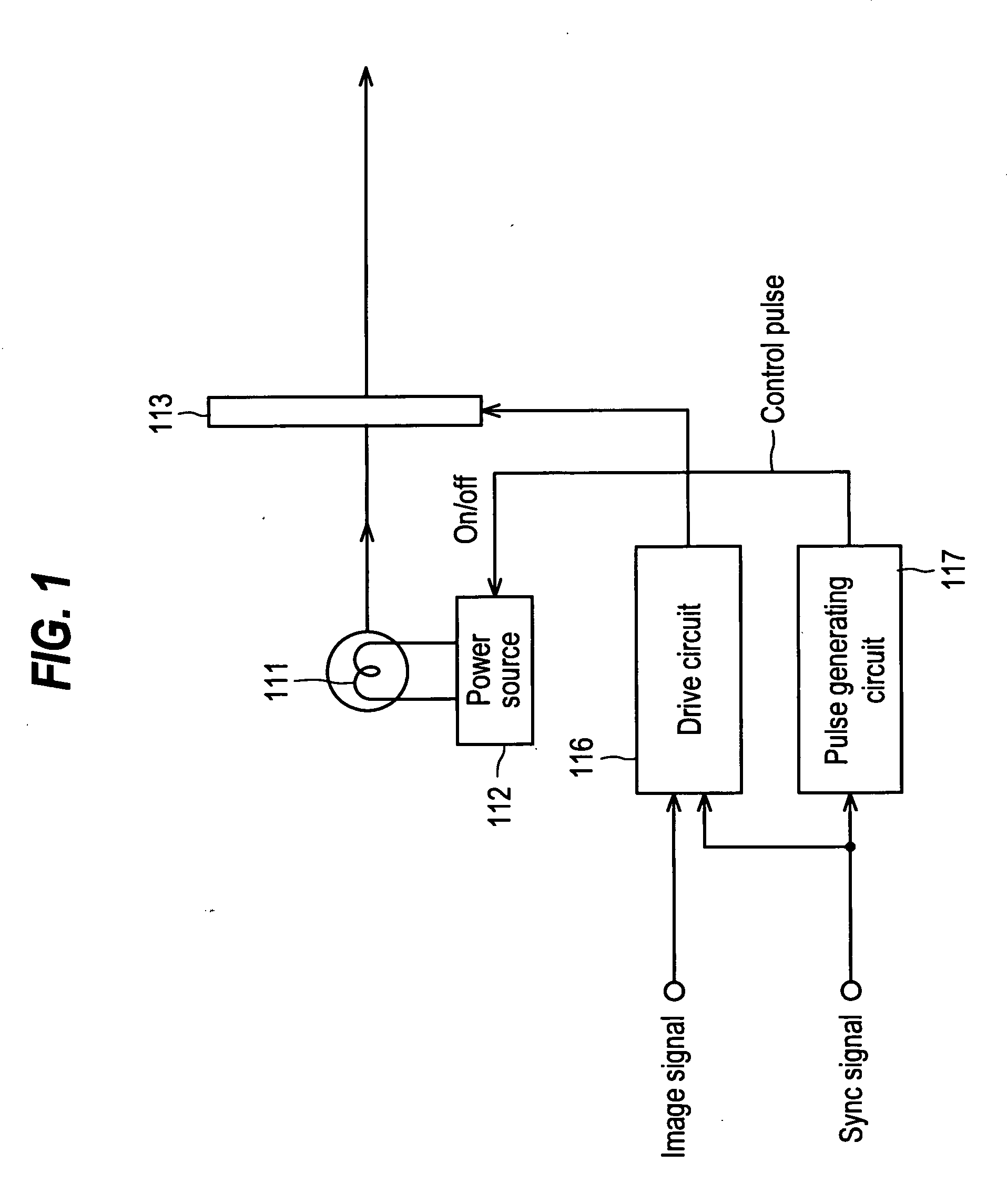
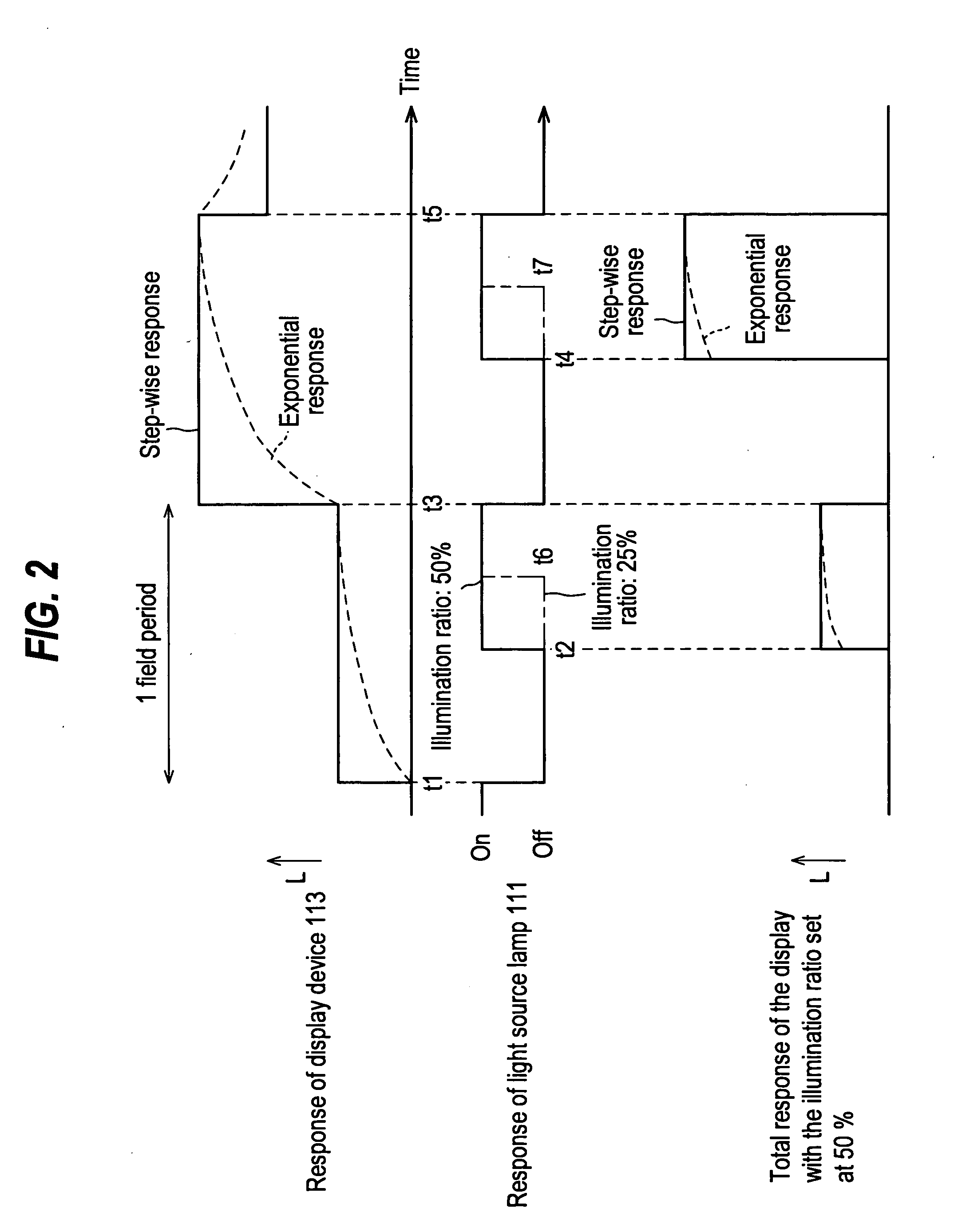
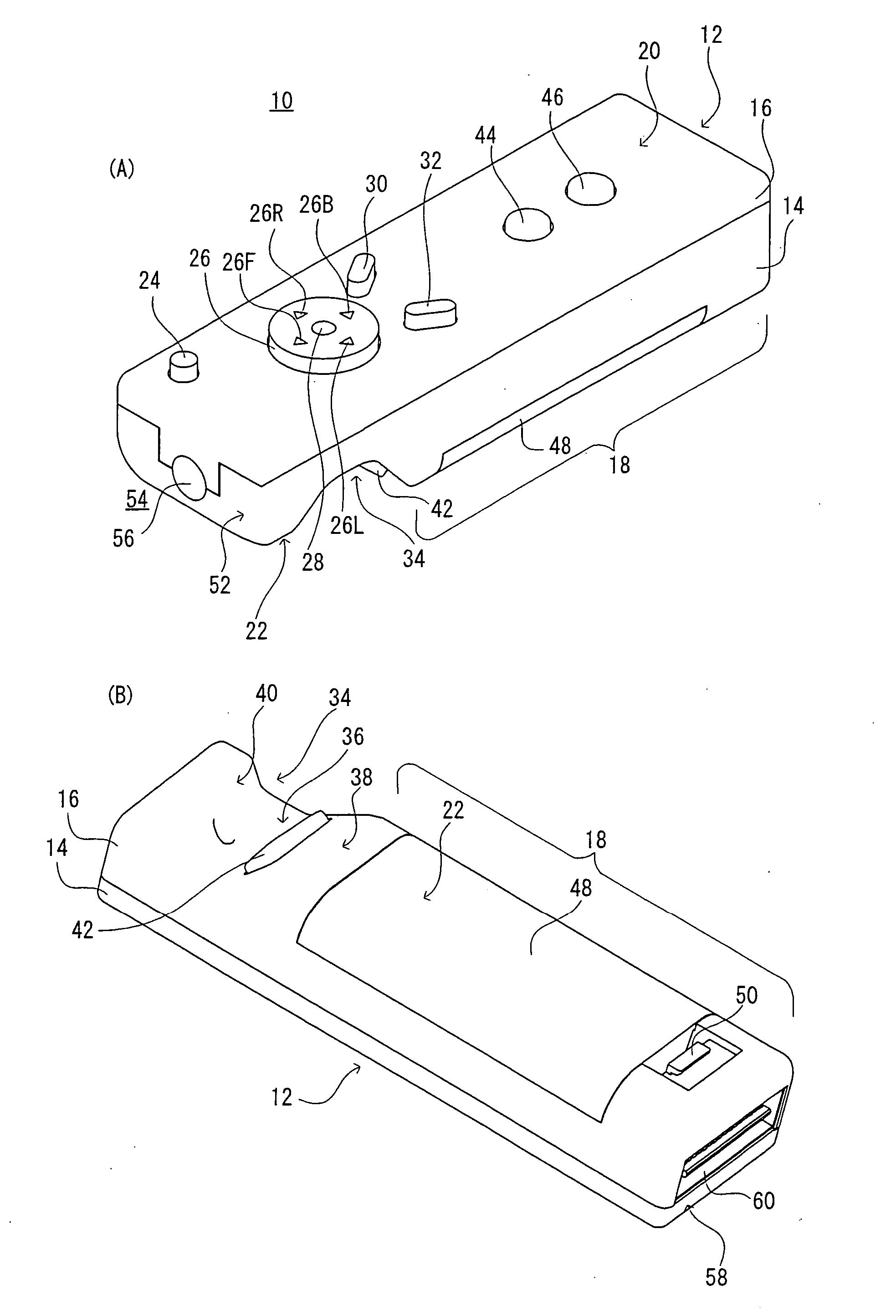
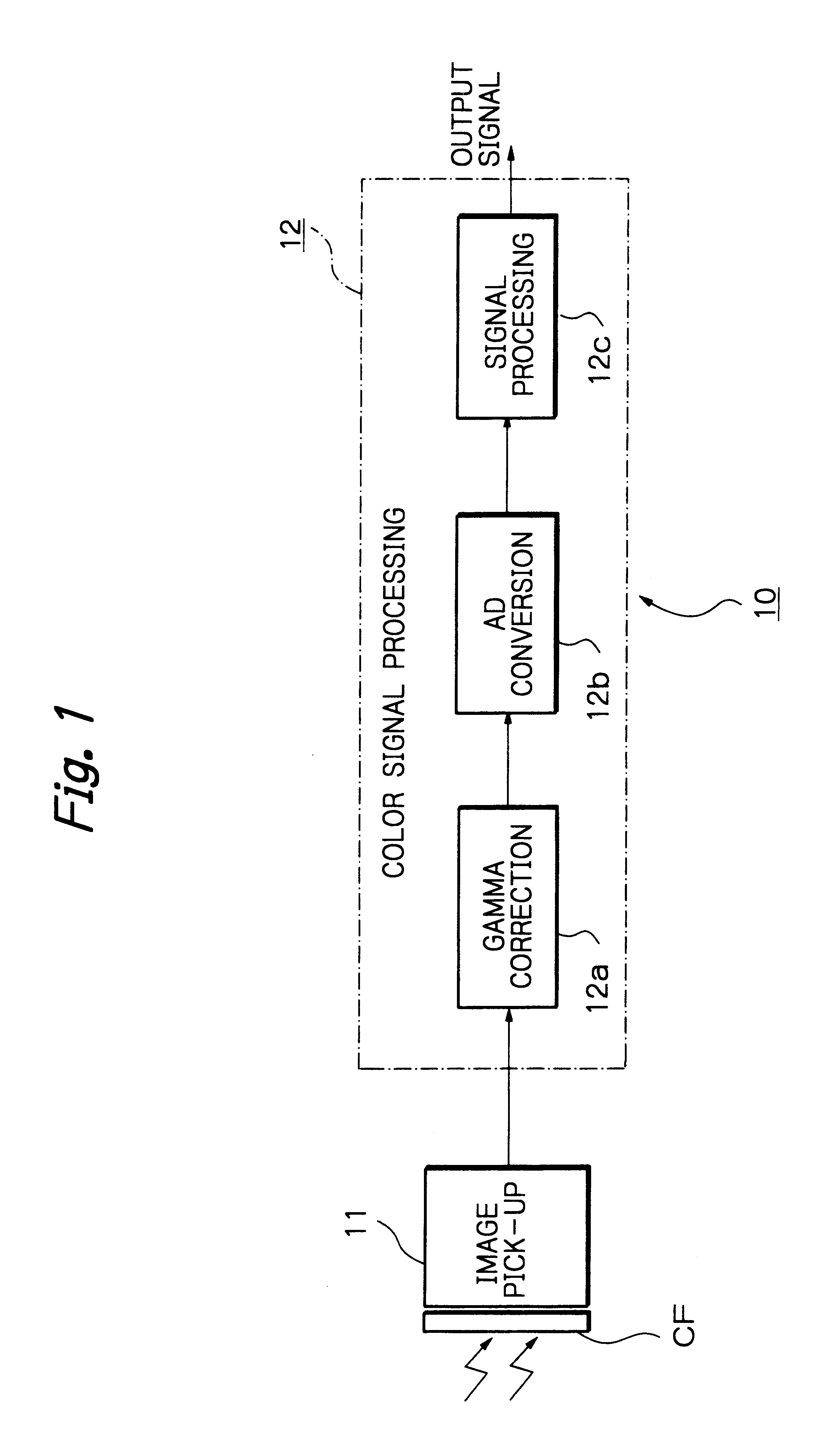
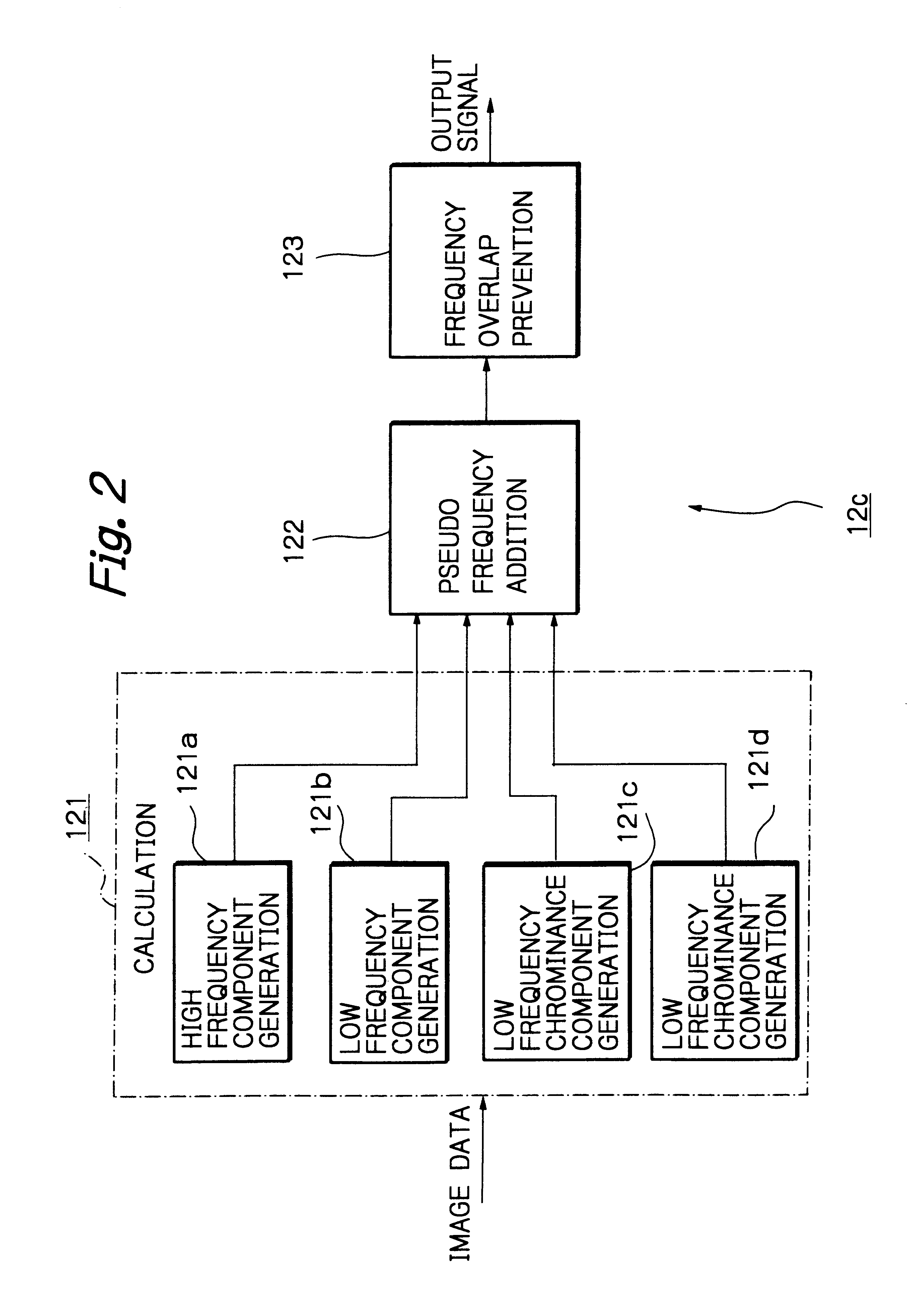
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
20596 results about "Image signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
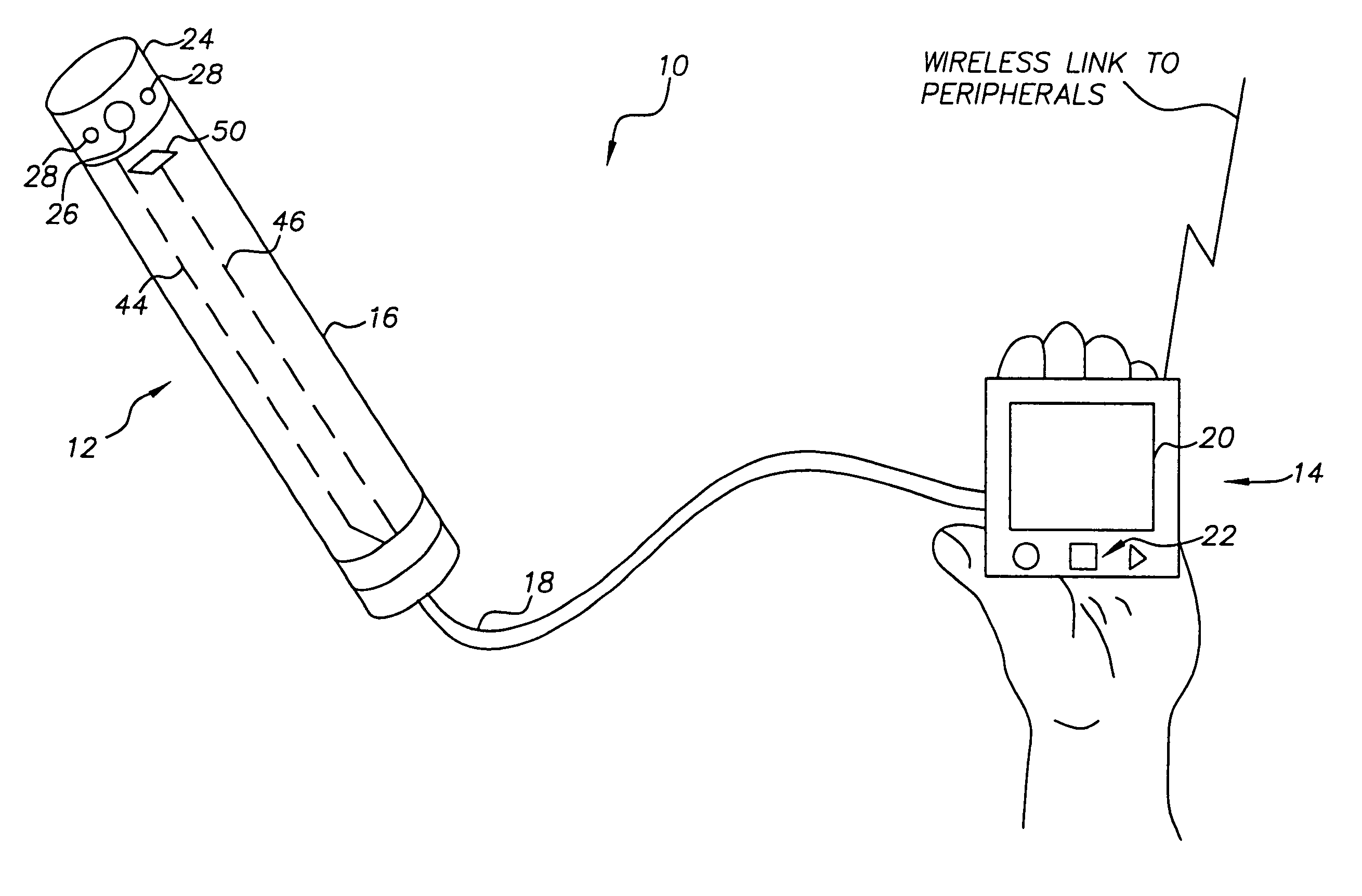
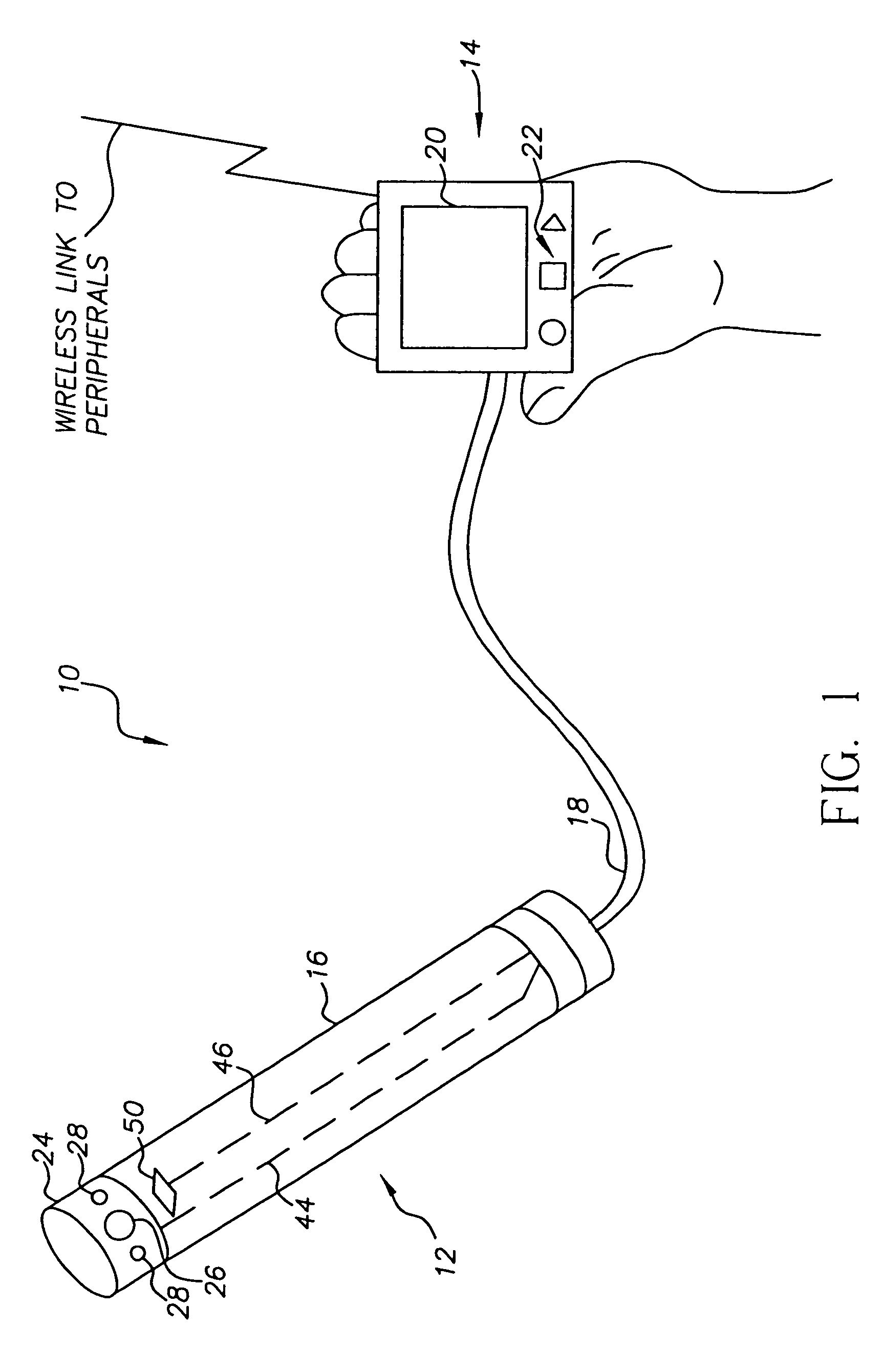
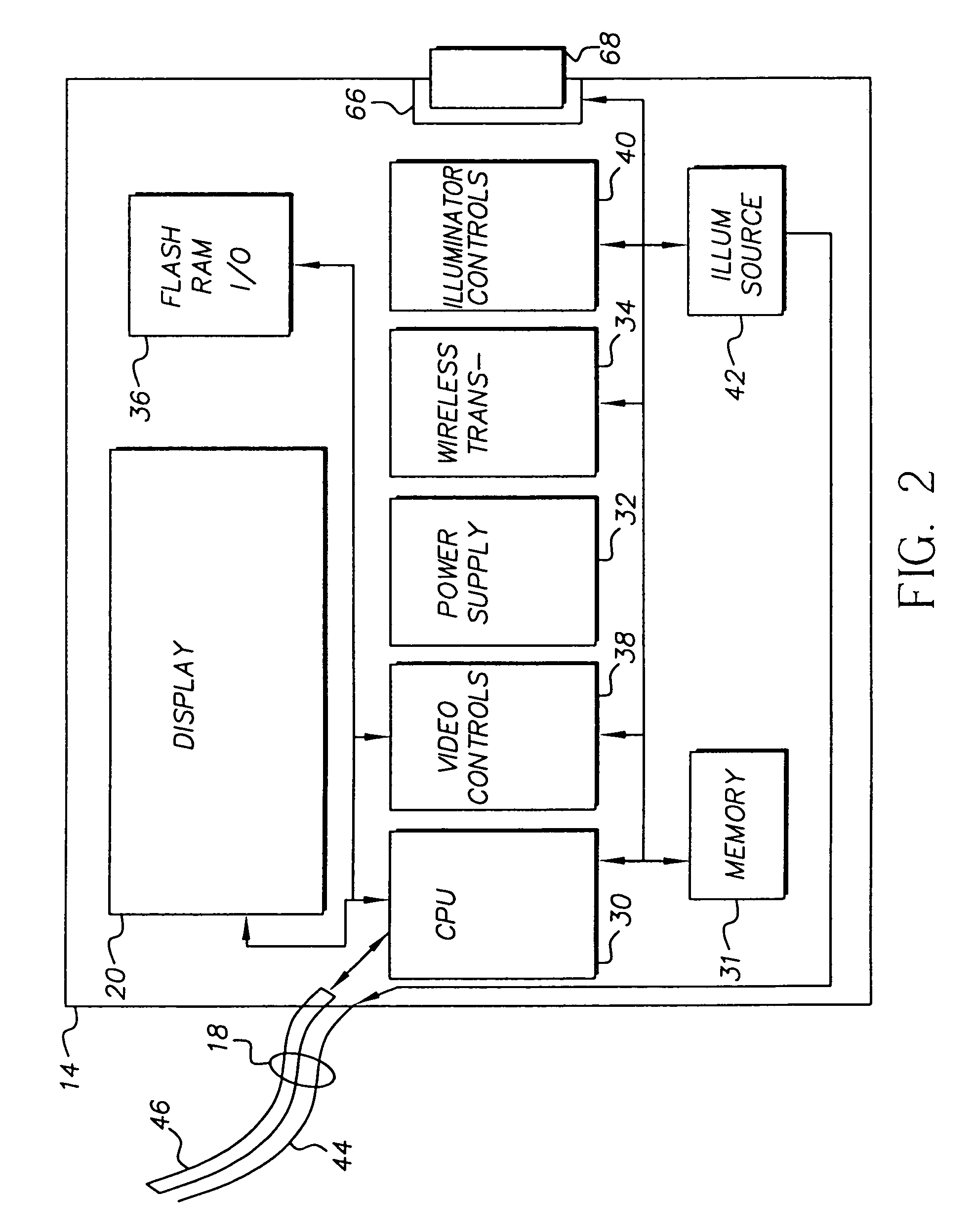
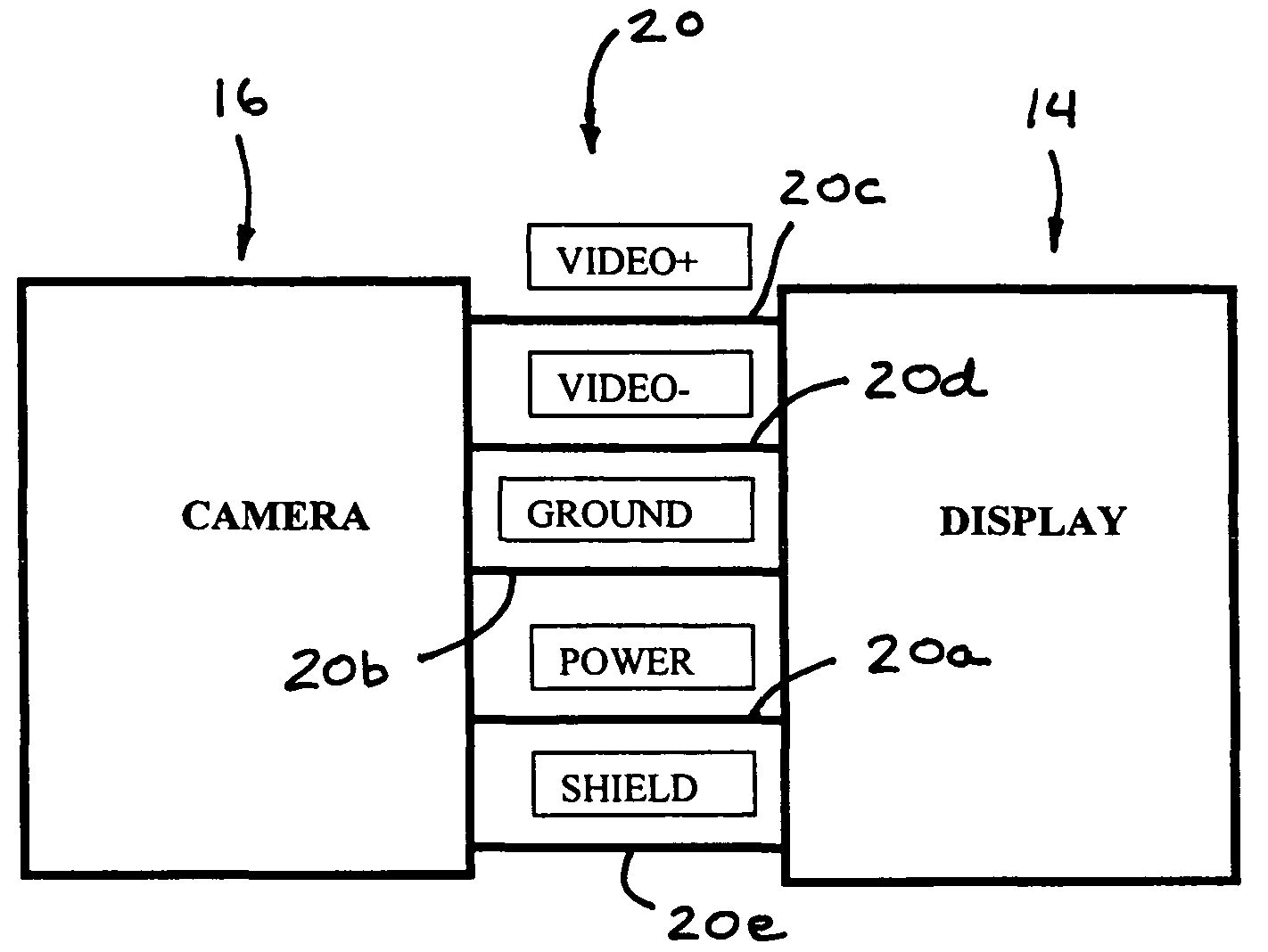
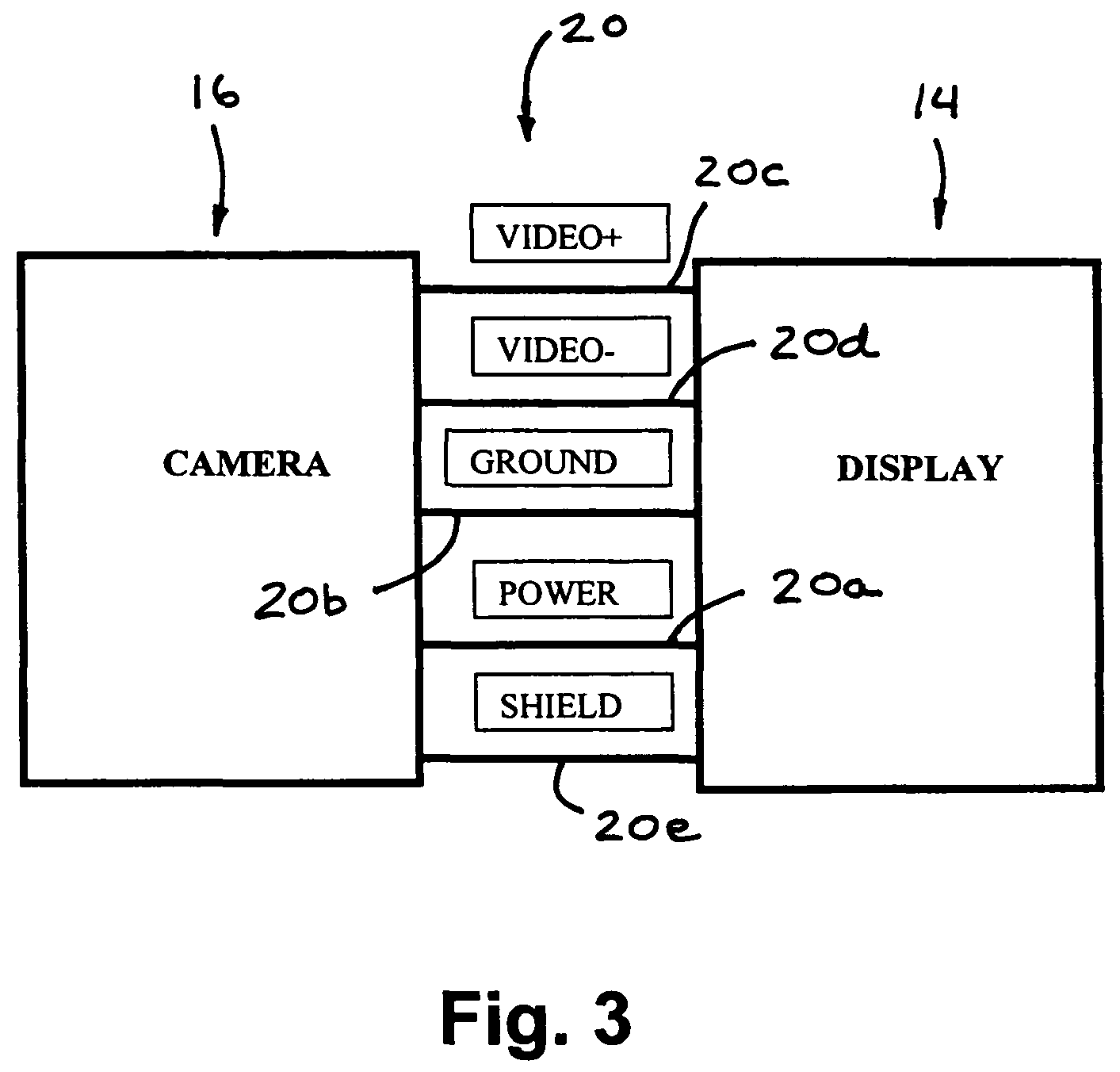
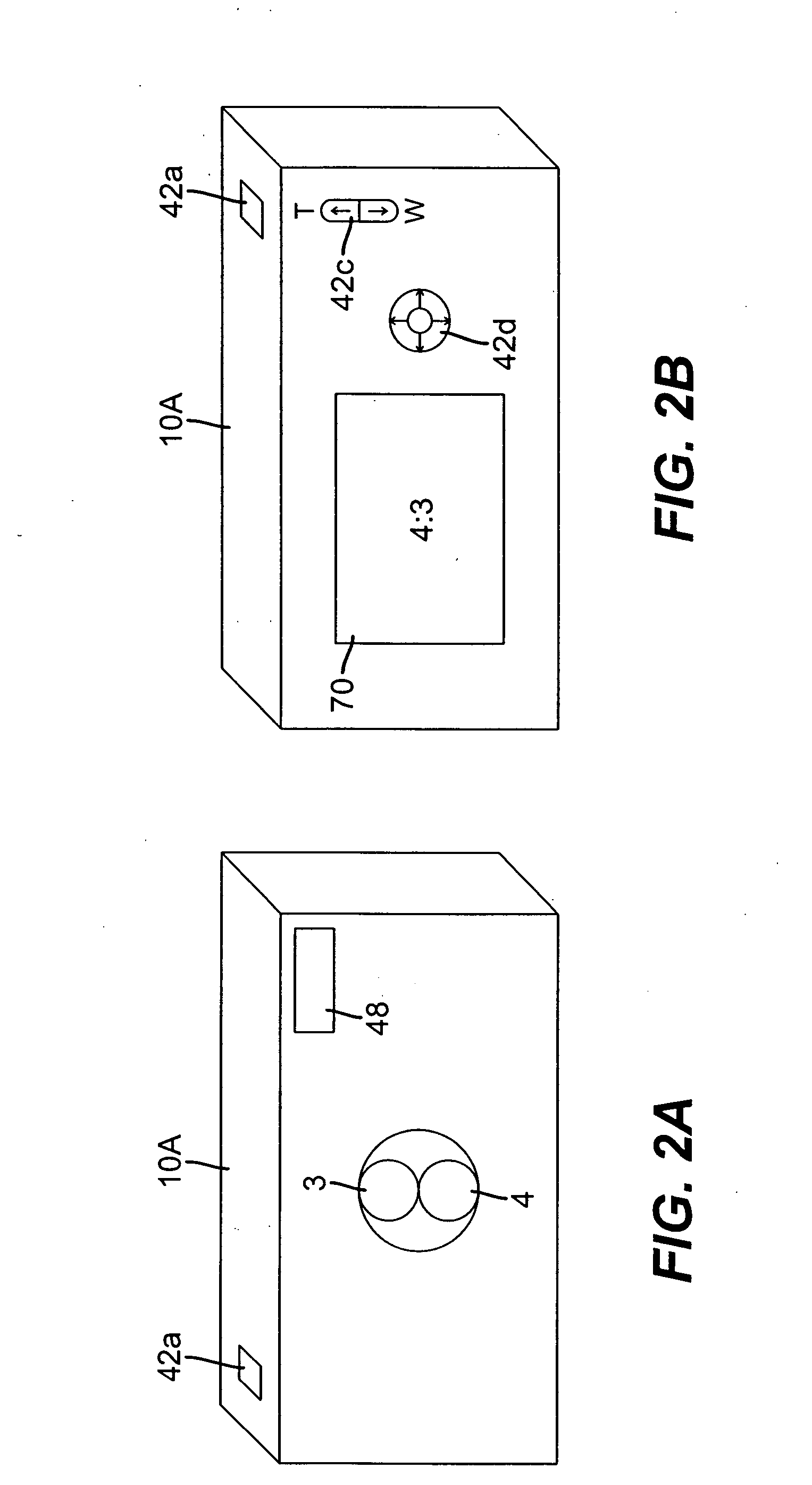
Intra-oral camera system with chair-mounted display
A portable intra-oral capture and display system, designed for use by a dental practitioner in connection with a patient seated in a dental chair, includes: a handpiece elongated for insertion into an oral cavity of the patient, where the handpiece includes a light emitter on a distal end thereof for illuminating an object in the cavity and an image sensor for capturing an image of the object and generating an image signal therefrom; a monitor interconnected with the handpiece, where the monitor contains electronics for processing the image for display and a display element for displaying the image, where the interconnection between the monitor and the handpiece includes an electrical connection for communicating the image signal from the image sensor in the camera to the electronics in the monitor; and a receptacle on the dental chair for receiving the monitor, wherein the receptacle conforms to the monitor such that the monitor may be withdrawn from the receptacle in order to allow the display element to be seen by the dental practitioner or the patient.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
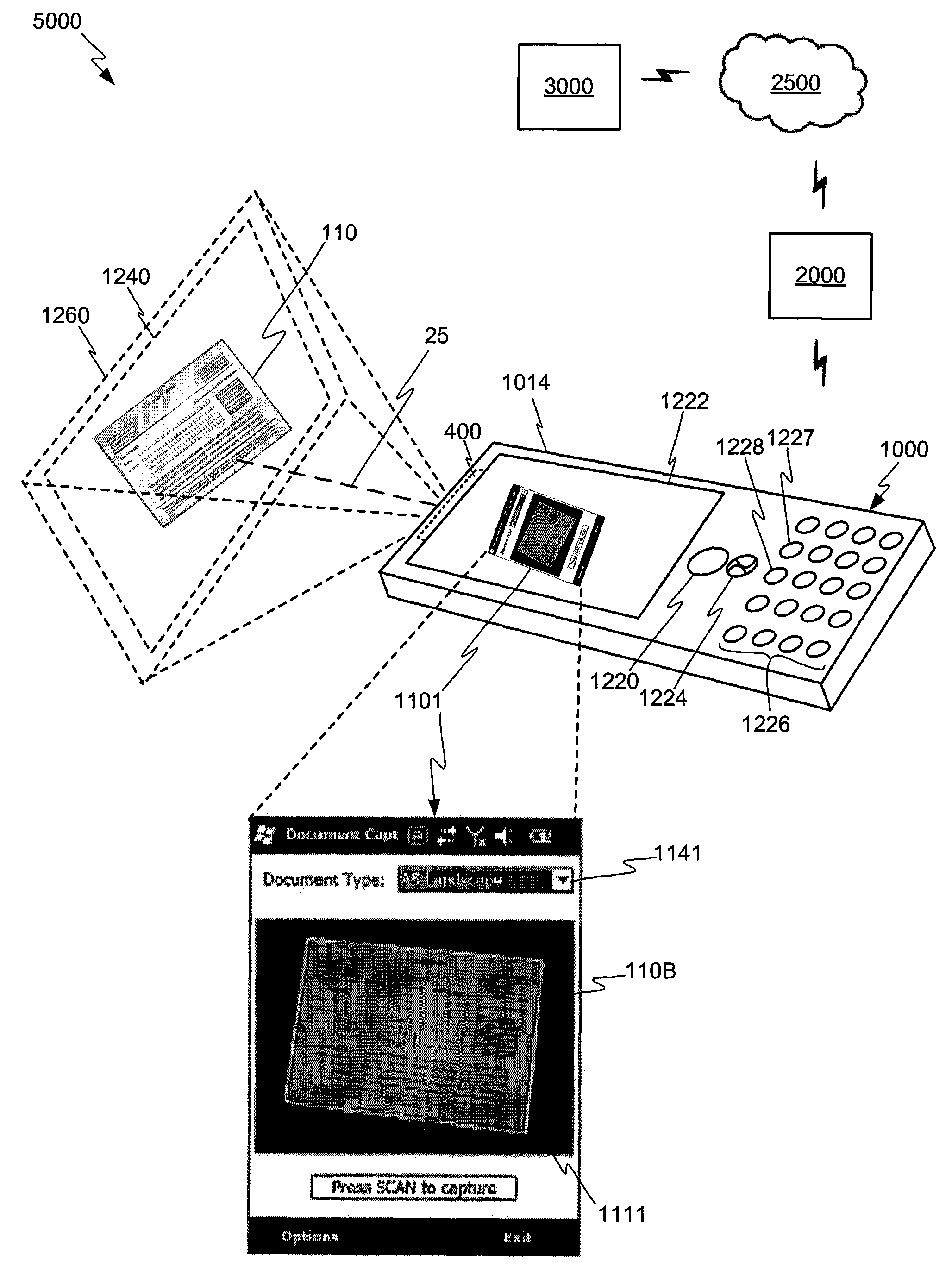
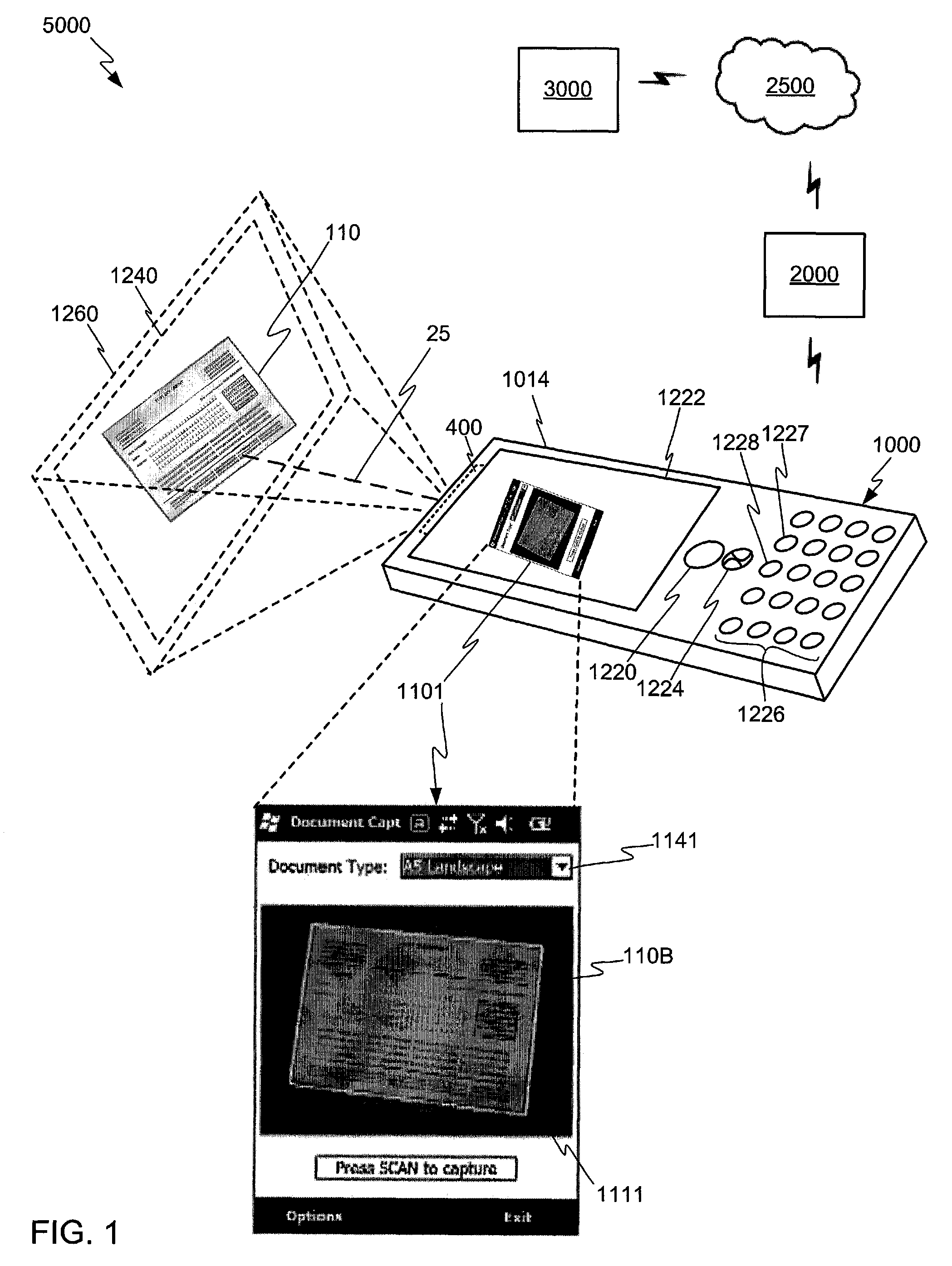
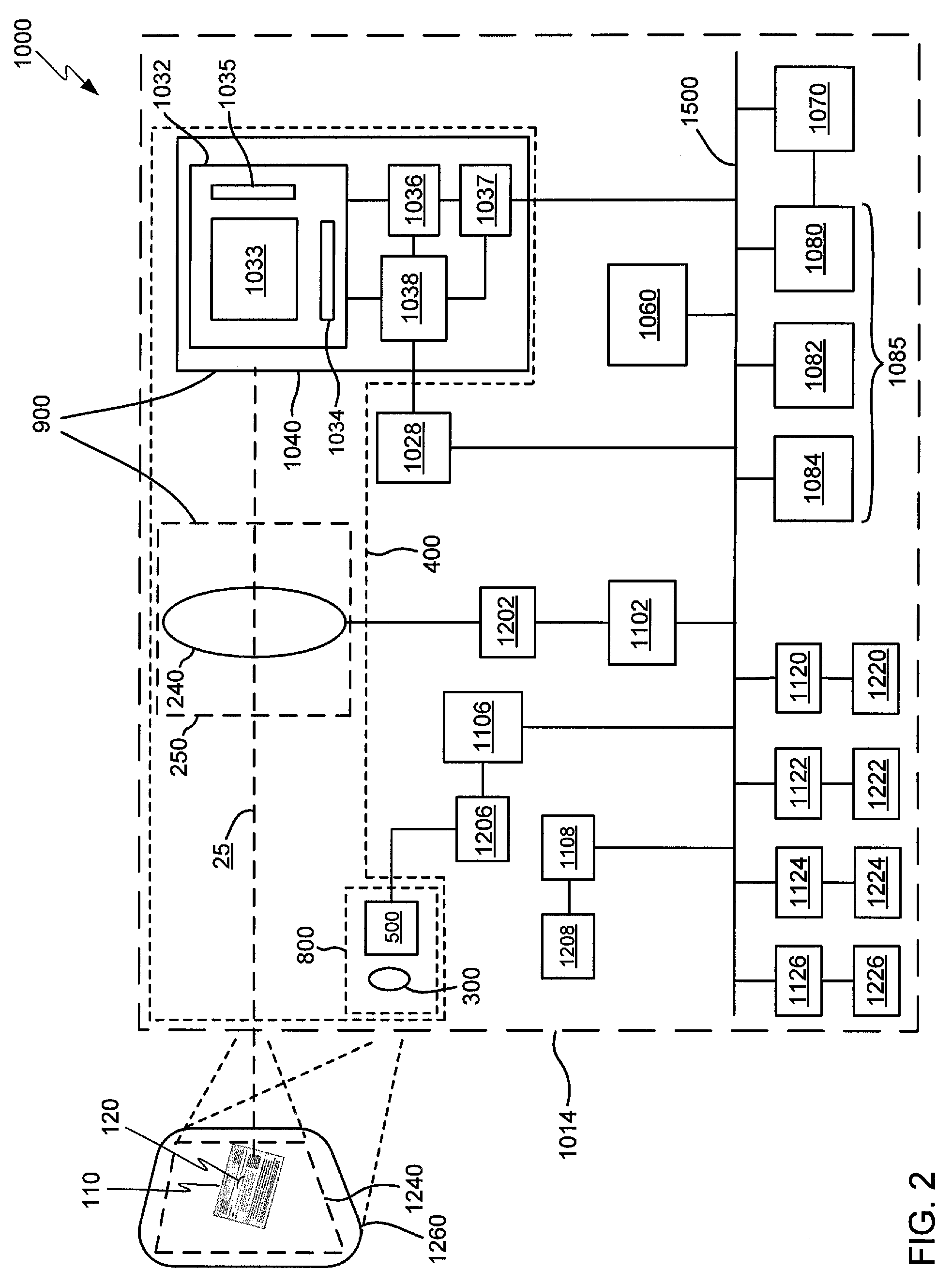
Interactive user interface for capturing a document in an image signal
ActiveUS9047531B2Improve abilitiesTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPaper documentImage signal
Devices, methods, and software are disclosed for an interactive user interface for capturing a frame of image data having a representation of a feature. In an illustrative embodiment, a device includes an imaging subsystem, one or more memory components, and one or more processors. The imaging subsystem is capable of providing image data representative of light incident on said imaging subsystem. The one or more memory components include at least a first memory component operatively capable of storing an input frame of the image data. The one or more processors may be enabled for performing various steps. One step may include receiving the image data from the first memory component. Another step may include attempting to identify linear features defining a candidate quadrilateral form in the image data. Another step may include providing user-perceptible hints for guiding a user to alter positioning of the device to enhance a capability for identifying the linear features defining a candidate quadrilateral form in the image data.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
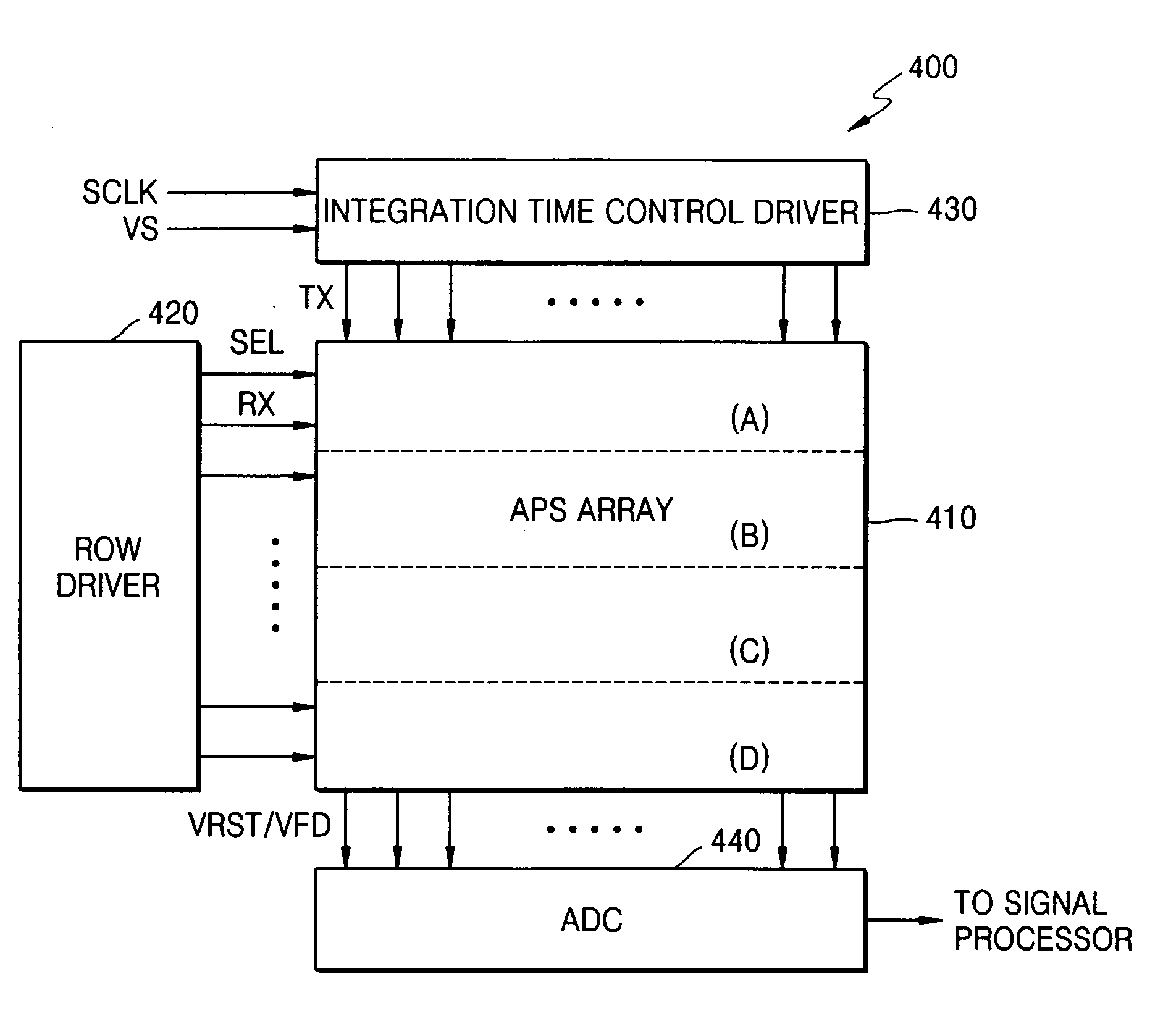
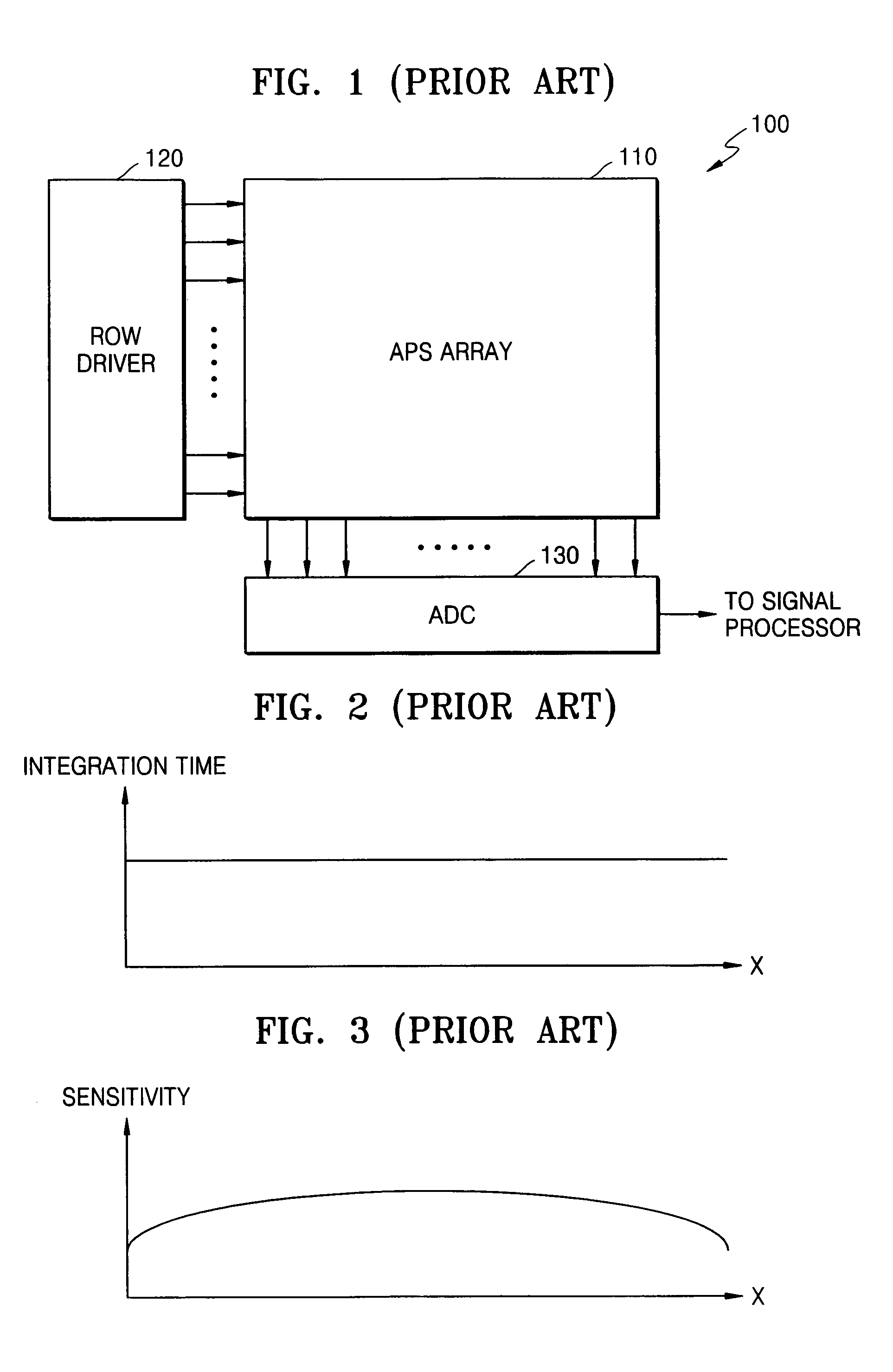
Solid-state image-sensing device that compensates for brightness at edges of a display area and a driving method thereof
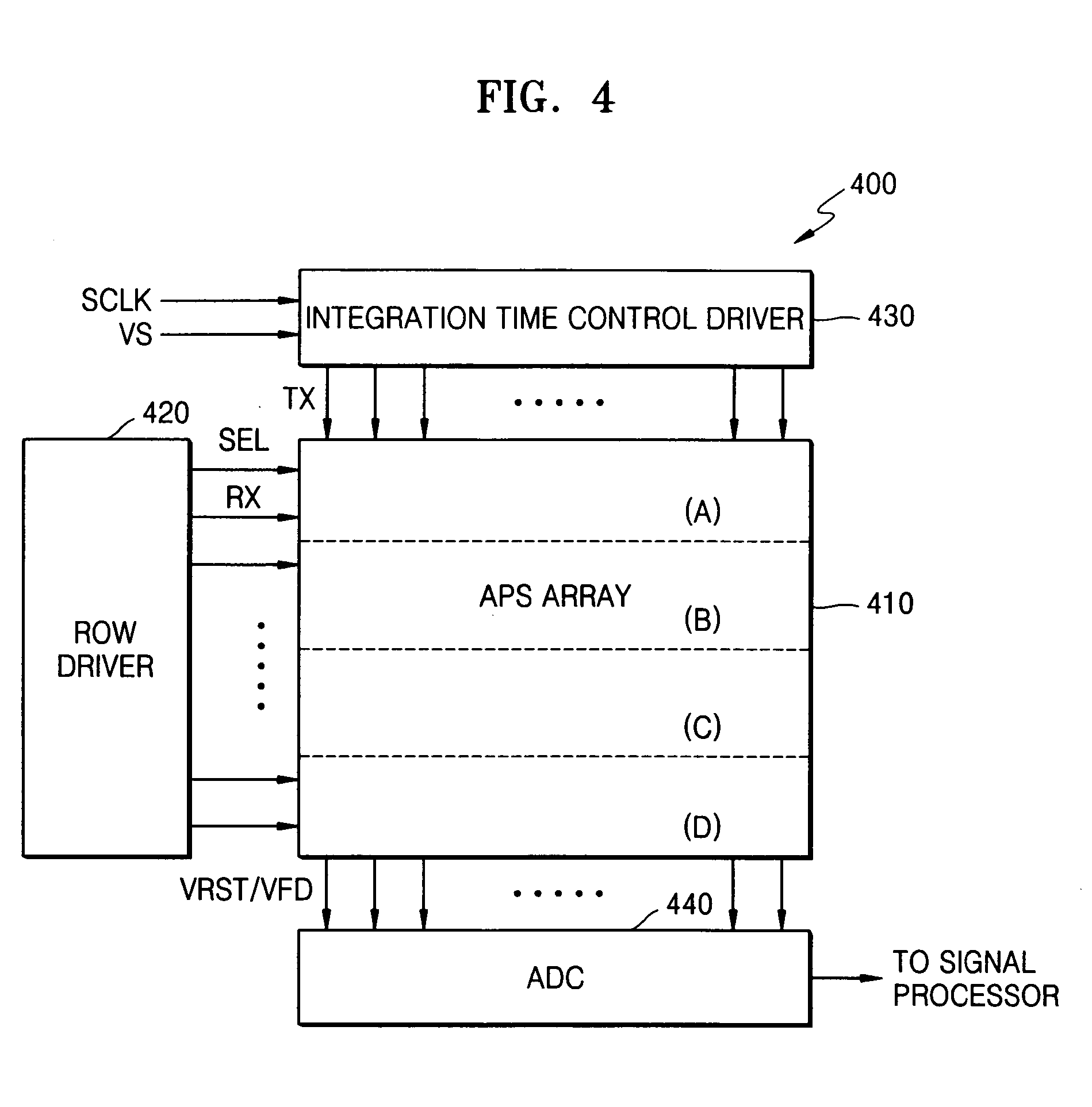
ActiveUS7193199B2Lower ratioImprove noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorControl signal
A solid-state image-sensing device that compensates for brightness at edges of a screen and a method of driving the device are provided. The solid-state image-sensing device comprises: an active pixel sensor (APS) array including pixels disposed in a two-dimensional matrix, each pixel for outputting a photoelectrically converted image signal generated by a photodiode in response to one of a plurality of transmission control signals transmitted to a selected row of the APS array, and for generating and outputting a reset signal in response to a reset control signal; a row driver for selecting a row of the APS array by generating row selection signals and for generating the reset control signal; an integration time control driver for generating the transmission control signals for setting non-uniform integration times of the photodiodes in each pixel; and an analog-digital converter for converting an analog signal corresponding to a difference between the image signal and the reset signal into a digital signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
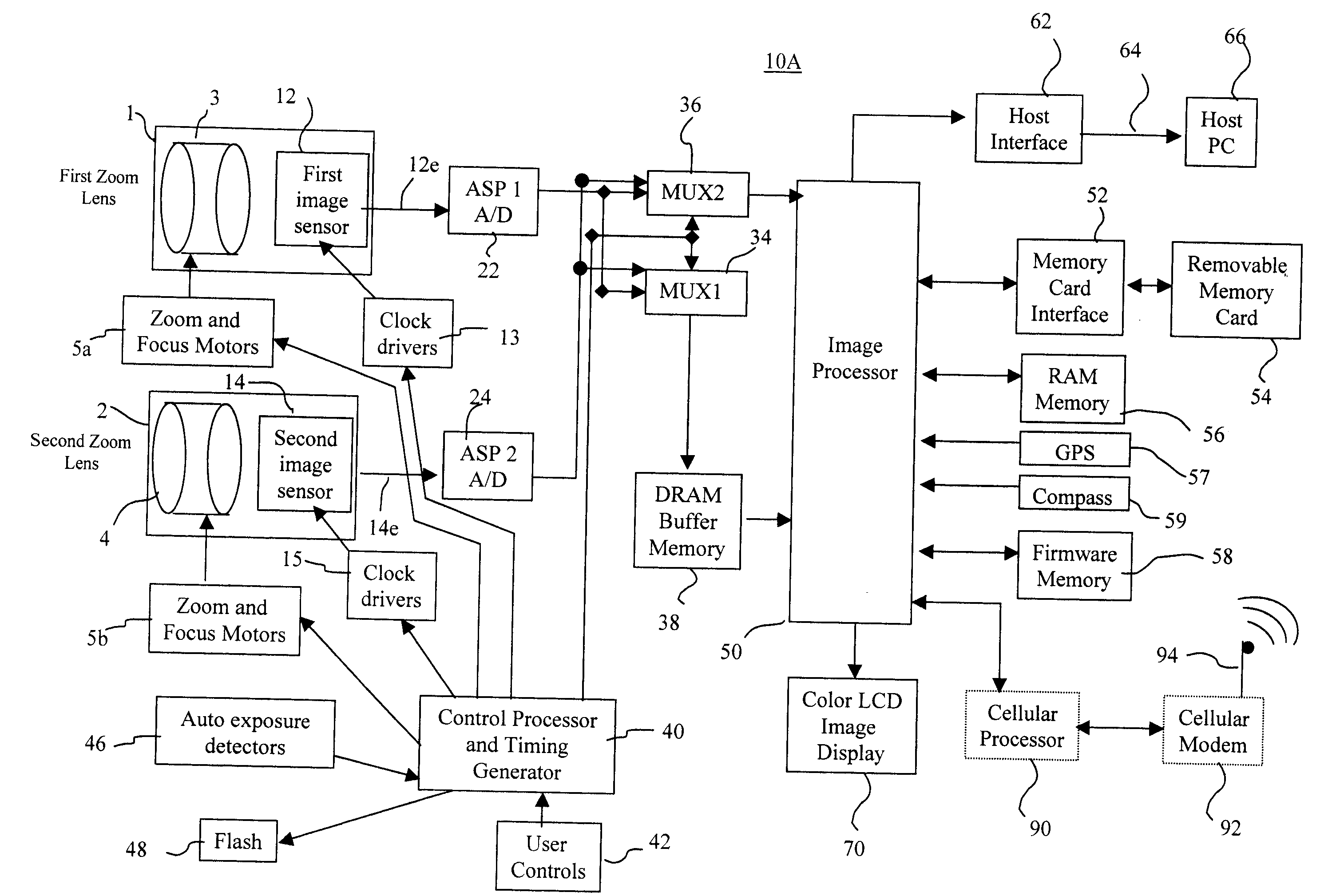
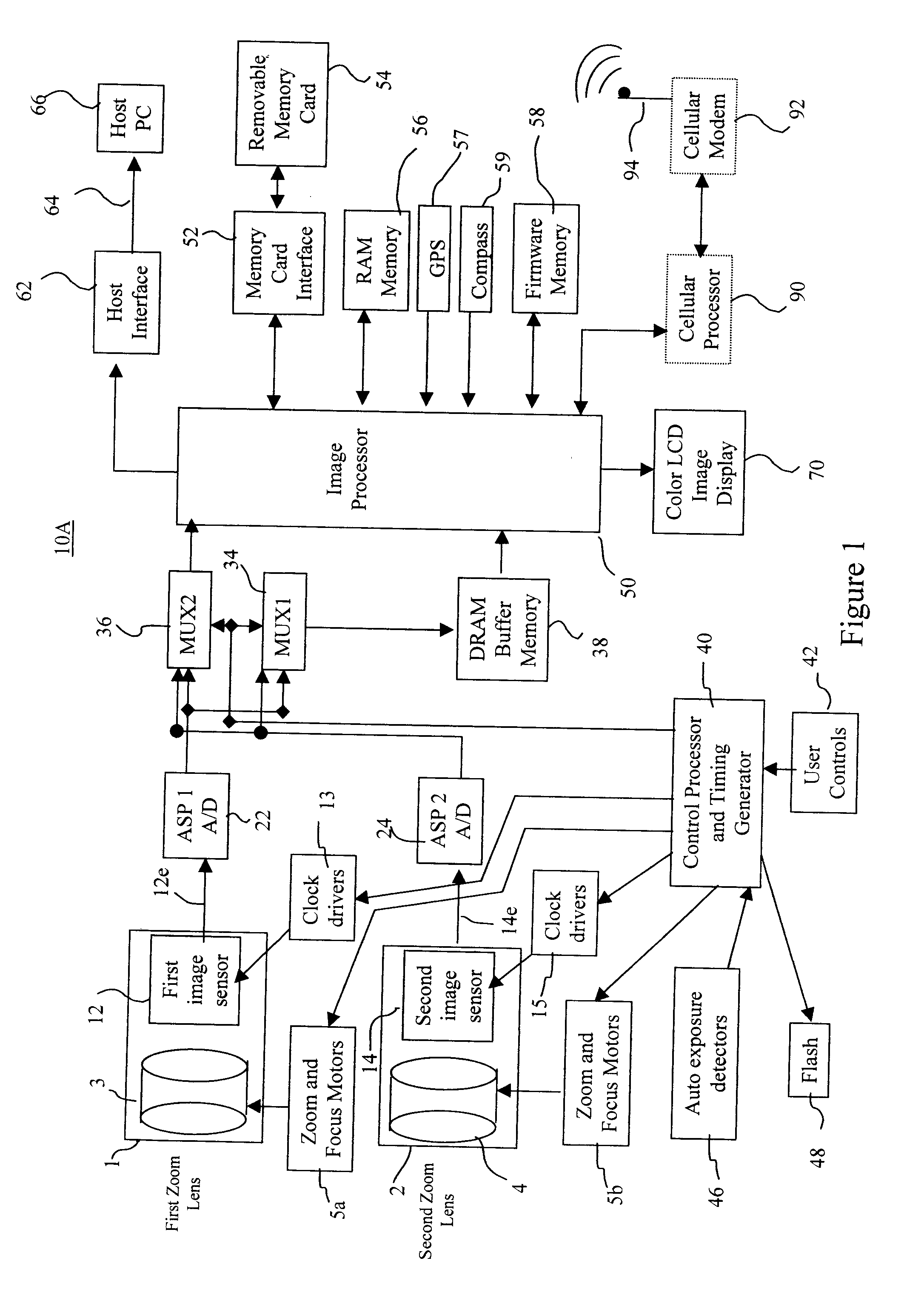
Camera using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide improved focusing capability
InactiveUS20080219654A1Increasing sizeIncreasing costTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensImage signal
An electronic camera for producing an output image of a scene from a captured image signal includes: (a) a first imaging stage comprising a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output; a first lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor; and a first lens focus adjuster for adjusting focus of the first lens responsive to a first focus detection signal; and (b) a second imaging stage comprising a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output; a second lens for forming a second image of the scene on the second image sensor; and a second lens focus adjuster for adjusting focus of the second lens responsive to a second focus detection signal. A processing stage either (a) selects the sensor output from the first imaging stage as the captured image signal and uses the sensor output from the second imaging stage to generate the first focus detection signal for the selected imaging stage, or (b) selects the sensor output from the second imaging stage as the captured image signal and uses the sensor output from the first imaging stage to generate the second focus detection signal for the selected imaging stage.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
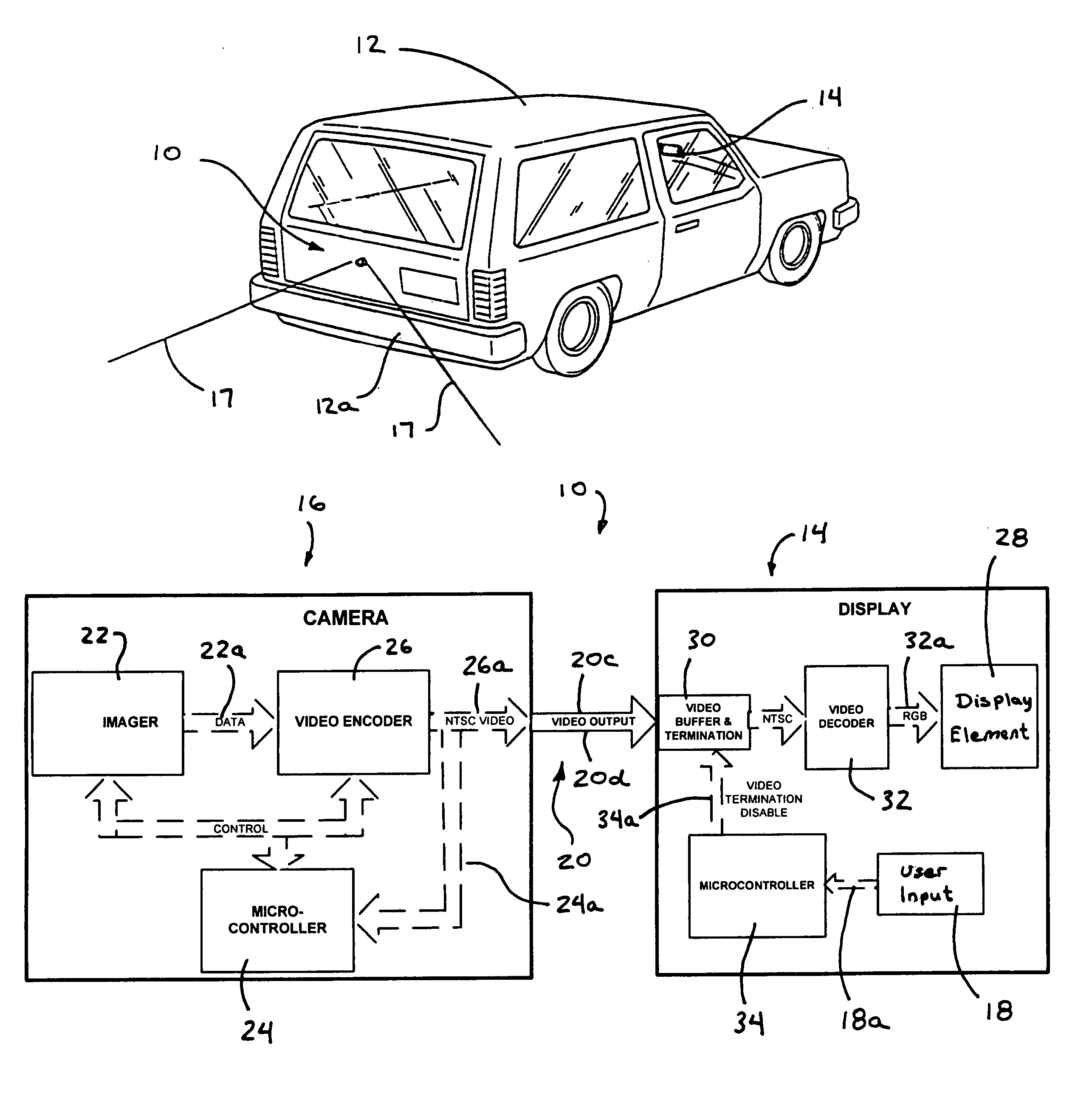
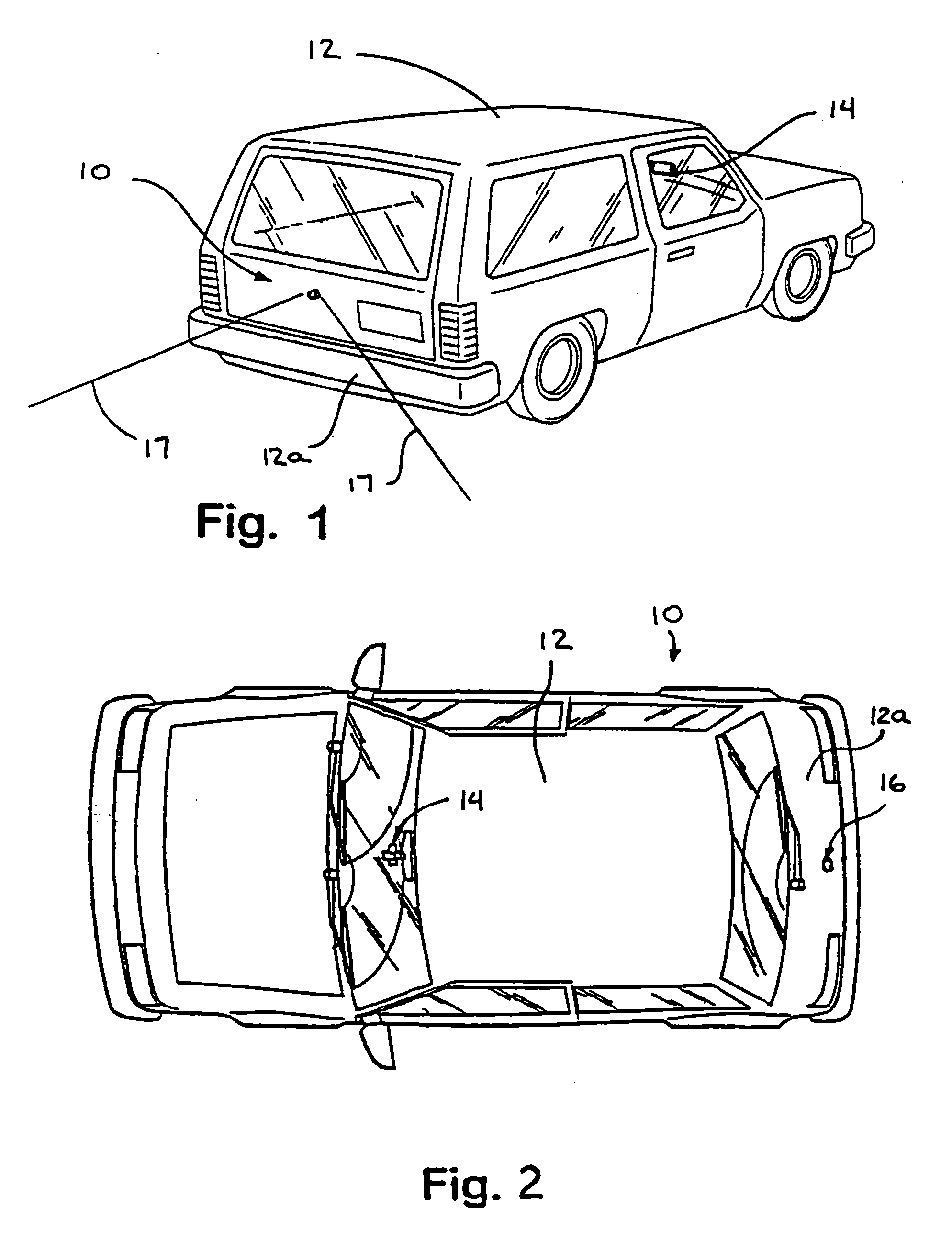
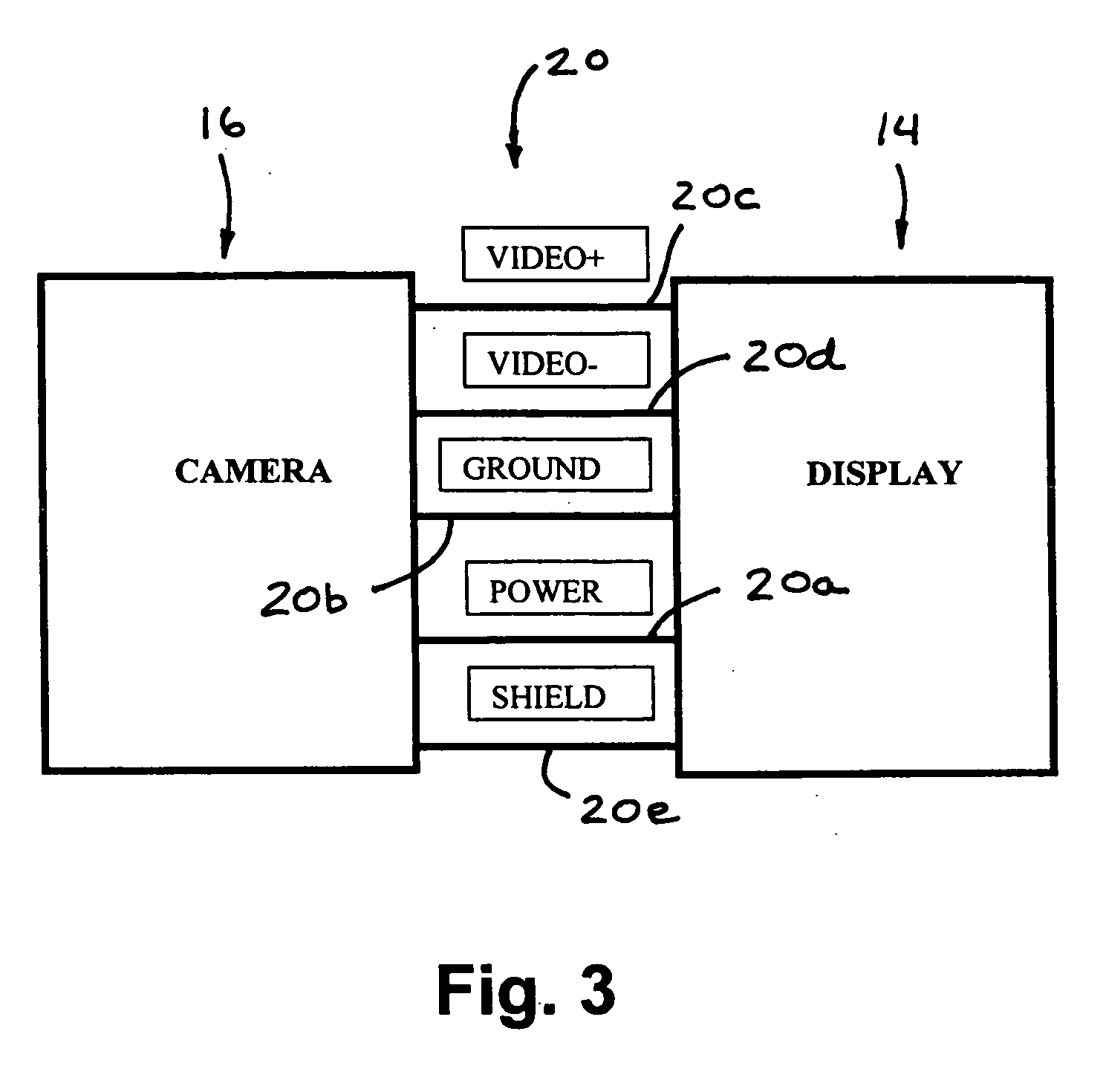
Vision system for vehicle
InactiveUS7881496B2Enhance the imageEasy to captureDetection of traffic movementIndication of parksing free spacesMicrocontrollerTelecommunications link
A vision system for a vehicle includes an imaging device having an imaging sensor, a camera microcontroller, a display device having a display element, a display microcontroller, and at least one user input selectively actuatable by a user. The imaging device communicates an image signal to the display device via a communication link. The display microcontroller affects the image signal in response to the at least one user input. The camera microcontroller monitors the image signal on the communication link and adjusts a function of the imaging device in response to a detection of the affected image signal. The vision system may adjust a display or sensor of the system in conjunction with a distance detecting system.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
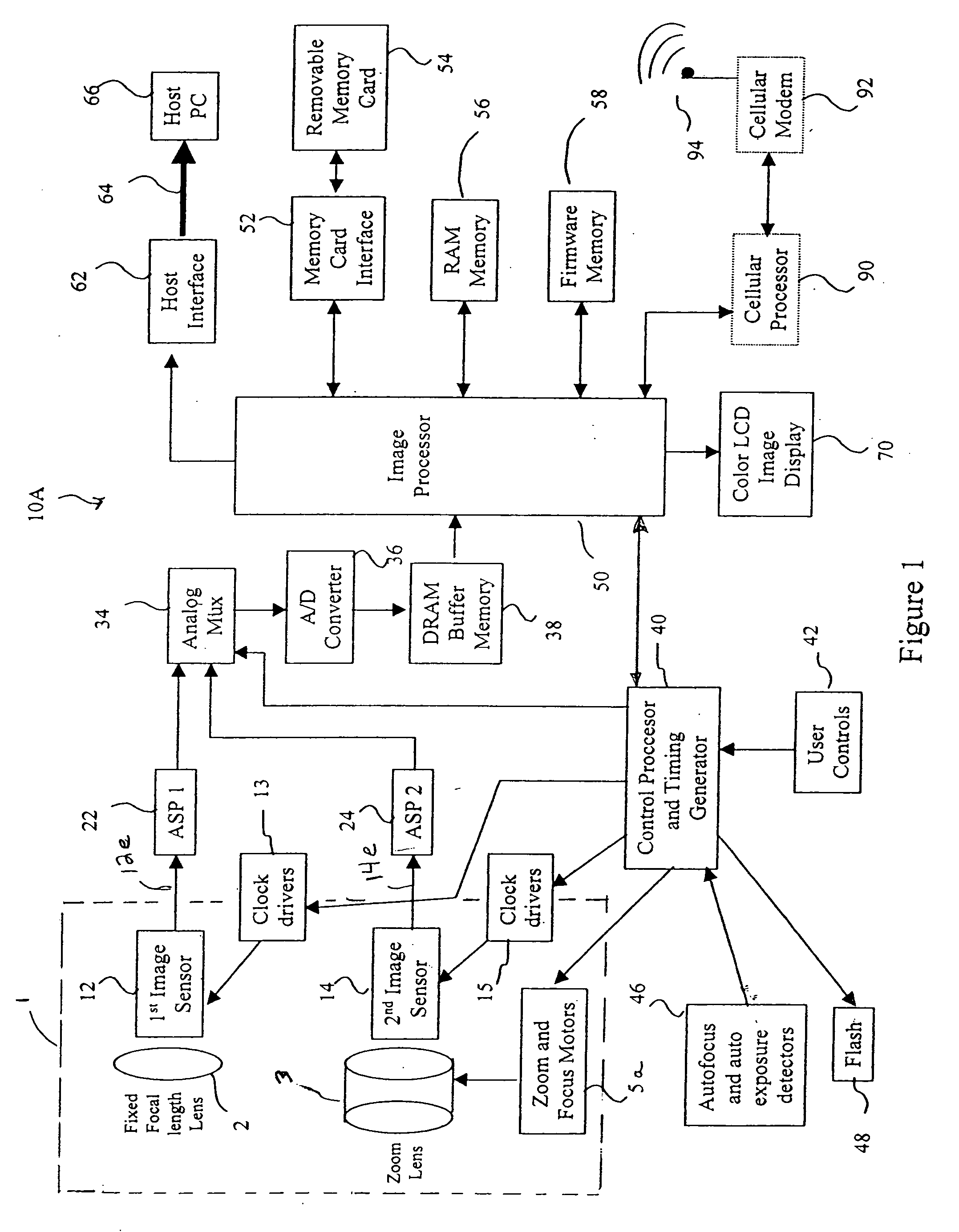
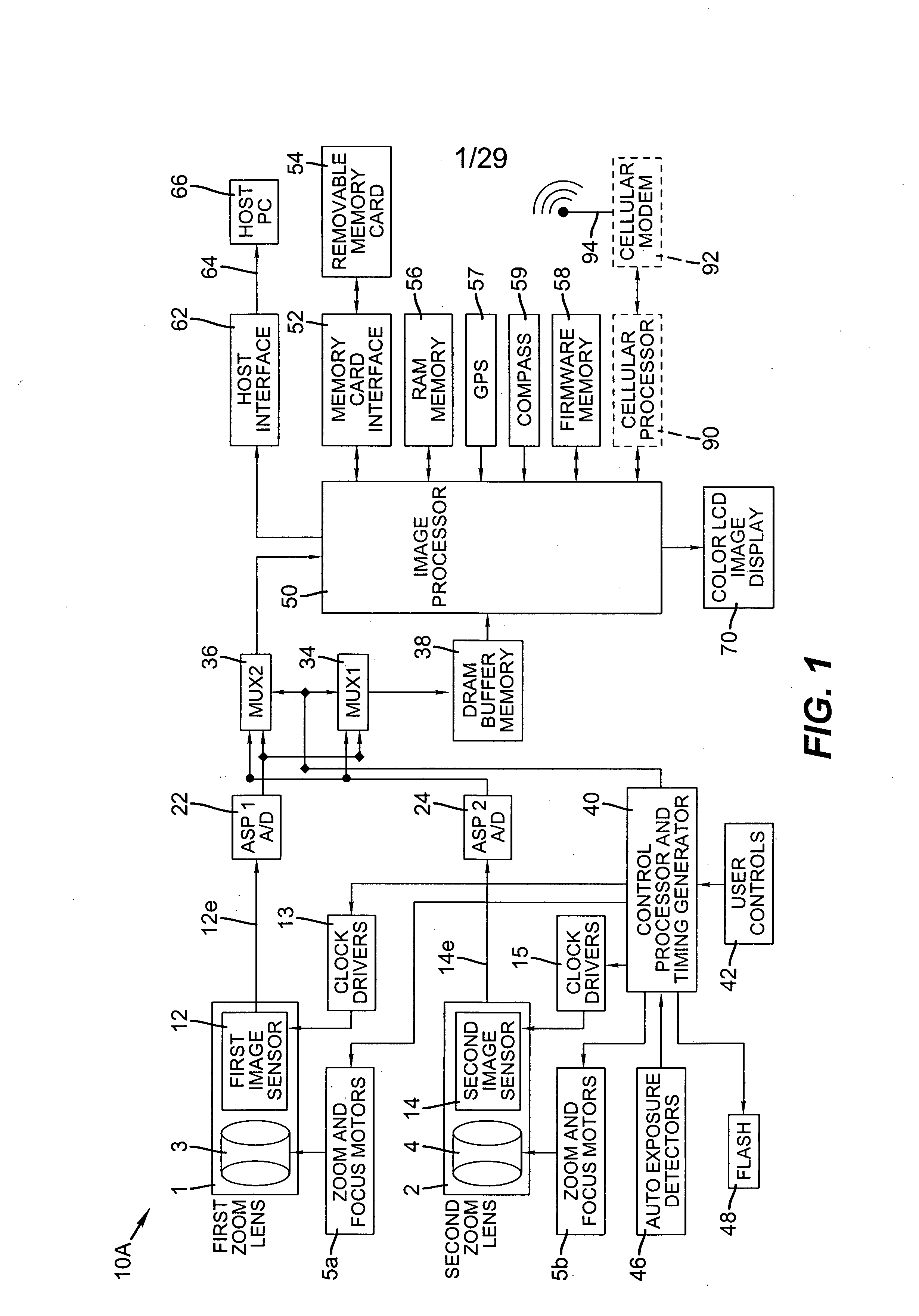
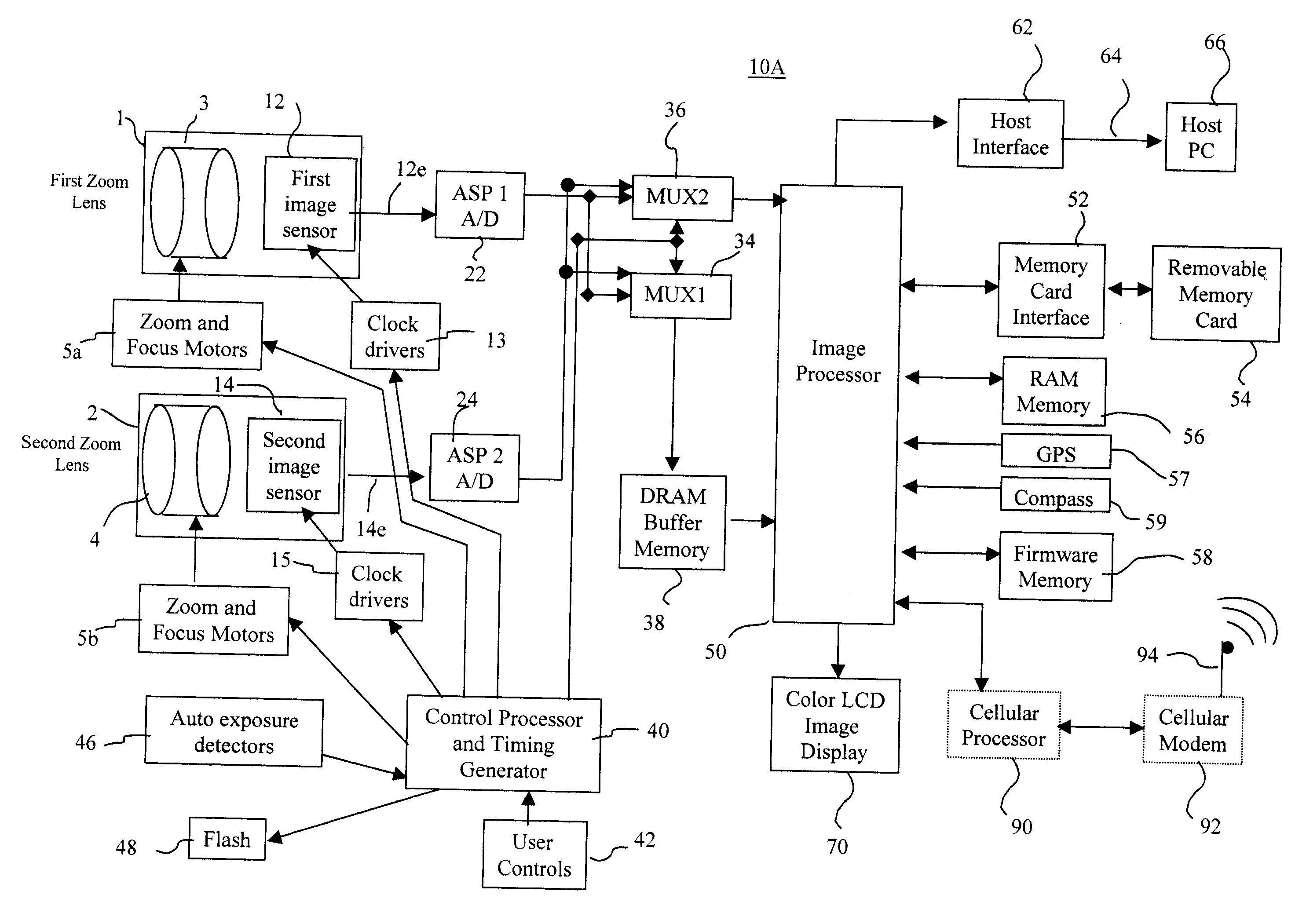
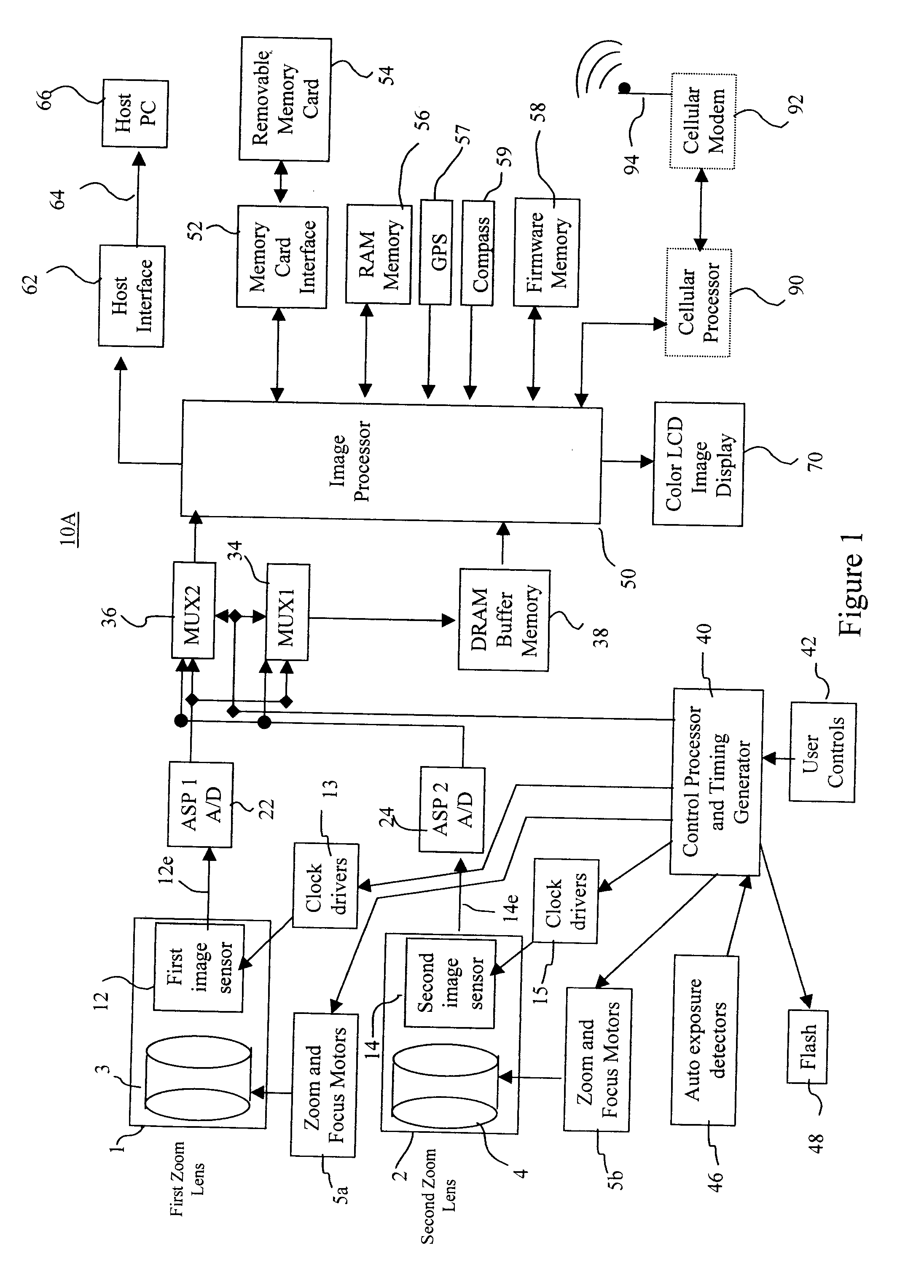
Camera phone using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide an extended zoom range
InactiveUS20060187338A1Low costHigh quality optical resultTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceCamera phoneTelephoto lens
A camera phone includes a phone stage for generating voice signals, a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output, a first fixed focal length wide angle lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor, a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output, and a second fixed focal length telephoto lens pointing in the same direction as the first lens and forming a second image of the same scene on the second image sensor. A control element selects either the first sensor output from the first image sensor or the second sensor output from the second image sensor. A processing section produces the output image signals from the selected sensor output, and a cellular stage processes the image and voice signals for transmission over a cellular network.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method and apparatus for operating a dual lens camera to augment an image
ActiveUS20080218611A1Reduce noiseImprove clarityTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceCamera lensImage signal
An electronic camera for producing an output image of a scene from a captured image signal includes a first imaging stage comprising a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output and a first lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor, and a second imaging stage comprising a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output and a second lens for forming a second image of the scene on the second image sensor. The sensor output from the first imaging stage is used as a primary output image for forming the captured image signal and the sensor output from the second imaging stage is used as a secondary output image for modifying the primary output image, thereby generating an enhanced, captured image signal.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Vision system for vehicle
InactiveUS20060125919A1Enhance the imageEasy to captureDetection of traffic movementIndication of parksing free spacesMicrocontrollerTelecommunications link
A vision system for a vehicle includes an imaging device having an imaging sensor, a camera microcontroller, a display device having a display element, a display microcontroller, and at least one user input selectively actuatable by a user. The imaging device communicates an image signal to the display device via a communication link. The display microcontroller affects the image signal in response to the at least one user input. The camera microcontroller monitors the image signal on the communication link and adjusts a function of the imaging device in response to a detection of the affected image signal. The vision system may adjust a display or sensor of the system in conjunction with a distance detecting system.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Camera using multiple lenses and image sensors in a rangefinder configuration to provide a range map
ActiveUS20080218612A1Increasing size and costPrecise and rapid autofocusTelevision system detailsPrintersComputer graphics (images)Radiology
An electronic camera for producing an output image of a scene from a captured image signal includes a first imaging stage comprising a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output and a first lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor, and a second imaging stage comprising a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output and a second lens for forming a second image of the scene on the second image sensor, where the lenses have different focal lengths. A processing stage uses the sensor output from one of the imaging stages as the captured image signal and uses the images from both imaging stages to generate a range map identifying distances to the different portions of the scene.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
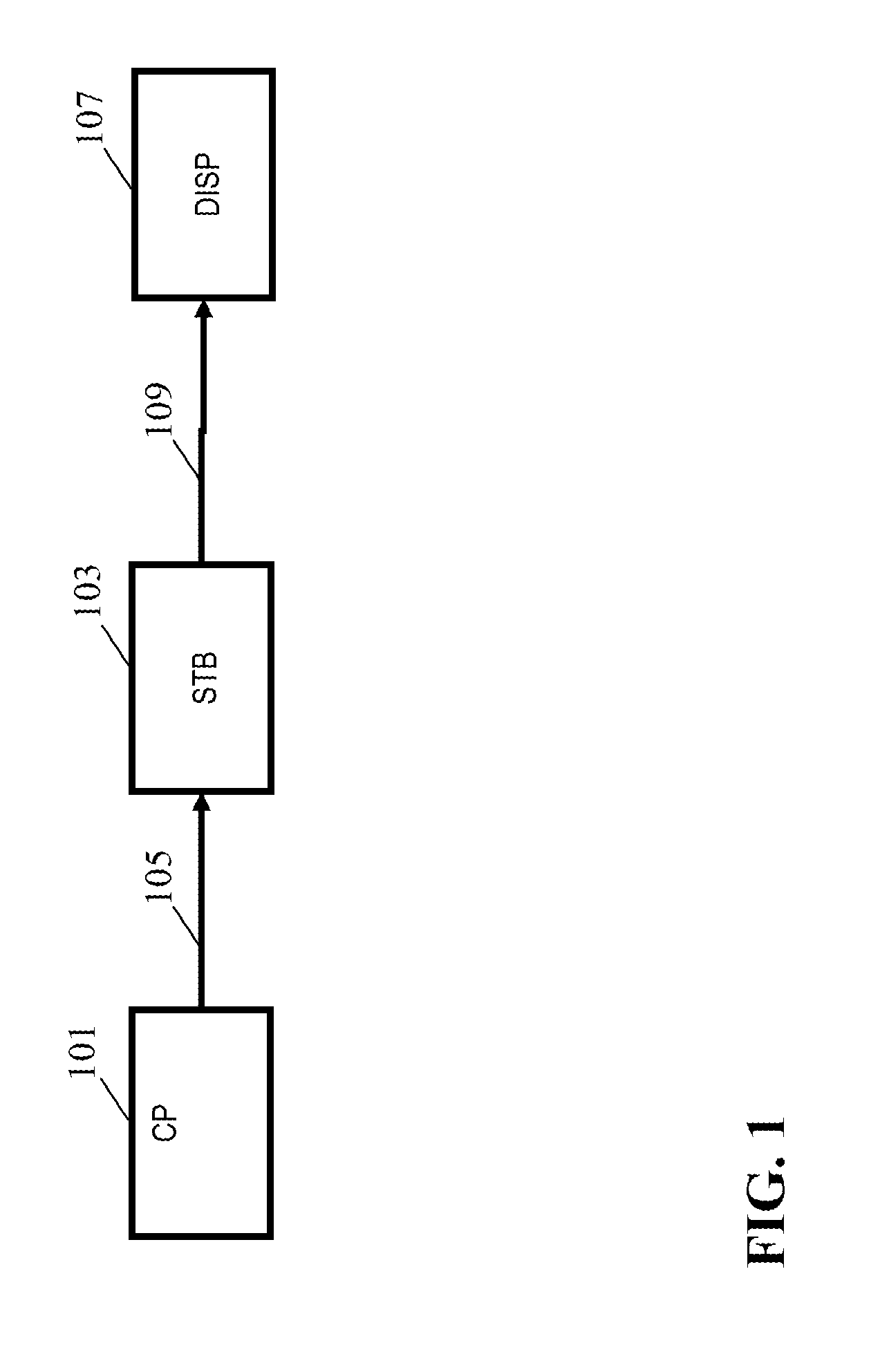
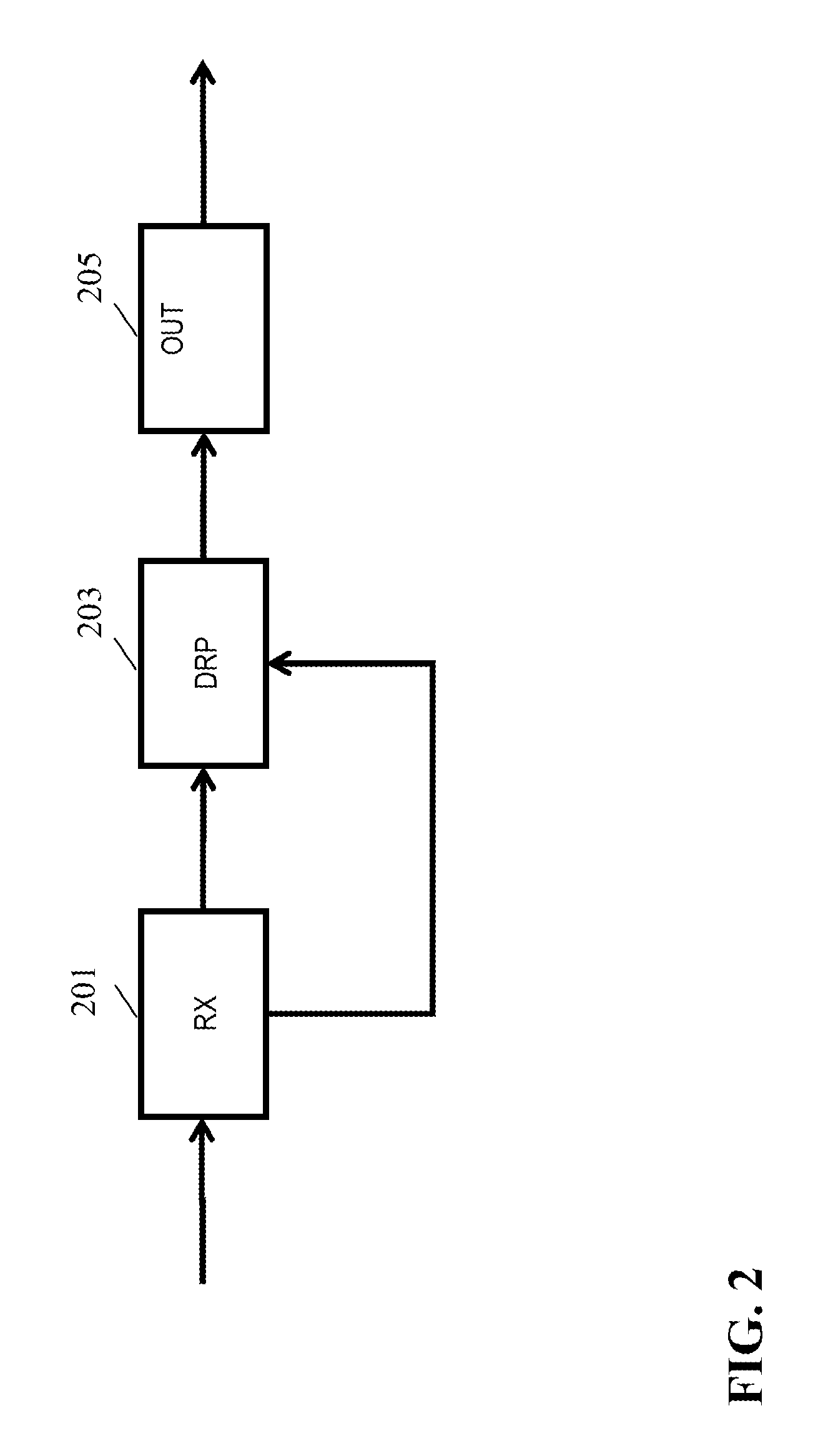
Apparatus and method for dynamic range transforming of images
ActiveUS20140210847A1Improved dynamic range transformsImprove dynamic rangeImage enhancementRecording carrier detailsImaging processingDisplay device
An image processing apparatus comprises a receiver (201) for receiving an image signal which comprises at least an encoded image and a target display reference. The target display reference is indicative of a dynamic range of a target display for which the encoded image is encoded. A dynamic range processor (203) generates an output image by applying a dynamic range transform to the encoded image in response to the target display reference. An output (205) then outputs an output image signal comprising the output image, e.g. to a suitable display. The dynamic range transform may furthermore be performed in response to a display dynamic range indication received from a display. The invention may be used to generate an improved High Dynamic Range (HDR) image from e.g. a Low Dynamic Range (LDR) image, or vice versa.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
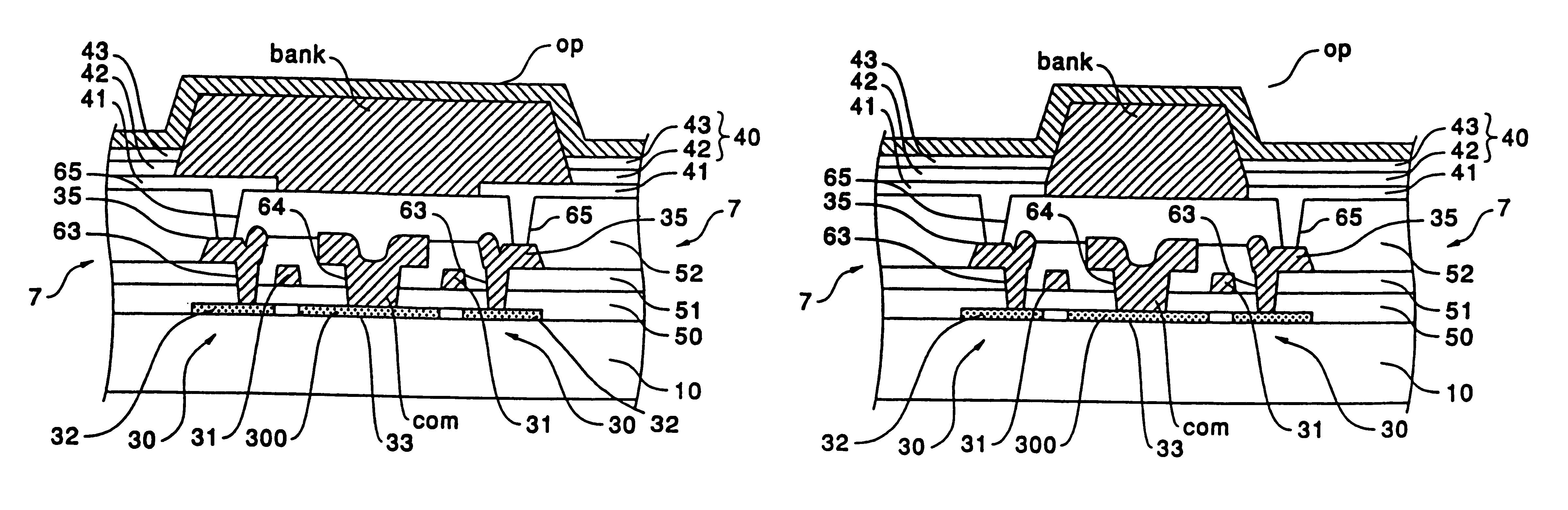
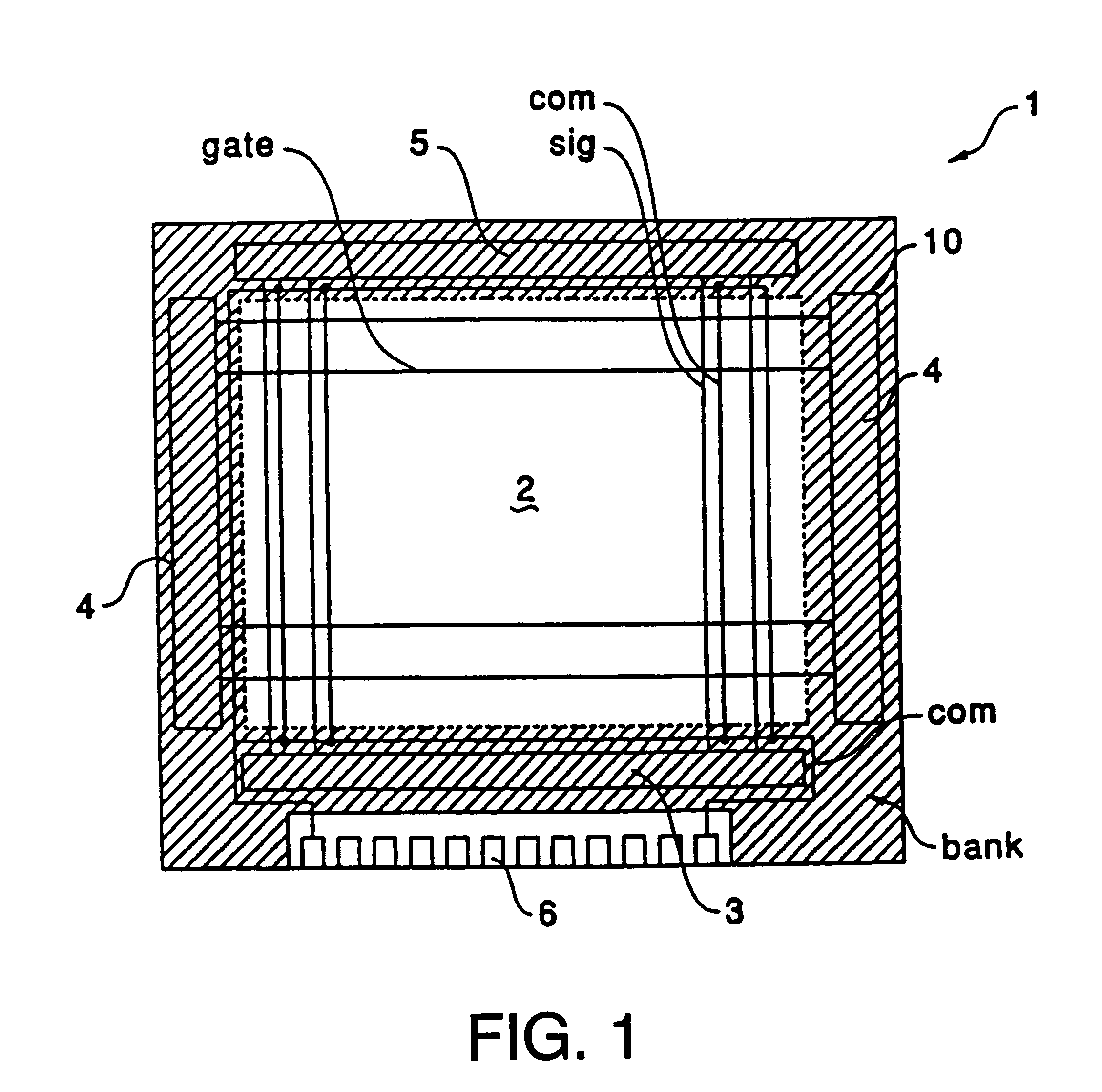
Display device
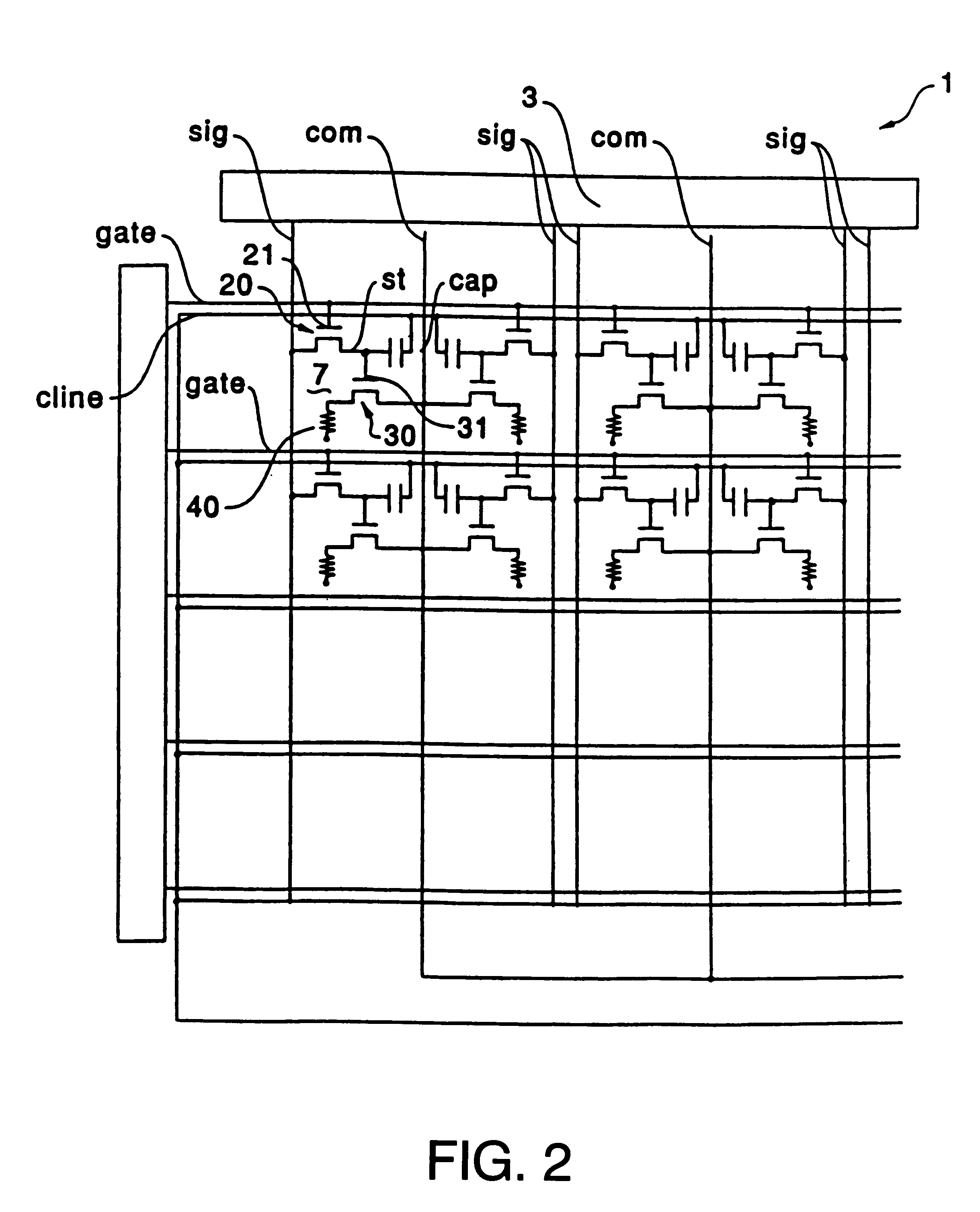
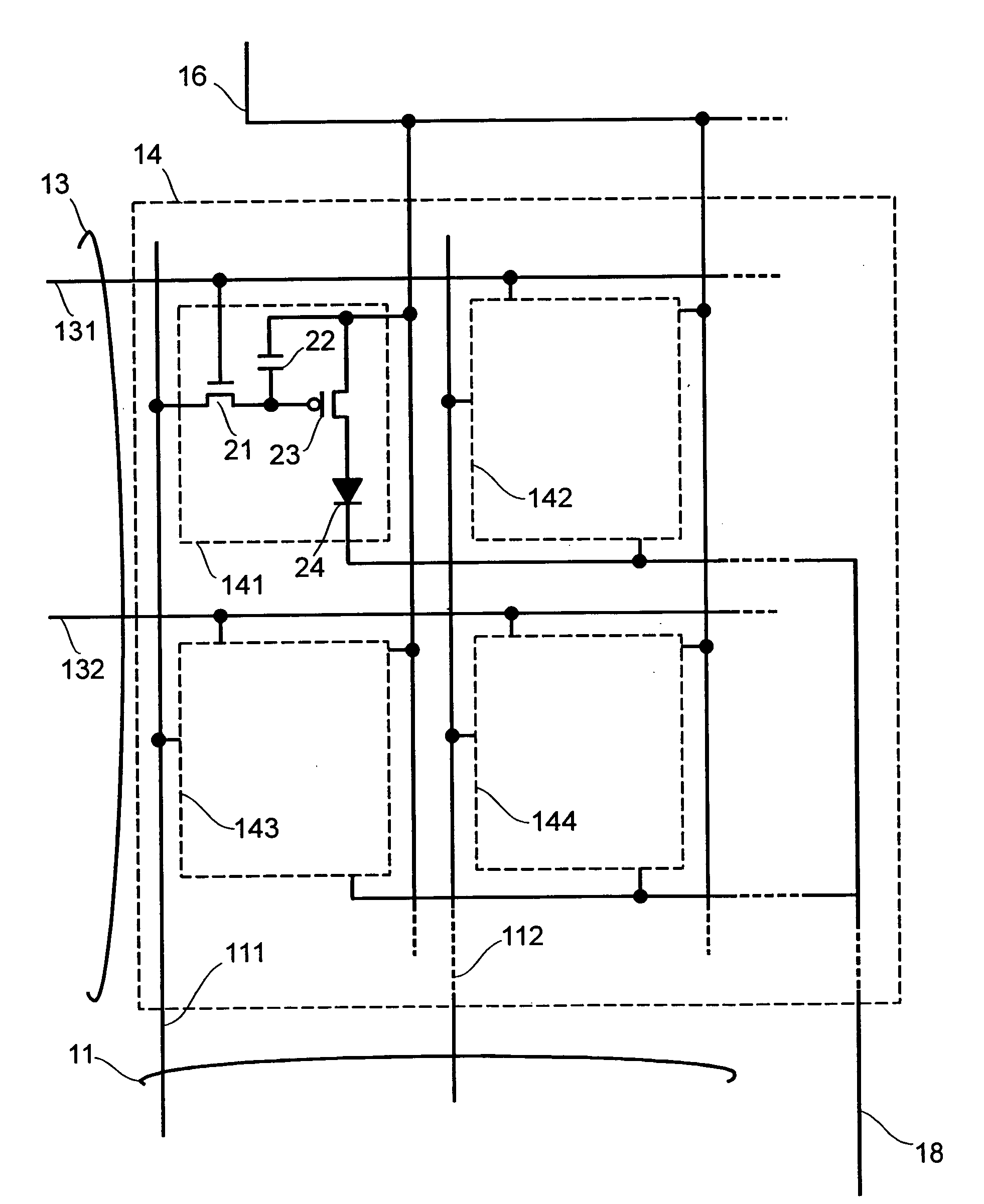
The invention provides a display device in which parasitic capacitance associated with data lines and driving circuits is prevented using a bank layer whose primary purpose is to define areas on a substrate in which an organic semiconductor film is formed. When the organic semiconductor film for forming a luminescent element such as an electroluminescent element or an LED is formed is formed in pixel regions (7), the organic semiconductor film is formed in the areas surrounded by the bank layer (bank) formed of a black resist. The bank layer (bank) is also formed between an opposite electrode (op) and data lines (sig) for supplying an image signal to first TFTs (20) and holding capacitors (cap) in the pixel regions (7) thereby preventing parasitic capacitance associated with the data lines (sig).
Owner:INTELLECTUAL KEYSTONE TECH LLC
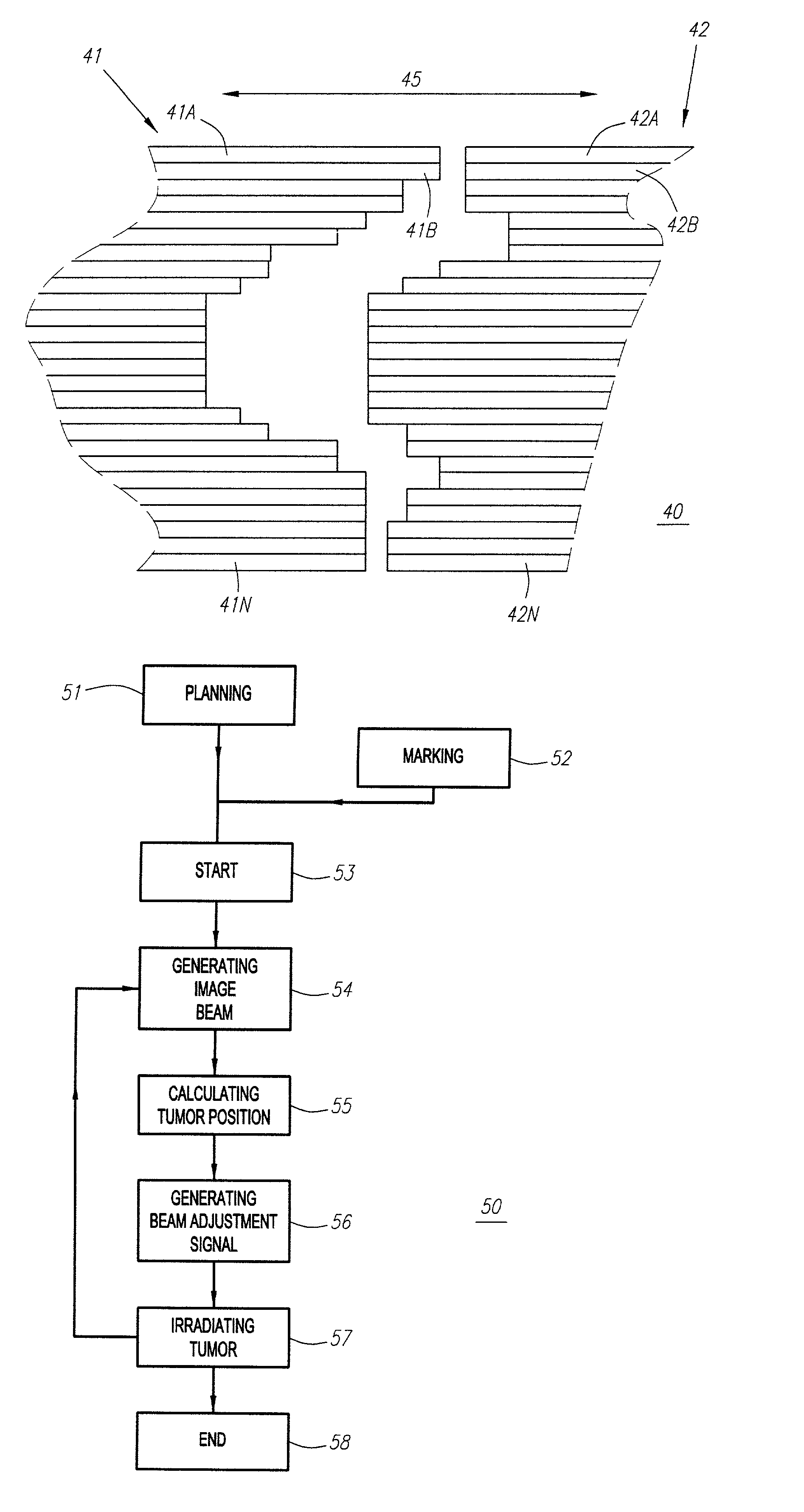
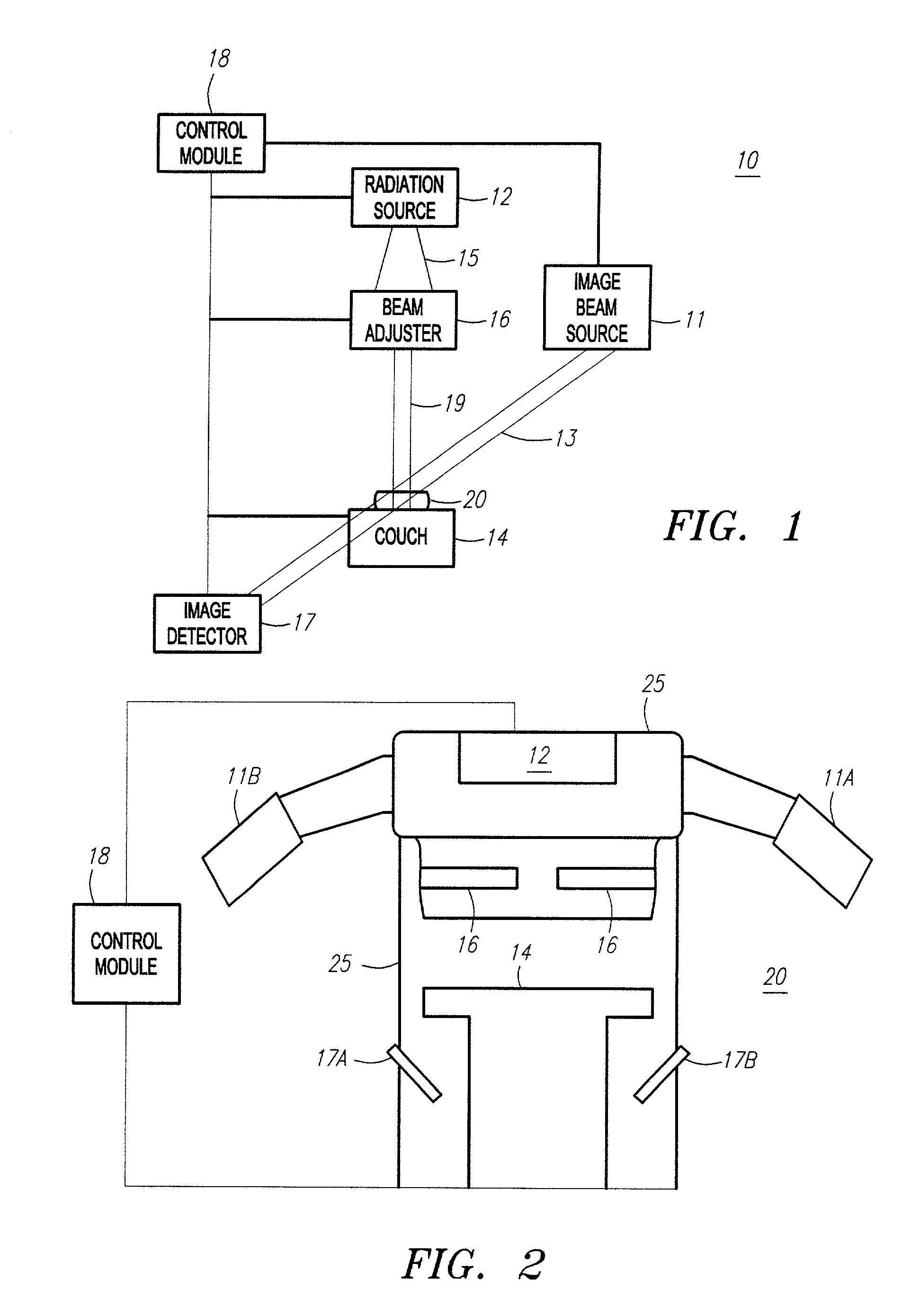
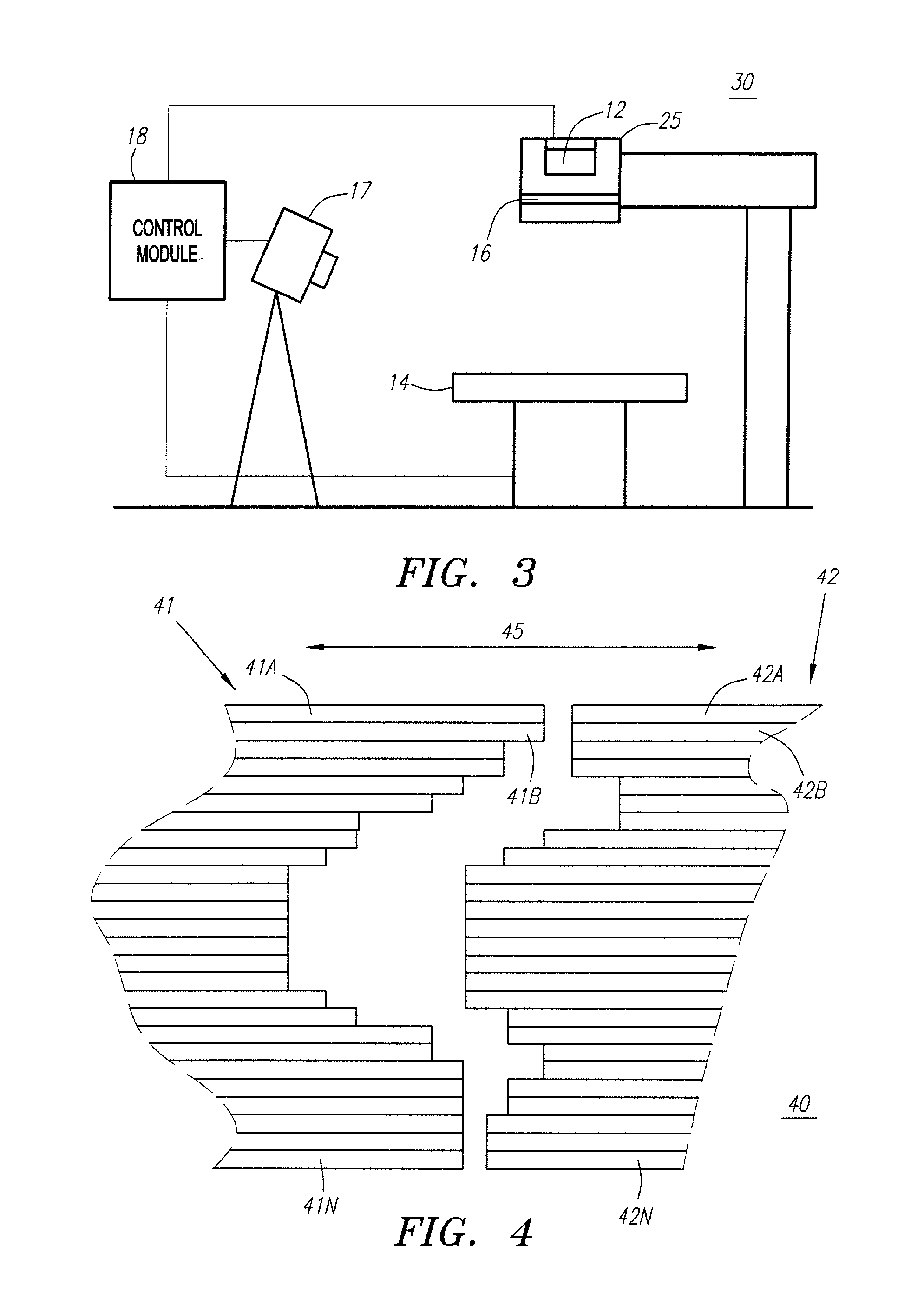
Method and apparatus for irradiating a target
An apparatus (10) for irradiating a target includes a radiation source (12) for generating a radiation beam and a multiple leaf beam adjuster (16) for collimating and adjusting the shape of the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) that would be projected on the target. An image detector (17) detects generates an image signal of the target. In response to the image signal, a control module (18) generate a beam adjustment signal for controlling the beam adjuster (16), thereby enabling the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) to track the movement of the target.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
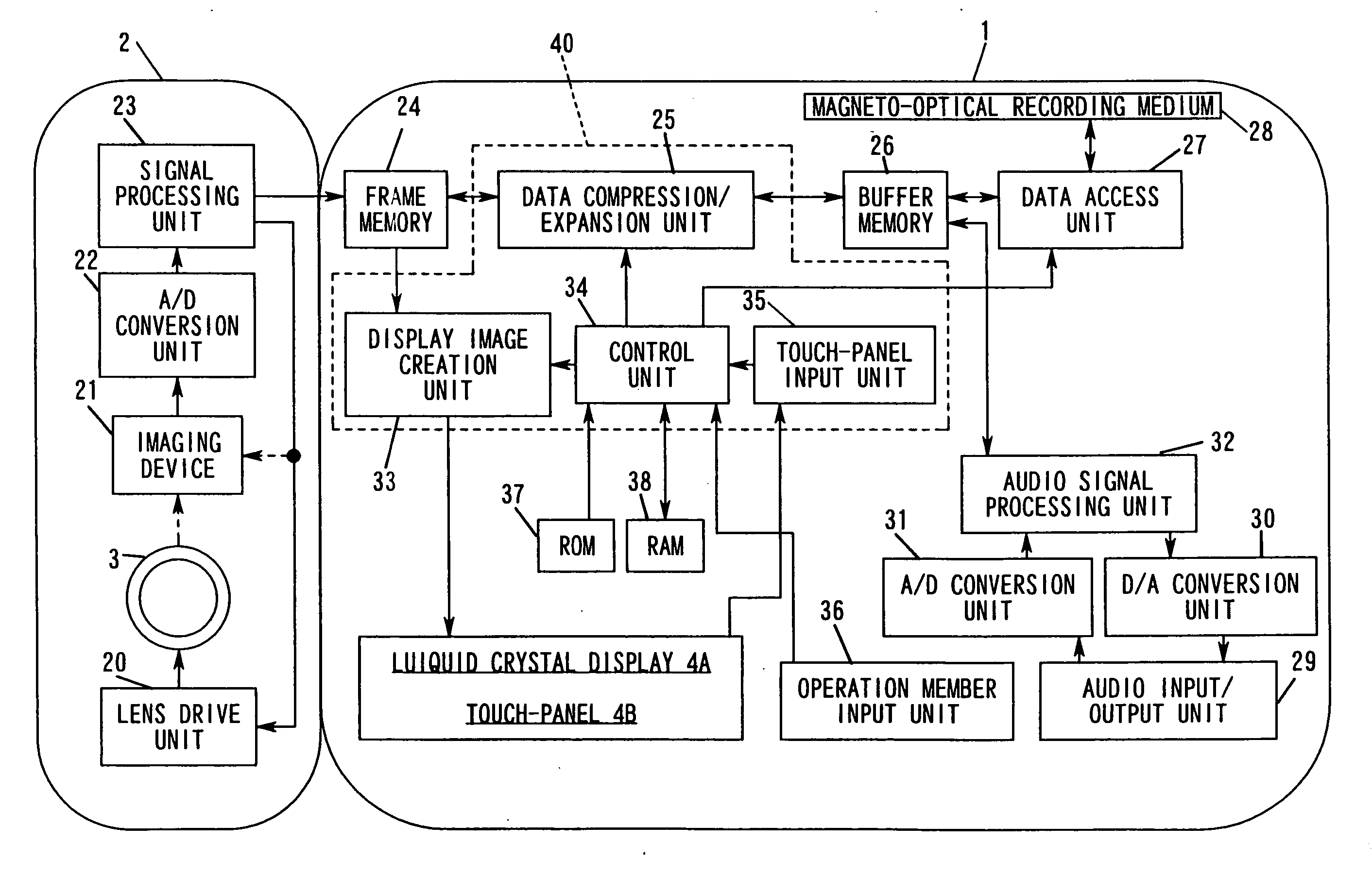
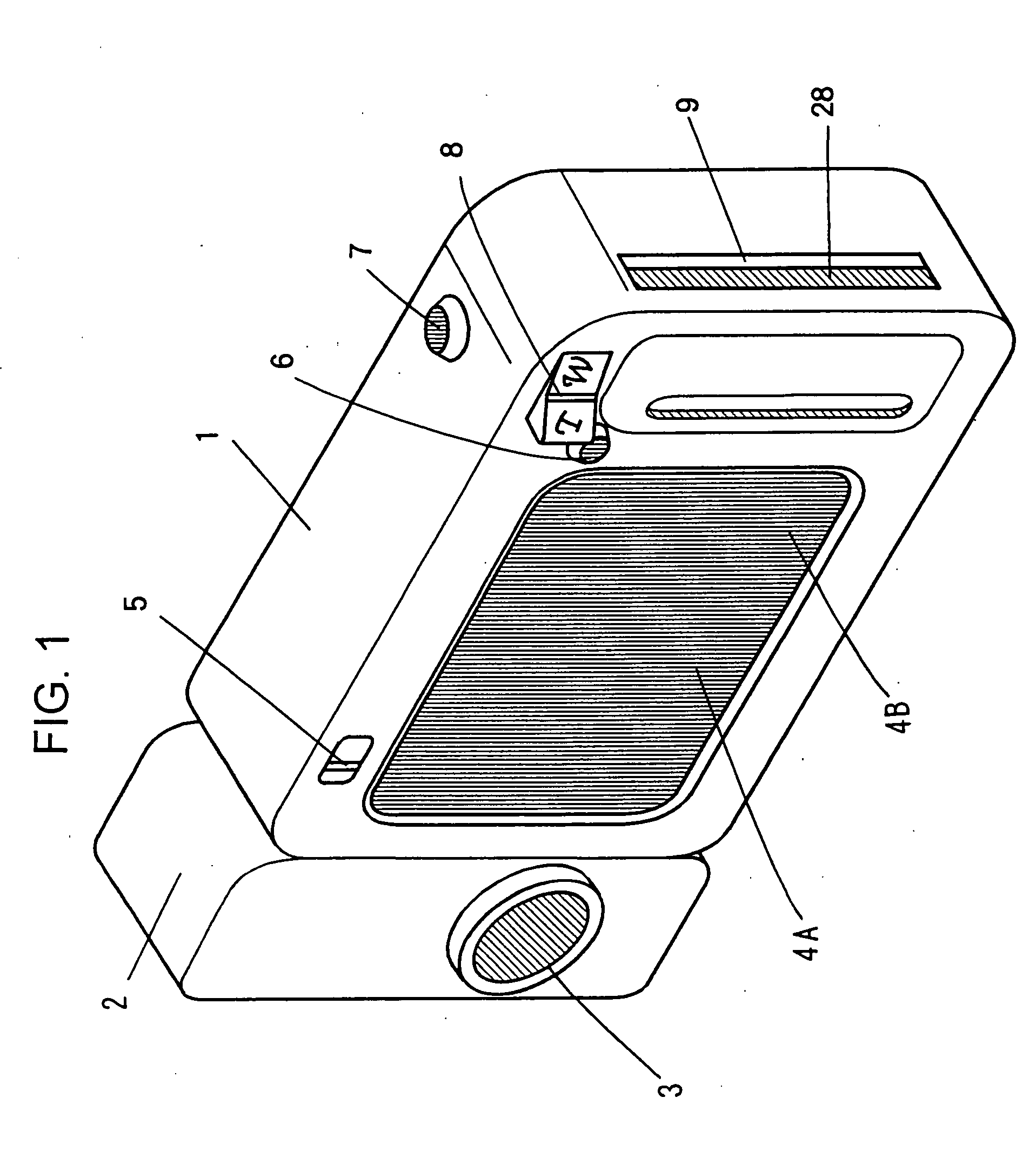
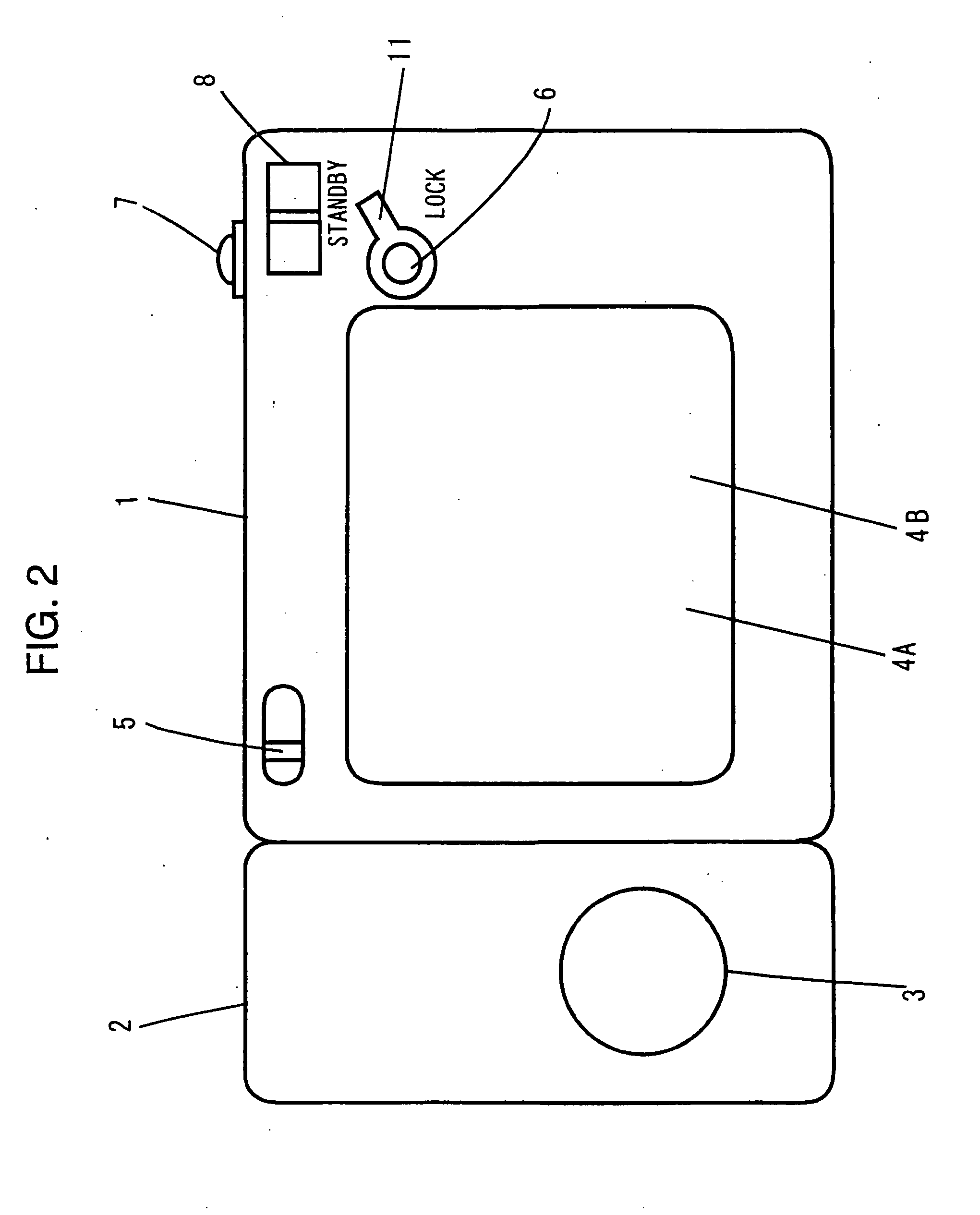
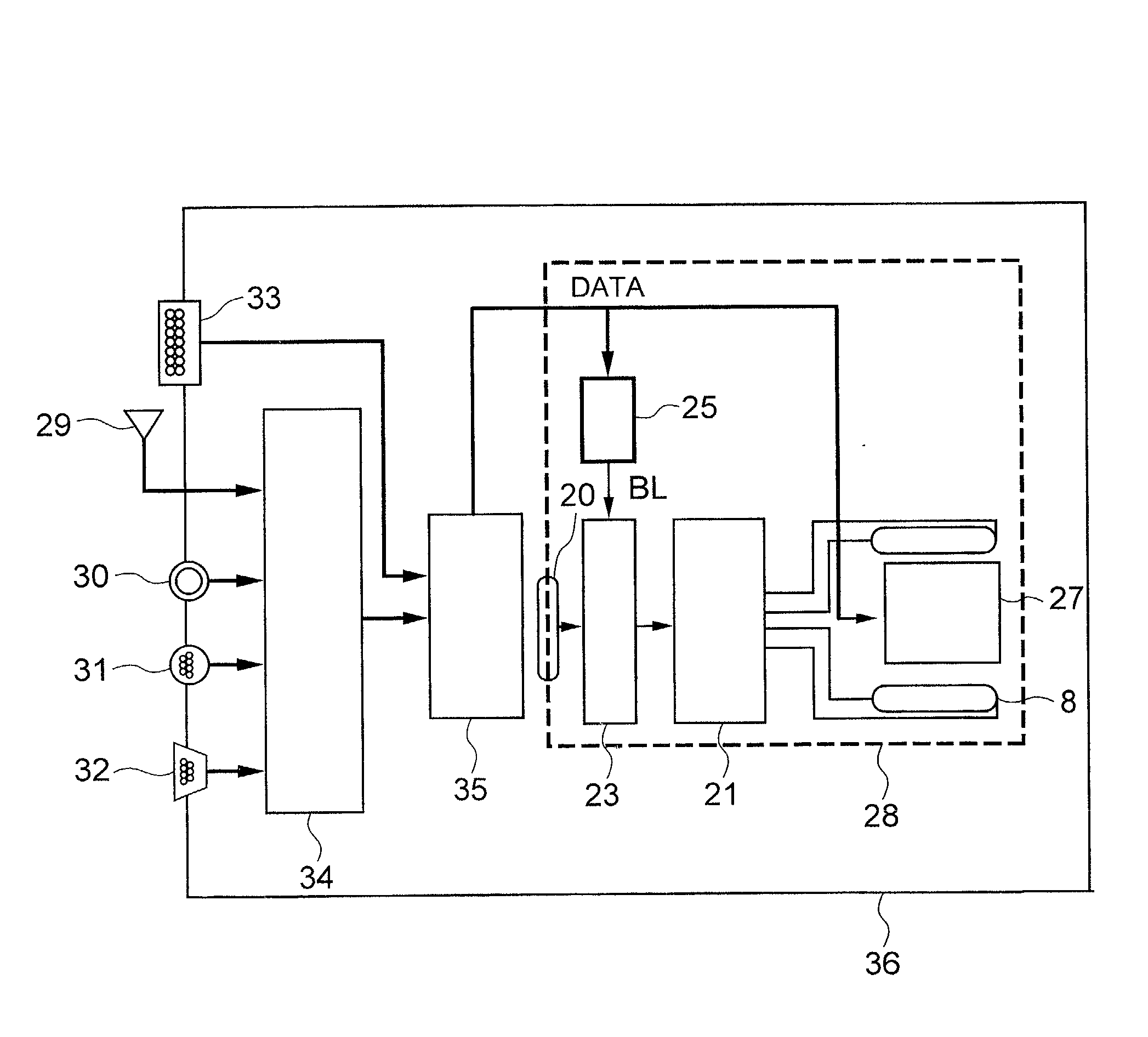
Image signal recording/reproduction apparatus, method employed therein, and image signal recording apparatus
InactiveUS20080025701A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingComputer hardwareLiquid-crystal display
A dynamic image recording button and a still image recording button are provided at the main unit of a movie camera. A magneto-optical recording medium is loaded in a slot. If the dynamic image recording button or the still image recording button is operated during a reproduction operation, the reproduction operation is interrupted in a state in which the mechanical drive (rotation) of the magneto-optical recording medium is sustained. At this point, a dynamic image signal or a still image signal obtained through a photographing operation performed at the camera unit is temporarily recorded in a buffer memory, and is written in the magneto-optical recording medium when a write in the magneto-optical recording medium becomes enabled. Instructions to record dynamic images and to record still images can be issued to the movie camera through a touch-panel provided on the screen of a liquid crystal display unit. Even when operation cannot be performed through the touch-panel, the instructions can be issued through the dynamic image recording button or the still image recording button.
Owner:NIKON CORP
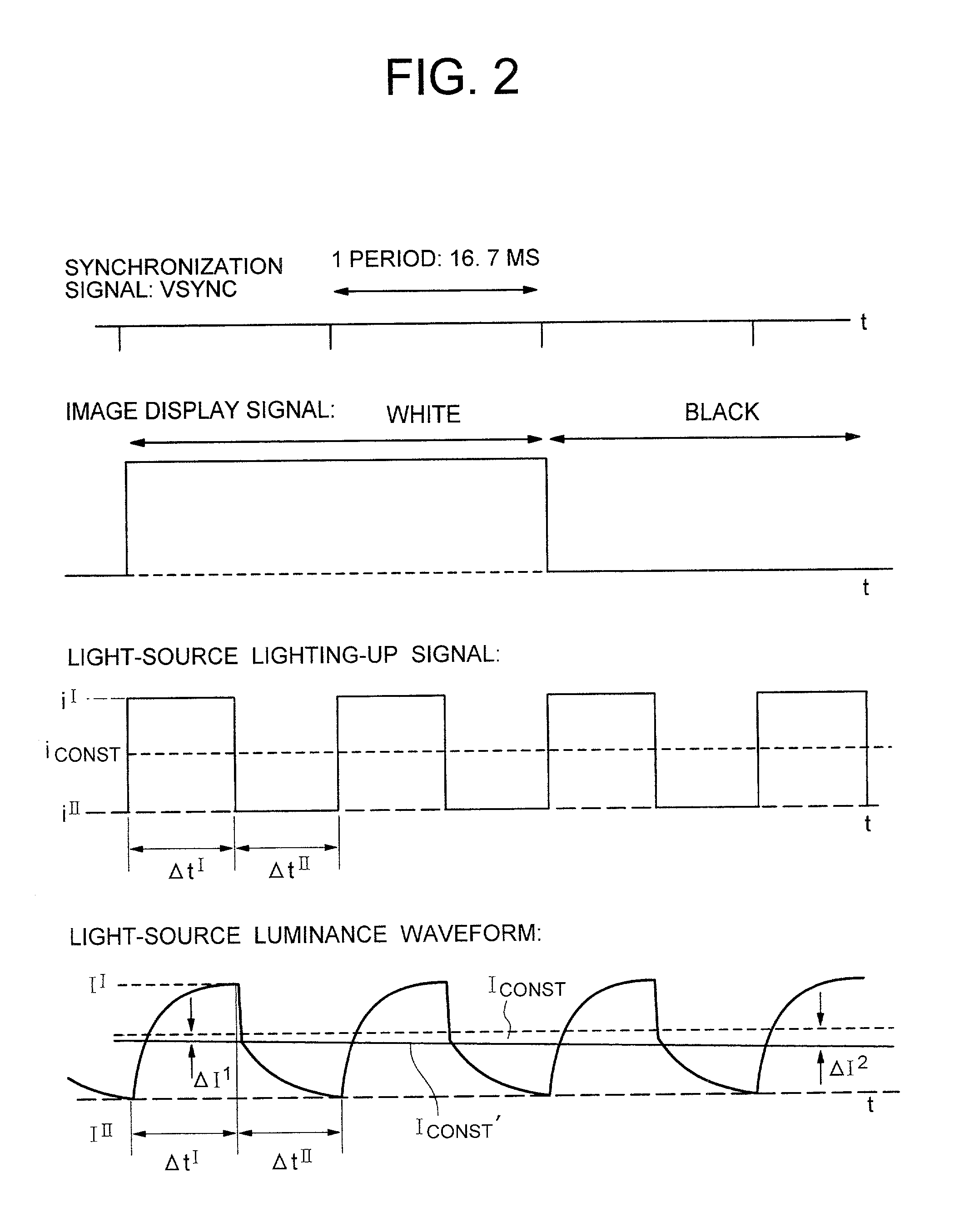
Liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20020057238A1Static indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayControl circuit
The present invention includes a panel on which a plurality of pixels are located, a light-source for visualizing an image displayed on the plurality of pixels, a controlling circuit for controlling the light-source, and an image-signal tone characteristic controlling circuit. Moreover, the light-source controlling circuit has a function of repeating a period. Here, the period includes a 1st time-period during which an electric current having a 1st intensity is fed to the light-source, and a 2nd time-period during which an electric current having a 2nd intensity differing from the 1st intensity is fed to the light-source. The light-source controlling circuit controls the 1st time-period and the 2nd time-period in accordance with display information. Also, in accordance with the display information as well, the tone characteristic controlling circuit is controlled so that the excellent contrast will be always available.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS +1
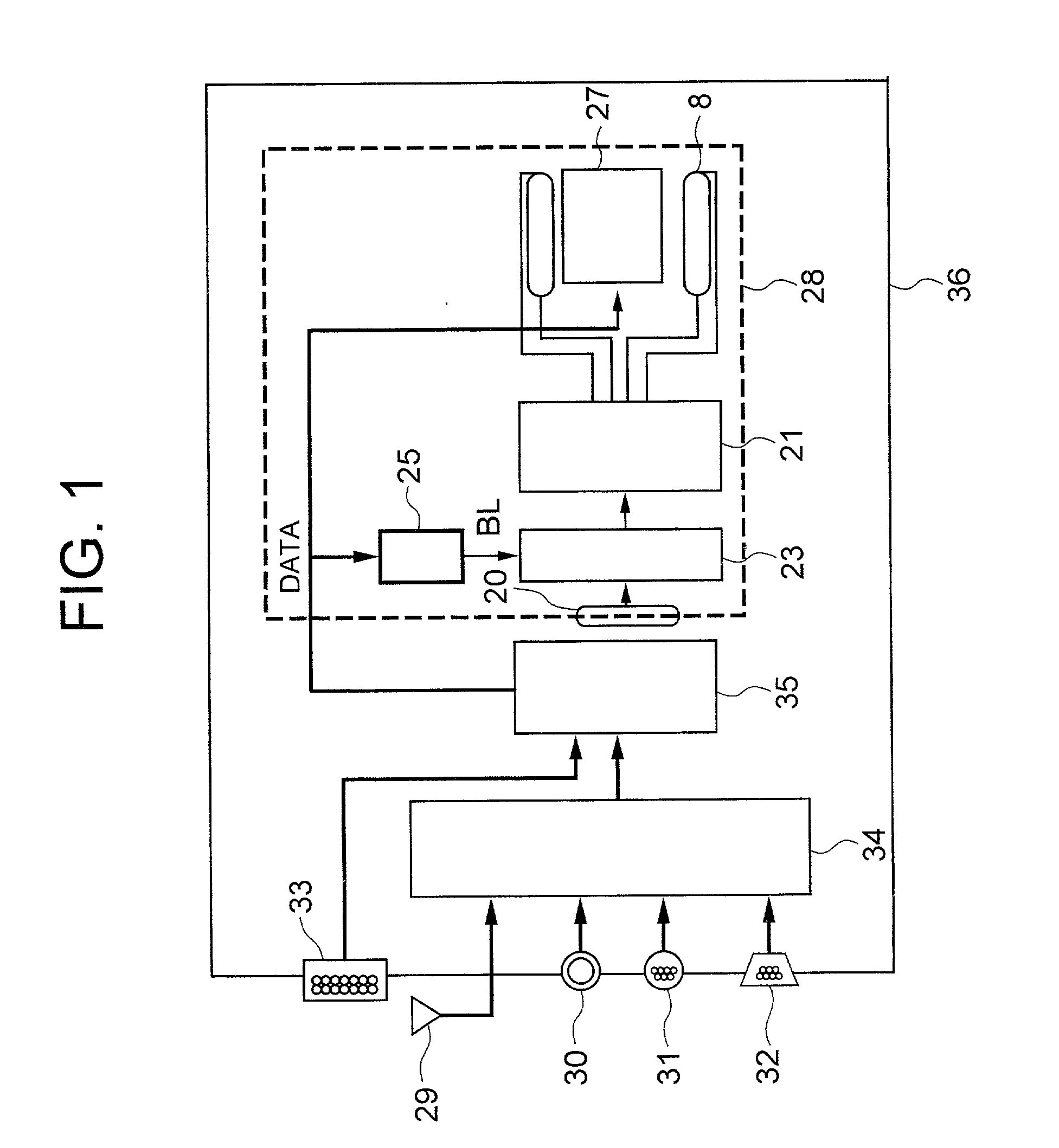
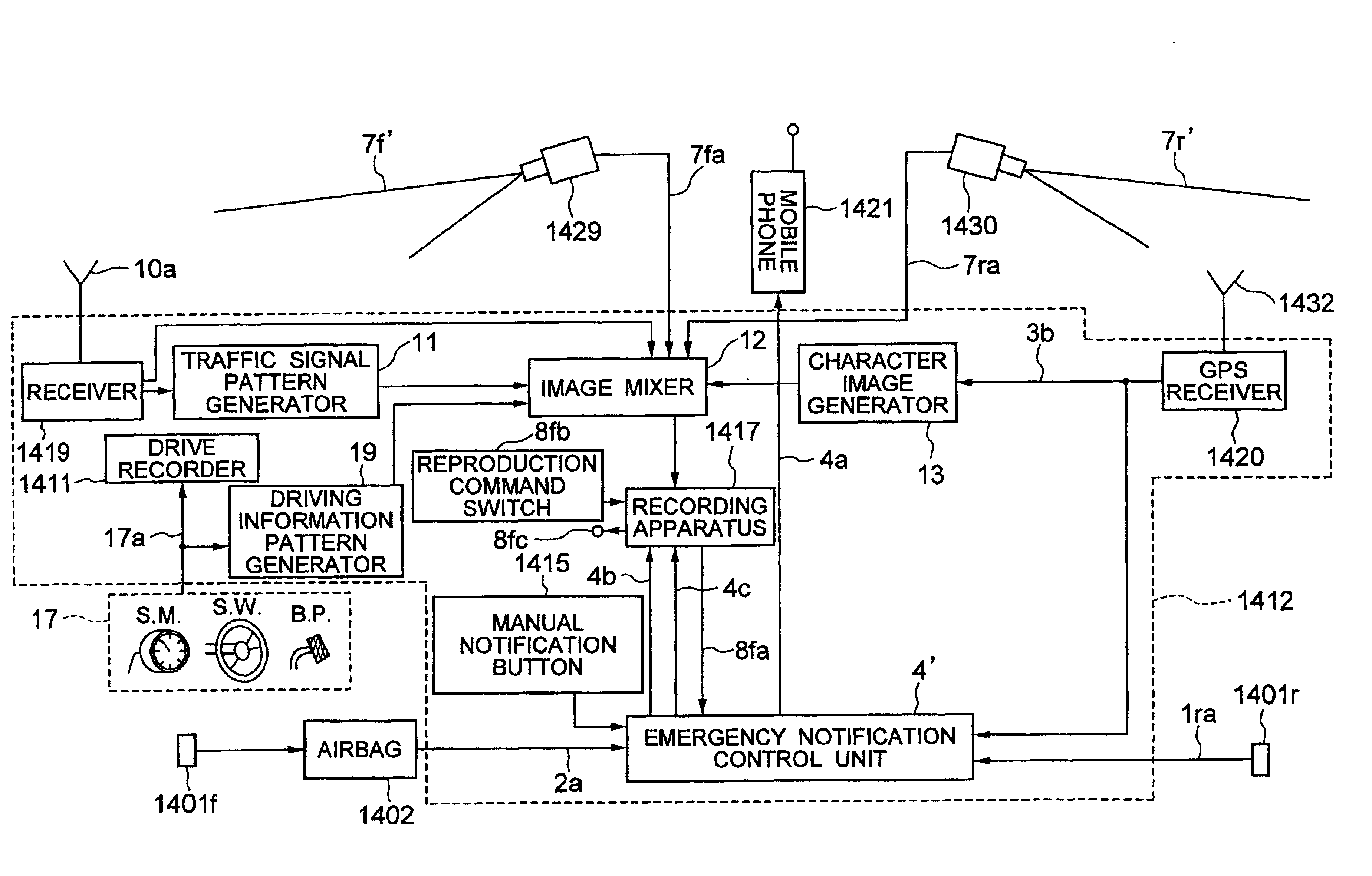
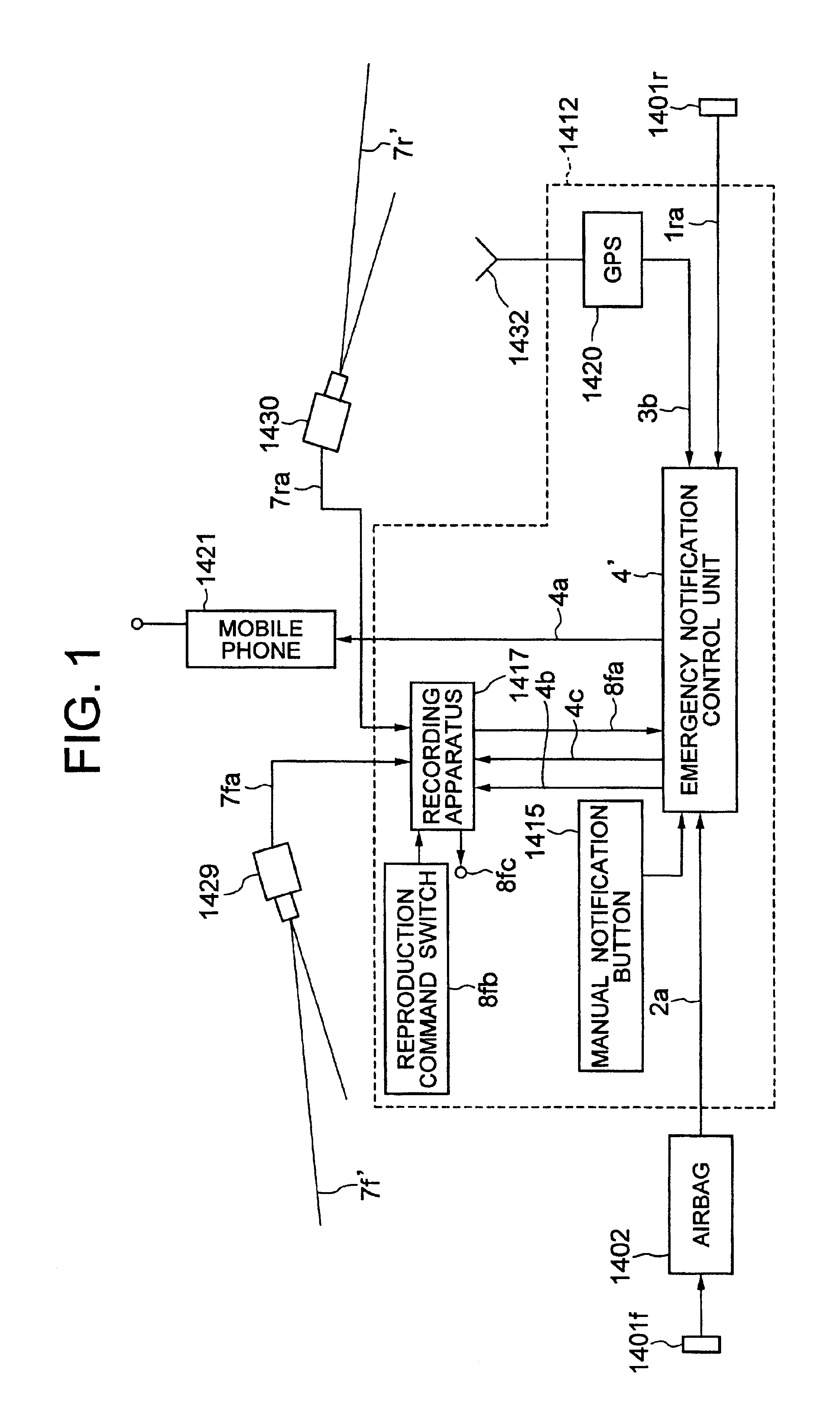
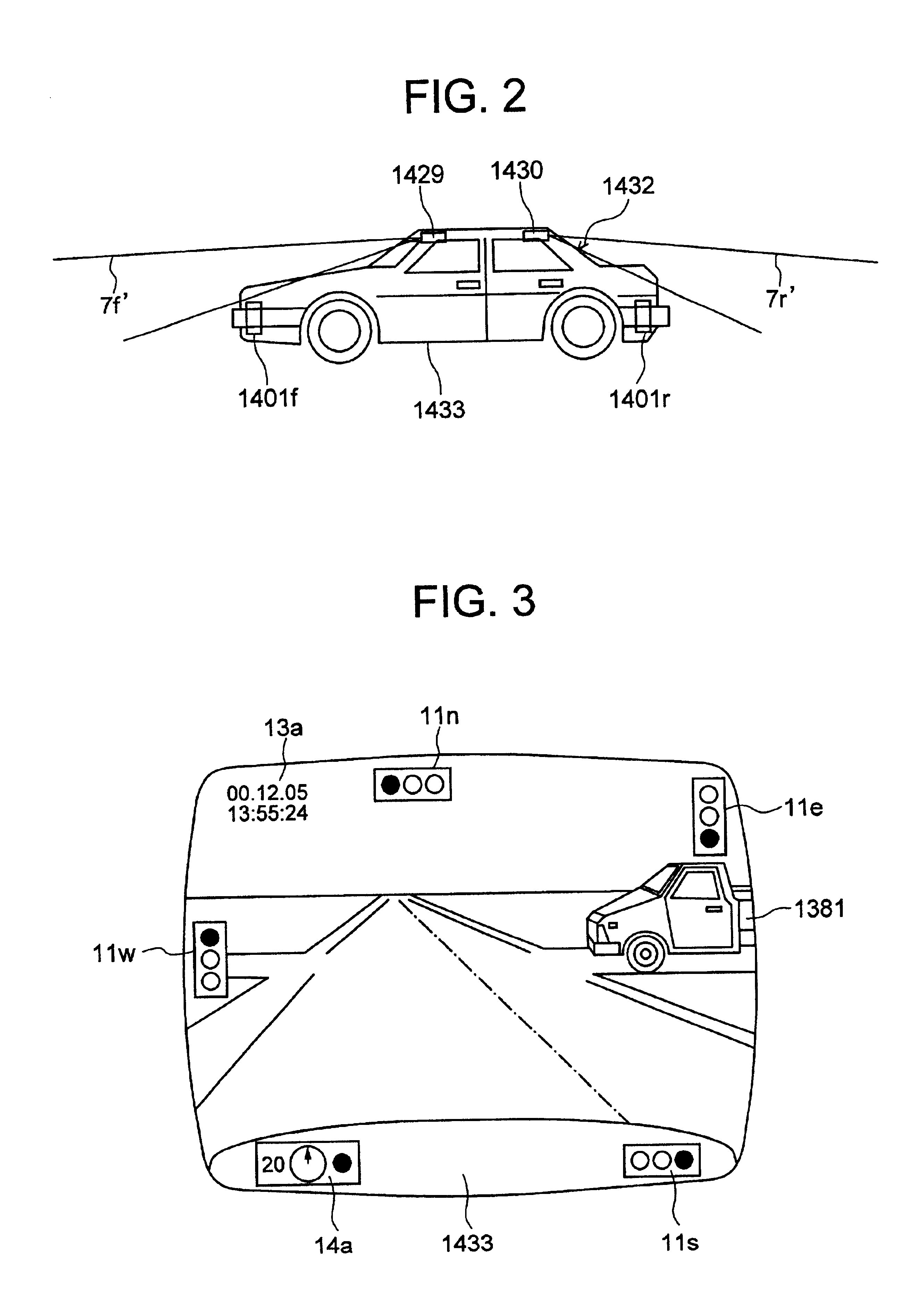
Emergency information notifying system, and apparatus, method and moving object utilizing the emergency information notifying system
InactiveUS7133661B2Enhance first aidEnhance critical care effectVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesVideo recordVideo recording
An emergency notifying apparatus of a moving object, having: image pick-up devices for picking up a part of the moving object and surroundings thereof, a video recording apparatus for recording signals related to the images taken by the image pick-up devices according to an output from at least one of shock sensors for detecting a shock applied to the moving object, a thermal sensor for detecting a heat or a temperature in a given portion of the moving object, and a manual switch, and a control unit for generating a signal for transmitting the image signals recorded in the recording apparatus to a given station via a radio communication device.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Camera device with selectable image paths
A combination mobile terminal and camera with multiple light apertures in the housing. One aperture is disposed on a front side of the housing while another aperture is disposed on a rear side of the housing. The device has an image sensor disposed within the housing for converting images formed by light directed onto the image sensor into electrical signals. The device also has a movable optical system for selectively directing light passing through one of the light apertures onto the image sensor. The device also includes an image processor coupled to an output of the image sensor for processing the electrical signals from the image sensor to produce image signals. The device also has a position detector to detect the position of the movable optics and for directing the image processor to invert the images as needed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
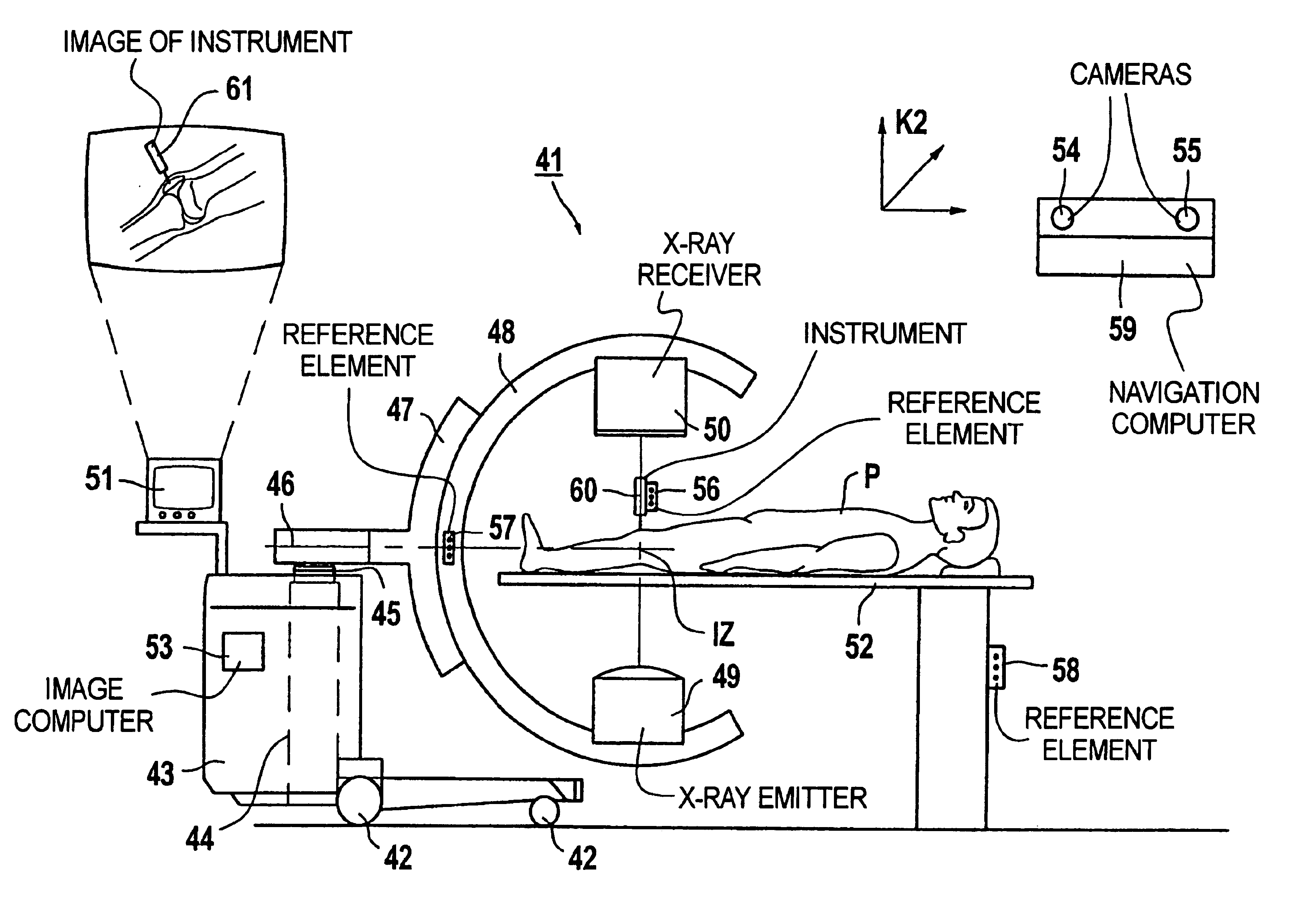
Medical workstation, imaging system, and method for mixing two images
InactiveUS6895268B1Well mixedEffective supportGeometric image transformationSurgeryWorkstationComputer science
In a system, method and workstation, images of a first subject are acquired with an image signal acquisition unit, the position of the image signal acquisition unit is determined, the position of a second subject is determined and the position of the second subject relative to the image signal acquisition unit is also determined and an image of the second subject is mixed into an image of the first subject acquired with the image signal acquisition unit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
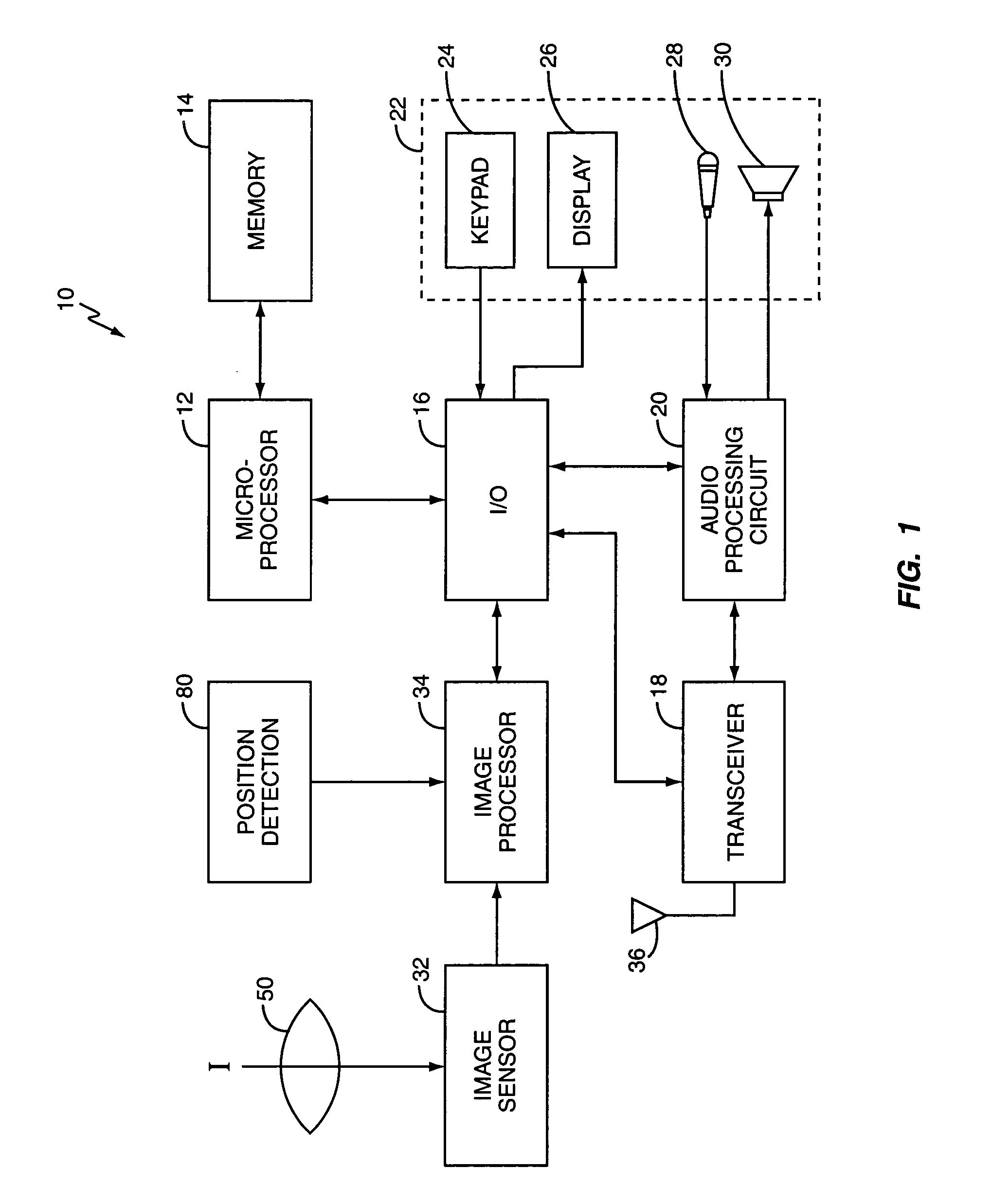
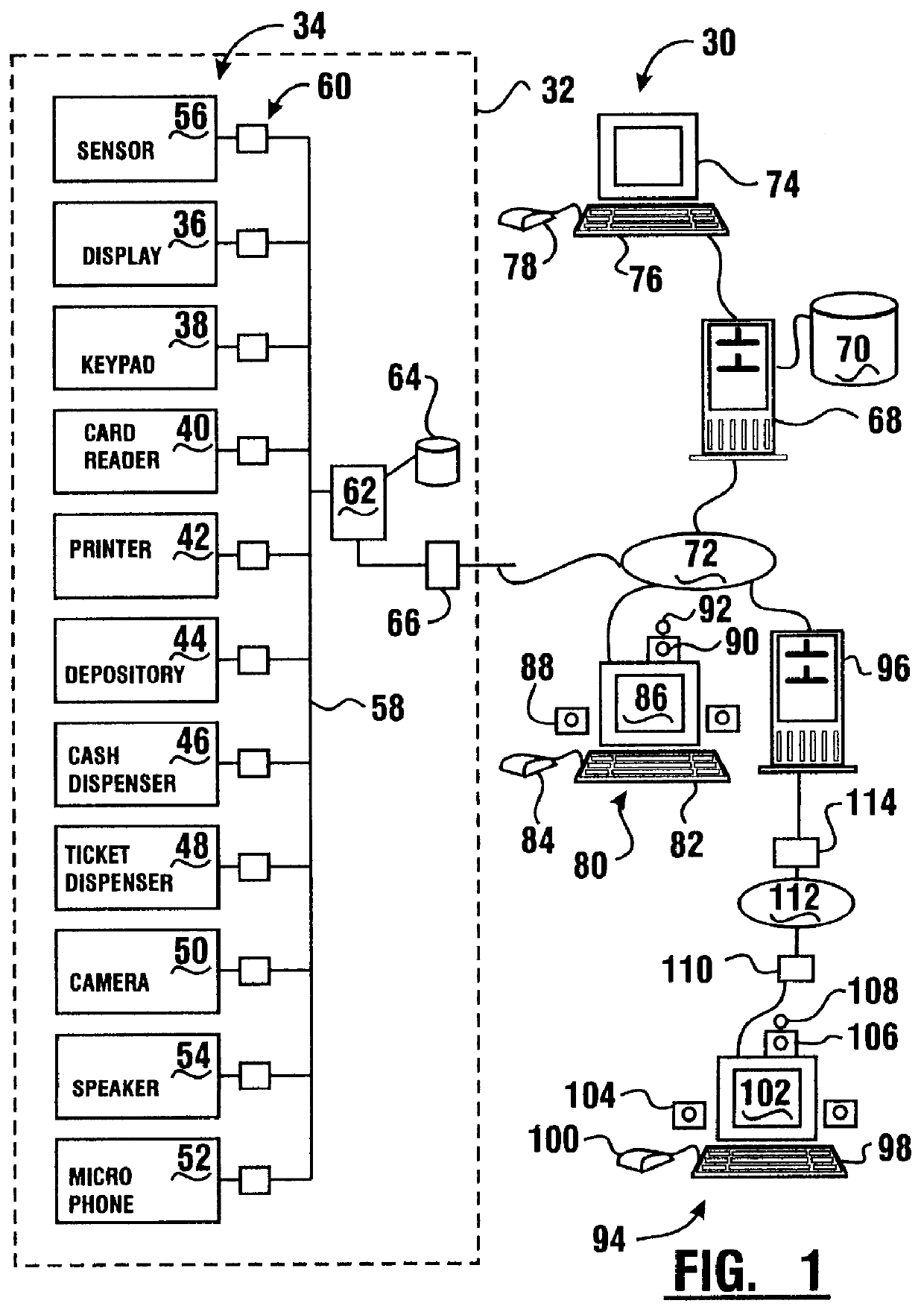
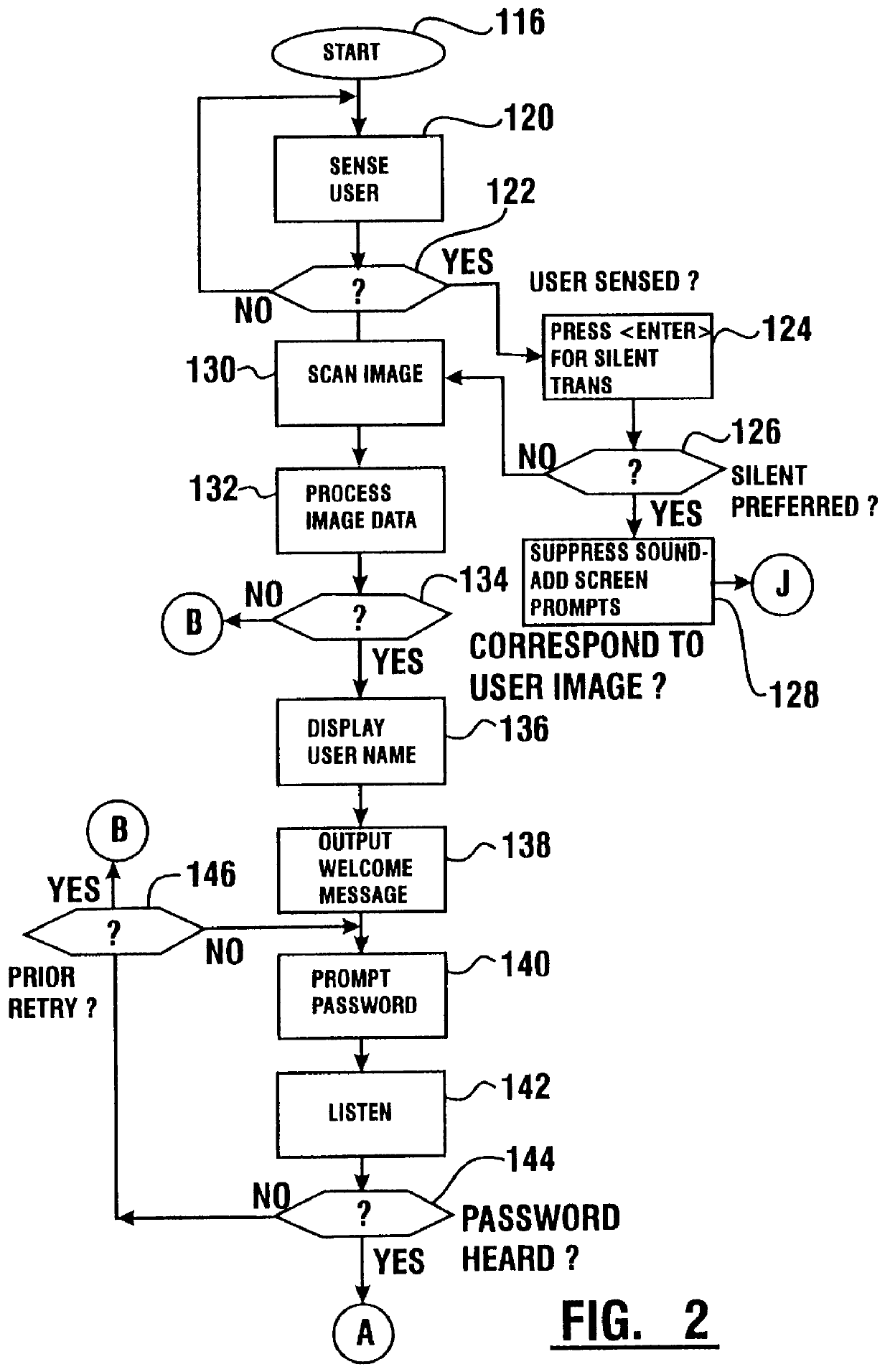
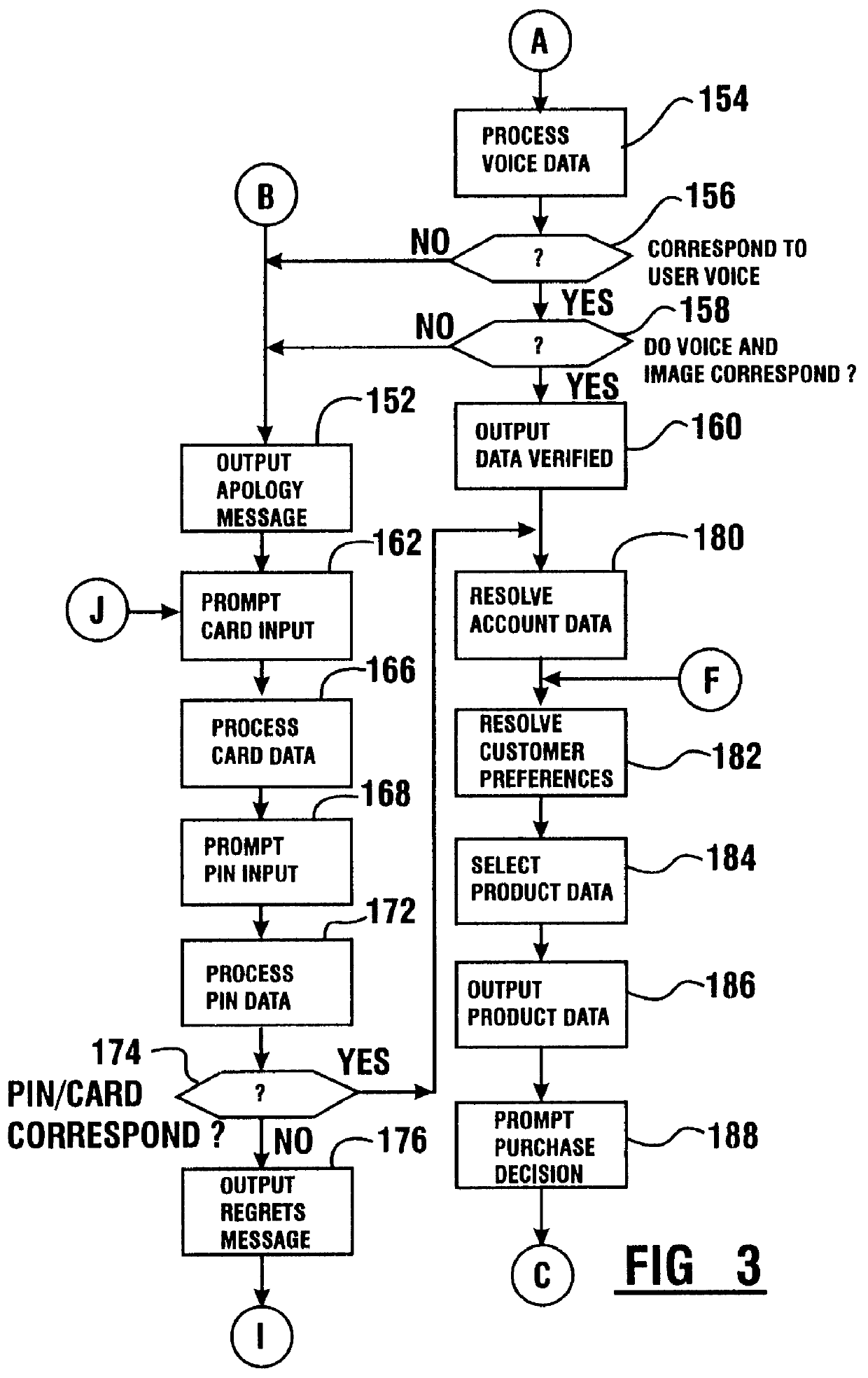
Transaction apparatus and method that identifies an authorized user by appearance and voice
A financial transaction apparatus (30) includes a financial transaction machine (32). The machine includes devices (34) including transaction function devices (42, 44, 46, 48) for carrying out operations associated with financial transactions. The terminal also includes an imaging device (50) and an audio input device (52), as well as a visual output device (36) and an audio output device (54). Terminal (32) is connected to a computer (68) which has an associated data store (70). The data store includes user data including image data and voice data corresponding to authorized users. The identity of a customer operating the machine is determined by resolving first identity data based on image signals from the imaging device which correspond to a user's appearance. Second identity data is resolved by the processor from voice signals from the audio input device corresponding to the user's voice. The computer enables operation of the transaction function devices if the level of correlation between the first and second identity data is sufficient to establish that the image and voice signals originate from a single authorized user.
Owner:DIEBOLD NIXDORF
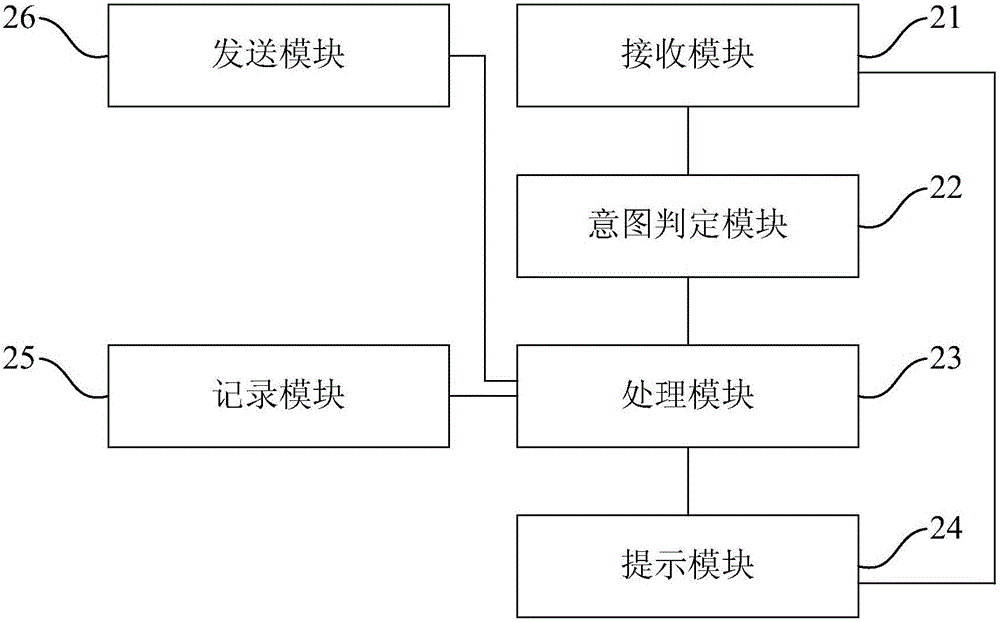
Man-machine interaction method and device based on artificial intelligence and terminal equipment
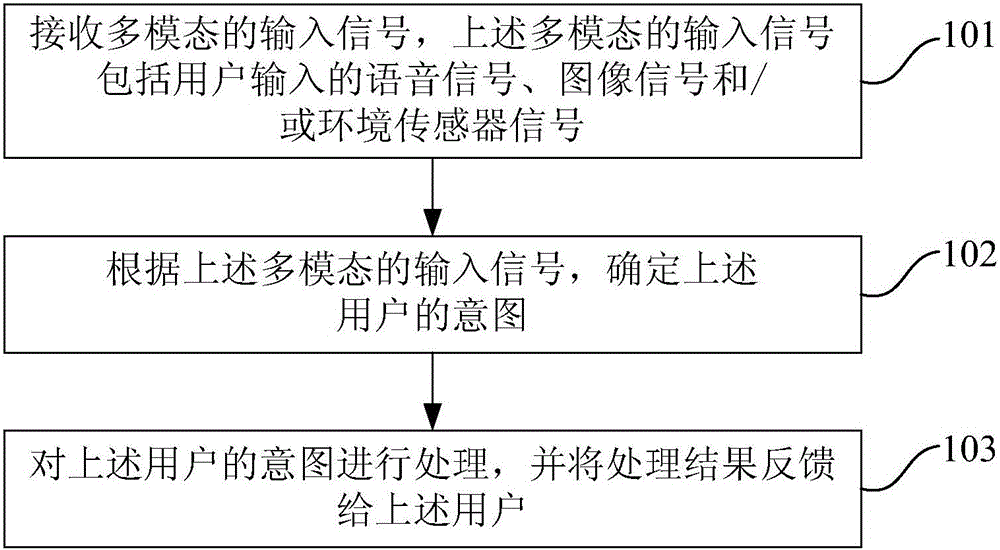
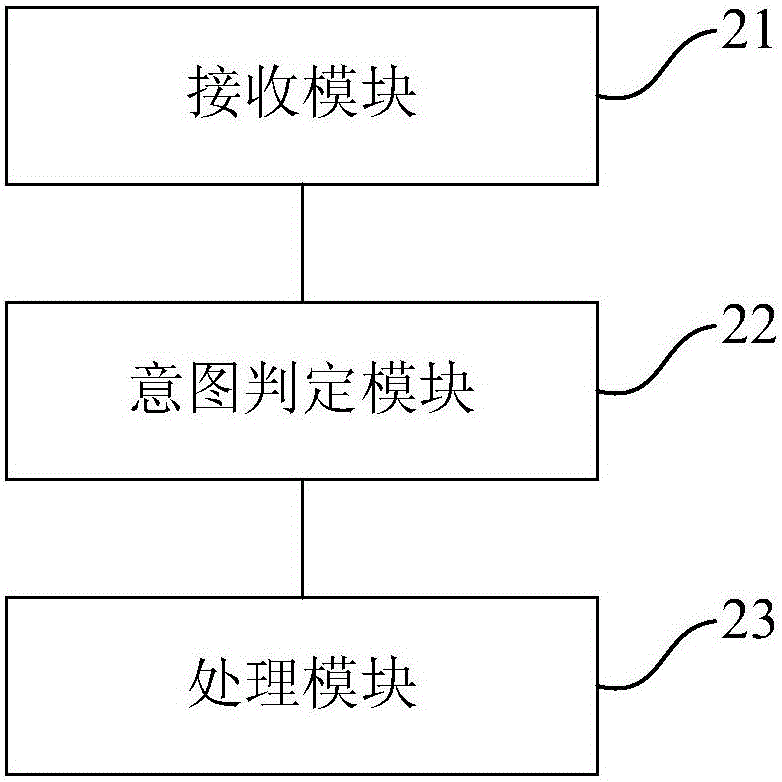
InactiveCN104951077AImprove experienceGood human-computer interaction functionInput/output for user-computer interactionArtificial lifeUser inputTerminal equipment
The invention provides a man-machine interaction method and device based on artificial intelligence and terminal equipment. The man-machine interaction method based on artificial intelligence comprises the steps of receiving multi-modal input signals, wherein the multi-modal input signals comprise voice signals, image signals and / or environment sensor signals input by a user; determining the intention of the user according to the multi-modal input signals; processing the intention of the user and feeding the processing result back to the user. The man-machine interaction method and device based on artificial intelligence and the terminal equipment can achieve the good man-machine interaction function and high-functioning and high-accompany type intelligent man-machine interaction.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
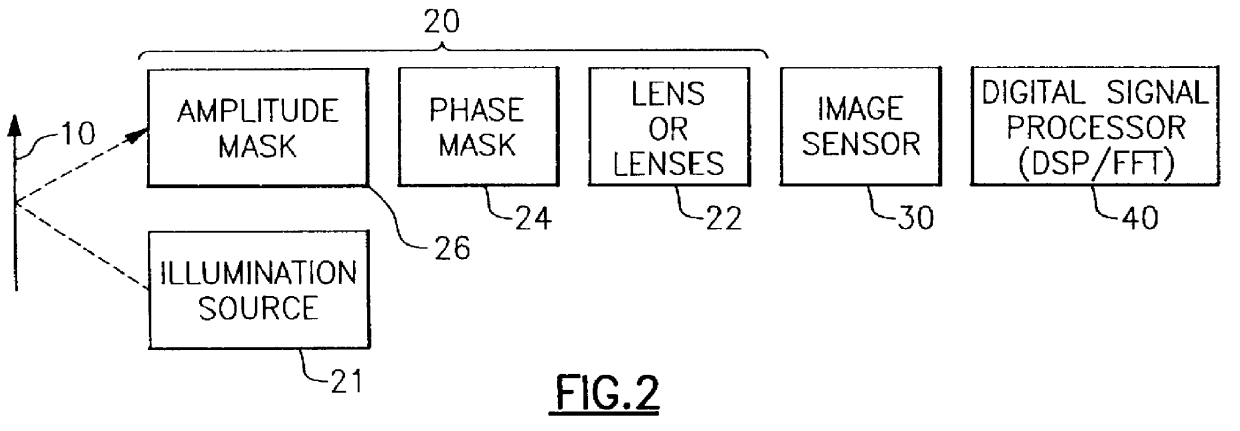
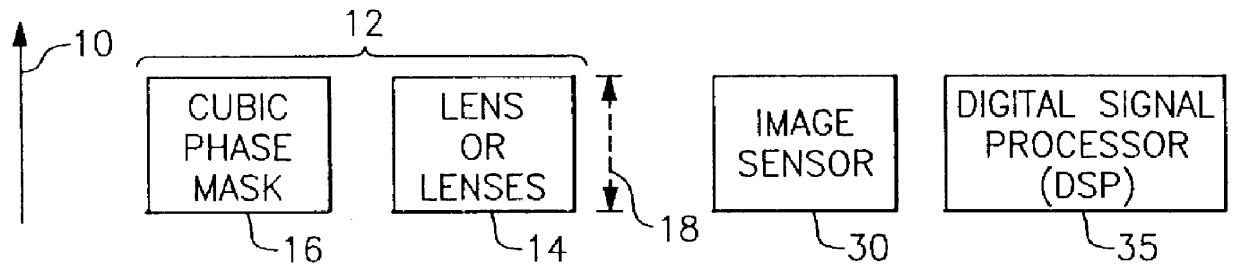
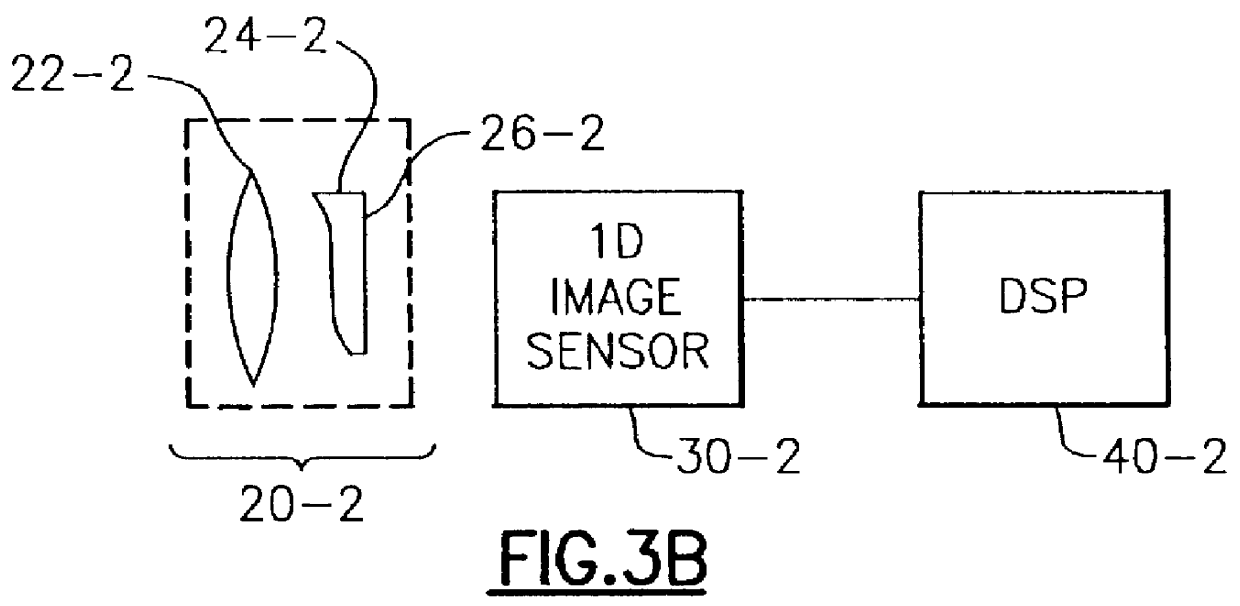
Apparatus and method for reducing imaging errors in imaging systems having an extended depth of field
An improved opto-electronic imaging system which is adapted for use with incoherently illuminated objects, and which produces final images having a reduced imaging error content. The imaging system includes an optical assembly for forming an intermediate image of the object to be imaged, an image sensor for receiving the intermediate image and producing an intermediate image signal, and processing means for processing the intermediate image signal to produce a final image signal having a reduced imaging error content. A reduction in imaging error content is achieved, in part, by including in the optical assembly a phase mask for causing the OTF of the optical assembly to be relatively invariant over a range of working distances, and an amplitude mask having a transmittance that decreases continuously as a function of distance from the center thereof. The reduction in imaging error content is also achieved, in part, by including in the processing means an improved generalized recovery function that varies in accordance with at least the non-ideal calculated IOTF of the optical assembly under a condition of approximately optimum focus.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Patient positioning device and patient positioning method
InactiveUS7212608B2Improve accuracyAvoid accuracyBuilding locksPatient positioning for diagnosticsPattern matchingX-ray
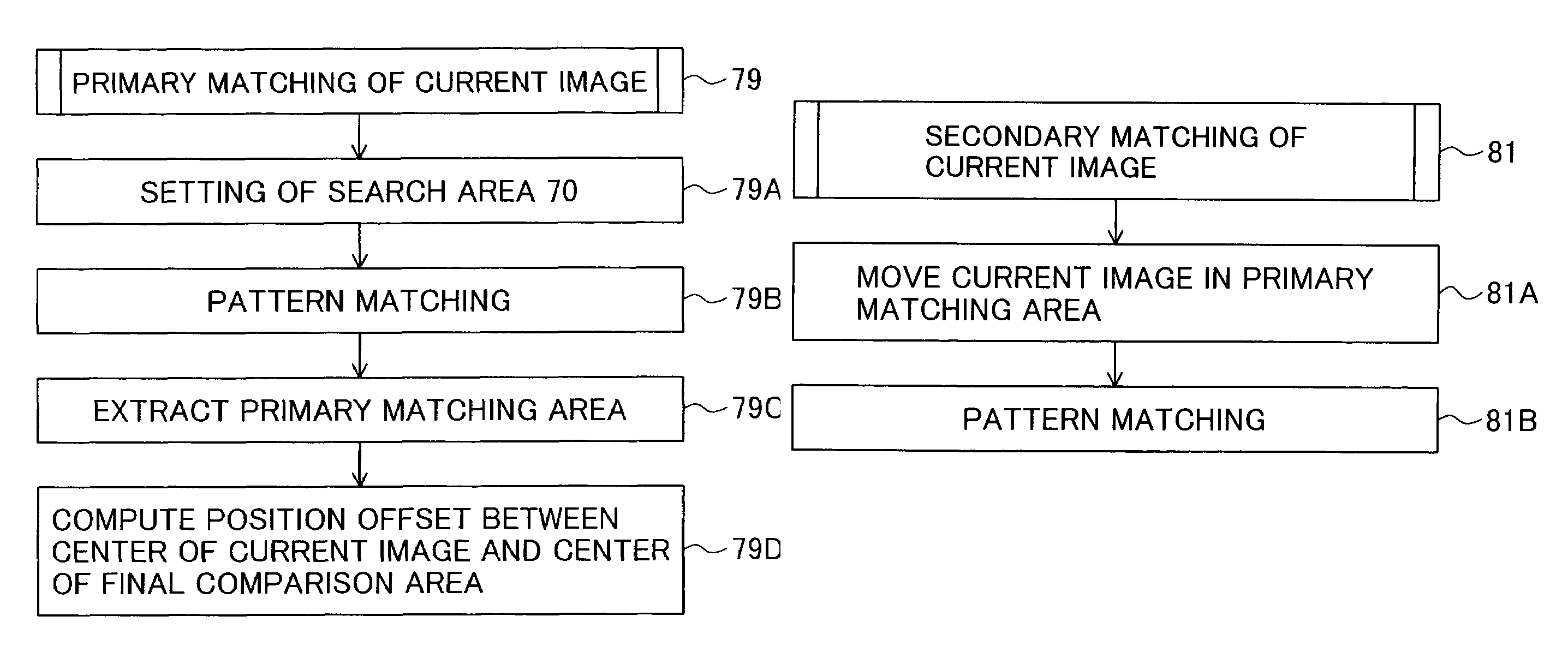
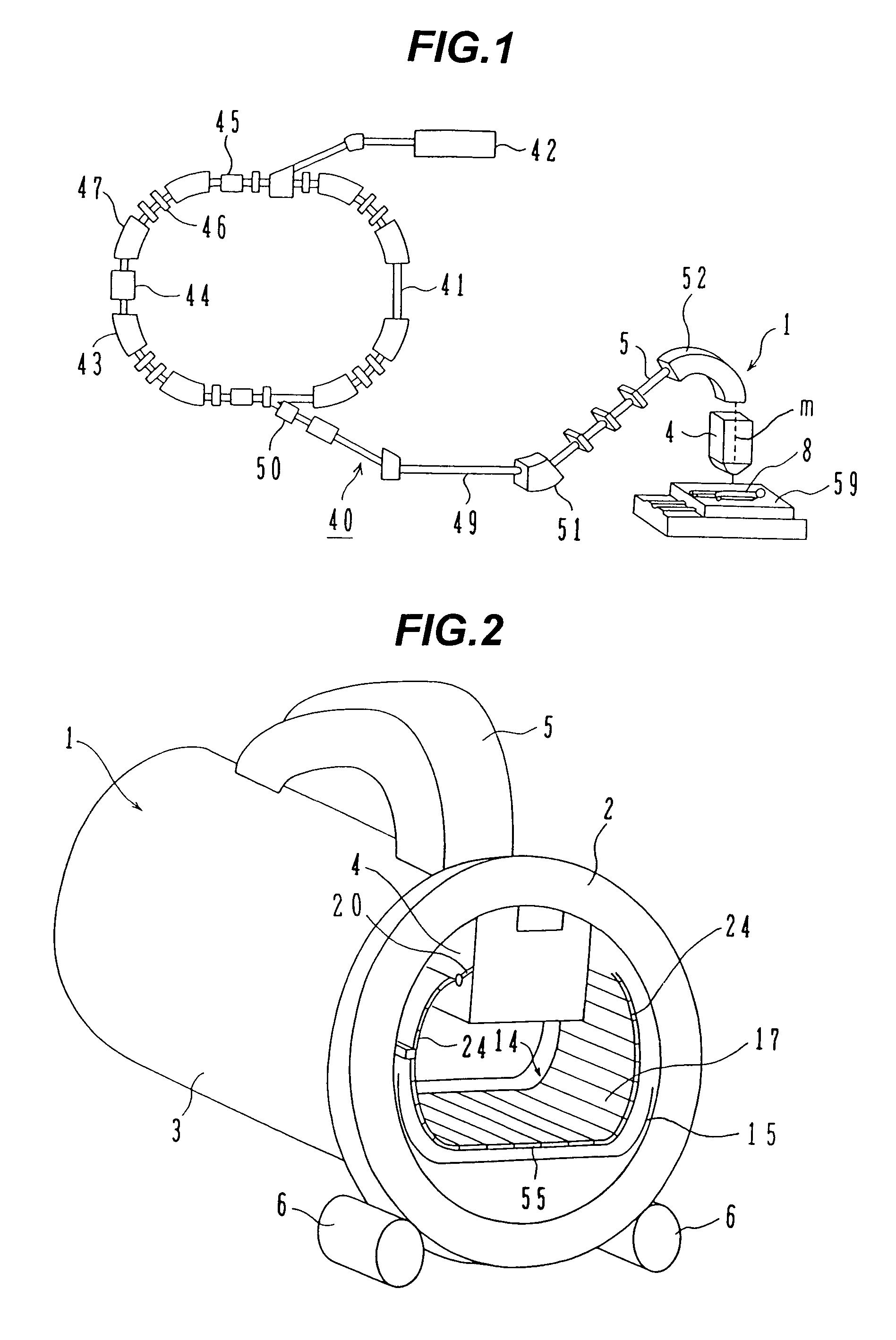
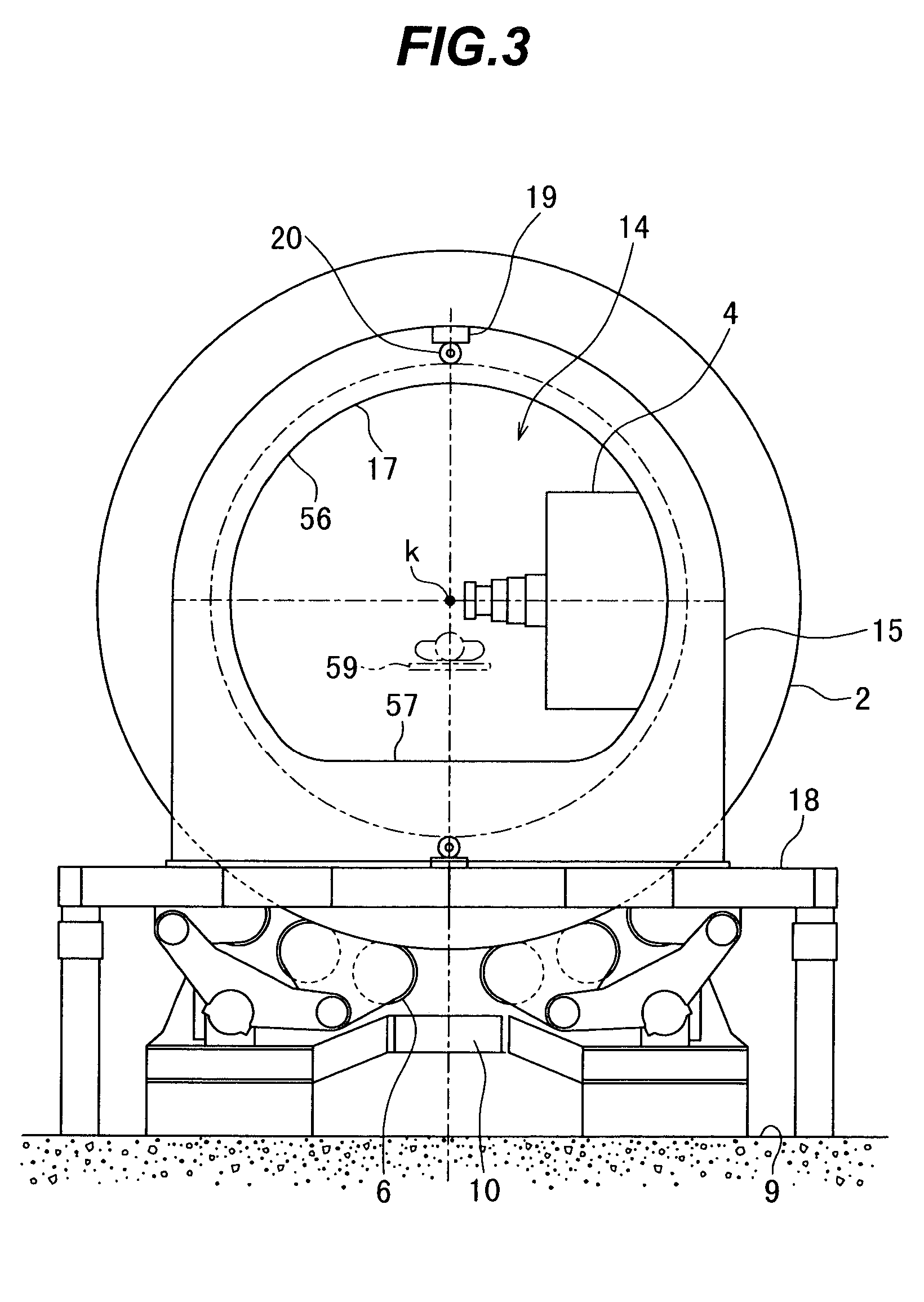
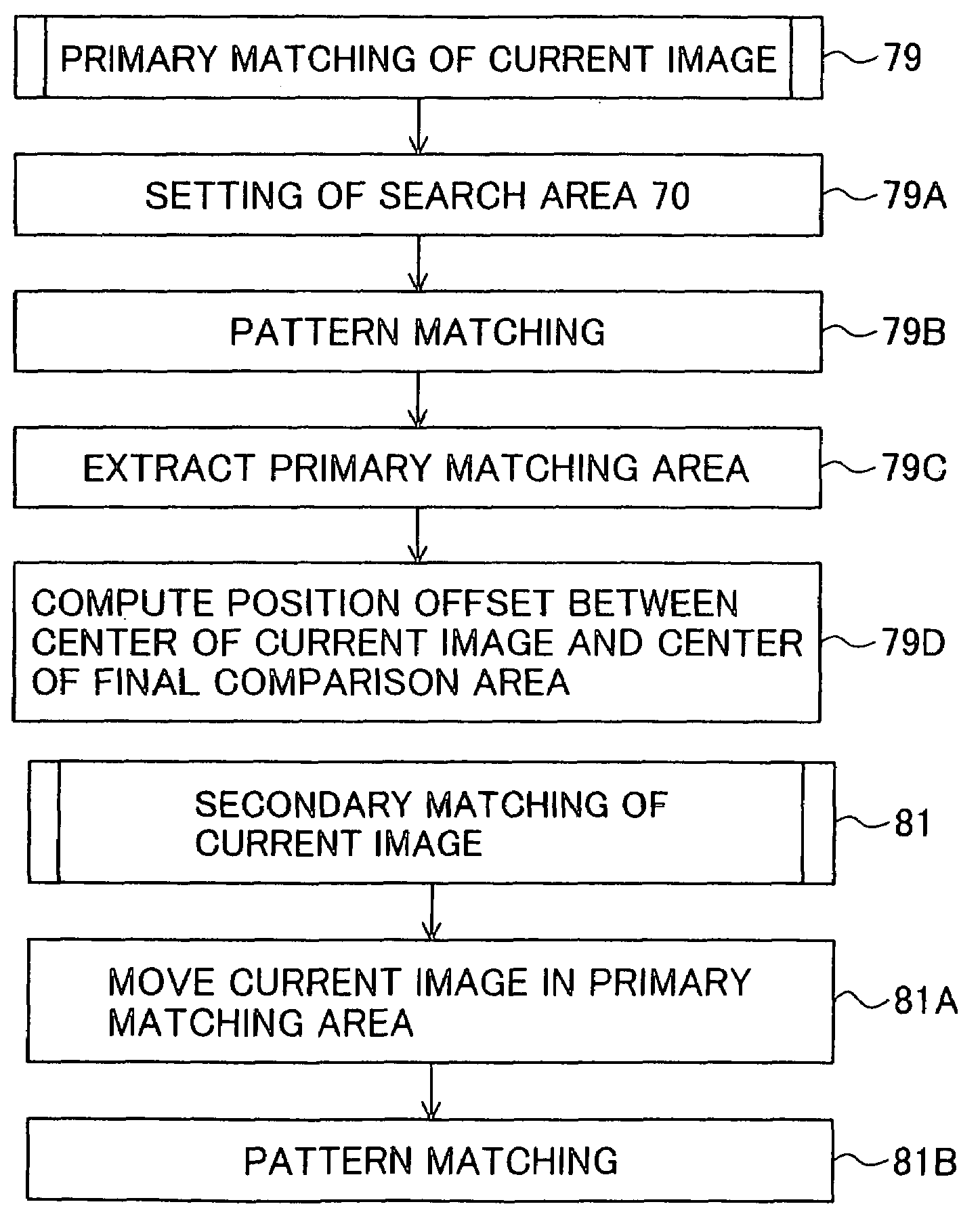
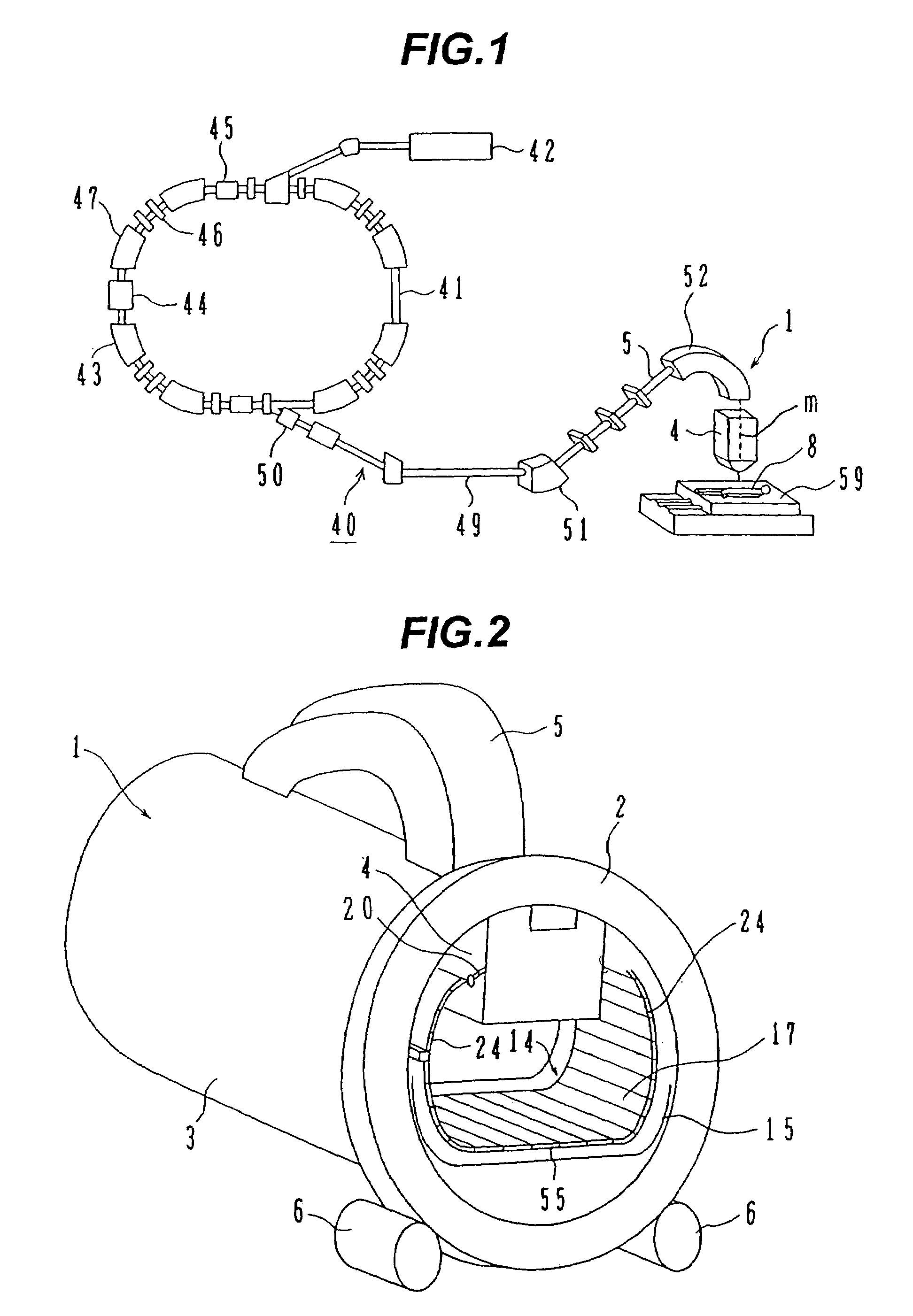
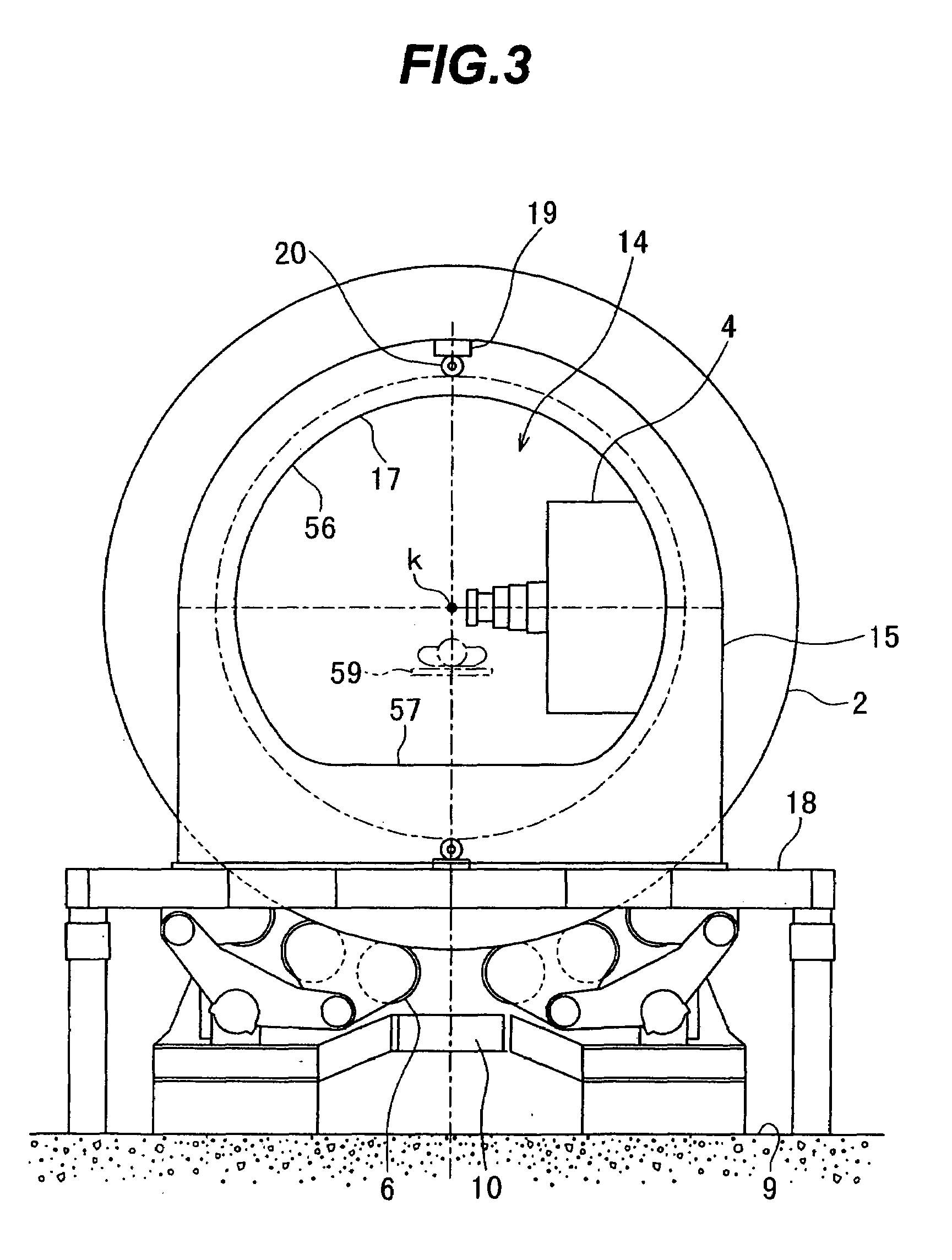
The invention is intended to always ensure a sufficient level of patient positioning accuracy regardless of the skills of individual operators. In a patient positioning device for positioning a patient couch 59 and irradiating an ion beam toward a tumor in the body of a patient 8 from a particle beam irradiation section 4, the patient positioning device comprises an X-ray emission device 26 for emitting an X-ray along a beam line m from the particle beam irradiation section 4, an X-ray image capturing device 29 for receiving the X-ray and processing an X-ray image, a display unit 39B for displaying a current image of the tumor in accordance with a processed image signal, a display unit 39A for displaying a reference X-ray image of the tumor which is prepared in advance, and a positioning data generator 37 for executing pattern matching between a comparison area A being a part of the reference X-ray image and including an isocenter and a comparison area B or a final comparison area B in the current image, thereby producing data used for positioning of the patient couch 59 during irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20050259064A1Avoid injuryImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayImaging quality
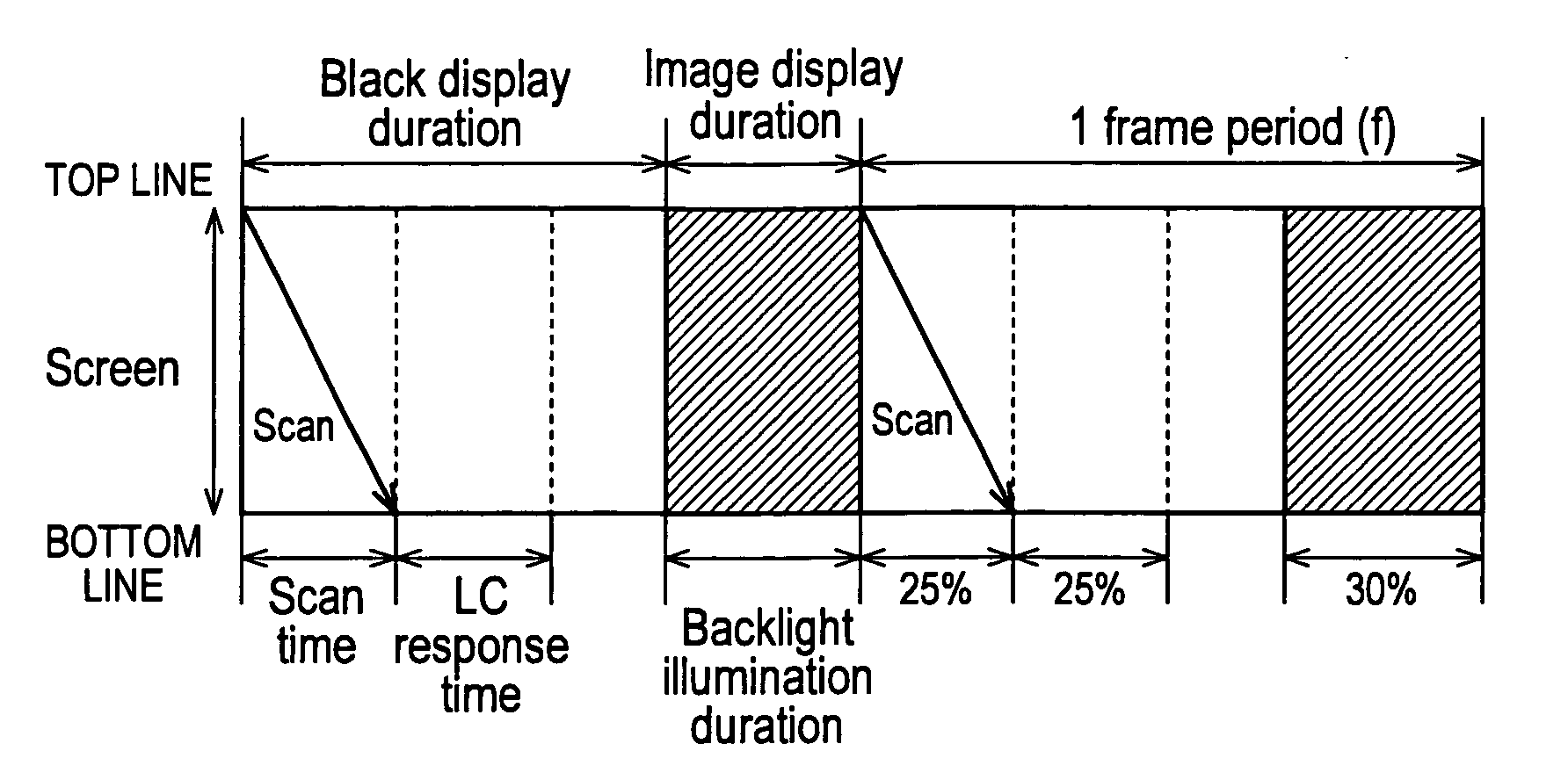
A liquid crystal display device in which a frame of the image signal to be displayed is written into a liquid crystal display panel while a backlight is activated intermittently within one frame period so as to prevent blur injury arising when displaying motion pictures includes: sections and for variably controlling the illumination duration of the backlight based on the detected type of the image content to be displayed. This configuration makes it possible to appropriately control the image quality degradation caused by blur injury, stroboscopic effect and flickering, hence realize total image quality improvement.
Owner:SHARP KK
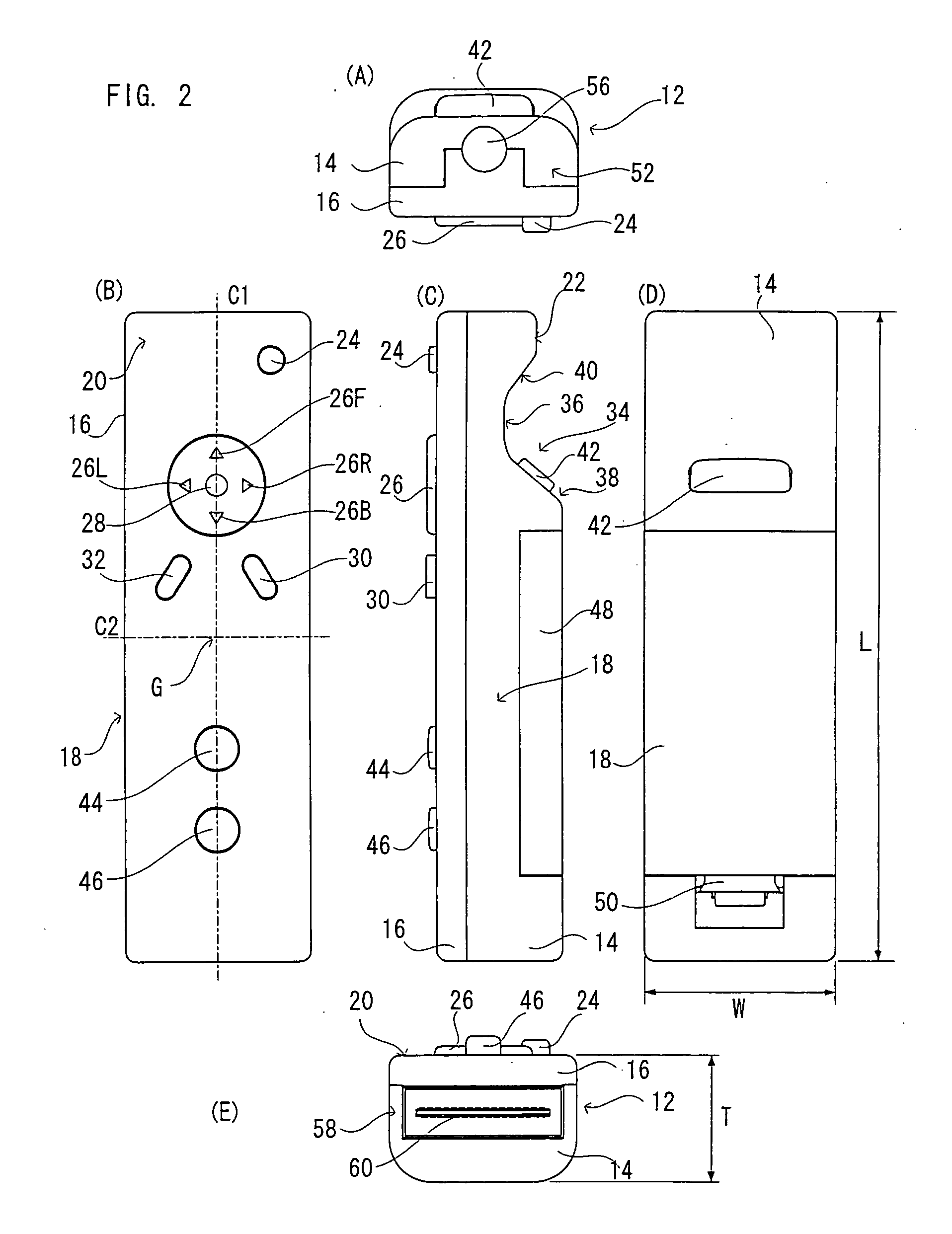
Game operating device
ActiveUS20070052177A1Stable changeIncrease flexibilityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsInfraredHand held
A game operating device (controller) includes a longitudinal housing, and a holding portion held by hand to be wrapped by its palm it is formed in the housing. A direction switch is provided on an upper surface at a position where it can be operated by thumb of the hand holding the holding portion, and a start switch and a select switch are provided backward thereof. An X button 46 and a Y button are further arranged in line on the upper surface of the housing. An imaging information arithmetic unit is provided at a front end of the housing in a longitudinal direction in such a manner that an imaging device thereof is exposed from a front-end surface. A concave portion is formed on a lower surface at a position corresponding to the direction switch. The concave portion includes a valley and two inclined surfaces. An A button capable of being operated by index finger of the hand holding the holding portion is provided on the backward inclined surface. By processing an image signal obtained by imaging an infrared ray from LED modules by the imaging device, it is possible to obtain an operation signal varying according to a position and / or attitude of the controller.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
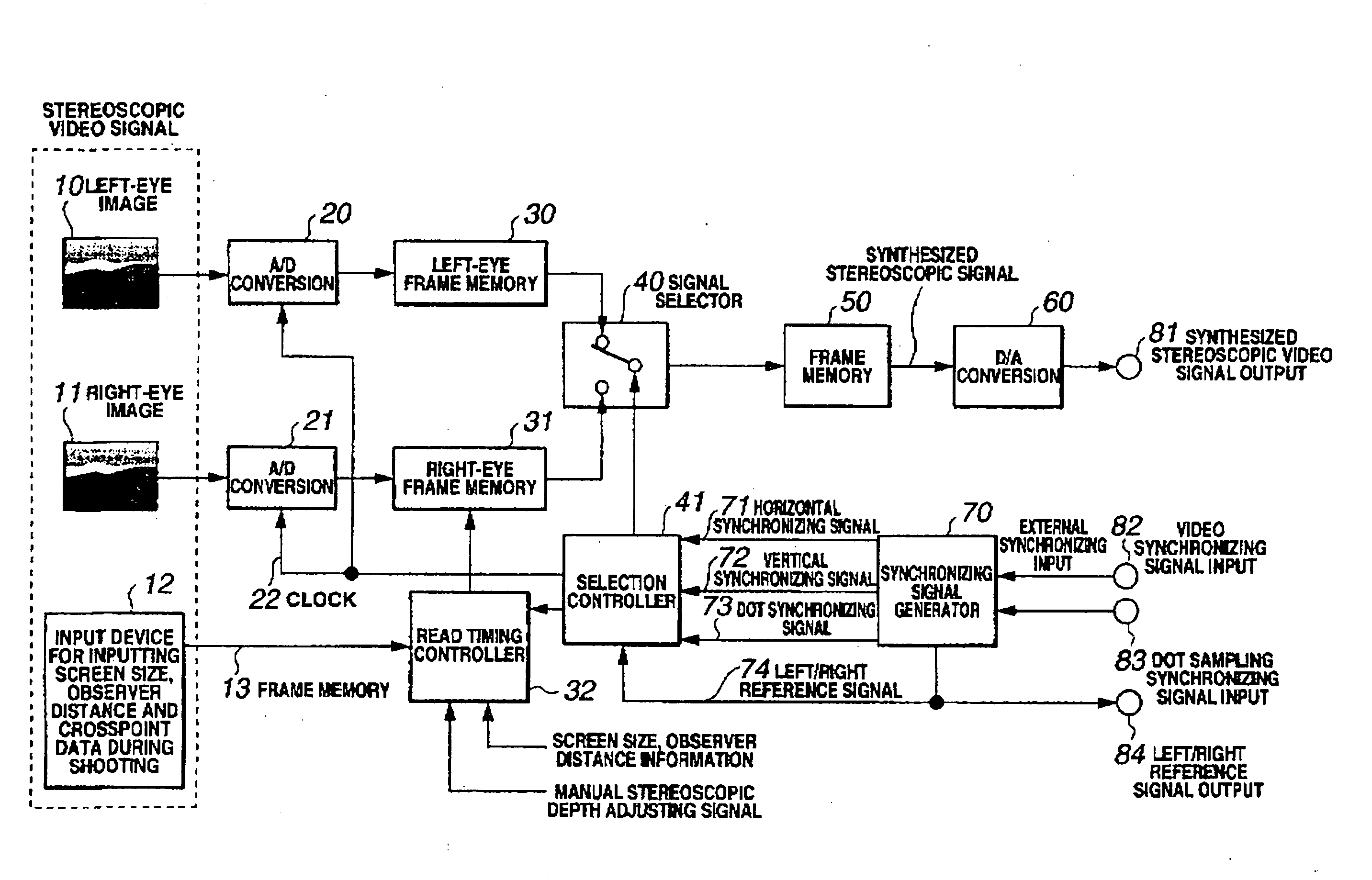
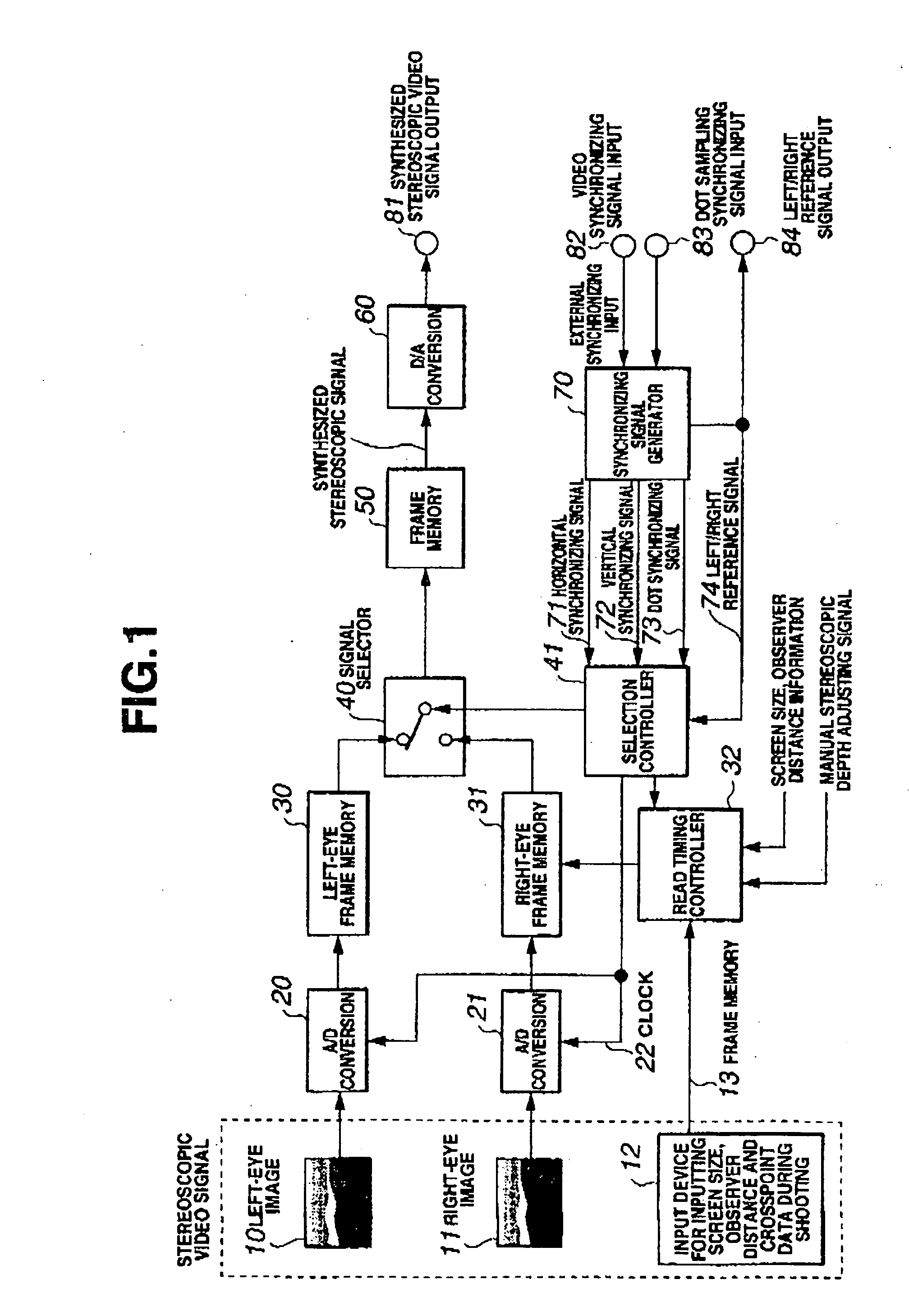
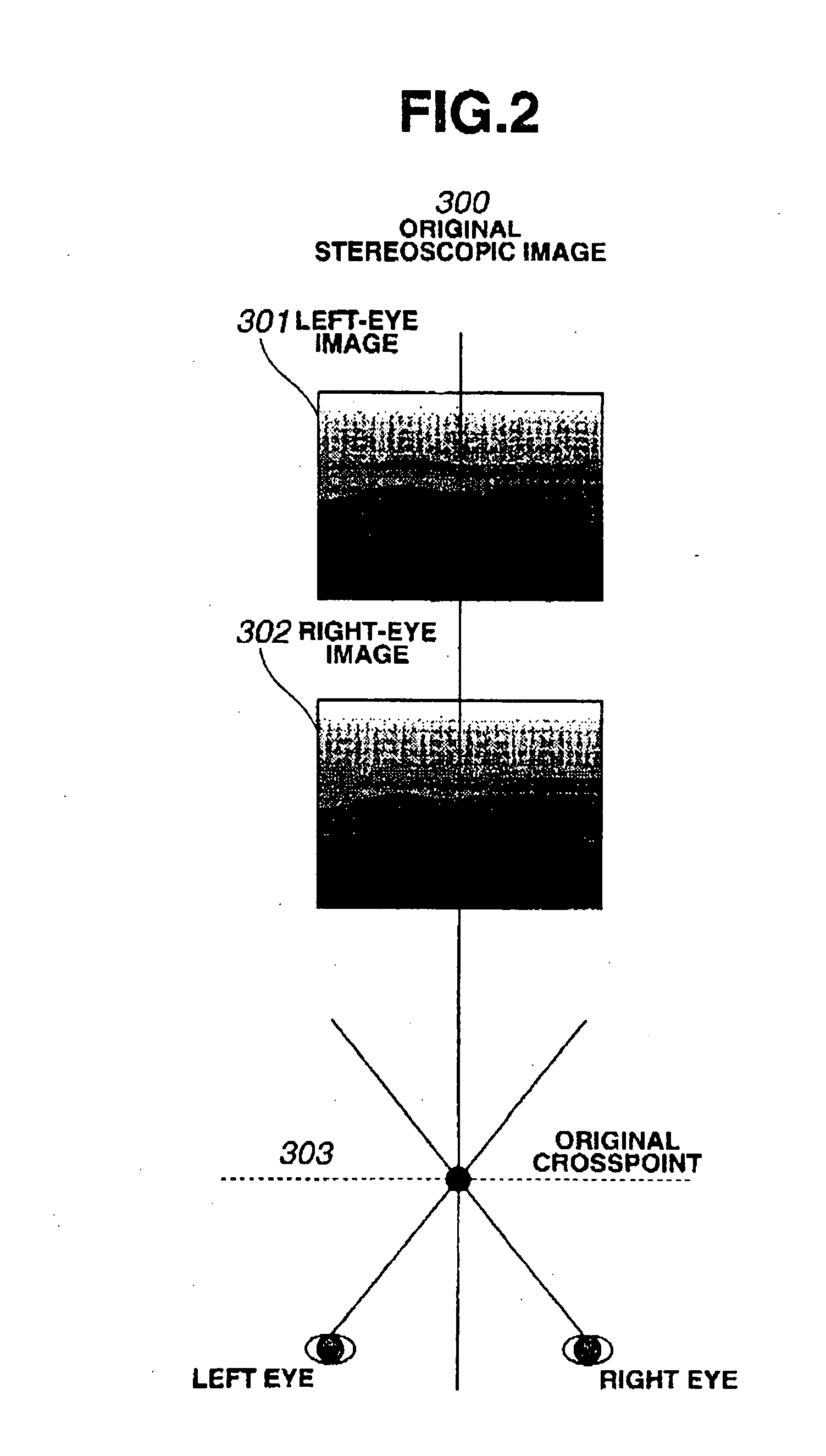
There dimensional image signal producing circuit and three-dimensional image display apparatus
A three-dimensional display is provided which can produce a stereoscopic image with a natural stereoscopic depth even on different screen sizes. A stereoscopic video signal generation circuit, which supplies a stereoscopic video signal to the three-dimensional display that forms a stereoscopic image by taking advantage of binocular disparity parallax, comprises: an information retrieving means for retrieving video information on the stereoscopic image and display information on the three-dimensional display; and an offset setting means for offsetting a left-eye image and a right-eye image relative to each other according to the video information and the display information to adjust the stereoscopic depth of the image displayed.
Owner:TOMITA SEIJIRO
Patient positioning device and patient positioning method
InactiveUS7212609B2Improve accuracyAvoid accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPattern matchingX-ray
The invention is intended to always ensure a sufficient level of patient positioning accuracy regardless of the skills of individual operators. In a patient positioning device for positioning a patient couch 59 and irradiating an ion beam toward a tumor in the body of a patient 8 from a particle beam irradiation section 4, the patient positioning device comprises an X-ray emission device 26 for emitting an X-ray along a beam line m from the particle beam irradiation section 4, an X-ray image capturing device 29 for receiving the X-ray and processing an X-ray image, a display unit 39B for displaying a current image of the tumor in accordance with a processed image signal, a display unit 39A for displaying a reference X-ray image of the tumor which is prepared in advance, and a positioning data generator 37 for executing pattern matching between a comparison area A being a part of the reference X-ray image and including an isocenter and a comparison area B or a final comparison area B in the current image, thereby producing data used for positioning of the patient couch 59 during irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Display apparatus and display control method
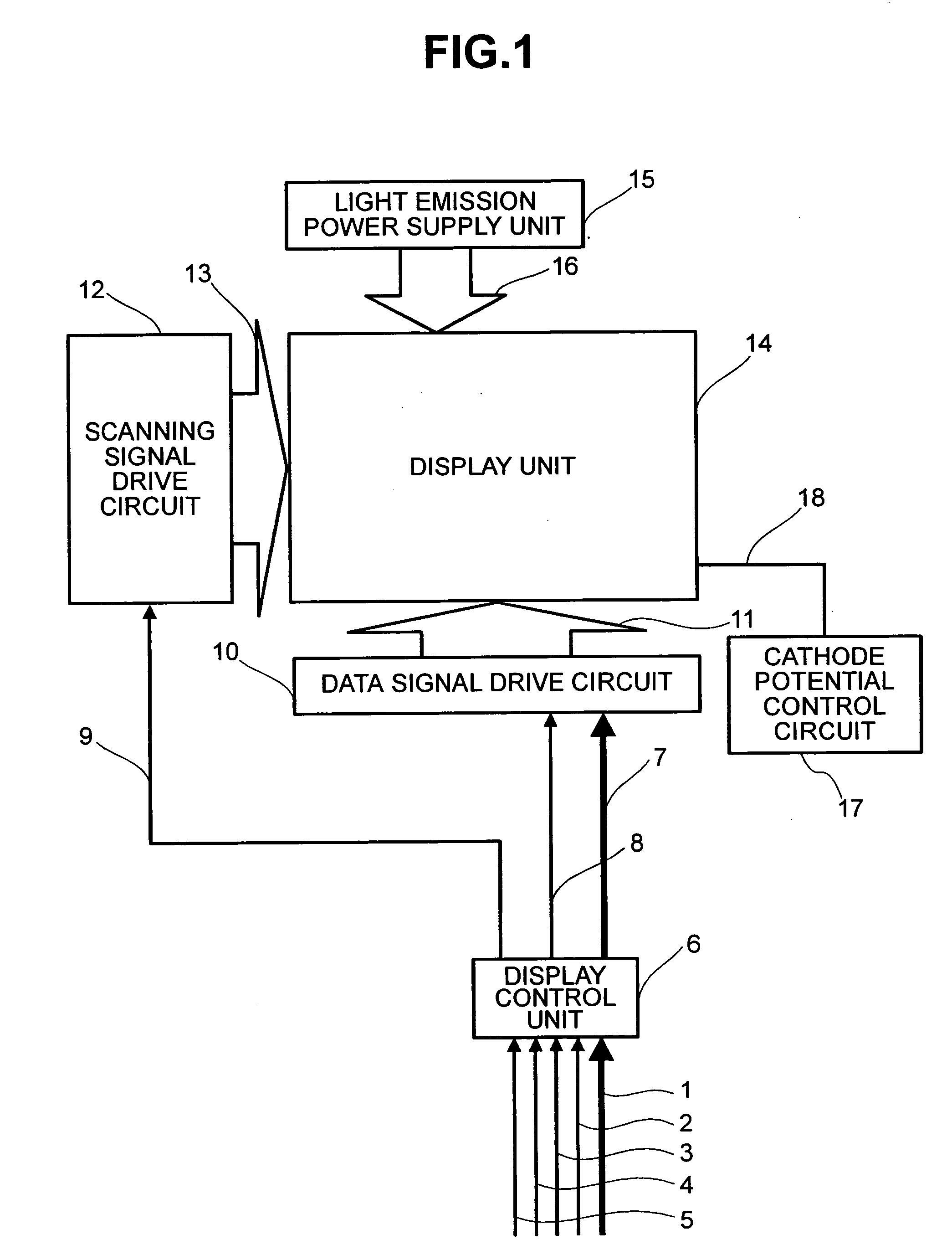
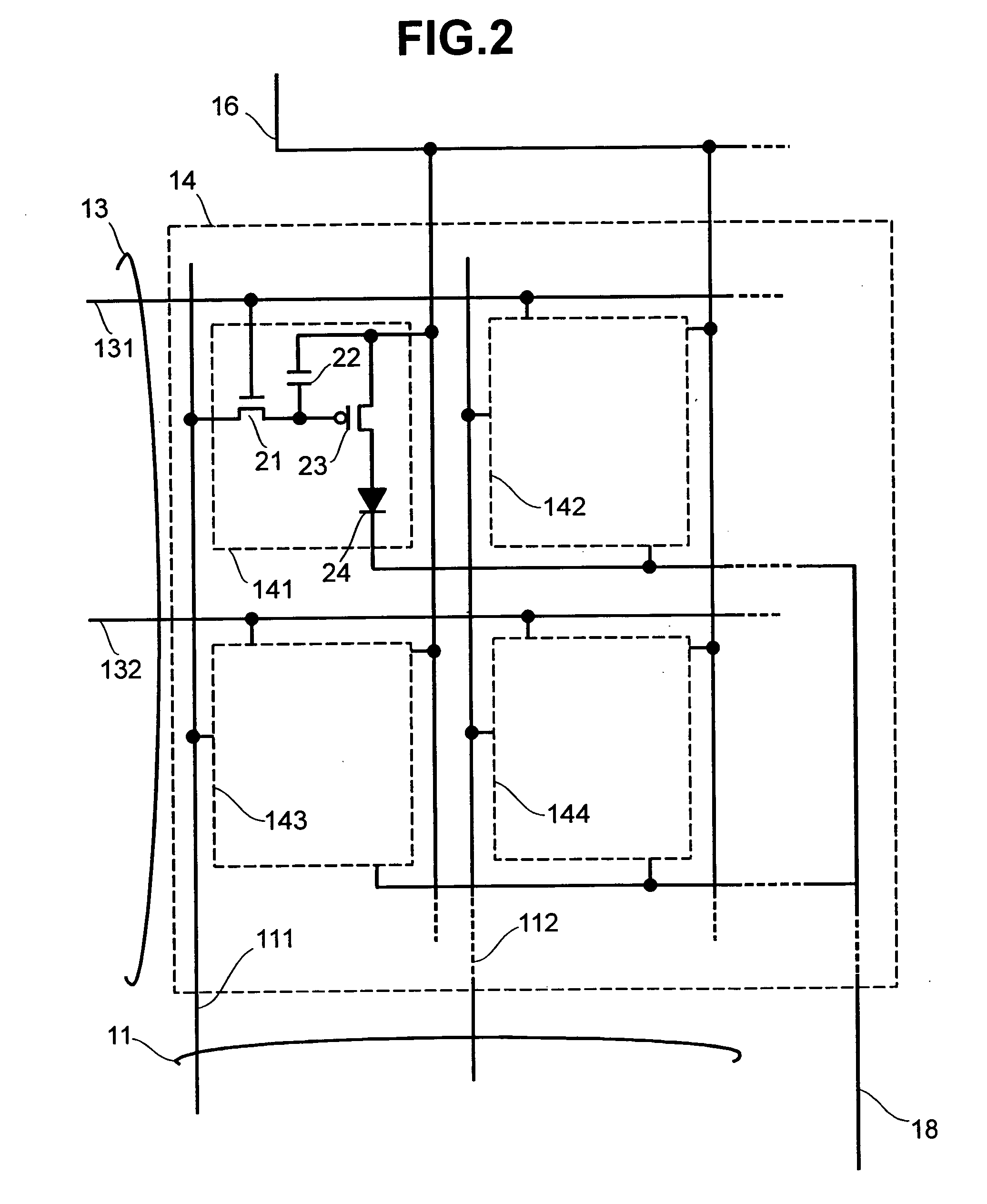
ActiveUS20050068270A1Peak luminance can be increasedDisplay luminance can be enhancedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriven elementLight emission
The present invention comprises: a display unit having a plurality of pixels arranged therein, each pixel including an organic EL element 24, a switching TFT, and a drive TFT; a data signal drive circuit for receiving image data for each frame period and outputting an image signal based on the image data; a scanning signal drive circuit for outputting a scanning signal for controlling a timing at which the switching element of each of the plurality of pixels receives the image signal; and a current source (a light emission power supply unit and a cathode potential control circuit together) for outputting a current supplied to the light emitting unit of each of the plurality of pixels through its drive element; wherein the current source modulates the value of the output current within each frame period.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Image sensing apparatus and its control method, control program, and storage medium
InactiveUS7262799B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionImage signal
This invention has as its object to provide an image sensing apparatus which can satisfactorily correct misregistration among images, and can composite the images. To achieve this object, an image sensing apparatus includes: a plurality of apertures that receives external light from different positions; a plurality of image sensing units that outputs image signals obtained by independently receiving light that comes from an identical position of an object and is received via the plurality of apertures, and independently extracting predetermined color components for each received light; and a signal processing device that forms a signal that outputs an object image by mixing the image signals output from the plurality of image sensing units. When it is determined that a predetermined position deviation occurs between the image signals upon forming the signal that outputs the object image, the signal processing device corrects the predetermined position deviation by a signal process, and forms the signal that outputs the object image.
Owner:CANON KK
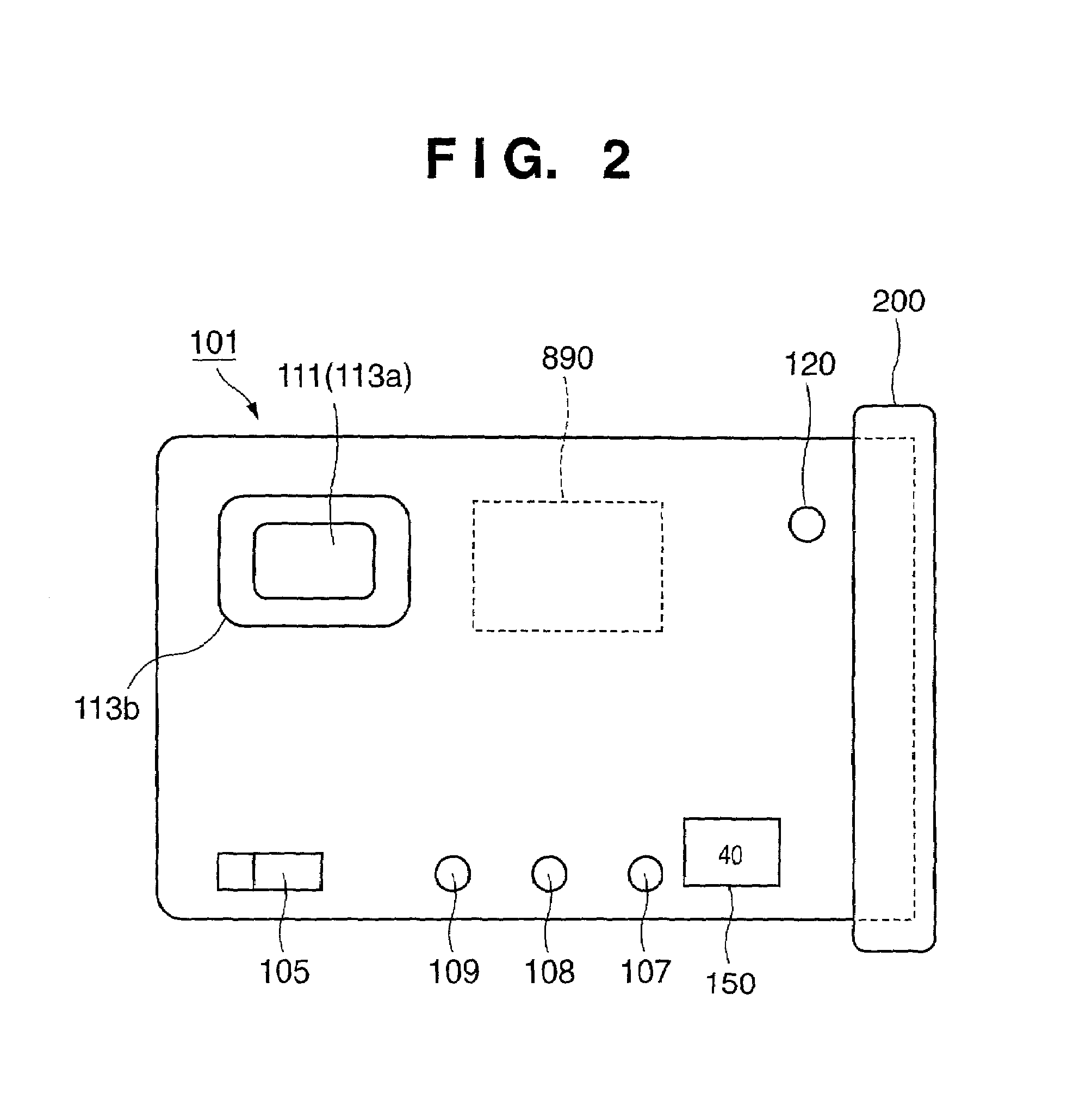
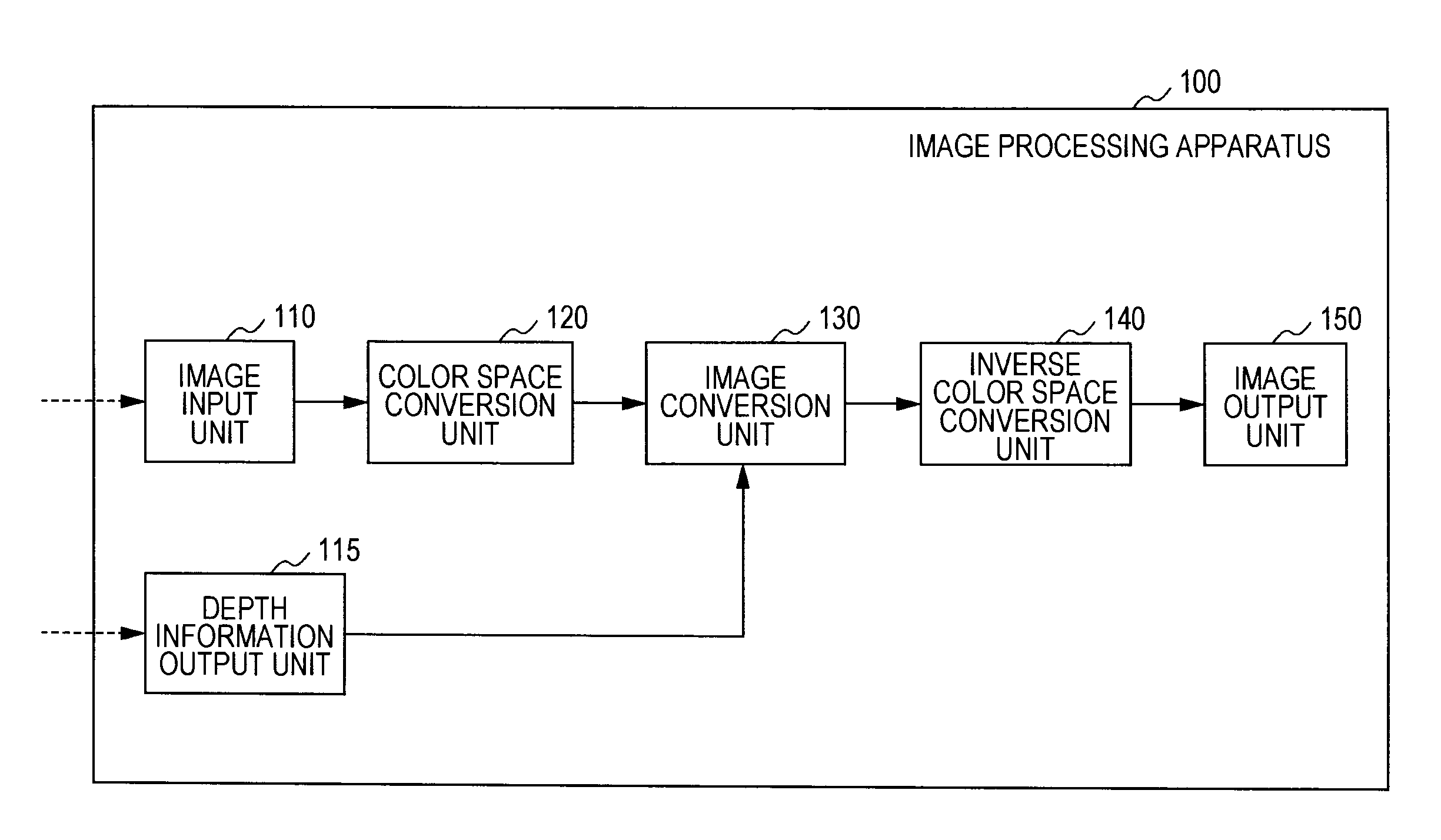
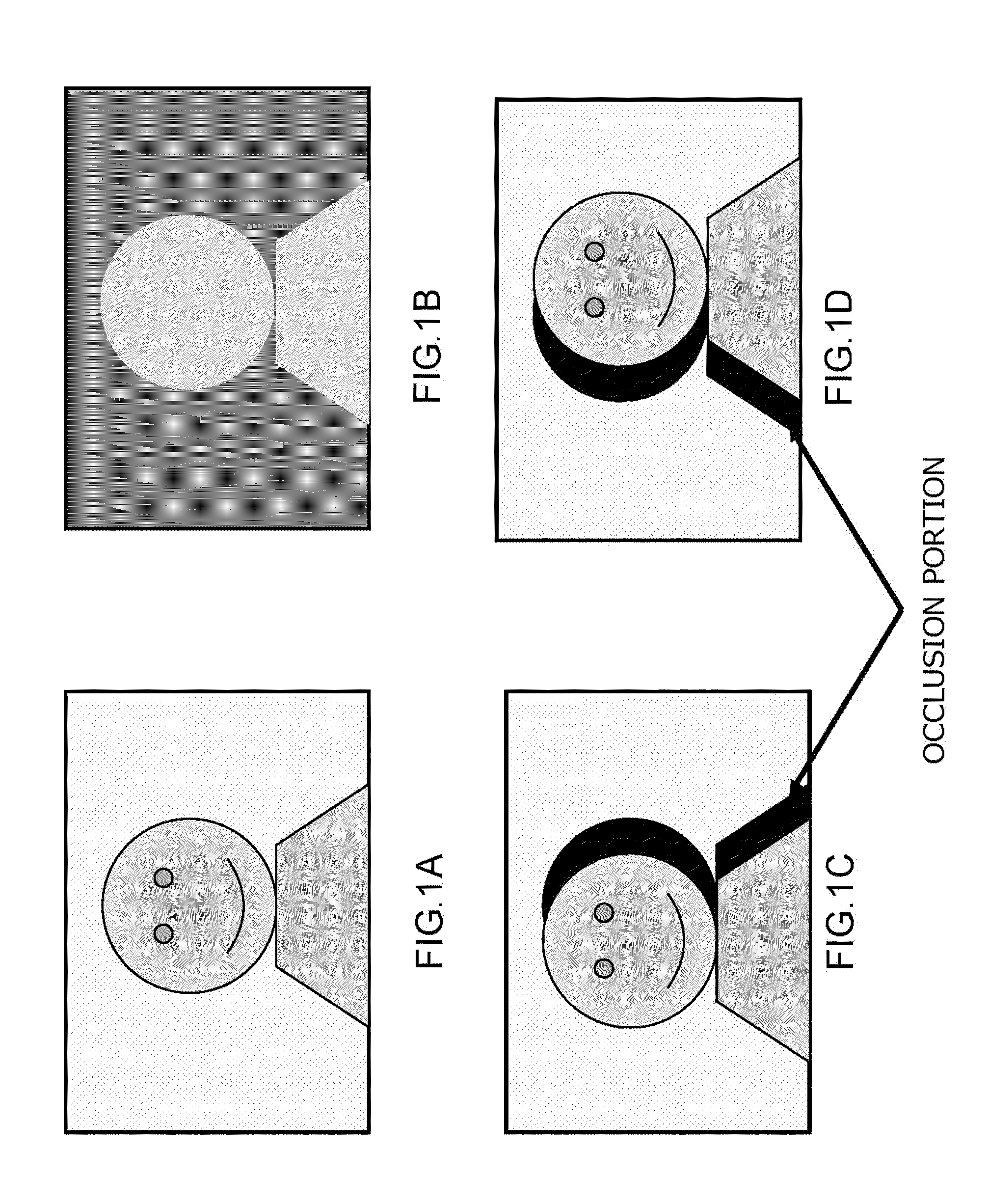
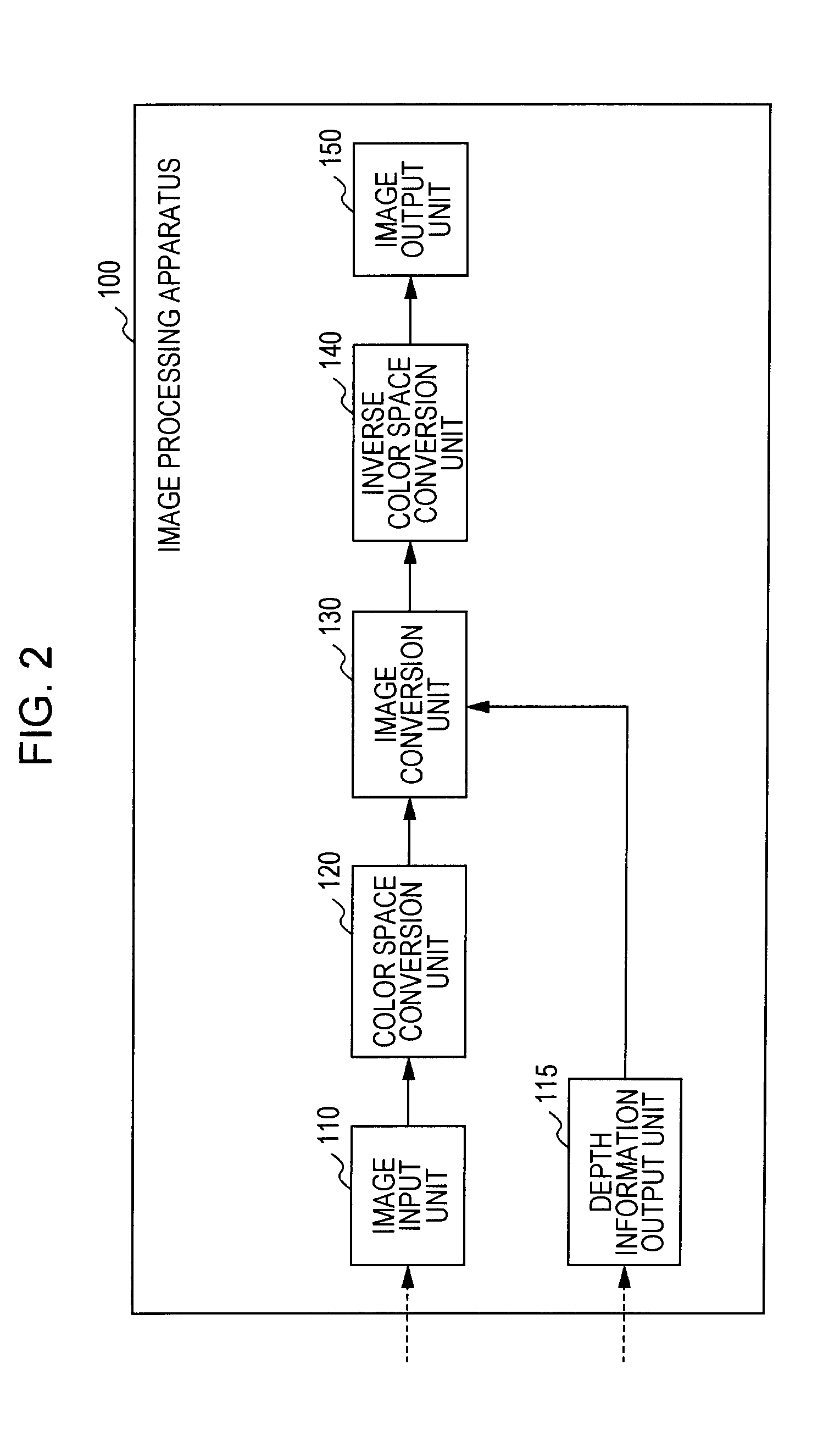
Image processing apparatus, image processing method and program
An image processing apparatus includes an image input unit that inputs a two-dimensional image signal, a depth information output unit that inputs or generates depth information of image areas constituting the two-dimensional image signal, an image conversion unit that receives the image signal and the depth information from the image input unit and the depth information output unit, and generates and outputs a left eye image and a right eye image for realizing binocular stereoscopic vision, and an image output unit that outputs the left and right eye images. The image conversion unit extracts a spatial feature value of the input image signal, and performs an image conversion process including an emphasis process applying the feature value and the depth information with respect to the input image signal, thereby generating at least one of the left eye image and the right eye image.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Information processing apparatus, information processing system, and dialogist displaying method
InactiveUS20050175257A1Improve the display effectImage analysisGeometric image transformationInformation processingImaging processing
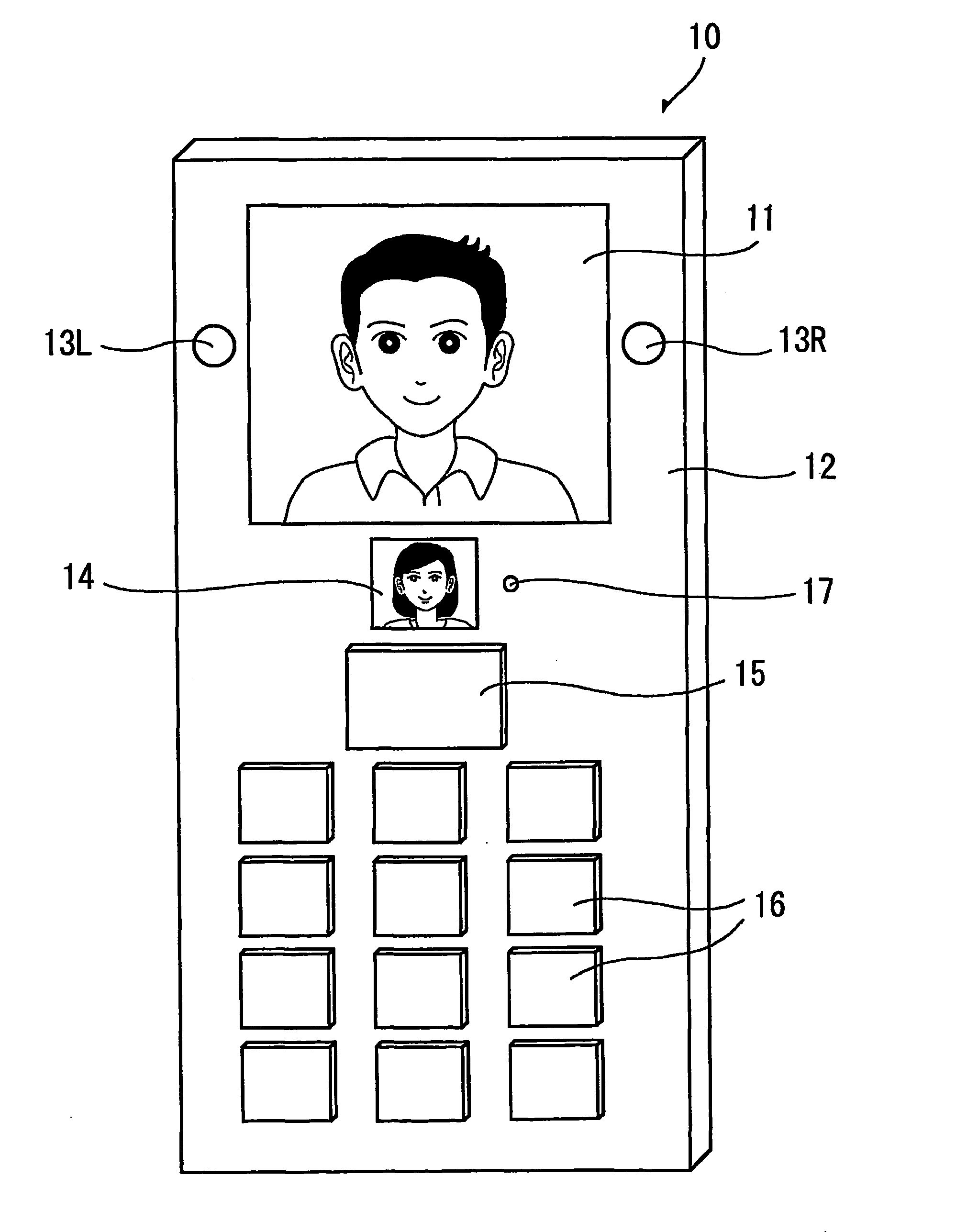
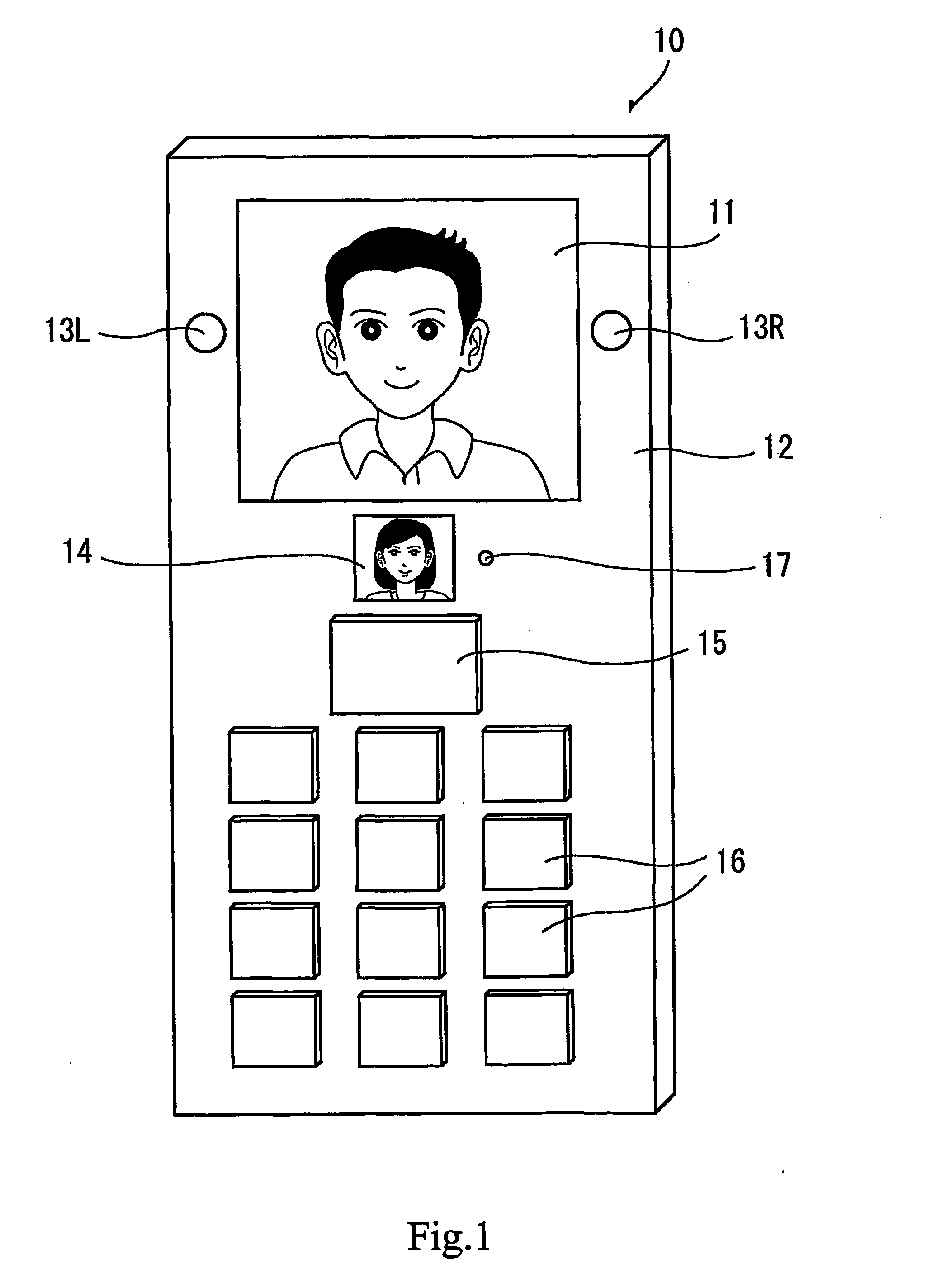
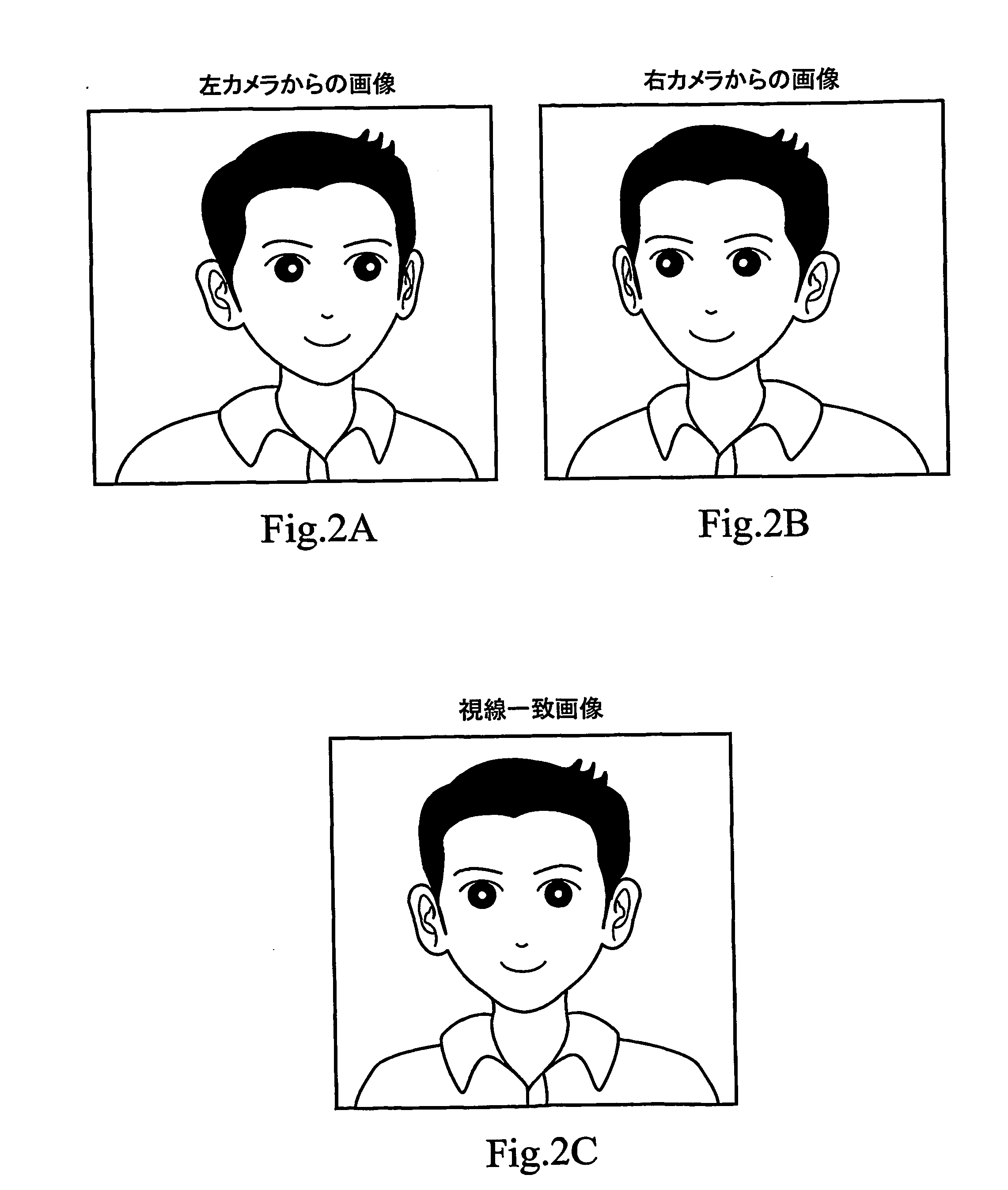
An image processing apparatus comprises an image display unit for displaying a desired image in accordance with an image signal, and image pickup units disposed respectively on the left and right sides of the image display unit. An image picked up from the left side and an image picked up from the right side are displayed together to be synthesized as the desired image in an image display unit of, e.g., a terminal of a conversation partner. Display in eye-to-eye matching with the conversation partner is thereby realized. An image processing apparatus, such as a portable communication terminal, capable of realizing conversation in a natural eye-to-eye matching state with the conversation partner can be provided.
Owner:SONY CORP
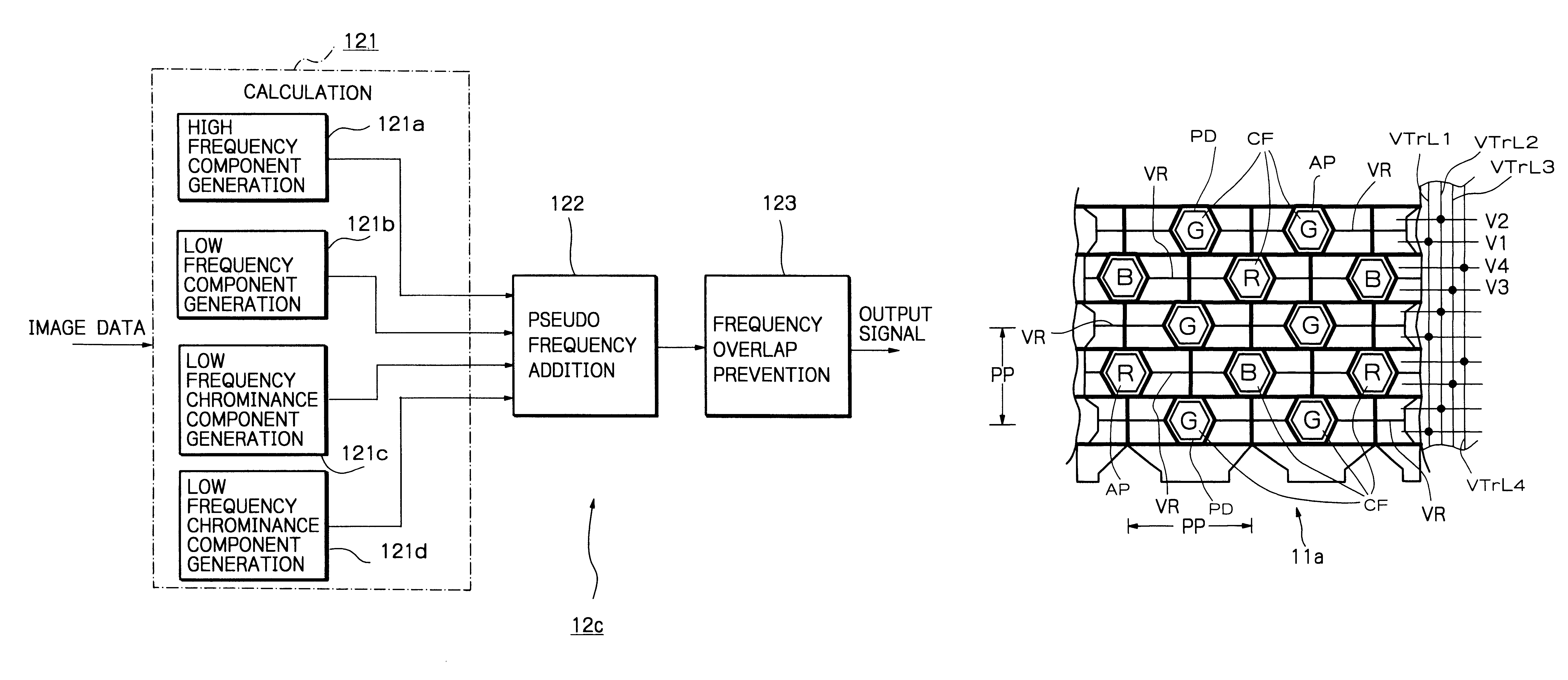
Solid-state imaging apparatus and signal processing method for transforming image signals output from a honeycomb arrangement to high quality video signals
InactiveUS6882364B1High outputWithout delayTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLow-pass filterFalse color
A solid-state imaging apparatus includes an image pick-up section in which photosensitive devices are arranged in, e.g., a honeycomb G square lattice, RB full-checker pattern due to shifted pixels. Regions void of the photosensitive devices are assumed to be virtual photosensitive devices. A signal processing section generates data for the virtual photosensitive devices by using the data of surrounding photosensitive devices while attaching importance to accurate color reproduction and horizontal and / or vertical resolution. As a result, the number of pixel data are increased in a square lattice arrangement. Therefore, high quality image signals are readily achievable with a smaller number of photosensitive devices than conventional with a conventional apparatus. Interpolation can be executed with the high quality signals to the limit of resolution with an adequate circuit scale. The honeycomb arrangement guarantees the required size of the individual pixel and thereby the sensitivity of the entire apparatus while increasing yield on a production line. False colors particular to a single photosensitive portion can be reduced by, e.g., uniform interpolation. Particularly, when a digital camera is constructed by using an imaging apparatus including optics operable with a silver halide sensitive type of film, false colors can be reduced without resorting to an optical low pass filter.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com