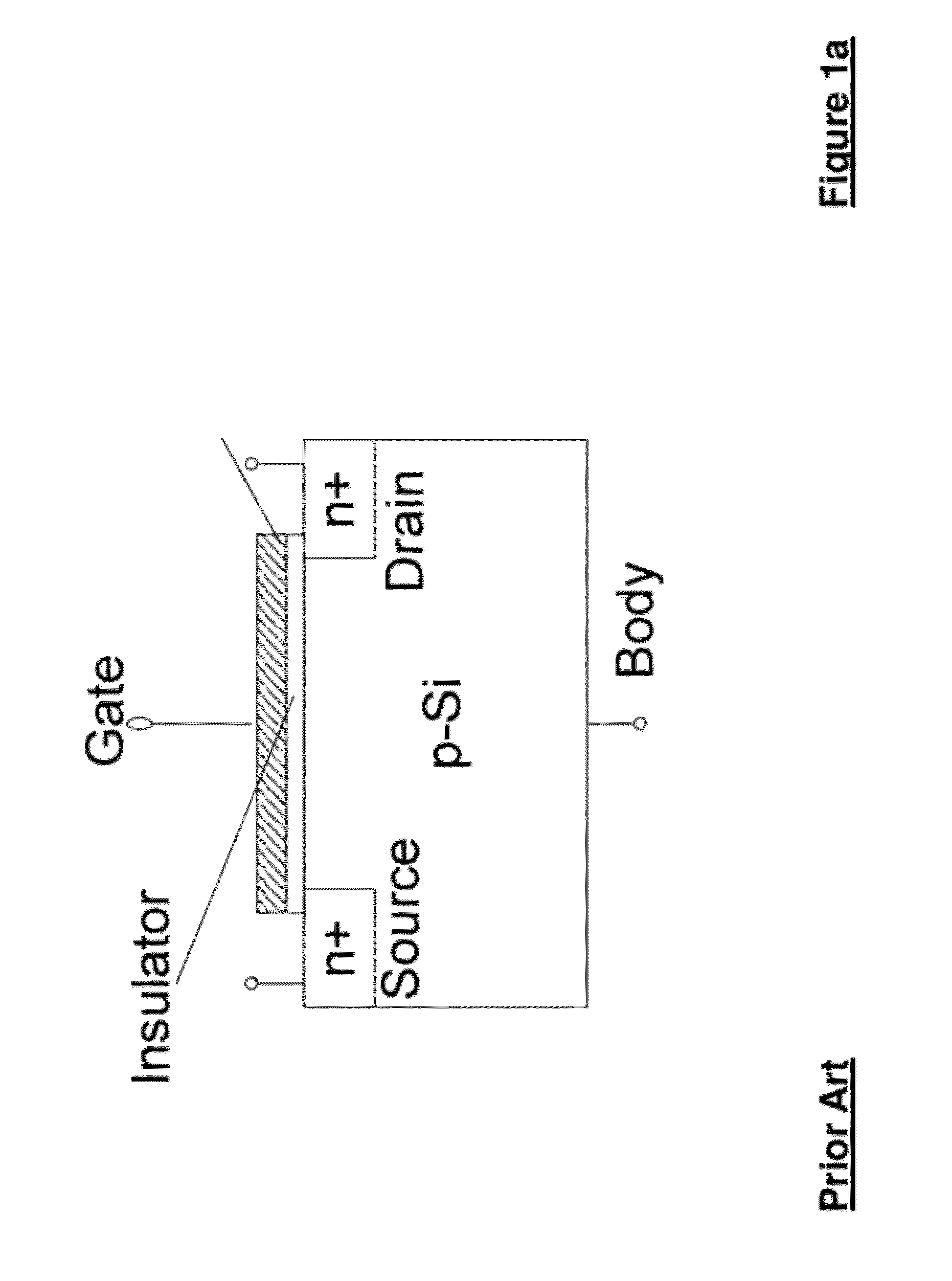
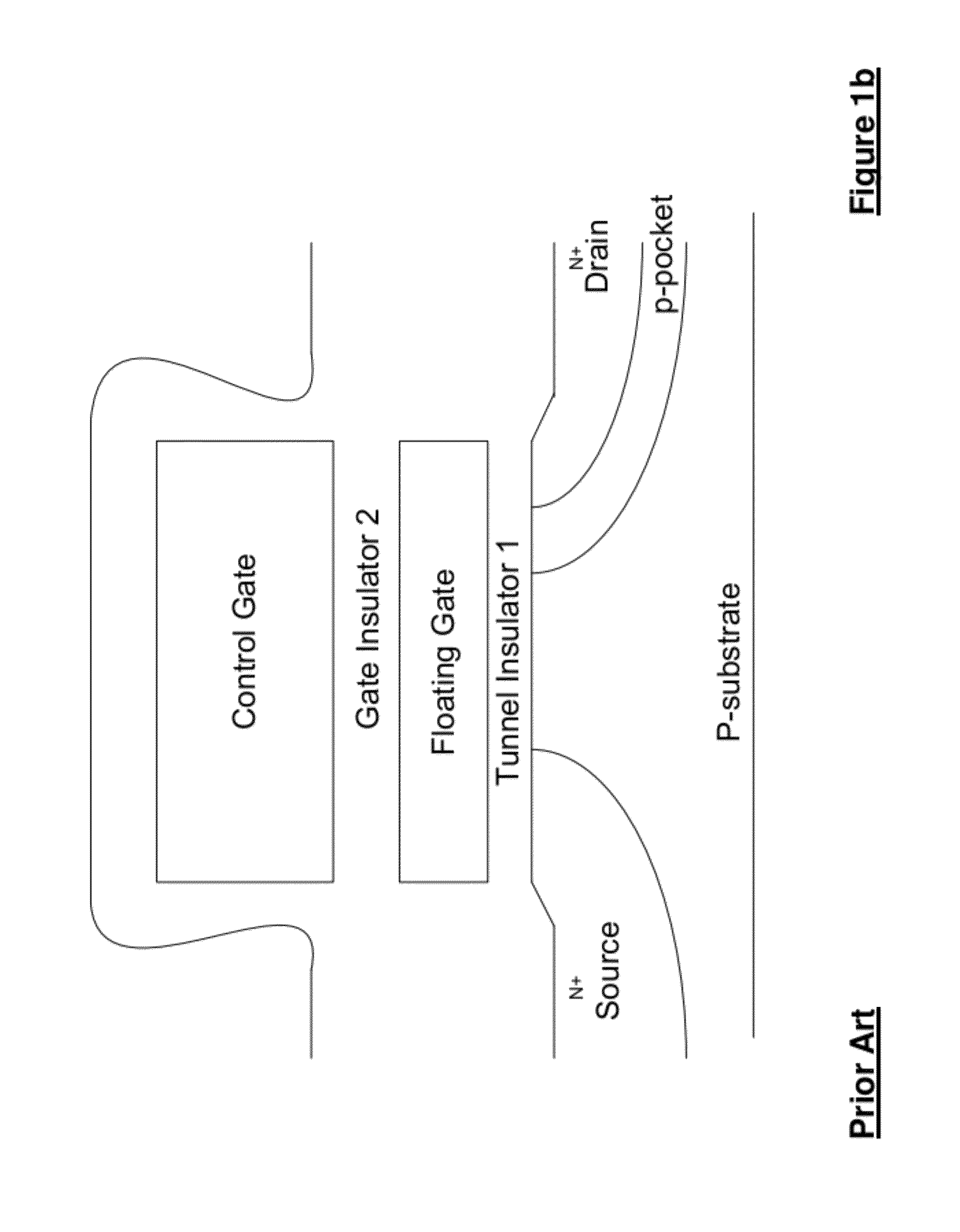
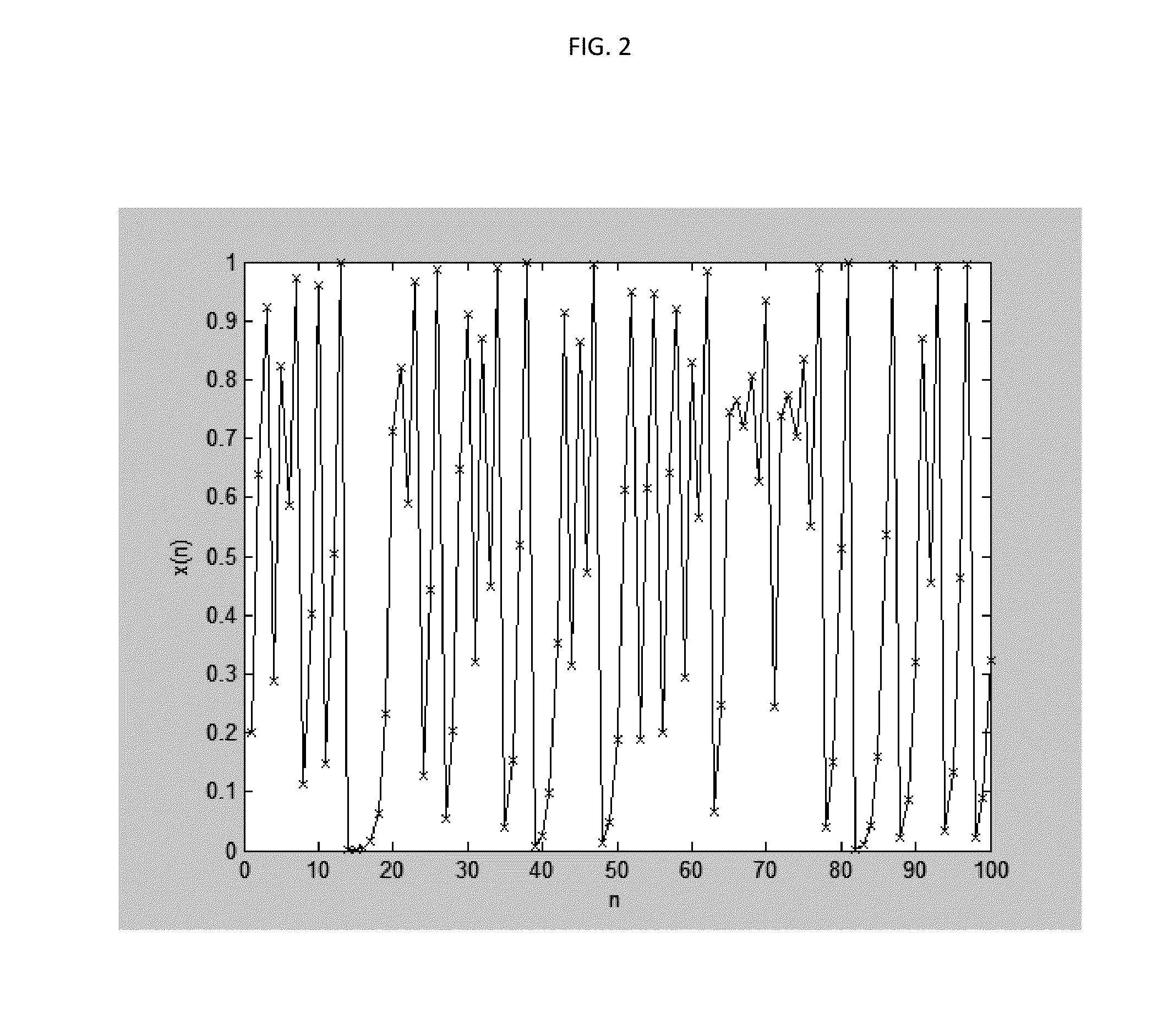
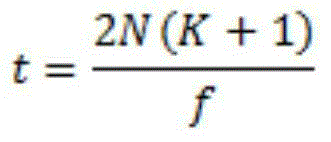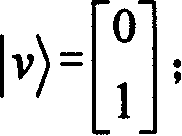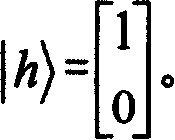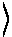Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
287 results about "Quantum channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
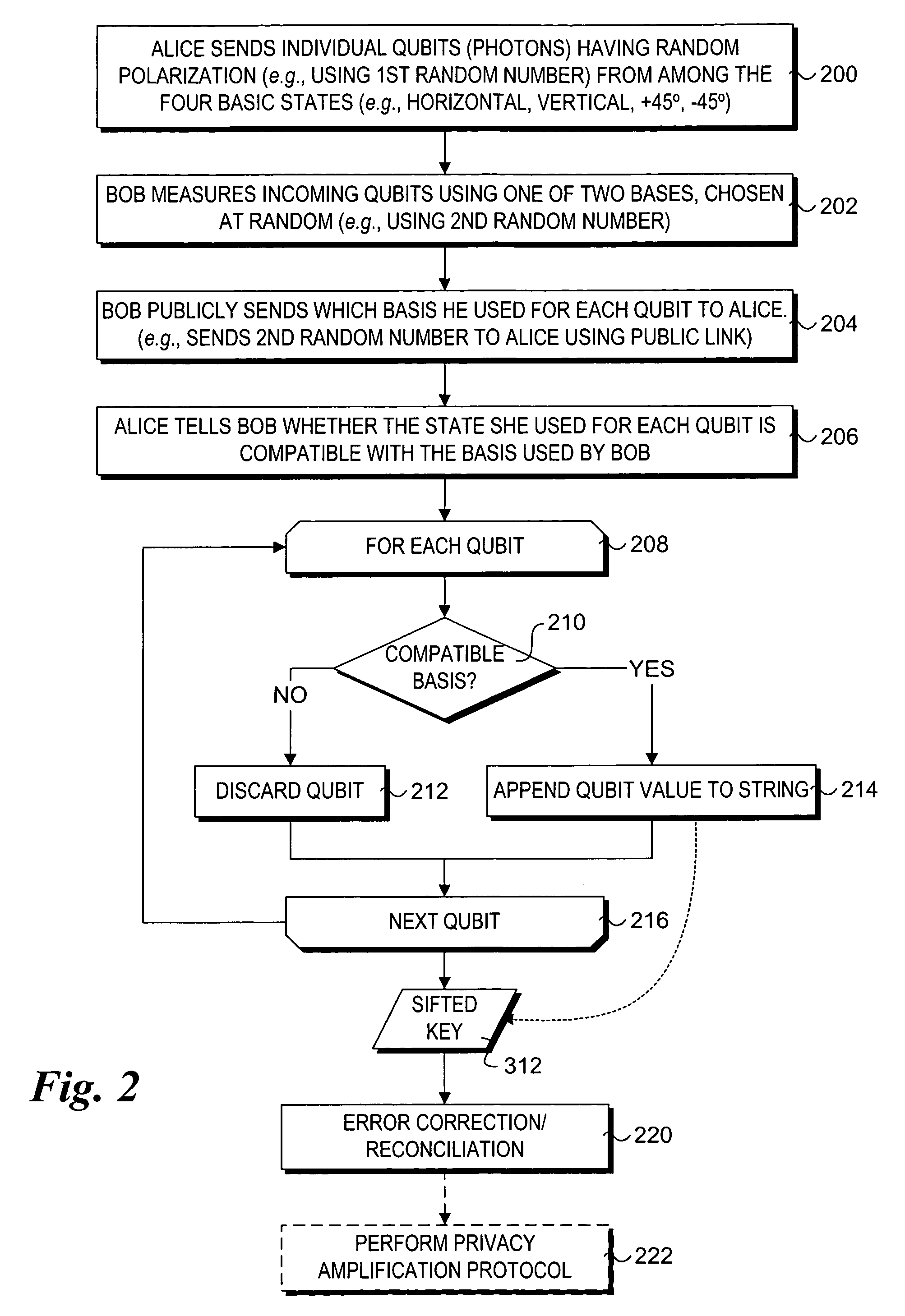
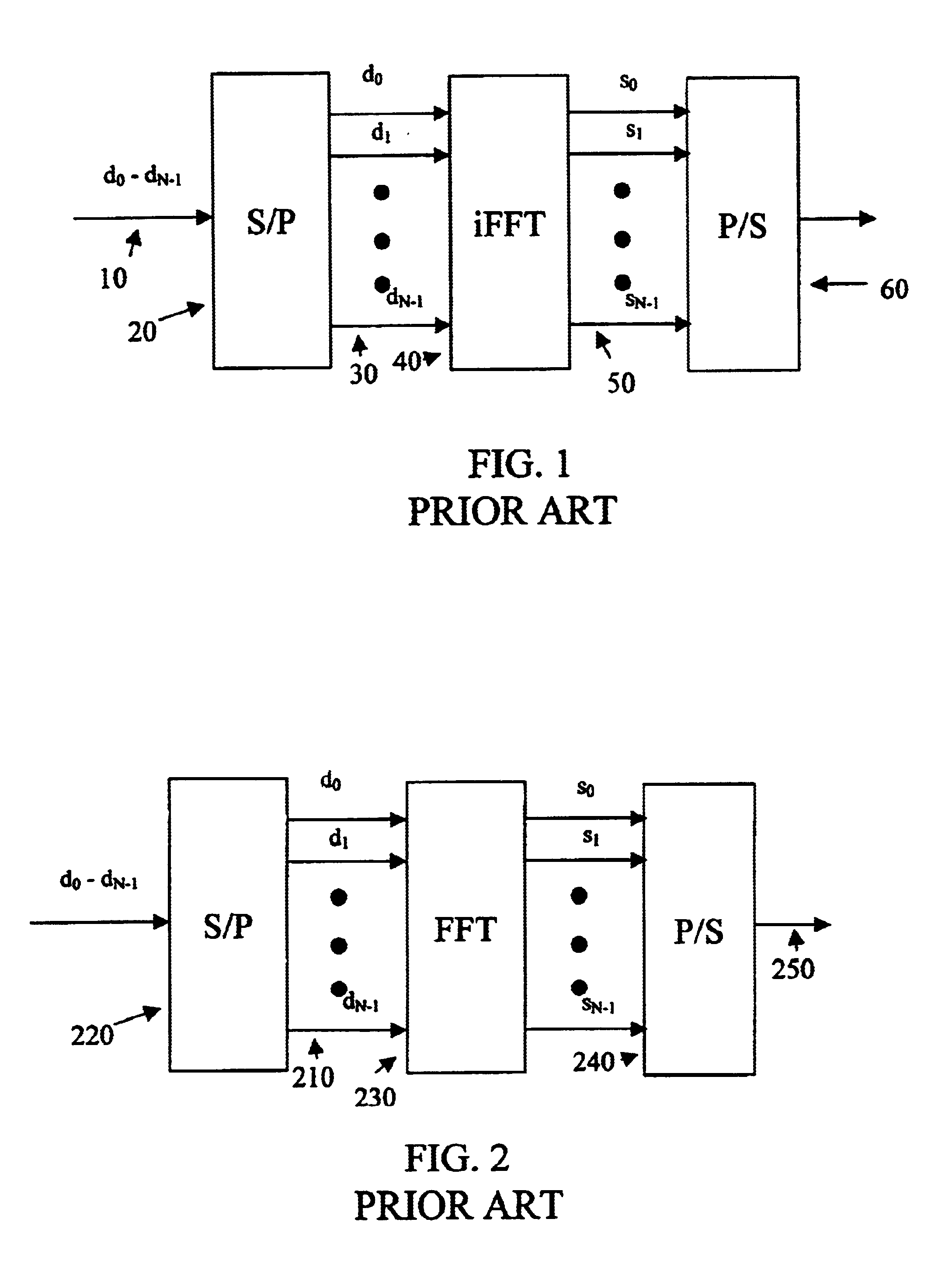
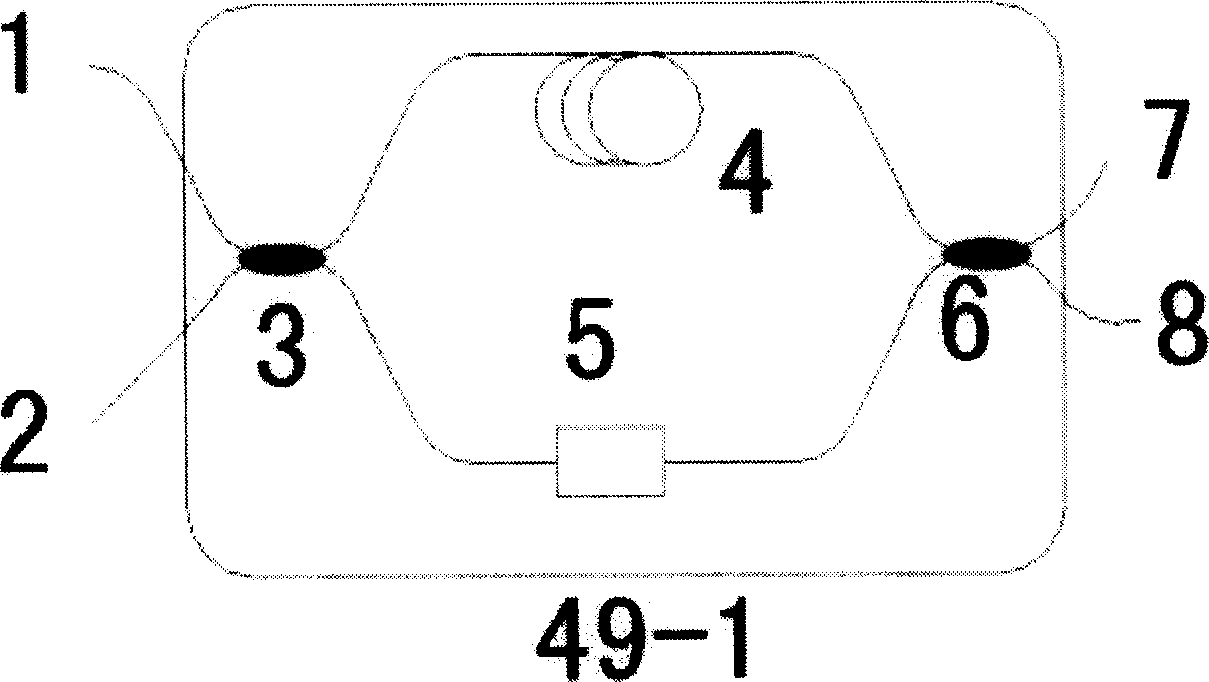
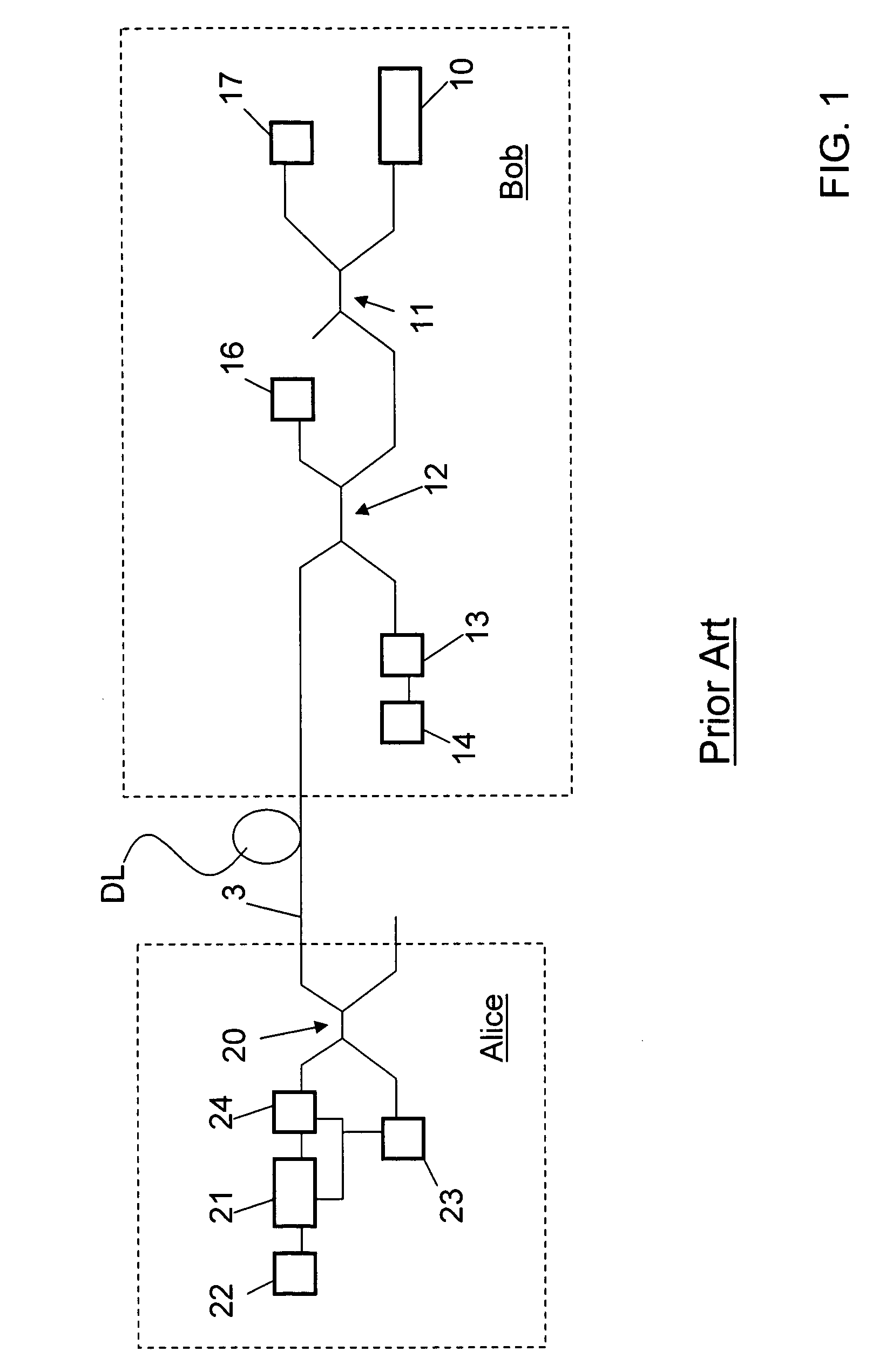
In quantum information theory, a quantum channel is a communication channel which can transmit quantum information, as well as classical information. An example of quantum information is the state of a qubit. An example of classical information is a text document transmitted over the Internet.
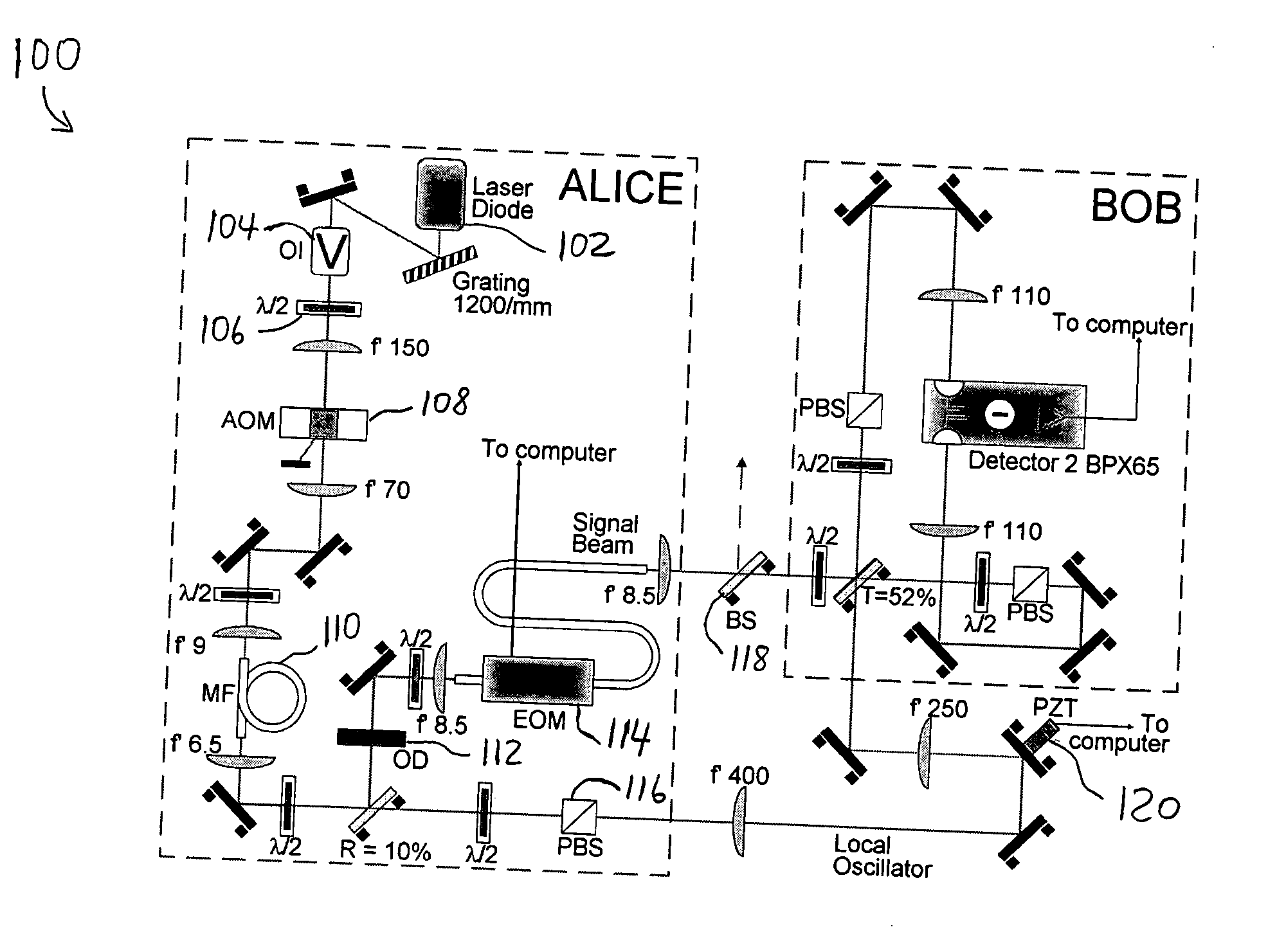
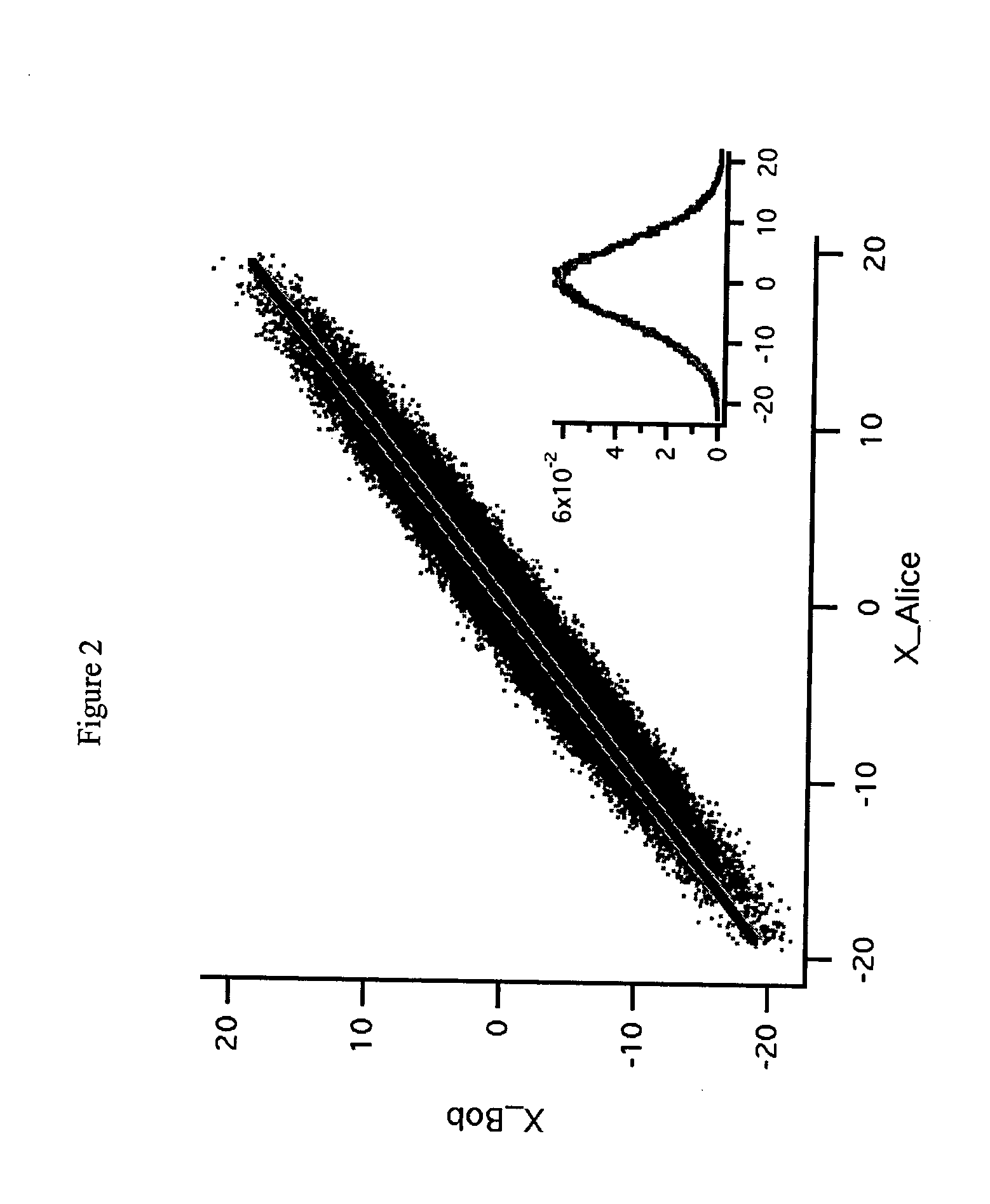
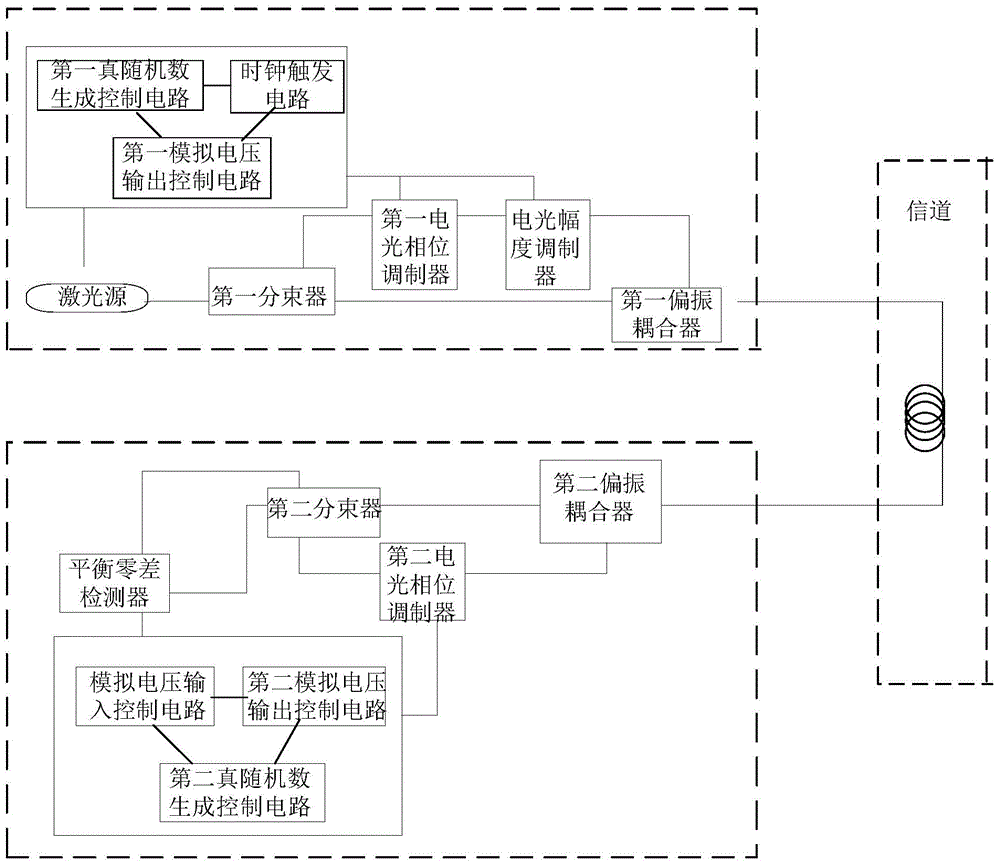
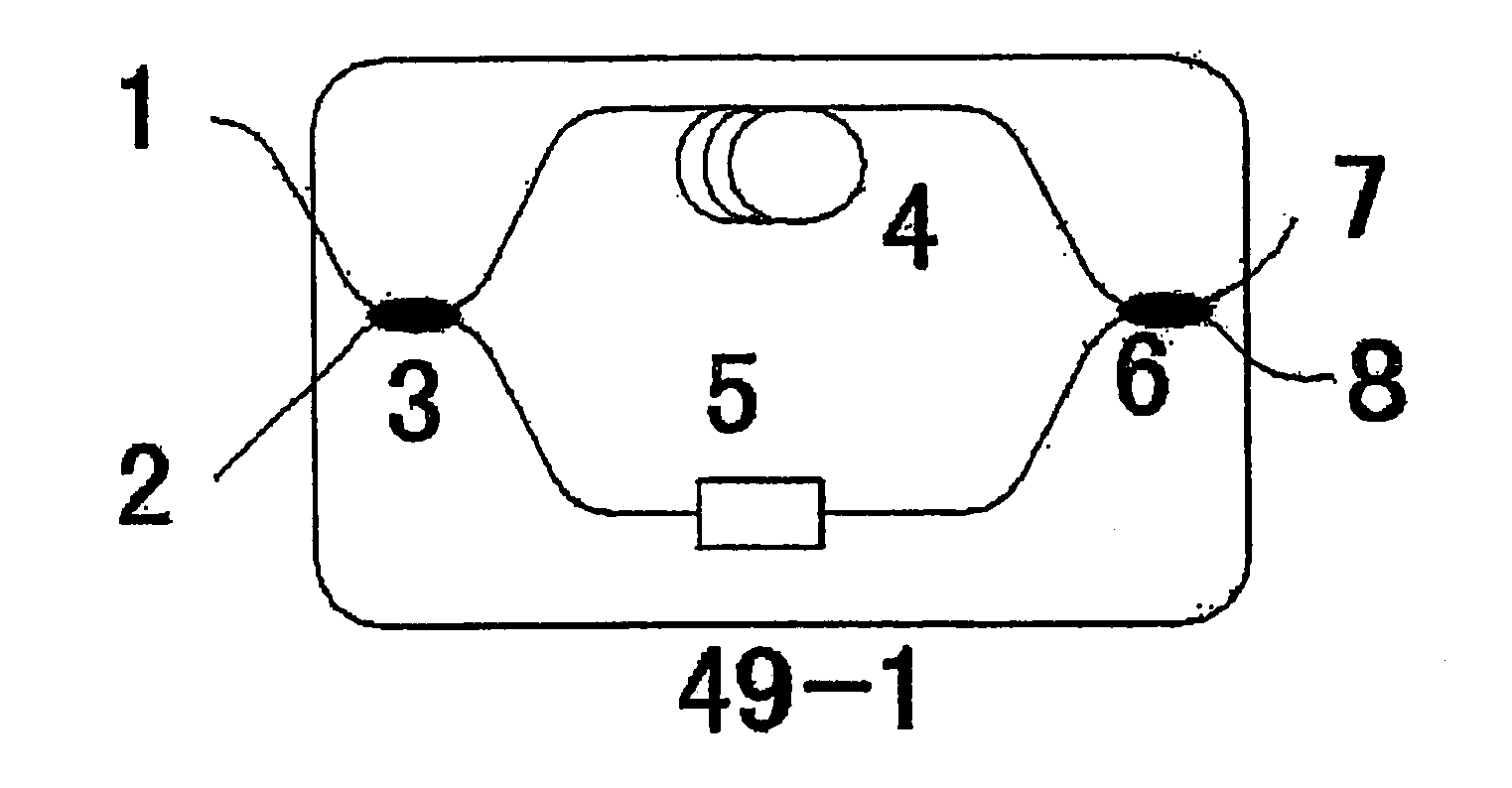
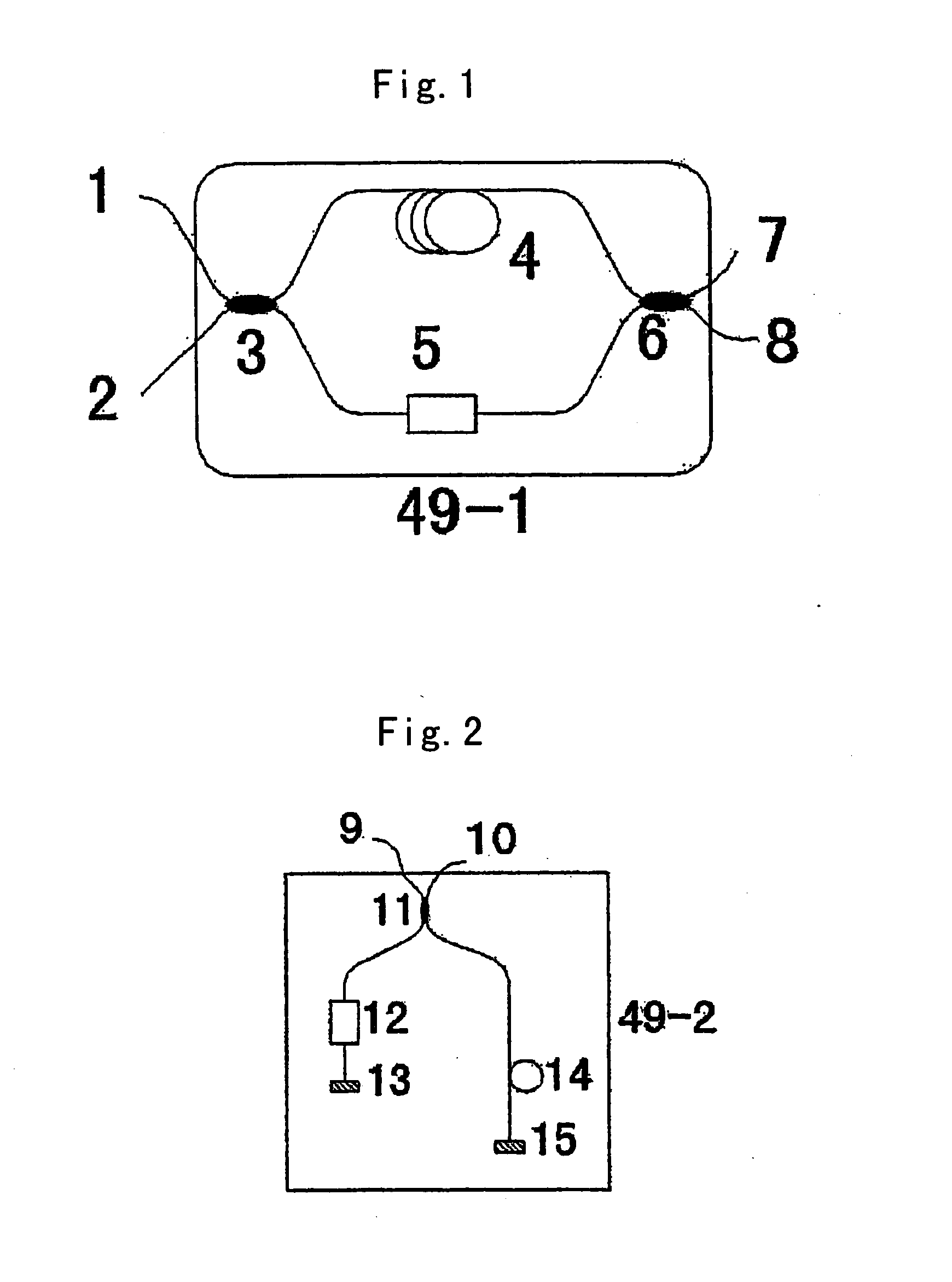
High-rate quantum key distribution scheme relying on continuously phase and amplitude-modulated coherent light pulses
InactiveUS20040109564A1Level of securityIncrease chanceKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationHigh rateCoherent states
One aspect of the present invention is related to a quantum cryptographic scheme comprising at least one sending unit including a physical means of encoding and distributing a raw key in the quadrature components of quantum coherent states that are continuously modulated in phase and amplitude, at least one receiving unit containing a physical means of performing homodyne detection of the quantum coherent states in order to measure the quadrature components of the states, a quantum channel for connecting the sending unit to the receiving unit, a two-way authenticated public channel for transmitting non-secret messages between the sending unit and the receiving unit, a quantum key distribution protocol ensuring that the information tapped by a potential eavesdropper can be estimated from the quantum channel parameters, and a direct or reverse reconciliation protocol that converts the raw continuous data into a common binary key.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
Quantum cryptography
ActiveUS20050036624A1Reduce bitrateIncrease bitrateKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum channelHilbert space
A method of establishing a shared secret random cryptographic key between a sender and a recipient using a quantum communications channel is described. The method comprises: generating a plurality of random quantum states of a quantum entity, each random state being defined by a randomly selected one of a first plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting the plurality of random quantum states of the quantum entity via the quantum channel to a recipient, measuring the quantum state of each of the received quantum states of the quantum entity with respect to a randomly selected one of a second plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting to the recipient composition information describing a subset of the plurality of random quantum states, analysing the received composition information and the measured quantum states corresponding to the subset to derive a first statistical distribution describing the subset of transmitted quantum states and a second statistical distribution describing the corresponding measured quantum states, establishing the level of confidence in the validity of the plurality of transmitted random quantum states by verifying that the first and second statistical distributions are sufficiently similar, deriving a first binary sting and a second binary string, correlated to the first binary string, respectively from the transmitted and received plurality of quantum states not in the subset, and carrying out a reconciliation of the second binary string to the first binary string by using error correction techniques to establish the shared secret random cryptographic key from the first and second binary strings.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
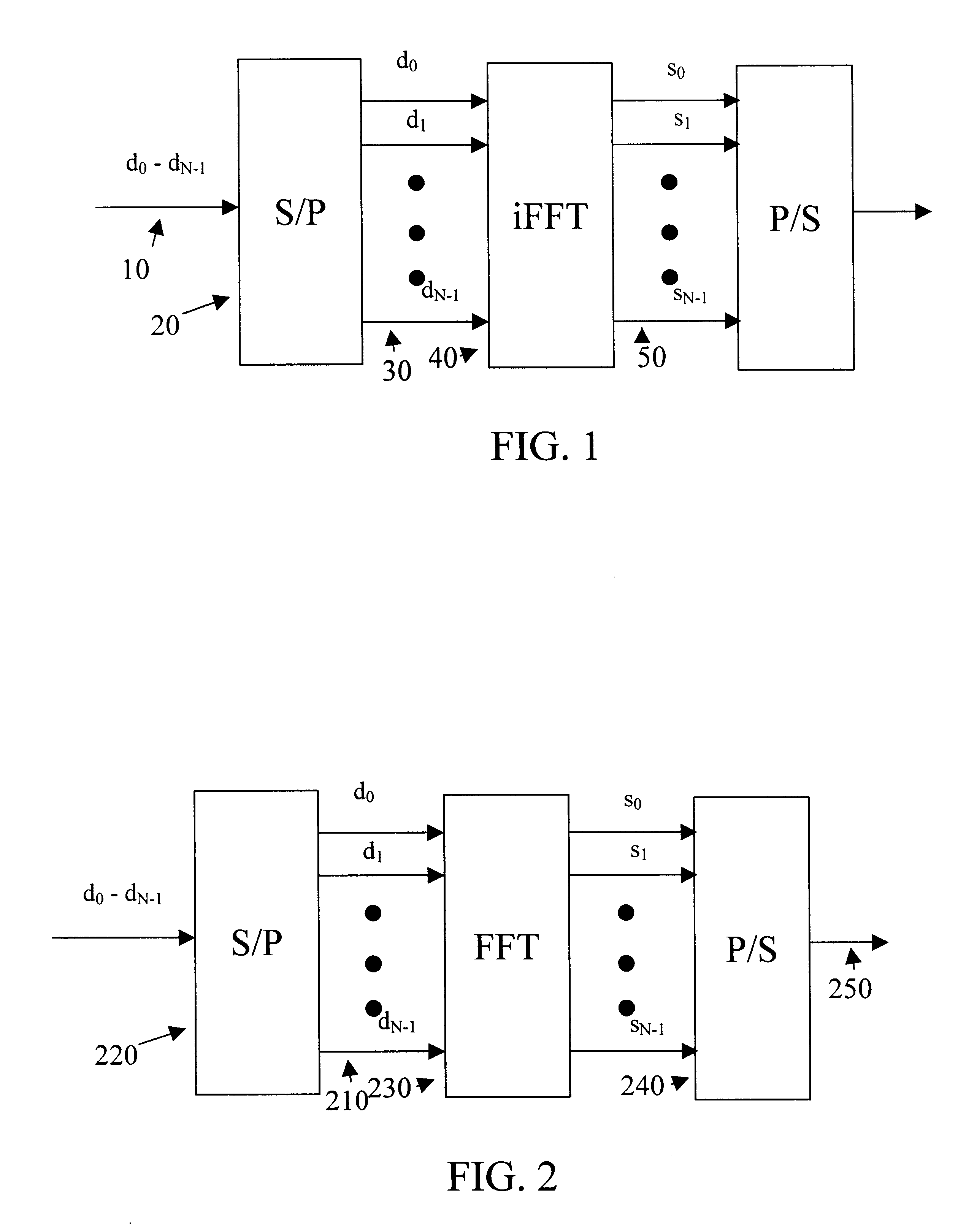
Modulating and coding apparatus and method in a high-rate wireless data communication system
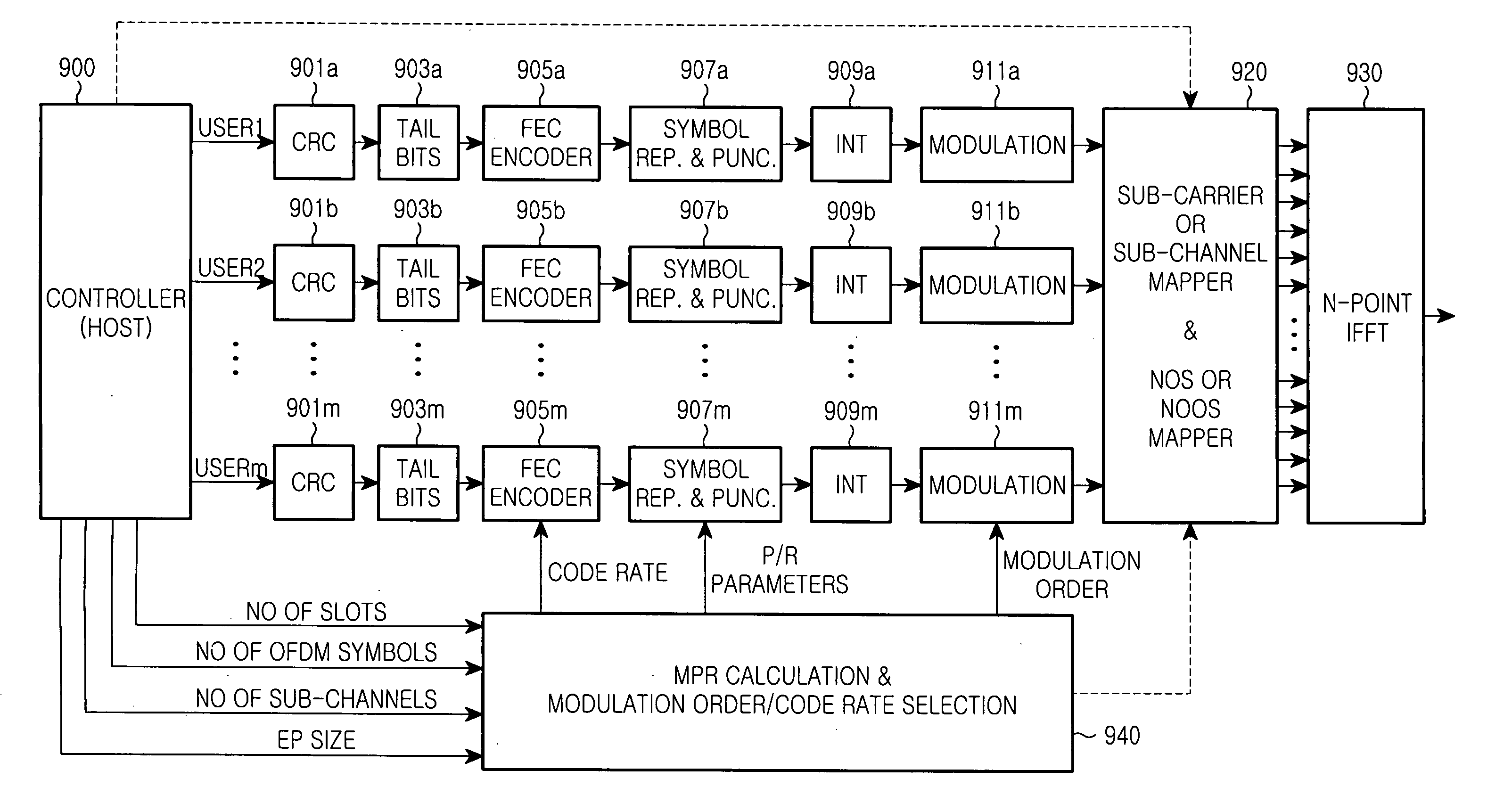
InactiveUS20050157803A1Data transmission efficiency is maximizedMaximize efficiencyDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusHigh rateEncoder packet
An apparatus and method for determining a modulation order of packet data to be transmitted through a subcarrier in a transmission apparatus. In the apparatus and method, transmitter physical channels encode and modulate data to transmit the user data with OFDM symbols. A controller outputs packet data to the transmitter physical channels, and determines the number of transmission slots, the number of OFDM symbols, the number of subchannels, and a size of an encoder packet. A modulation order and code rate decider receives, from the controller, the number of transmission slots, the number of OFDM symbols, the number of subchannels, and a size of an encoder packet, calculates a Modulation order Product code Rate (MPR), determines a modulation order according to the MPR, and outputs the determined modulation order to a corresponding physical channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
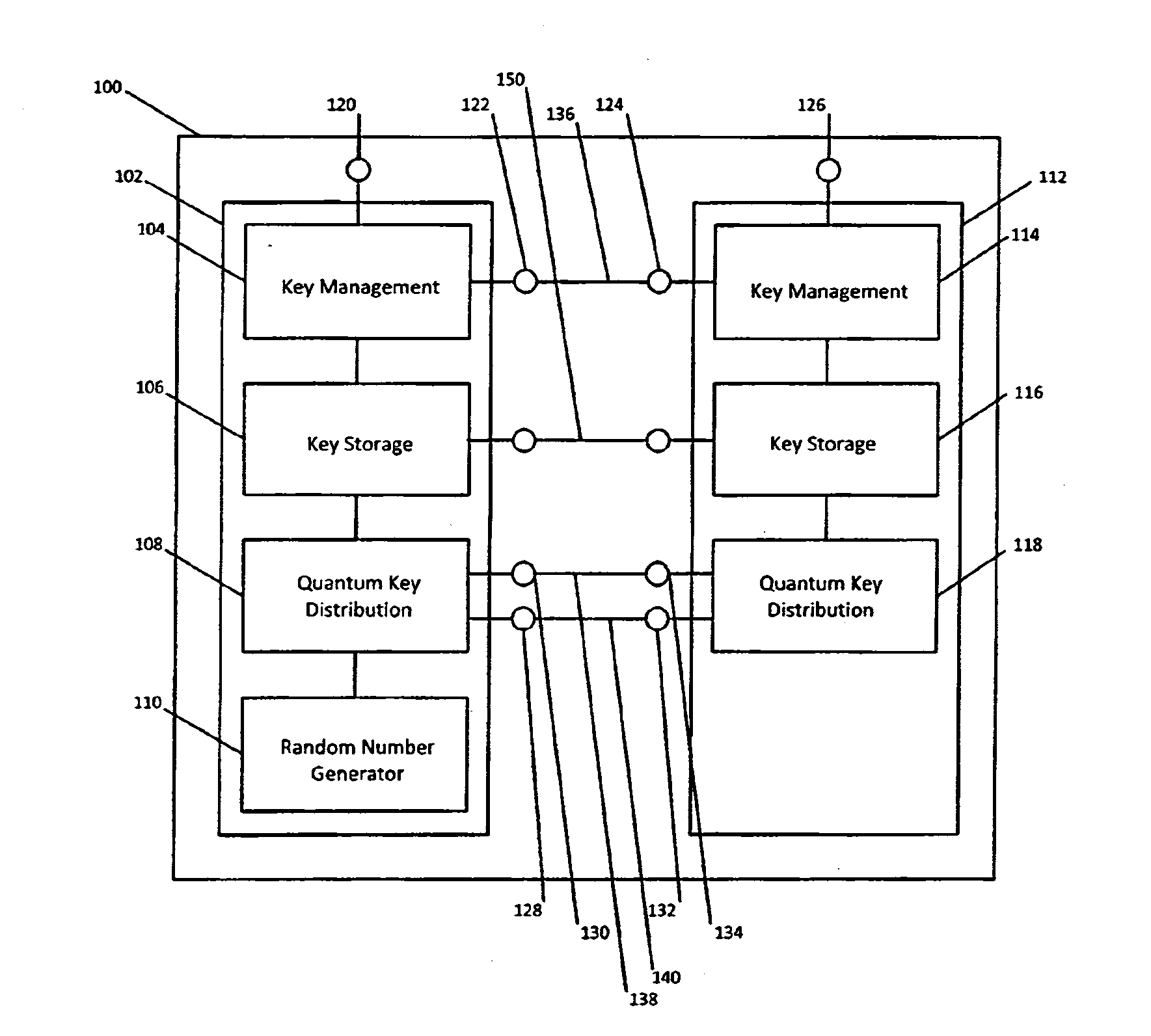
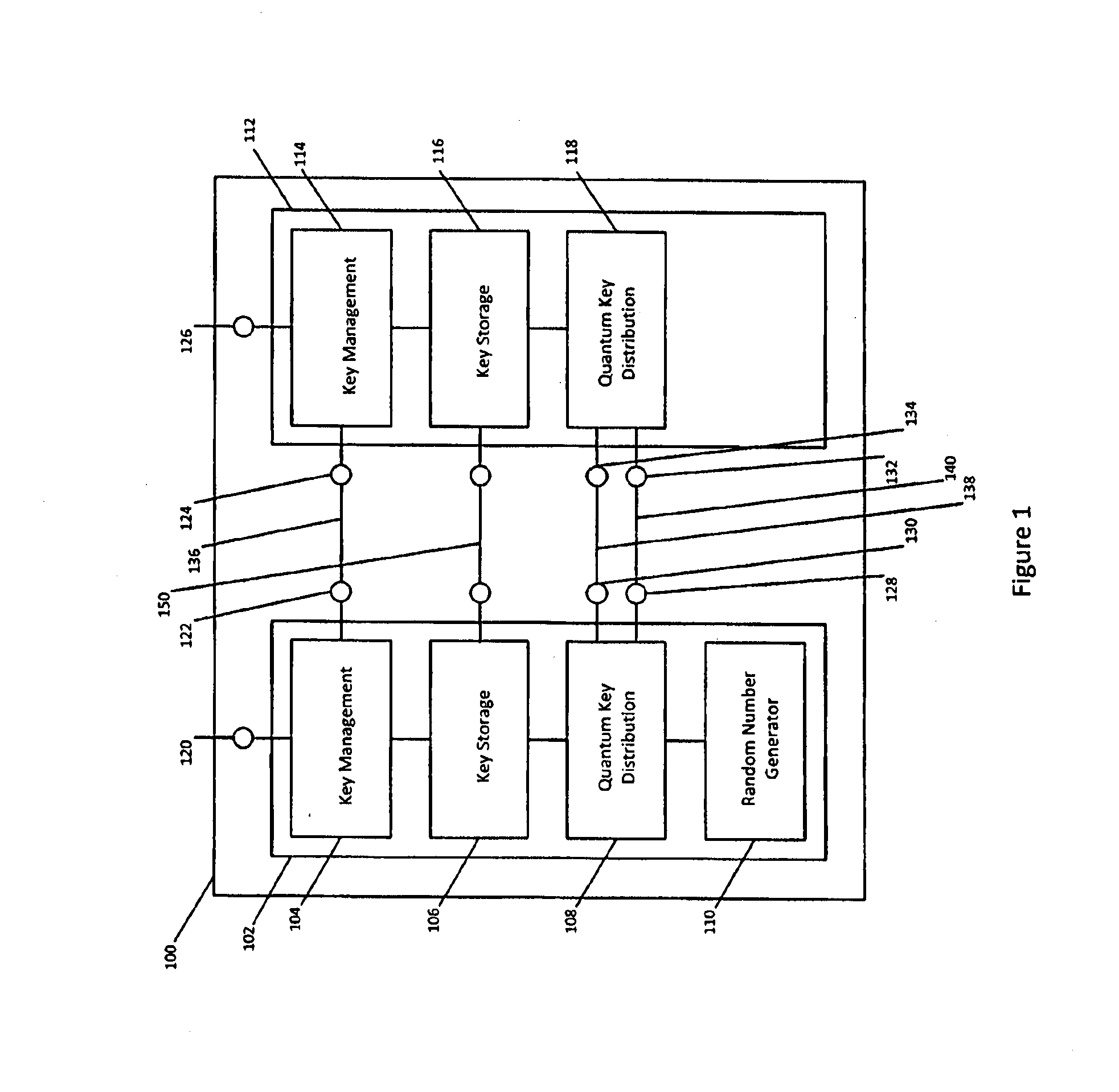
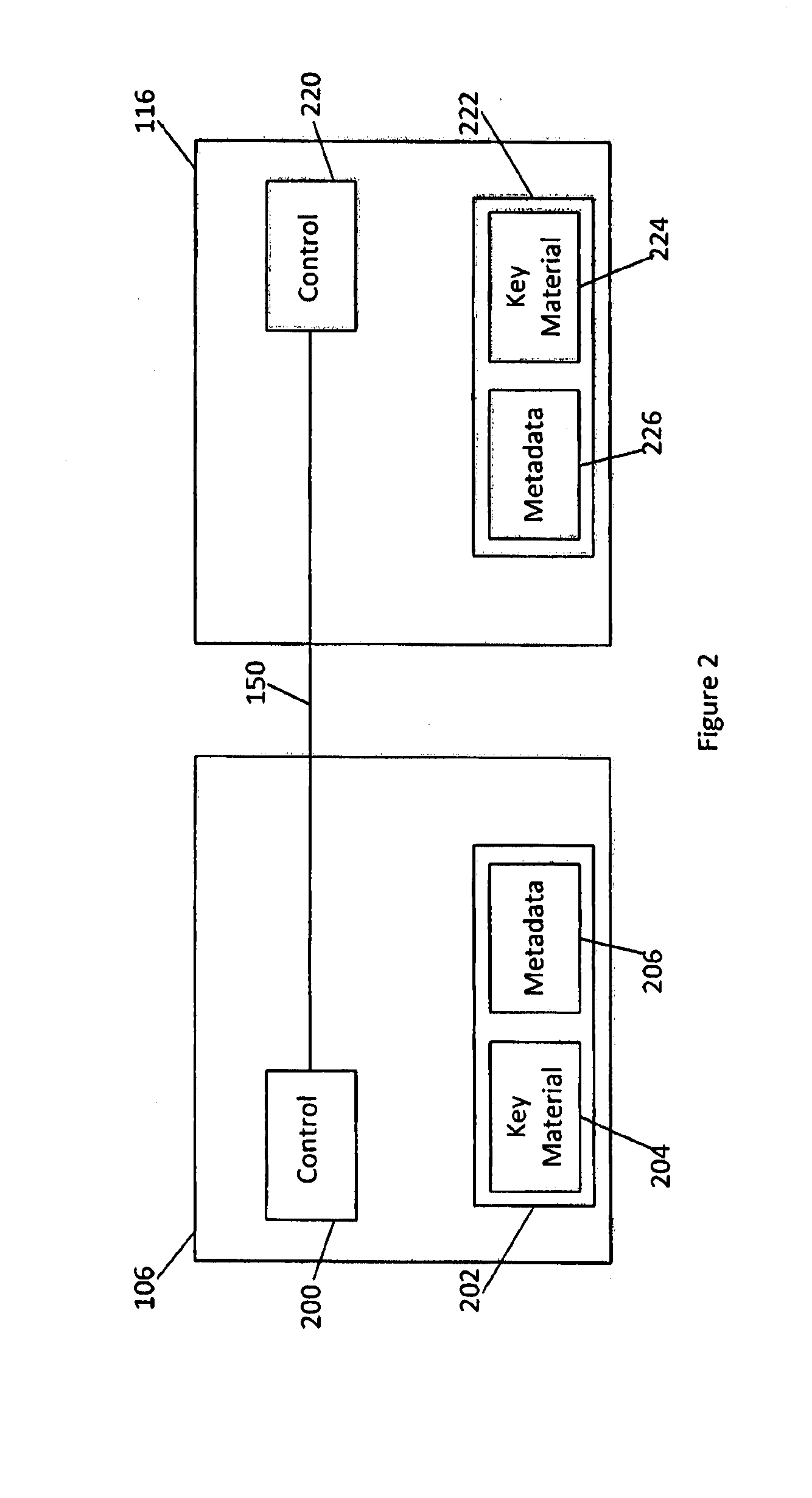
Qkd key management system
ActiveUS20140331050A1Enabling detectionEfficient management and deliveryKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCryptosystemQuantum channel
Owner:QUINTESSENCELABS
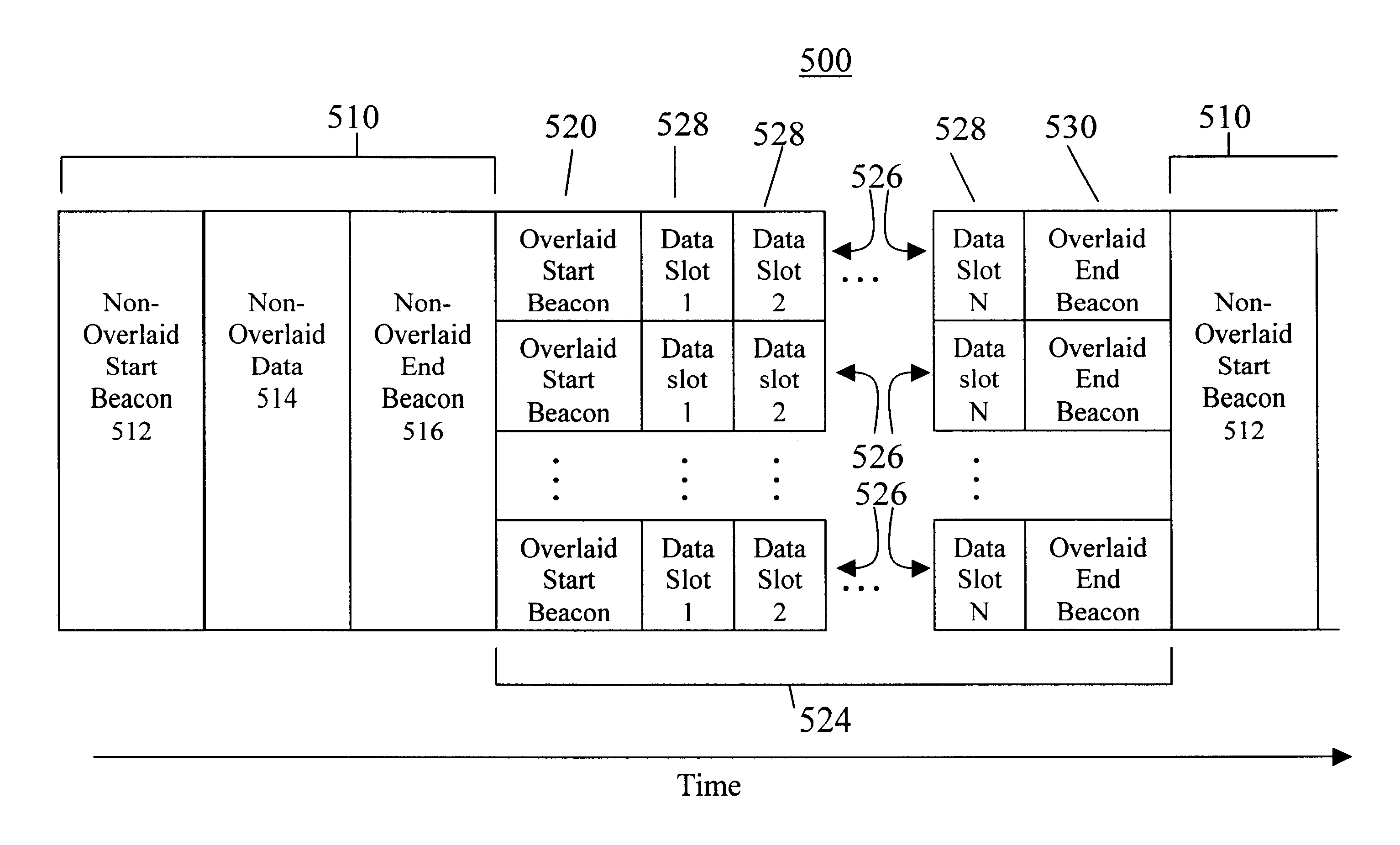
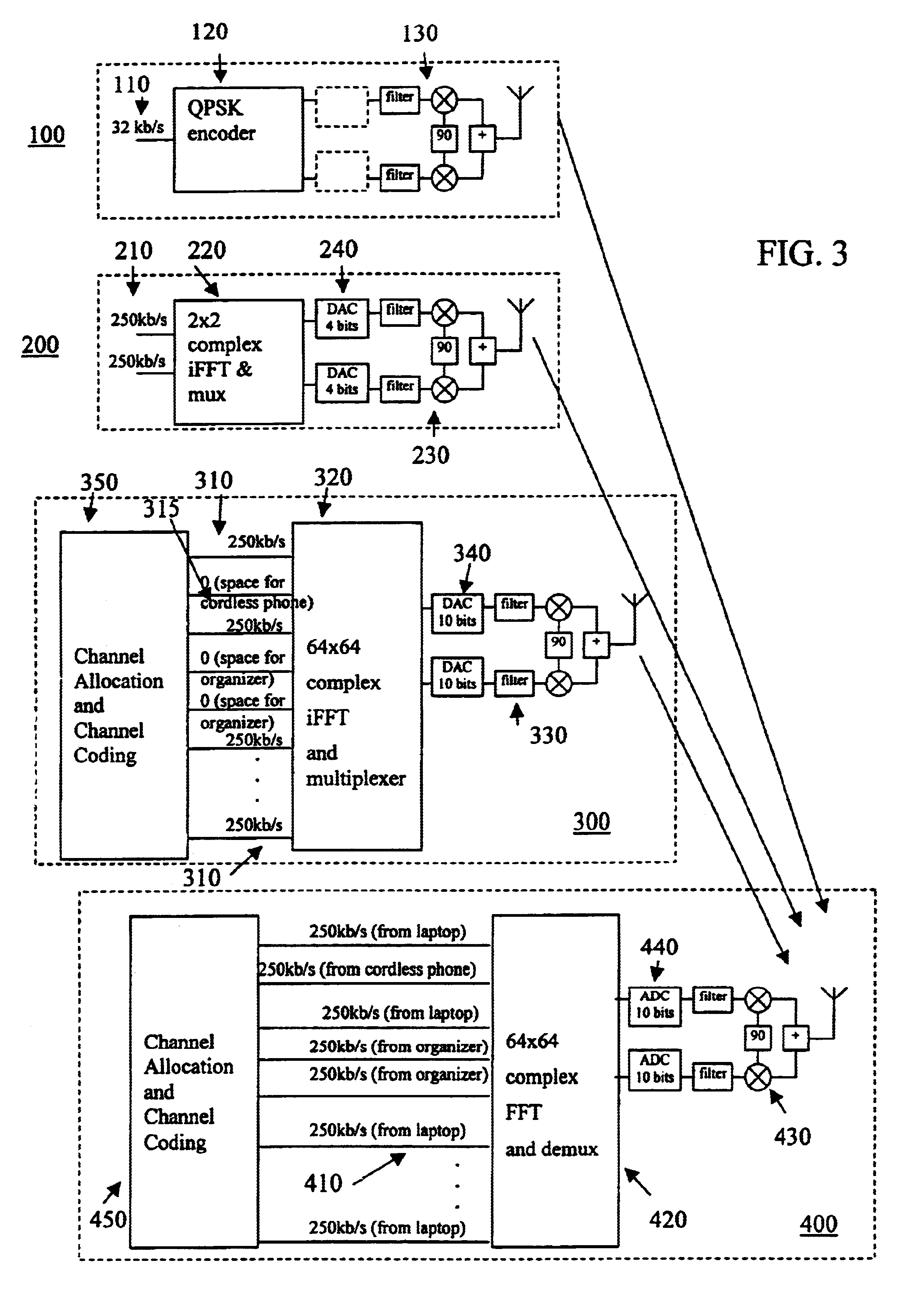
Protocols for scalable communication system using overland signals and multi-carrier frequency communication
A communication system such as an OFDM or DMT system has nodes which are allowed to transmit continuously on one or just a few of the system's frequency sub-channels, while the other nodes avoid putting any signal into those sub-channels. Simple low data rate nodes are allowed to use a small number of sub-channels while more complicated nodes use the remainder. A control protocol allows the sharing in time of communications using overlaid and non-overlaid multi-carrier communication techniques. The sharing in time can be done using TDMA, CSMA or polling techniques. In each case, mechanisms are provided for bringing new nodes into the network and for insuring the time alignment of overlaid transmissions. Reliable transmissions are insured through acknowledgement and retransmission facilities.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method to support secure network booting using quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution
A method and system to support secure booting and configuration. The mechanism employs an optical link comprising a quantum channel that is used to send data encoded as quantum bits (qubits) via respective photons. Qubits encoded using a first random basis at the client and are sent to the boot server, which processes the qubits using a second random basis to extract the encoded data. A public channel is used to send data indicative of the second random basis to the client. A symmetric quantum key is then derived a both the client and the boot server using a comparison of the random basis' and the original and extracted data. The scheme enables the presence of an eavesdropper to be detected on the quantum channel. A DHCP message exchange is employed to obtain a network address, and, optionally, be provided with a network address for one or more boot servers. A boot image request is made to the boot server by the client, and a subsequent boot image is downloaded via a secure channel facilitated by the symmetric quantum key.
Owner:INTEL CORP
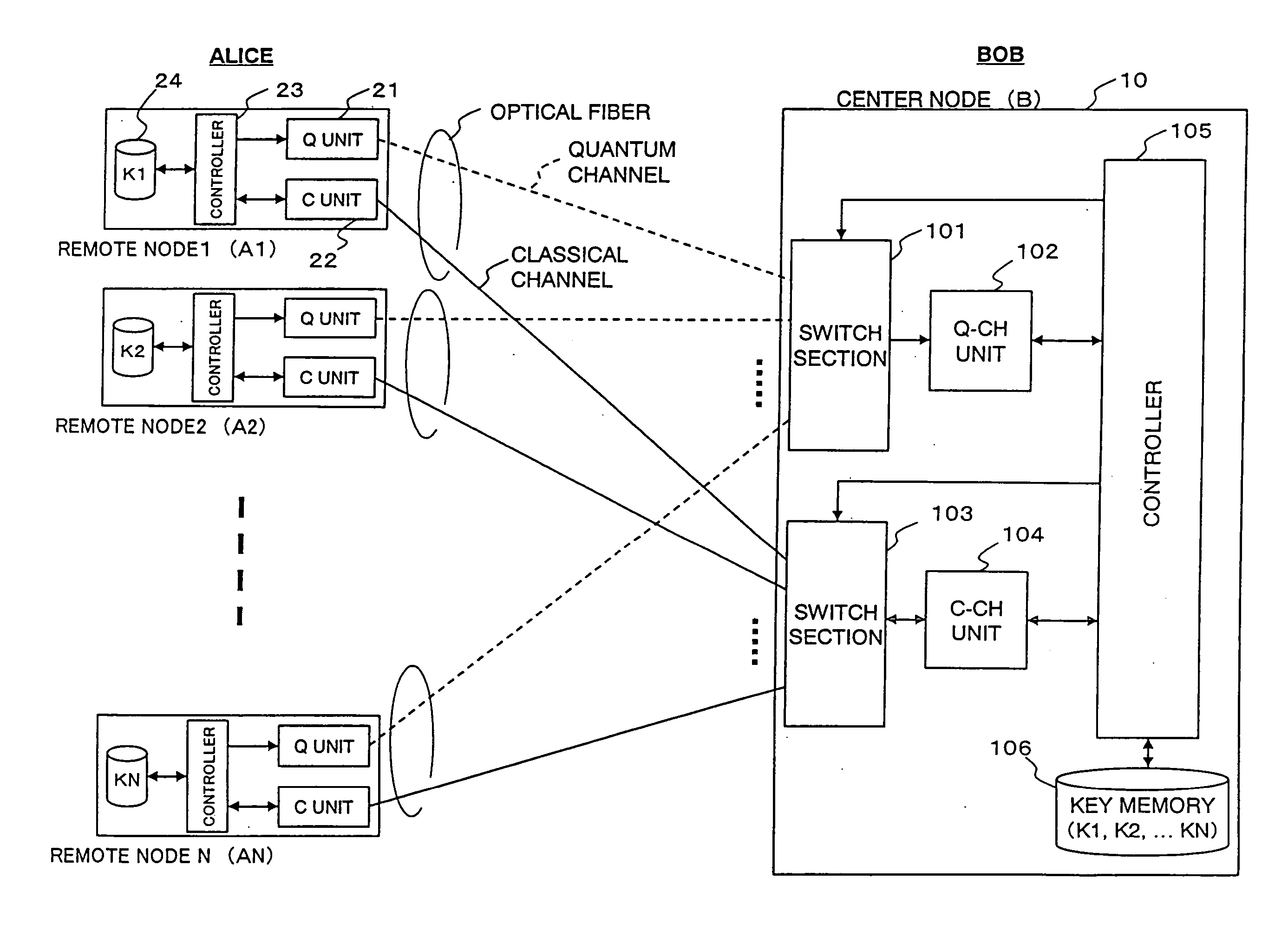
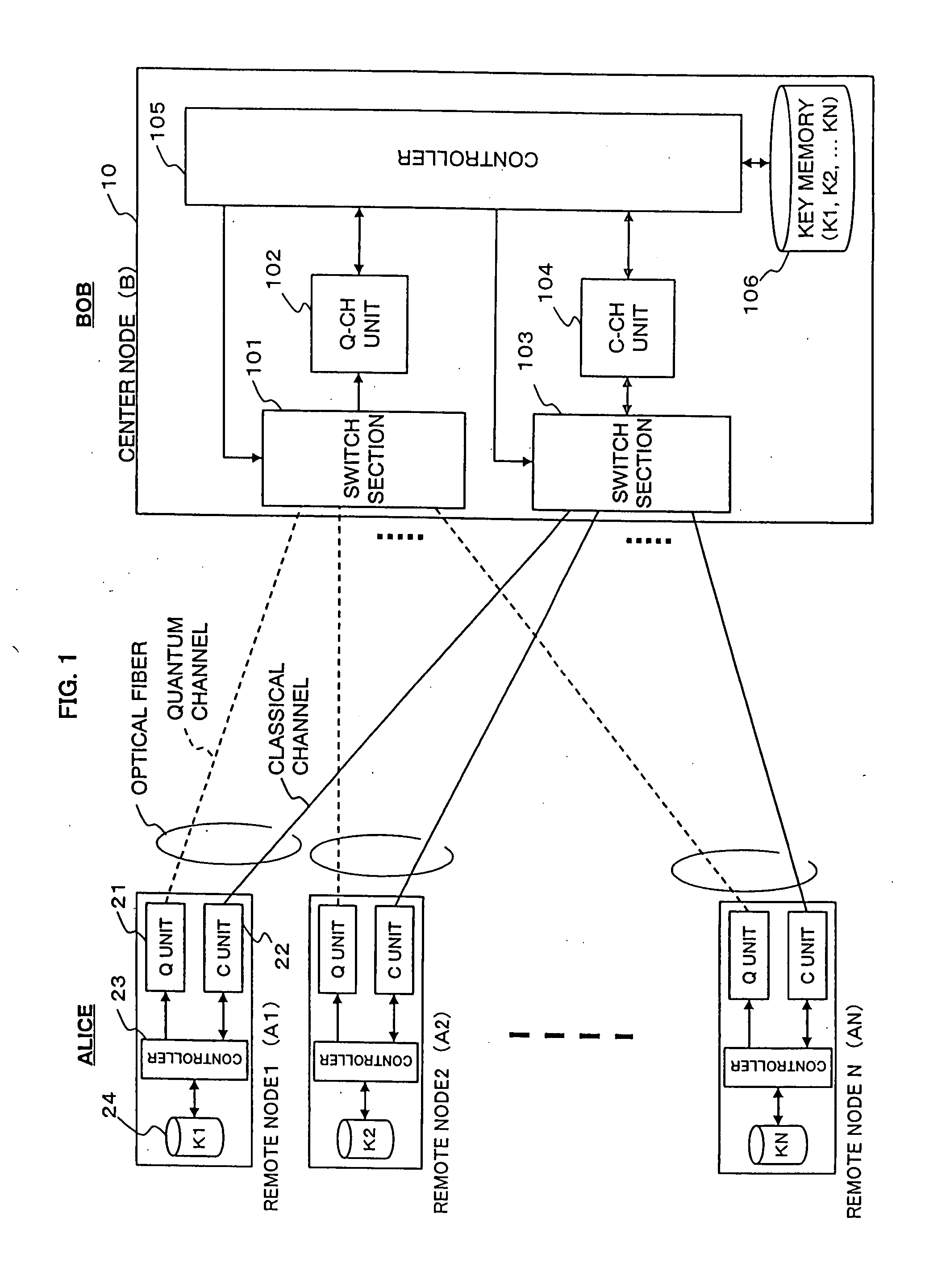
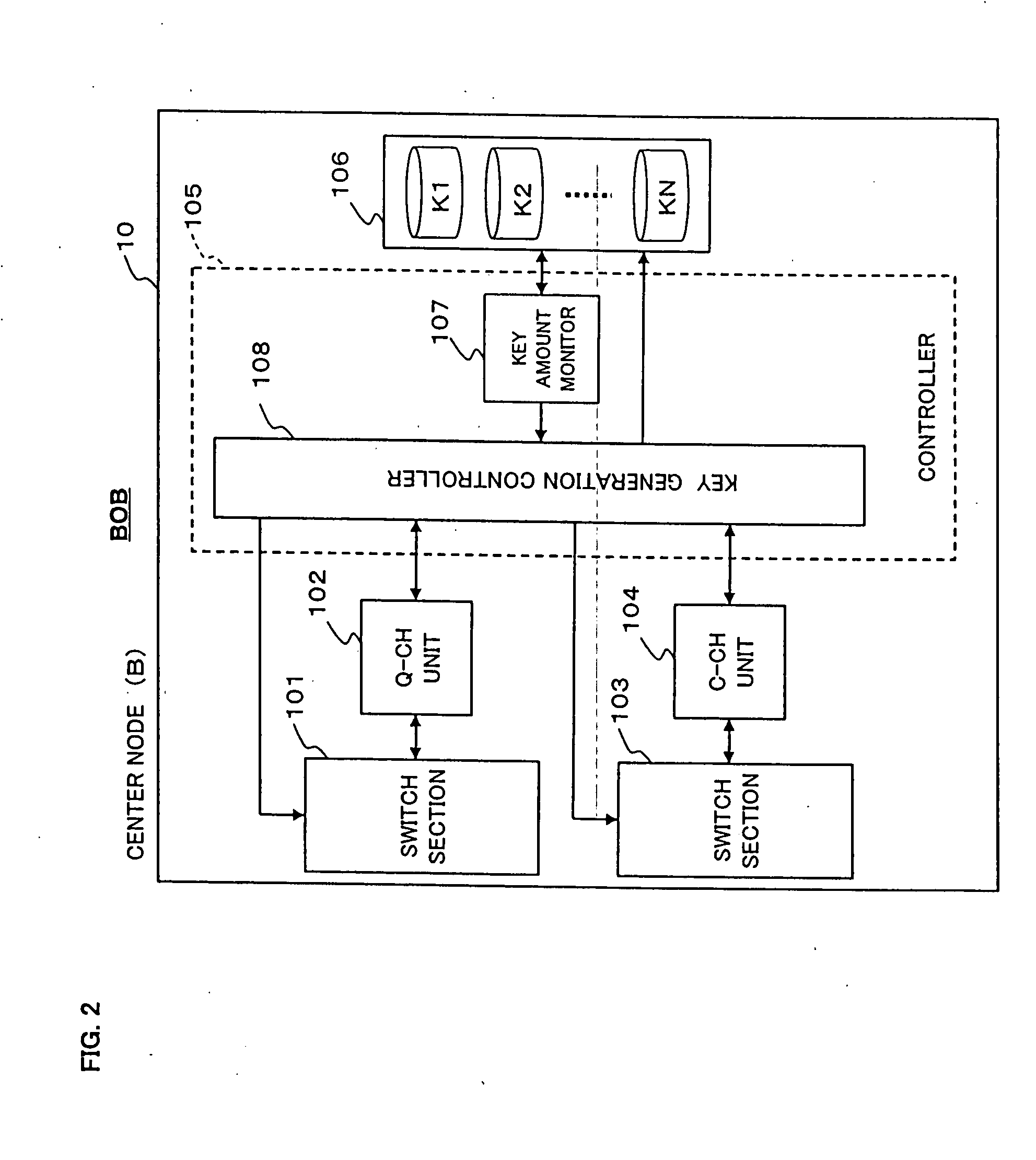
Secret communications system and channel control method
ActiveUS20080013738A1Generate efficientlyGuaranteed normal transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationInformation technology support systemComputer hardwareHandoff control
A secret communications system realizes point-to-multipoint or multipoint-to-multipoint connections of both quantum channels and classical channels. Multiple remote nodes are individually connected to a center node through optical fiber, and random-number strings K1 to KN are individually generated and shared between the respective remote nodes and the center node. Encrypted communication is performed between each remote node and the center node by using the corresponding one of the shared random-number strings K1 to KN as a cryptographic key. The center node is provided with a switch section for quantum channels and a switch section for classical channels. Switching control on each of these switch sections is performed independently of the other by a controller.
Owner:NEC CORP
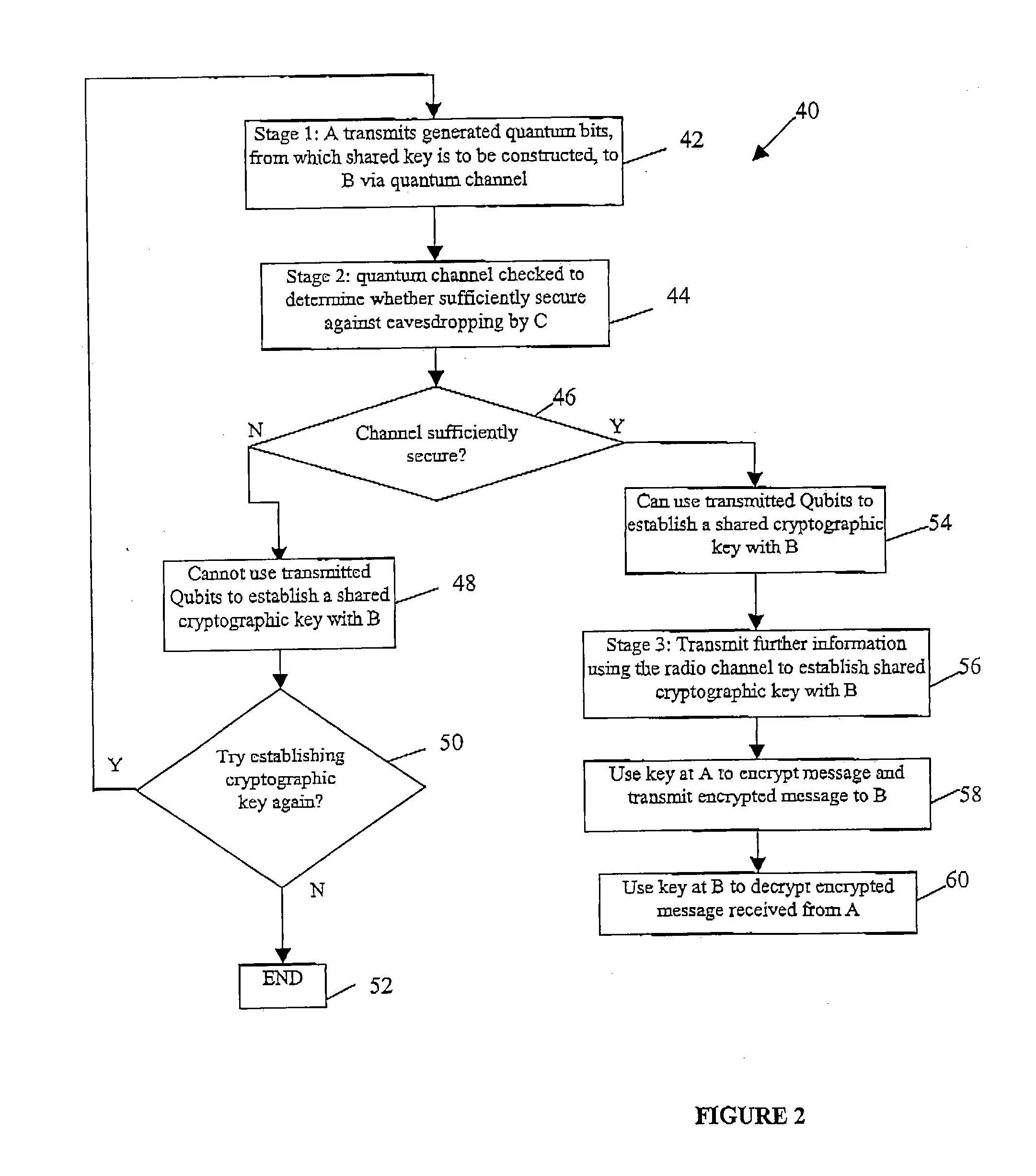
Scalable communication system using overlaid signals and multi-carrier frequency communication
InactiveUS6628673B1Reliable controlError preventionFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemLow data rate
A communication system such as an OFDM or DMT system has nodes which are allowed to transmit continuously on one or just a few of the sysiem's frequency sub-channels, while the other nodes avoid putting any signal into those sub-channels. Simple low data rate nodes are allowed to use a small number of sub-channels while more complicated nodes use the remainder, and preferably functionality is provided to ensure that adjacent sub-channels are reliably spaced apart in frequency so that they do not bleed over into one another; to ensure that signals from all nodes arrive at the base station with well-aligned symbol transitions; and to ensure that signals from the various nodes arrive at the base station with similar power levels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Cryptographic key distribution system
ActiveUS20130208894A1Mitigate such drawbackKey distribution for secure communicationNanotechQuantum channelKey distribution
The invention concerns a or key distribution system comprising a server node, a repeater network connected to the server node through a quantum channel, and a client node connected to the repeater network through a quantum channel; wherein in use the repeater network and the client node cooperatively generate a transfer quantum key which is supplied to a system subscriber by the client node; the server node and the repeater network cooperatively generate a link quantum key; the repeater network encrypts the link quantum key based on the transfer quantum key and sends the encrypted link quantum key to the system subscriber through a public communication channel; the node encrypts a traffic cryptographic key based on the link quantum key and a service an key and sends the encrypted traffic cryptographic key to the system subscriber through a public communication channel.
Owner:SELEX SISTEMI INTEGRATI
System and methods for quantum key distribution over WDM links
InactiveUS20070065155A1Easy to optimizeKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal onQuantum channel
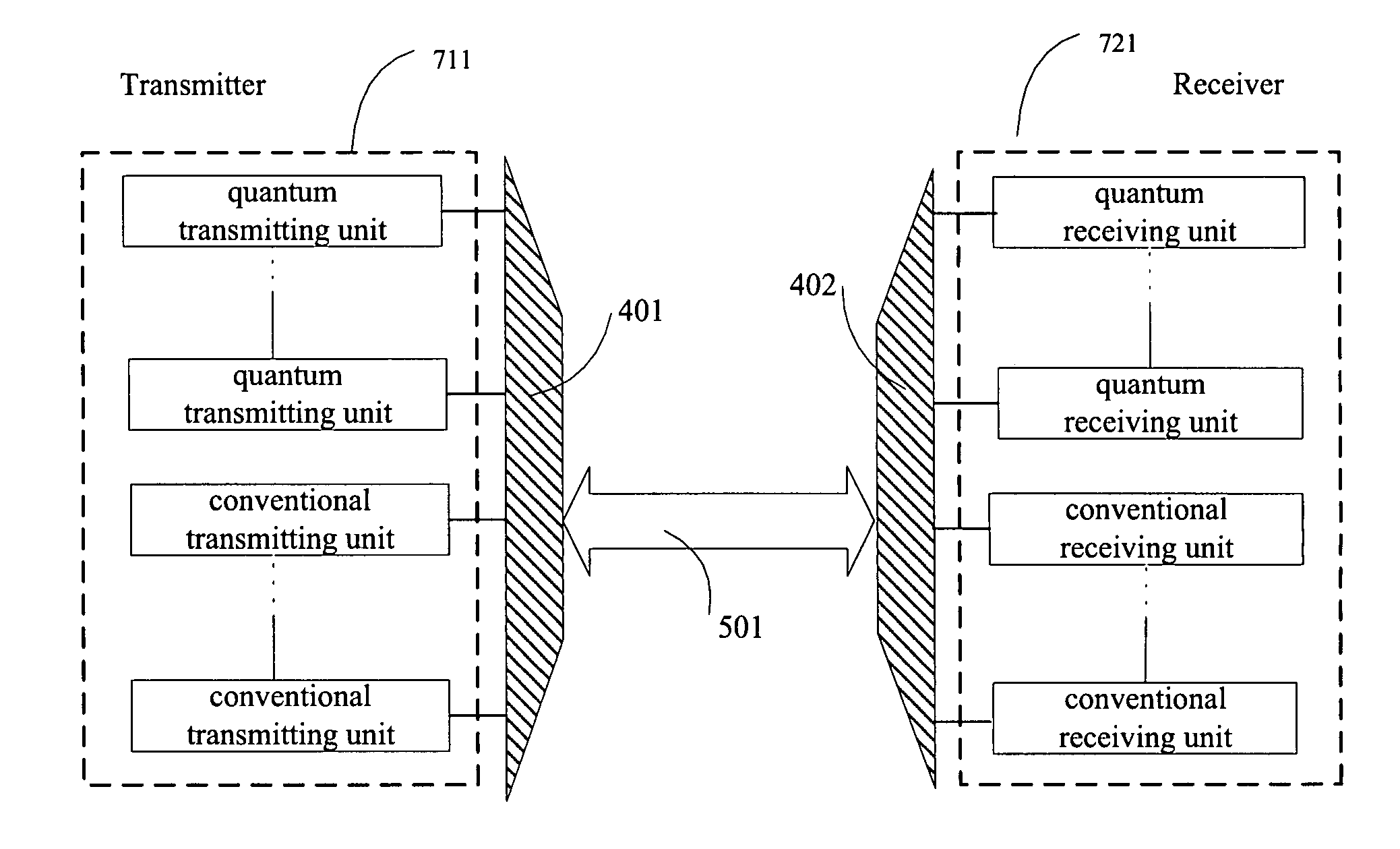
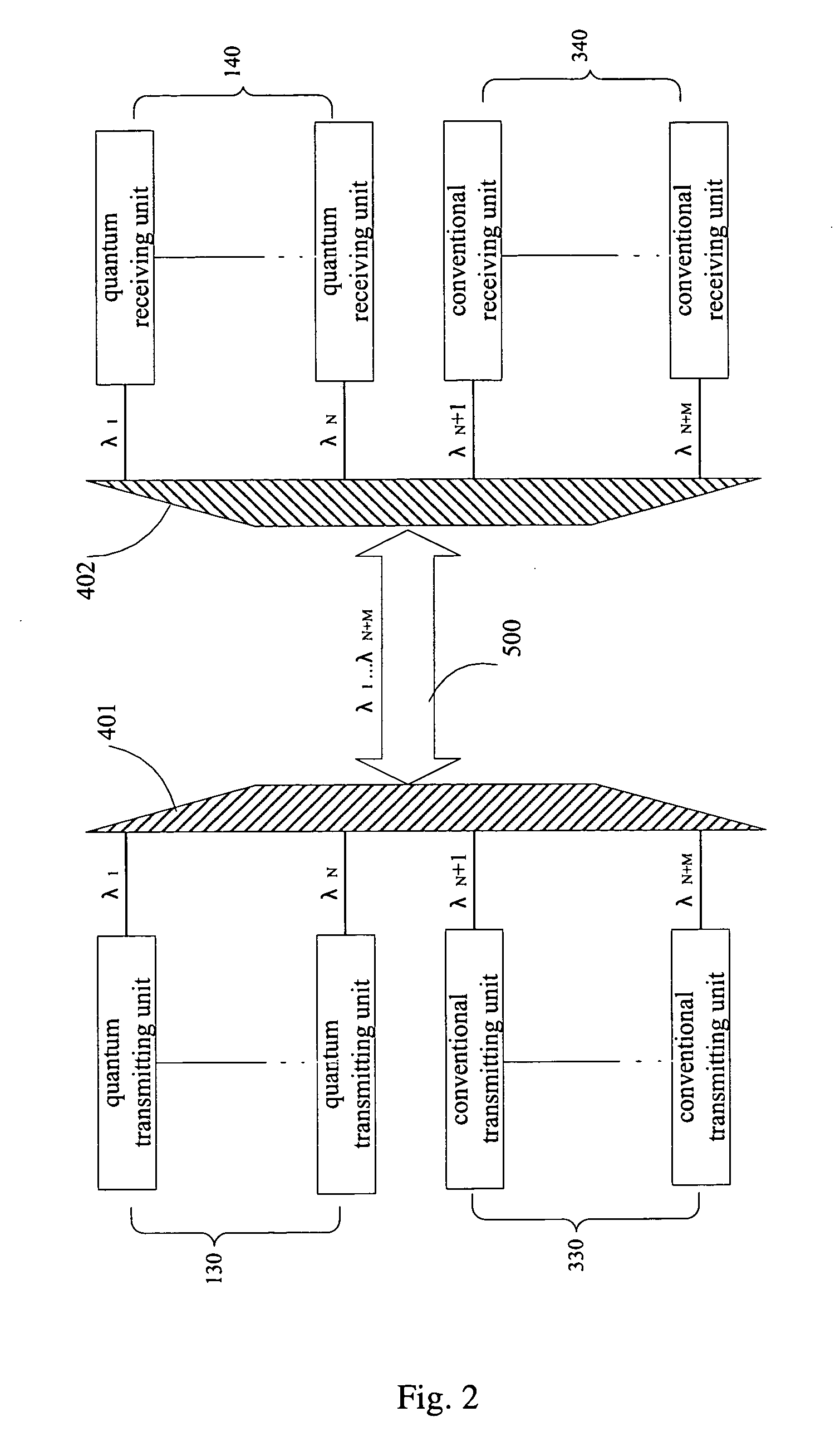
A system and a method for quantum key distribution between a transmitter and a receiver over wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) link are disclosed. The method includes providing one or more quantum channels and one or more conventional channels over the WDM link; assigning a different wavelength to each of the one or more quantum channels and each of the one or more conventional channels; transmitting single photon signals on each of the one or more quantum channels; and transmitting data on each of the one or more conventional channels. The data comprises either conventional data or trigger signals for synchronizing the transmission of the single photon signals on the quantum channels. All channels have wavelengths around 1550 nm. The WDM link can be a 3-channel WDM link comprising two quantum channels for transmitting single photon signals and one conventional channel for transmitting conventional data or triggering signals.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
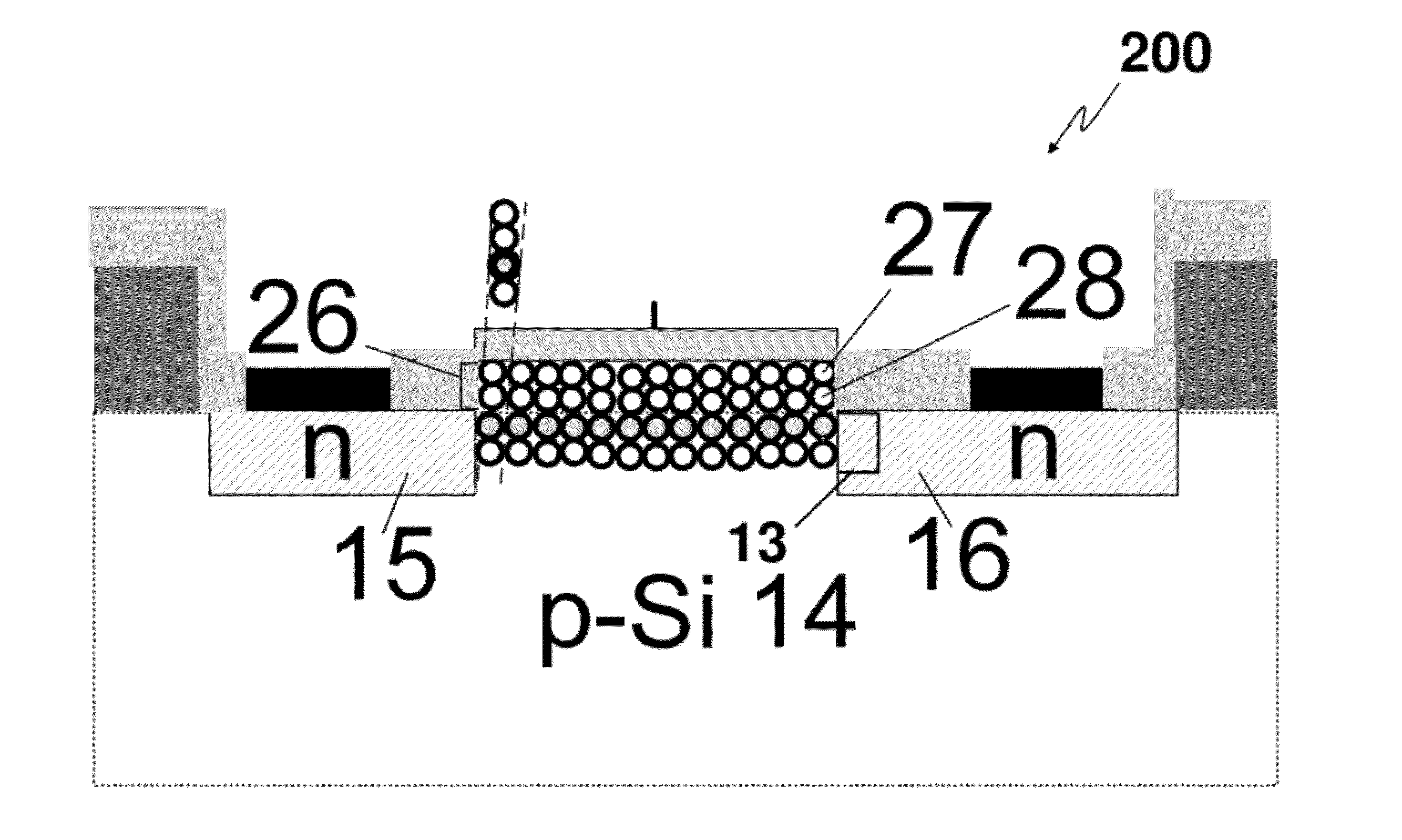
Quantum dot channel (QDC) quantum dot gate transistors, memories and other devices
This invention describes a field-effect transistor in which the channel is formed in an array of quantum dots. In one embodiment the quantum dots are cladded with a thin layer serving as an energy barrier. The quantum dot channel (QDC) may consist of one or more layers of cladded dots. These dots are realized on a single or polycrystalline substrate. When QDC FETs are realized on polycrystalline or nanocrystalline thin films they may yield higher mobility than in conventional nano- or microcrystalline thin films. These FETs can be used as thin film transistors (TFTs) in a variety of applications. In another embodiment QDC-FETs are combined with: (a) coupled quantum well SWS channels, (b) quantum dot gate 3-state like FETs, and (c) quantum dot gate nonvolatile memories.
Owner:JAIN FAQUIR CHAND
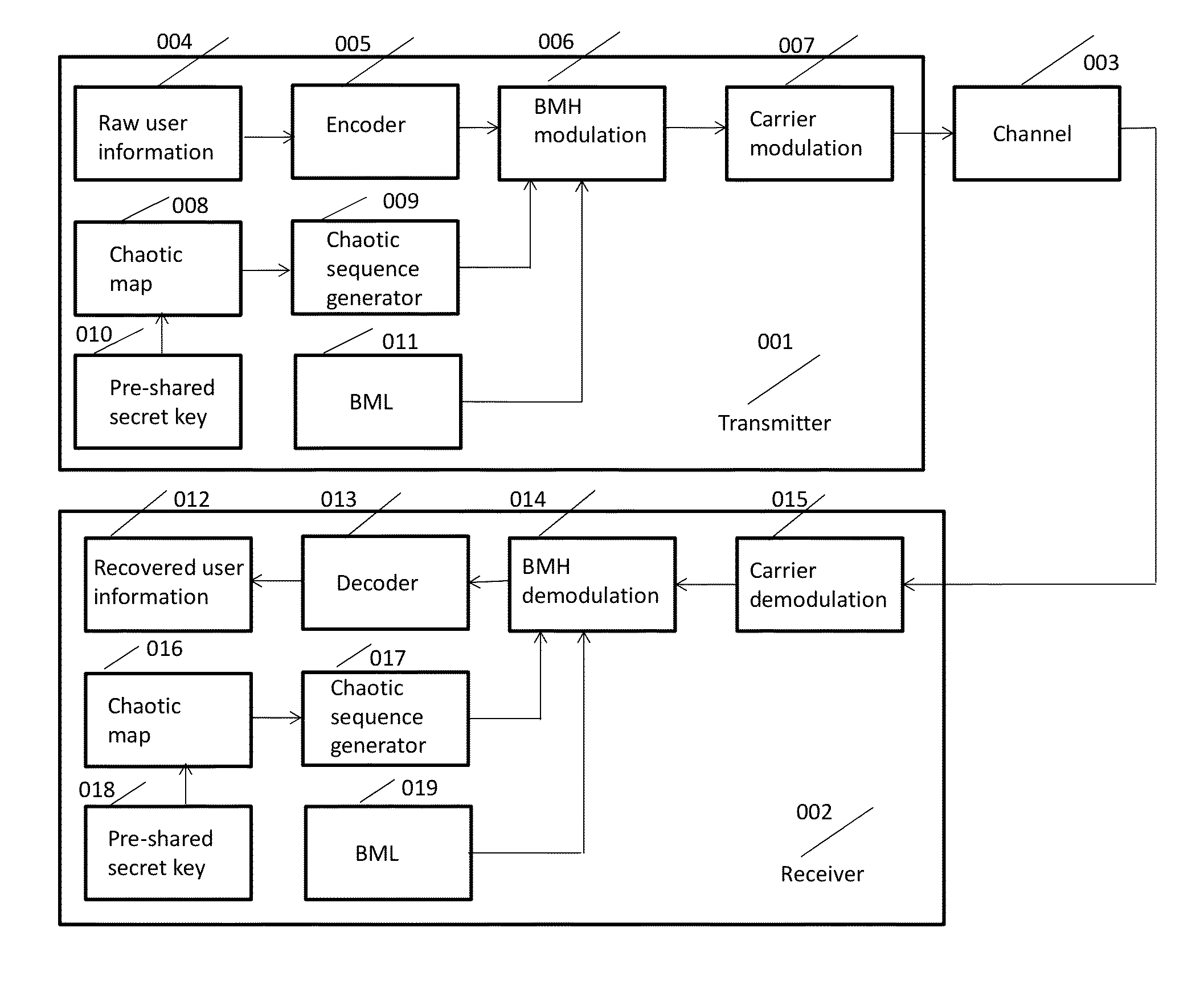
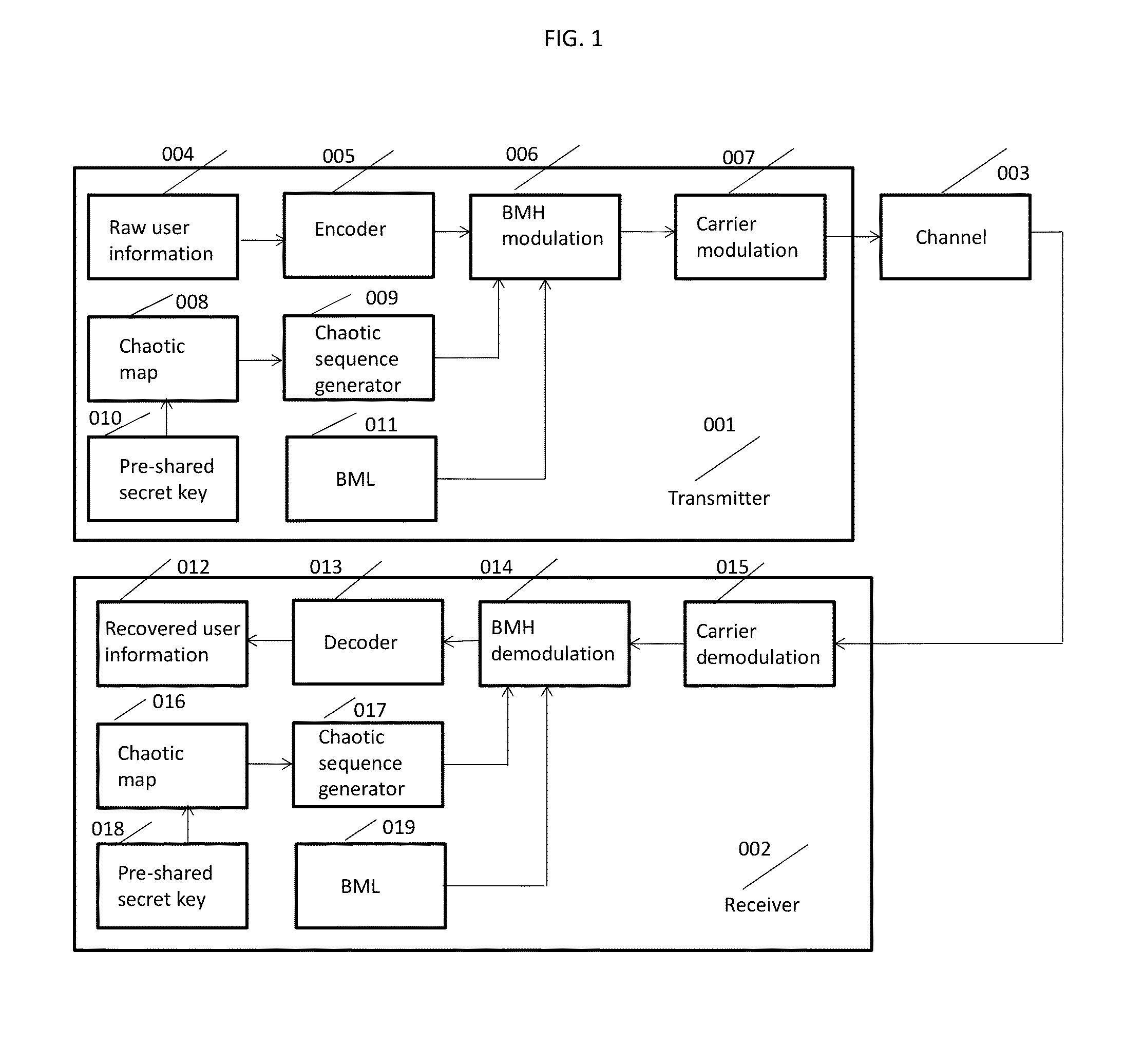
Chaotic Baseband Modulation Hopping Based Post-Quantum Physical-Layer Encryption
A post-quantum physical-layer encryption / decryption system based on chaotic Baseband Modulation Hopping (BMH). The baseband constellation, mapping, power level, and phase will vary symbol-by-symbol according to assigned random sequences. Pre-shared secret keys are used as the chaotic system parameters, initialization, and quantization parameters to generate the BMH codes. The BMH physical-layer encryption / decryption system can be combined with digital-domain based encryption algorithms such as AES, code-based post-quantum cryptography, and other physical-layer secure communication techniques such as Frequency Hopping (FH) and Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS). It can also be combined with Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) to provide mutual authenticated key distribution. This invention can be applied to all kinds of communication systems including wireless (radio frequency, optical, quantum channel, sonar) and wire (optical fiber, power-line, telephone line, wire quantum channel, etc.), single carrier and multi-carrier, OFDM, MIMO channels.
Owner:LI WENHUA +1
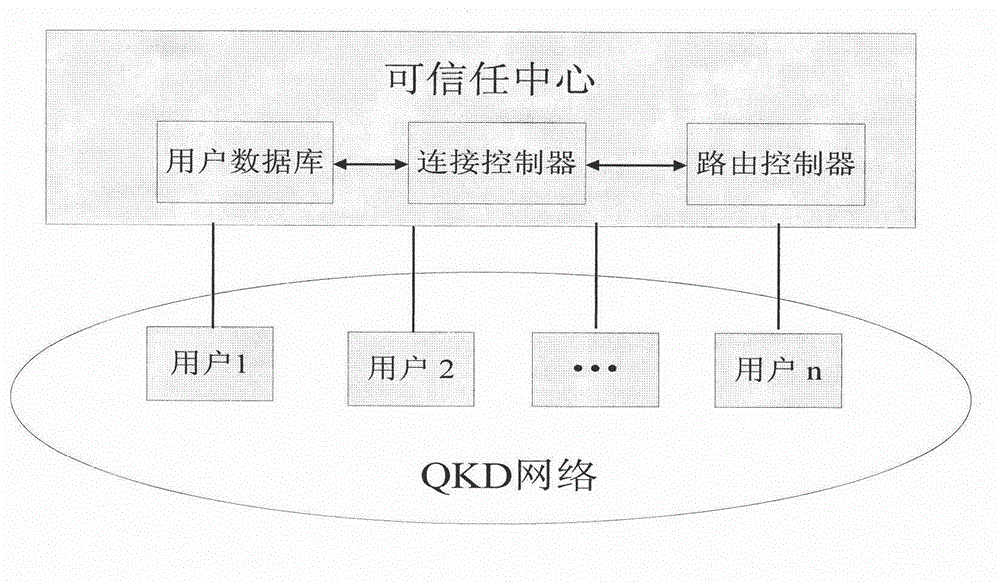
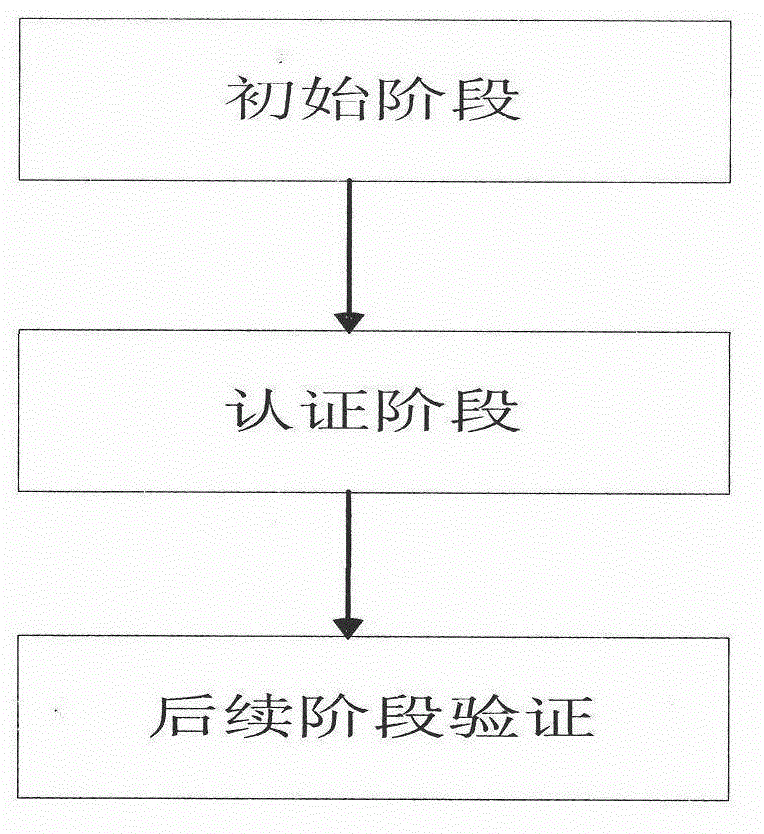
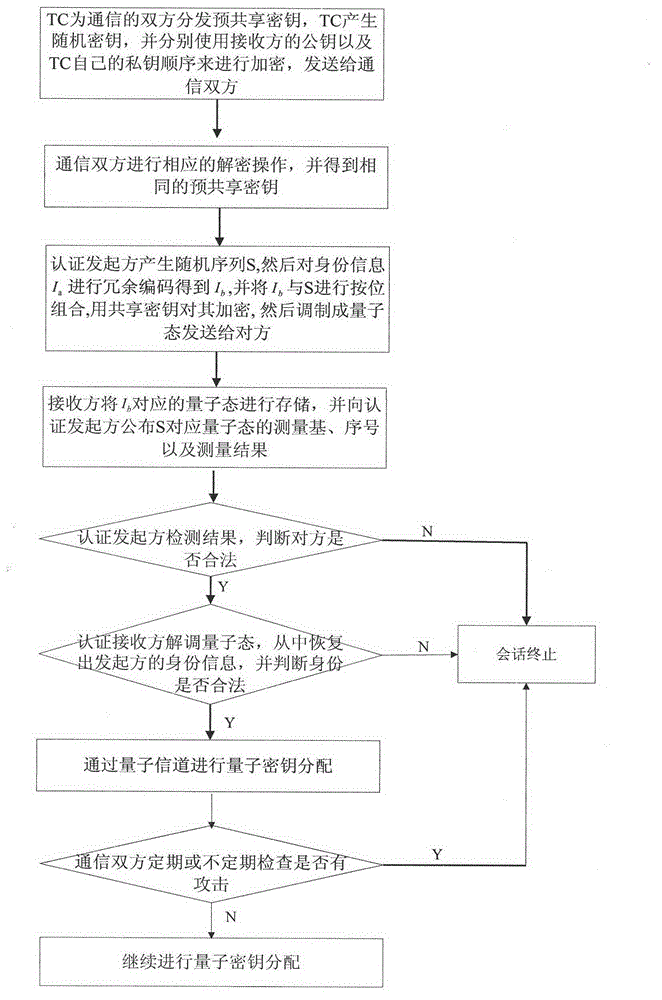
Model and method for user authentication for quantum key distribution network
ActiveCN102946313AAvoid Intermittent AttacksPrevent theftKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunications securityMan-in-the-middle attack
The invention provides a model and a method for user authentication based on a trusted center in a quantum key distribution network, specifically, a user authentication model based on the trusted center is provided and an implementation method is described in detail, in order to realize the communication security between any two users in the network and prevent a man-in-the-middle attack. Based on the model, the invention further provides a method for user authentication, which comprises the following steps that: 1, any user requesting for communication in the network sends a connection request to the trusted center; 2, the trusted center sends a pre-shared key to the two communication parties respectively; 3, the two communication parties set up a quantum channel and are authenticated; and 4, the two parties are authenticated regularly or irregularly in the subsequent communication process. According to the invention, by fully considering the development status of the current quantum key distribution network and by combining with the actual requirement, a quantum communication channel can be set up securely between any two nodes in the network, so that the communication security between users can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
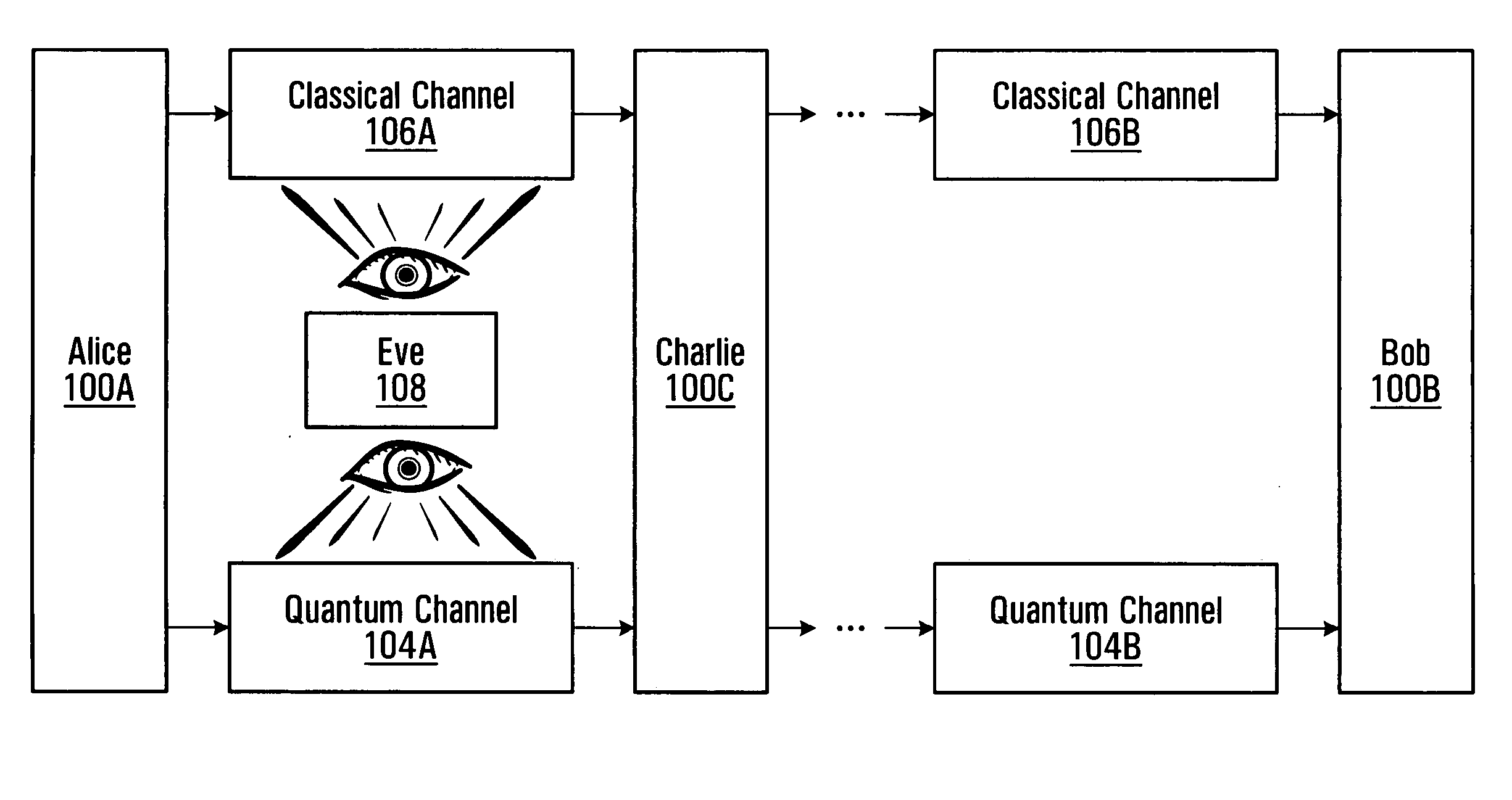
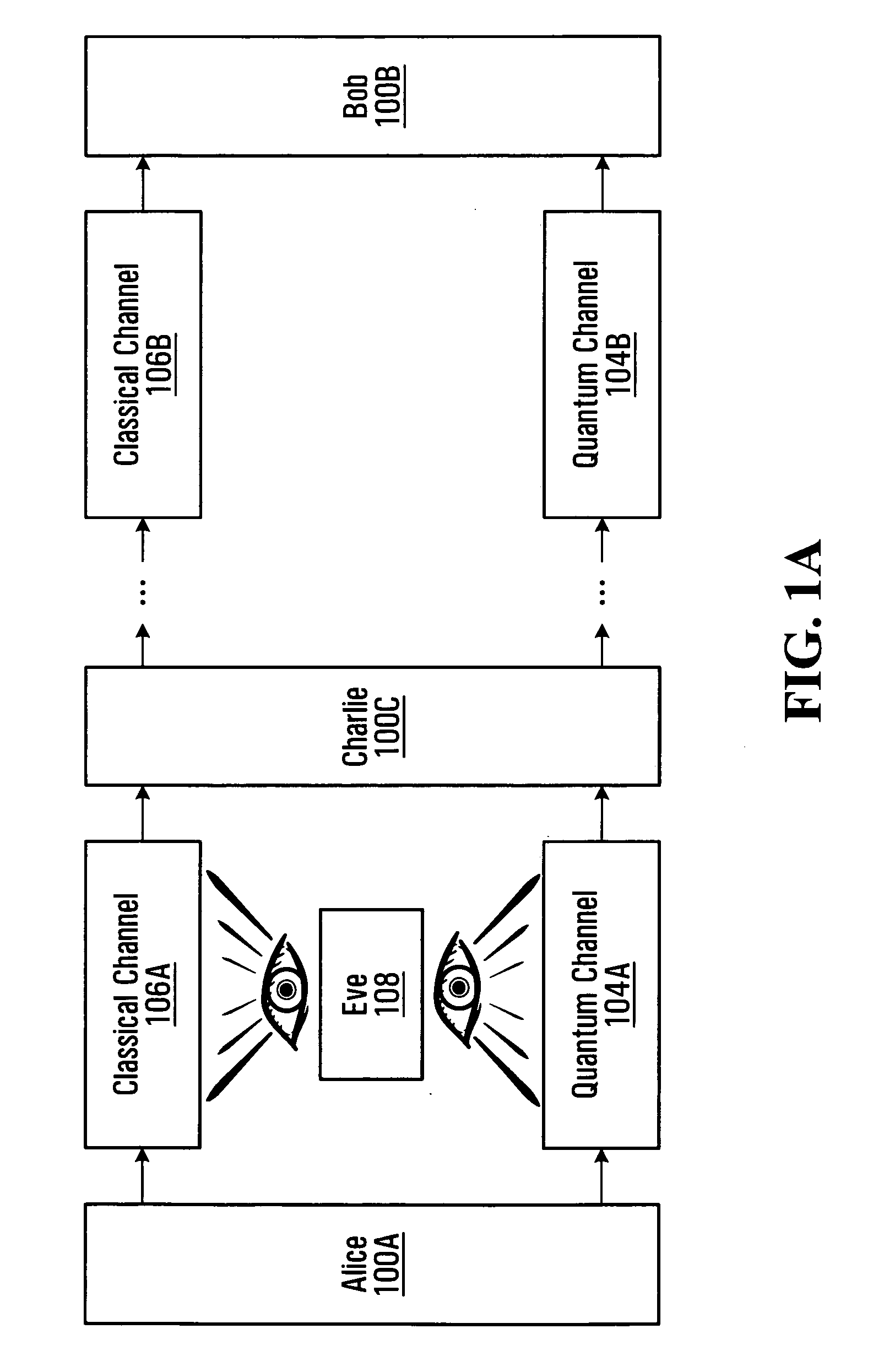
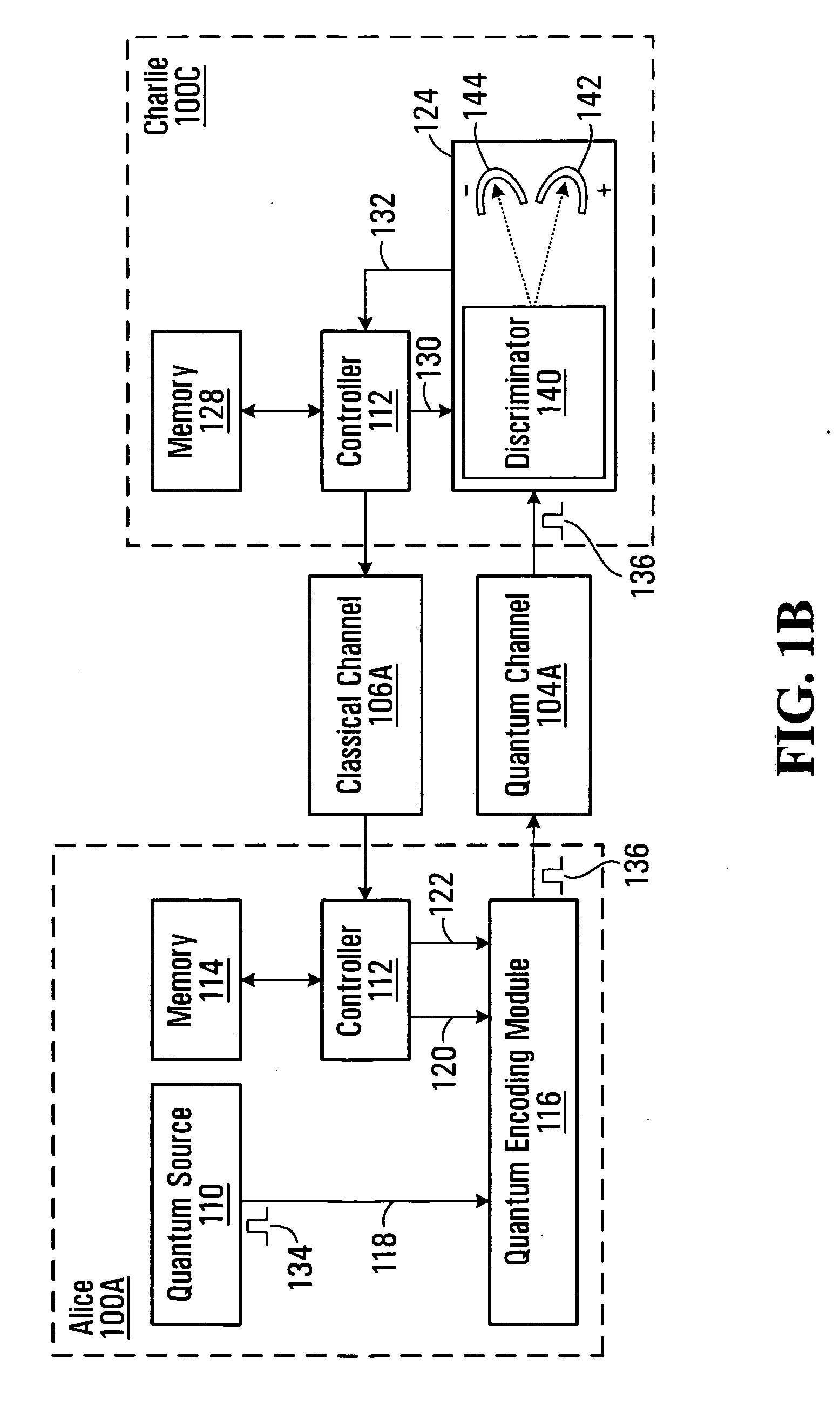
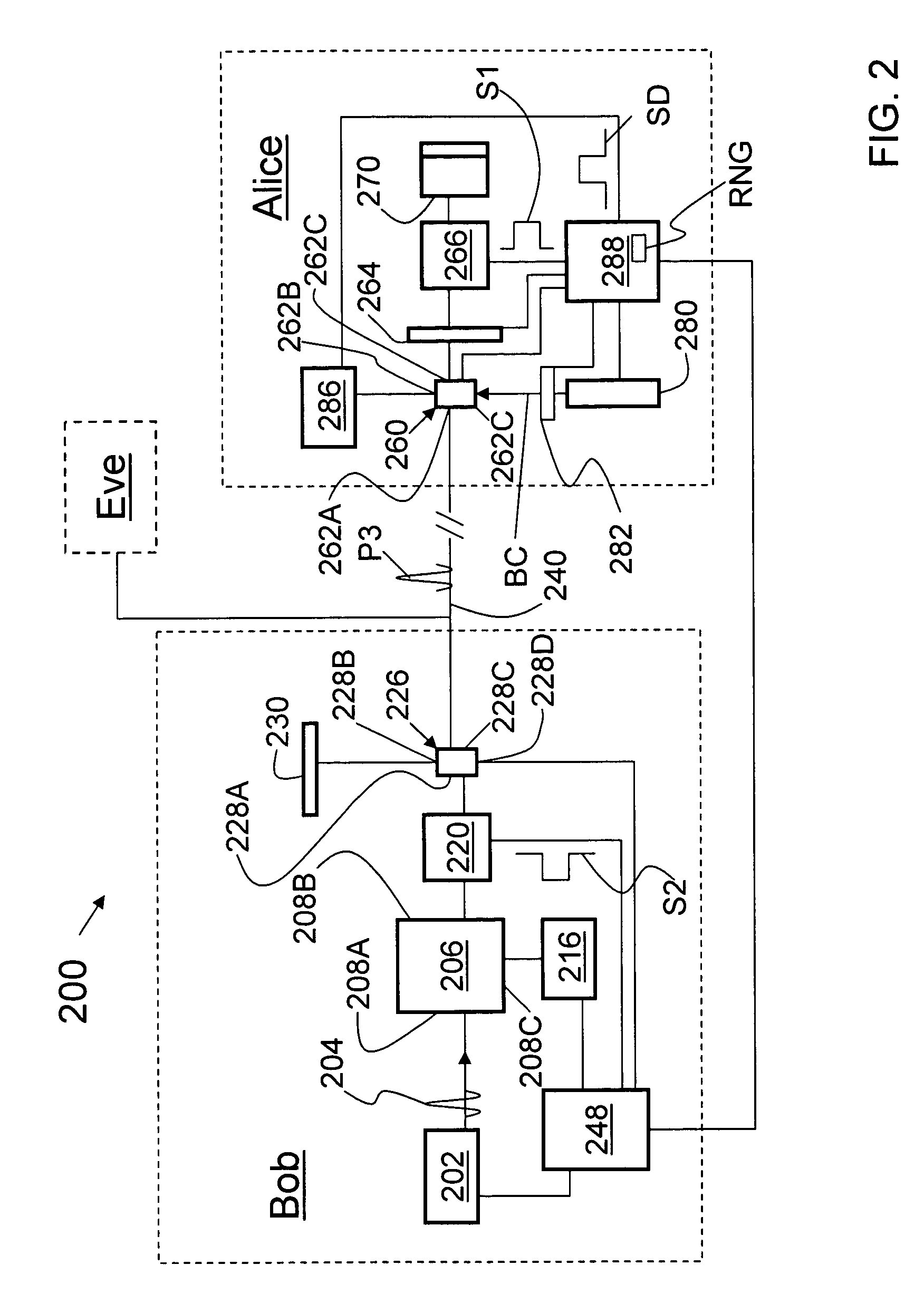
Methods and systems for communicating over a quantum channel
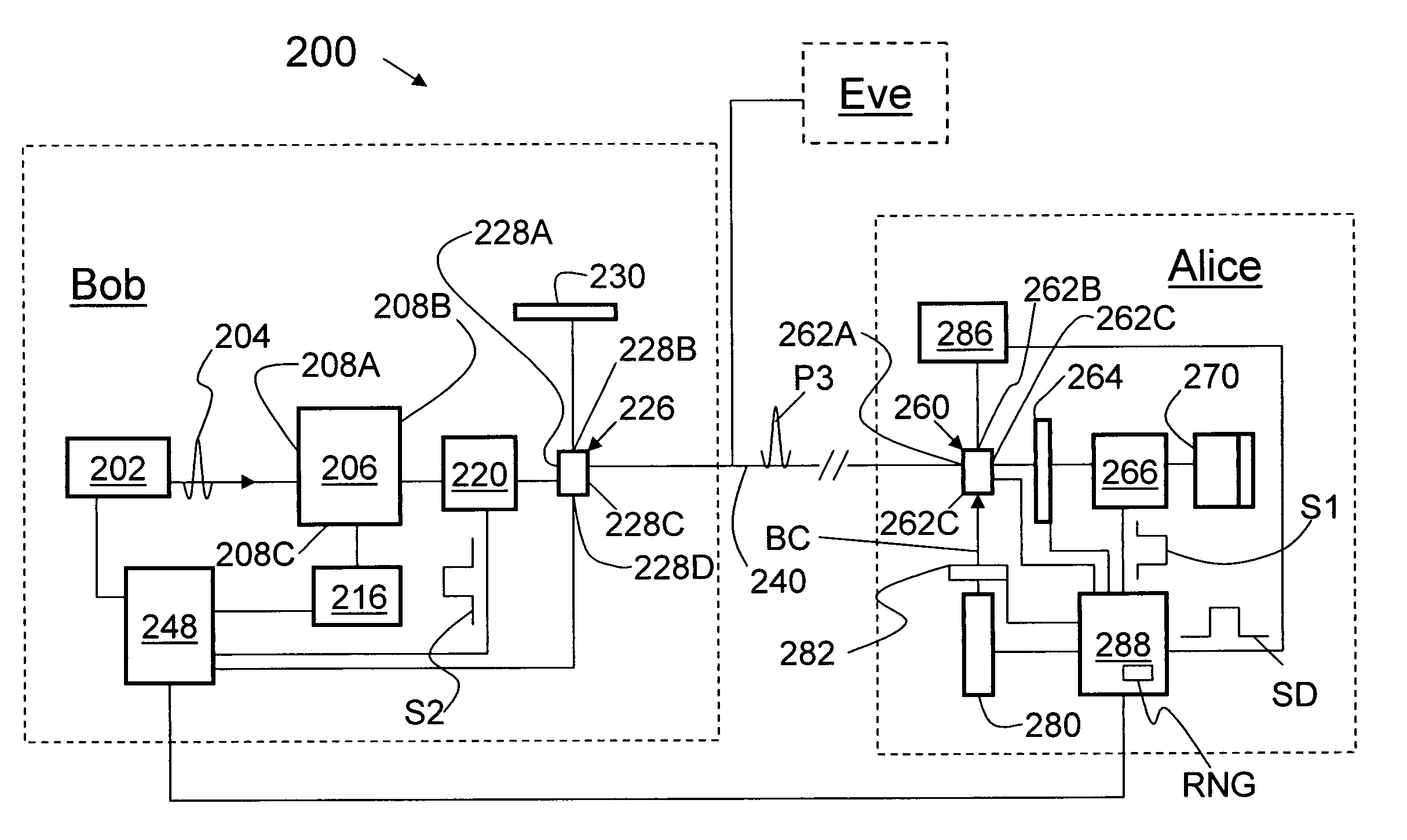
Alice generates a sequence of key bits forming an initial cryptographic key. Alice then uses the sequence of key bits and a sequence of cipher bits to control respective control parameters of a quantum encoding process applied to a sequence of quantum pulses, where the sequence of cipher bits used is known to Bob. Alice then releases the encoded pulses towards Bob over a quantum channel. Bob uses the previously agreed-upon sequence of cipher bits to control a control parameter, such as the quantum basis, of a quantum detection process applied to the pulses received from Alice, thus producing a detection outcome for each received pulse. Bob then derives a final cryptographic key from the detection outcomes. Because the cipher bits used to select the quantum bases used by both Alice and Bob are known by both parties, the method allows the final cryptographic key to be distributed with full basis alignment compared to 50% for BB84, thus allowing efficient quantum key distribution over multiple hops.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
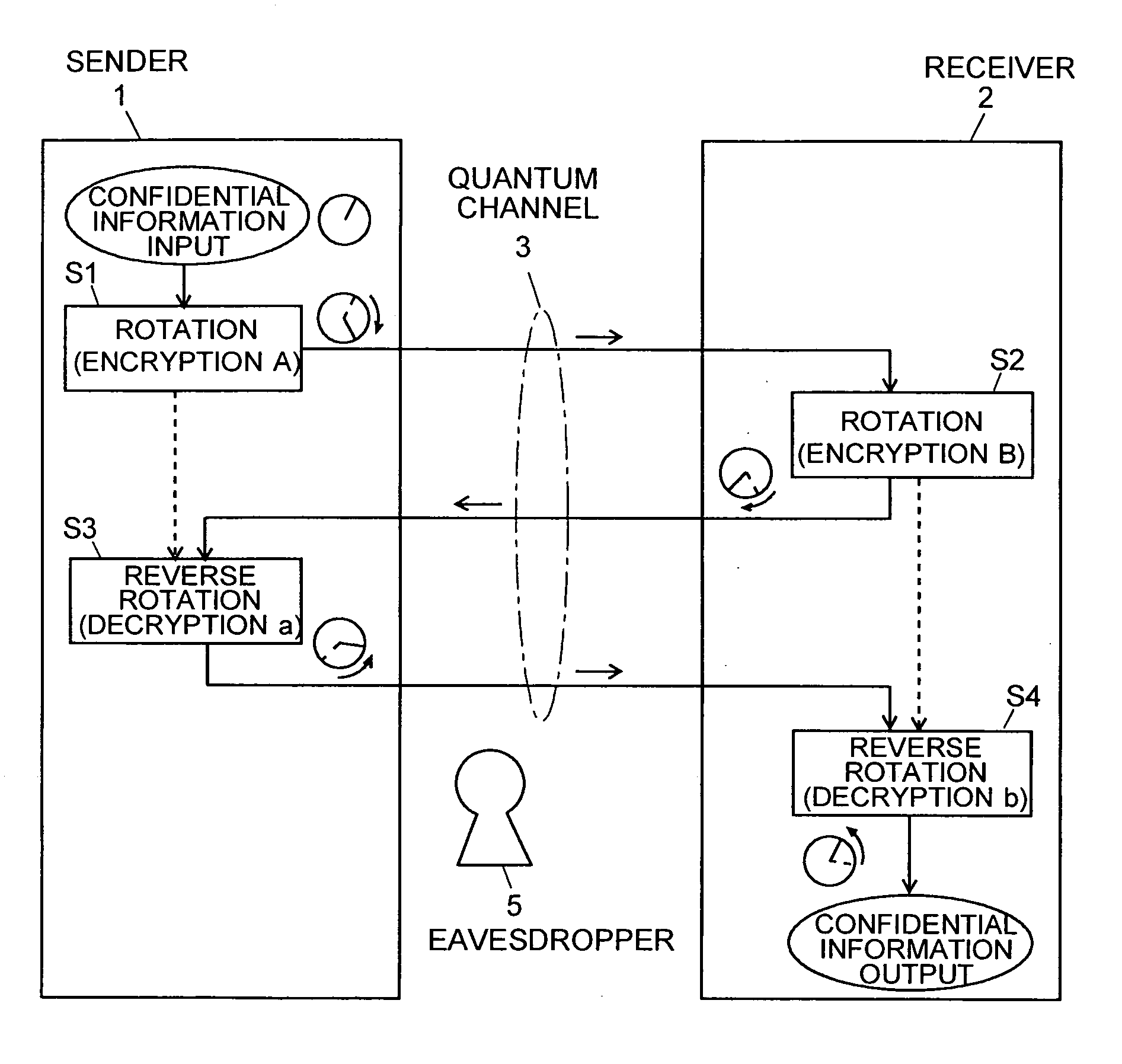
Quantum Cryptographic Communication Method
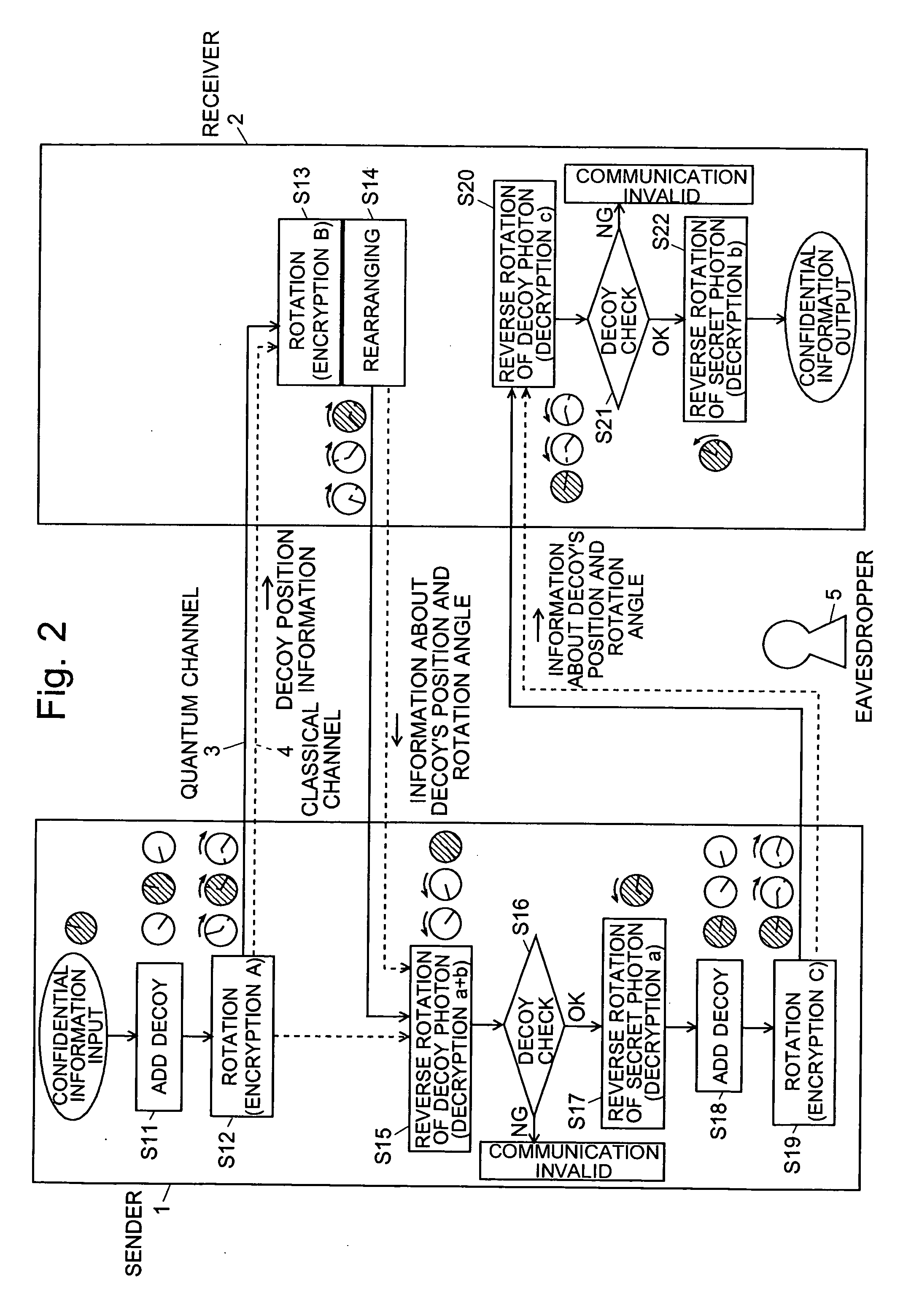
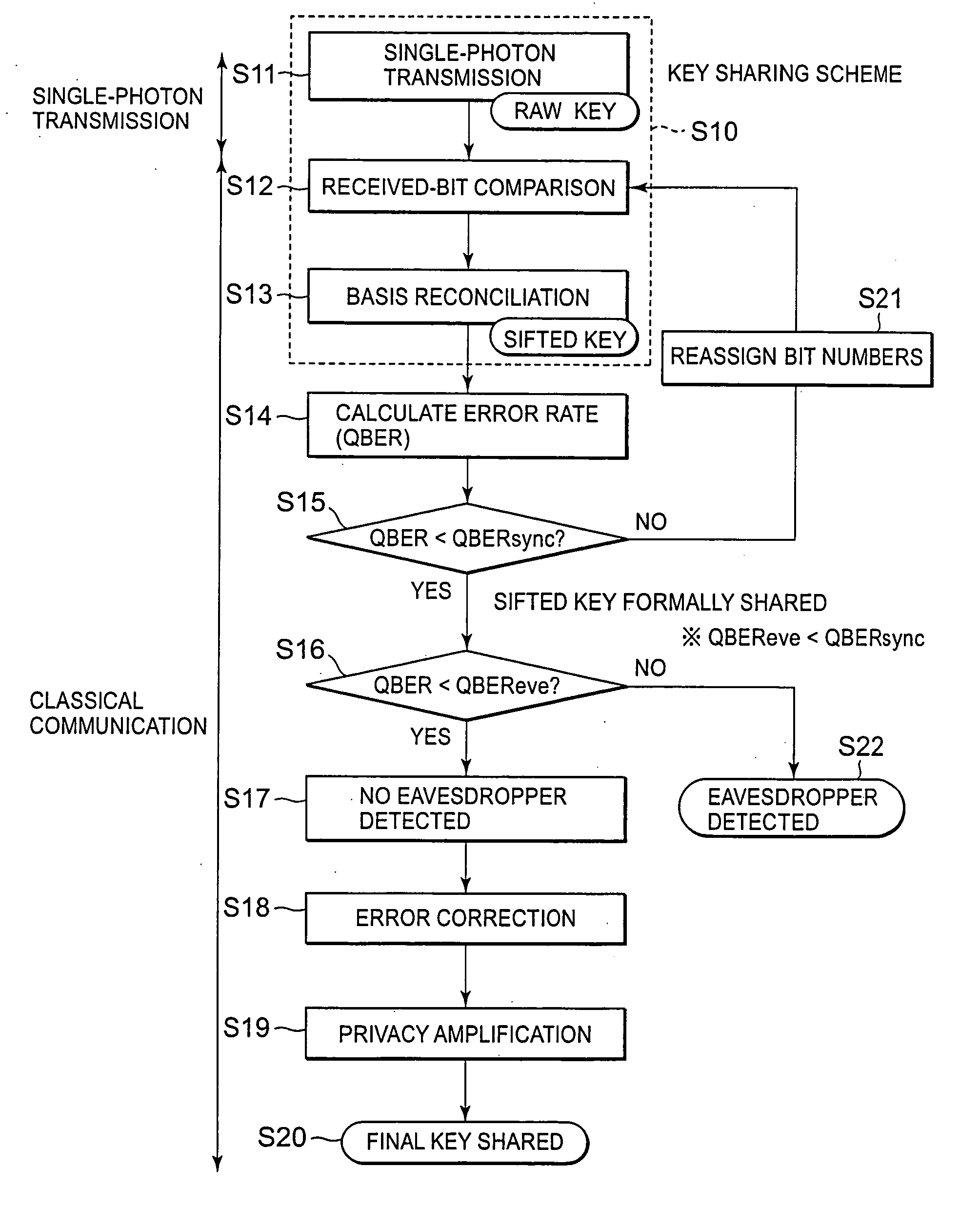
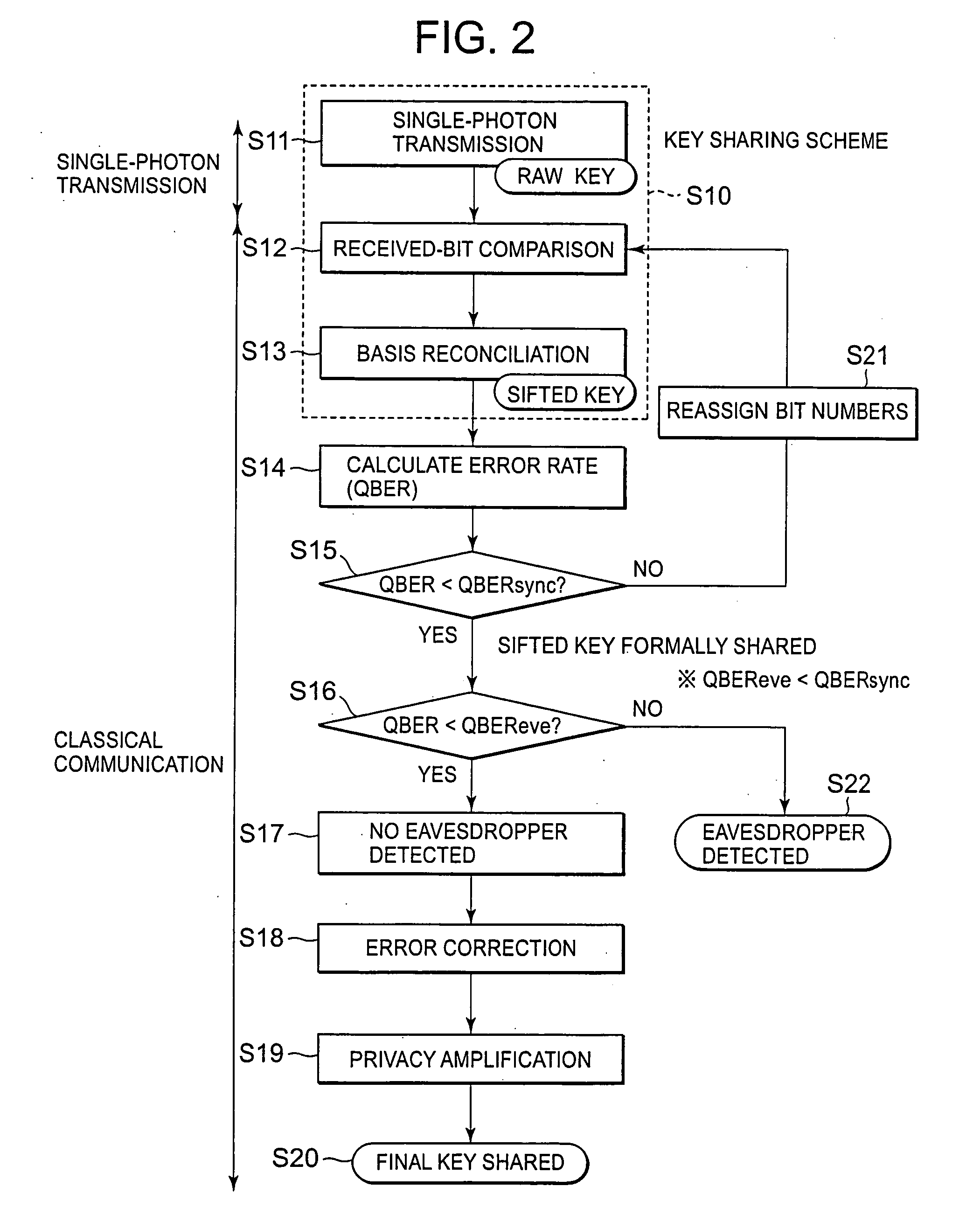
A sender (1) adds decoy photons to a secret photon having confidential information, then, subjects each photon to a different rotational manipulation, and passes the photons along a quantum channel (3) (S11 and S12). A receiver (2) receives those photons and then obtains information about the position of the decoy photons from the sender (1) through a classical channel (4). Using the information, the receiver (2) subjects each of the decoy and secret photons to a different rotational manipulation and transmits the photons in a rearranged order (S13 and S14). The receiver (1) obtains information about the position and manipulation quantities of the decoy photons from the receiver (2) and decodes the decoy photons. If the quantum state of the decoys is identical to their initial quantum state, the sender (1) determines that no eavesdropper (5) should be present (S15 and S16), cancels only the encryption of the secret photon performed by himself or herself in S12, and transmits the secret photon (S17). The receiver (2) cancels the encryption of the secret photon performed by himself or herself in S13 and thereby obtains the confidential information (S18). The present method can securely send quantum information as well as classical information such as key information, and also effectively detect eavesdropping.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
High-speed continuous variable quantum key distribution system and bit frame synchronization method thereof
ActiveCN104065475AAvoid interferenceKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising arrangementCoherent statesQuantum channel
The invention provides a high-speed continuous variable quantum key distribution system and a bit frame synchronization method thereof. The bit frame synchronization method comprises the following steps: Step one, a sender generates a set of special data used as a synchronous frame; Step two, the sender sends a coherent state to a receiver through a quantum channel; Step three, the receiver uses a balance homodyne detector to measure the displacement component of the coherent state; Step four, the receiver selects an appropriate alternate voltage determining threshold and a frame synchronization segment determining threshold to determine the synchronous frame according to structure information of the special data acquired through a classical channel in Step one; and Step five, synchronization fails if the receiver does not search the synchronous frame in the specified time, and the receiver needs to adjust the value of the alternate voltage determining threshold and the value of the frame synchronization segment determining threshold and reestablishes communication. According to the invention, the interference of external environmental factors to synchronization signals in the process of quantum key distribution can be effectively overcome, and synchronization between both sides of communication can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA INTELLECTUAL PORPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD +1
Electric power security communication network based on quantum key distribution technology
ActiveCN103763099AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationPower distribution line transmissionQuantum channelQuantum network
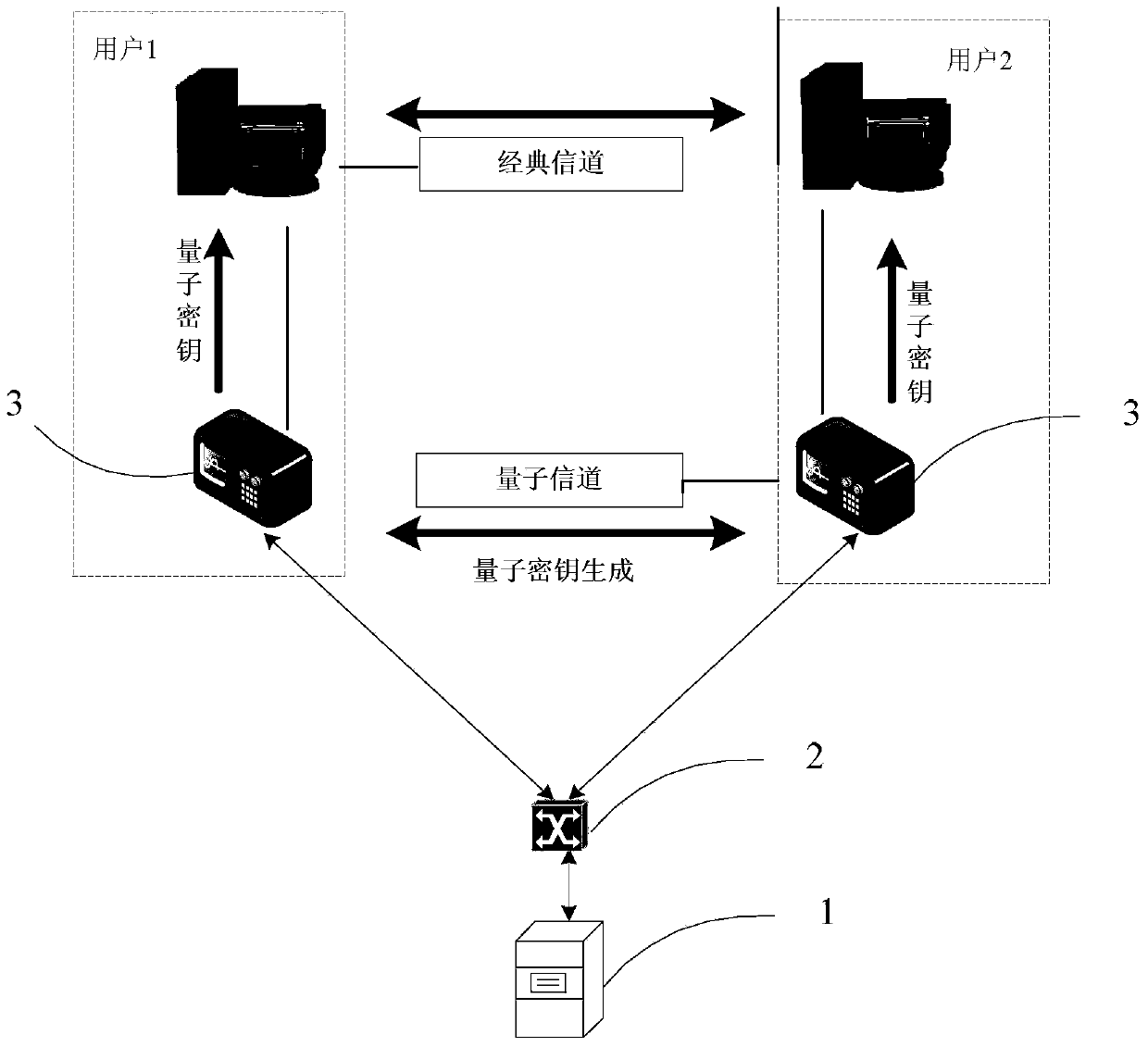
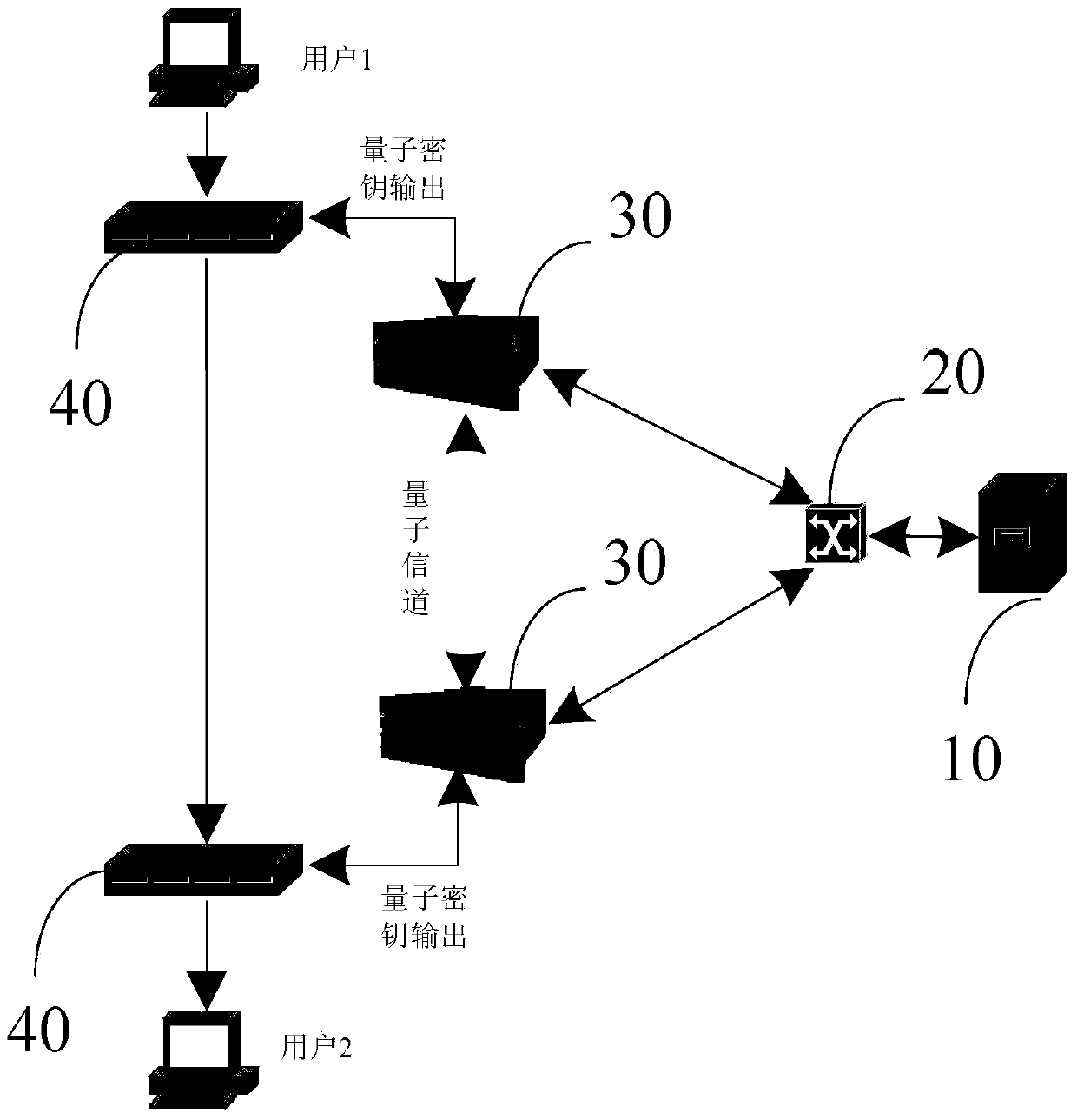
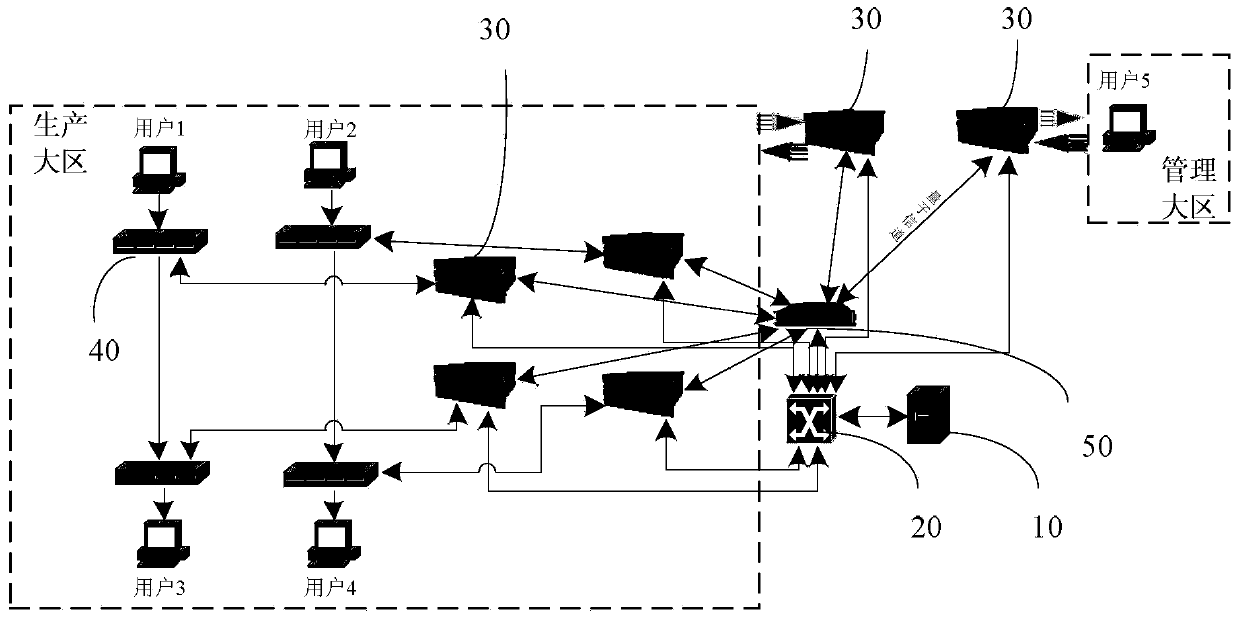
An electric power security communication network based on quantum key distribution technology comprises a power longitudinal encryption authentication device, a key generation control server, a classic switch, and a QKD system. The key generation control server is connected to the QKD system through the classic switch. Each power longitudinal encryption authentication device is provided with a QKD system which is connected to the power longitudinal encryption authentication device. The quantum key distribution is achieved through quantum channels among QKD systems. Communication among power longitudinal encryption authentication devices is achieved through classical channels. The power longitudinal encryption authentication device includes a quantum key transmission unit, a quantum key processing unit and an electric power communication data encryption unit, which are connected in sequence. Under a multi-user application situation, the interconnection among all the QKD systems will be achieved through all-pass typed light quantum switches. The invention further discloses an embodiment of integration of the electric power communication network and the quantum network. The electric power security communication network based on quantum key distribution technology has the advantage that the security in electric power communication network data transmission can be greatly improved by applying quantum communication technology into the traditional electric power communication network.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
High-speed autocompensation scheme of quantum key distribution
ActiveUS20180191496A1Key distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBeam splitterQuantum channel
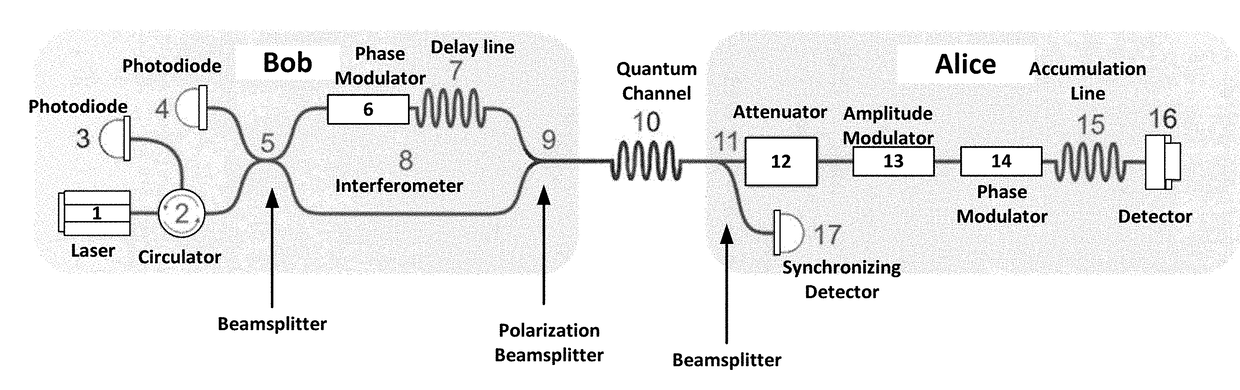
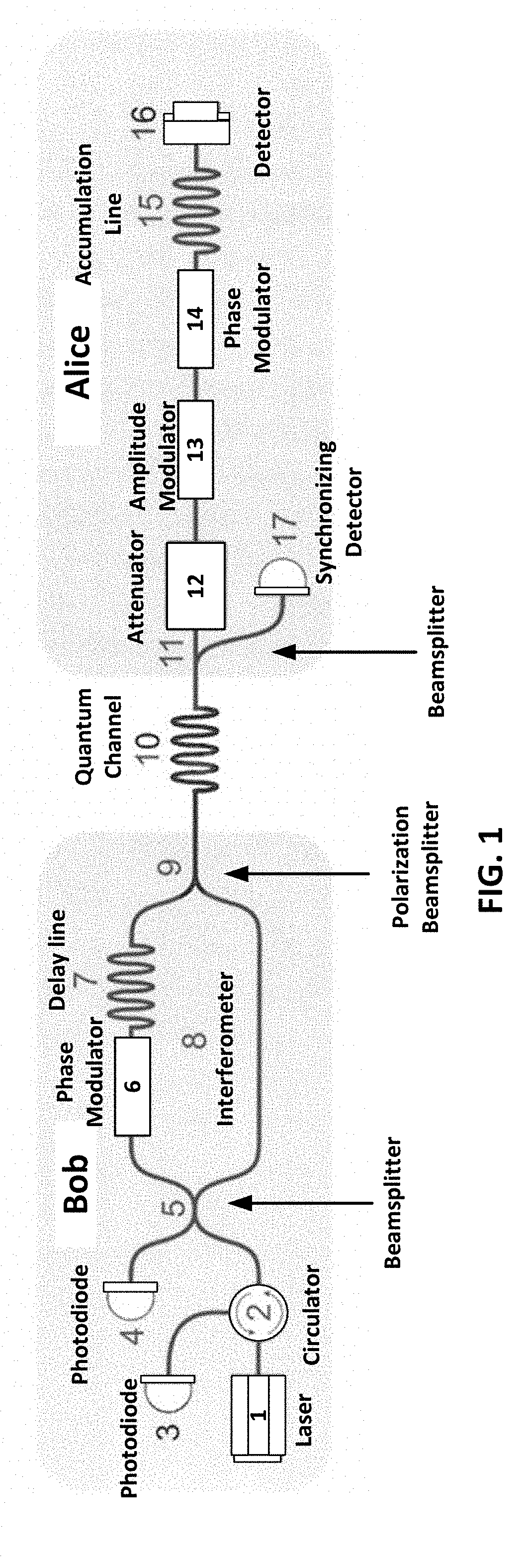
The invention relates to quantum cryptography, and includes a communication system for transmitting a cryptographic key between the ends of a channel, including a transmitting node (Alice) comprising a beam splitter, an electro-optical attenuator, an amplitude modulator, a phase modulator, a storage line, a Faraday mirror, a synchronization detector; a receiving node (Bob) that includes avalanche photodiodes, a beam splitter, a circulator, a delay line, a phase modulator, a polarizing beam splitter, a Mach-Zehnder interferometer, and also a quantum channel for connecting these nodes. In this case, for the storage line is placed between the electro-optical phase modulator of the sender and the Faraday mirror. The limiting frequency of the laser pulse repetition at a fixed value of their width is increased, which makes it possible to use an autocompensation circuit at a frequency corresponding to the width of the laser pulse, which is the maximum possible result.
Owner:QRATE LLC
Flexible three-dimensional force touch sensor of multi-fingered hands of human-simulated robot and three-dimensional force detecting system thereof
ActiveCN102706489AFlexibleBroaden applicationForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsManipulatorTouch PerceptionQuantum channel
The invention discloses a flexible three-dimensional force touch sensor of multi-fingered hands of a human-simulated robot and a three-dimensional force detecting system, relating to the field of touch sensors of robots. The invention aims at solving the problem that more touch sensors only can acquire normal force but can not detect the normal force and the force simultaneously like the human hands. A sensor body consists of a force-transferring hemispherical layer, a flexible top-level electrode layer, a composite material QTC (Quantum Tunneling Composites) with quantum channel effect and a flexible bottom-level electrode layer which are arranged in sequence from top to bottom; a signal acquisition circuit consists of a mixed-signal array programmable on-chip system and an analog multiplex selection module; the on-chip system comprises a digital logic module, an analog digital conversion module ADC, a digital analog conversion module DAC, an analog signal register I, an analog signal register II, a voltage amplifying circuit and a multi-way switch; and the analog multiplex selection module comprises an analog multi-way switch I and an analog multi-way switch II. The invention is used for the touch sensor for detecting the three-dimensional force of the multi-fingered hands of the human-simulated robot.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
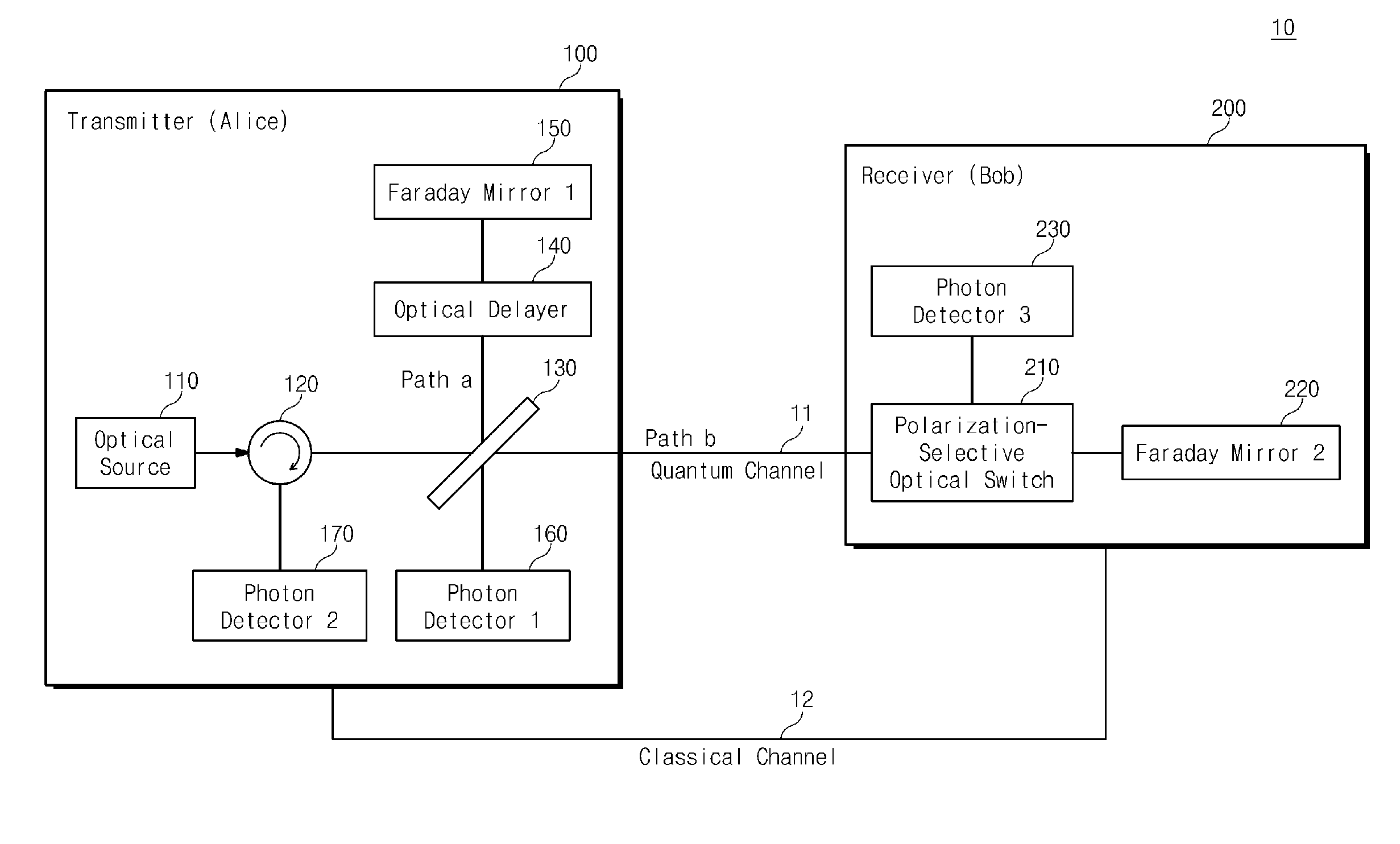
Polarization-Controlled Encoding Method, Encoder, And Quantum Key Distribution System
ActiveUS20080037998A1Environment requirement of largelyImprove system stabilityKey distribution for secure communicationCoupling light guidesQuantum channelKey distribution
The invention relates to a polarization-controlled encoding method, encoder and quantum key distribution system, which is characterized in that polarization maintaining light path or 90 degree rotation Faraday mirror are used inside the encoder to keep the polarization of the output pulses same, and that in the quantum key distribution system employing the polarization-controlled encoder the pulse emitted from transmitter is unidirectional-transmitted to receiver and then quantum key distribution is implemented using interference in the pulses according to the quantum key distribution protocol. The quantum key distribution system using the polarization-controlled encoder of the invention has the ability of avoiding the wiretapping to transmitter, receiver and quantum channel. Detection units each of which separates reversed photon from other photons are added at the out port of the transmitter and the in port of receiver, respectively, so that Trojan horse is prevented from entering and photons with phase modulated information are prevented from leaving the safe area in receiver. Unconditionally safe key distribution can be accomplished by using the quantum key distribution system of the invention.
Owner:ANHUI QASKY QUANTUM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method and system for generating shared information
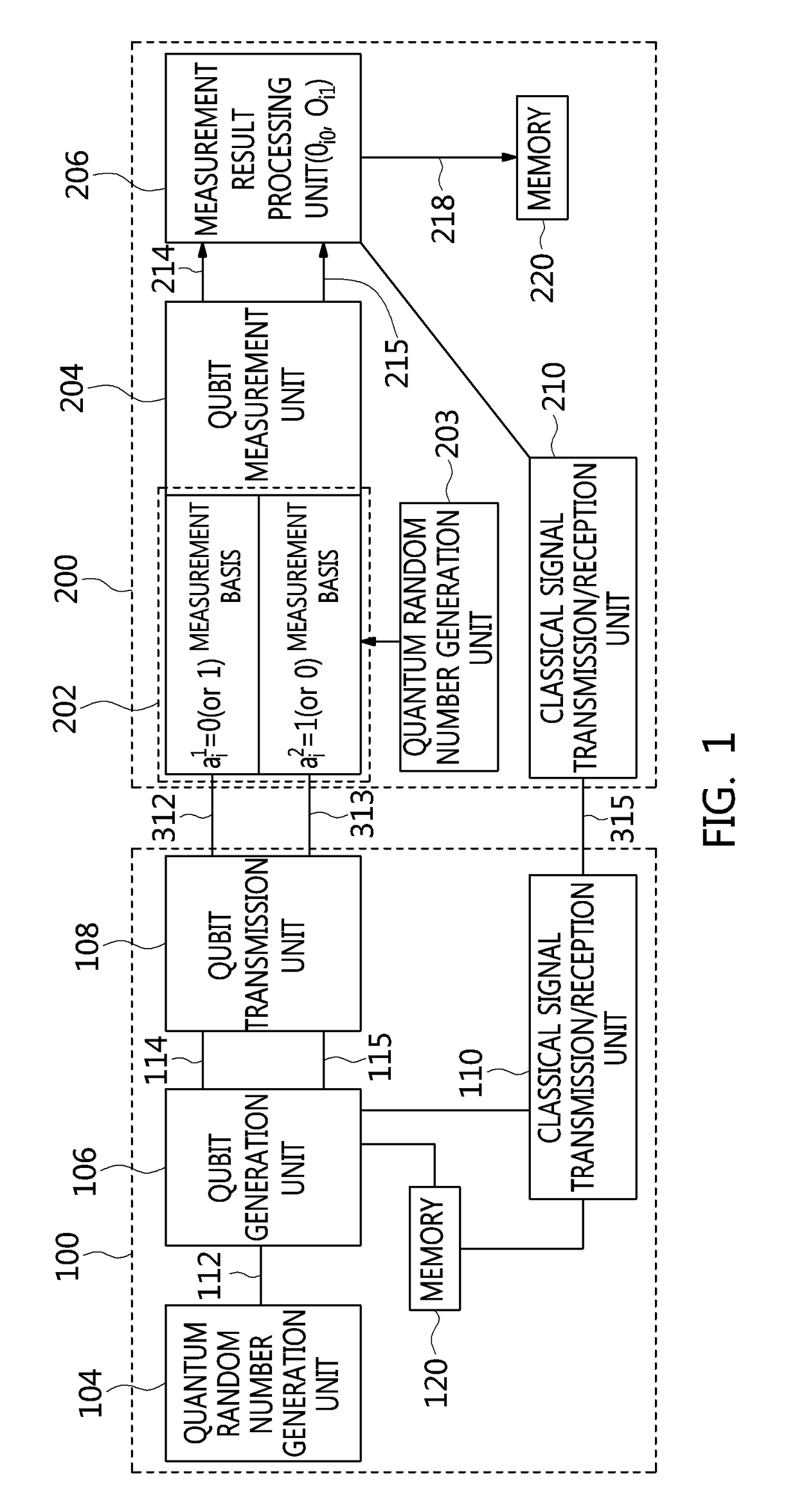
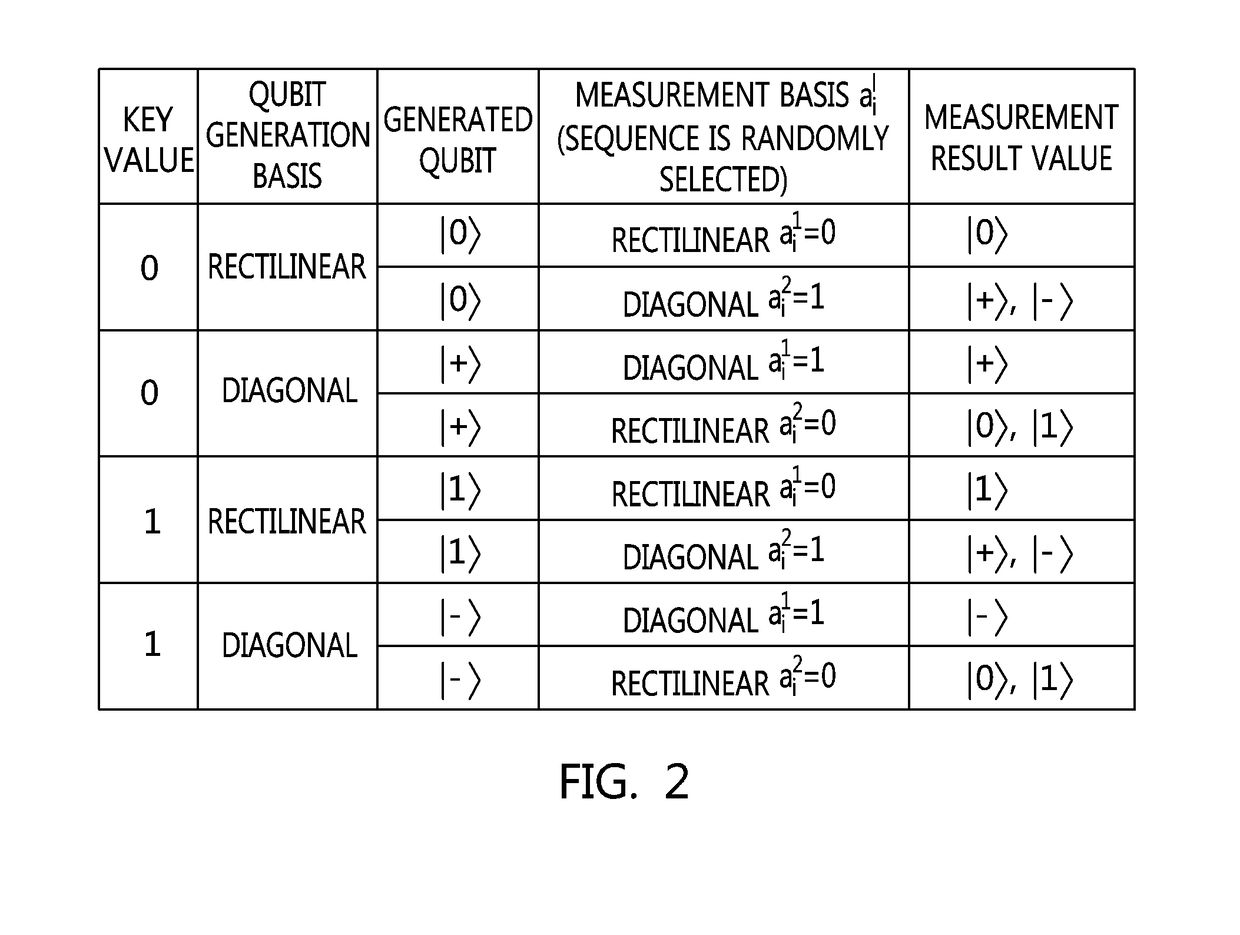
ActiveUS20060093143A1Stably and efficiently generatingEfficient sharing of informationKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesQuantum channelBit numbering
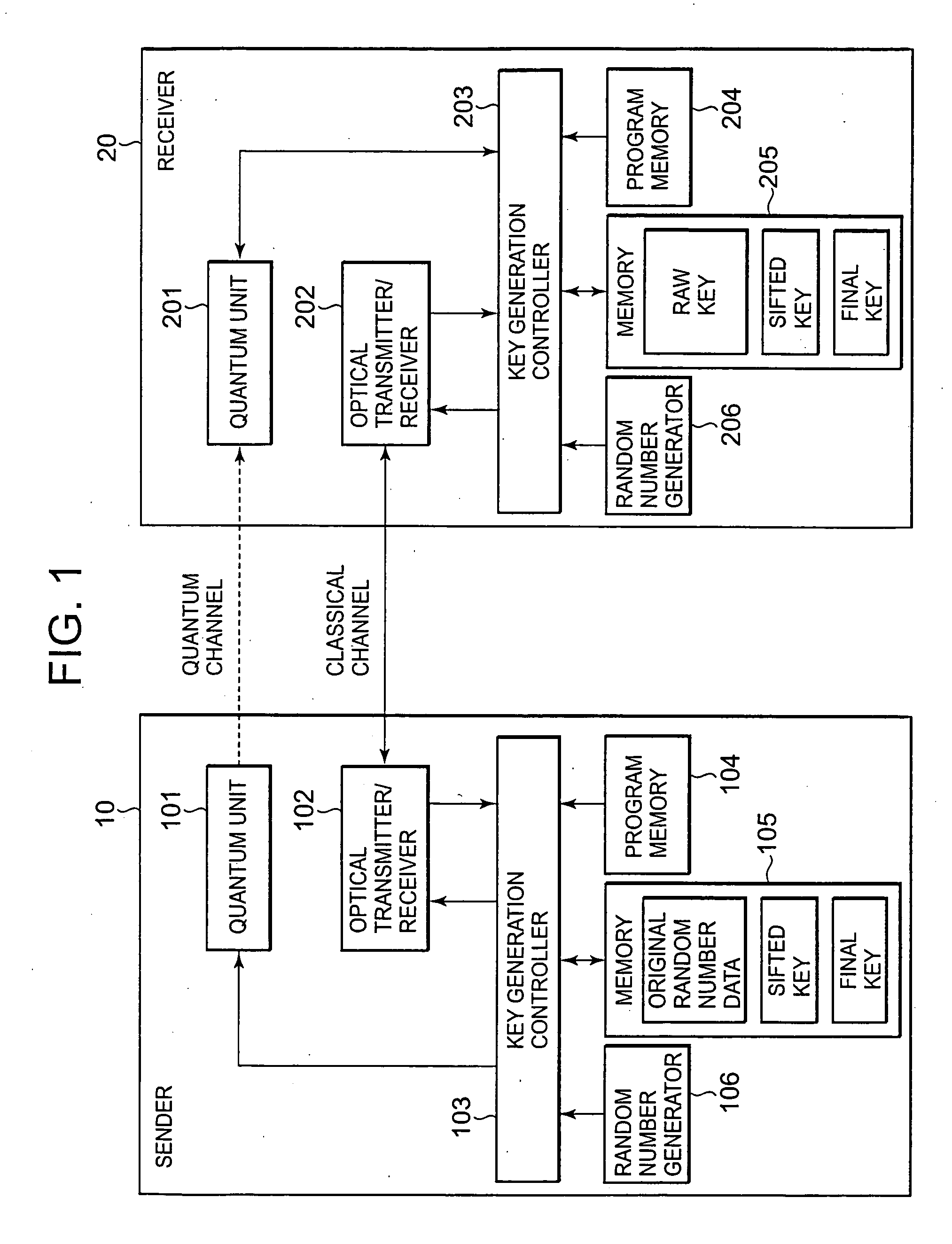
A sender sends original random-number data to a receiver through a quantum channel. The receiver generates a raw key from information received through the quantum channel and notifies the received information to the sender. The sender performs received-bit comparison and basis reconciliation based on the received information and provisionally shares a sifted key with the receiver. The receiver sends part of its version of the sifted key to the sender, by which an error rate is calculated. The calculated error rate is compared with a predetermined threshold value for bit position synchronization determination. When the calculated error rate is larger, the sender notifies the receiver that bit position synchronization is not established. The receiver reassigns bit numbers to the sifted key, and received-bit comparison and basis reconciliation are performed again. This procedure is repeated until the calculated error rate becomes smaller than the threshold value.
Owner:NEC CORP
Key distribution system and key distribution method based on multiuser remote communication
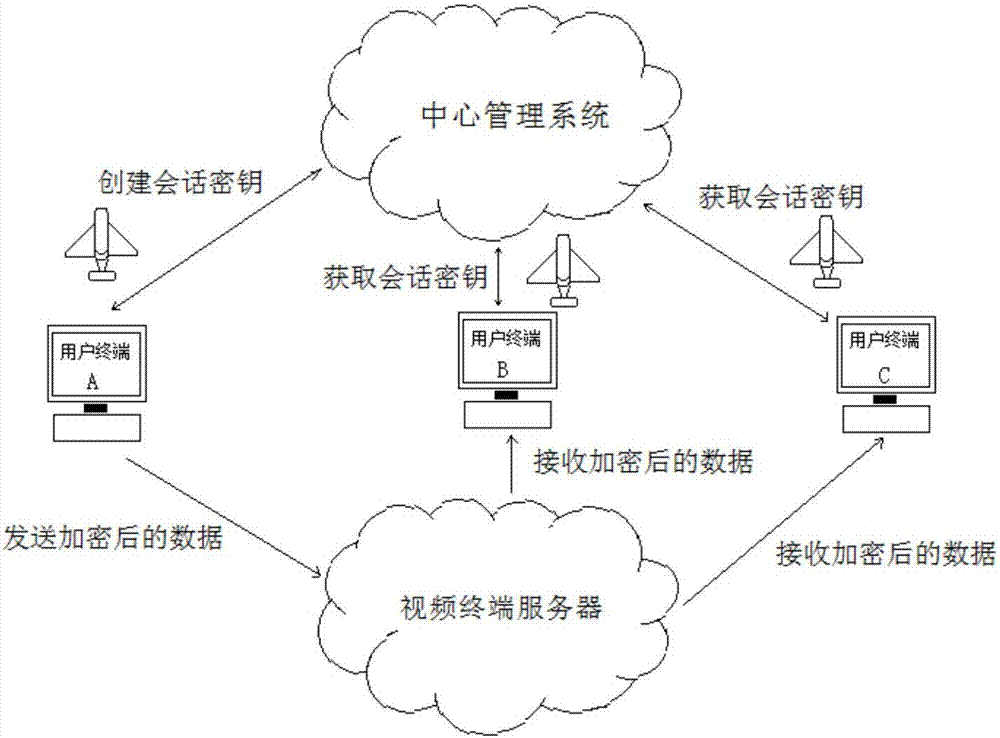
PendingCN107040378AGuaranteed absolute securityAvoid high standardsKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesQuantum channelKey distribution
The invention discloses a key distribution system and a key distribution method based on multiuser remote communication. Quantum key synchronization between each user terminal and a central management system is realized in a manner of carrying a key relay server by an aerial vehicle. Then the central management system distributes a session key to a user terminal which requires participation into communication in a quantum key encrypted session key manner. A data packet only requires session key encryption, thereby realizing a purpose of multi-user-terminal communication. The key distribution system and the key distribution method ensure absolute safety in multiple-party communication and prevent a high-standard requirement for a QKD system in a one-packet and one-key manner so that quantum encrypted communication is suitable for a large-scale multiple-party communication occasion. Furthermore, establishing of a quantum channel between each user terminal and the central management system is not required. Not only is a problem of quantum information attenuation in remote channel transmission settled, but also a problem of difficult quantum channel disposition is alleviated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG QUANTUM TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for multi-user quantum key distribution
ActiveUS20180069698A1Constant efficiencyEasy to implementKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageQuantum channelKey distribution
An apparatus and method for multi-user quantum key distribution. The method for multi-user quantum key distribution is performed using a multi-user quantum key distribution apparatus and a quantum key client device, and includes generating, by the multi-user quantum key distribution apparatus, transmission qubit pairs based on a key bit string of a shared key to be distributed to the quantum key client device, measuring, by the quantum key client device, the transmission qubit pairs, received from the multi-user quantum key distribution apparatus through a quantum channel, based on a measurement basis, verifying security of the quantum channel using the transmission qubit pairs, and if the security has been verified, decoding qubit measurement values of the transmission qubit pairs into the shared key.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
A quanta secret key distribution system for phase coding polarization detection
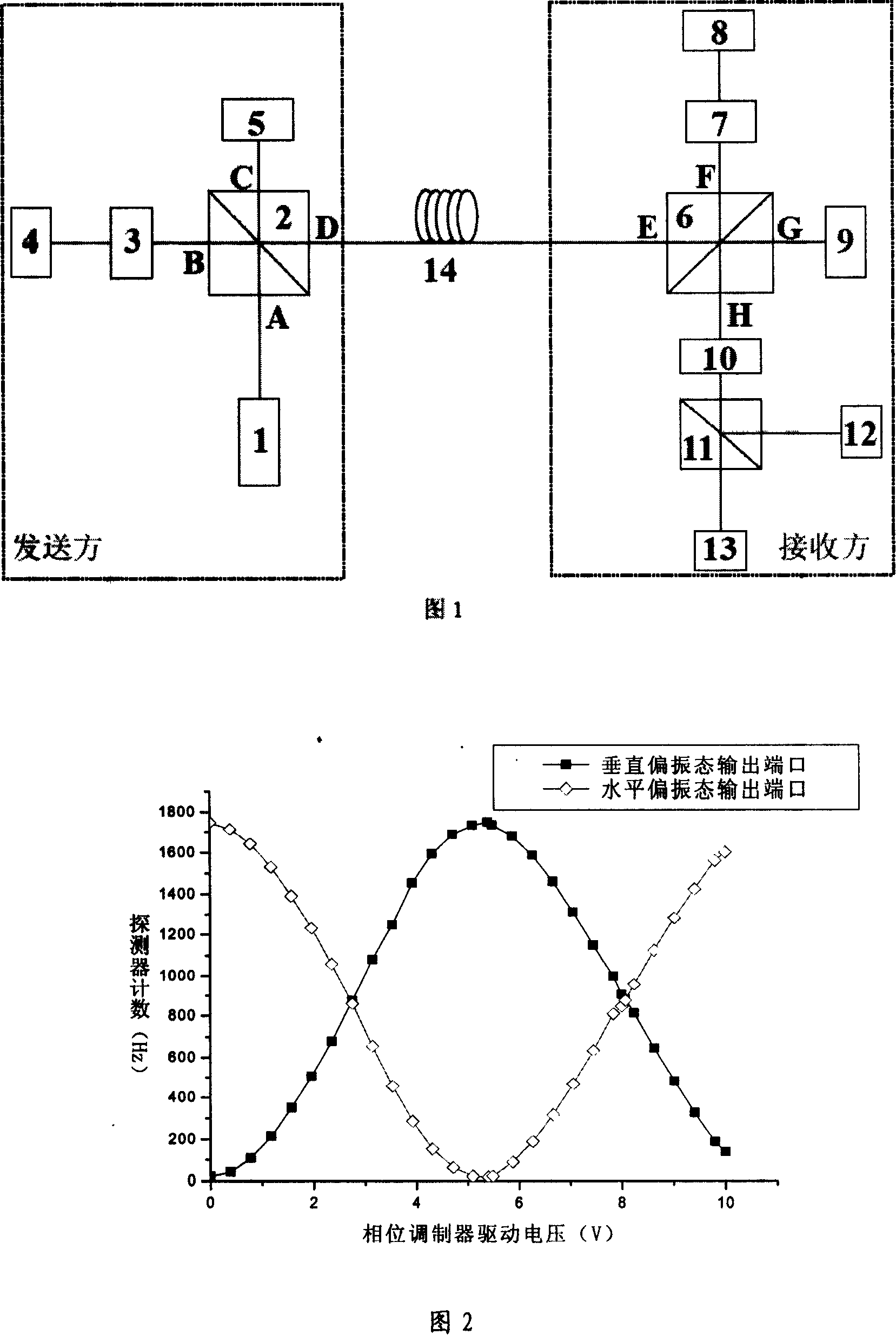
InactiveCN101150371ARealize unconditional security distribution systemSimple structureKey distribution for secure communicationCoupling light guidesBeam splittingQuantum channel
This invenion discloses a distribution system for quantum ciphered keys testing polarization of phase coding, in which, a transmitting party is connected with a receiving party by a quantum channel and either of which includes a same polarized beam splitting and merging device with four ports, the reflection port of which is connected with a phase modulator and a 90deg. rotation Faraday mirror orderly to form a long circuit and a transmission port of which is conneted with the 90deg. rotation Faraday mirror to form a short circuit, the incident port of the beam splitting and merging device is connected with a single photon source and the exit port is connected to a common port of a lambda / 2 wave plate and a three-port polarized splitting / merging device, the reflection and the transmission ports of which are connected with a single-photon detector.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
One-dimensional modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on heterodyne detection, and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN107612686ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costKey distribution for secure communicationManufacturing cost reductionBeam splitter
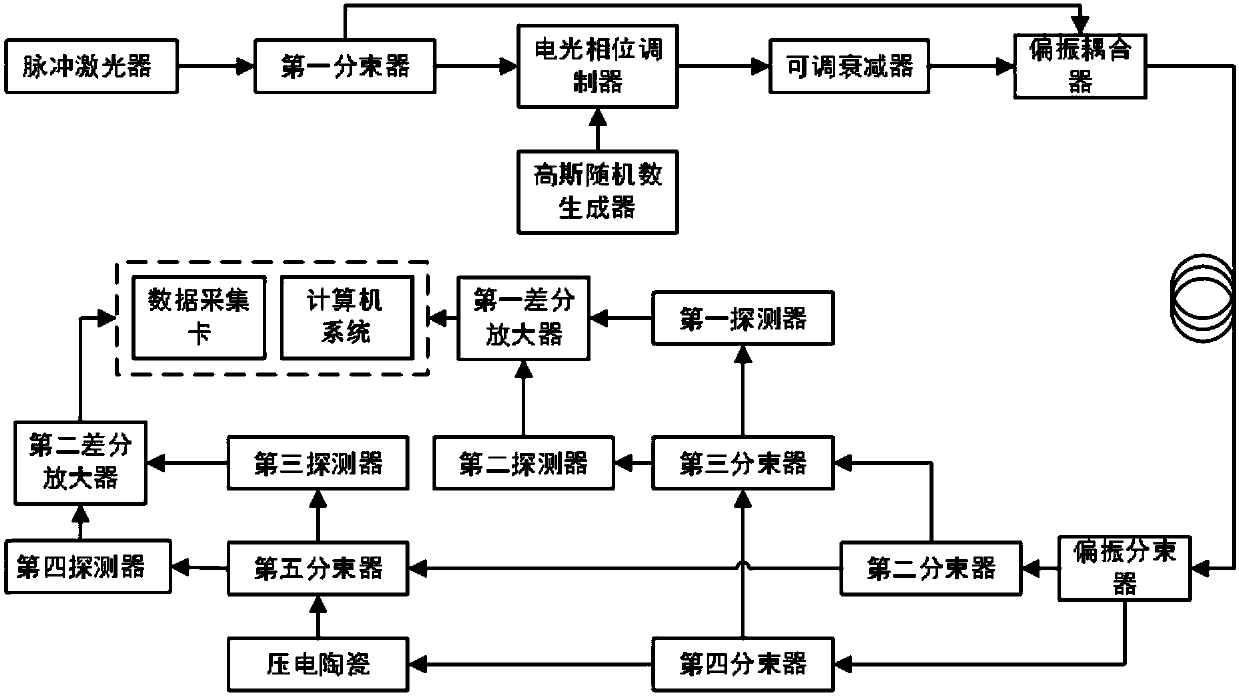
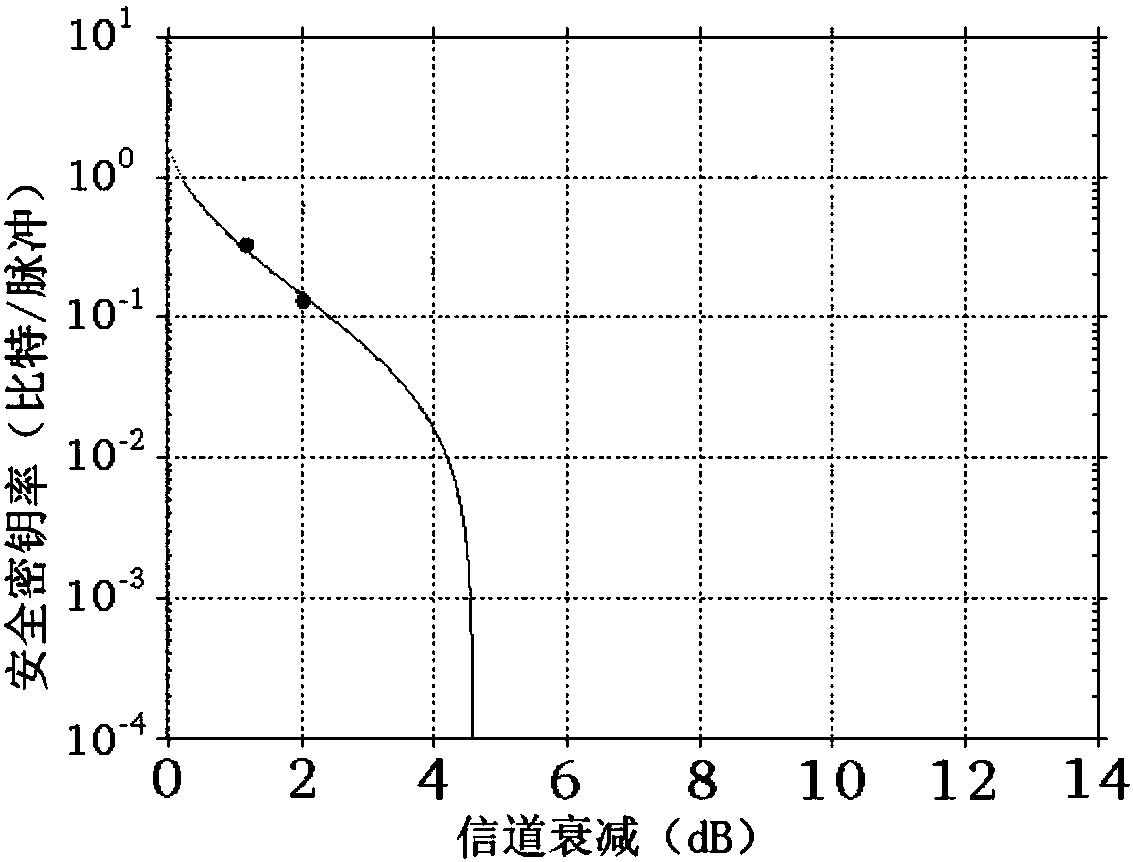
The invention discloses a one-dimensional modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on heterodyne detection, and an implementation method thereof. Pulse laser is divided bya first beam splitter into signal light and local oscillator light at a sending end, an electro-optic phase modulator modulates the signal light, and the modulated signal light is attenuated to a quantum level by an adjustable light attenuator; the signal light at the quantum level is merged with the local oscillator light by a polarization coupler and is transmitted to a receiving end by a quantum channel; signal detection is performed on the receiving end by the heterodyne detection technology, the output information of a first differential amplifier and a second differential amplifier are sent to a data collection card and a computer system for collection and analysis processing, and a group of safe quantum keys is obtained on the sending end and the receiving end separately. Accordingto the one-dimensional modulation continuous variable quantum key distribution system, the modulation process in the continuous variable quantum key distribution system can be achieved just by one electro-optic phase modulator, thereby effectively simplifying the system structure, reducing the volume of the device, reducing the data processing volume and reducing the manufacturing cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
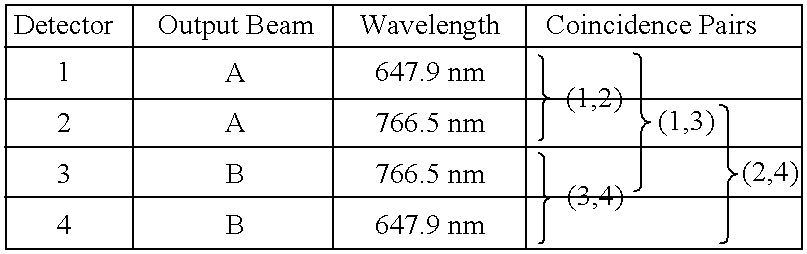
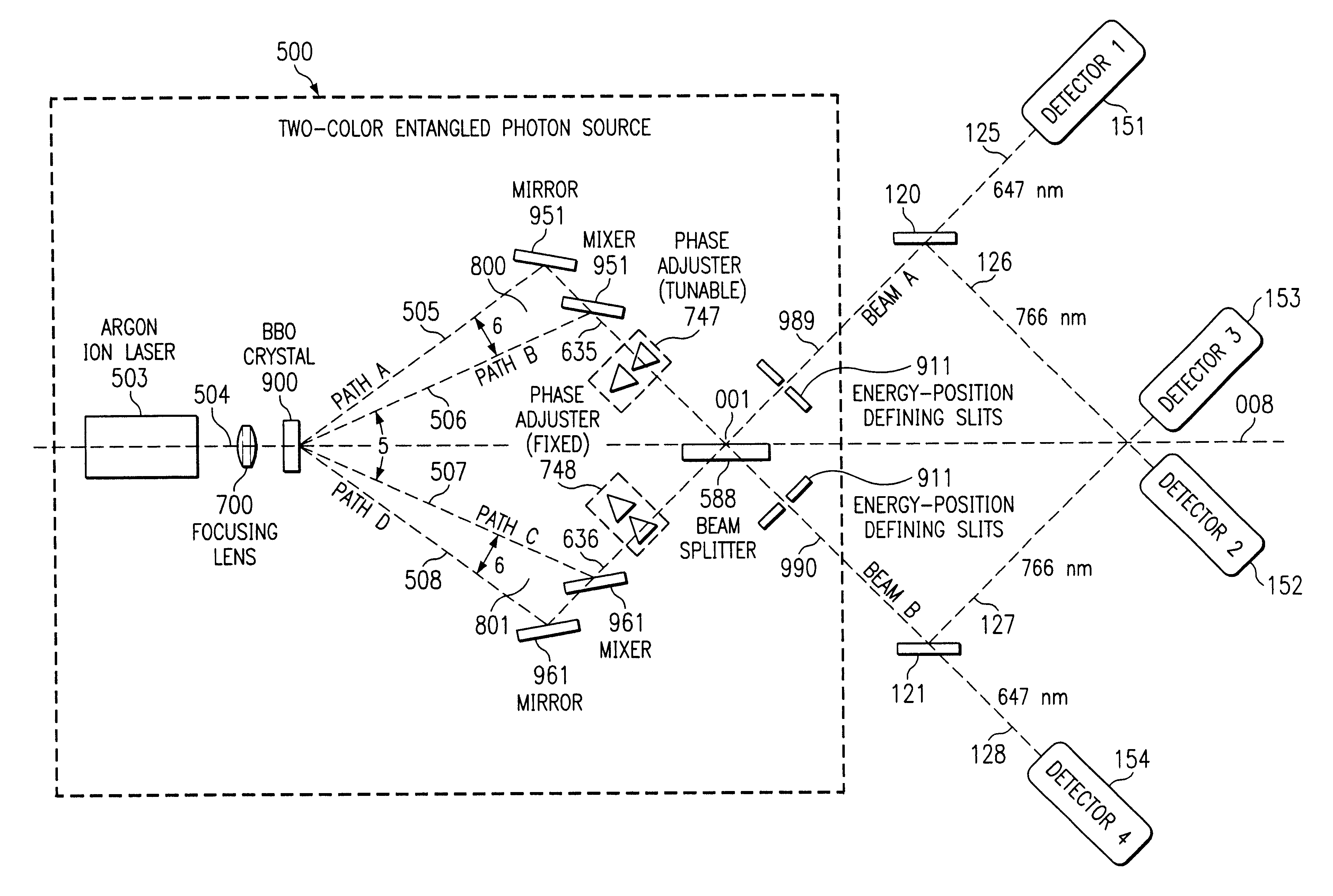
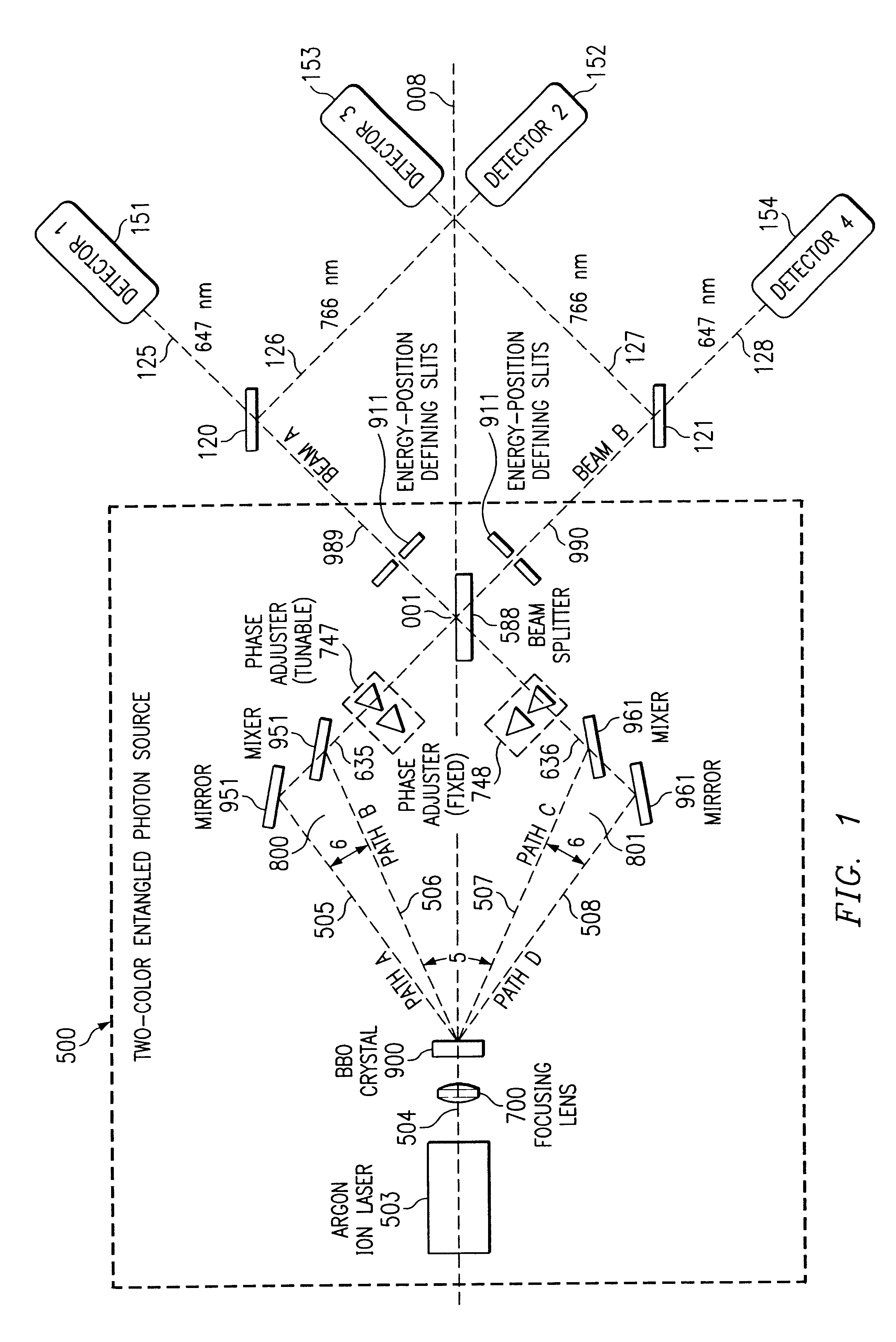
Quantum channel for the transmission of information
Systems and methods are described for a quantum channel for the transmission of information. A method includes: down converting a beam of coherent energy to provide a beam of multi-color entangled photons; converging two spatially resolved portions of the beam of multi-color entangled photons into a converged multi-color entangled photon beam; changing a phase of at least a portion of the converged multi-color entangled photon beam to generate a first interferometric multi-color entangled photon beam; combining the first interferometric multi-color entangled photon beam with a second interferometric multi-color entangled photon beam within a single beam splitter; wherein combining includes erasing energy and momentum characteristics from both the first interferometric multi-color entangled photon beam and the second interferometric multi-color entangled photon beam; splitting the first interferometric multi-color entangled photon beam and the second interferometric multi-color entangled photon beam within the single beam splitter, wherein splitting yields a first output beam of multi-color entangled photons and a second output beam of multi-color entangled photons; and modulating the first output beam of multi-color entangled photons.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
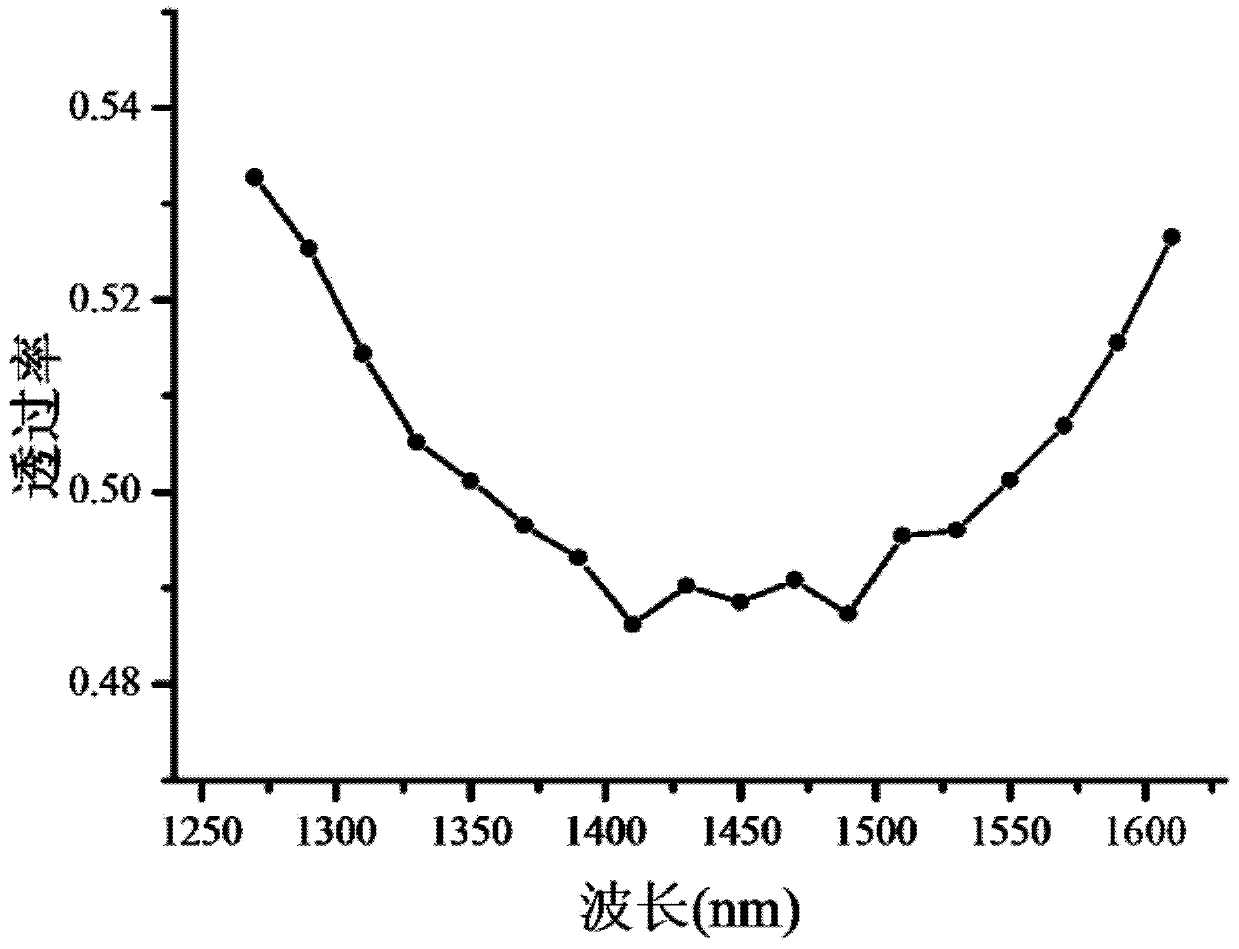
Monitoring method for continuous-variable quantum key distribution system
ActiveCN103780378AListening is validCancel noiseKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum channelTransmittance
The invention discloses a monitoring method for a continuous-variable quantum key distribution system. The method is used for monitoring a quantum channel between a sender and a receiver of the continuous-variable quantum key distribution system. The receiver comprises a balanced homodyne detector. The balanced homodyne detector comprises a 50:50 BS and an AM. According to the non-ideality of relevance between the transmittance and the wave length of the 50:50 BS of the balanced homodyne detector, two kinds of de-noising light are introduced besides spurious signal light and spurious local oscillation light, and therefore the extra noise caused by acquiring and resending behaviors of a monitor is eliminated.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for quantum cryptography
InactiveUS20110075839A1Guaranteed safe generationEfficient detectionKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum channelQuantum system
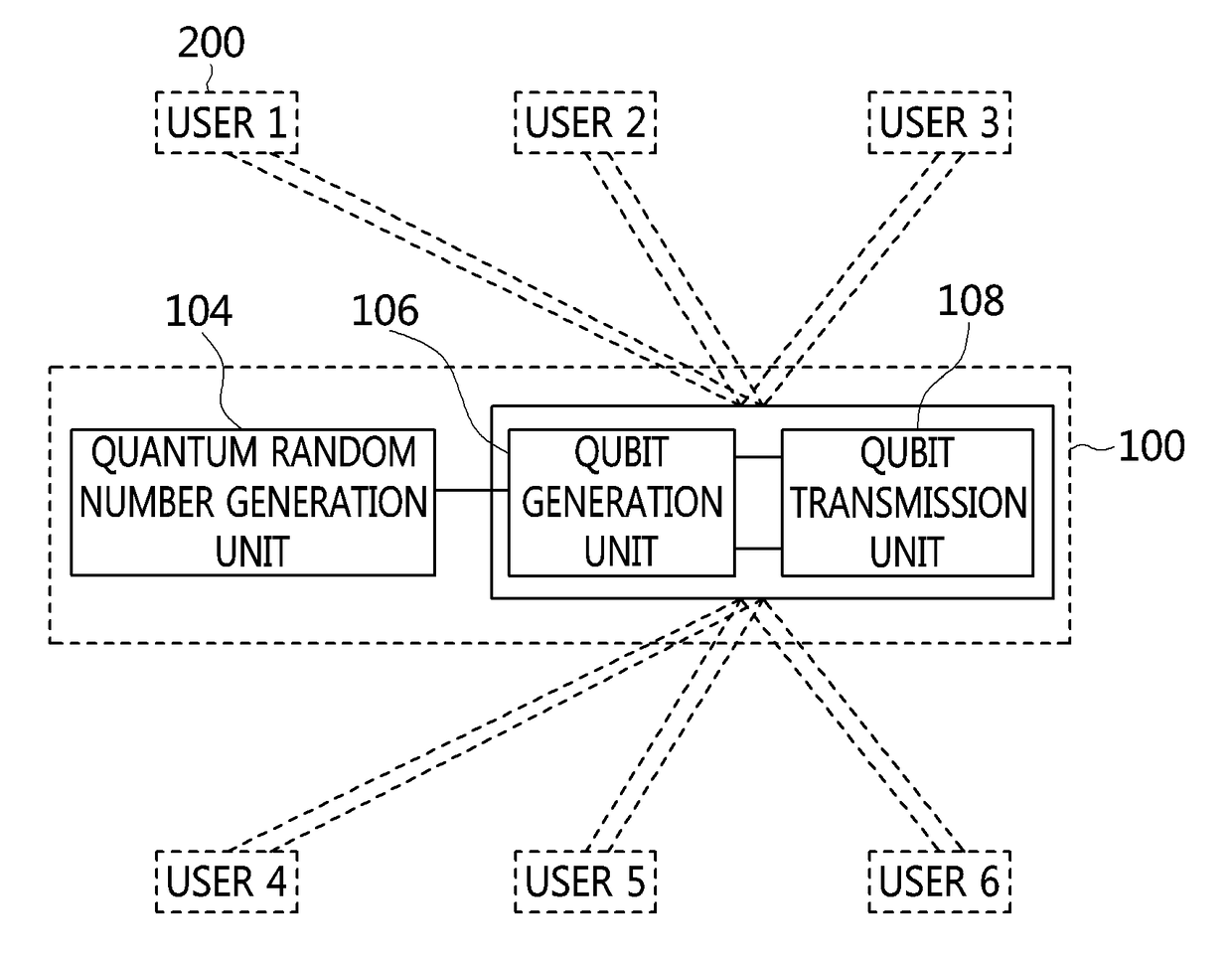
Provided are a system and a method for quantum cryptography. The method includes generating the same quantum cryptography key in a transmitter and a receiver by measuring a composite-quantum-system made of a plurality of sub-quantum-systems in each of the transmitter and the receiver connected to each other through a quantum channel, wherein a part of the sub-quantum-systems is confined within the transmitter in order not to expose the entire composite-quantum-system to an outside of the transmitter and the composite-quantum-system cannot be determined without disturbing the composite-quantum-system at the outside of the transmitter.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Polarization control coding method coder and quantum key distributing system
InactiveCN1651947ALower requirementReduce speed requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationCoupling light guidesMirror reflectionQuantum channel
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com