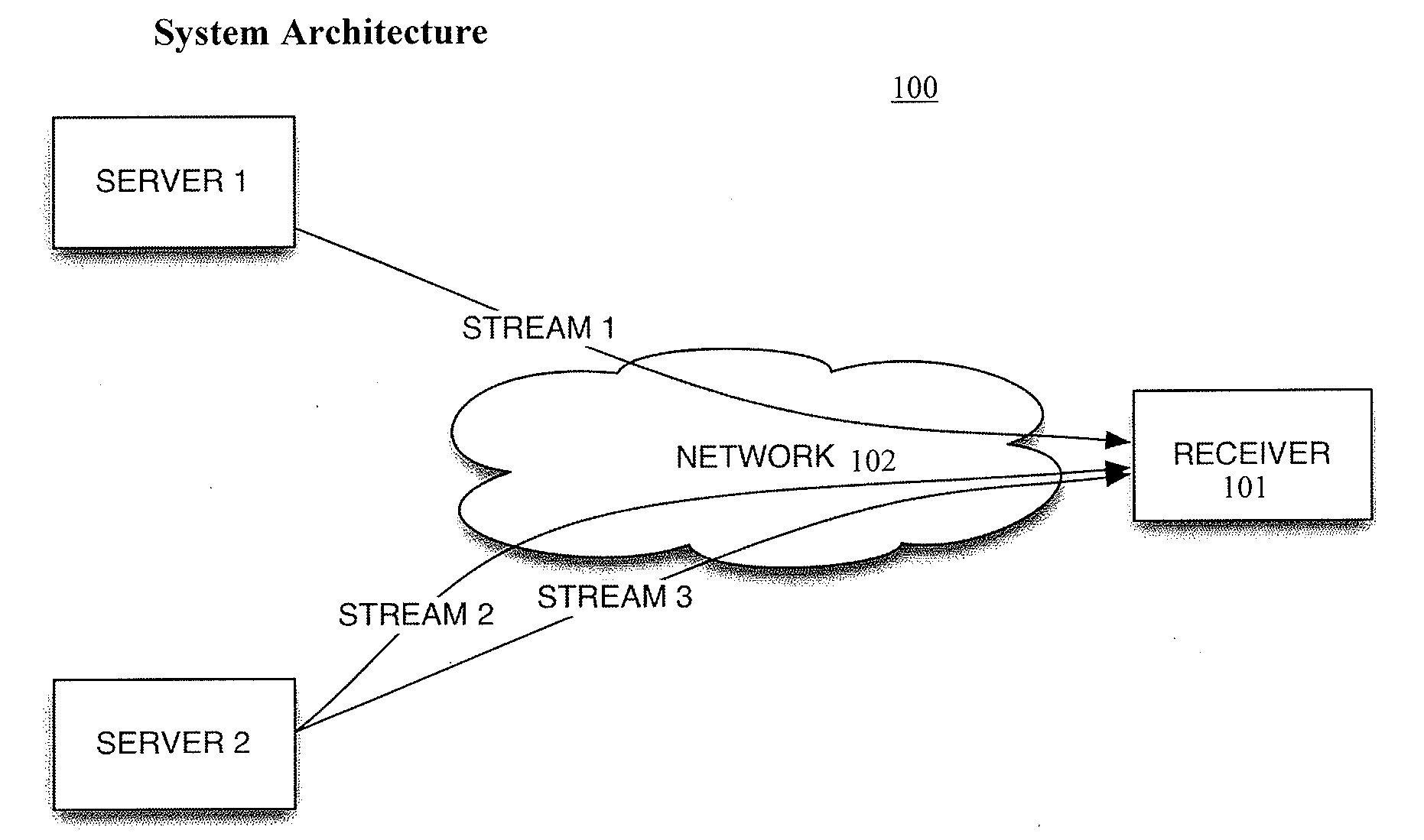
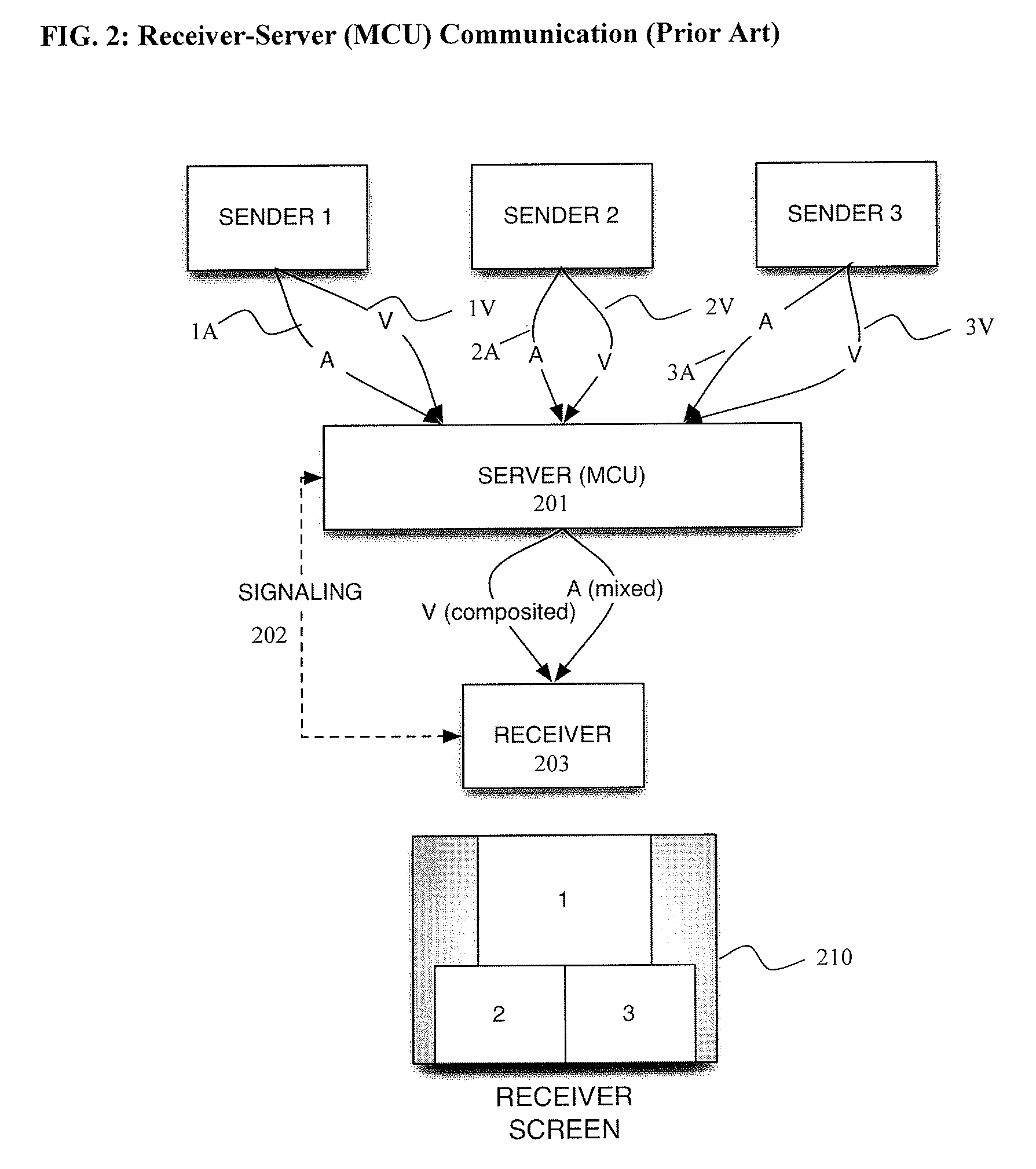
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
480results about How to "Reduce bitrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
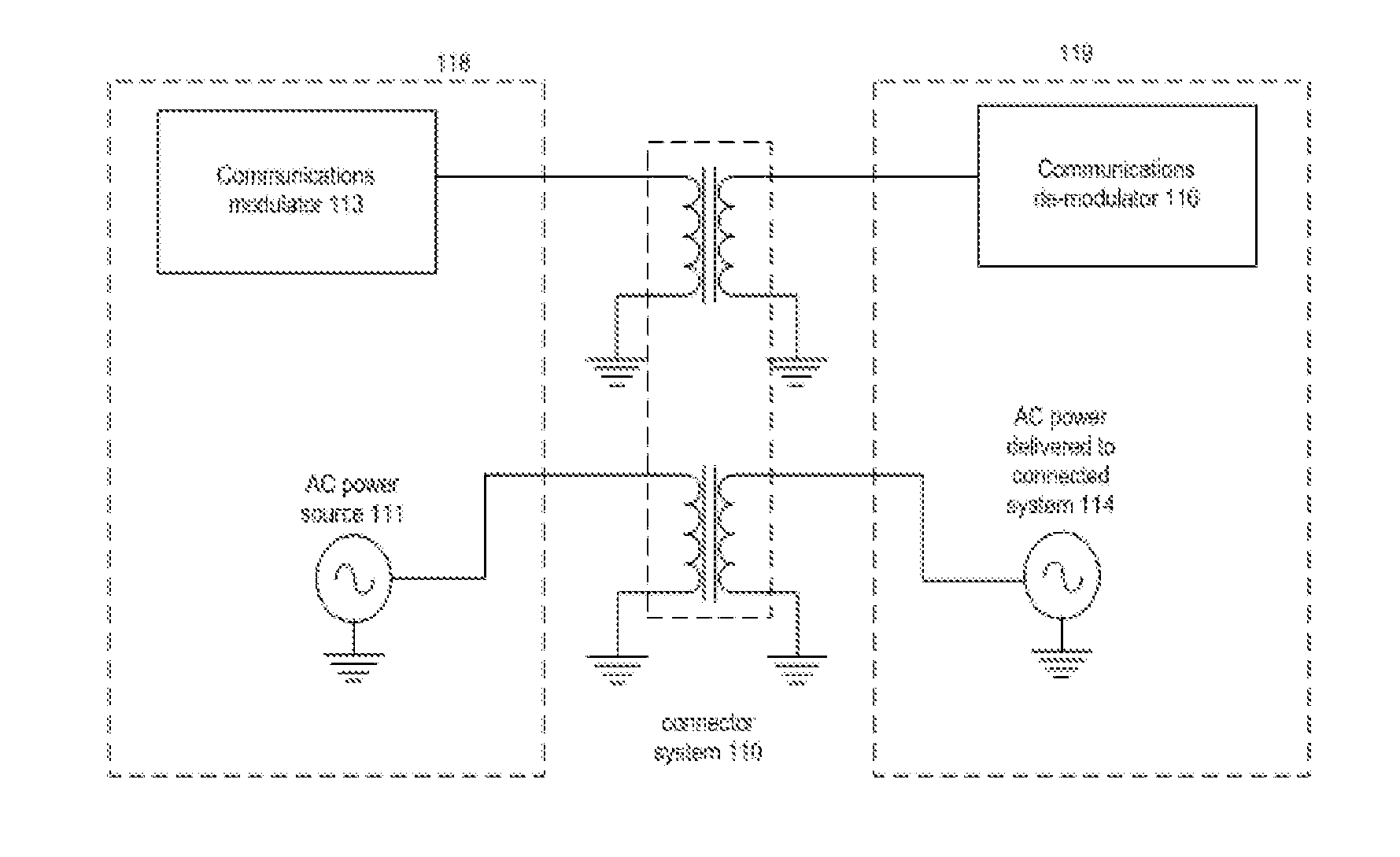
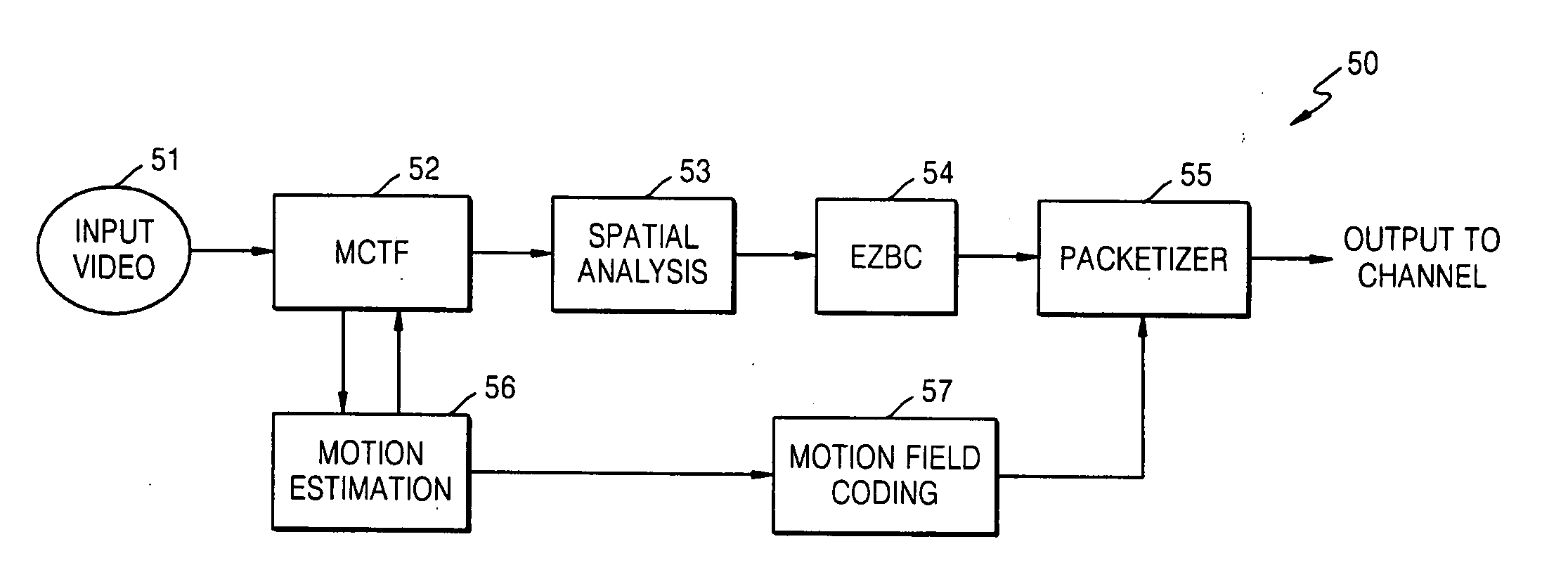
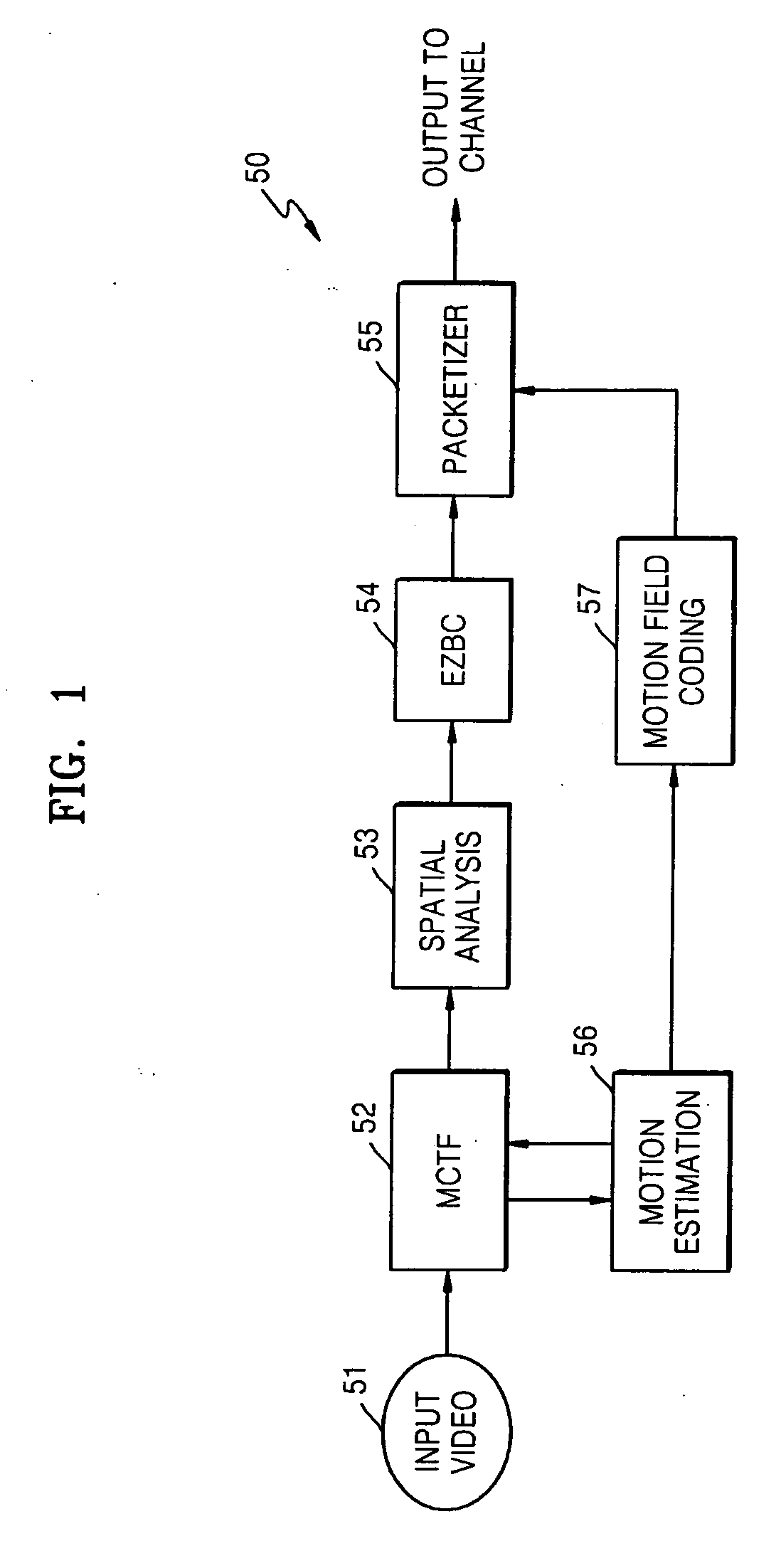
Rotary data and power transfer system
InactiveUS20120007442A1Increase distanceIncreases useful information rateElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersElectricityElectric power transmission
A data and power transfer system comprising a first system unit which includes a first communication element operable to transfer communication signals and a first connector element operable to transfer electrical power; and a second system unit which includes a second communication element operable to transfer communication signals and a second connector element operable to transfer electrical power, wherein the first communication element and second communication element are operable to transfer data between one another and the first connector element and second connector element are operable to transfer electrical power whilst electrically insulated from one another.
Owner:WFS TECH
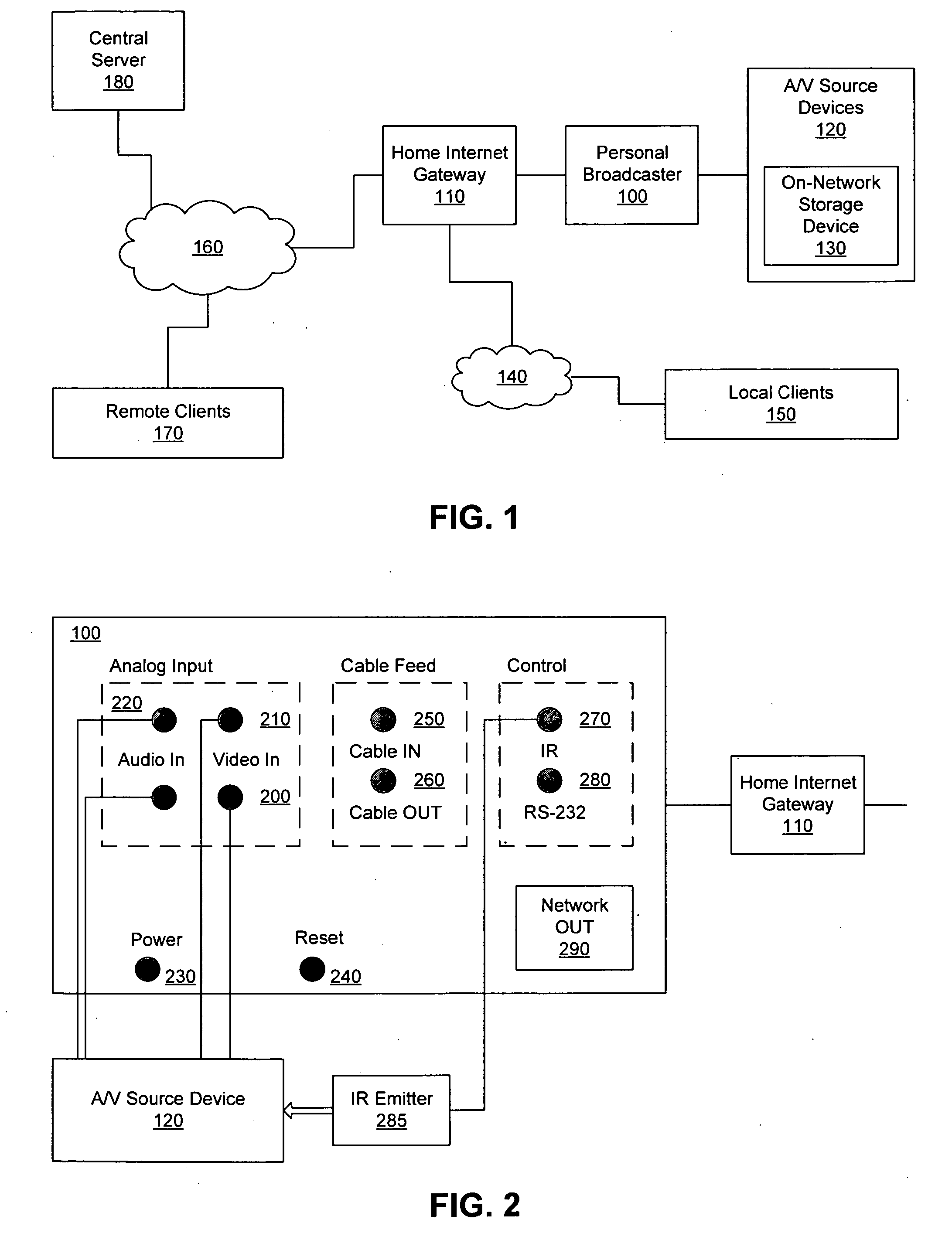
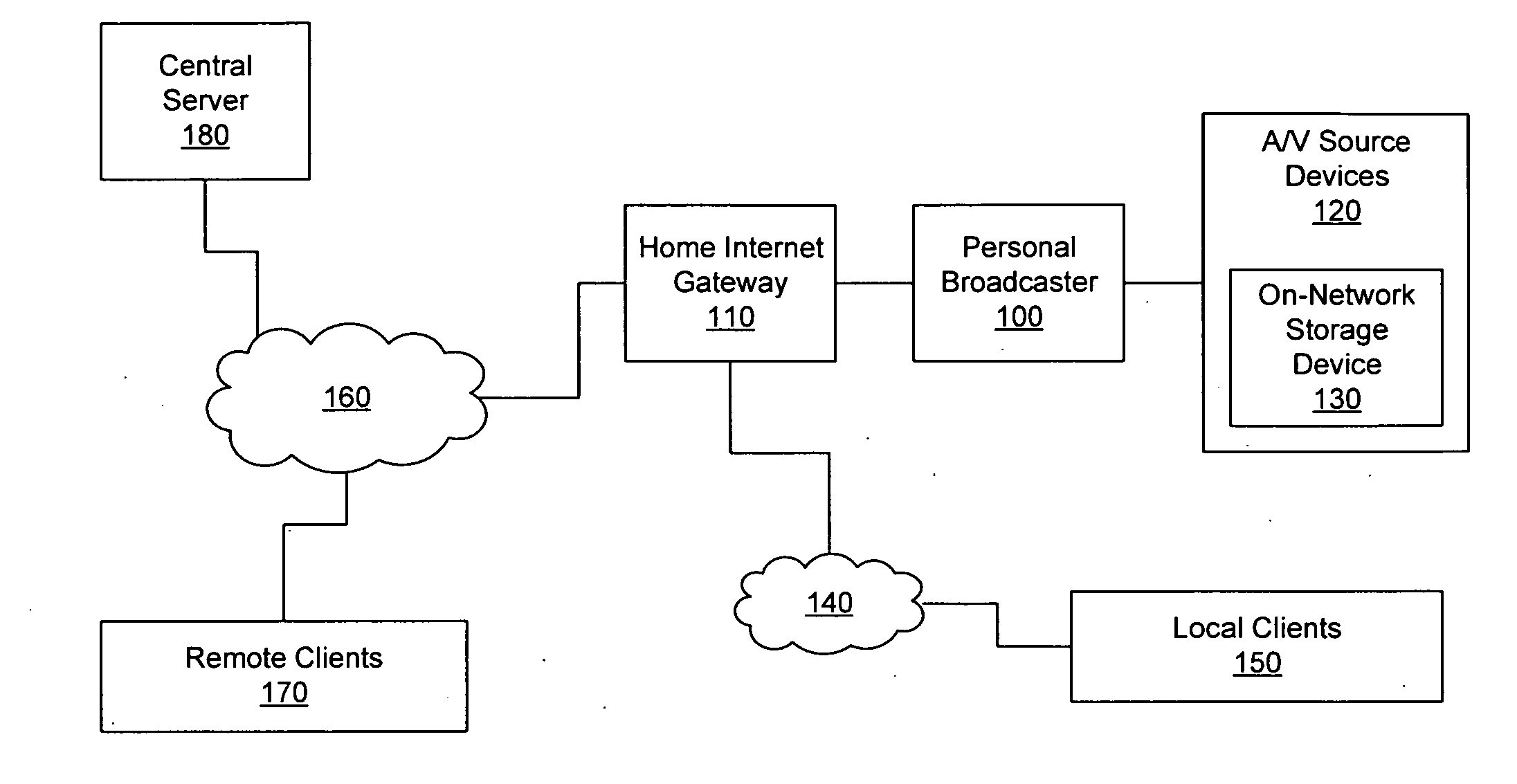
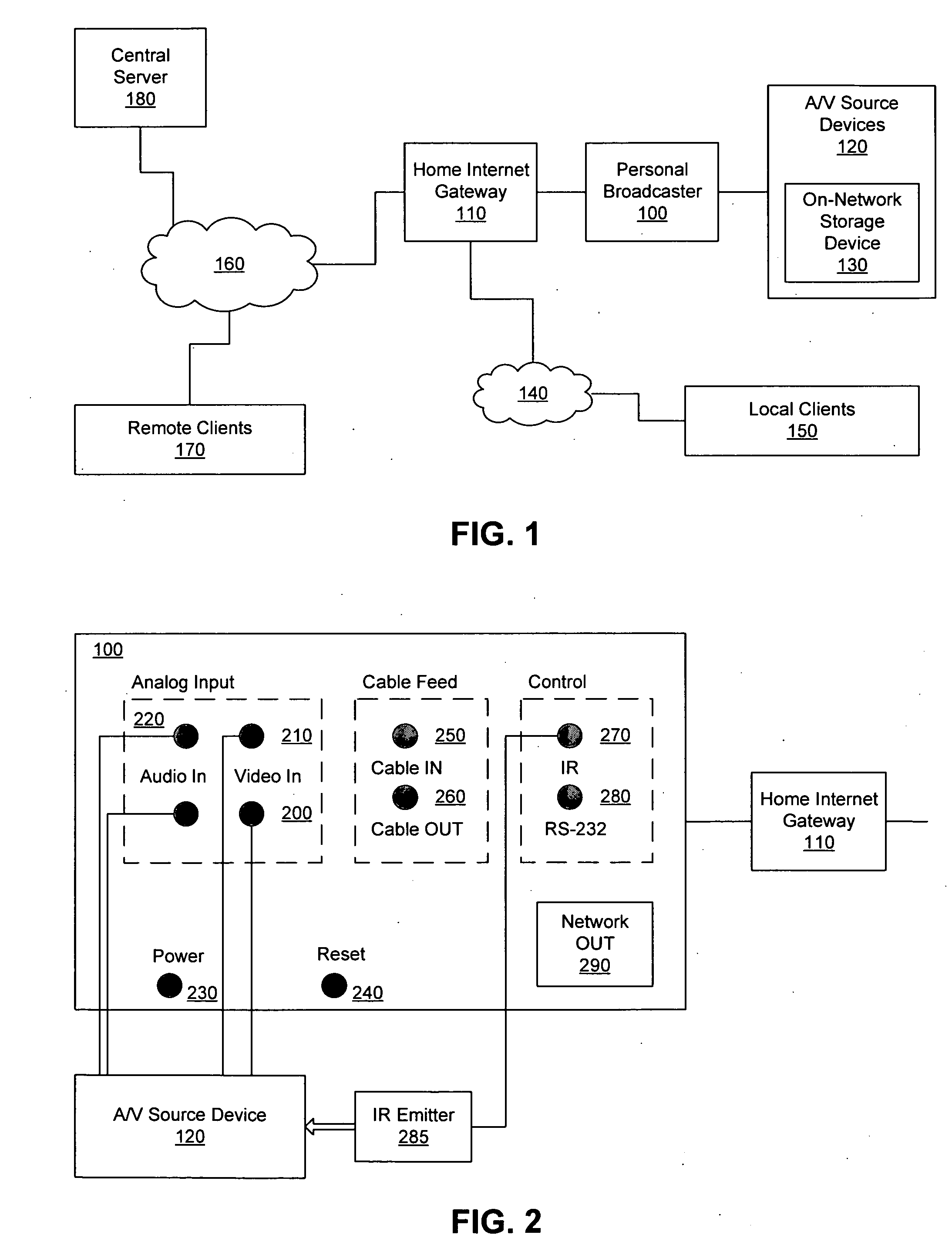
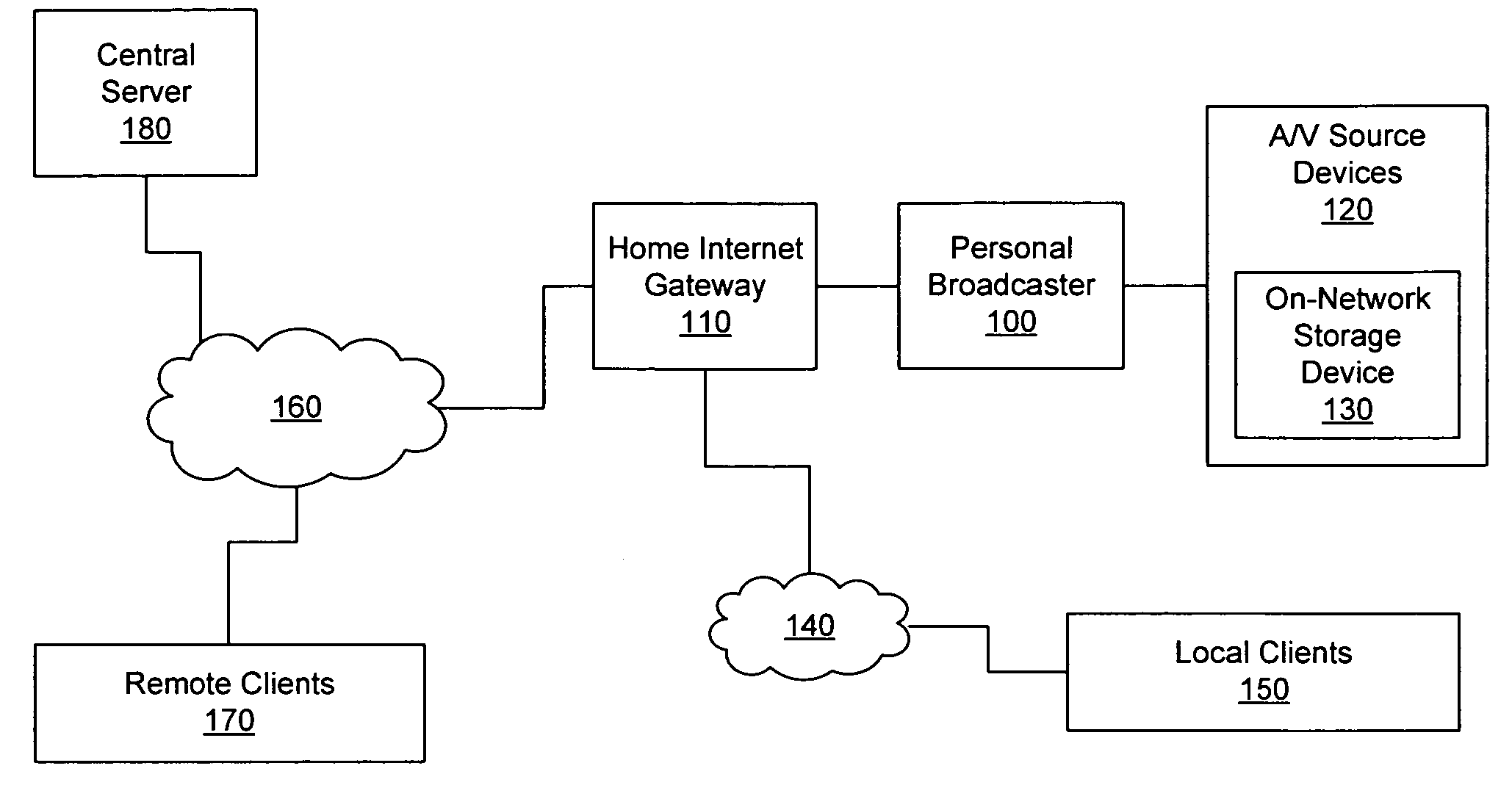
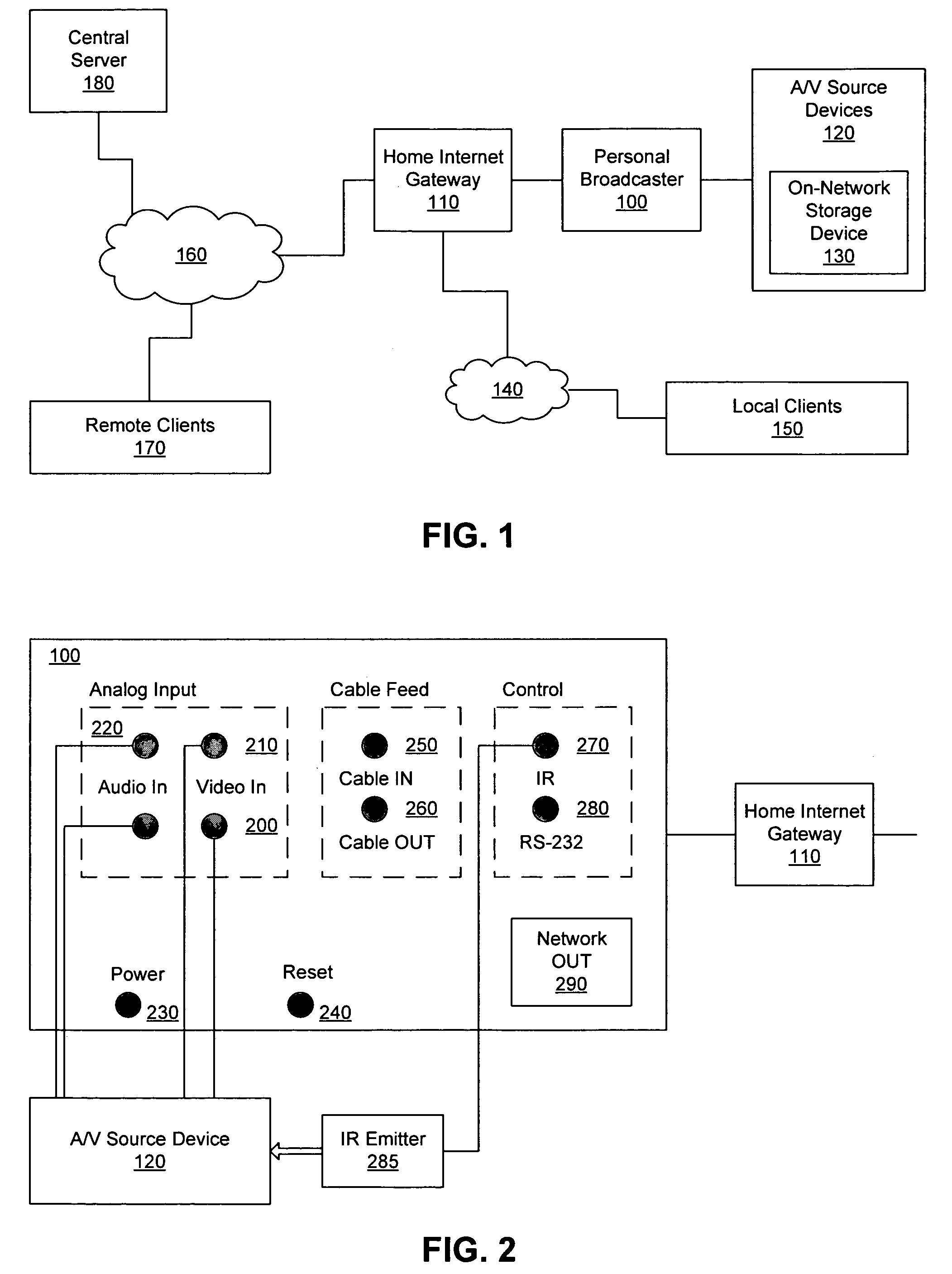
Personal media broadcasting system with output buffer
ActiveUS20060095401A1Improve experienceReduce bitratePulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast-related systemsClient-sideDigitization
A personal media broadcasting system enables video distribution over a computer network and allows a user to view and control media sources over a computer network from a remote location. A personal broadcaster receives an input from one or more types of media sources, digitizes and compresses the content, and streams the compressed media over a computer network to a media player running on any of a wide range of client devices for viewing the media. The system may allow the user to issue control commands (e.g., “channel up”) from the media player to the broadcaster, causing the source device to execute the commands. The broadcaster and the media player may employ several techniques for buffering, transmitting, and viewing the content to improve the user's experience.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
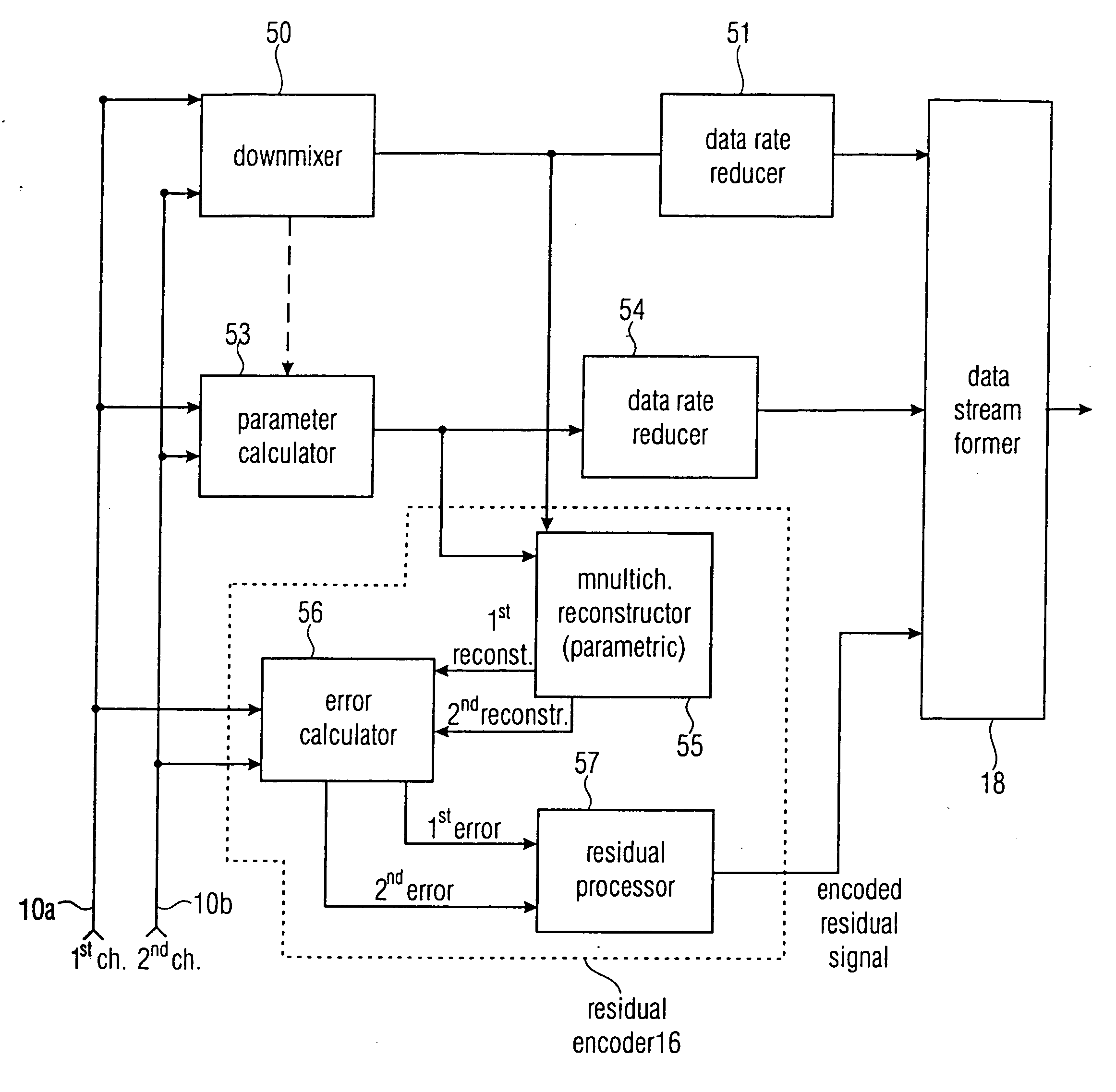
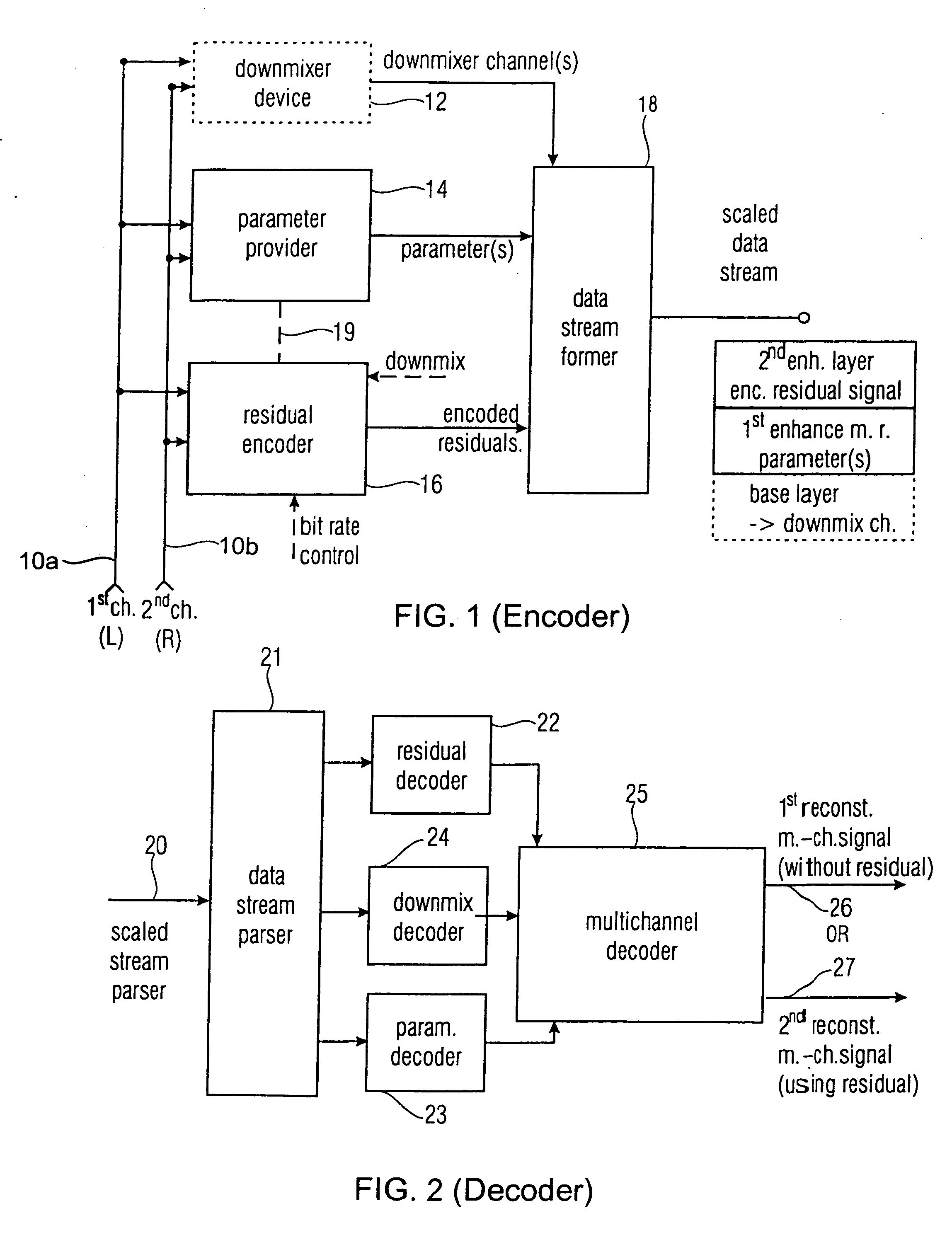
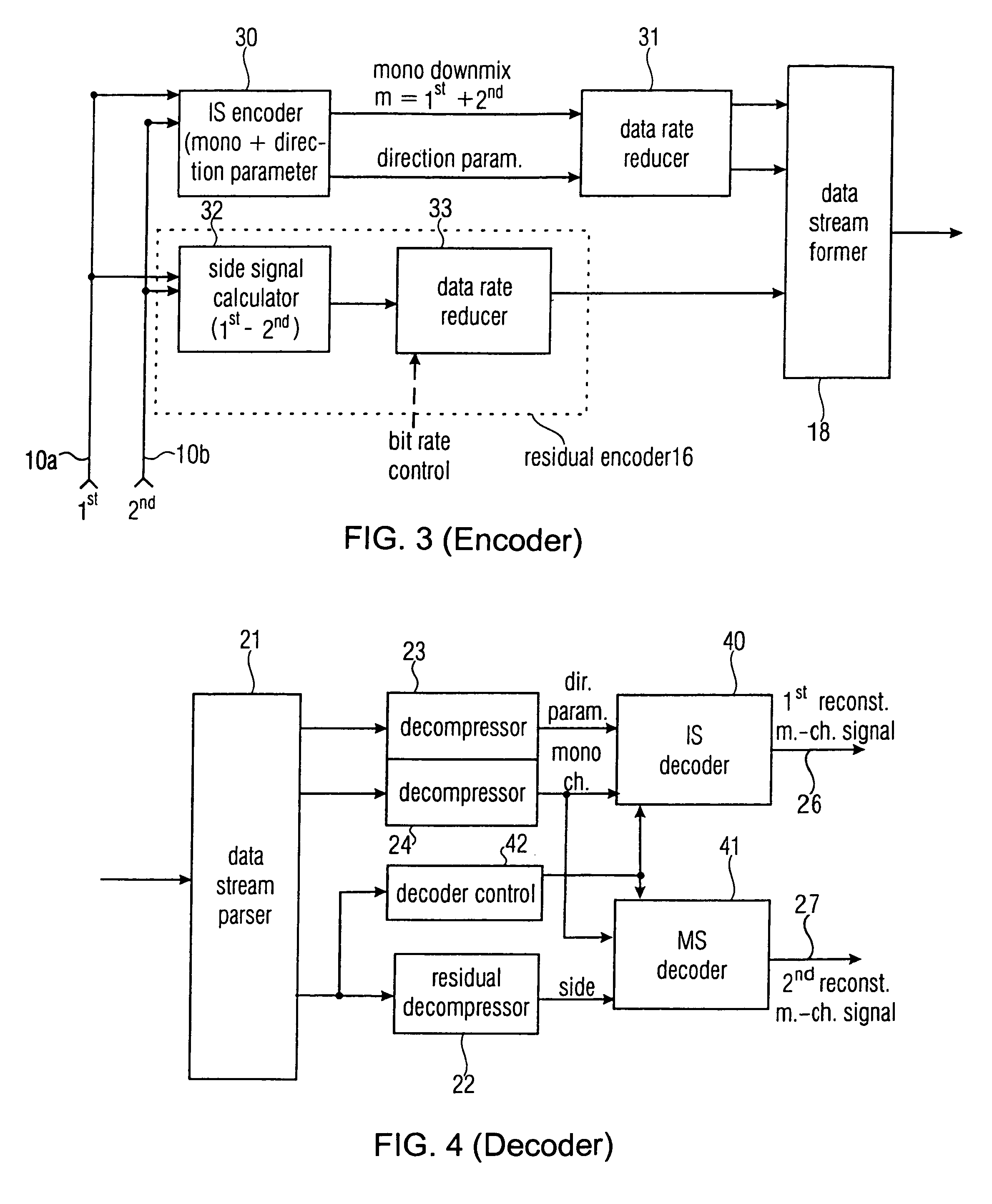
Near-transparent or transparent multi-channel encoder/decoder scheme
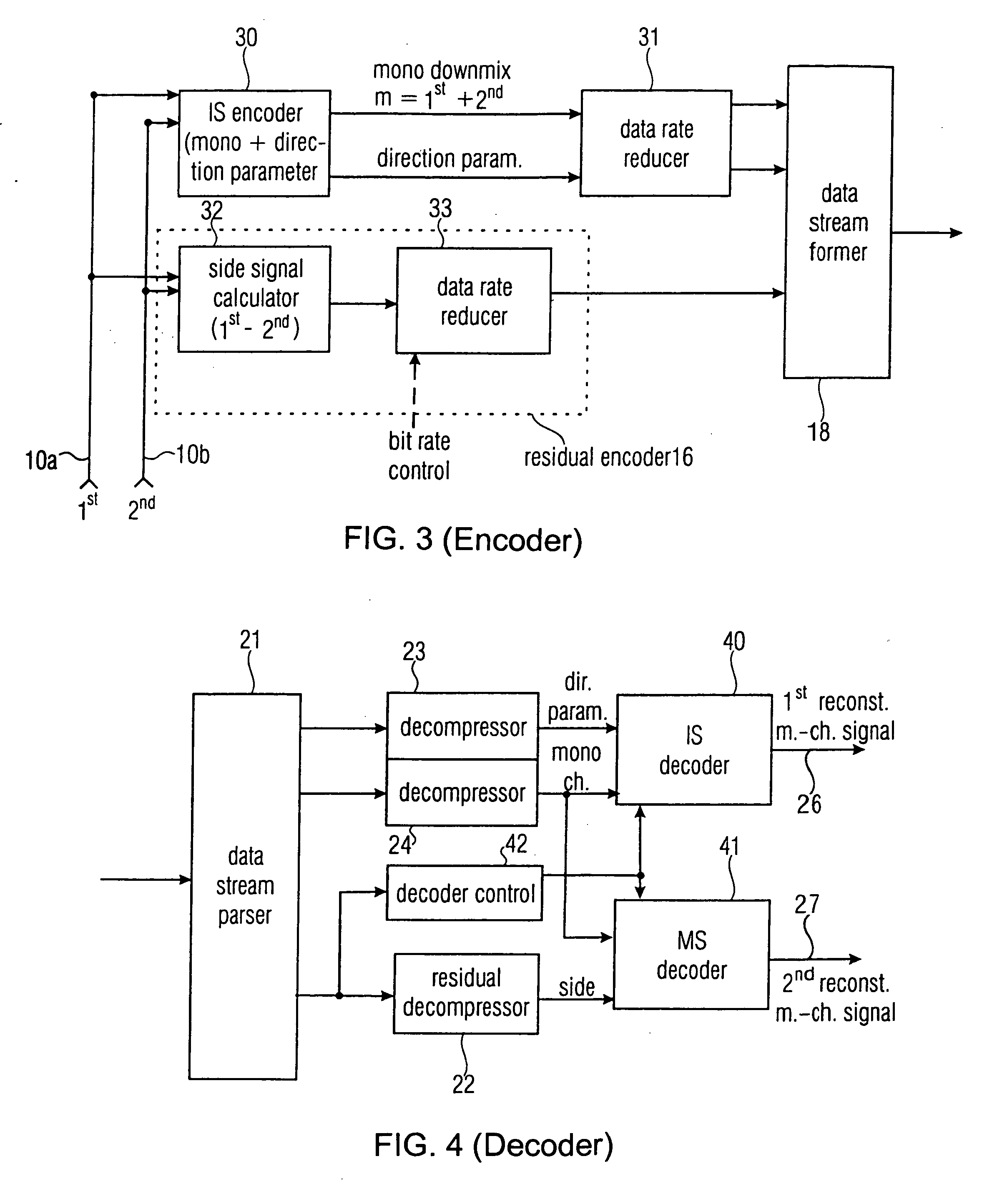
ActiveUS20060190247A1Quality improvementReduce bitrateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel decoderComputer science
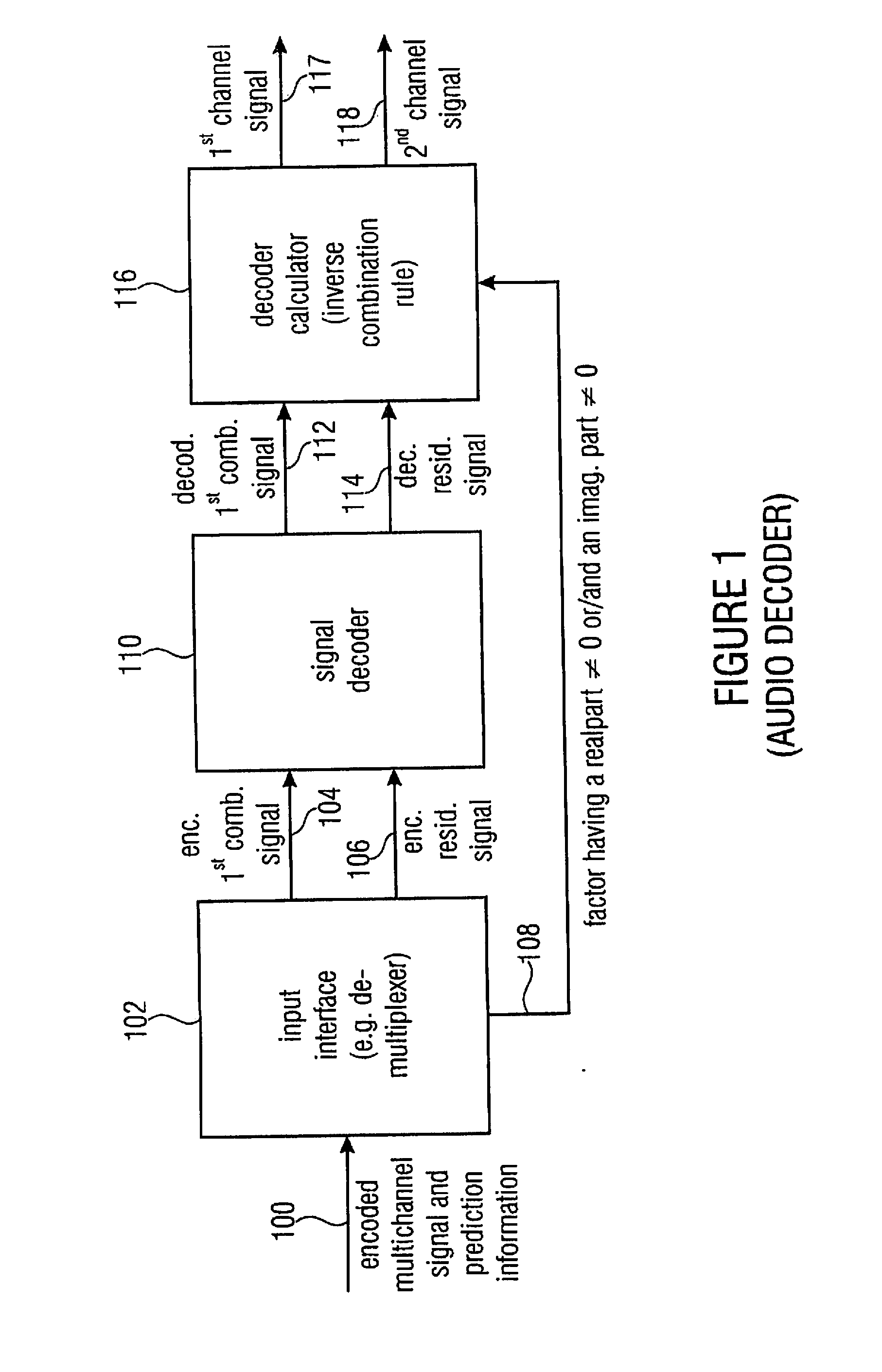
A multi-channel encoder / decoder scheme additionally preferably generates a waveform-type residual signal. This residual signal is transmitted together with one or more multi-channel parameters to a decoder. In contrast to a purely parametric multi-channel decoder, the enhanced decoder generates a multi-channel output signal having an improved output quality because of the additional residual signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
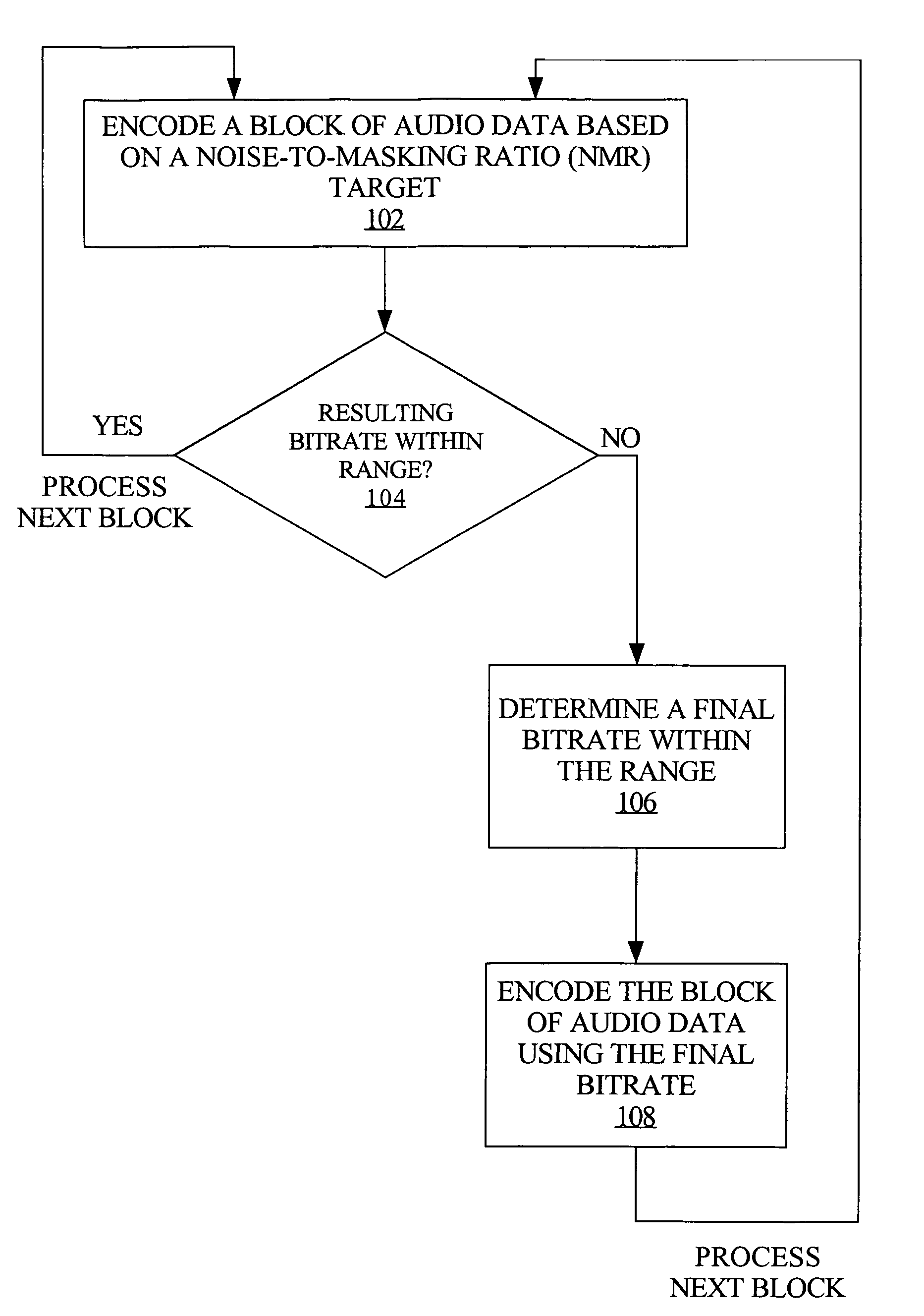
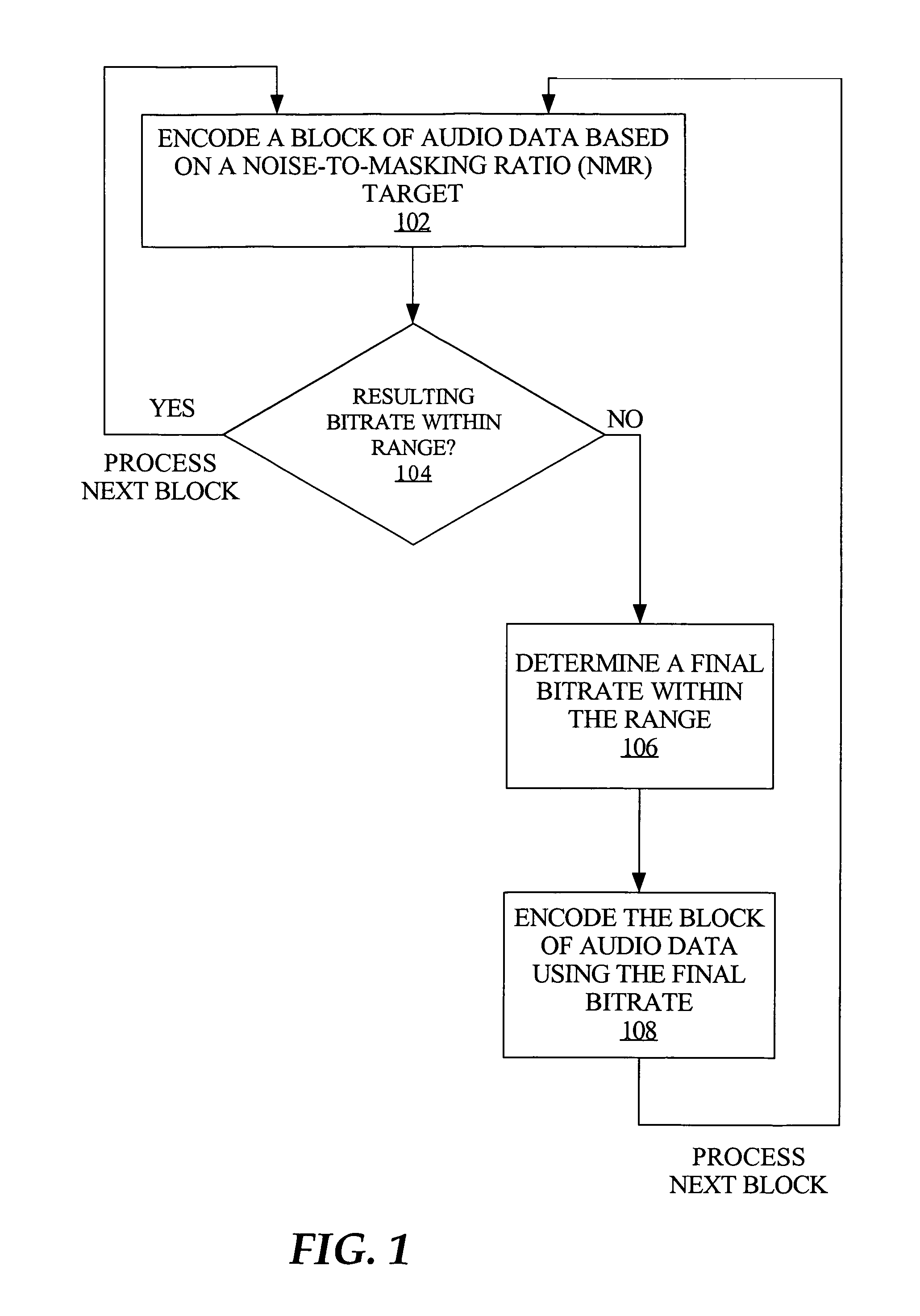
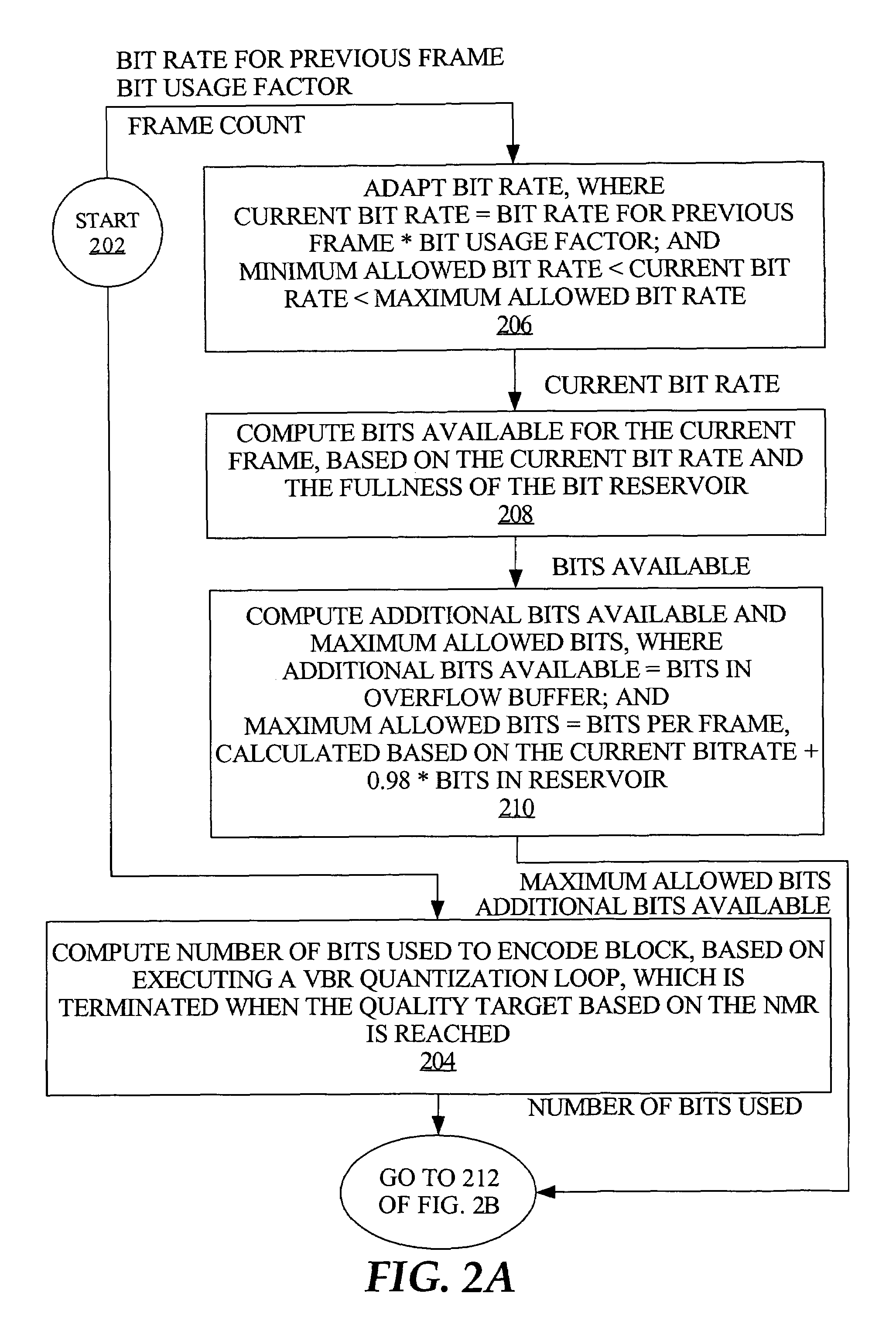
Bitrate constrained variable bitrate audio encoding
ActiveUS7634413B1Excessively high bitratesImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisCoding blockSound quality
A hybrid audio encoding technique incorporates both ABR, or CBR, and VBR encoding modes. For each audio coding block, after a VBR quantization loop meets the NMR target, a second quantization loop might be called to adaptively control the final bitrate. That is, if the NMR-based quantization loop results in a bitrate that is not within a specified range, then a bitrate-based CBR or ABR quantization loop determines a final bitrate that is within the range and is adaptively determined based on the encoding difficulty of the audio data. Excessive bitrates from use of conventional VBR mode are eliminated, while still providing much more constant perceptual sound quality than use of conventional CBR mode can achieve.
Owner:APPLE INC
Personal media broadcasting system
ActiveUS20060095471A1Improve experienceReduce bitratePulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast-related systemsClient-sideDigitization
A personal media broadcasting system enables video distribution over a computer network and allows a user to view and control media sources over a computer network from a remote location. A personal broadcaster receives an input from one or more types of media sources, digitizes and compresses the content, and streams the compressed media over a computer network to a media player running on any of a wide range of client devices for viewing the media. The system may allow the user to issue control commands (e.g., “channel up”) from the media player to the broadcaster, causing the source device to execute the commands. The broadcaster and the media player may employ several techniques for buffering, transmitting, and viewing the content to improve the user's experience.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
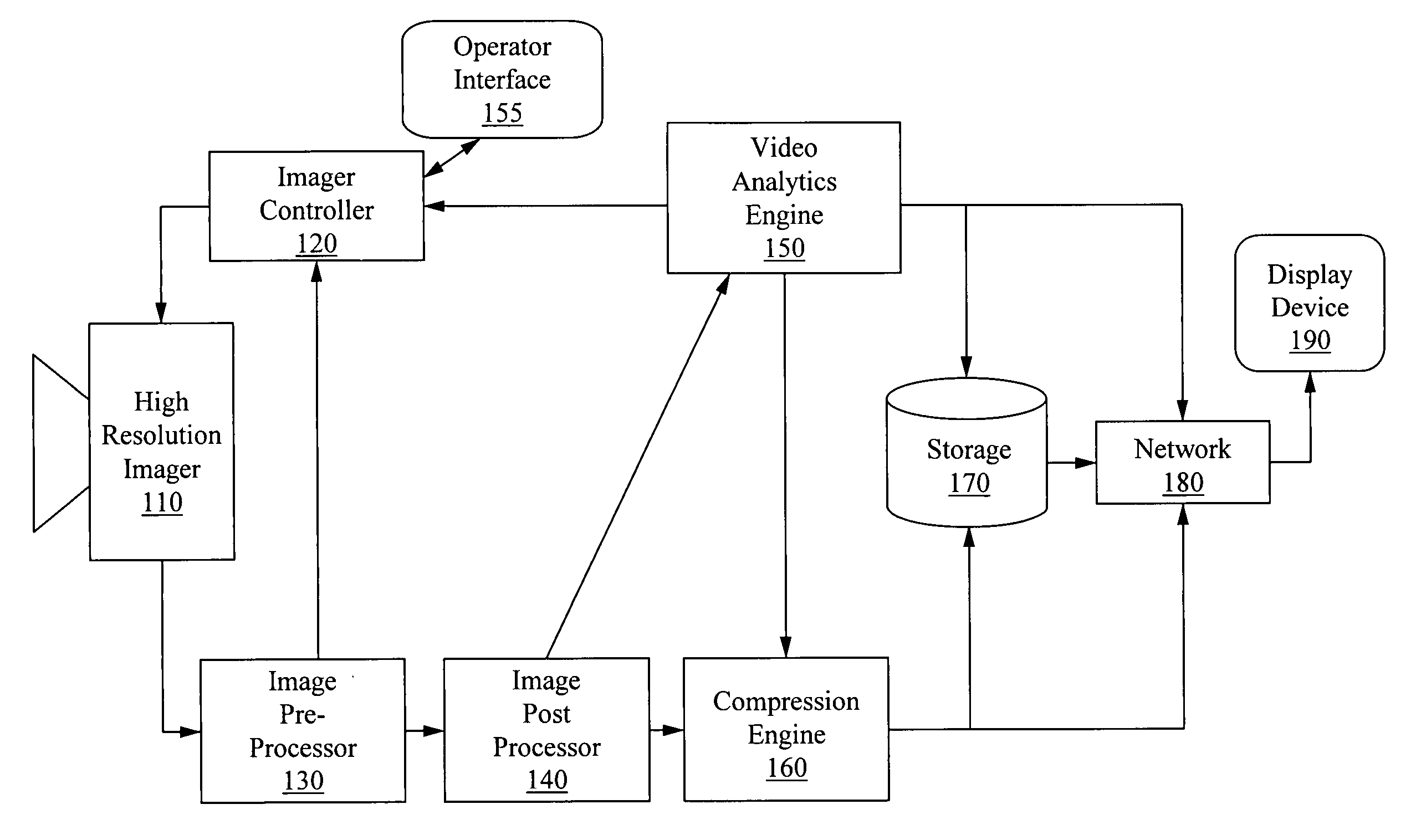
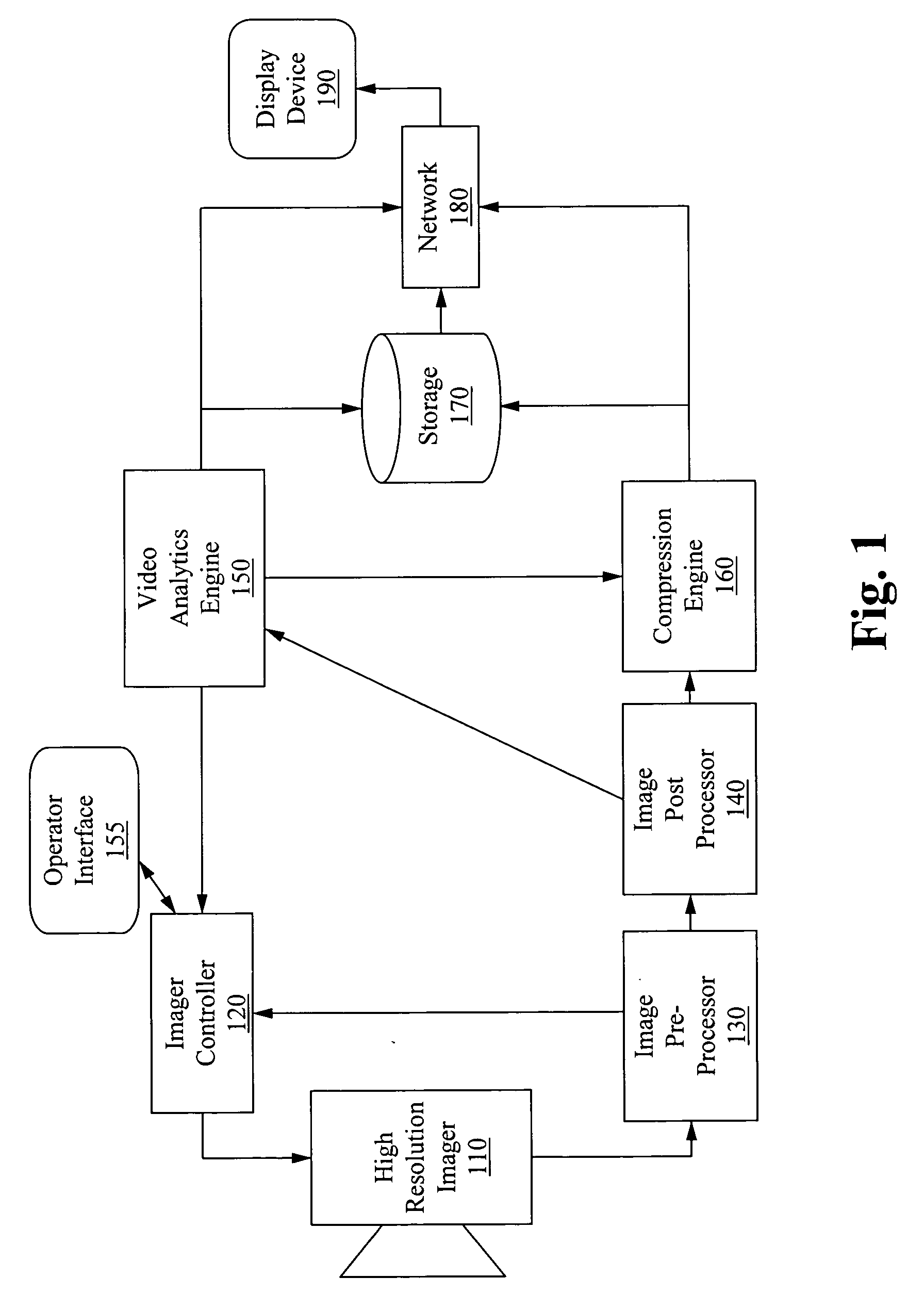
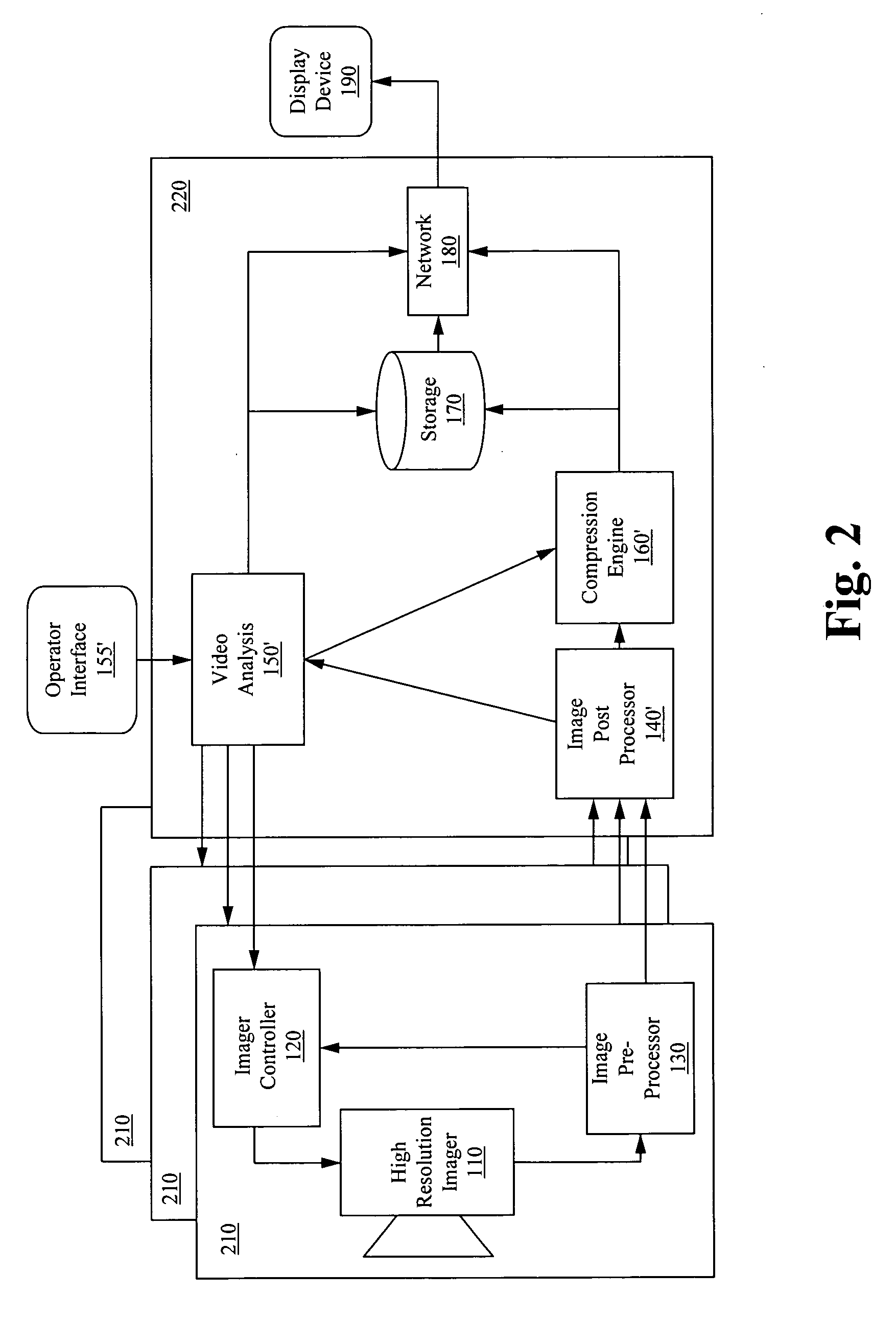
Apparatus for image capture with automatic and manual field of interest processing with a multi-resolution camera
InactiveUS20080129844A1Resolution and frame rate and clarityHigh compression levelTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRegion of interestDistinctness of image
An apparatus for capturing a video image comprising a means for generating a digital video image, a means for classifying the digital video image into one or more regions of interest and a background image, and a means for encoding the digital video image, wherein the encoding is selected to provide at least one of; enhancement of the image clarity of the one or more ROI relative to the background image encoding, and decreasing the video quality of the background image relative to the one or more ROI. A feedback loop is formed by the means for classifying the digital video image using a previous video image to generate a new ROI and thus allow for tracking of targets as they move through the imager field-of-view.
Owner:AGILENCE
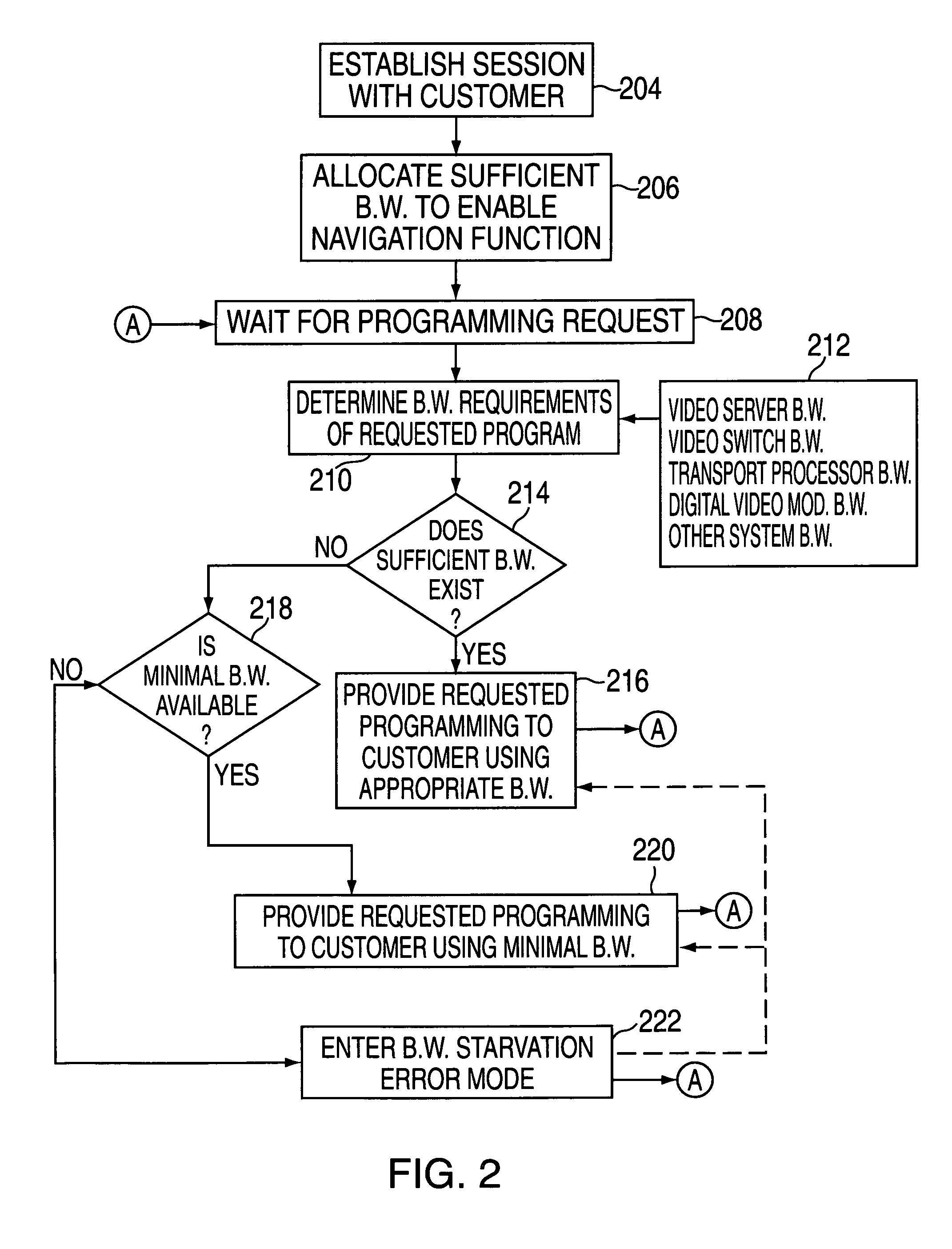
Service rate change method and apparatus
InactiveUS7086077B2Reduce bitrateMinimally acceptable qualityTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionDistribution systemTelecommunications
A method and apparatus for allocating bandwidth within a bandwidth constrained interactive information distribution system. The system determined if a requested information stream may be provided to a requesting subscriber at an appropriate bandwidth level (i.e., appropriate bitrate providing full quality), a minimal bandwidth level (i.e., a reduced bitrate providing minimally acceptable quality) or not at all. Each information stream and any ancillary streams may be stored twice by the system, once at an appropriate encoded bitrate and once at a minimal encoded bitrate.
Owner:COX COMMUNICATIONS +1
Method and apparatus for scalable motion vector coding
InactiveUS20060193388A1Improve visual qualityReduce resolutionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorComputer science
A method and apparatus for scalable coding of a motion vector generated during motion estimation, in which a generated motion vector field is separated into a base layer and an enhancement layer according to pixel accuracies to obtain a layered structure for a motion vector. In addition, the motion vector field has a layered structure including a base layer composed of motion vectors of blocks larger than or equal to a predetermined size and at least one enhancement layer composed of motion vectors of blocks smaller than a predetermined size.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
System And Method For Improved View Layout Management In Scalable Video And Audio Communication Systems
ActiveUS20100002069A1Reduce bitratePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningCommunications systemAudio frequency
A system and method for transmitting a plurality of video signals scalably coded into layers including a base layer and one or more enhancement layers and associated audio signals, if any, over a communication network for presentation to one or more end users. A layout to display the plurality of video signals is determined based on a set of criteria and only the data of the video signal layers that are necessary for displaying the video signals in the determined layout, and any associated audio signals, is selectively transmitted over the communication network.
Owner:VIDYO
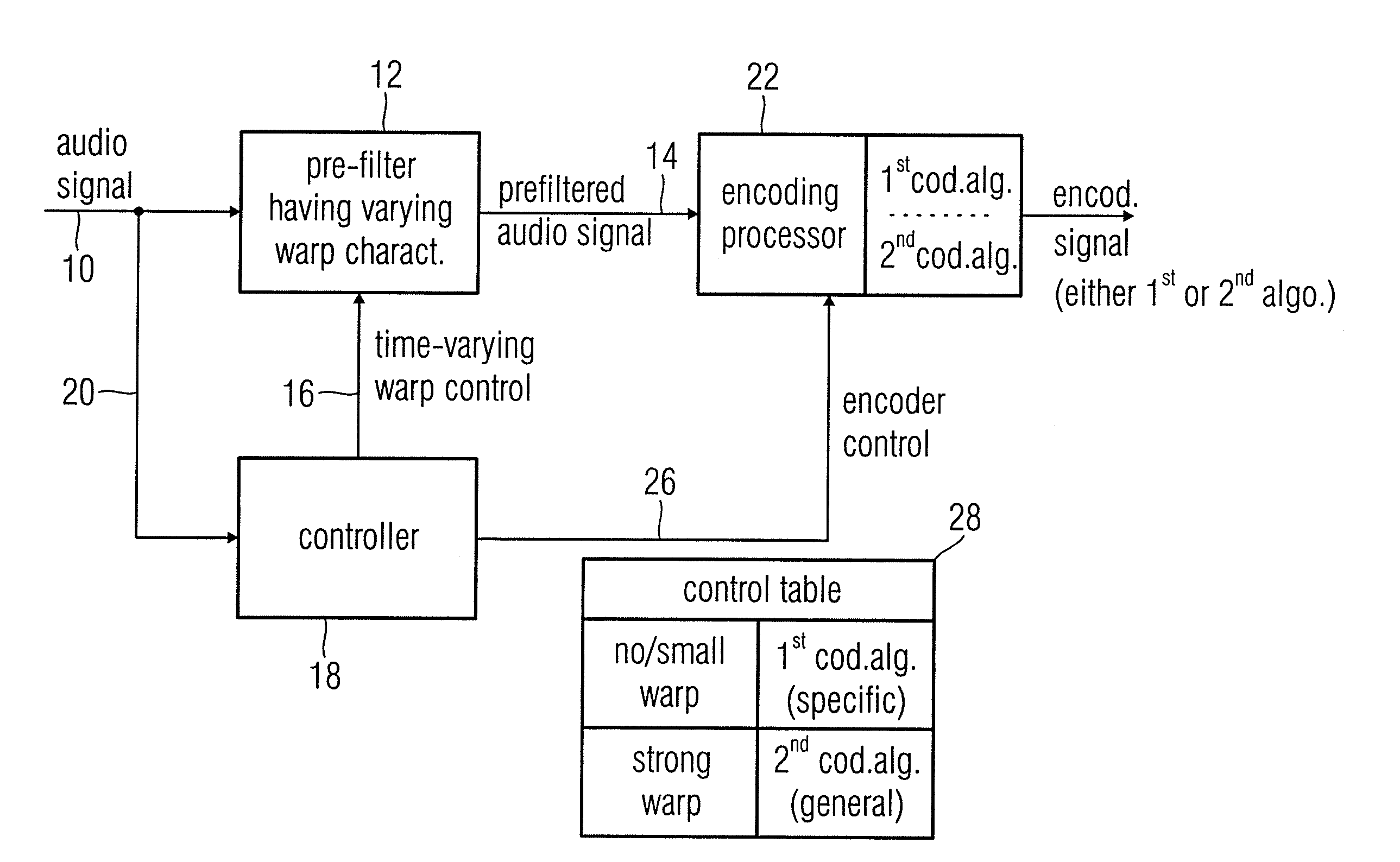
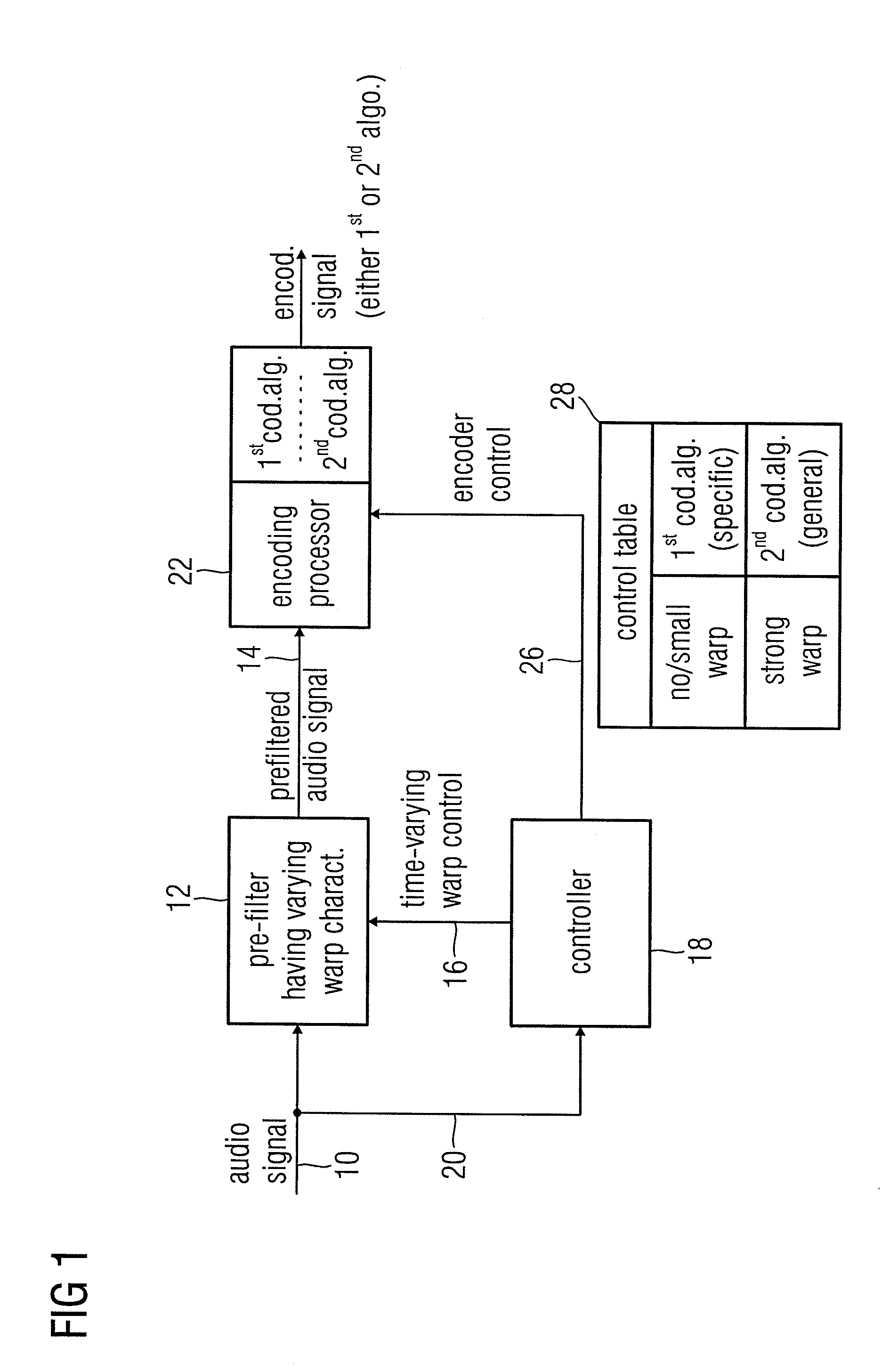
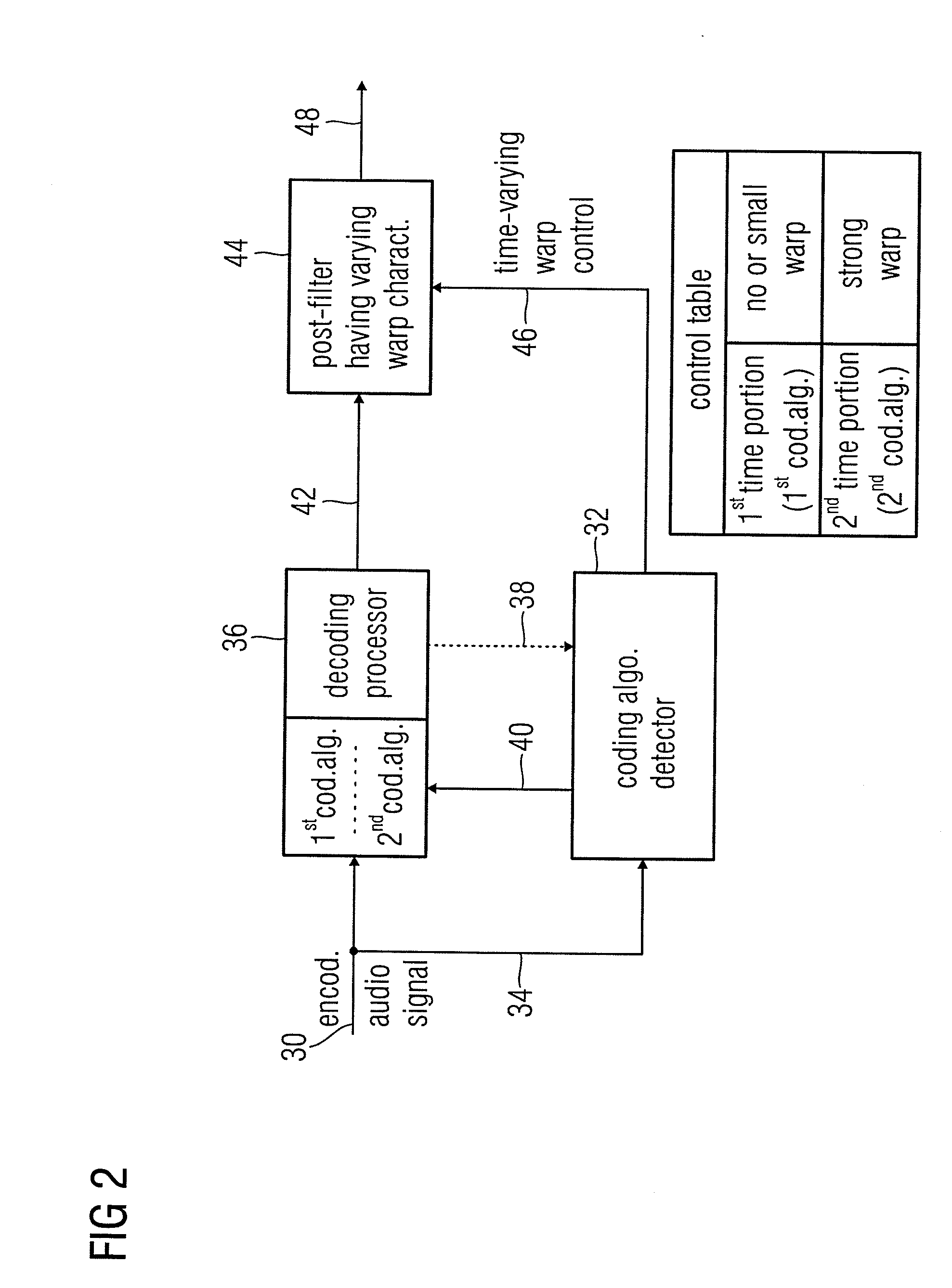
Audio Encoder, Audio Decoder and Audio Processor Having a Dynamically Variable Warping Characteristic
ActiveUS20080004869A1High audio qualityStrong characteristicSpeech analysisSpeech recognitionAudio signal
An audio encoder, an audio decoder or an audio processor includes a filter for generating a filtered audio signal, the filter having a variable warping characteristic, the characteristic being controllable in response to a time-varying control signal, the control signal indicating a small or no warping characteristic or a comparatively high warping characteristic. Furthermore, a controller is connected for providing the time-varying control signal, which depends on the audio signal. The filtered audio signal can be introduced to an encoding processor having different encoding algorithms, one of which is a coding algorithm adapted to a specific signal pattern. Alternatively, the filter is a post-filter receiving a decoded audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Fast-start streaming and buffering of streaming content for personal media player
ActiveUS7647614B2Improve experienceReduce bitratePulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast-related systemsClient-sideComputer science
A personal media broadcasting system enables video distribution over a computer network and allows a user to view and control media sources over a computer network from a remote location. A personal broadcaster receives an input from one or more types of media sources, digitizes and compresses the content, and streams the compressed media over a computer network to a media player running on any of a wide range of client devices for viewing the media. The system may allow the user to issue control commands (e.g., “channel up”) from the media player to the broadcaster, causing the source device to execute the commands. The broadcaster and the media player may employ several techniques for buffering, transmitting, and viewing the content to improve the user's experience.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
Apparatus and methods for multichannel digital audio coding
ActiveUS20060074642A1Low bit-rate codingSame level of compressionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionVocal tract
A low bit rate digital audio coding system includes an encoder which assigns codebooks to groups of quantization indexes based on their local properties resulting in codebook application ranges that are independent of block quantization boundaries. The invention also incorporates a resolution filter bank, or a tri-mode resolution filter bank, which is selectively switchable between high and low frequency resolution modes or high, low and intermediate modes such as when detecting transient in a frame. The result is a multichannel audio signal having a significantly lower bit rate for efficient transmission or storage. The decoder is essentially an inverse of the structure and methods of the encoder, and results in a reproduced audio signal that cannot be audibly distinguished from the original signal.
Owner:DIGITAL RISE TECH CO LTD
Adaptive transmission rate and fragmentation threshold mechanism for local area networks
ActiveUS7388903B2Reduce the possibilityError rateEnergy efficient ICTError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTelecommunicationsWireless transceiver
An apparatus for adjusting the transmission bit rate and fragmentation threshold of a wireless station in response to transmission errors is disclosed. In particular, the illustrative embodiment of the present invention is based on a wireless station that employs both an IEEE 802.11 radio and a Bluetooth radio, and determines whether transmission errors of the IEEE 802.11 radio are due to fading, or interference from the Bluetooth radio. It will be clear to those skilled in the art how to make and use alternative embodiments of the present invention for protocols other than IEEE 802.11 and Bluetooth, as well as stations that employ wireline or non-RF-wireless transceivers.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Tunneled datagram switching
InactiveUS7136377B1Improve scalabilityCall control can be simplifiedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationState dependentReal-time data
A method for transporting real-time data such as voice over a packet-based infrastructure, and a switch for use with that method, are disclosed. In this method, datagrams from multiple data streams are packaged in a single tunnel packet for transport across a network to an intermediate switching point (switch). To reduce bandwidth, each datagram in the tunnel packet (e.g., tunneled datagram) can be sent in a compressed-header format identified by a context identifier (CID) for its data stream. The switch saves context state for each tunnel and CID it is receiving packets for. The switch deaggregates received tunnel packets into tunneled datagrams and associates each datagram with its context state. Based on the destination indicated in its context state, each datagram it re-aggregated in an outgoing tunnel packet bound for a next switch or the destination endpoint itself.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
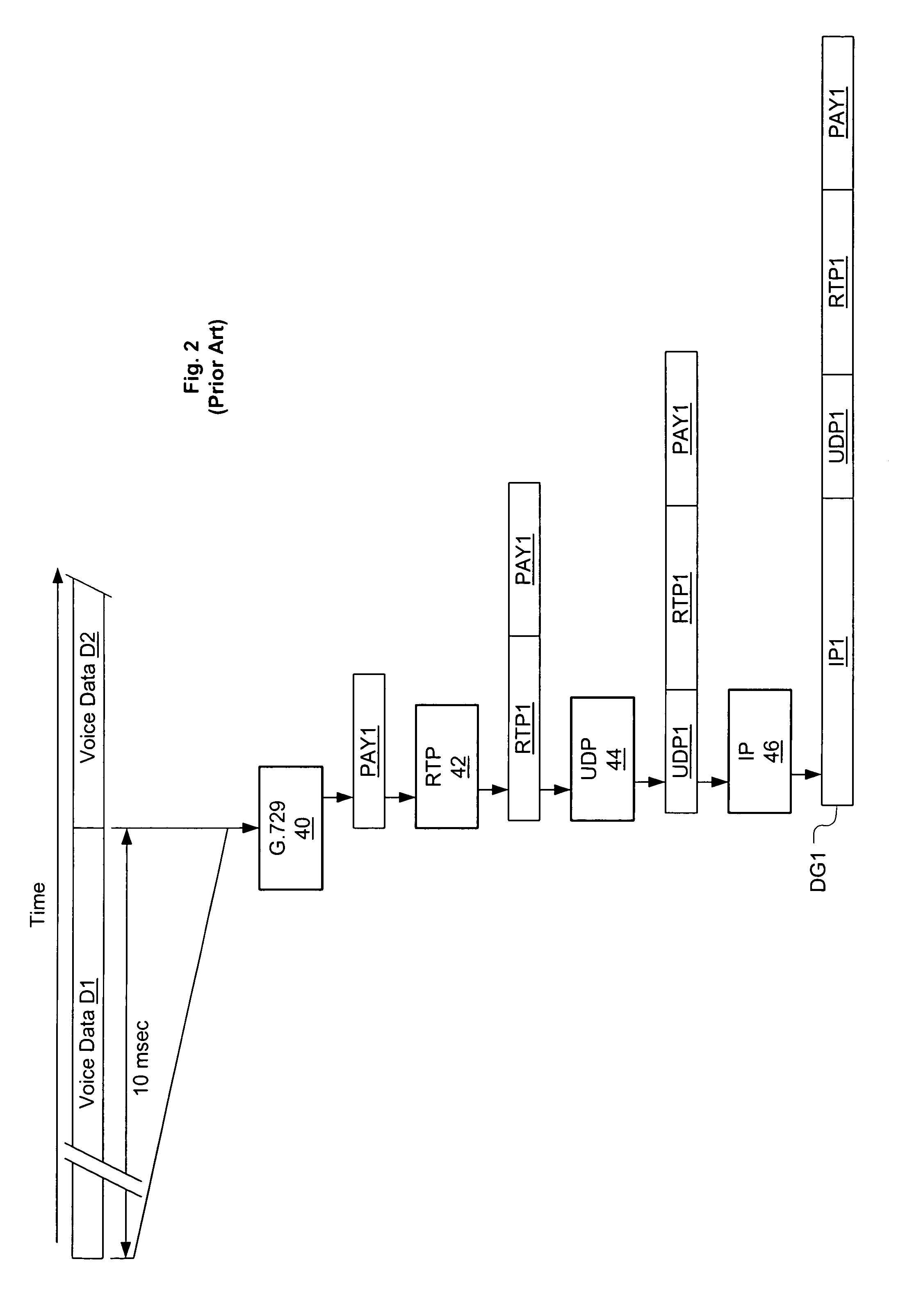
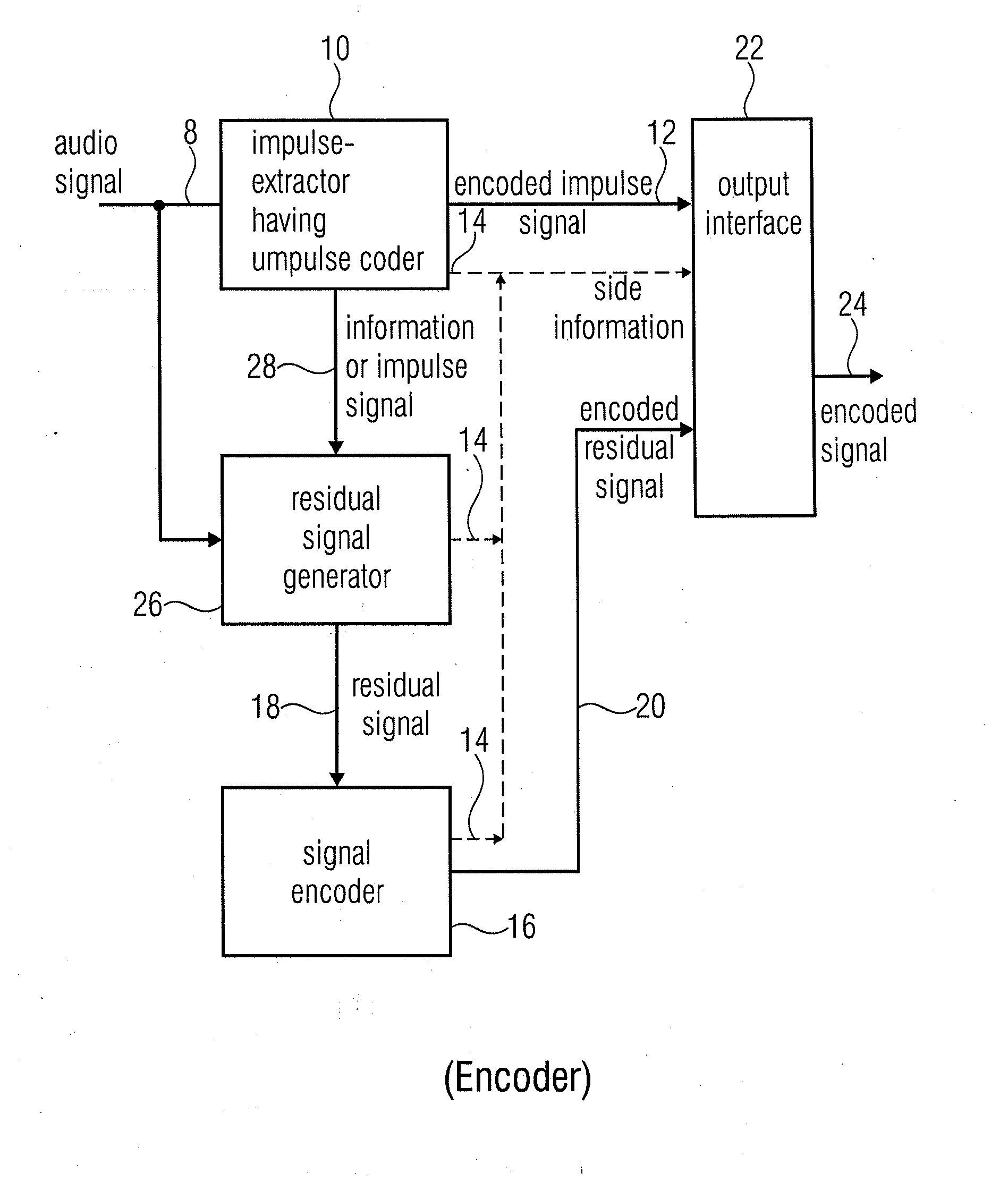
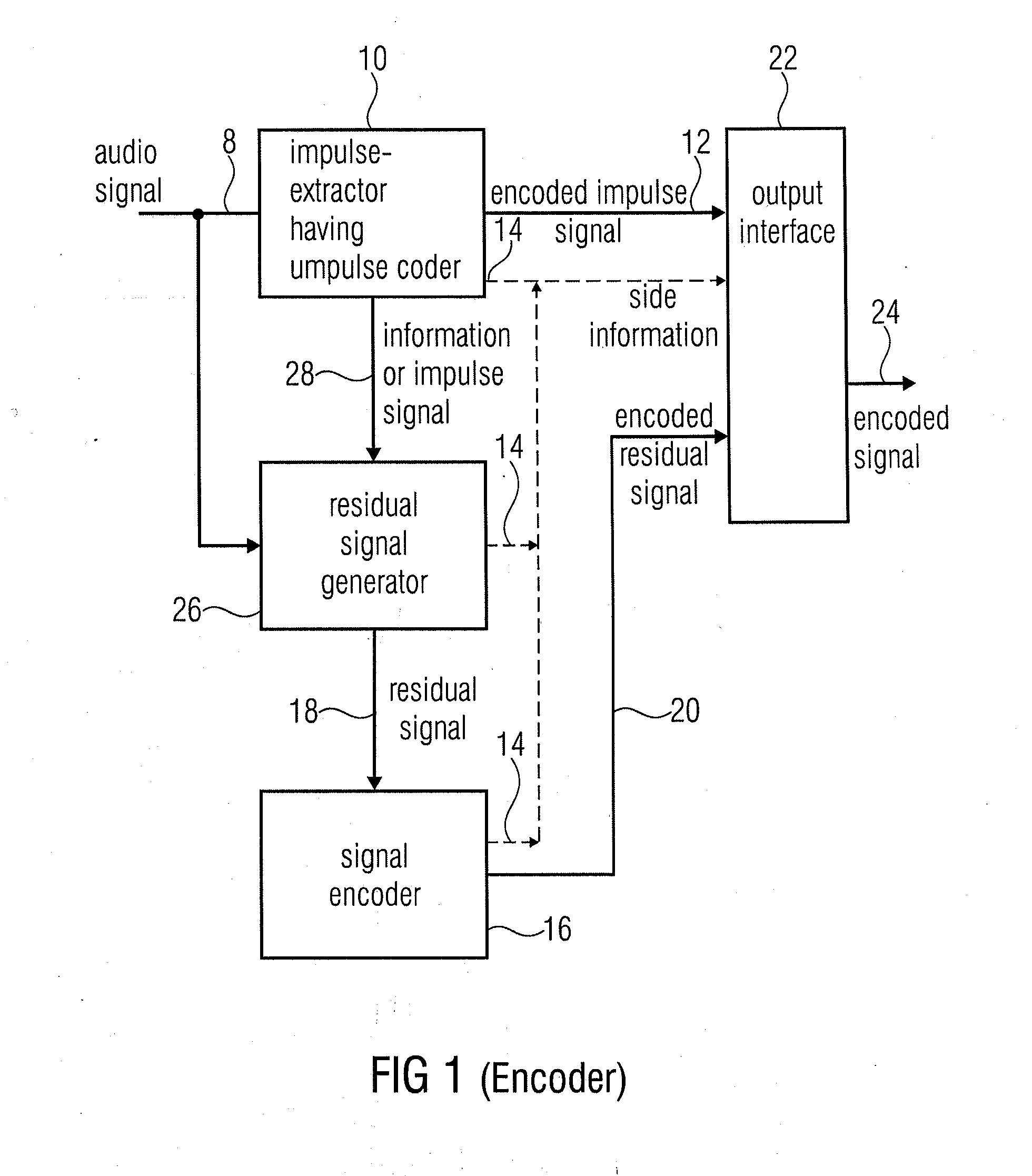
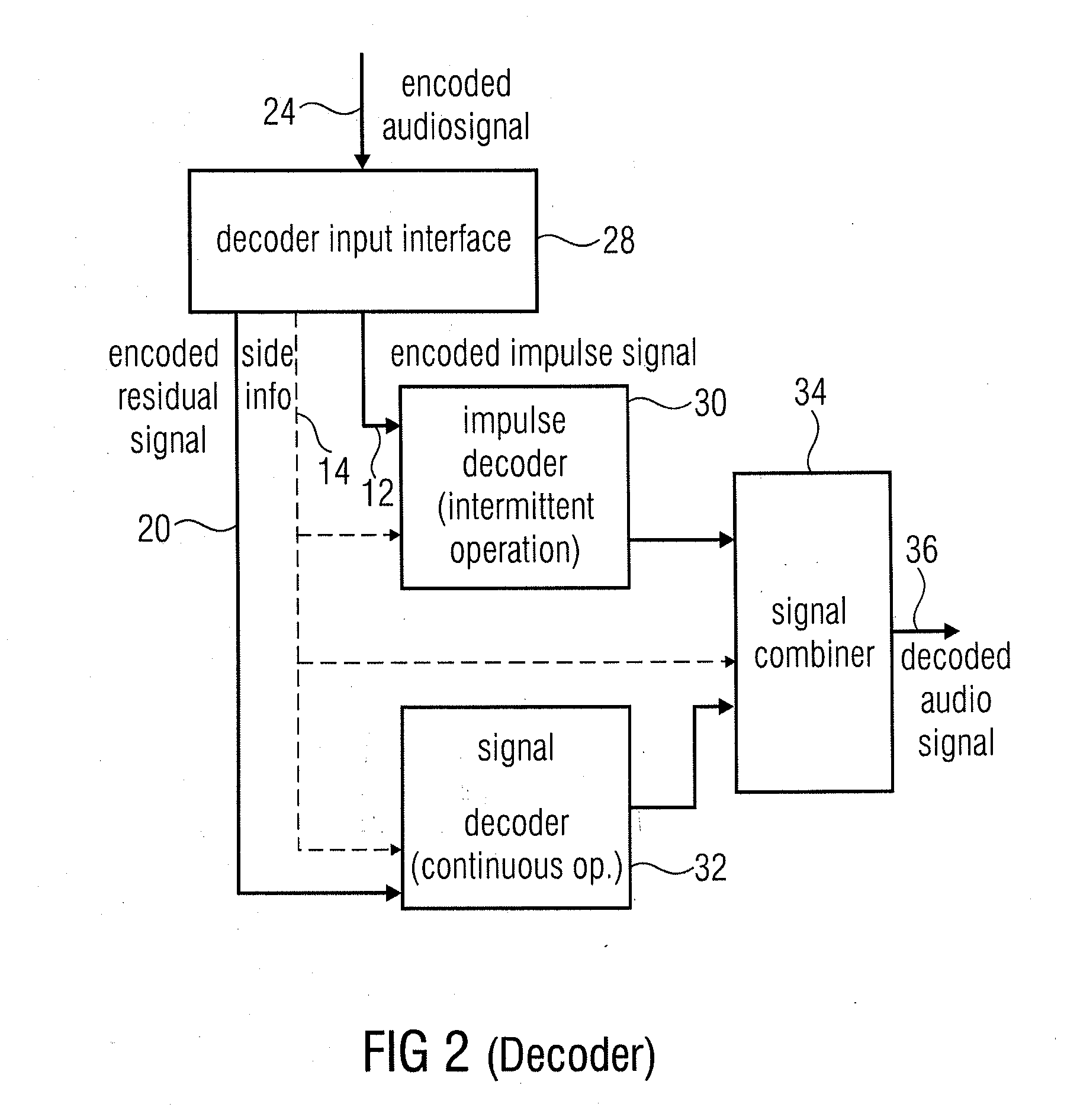
Audio encoder for encoding an audio signal having an impulse-like portion and stationary portion, encoding methods, decoder, decoding method, and encoding audio signal
ActiveUS20100262420A1Reduce data rateImprove efficiencySpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsAudio signal flow
An audio encoder for encoding an audio signal includes an impulse extractor for extracting an impulse-like portion from the audio signal. This impulse-like portion is encoded and forwarded to an output interface. Furthermore, the audio encoder includes a signal encoder which encodes a residual signal derived from the original audio signal so that the impulse-like portion is reduced or eliminated in the residual audio signal. The output interface forwards both, the encoded signals, i.e., the encoded impulse signal and the encoded residual signal for transmission or storage. On the decoder-side, both signal portions are separately decoded and then combined to obtain a decoded audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Wireless video camera and connection methods including multiple video streams
ActiveUS20140043485A1Reduce bitrateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl signalWireless video
Systems and methods for streaming video and / or audio from multiple devices are provided. A camera may include an optical sensor, a wireless communication device, and a processor configured to establish a first connection with a remote location, establish a second connection with one or more other cameras, and stream video from the cameras to the remote location. The remote location may be, for example, a remote website, a remote server, or a remote client device. The camera may be further configured to provide control signals to the other cameras, such as for controlling applications running on the other cameras.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
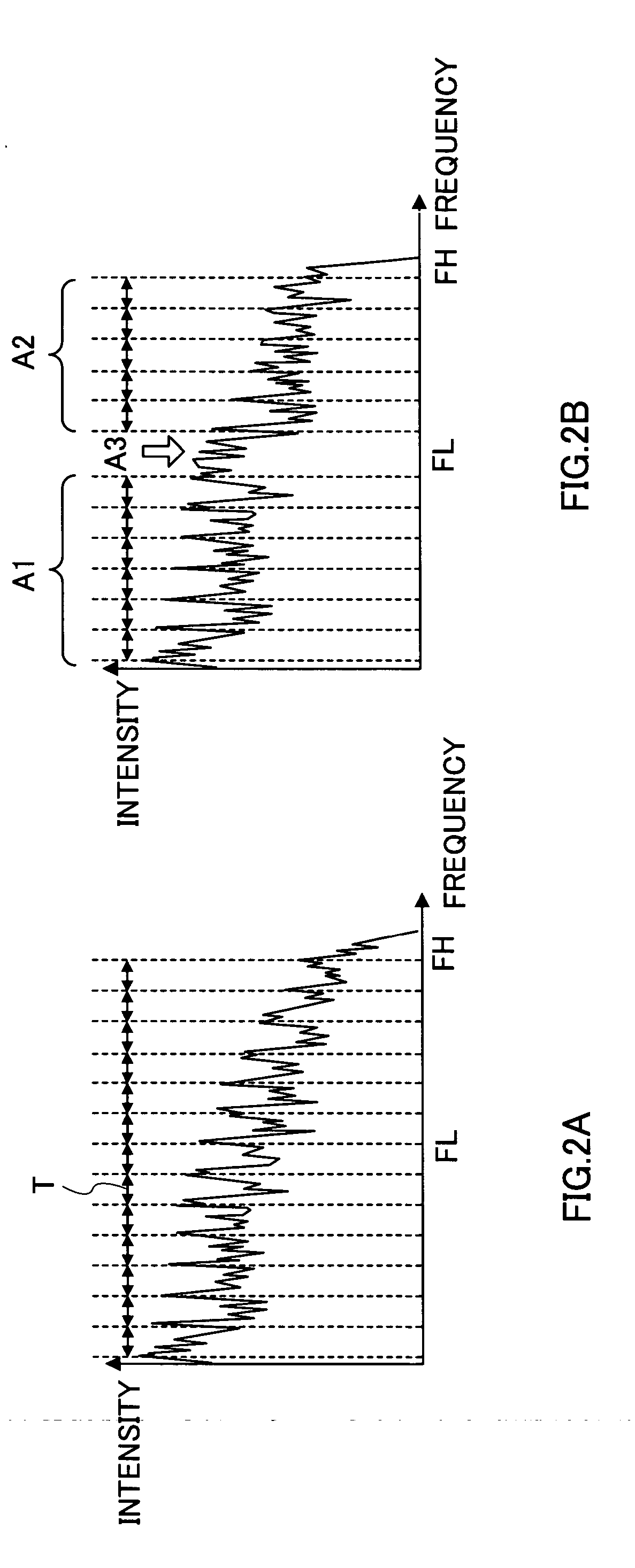
Coding device, decoding device, coding method, and decoding method
ActiveUS20050163323A1High-quality codingLow bit rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSubtractorComputer science
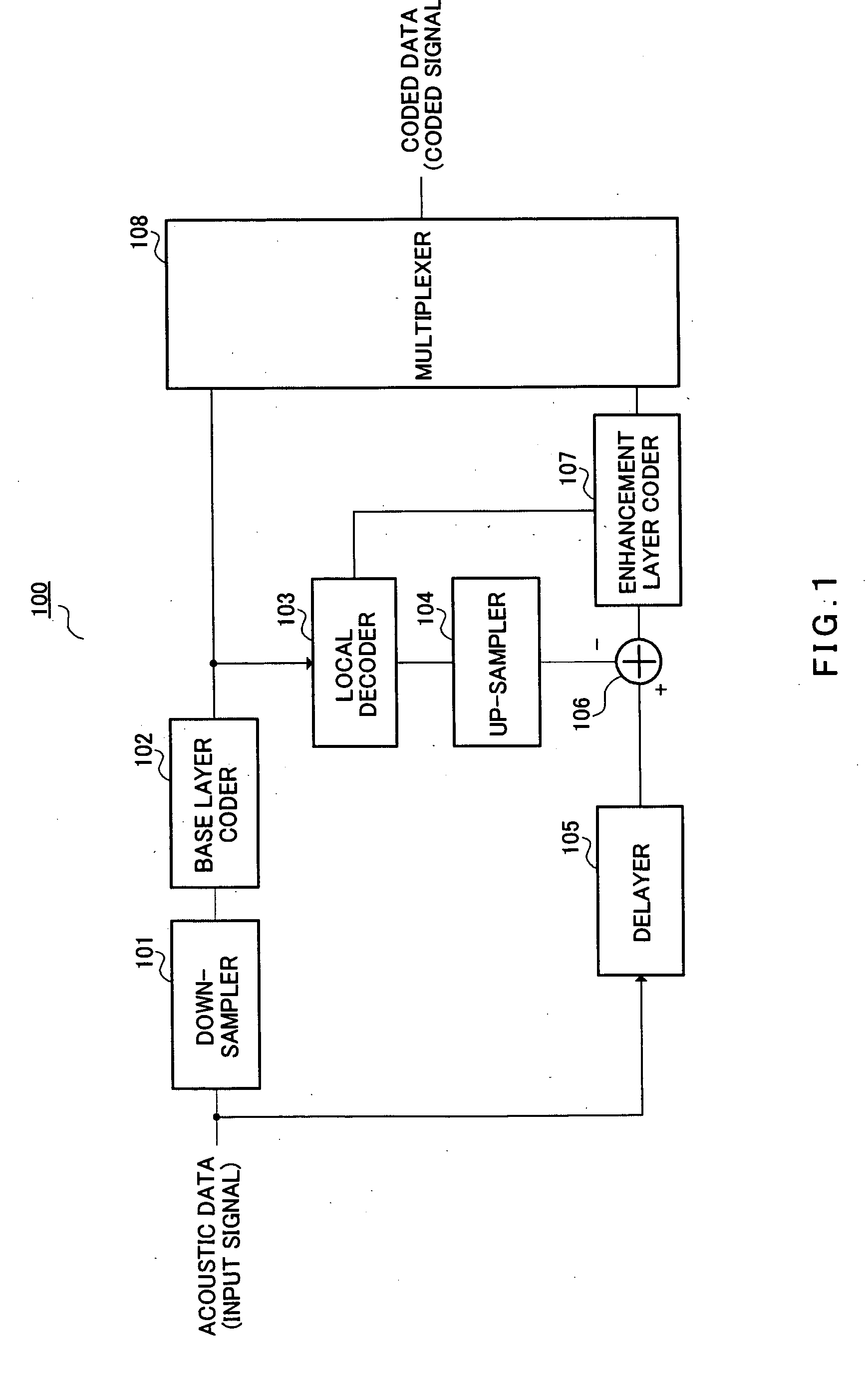
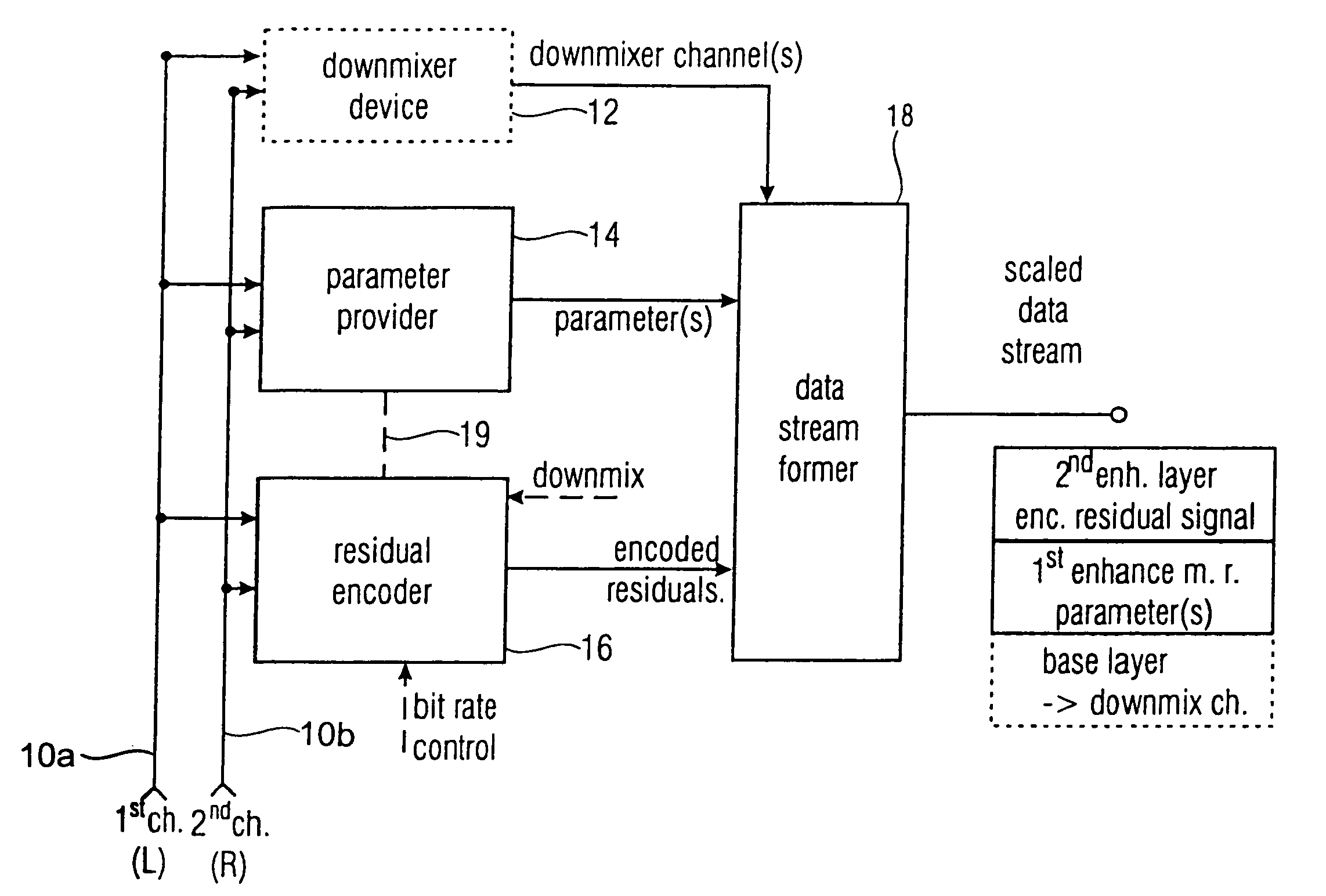
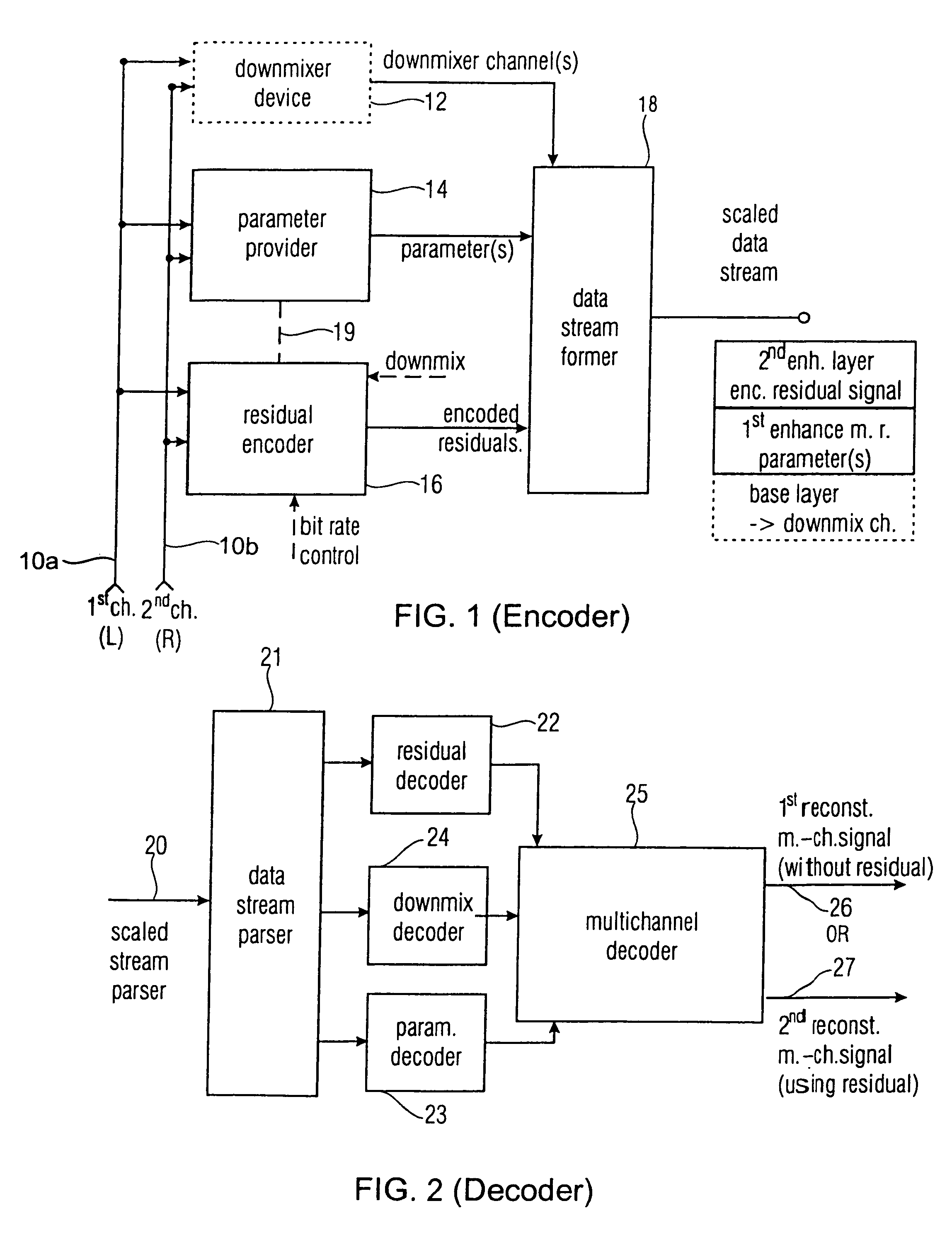
A down-sampler 101 down-samples the sampling rate of an input signal from sampling rate FH to sampling rate FL. A base layer coder 102 encodes the sampling rate FL acoustic signal. A local decoder 103 decodes coding information output from base layer coder 102. An up-sampler 104 raises the sampling rate of the decoded signal to FH. A subtracter 106 subtracts the decoded signal from the sampling rate FH acoustic signal. An enhancement layer coder 107 encodes the signal output from subtracter 106 using a decoding result parameter output from local decoder 103.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
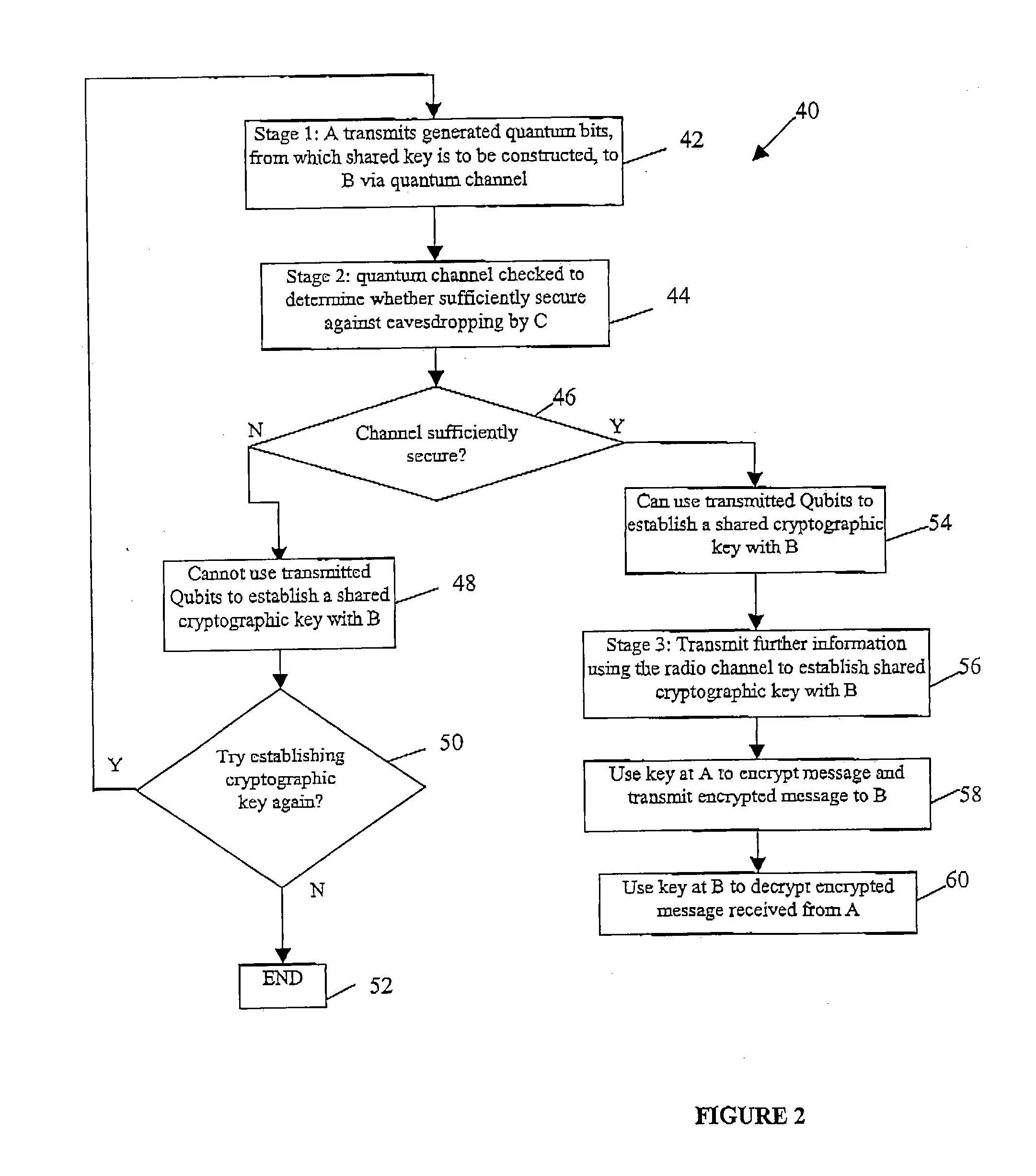
Quantum cryptography
ActiveUS20050036624A1Reduce bitrateIncrease bitrateKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum channelHilbert space
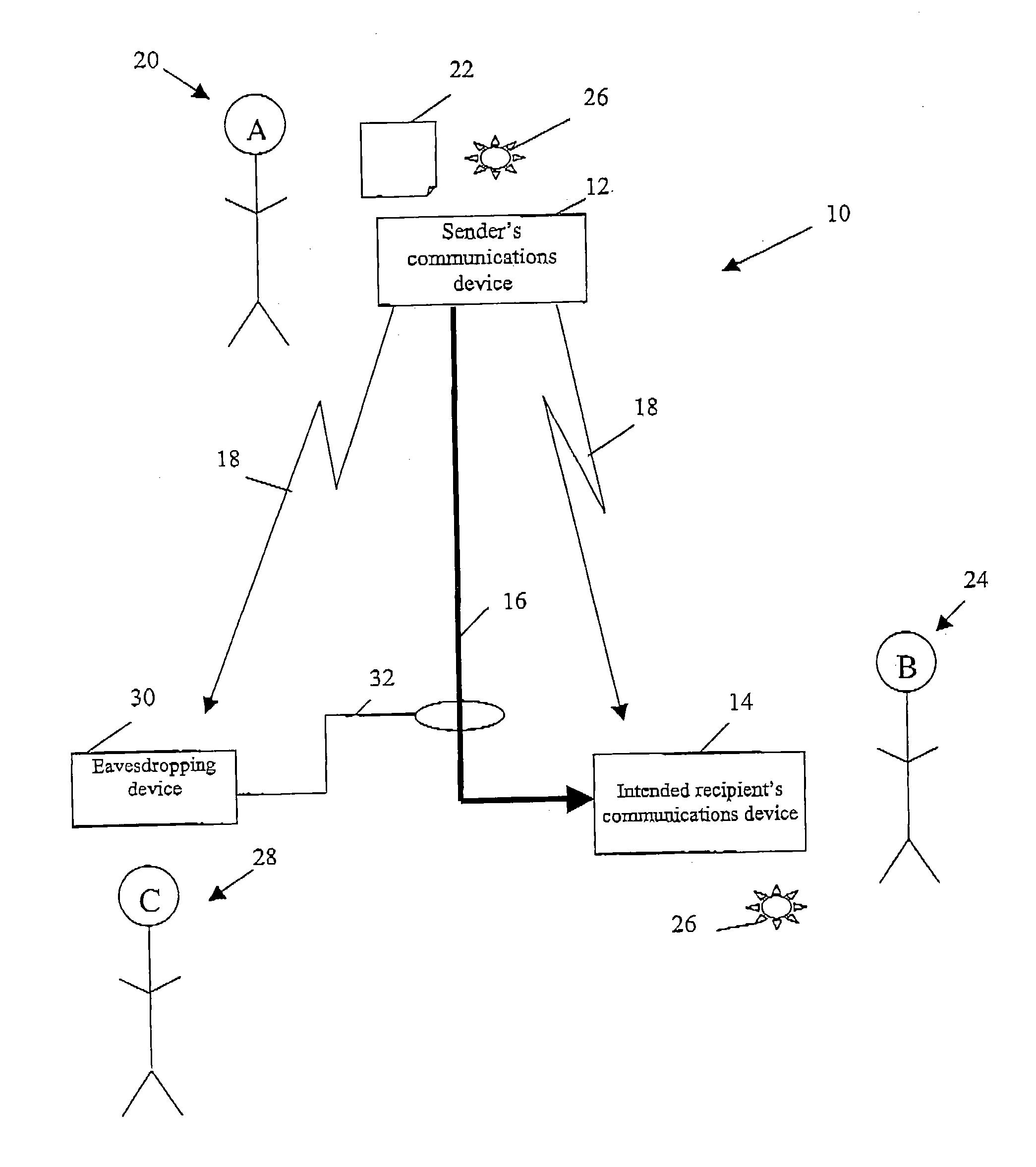
A method of establishing a shared secret random cryptographic key between a sender and a recipient using a quantum communications channel is described. The method comprises: generating a plurality of random quantum states of a quantum entity, each random state being defined by a randomly selected one of a first plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting the plurality of random quantum states of the quantum entity via the quantum channel to a recipient, measuring the quantum state of each of the received quantum states of the quantum entity with respect to a randomly selected one of a second plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting to the recipient composition information describing a subset of the plurality of random quantum states, analysing the received composition information and the measured quantum states corresponding to the subset to derive a first statistical distribution describing the subset of transmitted quantum states and a second statistical distribution describing the corresponding measured quantum states, establishing the level of confidence in the validity of the plurality of transmitted random quantum states by verifying that the first and second statistical distributions are sufficiently similar, deriving a first binary sting and a second binary string, correlated to the first binary string, respectively from the transmitted and received plurality of quantum states not in the subset, and carrying out a reconciliation of the second binary string to the first binary string by using error correction techniques to establish the shared secret random cryptographic key from the first and second binary strings.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
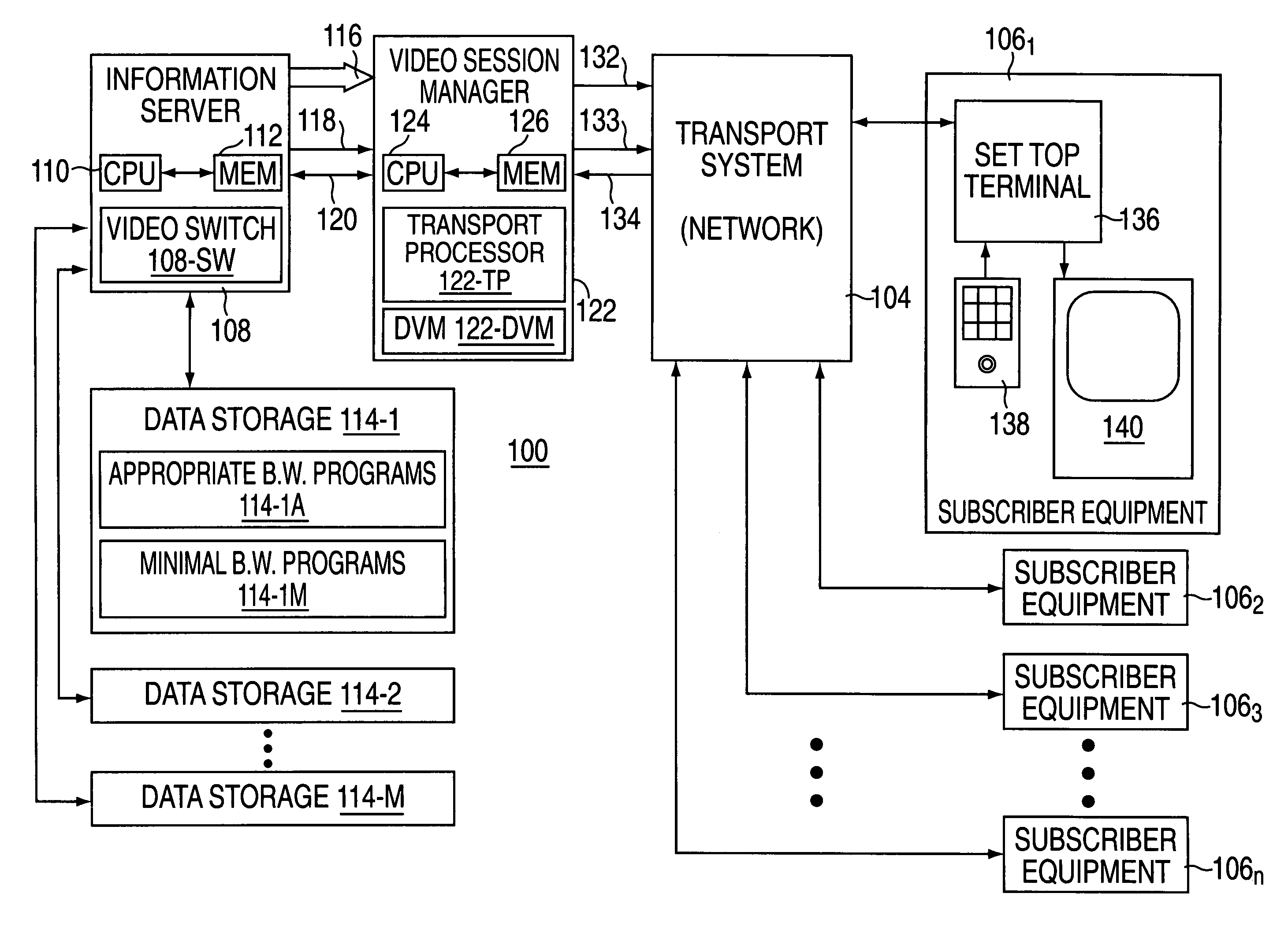
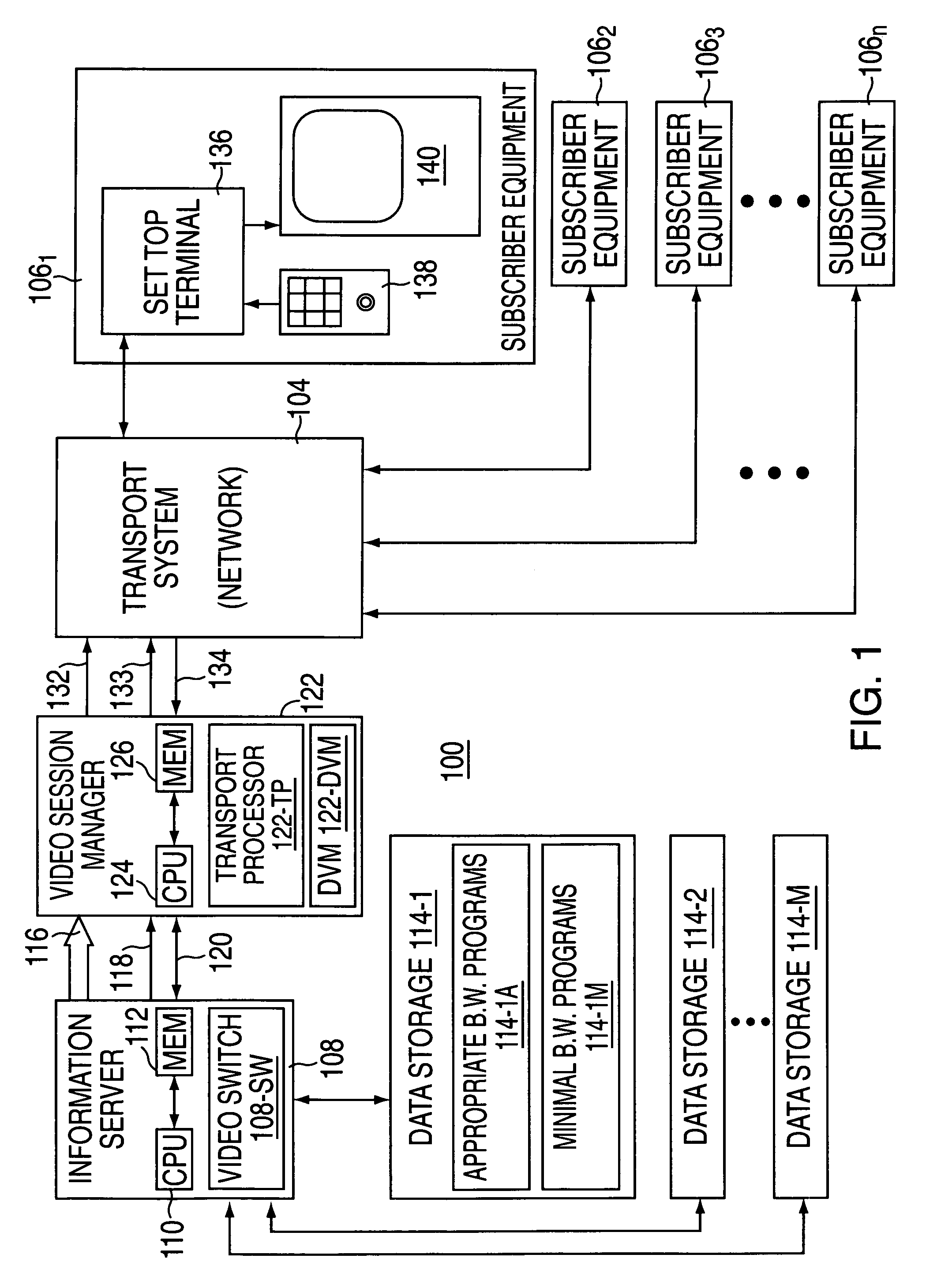
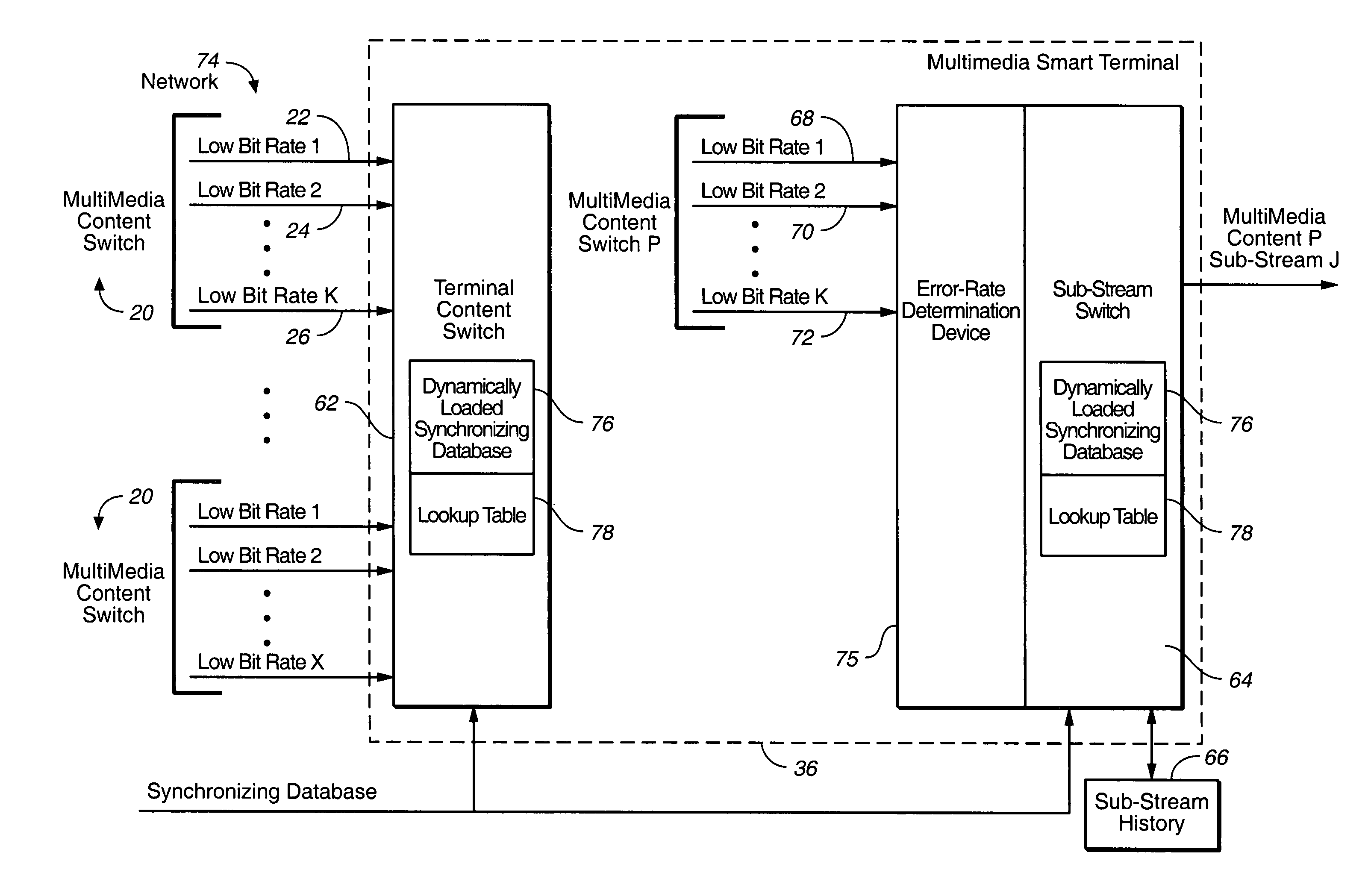
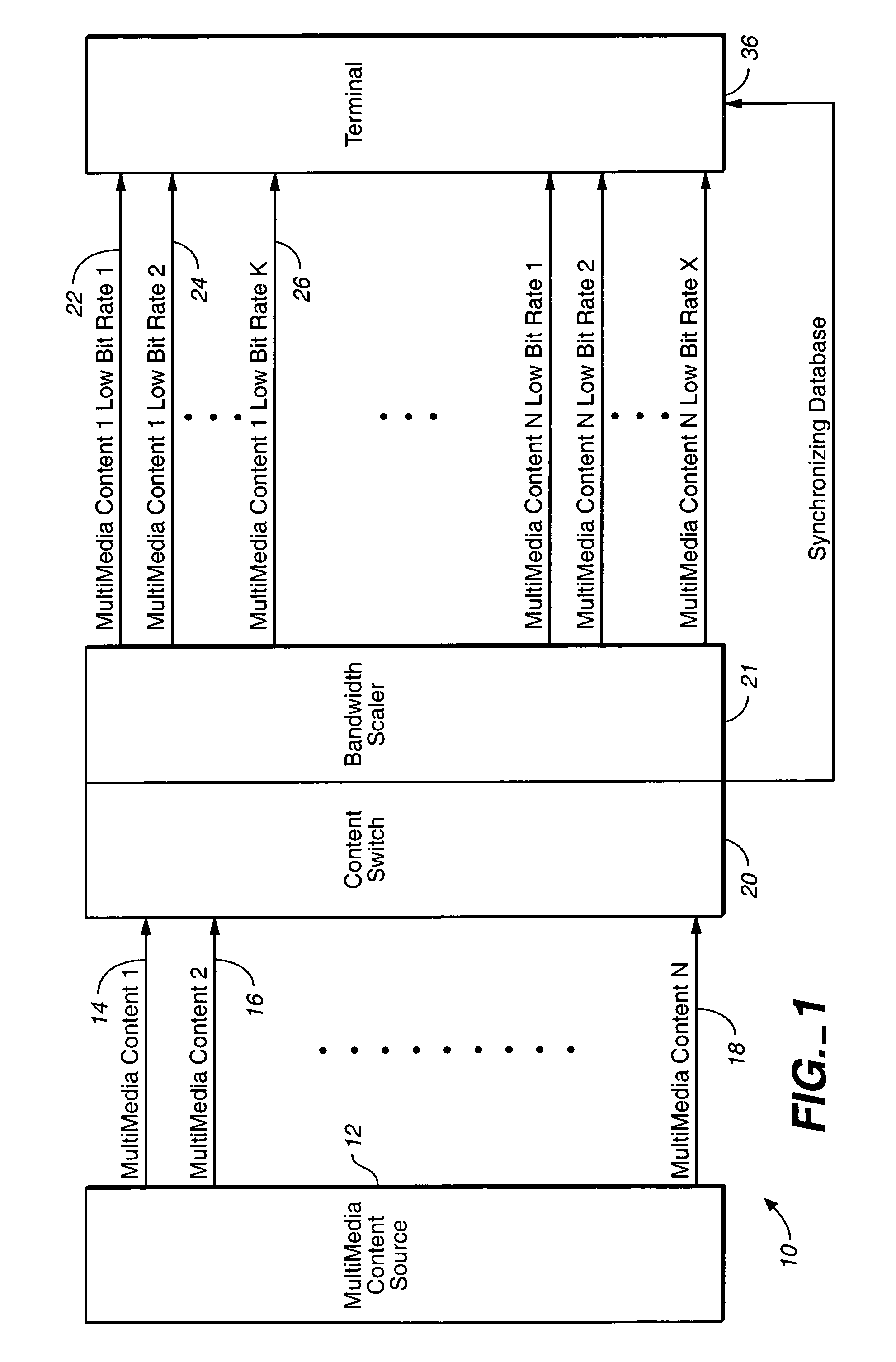
Multicasting transmission of multimedia information
InactiveUS7003794B2Easy to receiveSmooth transitionBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexComputer networkMulticast transmission
A multicasting system for reception of multimedia information comprising: a content switch coupled to a multimedia content source and at least one multimedia smart terminal. The multimedia content source includes a plurality of multimedia contents, wherein each multimedia content is supported by a primary multimedia stream transmitted over a primary dedicated channel having a primary bandwidth. At least one multimedia smart terminal is configured to receive from the content switch over a network each multimedia content as a secondary multimedia stream transmitted over a secondary channel having a secondary bandwidth. The content switch includes a bandwidth scaler configured to scale each primary multimedia stream to a plurality of secondary multimedia sub-streams that are substantially synchronized. The multimedia smart terminal includes a smart terminal sub-stream switch configured to switch among the plurality of secondary multimedia sub-streams in order to select a substantially optimum secondary multimedia sub-stream. The substantially optimum secondary multimedia sub-stream includes a substantially optimum relationship between an error rate level determined at the time of reception of a multimedia content and the quality of reception of a multimedia content.
Owner:RUNCOM TECH LTD
Encoding Device, Decoding Device, and Method Thereof
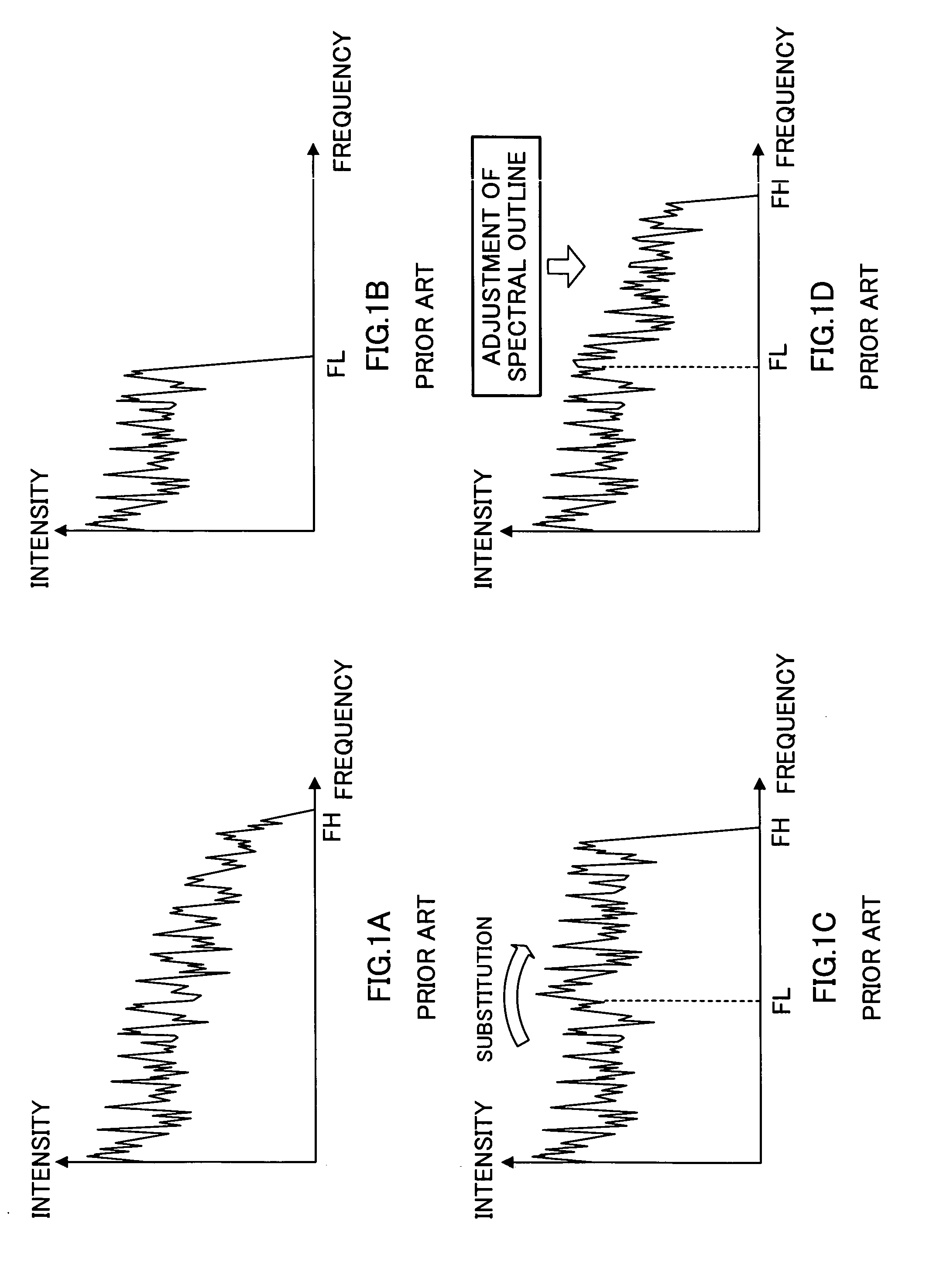
ActiveUS20080262835A1Reduce bitrateHigh similaritySpeech analysisCode conversionBand spectrumFrequency spectrum
There is disclosed an encoding device capable of improving similarity between the high frequency band spectrum of the original signal and a new spectrum to be generated while realizing a low bit rate when encoding a wide-band signal spectrum. The encoding device has sub-band amplitude calculation units (122, 128) for calculating the amplitude of the respective sub-bands for the high frequency band spectrum obtained from the wide-band signal. A search unit (124) and a gain codebook (125) select some sub-bands from a plurality of sub-bands and only the gain of the selected sub-bands is subjected to encoding. An interpolation unit (126) expresses the gain of the sub-band not selected, by mutually interpolating the selected gains.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Audio signal coding apparatus, audio signal decoding apparatus, and audio signal coding and decoding apparatus
InactiveUS6871106B1Scalable and adaptableImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisCode conversionAudio signal flowAudio frequency
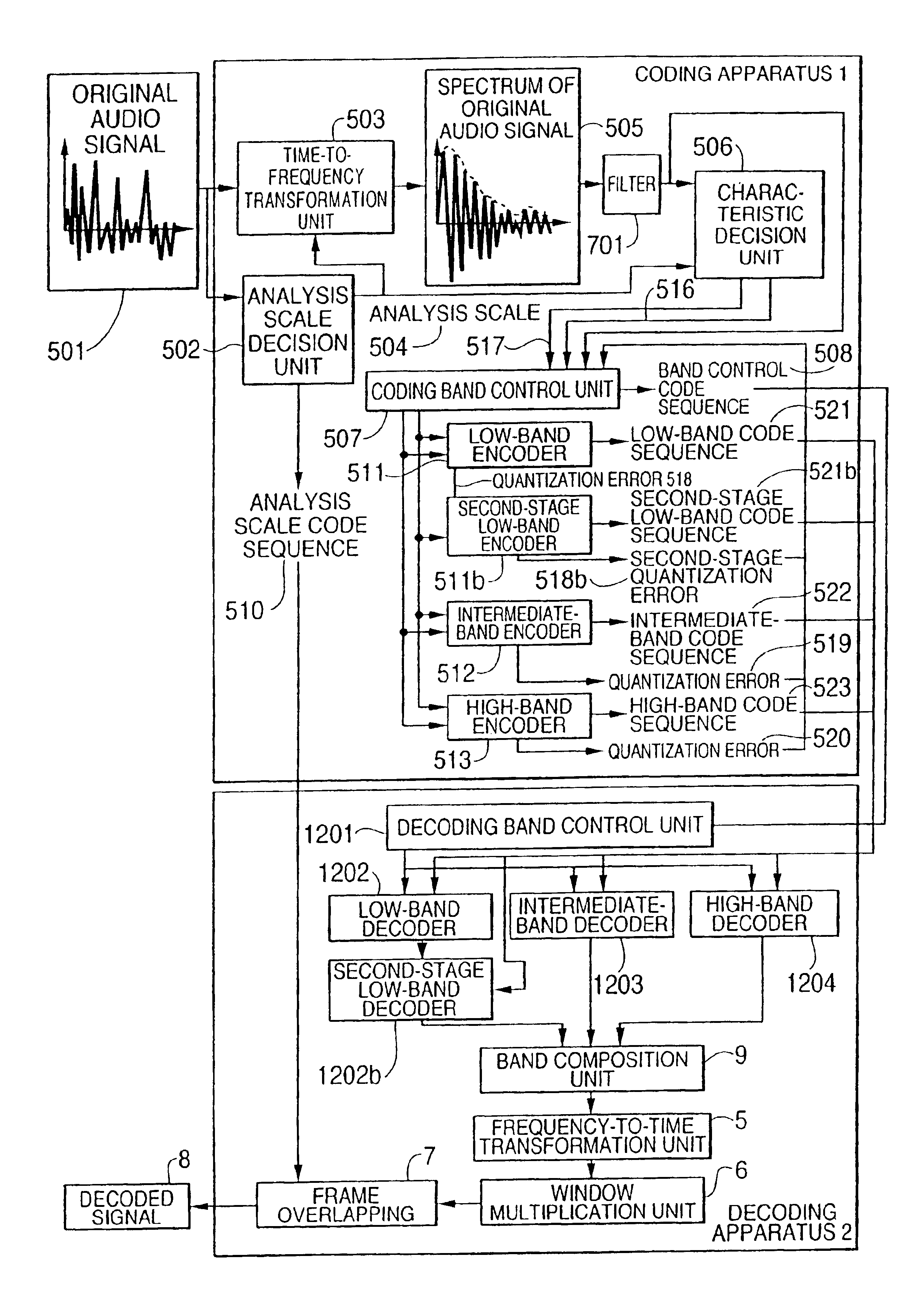
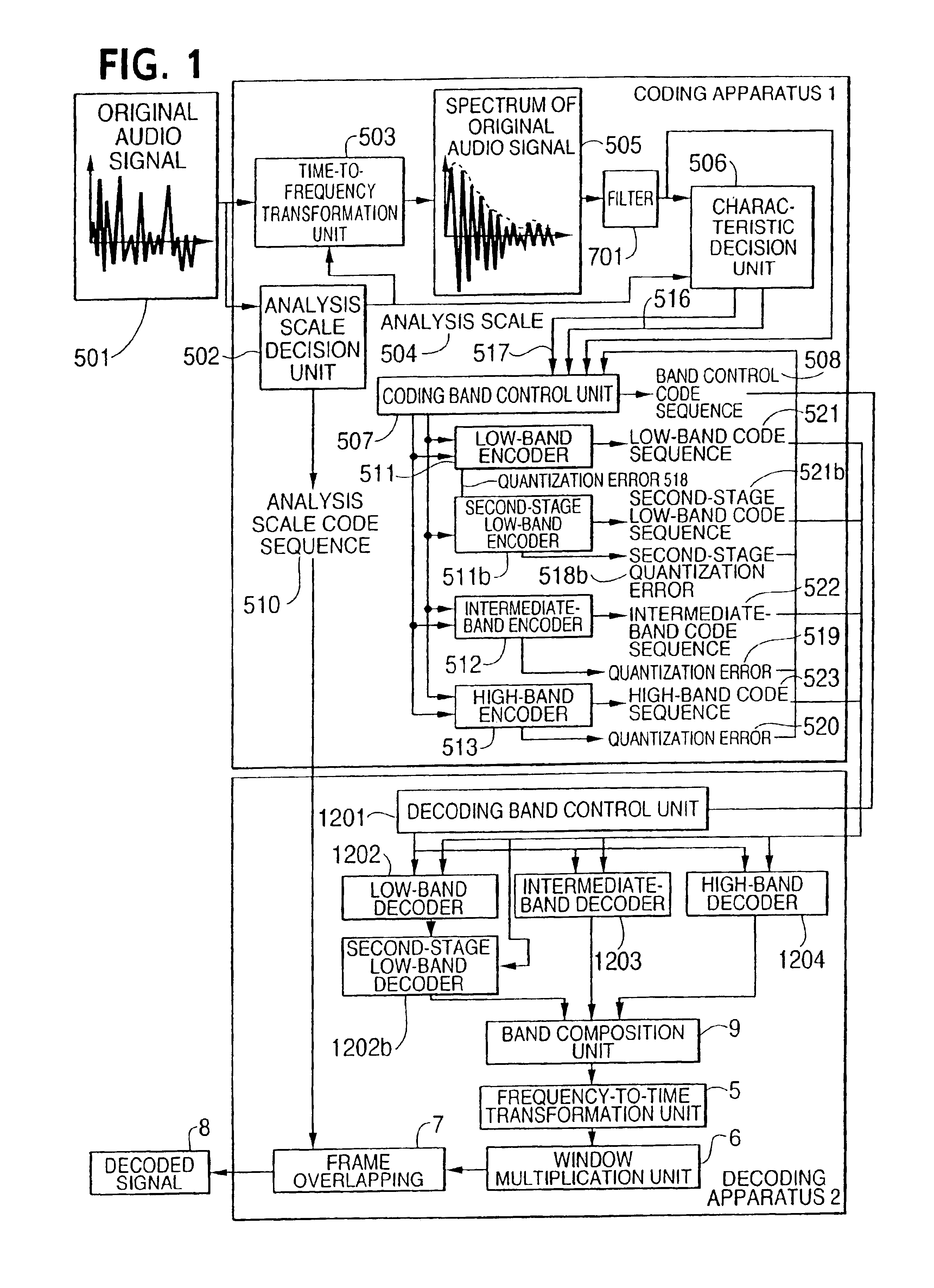
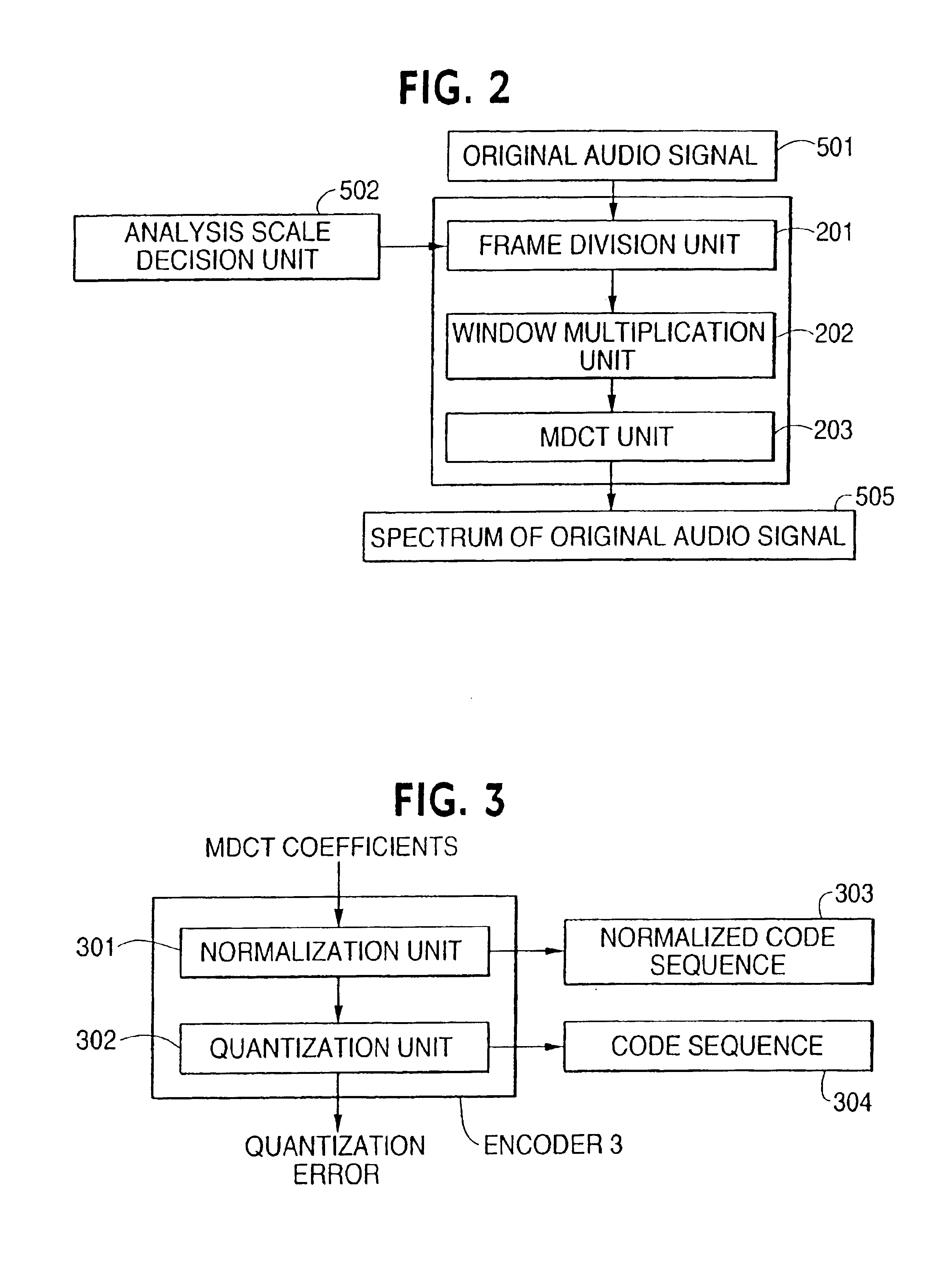
An audio signal coding apparatus includes a first-stage encoder for quantizing the time-to-frequency transformed audio signal and second-and-subsequent-stages of encoders each for quantizing a quantization error output from the previous-stage encoder A characteristic decision unit is provided which decides the frequency band of an audio signal to be quantized by each encoder of multiple-stage encoders, and a coding band control unit receives the frequency band decided by the characteristic decision unit and the time-to-frequency transformed audio signal, decides the order of connecting the respective encoders, and transforms the quantization bands of the encoders and the connecting order to code sequences. Therefore, it is possible to provide an audio signal coding apparatus performing adaptive scalable coding, which exhibits sufficient performance when coding various audio signals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
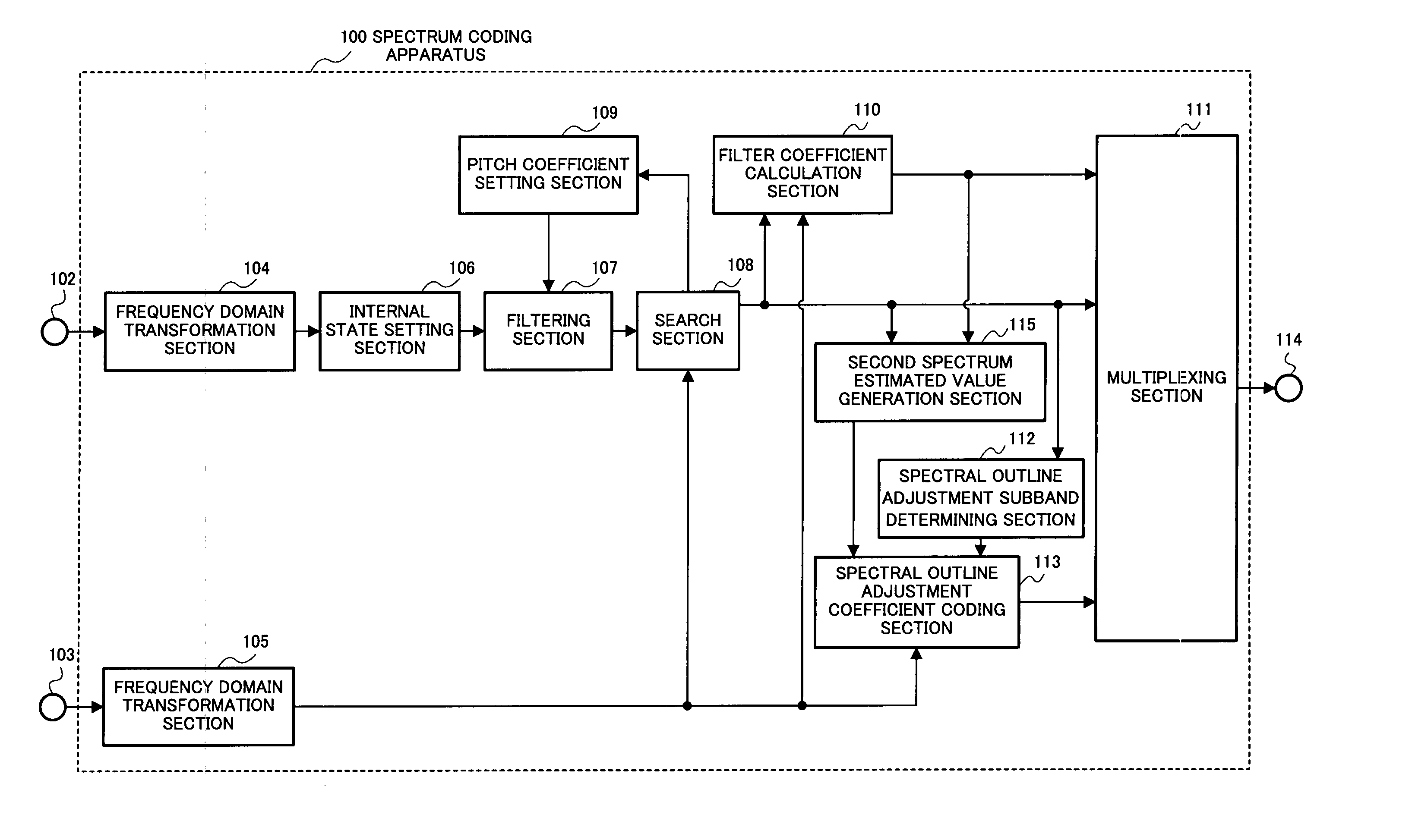
Spectrum coding apparatus, spectrum decoding apparatus, acoustic signal transmission apparatus, acoustic signal reception apparatus and methods thereof
ActiveUS20070071116A1Reduce bitrateQuality improvementSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementFrequency spectrumWave band
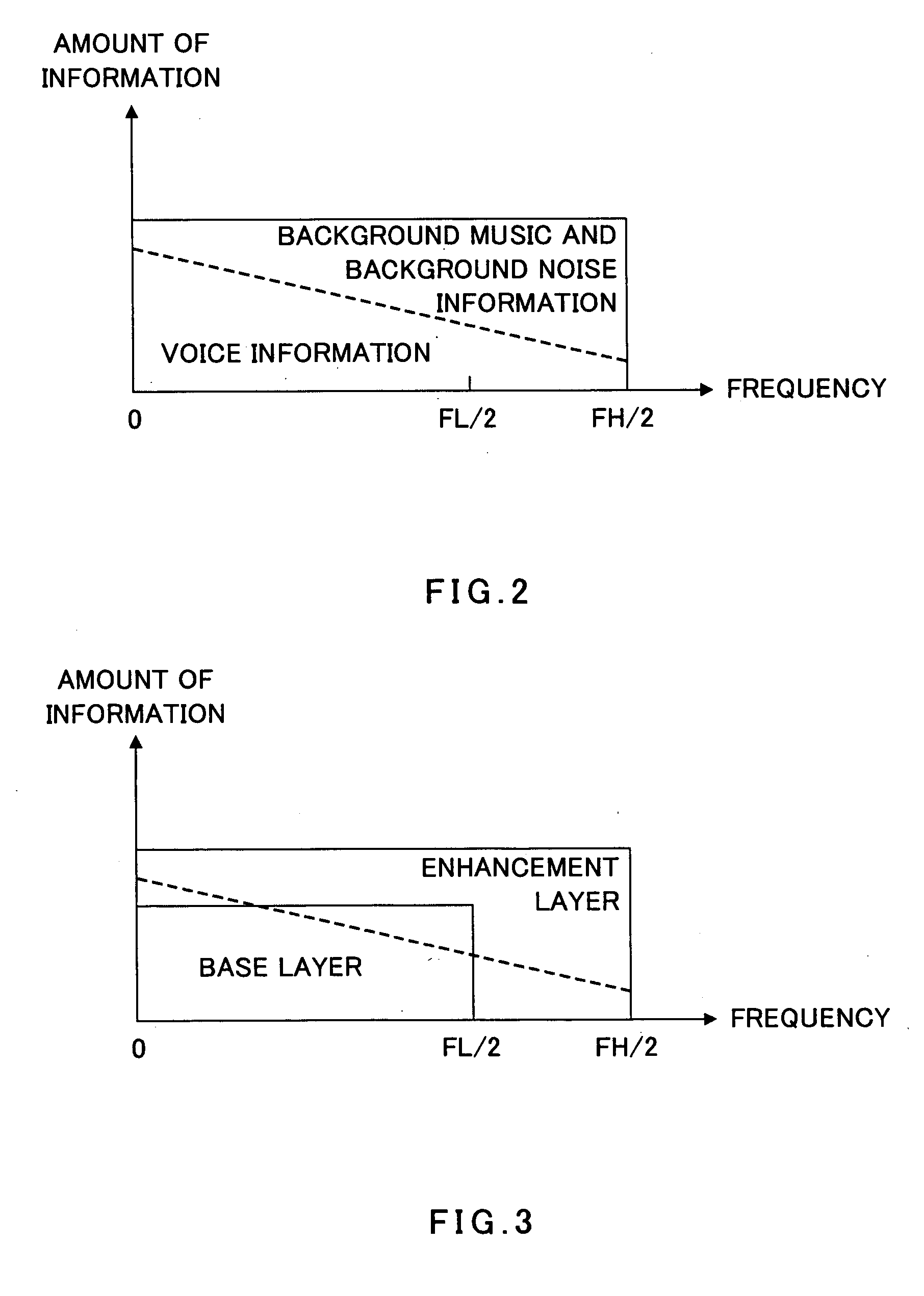
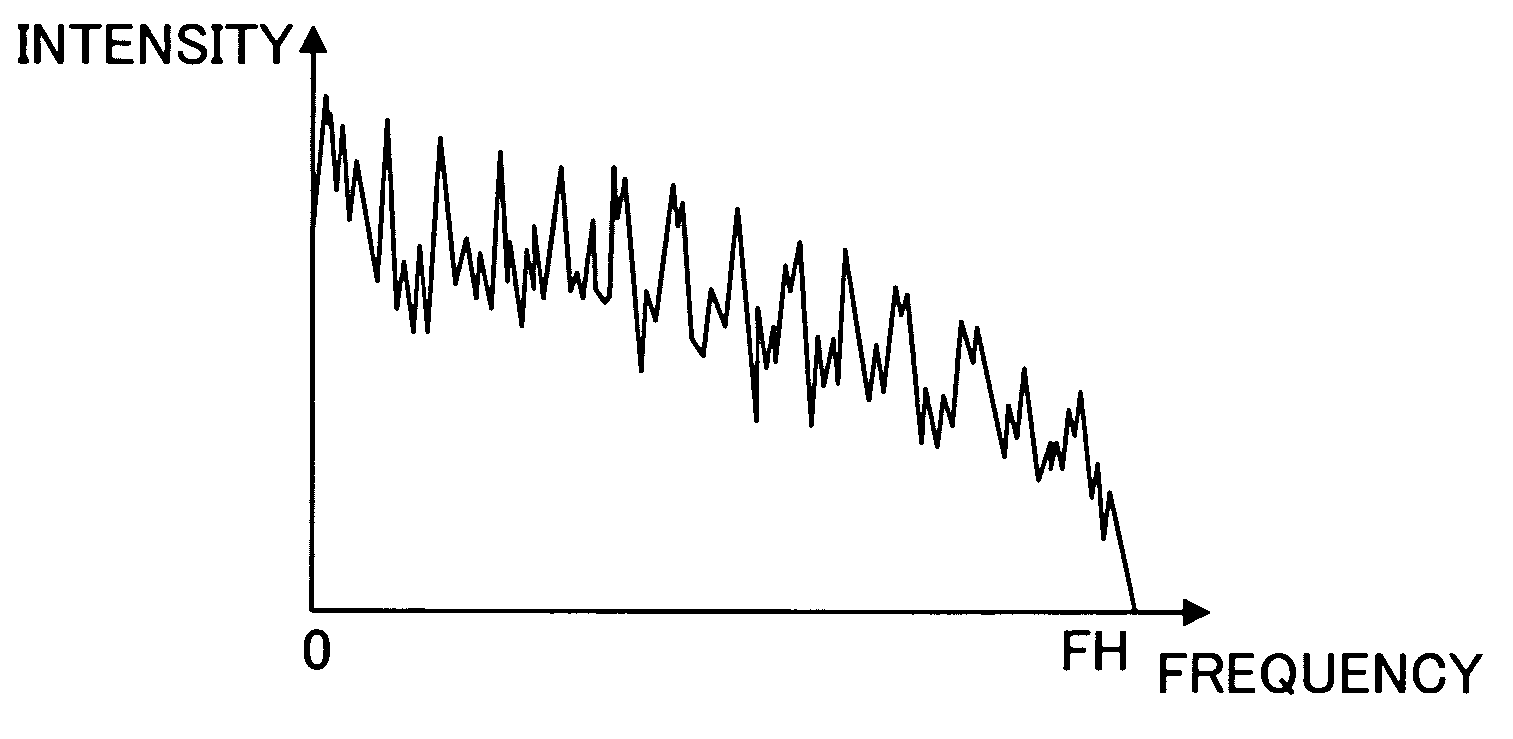
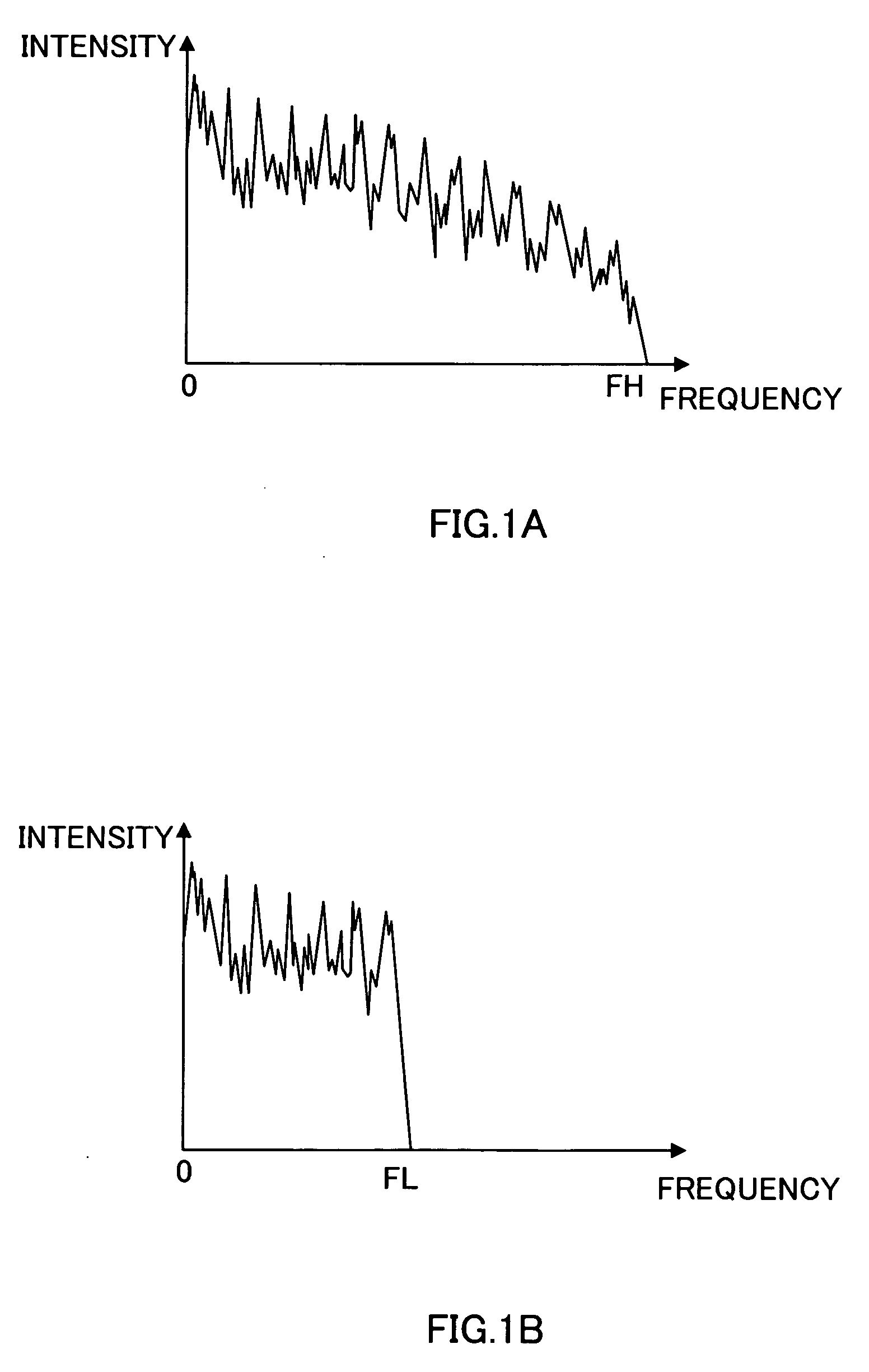
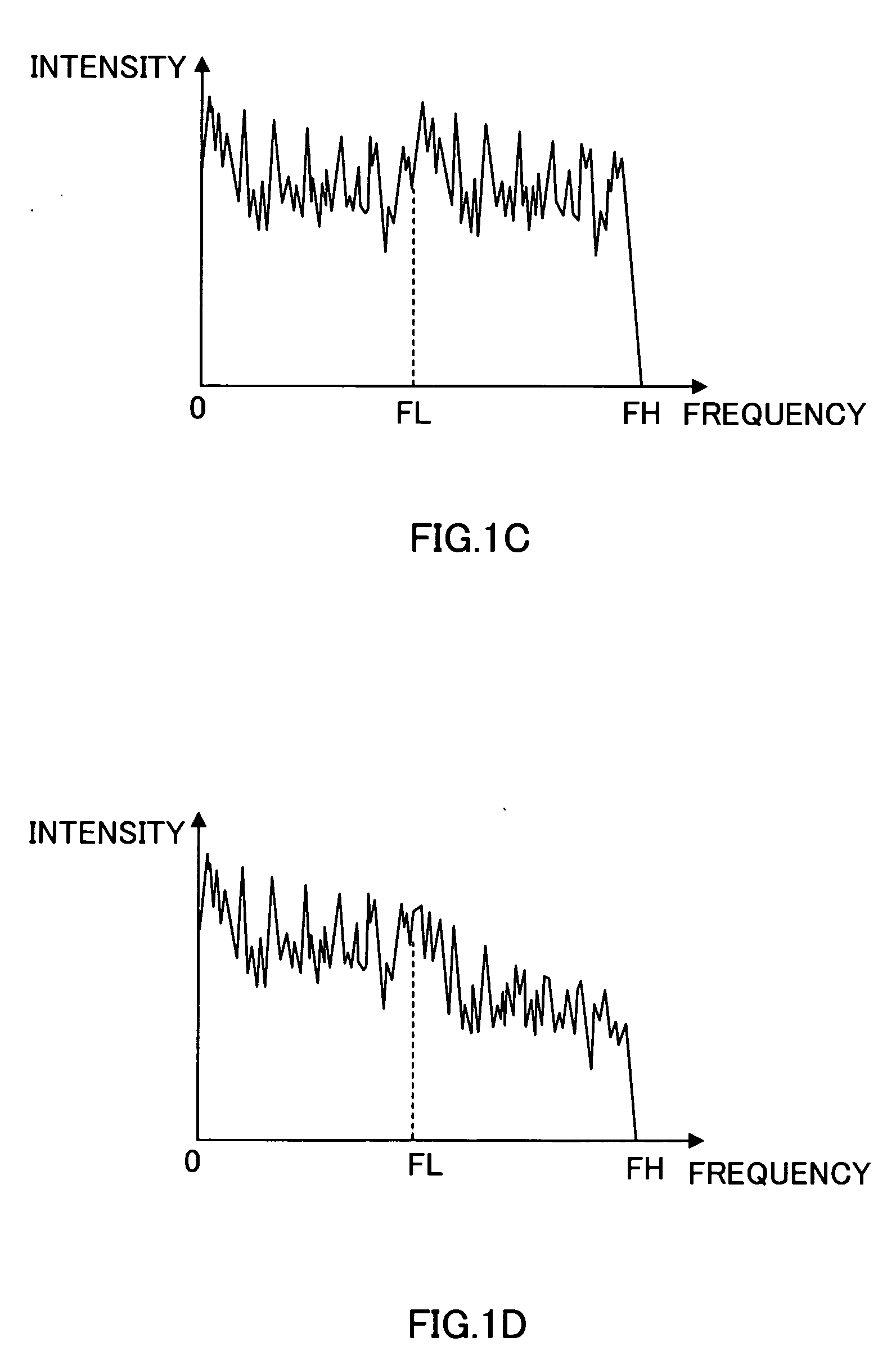
A spectrum coding apparatus capable of performing coding at a low bit rate and with high quality is disclosed. This apparatus is provided with a section that performs the frequency transformation of a first signal and calculates a first spectrum, a section that converts the frequency of a second signal and calculates a second spectrum, a section that estimates the shape of the second spectrum in a band of FL≦k<FH using a filter having the first spectrum in a band of 0≦k<FL as an internal state and a section that codes an outline of the second spectrum determined based on a coefficient indicating the characteristic of the filter at this time.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
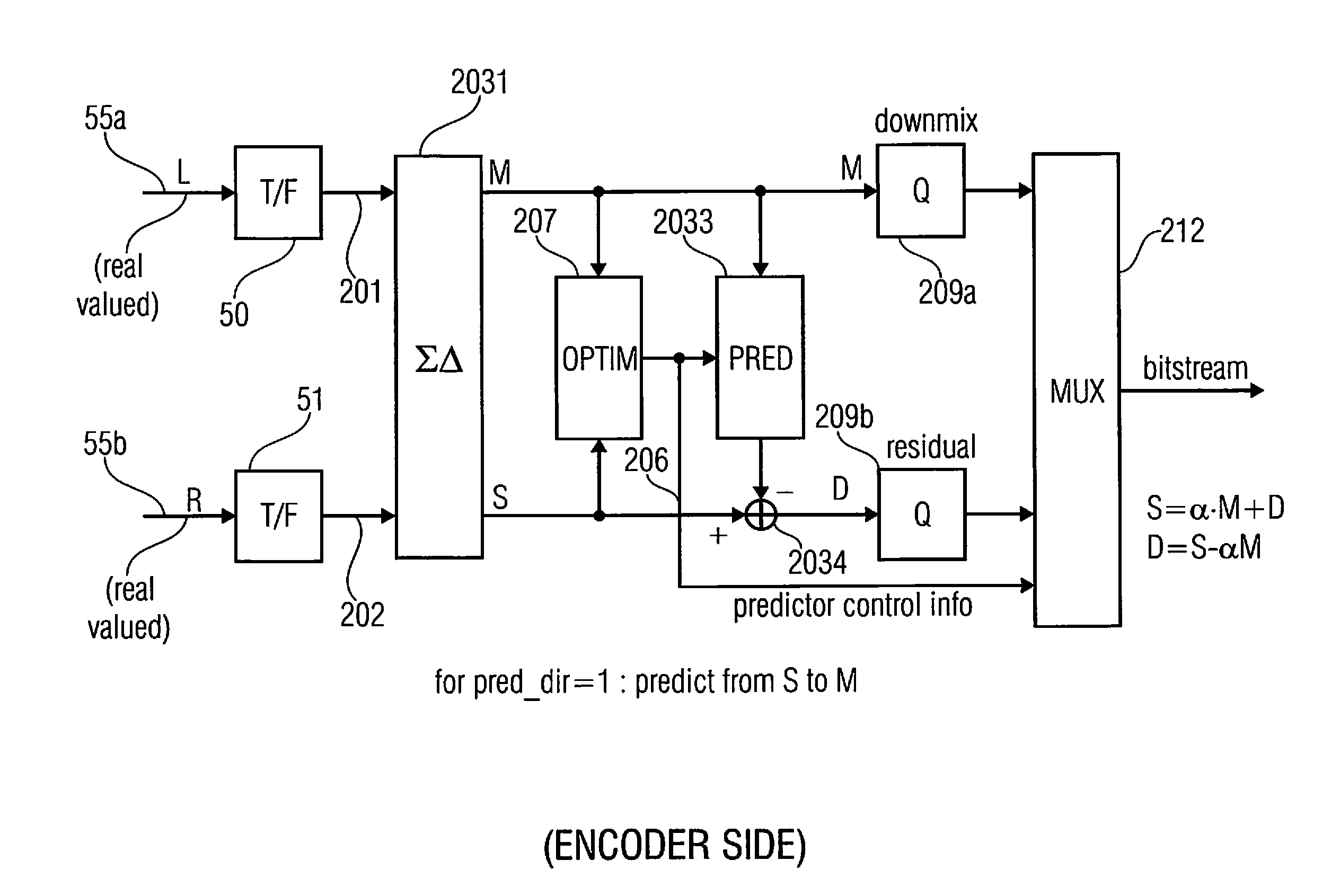
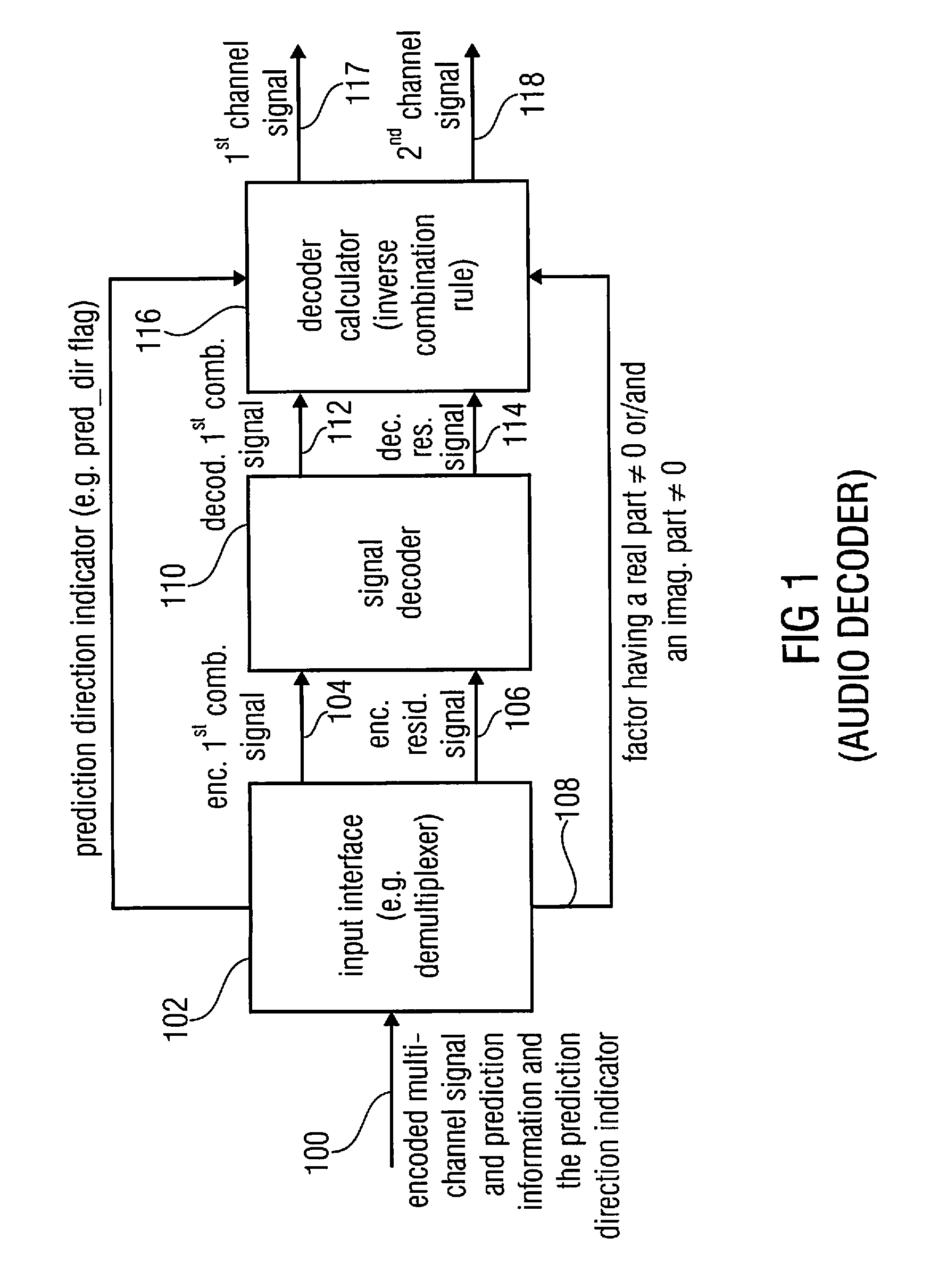
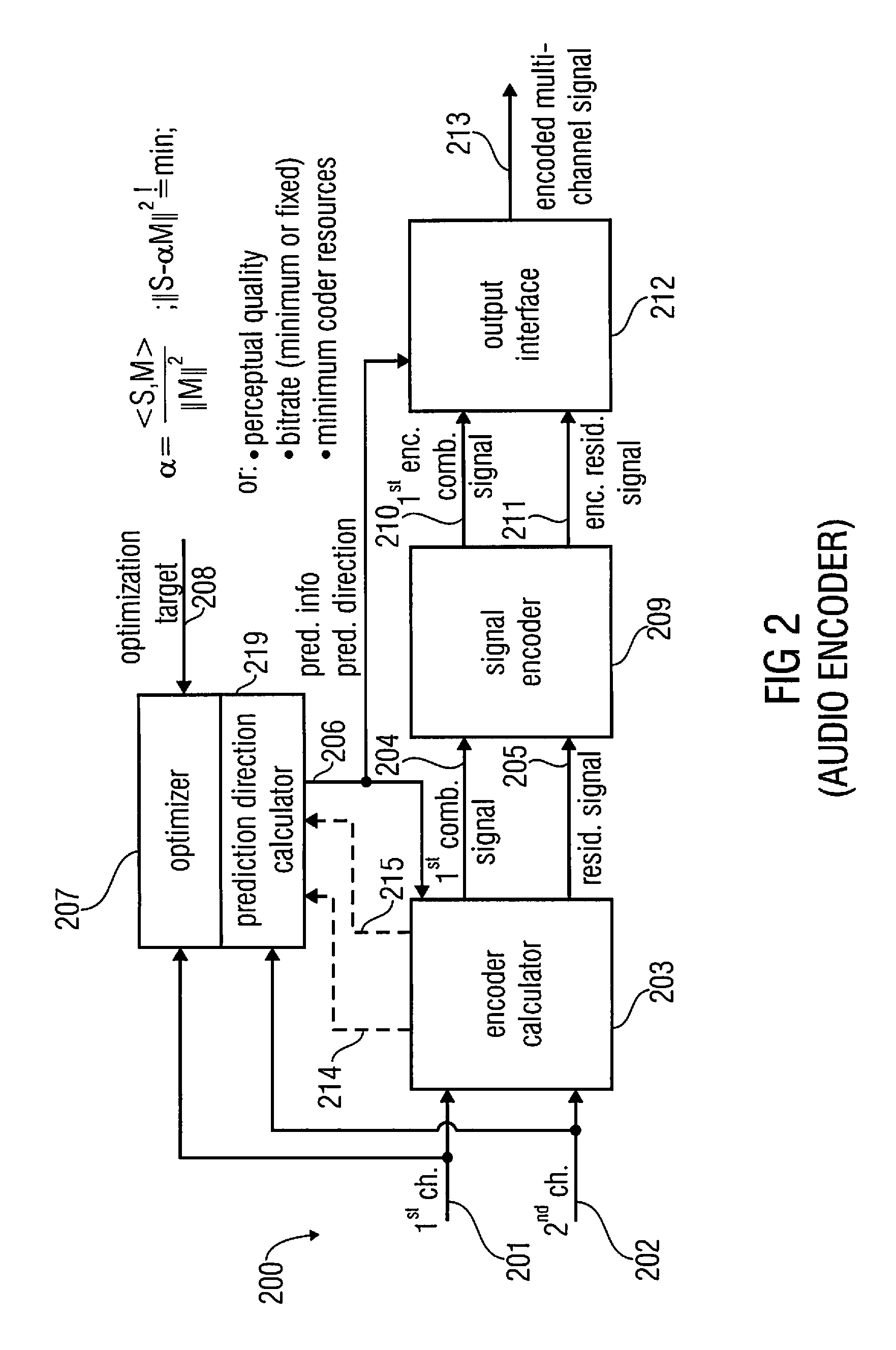
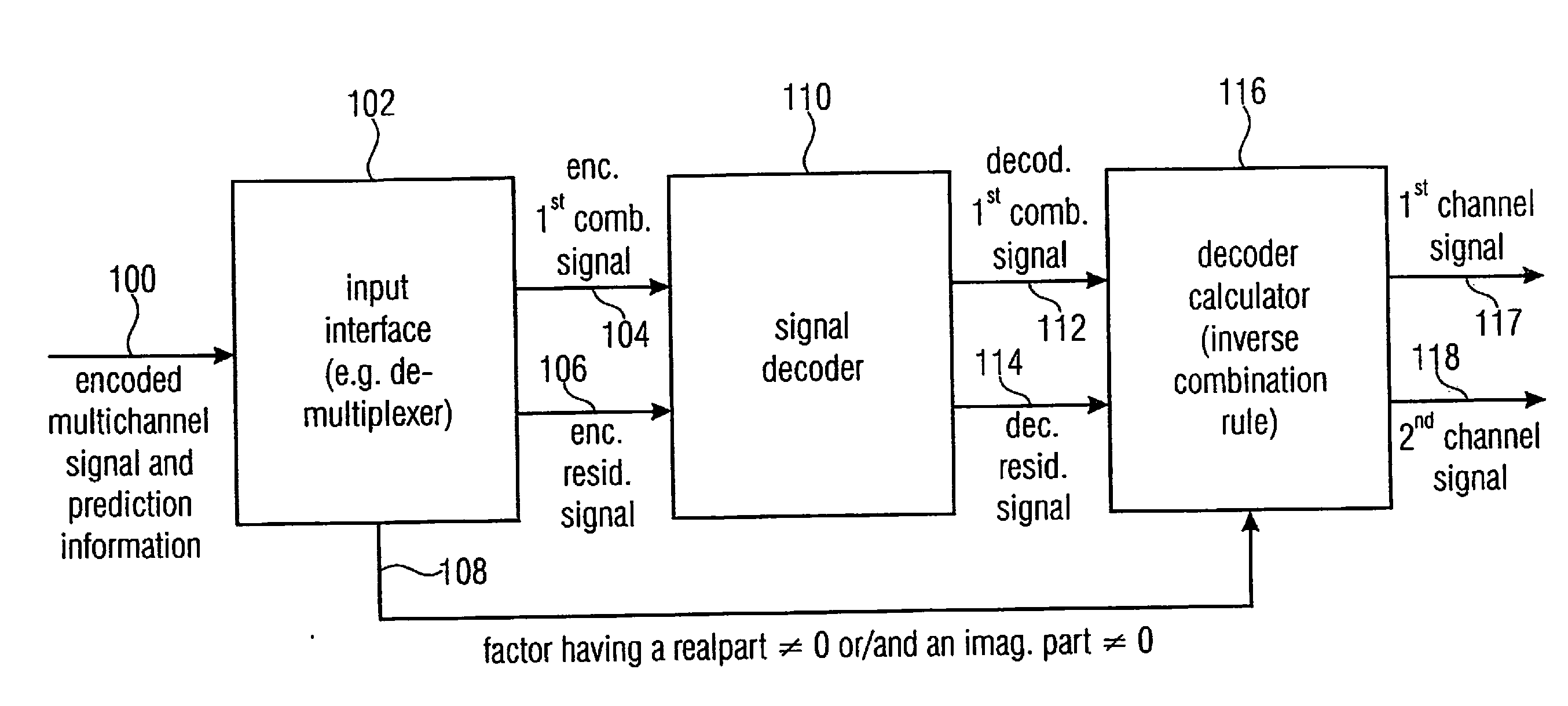
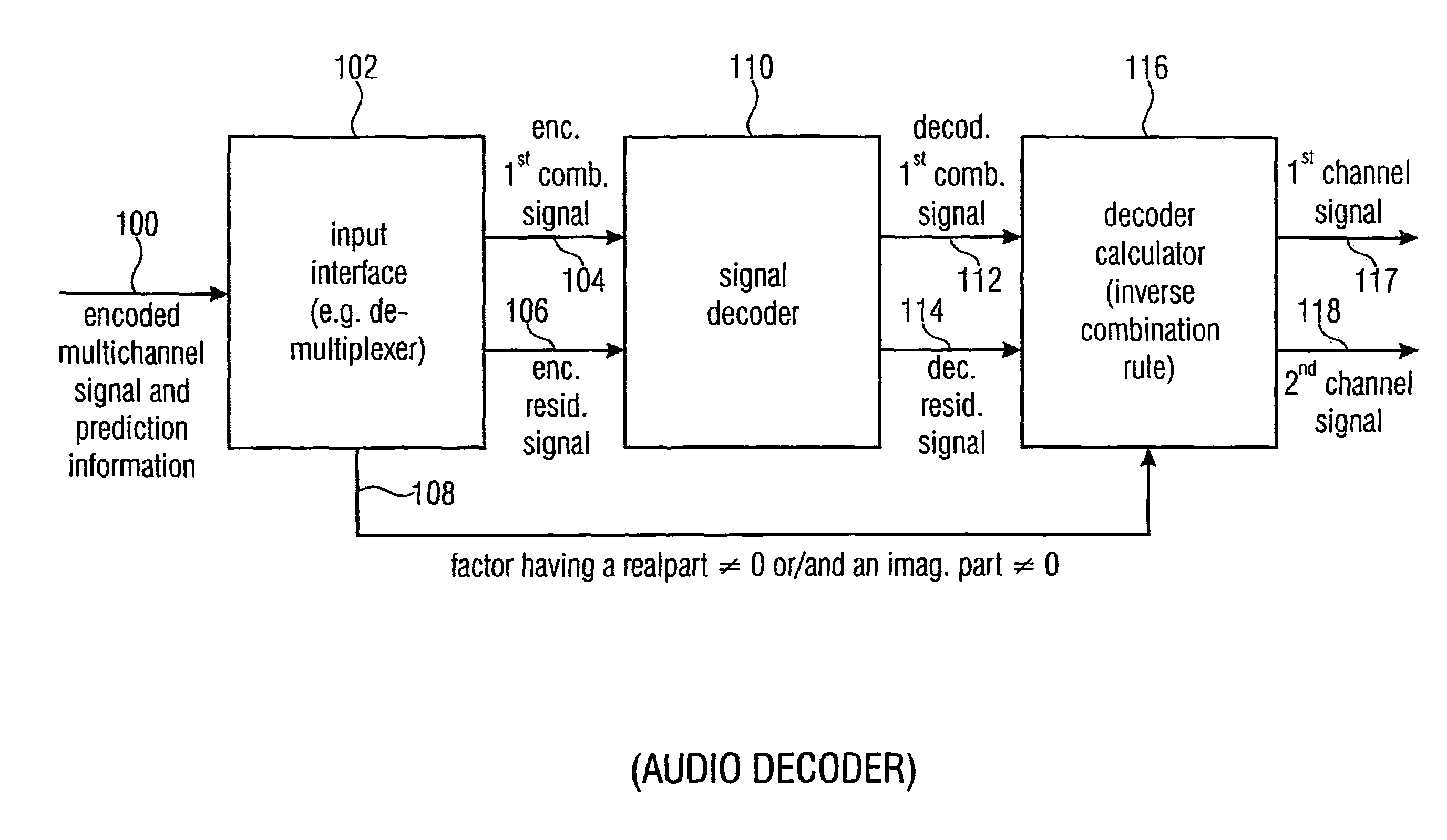
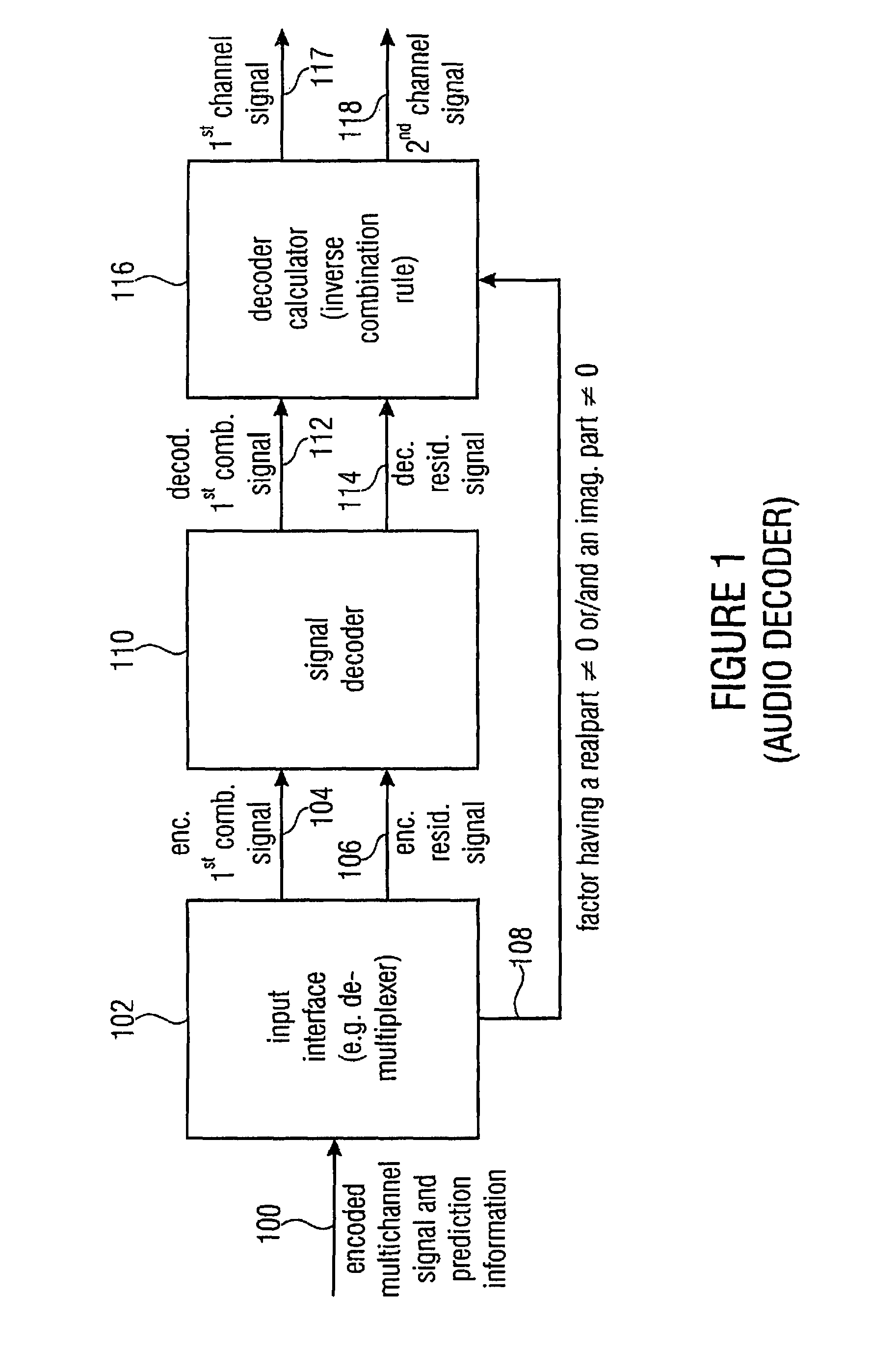
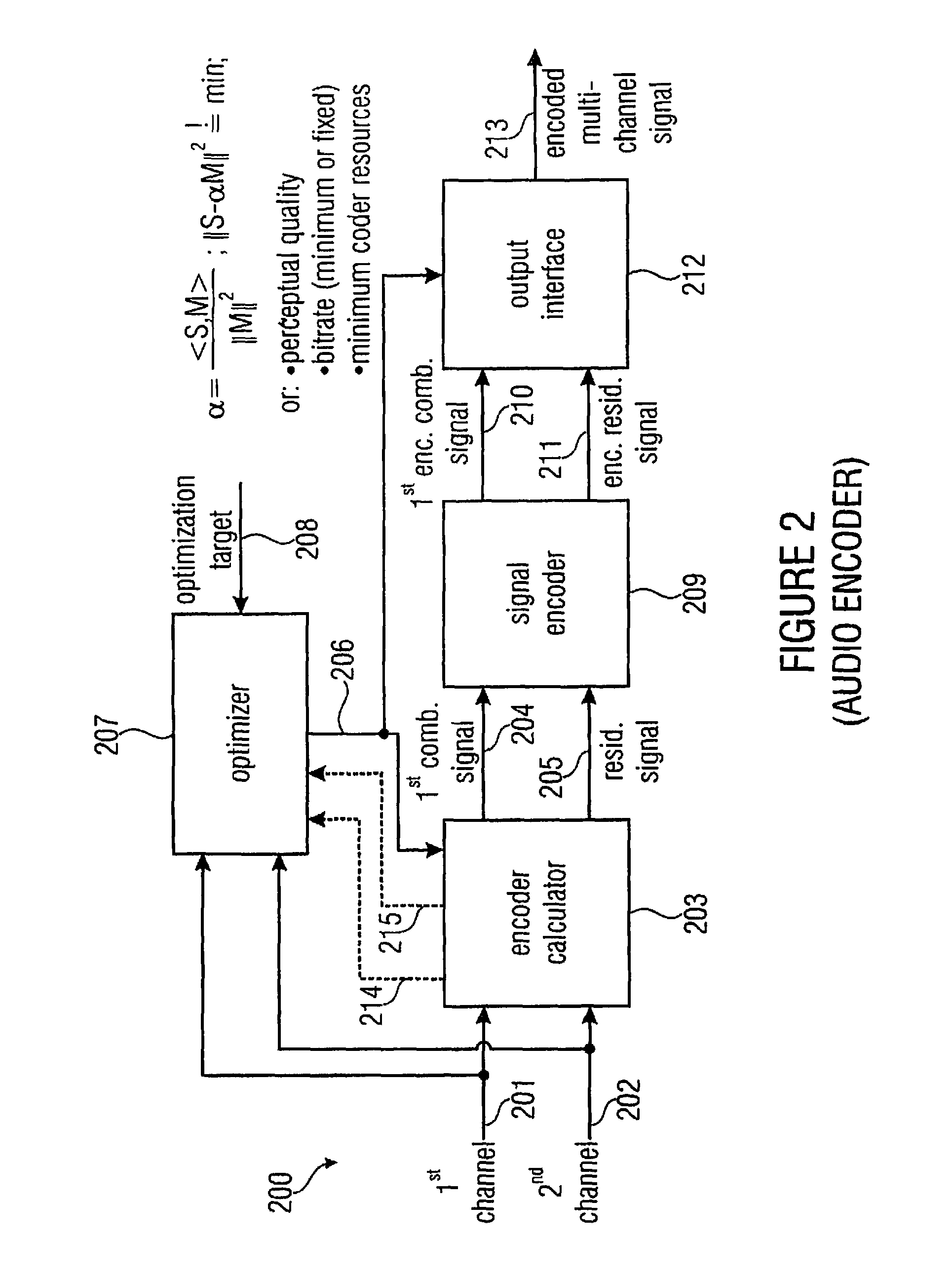
Audio or video encoder, audio or video decoder and related methods for processing multi-channel audio or video signals using a variable prediction direction
ActiveUS20130121411A1Enhanced audio and video qualityReduce bit rateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVIT signalsAudio frequency
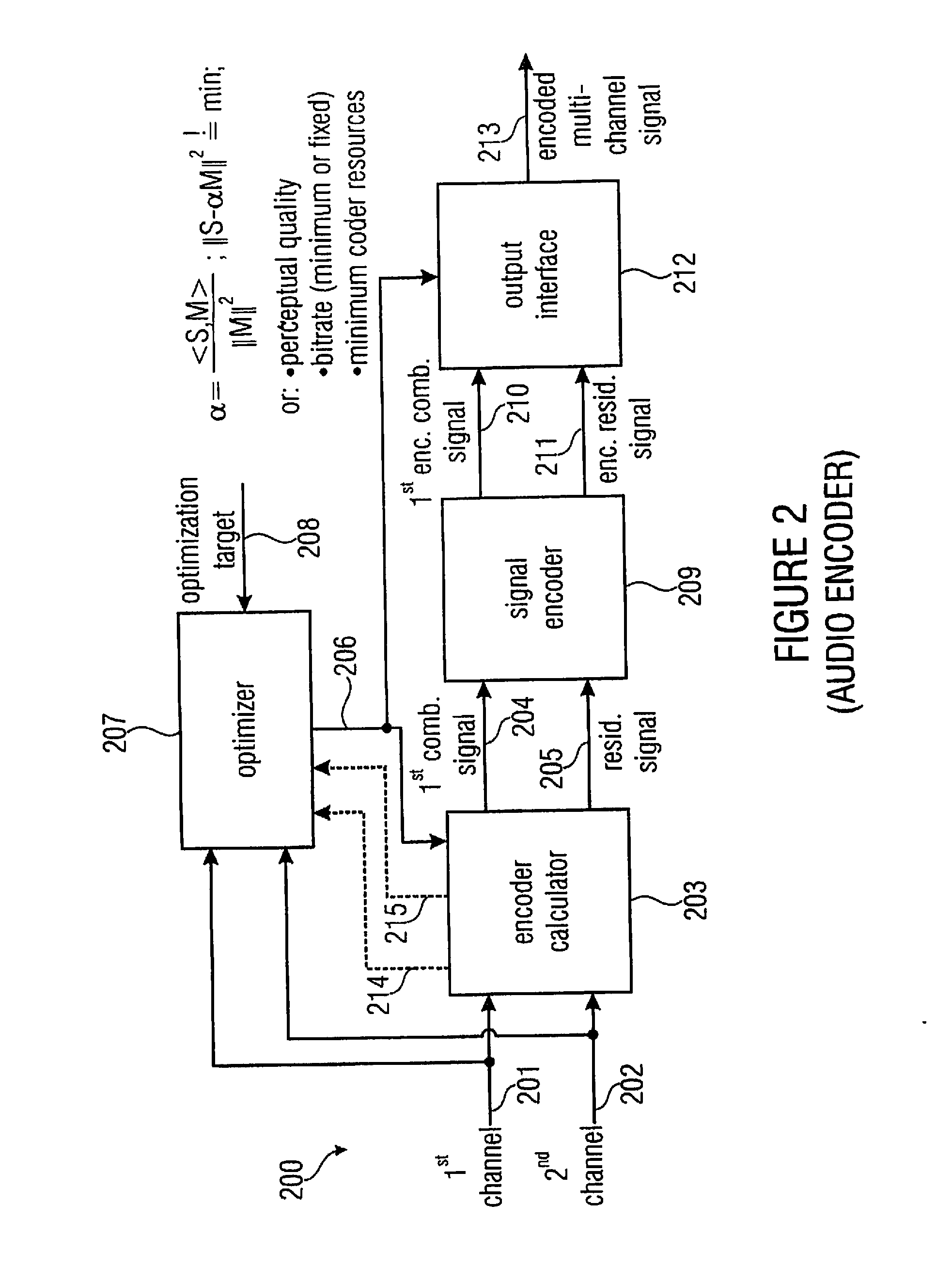
An encoder / decoder is based on a combination of two audio or video channels to obtain a first combination signal as a mid-signal and a residual signal derivable using a predicted side signal derived from the mid-signal. A decoder uses the prediction residual signal, the first combination signal, a prediction direction indicator and prediction information to derive decoded first channel and second channel signals. A real-to-imaginary transform can be applied for estimating the imaginary part of the spectrum of the first combination signal. The prediction signal used in the derivation of the prediction residual signal, the real-valued first combination signal is multiplied by a real portion of the complex prediction information and the estimated imaginary part of the first combination signal is multiplied by an imaginary portion of the complex prediction information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
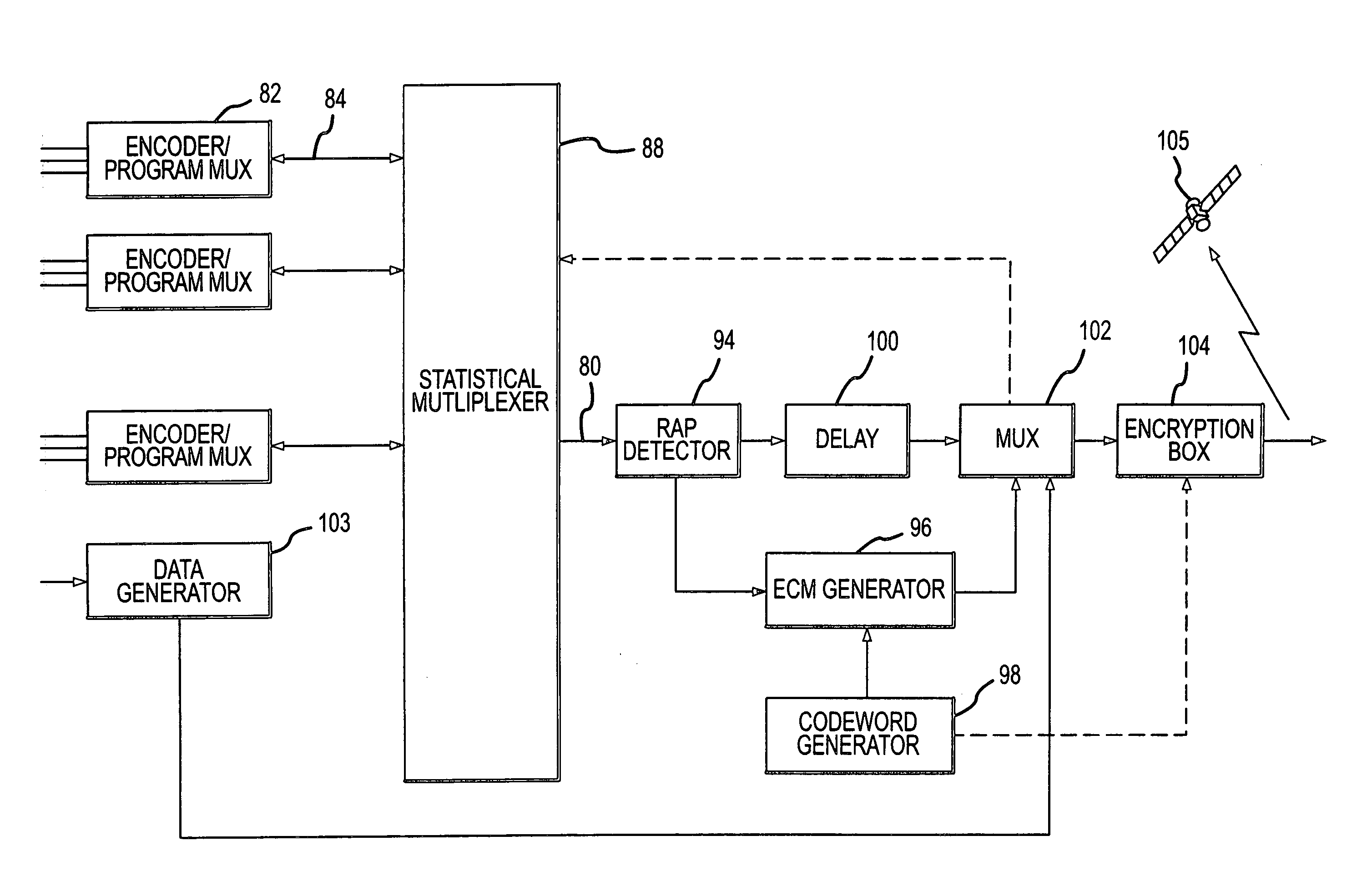
Just in time delivery of entitlement control message (ECMs) and other essential data elements for television programming
InactiveUS7912219B1Reduces overhead bit rateReduce rateDigital data processing detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesBit rateSatellite
Essential data elements, particularly entitlement control messages (ECMs), are inserted in a manner that reduces the overhead bit rate without effecting overall tuning time at the customer receiver or security in satellite, cable or other programming networks. ECMs are inserted into the transport stream by detecting random access points (RAPS) in the encoded programming and inserting the ECM packets in a window just ahead of the RAP.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GROUP
Audio encoder, audio decoder and related methods for processing multi-channel audio signals using complex prediction
ActiveUS20130030819A1Reduce complexityImprove audio qualityPulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumData stream
An encoder, based on a combination of two audio channels, obtains a first combination signal as a mid-signal and a residual signal derivable using a predicted side signal derived from the mid signal. The first combination signal and the prediction residual signal are encoded and written into a data stream together with the prediction information. A decoder generates decoded first and second channel signals using the prediction residual signal, the first combination signal and the prediction information. A real-to-imaginary transform may be applied for estimating the imaginary part of the spectrum of the first combination signal. For calculating the prediction signal used in the derivation of the prediction residual signal, the real-valued first combination signal is multiplied by a real portion of the complex prediction information and the estimated imaginary part of the first combination signal is multiplied by an imaginary portion of the complex prediction information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Near-transparent or transparent multi-channel encoder/decoder scheme
ActiveUS7573912B2Quality improvementReduce bitrateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWave shapeComputer science
A multi-channel encoder / decoder scheme additionally preferably generates a waveform-type residual signal. This residual signal is transmitted together with one or more multi-channel parameters to a decoder. In contrast to a purely parametric multi-channel decoder, the enhanced decoder generates a multi-channel output signal having an improved output quality because of the additional residual signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Audio encoder, audio decoder and related methods for processing multi-channel audio signals using complex prediction
ActiveUS8655670B2Quality improvementLittle overheadPulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisData streamFrequency spectrum
An encoder, based on a combination of two audio channels, obtains a first combination signal as a mid-signal and a residual signal derivable using a predicted side signal derived from the mid signal. The first combination signal and the prediction residual signal are encoded and written into a data stream together with the prediction information. A decoder generates decoded first and second channel signals using the prediction residual signal, the first combination signal and the prediction information. A real-to-imaginary transform may be applied for estimating the imaginary part of the spectrum of the first combination signal. For calculating the prediction signal used in the derivation of the prediction residual signal, the real-valued first combination signal is multiplied by a real portion of the complex prediction information and the estimated imaginary part of the first combination signal is multiplied by an imaginary portion of the complex prediction information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Frequency division multiplexing system with selectable rate
InactiveUS6992972B2Increase delayIncrease rangeLine-faulsts/interference reductionMulti-frequency code systemsFourier transform on finite groupsCarrier signal
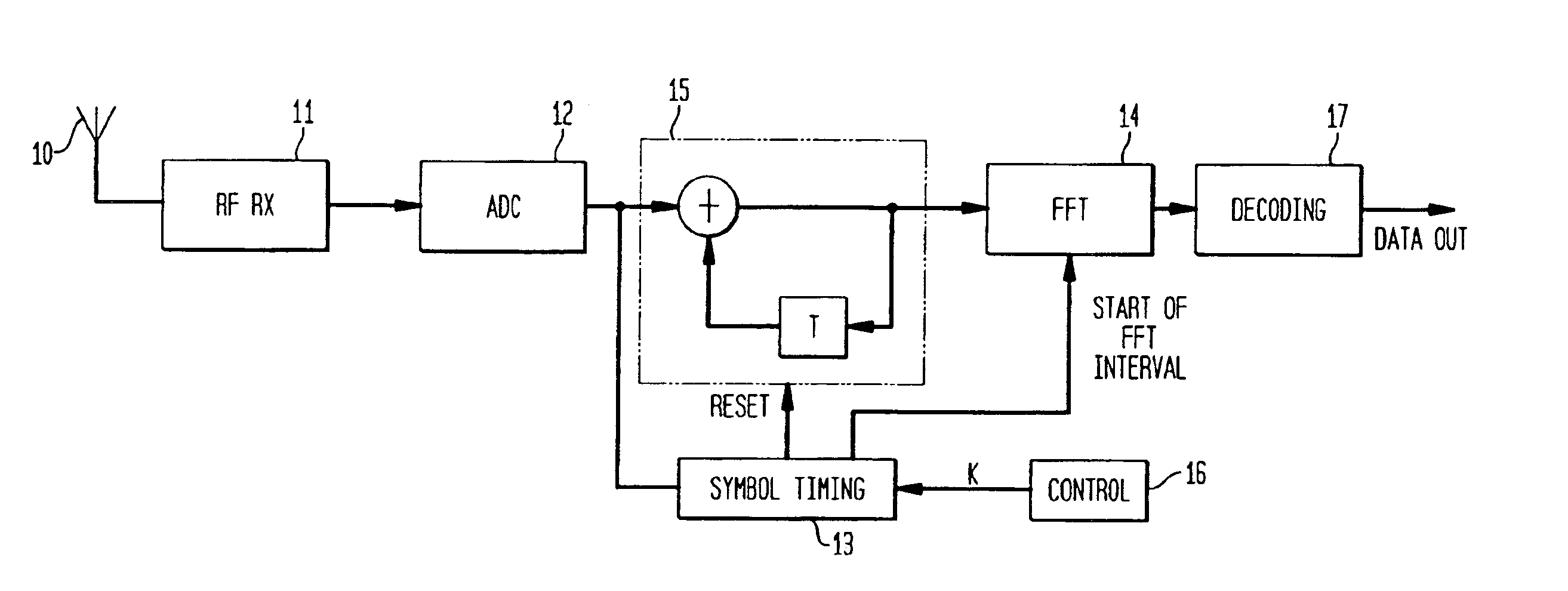
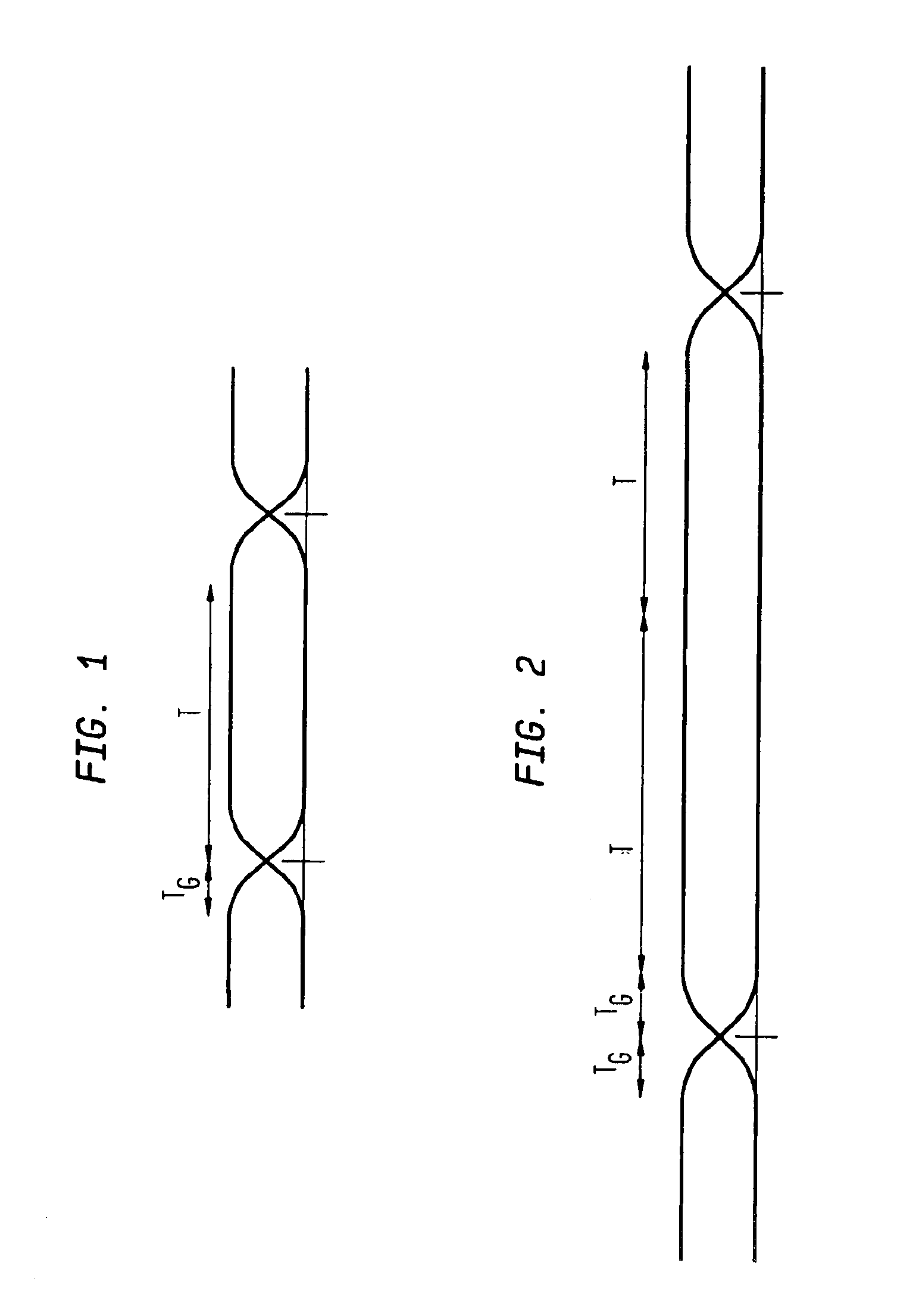
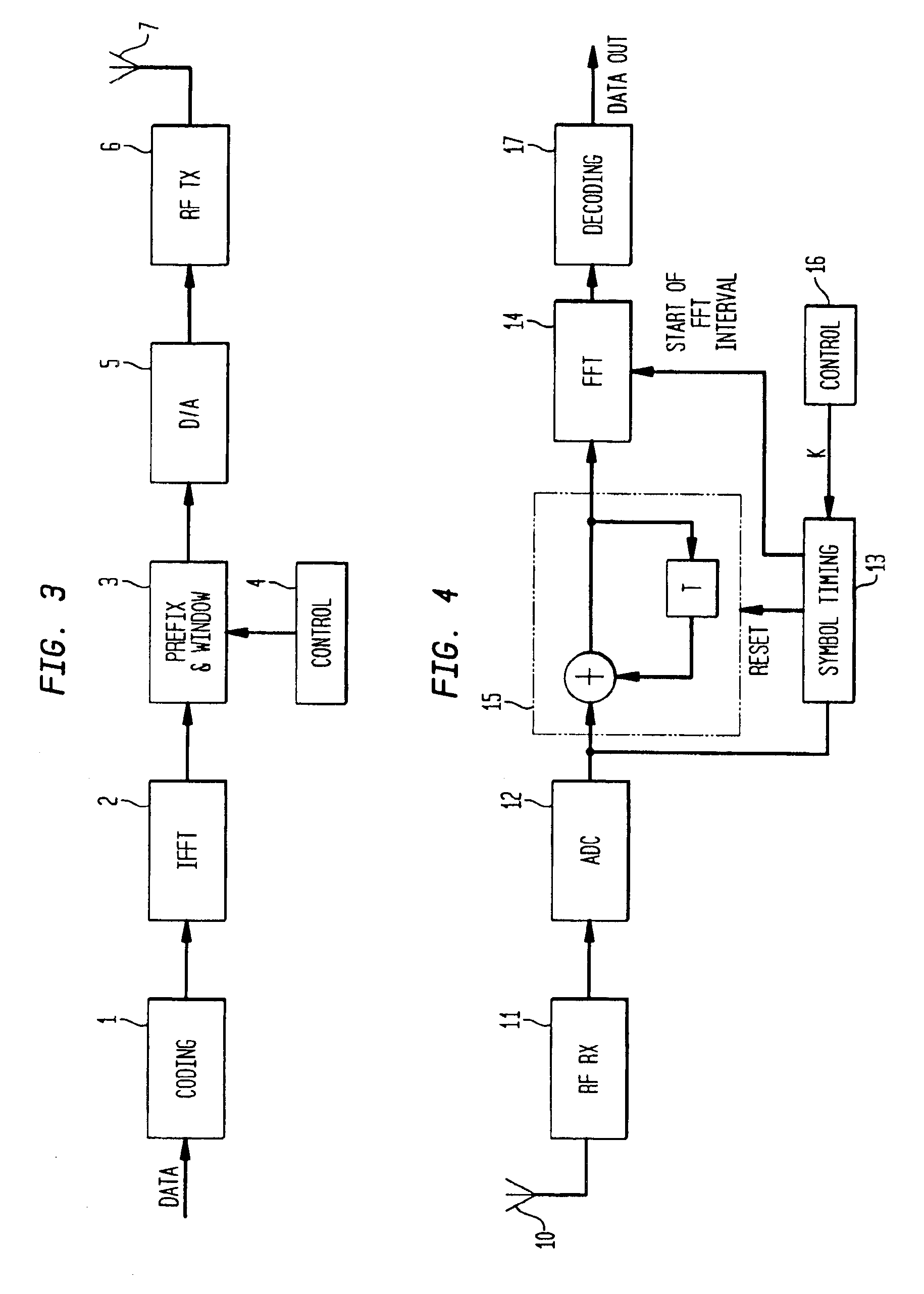
An OFDM system uses a normal mode which has a symbol length T, a guard time TG and a set of N sub-carriers, which are orthogonal over the time T, and one or more fallback modes which have symbol lengths KT and guard times KTG where K is an integer greater than unity. The same set of N sub-carriers is used for the fallback modes as for the normal mode. Since the same set of sub-carriers is used, the overall bandwidth is substantially constant, so alias filtering does not need to be adaptive. The Fourier transform operations are the same as for the normal mode. Thus fallback modes are provided with little hardware cost. In the fallback modes the increased guard time provides better delay spread tolerance and the increased symbol length provides improved signal to noise performance, and thus increased range, at the cost of reduced data rate.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Image encoding method
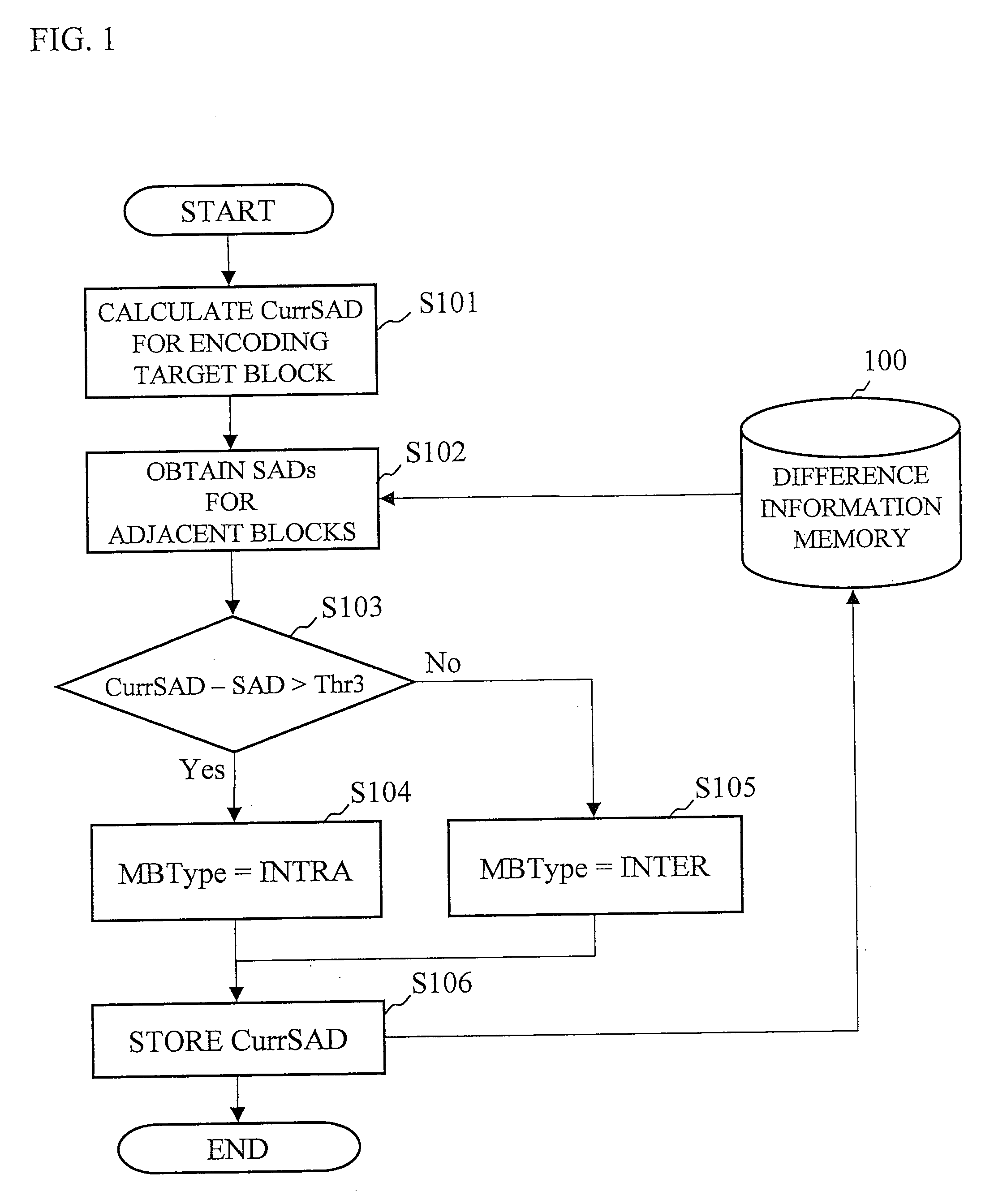
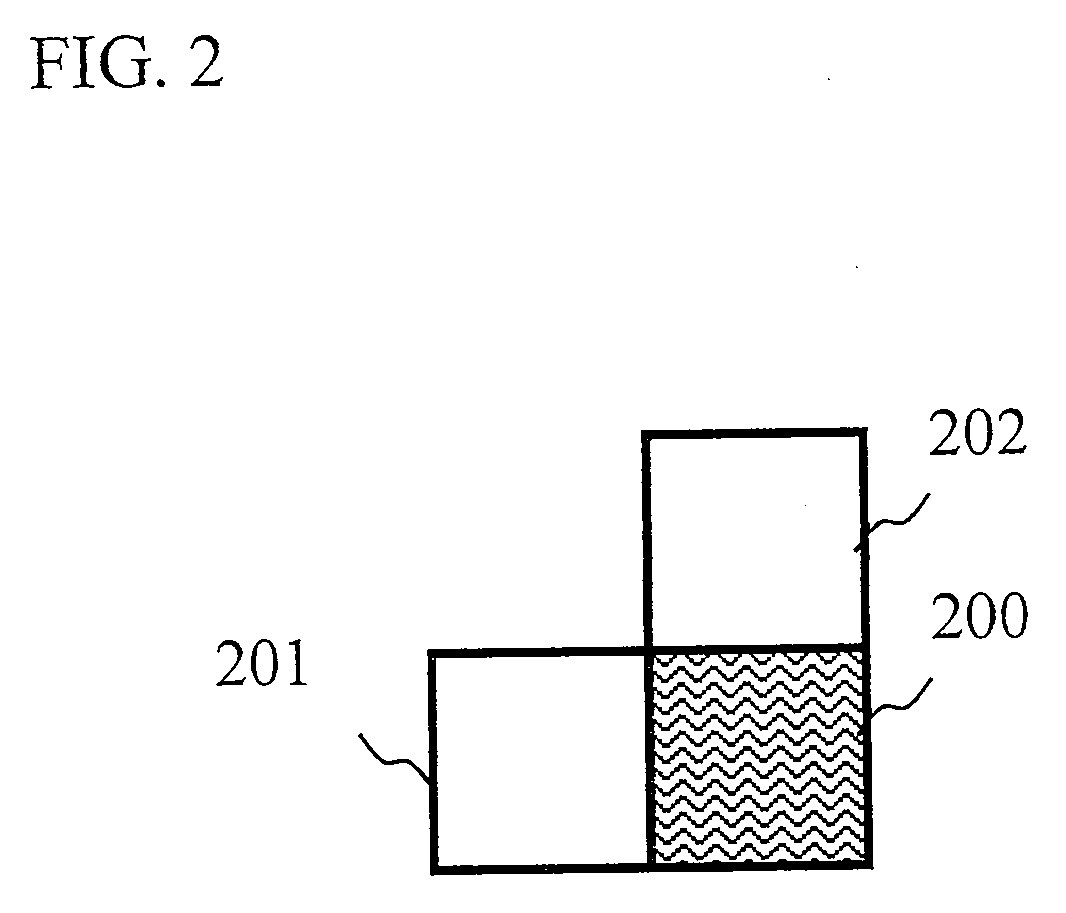
InactiveUS20090190660A1Suppresses increase in amount of codePrevent image degradationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer scienceIntra mode
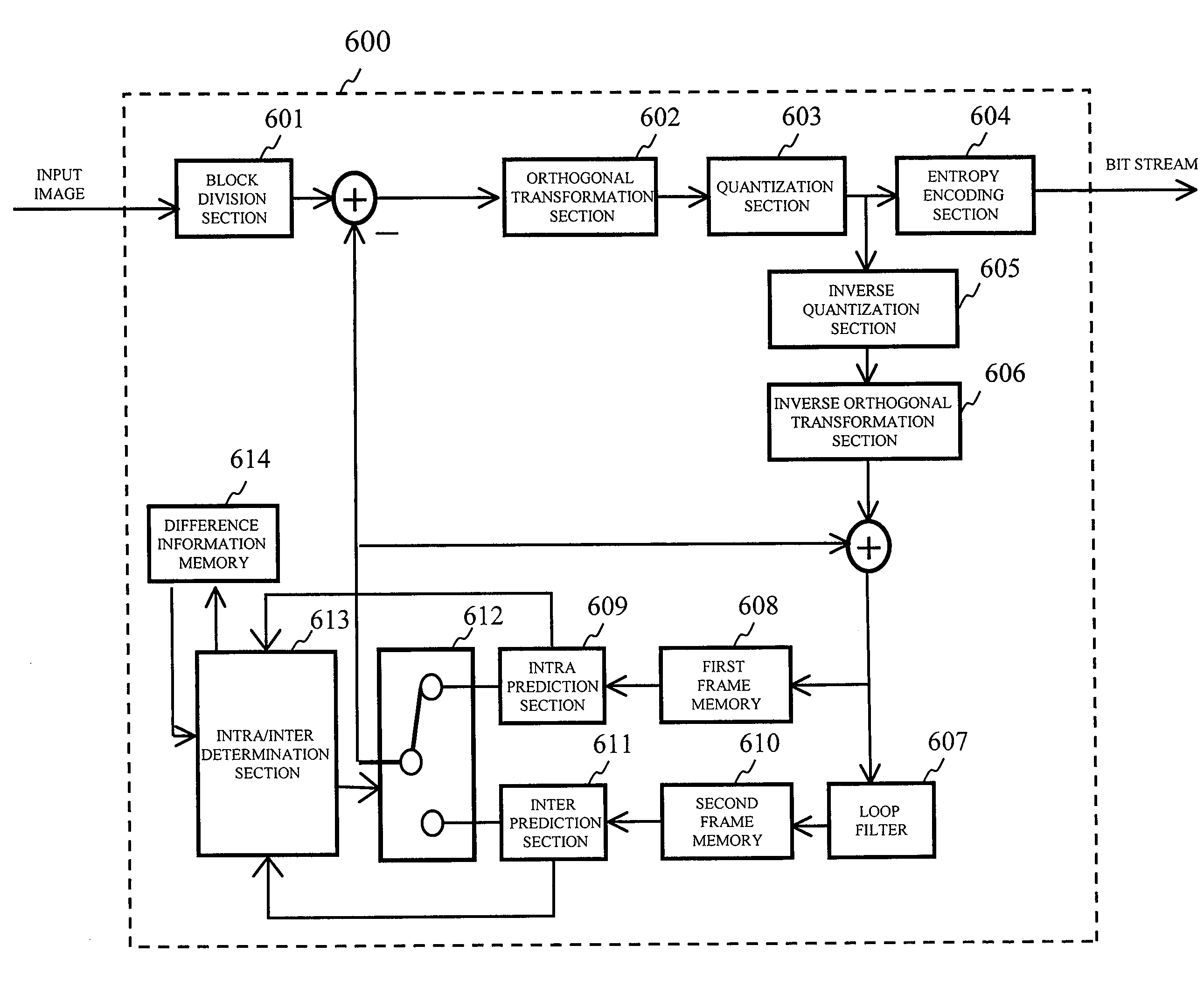
An image encoding method according to the present invention calculates first difference information of an encoding target block and second difference information of an adjacent block, calculates a difference between the first difference information and the second difference information, and uses an intra mode only for blocks where a residual image noise occurs by selecting the intra mode when the difference is larger than a predetermined threshold, and selecting an inter mode when the difference is smaller than the predetermined threshold.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of digital video reference frame compression
ActiveUS20080170626A1High complexityAccelerated programColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoLossless compression algorithm
The digital video referencing frame image is compressed block by block by applying lossless compression algorithm to pixel components with full length, or 1 bit, 2 bits, 3 bits or 4 bits LSB bits truncation. If a sub-block has high complexity which results in more than 3 bits error for most pixel components, a transfer algorithm with quantization and VLC coding is applied to compress this sub-block. Should the complexity is higher than a threshold or at least one sub-block having error of more than 3 bits for most pixel components, truncating 1 LSB bit of sub-block with simple pattern to save more bits to be allocate to code the sub-block with highest complex pattern.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com