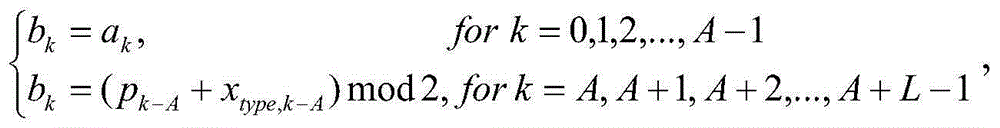Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "NodeB" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
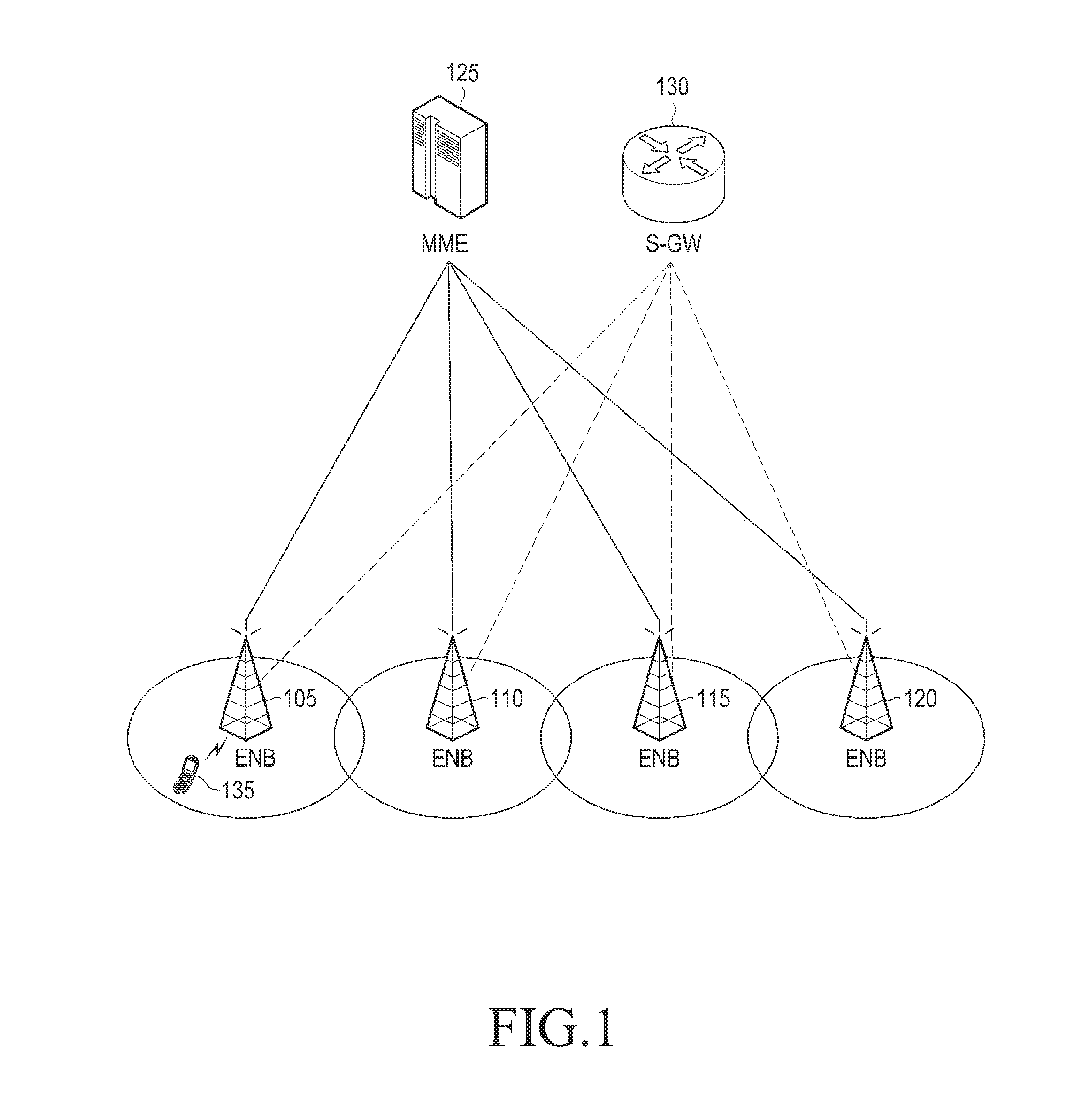
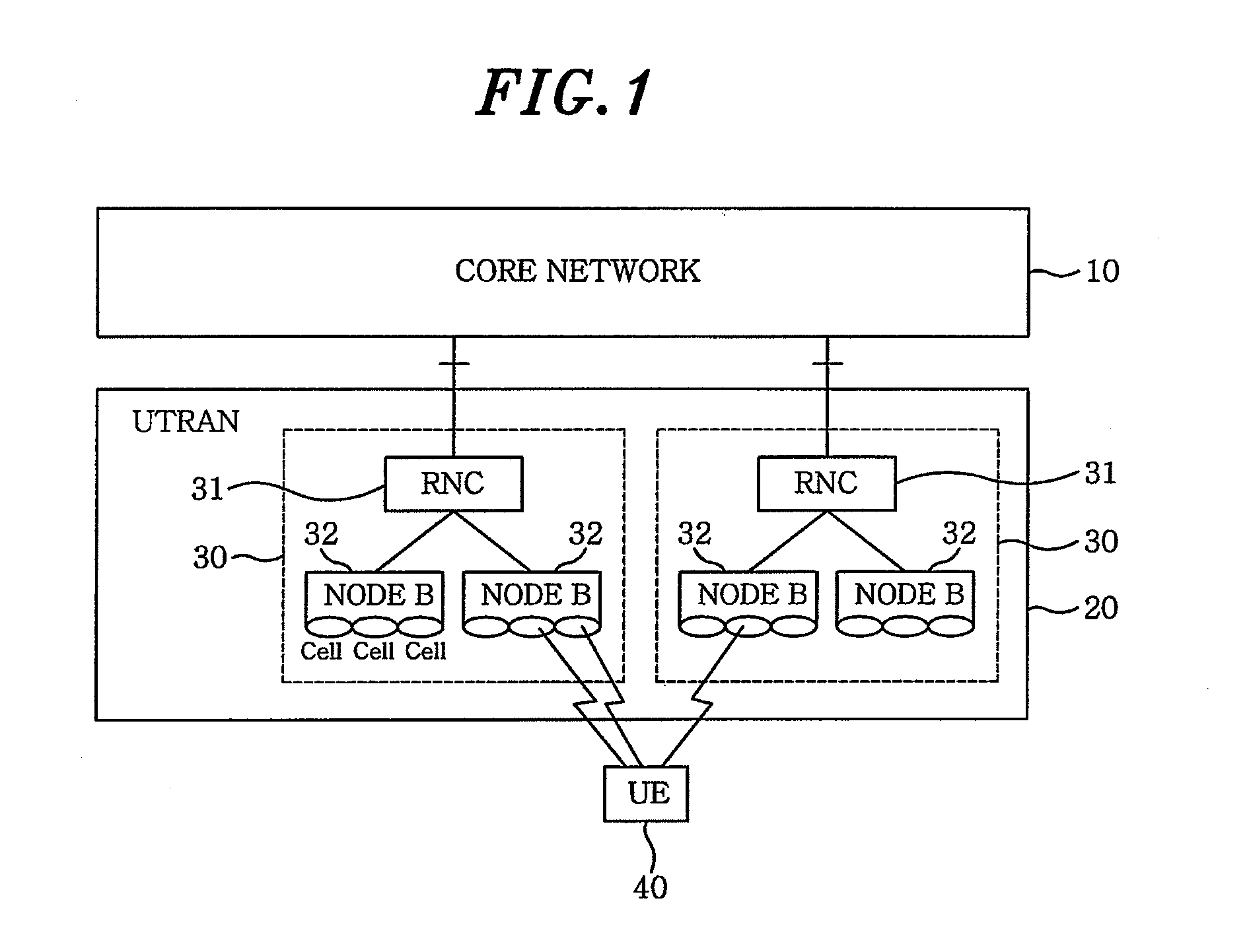
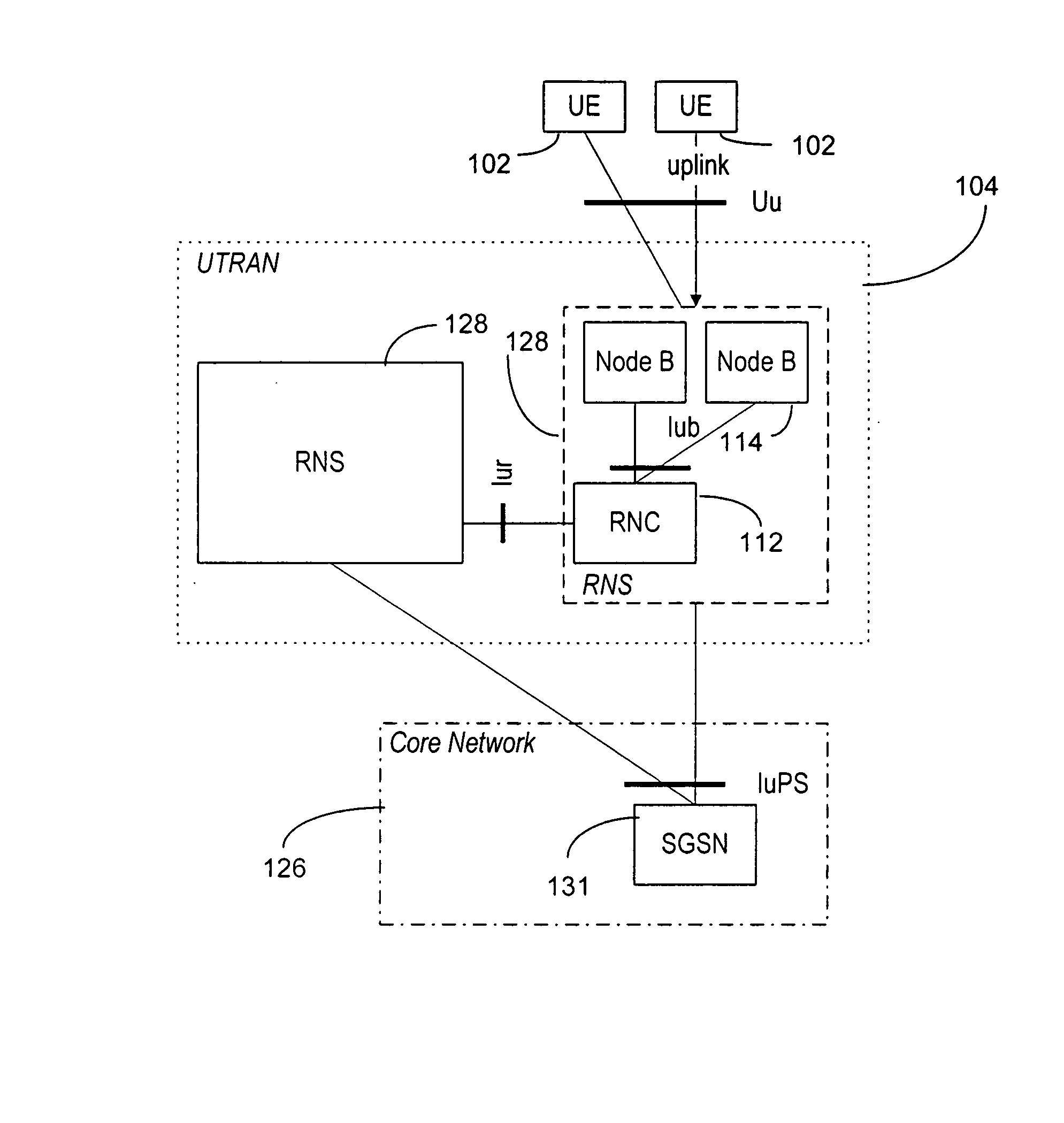
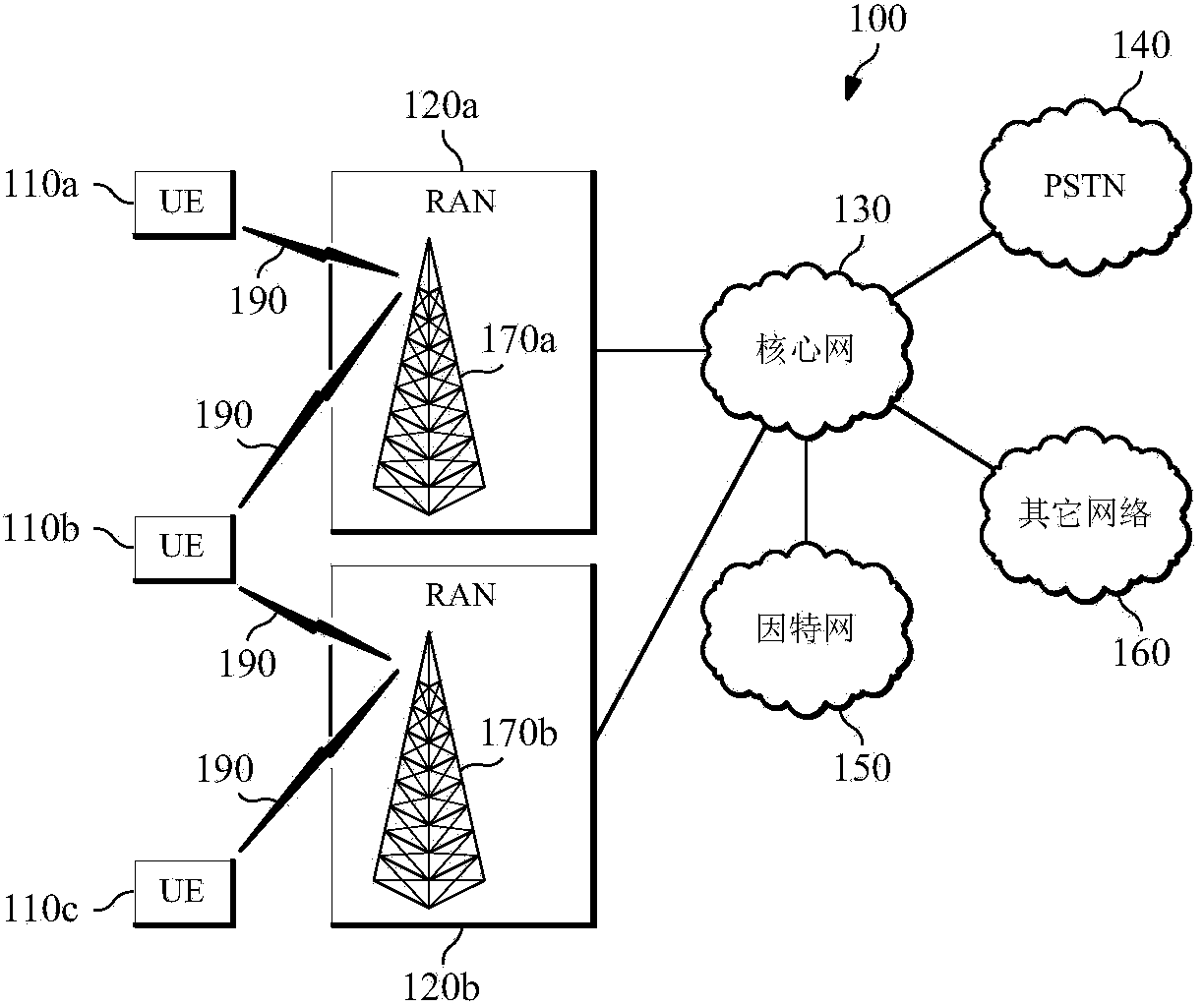
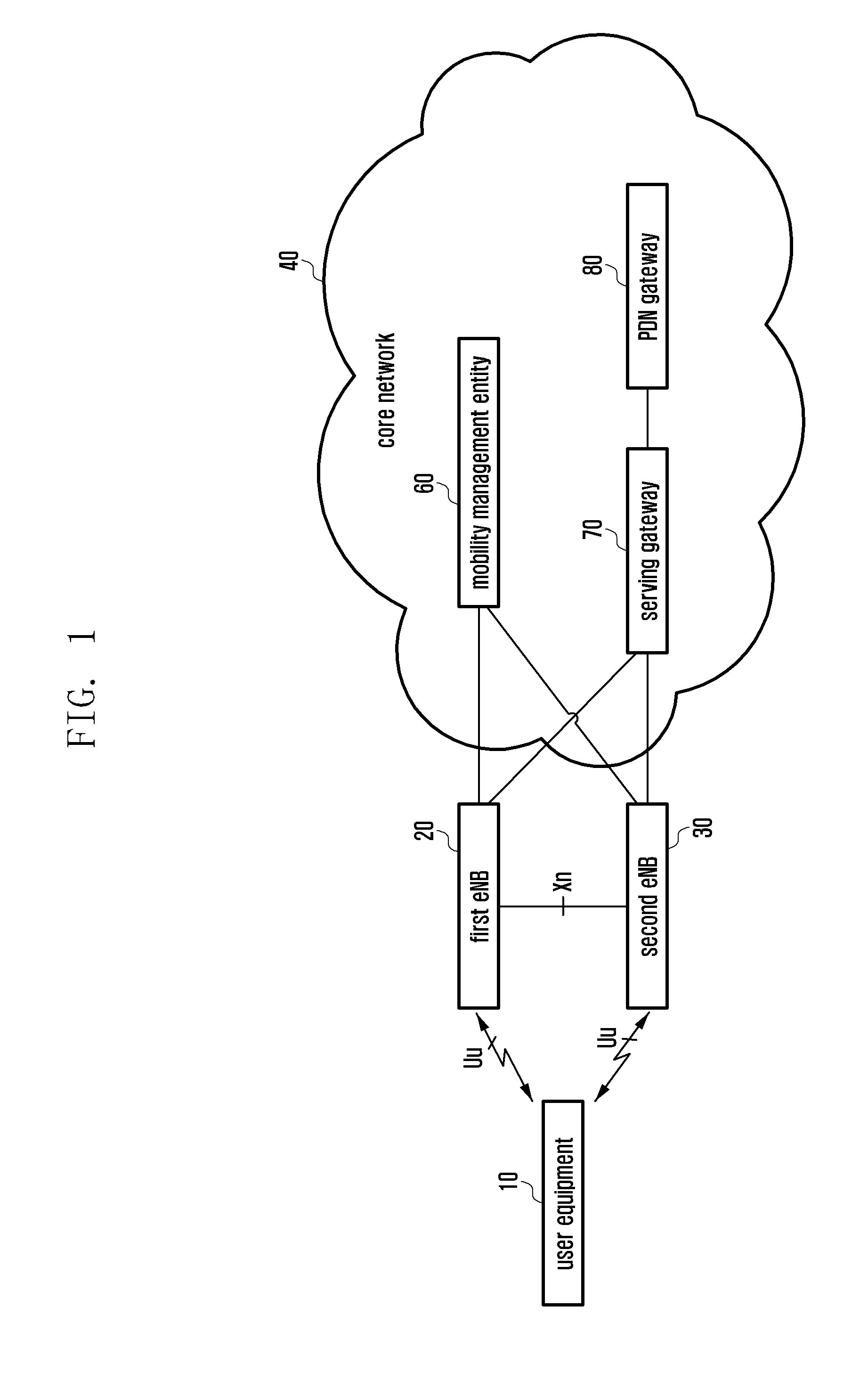
Node B is the telecommunications node in particular mobile communication networks, namely those that adhere to the UMTS standard. The Node B provides the connection between mobile phones (UEs) and the wider telephone network. UMTS is the dominating 3G standard.
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving uplink power offset information in a mobile communication system supporting HSDPA
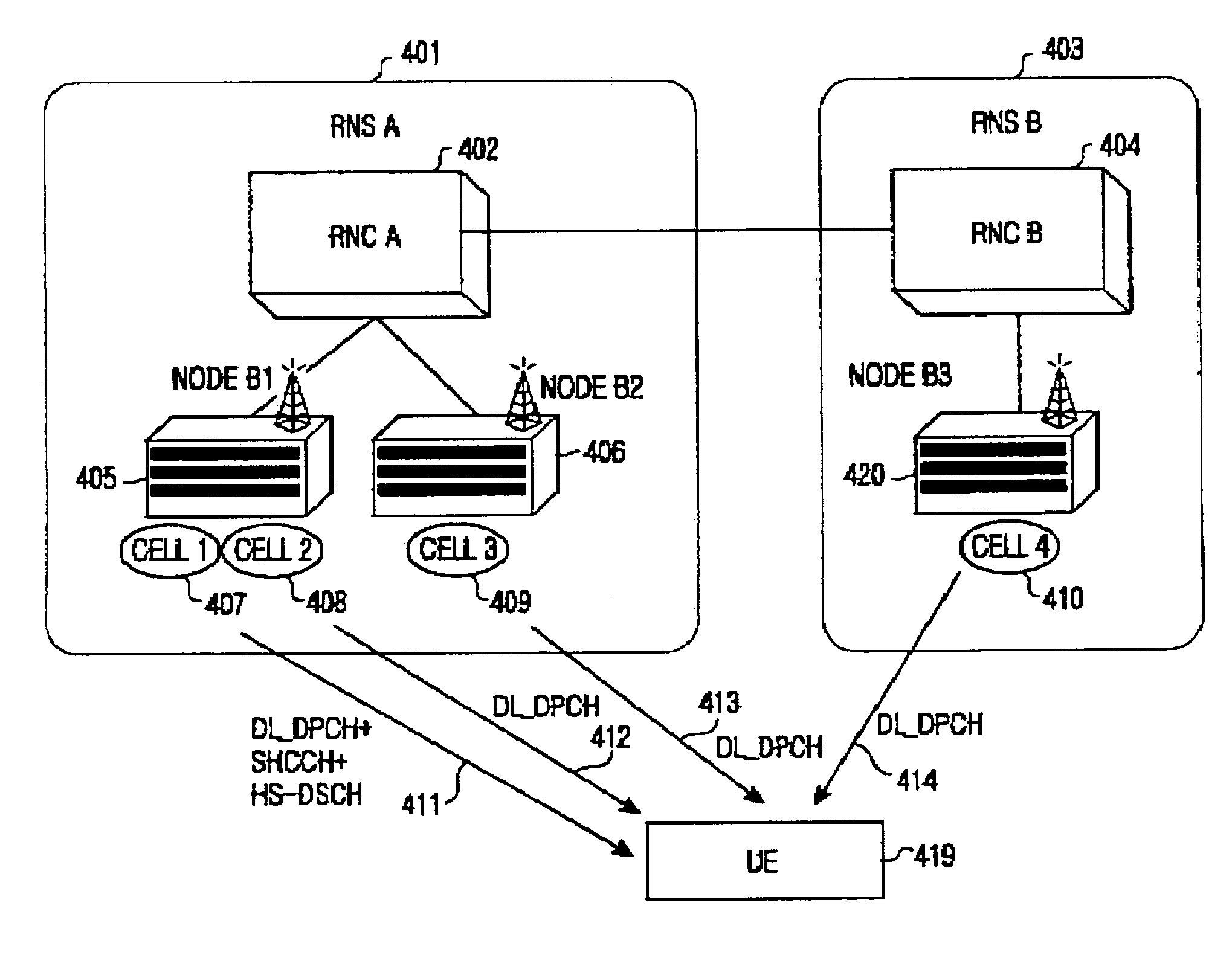
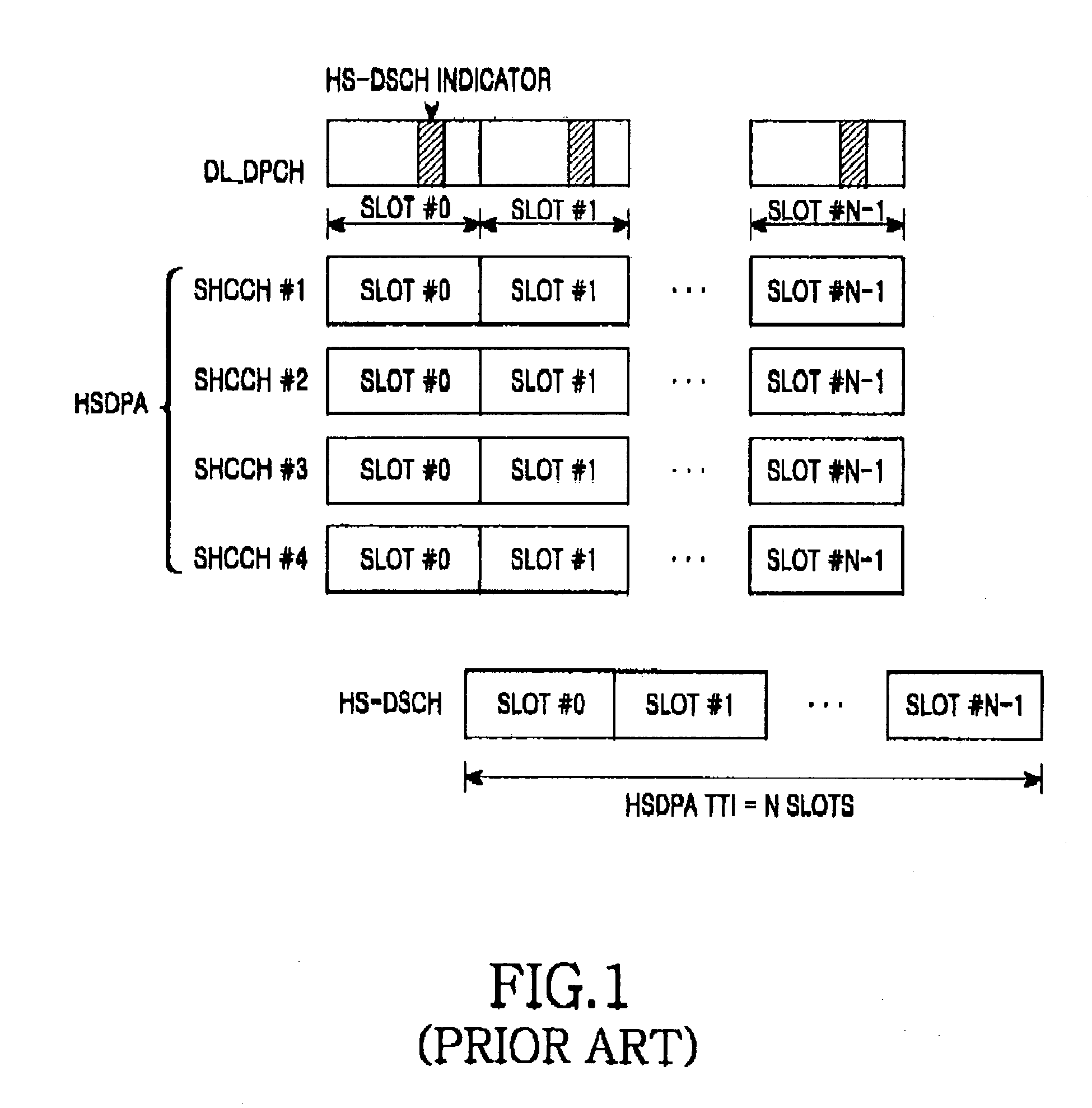
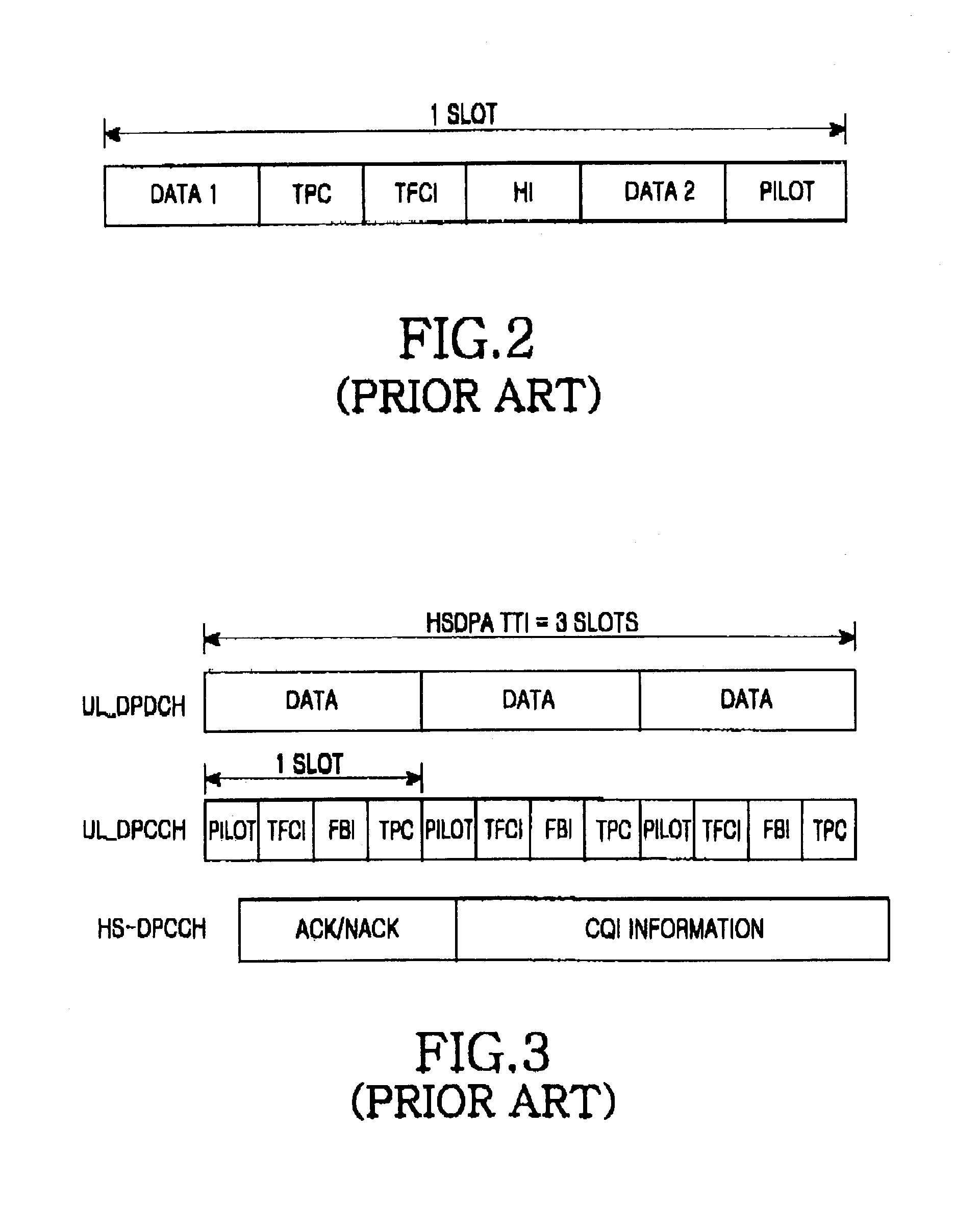
A radio network controller (RNC) transmits a power offset for controlling transmission power of an uplink high-speed dedicated physical control channel (HS-DPCCH) when a user equipment (UE) enters a handover region, in a mobile communication system including the RNC, a Node B connected to the RNC, and the UE located in one of at least two cell areas occupied by the Node B. The Node B transmits data to the UE over a high-speed downlink shared channel (HS-DSCH) and the UE transmits information indicating reception of the data to the Node B over the uplink HS-DPCCH. The RNC informs the UE of a power offset for determining a transmission power increment of the uplink HS-DPCCH, if it is determined that the UE is located in the handover region. The RNC informs the Node B of the power offset so that the Node B can determine a threshold value for determining information indicating reception of the data, depending on the power offset.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for optimized reference signal downlink transmission in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080260062A1Reduce MAISignal allocationFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemNetwork conditions
A method and system optimizes the transmission of a downlink reference signal (DLRS) in a wireless communication system that uses orthogonal division multiple access (OFDMA) for the downlink. Each Node-B (base station) is capable of transmitting the DLRS reference symbols in different subframes of the OFDM radio frame and changing both the number and location of the subframes in response to changing network conditions. The network conditions include the number of terminals being served by the Node-B and multiple access interference (MAI) from adjacent Node-Bs.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
System and method for controlling a TTI in a W-CDMA communication system supporting enhanced uplink dedicated transport channel
InactiveUS20050073985A1Error preventionRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemMobile communication systems
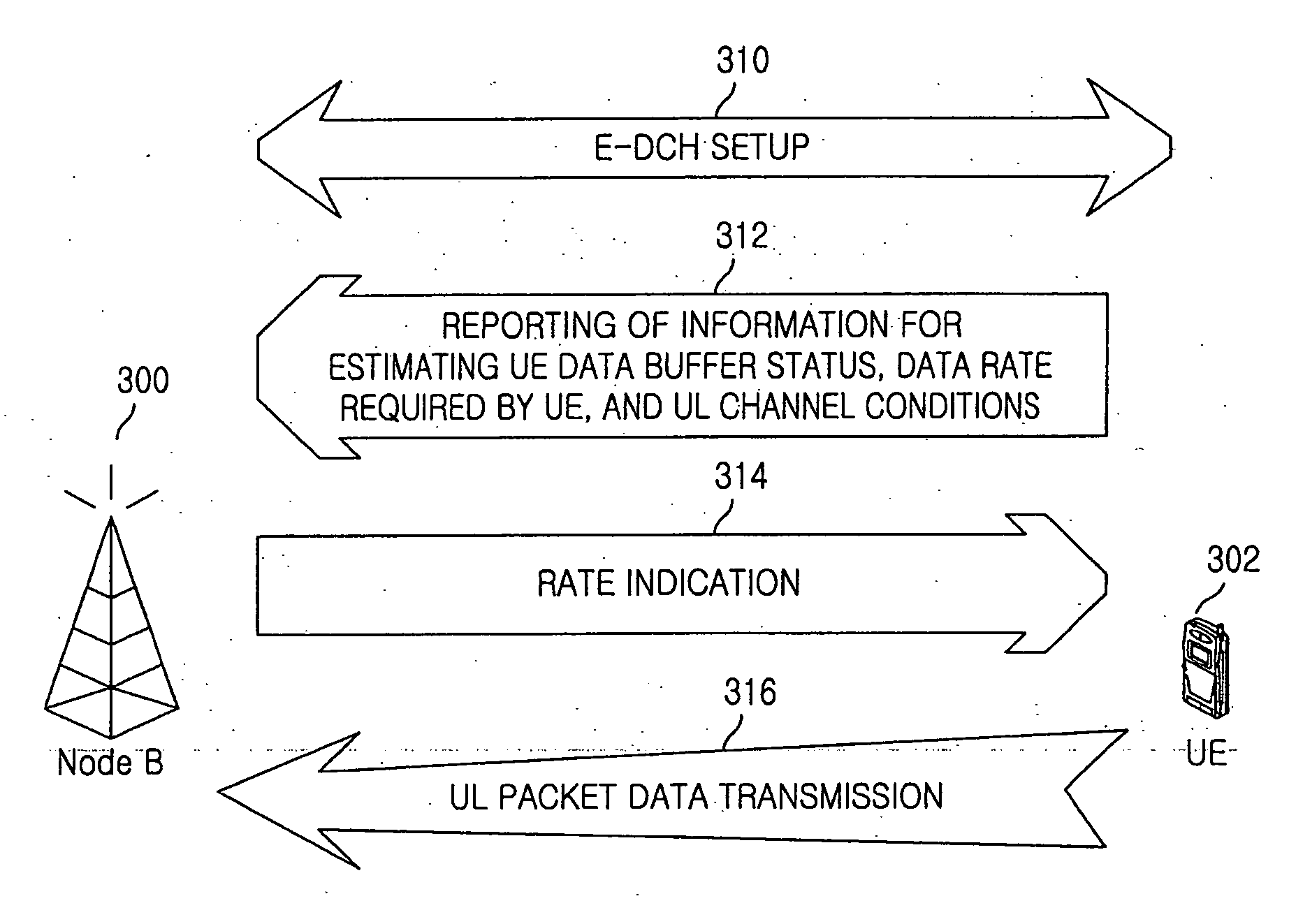
A system and a method for enabling a node B to control a transmission time interval (TTI) in consideration of radio resources of a cell, a channel environment of a UE, and a buffer state of the UE, in an asynchronous wideband code division multiple access (W-CDMA) mobile communication system that supports a packet data service through an enhanced uplink dedicated transport channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
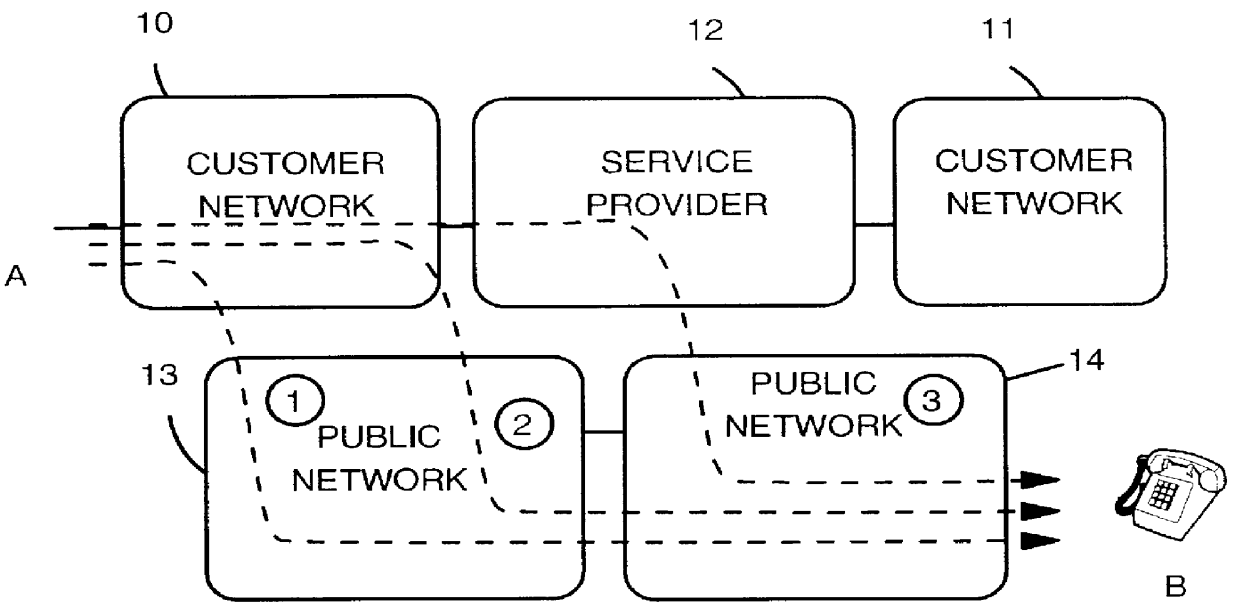
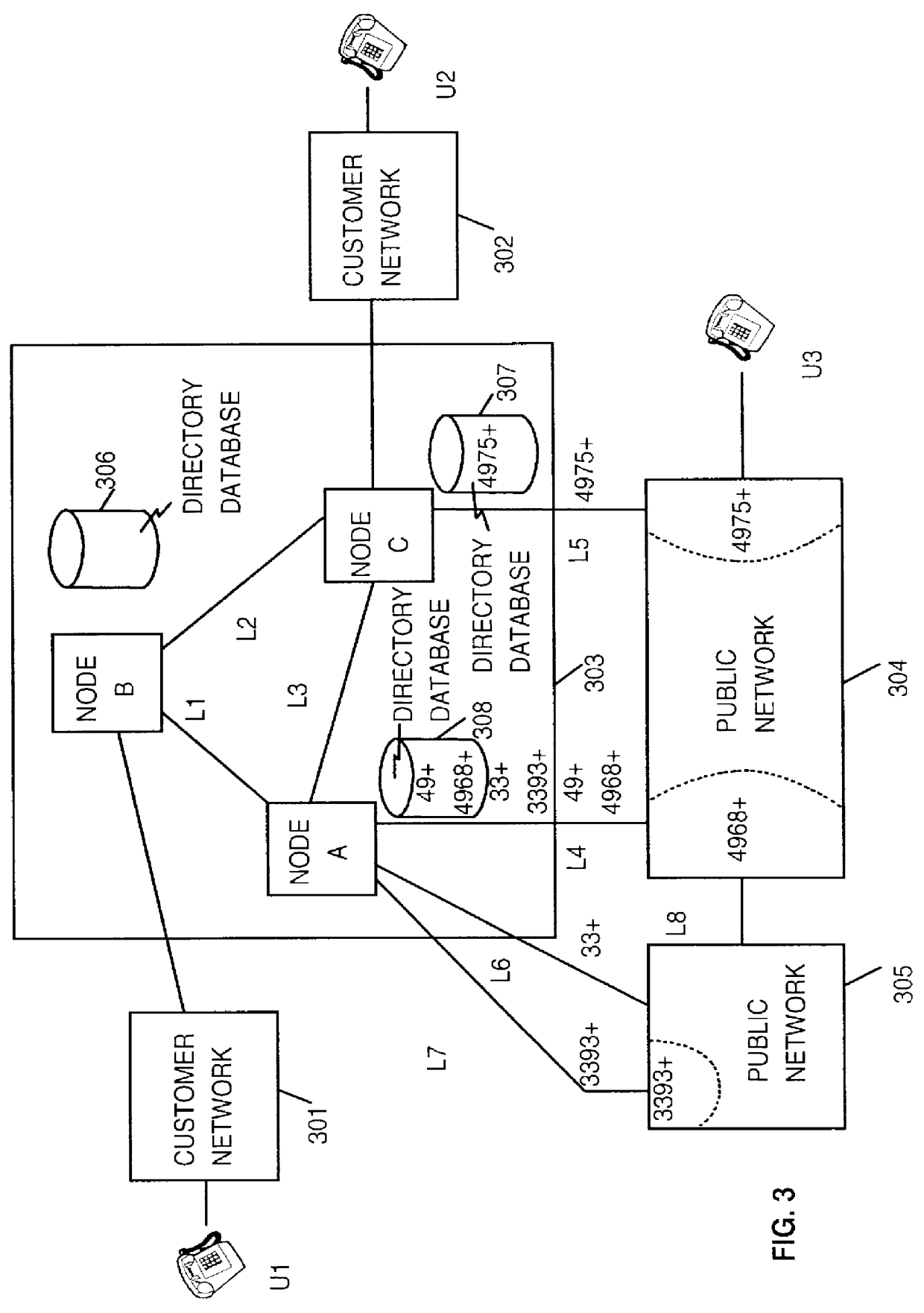
Method and system for performing a least cost routing function for data communications between end users in a multi-network environment
InactiveUS6104701ALow costLeast Cost RoutingInterconnection arrangementsError preventionPrivate networkLeast cost
A method and system for determining the best data path in a communication network is presented. A Least Cost Routing path between end users in a multi-network environment, including both public and private networks, is determined based upon a longest prefix match. At network activation time, the numbers or prefixes of numbers of end users attached to the public network (304, 305) are stored in entry node data bases A and C of the private network (303). Assuming an end user terminal U1 calls a target end user U3, an entry node B first checks for a longest prefix match between the called number and numbers already stored into its memory. If this is the first time U3 is called via node B, no match will occur and node B will then broadcast a Query to all nodes in the private network (i.e. Nodes A and C). Only those nodes providing possible access to U3 answer this Query. Node B then determines the longest prefix match with the called number amongst the various query answers, and sets the data path via that node having the longest prefix match.
Owner:IBM CORP
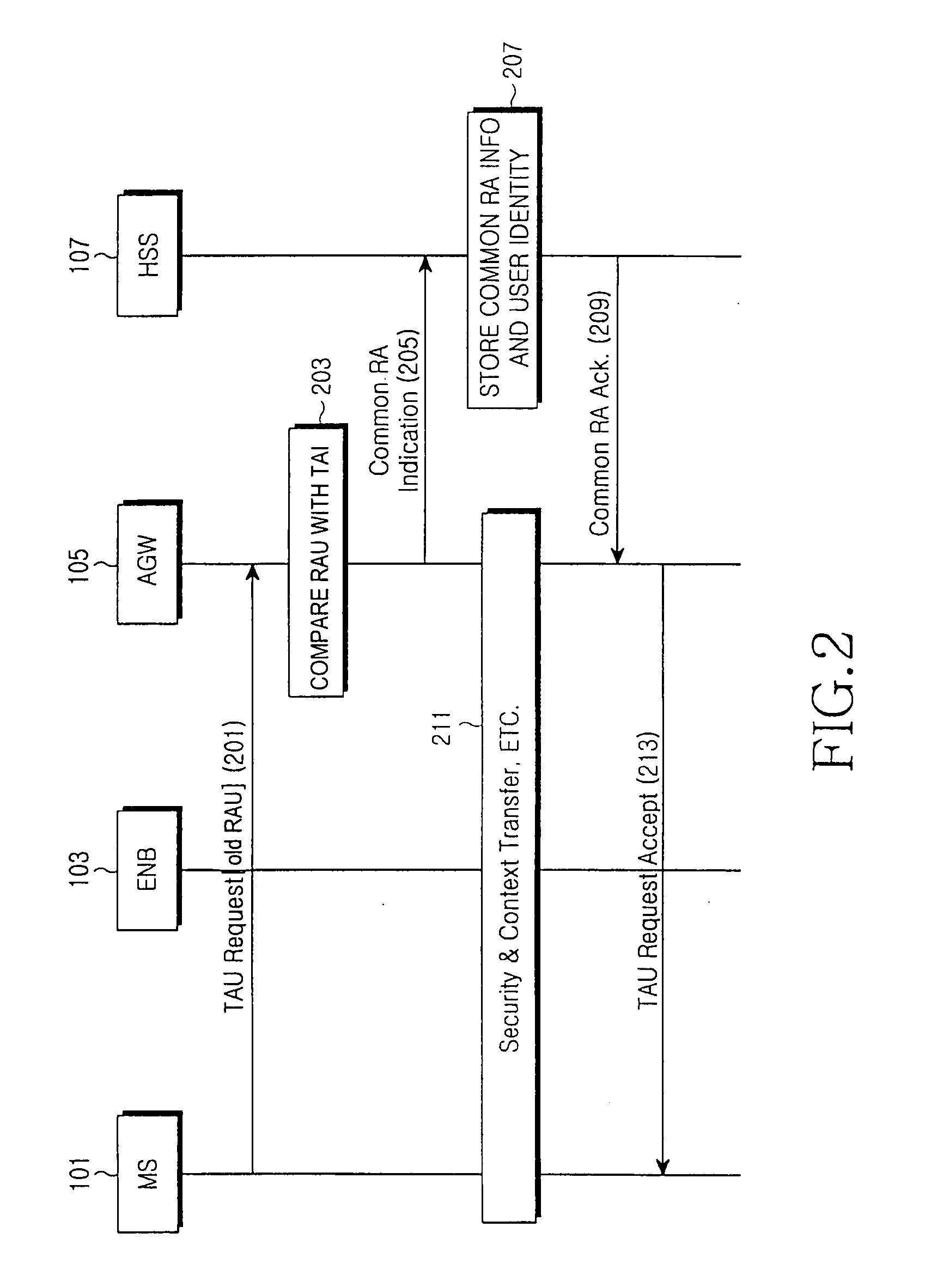
Method and apparatus for supporting communication service of idle user terminal located in common routing area in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20080020745A1Minimize unnecessary signalingReduce interworking overheadRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesThird generationMobile communication systems
A method for supporting a communication service of an idle mode terminal located in a common routing area in a mobile communication system that includes a Node B, an Access Gateway (AGW), and a Home Subscriber Server (HSS), and has a Long Term Evolution (LTE) network and a 3rd Generation (3G) network connected to each other to perform transmission / reception. The AGW receives tracking area information of the LTE network, including routing area information of the 3G network, from the idle mode terminal via the Node B. The AGW sends common routing area indication information and identification information of the terminal to the HSS if the routing area information is coincident with the tracking area information. The HSS stores the common routing area indication information and the identification information of the terminal, and sends a response message according to the indication information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Access admission control method and system for mobile communication system
ActiveUS20100075635A1Effective controlUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAssess restrictionMobile communication systemsWhitelist
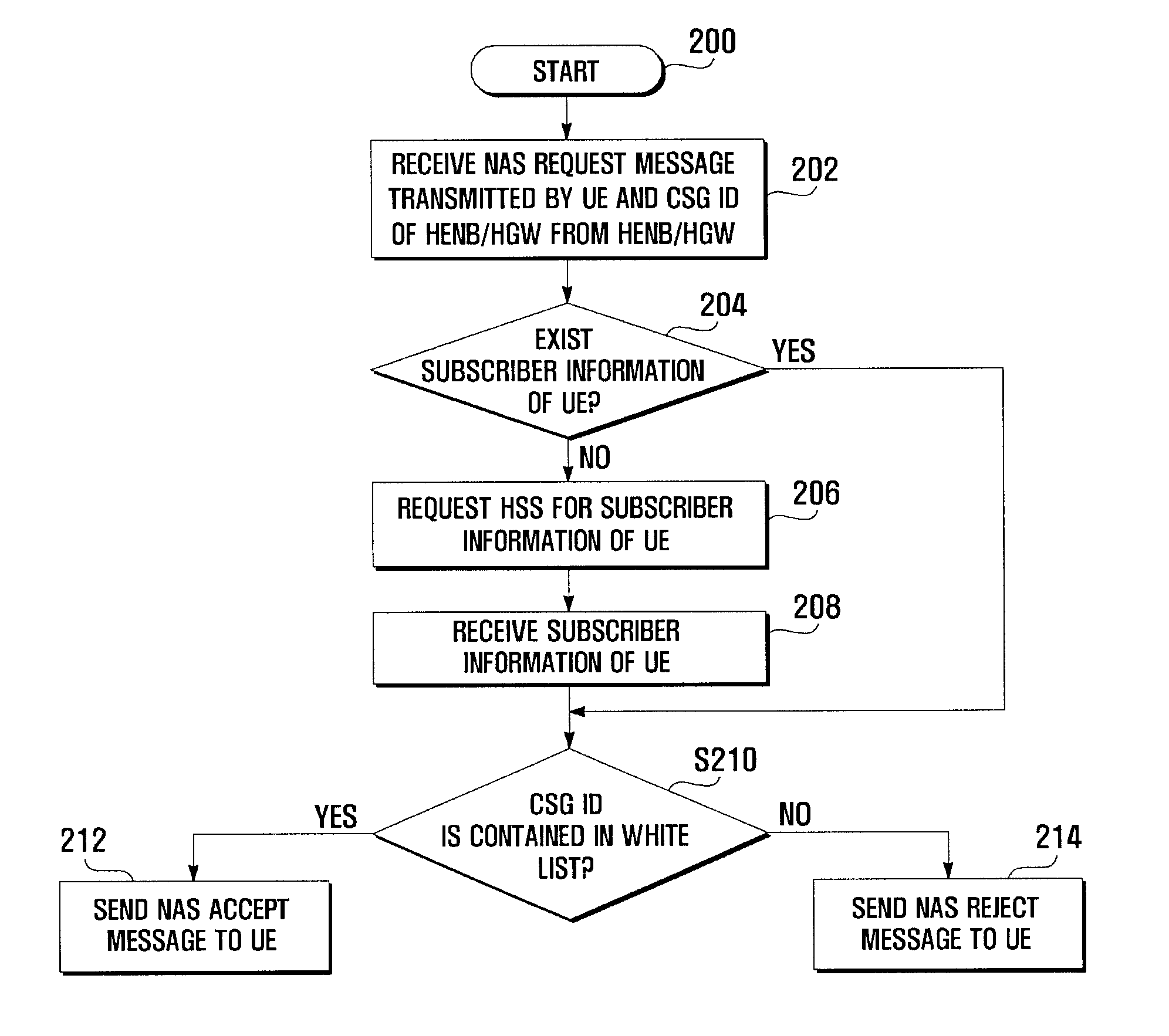
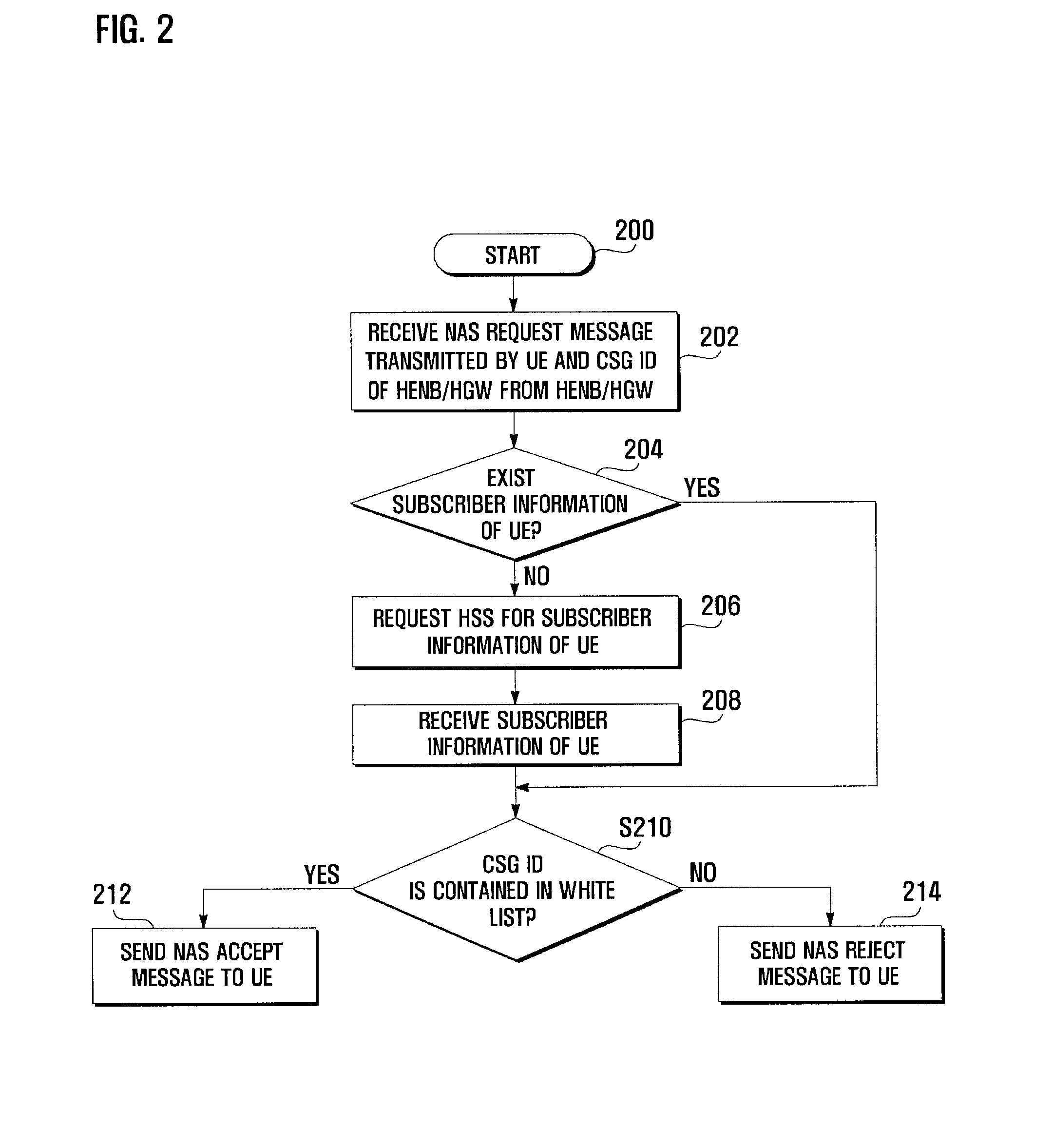
An access admission control method and system for and SAE / LTE system is provided for determining whether to accept or reject an access of a User Equipment (UE) to a Home evolved Node B (HeNB) based on the subscriber information of the UE. In an access admission control method according to the present invention, a HeNB or HeNB Gateway (HGW) transmits, when an access request message is received from a UE, the access request message to a Mobility Management Entity (MME) together with a CSG ID of the HeNB, and the MME determines, whether to accept or reject the access of the UE to the HeNB based on whether the CSG ID is contained in a white list associated with the UE.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for sending state indication of voice packet by user equipment in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20080084851A1Time-division multiplexWireless communicationMobile communication systemsReal-time computing
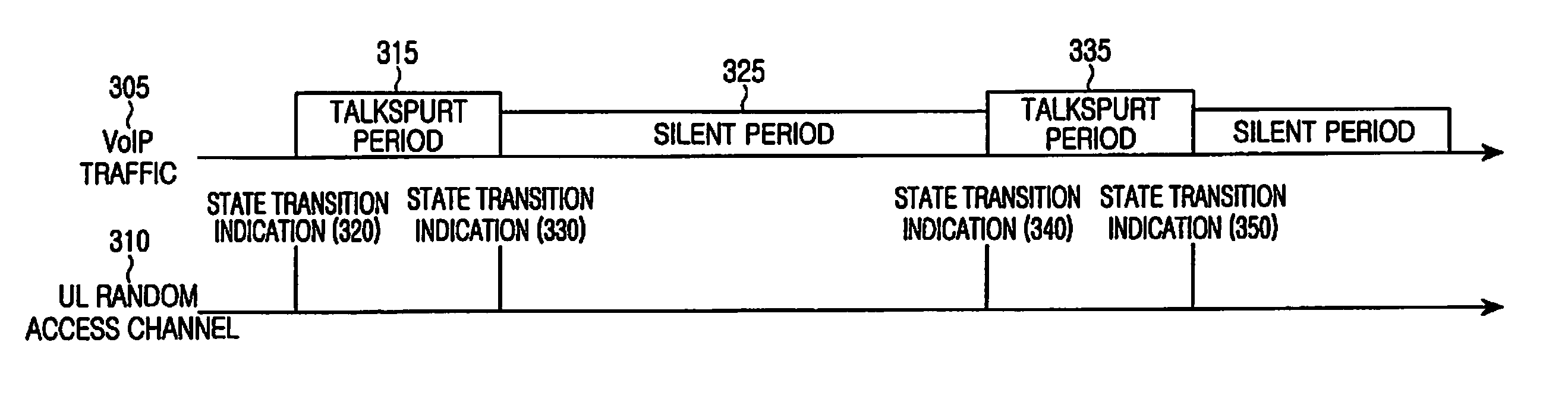
Provided is a method for receiving allocated transmission resources by a User Equipment (UE) in a mobile communication system supporting a voice packet service. The method includes determining whether there is a state transition of a desired current transmission voice packet, using at least one state transition indication generation condition determined according to a codec mode of the UE; if it is determined that the state of the current voice packet has transitioned from a state of an old voice packet, generating state transition indication of the voice packet and transmitting the state transition indication to an Evolved Node B (ENB); and receiving allocated transmission resources corresponding to the state transition indication from the ENB, and transmitting the voice packet using the allocated transmission resources.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
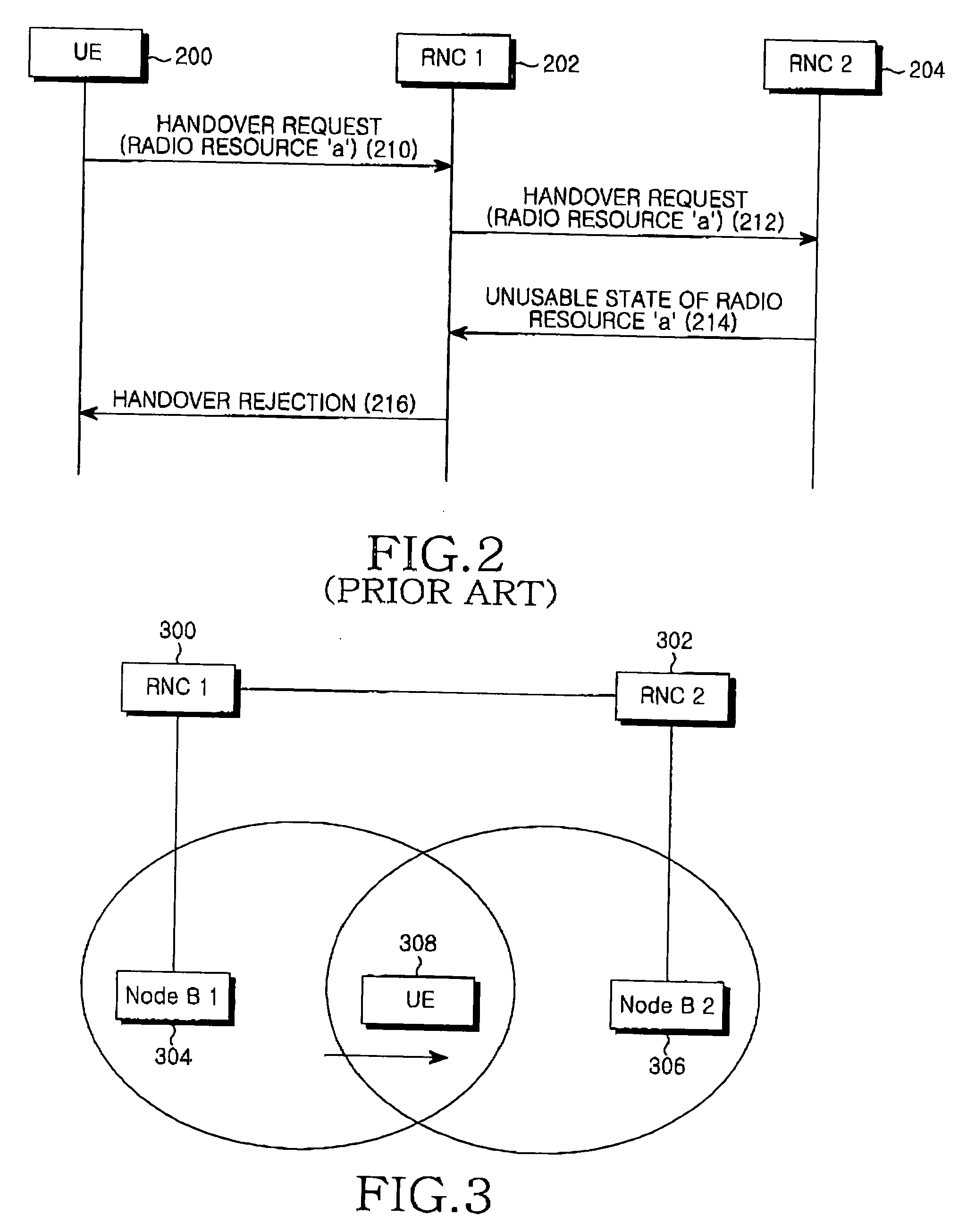
System and method for performing a handover in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050026615A1Efficient managementTelephonic communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsResource informationMobile communication systems
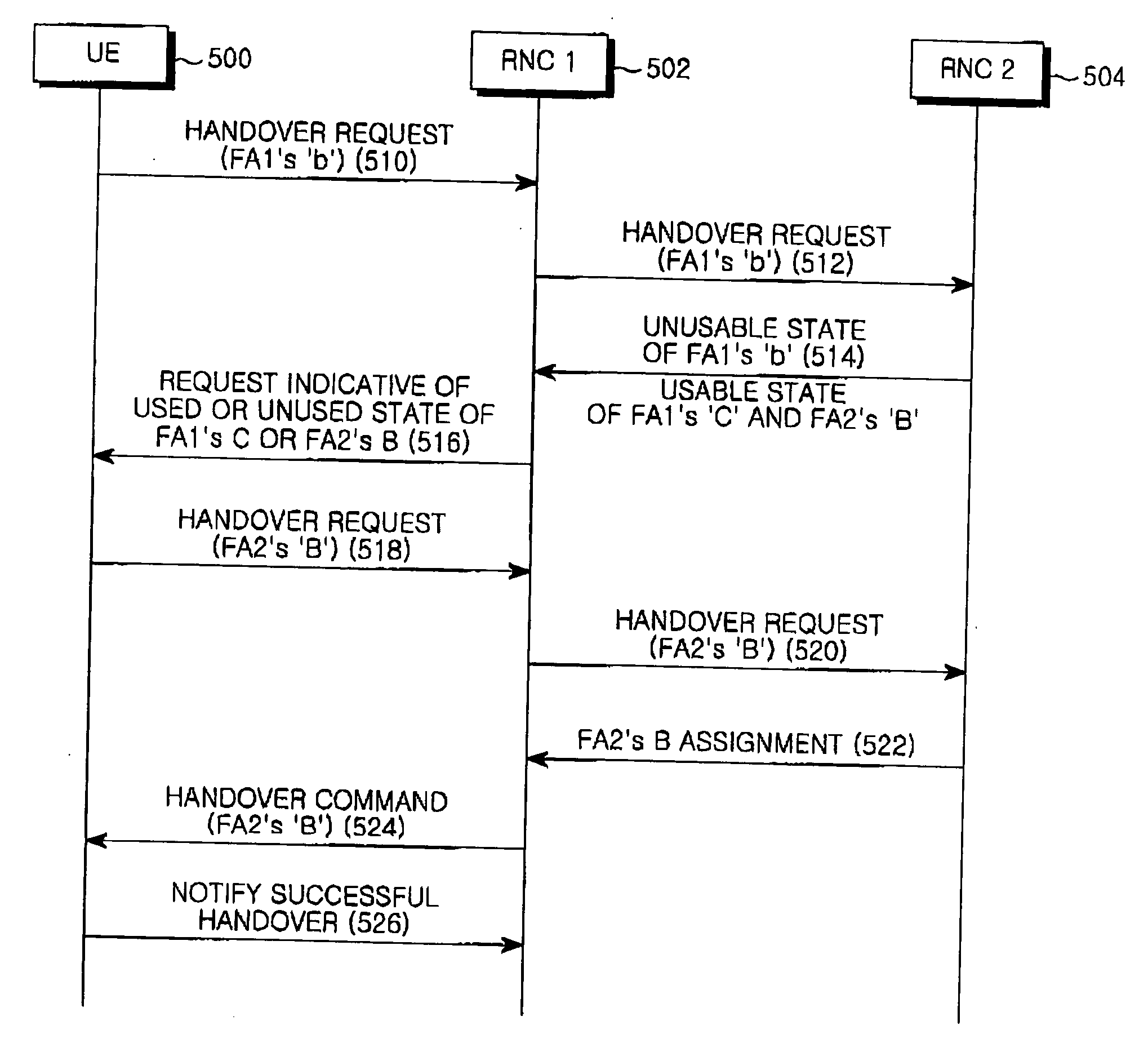
A system and method for performing a handover function in a mobile communication system. The system and method for controlling a User Equipment (UE) to perform a handover from a first Node B to a second Node B in a mobile communication system including a first Radio Network Controller(RNC) for managing the first Node B communicating with the UE and a second RNC for managing the second Node B to which the UE is to be handed over. The system and method comprise transmitting a handover request message including a resource to be assignment-requested to the second RNC over the first RNC; receiving resource information indicative of other assignable resources from the second RNC over the first RNC when the second Node B cannot assign the assignment-requested resource to the UE; and performing the handover using the received resource information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Signal measurement apparatus and method for handover in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS7200124B2Effective distributionIncrease the lengthNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexMobile communication systemsHandover
An RNC determines parameters available for measurement of a synchronization signal and second Node B information from a second Node B, transmits the determined parameters to a first Node B during radio link setup and to a UE during radio bearer setup, and transmits parameter selection information to the first Node B and the UE, if it is recognized that measurement of the synchronization signal and the second Node B information is necessary. The first Node B changes a position of a downlink time period over which a downlink channel is transmitted from the first Node B to the UE and a position of an uplink time period over which an uplink channel is transmitted from the UE to the first Node B, according to parameters selected from the parameters. The UE receives the synchronization signal and the second Node B information in the remaining time periods except the changed downlink time period and the changed uplink time period among the plurality of time periods.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
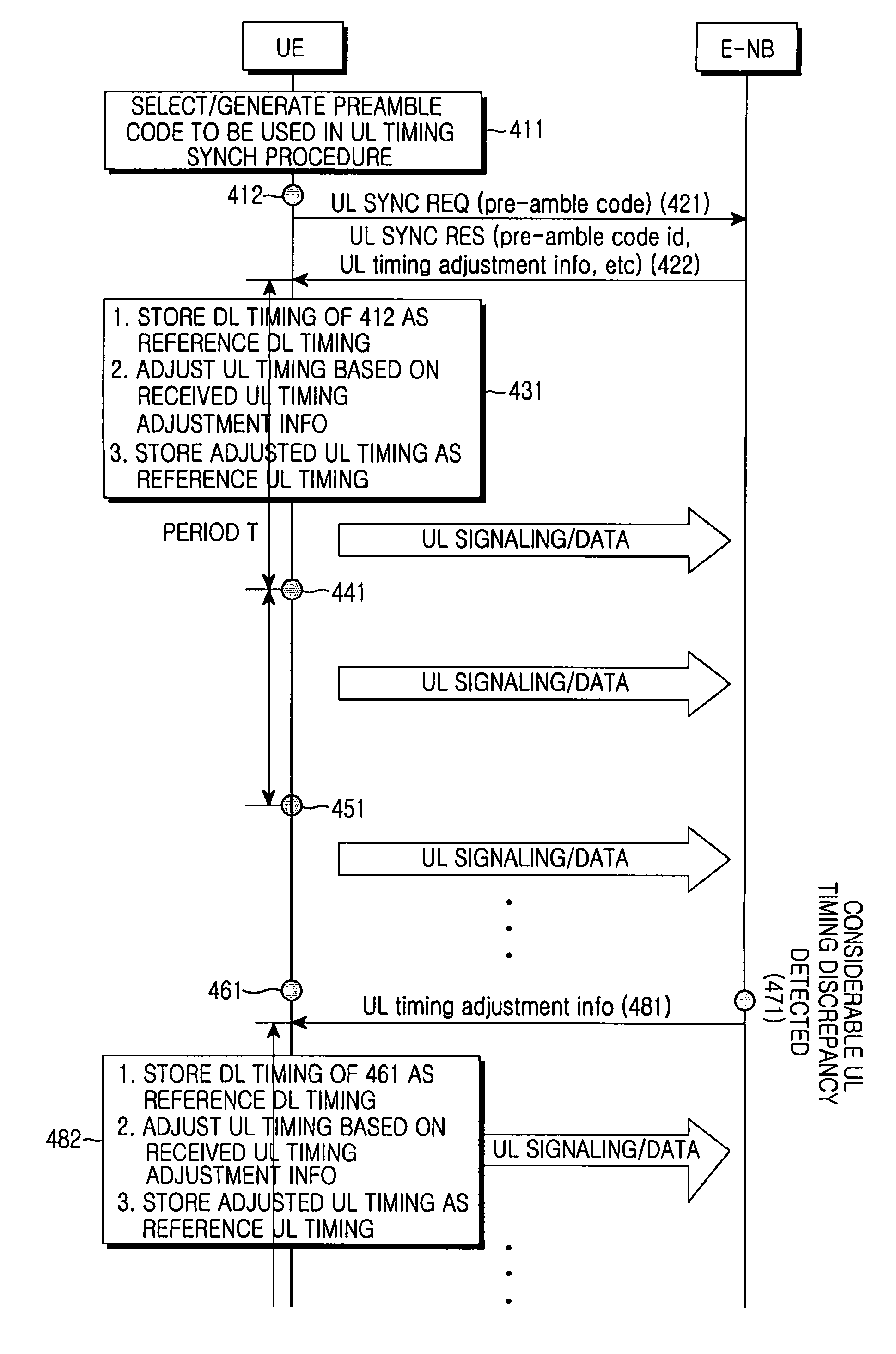
Method for maintaining uplink timing synchronization in a mobile communication system and user equipment apparatus for the same
ActiveUS20080002660A1Timely maintenanceSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsUplink transmission
Disclosed is a method for maintaining uplink timing synchronization by a User Equipment (UE) in a mobile communication system, without uplink transmission of a preamble from a UE or without transmission of uplink timing difference information from an Evolved Node B (E-NB) to solve the inefficient use problem of radio resources, occurring due to periodic transmission of uplink signaling and downlink signaling during maintenance of the uplink timing synchronization, and a UE apparatus for the same.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
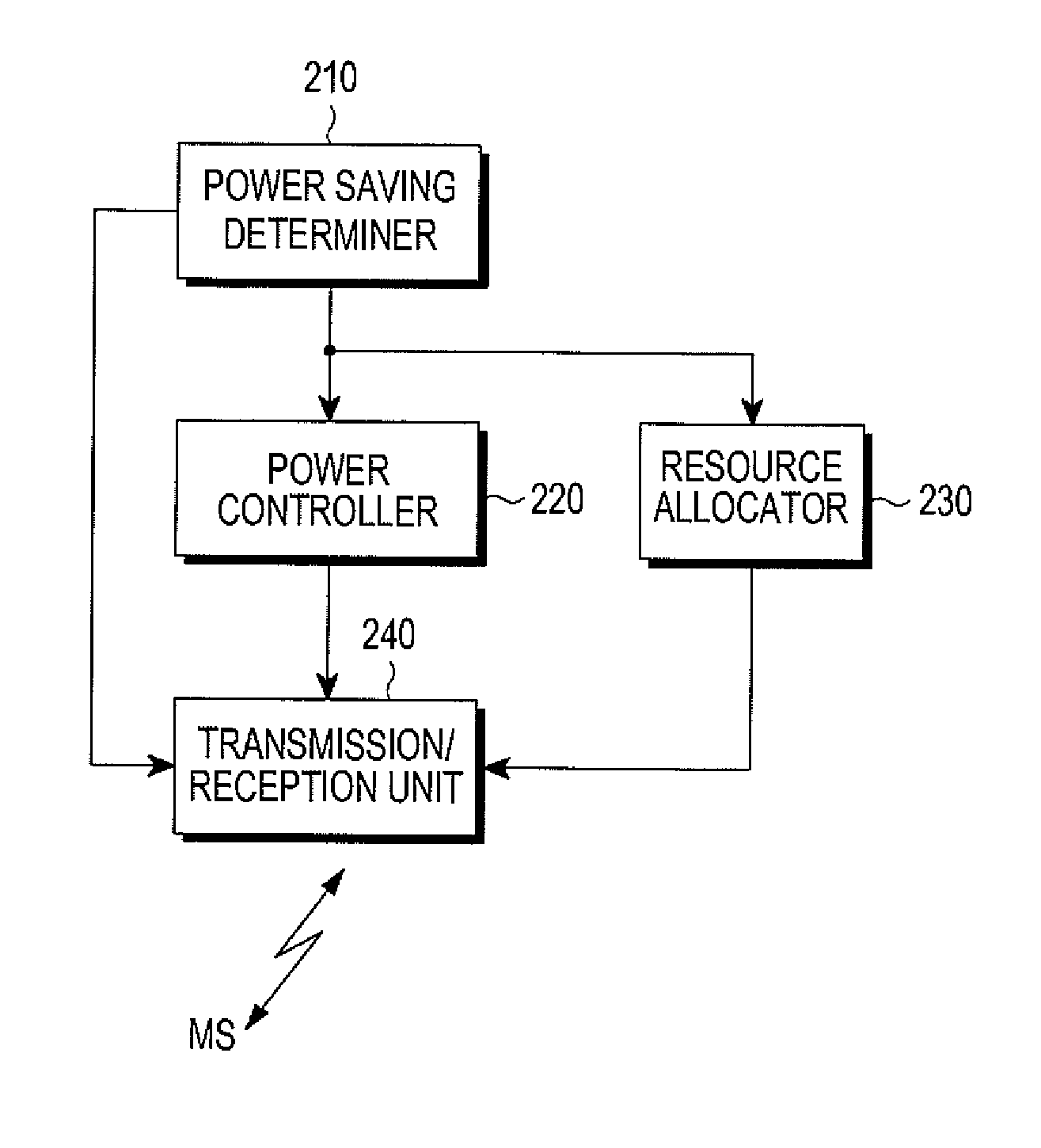
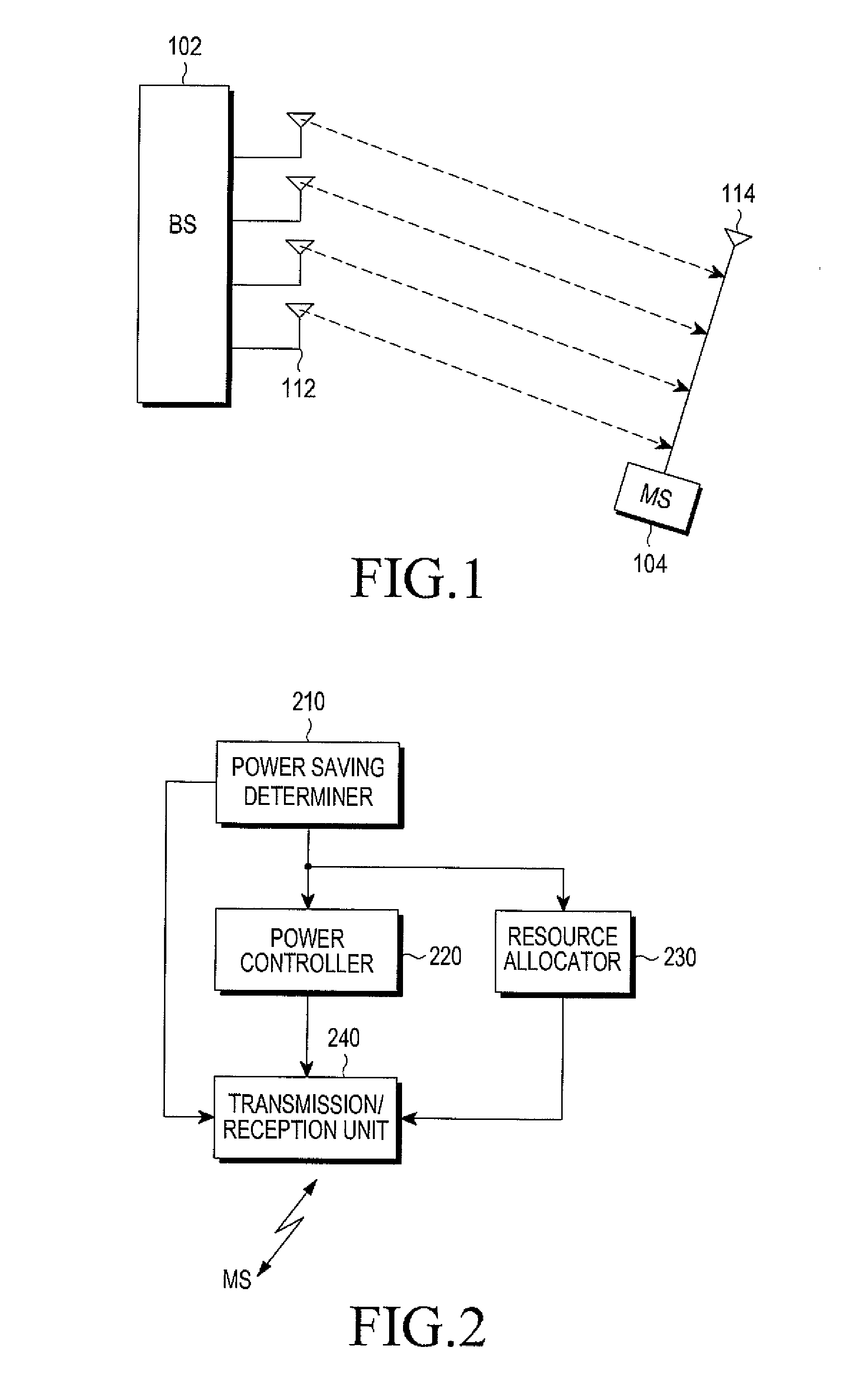
Method and apparatus for power saving in wireless communication node b
ActiveUS20110195741A1Reduce in quantityReduce power consumptionPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
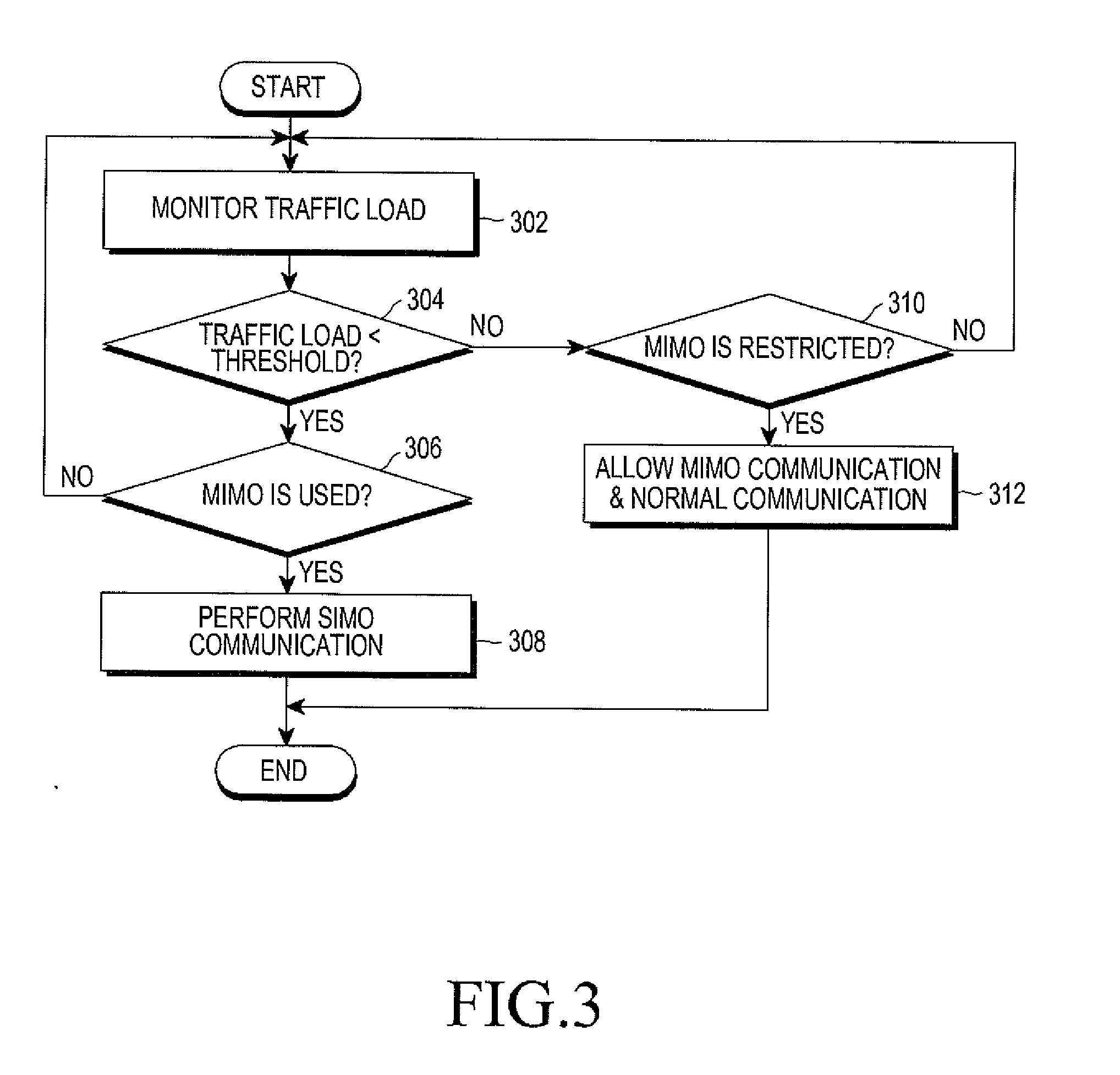
A method and an apparatus reduce power used when a traffic load is low in a base station of a wireless communication system. The base station monitors a traffic load. When the traffic load is lower than a predetermined threshold and a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) mode is used to communicate with a mobile station, the MIMO mode is converted to a Single Input Multiple Output (SIMO) mode. The base station performs communication with the mobiles stations by using the SIMO mode. According to another embodiment, when the traffic load is lower than a predetermined threshold, the base station limits the number of Resource Blocks (RBs) that may be allocated to a coverage area of the base station. A Power Amplifier (PA) bias related to a transmission output of the base station is reduced based on the limited number of RBs, thereby saving power consumption of the base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmitting Node B Load Status Information in a Self Organising Network
ActiveUS20110038431A1Modulated-carrier systemsNetwork topologiesWireless transmissionSelf-organizing network
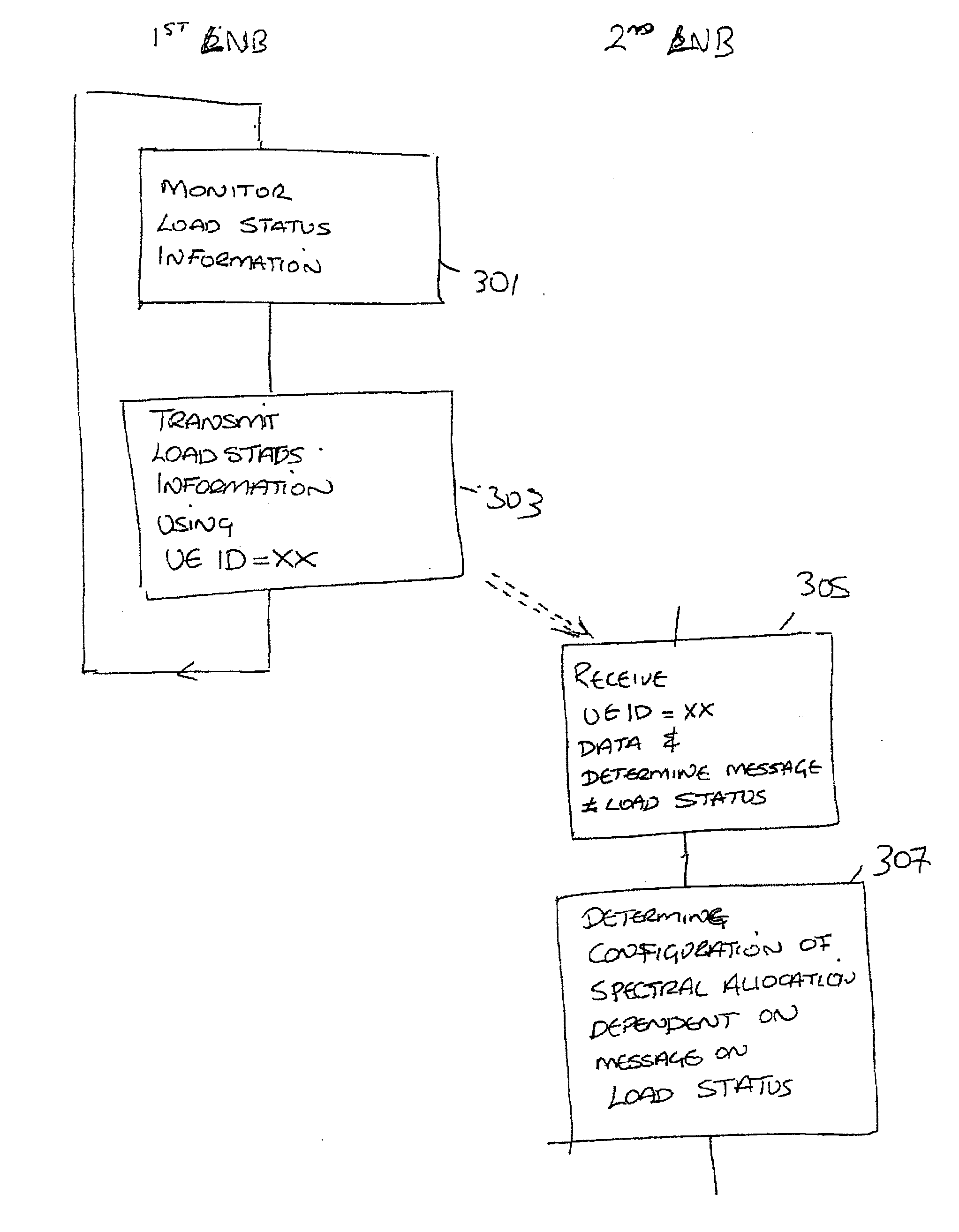
The application relates to wireless transmission of load status information for load balancing among Home Node Bs (HNB) or Local Area Node Bs (LNB) for which an X2 interface is not available. In particular, an LNB may pretend to be a user equipment with a specific predefined user equipment ID value. A neighbouring LNB which receives a data packet with this user equipment ID value knows that the data packet contains load information monitored, by a neighbouring LNB.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method and apparatus for signaling control information of uplink packet data service in mobile telecommunication system
Disclosed is a mobile telecommunication system in which packet data is transmitted over an uplink, and particularly a method and an apparatus for transmitting control information from a UE to a Node B. By multiplexing, several upper layer data units and MAC layer control information are included in a packet which the UE transmits during one transmission period in the uplink. A header of the packet accommodates multiplexing information, and thus the Node B uses the multiplexing information for demultiplexing upper layer data units from the packet. When the packet accommodates only the MAC layer control information, the UE does not insert the header into the packet, thereby reducing the packet size. The Node B then determines whether the packet includes only the control information or the upper layer data units together with the header.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for selecting wireless local area network to be accessed by a user equipment within a cell in a mobile communication system
A method and apparatus for selecting a wireless Local Area Network (LAN) within a cell to be accessed by a User Equipment (UE) in a mobile communication system are provided. The method includes performing, when a request for information regarding wireless LAN Access Points (APs) within the cell is received, a search for the wireless LAN APs and transmitting a report indicating a search result to a serving Evolved Node B (ENB); receiving, from the serving ENB, updated information on wireless LAN APs based on report indicating the search result; determining whether to perform a re-search for the wireless LAN APs based on the updated information on the wireless LAN APs; and performing, in response to determination to perform the re-search for the wireless LAN APs, the re-search and selecting APs to be accessed based on a result of the re-search.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
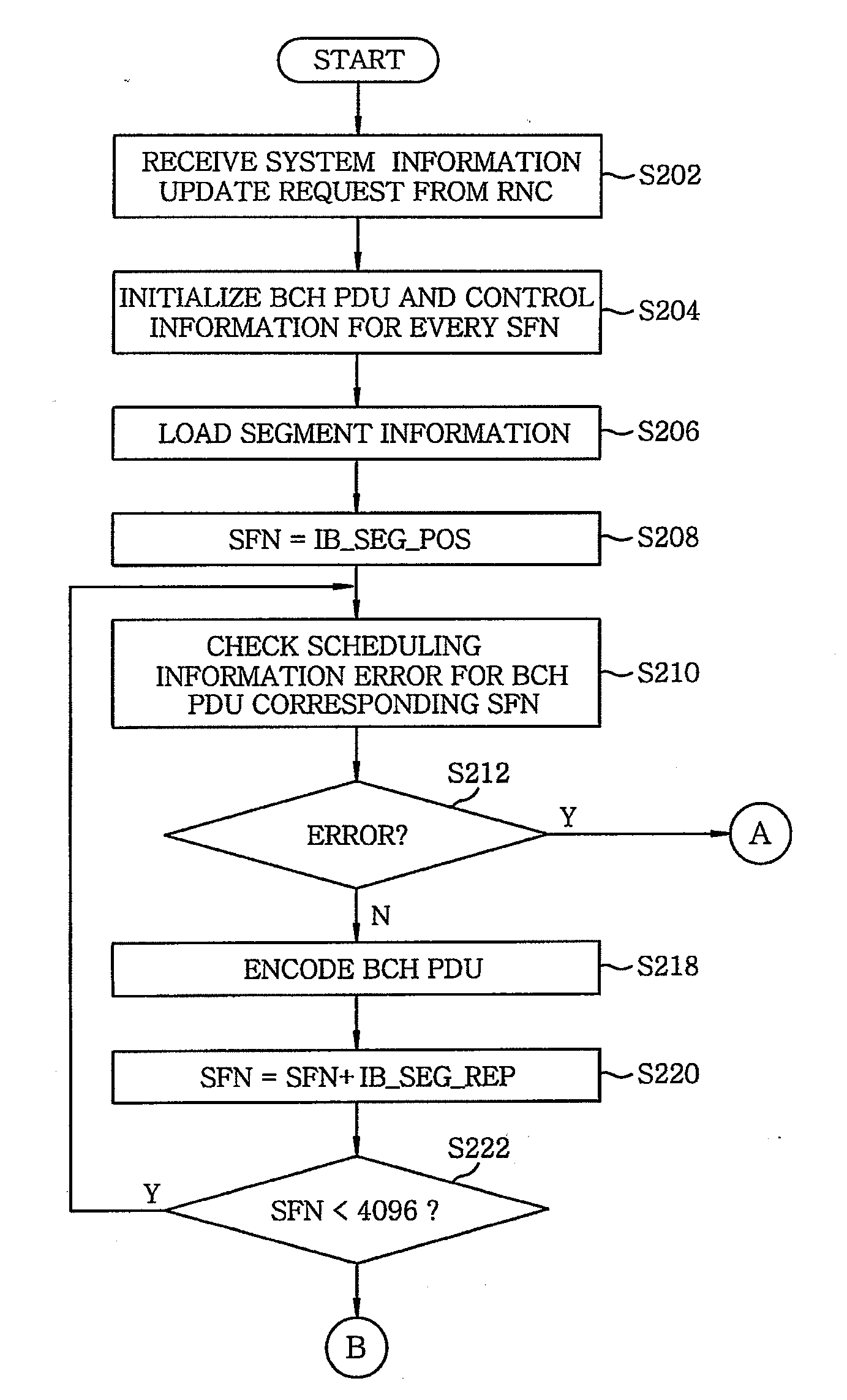
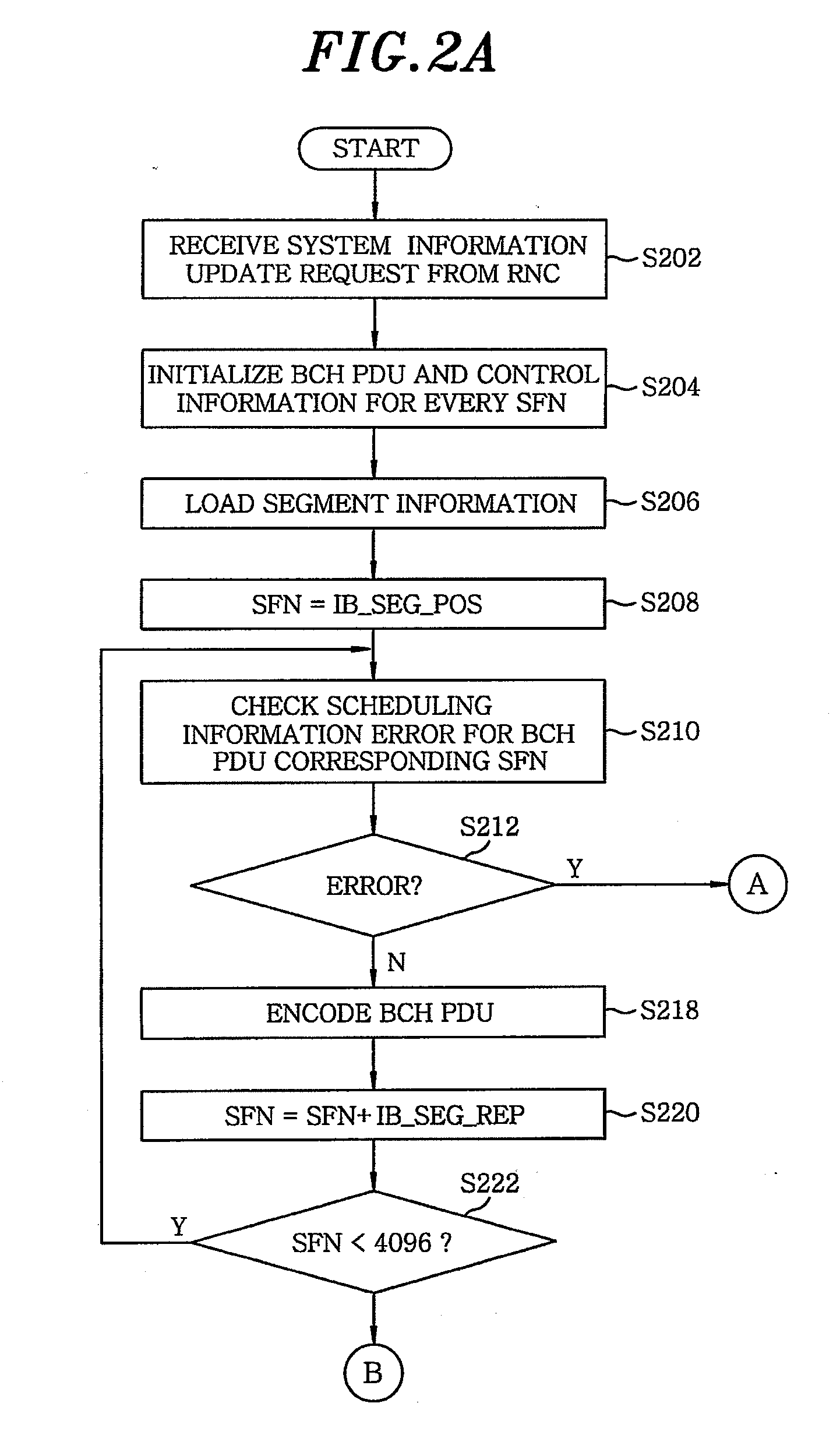
Method for encoding broadcast channel protocol data unit based on broadcast control channel scheduling error in universal mobile telecommunications system
ActiveUS20080137637A1Avoid problemsError preventionTransmission systemsBroadcast channelsRadio networks
A method for encoding a broadcast channel protocol data unit (BCH PDU) based on a broadcast control channel (BCCH) scheduling error in a universal mobile telecommunications system (UMTS) having a Node B and a radio network controller includes setting up a call between the radio network controller and the Node B to receive system information and scheduling information for a system information update from the radio network controller; initializing broadcast channel protocol data units and control information for every system frame number (SFN) at the Node B; and detecting the broadcast control channel scheduling error on the scheduling information for the system information update based on segment types of the system information when combining the system information for every system frame number. In case the broadcast control channel scheduling error is not detected, the broadcast channel protocol data units are encoded to be incorporated therein the system information.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
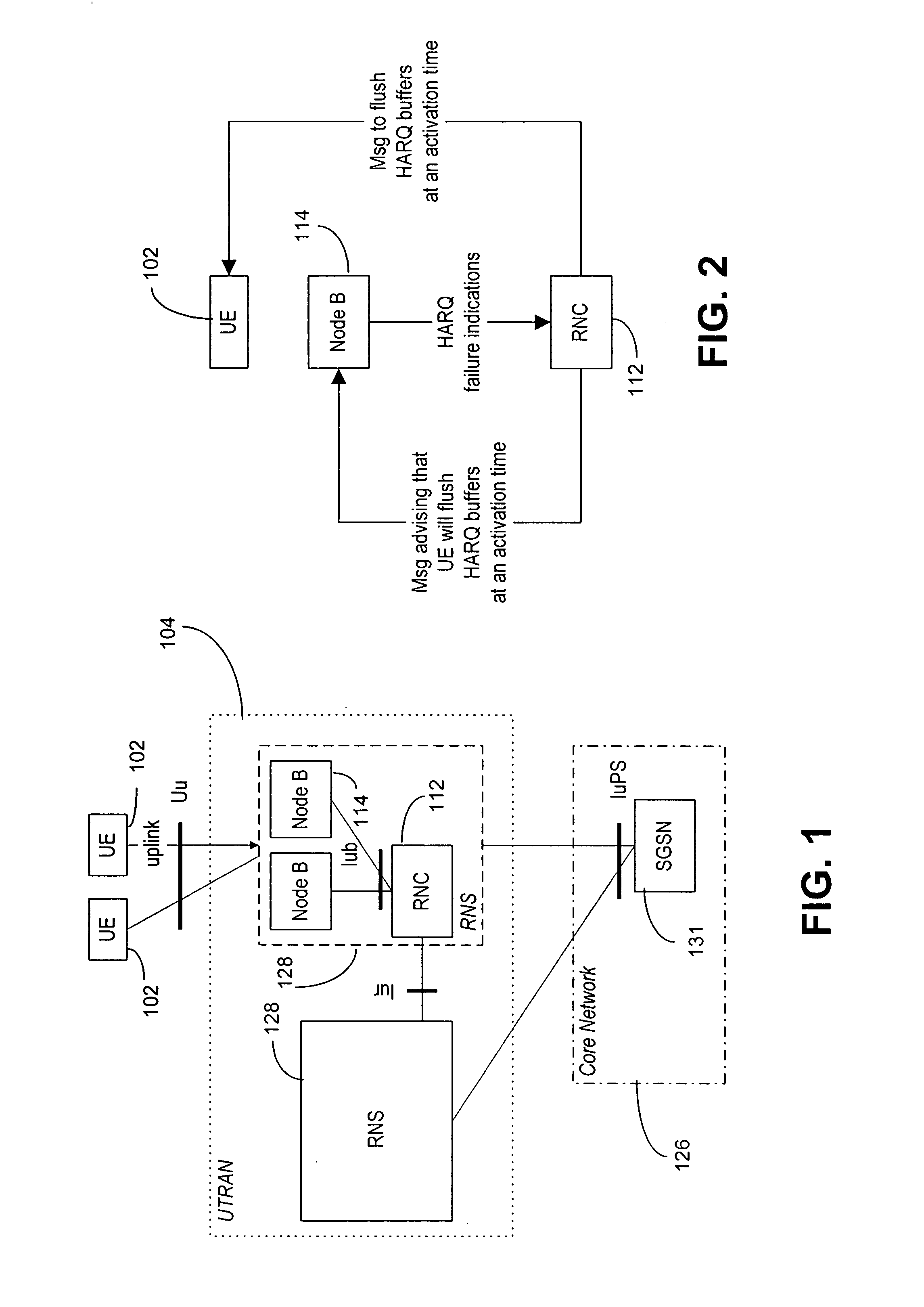
Method, apparatus and computer program for handling hybrid automatic repeat request failure
ActiveUS20080026741A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelAutomatic exchangesHybrid automatic repeat requestSoftware
A method by which a Node B is informed by a serving RNC that a MAC-e reset is to be performed by a UE in communication with the Node B, so that the Node B can then provide failure indications of all HARQ processes that are not decoded by the time of the MAC-e reset. Corresponding equipment and software is also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
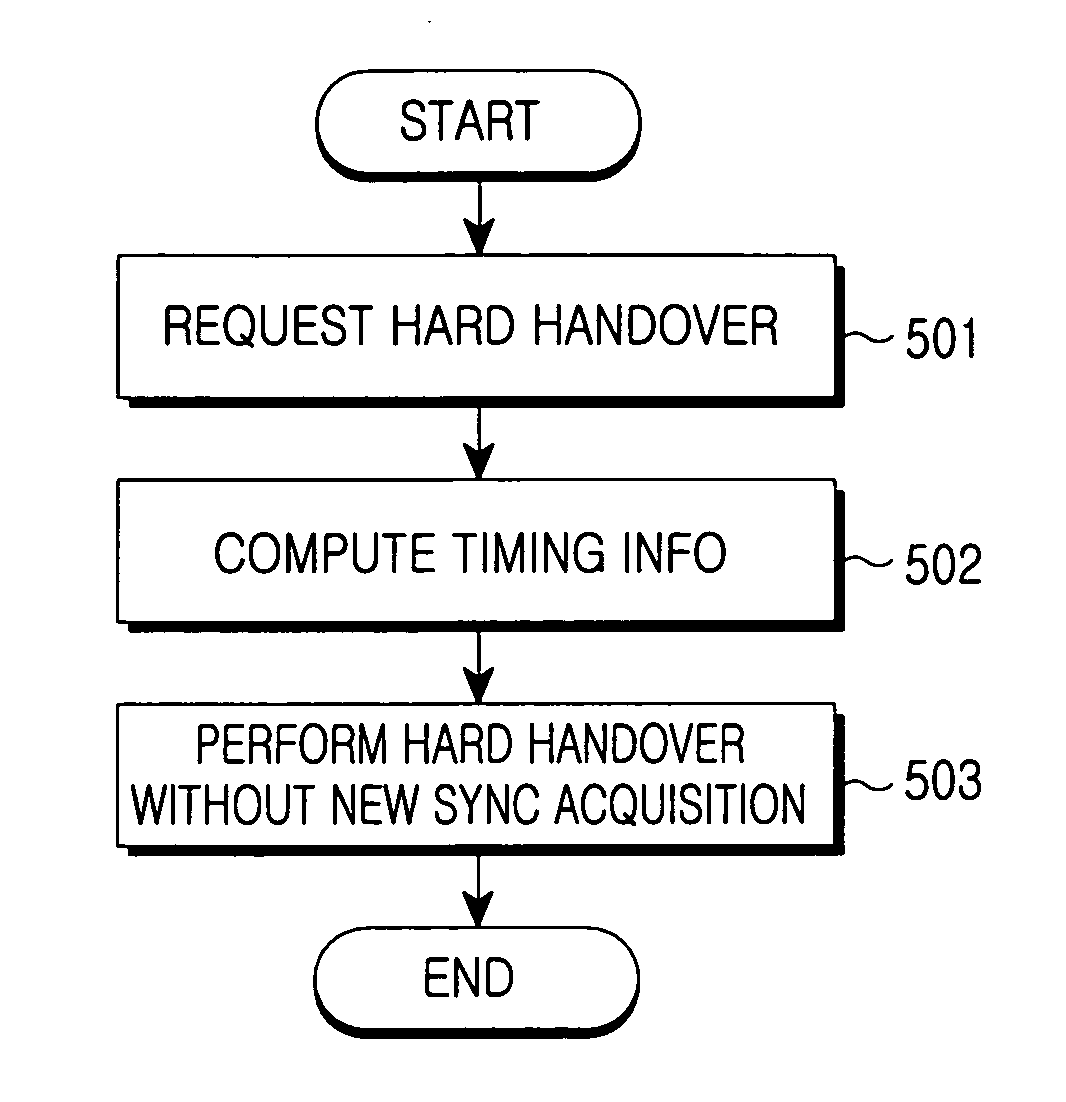
Hard handover method and radio network controller therefor in a mobile telecommunication system
InactiveUS20060270406A1Increase the likelihood of successShorten cut-off timeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemMobile communication systems
A hard handover method and a Radio Network Controller (RNC) therefor in a mobile telecommunication system are provided which can improve the performance of an interfrequency hard handover. The RNC stores information about a timing difference between first and second Node Bs for supporting a soft handover. When receiving, from a User Equipment (UE), a request for a hard handover from the first Node B to the second Node B, the RNC computes information about a timing difference between the Node Bs for the hard handover using the information about the timing difference between the Node Bs stored at a soft handover time. The RNC commands the second Node B and the UE to operate for the hard handover using the computed timing difference information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Arrangements and method for handling macro diversity in a universal mobile telecommunications system
InactiveUS20070197222A1Facilitates RNCsReduce transmission costsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionTransport layerTelecommunications network
The present invention relates to methods and arrangements for providing macro diversity, also referred to as diversity handover, DHO, related instructions to a node, e.g. a Node B, that is a part of a DHO connection in a mobile telecommunication network wherein the macro diversity functionality is distributed to a Radio Network Controller, RNC, and its connected Node Bs in said network. The method comprises the steps of: including in a signaling message one or more transport layer addresses and one or more transport bearer reference parameters in order to direct one or more data flows of the DHO connection, and sending said signaling message to said node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for transmission and reception of signals and related method of signaling
A base station (e.g., an evolved Node B) (300) determines whether the physical broadcast channel (PBCH), reference signals (SCH) and common reference signals (CRS) are transmitted (or awaiting transmission) on a secondary component carrier (Scell) with the cell (506). The determination information is transmitted to a user equipment (UE) (110) to inform the UE that the Scell transmissions do not include PBCH / SCH / CRS (508). As a result, the resource elements (REs) normally used to carry system information in the PBCH / SCH / CRS can be dynamically assigned (or reassigned) to the data channel. In this manner, the physical downlink shared channel (PBSCH) bandwidth can be increased by utilizing those resource elements that are normally reserved / assigned to the PBCH / SCH / CRS.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
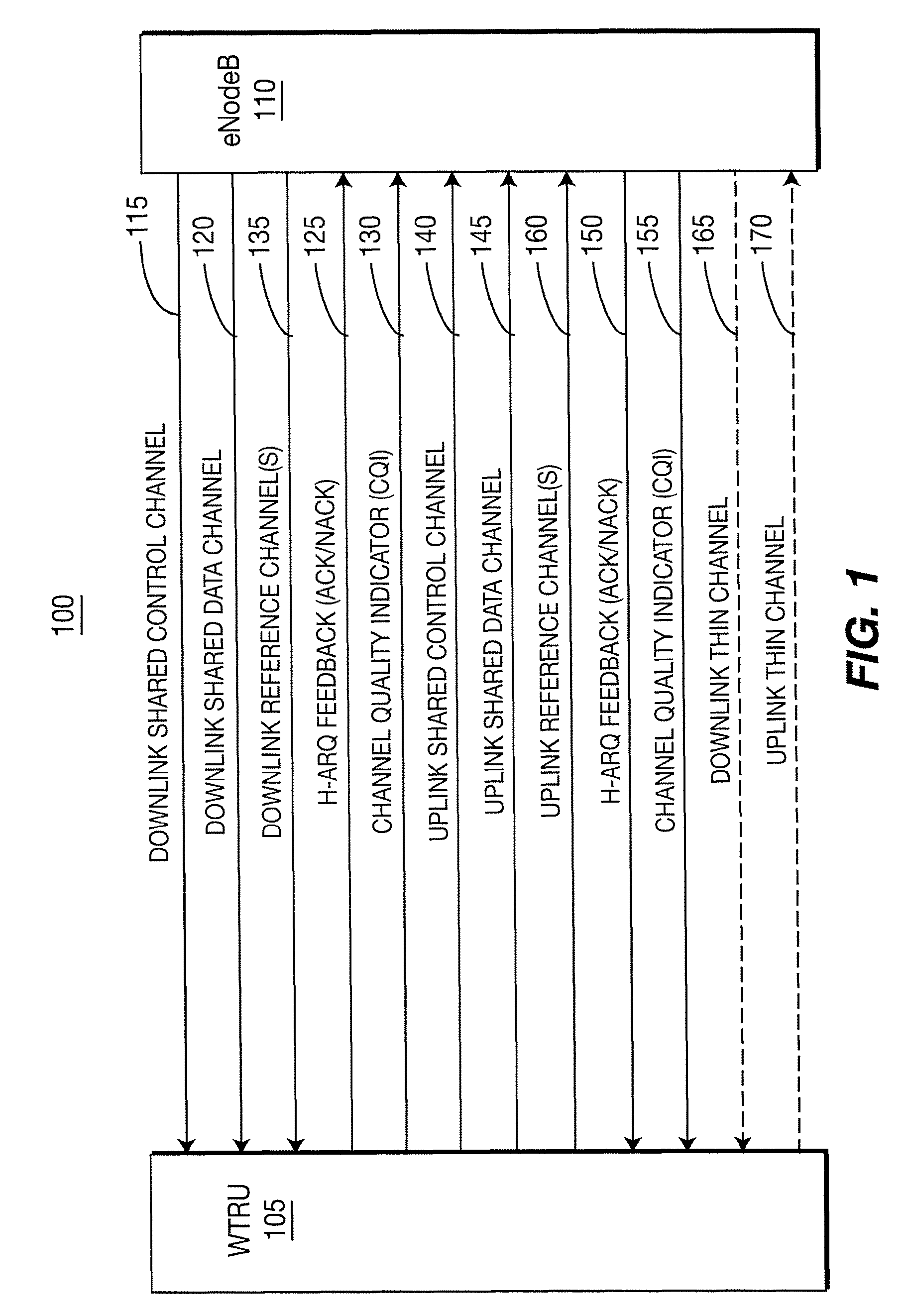
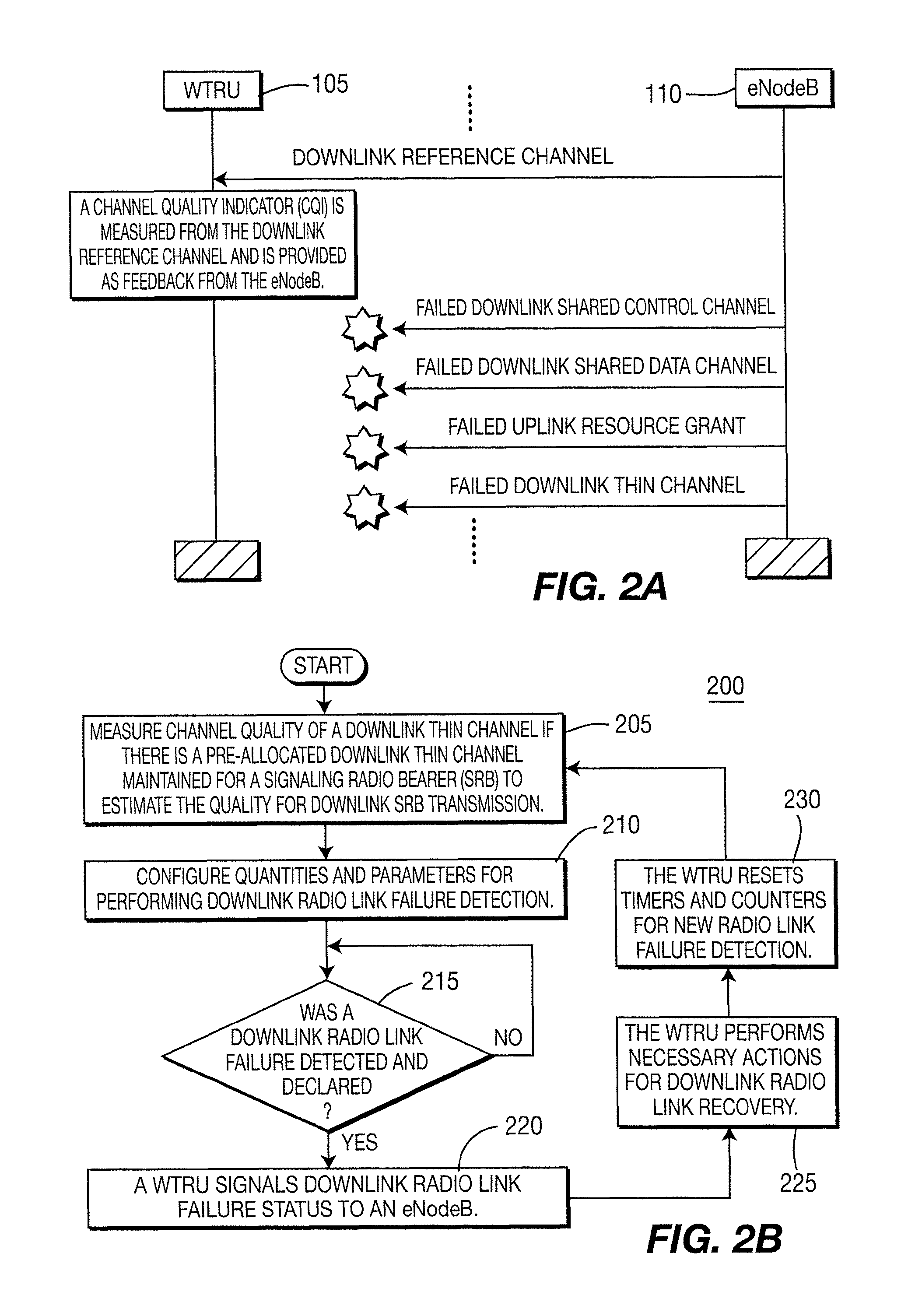
Radio link failure detection procedures in long term evolution uplink and downlink and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS8126021B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelSynchronisation arrangementCommunications systemRadio link failures
Owner:GUANGDONG NUFRONT COMP SYST CHIP +1
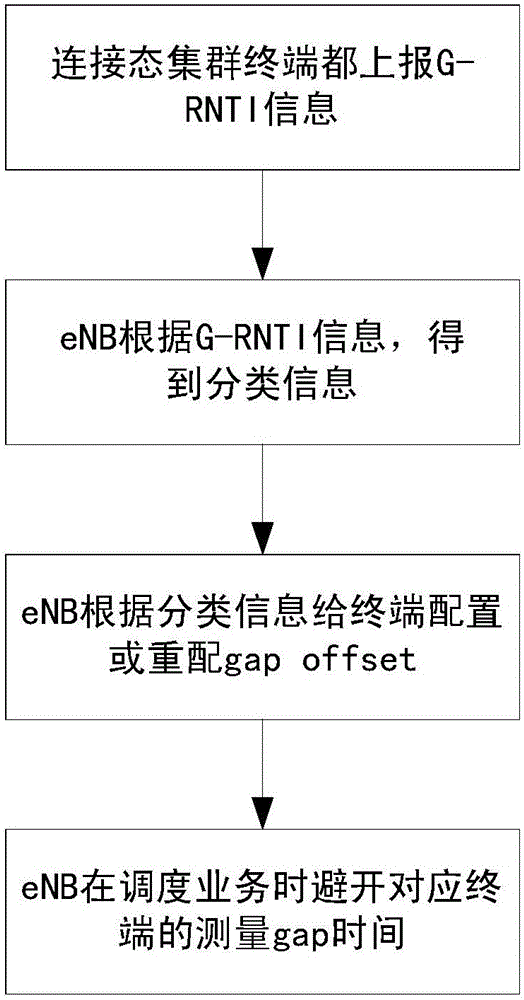
LTE (Long Term Evolution) trunking service and non-trunking service-coexisting measurement gap allocation method
InactiveCN106304133ADoes not affect mobilityAvoid wastingConnection managementTrunkingRadio network temporary identifier
The present invention provides an LTE (Long Term Evolution) trunking service and non-trunking service-coexisting measurement gap allocation method. The method includes the following steps that: trunking terminals in connection states all report G-RNTI (Group Radio Network Temporary Identifier) information; an eNB (Evoluted Node B) obtains the classification information of trunking terminals and non-trunking terminals according to the received G-RNTI information; the eNB allocates or re-allocates gap offset for the terminals according to allocation principles and based on the received classification information, wherein the allocation principles are that: the gap offset of all the trunking terminals is identical, the gap offset of the non-trunking terminals is different from the gap offset of the trunking terminals, and the gap offset of the non-trunking terminals is different from each other; and when carrying out service dispatching, the eNB avoids the measurement gap time of corresponding terminals. With the measurement gap allocation method of the invention adopted, the trunking services of the trunking terminals in connection states are not affected, the mobility of the terminals is not be affected, and resource waste can be avoided.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Method and system for optimized reference signal downlink transmission in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS7808882B2Reduce MAISignal allocationFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemNetwork conditions
A method and system optimizes the transmission of a downlink reference signal (DLRS) in a wireless communication system that uses orthogonal division multiple access (OFDMA) for the downlink. Each Node-B (base station) is capable of transmitting the DLRS reference symbols in different subframes of the OFDM radio frame and changing both the number and location of the subframes in response to changing network conditions. The network conditions include the number of terminals being served by the Node-B and multiple access interference (MAI) from adjacent Node-Bs.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
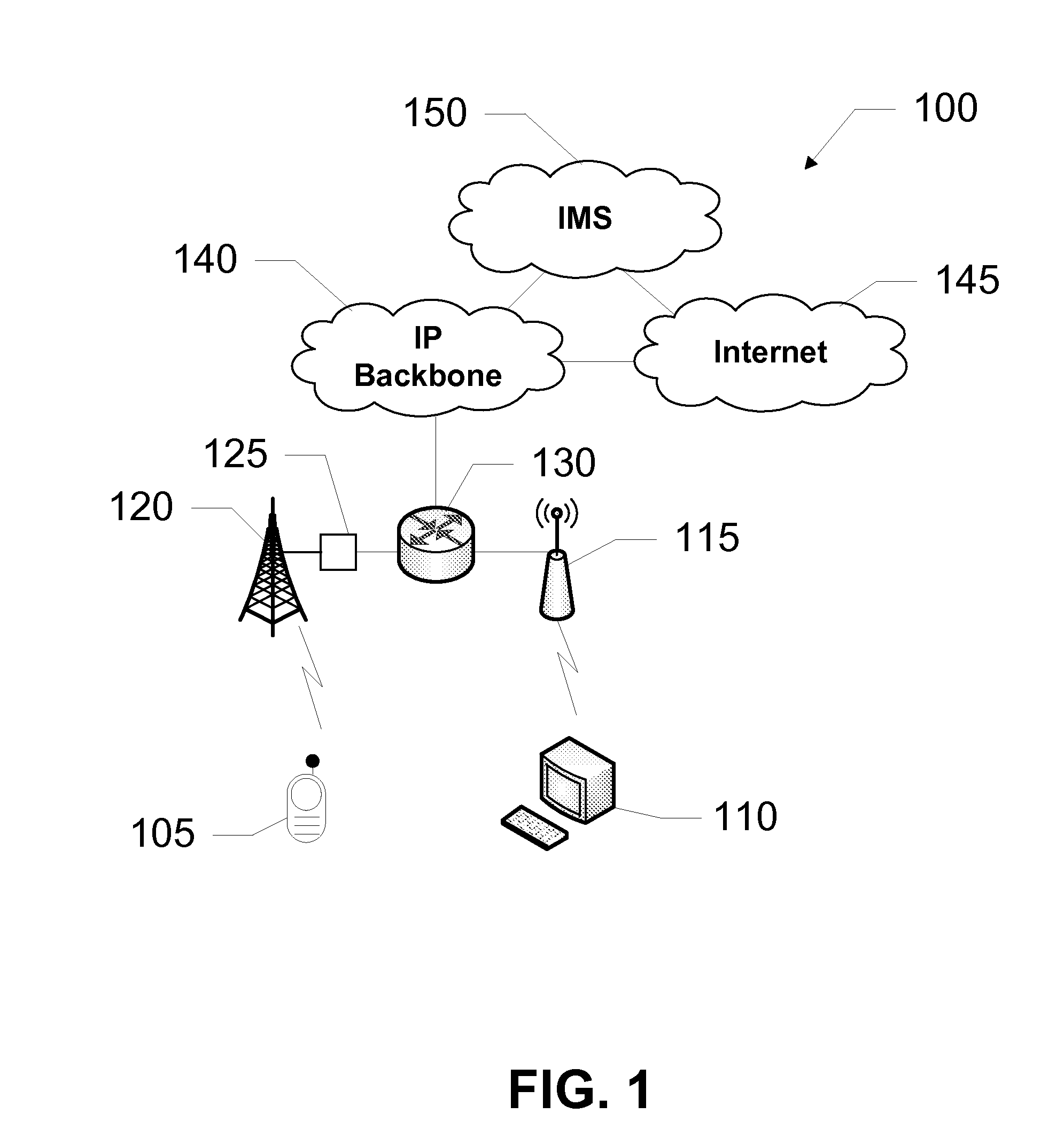
Mobile communication base station and system
ActiveCN1859656ARealize the establishmentAchieve connectionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksData terminalTelecommunications
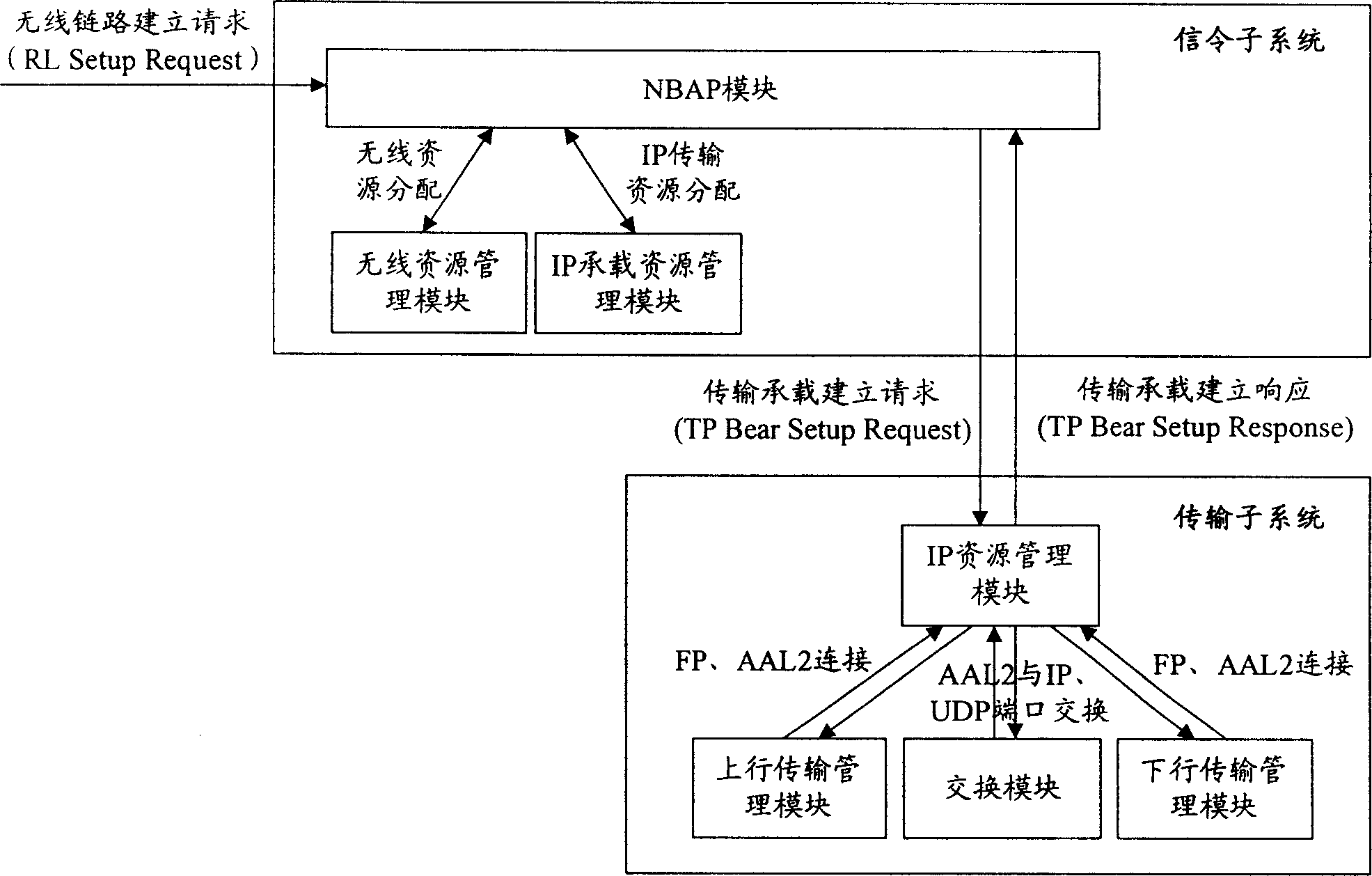
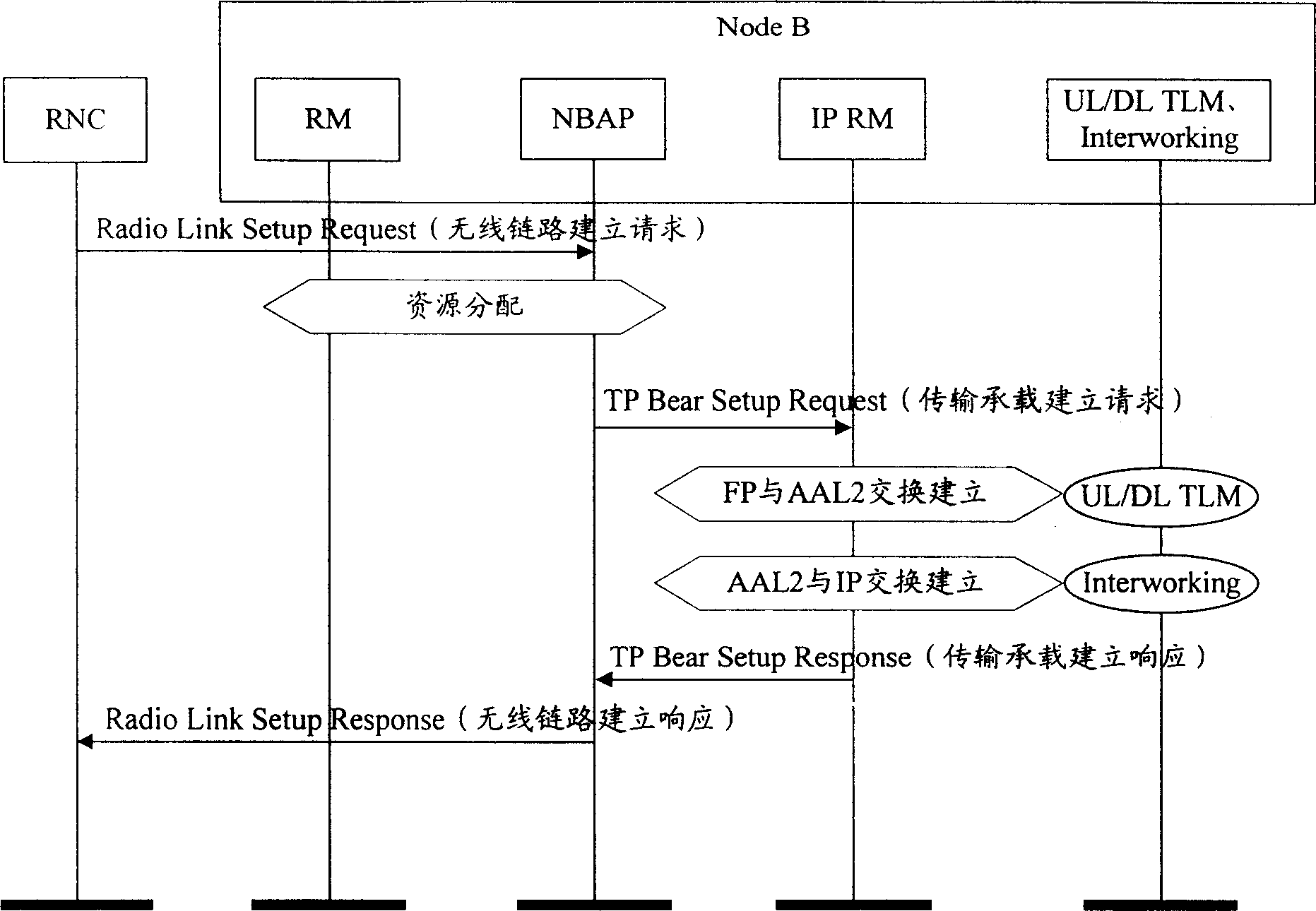
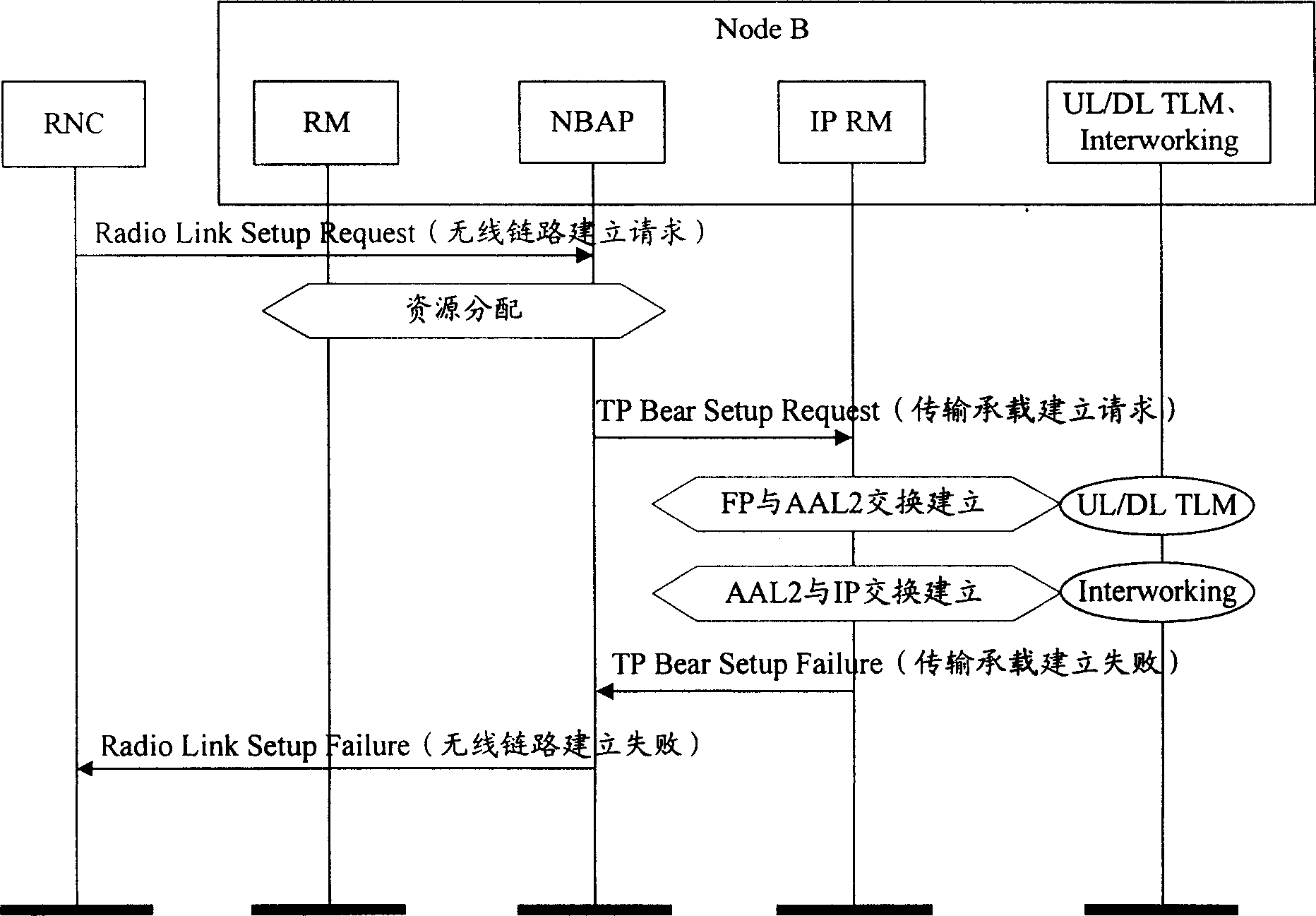
The present invention provides mobile base station and system suitable for mobile communication field. It contains signaling subsystem and transmission subsystem, wherein said signaling subsystem corresponding signaling control surface, said transmission subsystem corresponding transport network control surface, said signaling subsystem and transmission subsystem through transmission bearing establishing message distribution relating to transmission wireless resource and IP transmission bearing resource, establishing base station inner transmission channel; said relating to transmission wireless resource including uplink wireless link resource and downlink wireless link resource; said IP transmission bearing resource including said base station IP address and user data terminal number. The present invention can establish IP mode Node B interior transmission channel, and connection between Node B internal interface and Iub interface.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
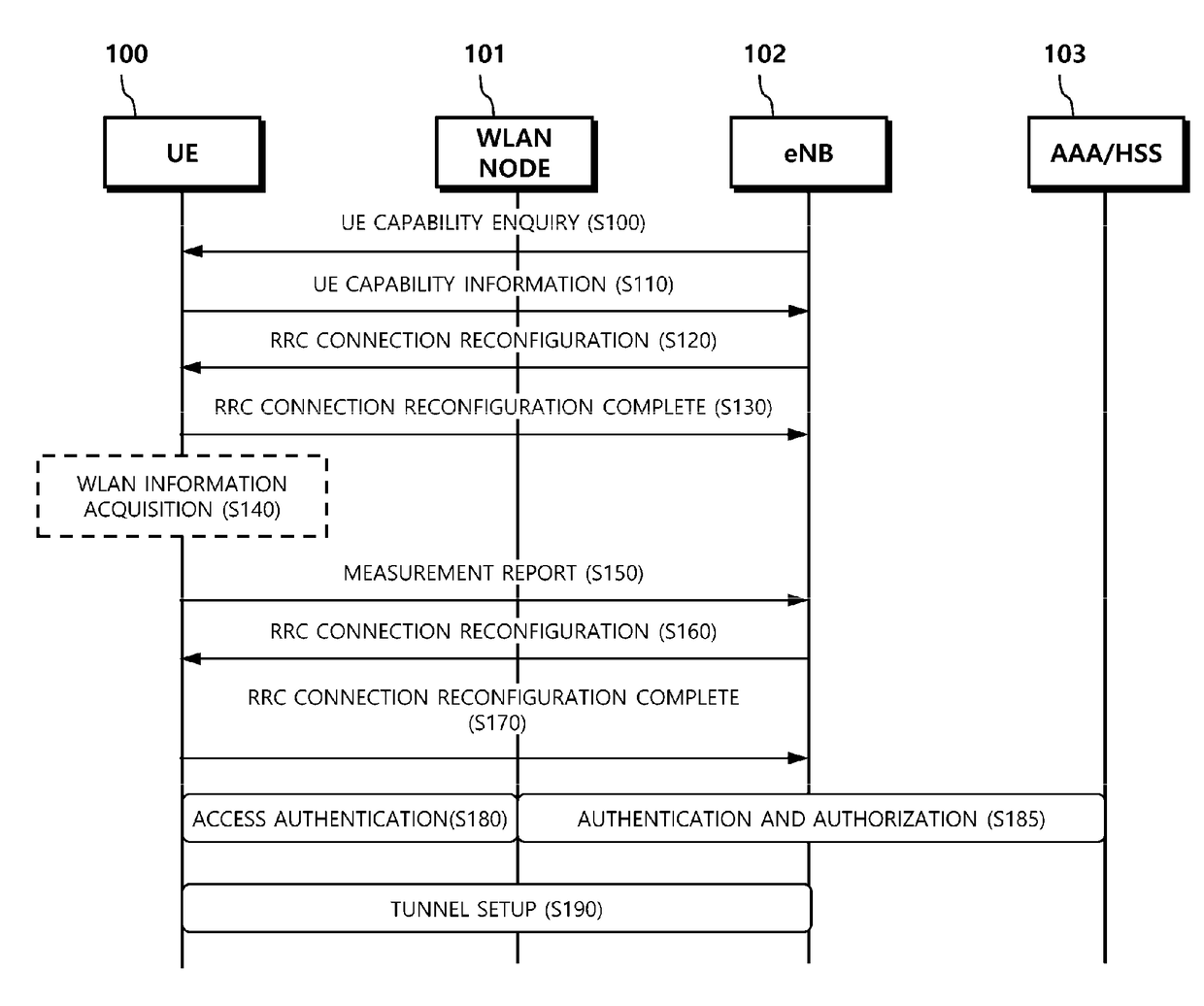
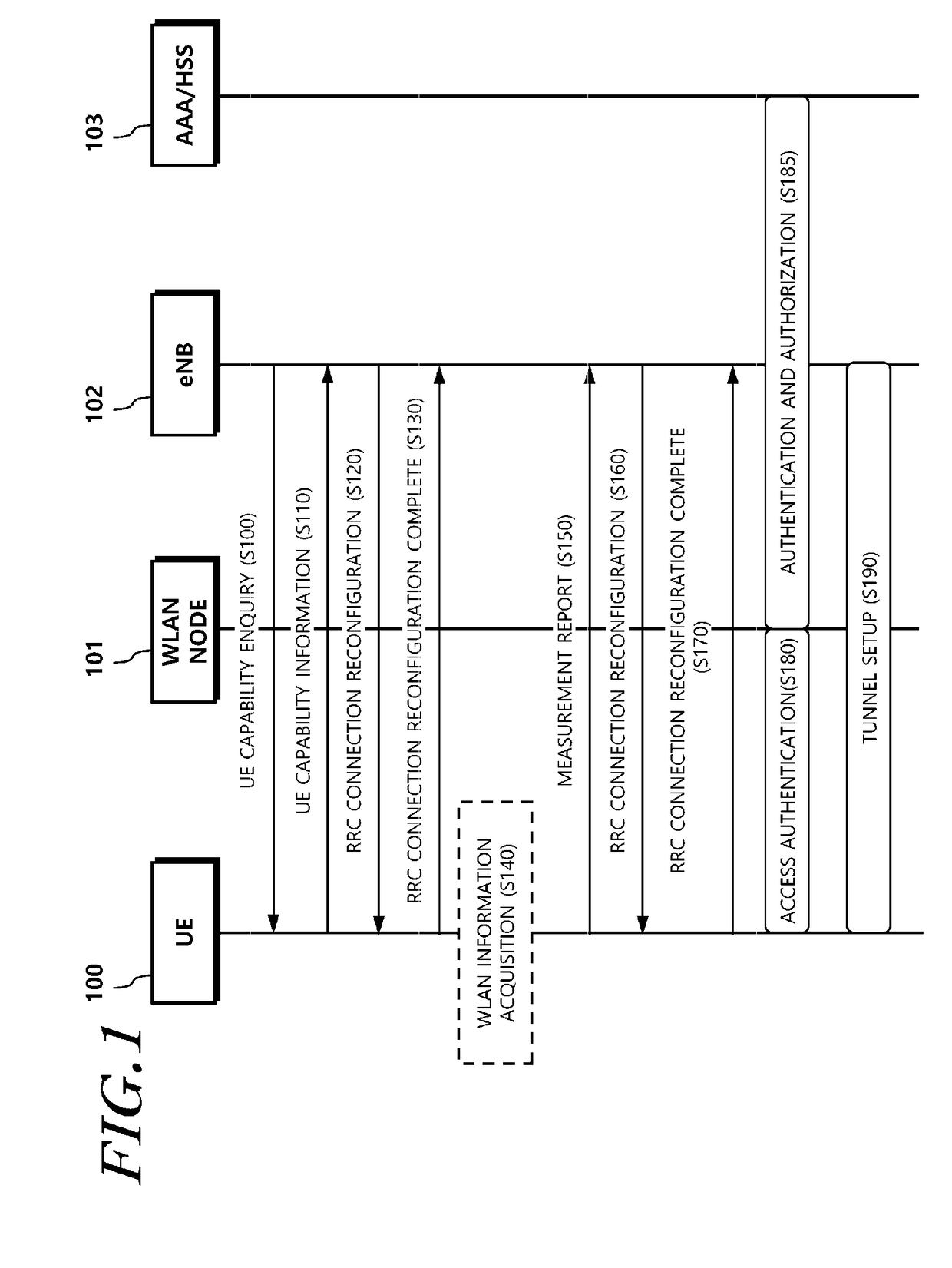
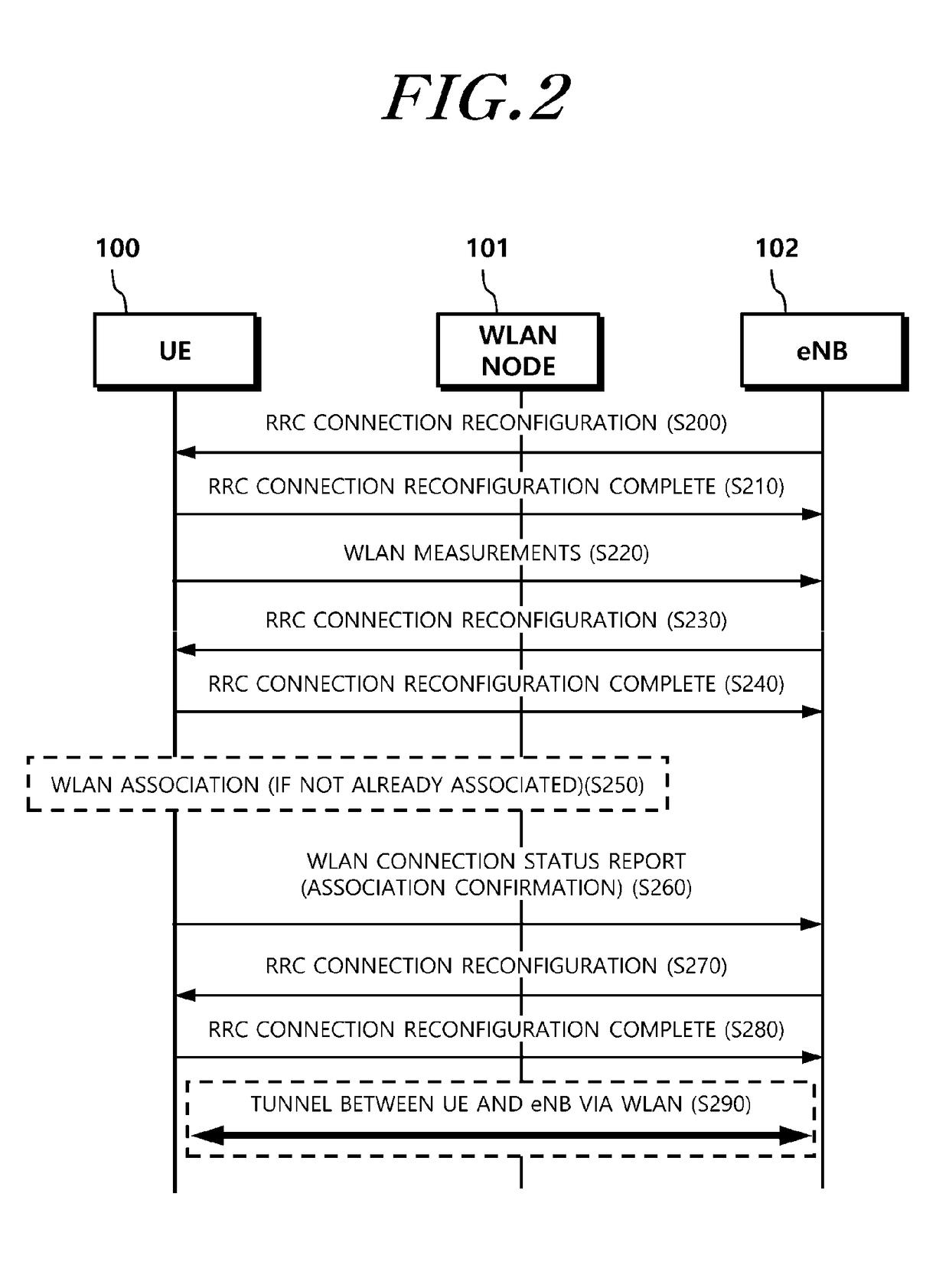
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving data using WLAN radio resources
ActiveUS20170094700A1Increase capacityImprove processing speedAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsRadio access network
Provided is a method and apparatus for processing control plane data to enable an evolve Node B (eNB) and a User Equipment (UE) to transmit and / or receive user plane data through a WLAN carrier when the user plane data is transmitted by adding a WLAN radio resource to an E-UTRAN carrier in a radio access network (RAN) level. Particularly, provided is a method for a UE to transmit and receive data, the method including: receiving, from an eNB, wireless local area network (WLAN) cell configuration information which is for transmitting and receiving data using a WLAN radio resource; performing WLAN association based on the WLAN cell configuration information; transmitting a WLAN access confirmation message to the eNB; and receiving, from the eNB through a higher layer signaling, tunnel configuration information which is for the UE to set up a tunnel with the eNB through the WLAN radio resource.
Owner:KT CORP
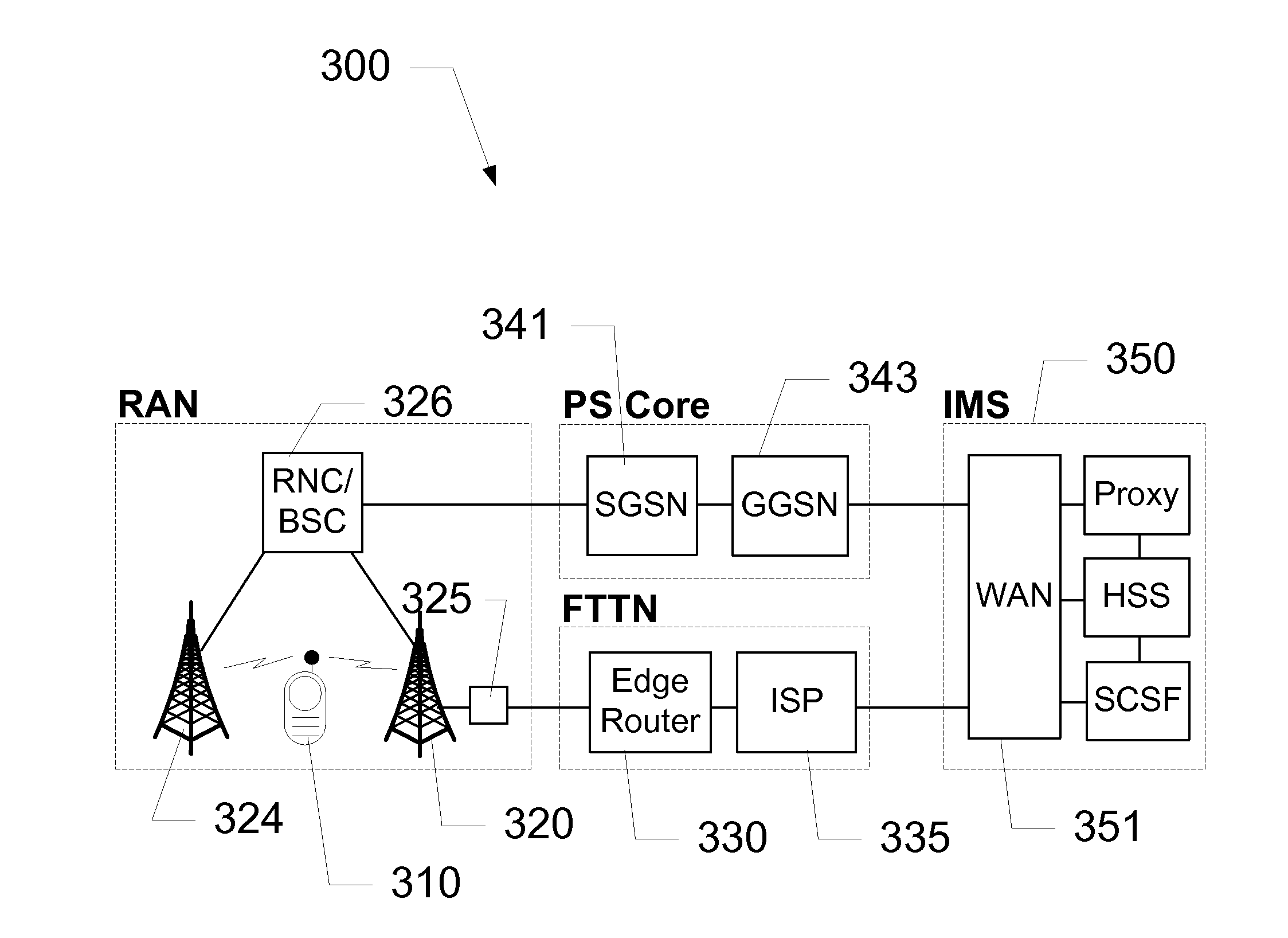
Radio Access Network Node With IP Interface
ActiveUS20120014317A1Wireless network protocolsWireless commuication servicesGPRS core networkRadio access network
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed to directly connect a node of a Radio Access Network (RAN) with an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The node is provided with an interface to a broadband local loop network. Access to the local loop network or last mile enables the node to communicate directly with an IP network, including an IP Multimedia System (IMS) core. The node need not access a packet-switched core network via a controller. Embodiments include a Node B with an IP interface in a UMTS system and a Base Transceiver Station (BTS) with an IP interface in a GSM system.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
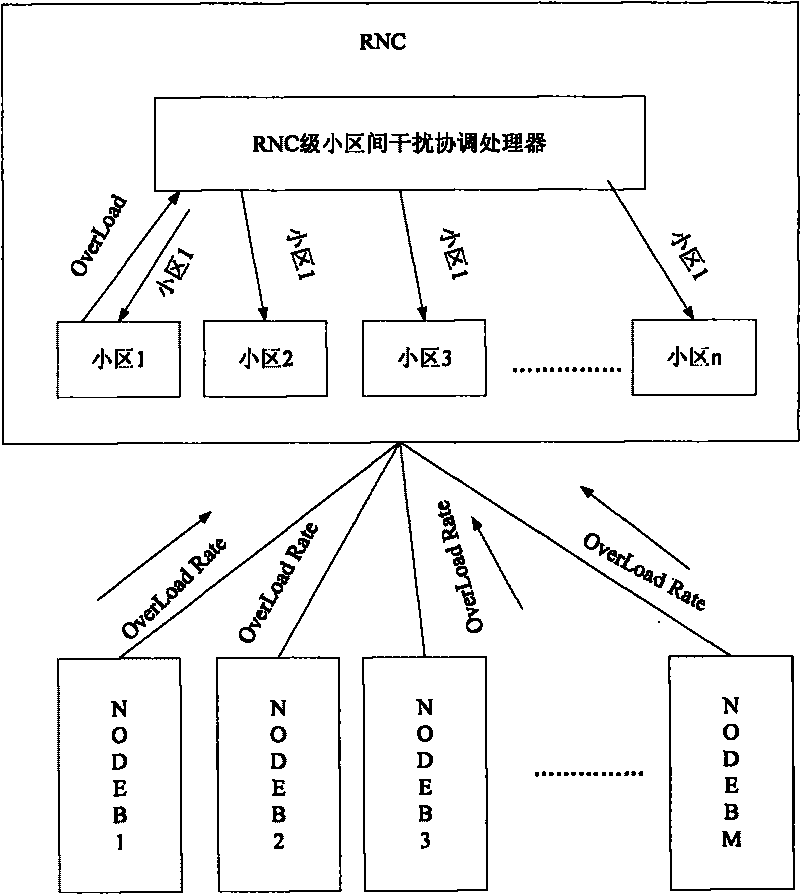
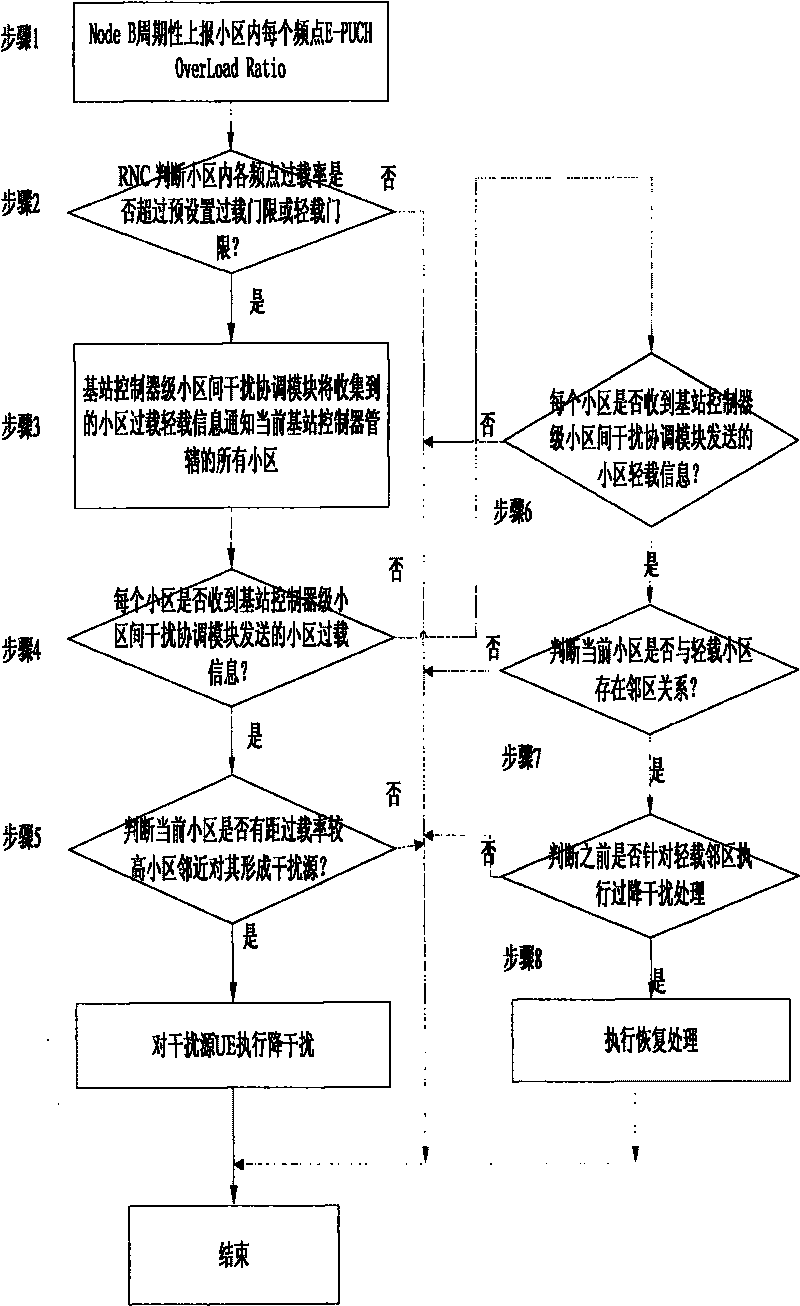
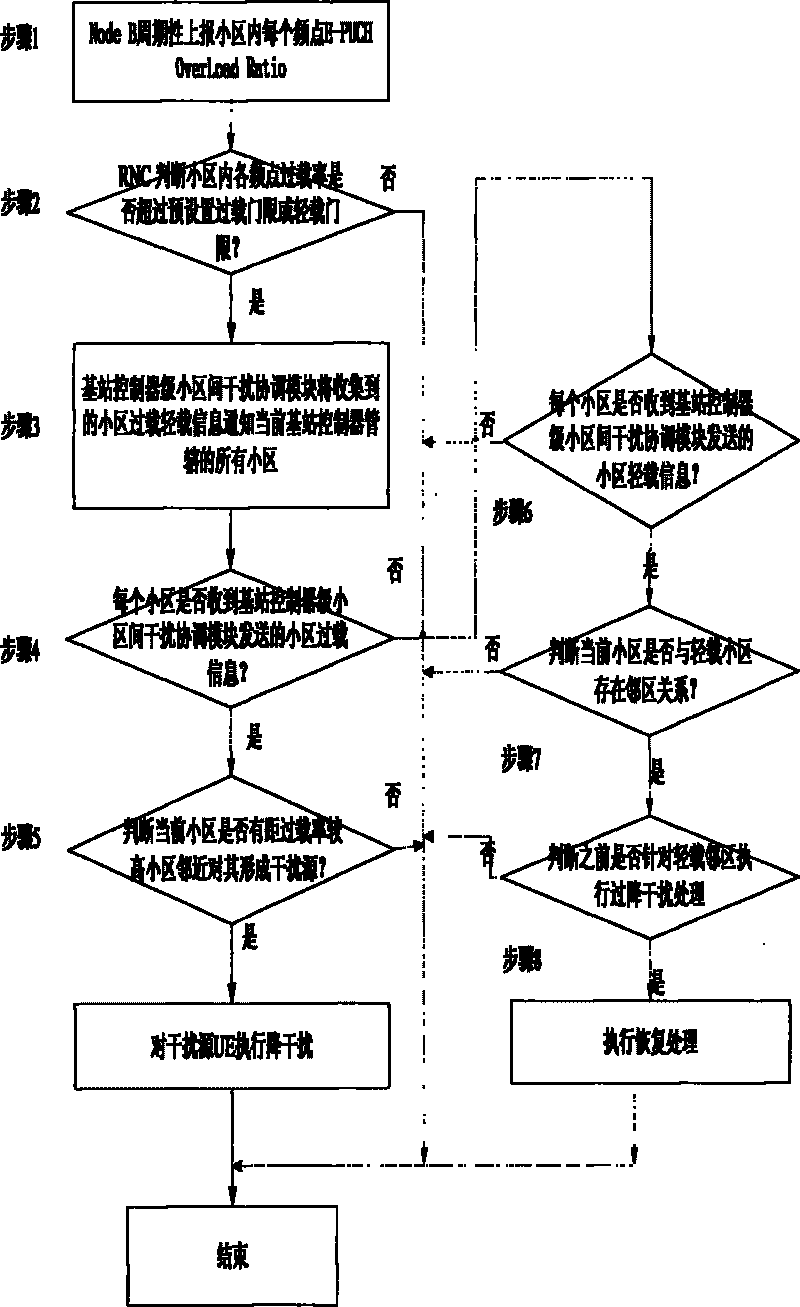
Method for coordinating interferences among HSUPA substricts in TD - SCDMA system
InactiveCN101765141AReduce the impactImprove throughputTransmissionWireless communicationEngineeringThroughput
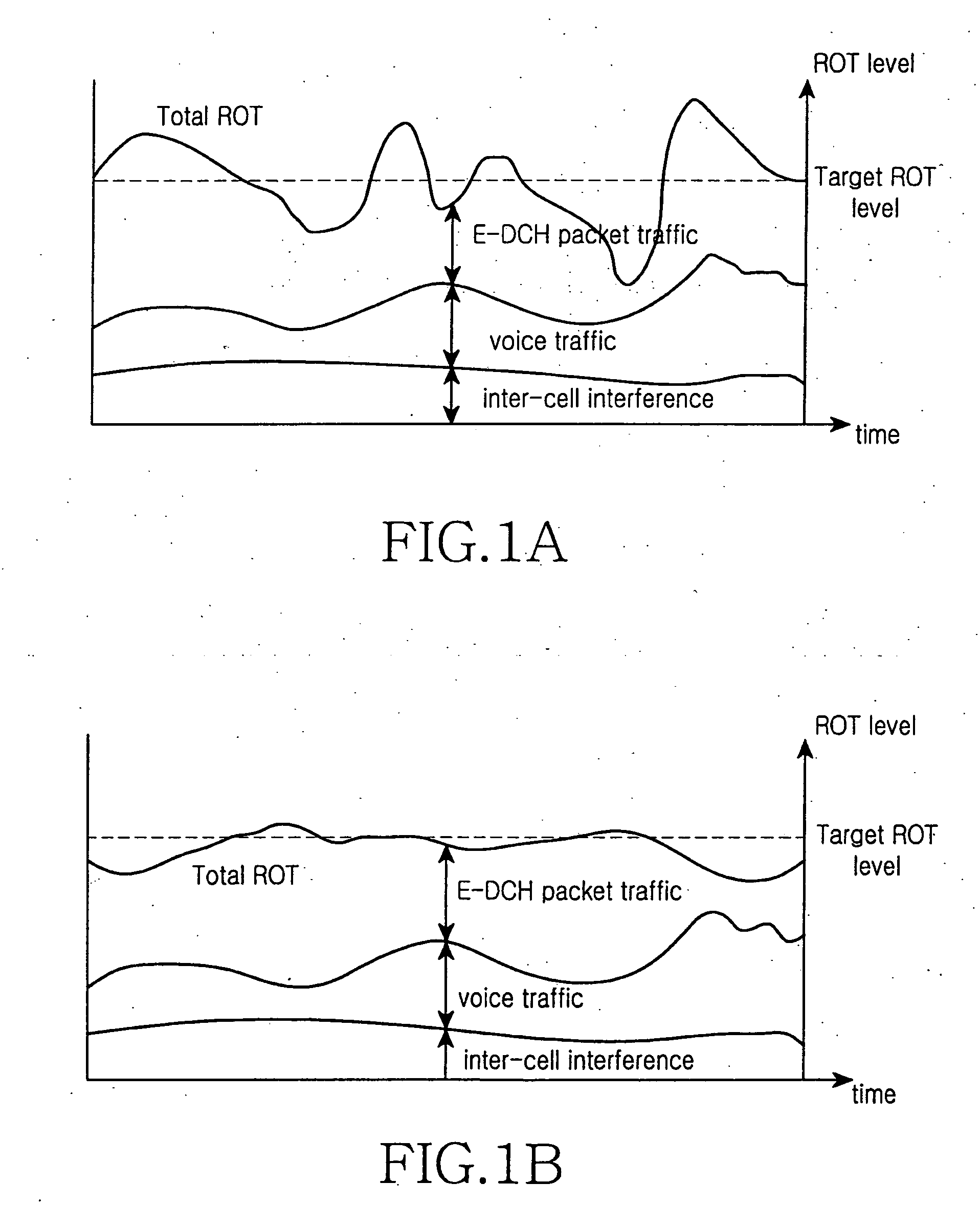
The present invention provides new public measurement of E-PUCH Overload Ratio, which is defined as the following: the E-PUCH Overload Ratio: the ratio of times that the average interference of time gaps for loading E-PUCH source in every 5ms TTI is above ROT threshold to the total number of TTI in an appointed period is counted in a base station (Node B) in an appointed period. The new public measurement can support period reporting. By the present invention, interference sources in nearby regions which bring the overload ratio of some subdistrict to high can be detected by the tactic of grades of a base station controller (RNC), and the effect of the interference sources is reduced by reasonable measures. Disadvantages that the base station (Node B) can not know the information of the nearby regions, and a high overload ratio condition of the subdistrict can not be solved by controlling the interference of the nearby regions are solved well, and the HSUPA throughput ratio of a whole net can be effectively improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method, user equipment and base station for controlling discontinuous reception (DRX) in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20150327169A1Effective controlReduce power consumptionPower managementTransmission systemsCommunications systemComputer science
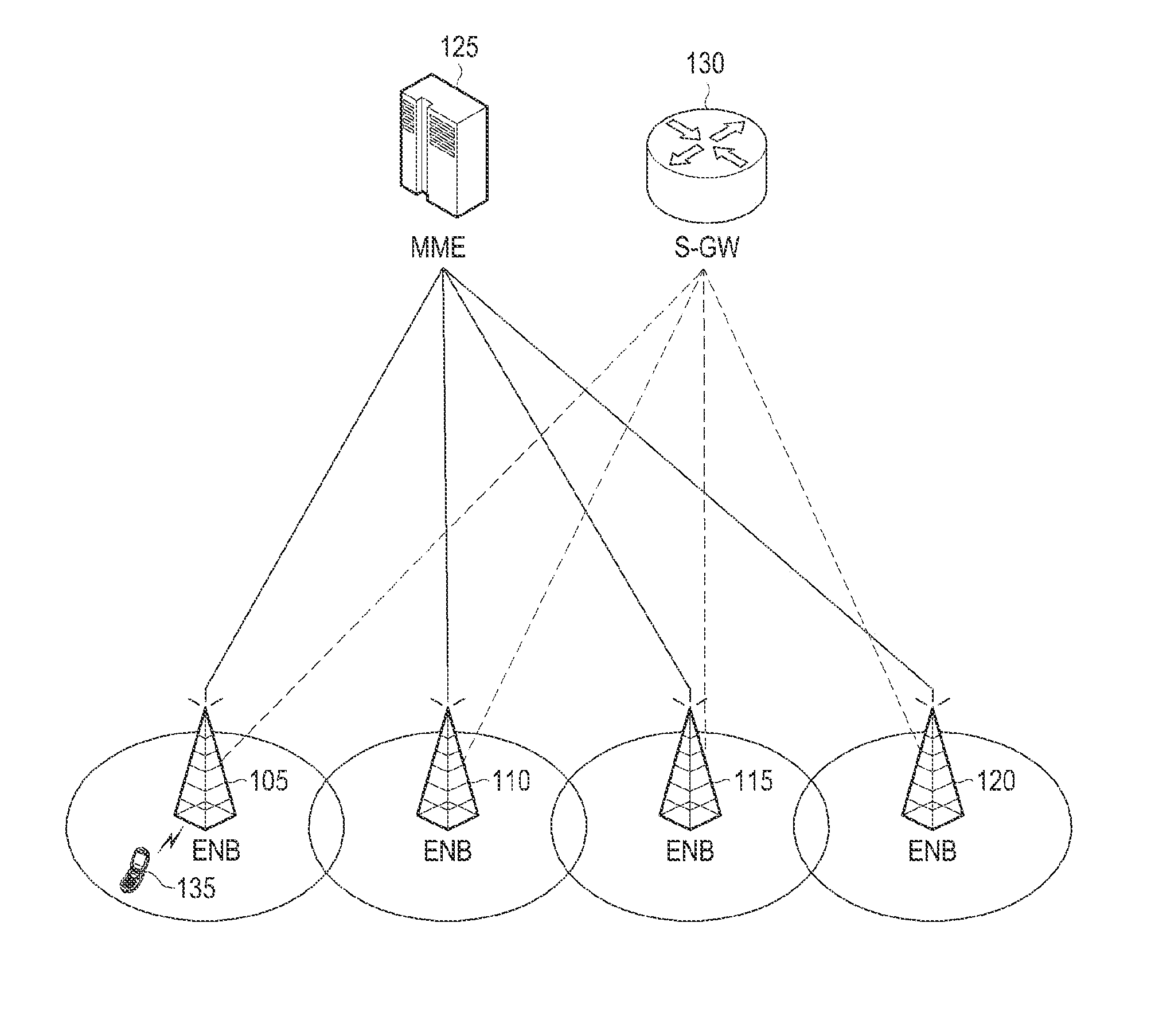
A method, a user equipment, an eNB are provided for controlling DRX in a wireless communication system. A method includes receiving, from a master evolved Node B (MeNB), an indication that a Slave eNB (SeNB) is to be monitored; and monitoring the SeNB, in response to the indicator. The present disclosure relates to a pre-5th-Generation (5G) or 5G communication system to be provided for supporting higher data rates Beyond 4th-Generation (4G) communication system such as Long Term Evolution (LTE).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
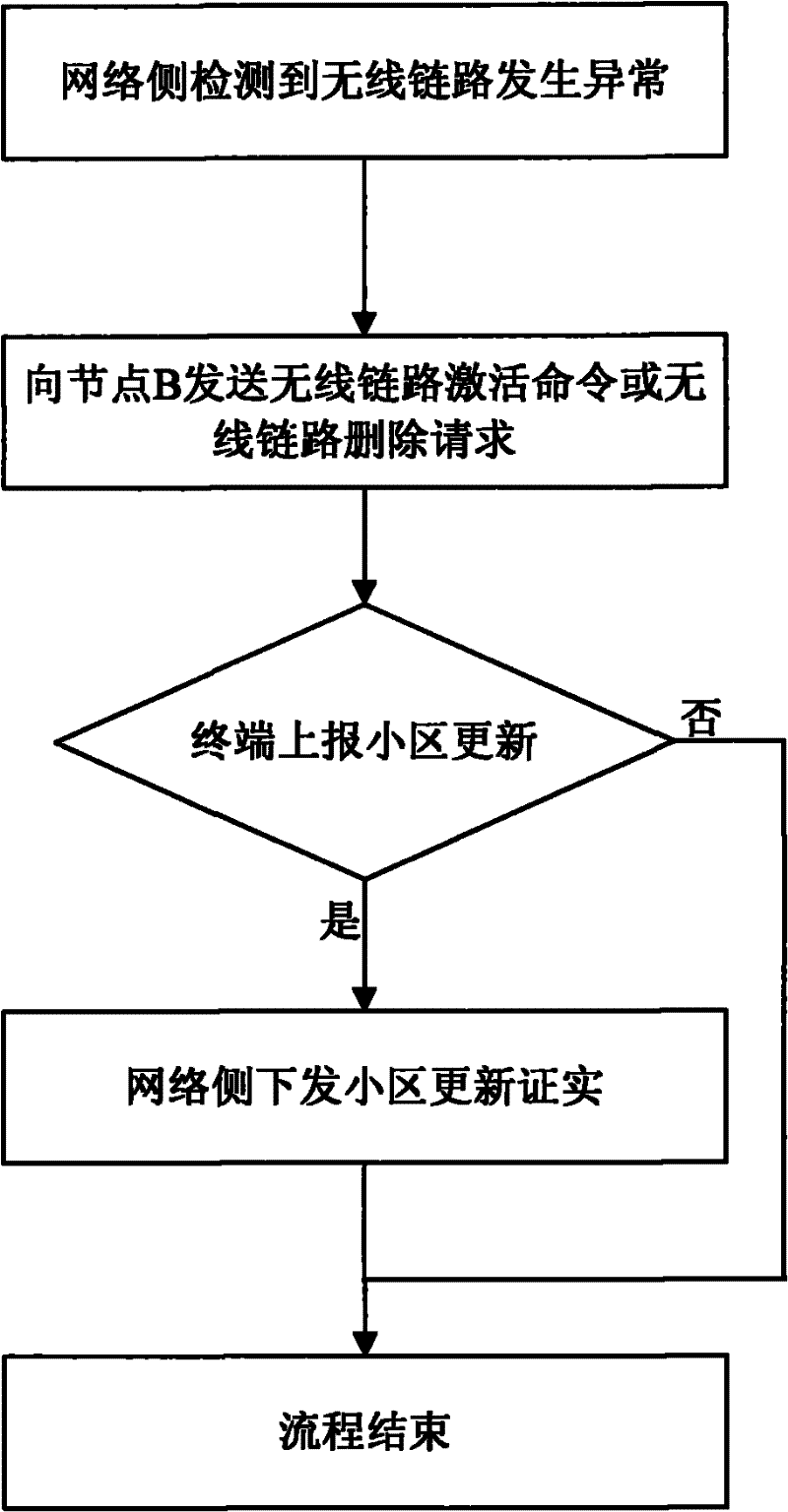
A Network Side Rescue Method for Service Abnormality in the Third Generation Communication Network
ActiveCN102291710ASave dropped callsImprove drop call rate indicatorsConnection managementNetwork data managementUser needsTelecommunications
The present invention discloses a network-side rescue method for service abnormality in a third-generation communication network. The steps of the rescue method include: after the wireless network controller judges that the wireless link is abnormal, the node B stops the downlink power transmission, and makes the terminal in the downlink direction If the wireless link fails, actively search for the cell and report the cell update message to the radio network controller; the radio network controller receives the cell update message, deletes the wireless link, establishes a new wireless link, and sends a cell update confirmation to the terminal The message enables the terminal to synchronize on the new wireless link, and sends physical channel reconfiguration, transport channel reconfiguration, and radio bearer reconfiguration completion messages to the network side. According to the feature that the terminal actively reports the cell update to the network side when the downlink is out of sync, the present invention saves the call drop when the wireless environment or the network is abnormal, so that the user does not need to re-initiate the call operation, and not only improves the call drop rate index of the system , and bring convenience to users.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGXING SOFTWARE
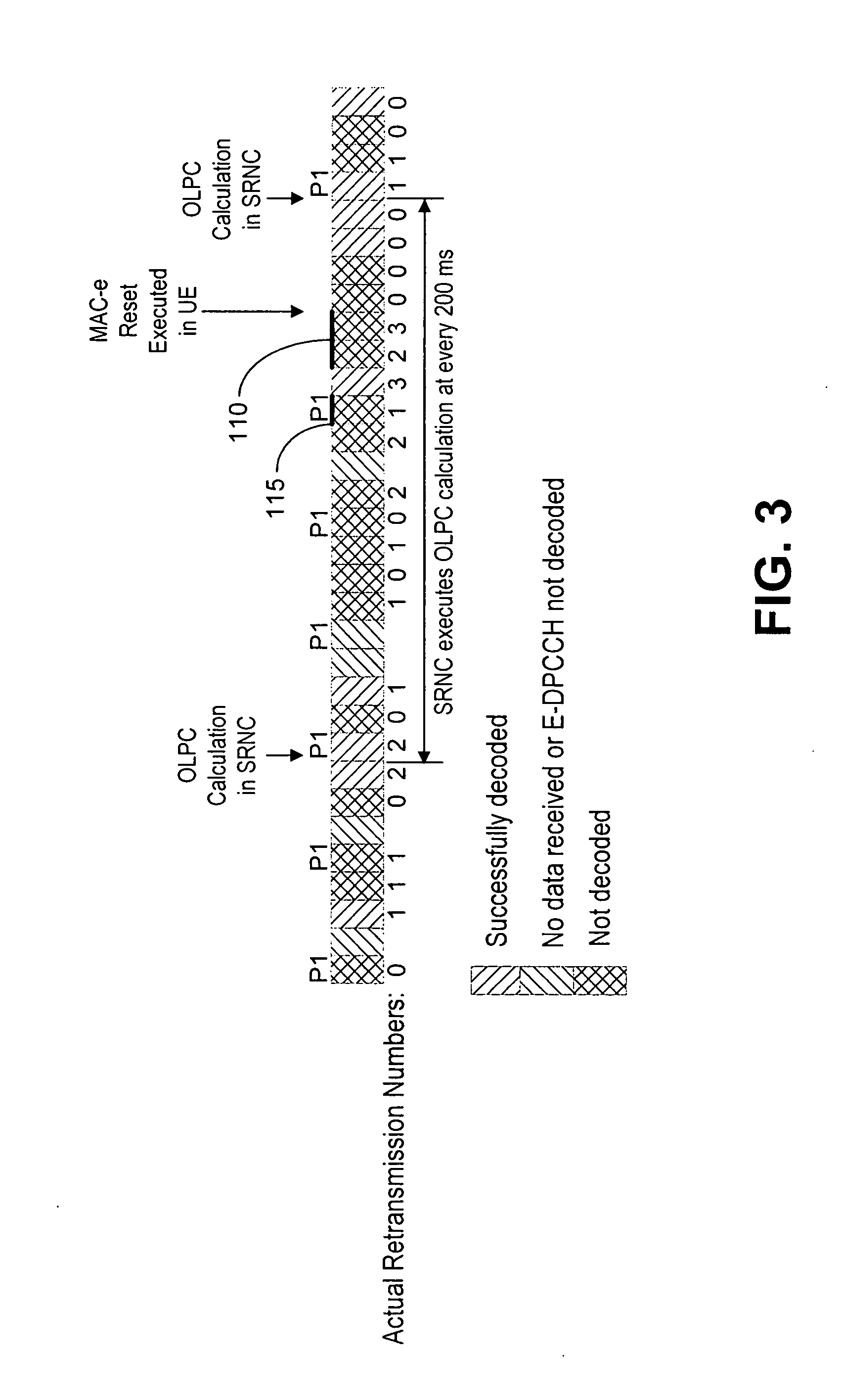
Equipment and method for controlling retransmission data ROT
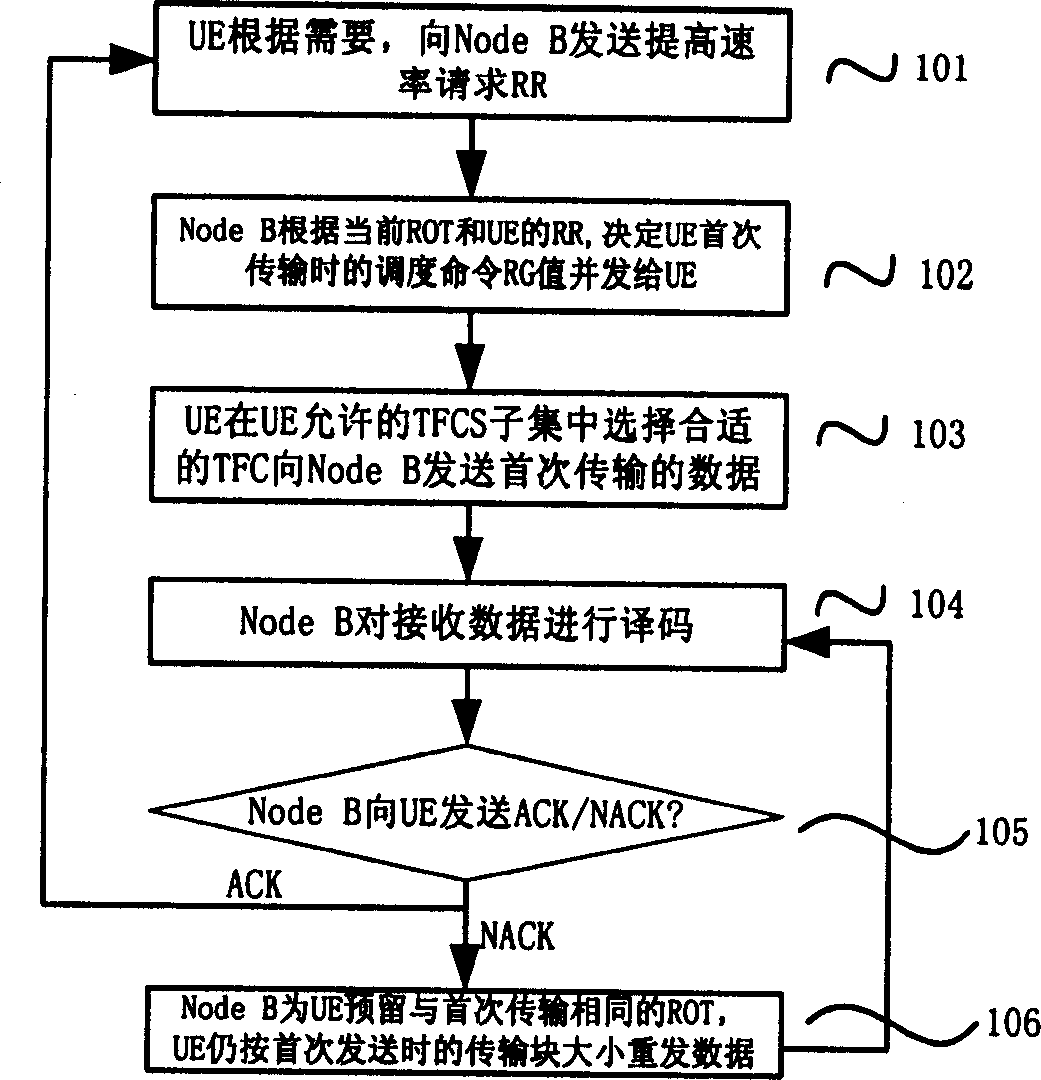
A method for controlling retransmission data ROT in the mode of speed regulation.This method includes the following steps:Node B decodes after receiving the data from UE,if coding is wrong,Node B sends NACK to UE and asks UE to retransmit the data.when retransmitting the data,Node B determines the change of aim ROT which is needed to retransmit data.Node B indicates the largest speed lifting that UE can use when retransmit by dispatching command RG.UE reckons the virtual transmission format combination according to the dispatching command RG from Node B so as to deduces the transmission power of the E-DPDCH channel when retransmitting.UE sends retransmission data with the same virtual transmission format combination used in the first time and the transmission power.Node B determines the anticipant ROT in retransmission process according to the ROT of the current base station and the power of E-DPDCH coding correctly and indicates by dispitching command of physical layer.The dispatching command does not indicate the actual transmission speed but the virtual transmission speed which is the one that Node B expects the UE reach when retransmission.
Owner:BEIJING SAMSUNG TELECOM R&D CENT +1
Method and an arrangement for transport layer control signalling in utran supporting both atm and ip transport technologies
InactiveUS20070058553A1Reduces required signallingReduce stepsError preventionTransmission systemsTransport layerControl signal
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for controlling the user plane of a UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network, UTRAN, comprising a first edge node connected via a Transport Network Layer to a second edge node, by using Transport Network Layer, TNL, signalling. A radio link is set up by using the Node B Application Part between the first and second edge nodes of the UTRAN, RSVP-TE based TNL signalling messages are transmitted between said first and second edge nodes for each TNL flow, and each TNL flow is identified by using RSVP-TE messages, wherein the object SESSION and SENDER_TEMPLATE comprises an IP based 5-tuple flow information, which is adapted to be used as a TNL flow identity.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com