Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10779 results about "Time control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
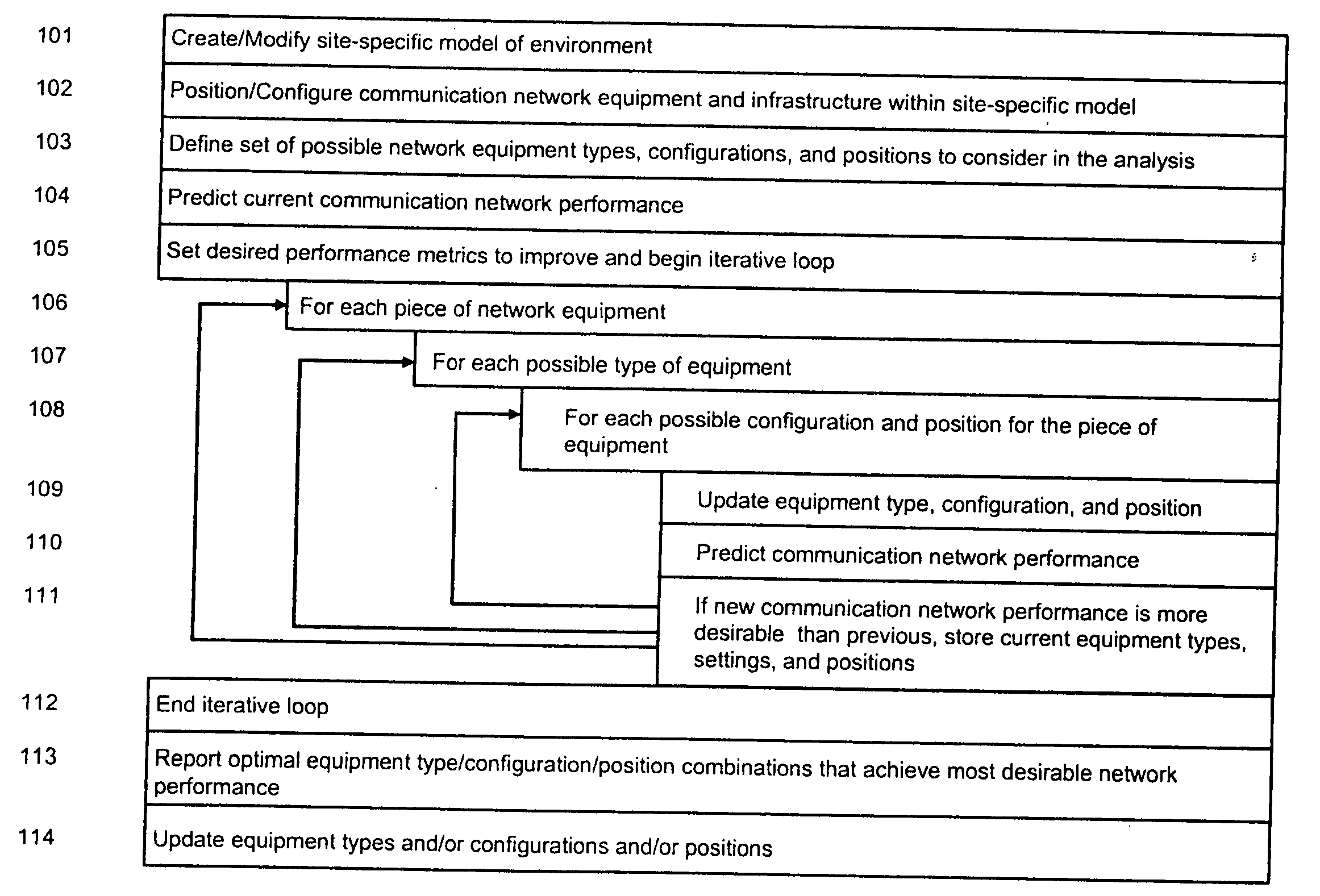
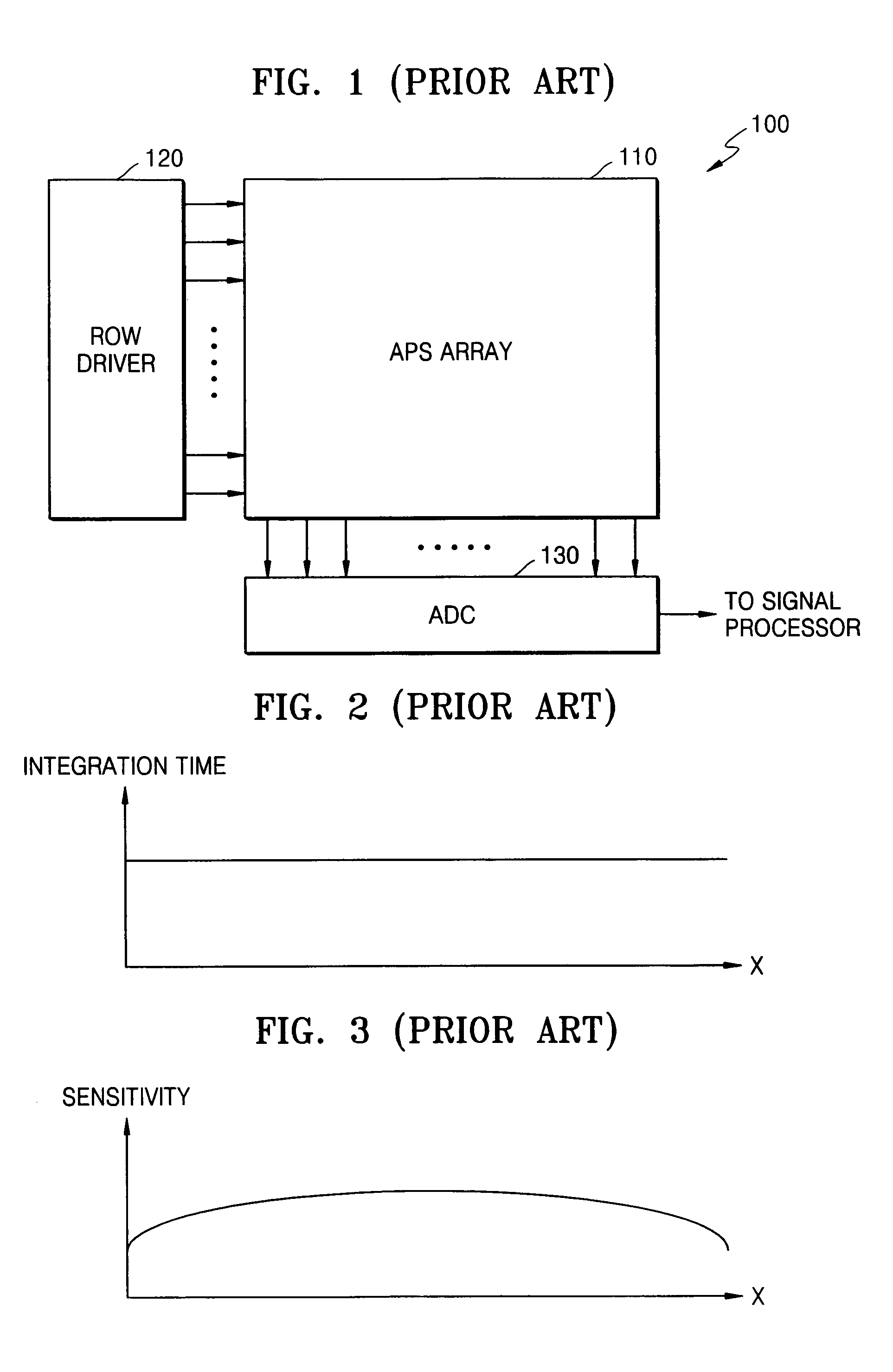
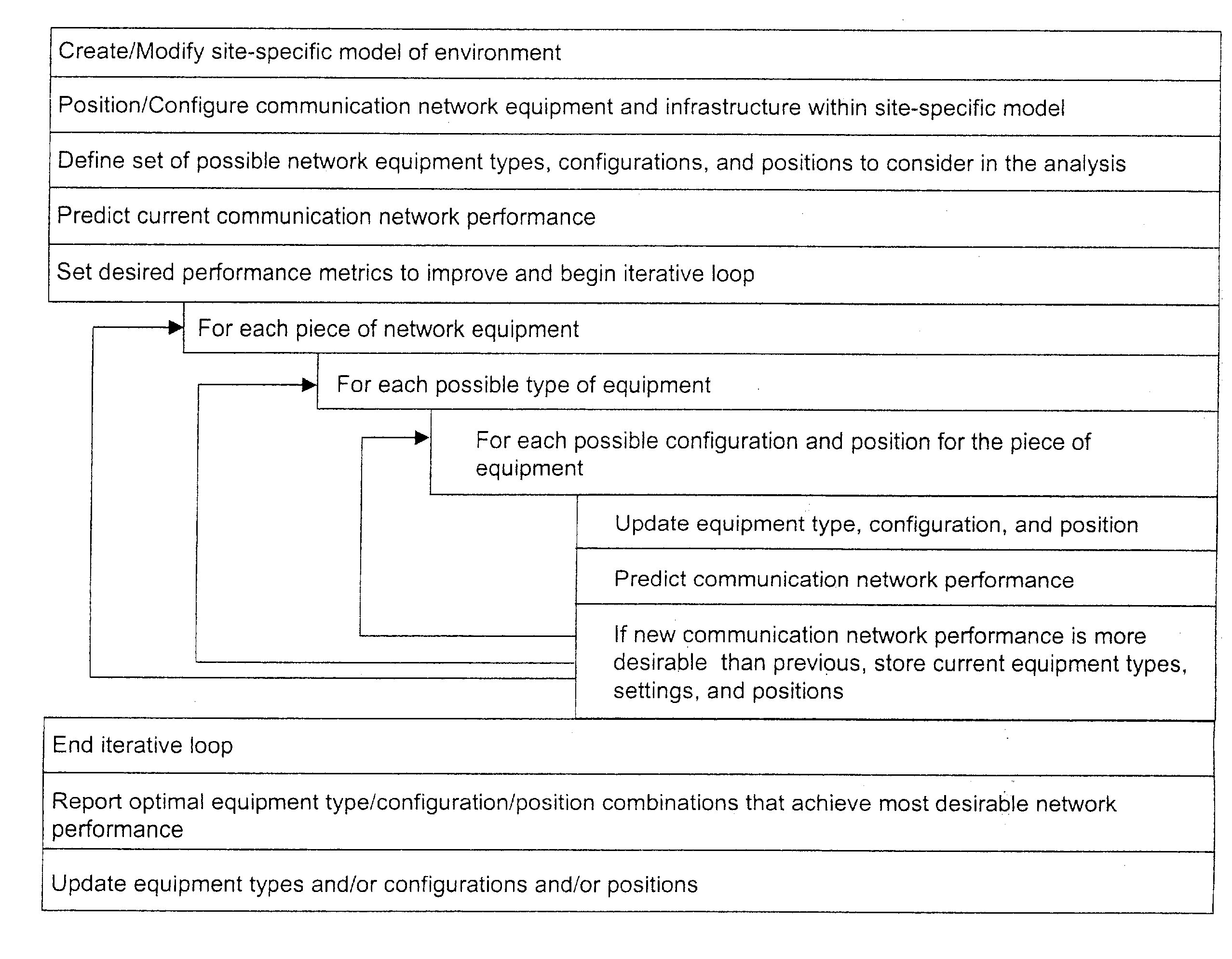
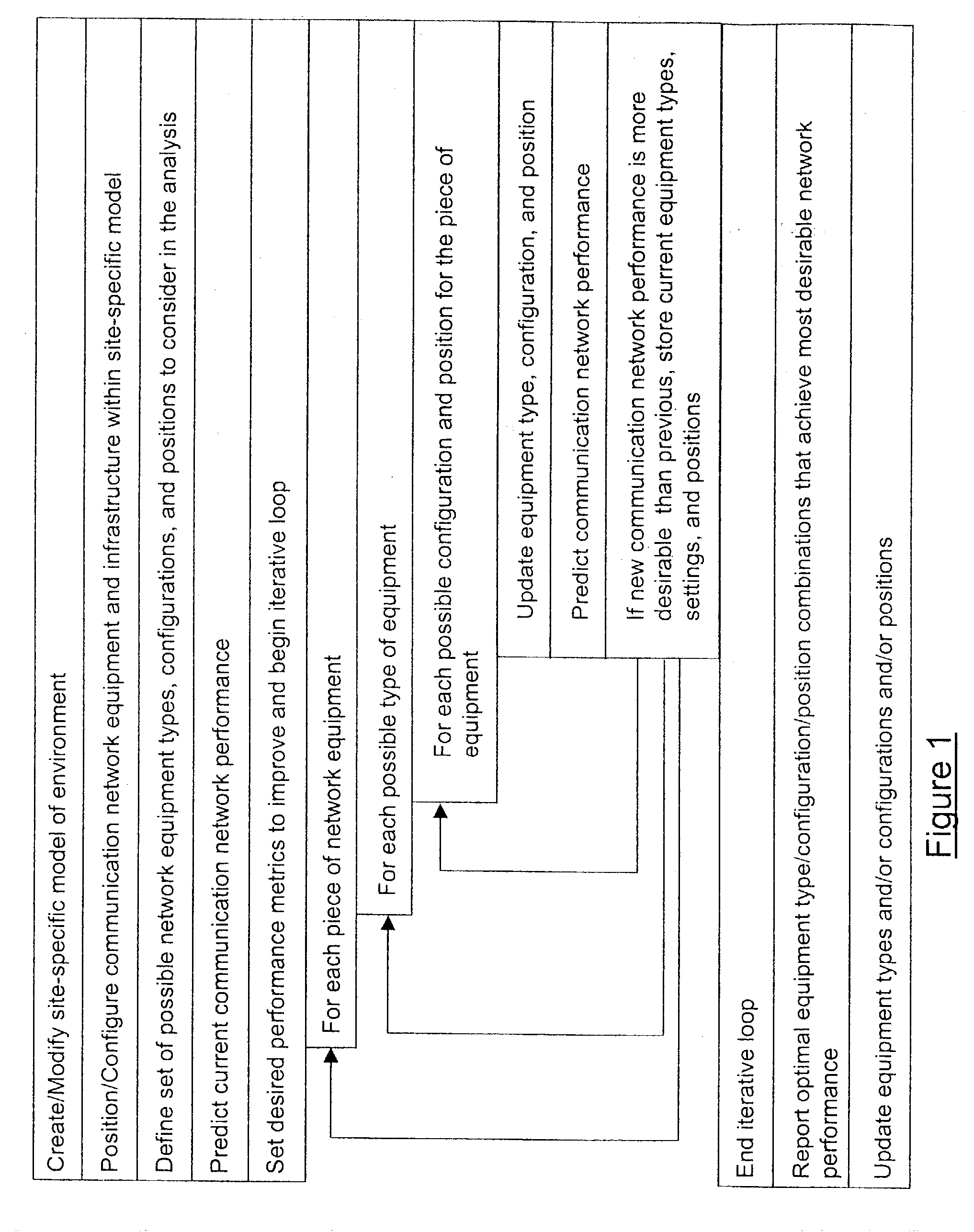
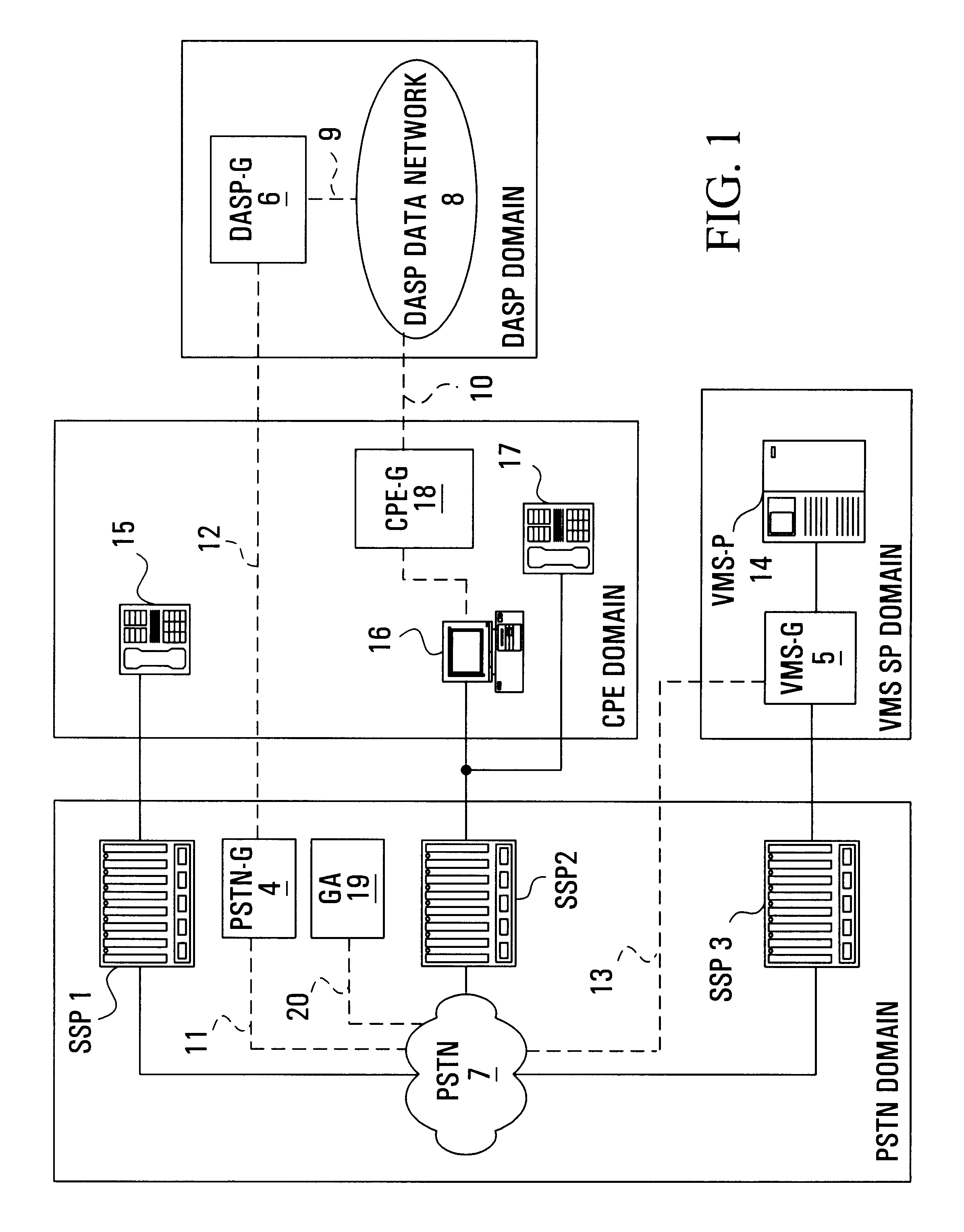
System and method for automated placement or configuration of equipment for obtaining desired network performance objectives and for security, RF tags, and bandwidth provisioning
ActiveUS20040236547A1Significant valueEasy to explainGeometric CADData taking preventionHard disc driveThe Internet
A method is presented for determining optimal or preferred configuration settings for wireless or wired network equipment in order to obtain a desirable level of network performance. A site-specific network model is used with adaptive processing to perform efficient design and on-going management of network performance. The invention iteratively determines overall network performance and cost, and further iterates equipment settings, locations and orientations. Real time control is between a site-specific Computer Aided Design (CAD) software application and the physical components of the network allows the invention to display, store, and iteratively adapt any network to constantly varying traffic and interference conditions. Alarms provide rapid adaptation of network parameters, and alerts and preprogrammed network shutdown actions may be taken autonomously. A wireless post-it note device and network allows massive data such as book contents or hard drive memory to be accessed within a room by a wide bandwidth reader device, and this can further be interconnected to the internet or Ethernet backbone in order to provide worldwide access and remote retrieval to wireless post-it devices.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
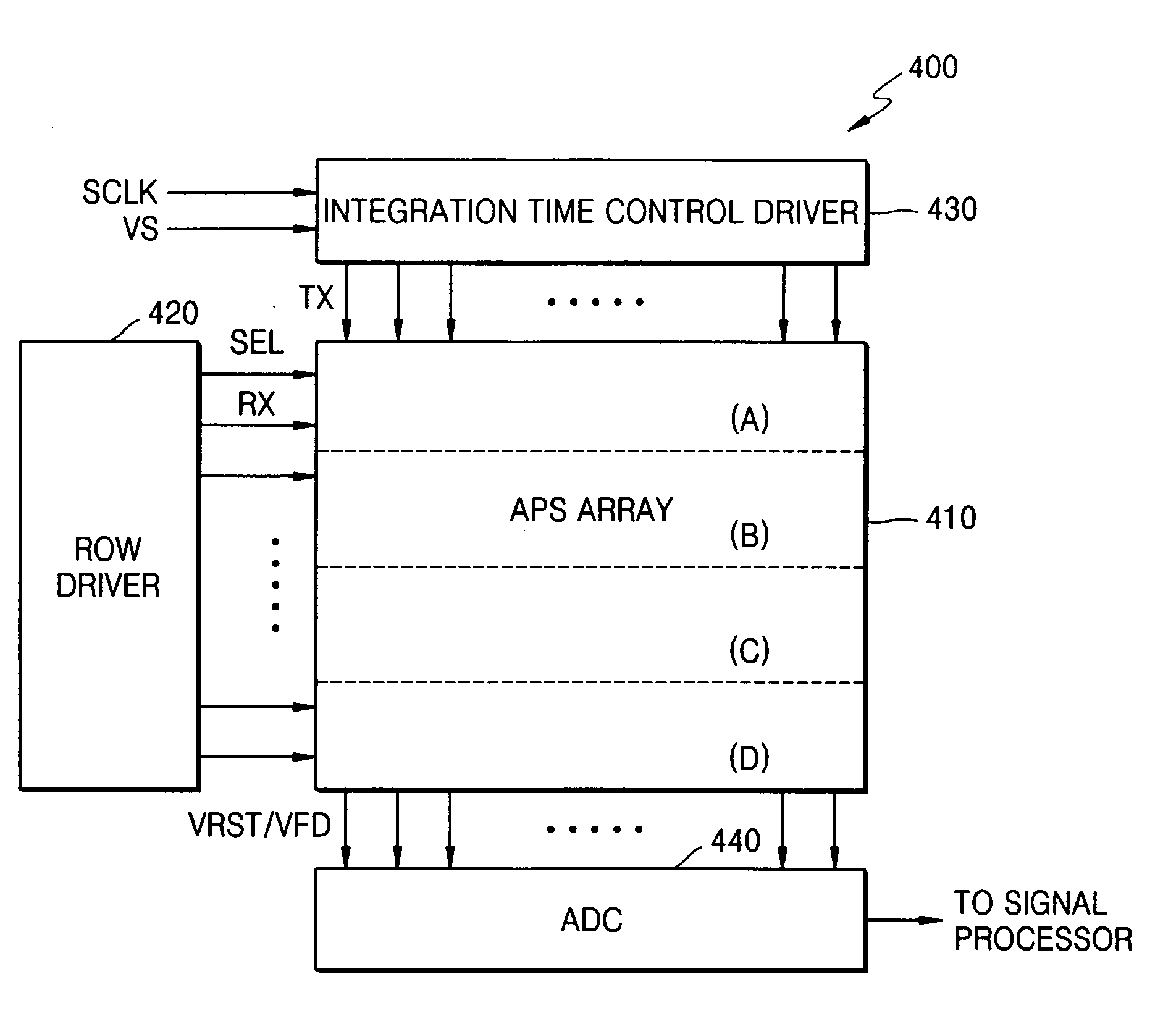
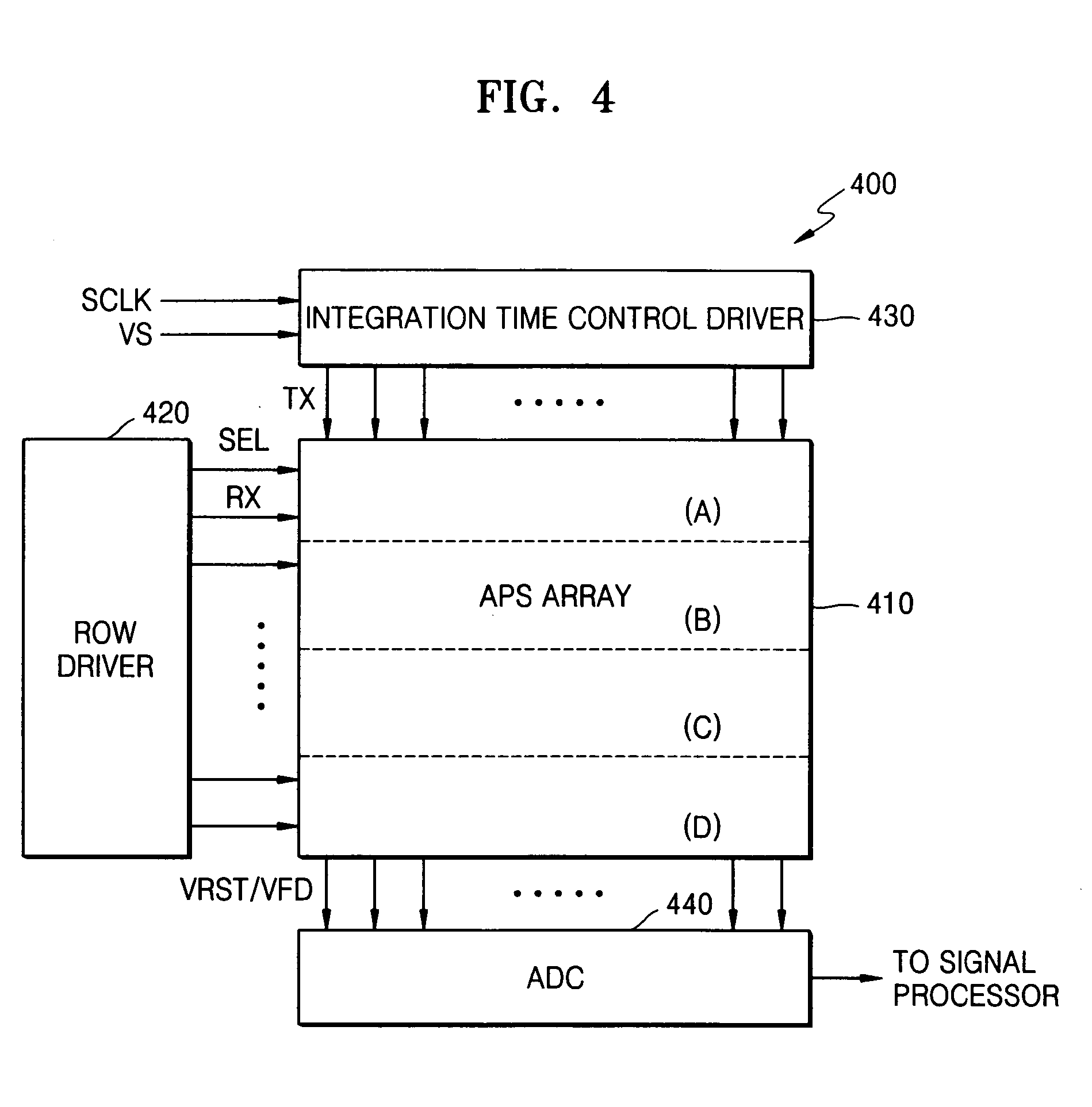
Solid-state image-sensing device that compensates for brightness at edges of a display area and a driving method thereof
ActiveUS7193199B2Lower ratioImprove noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorControl signal
A solid-state image-sensing device that compensates for brightness at edges of a screen and a method of driving the device are provided. The solid-state image-sensing device comprises: an active pixel sensor (APS) array including pixels disposed in a two-dimensional matrix, each pixel for outputting a photoelectrically converted image signal generated by a photodiode in response to one of a plurality of transmission control signals transmitted to a selected row of the APS array, and for generating and outputting a reset signal in response to a reset control signal; a row driver for selecting a row of the APS array by generating row selection signals and for generating the reset control signal; an integration time control driver for generating the transmission control signals for setting non-uniform integration times of the photodiodes in each pixel; and an analog-digital converter for converting an analog signal corresponding to a difference between the image signal and the reset signal into a digital signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for automated placement or configuration of equipment for obtaining desired network performance objectives
ActiveUS20040143428A1Significant valueEasy to explainGeometric CADProgram controlHard disc driveThe Internet
A method is presented for determining optimal or preferred configuration settings for wireless or wired network equipment in order to obtain a desirable level of network performance. A site-specific network model is used with adaptive processing to perform efficient design and on-going management of network performance. The invention iteratively determines overall network performance and cost, and further iterates equipment settings, locations and orientations. Real time control is between a site-specific Computer Aided Design (CAD) software application and the physical components of the network allows the invention to display, store, and iteratively adapt any network to constantly varying traffic and interference conditions. Alarms provide rapid adaptation of network parameters, and alerts and preprogrammed network shutdown actions may be taken autonomously. A wireless post-it note device and network allows massive data such as book contents or hard drive memory to be accessed within a room by a wide bandwidth reader device, and this can further be interconnected to the internet or Ethernet backbone in order to provide worldwide access and remote retrieval to wireless post-it devices.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
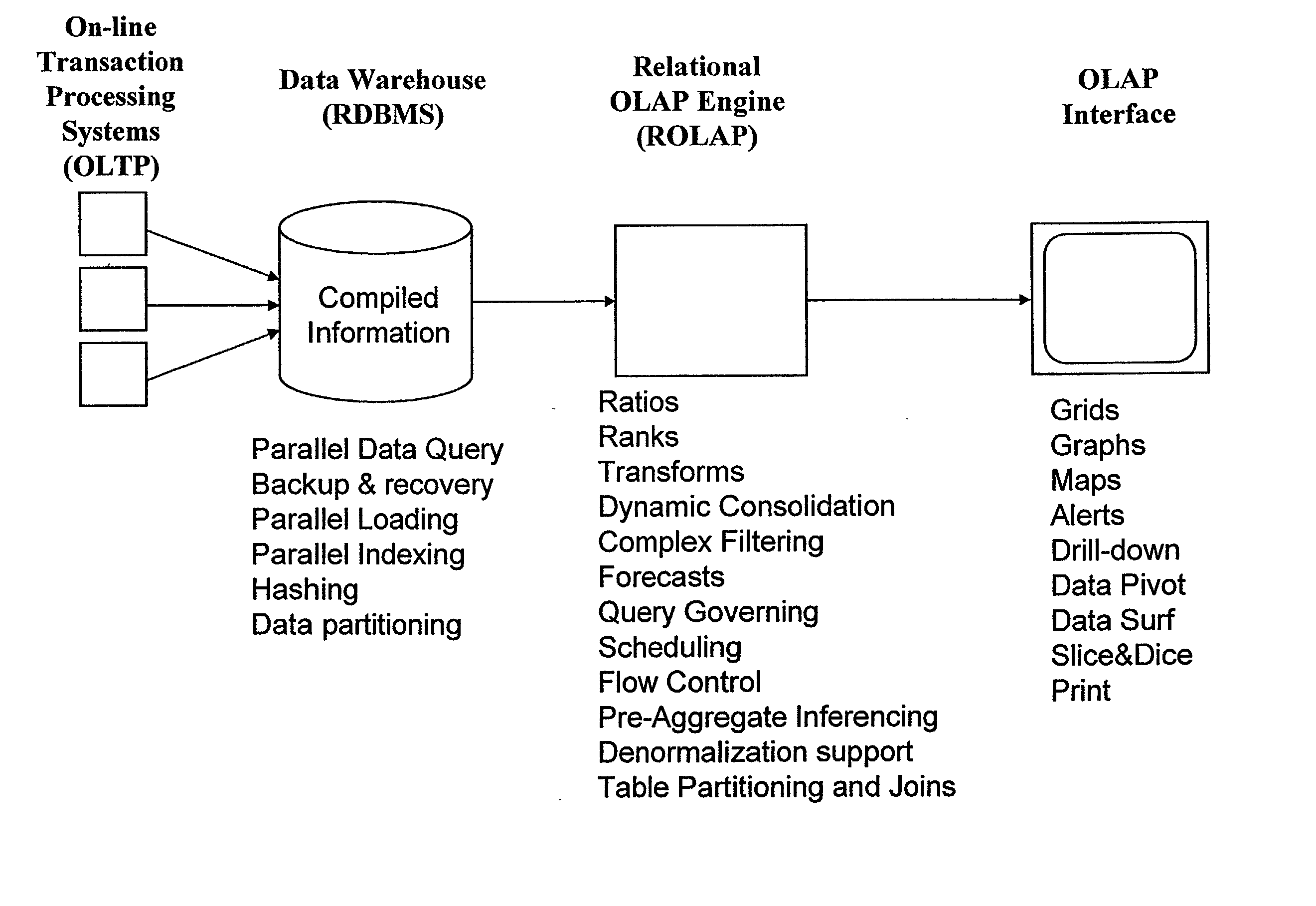
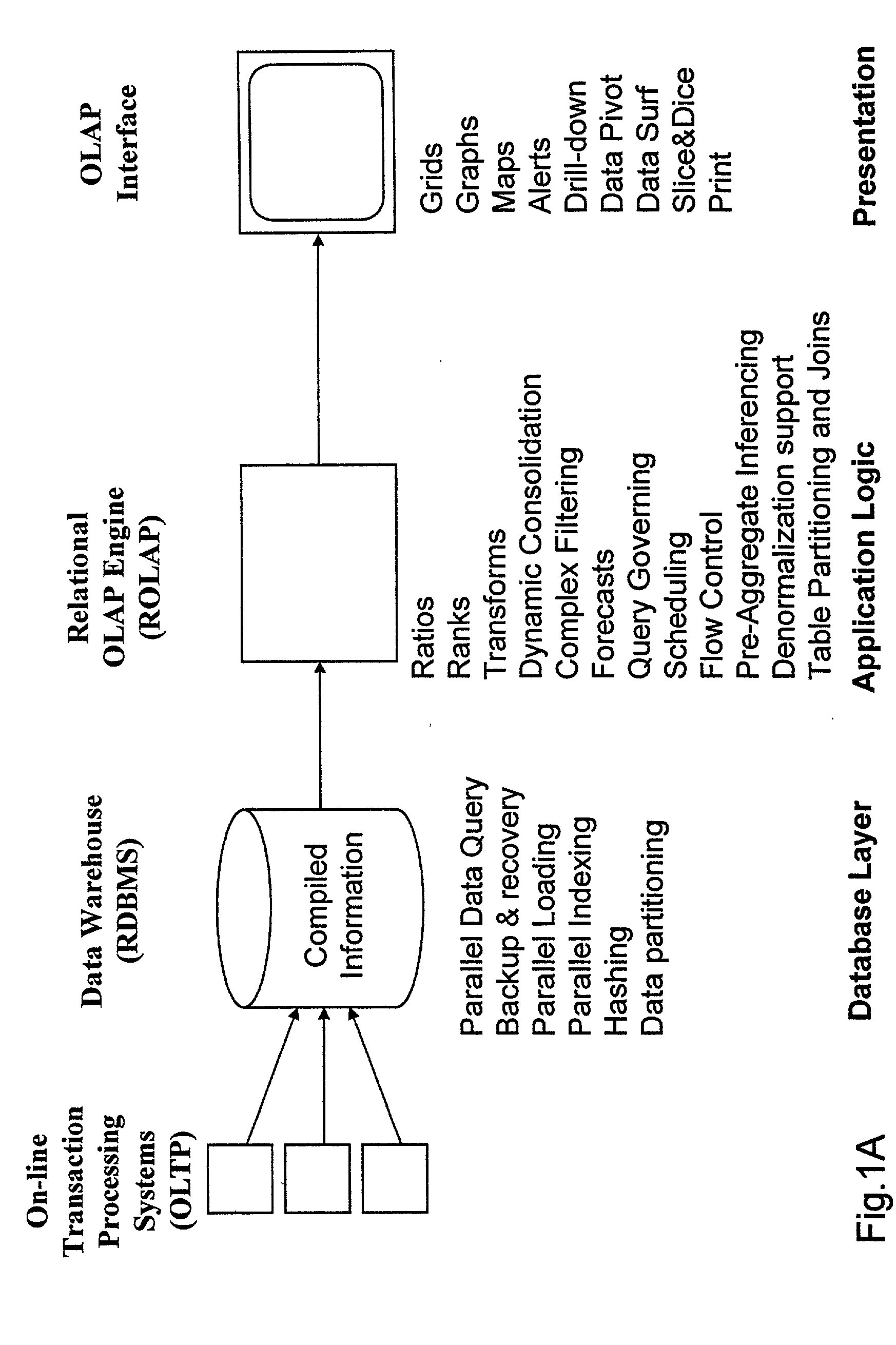
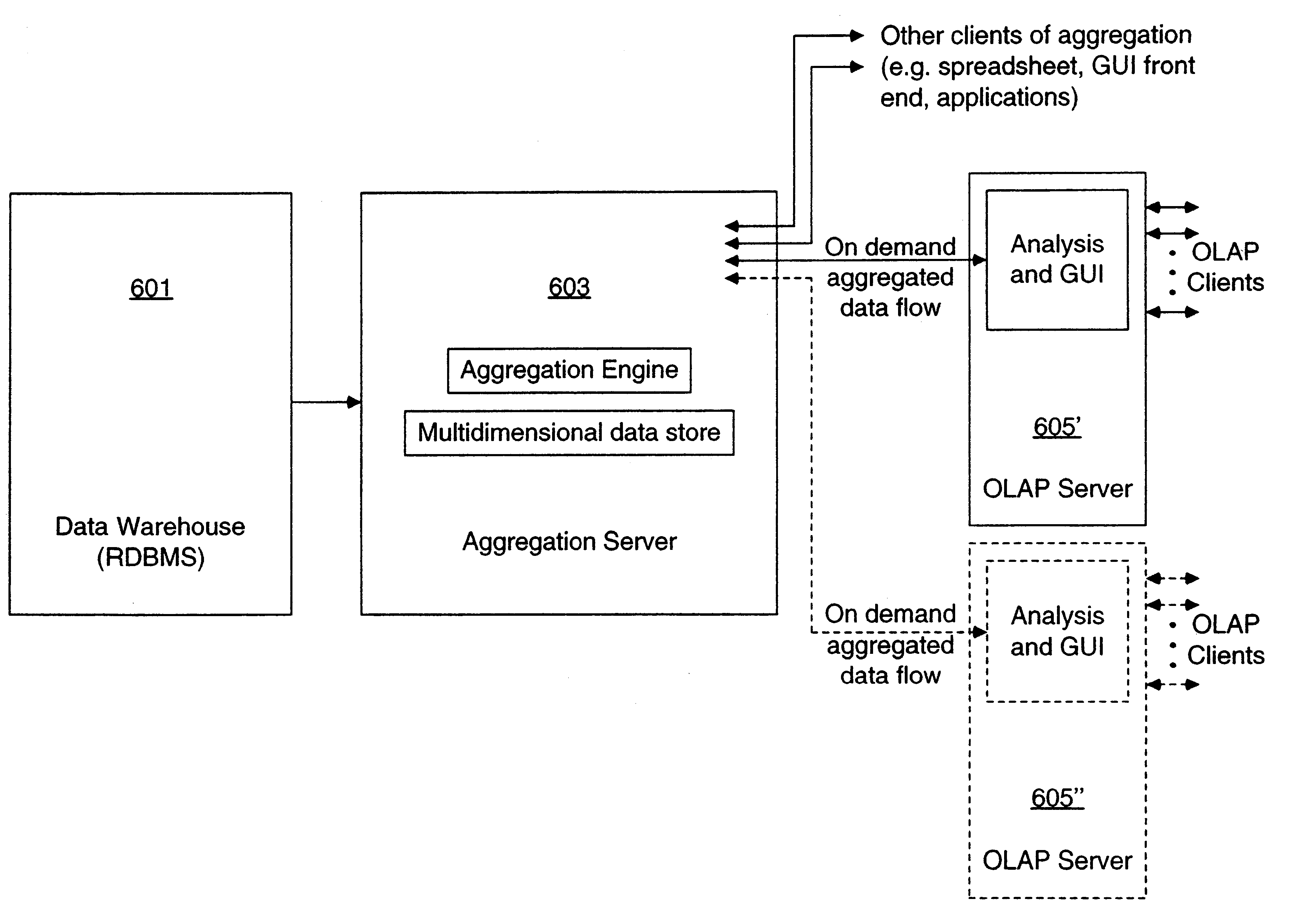
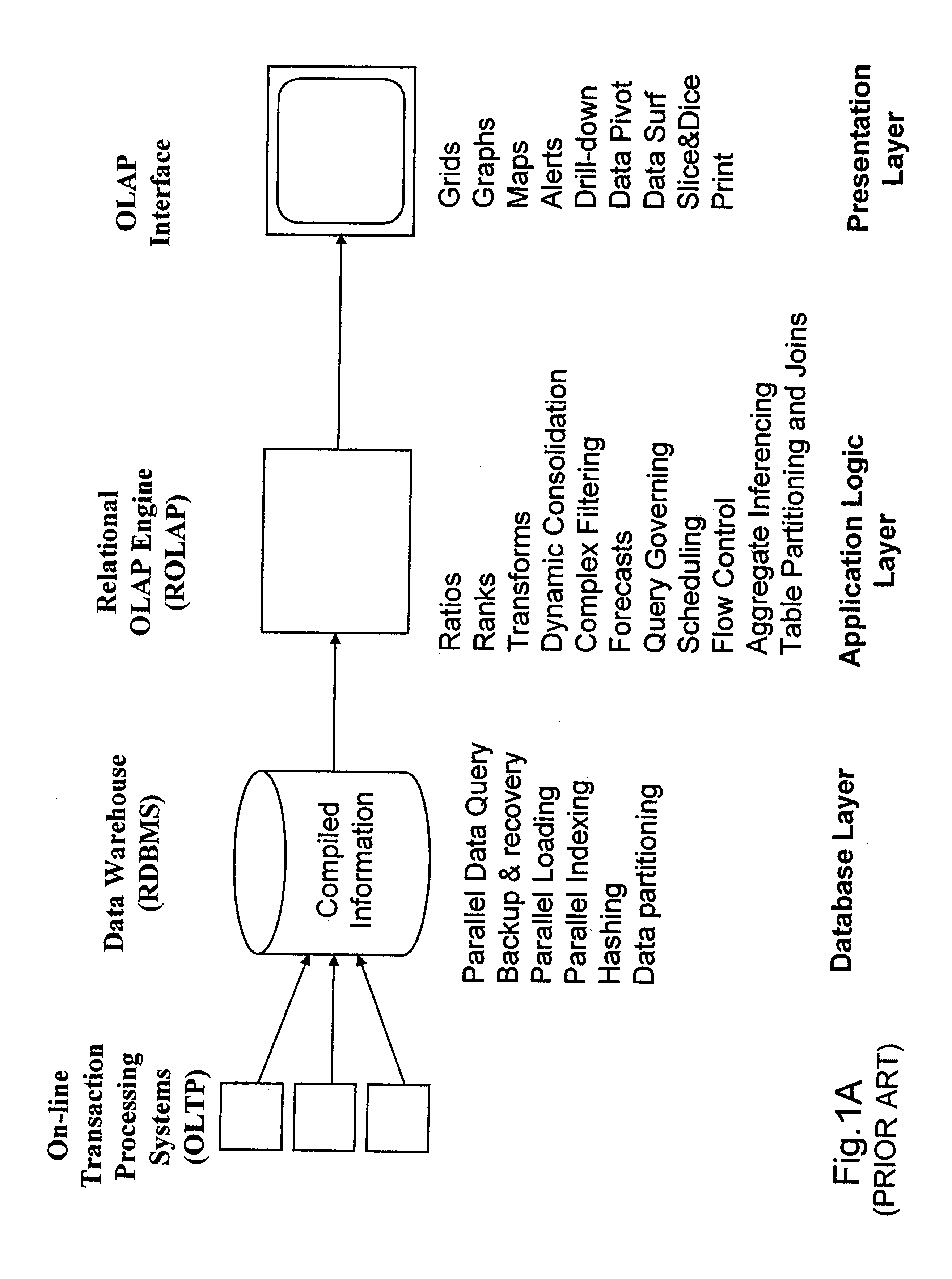
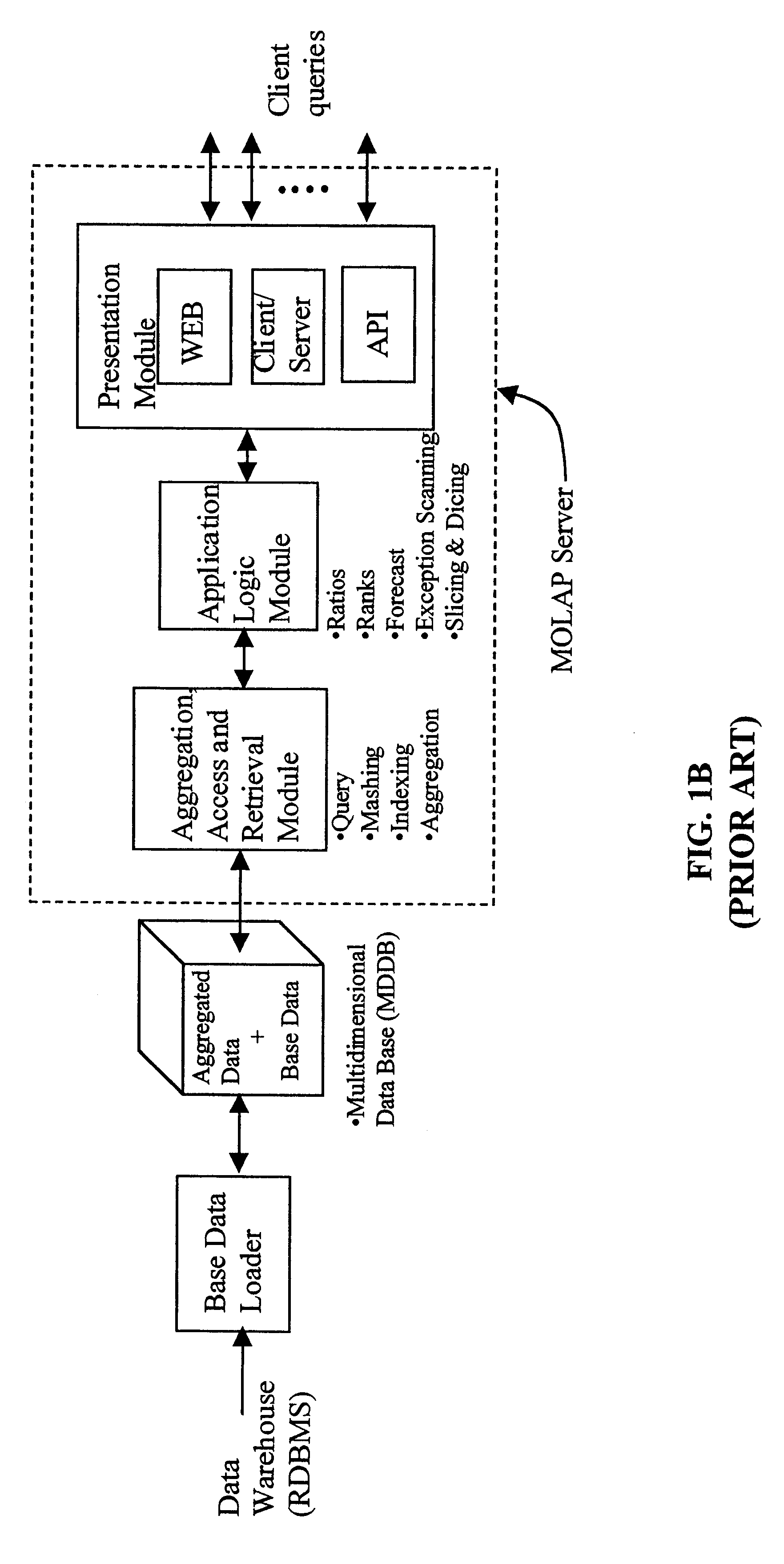
Data aggregation server for managing a multi-dimensional database and database management system having data aggregation server integrated therein
InactiveUS20020029207A1Reduce the burden onImprove system performanceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData aggregatorThe Internet
Improved method of and apparatus for aggregating data elements in multidimensional databases (MDDB). In one aspect of the present invention, the apparatus is realized in the form of a high-performance stand-alone (i.e. external) aggregation server which can be plugged-into conventional OLAP systems to achieve significant improments in system performance. In accordance with the principles of the present invention, the stand-alone aggregation server contains a scalable MDDB and a high-performance aggregation engine that are integrated into the modular architecture of the aggregation server. The stand-alone aggregation server of the present invention can uniformly distribute data elements among a plurality of processors, for balanced loading and processing, and therefore is highly scalable. The stand-alone aggregation server of the present invention can be used to realize (i) an improved MDDB for supporting on-line analytical processing (OLAP) operations, (ii) an improved Internet URL Directory for supporting on-line information searching operations by Web-enabled client machines, as well as (iii) diverse types of MDDB-based systems for supporting real-time control of processes in response to complex states of information reflected in the MDDB. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus is integrated within a database management system (DBMS). The improved DBMS can be used to realize achieving a significant increase in system performance (e.g. deceased access / search time), user flexibility and ease of use. The improved DBMS system of the present invention can be used to realize an improved Data Warehouse for supporting on-line analytical processing (OLAP) operations or to realize an improved informational database system, operational database system, or the like.
Owner:YANICKLO TECH LIABILITY +1
Systems and methods for additive manufacturing and repair of metal components
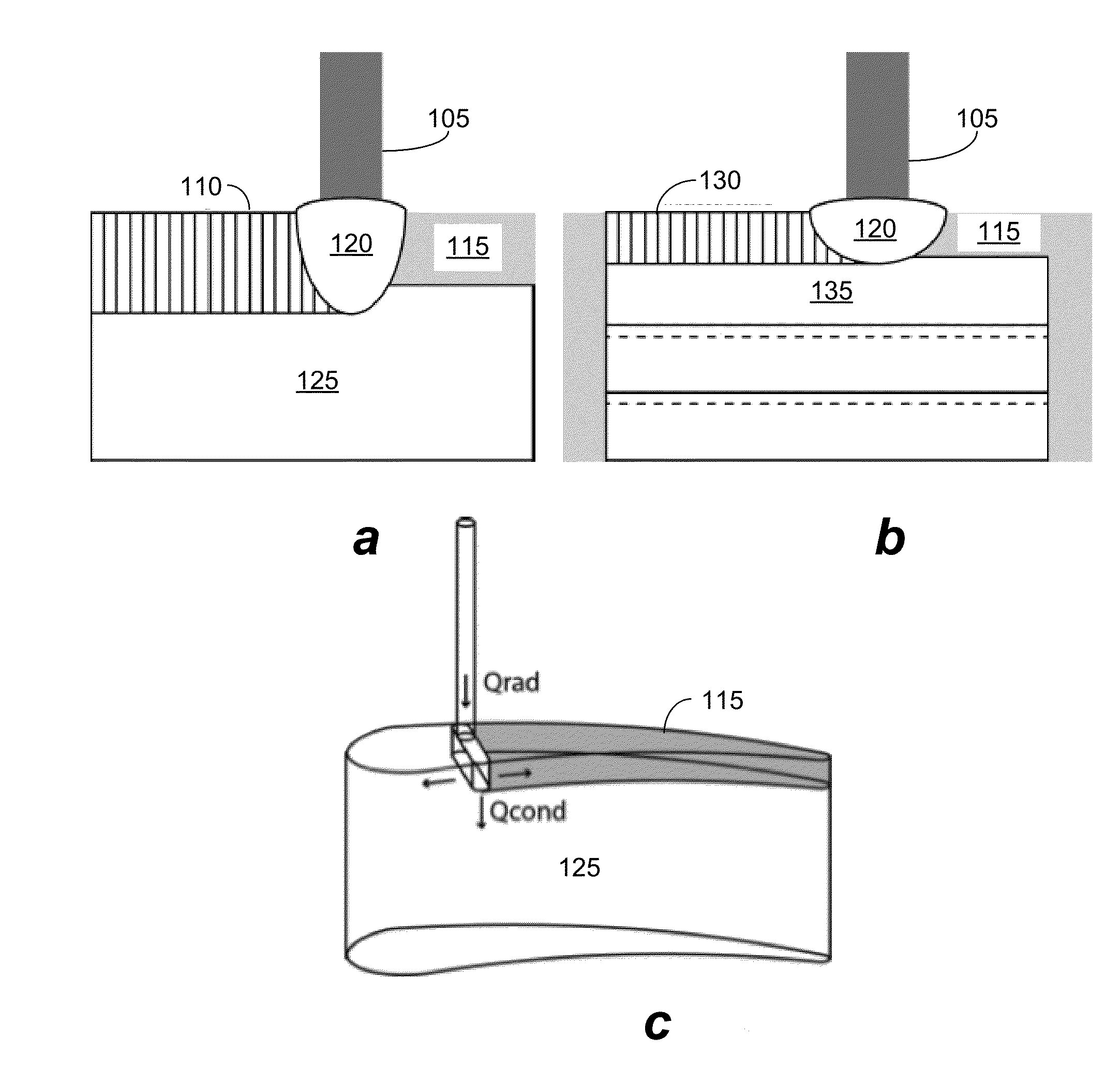
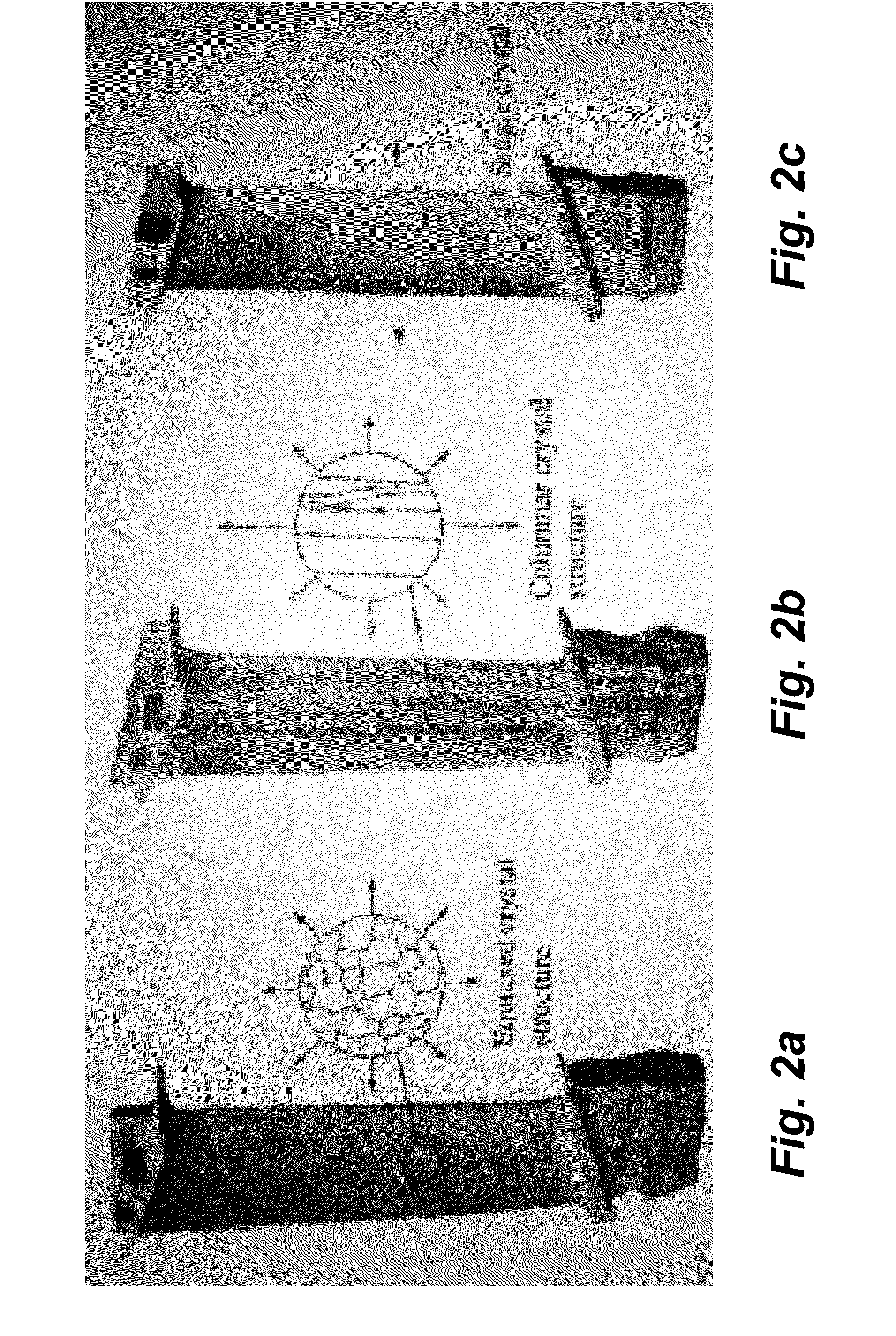
Scanning Laser Epitaxy (SLE) is a layer-by-layer additive manufacturing process that allows for the fabrication of three-dimensional objects with specified microstructure through the controlled melting and re-solidification of a metal powders placed atop a base substrate. SLE can be used to repair single crystal (SX) turbine airfoils, for example, as well as the manufacture functionally graded turbine components. The SLE process is capable of creating equiaxed, directionally solidified, and SX structures. Real-time feedback control schemes based upon an offline model can be used both to create specified defect free microstructures and to improve the repeatability of the process. Control schemes can be used based upon temperature data feedback provided at high frame rate by a thermal imaging camera as well as a melt-pool viewing video microscope. A real-time control scheme can deliver the capability of creating engine ready net shape turbine components from raw powder material.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
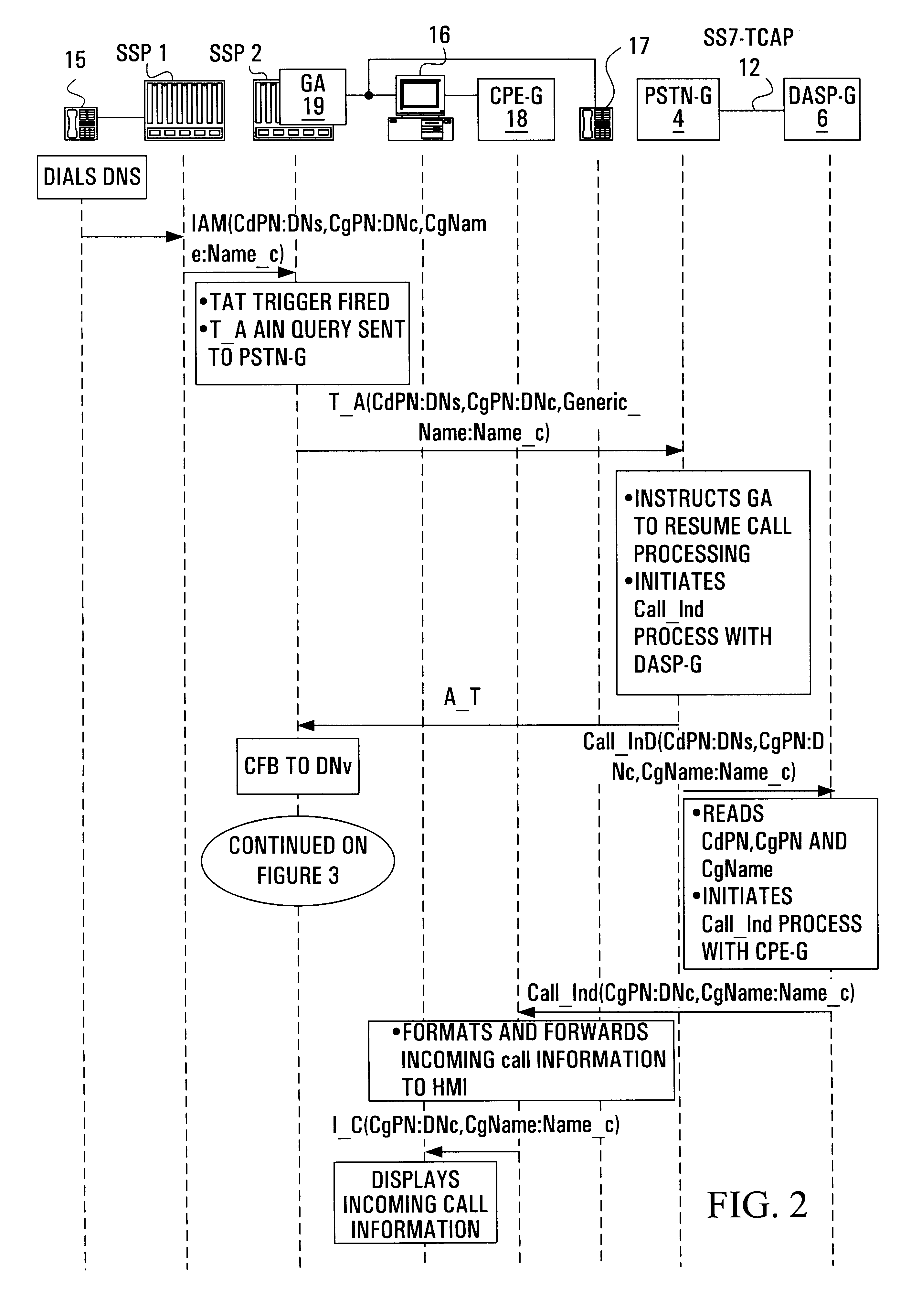
Internet-based telephone call manager
InactiveUS6212261B1Improve handlingImprove abilitiesInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersData connectionData information
A method is provided that allows data access service provider subscribers to manage their telephone service through a data connection. The subscriber is enabled to obtain call data information and is provided real time control. During a data call, a visual incoming call indicator informs the subscriber, through a popup window, connected to the data access service provider that there is a call attempt. A visual message waiting indicator allows a subscriber, connected to the data access service provider to be notified of a pending message on the voice message system. A visual call disposition allows the subscriber, through the data connection, to dispose of calls. The call disposition options include forwarding a call to voice mail, playing an announcement to the calling party, forwarding the call to another line, sending a text message which could be converted to speech using text to speech technology, answering the call using voice over data call or terminating the data connection in order to accept the call.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
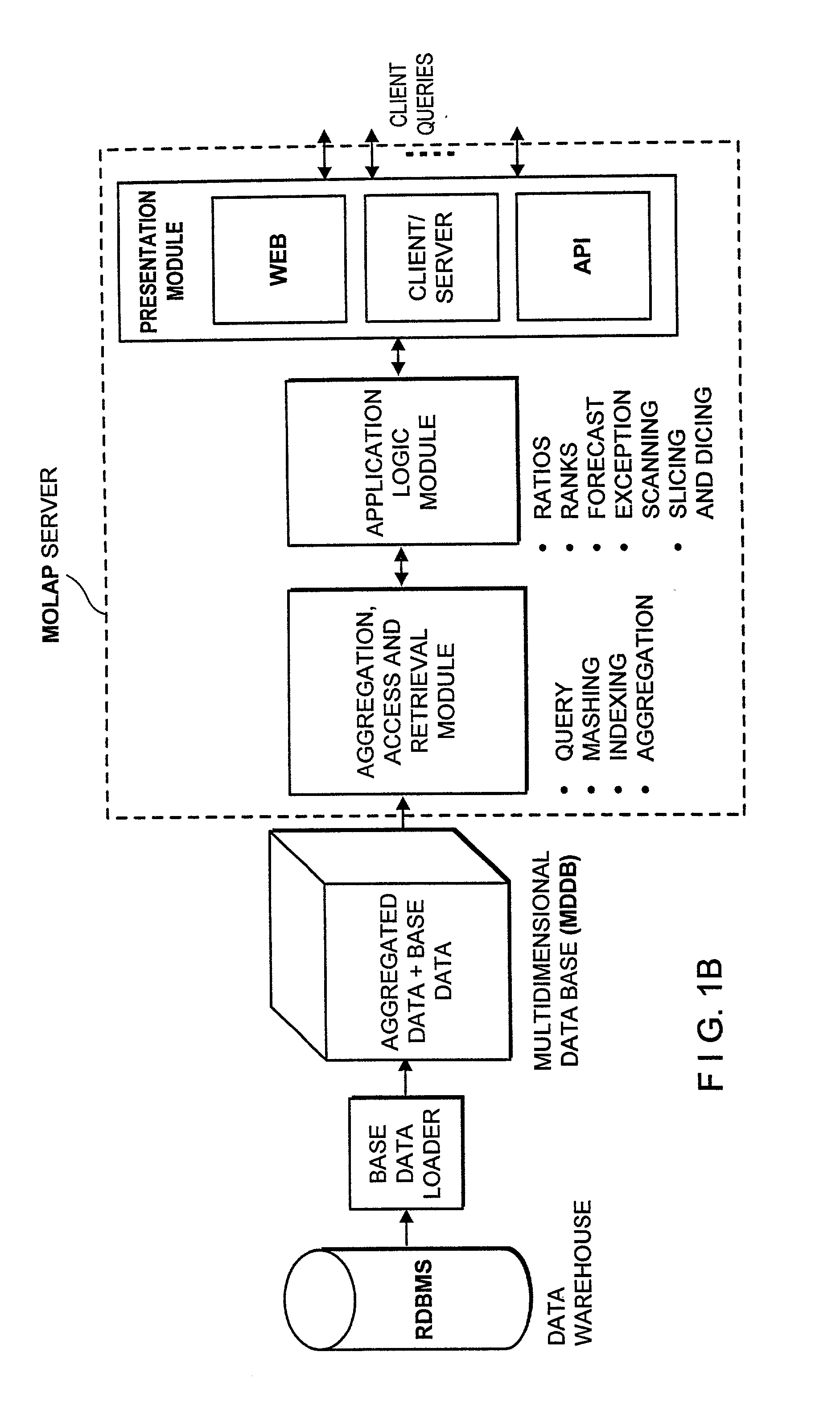
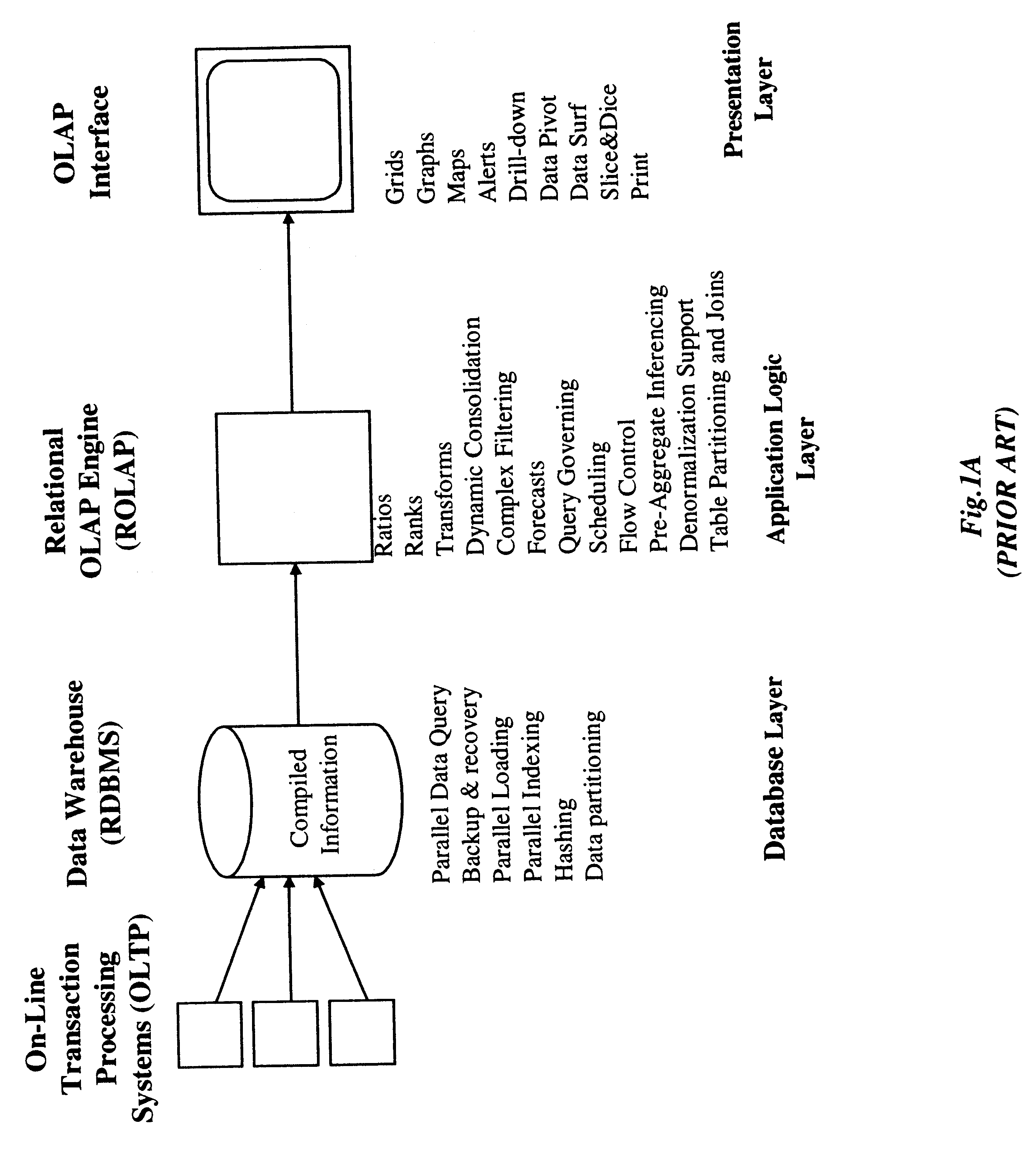
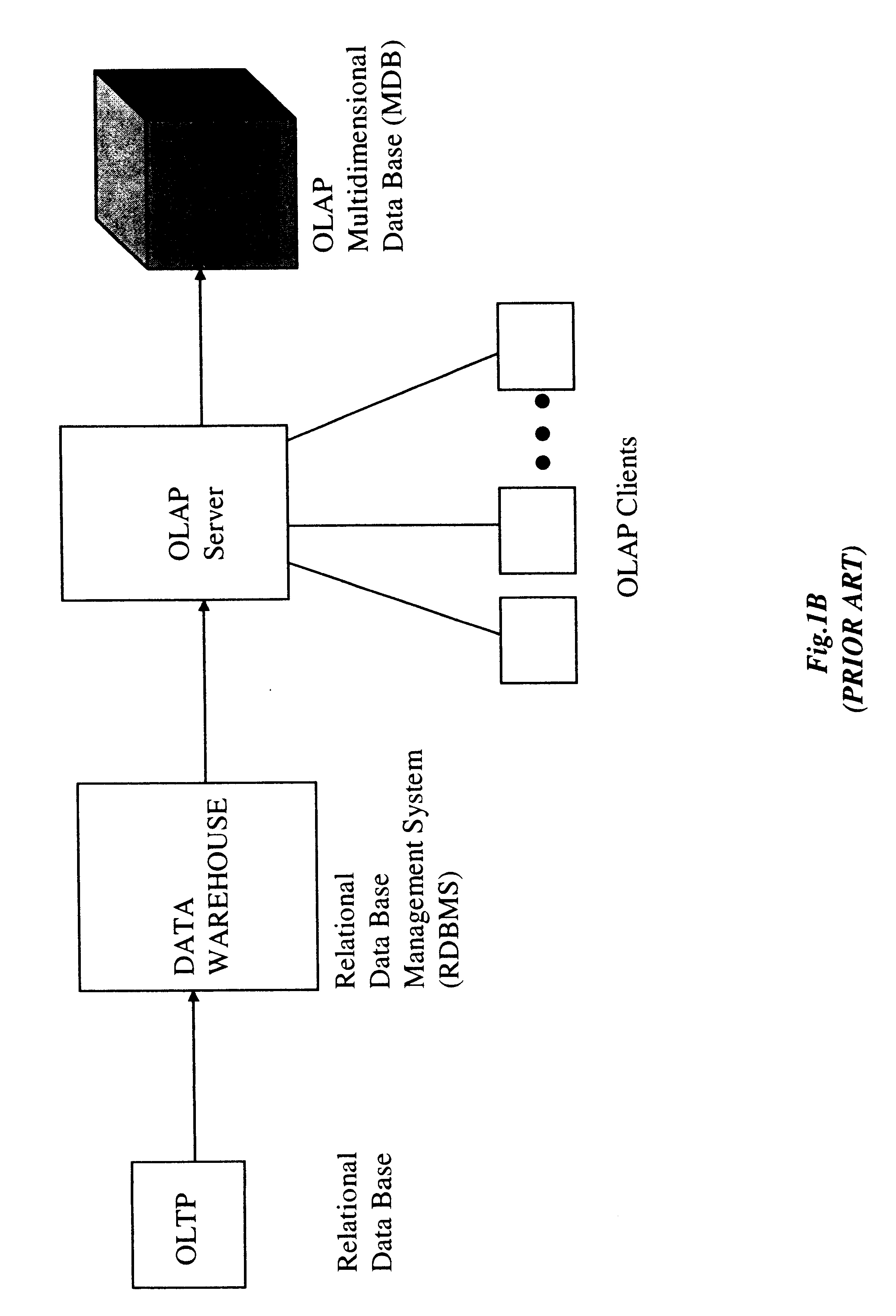
Stand-alone cartridge-style data aggregation server providing data aggregation for OLAP analyses
InactiveUS6434544B1Improve system performanceQuick searchData processing applicationsMulti-dimensional databasesData aggregatorThe Internet
An improved method of and apparatus for aggregating data elements in multidimensional databases (MDDB) realized in the form of a high-performance stand-alone (i.e. external) aggregation server which can be plugged-into conventional OLAP systems to achieve significant improvements in system performance. In accordance with the principals of the present invention, the stand-alone aggregation server contains a scalable MDDB and a high-performance aggregation engine that are integrated into the modular architecture of the aggregation server. The stand-alone aggregation server of the present invention can uniformly distributed data elements among a plurality of processors, for balanced loading and processing, and therefore is highly scalable. The stand-alone aggregation server of the present invention can be used to realize (i) an improved MDDB for supporting on-line analytical processing (OLAP) operations, (ii) an improved Internet URL Directory for supporting on-line information searching operations by Web-enabled client machines, as well as (iii) diverse types of MDDB-based systems for supporting real-time control of processes in response to complex states of information reflected in the MDDB.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES ASSETS 114 LLC +1
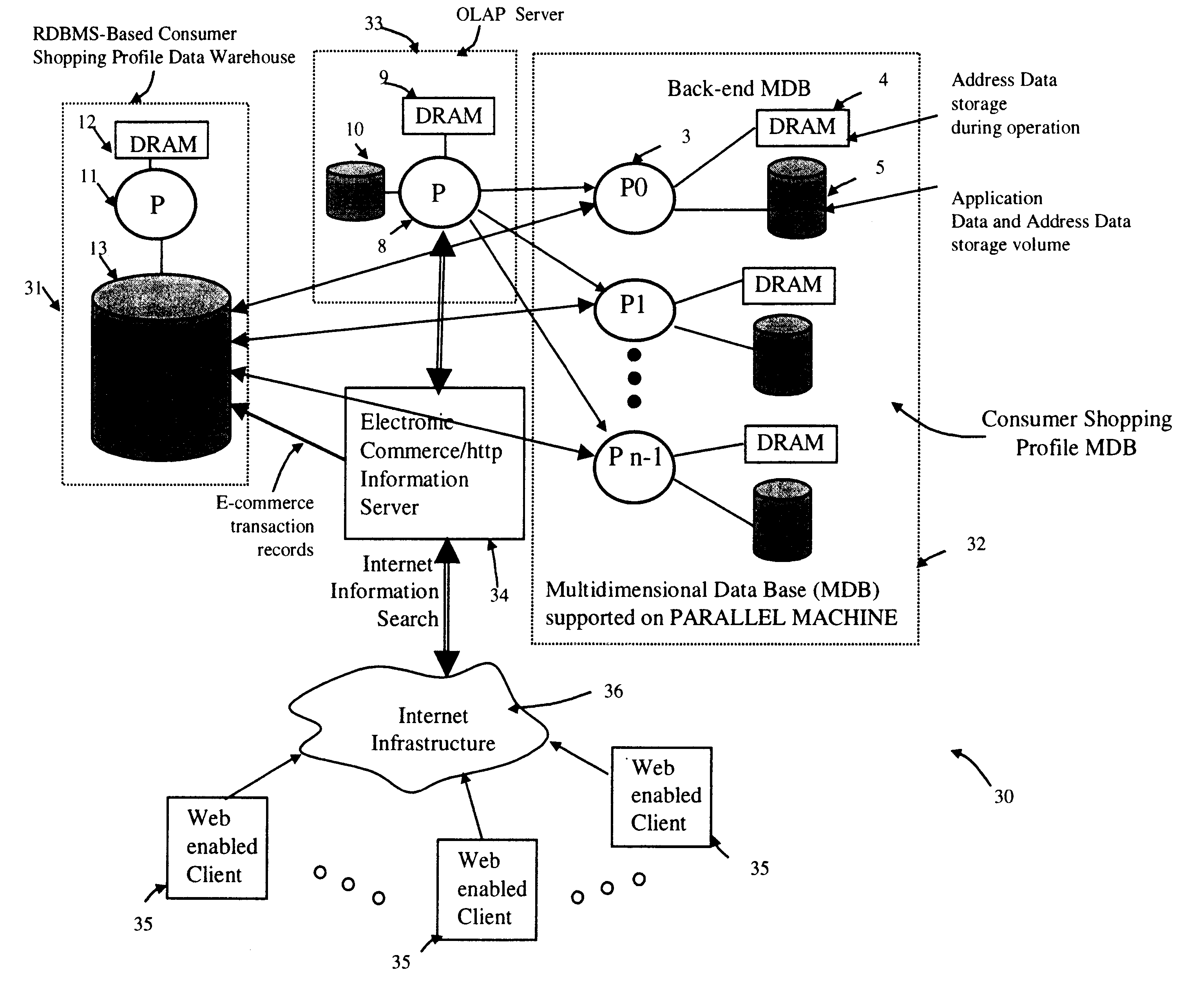
Method of and system for managing multi-dimensional databases using modular-arithmetic based address data mapping processes on integer-encoded business dimensions
InactiveUS6408292B1Improve performanceFast knowledge discoveryData processing applicationsMulti-dimensional databasesData warehouseThe Internet
An improved method of and a system for managing data elements in a multidimensional database (MDB) supported upon a parallel computing platform using modular-arithmetic based address data mapping (i.e. translation) processes on integer-encoded business dimensions. The parallel computing platform has a plurality of processors and one or more storage volumes for physically storing data elements therein at integer-encoded physical addresses in Processor Storage Space (i.e. physical address space in the one or more storage volumes associated with a given processor). The location of each data element in the MDB is specified in MDB Space by integer-encoded business dimensions associated with the data element. A data loading mechanism loads the integer-encoded business dimensions and associated data elements from a data warehouse. The address data mapping mechanism performs a two part address mapping processing. The first step maps the integer-encoded business dimensions associated with each data element to a given processor identifier (which uniquely identifies the processor amongst the plurality of processors of the parallel computing platform). The second step maps the integer-encoded business dimensions associated with each data element into an integer-encoded physical data storage address in Processor Storage Space associated with the processor identified by the processor identifier generated in the first mapping step. The mapping performed in this second step is based upon size of the integer encoded business dimensions. The data management mechanism manages the data elements stored in the storage volumes using the integer-encoded data storage addresses generated during the two-part address data mapping process. The use of modular-arithmetic functions in the two-part address data mapping mechanism ensures that the data elements in the MDB are uniformly distributed among the plurality of processors for balanced loading and processing. The present invention can be used to realize (i) an improved MDB for supporting on-line analytical processing (OLAP) operations, (ii) an improved Internet URL Directory for supporting on-line information searching operations by Web-enabled client machines, as well as (iii) diverse types of MDB-based systems for supporting real-time control of processes in response to complex states of information reflected in the MDB.
Owner:MEC MANAGEMENT LLC +1
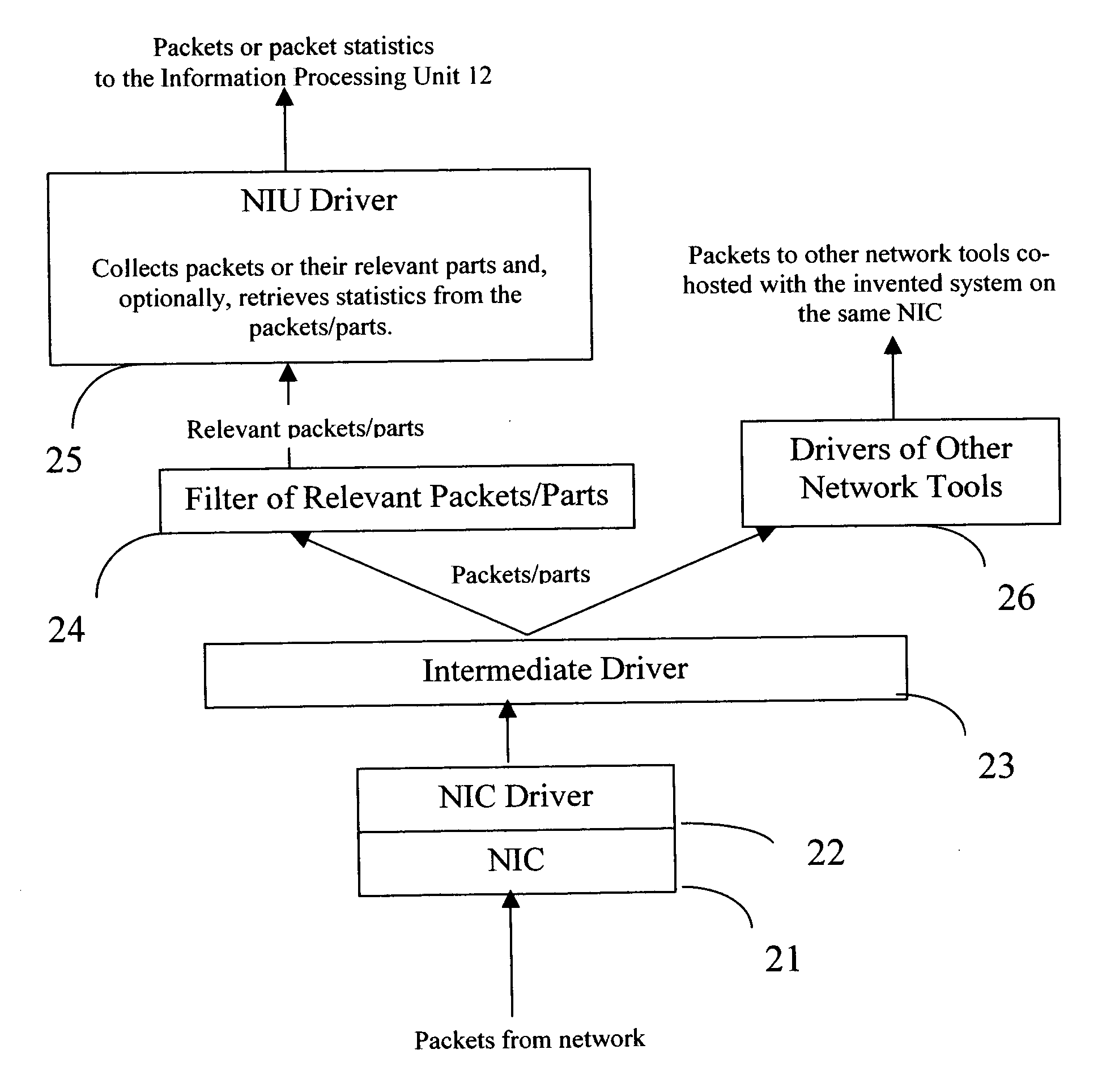
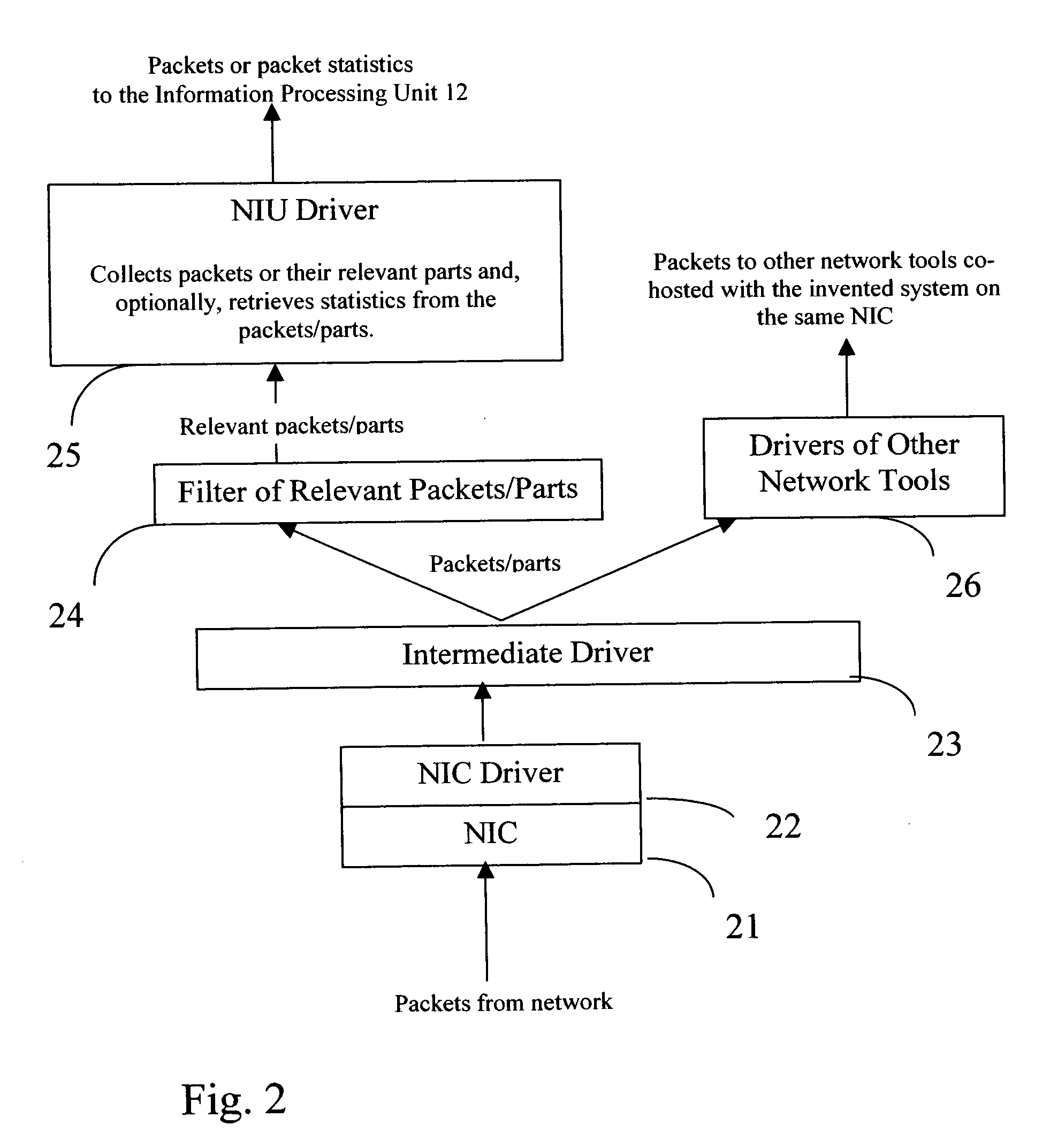
Flows based visualization of packet networks with network performance analysis, troubleshooting, optimization and network history backlog
InactiveUS20060028999A1Improve network securityEasy to highlightError preventionTransmission systemsProcess informationStreamflow
The present invention is a computer system and a method for gathering, processing and analysis of network information resulting in presentation and visualization of packet networks in the form of individual virtual flows, sometimes also called connections or sessions, containing their statistical characteristics in a time-sampled dynamics. The system, deployed as a separate device or co-hosted with other network devices, collects and processes information from all valid packets in network, classifies and maps gathered statistics to the statistics of relevant virtual flows. The statistical information is further processed by the system to provide near-real presentation, as well as stored in a searchable database for future analyses. The invention to be used by network engineers and administrators as a tool for a near real-time control of network traffic, as an analytical tool for solving network bottlenecks, network performance optimization and troubleshooting analyses, cutting costs by optimizing network layout, appropriate organization of traffic and intelligent configuration of QoS, routers and other network devices.
Owner:IAKOBASHVILI ROBERT +1
Method and apparatus for path planning, selection, and visualization
InactiveUS20100241289A1Suffer from effectKeep movingProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorGraphicsThree-dimensional space
New and Improved methods and apparatus for robotic path planning, selection, and visualization are described A path spline visually represents the current trajectory of the robot through a three dimensional space such as a room By altering a graphical representation of the trajectory—the path spline—an operator can visualize the path the robot will take, and is freed from real-time control of the robot Control of the robot is accomplished by periodically updating the path spline such that the newly updated spline represents the new desired path for the robot Also a sensor that may be located on the robot senses the presence of boundaries (obstacles) in the current environment and generates a path that circumnavigates the boundaries while still maintaining motion in the general direction selected by the operator The mathematical form of the path that circumnavigates the boundaries may be a spline
Owner:SANDBERG ROY
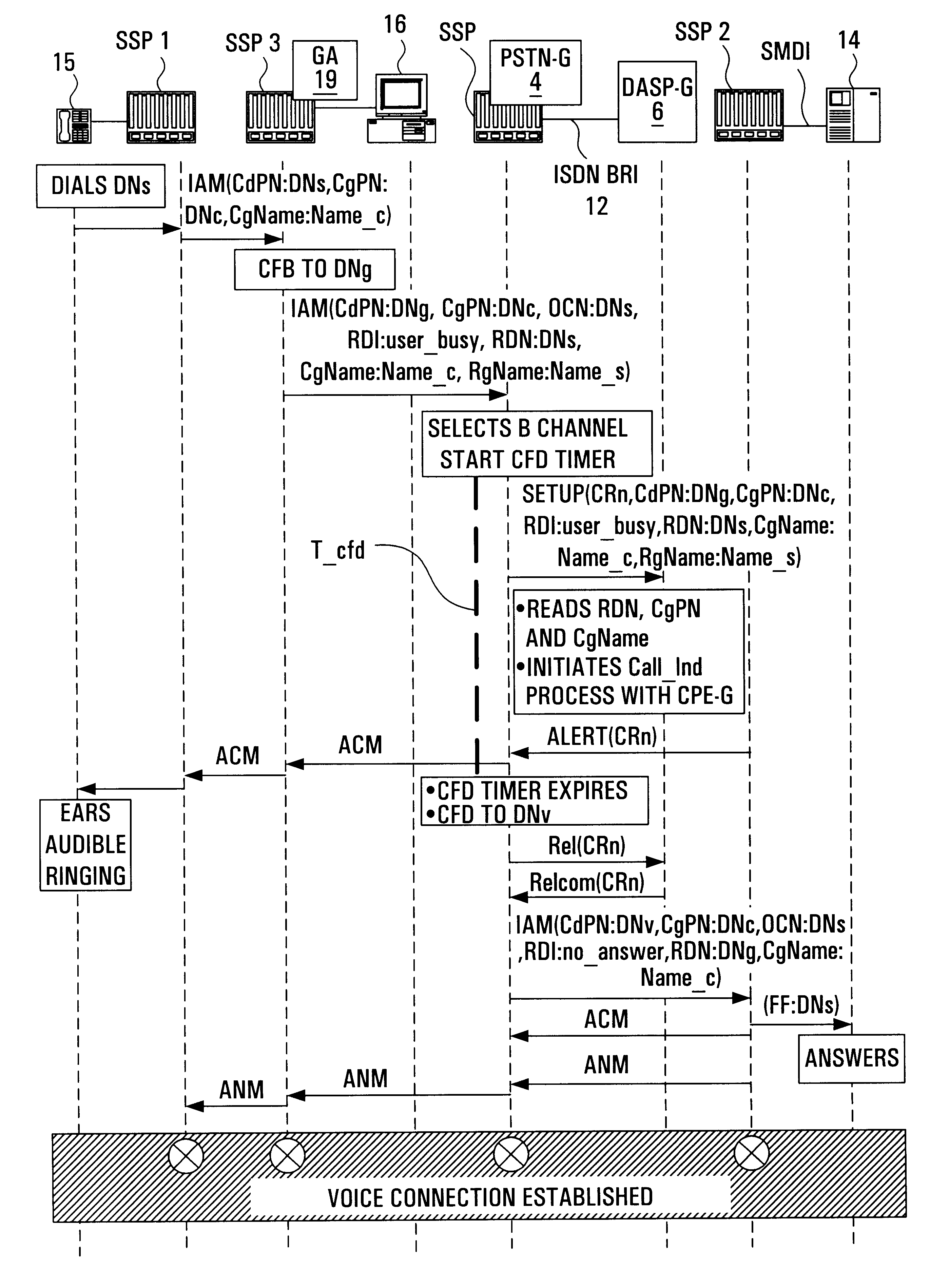
Method and apparatus for providing extended call setup and control features using a short message service
InactiveUS20050078612A1Simple and convenient and powerfulMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationShort Message ServiceConference call
A system for enabling setup and control of conference calls using short message service (SMS) messages (SMs). The SMS messages may be used to set up, or control a scheduled or real-time conference call. The SMS messages can also be used to exercise real-time control over a conference call. Invitations can be sent in real time to add participants to a call in progress, or to transfer the call from any participant's telephone to another telephone connected to the PSTN.
Owner:LANG ALEXANDER C
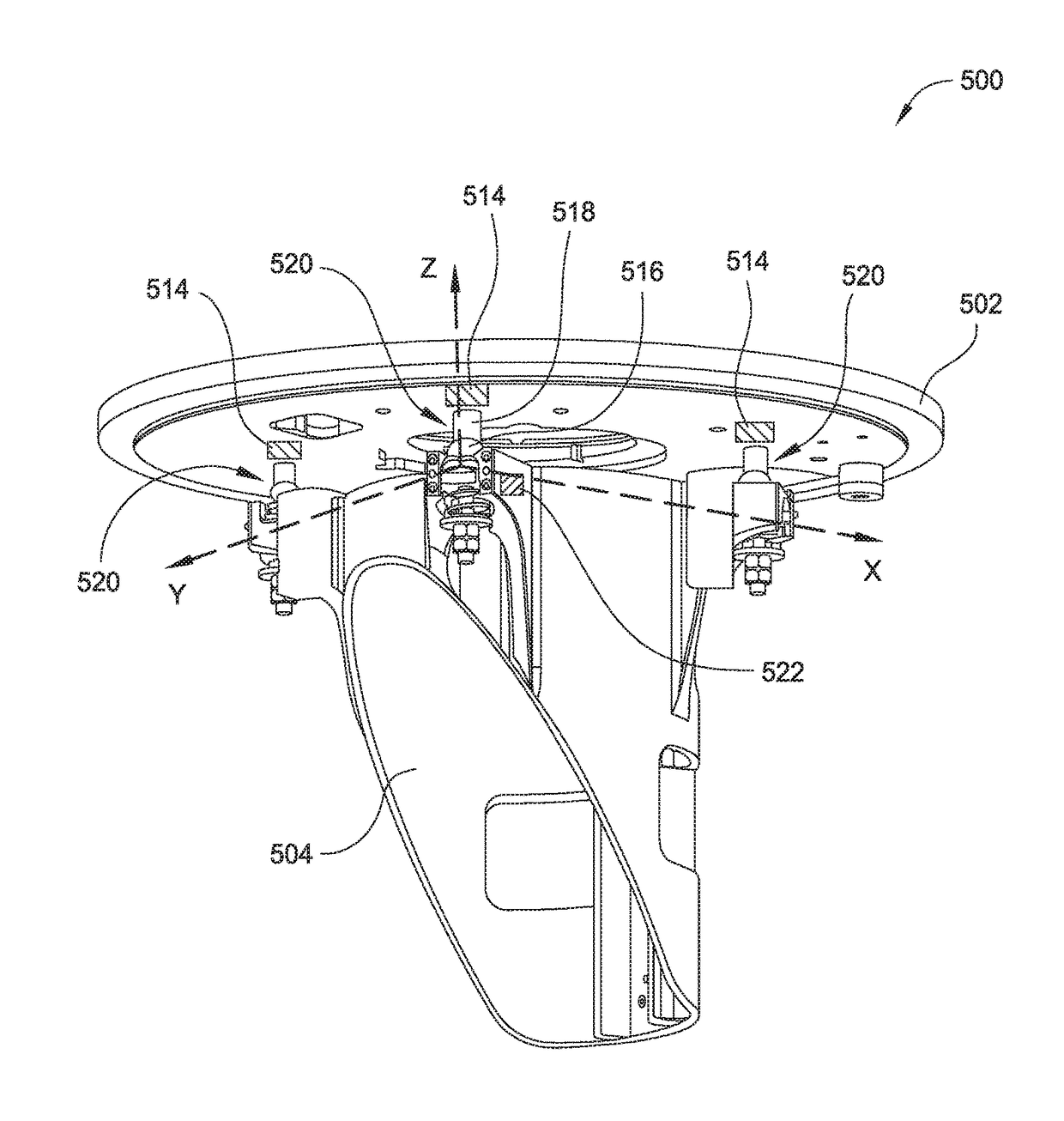
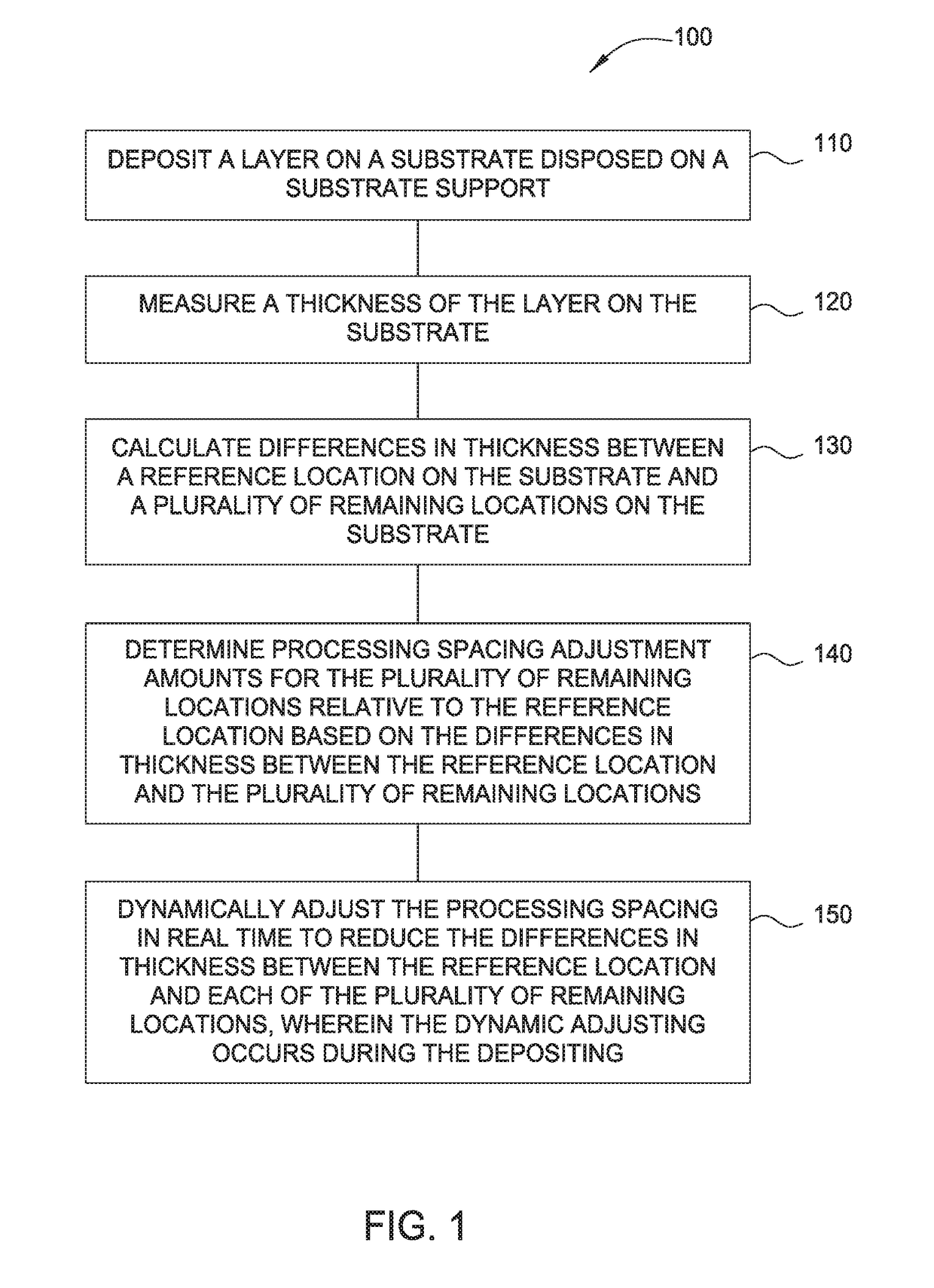
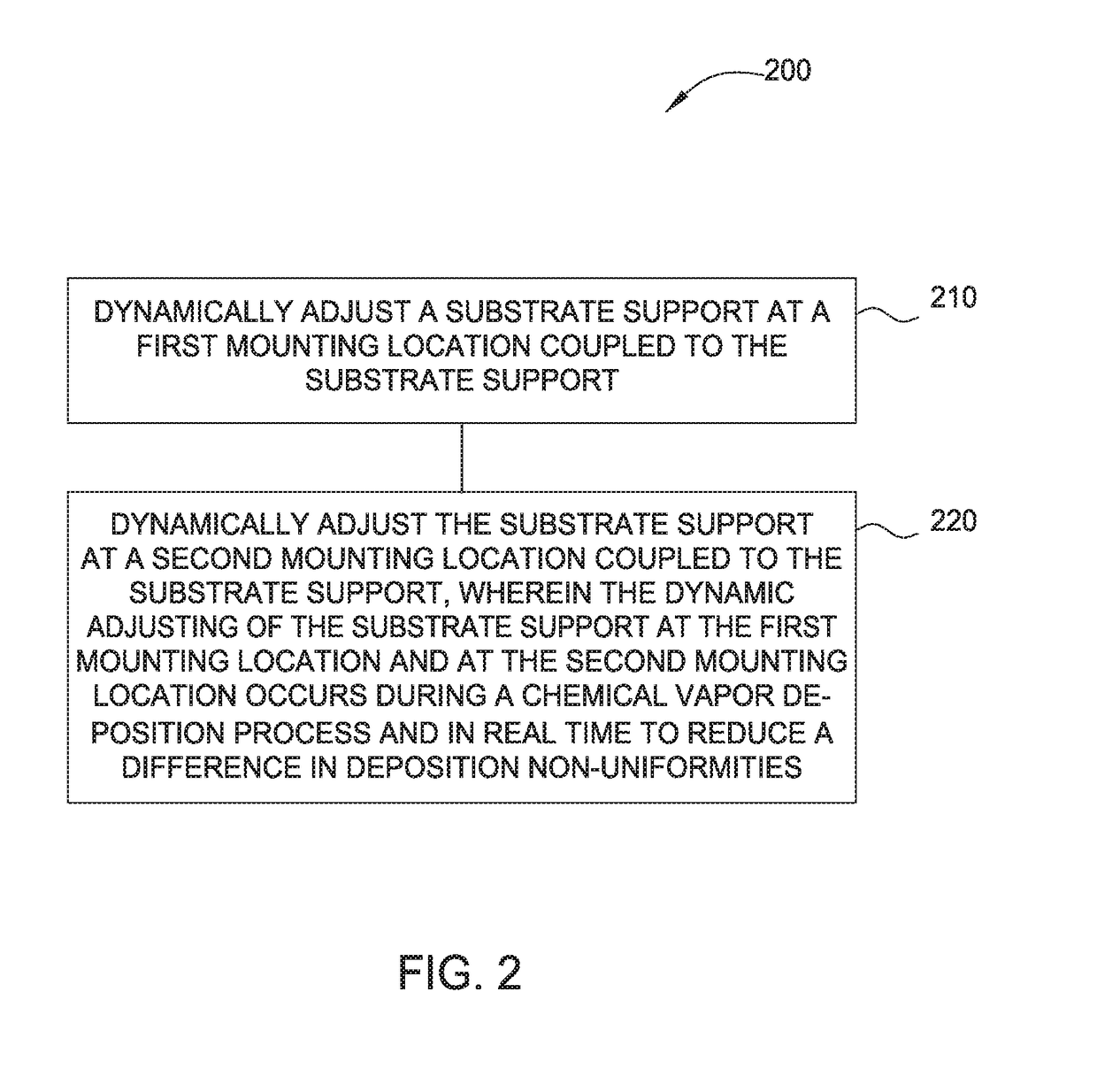
Dynamic wafer leveling/tilting/swiveling during a chemical vapor deposition process
ActiveUS20170309528A1Good film uniformityImprove the deposition effectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseDegrees of freedom
The implementations described herein generally relate to the dynamic, real-time control of the process spacing between a substrate support and a gas distribution medium during a deposition process. Multiple dimensional degrees of freedom are utilized to change the angle and spacing of the substrate plane with respect to the gas distributing medium at any time during the deposition process. As such, the substrate and / or substrate support may be leveled, tilted, swiveled, wobbled, and / or moved during the deposition process to achieve improved film uniformity. Furthermore, the independent tuning of each layer may be had due to continuous variations in the leveling of the substrate plane with respect to the showerhead to average effective deposition on the substrate, thus improving overall stack deposition performance.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
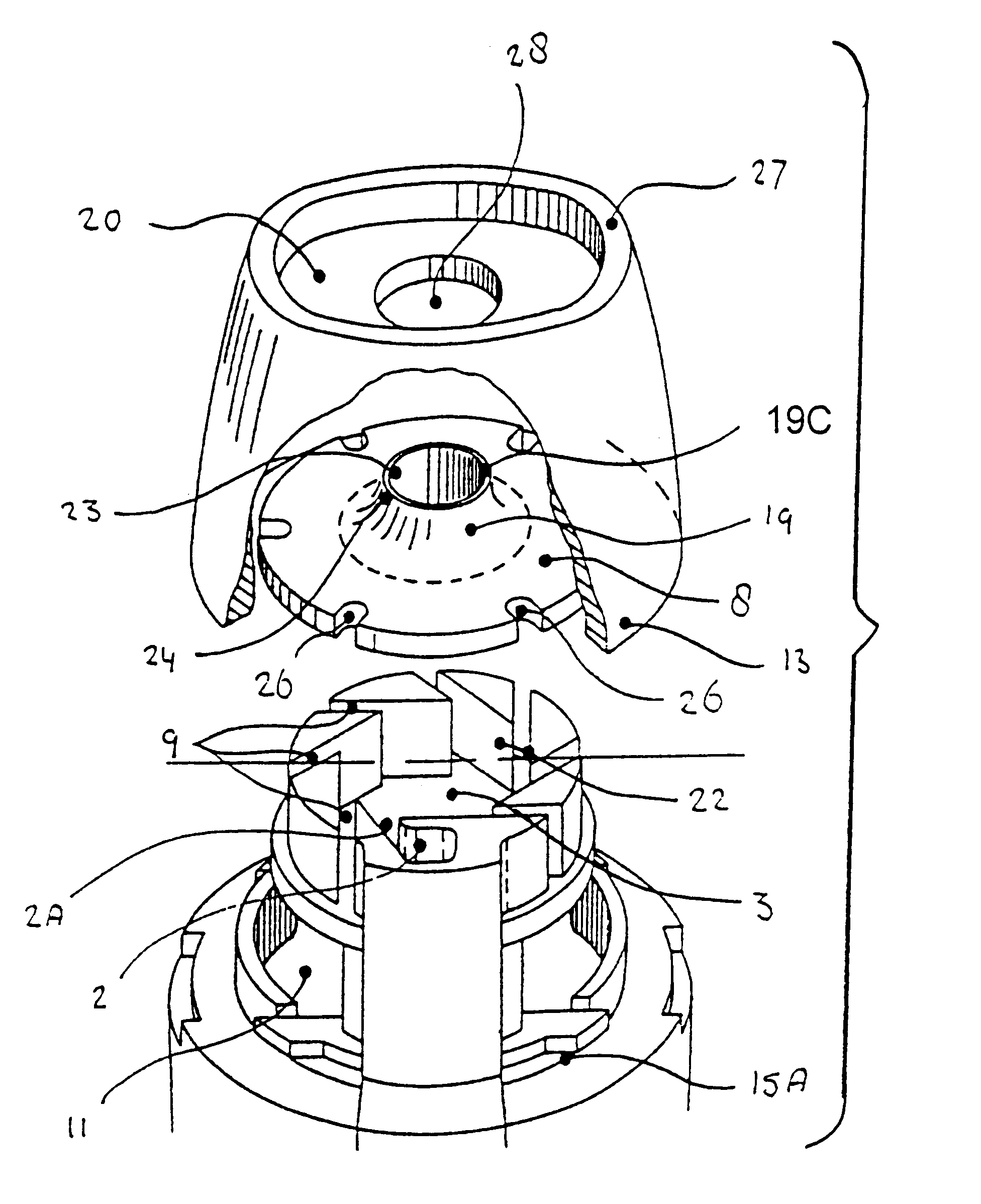
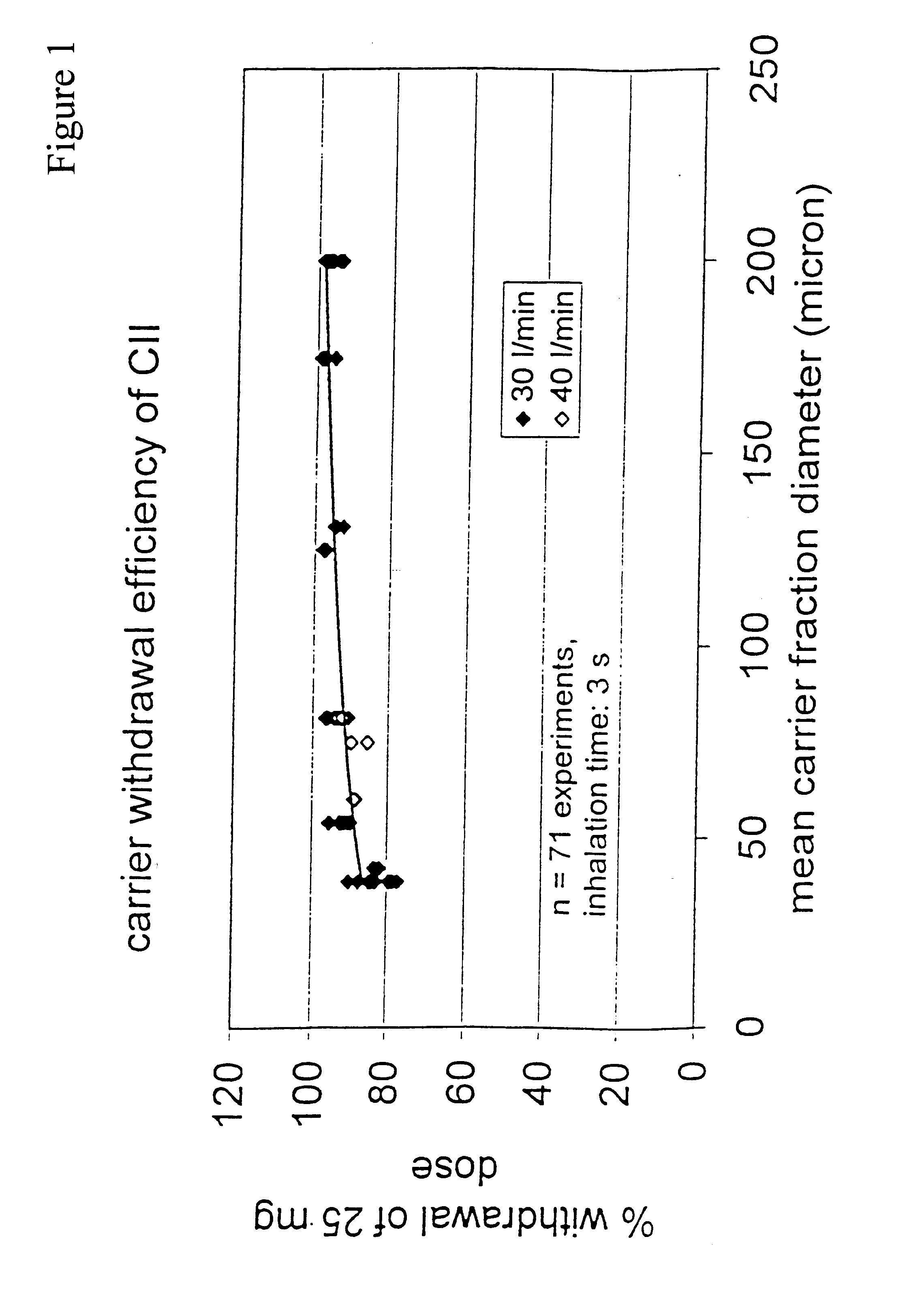
Powder formulation disintegrating system and method for dry powder inhalers
A disperser for dry powders which can be used with different dose systems, dose weights ranging from 2 to 25 mg and different types of powder formulation. In one embodiment, the disperser acts both as a de-agglomeration (disintegration; aerosolization) means and as an air classifier for especially adhesive mixtures. Only fine drug particles are emitted whereas the larger agglomerates and carrier crystals are retained by the disperser. Another embodiment enables time controlled release of carrier crystals in these mixtures. Yet another embodiment has optimized performance with spherical pellets, containing no carrier crystals. Other possible embodiments of the invention make it possible to control the total inhaler resistance and the powder deposition in the upper respiratory tract by means of the addition of a so-called sheath flow of clean air. Modifications also enable carrier retainment in the mouthpiece and elimination of the tangential flow component of the discharge cloud.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Method and system for controlled thermal injury of human superficial tissue
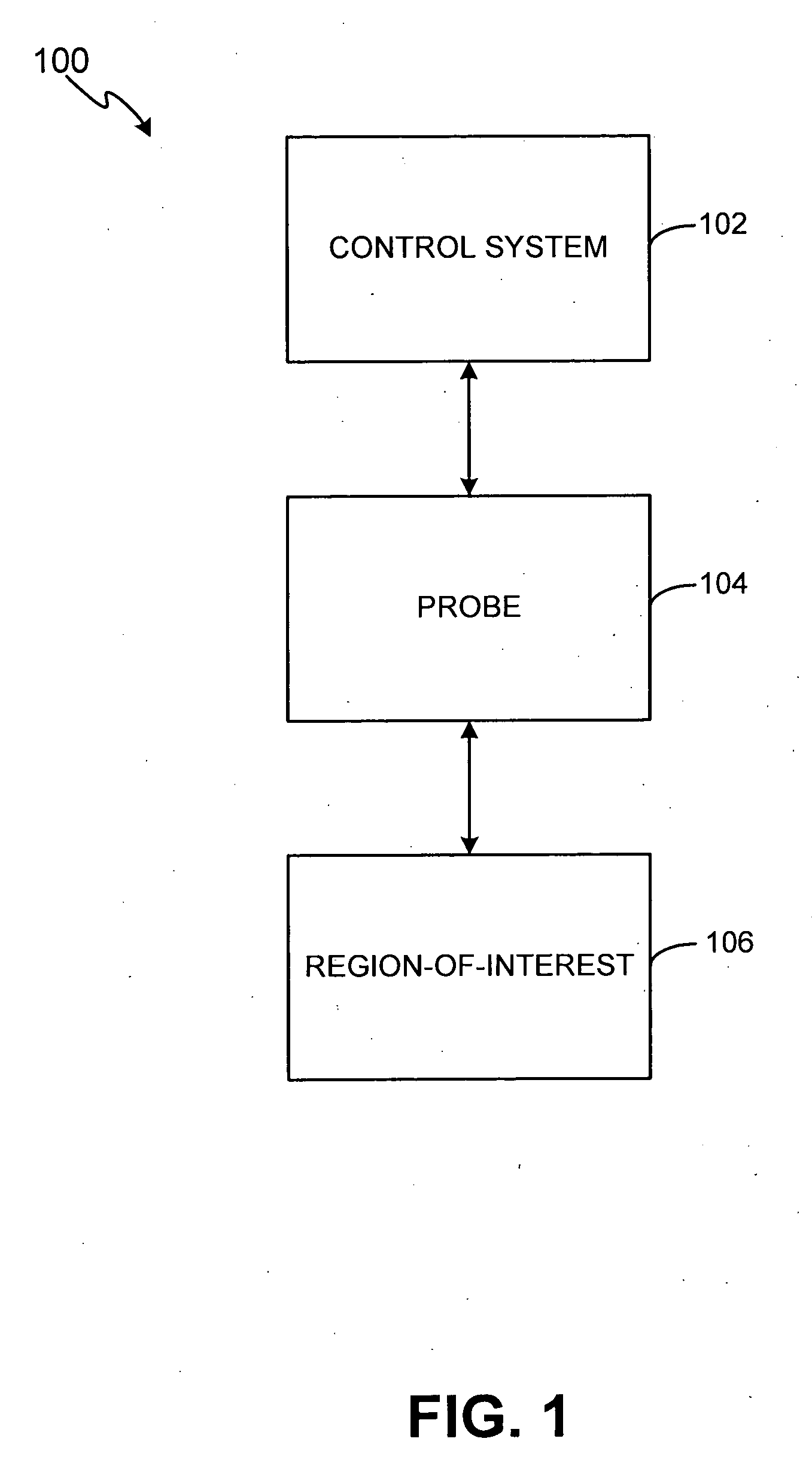
InactiveUS20060116671A1Produce lesionRestricted in mannerUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionThermal injuryControl system
A method and system for controlled thermal injury of human superficial tissue based on the ability to controllably create thermal lesions of variable shape, size, and depth via precise spatial and temporal control of acoustic energy deposition. The apparatus includes a control system and probes that facilitate treatment planning, control and delivery of energy, and monitoring of treatment conditions.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Management interface for a system that provides automated, real-time, continuous data protection
ActiveUS20060101384A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionDisplay deviceContent Time
A data management system that protects data into a continuous object store includes a management interface having a time control. The time control allows an administrator to specify a “past” time, such as a single point or range. When the time control is set to a single point, a hierarchical display of data appears on a display exactly as the data existed in the system at that moment in the past. Preferably, the visualization includes both the structure of the hierarchy (e.g., the identity of the directories, their files, databases, and the like) and also the contents of the data objects themselves (i.e., what was in the files and databases). The time control enables the management interface to operate within a history mode in which the display provides a visual representation of a “virtual” point in time in the past during which the data management system has been operative to provide the data protection service. In addition, the management interface can be toggled to operate in a real-time mode, which provides an active view of the system data as it changes in real-time, typically driven by changes to primary storage. This real-time mode provides the user with the ability to view changes that occur to a set of data currently visible on the display screen. The interface also allows an administrator to specify and manage policy including, without limitation, how long data is retained in the management system. A policy engine enables the user to assert “temporal-based” policy over data objects.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
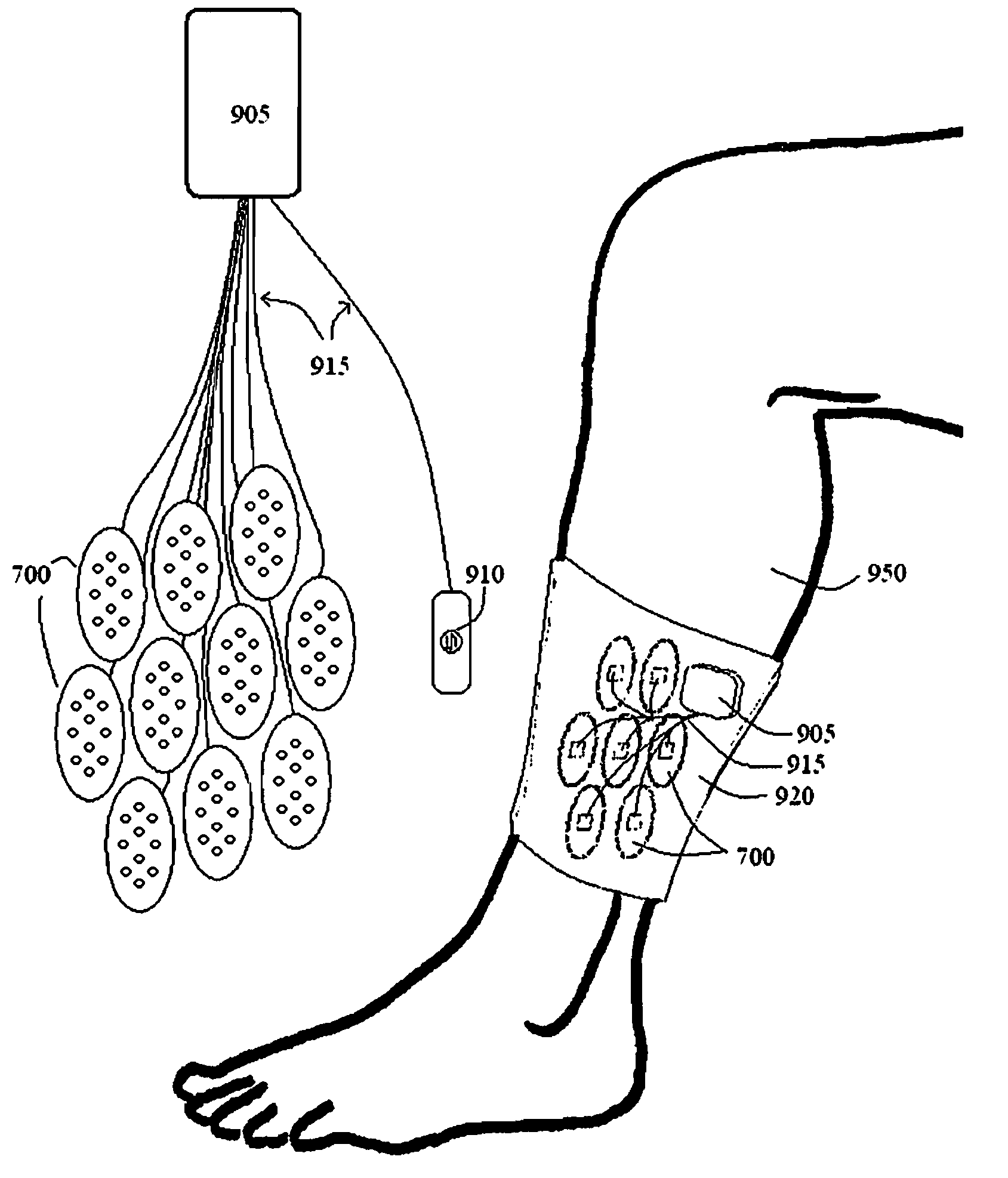
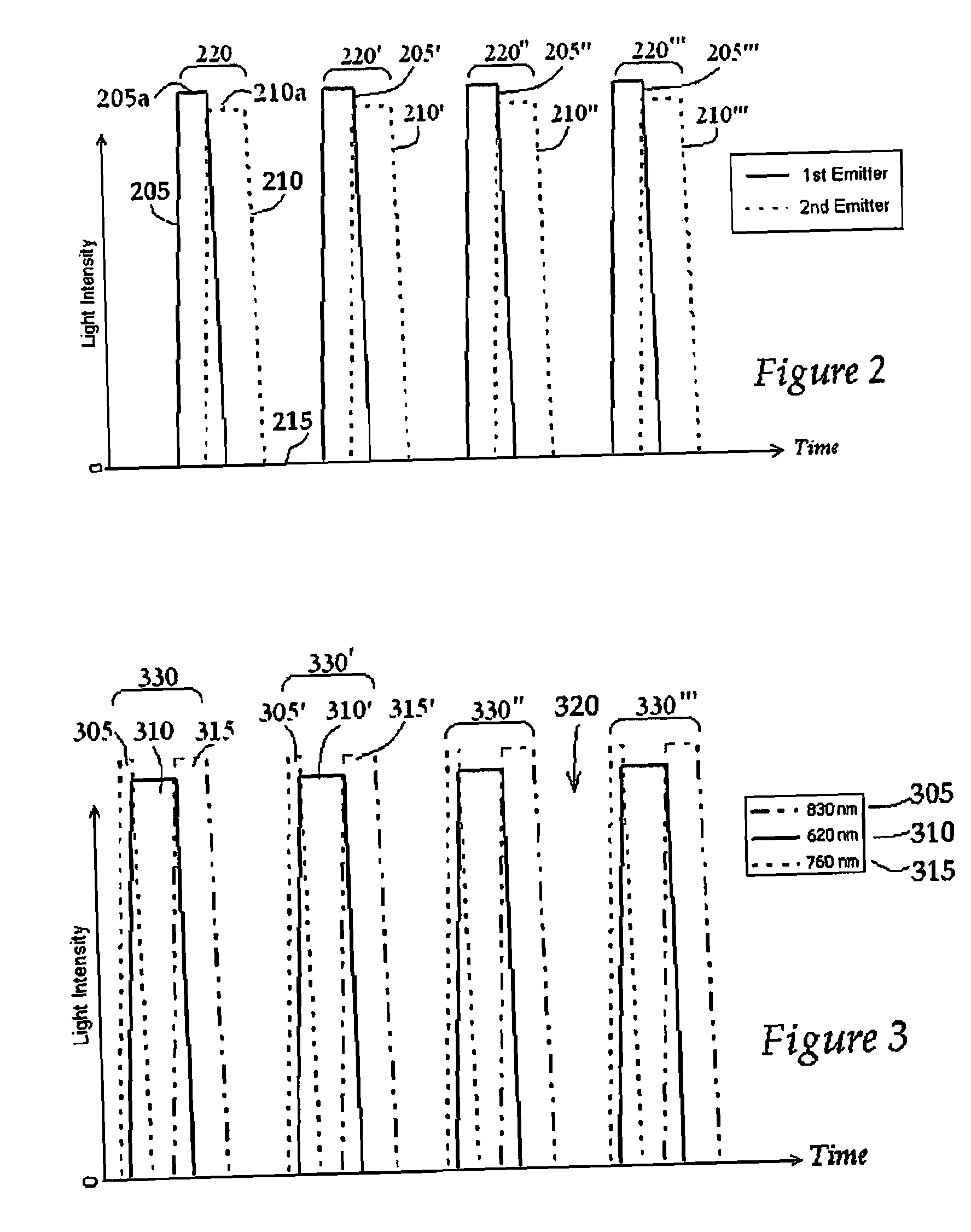
Temporal control in phototherapy
InactiveUS20080269849A1Improve efficiencySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyPhototherapy unitPeak value
An apparatus for delivering phototherapy includes at least one substrate, at least one emitter mounted on the substrate, and which emits at least two peak wavelengths of light, and an electronic circuit that controls emitter timing. The apparatus is configured as a dressing. A corresponding method includes delivering a first pulse of light to the target tissue from the emitter with a peak wavelength of light, and delivering at least a second pulse of light having a peak wavelength of light that is different from the peak wavelength of the first pulse of light, and the steps define a method of delivering a series of pulse sets of light, and the first and second pulses of light define a pulse set of light. Also disclosed are modular phototherapy units, control of timing of phototherapy by a perfusion detector, and use of long wavelength light for hyperbilirubinemia.
Owner:MERGENET MEDICAL
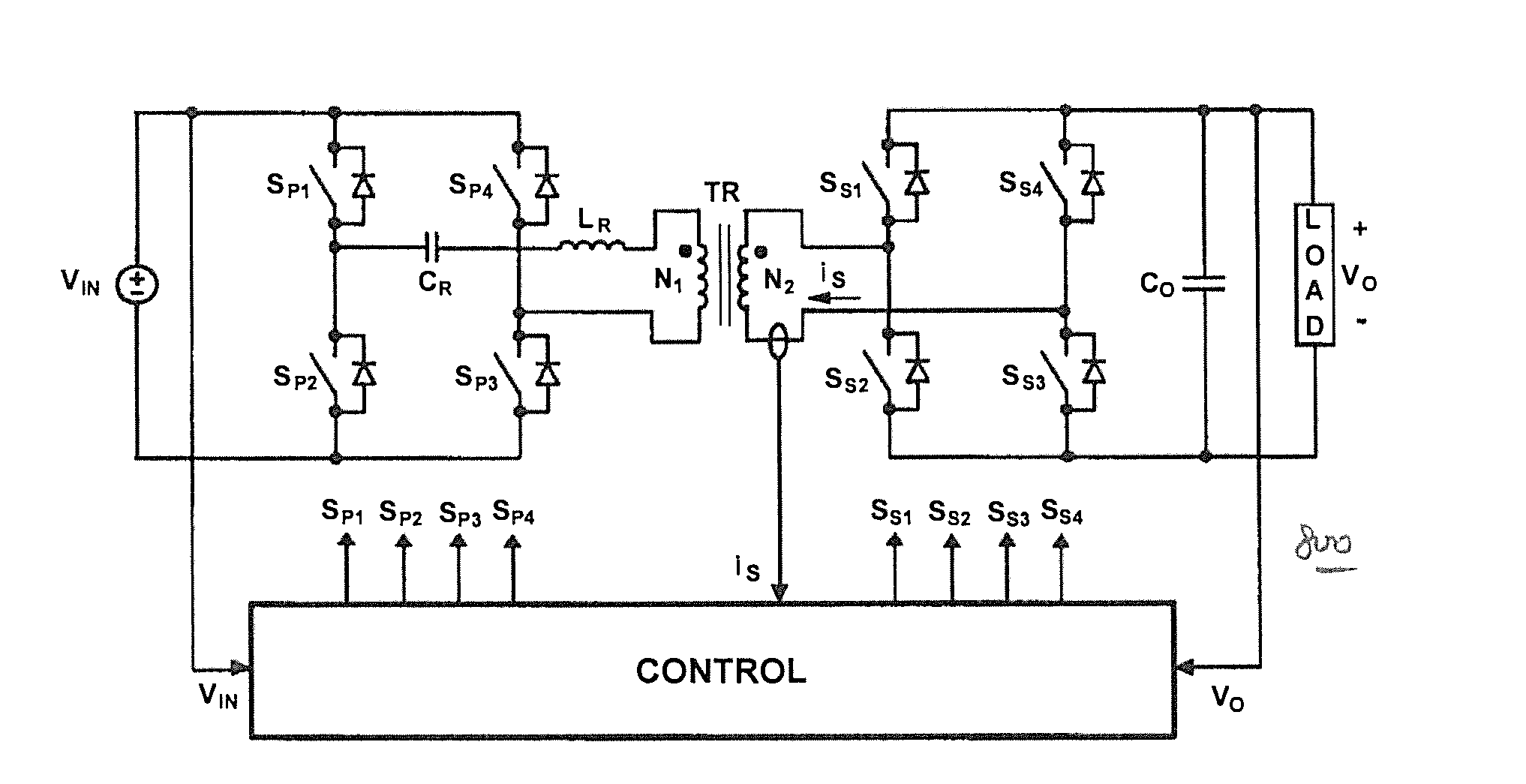
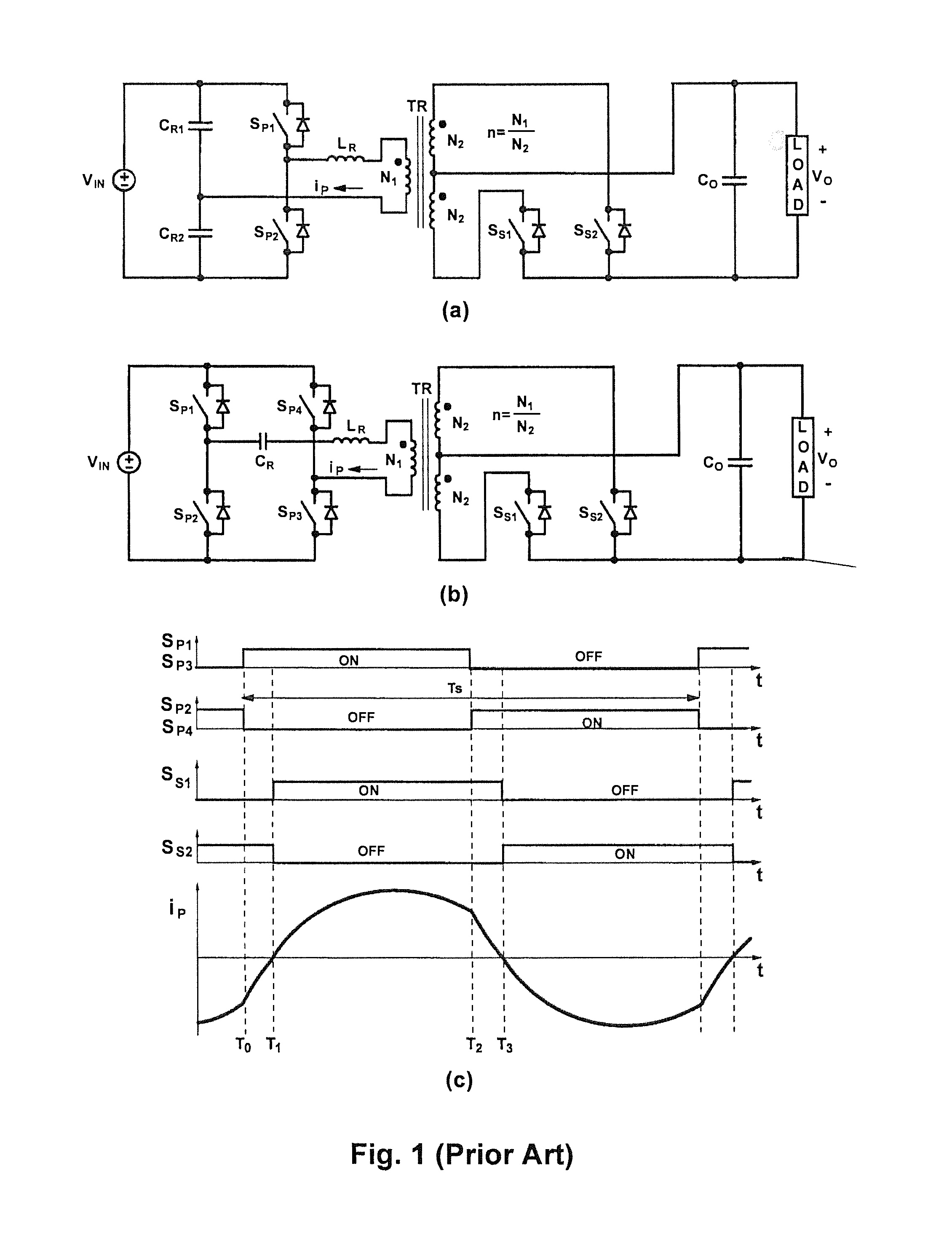
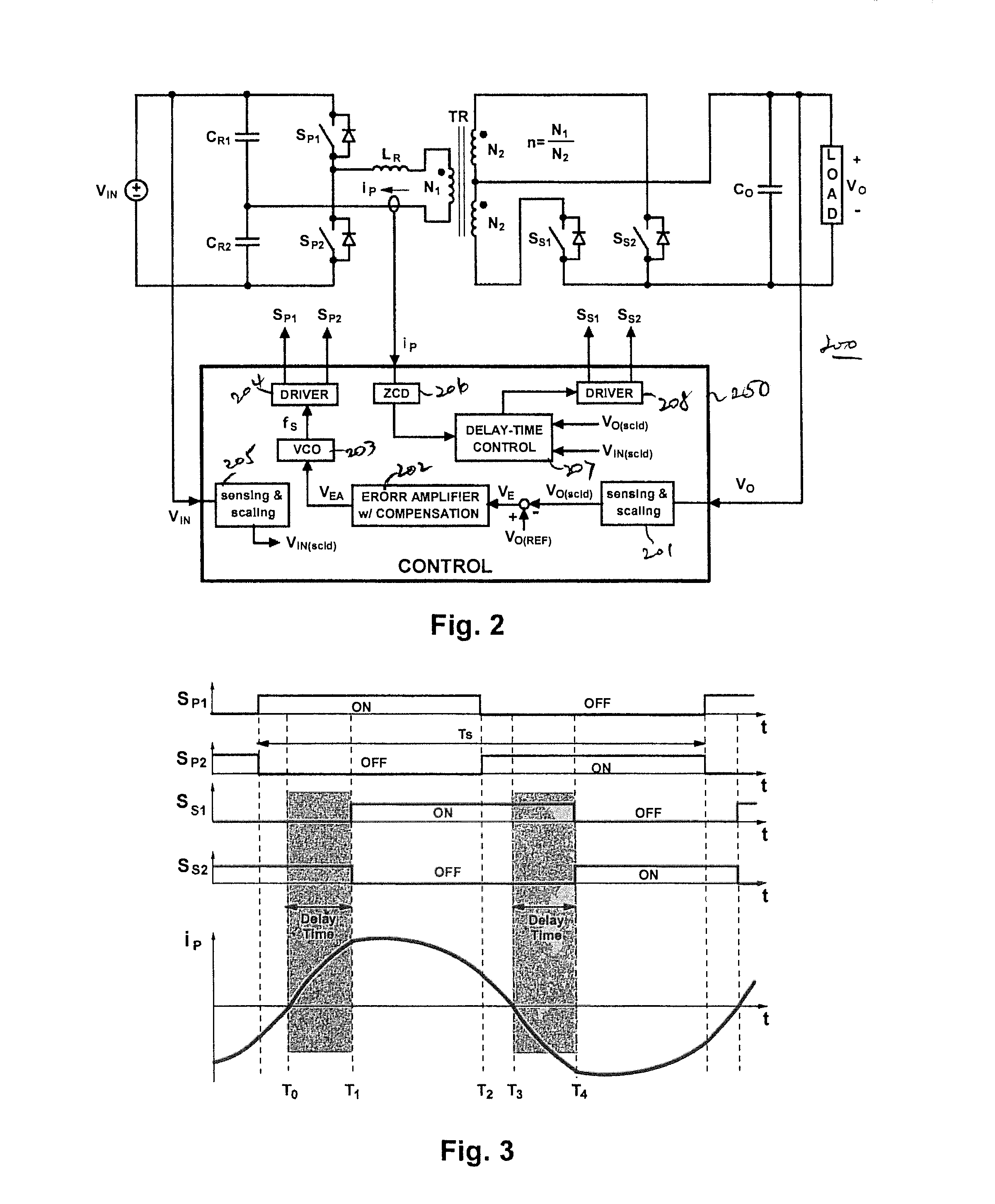
Resonant converters and control methods thereof
ActiveUS20150229225A1Improve performanceReducing switching-frequency rangeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTime delaysEngineering
Control methods for resonant converters offer improved performance in resonant converters that operate with a wide input-voltage range or a wide output-voltage range (or both) by substantially reducing the switching-frequency range. Reduction in the switching frequency range is achieved by controlling the output voltage with a combination of variable-frequency control and time-delay control. Variable-frequency control may be used to control the primary switches of an isolated resonant converter, while delay-time control may be used to control secondary-side rectifier switches provided in place of diode rectifiers. The secondary-side control may be implemented by sensing the secondary current or the primary current (or both) and by delaying the turning-off of the corresponding secondary switch with respect to the zero crossings in the secondary current or the primary current.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
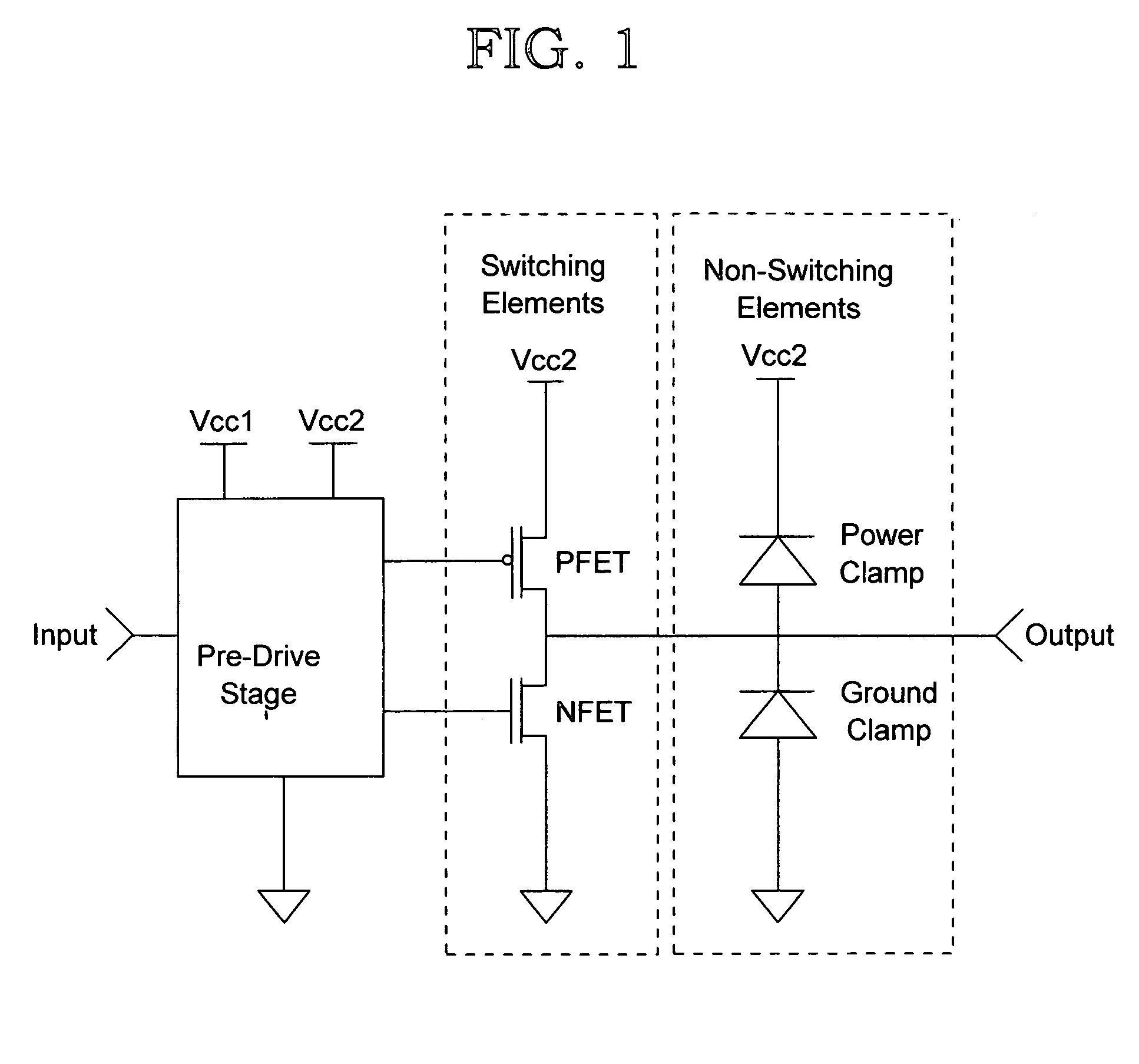
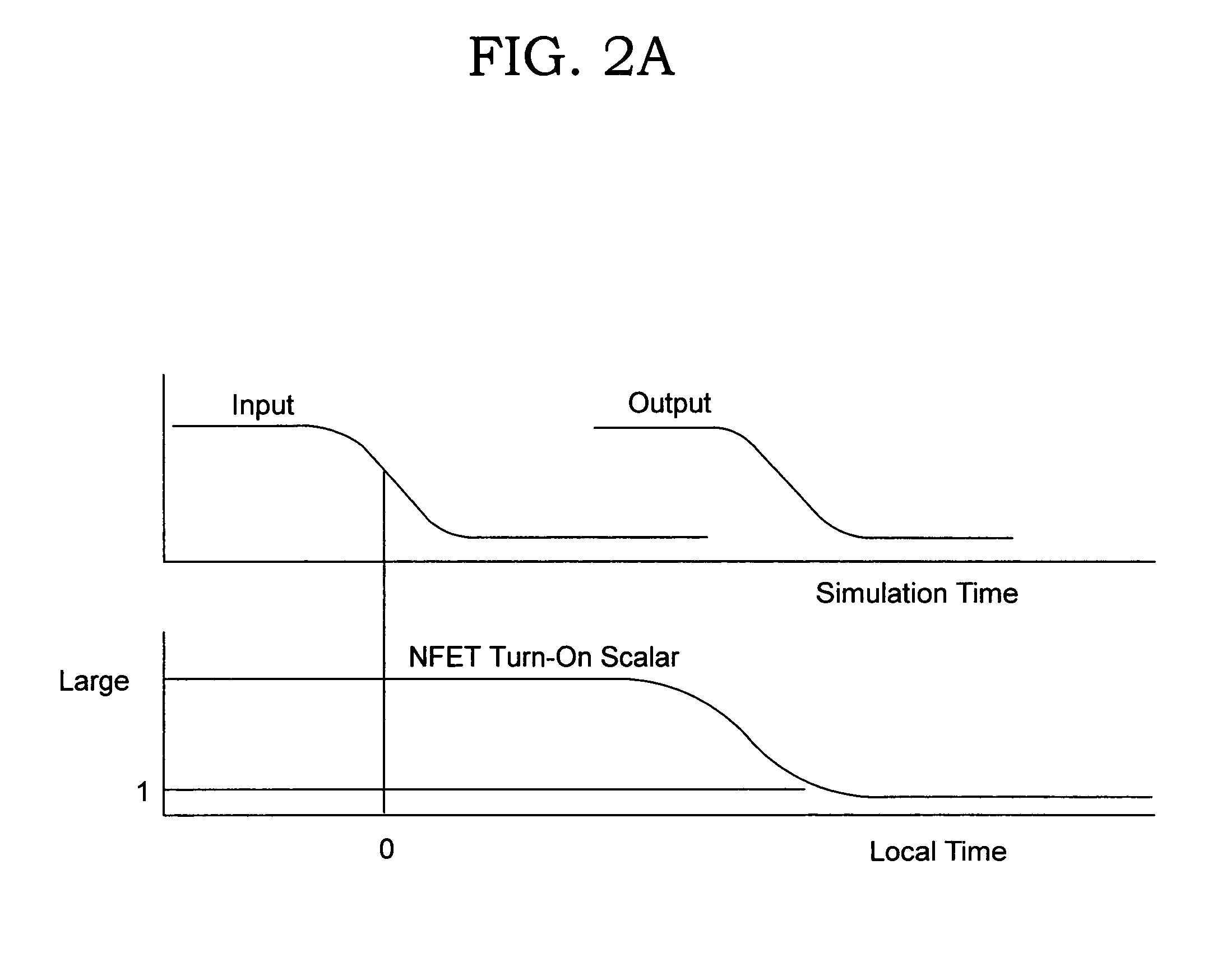
Circuit and method for modeling I/O
InactiveUS6983432B2Reduction in size of cross sectionReadily availableComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designBehavioral modelingTime control
A behavioral modeling technique that captures driver delay. The output characteristics of a typical driver are represented by two basic element types: switching and non-switching. Switching elements are functions of both time-varying and non-time-varying parameters, and non-switching elements are functions of non-time-varying parameters only. The outputs of these elements are characterized and tabulated by applying a DC voltage on the output of the driver and measuring the current through each element. The time-varying switching element are represent by time-controlled resistors. The invention provides a methodology to account for variations in input transition rate, supply voltage(s) or temperature.
Owner:IBM CORP
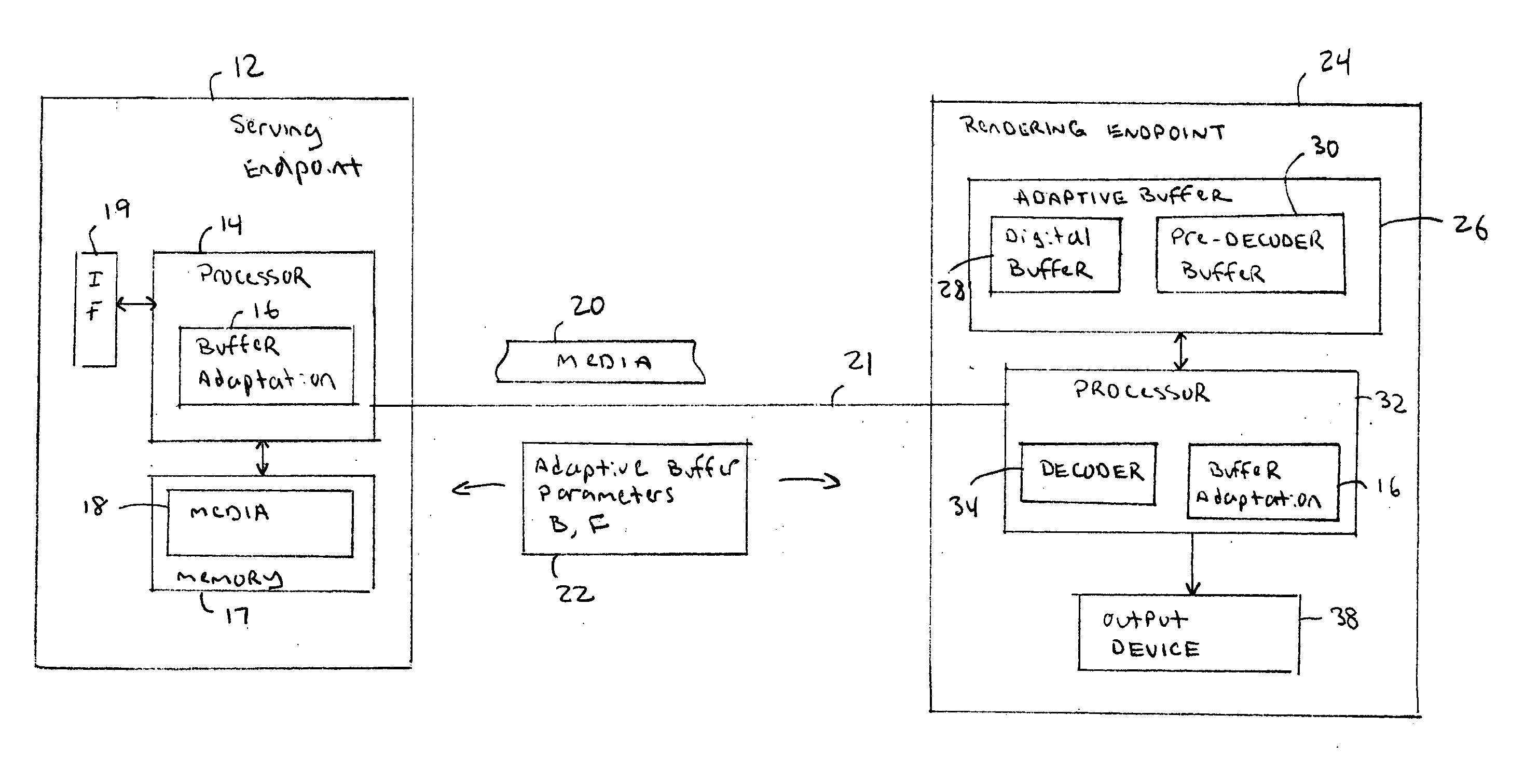
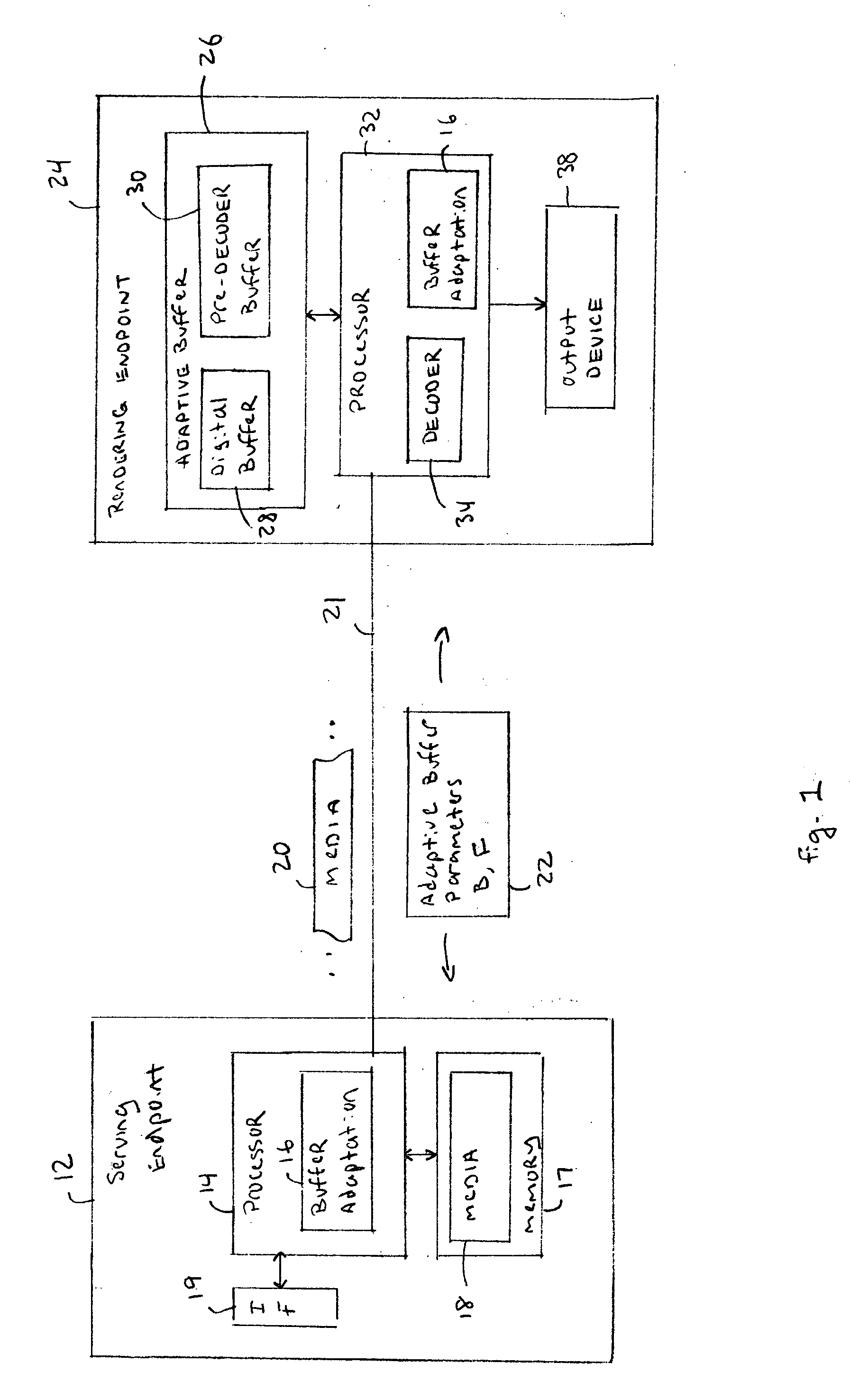
Method and apparatus for adaptive buffering
InactiveUS20060109856A1Efficient transportReadily apparentNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTime controlReal-time Transport Protocol
An adaptive buffering scheme allows more effective media transport and buffering. In one aspect of the adaptive buffering scheme, buffering parameters are adapted to different media characteristics, such as media play commands or the amount of encoding / transcoding required for the particular media stream. In another aspect of the adaptive buffering scheme, buffering is adapted to different transmission or memory conditions, such as transmission rate, packet jitter, or the amount of available buffer memory. In one example, the adaptive buffering is supported using Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), and / or Real Time Transport Protocol (RTP) and associated Real Time Control Protocol (RTCP), and / or Session Description Protocol (SDP) messages.
Owner:SHARP KK
Hydrocephalus valve
In order to allow improved adaptation to the situation existing in a patient in the case of a hydrocephalus valve with an electric actuating system comprising a control system opening and closing the hydrocephalus valve, it is proposed that the control system is a time control system.
Owner:MIETHKE CHRISTOPH
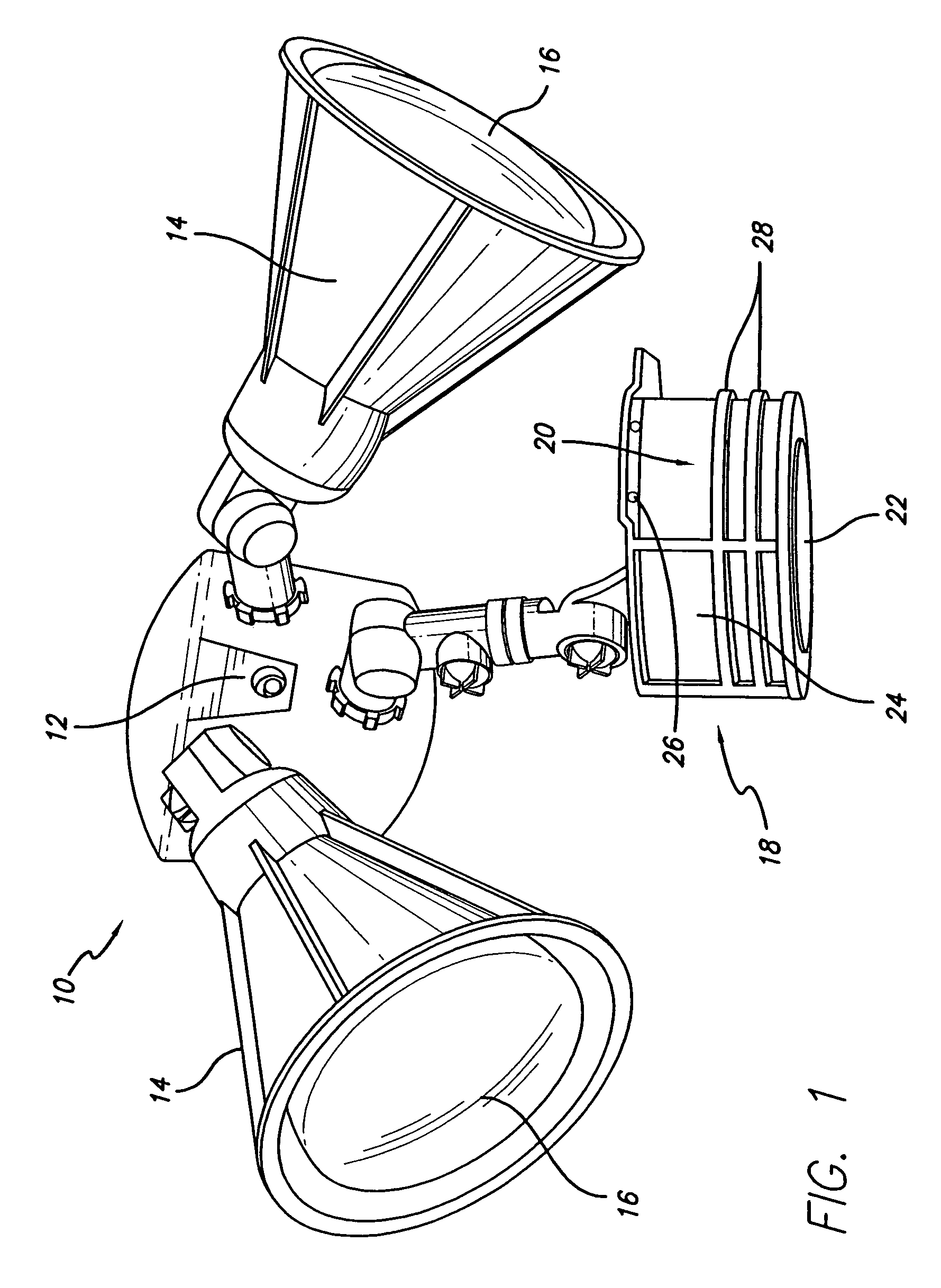
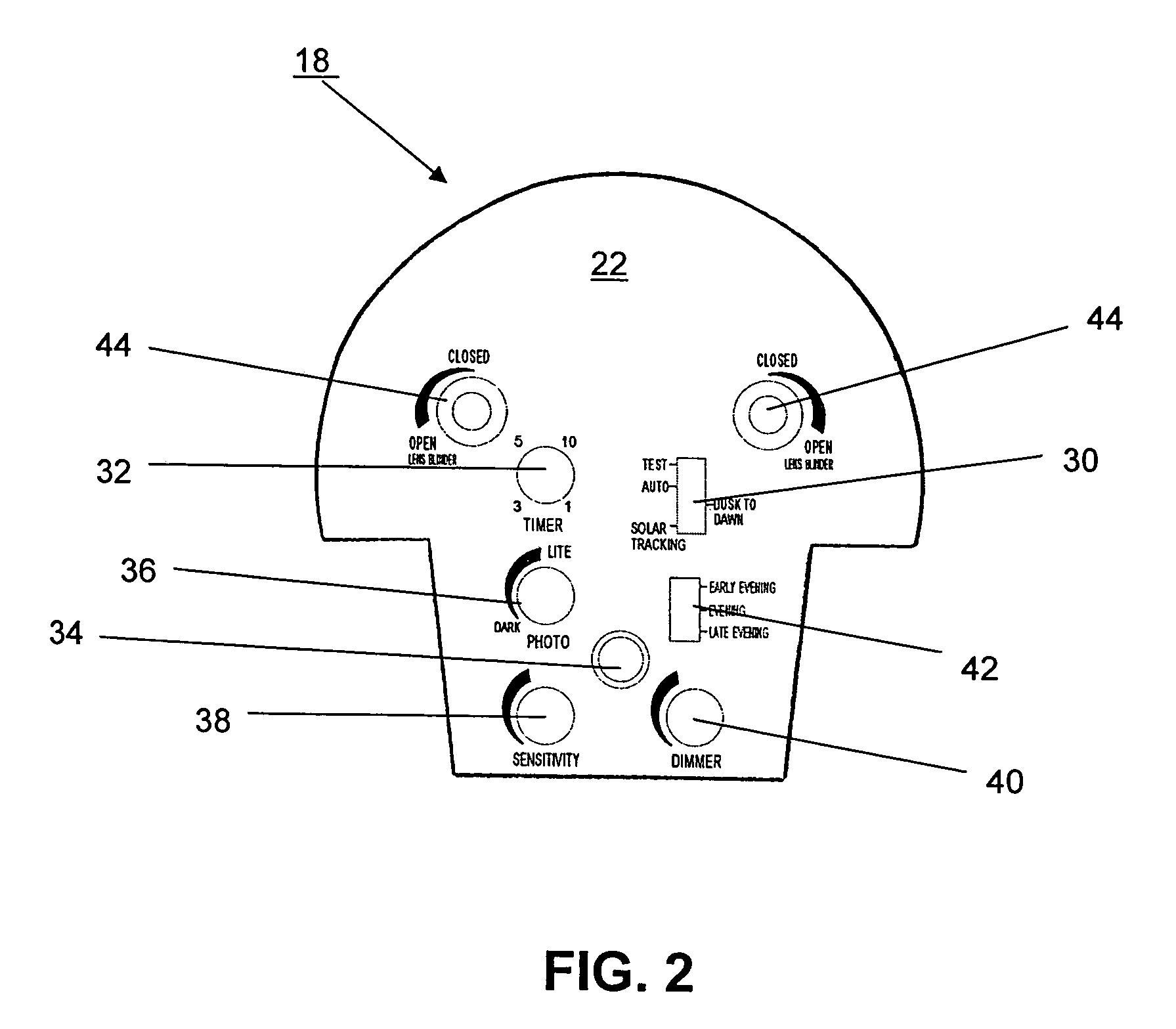
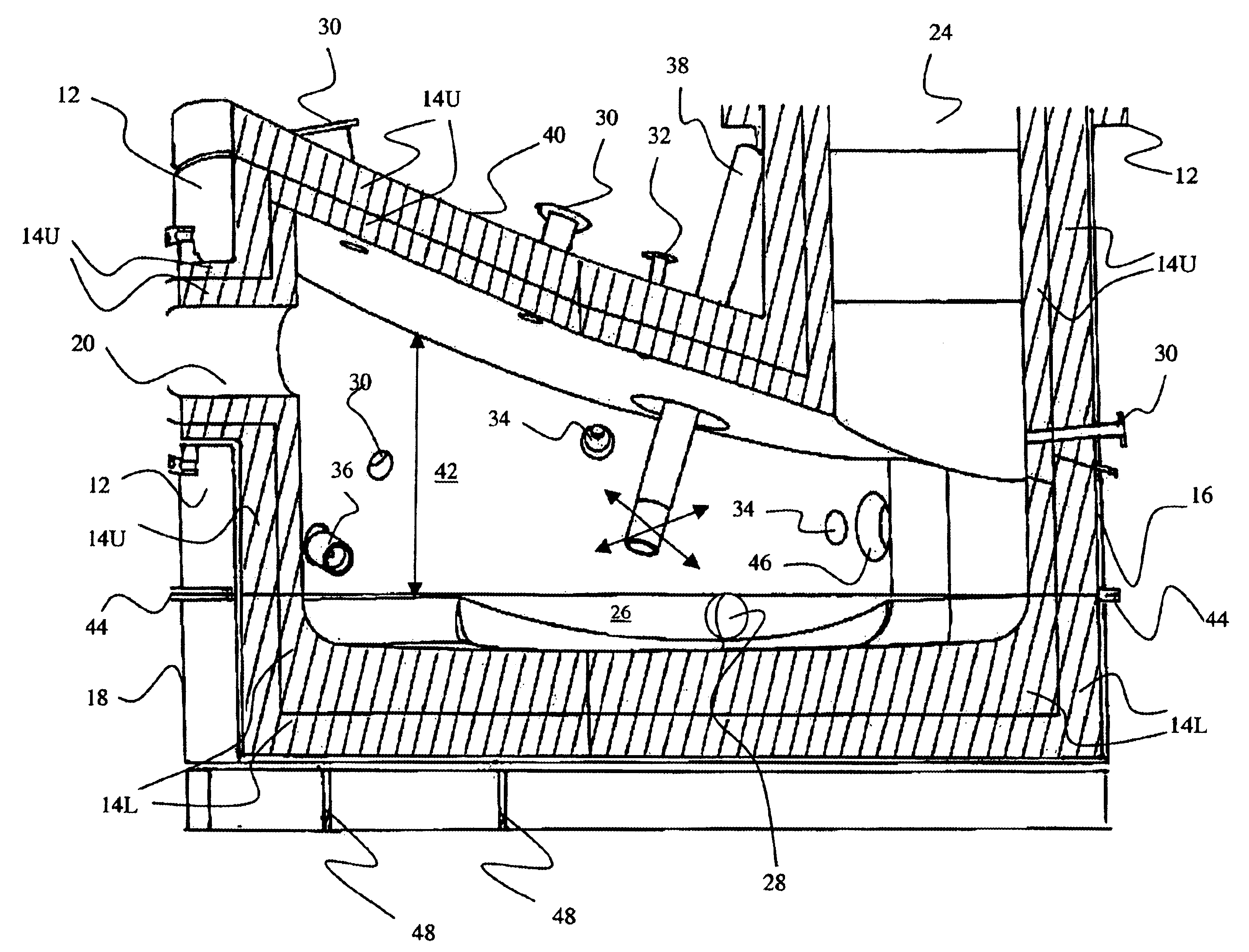
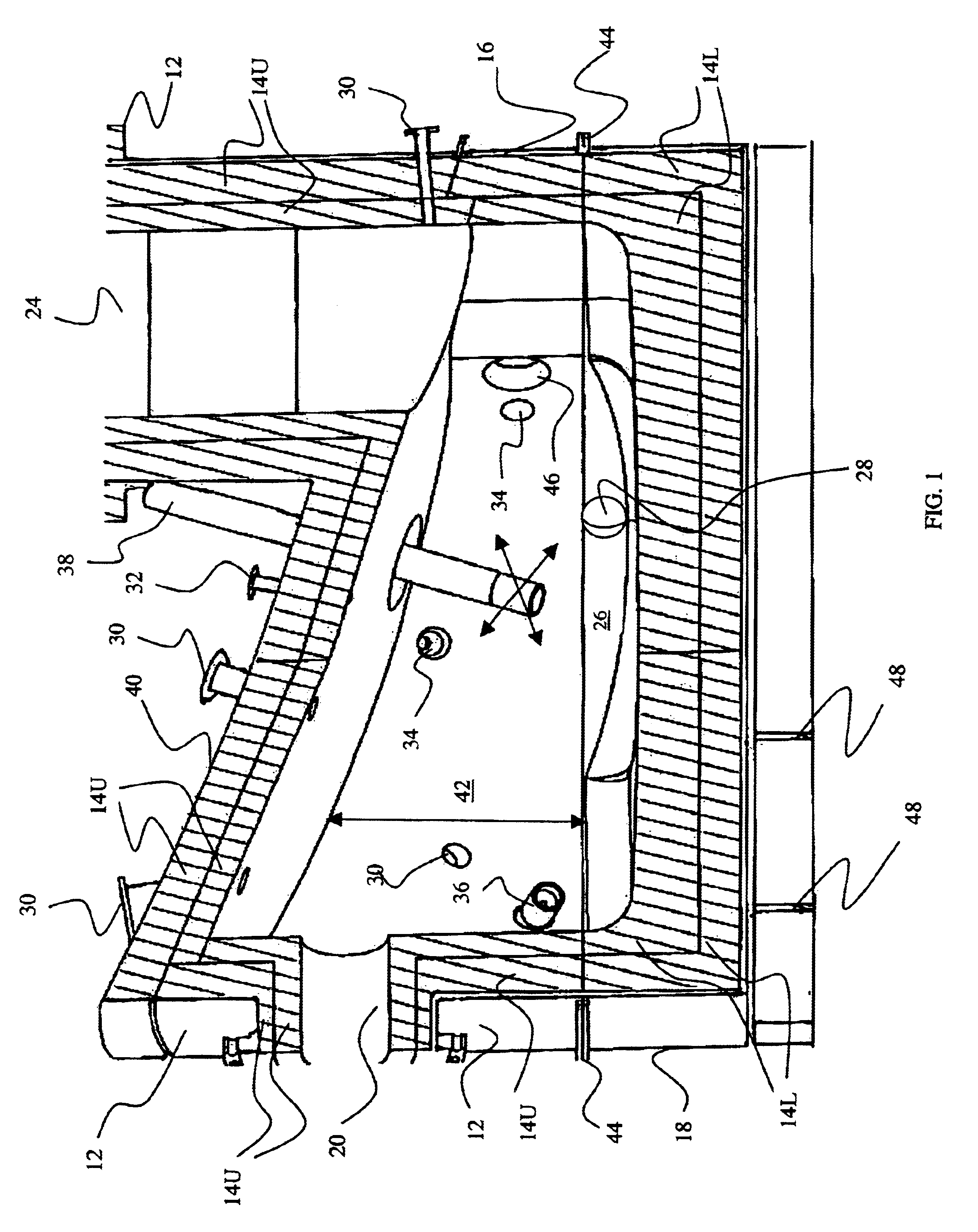
Nighttime-controlled lighting system
A time-controlled security lighting system records the length of nighttime and is capable of automatically adjusting for seasonal nighttime hours. The time duration between the initial nighttime darkness and the light of dawn, as sensed from the prior day by a photocell, is measured and recorded in memory. As the surrounding area becomes dark, the lighting system is activated to provide the illumination for the area. The duration of illumination is determined based on a predetermined fraction of the recorded length of nighttime from the previous night. The control system can adjust the duration of illumination according the recorded nighttime durations from the previous night. The control system can also adjust the level of illumination based on the signals from a motion detector, where the lights are set at a higher brightness for a predetermined amount of time upon detection of motion.
Owner:CORDELIA LIGHTING
Multiple plasma generator hazardous waste processing system
A waste processing system is provided herein which entails the use of at least one fixed-position plasma arc generator for primary processing and at least one moveable plasma arc generator for secondary processing assistance and / or final conditioning of the slag prior to exit from the reactor vessel. This optimum processing environment is provided by control of reactor vessel configuration and real time control of processing characteristics to ensure maximum processing efficiency.
Owner:PLASCO ENERGY GROUP INC
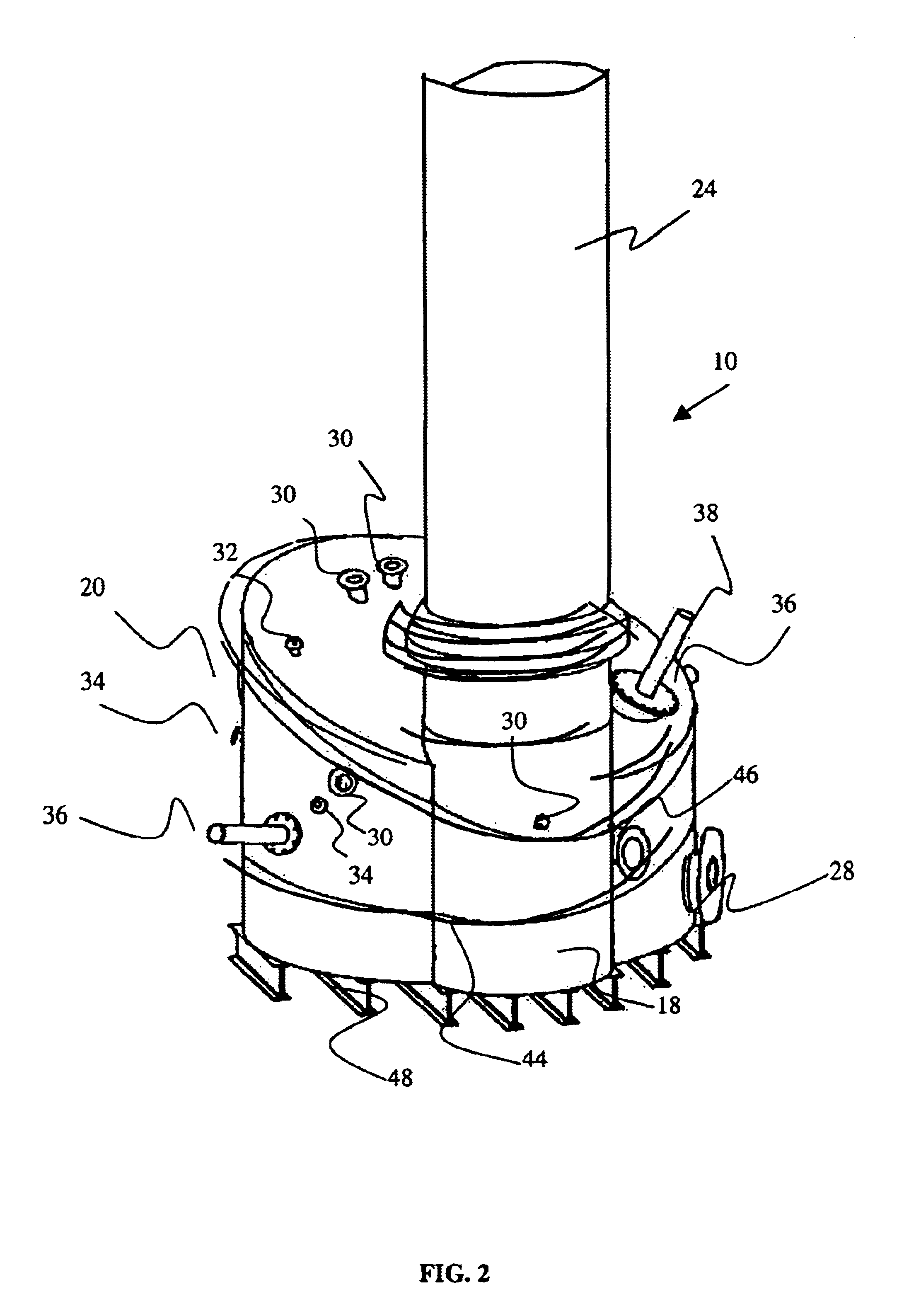
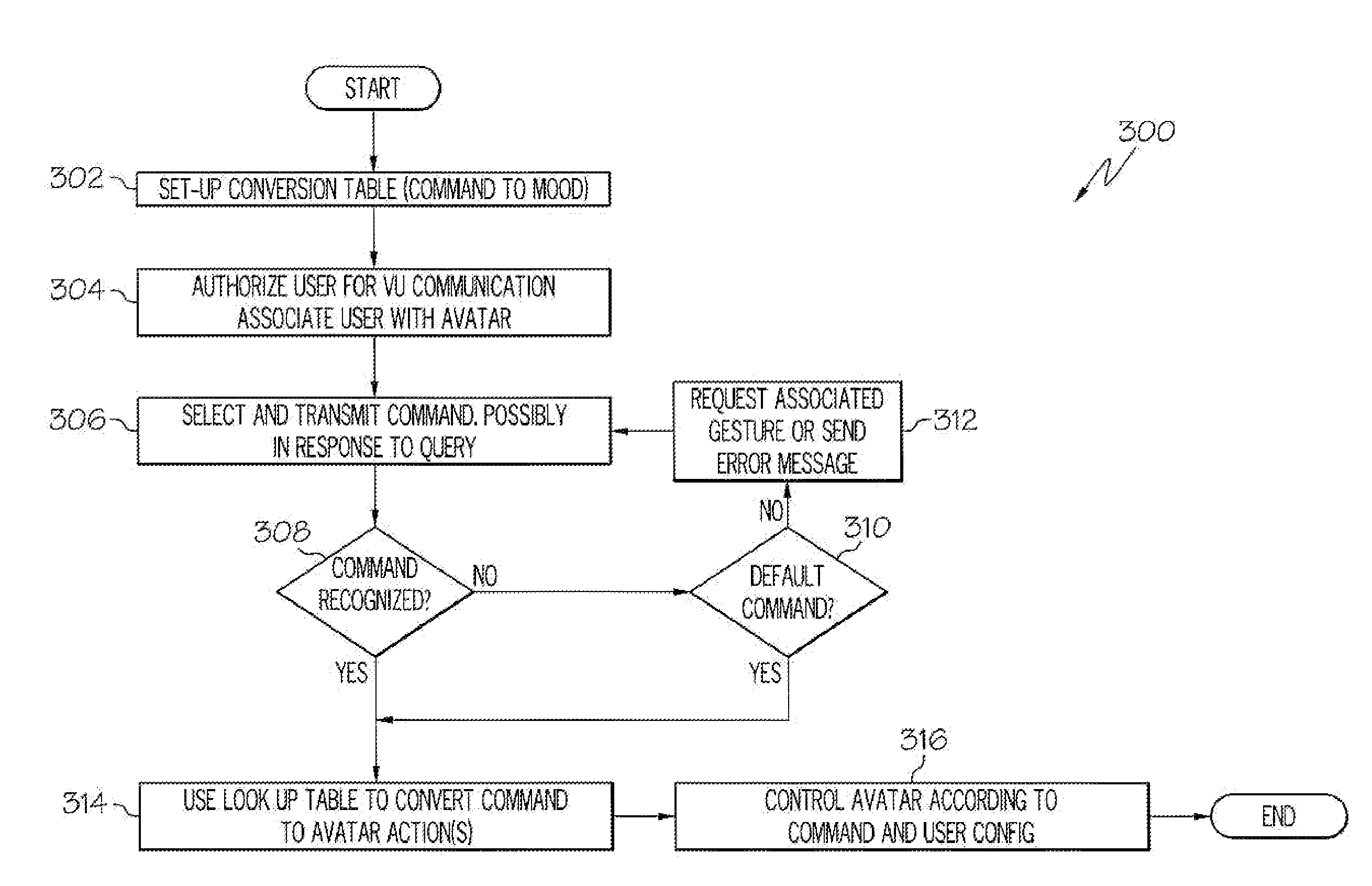
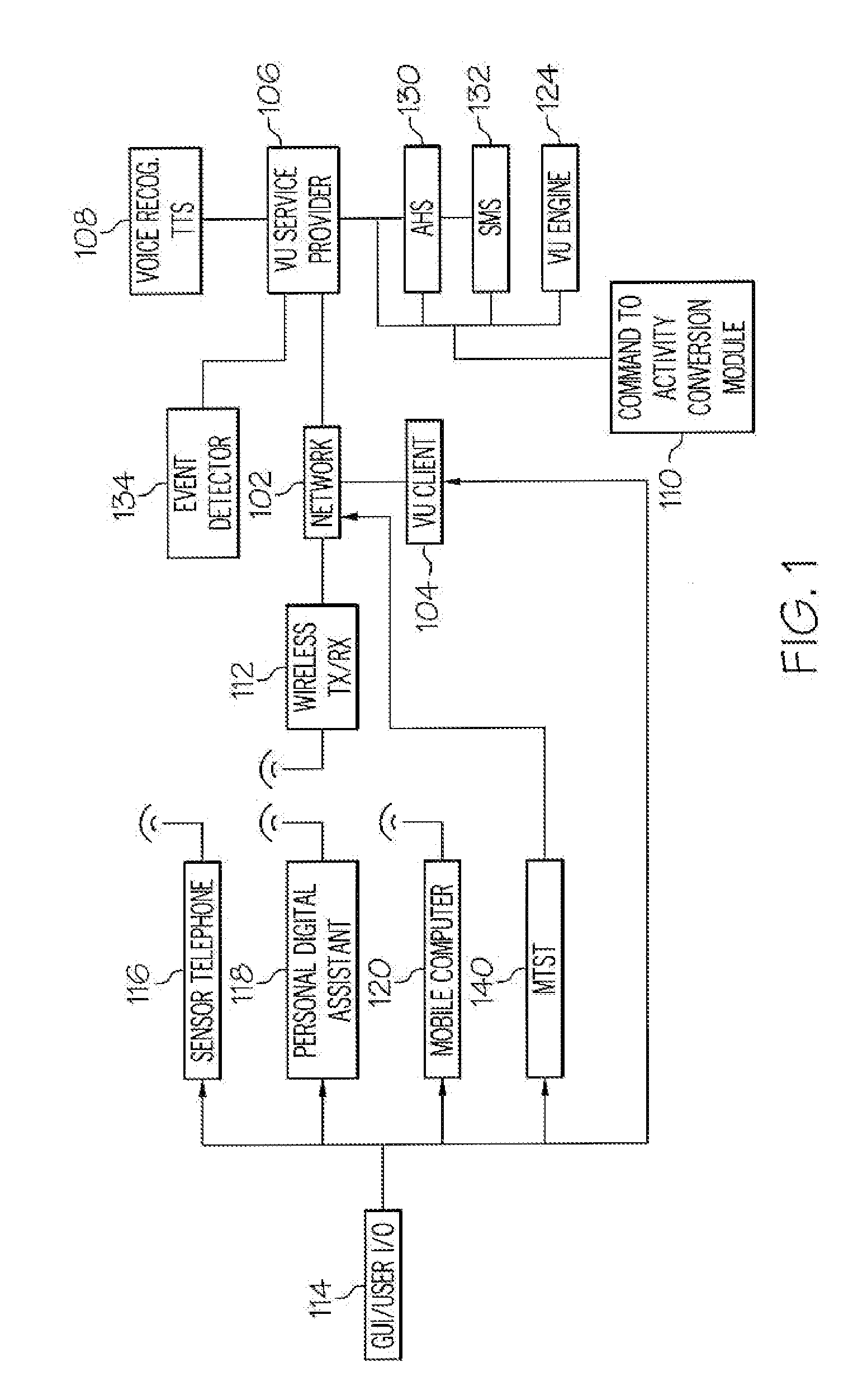
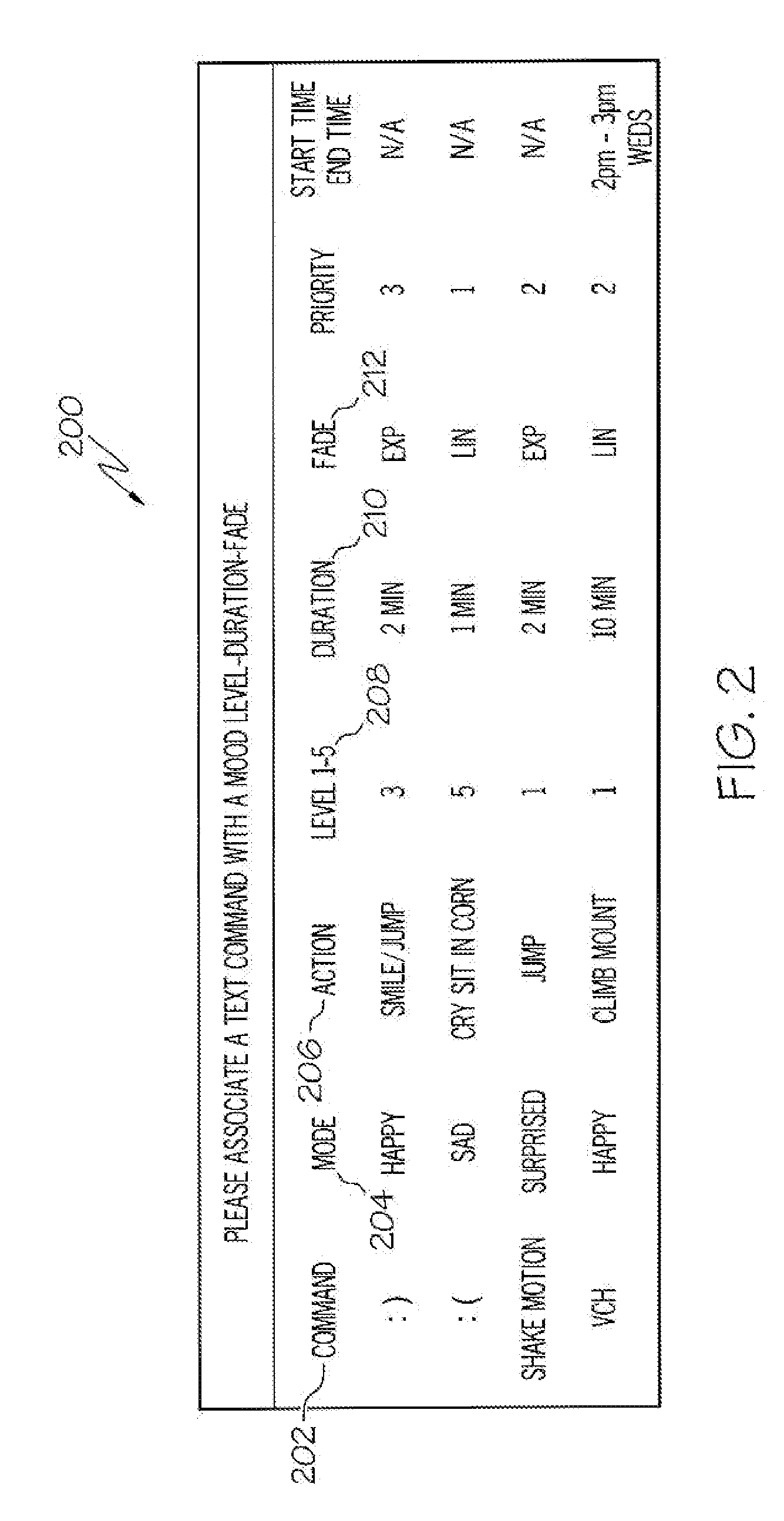
Arrangements for controlling activites of an avatar
Systems are disclosed herein that allow a participant to be associated with an avatar and receive a transmission from the participant in response to a participant activated transmission. The transmission can include a participant selectable and time delayed mood and / or activity command which can be associated with a user configurable command to avatar activity conversion table. The associated avatar activity table can provide control signal to the VU system controlling the participant's avatar for extended time periods, where the activity commands allow the avatar to exhibit a mood and to conduct an activity. The preconfigured time controlled activity commands allow the user to control their avatar without being actively engaged in a session with a virtual universe client or logged on and the control configuration can be set up such that a single mood / activity control signal can initiate moods and activities that occur over an extended period of time.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
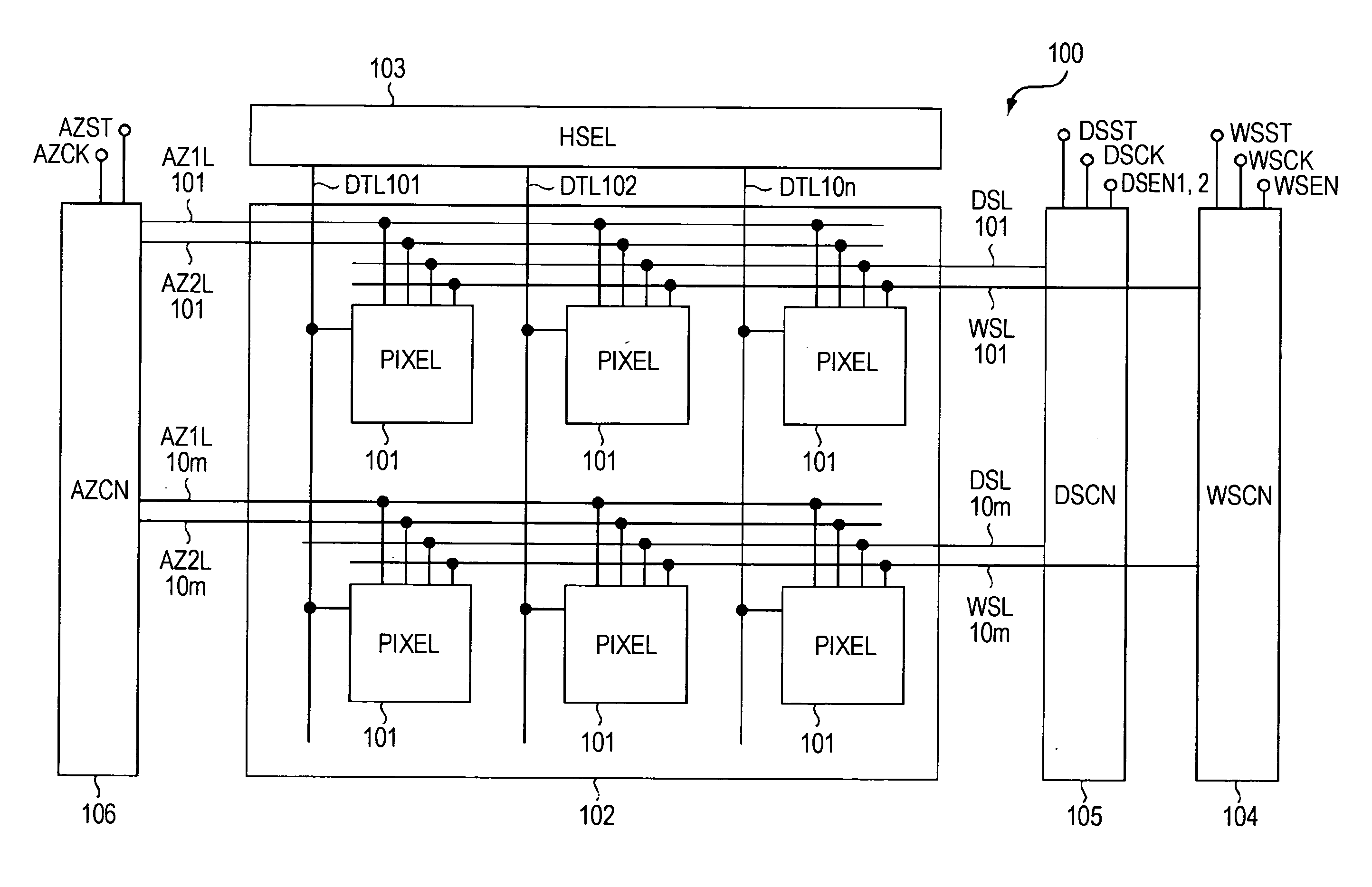
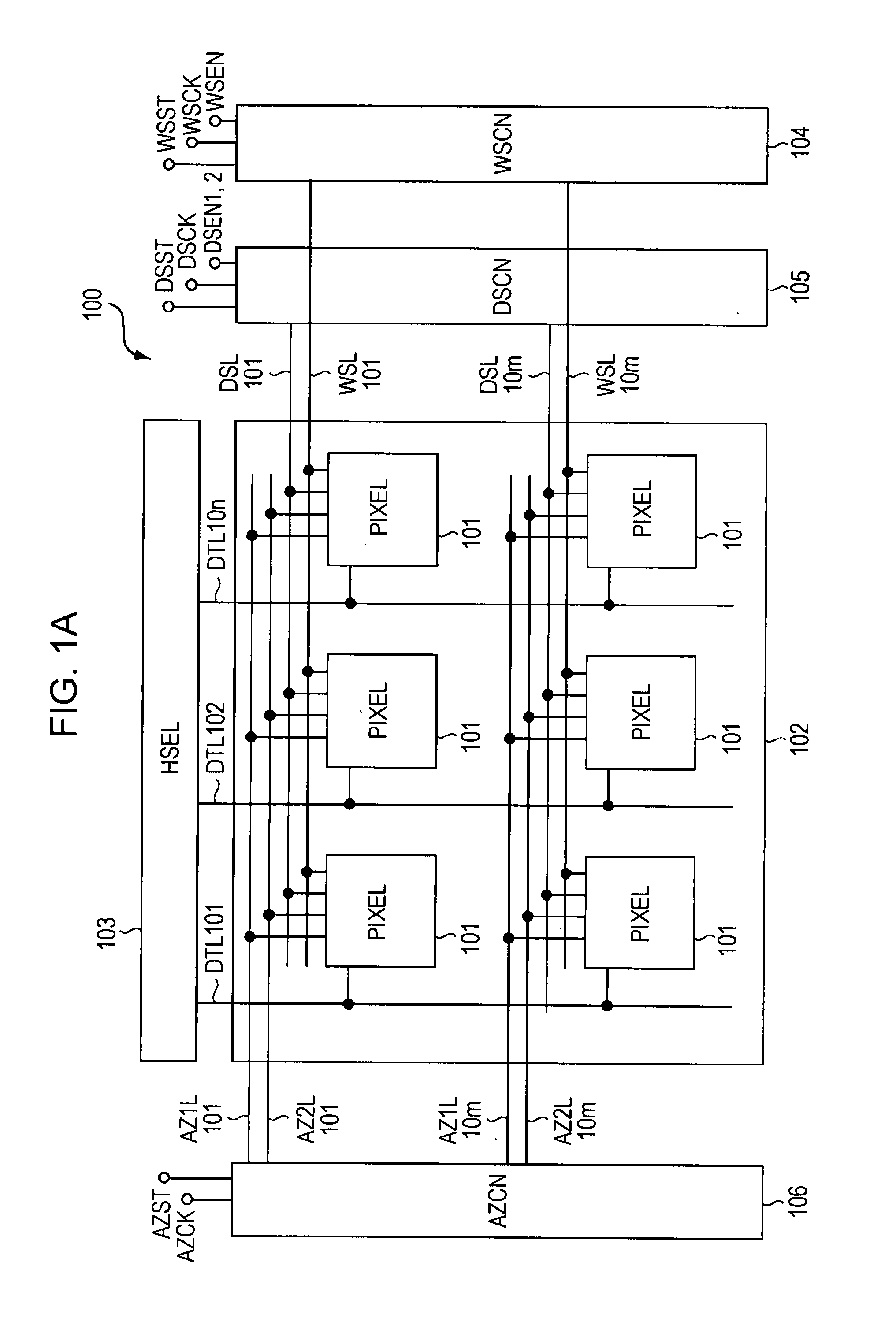
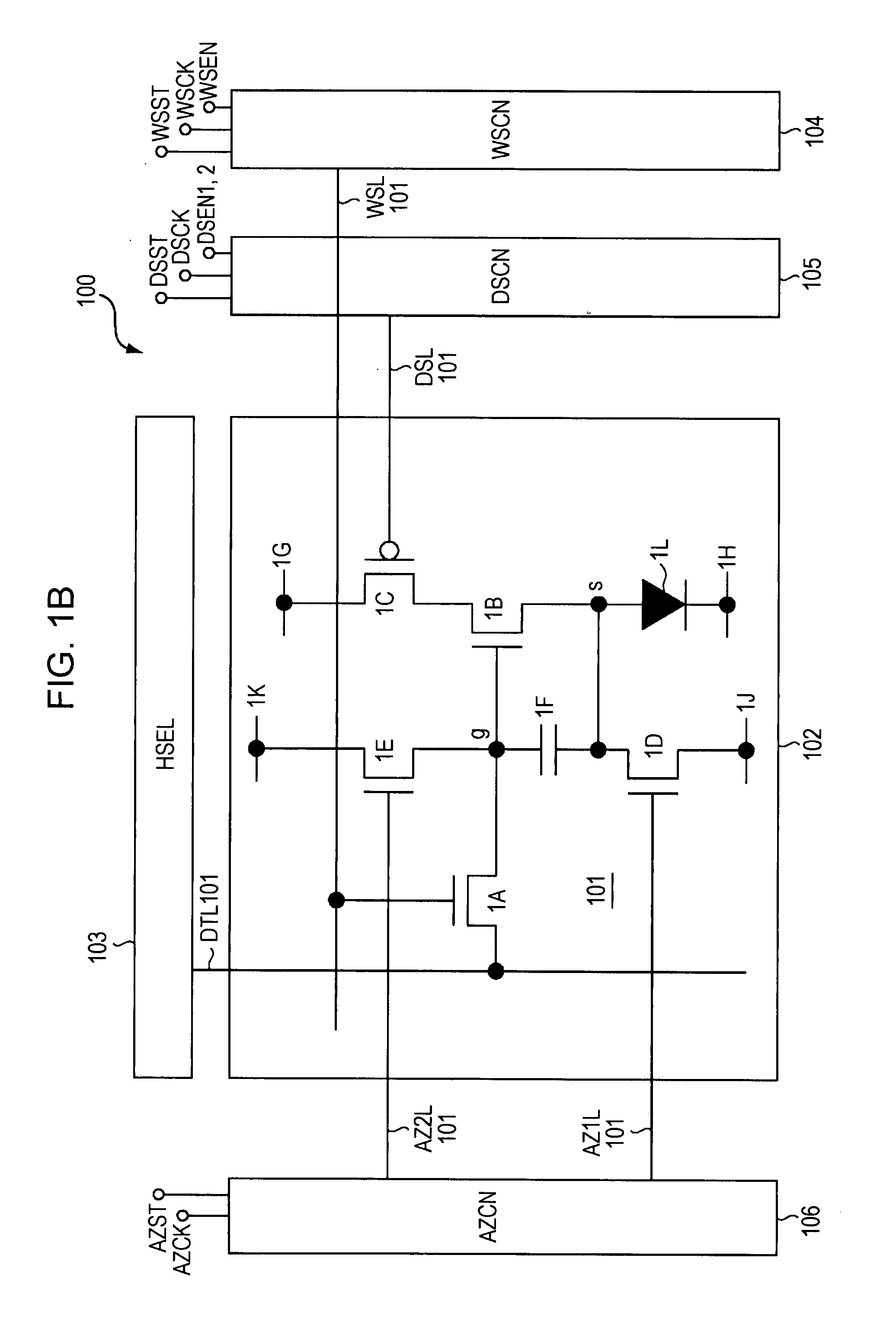
Display device, method for driving the same, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20080111766A1Influence on image quality in a display deviceCorrection of mobilityElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceDisplay device
A display device includes a pixel array unit and a peripheral circuit unit. The pixel array unit includes first scanning lines arranged in rows; second scanning lines arranged in rows; signal lines arranged in columns; and pixels arranged in a matrix pattern at intersections of the scanning lines and the signal lines. The peripheral circuit unit includes a first scanner to supply first control pulses to the first scanning lines; a second scanner to supply second control pulses to the second scanning lines; and a signal driver to supply video signals to the signal lines. Each of the pixels includes at least a sampling transistor; a driving transistor; an emission time controlling transistor; a holding capacitance; and a light-emitting element.
Owner:SONY CORP
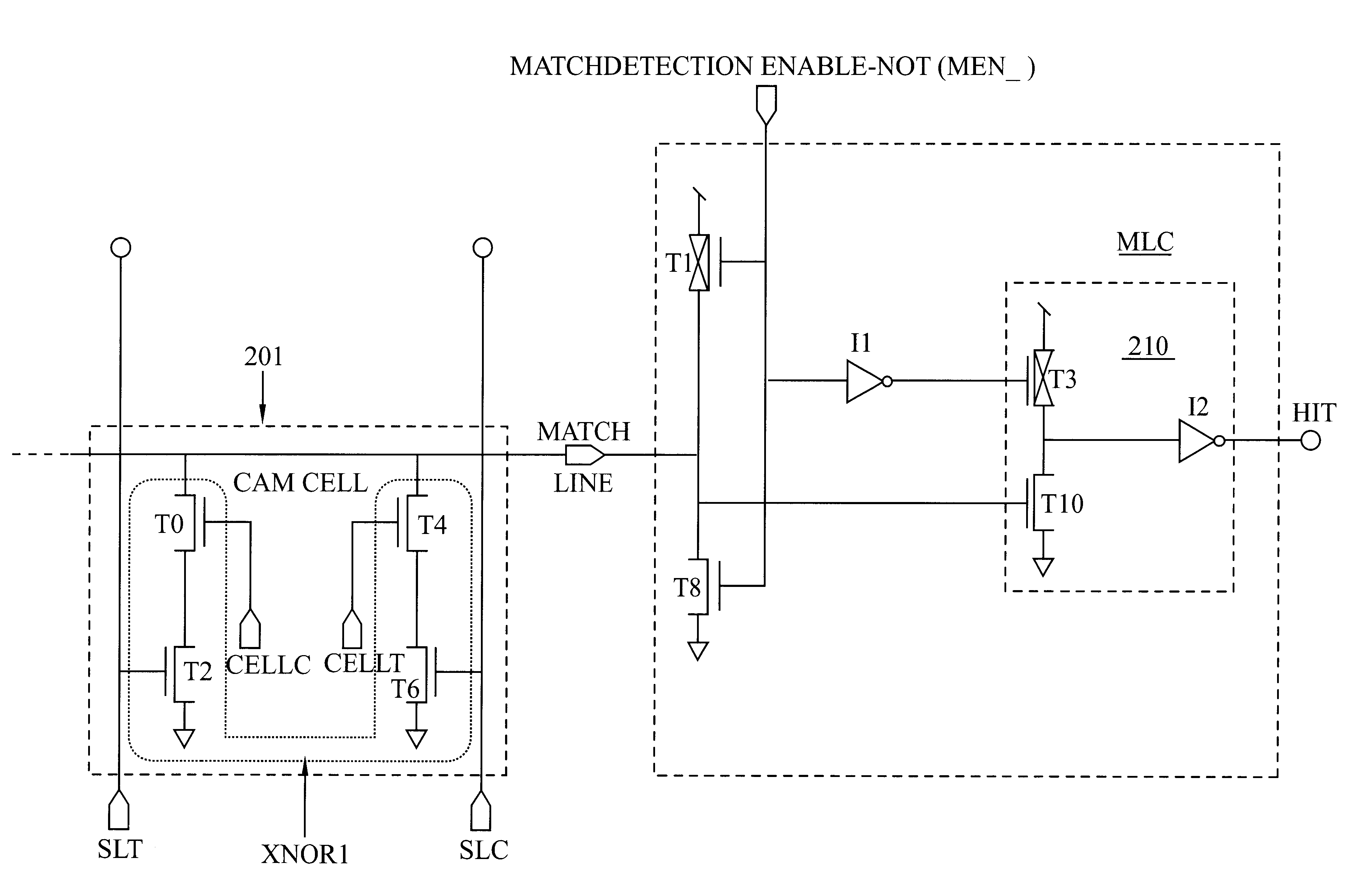
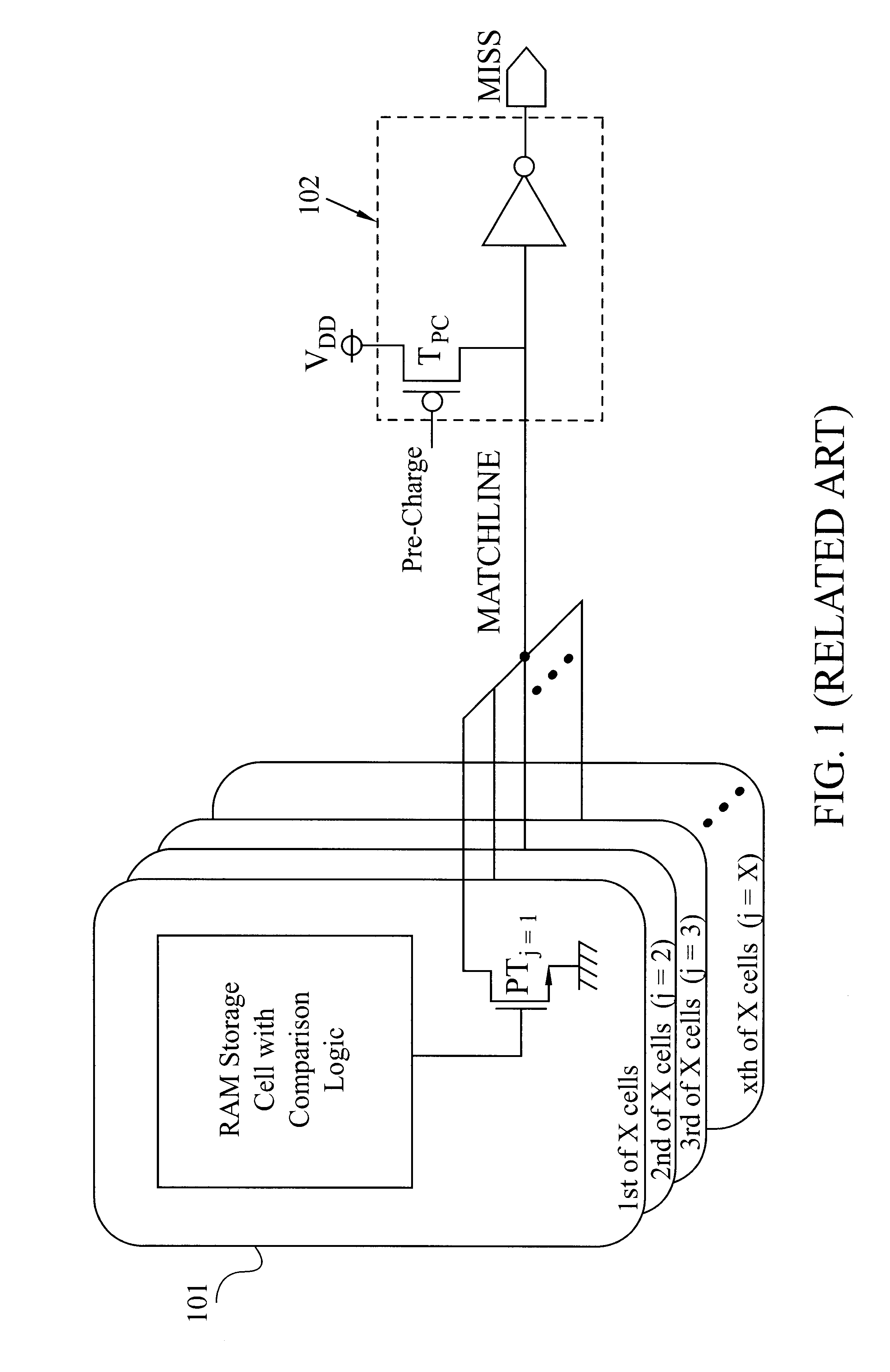
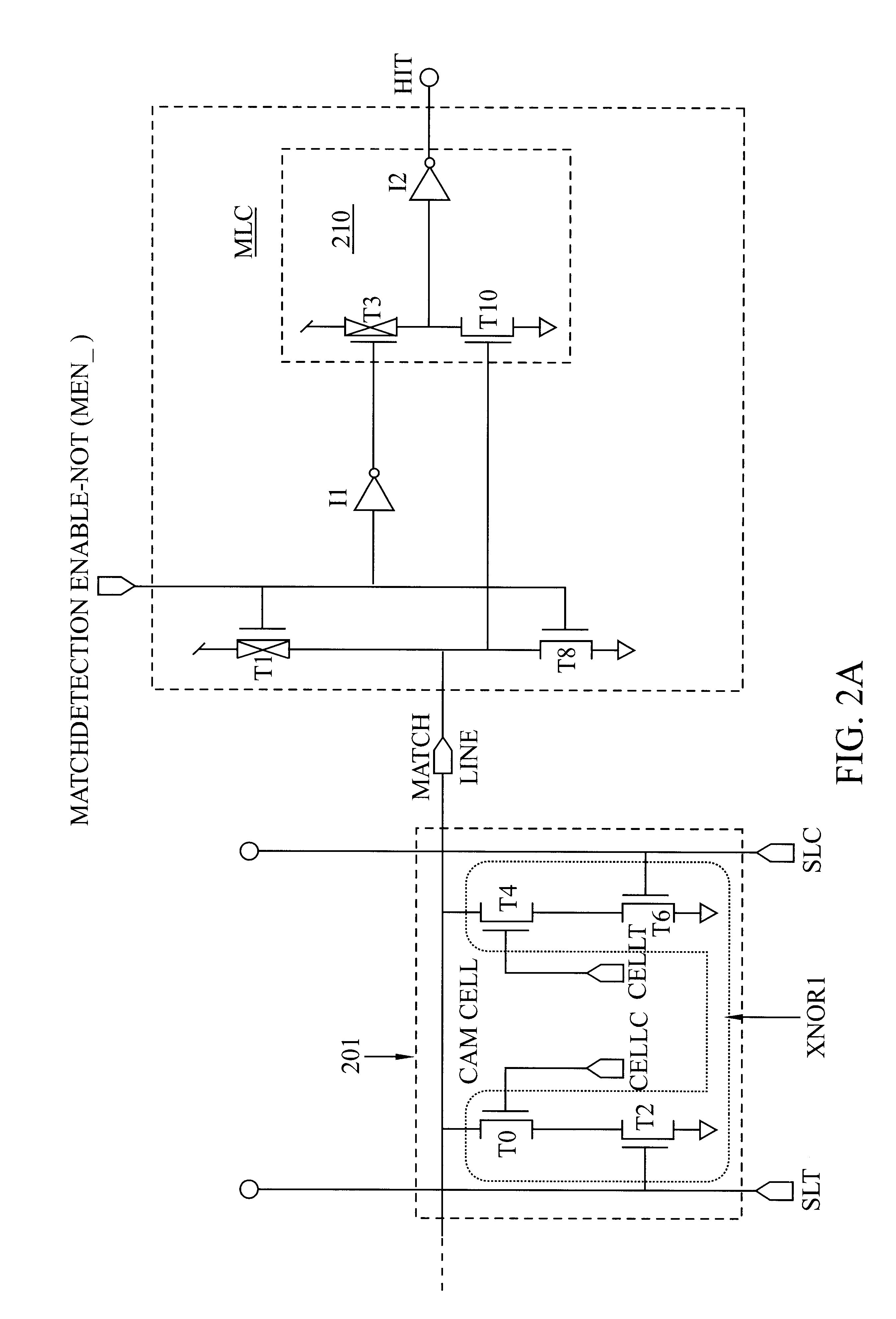
Low power CAM match line circuit
A Match-Detection Circuit and Match-Detection method, for low-power-consuming searches in a Content Addressable Memory. A HIT is output when the Match Line rises from a Low voltage level to a higher Match Detection Voltage. The Match Detection Voltage is approximately the conducting threshold voltage of an N-channel Field Effect Transistor (FET), and is normally less than One Half of the Power Supply Voltage. Circuits and methods to turn of the through-current in each MISS-ing entry by a carefully timed control signal at the end of a brief Match Detection Period, are disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
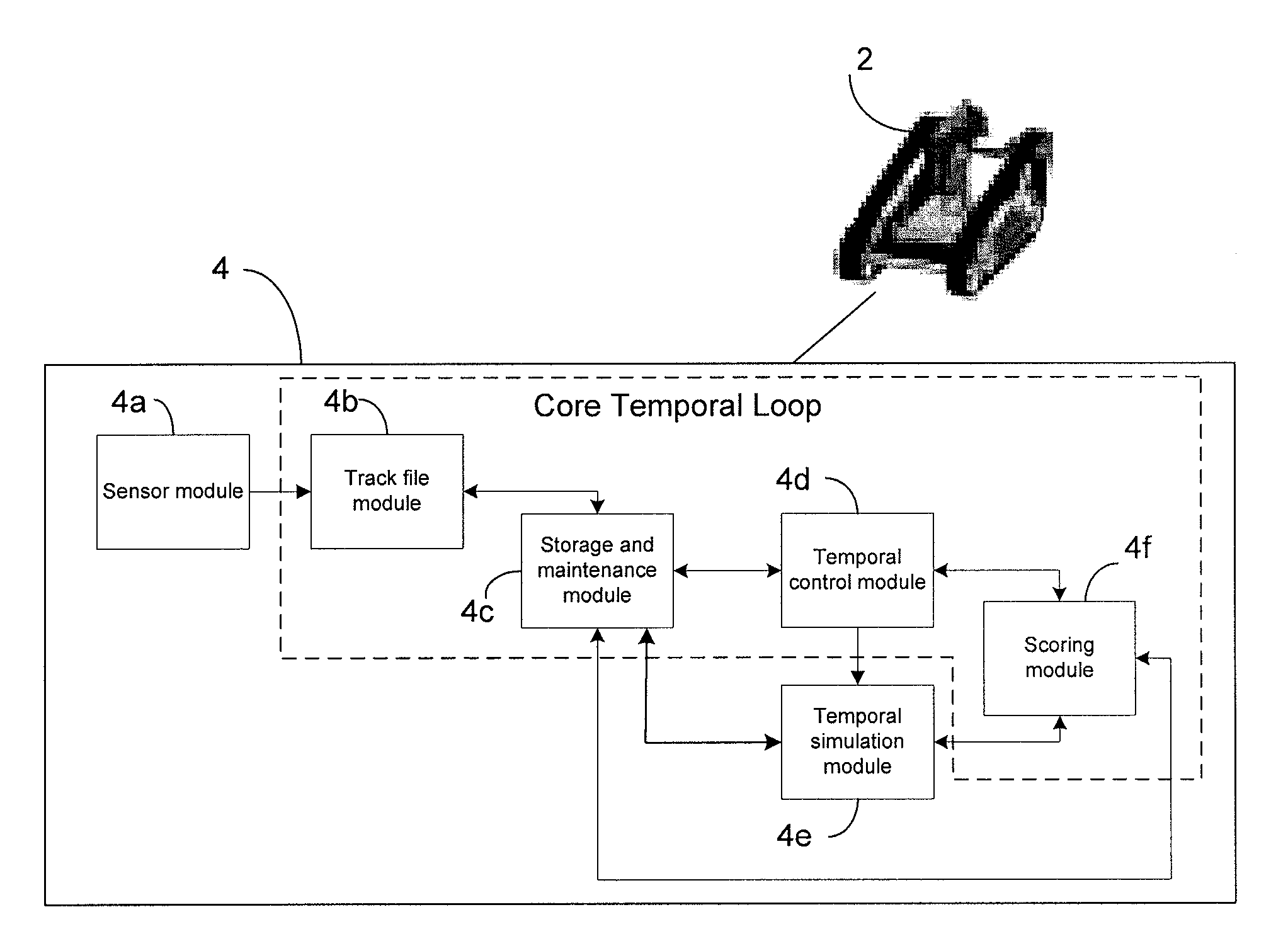
Temporal tracking robot control system
ActiveUS20110231016A1Autonomous decision making processNavigational calculation instrumentsObject basedHypothesis
A temporal controller for mobile robot path planning includes a sensor module for receiving data corresponding to spatial locations of at least one object, and a temporal control module operatively coupled to the sensor module, the temporal control module configured to predict future locations of the at least one object based on data received by the sensor module. The controller further includes a temporal simulation module operatively coupled to the temporal control module, wherein the temporal simulation module configured to use the predicted future locations of the at least one object to simulate multiple robot motion hypothesis for object avoidance and trajectory planning.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and apparatus for monitoring and controlling laser-induced tissue treatment
ActiveUS20050154380A1Great safety and efficiency and uniformity and continuityImprove the quality of treatmentControlling energy of instrumentLight therapyLight beamEngineering
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for controlling light-induced tissue treatment. In accordance with various aspects of the present invention, the invention provides for improved, real-time control of the light beam operational parameters which enables greater safety, efficiency, uniformity and continuity of the treatment process.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
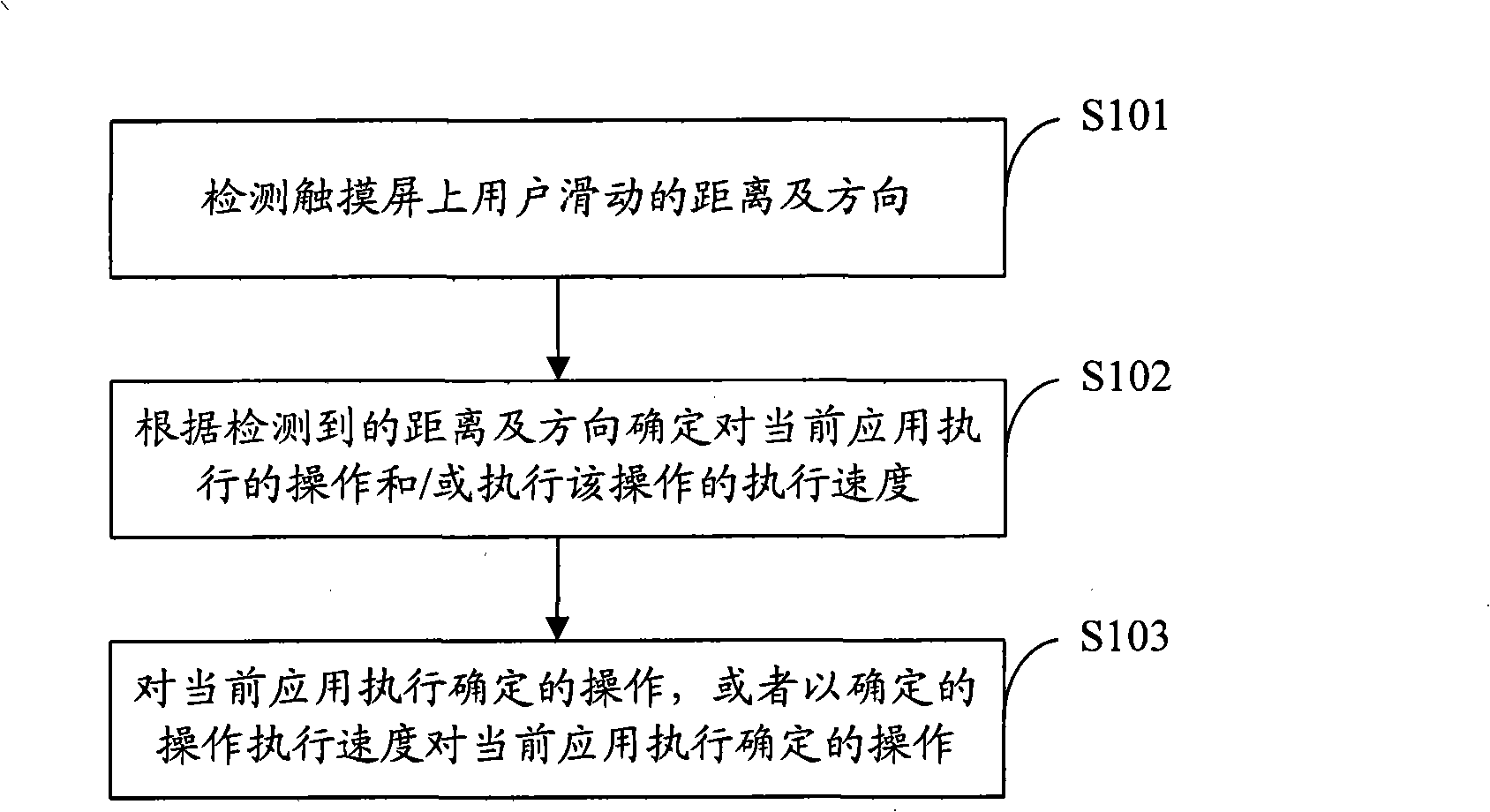
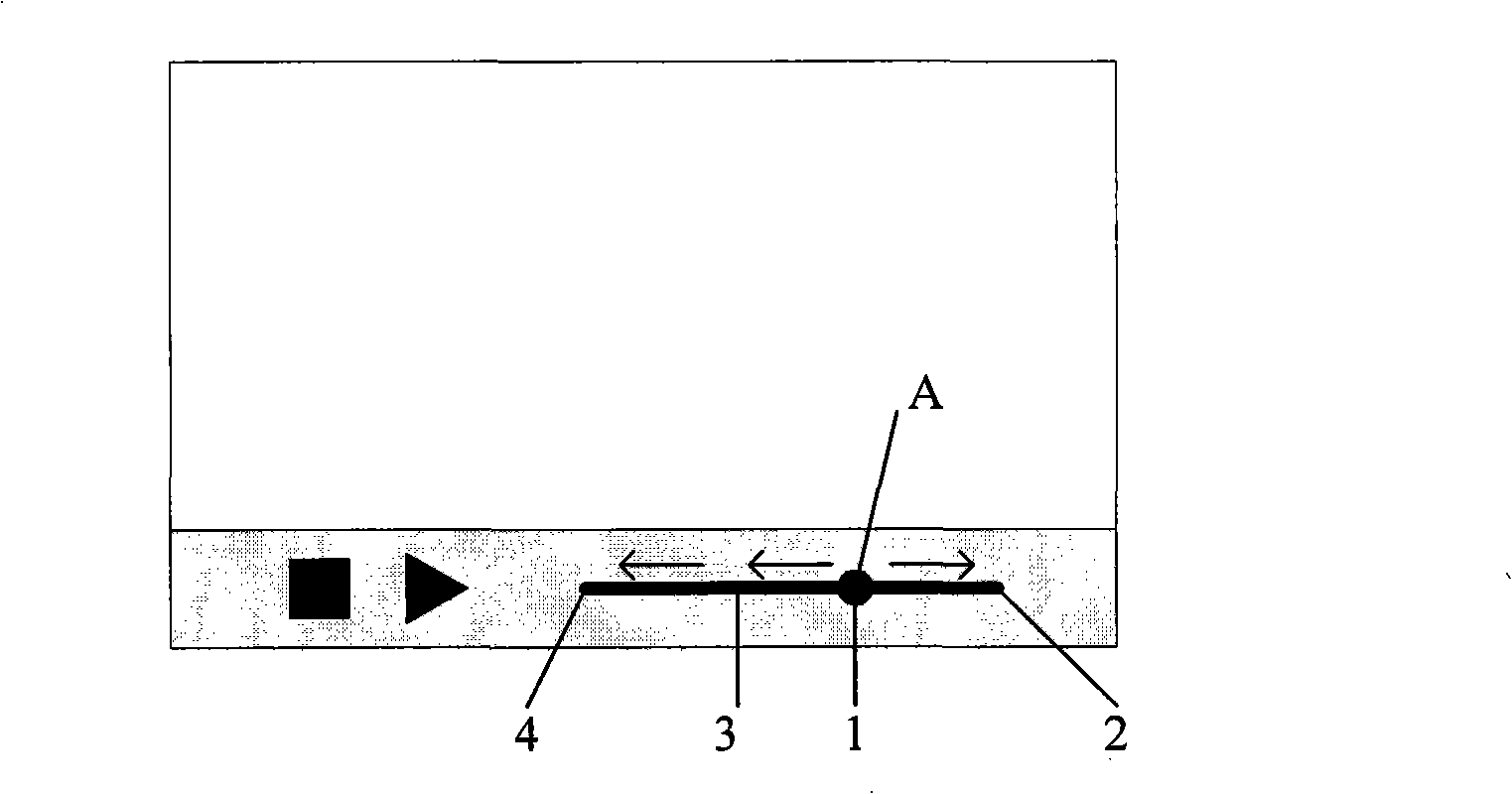
Interaction control method and system based on touch screen
InactiveCN101308440AAchieve accelerationAchieve a controlTelephone sets with user guidance/featuresInput/output processes for data processingInteraction controlTime control
The invention is applied to the field of information technology and provides a touch screen-based interactive control method and a system; the method comprises the following steps: to detect the sliding distance and direction of the user on a touch screen; to determine the operation of the current application implementation and / or the implementation speed for implementing the operation, according to the detected distance and direction; to operate the determination of the current application implementation, or to operate the determination of the current application implementation at a determined operating implementation speed. In an embodiment of the invention, the corresponding functions pre-installed with the system can be continuously implemented through detecting the sliding distance and direction of the user on the touch screen, so as to achieve that the acceleration of the corresponding function application can be controlled through the sliding distance; meanwhile, the purpose of continuously implementing the corresponding function application upon one-time control can be effectively achieved.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
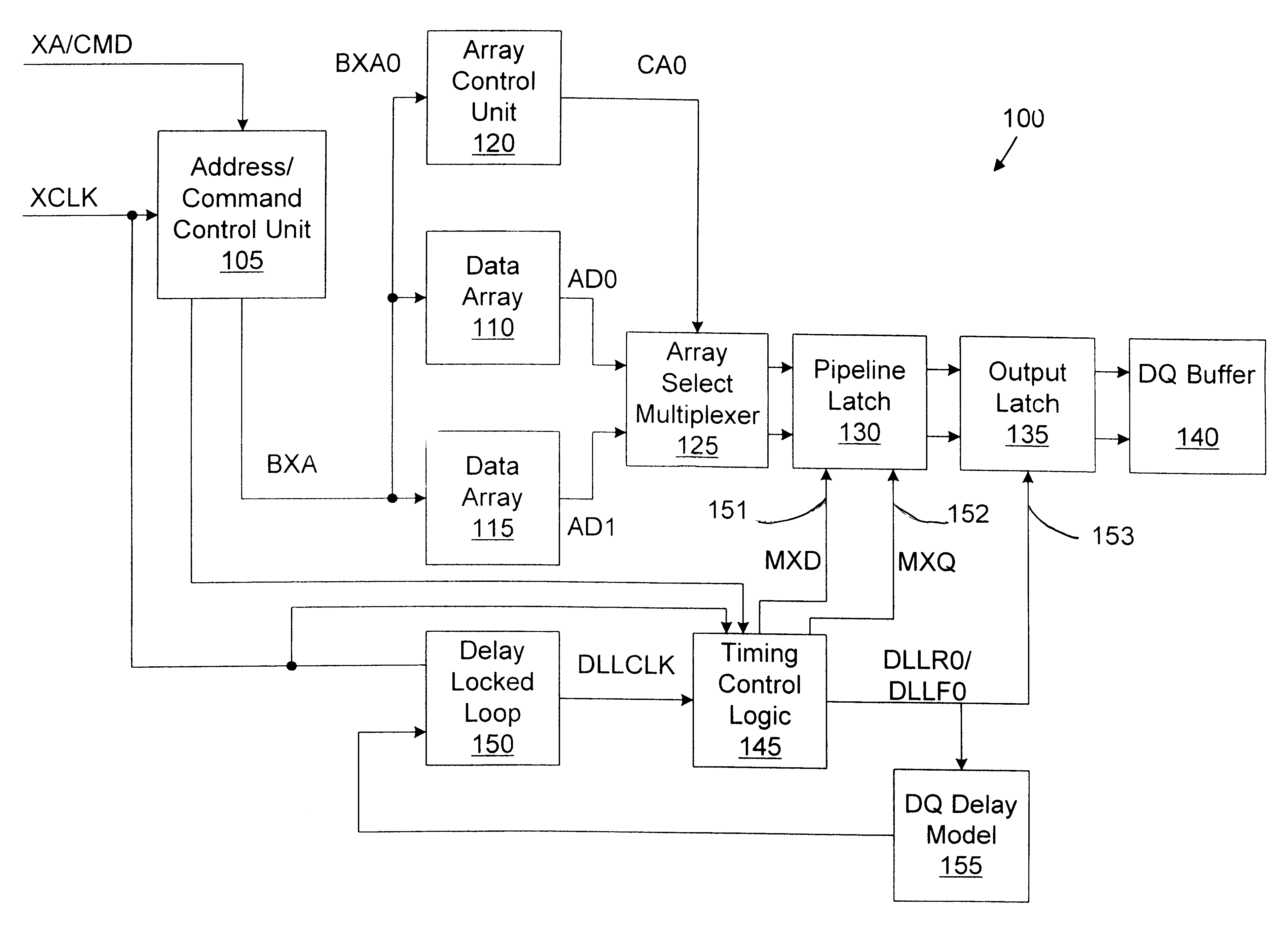
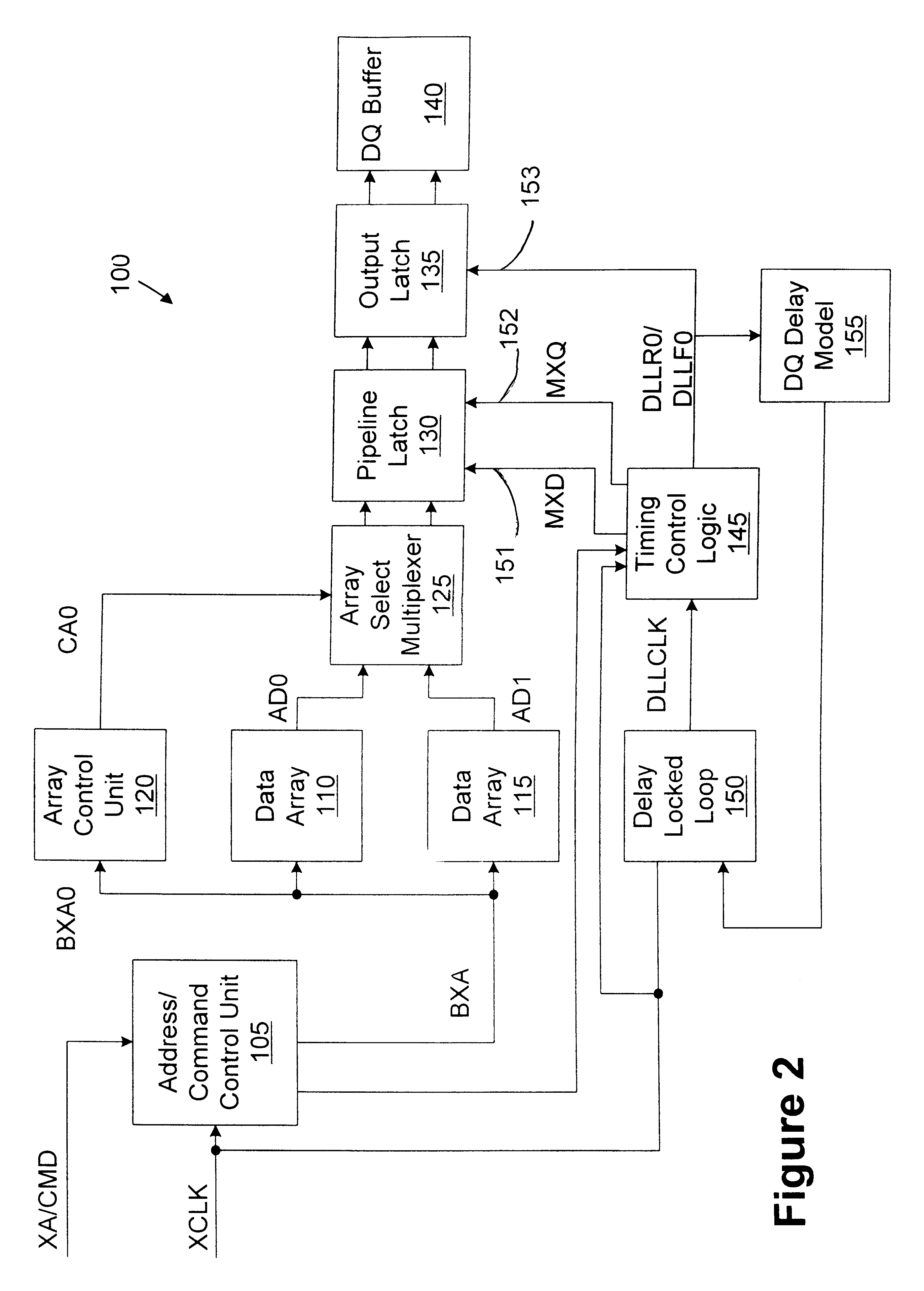
Memory device with synchronized output path
A memory device includes a data array, array control logic, a delay locked loop circuit, timing control logic, and a first storage device. The array control logic is adapted to receive a read command synchronized with an external clock signal and to read at least a first data element from the data array based on the read command. The delay locked loop circuit is adapted to receive the external clock signal and delay the external clock signal by a programmable amount to generate a delay locked loop clock signal. The timing control logic is adapted to generate a first input enable signal based on the external clock signal and a first output enable signal based on the delay locked loop clock signal. The first storage device adapted to receive the first data element. The first storage device has an input terminal enabled in response to the first input enable signal and an output terminal enabled in response to the first output enable signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
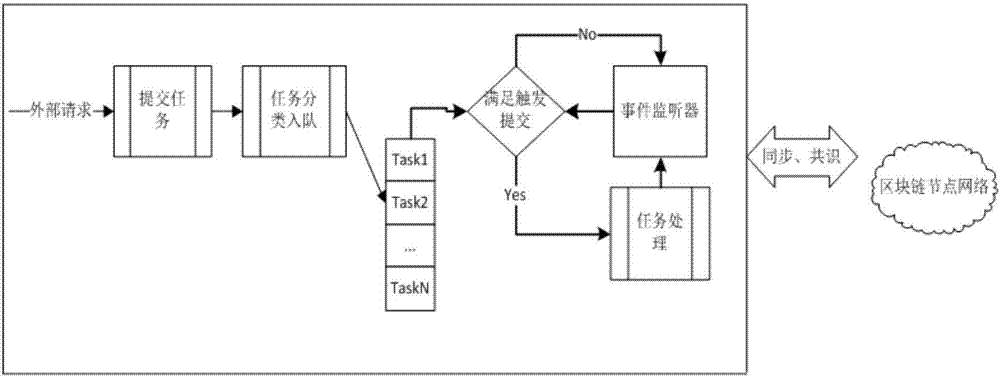
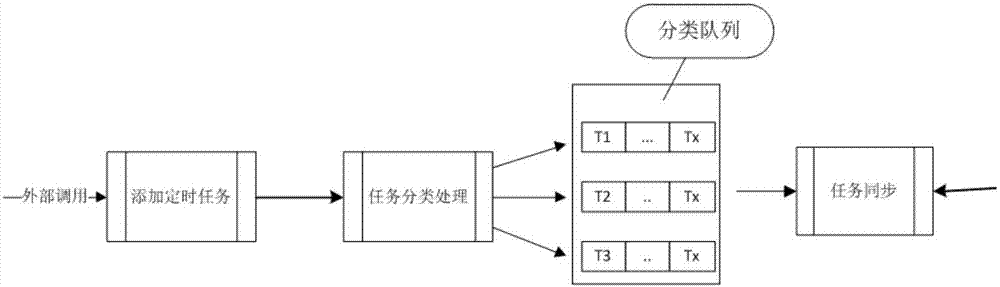
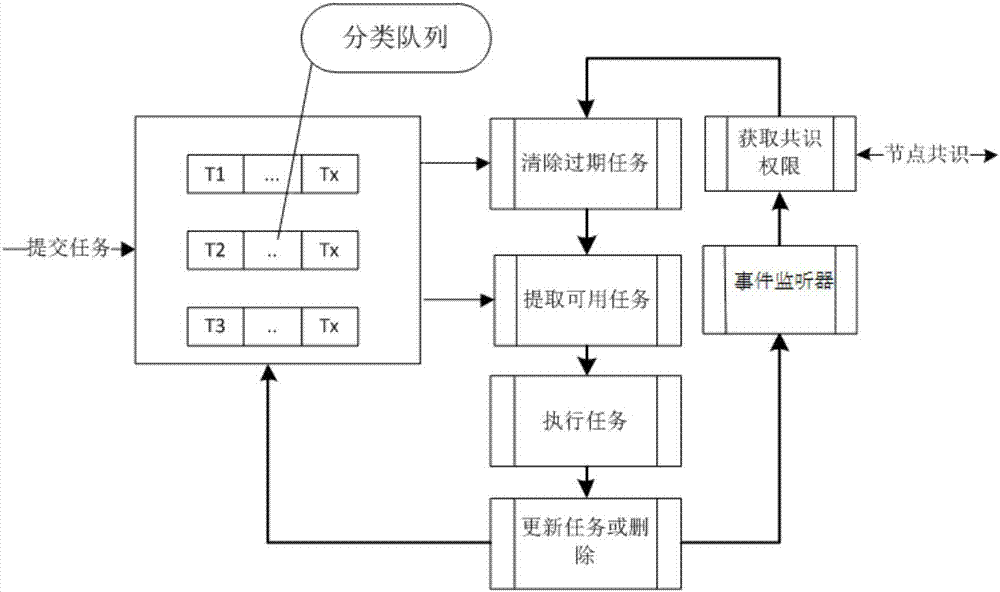
Block chain intelligent contract timed task dispatching method
InactiveCN106874087APrecise time controlIncrease flexibilityProgram initiation/switchingTime controlDistributed computing
The invention relates to the technical field of block chains, and specifically relates to a block chain intelligent contract timed task dispatching method. The method comprises: (1) adding a timed task, configuring execution requirement of the timed task, submitting the timed task to a block chain processing node; (2) performing classified processing on the timed task, and adding to a task processing queue; (3) selecting a consensus node of the block chain, the consensus node obtaining consensus permission; (4) when the timed task reaches the execution requirement, the consensus node performing task processing on the timed task; (5) after the task is processed, synchronizing the state of the timed task to other nodes, after other nodes obtain consensus permission, according to the state of the timed task, performing next task processing on the timed task which is not executed. The dispatching method is high in flexibility and accuracy, and can realize accurate time control, and can accurately and efficiently process tasks.
Owner:上海钜真金融信息服务有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com