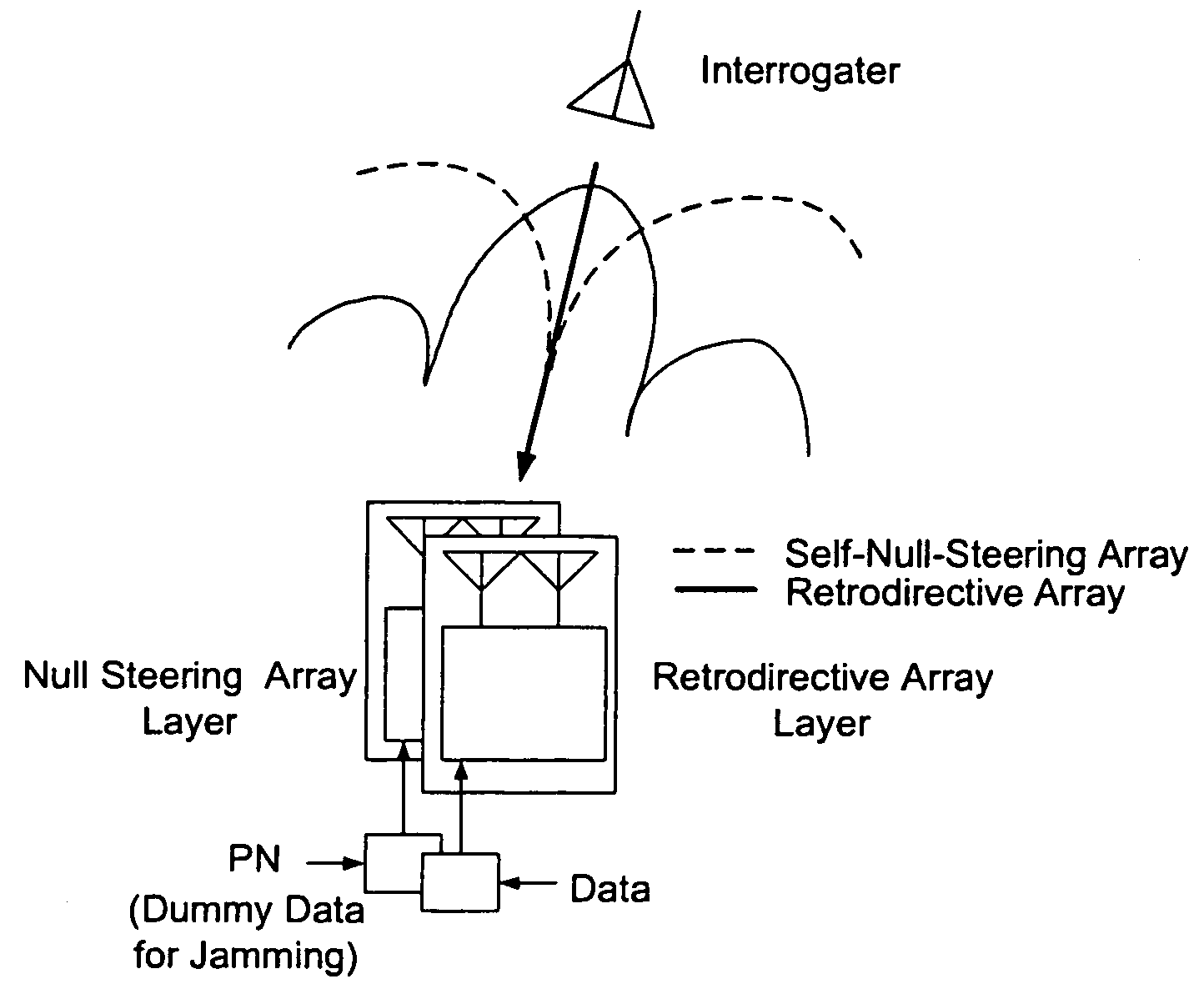
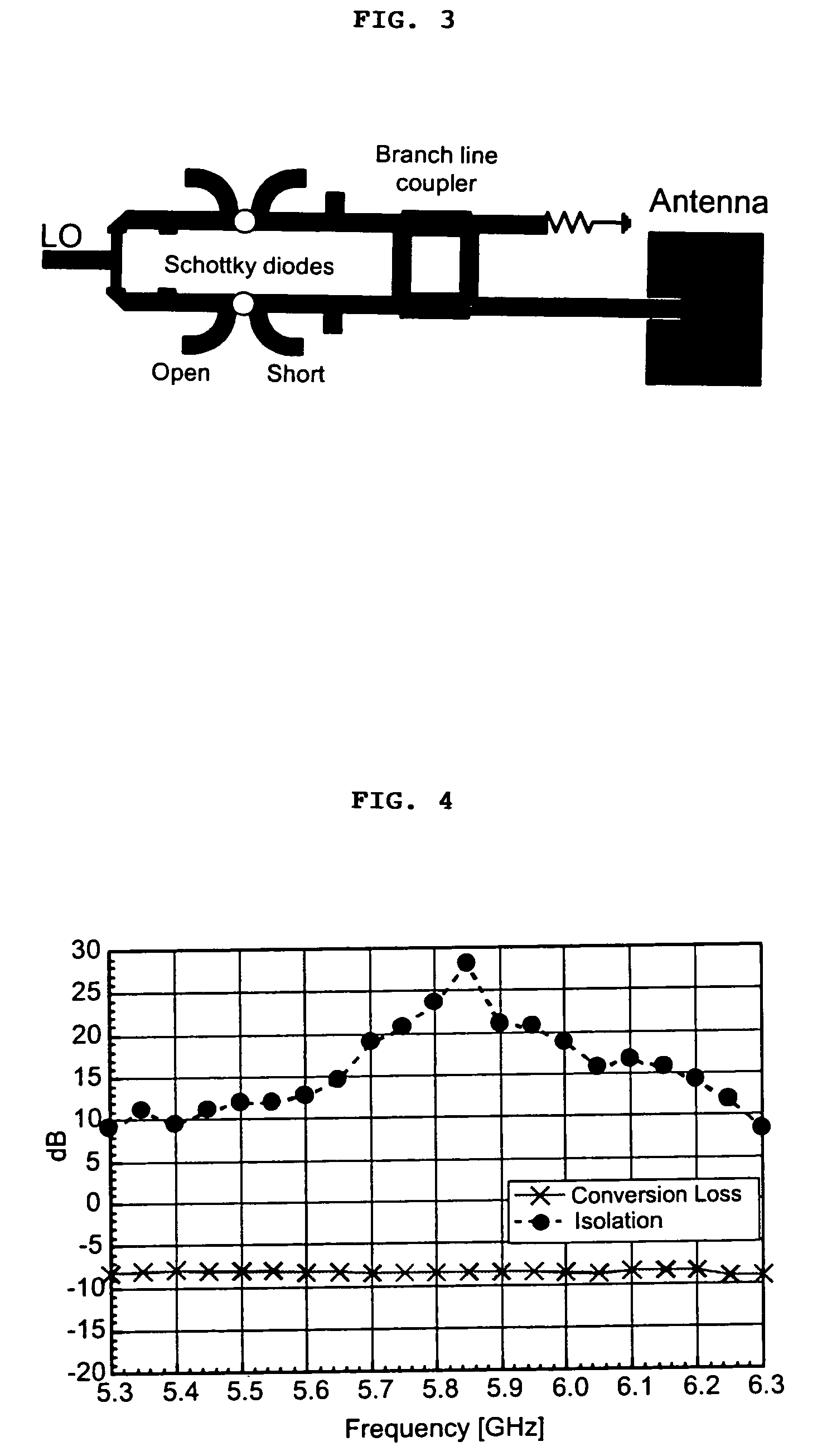
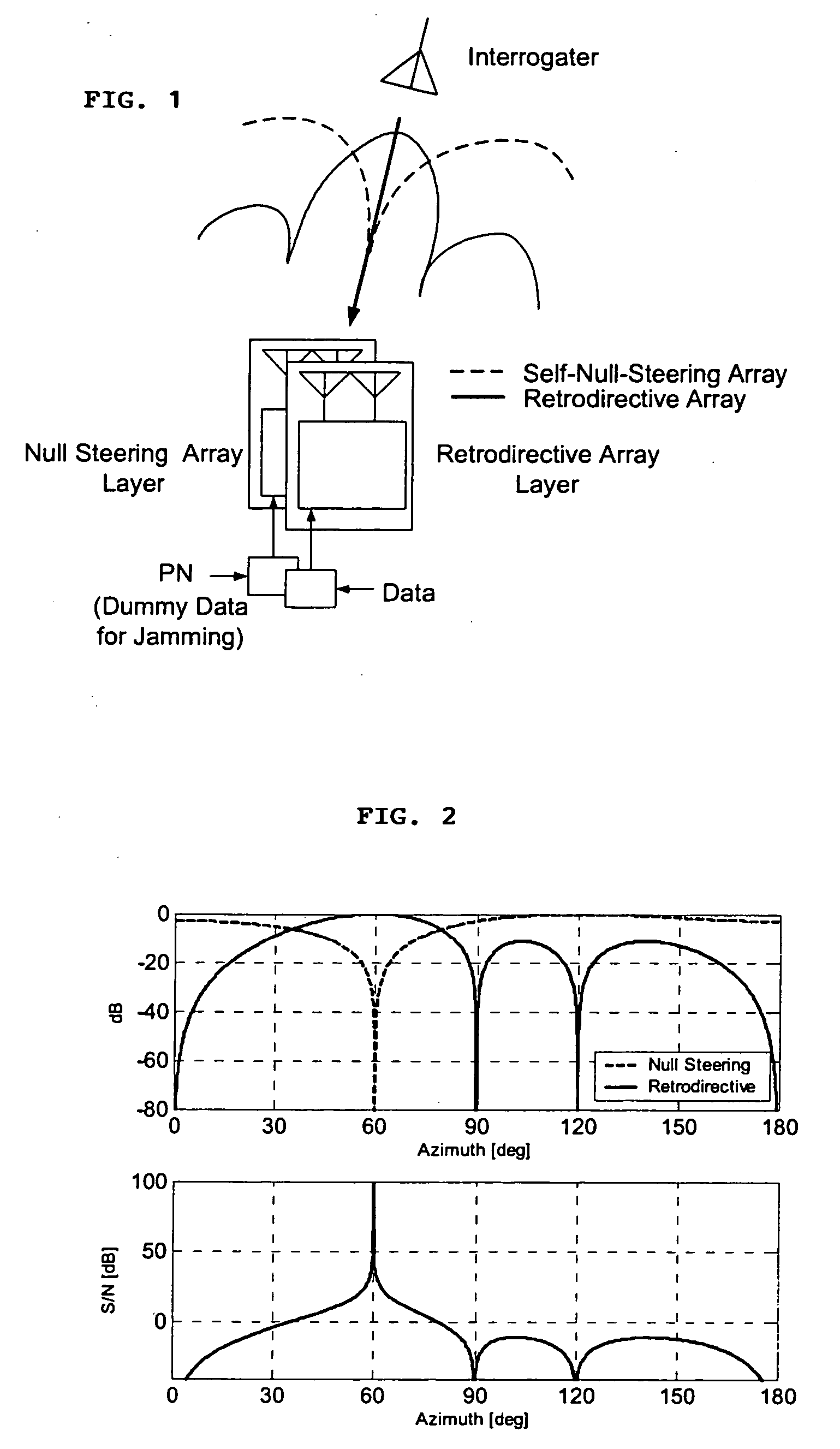
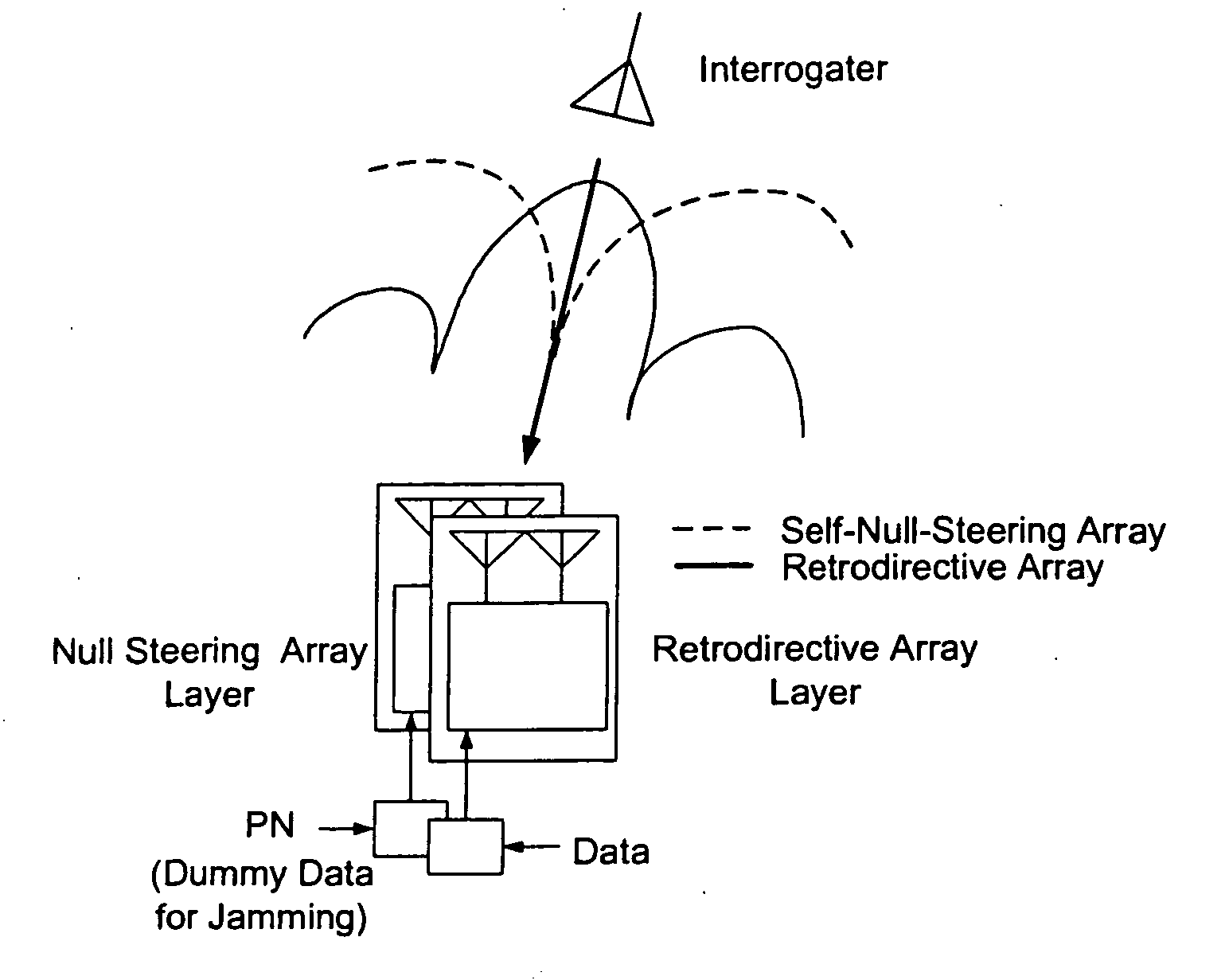
Microwave self-phasing antenna arrays for secure data transmission & satellite network crosslinks
ActiveUS7006039B2Increase user capacityImprove directivityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAntenna supports/mountingsTactical communicationsFrequency spectrum
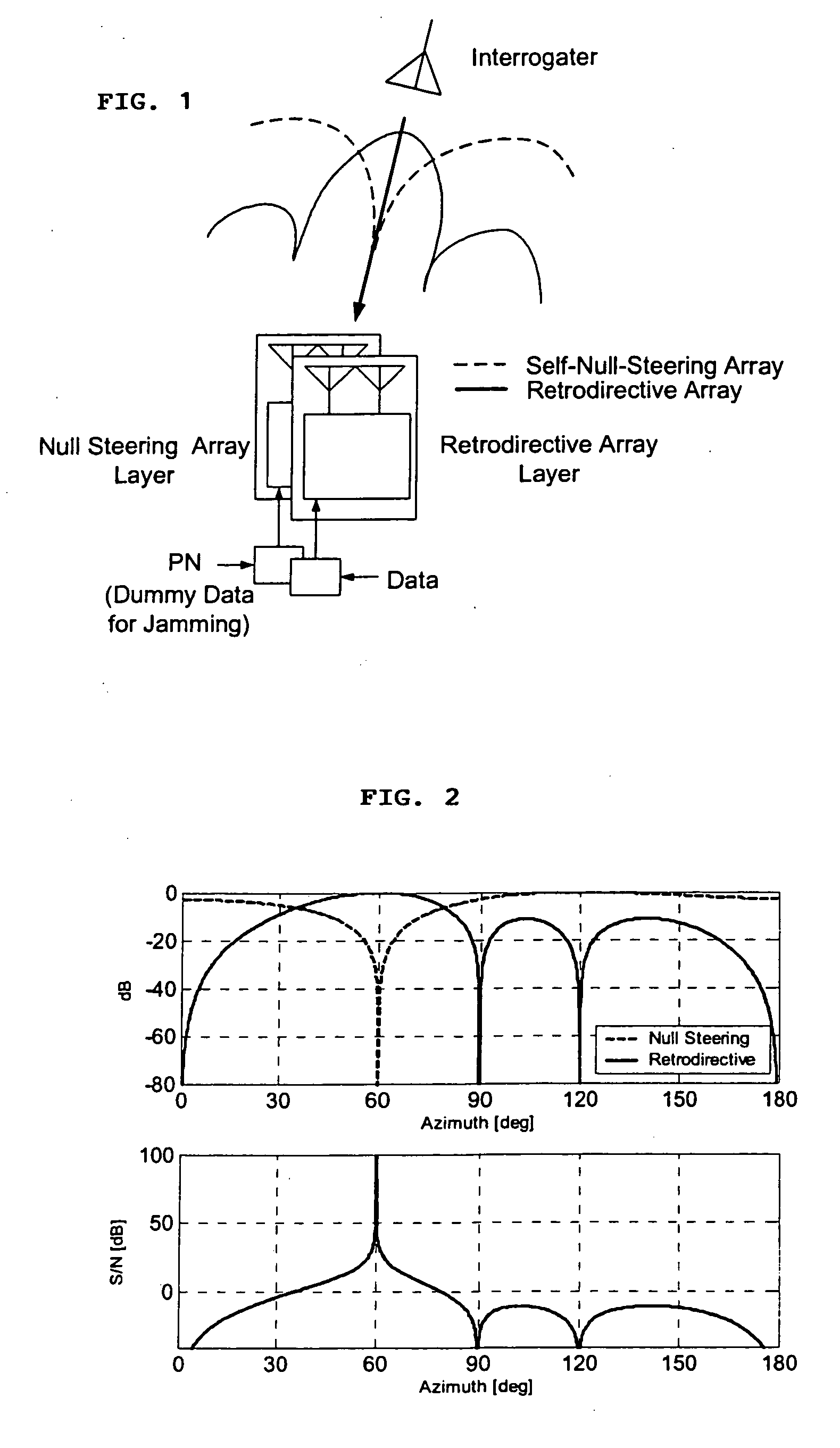
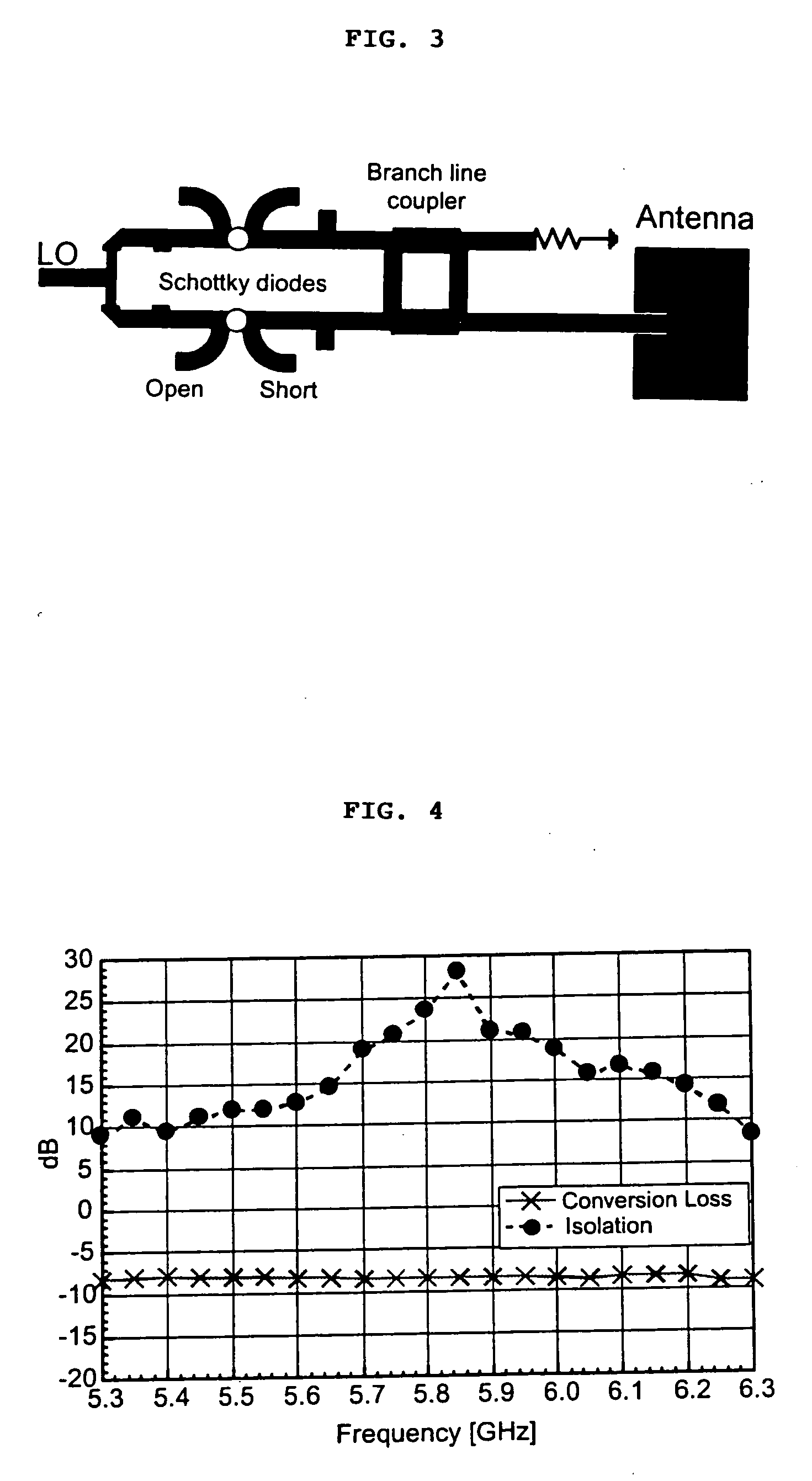
A high-directivity transponder system uses a dual system of a retrodirective array transmitting a data signal peak toward an interrogator source, and a self-null-steering array transmitting a null toward the interrogator source and a jamming signal elsewhere, resulting in high S / N reception at the interrogator source and avoidance of interception. Integrating modulators would allow each array to transmit different data while the spectra of the transmitted signals are identical, thus disabling interception. The system enables secure point-to-point communications and can be used for short-distance wireless data transmission systems such as wireless LAN and RFID servers. As another aspect, self-steering signal transmission is employed for randomly oriented satellites using circularly polarized, two-dimensional retrodirective arrays. Quadruple subharmonic mixing is used as an effective means of achieving phase conjugation when a high-frequency LO is not feasible or inapplicable. These features may be used for small-satellite communications, secure tactical communications, search and rescue, enemy location fixing and tracking, UAV command and control, forest fire detection, marine-based tracking, and many other applications requiring secure communications with high signal directivity.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
IEC61850-based detection method and system for detecting power industrial control network intrusions
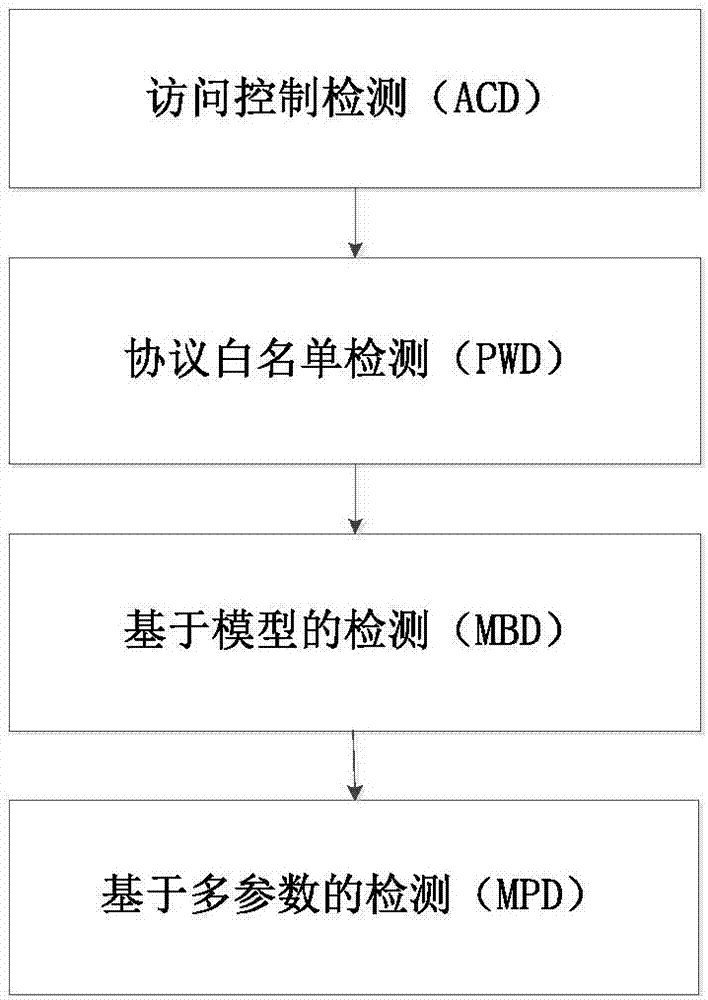
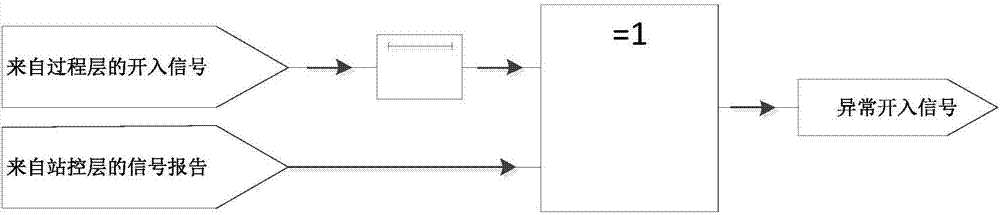
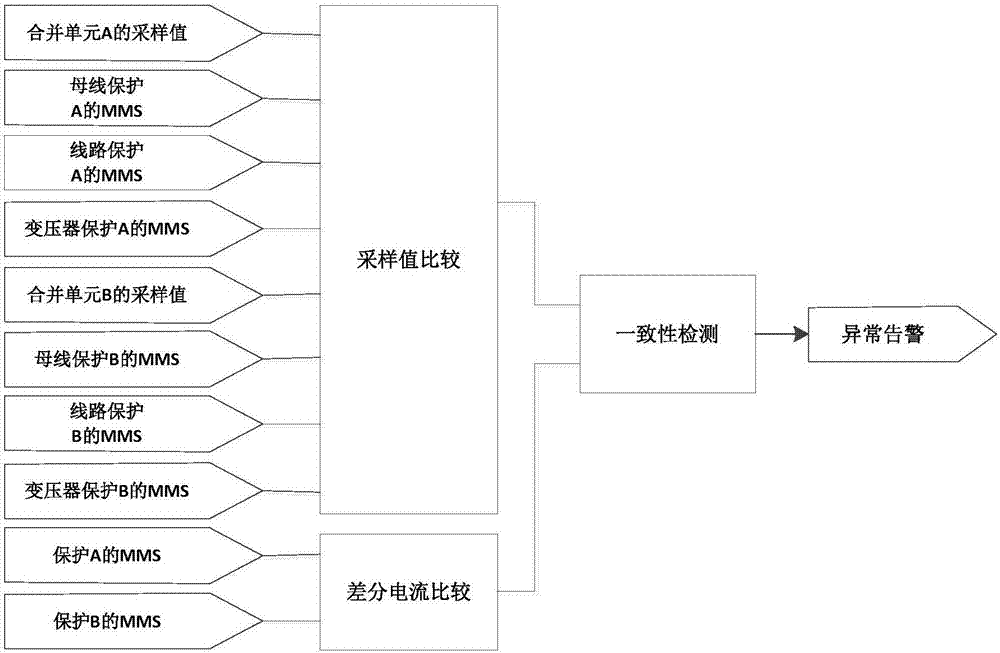
The invention discloses an IEC61850-based detection method and system for detecting power industrial control network intrusions; the method comprises access control detection, protocol white list detection, model-based detection and multiple-parameter-based detection, wherein through the access control detection, it is possible to prevent malware intending to communicate with a control server from acting and attacking, and the effect is particularly good in the initial infection stage; through the protocol white list detection, it is possible to detect abnormal protocol traffic in station control layer and process layer network of a substation and give a warning; the model-based anomaly detection has the potential to discover hostile attack or untended anomalies in the station control layer and process layer network; in the multiple-parameter-based detection, possible threats to an industrial control system due to internal untended misuse or external hostile attack can be recognized by monitoring the most sensitive parameters of an intelligent substation. Validation on a network physical test platform for simulating actual 500 kV intelligent substations shows that the method is timely and practical.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Killing login-based sessions with a single action
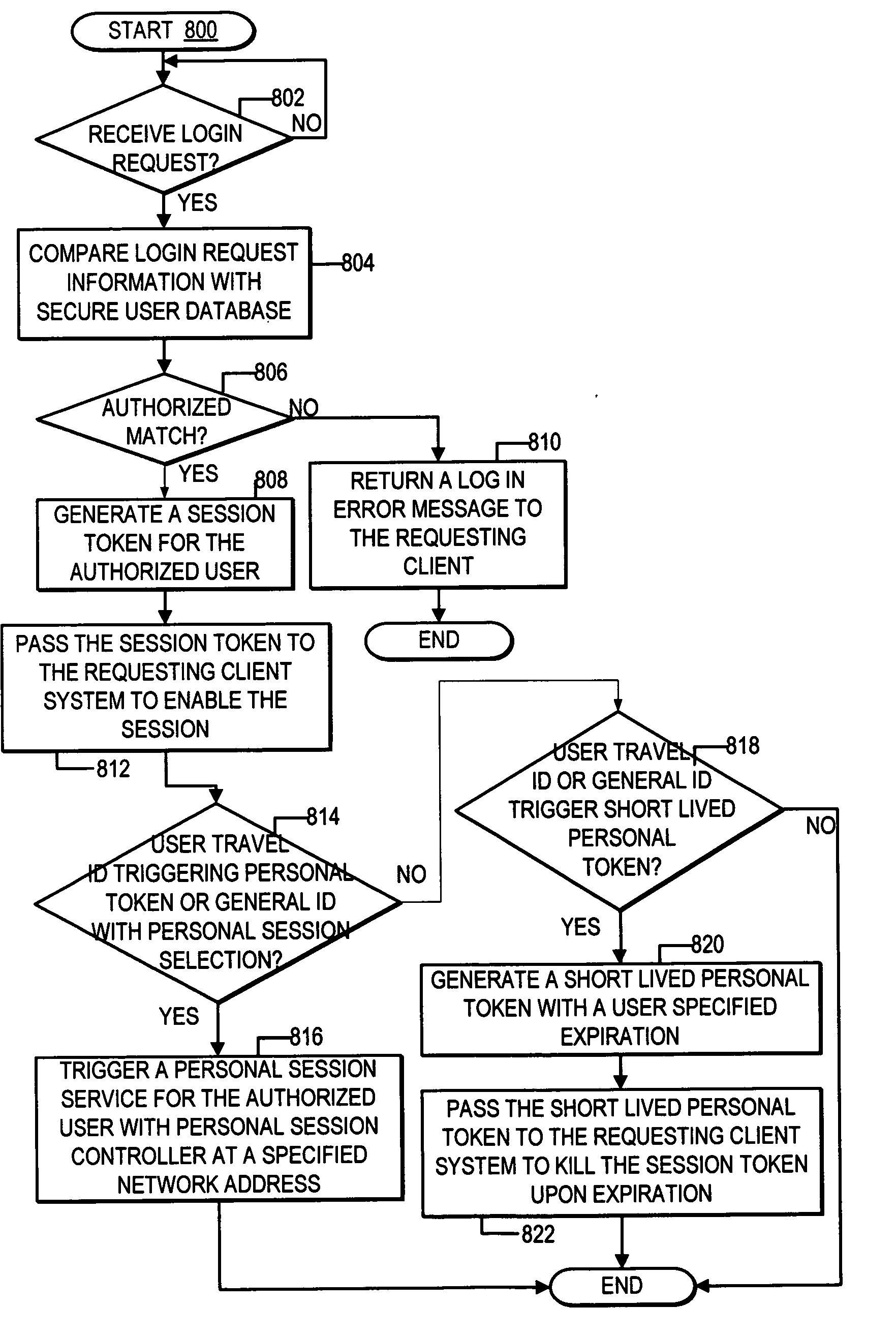
ActiveUS20070169175A1Improve network securityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationClient-sideNetwork service
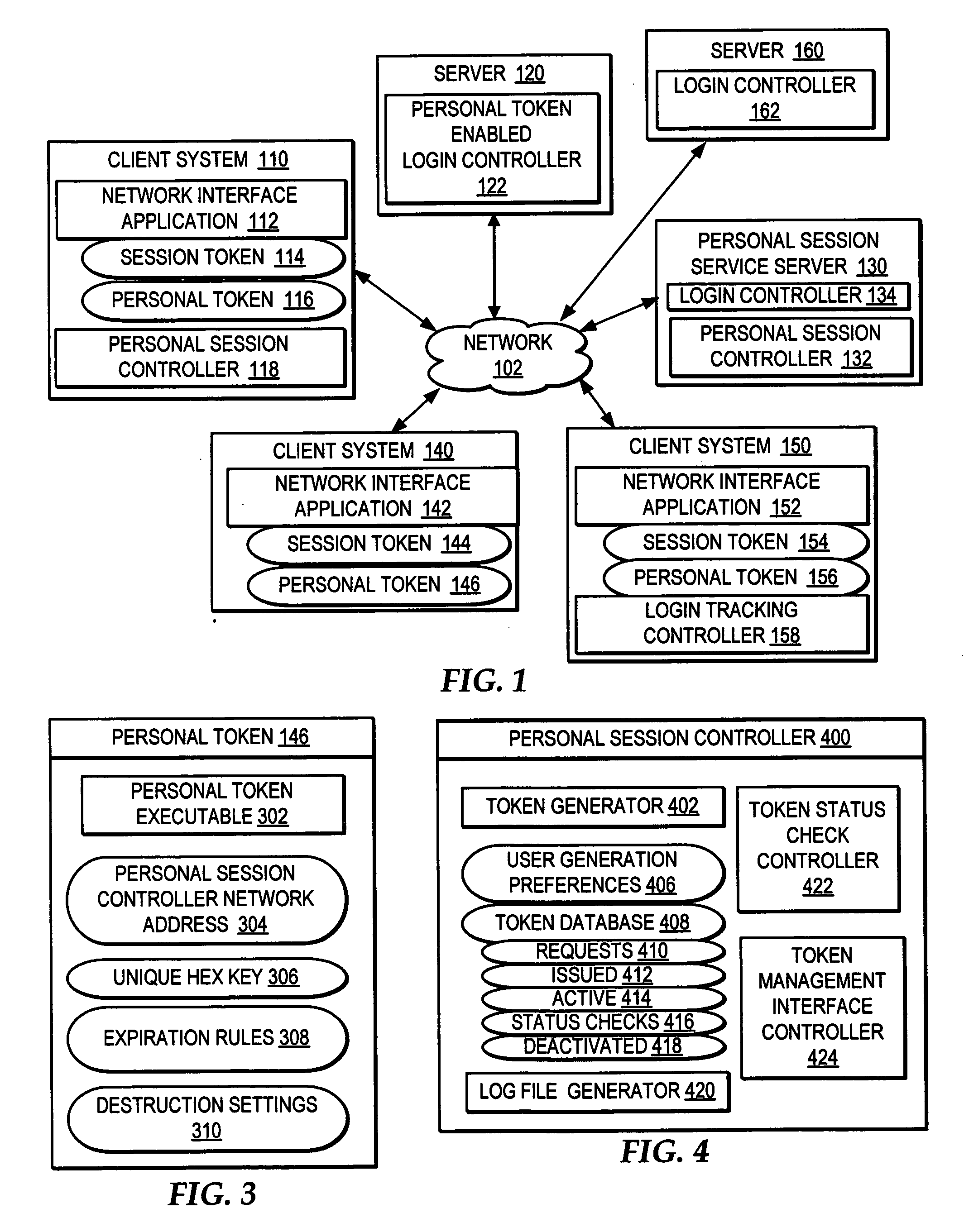
A method, system, and program are provided for killing login-based sessions with a single action. In addition to issuing a session token to a client system upon login by a user to a network service, a personal token is issued to the client system. The personal token is executable at the client system to trigger accesses to a personal session controller and to automatically disallow the session token if the personal session controller indicates that the personal token is deactivated. The personal session controller enables an interface through which a user is enabled select to deactivate all active personal tokens with a single action, such that a user manages killing login-based sessions independent of the server system authorizing each login-based session and independent of the client system to which the login-based session was authorized.
Owner:MACHINES CORP INT BUSINESS +1
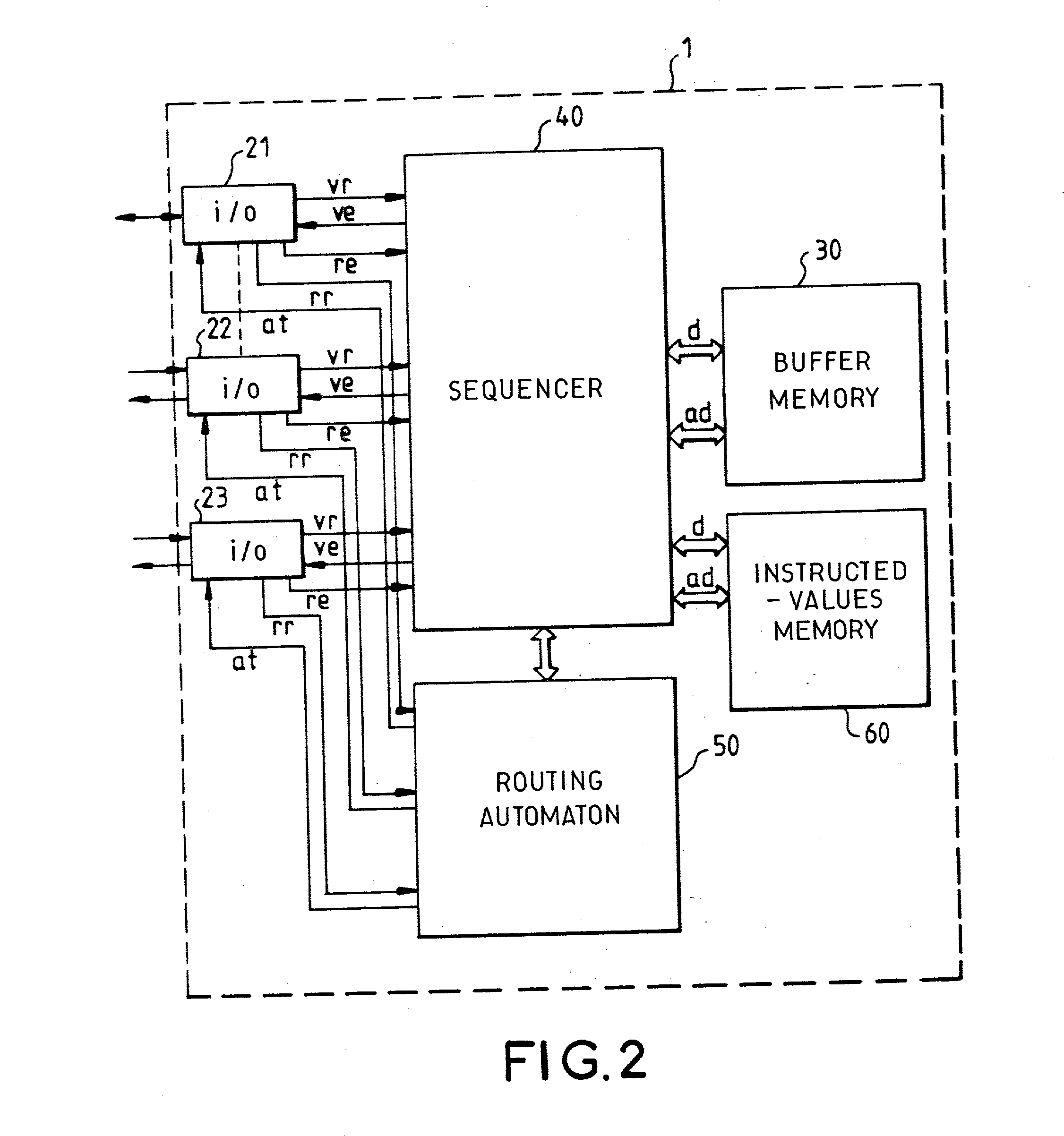
Task management method for a packet switch routing automaton forming part of a secured packet-switching transmission network
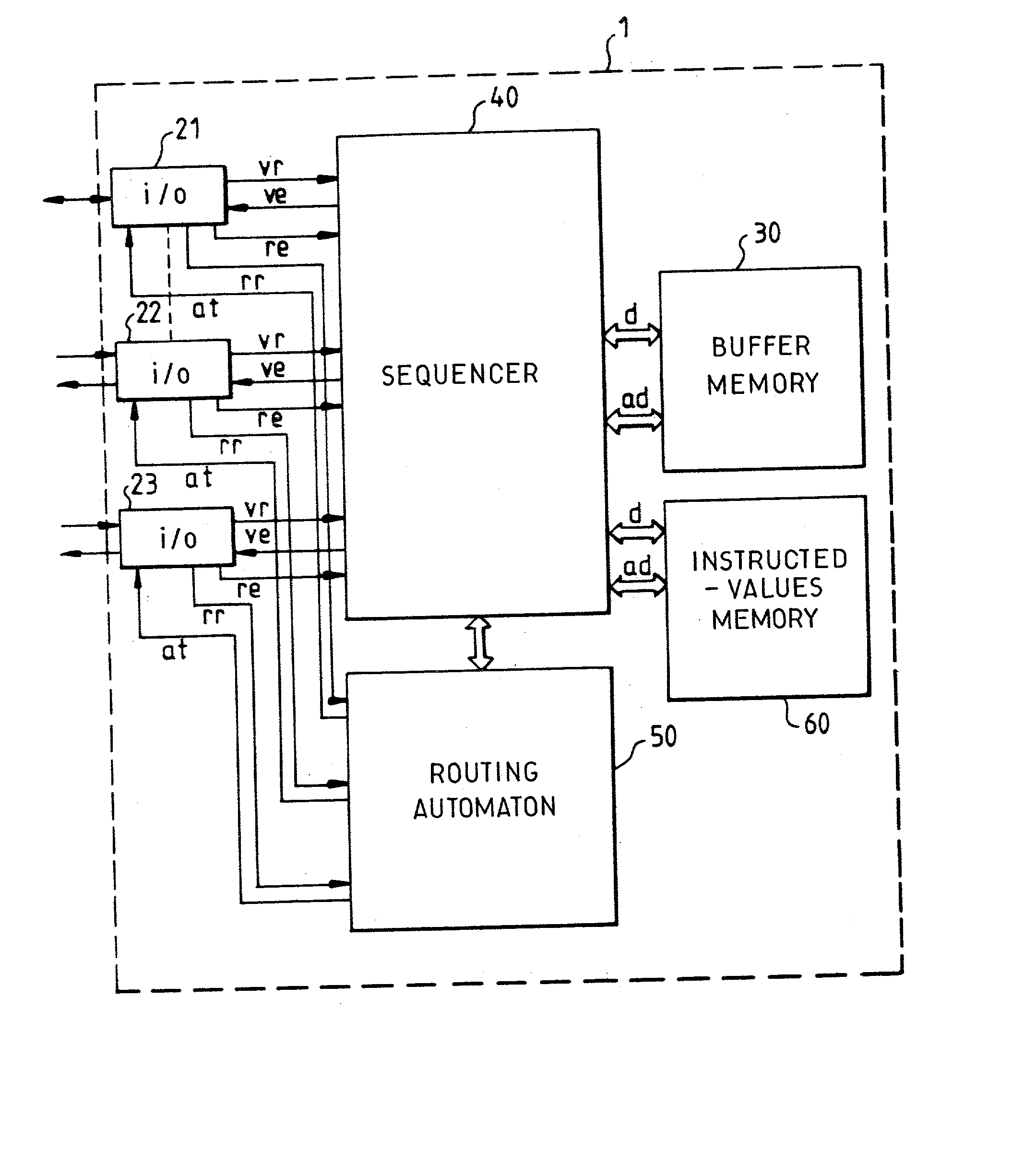
ActiveUS20030076780A1Improve network securityReduce wiring timeError preventionTransmission systemsRepetitive SequencesRandom access memory
This method consists in making a routing automaton (50) carry out verifications on the integrity of the packets arriving at the packet switch (1), their periods of stay in the packet switch (1), their matching with the virtual paths that they claim to take as well as the routings proper, within the packet switch (1), of the datagrams that have satisfactorily undergone the verification. The routing automaton (50) is provided with a random access memory of instructed values (60) containing a table of virtual path local descriptors. The processing time of the automaton is divided into a repetitive sequence of time slots individually allocated to the different input ports (21, 22, 23) of the packet switch (1).
Owner:THALES SA
Identification of an attacker in an electronic system
InactiveUS7140039B1Improve network securityLimited accessDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationElectronic systemsElectronic security
A method for identifying a particular component of an electronic system that accesses a resource of the electronic system using electronic security value units is described. First, electronic security value units are selectively distributing to a plurality of components, such as to a client, of the electronic system. Next, a unique first association is created with each individual component to which the security electronic security value units are distributed. Further, upon a particular access to a resource, a unique second association is created between particular ones of security electronic security value units and the particular access to the resource. In addition, the unique second association is analyzed to determine which particular security electronic security value units were used to access the particular resource. Then, the first association of the particular security electronic security value units is analyzed to determine the identity of the component which accessed the resource.
Owner:COLUMBIA INNOVATION ENTERPRISE +1
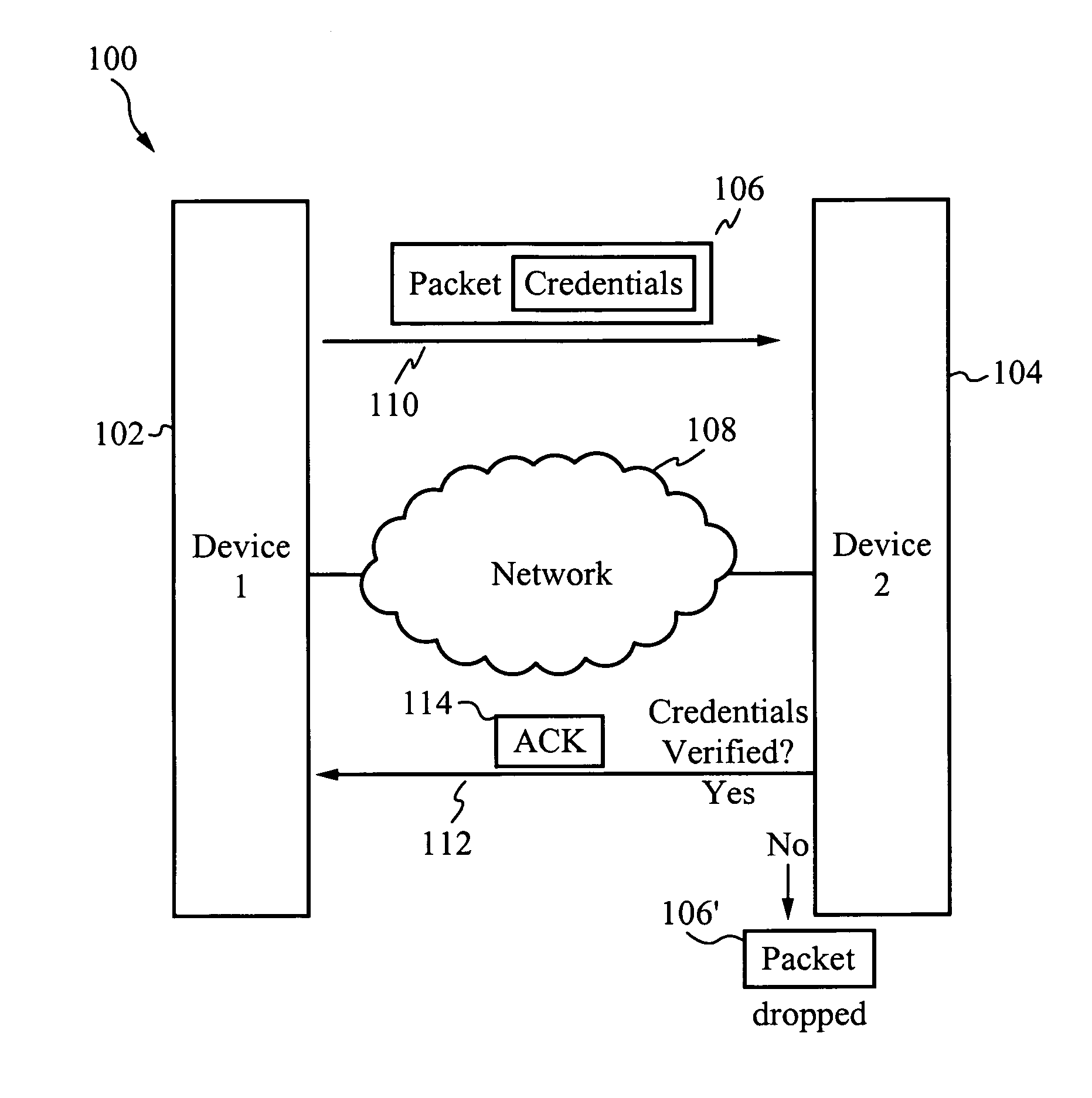
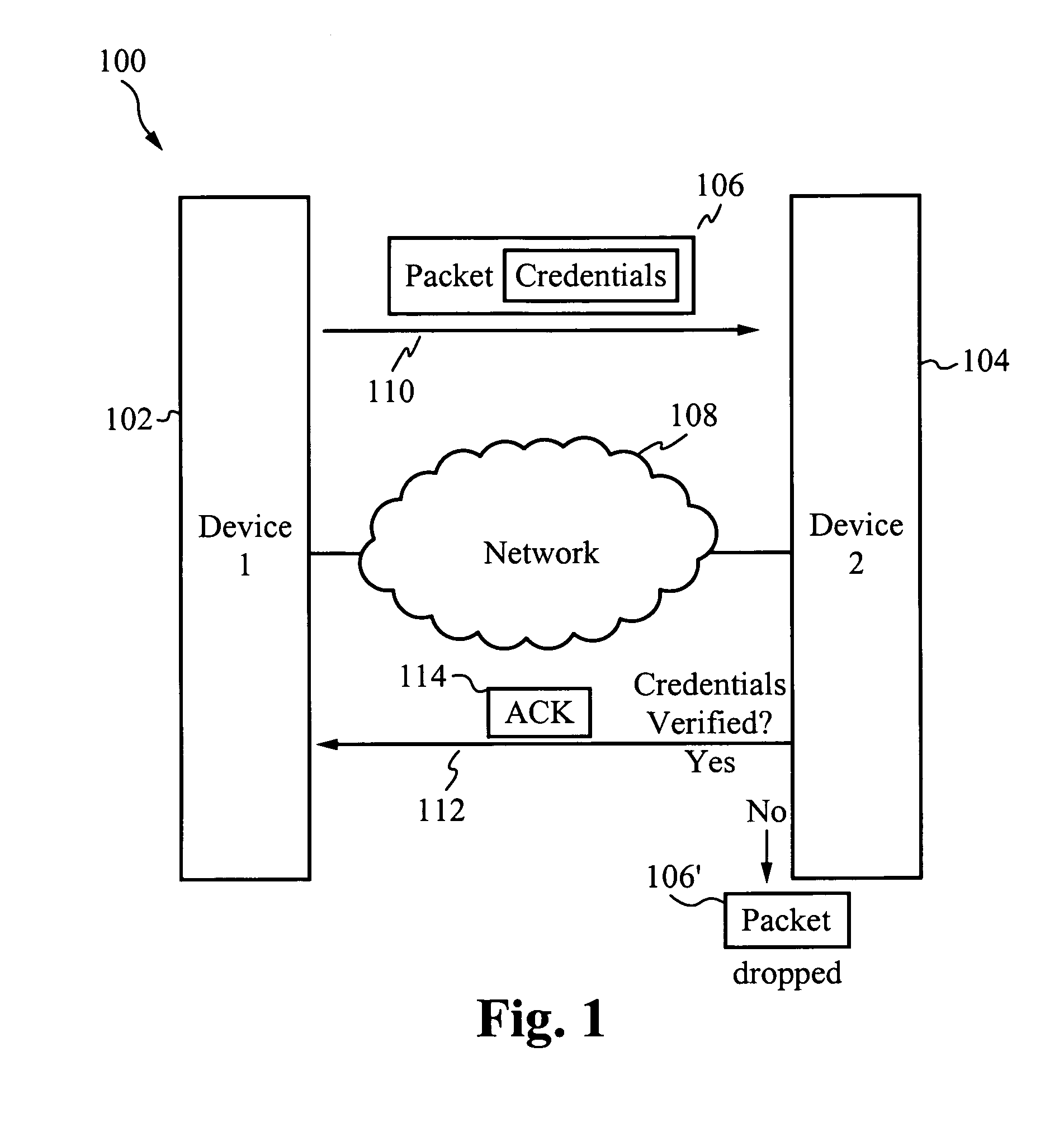
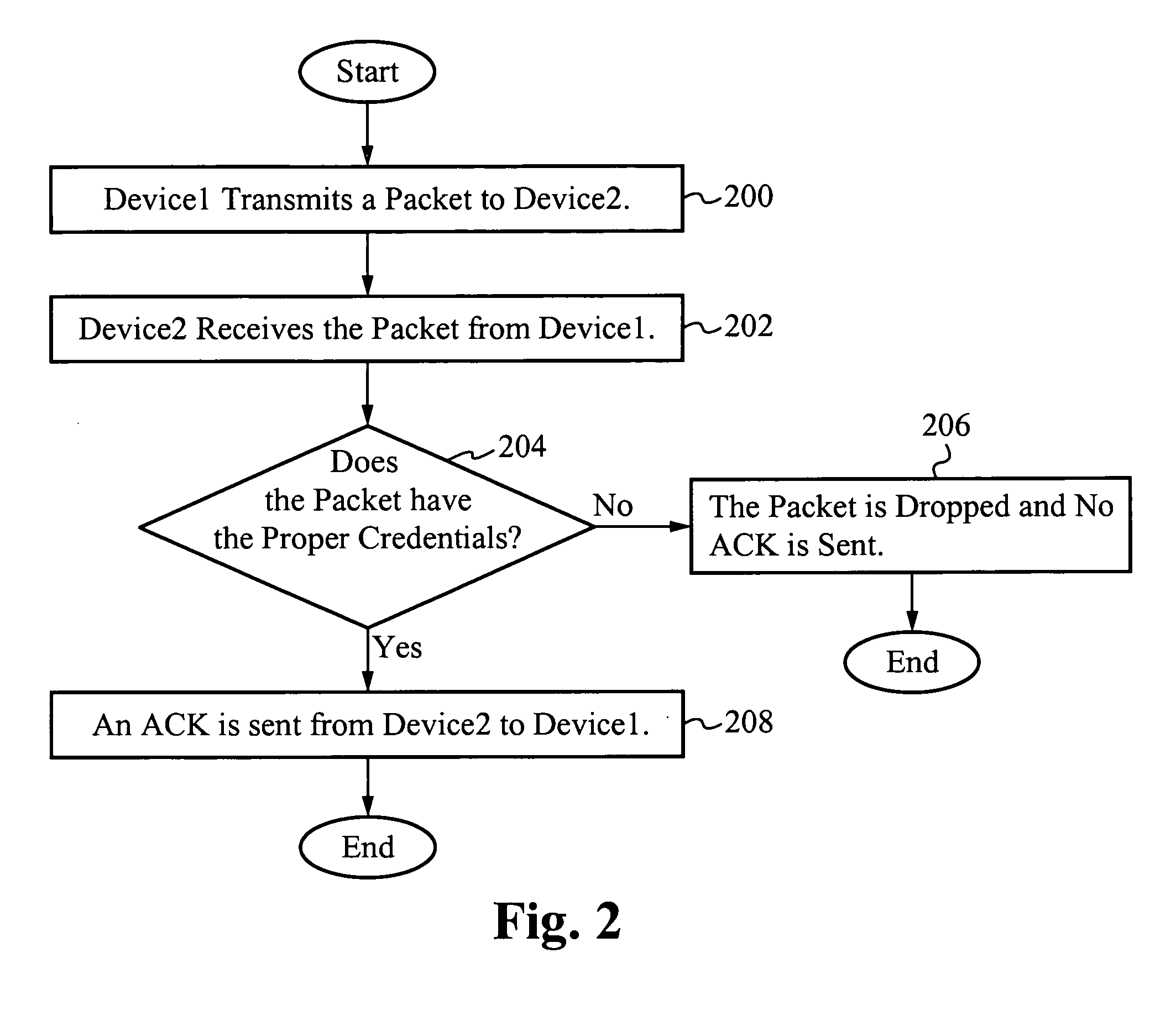
System for and method of securing a network utilizing credentials
InactiveUS20070274315A1Improve network securityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareSoftware
A system for and method of securing a network are described herein. A receiving device listens for packets with proper credentials. If a transmitting device sends the correct credentials, the receiving device will respond with an acknowledgment and further data is able to be transmitted. However, if the transmitting device does not send a packet with the proper credentials, then the receiving device will drop the packet and not respond. Thus, the transmitting device will be unaware of the presence of the receiving device, in particular when hackers are using scanning software to locate target devices.
Owner:GOODRICH JOHN B +1
Microwave self-phasing antenna arrays for secure data transmission & satellite network crosslinks
ActiveUS20050030226A1Improve directivityMaximizes signal-to-noise (SNR) ratioRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsClimate change adaptationTactical communicationsCommunications security
A high-directivity transponder system uses a dual system of a retrodirective array transmitting a data signal peak toward an interrogator source, and a self-null-steering array transmitting a null toward the interrogator source and a jamming signal elsewhere, resulting in high S / N reception at the interrogator source and avoidance of interception. Integrating modulators would allow each array to transmit different data while the spectra of the transmitted signals are identical, thus disabling interception. The system enables secure point-to-point communications and can be used for short-distance wireless data transmission systems such as wireless LAN and RFID servers. As another aspect, self-steering signal transmission is employed for randomly oriented satellites using circularly polarized, two-dimensional retrodirective arrays. Quadruple subharmonic mixing is used as an effective means of achieving phase conjugation when a high-frequency LO is not feasible or inapplicable. These features may be used for small-satellite communications, secure tactical communications, search and rescue, enemy location fixing and tracking, UAV command and control, forest fire detection, marine-based tracking, and many other applications requiring secure communications with high signal directivity.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Systems and methods for detecting network intrusions
InactiveUS7500266B1Improve abilitiesImprove network securityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer science
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP +1
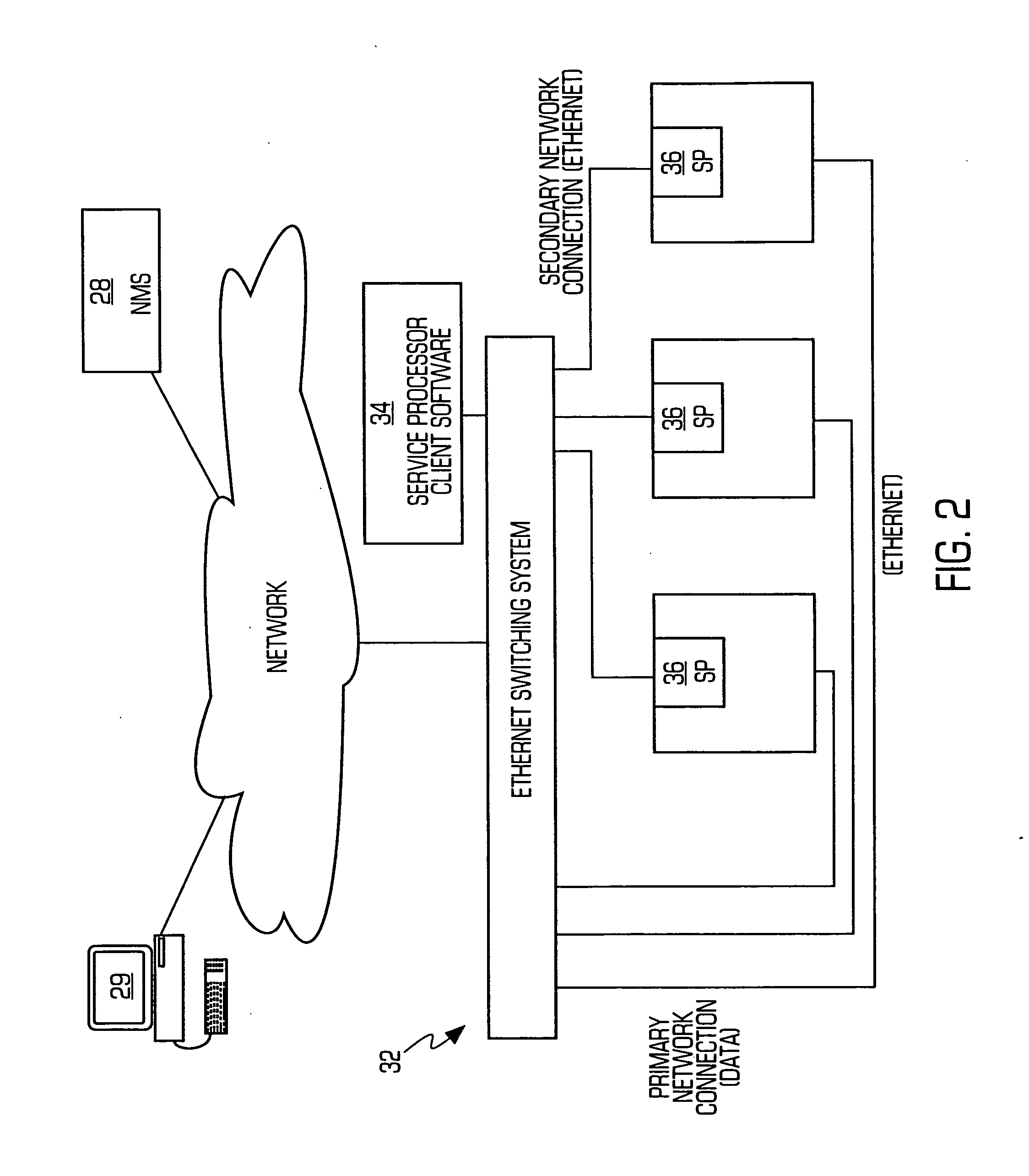
Service processor gateway system and appliance
ActiveUS7466713B2Reduce complexityLow costDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationNetworking protocolSecure transmission
A system for physically consolidating and securing access to service processors and management modules in computer, telecommunication and networking equipment is provided that isolates the management ports from the data network. The system converts low-level management protocols into higher-level network protocols suitable for secure transport over the data network. The system may encrypt the common format management data. The system may also authenticate each user that attempts to access the management interfaces.
Owner:VERTIV IT SYST INC
Microwave self-phasing antenna arrays for secure data transmission & satellite network crosslinks
InactiveUS20060238414A1Increase user capacityImprove directivityDirection finders using radio wavesAntenna supports/mountingsTactical communicationsCommunications security
A high-directivity transponder system uses a dual system of a retrodirective array transmitting a data signal peak toward an interrogator source, and a self-null-steering array transmitting a null toward the interrogator source and a jamming signal elsewhere, resulting in high S / N reception at the interrogator source and avoidance of interception. Integrating modulators would allow each array to transmit different data while the spectra of the transmitted signals are identical, thus disabling interception. The system enables secure point-to-point communications and can be used for short-distance wireless data transmission systems such as wireless LAN and RFID servers. As another aspect, self-steering signal transmission is employed for randomly oriented satellites using circularly polarized, two-dimensional retrodirective arrays. Quadruple subharmonic mixing is used as an effective means of achieving phase conjugation when a high-frequency LO is not feasible or inapplicable. These features may be used for small-satellite communications, secure tactical communications, search and rescue, enemy location fixing and tracking, UAV command and control, forest fire detection, marine-based tracking, and many other applications requiring secure communications with high signal directivity.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Method, device, and system for deriving keys
ActiveUS20120077501A1Improve network securitySecurity arrangementSecuring communicationRadio networksRadio access network
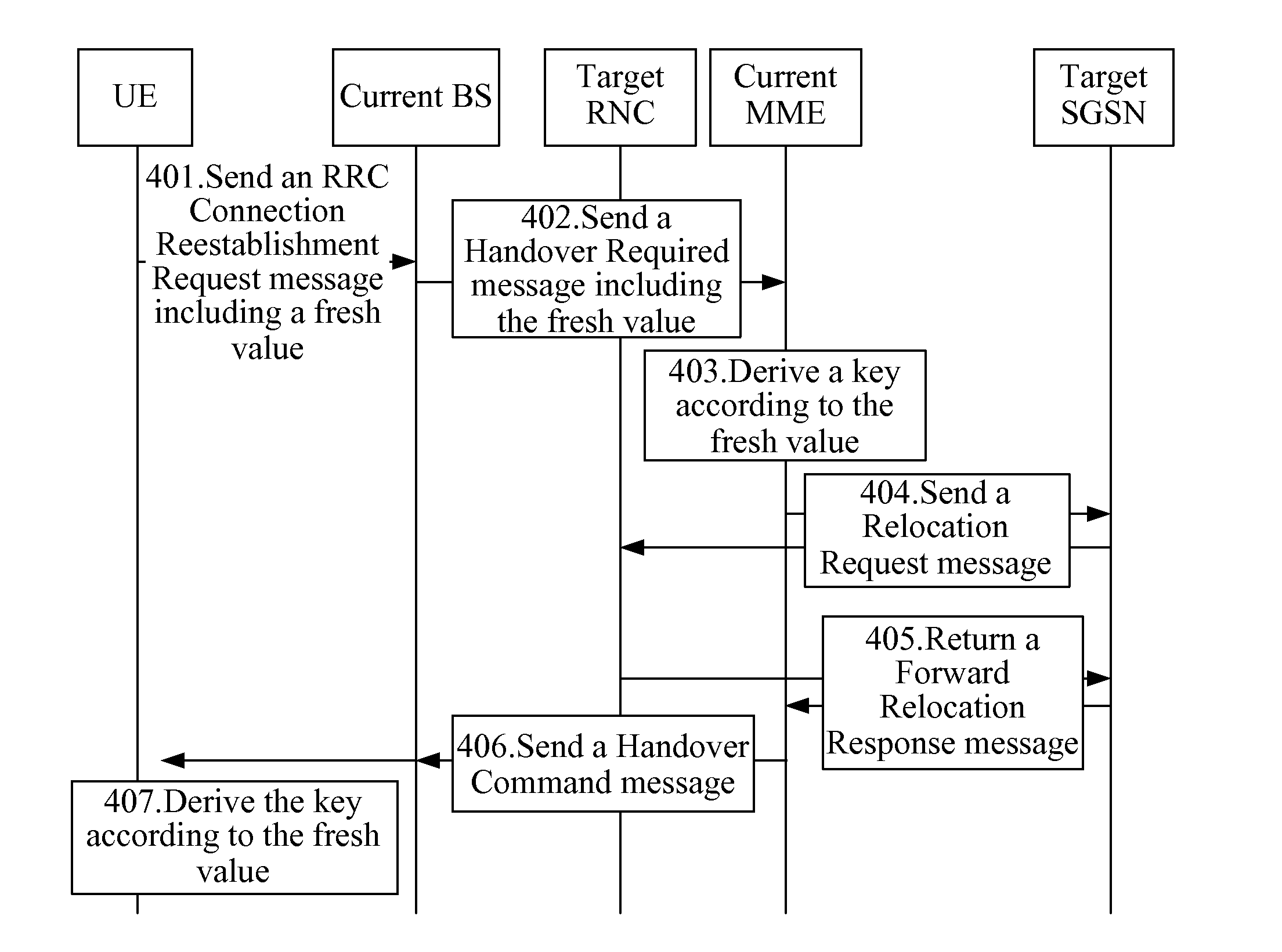
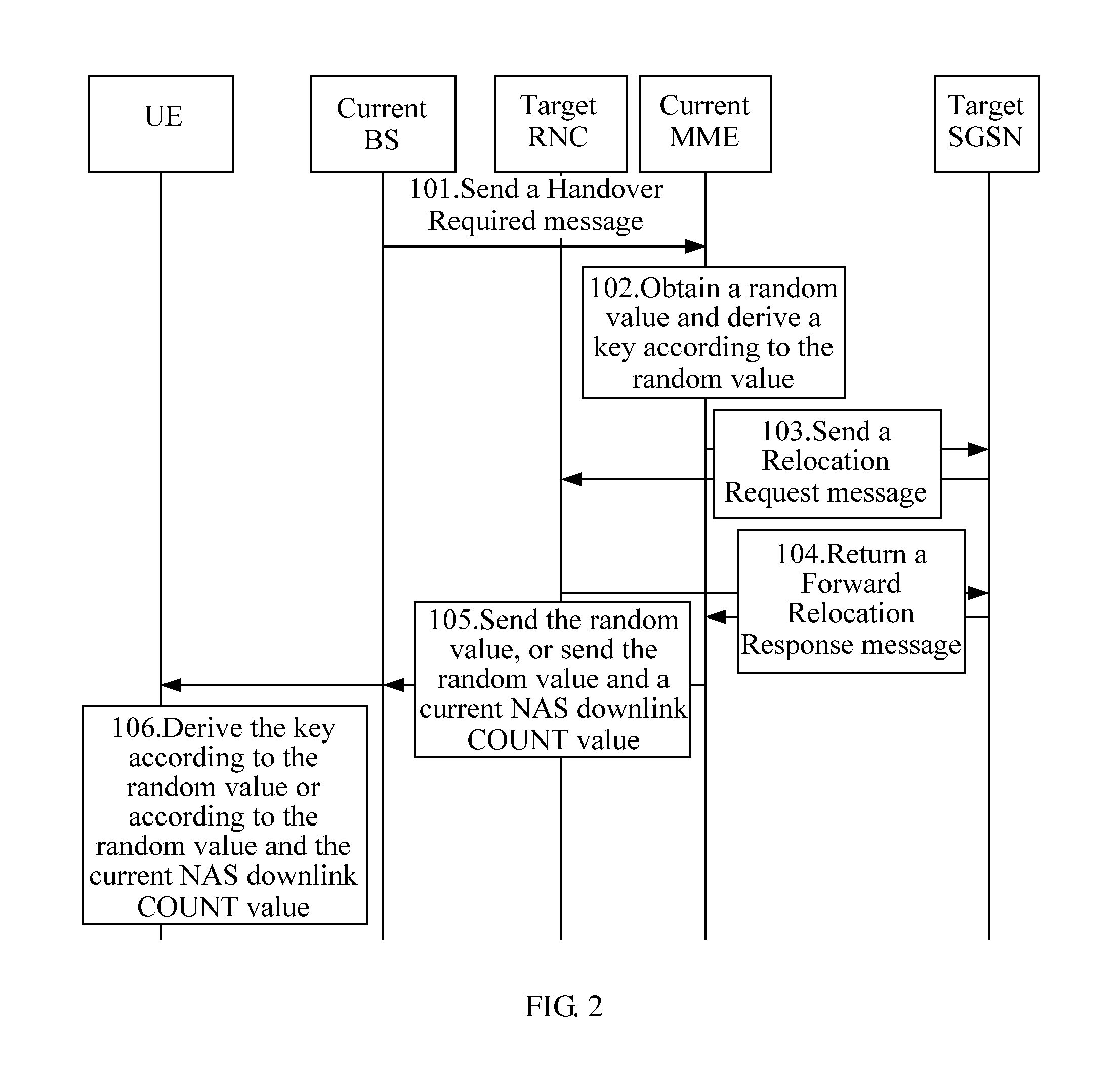
Method, device, and system for deriving keys are provided in the field of mobile communications technologies. The method for deriving keys may be used, for example, in a handover process of a User Equipment (UE) from an Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (EUTRAN) to a Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN). If a failure occurred in a first handover, the method ensures that the key derived by a source Mobility Management Entity (MME) for a second handover process of the UE is different from the key derived for the first handover process of the UE. This is done by changing input parameters used in the key derivation, so as to prevent the situation in the prior art that once the key used on one Radio Network Controller (RNC) is obtained, the keys on other RNCs can be derived accordingly, thereby enhancing the network security.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
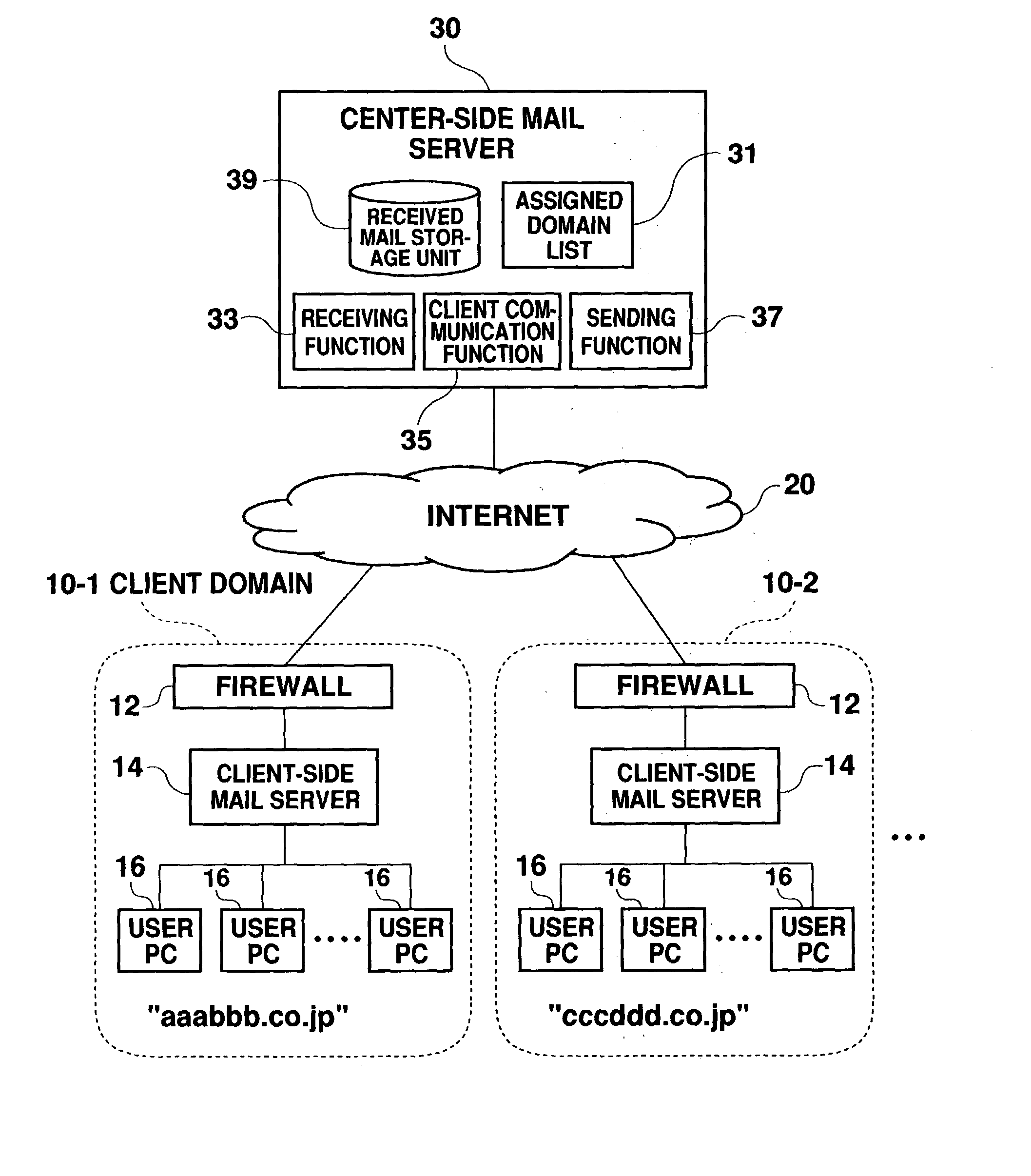
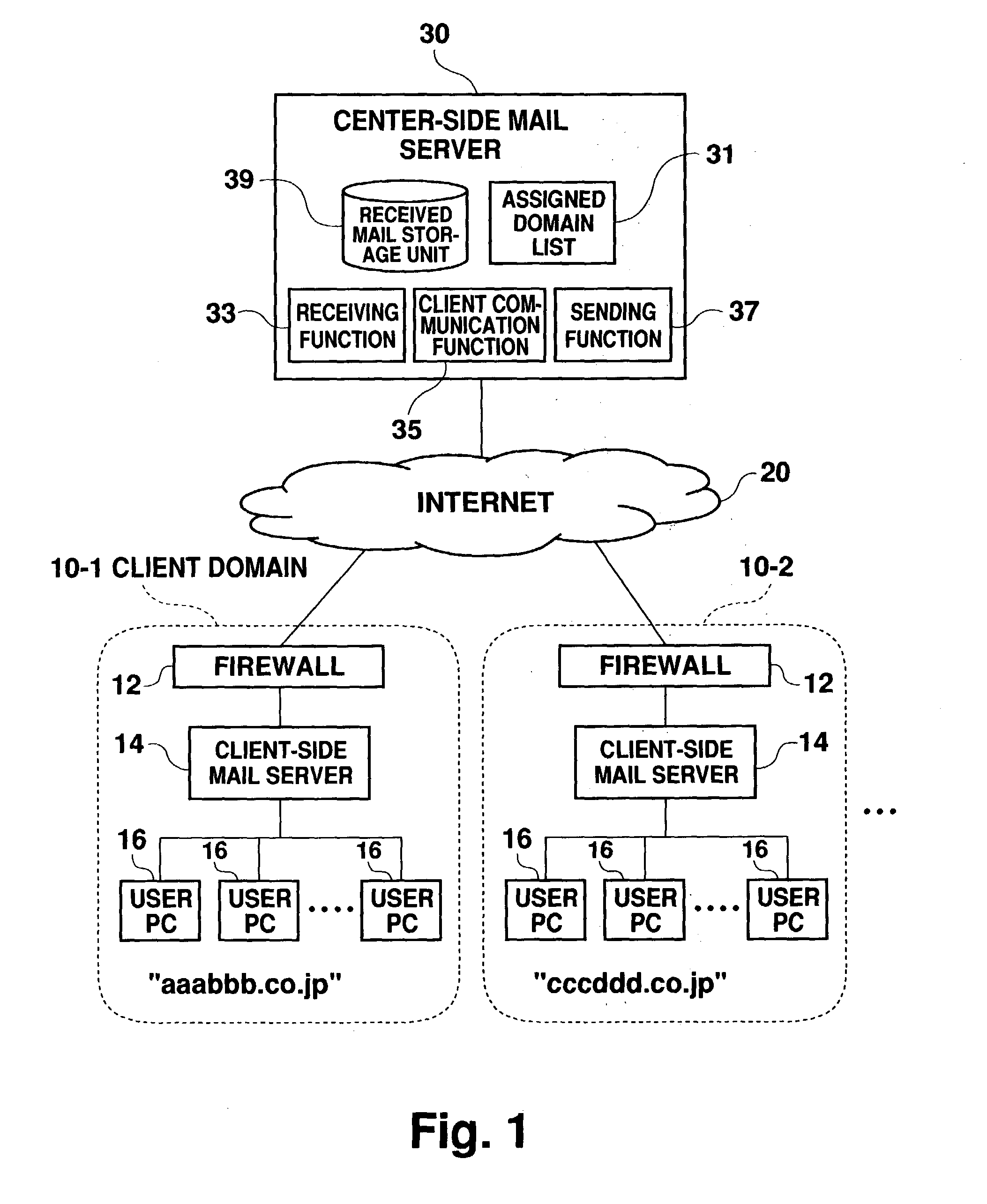
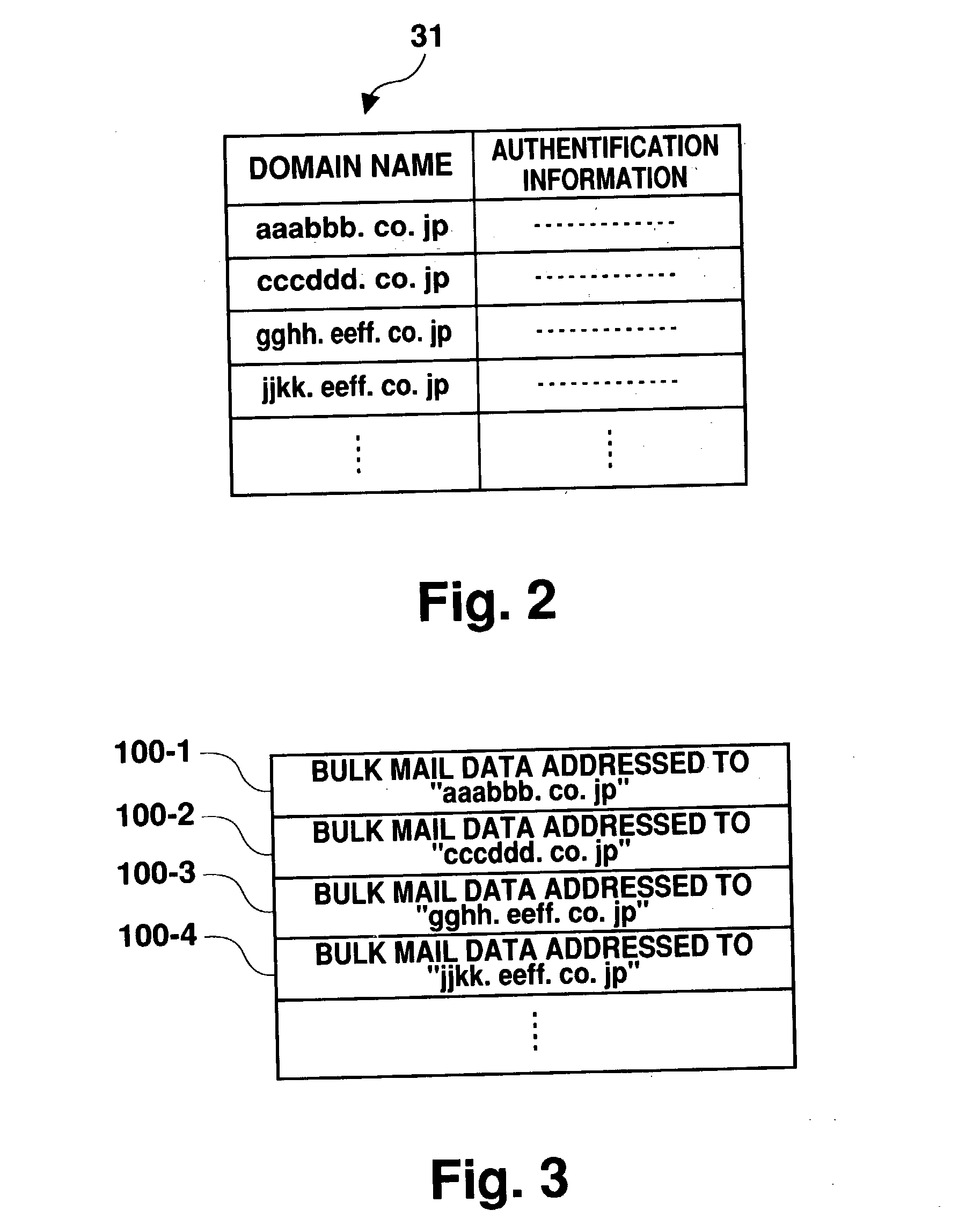
Mail processing system
InactiveUS20040049546A1Reduce loadReduce processing loadData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideHandling system
The present invention provides a mail processing system which reduces the load on an e-mail hosting. A center-side mail server (30) receives electronic mail addressed to client domains (10) and combines the electronic mail into one file (bulk mail data) for each domain. A client-side mail server (14) in the client domain (10) regularly accesses the center-side mail server (30) to download the bulk mail data, which is addressed to the client domain (10), from the server (30). The client-side mail server (14) disassembles the downloaded bulk mail data into individual electronic mail data and saves it in respective destination mailboxes. A user PC (16) in the client domain (10) can receive electronic mail, which is addressed to the user PC, from the client-side mail server (14) using a protocol such as POP3.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
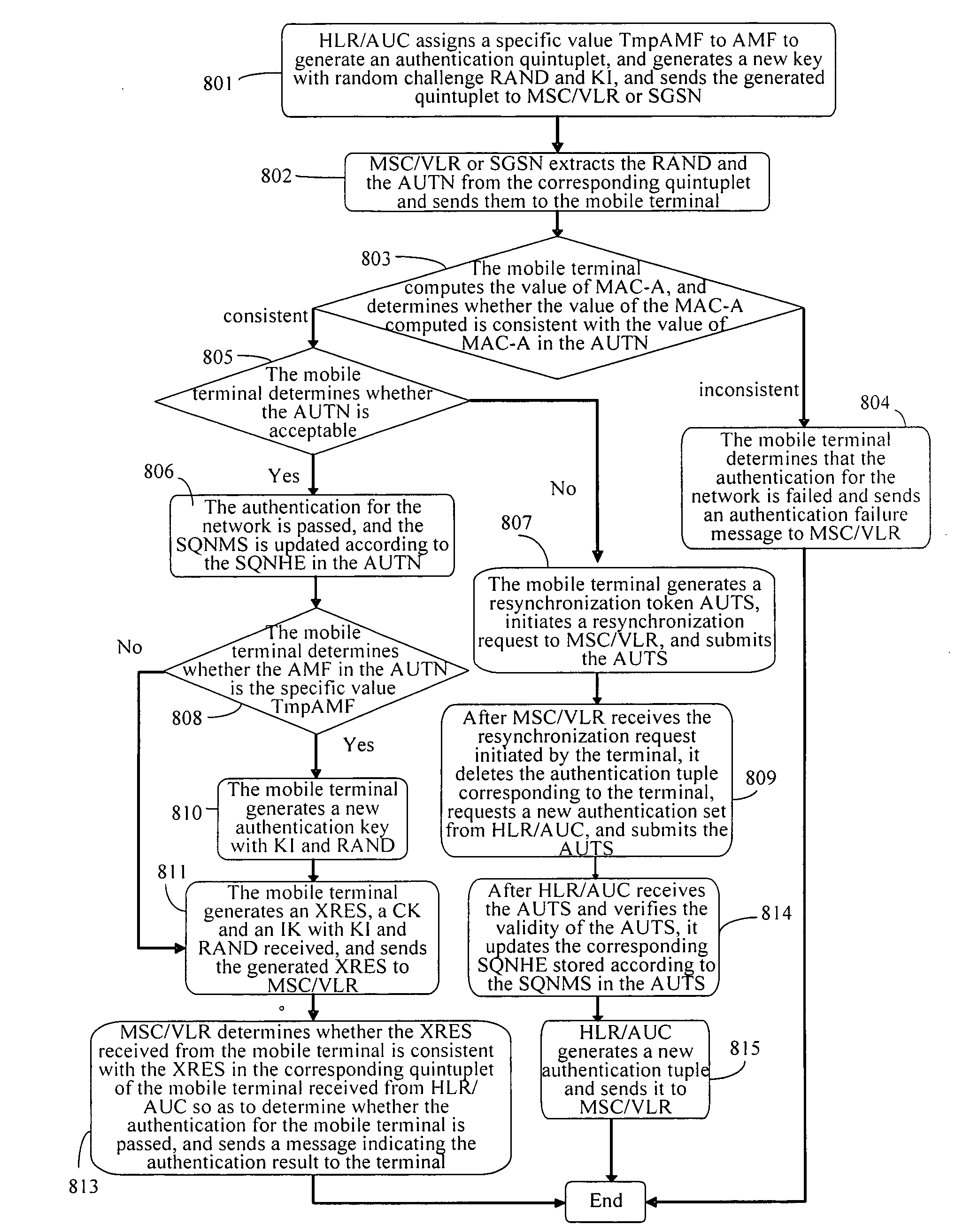
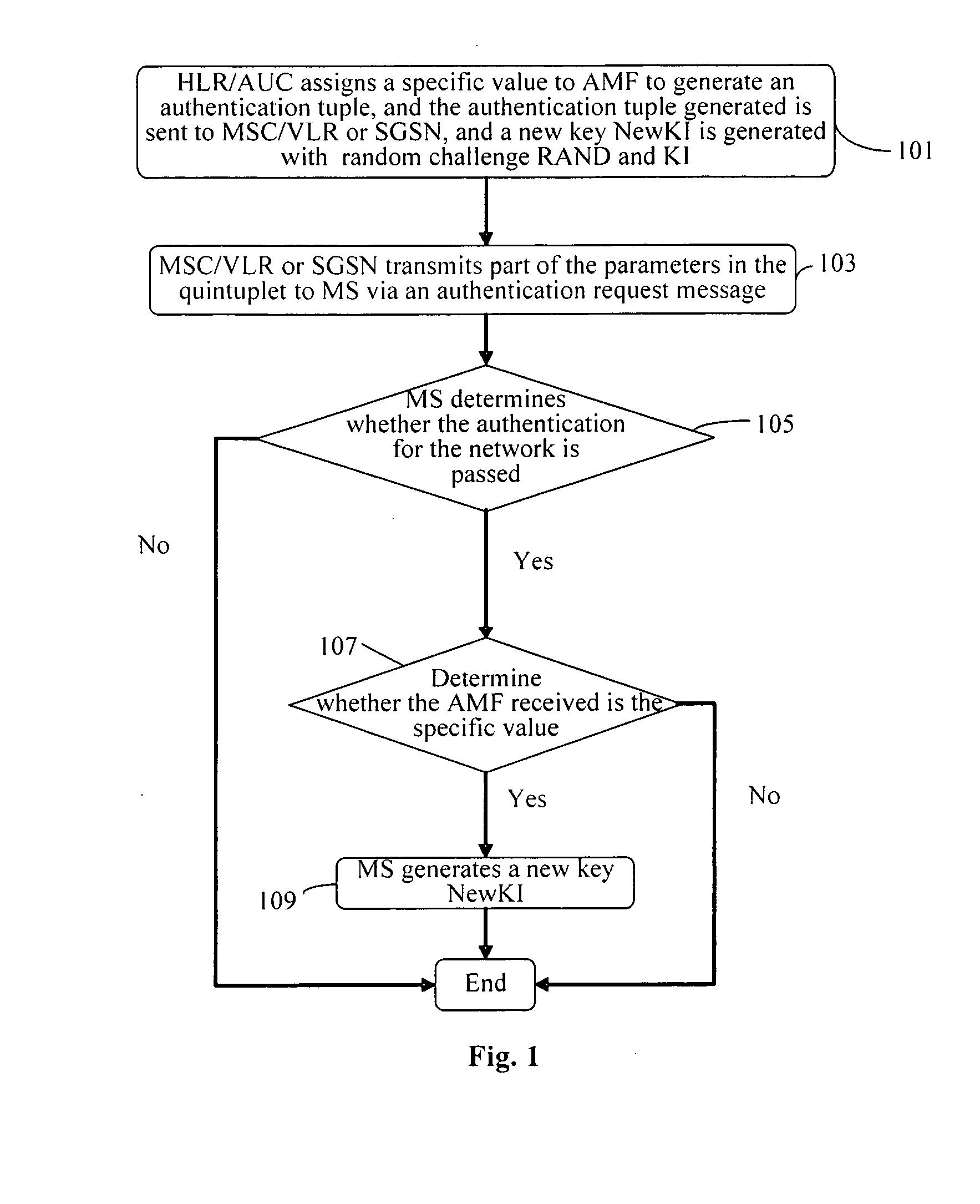
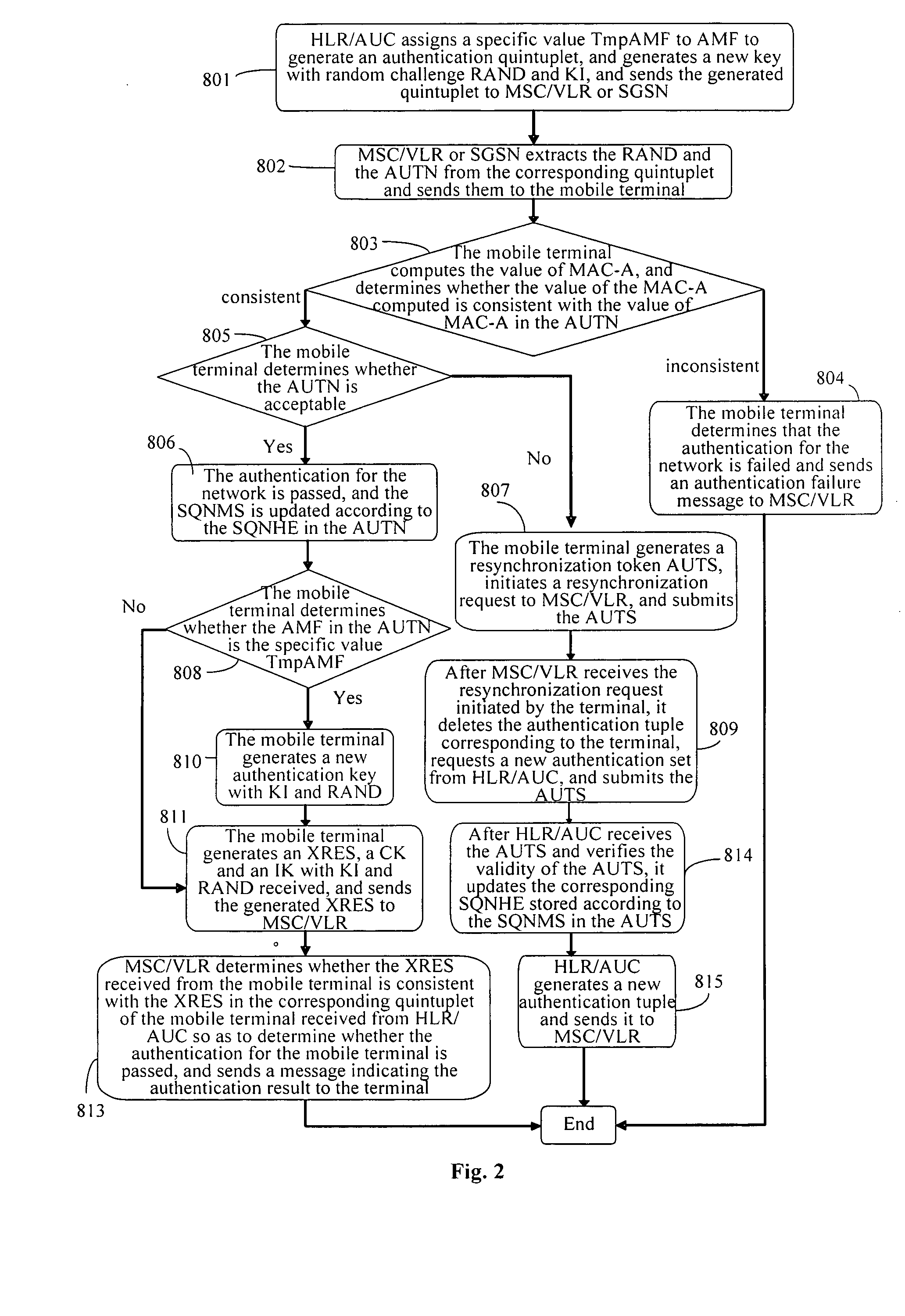
Method and device for updating a key
ActiveUS20100064344A1Improve safetyConveniently updateDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsNetwork securityAuthentication
A method for updating a key includes: assigning, by a network, a stipulated specific value to an authentication management field AMF and generating a corresponding authentication tuple, and sending corresponding parameters in the authentication tuple to the terminal when an authentication request is initiated to the terminal, and generating a new authentication key for use in the next authentication; generating, by the terminal, a new authentication key corresponding to the network for use in the next authentication, when the corresponding parameters are received and it is determined that the authentication for the network is passed and the authentication management field in the corresponding parameters is with the predetermined value. According to the method for updating the key according to the invention, the key may be updated conveniently without adding to or modifying the existing signaling resources or the authentication parameters, so that network security may be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for improving network connection security with one or more cross-wired adapters
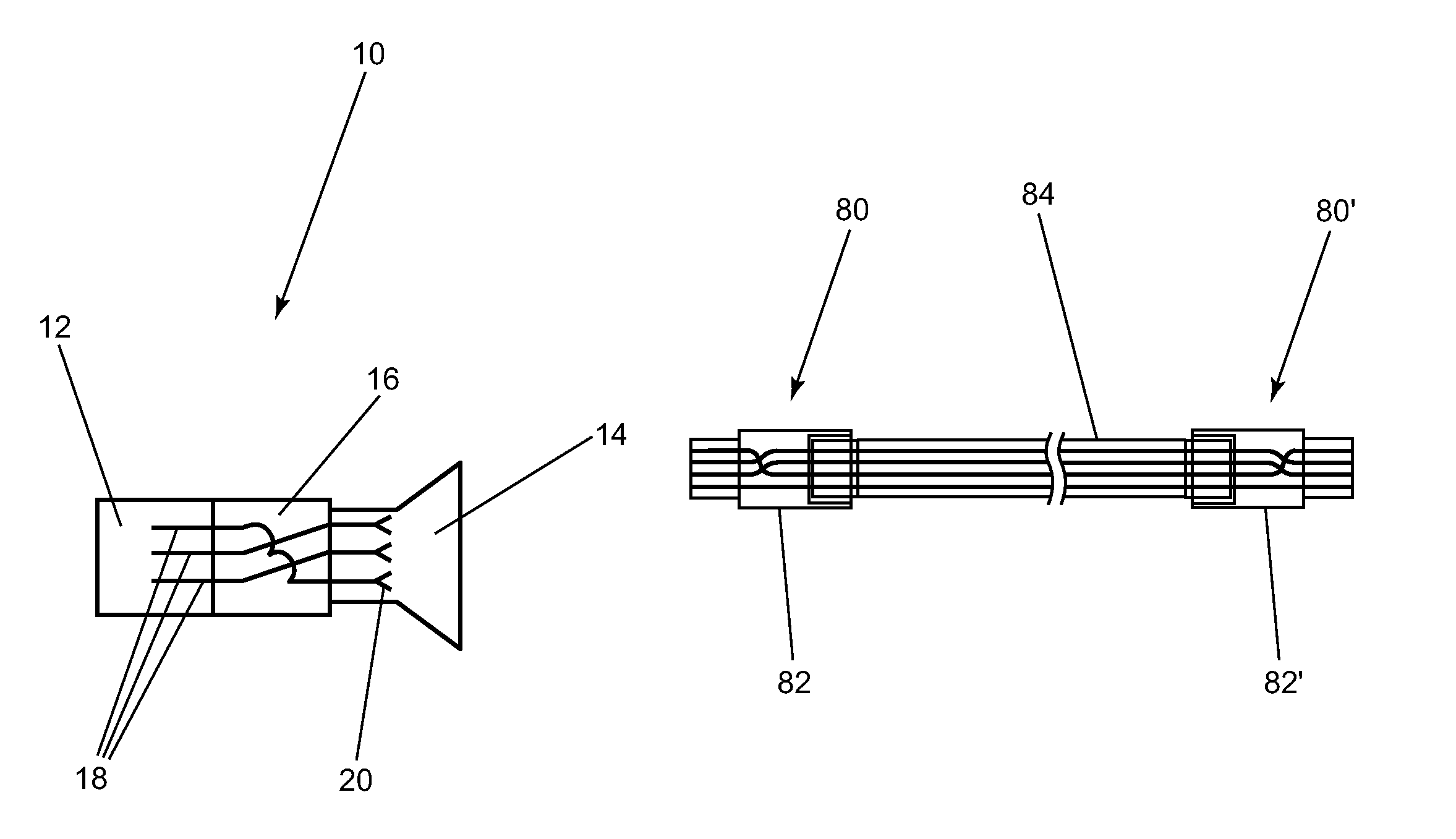
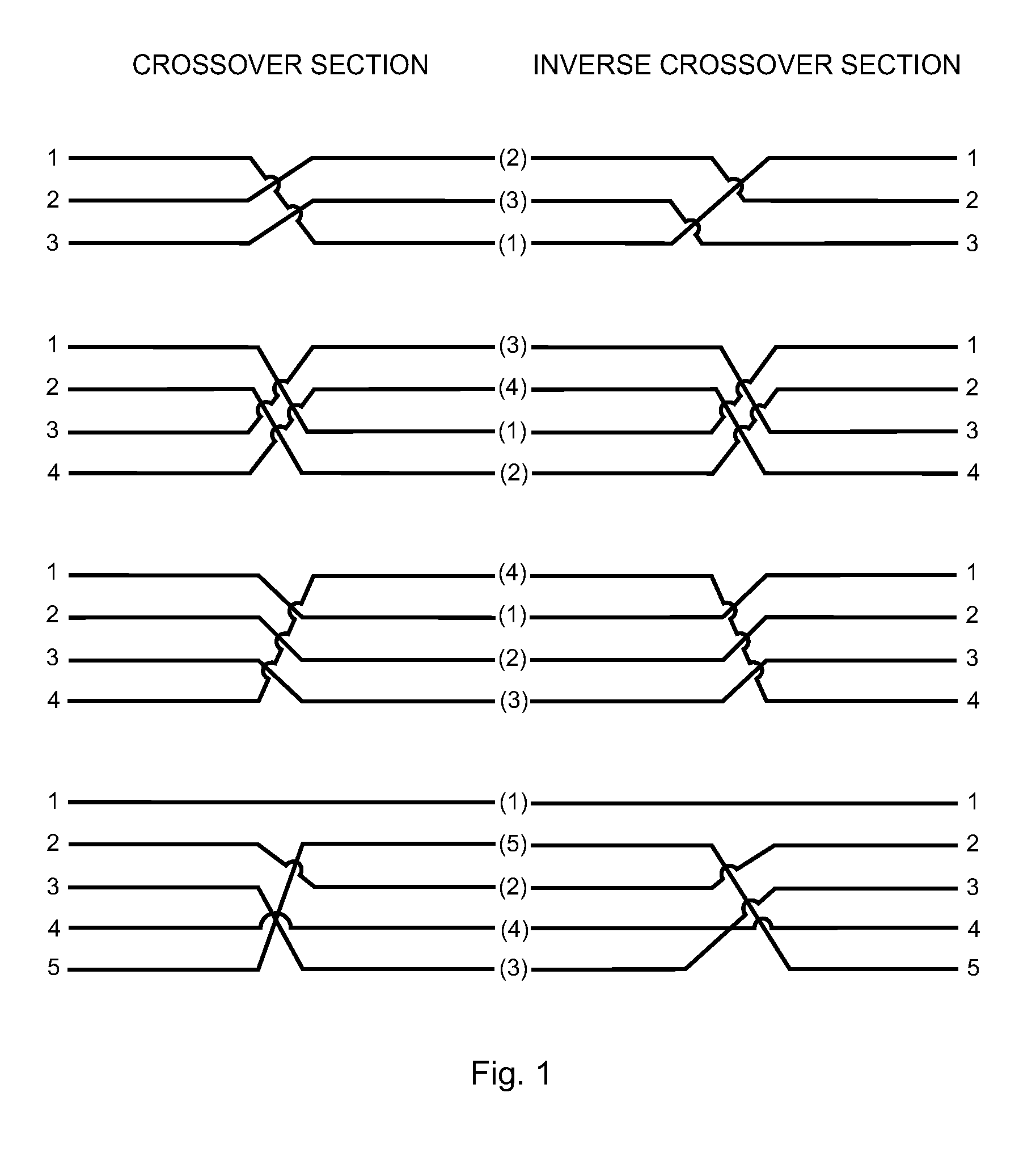
ActiveUS7377819B1Improve network securityIncorrect coupling preventionTwo-part coupling devicesNetwork connectionEngineering
A method and apparatus for improving network connection security. An adapter having a cross-wiring section which alters the pin out of the network from a standard wiring pattern to a non-standard wiring pattern is preferably connected to two or more connection points for the network.
Owner:ARROWHEAD CENT
Method and apparatus for providing network security using security labeling
ActiveUS7836490B2Reduces potential leakageImprove network securityDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsNetwork security policySecurity level
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com