Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2762 results about "Epitaxy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
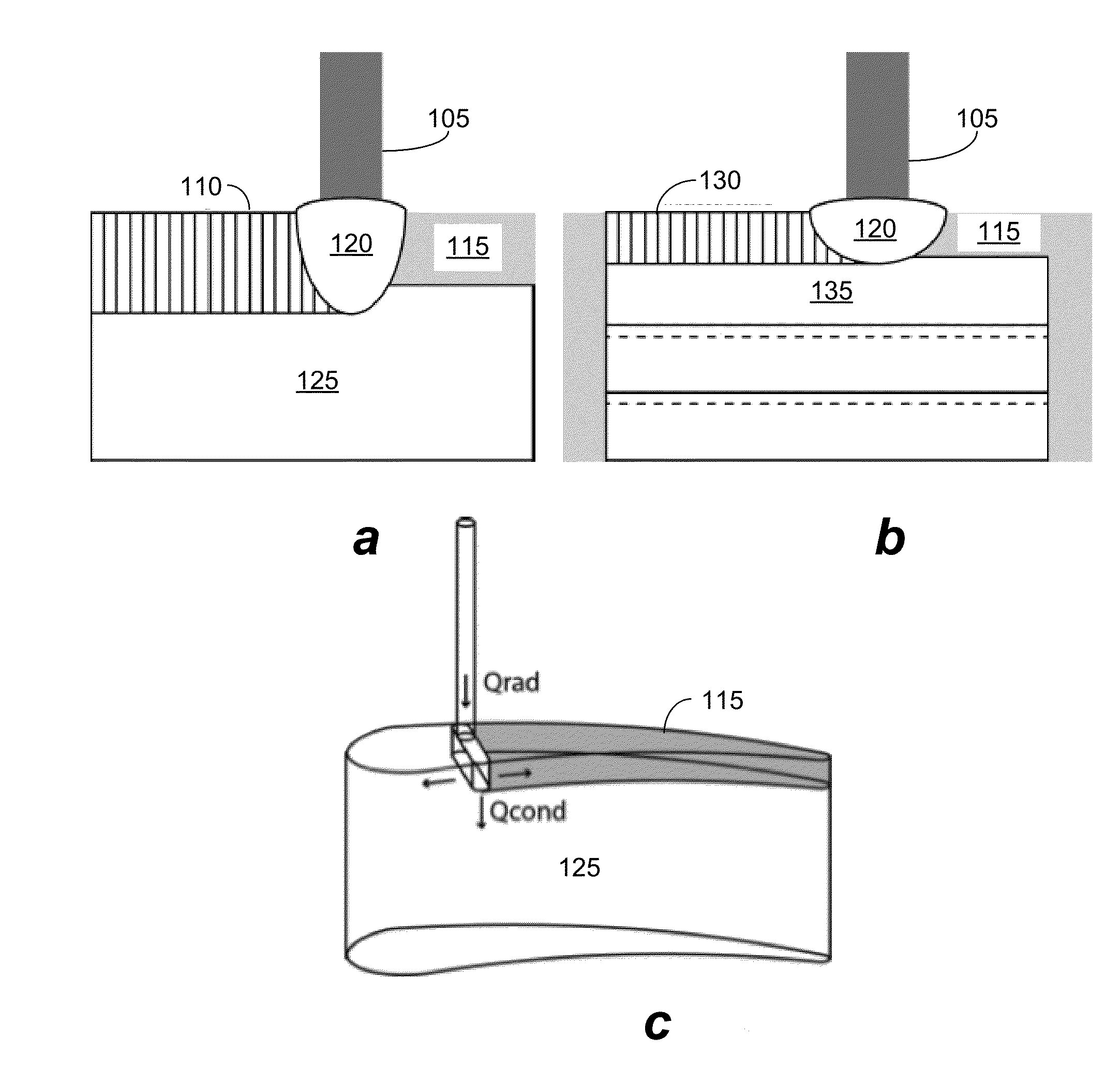
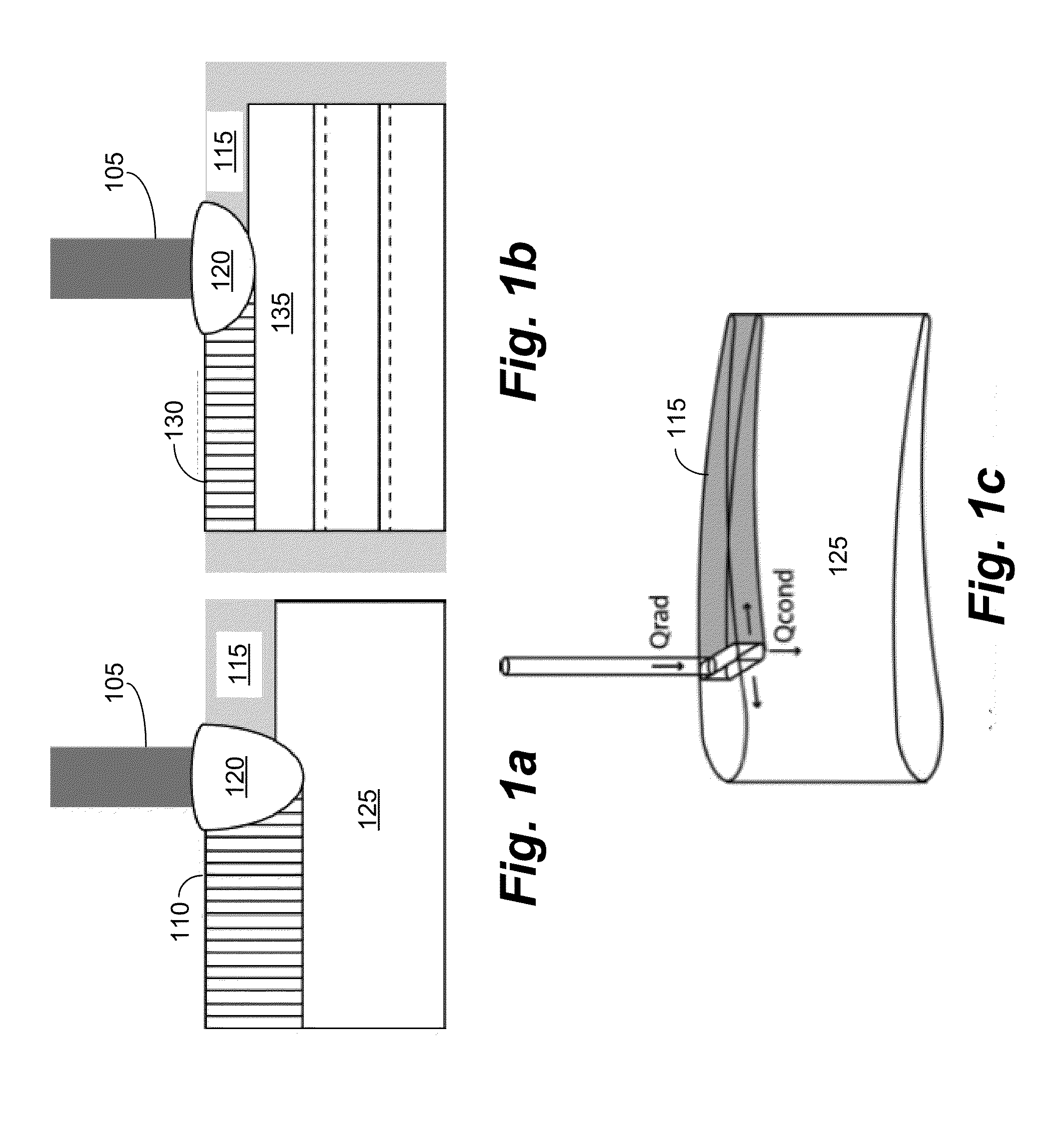
Epitaxy refers to a type of crystal growth or material deposition in which new crystalline layers are formed with a well-defined orientation with respect to the crystalline substrate. The new layers formed are called the epitaxial film or epitaxial layer. The relative orientation of the epitaxial layer to the crystalline substrate is defined in terms of the orientation of the crystal lattice of each material. For epitaxial growth, the new layer will be crystalline and will all have a single orientation relative to the substrate; amorphous growth or multicrystalline growth with random crystal orientation does not meet this criteria.
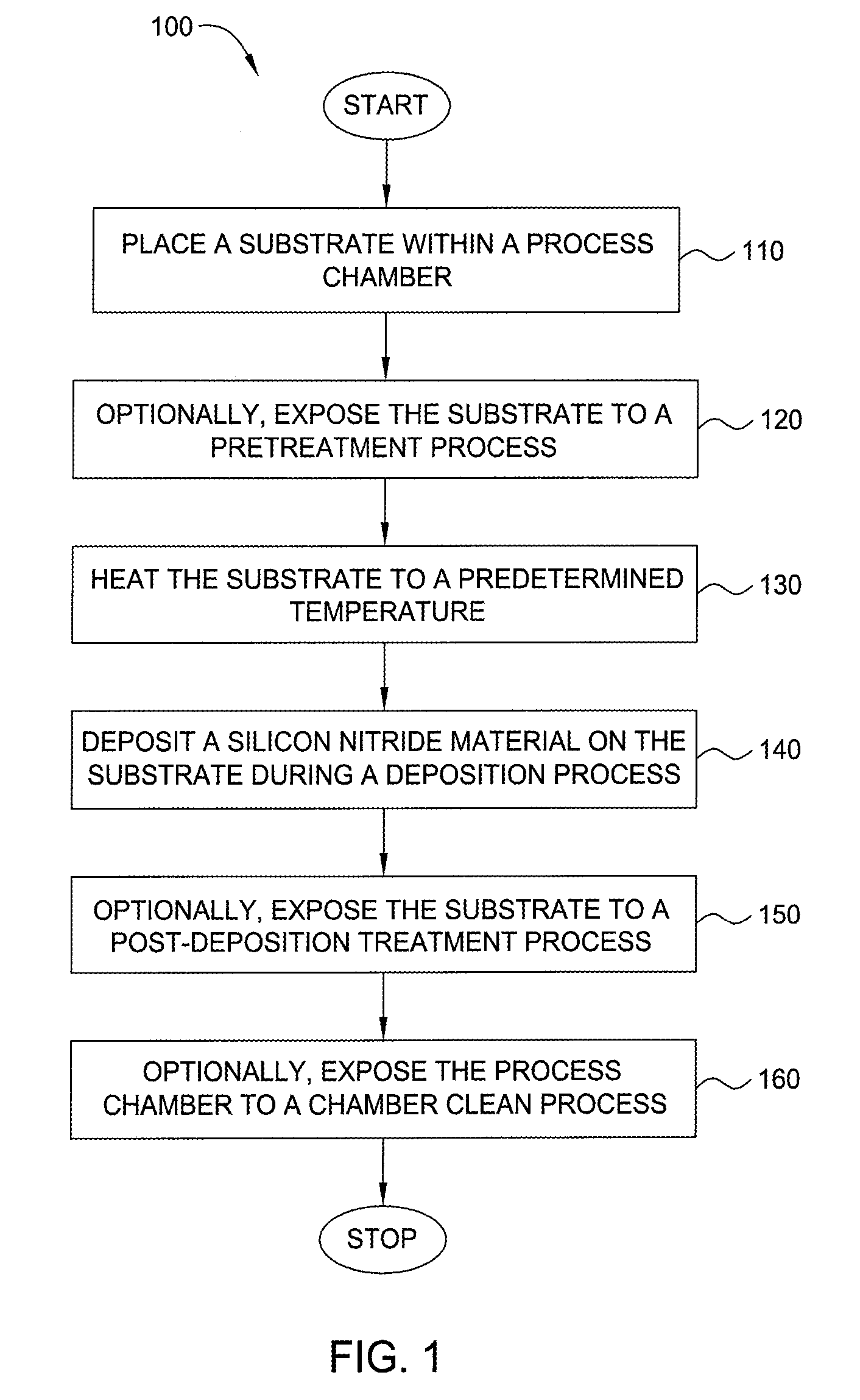
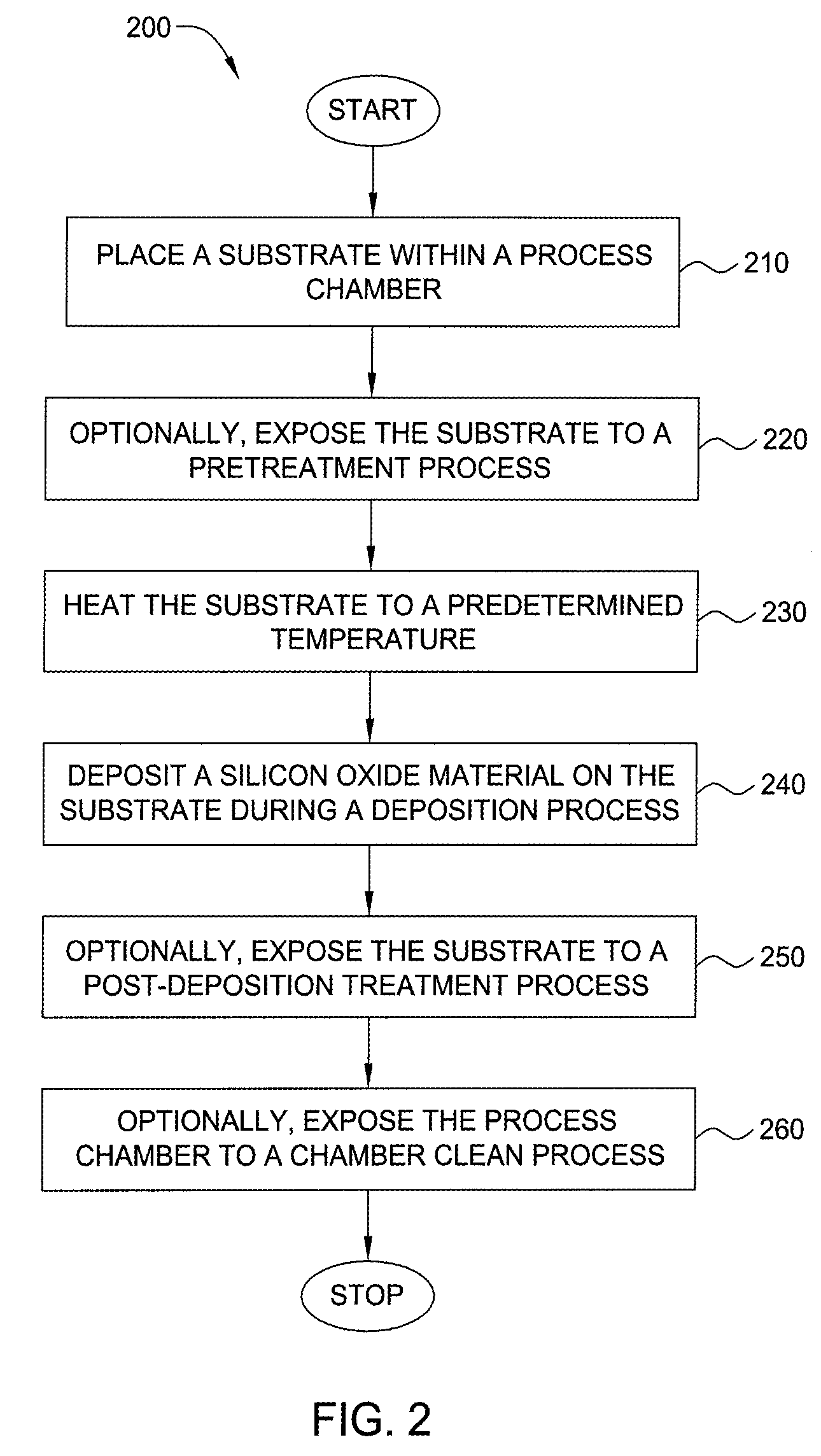
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286774A1Enhance chamber cleaning processHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolatilesSilicon oxide
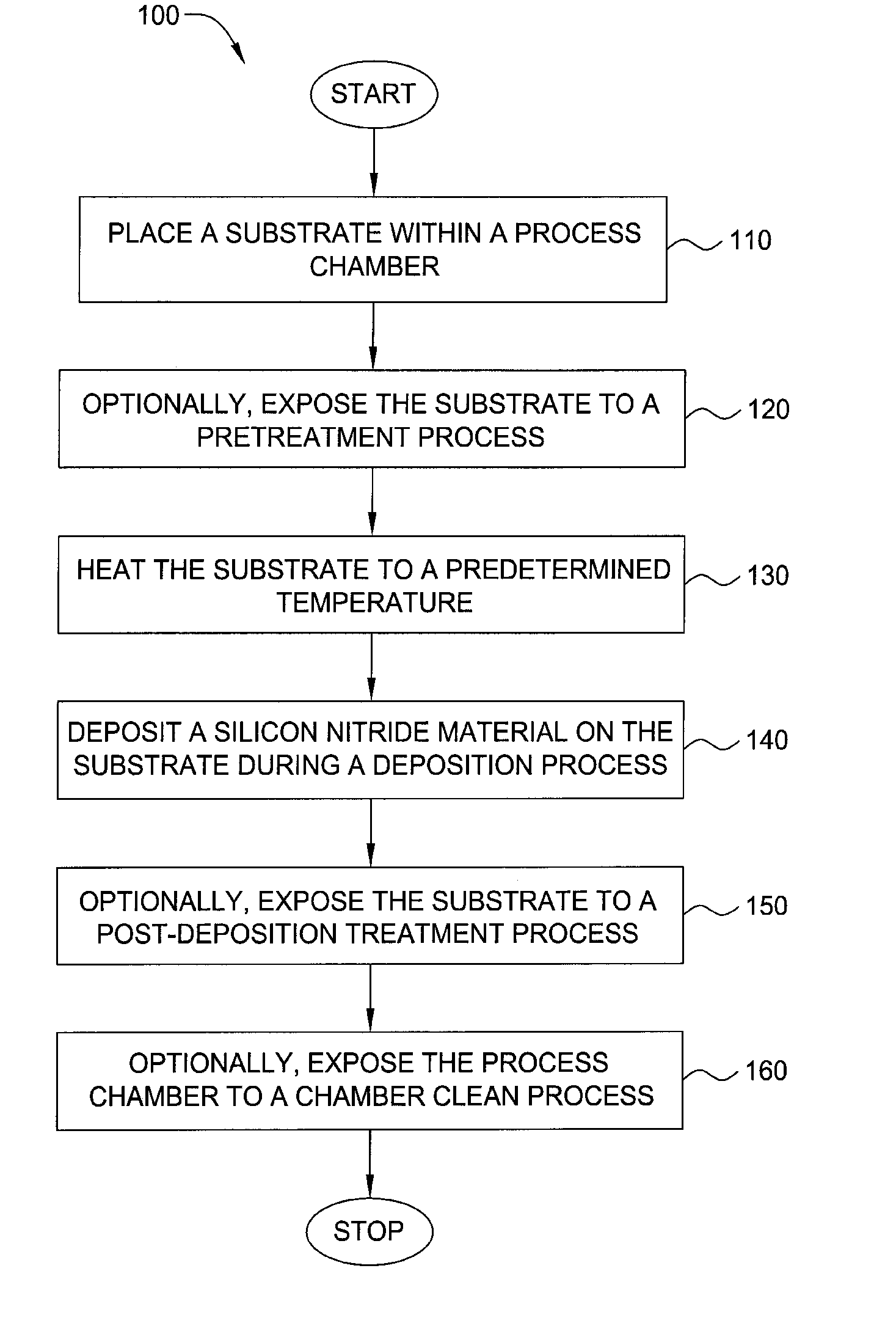
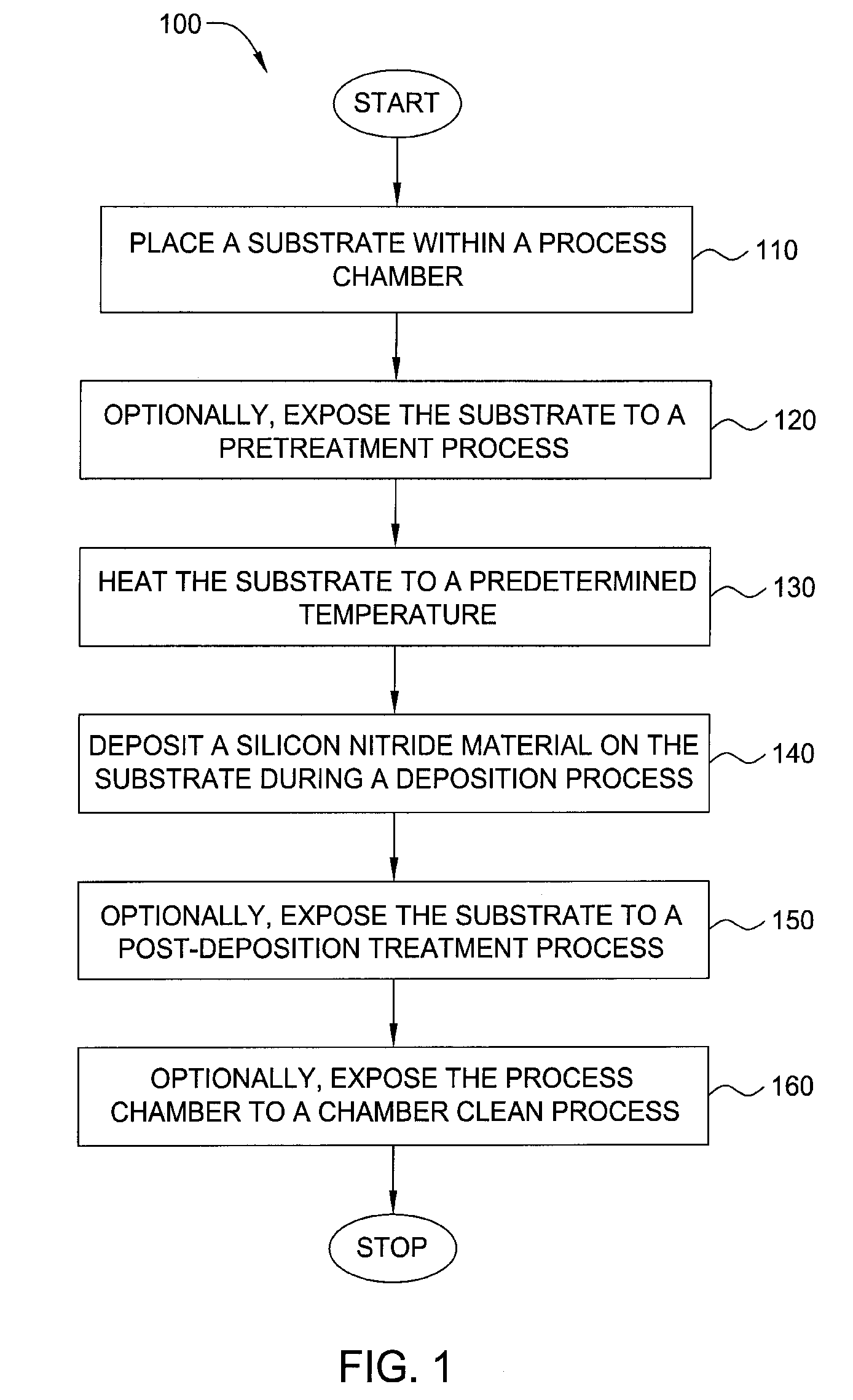
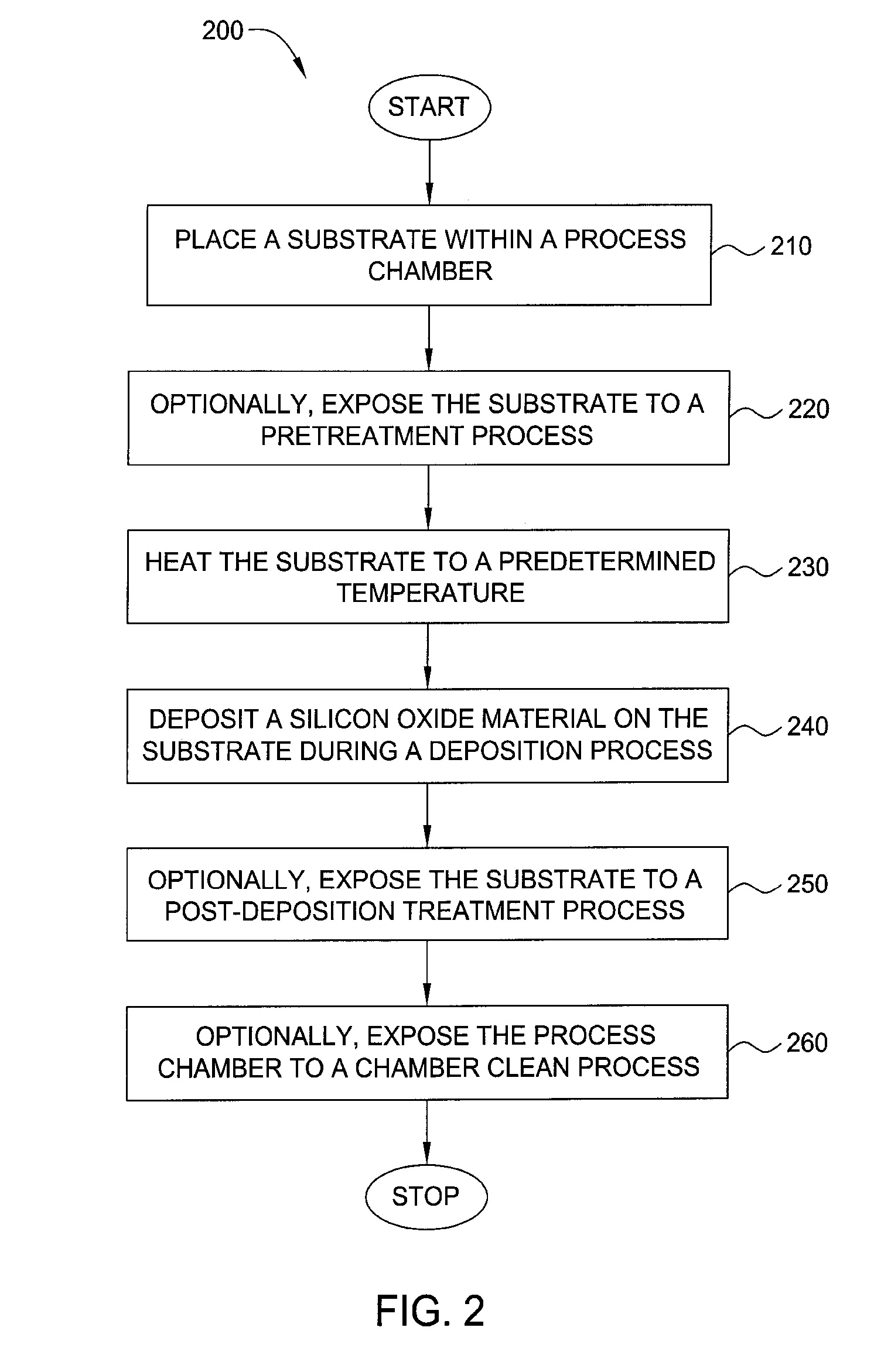
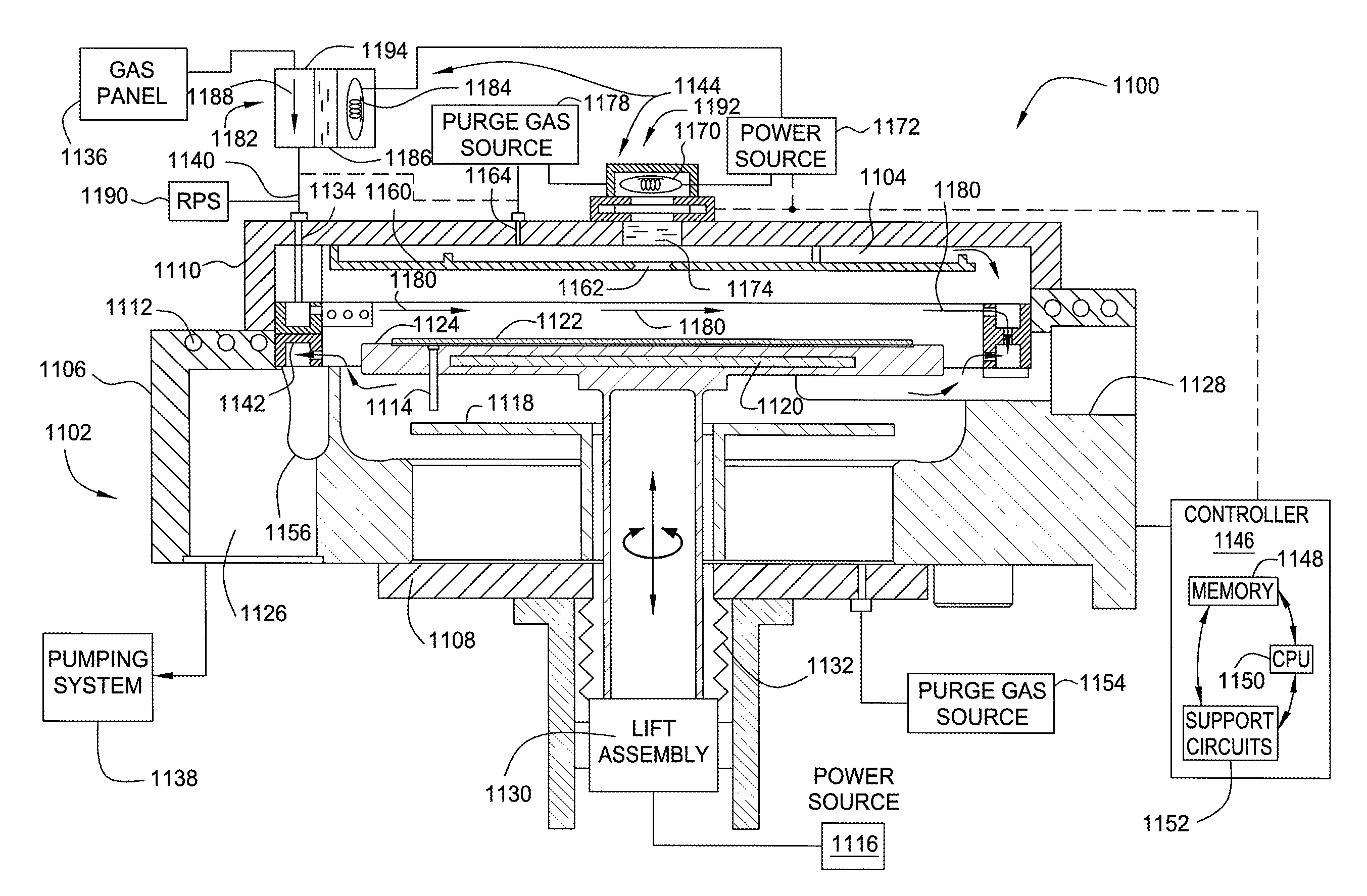
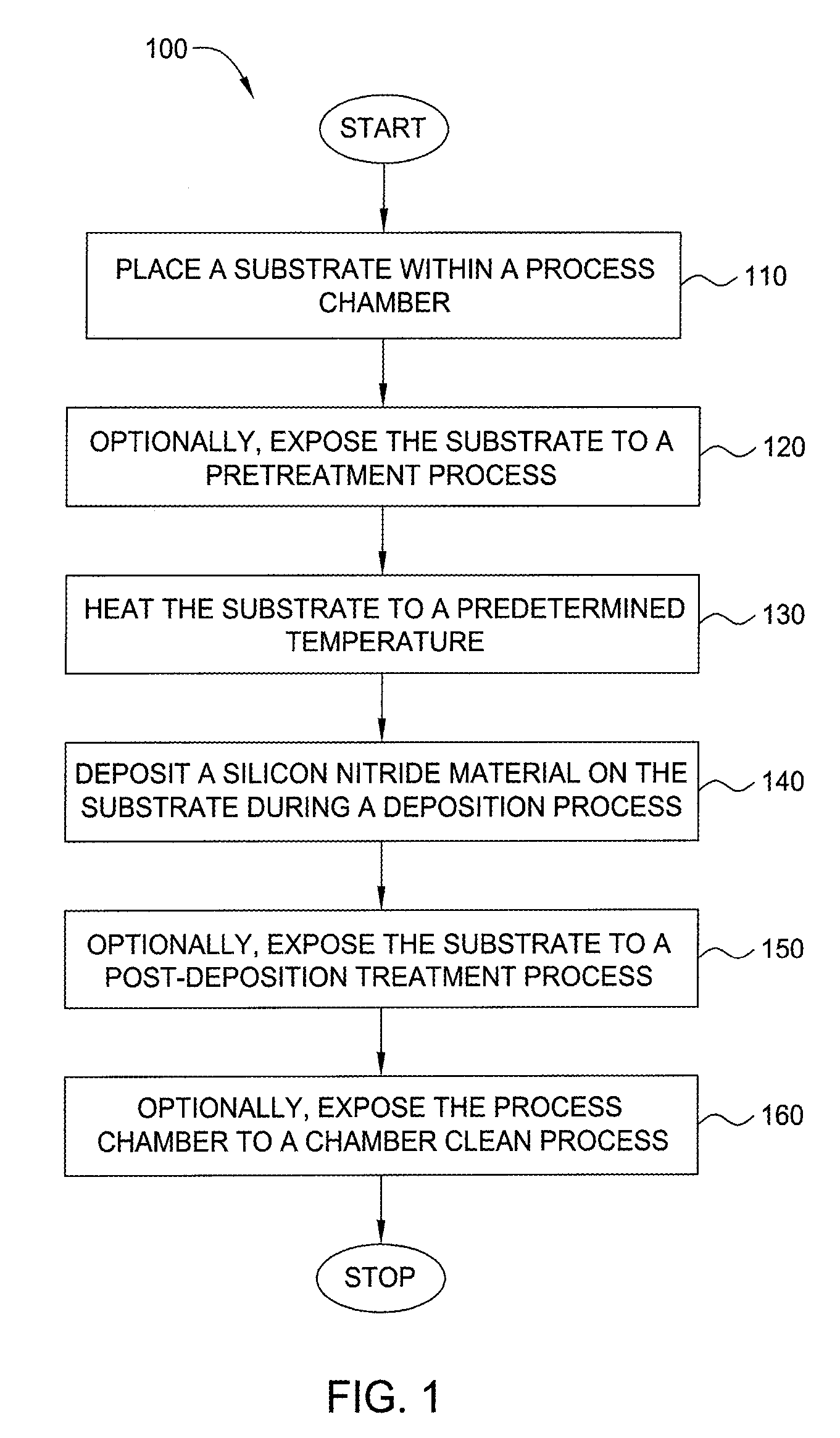
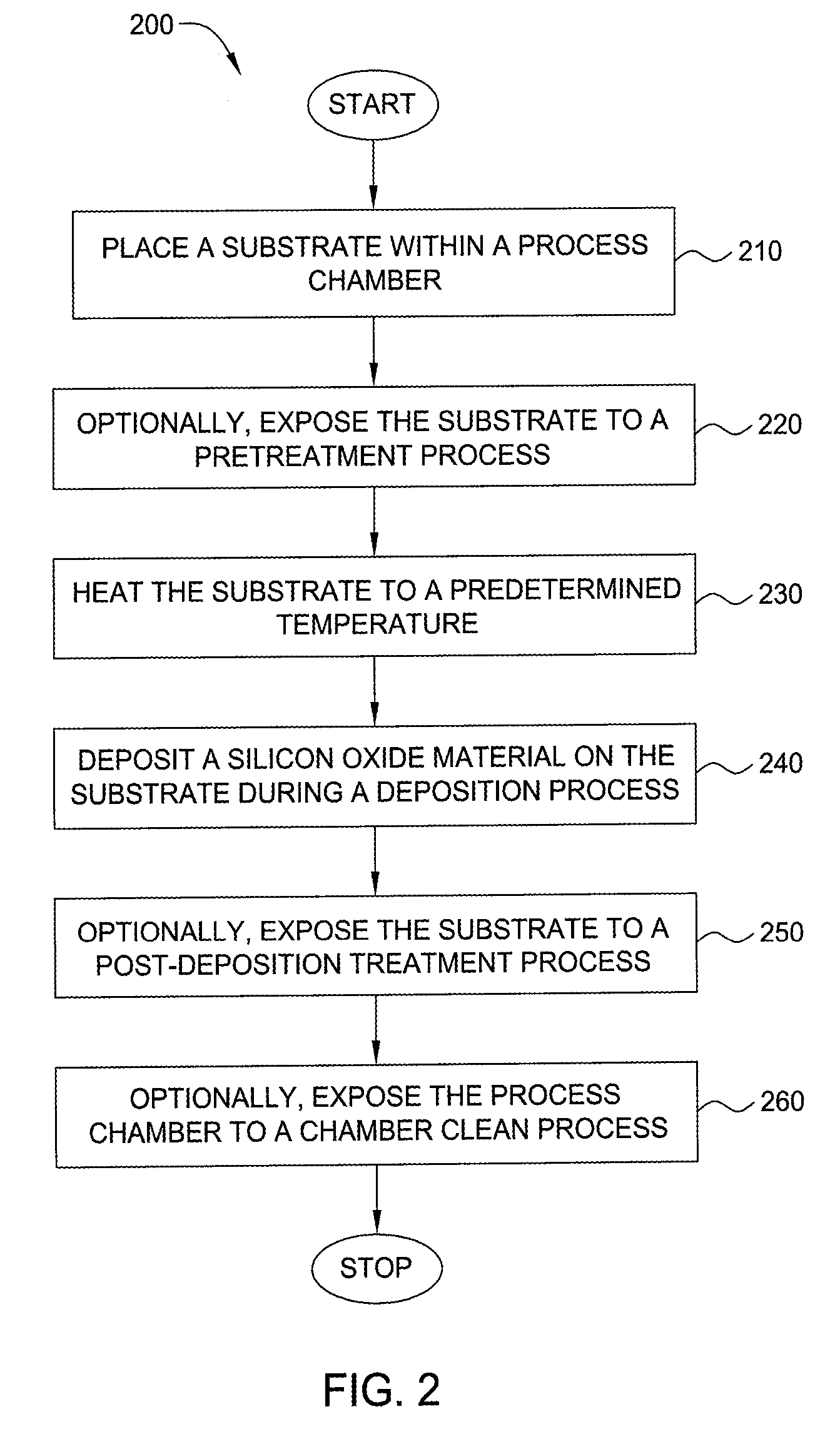
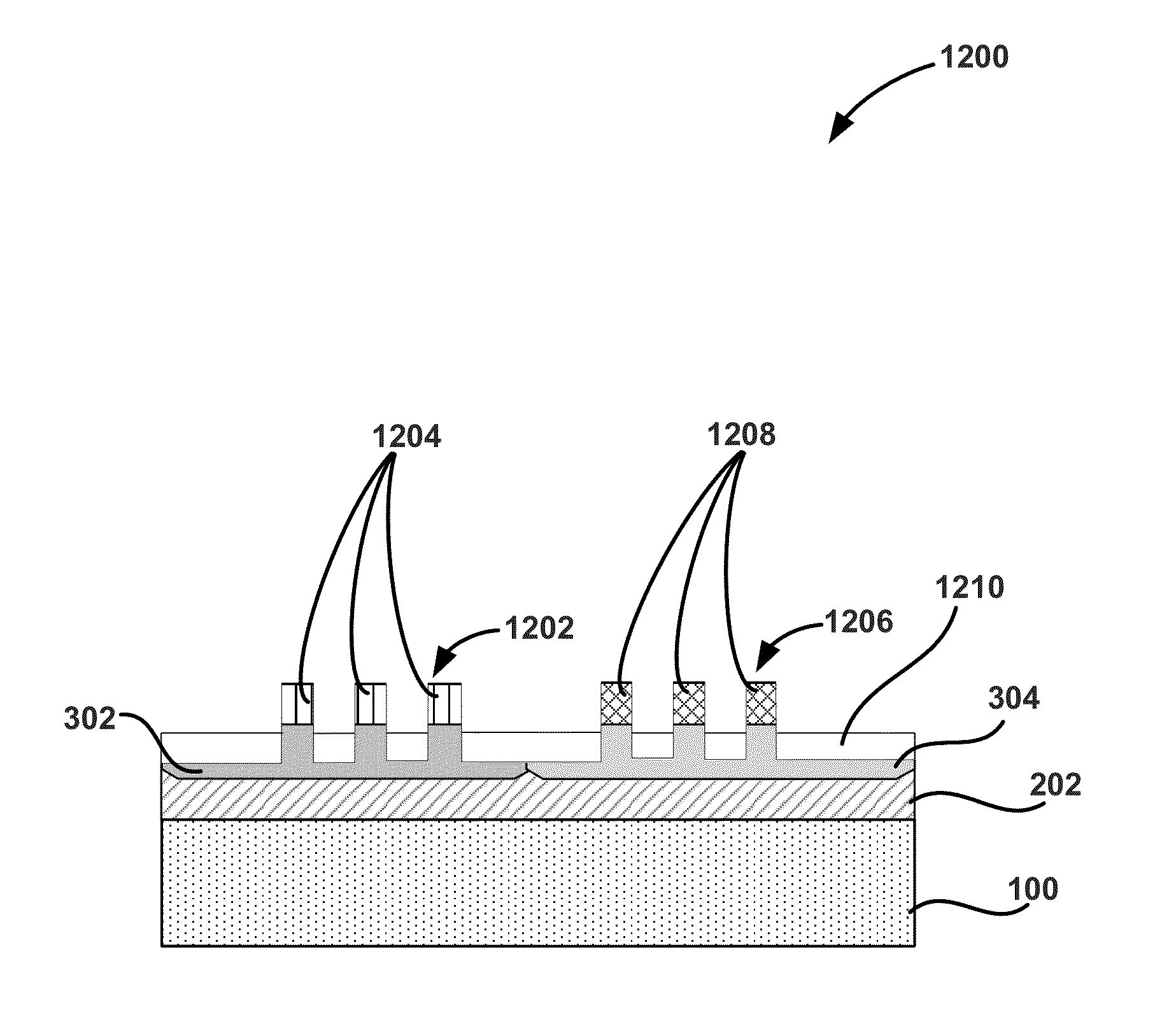
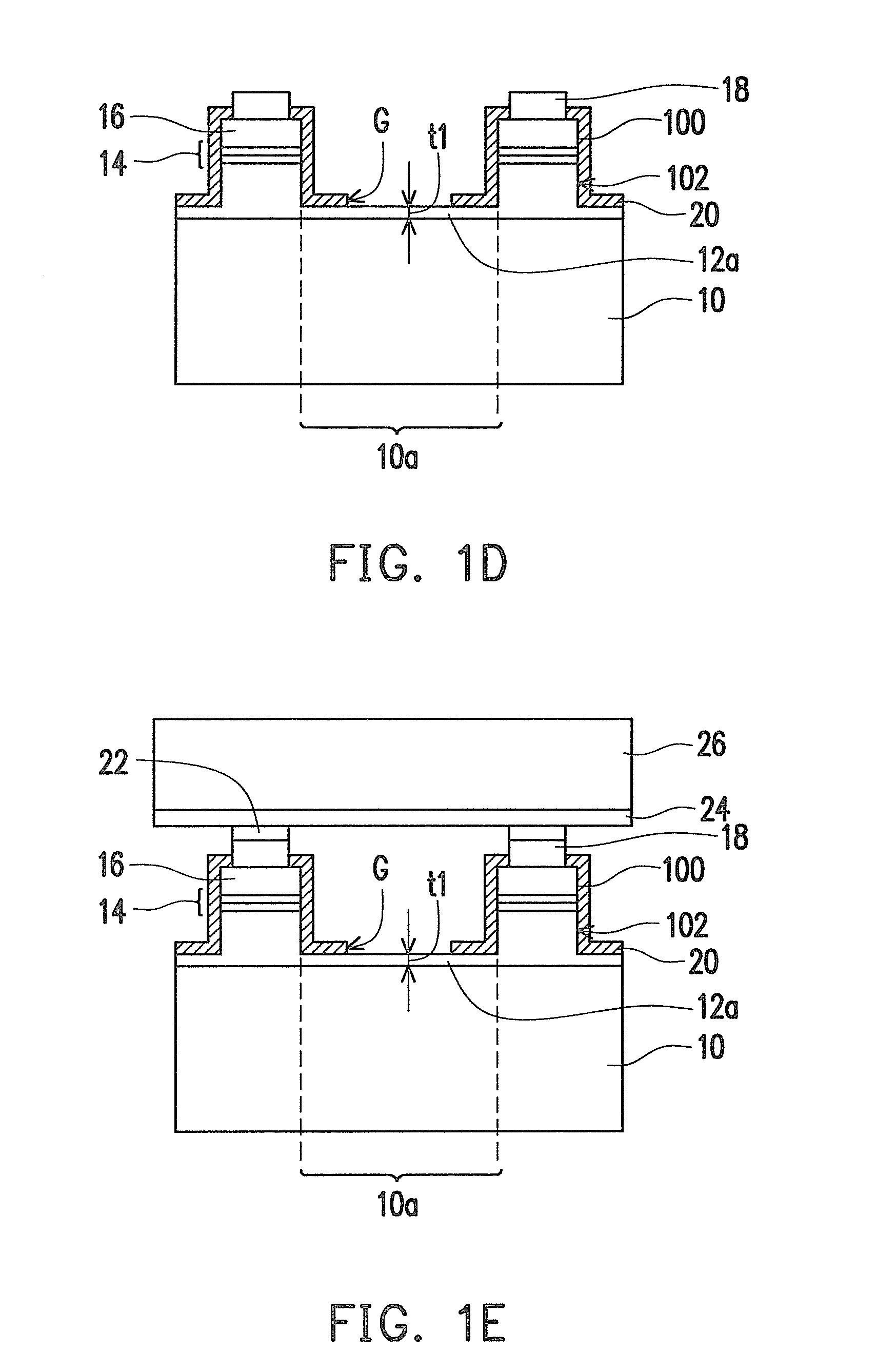
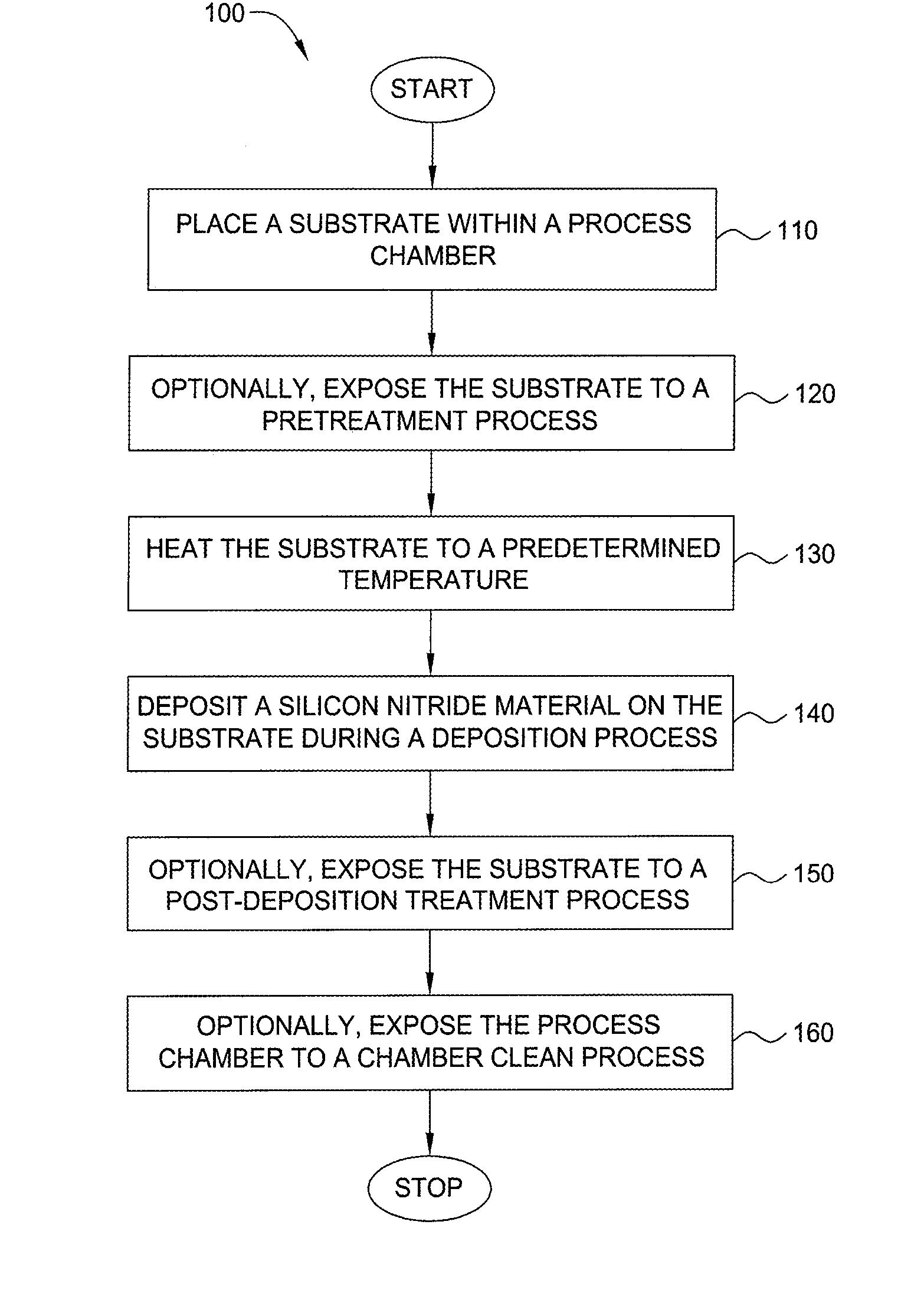
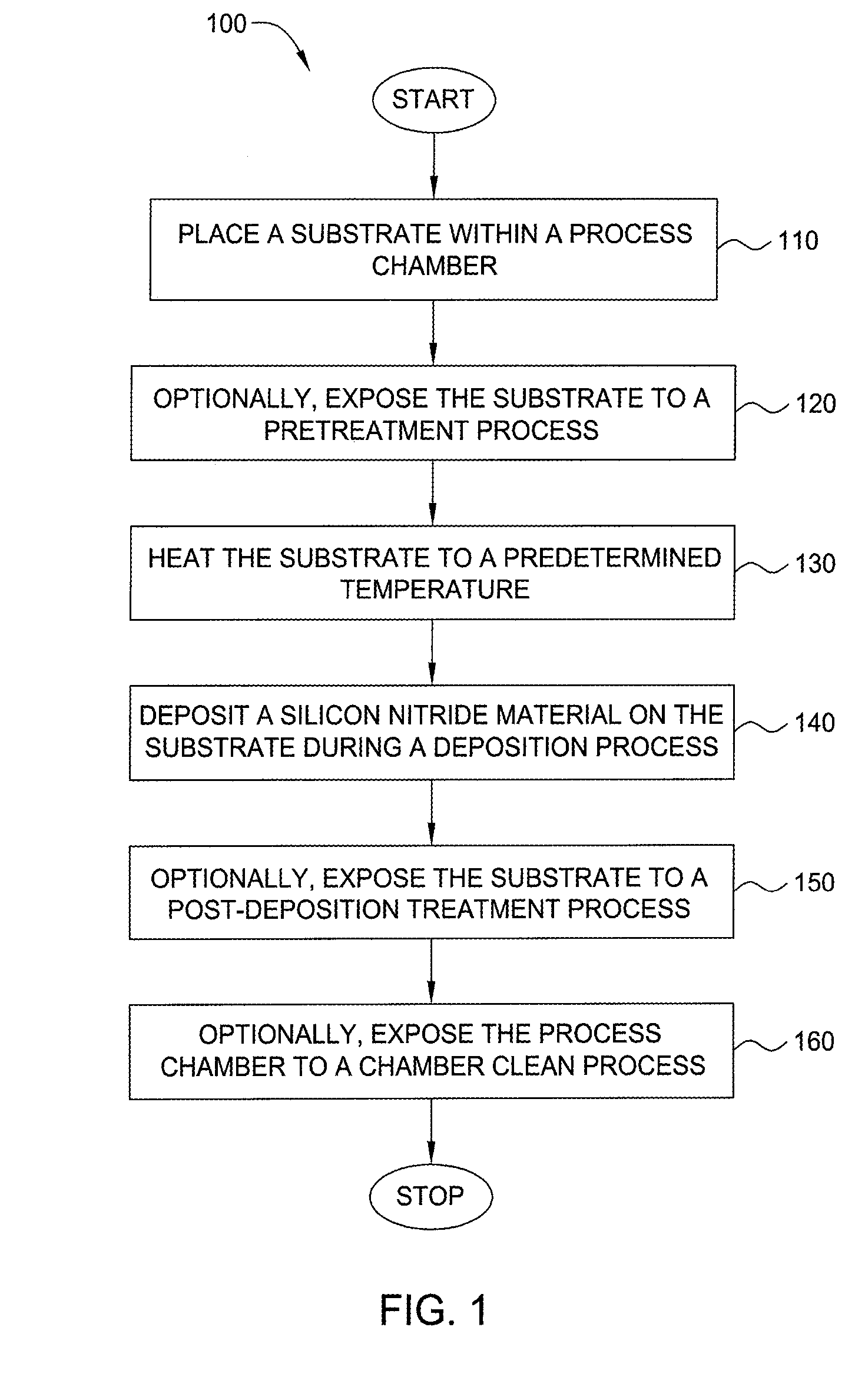
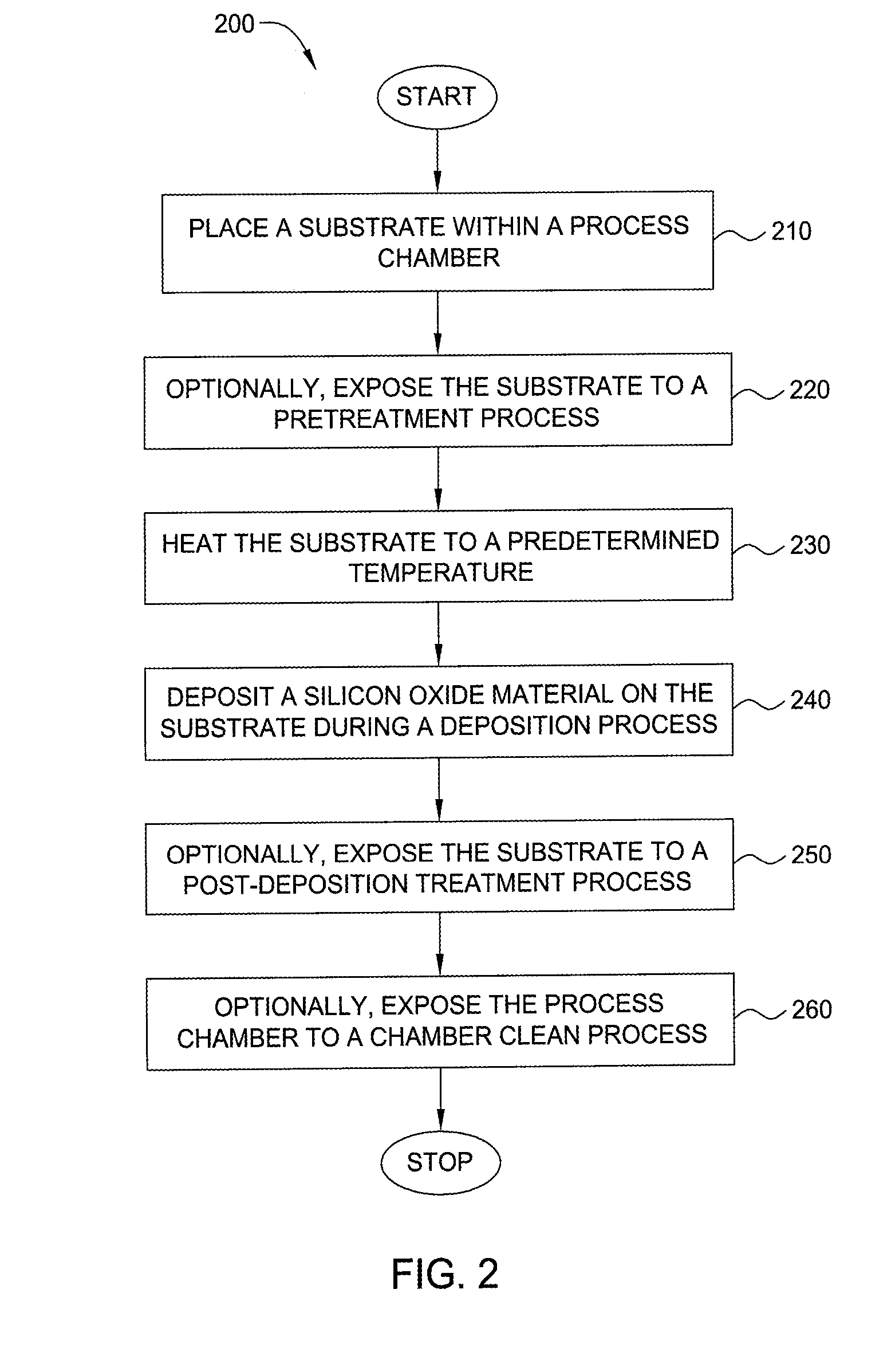
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor structure and device and methods of forming same using selective epitaxial process
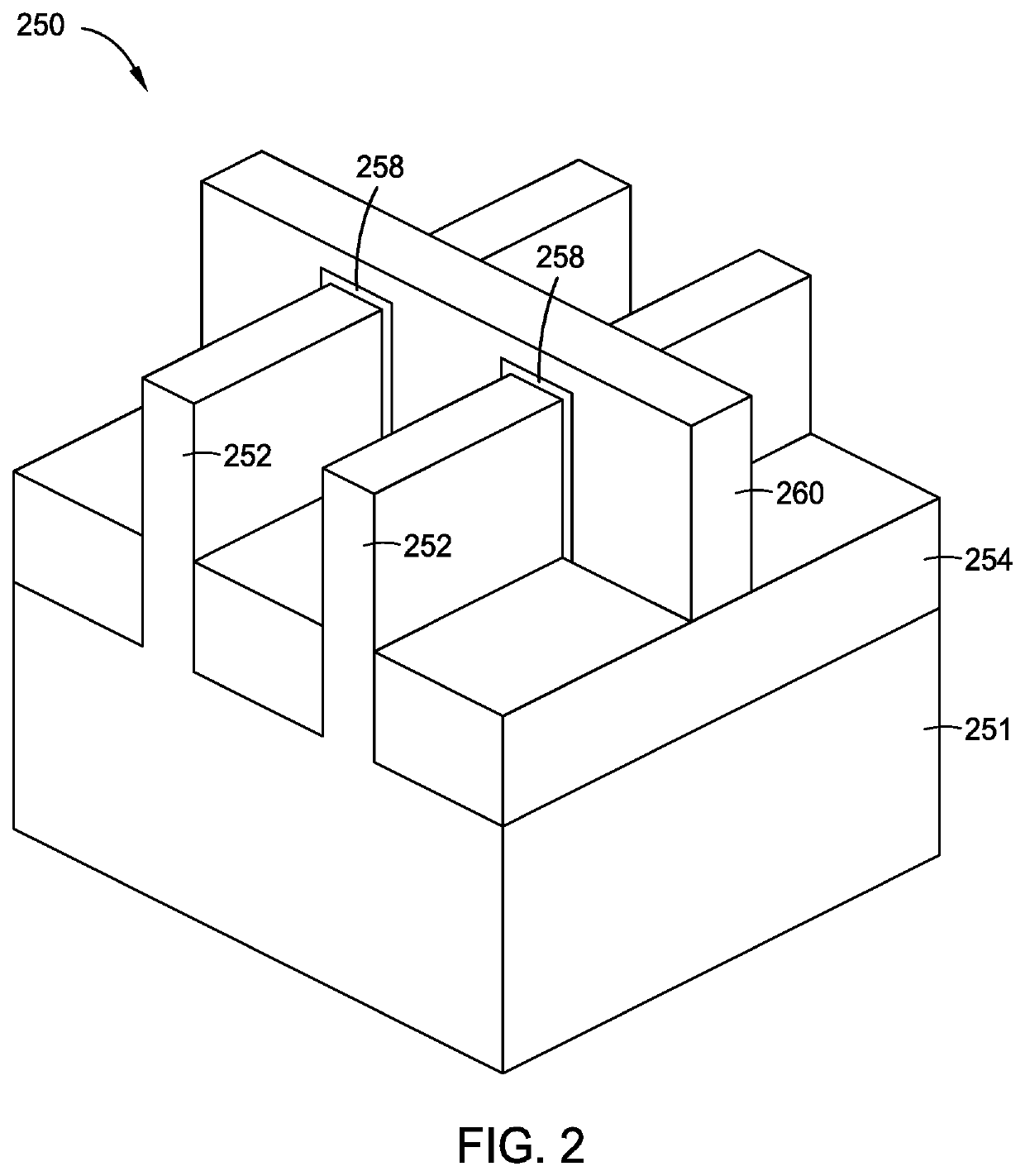
Semiconductor structures, devices, and methods of forming the structures and device are disclosed. Exemplary structures include multi-gate or FinFET structures that can include both n-channel MOS (NMOS) and p-channel MOS (PMOS) devices to form CMOS structures and devices on a substrate. The devices can be formed using selective epitaxy and shallow trench isolation techniques.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS7651955B2Easy to cleanHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutoxidationDeposition temperature
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor structure and device and methods of forming same using selective epitaxial process
Semiconductor structures, devices, and methods of forming the structures and device are disclosed. Exemplary structures include multi-gate or FinFET structures that can include both re-channel MOS (NMOS) and p-channel MOS (PMOS) devices to form CMOS structures and devices on a substrate. The devices can be formed using selective epitaxy and shallow trench isolation techniques.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Semiconductor structure and device and methods of forming same using selective epitaxial process
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS7648927B2Easy to cleanHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutoxidationDeposition temperature
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for achieving improved epitaxy quality (surface texture and defect density) on free-standing (aluminum, indium, gallium) nitride ((al,in,ga)n) substrates for opto-electronic and electronic devices
A III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structure comprising a III-V nitride homoepitaxial epi layer on a III-V nitride material substrate, e.g., of freestanding character. Various processing techniques are described, including a method of forming a III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer on a corresponding III-V nitride material substrate, by depositing the III-V nitride homoepitaxial layer by a VPE process using Group III source material and nitrogen source material under process conditions including V / III ratio in a range of from about 1 to about 105, nitrogen source material partial pressure in a range of from about 1 to about 103 torr, growth temperature in a range of from about 500 to about 1250 degrees Celsius, and growth rate in a range of from about 0.1 to about 500 microns per hour. The III-V nitride homoepitaxial microelectronic device structures are usefully employed in device applications such as UV LEDs, high electron mobility transistors, and the like.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Systems and methods for additive manufacturing and repair of metal components
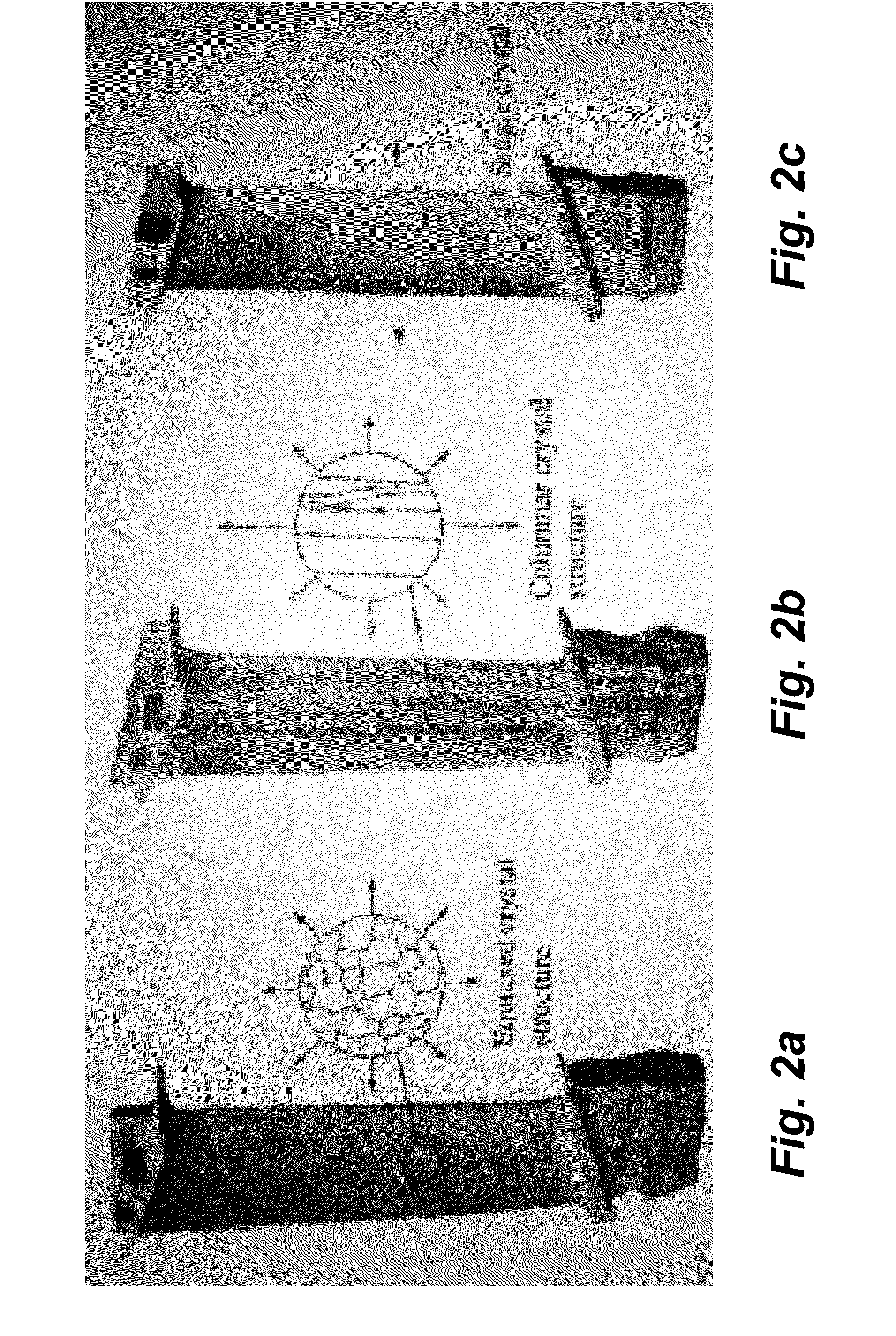
Scanning Laser Epitaxy (SLE) is a layer-by-layer additive manufacturing process that allows for the fabrication of three-dimensional objects with specified microstructure through the controlled melting and re-solidification of a metal powders placed atop a base substrate. SLE can be used to repair single crystal (SX) turbine airfoils, for example, as well as the manufacture functionally graded turbine components. The SLE process is capable of creating equiaxed, directionally solidified, and SX structures. Real-time feedback control schemes based upon an offline model can be used both to create specified defect free microstructures and to improve the repeatability of the process. Control schemes can be used based upon temperature data feedback provided at high frame rate by a thermal imaging camera as well as a melt-pool viewing video microscope. A real-time control scheme can deliver the capability of creating engine ready net shape turbine components from raw powder material.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
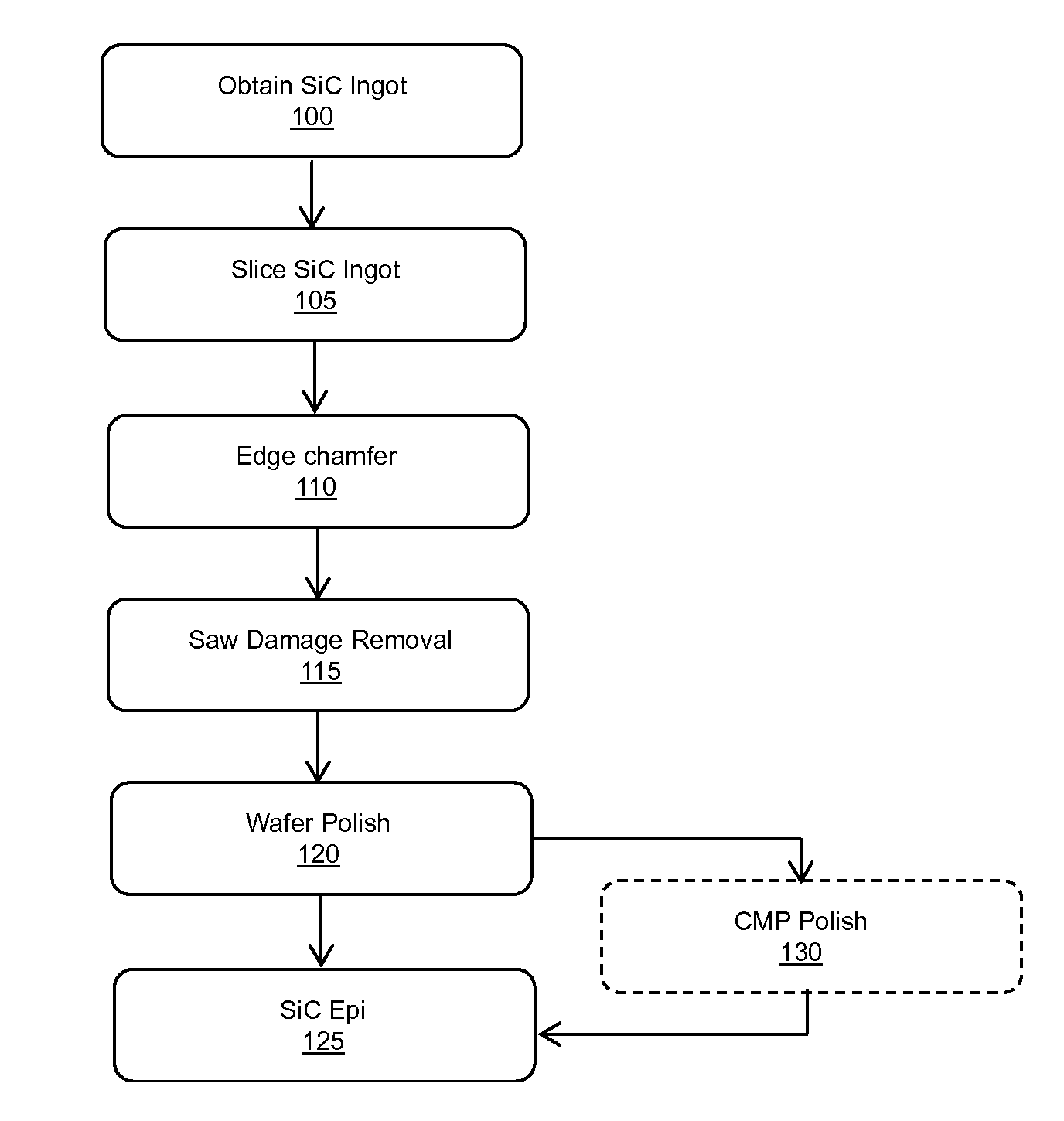
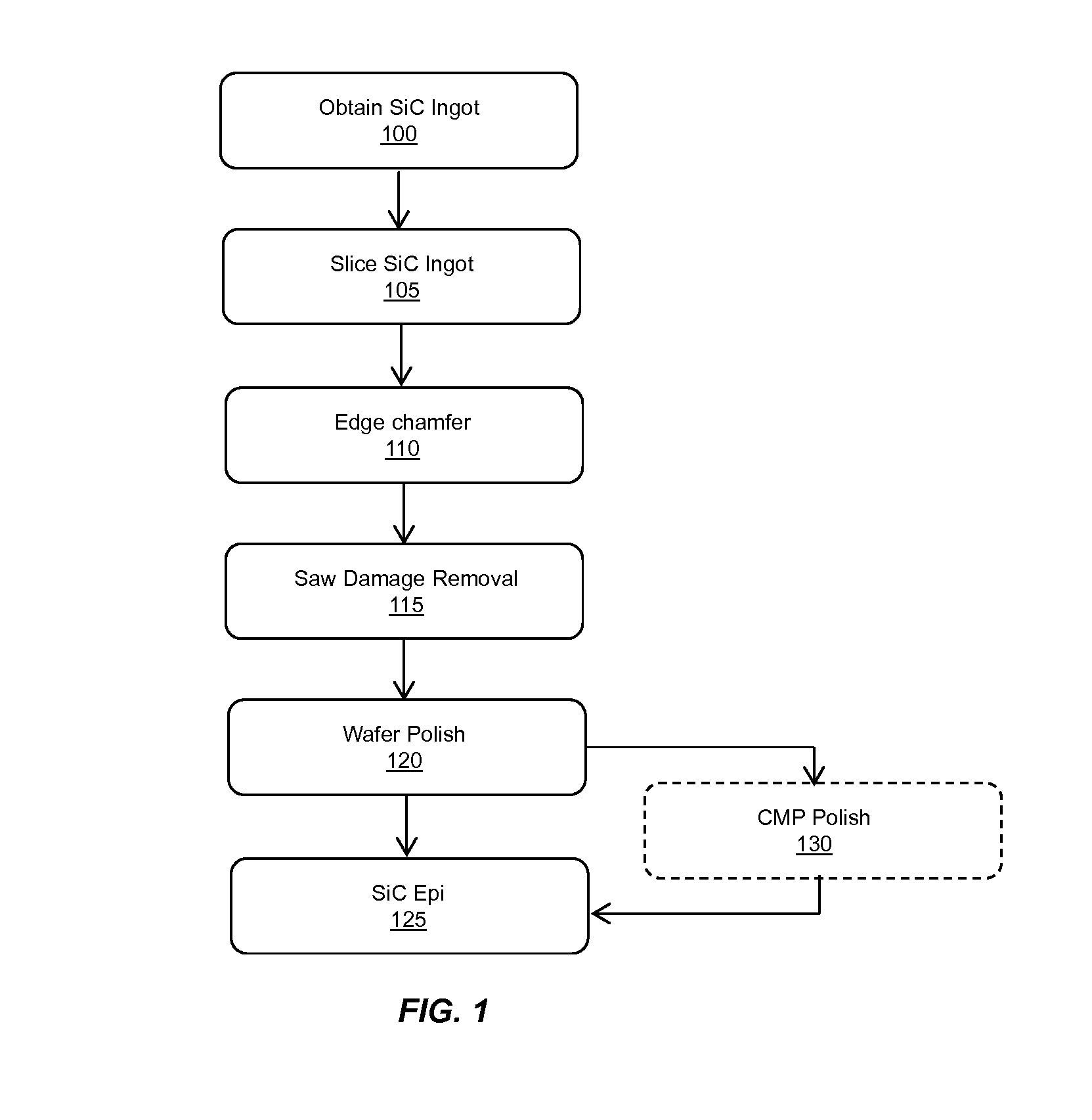
Flat sic semiconductor substrate
ActiveUS20140117380A1Efficient polishingImprove performanceEdge grinding machinesPolycrystalline material growthCrystallographyWafering
Methods for manufacturing silicon carbide wafers having superior specifications for bow, warp, total thickness variation (TTV), local thickness variation (LTV), and site front side least squares focal plane range (SFQR). The resulting SiC wafer has a mirror-like surface that is fit for epitaxial deposition of SiC. The specifications for bow, warp, total thickness variation (TTV), local thickness variation (LTV), and site front side least squares focal plane range (SFQR) of the wafer are preserved following the addition of the epitaxy layer.
Owner:SK SILTRON CSS LLC
Methods for Selective and Conformal Epitaxy of Highly Doped Si-containing Materials for Three Dimensional Structures
InactiveUS20140120678A1Improve crystal qualityIncreased junctionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantPhosphate
The present invention addresses the key challenges in FinFET fabrication, that is, the fabrications of thin, uniform fins and also reducing the source / drain series resistance. More particularly, this application relates to FinFET fabrication techniques utilizing tetrasilane to enable conformal deposition with high doping using phosphate, arsenic and boron as dopants thereby creating thin fins having uniform thickness (uniformity across devices) as well as smooth, vertical sidewalls, while simultaneously reducing the parasitic series resistance.
Owner:MATHESON TRI GAS INC
Deposition of silicon germanium on silicon-on-insulator structures and bulk substrates
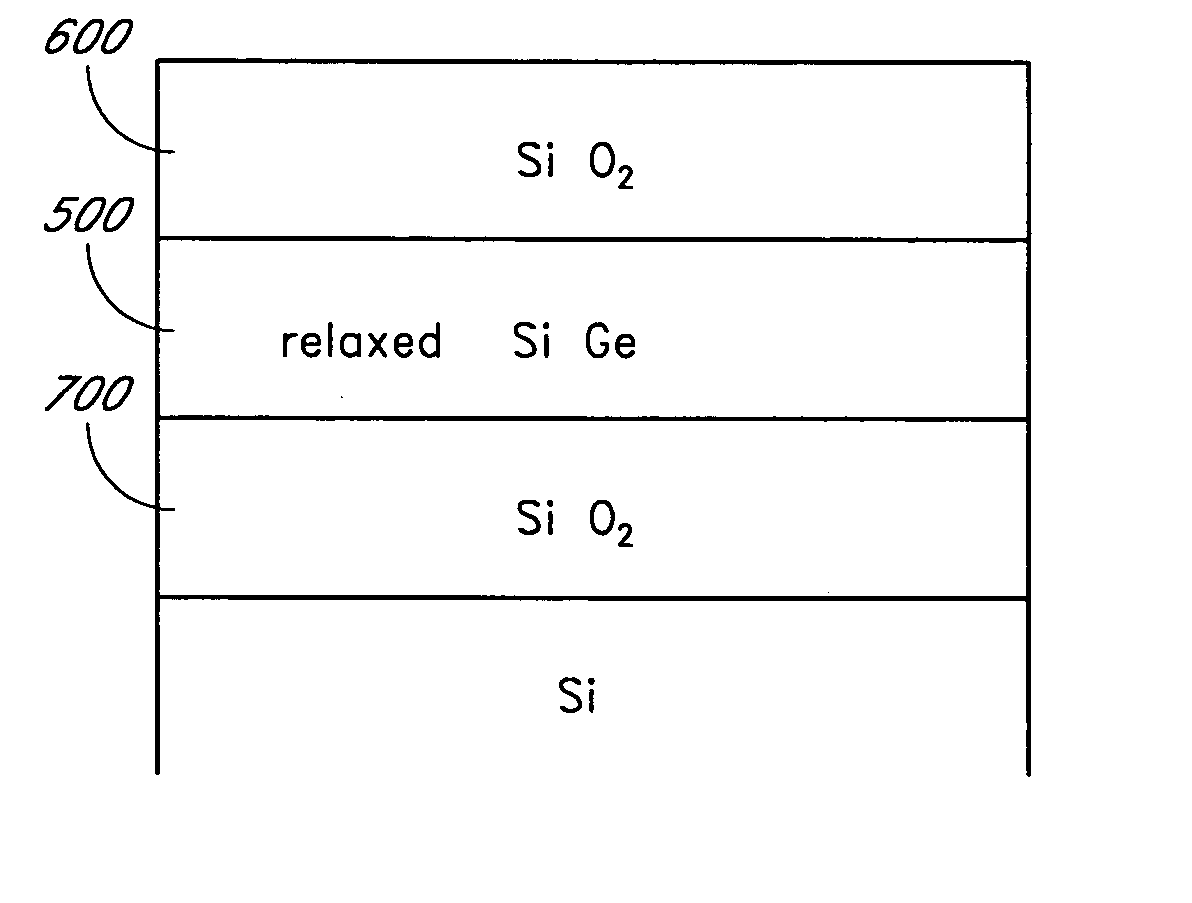
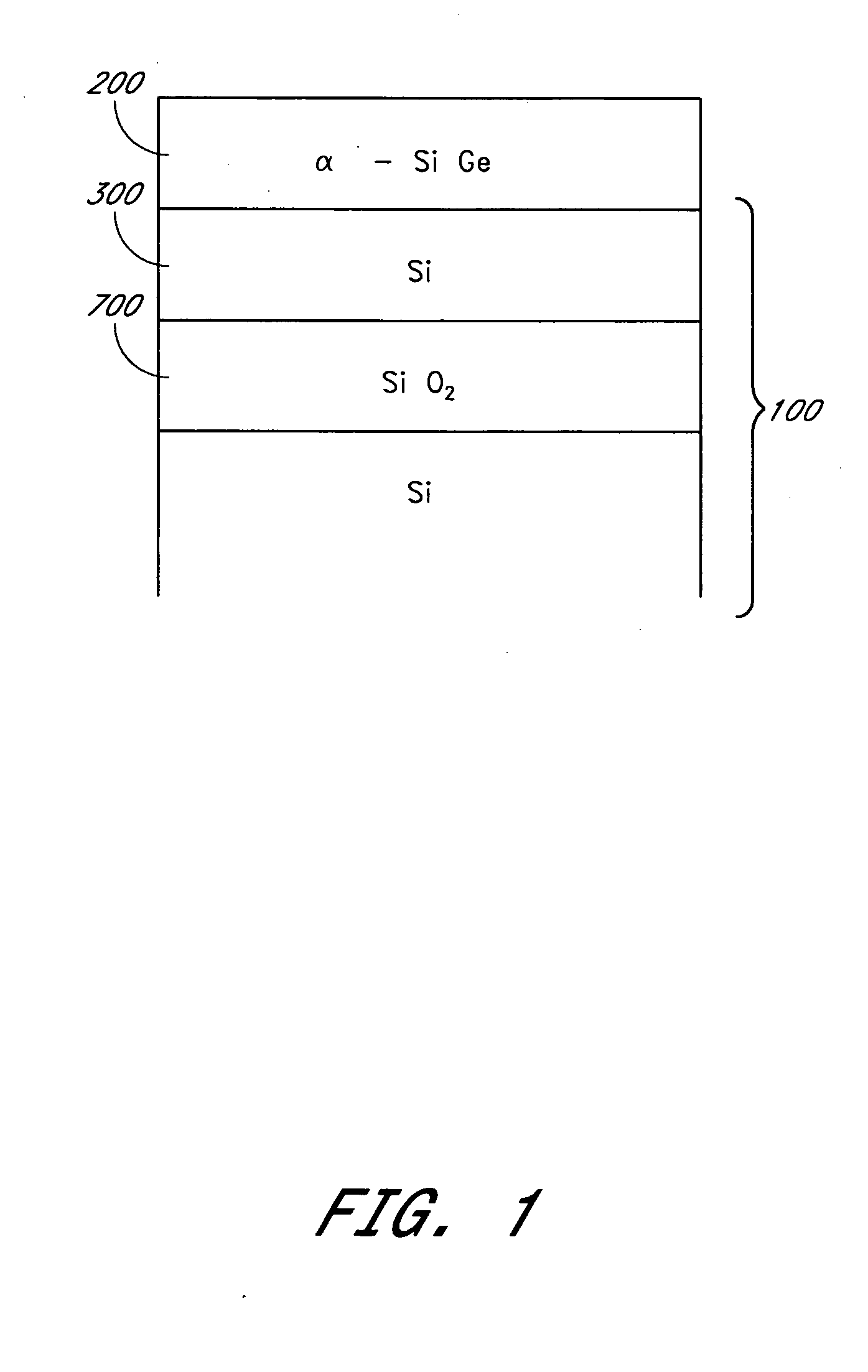
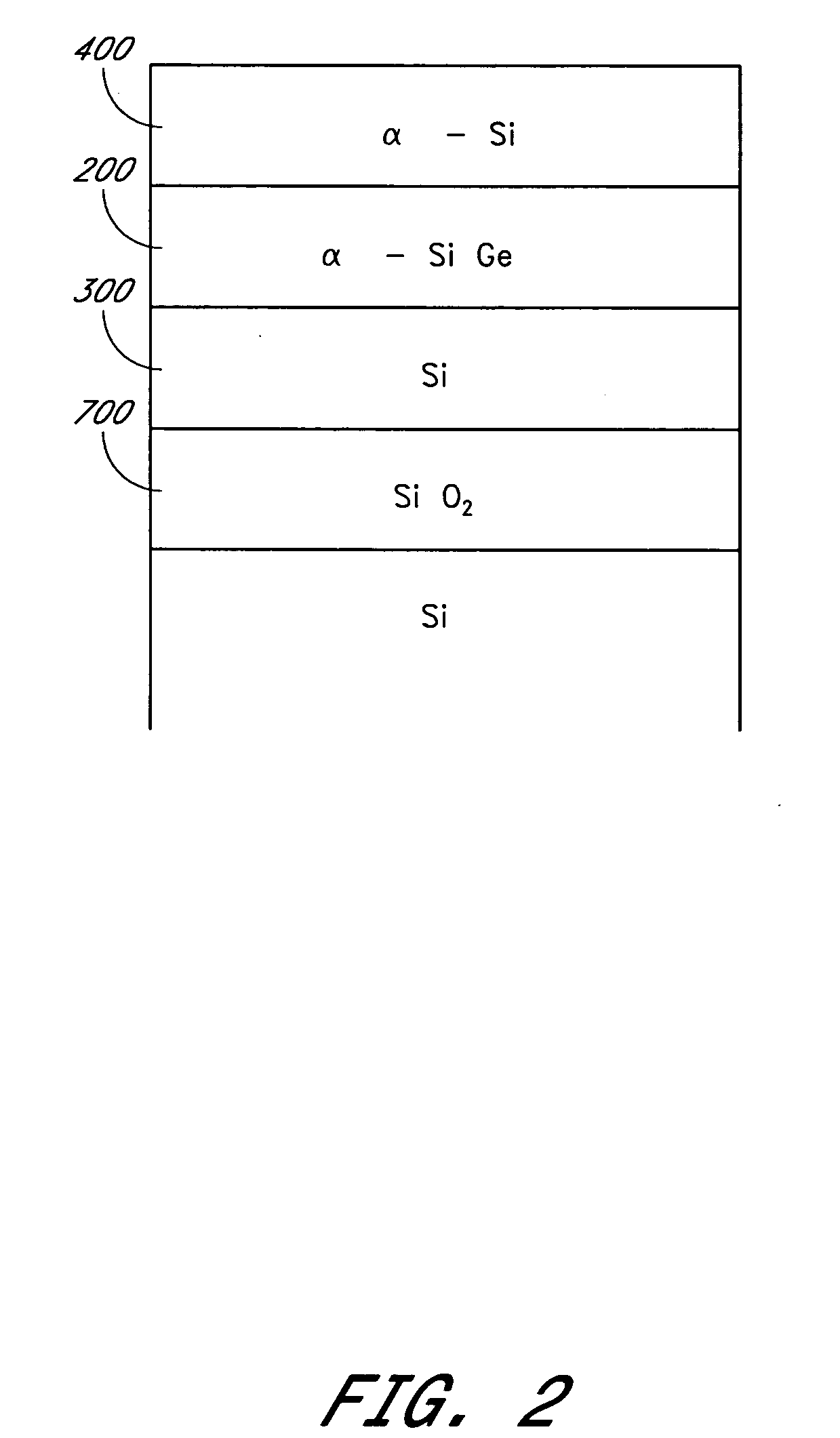
Methods are provided for producing SiGe-on-insulator structures and for forming strain-relaxed SiGe layers on silicon while minimizing defects. Amorphous SiGe layers are deposited by CVD from trisilane and GeH4. The amorphous SiGe layers are recrystallized over silicon by melt or solid phase epitaxy (SPE) processes. The melt processes preferably also cause diffusion of germanium to dilute the overall germanium content and essentially consume the silicon overlying the insulator. The SPE process can be conducted with or without diffusion of germanium into the underlying silicon, and so is applicable to SOI as well as conventional semiconductor substrates.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
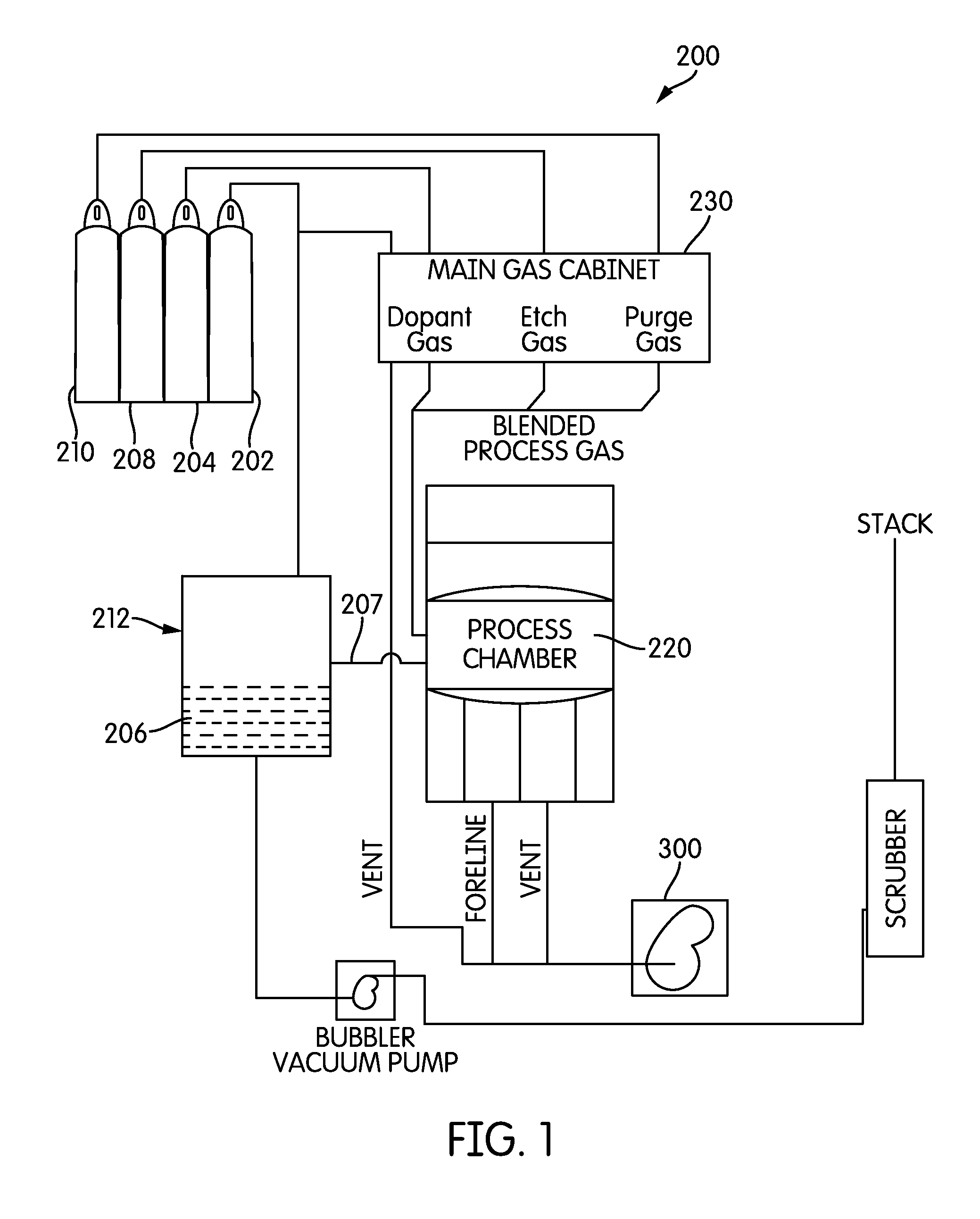
Epitaxial deposition process and apparatus
InactiveUS7494545B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReactive gasDeposition process
An epitaxial deposition process including a dry etch process, followed by an epitaxial deposition process is disclosed. The dry etch process involves placing a substrate to be cleaned into a processing chamber to remove surface oxides. A gas mixture is introduced into a plasma cavity, and the gas mixture is energized to form a plasma of reactive gas in the plasma cavity. The reactive gas enters into the processing chamber and reacts with the substrate, forming a thin film. The substrate is heated to vaporize the thin film and expose an epitaxy surface. The epitaxy surface is substantially free of oxides. Epitaxial deposition is then used to form an epitaxial layer on the epitaxy surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
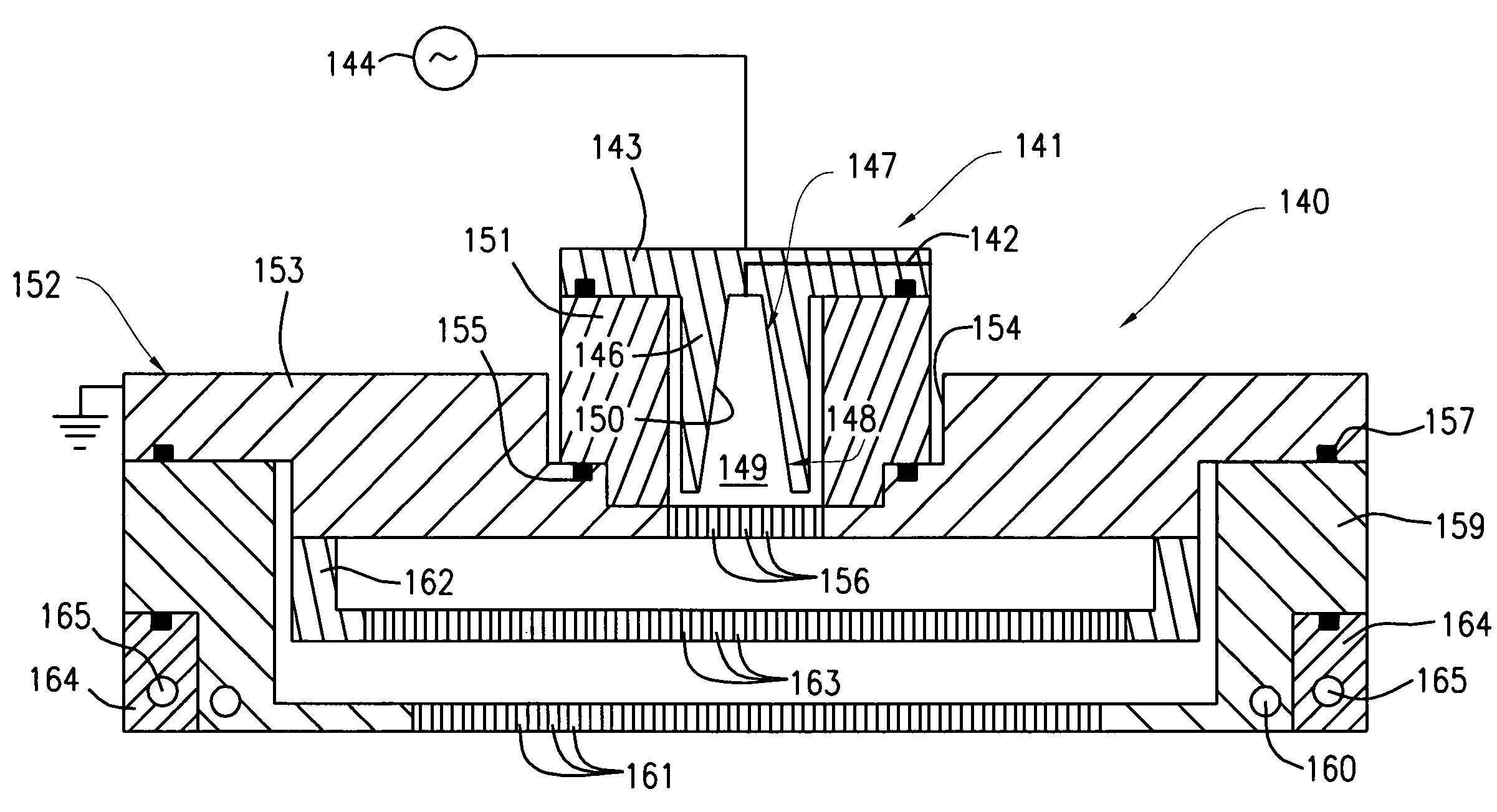
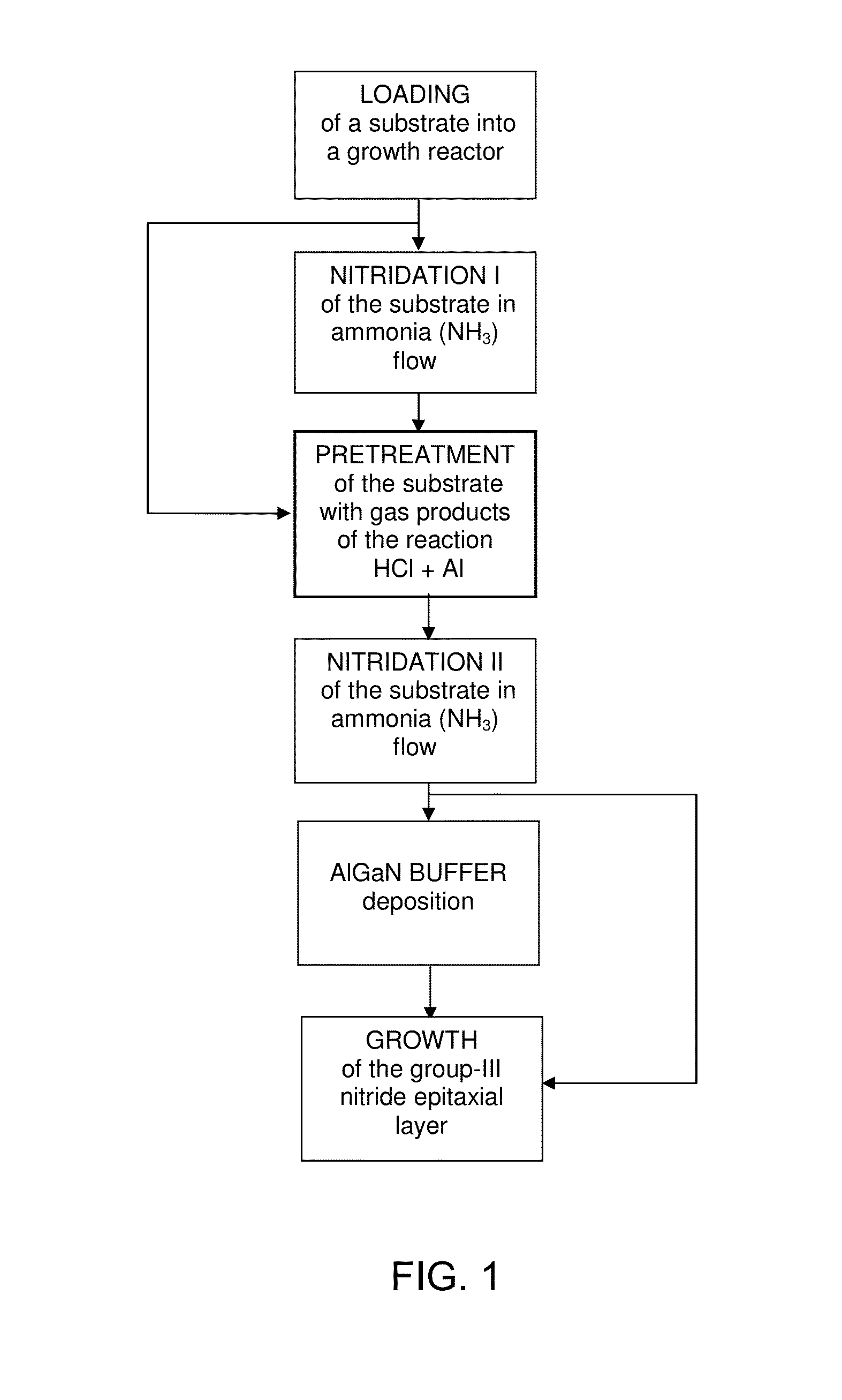
Method for Substrate Pretreatment To Achieve High-Quality III-Nitride Epitaxy
The present invention relates to a method for producing a modified surface of a substrate that stimulates the growth of epitaxial layers of group-III nitride semiconductors with substantially improved structural perfection and surface flatness. The modification is conducted outside or inside a growth reactor by exposing the substrate to a gas-product of the reaction between hydrogen chloride (HCl) and aluminum metal (Al). As a single-step or an essential part of the multi-step pretreatment procedure, the modification gains in coherent coordination between the substrate and group-III nitride epitaxial structure to be deposited. Along with epilayer, total epitaxial structure may include buffer inter-layer to accomplish precise substrate-epilayer coordination. While this modification is a powerful tool to make high-quality group-III nitride epitaxial layers attainable even on foreign substrates having polar, semipolar and nonpolar orientation, it remains gentle enough to keep the surface of the epilayer extremely smooth. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:OSTENDO TECH INC
Concentric-ring sprayer structure for material vapor phase epitaxy
InactiveCN103014846ANo effect on growthGrowth impactFrom chemically reactive gasesVapour phase epitaxySprayer
The invention discloses a concentric-ring sprayer structure for material vapor phase epitaxy, which solves the problem that the large-area deposition region provides a uniform flow field of a precursor gas mixture in a large-substrate or multi-substrate crystal growth process. The sprayer structure comprises more than one independent air inlet pipeline, wherein each air inlet pipeline is provided with a controller for monitoring and regulating inlet gas flow speed and flow rate; the bottom of the sprayer is provided with an air outlet baffle; more than one concentric ring is arranged in the sprayer; independent cavities are formed among the concentric rings and are mutually separated; the top end of each concentric ring is connected with one independent air inlet pipeline; and the air outlet baffle at the bottom end of each concentric ring is provided with one or more air outlets. The air sources are mutually separated and independently controlled; and the multi-sprayer integrated use mode obviously improves the quality of the large-area deposited grown crystal, and greatly enhances the production efficiency.
Owner:SINO NITRIDE SEMICON +1
Precursors and processes for low temperature selective epitaxial growth
InactiveUS20090087967A1Practical and cost-effective SEGReduce processingDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBromineGas phase
This invention generally relates to low temperature epitaxy. More specifically, this invention relates to processes for achieving low temperature selective epitaxial growth by chemical vapor deposition of source precursors containing Si or Ge in the presence of bromine or iodine, compositions containing precursors and brominated or iodinated compounds suitable for achieving selective epitaxial growth using the processes, epitaxial layers made using the processes, devices and other types of structures made using the processes, and processes for cleaning epitaxy reactor chambers using a bromine etchant source.
Owner:TODD MICHAEL A
SiGe (silicon germanium) source and drain area manufacturing method
ActiveCN104201108AReduce thicknessAvoid stress relaxationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationEngineering
The invention discloses a SiGe (silicon germanium) source and drain area manufacturing method. A multi-layer structure which comprises alternately stacked buffer layers and main body layers is formed by a method that the SiGe epitaxial growth of the buffer layer and the main body layers is alternated repeatedly and accordingly the thickness of every high Ge concentration of SiGe main body layer is effectively reduced and shared into every layer of main body layer and accordingly the stress relaxation due to the fact that thickness of every main body layer exceeds the critical thickness is avoided; the Ge content of every layer of SiGe main body layer is further improved to enable the stress of the SiGe source leakage on a channel to be increased; an SiGe process window is enlarged due to the repeated epitaxy and accordingly the process stability is enhanced and accordingly the device performance is improved; the stress can be effectively improved without increase of the process difficulty and accordingly the process is stable and controllable and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
SiGe selective growth without a hard mask
InactiveUS20080083948A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTensile strainCharge carrier mobility
MOS transistors having localized stressors for improving carrier mobility are provided. Embodiments of the invention comprise a gate electrode formed over a substrate, a carrier channel region in the substrate under the gate electrode, and source / drain regions on either side of the carrier channel region. The source / drain regions include an embedded stressor having a lattice spacing different from the substrate. In a preferred embodiment, the substrate is silicon and the embedded stressor is SiGe or SiC. An epitaxy process that includes using HCl gas selectively forms a stressor layer within the crystalline source / drain regions and not on polycrystalline regions of the structure. A preferred epitaxy process dispenses with the source / drain hard mask required of conventional methods. The embedded SiGe stressor applies a compressive strain to a transistor channel region. In another embodiment, the embedded stressor comprises SiC, and it applies a tensile strain to the transistor channel region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method of manufacturing a light emitting diode element
ActiveUS20110003410A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight-emitting diodeSemiconductor
A method of manufacturing a light emitting diode element is provided. A first patterned semi-conductor layer, a patterned light emitting layer, and a second patterned semi-conductor layer are sequentially formed on an epitaxy substrate so as to form a plurality of epitaxy structures, wherein the first patterned semi-conductor layer has a thinner portion in a non-epitaxy area outside the epitaxy structures. A passivation layer covering the epitaxy structures and the thinner portion is formed. The passivation layer covering on the thinner portion is partially removed to form a patterned passivation layer. A patterned reflector is formed directly on each of the epitaxy structures. The epitaxy structures are bonded to a carrier substrate. A lift-off process is performed to separate the epitaxy structures from the epitaxy substrate. An electrode is formed on each of the epitaxy structures far from the patterned reflector.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286776A1Enhance chamber cleaning processHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolatilesSilicon oxide
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
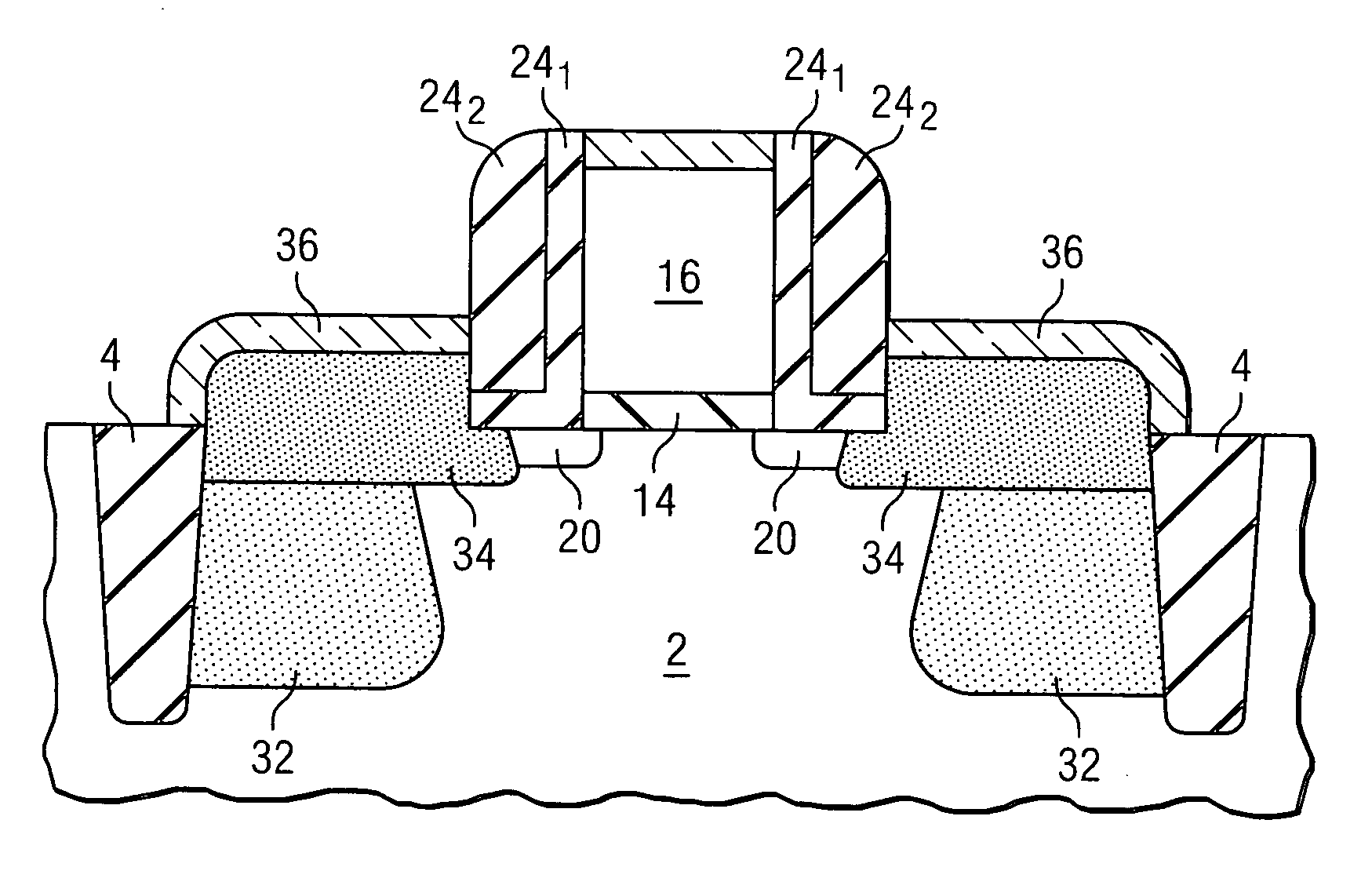
Self-aligned double-gate MOSFET by selective epitaxy and silicon wafer bonding techniques
InactiveUS6365465B1Controlled diffusionReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
A structure and a method of manufacturing a double-gate metal oxide semiconductor transistor includes forming a laminated structure having a single crystal silicon channel layer and insulating oxide and nitride layers on each side of the single crystal silicon channel, forming openings in the laminated structure, forming drain and source regions in the openings, doping the drain and source regions, forming a mask over the laminated structure, removing portions of the laminated structure not protected by the mask, removing the mask and the insulating oxide and nitride layers to leave the single crystal silicon channel layer suspended from the drain and source regions, forming an oxide layer to cover the drain and source regions and the channel layer, and forming a double-gate conductor over the oxide layer such that the double-gate conductor includes a first conductor on a first side of the single crystal silicon channel layer and a second conductor on a second side of the single crystal silicon channel layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low-temperature selective epitaxial growth of silicon for device integration
InactiveUS20150247259A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDeposition temperaturePhysical chemistry
An epitaxy method includes providing an exposed crystalline region of a substrate material. Silicon is epitaxially deposited on the substrate material in a low temperature process wherein a deposition temperature is less than 500 degrees Celsius. A source gas is diluted with a dilution gas with a gas ratio of dilution gas to source gas of less than 1000.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
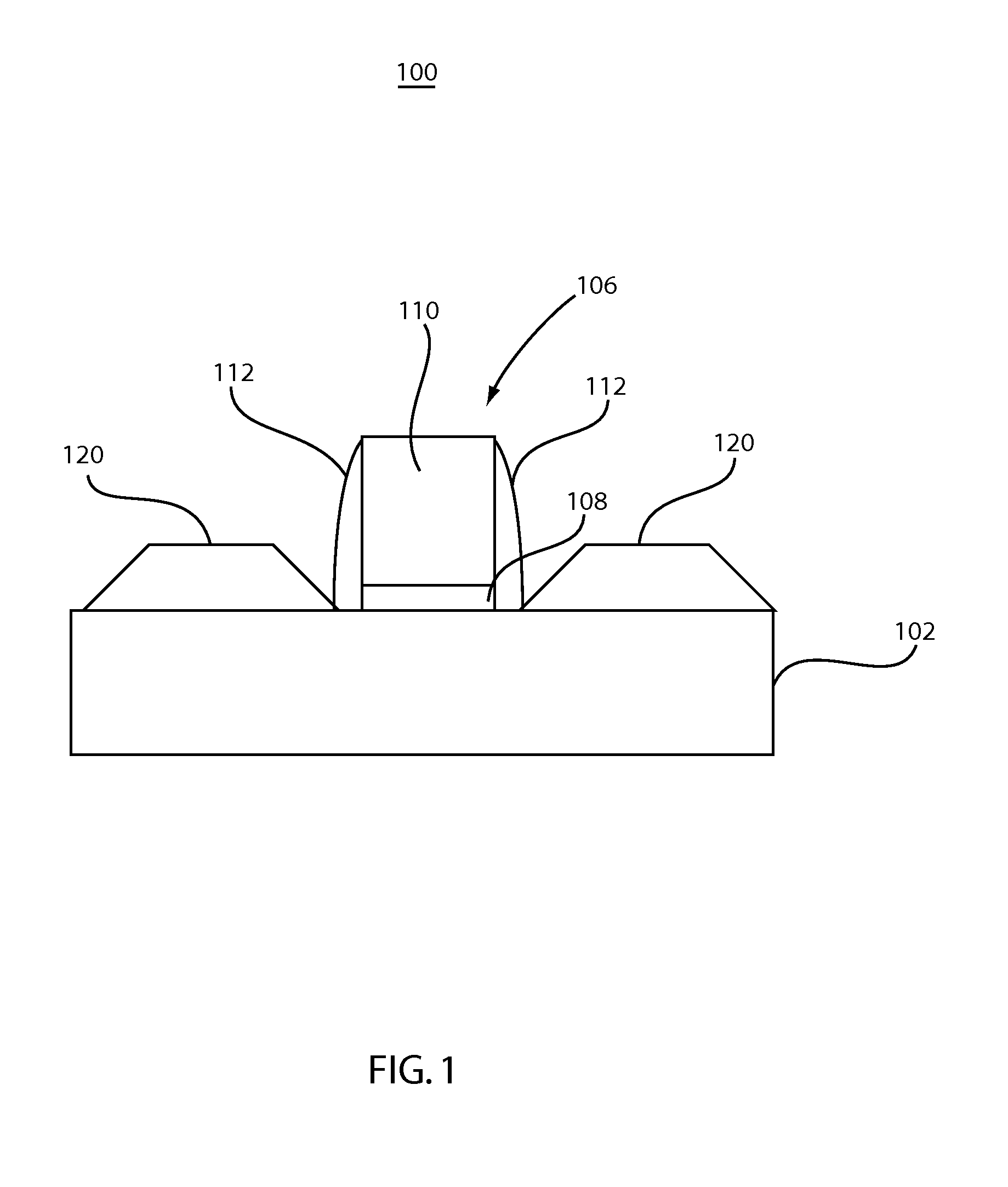
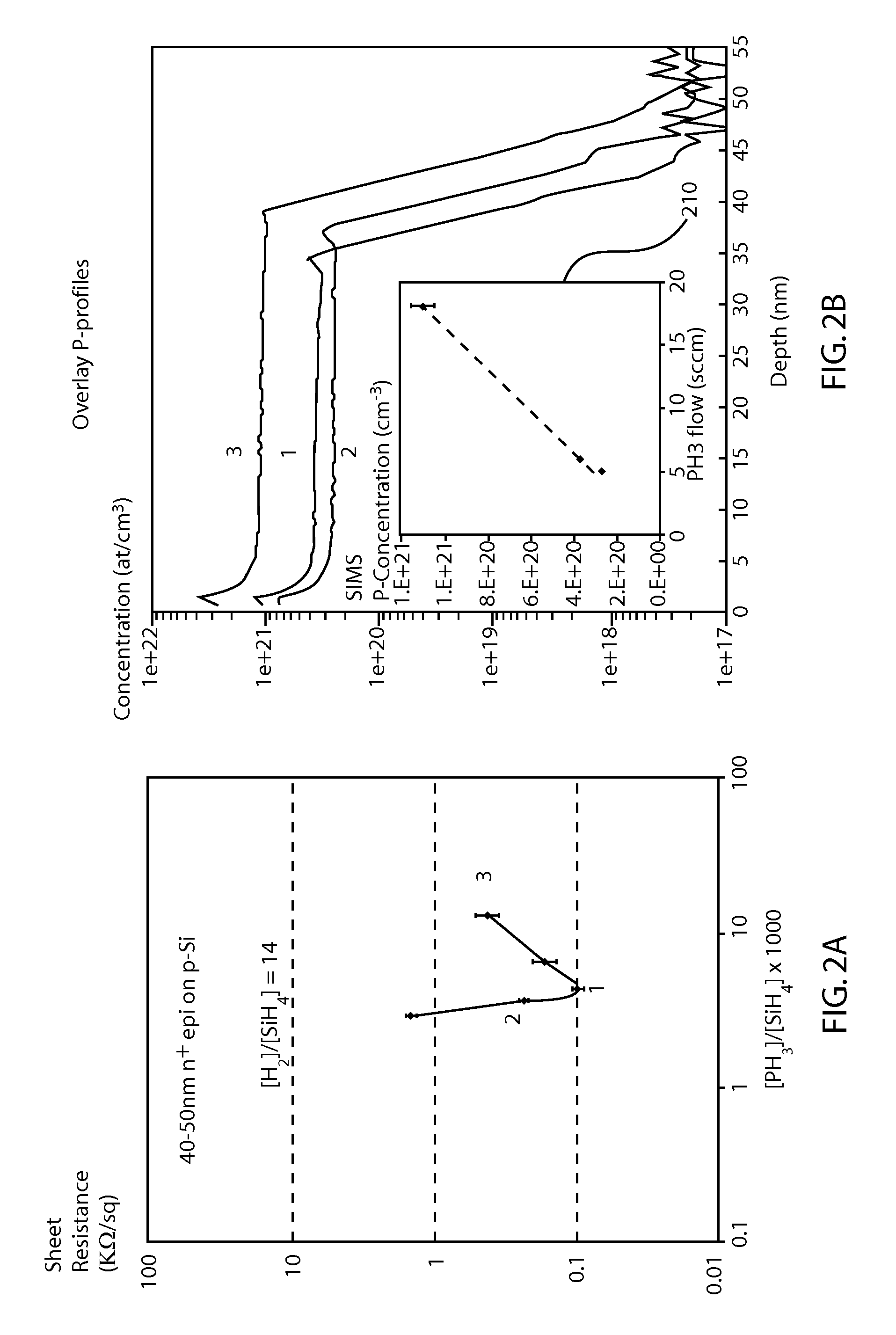
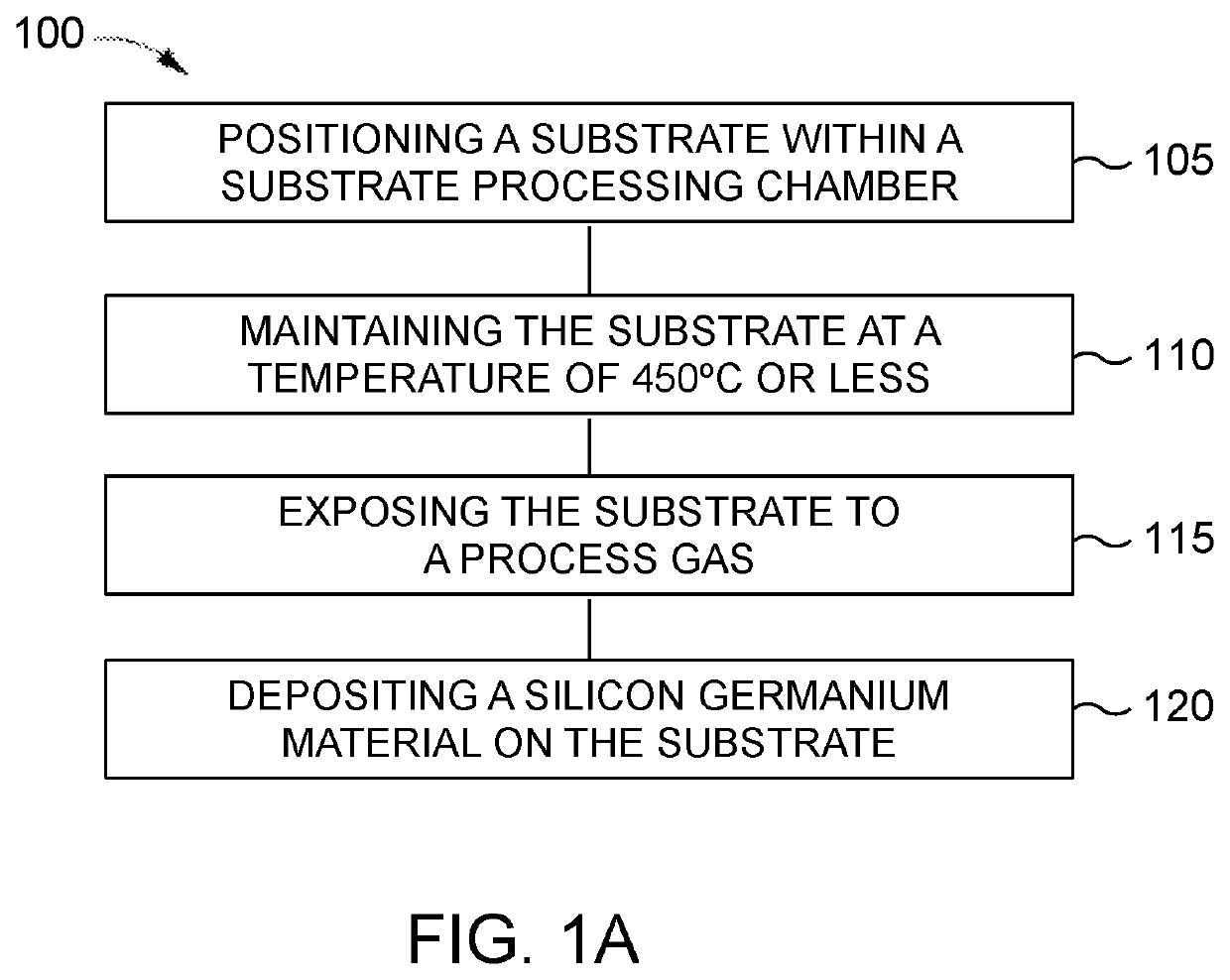
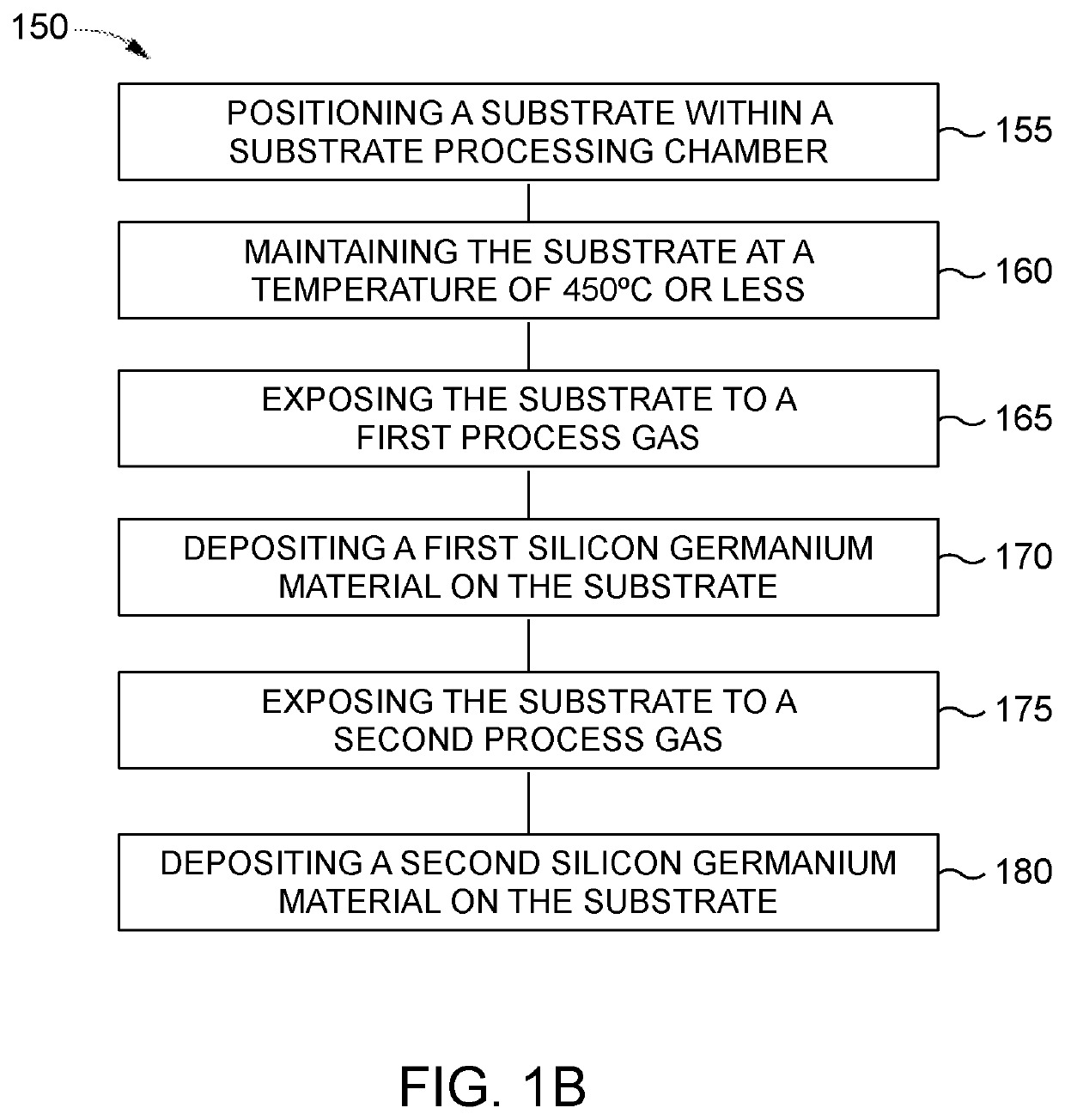
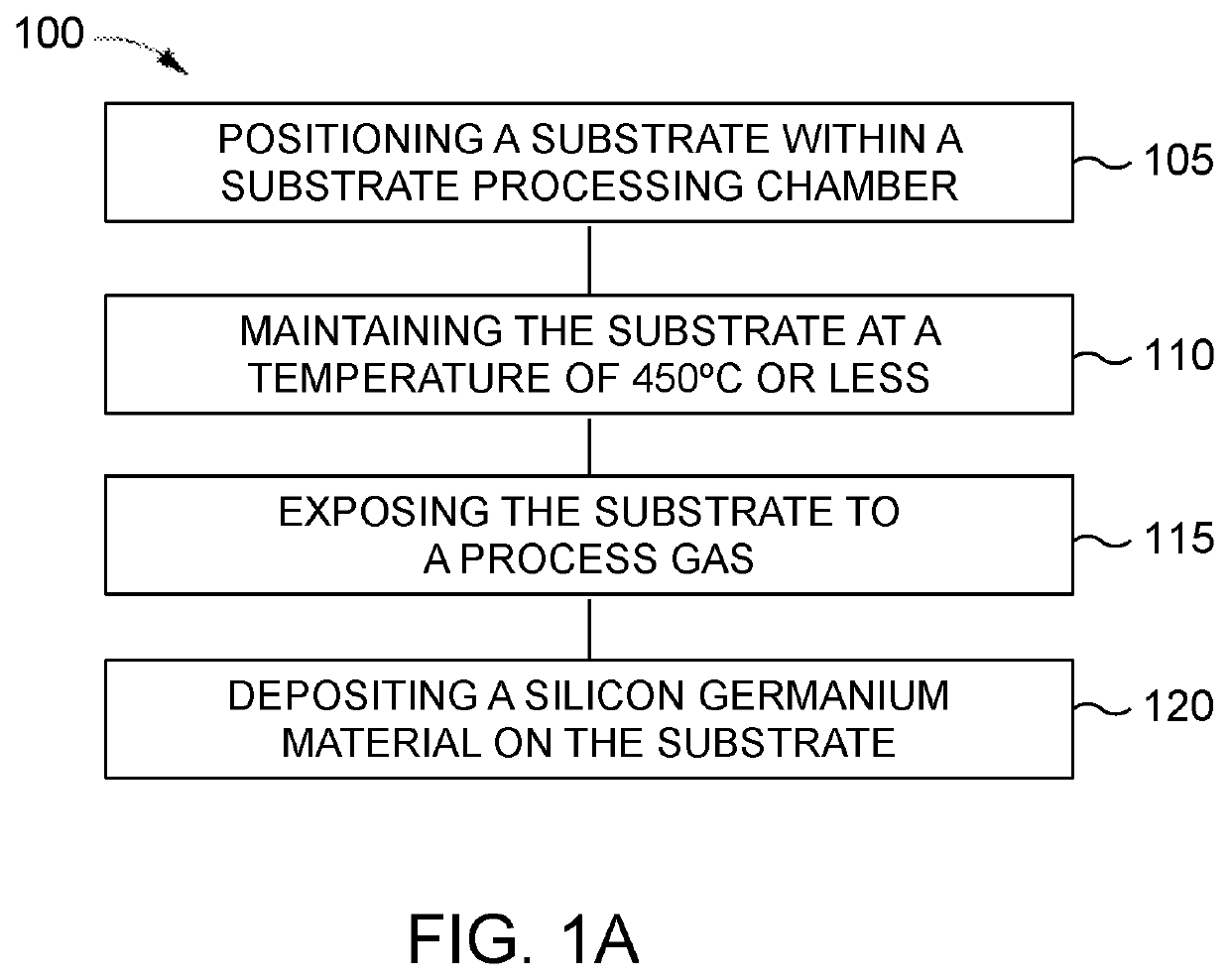
Method of selective silicon germanium epitaxy at low temperatures
In an embodiment, a method of selectively depositing a silicon germanium material on a substrate is provided. The method includes positioning the substrate within a substrate processing chamber, the substrate having a dielectric material and a silicon containing single crystal thereon; maintaining the substrate at a temperature of about 450° C. or less; exposing the substrate to a process gas comprising: a silicon source gas, a germanium source gas, an etchant gas, a carrier gas, and at least one dopant source gas; and epitaxially and selectively depositing a first silicon germanium material on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dsa grapho-epitaxy process with etch stop material
InactiveUS20140256145A1Reduce widthForming accuratelySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistReactive-ion etching
A method for defining a template for directed self-assembly (DSA) materials includes forming an etch stop layer on a neutral material, forming a mask layer on the etch stop layer and forming an anti-reflection coating (ARC) on the mask layer. A resist layer is patterned on the ARC using optical lithography to form a template pattern. The ARC and the mask layer are reactive ion etched down to the etch stop layer in accordance with the template pattern to form a template structure. The ARC is removed from the mask layer and the template structure is trimmed to reduce a width of the template structure. A wet etch is performed to remove the etch stop layer to permit the neutral material to form an undamaged DSA template for DSA materials.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low temperature fabrication of discrete silicon-containing substrates and devices
InactiveUS20070262363A1Less timeLess moneySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETEtching
Fabrication methods and processes are described, the methods and processes occurring at a low-temperature and involving passivation. The methods and processes easily incorporate annealing, deposition, patterning, lithography, etching, oxidation, epitaxy and chemical mechanical polishing for forming suitable devices, such as diodes and MOSFETs. Such fabrication is a suitable and more cost-effective alternative to a process of diffusion or doping, typical for forming p-n junctions. The process flow does not require temperatures above 700 degrees Centigrade. Formation of p-n junctions in discrete silicon diodes and MOSFETs are also provided, fabricated at low temperatures in the absence of diffusion or doping.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method of selective silicon germanium epitaxy at low temperatures
In an embodiment, a method of selectively depositing a silicon germanium material on a substrate is provided. The method includes positioning the substrate within a substrate processing chamber, the substrate having a dielectric material and a silicon containing single crystal thereon; maintaining the substrate at a temperature of about 450° C. or less; exposing the substrate to a process gas comprising: a silicon source gas, a germanium source gas, an etchant gas, a carrier gas, and at least one dopant source gas; and epitaxially and selectively depositing a first silicon germanium material on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods for repairing substrate lattice and selective epitaxy processing
ActiveUS20190362970A1Weaken energyHigh energySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantDielectric
The present disclosure describes patterned devices and methods for repairing substrate lattice damage in a patterned device. The patterned device includes a substrate, an alternating conductor and dielectric stack atop the substrate, a channel hole extending through the alternating conductor and dielectric stack to the substrate, and an epitaxial grown layer at a bottom of the channel hole and a top surface of the substrate. A part of the substrate in contact with the epitaxial grown layer has a dopant or doping concentration different from an adjacent part of the substrate. The method includes forming a channel hole in an insulating layer atop a substrate, forming an amorphous layer in a top side of the substrate below the channel hole, heating to crystallize the amorphous layer, and growing an epitaxial layer on the crystallized layer in the channel hole.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
Bulk nitride mono-crystal including substrate for epitaxy
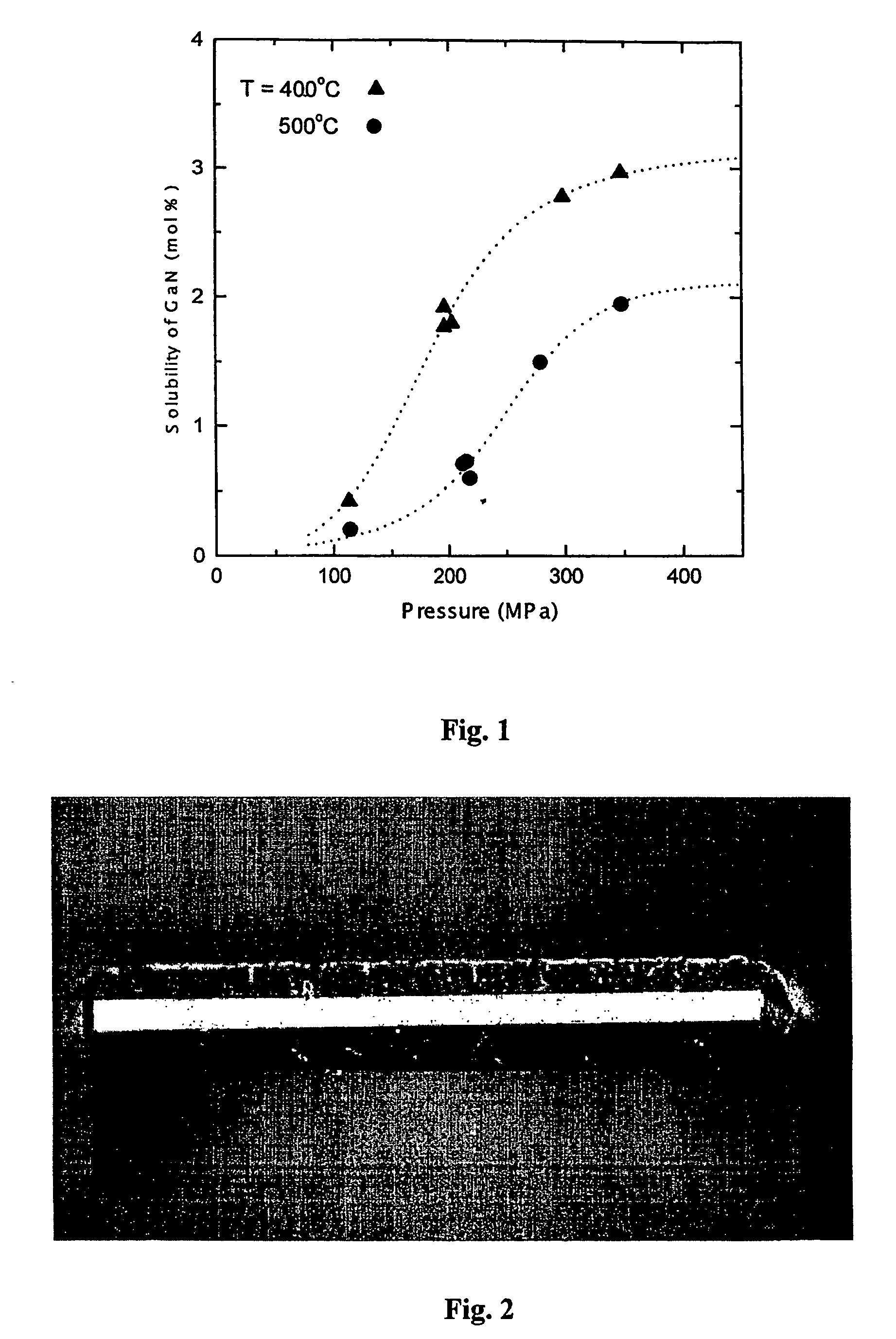
InactiveUS7132730B2Reduced life-timeLaser detailsFrom normal temperature solutionsDissolutionSolvent
The invention relates to a substrate for epitaxy, especially for preparation of nitride semiconductor layers. Invention covers a bulk nitride mono-crystal characterized in that it is a mono-crystal of gallium nitride and its cross-section in a plane perpendicular to c-axis of hexagonal lattice of gallium nitride has a surface area greater than 100 mm2, it is more than 1.0 μm thick and its C-plane surface dislocation density is less than 106 / cm2, while its volume is sufficient to produce at least one further-processable non-polar A-plane or M-plane plate having a surface area at least 100 mm2. More generally, the present invention covers a bulk nitride mono-crystal which is characterized in that it is a mono-crystal of gallium-containing nitride and its cross-section in a plane perpendicular to c-axis of hexagonal lattice of gallium-containing nitride has a surface area greater than 100 mm2, it is more 1.0 μm thick and its surface dislocation density is less than 106 / cm2. Mono-crystals according to the present invention are suitable for epitaxial growth of nitride semiconductor layers. Due to their good crystalline quality they are suitable for use in opto-electronics for manufacturing opto-electronic semiconductor devices based on nitrides, in particular for manufacturing semiconductor laser diodes and laser devices. The a.m bulk mono-crystals of gallium-containing nitride are crystallized on seed crystals. Various seed crystals may be used. The bulk mono-crystals of gallium-containing nitride are crystallized by a method involving dissolution of a gallium-containing feedstock in a supercritical solvent and crystallization of a gallium nitride on a surface of seed crystal, at temperature higher and / or pressure lower than in the dissolution process.
Owner:AMMONO SP Z O O (PL) +1
Selective epitaxy process with alternating gas supply
ActiveUS20060115934A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle crystalGas supply
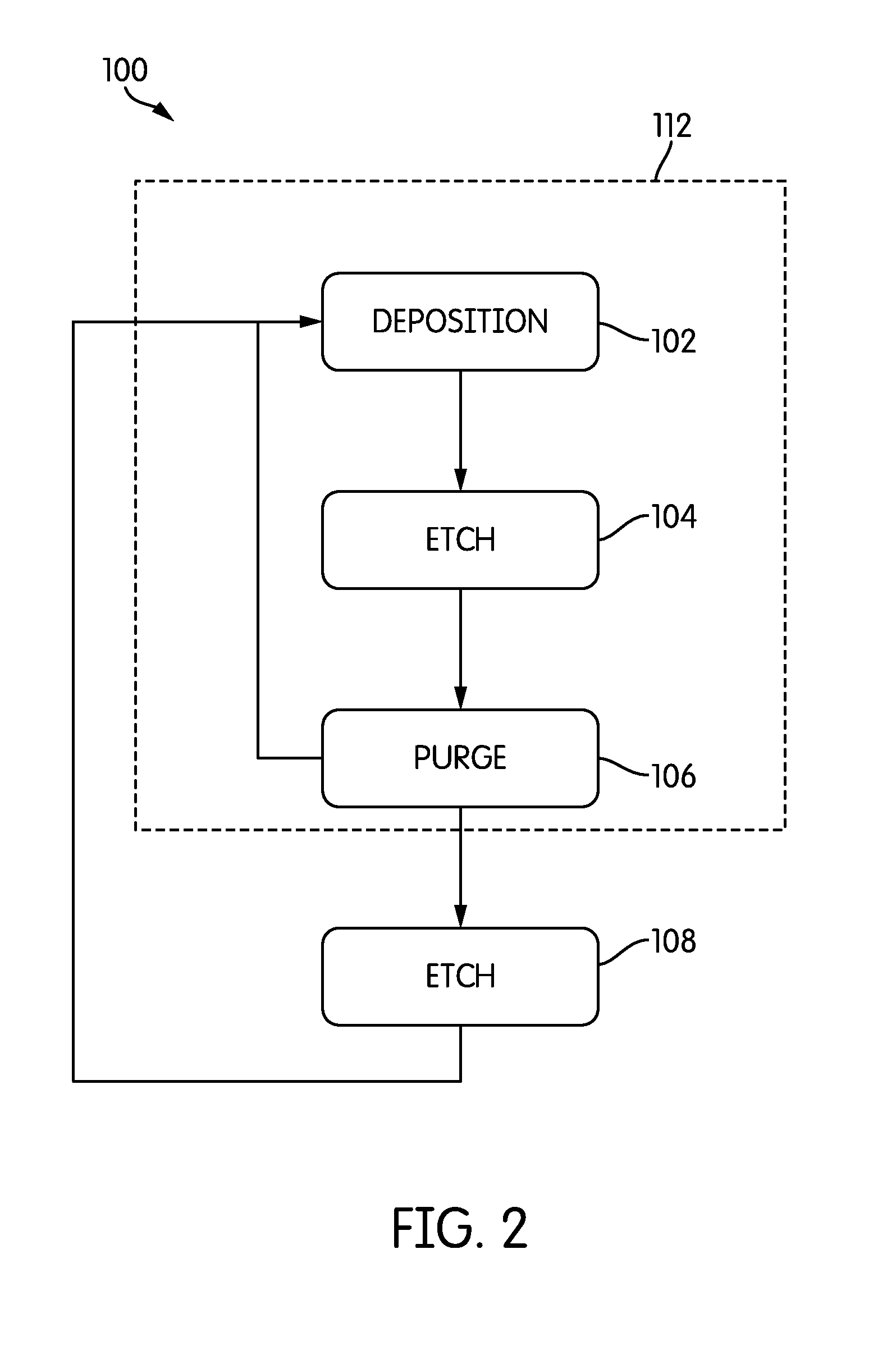
In one example, a method of epitaxially forming a silicon-containing material on a substrate surface is presented which includes positioning a substrate into a process chamber. The substrate has a monocrystalline surface and at least a second surface, such as an amorphous surface and / or a polycrystalline surface. The substrate is exposed to a deposition gas to deposit an epitaxial layer on the monocrystalline surface and a polycrystalline layer on the second surface. The deposition gas preferably contains a silicon source and at least a second elemental source, such as a germanium source, a carbon source and / or combinations thereof. Thereafter, the method further provides exposing the substrate to an etchant gas to etch the polycrystalline layer and the epitaxial layer in a manner such that the polycrystalline layer is etched at a faster rate than the epitaxial layer. The method may further include a deposition cycle that includes repeating the exposure of the substrate to the deposition and etchant gases to form a silicon-containing material with a predetermined thickness.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Growth of multi-junction LED film stacks with multi-chambered epitaxy system
InactiveUS20110204376A1Reduce impactHigh bulk densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantLed array
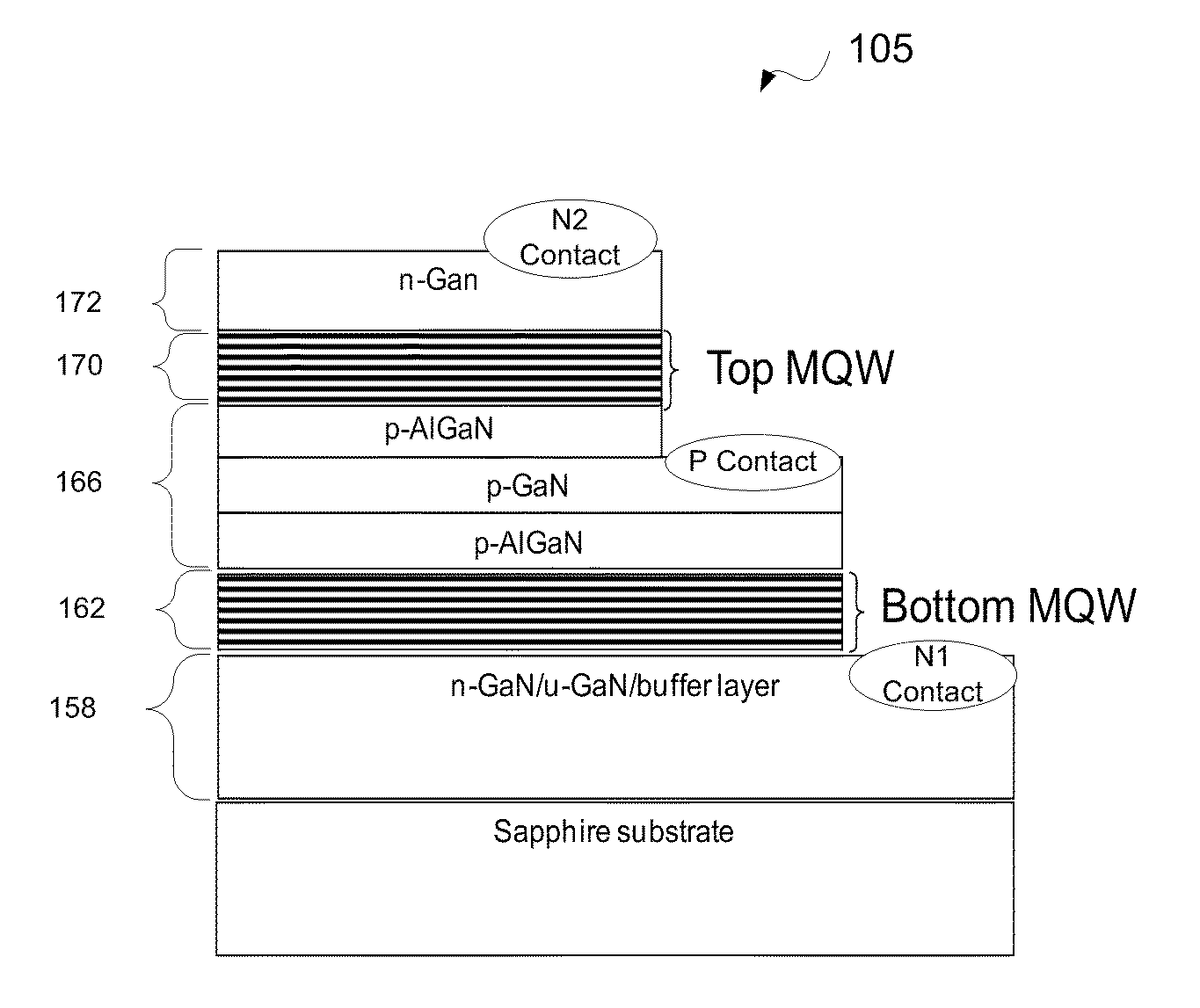
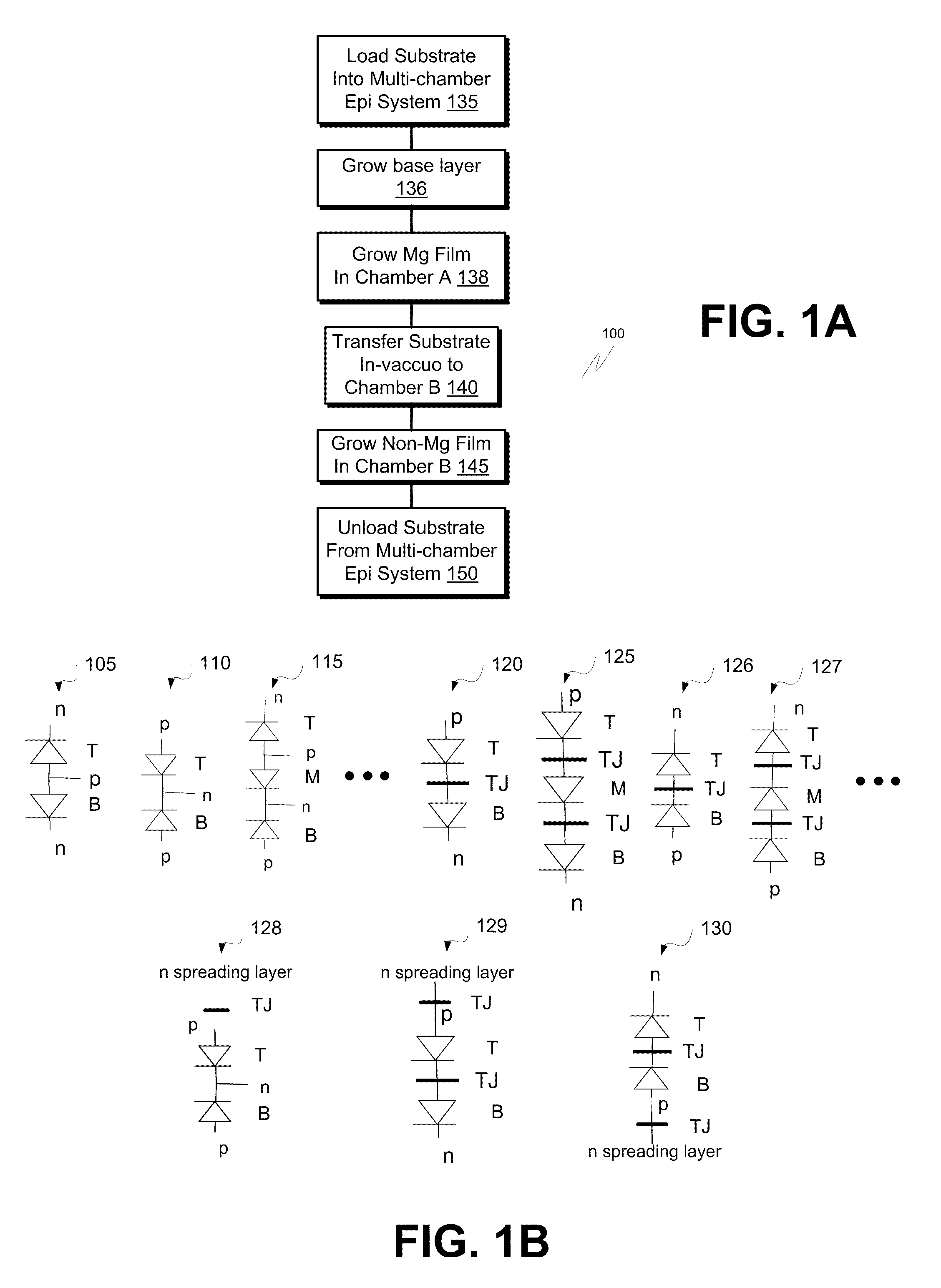
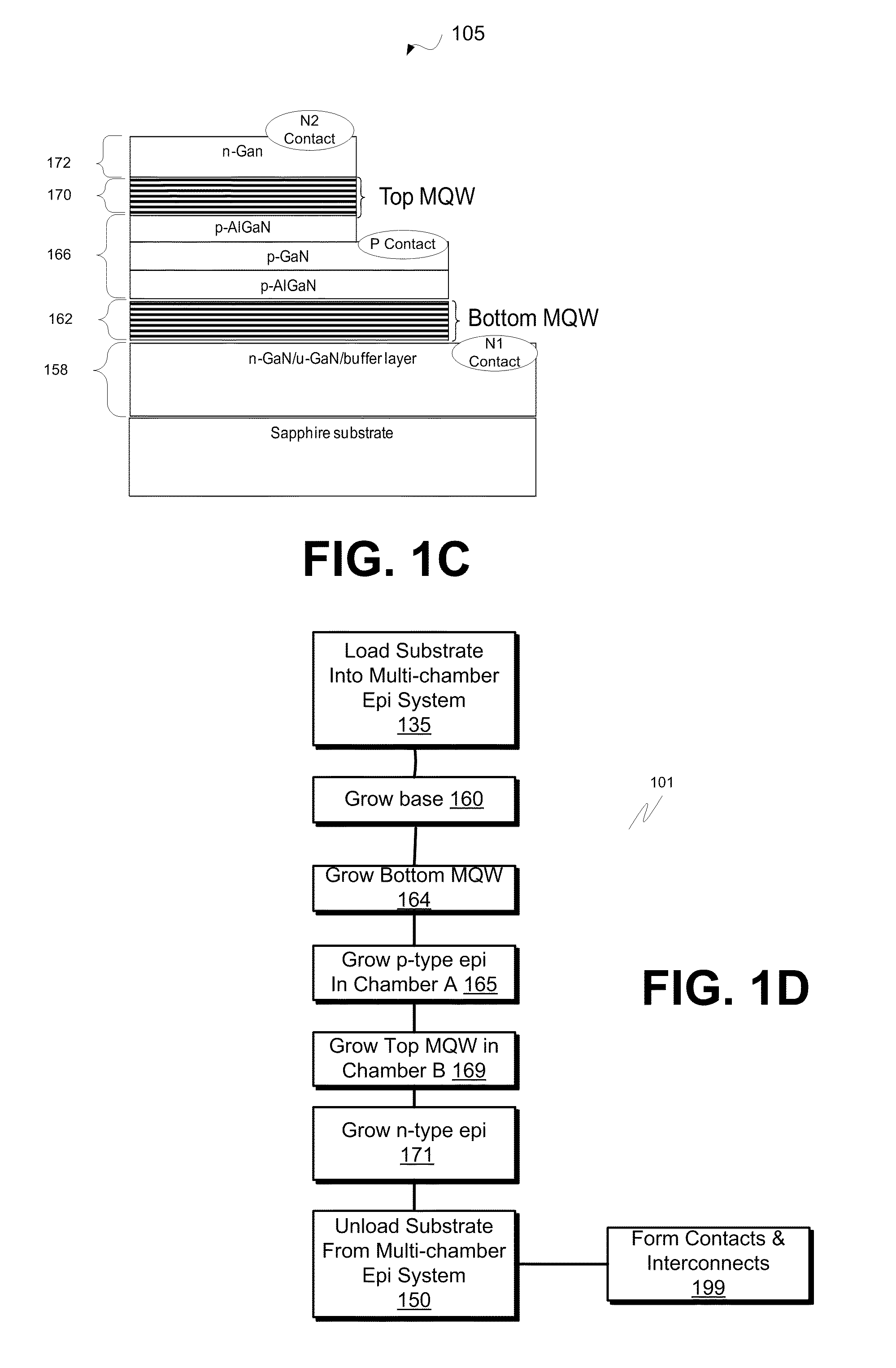
Apparatus and method for growth of non-p-type GaN layers over p-type GaN layers. Embodiments include multi-junction LED film stacks, multi-junction LED devices paired into units and multi-junction LED arrays of the paired units. Epitaxial growths of p-type and non-p-type material layers are split between epitaxial chambers clustered onto a single platform to reduce p-type dopant cross-contamination. Arrayed multi-junction LED devices provide improved packing density and reduced blinking during AC operation.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dual-SiGe epitaxy for MOS devices
ActiveUS20080128746A1Increase pressureReduce impurity diffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate stackStressor
A semiconductor includes a semiconductor substrate, a gate stack on the semiconductor substrate, and a stressor having at least a portion in the semiconductor substrate and adjacent to the gate stack. The stressor includes a first stressor region and a second stressor region on the first stressor region, wherein the second stressor region extends laterally closer to a channel region underlying the gate stack than the first stressor region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com