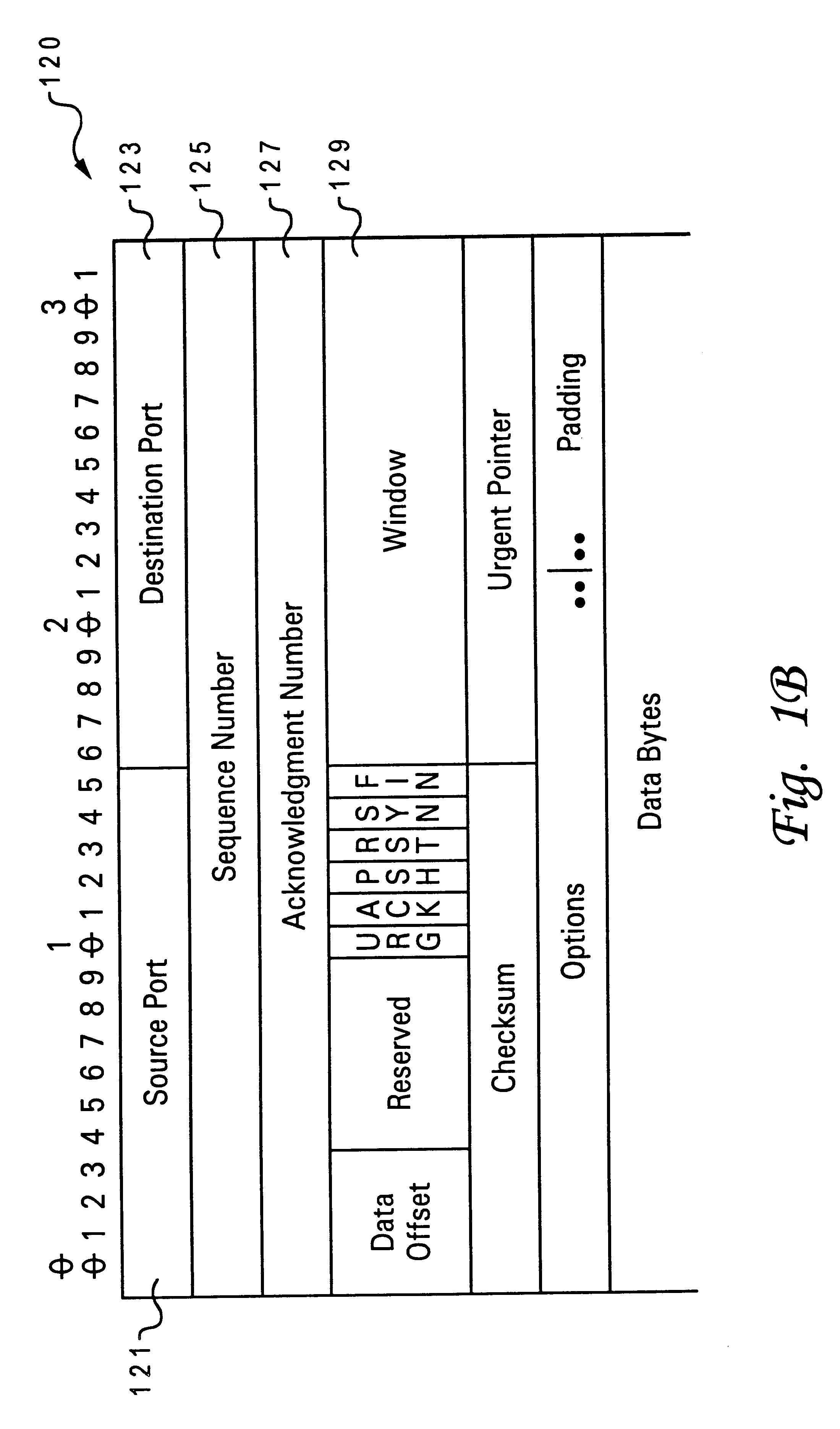
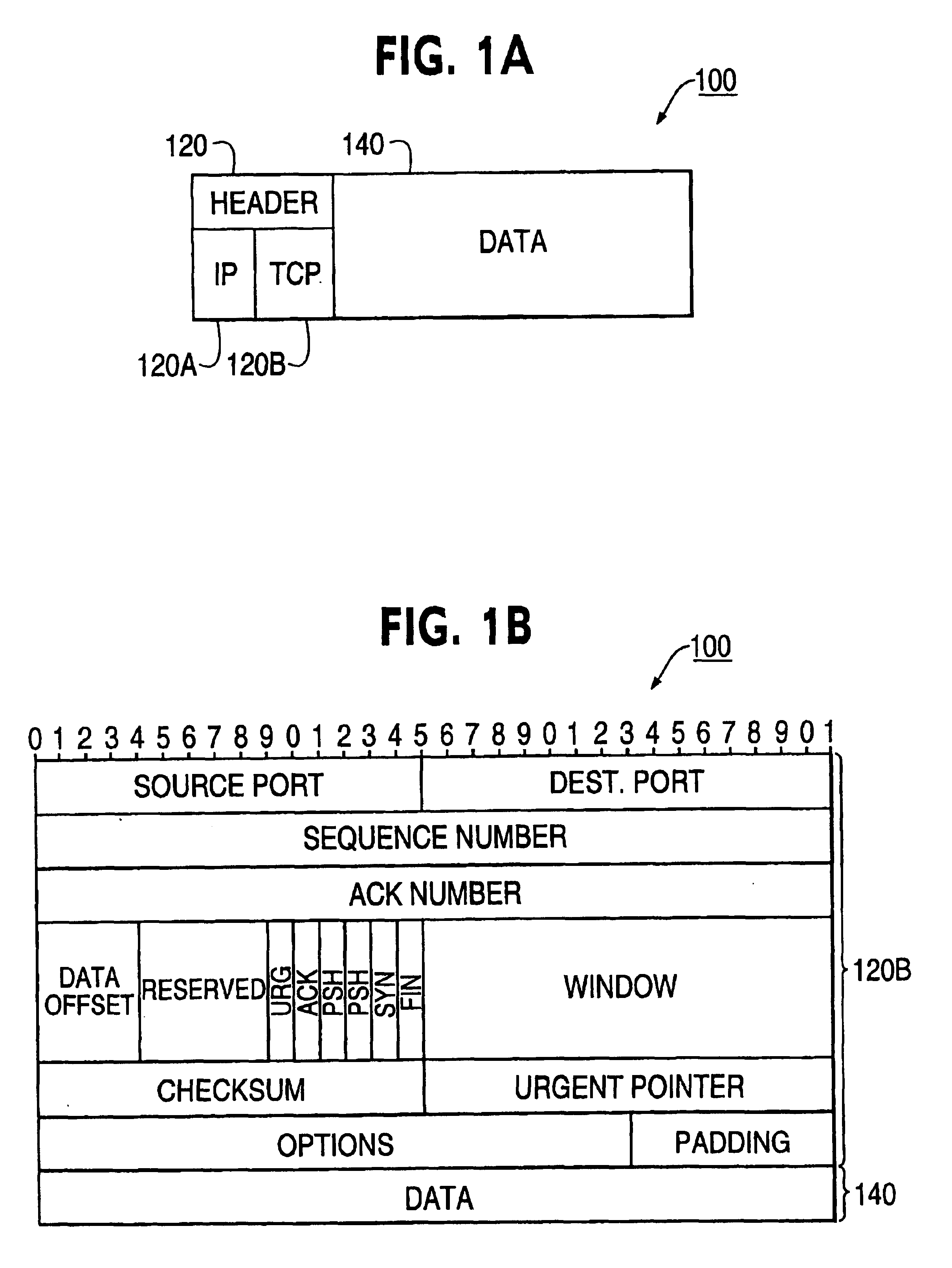
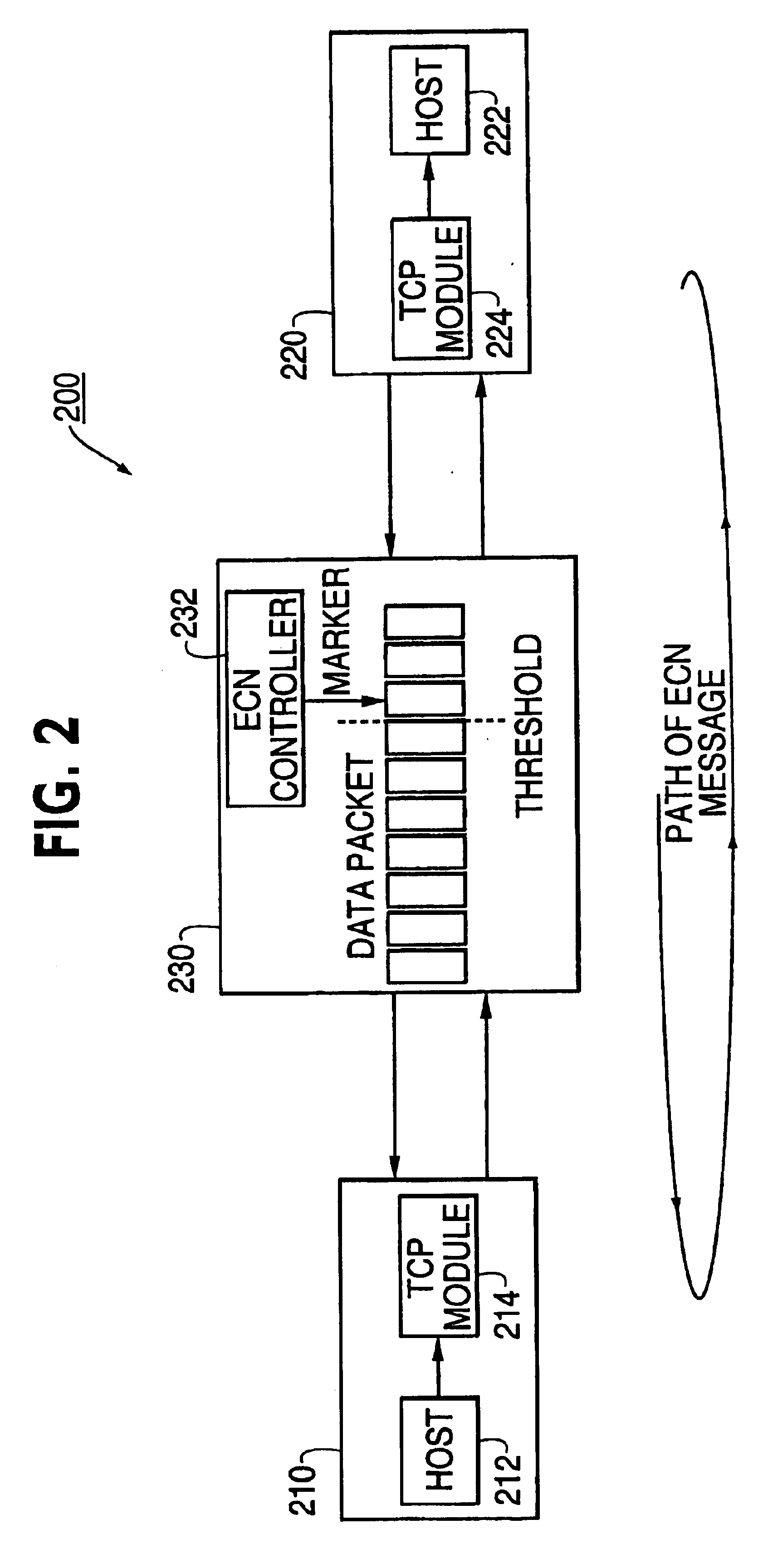
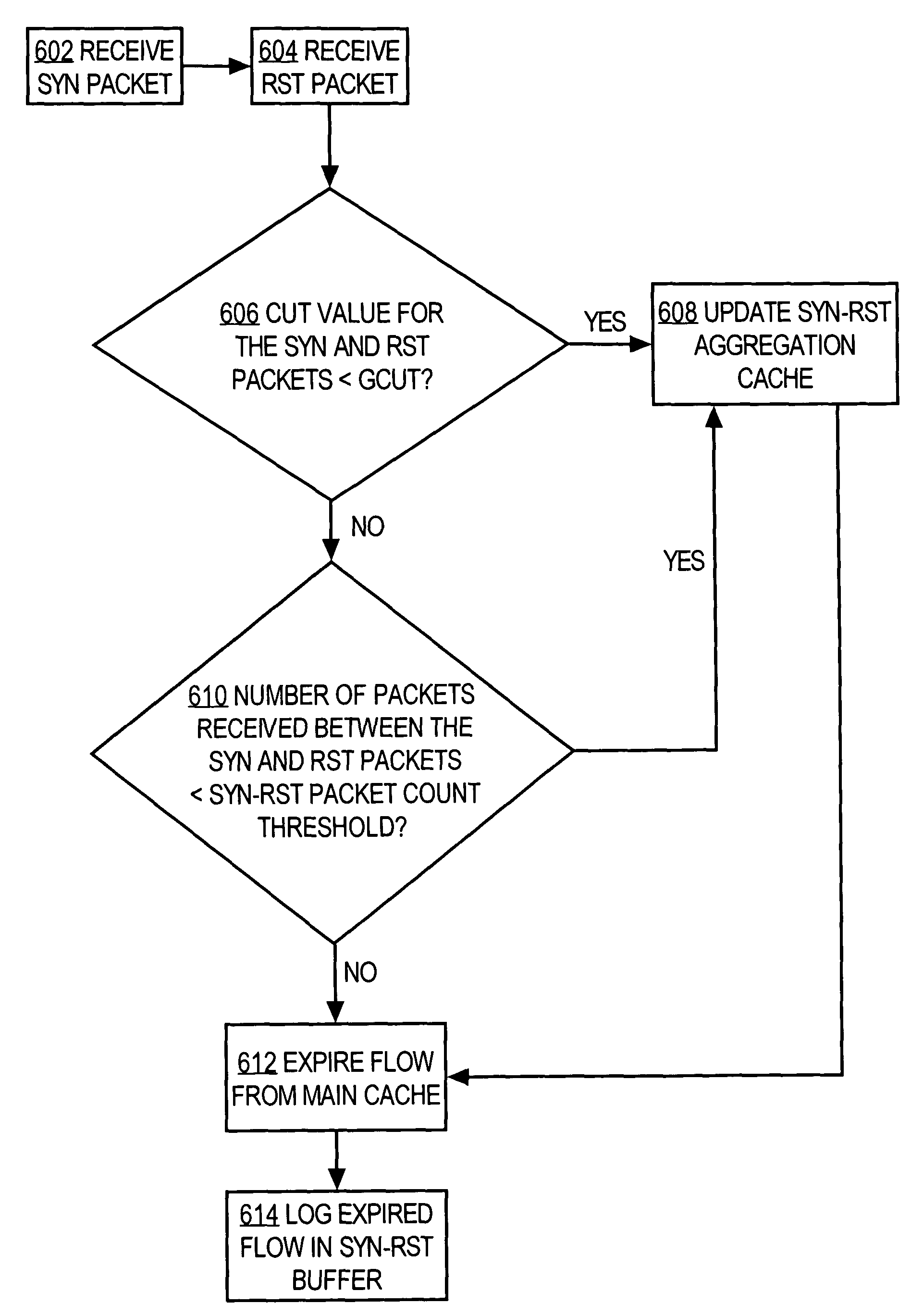
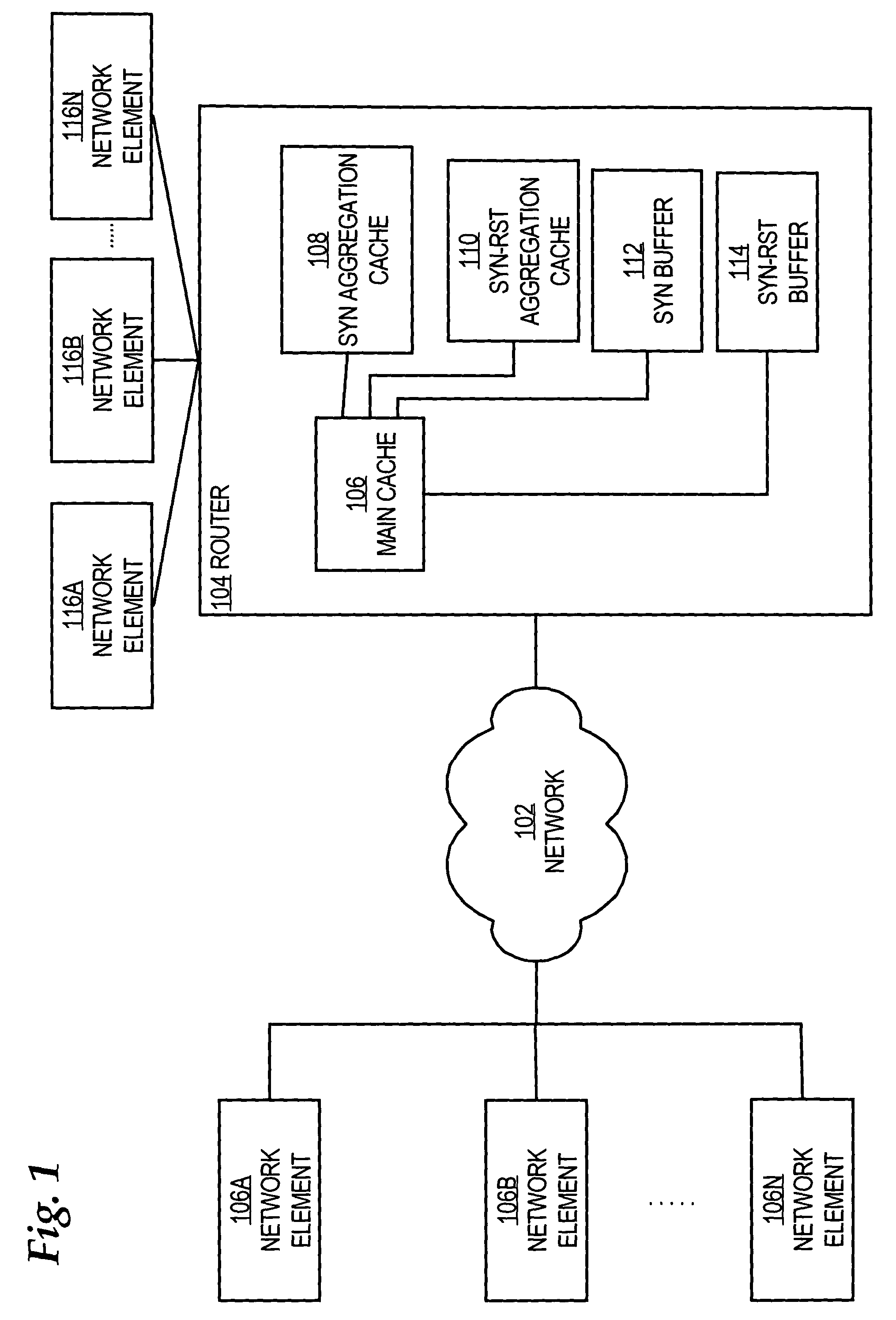
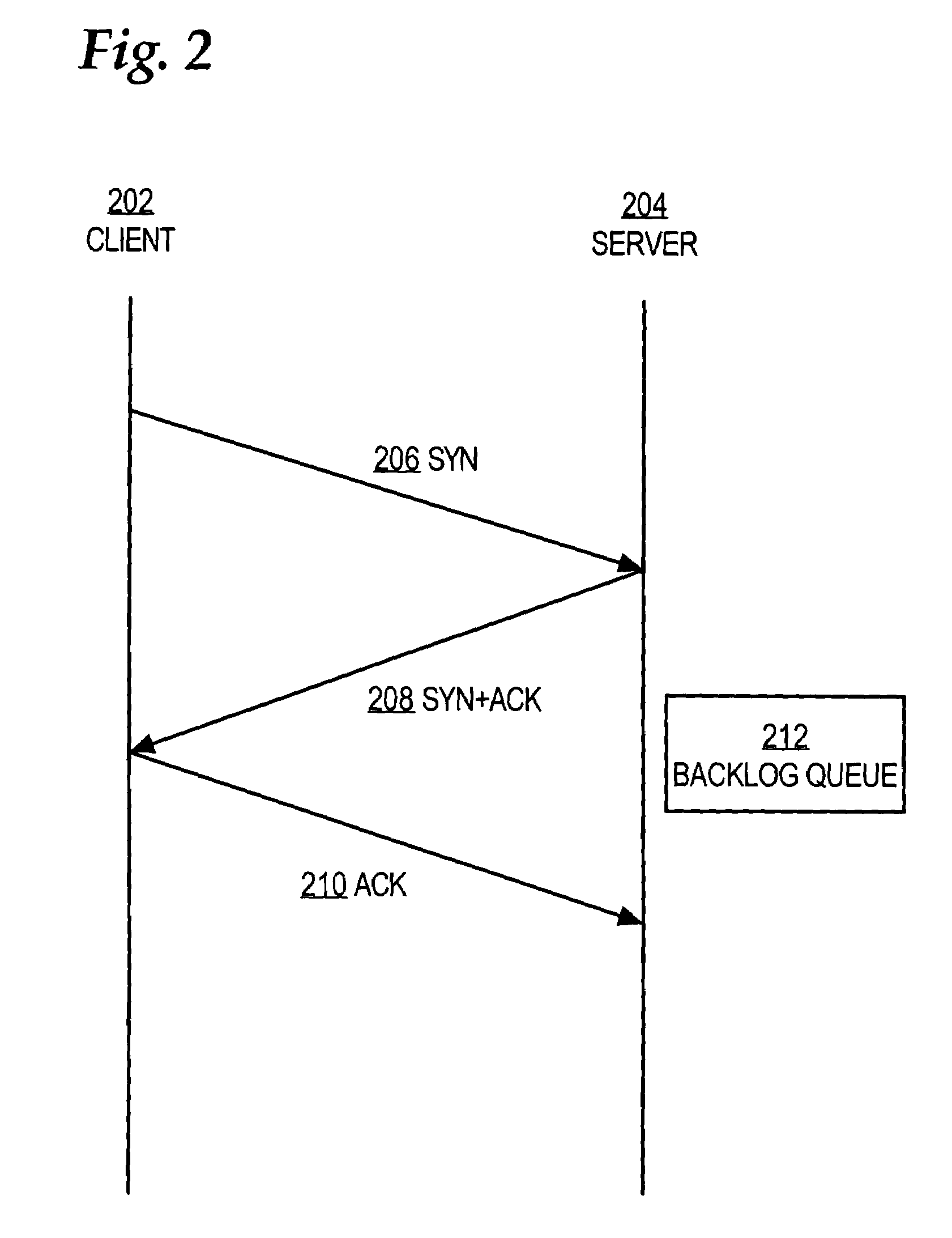
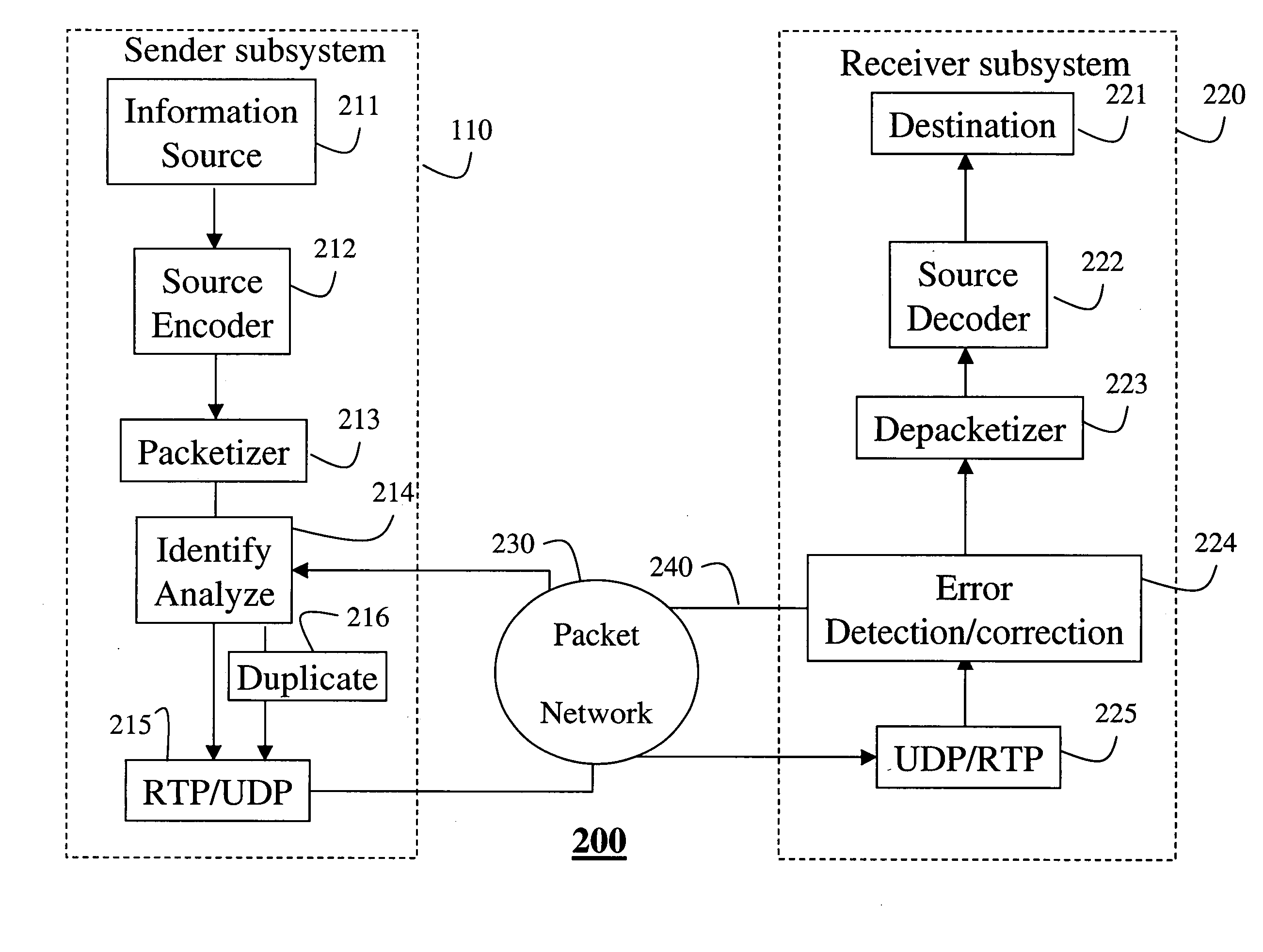
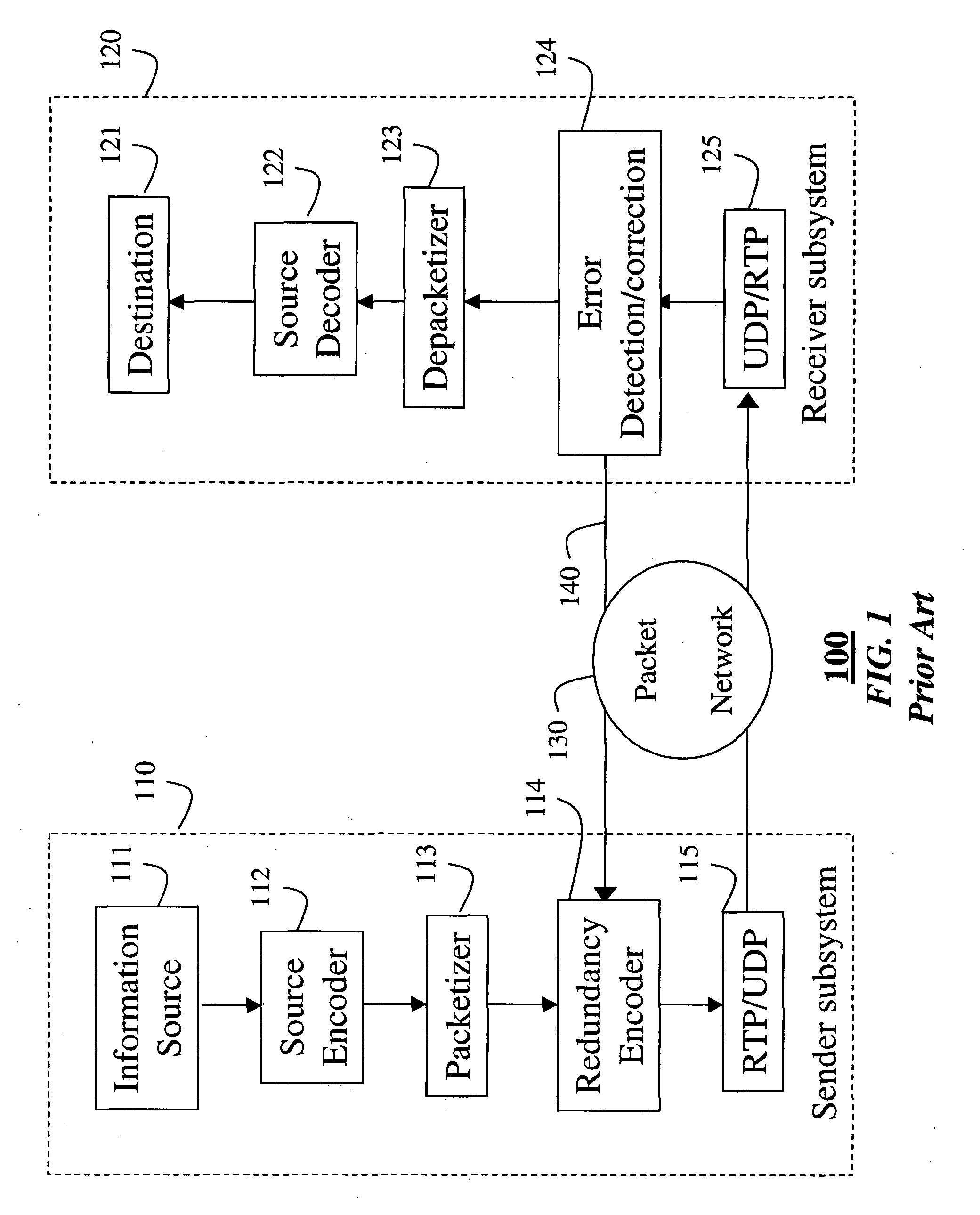
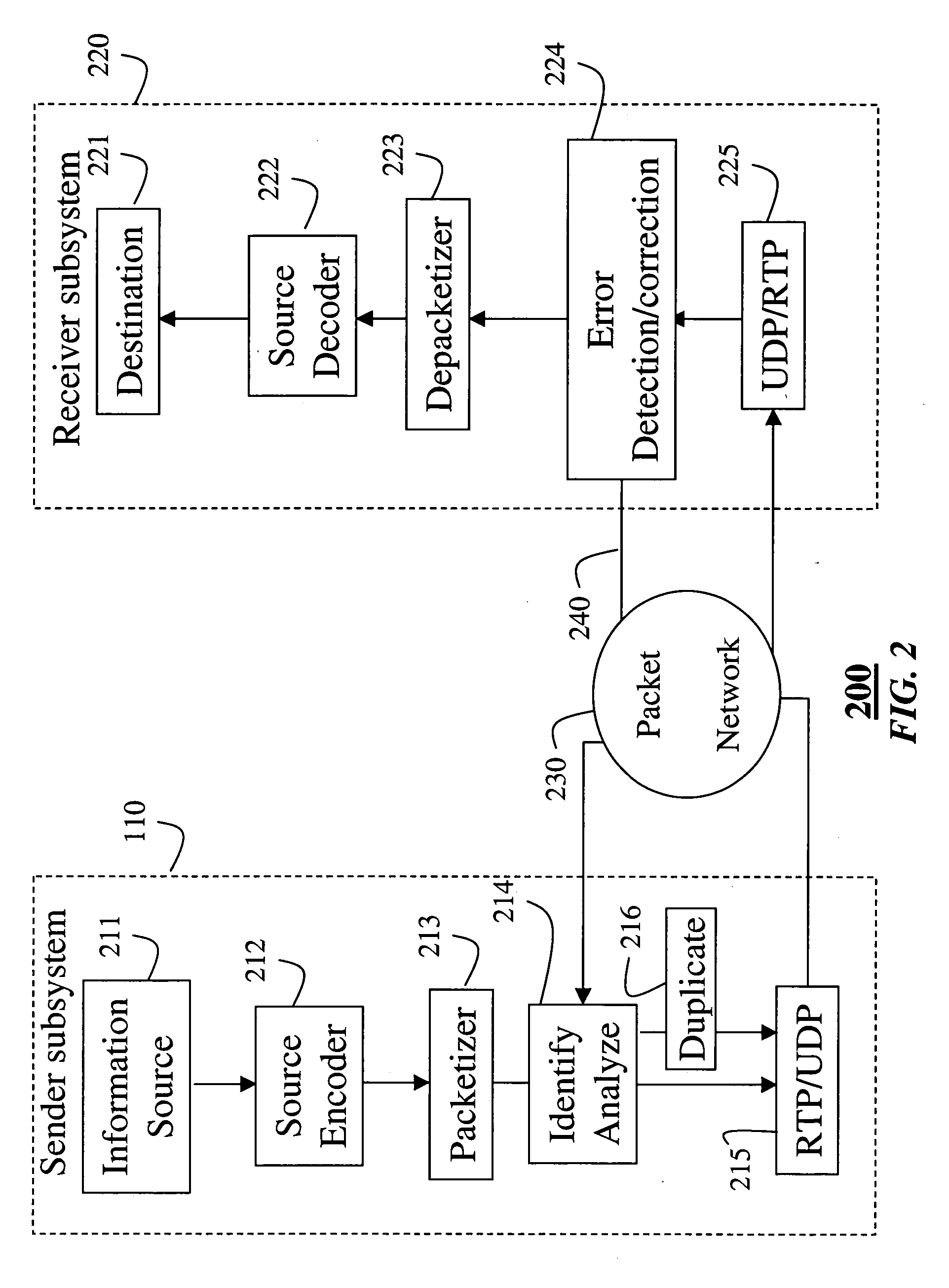
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4996 results about "Packet loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Packet loss occurs when one or more packets of data travelling across a computer network fail to reach their destination. Packet loss is either caused by errors in data transmission, typically across wireless networks, or network congestion. Packet loss is measured as a percentage of packets lost with respect to packets sent.
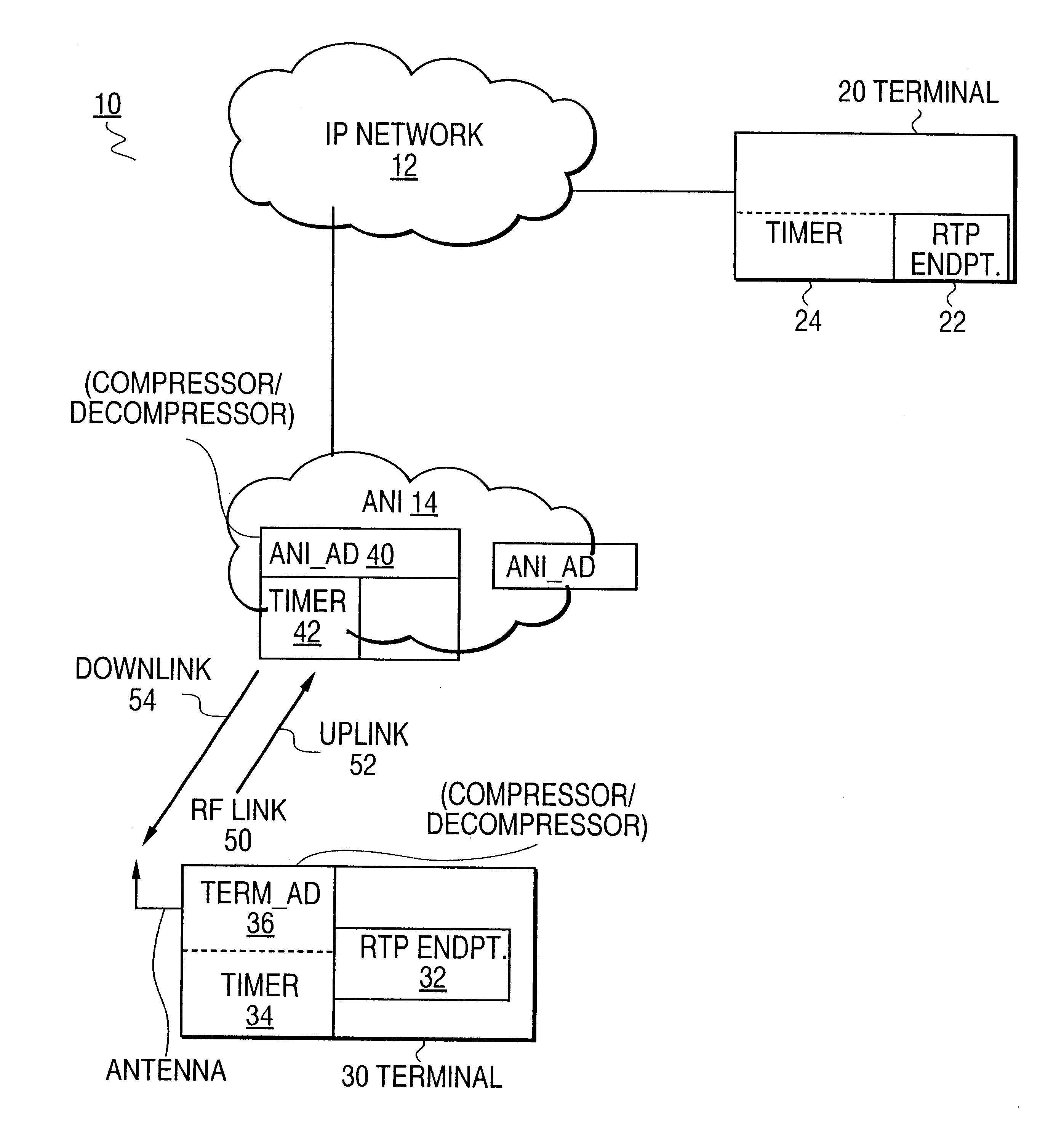
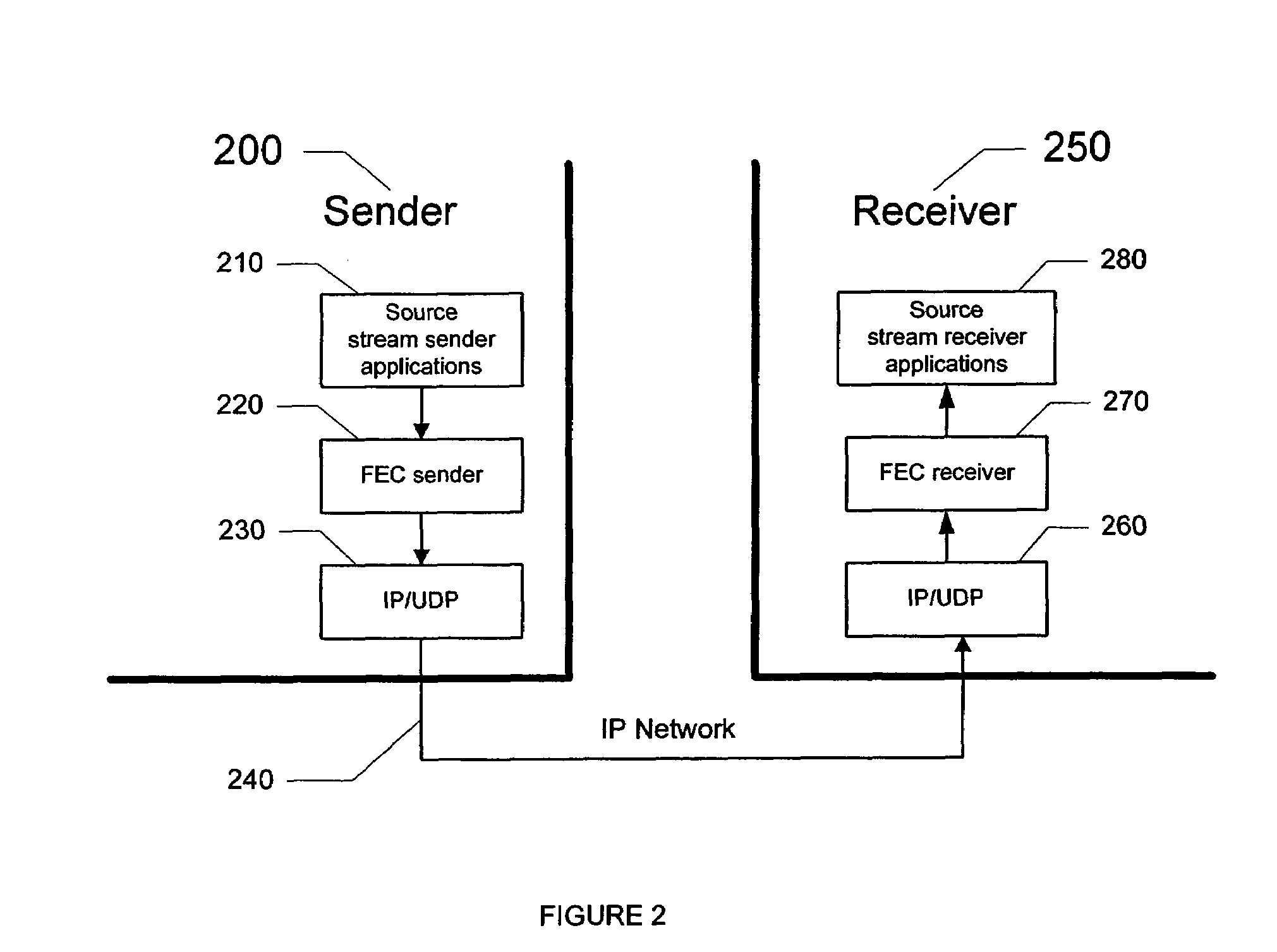
System and method for achieving robust IP/UDP/RTP header compression in the presence of unreliable networks
A robust IP / UDP / RTP header compression mechanism is provided to correctly reconstruct IP / UDP / RTP headers in the presence of packet losses and errors of unreliable networks. The header compression mechanism may include a compressor / de-compressor implemented for operation similarly to RFC 2508 but designed specifically to address robustness when employed in lossy and error-prone networks. The robust header compression scheme requires that, when a second-order difference of a field is non-zero, not only a particular RTP packet whose second-order difference is non-zero is sent with the new first-order difference, but also those following packets are also sent with the new first-order difference as long as: (a) a period pre-determined by factors such as channel characteristics (e.g., link round-trip time RTT / inter-packet separation); or (b) a positive confirmation is received by the compressor that the new first-order difference has been correctly received. In addition, during a period of communicating with the new first-order difference, if the corresponding RTP field changes again with non-zero second-order difference, the "new" first-order difference is combined with the original first-order difference such that the two first-order differences may be appended together as a simple means of communicating the two first-order differences reliably.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Peer-to-peer method of quality of service (QoS) probing and analysis and infrastructure employing same
InactiveUS7133368B2Improve gaming experienceImprove performanceError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
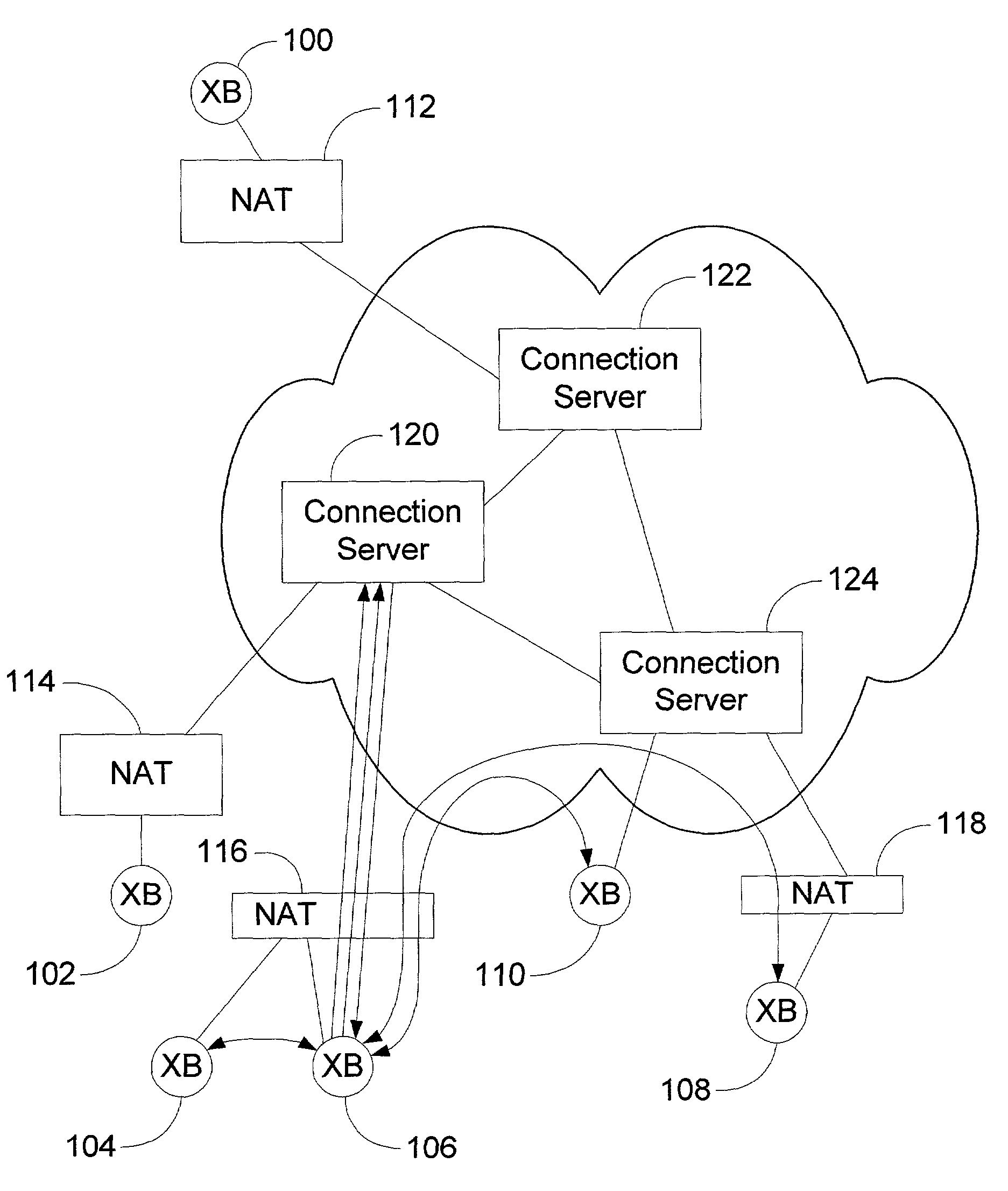
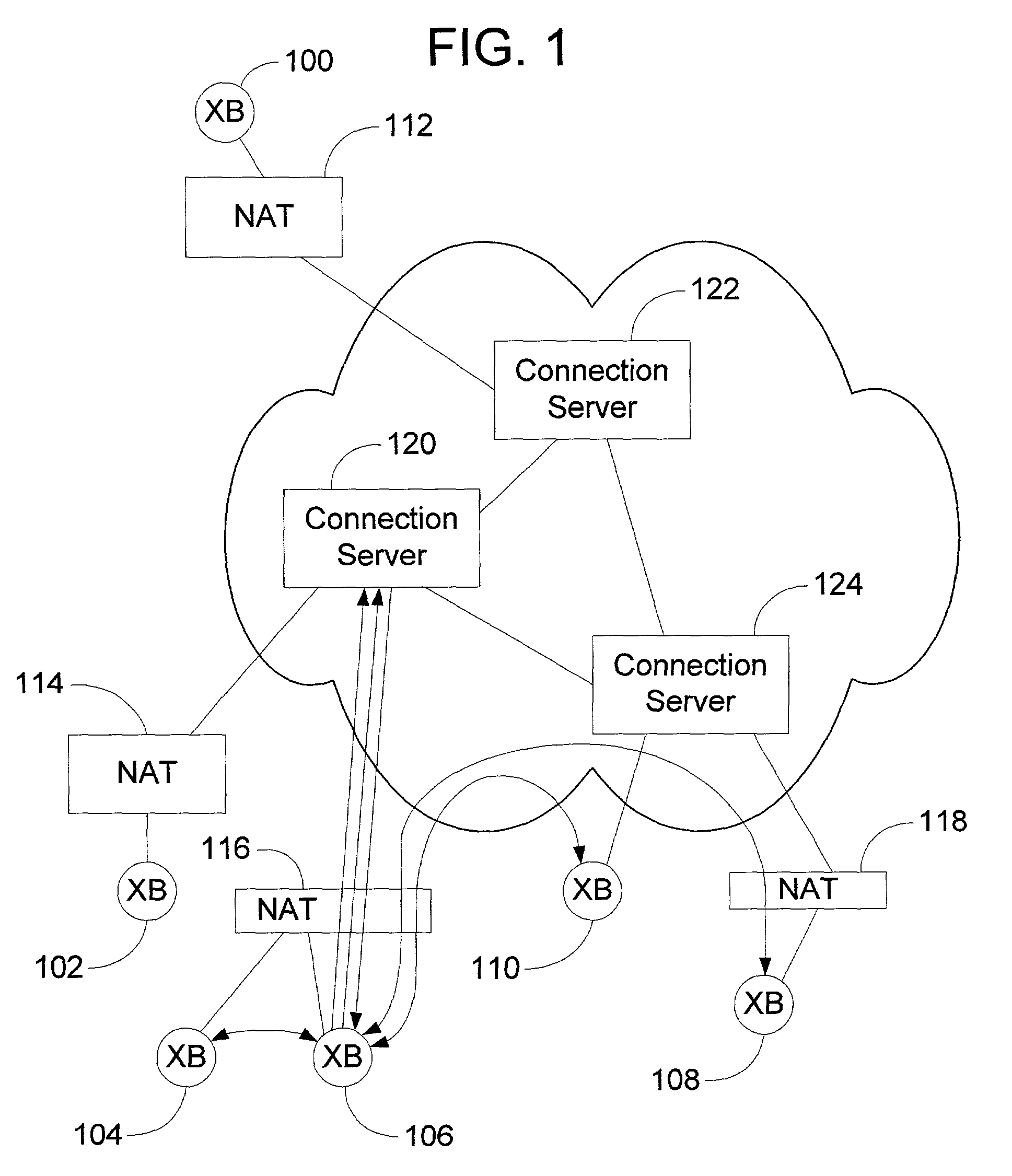
A peer-to-peer (P2P) probing / network quality of service (QoS) analysis system utilizes a UDP-based probing tool for determining latency, bandwidth, and packet loss ratio between peers in a network. The probing tool enables network QoS probing between peers that connect through a network address translator. The list of peers to probe is provided by a connection server based on prior probe results and an estimate of the network condition. The list includes those peers which are predicted to have the best QoS with the requesting peer. Once the list is obtained, the requesting peer probes the actual QoS to each peer on the list, and returns these results to the connection server. P2P probing in parallel using a modified packet-pair scheme is utilized. If anomalous results are obtained, a hop-by-hop probing scheme is utilized to determine the QoS of each link. In such a scheme, differential destination measurement is utilized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
TCP-aware agent sublayer (TAS) for robust TCP over wireless
InactiveUS6208620B1Improve performanceMinimize impactError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCongestion windowTransport control protocol
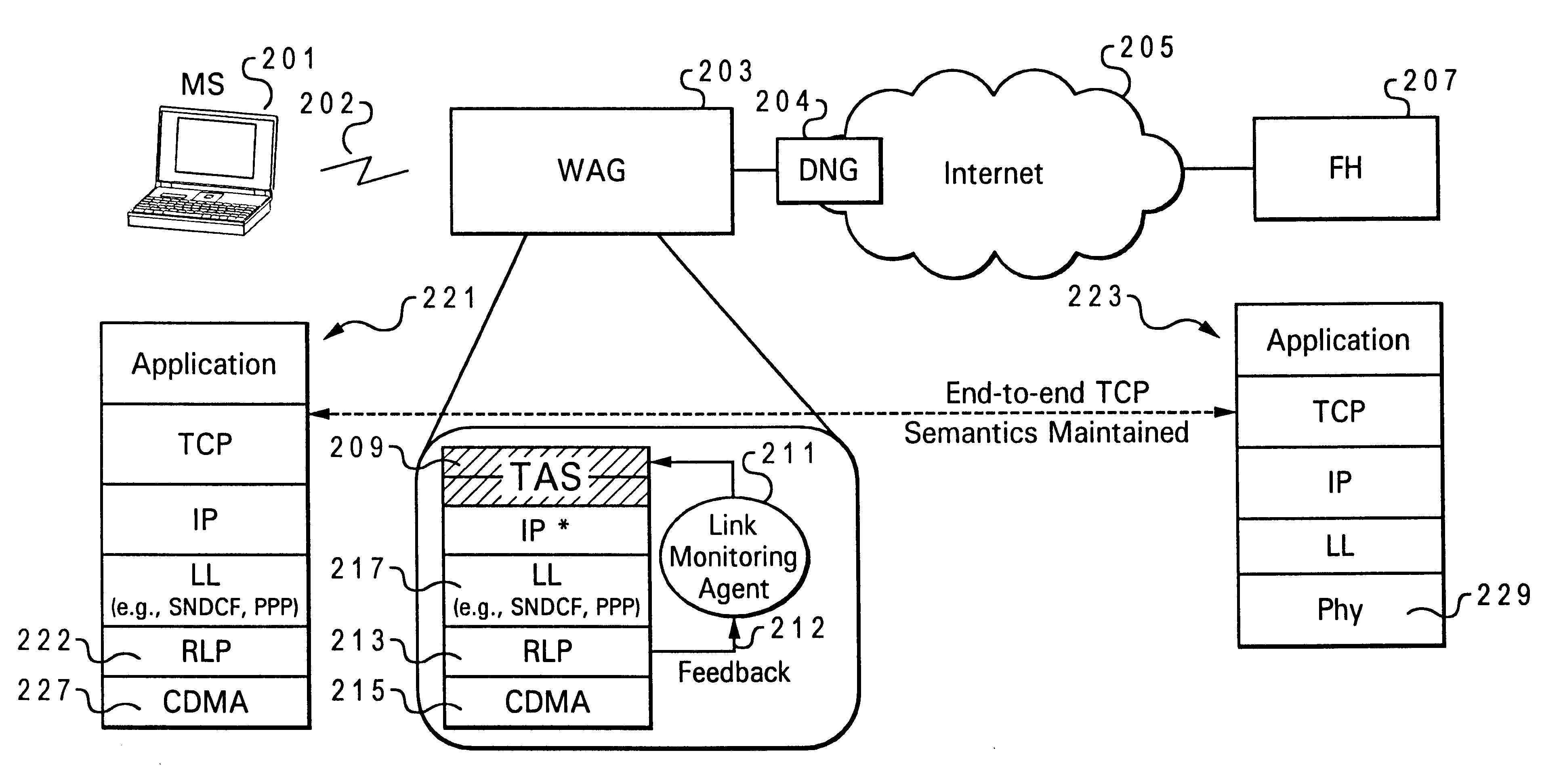
Disclosed is a system for minimizing the effects of faults over an air link of a wireless transmission channel utilizing Transport Control Protocol (TCP). The system includes a TCP-Aware Agent Sublayer (TAS) in a protocol stack, which has a mechanism for caching both TCP packets during forward transmission and acknowledgment (ACK) return packets. The caching mechanism is located near a wireless link of the wireless transmission channel. The system also includes a link monitoring agent coupled to the TAS. The link monitoring agent monitors the condition of the wireless transmission channel for an occurrence of a predefined fault. Once a predefined fault is detected, a system response is implemented based on the type of fault encountered. When the fault is an air link packet loss, an associated packet is immediately retransmitted from the cache, and when the fault is a temporary disconnect, a congestion window of the TCP source is closed.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
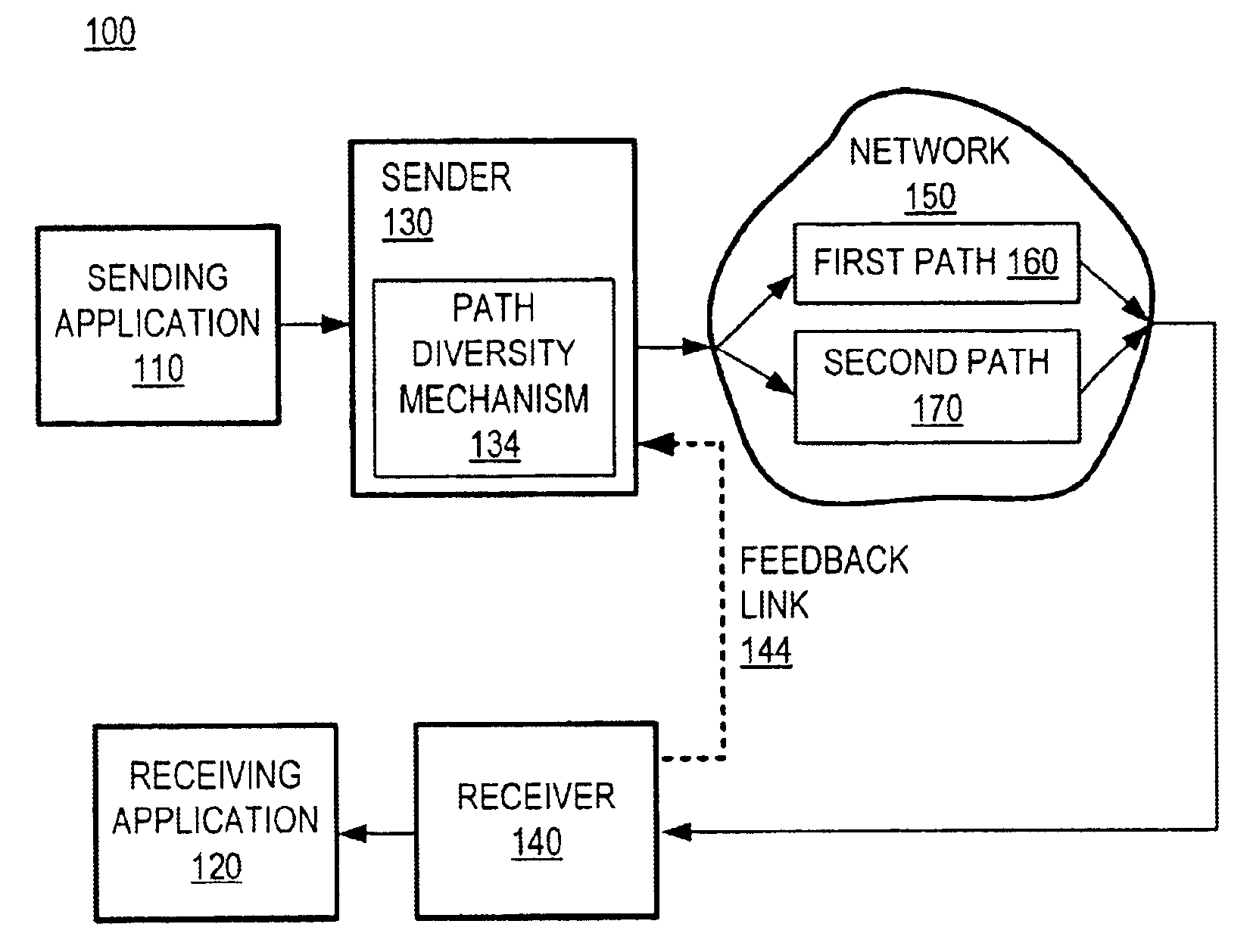
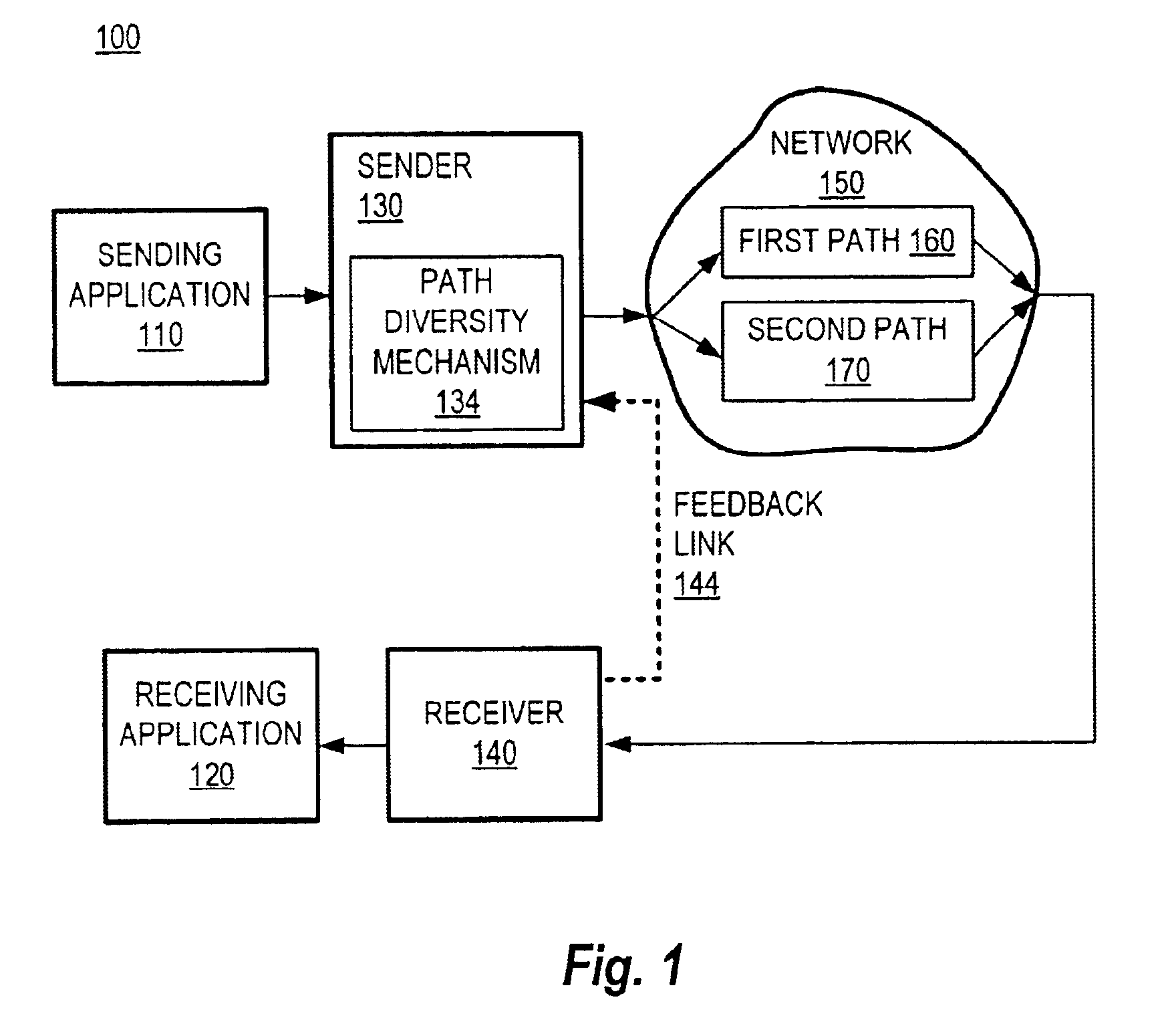
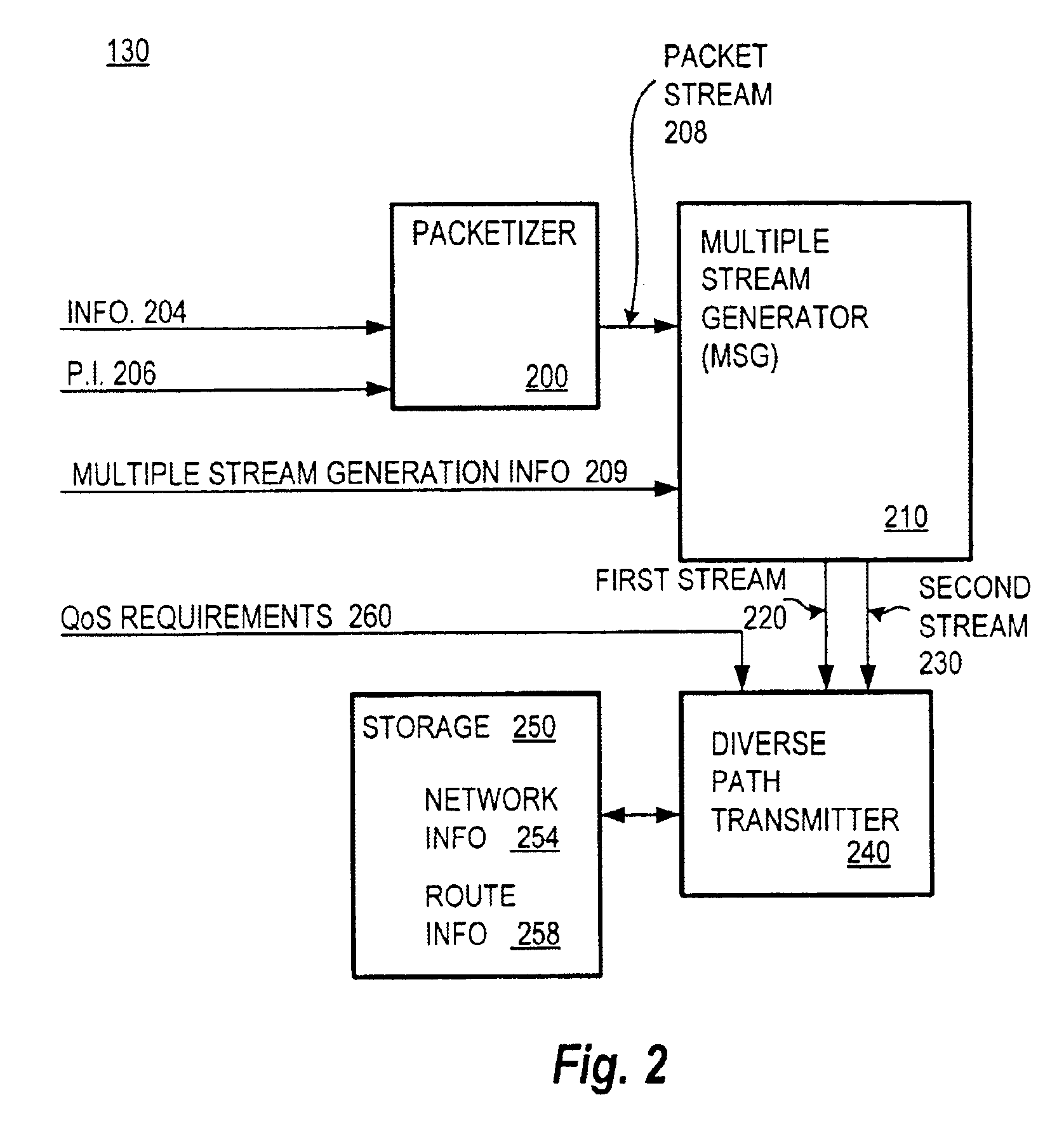
Method and system for packet communication employing path diversity
InactiveUS6868083B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationPacket loss
Communication over lossy packet networks such as the Internet is hampered by limited bandwidth and packet loss. The present invention provides a path diversity transmission system for improving the quality of communication over a lossy packet network. The path diversity transmission system explicitly sends different subsets of packets over different paths, thereby enabling the end-to-end application to effectively see an average path behavior. Generally, seeing this average path behavior provides better performance than seeing the behavior of any individual random path. For example, the probability that all of the multiple paths are simultaneously congested is much less than the probability that a single path is congested. The resulting path diversity can provide a number of benefits, including enabling real-time multimedia communication and simplifying system design (e.g., error correction system design). Two exemplary architectures for achieving path diversity are described herein. The first architecture is based on source routing, and the second architecture is based on a relay infrastructure. The second architecture routes traffic through semi-intelligent nodes at strategic locations in the Internet, thereby providing a service of improved reliability while leveraging the infrastructure of the Internet.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
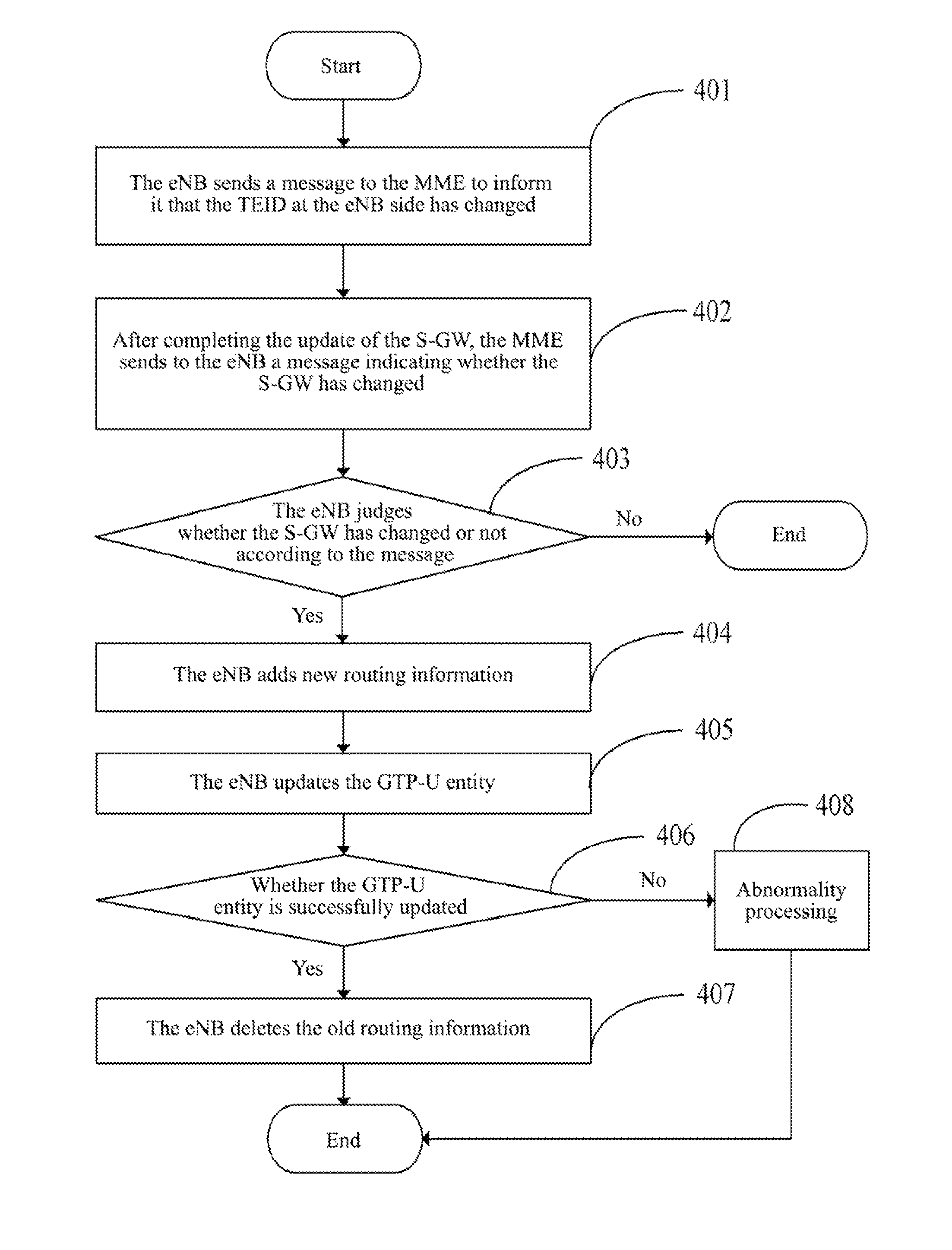
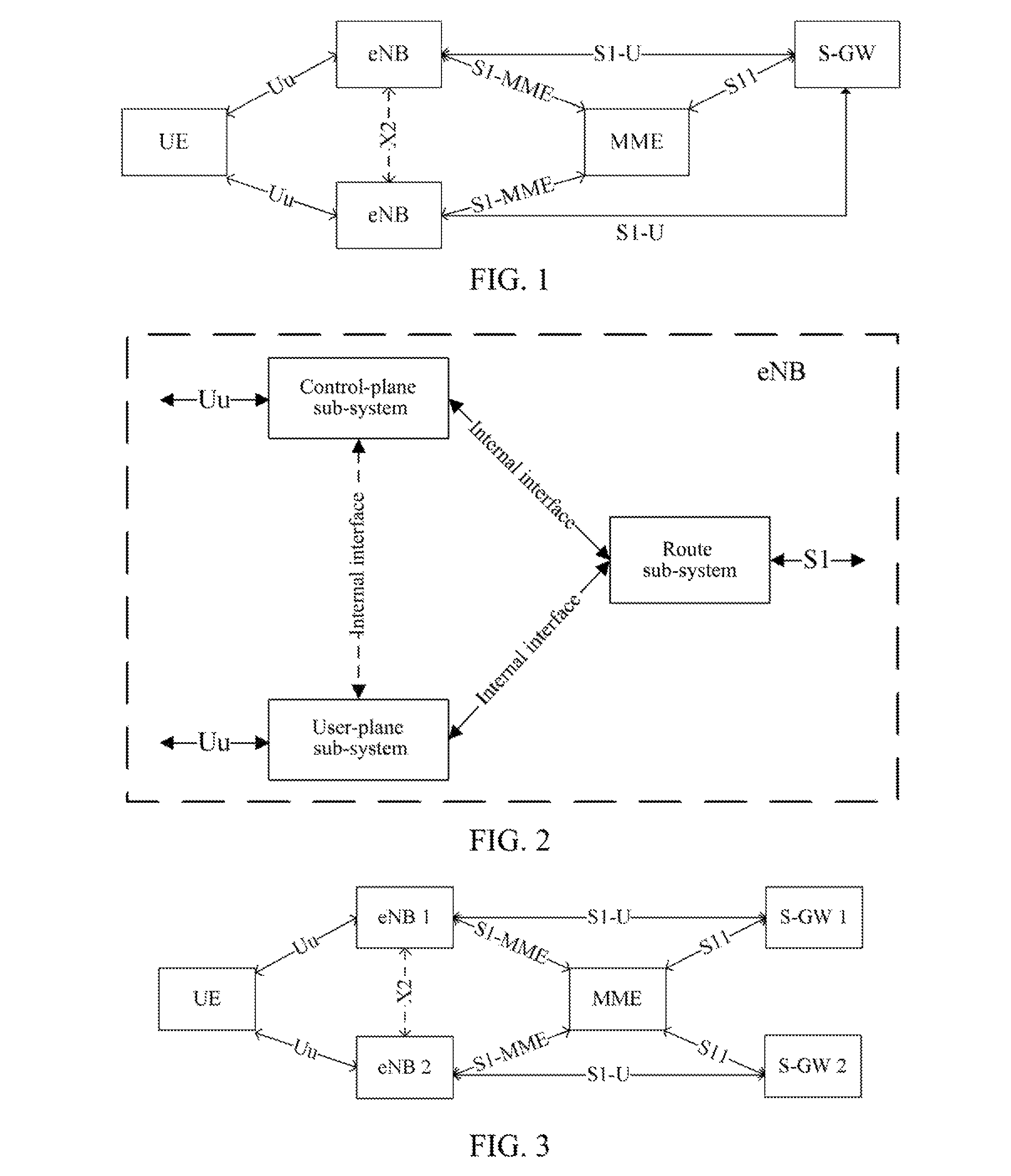
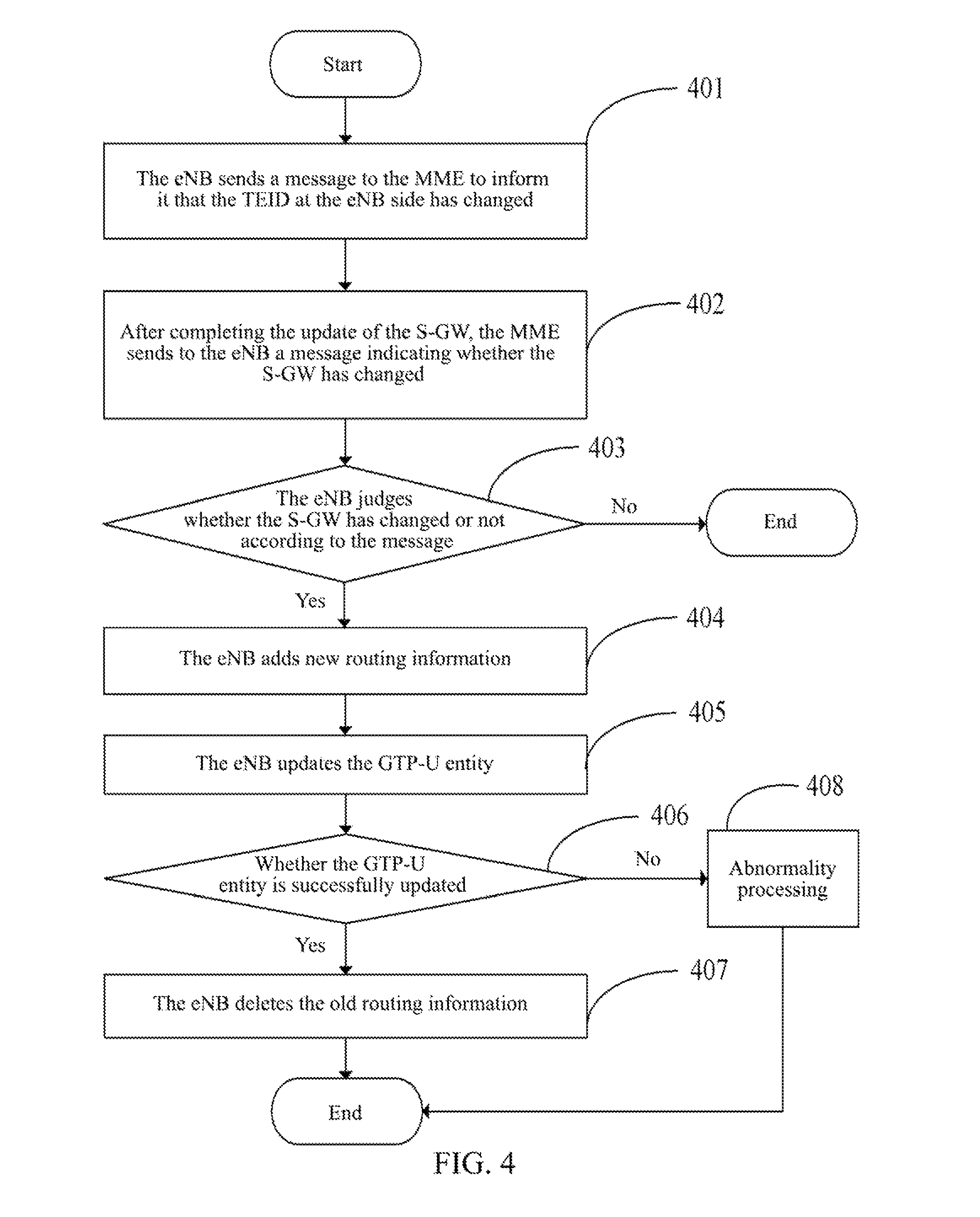
Method, system and evolved NodeB apparatus for implementing inter-evolved NodeB handover
ActiveUS8804667B2Avoid it happening againConnection managementData switching by path configurationGeneral Packet Radio ServiceRouting table
A method, a system and an evolved NodeB (eNB) apparatus for implementing inter-eNB switch are disclosed in the present invention. The method includes: when a user equipment switches from a source-side eNB to a target-side eNB, if the target-side eNB acquires via the Mobility Management Entity (MME) that the Serving Gateway (S-GW) has changed, the target-side eNB adds the new route relation of the S-GW and then updates the General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Tunnelling Protocol User Plane (GTP-U) entity. The present invention can effectively solve the problem of the uplink data packet loss due to the time difference existing between the update to the Tunnel Endpoint Identifier (TEID) and the routing table by the eNB when inter-eNB switch is performed via X2 and the S-GW has changed, thus enhancing the user experience during the switch.
Owner:ZTE CORP
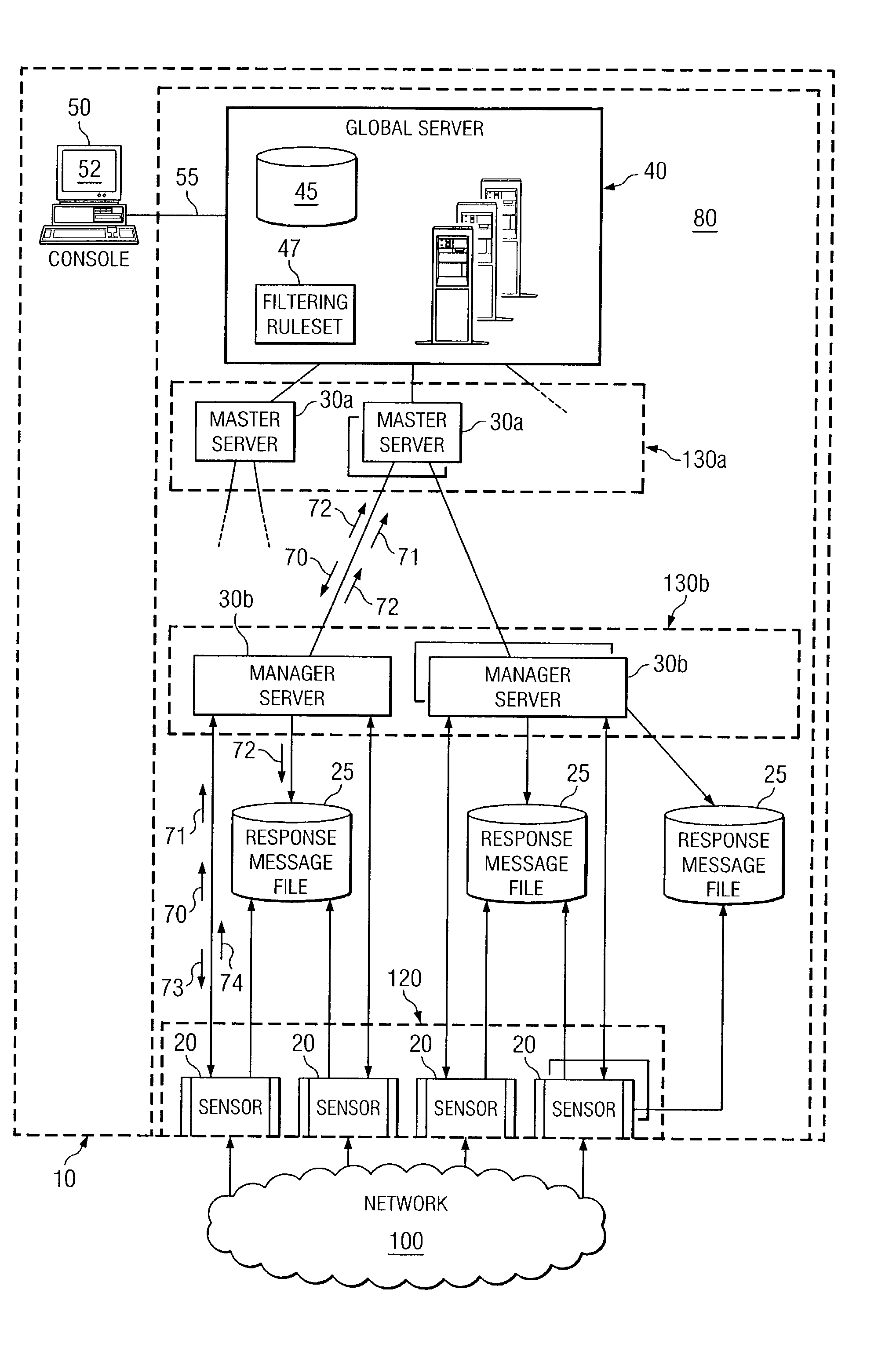
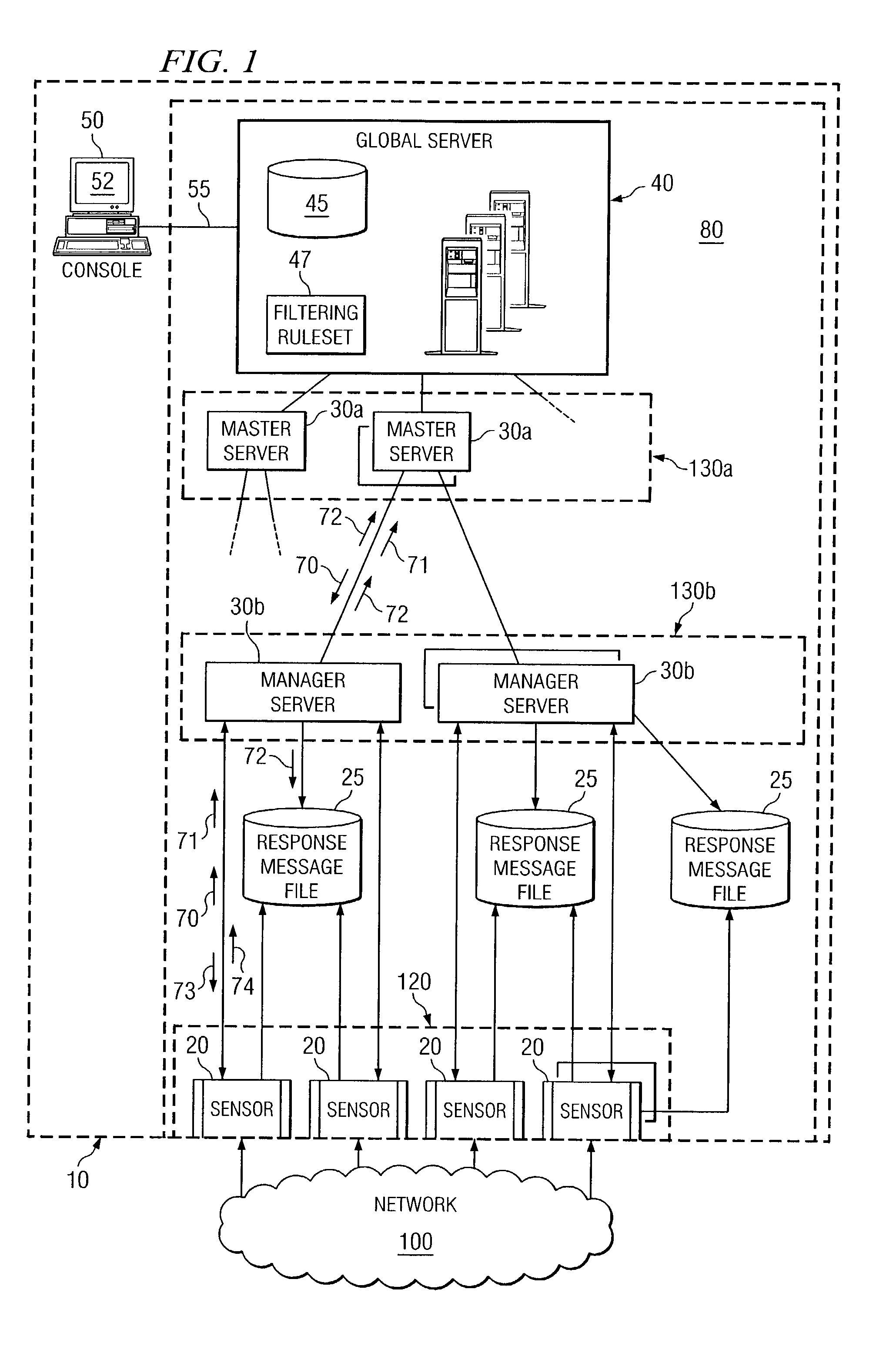
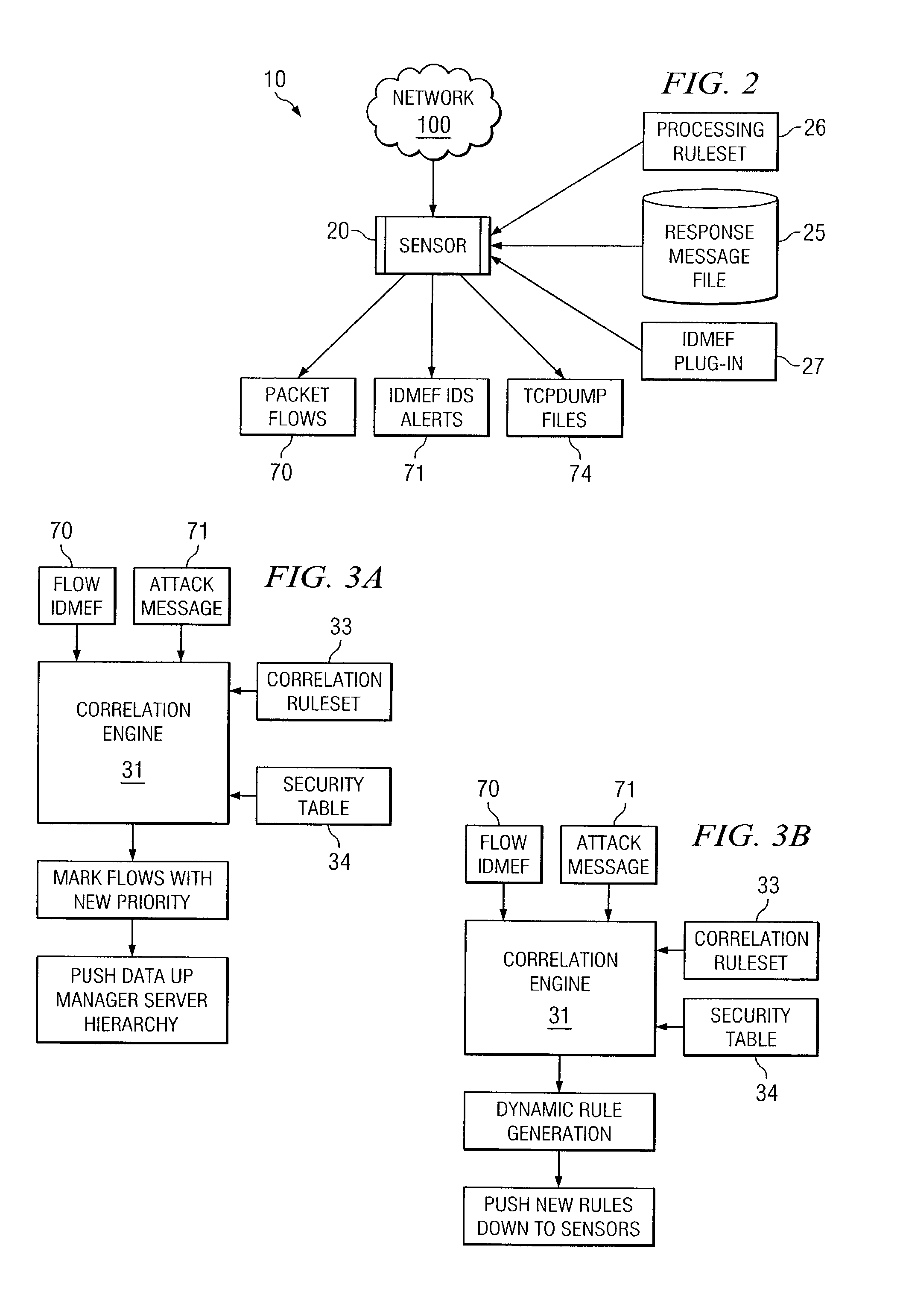
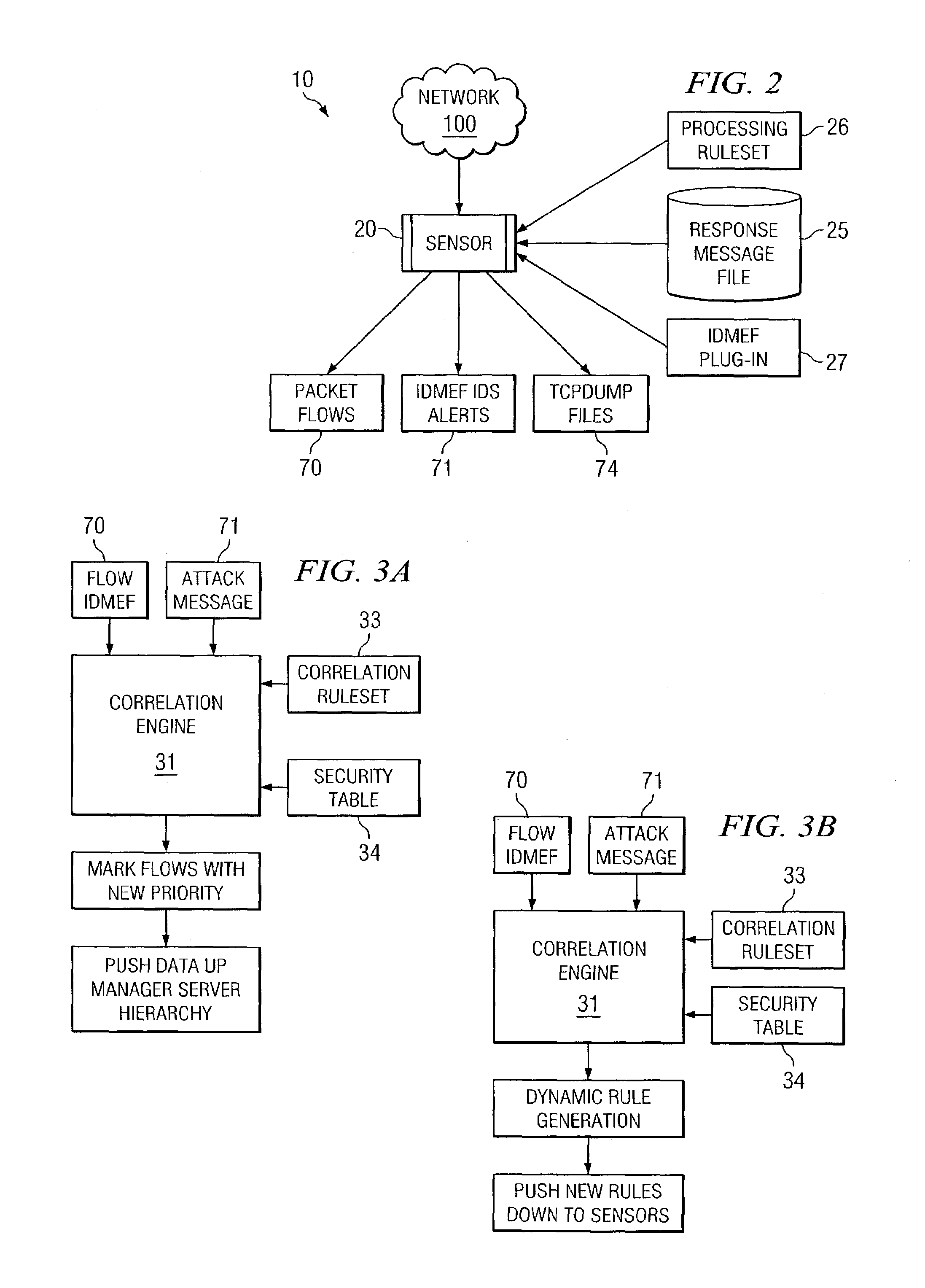
Dynamic rule generation for an enterprise intrusion detection system
ActiveUS7895649B1Lower the volumeReadily apparentMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsPacket lossEnterprise system
A method for dynamically generating rules for an enterprise intrusion detection system comprises receiving a packet flow from a sensor. The packet flow is dynamically processed to detect if the packet flow represents an attack on the enterprise system. A response message is automatically generated in response to the attack, the response message comprising a signature to identify the attack. The response message is automatically communicated to a response message file, the response message file comprising at least one response message.
Owner:FORCEPOINT FEDERAL
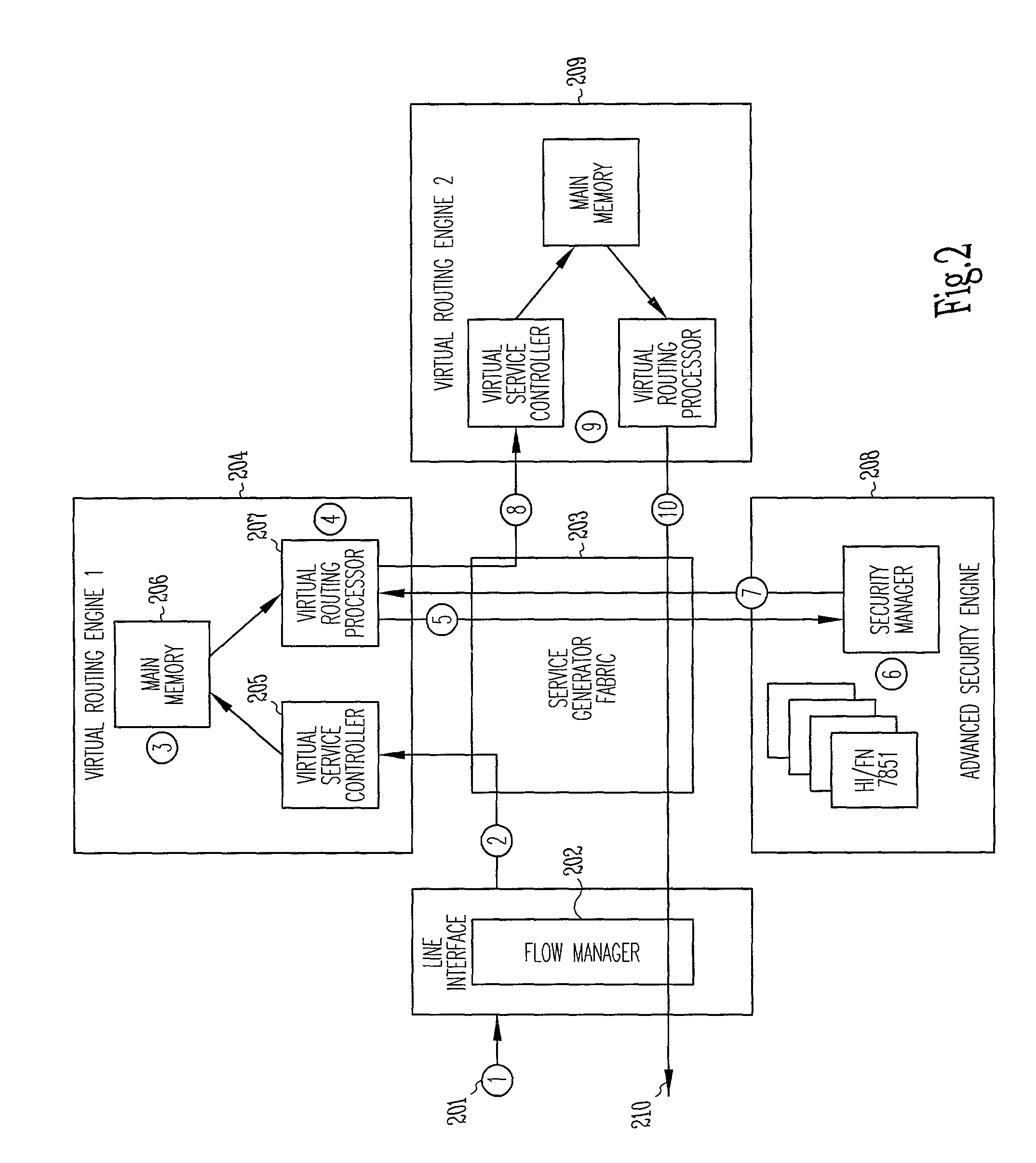
System and method for controlling routing in a virtual router system
ActiveUS7340535B1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationPacket lossNetwork data
One or more functions are applied to network data packets in a virtual router. A packet comprising part of a packet flow is received, and the packet is evaluated to determine which of the one or more functions are to be applied to the flow. The results of the evaluation are stored in a record, and the functions indicated in the stored record are applied to subsequent packets in the packet flow.
Owner:FORTINET
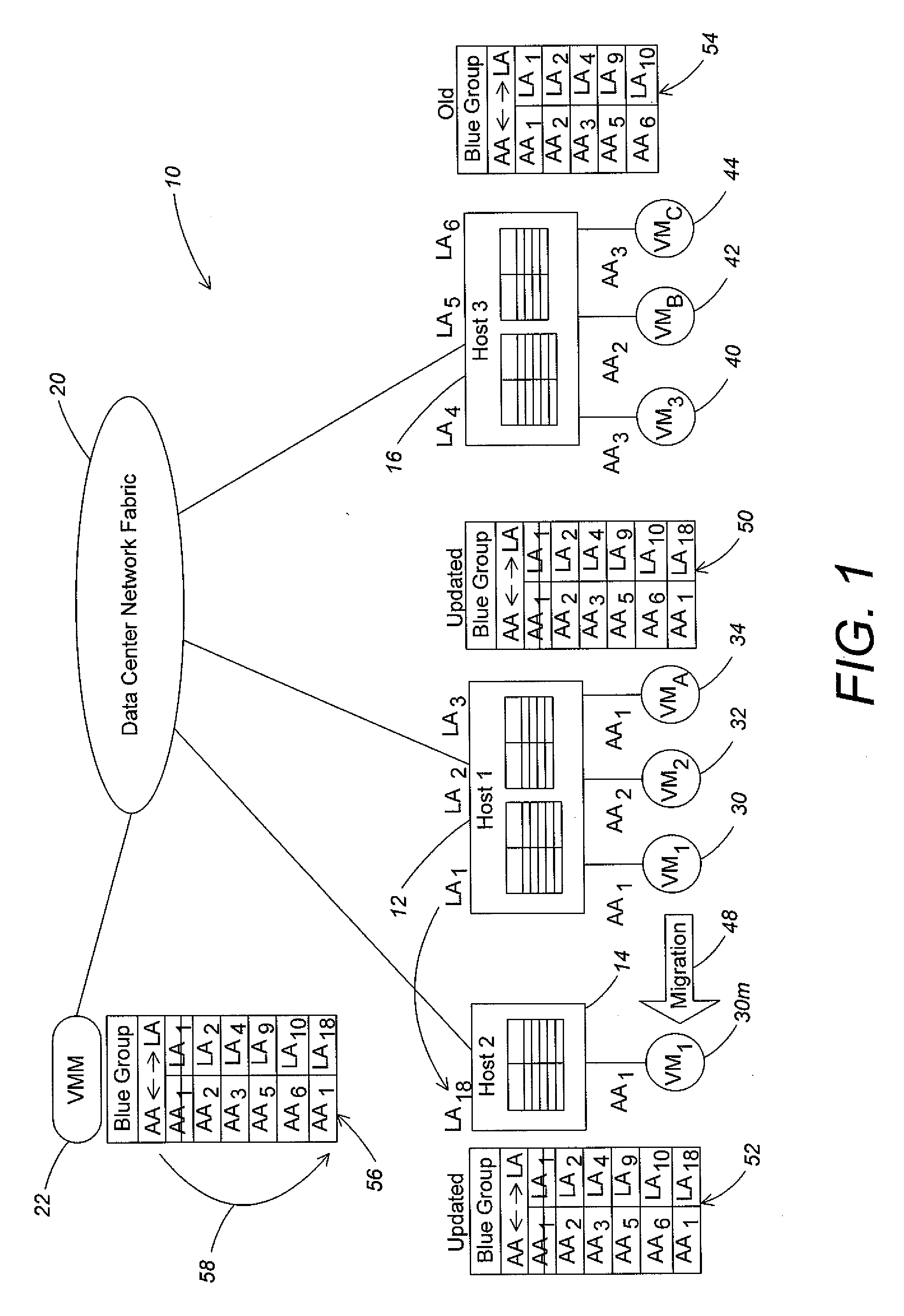
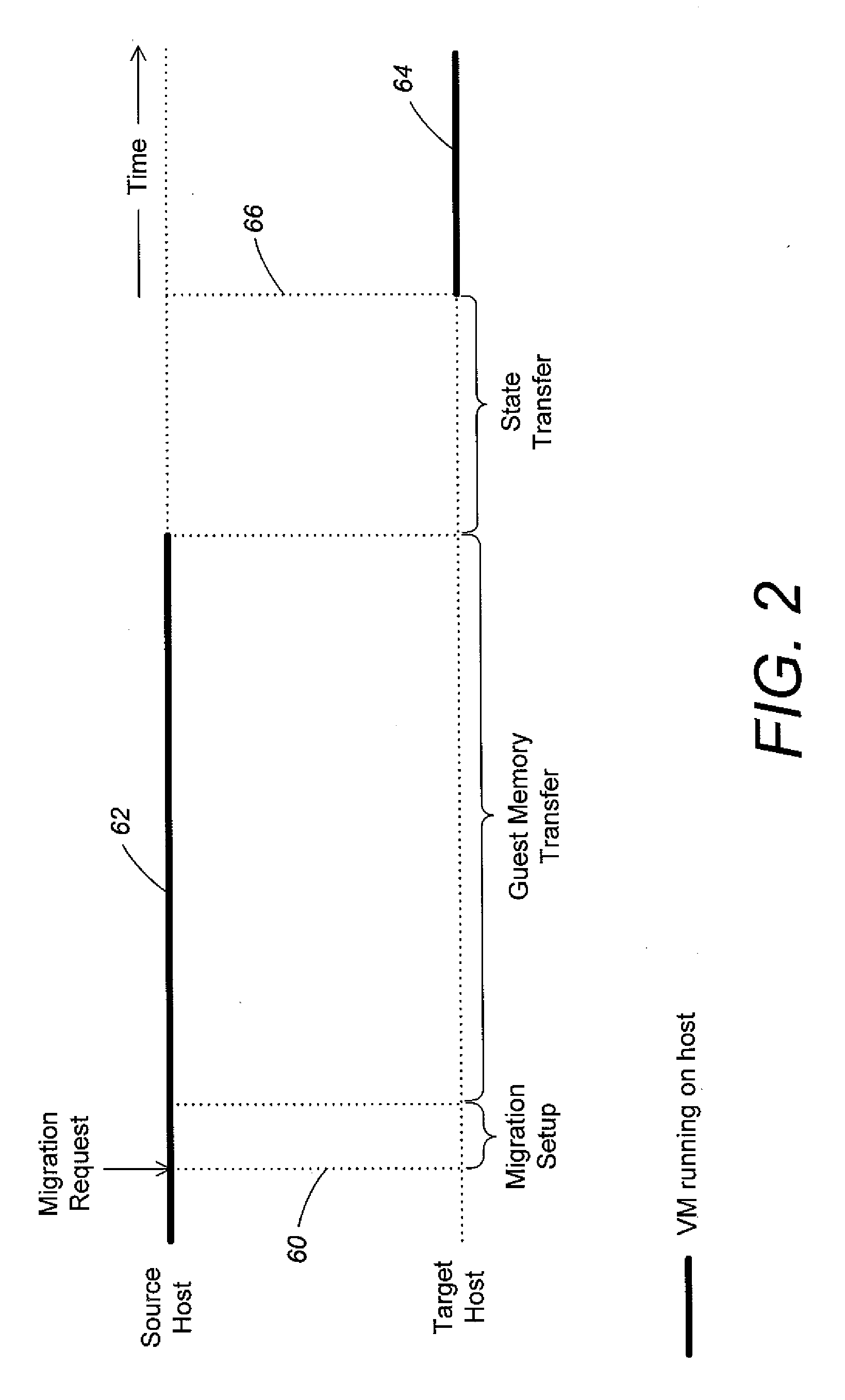
Virtual machine migration to minimize packet loss in virtualized network
ActiveUS20130031544A1Effective distributionError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsPacket lossData center
Methods and apparatus are provided for controlling live migration of a virtual machine from a first host to a second host in a data center. A virtual machine manager may distribute to at least one host in a virtual network an updated mapping policy that maps a customer address of the virtual machine to a provider address of the migrated virtual machine. The updated mapping policy enables hosts in the virtual network to communicate with the migrated virtual machine. The updated mapping policy can be a shadow policy. The shadow policy is transmitted to hosts in the virtual network by the virtual machine manager before live migration of the virtual machine completes and is maintained by recipient hosts in an inactive state until triggered. The virtual machine manager notifies hosts in the virtual network to activate the shadow policy when live migration completes.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Congestion control method for a packet-switched network
InactiveUS7369498B1Increase profitError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket loss
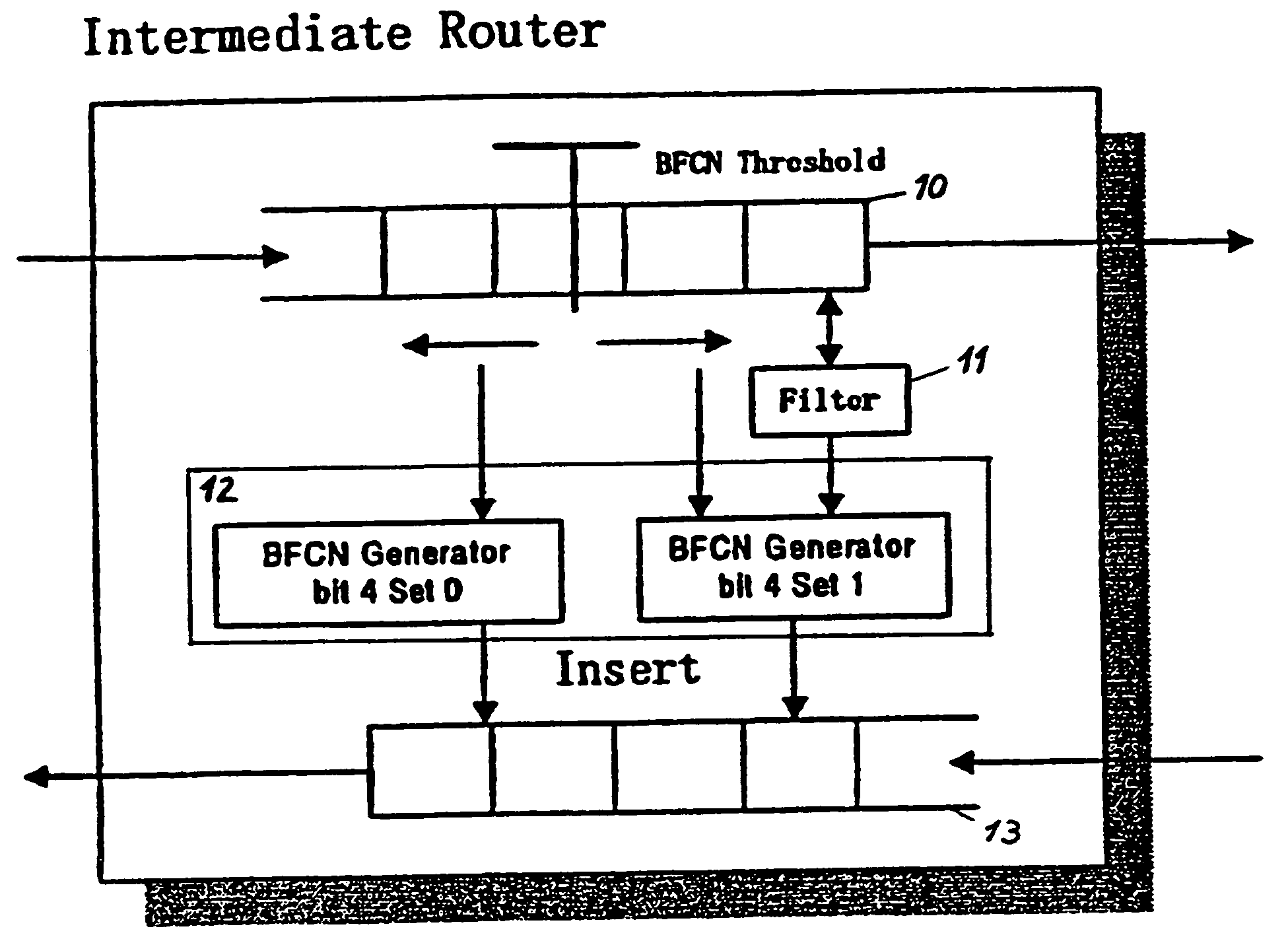
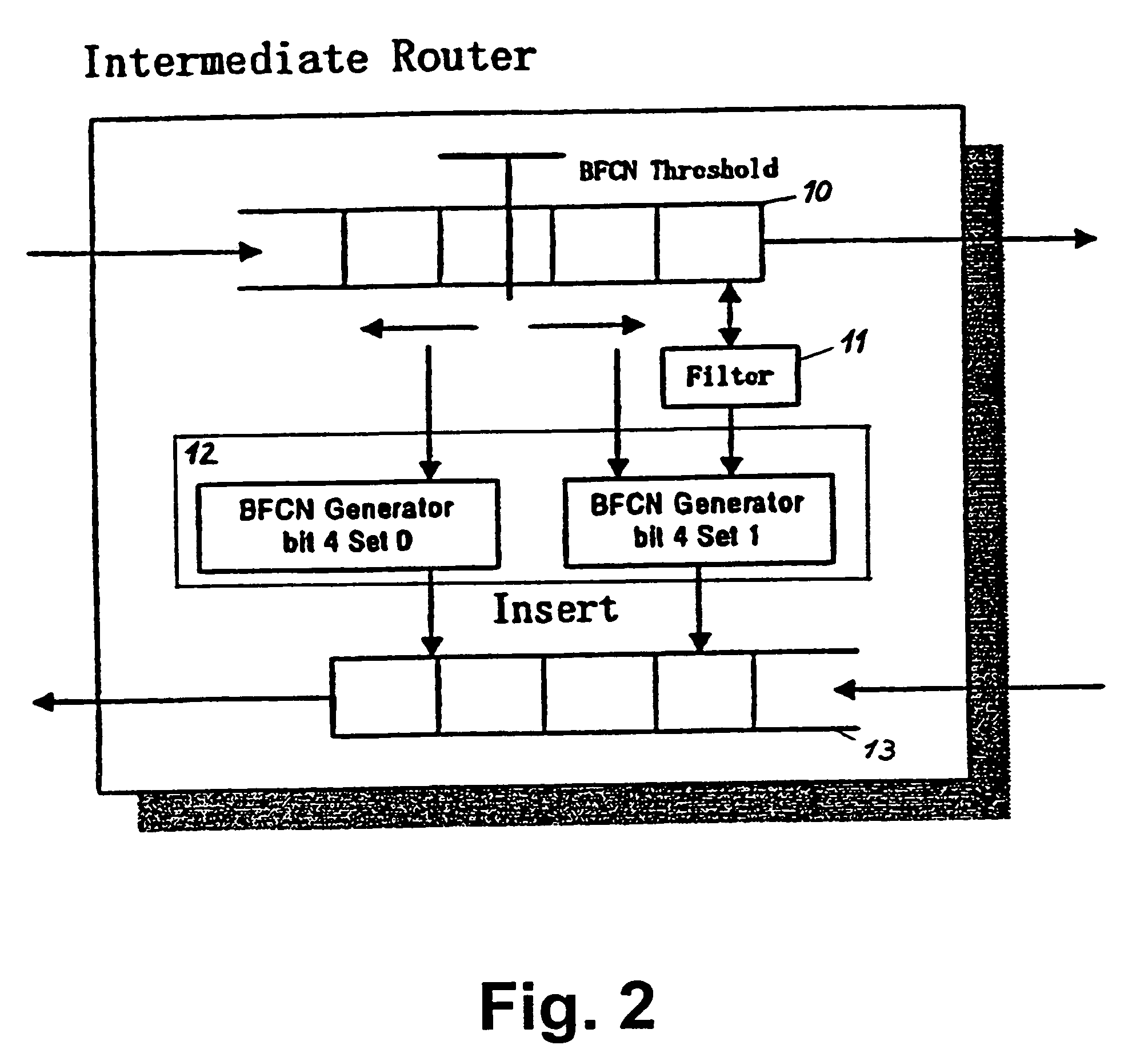
The present invention relates to a method and network for controlling congestion in a packet-switched network, comprising traffic sources, traffic destinations and network nodes, wherein a packet queue length in a network node is determined and a congestion notification is transmitted back towards the source address of an incoming data packet received at the network node, if the detected packet queue length exceeds a predetermined threshold. Then, congestion control is performed at a predetermined intermediate network node in response to the receipt of the congestion notification. Thereby, burts of source traffic can be constrained and unnecessary packet losses can be avoided already at an intermediate access node and within the network. The congestion notification message generated due to an incipient congestion is immediately routed back according to its source address. As a result, control delay time is shortened, such that buffer size requirements and number of congestion notification messages are reduced.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
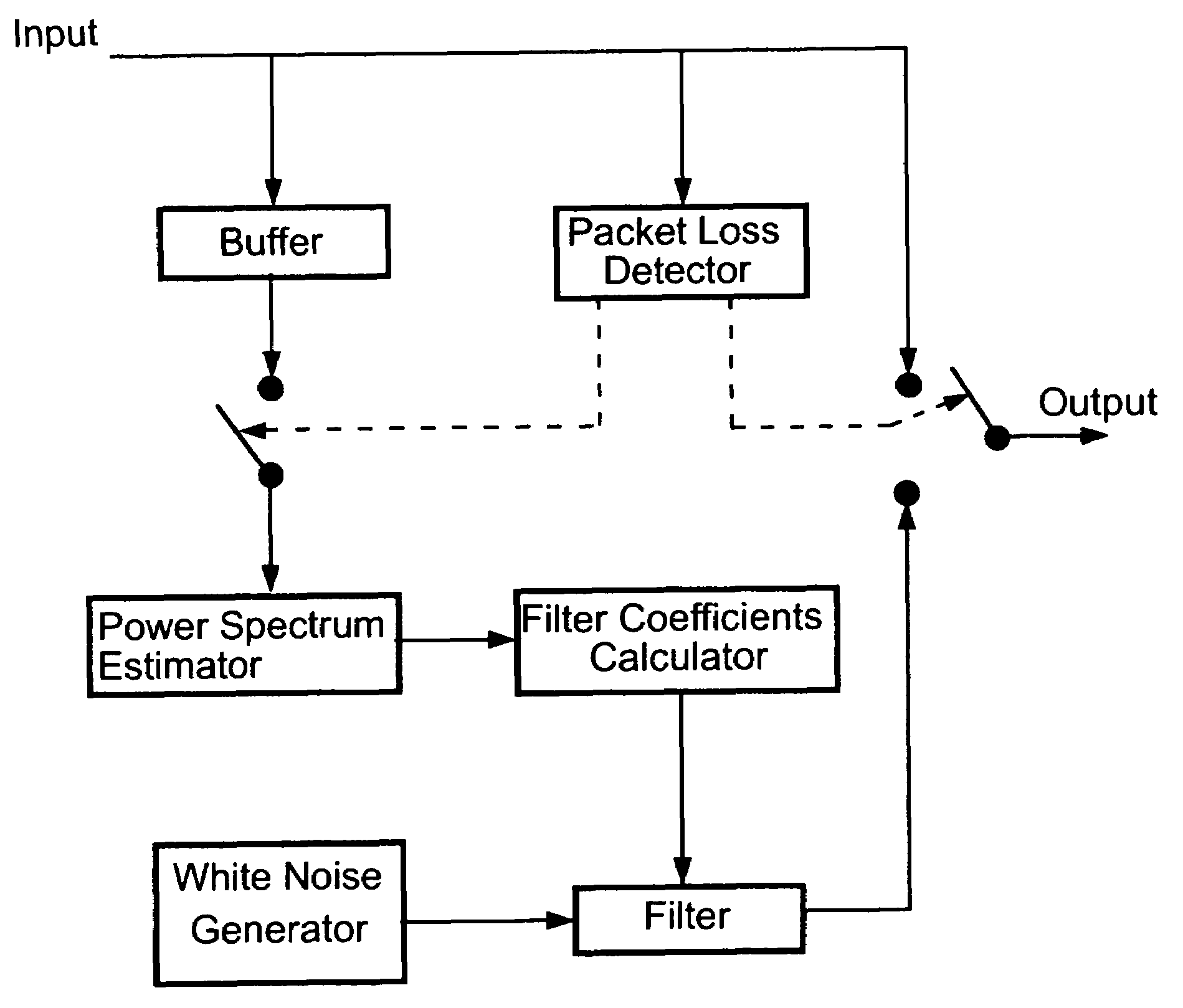
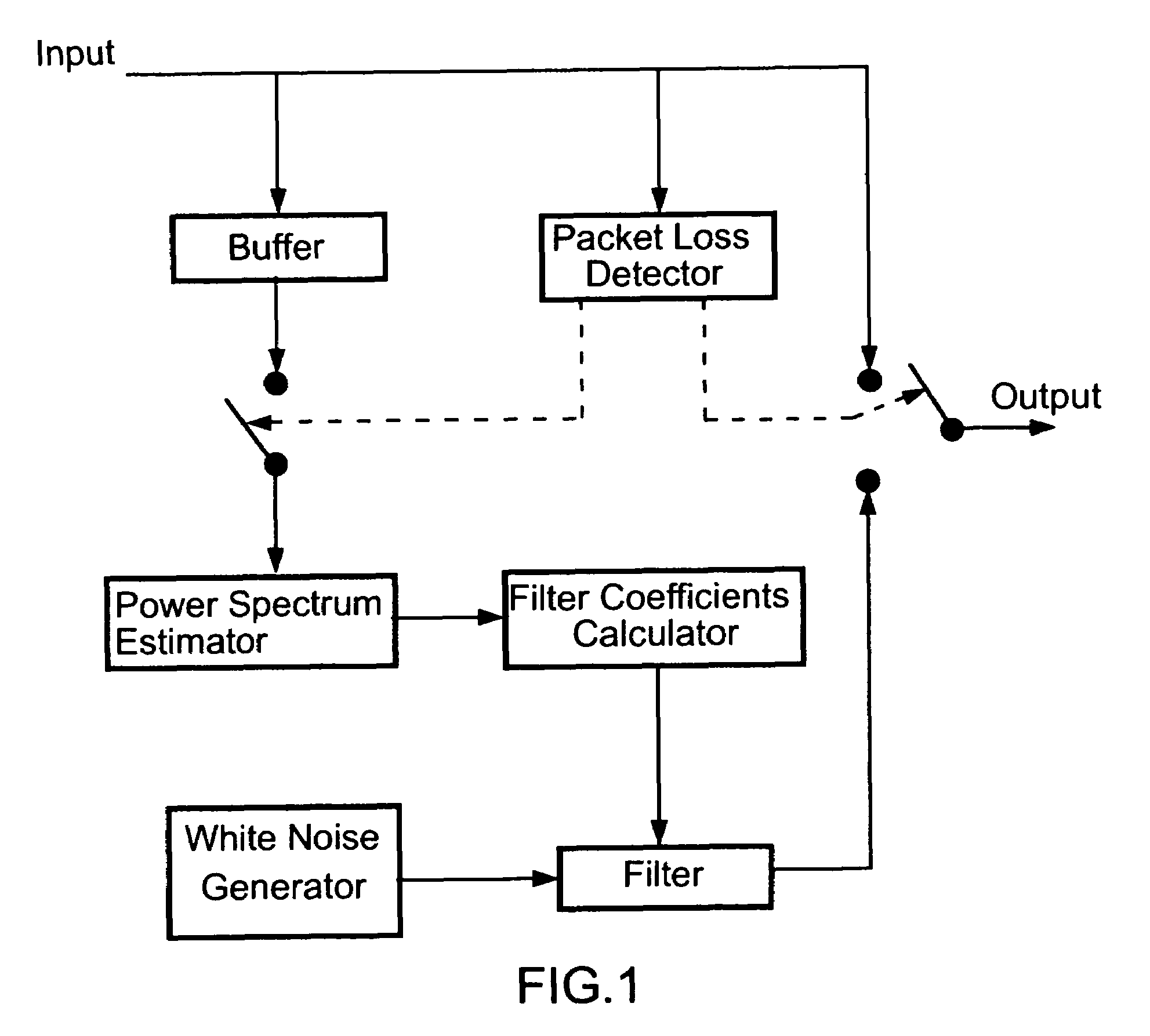
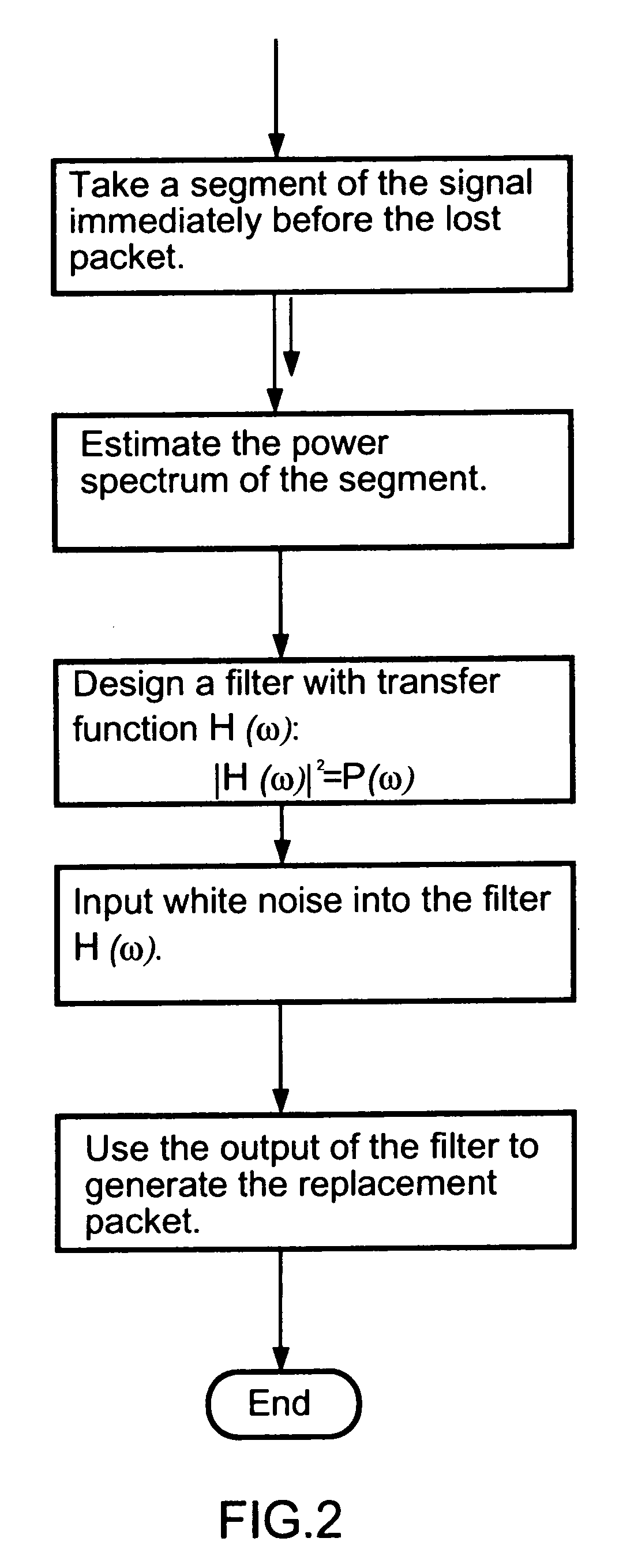
Packet loss compensation method using injection of spectrally shaped noise
An insertion-based error concealment method and apparatus are provided whereby, instead of directly inserting white noise, a filter is created to shape the white noise. The filtered white noise is then used to replace lost data. The method of the present invention is implemented by first estimating the power spectrum of the previous frame; then designing a filter with transfer function H(f), where |H(f)|2=the estimated power spectrum; and finally generating the replacement packet using noise which has been spectrally modified by the filter. The resulting filtered noise has the same power spectrum as the previous packet but is not highly correlated with it.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
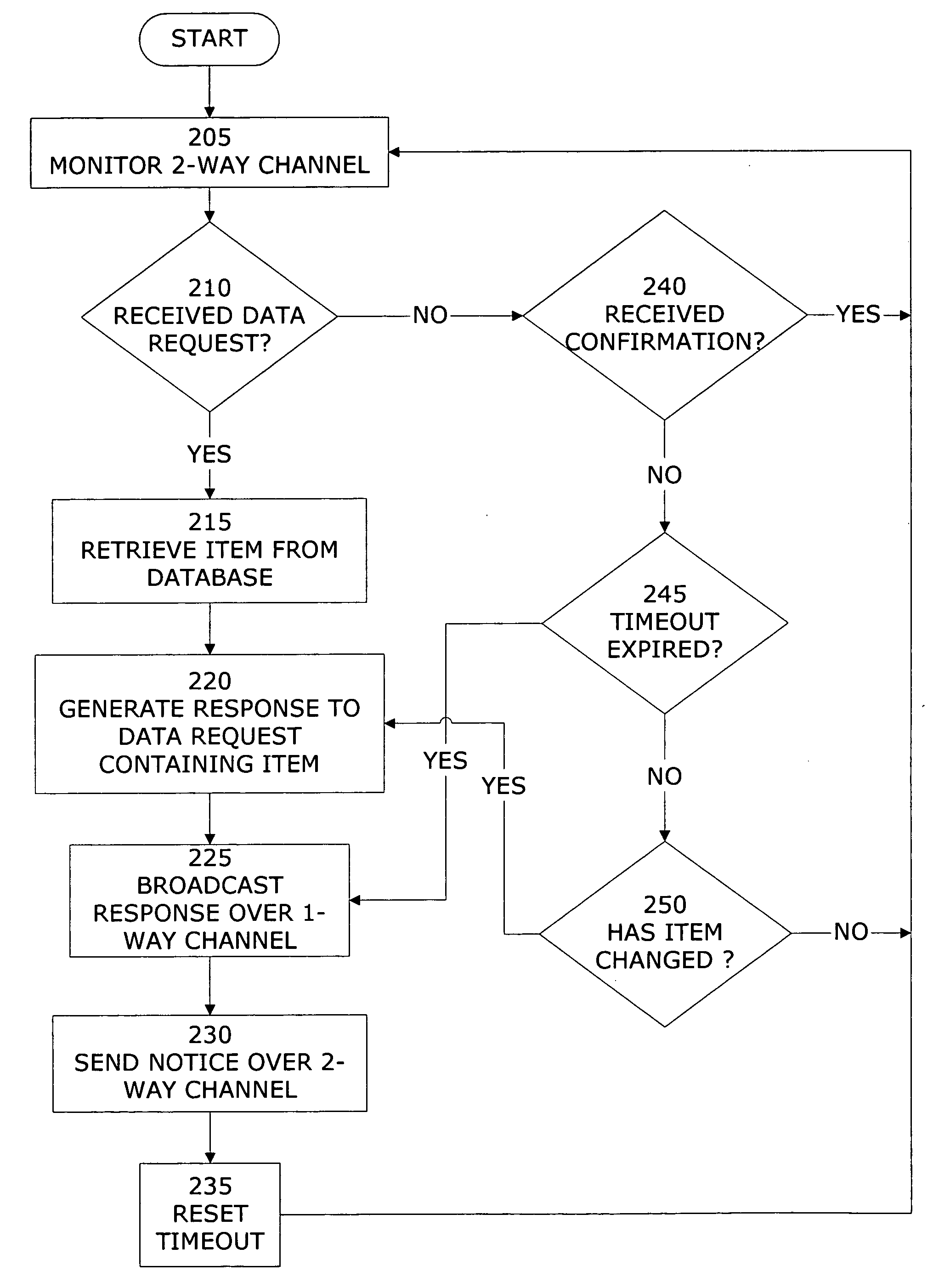
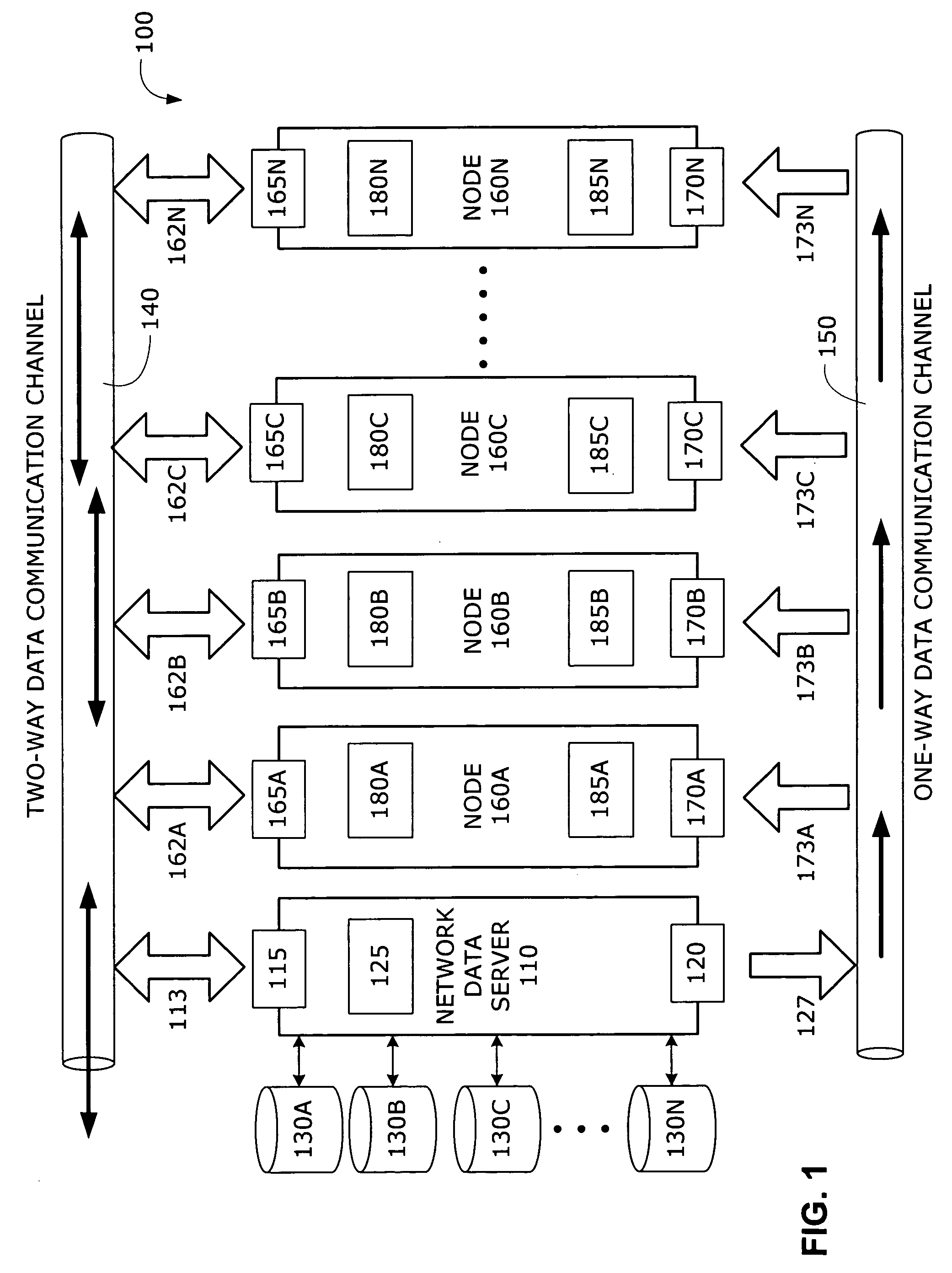
Network data distribution system and method
ActiveUS20060271617A1GHz frequency transmissionMultiple digital computer combinationsData packPacket loss
Embodiments of a system and method for distributing network data to multiple nodes in a data communications network is described. Two data communication channels are provided for each node in the network. While one of the communication channels carries routing and flow control protocol messages, as well as data, in both directions between network nodes, the other communication channel is configured to transmit data traffic—and only data traffic—in a single direction from the network data server toward all of the other nodes in the network. By using 100% of the available bandwidth for data traffic only, the speed at which data may be distributed throughout the network is maximized and the performance degradation caused by the congestion, collisions or packet loss that typically occurs in two-way data communication channels is avoided.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
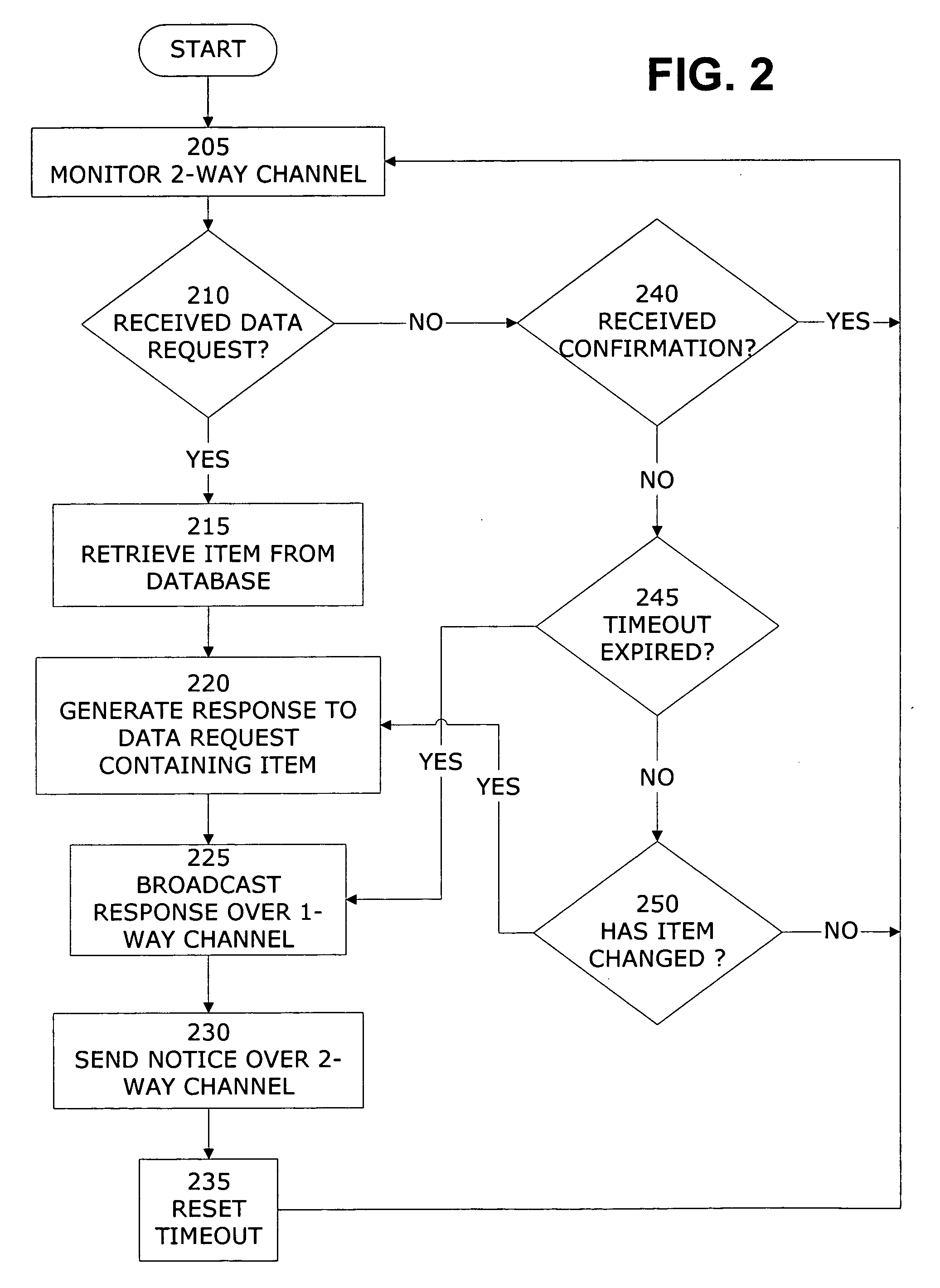
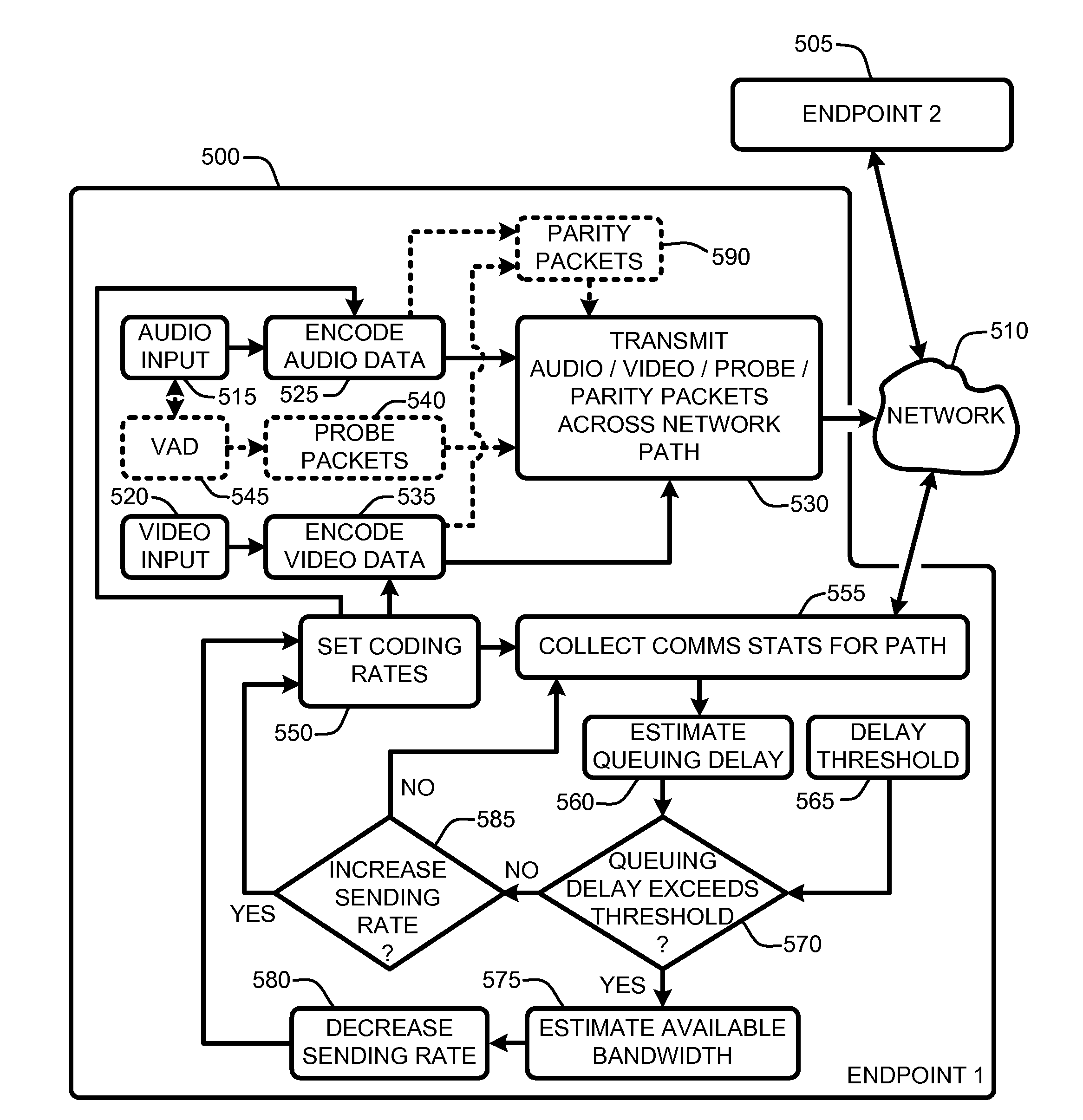
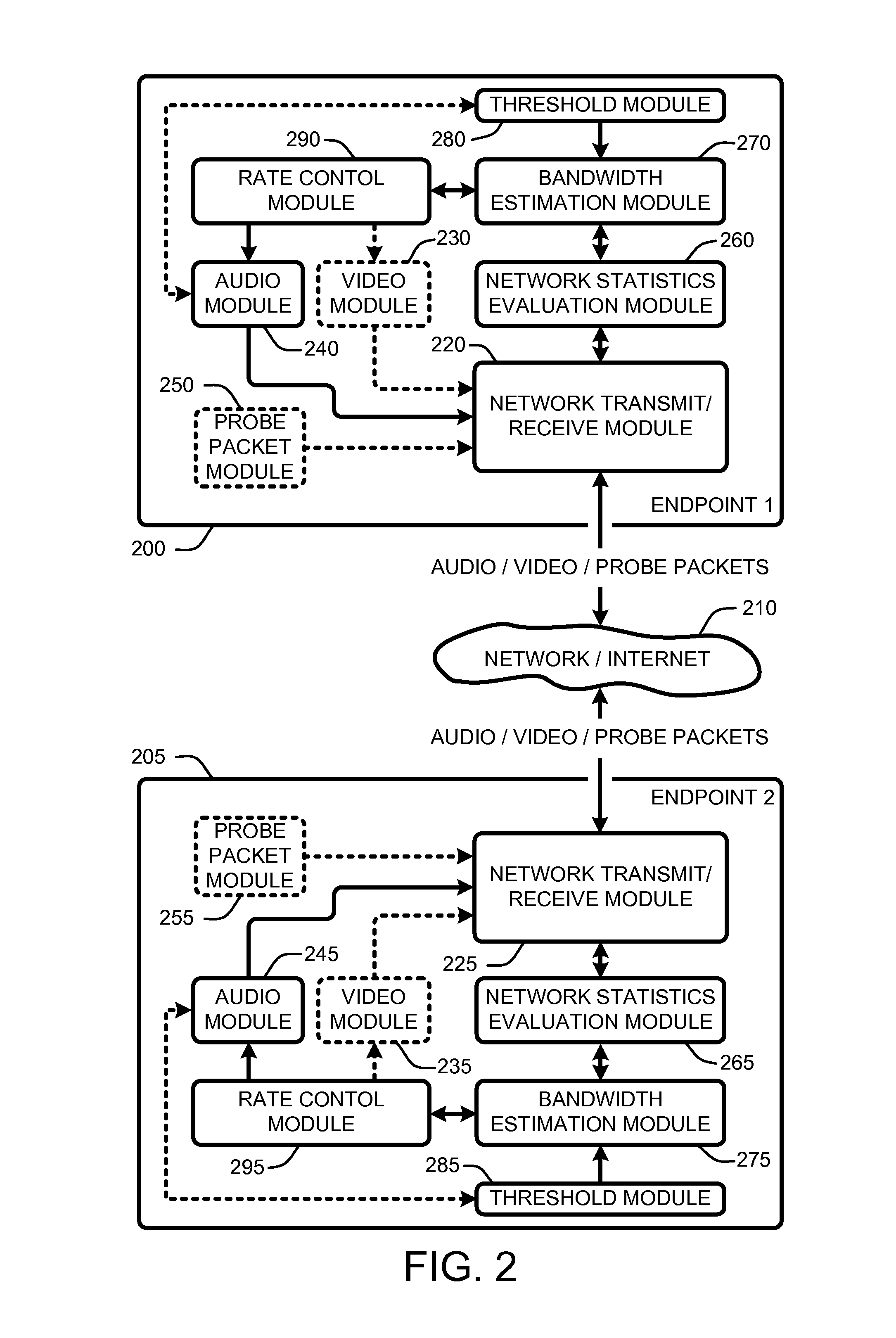
Application aware rate control
InactiveUS20090164657A1Maximize qualityMaximizing conferencing qualityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPacket lossThe Internet
A “communications rate controller” provides various techniques for maximizing a quality of real-time communications (RTC) (including audio and / or video broadcasts and conferencing) over multi-hop networks such as, for example, the Internet. Endpoints in such networks generally communicate via a segmented path that extends through one or more routers between each endpoint. Maximization of conferencing quality is generally accomplished by providing in-session bandwidth estimation across segments of the network path between endpoints (i.e., communication / conference participants) in combination with a robust non-oscillating dynamic rate control strategy for maximizing usage of available bandwidth between RTC endpoints. Further, the dynamic rate control techniques provided by the communications rate controller are designed to prevent degradation in end-to-end delay, jitter, and packet loss characteristics of the RTC.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Medium streaming distribution system
ActiveUS20050180415A1Improve communication qualityReduce impactError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket lossDistribution system
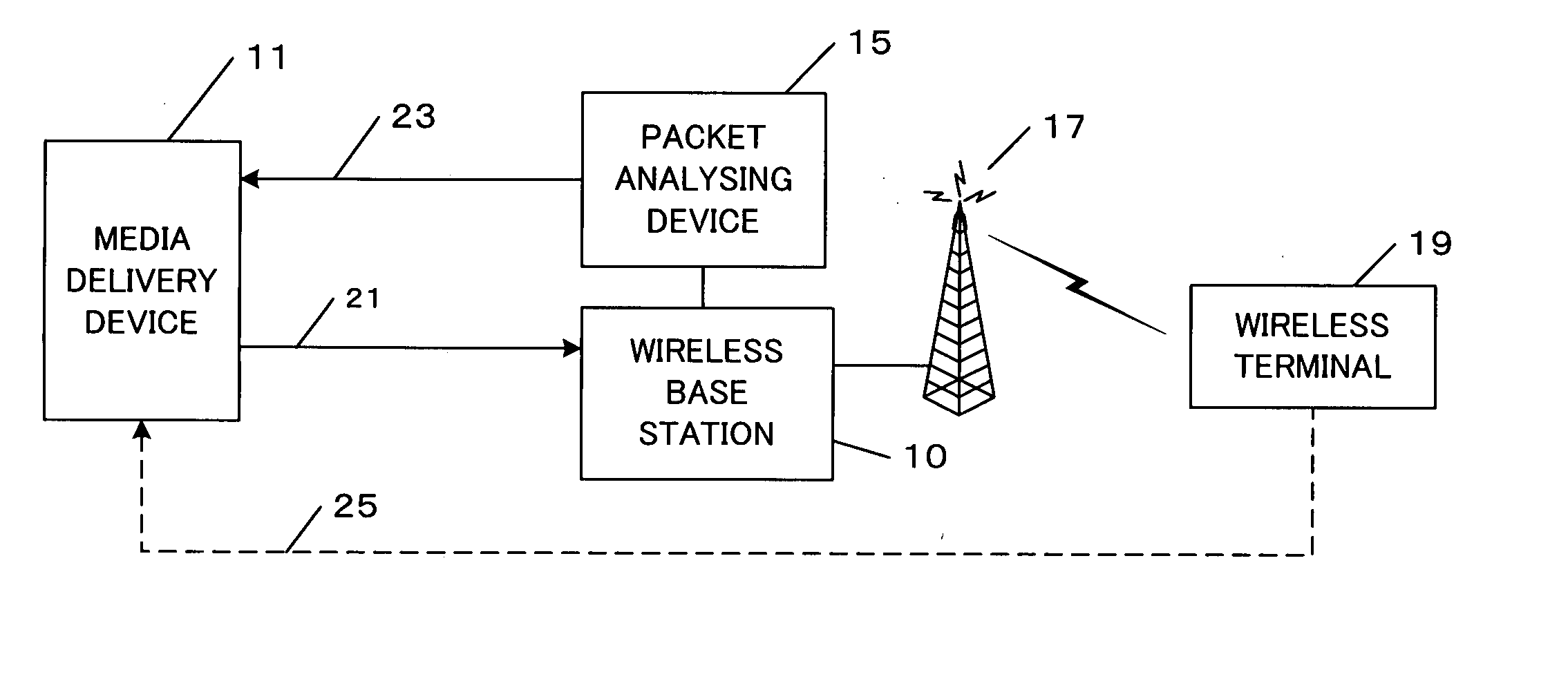
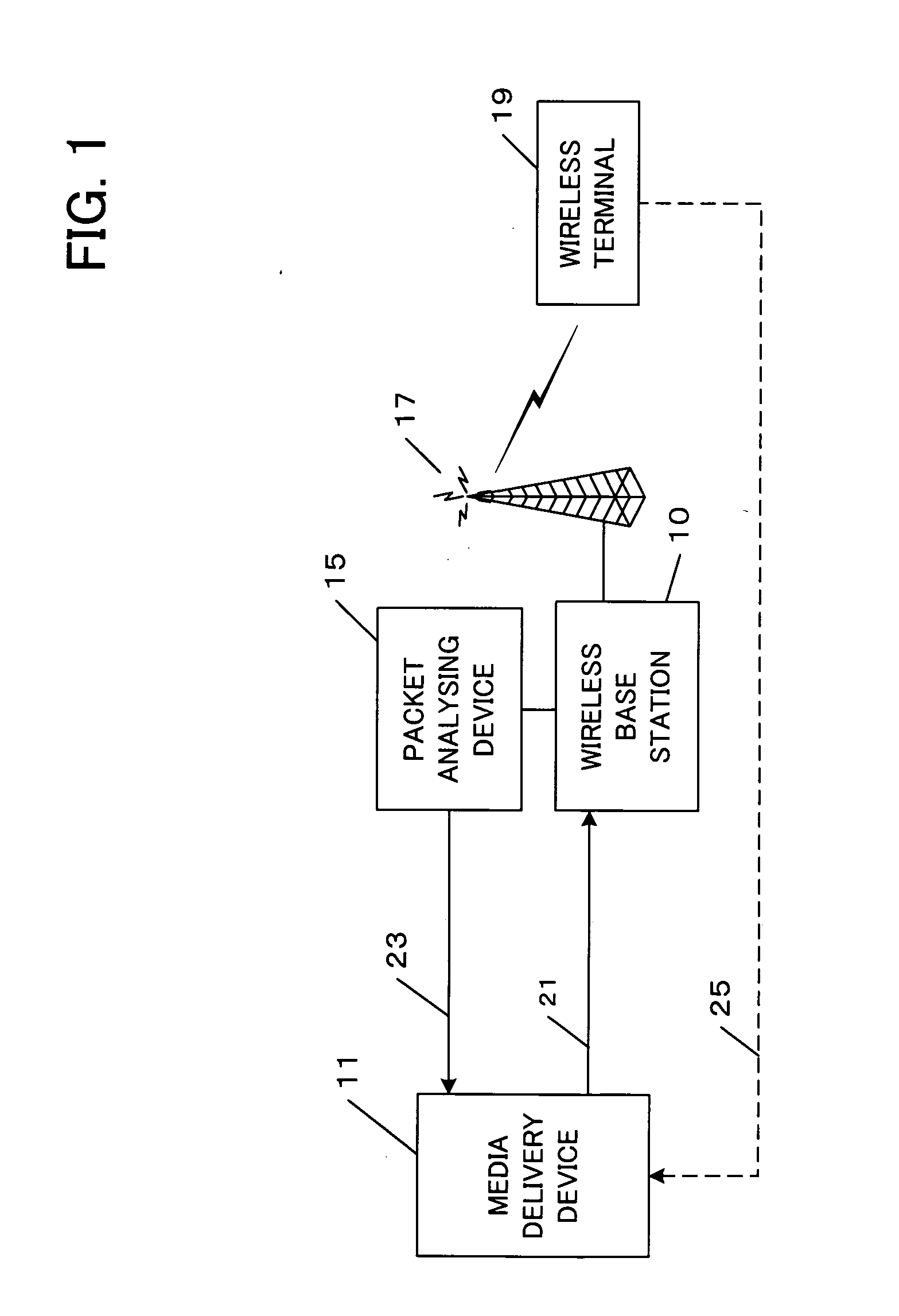
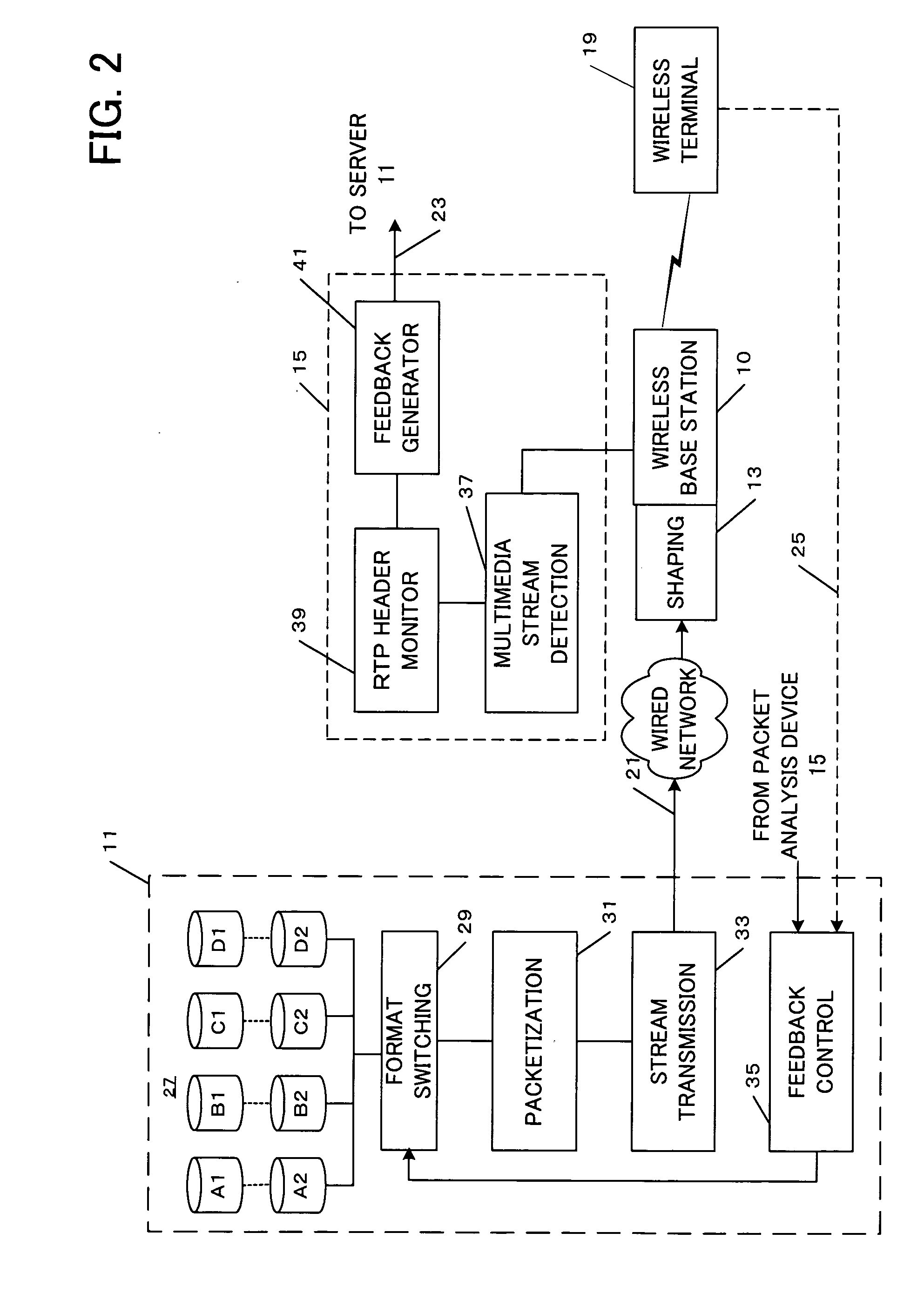
A medium streaming distribution system reduces effects of packet loss in a network before the packet reaches radio base station. A medium distribution device for packet-transmits via the base station, a medium stream to the network by a real time transmission protocol. A packet analyzer monitors the packet arriving at the radio base station and transmits feedback Information associated with loss of a packet to the medium distribution device. Based on the feedback from a relay device and a terminal device of the medium stream, the transmission rates from the medium distribution device to the relay device and from the relay device to the terminal device are obtained to provide a greater transmission rate in a surplus band for re-transmission or a forward error correction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Enhancement of explicit congestion notification (ECN) for wireless network applications
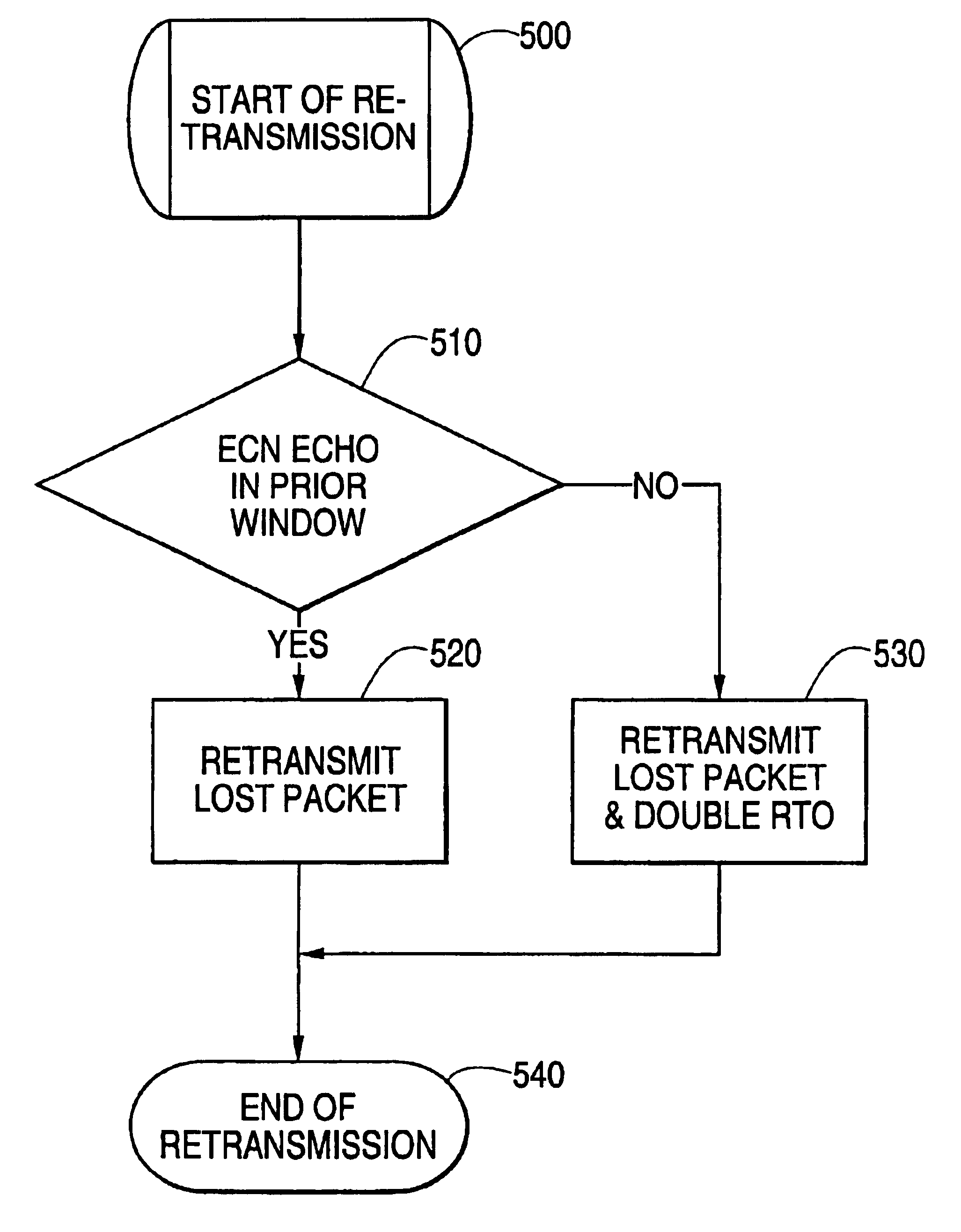
An Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) method is disclosed for wireless applications to avoid network congestion in a TCP / IP packet-switched network. Such method comprises transmitting, at a source node, data packets to a destination node, via at least an intermediate node; determining, at the intermediate node, if an incipient congestion is encountered, setting a Congestion Experienced (CE) flag in each data packet to notify congestion; sending, at the destination node, an ECN-Echo acknowledgment packet back to the source node to inform congestion; reducing, at the source node, a congestion window and a transmission rate to avoid congestion; if the packet loss is due to congestion, re-transmitting, at the source node, only a lost packet to the destination node; alternatively, if the packet loss is due to transmission error, re-transmitting, the lost packet to the destination node, while increasing a round-trip timeout but maintaining the same congestion window.
Owner:VRINGO INFRASTRUCTURE +2
Detecting network denial of service attacks
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Redundant packets for streaming video protection
InactiveUS20050013249A1Reduce complexitySimple methodError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsPacket lossLive feedback
A method transmits a video over a network as a bit stream of packets. Real-time feedback information on conditions of the network is received while transmitting the packets. A probability of packet loss is based on the real-time feedback. Then, redundant packets are generated for selected packets of the bit stream if the probability of packet loss is greater than a predetermined threshold.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Dynamic stream interleaving and sub-stream based delivery
ActiveUS20080256418A1Convenient amountLoss of protectionFault responseCode conversionPacket lossCommunications system
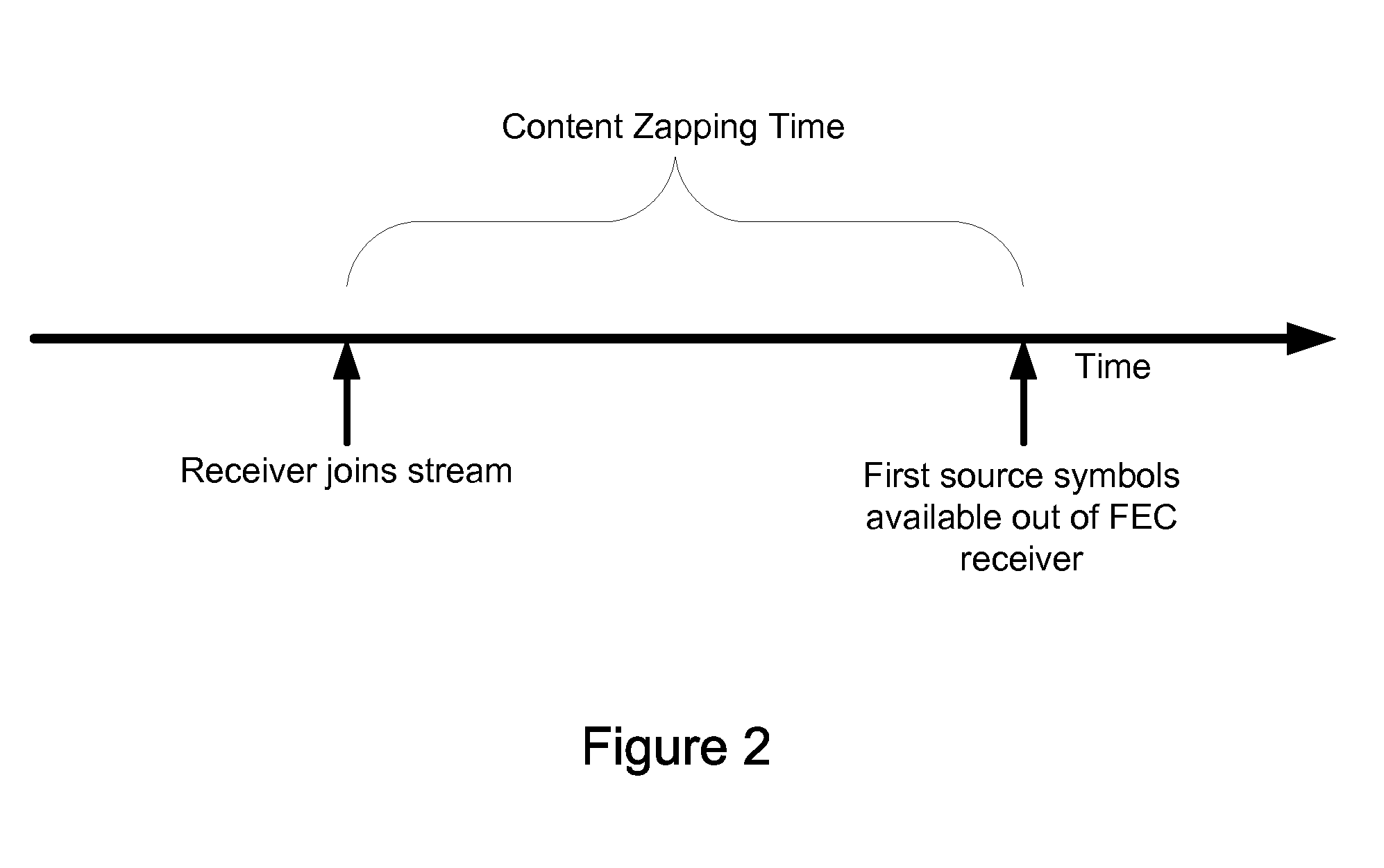
A communications system can provide methods of dynamically interleaving streams, including methods for dynamically introducing greater amounts of interleaving as a stream is transmitted independently of any source block structure to spread out losses or errors in the channel over a much larger period of time within the original stream than if interleaving were not introduced, provide superior protection against packet loss or packet corruption when used with FEC coding, provide superior protection against network jitter, and allow content zapping time and the content transition time to be reduced to a minimum and minimal content transition times. Streams may be partitioned into sub-streams, delivering the sub-streams to receivers along different paths through a network and receiving concurrently different sub-streams at a receiver sent from potentially different servers. When used in conjunction with FEC encoding, the methods include delivering portions of an encoding of each source block from potentially different servers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Self-adapting transmission method and system in ascending honeycomb video communication
InactiveCN101222296AImprove playback qualityReduce packet loss eventsError preventionData streamPacket loss
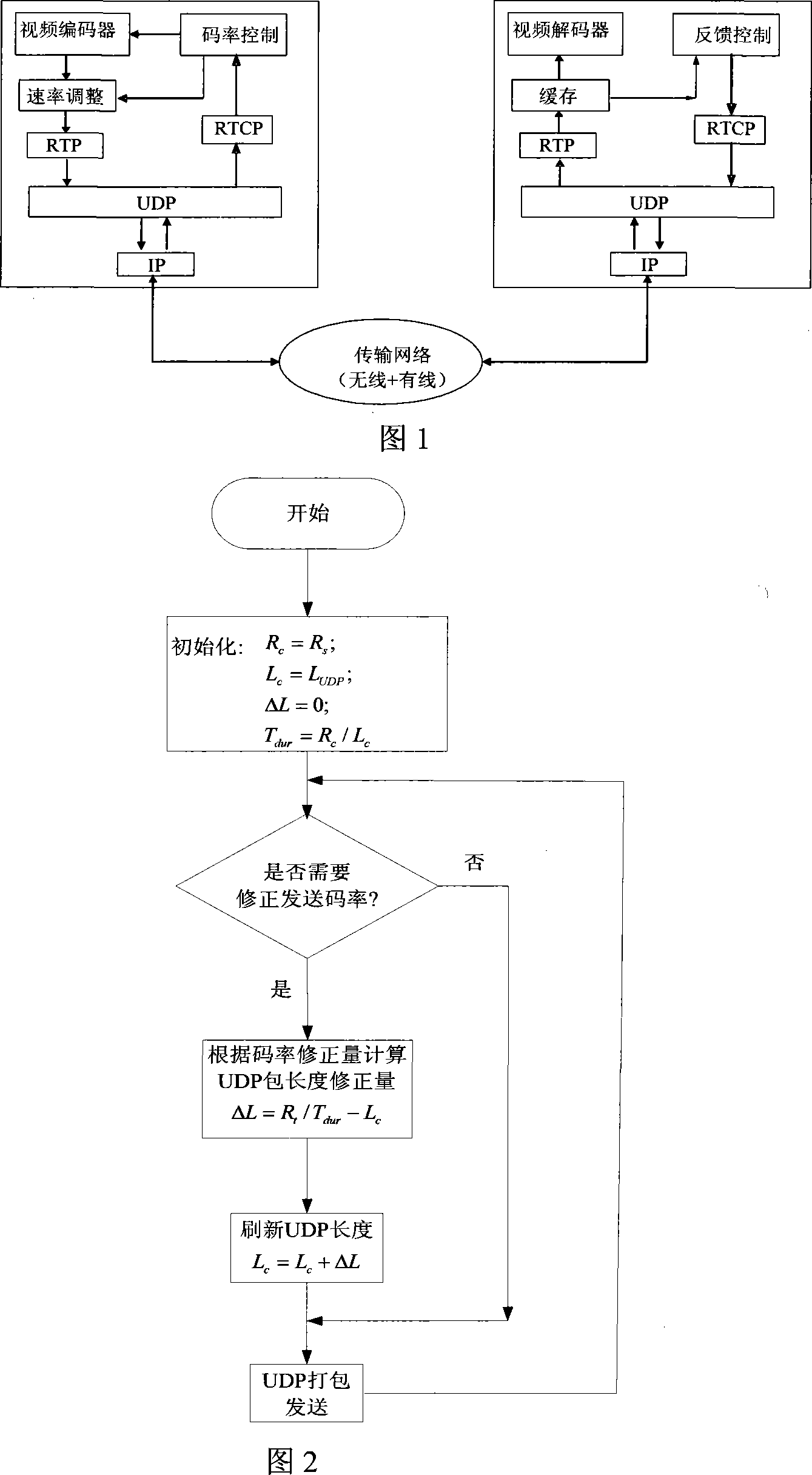
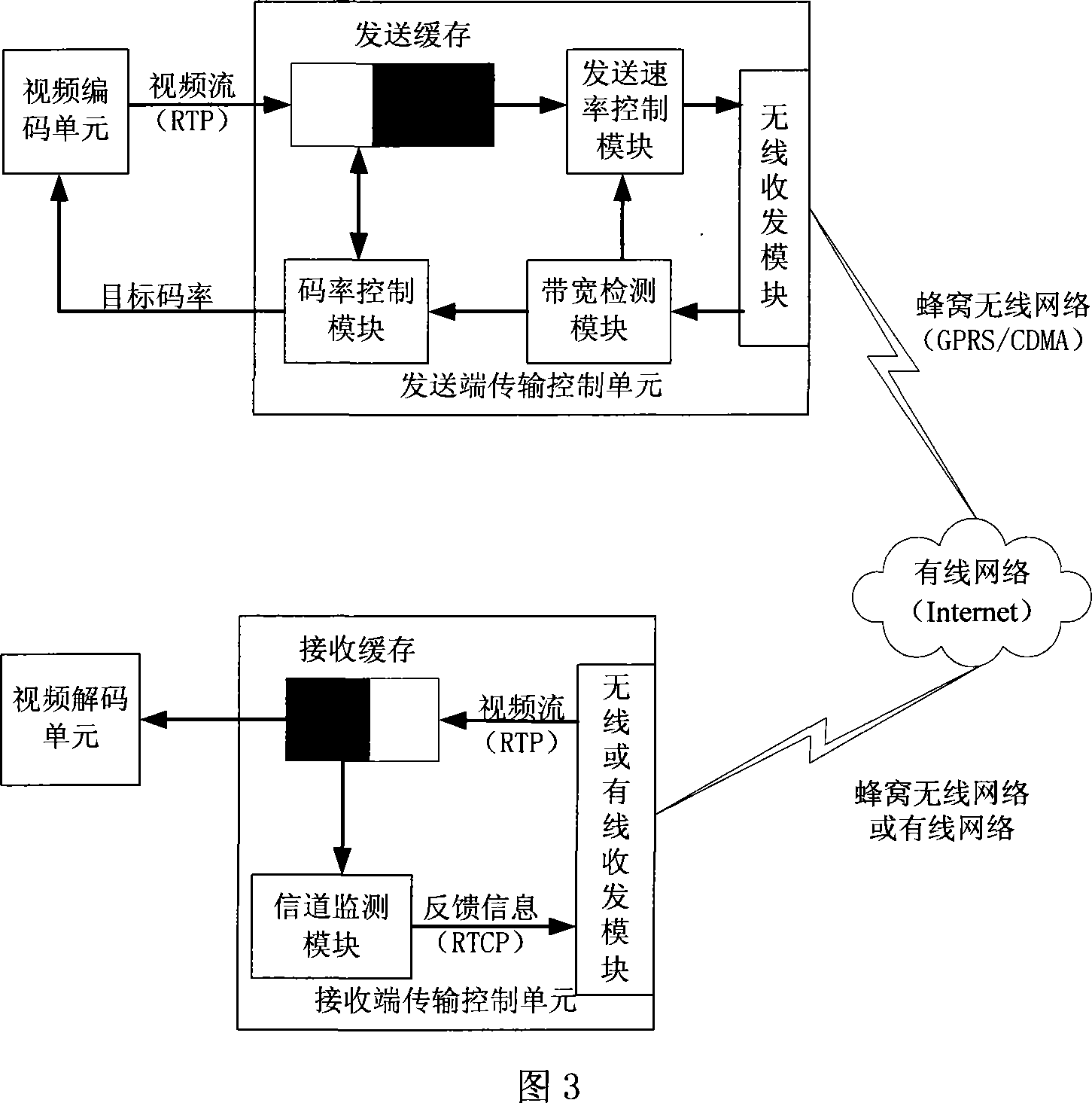
The invention discloses a self-adaptive transmission method and a self-adaptive transmission system in the uplink cellular video communication of the wireless multimedia communication technical field. The method is that: a feedback-based channel effectively transmits bandwidth perceiving; the sending speed of a data flow is adjusted according to the perceived effective transmission bandwidth, the adjustment of the sending rate is realized by changing the packet length of the data flow; two-stage information resource rate control based on cache cleaning and rate control of an encoder is used. The device comprises a sending end, a transmission network and a receiving end, wherein the sending end comprises a video encoding unit and a transmission control unit, the receiving end comprises a transmission control unit and a video decoding unit, the sending end and the receiving end transmit messages through the transmission network. The sending rate of the invention can automatically adapt to the change of the channel bandwidth, decreases the probability of packet loss caused by the fluctuation of the wireless channel bandwidth, and realizes that the customer side can obtain the best possible playing quality under the condition of constant change of network operation conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
QoS-awar handover procedure for IP-based mobile ad-hoc network environments
InactiveUS20040228304A1Packet loss can be avoidedReduce the impactSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTraffic capacityData stream
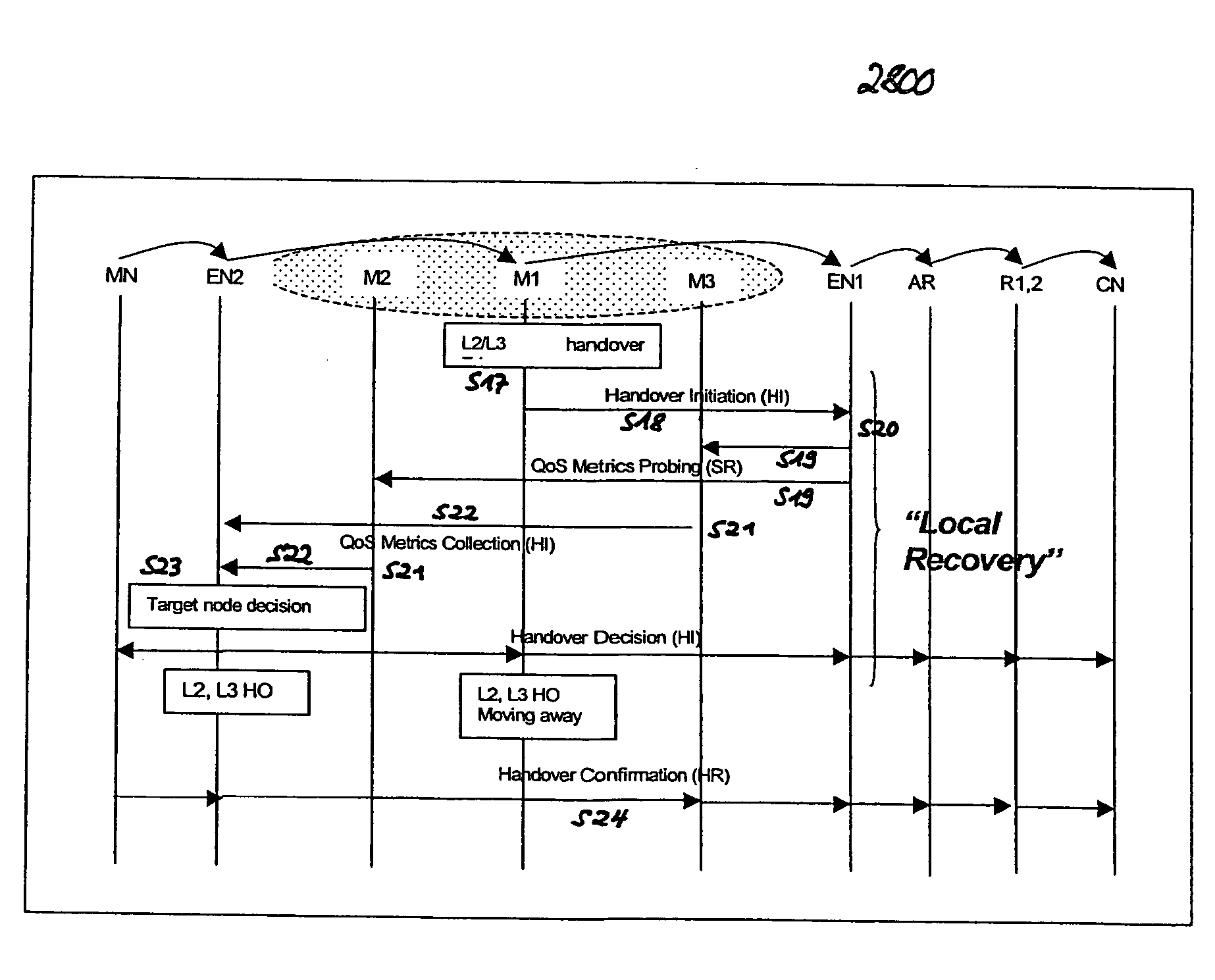
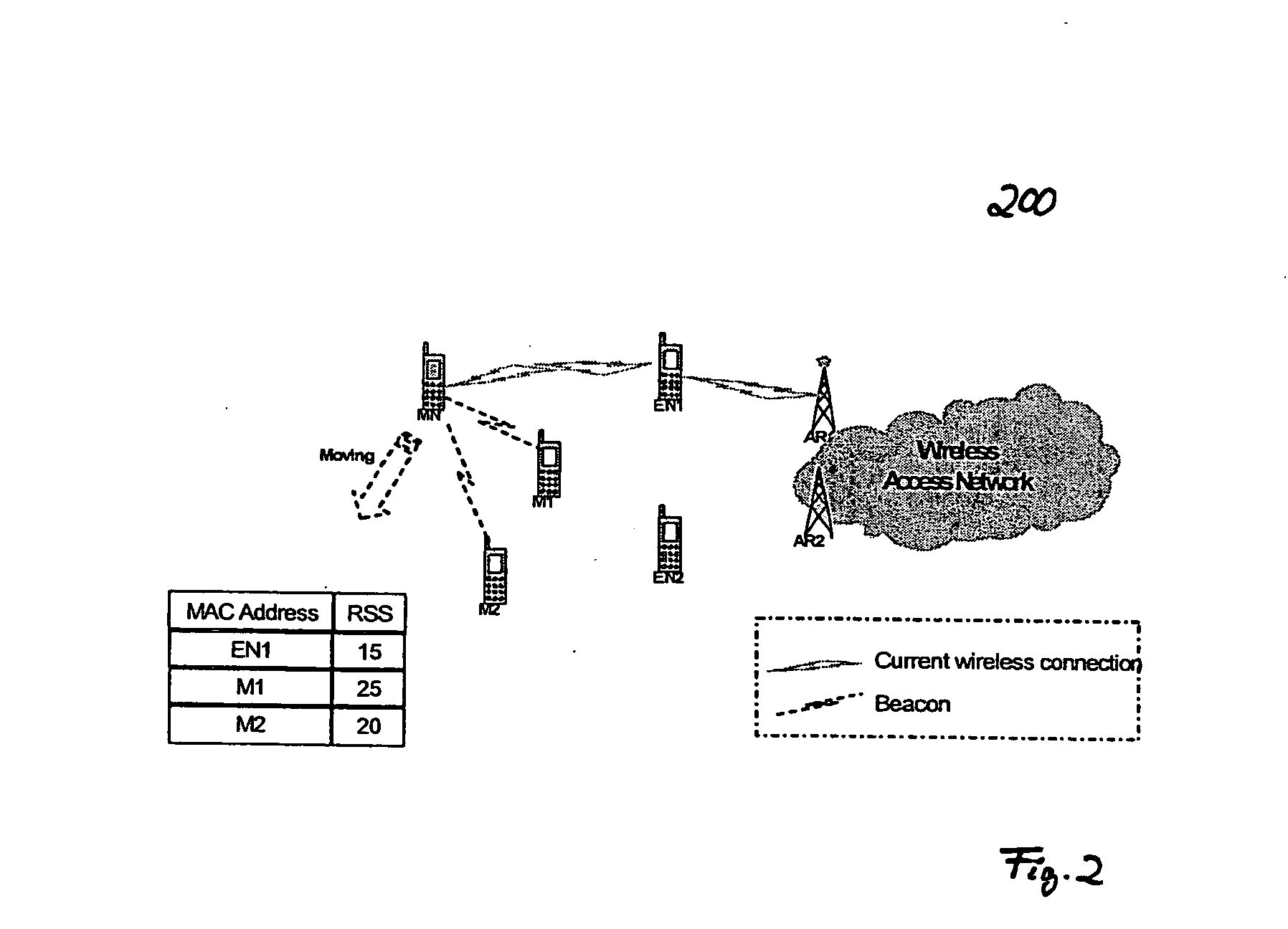
The invention targets at a QoS-aware handover procedure in a typical dynamic mobile ad-hoc scenario (cf. FIGS. 23 to 27) wherein the connectivity of fixed (AR1, AR2, CN) and / or mobile nodes (MN, M1, M2, M3, M4, EN1, EN2) is unpredictably time-varying and, due to the mobility of mobile nodes, handovers will inevitably frequently occur. Thereby, resources are pre-allocated along potential routing paths in advance, and the flow traffic is redirected to the path having the best available QoS capabilities. According to the new QoS situation of the selected path, adaptive real-time applications can have the opportunity to individually adjust traffic generation. With this concept, packet loss can be avoided and degradation effects on the running real-time application during the QoS-aware handover can be minimized. The QoS-aware handover procedure comprises the steps of handover candidates selection, handover initiation, QoS metrics probing and resource pre-allocation (soft reservation), QoS metrics collection, handover decision, handover confirmation (hard reservation), and reservation release. In particular, the proposed solution thereby pertains to a method for proactively probing the QoS situation of each potential routing path, pre-allocating resources along the best available QoS path before the handover of the QoS data flow to be transmitted to a new access point (AP) is initiated, providing efficient resource reservation management and maintenance within the underlying mobile ad-hoc networks and incorporating advanced QoS support features offered by adaptive real-time applications. The invention further proposes an "information dissemination" approach, which optimizes prior-art address resolution mechanisms.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Method and system for identifying reasons of ZigBee sensor network packet loss
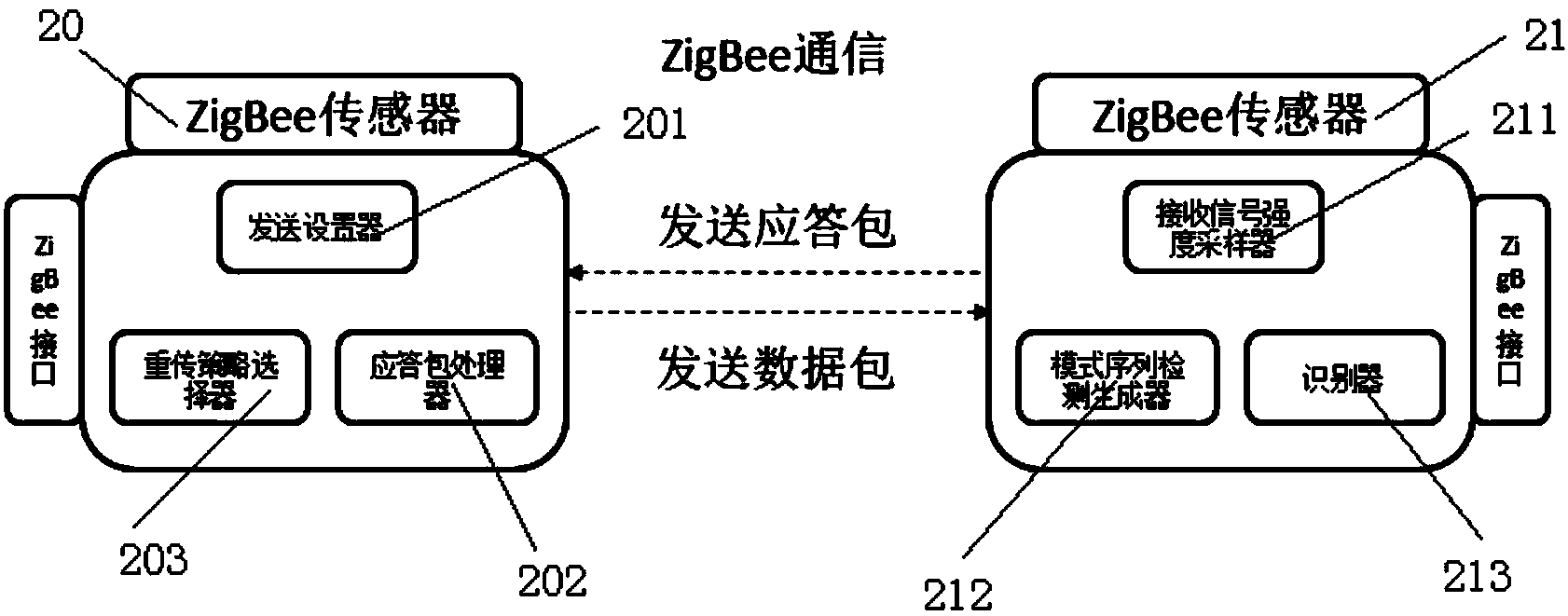
ActiveCN103716137AImprove throughputReduce the number of retransmissionsEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelPacket lossZigbee sensor network
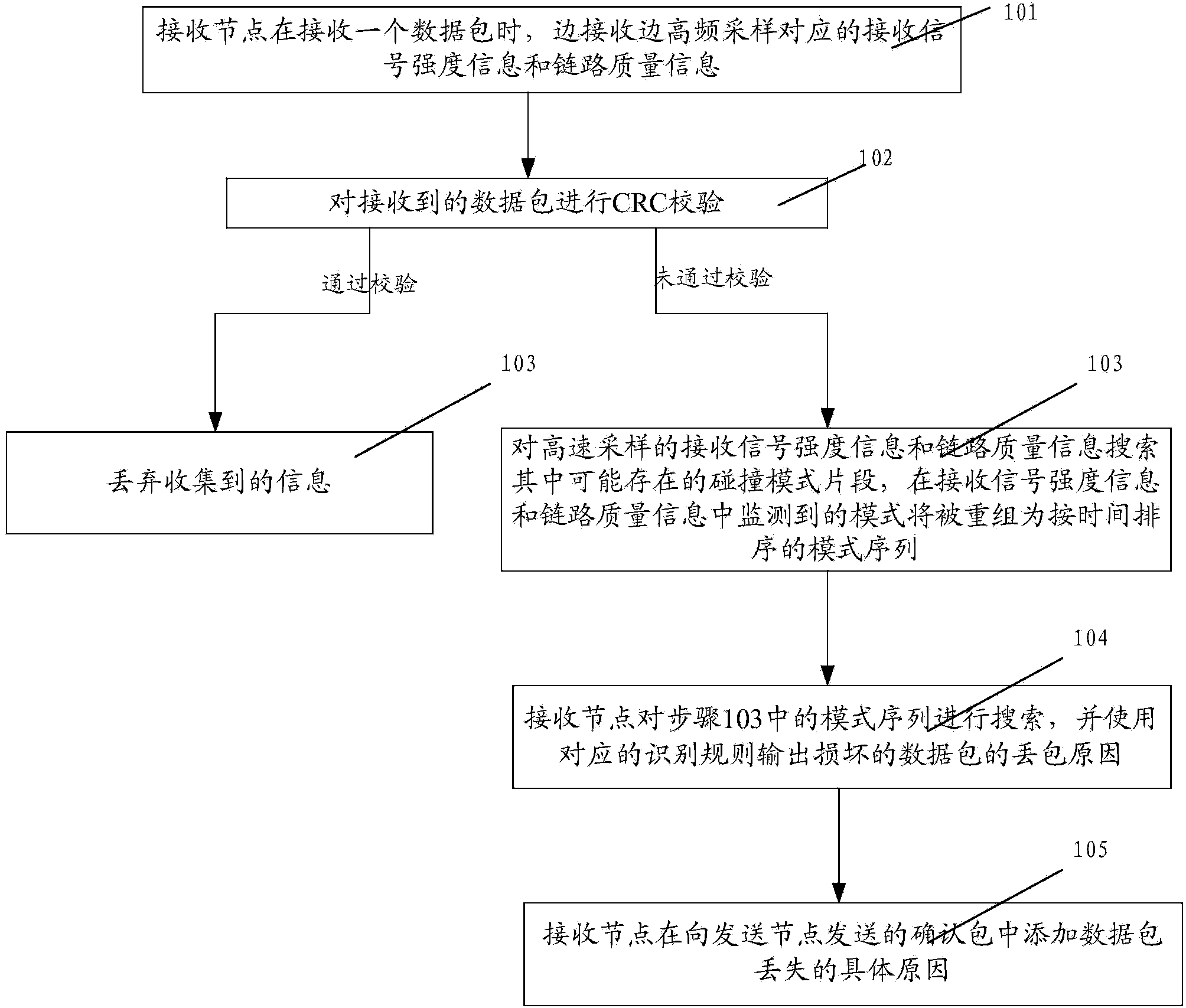
The invention discloses a method and system for identifying reasons of ZigBee sensor network packet loss. The method includes the steps that a receiving node carries out high-frequency sampling on corresponding receiving signal strength information and link quality information while receiving a data package; if the received data package fails to pass the cyclic redundancy check, collision mode fragments possibly existing in the high-frequency sampled receiving signal strength information and the high-frequency sampled link quality information are searched, and the modes monitored in the receiving signal strength information and the link quality information will be regrouped into a time-ordered mode sequence; the receiving node searches for the generated mode sequence and outputs the packet loss reasons of the damaged data package by using corresponding identifying rules; the receiving node adds the specific reasons of data package loss in an acknowledgment packet sent to a sending node. Through the method, network throughput can be improved and retransmission frequency can be reduced, so the purposes of saving energy and prolonging working time can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
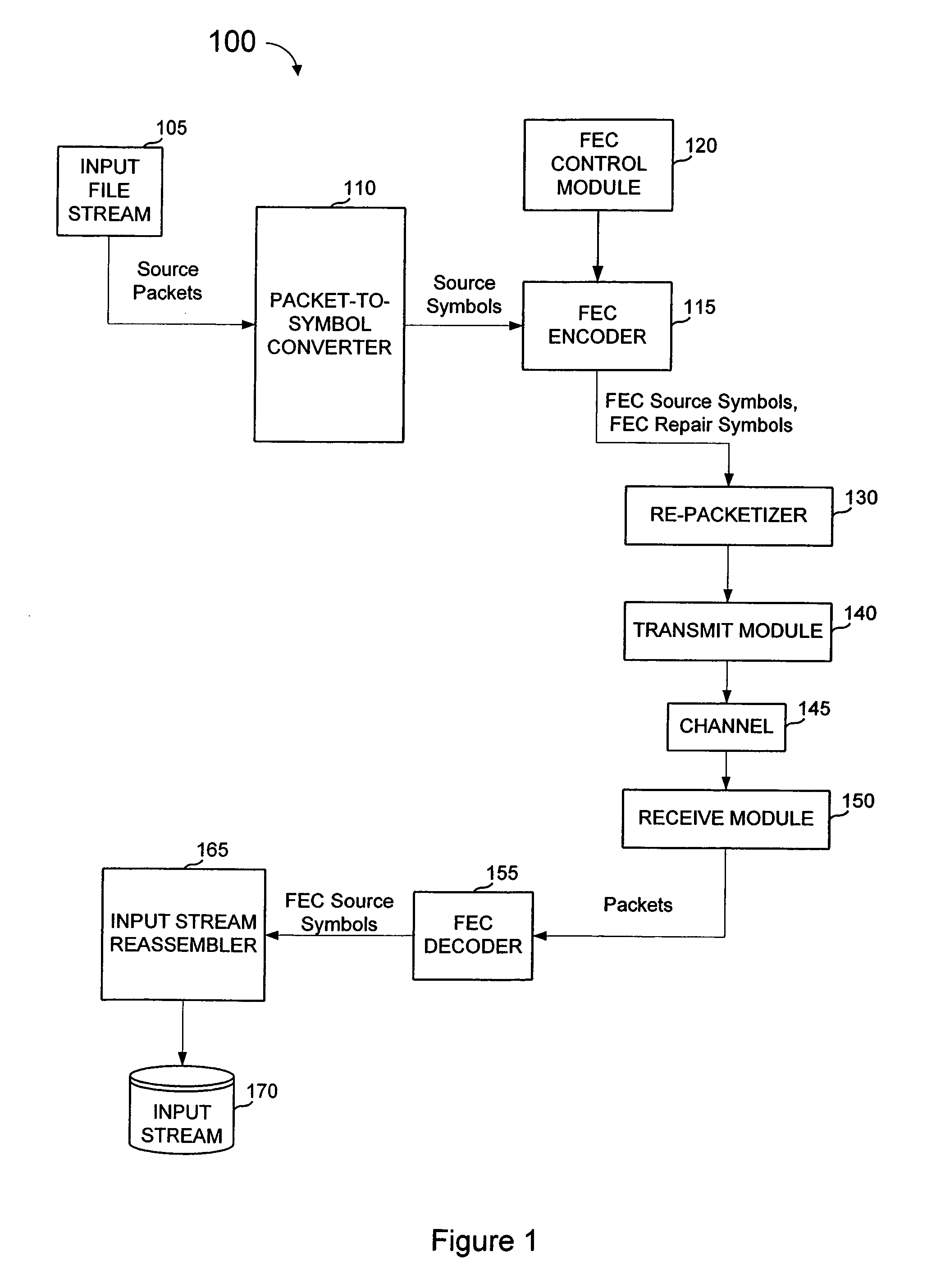
FEC architecture for streaming services including symbol-based operations and packet tagging
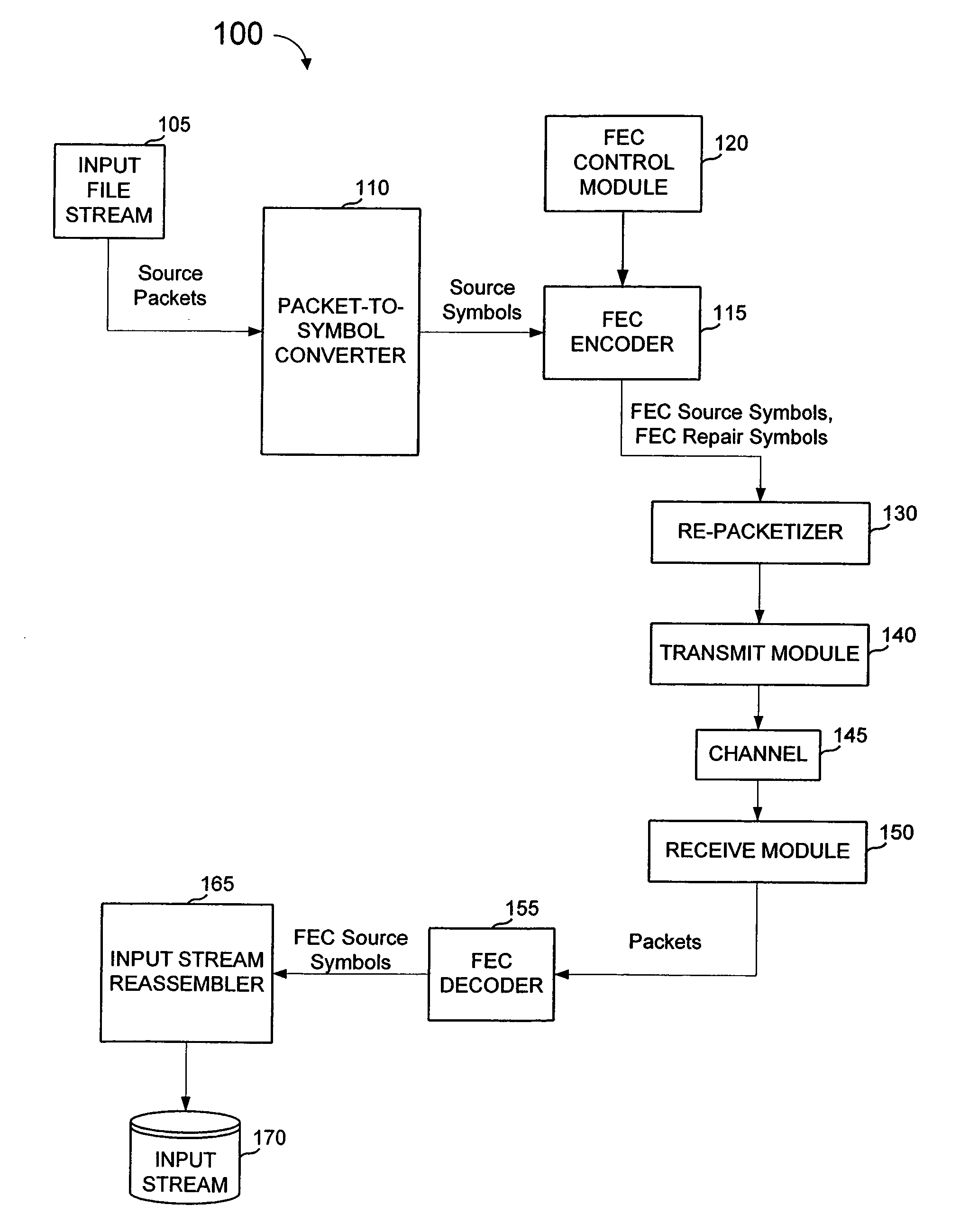
ActiveUS7660245B1Loss of protectionEfficiently recreateTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationStreaming data
In a packet communications system stream data is transported over a channel over which packet loss or corruption is possible, with forward error correction (“FEC”) information. A transmitter receives source packets comprising source data, generates FEC source packets formatted to allow for identification of lost or corrupted source packets at a receiver, arranges source data from the source packets into a plurality of source symbols wherein at least one source packet is arranged into more than one source symbol, associates a plurality of source symbols with a source block, generates a plurality of repair symbols from the source block according to a predetermined FEC encoding process and groups the plurality of repair symbols into one or more FEC repair packets associated with the source block. A receiver can use the FEC repair symbols from the FEC repair packets to recover source symbols, as needed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Hierarchical metering in a virtual router-based network switch
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for monitoring latency, jitter, packet throughput and packet loss ratio between two points on a network
InactiveUS7961637B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCorrect operation testingPacket lossWaiting time
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
Forward error correction system for packet based data and real time media, using cross-wise parity calculation
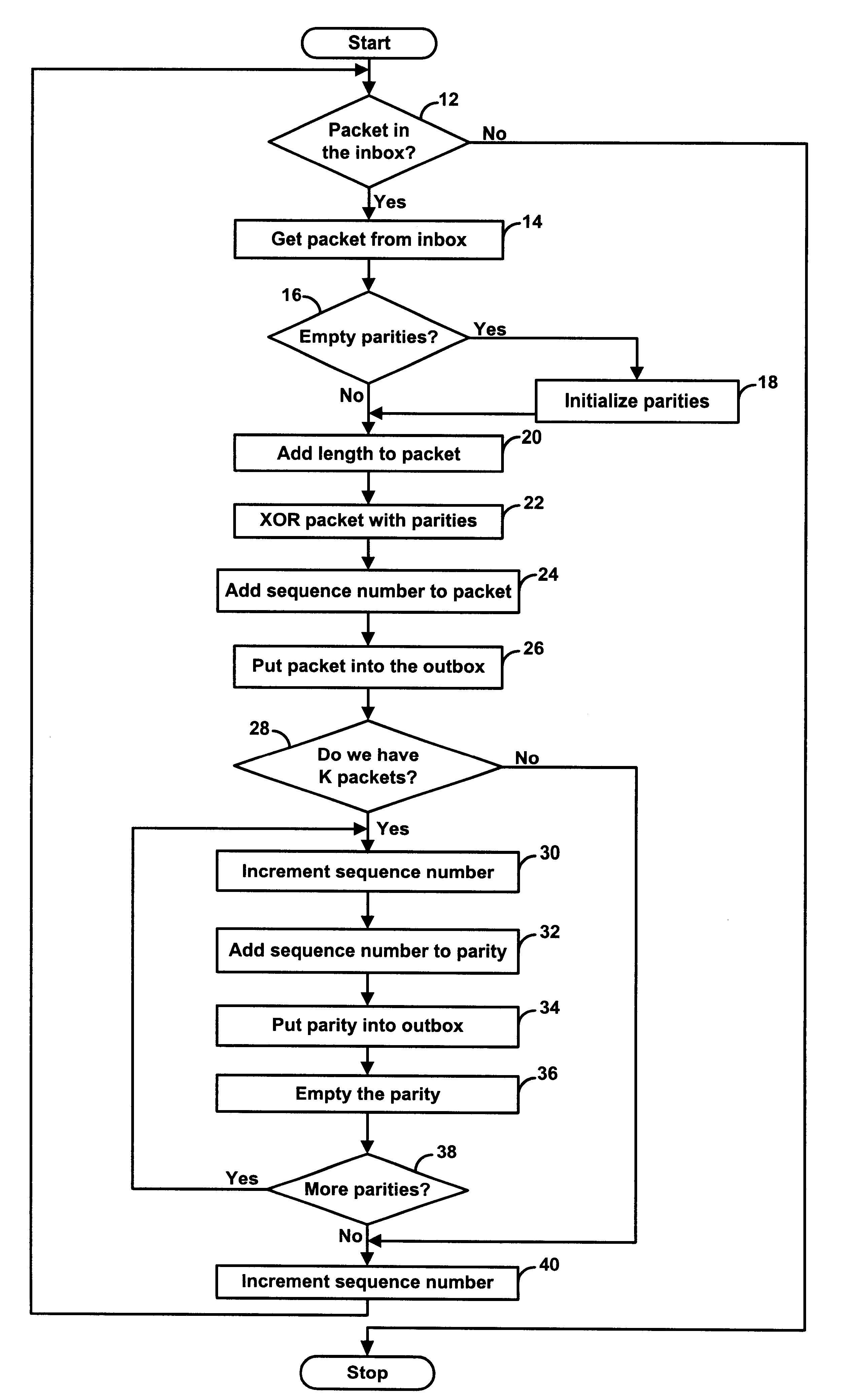
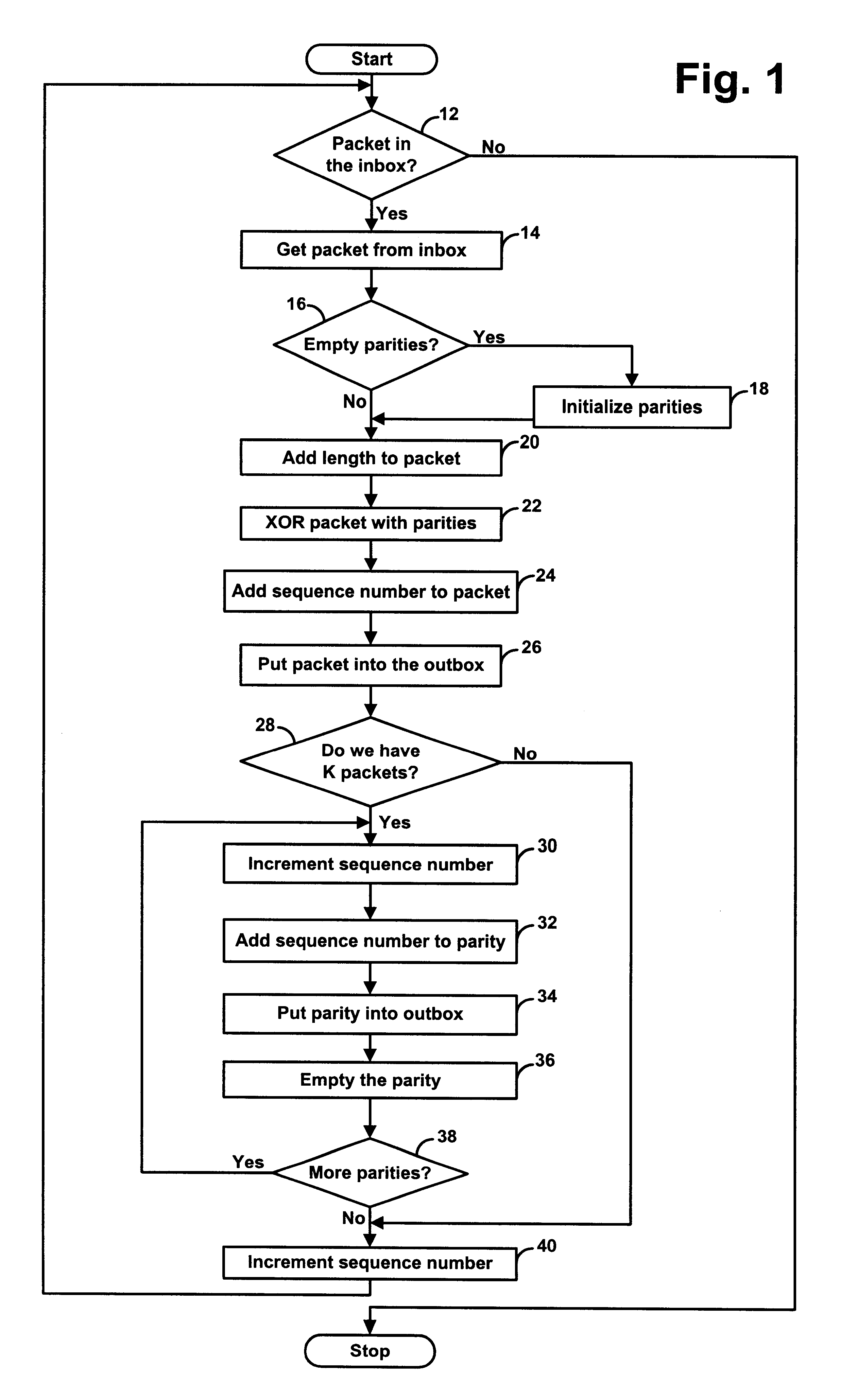
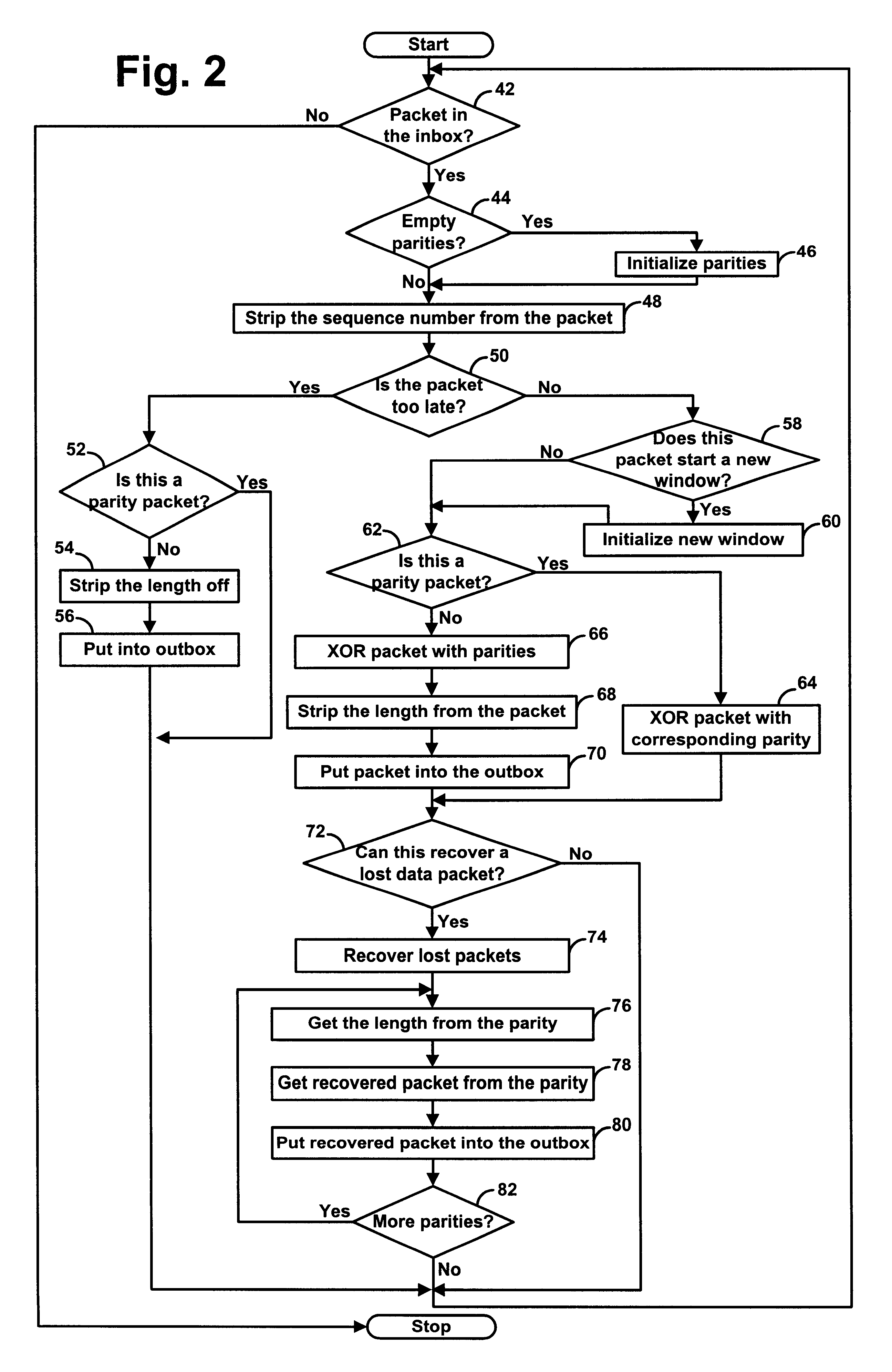
A computationally simple yet powerful forward error correction code scheme for transmission of real-time media signals, such as digitized voice, video or audio, in a packet switched network, such as the Internet. For each window of k data packets, the invention generates and transmits at least one cross-wise parity packet taken as an index-shifted function over the k data packets. The invention thereby enables a receiving end to recover from packet loss.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
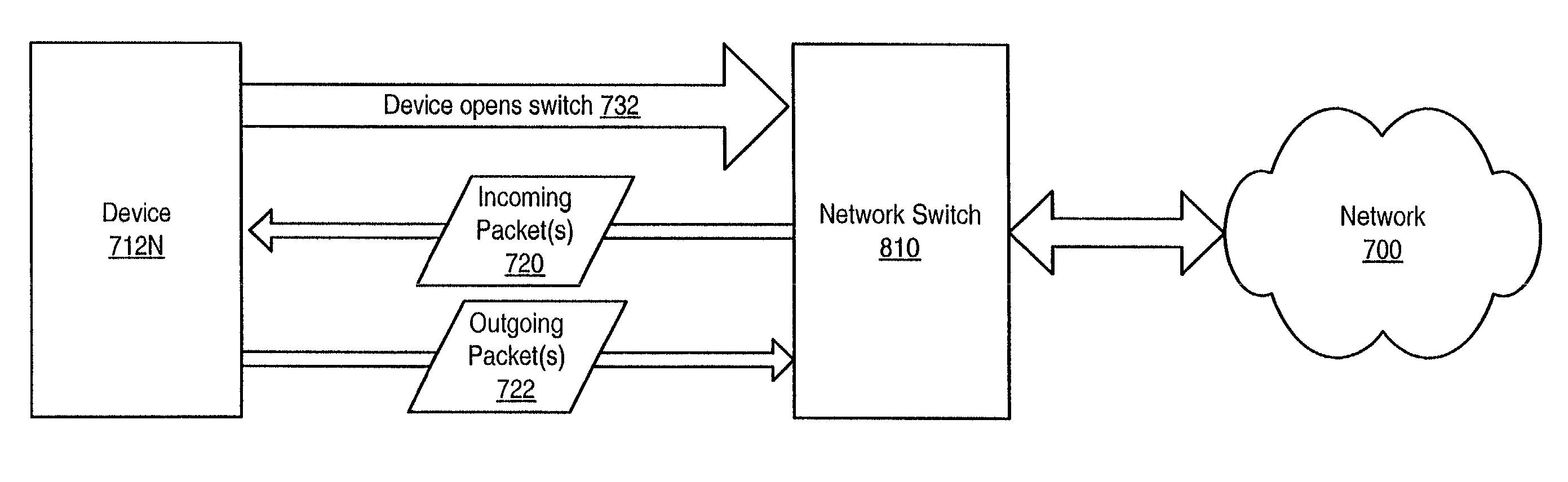
Method and apparatus for scheduling packet flow on a fibre channel arbitrated loop
A system and method for enabling a network switch to transmit queued packets to a device when opened by the device, and thus to utilize the Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL) in full-duplex mode when possible. The switch may include a plurality of queues each associated with a device on the FC-AL for queuing incoming packets for the device. The switch may determine a next non-empty queue, open the device associated with the queue, and send packets to the device. The device may send packets to the switch concurrently with receiving packets from the switch, thus utilizing the FC-AL in full-duplex mode. When a device opens the switch to transmit packets to the switch, the switch may determine if there are packets for the device in the queue and, if so, send packets to the device concurrently with receiving packets from the device, thus utilizing the FC-AL in full-duplex mode.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
Graphical user interface for an enterprise intrusion detection system
ActiveUS7293238B1Improve efficiencyReliable detectionDigital computer detailsHardware monitoringGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method for interfacing with a user of an enterprise intrusion detection system, the method comprises receiving at least one packet flow, each packet flow originating from a unique node in the intrusion detection system and comprising descriptive information and a plurality of packet headers. The descriptive information of a first subset of the received packet flows is communicated to a user based at least in part on a filtering ruleset. A second subset of the received packet flows is concealed from the user based at least in part on the filtering ruleset. In response to receiving a command from the user, the plurality of packet headers for at least one packet flow in the first subset is communicated to the user.
Owner:FORCEPOINT FEDERAL
Link status monitoring based on packet loss detection
In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, special metadata is added to link monitoring protocol messages exchanged by pairs of adjacent nodes to allow such nodes to detect communication link failures and determine whether the failure affects an incoming communication link or an outgoing communication link. The link monitoring protocol messages may be augmented BFD messages.
Owner:128 TECH
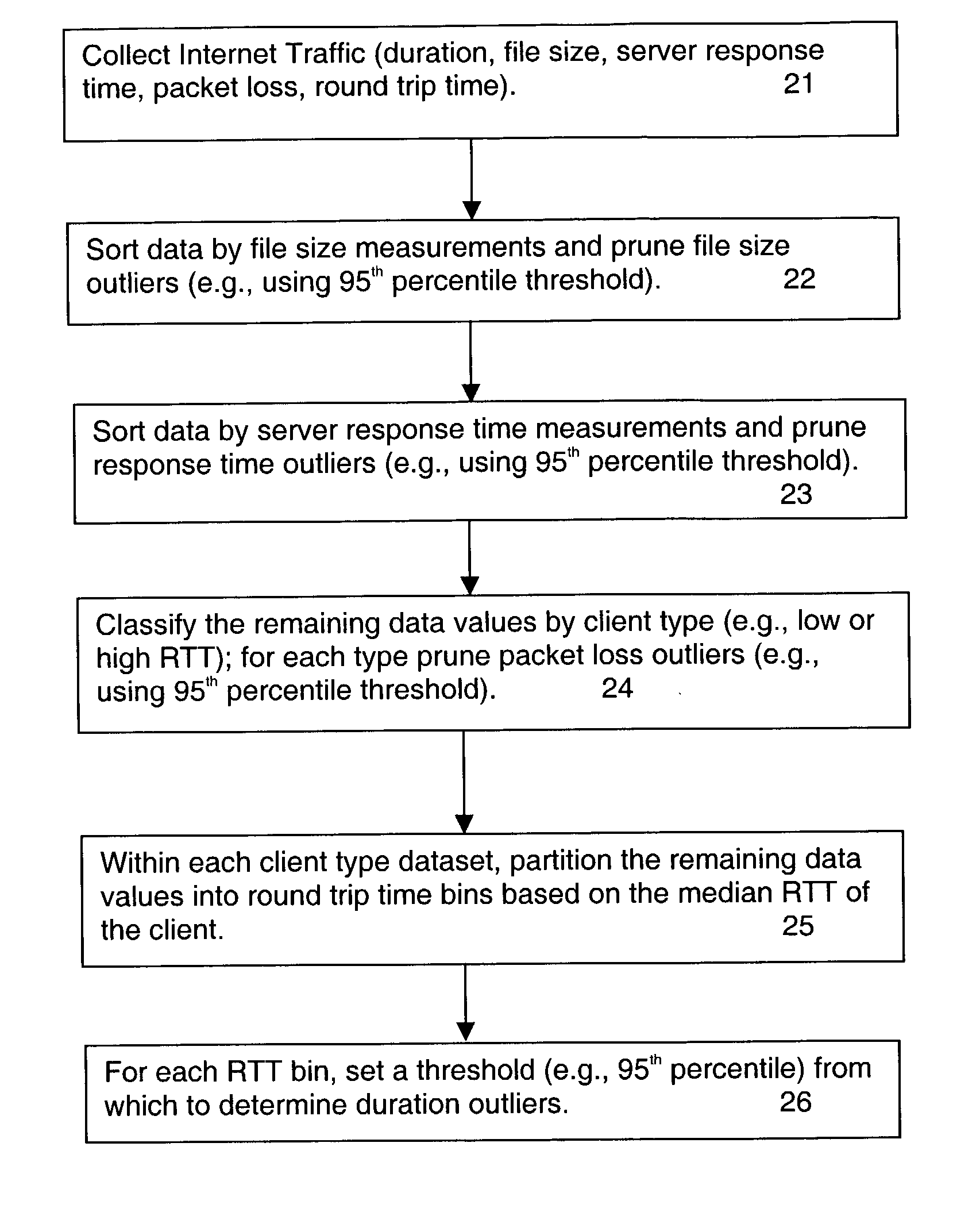
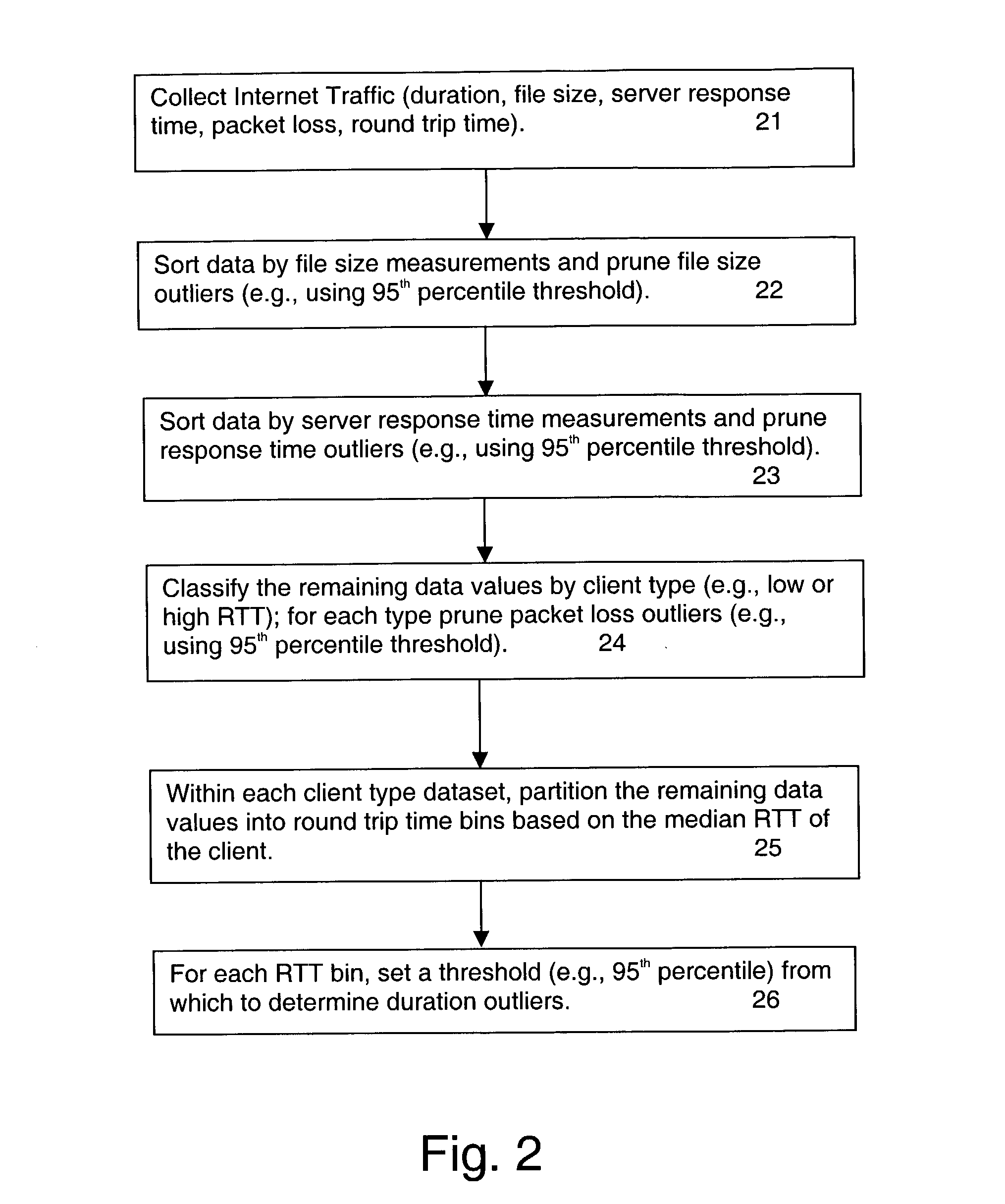
Method for detecting congestion in internet traffic
A baseline for internet traffic duration is established by (i) collecting internet traffic data regarding file size, server response time, packet loss and round trip time, (ii) removing from this data outliers associated with file size, server response time and packet loss per client type, and (iii) organizing any remaining data into round trip time bins according to median values of round trip time per client type. Thereafter, historical or newly collected Internet traffic data is compared against threshold values for each round trip time bin to locate duration outliers. These duration outliers are indicators of congestion and congestion episodes may be identified by the continued presence of such outliers over successive time intervals.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
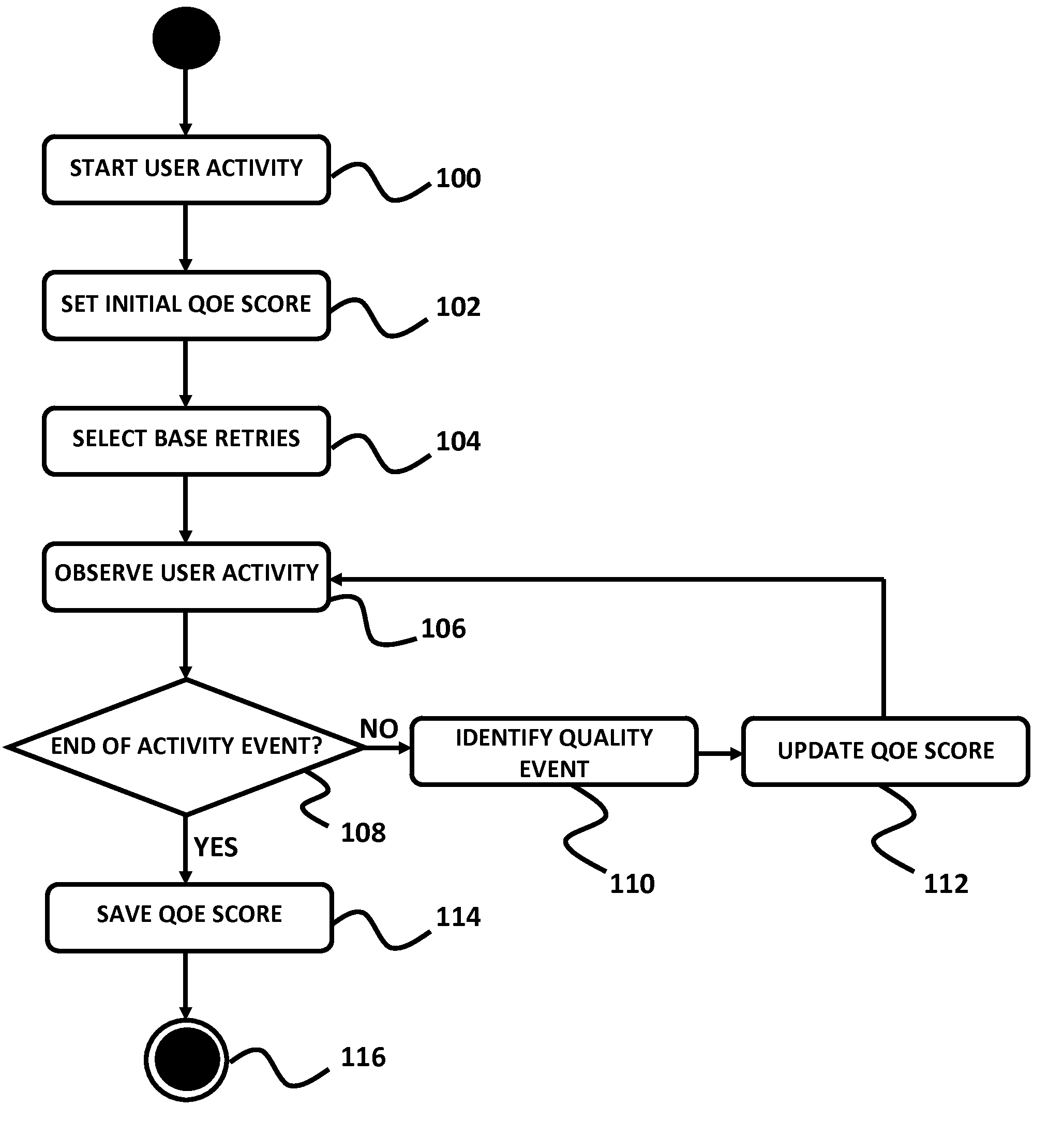
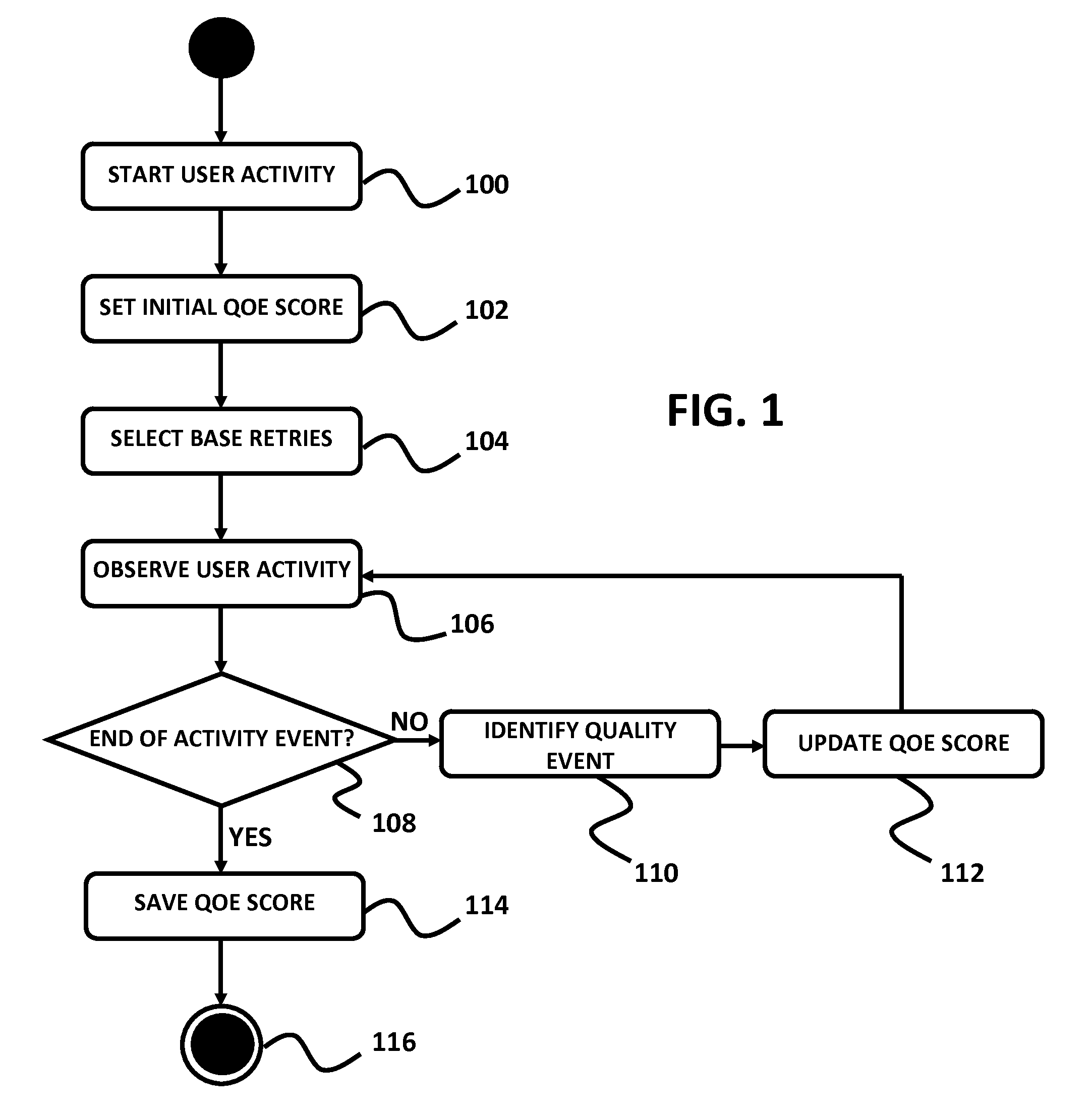
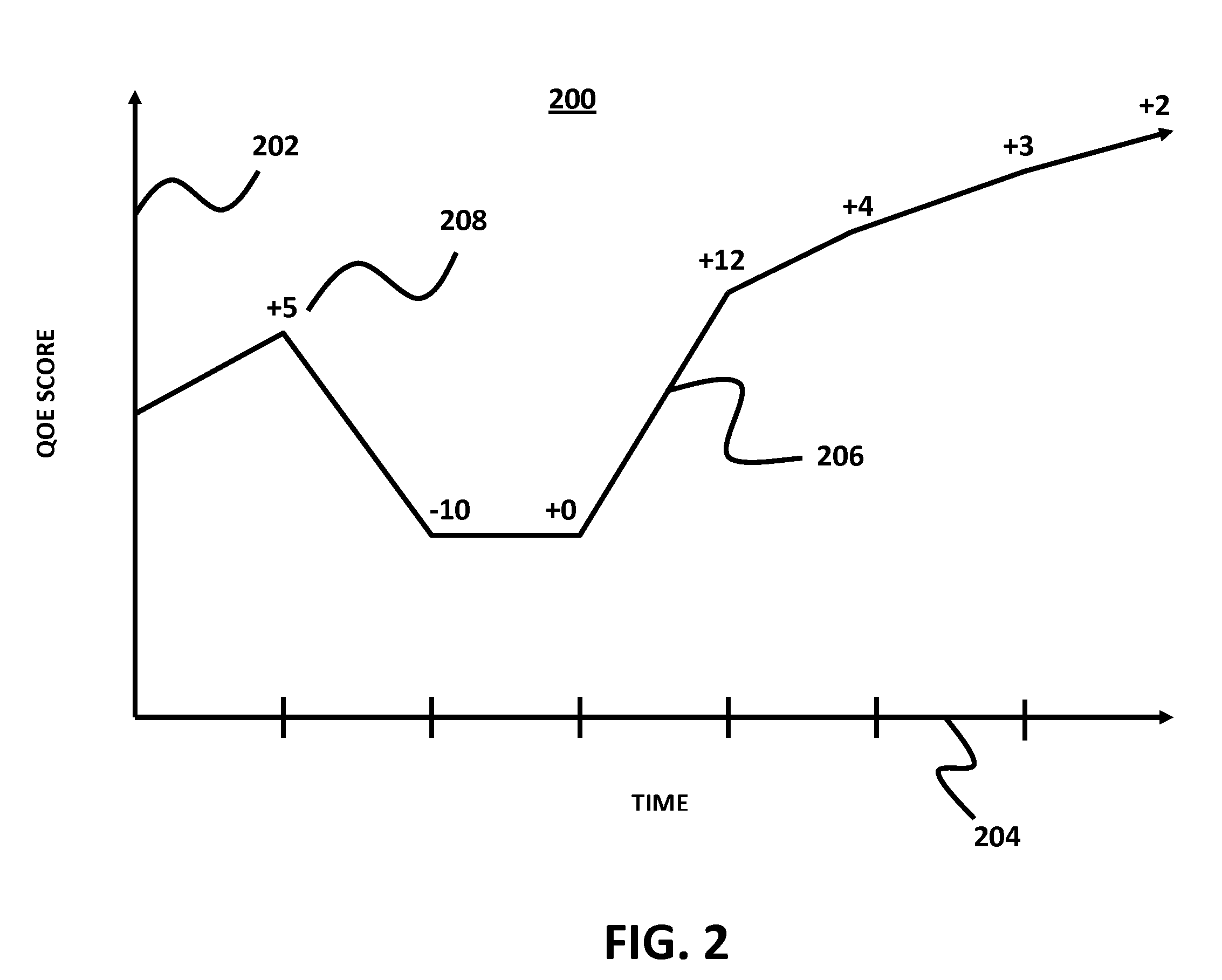
Method For Determining A Quality Of User Experience While Performing Activities in IP Networks
ActiveUS20100269044A1Telephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsPacket lossQuality of experience
An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for establishing Quality of Experience (QoE) measurements and metrics for different types of actual user activities over IP networks. These activities include, but are not limited to web browsing, sending and receiving email, file downloading and uploading, peer to peer (P2P) networking, VoIP, online gaming, and media streaming. The measurement of the QoE metrics is based on both objective and subjective metrics, including network characteristics, such as packet loss and latency, along with empirical observations of the user activities.
Owner:EMPIRIX
Efficient one-to-many content distribution in a peer-to-peer computer network
InactiveUS7593333B2Large throughputEfficiently contentSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelContent distributionPacket loss
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com