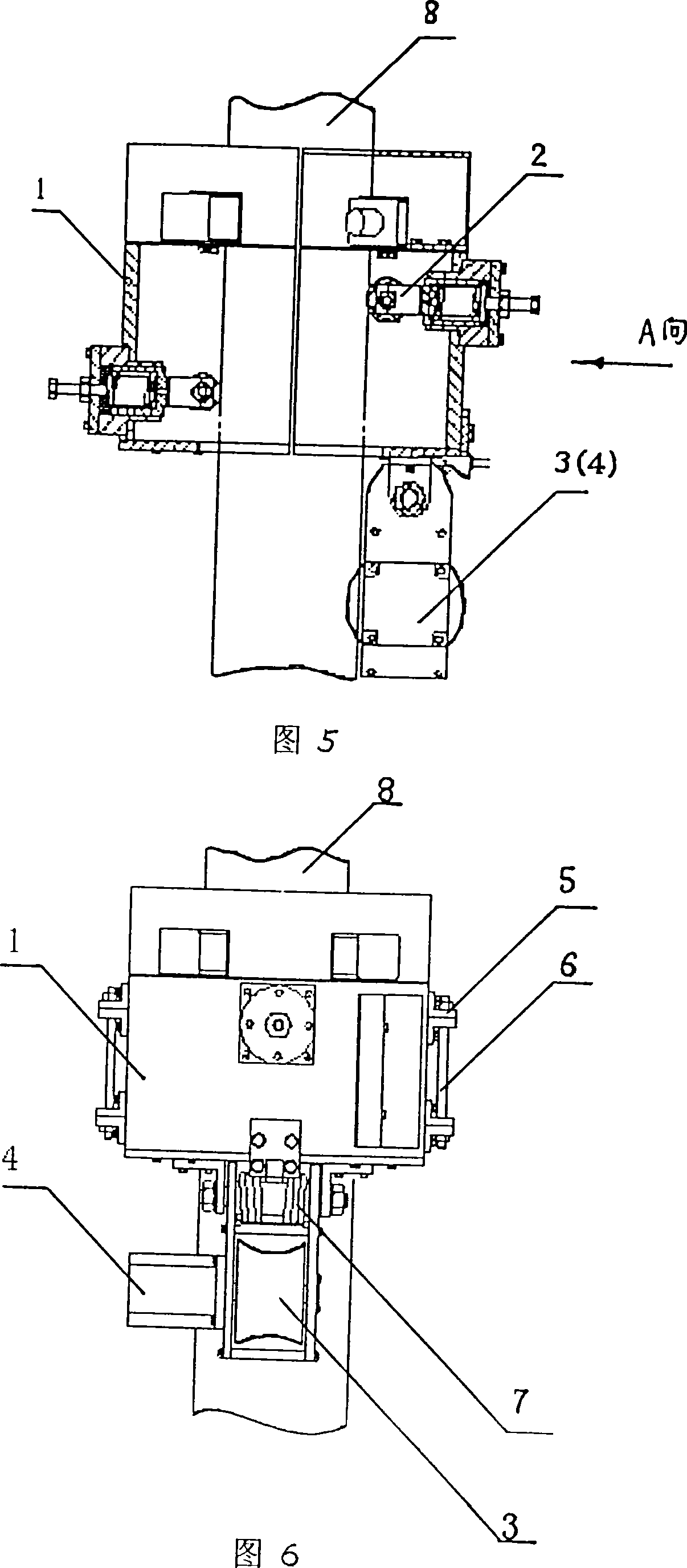
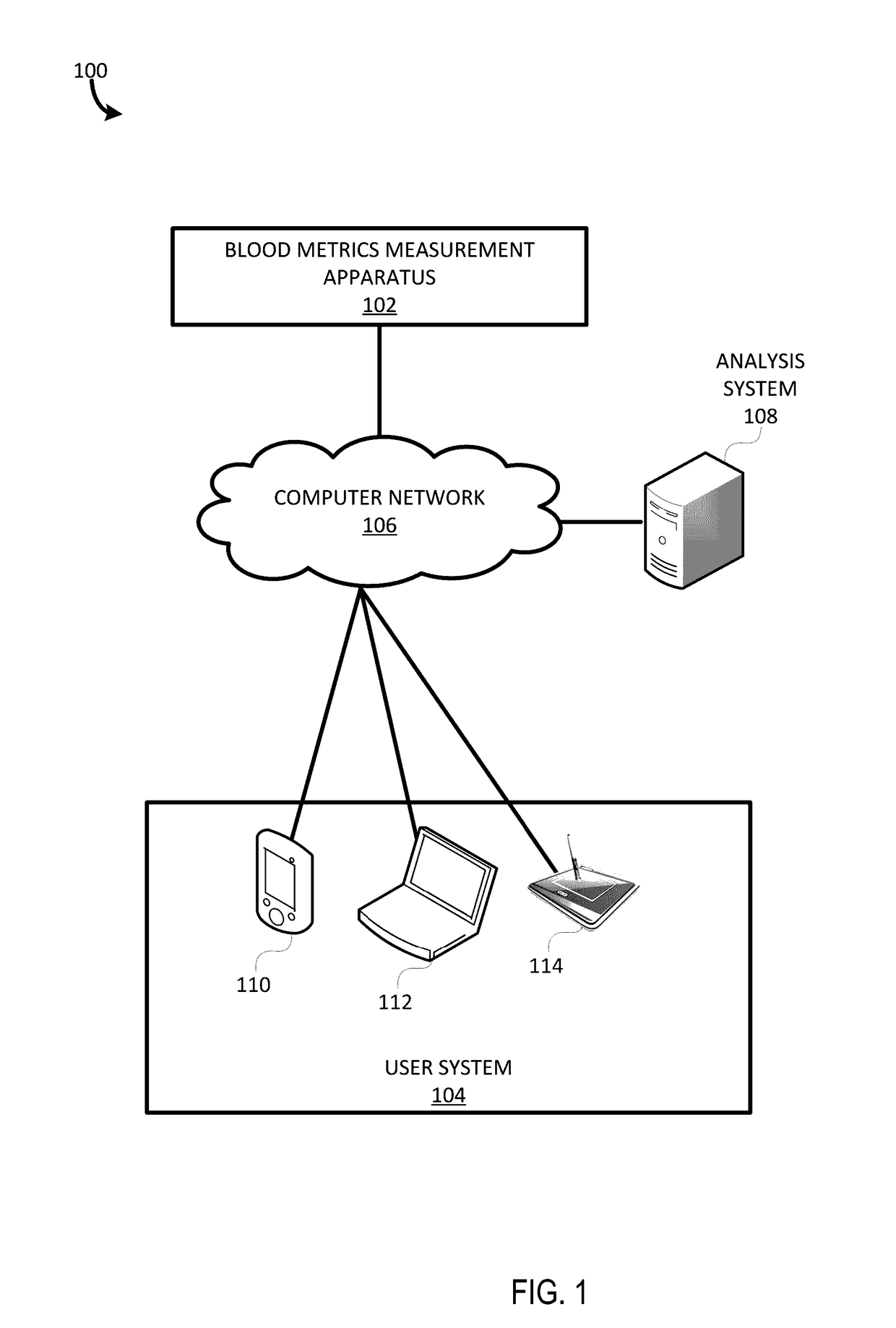
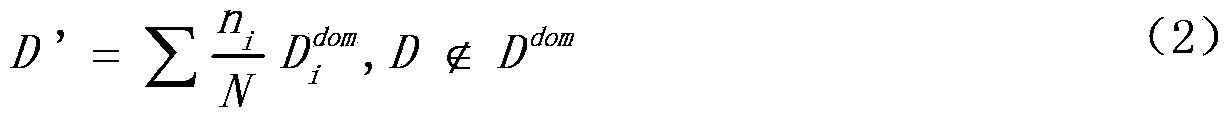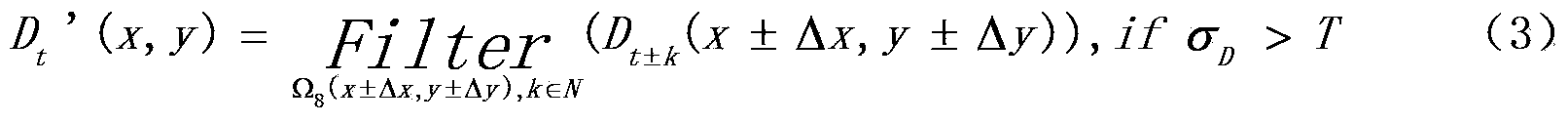Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
807 results about "Filter noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
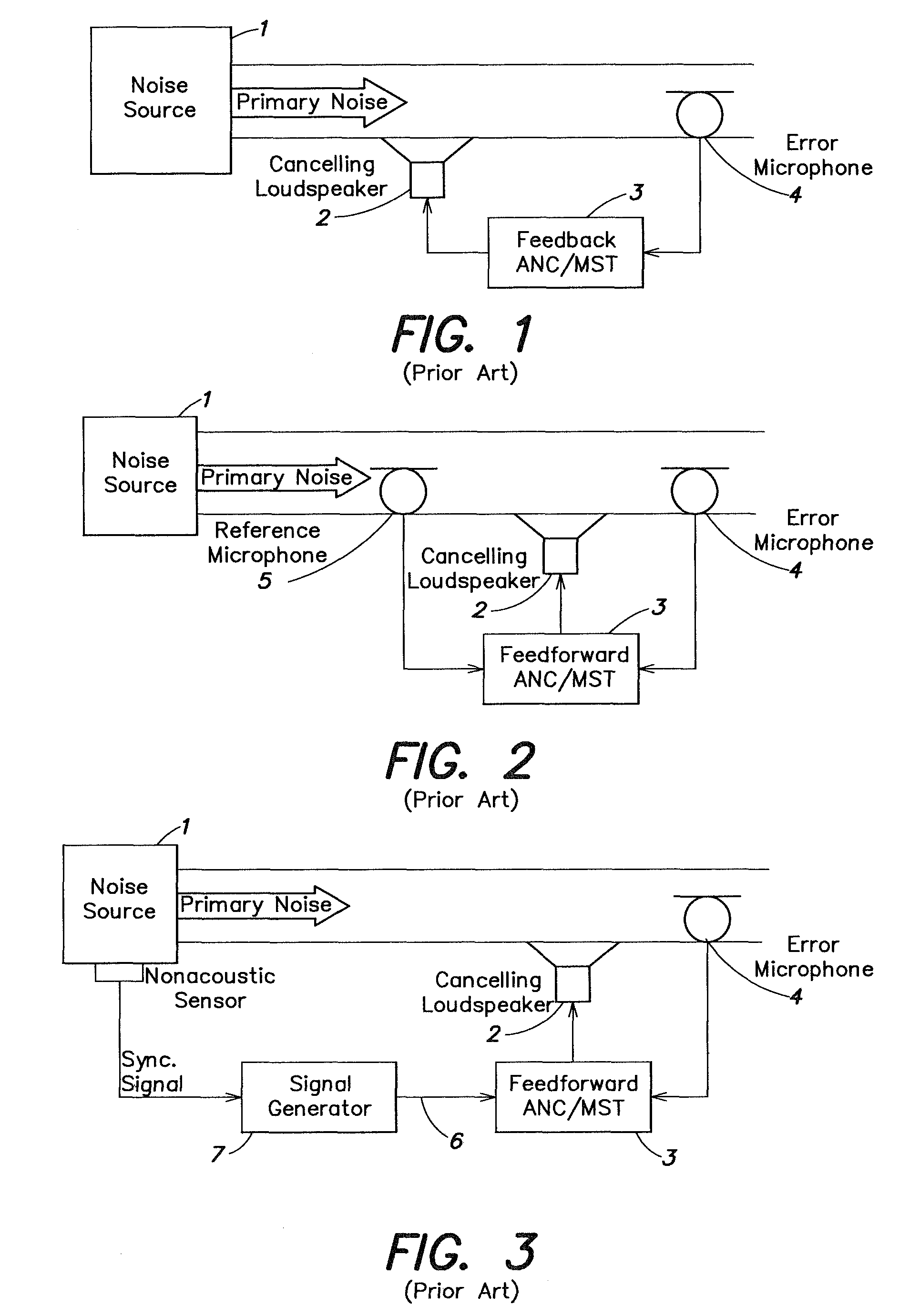
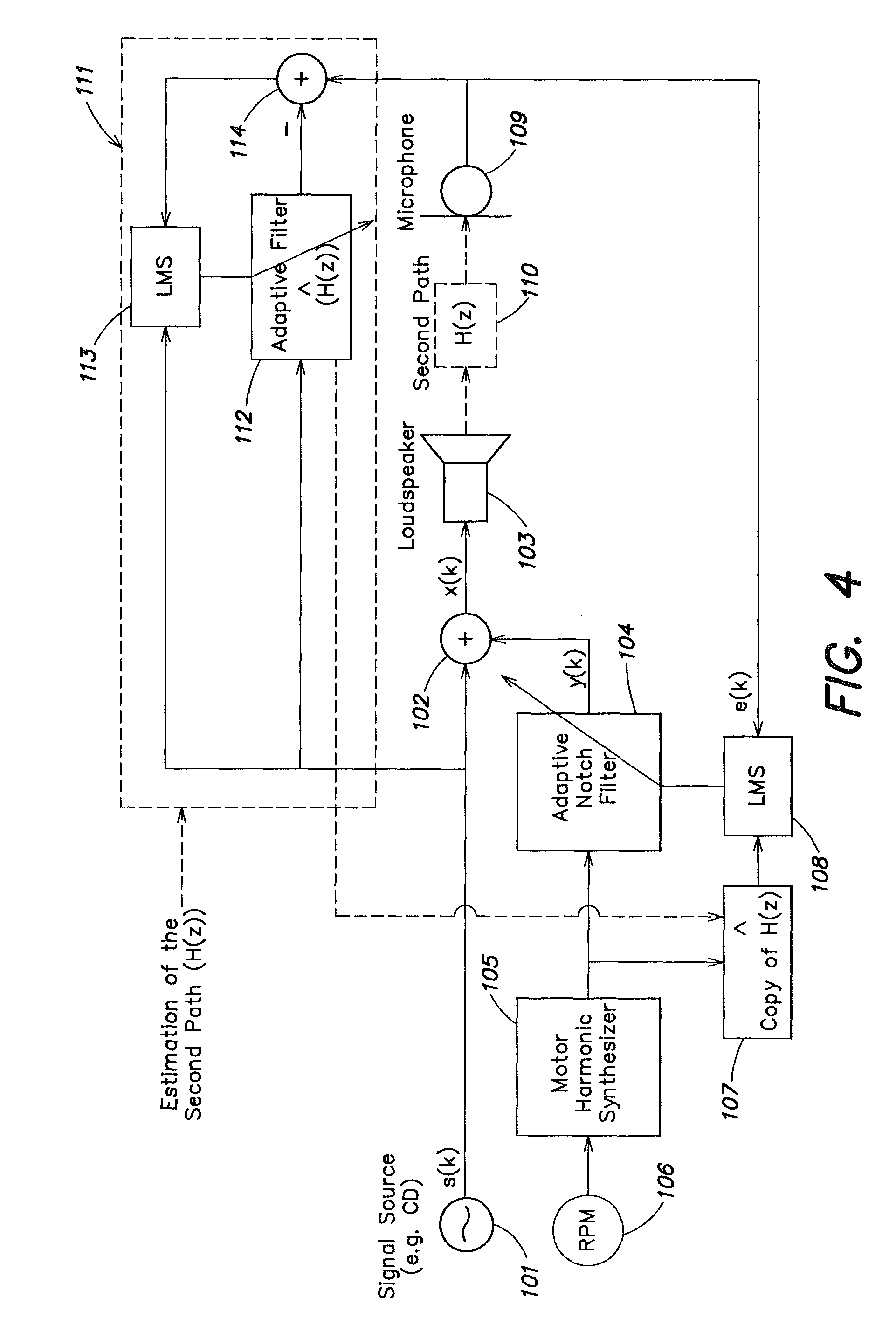
Active noise tuning system
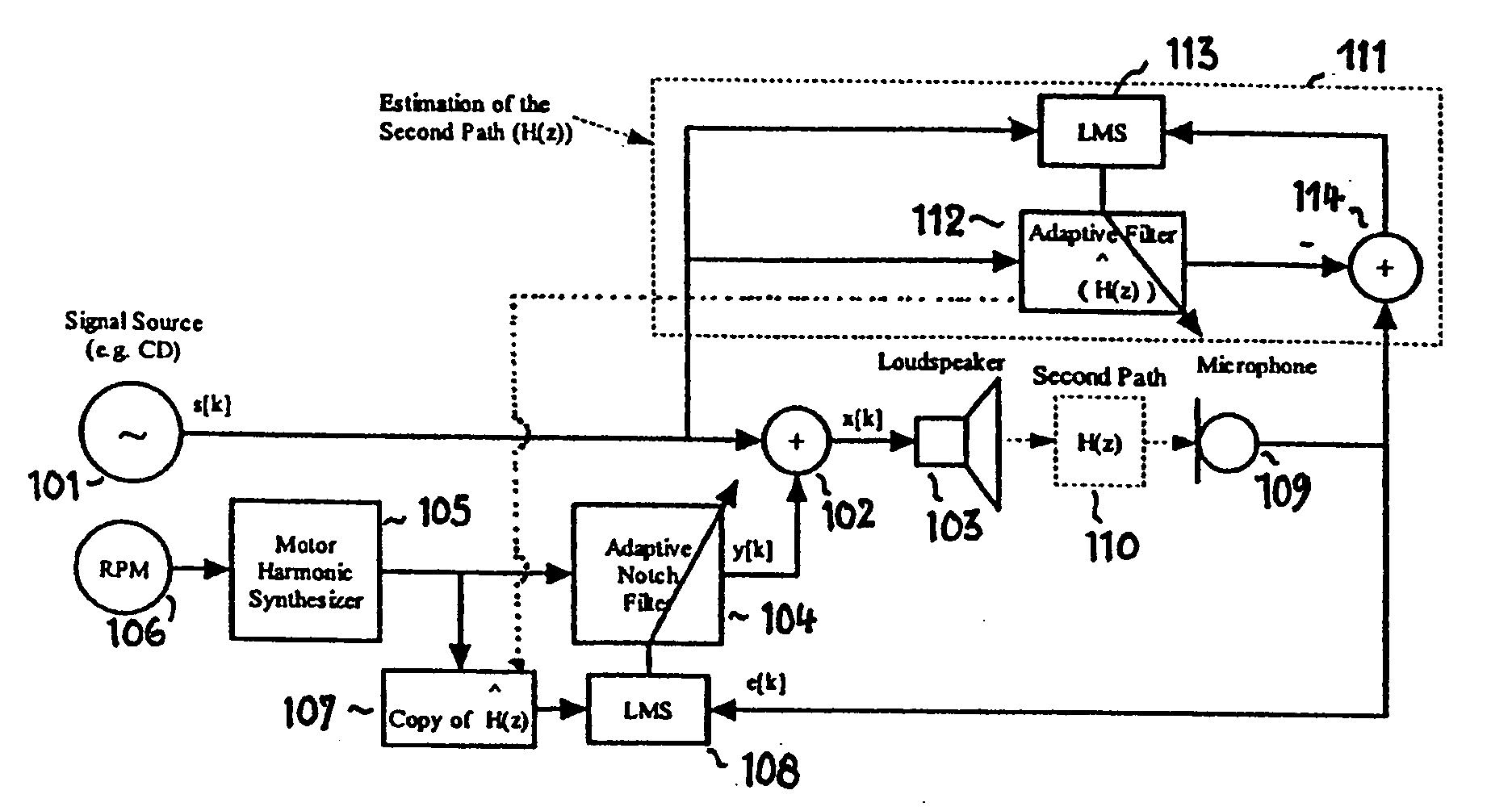
ActiveUS20050207585A1Improved noise suppressionEar treatmentSpeech analysisNoise controlControl signal
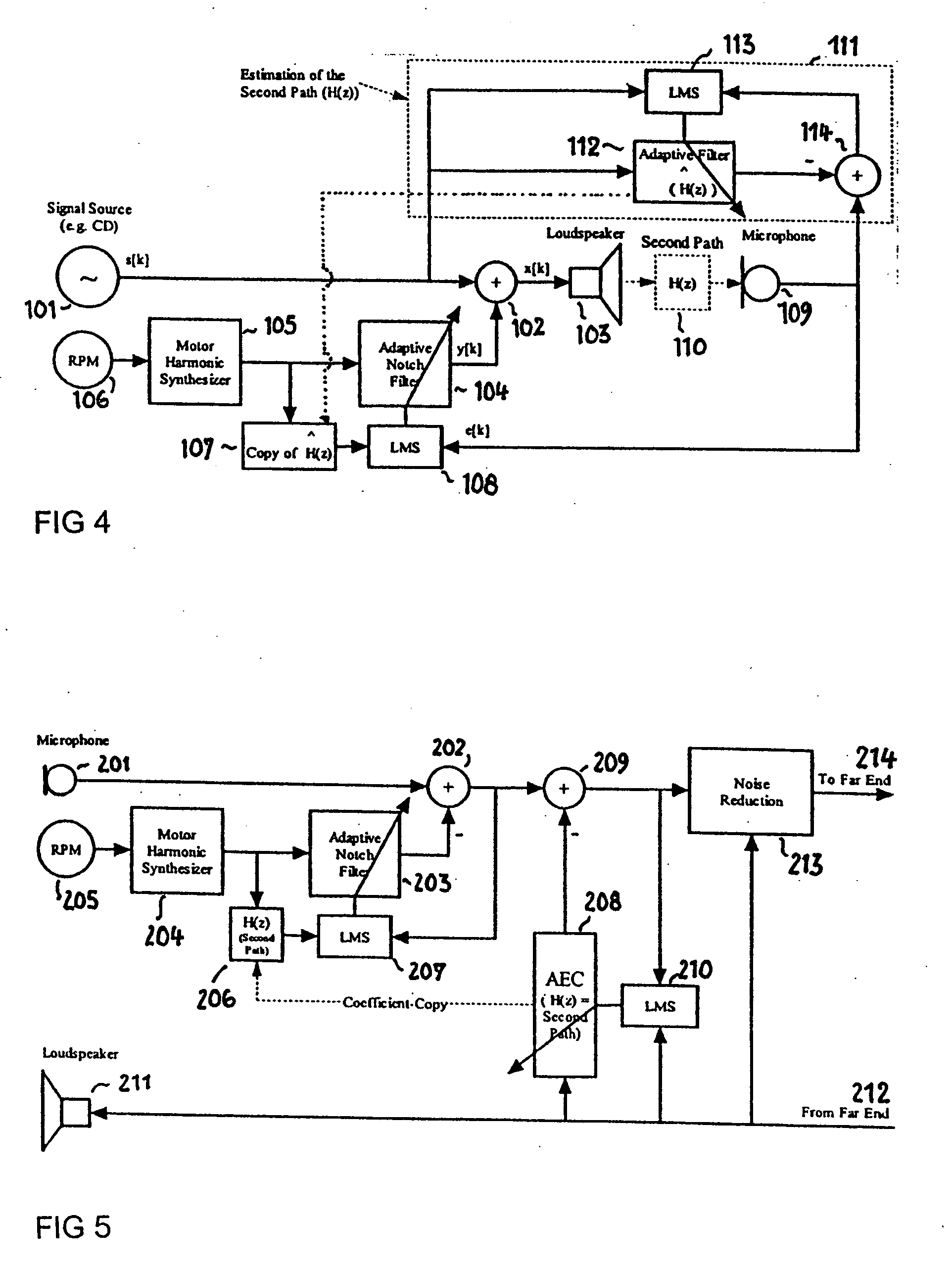
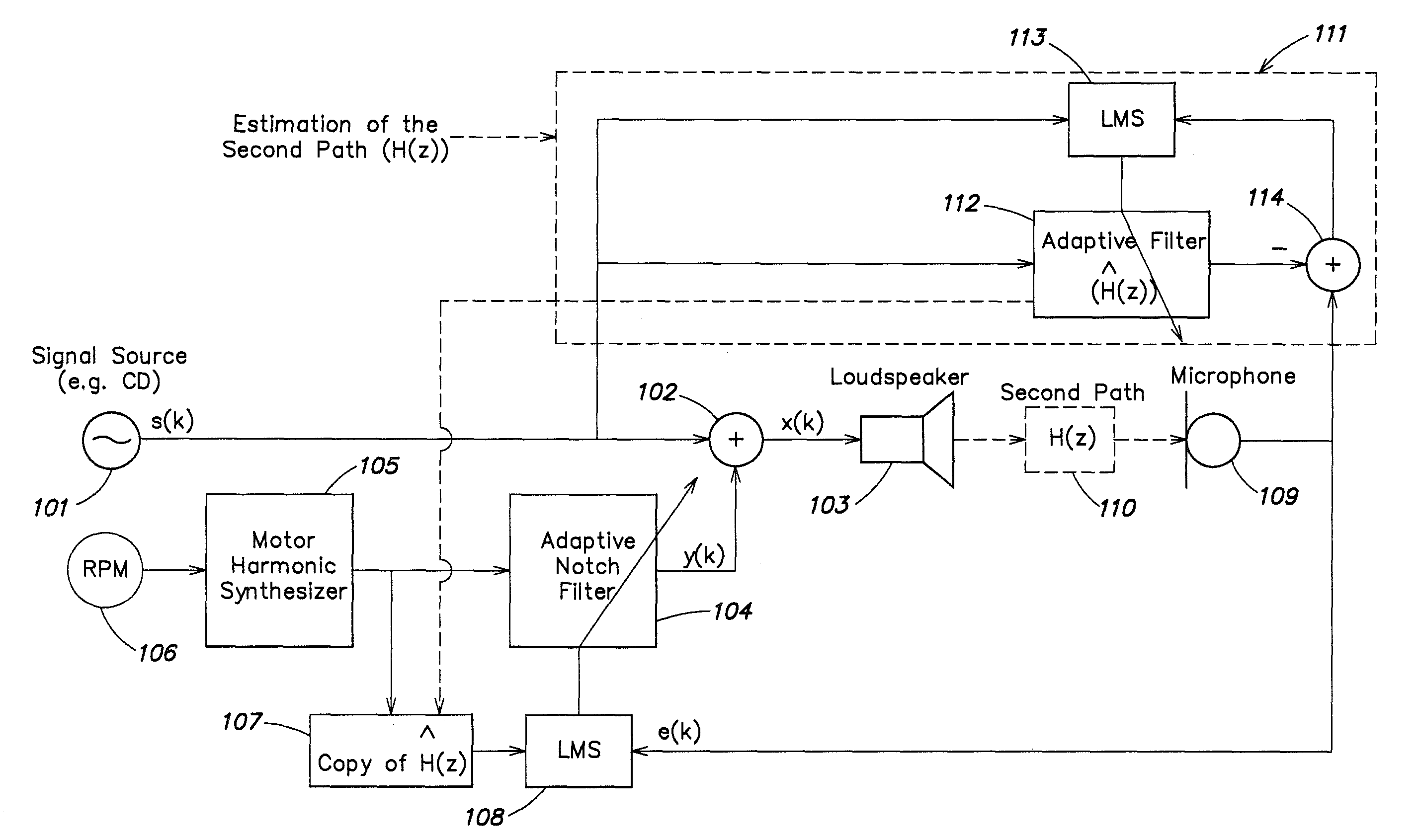
Active noise control system and method for controlling an acoustic noise generated by a noise source at a listening location, in which system and method sound is picked up in the surroundings of the listening location by a sound sensor; an electrical noise signal which corresponds to the acoustic noise of the noise source is generated and filtered adaptively in accordance with control signals. The adaptively filtered noise signal is irradiated into the surroundings of the listening location by a sound reproduction device, where a secondary path transfer function extends between the sound reproduction device and sound sensor. The noise signal is filtered with a transfer function that models the secondary path transfer function. The signals which provided by the sound sensor after first filtering serve as control signals for the adaptive filtering.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Integrated Biometric Sensing and Display Device
InactiveUS20120271121A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyBiometric dataWavelength filter
A biometric device configured to be attached to a portion of a body of a user measures biometric data of the user. The device includes an optical emitter, a wavelength filter, an optical sensor and a processor, for sending a light to the body of a user, receiving light received from the user, filtering and processing it to measure biometric data of the user, including for example, heart rate and blood flow rate. In addition, the biometric device may include other sensors, such as a galvanic skin response sensor, an ambient temperature sensor, skin temperature, motion sensor, etc., to enable the biometric device to measure arousal or conductivity changing events, ambient temperature, user temperature and motion associated with the user. Additionally, information from each sensor may be used to further filter noise in one or more signals received by the sensors to provide biometric data to the user.
Owner:INTEL CORP
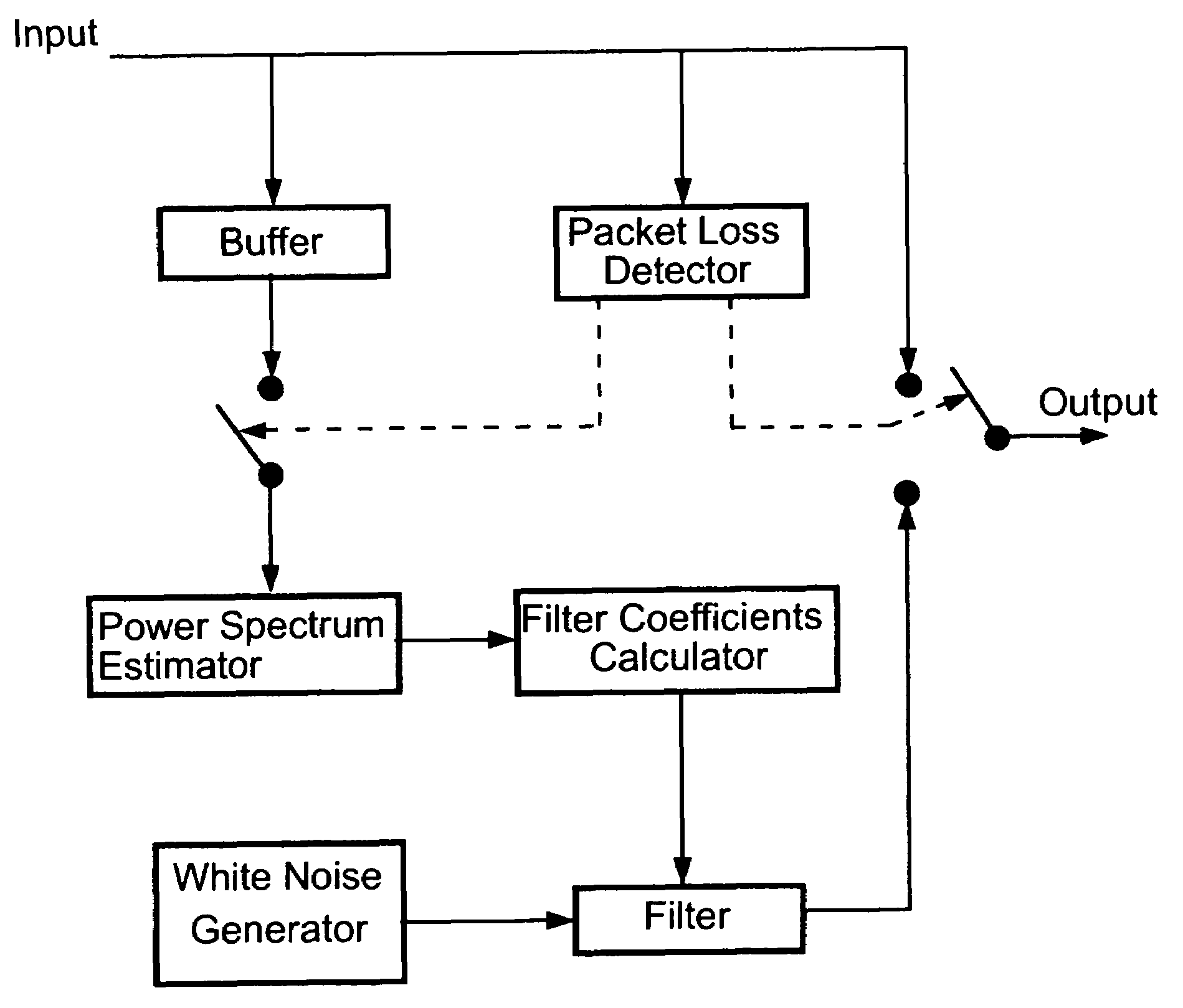
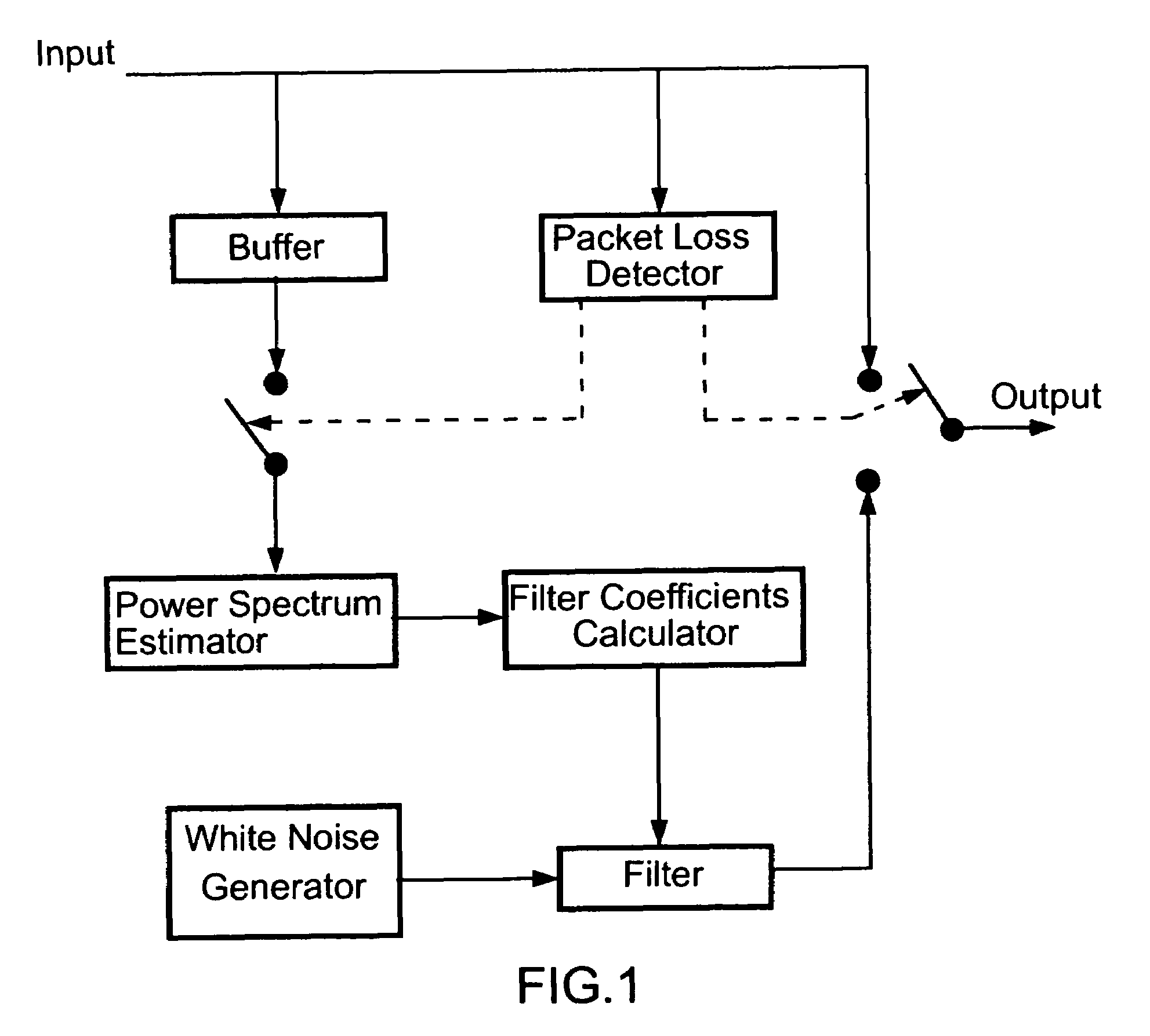
Packet loss compensation method using injection of spectrally shaped noise
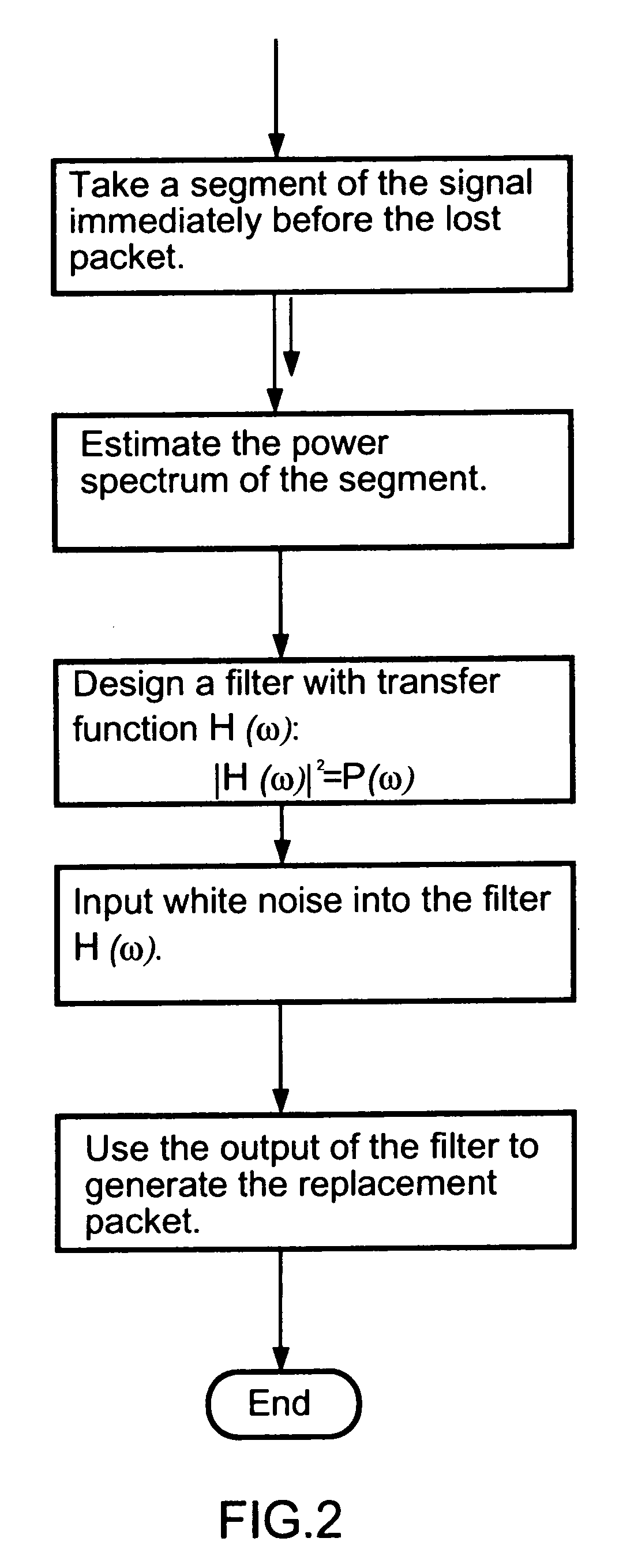
An insertion-based error concealment method and apparatus are provided whereby, instead of directly inserting white noise, a filter is created to shape the white noise. The filtered white noise is then used to replace lost data. The method of the present invention is implemented by first estimating the power spectrum of the previous frame; then designing a filter with transfer function H(f), where |H(f)|2=the estimated power spectrum; and finally generating the replacement packet using noise which has been spectrally modified by the filter. The resulting filtered noise has the same power spectrum as the previous packet but is not highly correlated with it.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
Quantization in perceptual audio coders with compensation for synthesis filter noise spreading and the overlap-add process
InactiveUS6363338B1Improve performanceAccurate noiseSpeech analysisCode conversionBit allocationAlgorithm
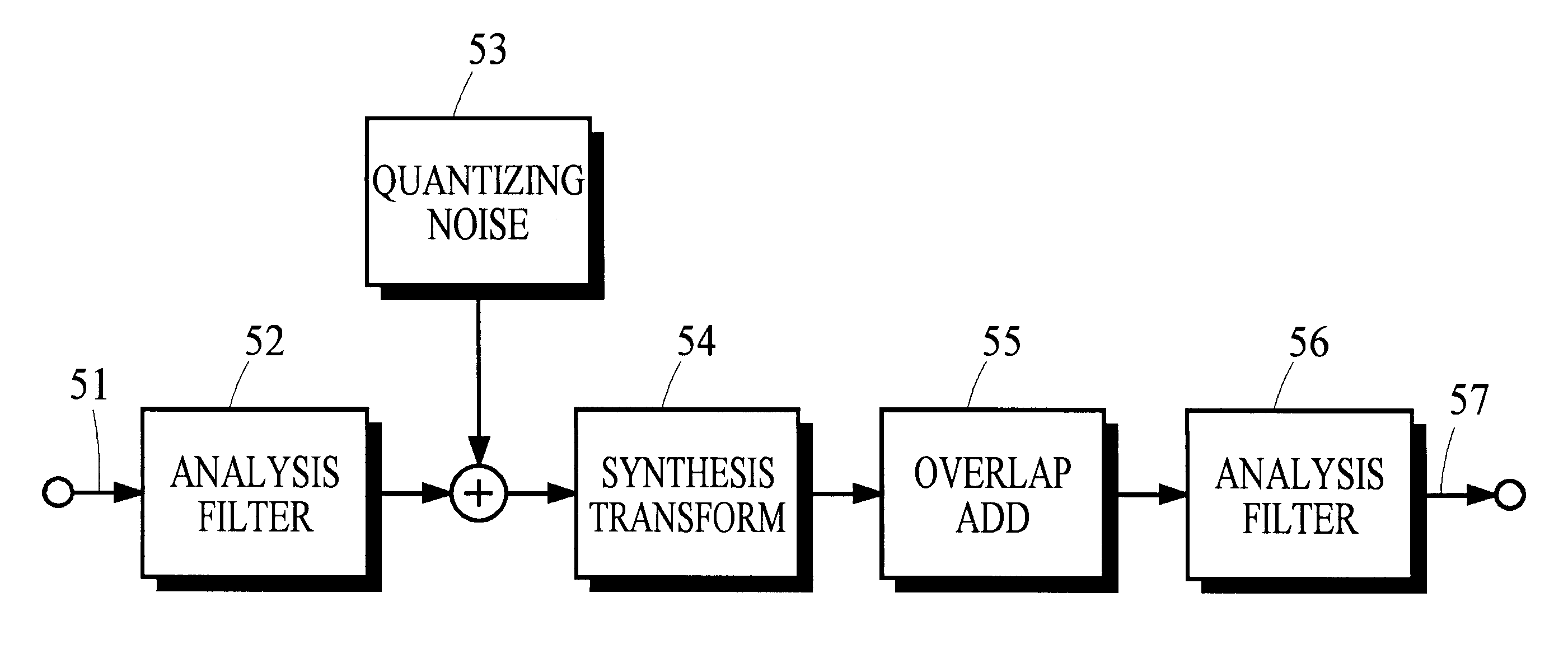
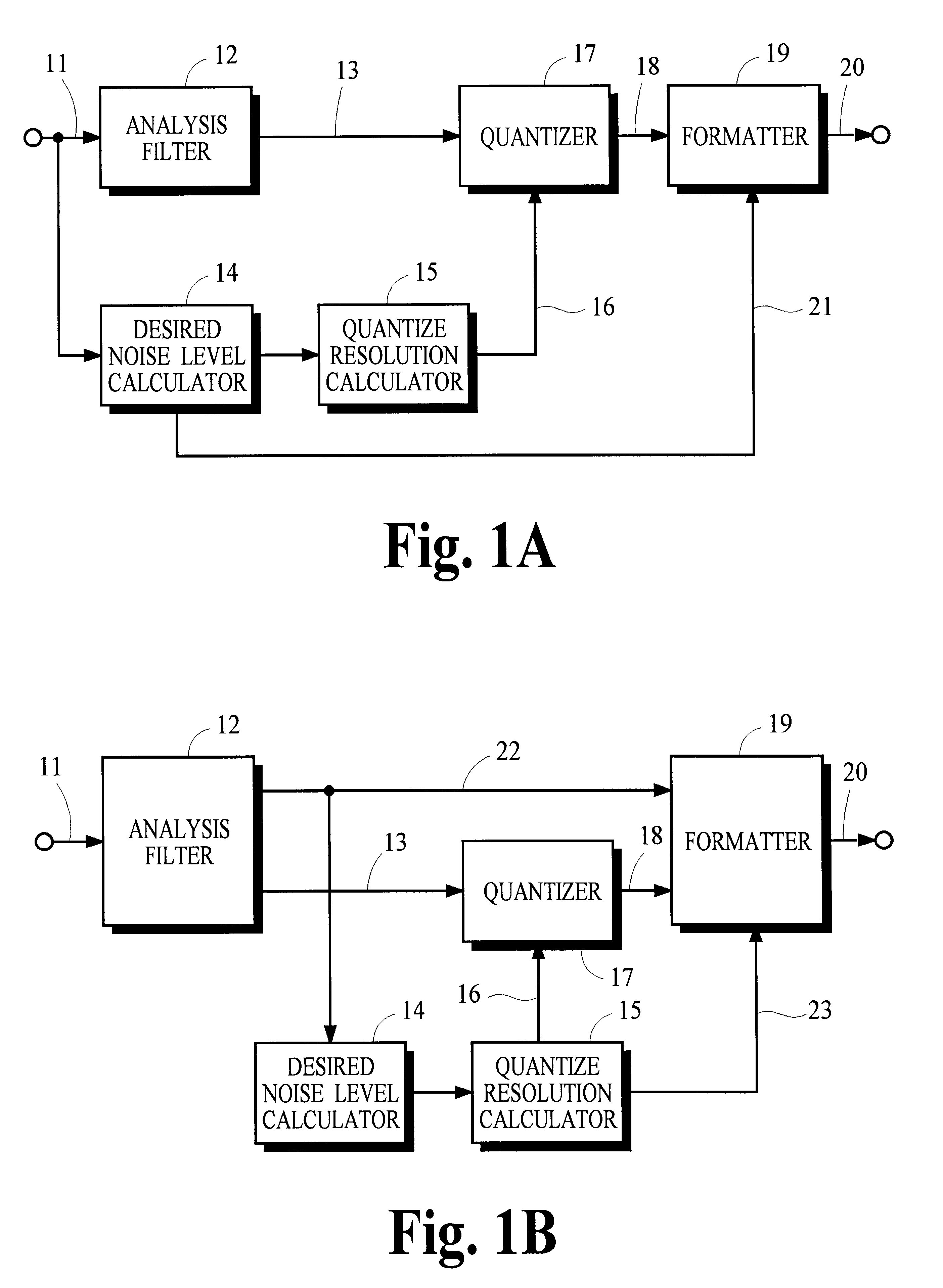
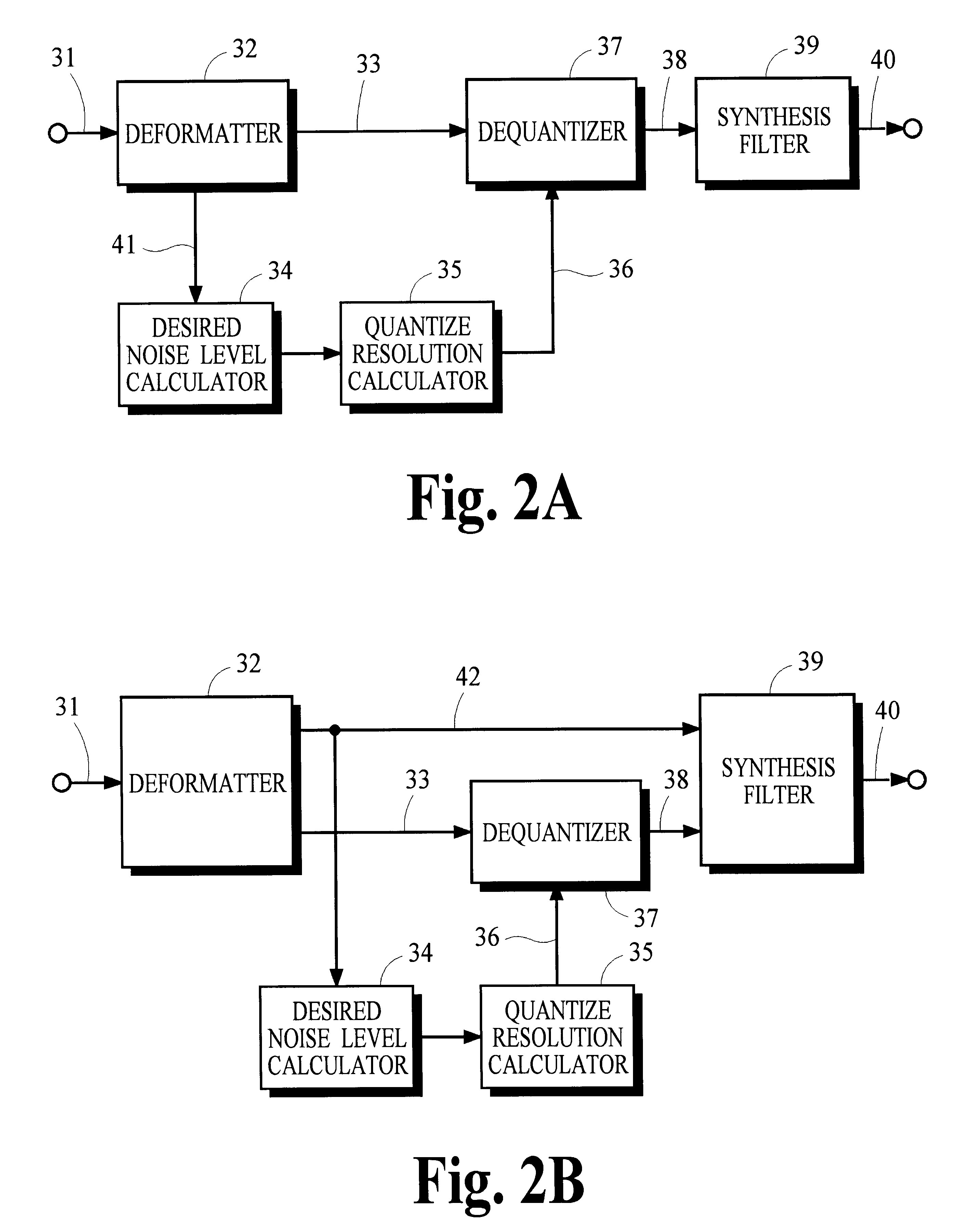
Many perceptual split-band coding systems that use analysis and synthesis filters assume the quantization noise introduced by quantizing split-band signals is substantially the same as the noise that results in the output signal obtained by applying the synthesis filters to the quantized split-band signals. In general, this assumption is not true because the synthesis filters modify or spread the quantization noise. A theoretical framework for deriving an optimum bit allocation that accounts for synthesis-filter noise spreading and the overlap-add process is disclosed. In concept, the problem of finding an optimal bit allocation can be expressed as a linear optimization problem in a multidimensional coordinate space. Simplified processes derived from this theoretical framework are disclosed that can obtain near-optimal solutions using modest computational resources.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method for extracting text-oriented field term and term relationship
InactiveCN102360383AEfficient removalImprove term recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsNODALConditional random field
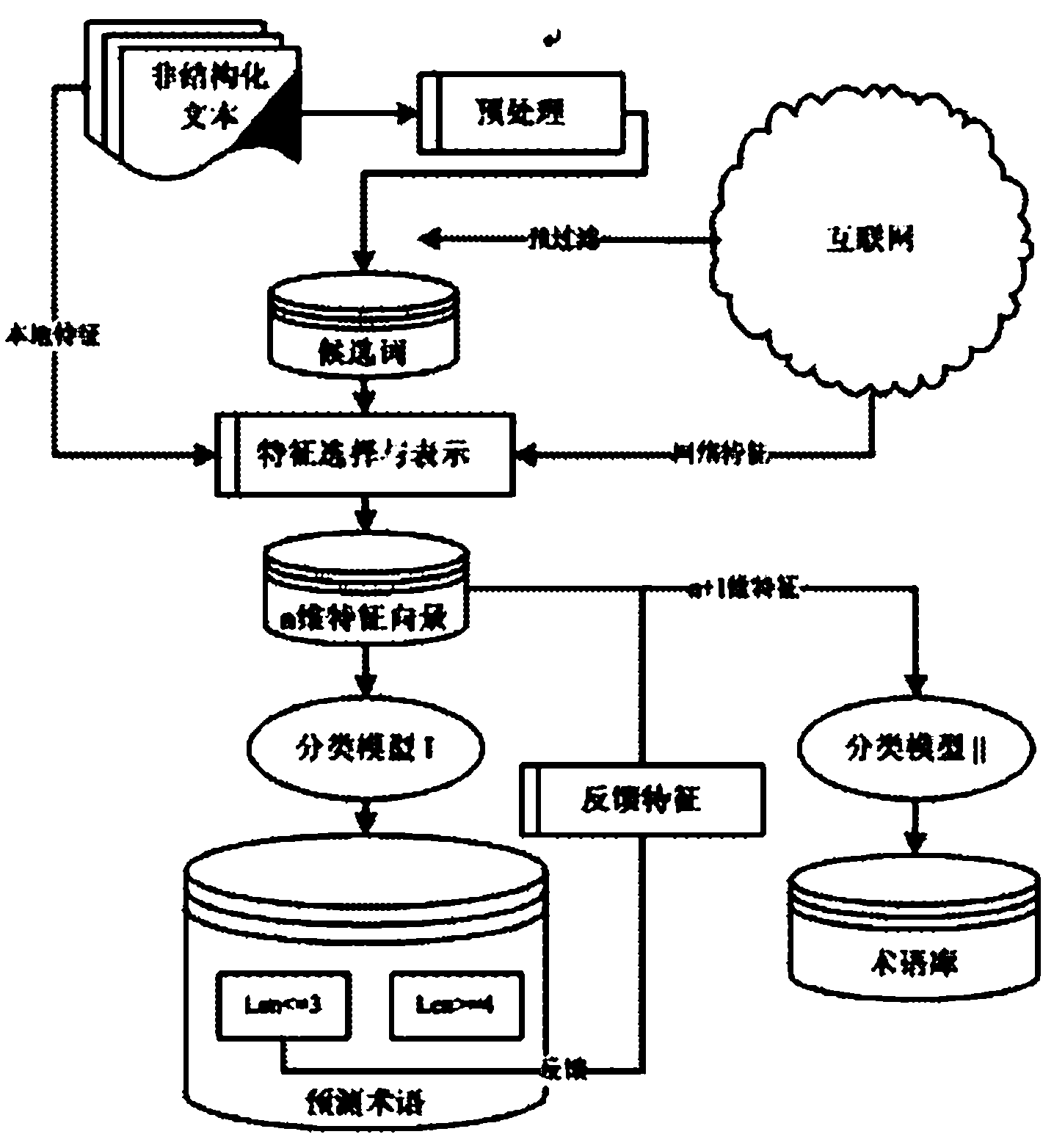
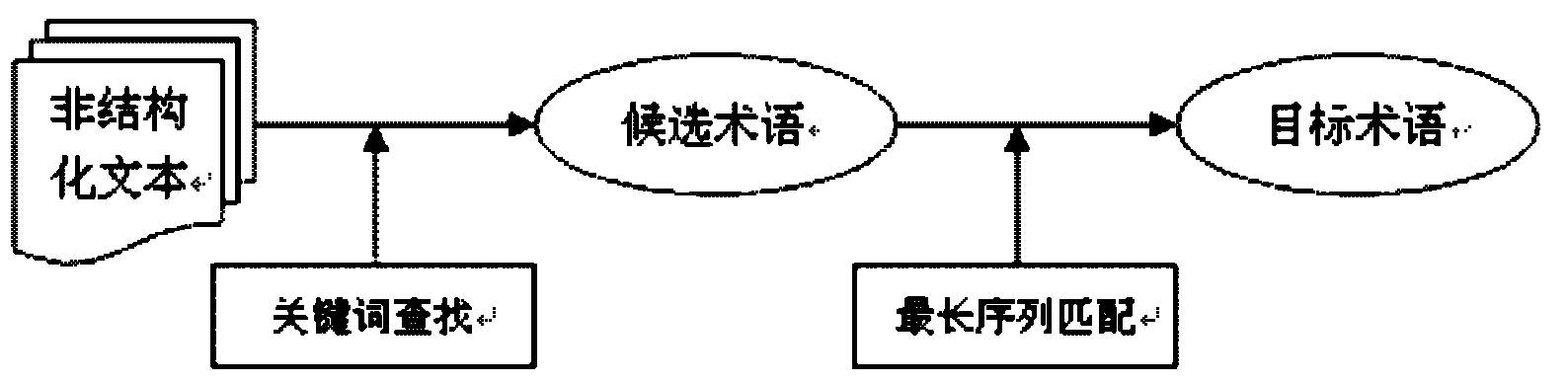
The invention discloses a method for extracting a text-oriented field term and term relationship. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, preprocessing original linguistic data to obtain a candidate word set including clauses, participles and part of speech tagging, and filtering noise words; secondly, extracting term characteristics from the original linguisticdata and the Internet, and separating terms from candidate words by combining with a dual-model structure algorithm; thirdly, constructing a term dictionary by adopting an inverted index method, and tagging the terms in a text to be identified by using a longest match algorithm; and finally, carrying out multilevel sign sequence tagging through a conditional random field model according to a multi-dimensional node signing rule to obtain a relationship among the terms in the text to be identified.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Active noise tuning system
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Method and device for noise reduction
ActiveUS20070055505A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSignal processingNoise reductionComputer science
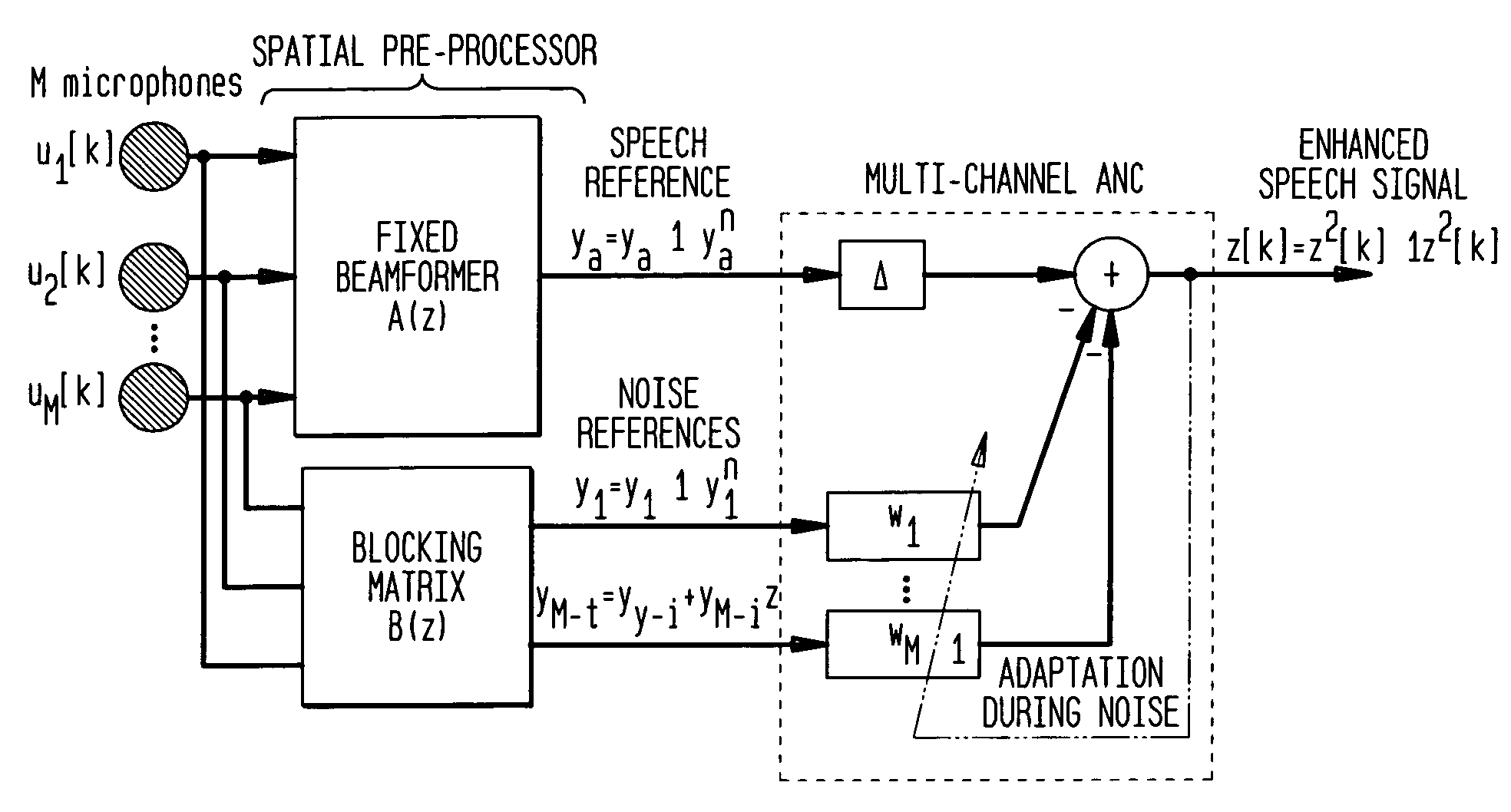
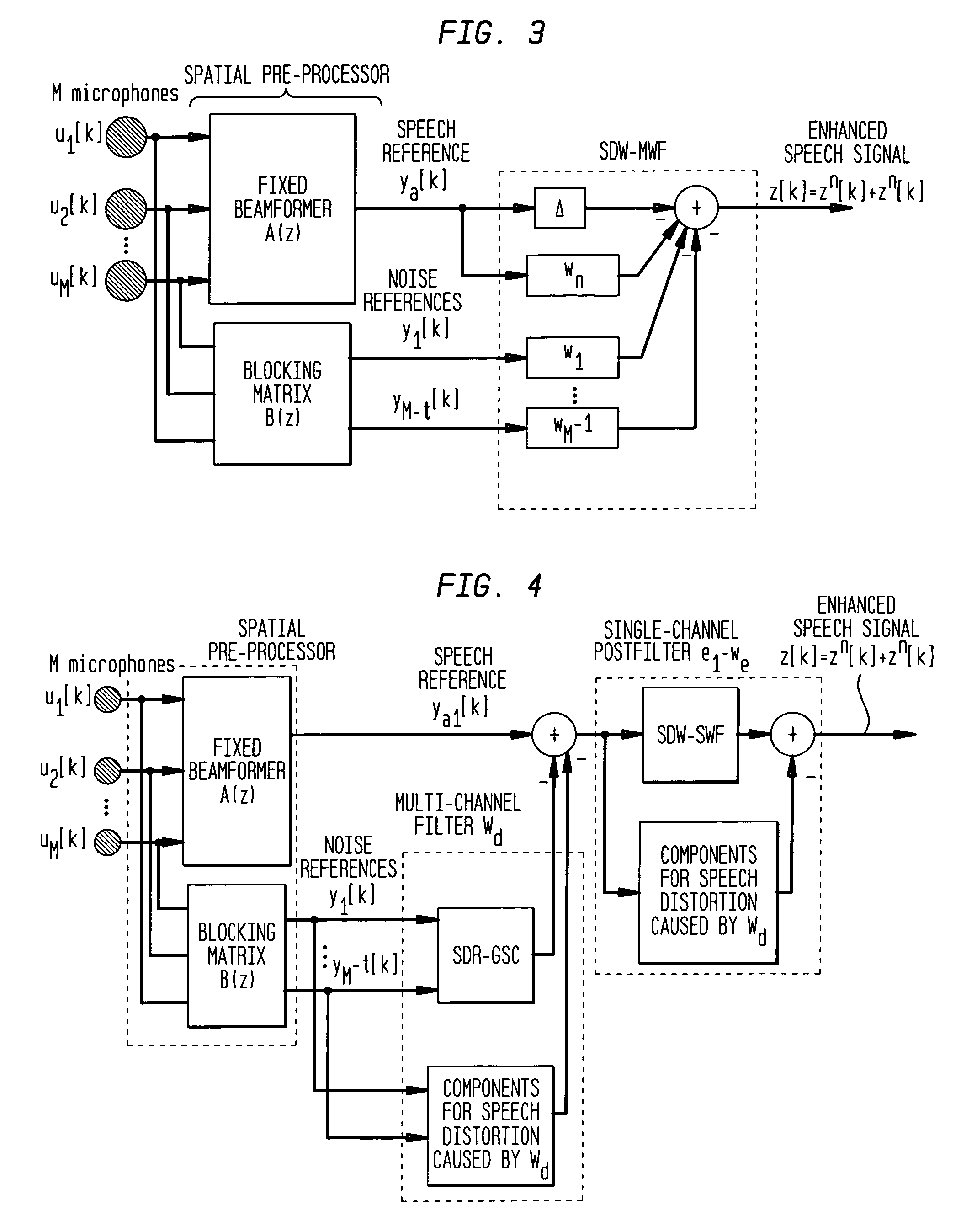
In one aspect of the present invention, a method to reduce noise in a noisy speech signal is disclosed The method comprises applying at least two versions of the noisy speech signal to a first filter, whereby that first filter outputs a speech reference signal and at least one noise reference signal, applying a filtering operation to each of the at least one noise reference signals, and subtracting from the speech reference signal each of the filtered noise reference signals, wherein the filtering operation is performed with filters having filter coefficients determined by taking into account speech leakage contributions in the at least one noise reference signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
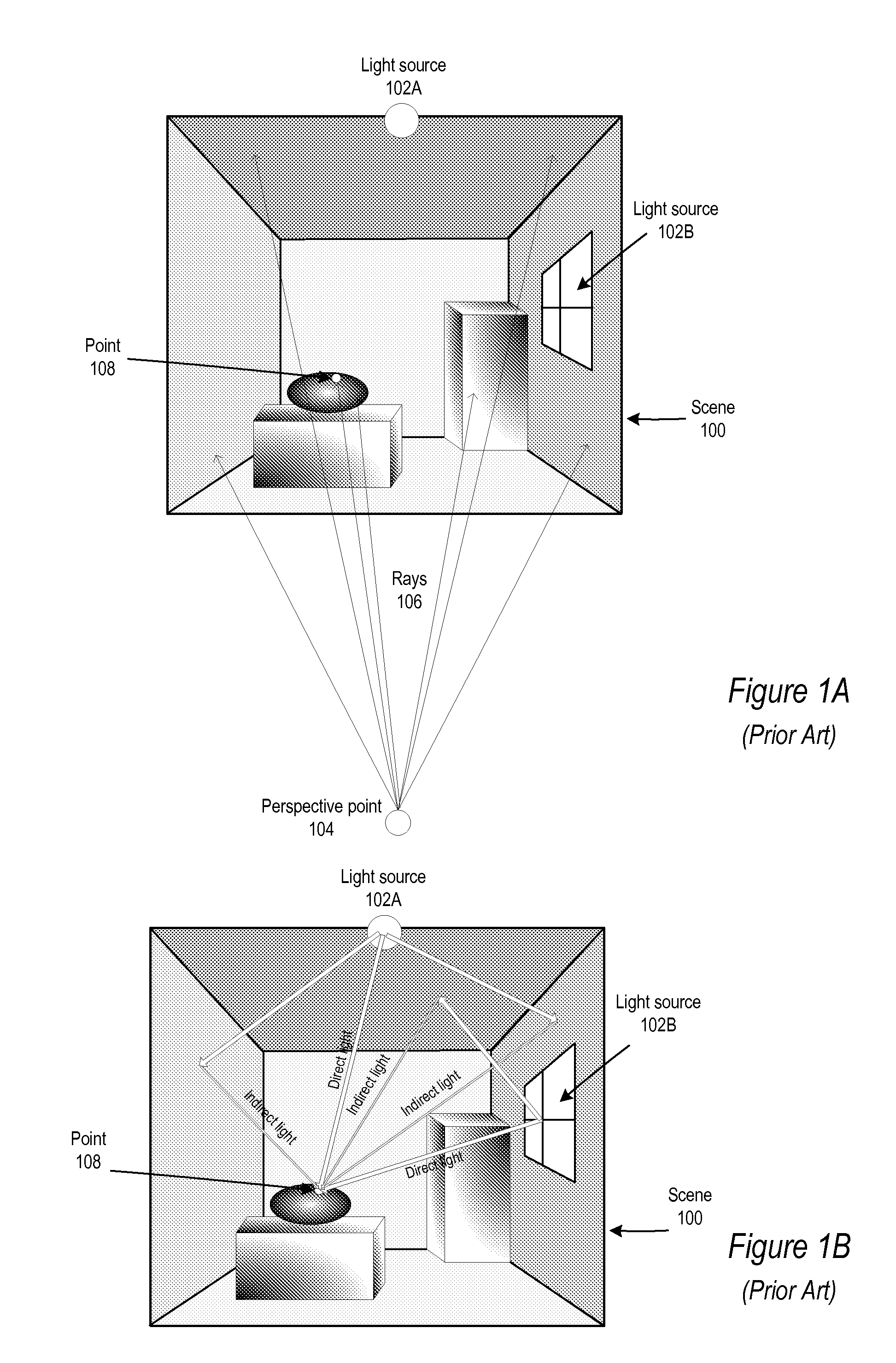
Methods and Apparatus for Diffuse Indirect Illumination Computation using Progressive Interleaved Irradiance Sampling
InactiveUS20130120385A1Quality improvementUniform coverage3D-image renderingDiffuse reflectionBilateral filter
Methods and apparatus for diffuse indirect illumination computation using progressive interleaved irradiance sampling. Embodiments may implement a method that amortizes the cost of computing the irradiance integral for diffuse indirect illumination both temporally and spatially in screen space. For each pixel, only one secondary ray is fired. By carefully arranging different secondary ray directions for different pixels according to a sampling sequence, embodiments may filter the noisy estimate so that each pixel receives a relatively uniform coverage of the integrated hemisphere. Some embodiments may use a bilateral filter so that the geometric discontinuities are respected. The sequence may continue to a higher-level of stratification in each frame. This ensures that the rendering is converging to a noise-free result.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Lithium battery system
A lithium battery system for providing power to a load and a method for controlling the same. The system includes an alternator and a battery pack coupled in parallel with the alternator and the load via a vehicle voltage bus. The battery pack includes a lithium battery having a plurality of cells connected to the vehicle voltage bus to filter noise thereon and a battery management system coupled to the lithium battery. The battery management system is configured to vary a voltage output of the alternator based on a voltage and / or a current of the lithium battery. The noise along the vehicle voltage bus is reduced by the placement of the lithium battery.
Owner:AIRPORTS AUTHORITY OF INDIA
Noise filtering method for touch screen
InactiveCN1811680AIncrease jitterImproving falsely detected phenomenaInput/output processes for data processingPattern recognitionSimulated data
Owner:LG ELECTRONIC (HUIZHOU) CO LTD
Container number identification method
InactiveCN102024144AEfficient extractionEffectively extract and identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmRapid identification
The invention discloses a container number identification method which comprises the following steps of, firstly, after acquiring pictures of a container number, searching a frame of a container, calculating the inclination with the frame as a reference line, and intercepting pictures in the frame subjected to correction; secondly, carrying out graying and dynamic binarization on the intercepted pictures, and filtering noise interference; thirdly, scanning and segmenting container number character pictures which satisfy the conditions one by one through a rank scanning method; fourthly, accurately extracting 11-bit container number characters which satisfy the conditions by determining an equipment identifier; and fifthly, extracting character characteristics one by one to finish the identification process, and judging whether the container number is correct by combining a check bit. The invention improves the process of respectively carrying out location, segmentation and identification of the traditional container number identification algorithm, enhances the continuity of a whole system and also has the advantages of rapid identification speed and high accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Adaptive filter for LED dimmer
InactiveUS20130249437A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesAdaptive filterHigh bandwidth
A dimming controller for an LED lamp controls dimming using an adaptive filter to reduce or eliminate perceivable flickering and to provide smooth transitions during active dimming. During stable conditions, the adaptive filter operates with a relatively narrow bandwidth to filter noise that may lead to perceivable flickering. During active or startup conditions, the adaptive mapping filter operates with a high bandwidth to provide a quick response to the dimmer switch.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Method and device for noise reduction
ActiveUS7657038B2Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSignal processingNoise reductionComputer science
In one aspect of the present invention, a method to reduce noise in a noisy speech signal is disclosed The method comprises: applying at least two versions of the noisy speech signal to a first filter, whereby that first filter outputs a speech reference signal and at least one noise reference signal, applying a filtering operation to each of the at least one noise reference signals, and subtracting from the speech reference signal each of the filtered noise reference signals, wherein the filtering operation is performed with filters having filter coefficients determined by taking into account speech leakage contributions in the at least one noise reference signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Trade-mark searching method
InactiveCN1581159AHigh precisionOvercoming technical deficienciesSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionTrademark
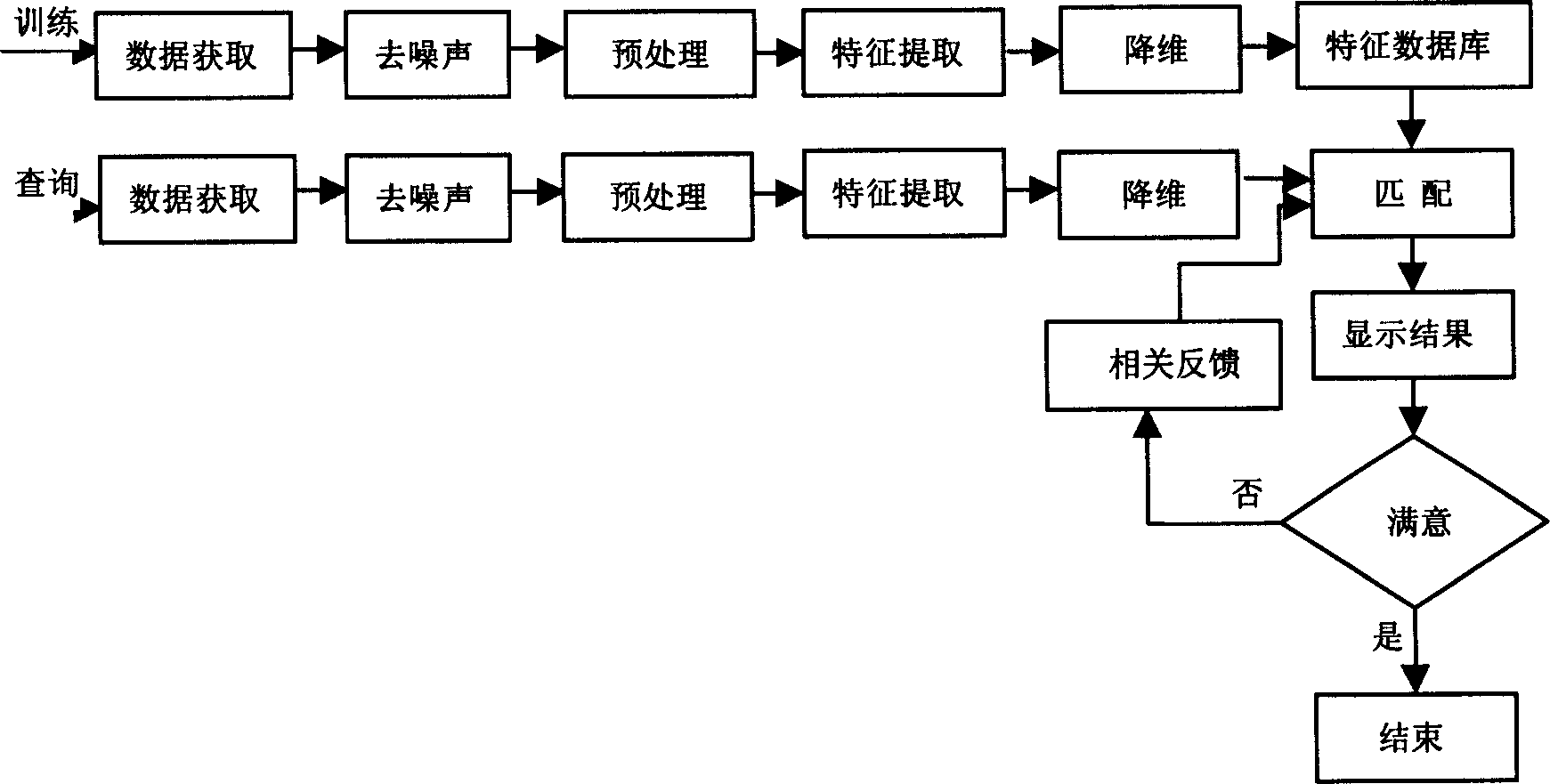
The present invention relates to a trademark searching method. Said method includes the following steps: obtaining trademark image; filtering noise in the trademark image; pretreatment, extracting a group of characteristics with separability from the filtered image; storing the extracted characteristics into characteristic dictionary; reducing dimensionality; utilizing existed characteristics and characteristic dictionary to make matching, calculating similarity and returning a group of most similar images as inquiry result; and utilizing related feedback to optimize search result.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for counteracting environment noise and active noise reduction earphone
PendingCN106792315AGood noise reduction experienceImprove noise reductionMicrophonesLoudspeakersEnvironmental noiseEngineering
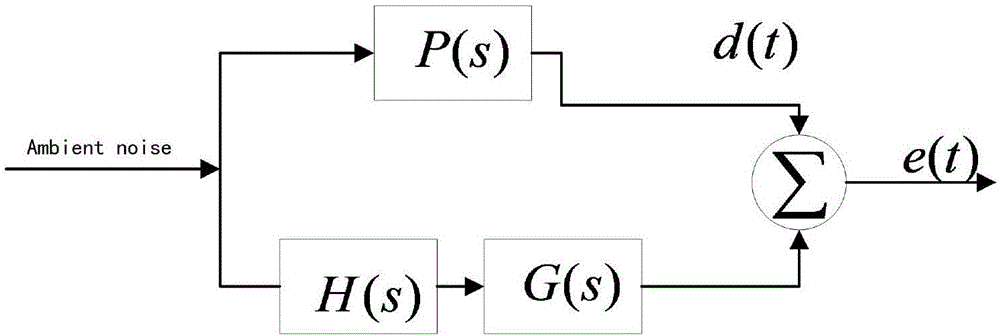
The invention discloses a method and device for counteracting environment noise and an active noise reduction earphone. The device comprises a microphone, a DSP chip, an active noise reduction controller, and a loudspeaker, wherein the microphone is used as a feed-forward noise reduction microphone and an environmental noise monitoring microphone so as to acquire the environmental noise in real time; the DSP chip periodically selects a noise reduction mode best-matched with the current environment according to the environmental noise acquired by the microphone, and sending a corresponding noise reduction parameter to the active noise reduction controller; the active noise reduction controller performs the feed-forward filter noise reduction according to the noise reduction parameter sent by the DSP chip, and outputs the waveform for counteracting the environmental noise; and the loudspeaker plays the corresponding sound signal according to the waveform to counteract the environmental noise at the ear, thereby achieving the optimal noise reduction effect under various different environments, and the switching of the noise reduction mode is self-adaptively performed aiming at different noise environments, thereby guaranteeing that the best noise reduction experience can be provided under various different environments.
Owner:GEER TECH CO LTD
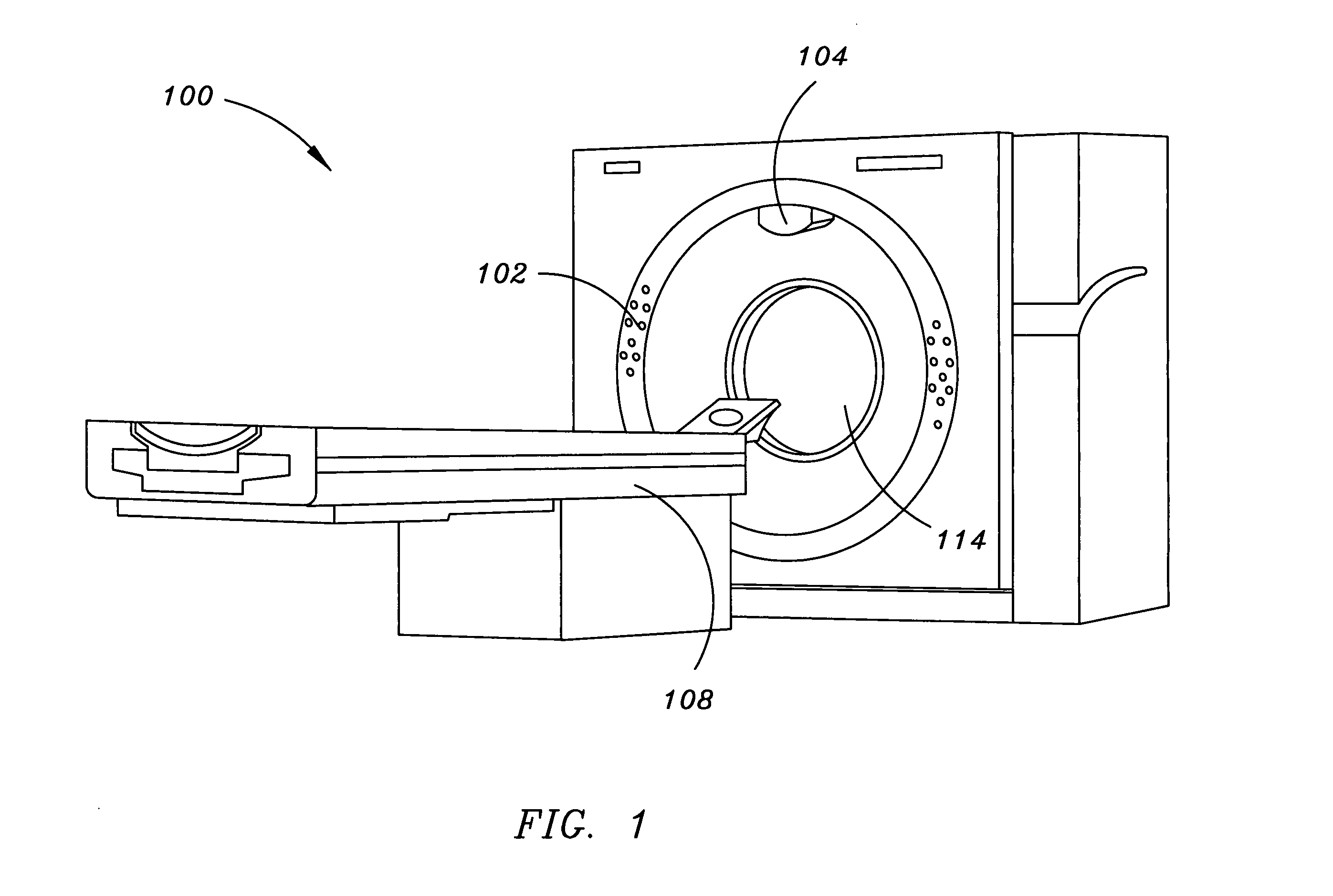
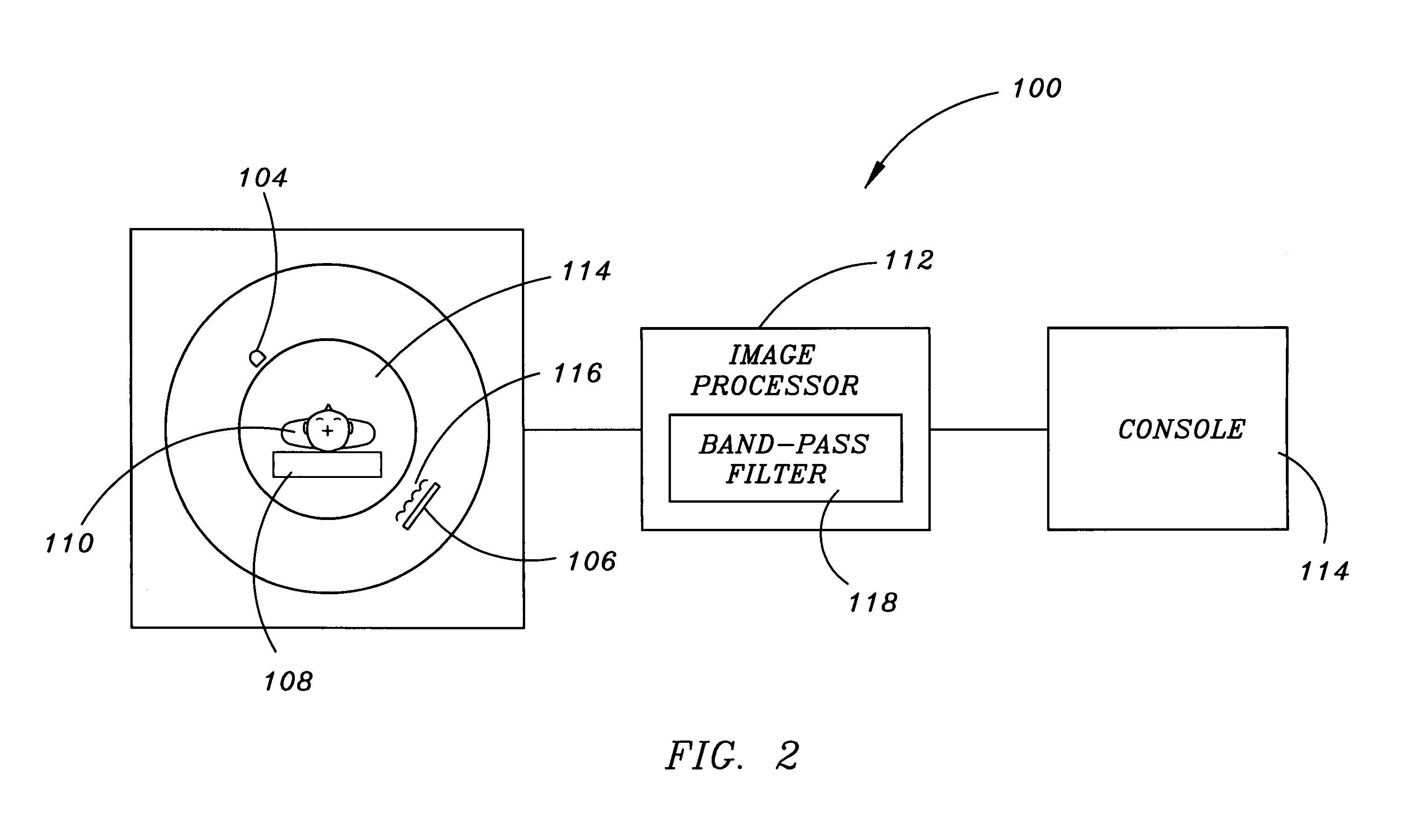
System and method for filtering noise from a medical image
ActiveUS7502499B2Increase and decrease amount of removedIncrease and decrease in densityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionFilter noise
A system and method for filtering noise from a medical image are provided. A method for filtering noise from an image comprises: generating a weighted graph representing the image; selecting a plurality of nodes from the image to retain grayscale values of the plurality of nodes; and determining filtered grayscale values of the plurality of nodes.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Automated methods for pre-selection of voxels and implementation of pharmacokinetic and parametric analysis for dynamic contrast enhanced MRI and CT
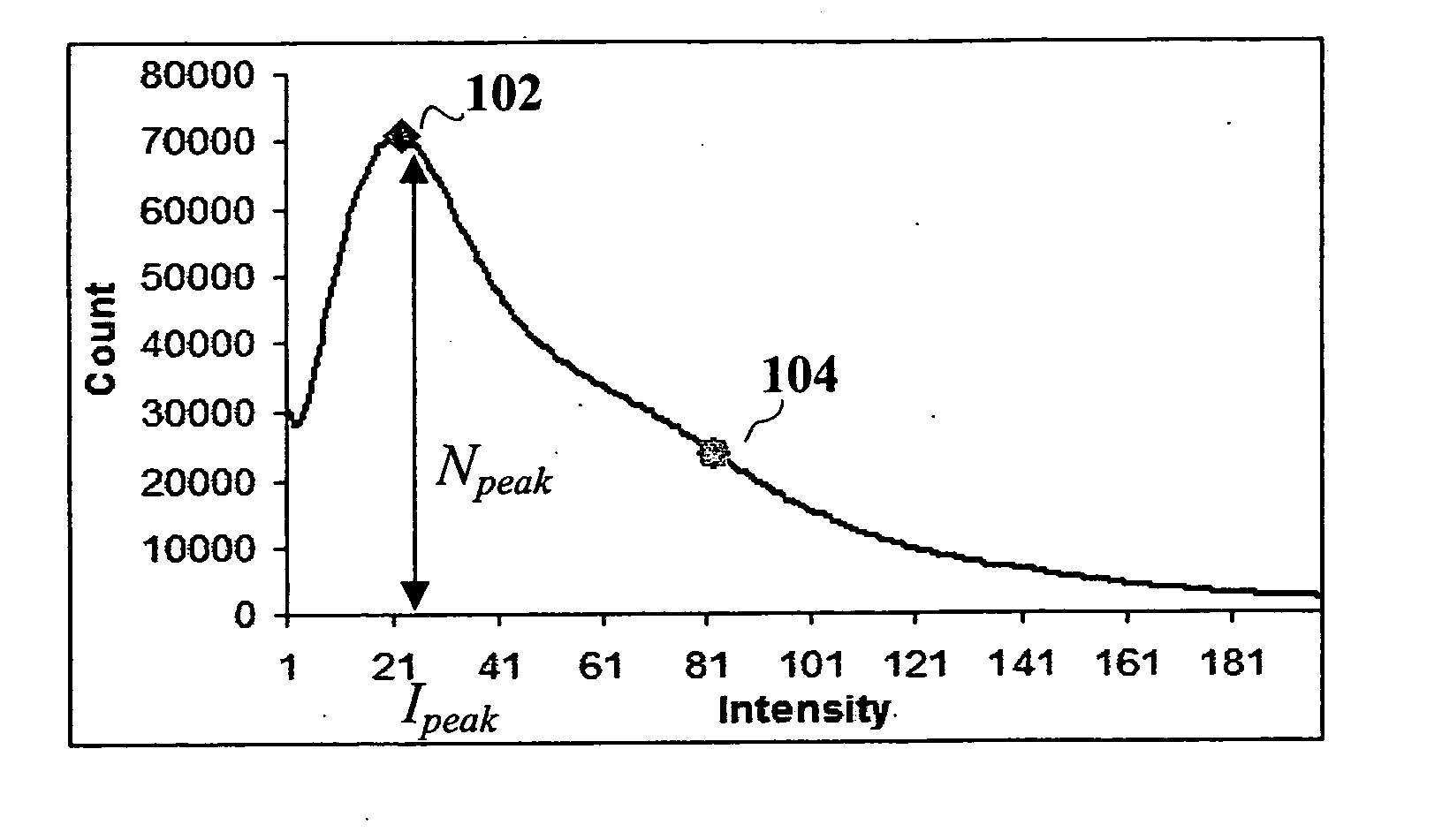
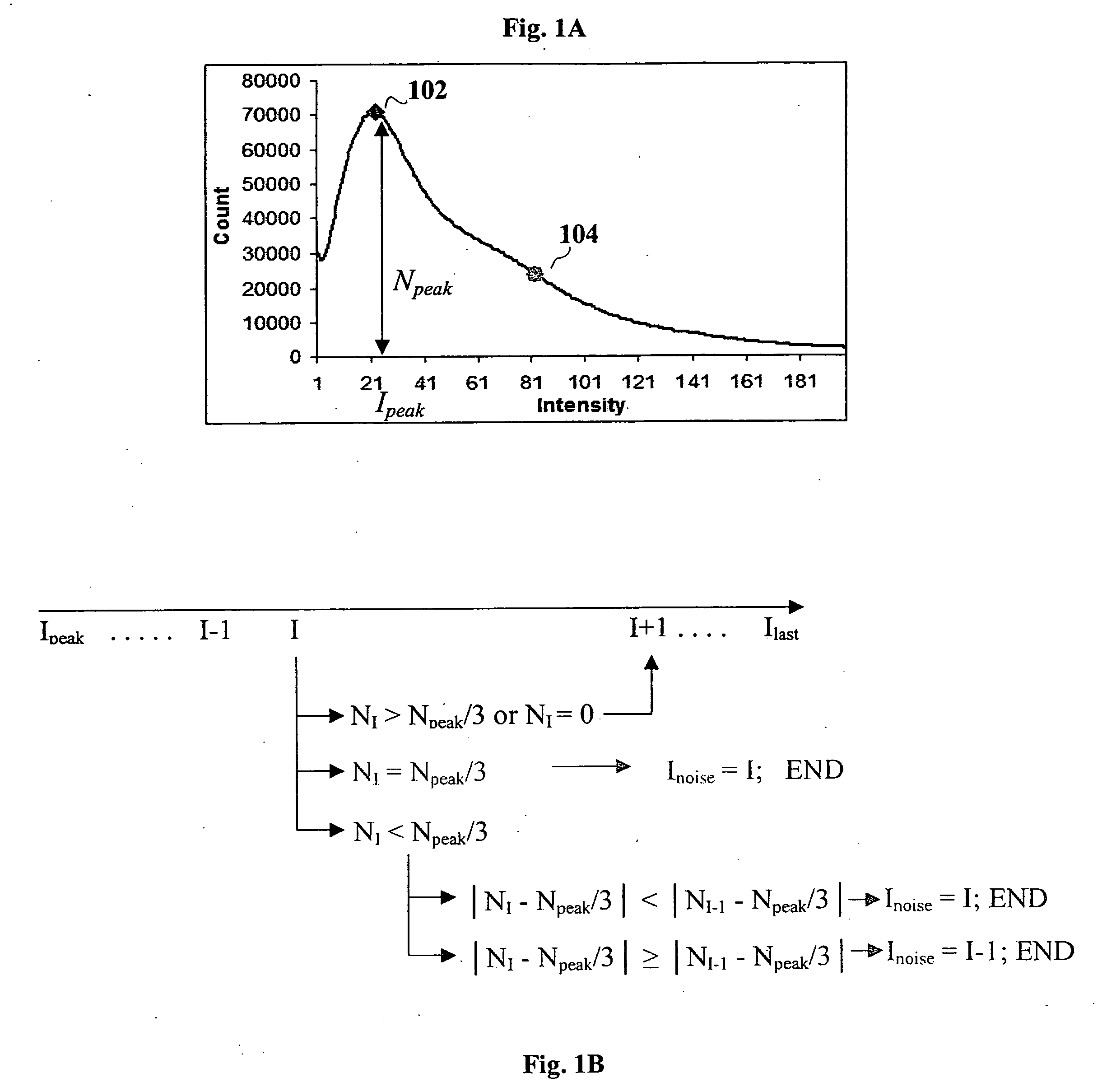
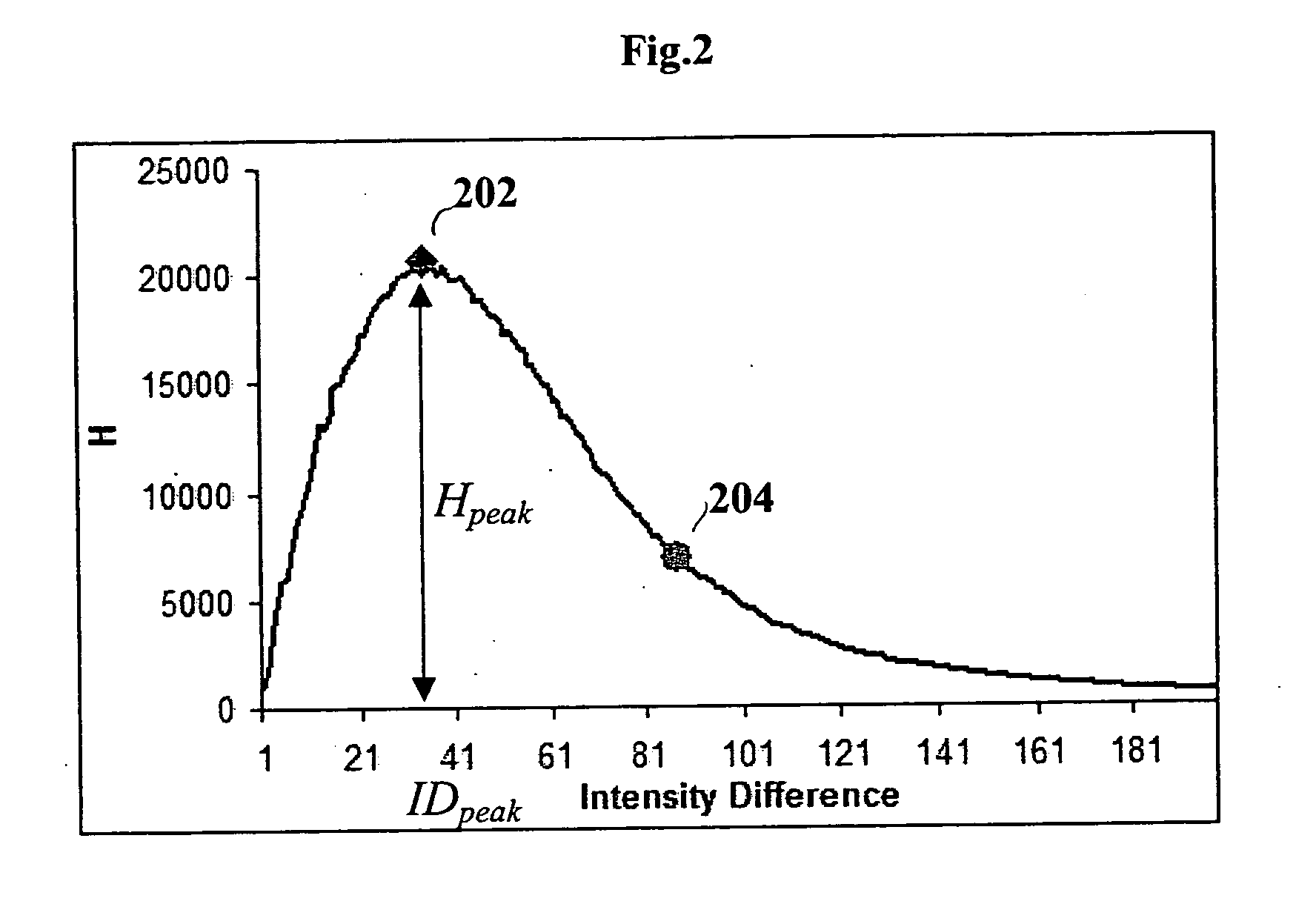
A method, system and computer-readable medium of filtering noise pixels and other extraneous data, including saturated fat tissue and air data in image data is provided. Examples of image data may include but are not limited to magnetic resonance imaging data and computed tomography data. The method includes receiving pixel count for each signal intensity value of the image data; determining a signal intensity value, Ipeak, corresponding to a pixel count of a greatest number of pixels, Npeak; setting a noise threshold at a signal intensity value, Inoise, corresponding to a pixel count, NI, such that NI, is determined based on Npeak; and filtering from the image data one or more pixels with signal intensity values below the noise threshold. NI, may be determined such that NI=Npeak / 3 or close to Npeak / 3.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for segmenting cervix uteri liquid base cell image
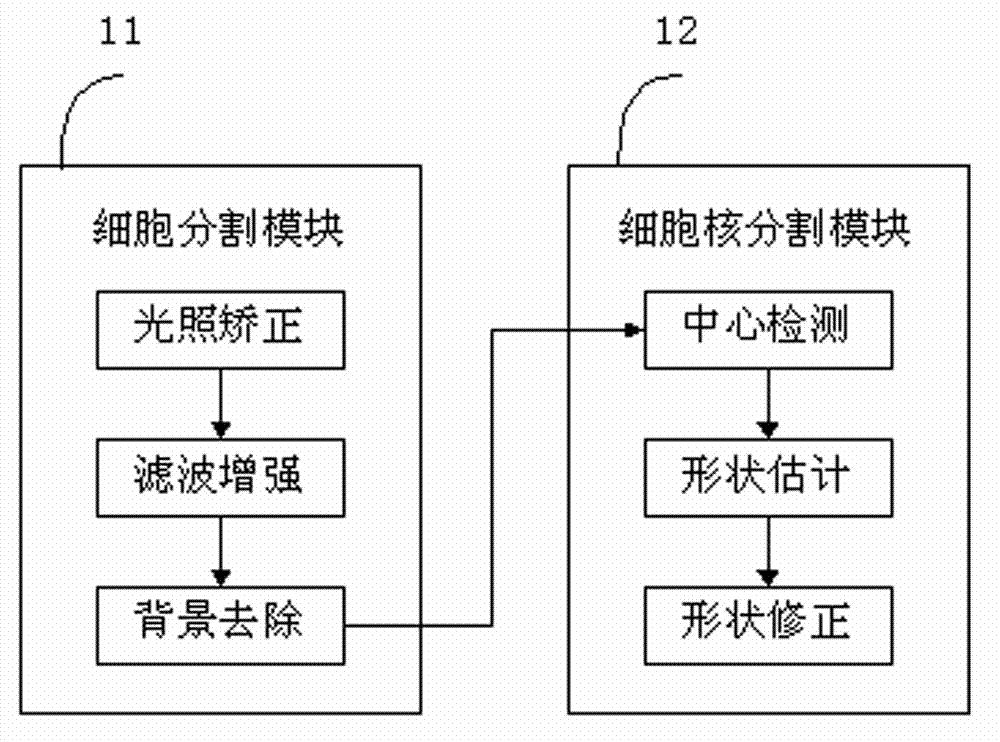
ActiveCN102831607ASegmentation is reliable and preciseOvercome lighting changesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCervix
The invention discloses a method for segmenting a cervix uteri liquid base cell image. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, cell segmentation: performing illumination correction on an image, filtering noises and enhancing a cell boundary; and dividing the image into three types of cytoplasm, nucleus and background to eliminate a background class area; 2, nucleus segmentation: detecting centers of each of nucleuses in the cell area, estimating the approximate shapes of the nucleuses close to the centers of the nucleuses and correcting the shapes of the nucleuses to acquire an accurate boundary. The method is applied to cervix uteri cells and cell masses in a wide vision range, so that the phenomena of changed illumination, non-uniform dyeing and noise influence to a certain extent are avoided, and the cytoplasm, the single nucleus and adhesion nucleus can be segmented reliably and accurately.
Owner:SHENZHEN MICRO BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Bridge cable surface damage dynamic detection method and device
InactiveCN101169380ASmall impact on test resultsTime-consuming and laborious to solveImage enhancementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationImaging processingEngineering
The present invention provides a dynamic detection method and device for surface damage of bridge cables. An intelligent detection device is arranged radially on the surface of bridge cables. The intelligent detection device travels at a constant speed on the surface of bridge cables through a driving device. A camera collects the surface image of the bridge cable and sends it to the image processing and recording system; the bridge cable surface damage dynamic detection algorithm program solidified in the system DSP chip judges whether there is damage in the collected image, and records the position of the positioning mechanism if there is damage Move the distance to accurately locate the injury site. The processing steps of the cable surface image are: parallel image acquisition; effective information interception; filtering and noise reduction; curved surface projection correction; target segmentation; defect identification and information storage. Through the above algorithm, the rapid identification, location and storage of the surface damage of the bridge cable are completed, so as to realize the purpose of dynamic detection of the surface damage of the bridge cable.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Systems and methods for non-invasive respiratory rate measurement
Systems and methods for non-invasive respiratory rate measurement are disclosed. In some embodiments, a system comprises a wearable member including an energy transmitter configured to project energy into tissue of a user. An energy receiver generates a multichannel signal based on a first received portion of the energy, the received portion of energy being received through the tissue of the user. A respiratory rate calculation system includes a pre-processing module for filter noise from the signal. A spectrum module determines a spectrum of the signal. A respiratory rate processing module determines a first respiratory rate from the spectrum of the signal. A noise reference and one or more second respiratory rates are obtained. A third respiratory rate is determined based on the first respiratory rate, the noise reference, and the one or more second respiratory rates. A communication module provides a message based on the third respiratory rate.
Owner:ITAMAR MEDICAL SPRY 2021 LLP
Depth enhancing method based on texture distribution characteristics
ActiveCN103413276AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove continuityImage enhancementTime domainPattern recognition
A depth enhancing method based on texture distribution characteristics comprises the steps of A1, inputting texture images of adjacent frames on the time domain and corresponding depth images collected by a low end depth transducer, wherein the number of frames is N, and the N is larger than or equal to 2; A2, extracting the boundaries of the texture images of all the frames, and dividing the depth images into non-boundary areas and boundary areas, wherein the non-boundary areas do not contain texture boundaries, and the boundary areas contain the texture boundaries; A3, aiming at the boundary areas of the depth images, selectively modifying the depth of pixels to carry out depth enhancing according to the distribution characteristics of the depth values of the pixels on the two sides of the texture boundaries in the boundary areas of all the adjacent frames on the time domain, and carrying out filtering noise reduction processing on the boundary area when the processing is judged to be necessary; A4, aiming at the non-boundary areas of the depth images, acquiring time-domain prediction blocks of current depth blocks through texture matching results of all the frames in the time domain, repairing the current depth blocks according to the pixel information of the prediction blocks, and carrying out filtering noise reduction processing. By the adoption of the depth enhancing method based on the texture distribution characteristics, the accuracy and the time-domain consistency of the depth images collected by the low end depth transducer can be improved remarkably.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Camera calibrating method and its implementing apparatus
InactiveCN1455222AHigh speedHigh degree of automationTelevision system detailsPicture taking arrangementsOptical axisEllipse
In the invention, the mark aperture radius of the circular target drone is 120%-150% of the rest aperture. In the process, according to the filtering noise of images, threshold segmentation, contour tracing, ellipse recognition, ellipse fitting and center extraction are utilized. Based on the spetial position between the center of the marked aperture and the center of the nearest aperture as well as the distances between the center of the marked aperture and the centers of other apertures and the distance of moving the circular target drone along a certain direction, the position of the camera is determined by using the unique point space orientation method. The invention is suitable to calibration of camera in order to obtain the coincidence relation between the point in 3D space and the pixel in computer image.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
X-ray scatter elimination by frequency shifting
InactiveUS7046757B1Reduce noiseImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayGrating
A method for separating and filtering noise caused by X-ray scatter contaminations from the primary signal component of the signal produced by the detector assembly of a radiographic imaging device employs a scatter removal screen or grating disposed between the object being imaged and the detector assembly. The grating has an absorption that varies periodically for varying the intensity of the X-ray radiation passed through the grating. This variation in intensity of the X-ray radiation causes the signal produced by the detector assembly to be amplitude modulated so that the frequency of the primary signal component is shifted from noise components of the signal caused by X-ray scatter contamination allowing the noise components to be filtered from the primary signal component so that scatter induced noise may be reduced or eliminated from the signal.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
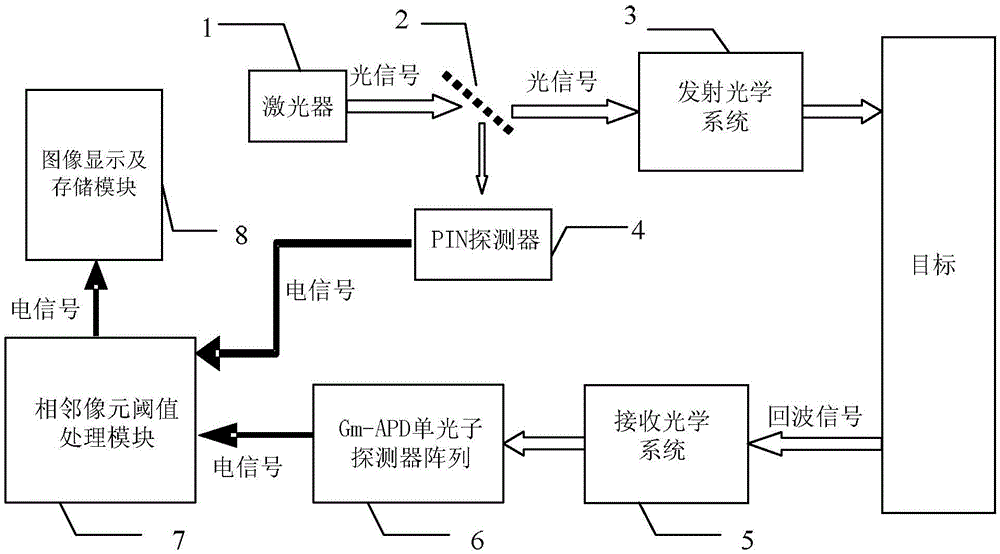
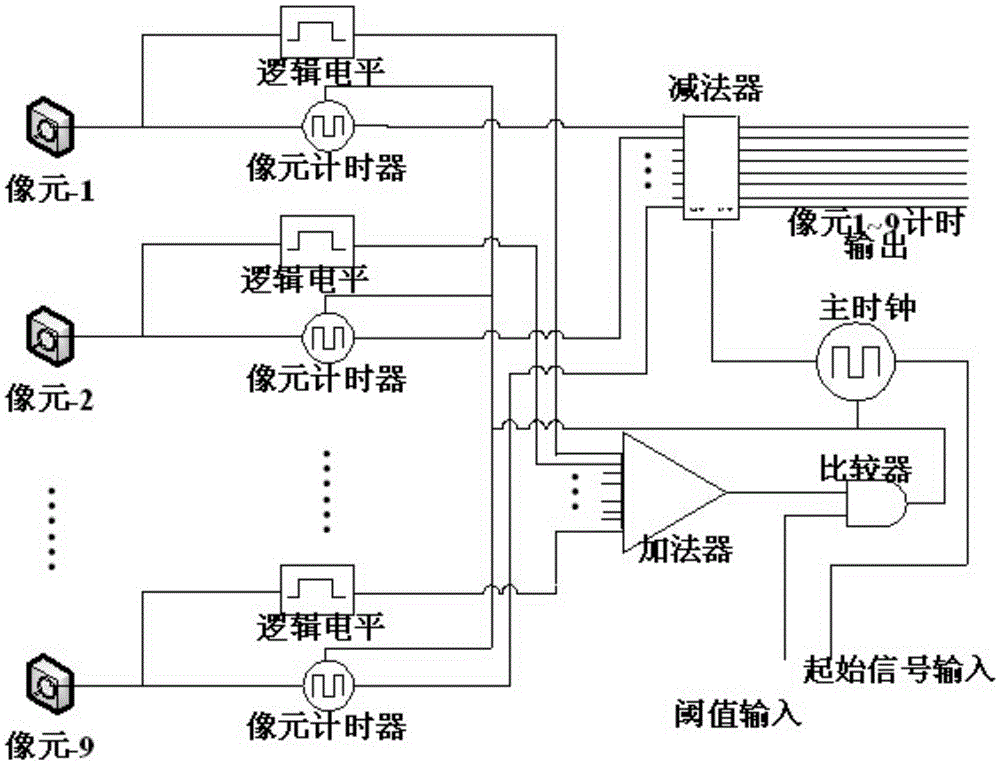
Photon-counting imaging laser radar for filtering noise in real time by adopting adjacent pixel element threshold value method
InactiveCN105607073AImprove performanceReduce volumePhotometry using electric radiation detectorsElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splitterTime correlation
The invention relates to a photon-counting imaging laser radar for filtering noise in real time by adopting an adjacent pixel element threshold value method, and the radar relates to the technical field of laser radar. The problem that the photon-counting imaging laser radar noise filtering technology can not meet the real-time application requirement is solved. A pulse laser signal enters a beam splitter to form two signals; one signal is processed through a PIN detector and is outputted to an adjacent pixel element threshold value processing module; the other signal is collimated through a optical transmitting system to radiate a target; the other signal is spread by the target and outputted an echo signal, the echo signal passes through a receiving optical system and a Gm-APD single-photon detector array, the adjacent pixel element threshold value processing module records the echo signal comprising time correlation and compares the signal with an initial signal, so as to obtain the round-trip time difference of the pixel corresponding to the Gm-APD single-photon detector array, the round-trip time difference is calculated to obtain a distance value of the corresponding pixel target, and a target 3D distance image is obtained finally. The radar is suitable for filtering the noise in laser imaging.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
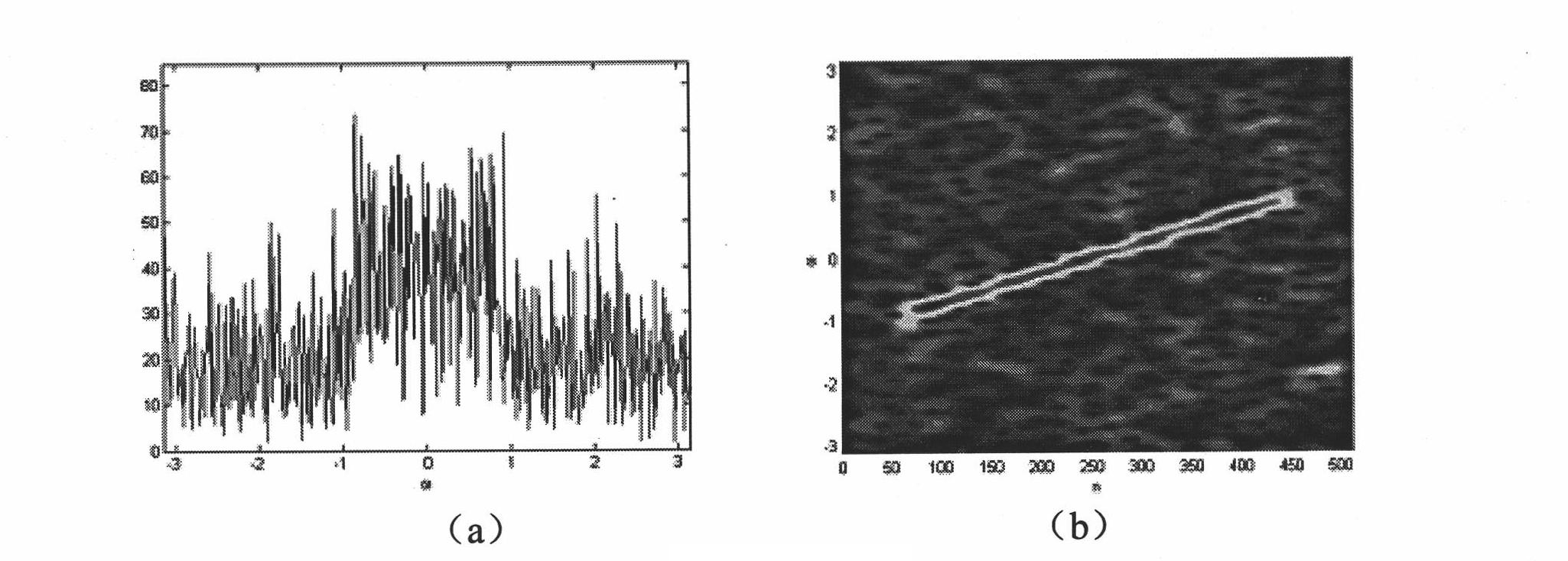
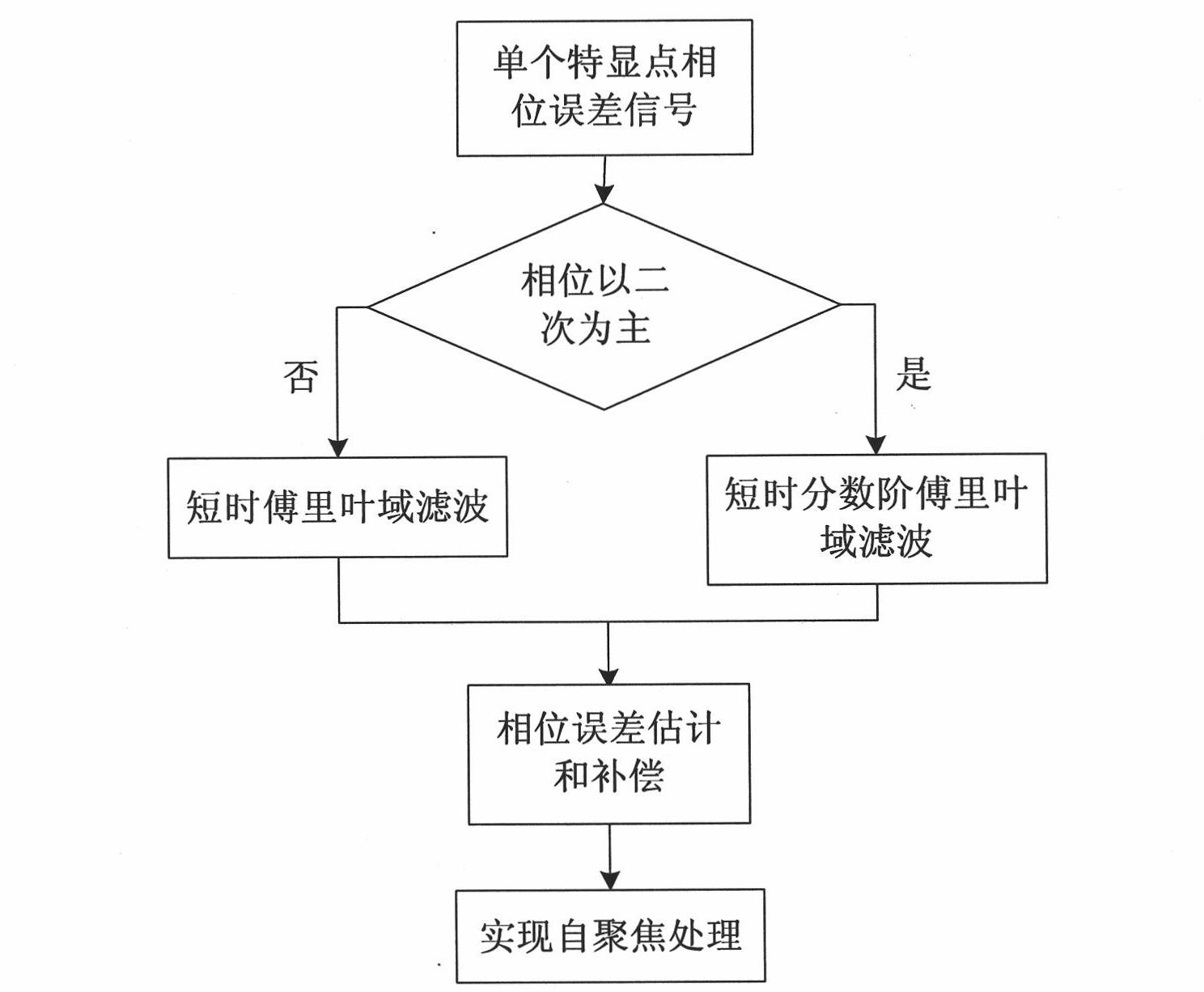
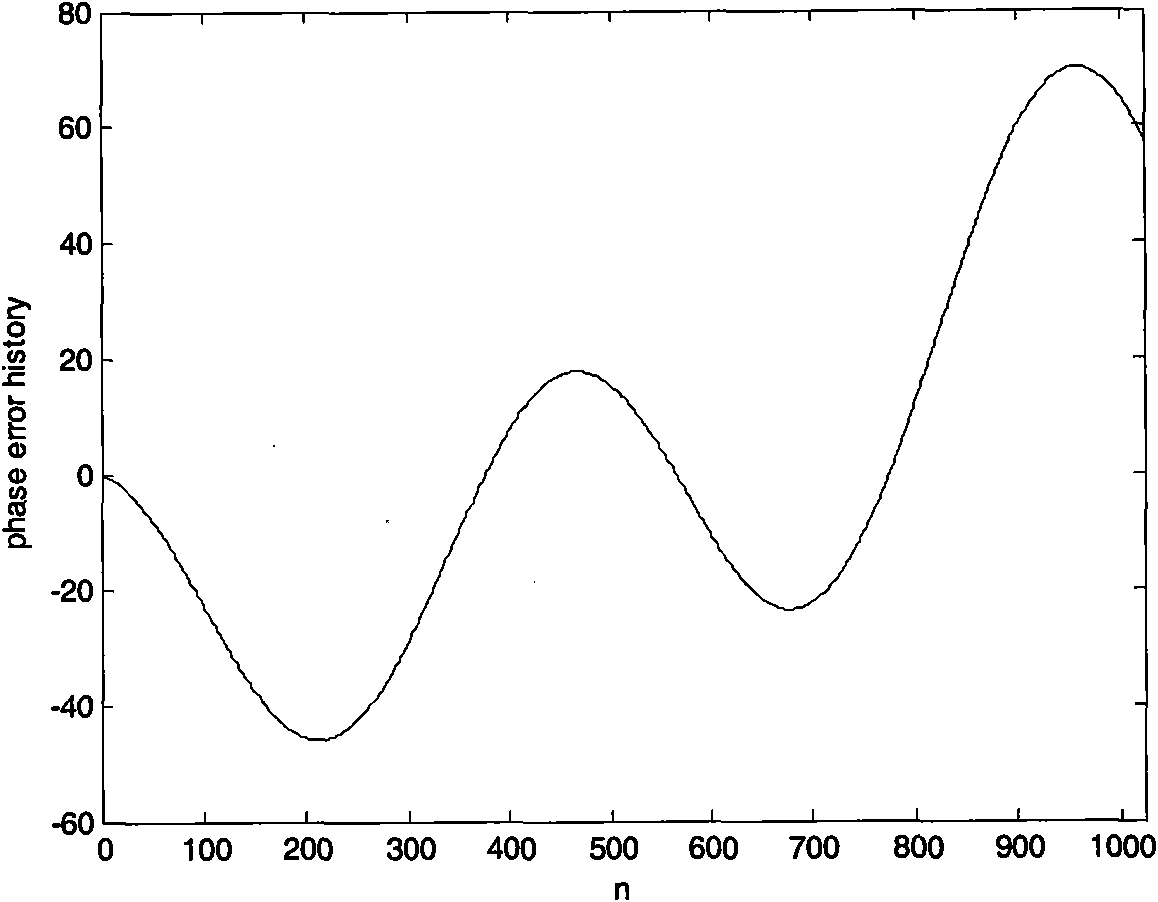
Self-focusing preprocessing method based on short-time fractional order Fourier domain filter
InactiveCN101963662AImprove matchHigh two-dimensional aggregationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to a self-focusing preprocessing method based on a short-time fractional order Fourier domain filter, which belongs to the field of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) signal processing. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting a phase error signal of a single special showing point; (2) judging whether the phases of the phase error signal mainly are quadratic phase or not; (3) filtering noise in a transform domain: if the phases mainly are quadratic phases, using short-time fractional order Fourier domain filter; otherwise, using short-time Fourier domain filter; and (4) inversely transforming result time frequency to a time domain, estimating and compensating the phase error and realizing self-focusing preprocessing. The method effectively solves the problems of estimation and compensation of the phase error in a low-signal-to-noise ratio environment, especially the estimation and compensation of the quadratic phase error, and can obtain the main part of a phase error course and greatly improve the imaging quality after removing the phase error course from an original signal, thereby improving the signal-to-noise ratio of a special showing point signal.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
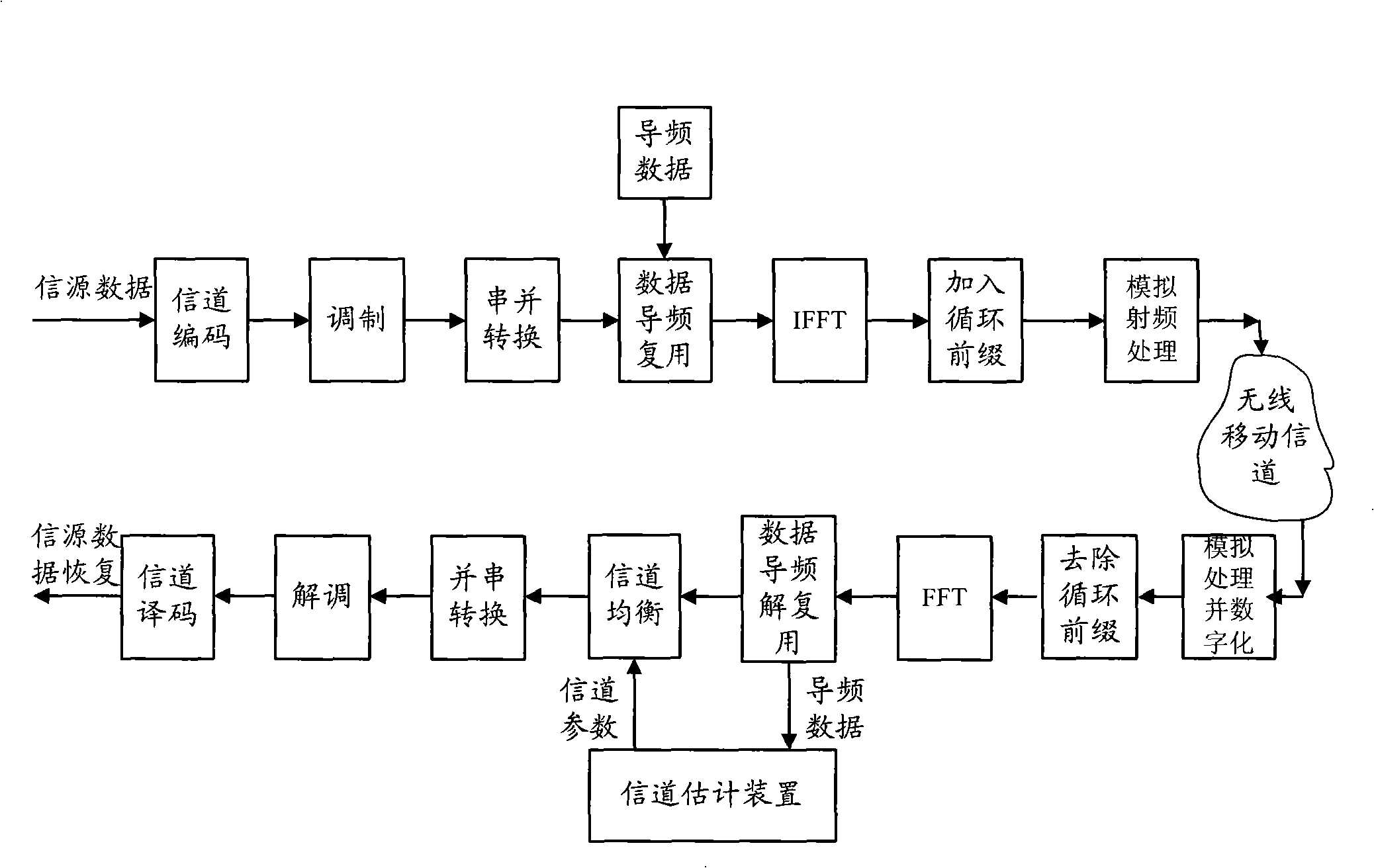
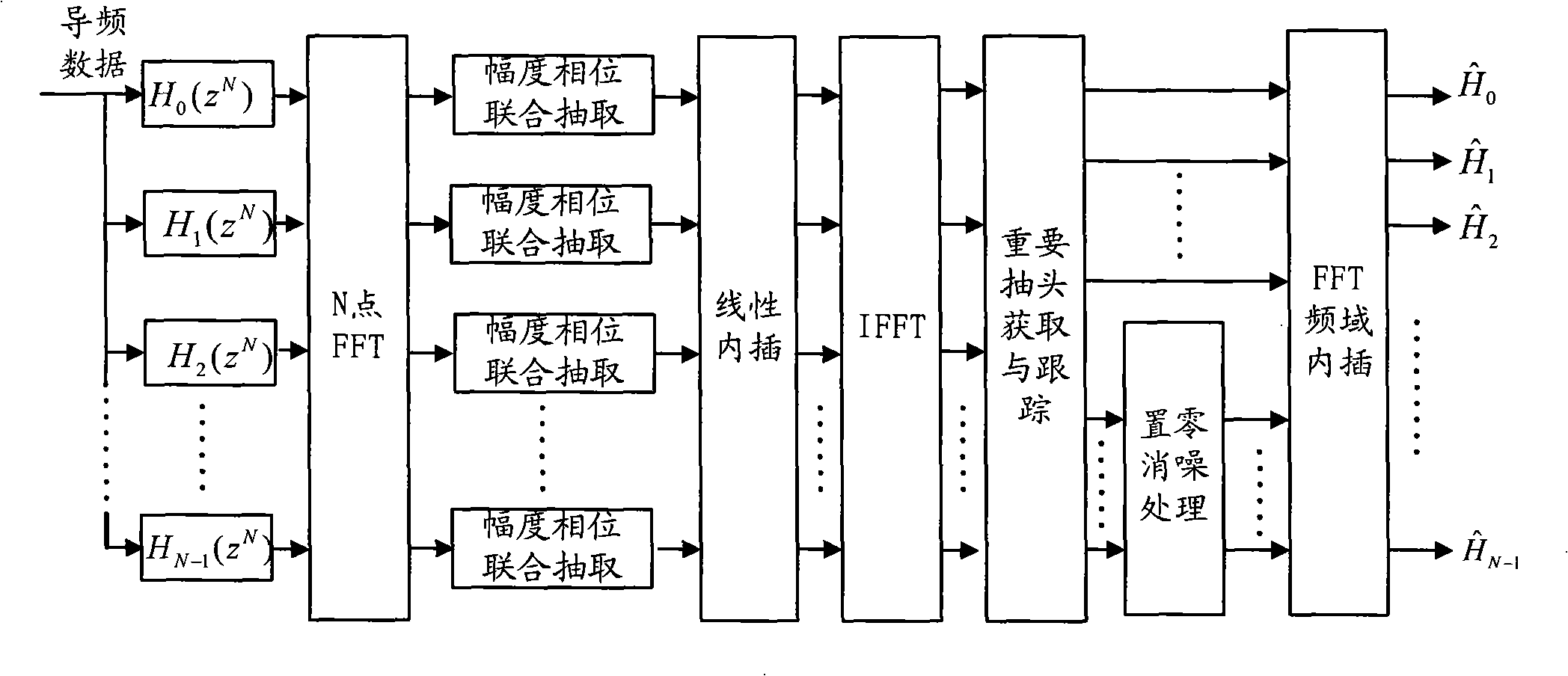
An OFDM time shift channel measuring method
InactiveCN101267421AImprove meter accuracyReduce computational complexityBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsChannel parameterCarrier signal
The invention provides an OFDM time-varying channel measuring method, comprising the following steps: generating complex exponential pilot frequency data having the same central frequency point as that of an OFDM sampling sub-carrier, multiplexing the data with data to be transmitted at a transmitting terminal in comb-like format, sending the pilot frequency data received by a receiving terminal in corresponding pilot frequency positions to a multi-phase filter bank realized by N points FFT, amplitude phase united extracting the data outputted by each corresponding passage to obtain initial channel frequency measuring data on a corresponding pilot frequency sub-carrier, obtaining initial channel frequency measuring data on all pilot frequency sub-carriers by linear interpolating, performing IFFT, and acquiring and tracking L-point important taps in time frequency. Finally, the L-point important taps coefficients are zero padded and FFT processed, interpolation in frequency domain is carried out to obtain channel parameters in all sub-carriers positions. By filtering noise by multi-phase filter, the measuring accuracy of parameters of an OFDM time-varying channel in low Signal-to-Noise condition is improved, and the invention has the characteristic of low bit error floor.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Spam identification using an algorithm based on histograms and lexical vectors (one-pass algorithm)
ActiveUS8001195B1Eliminate disadvantagesMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksOne passNatural language processing
A system, method and computer program product for identifying spam in email messages, including (a) identifying unique words and all their variations in the text of the email; (b) filtering noise words from the text; (c) determining how many times each unique word or its morphological variations is found in the text; (d) assigning an identifier to each unique word in the text based on the number of times the unique word is found; (e) creating a lexical vector of the text based on all the identifiers assigned; (f) generating a histogram based on the lexical vector; (g) comparing the histogram against the histograms of lexical vectors corresponding to known spam texts stored in the database; (h) if the histograms coincide within a certain threshold, then the email text is identified as spam.
Owner:AO KASPERSKY LAB
Full-waveform laser radar echo data gaussian decomposition method based on genetic algorithm
The invention discloses a full-waveform laser radar echo data gaussian decomposition method based on a genetic algorithm. The method is mainly formed by five steps including echo denoising, initial wave crest extracting, initial parameter estimating, waveform fitting and precision judging; when the precision of initial fitting meets the requirements, second fitting is not carried out, when the precision of the initial fitting does not meet the requirements, iteration fitting is carried out, and in each iteration, the fitting precision is improved by a method of increasing a gaussian component until a stopping condition is met; a gaussian function is used for fitting echo data of a full-waveform laser radar; and a gaussian filter method is adopted to filter noise of the echo data of the full-wave form laser radar, the number of initial gaussian components is confirmed by extracting a peak value point, an initial parameter range is estimated, fitting and precision adjusting are carried out on the echo data of the full-waveform laser through the genetic algorithm, an echo gaussian decomposition software system based on the genetic algorithm is manufactured, and echo decomposition operation is simplified.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and Method For Myocardium Segmentation In Realtime Cardiac MR Data
A method for cardiac segmentation includes providing a plurality of digitized medical images, each image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a domain of points on an 2-dimensional grid, the plurality of images forming a sequence of cardiac images acquired at different time points, filtering noise from the sequence of images, approximating the endocardium with a first circle, approximating the epicardium with a second circle, finding candidate points for the endocardium, finding candidate points for the epicardium, and interpolating gaps between points of the endocardium and between points of the epicardium wherein the myocardium is segmented.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Line feature map creation method of mobile robot based on laser range finder
InactiveCN103198751ASmall amount of calculationImprove speedImage enhancementImage analysisLaser rangingLaser data
The invention discloses a line feature map creation method of a mobile robot based on a laser range finder and belongs to the technical field of mobile robot map creation. The line feature map creation method of the mobile robot based on the laser range finder includes the following steps: firstly, starting the laser range finder to scan an external environment, then preprocessing scanned laser data through an average filtering method to filter noise points; utilizing exponential distribution to approximate posterior distribution of laser data points, conducting region segmentation on the laser measurement data points through a dynamic threshold method, dividing the laser measurement data points into N region pieces after the region segmentation, and conducting segment fitting on the data points in the regions through a golden section method; and extracting feature corners through a method of combining Hough transformation and an area threshold value, achieving transition from an image space to a parameter space, building local environment maps, and achieving the fusion of the local environment maps by utilizing a sector matching method. The line feature map creation method of the mobile robot based on the laser range finder has the advantages of being easy in calculation and high in accuracy and improving rapidity of algorithm execution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com