Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13753 results about "Wave band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultraviolet laser apparatus and exposure apparatus using same
InactiveUS7023610B2Easy to getReduce spatial coherenceLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberUltraviolet lights
An ultraviolet laser apparatus having a single-wavelength oscillating laser generating laser light between an infrared band and a visible band, an optical amplifier for amplifying the laser light, and a wavelength converting portion converting the amplified laser light into ultraviolet light using a non-linear optical crystal. An exposure apparatus transfers a pattern image of a mask onto a substrate and includes a light source having a laser apparatus emitting laser light having a single wavelength, a first fiber optical amplifier for amplifying the laser light, a light dividing device for dividing or branching the amplified laser light into plural lights, and second fiber optical amplifiers for amplifying the plural divided or branched lights, respectively, and a transmission optical system for transmitting the laser light emitted from the light source to the exposure apparatus.
Owner:NIKON CORP
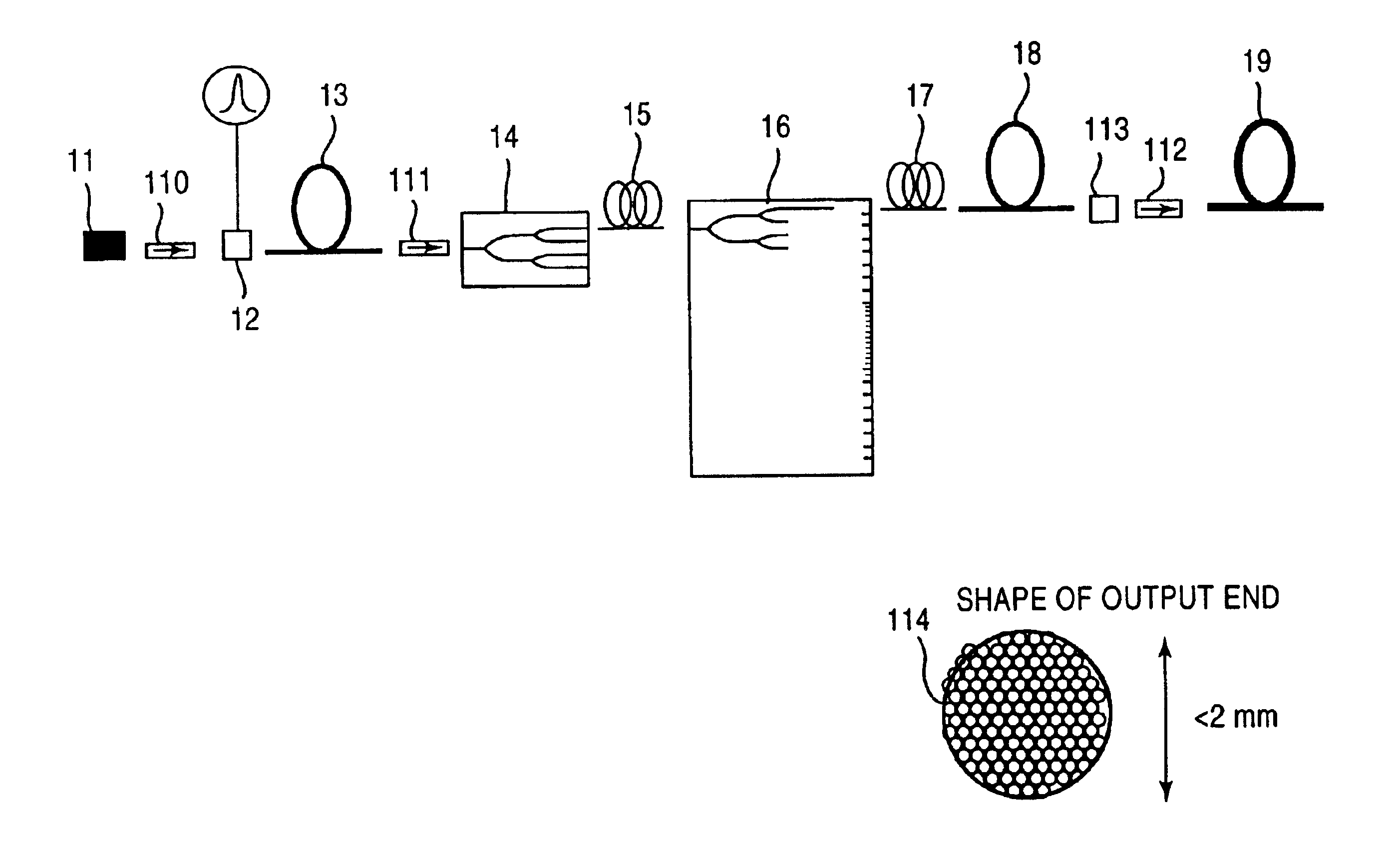
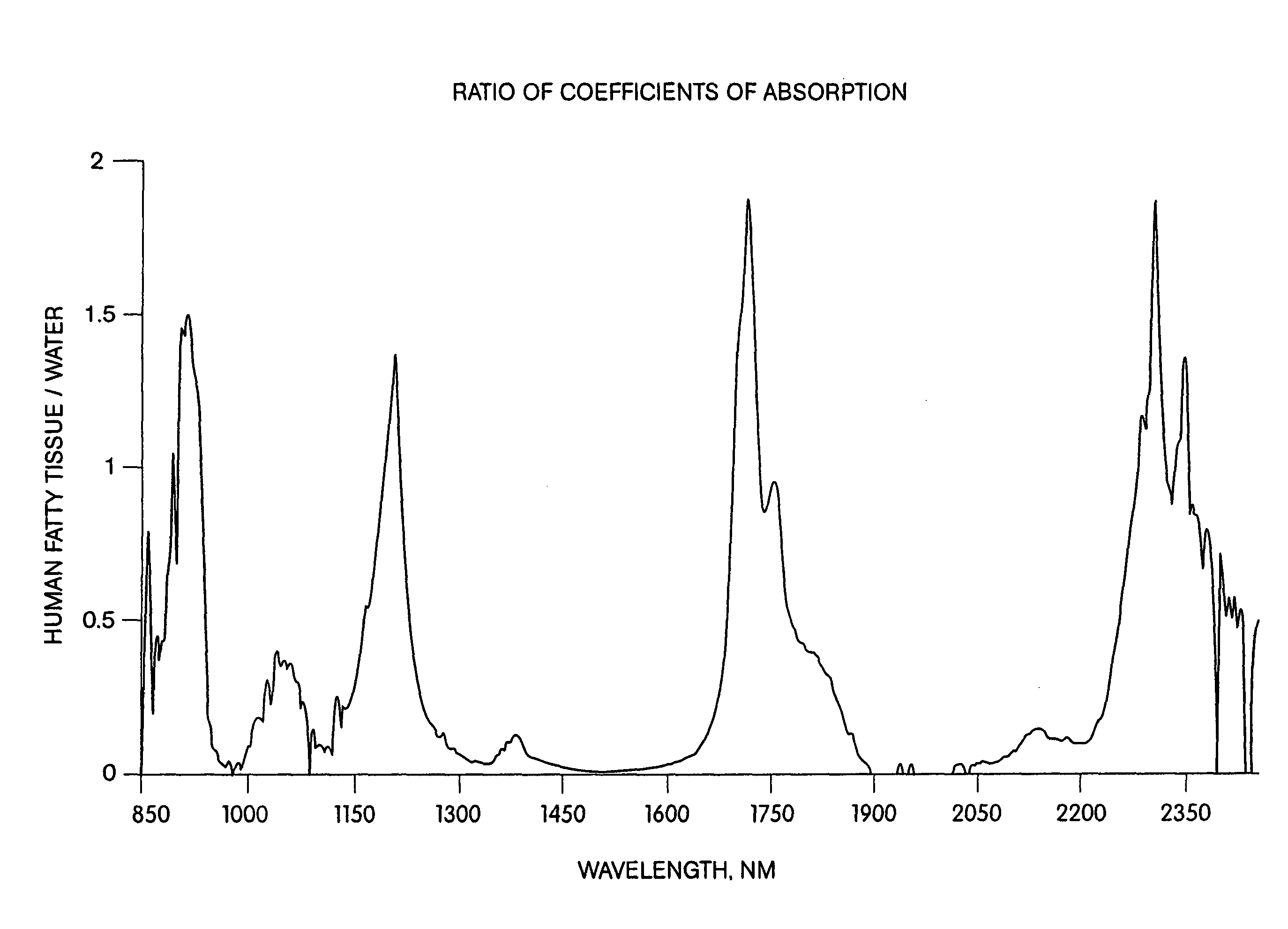
Method and apparatus for the selective targeting of lipid-rich tissues
InactiveUS7060061B2Desired treatmentSufficient durationSurgical instrument detailsSurgical pincettesHair removalLipid formation
A method and apparatus are provided for targeting lipid-rich tissue to effect a desired, the method / apparatus involving irradiating the lipid-rich tissue with energy at a wavelength preferentially absorbed by lipid cells, such wavelength being preferably in a band between 880 nm and 935 nm, 1150 nm and 1230 nm, 1690 nm to 1780 nm, or 2250 nm to 2450 nm with a fluence and duration sufficient to achieve a desired treatment. For preferred embodiments, the irradiation wavelength is between 900–930 nm, 1190–1220 nm, 1700–1730 nm, or 2280–2350 nm. The method and apparatus may for example be used to target one or more sebaceous glands for the treatment of acne or hair removal, to target subcutaneous fat for removal thereof or for targeting fat on anatomical elements for various purposes.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
Low cost multi-beam, multi-band and multi-diversity antenna systems and methods for wireless communications
ActiveUS7075485B2Low costImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandCommunications system
Systems and methods for employing switched phase shifters and a feed network to provide a low cost multiple beam antenna system for wireless communications. The present systems and methods may also facilitate multi-band communications and employ multi-diversity. The present systems and methods allow communication systems to achieve enhanced performance for communication or other services such as location tracking. The present systems and methods may employ switched phase shifters, multiple diversity antennas and / or a feed network having a multi-layer construction to provide an antenna system with low losses, low external component count and / or which is thin and compact.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Integrated traffic surveillance apparatus
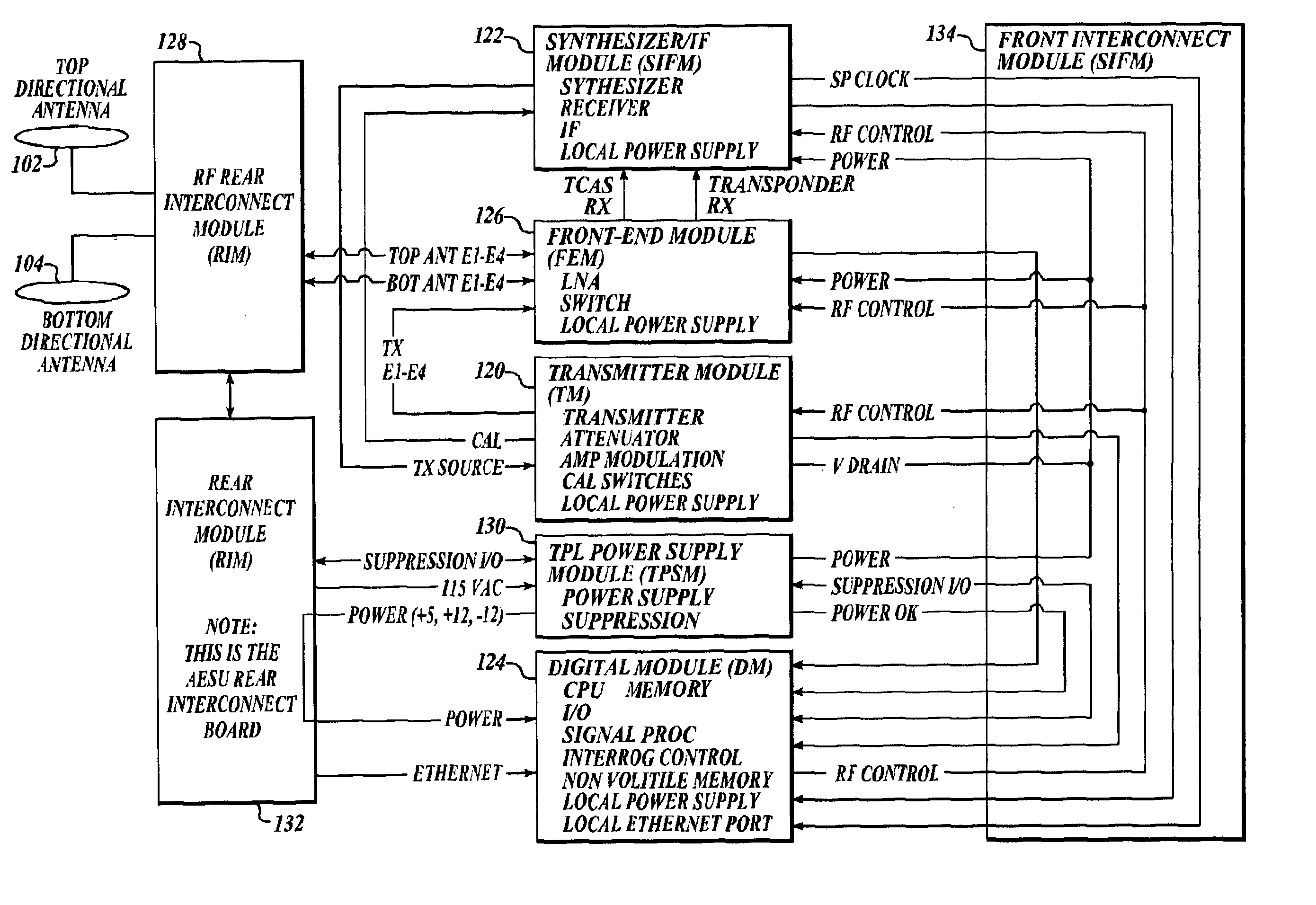
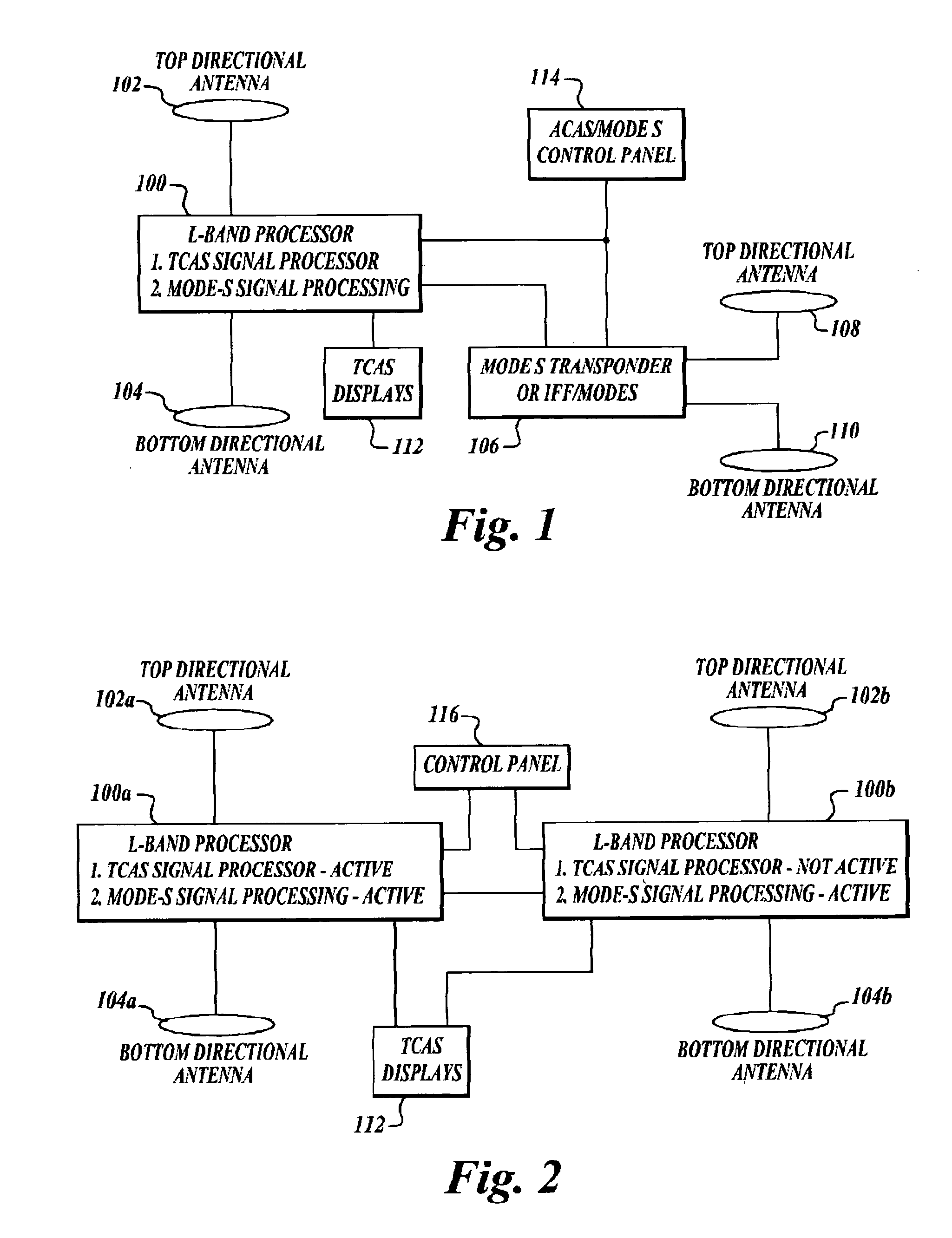
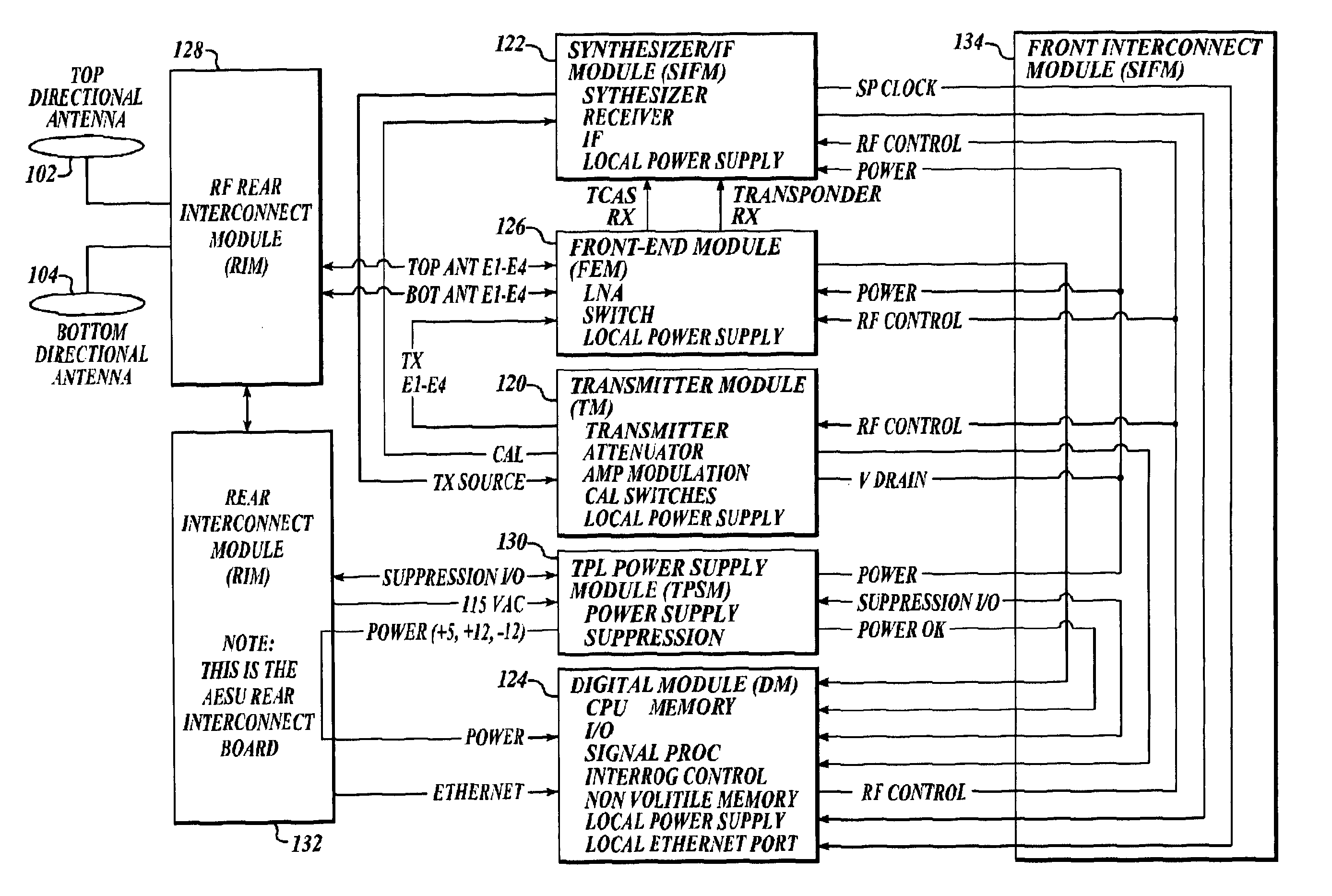
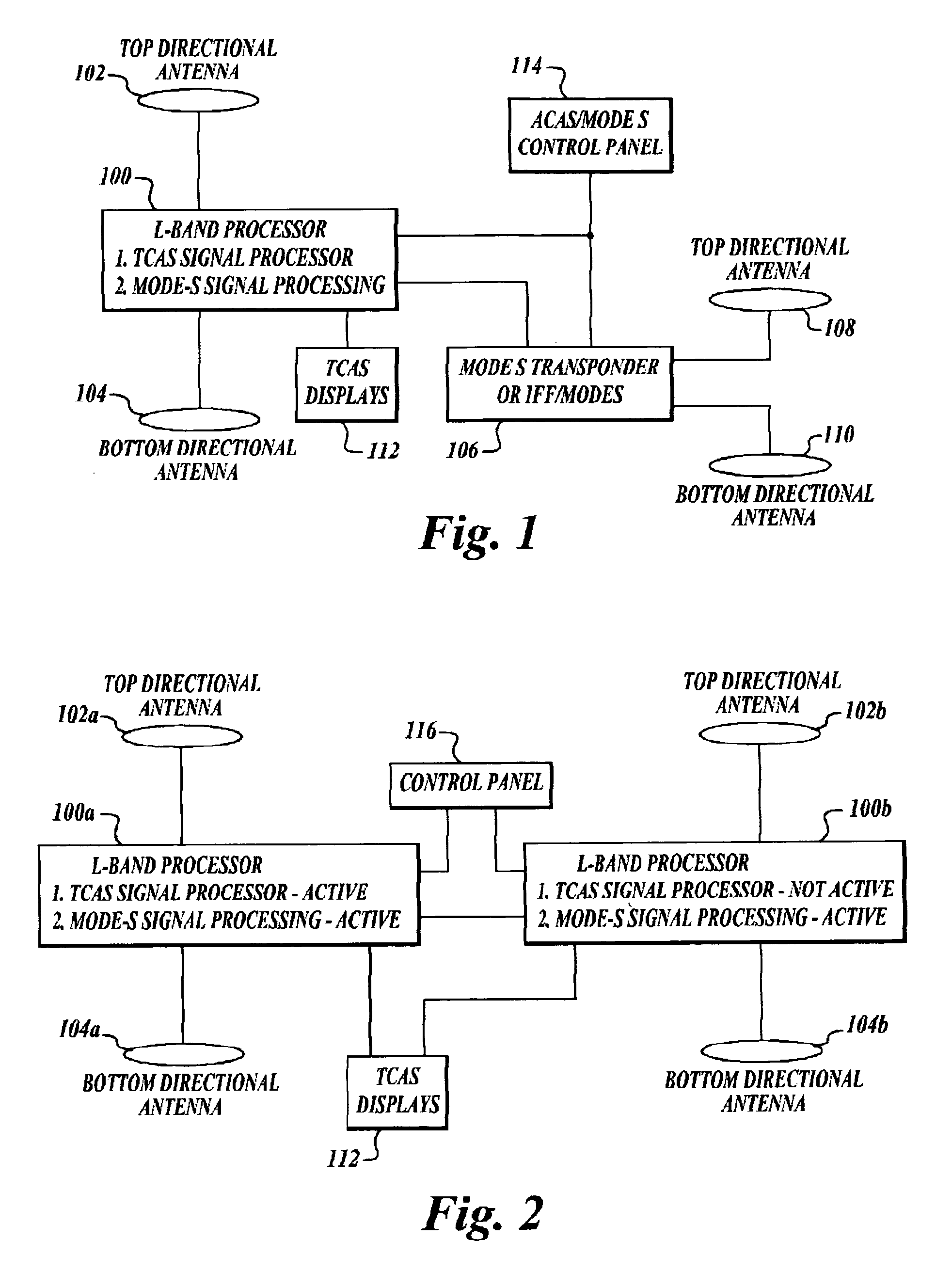
ActiveUS20050156777A1Improve reliabilityReduce weightRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadio wave finder monitoring/testingMonitoring systemEngineering
An apparatus and method for combining the functionality of multiple airborne traffic surveillance systems that operate in the L-band frequency range. The apparatus and method combine the functionality of both a Traffic Alert Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) and a Mode-Select (Mode-S) transponder in an integrated L-band traffic surveillance apparatus having a single processor that is embodied in a single Line Replaceable Unit.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
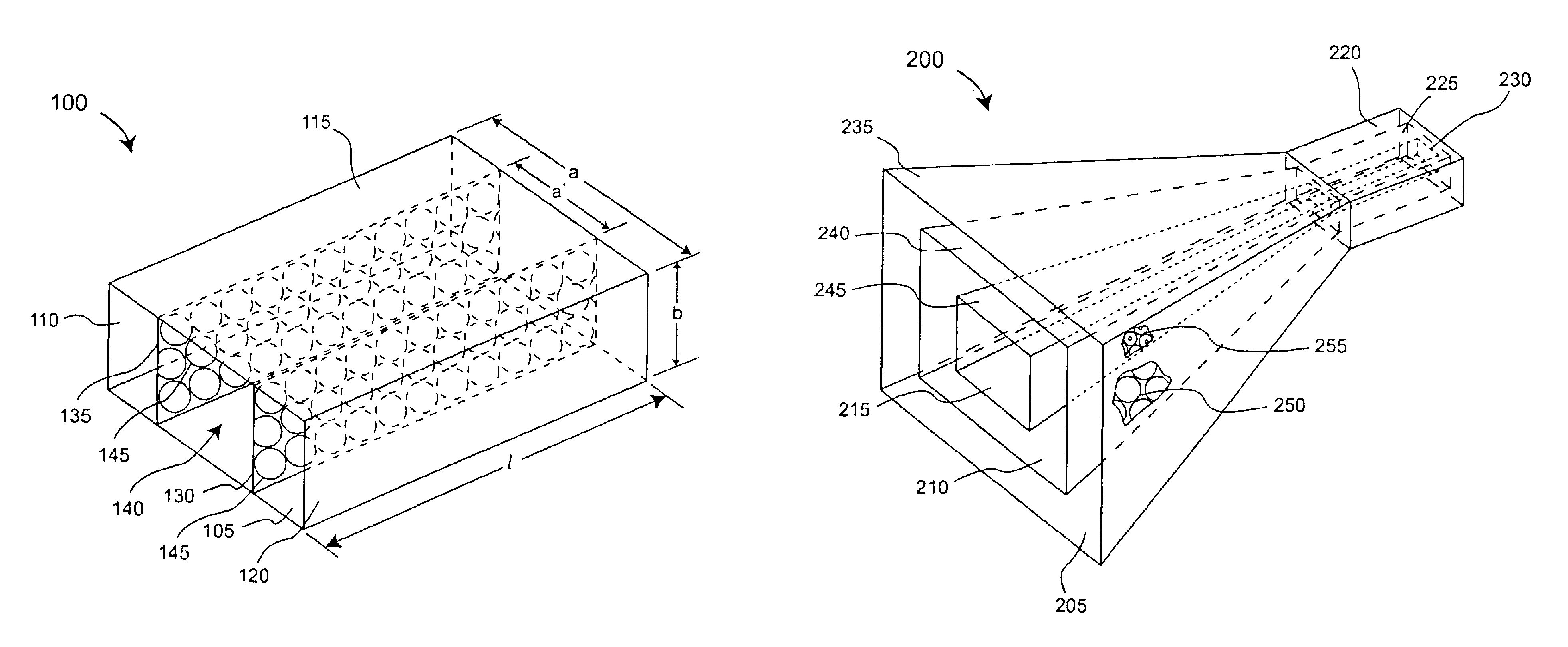
Multi-band horn antenna using frequency selective surfaces
InactiveUS6985118B2Grating lobe of the antenna is reducedImprove permeabilityWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsMulti bandHorn antenna
A waveguide (100) including at least one outer surface (105, 110, 115, 120) defining a waveguide cavity (140) and at least one inner surface (130, 135) positioned within the waveguide cavity (140). The inner surface (130, 135) includes a frequency selective surface (FSS) having a plurality of FSS elements (145) coupled to at least one substrate. The substrate defines a first propagation medium such that an RF signal having a first wavelength in the first propagation medium can pass through the FSS (130, 135). The FSS (130, 135) is coupled to a second propagation medium such that in the second propagation medium the RF signal has a second wavelength which is at least twice as long as a physical distance between centers of adjacent FSS elements (145). The second wavelength can be different than the first wavelength.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
FSS feeding network for a multi-band compact horn
A feed structure (105) for a horn antenna (100). The feed structure can include a first waveguide (110) and a second waveguide (115) having a first portion at least partially disposed within the first waveguide. The second waveguide also can include a second portion intersecting a first wall (240) of the first waveguide. The first wall can include a first frequency selective surface (244) at an intersection (280) of the first wall and the second portion of the second waveguide. The first waveguide can be operatively coupled to a first horn section (130) and the second portion can be operatively coupled to a second horn section (135).
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Small wave-guide radiators for closely spaced feeds on multi-beam antennas
Owner:PRO BRAND INT
Integrated traffic surveillance apparatus
ActiveUS7006032B2Improve reliabilityReduce weightRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadio wave finder monitoring/testingMonitoring systemEngineering
An apparatus and method for combining the functionality of multiple airborne traffic surveillance systems that operate in the L-band frequency range. The apparatus and method combine the functionality of both a Traffic Alert Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) and a Mode-Select (Mode-S) transponder in an integrated L-band traffic surveillance apparatus having a single processor that is embodied in a single Line Replaceable Unit.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
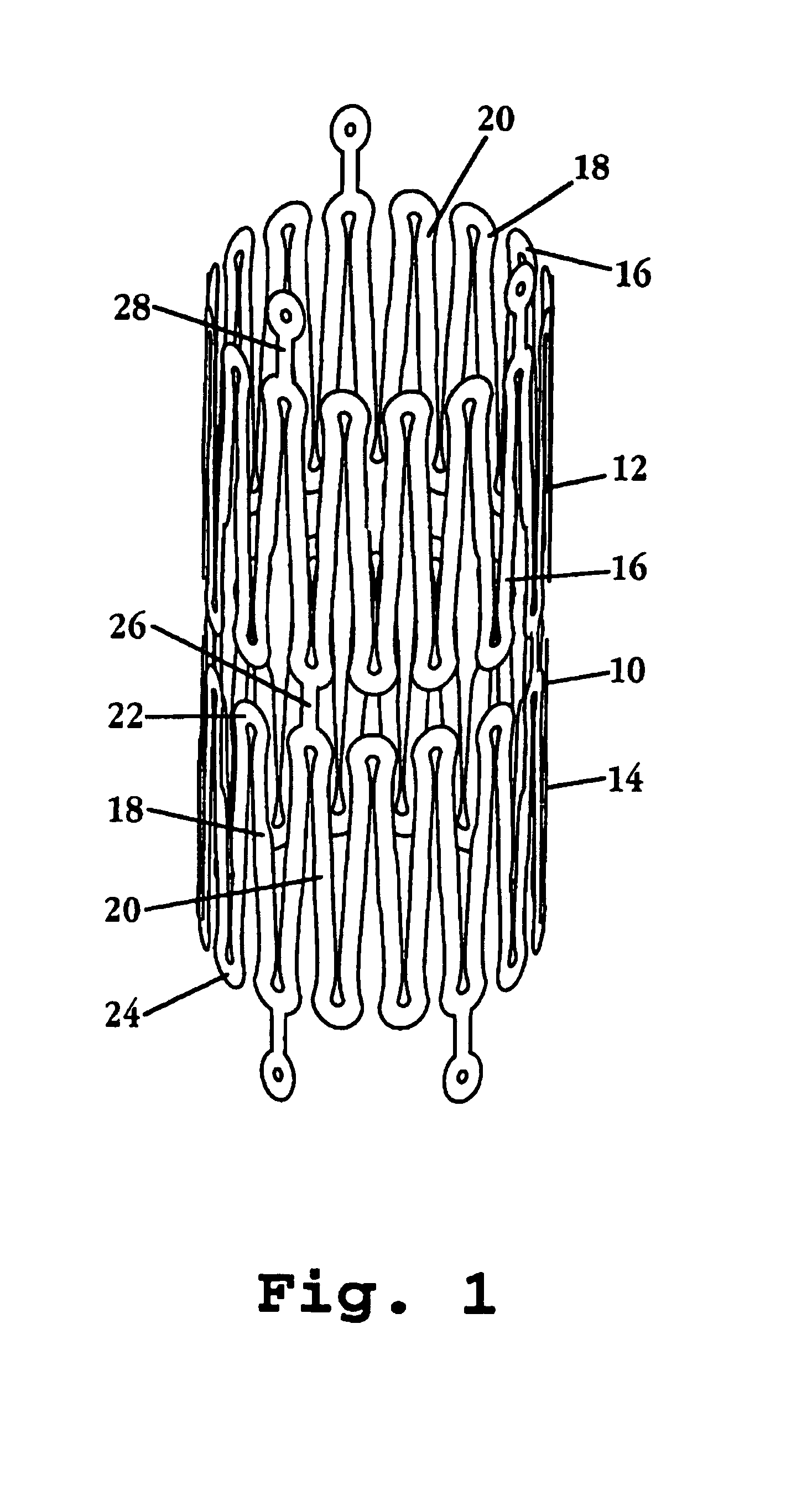
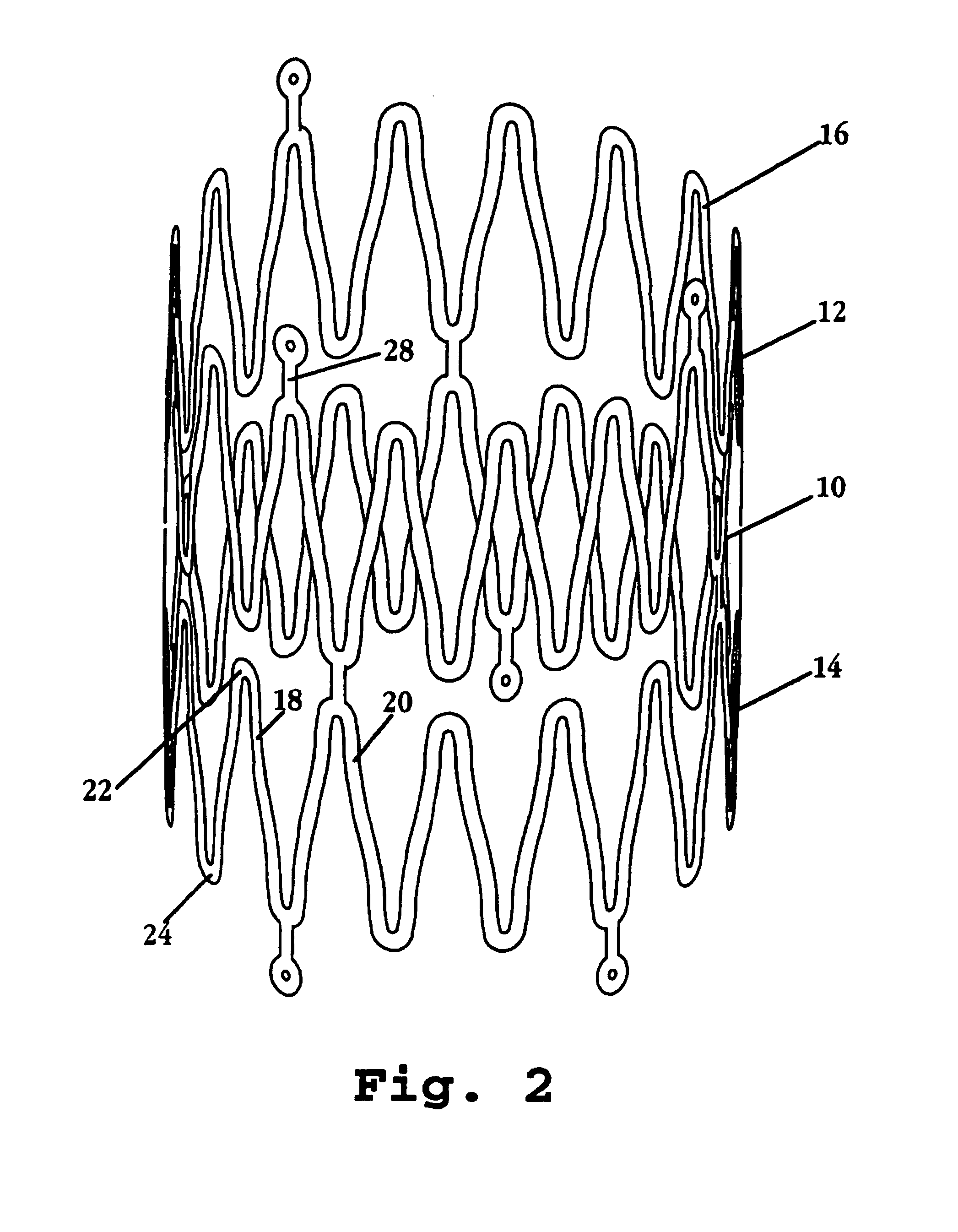
Neurovascular stent and method
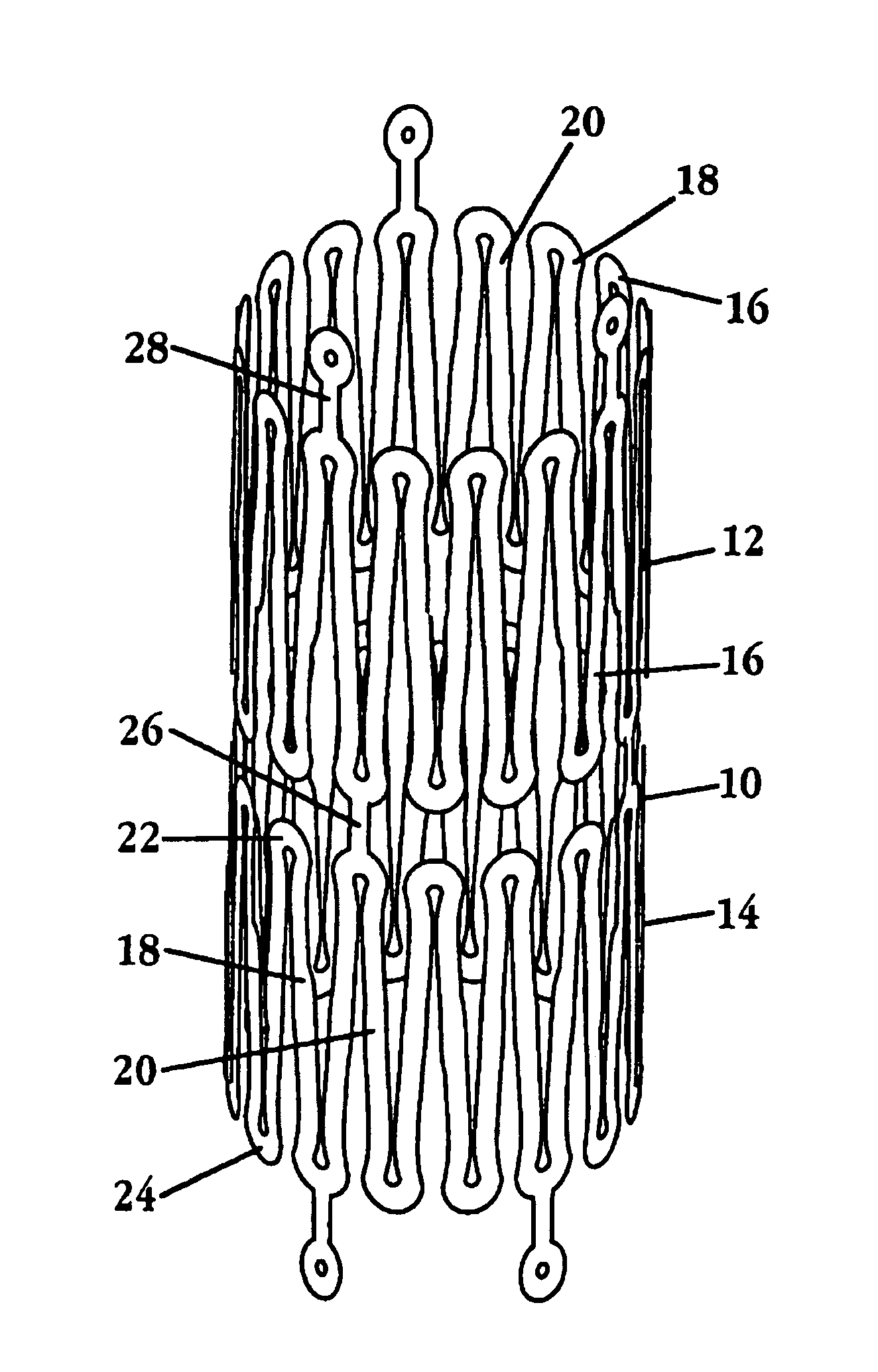
A stent designed for catheter delivery to a target neurovascular site via a tortuous path, in a contracted state, and deployment at the target site, in an expanded state, is disclosed. The stent includes a plurality of expandable tubular members, where member is composed of a continuous wire element forming a plurality of wave segments, and segment contains a pair of opposite looped peaks having a wave shape such that the distance between adjacent sides of a wave, on proceeding from a peak toward opposite peaks, increases monotonically with an inflection point therebetween. The expandable tubular members are joined through adjacent peaks by axial connectors Radial expansion of the stent from a contracted to expanded state is accommodated by movement of adjacent wave-segment peaks away from one another, without significant change in the axial dimension of the stent. Also disclosed are a system incorporating the stent, and a method of treating a neurovascular abnormality.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
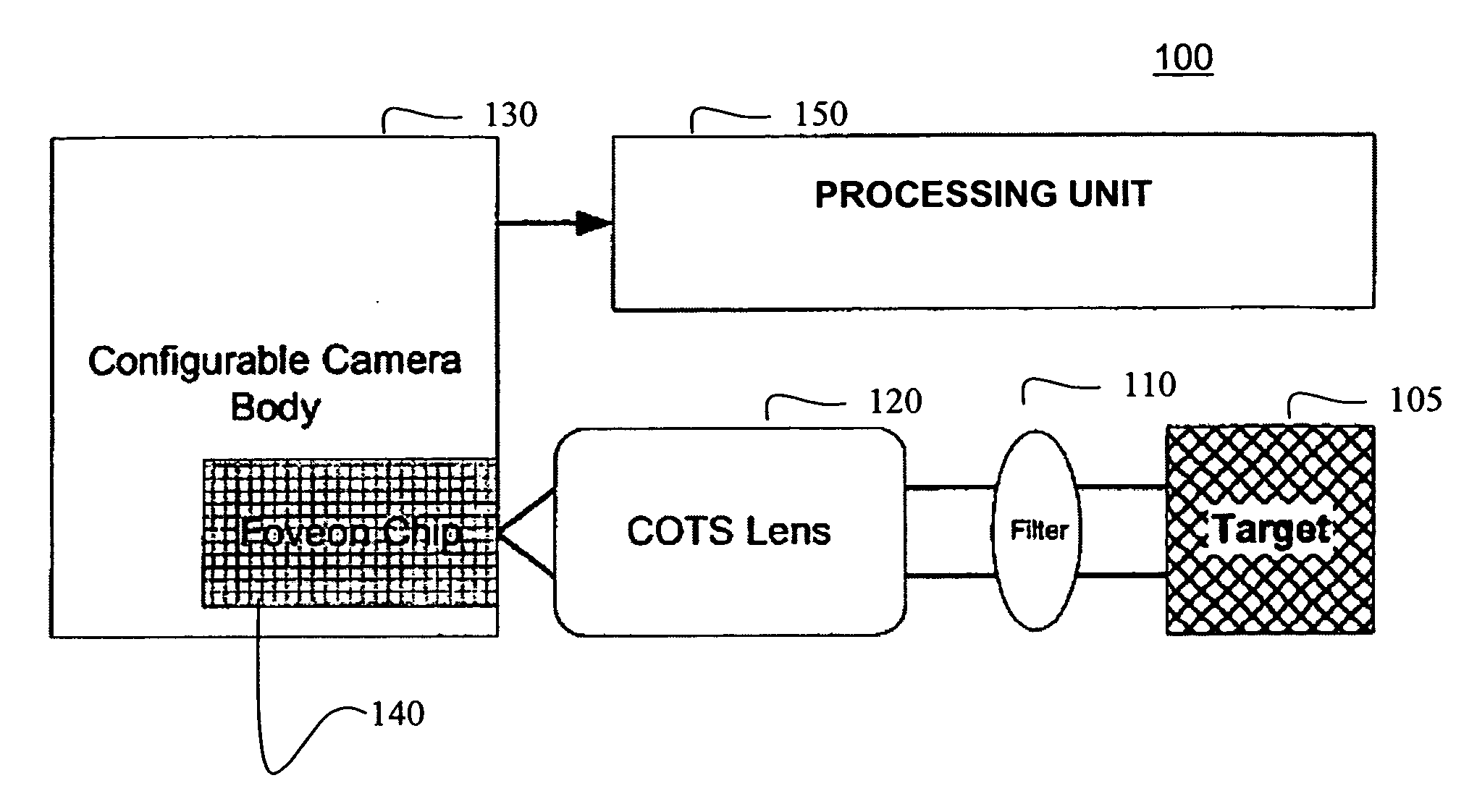
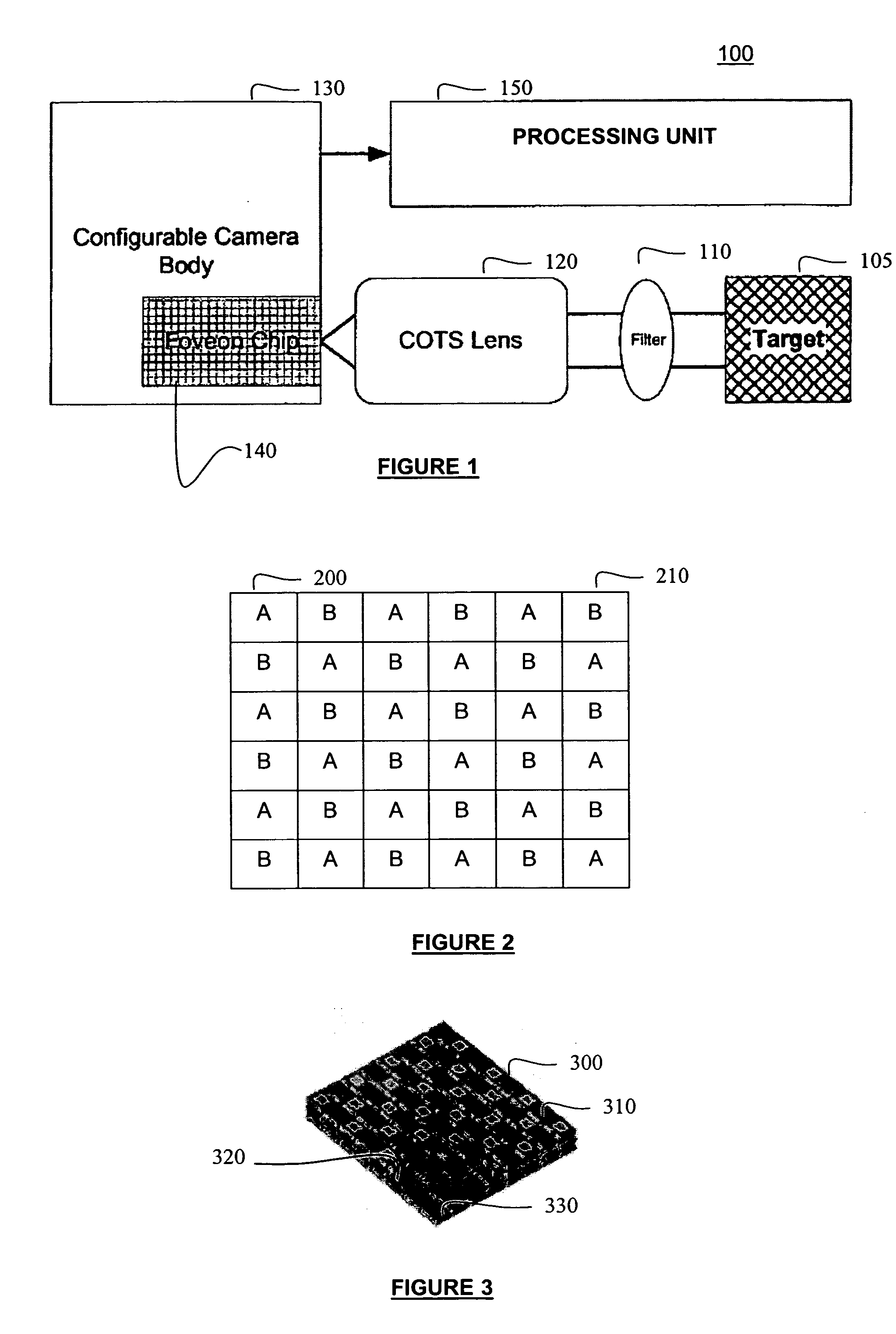
Single camera multi-spectral imager
ActiveUS20070159541A1Improve discriminationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMulti bandSpectral bands
An imaging system has a single focal plane array that does not require the precise alignment of multiple cameras relative to one another. It incorporates a multi-band, band pass filter that includes filter elements corresponding to pixel regions of a detector within a camera. The imaging system may further incorporate a detector that vertically discriminates among radiation in different spectral bands incident on an image plane of the detector. In this manner, spectral content may be determined in each spatial region without the need for beam splitting or multiple cameras. The filter itself may further comprise different filter elements, for example, filter elements A and B arranged in a checkerboard pattern, where filter element A passes different spectral bands than filter element B. In this manner, multi-spectral, high resolution images may be generated using a single camera that significantly improves upon image discrimination as compared to, for example, the Bayer color filter array pattern. The single camera implementation is well suited for incorporation into marine, land and air vehicles.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Dual feel multi-band planar antenna
InactiveUS6670923B1Reduce Design ComplexityCompromise performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandPlanar inverted f antenna
A three-band, two-antenna, assembly includes a planar inverted-F antenna (PIFA) having a radiating / receiving element that is spaced from and extends generally parallel to a ground plane element. The planar radiating / receiving element of an inverted-F antenna (IFA) is located in an open space that exists between the radiating / receiving element of the PIFA and the ground plane element. The radiating / receiving element of the IFA extends either perpendicular to, or parallel to, the radiating / receiving element of the PIFA. The radiating / receiving element of the PIFA includes one or more open slot configurations that operate to provide dual resonant frequencies for the IPFA (AMPS / PCS or GSM / DCS). The radiating / receiving element of the IFA operates in a non-cellular frequency band (ISM or GPS).
Owner:LAIRD CONNECTIVITY LLC
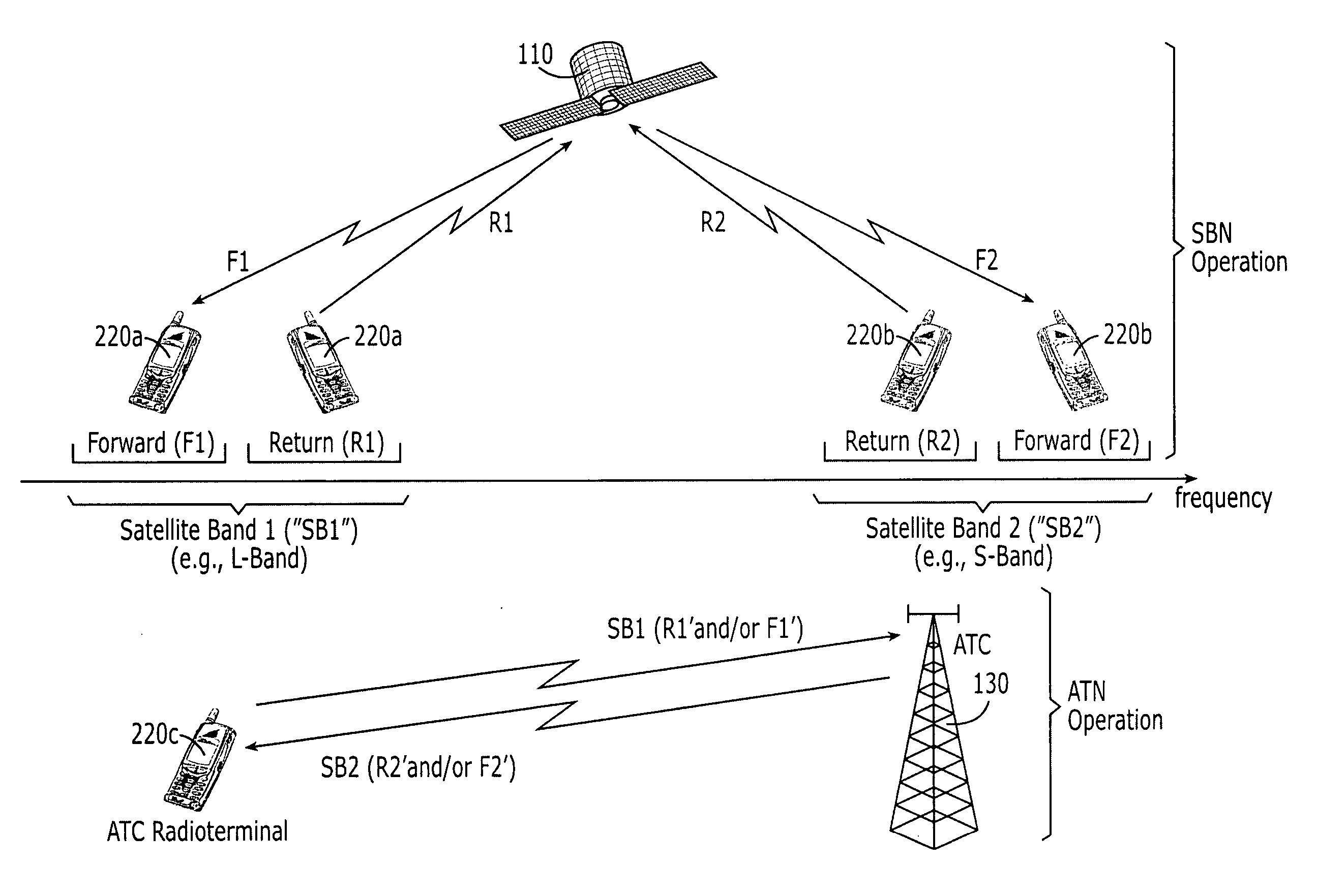
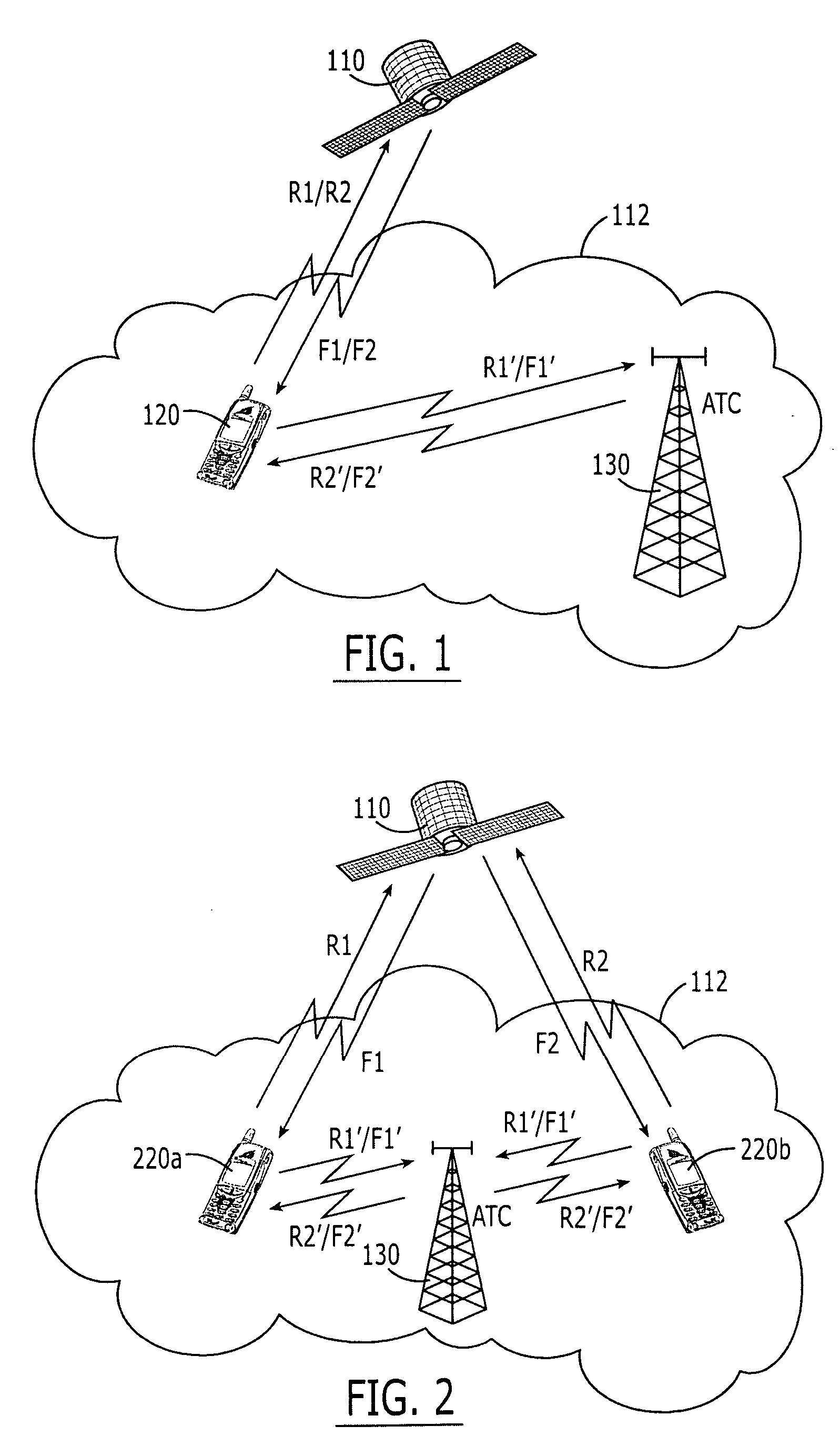
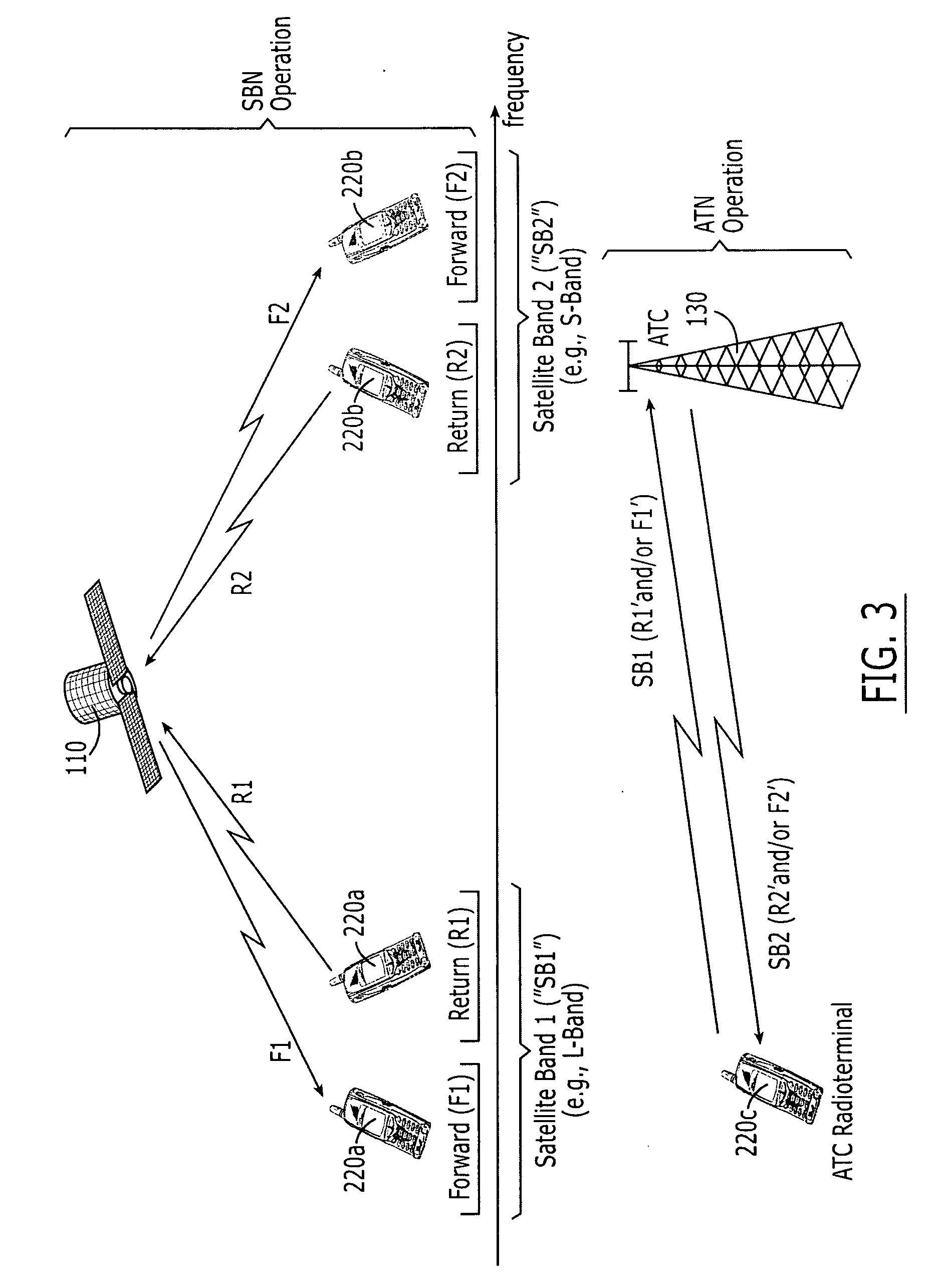
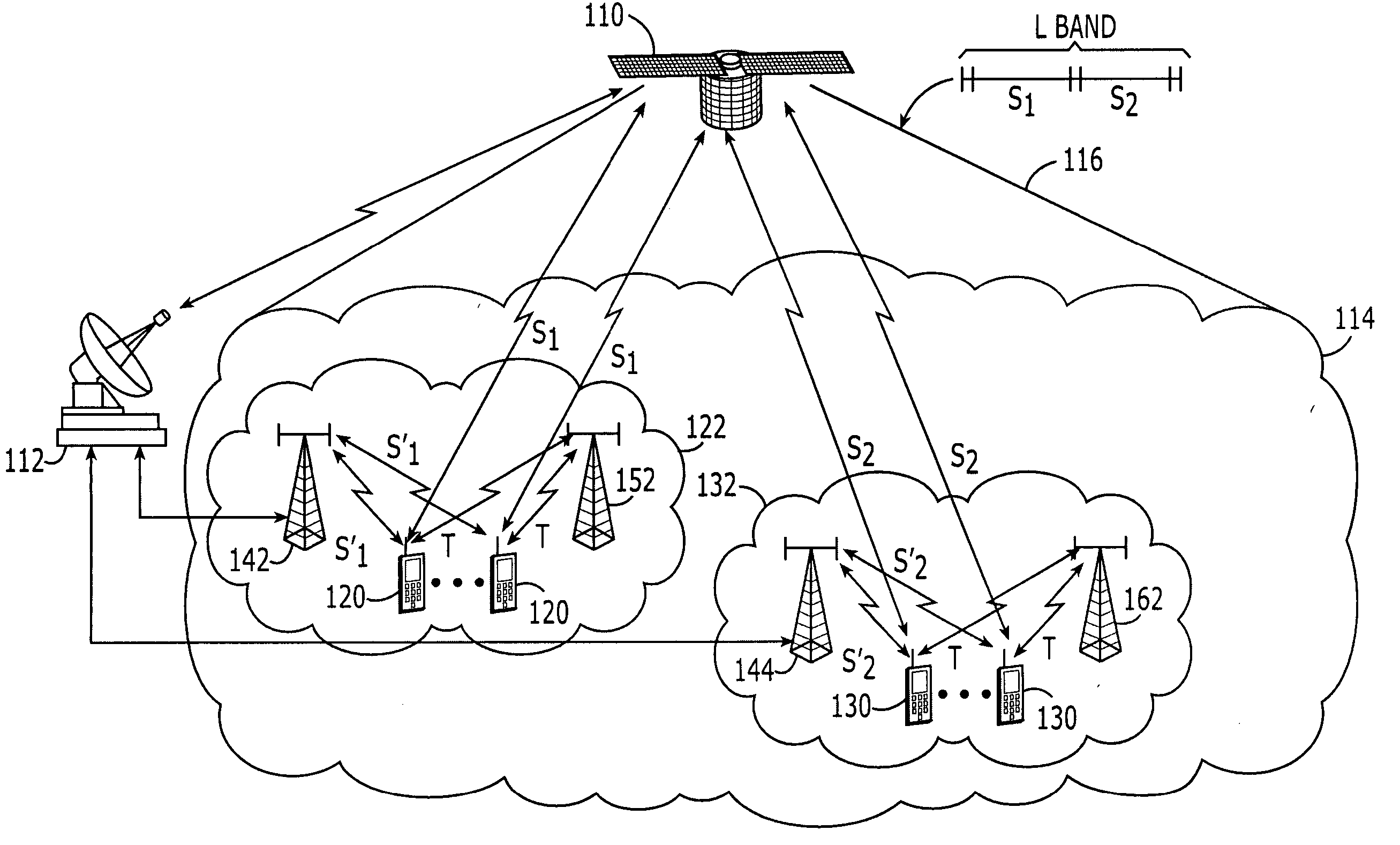
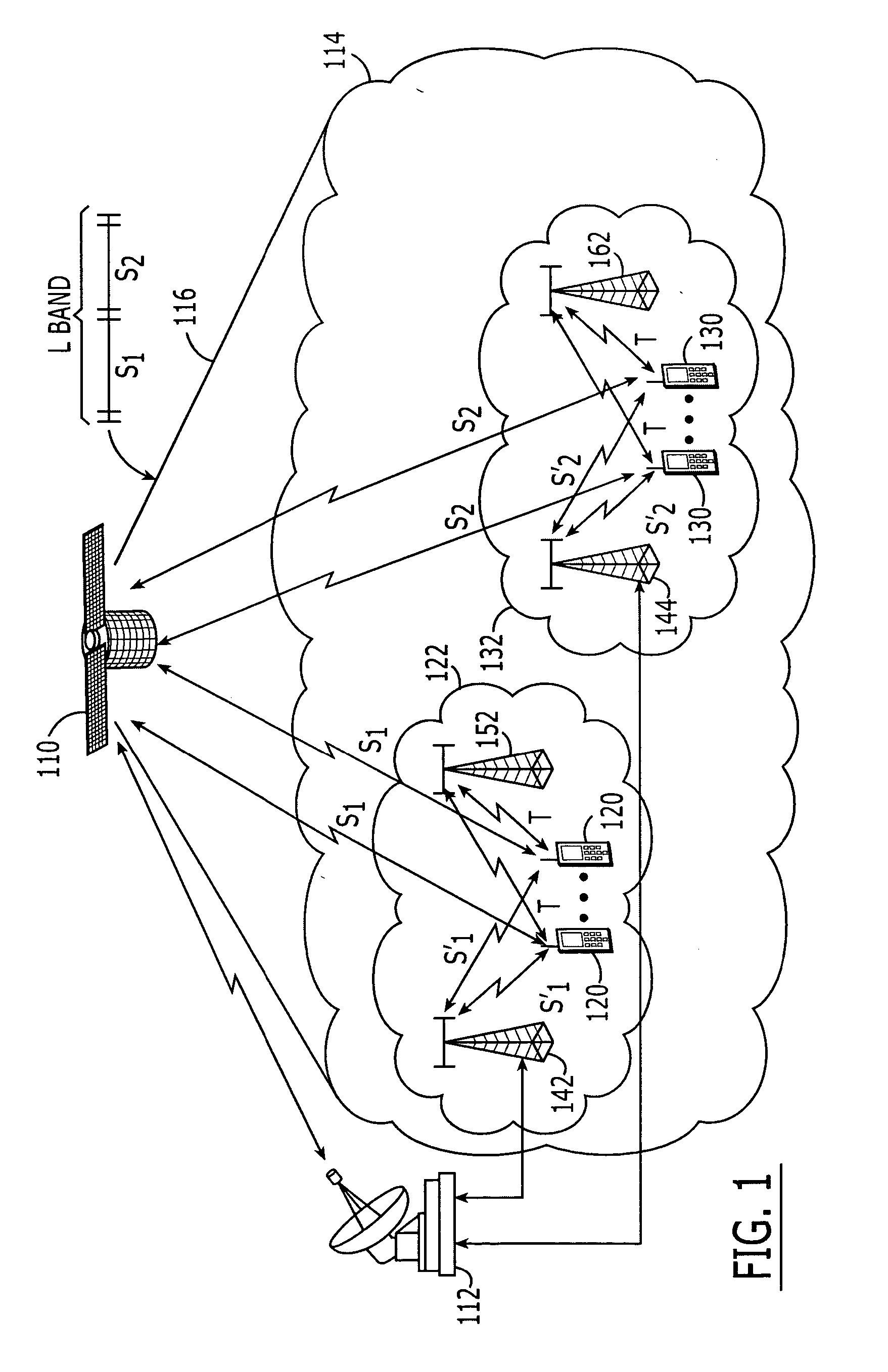
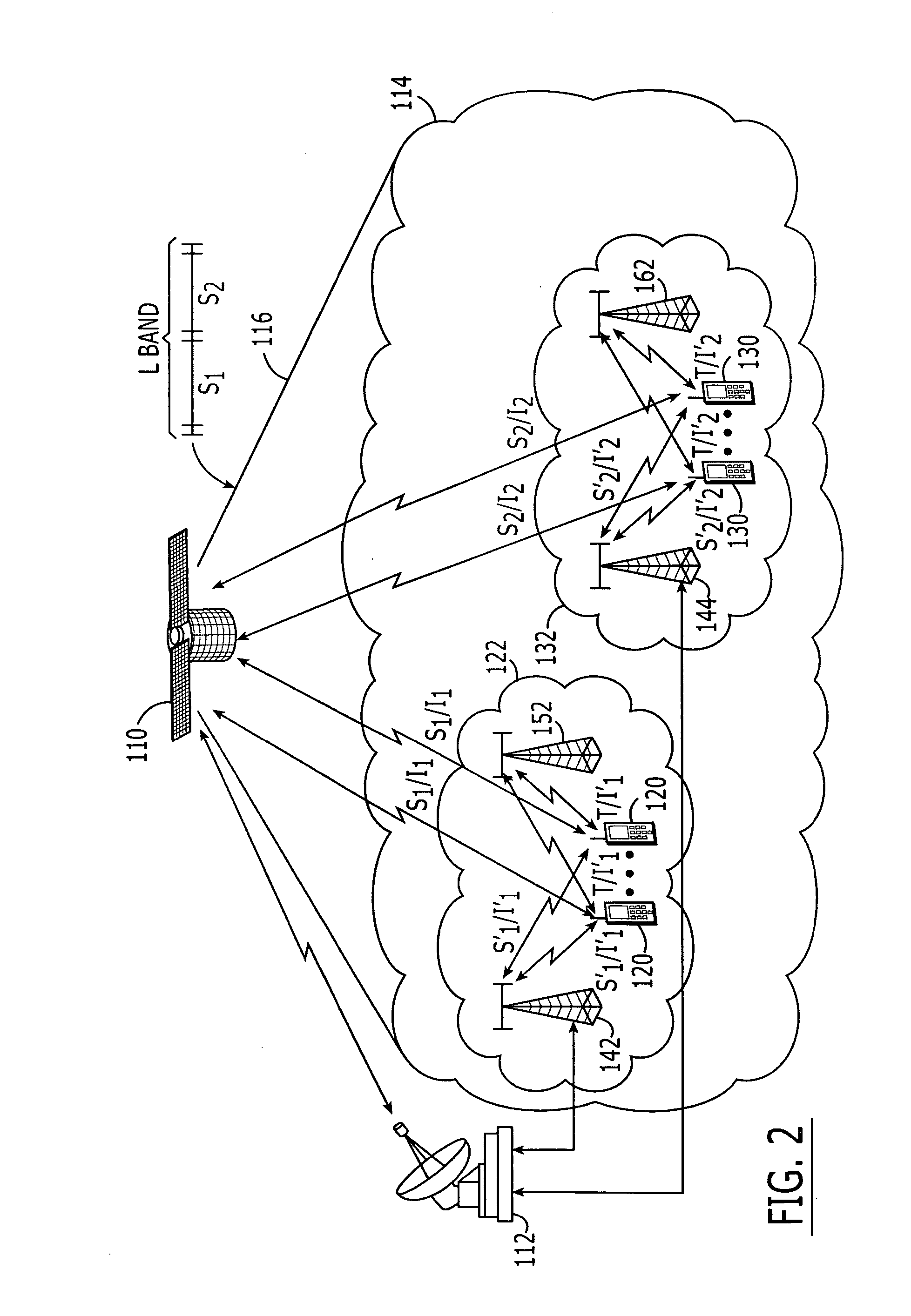
Systems and methods with different utilization of satellite frequency bands by a space-based network and an ancillary terrestrial network
ActiveUS20050239403A1Active radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemWave band
A radioterminal communications system includes an ancillary terrestrial component configured to receive from at least some of a plurality of radioterminals using frequencies from a first satellite frequency band (e.g., an L-band) and to transmit to at least some of the plurality of radioterminals using frequencies from a second satellite frequency band (e.g., an S-band). The system further includes a space-based component configured to communicate with the plurality of radioterminals using at least some of the frequencies from the first satellite frequency band and / or at least some of the frequencies from the second satellite frequency band. In some embodiments the ancillary terrestrial component communicates with radioterminals using a Time Division Duplex (TDD) mode and the space-based component communicates with the same or other radioterminals using a Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and / or a TDD mode.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Transmission/reception sources of electromagnetic waves for multireflector antenna
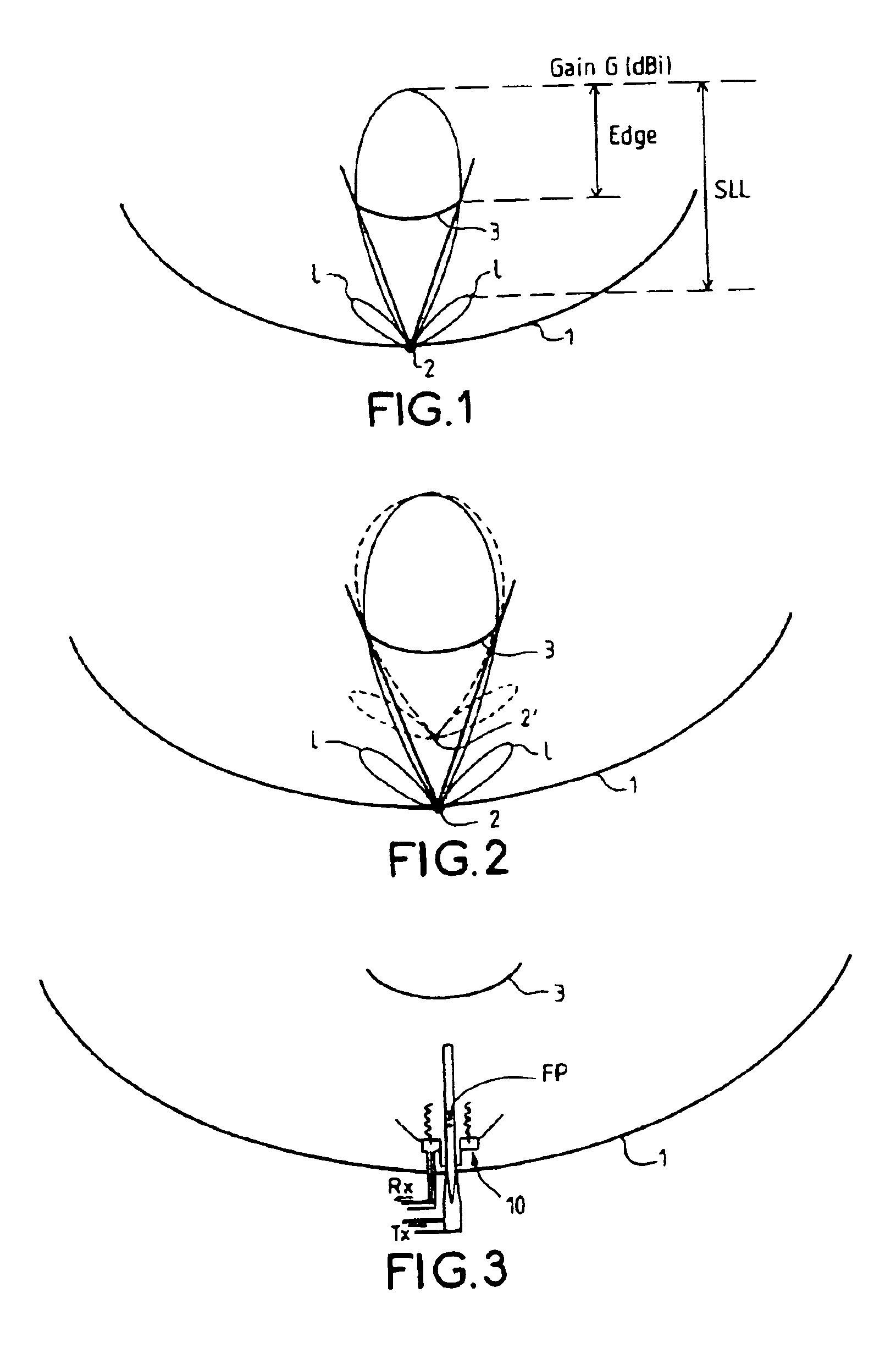
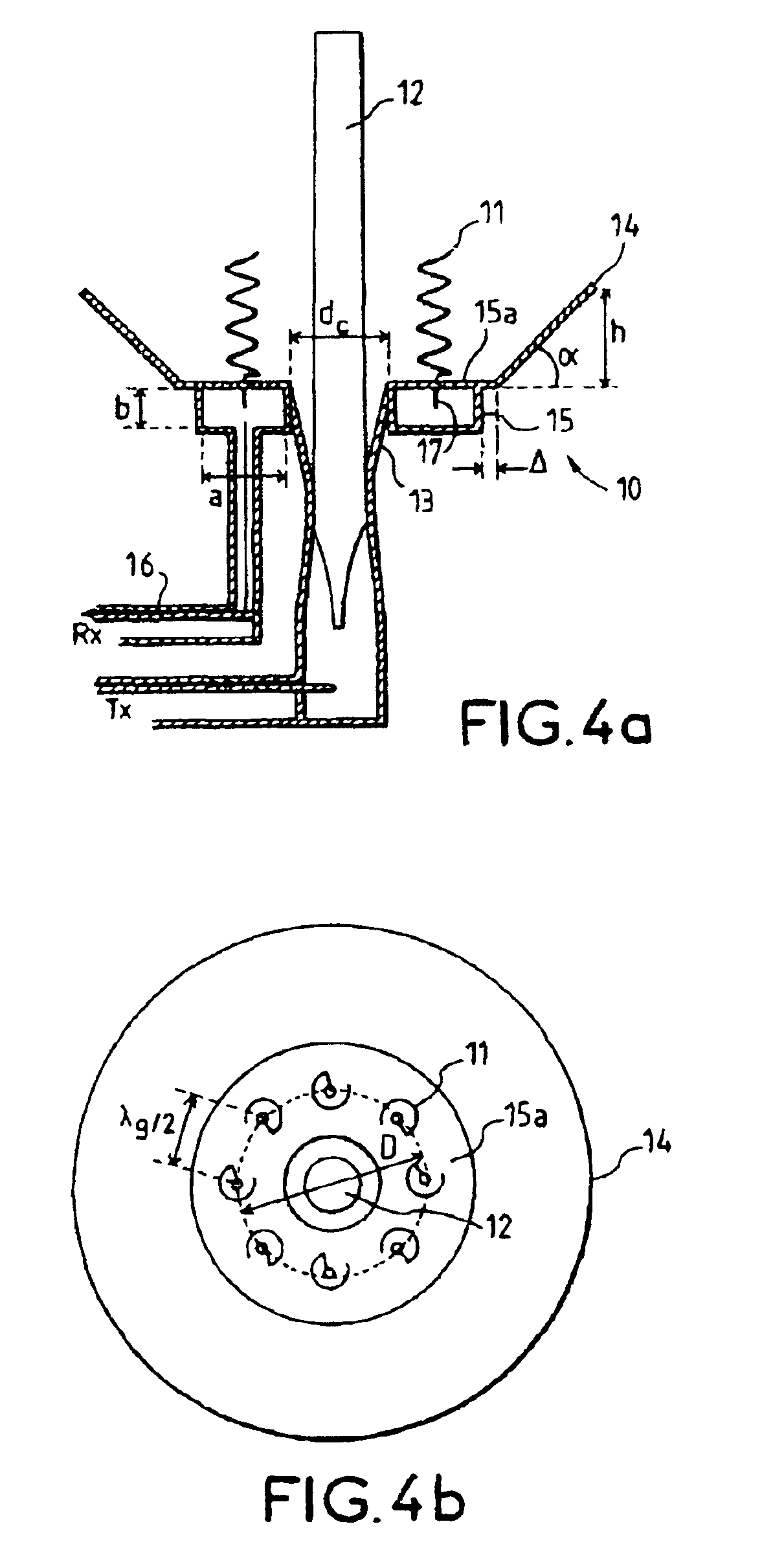
InactiveUS6861998B2Reduce sidelobeReducing side lobe level SLLLogperiodic antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsElectromagnetic wave transmissionWaveguide
The present invention relates to an electromagnetic wave transmission / reception source for a multireflector antenna of the Cassegrain type comprising longitudinal-radiation means operating in a first frequency band and an array of n radiating elements of the travelling-wave type operating in a second frequency band with the n radiating elements arranged symmetrically around the longitudinal-radiation means, the array and the longitudinal-radiation means having an approximately common phase centre, the array of n radiating elements being excited by a waveguide of polygonal cross section. The invention applies especially in satellite communication systems operating in the C-, Ku- or Ka-bands.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
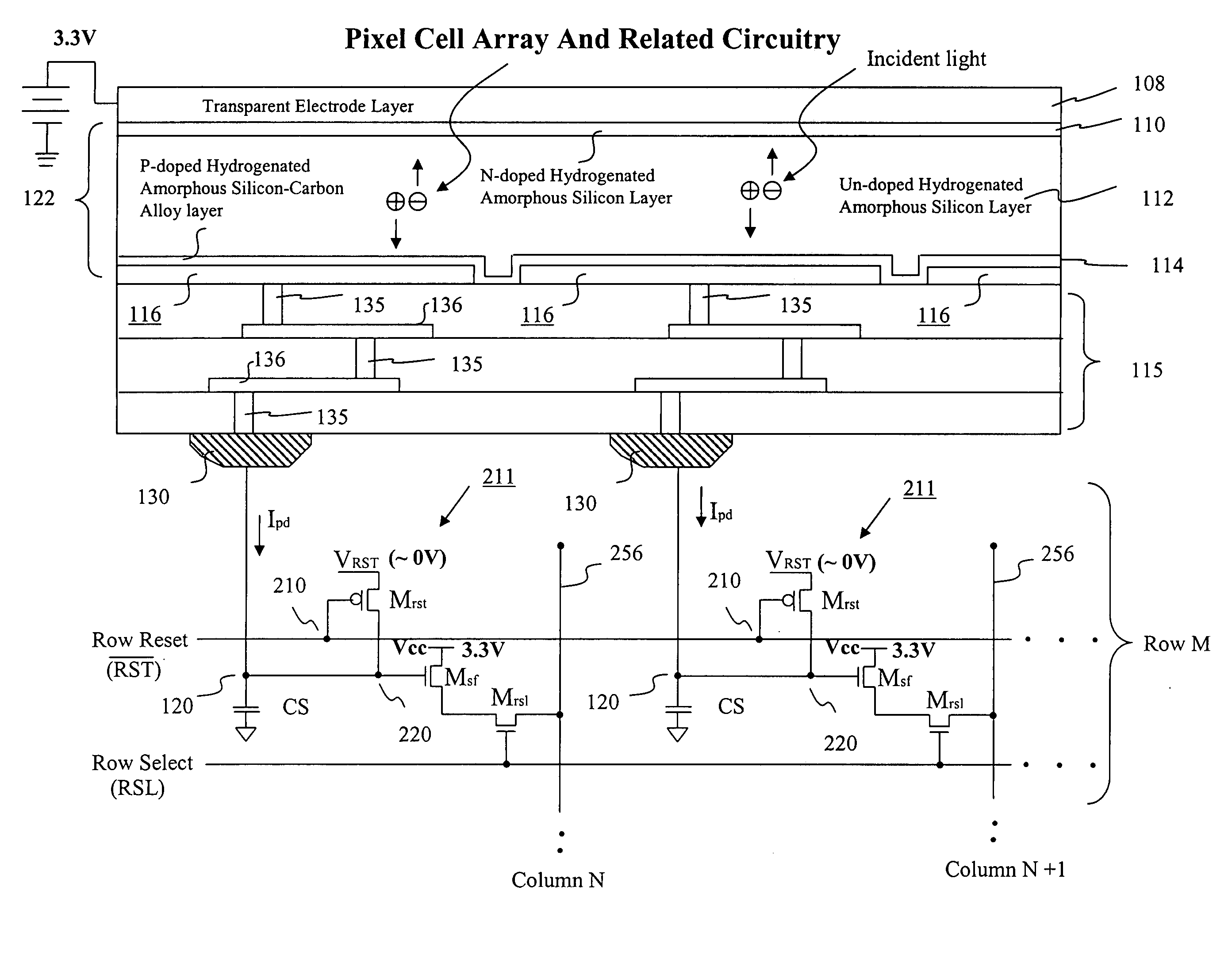
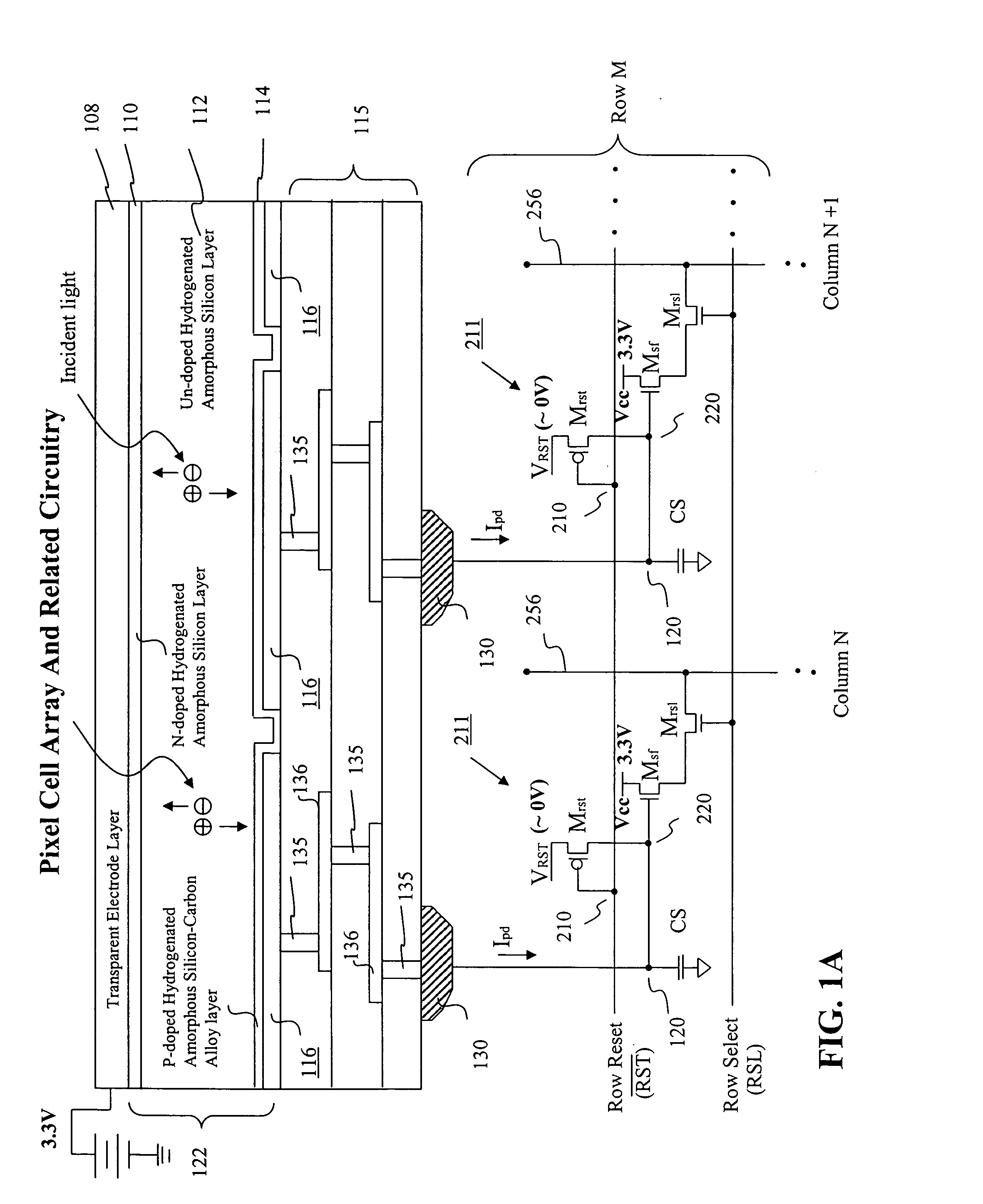
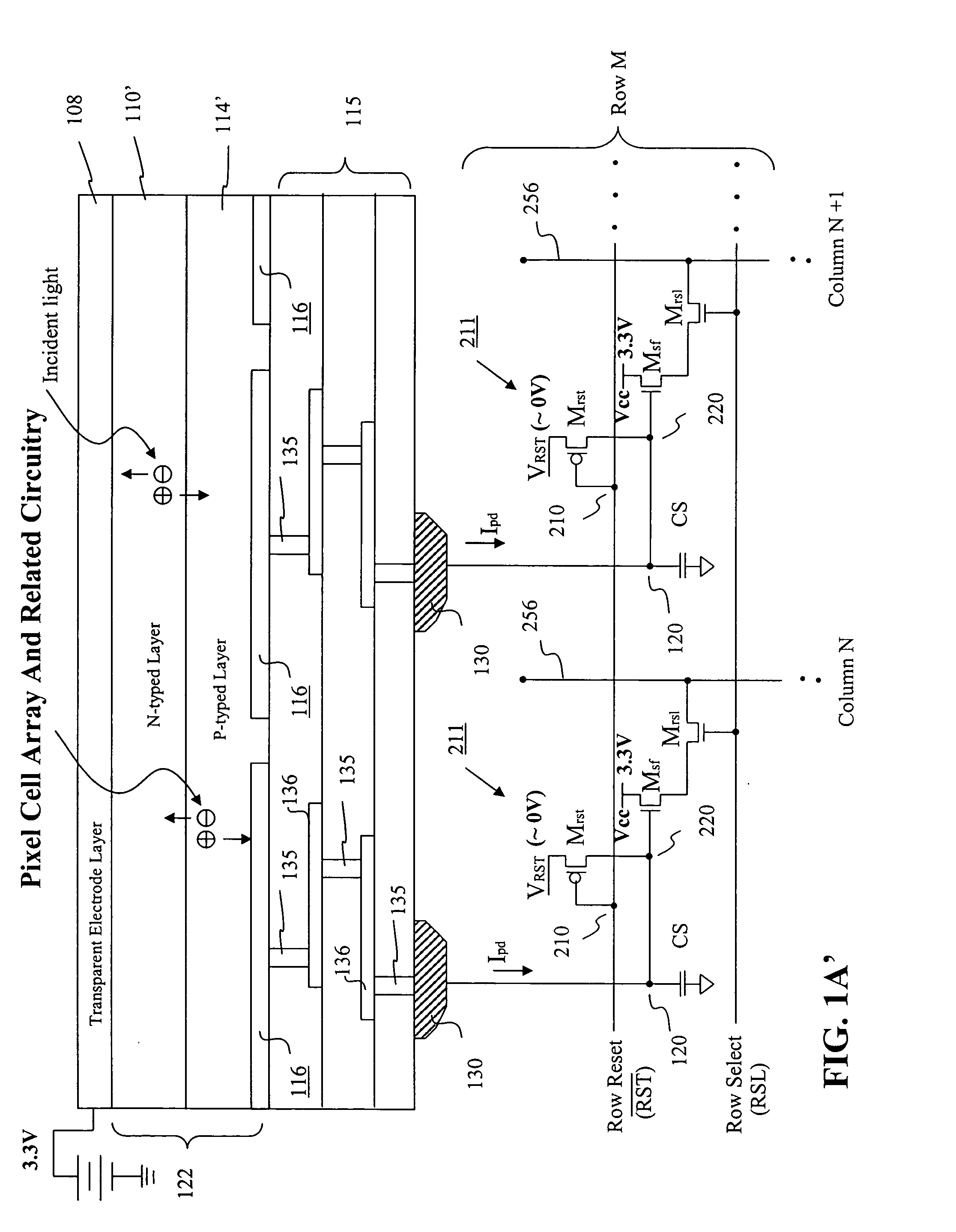
Visible/near infrared image sensor
InactiveUS20050104089A1Improve performanceHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow earth orbitBeam steering
A MOS or CMOS sensor for high performance imaging in broad spectral ranges including portions of the infrared spectral band. These broad spectral ranges may also include portions or all of the visible spectrum, therefore the sensor has both daylight and night vision capabilities. The sensor includes a continuous multi-layer photodiode structure on a many pixel MOS or CMOS readout array where the photodiode structure is chosen to include responses in the near infrared spectral ranges. A preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline copper indium diselenide / cadmium sulfide photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. An alternate preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline silicon germanium photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. Each of these embodiments provides night vision with image performance that greatly surpasses the GEN III night vision technology in terms of enhanced sensitivity, pixel size and pixel count. Further advantages of the invention include low electrical bias voltages, low power consumption, compact packaging, and radiation hardness. In special preferred embodiments CMOS stitching technology is used to provide multi-million pixel focal plane array sensors. One embodiments of the invention made without stitching is a two-million pixel sensor. Other preferred embodiments available using stitching techniques include sensors with 250 million (or more) pixels fabricated on a single wafer. A particular application of these very high pixel count sensors is as a focal plane array for a rapid beam steering telescope in a low earth orbit satellite useful for tracking over a 1500-meter wide track with a resolution of 0.3 meter.
Owner:C PHOCUS
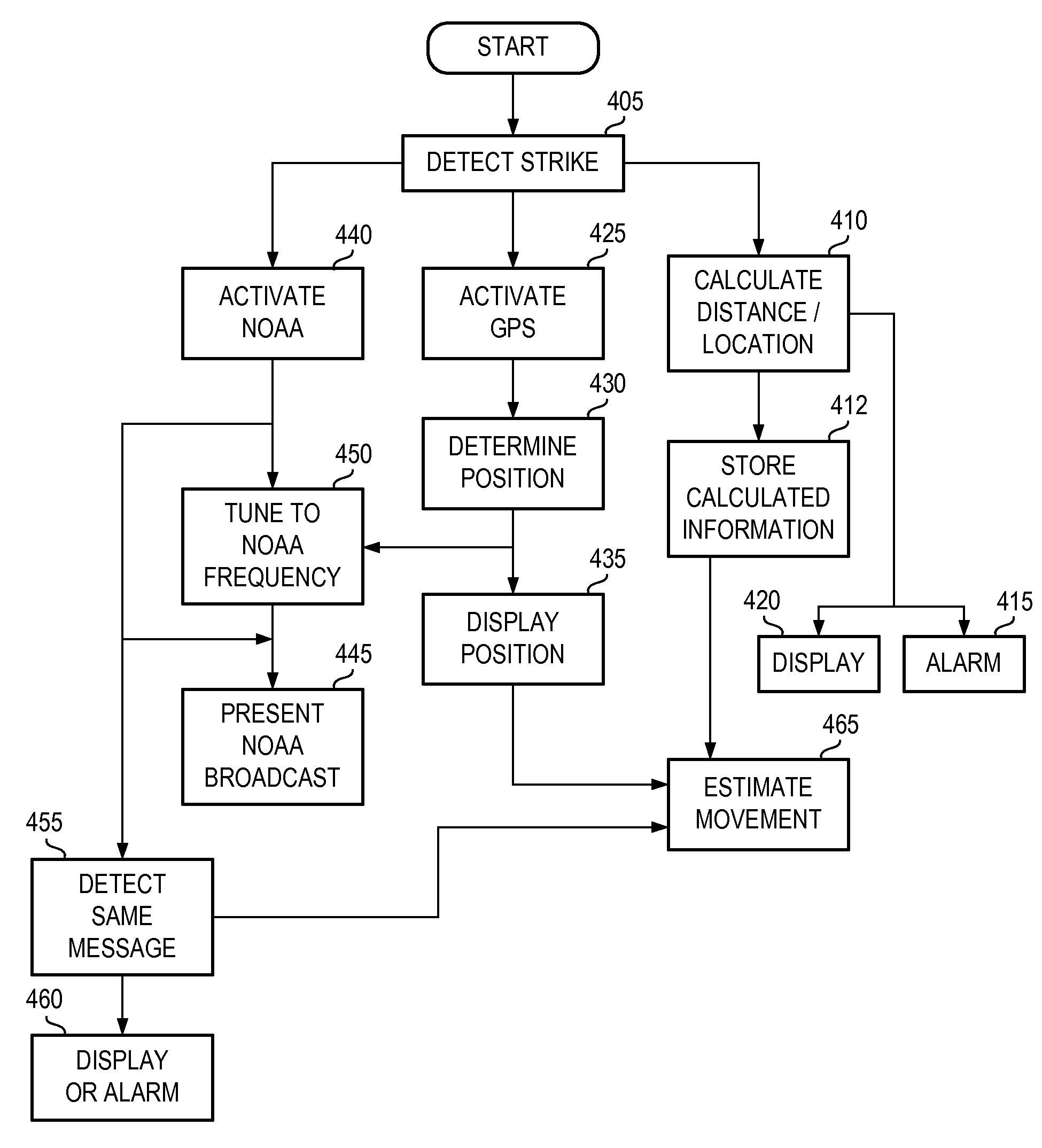
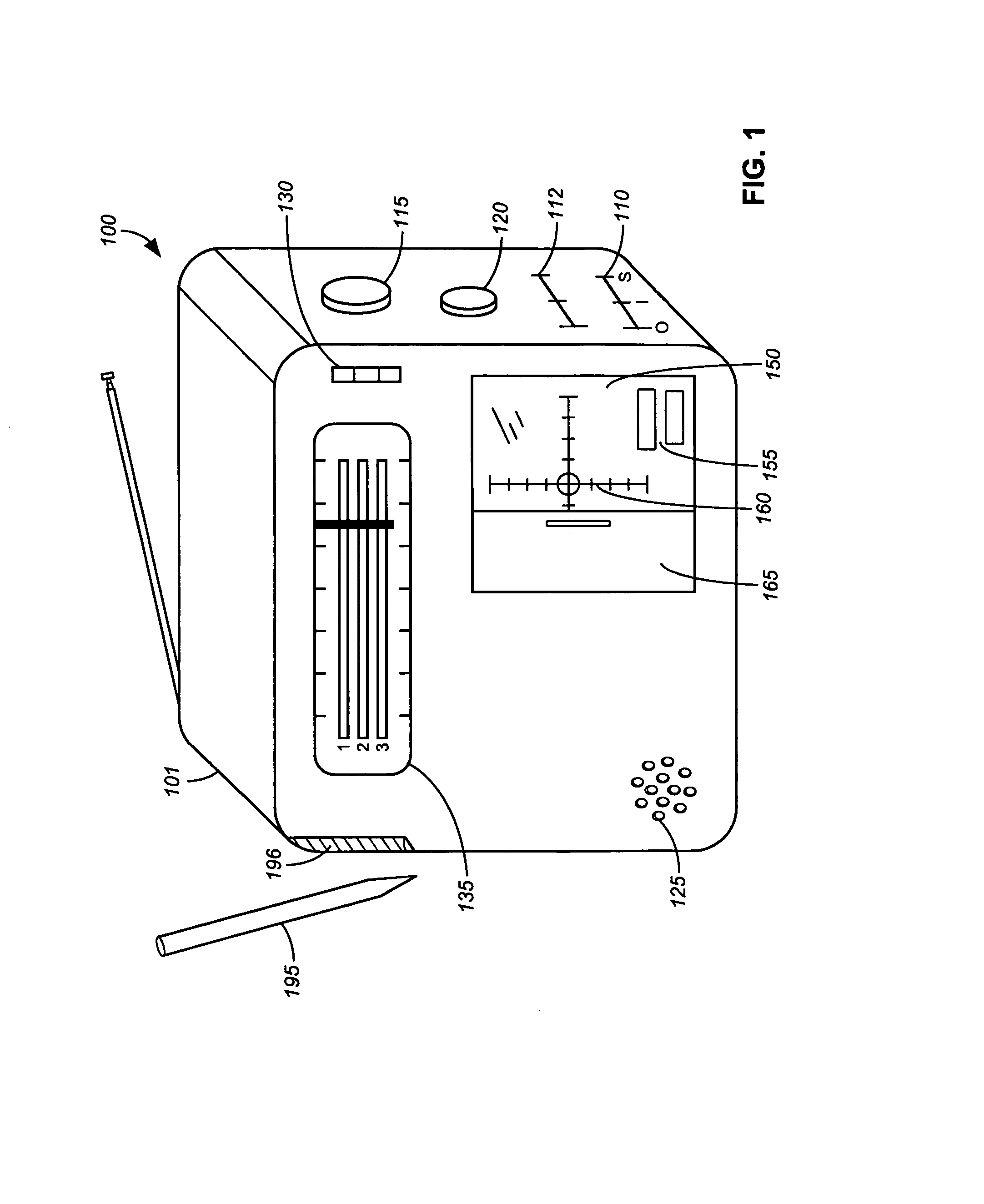
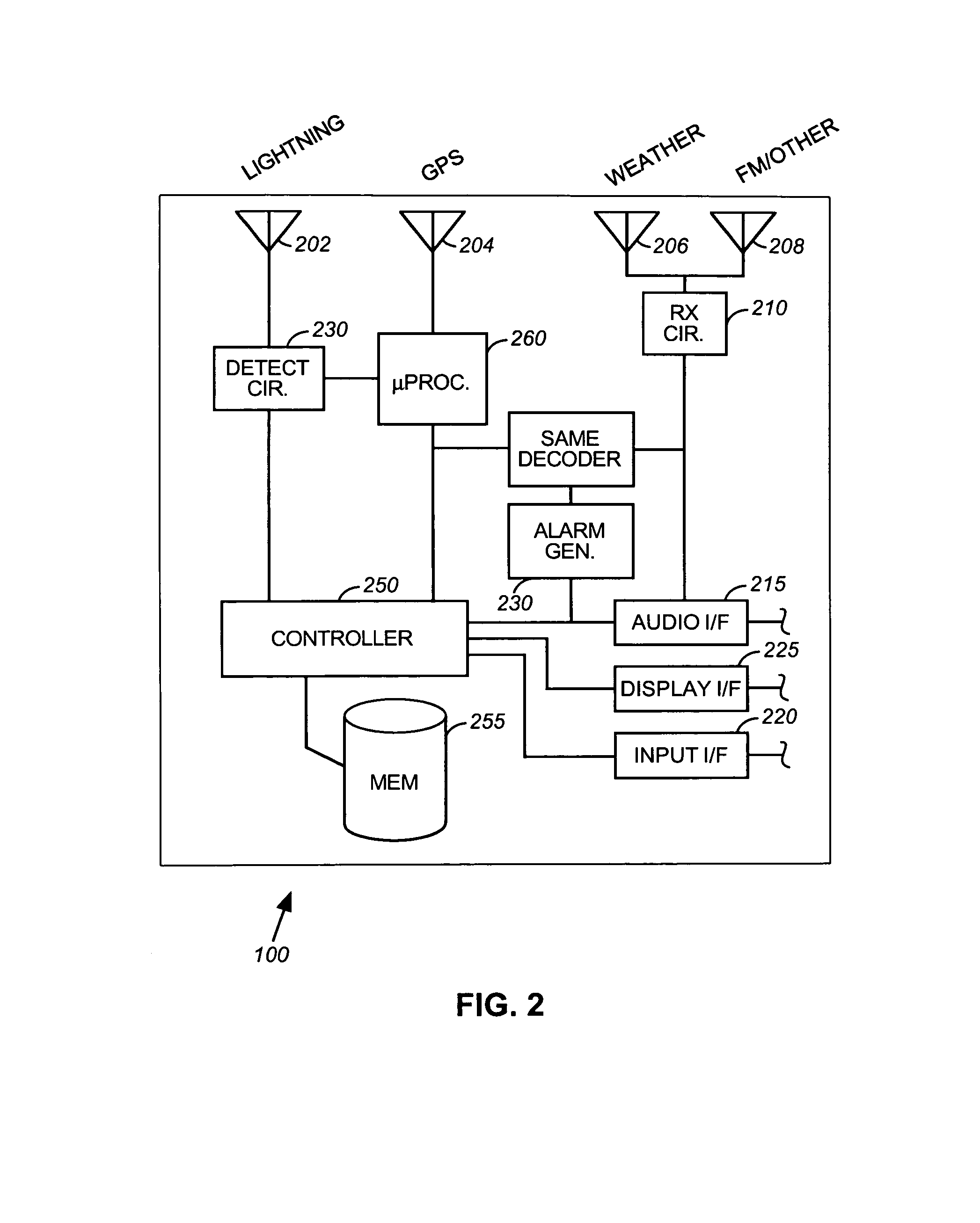
Weather station
ActiveUS7171308B2Special data processing applicationsAtmospheric potential difference measurementLightning strikeThunderstorm
A weather station for providing weather information to a user, especially weather information related to lightning and severe thunderstorm activity. In accordance with the present invention, the weather station includes one or more antennas for receiving GPS transmissions, weather radio transmissions, and a separate radio band, such as the AM radio band for use in detecting lightning strikes. The GPS signal is used to determine the position of the user. A lightning detector coupled to the antenna for receiving the AM (or other band) signal calculates the proximity of any detected lightning strikes. The national weather radio band antenna receives information from NOAA and similar organizations and presents it to the user in the normal fashion. In accordance with the present invention, the weather station may take storm data from NOAA and compare it to lightning proximity data that it has already obtained at a particular location and present to the user an indication of the relative location of the severe thunderstorm activity and its direction of movement.
Owner:RADIOSHACK ONLINE IPCO LLC +1
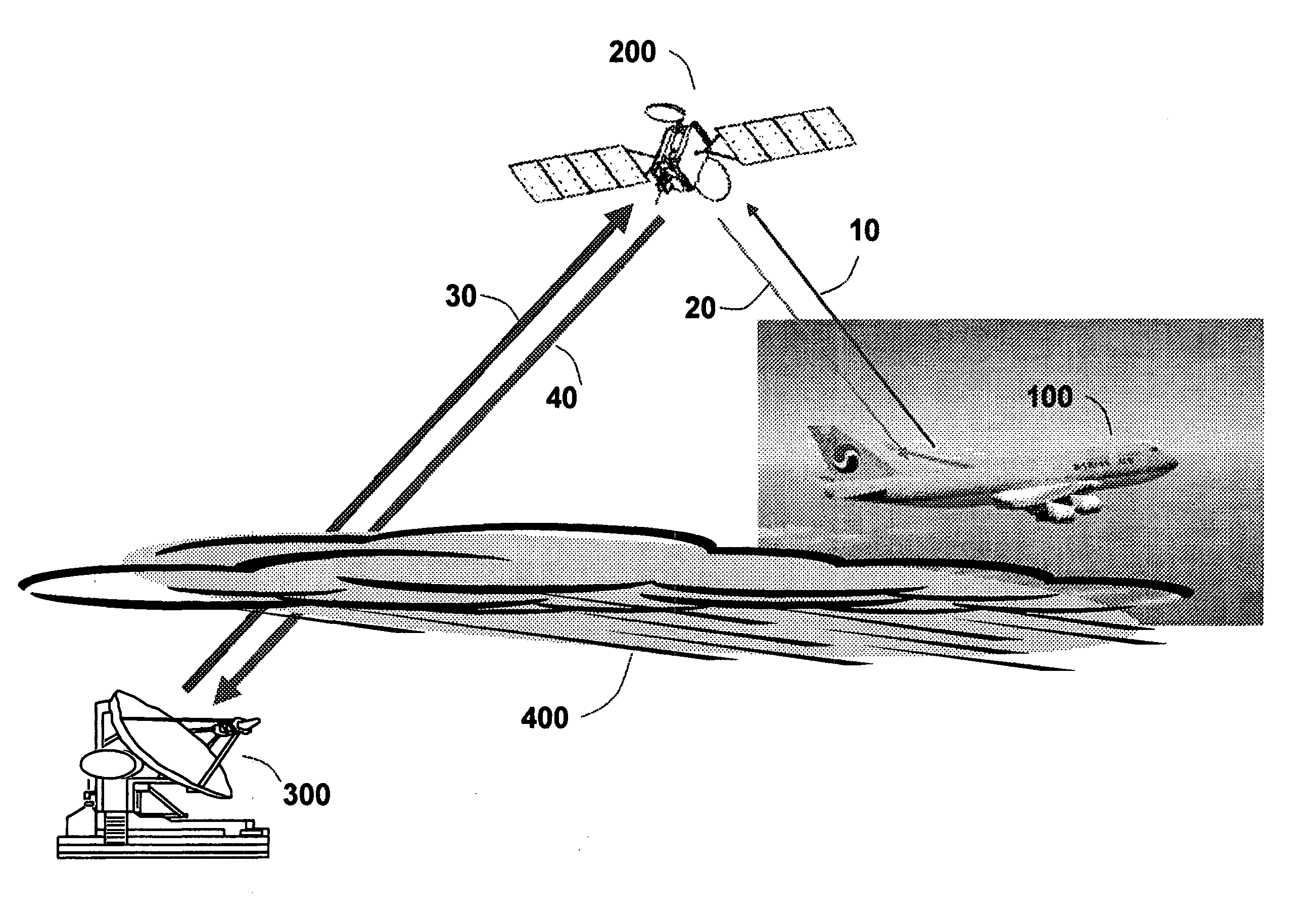
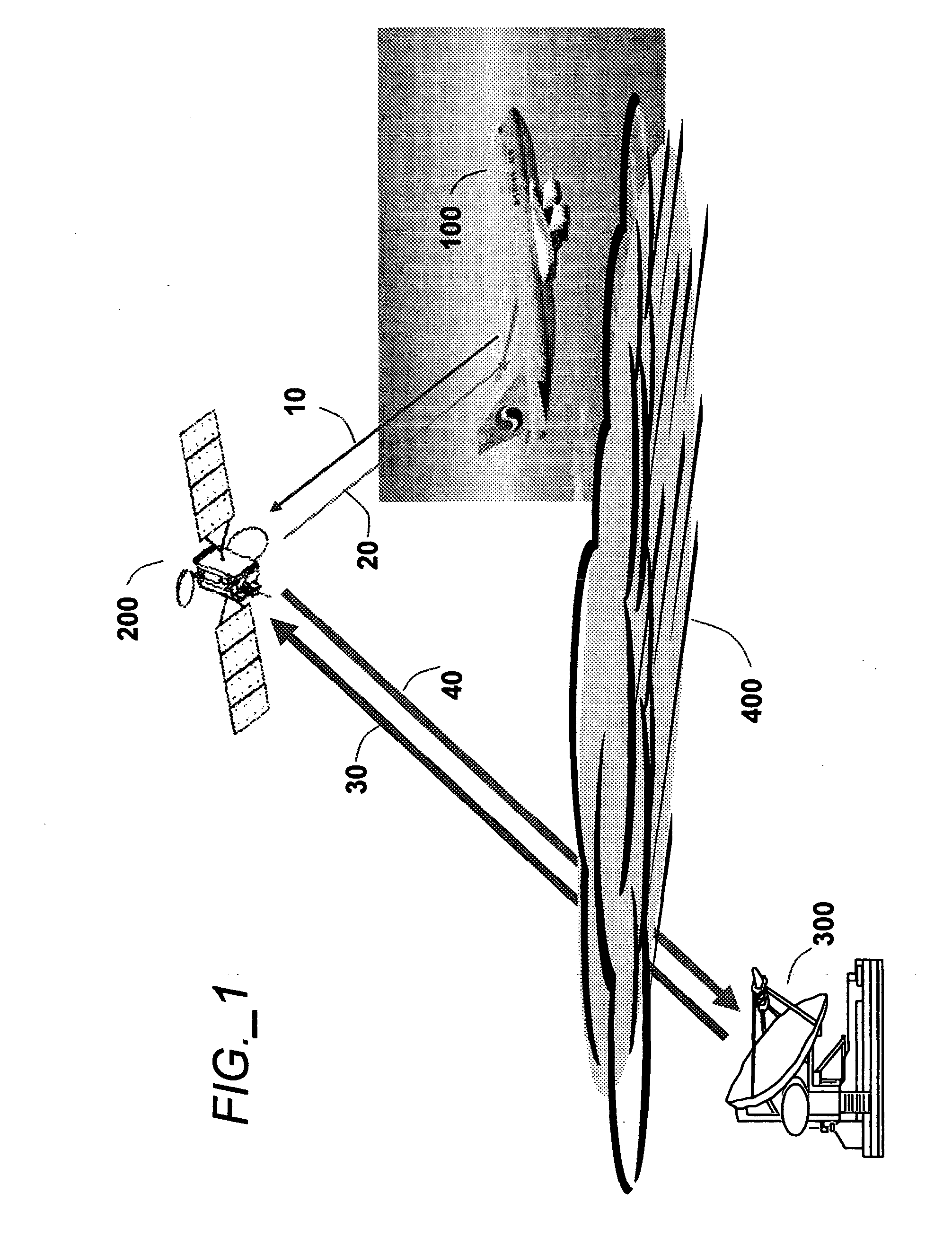
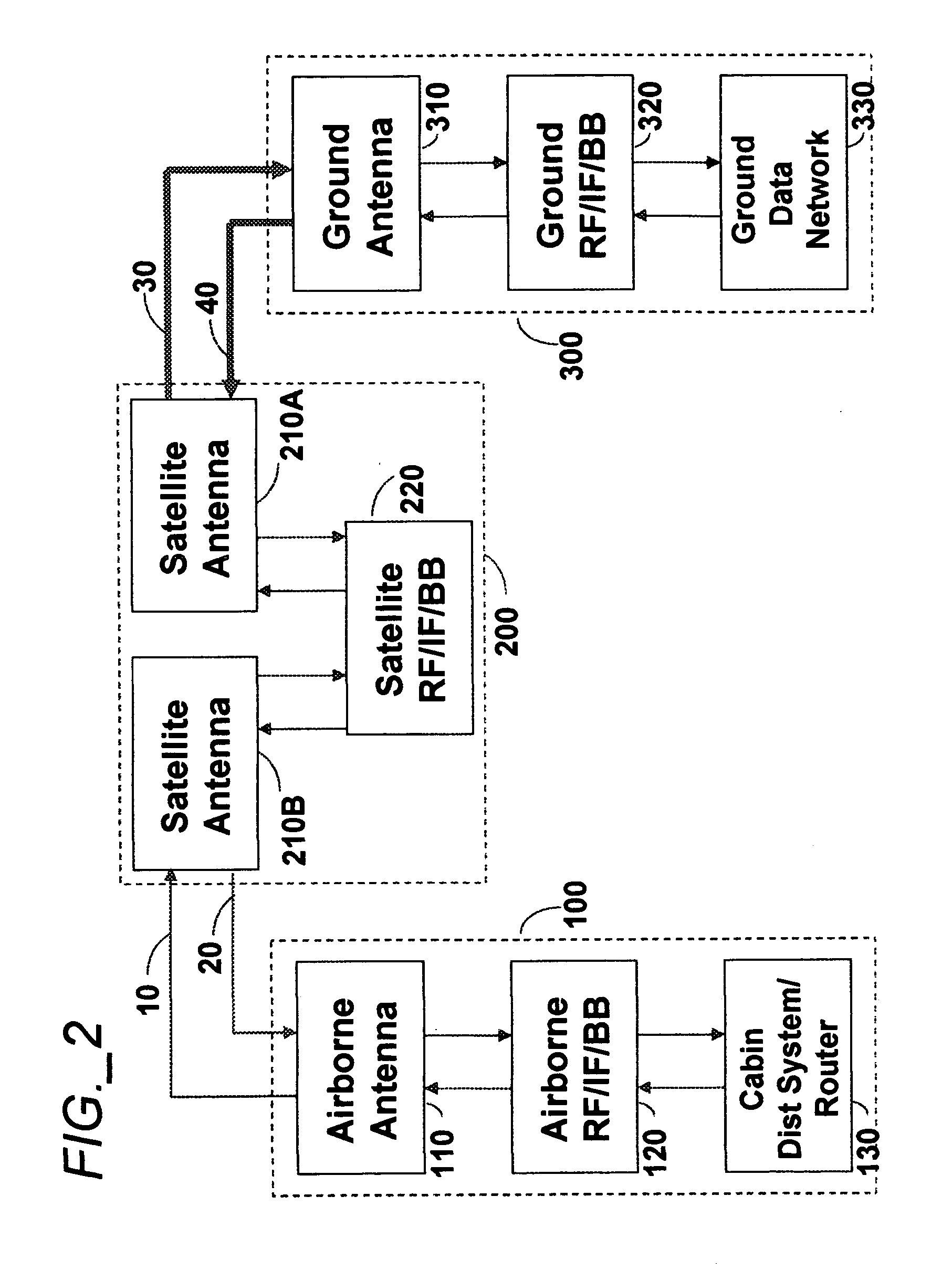
Aeronautical broadcast and communication system
ActiveUS20060040612A1Relatively large bandwidthMore bandwidthActive radio relay systemsWireless commuication servicesJet aeroplaneAviation
A method and system for a plurality of airplanes in flight to receive from and send to a plurality of ground stations broadcast and communication signals through a single or a plurality of geostationary satellites, wherein at least the mobile link between said airplanes and said satellite, uplink or downlink, uses the high frequency radio waves at 17 GHz or higher, such as Ka-band. The fixed link between said satellite and said ground stations may use any radio frequencies below the frequencies used to communicate between the satellite and the aircraft. The lower frequencies tend to be less susceptible to rain attenuation and hence suitable for closing the fixed broadcast and communication link. Frequencies such as C-band or Ku-band, or even Ka-band, are applied between satellite and ground such that the available link margin is sufficient to overcome rain attenuation at said ground stations. Said satellite carries a plurality of transponders that may include a plurality of frequency converters to enable the conversion between different frequencies. Said satellite generates a plurality of spot beams, shaped or unshaped, which collectively cover the flight routes of said airplanes, preferably the geodesic path between two highly populated regions.
Owner:NUBRON
Low cost multi-beam, multi-band and multi-diversity antenna systems and methods for wireless communications
InactiveUS7525504B1Low costImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandCommunications system
Systems and methods for employing switched phase shifters and a feed network to provide a low cost multiple beam antenna system for wireless communications. The present systems and methods may also facilitate multi-band communications and employ multi-diversity. The present systems and methods allow communication systems to achieve enhanced performance for communication or other services such as location tracking. The present systems and methods may employ switched phase shifters, multiple diversity antennas and / or a feed network having a multi-layer construction to provide an antenna system with low losses, low external component count and / or which is thin and compact.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
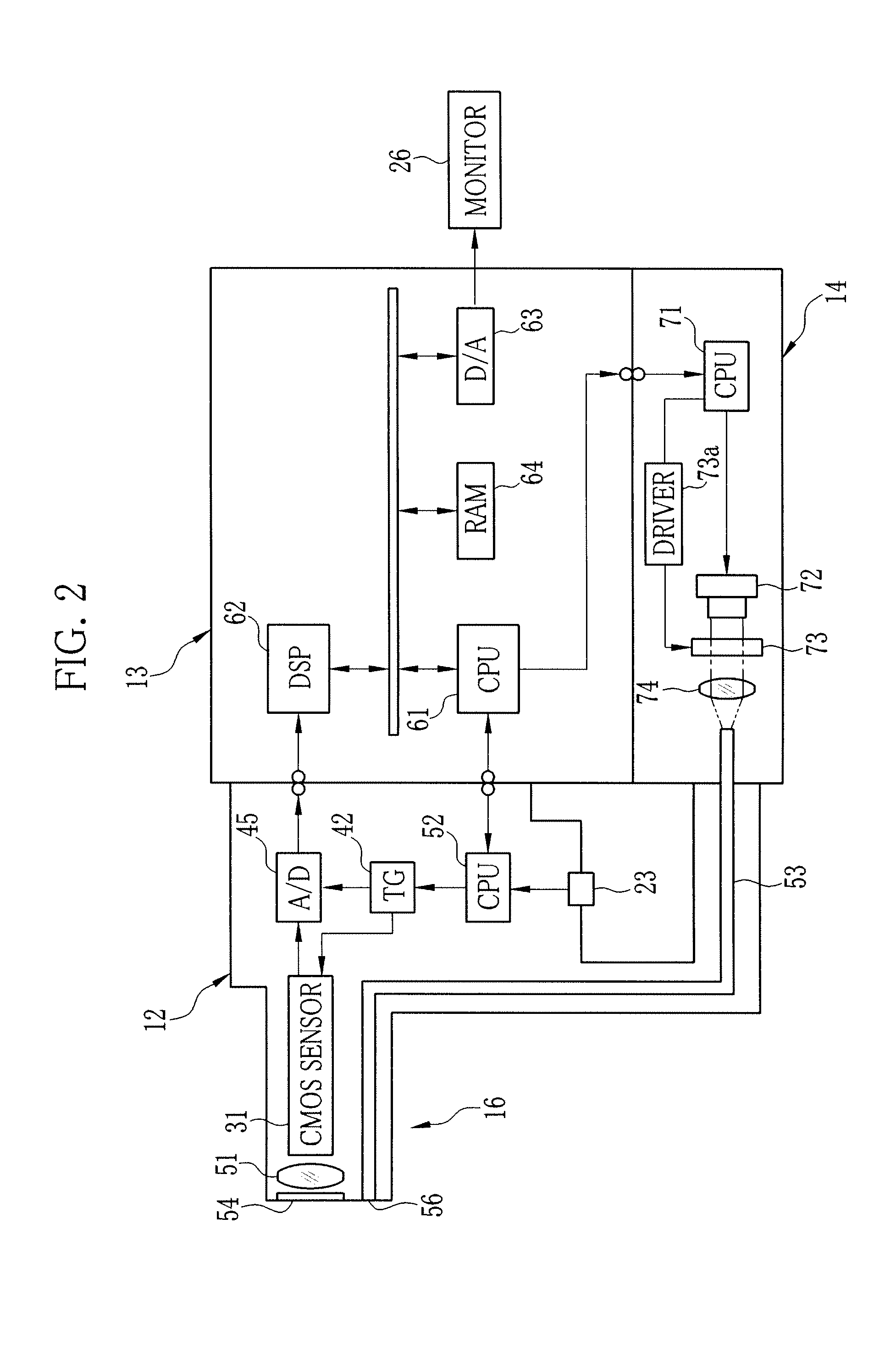
Electronic endoscope system
ActiveUS20100069713A1Image can be preventedSimplify the electronic structureTelevision system detailsSurgeryCMOSLength wave
An electronic endoscope system includes an electronic endoscope having a CMOS image sensor on the tip of an insertion section, a light source device for illuminating the interior of a patient's body, and a processing device for reading out image signals from the CMOS image sensor. The electronic endoscope system can operate with a standard imaging mode and a special imaging mode. When the time taken to read out the image signals from all the pixels in the standard mode is defined as T, the light source device in the special imaging mode emits illumination light in every first half period T / 2 while switching a wavelength of the illumination light between two different wavebands. In every second half period T / 2, the processing device reads out the image signals from the half of the pixels.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
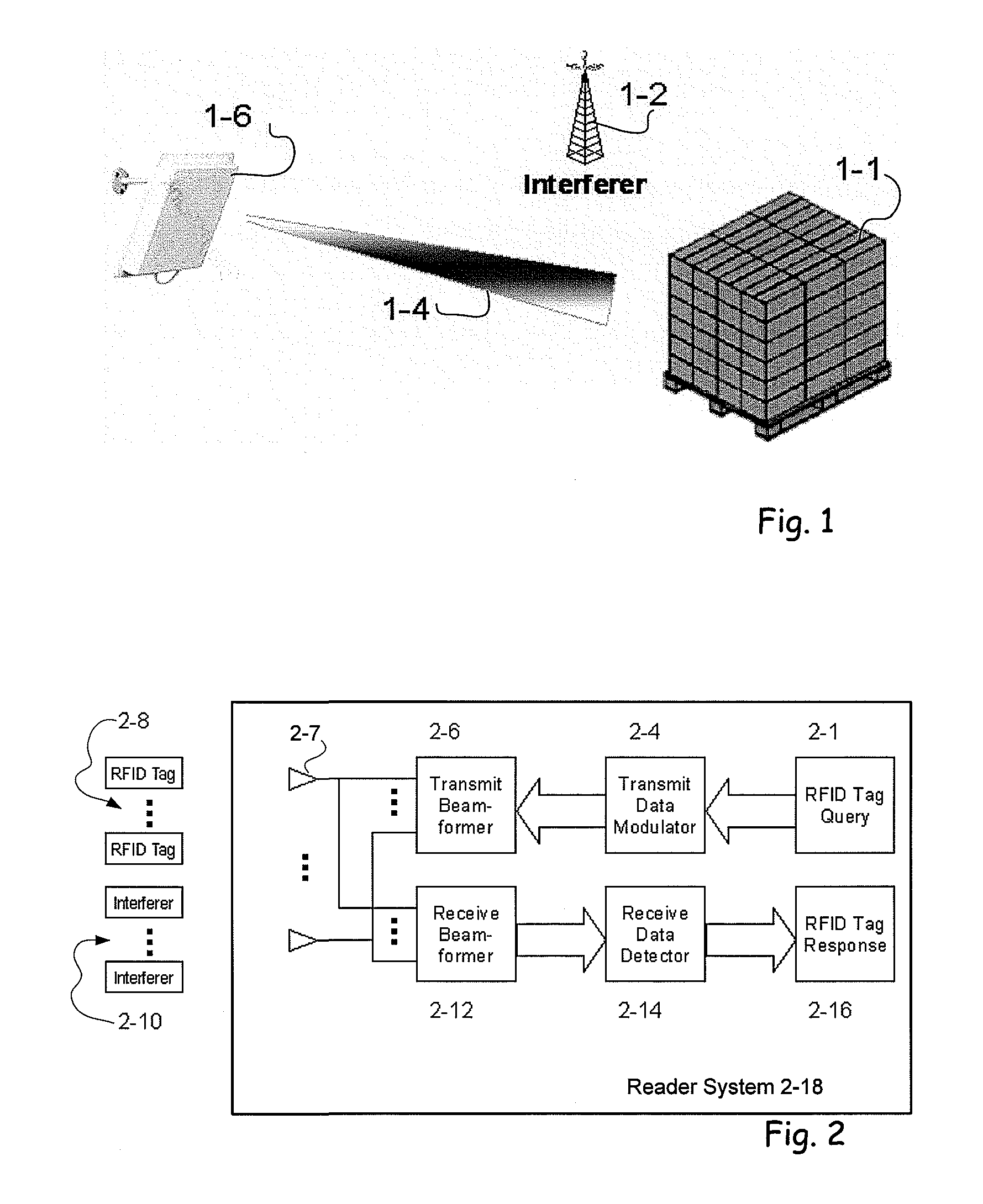
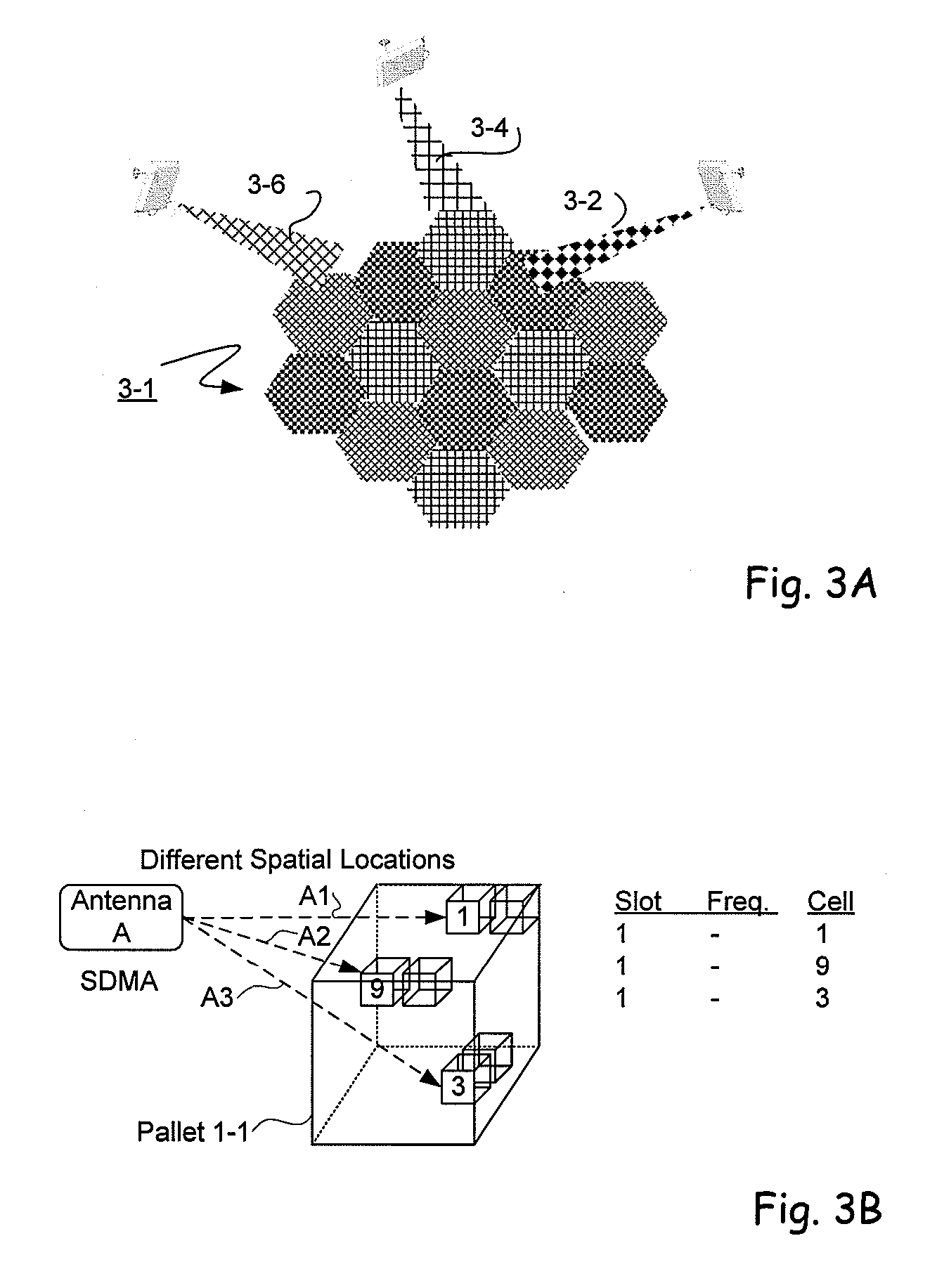
RFID beam forming system
ActiveUS20080012710A1Improve accuracyReduce multipath effectsMemory record carrier reading problemsBroadcast transmission systemsMulti bandLight beam
A multi-protocol, multi-band array antenna system may be used in Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system reader and sensory networks. The antenna array may include array elements with an integrated low noise amplifier. The system may employ digital beam forming techniques for transmission and steering of a beam to a specific sensor tag or group of tags in an cell. The receive beam forming network is optimized for detecting signals from each sensor tag. Narrow and wideband interferences may be excised by an interference nulling algorithm. Space division multiplexing may be used by the antenna system to enhance system processing capacity.
Owner:MOJIX
Waveguide to stripline transition with via forming an impedance matching fence
InactiveUS6958662B1Easy to manufactureLess expensiveMultiple-port networksOne-port networksMulti bandCoupling
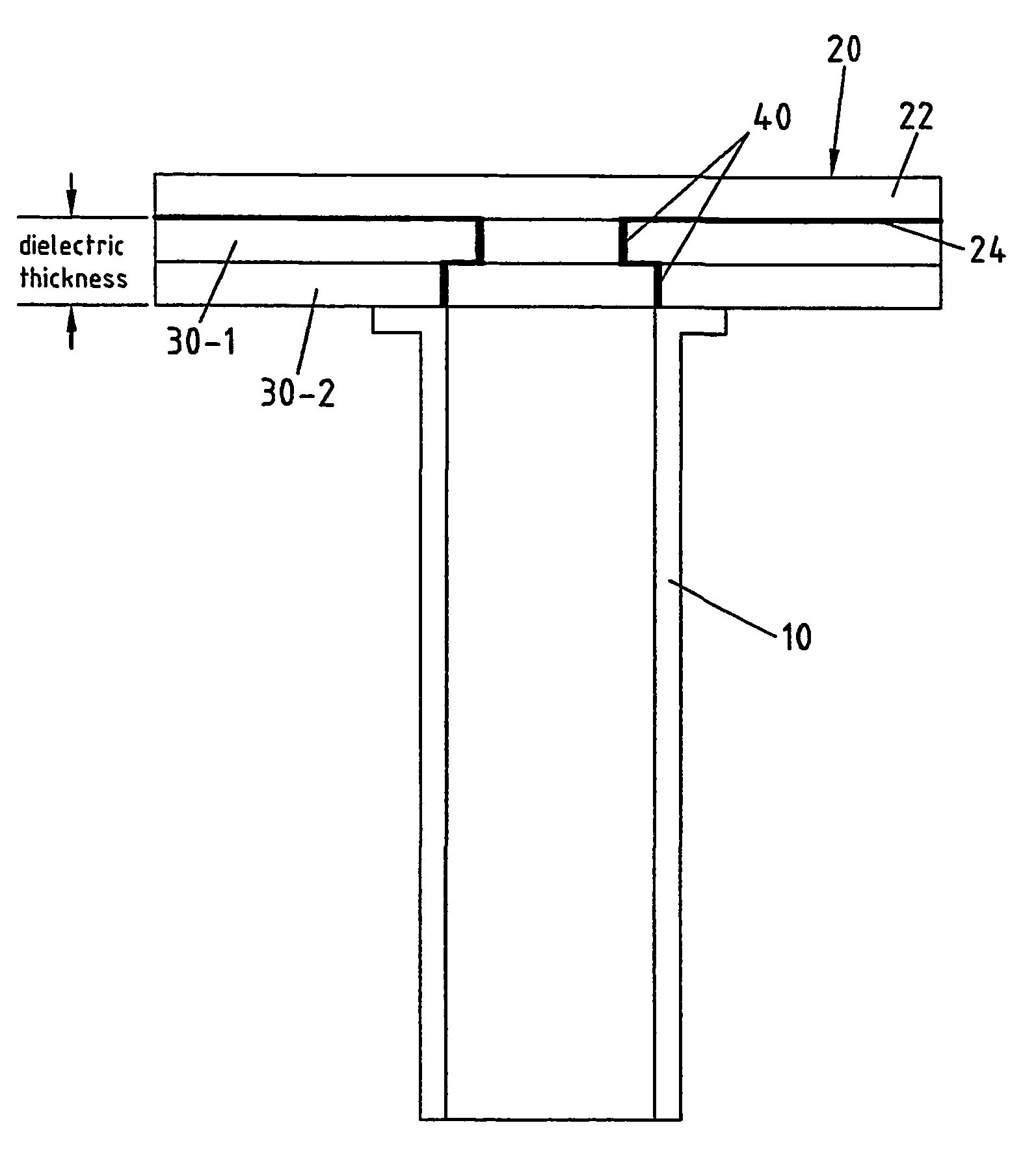
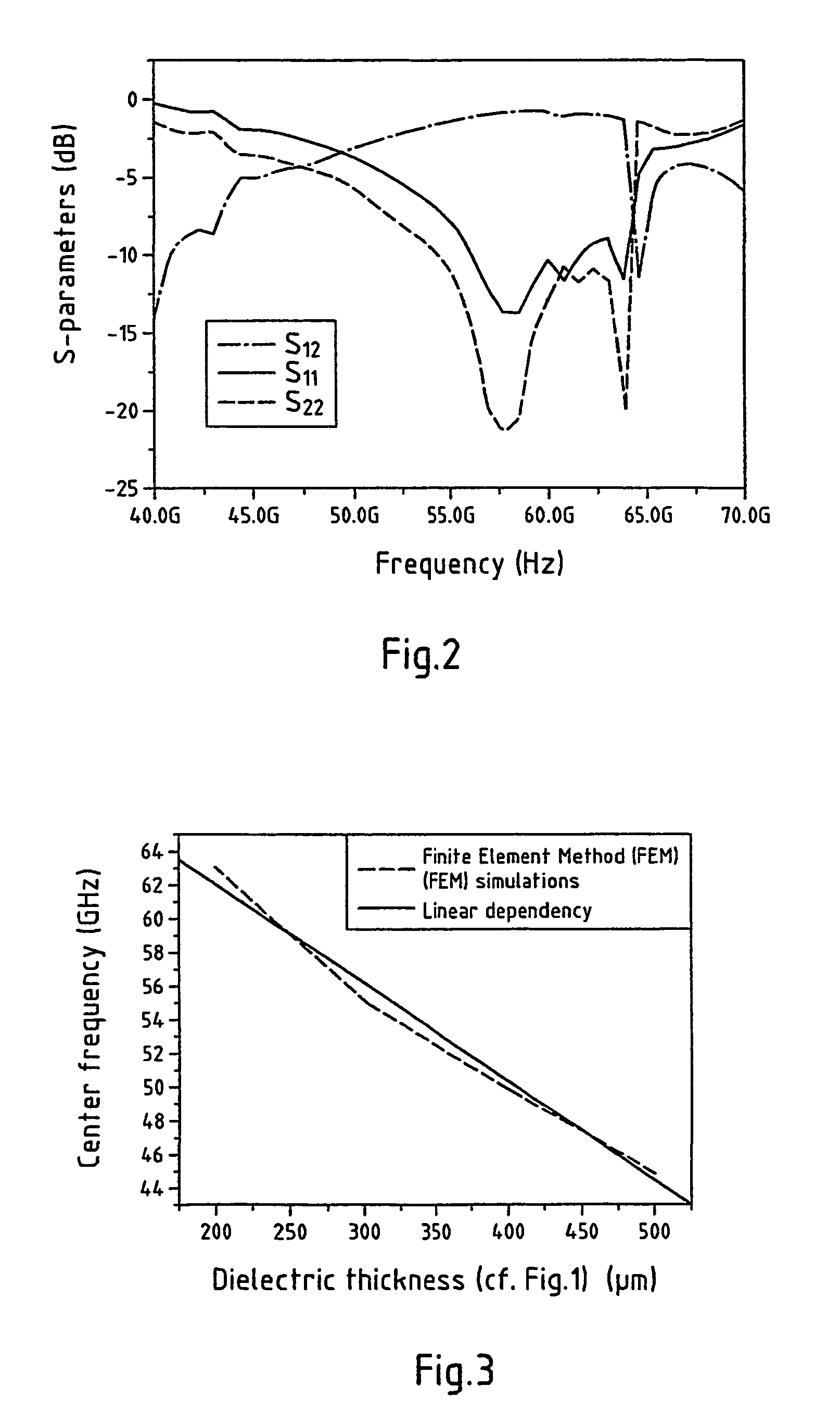
The invention relates to a device for guiding electromagnetic waves from a wave guide (10), in particular a multi-band wave guide, to a transmission line (20), in particular a micro strip line, arranged at one end of the wave guide (10), comprising coupling means (30-1, . . . , 30-7) for mechanical fixation and impedance matching between the wave guide (10) and the transmission line (20). It is the object of the invention to improve such a structure in the way that manufacturing is made easier and less expensive than according to prior art. According to the present invention that object is solved in the way that the coupling means comprises at least one dielectric layer (30) being mechanically connected with the main plane of the transmission line, the geometric dimension of that at least one dielectric layer extending along the propagation direction of the electromagnetic waves being correlated with the center frequency of electromagnetic waves in order to achieve optimised impedance matching.
Owner:RPX CORP
Multi frequency band/multi air interface/multi spectrum reuse cluster size/multi cell size satellite radioterminal communicaitons systems and methods
InactiveUS20060094420A1Enhance effective gain and selectivityReduce fadingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
Satellite radioterminal communications systems, methods and components thereof, can use multiple frequency segments of at least one satellite frequency band, multiple air interfaces, multiple spectrum reuse cluster sizes and / or multiple geographic cell sizes. For example, a space-based component is configured to communicate with first radioterminals in first satellite cells over a first frequency segment of a satellite frequency band, such as a first frequency segment of a satellite L-band, and to communicate with second radioterminals in second satellite cells over a second frequency segment of the same or different satellite frequency band. The space-based component also may be configured to communicate with a first radioterminal over a first air interface and to communicate with the second radioterminals over a second air interface.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Fluorescence polarization assay system and method
An instrument is disclosed for fluorescence assays which is capable of reading many independent samples at the same time. This instrument provides enhanced throughput relative to single-sample instruments, and is well-suited to use in general fluorescence, time-resolved fluorescence, multi-band fluorescence, fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), and fluorescence polarization. This invention is beneficial in applications such as high-throughput drug screening, and automated clinical testing. Also disclosed are means and methods for a fluorescence polarization measurement which is highly sensitive, inherently self-calibrated, and unaffected by lamp flicker or photobleaching. This fluorescence polarization invention can be practiced on a variety of fluorescence instruments, including prior-art equipment such as microscopes and multi-well plate readers.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
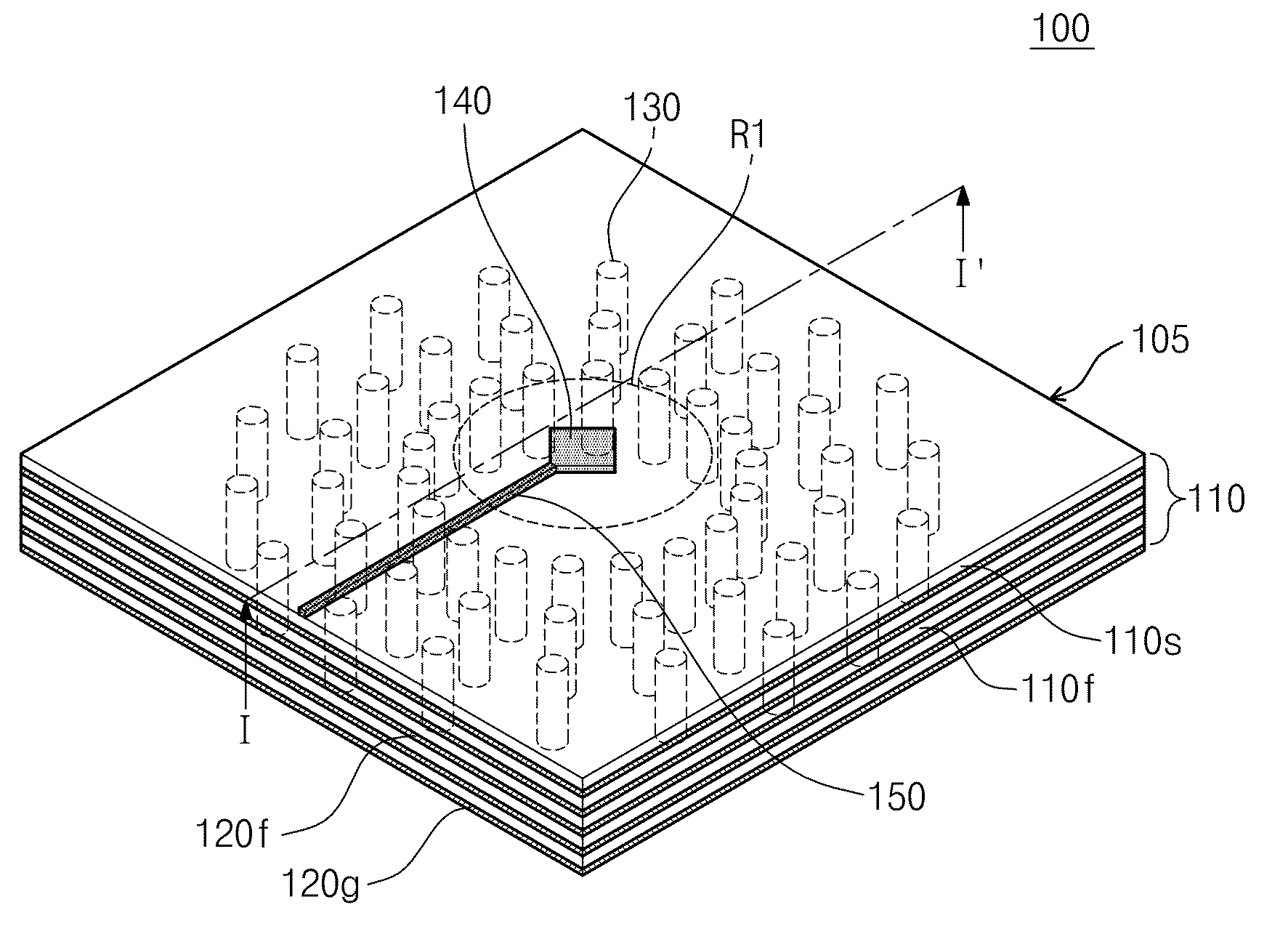
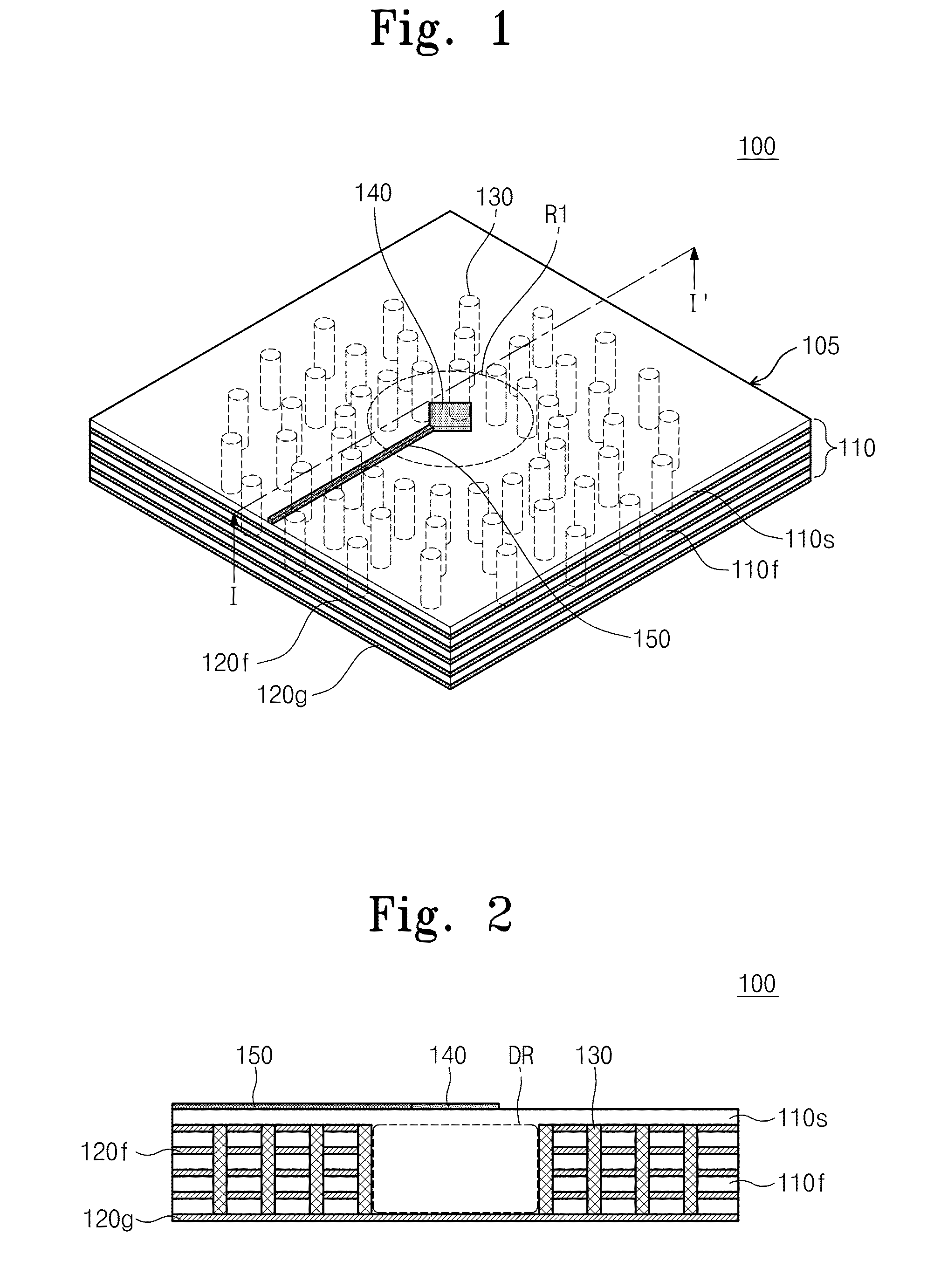
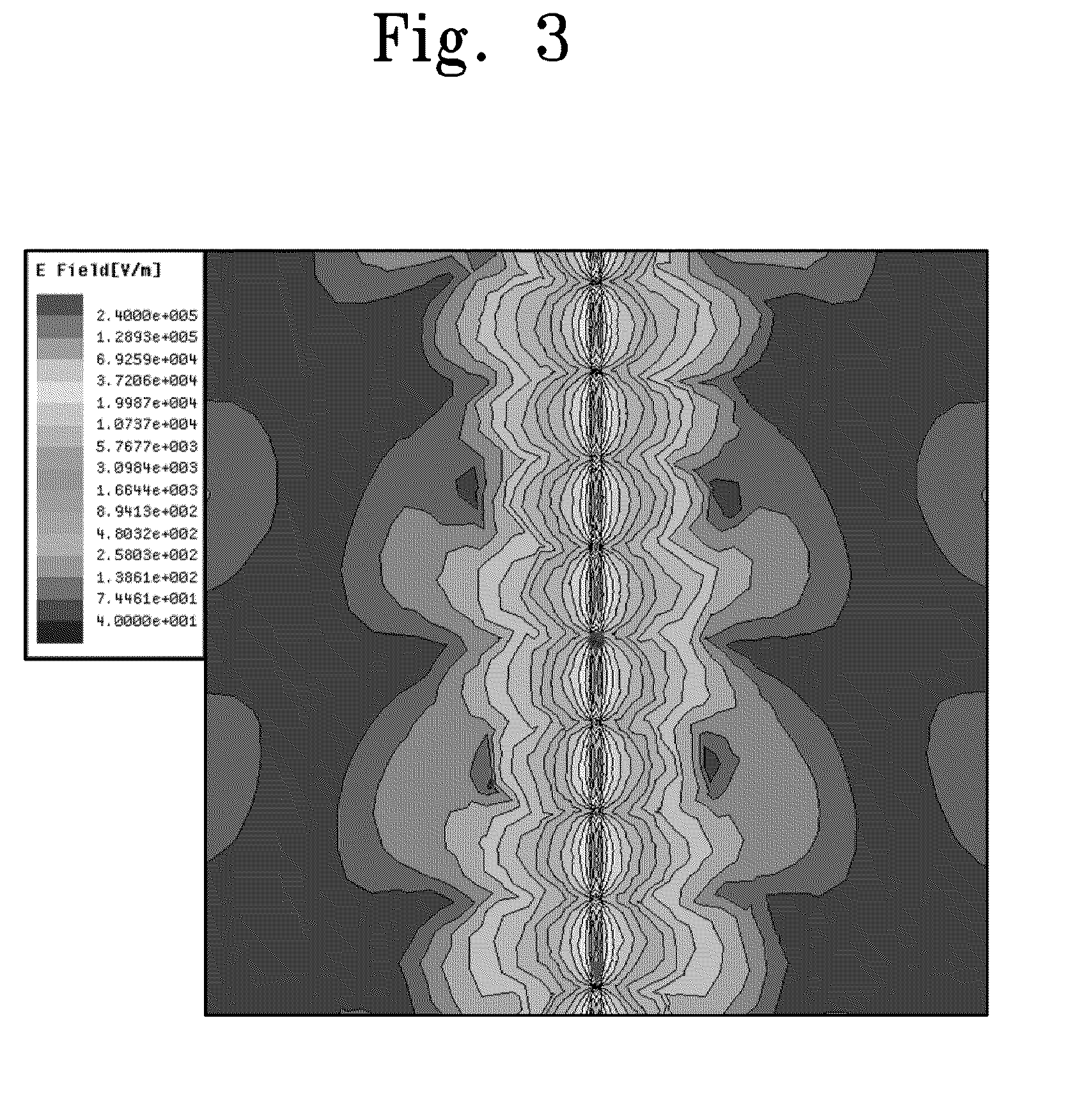
Patch antenna with wide bandwidth at millimeter wave band
InactiveUS20110057853A1Suppress signal leakageReduce size and manufacturing costSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrically long antennasGround planeWide band
Provided is a millimeter wave band patch antenna. The patch antenna includes a multi-layer substrate, at least one metal pattern layer, an antenna patch, a ground layer, and a plurality of vias. In the multi-layer substrate, a plurality of dielectric layers are stacked. The metal pattern layer is disposed between the dielectric layers except for a center region of the multi-layer substrate. The antenna patch is disposed on an upper surface of the multi-layer substrate in the center region. The ground layer is disposed on a lower surface of the multi-layer substrate opposing to the upper surface. The vias is disposed around the center region through the dielectric layers for electrically connecting the metal pattern layer to the ground layer. The center region, which is surrounded by the ground layer and the vias, functions as a resonator.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
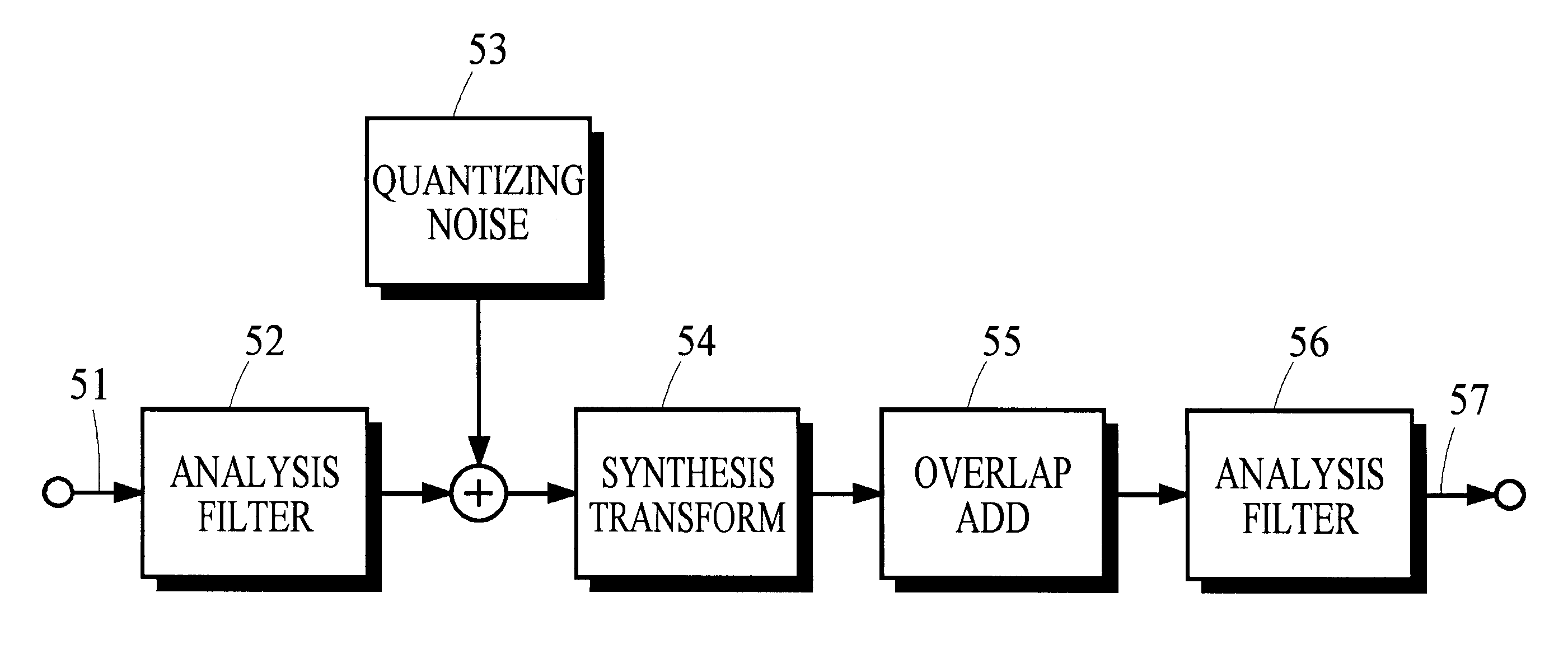
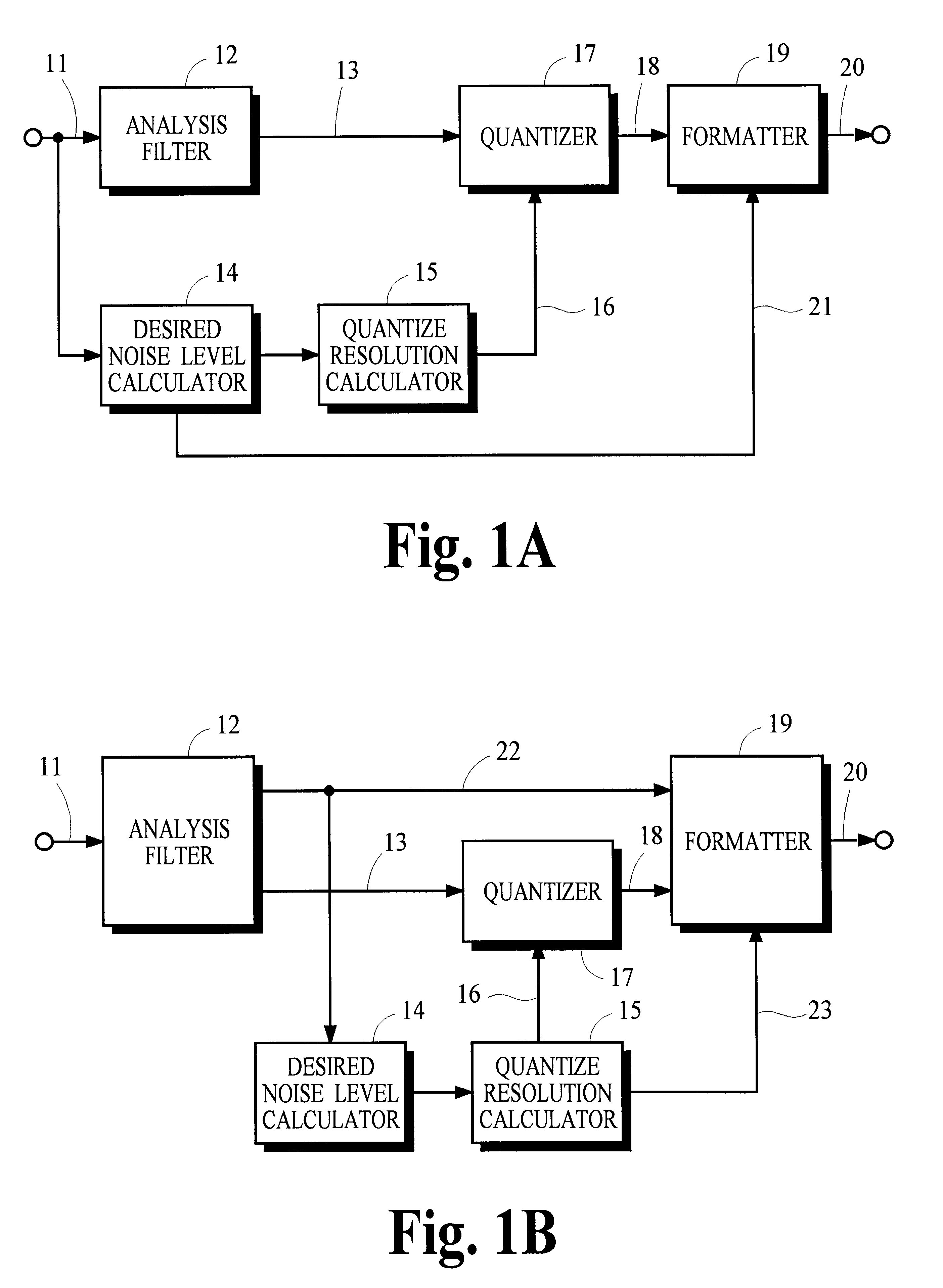
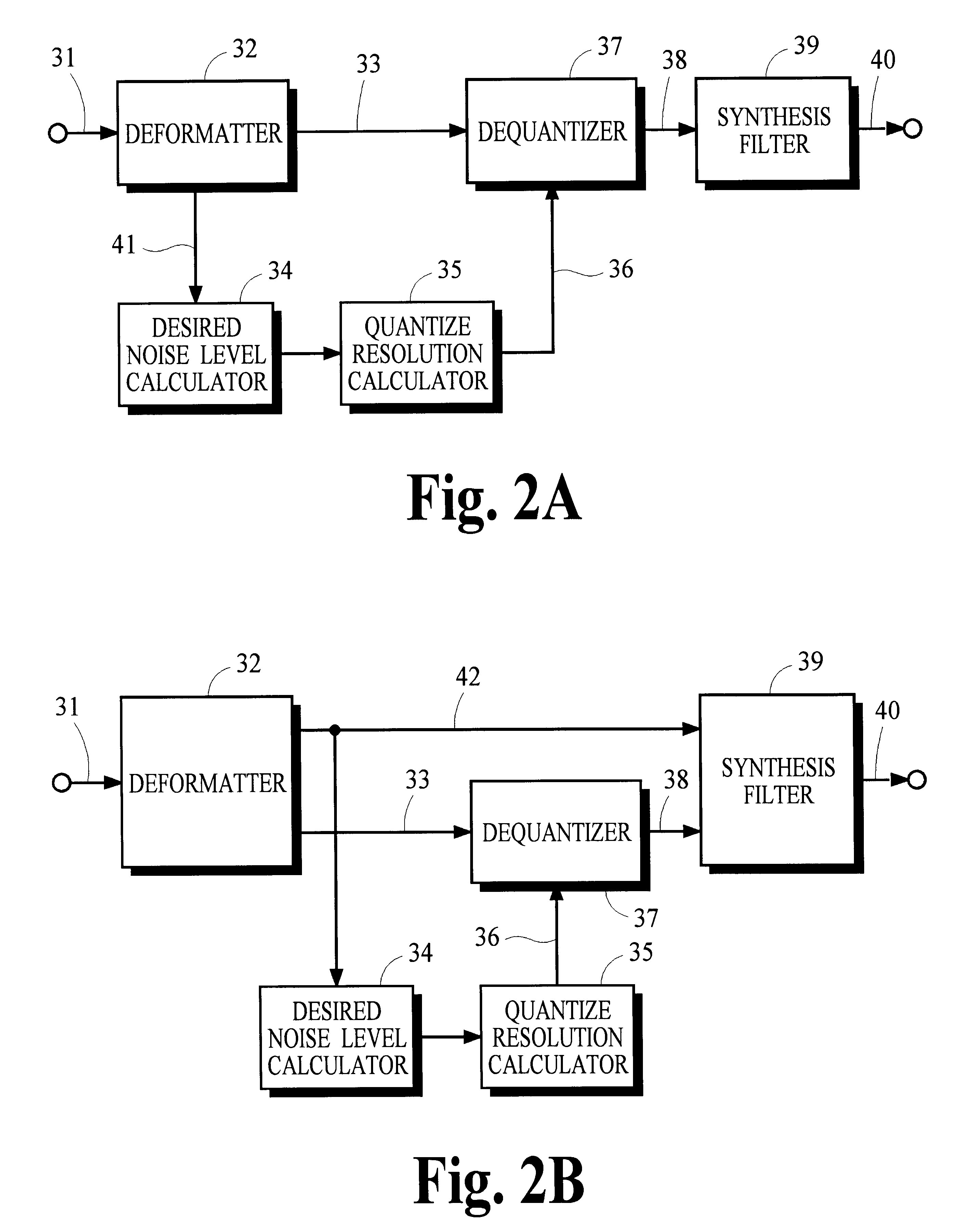
Quantization in perceptual audio coders with compensation for synthesis filter noise spreading and the overlap-add process
InactiveUS6363338B1Improve performanceAccurate noiseSpeech analysisCode conversionBit allocationAlgorithm
Many perceptual split-band coding systems that use analysis and synthesis filters assume the quantization noise introduced by quantizing split-band signals is substantially the same as the noise that results in the output signal obtained by applying the synthesis filters to the quantized split-band signals. In general, this assumption is not true because the synthesis filters modify or spread the quantization noise. A theoretical framework for deriving an optimum bit allocation that accounts for synthesis-filter noise spreading and the overlap-add process is disclosed. In concept, the problem of finding an optimal bit allocation can be expressed as a linear optimization problem in a multidimensional coordinate space. Simplified processes derived from this theoretical framework are disclosed that can obtain near-optimal solutions using modest computational resources.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
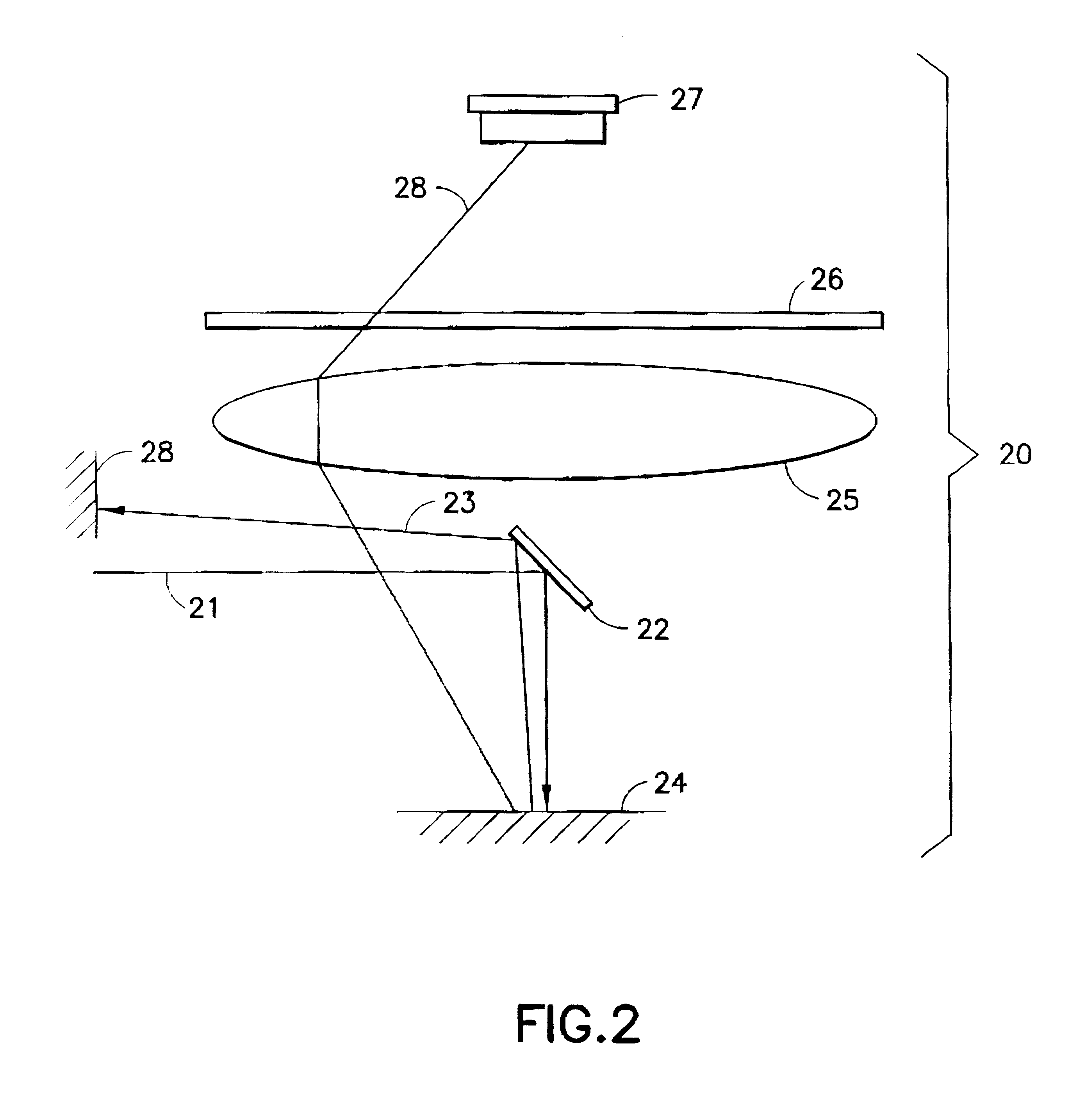
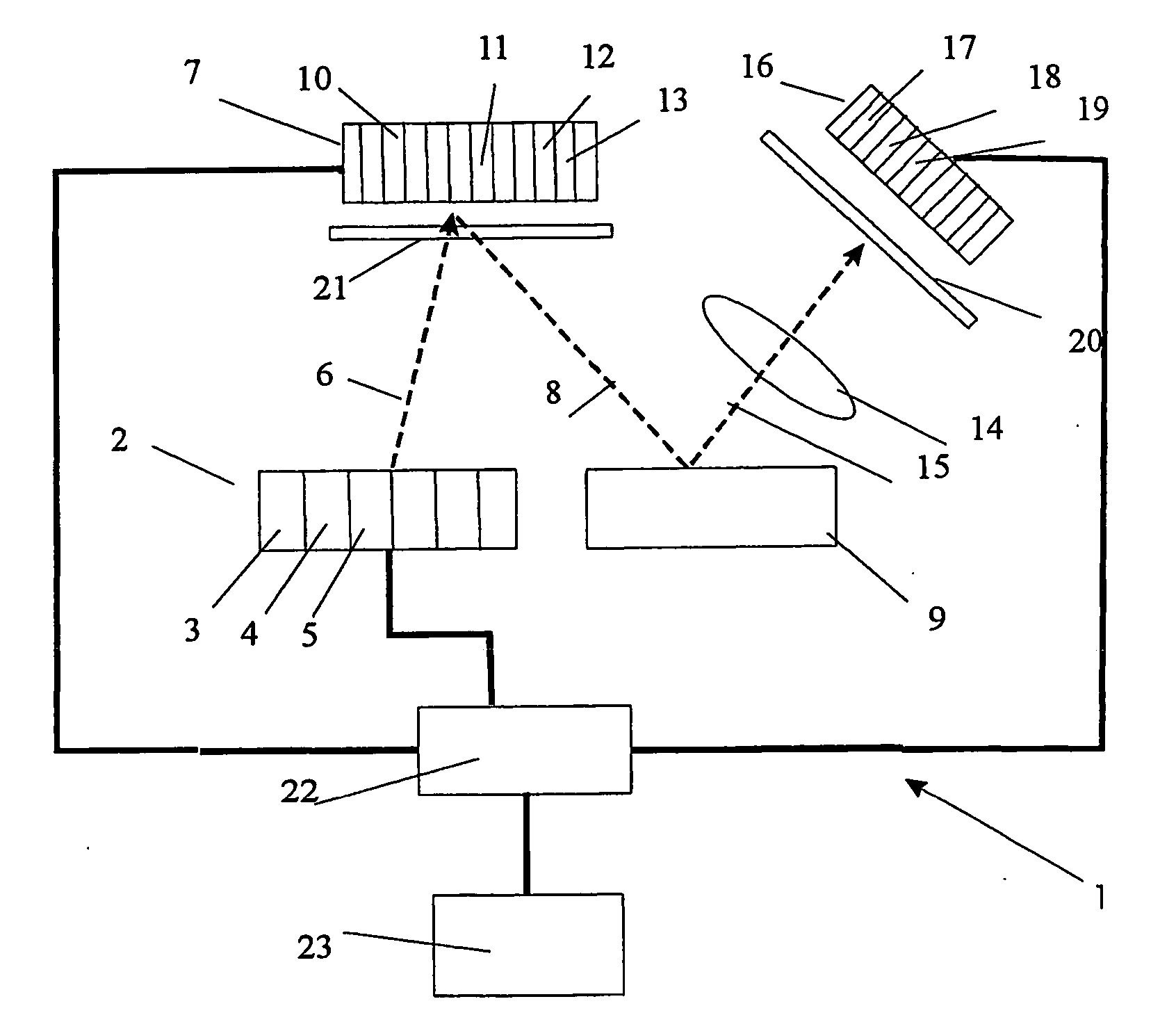
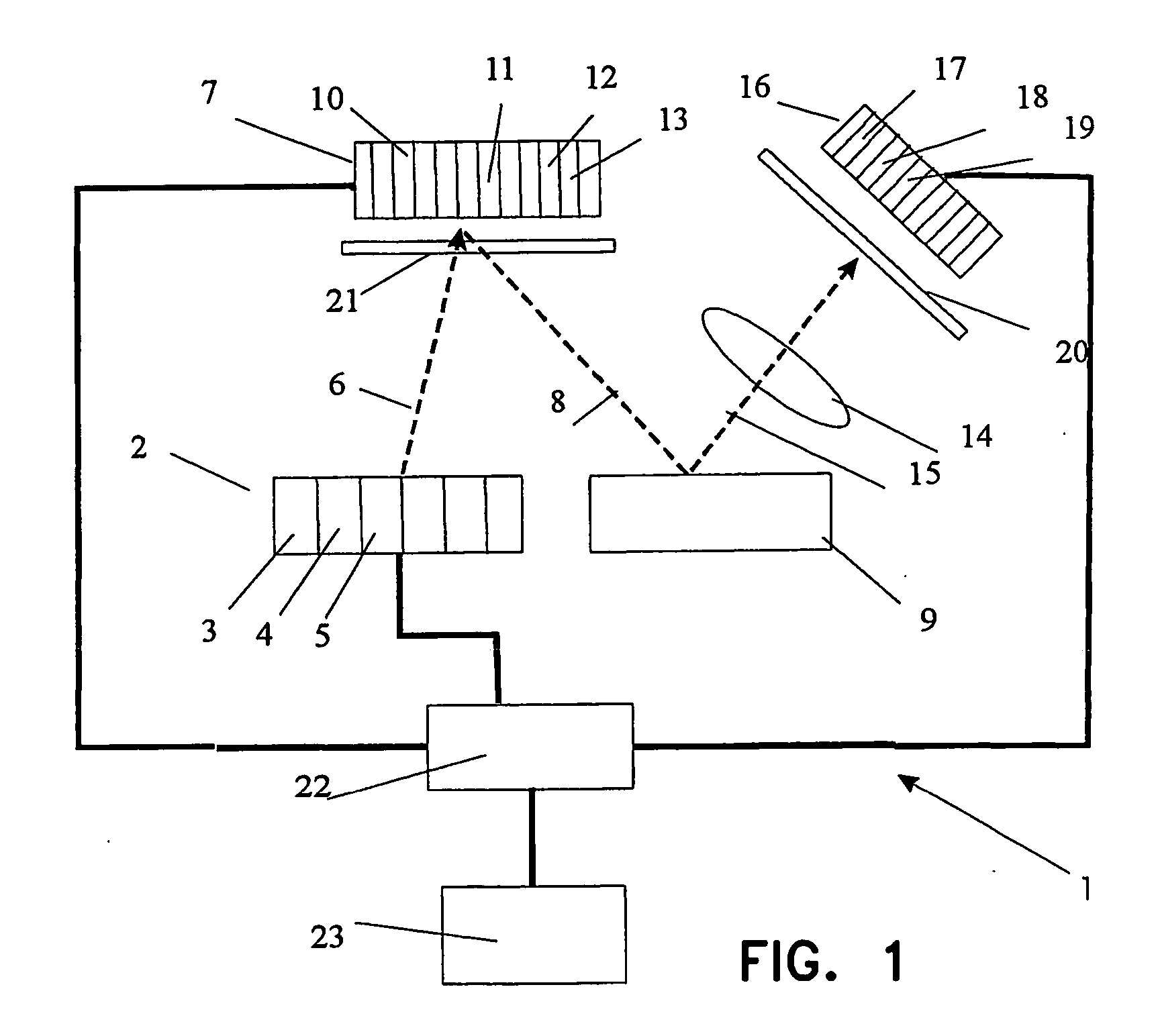
Method for forming the image in millimetre and sub-millimetre wave band (variants), system for forming the image in millimetre and sub-millimeter wave band (variants), diffuser light (variants) and transceiver (variants)
InactiveUS20060273255A1Minimize level of disturbanceDecrease of its informational contentRadiation pyrometryPhotometryPhysicsWave band
The invention relates to the field of computer diagnostics. The method consists in the steps of forming radiation forming in this wave range, consisting of separate partial radiations, which are different from each other by values of their physical features, directing of the formed radiations into a side of the observed object, receiving a radiation, dispersed from the observed object, through a focusing element, transforming of the received radiation in electrical signals and forming a synthesized enhance image of the observed object by combining said given electrical signals. Besides, each separate partial radiation is additionally distinctly encoded for example by means of its modulation, which differs from a modulation of other partial radiations, the partial radiations are directed to a diffuser for decreasing their spatial coherence and / or their dispersing by means of different portions of the diffuser in order to create an additional distinctly encoded partial radiations with an additional modulation, corresponding to an angle of impingement onto the observed object. After reflecting of the radiation from the observed object the step of focusing of this radiation to a receiving device is realized, which accomplishes a transforming of set of partial radiations in a corresponding array set of electrical signals, there is realized the step of decoding of partial electrical signals, corresponding to said partial radiations, from each of said electrical signals of said array set there are formed partial images from array sets with various partial electrical signals and then an combination of the partial images or their portions is realized in order to form enhanced resultant image of the object.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
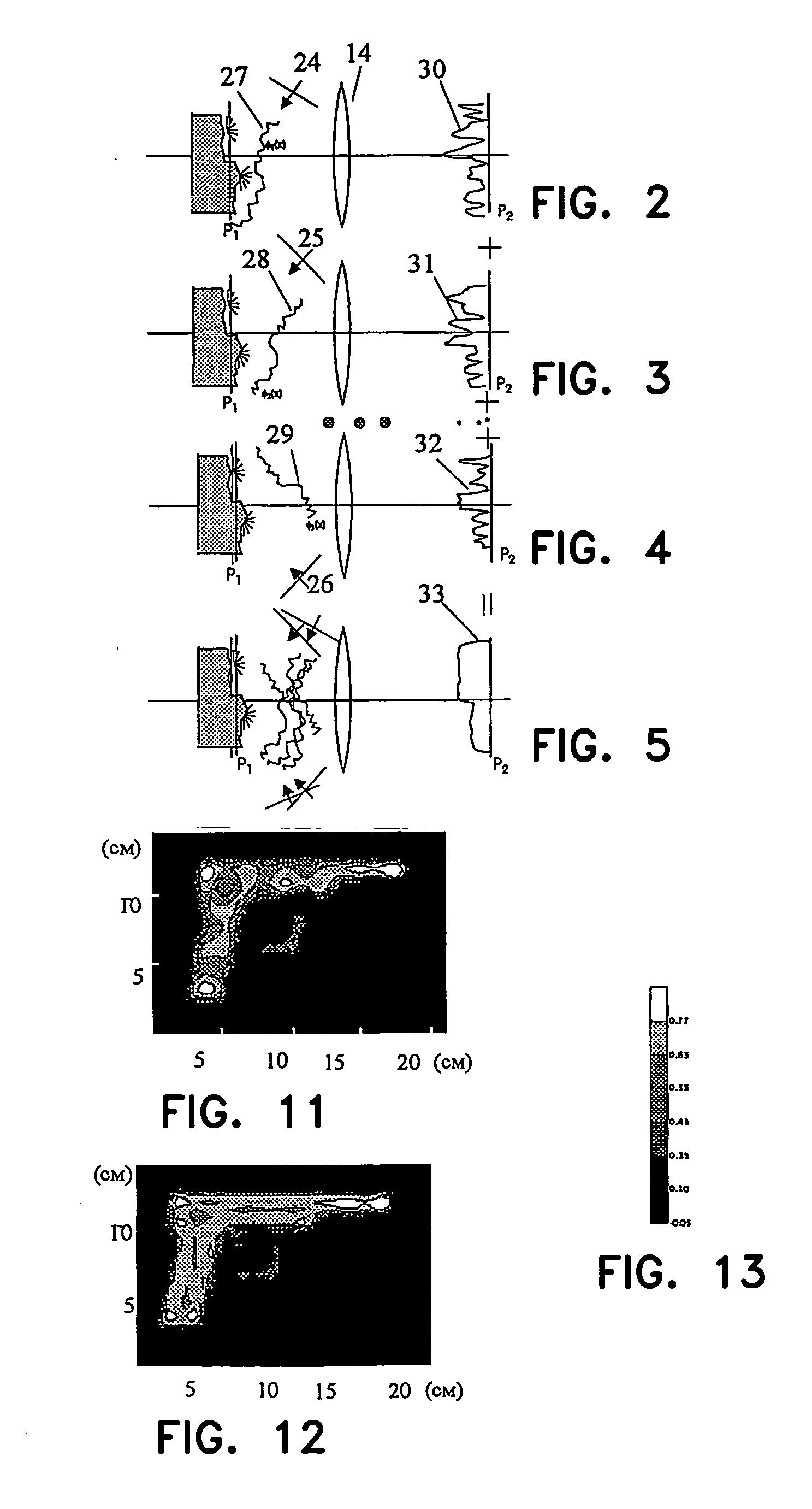
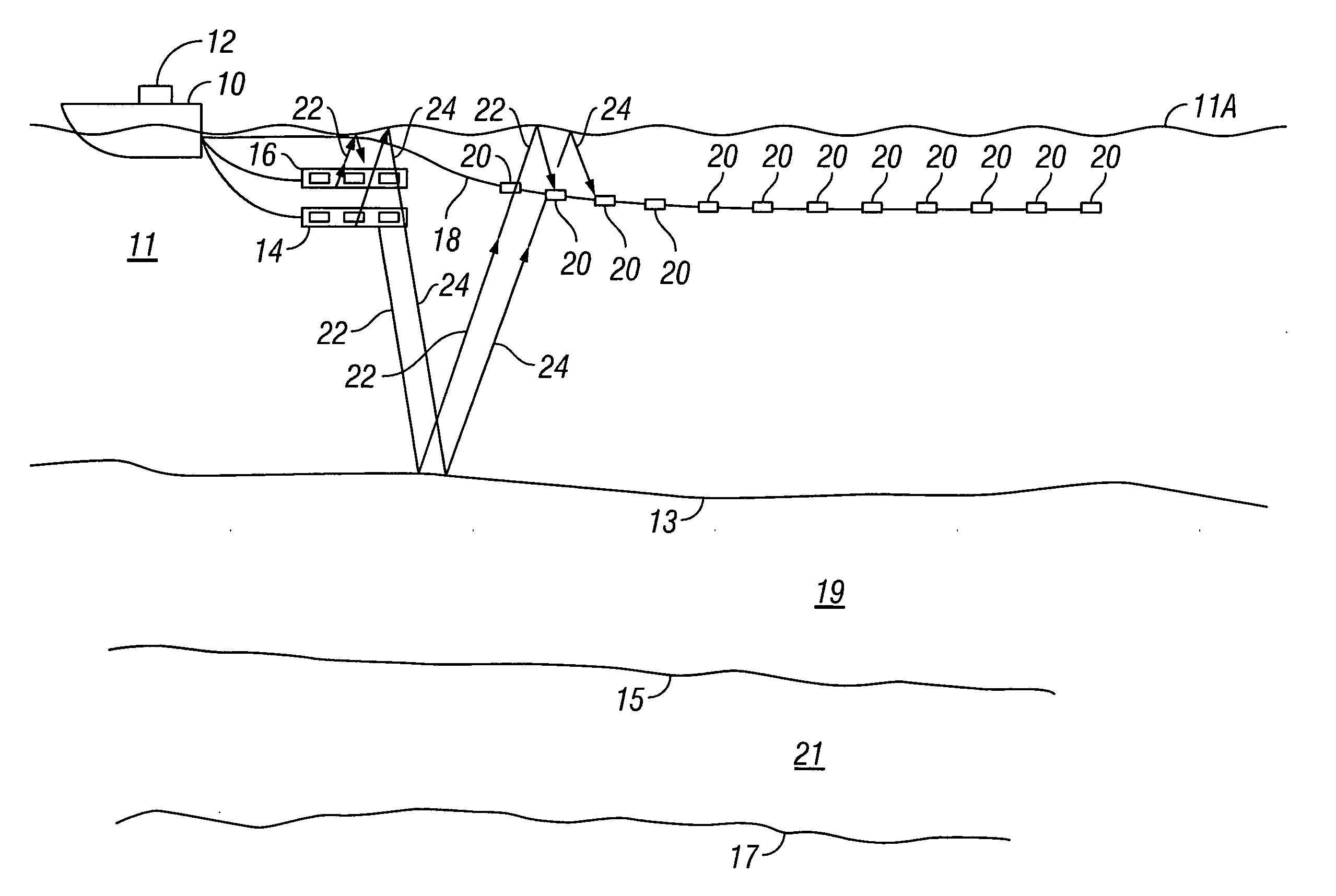
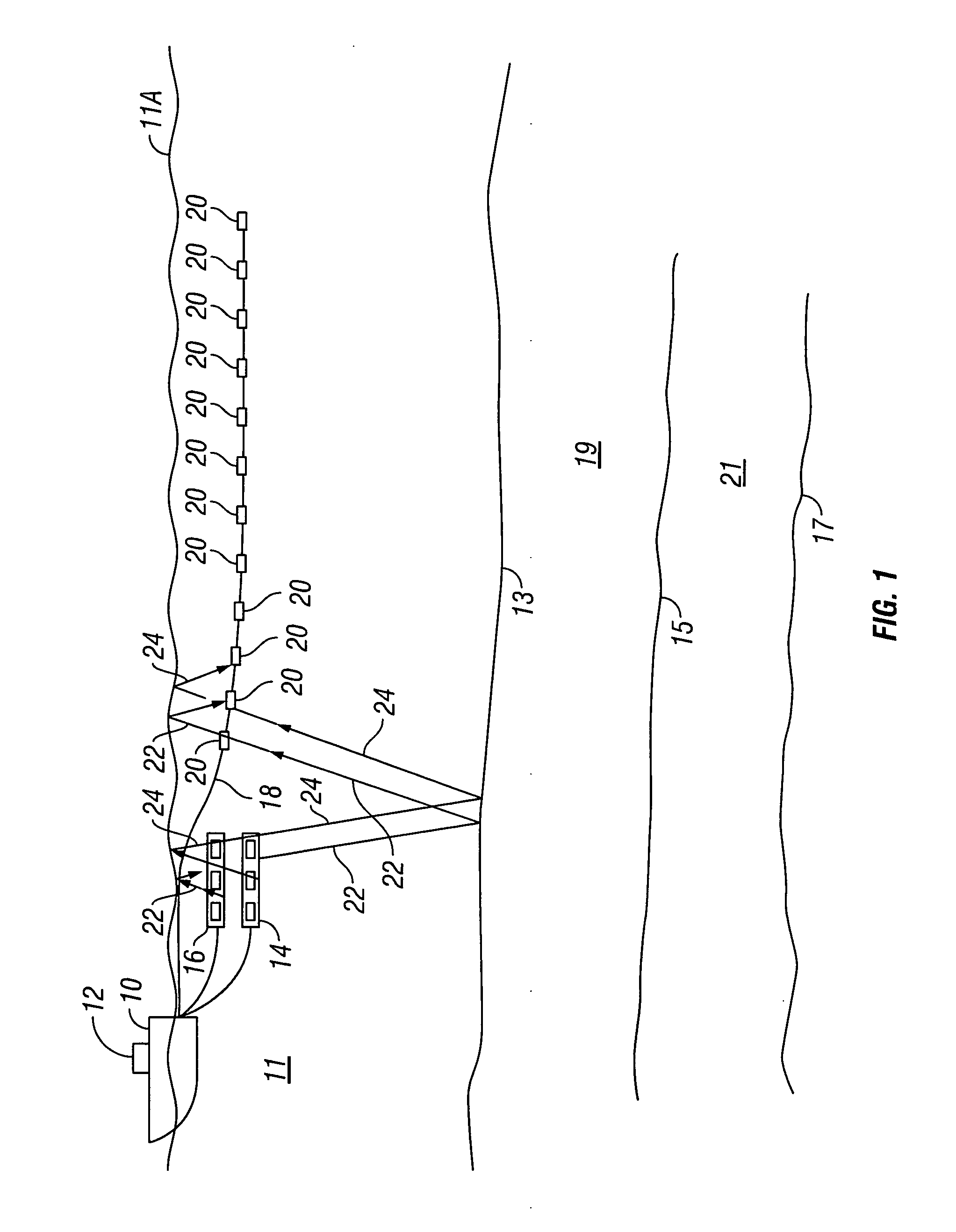
Method for aquiring and processing marine seismic data to extract and constructively use the up-going and down-going wave-fields emitted by the source(s)
InactiveUS20100008184A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSeismic signal processingSurface oceanPhase shifted
A method for acquisition and processing of marine seismic signals to extract up-going and down- going wave-fields from a seismic energy source includes deploying at least two marine seismic energy sources at different depths in a body of water. These seismic energy sources are actuated with known time delays that are varied from shot record to shot record. Seismic signals from sources deployed at different depths are recorded simultaneously. Seismic energy corresponding to each of the sources is extracted from the recorded seismic signals. Up-going and down-going wave-fields are extracted from the sources deployed at different depths using the extracted seismic energy therefrom. A method includes the separated up-going and down-going wave-fields are propagated to a water surface or a common reference, the up-going or the down-going wave-field is 180 degree phase shifted, and the signals from these modified up-going and down-going wave-fields are summed.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Apparatus and method and techniques for measuring and correlating characteristics of fruit with visible/near infra-red spectrum
InactiveUS6847447B2Better signal to noise ratioImproves Brix prediction accuracyRadiation pyrometryInvestigation of vegetal materialBrixPeak value
This disclosure is of 1) the utilization of the spectrum from 250 nm to 1150 nm for measurement of prediction of one or more parameters, e.g., brix, firmness, acidity, density, pH, color and external and internal defects and disorders including, for example, surface and subsurface braises, scarring, sun scald, punctures, in N—H, C—H and O—H samples including fruit; 2) an apparatus and method of detecting emitted light from samples exposed to the above spectrum in at least one spectrum range and, in the preferred embodiment, in at least two spectrum ranges of 250 to 499 nm and 500 nm; 3) the use of the chlorophyl band, peaking at 690 nm, in combination with the spectrum from 700 nm and above to predict one or more of the above parameters; 4) the use of the visible pigment region, including xanthophyll, from approximately 250 nm to 499 nm and anthocyanin from approximately 500 to 550 nm, in combination with the chlorophyl band and the spectrum from 700 nm and above to predict the all of the above parameters.
Owner:FPS FOOD PROCESSING SYST BV
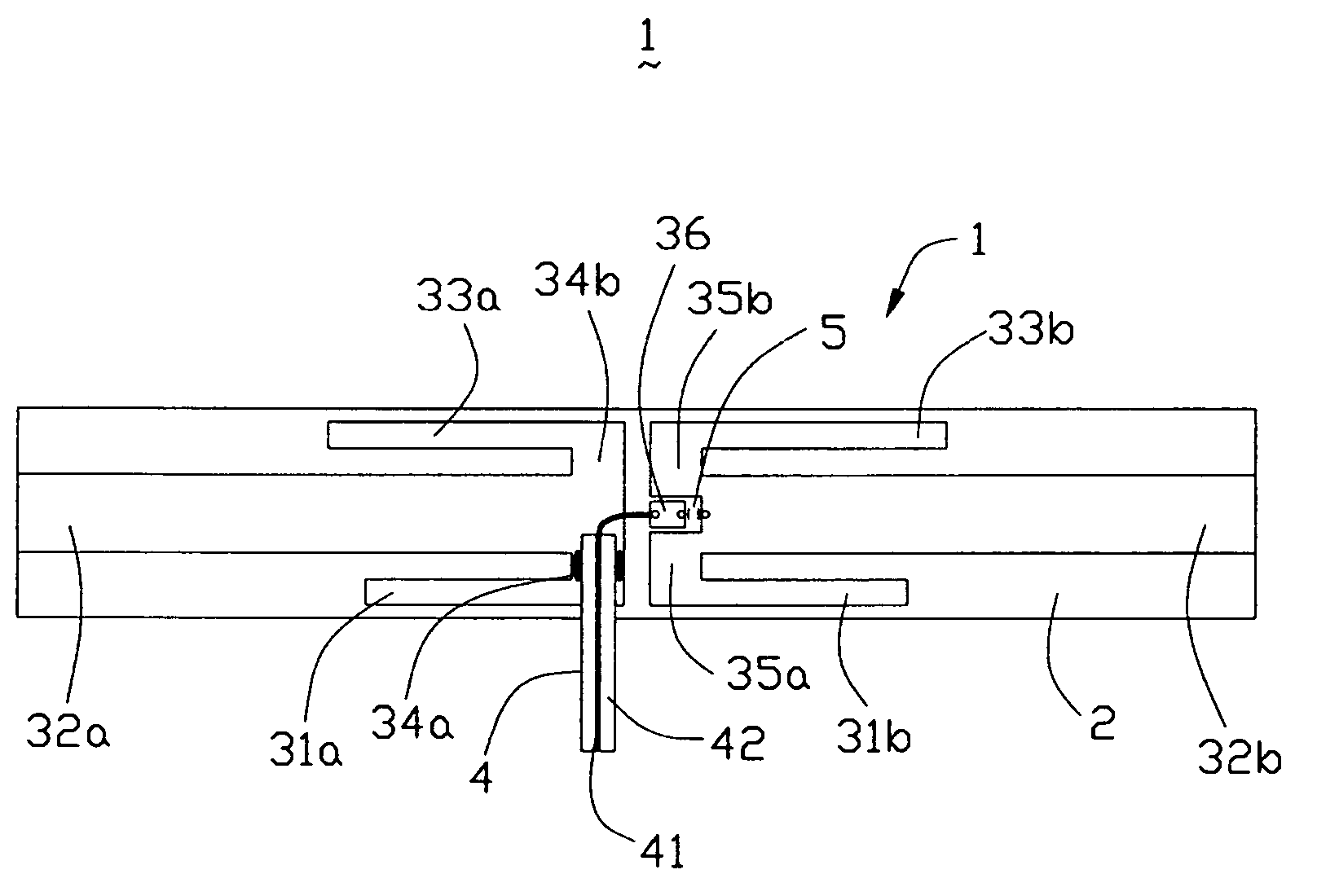
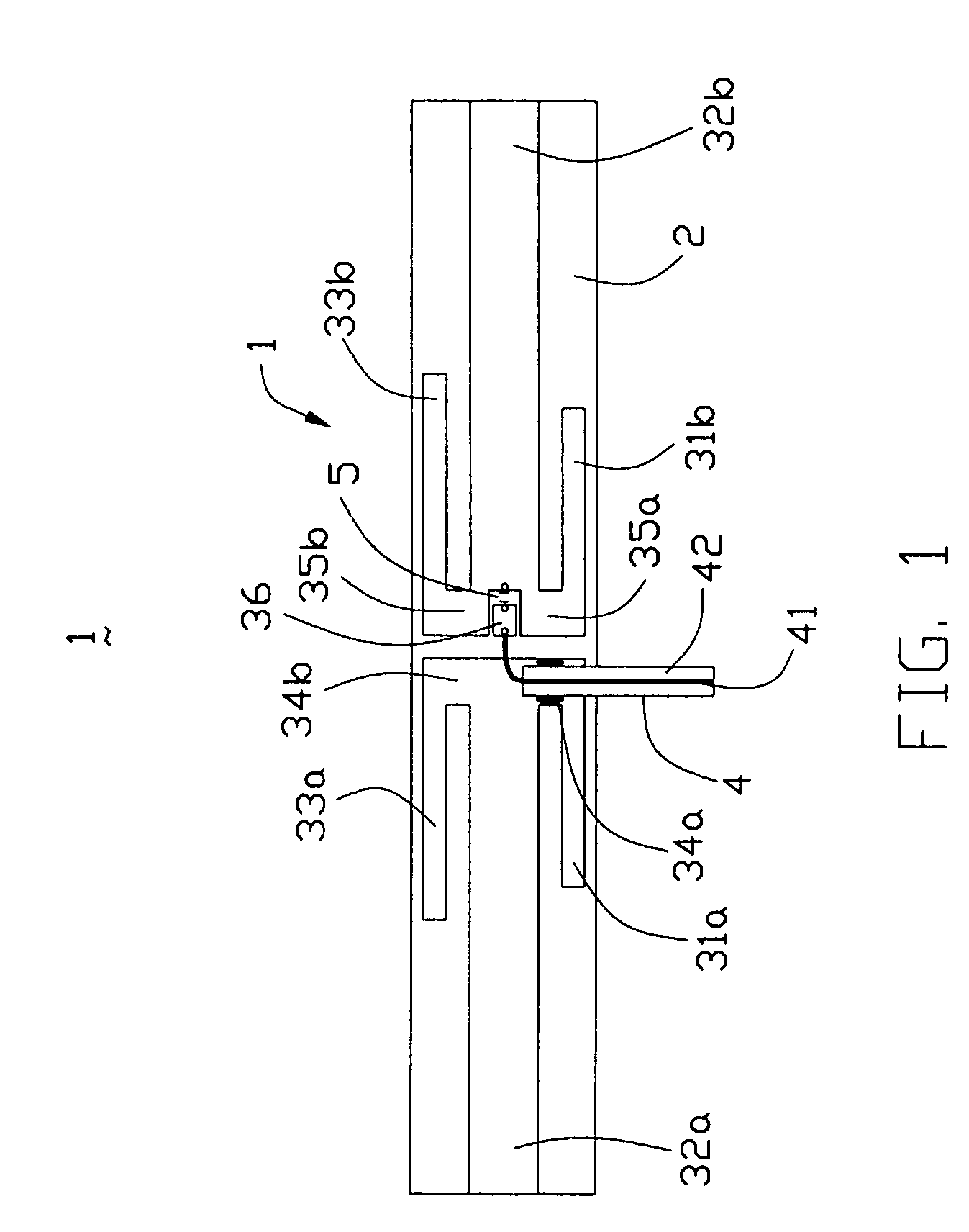
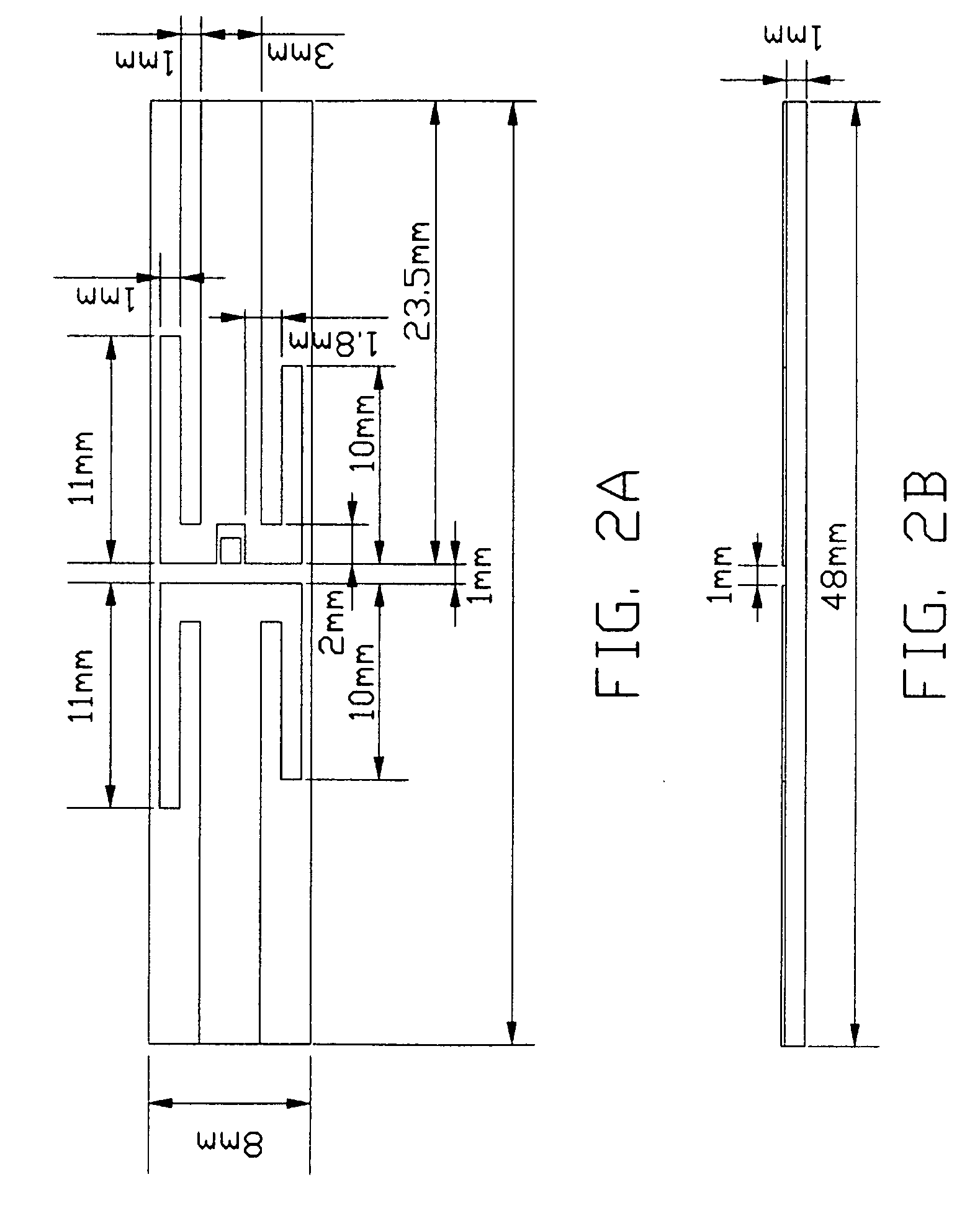
Multi-band printed dipole antenna
InactiveUS20050035919A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntennas with plural divergent straight elementsMulti bandImpedance matching
A multi-band printed dipole antenna (1) for an electronic device includes an elongate insulative substrate (2), a first, second and third pairs of dipole elements (31a, 31b, 32a, 32b, 33a, 33b) closely and parallelly disposed on the substrate, a capacitor (5) and a feeder cable (4). The first, second and third pair of dipole elements respectively couple with the feeder cable to form a first, second and third dipole antennas. The capacitor is used to improve the impedance matching of the second dipole antenna.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Method and spectral/imaging device for optochemical sensing with plasmon-modified polarization
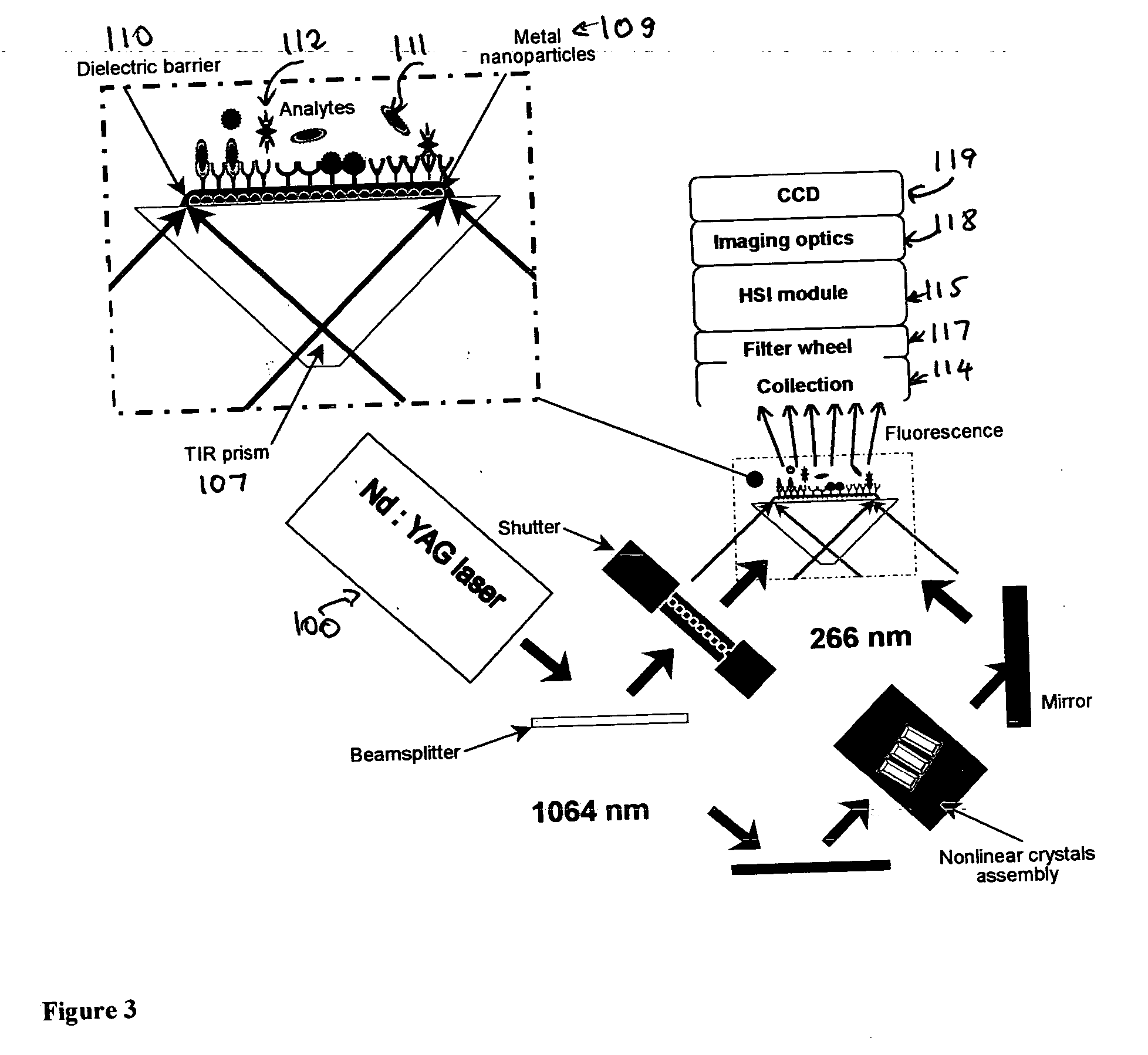
InactiveUS20050186565A1Low fluorescence quantum yieldHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberFluorescence
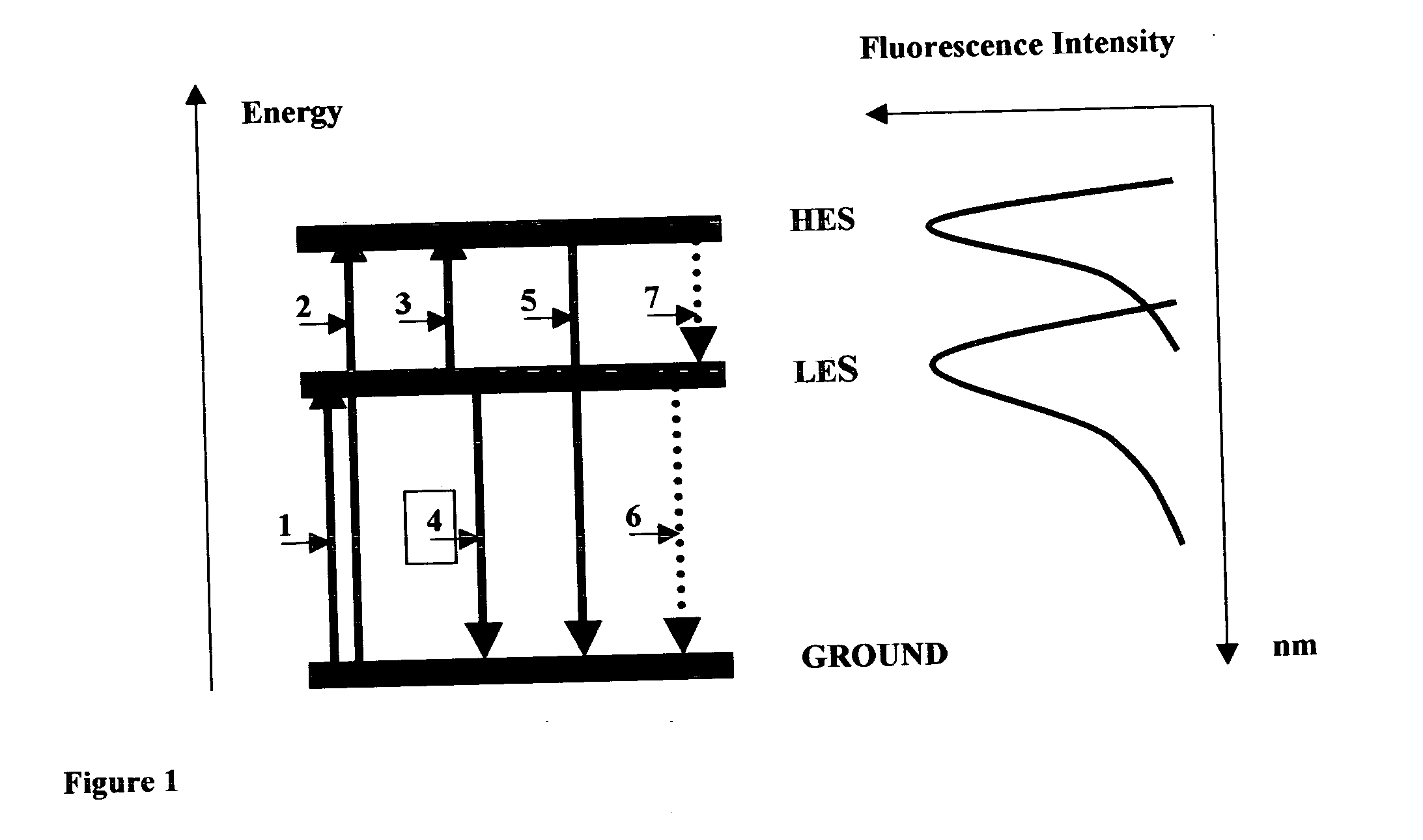
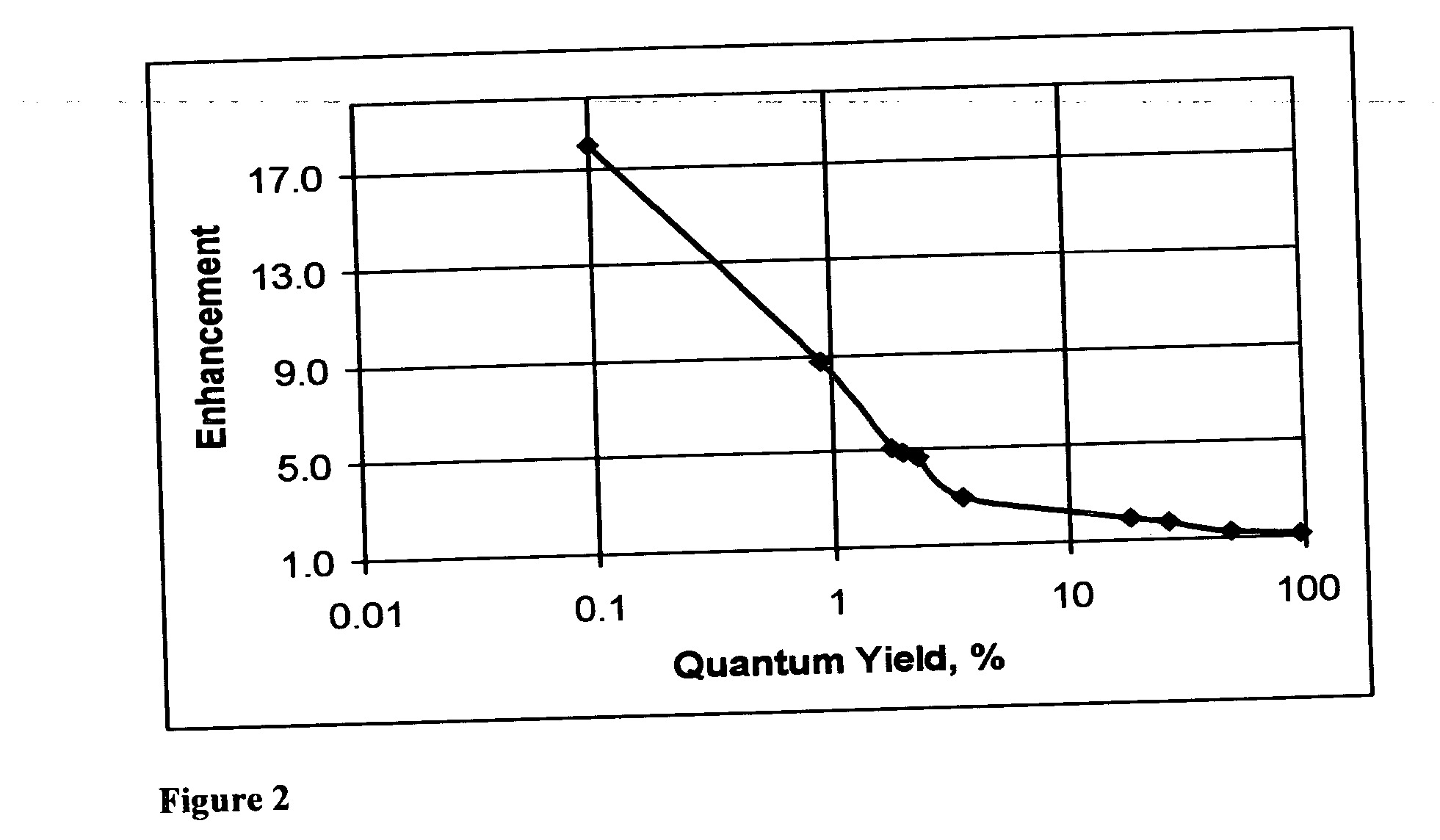
The invention discloses a method and spectral-imaging device for optochemical sensing with plasmon-modified multiband fluorescence polarization and with plasmon-modified polarization phase shift changes of a light beam reflected and / or passed through a total internal reflection conducting structure. The optochemical sensing is performed for molecules placed nearby the conducting structure and being excited by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to lower excited state (LES) and / or to higher excited states (HES). The invention also describes the spectral imaging device with an improved sensitivity of several orders of magnitude. The disclosed method and imaging device may find applications in clinical diagnostics, pharmaceutical screening, biomedical research, biochemical-warfare detection and other diagnostic techniques. The device can be used in bio-chip and micro-array technologies, flowcytometer, fiber optic and other types of diagnostic devices.
Owner:AMERICAN ENVIRONMENTAL SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com