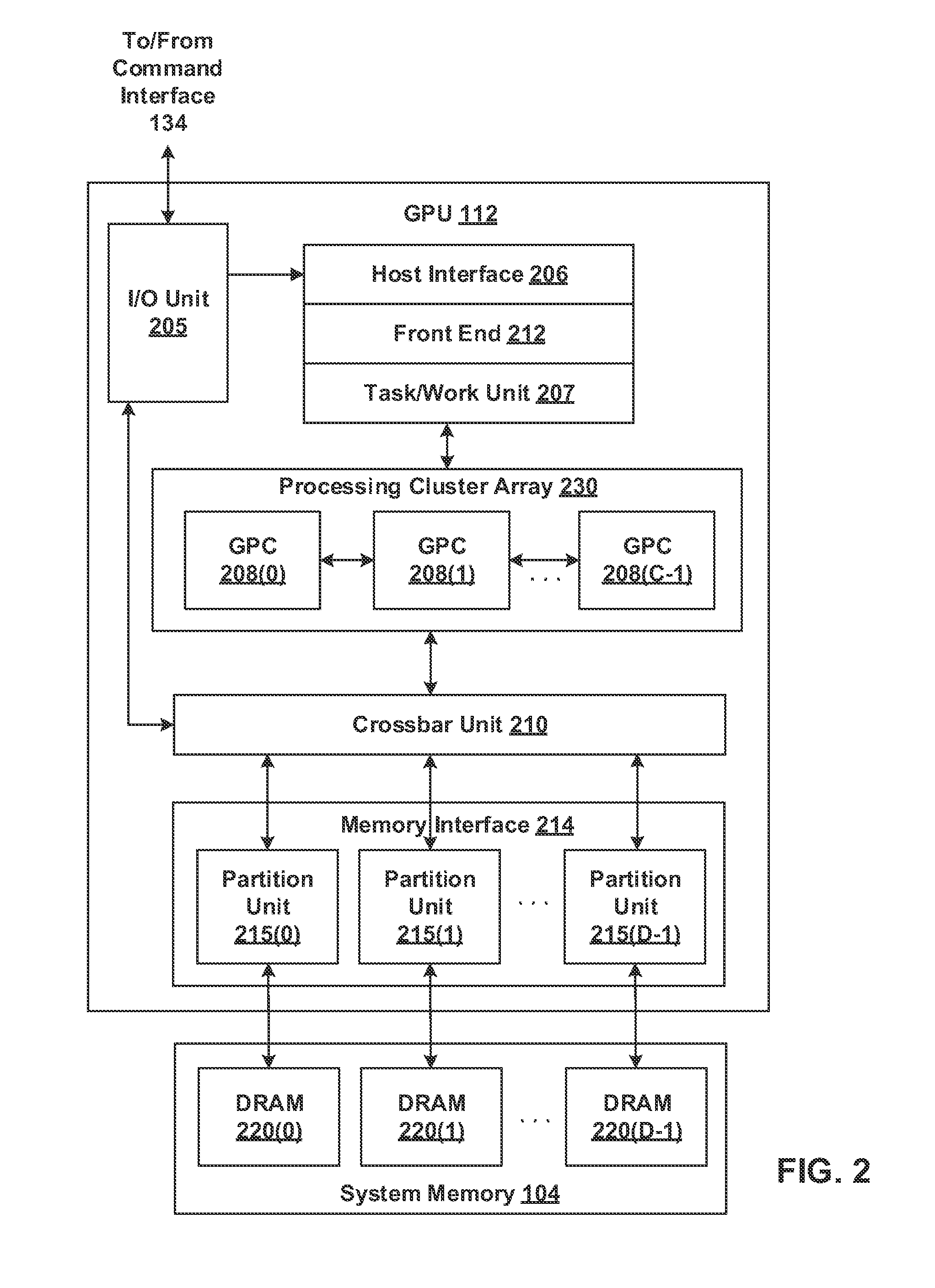
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10107 results about "Synchronization signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Signal Synchronization. Signal Synchronization Signal synchronization is a standard procedure of signal timing. It may be provided by triggers. A trigger is the easiest device used to avoid spurious pulses of combinational circuit output which occur if several input signals are changed almost at the same time.
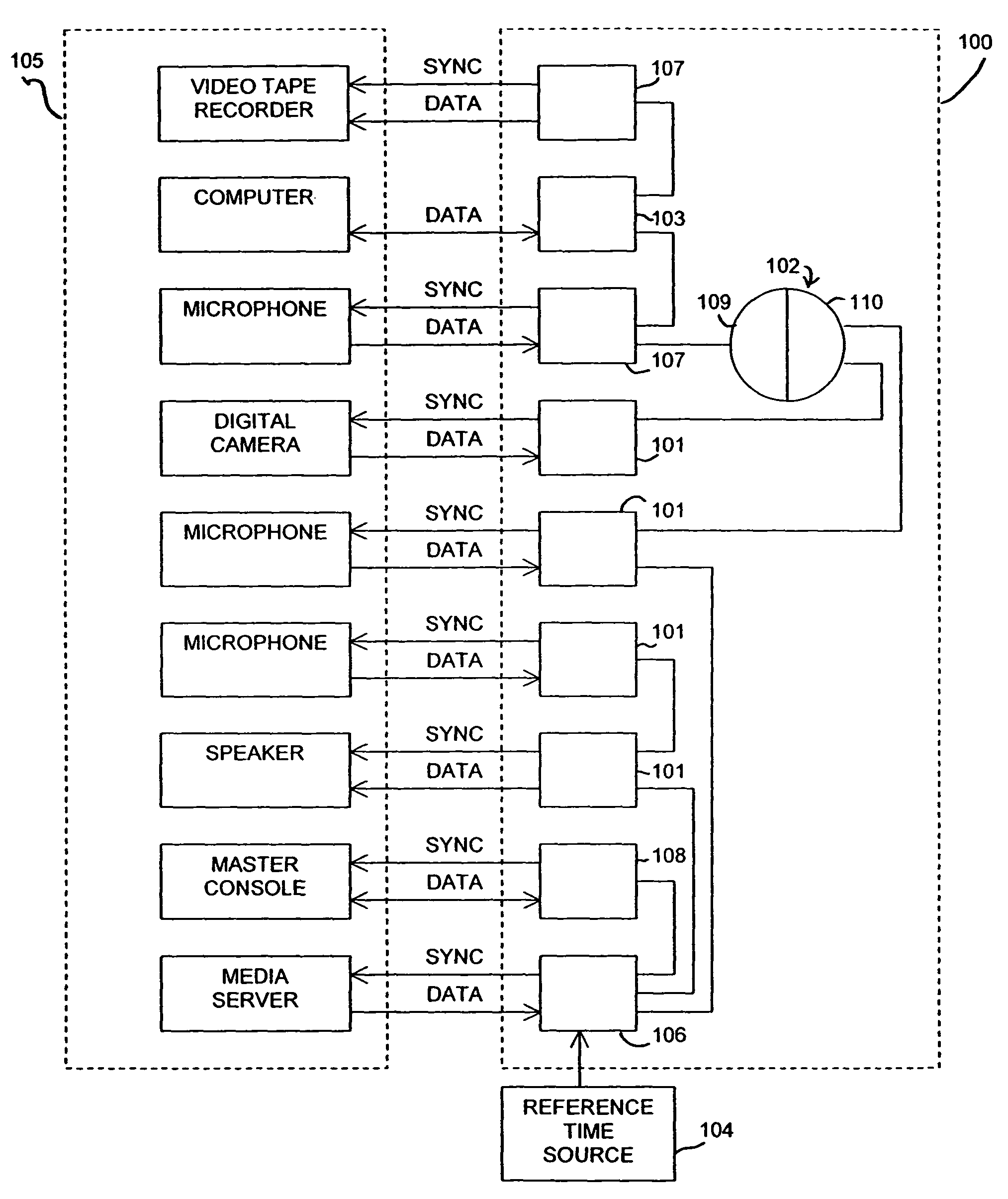
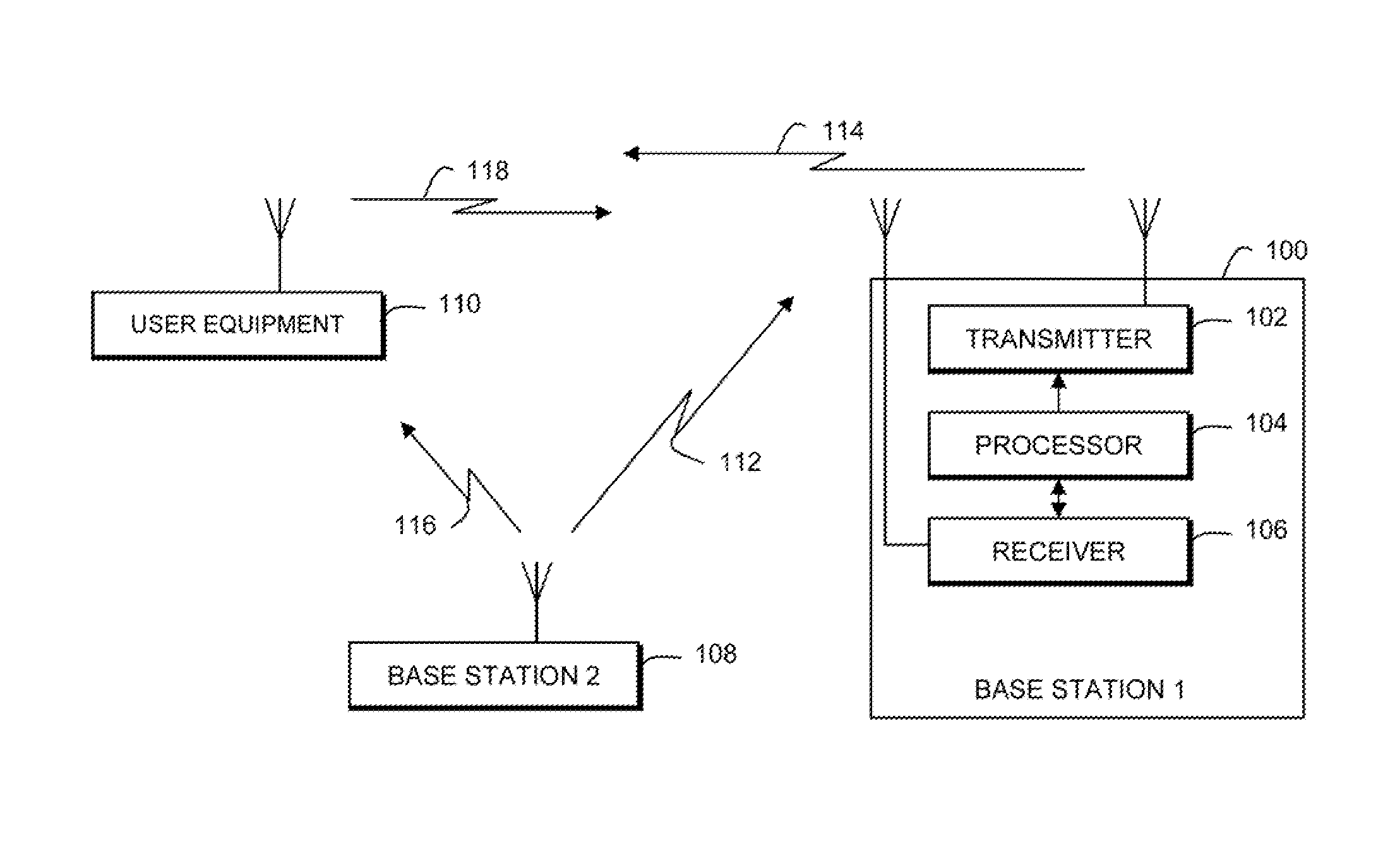
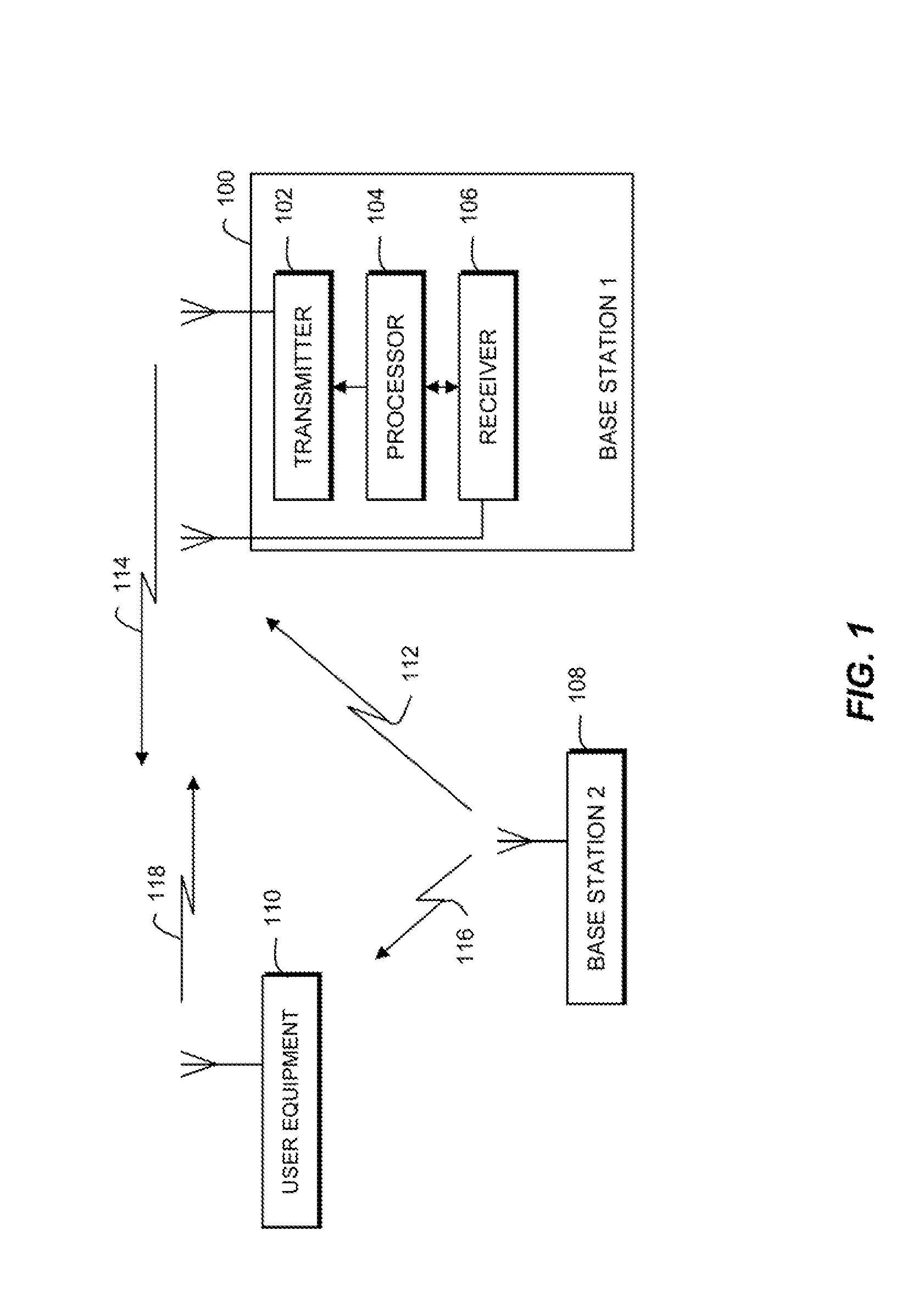
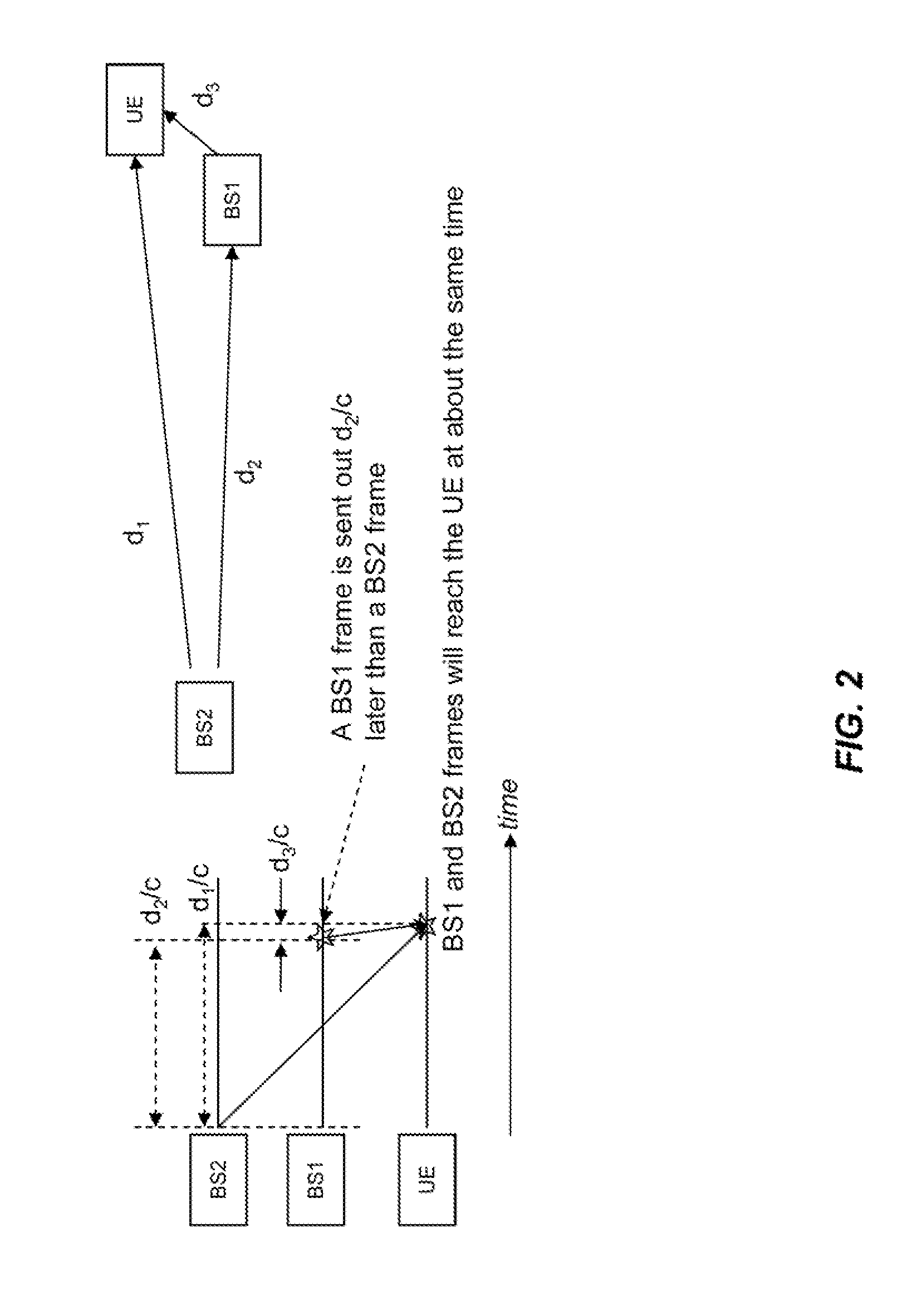
Reference time distribution over a network
InactiveUS8014423B2Time-division multiplexGenerating/distributing signalsTime informationData stream
A reference time distribution system and method use a data transmission network having a plurality of nodes to distribute the House Sync signal. A network-wide time signal is generated using a reference time generator, and the network-wide time signal is then distributed over the network to the plurality of nodes. At each node, the network-wide time signal is converted to a local synchronization signal for use in performing synchronization of the timing of each node. Either network-inherent timing and / or additional time signaling is used to provide the nodes attached to this network with a network-wide notion of time. The time information is converted locally into synchronization signals or time information as required by a respective application. When data is transported over the network, delay compensation is performed to simultaneously output different data streams that have been synchronously input into the network, regardless of the data path.
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
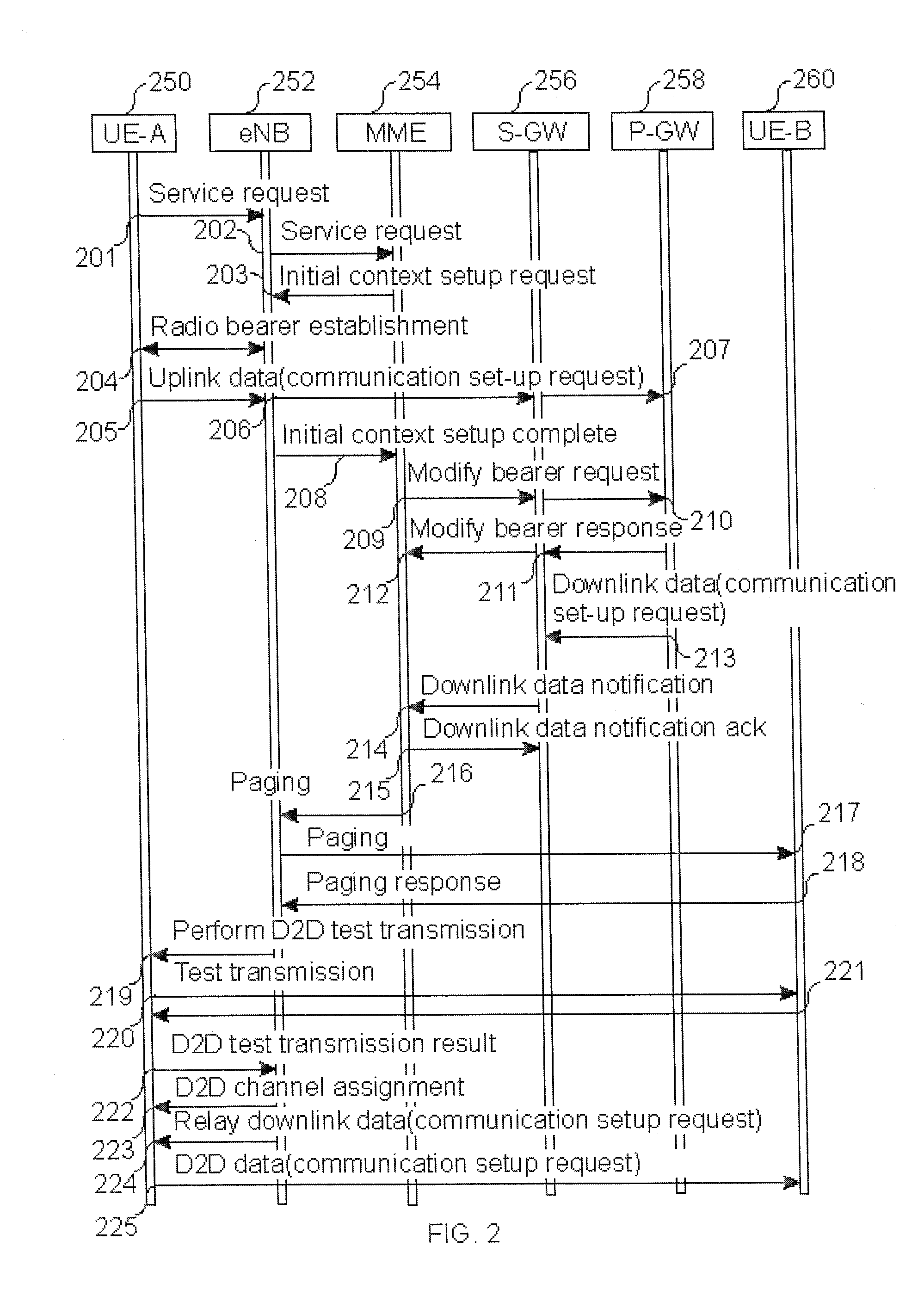
Method and apparatus for performing synchronization in device-to-device network
ActiveUS20130308625A1Perform synchronizationSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexComputer sciencePhase adjustment
A method and an apparatus for performing synchronization by a first device in a Device-to-Device (D2D) network are provided. The method includes detecting a synchronization signal from at least one second device during one period, determining a phase adjustment value depending on a number of synchronization signals, which have been detected from the at least one second device during the one period, adjusting a phase value of a first device using the phase adjustment value, and transmitting a synchronization signal if the phase value of the first device reaches a predetermined specific value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dynamic parameter adjustment for LTE coexistence
Coexistence gaps may permit one radio access technology (RAT) to coexists with another RAT by providing period in which one RAT may be silent and another may transmit. Methods may account for the RAT traffic and for the presence of other secondary users in a channel. Methods may be provided to dynamically change the parameters of a coexistence gap pattern, such as the duty cycle, to adapt to both the RAT traffic and the presence of other secondary users. Methods may include PHY methods, such as synchronization signal (PSS / SSS) based, MIB based, and PDCCH based, MAC CE based methods, and RRC Methods. Measurements may be provided to detect the presence of secondary users, and may include reporting of interference measured during ON and OFF durations, and detection of secondary users based on interference and RSRP / RSRQ measurements.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
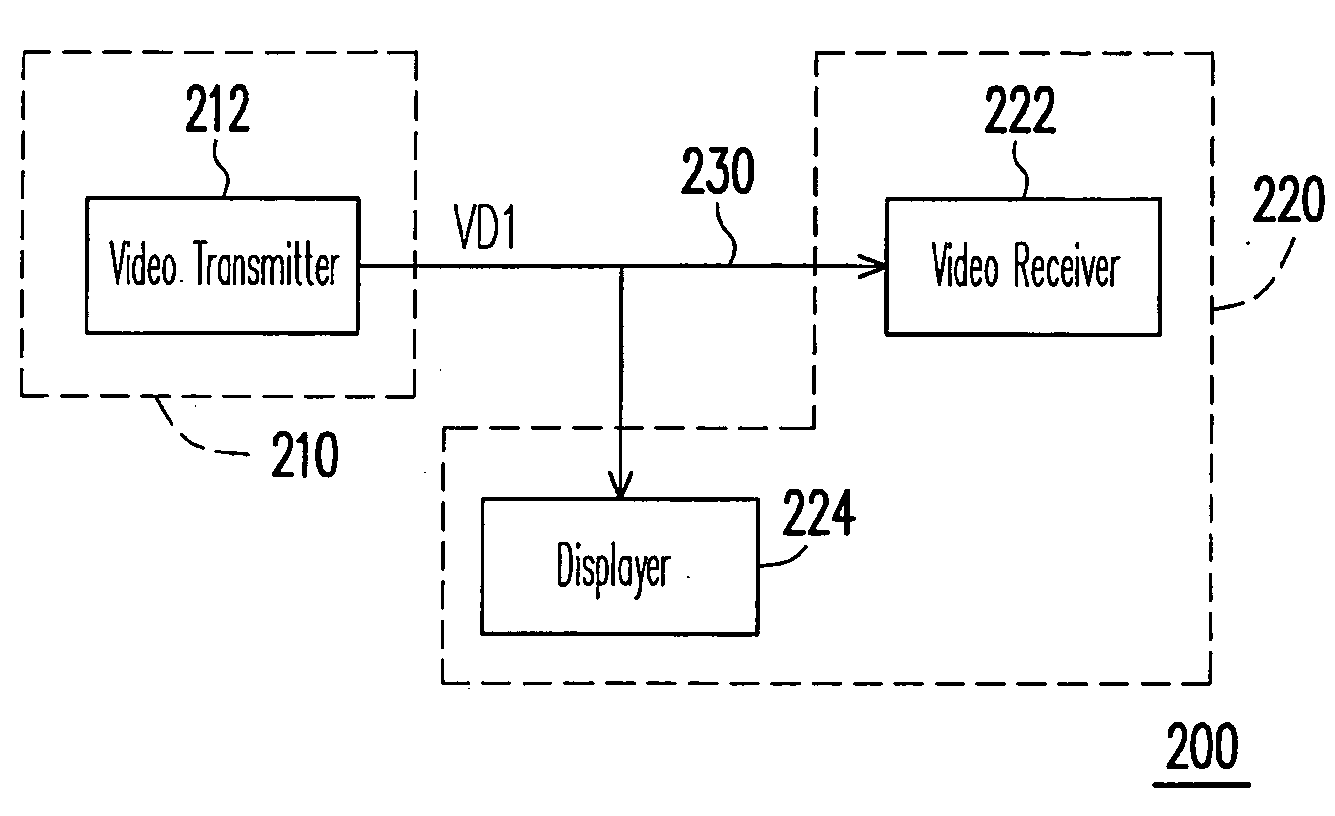
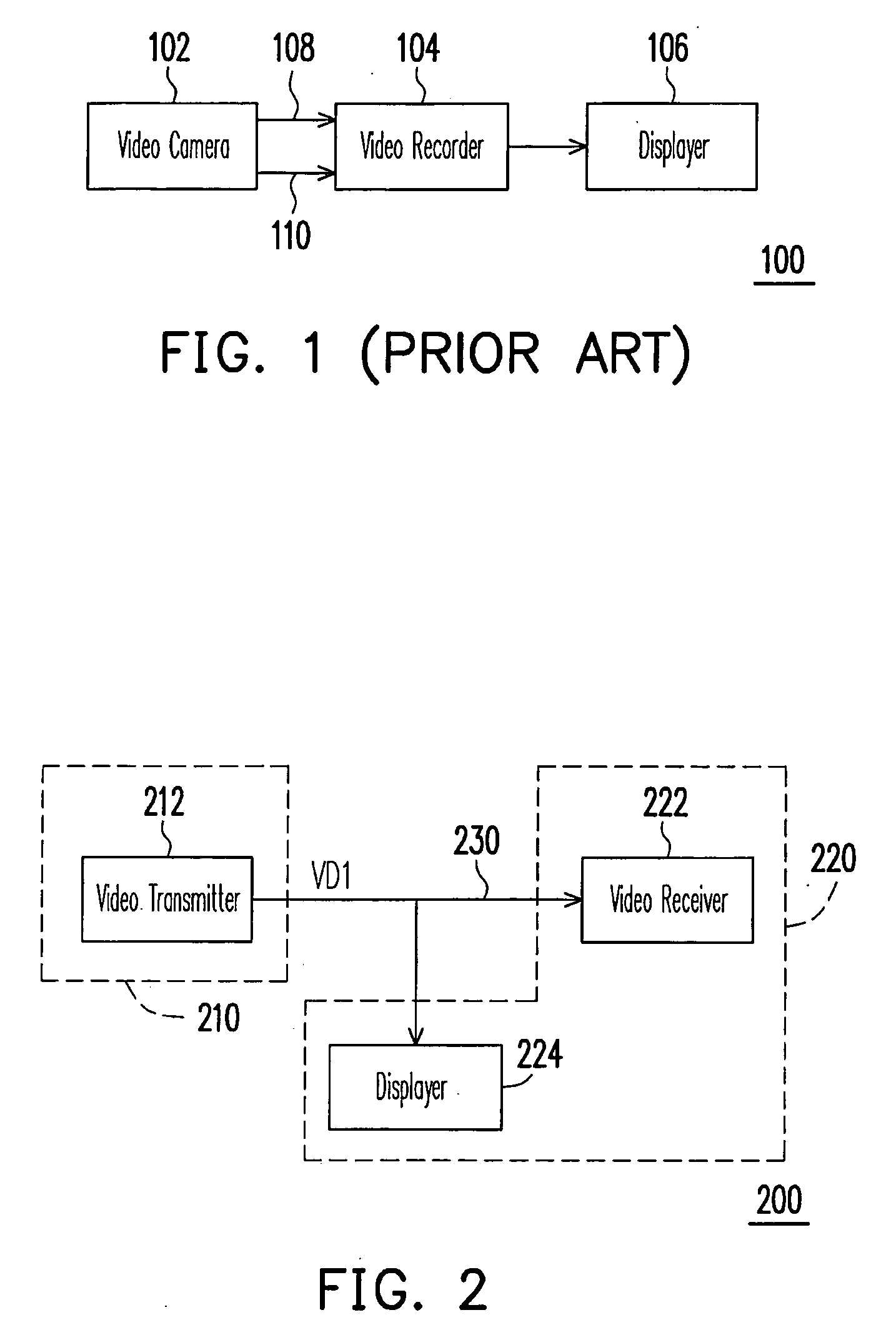
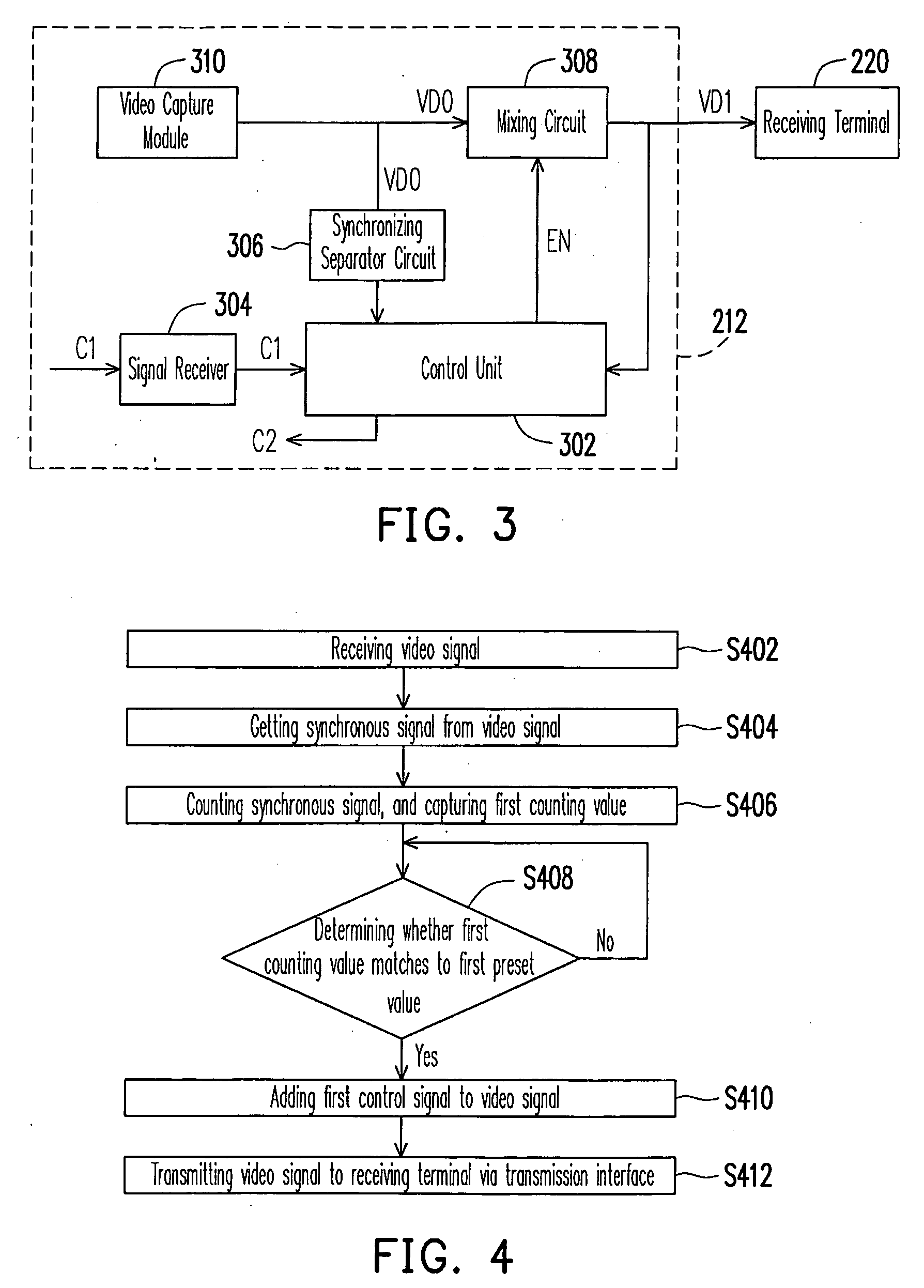
Video system, video transmitter, video receiver and control method for the same
InactiveUS20090113509A1Reduce hardware costsEliminate needTelevision system detailsTwo-way working systemsComputer hardwareControl signal
A video system with a bi-directional transmission function is provided. The video system includes an video transmitter, a transmission interface and a video receiver. The video transmitter is coupled to the video receiver via the transmission interface (coaxial cable). The video transmitter is used for inserting a first control signal into the video signal according a synchronous signal of the video signal. The video transmitter is used for outputting the video signal with the first control signal to the video receiver via the transmission interface. The video receiver receives the video signal with the first control signal, and gets the first control signal from the video signal according to the synchronous signal of the video signal. In addition, the video receiver can insert a second control signal into the video signal and feedback the second control signal to the video transmitter via the transmission interface.
Owner:AVTECH
Clock reproduction circuit that can reproduce internal clock signal correctly in synchronization with external clock signal
InactiveUS6166990ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrequency determinationPhase synchronization
A frequency determination circuit generating a clock signal phase-locking with an external clock signal at a coarse precision and a fine adjust circuit generating an internal synchronizing signal phase-locking with the external clock signal at a fine precision are provided. The fine adjust circuit has a function of adjusting the phase of the frequency determination circuit when phase synchronization is to be carried out exceeding the adjust range thereof. The frequency determination circuit and the fine adjust circuit receive a clock power supply voltage. A clock reproduction circuit is provided which generates an internal clock signal phase-locking with an external clock signal or a reference clock signal stably even when the operating environment changes.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +2
Synchronization for femto-cell base stations
Timing synchronization between base stations of uncoordinated communication networks includes obtaining timing synchronization information from one base station, and adjusting a clock of the other station in response to the synchronization information. The timing synchronization information can be identified from a strongest synchronization signal from nearby uncoordinated base stations. The timing synchronization can accommodate clock offsets and frequency offsets.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
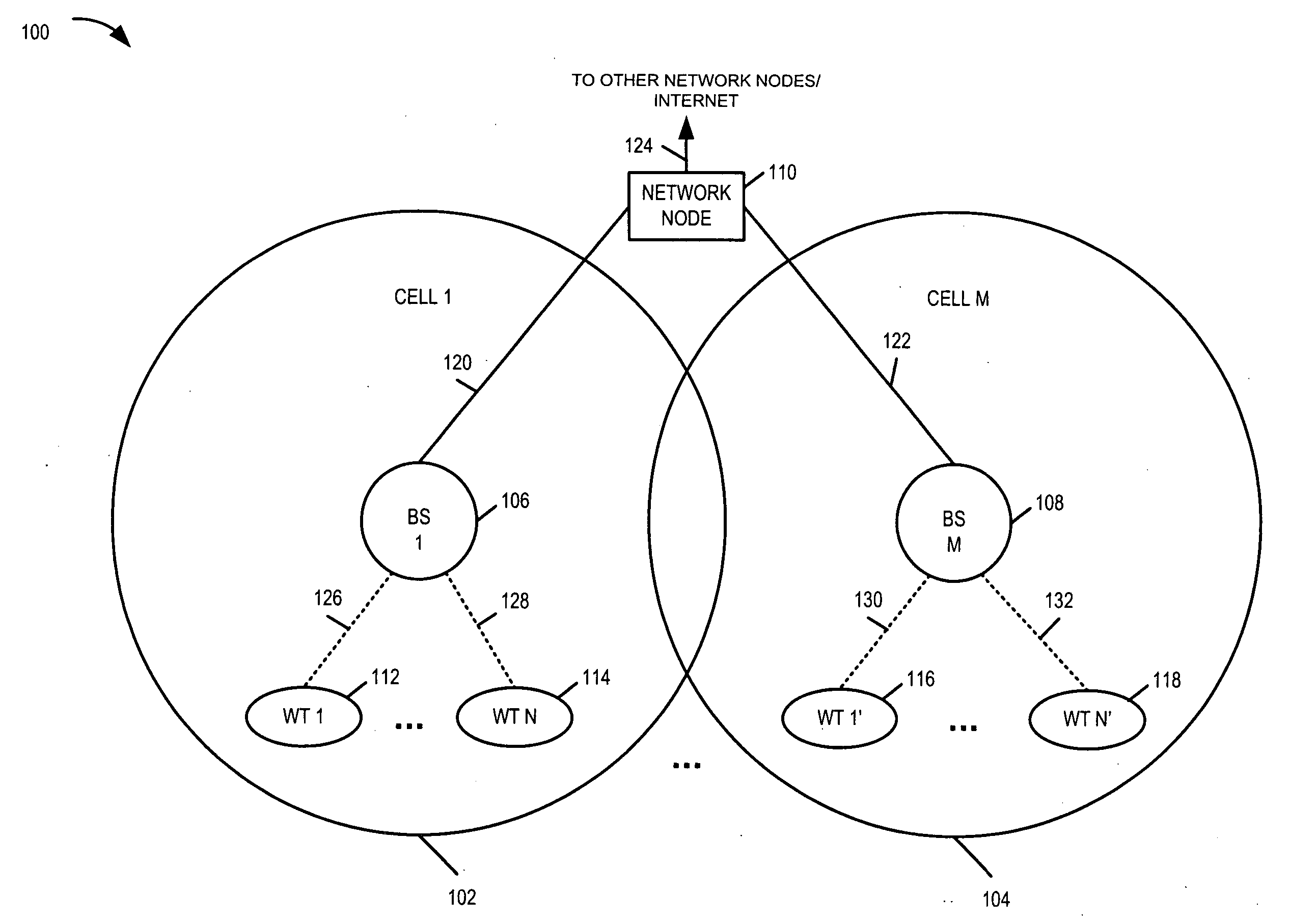
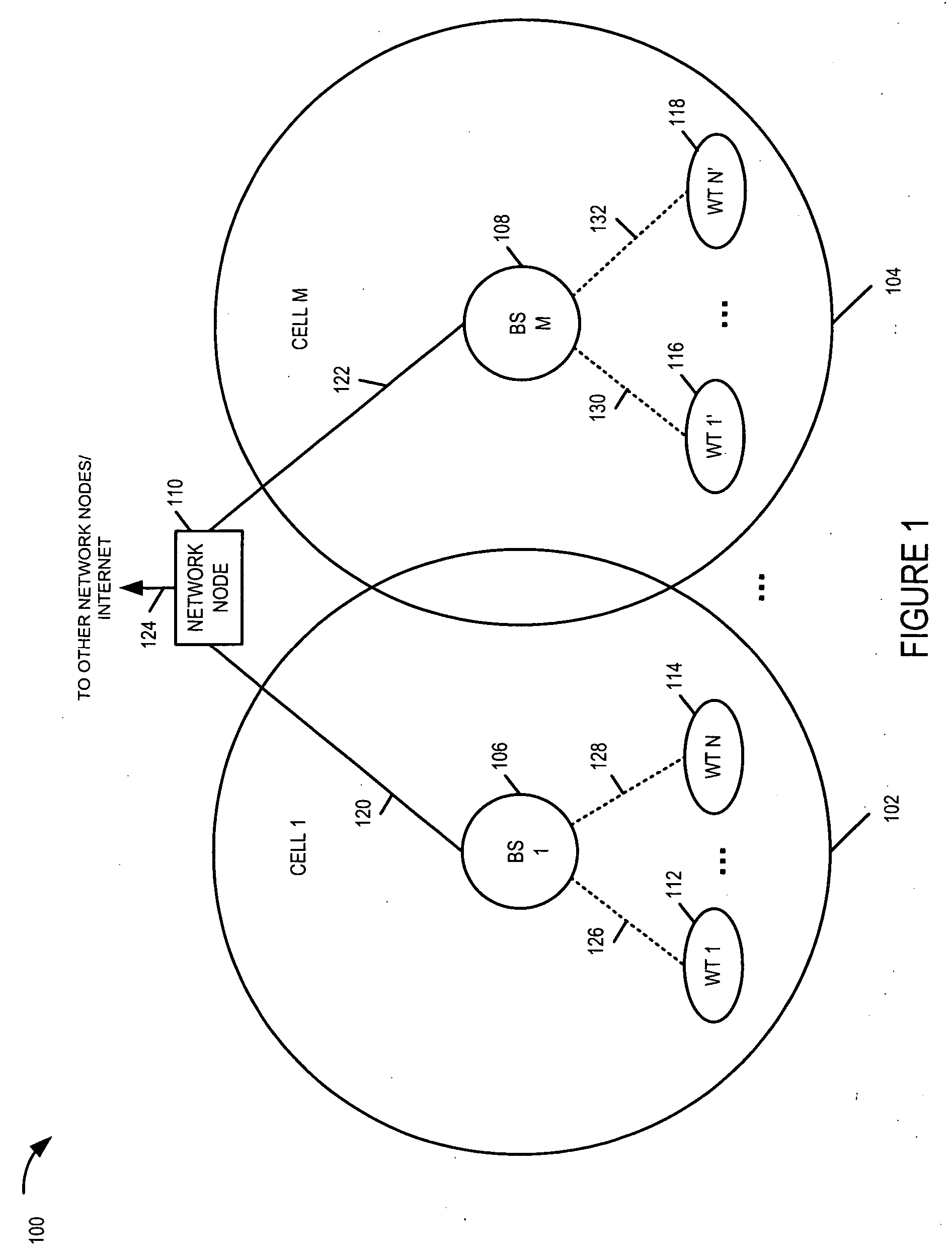
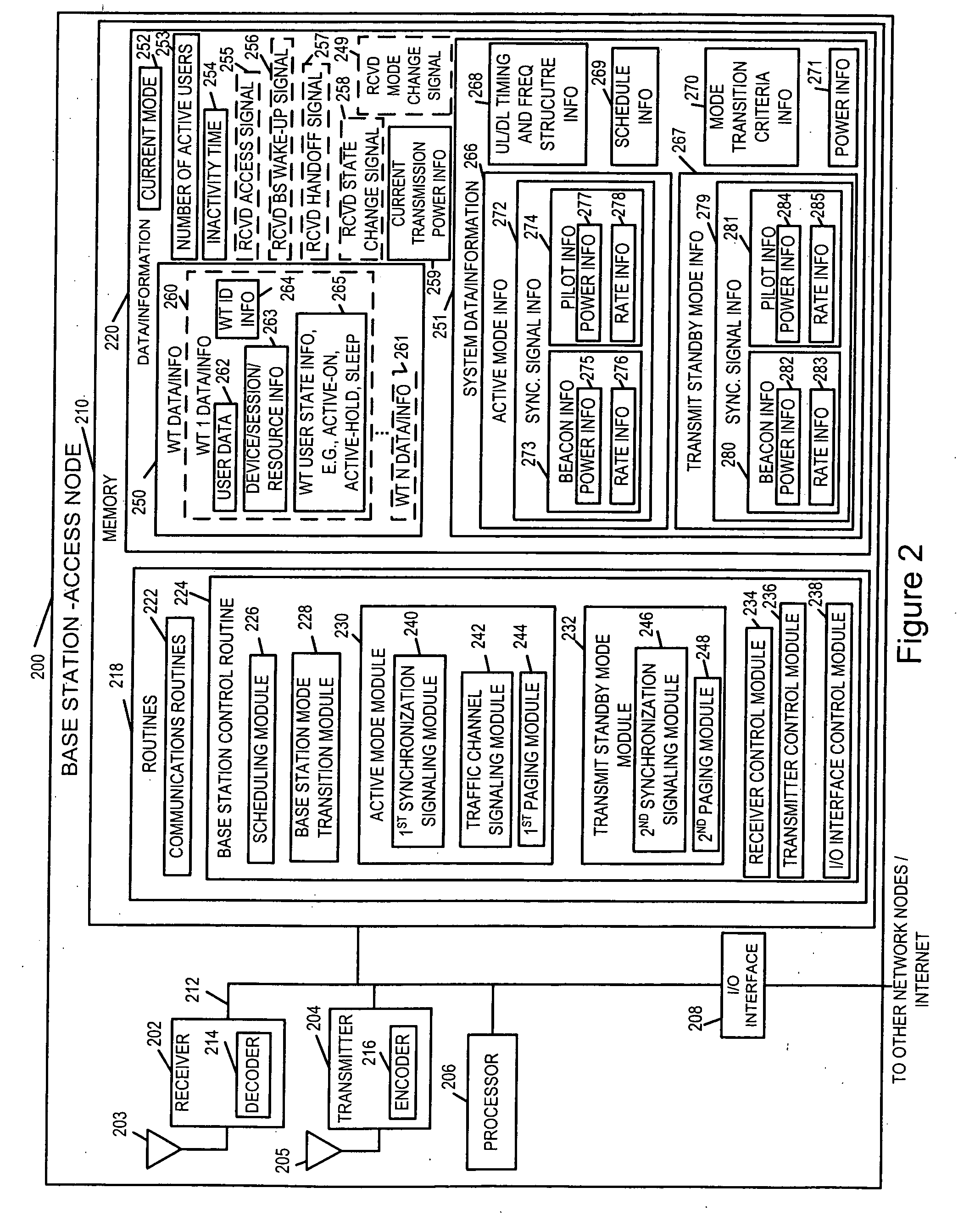
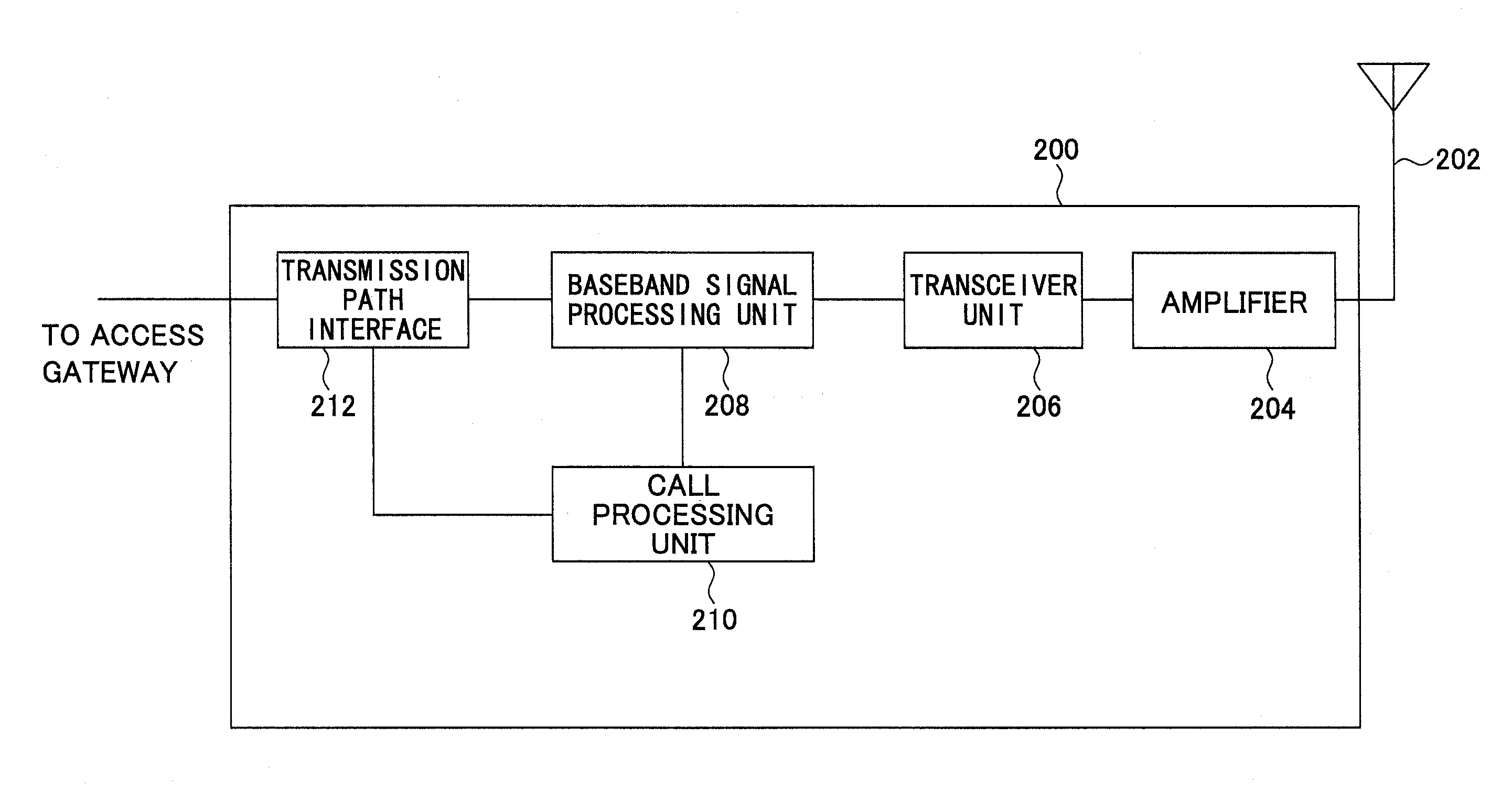
Methods and apparatus for use in a wireless communications system that uses a multi-mode base station
ActiveUS20070066329A1Improve throughputReducing base stationEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemSleep state
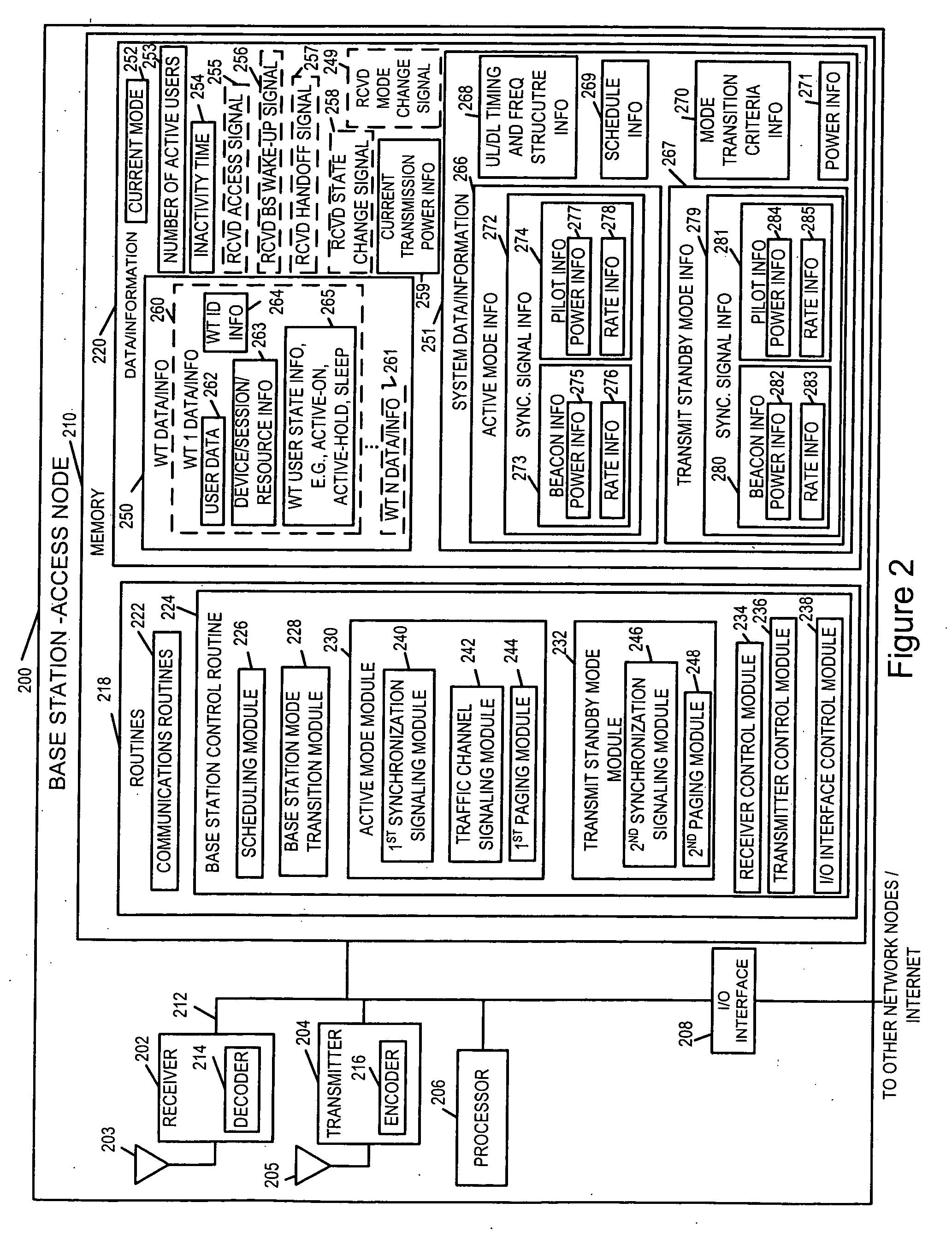
A multi-mode base station includes a transmit standby mode and an active mode. Transmit standby mode of base station operation is a low power / low interference level of operation as compared to active mode. In transmit standby mode at least some of the synchronization signaling such as pilot tone signaling is reduced in power level and / or rate with respect to the active mode. In transmit standby mode, the base station has no active state registered wireless terminals being serviced but may have some sleep state registered wireless terminals being serviced. Mode transitions from active to transmit standby may be in response to: a detected period of inactivity, scheduling information, base station mode change signals, and / or detected wireless terminal state transition. Mode transitions from transmit standby to active may be in response to: scheduling information, access signals, wake-up signals, hand-off signals, wireless terminal state change signals, and / or base station mode change signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
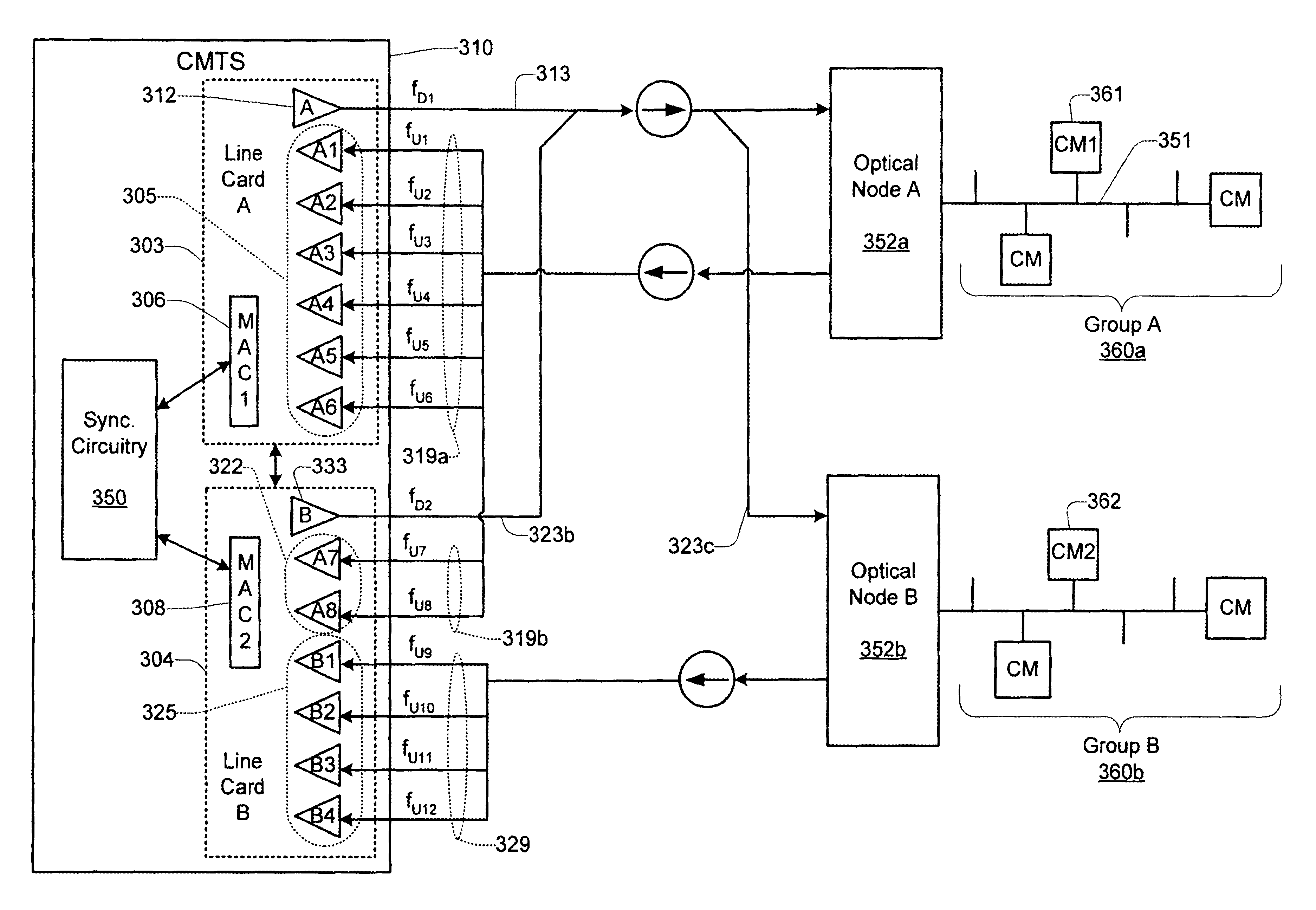
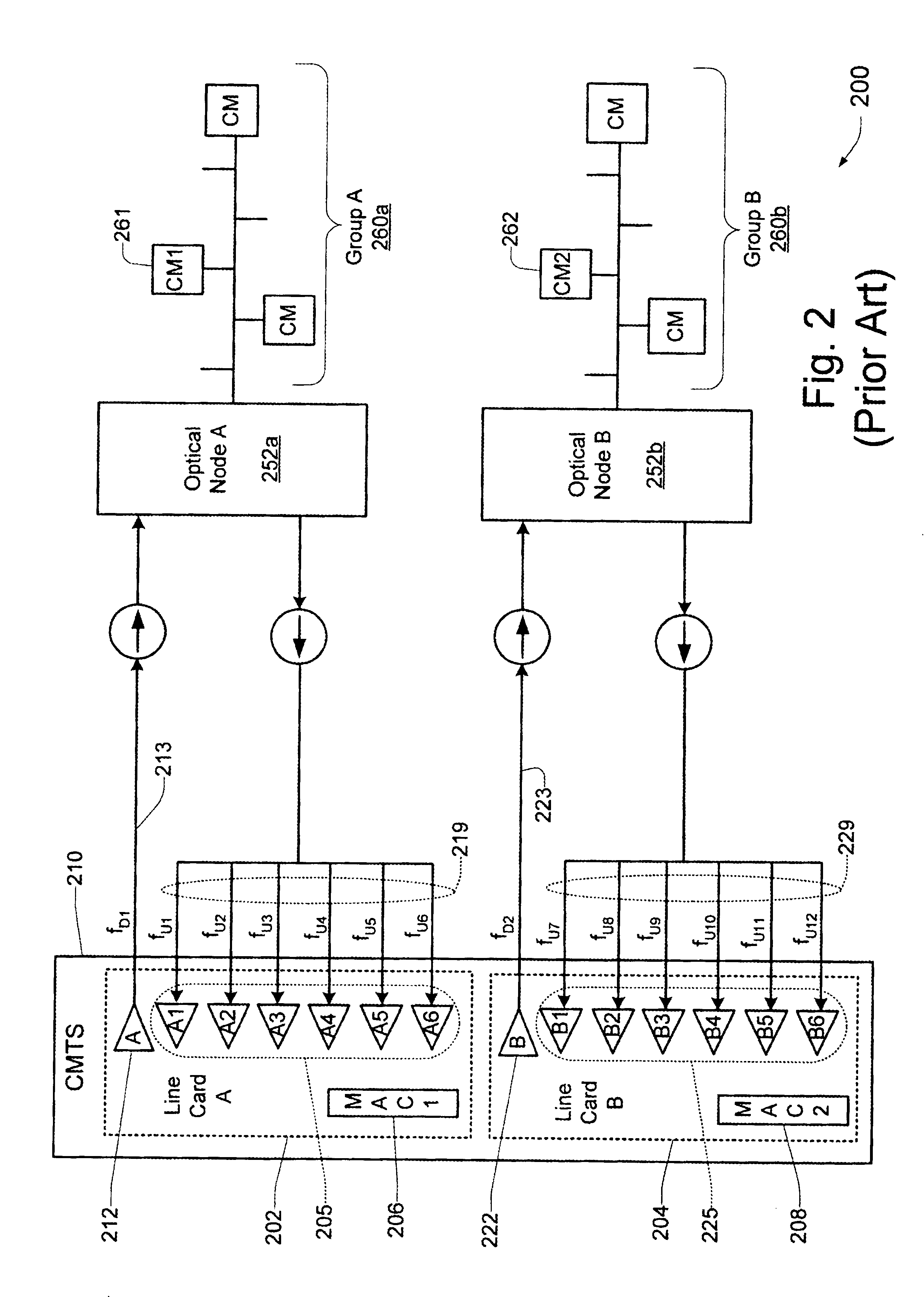
Technique for synchronizing multiple access controllers at the head end of an access network
InactiveUS7065779B1Broadband local area networksAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsAccess networkTimestamp
A technique is described which may be used to synchronize a plurality of different access controllers which control a plurality of distinct ports at the Head End of an access network. In the context of a cable network, the technique of the present invention may be used to synchronize desired upstream and / or downstream channels across different line cards within a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS). The technique involves utilizing a master time reference device which maintains and updates a current time reference, and periodically distributes synchronization signals to desired line cards in the system in order to synchronize these line cards. In a specific embodiment, the synchronization signals include current timestamp data generated from the master time reference device and distributed to all (or selected) line cards in the system. A slave time reference device on each of the line cards receives the periodic synchronization updates and uses the synchronization data to remain synchronized with the master time reference device. There are also provisions in this protocol to allow for hot insertion and removal of line cards, software reset or loading of the master and / or slave time reference devices, and redundant master time reference devices, including master time reference device fault detection and automatic fail over.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and base station for receiving reference signal, and method and user equipment for receiving reference signal
ActiveUS20110235743A1Improve transmission efficiencyModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionResource blockUser equipment
A base station does not transmit any reference signal (RS) for channel measurement in a subframe in which transmission of an RS collides with transmission of a synchronization signal or a broadcast signal or in a resource block including the synchronization signal or the broadcast signal in the subframe. A user equipment assumes that any RS for channel measurement is not transmitted in a subframe or in a resource block when transmission of an RS collides with transmission of a synchronization signal or a broadcast signal in the subframe or in the resource block.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Wireless terminal methods and apparatus for use in a wireless communications system that uses a multi-mode base station
ActiveUS20070066273A1Improve throughputReducing base stationPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemSleep state
Wireless terminal for use with a multi-mode base station that supports a transmit standby mode and an active mode is described. Transmit standby mode of base station operation is a low power / low interference level of operation as compared to active mode. In transmit standby mode at least some of the synchronization signaling such as pilot tone signaling is reduced in power level and / or rate with respect to the active mode. In transmit standby mode, the base station has no active state registered wireless terminals being serviced but may have some sleep state registered wireless terminals being serviced. Mode transitions from active to transmit standby may be in response to: a detected period of inactivity, scheduling information, base station mode change signals, and / or detected wireless terminal state transition. Mode transitions from transmit standby to active may be in response to: scheduling information, access signals, wake-up signals from the wireless terminal, hand-off signals, etc.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
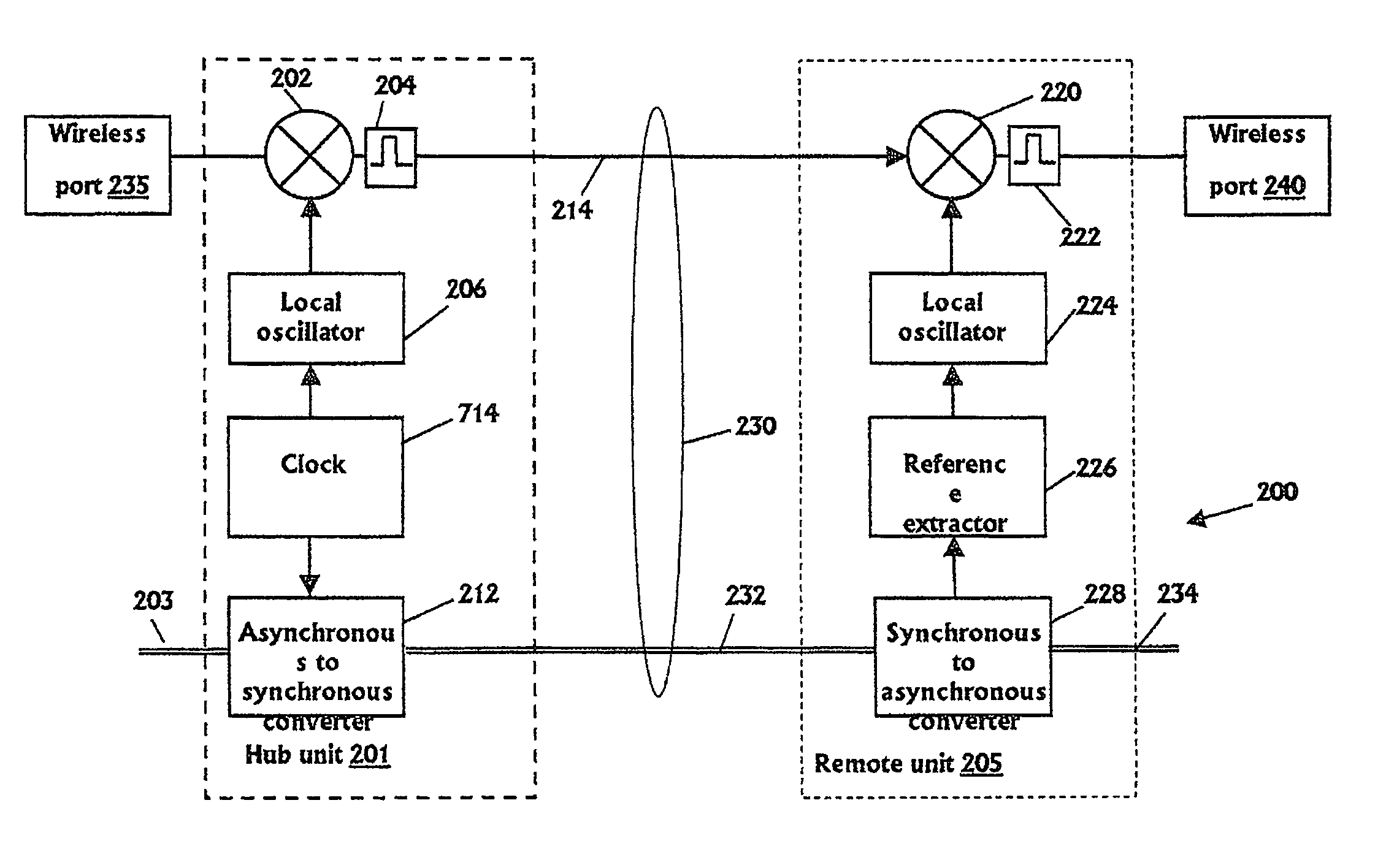
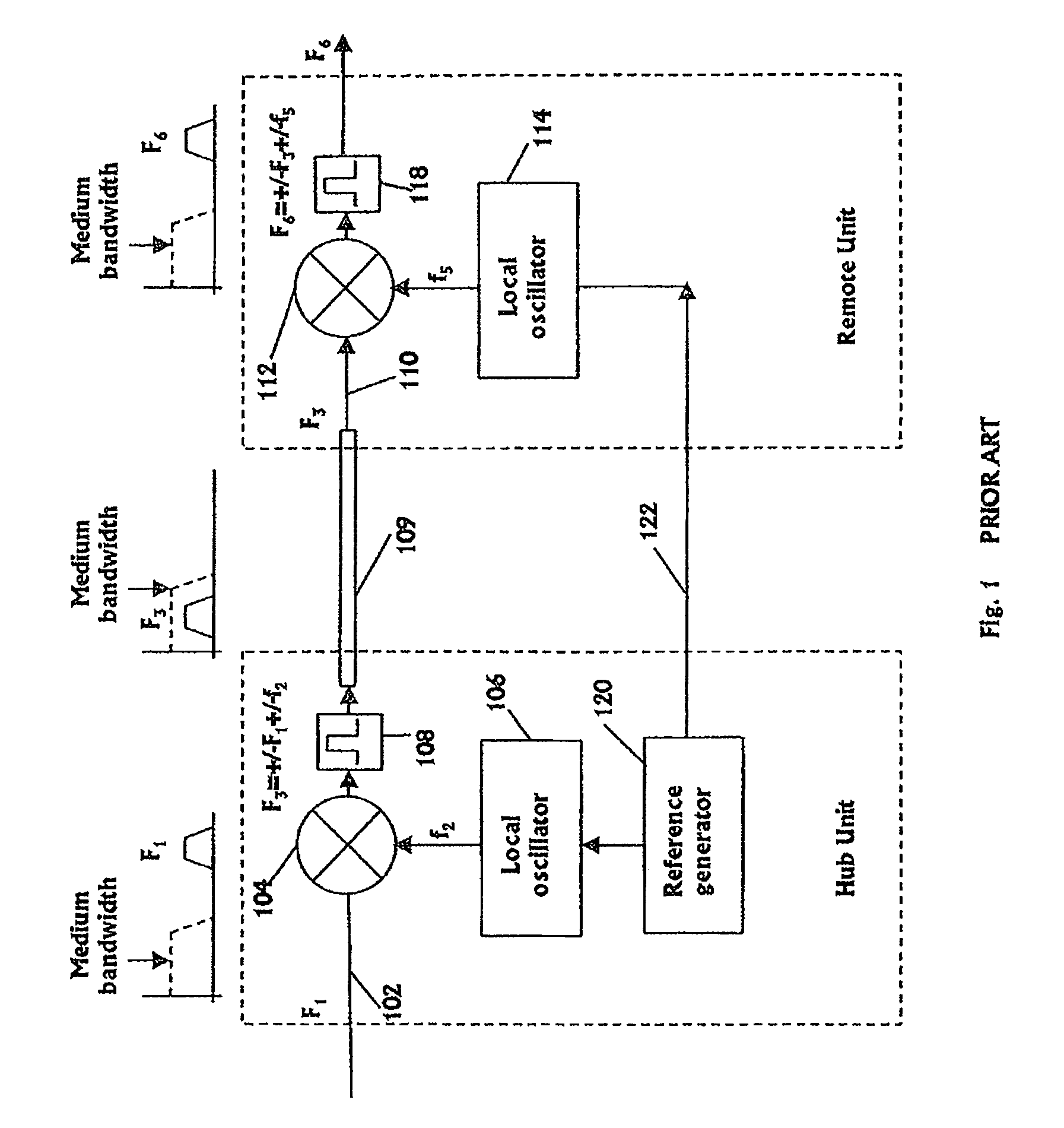
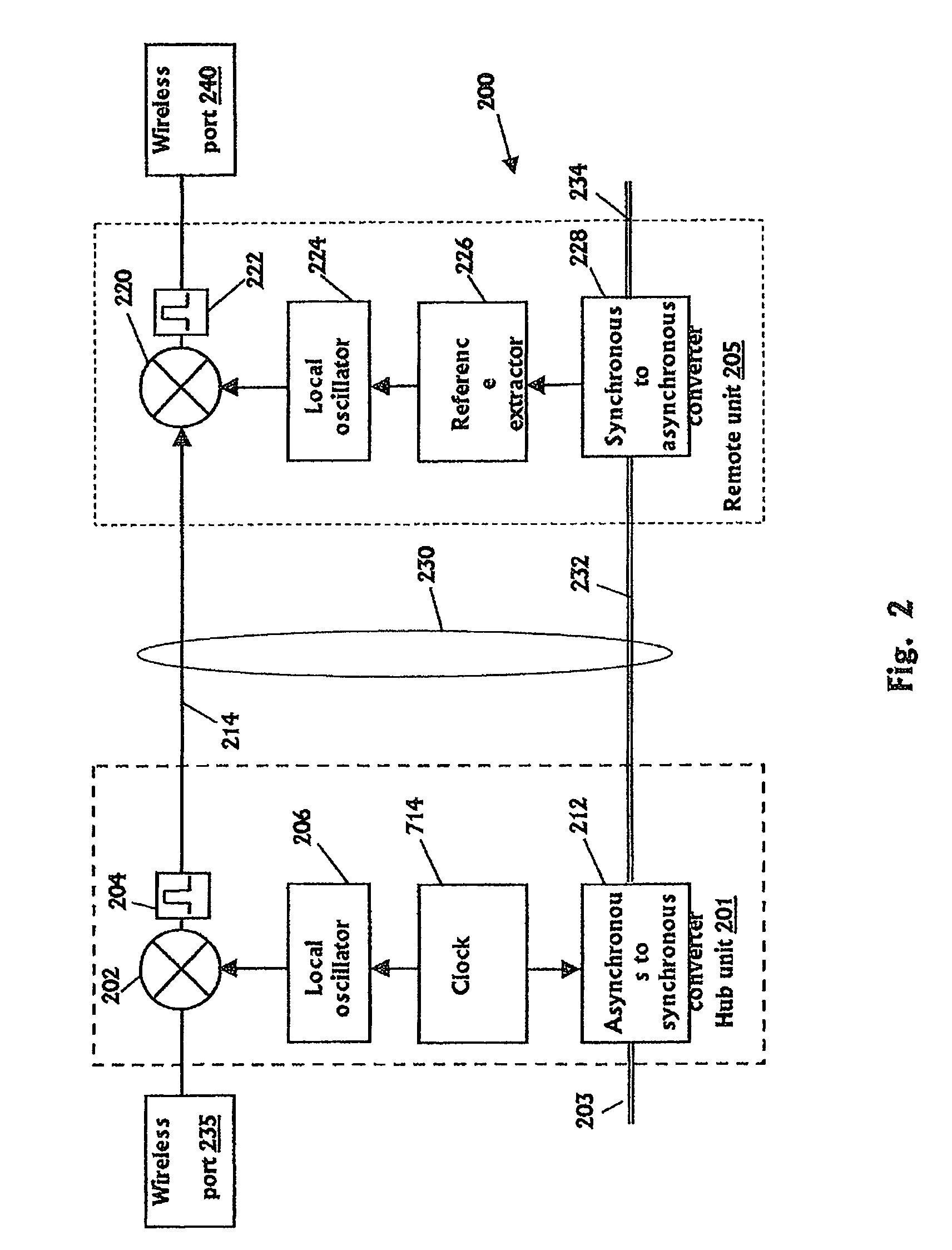
Communication system using cables carrying ethernet signals
ActiveUS8897215B2Wireless commuication servicesData switching networksCommunications systemLocal oscillator
It is provided a method for transmitting a wireless signal on Ethernet wiring The wireless signal is received in a hub unit for delivery to a remote unit In the hub unit the wireless signal is down converted to a down-converted frequency band for propagation on the Ethernet wiring A reference signal associated with a local oscillator used for the down conversion is embedded on a synchronous Ethernet stream that may include Ethernet data received at hub unit The synchronous Ethernet stream and the down converted wireless signal are submitted through the Ethernet wiring to the remote unit. The synchronous Ethernet stream may include data for management of electronic circuits installed in the remote unit, as well as a synchronization signal used thereof A converted replica of the first signal may be included in digital form in frames of the synchronous Ethernet stream.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
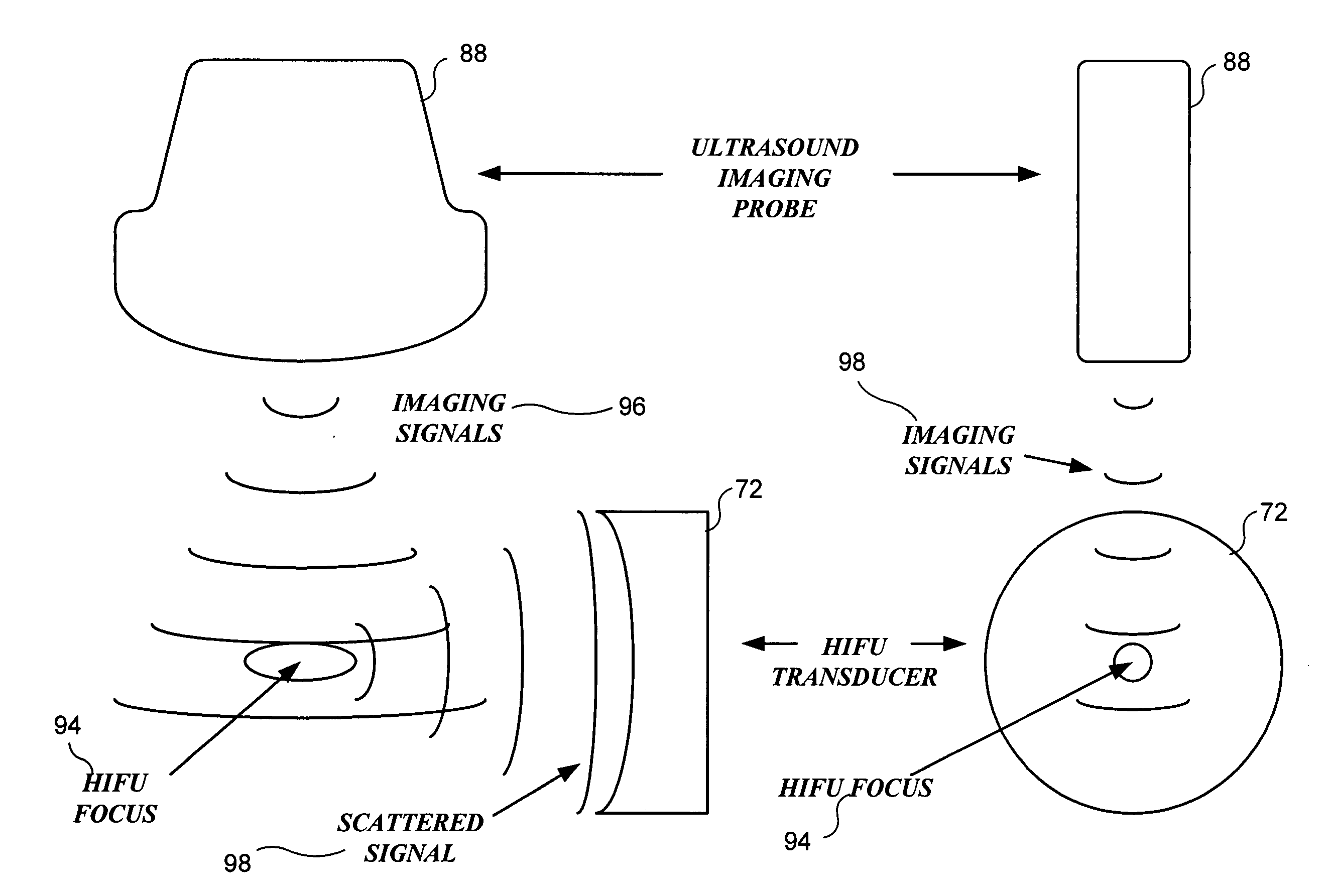
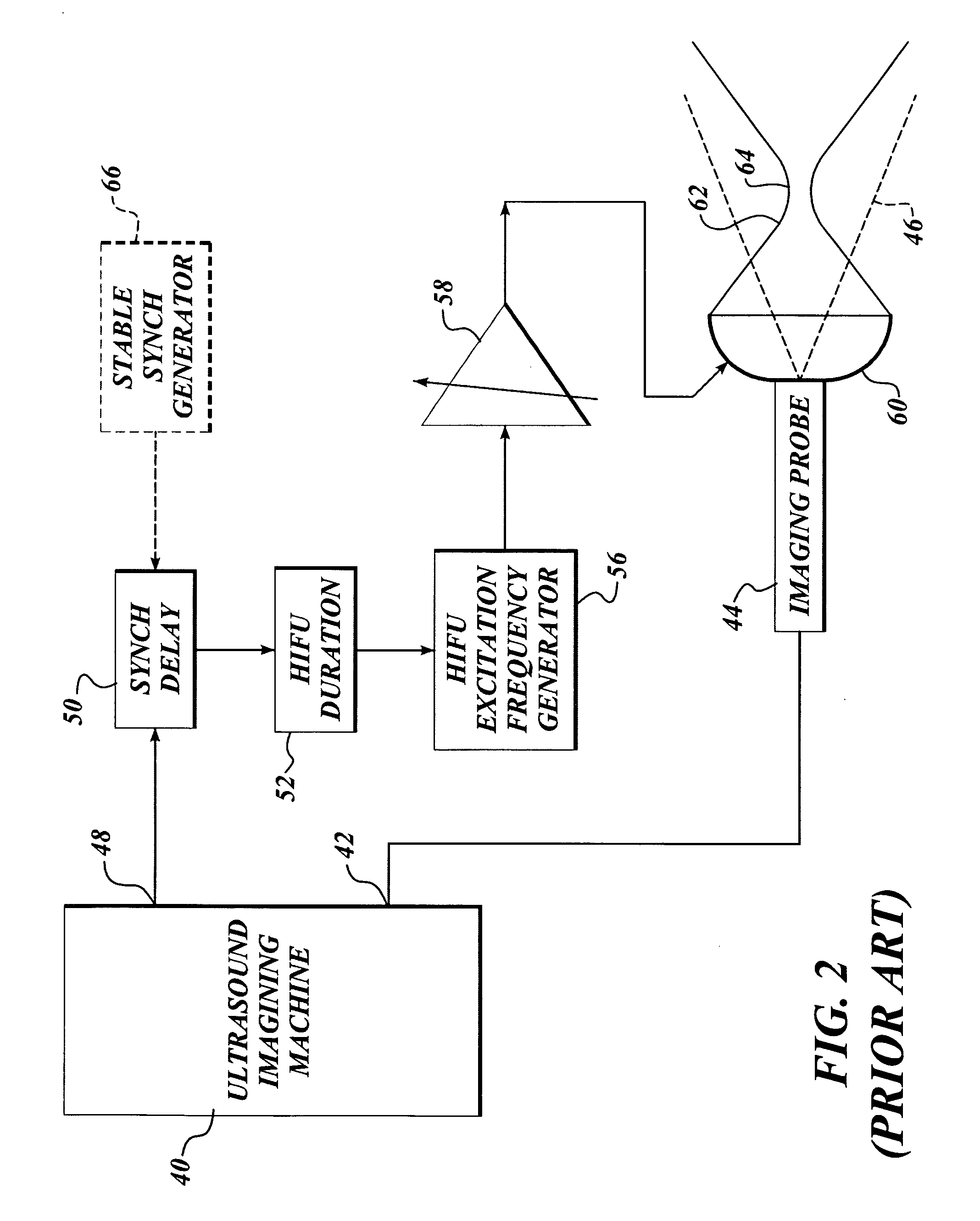
Method and system to synchronize acoustic therapy with ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20070055155A1Synchronization is simpleGood synchronizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound imagingSonification
Interference in ultrasound imaging when used in connection with high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is avoided by employing a synchronization signal to control the HIFU signal. Unless the timing of the HIFU transducer is controlled, its output will substantially overwhelm the signal produced by ultrasound imaging system and obscure the image it produces. The synchronization signal employed to control the HIFU transducer is obtained without requiring modification of the ultrasound imaging system. Signals corresponding to scattered ultrasound imaging waves are collected using either the HIFU transducer or a dedicated receiver. A synchronization processor manipulates the scattered ultrasound imaging signals to achieve the synchronization signal, which is then used to control the HIFU bursts so as to substantially reduce or eliminate HIFU interference in the ultrasound image. The synchronization processor can alternatively be implemented using a computing device or an application-specific circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
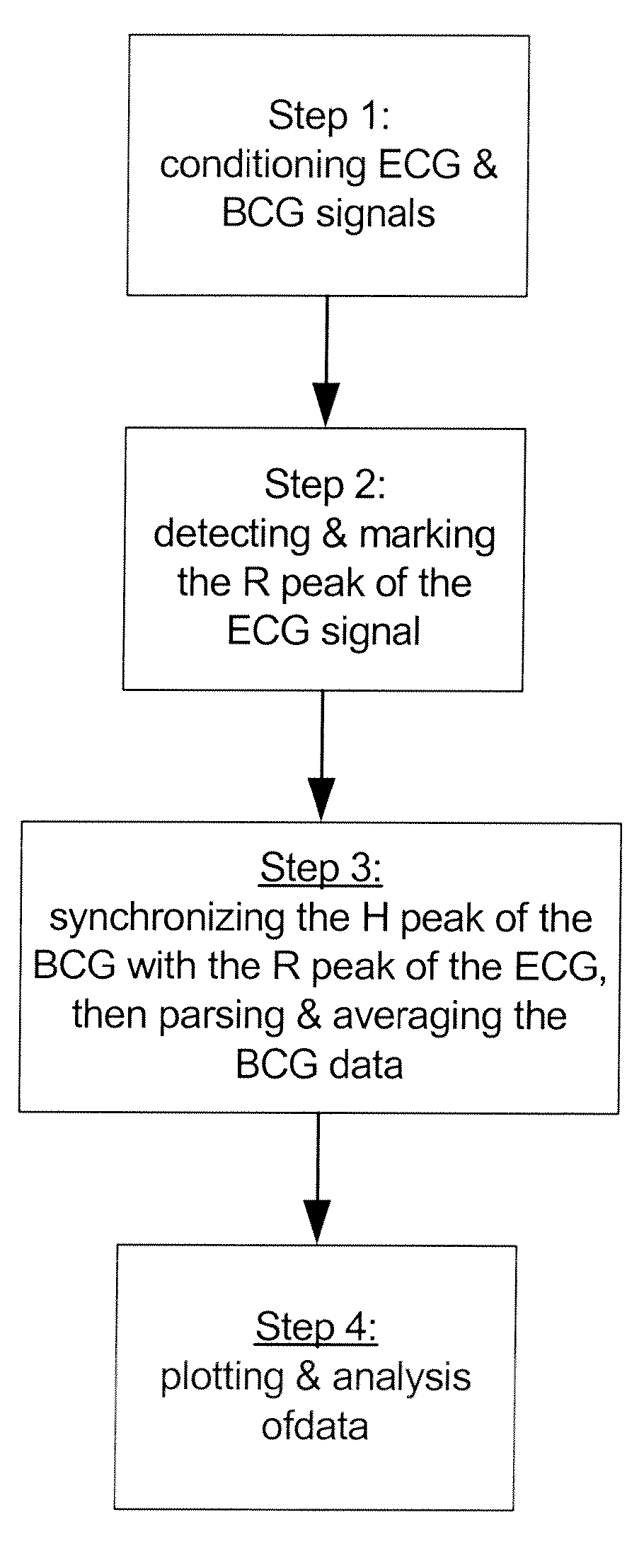
Monitoring physiological condition and detecting abnormalities
ActiveUS20080194975A1Monitoring usingElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsMedicineReference designator
A system for monitoring an individual's physiological condition and detecting abnormalities therein, comprising concurrently receiving at least a first signal and a second signal. The first and second signals are conditioned to minimize background extraneous noise after which, each signal is concurrently processed and analyzed to detect repeating cyclical patterns and further characterized to identify individual components of the repeating cycles. At least one individual component in one signal is selected as a reference marker for a selected component in the other signal. The two signals are then synchronized, outputs produced therefrom and stored in a database. The system is provided with a plurality of devices for acquiring, transmitting and conditioning at least two physiological signals, a software program cooperable with a microprocessor configured for receiving said transmitted signals and conditioned signals, and processing said signals to characterize and synchronize said signals and provide signal outputs derived therefrom, a database for storing said transmitted signals, conditioned signals, synchronized signals, and output signals derived therefrom. The output signals are useful for reporting and optionally for retransmission to the individual's body and providing physiologically stimulatory signals thereto.
Owner:HEART FORCE MEDICAL
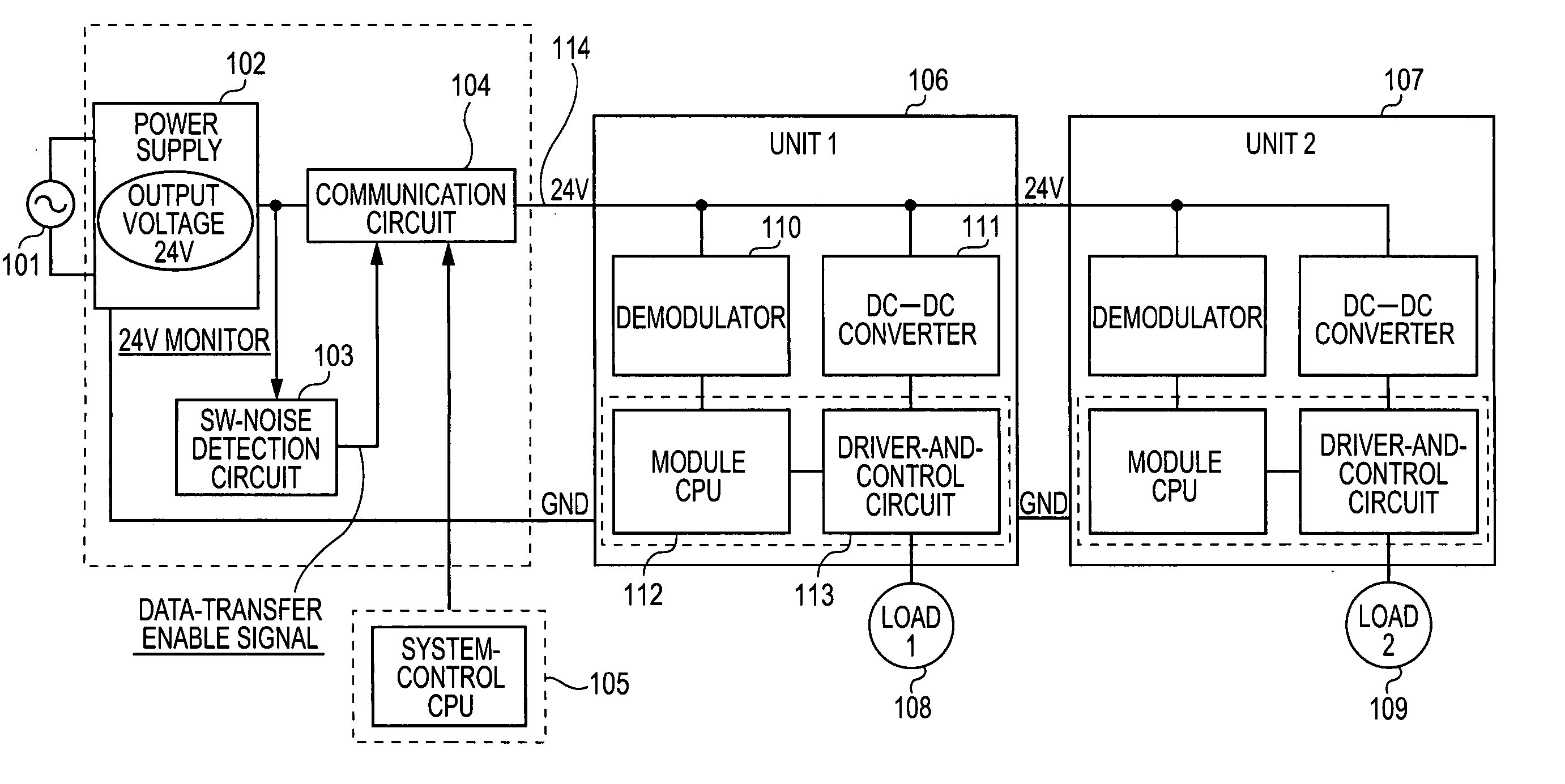
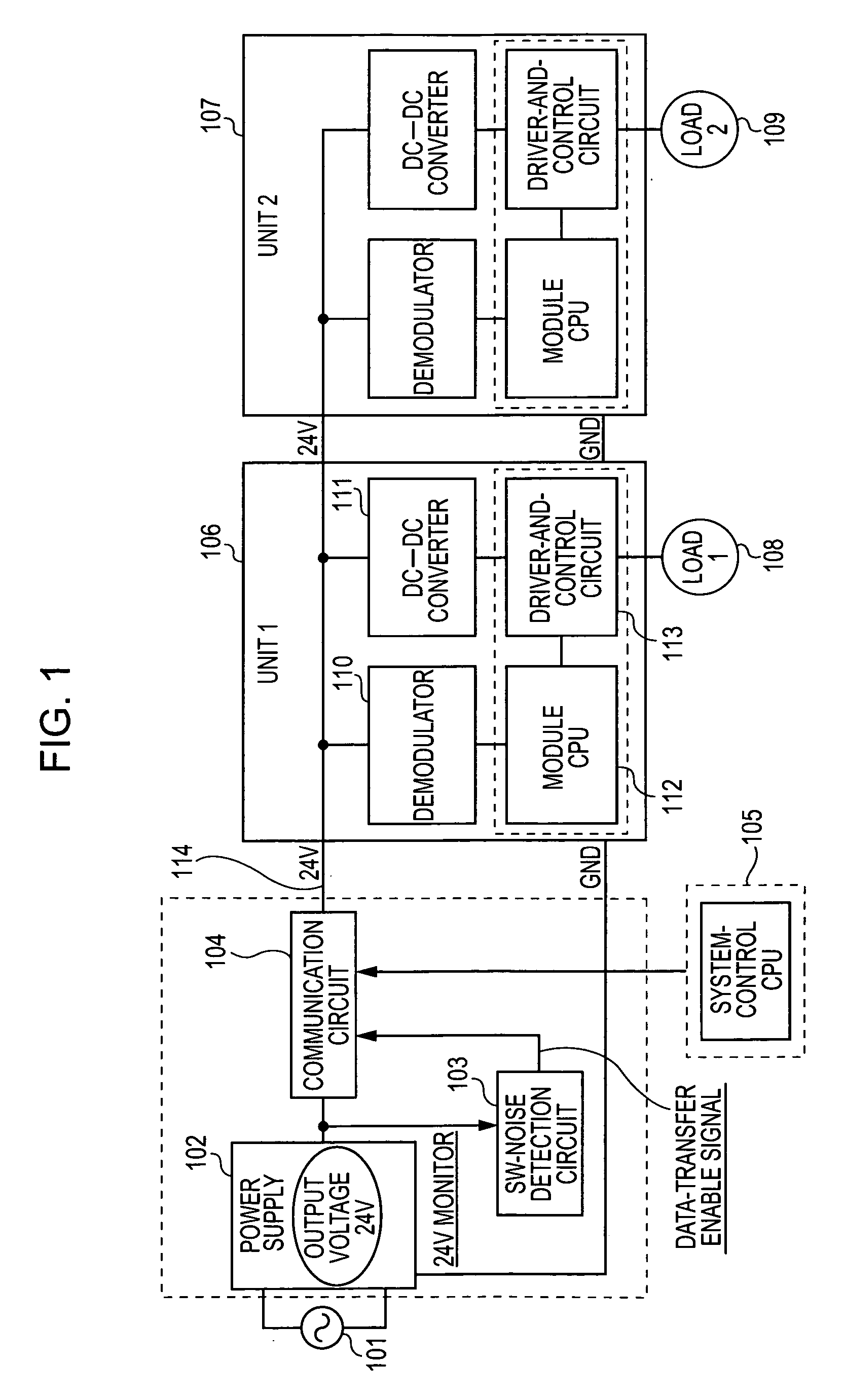
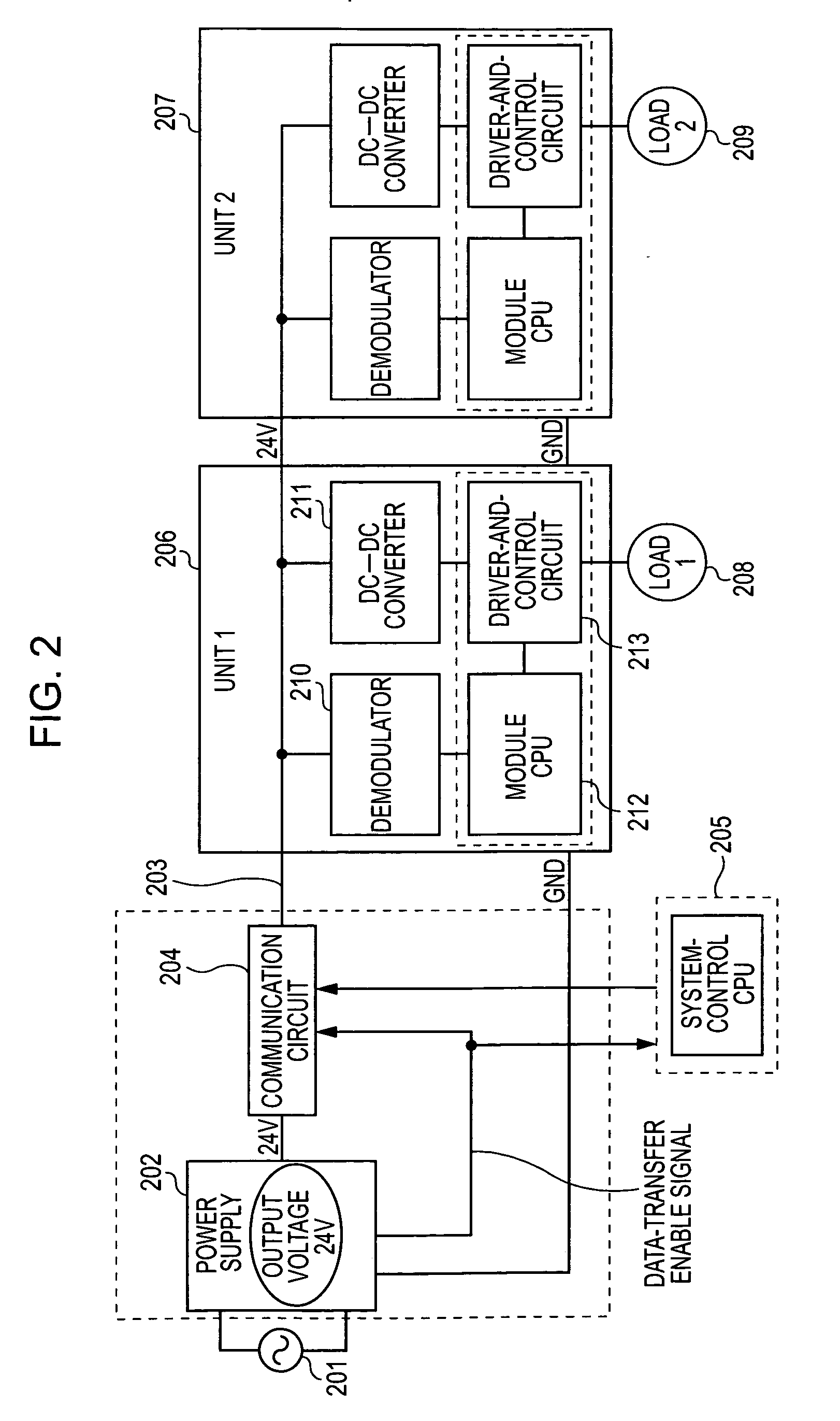
Power-line communication device
InactiveUS20060077046A1Reduce in quantitySystems using filtering and bypassingElectric signal transmission systemsControl signalEngineering
A power-line communication device in which a control signal is superimposed on a power line between a switching power supply and a unit to be controlled to which an output of the switching power supply is supplied, so that the control signal is transmitted to the unit. At the same time, a switching noise generated by the switching power supply is monitored and communication is started by using the switching noise, as a synchronizing signal. Subsequently, communication can be performed during the intervals between the switching noises so that erroneous signal detection is reduced.
Owner:CANON KK
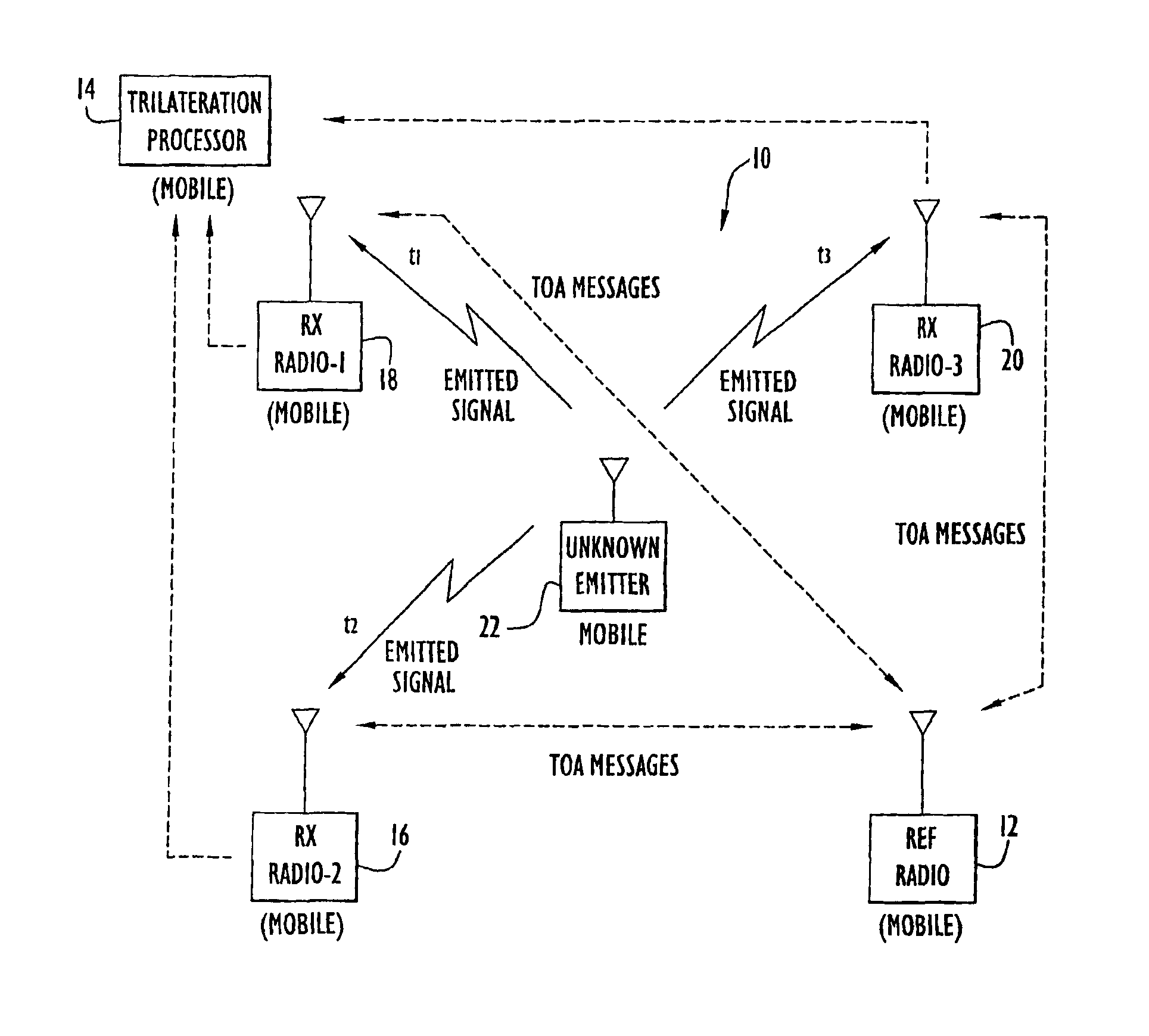
System for determining position of an emitter
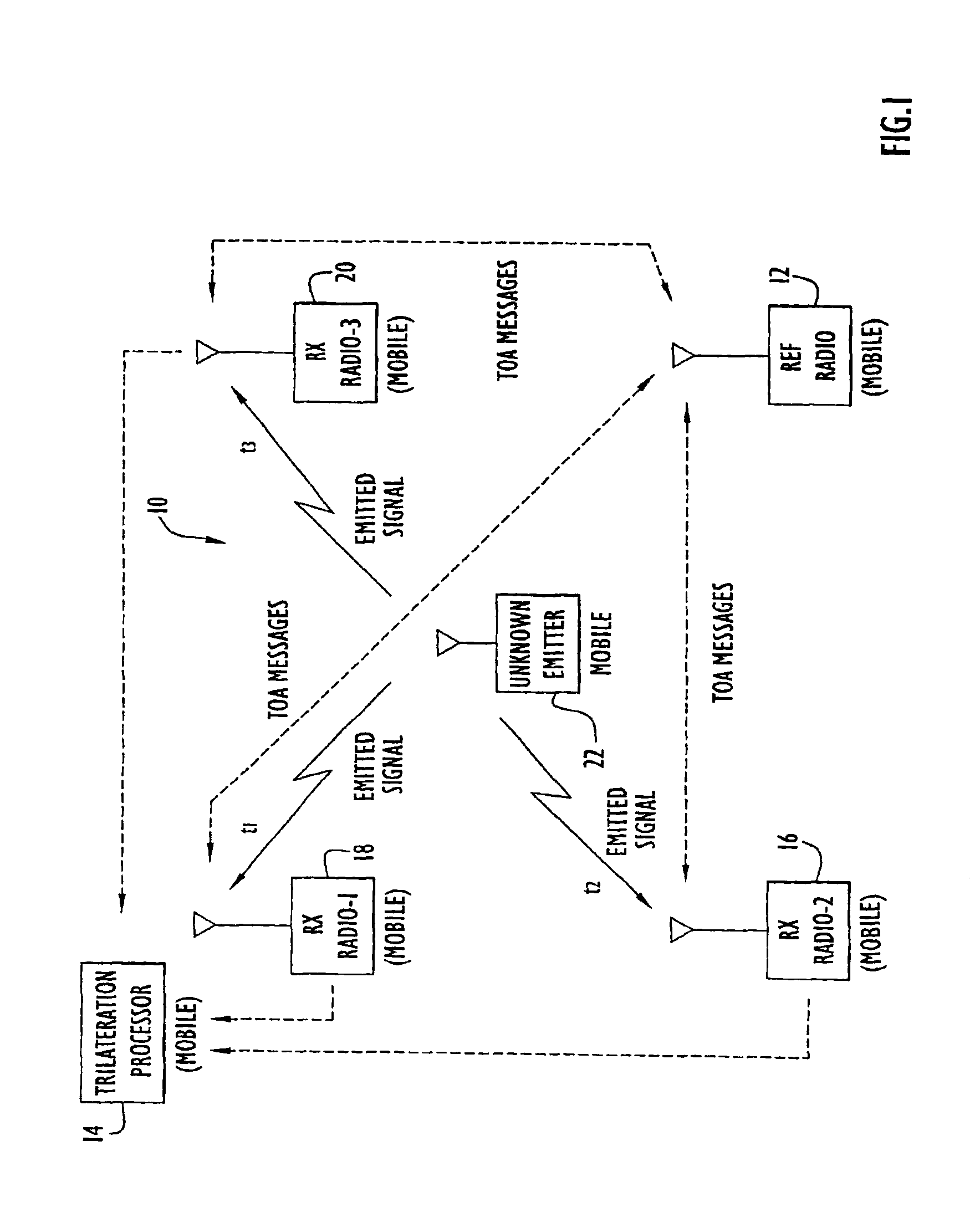
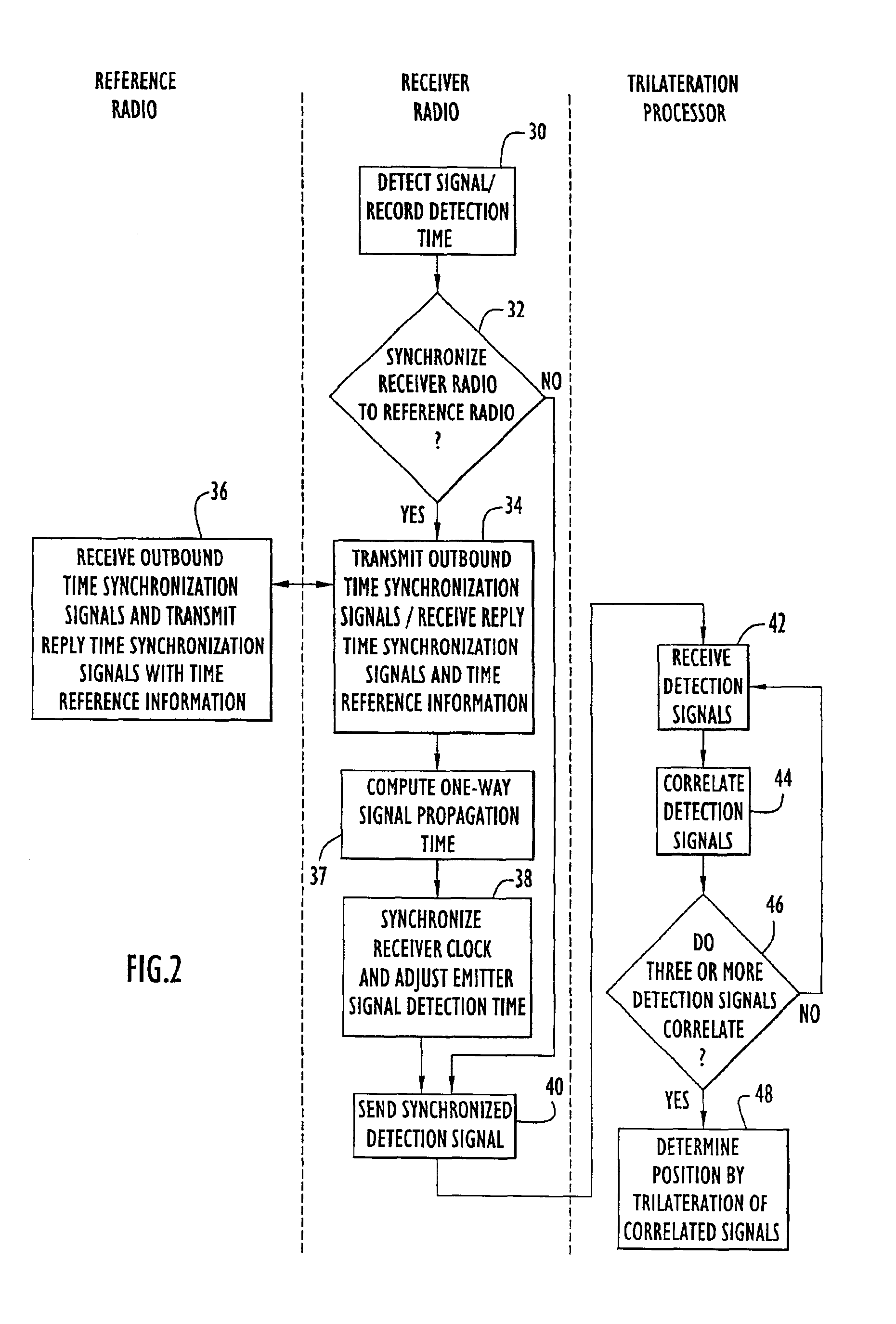
InactiveUS6861982B2Improve accuracyMinimizes designDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPropagation timeExchange time
The position of a non-cooperating emitter is determined by detecting a signal from the emitter at three or more receiver communication devices positioned at different locations. The receiver communication devices determine respective detection times of the emitted signal in respective local time reference frames. To establish a common time reference frame for the emitted signal detections, each receiver communication device exchanges time synchronization signals with a reference communication device. Since any of the receiver communication devices and the reference communication device may be mobile, the signal exchange allows each receiver communication device to accurately determine the signal propagation time between itself and the reference communication device and factor the signal propagation time into an accurate adjustment of the local time reference frame. Using trilateration, the position of the emitter is determined from known positions of the receiver communication devices and the emitted signal detection times from the receiver communication devices.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Apparatus and Method for Direct Device-to-Device Communication in a Mobile Communication System
InactiveUS20120294163A1Improve data transfer performanceAvoid interferenceSynchronisation arrangementError preventionResource elementMobile communication systems
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
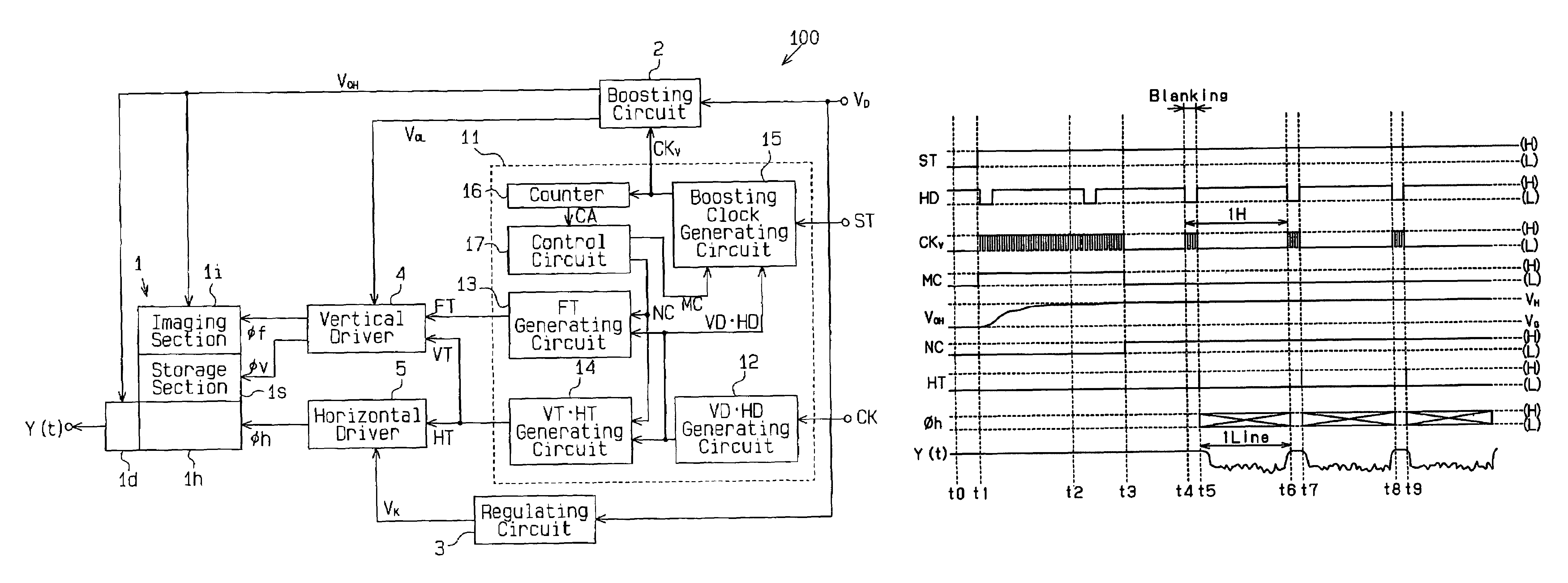
Imaging device with boosting circuit
ActiveUS7310115B2Television system detailsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEngineeringImage signal
An imaging device that is activated quickly and prevents deterioration of an image signal. The imaging device includes a boosting circuit for boosting an input voltage to generate a boosted voltage. A solid state imaging device receives the boosted voltage and generates the image signal. A clock signal generation unit is connected to the boosting circuit to determine a timing for generating the image signal in correspondence with a vertical synchronization signal and a horizontal synchronization signal and to generate a boosting clock signal for operating the boosting circuit. The clock signal generation unit continuously generates the boosting clock signal during a predetermined period in which the imaging operation starts and, after the predetermined period, generates the boosting clock signal during at least part of a blanking period of the vertical synchronization signal and the horizontal synchronization signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
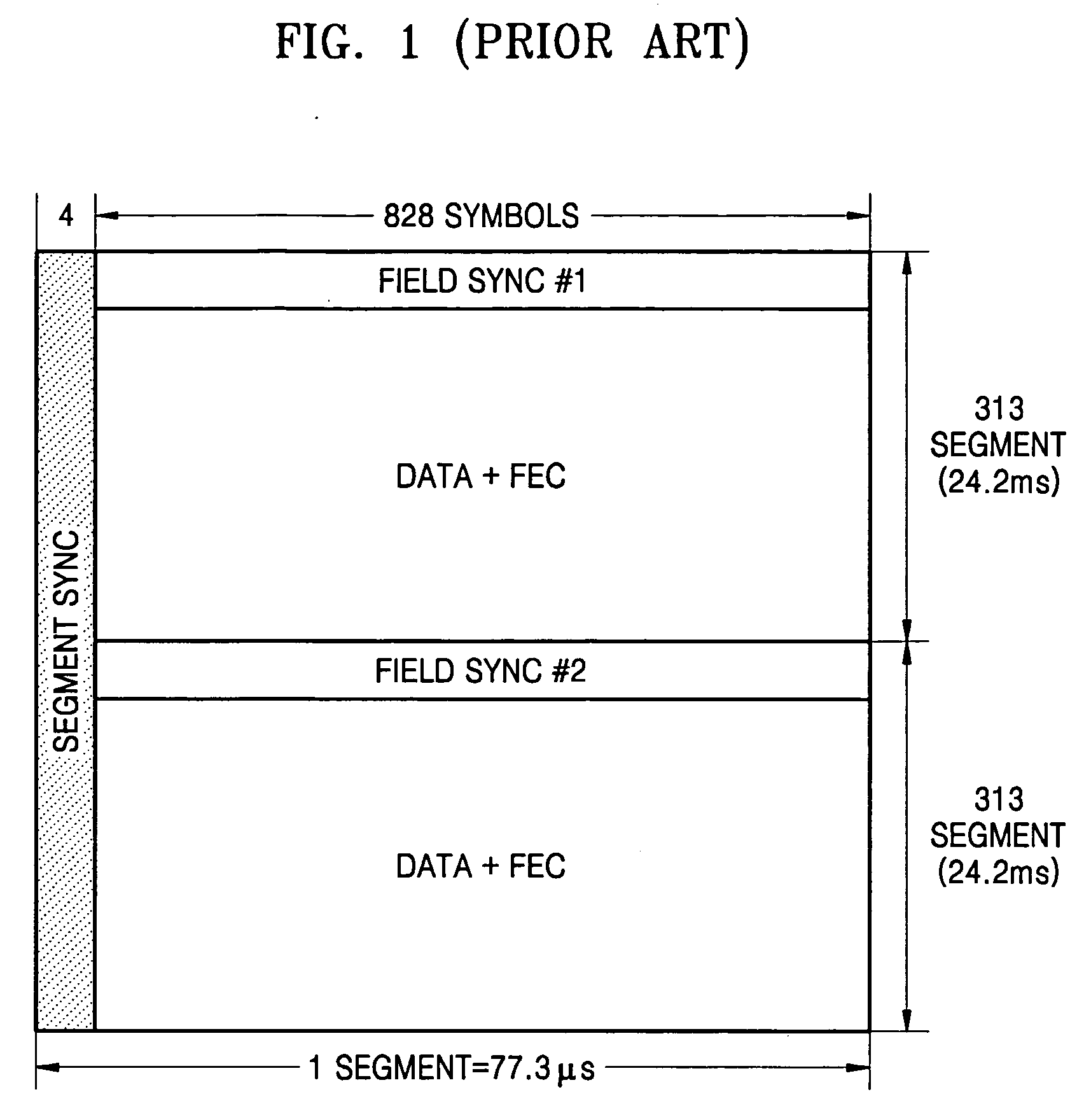
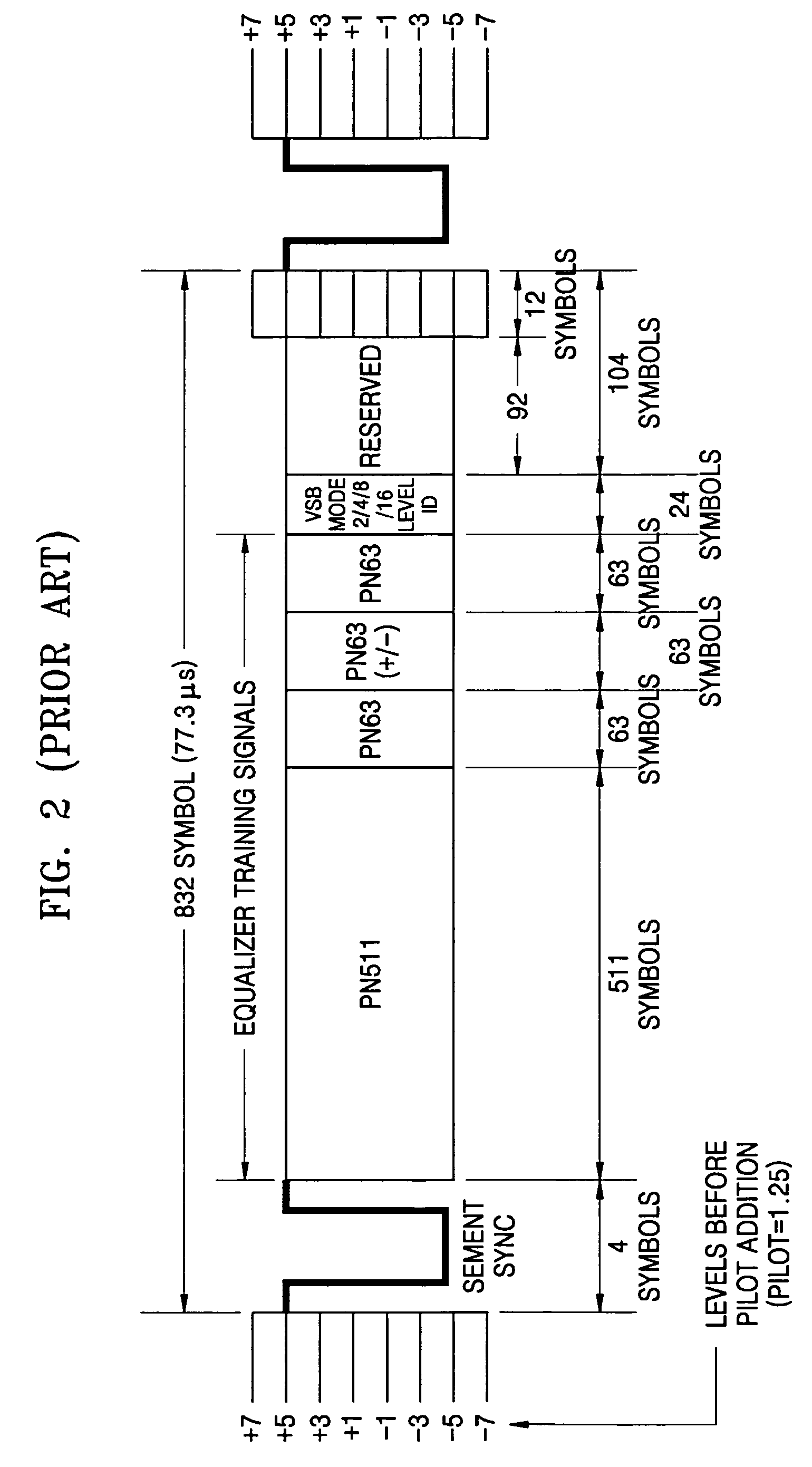
VSB communication system
InactiveUS6947487B2Noise robustRobust to ghostTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiplexingCommunications system
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Acoustic Robust Synchronization Signaling for Acoustic Positioning System
InactiveUS20080084789A1Improve accuracyDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationLocation detectionEngineering
A position detection system comprising positional element and positioning device, wherein the positional element transmits a continuously modulated acoustic waveform and a synchronization signal that is a sequence of at least two synchronization packets, each bearing timing data for the continuously modulated acoustic waveform. Additionally, the synchronization signal uses time hopping to support concurrent positioning of a plurality of positional elements.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
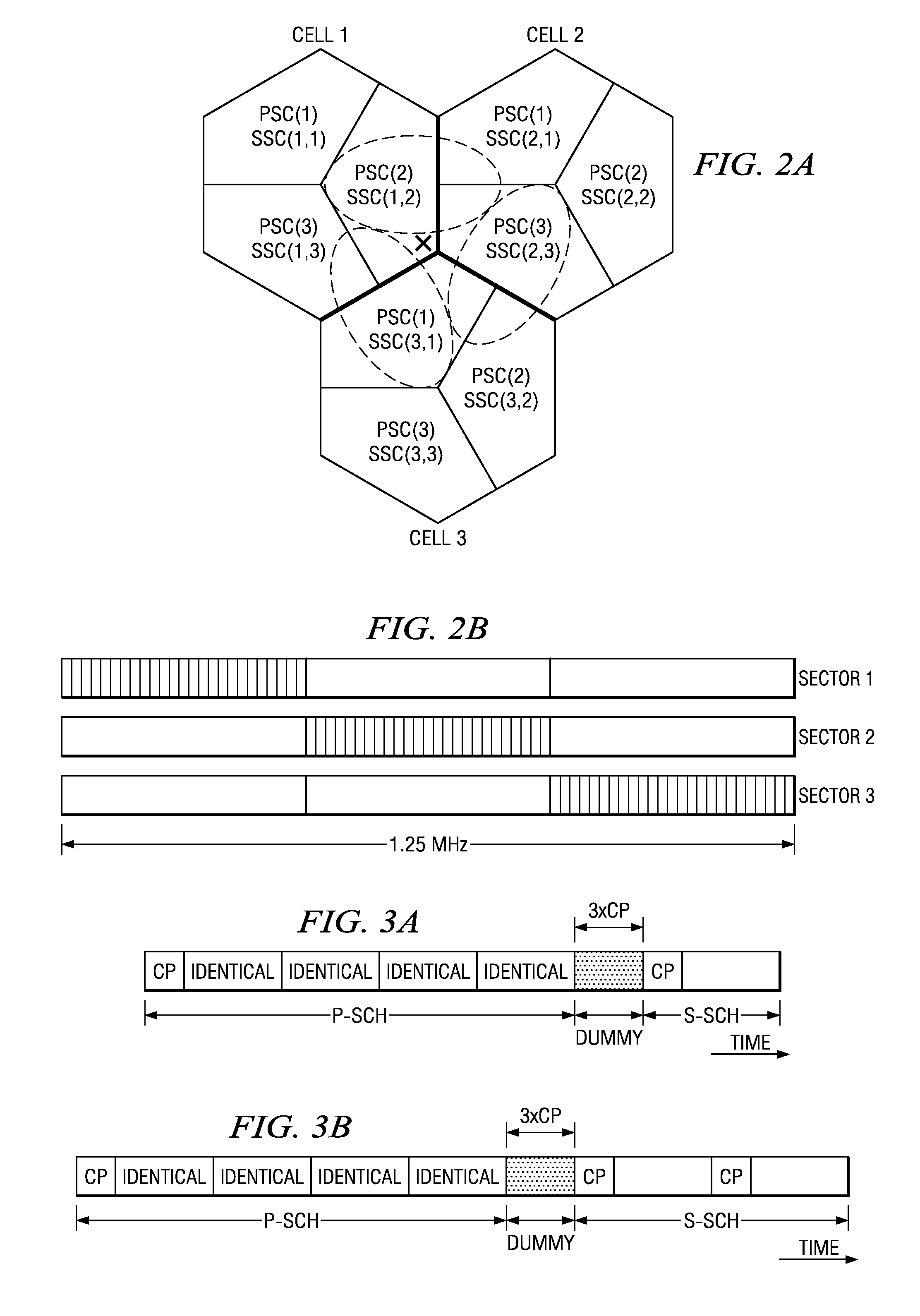
Base station, mobile station, and synchronization channel transmission method
ActiveUS20100135257A1Reduce in quantitySynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsCell specificCommunications system
A base station communicating with a mobile station in a radio communication system by using OFDM for downlink is disclosed. The base station includes a sequence selecting unit configured to select multiple synchronization signal sequences; a synchronization signal generating unit configured to generate a secondary synchronization channel based on a part of the selected synchronization signal sequences and another part of the selected synchronization signal sequences; and a transmitting unit configured to transmit the secondary synchronization channel. The secondary synchronization channel is used to detect cell-specific information.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
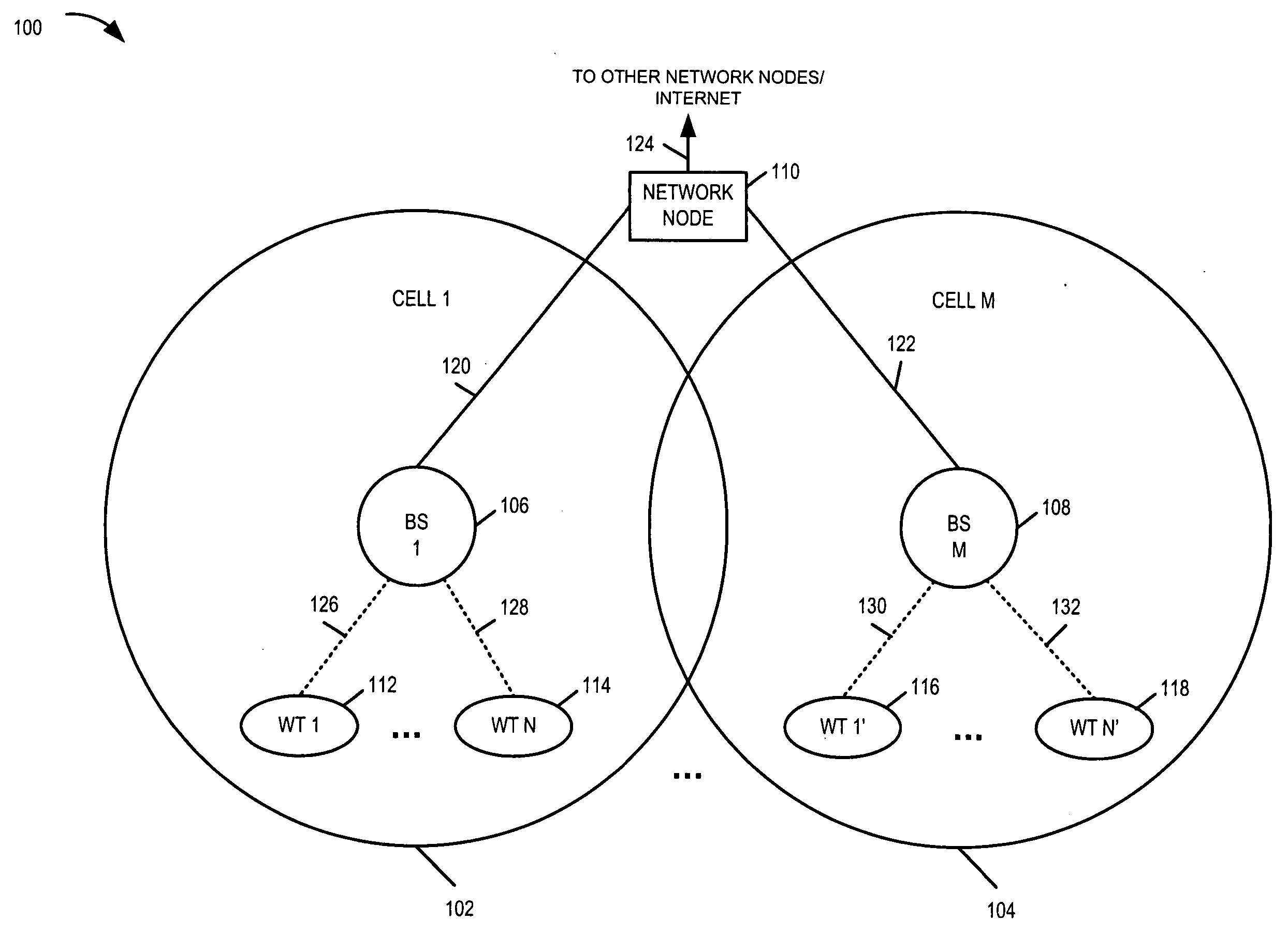
Adaptive communications methods for multiple user packet radio wireless networks
InactiveUS7110349B2Adapts quicklyGood estimateTime-division multiplexTransmitter/receiver shaping networksRadio networksOptimal weight
An exemplary wireless communication network that includes a base that communicates with remote units located in a cell of the network. A base concatenates information symbols with a preamble corresponding to a destination remote unit. One or more remote units communicating with a base each concatenates information symbols with a preamble corresponding to that remote unit. An adaptive receiver system for a base unit rapidly adapts optimal despreading weights for reproducing information symbols transmitted from multiple remote units. A transmitter system for a base unit concatenates information symbols with a preamble associated with a remote unit in the cell. An adaptive receiver system for a remote unit in a communication network rapidly adapts optimal weights for reproducing a signal transmitted to it by a specific base unit in the network. A transmitter system for a remote unit in a cell of a communication network which concatenates information symbols with preamble associated with the remote unit. A base initiates communication with a desired remote unit by transmitting an initiation codeword in a selected entry slot. One or more remote units each initiates communication with a bse by transmitting an initiation codeword associated with the remote unit in a selected entry slot. A remote unit synchronizes in time and frequency to the base using a sequence of synchronization signals transmitted by the base in a number of entry slots.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GROUP
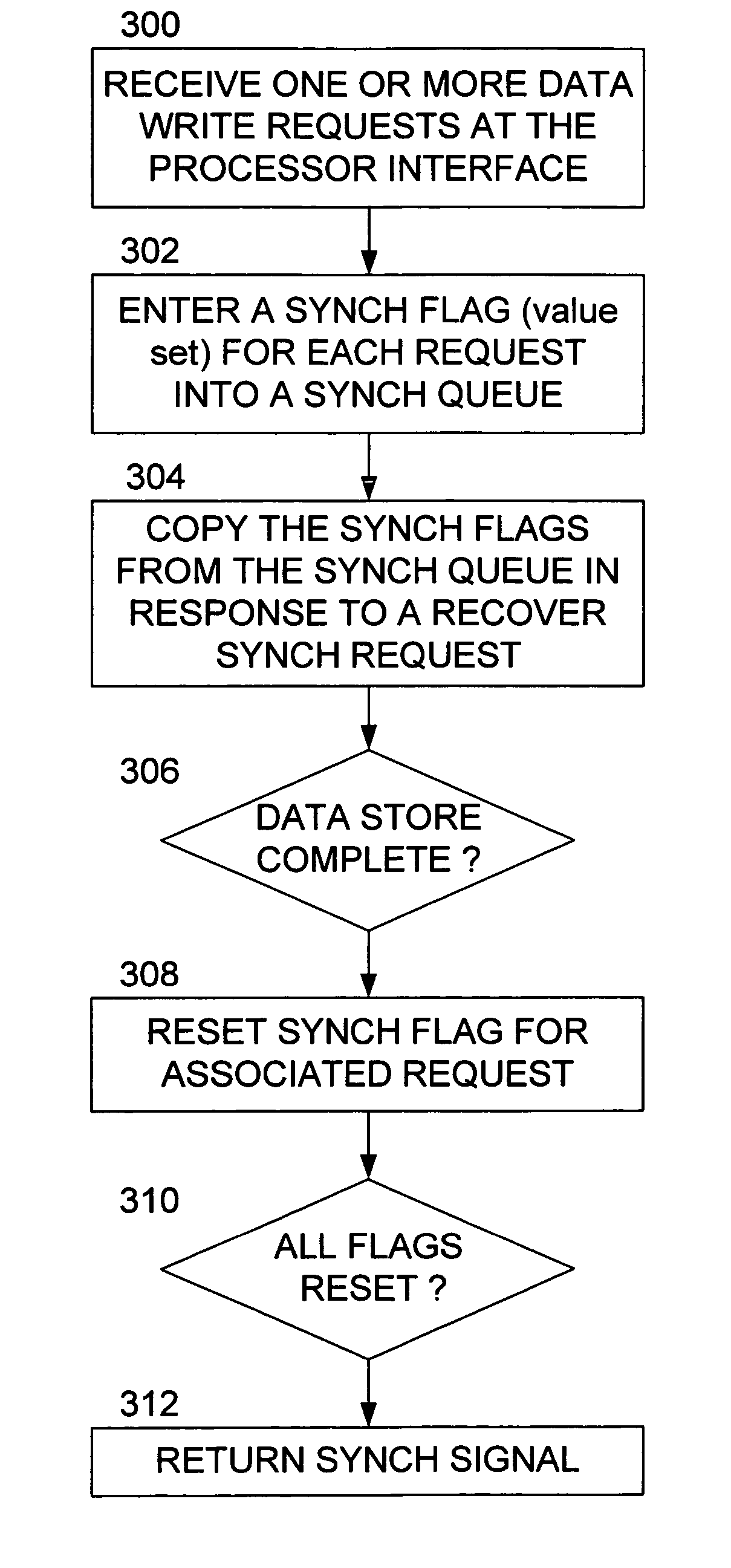
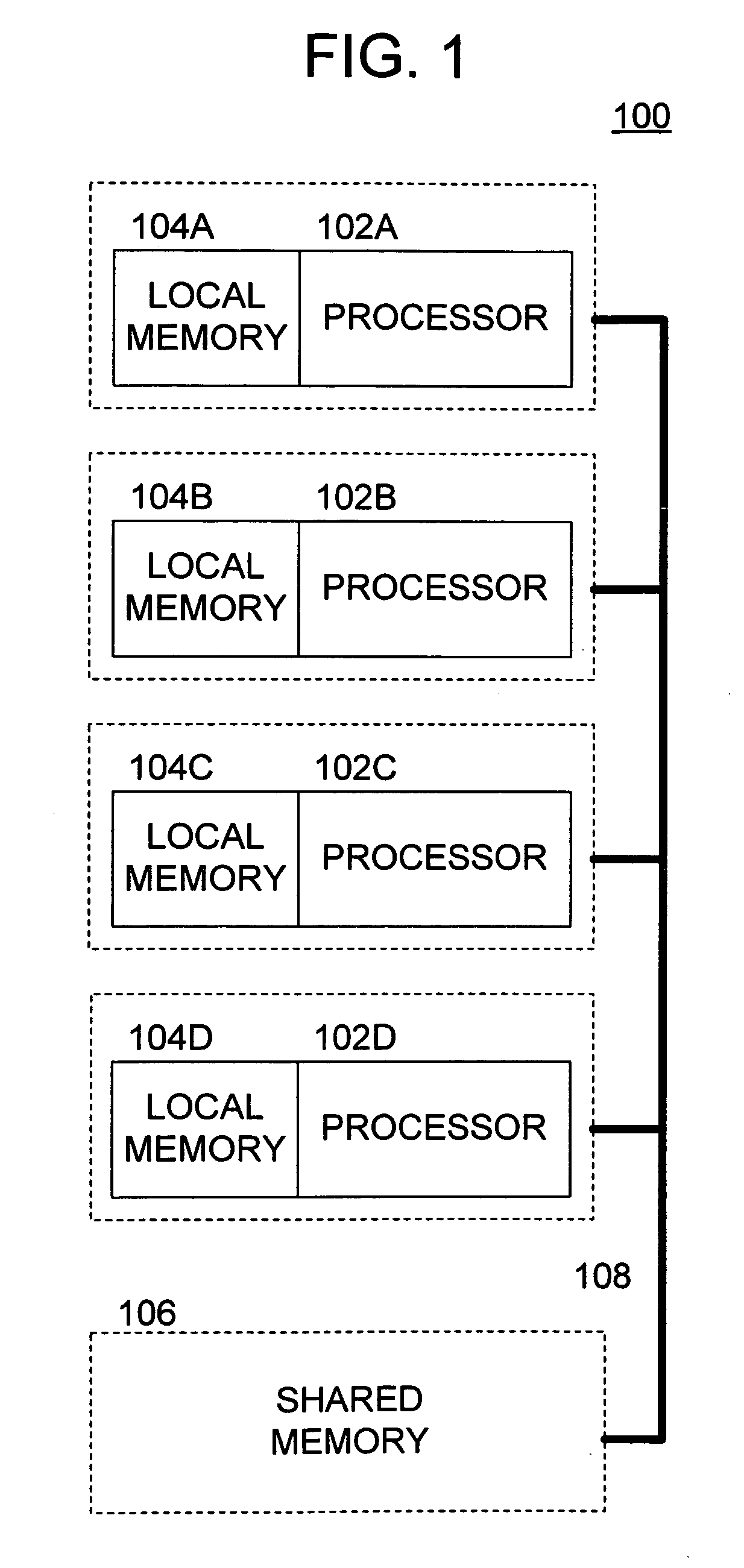
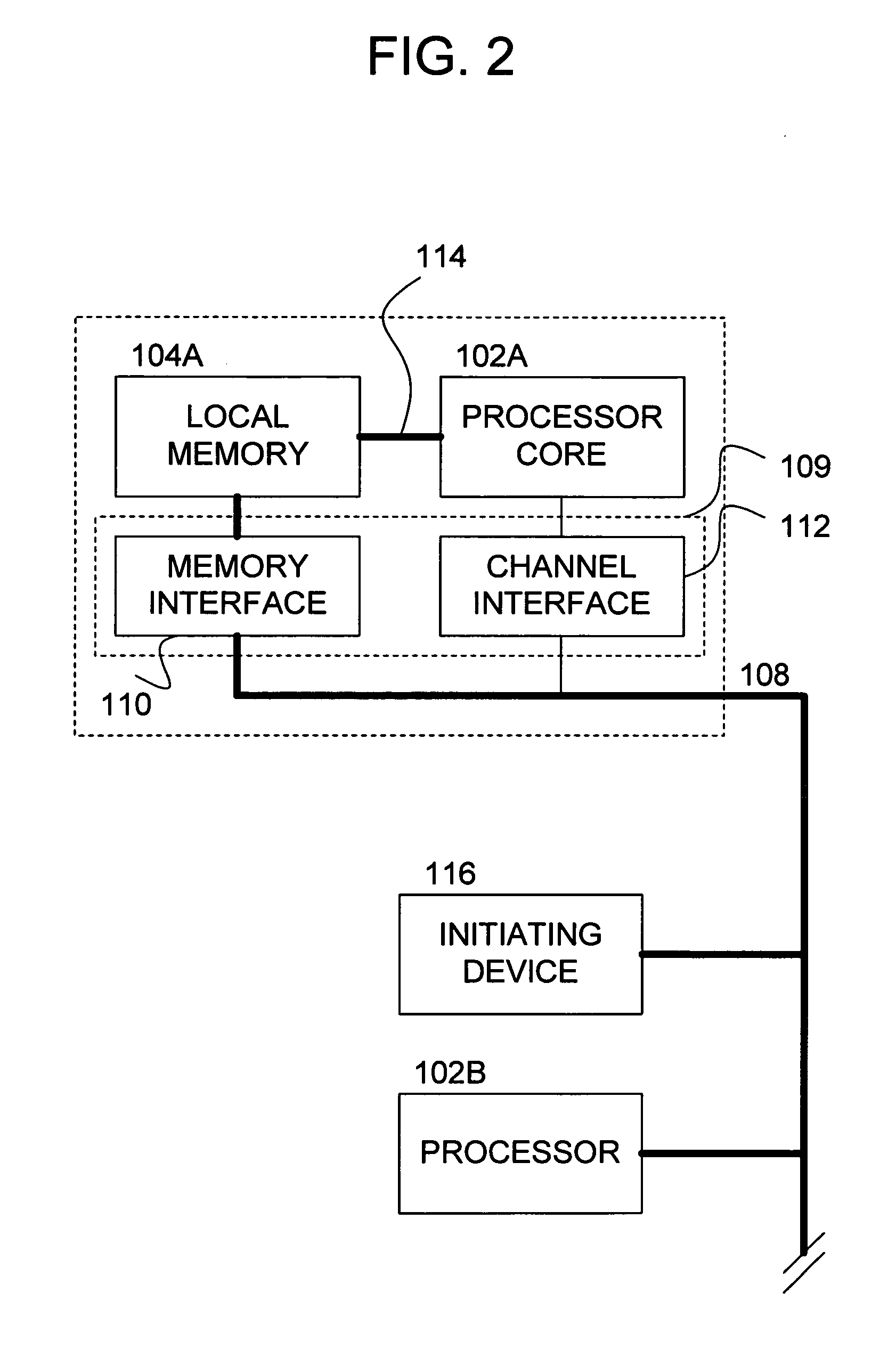
Methods and apparatus for synchronizing data access to a local memory in a multi-processor system
Methods and apparatus provide for receiving a request from an initiating device to initiate a data transfer into a local memory for execution of one or more programs therein, the local memory being operatively coupled to a first of a plurality of parallel processors capable of operative communication with a shared memory; facilitating the data transfer into the local memory; and producing a synchronization signal indicating that the data transfer into the local memory has been completed.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Neuromorphic Circuit
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to neuromorphic circuits containing two or more internal neuron computational units. Each internal neuron computational unit includes a synchronization-signal input for receiving a synchronizing signal, at least one input for receiving input signals, and at least one output for transmitting an output signal. A memristive synapse connects an output signal line carrying output signals from a first set of one or more internal neurons to an input signal line that carries signals to a second set of one or more internal neurons.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
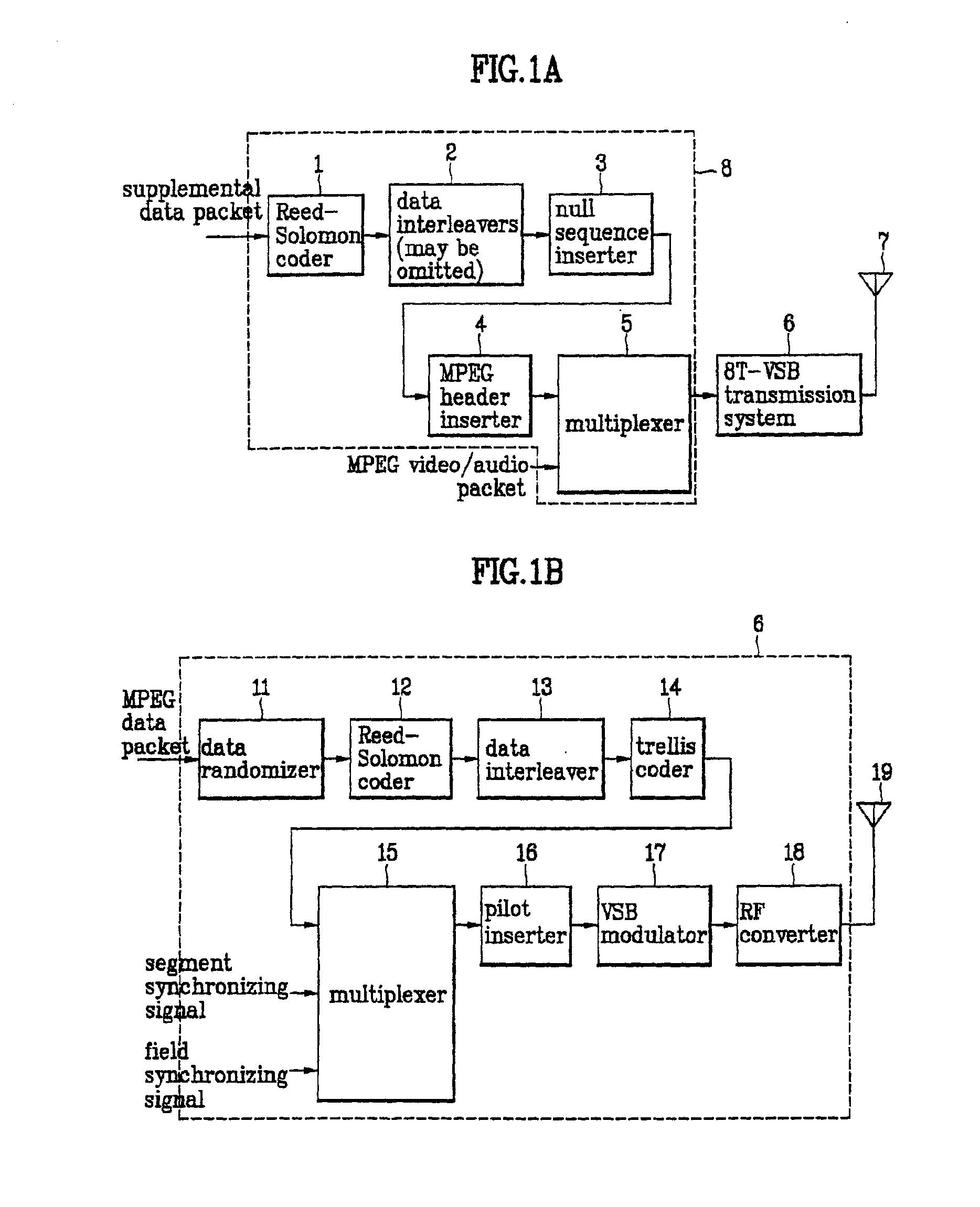
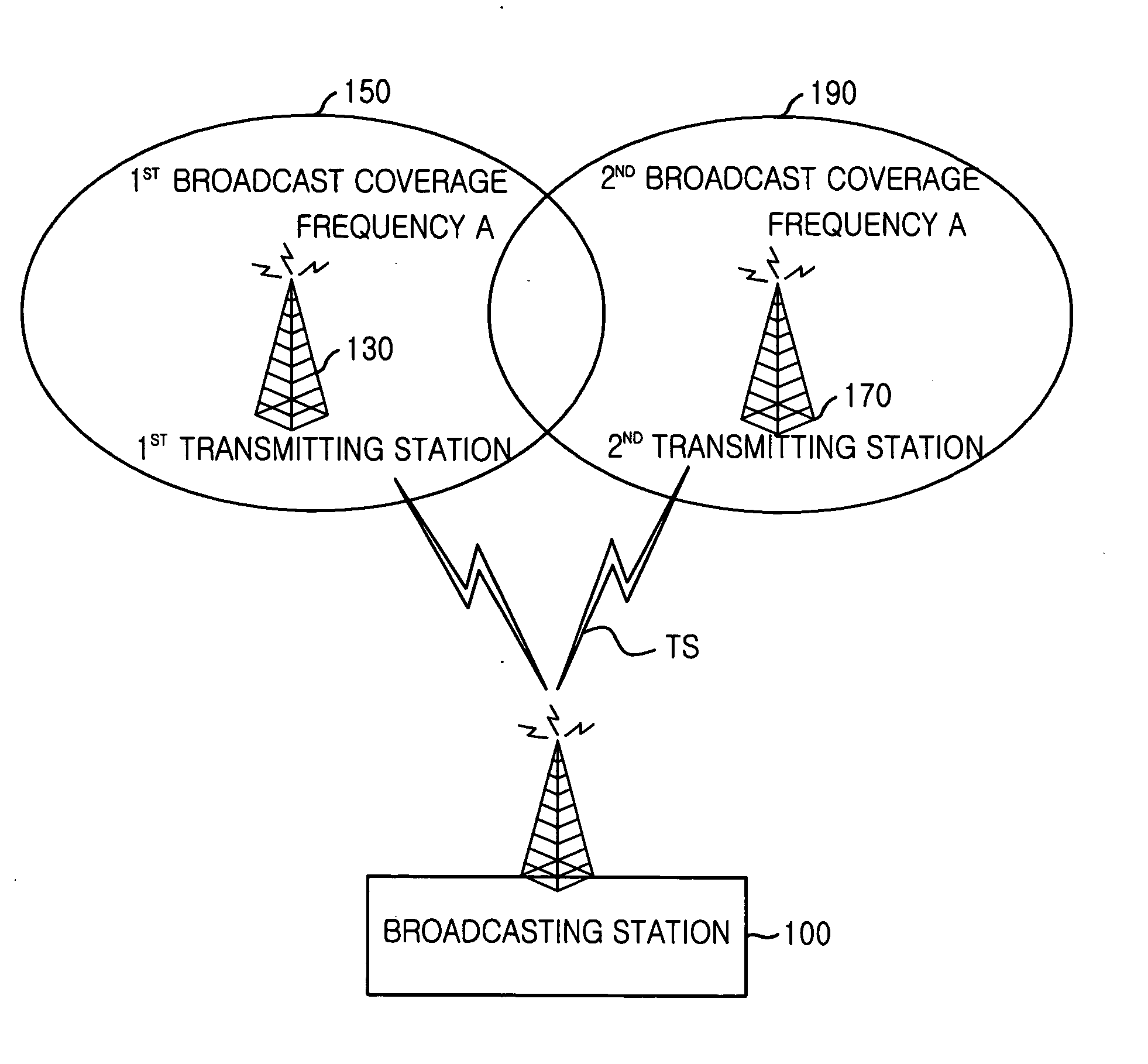
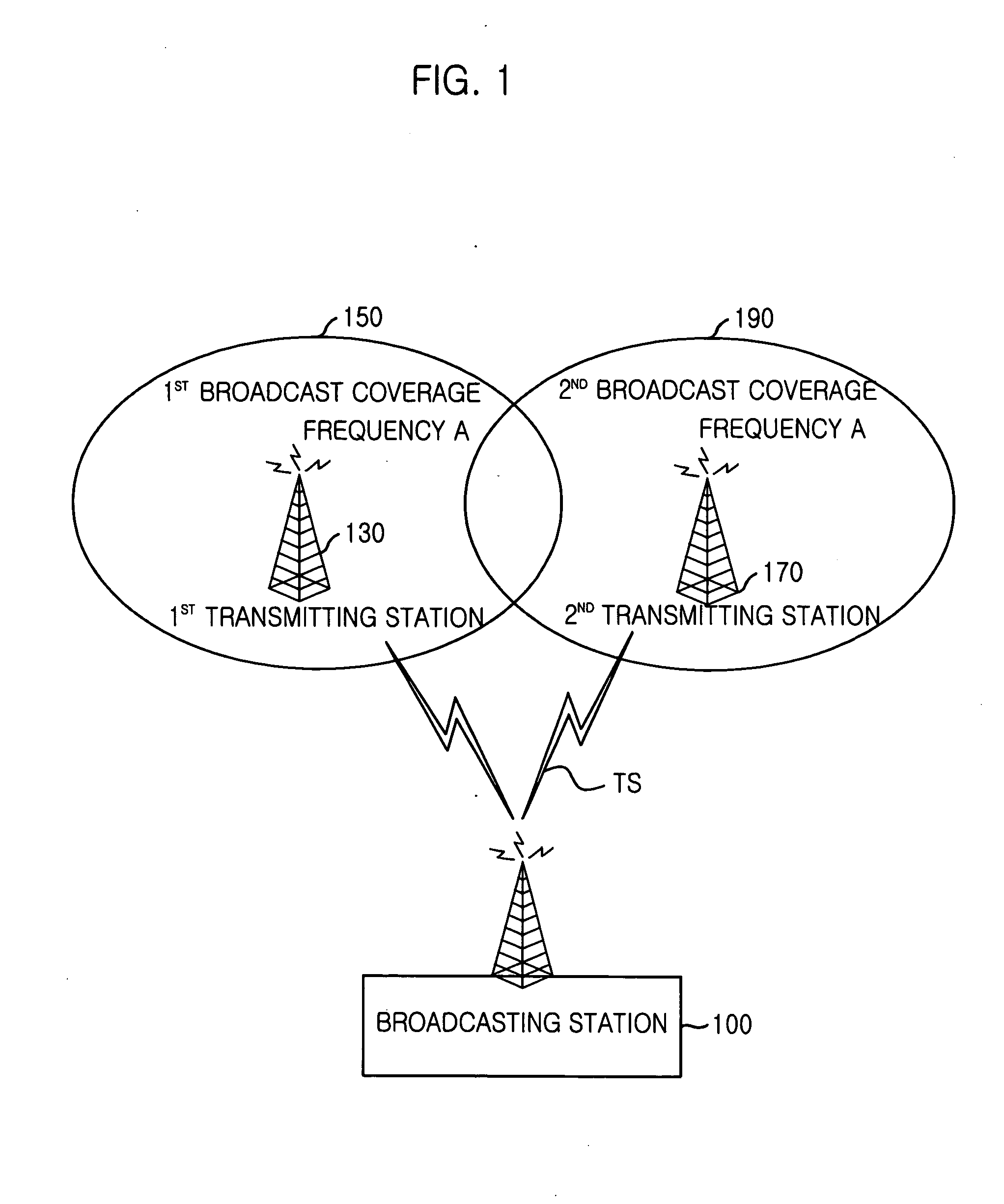
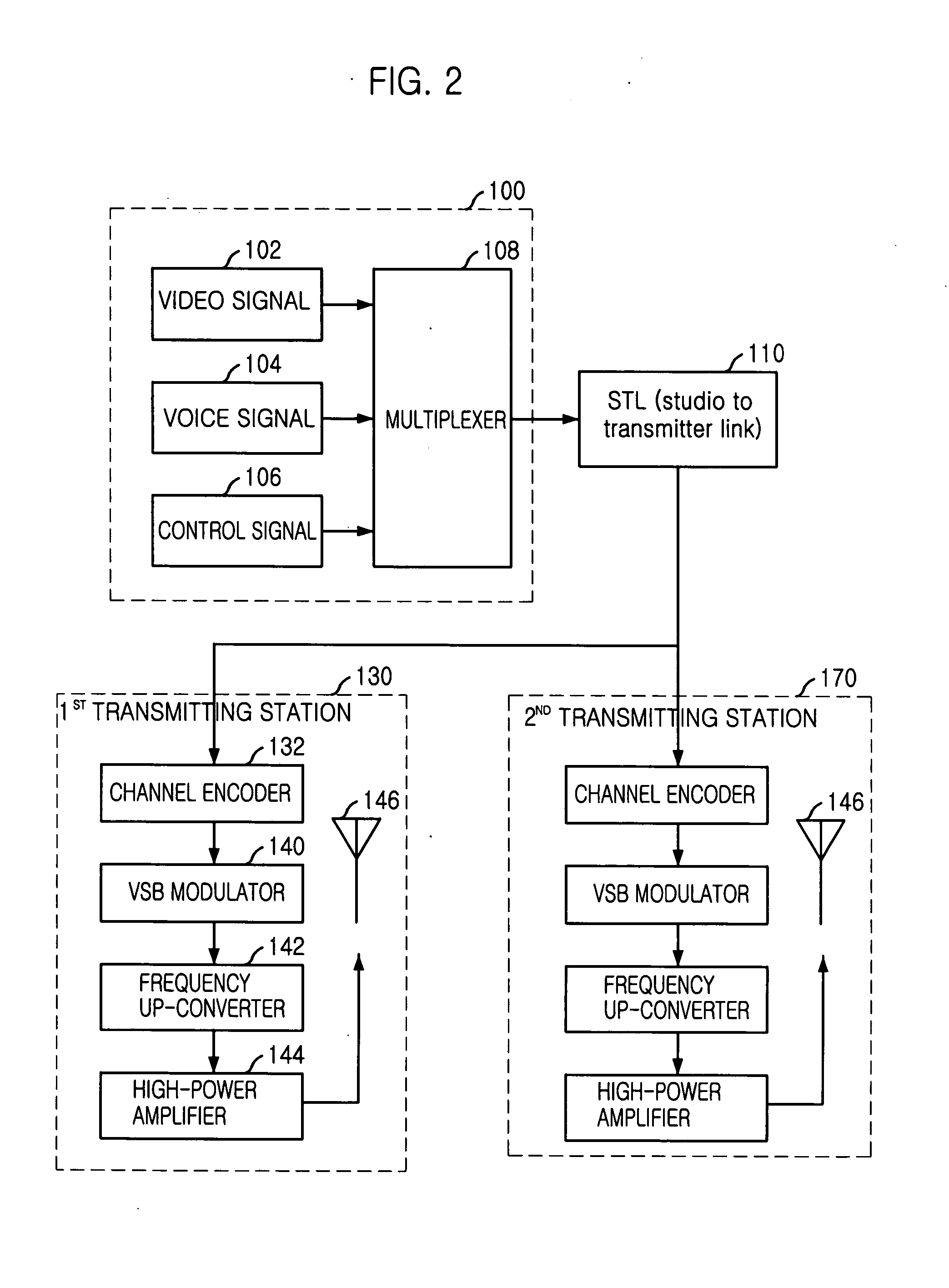
System and method for providing terrestrial digital broadcasting service using single frequency network
InactiveUS20060253890A9Television system detailsData representation error detection/correctionMultiplexingInit
Provided is a system and method for terrestrial digital broadcasting service using a single frequency network without additional equipment. The system and method synchronizes input signals into transmitting stations by inserting a transmission synchronization signal into a header of TS periodically, and solves the problematic ambiguity of the trellis encoder by including a trellis encoder switching unit separately and initializing a memory of the trellis encoder. The terrestrial digital broadcasting system includes: a broadcasting station for multiplexing video, voice and additional signals into transport stream (TS) and transmitting the TS to the transmitting stations and a transmitting stations for receiving the TS and broadcast the TS to receiving stations through a single frequency network
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
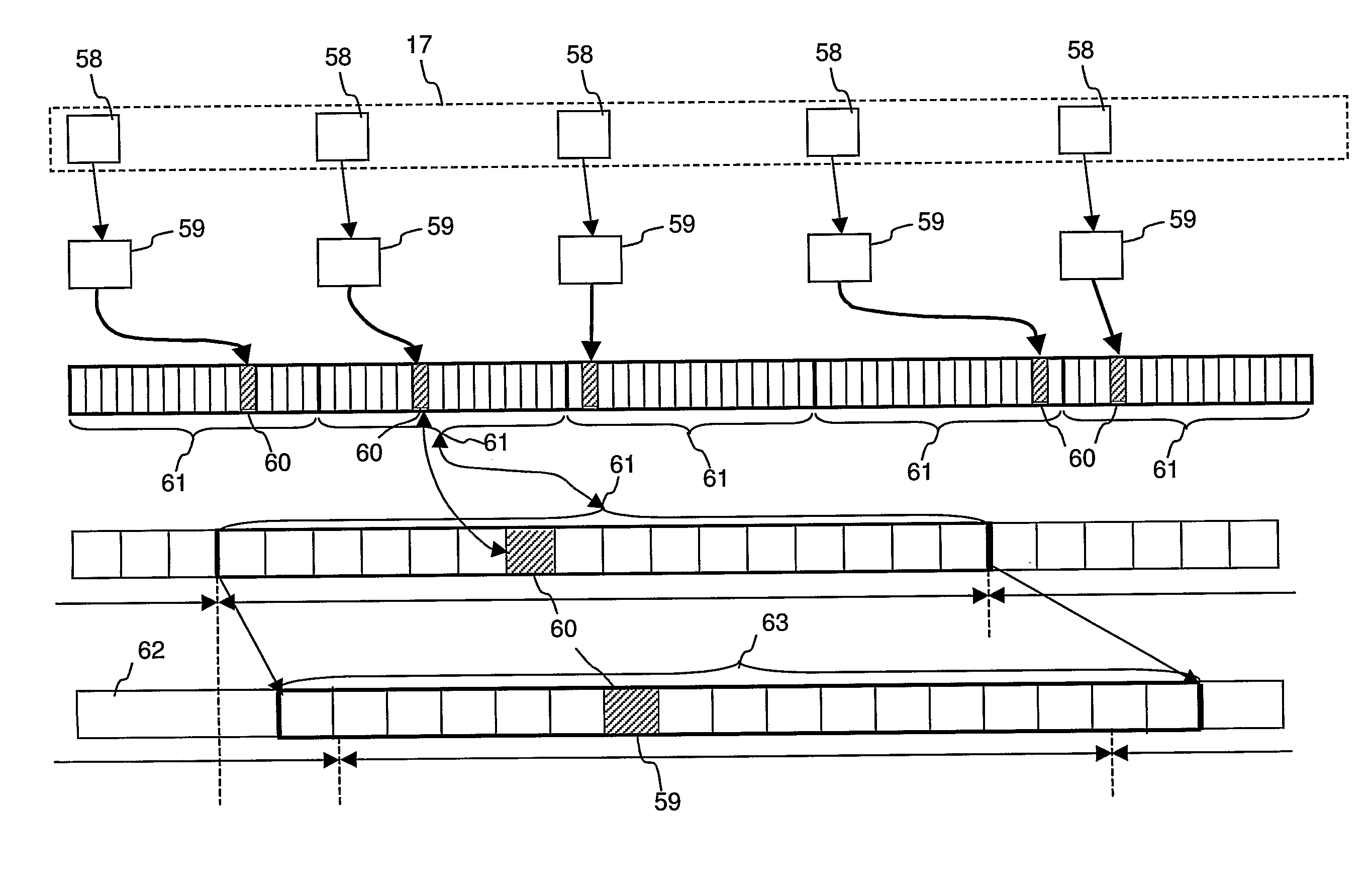
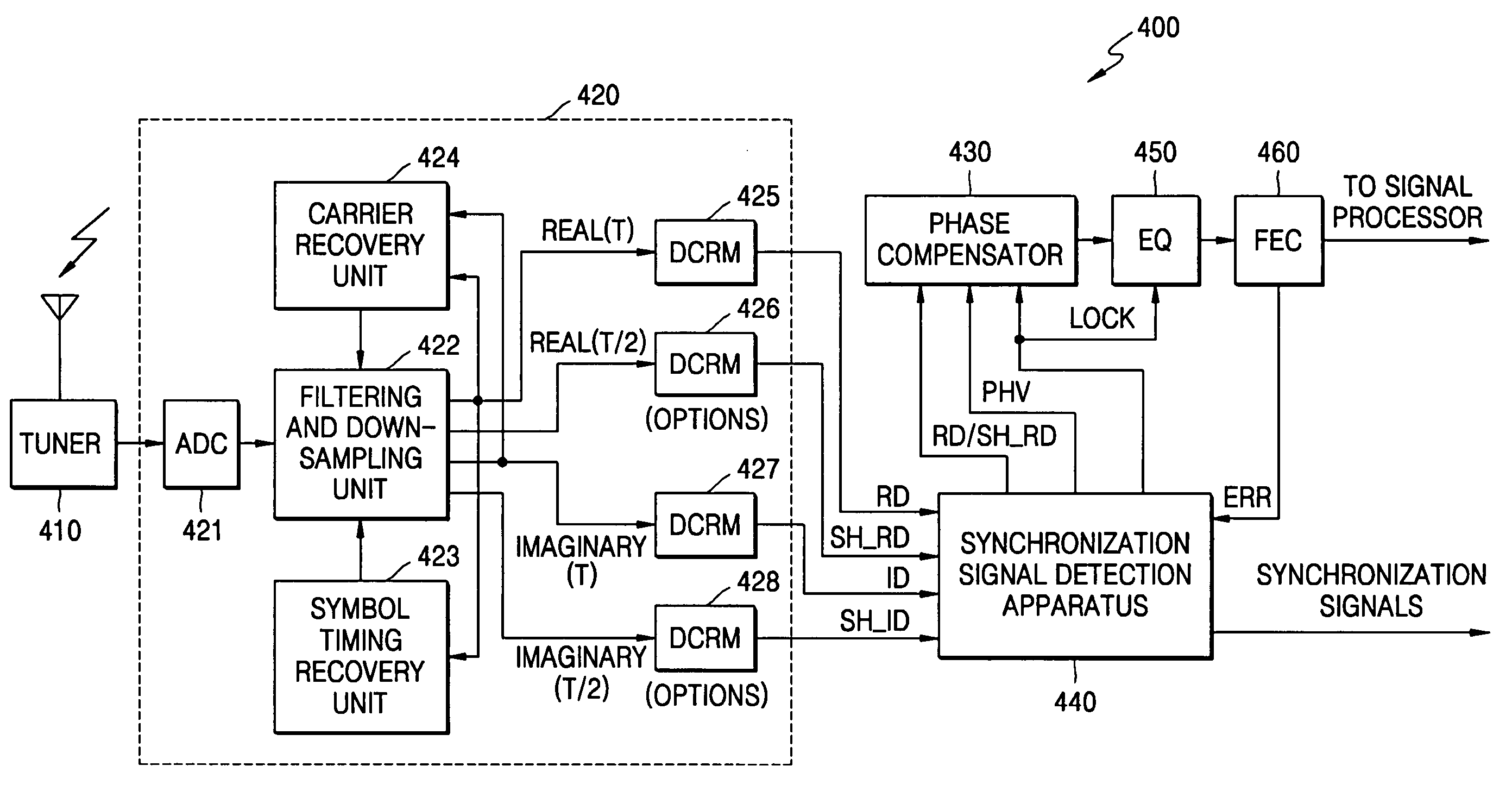
Synchronization signal detection circuit and method of digital television (DTV) receiver
InactiveUS20060078072A1Guaranteed uptimeStable operation can be assuredTelevision system detailsColor burst signal generation/insertionControl signalDTV receiver
A synchronization signal detection circuit and method of a digital TV (DTV) receiver are provided. The synchronization signal detection circuit determines a precise main path by determining powers in consideration of the influence of multiple paths near signals located at a peak value location and guarantees a stable operation of an equalizer by using error values output from a decoder to generate a synchronization locking control signal. A power signal based on the correlation of the received signal with a PN511 sequence is filtered to compensate for a dynamic multipath distortion (e.g., due to other multipath signals near signals located at a peak value location). The magnitude of the filtered power signal is then compared (e.g., with a predetermined threshold value) to determine the position of the main path (e.g., at the peak value location, or at a pre or post multipath signal location).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
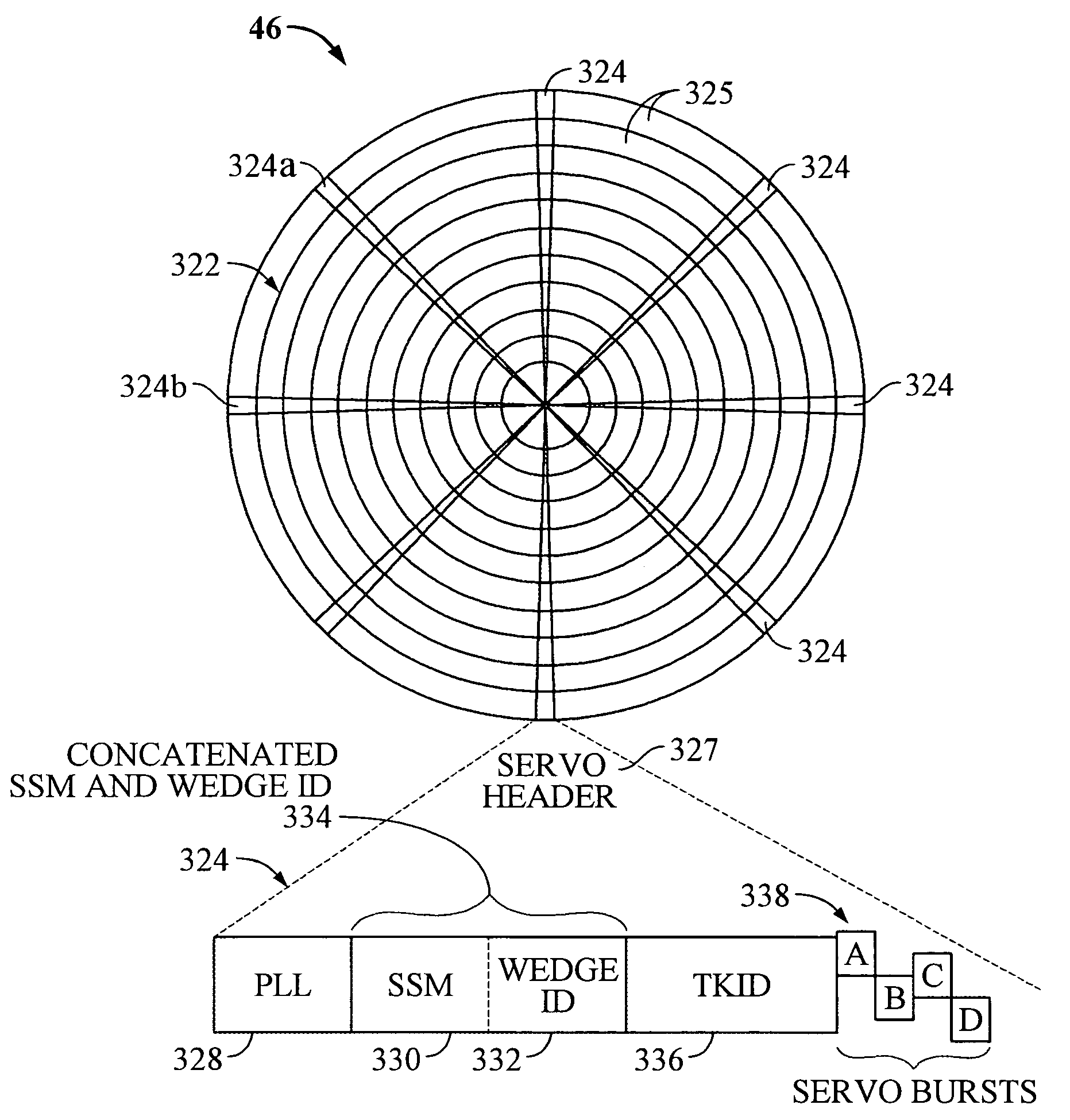
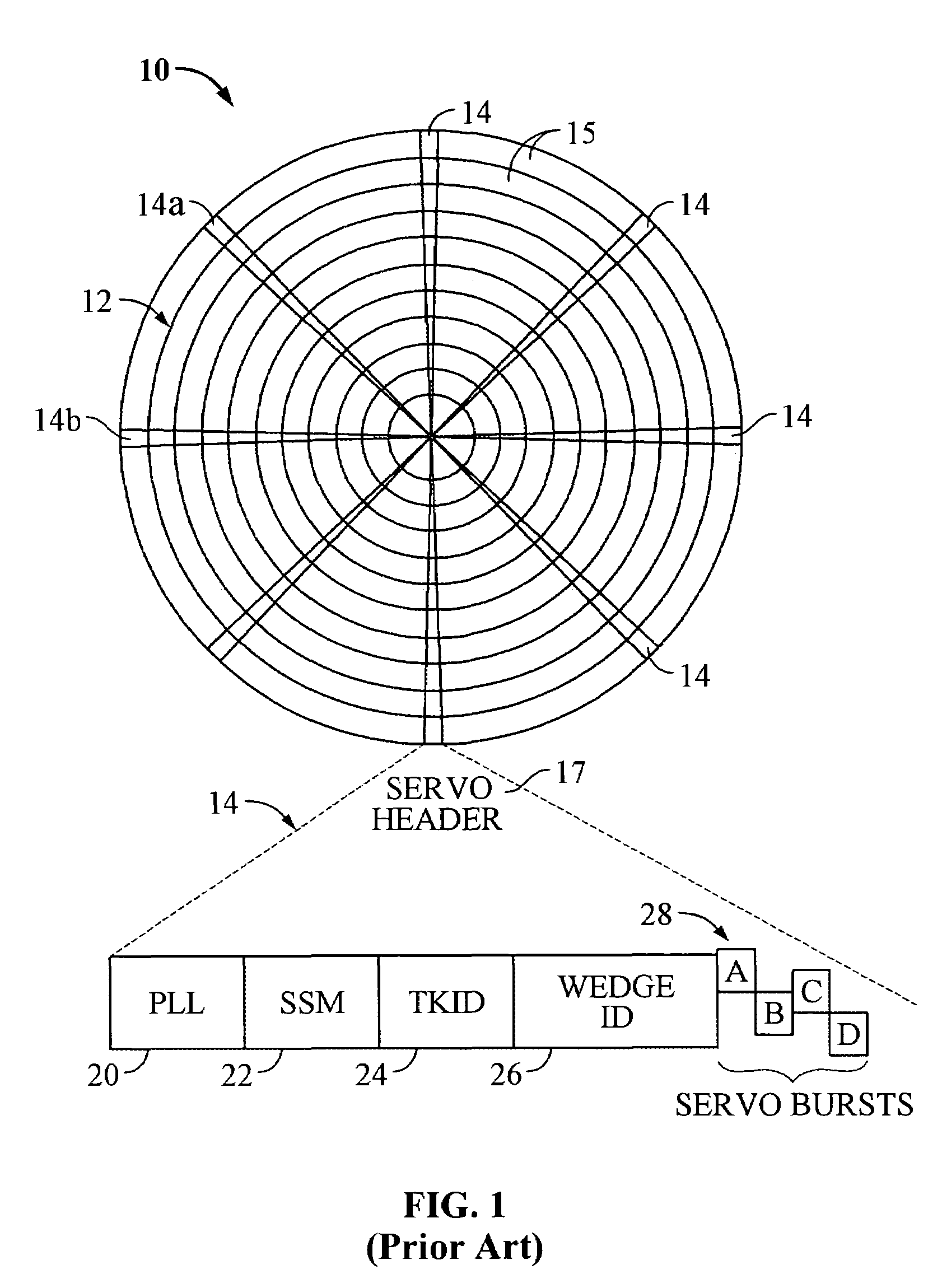
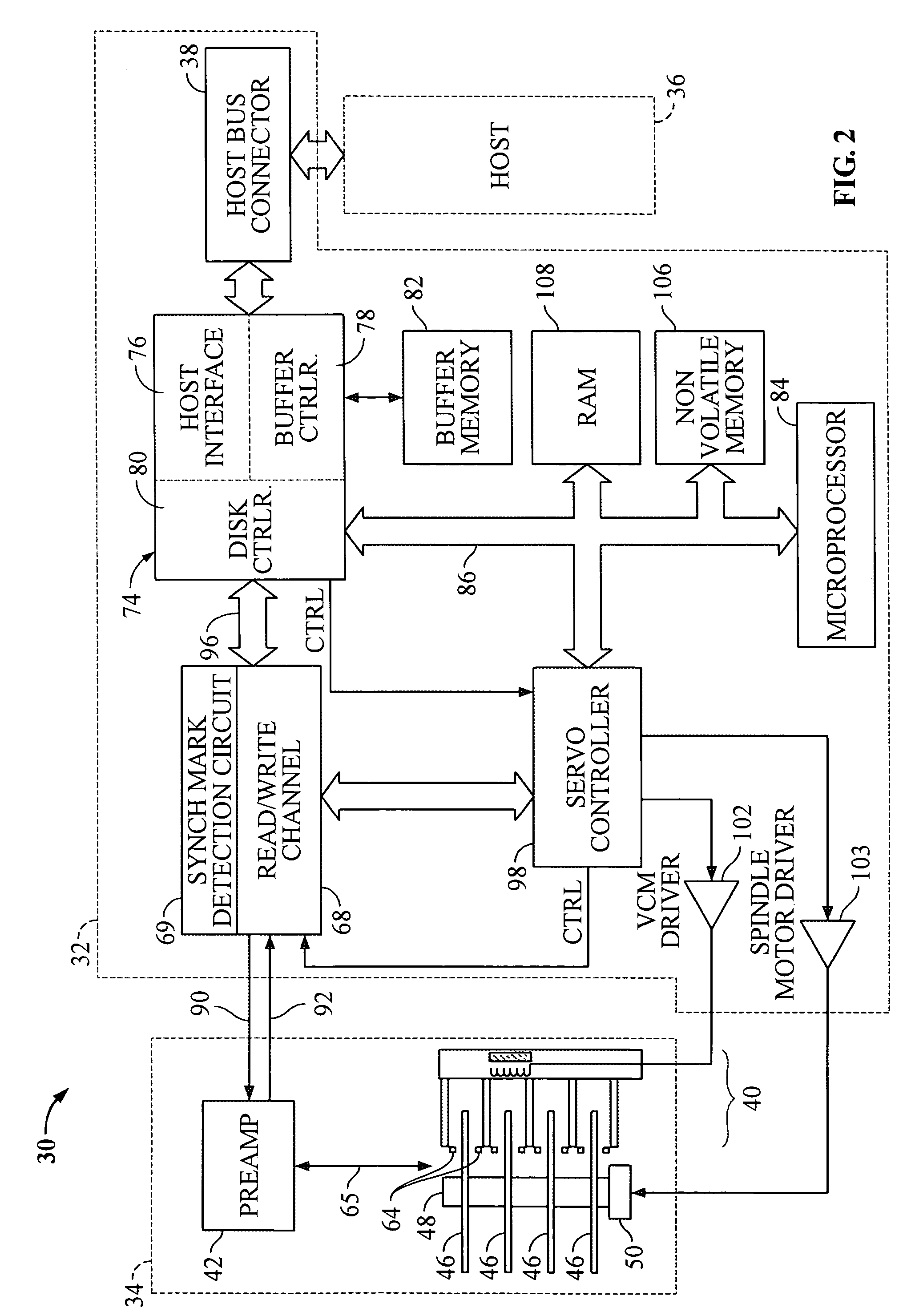
Servo synchronization validation techniques based on both servo synch marks and wedge identifiers in a rotating media storage device
Disclosed is a rotatable media storage device (RMSD) connectable to a host. The RMSD include a movable head to perform track following, a disk, and a synch mark detection circuit. The disk includes a circumferential track that has a plurality of embedded servo wedges utilized in track following. The synch mark detection circuit has a first detection mode and a second detection mode. In the first detection mode, the synch mark detection circuit detects a servo synchronization signal based on the head reading a SSM of a servo header of an embedded servo wedge. In the second detection mode, the synch mark detection circuit detects a servo synchronization signal based on the head reading a SSM and a wedge identifier of a servo header of an embedded servo wedge. The wedge ID is utilized in conjunction with the SSM to validate the servo synchronization signal.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
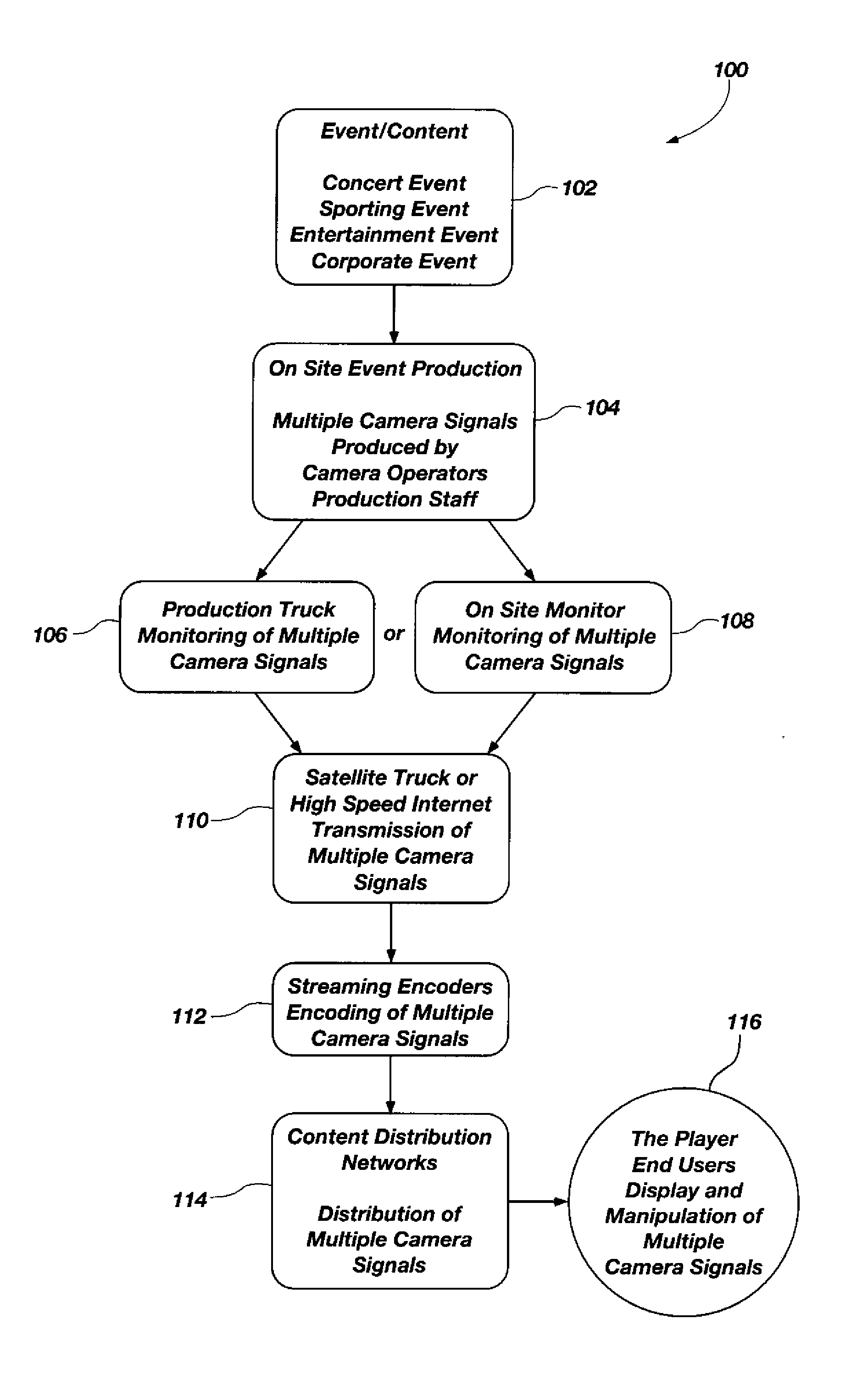
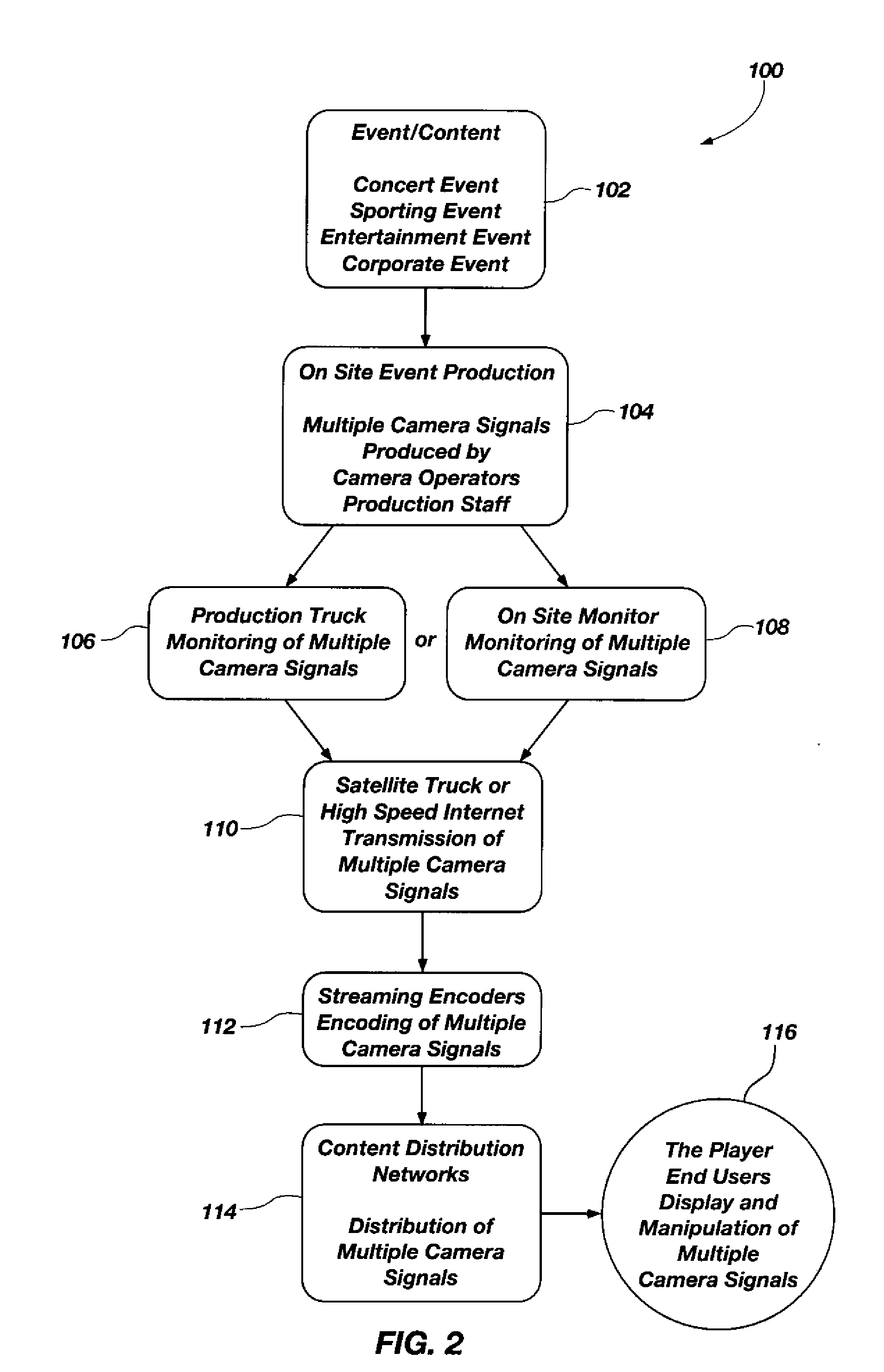
Media systems and methods for providing synchronized multiple streaming camera signals of an event
InactiveUS20100208082A1Television system detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer graphics (images)The Internet
A media system is provided having synchronized multiple camera signals of at least one event or activity for transmission over the internet to end users for selective display and / or manipulation. The media system may provide that end users are able to select and view and manipulate one or more of the multiple streaming video signals at will. The media system may be used in connection with a great variety of events or activities, including without limitation concerts, sports events, political events, sales events, movie premiers, public events, training events and religious events. A method is also provided having synchronized camera signals of at least one event or activity for transmission over the internet to end users for selective display and / or manipulation. The multiple camera signals are provided to end users for selective display and / or manipulation by end users. A media player is also provided for processing synchronized camera signals representing different views of at least one event or activity and providing end users of the media player the options of selectively displaying and / or manipulating at least one of the views at will.
Owner:BAND CRASHERS
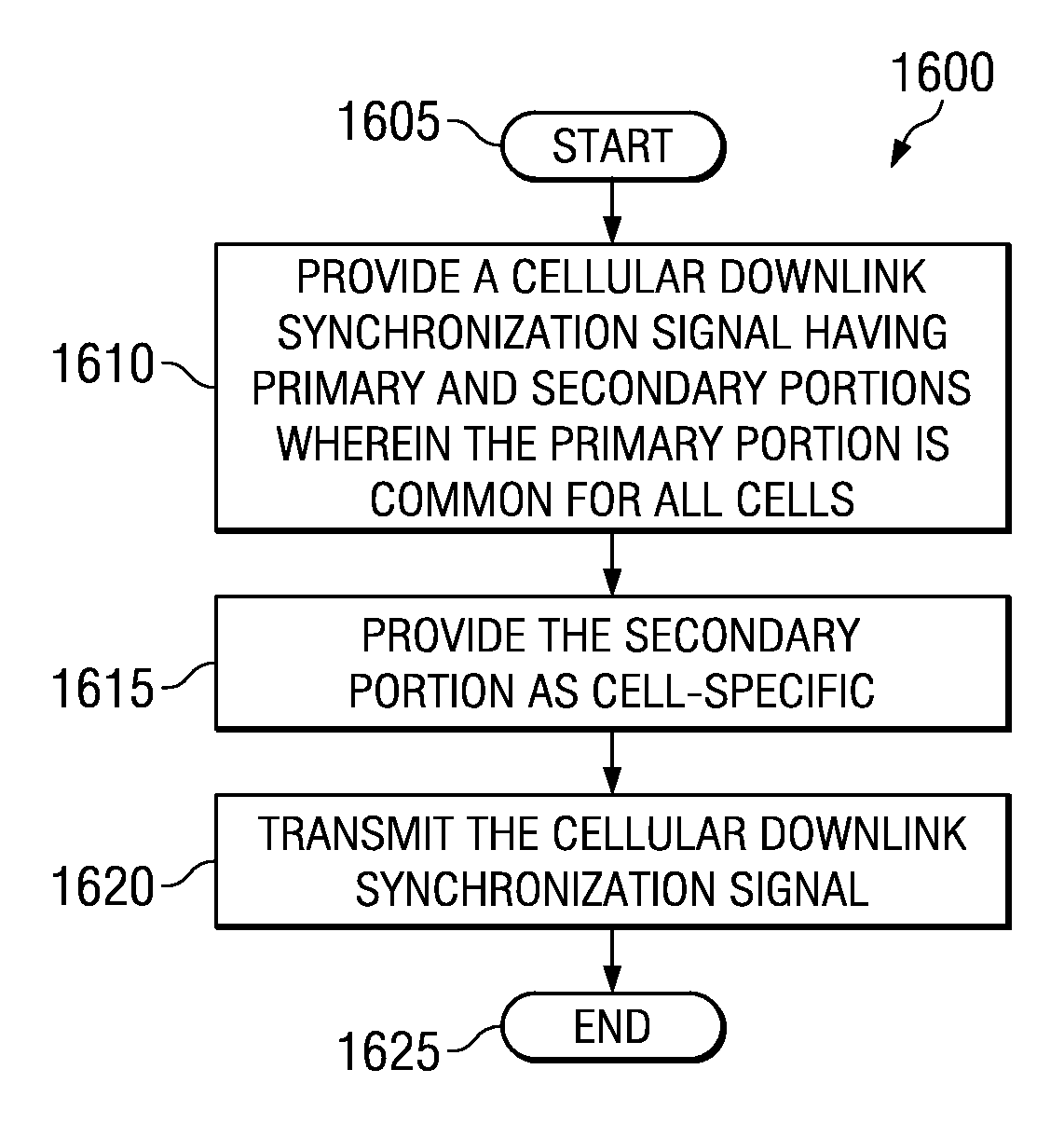
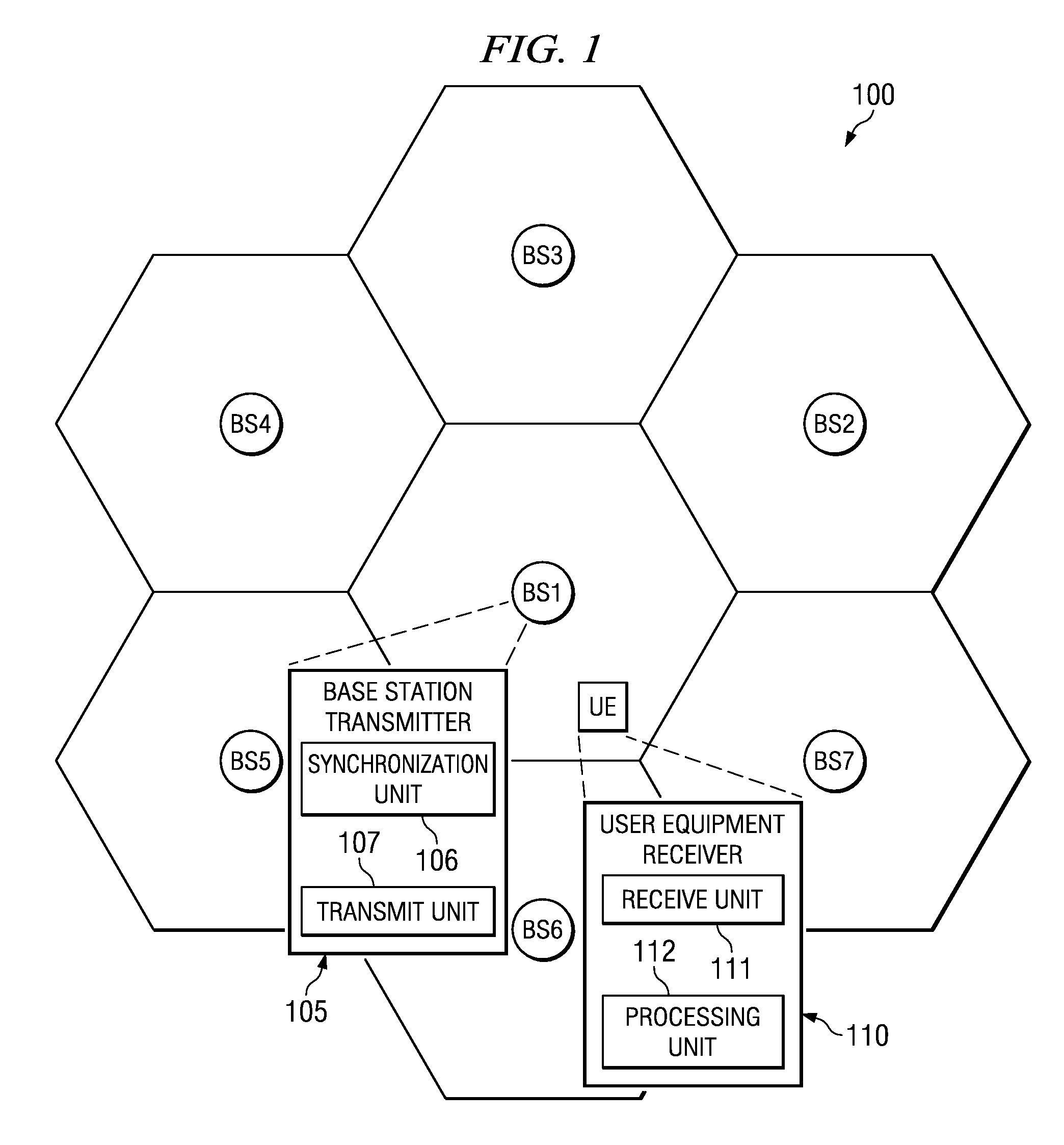
Downlink synchronization for a cellular OFDM communication system
ActiveUS20080019350A1Modulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCell specificOfdm communication system
The present invention provides a method of operating a base station transmitter. In one embodiment, the method includes providing a cellular downlink synchronization signal having primary and secondary portions, wherein the primary portion is common for all cells and the secondary portion is cell-specific and transmitting the cellular downlink synchronization signal. In another embodiment, the method includes providing a cellular downlink synchronization signal having primary and secondary portions wherein the primary portion employs a corresponding one of a plurality of different primary signals allocated to adjoining transmission cells. The method also includes further providing cell-specific information in the secondary portion and transmitting the cellular downlink synchronization signal. The present invention also provides a method of operating user equipment. The method includes receiving a cellular downlink synchronization signal having primary and secondary portions wherein the secondary portion provides cell-specific parameters and identifying and extracting the secondary portion.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Generating a low-latency transparency effect
InactiveUS20150194128A1Efficiently display deviceTransparency effectImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDisplay deviceLatency (engineering)
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for generating a transparency effect for a computing device. The technique includes transmitting, to a camera, a synchronization signal associated with a refresh rate of a display. The technique further includes determining a line of sight of a user relative to the display, acquiring a first image based on the synchronization signal, and processing the first image based on the line of sight of the user to generate a first processed image. Finally, the technique includes compositing first visual information and the first processed image to generate a first composited image, and displaying the first composited image on the display.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
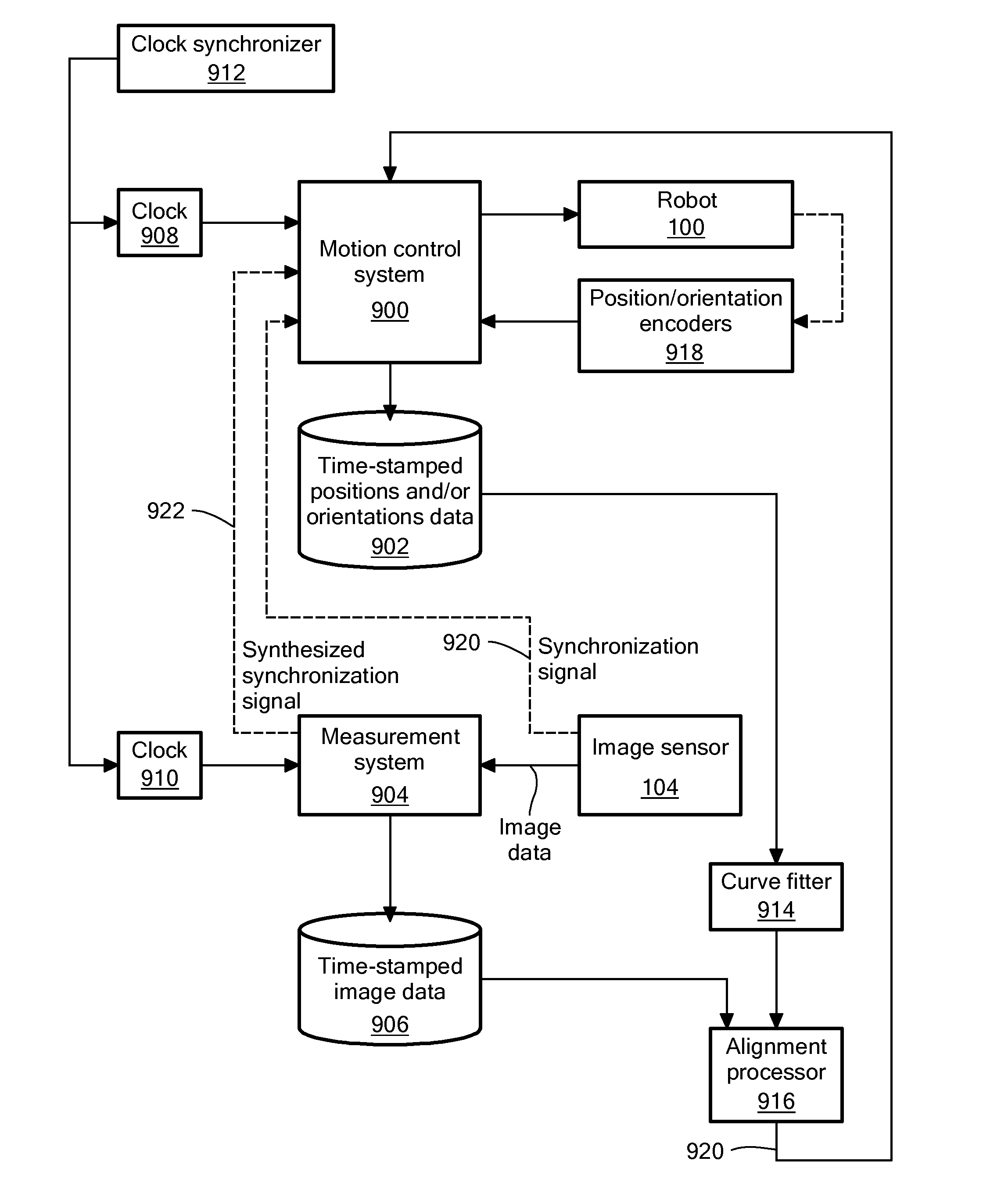
Active Alignment Using Continuous Motion Sweeps and Temporal Interpolation
Methods and apparatus for actively aligning a first optical element, such as a lens, to a second optical element, such as an image sensor, use continuous scans, even absent a synchronization signal from one of the optical elements. During a scan, timed position information about the scanned optical element is collected, and then a relationship between position of the scanned optical element and time is estimated, such as by fitting a curve to a set of position-time pairs. This relationship can then be used to estimate locations of the scanned optical element at times when image data or other alignment quality-indicating data samples are acquired. From this alignment quality versus location data, an optimum alignment position can be determined, and the scanned optical element can then be positioned at the determined alignment position.
Owner:AUTOMATION ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com