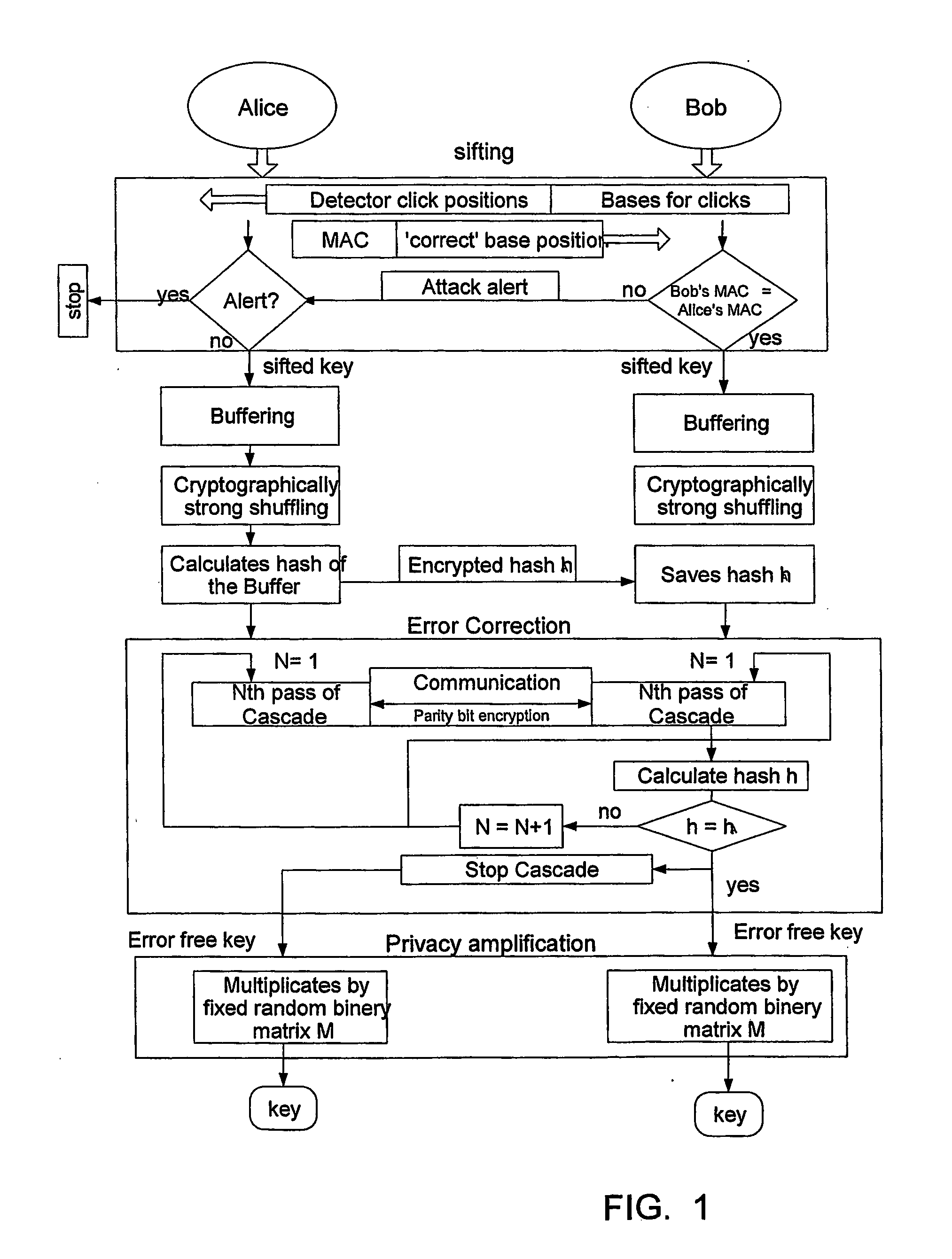
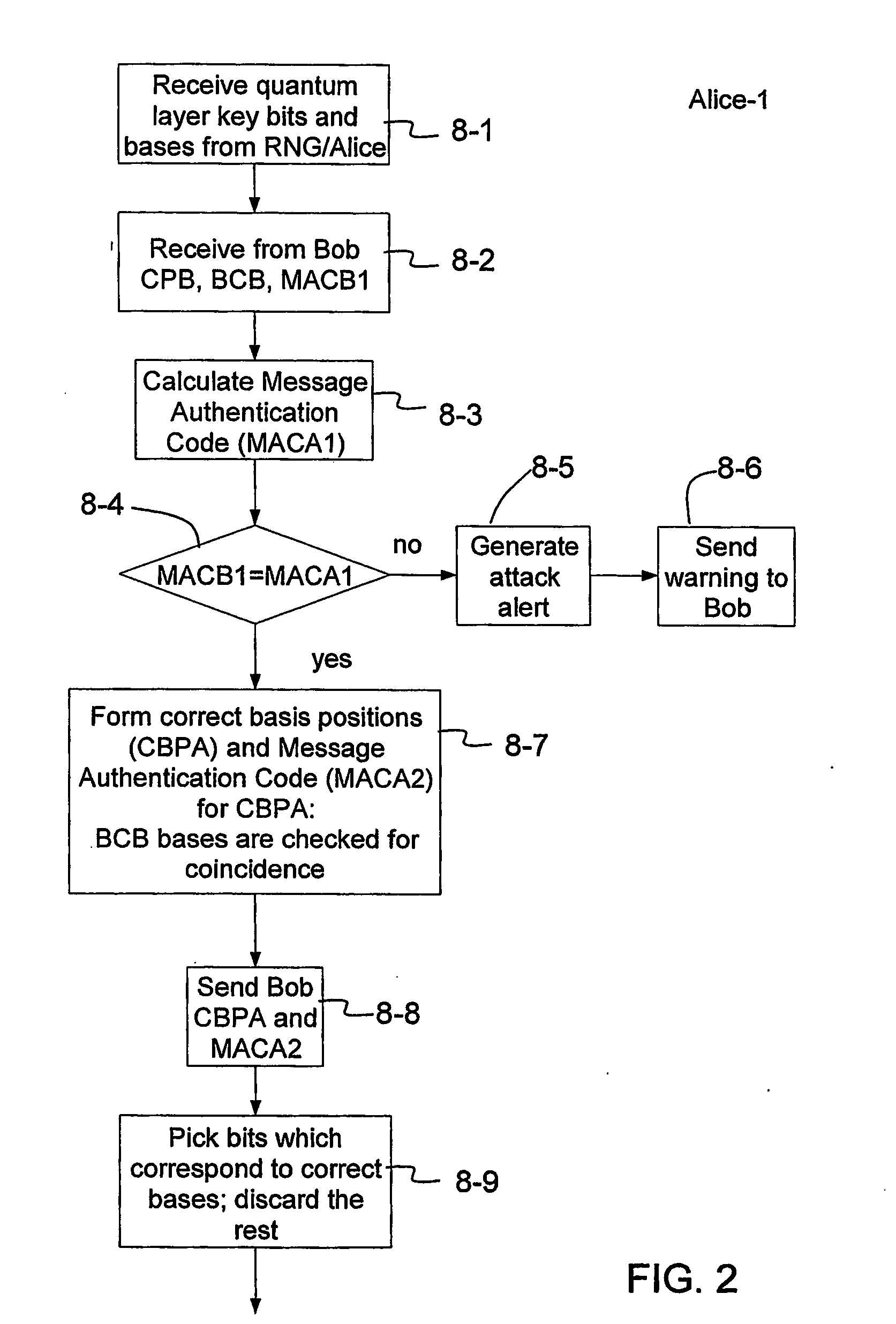
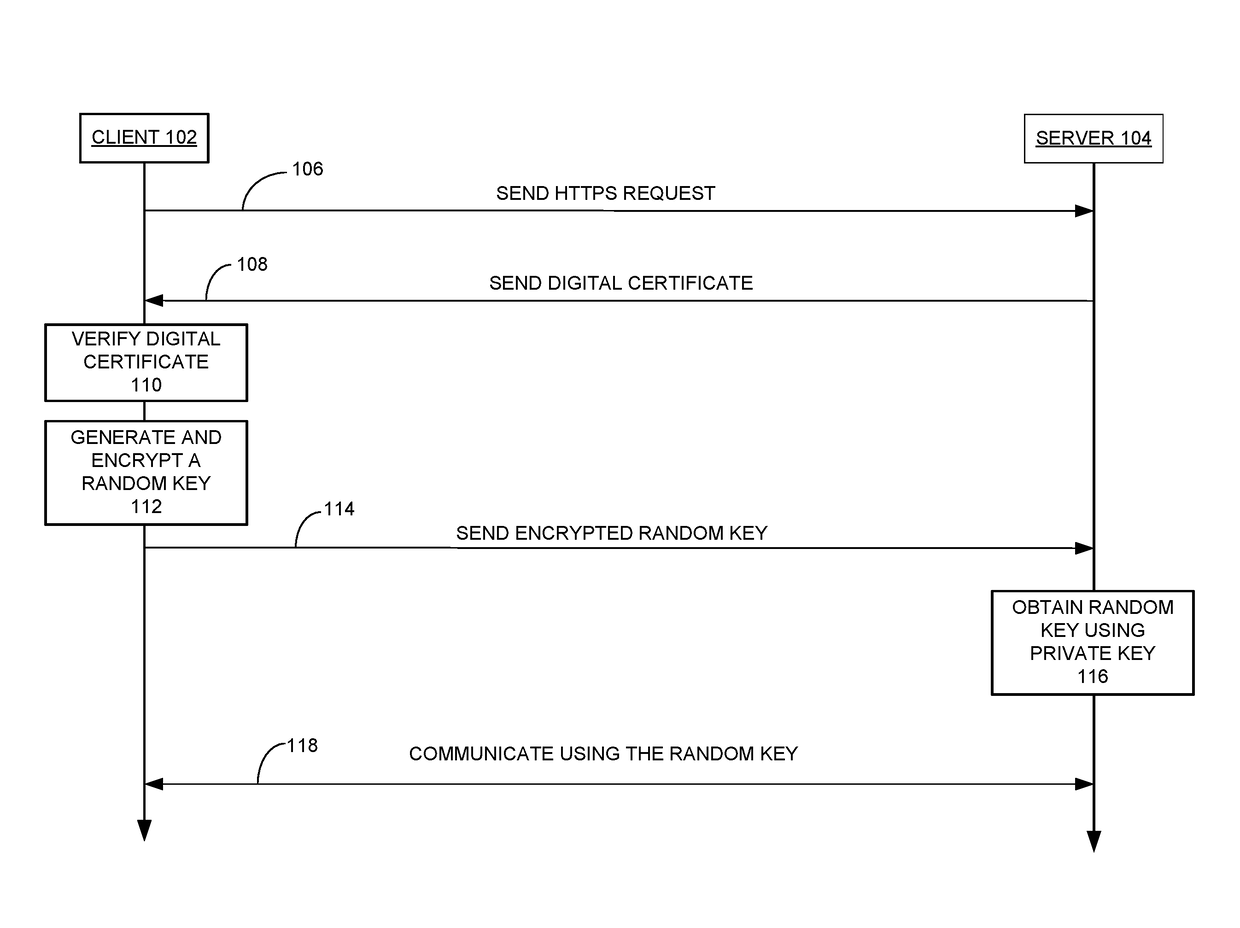
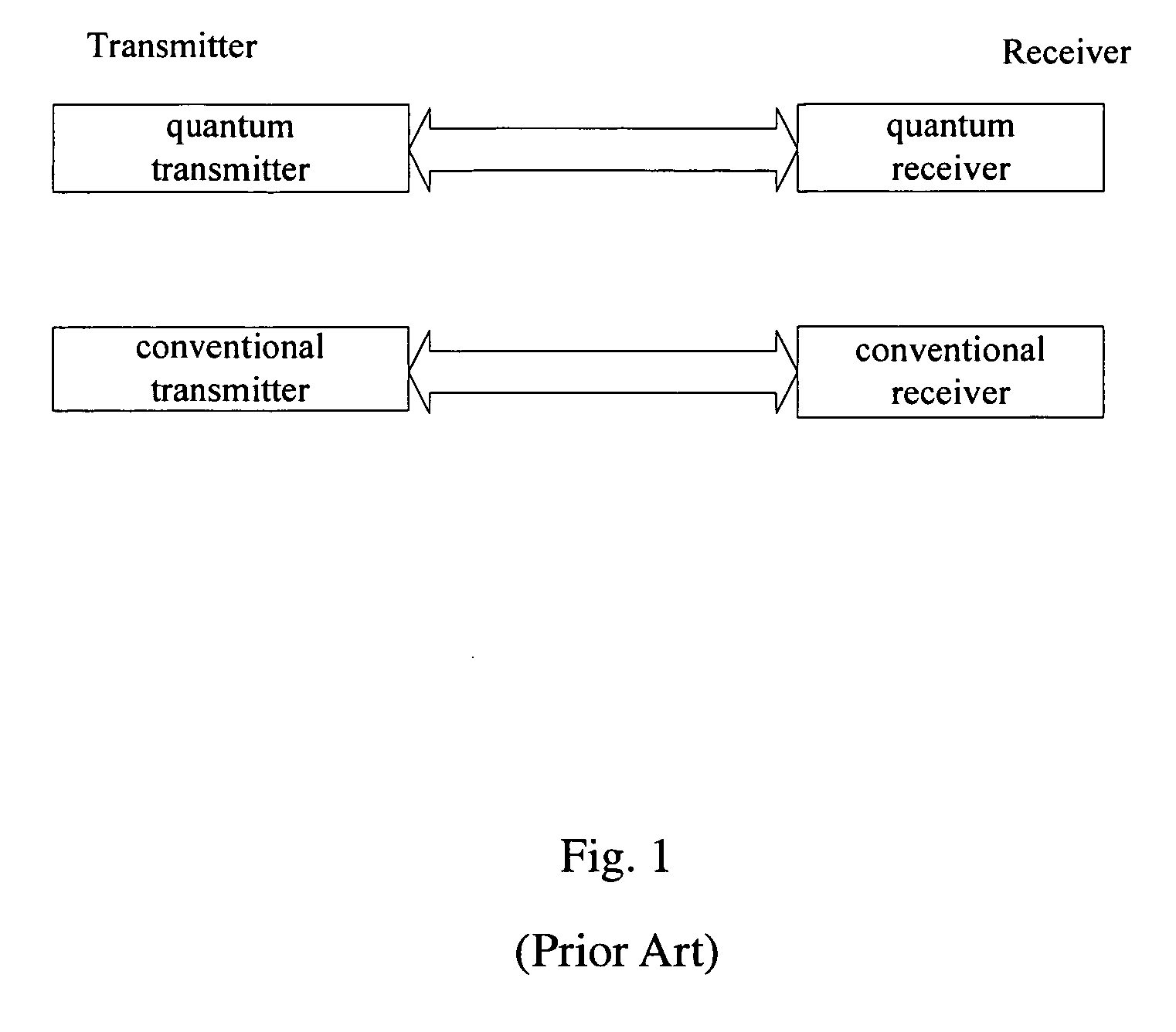
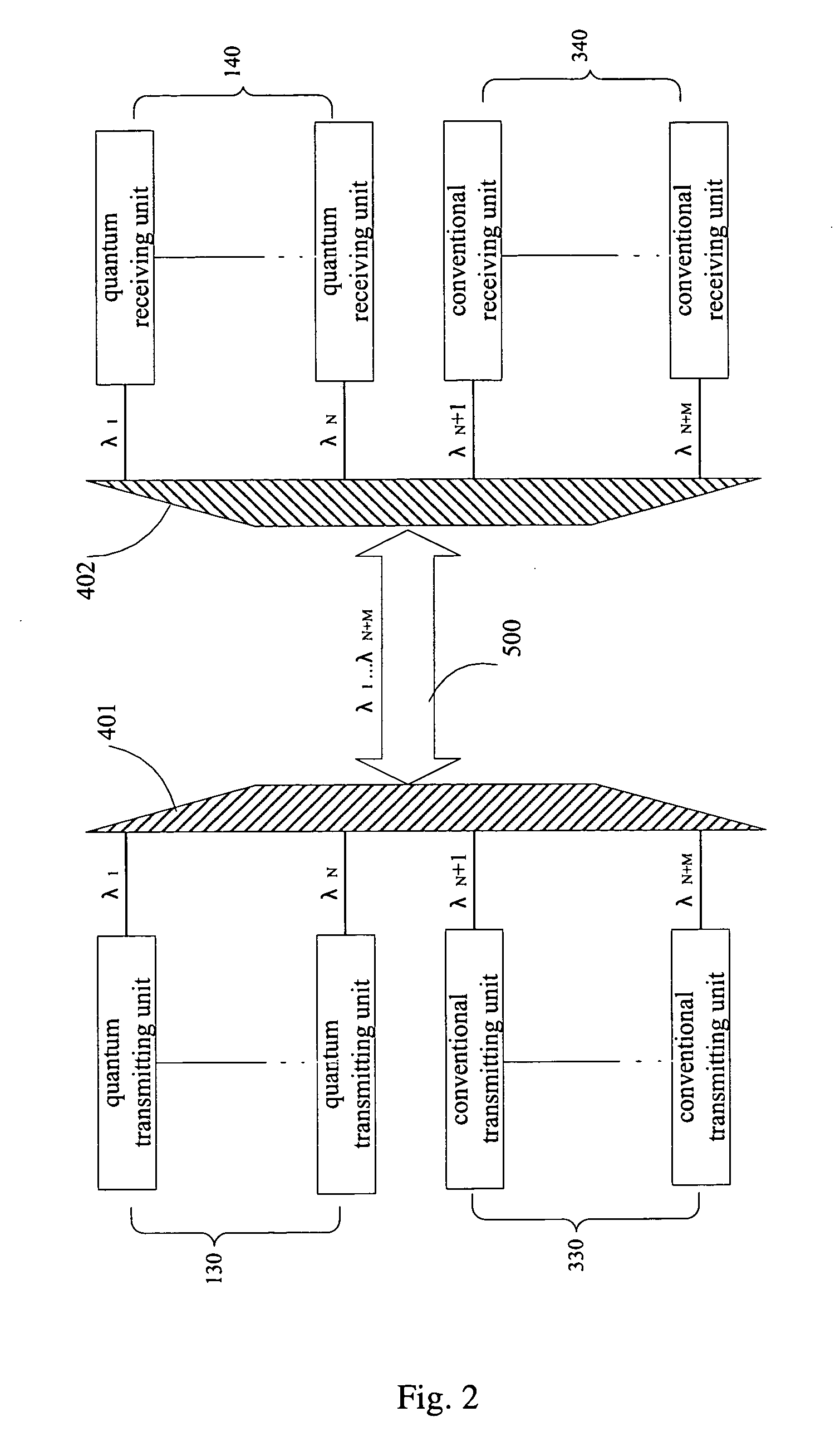
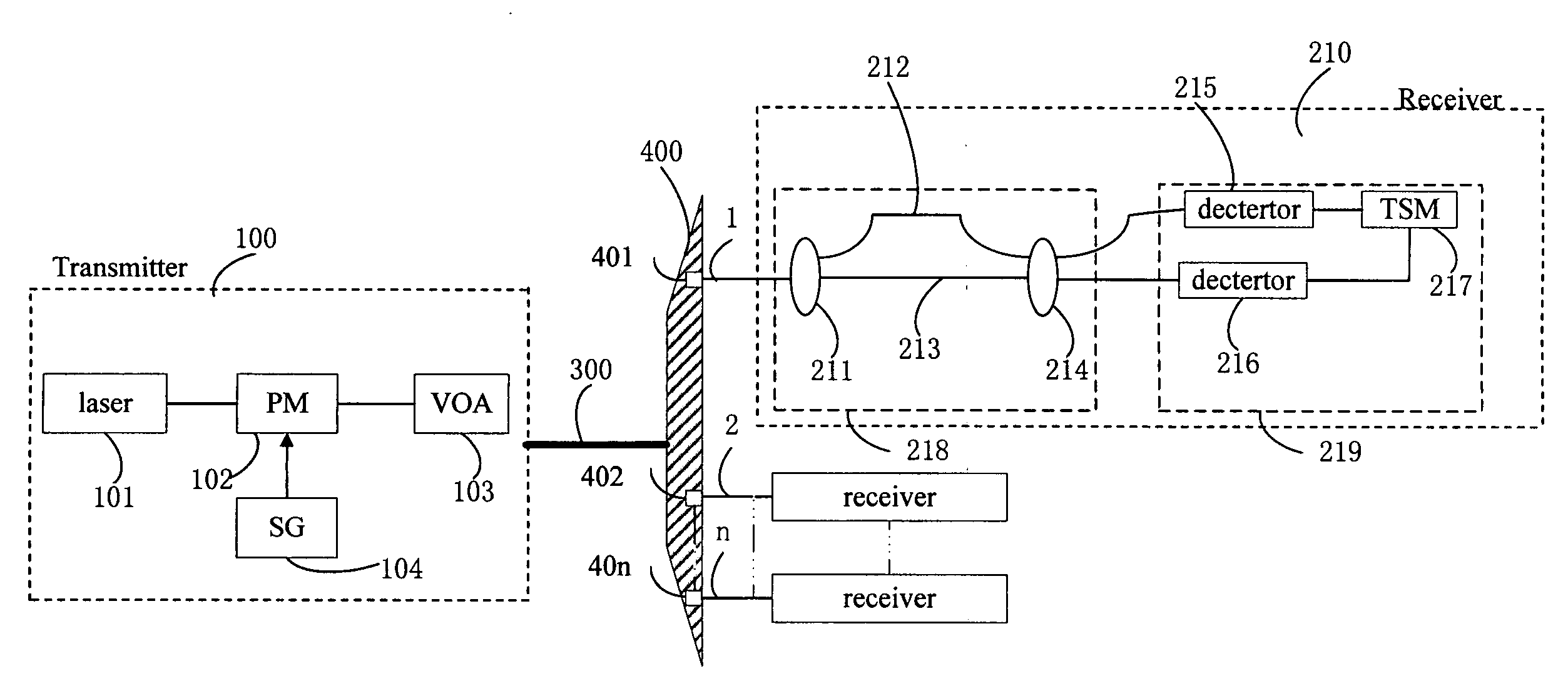
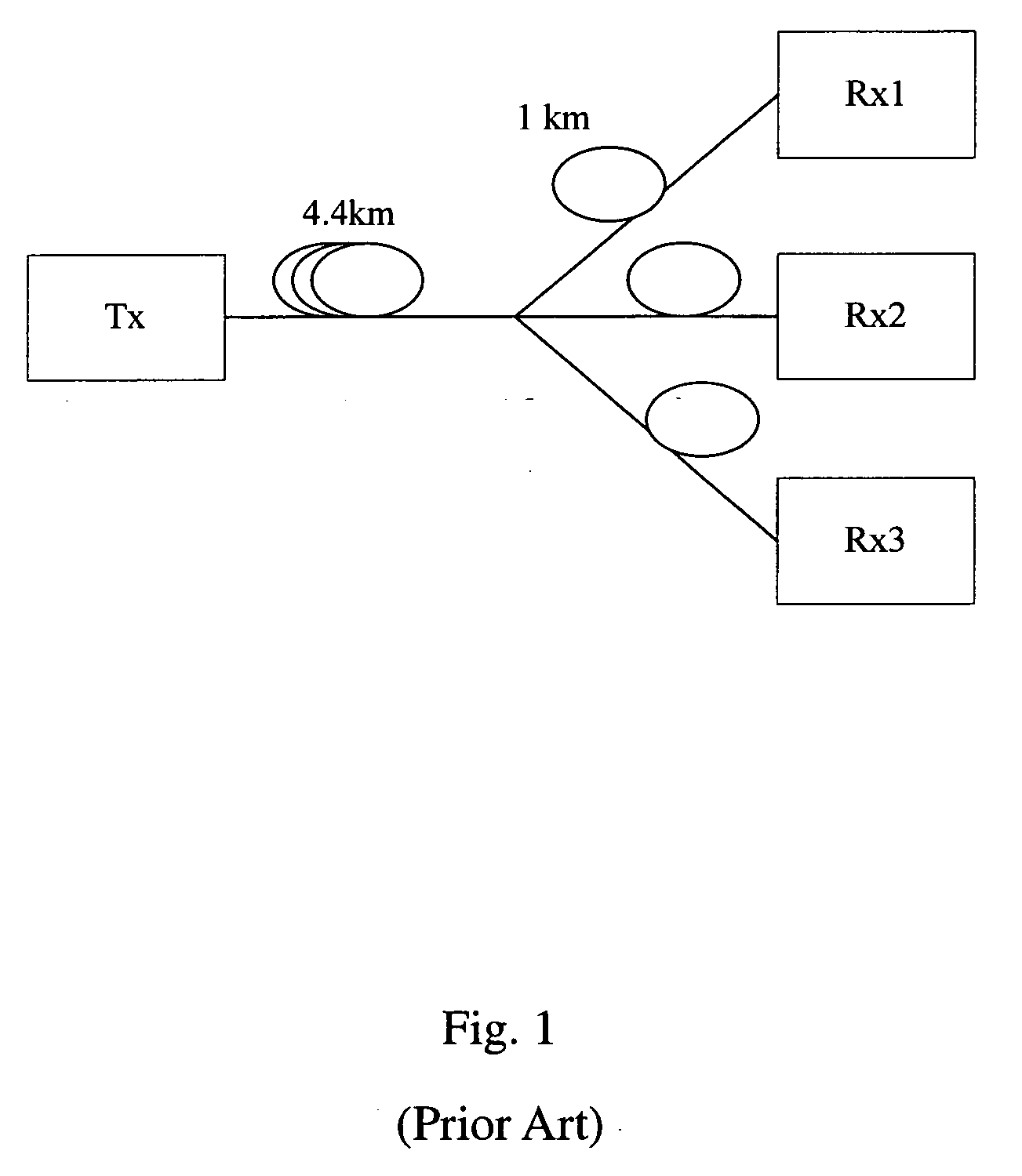
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1628 results about "Quantum key distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
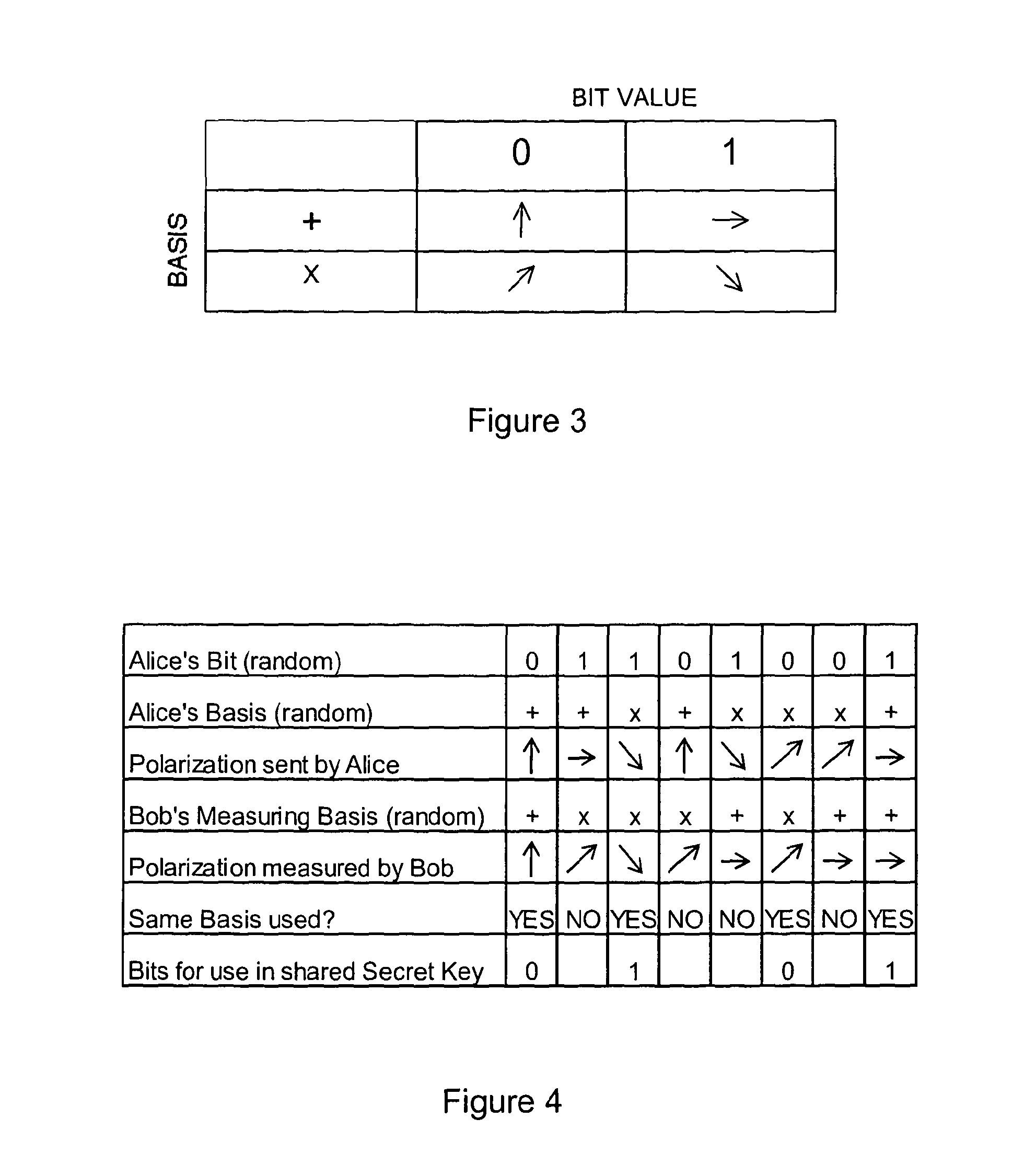
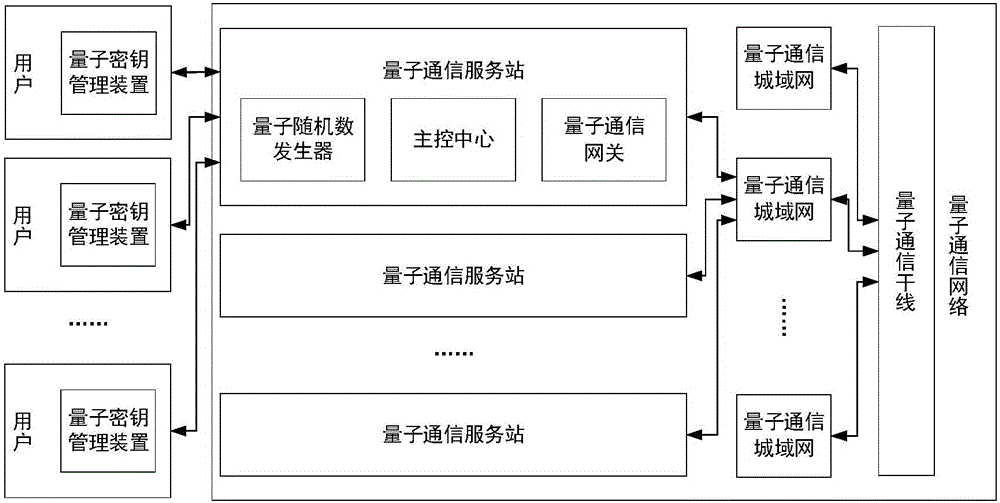
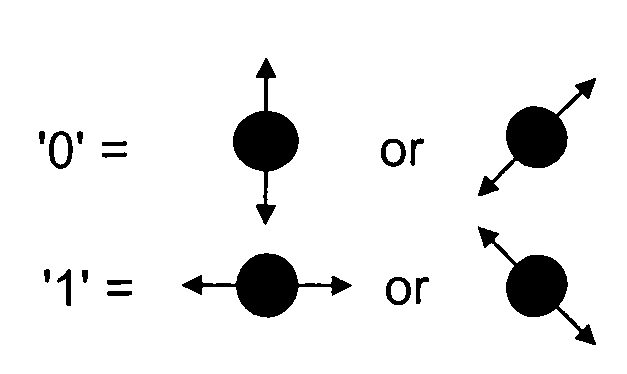
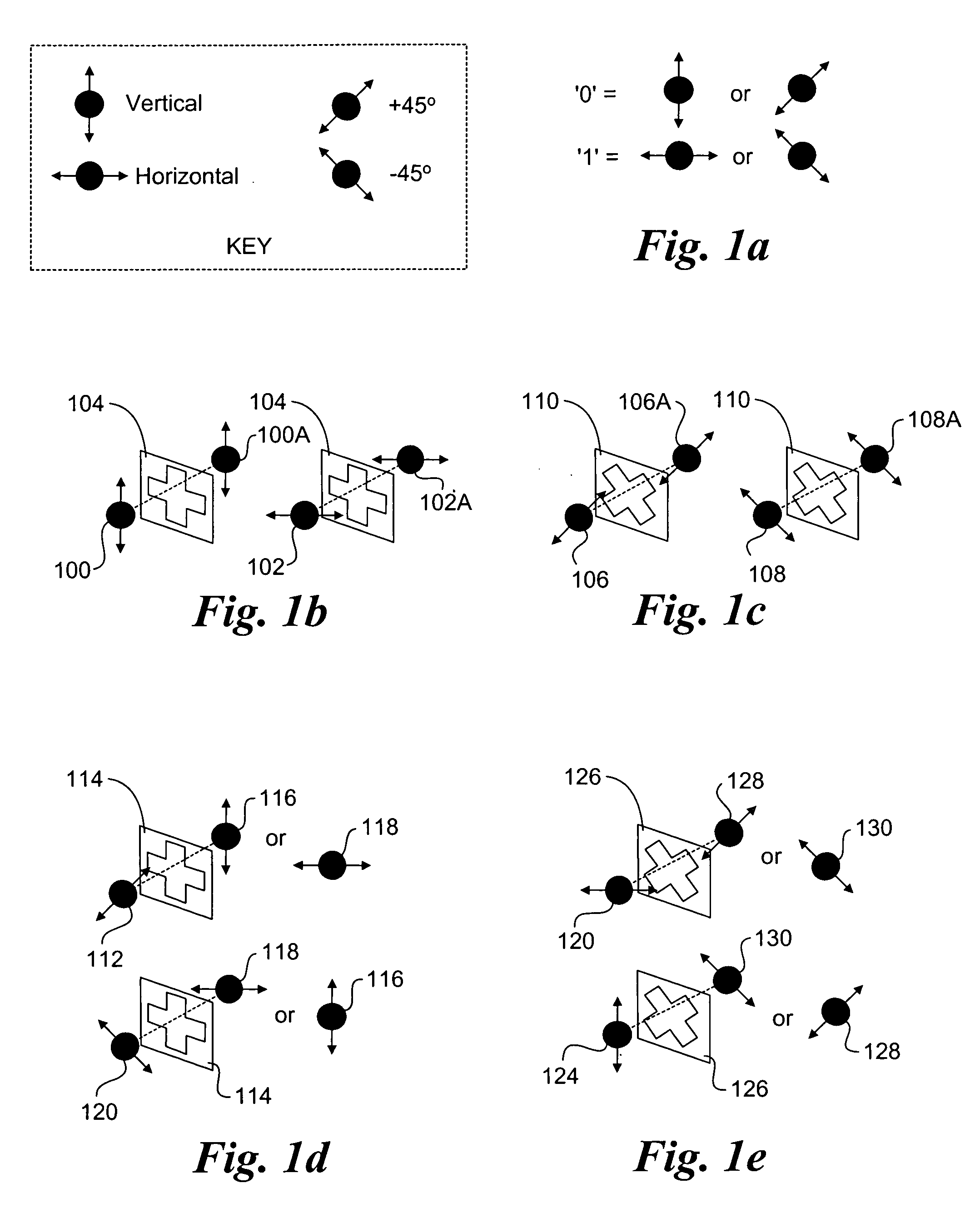
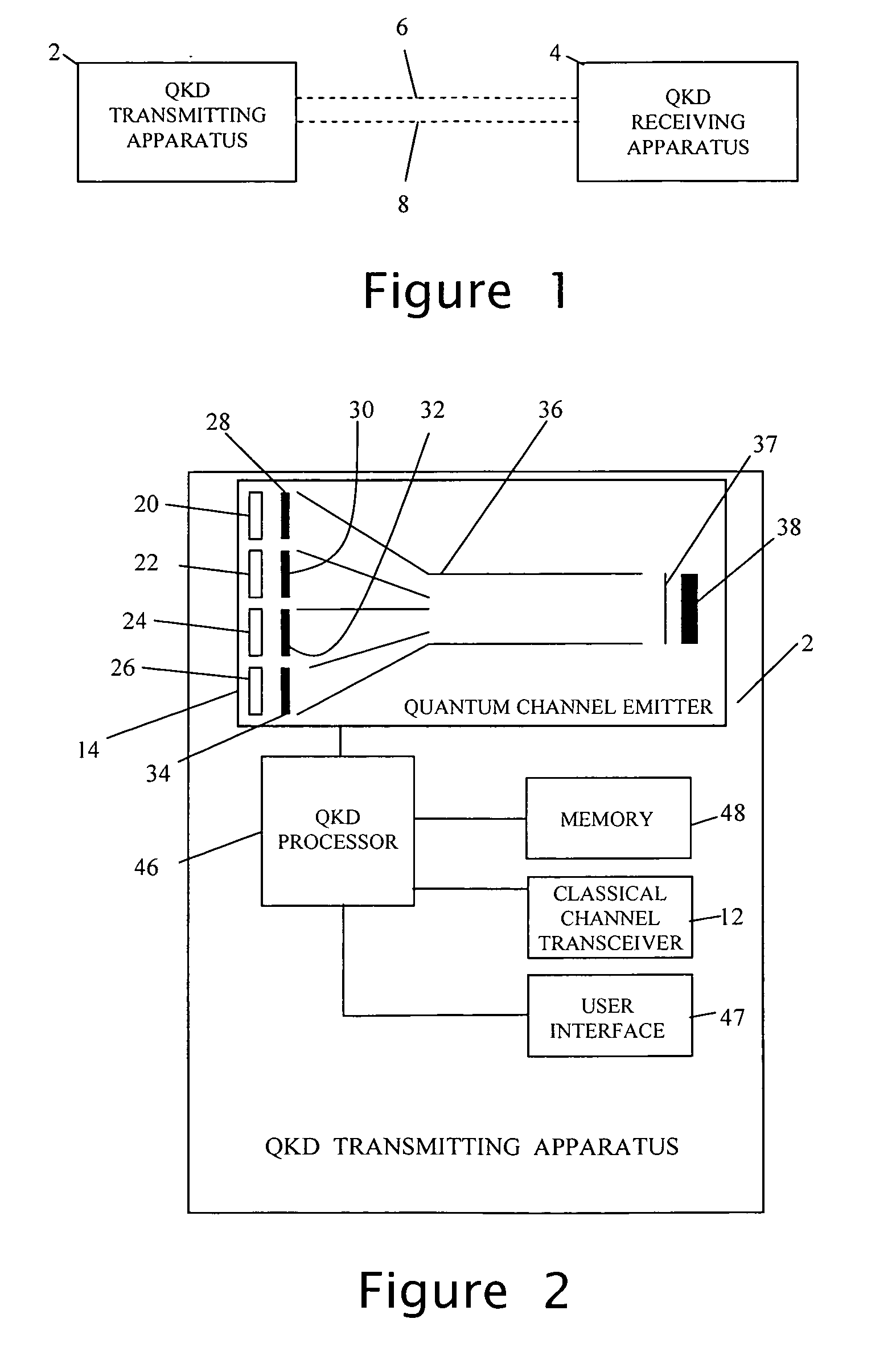
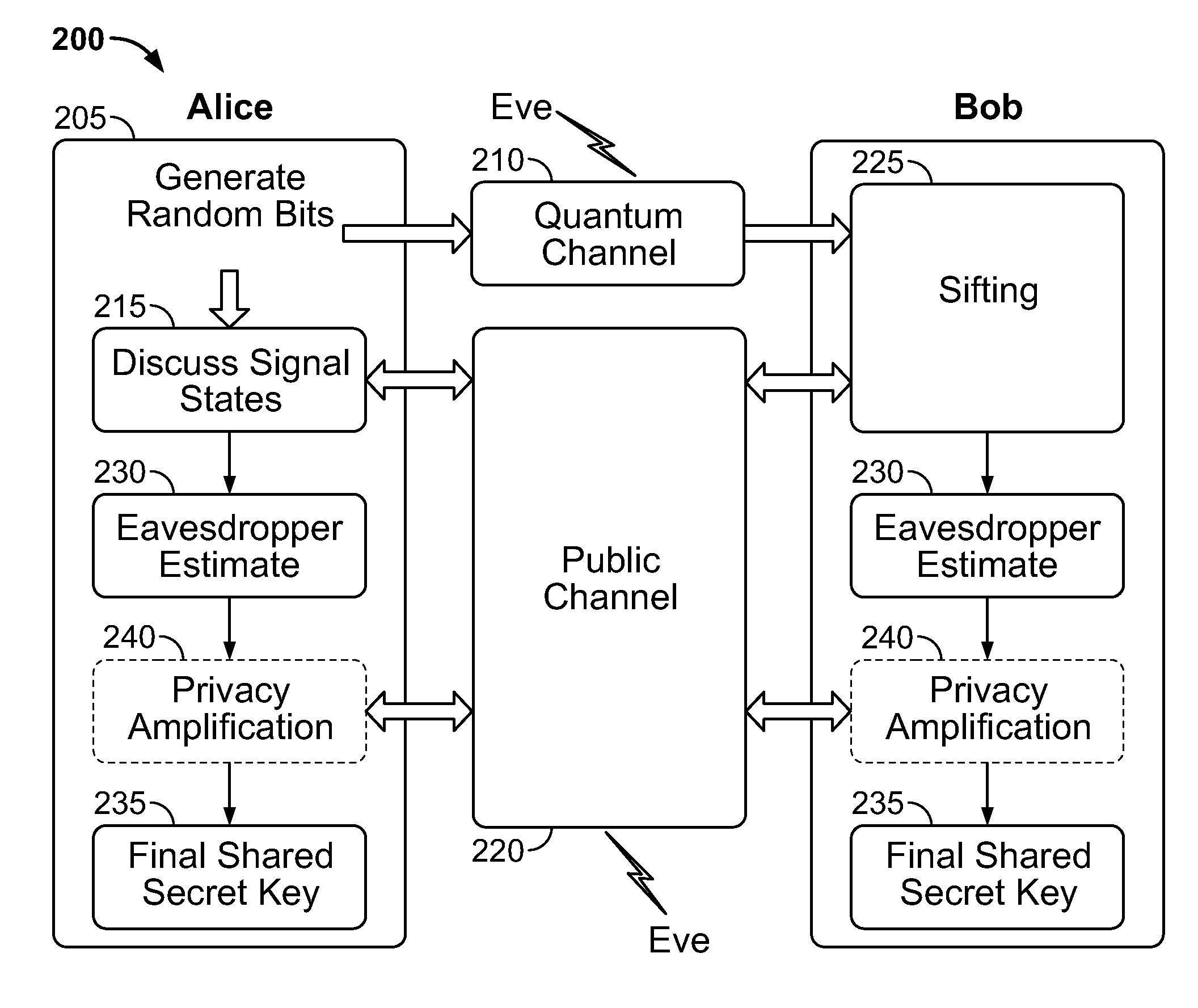
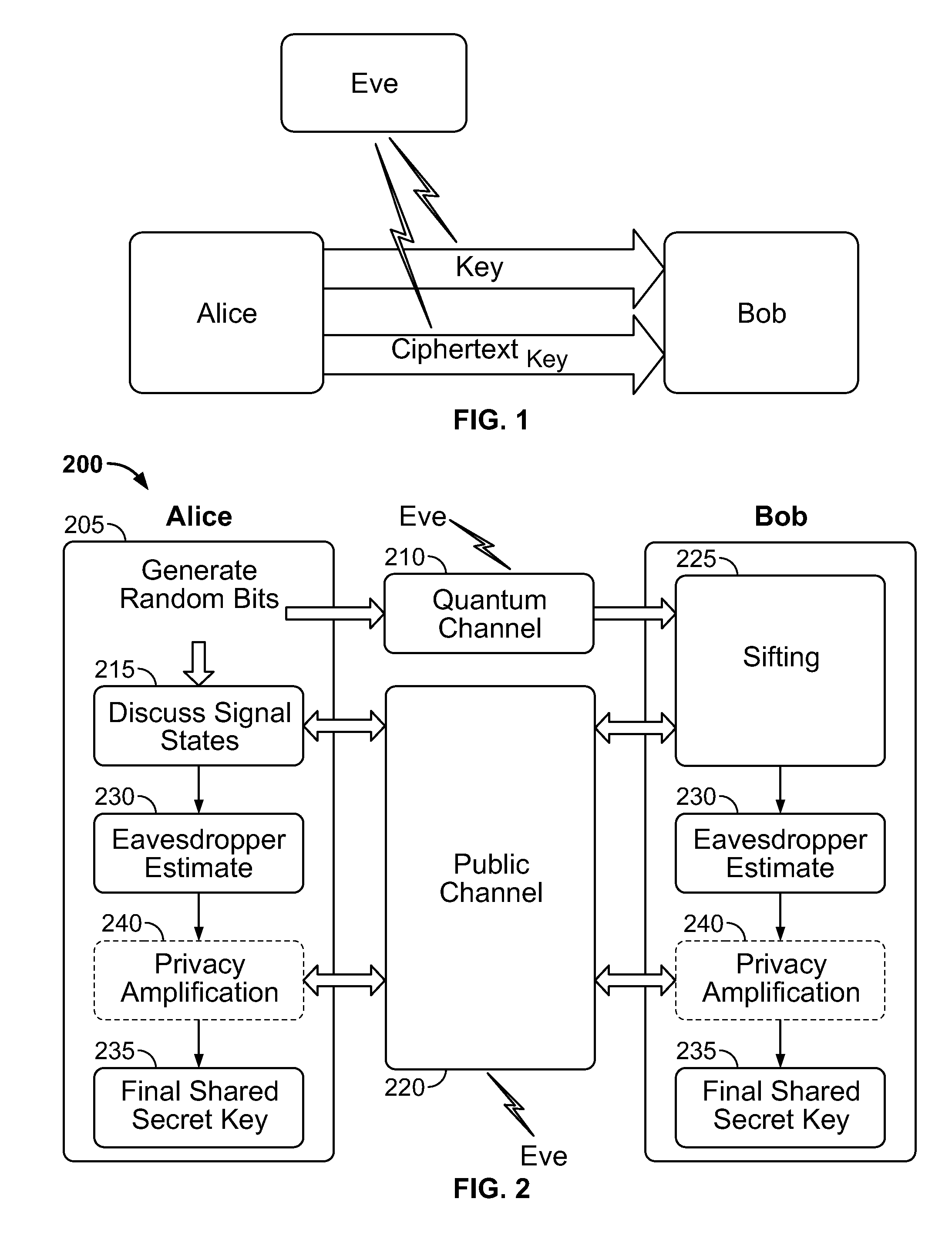
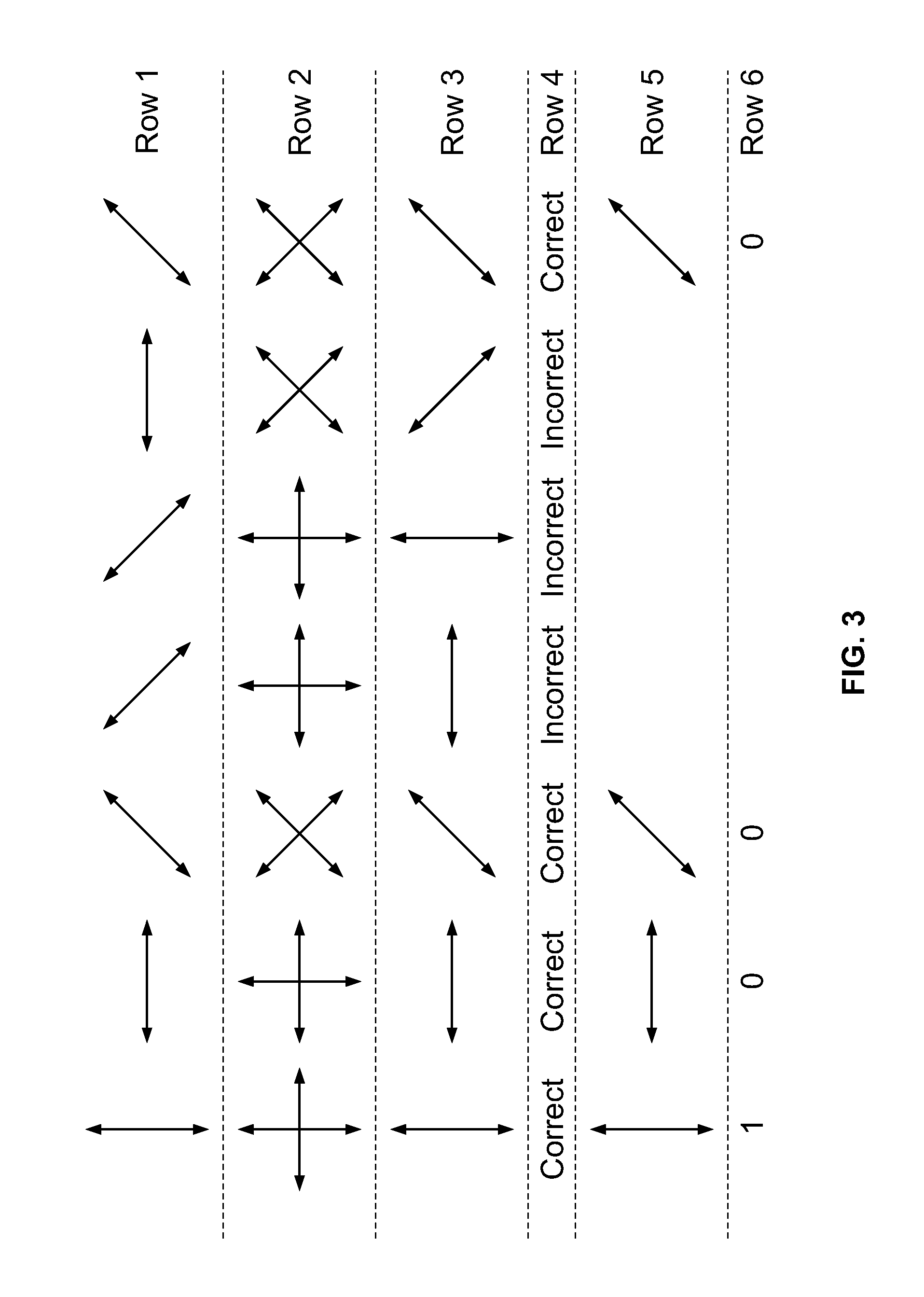
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a secure communication method which implements a cryptographic protocol involving components of quantum mechanics. It enables two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is often incorrectly called quantum cryptography, as it is the best-known example of a quantum cryptographic task.
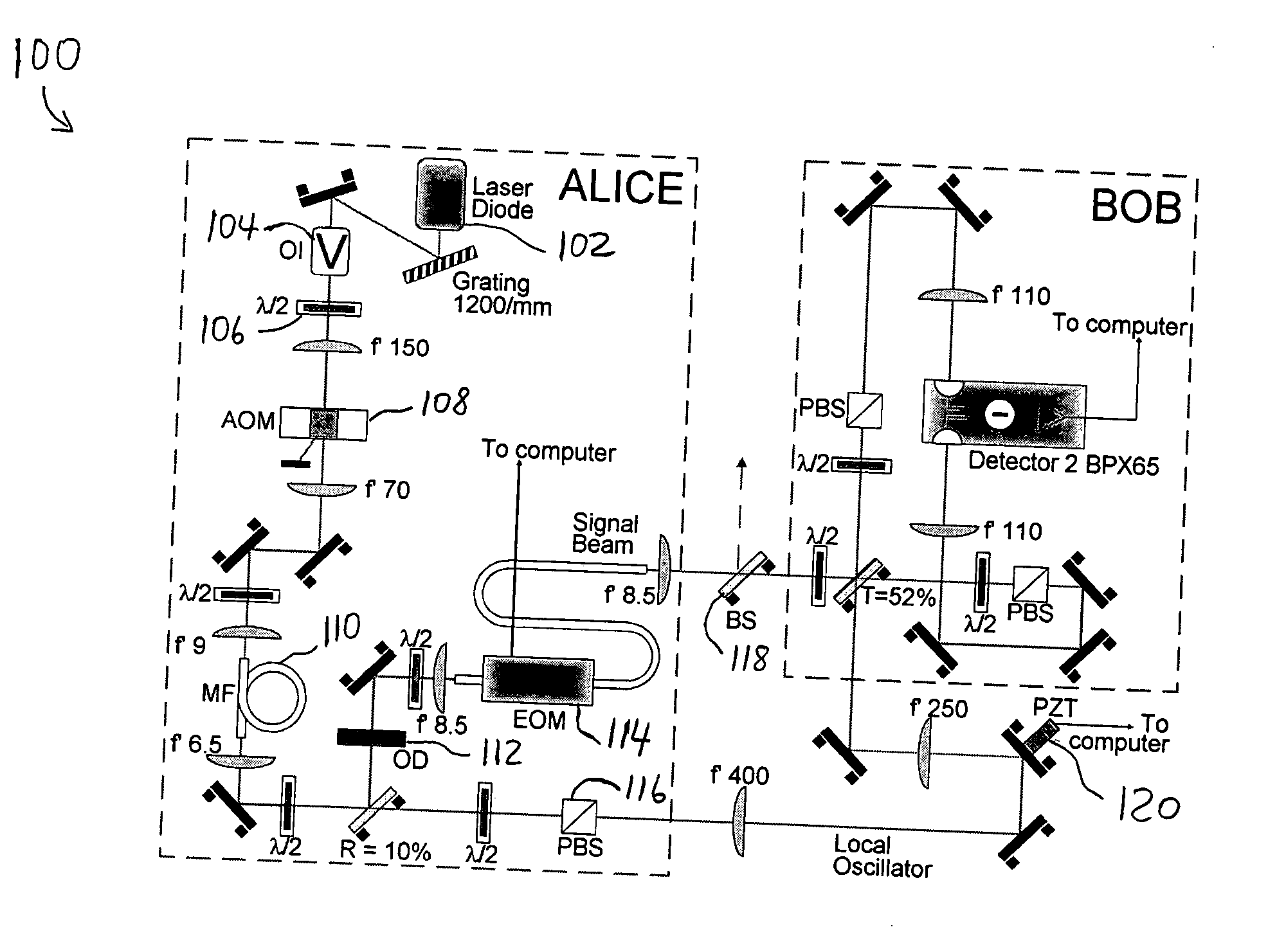
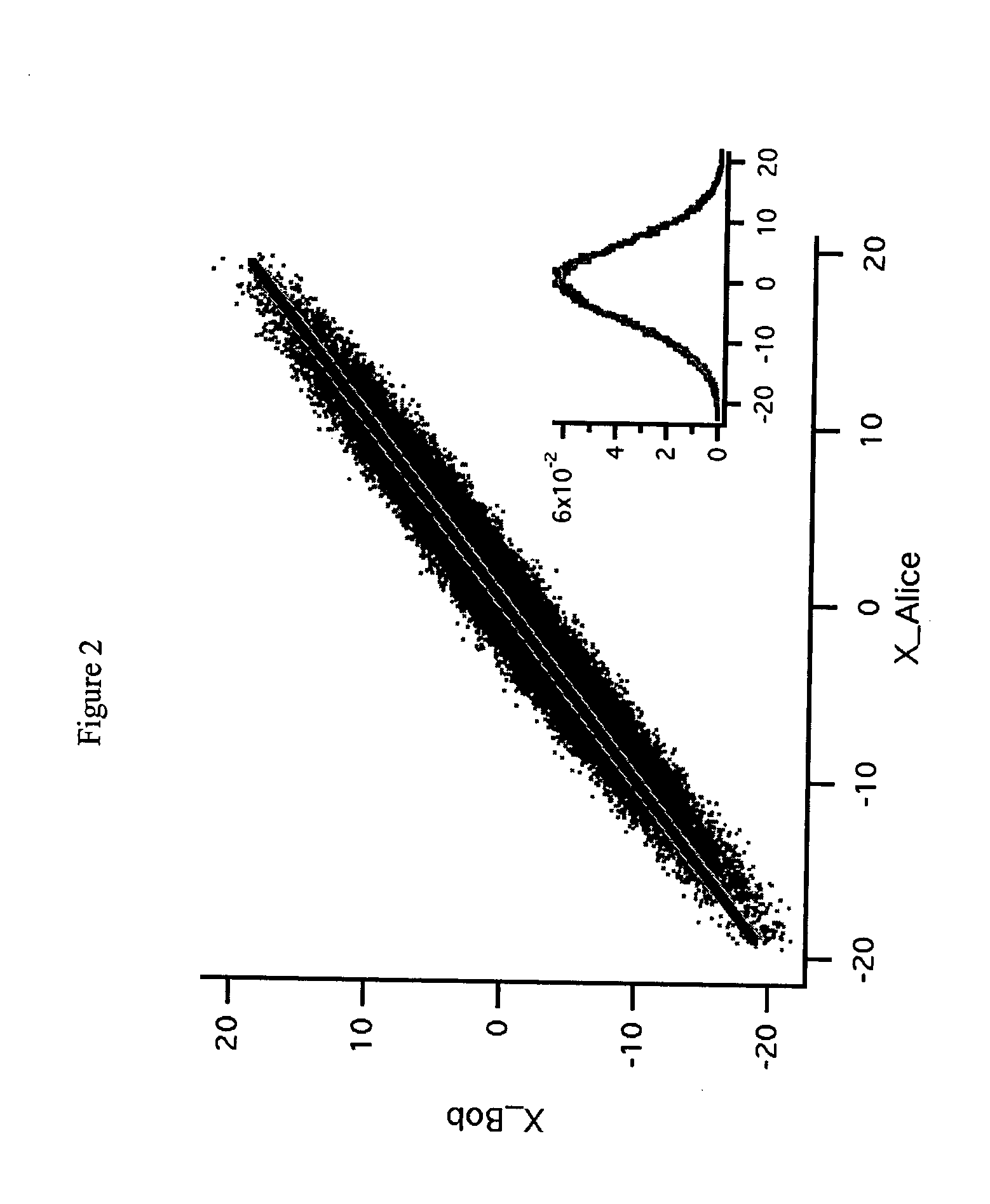
High-rate quantum key distribution scheme relying on continuously phase and amplitude-modulated coherent light pulses
InactiveUS20040109564A1Level of securityIncrease chanceKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationHigh rateCoherent states
One aspect of the present invention is related to a quantum cryptographic scheme comprising at least one sending unit including a physical means of encoding and distributing a raw key in the quadrature components of quantum coherent states that are continuously modulated in phase and amplitude, at least one receiving unit containing a physical means of performing homodyne detection of the quantum coherent states in order to measure the quadrature components of the states, a quantum channel for connecting the sending unit to the receiving unit, a two-way authenticated public channel for transmitting non-secret messages between the sending unit and the receiving unit, a quantum key distribution protocol ensuring that the information tapped by a potential eavesdropper can be estimated from the quantum channel parameters, and a direct or reverse reconciliation protocol that converts the raw continuous data into a common binary key.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
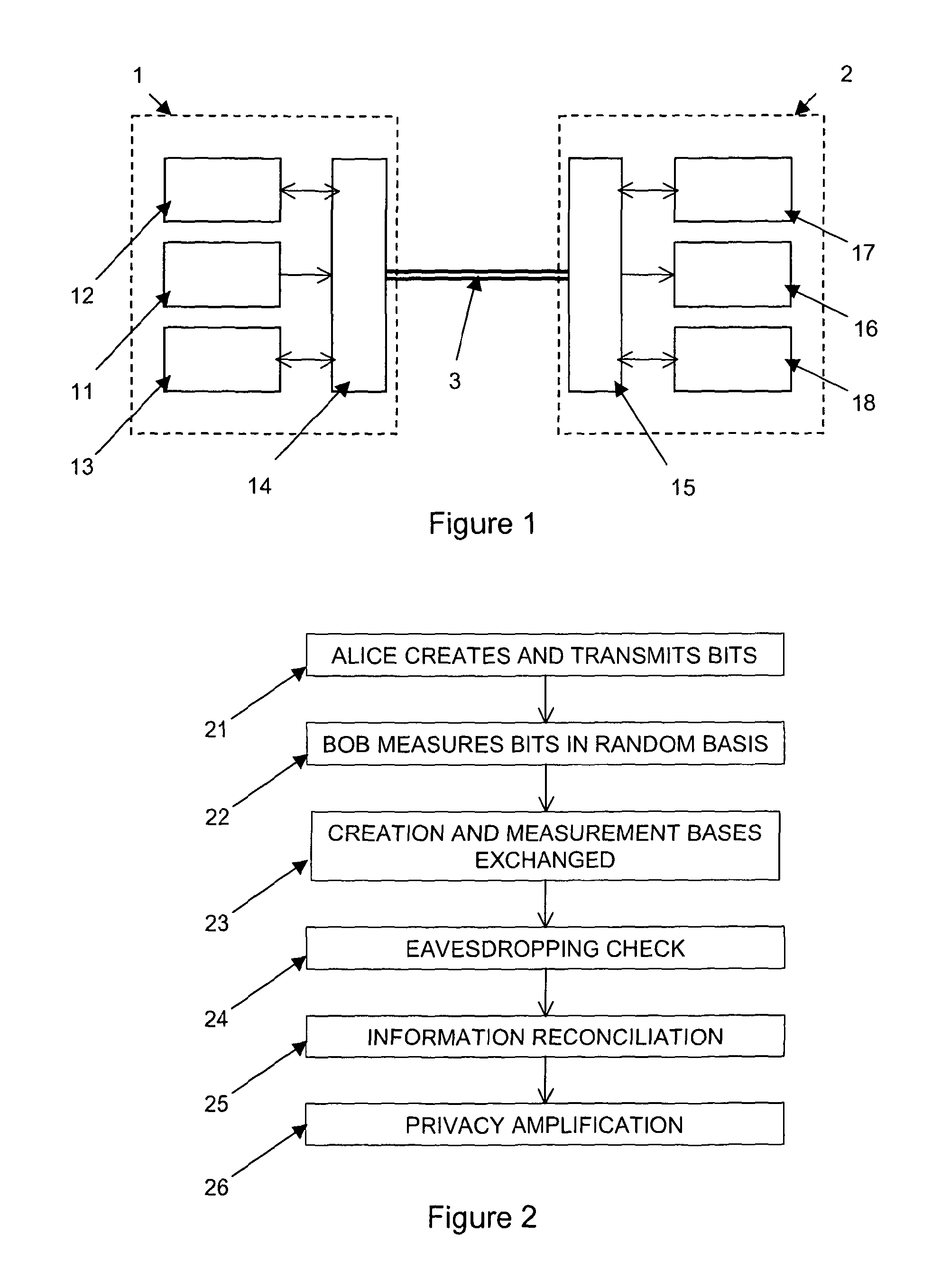
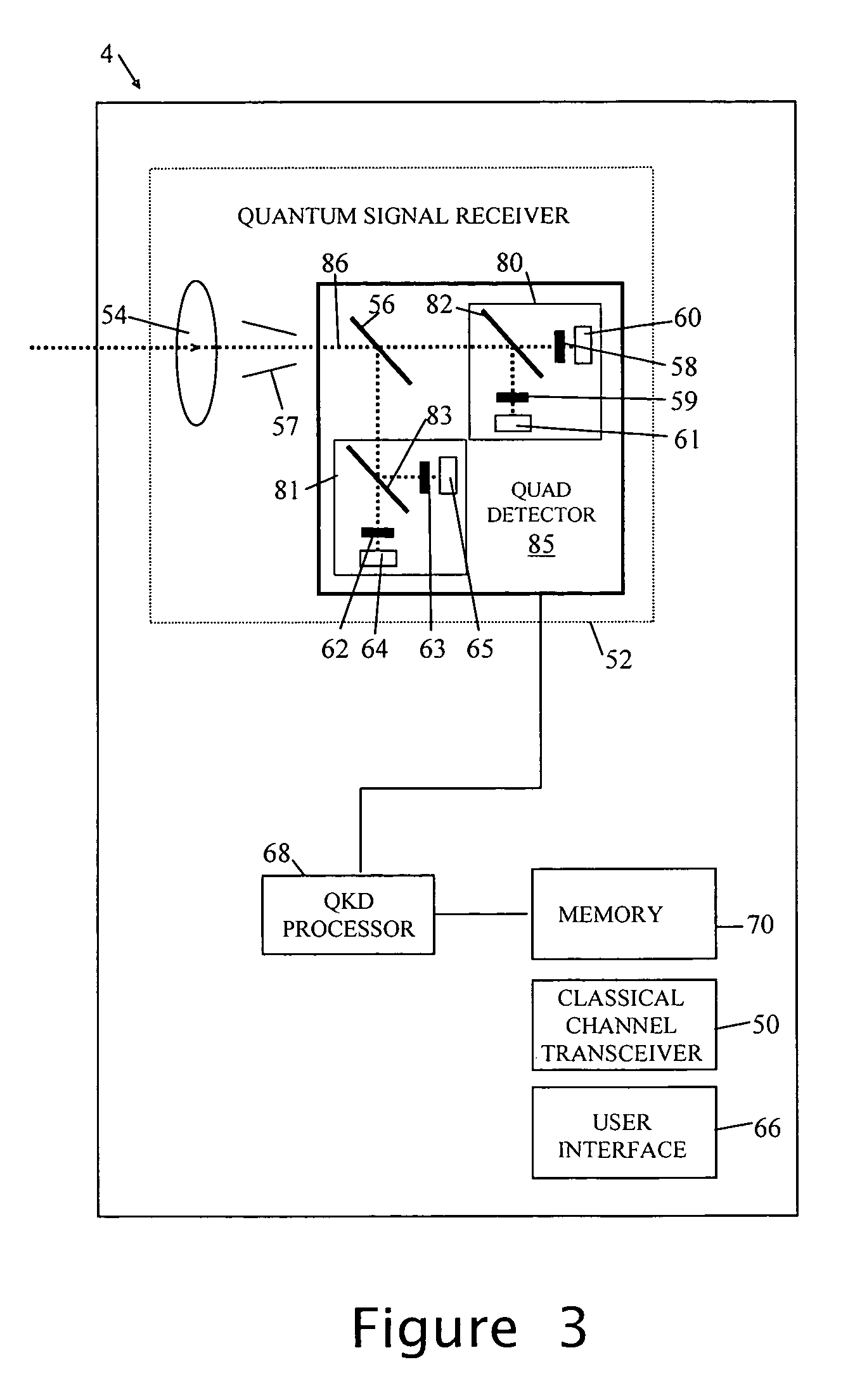
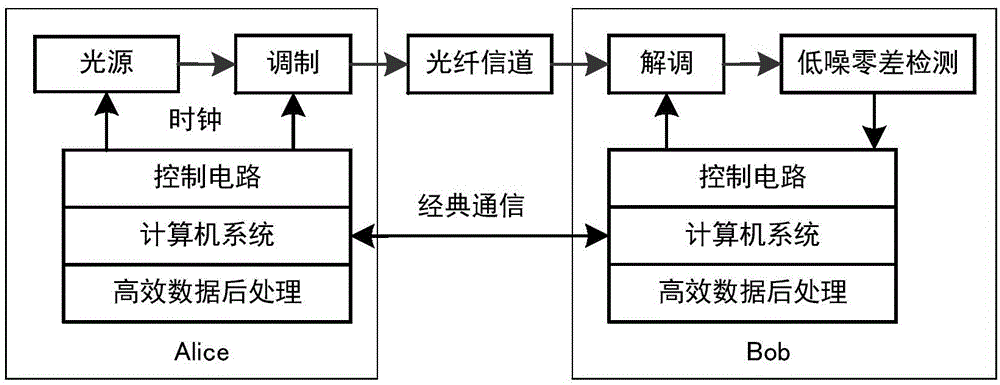
Methods and apparatus for use in quantum key distribution
ActiveUS20120177201A1Without prohibitive costEfficient executionKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationComputer hardwareFiber
Methods and apparatus for use in quantum key distribution (QKD) are described. A quantum QKD signal is generated at a source and transmitted through a fibre optic network to an endpoint, a key being agreed with communication over a classical QKD channel. The classical QKD channel contains additional information relevant to a network over which keys are distributed, and may be processed at nodes intermediate between the source and the endpoint.
Owner:QUBITEKK
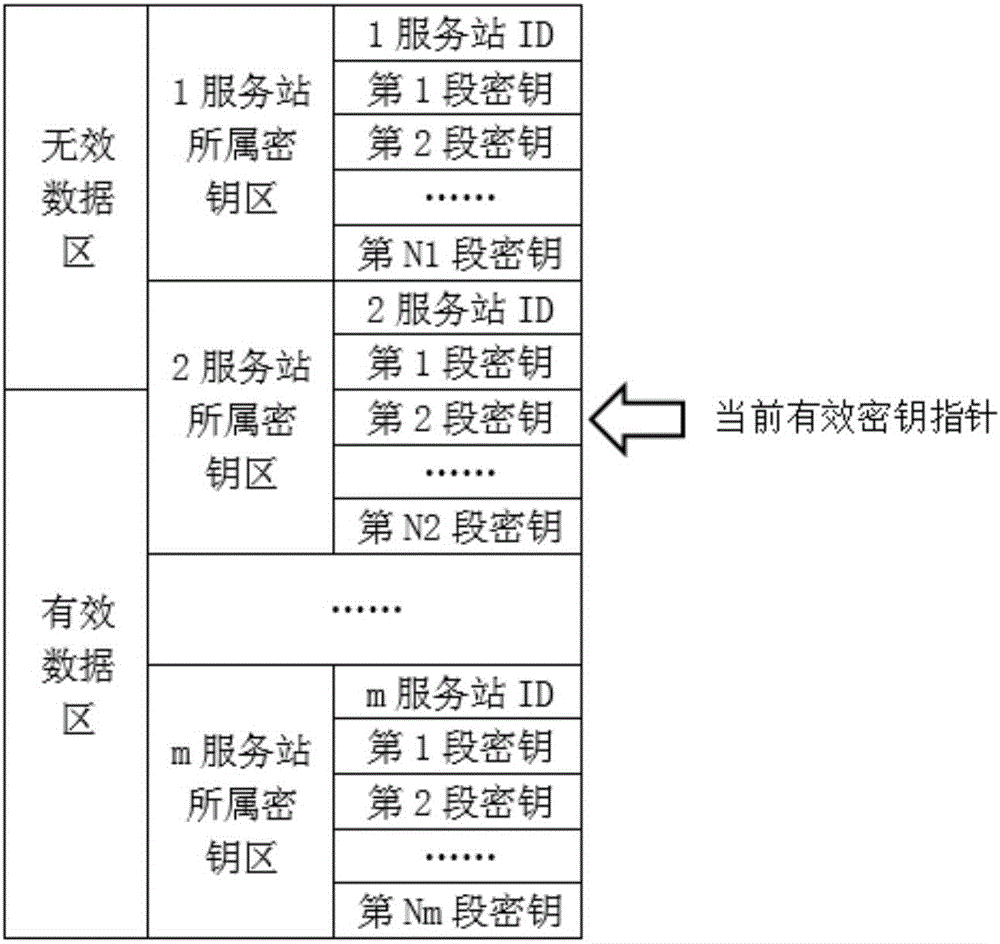
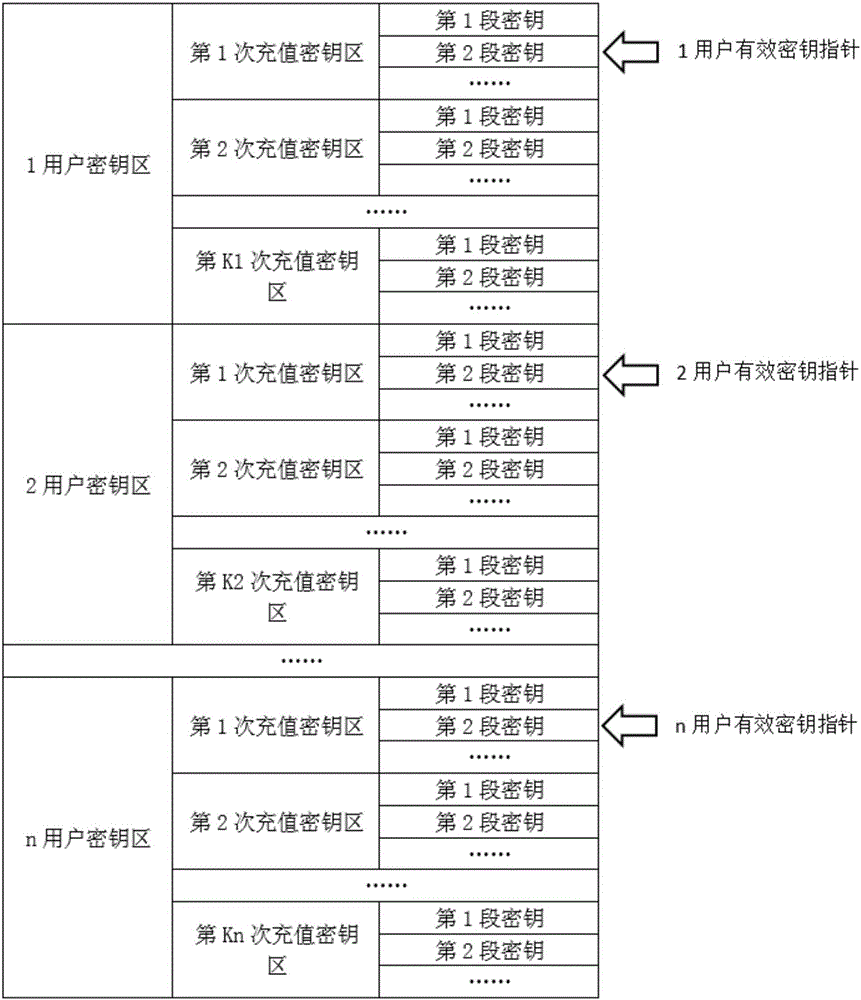
Quantum communication service station, quantum key management device, key configuration network, and key configuration method
ActiveCN106452740AAddress access security issuesAchieve coverageKey distribution for secure communicationSecurity questionKey distribution
The invention discloses a quantum communication service station, a quantum key management device, a key configuration network, and a key configuration method. The key configuration method comprises the following steps: responding to a key distribution request; authenticating a user of the key distribution request; writing a key generated with a true random number into a quantum key management device of the authenticated user. The key configuration method is different from the existing quantum key distribution QKD method in that key distribution of ultra high security is realized by pairing quantum key management devices and service stations at the end of a quantum communication network, the problem about access security at the end of a quantum communication network is solved, and terminal access is not a weak link of a quantum communication scheme. The quantum communication network can completely cover and replace the classic communication network in service.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENZHOU QUANTUM NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Quantum key distribution system
ActiveUS20070076884A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey generationTransmitter
A method is provided for distributing quantum cryptographic keys. The method includes receiving a first quantum signal from an initial quantum key generating transmitter. Following correspondence with the initial quantum key generating transmitter, a first quantum key is generated. A second quantum signal is transmitted to a recipient quantum key generating transmitter. Following correspondence with the recipient quantum key generating receiver, a second quantum key is generated. The first quantum key is encoded using the second quantum key. The encoded first quantum key is transmitted to the recipient quantum key generating receiver using the second quantum key.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
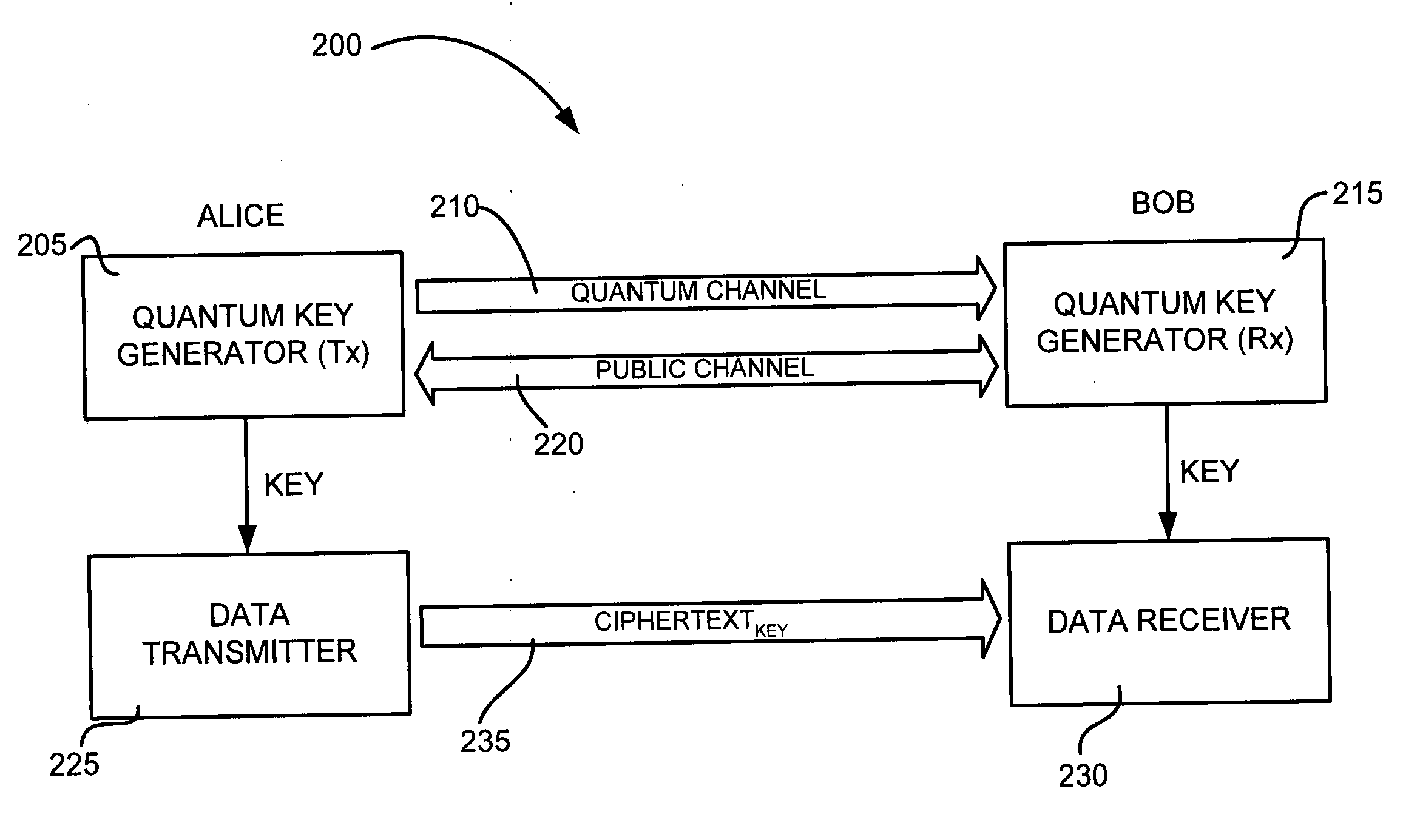
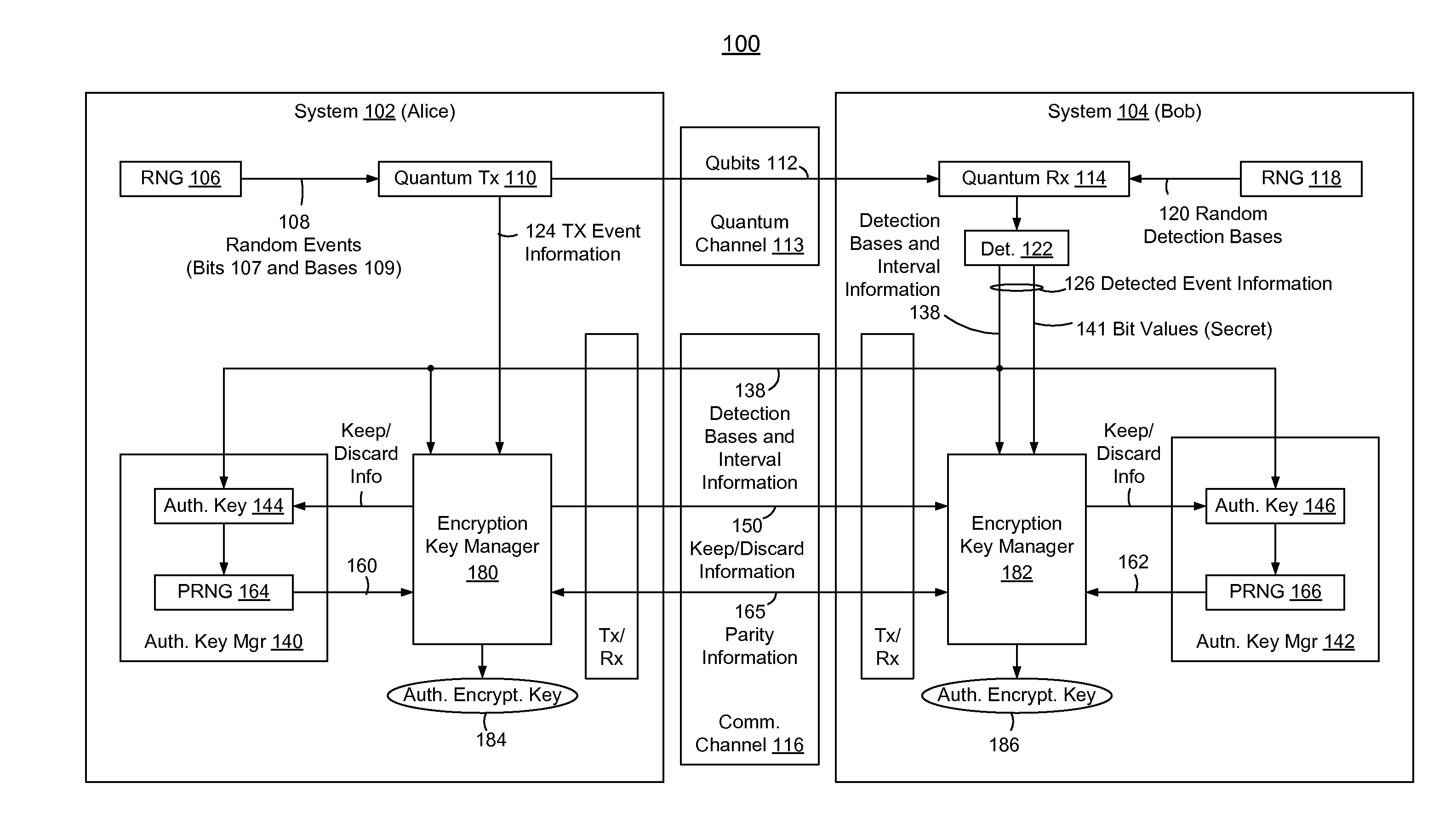
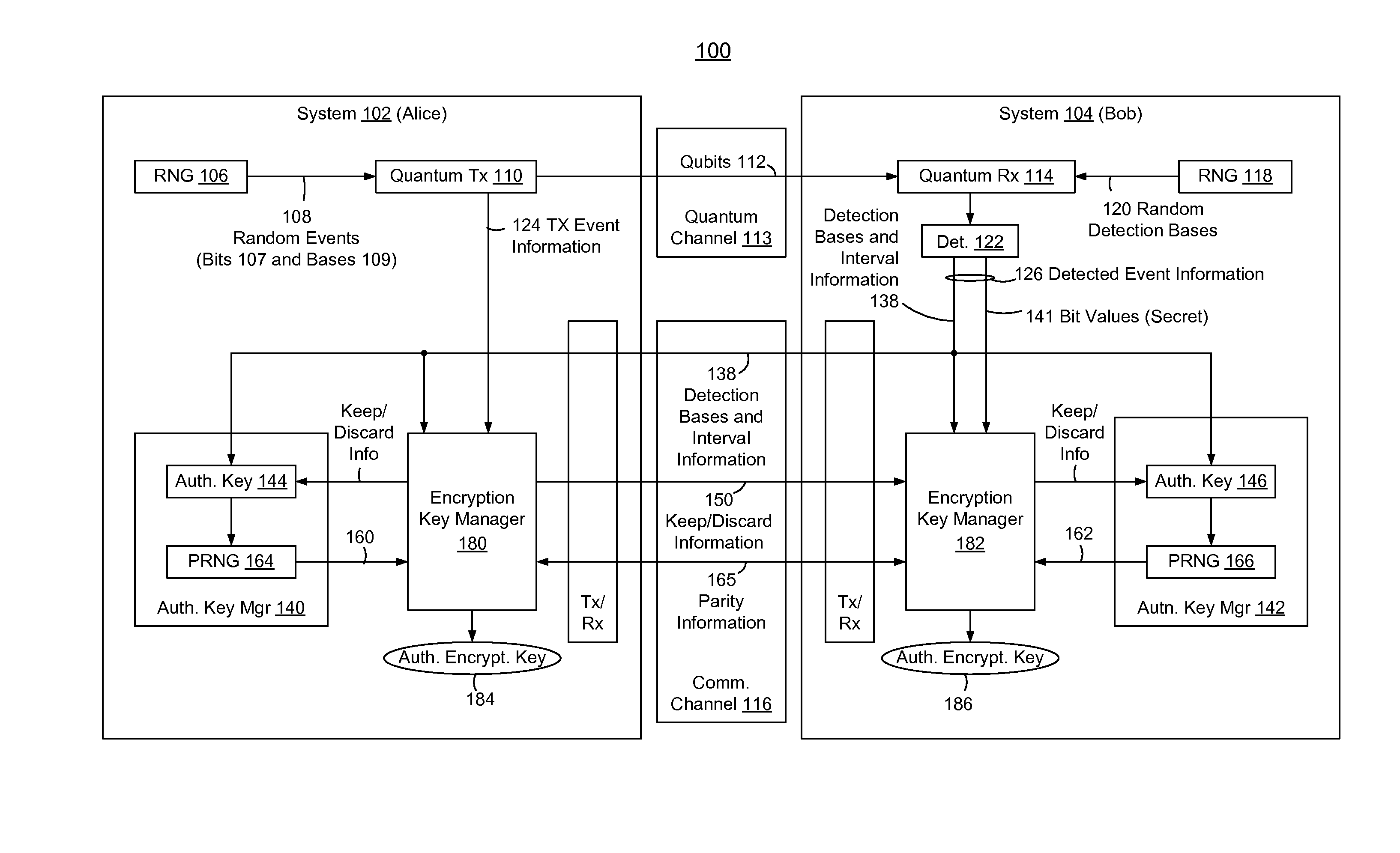
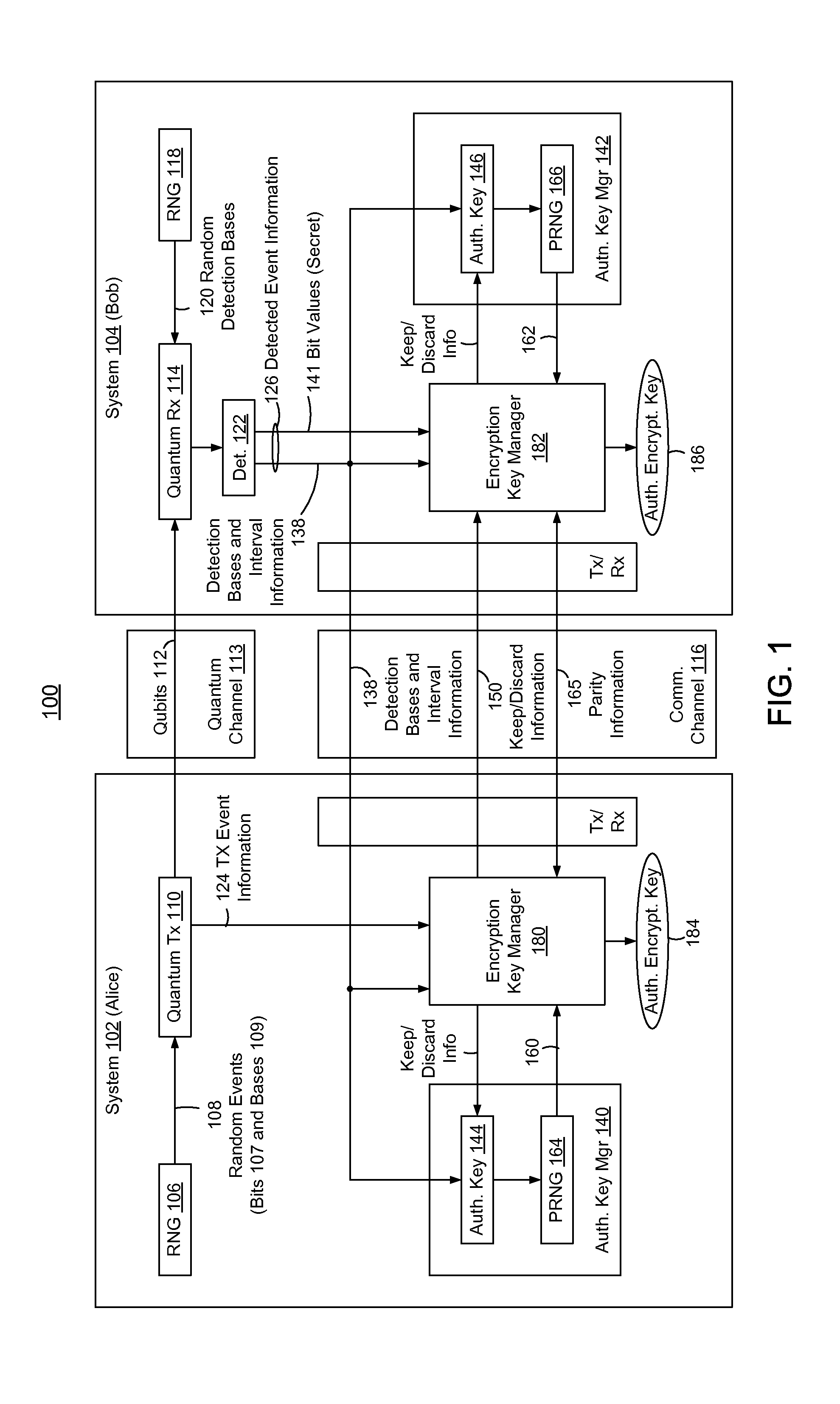
Embedded Authentication Protocol for Quantum Key Distribution Systems
ActiveUS20130315395A1Reduction of informationReduce overheadKey distribution for secure communicationAuthenticated encryptionQuantum key distribution
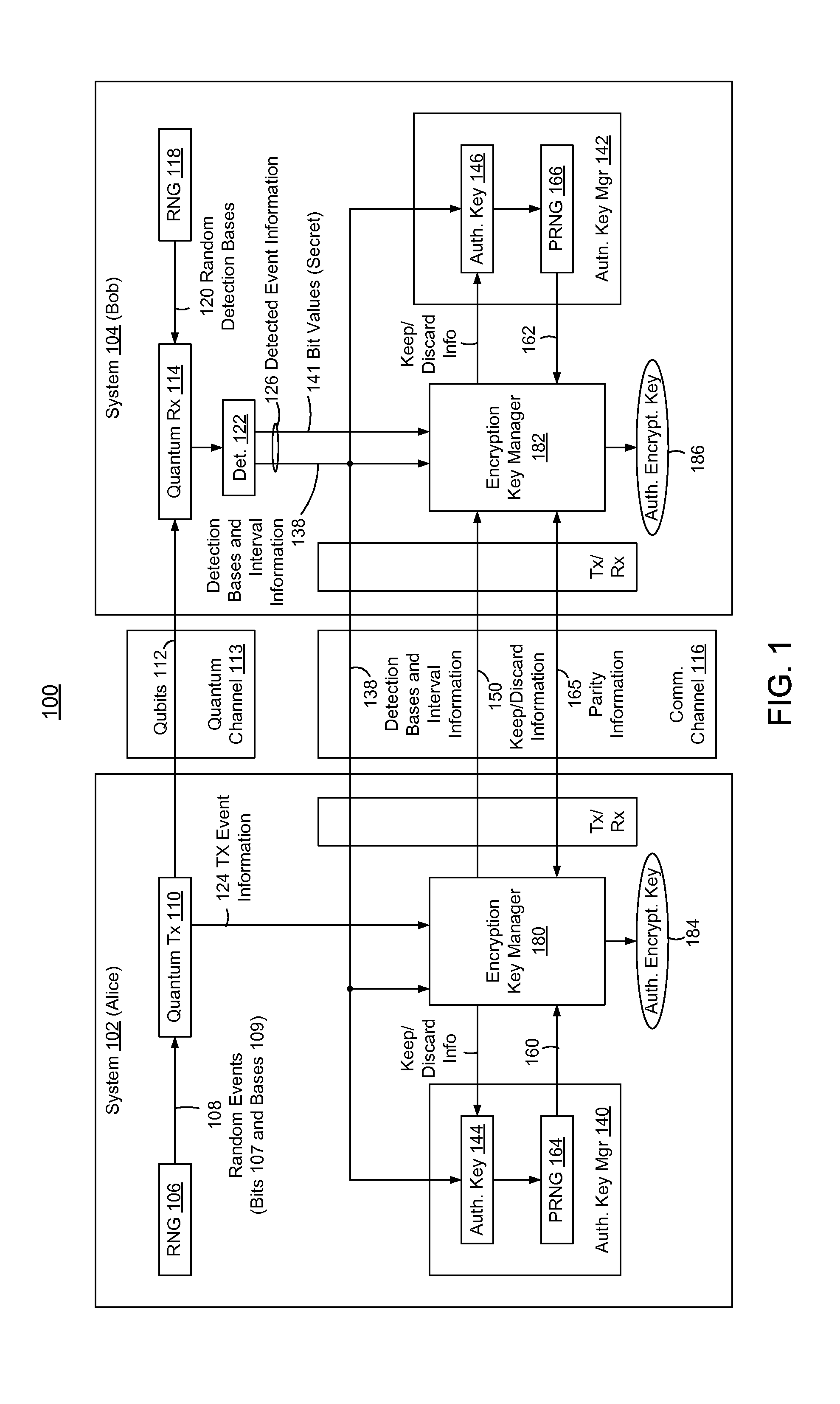
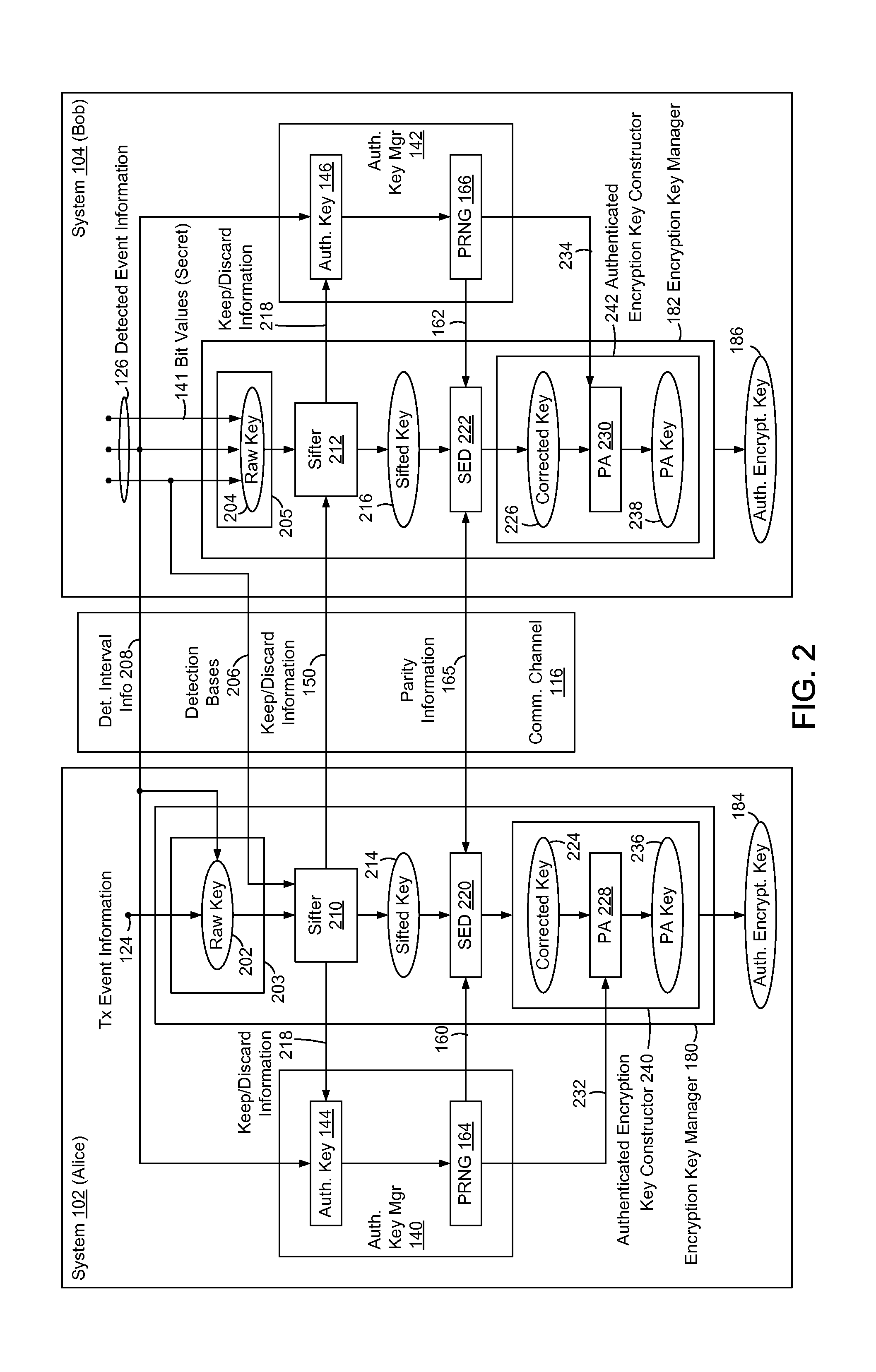
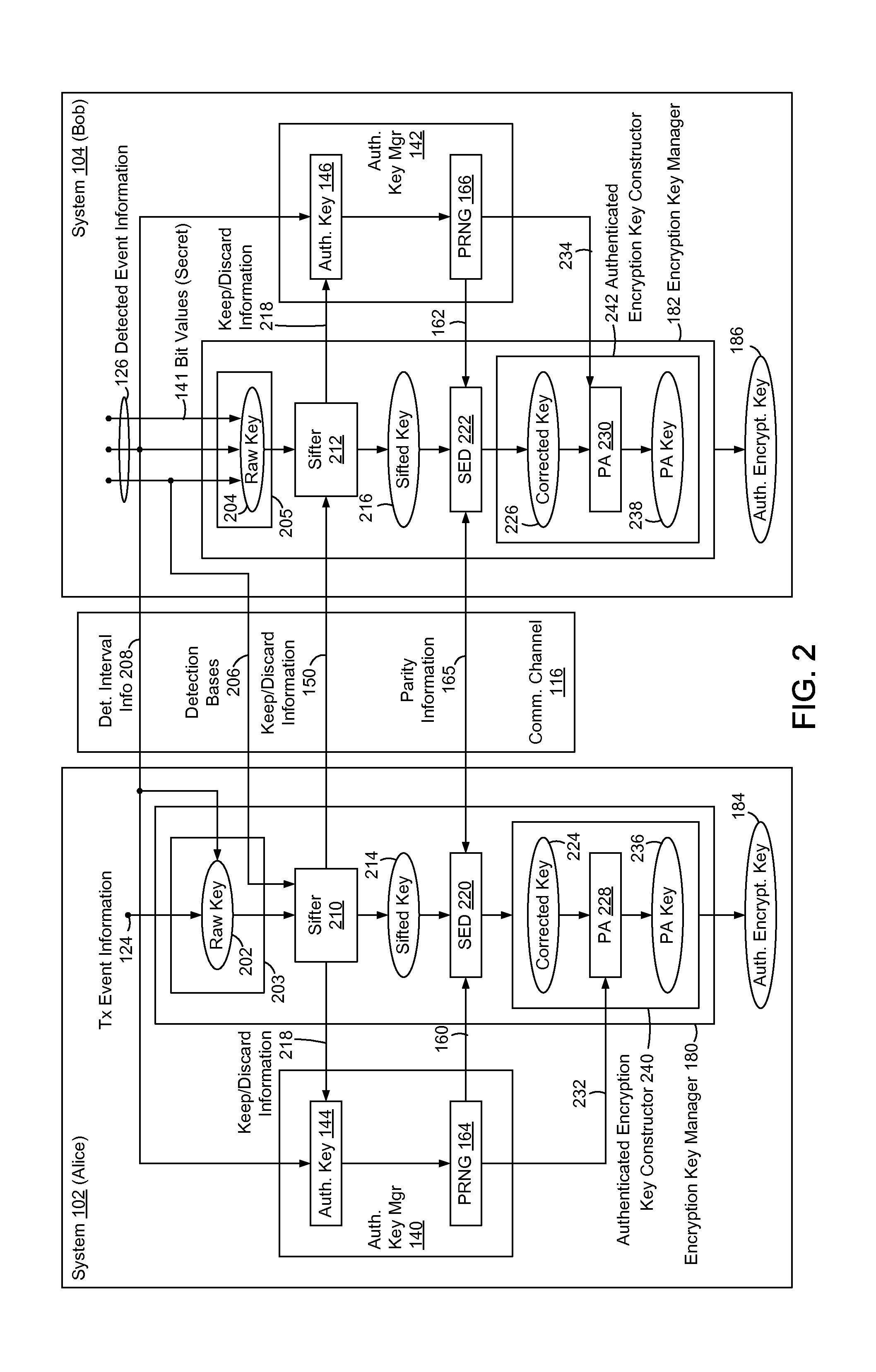
In methods and systems to authenticate systems in a quantum key distribution environment based on limited disclosures and identical, re-usable, pre-provisioned authentication keys, each system constructs an encryption key based on a corresponding one of transmitted events and detected events. Basis-sifting, error detection, error correction, and / or privacy amplification (PA) may be performed on the encryption keys based on limited disclosures (e.g., detection interval information, basis-sifting information, associated detection basis information, and / or parity measures). The authenticated keys may be modified based on disclosed detection information. Error detection and / or PA may be performed with identical pre-provisioned algorithms and pseudo-random values generated from the authenticated keys or modified authenticated keys. Final authenticated encryption keys are selectively constructed depending upon an extent of detected errors. Construction of authenticated encryption keys indicates authentication of the systems. None of the pre-provisioned authentication keys or modified authentication keys is disclosed and may thus be reused.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Quantum key distribution
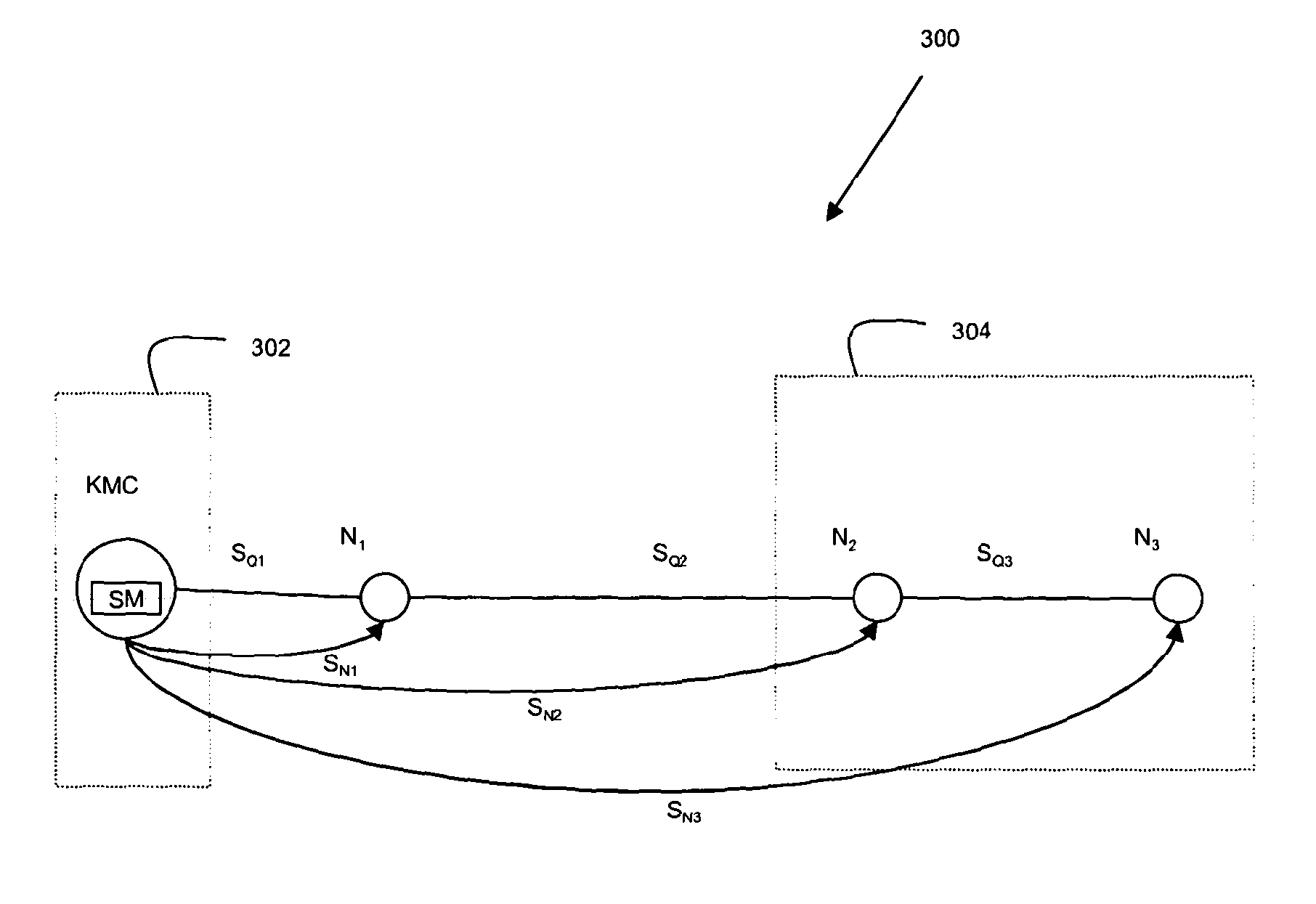
ActiveUS20130251145A1Improve network securityIncrease ratingsKey distribution for secure communicationKey distributionQuantum key distribution
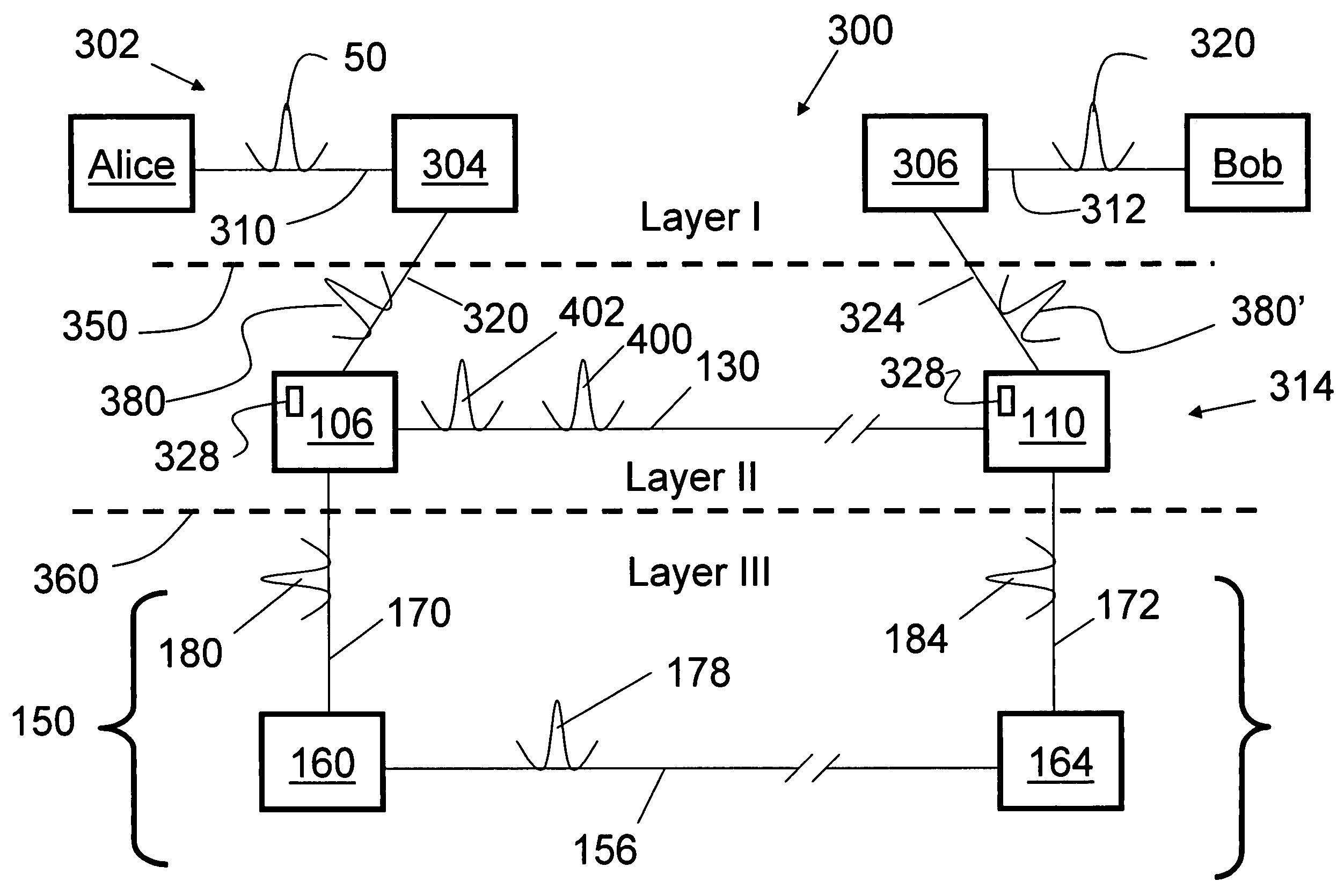
Methods and apparatus for quantum key distribution are described, in particular including methods and networks 300 arranged to improve and / or ensure the security of data transmitted thereby by (i) ensuring a certain level of loss within at least part of the network, (ii) placing a penultimate and an endpoint nodes in situated in a secure second enclave, (iii) analysing a transmitted bit stream to ensure that it does not provide an unacceptable amount of information about the key that may be generated therefrom, and / or (iv) varying the order in which bits are used to generate a key.
Owner:QUBITEKK
Secure quantum key distribution using entangled photons
InactiveUS20050135620A1High data rateImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer hardwareData rate
A system and method of implementing quantum key distribution are provided that possess increased data rates and enhanced security. These increased data rates are provided through the use of biphotons. Through encoding bits of information on the intra-biphoton delay time and enabling separate polarization bases for each of the photons comprising each biphoton, the system and method increase data bandwidth available for quantum key distribution.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS ADVANCED INFORMATION SYSTEMS
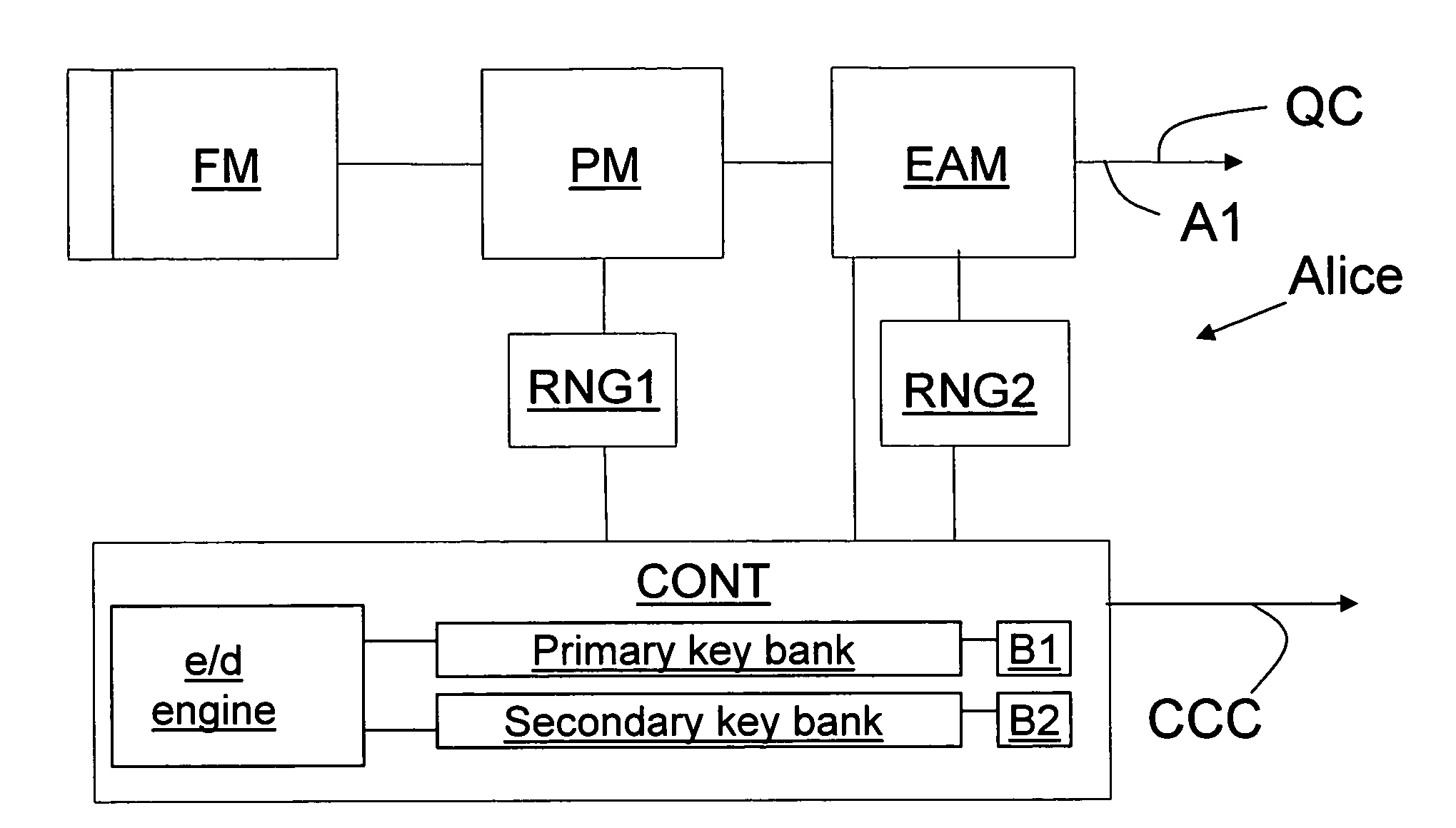
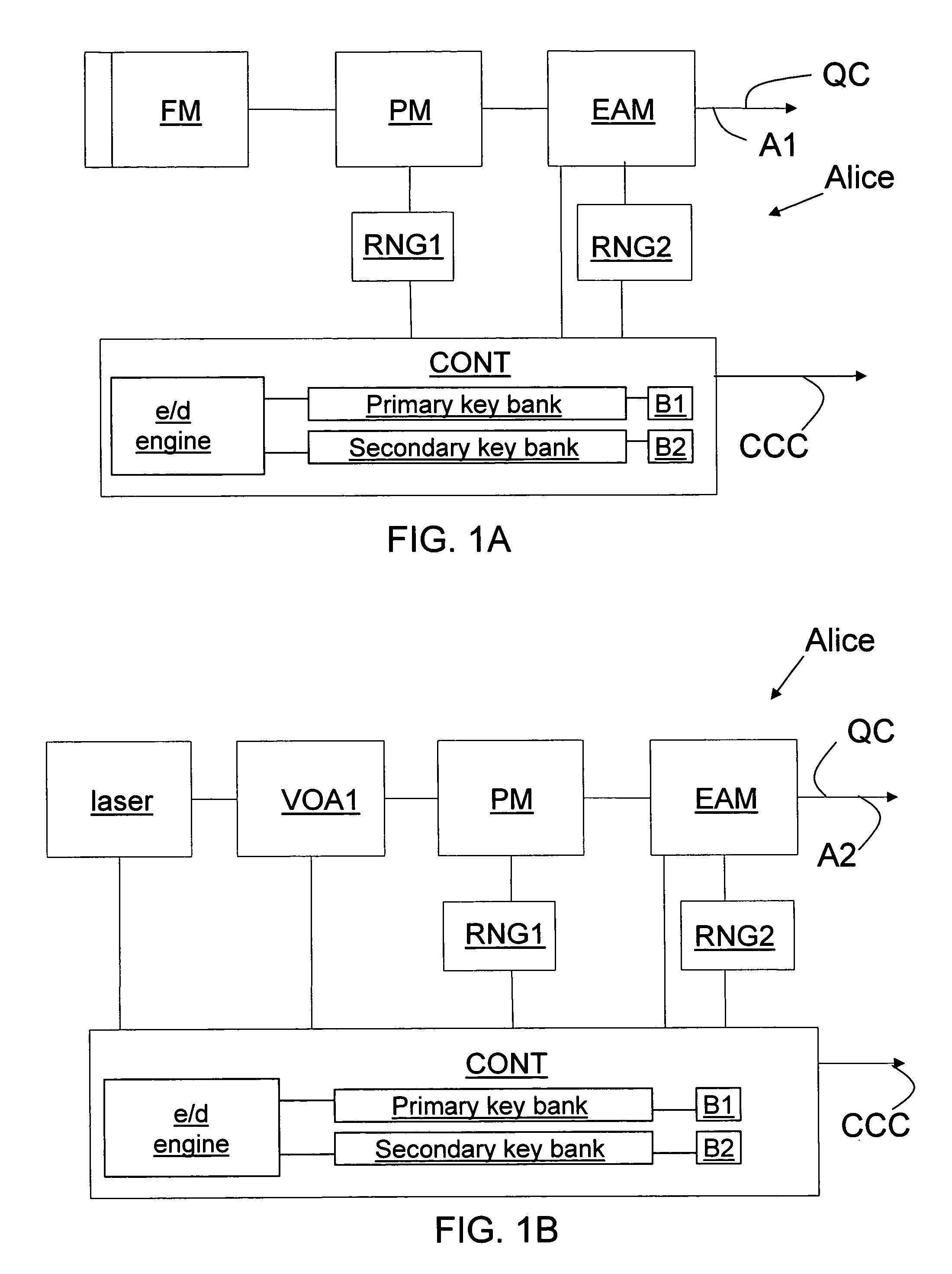
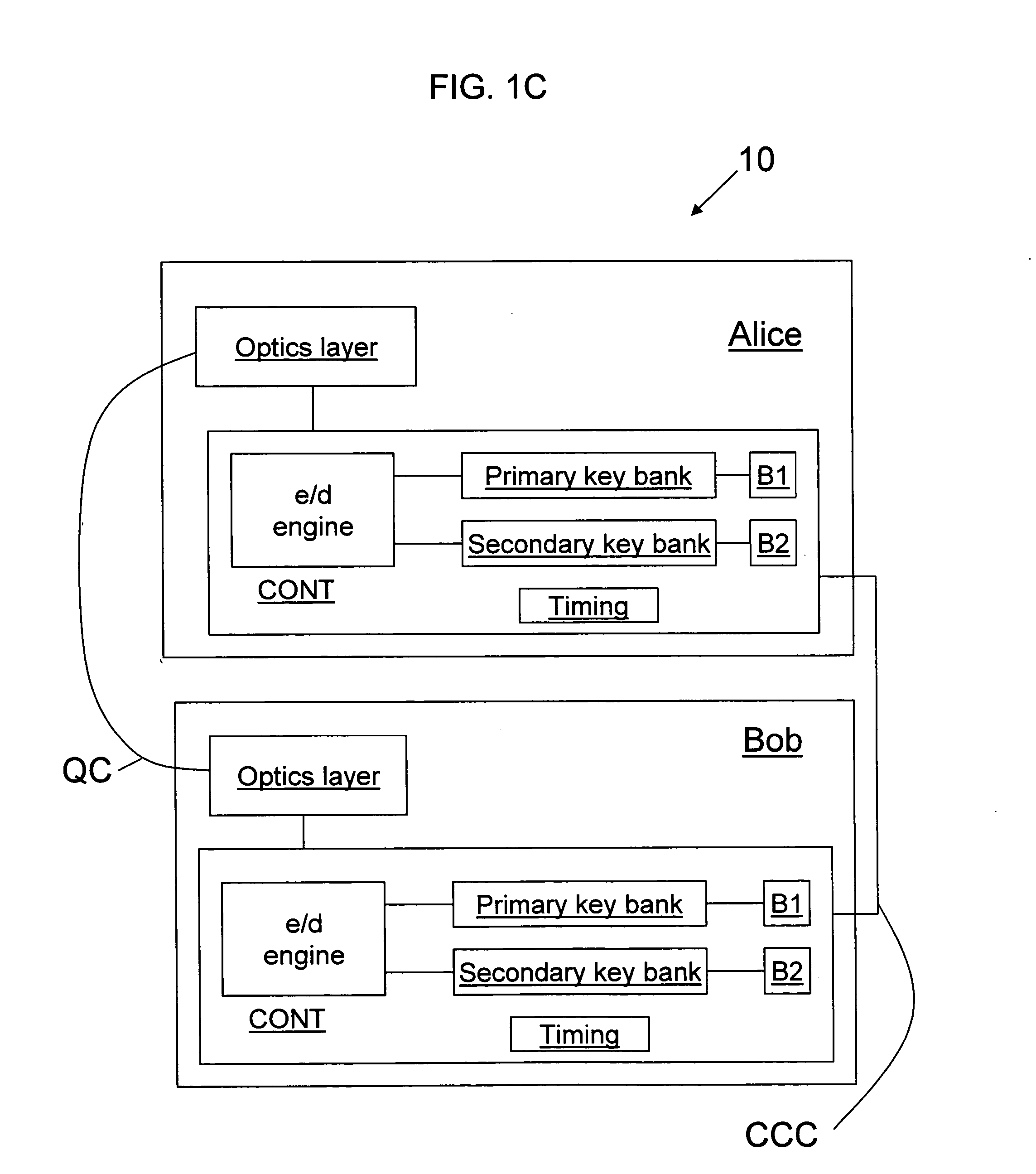
Key bank systems and methods for QKD
ActiveUS20050259825A1Increase distanceIncrease in key generation rateKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationAuthenticationQuantum key distribution
Key banking methods and systems for quantum key distribution (QKD) are disclosed. A method of the invention includes establishing a primary key bank that stores perfectly secure keys associated with exchanging true quantum pulses between two QKD stations Bob and Alice. The method also includes establishing a secondary key bank that stores less-than-perfectly secure keys associated with exchanging relatively strong quantum pulses between Bob and Alice. The primary keys are used for select applications such as authentication that are deemed to require the highest security, while the secondary keys are used for applications, such as encrypted bit sifting, that are deemed to require less-than-perfect security. A benefit of the two-key-bank architecture is that exchanging primary and secondary keys actually allows for an increase in the distance over which the primary keys can be securely distributed
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
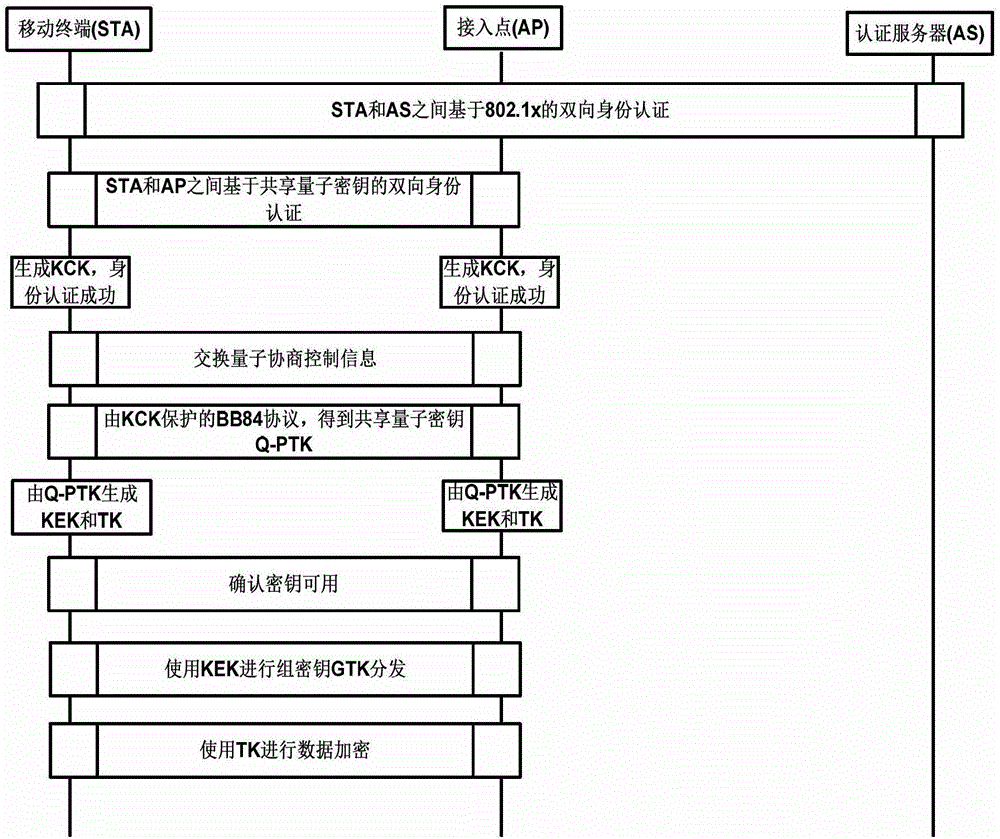
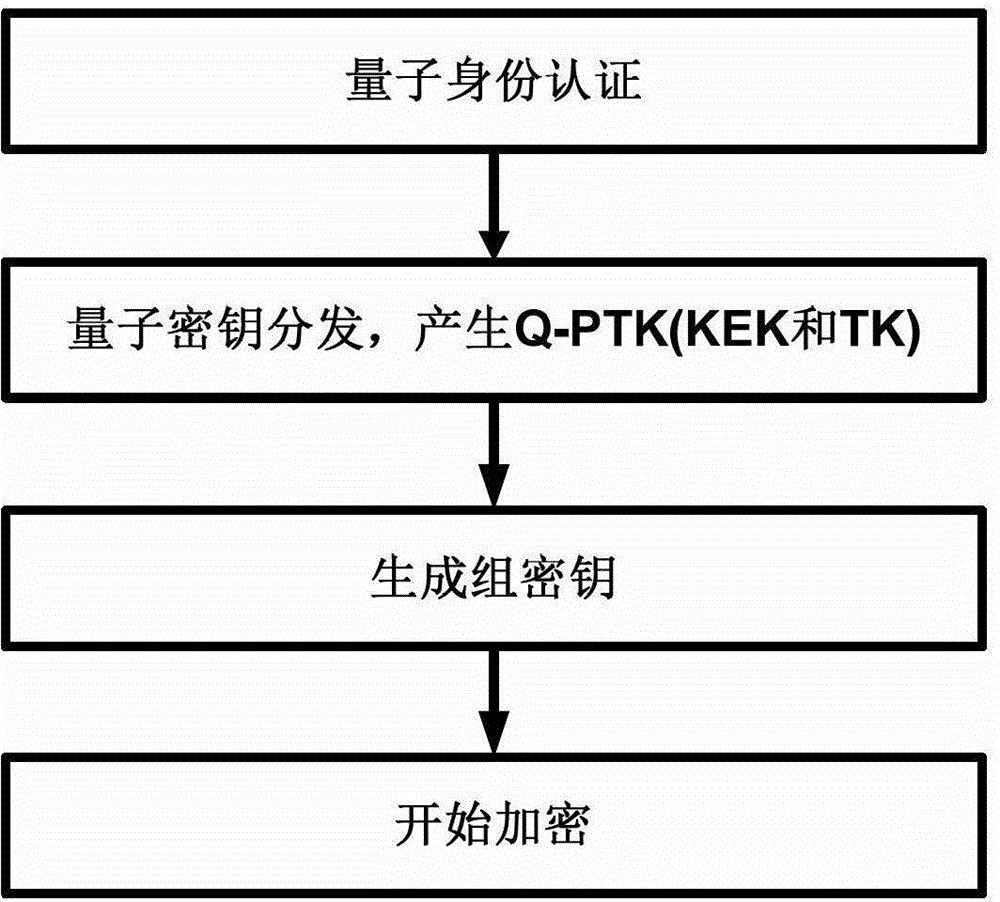
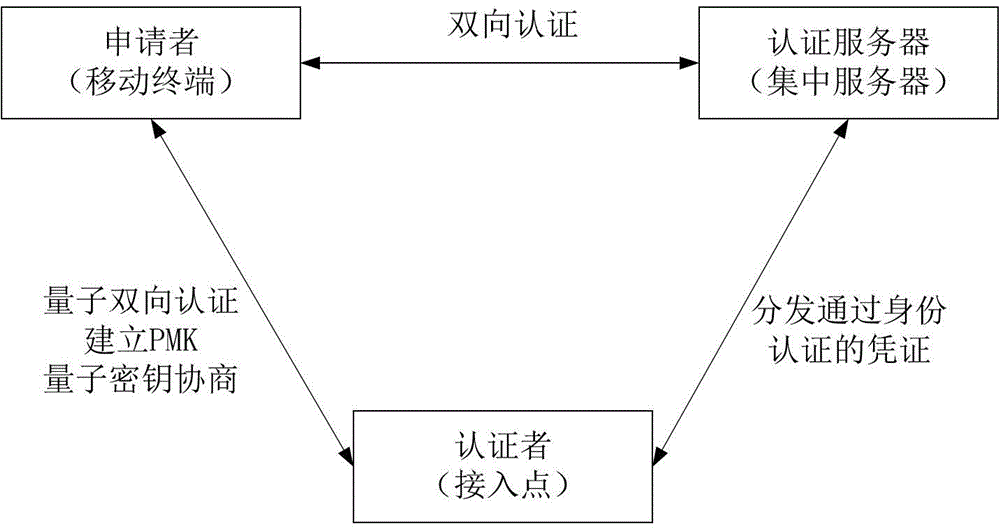
Wireless local area network security communication method based on quantum key distribution
InactiveCN103338448AImprove securityTamper-proofKey distribution for secure communicationSecurity arrangementQuantum technologyAuthentication server
The invention provides a wireless local area network security communication method based on quantum key distribution. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) identity authentication based on quantum keys is carried out; (2) quantum key negotiation is carried out; and (3) encryption is started. With the method of the invention adopted, information exchange between a faked access point and an applicant, the waste of system resources or a caused denial of service attack can be can avoided; bidirectional authentication between the applicant and an authentication server as well as between the applicant and an authenticator can be realized, and therefore, the security of the identity authentication is greatly improved; keys produced in the identity authentication can be adopted to protect message authentication in key negotiation, and therefore, attacks such as the tamper of a intermediary can be prevented; the security of key negotiation based on quantum technology is guaranteed by physical laws, and therefore, the key negotiation based on quantum technology has undecodability, and can withstand the decoding of a quantum computer with strong computational ability, and therefore, the security of a whole system can be enhanced.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
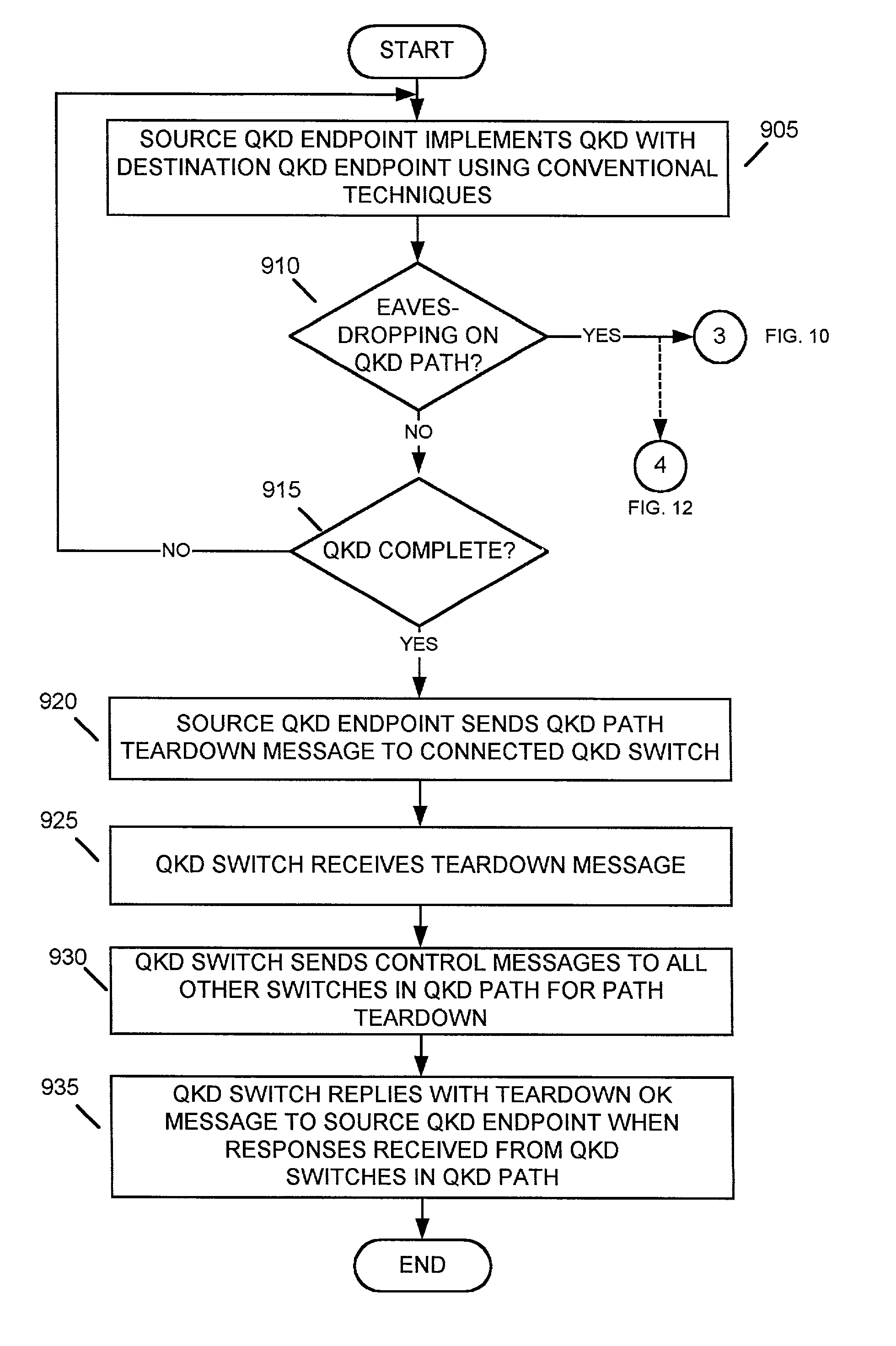
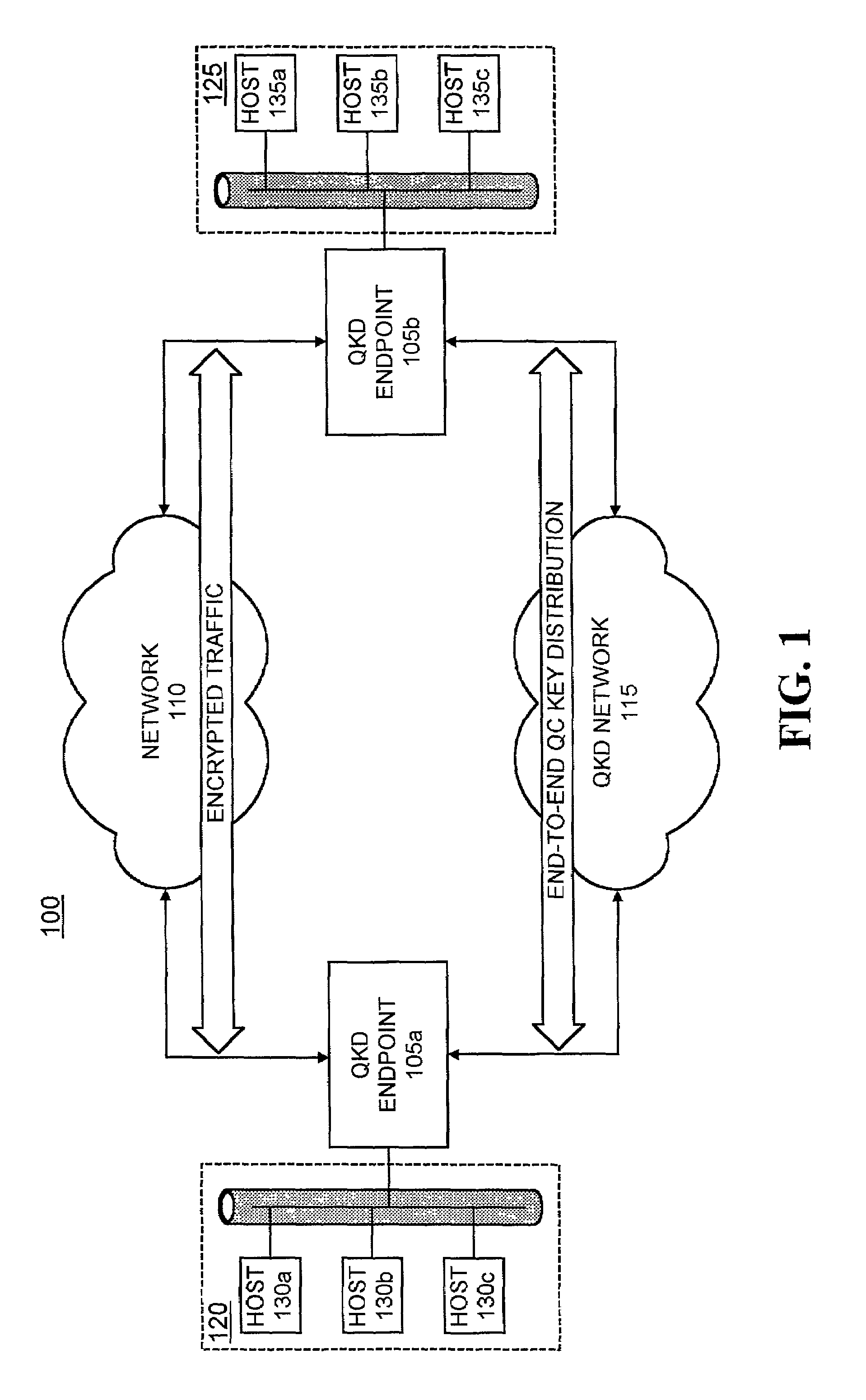
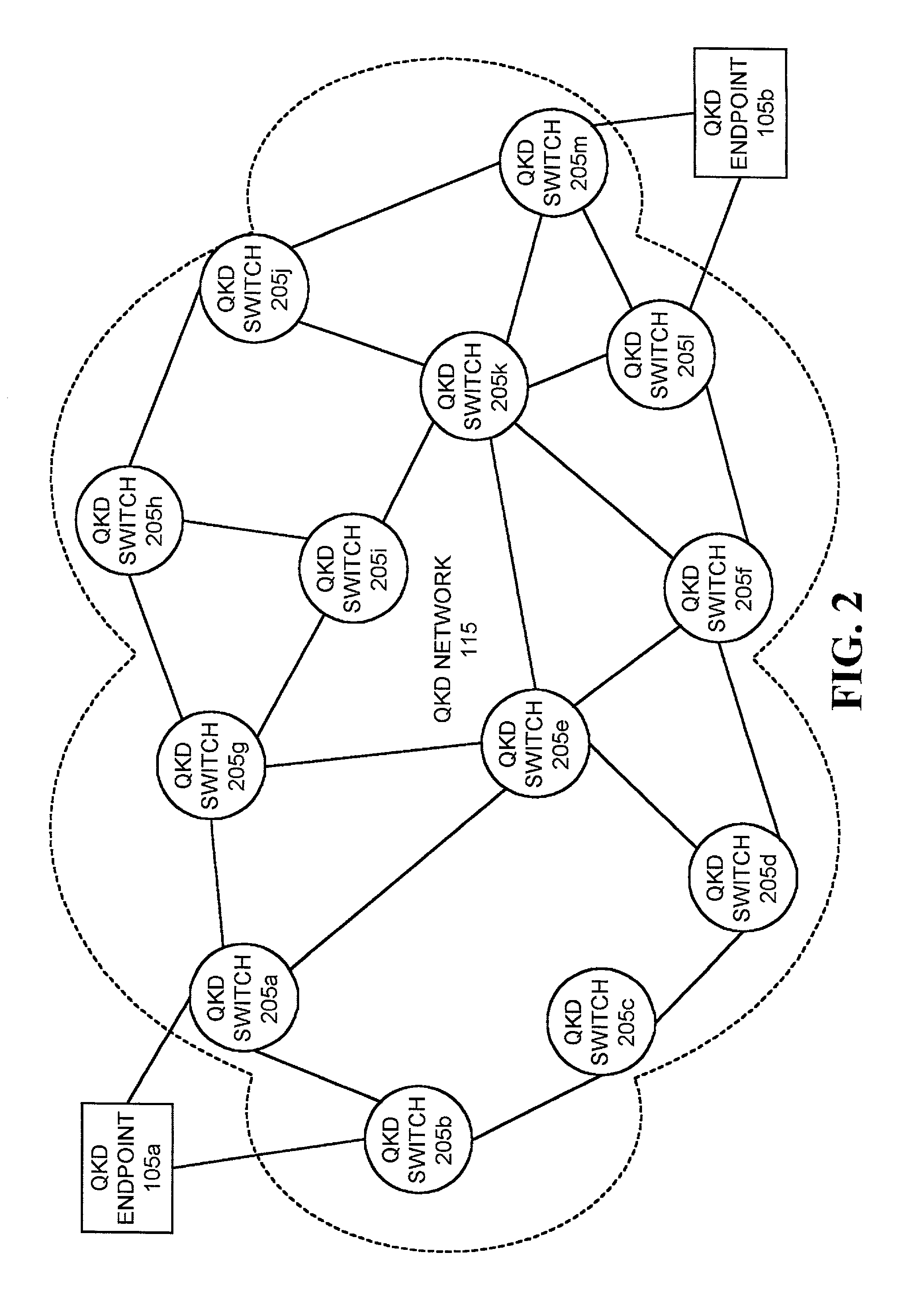
Systems and methods for path set-up in a quantum key distribution network
InactiveUS7068790B1Low costReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsKey distributionEavesdropping
A system establishes a path for distributing data through an optical network (115). The system includes an optical switch (205a) and a data distribution endpoint (105a). The optical switch (205a) establishes a first encryption key distribution path through the optical network (115), the first encryption key distribution path including multiple optical switches and optical links. The data distribution endpoint (105a) determines whether eavesdropping has occurred on the first encryption key distribution path using quantum cryptography. The optical switch (205a) further establishes a second data distribution path through the optical network (115) responsive to the eavesdropping determination. The second encryption key distribution path includes multiple optical switches and optical links.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Method to support secure network booting using quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution
A method and system to support secure booting and configuration. The mechanism employs an optical link comprising a quantum channel that is used to send data encoded as quantum bits (qubits) via respective photons. Qubits encoded using a first random basis at the client and are sent to the boot server, which processes the qubits using a second random basis to extract the encoded data. A public channel is used to send data indicative of the second random basis to the client. A symmetric quantum key is then derived a both the client and the boot server using a comparison of the random basis' and the original and extracted data. The scheme enables the presence of an eavesdropper to be detected on the quantum channel. A DHCP message exchange is employed to obtain a network address, and, optionally, be provided with a network address for one or more boot servers. A boot image request is made to the boot server by the client, and a subsequent boot image is downloaded via a secure channel facilitated by the symmetric quantum key.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Quantum-key-distribution-network-based mobile encryption system and communication method thereof
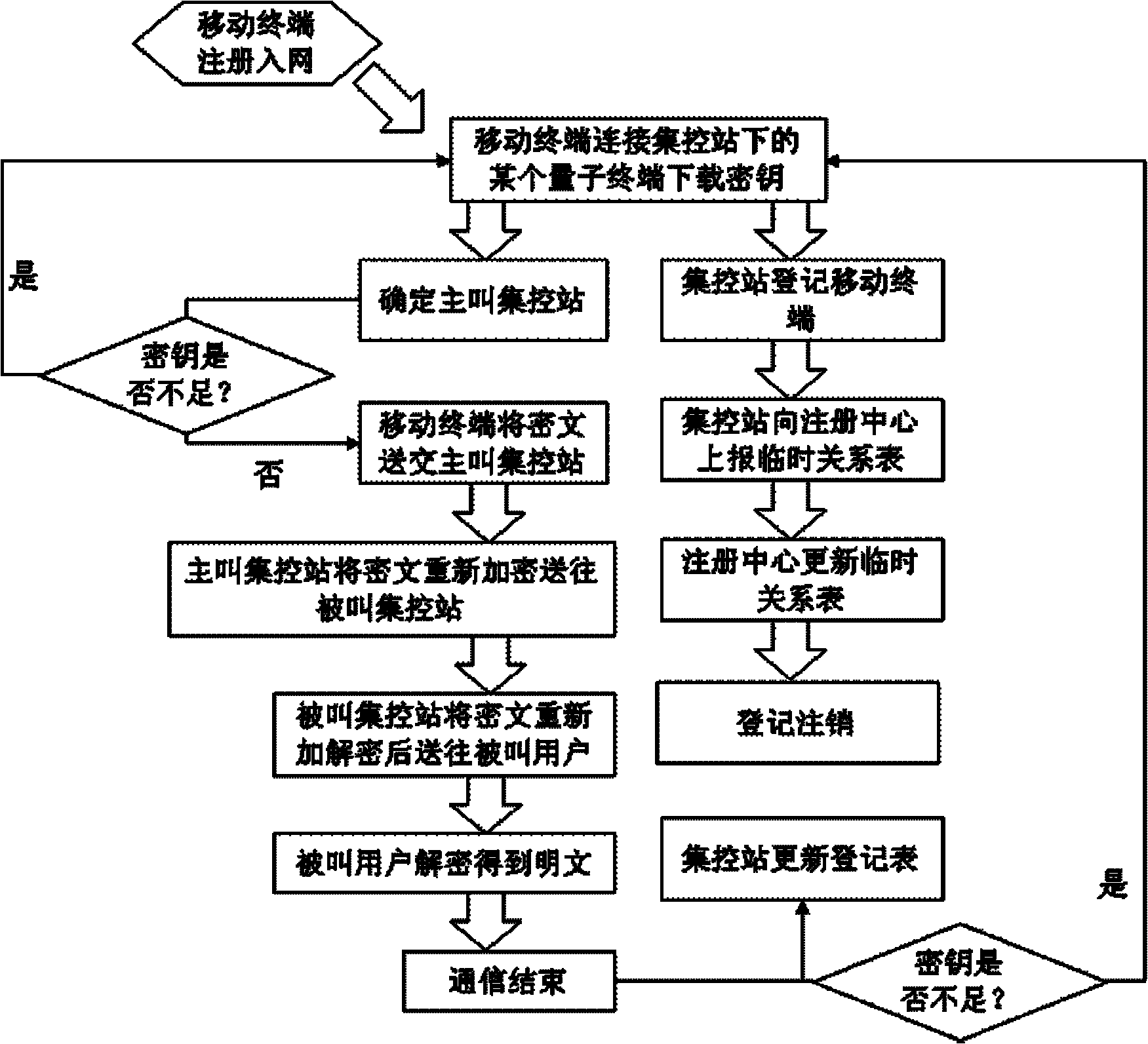
ActiveCN102196425AReduce computationGuaranteed distribution securitySecurity arrangementPlaintextTelecommunications
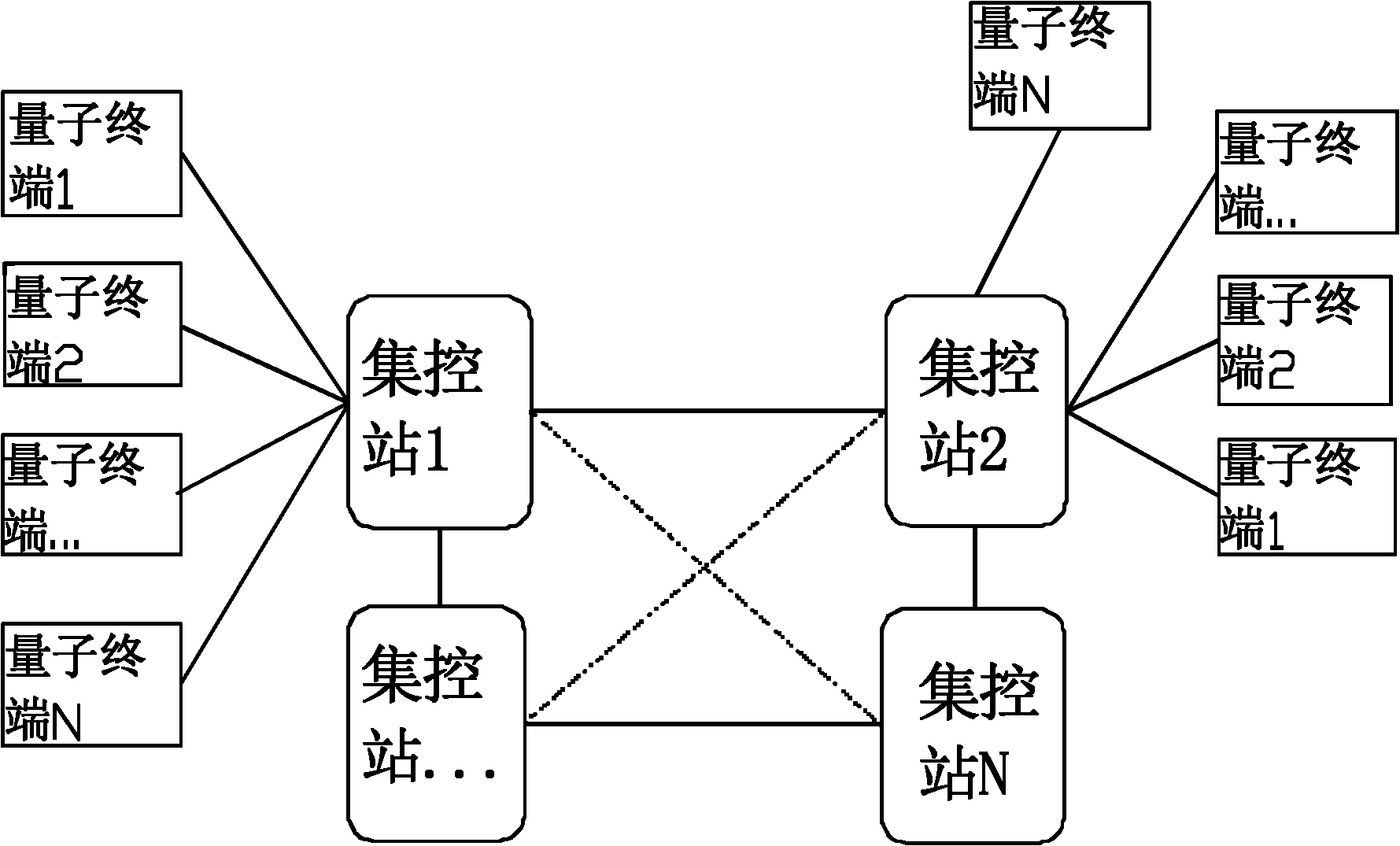
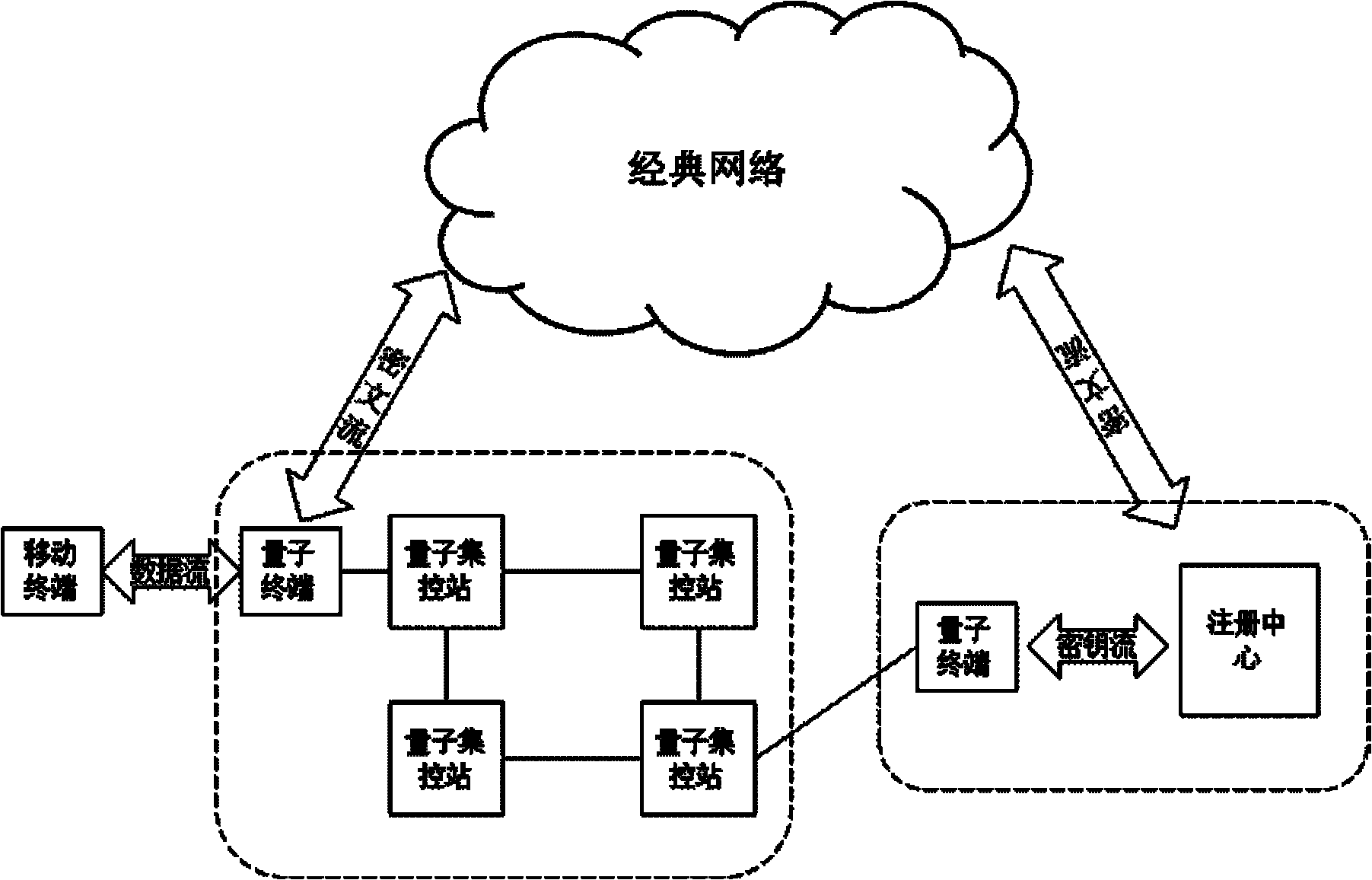
The invention discloses a quantum-key-distribution-network-based mobile encryption system and a communication method thereof. The method comprises that: a mobile terminal is registered in a network; the registered mobile terminal is connected with any quantum terminal by a key updating interface, and applies for the downloading of shared keys in a certain data volume to the quantum terminal; after the mobile terminal downloads the keys, the quantum terminal transmits a quantum centralized control station address to the mobile terminal for updating, and the mobile terminal takes a centralized control station on the quantum centralized control station address as a calling centralized control station; after the calling centralized control station is determined, the mobile terminal submits a cipher text to the calling centralized control station; the calling centralized control station re-encrypts the cipher text, and transmits the re-encrypted cipher text to a called centralized control station; the called centralized control station re-encrypts the cipher text, and transmits the re-encrypted cipher text to a called user; and after the called user decrypts the re-encrypted cipher text to obtain a plaintext, the communication is finished. In the method, the encryption does not require multiple matrix multiplication operations, so the computational load of the encryption is greatlyreduced; and simultaneously, the key distribution security of the highest level can be ensured in the key distribution of a quantum key distribution network.
Owner:QUANTUMCTEK +1
Key expansion for qkd
InactiveUS20060059343A1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronisation information channelsKey exchangeKey schedule
A method of encrypting information using an encryption pad based on keys exchanged between quantum key distribution (QKD) stations is disclosed. The method includes establishing raw keys between two stations using QKD, processing the keys to establish a plurality of matching privacy amplified keys at each station and buffering the keys in a shared key schedule. The method also includes the option of expanding one or more of the keys in the shared key schedule using a stream cipher to create a supply of expanded keys that serve as pads for one-time-pad encryption.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Method and system for secure data transmission
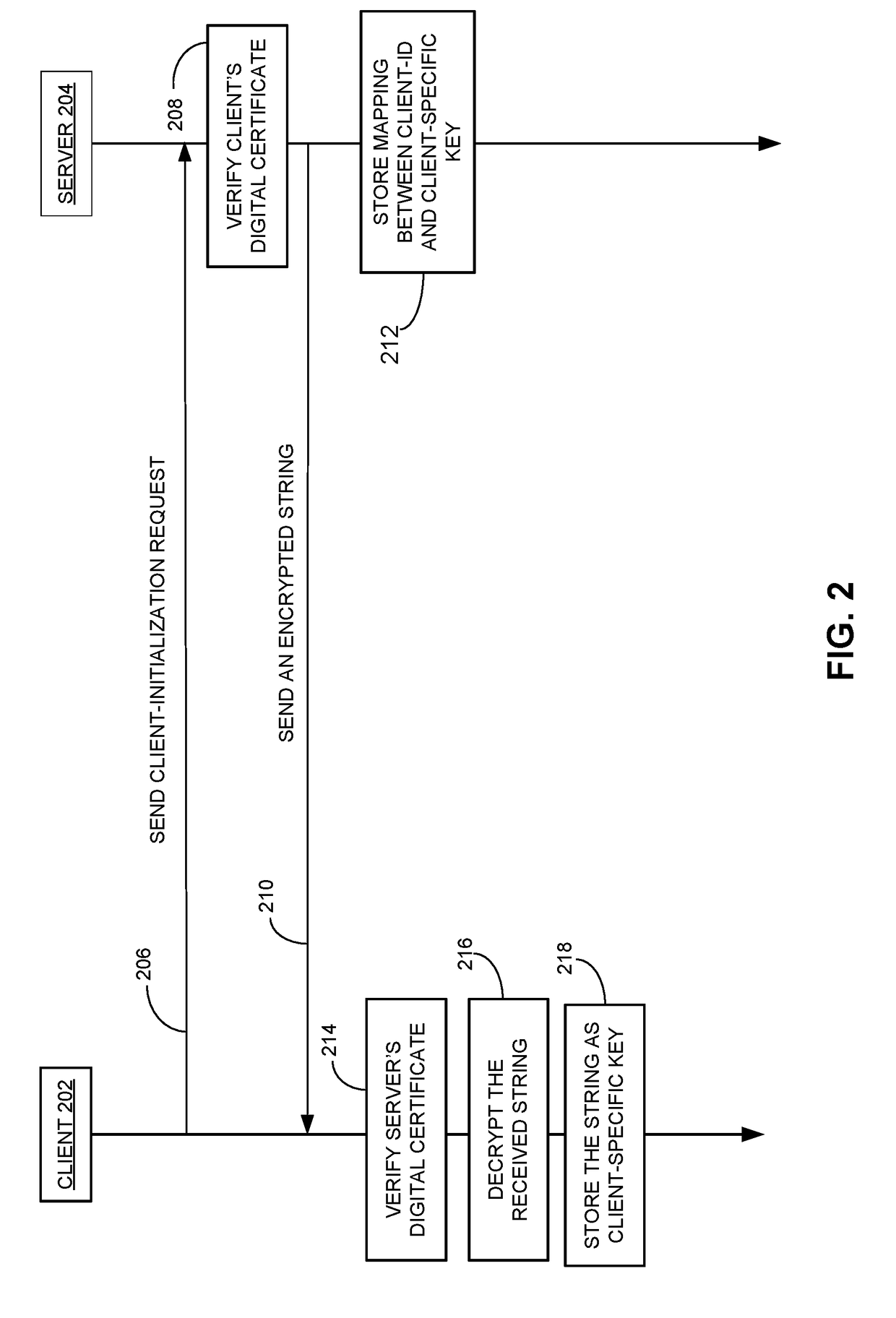
ActiveUS20170338951A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecure communicationClient-side
One embodiment described herein provides a system and method for establishing a secure communication channel between a client and a server. During operation, the client generates a service request comprising a first dynamic message, transmits the first service request to the server, which authenticates the client based on the first dynamic message, and receives a second dynamic message from the server in response to the first dynamic message. The client authenticates the server based on the second dynamic message, and negotiates, via a quantum-key-distribution process, a secret key shared between the client and the server. The client and server then establish a secure communication channel based on at least a first portion of the secret key.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
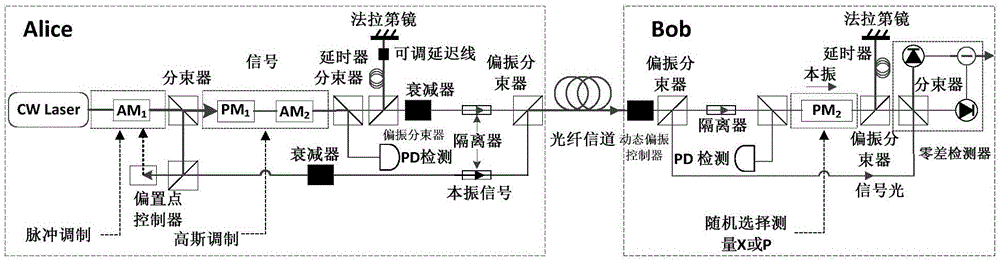
Continuous variable quantum key distribution system and synchronous realization method thereof
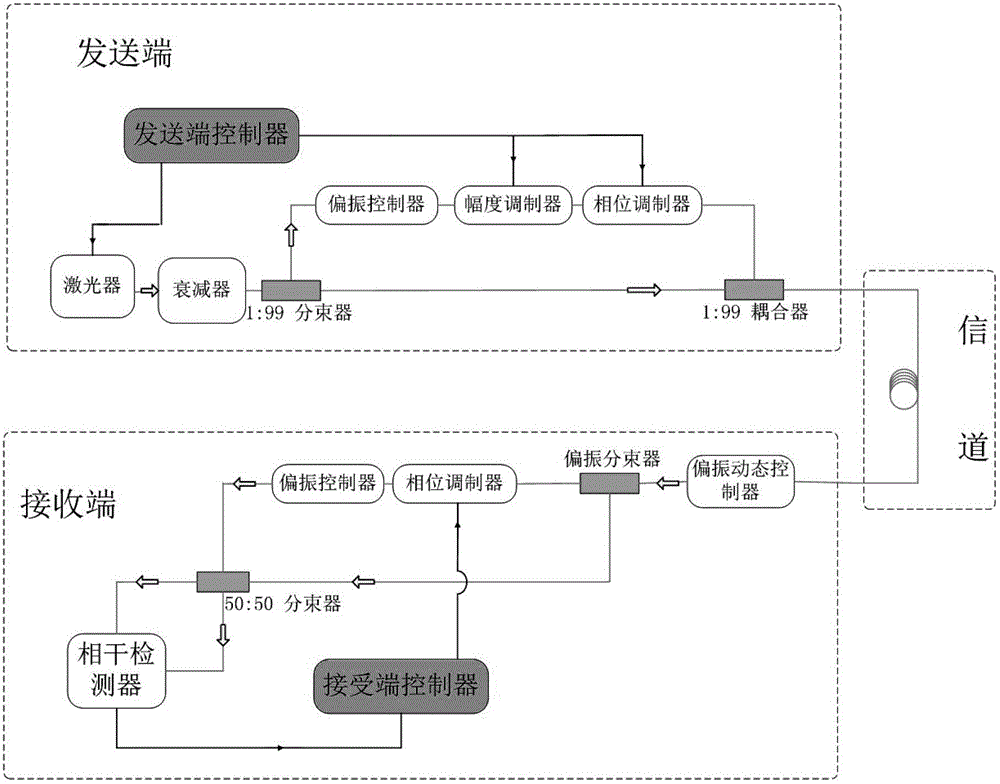
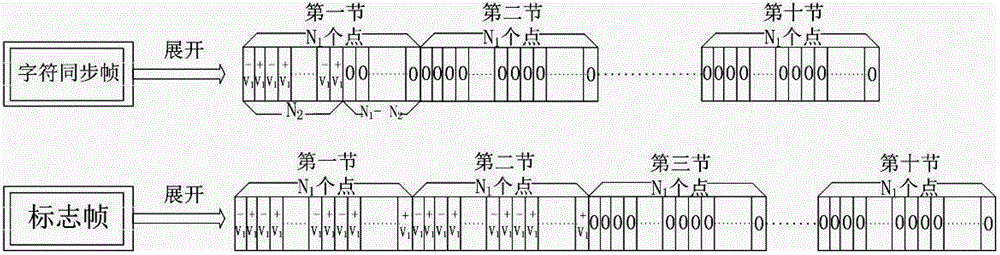
ActiveCN102724036AImprove bit error rateAvoid interferenceKey distribution for secure communicationMulti-frequency code systemsBeam splitterAmplitude control
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution system and a synchronous realization method thereof. The continuous quantum key distribution system consists of a light path part and a circuit control part, wherein the light path part mainly consists of a laser, an attenuator, a beam splitter, a polarization controller, am amplitude controller, a phase controller and a coupler. A control part is a transmission end controller module and consists of a true random key generator, an analog voltage output and a trigger clock output. The synchronous method comprises a bit synchronizing step and a frame synchronizing step. The invention provides a completely novel synchronous realization scheme based on properties of continuous variable quantum in an optical fiber, the practical orientation of the continuous variable quantum key distribution system is promoted, and the interference that the continuous variable quantum on the synchronous realization in the optical communication process also can be effectively overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA INTELLECTUAL PORPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD +1
Quantum key distribution method and apparatus
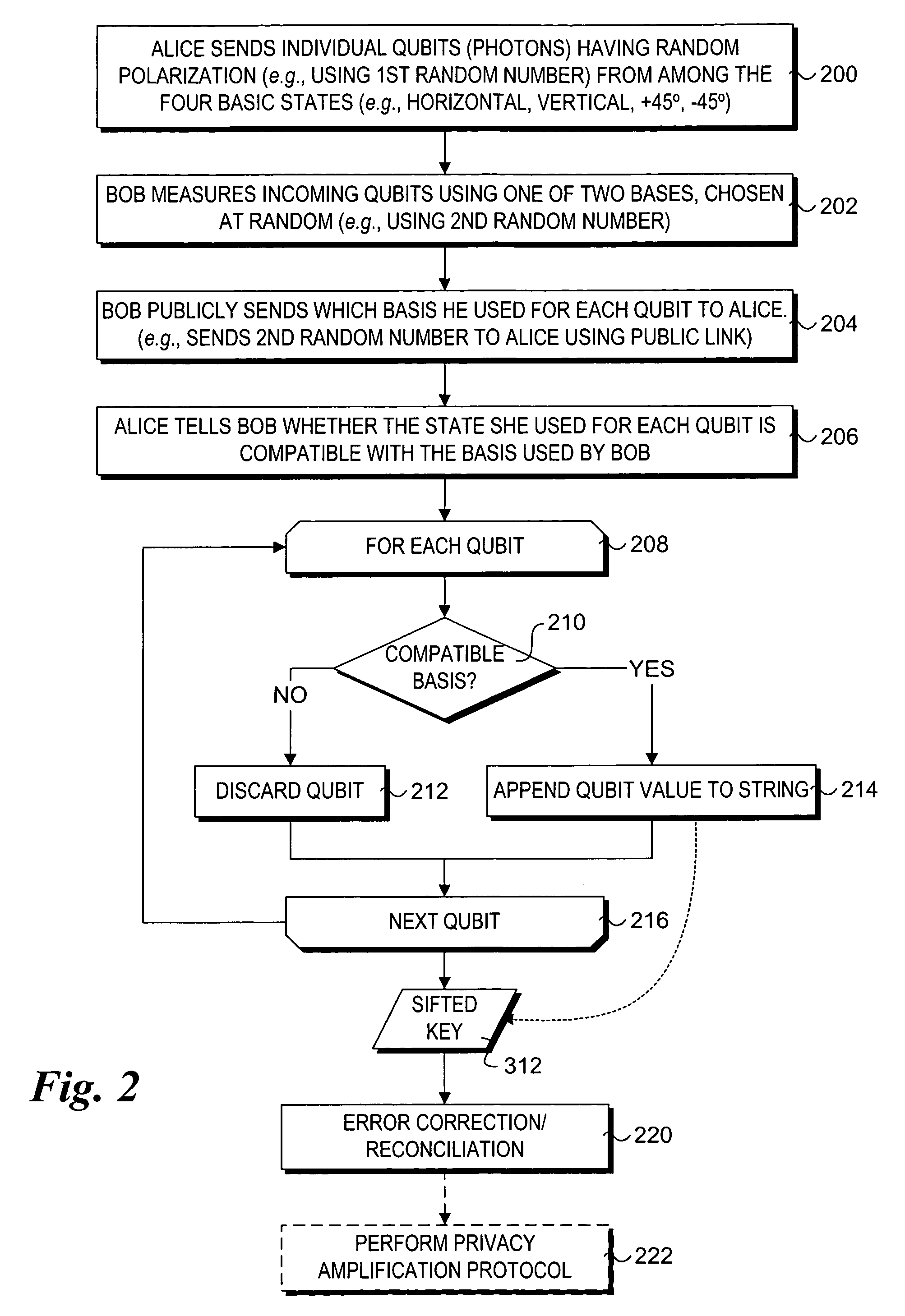
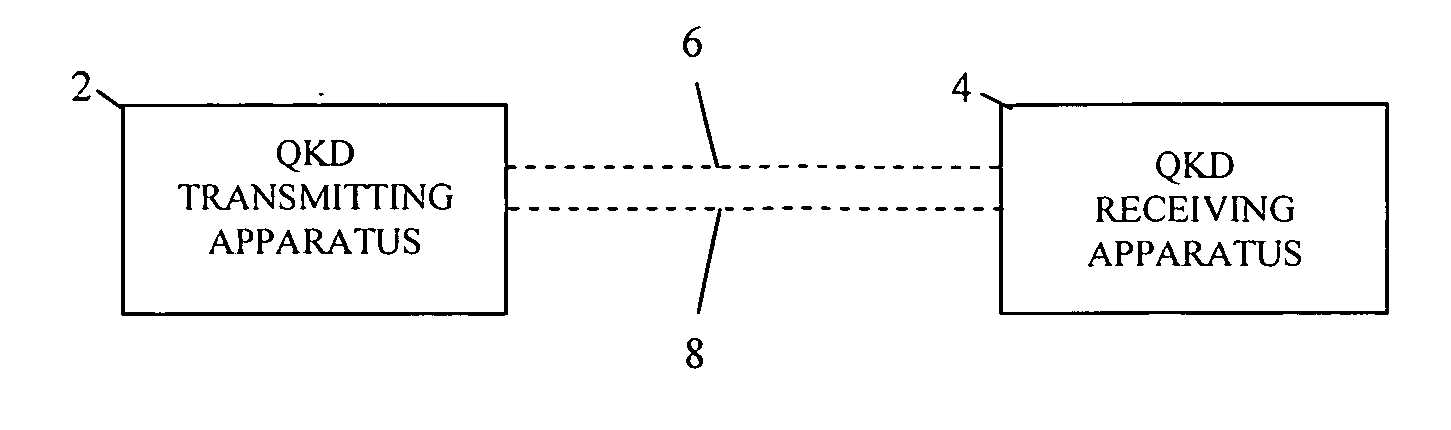
InactiveUS20070014415A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsData setComputer science
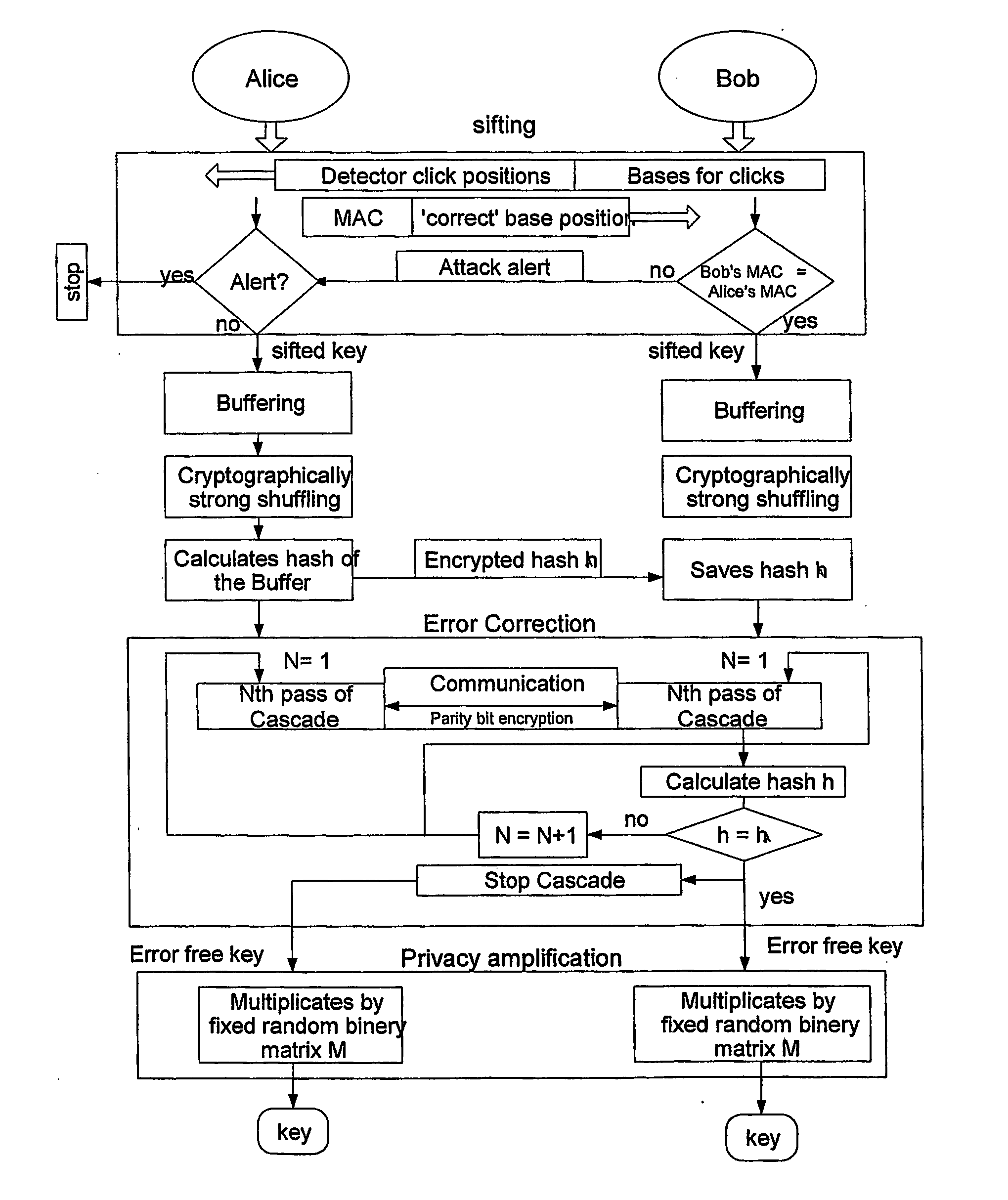
A quantum key distribution (QKD) method involves the sending of random data from a QKD transmitter to a QKD receiver over a quantum signal channel, and the QKD transmitter and receiver respectively processing the data transmitted and received over the quantum signal channel in order to seek to derive a common random data set. This processing is effected with the aid of messages exchanged between QKD transmitter and receiver over an insecure classical communication channel. The processing concludes with a check, effected by an exchange of authenticated messages over the classical communication channel, that the QKD transmitter and receiver have derived the same random data set. At least some of the other messages exchanged during processing are exchanged without authentication and integrity checking. A QKD transmitter and QKD receiver are also disclosed.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Long range continuous variablequantum key distribution method based on Gaussian-modulationcoherent state
ActiveCN105024809ASafe communication distance extensionReduce noiseKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareCoherent states
The invention discloses a long range CVQKD (Continuous Variable Quantum Key Distribution) method based on a Gaussian-modulationcoherent state. The method includes a step A of continuous variable initial key distribution which includes Gaussianmodulation of initial continuous key data through a coherent state by a sender Alice, long range transmission through an optical channel, demodulation and detection by a receiver Bob, and acquisition of initial continuous key data; and a step B of pre-treatment, error correction and confidentiality enhancement on acquired initial continuous key data by utilizing a data post-treatment algorithm and acquisition of a final binary digit safe key. According to the invention, the safe communication range of a CVQKD system based on the Gaussian-modulationcoherent state can be enlarged to 100-150 km.
Owner:上海循态量子科技有限公司
Simple untrusted network for quantum cryptography
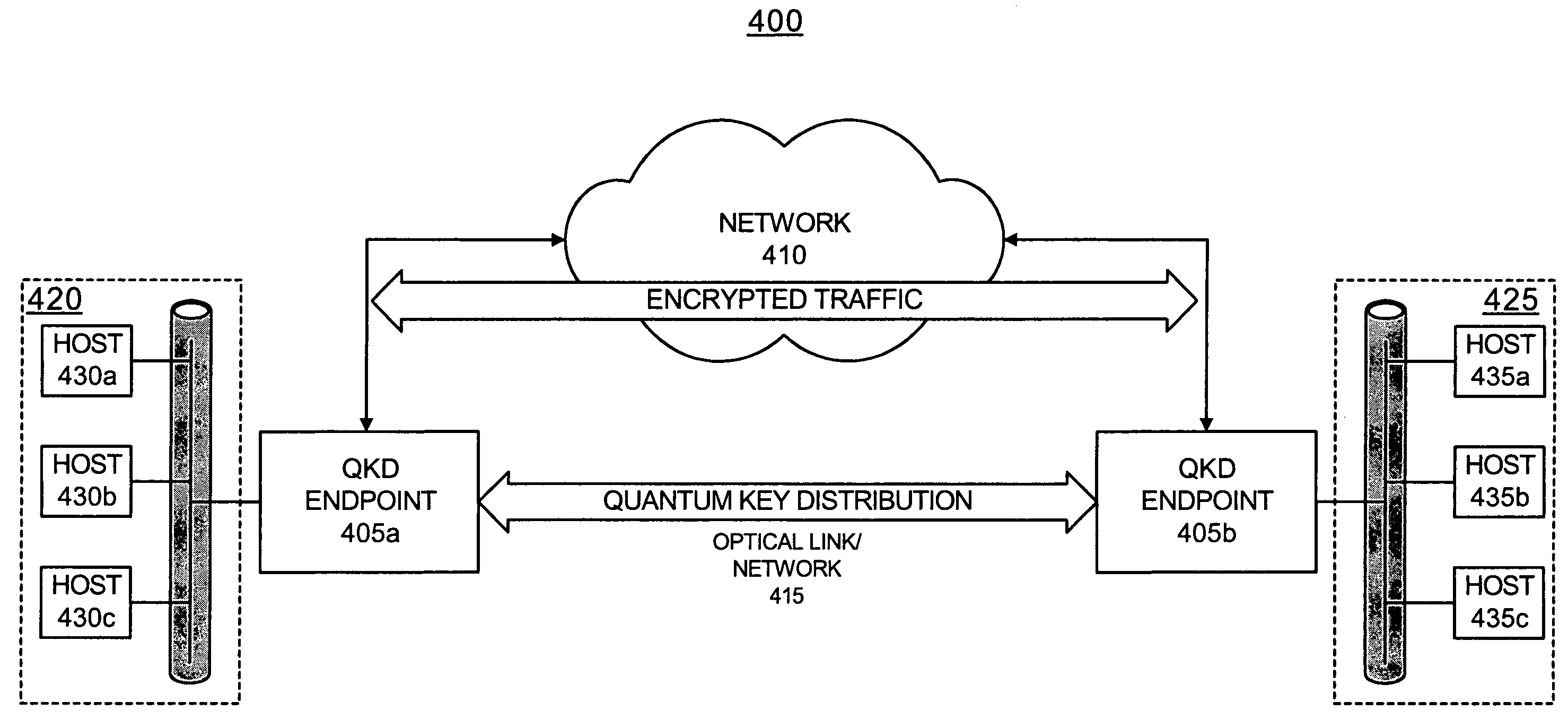
ActiveUS7430295B1Easy to shareKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationShared secretQuantum key distribution
A method and system for distributing quantum cryptographic keys among a group of user devices through a switch connected to the user devices are provided. A switch [1000] establishes a connection between two user devices [405a, 405b] according to a schedule. A Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) session is established between the two user devices [405a, 405b] to facilitate sharing of secret key material between the two user devices. Connections and QKD sessions may be established for different pairs of the user devices.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
System and methods for quantum key distribution over WDM links
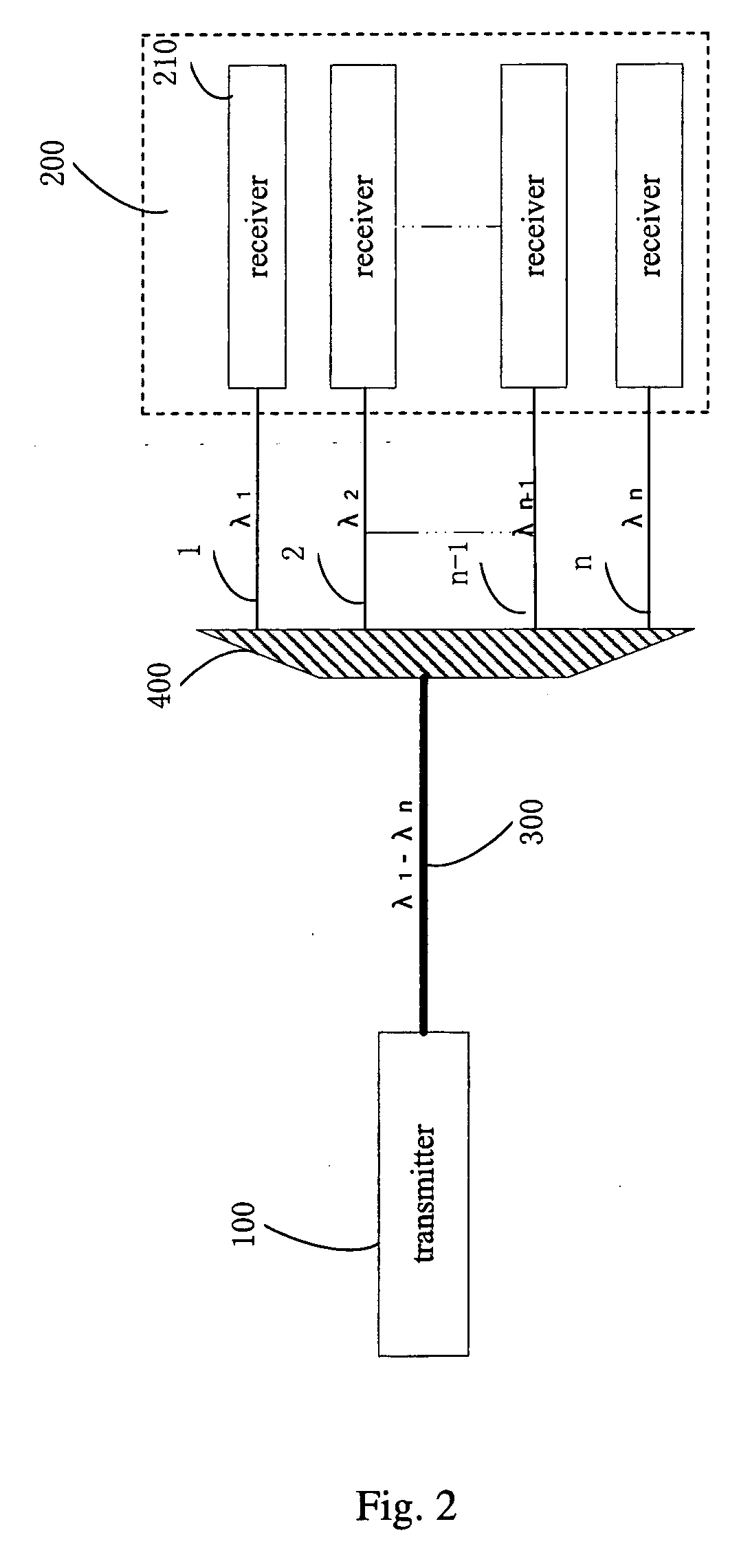
InactiveUS20070065155A1Easy to optimizeKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal onQuantum channel
A system and a method for quantum key distribution between a transmitter and a receiver over wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) link are disclosed. The method includes providing one or more quantum channels and one or more conventional channels over the WDM link; assigning a different wavelength to each of the one or more quantum channels and each of the one or more conventional channels; transmitting single photon signals on each of the one or more quantum channels; and transmitting data on each of the one or more conventional channels. The data comprises either conventional data or trigger signals for synchronizing the transmission of the single photon signals on the quantum channels. All channels have wavelengths around 1550 nm. The WDM link can be a 3-channel WDM link comprising two quantum channels for transmitting single photon signals and one conventional channel for transmitting conventional data or triggering signals.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods and system for quantum key distribution over multi-user WDM network with wavelength routing
ActiveUS20070065154A1Improve securitySystem simple and stableKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetwork linkLength wave
A system and a method for quantum key distribution over a multi-user wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) network are disclosed. The system comprises a tunable or multi-wavelength transmitter; a plurality of receivers, each assigned a receiving-wavelength; and a multi-user WDM network linking the transmitter to the receivers. The transmitter can select a receiver among the receivers to be communicated therewith and transmit quantum signals to the selected receiver over the WDM network. The quantum signals are at a wavelength equal to a receiving-wavelength of the receiver. Therefore the WDM network allows quantum signals to be communicated between the transmitter and the receivers by wavelength routing.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Systems and methods for stabilization of interferometers for quantum key distribution
InactiveUS20110280405A1Reduction in fidelityReduce and eliminate optical path length driftKey distribution for secure communicationPolarisation multiplex systemsTransceiverPath length
Systems and methods are described in which both a quantum key distribution (QKD) transmitter and QKD receiver may keep both of their two-path interferometers stable, with regard to path length drift, relative to an internal reference laser are described. Systems and methods are also proposed whereby the transmitter interferometer may have only a single path (e.g., Sagnac interferometers). The systems and methods described herein may greatly improve the performance of quantum cryptographic transceivers that may make use of these systems and methods.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
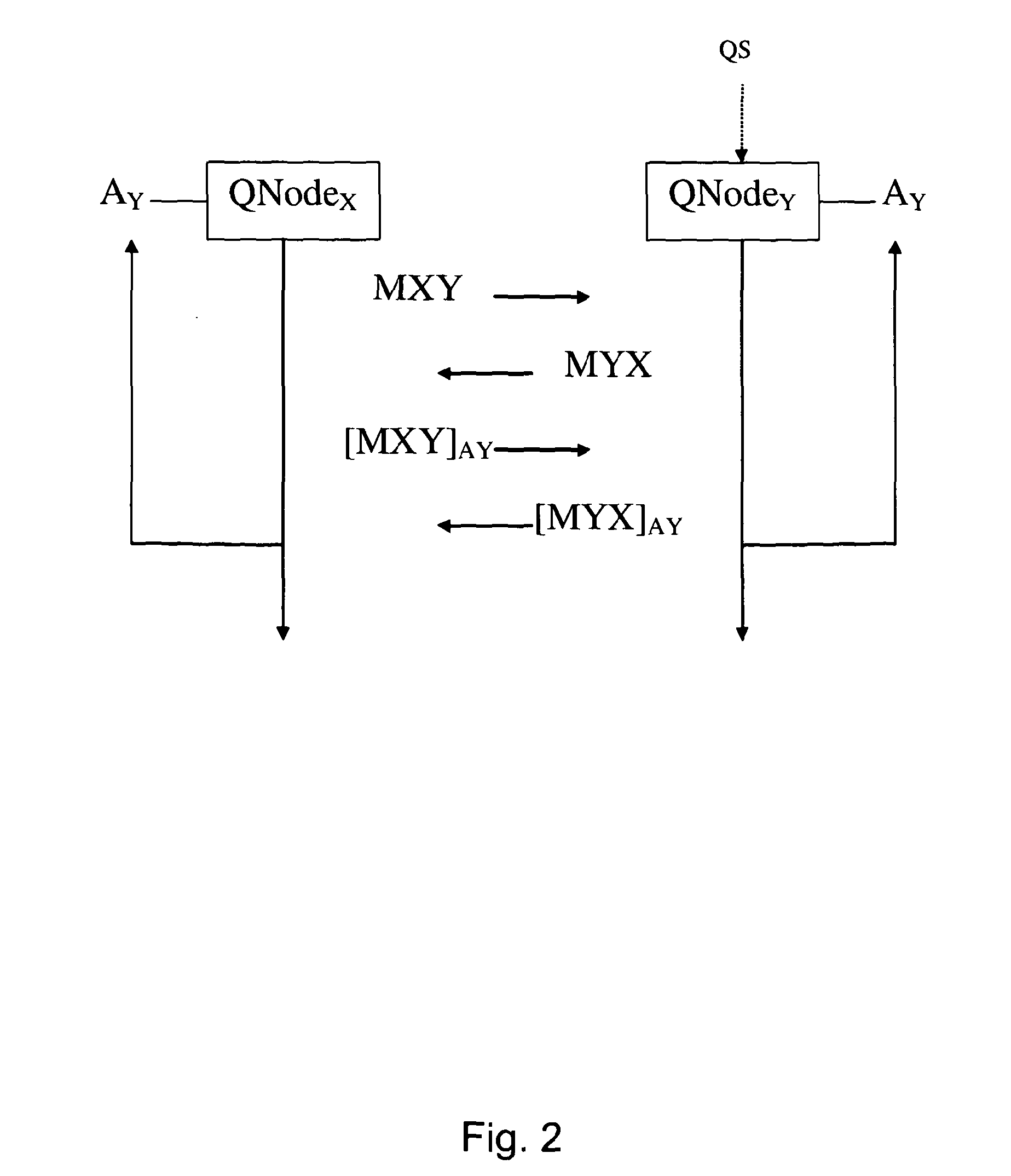
Quantum-key distribution method between a plurality of users or groups
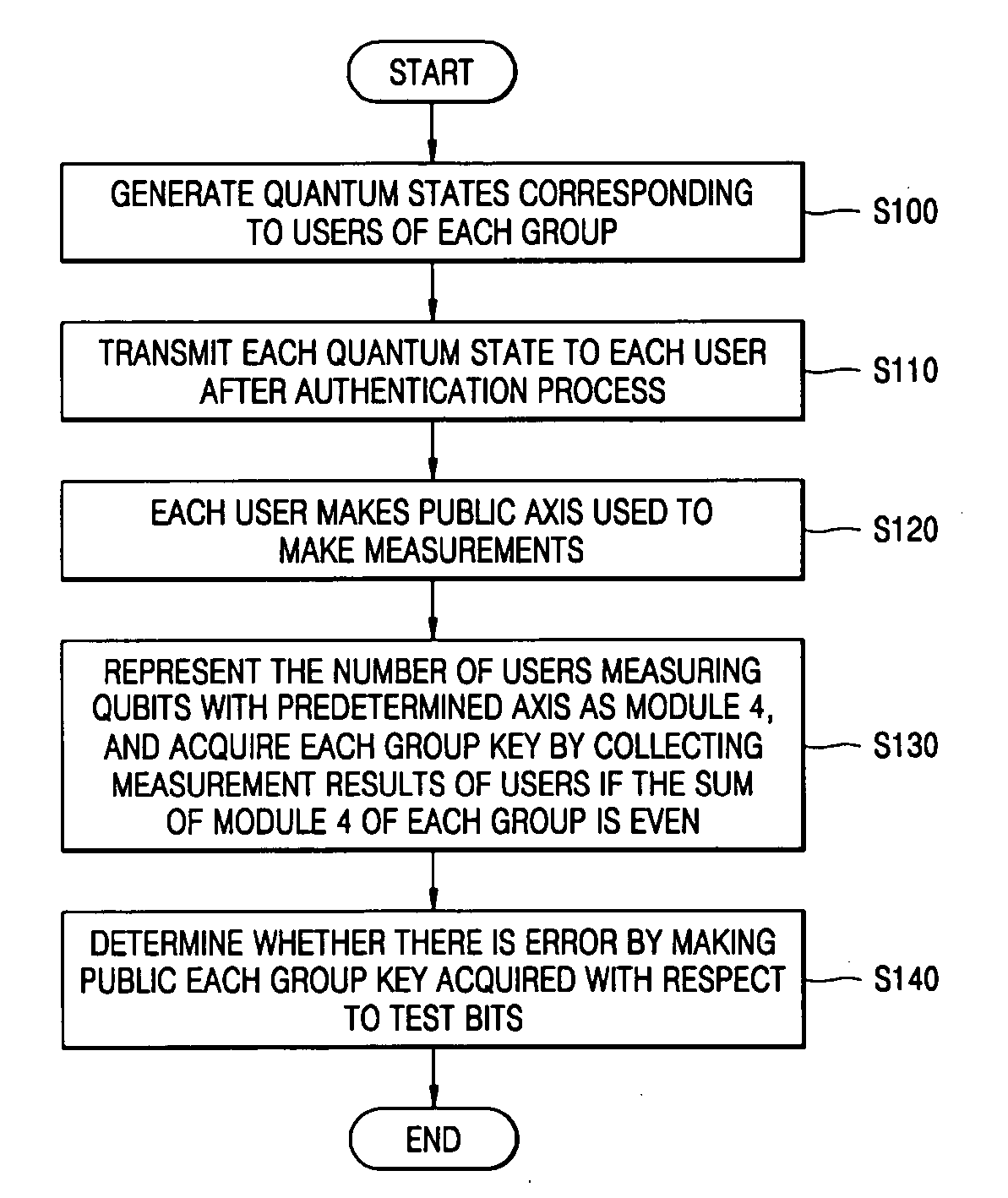
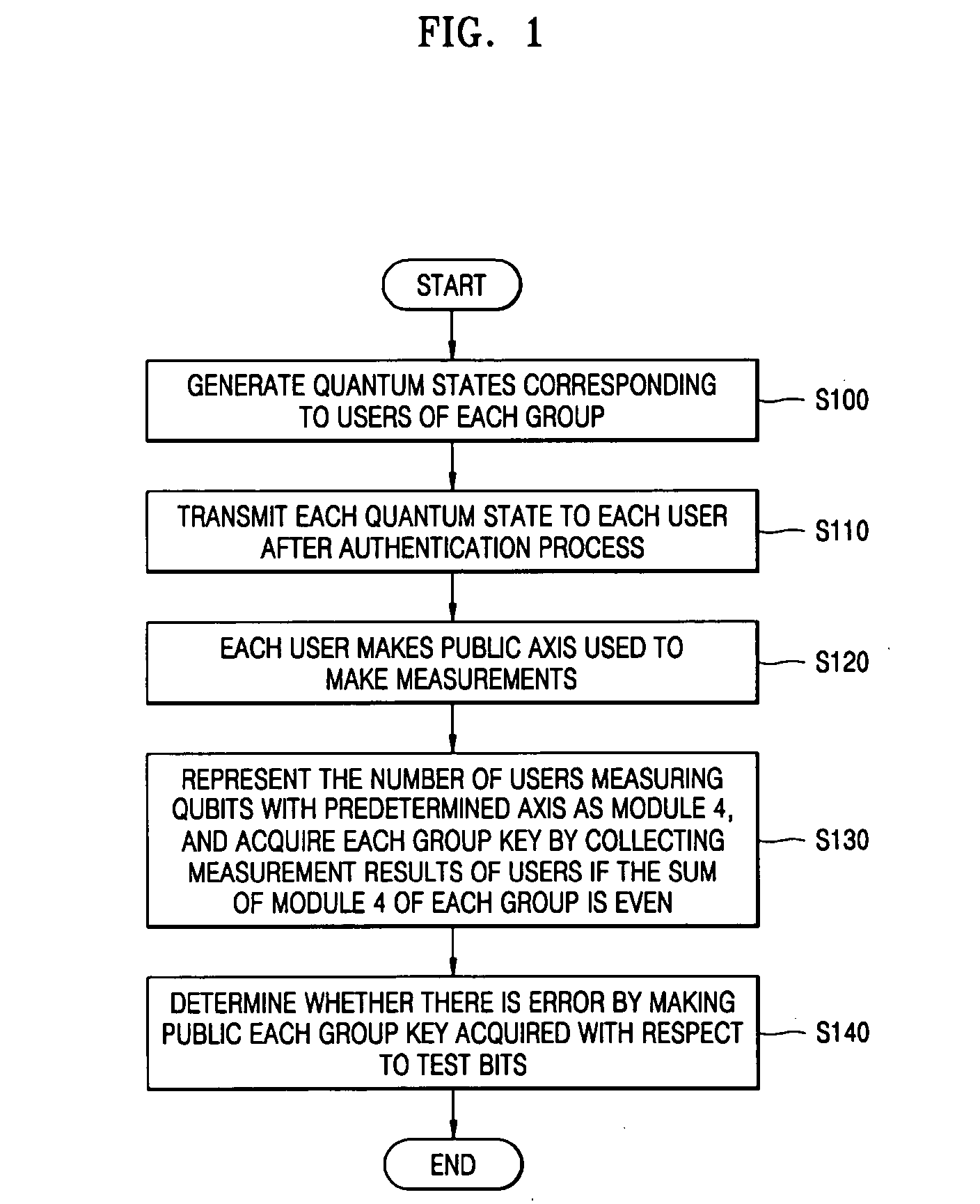
InactiveUS20050249352A1Improve securitySecure distributionKey distribution for secure communicationPump componentsComputer scienceQuantum state
There is provided a quantum-key distribution method between a plurality of users or groups. A center prepares a predetermined number of entangled states consisting of qubits equal to the number of the users, and generates quantum states consisting of the qubits belonging to each of the entangled states and corresponding to each of the users. The center transmits each of the quantum states to each of the users after an authentication process. Each of the users receiving the quantum state makes public an axis used to measure each of the qubits constituting the quantum states. The number of users in each group measuring the qubits with a predetermined axis is represented by module 4. If the sum of the module 4 of each group is even, each group collects the qubit measurement results of the users and acquires each group key. Therefore, it is possible to provide a high-security quantum-key distribution method between an unspecified number of users or groups.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
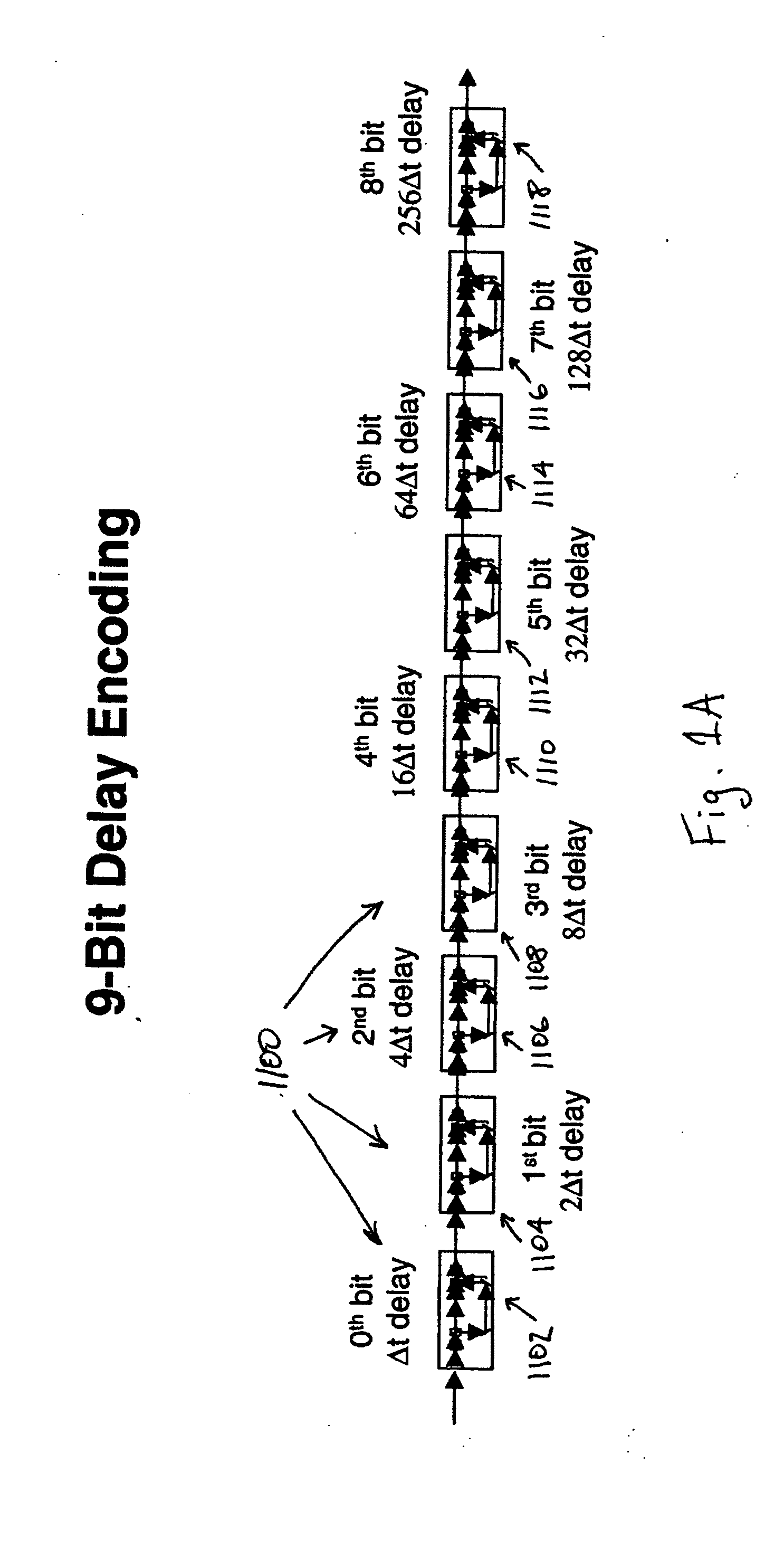
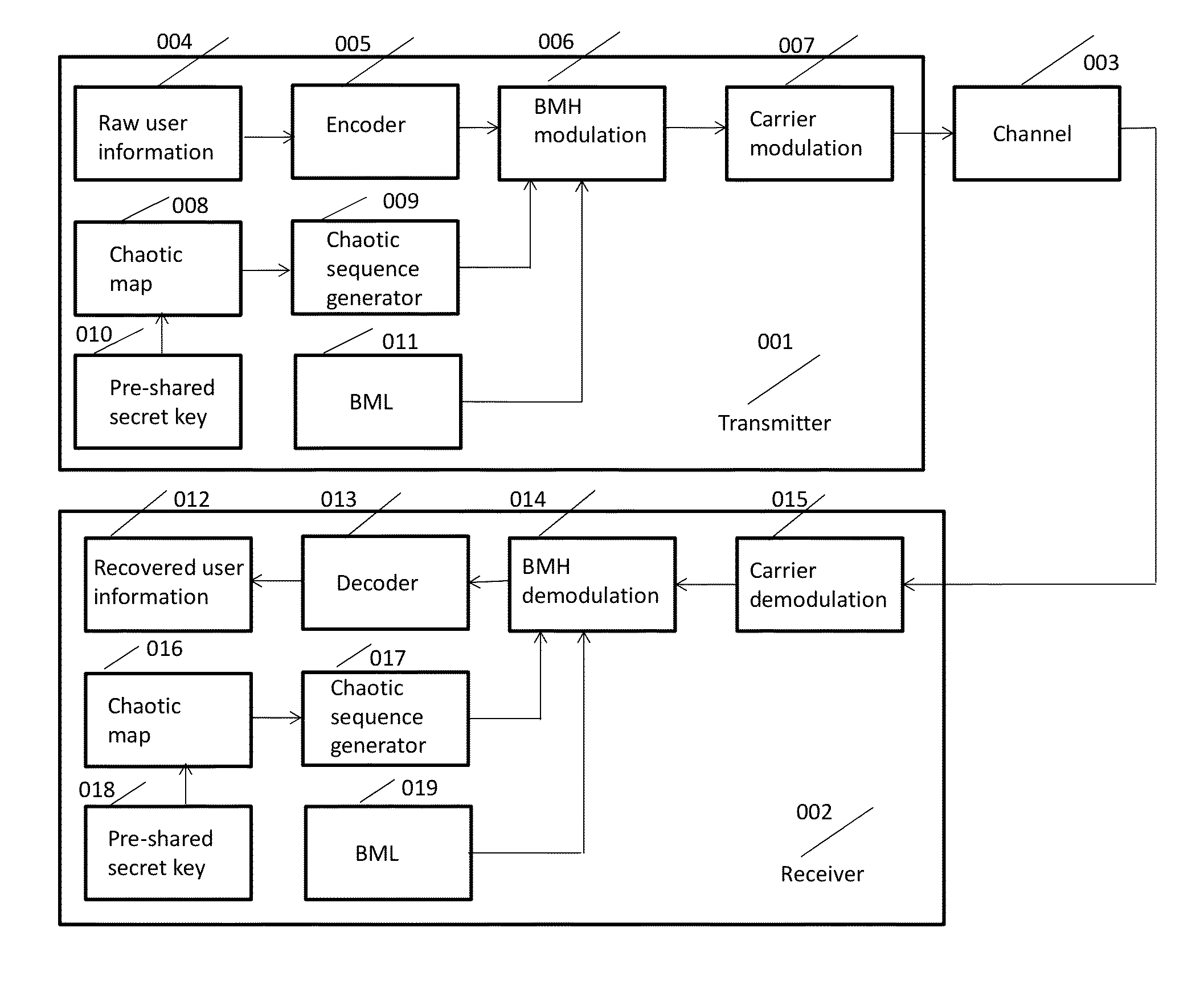
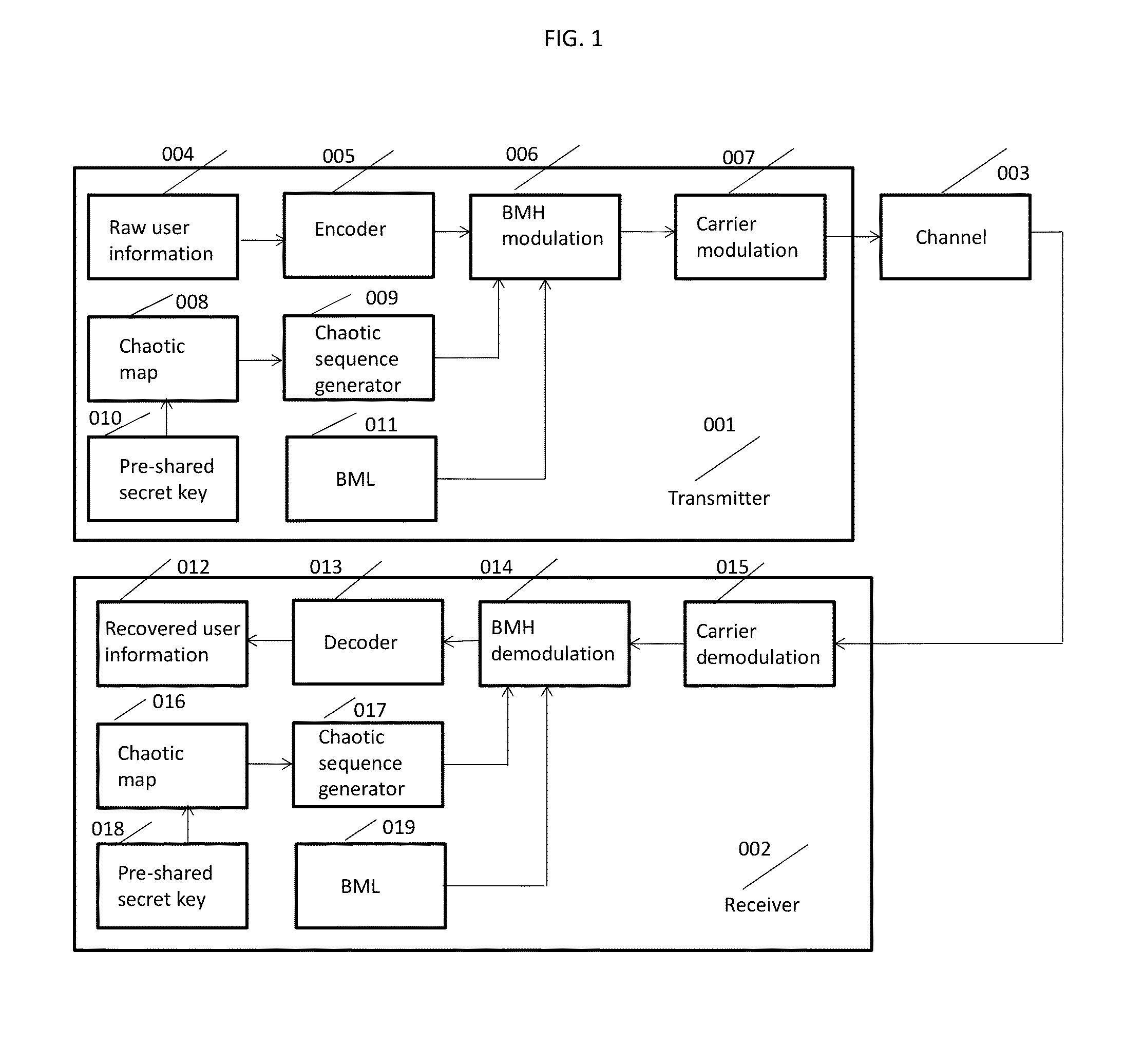
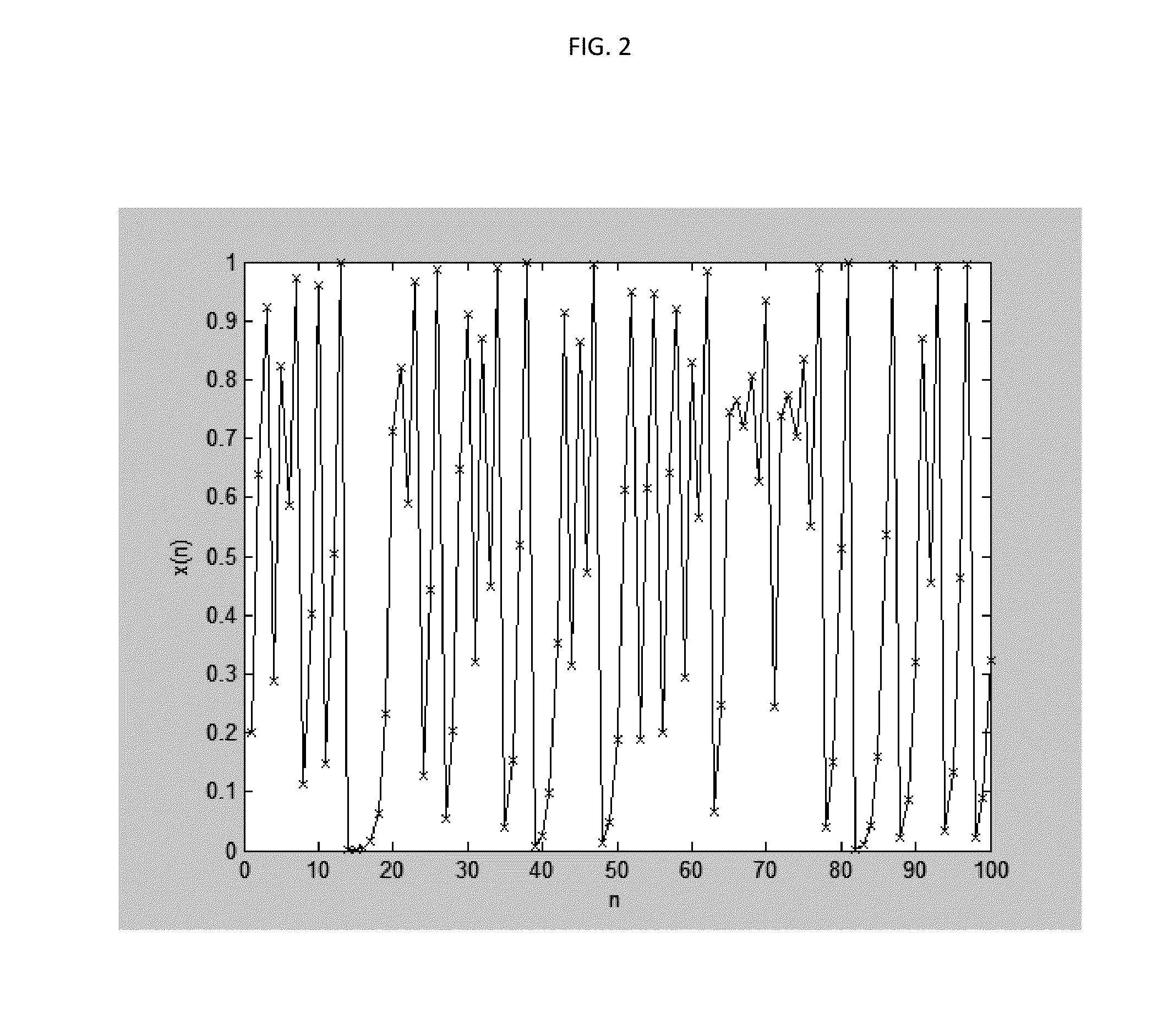
Chaotic Baseband Modulation Hopping Based Post-Quantum Physical-Layer Encryption
A post-quantum physical-layer encryption / decryption system based on chaotic Baseband Modulation Hopping (BMH). The baseband constellation, mapping, power level, and phase will vary symbol-by-symbol according to assigned random sequences. Pre-shared secret keys are used as the chaotic system parameters, initialization, and quantization parameters to generate the BMH codes. The BMH physical-layer encryption / decryption system can be combined with digital-domain based encryption algorithms such as AES, code-based post-quantum cryptography, and other physical-layer secure communication techniques such as Frequency Hopping (FH) and Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS). It can also be combined with Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) to provide mutual authenticated key distribution. This invention can be applied to all kinds of communication systems including wireless (radio frequency, optical, quantum channel, sonar) and wire (optical fiber, power-line, telephone line, wire quantum channel, etc.), single carrier and multi-carrier, OFDM, MIMO channels.
Owner:LI WENHUA +1
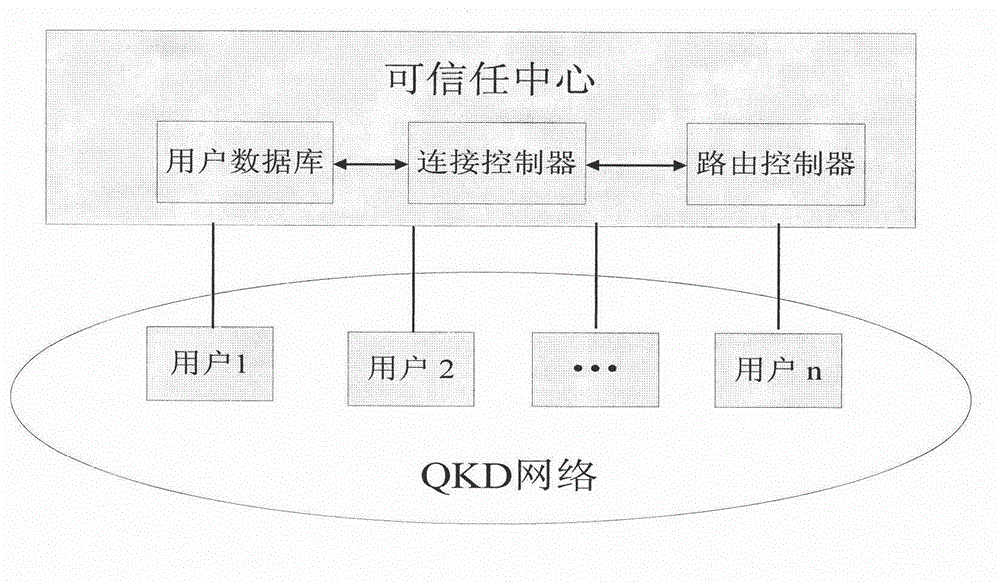
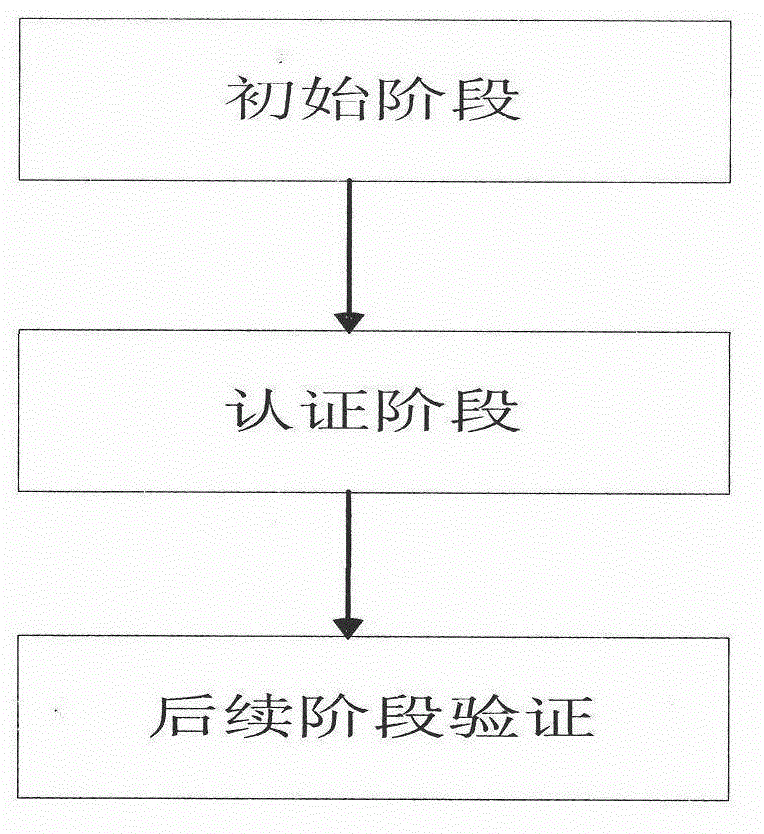
Model and method for user authentication for quantum key distribution network
ActiveCN102946313AAvoid Intermittent AttacksPrevent theftKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunications securityMan-in-the-middle attack
The invention provides a model and a method for user authentication based on a trusted center in a quantum key distribution network, specifically, a user authentication model based on the trusted center is provided and an implementation method is described in detail, in order to realize the communication security between any two users in the network and prevent a man-in-the-middle attack. Based on the model, the invention further provides a method for user authentication, which comprises the following steps that: 1, any user requesting for communication in the network sends a connection request to the trusted center; 2, the trusted center sends a pre-shared key to the two communication parties respectively; 3, the two communication parties set up a quantum channel and are authenticated; and 4, the two parties are authenticated regularly or irregularly in the subsequent communication process. According to the invention, by fully considering the development status of the current quantum key distribution network and by combining with the actual requirement, a quantum communication channel can be set up securely between any two nodes in the network, so that the communication security between users can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system and method based on time-phase encoding, transmitting end and receiving end
ActiveCN106161011AImprove bit rateKey distribution for secure communicationCode moduleComputer architecture
The invention discloses a plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system and method based on time-phase encoding, a transmitting end and a receiving end. The plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system comprises the transmitting end and the receiving end which are in mutually optical connection, a coding module in the transmitting end comprises a Z basis vector time coding module coding optical signals according to any sequence and a phase coding module which is an X basis vector phase coding module, and a decoding module in the receiving end is matched with the coding module. The plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution method includes: after an Alice end receives and reflects optical signals from a Bob end, performing Z basis vector time coding and phase coding; sending the optical signals after going through Z basis vector time coding and phase coding to the Bob end for decoding and detecting, wherein phase coding refers to X basis vector phase coding. Improved time-phase coding is used, so that ultrahigh-contrast coding and decoding can be realized, and code generating rate can be increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENZHOU QUANTUM NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Methods and systems for communicating over a quantum channel
Alice generates a sequence of key bits forming an initial cryptographic key. Alice then uses the sequence of key bits and a sequence of cipher bits to control respective control parameters of a quantum encoding process applied to a sequence of quantum pulses, where the sequence of cipher bits used is known to Bob. Alice then releases the encoded pulses towards Bob over a quantum channel. Bob uses the previously agreed-upon sequence of cipher bits to control a control parameter, such as the quantum basis, of a quantum detection process applied to the pulses received from Alice, thus producing a detection outcome for each received pulse. Bob then derives a final cryptographic key from the detection outcomes. Because the cipher bits used to select the quantum bases used by both Alice and Bob are known by both parties, the method allows the final cryptographic key to be distributed with full basis alignment compared to 50% for BB84, thus allowing efficient quantum key distribution over multiple hops.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
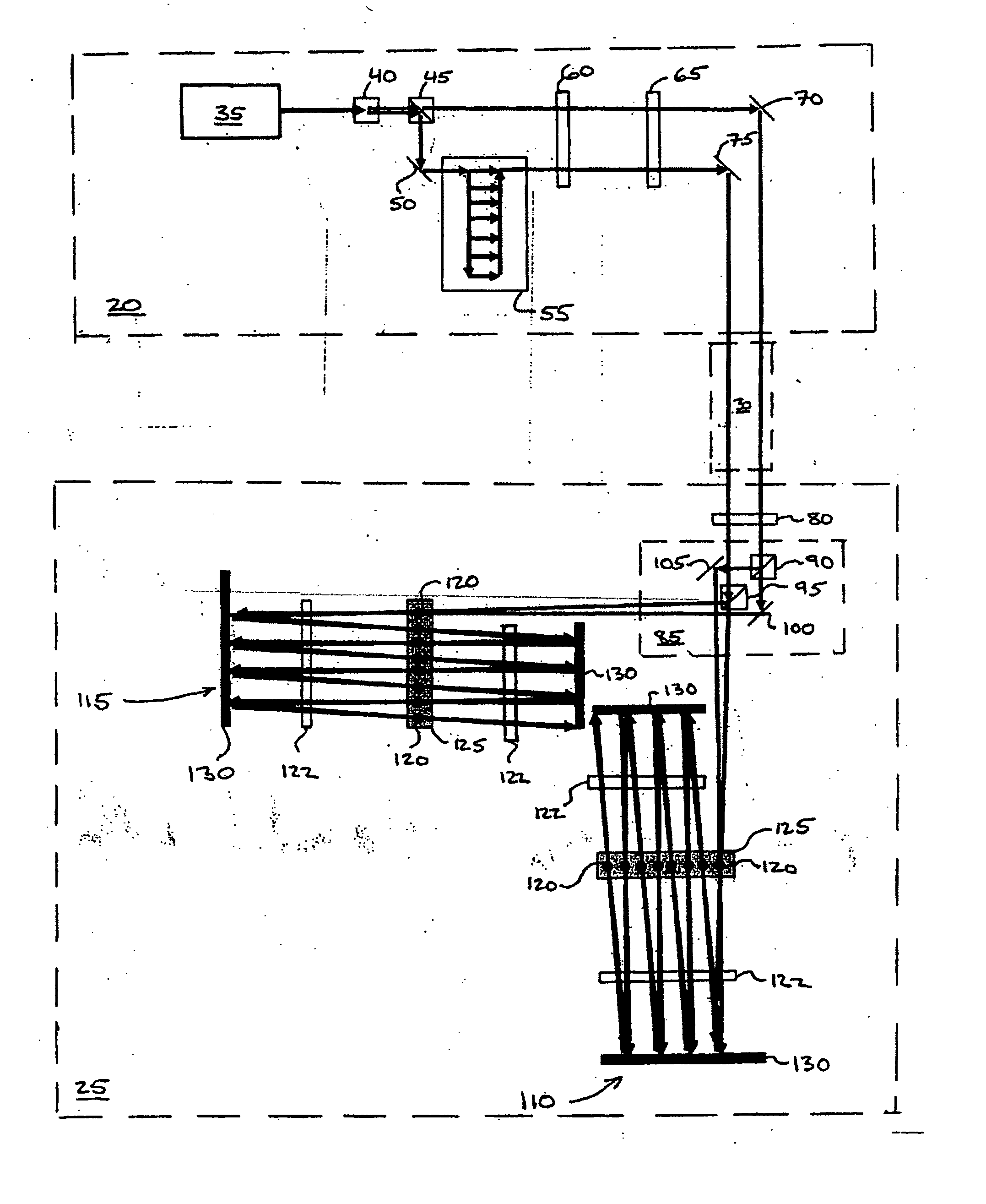
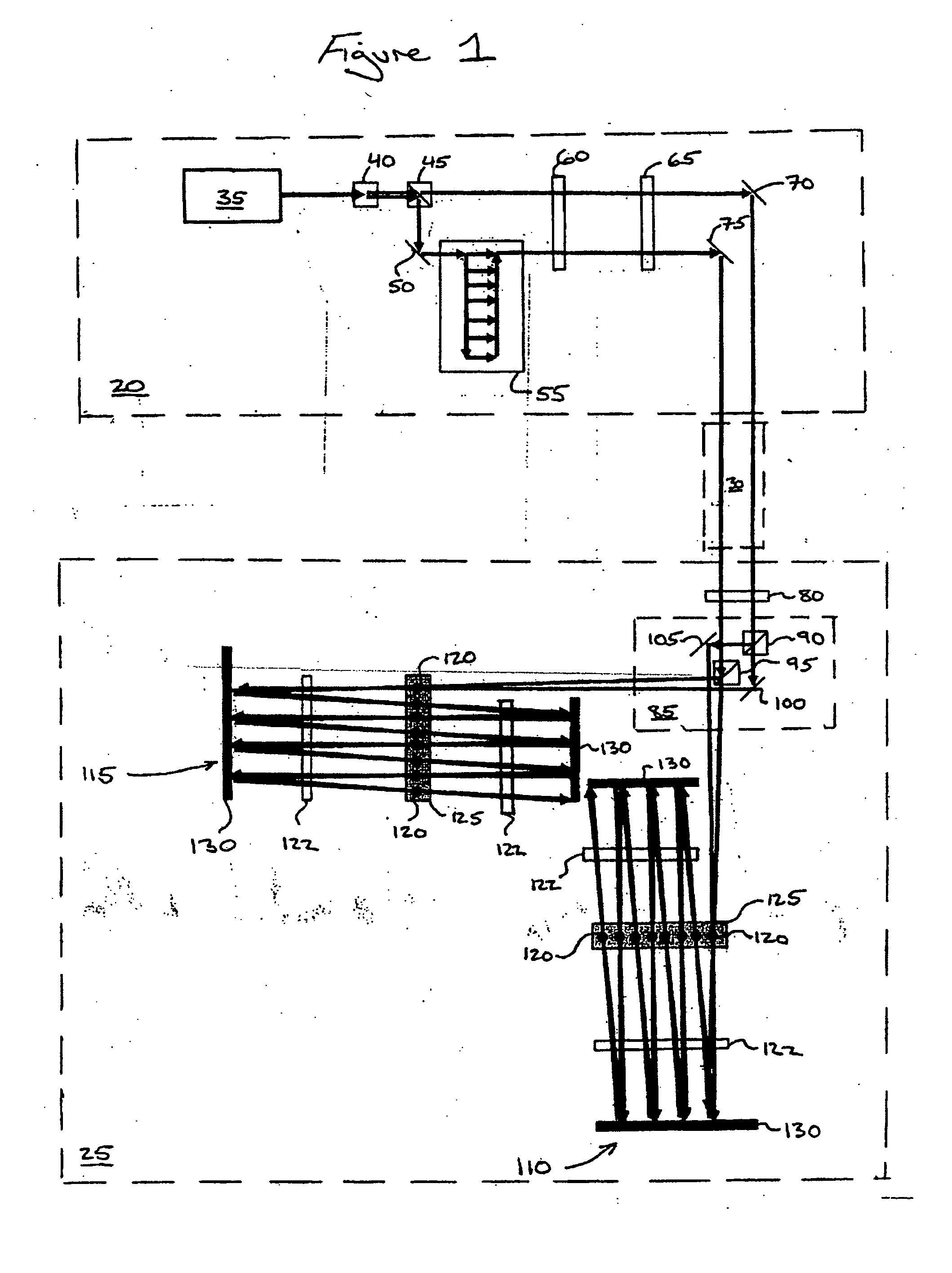
Quantum key distribution system and method using regulated single-photon source
InactiveUS20050094818A1Simpler practical realizationHigh key creation efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesBeam splitterPath length
A system and method for quantum key distribution uses a regulated single-photon source to sequentially generate a first photon and a second photon separated by a time interval Δt. The two photons are directed through a beam splitter that directs each photon to one of two transmission lines, which lead to two respective receivers. When one of the photons arrives at a receiver, it passes through an interferometer. One arm of the interferometer has a path length longer than the other arm by an amount equivalent to a photon time delay of Δt. The photon is then detected in one of three time slots by one of two single-photon detectors associated with each of the two interferometer outputs. Due to quantum-mechanical entanglement in phase and time between the two photons, the receivers can determine a secret quantum key bit value from their measurements of the time slots in which the photons arrived, or of the detectors where the photons arrived.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP +1
Embedded authentication protocol for quantum key distribution systems
ActiveUS8693691B2Reduction of informationReduce overheadKey distribution for secure communicationProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessKey generation
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Quantum key distribution system, optical transmitter, optical modulation control circuit, and optical modulation control method
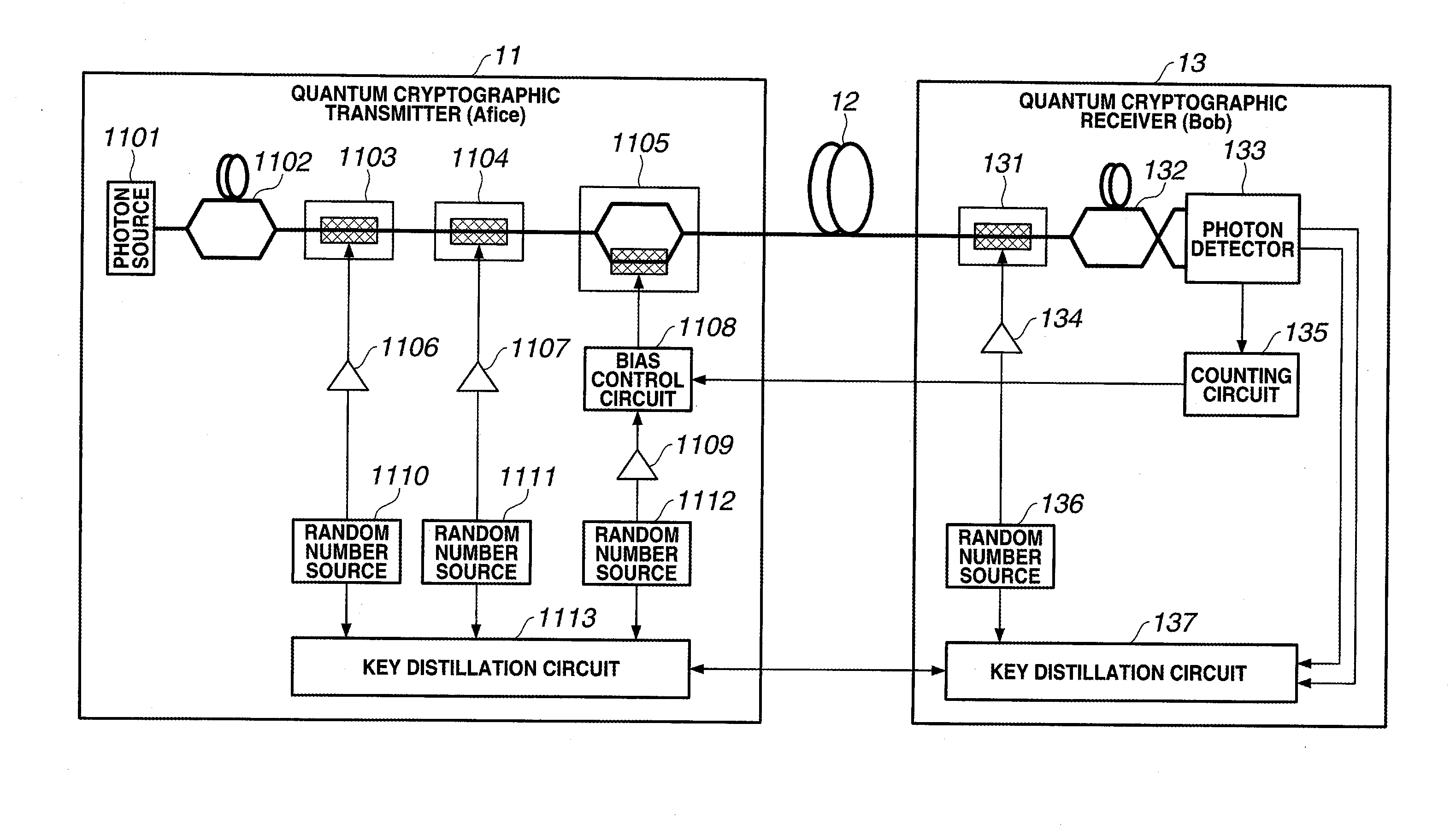
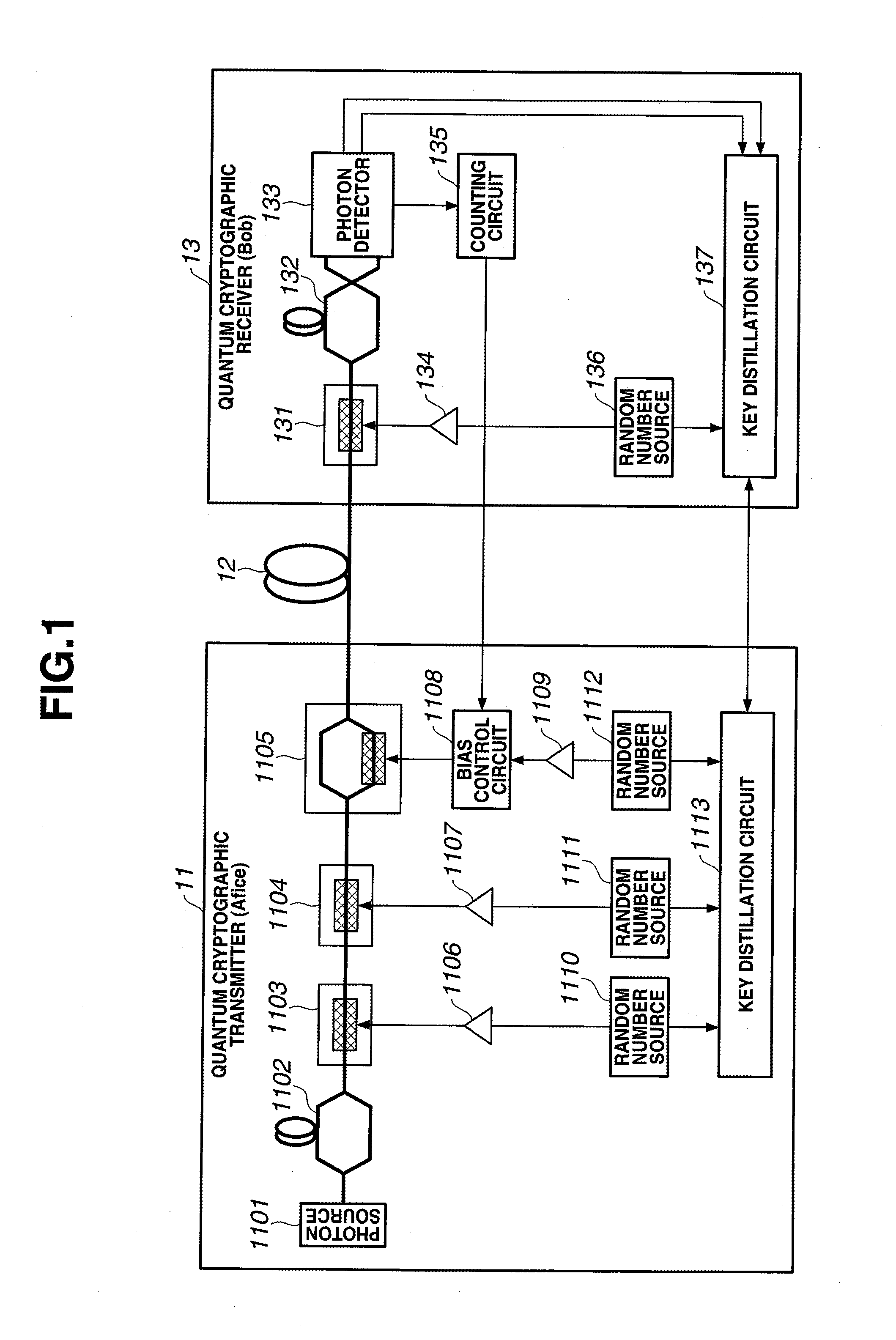
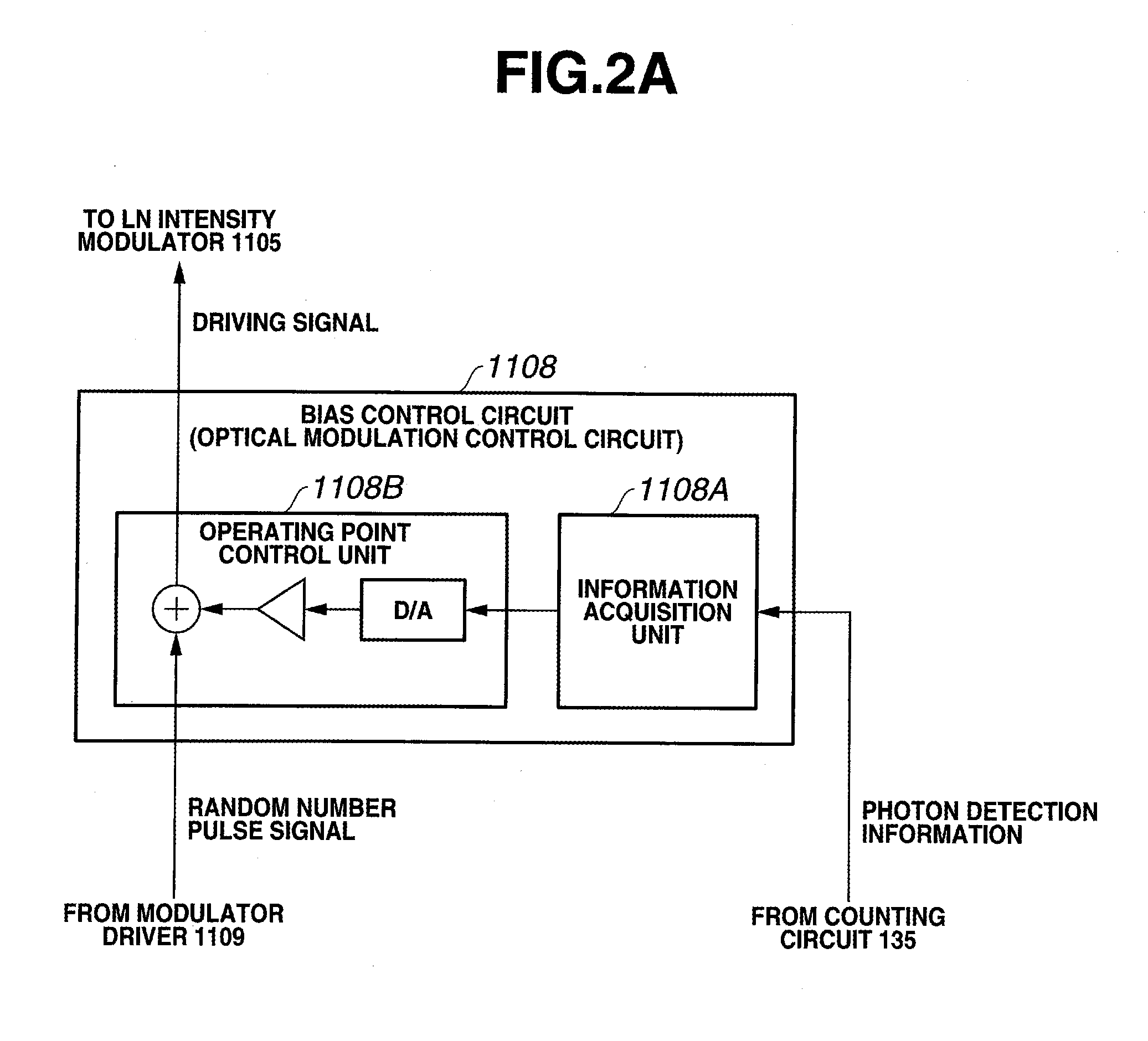
ActiveUS20100195831A1Stable optical modulation operationEasy to controlKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationOperating pointIntensity modulation
In a quantum cryptographic transmitter (11), a phase modulator (1103, 1104) and an LN intensity modulator (1105) apply optical phase modulation and light intensity modulation to an optical signal based on desired data to generate a desired optical signal to be transmitted to a quantum cryptographic receiver (13). Based on the number of photons detected from the desired optical signal, a bias control circuit (1108) controls an operating point in light intensity modulation of the LN intensity modulator (1105).
Owner:NEC CORP
Standards-compliant encryption with QKD
An encryption system and method that utilizes quantum key distribution (QKD) and that is compliant with industry and / or governmental standards for encryption is disclosed. One example embodiment of the system includes first and second transmitters / receivers operatively connected to respective first and second encryption / decryption (e / d) processors. The e / d processors are connected to a classical key distribution system as well as to a QKD system. The QKD system symmetrically provides quantum keys qi to the e / d processors, and the classical encryption system symmetrically provides classical keys ci to the e / d processors. The e / d processors then form session keys ki via the operation ki=ci XOR qi. The session keys are then used to encrypt and decrypt plaintext messages sent between two transmitting / receiving stations.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com