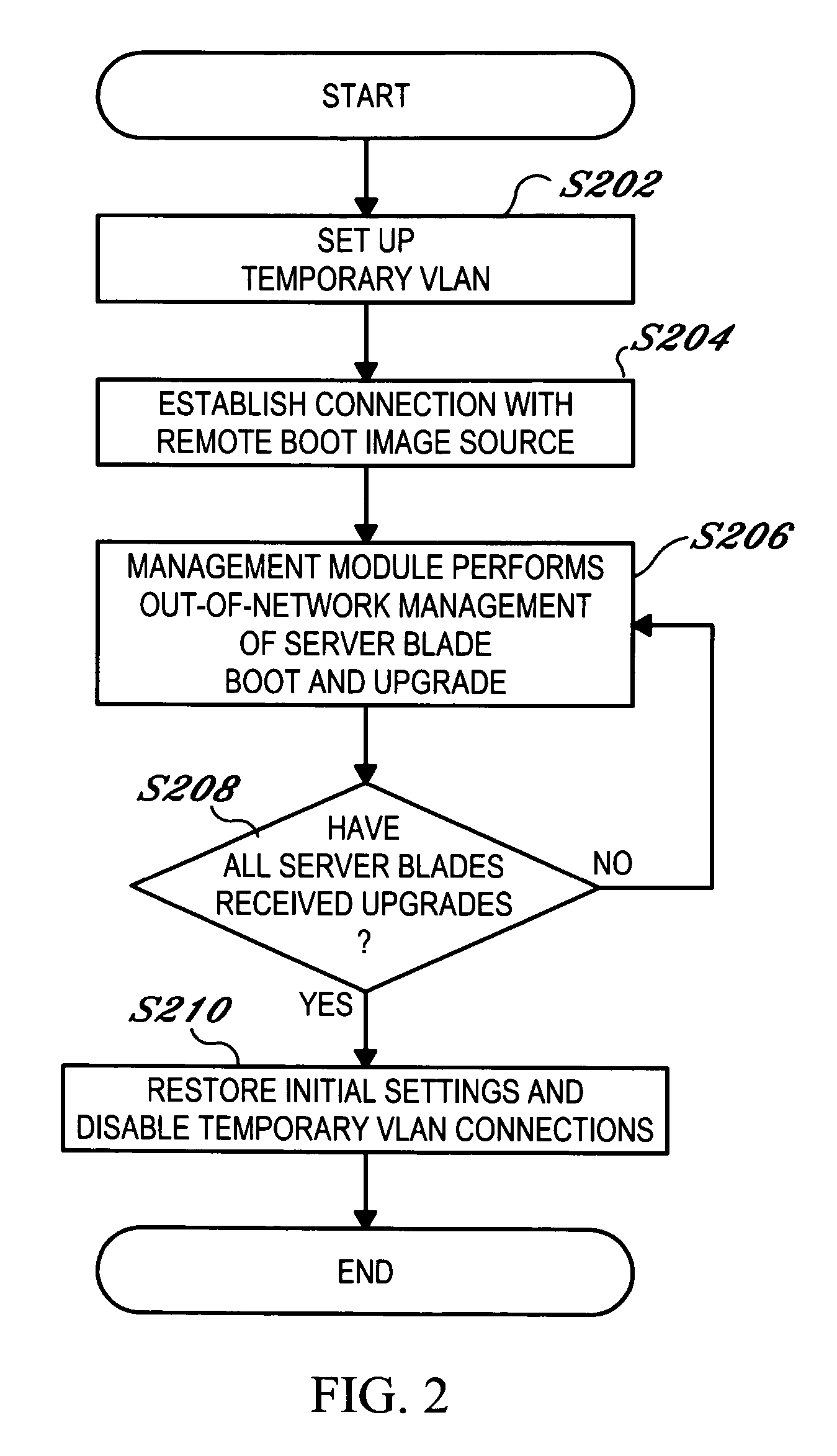
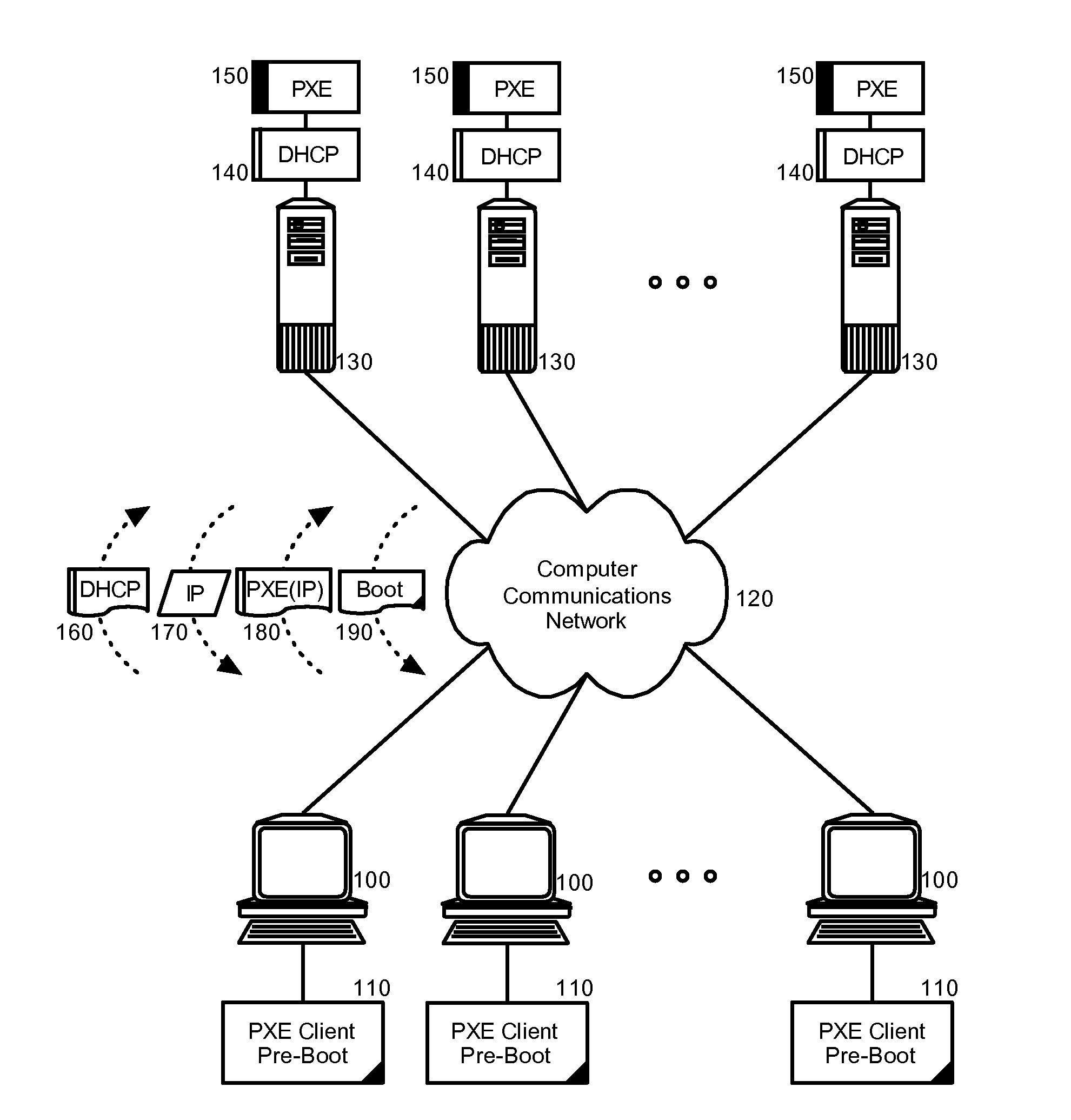
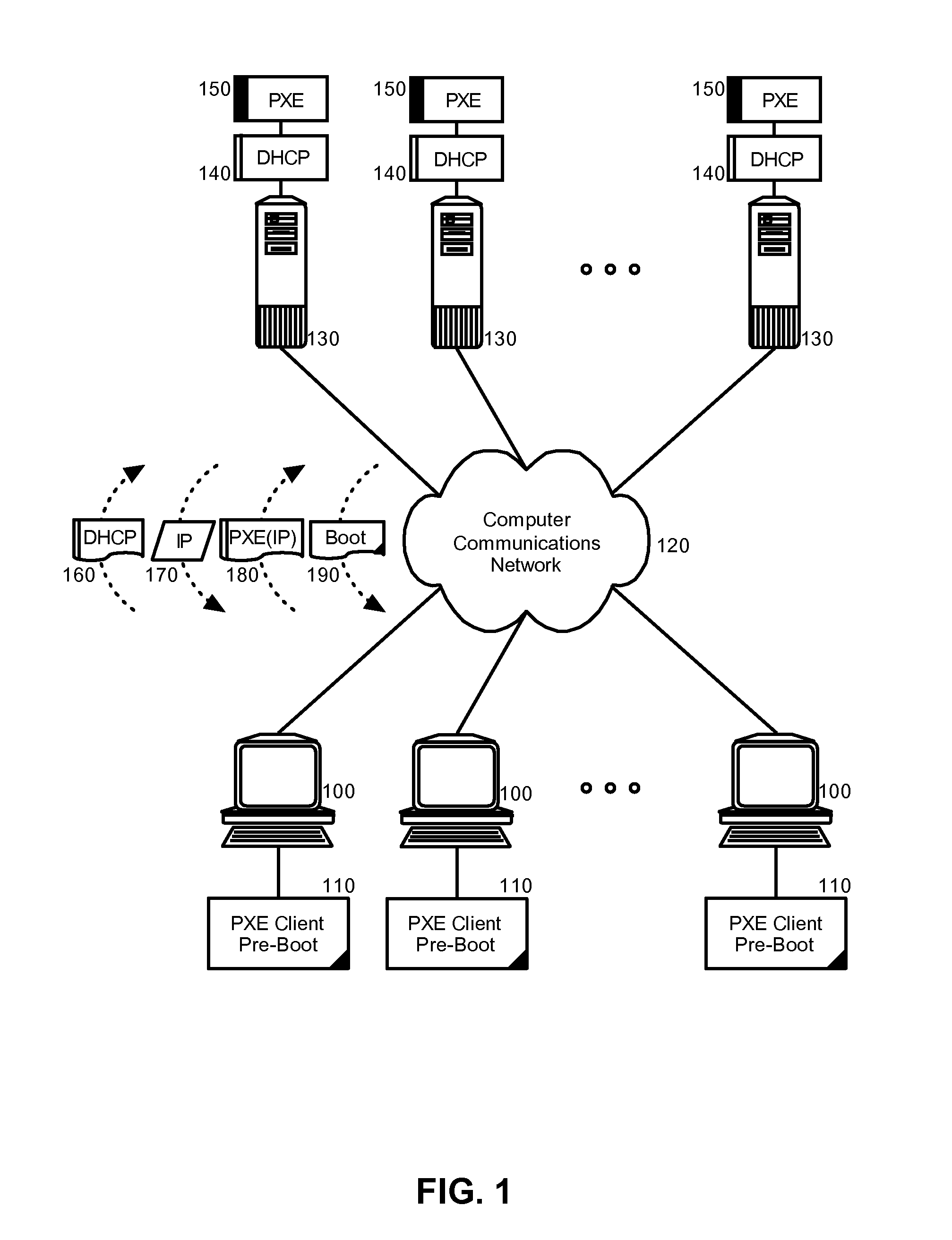
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117 results about "Network booting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
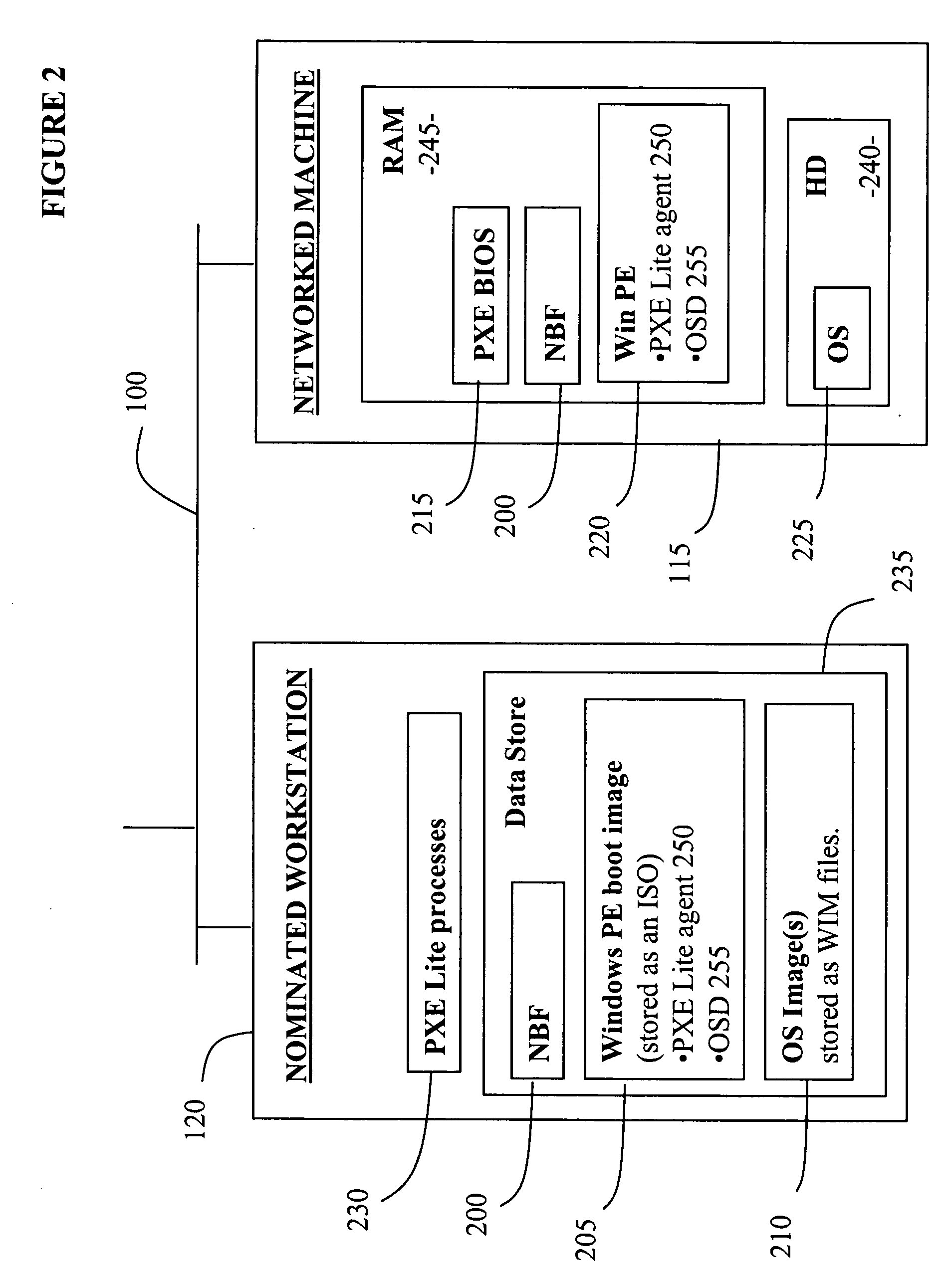
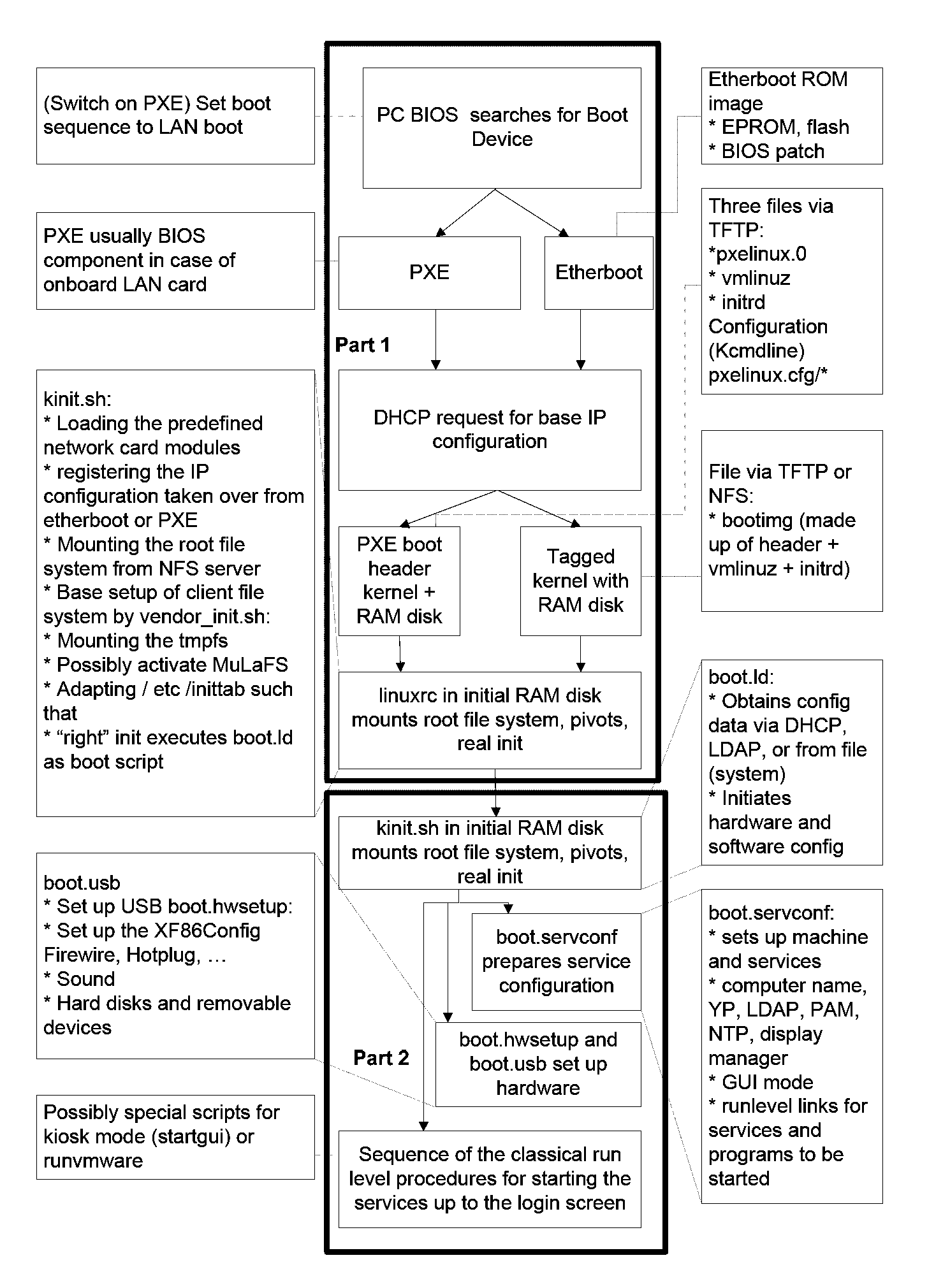
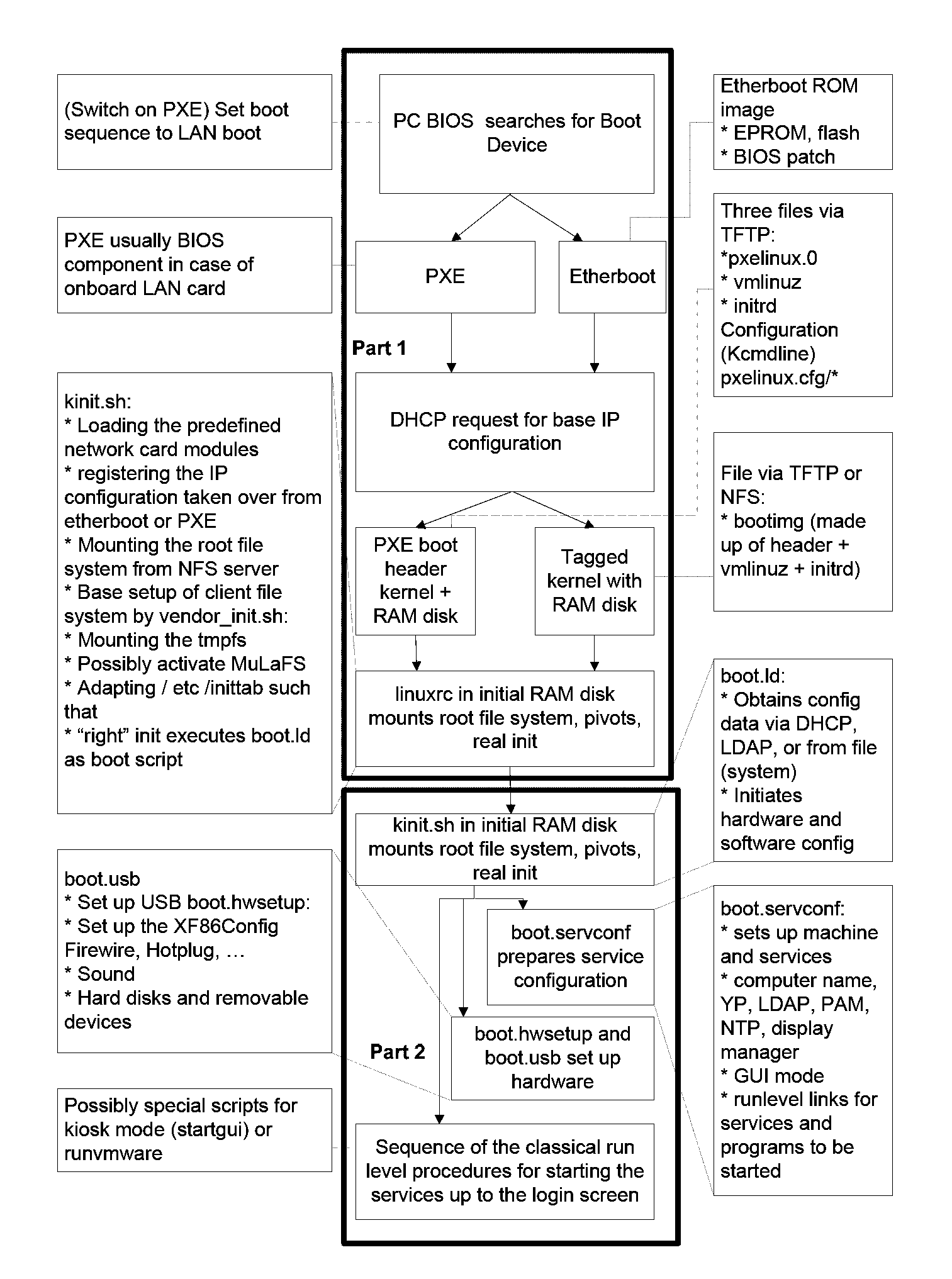
Network booting, shortened netboot, is the process of booting a computer from a network rather than a local drive. This method of booting can be used by routers, diskless workstations and centrally managed computers (thin clients) such as public computers at libraries and schools.
Method and apparatus to enhance platform boot efficiency
ActiveUS20060143432A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlNetwork bootingInternet traffic
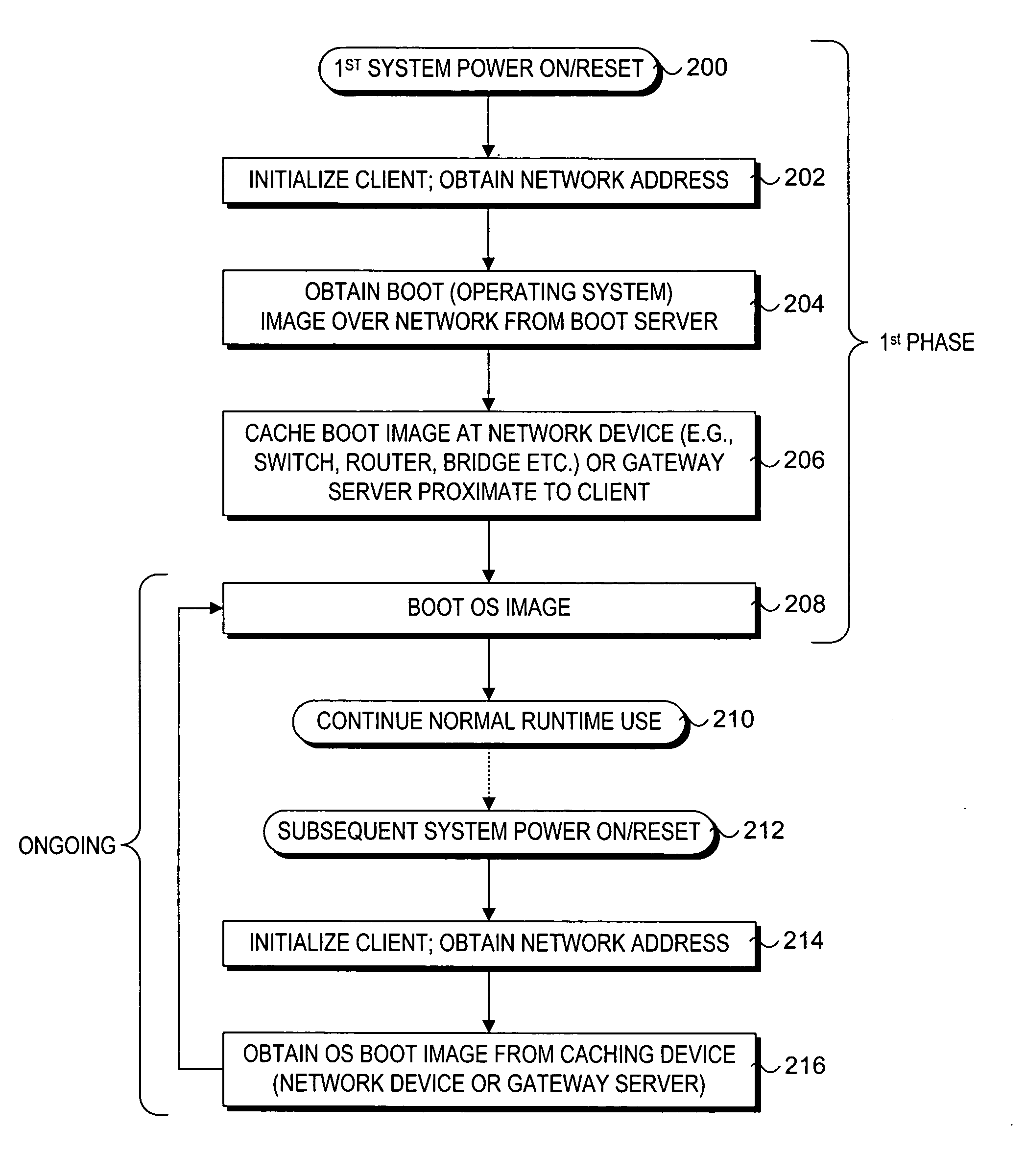
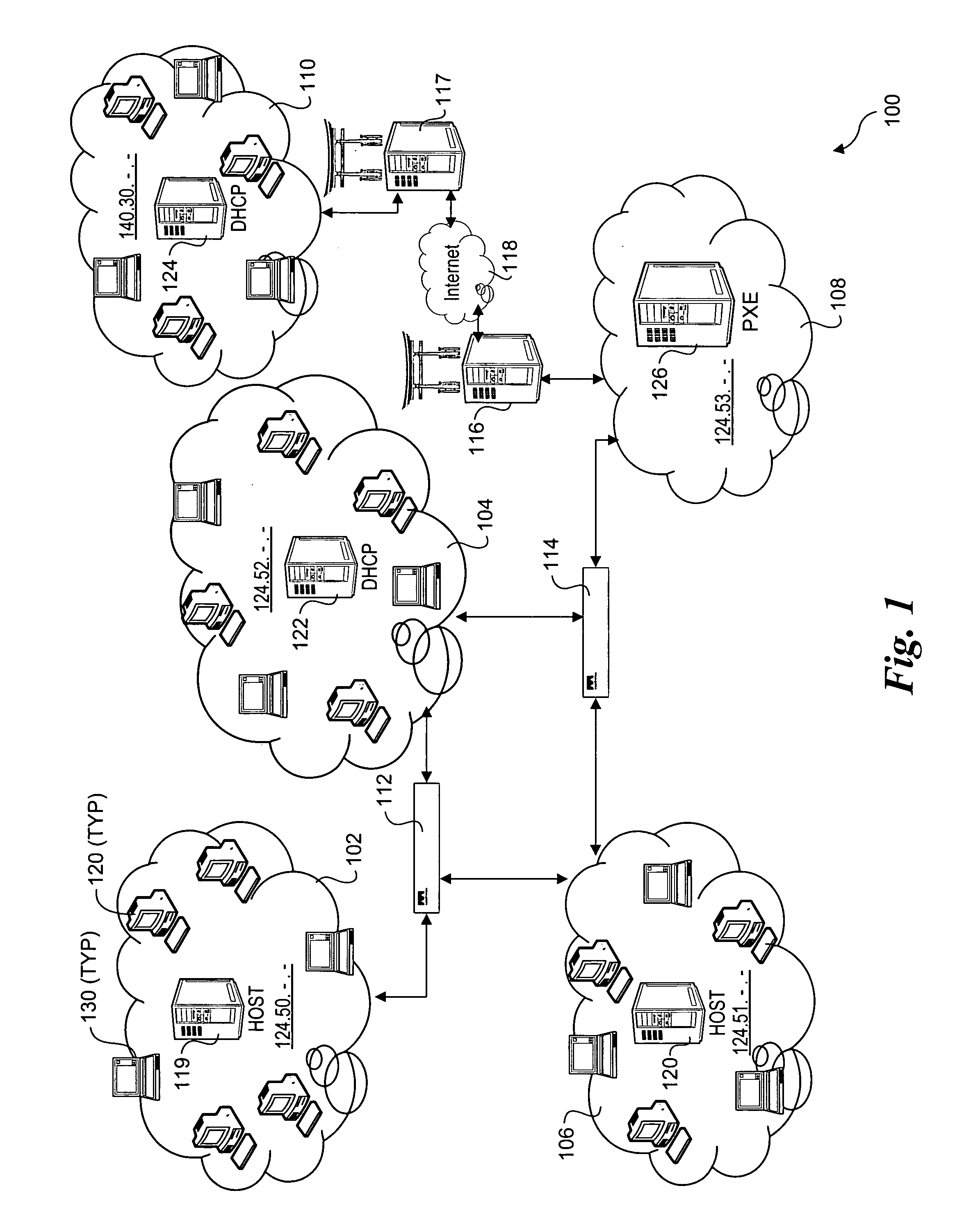
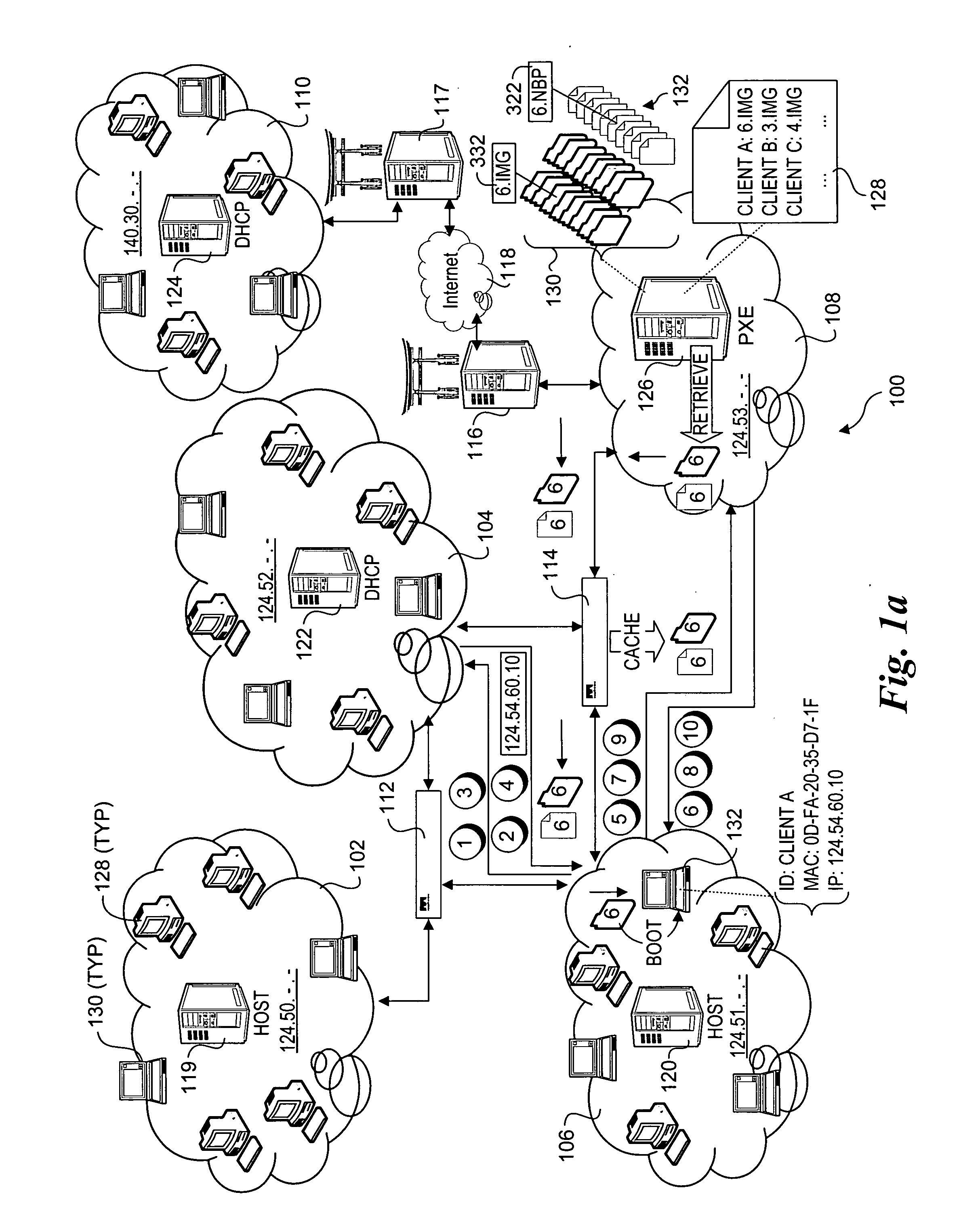
Methods and apparatus for improving network boot efficiency are disclosed. Under embodiments of the method, boot images that are initially sent from a boot server to various clients are cached at network devices along communication paths between the boot server and the clients. In response to subsequent boot image requests from the clients, boot images cached at the network devices are downloaded directly from the network devices rather than from the boot server, reducing network traffic to and from the boot server and domains in between. In addition, boot program bootstrap files may also be cached and downloaded in a similar manner. Techniques are also disclosed for intercepting boot image download and network bootstrap program requests at the network devices, and for maintaining valid boot image cache configurations across the network. The network devices generally include switches, routers, bridges, and gateway servers.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Providing a reliable operating system for clients of a net-booted environment
InactiveUS6751658B1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram loading/initiatingOperational systemNetwork booting
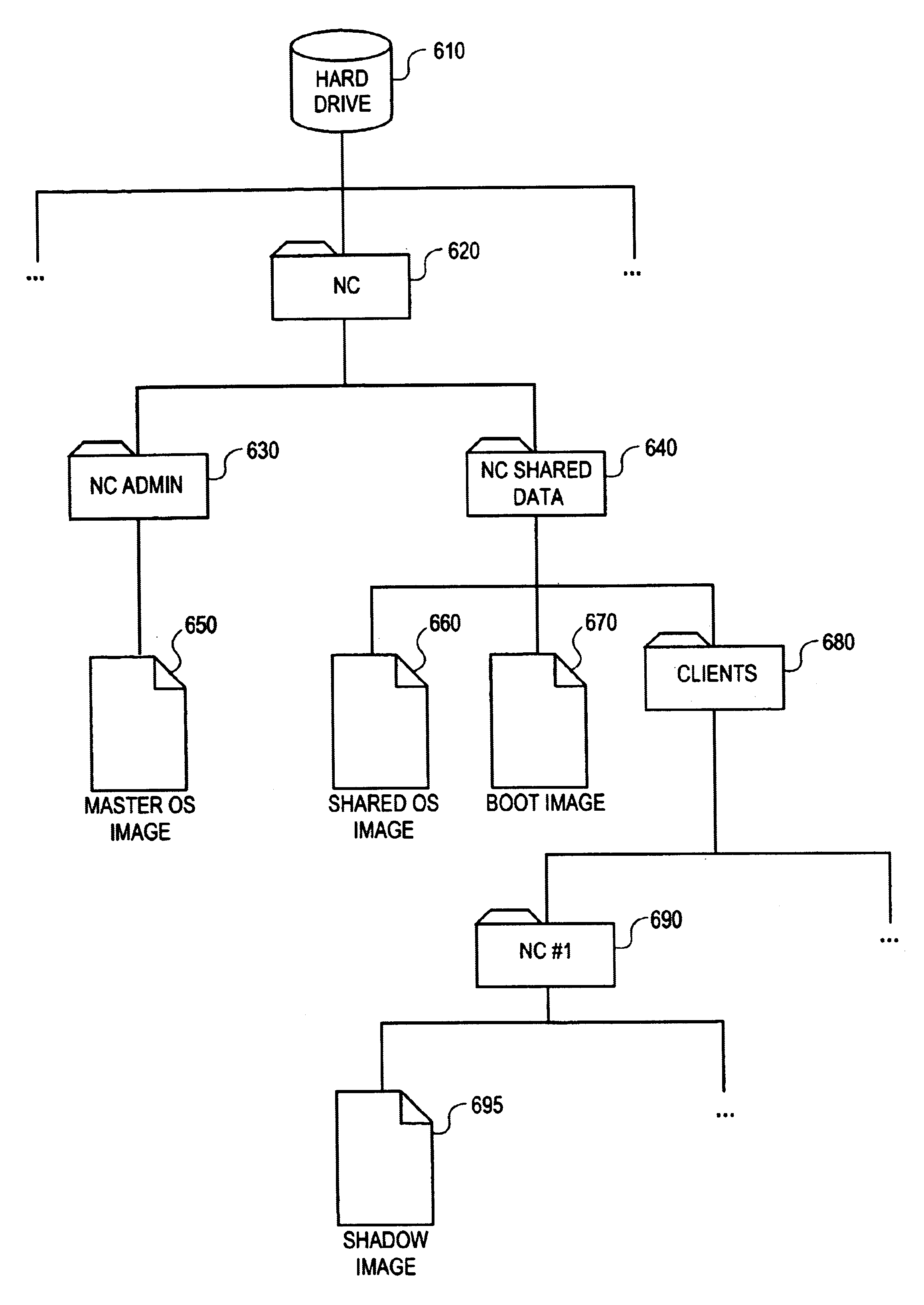
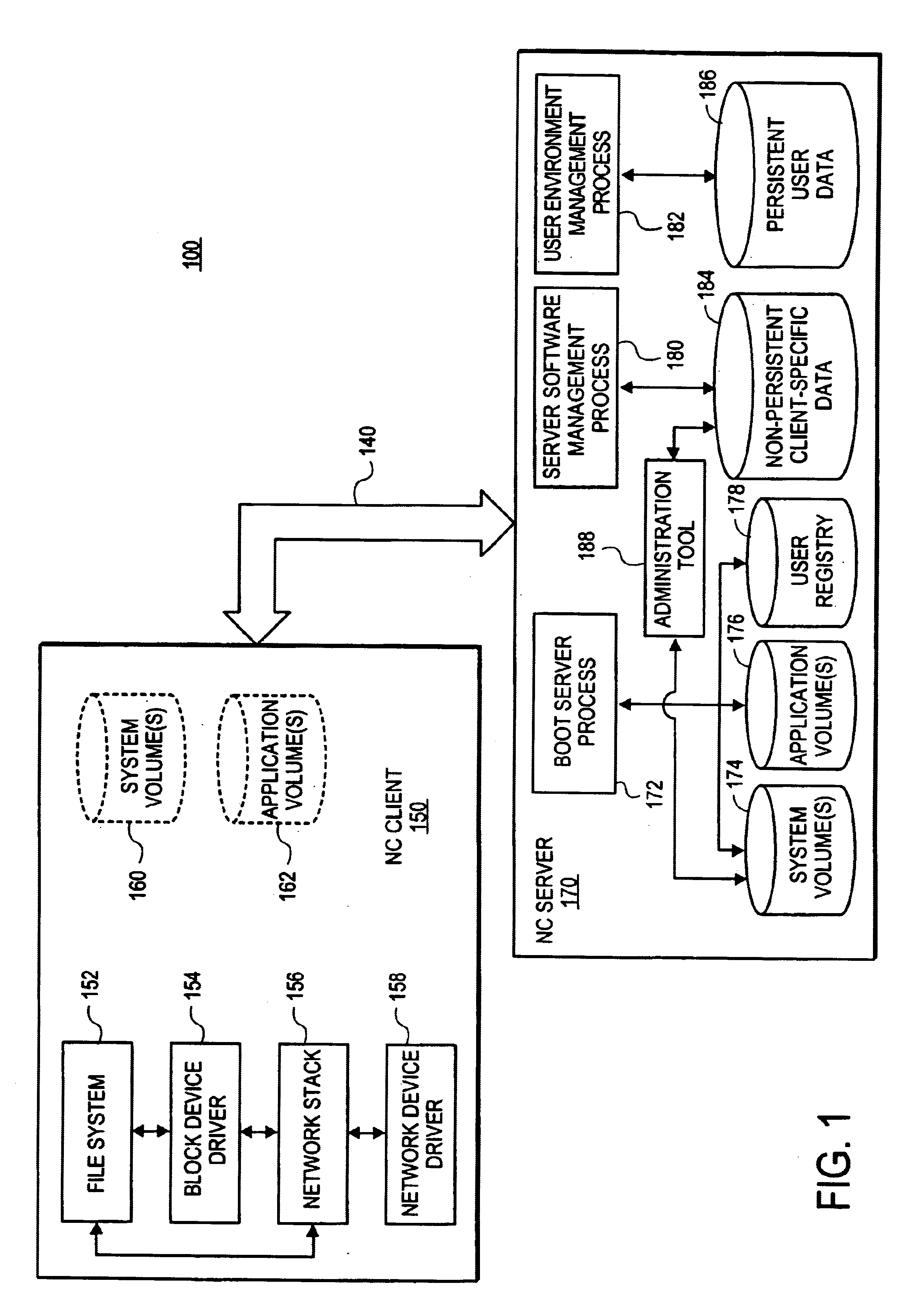
A method and apparatus are provided for supplying a reliable and maintainable operating system in a net-booted environment. According to one embodiment, a network computer (NC) client boots from a boot image provided by an NC server. The boot image includes information identifying the location of one or more system volumes on the NC server that contain operating system software. In response to an attempt to modify the contents of the one or more system volumes, the NC client causes information identifying the modification to be recorded on the NC server separate from the one or more system volumes in a storage area associated with the NC client.
Owner:APPLE INC
Network booting apparatus and method
ActiveUS20080155245A1Avoid problemsEasy to solveDigital computer detailsProgram controlOperational systemNetwork booting
An operating system deployment arrangement provides a database connected to a network for use in monitoring the boot status of machines connected to sub-networks of the network. A workstation connected to a sub-network is adapted to act as a server for a pre-installation environment to machines newly connecting to the sub-network or at the same geographical location. The workstation carries a program for detecting boot initiation messages broadcast on the sub-network and for progressing booting of newly connecting machines in accordance with boot action data held by the database. In particular, the workstation also sends a software agent and operating system deployment processes to a newly connected machine and the agent takes over progression of the booting process from the workstation. The data held in the database for any one machine is updated as booting progresses. Flexibility is provided both in administration of the boot action data held in the database and by means of user interaction software loaded to a newly connected machine in the course of booting.
Owner:1E LTD
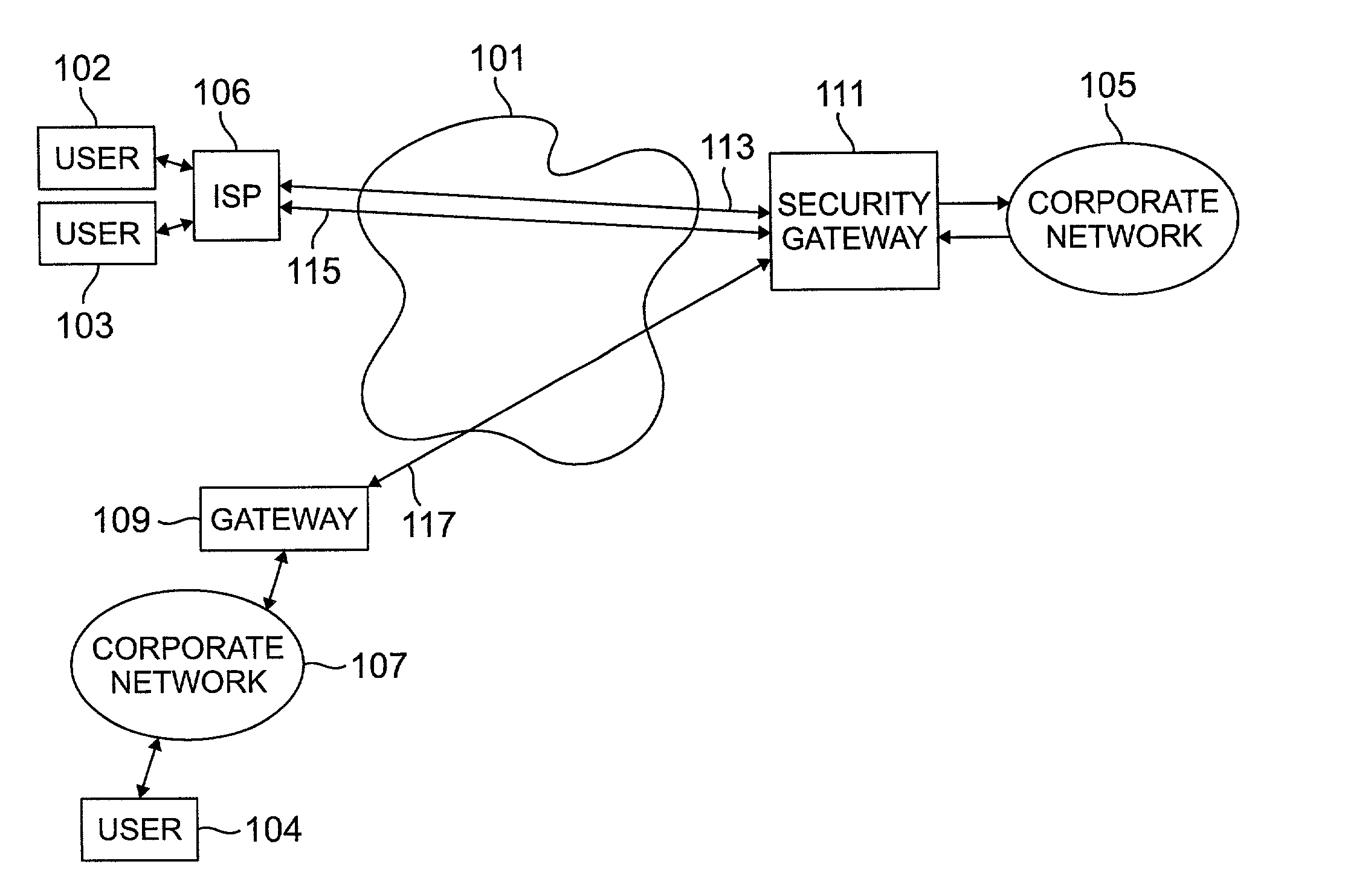
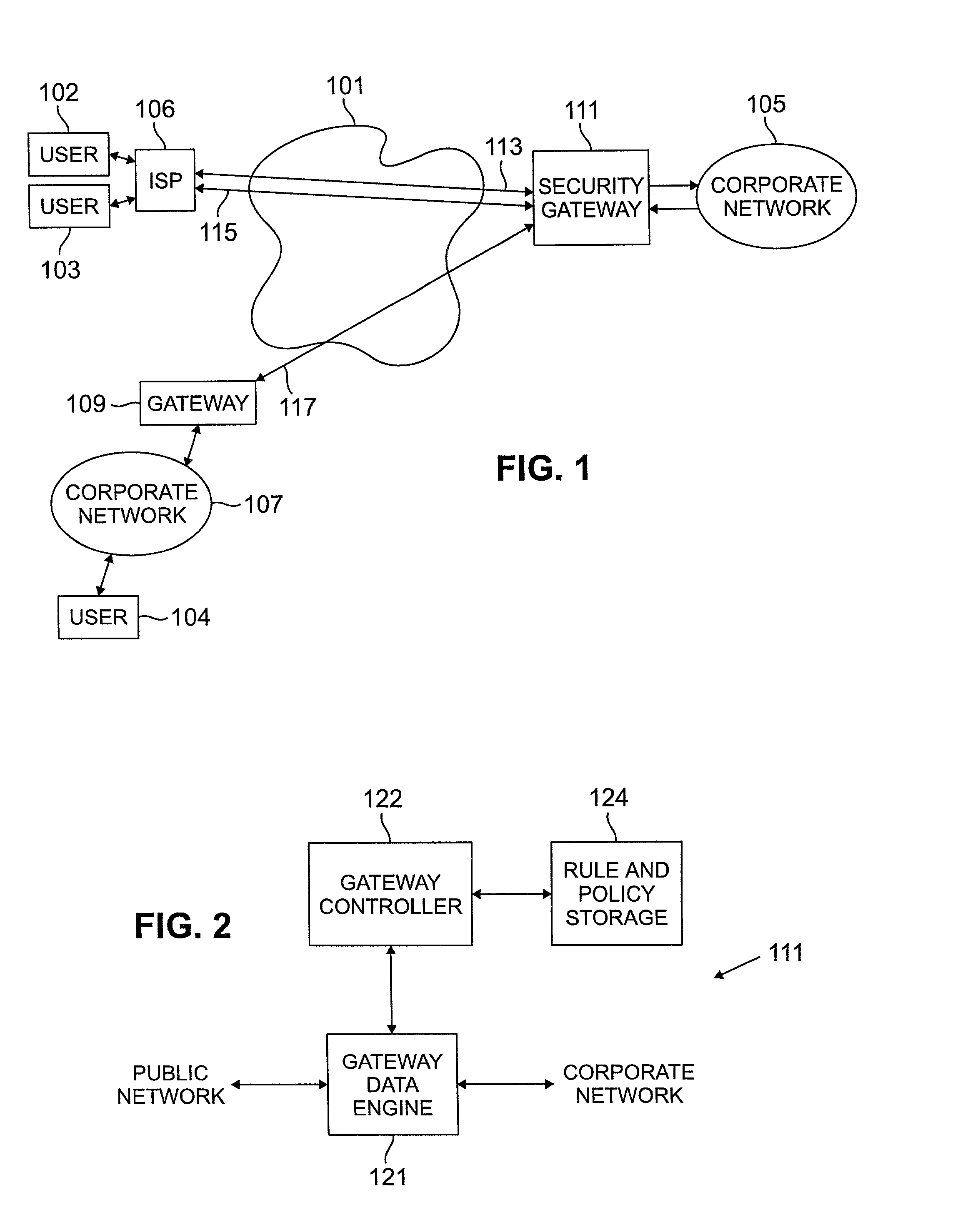
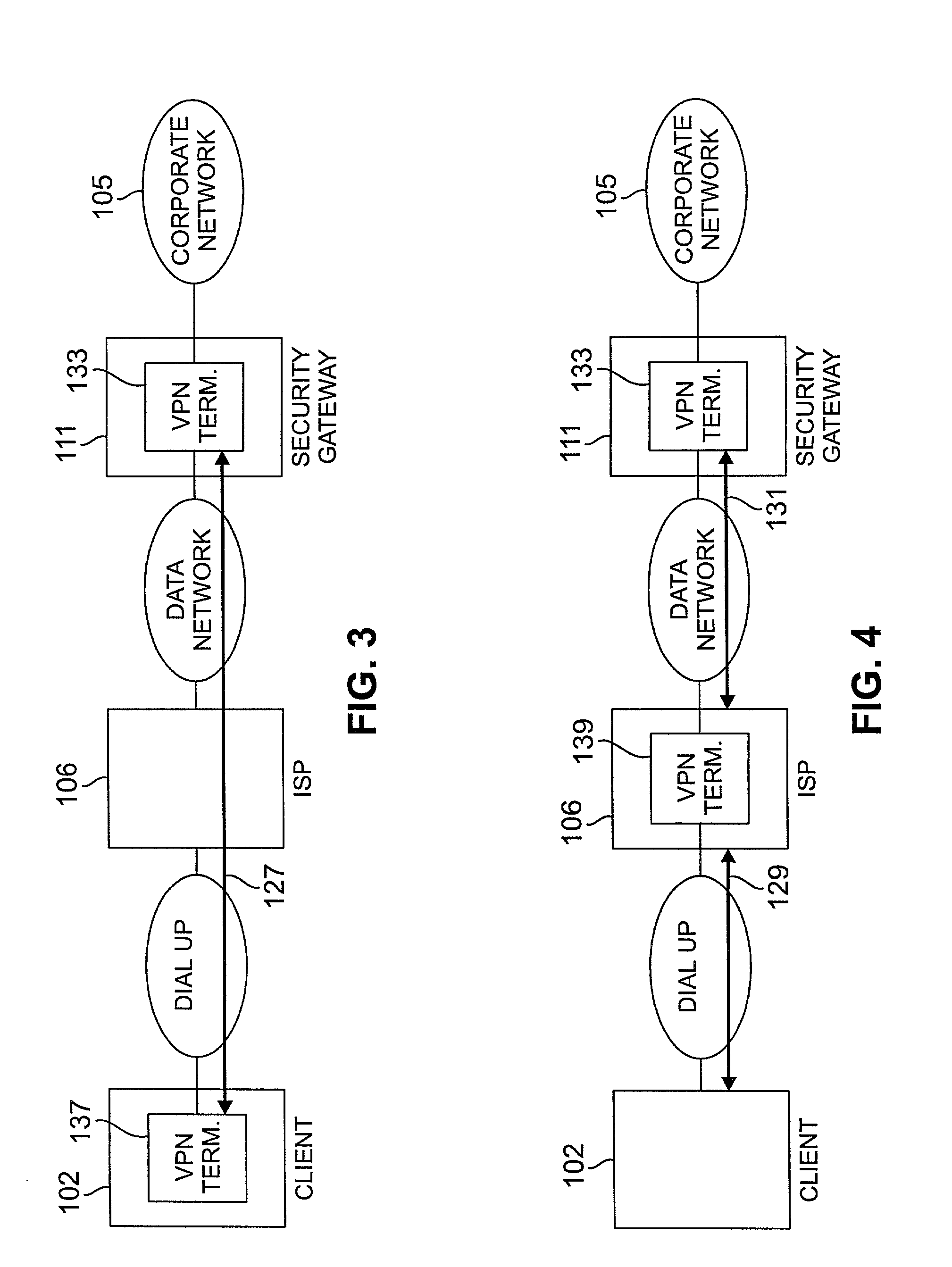
Method and apparatus for order independent processing of virtual private network protocols
InactiveUS20020129271A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlDiscriminatorProtocol processing
Methods and arrangements for virtual private network (VPN) data packets are disclosed. VPN packets include a payload having Internet Protocol (IP) addresses which guide the packet through a network to a security gateway. The payload may be encrypted and / or compressed and may include internal addresses to denote the real source and destination for a data portion of the payload. As initial control packets are received they are authenticated and rules and procedures are identified for proper treatment of VPN data packets bearing the same source IP address. The rules and procedures are stored in a gateway data engine having a plurality of protocol processing modules. VPN data packets are received by a protocol discriminator which reads the stored rules and procedures identified for the source IP address of the received packet. The discriminator passes the received packet to a first protocol module as identified in the stored rules and procedures. After the first module completes processing, the packet is passed back to the protocol discriminator which determines whether further protocol processing is required. When further protocol processing is required, the packet is passed to another protocol module for processing in accordance with another protocol. At the completion of processing, the second protocol module returns the packet to the protocol discriminator.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
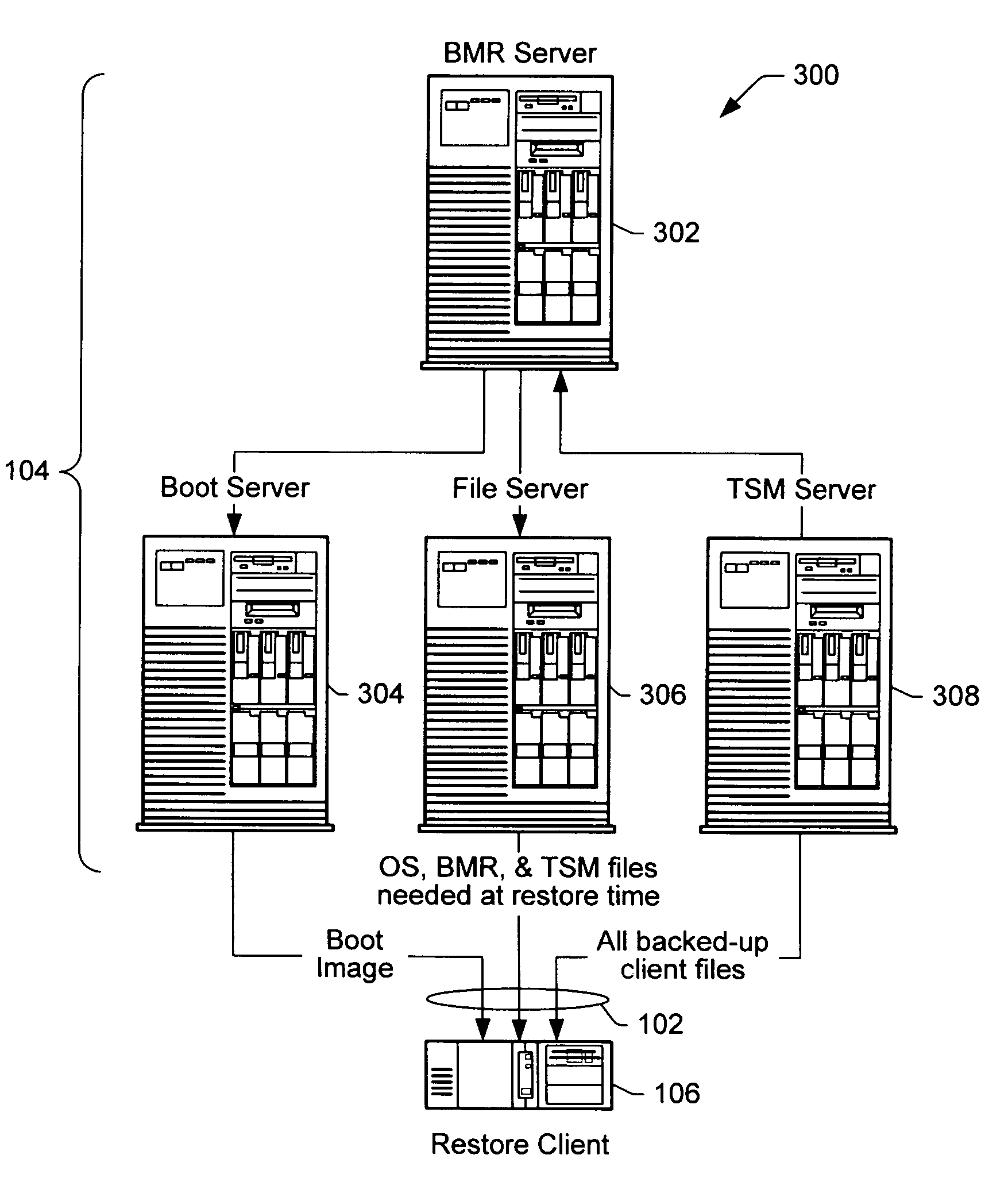
Computer restoration systems and methods
A method restores a client device of a network on major failure of the client device. The client device is incapable of automatically booting on its own. The network includes a server computer. The method includes booting the client device over the network in the restoration operation, configuring the client device according to the boot program and saved configuration states for the client device, and copying files to the client device in accordance with the configuration. The client computer has access to a storage manager application, such as a server computer of the network operating a storage management software program. All client files, including configuration files, as well as application and data files, of the client device are saved on the network by the storage manager application. The client device is booted over the network, rather than locally to the client device by boot disk or otherwise. The boot program is loaded to the client device, and the client device retrieves configuration and file information over the network from the storage manager application. The client device configures its disk according to the configuration information, and then all other files and data of the client device at the time of failure of the client device are saved on the disk substantially in the condition and state just prior to the failure and as most recently backed up to the storage manager application. Alternatively, the client device is reset and booted via a control device either locally or otherwise connected to the client device, and substantially according to the method of the network boot.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Method and apparatus to enhance platform boot efficiency
Methods and apparatus for improving network boot efficiency are disclosed. Under embodiments of the method, boot images that are initially sent from a boot server to various clients are cached at network devices along communication paths between the boot server and the clients. In response to subsequent boot image requests from the clients, boot images cached at the network devices are downloaded directly from the network devices rather than from the boot server, reducing network traffic to and from the boot server and domains in between. In addition, boot program bootstrap files may also be cached and downloaded in a similar manner. Techniques are also disclosed for intercepting boot image download and network bootstrap program requests at the network devices, and for maintaining valid boot image cache configurations across the network. The network devices generally include switches, routers, bridges, and gateway servers.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
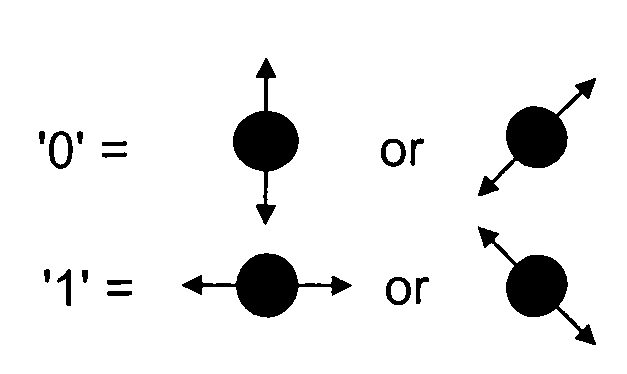
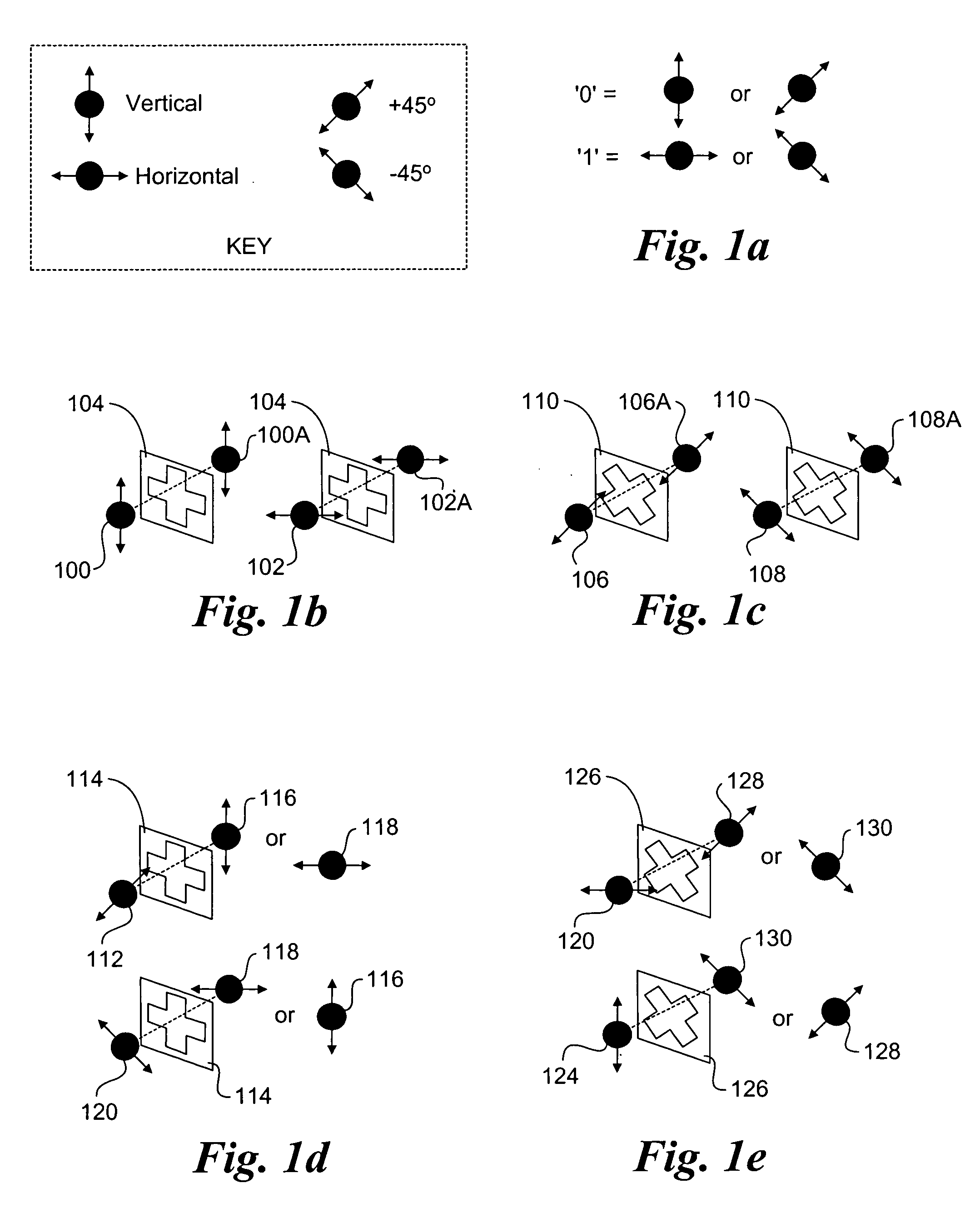
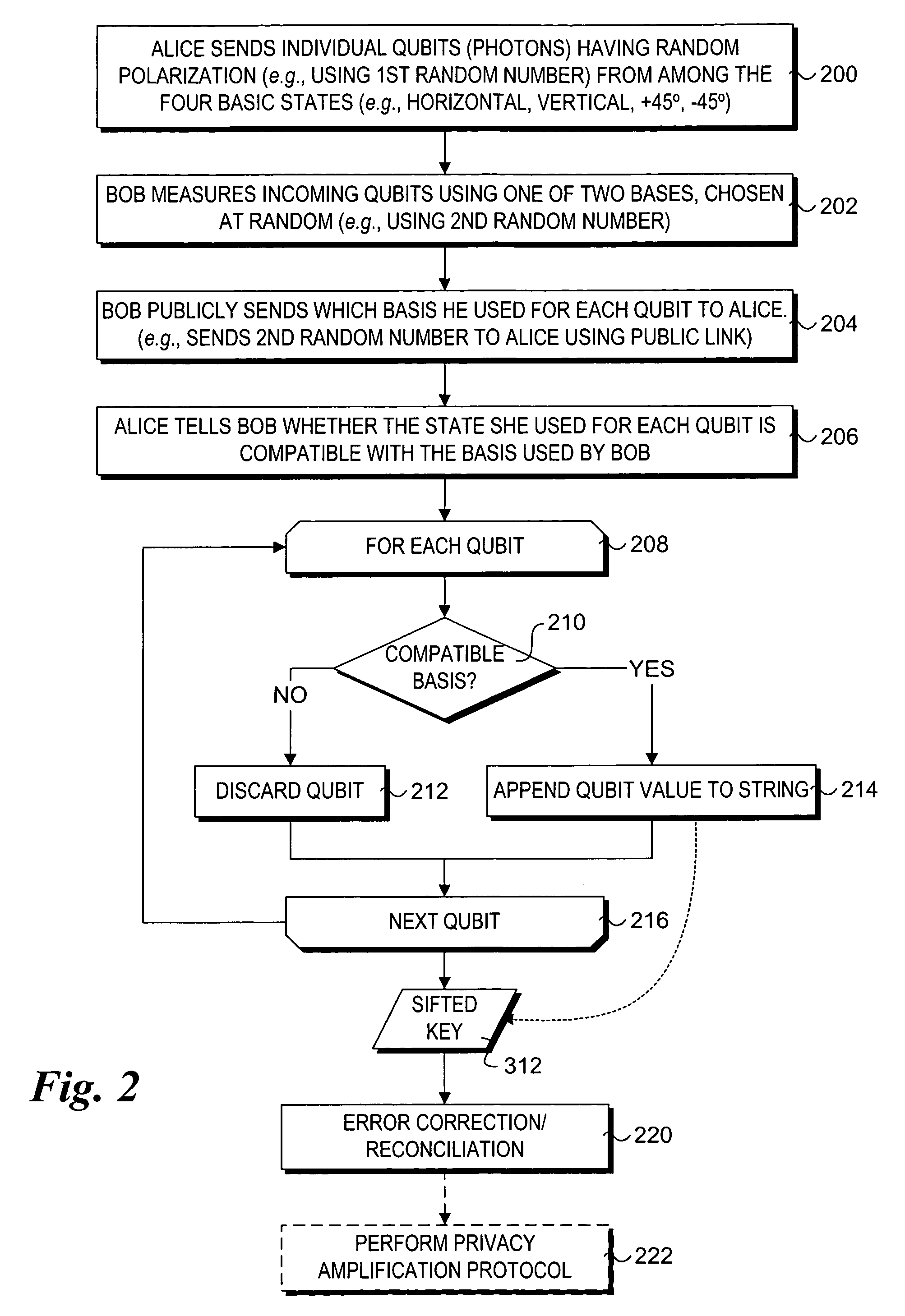
Method to support secure network booting using quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution
A method and system to support secure booting and configuration. The mechanism employs an optical link comprising a quantum channel that is used to send data encoded as quantum bits (qubits) via respective photons. Qubits encoded using a first random basis at the client and are sent to the boot server, which processes the qubits using a second random basis to extract the encoded data. A public channel is used to send data indicative of the second random basis to the client. A symmetric quantum key is then derived a both the client and the boot server using a comparison of the random basis' and the original and extracted data. The scheme enables the presence of an eavesdropper to be detected on the quantum channel. A DHCP message exchange is employed to obtain a network address, and, optionally, be provided with a network address for one or more boot servers. A boot image request is made to the boot server by the client, and a subsequent boot image is downloaded via a secure channel facilitated by the symmetric quantum key.
Owner:INTEL CORP
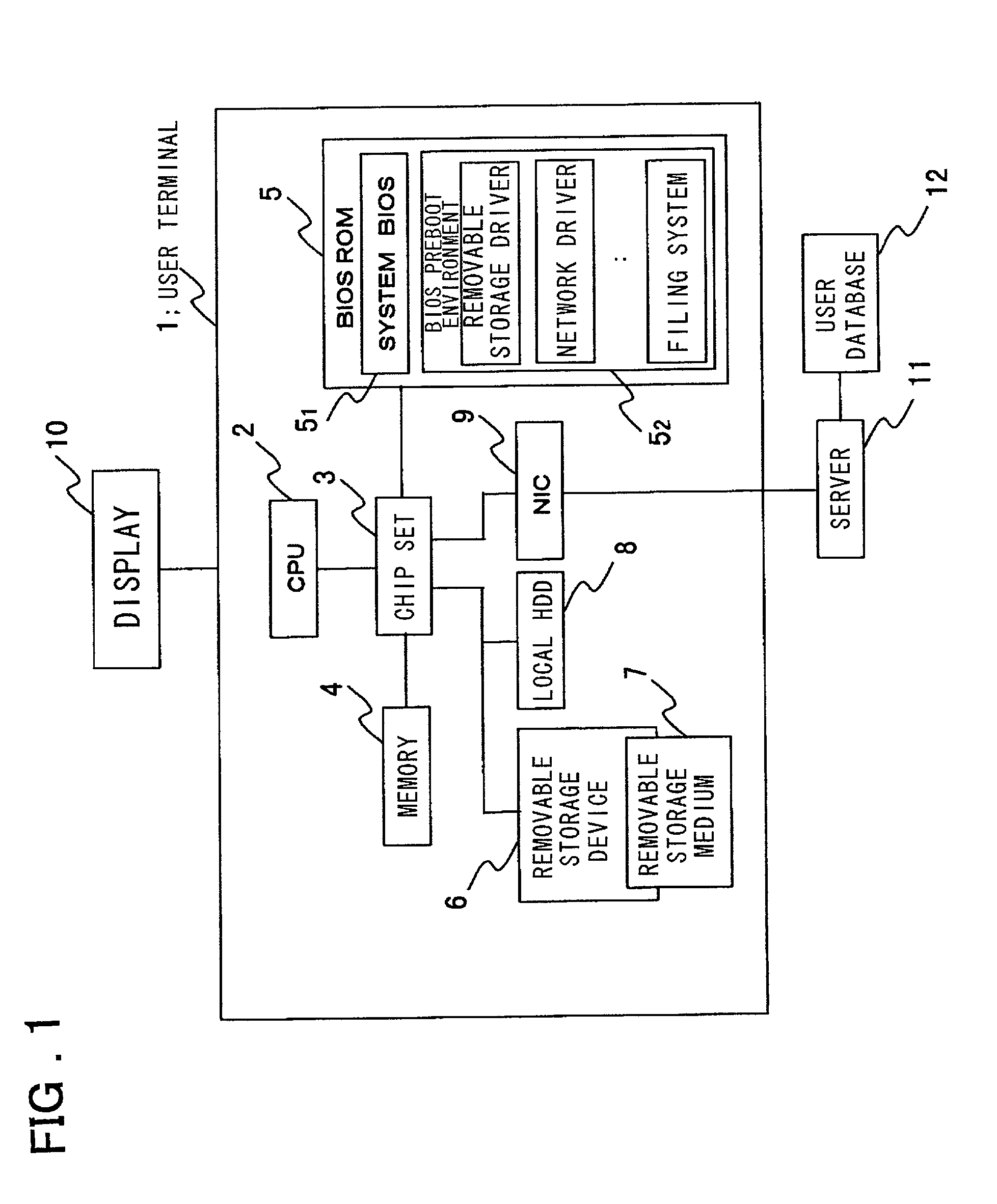
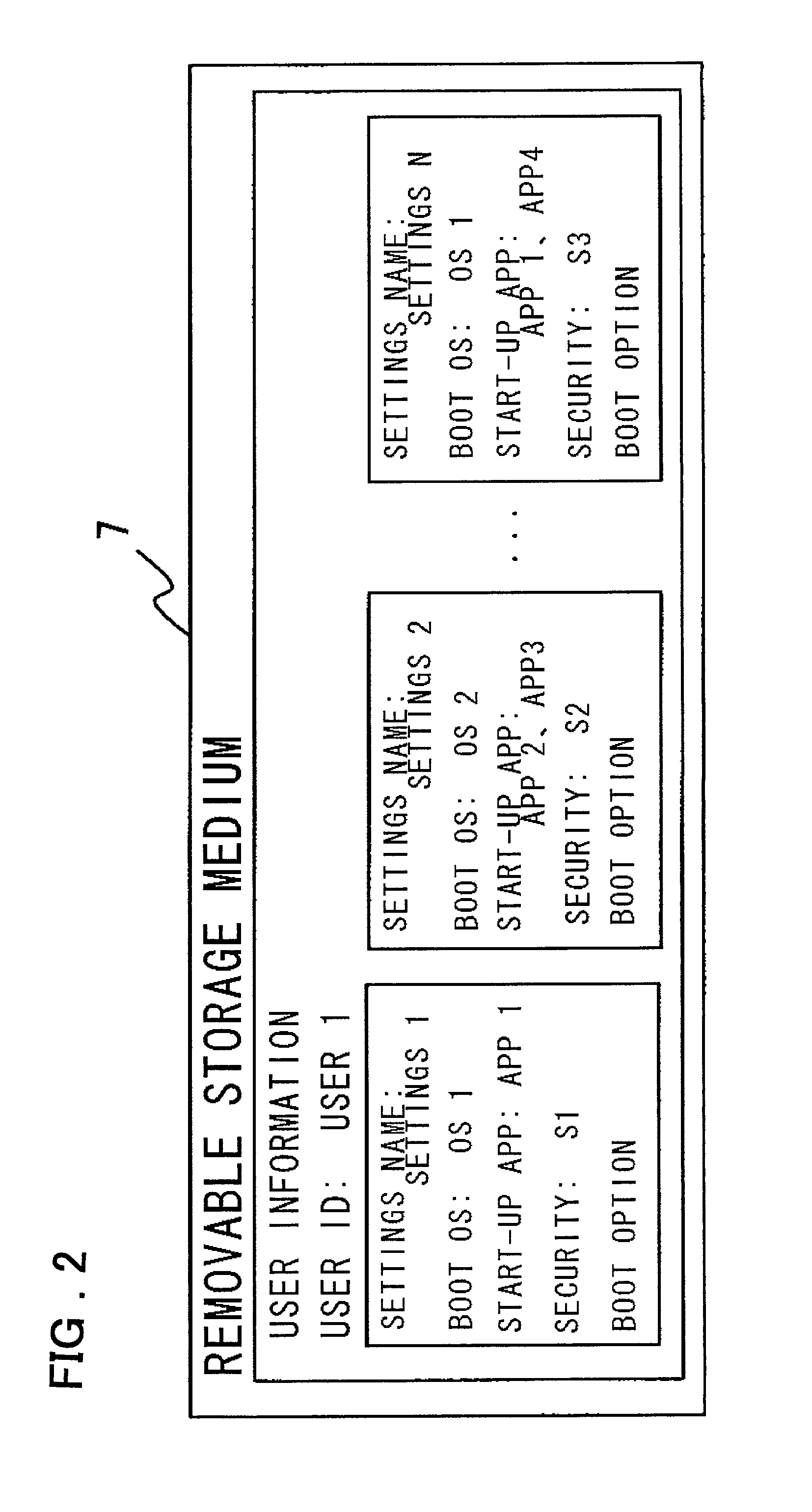
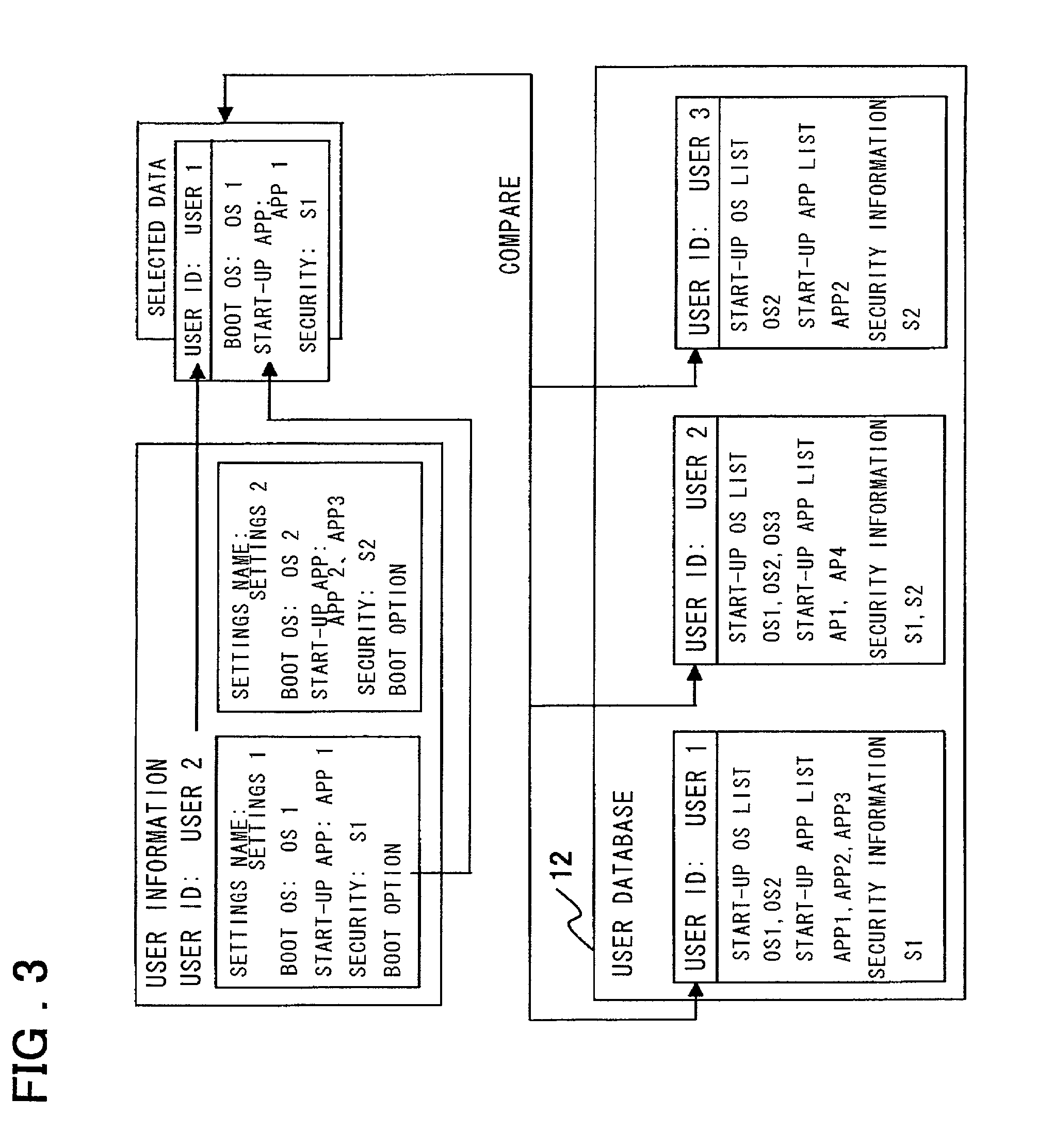
User-authentication-type network operating system booting method and system utilizing BIOS preboot environment
InactiveUS20010052069A1Easy to startImprove securityDigital computer detailsDigital data authenticationNetwork operating systemTerminal server
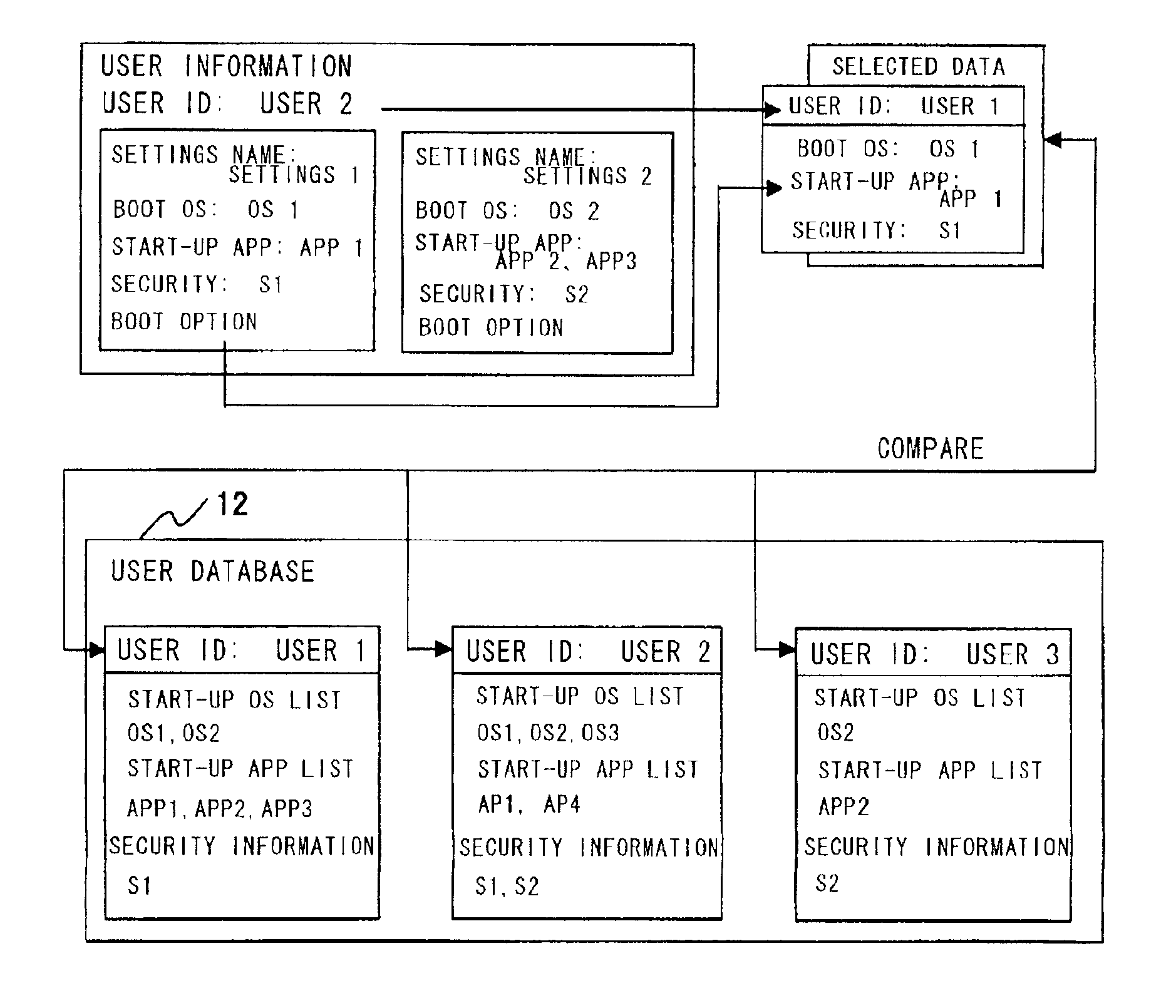
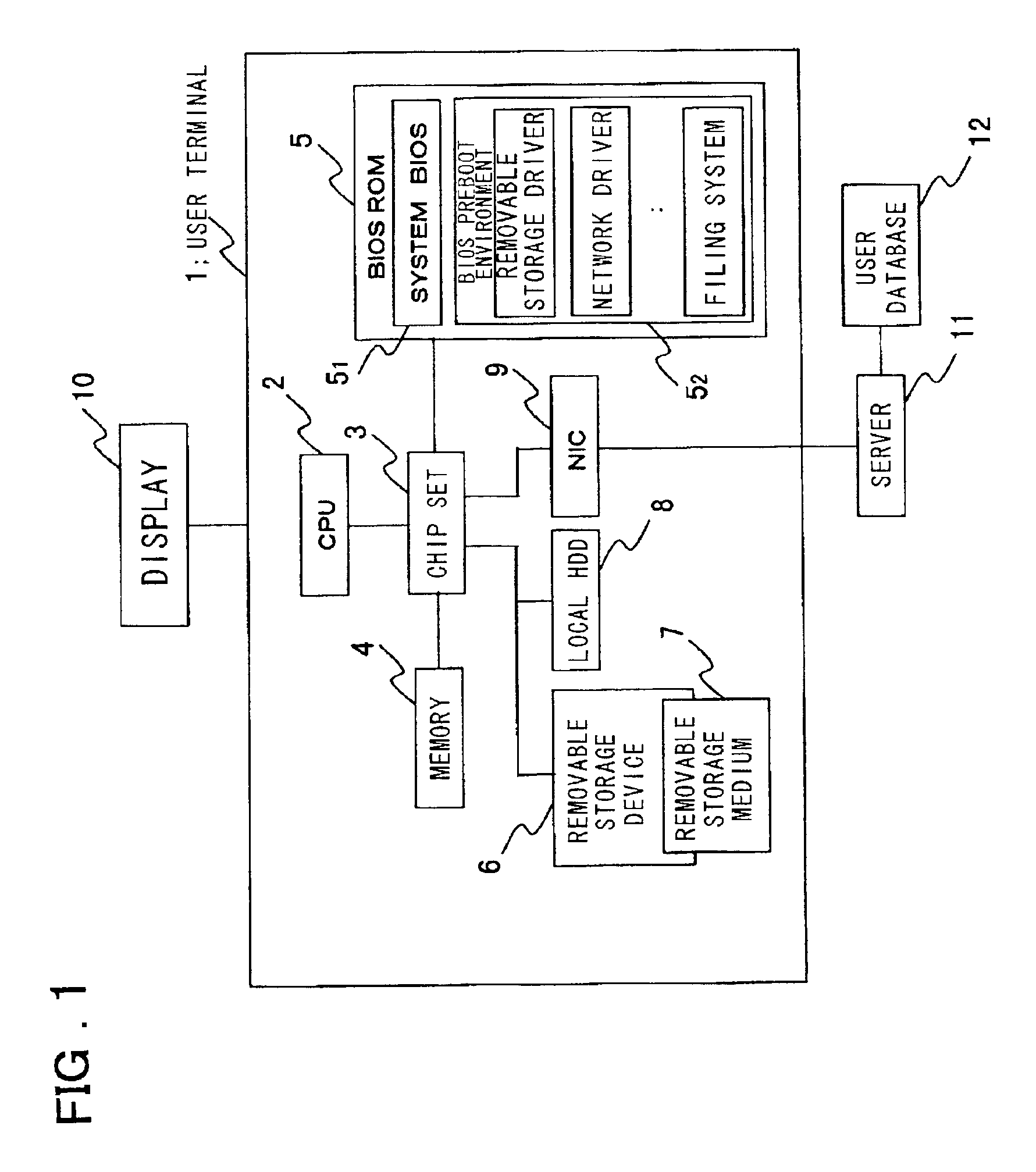
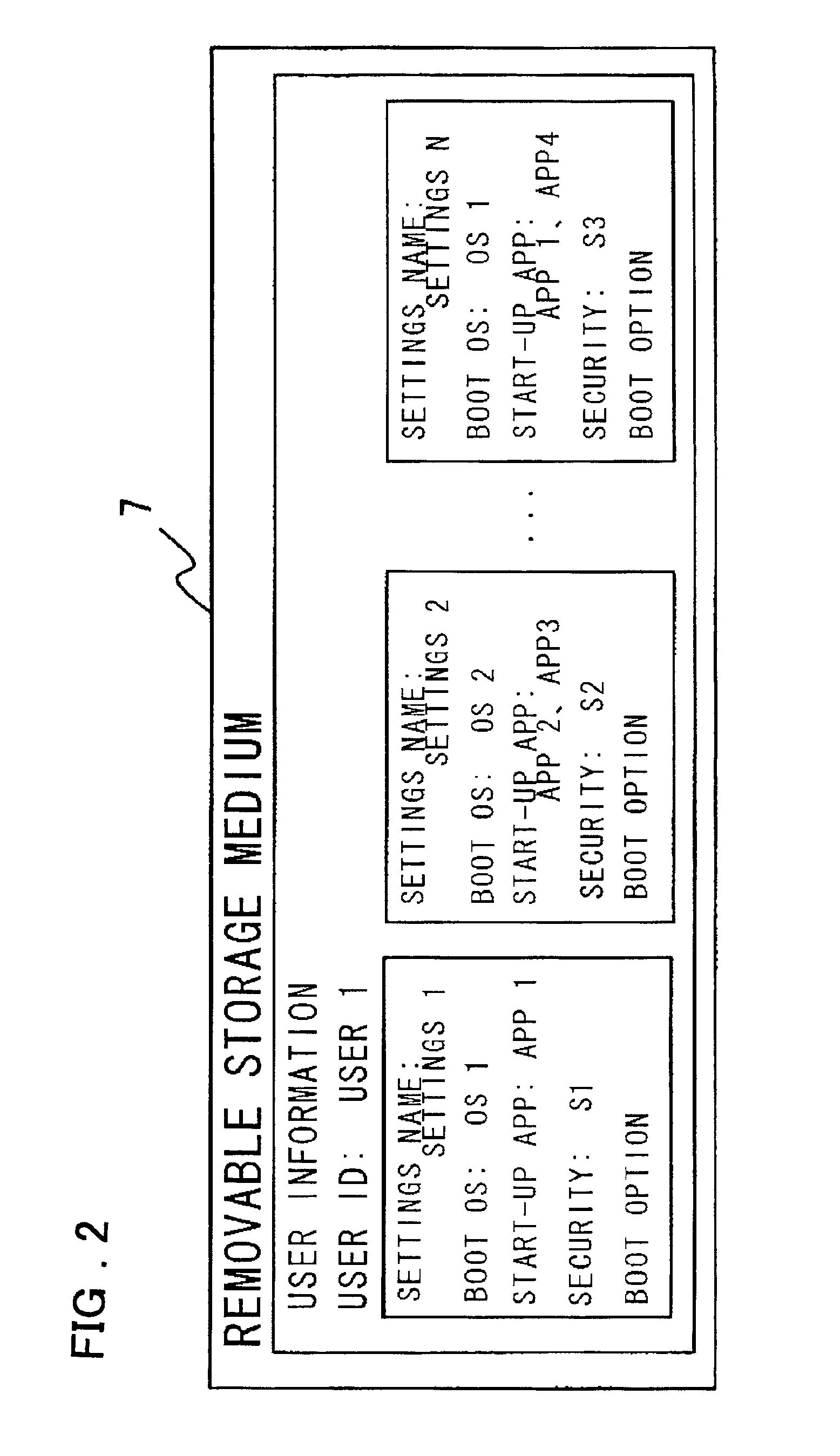
Disclosed is a system that make it possible for a user to readily boot an operating system from a user terminal with user-specific settings, thereby making it unnecessary for the server to register an image for each OS environment, as a result of which the required storage capacity of the server can be reduced. The user terminal, which is connected to the server by a network, is booted using an operating system stored in the server. In booting of the user terminal, user information that has been selected by the user from OS-booting user information stored on a removable storage medium of the user terminal is transmitted to the server under the control of a BIOS preboot environment stored in a storage device of the user terminal. On the basis of the user information, the server authenticates the user terminal, transmits the operating system to the user terminal and network-boots the operating system in a user-specific environment.
Owner:NEC CORP
Server blade network boot method that minimizes required network bandwidth
ActiveUS7350068B2Use minimizedMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlNetwork bootingEmbedded system
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Embedded OS PXE server
InactiveUS7085921B2Low costReduce developmentData resettingMultiple digital computer combinationsMicrocontrollerOperational system
A method of directing a computer network for booting using a prebooting execution environment (PXE) embedded OS based computer is provided in which the embedded OS based computer listens for PXE requests from PXE enabled target servers of the network and in response provides a netboot program and address information of a boot server. An embodiment of an embedded OS based computer is provided that has a network interface controller, a microcontroller, a display, an input device, and a processor. An embodiment of a system for booting a computer network using the embedded OS based computer is provided. The system has a target network of PXE enabled servers coupled to the embedded OS based computer and a boot server coupled to the embedded OS based computer and to the network. The system and the method are illustrated using Windows CE operating system as an example an embedded OS.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
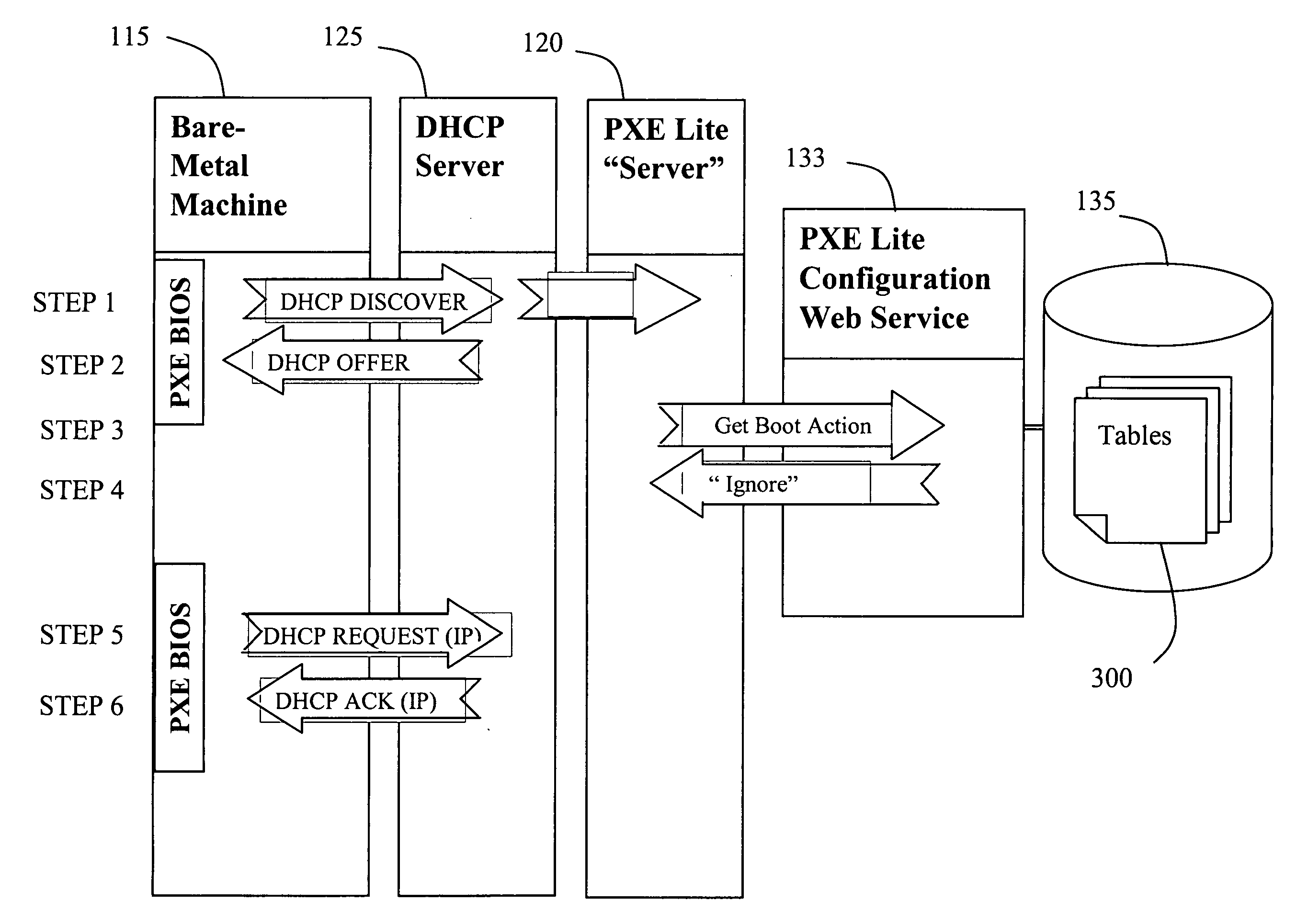
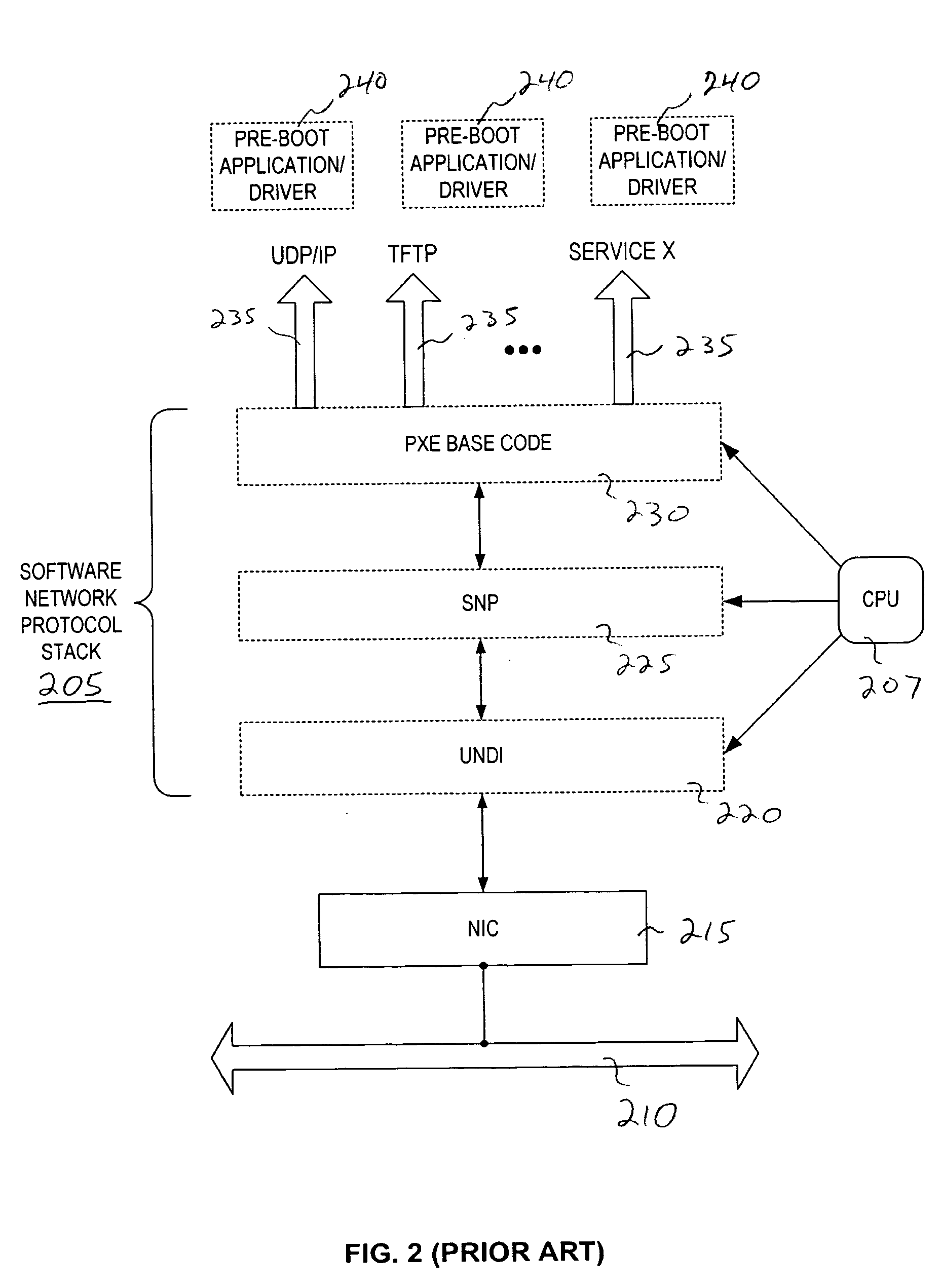
Selective sub-net filtering in a pre-boot execution environment (PXE)
Embodiments of the invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to PXE processing and provide a novel and non-obvious method, system and computer program product for selective PXE subnet filtering. In an embodiment of the invention, a PXE server subnet filtering method can be provided. The method can include selectively referring a PXE client to different boot logic depending upon at least a portion of a network assigned address for the PXE client. In this regard, selectively referring a PXE client to different boot logic depending upon at least a portion of a network assigned address for the PXE client can include selectively referring a PXE client to a different boot image notification layer (BINL) service providing a different filename for a different network bootstrap program depending upon at least a portion of an Internet protocol (IP) assigned address for the PXE client by a network resident dynamic host control protocol (DHCP) server in response to a previous DHCP request provided by the PXE client.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
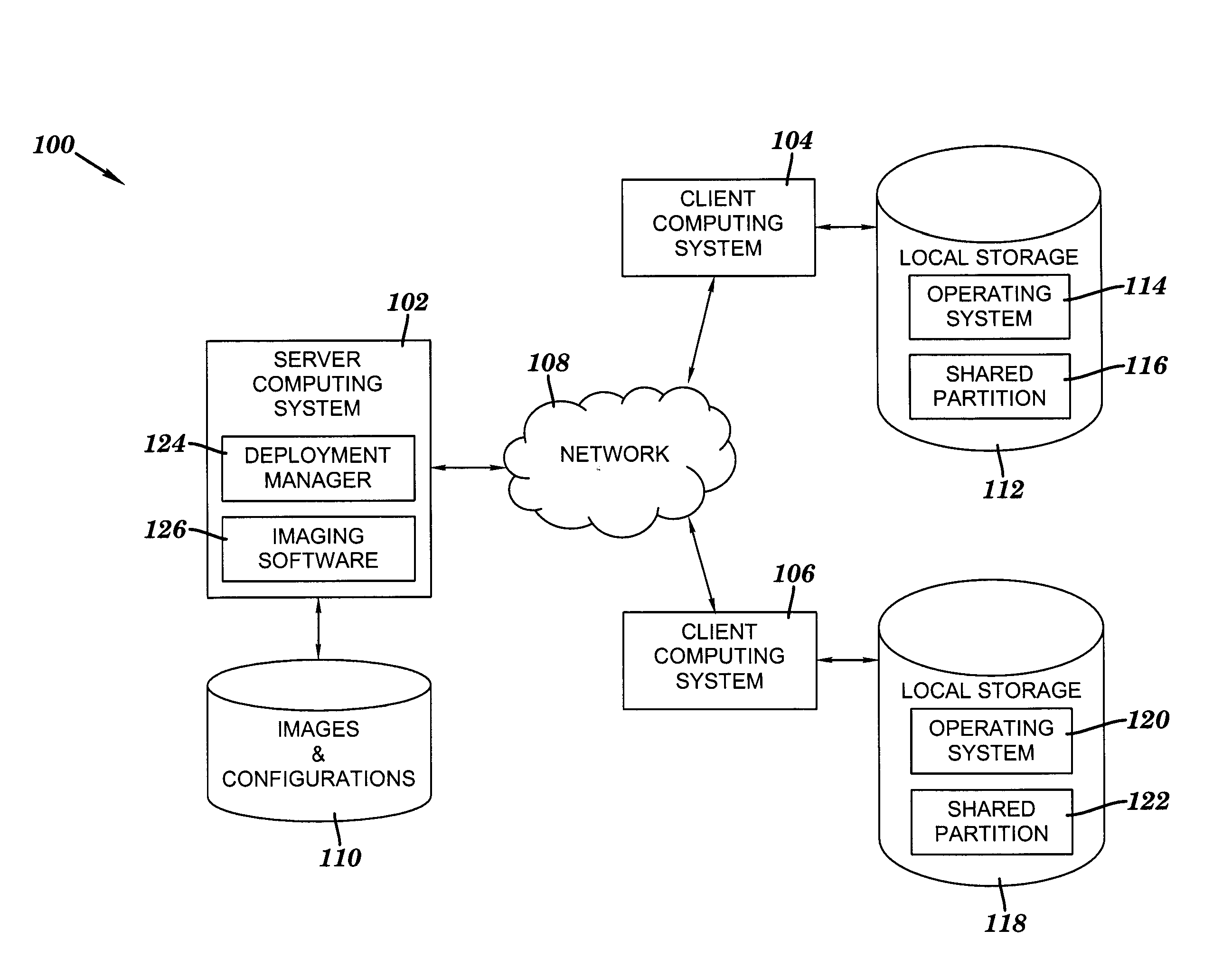
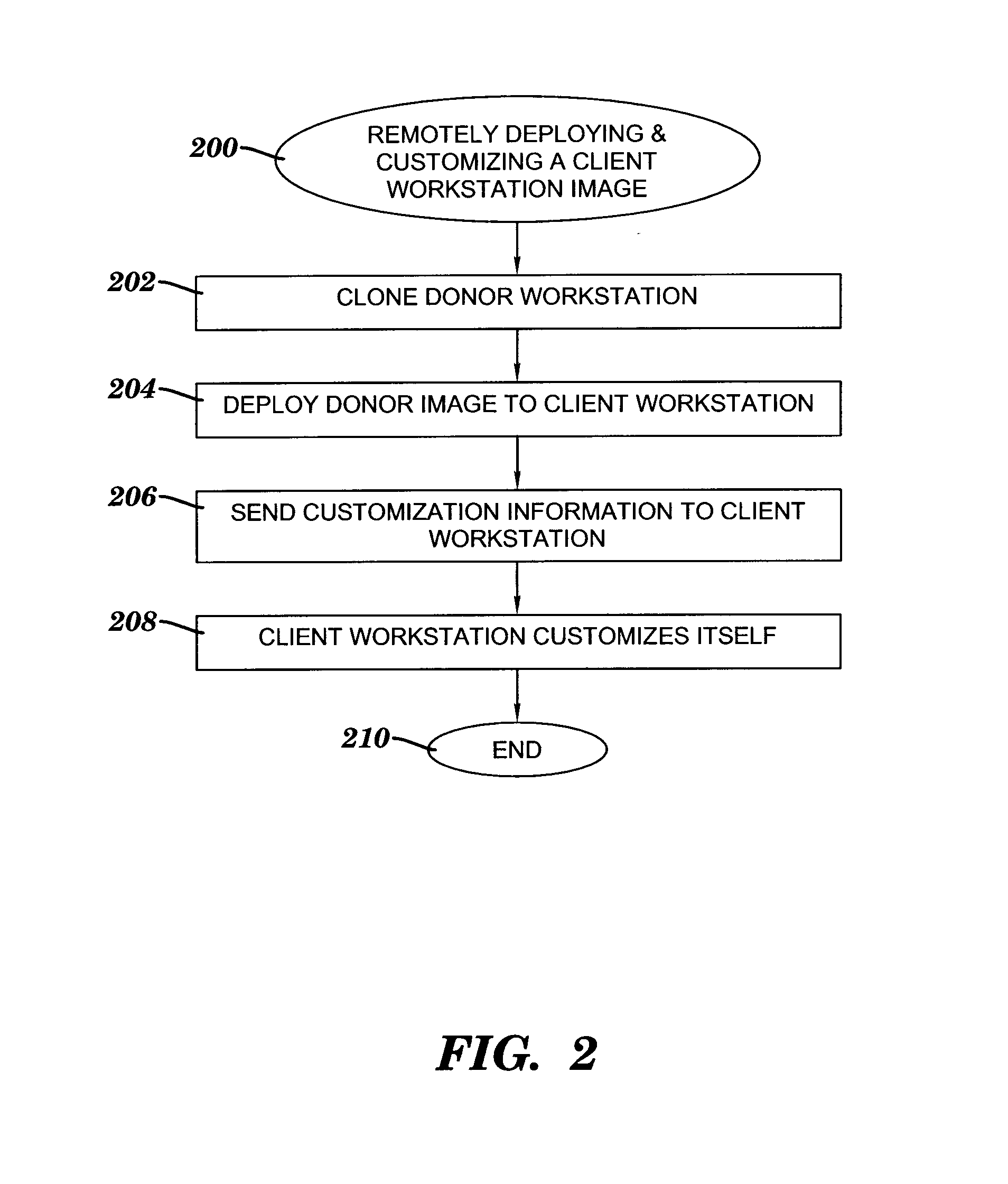
Method, system and program product for remotely deploying and automatically customizing workstation images
ActiveUS20080270583A1Low costSave effortDigital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork bootingFile system
A method, system and program product for remotely deploying and automatically customizing workstation images. A client's first partition receives a workstation image deployed from a server in communication with the client via a network. The image includes a customization script. The server remotely boots the client, which is pre-configured to be booted by the server via the network. The server writes a customization parameter to the client's shared partition. The shared partition has a file system type that is accessible by the server via the remote boot and by the deployed image. One or more subsequent reboots of the client include the deployed image obtaining the customization parameter from the shared partition, identifying the customization script by using the customization parameter, and executing the customization script to automatically customize the client.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
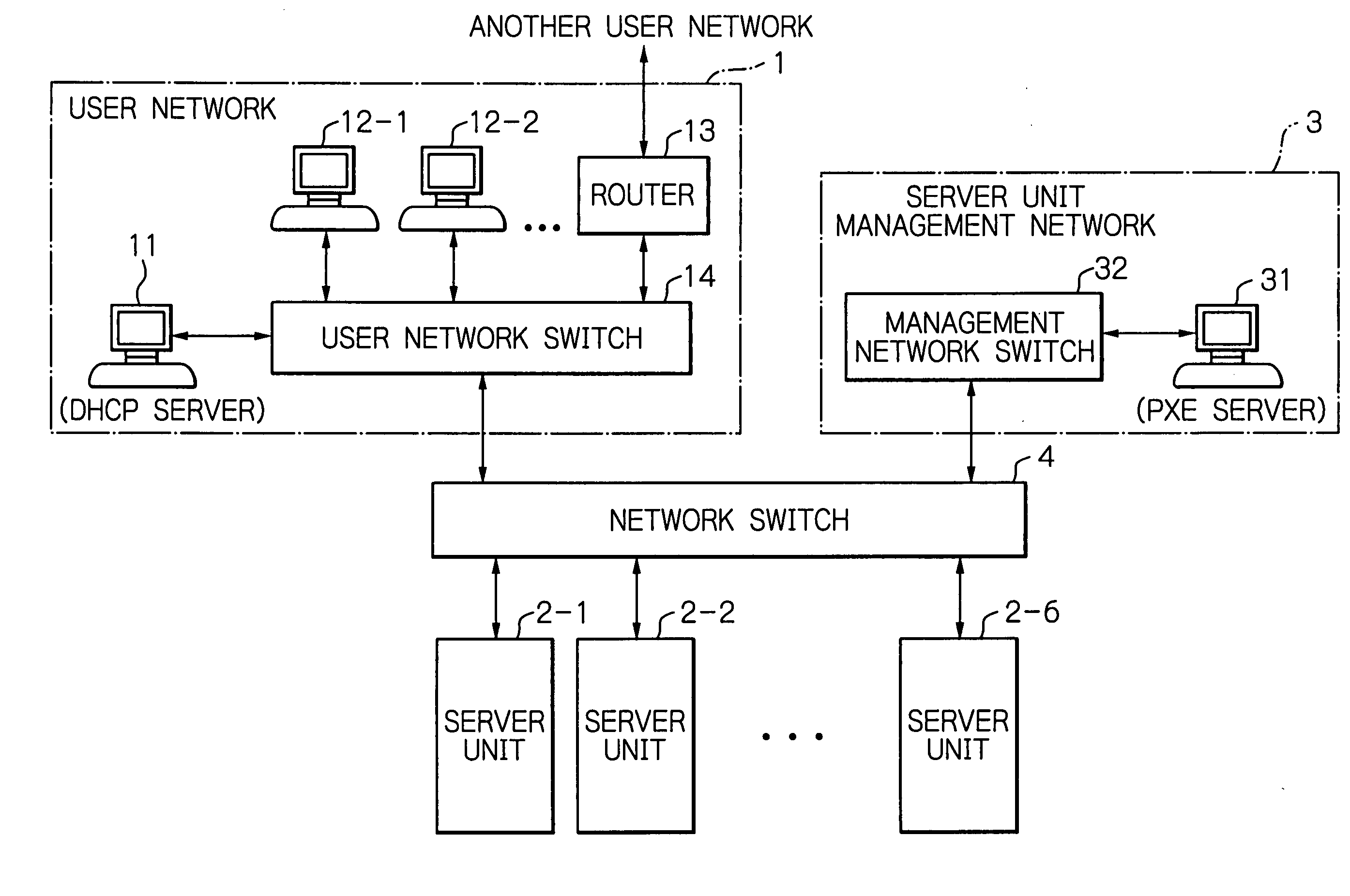
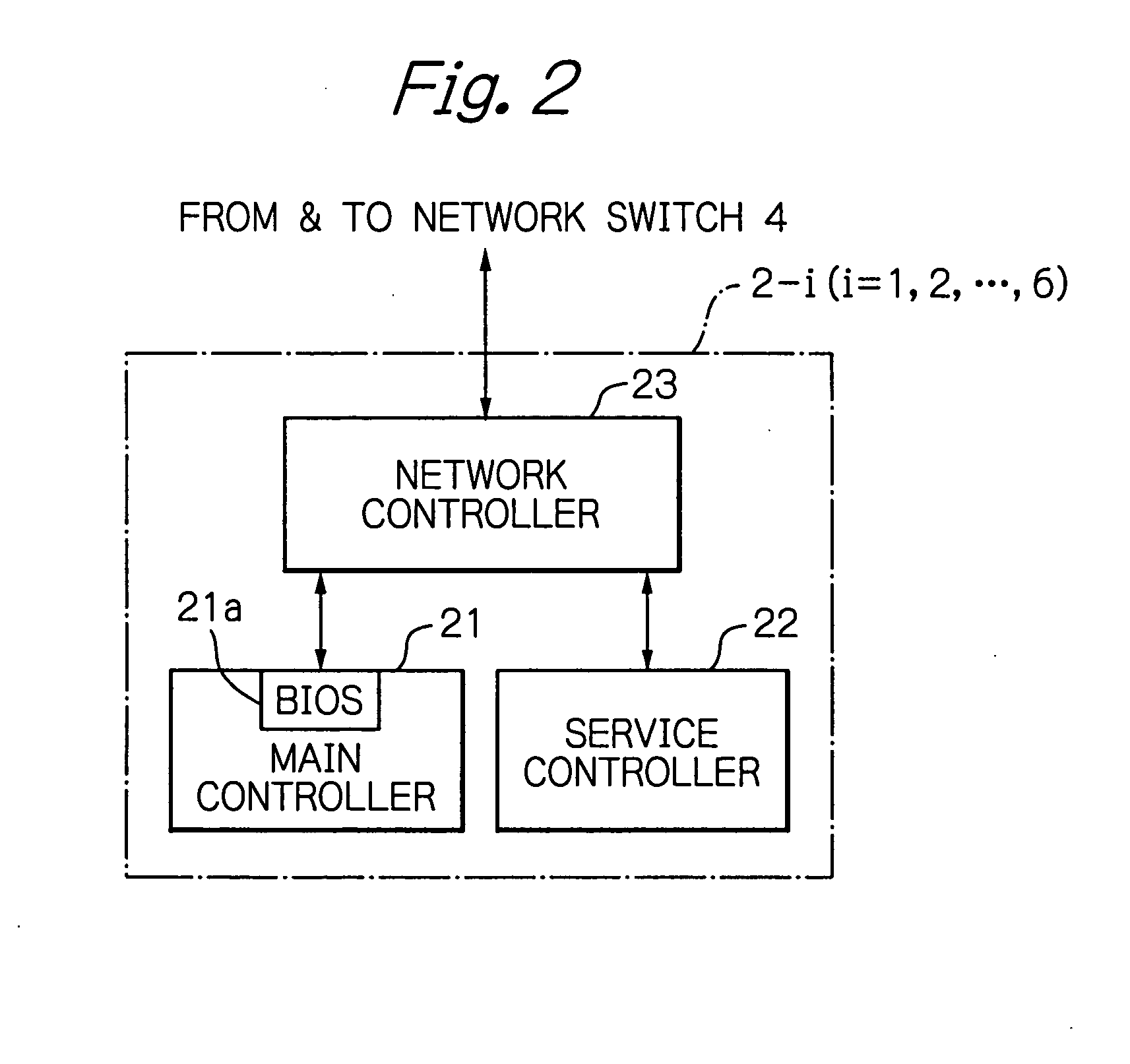
Network switch for logical isolation between user network and server unit management network and its operating method
InactiveUS20050091387A1Multiple digital computer combinationsStar/tree networksStore and forwardNetwork booting
In a network switch including a user network port connectable to a user network, a plurality of down link ports each connectable to one server unit, a server unit management network port connectable to a server unit management network for managing the server unit, a store-and-forward switching unit connected to the user network port, the down link ports and the server unit management network port, and a control unit connected to the store-and-forward switching unit, when a packet that has arrived at one of the down link ports is a dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) packet including a network boot option, the control unit operates the store-and-forward switching unit to transmit the packet to the server unit management network port.
Owner:NEC CORP
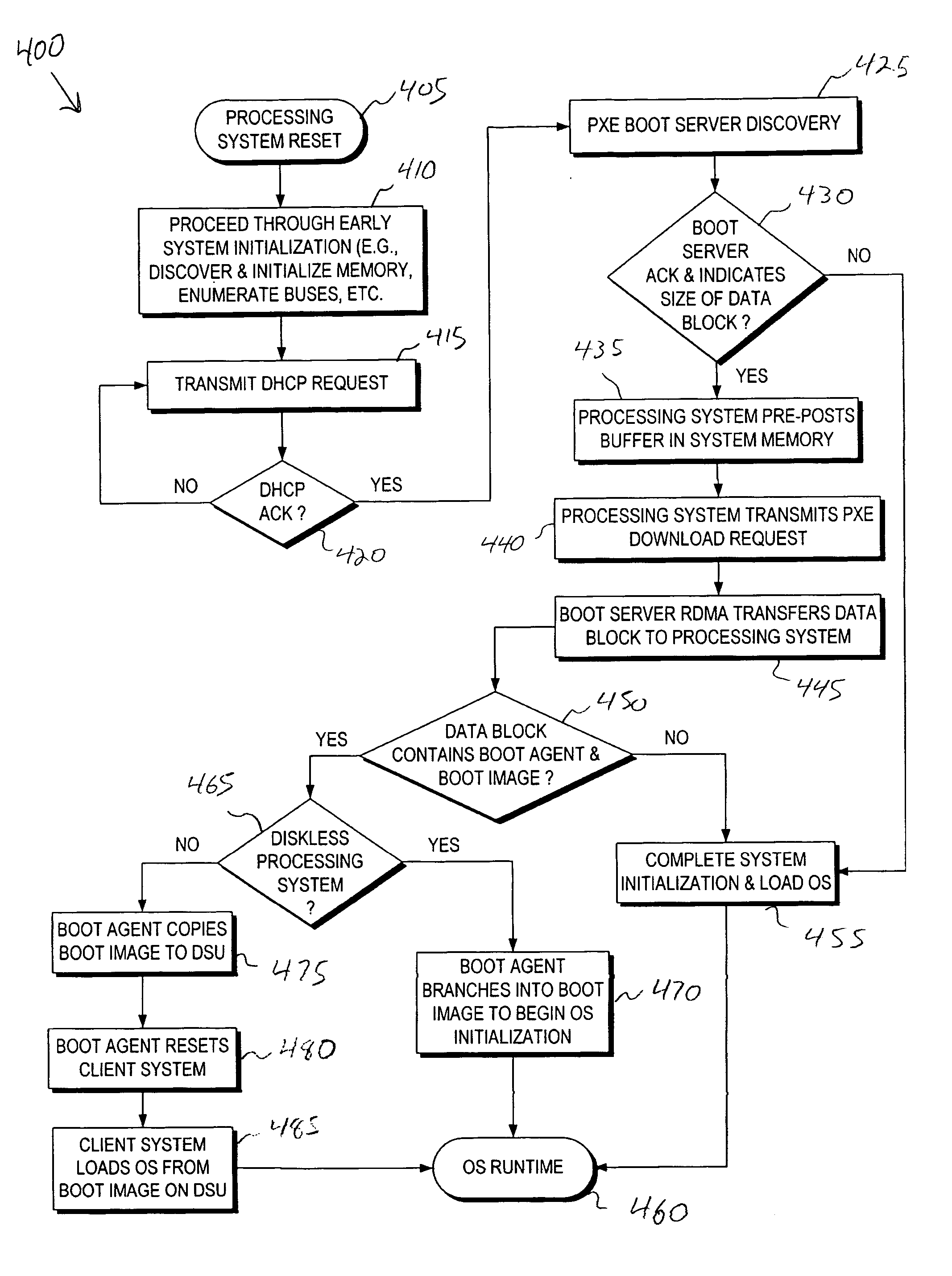
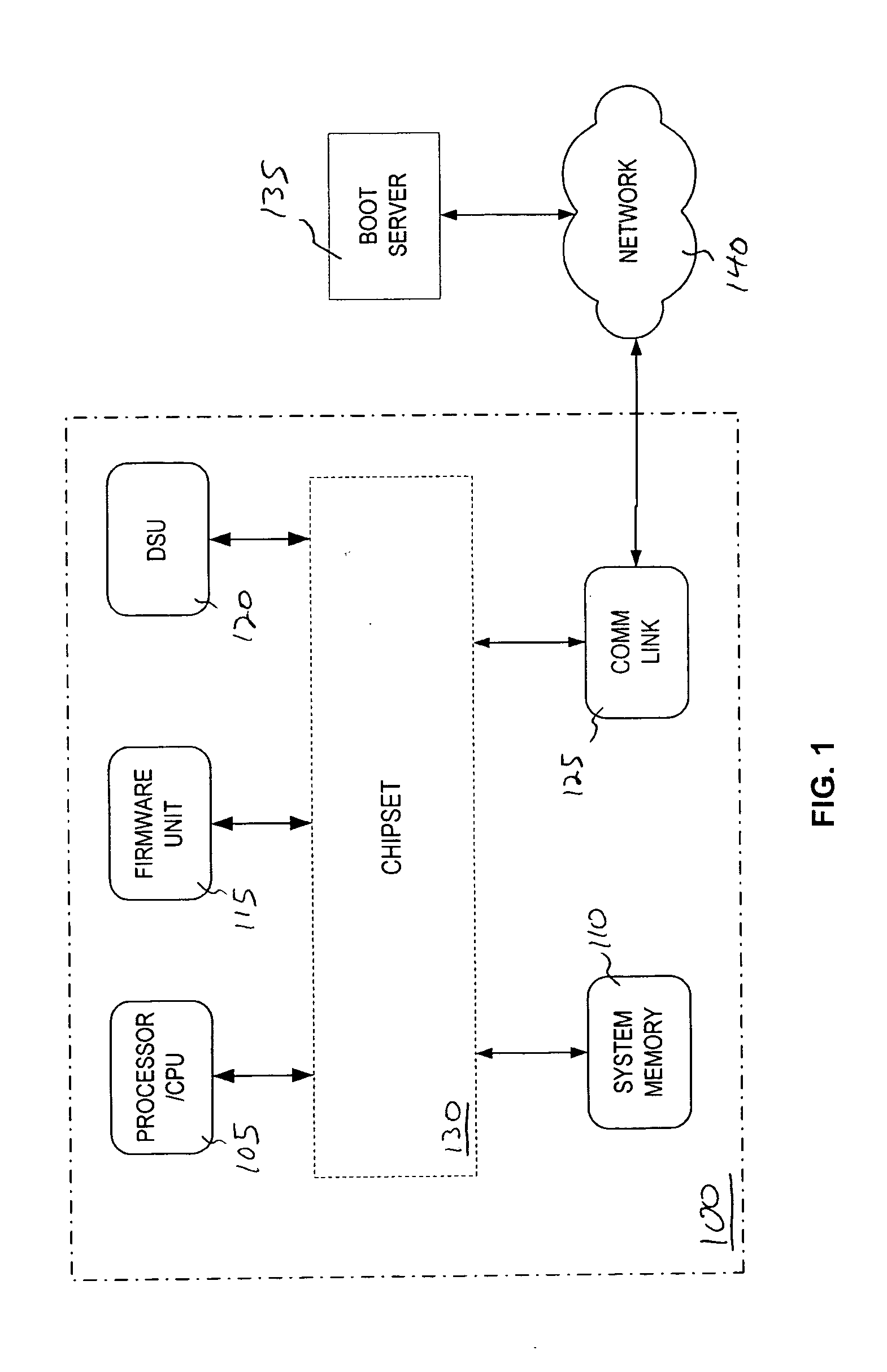
Firmware interfacing with network protocol offload engines to provide fast network booting, system repurposing, system provisioning, system manageability,and disaster recovery
InactiveUS20050071623A1Data resettingMultiple digital computer combinationsData segmentNetworking protocol
A system and method to quickly and efficiently transfer data over a network to a processing system during a pre-boot runtime of the processing system. During a pre-boot runtime of the processing system, a plurality of data packets is received via a network. Each of the plurality of data packets contains one of a corresponding plurality of data segments. The plurality of data packets are parsed using a network protocol stack to extract the plurality of data segments during the pre-boot runtime. A portion of the network protocol stack is executed in a hardware entity of the processing system. The plurality of data segments is transferred into system memory of the processing system during the pre-boot runtime.
Owner:INTEL CORP
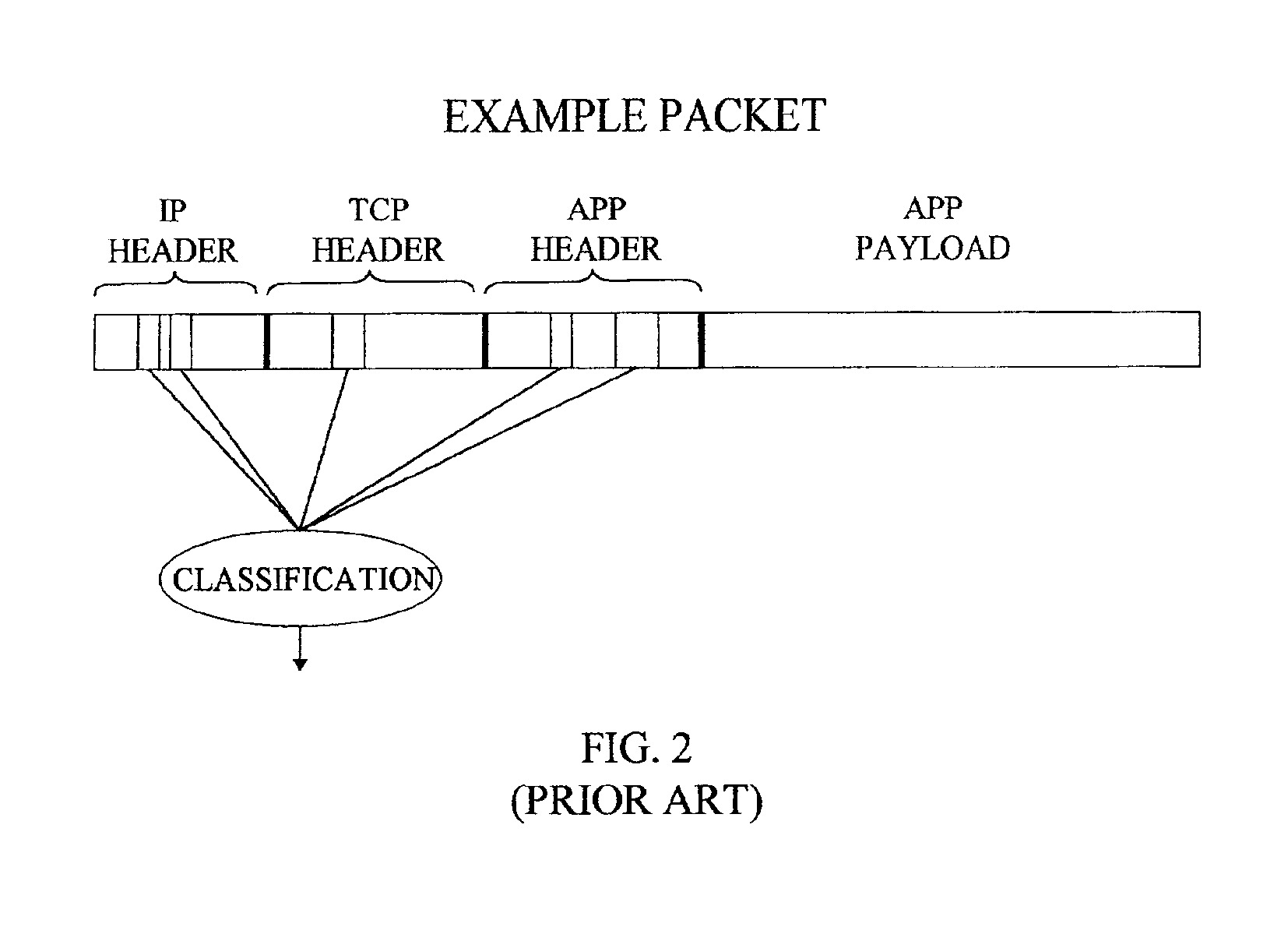
Apparatus and method for classifying packets
InactiveUS6940862B2Eliminate bottlenecksHandle classificationTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork bootingObject code
A method and apparatus can direct packets from a first network to a second network, e.g., a backbone network. Packets of the first network follow a predetermined protocol employing global addressing. Packets of the first network have a source identification code, a destination code, and a service code. The second network offers the benefit of one of a plurality of service classes. A host (in some case in cooperation with a gateway) can (a) originate at least some of the packets and set the source identification code, the destination code, and the service code for the packets, and (b) send the packets from the host on at least one hop consistent with the destination code. An edge router can transfer the packets to the second network offering the benefit of one or more service classes. The edge router has an input device and an output device. The input device can extract from the packets the source identification code and the service code. A table stored in the edge router can use the source identification code drawn from the input device to lookup a corresponding code indicating permission with respect to the service classes. A permissible one of the service classes is allocated consistent with the service code if the service code is consistent with the corresponding code. The output device communicates with the input device and can send the packets onto the second network with the benefit of the permissible one of the service classes.
Owner:GOUDREAU MARK
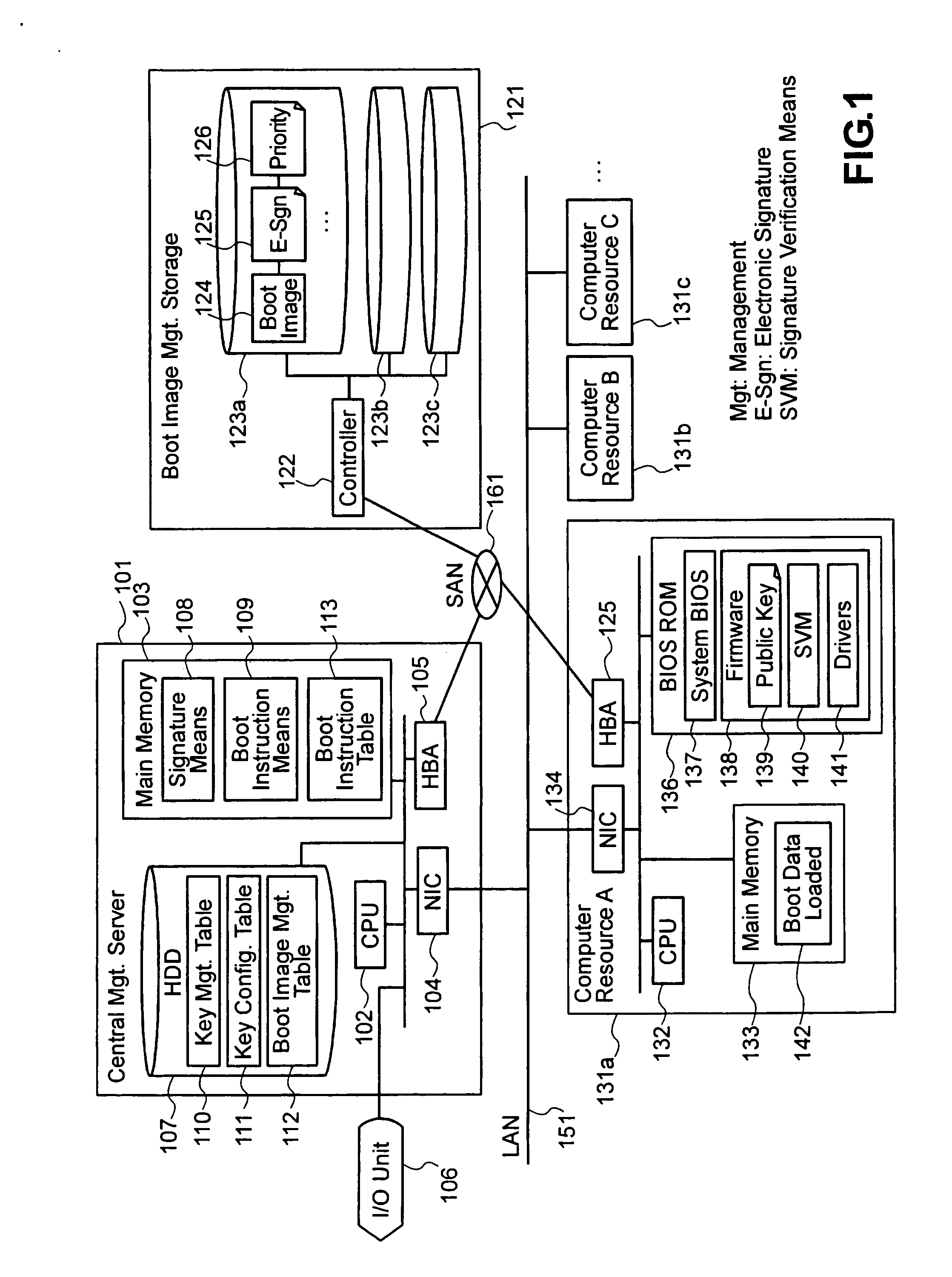
Method and system for setting up hosting environments in safety
InactiveUS20060026429A1Easy to set upSecurity is preservedUser identity/authority verificationProgram/content distribution protectionComputer resourcesData center
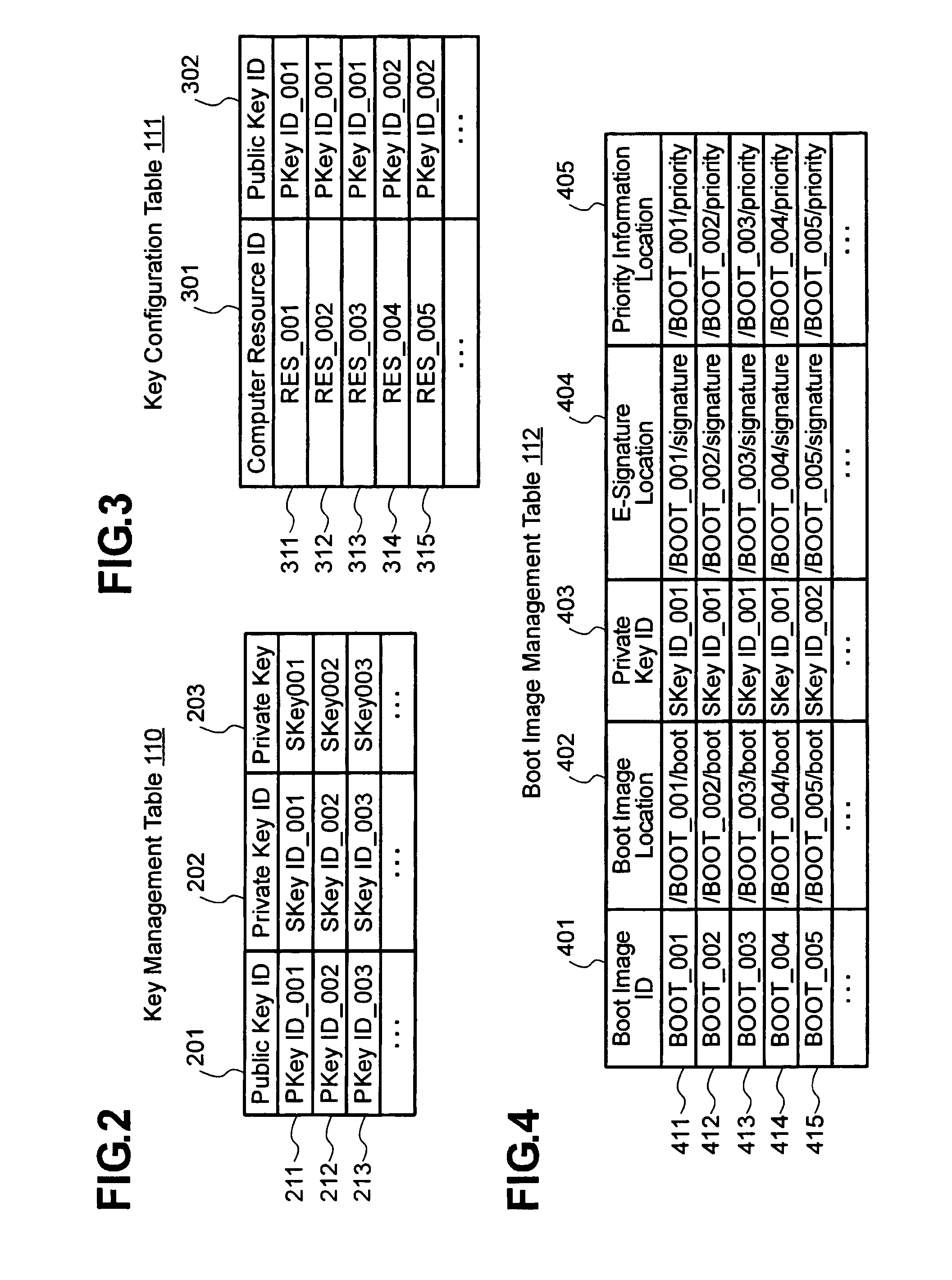
In a data center architecture or the like, the present invention provides a method for setting up hosting environments concurrently by loading a boot image by means of network boot or the like, allowing for fast booting even with a large boot image, while preserving security. A boot image is divided into a plurality of parts. Computer resources have their public keys stored in their BIOS ROMs and e-signatures are attached to the boot image parts with a private key corresponding to one of the public keys. Also, priority levels in e-signature verification are assigned to the boot image parts. A boot instruction includes priority level setting. Only for boot image parts with that priority level or higher, e-signature verification is performed. By this manner, booting can be performed faster than booting involving verification of the e-signature to a whole boot image.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
User-authentication-type network operating system booting method and system utilizing BIOS preboot environment
InactiveUS6928541B2Easy to startImprove securityDigital computer detailsDigital data authenticationNetwork operating systemOperational system
Disclosed is a system that make it possible for a user to readily boot an operating system from a user terminal with user-specific settings, thereby making it unnecessary for the server to register an image for each OS environment, as a result of which the required storage capacity of the server can be reduced. The user terminal, which is connected to the server by a network, is booted using an operating system stored in the server. In booting of the user terminal, user information that has been selected by the user from OS-booting user information stored on a removable storage medium of the user terminal is transmitted to the server under the control of a BIOS preboot environment stored in a storage device of the user terminal. On the basis of the user information, the server authenticates the user terminal, transmits the operating system to the user terminal and network-boots the operating system in a user-specific environment.
Owner:NEC CORP
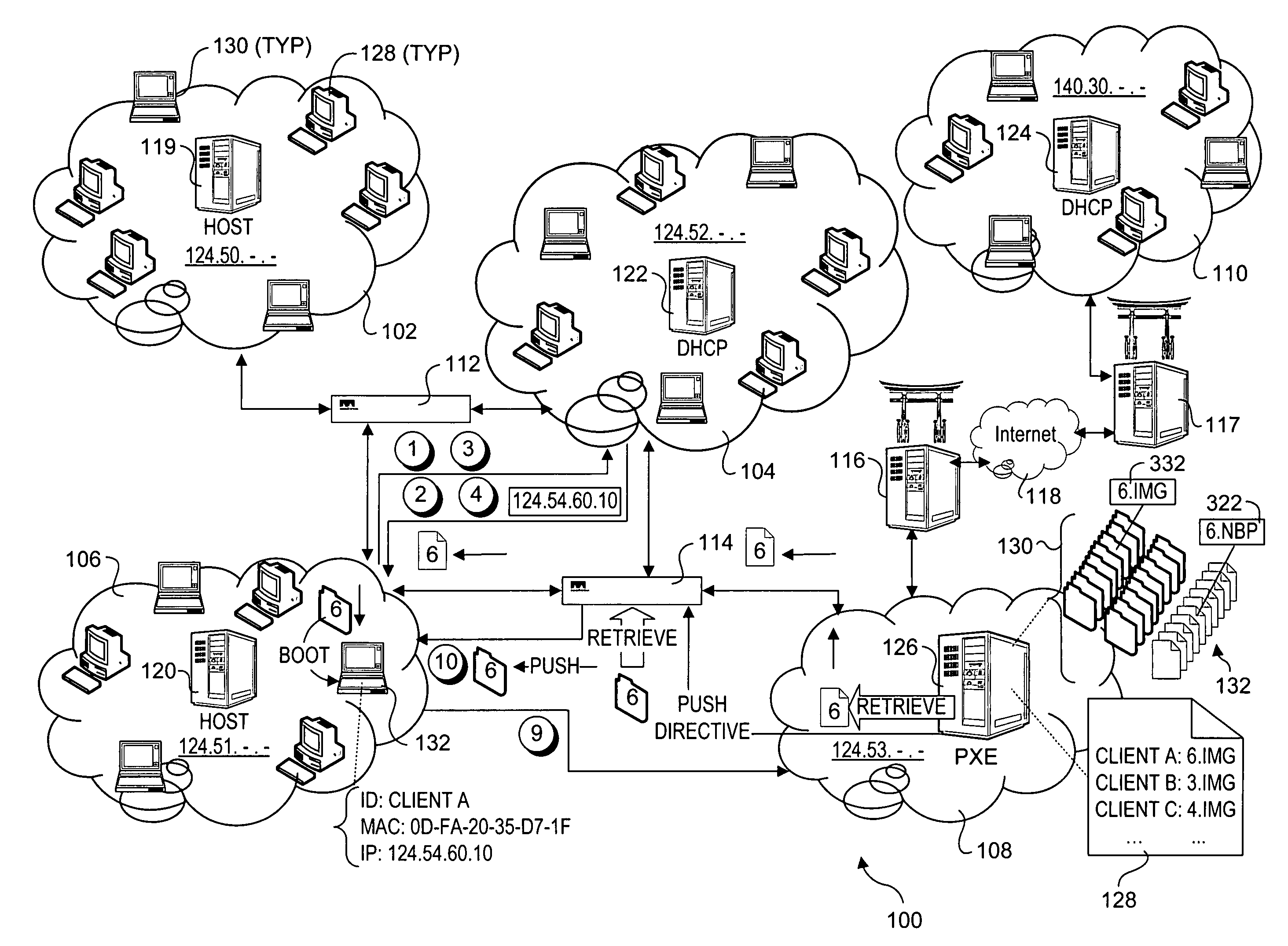
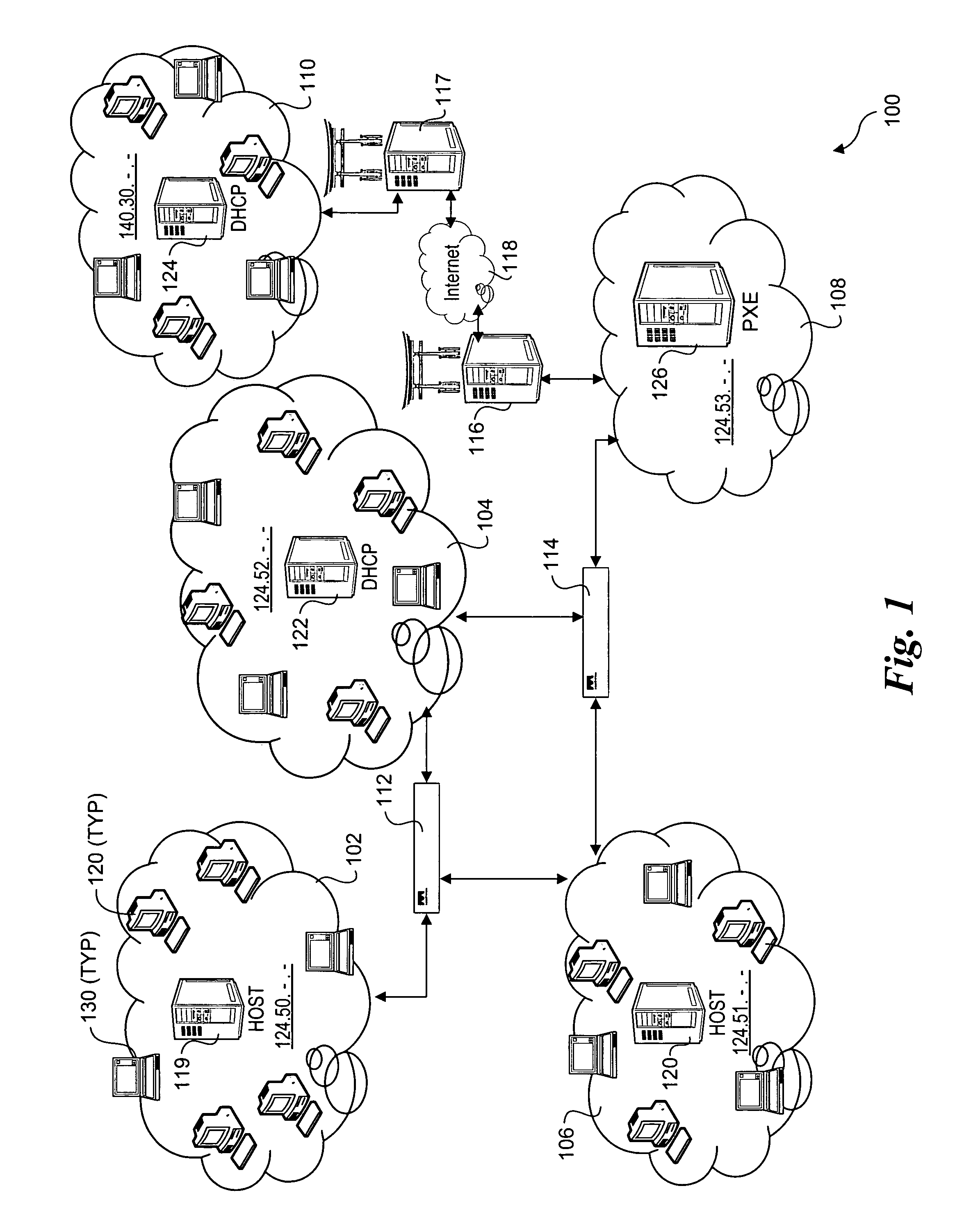
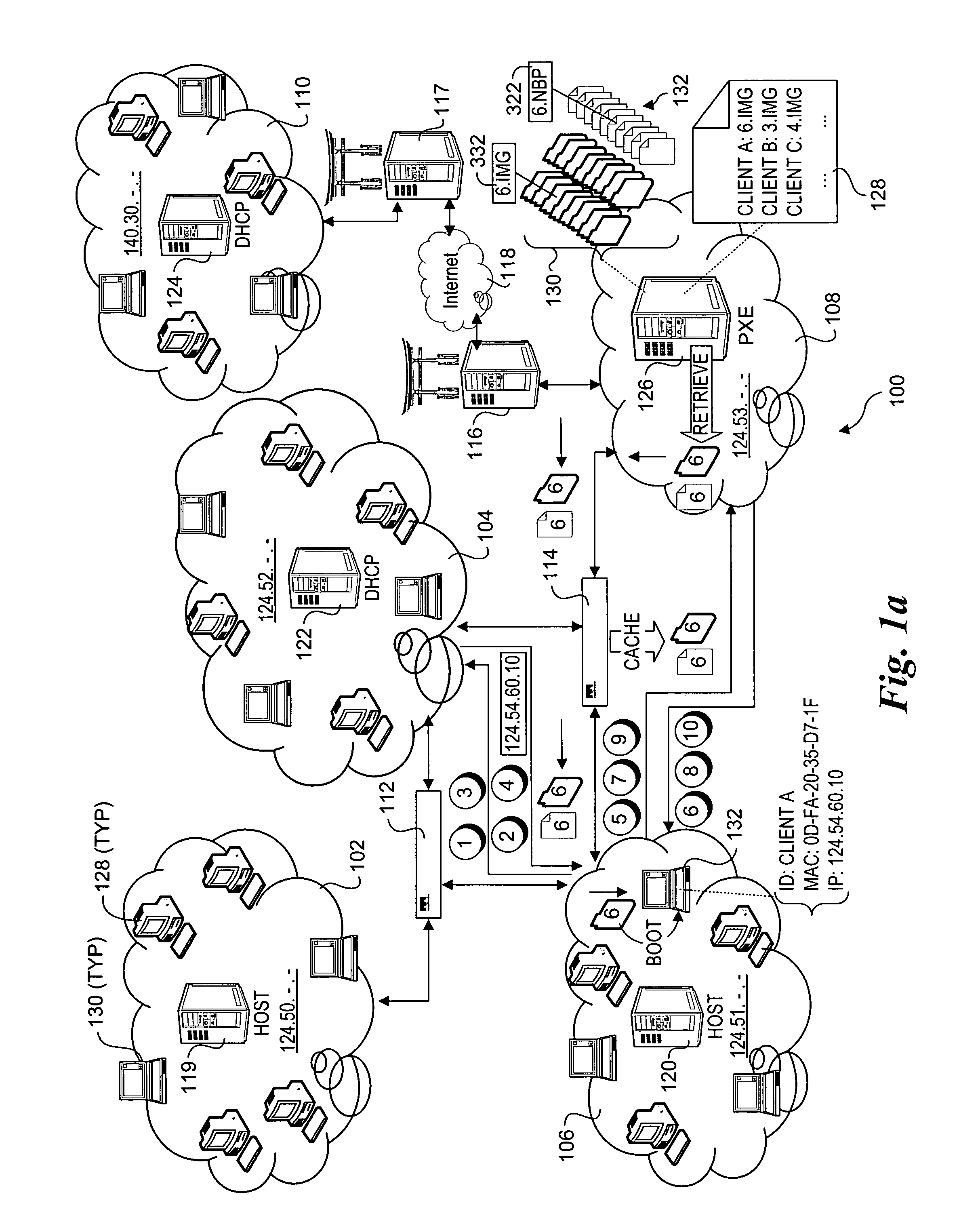
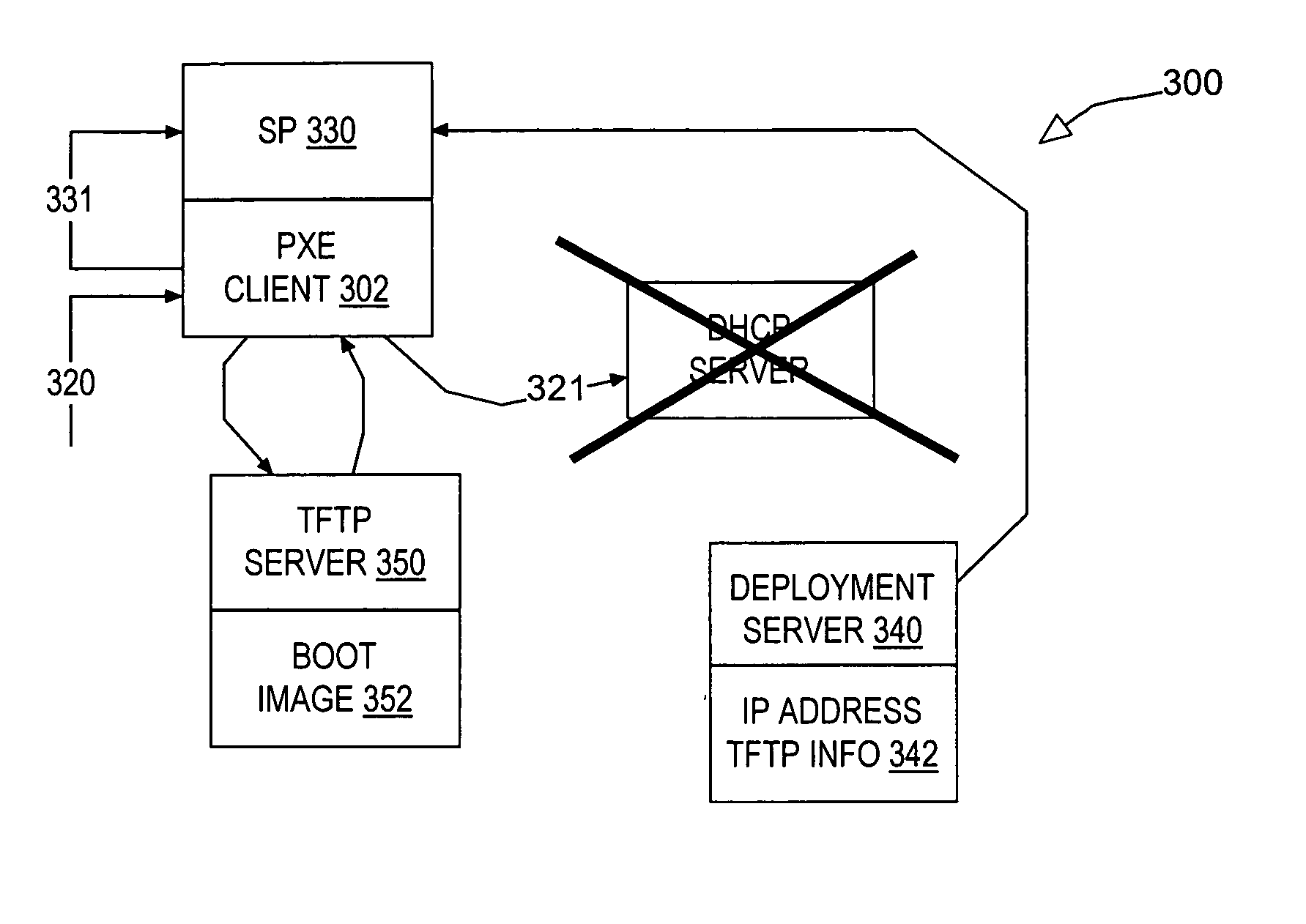
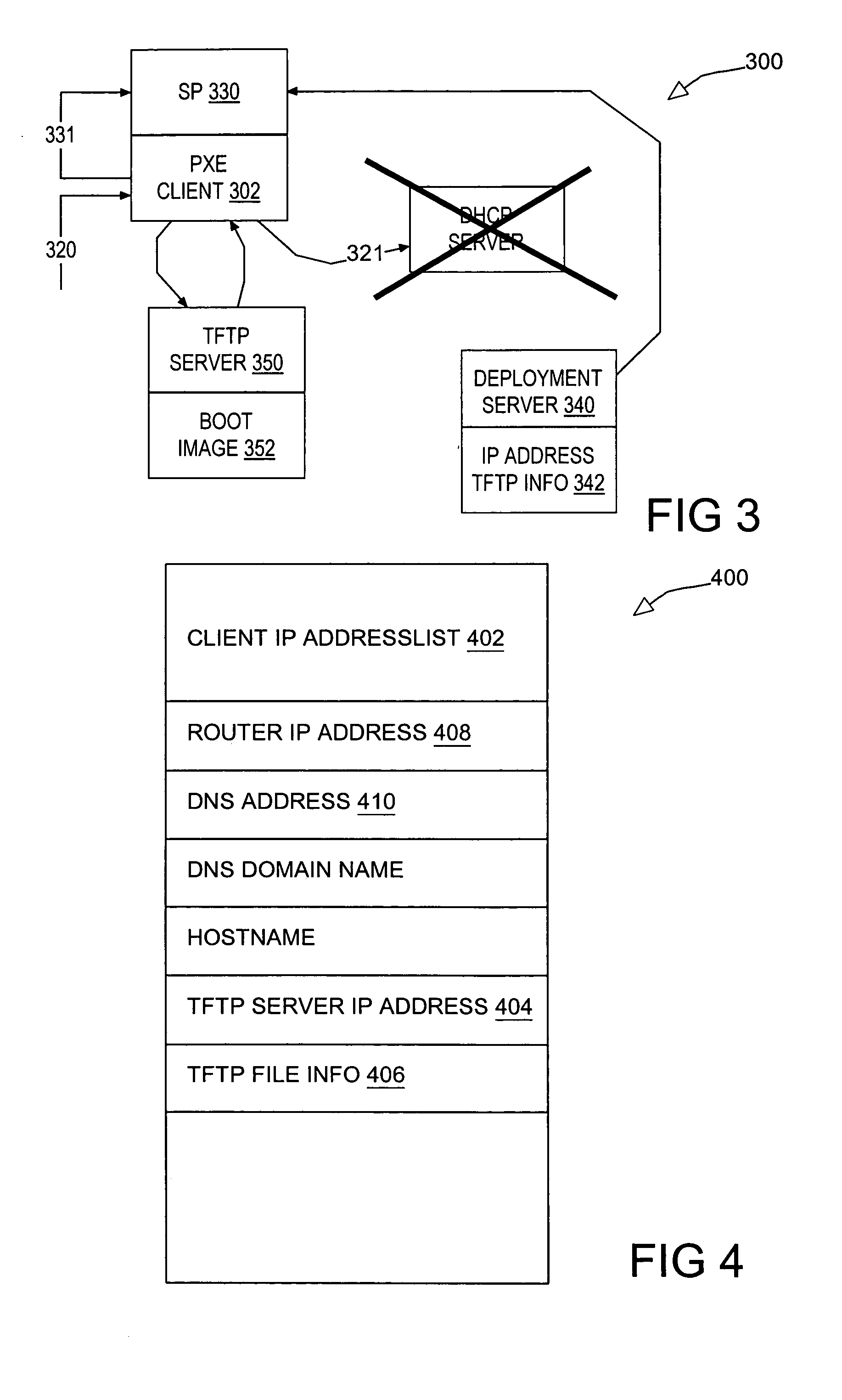
Network boot sequence in the absence of a DHCP server
A data processing system suitable for use as a client device in a network includes a service processor communicatively coupled to a general purpose processor of the system. The system is enabled to respond to a boot event by requesting boot information from a network device. If the boot information request expires unsuccessfully, the boot information is requested from the service processor. If the attempt to retrieve the boot information from the service processor is successful, the retrieved boot information is used to establish a network connection to a file transfer server. The file transfer server connection is then used to download an operating system image from the file transfer server to boot the operating system image and install an operating system on the client device. In one embodiment, the client device is a PXE client on a network lacking a DHCP server.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for the distribution of configurations to client computers
InactiveUS20090172136A1Significant positive effectSave storage spaceDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationOperational systemComputer configuration
A method for distributing computer configurations to at least one client from a server, comprising the following steps: Network-booting a first operating system for the clients from a server, automatically loading a virtual machine having an elective second operating system on the basis of the booted (first) operating system while taking into consideration one or more of the following parameters: user login, network address. Consequently, providing a full fat client (standard PC) functionality under an elective operating system on a (diskless) client hardware by using exclusively volatile storage media (on the new thin client system).
Owner:SCHULZ ULRICH +1
Redistribution of operating environments for the redeployment of grid clients
InactiveUS20060242228A1Reduced computing resourceMultiple digital computer combinationsMarketingOperational systemNetwork booting
A client-server network environment is temporarily transformed into a grid computing environment through the deployment of a network-booted grid operating system to each of a plurality of network clients. Each participating client operates in the client-server mode under a local operating system. At an appropriate time, a server transmits to each client a thin-client boot image (a dynamically built customized image or an image obtained from a store of predefined boot images) along with a grid application for which the thin-client has been optimized for peak performance. Each client re-boots using the thin-client image, thereby entering the grid mode and allowing substantially all of its computing resources to be dedicated to executing the grid application. At a later time, the server directs that each client terminate the grid application and re-boot in its respective local operating system, reverting again to the client-server mode.
Owner:IBM CORP
Firmware interfacing with network protocol offload engines to provide fast network booting, system repurposing, system provisioning, system manageability, and disaster recovery
InactiveUS7275152B2Data resettingMultiple digital computer combinationsData segmentNetworking protocol
A system and method to quickly and efficiently transfer data over a network to a processing system during a pre-boot runtime of the processing system. During a pre-boot runtime of the processing system, a plurality of data packets is received via a network. Each of the plurality of data packets contains one of a corresponding plurality of data segments. The plurality of data packets are parsed using a network protocol stack to extract the plurality of data segments during the pre-boot runtime. A portion of the network protocol stack is executed in a hardware entity of the processing system. The plurality of data segments is transferred into system memory of the processing system during the pre-boot runtime.
Owner:INTEL CORP
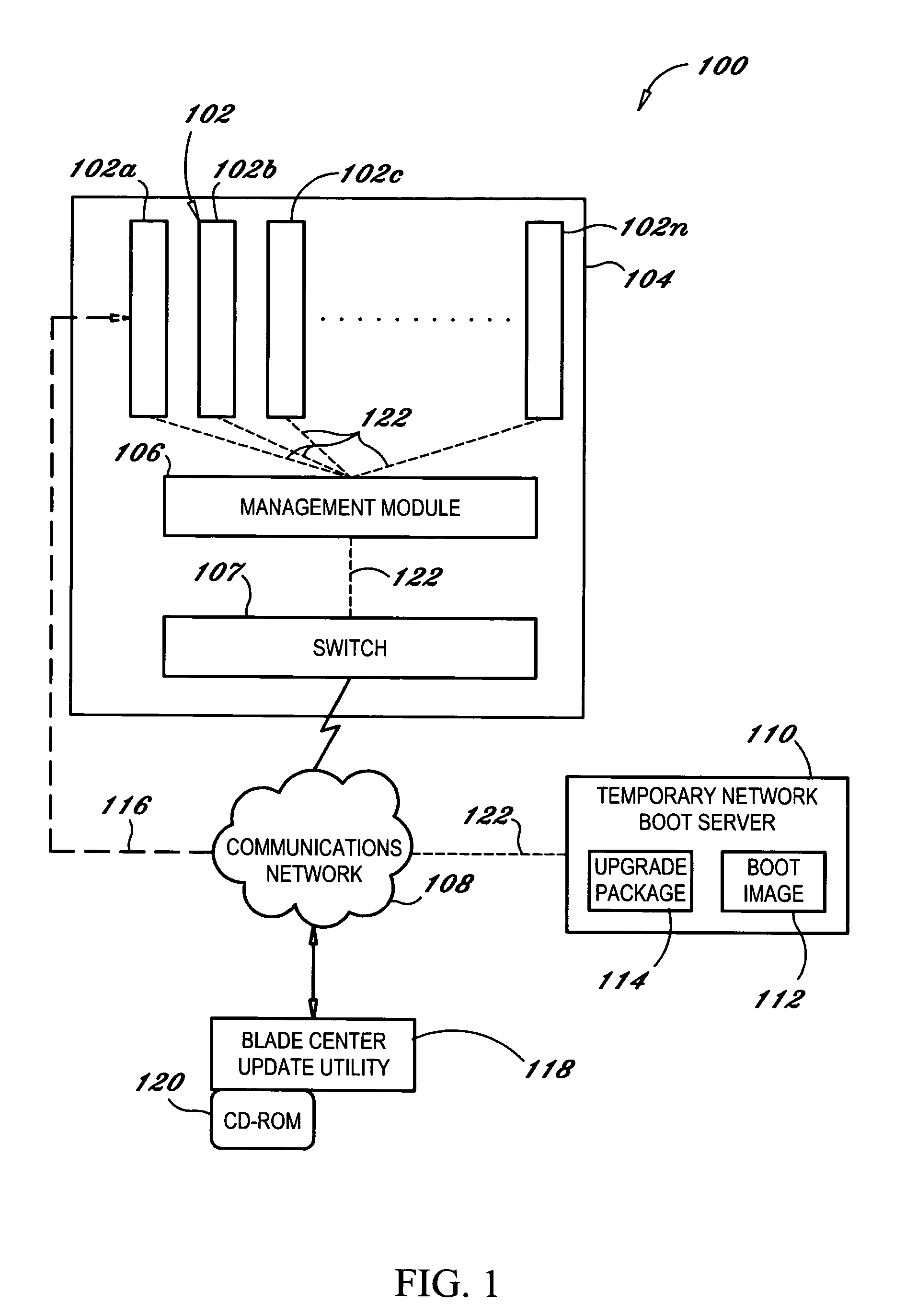
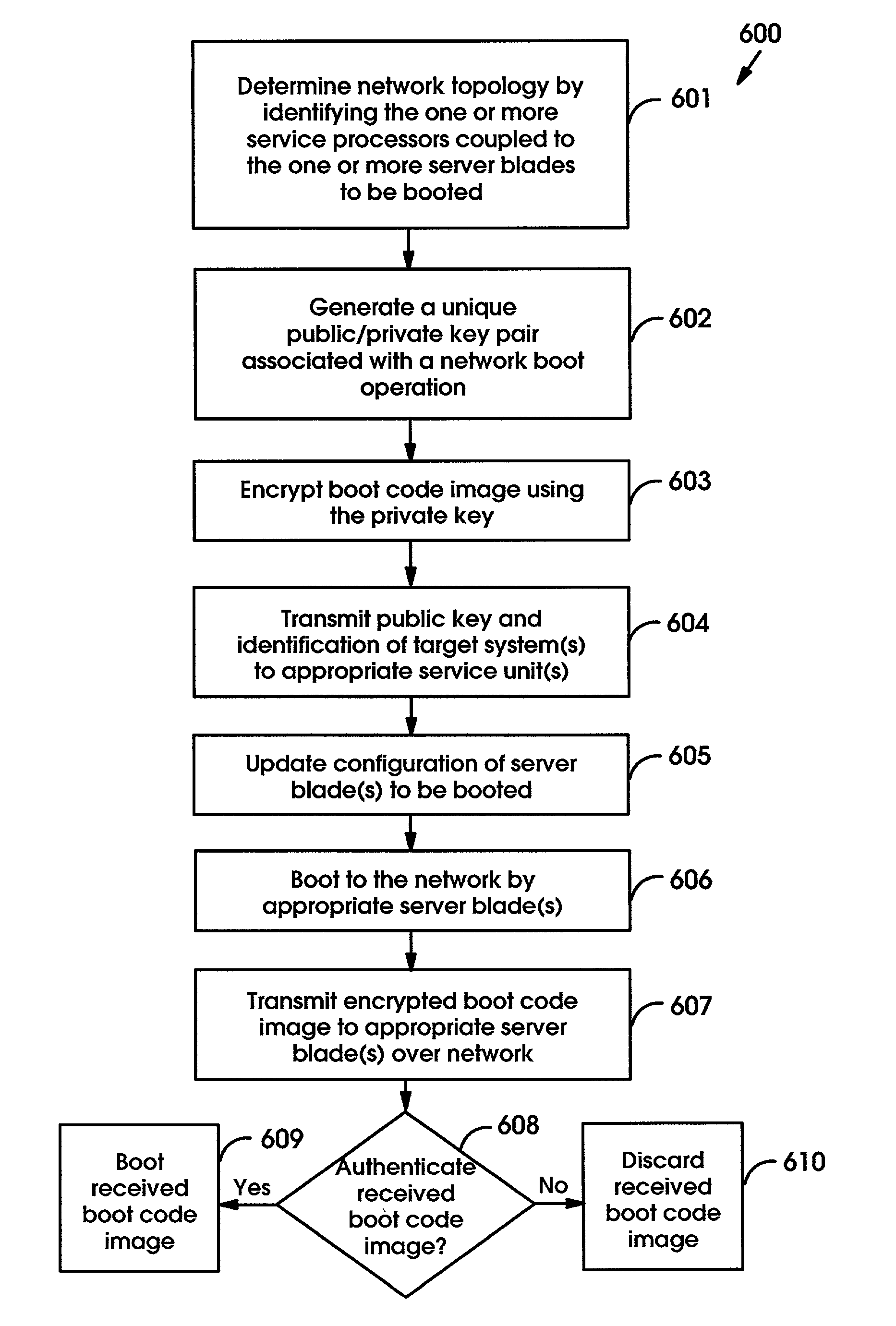
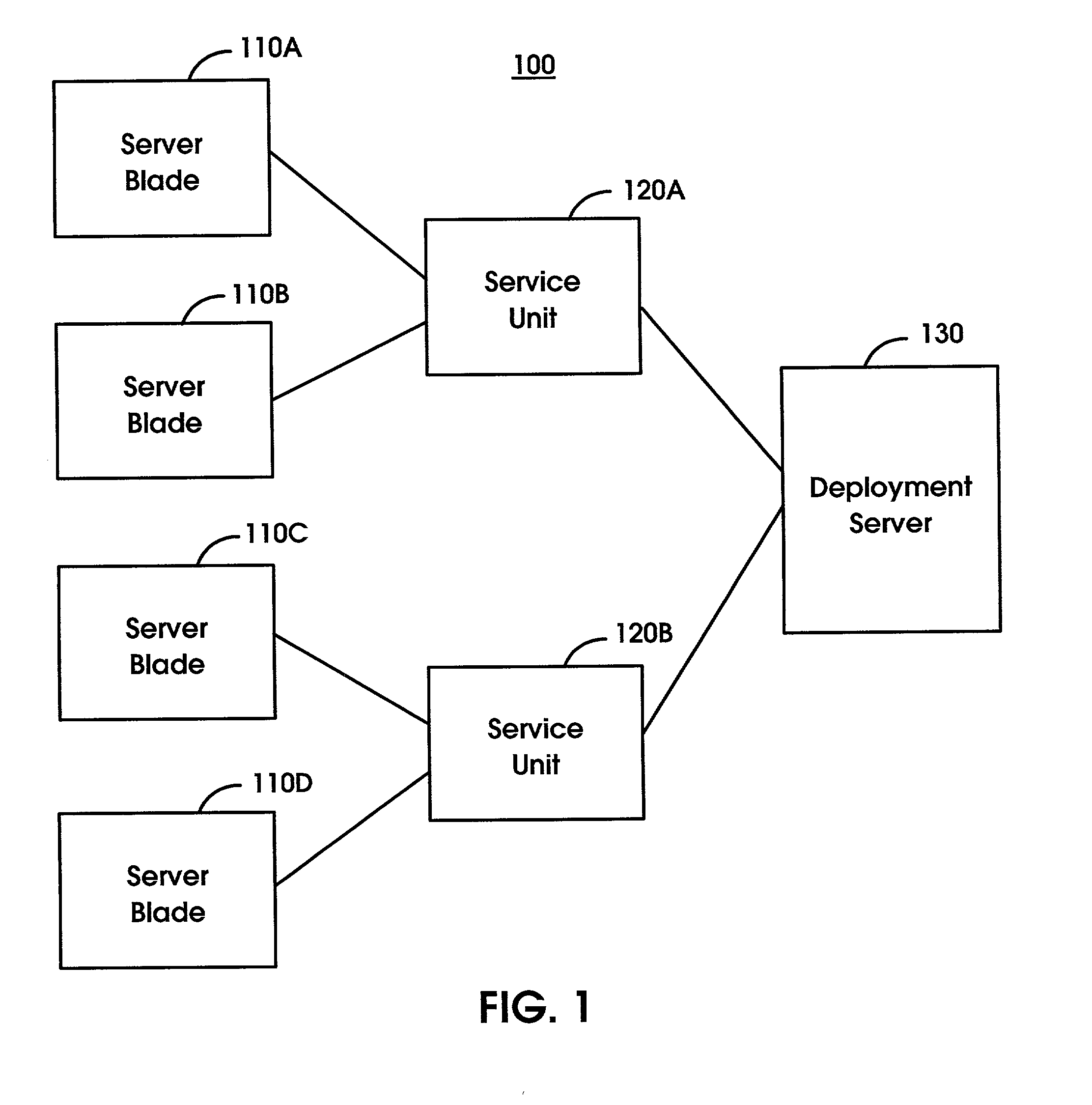
Remotely booting devices in a dense server environment without manually installing authentication parameters on the devices to be booted
ActiveUS7194619B2Reduce exposureDigital computer detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionNetwork bootingComputer science
A method, system and computer program product for remotely booting devices. A deployment server may remotely transmit authentication parameter(s), e.g., public key, secret key, to a service unit configured to establish a private connection between server blades and the deployment server. The service unit may remotely install the authentication parameter(s) onto the server blade(s) to be booted by either the deployment server or another boot server. By the service unit remotely installing the authentication parameter(s) onto the server blade(s), the need to manually install them during each network boot operation may be alleviated. By remotely transmitting authentication parameter(s) instead of manually installing them on the devices to be booted during each network boot operation, the deployment server may be able to generate unique authentication parameter(s), e.g., public / private key pair, secret key, for each network boot operation thereby substantially reducing the exposure to replay attacks.
Owner:IBM CORP
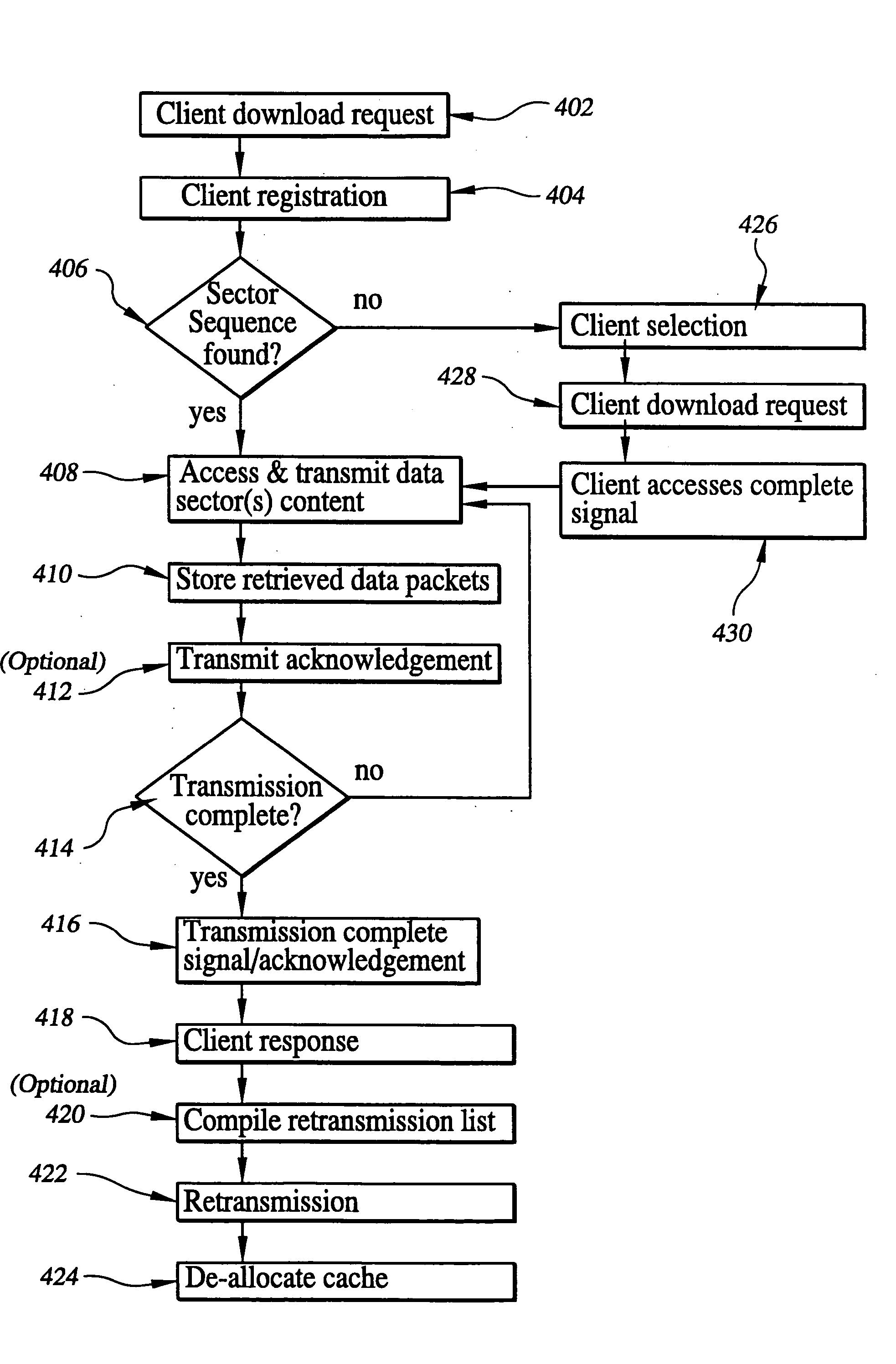
Method and system for automatic detection, inventory, and operating system deployment on network boot capable computers
A system for the automatic detection and inventory of a network boot capable computer and for the automatic deployment of an appropriate operating system to the network boot capable computer. First, an initial broadcast packet from the network boot capable computer is received. In response to receiving the initial broadcast packet, a discovery kernel is sent to the network boot capable computer. The discovery kernel generates a hardware details file. The hardware details file is received from the network boot capable computer and is analyzed. After the hardware details file is analyzed, an appropriate operating system is deployed to the network boot capable computer.
Owner:IBM CORP
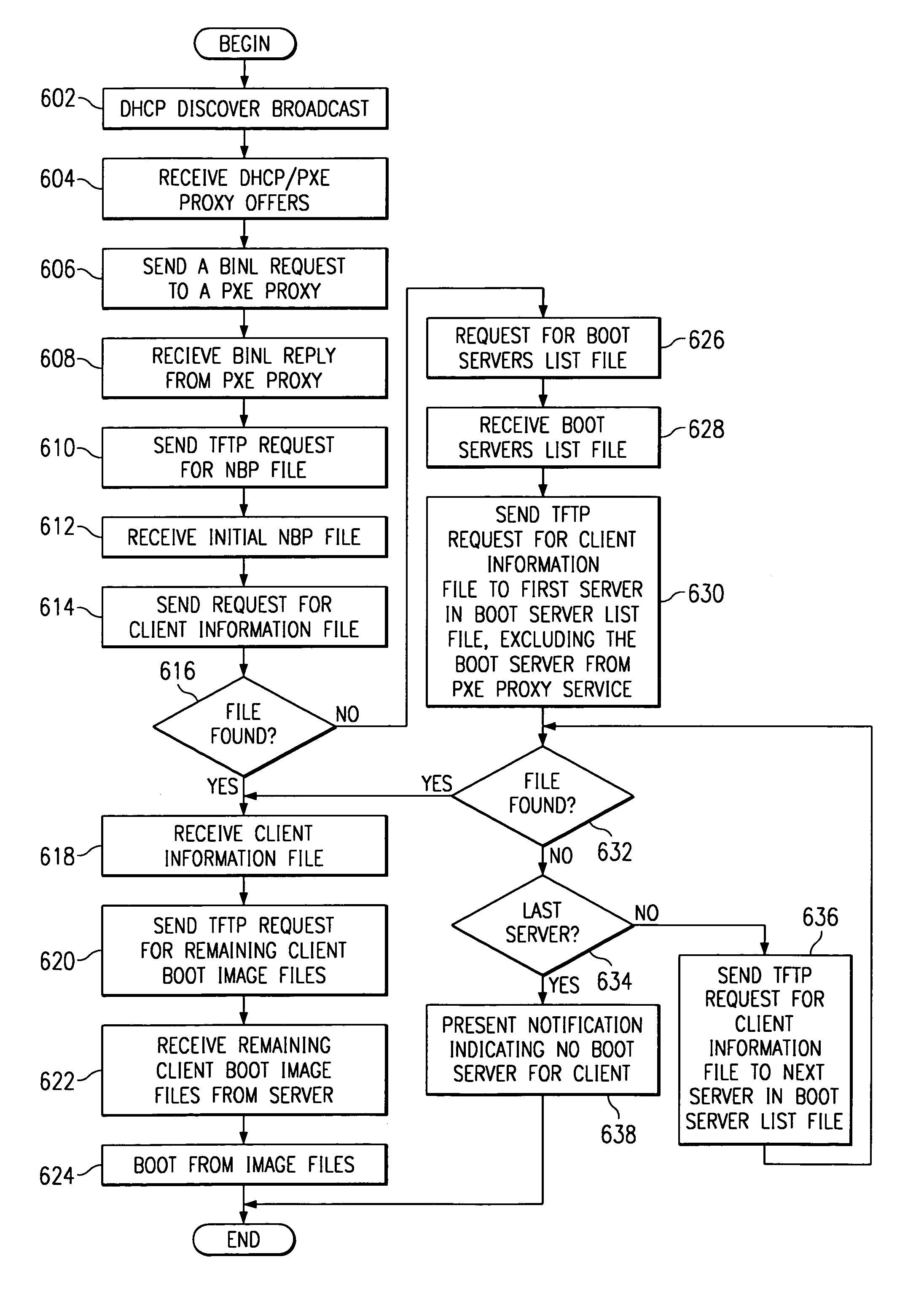
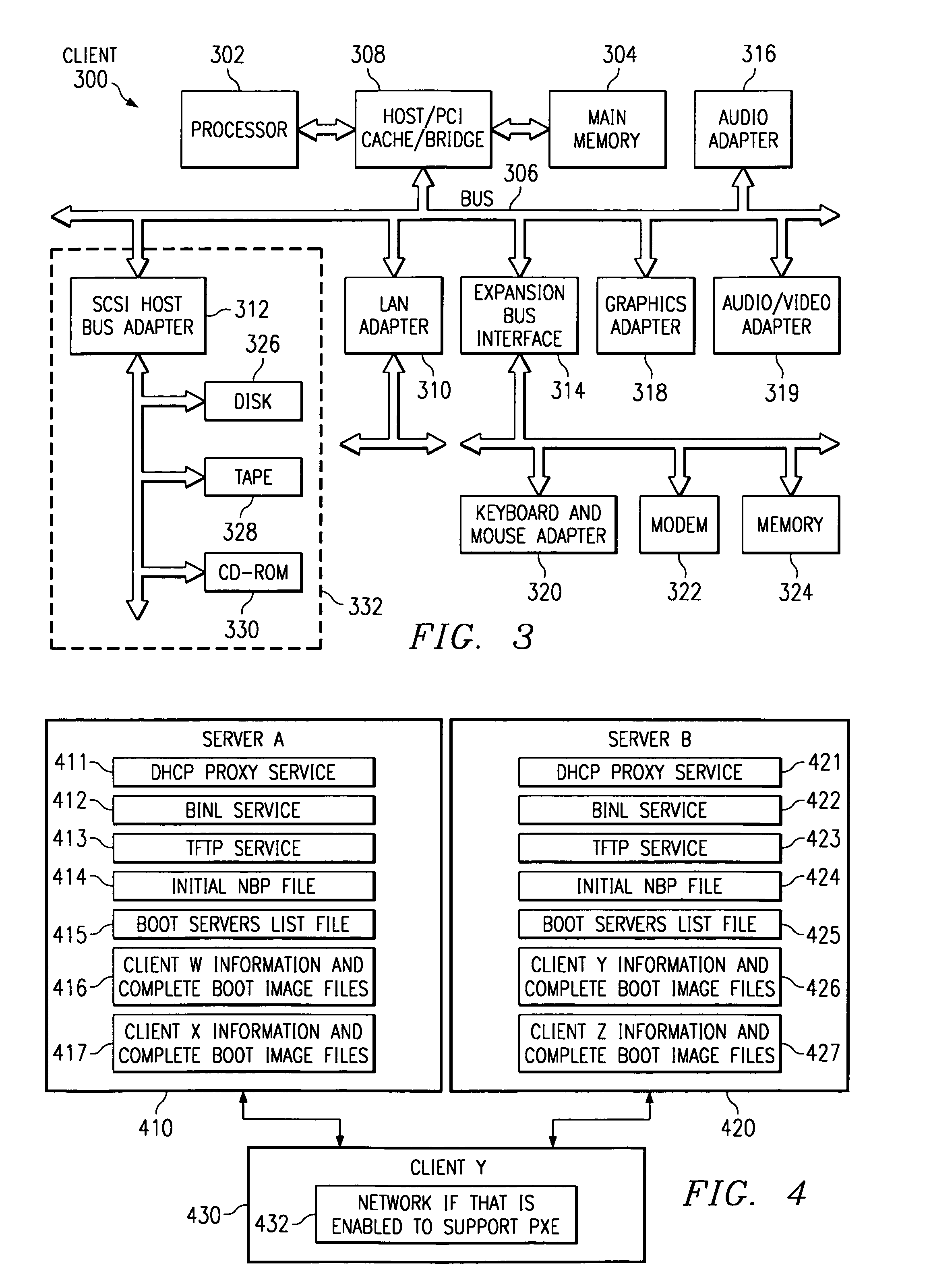
Method, apparatus, and program for server based network computer load balancing across multiple boot servers
A method, system, and program is provided to redirect a client computer to an appropriate boot server after it has been directed to any initial boot server by preboot execution environment (PXE) or similar services. An apparatus includes a data file containing a set of addresses of managed boot servers in any syntax and a program file containing a network bootstrap program (NBP) that interprets the syntax of the data file. These files are placed on every initial boot server. The NBP requests a file from the initial boot server whose name is identified with the client computer. The initial boot server will not return that file if it is not an appropriate server for booting the client. In that case, the NBP requests the data file containing the boot server addresses. The NBP then polls each of those boot servers by requesting the client's unique file. A boot server that returns the file is an appropriate boot server for the client computer. The data file containing boot server addresses is changed to reflect current boot server load balancing requirements without involving the configuration or affecting the availability of PXE or similar services.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multiple operation system switching method applicable to ARM (advanced risc machine) framework mobile equipment
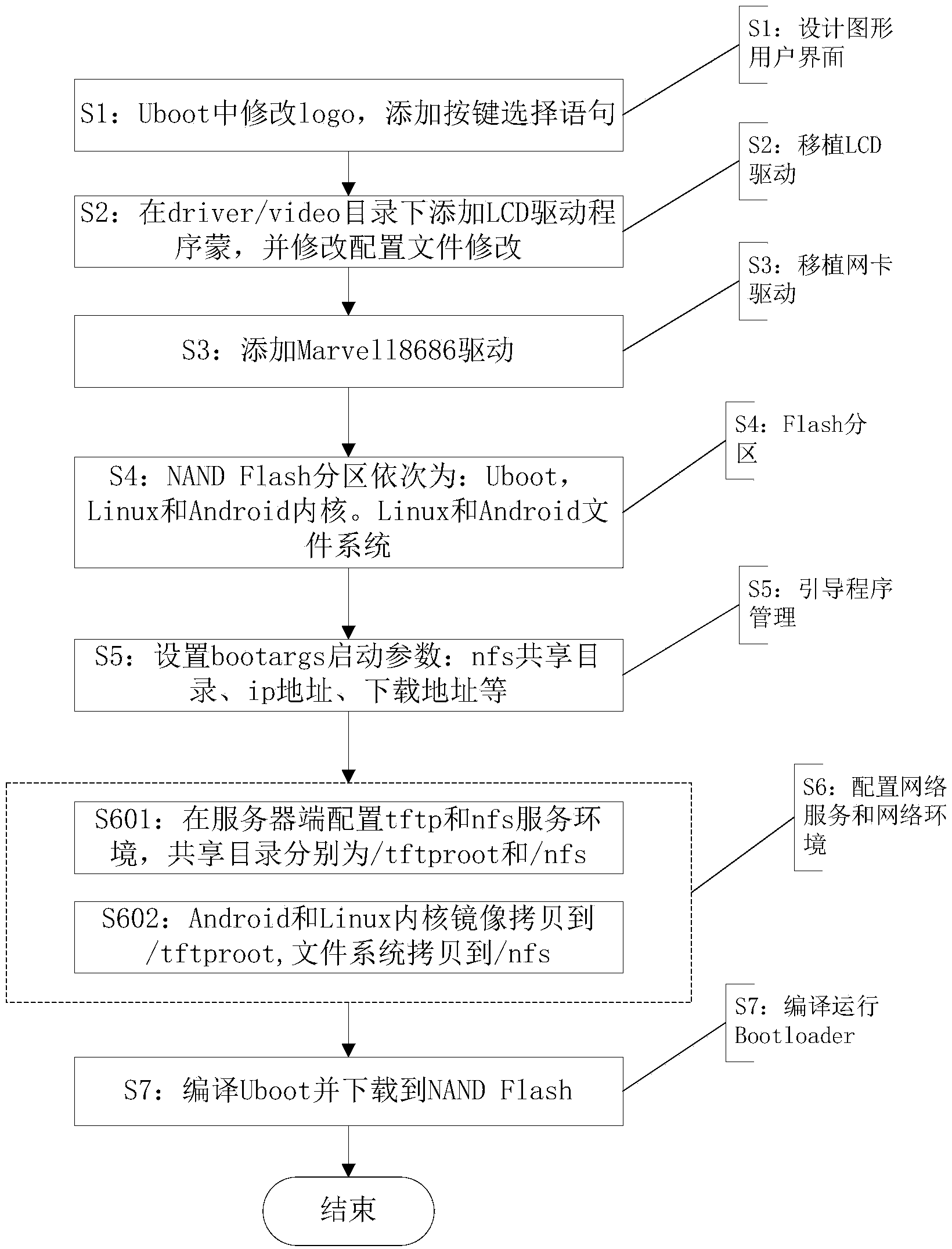
InactiveCN103761088AImplementation supportRealize switchingSpecific program execution arrangementsOperational systemNetwork booting
The invention discloses a multiple operation system switching method applicable to ARM (advanced risc machine) framework mobile equipment and belongs to the technical field of an operation system of mobile equipment. The multiple operation system switching method includes: initializing equipment for internal storage, internet equipment, a watchdog and I / O (input / output) firstly after the ARM framework mobile equipment boots, entering a selection interface of the operation system, setting corresponding booting parameters by a boot loader according to the operation system selected by a user, sending booting interrupt to a server end, searching a corresponding system kernel and file systems by a server after an interruption signal is truncated by the server, loading the system kernel to a client end in the form of files, burning into a set Flash partition before booting, mounting the file system under a root directory directly via an nfs (network file system) network protocol, and completing network booting of the operation system. By the aid of the multiple operation system switching method, preinstallation of the operation system on the ARM framework mobile terminal equipment is not required, and the purpose of realizing booting multiple operation systems via the network without local operation system is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
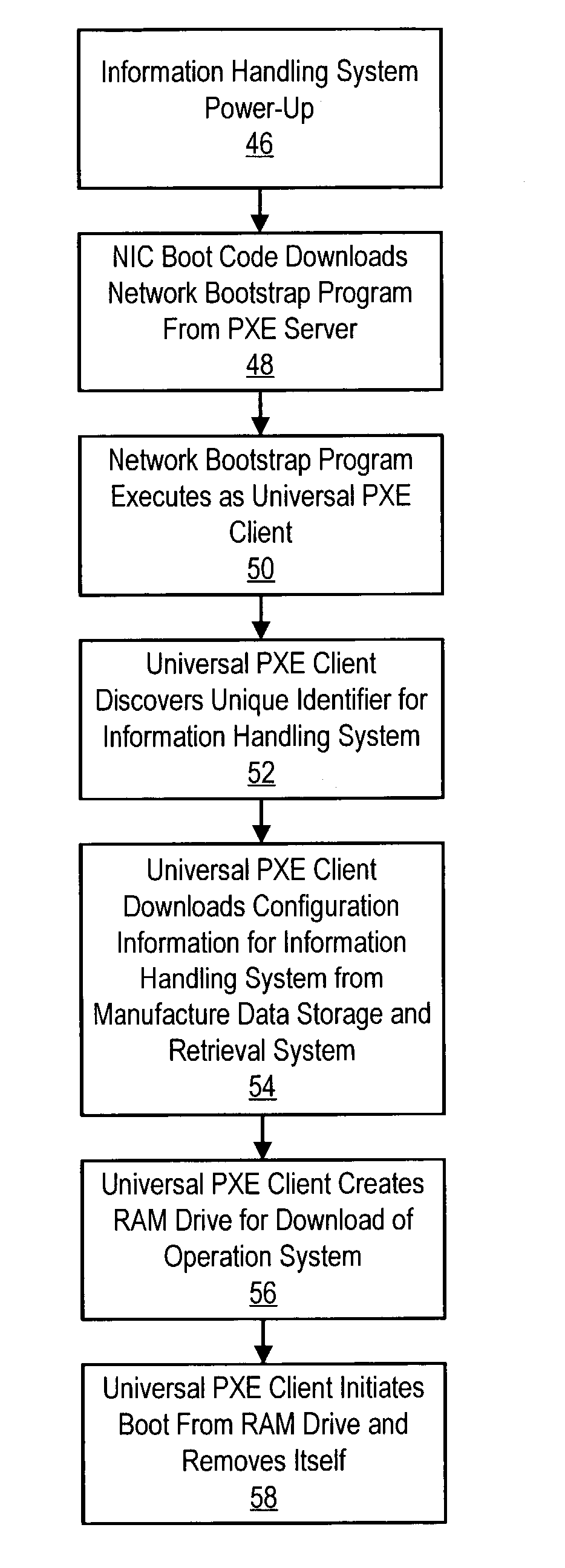
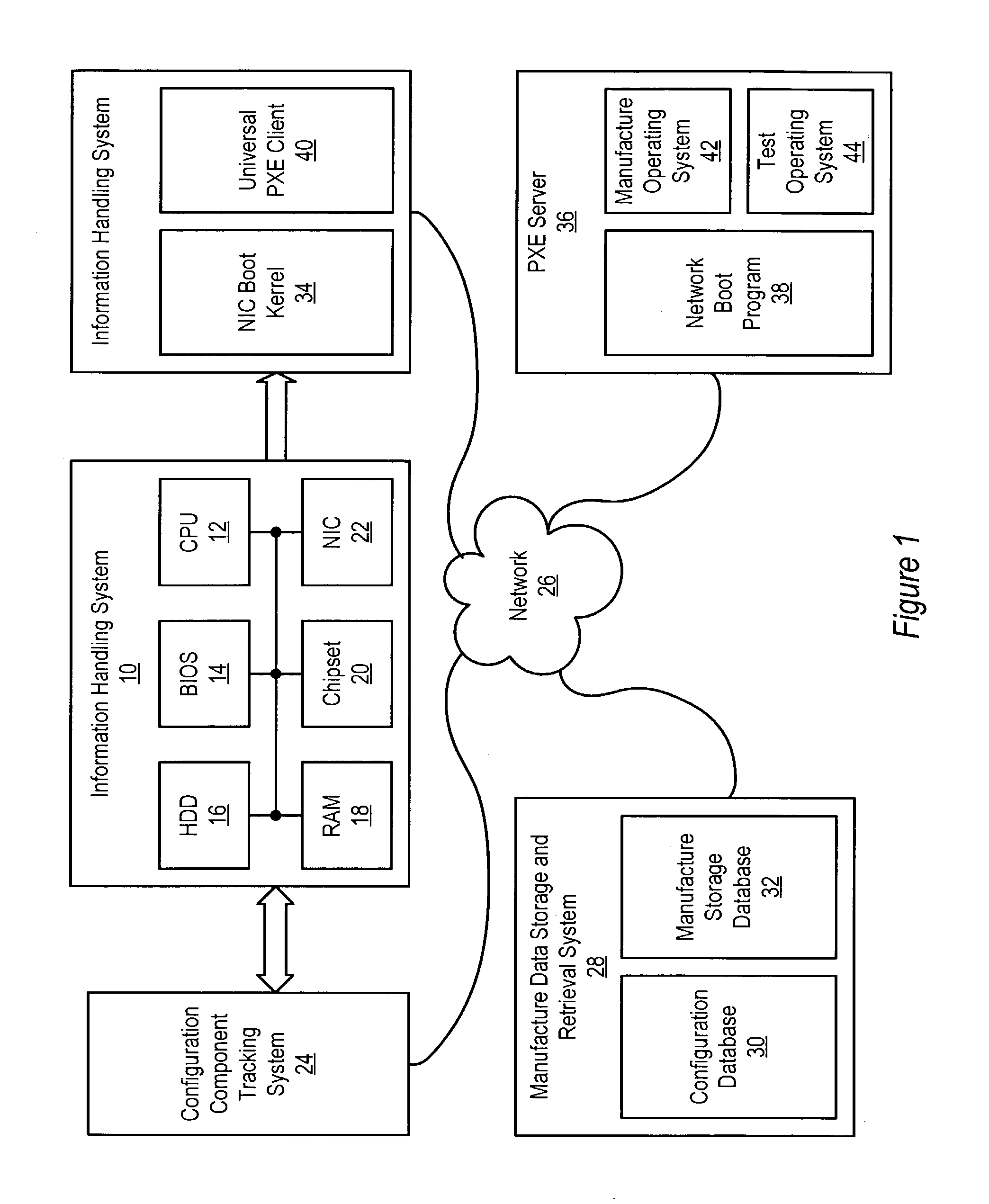
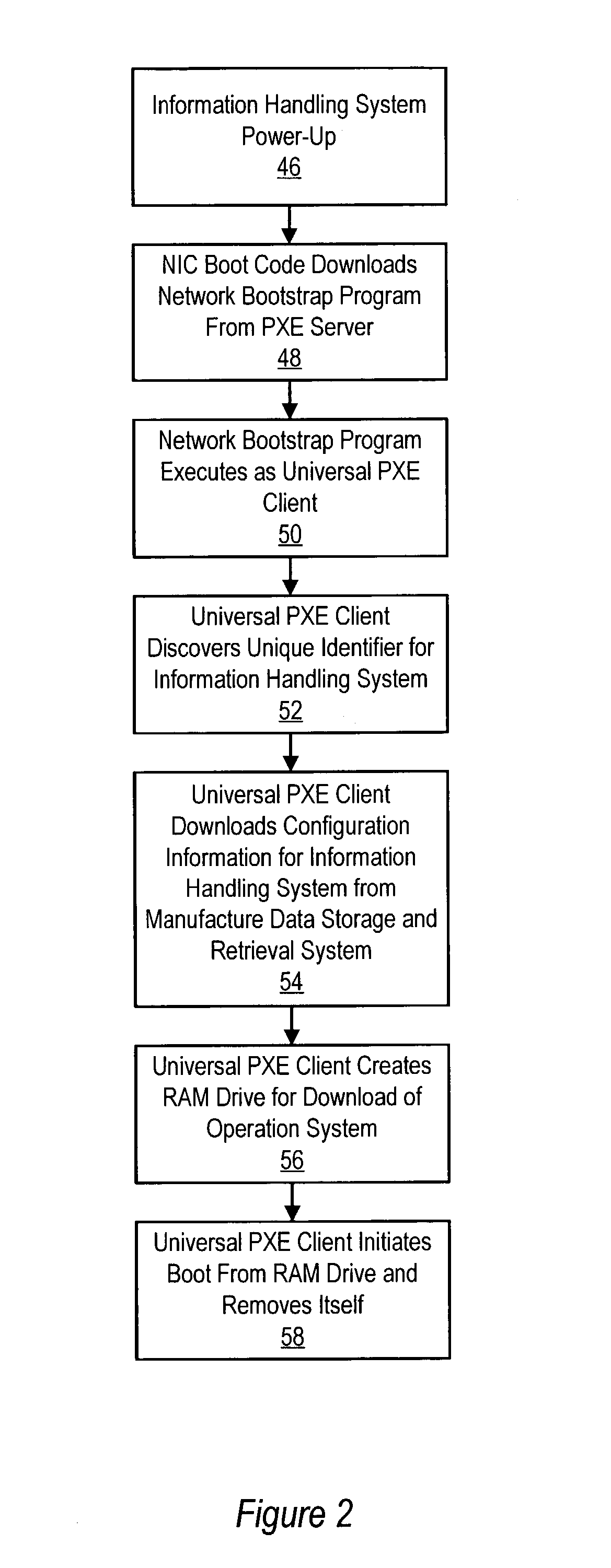
Information handling system manufacture method and system
ActiveUS7159106B2Allow useDigital computer detailsProgram loading/initiatingOperational systemNetwork booting
A universal PXE client obtains configuration information for an information handling system, applies the configuration information to create a drive on the information handling system and loads a manufacture operating system in the drive. The manufacture operating system runs a manufacture application that configures the software of the information handling system. The universal PXE client is generated by a scripting engine of a network boot program that is downloaded to the information handling system with a NIC boot kernel activated on power-up. The state of manufacture is periodically saved to a network location that tracks manufacture progress and persists manufacture state information through system re-boots.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
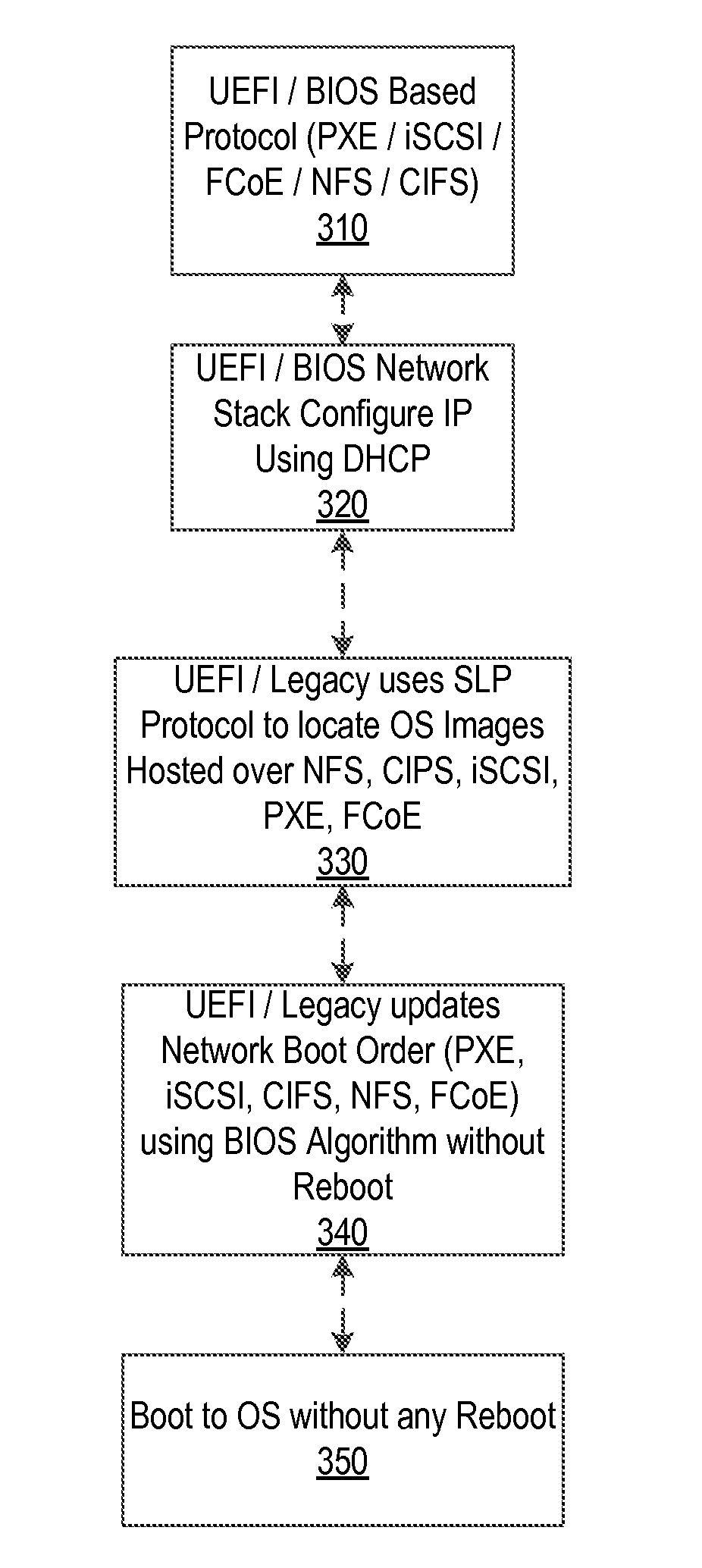
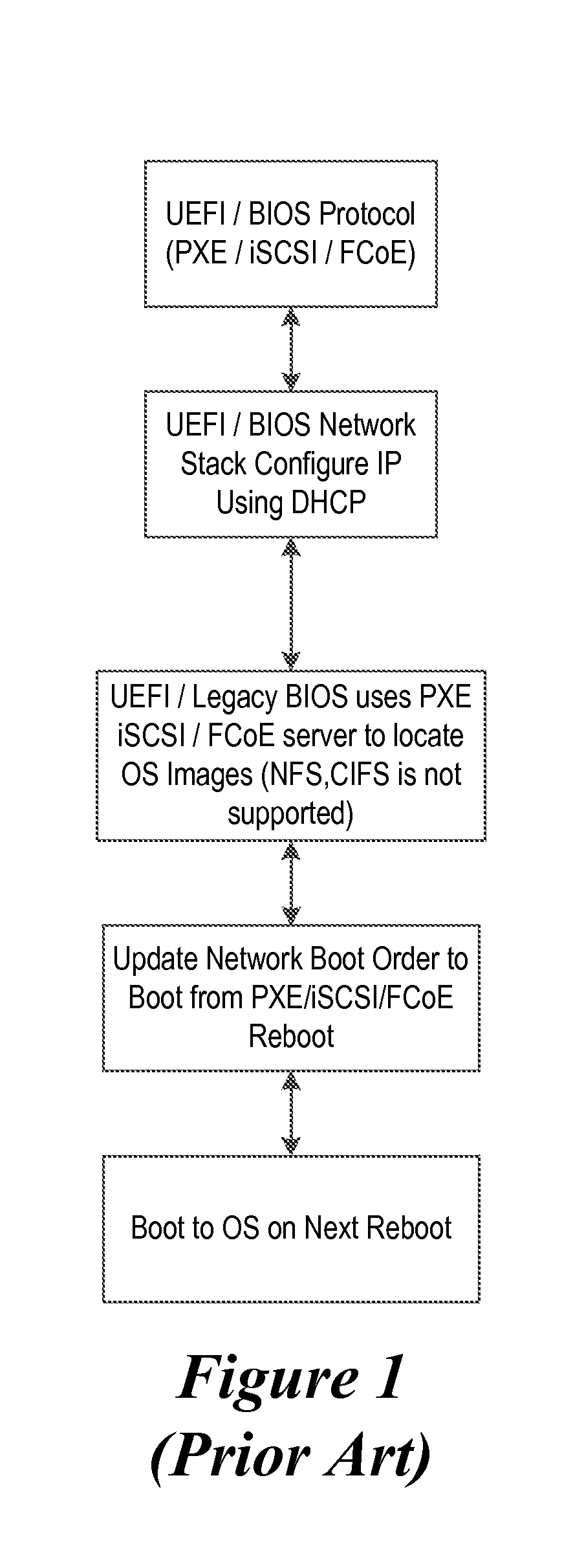
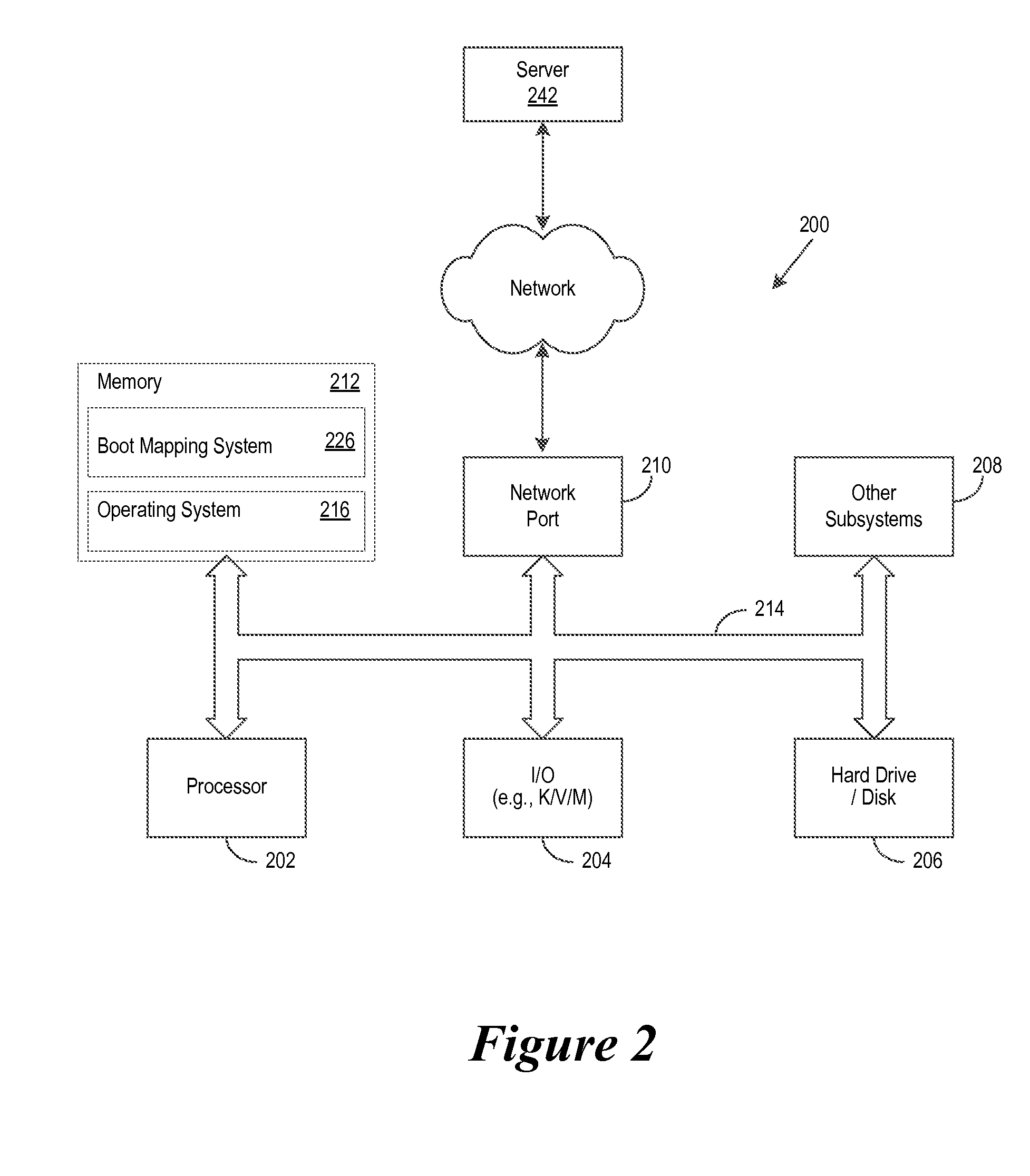
System and Method to Perform an OS Boot Using Service Location Protocol and Launching OS Using a Dynamic Update of Network Boot Order Without a Reboot
ActiveUS20150143094A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsNetwork bootingEngineering
A system, method, and computer-readable medium are disclosed for a boot mapping system. More specifically, in certain embodiments, BIOS of an information handling system includes a boot mapping system which allows the information handling system to boot up regardless of a boot order change in a network mode of operation or a BIOS boot order change. Additionally, in certain embodiments, the boot mapping system further includes a service location protocol (SLP) which locates operating system images based on the type of network protocol selected for deployment.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
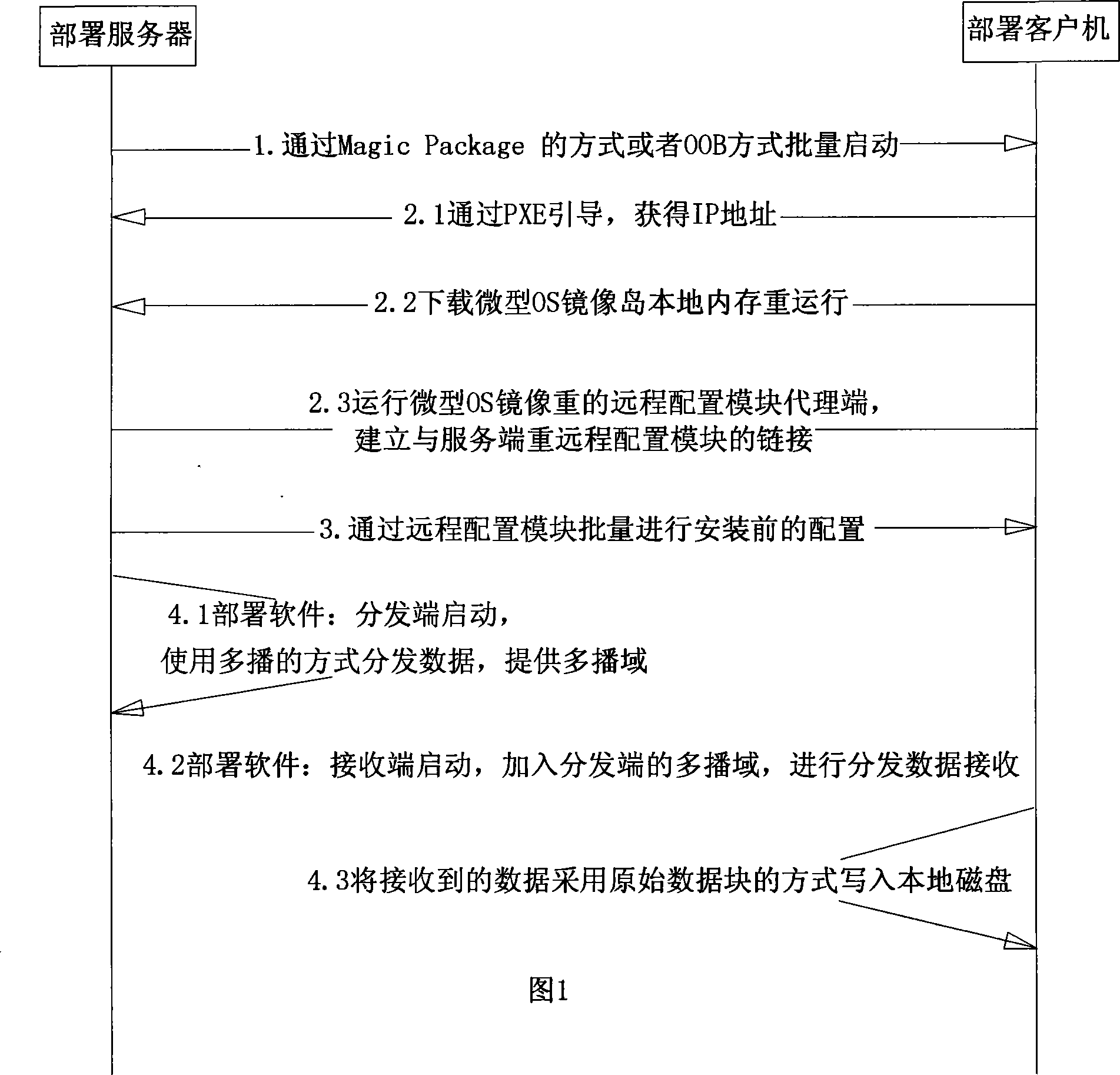
Method for allocating operating system through network guide
ActiveCN101232400AImprove transmission performanceData switching networksOperational systemIp address
The invention provides a method for deploying an operating system via a network guide. The method includes that a remote control module is adopted to remotely start a client computer by transmitting wake on Local Area Network (LAN) Magic Package or in an OOB management manner; the remote control module is used for concentratedly carrying out some necessary deployments to a multi-client terminal, and deploying starting / stopping of a software receiving terminal; a DHCP module is used for carrying out assignment of dynamic IP address to the client computer; and a micro OS mirror image operates on the client computer. The method is completely independent of a storage medium such as a local optical driver, a floppy drive, etc. and is suitable for various operating systems on an IA server. The method improves network transmission performance by using multi-cast technology, gets rid of limit of a file system by using the low-level implementation mechanism of primative data block, and can be widely applied in a large-scale computer system deploying field.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
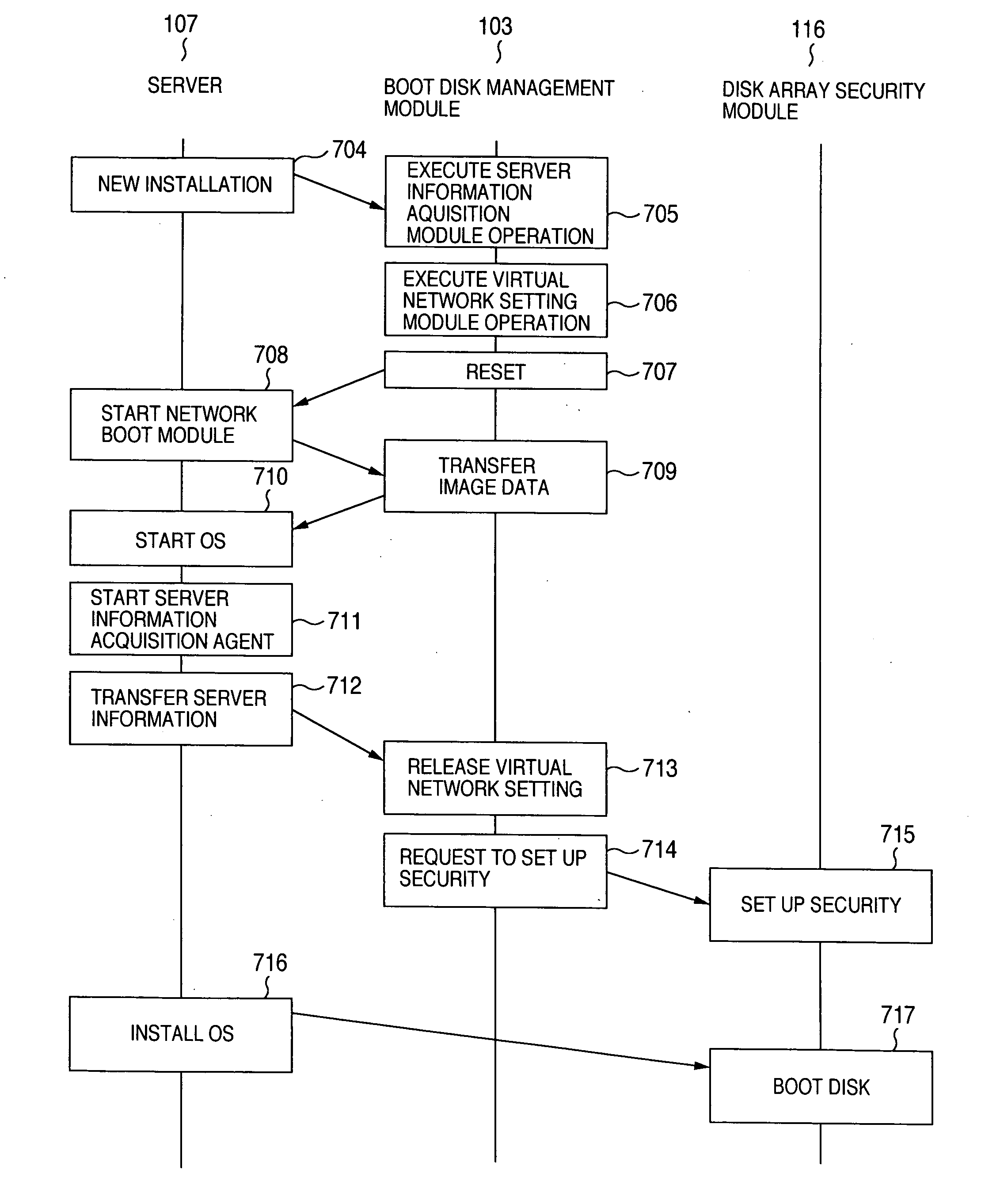
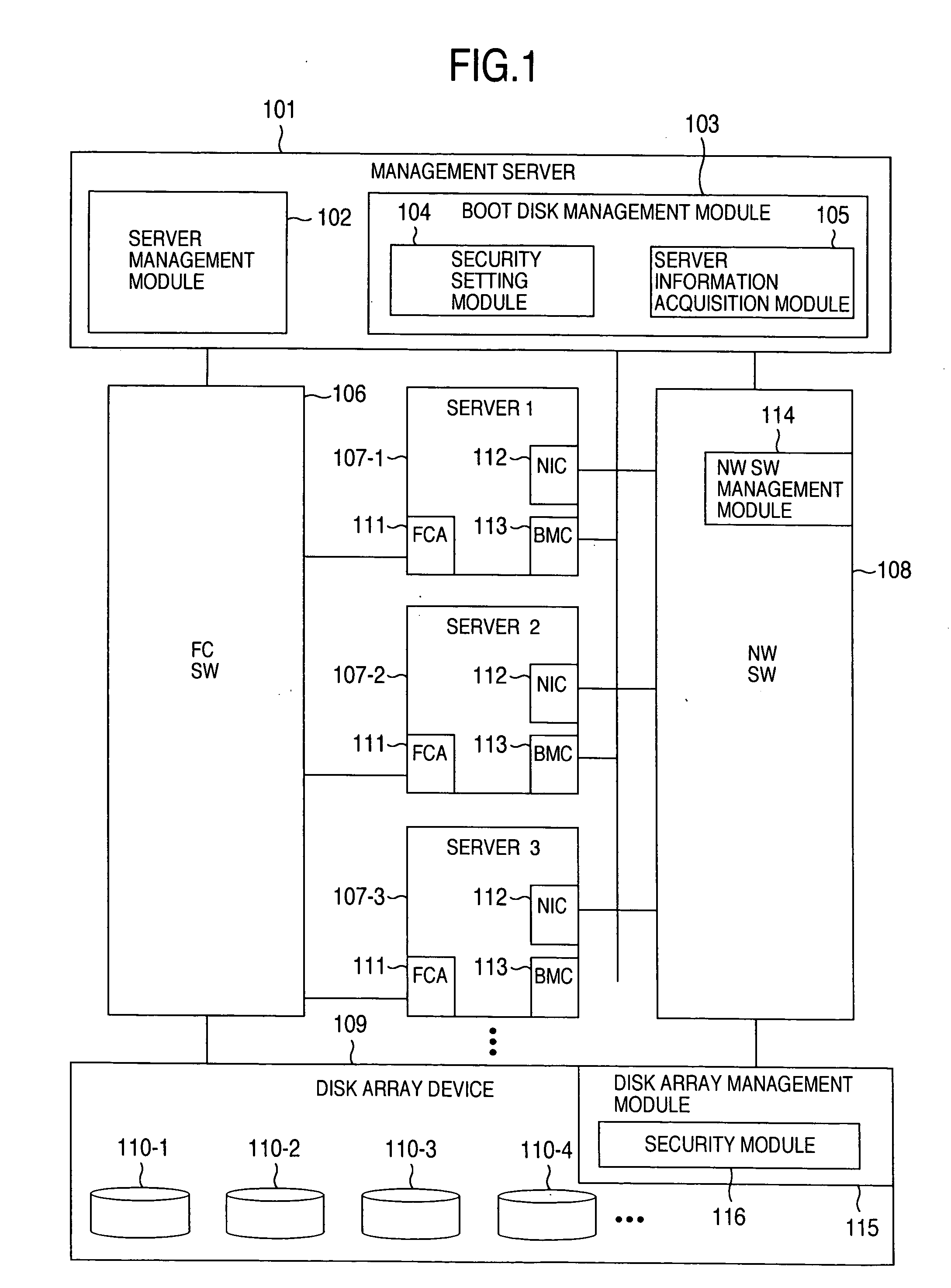
Method of booting an operating system
InactiveUS20060075217A1Automatic collectionReduce effortDigital computer detailsMemory systemsOperational systemNetwork booting
For use in a system where a plurality of servers are connected to an external disk device, a method is provided for a server to boot an operating system from the external disk device. The method includes the steps of searching for the port of a network switch to which the server is connected; establishing a network to which only the server and a management server belong; sending a server information acquisition program from the management server to the server via a network boot operation; acquiring, by the server information acquisition program, unique information owned by the storage interface of the server for transfer to the management server; and setting, by the management server, a disk within the external disk device accessible from the server based on the unique information.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
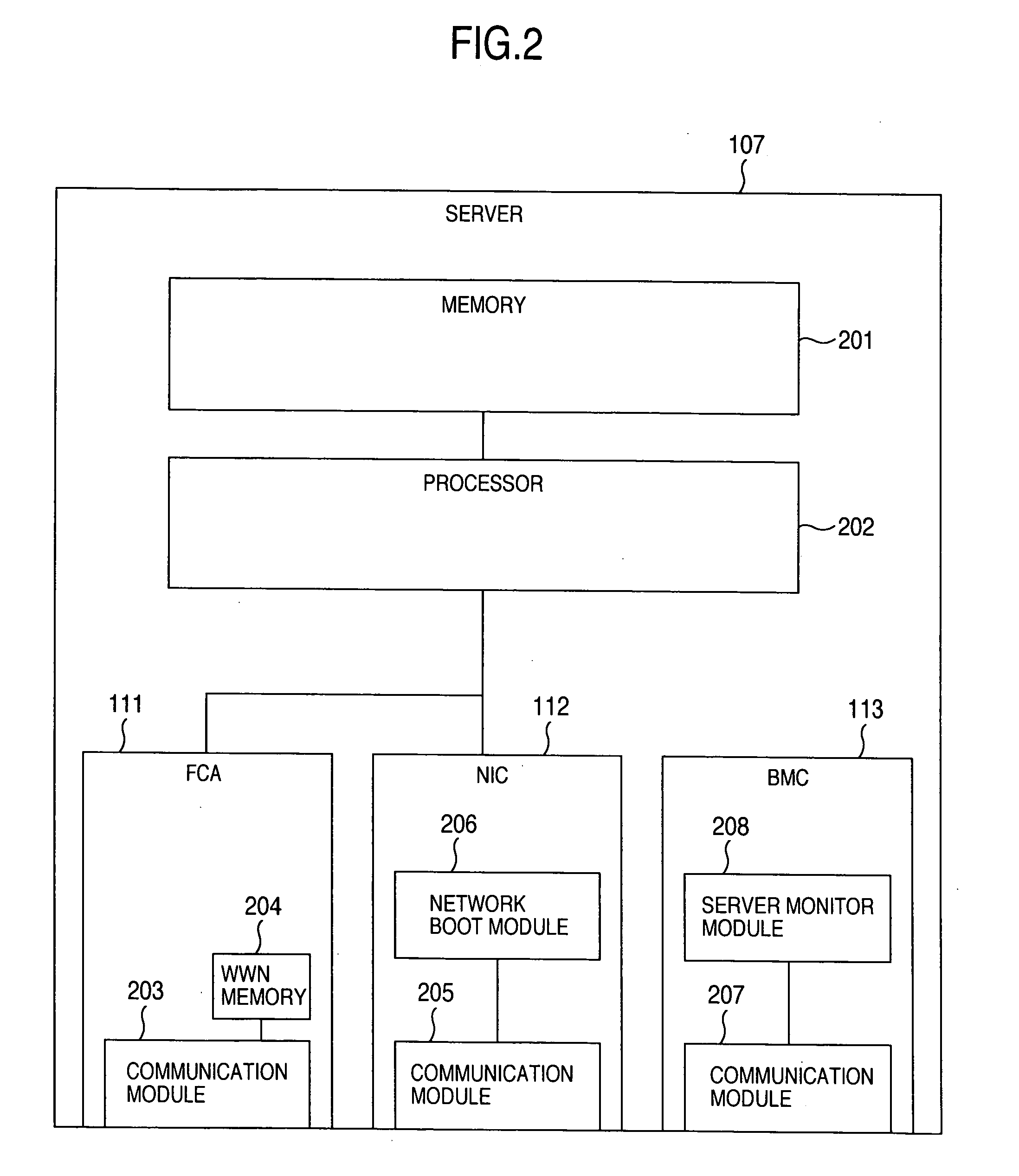
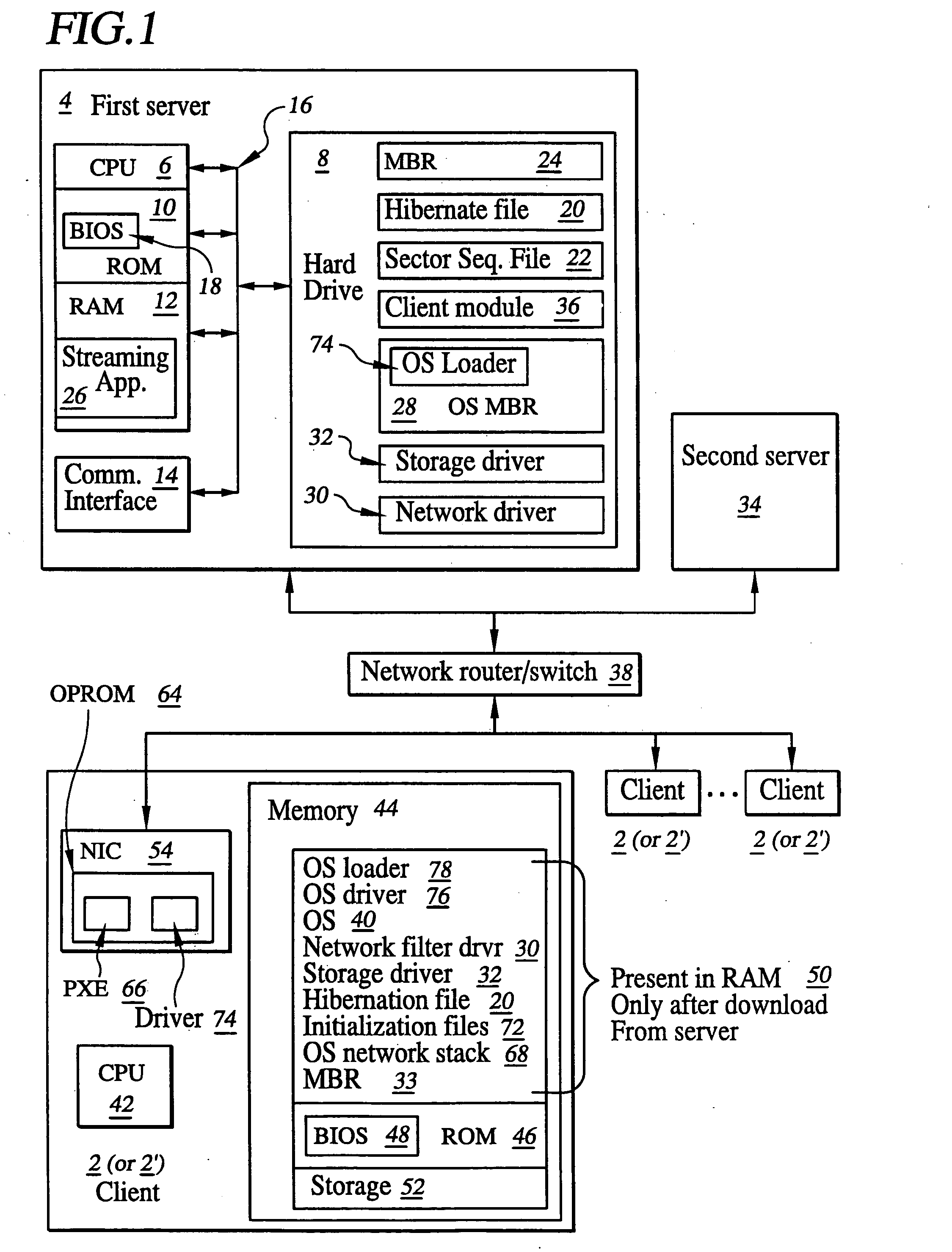
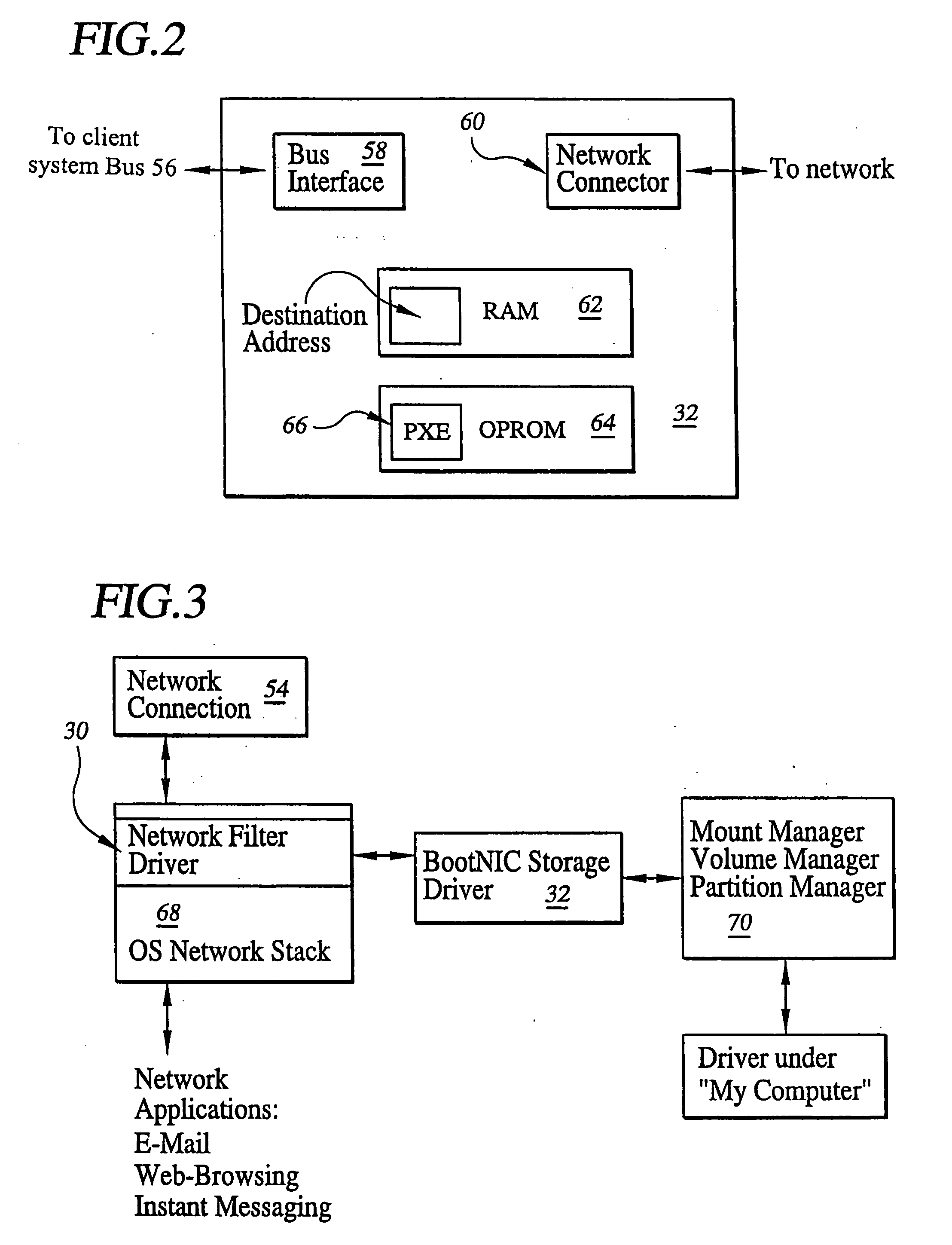
System for and method of network booting of an operating system to a client computer using hibernation
InactiveUS20060010316A1Easy to downloadFacilitates downloading of the hibernation fileDigital computer detailsData resettingOperational systemNetwork booting
A system for and method of network booting of an operating system (O / S) on one or more client devices, such as personal computers (PC's), employing a hibernation image. Remote booting of sets of client devices is facilitated by employing virtual disk emulation and, in certain preferred embodiments, broadcasting or multicasting of data residing on a network server which is necessary to appropriately boot and configure the one or more client devices, the data including hibernation, O / S and application files.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com