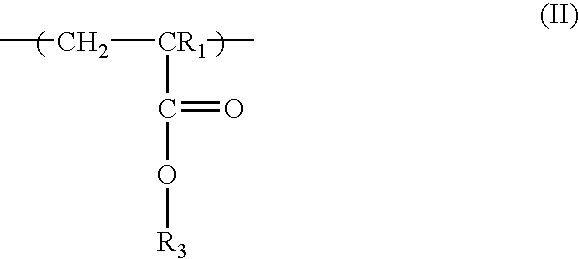Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1222 results about "Process window" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
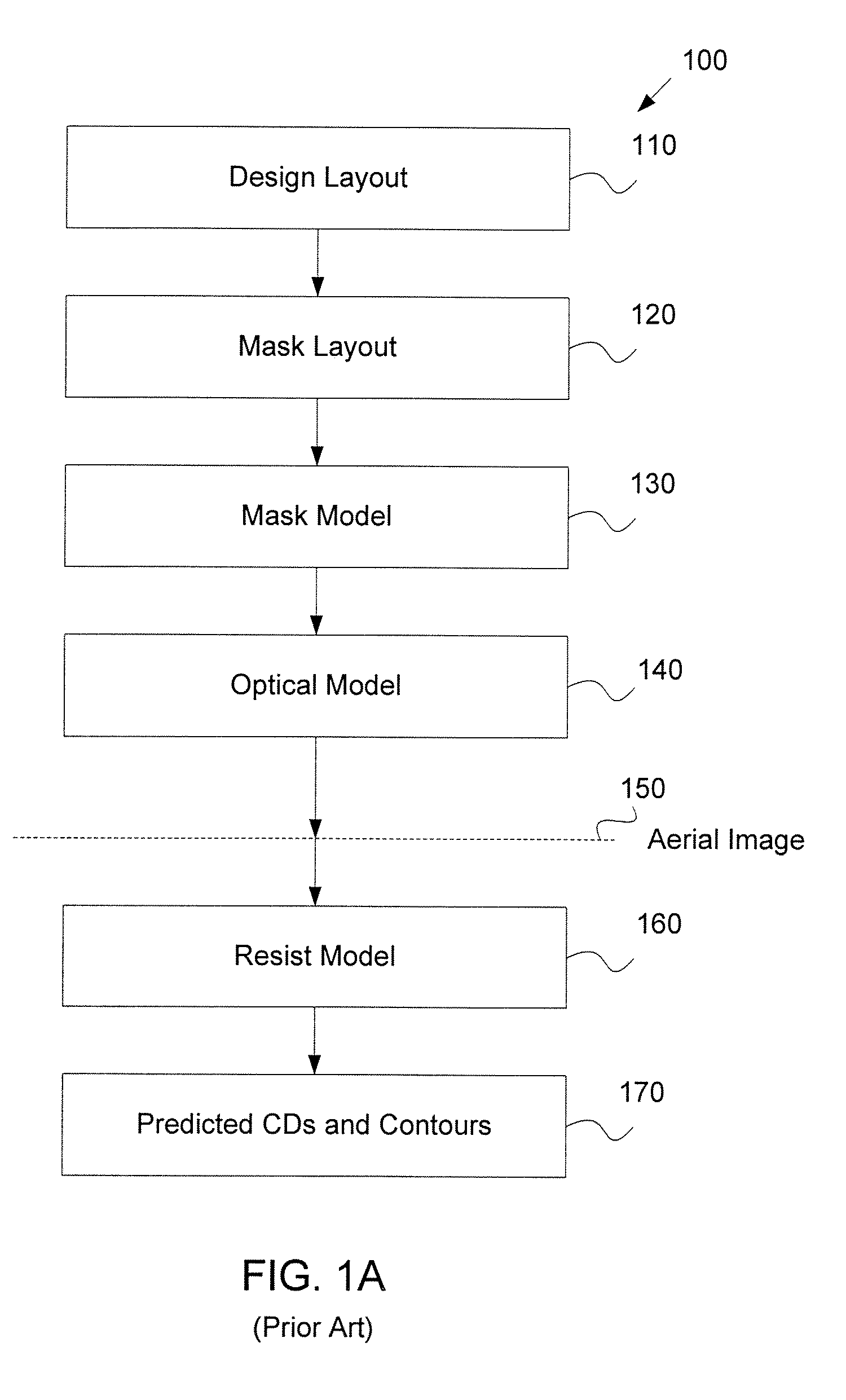
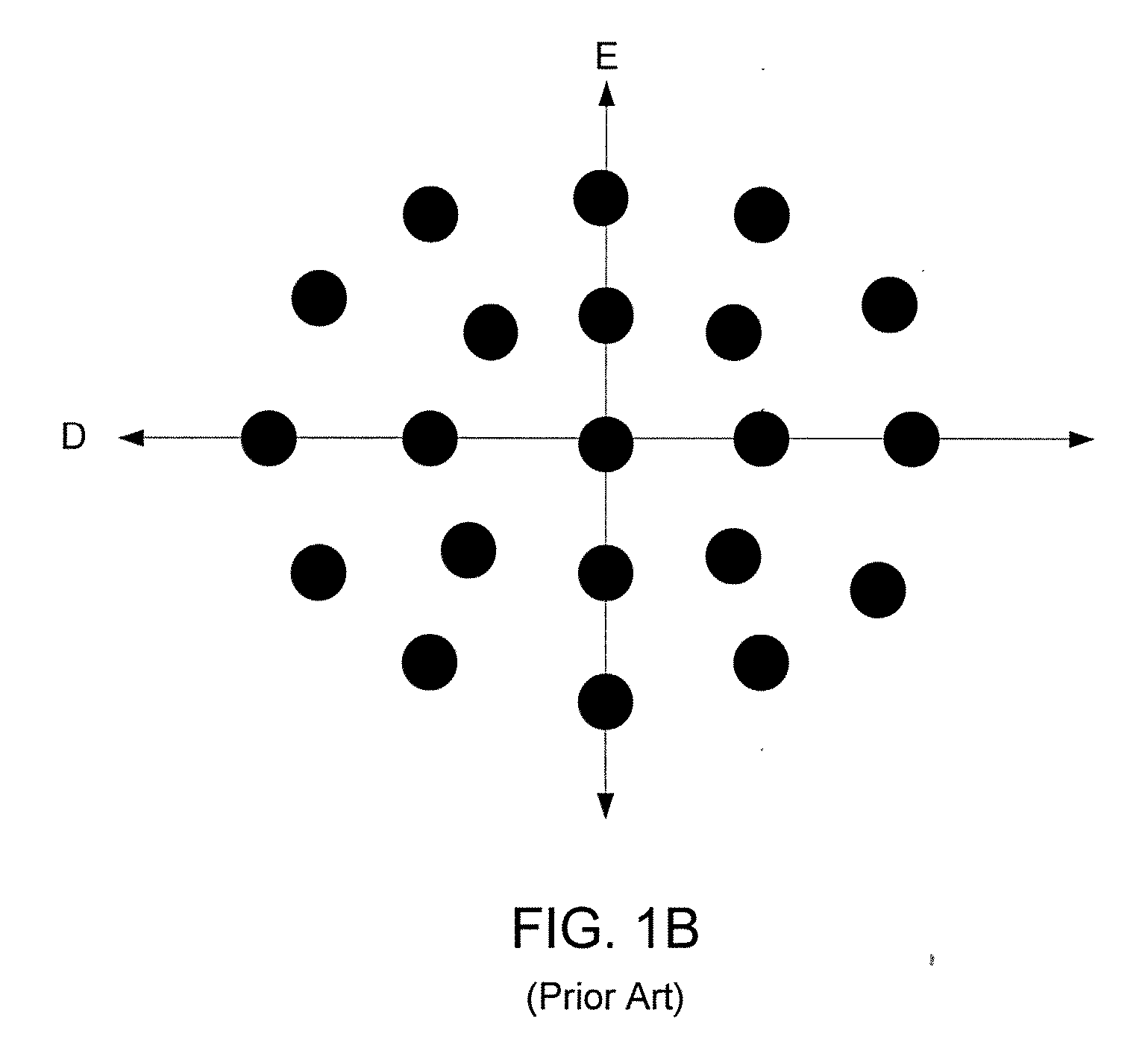
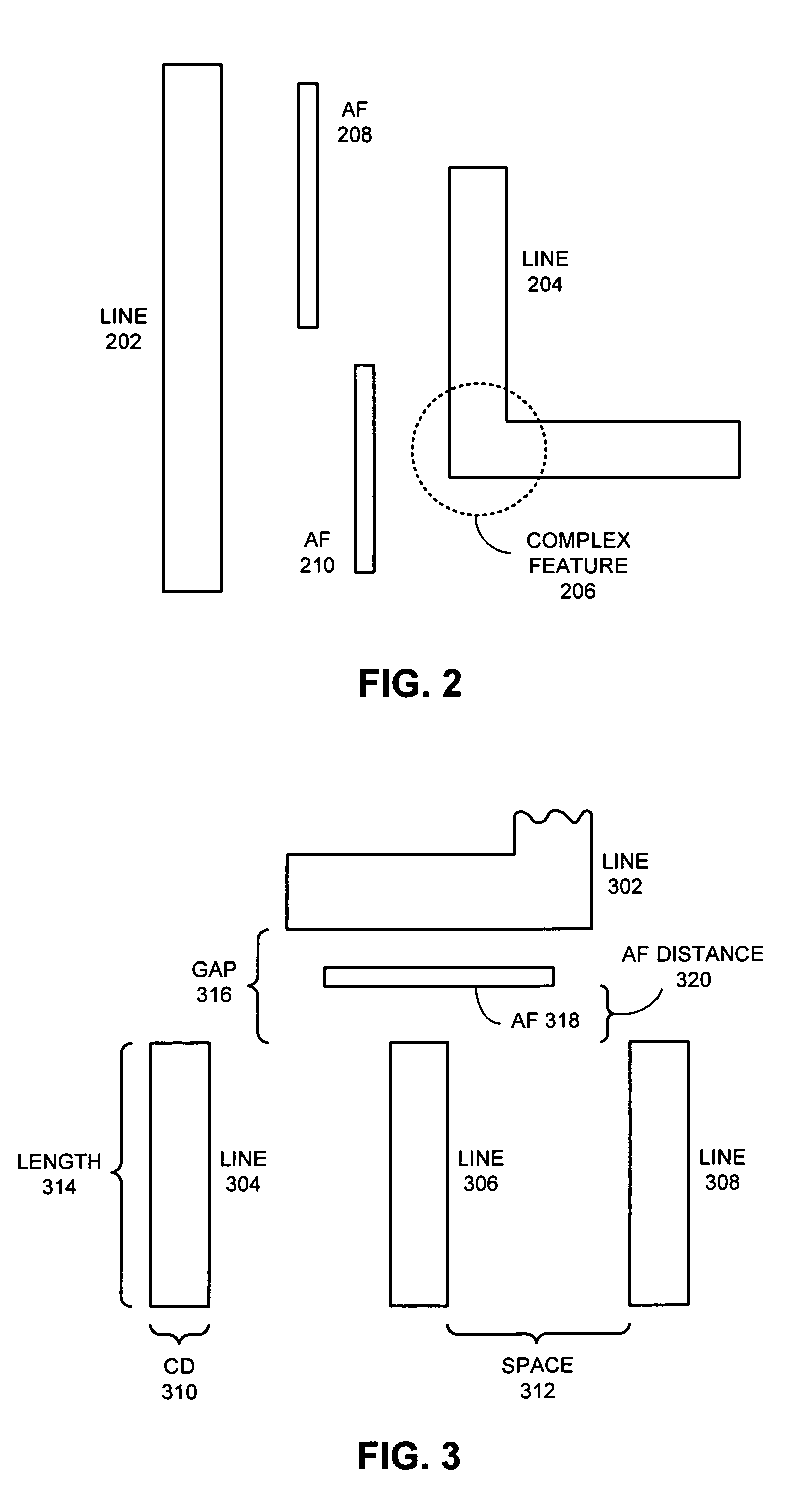
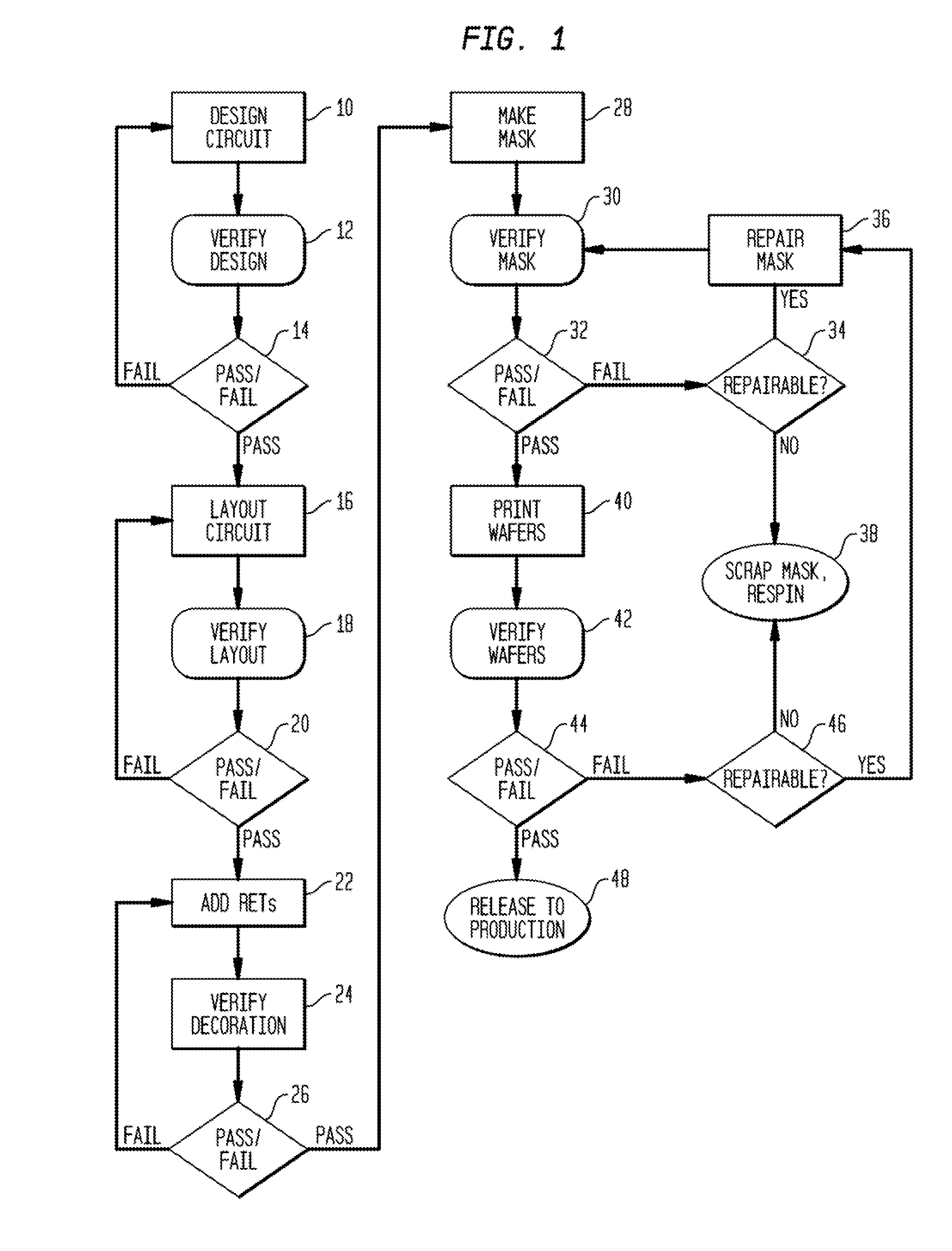
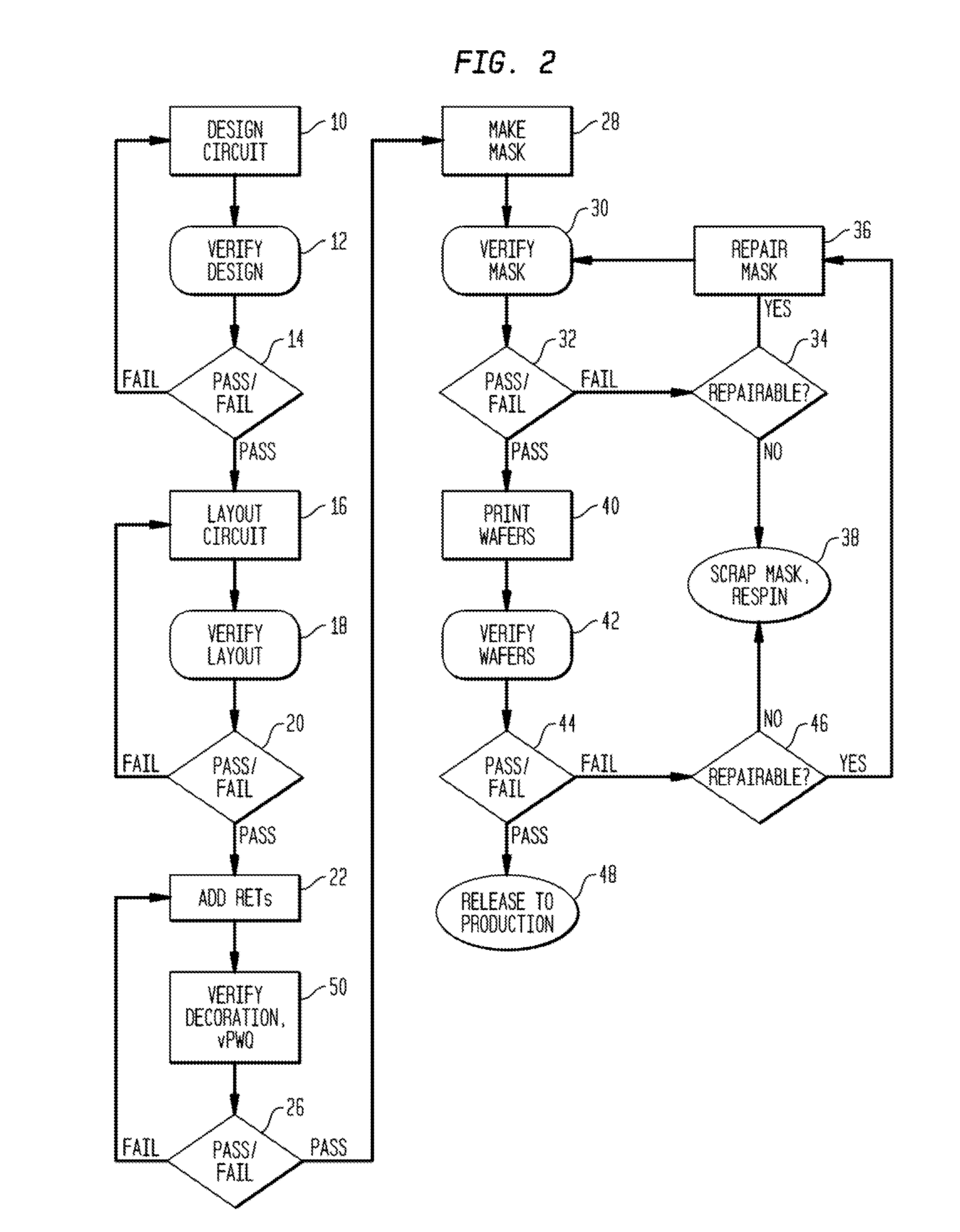
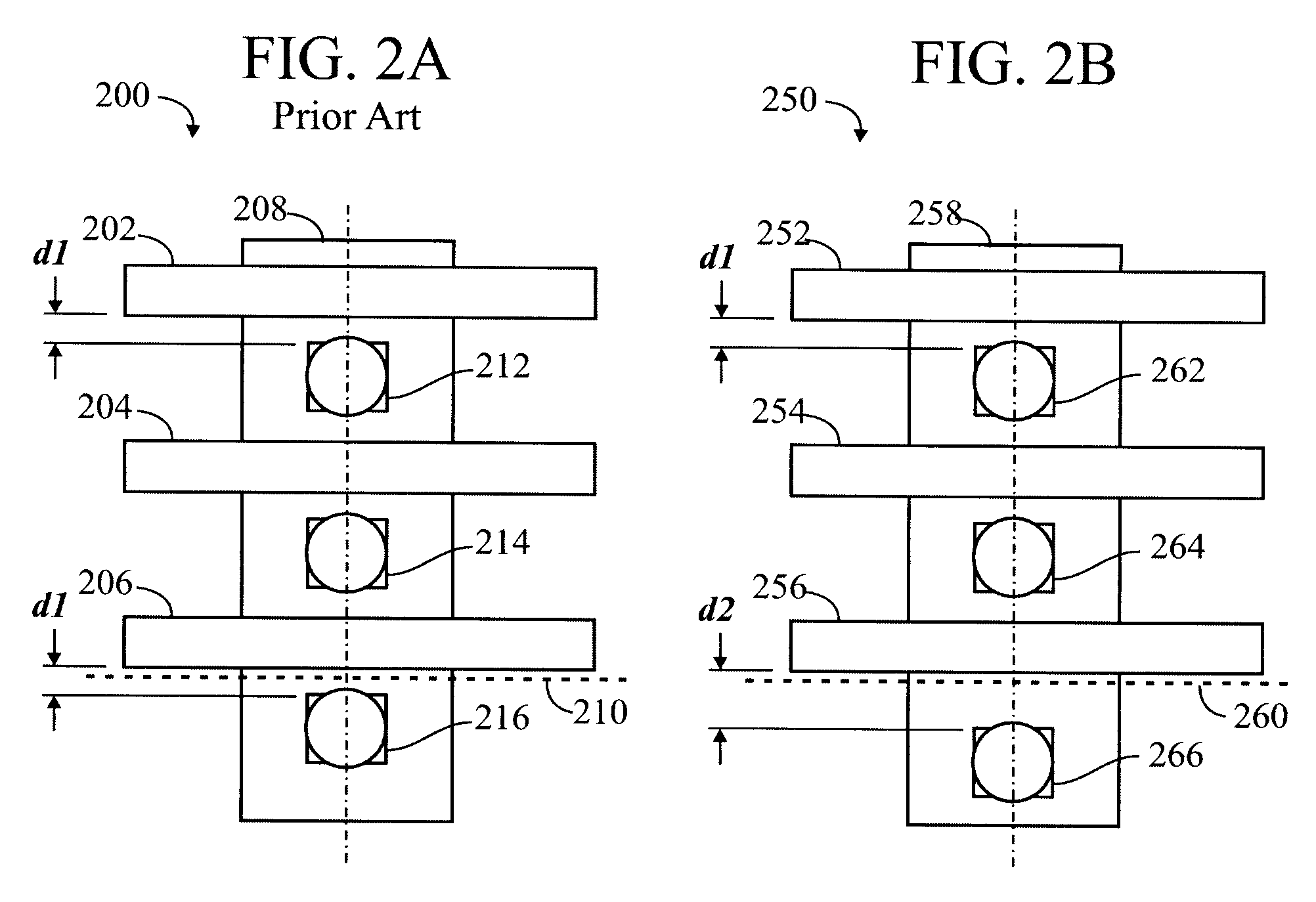
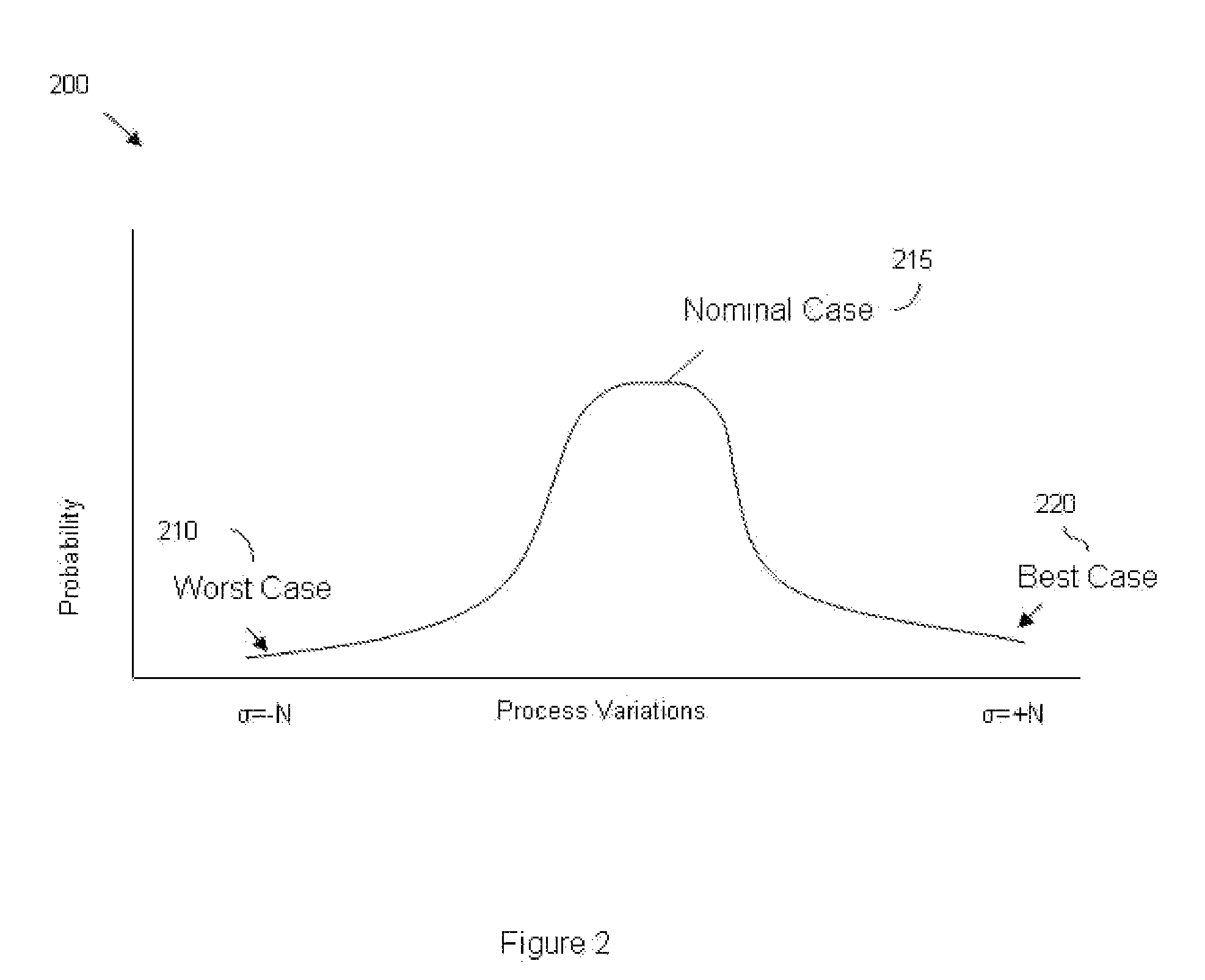
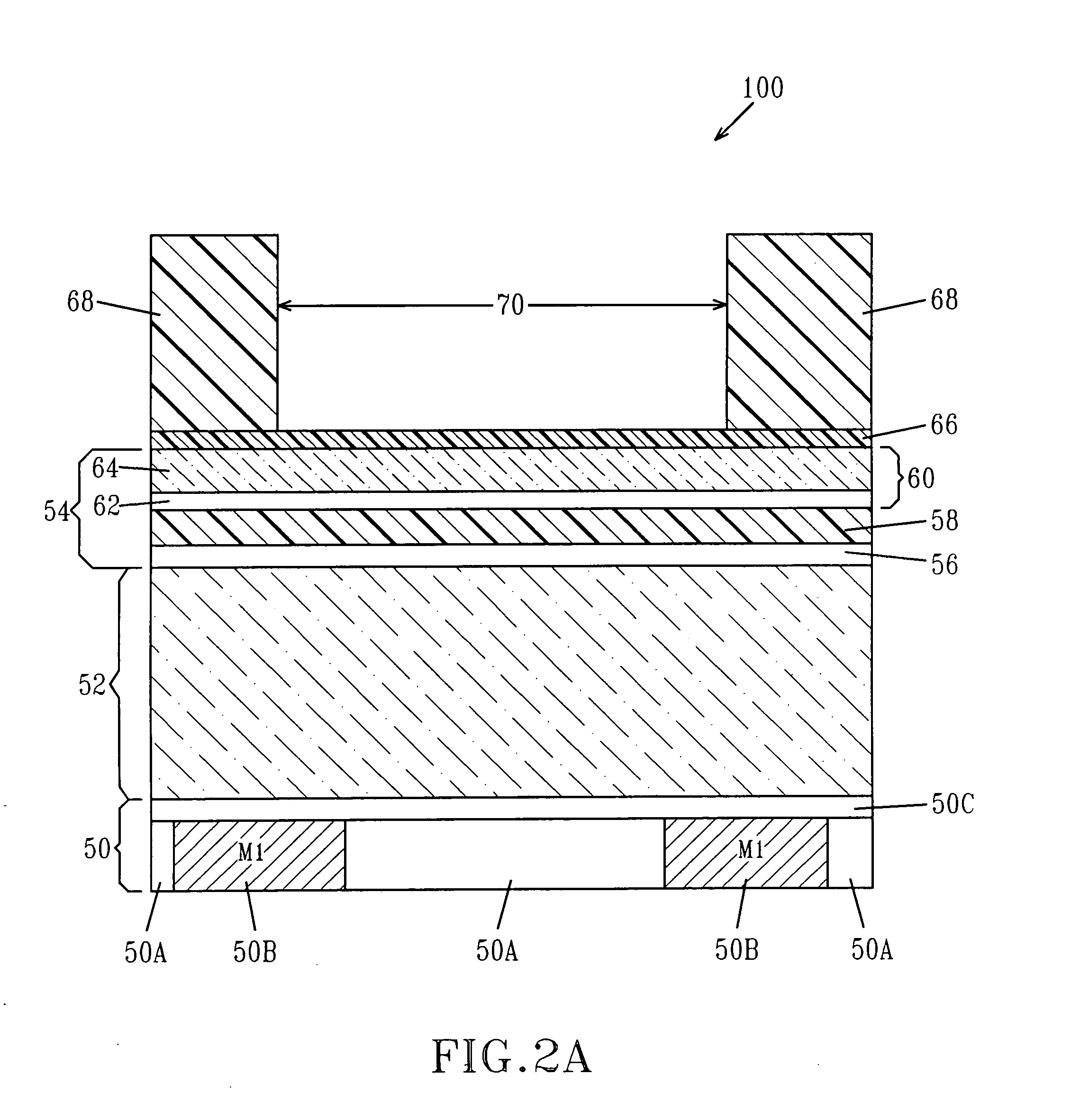
The process window is a graph with a range of parameters for a specific manufacturing process yields a defined result. Typically multiple parameters are plotted in such a graph with a central region where the process behaves well, while the outer borders define regions where the process becomes unstable or returns an unfavourable result. A statistical evaluation of the process performance is further performed by the calculation of the associated Process Window Index.
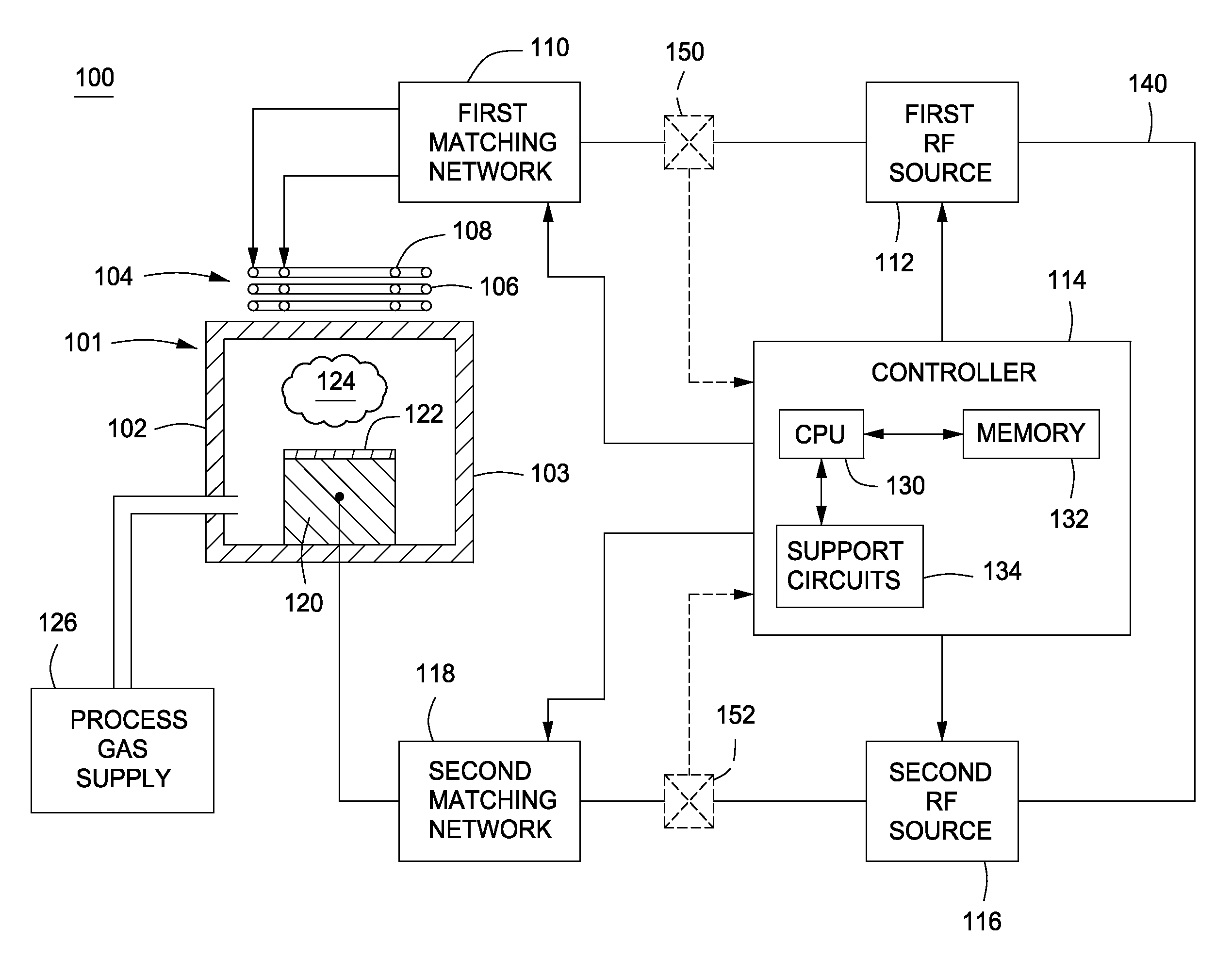
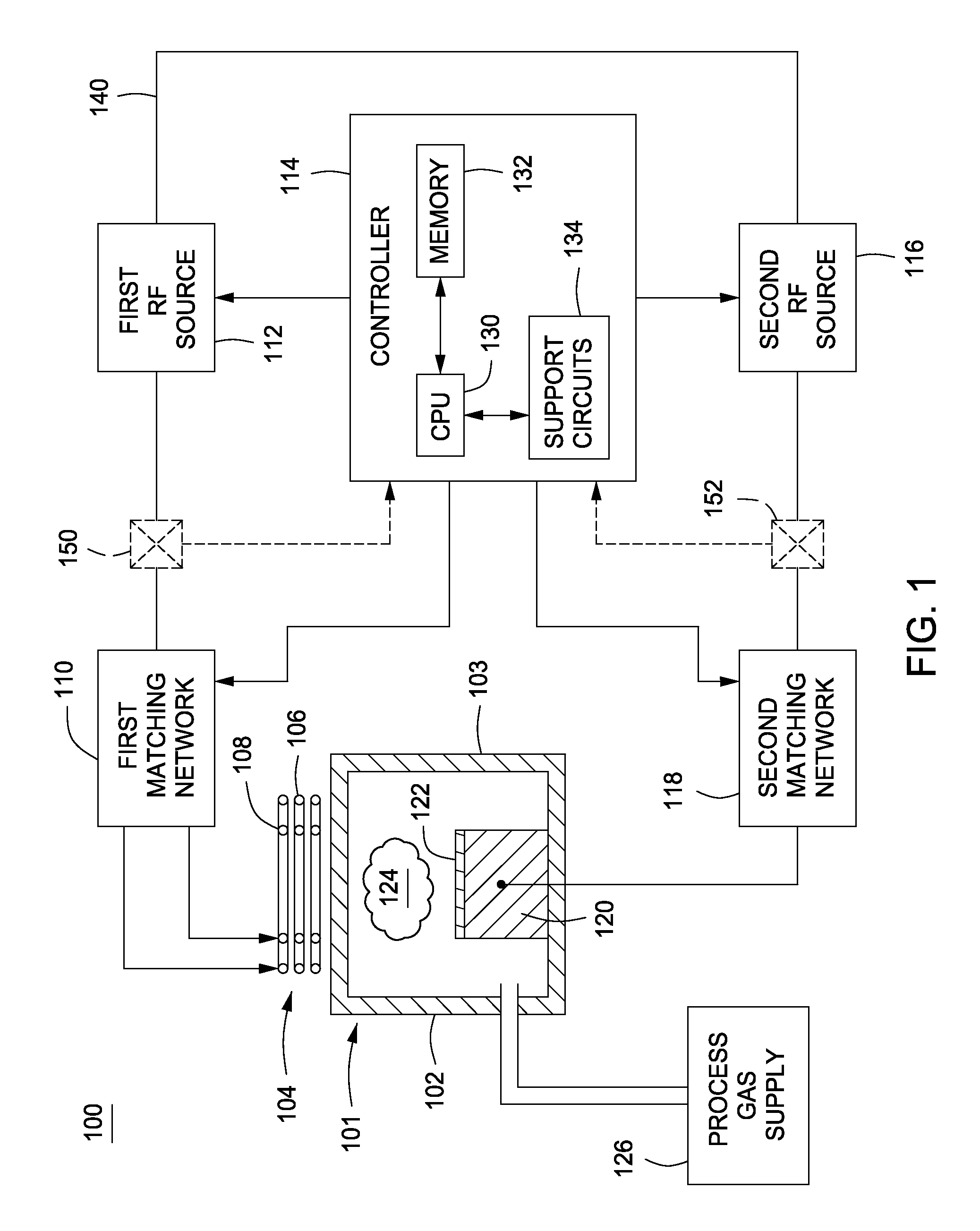
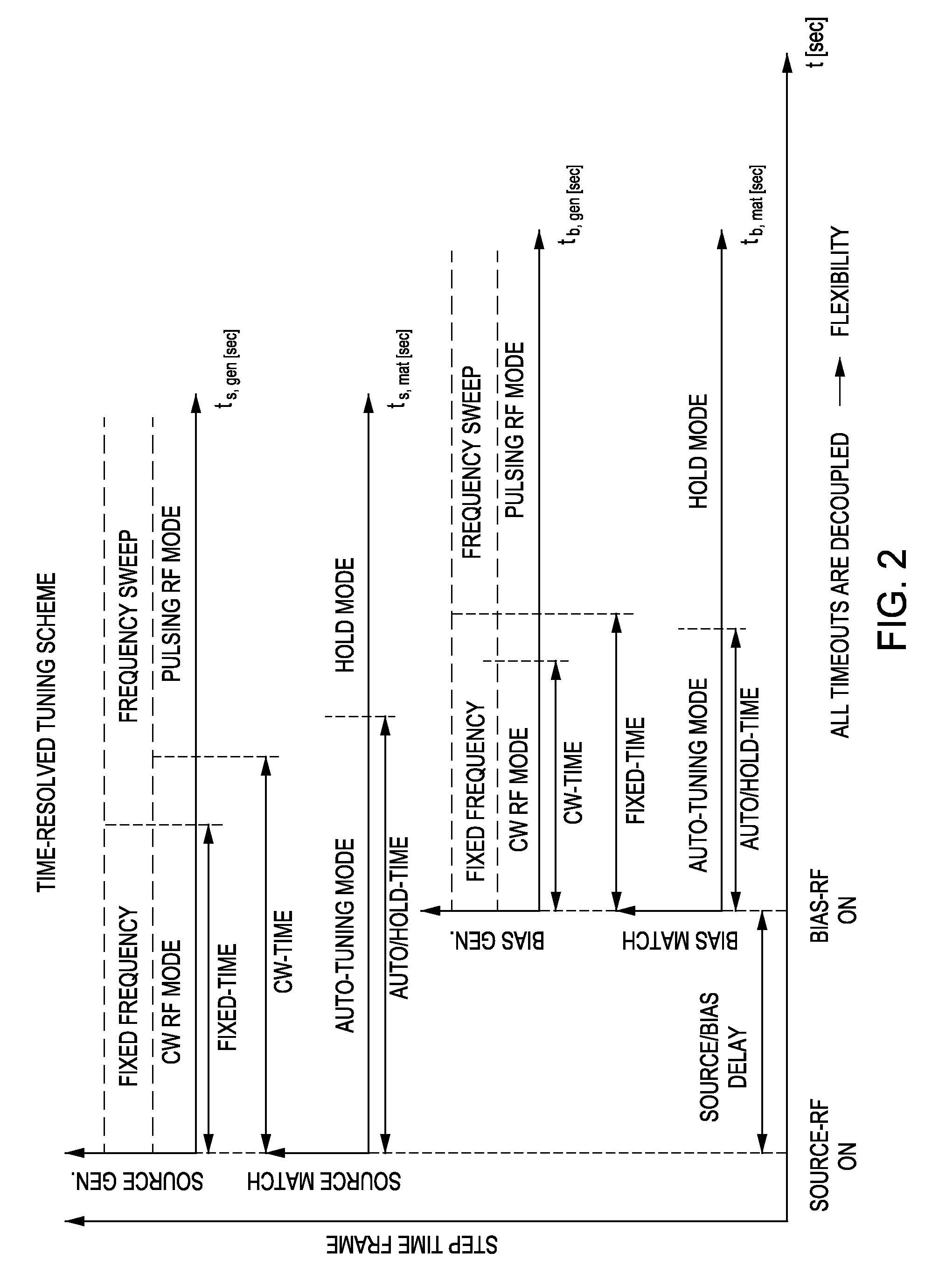
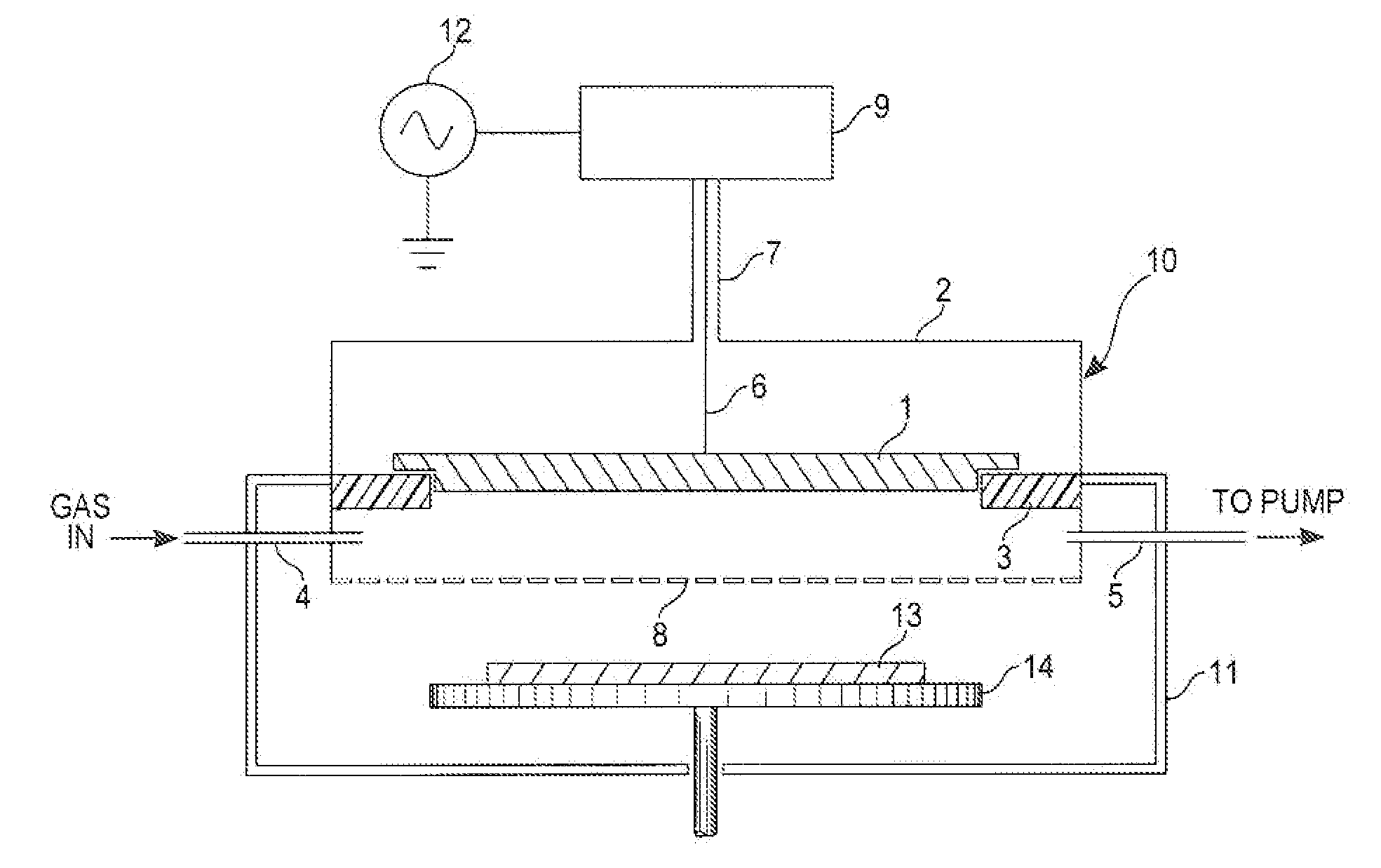
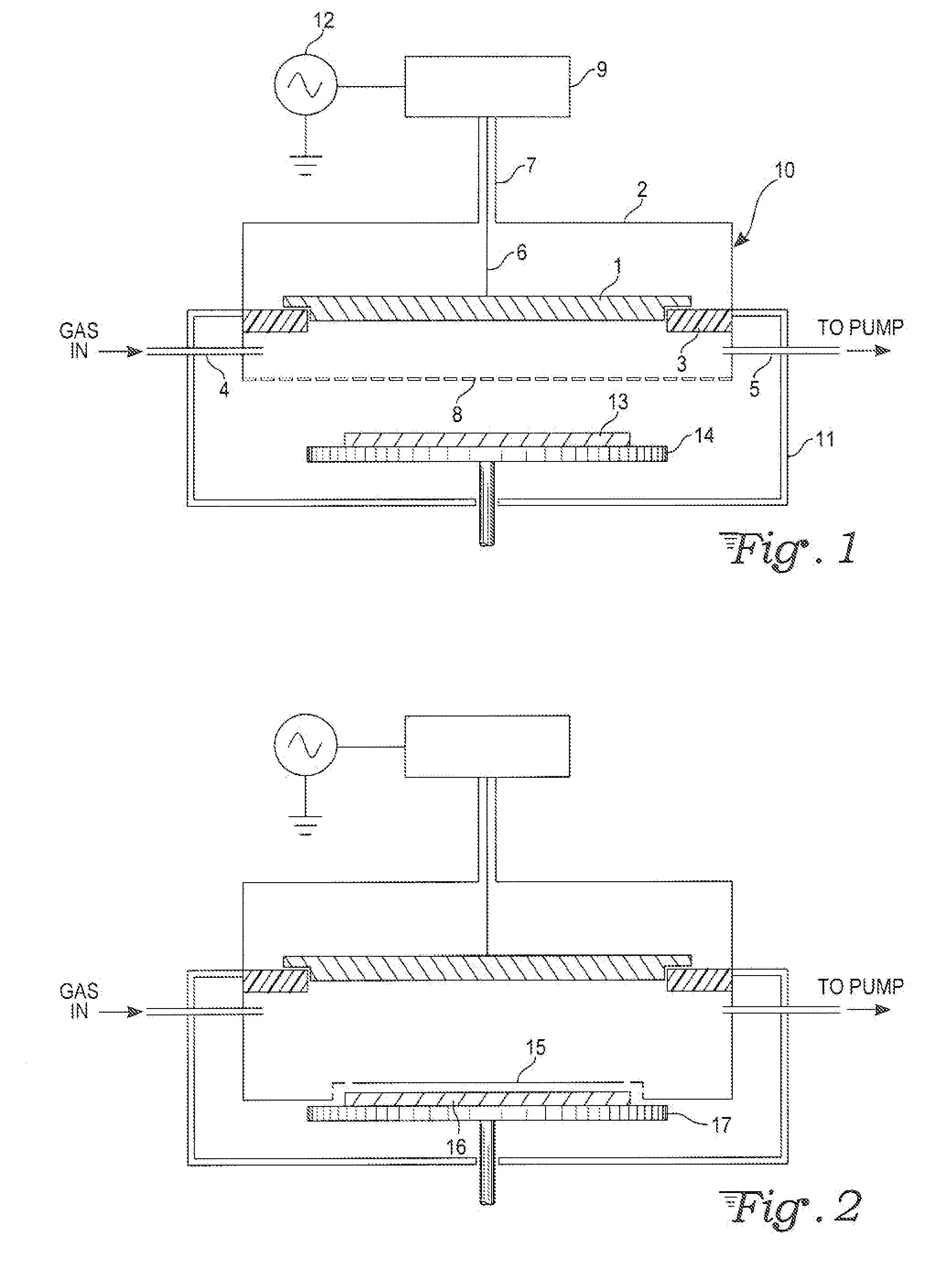
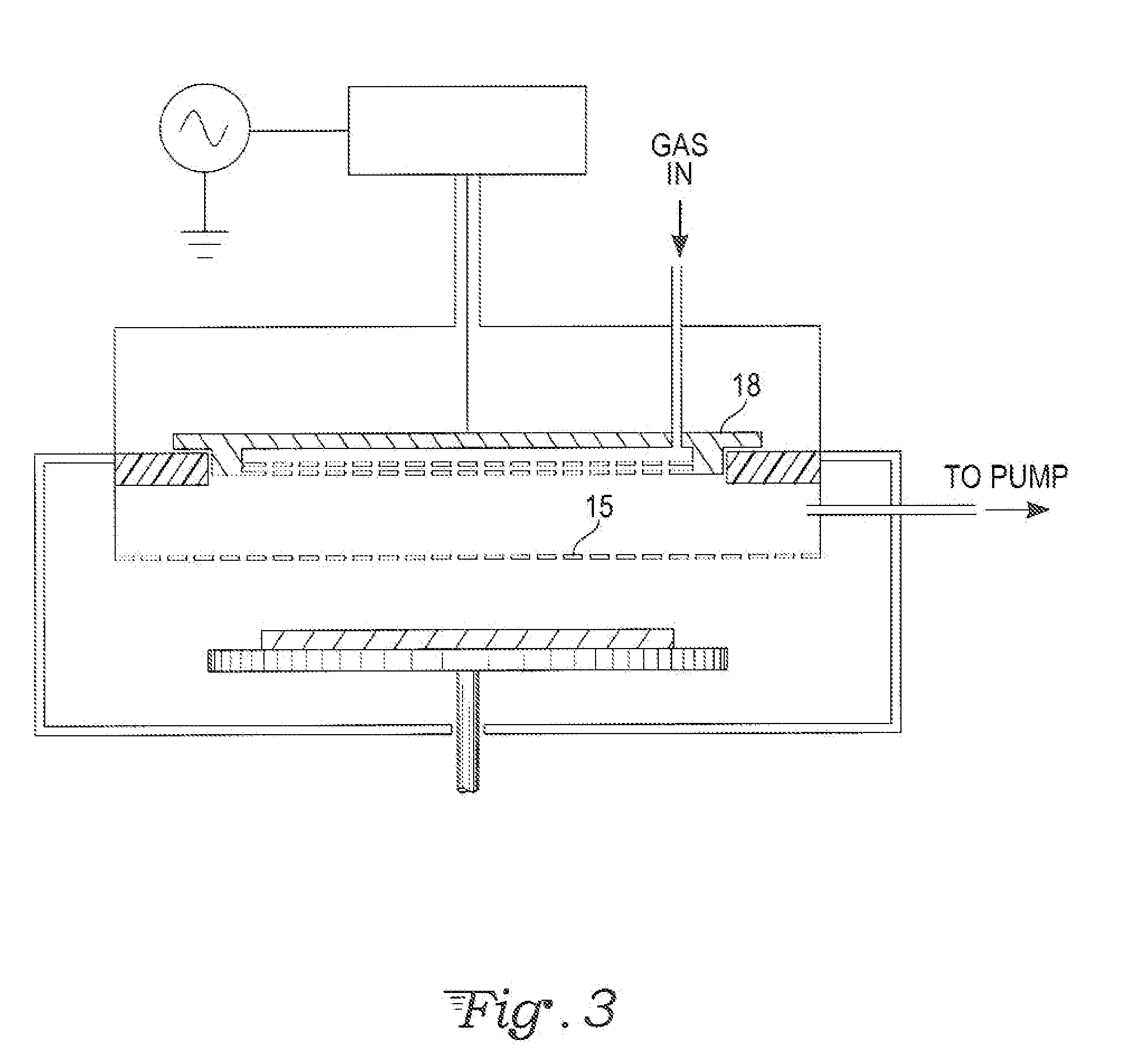
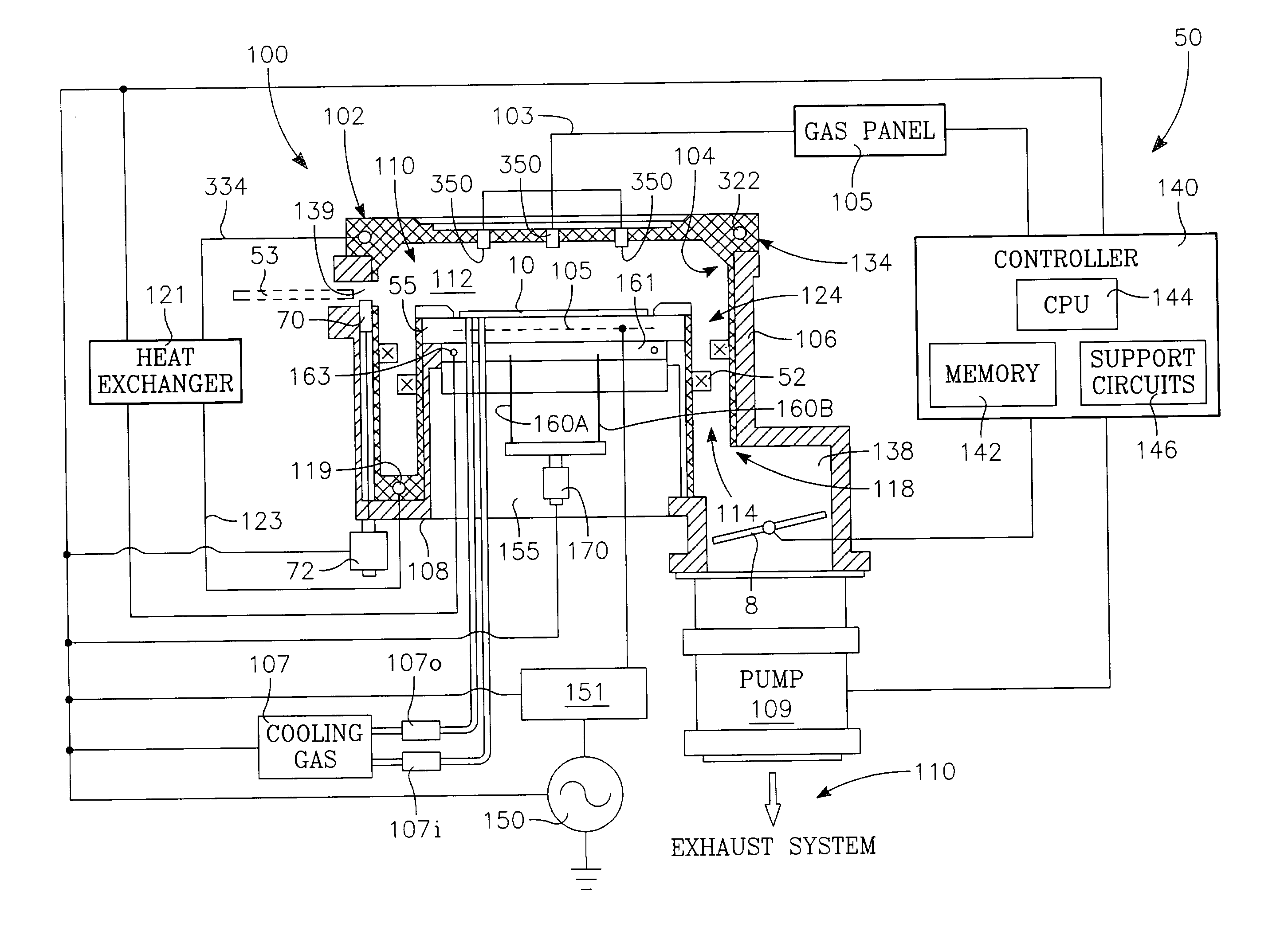
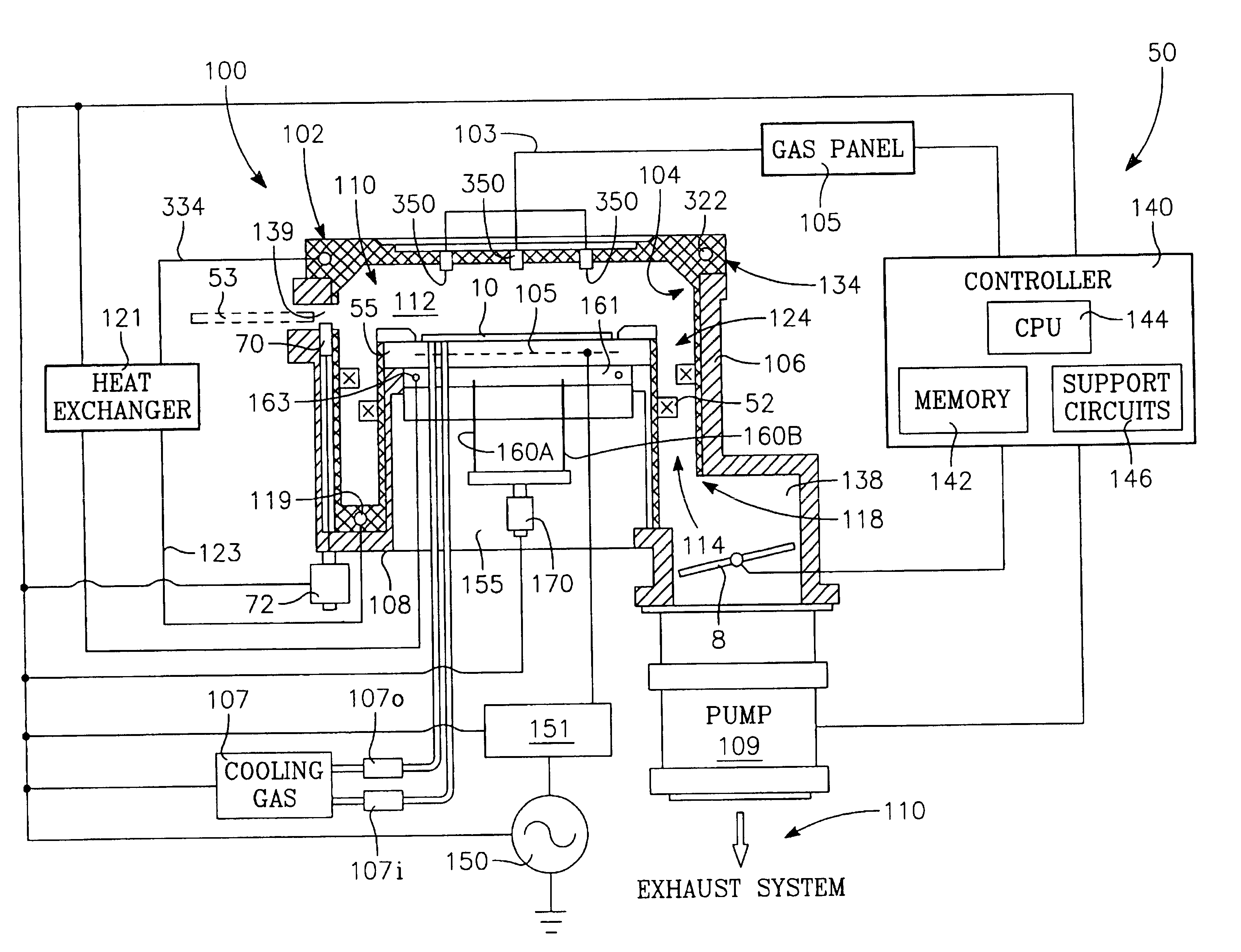
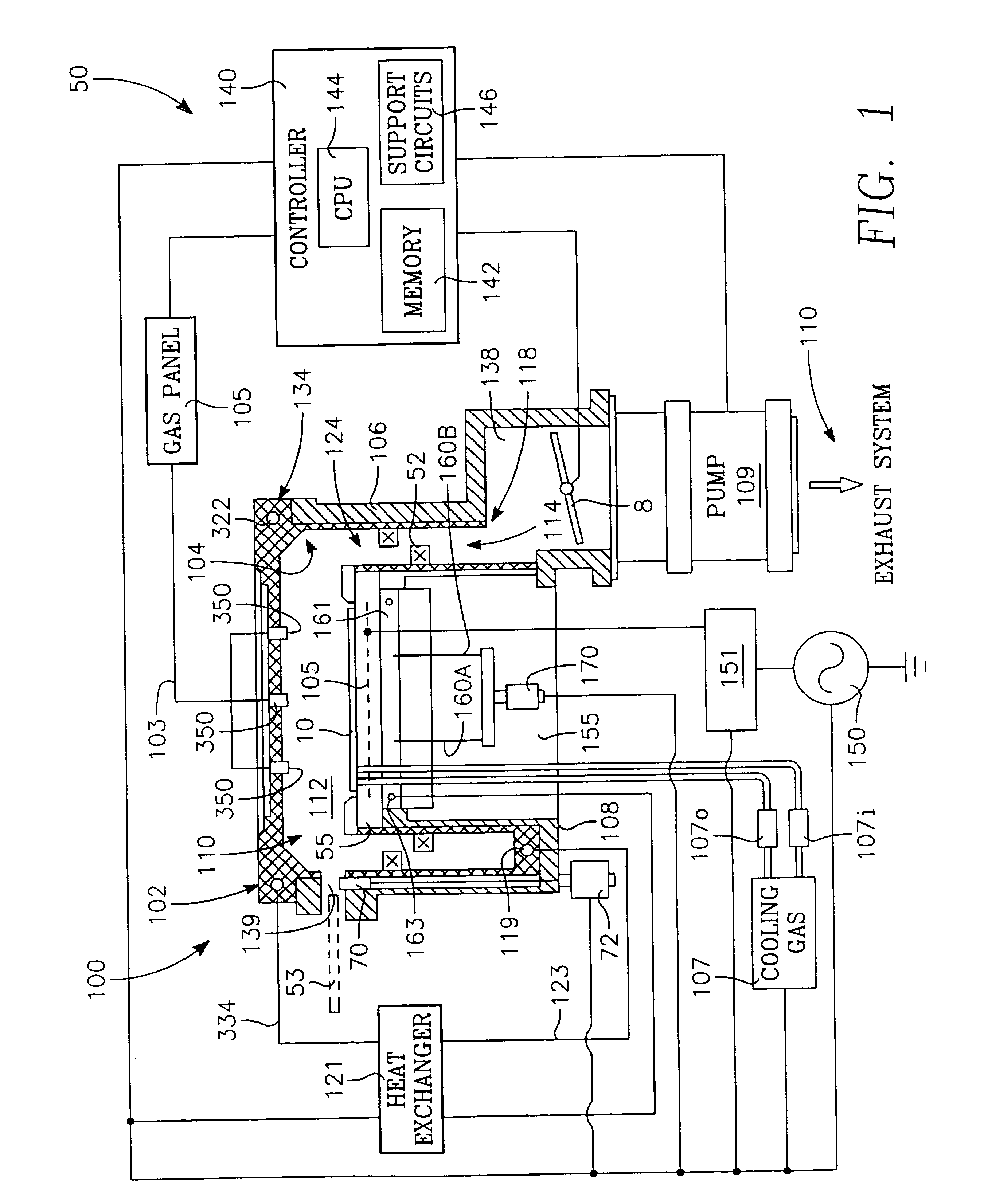
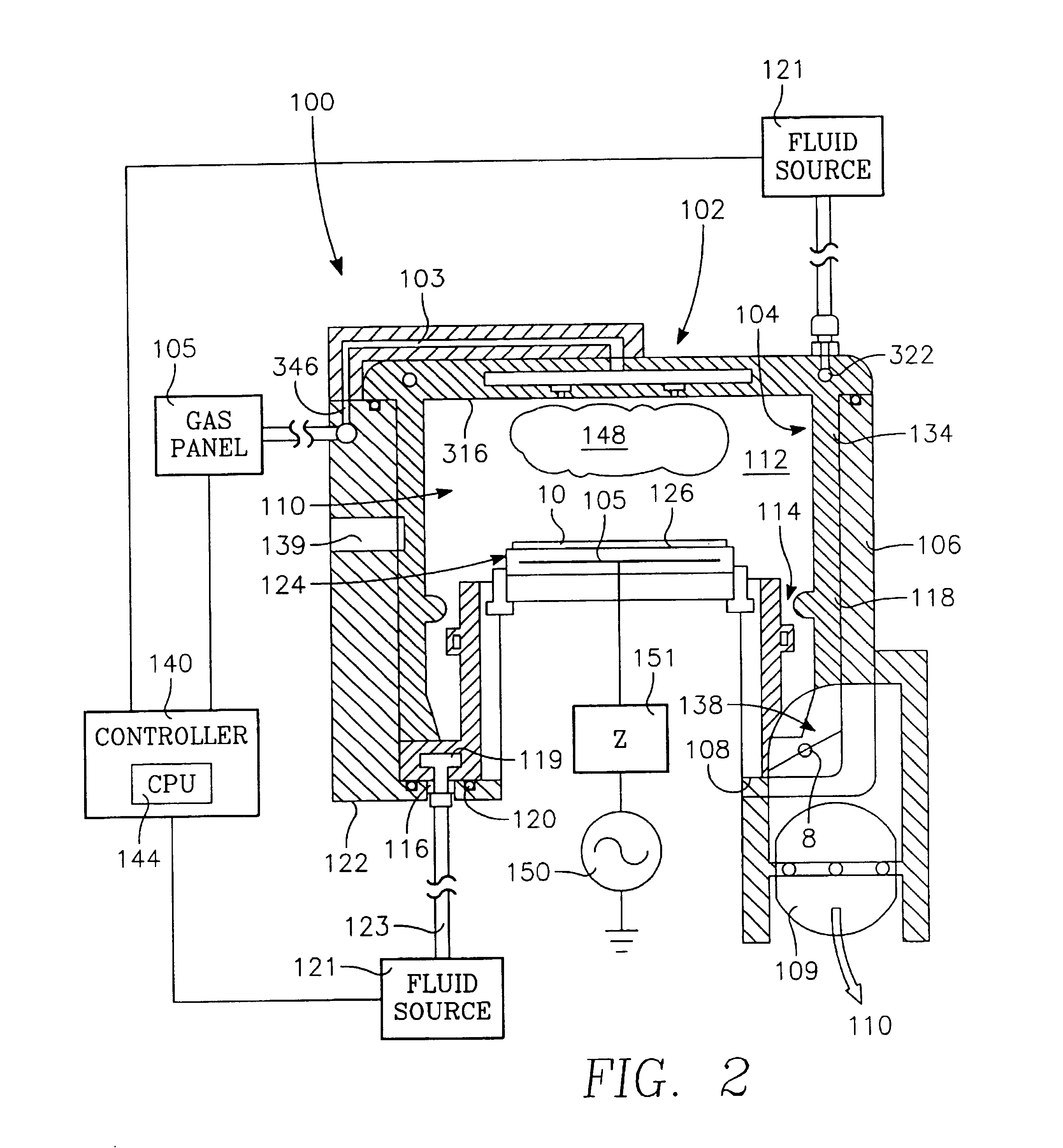
Method and apparatus for pulsed plasma processing using a time resolved tuning scheme for RF power delivery
ActiveUS20090284156A1Alternating current plasma display panelsElectric arc lampsProcess windowPlasma processing
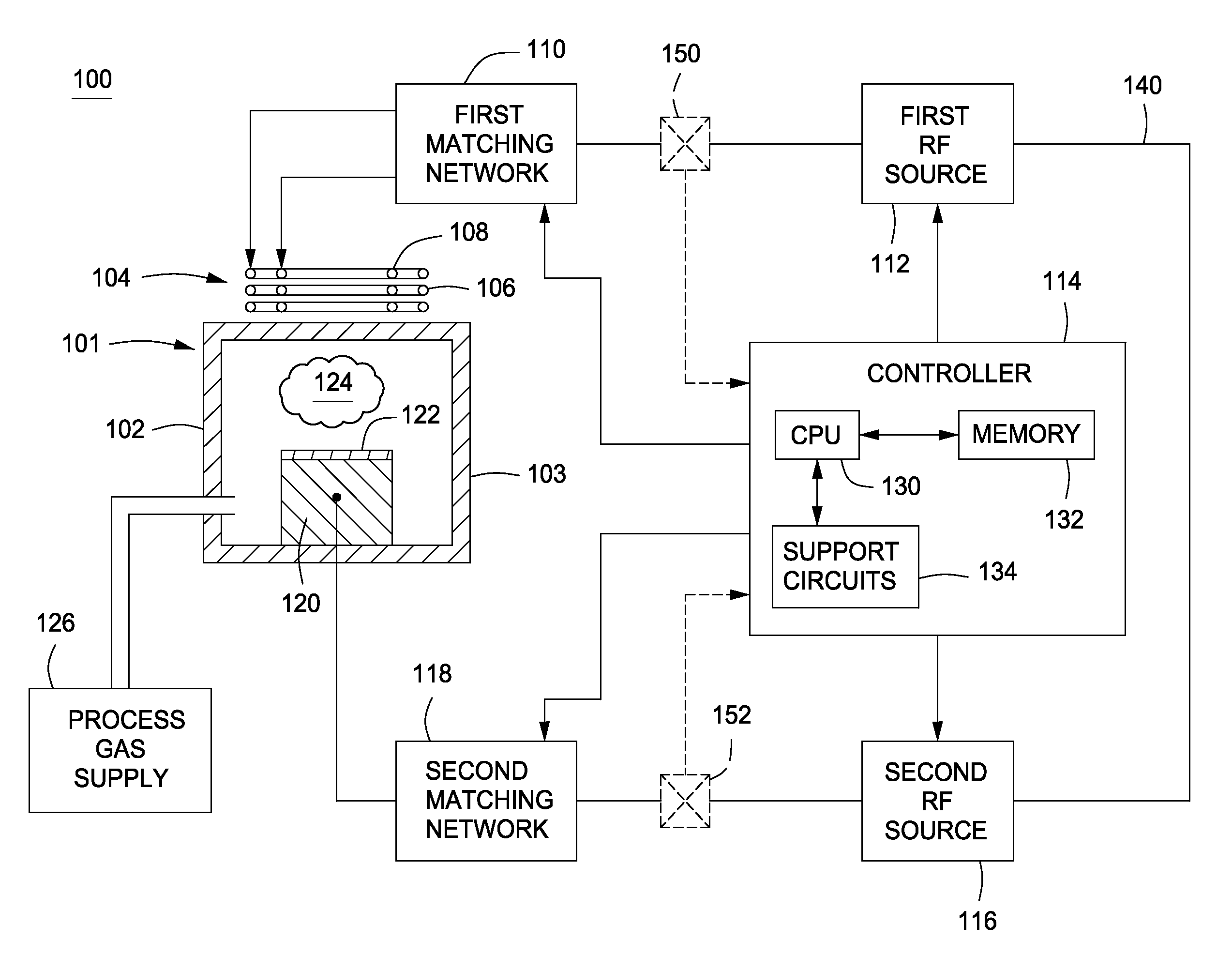
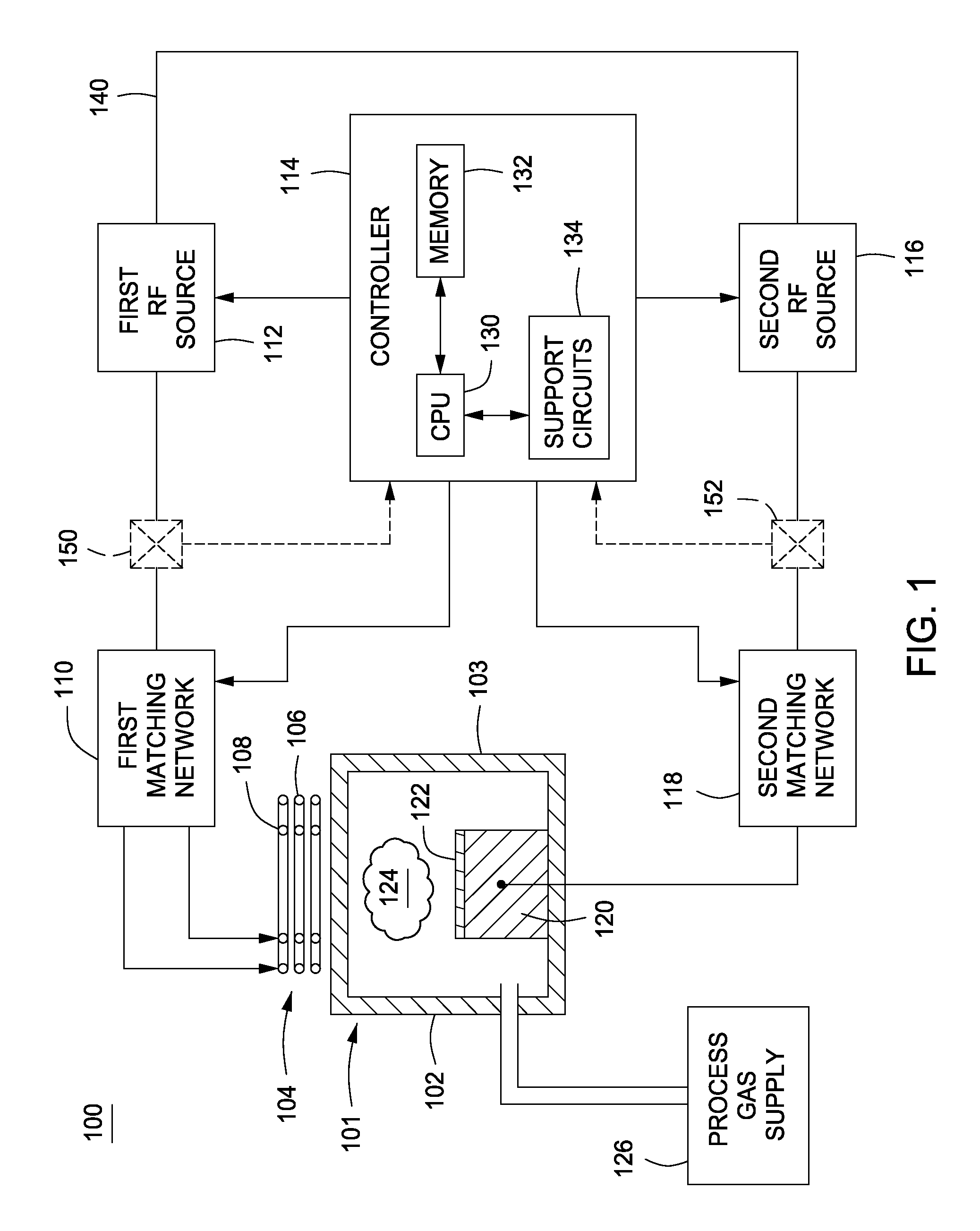
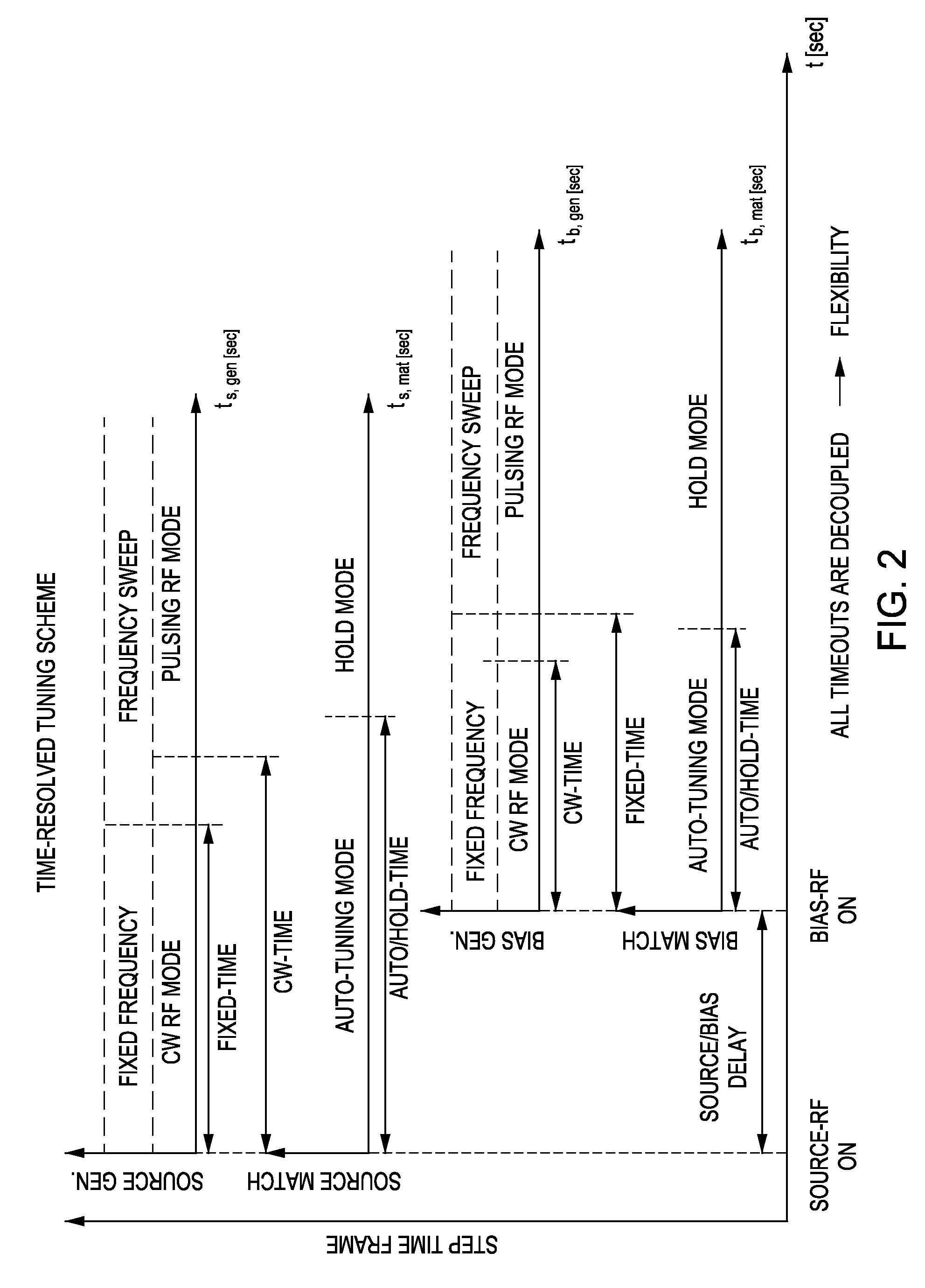
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide methods and apparatus for pulsed plasma processing over a wide process window. In some embodiments, an apparatus may include an RF power supply having frequency tuning and a matching network coupled to the RF power supply that share a common sensor for reading reflected RF power reflected back to the RF power supply. In some embodiments, an apparatus may include an RF power supply having frequency tuning and a matching network coupled to the RF power supply that share a common sensor for reading reflected RF power reflected back to the RF power supply and a common controller for tuning each of the RF power supply and the matching network.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
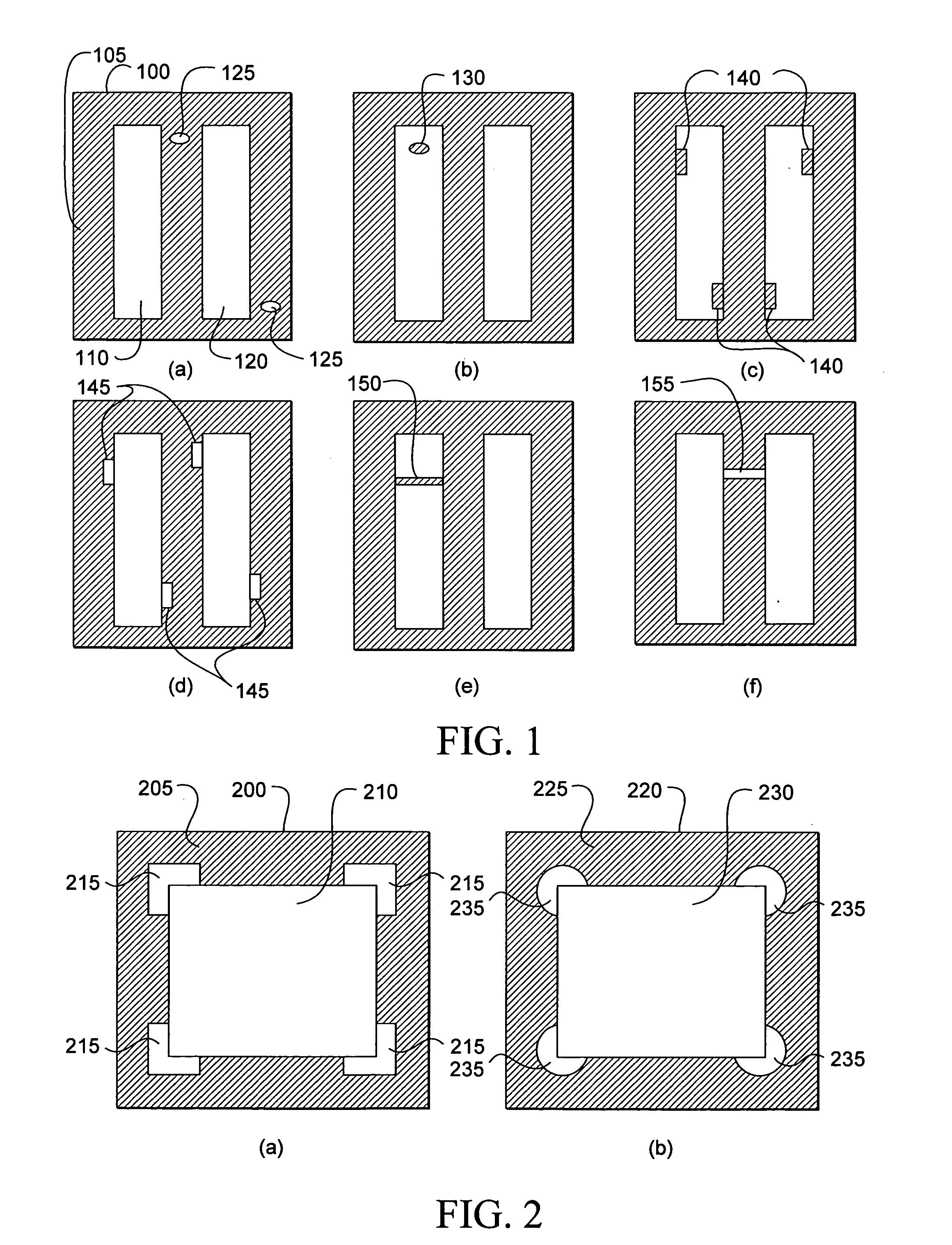
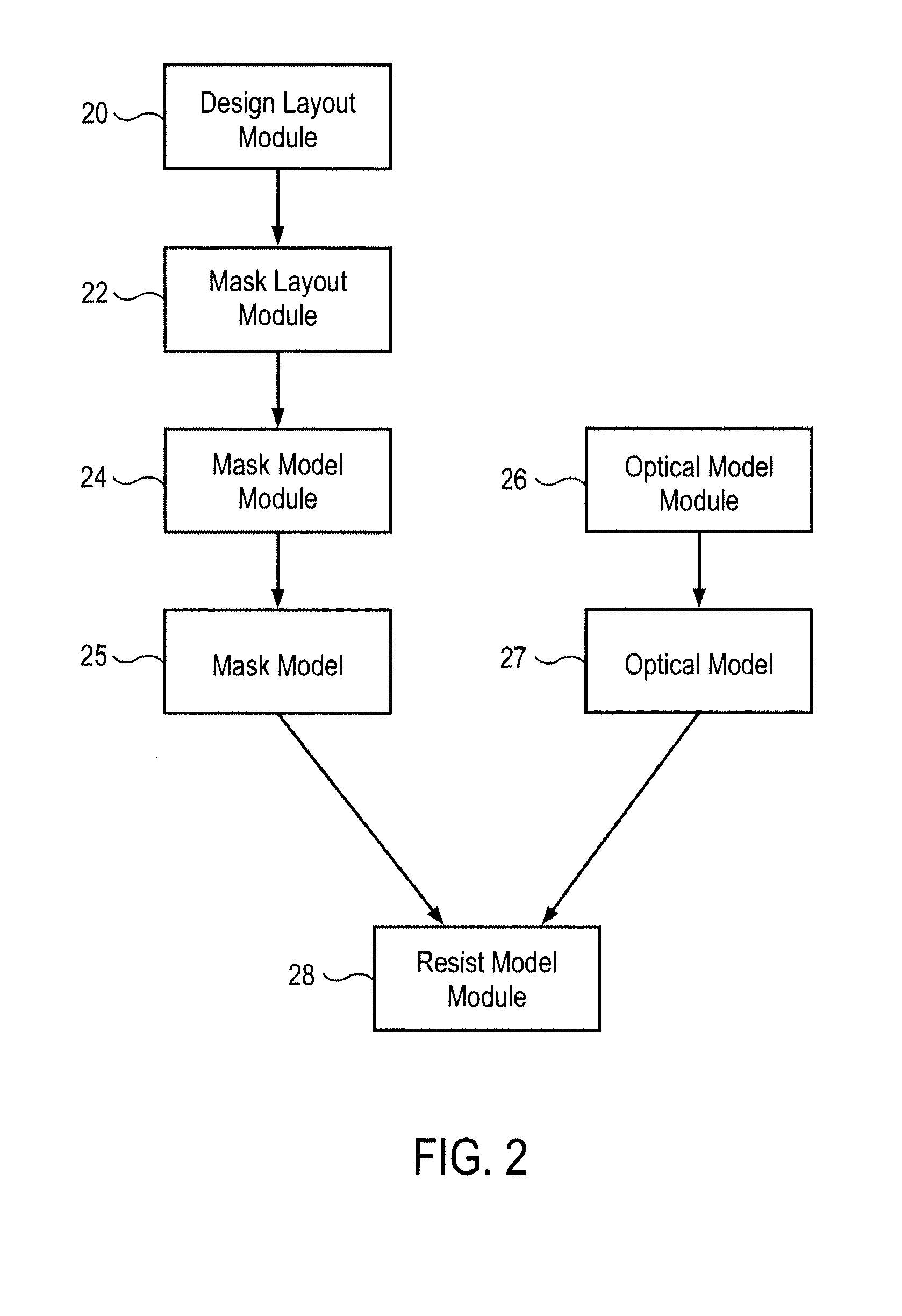
Mask material conversion
ActiveUS7910288B2Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconEngineering
The dimensions of mask patterns, such as pitch-multiplied spacers, are controlled by controlled growth of features in the patterns after they are formed. To form a pattern of pitch-multiplied spacers, a pattern of mandrels is first formed overlying a semiconductor substrate. Spacers are then formed on sidewalls of the mandrels by depositing a blanket layer of material over the mandrels and preferentially removing spacer material from horizontal surfaces. The mandrels are then selectively removed, leaving behind a pattern of freestanding spacers. The spacers comprise a material, such as polysilicon and amorphous silicon, known to increase in size upon being oxidized. The spacers are oxidized to grow them to a desired width. After reaching the desired width, the spacers can be used as a mask to pattern underlying layers and the substrate. Advantageously, because the spacers are grown by oxidation, thinner blanket layers can be deposited over the mandrels, thereby allowing the deposition of more conformal blanket layers and widening the process window for spacer formation.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor manufacturing process monitoring
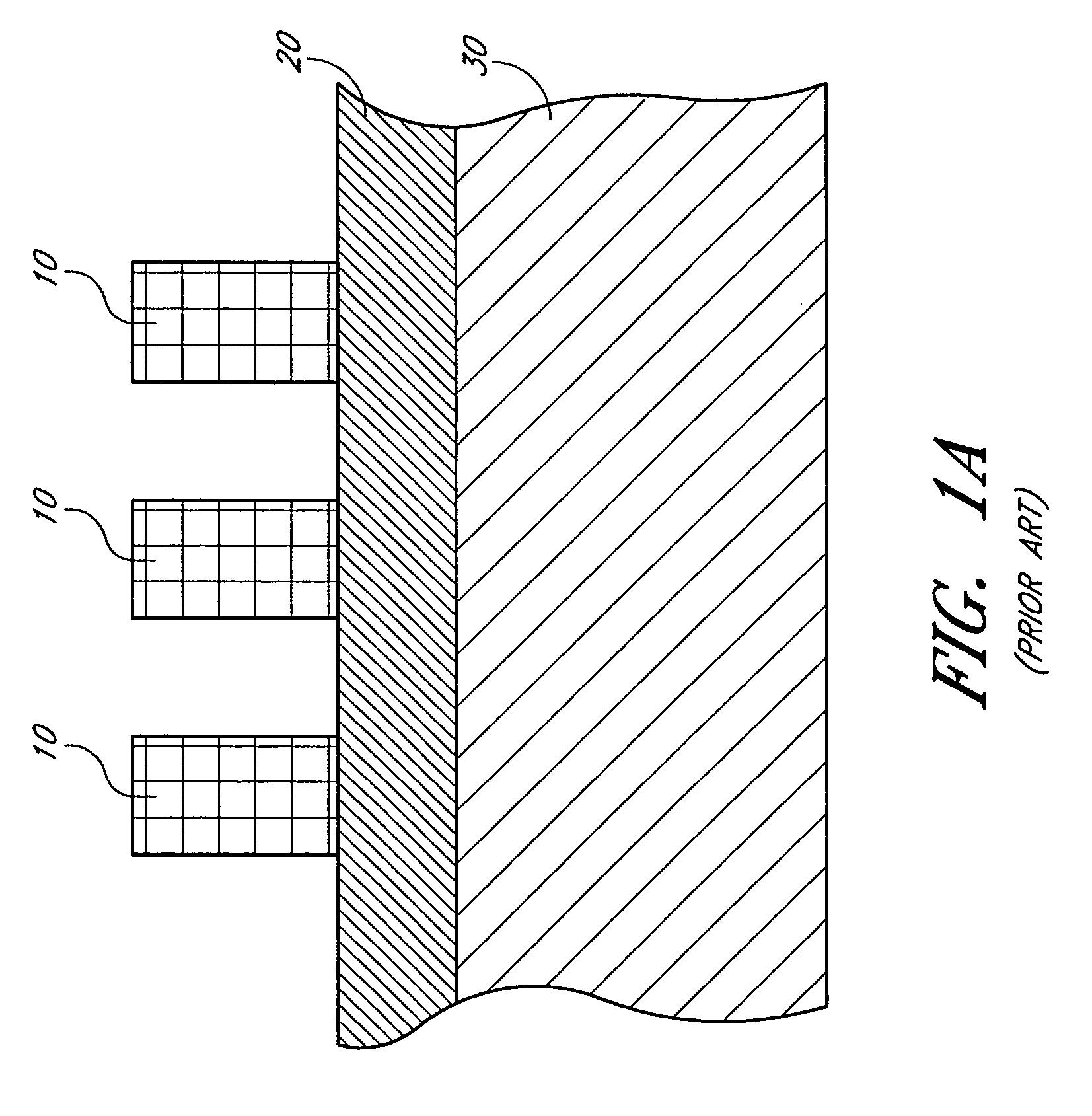
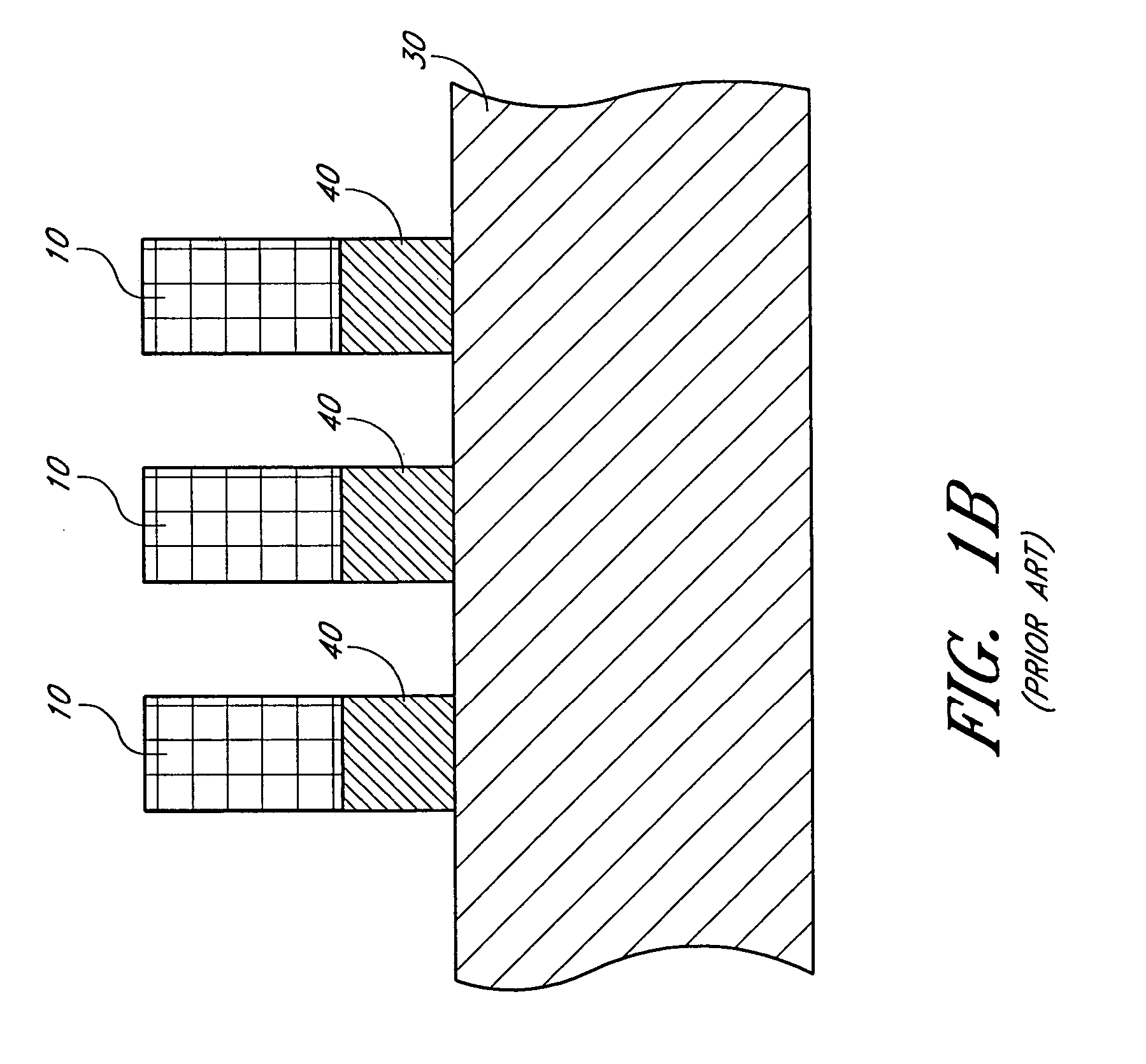
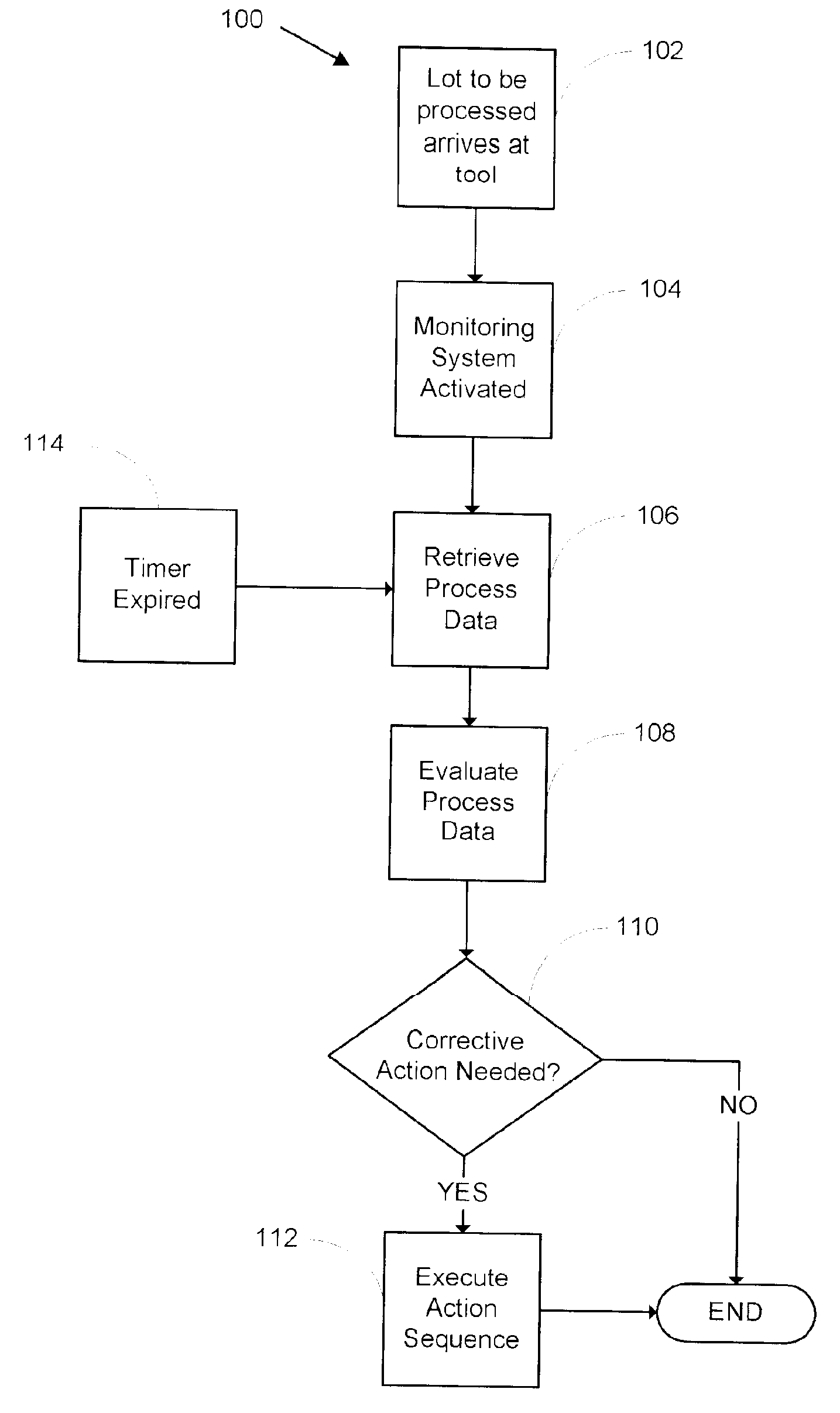
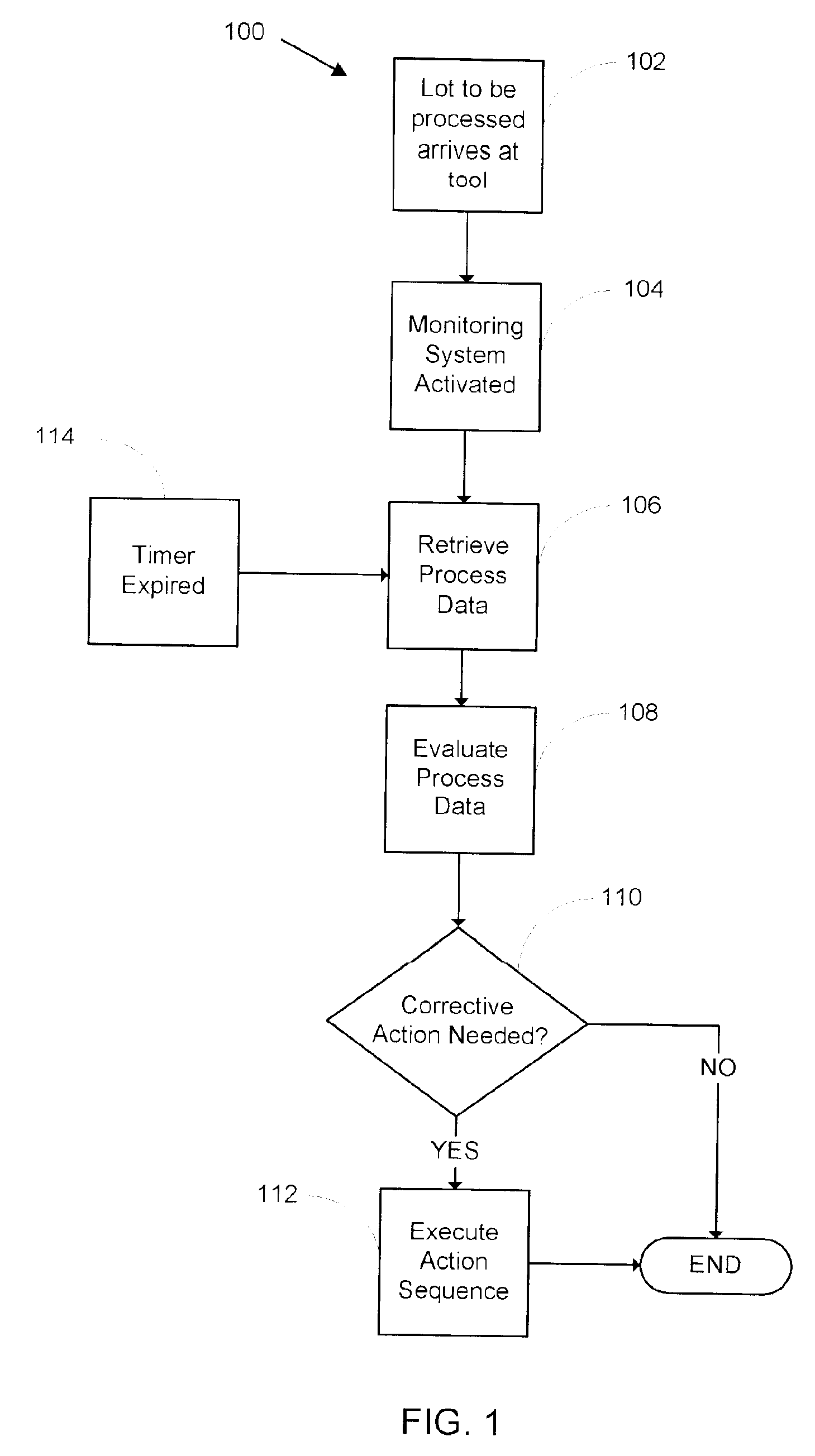
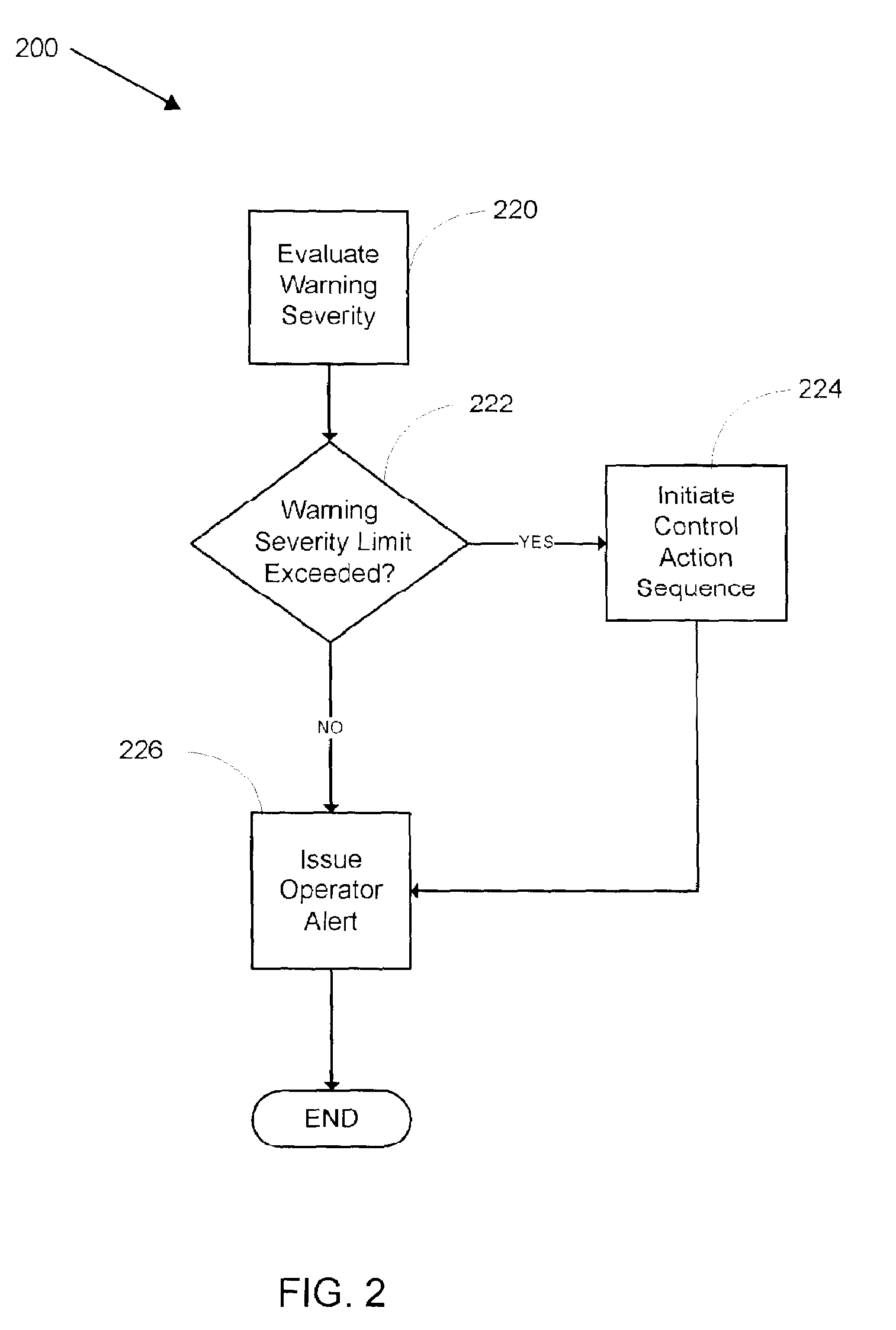
A system and method for monitoring a semiconductor manufacturing process is disclosed. The system communicates with one or more process tools, and monitors each tool during a predetermined process window time. Errors and warnings are provided to users, allowing corrective action to be taken. Additionally, the system of the present invention can initiate automatic adjustment of the process tools to maintain an efficient manufacturing operation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
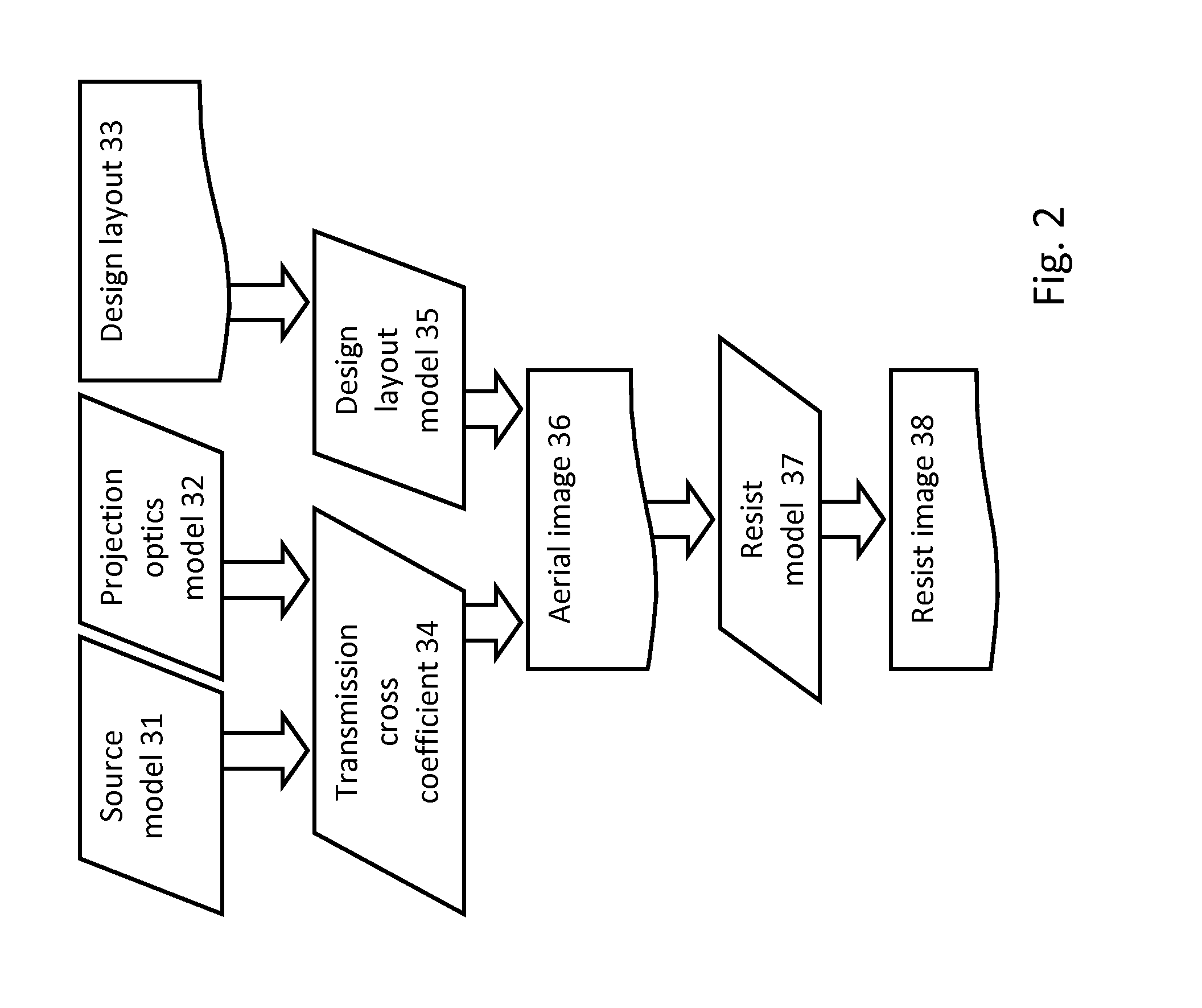
System and method for creating a focus-exposure model of a lithography process
ActiveUS20070031745A1Good accuracy and robustnessPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithography processAlgorithm
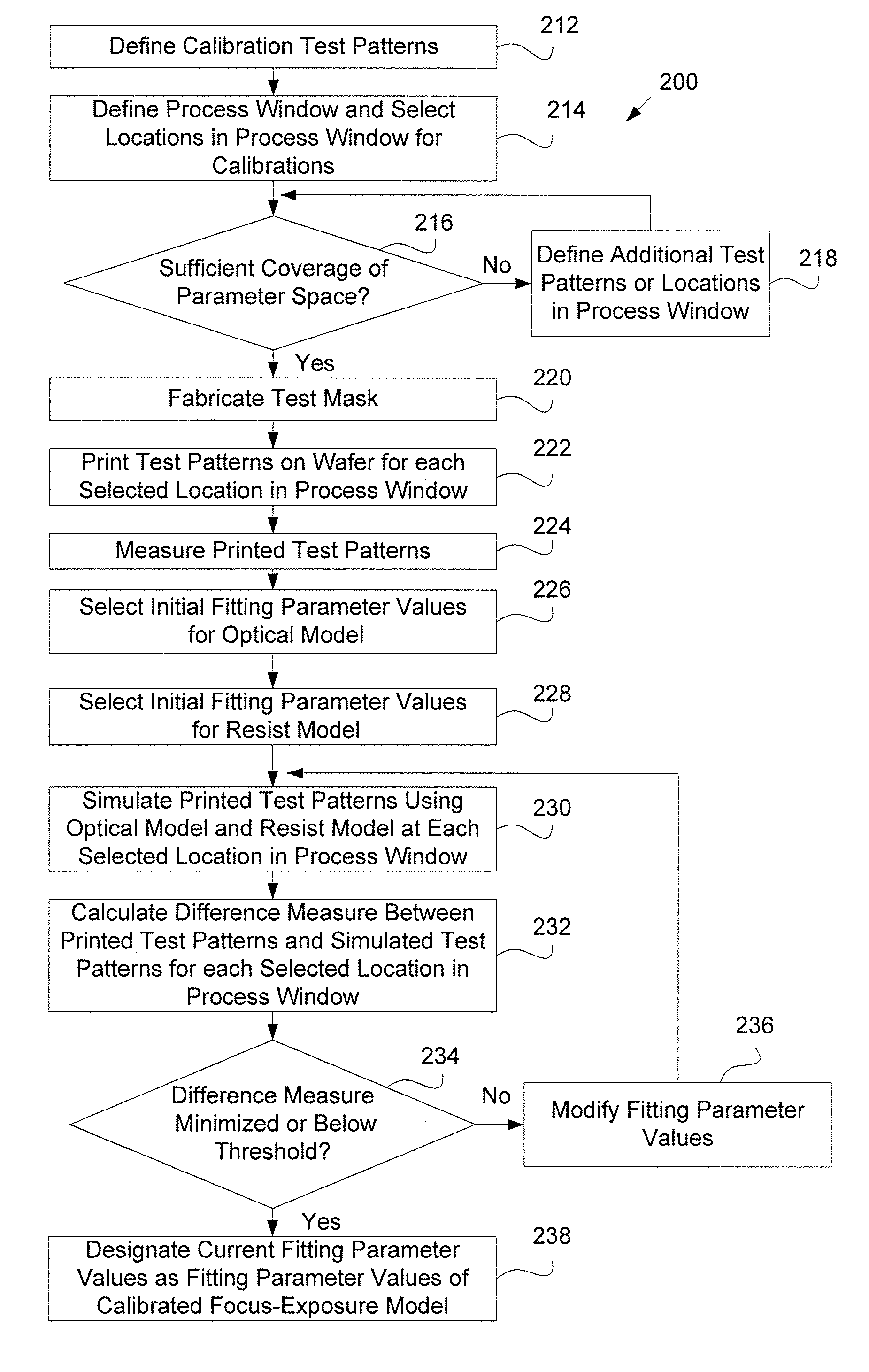
A system and a method for creating a focus-exposure model of a lithography process are disclosed. The system and the method utilize calibration data along multiple dimensions of parameter variations, in particular within an exposure-defocus process window space. The system and the method provide a unified set of model parameter values that result in better accuracy and robustness of simulations at nominal process conditions, as well as the ability to predict lithographic performance at any point continuously throughout a complete process window area without a need for recalibration at different settings. With a smaller number of measurements required than the prior-art multiple-model calibration, the focus-exposure model provides more predictive and more robust model parameter values that can be used at any location in the process window.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method to determine optical proximity correction and assist feature rules which account for variations in mask dimensions
InactiveUS6553559B2Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputational physicsProcess window
Optical proximity correction (OPC) and assist feature rules are generated using a process window (PW) analysis. A reference pitch is chosen and the mask bias is found that optimizes the process window. This can be done using standard process window analysis or through a weighted process window (WPW) analysis which accounts for focus and dose distributions that are expected in a real process. The WPW analysis gives not only the optimum mask bias, but also the center focus and dose conditions for the optimum process centering. A series of other pitches and mask biases are then analyzed by finding the common process window with the reference pitch. For the standard PW analysis, a common process window is found. For the WPW analysis, the WPW is computed at the center focus and dose conditions found for the reference pitch. If mask or lens errors are to be accounted for, then multiple structures can be included in the analysis. Once the common process windows for the mask features of interest have been computed, functional fits to the data can be found. Once the functional forms have been found for each of the OPC parameters, the rules table can be determined by solving for the spacings of interest in the design.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Process window based optical proximity correction of lithographic images
InactiveUS6578190B2Maximize rangeCharacter and pattern recognitionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusProcess windowPlanographic printing
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
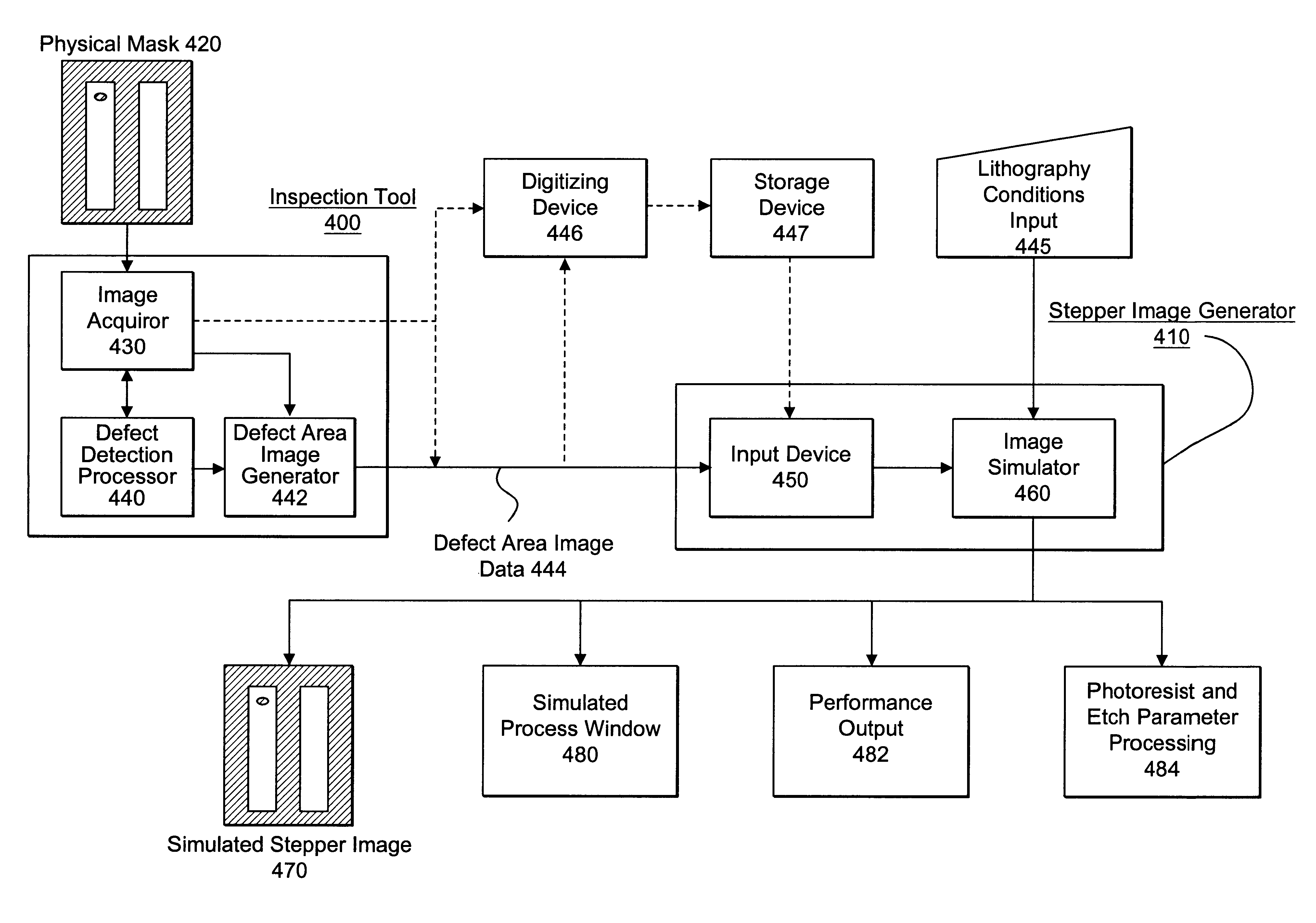
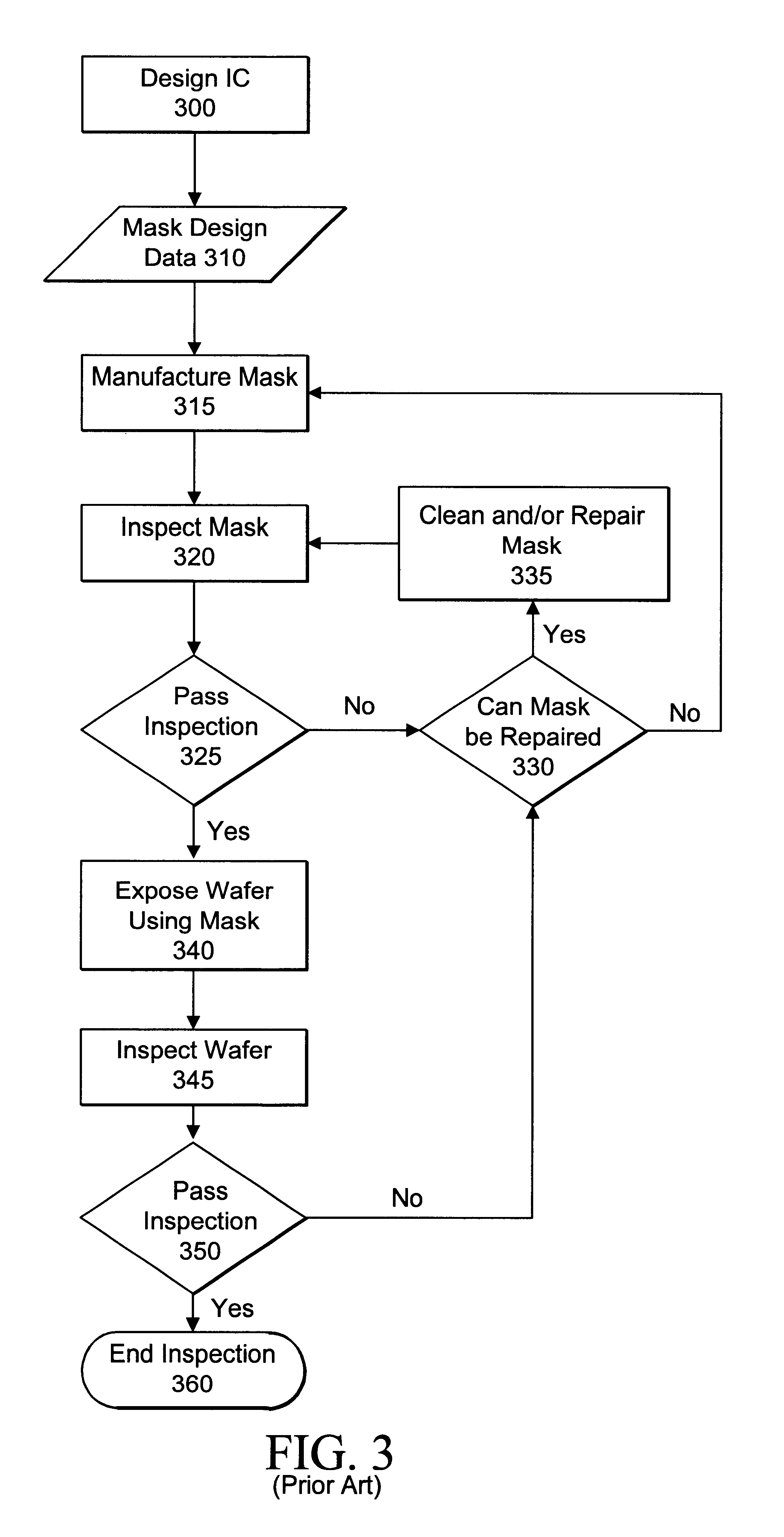
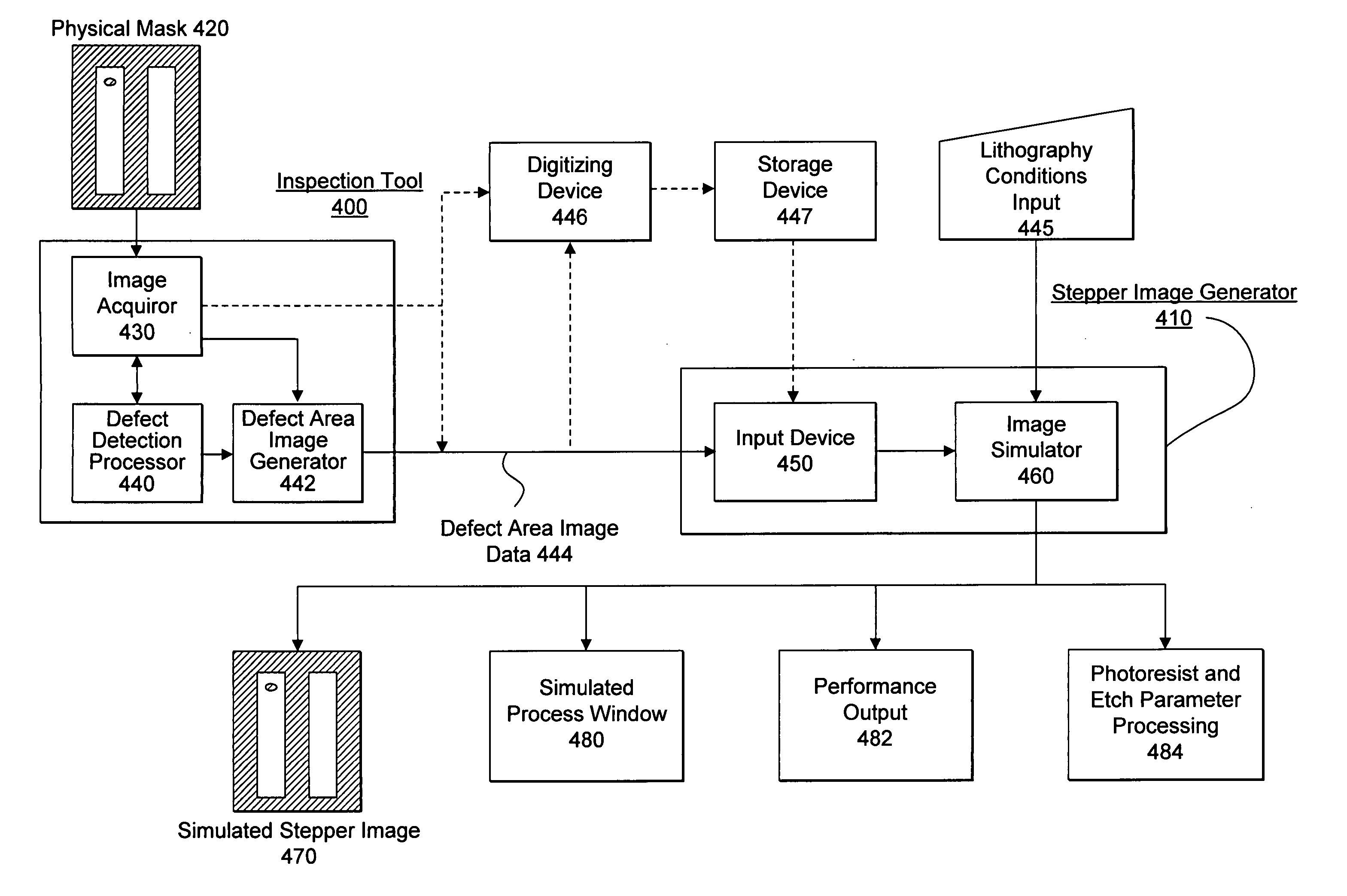
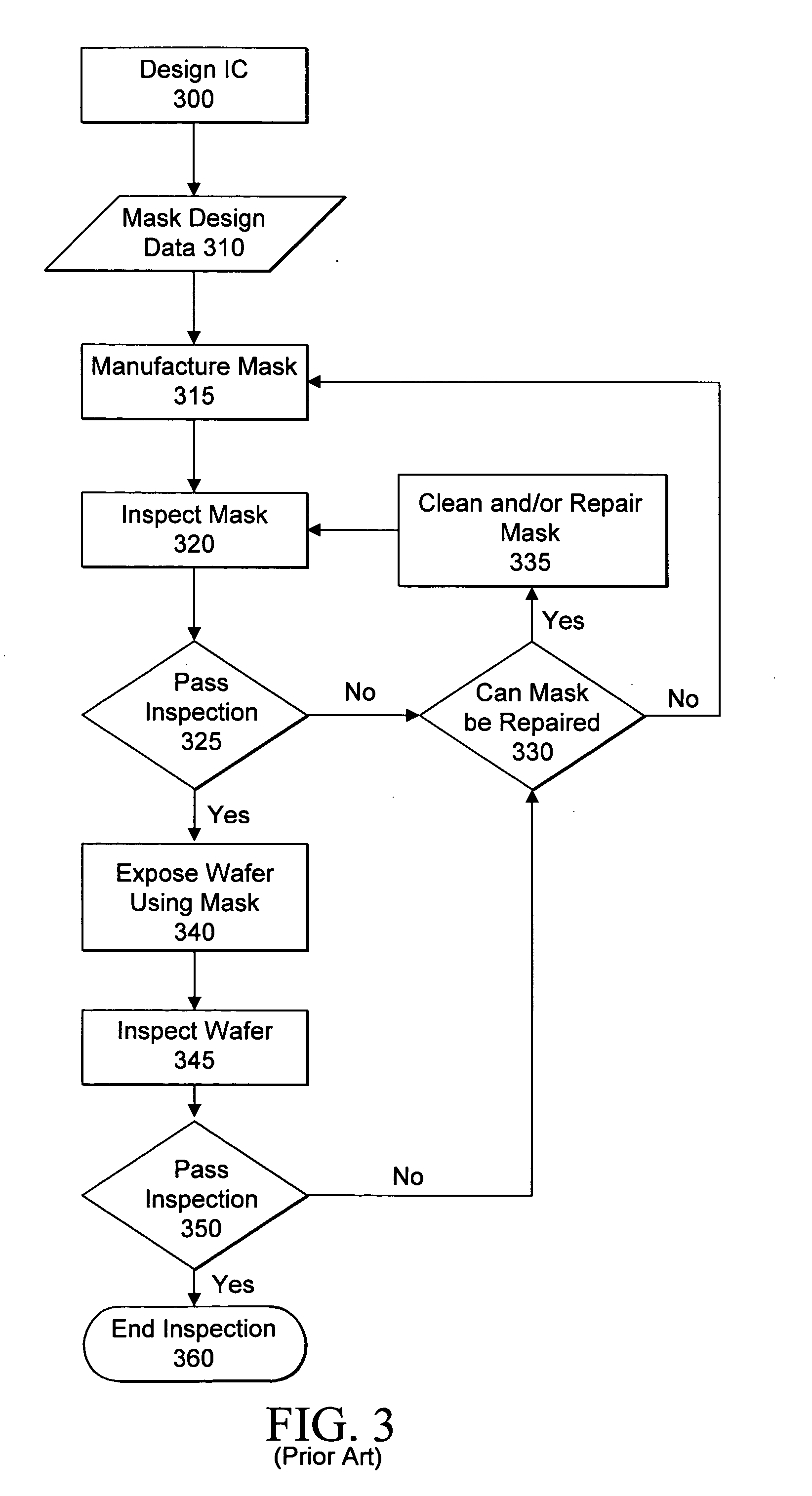
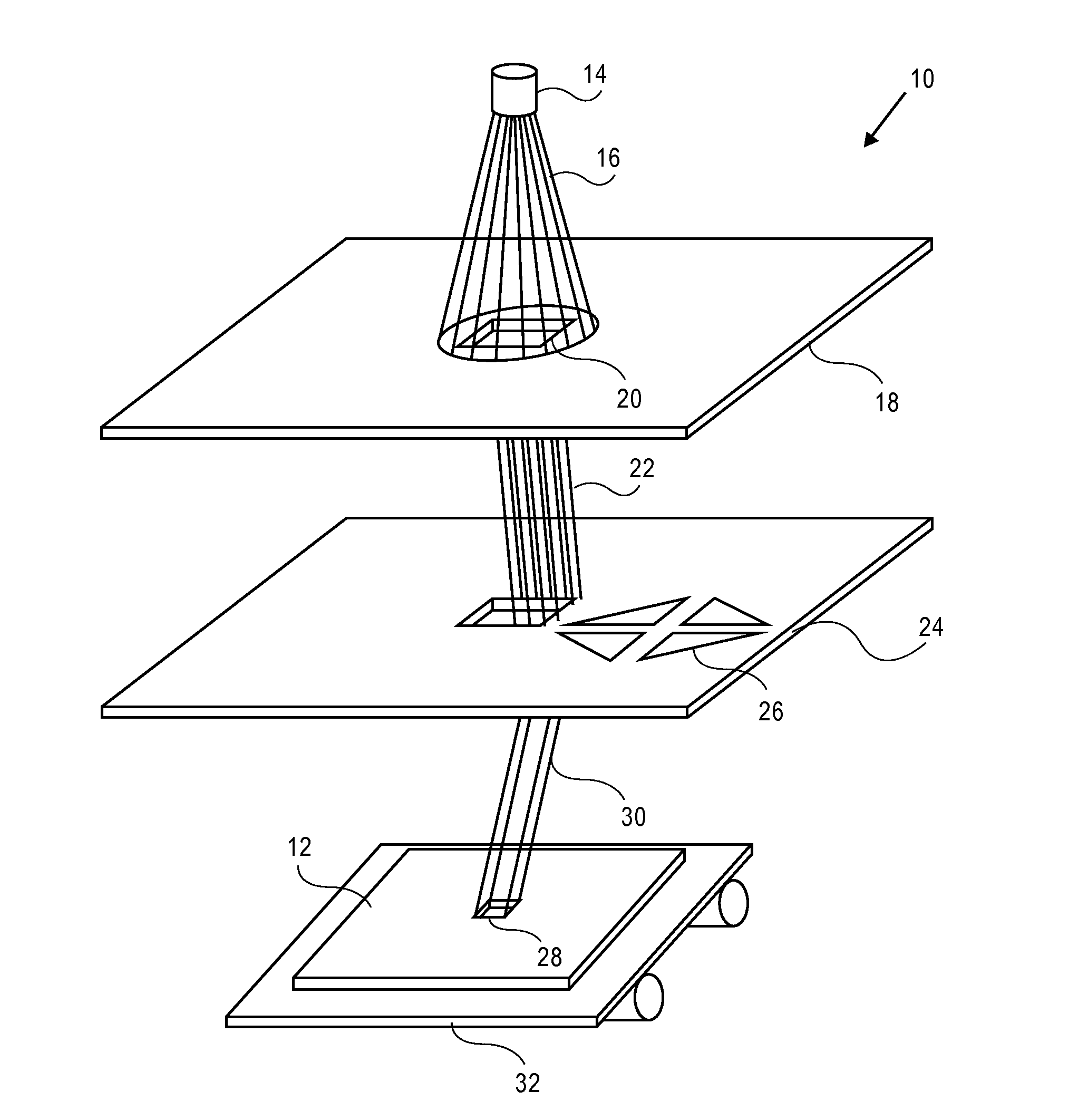
Visual inspection and verification system
A method and apparatus for inspecting a photolithography mask for defects is provided. The inspection method comprises providing a defect area image to an image simulator wherein the defect area image is an image of a portion of a photolithography mask, and providing a set of lithography parameters as a second input to the image simulator. The defect area image may be provided by an inspection tool which scans the photolithography mask for defects using a high resolution microscope and captures images of areas of the mask around identified potential defects. The image simulator generates a first simulated image in response to the defect area image and the set of lithography parameters. The first simulated image is a simulation of an image which would be printed on a wafer if the wafer were to be exposed to an illumination source directed through the portion of the mask. The method may also include providing a second simulated image which is a simulation of the wafer print of the portion of the design mask which corresponds to the portion represented by the defect area image. The method also provides for the comparison of the first and second simulated images in order to determine the printability of any identified potential defects on the photolithography mask. A method of determining the process window effect of any identified potential defects is also provided for.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Capacitively coupled remote plasma source with large operating pressure range
InactiveUS20100101727A1System costExtension of timeElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceRadio frequency
A radio frequency (RF) coaxial resonator feeding a saltshaker-like gas distributing electrode assembly forms a capacitively coupled plasma source. This apparatus can generate plasma of high density over a wide pressure range and large process window. The system may be used as a remote radical-rich plasma source for materials surface processing.
Owner:JI HELIN
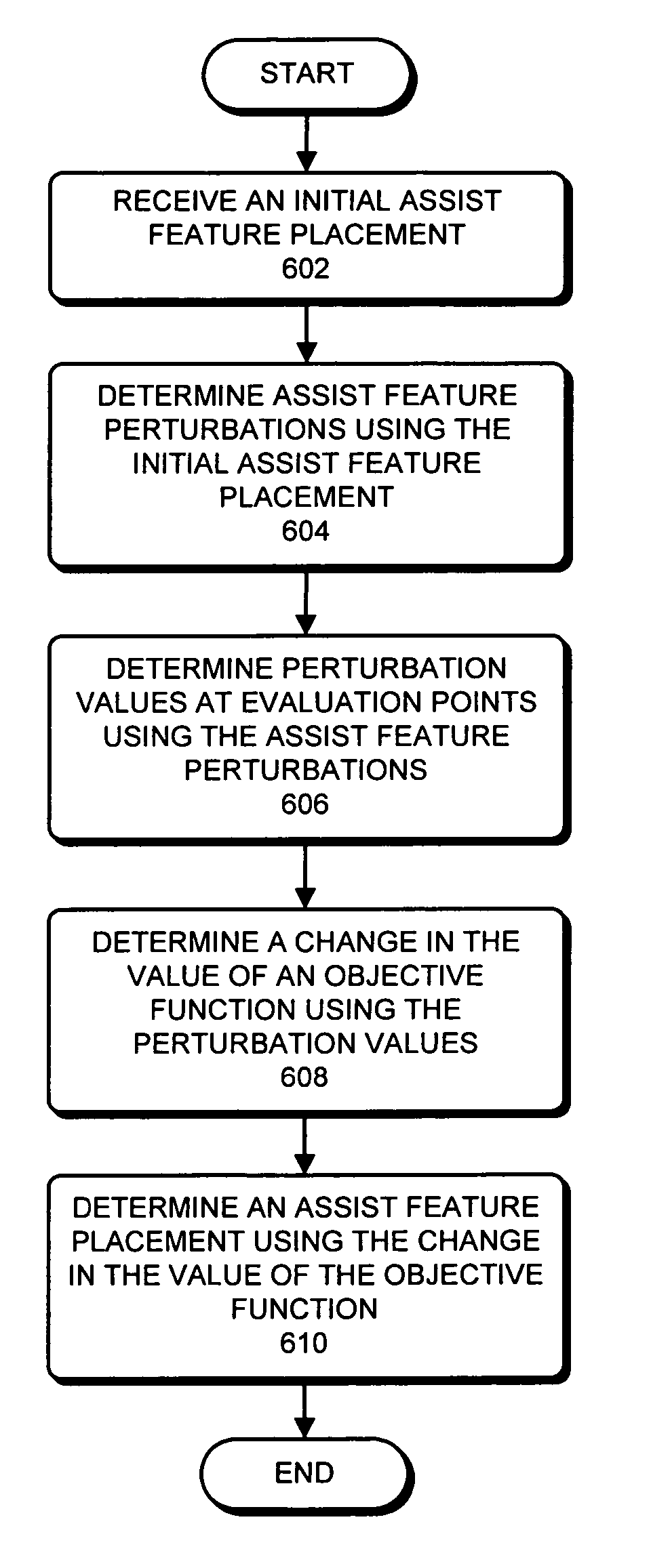
Assist feature placement using a process-sensitivity model
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Assist feature placement using a process-sensitivity model
ActiveUS20060206854A1CAD circuit designOriginals for photomechanical treatmentAlgorithmProcess window
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that determines an assist feature placement. During operation, the system receives an initial assist feature placement for a layout. Next, the system determines assist feature perturbations using the initial assist feature placement. An assist feature perturbation typically comprises a few simple polygons. The system then determines perturbation values at evaluation points in the layout using the assist feature perturbations and an analytical model. If a process-sensitivity model is used, the perturbation value at an evaluation point is associated with the change in the through-process window at that point in the layout. Next, the system determines a change in the value of an objective function using the perturbation values. The objective function can be indicative of the overall manufacturability of the layout. The system then determines an assist feature placement using the change in the value of the objective function. For example, the system can determine an assist feature placement using an assist feature perturbation which minimizes the objective function value.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
SiGe (silicon germanium) source and drain area manufacturing method
ActiveCN104201108AReduce thicknessAvoid stress relaxationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationEngineering
The invention discloses a SiGe (silicon germanium) source and drain area manufacturing method. A multi-layer structure which comprises alternately stacked buffer layers and main body layers is formed by a method that the SiGe epitaxial growth of the buffer layer and the main body layers is alternated repeatedly and accordingly the thickness of every high Ge concentration of SiGe main body layer is effectively reduced and shared into every layer of main body layer and accordingly the stress relaxation due to the fact that thickness of every main body layer exceeds the critical thickness is avoided; the Ge content of every layer of SiGe main body layer is further improved to enable the stress of the SiGe source leakage on a channel to be increased; an SiGe process window is enlarged due to the repeated epitaxy and accordingly the process stability is enhanced and accordingly the device performance is improved; the stress can be effectively improved without increase of the process difficulty and accordingly the process is stable and controllable and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
Qualifying patterns, patterning processes, or patterning apparatus in the fabrication of microlithographic patterns
InactiveUS6902855B2MaximizeIncrease catch ratePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess windowDesign rule checking
The invention is a method of determining the presence of an anomaly in qualifying a pattern, patterning process, or patterning apparatus used in the fabrication of microlithographic patterns. A preferred implementation of the method qualifies incoming reticles and process conditions on test wafers to maximize the available usable process window for a given reticle exposure tool combination. Practicing this method on test wafers enables the identification of spatial areas where a process will fail first and candidate regions for carrying out defect inspection and metrology. Other preferred implementations of the method qualify masks, reticles, or other patterns characterized by data bases on which are stored image data acquired by practice of aerial image measurement system (AIMS) or design rule checking (DRC) techniques.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
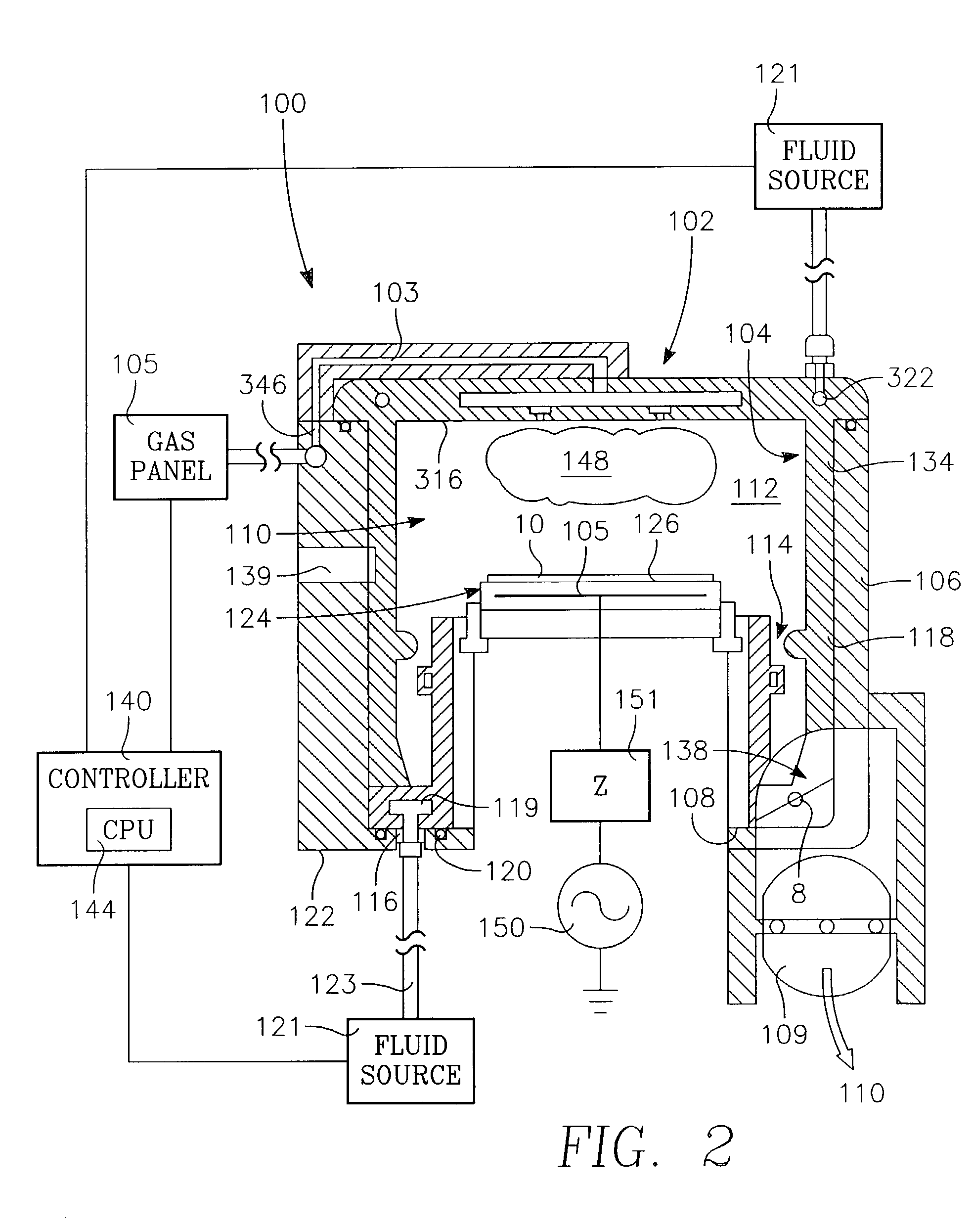
Dielectric etch chamber with expanded process window
InactiveUS20030037880A1Improve adhesionIncrease chanceElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDielectricCapacitive coupling
A capacitively coupled reactor for plasma etch processing of substrates at subatmospheric pressures includes a chamber body defining a processing volume, a lid provided upon the chamber body, the lid being a first electrode, a substrate support provided in the processing volume and comprising a second electrode, a radio frequency source coupled at least to one of the first and second electrodes, a process gas inlet configured to deliver process gas into the processing volume, and an evacuation pump system having pumping capacity of at least 1600 liters / minute. The greater pumping capacity controls residency time of the process gases so as to regulate the degree of dissociation into more reactive species.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
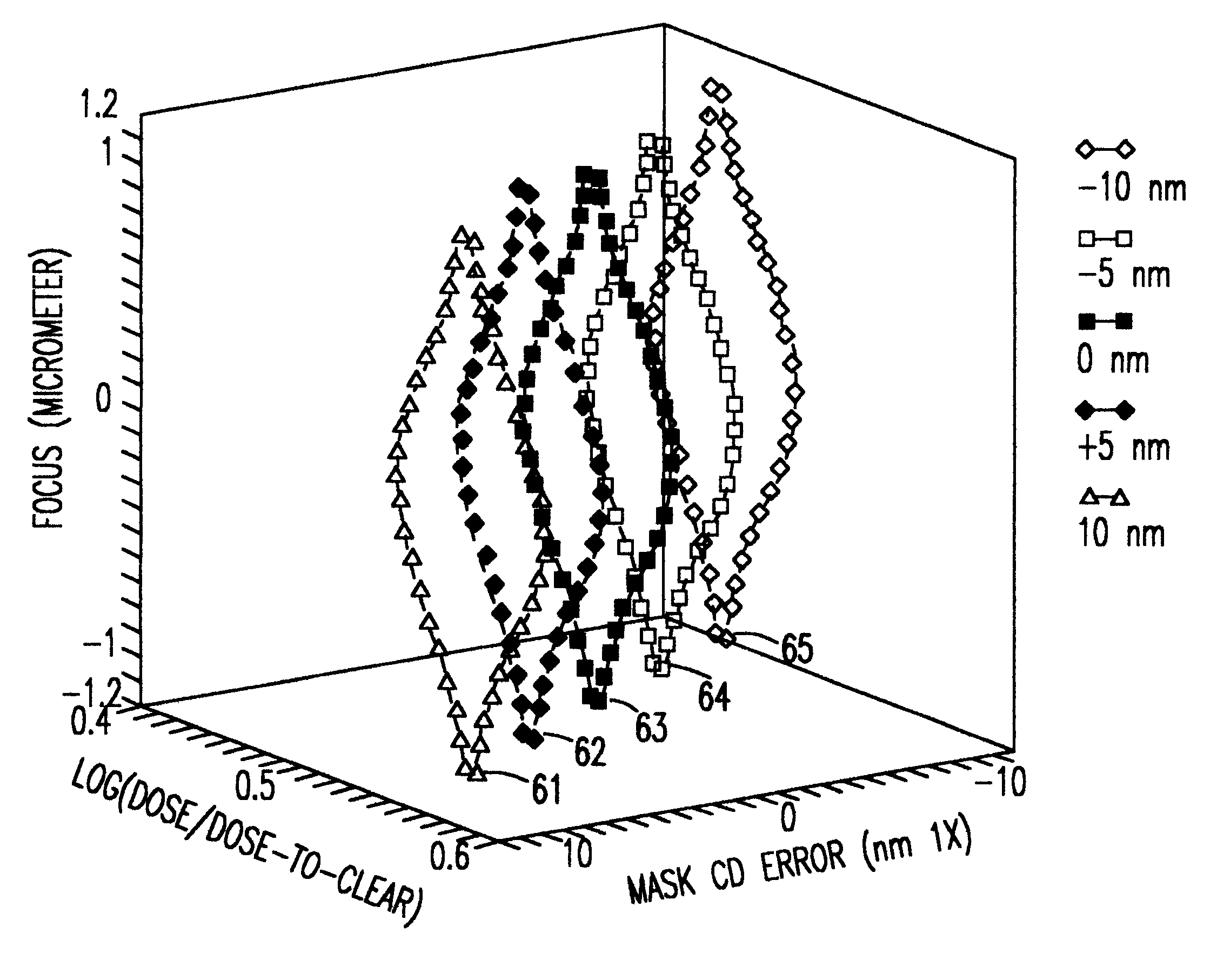
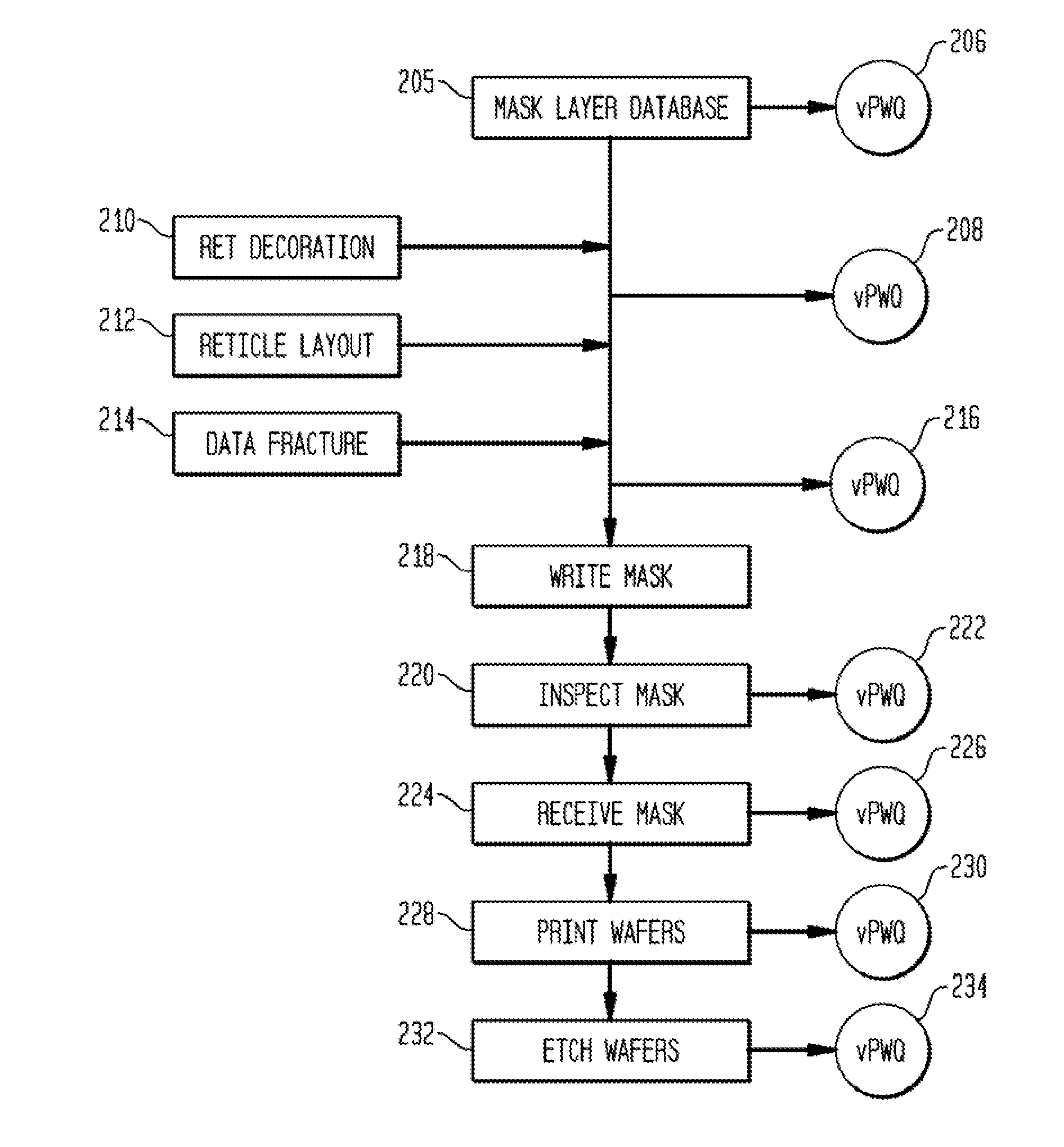
Computer-implemented methods and systems for determining different process windows for a wafer printing process for different reticle designs
ActiveUS20080072207A1Maximize distanceRecording apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentEngineeringProcess window
Computer-implemented methods and systems for determining different process windows for a wafer printing process for different reticle designs are provided. One method includes generating simulated images illustrating how each of the different reticle designs will be printed on a wafer at different values of one or more parameters of the wafer printing process. The method also includes detecting defects in each of the different reticle designs using the simulated images. In addition, the method includes determining a process window for the wafer printing process for each of the different reticle designs based on results of the detecting step.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Placement and optimization of process dummy cells
ActiveUS8225255B2Reduce probabilityImprove toleranceSolid-state devicesStatic storageInternal memoryVirtual cell
A method for laying out process dummy cells in relationship to inside memory cells of a memory array includes (a) calculating an initial process performance parameter for the memory array; (b) changing dummy cell layout configuration for a layer electrically connected to inside cells; (c) applying lithographic simulation and yield model for both the inside memory cells and the changed layout configuration process dummy cells; and (d) repeating steps (b) and (c) until yield is maximized. Checks may be performed to ensure that there is enough room to make the change and that there is no significant adverse effect to neighboring circuits. The process performance parameter may be yield or a process window for the inside memory cells.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
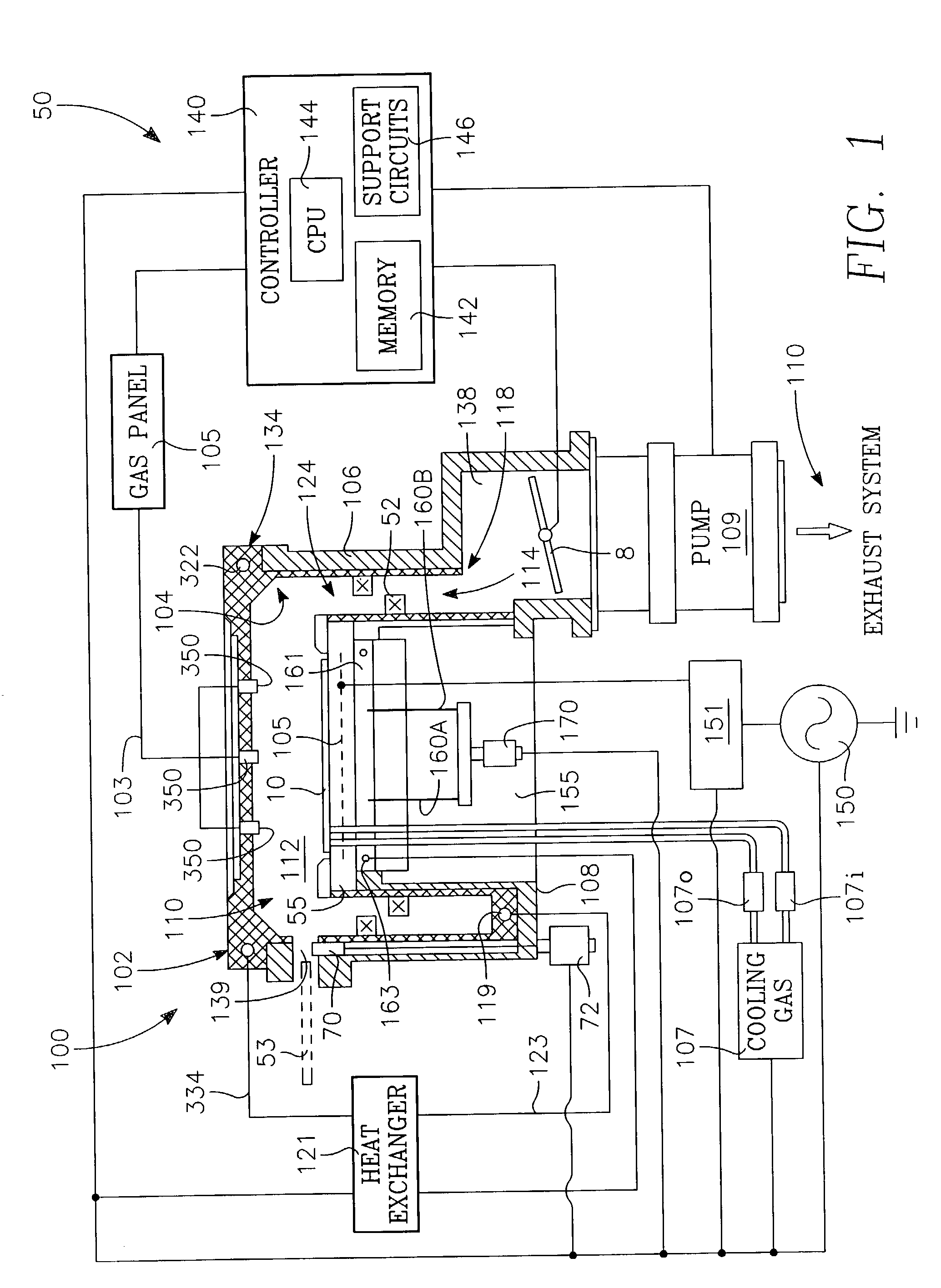
Method and apparatus for pulsed plasma processing using a time resolved tuning scheme for RF power delivery
ActiveUS8264154B2Alternating current plasma display panelsElectric arc lampsProcess windowPlasma processing
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide methods and apparatus for pulsed plasma processing over a wide process window. In some embodiments, an apparatus may include an RF power supply having frequency tuning and a matching network coupled to the RF power supply that share a common sensor for reading reflected RF power reflected back to the RF power supply. In some embodiments, an apparatus may include an RF power supply having frequency tuning and a matching network coupled to the RF power supply that share a common sensor for reading reflected RF power reflected back to the RF power supply and a common controller for tuning each of the RF power supply and the matching network.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dielectric etch chamber with expanded process window
InactiveUS6716302B2Improve adhesionIncrease chanceElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDielectricCapacitive coupling
A capacitively coupled reactor for plasma etch processing of substrates at subatmospheric pressures includes a chamber body defining a processing volume, a lid provided upon the chamber body, the lid being a first electrode, a substrate support provided in the processing volume and comprising a second electrode, a radio frequency source coupled at least to one of the first and second electrodes, a process gas inlet configured to deliver process gas into the processing volume, and an evacuation pump system having pumping capacity of at least 1600 liters / minute. The greater pumping capacity controls residency time of the process gases so as to regulate the degree of dissociation into more reactive species.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Visual inspection and verification system
A method and apparatus for inspecting a photolithography mask for defects is provided. The inspection method comprises providing a defect area image to an image simulator wherein the defect area image is an image of a portion of a photolithography mask, and providing a set of lithography parameters as a second input to the image simulator. The defect area image may be provided by an inspection tool which scans the photolithography mask for defects using a high resolution microscope and captures images of areas of the mask around identified potential defects. The image simulator generates a first simulated image in response to the defect area image and the set of lithography parameters. The first simulated image is a simulation of an image which would be printed on a wafer if the wafer were to be exposed to an illumination source directed through the portion of the mask. The method may also include providing a second simulated image which is a simulation of the wafer print of the portion of the design mask which corresponds to the portion represented by the defect area image. The method also provides for the comparison of the first and second simulated images in order to determine the printability of any identified potential defects on the photolithography mask. A method of determining the process window effect of any identified potential defects is also provided for.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
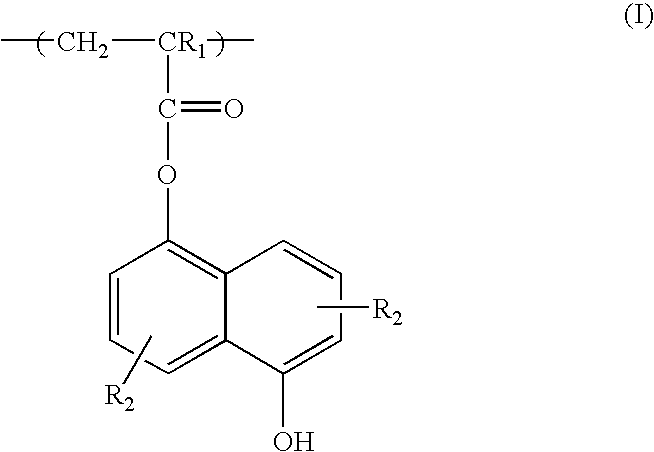
Positive resist containing naphthol functionality
ActiveUS20060105267A1Improve photolithographic effectExcellent etch resistancePhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersPhotosensitive material processingResistMethacrylate
Acid-catalyzed positive resist compositions which are imageable with 193 nm radiation are obtained using a polymer having acrylate / methacrylate monomeric units comprising a naphthol ester group. The resist may optionally contain polymer having acrylate / methacrylate monomeric units with fluorine-containing functional groups. The resists containing the polymer having acrylate / methacrylate monomeric units comprising a naphthol ester group have an improved process window, including improved etch resistance and reduced swelling compared to conventional fluorine-containing 193 nm resist.
Owner:IBM CORP
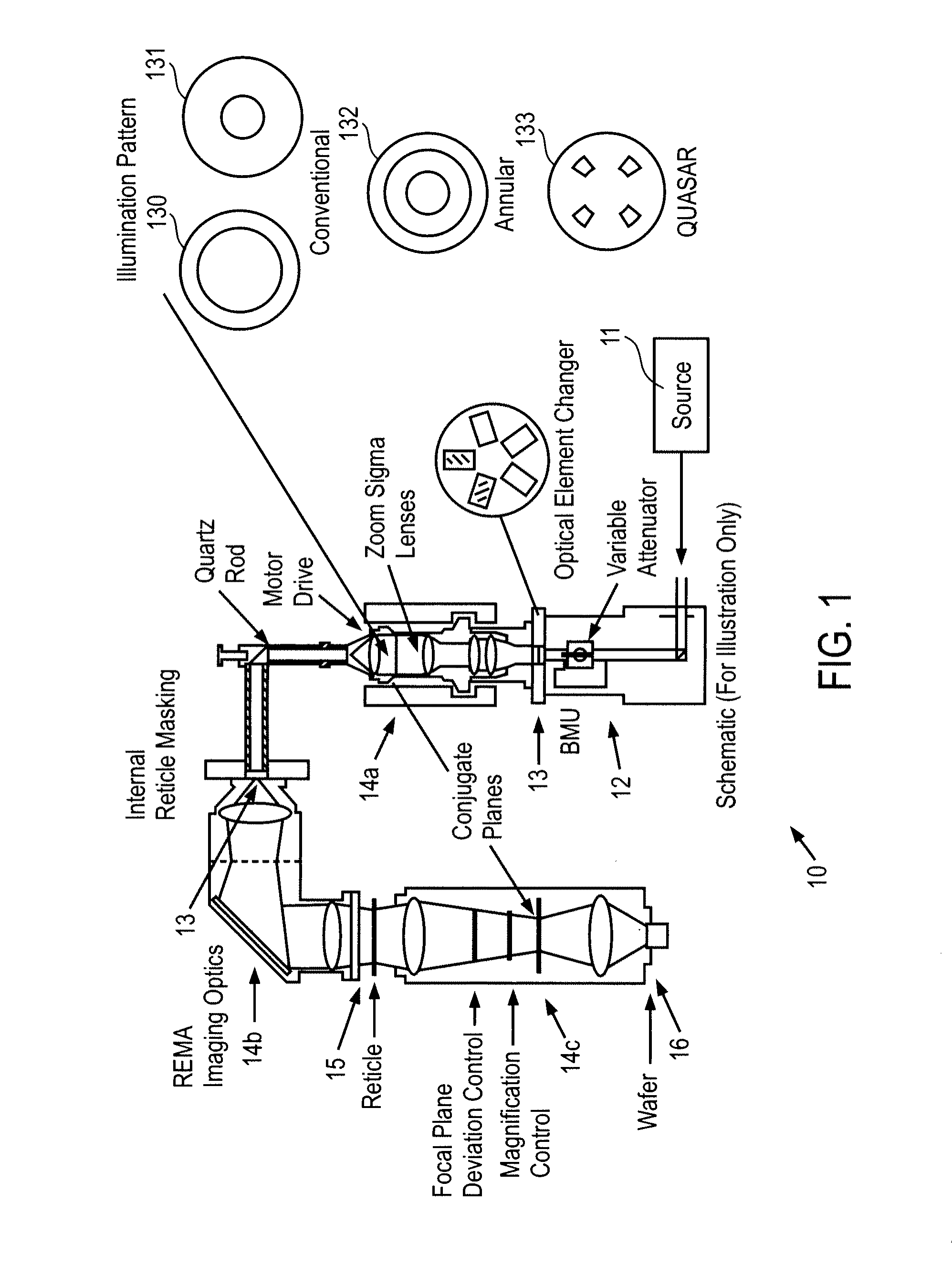
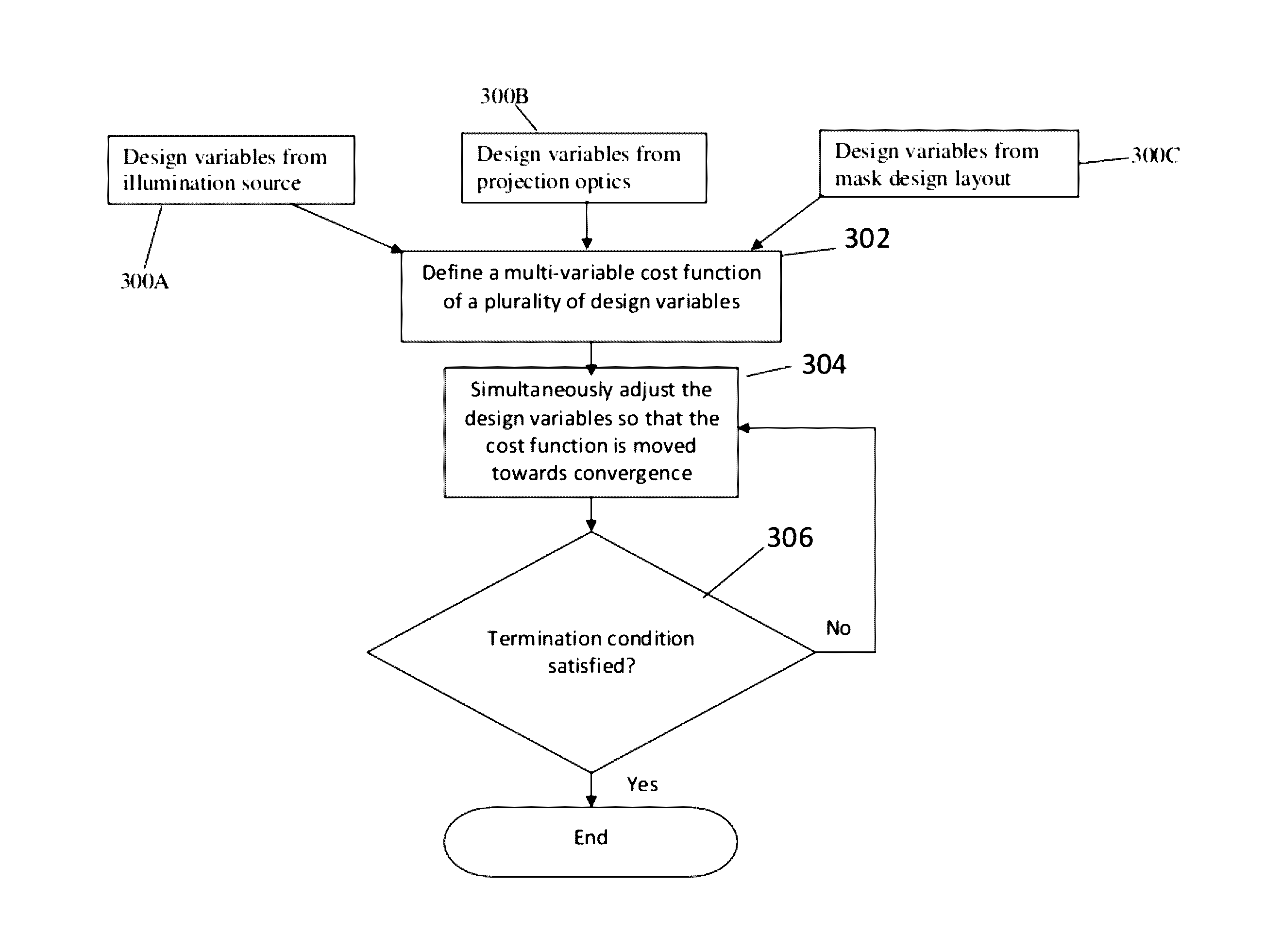
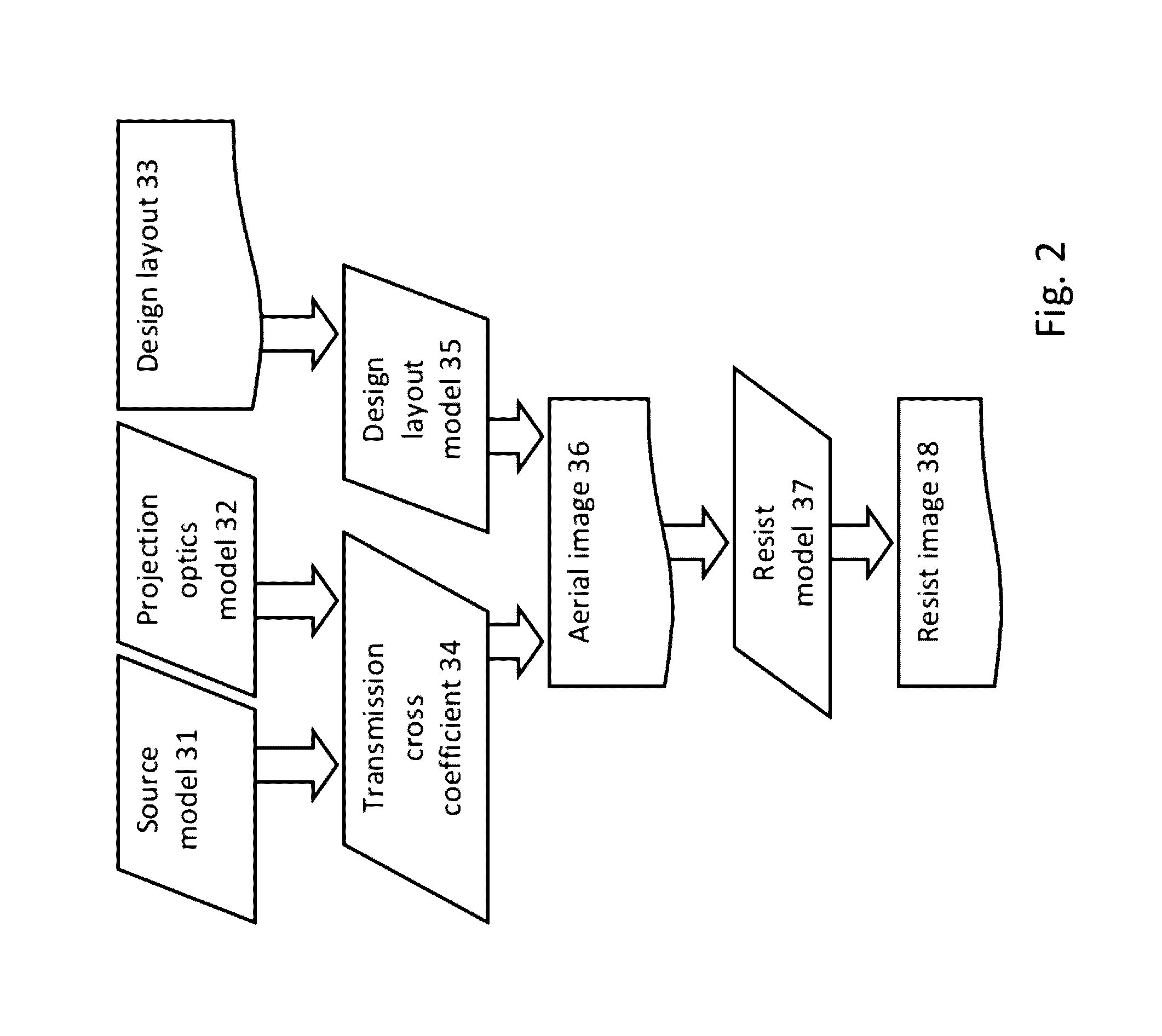
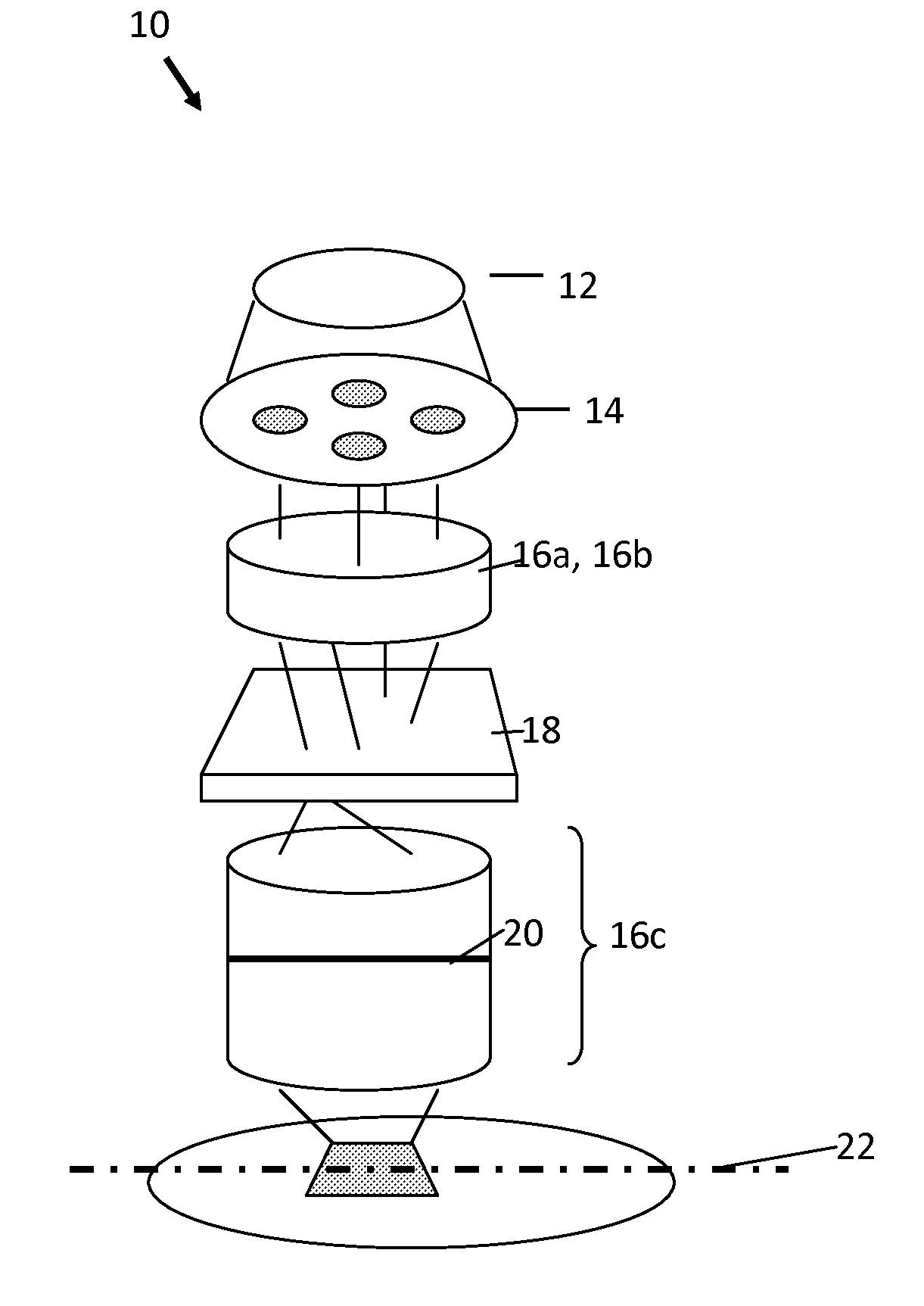
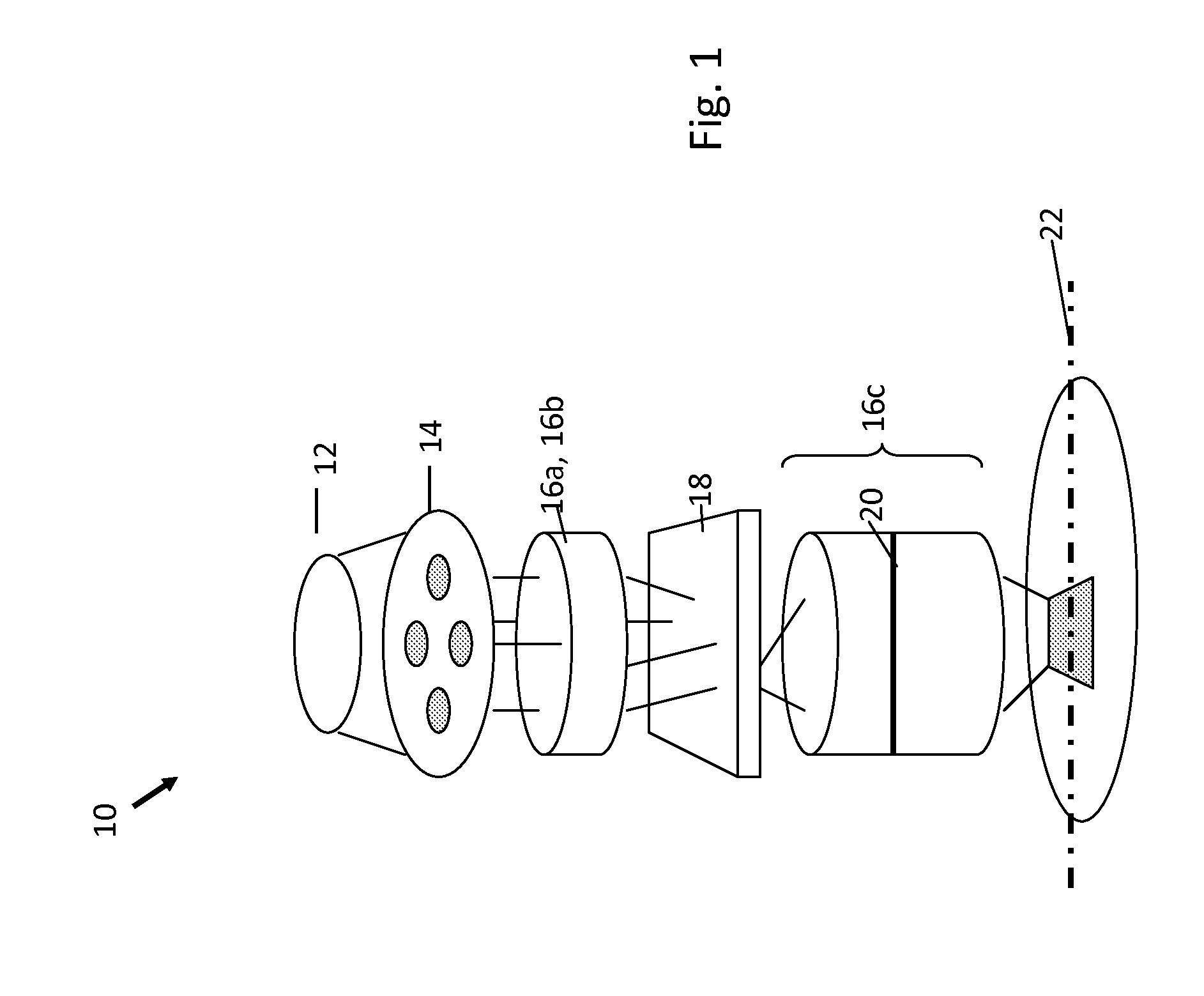
Optimization of Source, Mask and Projection Optics
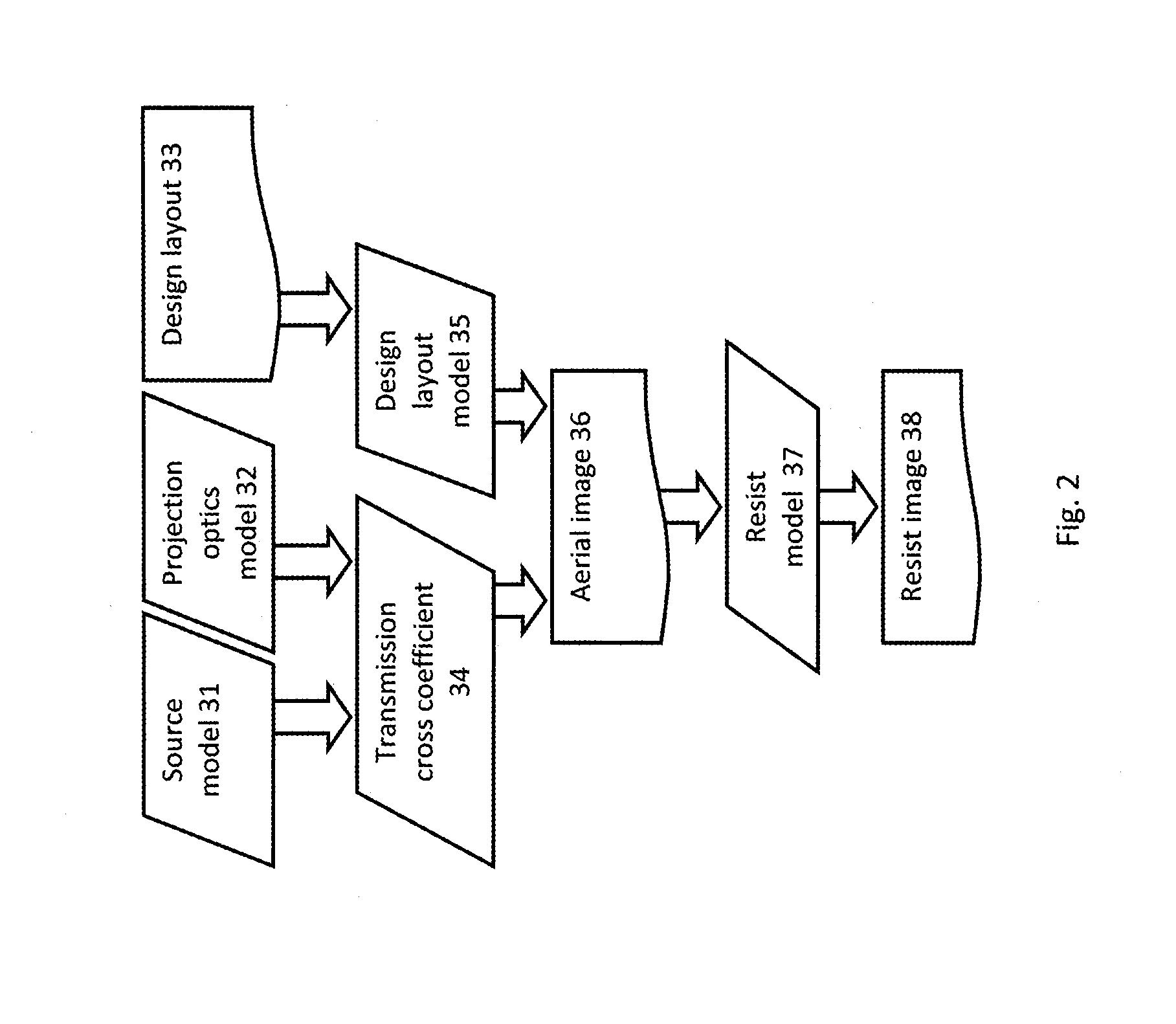
ActiveUS20120117522A1Optimize and improveEasy to optimizePhotomechanical apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationProjection opticsWavefront
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for optimizing a lithographic projection apparatus including optimizing projection optics therein, and preferably including optimizing a source, a mask, and the projection optics. The projection optics is sometimes broadly referred to as “lens”, and therefore the joint optimization process may be termed source mask lens optimization (SMLO). SMLO is desirable over existing source mask optimization process (SMO), partially because including the projection optics in the optimization can lead to a larger process window by introducing a plurality of adjustable characteristics of the projection optics. The projection optics can be used to shape wavefront in the lithographic projection apparatus, enabling aberration control of the overall imaging process. According to the embodiments herein, the optimization can be accelerated by iteratively using linear fitting algorithm or using Taylor series expansion using partial derivatives of transmission cross coefficients (TCCs).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
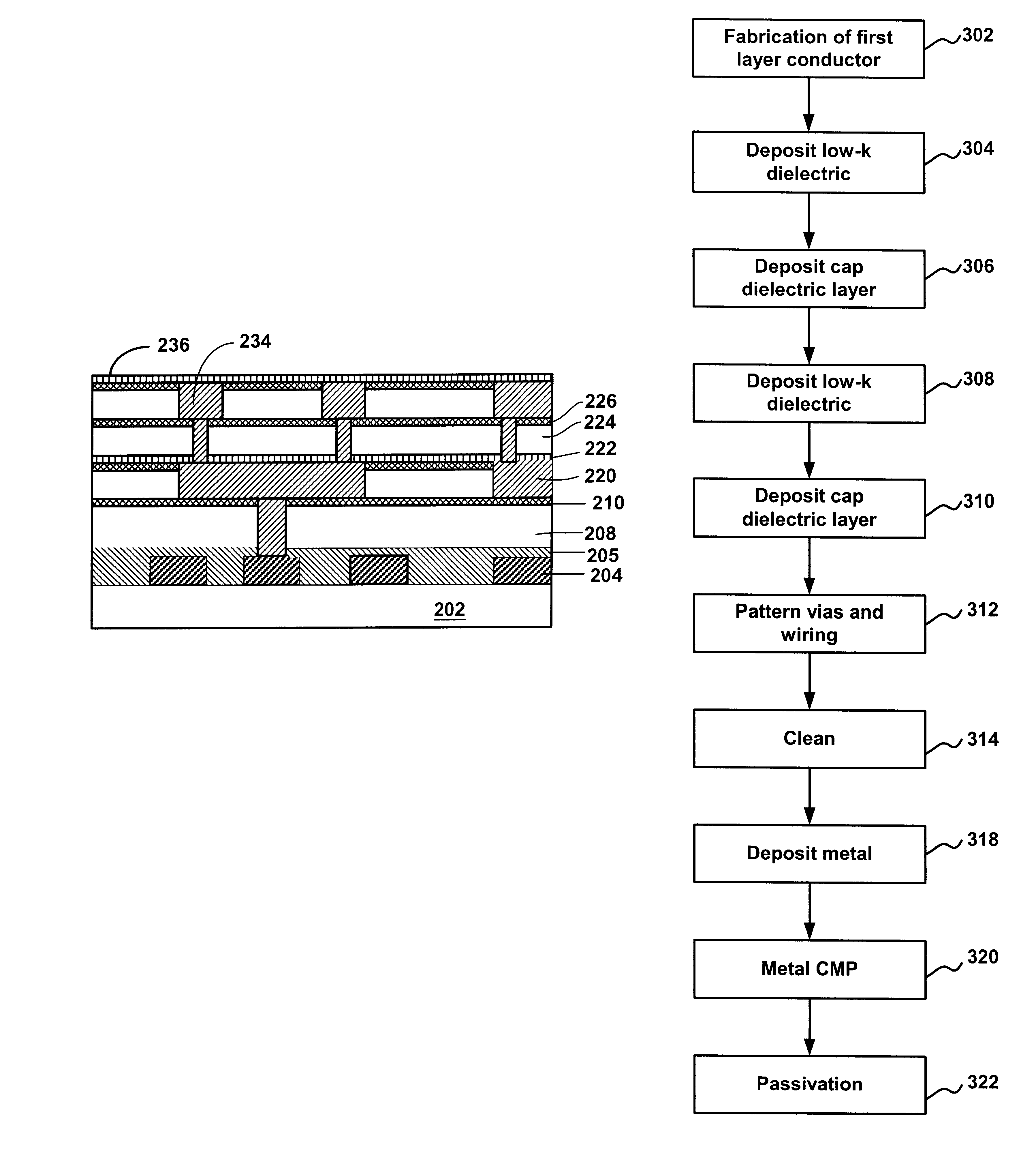
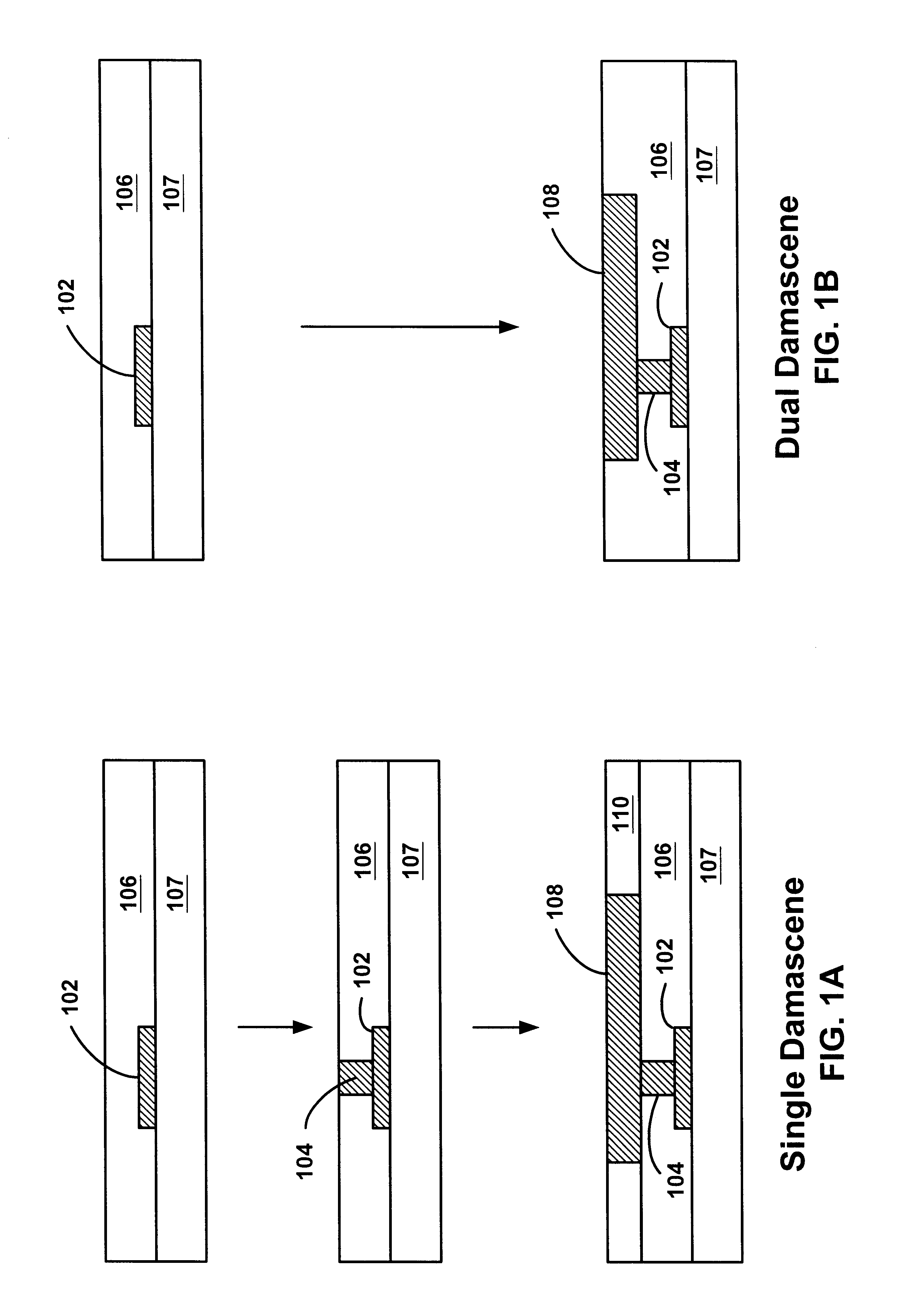
Method of forming dual-damascene interconnect structures employing low-k dielectric materials
InactiveUS6627539B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:NEWPORT FAB
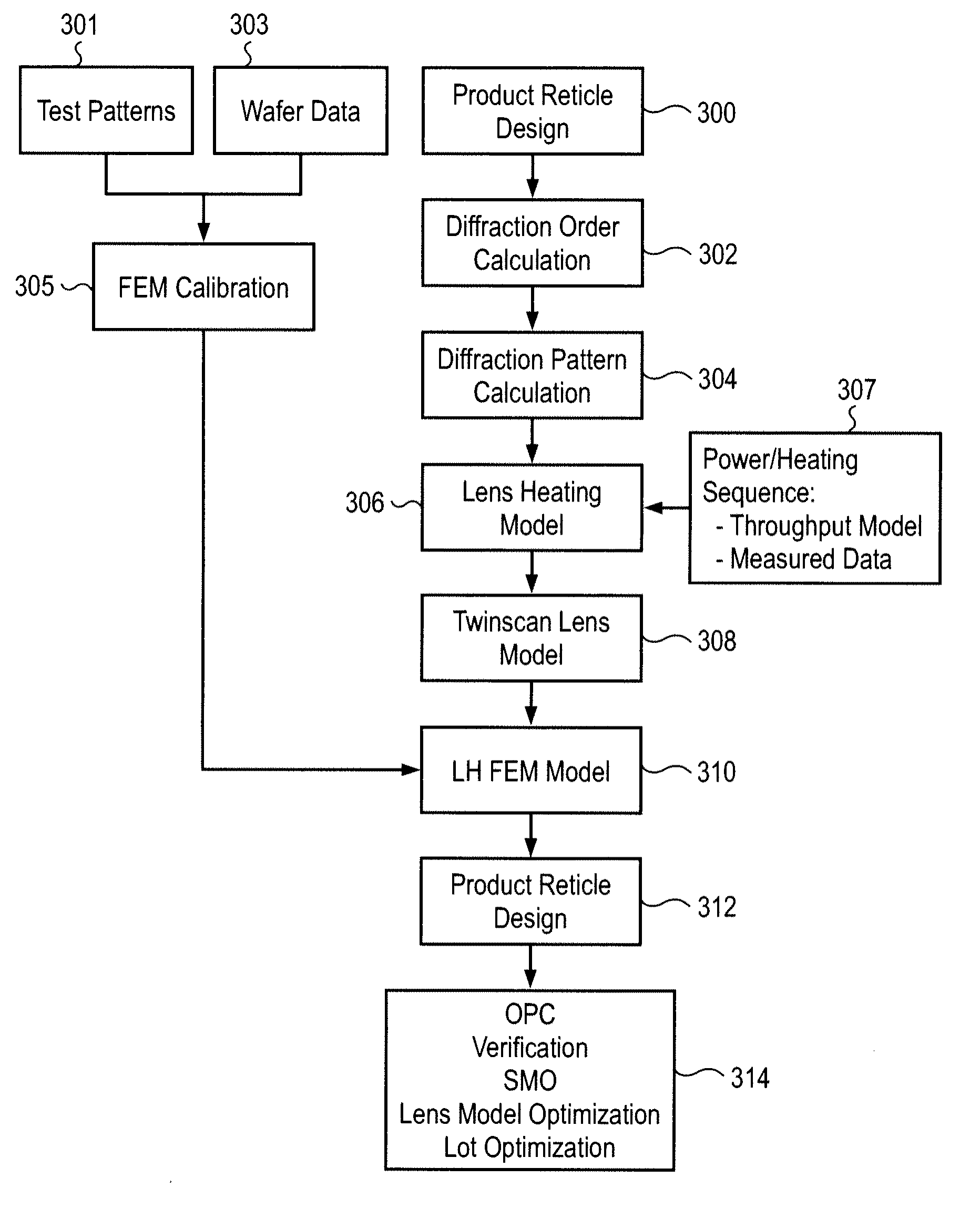
Lens heating compensation systems and methods
ActiveUS20090296055A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCamera lensProcess engineering
Methods for calibrating a photolithographic system are disclosed. A cold lens contour for a reticle design and at least one hot lens contour for the reticle design are generated from which a process window is defined. Aberrations induced by a lens manipulator are characterized in a manipulator model and the process window is optimized using the manipulator model. Aberrations are characterized by identifying variations in critical dimensions caused by lens manipulation for a plurality of manipulator settings and by modeling behavior of the manipulator as a relationship between manipulator settings and aberrations. The process window may be optimized by minimizing a cost function for a set of critical locations.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Optimization flows of source, mask and projection optics
ActiveUS9588438B2Improve or optimize the lithographic projection apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusProjection opticsWavefront
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for optimizing a lithographic projection apparatus including optimizing projection optics therein. The current embodiments include several flows including optimizing a source, a mask, and the projection optics and various sequential and iterative optimization steps combining any of the projection optics, mask and source. The projection optics is sometimes broadly referred to as “lens”, and therefore the optimization process may be termed source mask lens optimization (SMLO). SMLO may be desirable over existing source mask optimization process (SMO) or other optimization processes that do not include projection optics optimization, partially because including the projection optics in the optimization may lead to a larger process window by introducing a plurality of adjustable characteristics of the projection optics. The projection optics may be used to shape wavefront in the lithographic projection apparatus, enabling aberration control of the overall imaging process.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
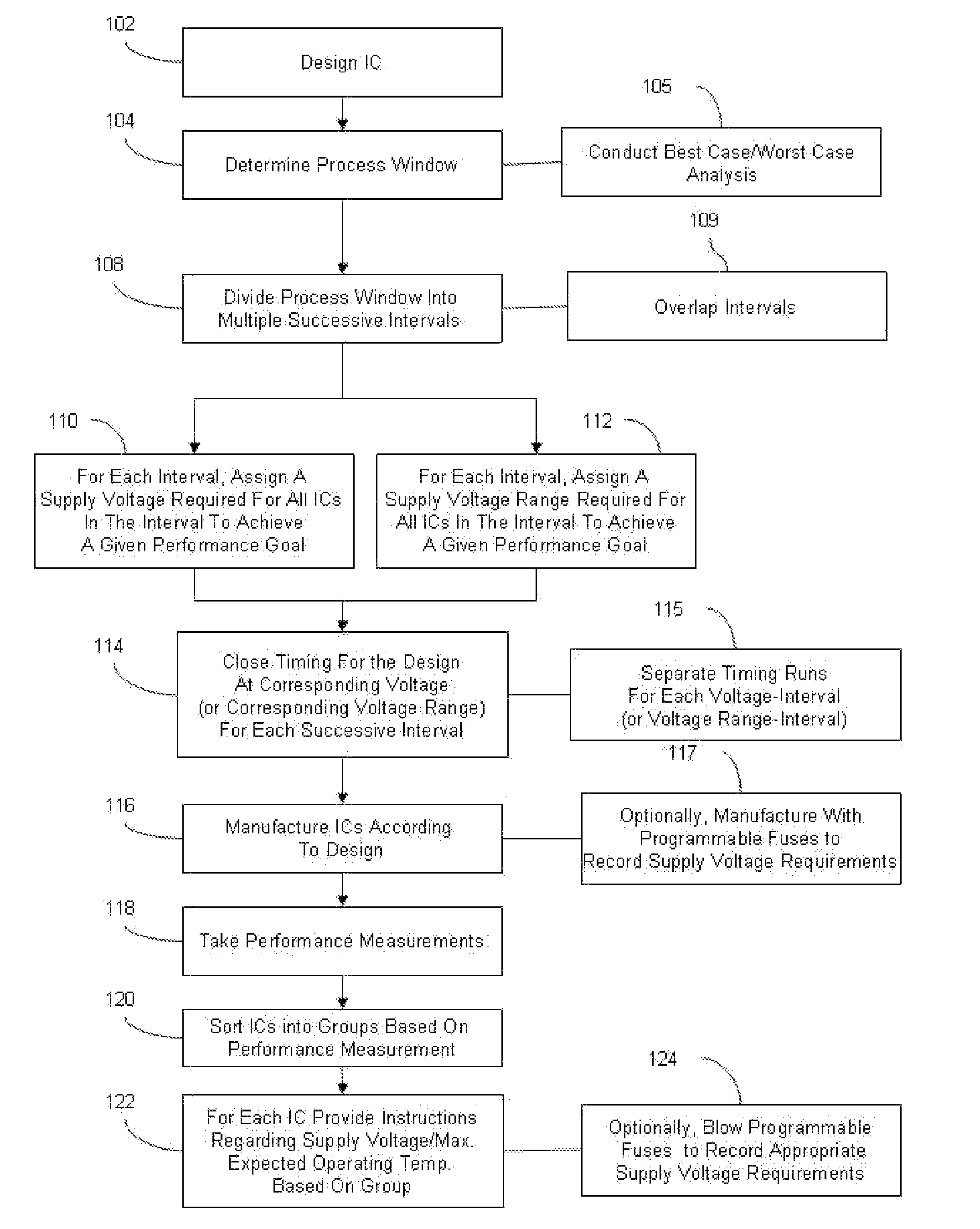
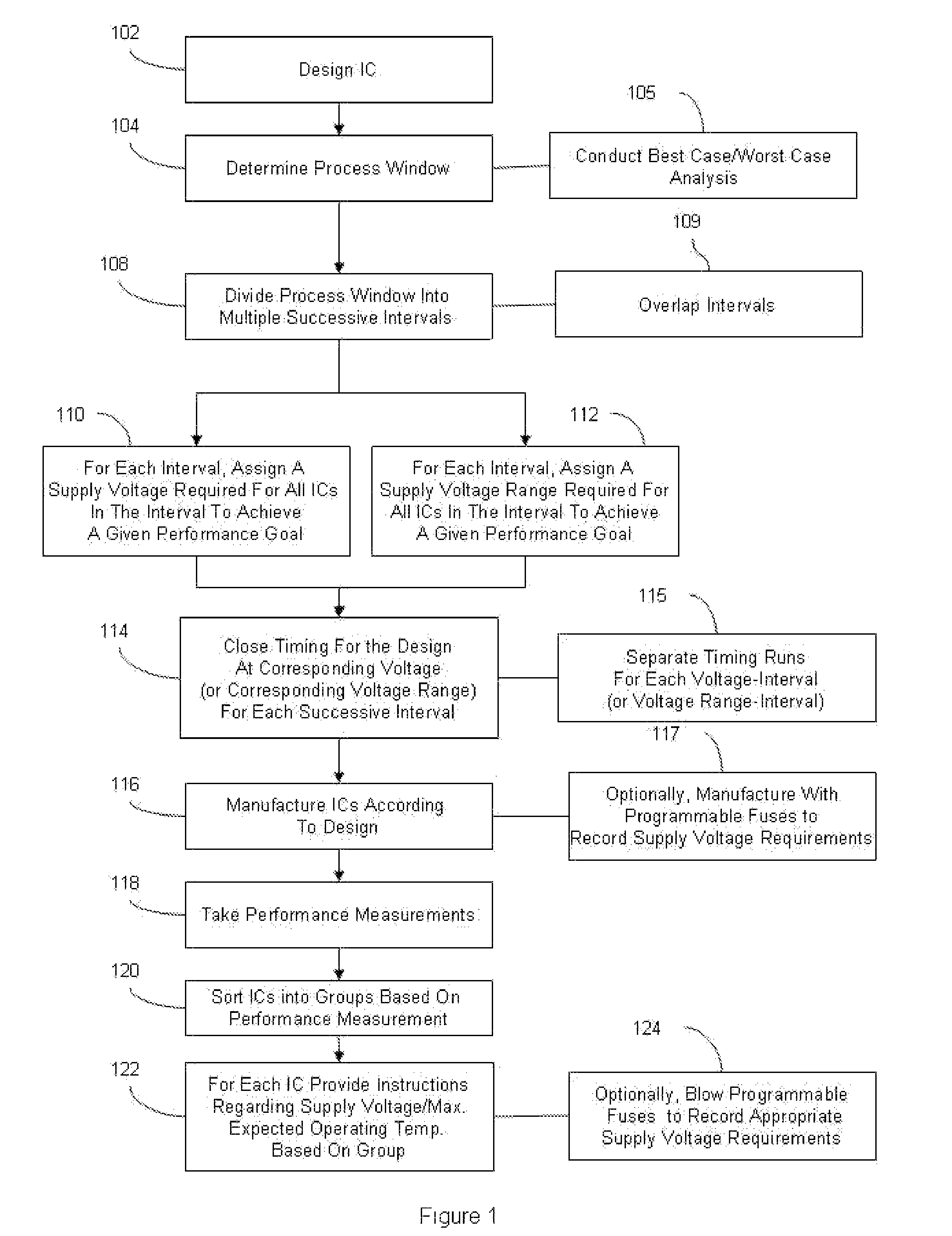
Integrated circuit design closure method for selective voltage binning
InactiveUS7475366B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProcess windowCircuit design
Disclosed are embodiments of a method of designing and producing an integrated circuit. During the pre-release chip design process, the method subdivides the overall process window for an integrated circuit design into smaller successive intervals corresponding to achievable performance. Each performance interval is independently optimized for performance versus power by assigning to each interval a different corresponding supply voltage. Timing for the design is then closed for each interval at each assigned voltage. After chip manufacturing, the method measures the performance of the integrated circuits that are manufactured according to the design. Using these performance measurements, the circuits are sorted into bins corresponding to each performance interval and appropriately labeled (e.g., with the performance goal and previously assigned supply voltage corresponding to the performance interval).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Optimization Flows of Source, Mask and Projection Optics
ActiveUS20120113404A1Improve or optimize the lithographic projection apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProjection opticsWavefront
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for optimizing a lithographic projection apparatus including optimizing projection optics therein. The current embodiments include several flows including optimizing a source, a mask, and the projection optics and various sequential and iterative optimization steps combining any of the projection optics, mask and source. The projection optics is sometimes broadly referred to as “lens”, and therefore the optimization process may be termed source mask lens optimization (SMLO). SMLO may be desirable over existing source mask optimization process (SMO) or other optimization processes that do not include projection optics optimization, partially because including the projection optics in the optimization may lead to a larger process window by introducing a plurality of adjustable characteristics of the projection optics. The projection optics may be used to shape wavefront in the lithographic projection apparatus, enabling aberration control of the overall imaging process.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
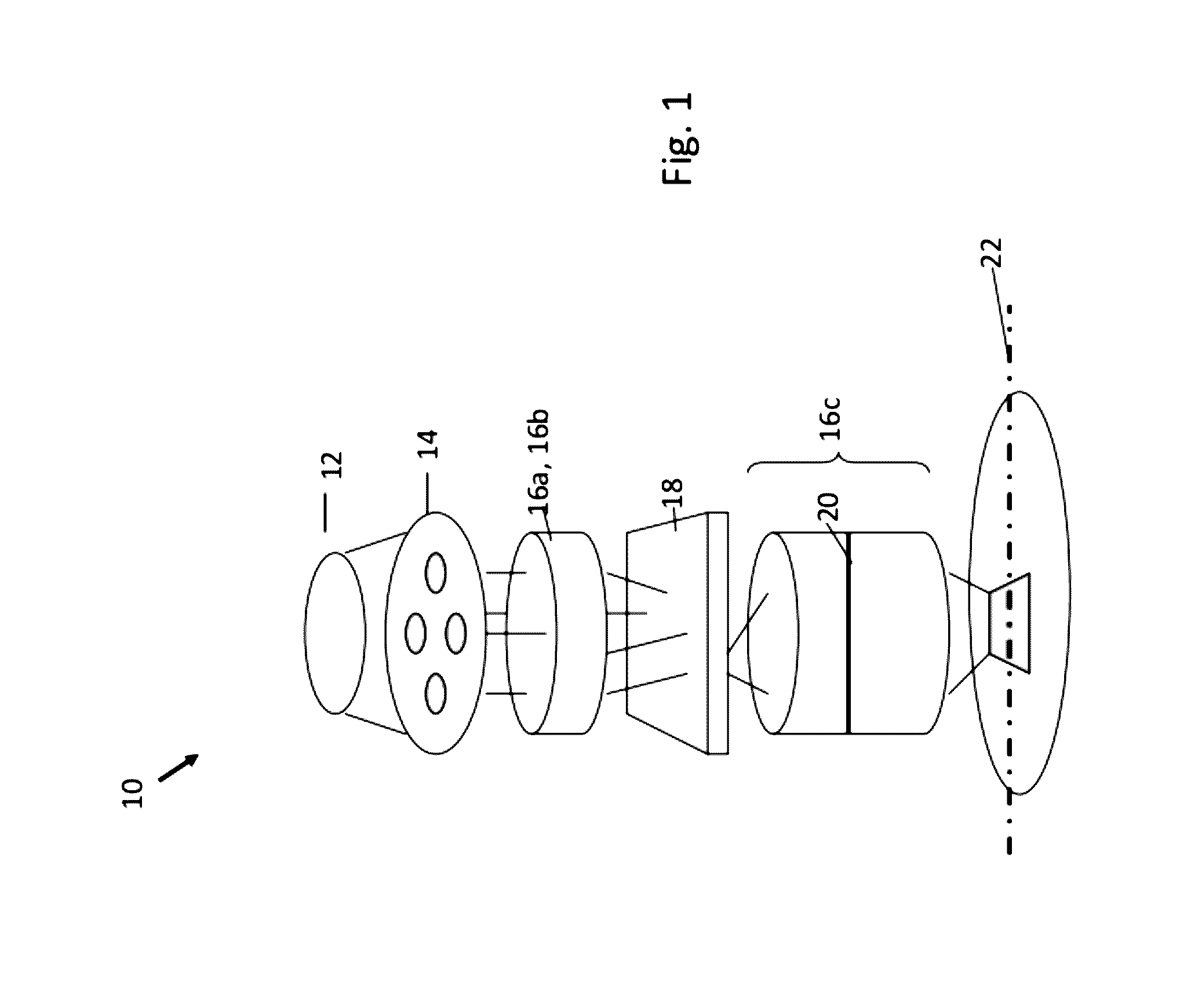
Method and System for Forming Patterns with Charged Particle Beam Lithography
ActiveUS20120329289A1Reduce sensitivityLower F0Electric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsLithography processProcess window
In a method for fracturing or mask data preparation or mask process correction for charged particle beam lithography, a plurality of shots are determined that will form a pattern on a surface, where shots are determined so as to reduce sensitivity of the resulting pattern to changes in beam blur (βf). At least some shots in the plurality of shots overlap other shots. In some embodiments, βf is reduced by controlling the amount of shot overlap in the plurality of shots, either during initial shot determination, or in a post-processing step. The reduced sensitivity to βf expands the process window for the charged particle beam lithography process.
Owner:D2S
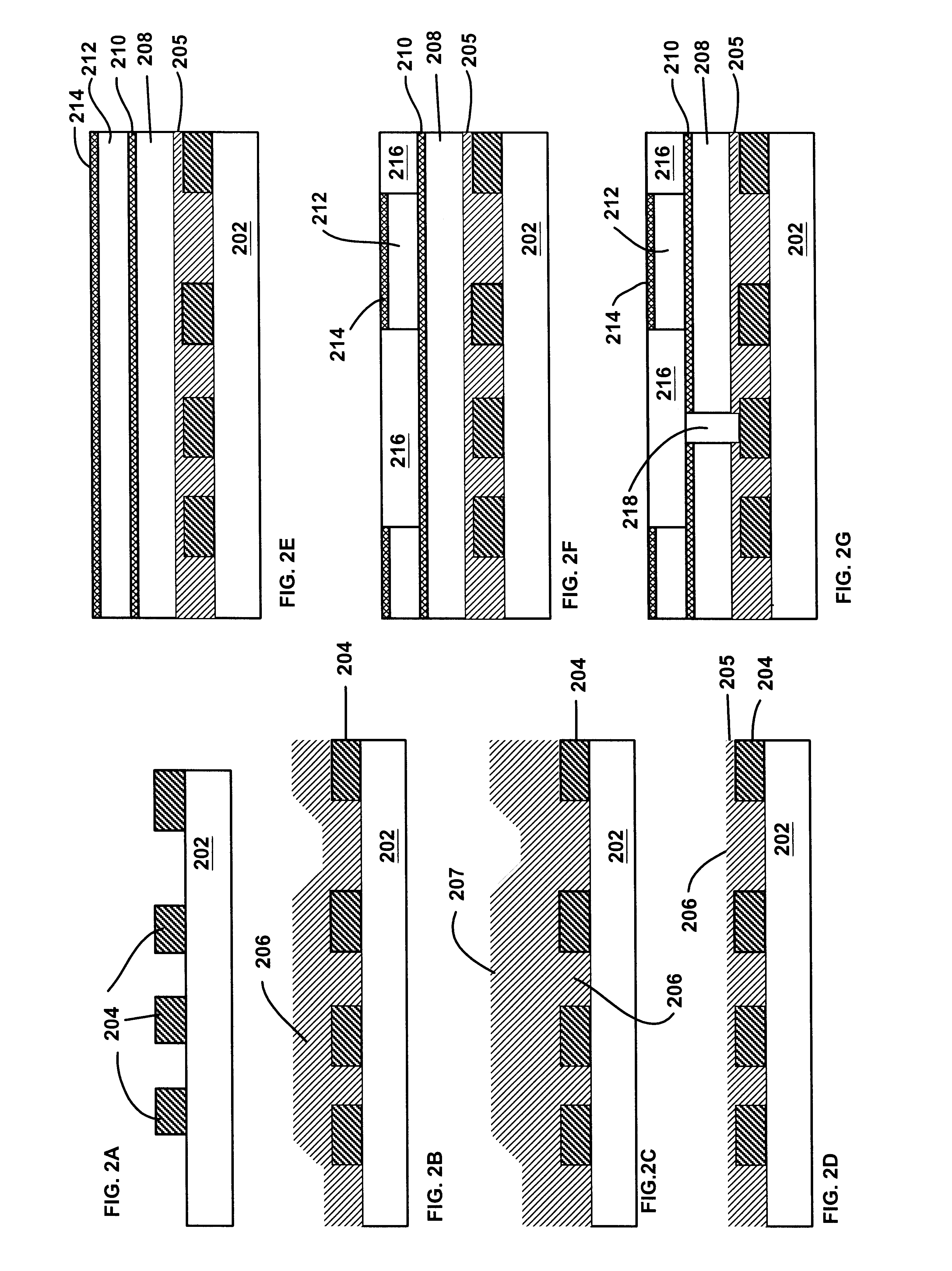
Multilayer hardmask scheme for damage-free dual damascene processing of SiCOH dielectrics
ActiveUS20060154086A1Easy to createImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricProcess window
Interconnect structures possessing an organosilicate glass based material for 90 nm and beyond BEOL technologies in which a multilayer hardmask using a line-first approach are described. The interconnect structure of the invention achieves respective improved device / interconnect performance and affords a substantial dual damascene process window owing to the non-exposure of the OSG material to resist removal plasmas and because of the alternating inorganic / organic multilayer hardmask stack. The latter feature implies that for every inorganic layer that is being etched during a specific etch step, the corresponding pattern transfer layer in the field is organic and vice-versa.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
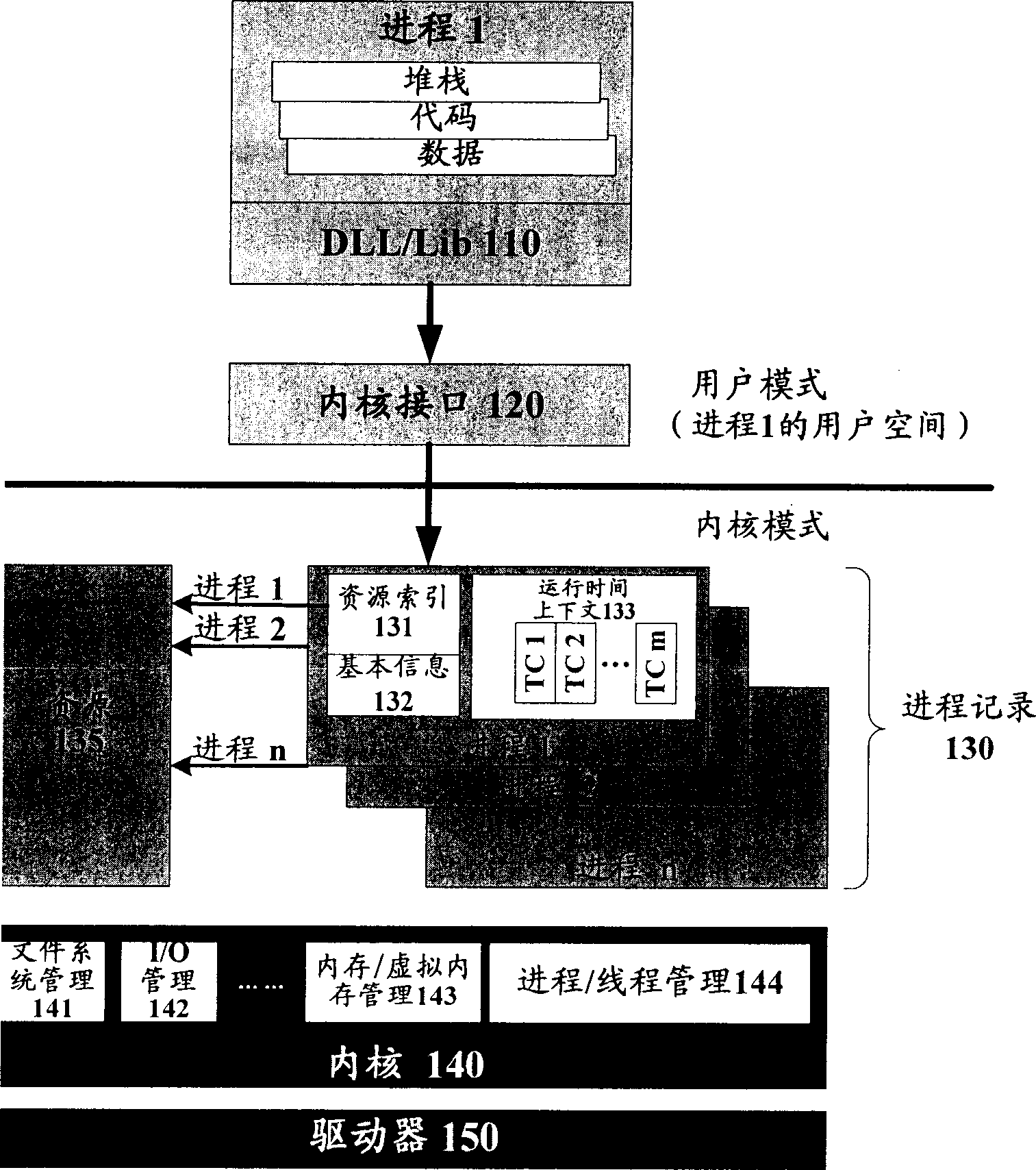
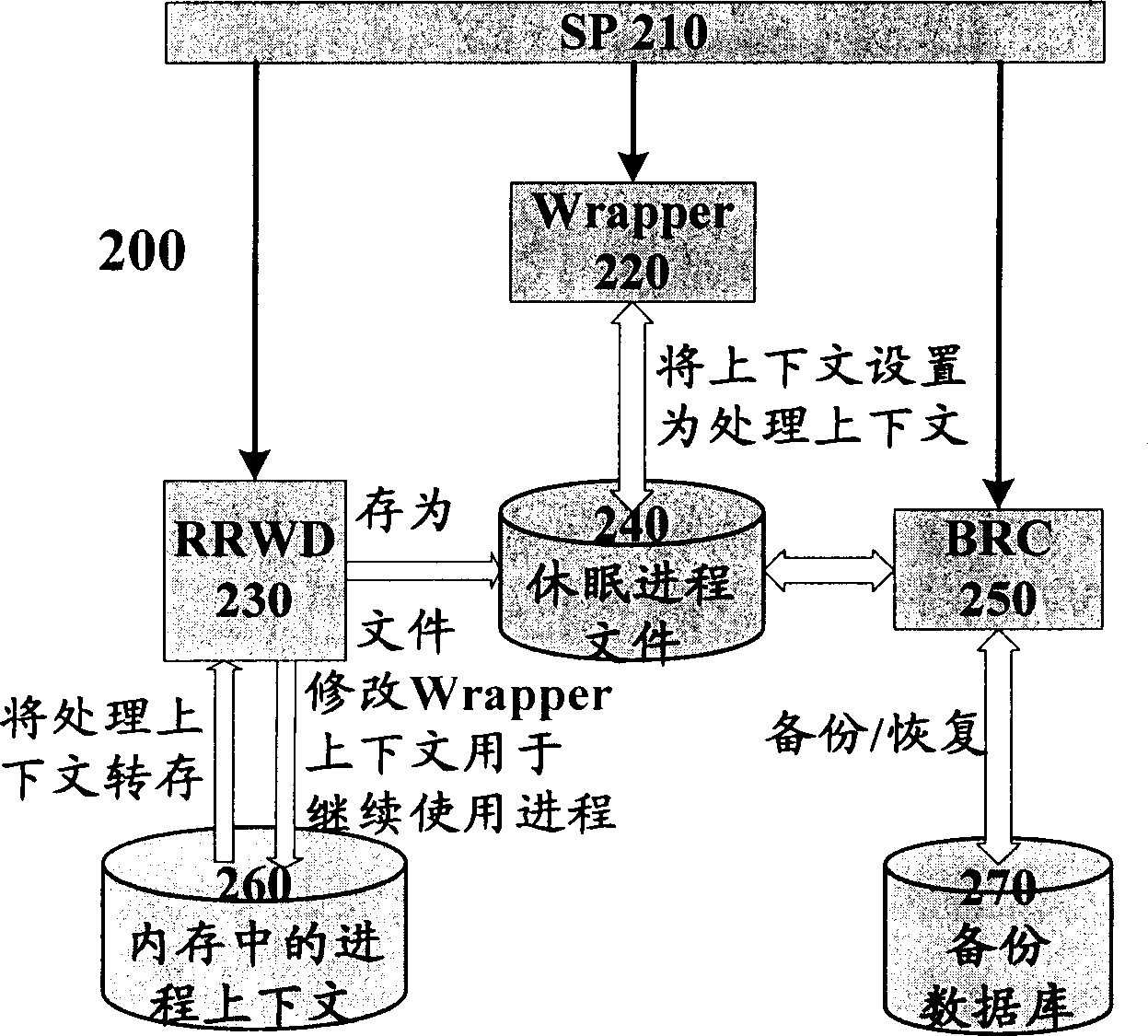
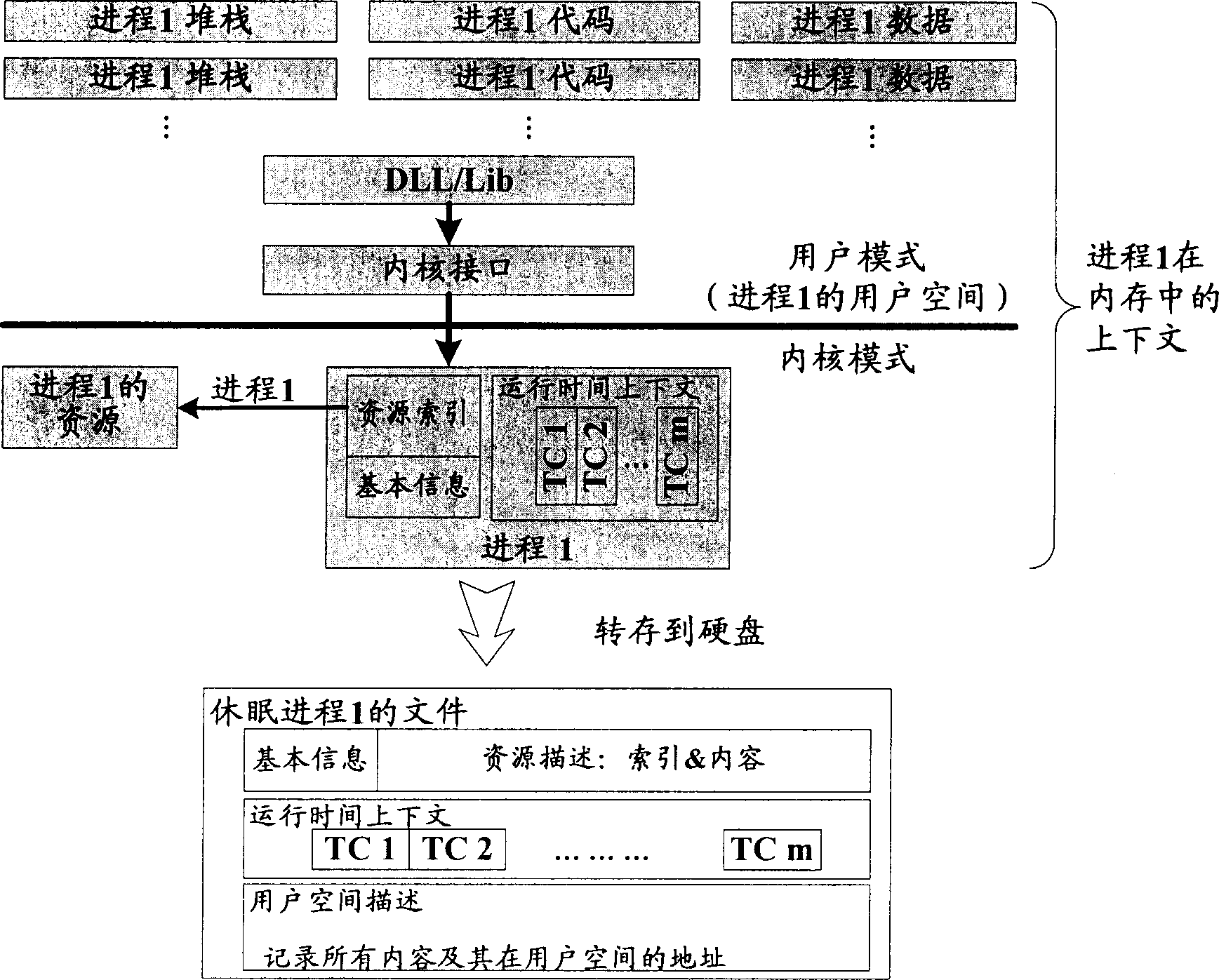
Method and system for implementing thread sleep in computer system
InactiveCN1801096AReduce stepsImprove performanceProgram initiation/switchingSingle processWorking environment
The invention discloses a single process dormant-and-arousing method and system in the computer system, wherein the dormant process comprises the following steps: concealing all process windows; suspending all process line-courses; recording all contexts; loading the dormant process file of context; terminating all process dormant; the arousing process comprises the following steps: structuring a packer similar to the context structure in the dormant process; restoring the dormant context; arousing all line-courses in the dormant process; displaying all windows to use the relative process continually. The invention reduces the operation of switch the applying program and optimizes the system resource, which stores the present working environment automatically and restores the entire environment when the accident occurs in the computer.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
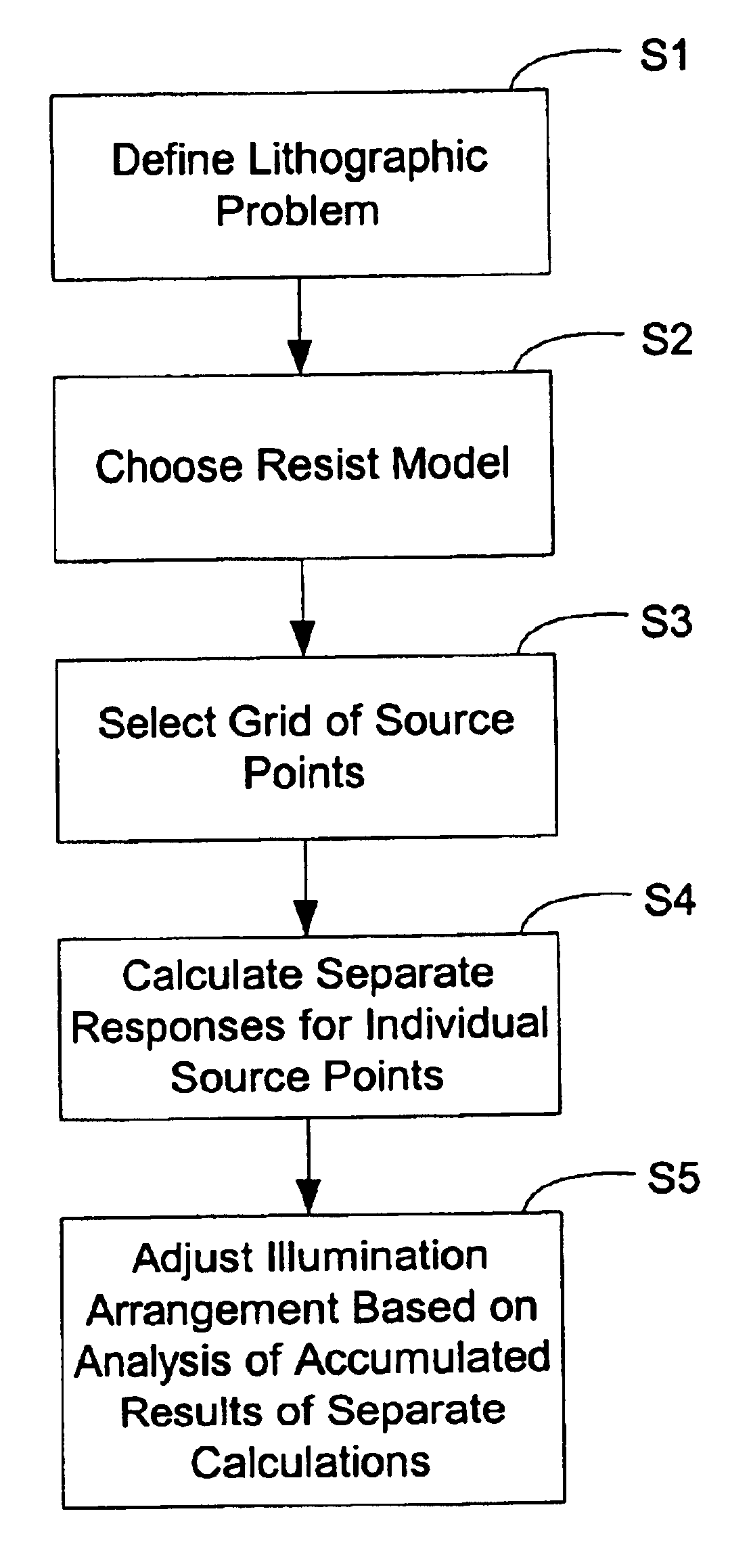
Method for optimizing an illumination source using full resist simulation and process window response metric
InactiveUS6839125B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusInvestigating moving sheetsResistProcess window
A method for optimizing the illumination conditions of a lithographic apparatus by computer simulation using full resist calculation, the lithographic apparatus comprising an illuminator, a projection system, and a mask having a pattern to be printed in a layer of photoresist material formed on a substrate. This method includes defining a lithographic 0problem, which may include a lithographic pattern to be printed on a wafer; choosing a resist model of a resist process to be used to print a pattern in the layer of photoresist material; selecting a grid of source points in a pupil plane of the illuminator; calculating separate responses for individual source points, each of the responses representing a result of a single or series of simulations using the resist model; and adjusting an illumination arrangement based on analysis of accumulated results of the separate calculations.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Printing a mask with maximum possible process window through adjustment of the source distribution
InactiveUS7057709B2Reduce lossesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansLight beamComputational physics
A lithographic mask is illuminated with light from different directions such that intensities of a plurality of incident beams of light provide a largest possible integrated process window defined in terms of an allowed range for defining shapes. Constrained sets of intensity parameters are imposed. A first set of intensity parameters represents maximum possible intensities that can be permitted for overexposed tolerance positions. A second set of intensity parameters represents minimum possible intensities that can be permitted for underexposed tolerance positions. Optimum source intensities of incident beams are defined using a linear program and constraints. The optimum source intensities maximize an integrated range of dose and focal variations without causing printed shapes to depart from the allowed range. Apparatus are detailed and variations are described.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com