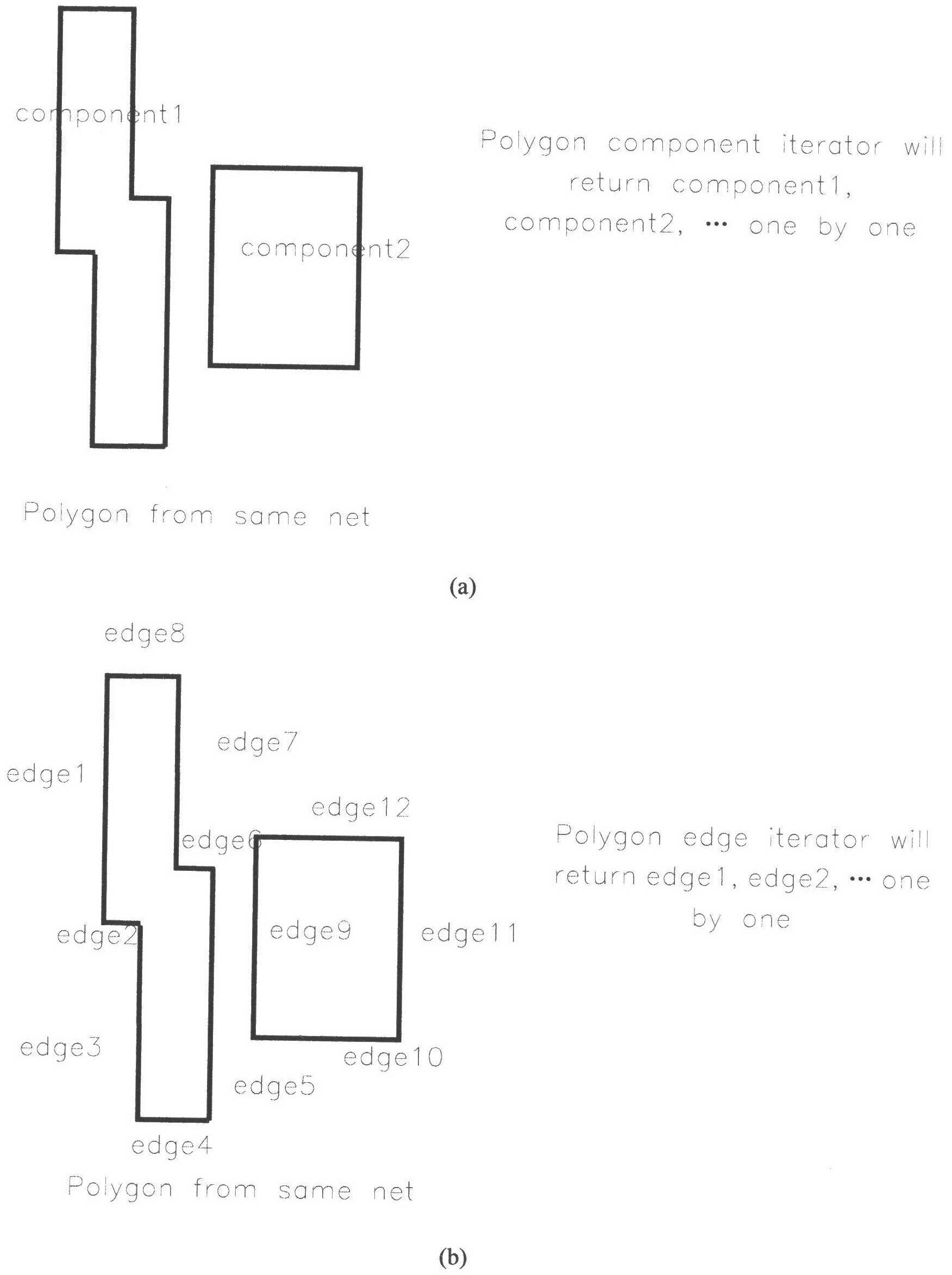
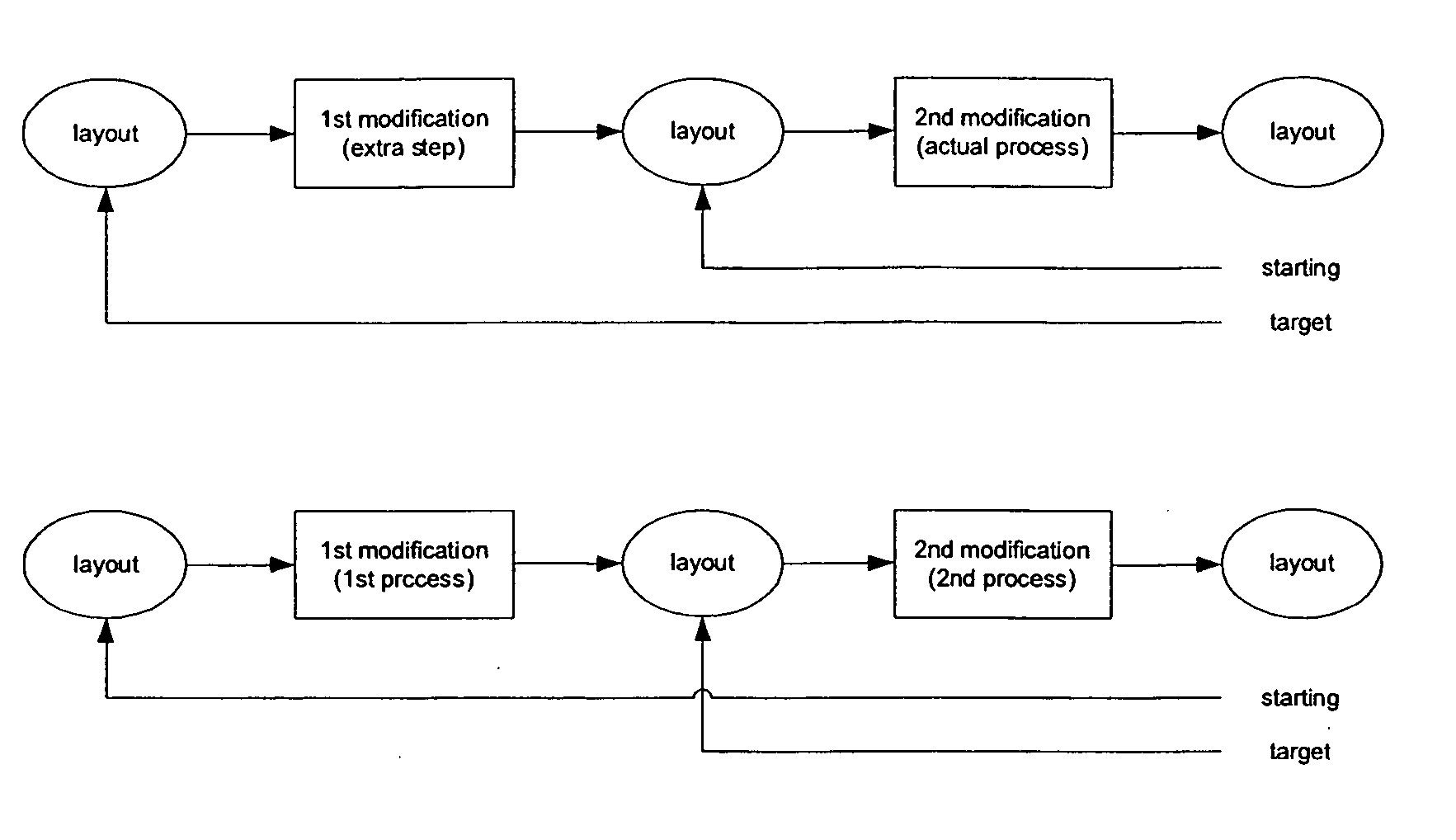
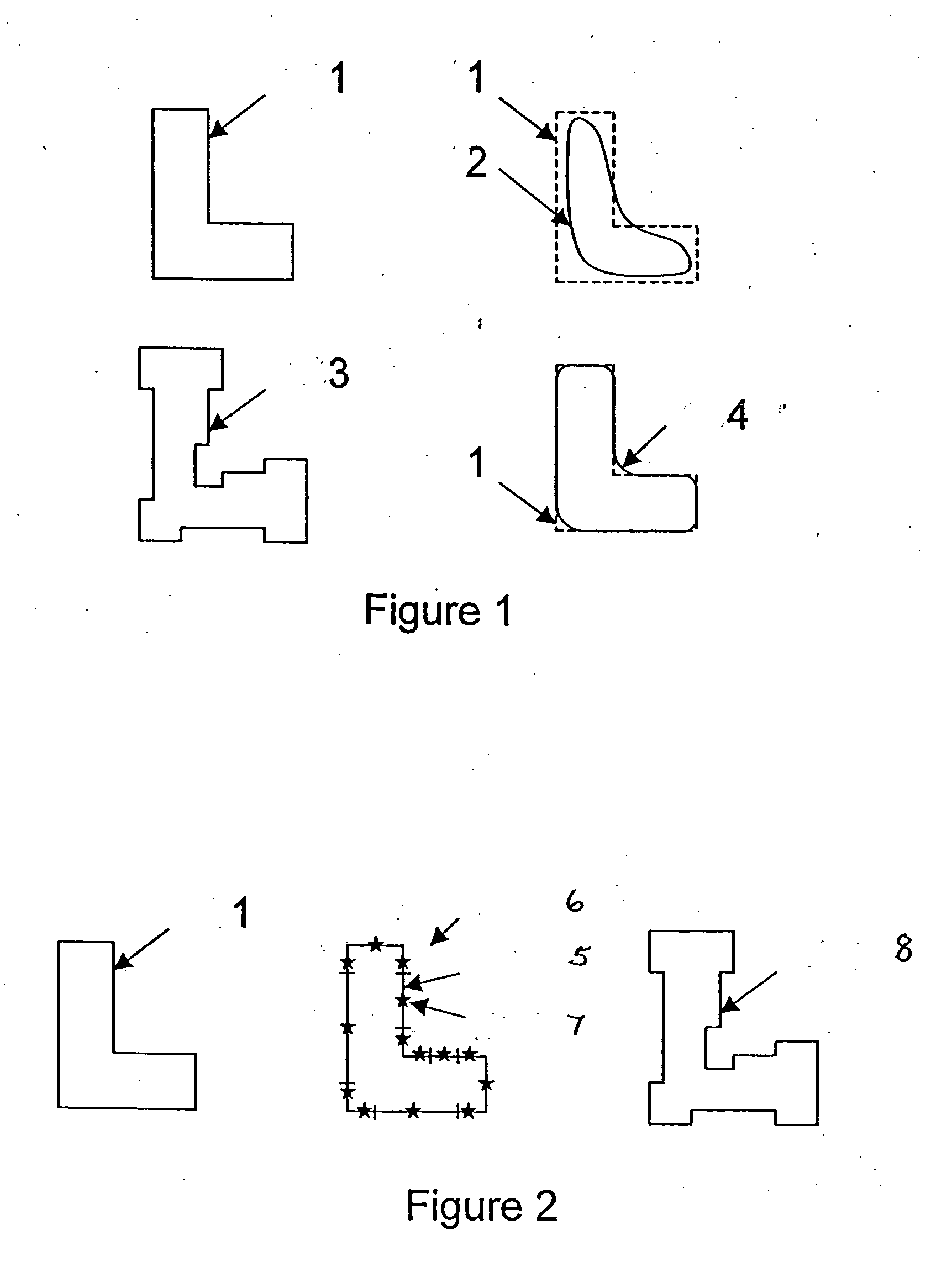
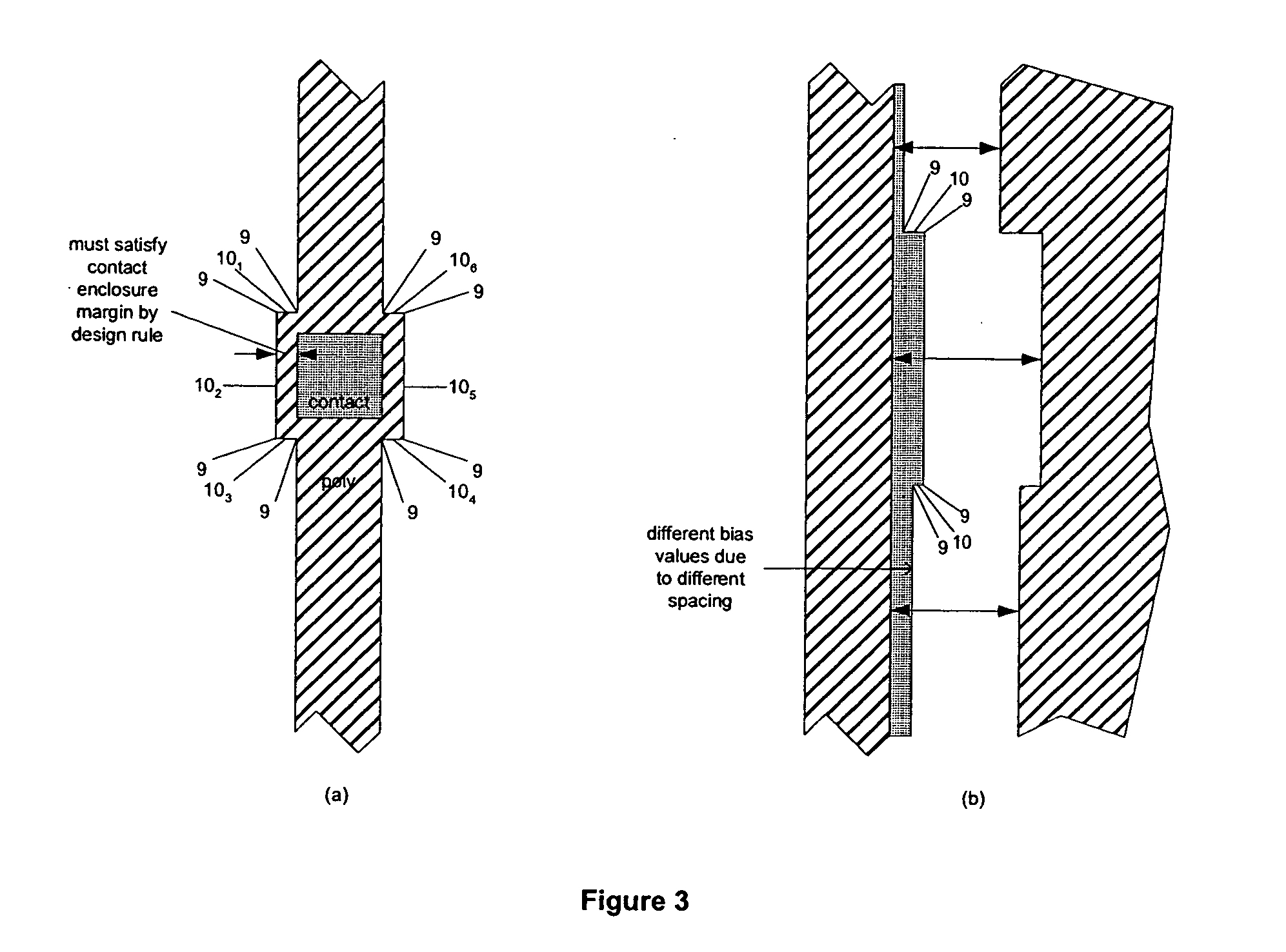
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
207 results about "Design rule checking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
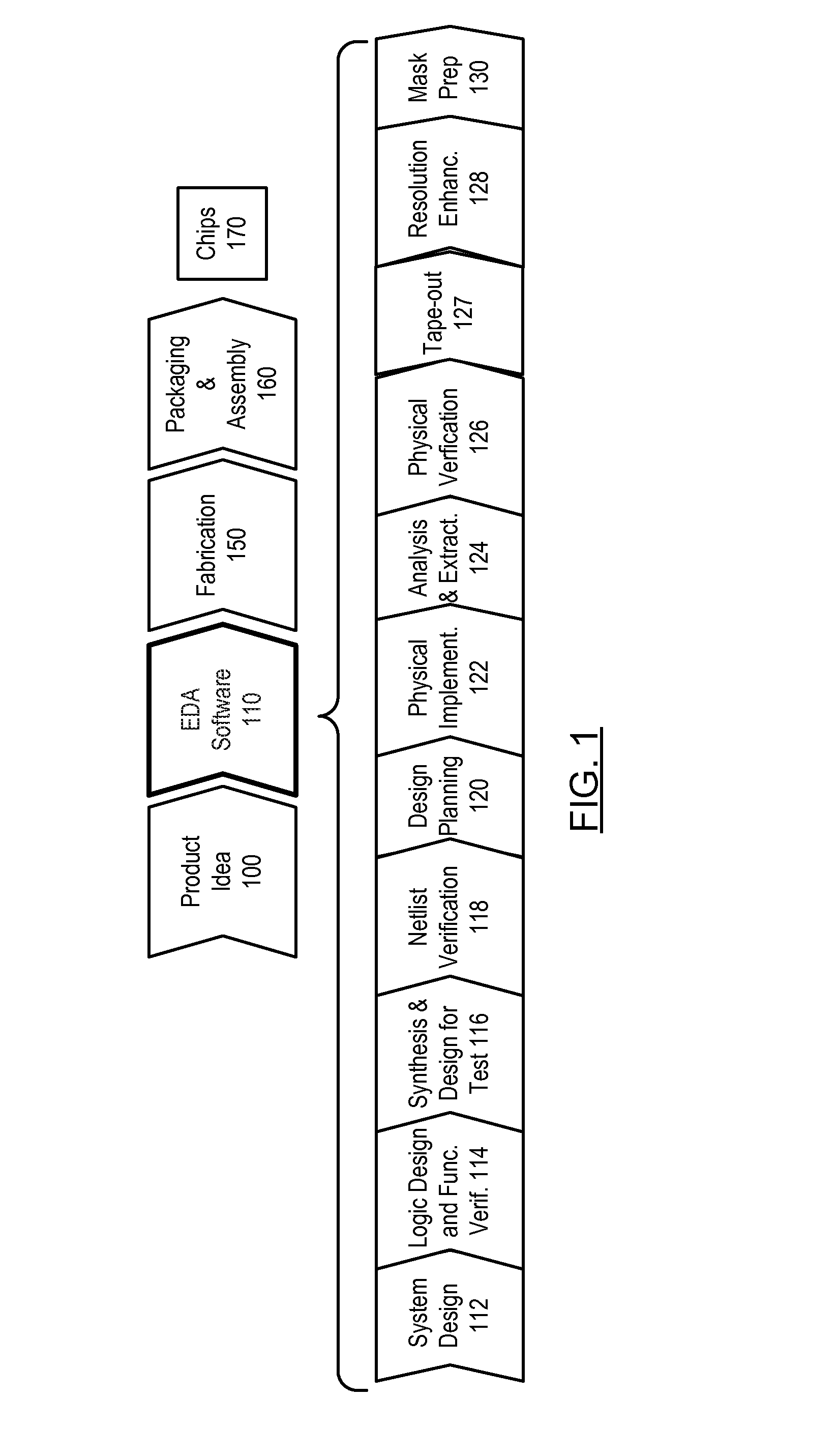
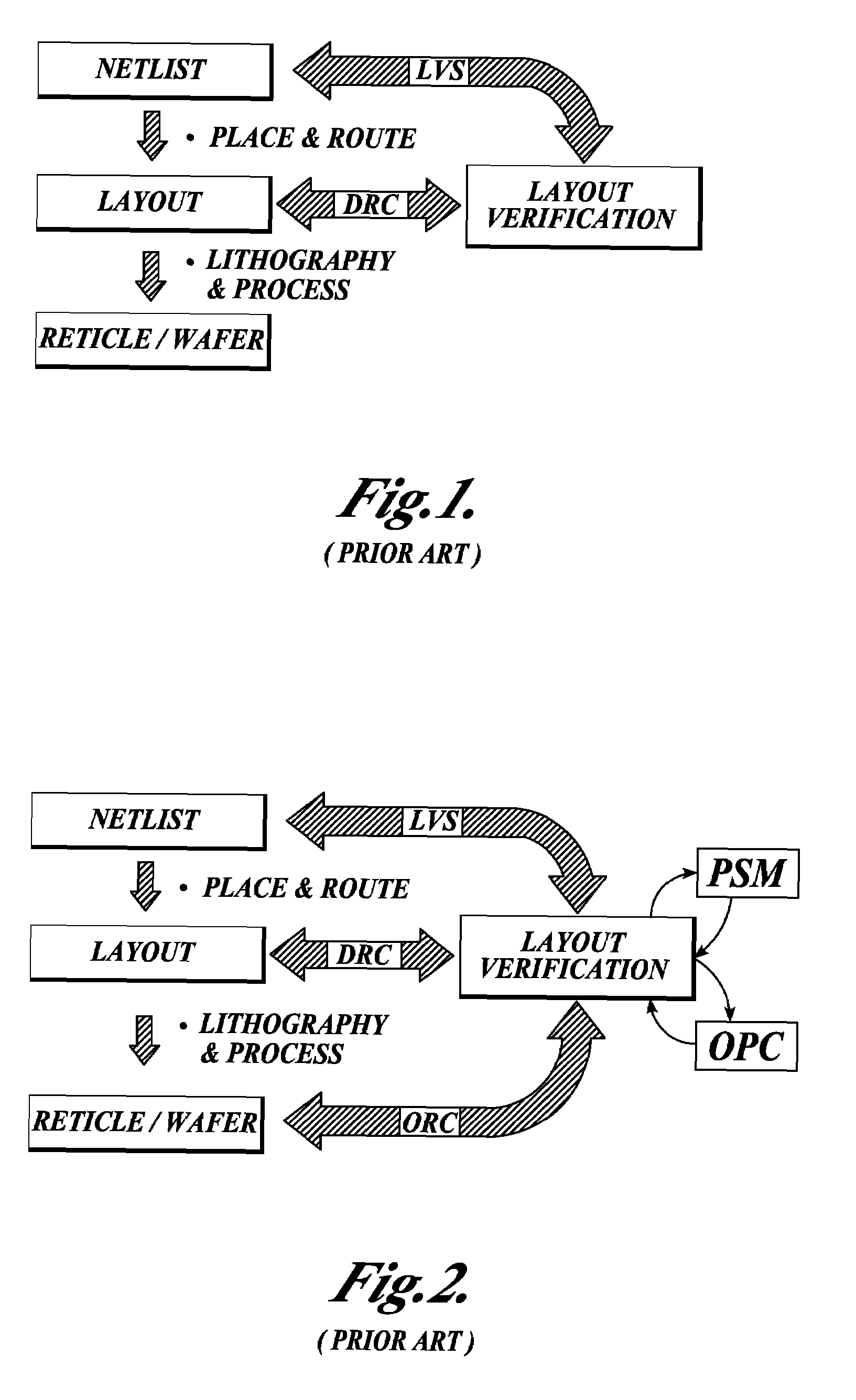
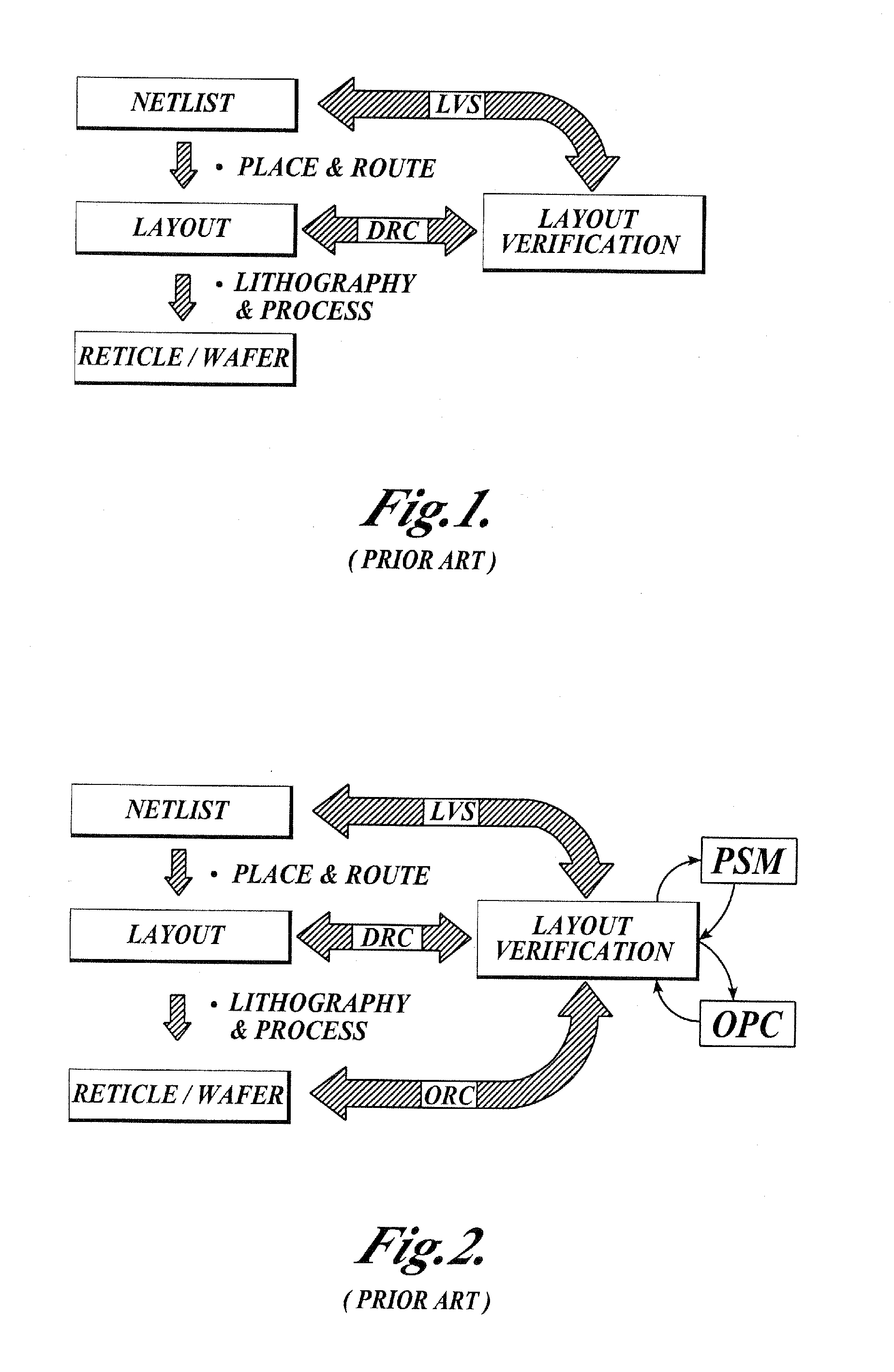
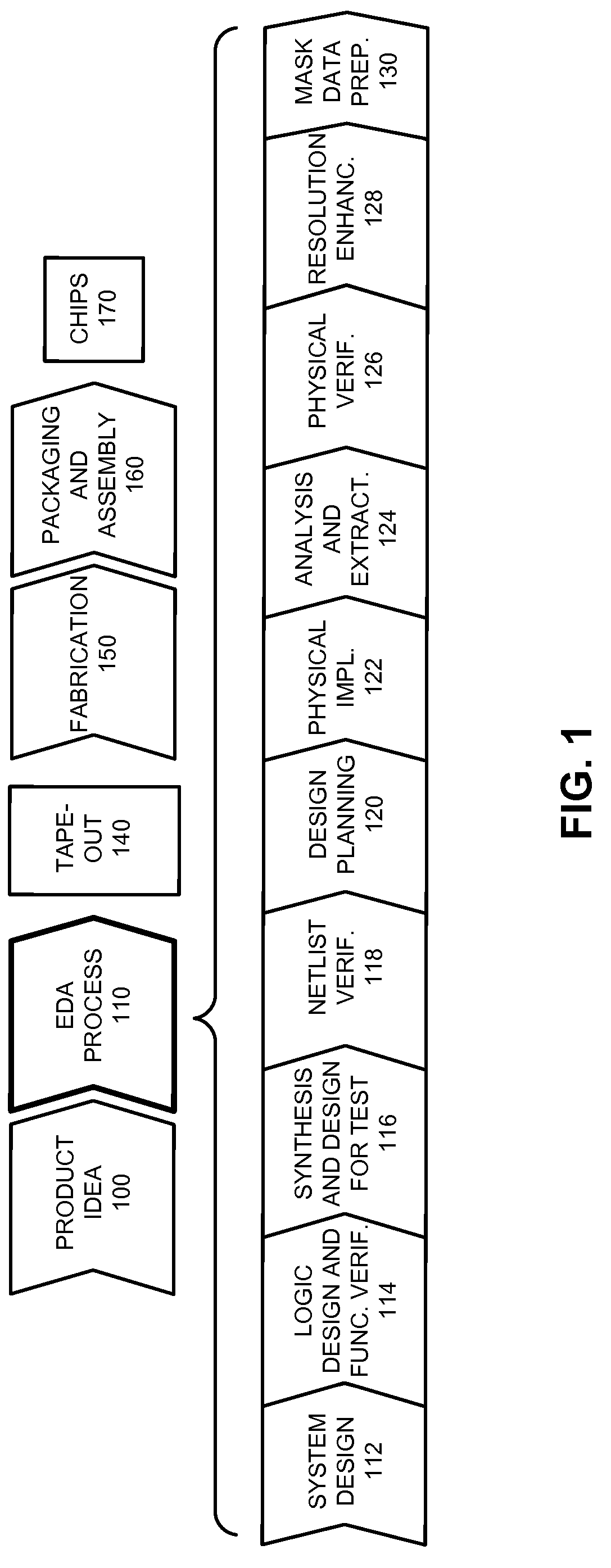
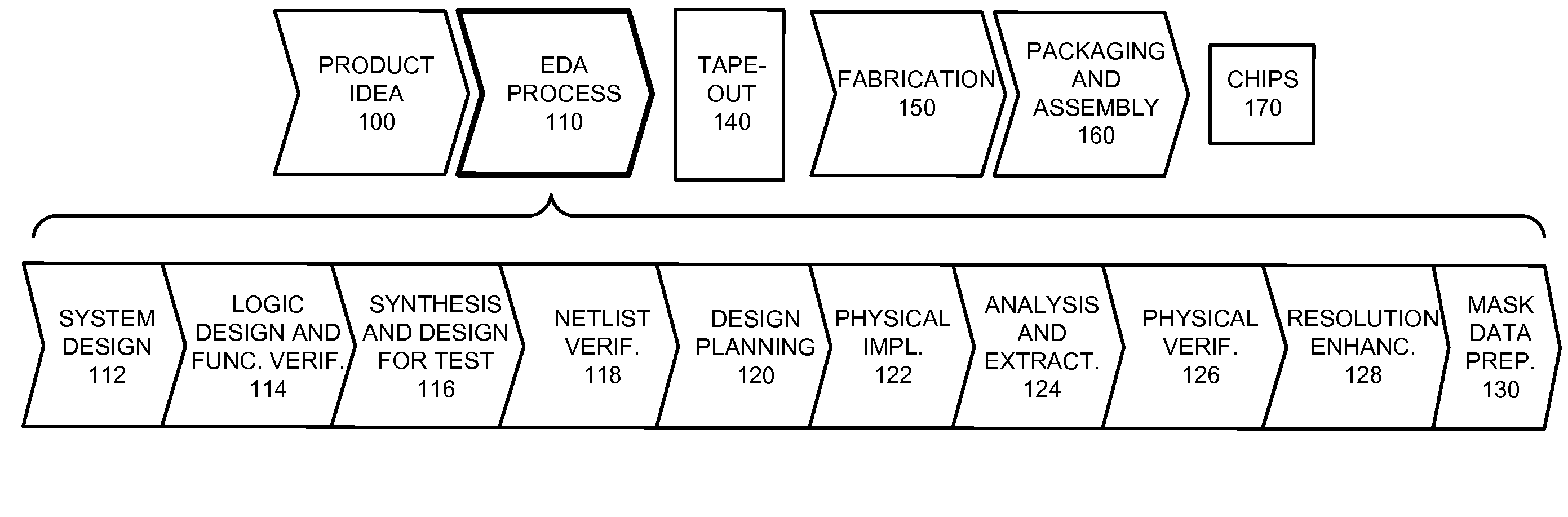
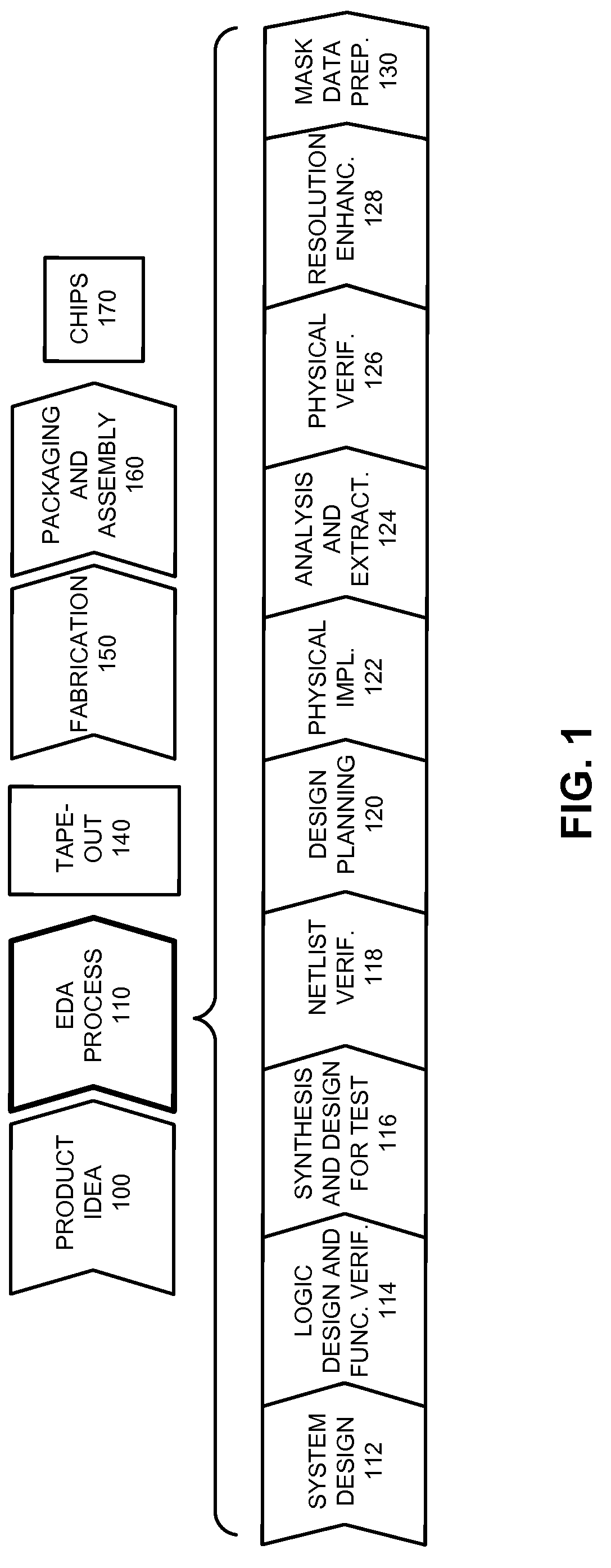
In electronics engineering, a design rule is a geometric constraint imposed on circuit board, semiconductor device, and integrated circuit (IC) designers to ensure their designs function properly, reliably, and can be produced with acceptable yield. Design rules for production are developed by process engineers based on the capability of their processes to realize design intent. Electronic design automation is used extensively to ensure that designers do not violate design rules; a process called design rule checking (DRC). DRC is a major step during physical verification signoff on the design, which also involves LVS (layout versus schematic) checks, XOR checks, ERC (electrical rule check), and antenna checks. The importance of design rules and DRC is greatest for ICs, which have micro- or nano-scale geometries; for advanced processes, some fabs also insist upon the use of more restricted rules to improve yield.
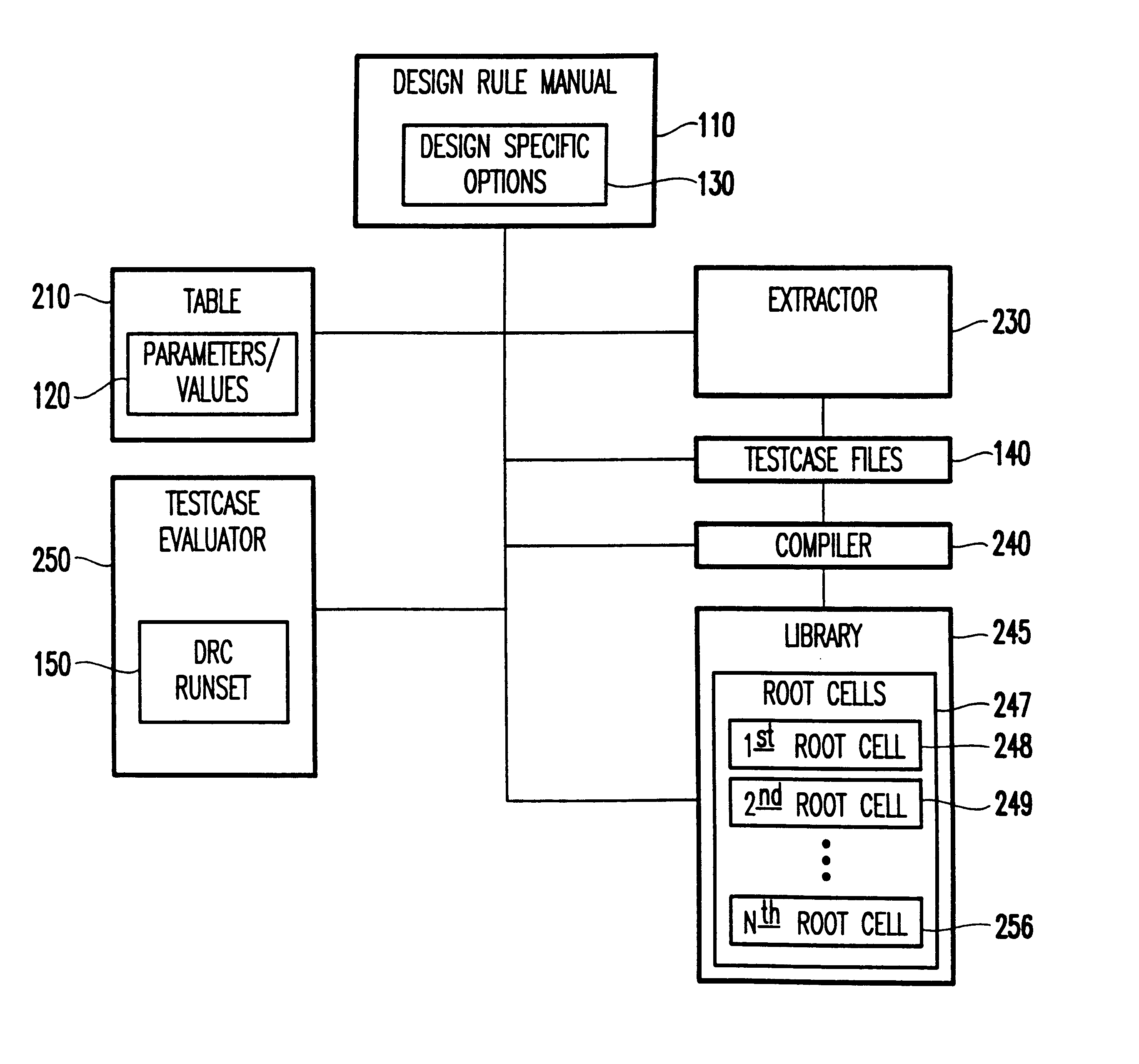
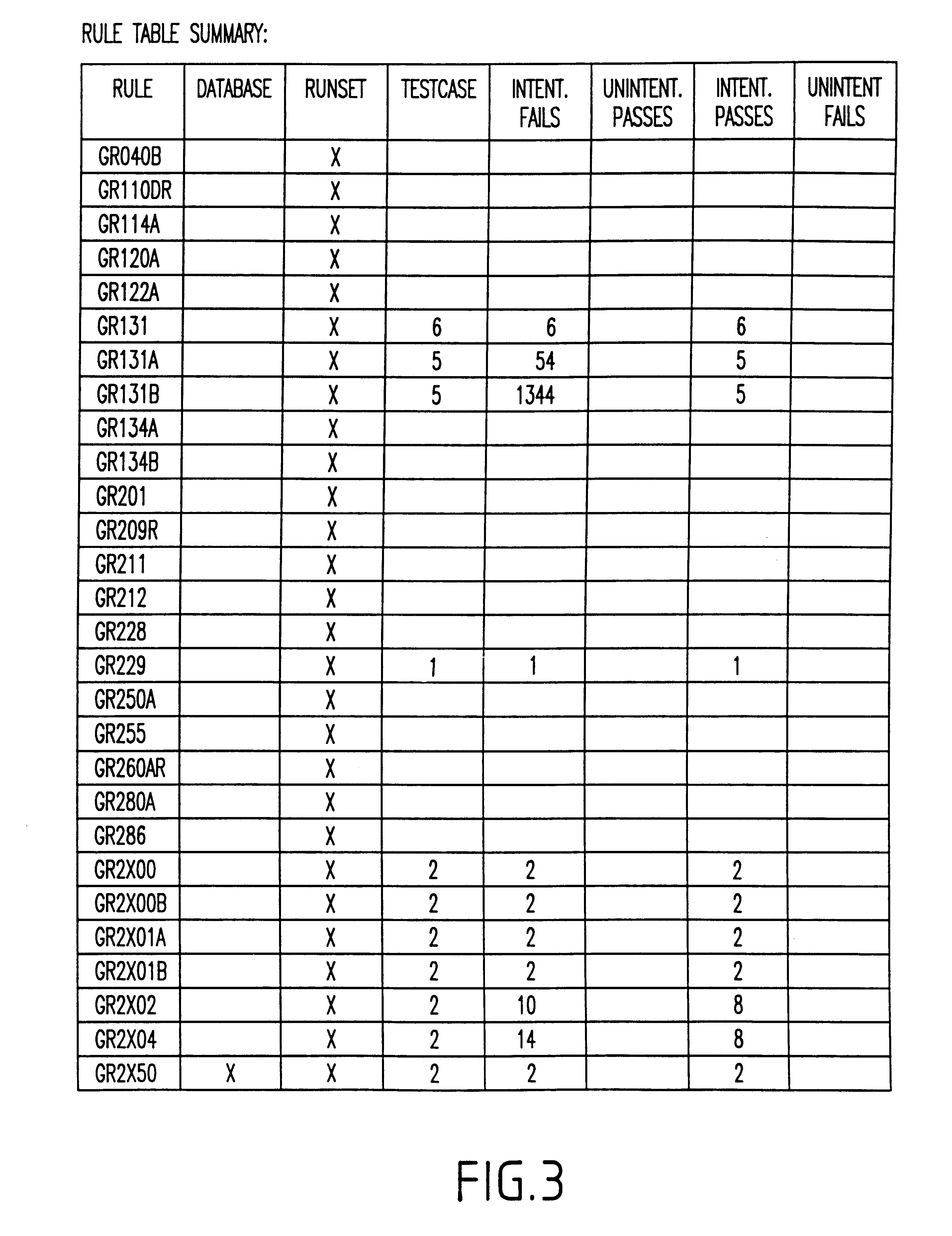
Method for comprehensively verifying design rule checking runsets
InactiveUS6732338B2Extraction of informationComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureDesign rule checking
A system and method for automatically creating testcases for design rule checking comprises first creating a table with a design rule number, a description, and the values from a design rule manual. Next, any design specific options are derived that affect the flow of the design rule checking, including back end of the line stack options. Then, the design rule values and any design specific options (including back end of the line stack options) are extracted into testcases. Next, the testcases are organized such that there is one library with a plurality of root cells, further comprising one root cell for checking all rules pertaining to the front end of the line, and another root cell for checking design specific options including back end of the line stack options. Finally, the DRC runset is run against the testcases to determine if the DRC runset provides for design rule checking.
Owner:IBM CORP
Qualifying patterns, patterning processes, or patterning apparatus in the fabrication of microlithographic patterns
InactiveUS6902855B2MaximizeIncrease catch ratePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess windowDesign rule checking
The invention is a method of determining the presence of an anomaly in qualifying a pattern, patterning process, or patterning apparatus used in the fabrication of microlithographic patterns. A preferred implementation of the method qualifies incoming reticles and process conditions on test wafers to maximize the available usable process window for a given reticle exposure tool combination. Practicing this method on test wafers enables the identification of spatial areas where a process will fail first and candidate regions for carrying out defect inspection and metrology. Other preferred implementations of the method qualify masks, reticles, or other patterns characterized by data bases on which are stored image data acquired by practice of aerial image measurement system (AIMS) or design rule checking (DRC) techniques.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Approach for routing an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7065729B1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsImage resolution
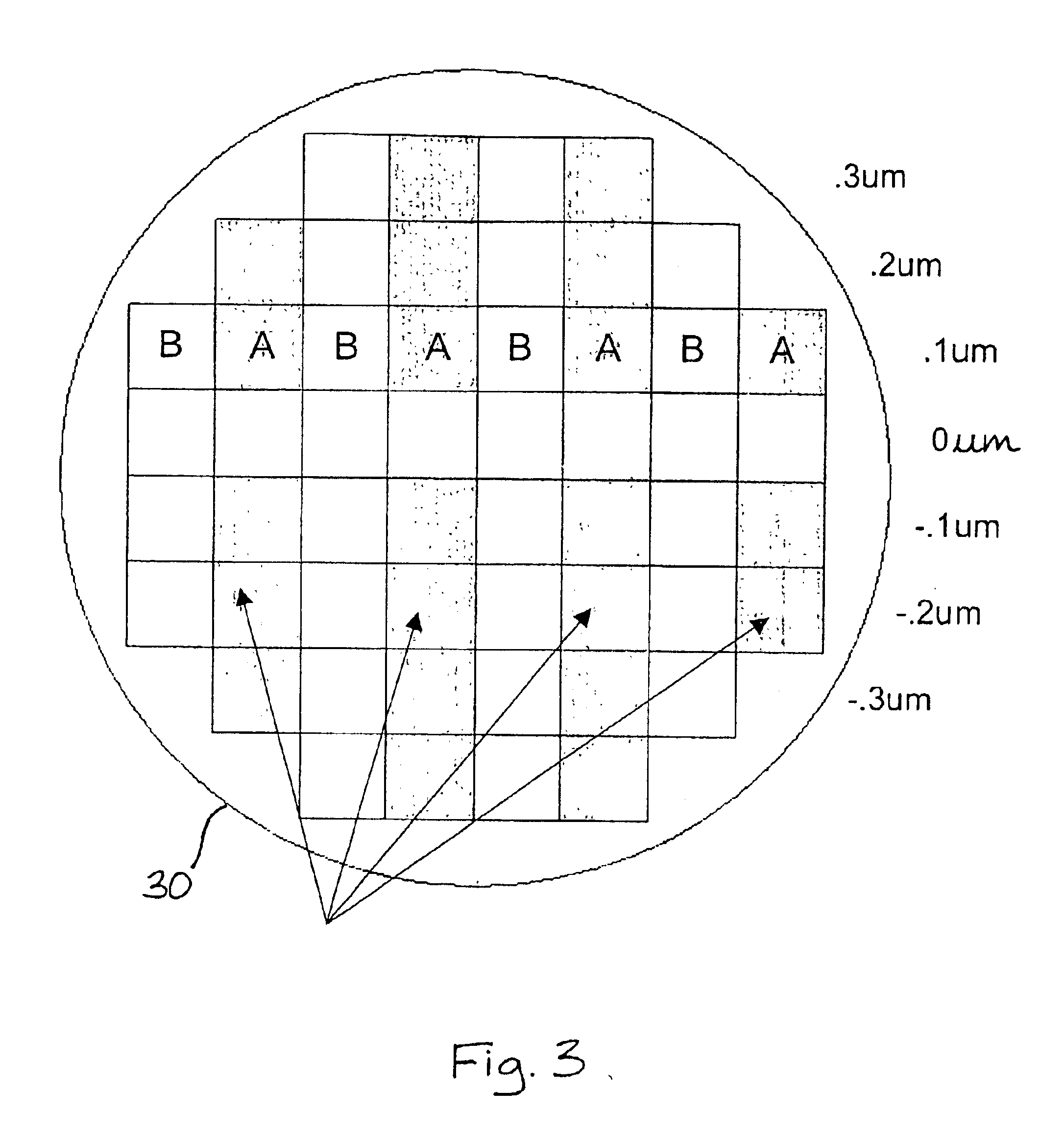
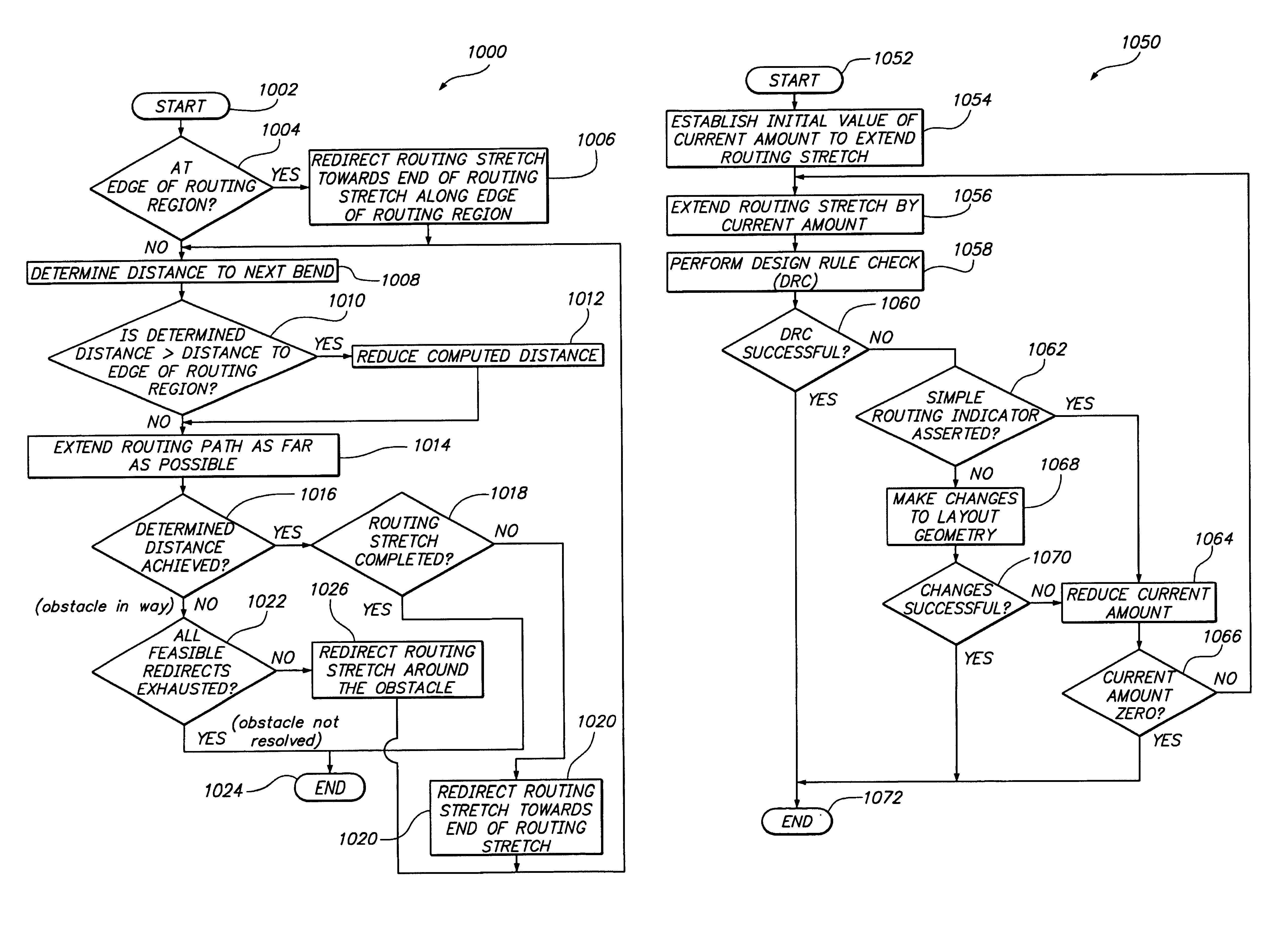
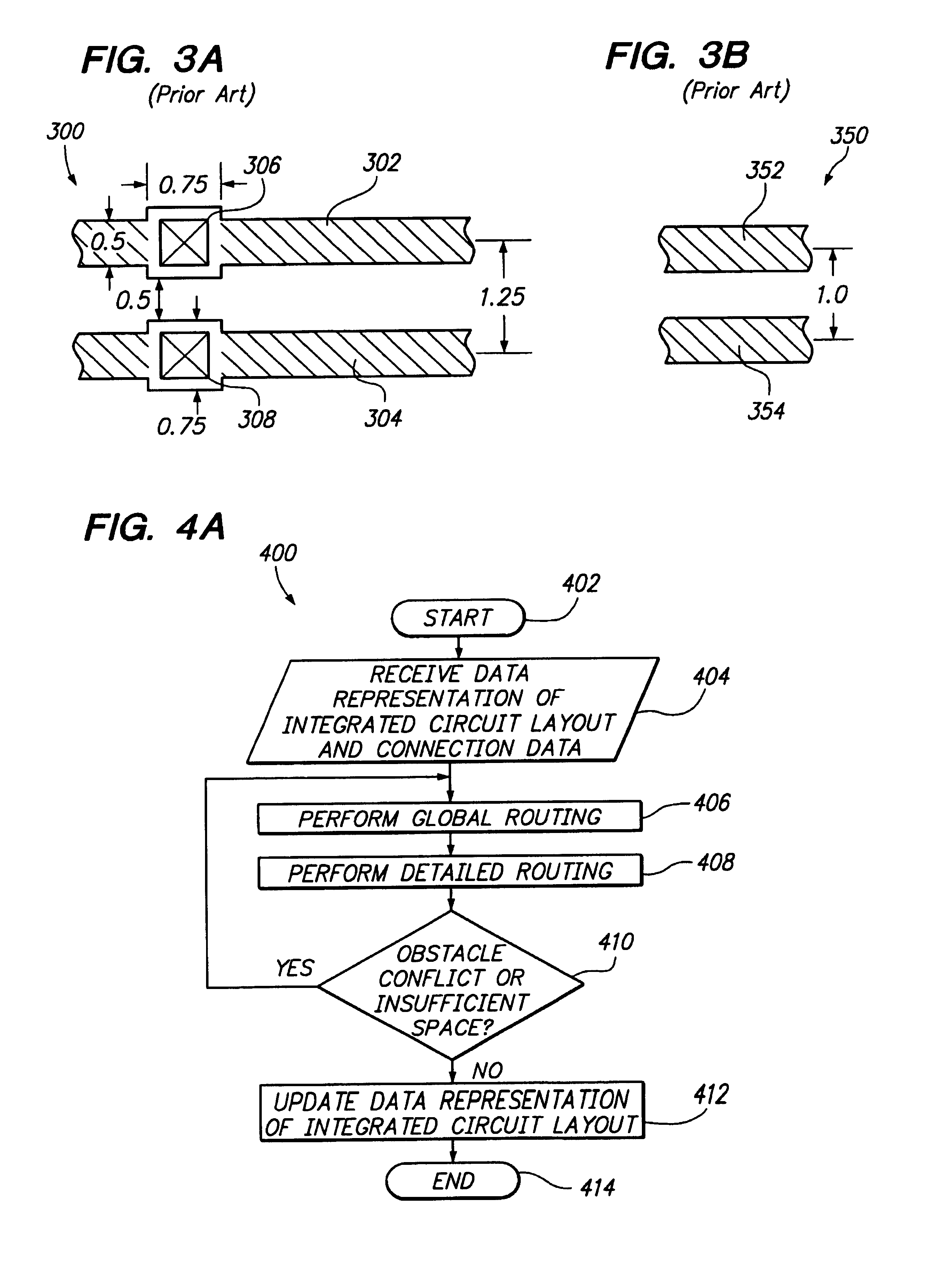
A computer-implemented approach for routing an integrated circuit using non-orthogonal routing is accomplished during two phases: a global routing phase and a detailed routing phase. During global routing, routing indicators, in the form of hint polygons, are added to the integrated circuit layout and strategy lists, that include bias directions and straying limits, are generated for the new wires to be added. The hint polygons and strategy lists are used during detailed routing to aid in placing the new wires. If obstacle conflicts or insufficient space problems prevent the detailed routing of a new wire, then an obstacle resolution portion of global routing is used to resolve the obstacle conflict and / or provide additional space in the integrated circuit layout to route the new wires. Obstacle resolution includes, without limitation, moving or changing layout geometry, changing or add hint polygons, changing the routing strategy by changing the bias direction and / or adjusting straying limits, inserting one or more layer changes, instructing the detailed router to backup and insert a bend, ripping-up and rerouting one or more wires, or routing the wire from the destination connection point. Also, a tight routing approach may be employed to accommodate constructing routing paths in tight layout areas. Object specific design rule checks are employed to increase routing flexibility optimize routing performance. “On-the-fly” design rule checks are performed on portions of routing paths as the routing paths are being constructed.
Owner:CHAPMAN DAVID C
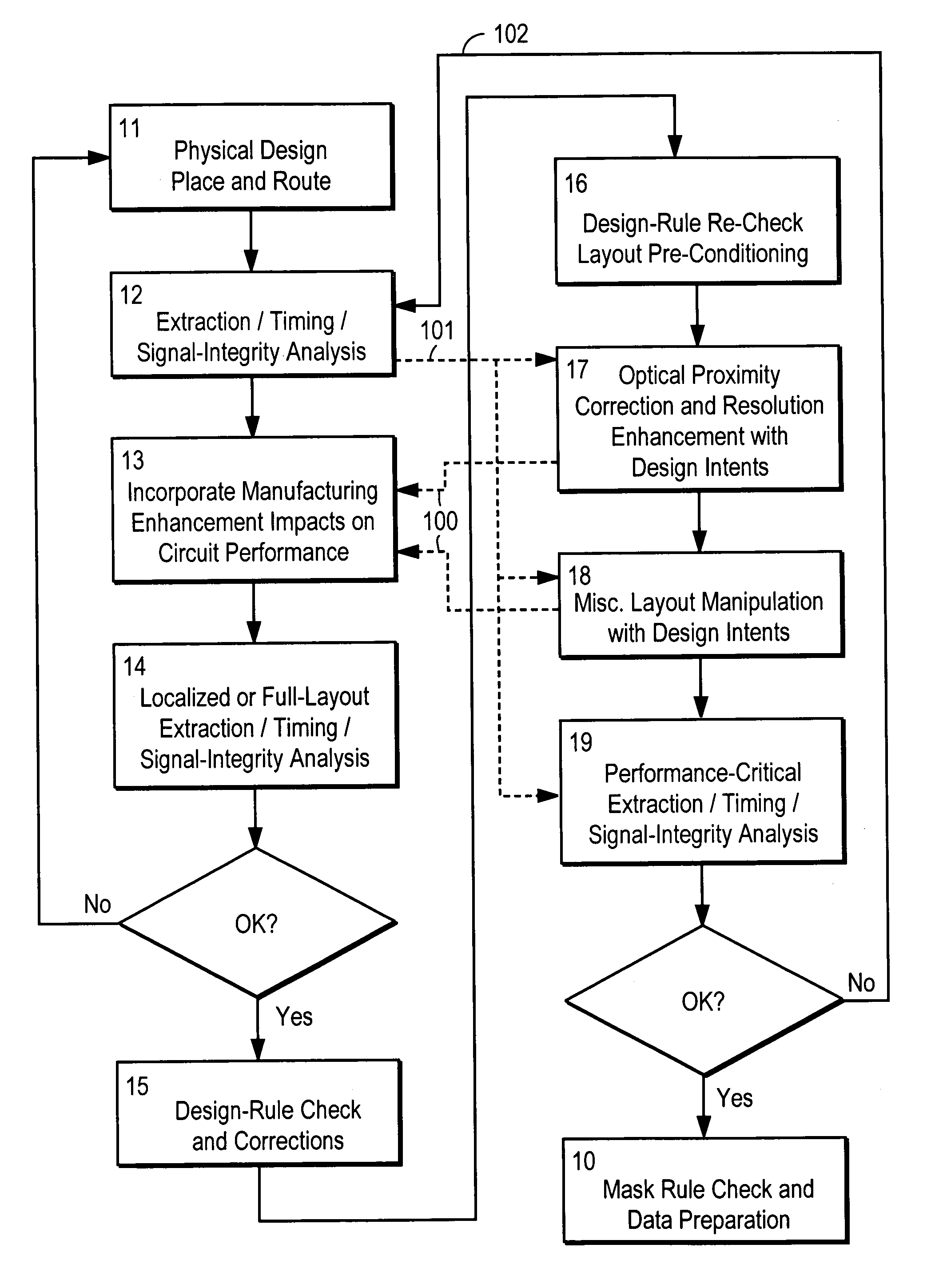
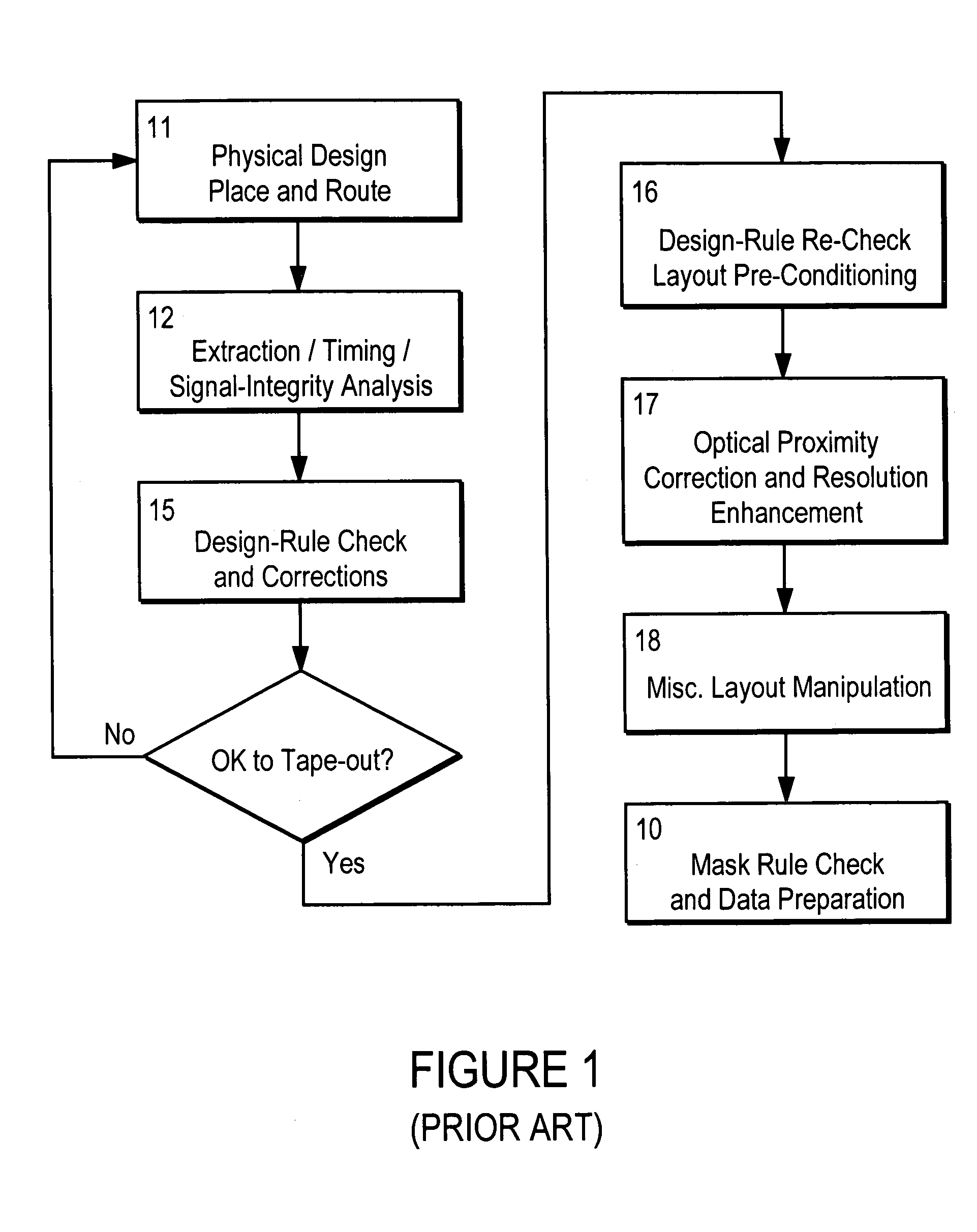
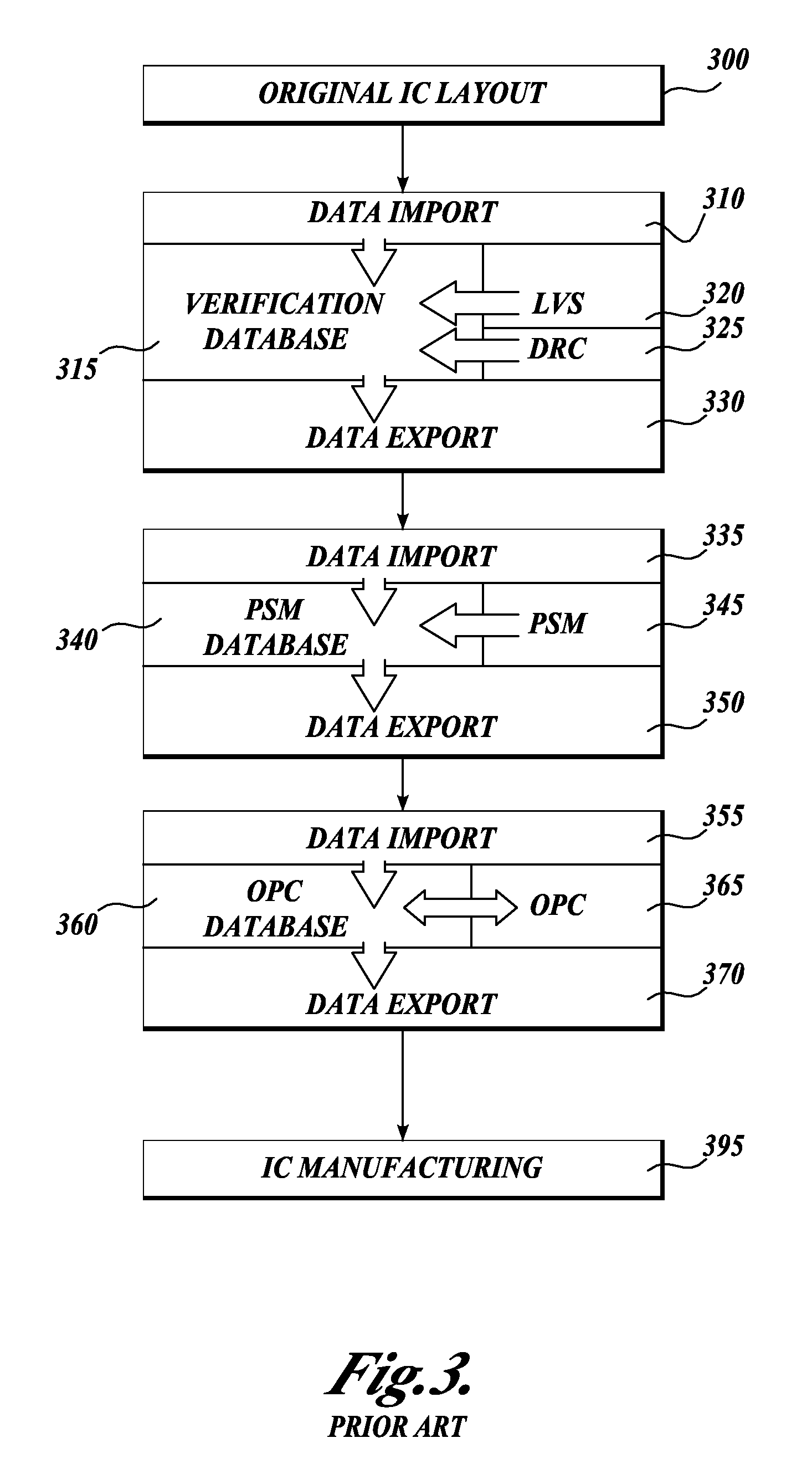
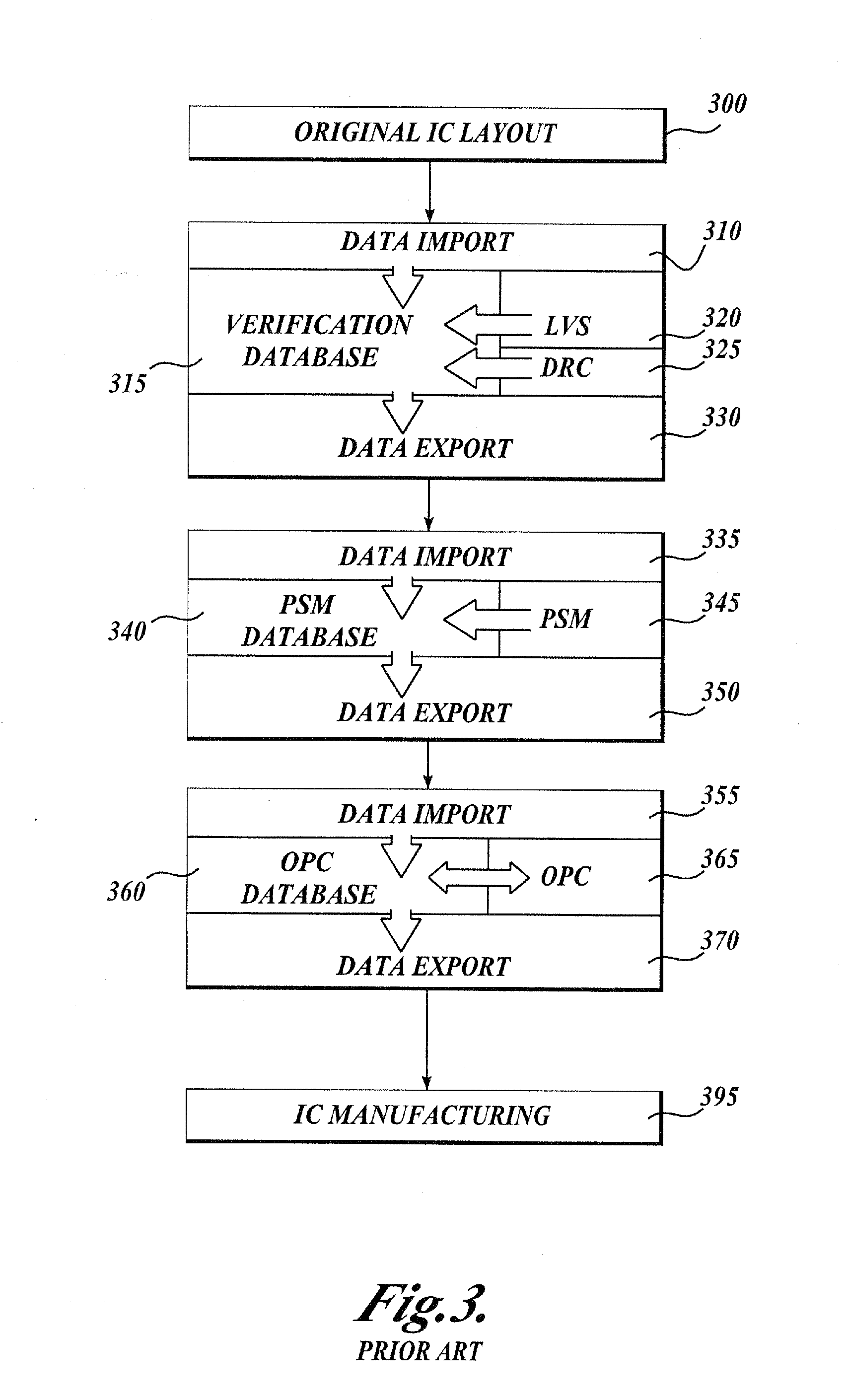
Method and platform for integrated physical verifications and manufacturing enhancements
InactiveUS20050044514A1High storageHigh memoryDigital computer detailsComputer aided designPhysical verificationEngineering
An automated design for manufacturability platform which provides integrated physical verification and manufacturing enhancement operations. The platform uses an efficient data structure capable of handling and manipulating both layout circuit and geometry characteristics, which permits a wide range of operations such as timing analysis, design-rule checking and optical proximity corrections on a single platform. This feature eliminates the need to translate layout representations between various tools without the requirement of using a common database. Moreover, the platform's common user interface enables encapsulated information exchange between the design and the manufacturing teams, permiting early consideration of manufacturing distortion or enhancement impact on circuit performance.
Owner:RPX CORP
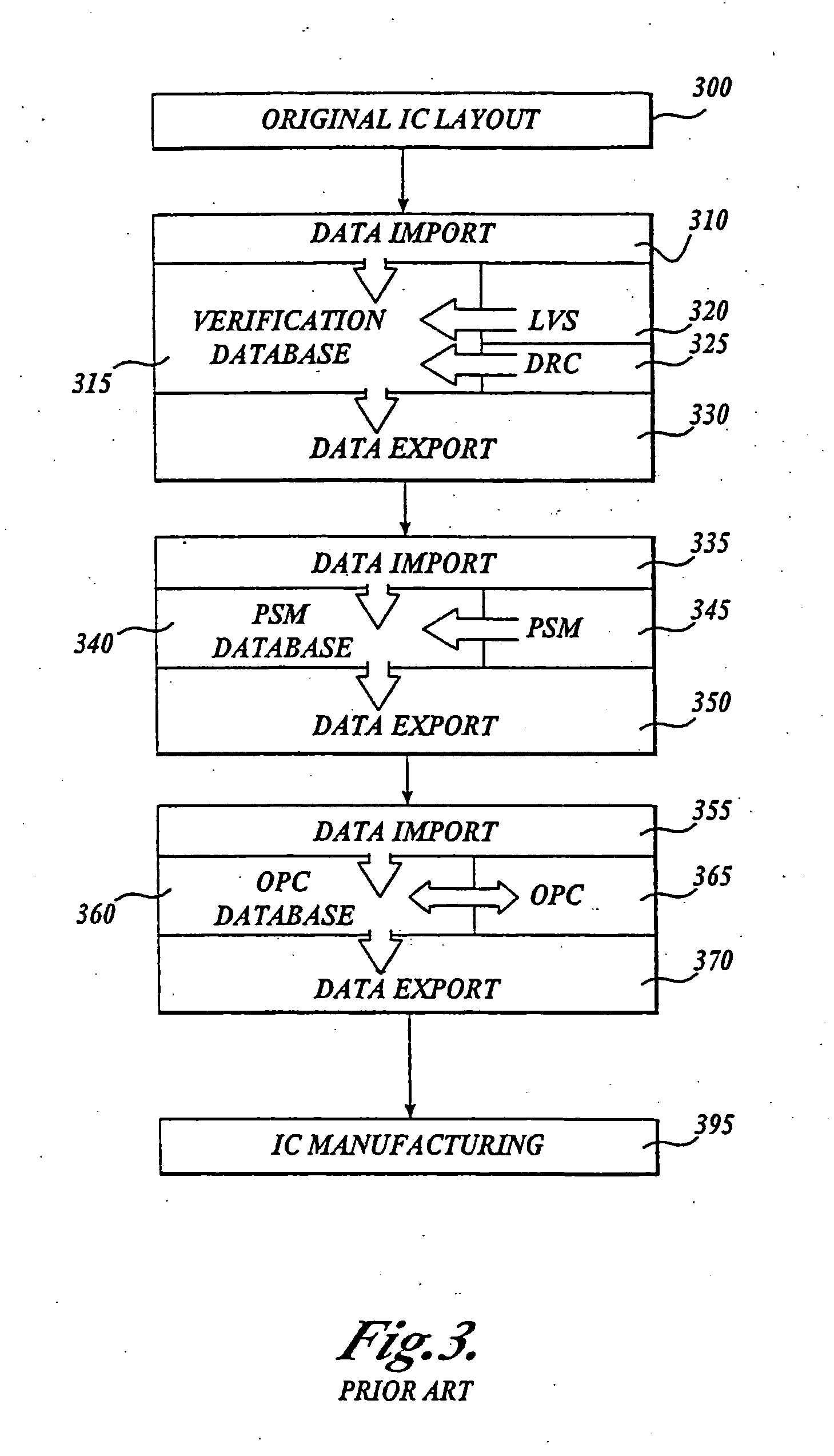
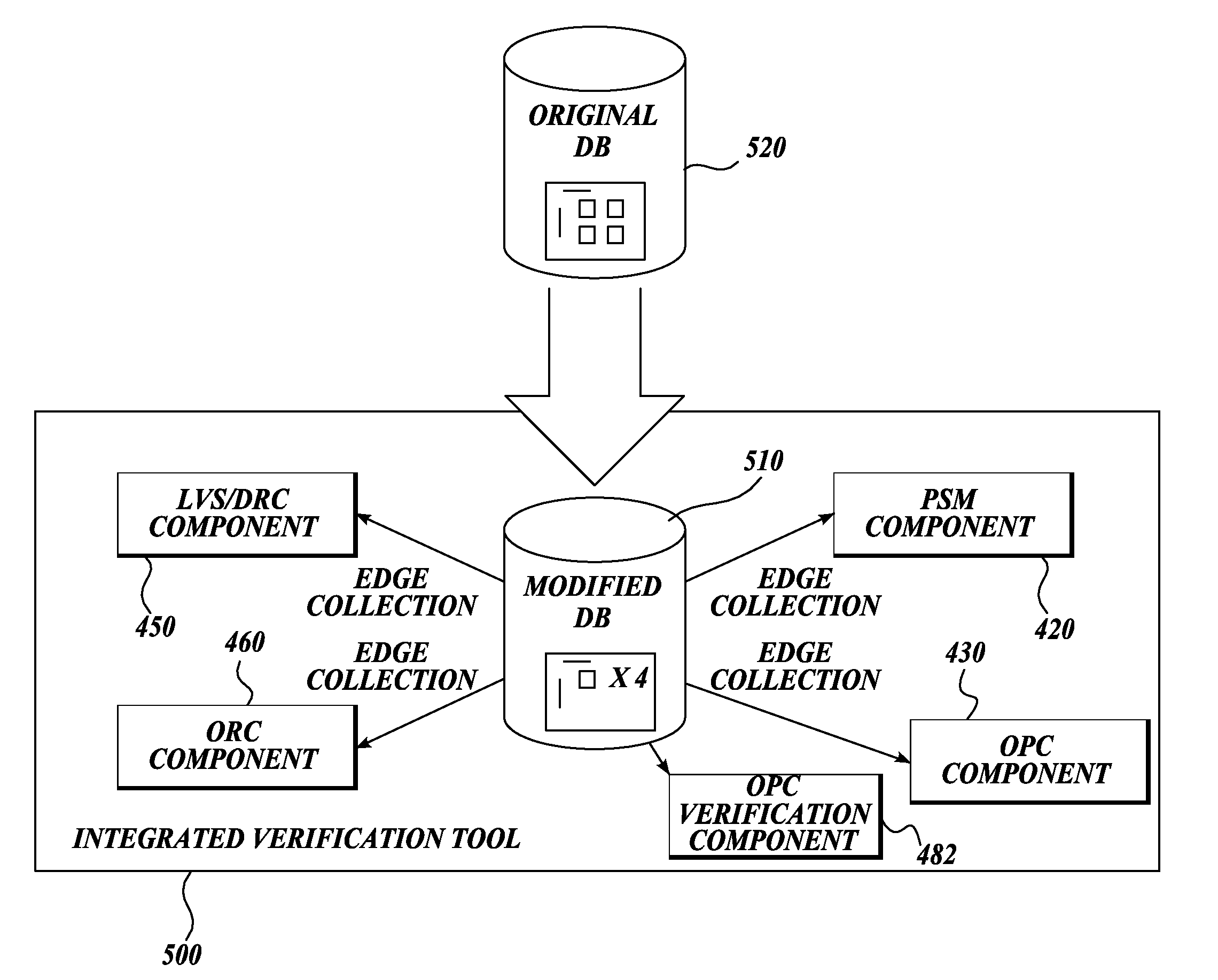
Integrated verification and manufacturability tool
InactiveUS7017141B2Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designComputer architectureInter layer
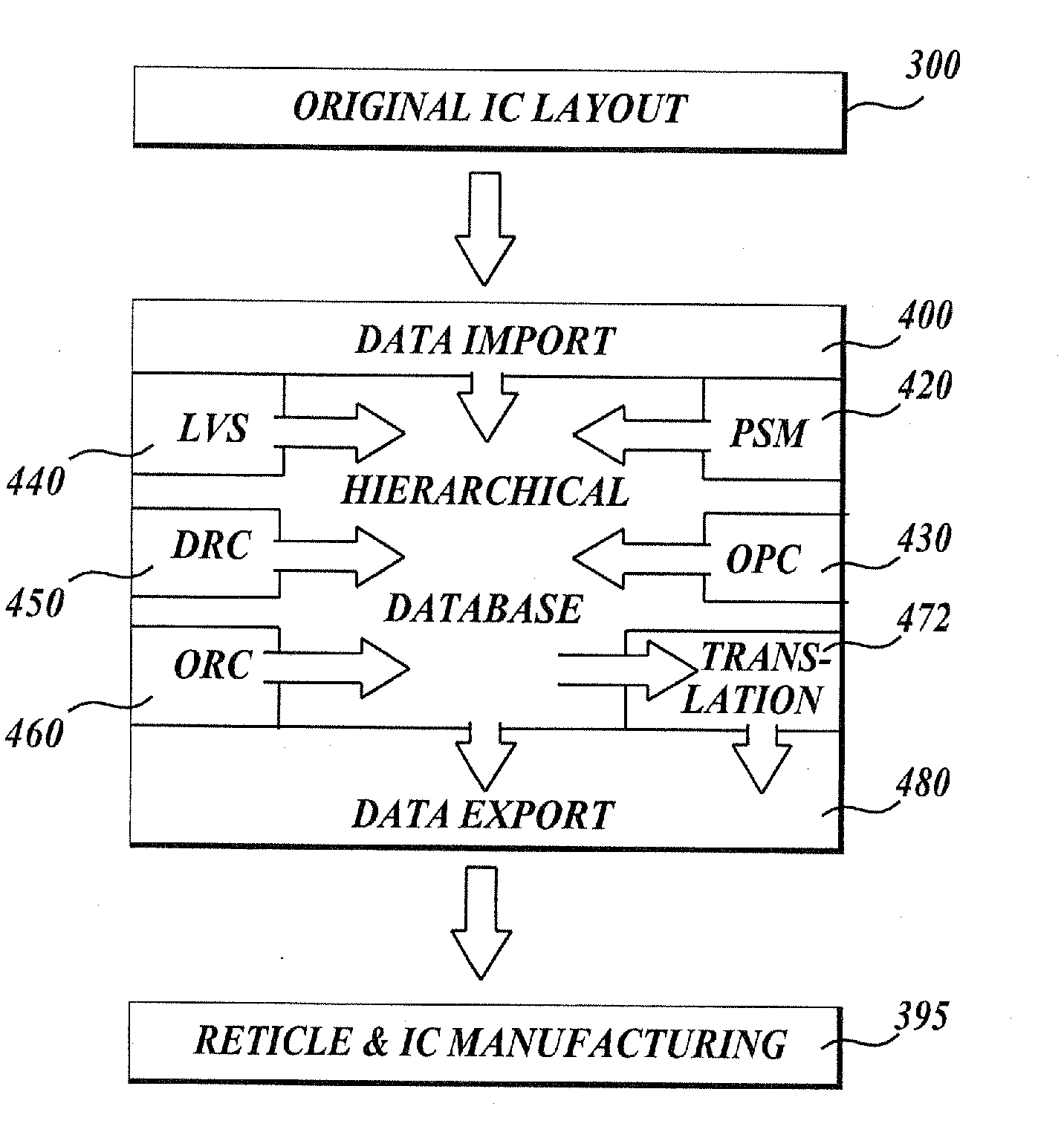
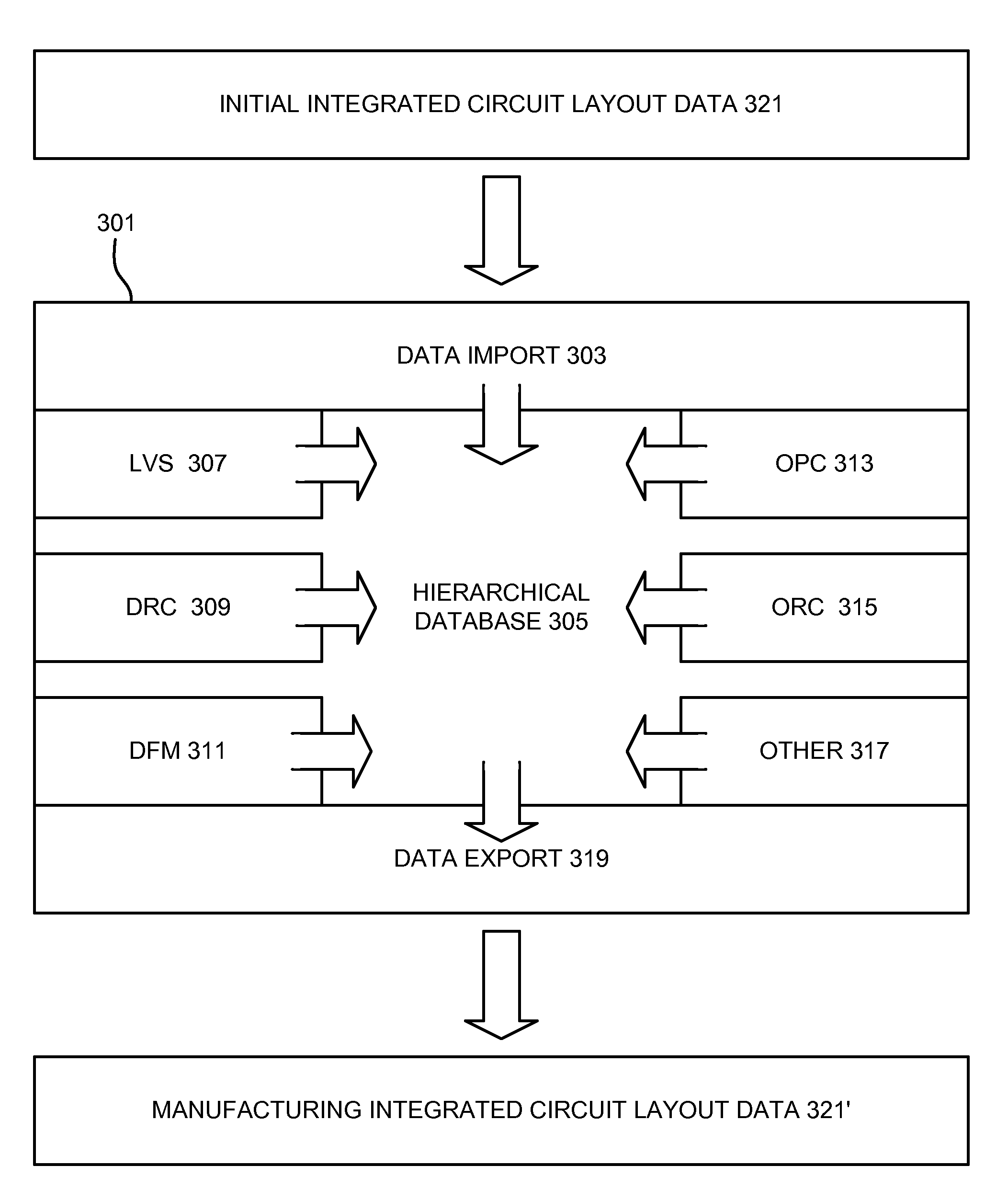
An integrated verification and manufacturability tool provides more efficient verification of integrated device designs than verification using several different verification tools. The integrated verification and manufacturability includes a hierarchical database to store shared design data accessed by multiple verification tool components (e.g., layout versus schematic, design rule check, optical process correction, phase shift mask assignment and machine language conversion). The hierarchical database includes representations of one or more additional, or intermediate layer structures that are created and used by the verification tool components for operations performed on the design being verified. Use of a single hierarchical database having shared data for access and use by multiple verification components streamlines the verification process, which provides an improved verification tool.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
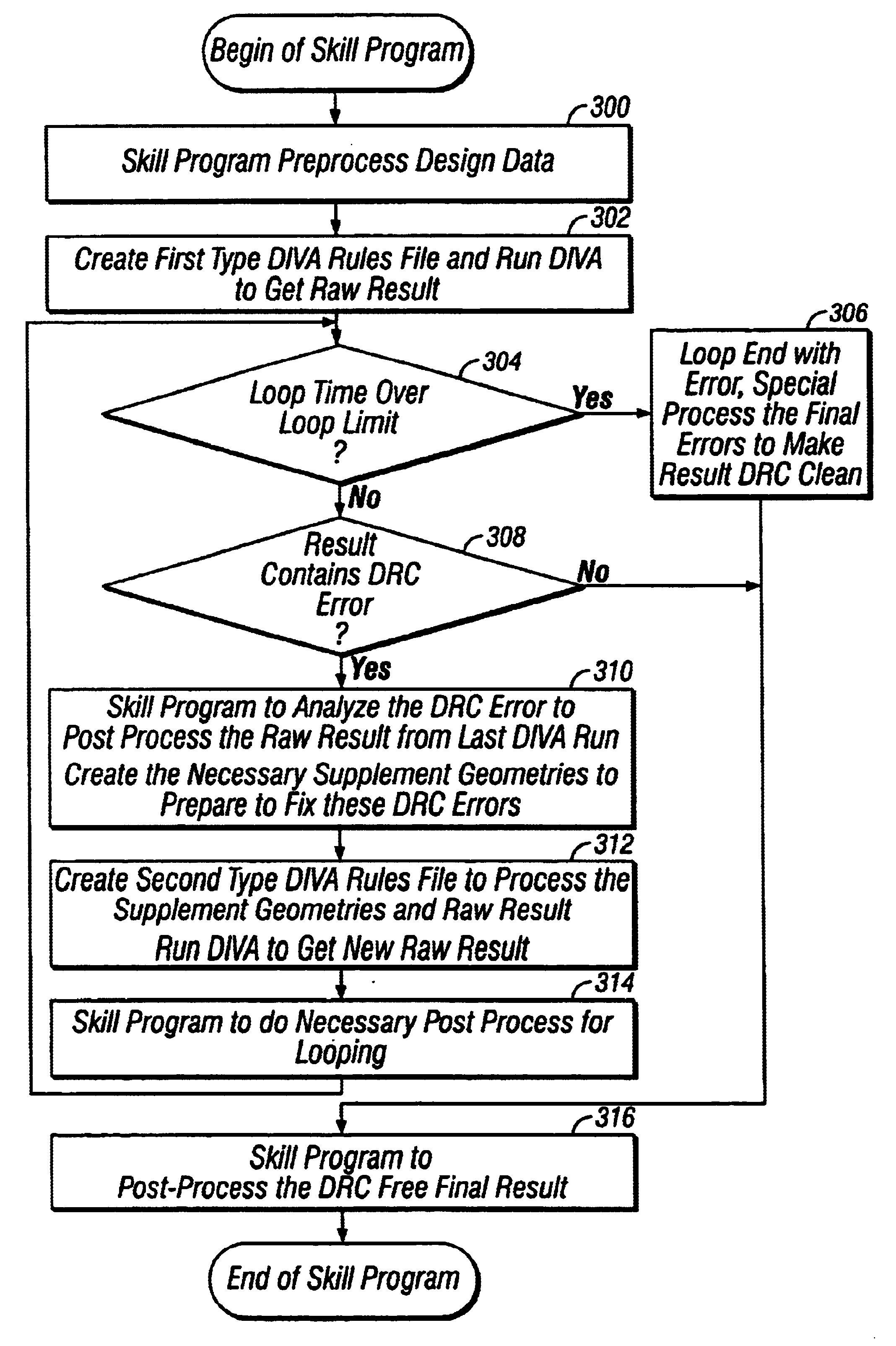
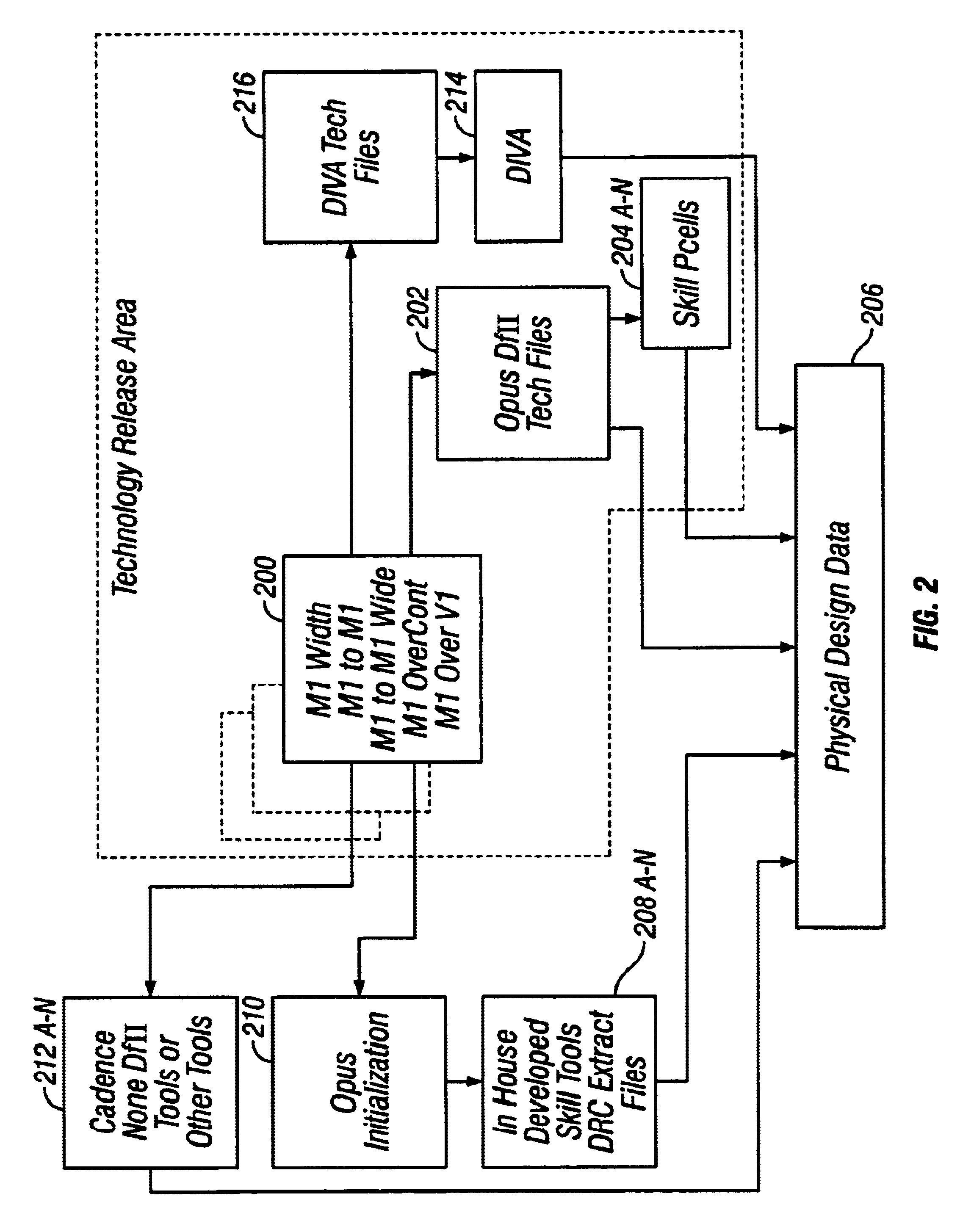
Method and system for automating design rule check error correction in a CAD environment
InactiveUS6637013B1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designComputer Aided DesignSoftware engineering
In a computer-aided design environment, a technique for automating design rule check error corrections in a CAD environment contemplates the use of an automation program, such as a SKILL program, to automatically and continuously run a design rule check utility program to generate intermediate results which are processed by the automation program and then supplied back to the design rule check utility program again for execution. The whole process is repeated, in an iterative manner, as many times as needed until a final result is achieved.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Design rule check method
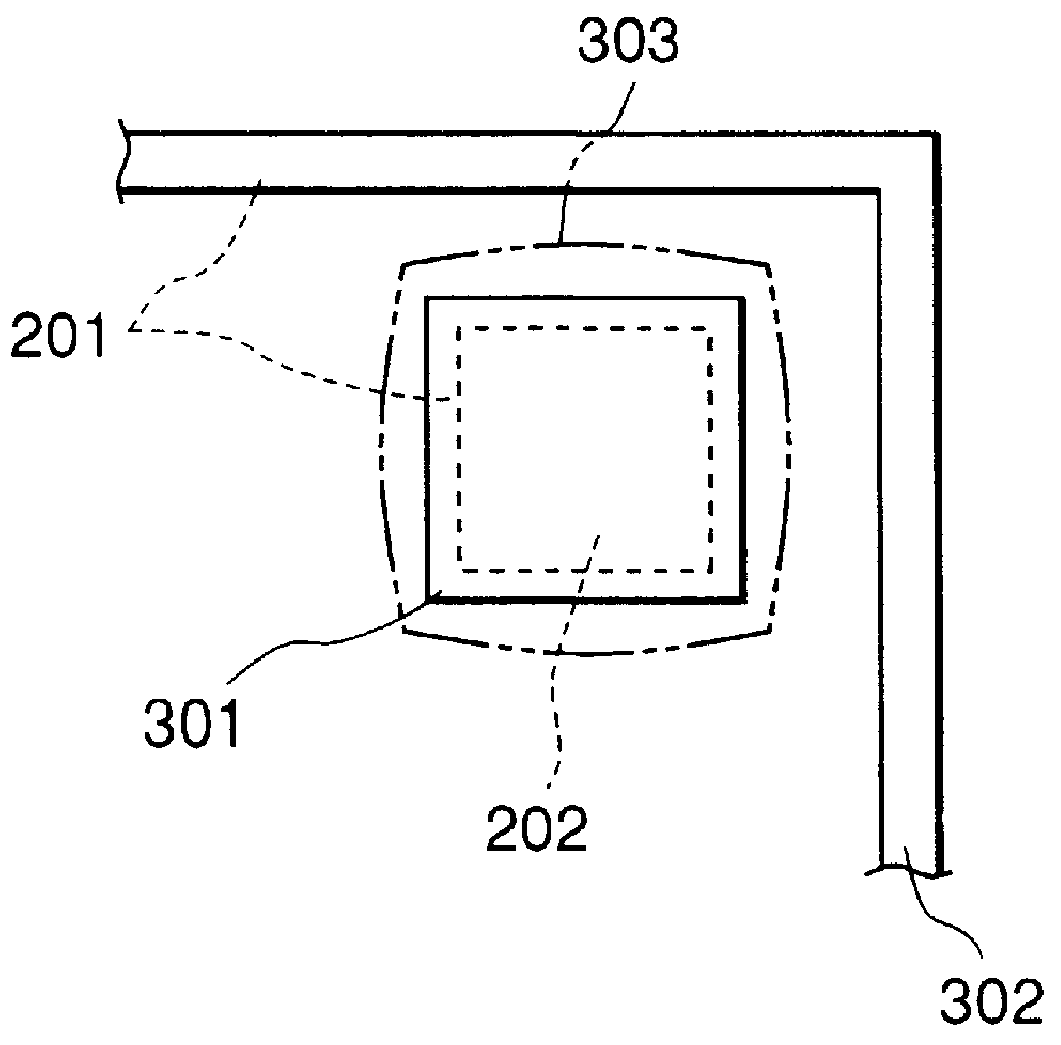
InactiveUS6078737ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDesign standardComputer architecture
A design rule check is to inspect whether mask pattern data of a semiconductor integrated circuit is correctly designed in accordance with a design standard or not. A design rule check method of the present invention is characterized in that design rule check errors occurring in the design rule check between a first error and a second error output in accordance with whether the design rule check errors overlap or not.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated OPC verification tool
InactiveUS20060005154A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
An integrated verification and manufacturability tool provides more efficient verification of integrated device designs than verification using several different verification components. The integrated verification and manufacturability includes a hierarchical database to store shared design data accessed by multiple verification components (e.g., layout versus schematic, design rule check, optical process correction, phase shift mask assignment and OPC verification and machine language conversion). The hierarchical database includes representations of one or more additional, or intermediate layer structures that are created and used by the verification components for operations performed on the design being verified. Use of a single hierarchical database having shared data for access and use by multiple verification components streamlines the verification process, which provides an improved verification tool.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
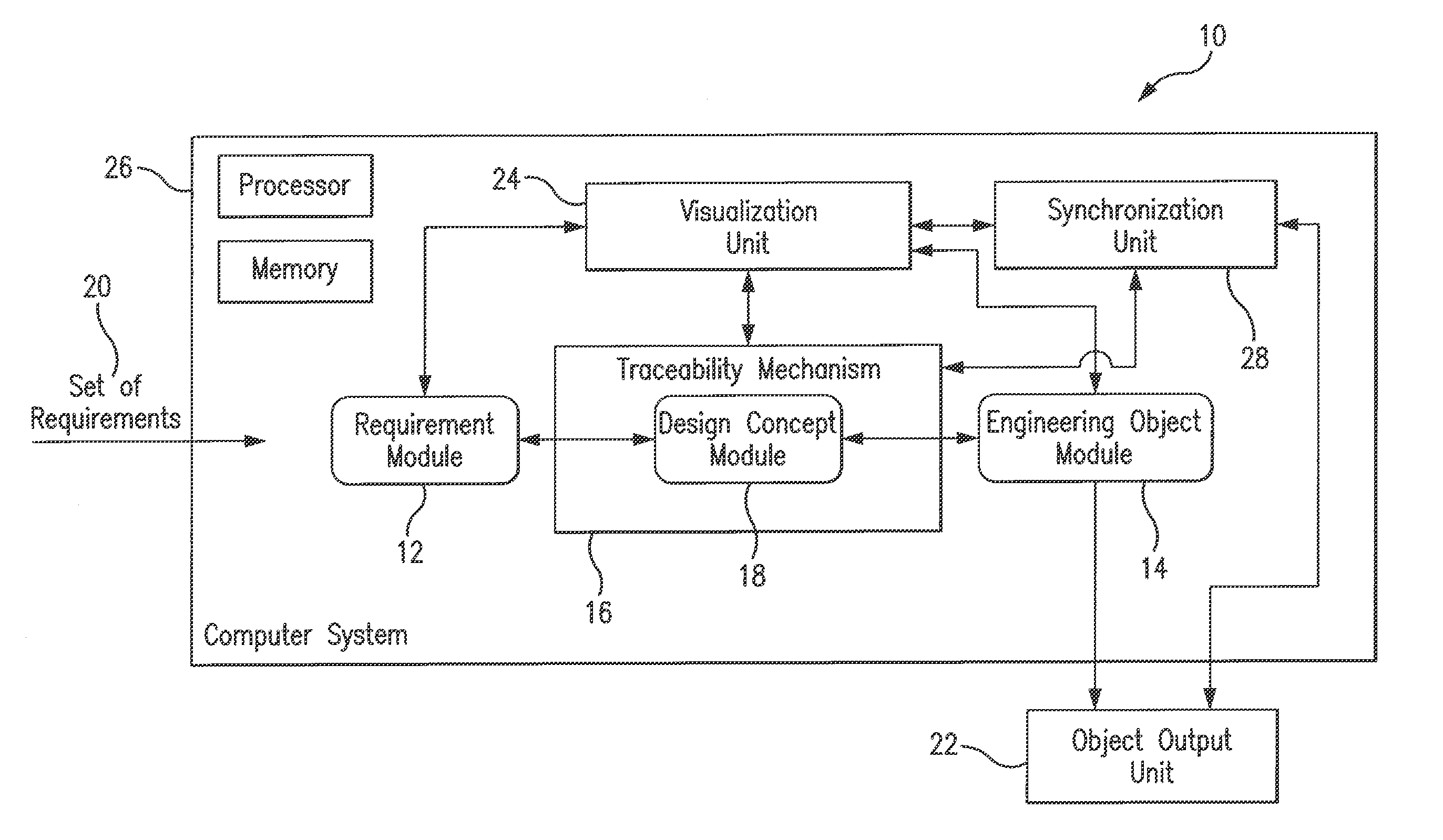
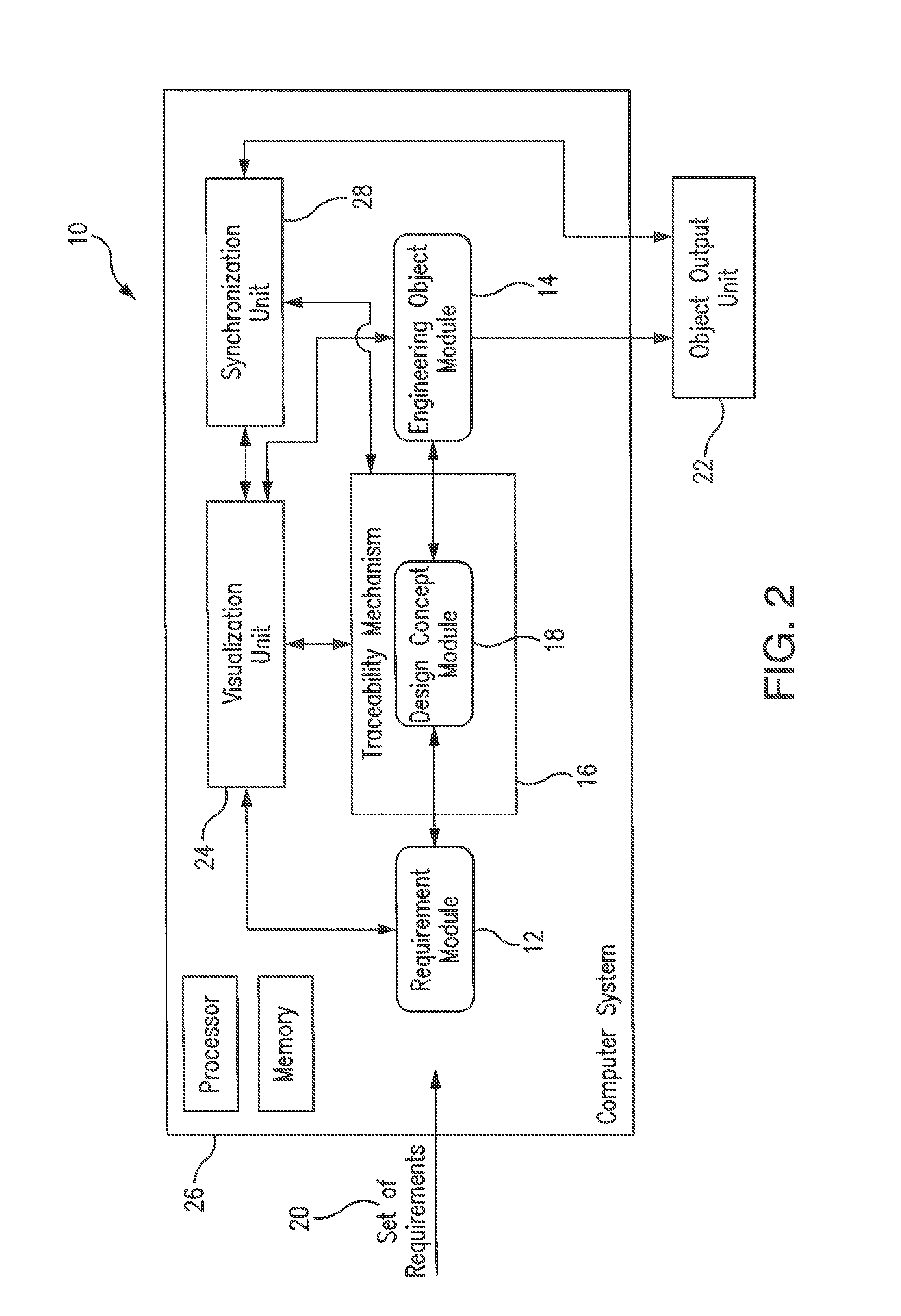
Method and system for ontology-enabled traceability in design and management applications
InactiveUS20120143570A1Enhanced Semantic RepresentationSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork management applicationDesign rule checking
A system and method for ontology-enhanced traceability in design and management applications employ ontology nodes embedded in a processor executable traceability link (network) coupling processor executable requirement modules to processor executable engineering object modules to facilitate in all stages of engineering object development. The engineering object development occurs through multiple models of computation, control, and visualization platform networked together via ontology-enhanced traceability mechanism. Processor executable design rule checking module embedded in the design concept nodes creates a pathway for the development process validation and verification at early stages of the object lifecycle. Linking of ontologies / meta-models is performed for the purposes of supporting ontology-enabled traceability across multiple domains.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Low-overhead multi-patterning design rule check
ActiveUS20130074024A1Avoid violationsComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationNODALDesign rule checking
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
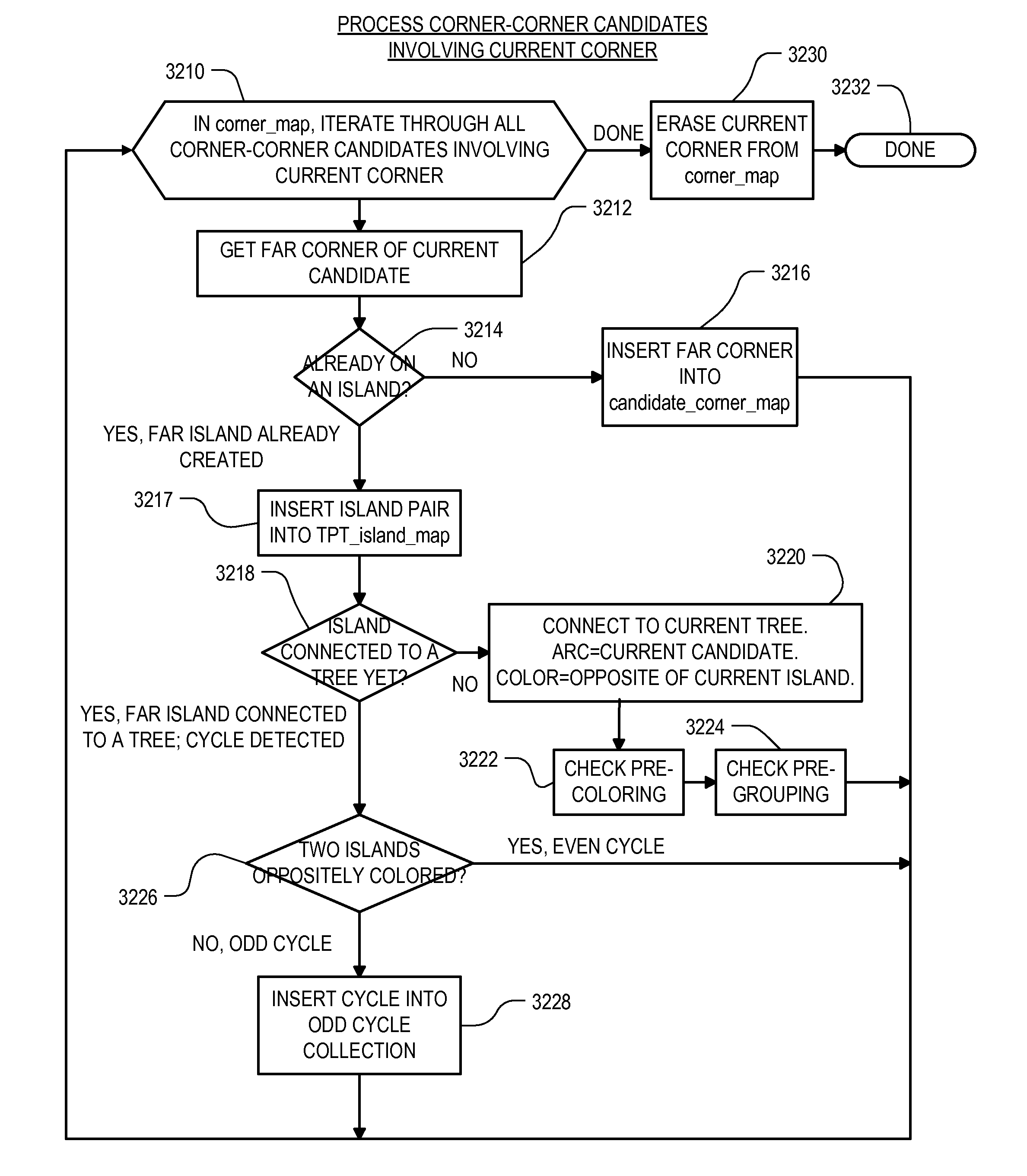
Topological Pattern Matching
InactiveUS20100185994A1Efficient identificationEfficient searchComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsPattern matchingSearch graph
Techniques for more efficiently identifying specific topological patterns in microdevice design data, such as layout design data. A user provides a topological pattern matching tool with a pattern template. In response, the topological pattern matching tool will analyze the pattern template to create a set of “design rule check” operations that can be performed to identify topological features of the layout design that will include the set of topological features specified for the template. The topological pattern matching tool also specifies properties that should be determined for each set of topological features identified by a design rule check operation. Once the design rule check operations have been created, the tool applies them to the layout design data being analyzed. The results produced by the design rule check operations will be a group of topological features in the layout design that encompass the topological features specified for the template. The results also will include a set of properties for each of the identified topological features. Next, the pattern matching tool creates a search graph based upon the results of the design rule check operations. Once the search graph is constructed, the pattern matching tool traverses the search graph to identify combinations of nodes connected by graph edges representing feature characteristics that match the constraints specified for the pattern template. For each such identified combination of nodes, the tool will output the arrangement of geometric elements corresponding to the nodes as a topological match to the original template.
Owner:PIKUS FEDOR G +1
Method and system for design rule checking of integrated circuit layout
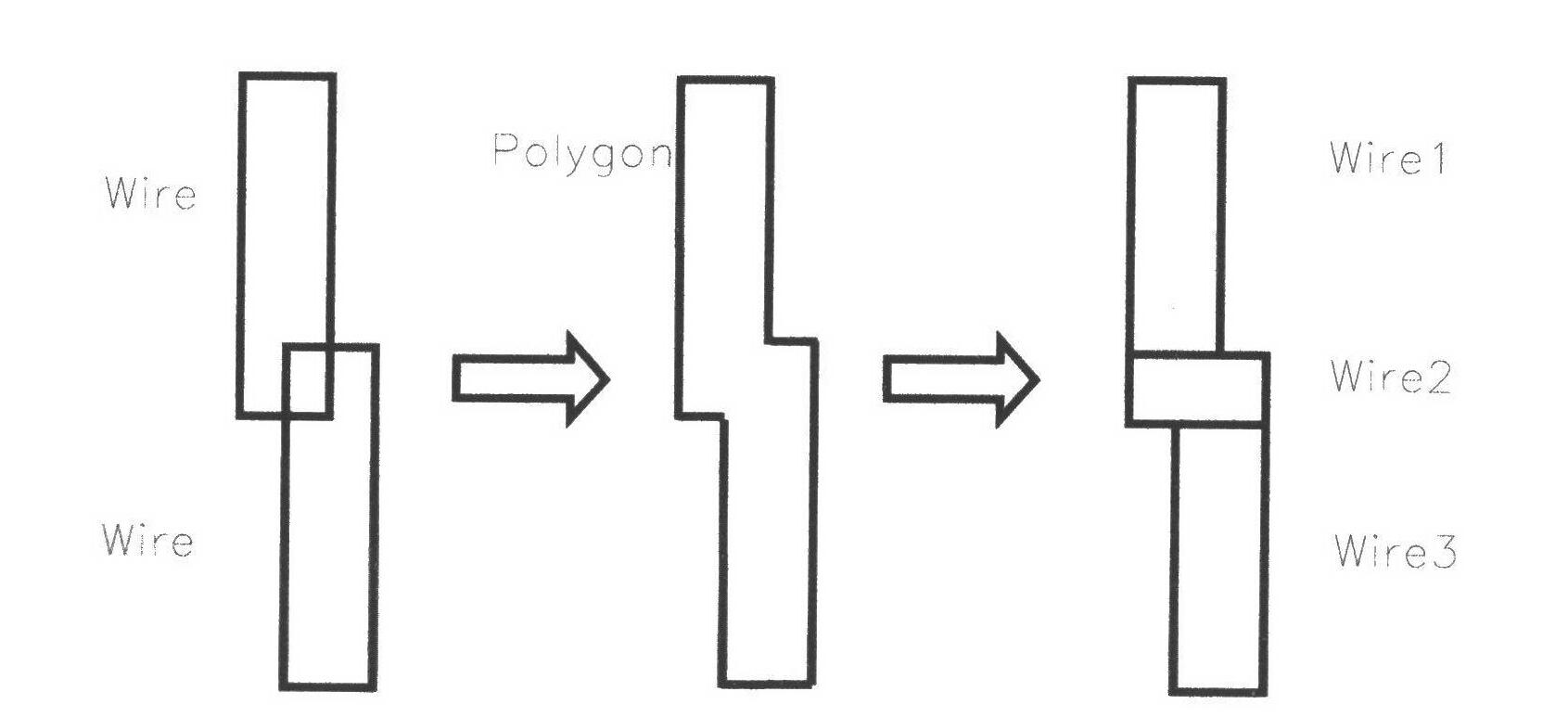
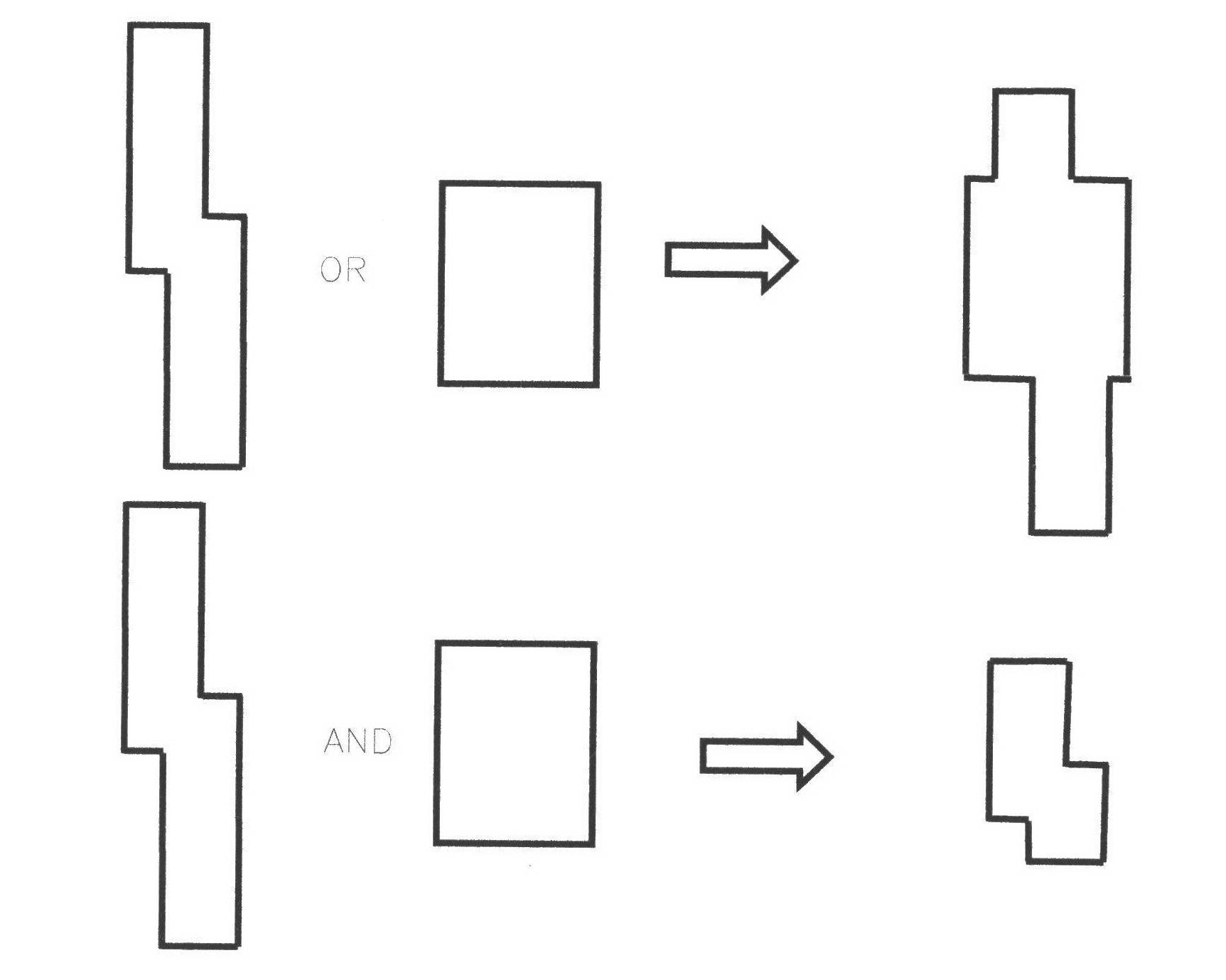
The invention discloses a method and a system for design rule checking of an integrated circuit layout. A layout graph is abstracted to be represented by polygon data defined by a series of horizontal borders, a polygon feature extraction method, a logical operation method among polygons and a method for enumeration and traverse operation of polygon connected regions and border edges are defined and achieved, and design rules are checked and marked on the basis. Data structure mutual transformation among interconnected rectangulars and layout polygons can be performed, the method for polygon operation and the enumeration and traverse operation of the polygon border edges is defined and achieved, and the design rules are checked on the basis. According to the method for the design rule checking of the integrated circuit layout, graph regions violating the design rules in the layout are also marked heuristically so as to enable local regions to be split and rerouted by automatic routing tools or designers to perform fine adjustment to the layout.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUDAN MICROELECTRONICS GROUP
Approach for routing an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7506289B1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsImage resolution
A computer-implemented approach for routing an integrated circuit using non-orthogonal routing is accomplished during two phases: a global routing phase and a detailed routing phase. During global routing, routing indicators, in the form of hint polygons, are added to the integrated circuit layout and strategy lists, that include bias directions and straying limits, are generated for the new wires to be added. The hint polygons and strategy lists are used during detailed routing to aid in placing the new wires. If obstacle conflicts or insufficient space problems prevent the detailed routing of a new wire, then an obstacle resolution portion of global routing is used to resolve the obstacle conflict and / or provide additional space in the integrated circuit layout to route the new wires. Obstacle resolution includes, without limitation, moving or changing layout geometry, changing or add hint polygons, changing the routing strategy by changing the bias direction and / or adjusting straying limits, inserting one or more layer changes, instructing the detailed router to backup and insert a bend, ripping-up and rerouting one or more wires, or routing the wire from the destination connection point. Also, a tight routing approach may be employed to accommodate constructing routing paths in tight layout areas. Object specific design rule checks are employed to increase routing flexibility optimize routing performance. “On-the-fly” design rule checks are performed on portions of routing paths as the routing paths are being constructed.
Owner:CHAPMAN DAVID C
System for simplifying layout processing
ActiveUS20050223350A1Promote generationImprove manufacturabilityComputer aided designTotal factory controlProcess deviationsEngineering
A system and method for integrated circuit design are disclosed to enhance manufacturability of circuit layouts by applying layout processing to handle imperfections such as jogs in integrated circuit design layouts. The layout processing may be applied to jogs in the original integrated circuit design layout or jogs created post-design by process biases, as well as design rule check and Boolean processes or process compensation.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and platform for integrated physical verifications and manufacturing enhancements
InactiveUS7100134B2Optimize circuit designDigital computer detailsComputer aided designPhysical verificationEngineering
An automated design for manufacturability platform which provides integrated physical verification and manufacturing enhancement operations. The platform uses an efficient data structure capable of handling and manipulating both layout circuit and geometry characteristics, which permits a wide range of operations such as timing analysis, design-rule checking and optical proximity corrections on a single platform. This feature eliminates the need to translate layout representations between various tools without the requirement of using a common database. Moreover, the platform's common user interface enables encapsulated information exchange between the design and the manufacturing teams, permiting early consideration of manufacturing distortion or enhancement impact on circuit performance.
Owner:RPX CORP
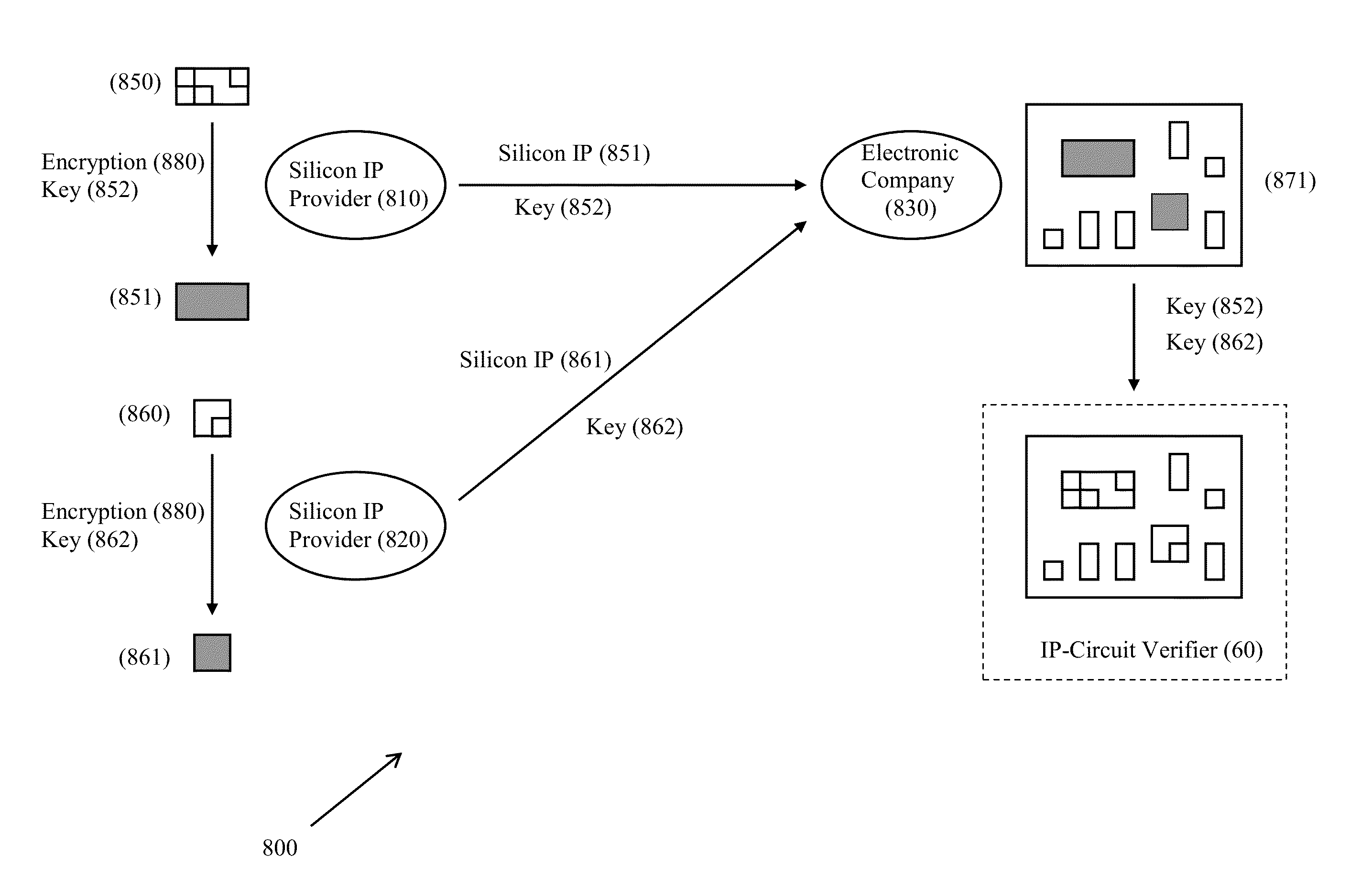
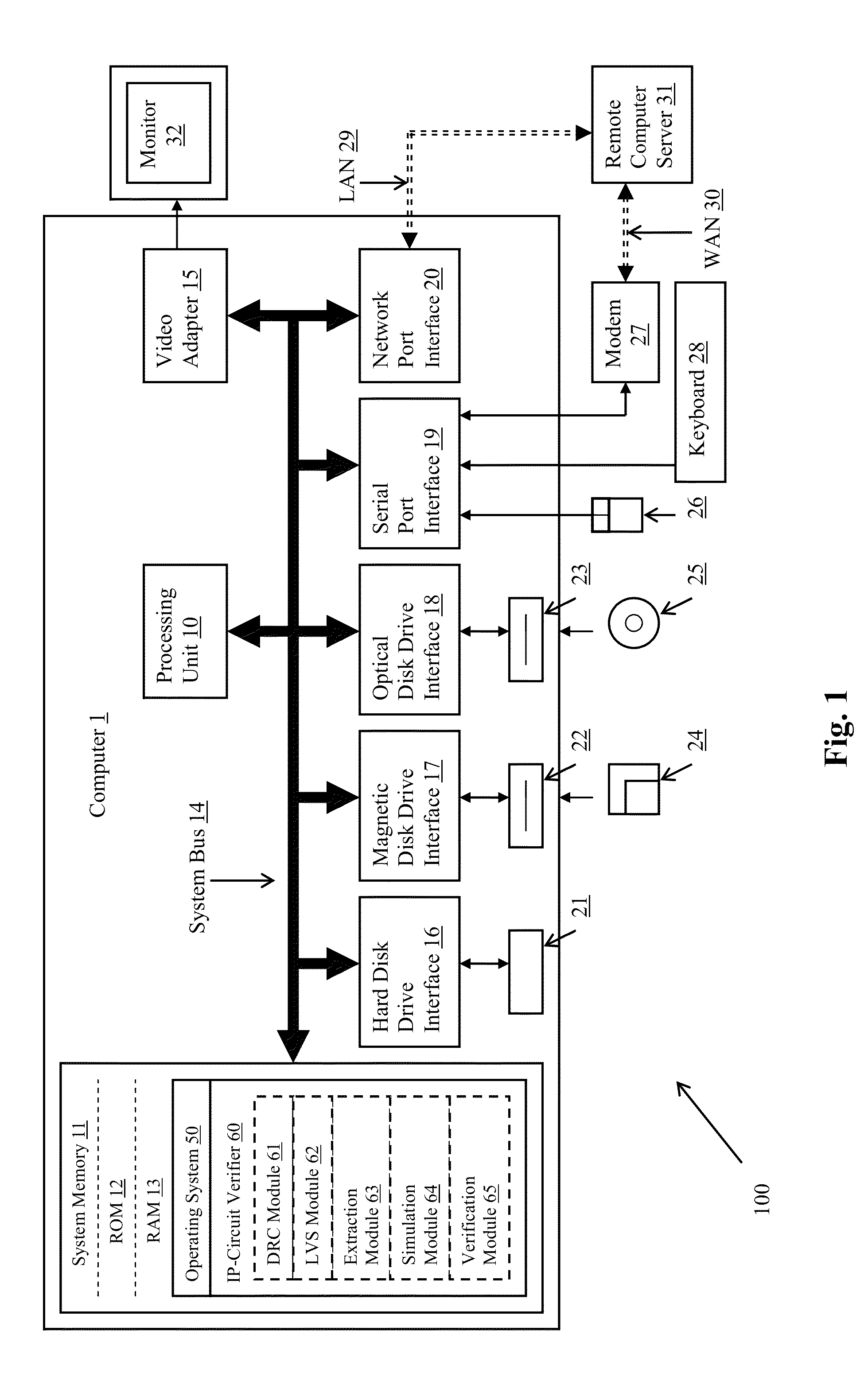
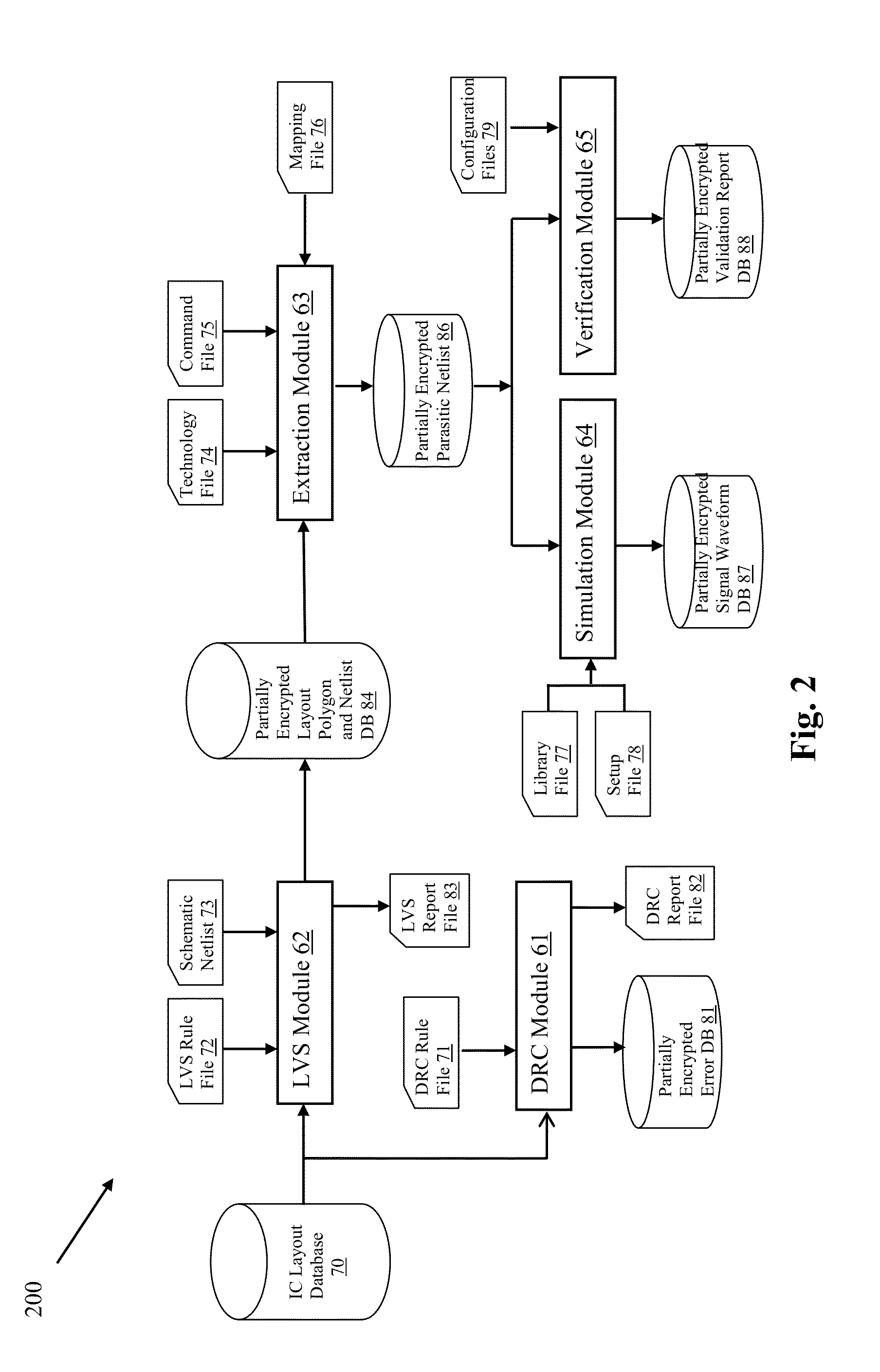
Validation of Integrated Circuit Designs Built With Encrypted Silicon IP Blocks
A method and system for validating integrated circuit designs that are built with encrypted silicon IP blocks decrypts the encrypted silicon IP blocks in the integrated circuit designs with the keys from IP providers. After decryption, various validation checks on the integrated circuit designs are done, such as design rule check (DRC), layout versus schematic (LVS) check, parasitic resistor capacitor (RC) extraction, circuit simulation, signal electro migration (EM) and voltage drop check, signal integrity (SI) check and static timing check, etc. After validation, any confidential data from the checking results related to the encrypted silicon IP blocks are themselves encrypted to protect the proprietary silicon IP blocks. The method and system work with silicon IP encryption technology to establish a low cost silicon IP usage and verification platform, and to enable a more cost efficient silicon IP business model.
Owner:ENCRIP
Low-overhead multi-patterning design rule check
ActiveUS8677297B2Avoid violationsQuick and accurate depictionComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationNODALDesign rule checking
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
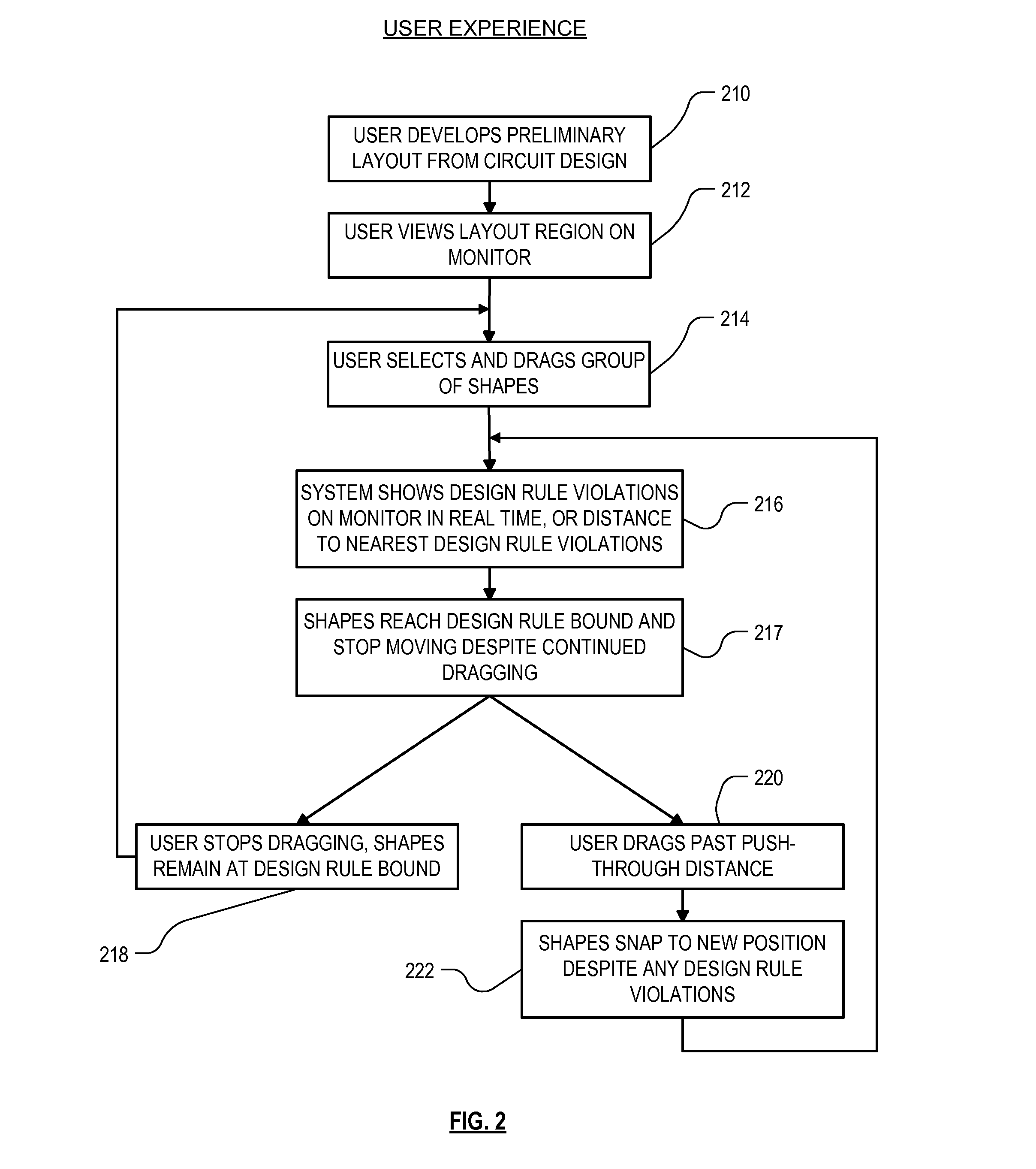
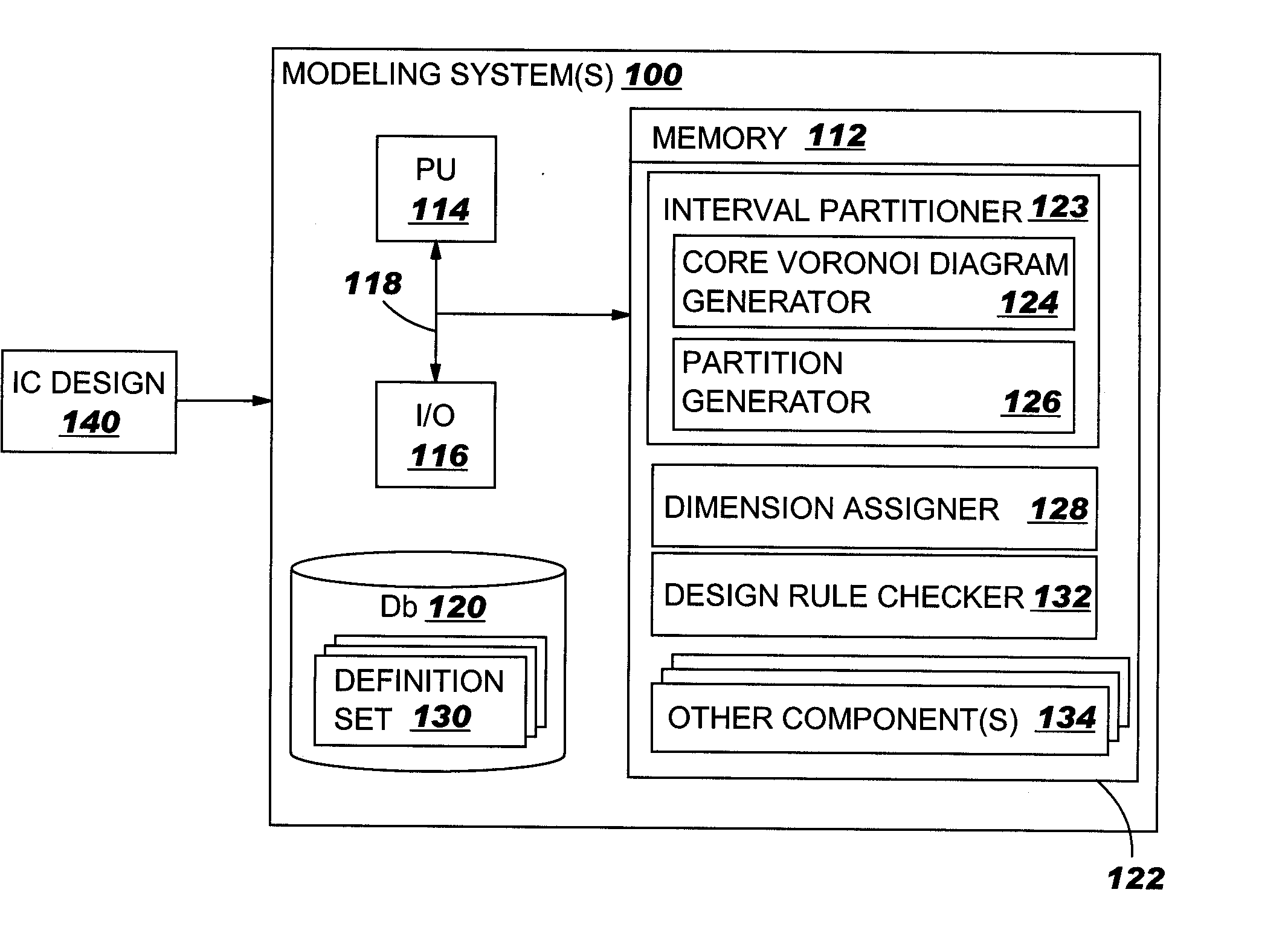
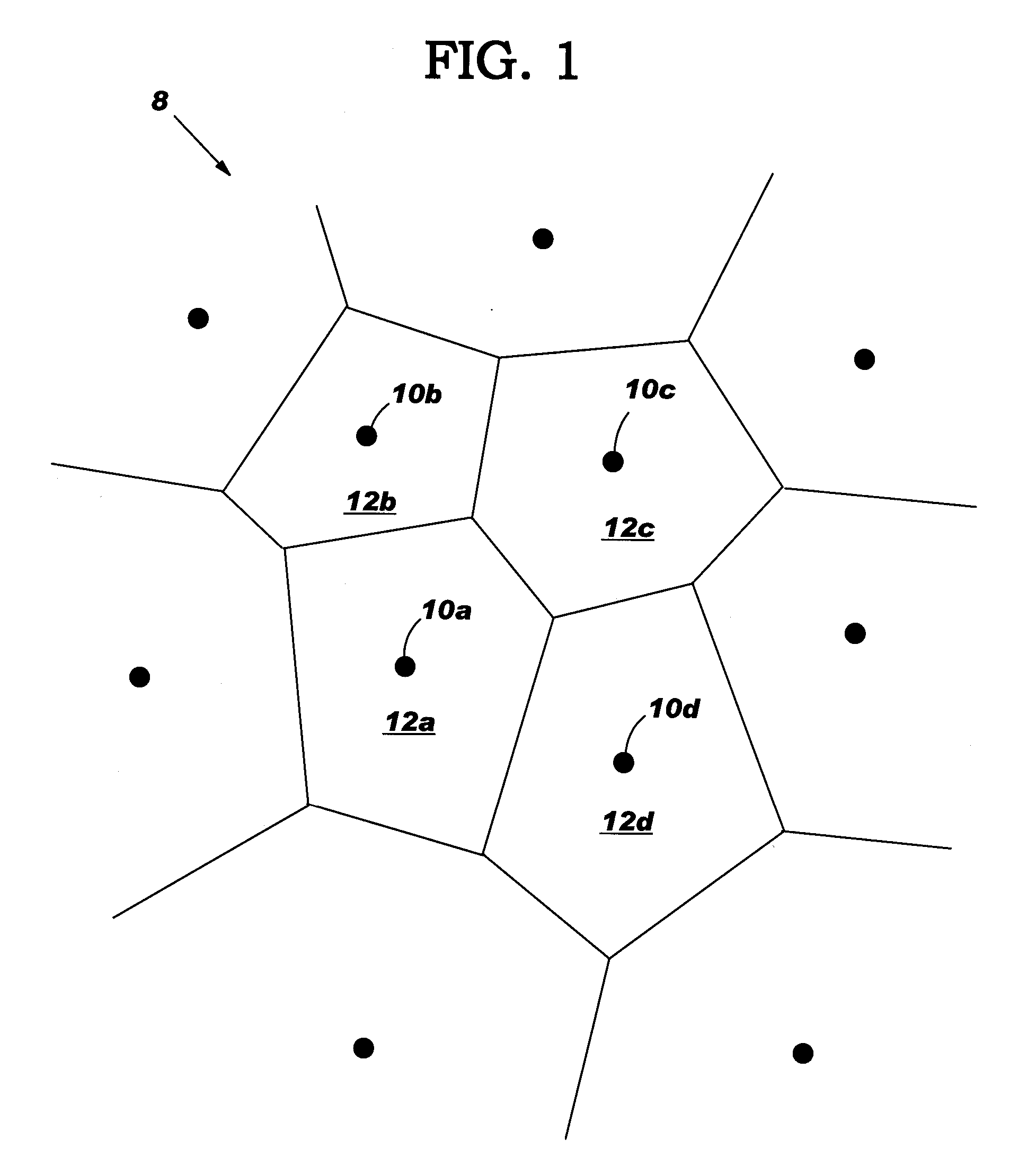
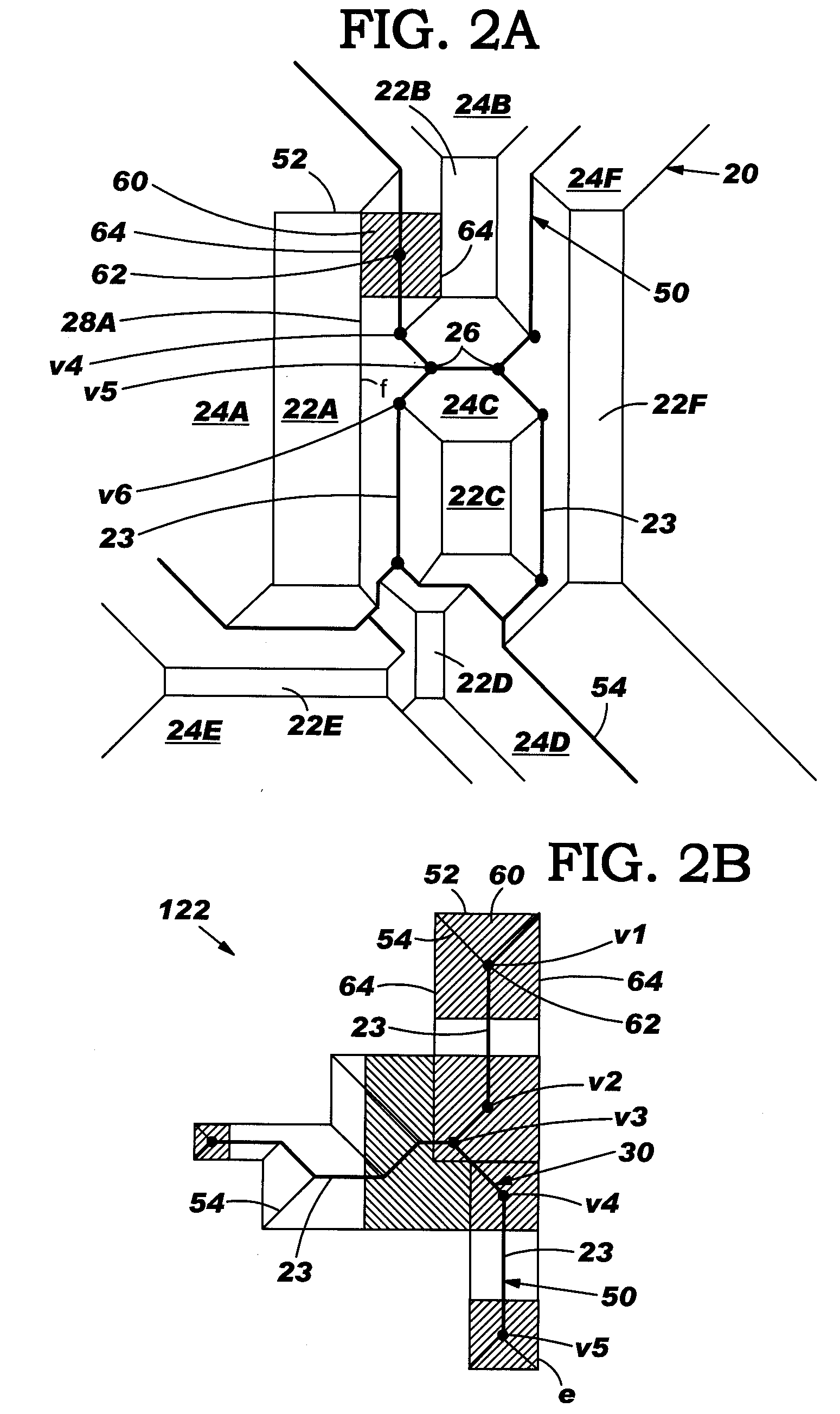
IC design modeling allowing dimension-dependent rule checking
ActiveUS20050172247A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureDesign rule checking
A method, system and program product to model an IC design to include dimensions such as a local width and spacing of IC shapes in a consistent fashion. In particular, the invention uses a core portion of Voronoi diagrams to partition edges of a shape into intervals and assigns at least one dimension to each interval such as a local width and spacing. Dimension assignment can be made as any desirable definition set for width and spacing, e.g., numerical values or continuous dimension-dependent design rules. Design rule checking for dimension-dependent spacing rules given in any arbitrary functional form of width and spacing is possible. Application of the invention can be made anywhere the width and spacing of VLSI shapes play a role, e.g., relative to a single edge, neighboring edges, neighboring shapes, and / or for edges in more than one layer of the IC design.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Integrated OPC verification tool
InactiveUS7412676B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designComputer architectureLayout Versus Schematic
An integrated verification and manufacturability tool provides more efficient verification of integrated device designs than verification using several different verification components. The integrated verification and manufacturability includes a hierarchical database to store shared design data accessed by multiple verification components (e.g., layout versus schematic, design rule check, optical process correction, phase shift mask assignment and OPC verification and machine language conversion). The hierarchical database includes representations of one or more additional, or intermediate layer structures that are created and used by the verification components for operations performed on the design being verified. Use of a single hierarchical database having shared data for access and use by multiple verification components streamlines the verification process, which provides an improved verification tool.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
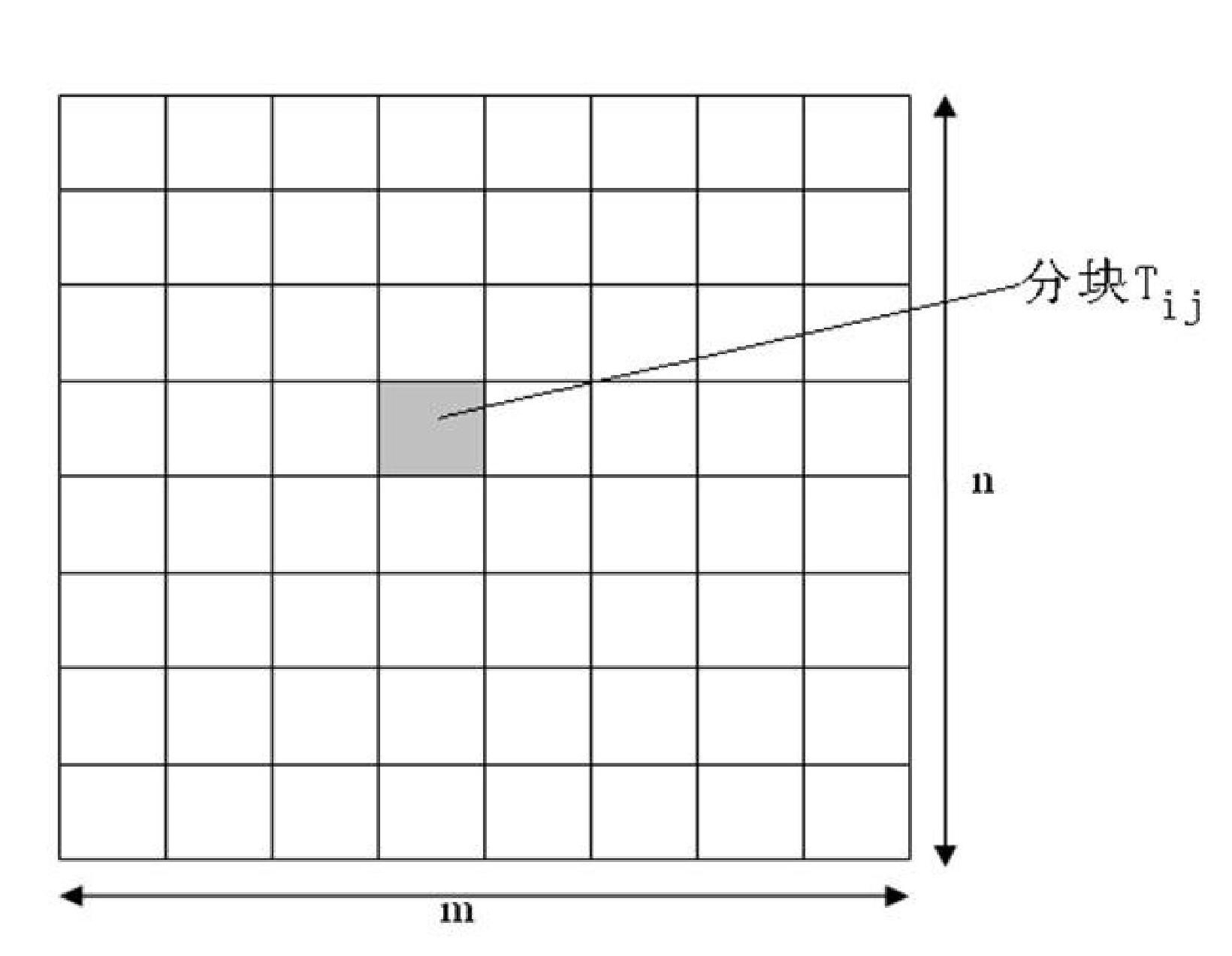
Preprocessing method using redundancy metal filling for realizing layout density uniformity
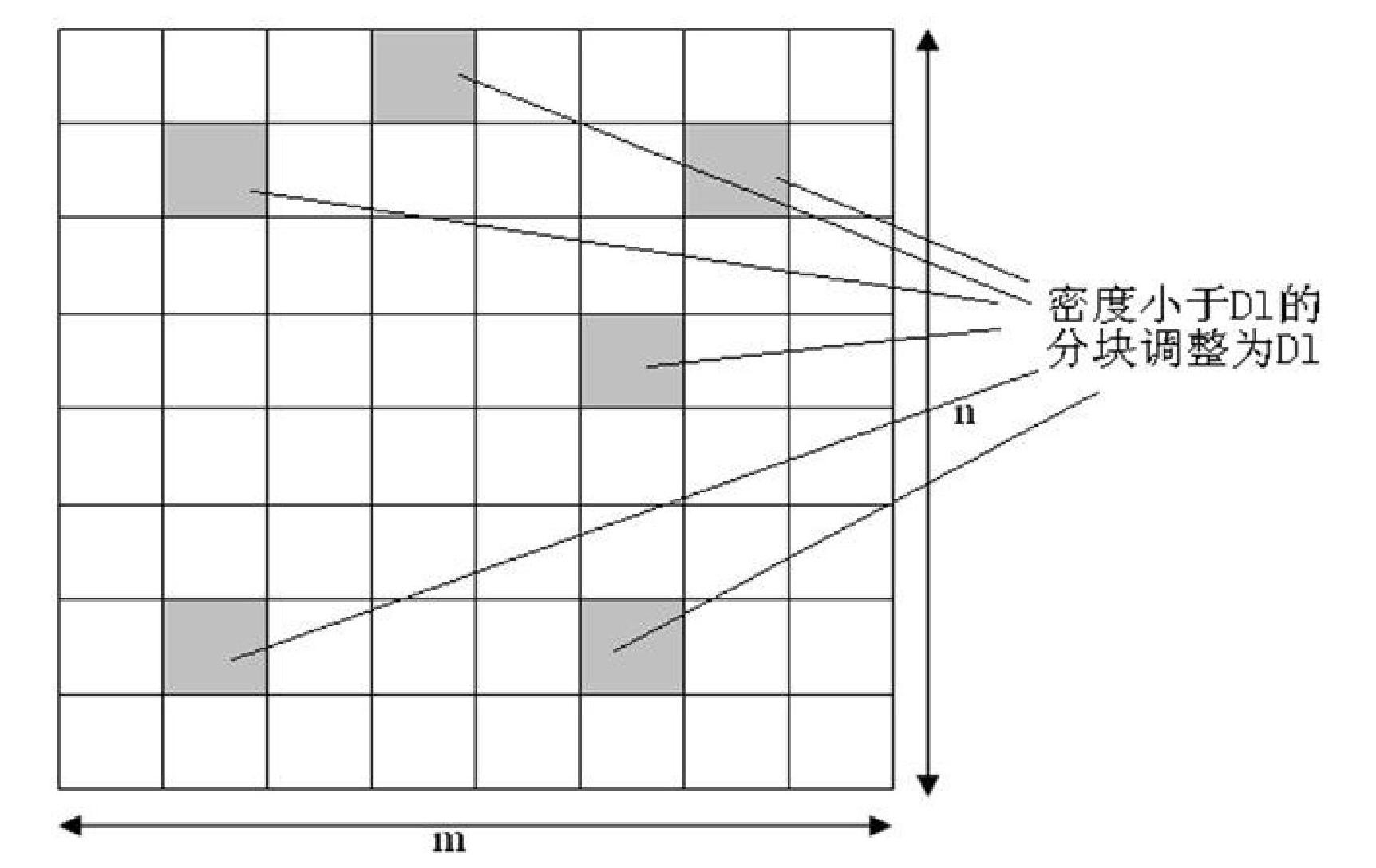
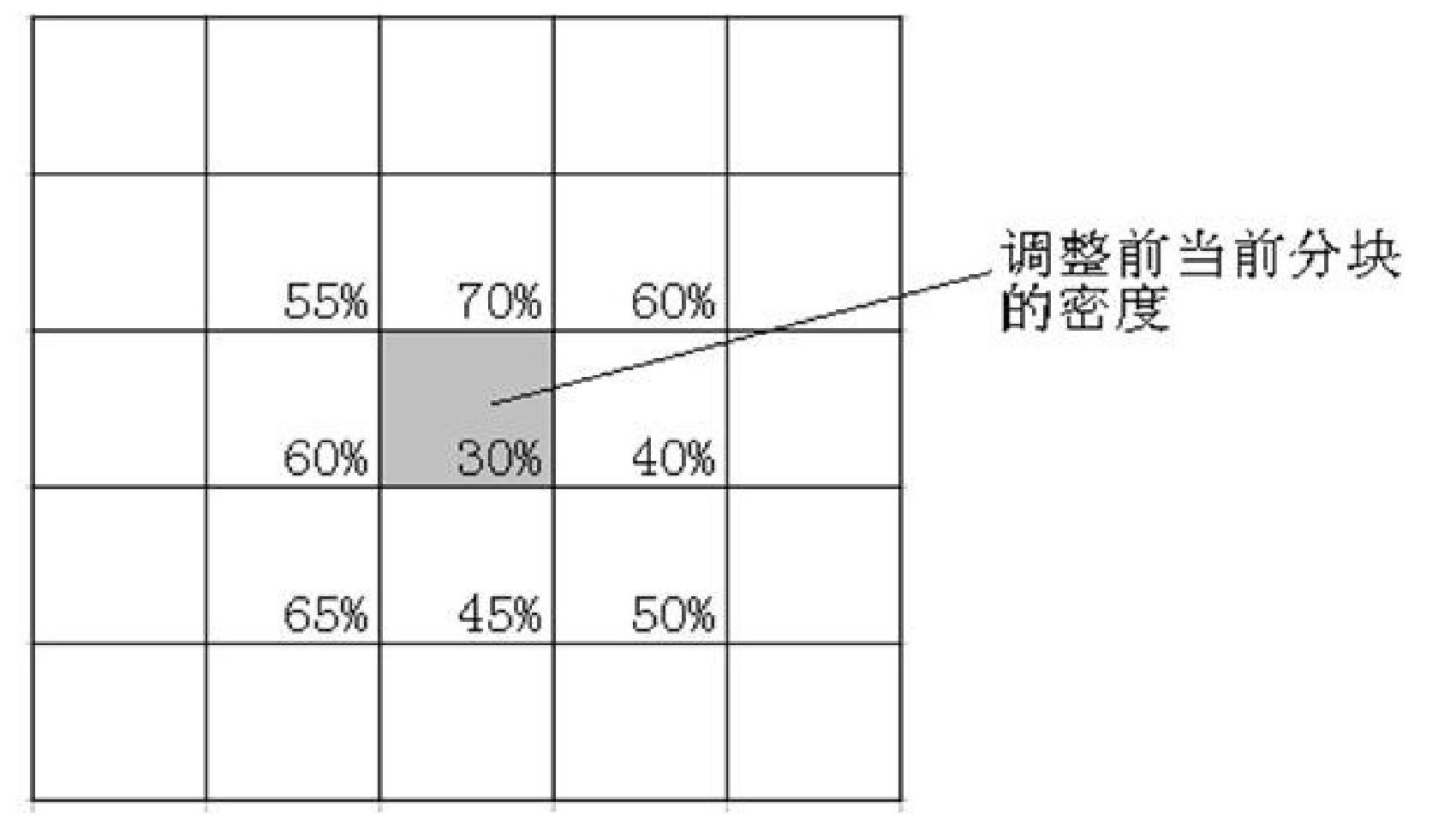
ActiveCN102117348AHomogenize Global DensitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial data processing applicationsLower limitPretreatment method
The invention relates to a preprocessing method using redundancy metal filling for realizing layout density uniformity, belonging to the technical field of integrated circuit manufacturing process and layout design. The method can determine the density of each block by a design rule check rule through a pre-setting the block density lower limit and pre-setting the allowable density undulating quantity and then dividing the layout into blocks having the same size. For the method, the density of each block is adjusted to be above the density lower limit, and then the density difference between each block and the adjacent blocks is limited within the preset allowable undulating quantity range, so that the density difference among different blocks is reduced, the uniformity of the metal wire density on the layout is improved, better smoothness is realized and chip quality is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
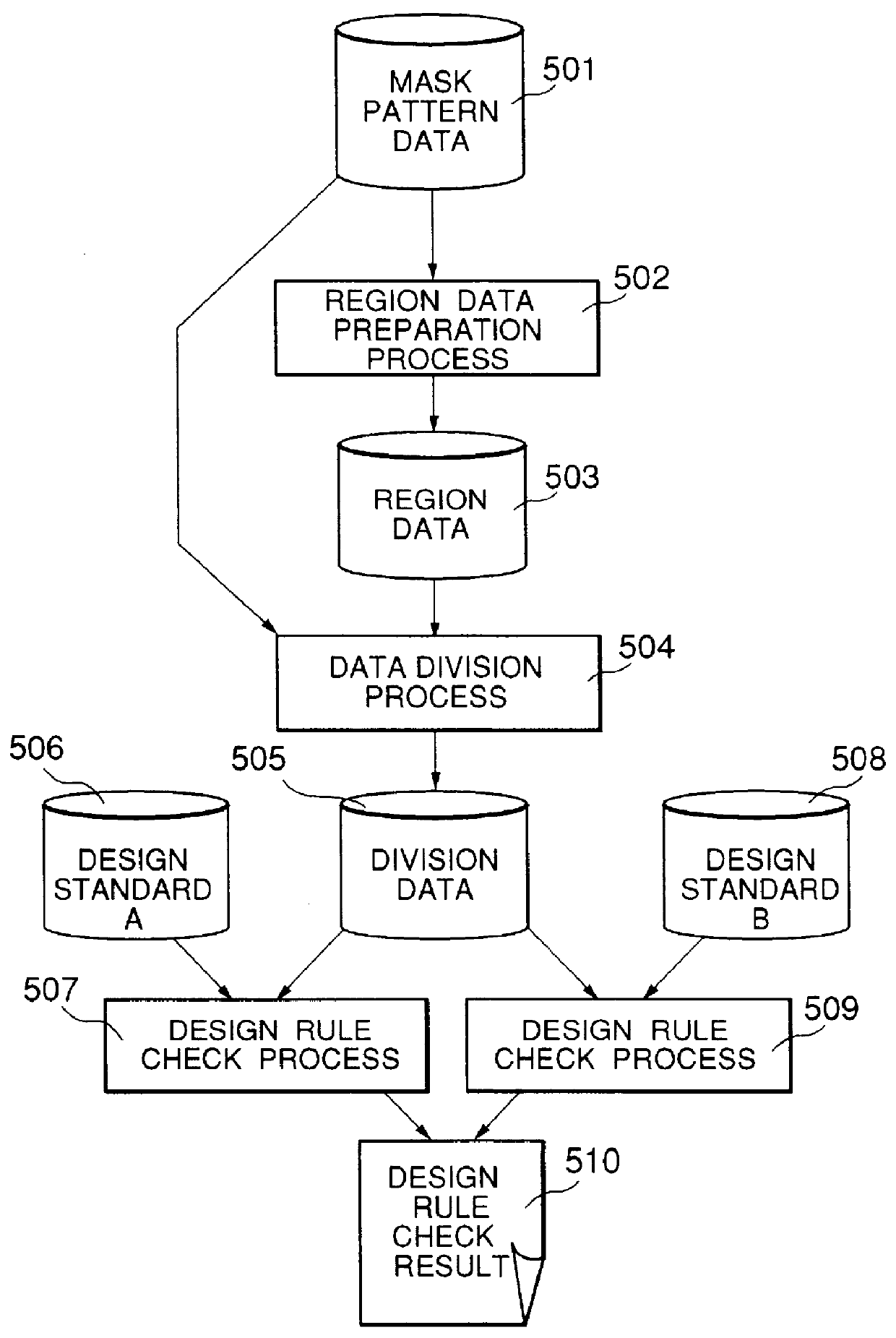
System & method for performing design rule check
InactiveUS20050086619A1Eliminate false errorError in design ruleComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureIntegrated circuit layout
An improved system and method is disclosed for performing a design rule check on a proposed integrated circuit (IC) layout, and for creating customized design rule check command files. The individual layers of the IC (a system on chip—SOC) are separated into different regions having different kinds of features (i.e., memory or logic). Each different type of region is then analyzed in accordance with the customized design rule command file so that so-called “false errors” are eliminated. The invention thus improves, among other things, a development time for getting a design implemented in silicon.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated opc verification tool
InactiveUS20080256500A1Digital data processing detailsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentInter layerComputer architecture
An integrated verification and manufacturability tool provides more efficient verification of integrated device designs than verification using several different verification components. The integrated verification and manufacturability includes a hierarchical database to store shared design data accessed by multiple verification components (e.g., layout versus schematic, design rule check, optical process correction, phase shift mask assignment and OPC verification and machine language conversion). The hierarchical database includes representations of one or more additional, or intermediate layer structures that are created and used by the verification components for operations performed on the design being verified. Use of a single hierarchical database having shared data for access and use by multiple verification components streamlines the verification process, which provides an improved verification tool.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
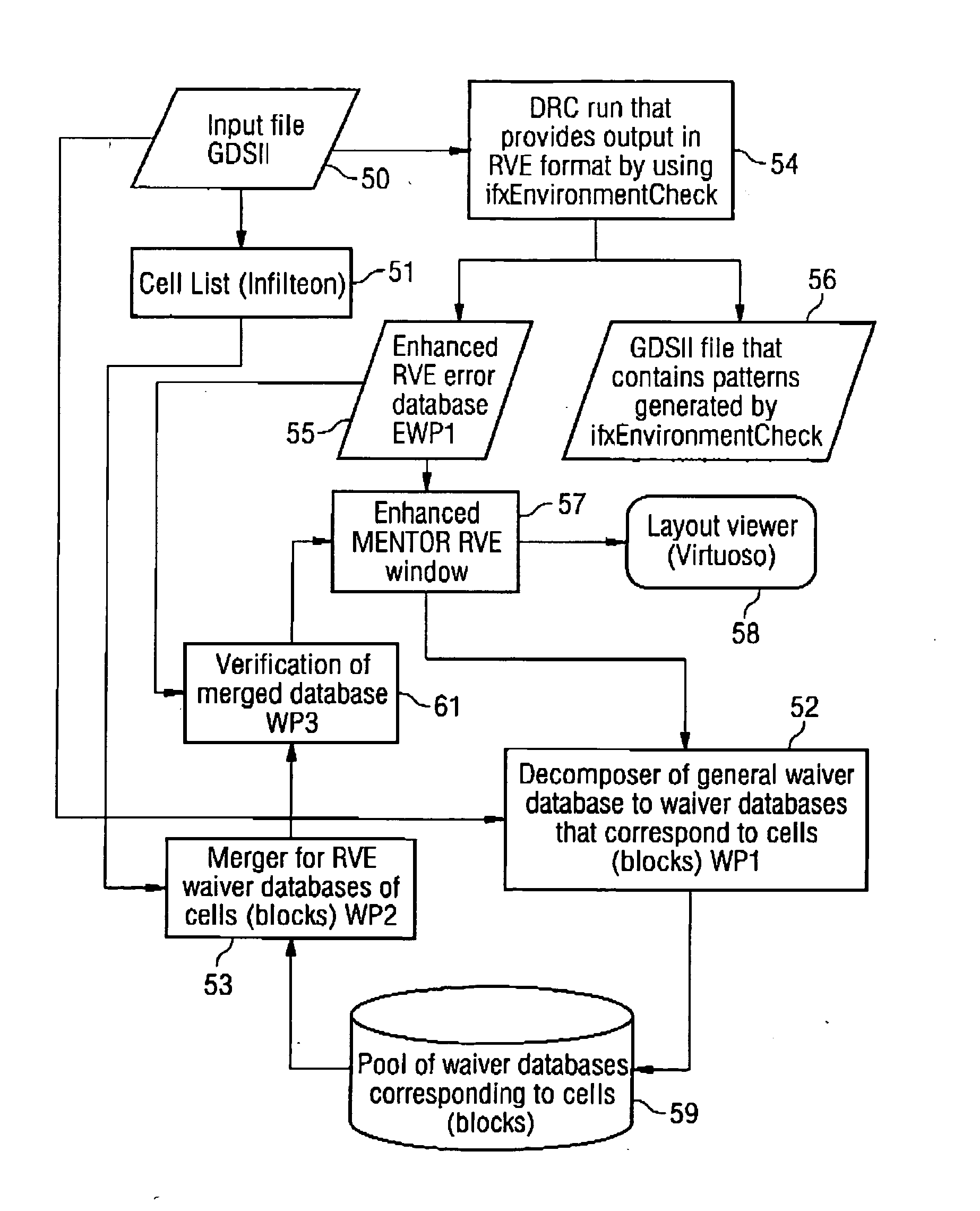
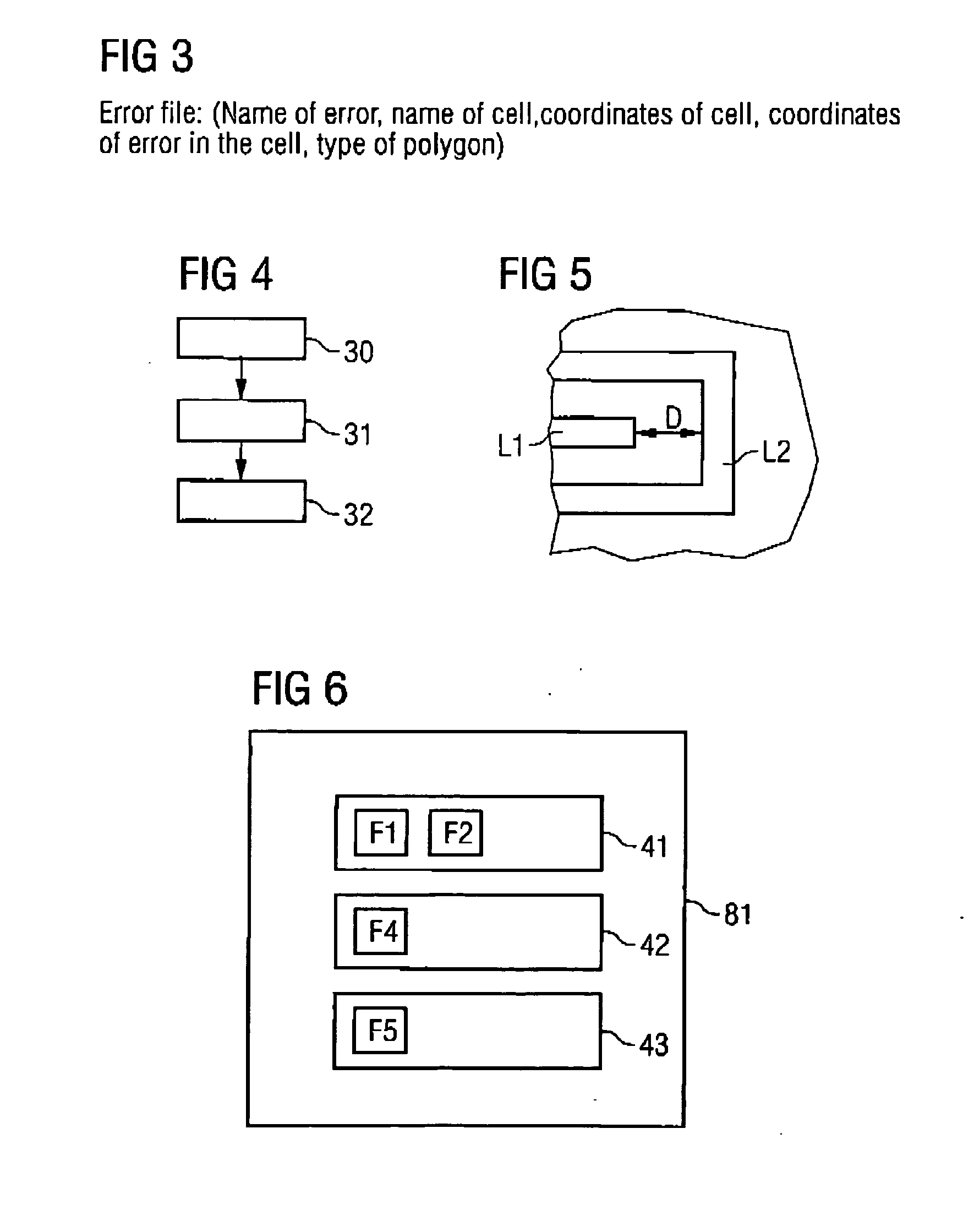
Method for treating design errors of a layout of an integrated circuit
InactiveUS20070192754A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProcess errorEngineering
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for treating errors during the checking of a design of an integrated circuit. In one embodiment, the method includes checking the design of the integrated circuit for errors using predetermined design rules, wherein the design includes a plurality of cells, detecting a design error when the design deviates from the predetermined design rules, writing the design error into a design error file, wherein at least one detected design error is written into a design waiver file if the design error is allowed as an allowed design error in spite of the deviation from the predetermined rules, and storing the allowed design error in the design waiver file with specification of a cell in which the design error occurs.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
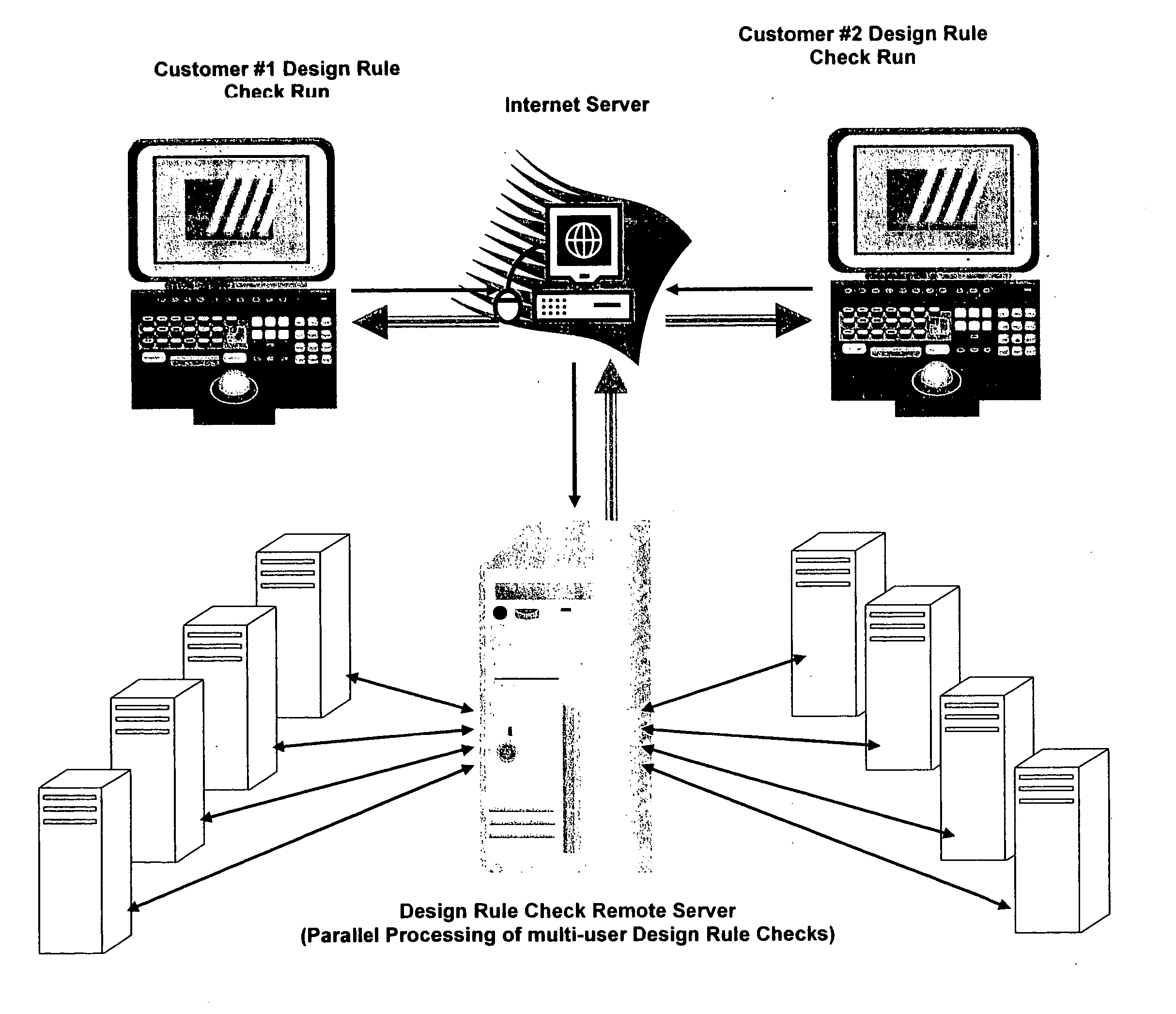
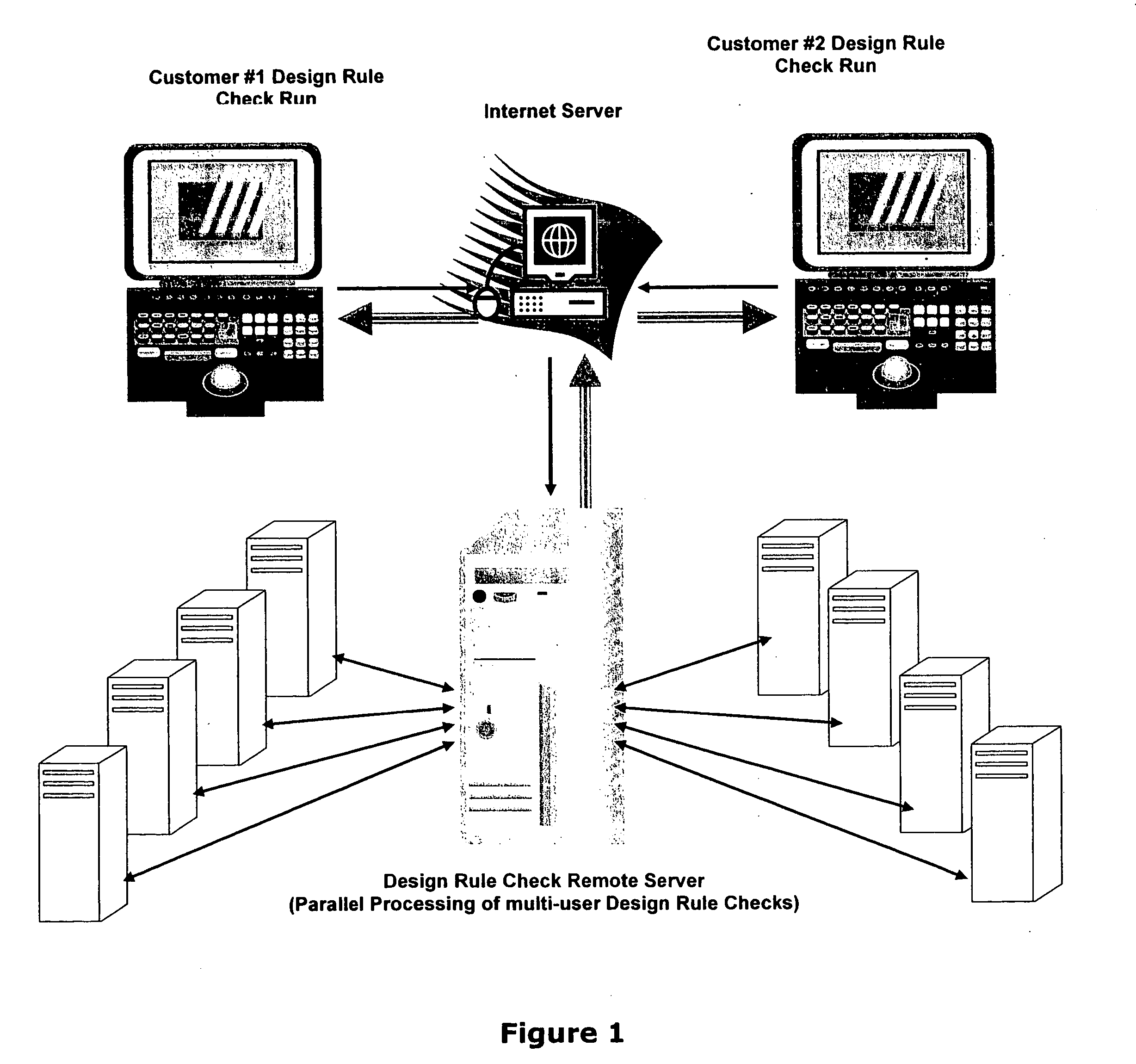
Design rule violations check (DRC) of IC's (integrated circuits) mask layout database, via the internet method and computer software
InactiveUS20060253813A1Fast resultsLow costComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGuidelineSoftware design
This paper describes method and EDA (Electronic Data Automation) computer software invention for design rule violations check of mask layout database (integrated circuits layout) via the internet. The technique takes advantage of a unique algorithm to analyze the mask layout database to find mask layout polygons that are less than the minimum design rules (distances) that are determined by the fabrication process. The computer program then creates an output file that marks all design rule violations location and type. The input of the tool is a mask layout database (i.e.: layout block / s) that is made manually by a mask design specialist or automatically by automatic IC layout tools. The output of the software tool is a guideline mechanism and file to mark all design rule violations for correction. This markers file can be loaded into any industry's standard IC mask layout database editor for viewing and correction. The software performs on individual mask layout blocks and / or on hierarchical structure of mask layout blocks. The system also checks mask layout database incrementally, means only blocks that have been changed are checked. The system is activated via the internet using secured protocol. In order to reduce the cost of DRC (design rule check) computer program, corporations may log in to a main server to submit complete DRC (Design Rule Check) run. User point reference files at a local location (User's local computer) and setup all parameters on a web based interface. The system collects all local information and run a complete design rule check locally or on remote server. The system offer a web based control panel to execute all necessary setups for submitting design rule check over the internet using any secured internet browser like MS Explorer and Netscape. The system offers the option to run on a local machine (user's computer) or on the main server over the internet. The system also offers a PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) interface to launch DRC runs via industry's standard PDA's. The procedure is fully secured by 128 bit security protocol. The system supports existing industry standard rule decks like: Mentor's Calibre, Cadence's Assura and Synopsys's Hercules. All design rules can be easily imported from these rule decks to be used by DRC program on the main server. All necessary files including mask layout GDSII (or GSIII) file and technology file are securely encrypted using 128 bit protocol and send to the remote server. These files are decrypted on the remote computer and submitted for design rule check. The main remote server is distributing the task among other computer system for advanced parallel processing to achieve fast results. All results log files are encrypted using 128 bit security protocol and available for download by the user. In case of local design rule check the results files are available on the user's local machine. This approach eliminates the purchase of a full local license and enables affordable price for small and medium size chip design firms. This fact significantly reduces integrated circuits design cost and time to market factor for chip design corporations, enabling faster deliveries to their end customers.
Owner:MICROLOGIC DESIGN AUTOMATION
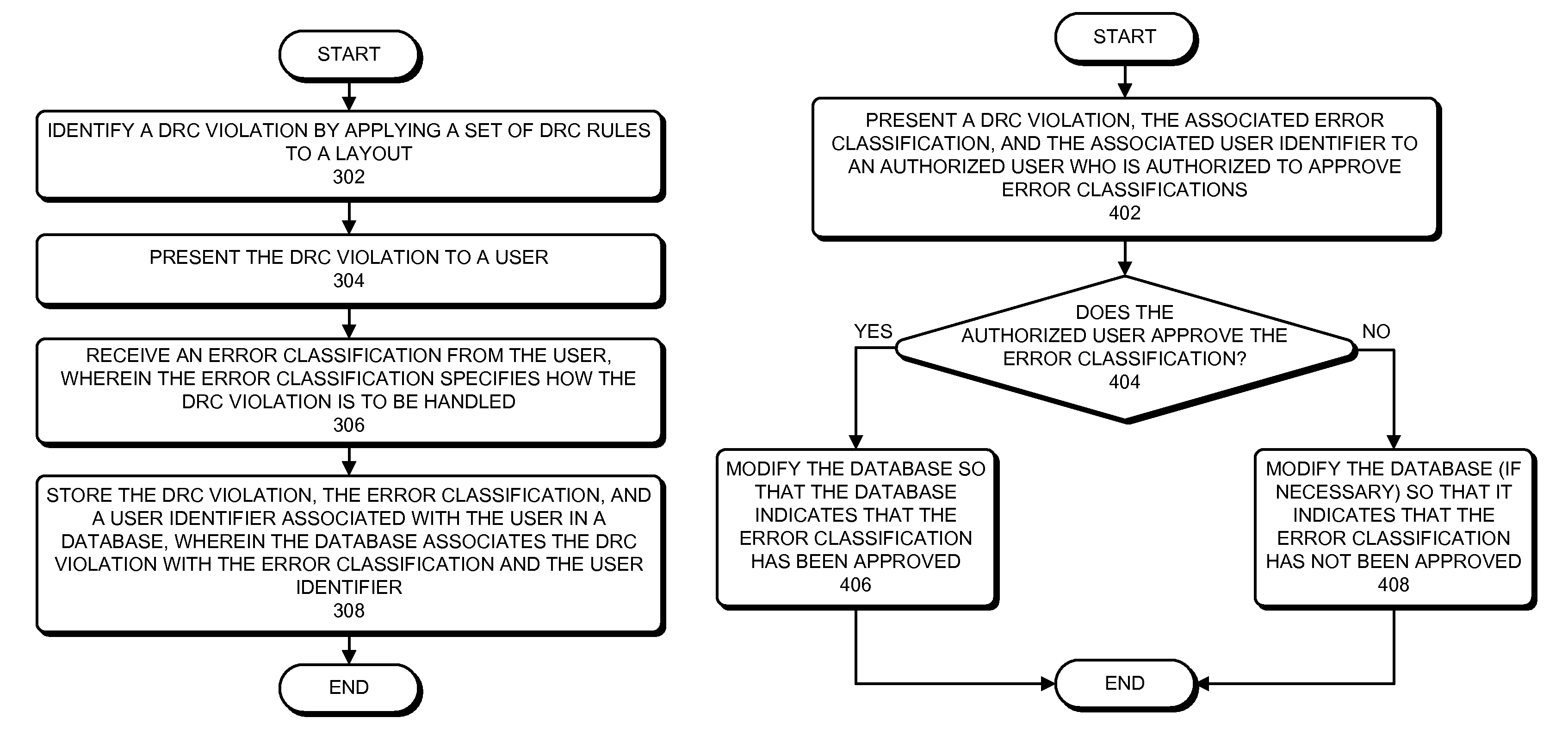
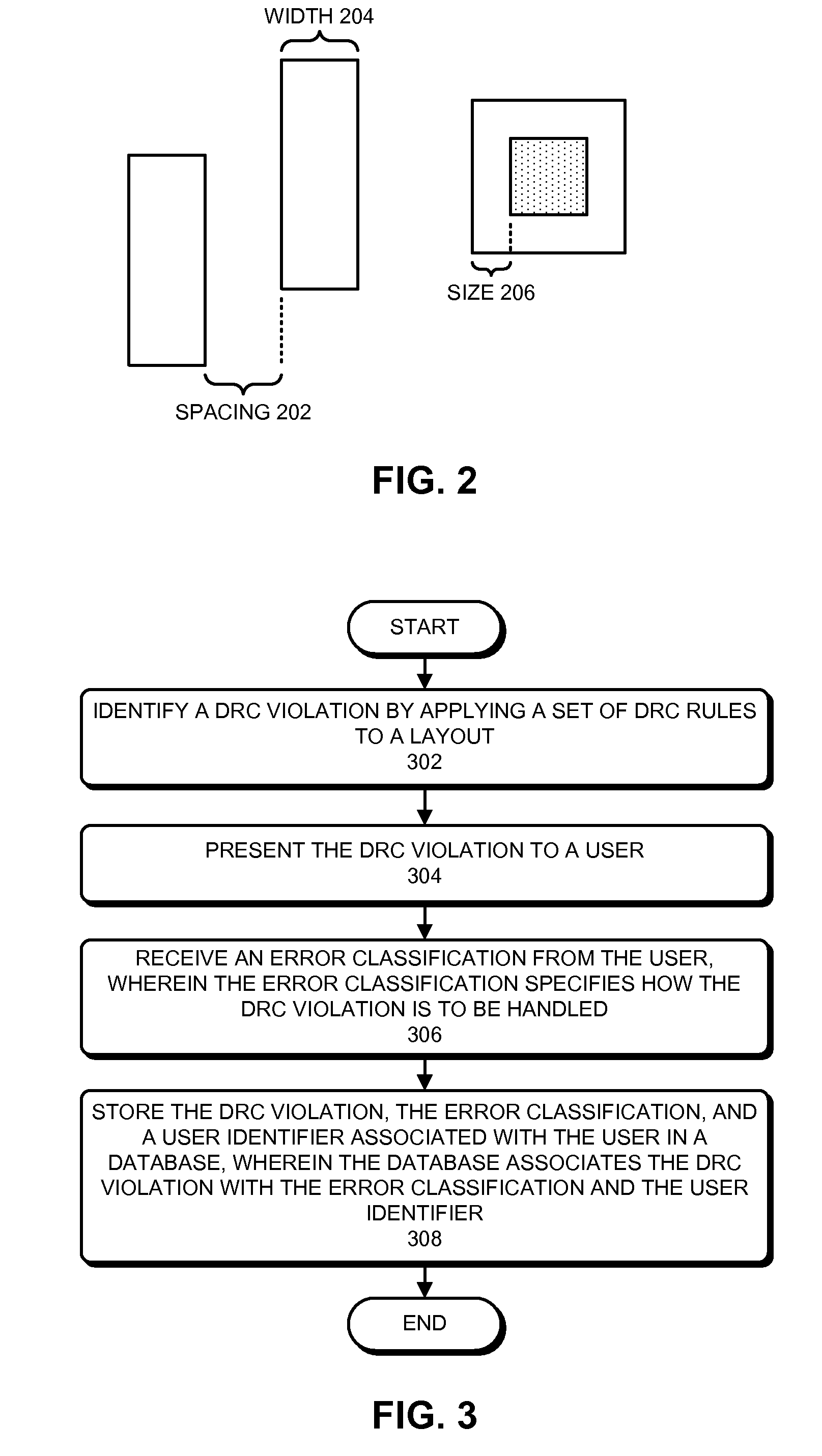
Method and apparatus for managing violations and error classifications during physical verification
ActiveUS8091055B2Increase probabilitySpeeding up applicationDigital data processing detailsComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionPhysical verificationUser identifier
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method and apparatus for managing violations and error classifications during physical verification
ActiveUS20100192113A1Increase probabilitySpeeding up applicationDigital data processing detailsComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionPhysical verificationUser identifier
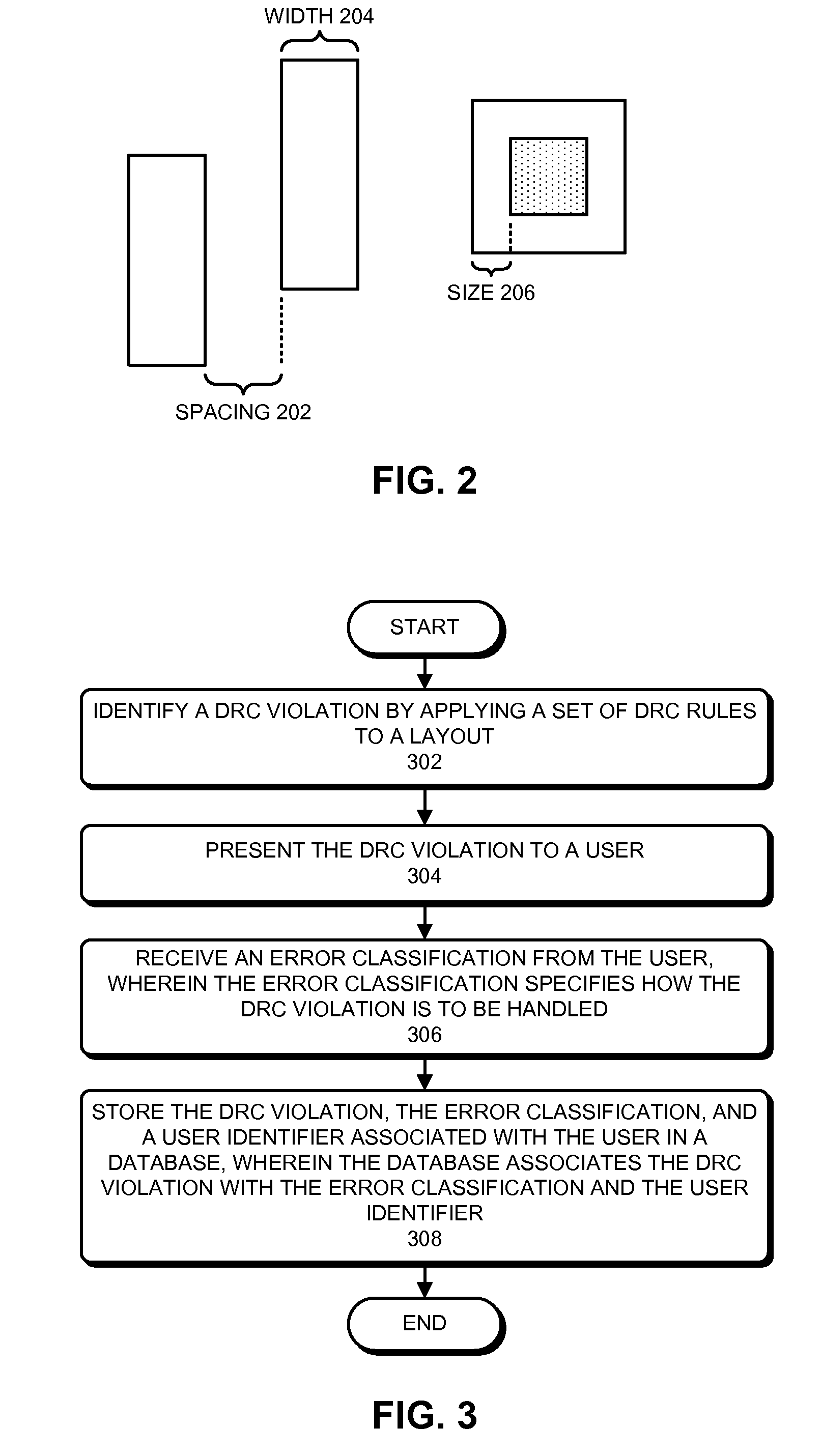
Some embodiments provide a system for managing violations during physical verification. The system may identify a design-rule-check (DRC) violation by applying a set of DRC rules to a layout. The system can then receive an error classification from the user which specifies how the DRC violation is to be handled. Next, the system can store the DRC violation, the user-selected error classification, and a user identifier associated with the user in a database. If the user is not authorized to approve the error classification, the database can indicate that the error classification has not been approved. Later, a user who is authorized to approve the error classification can approve the error classification. The system can determine if a cell is known, and if so, the system can use the violations and error classifications stored in the database to speed up the verification process.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Optimization method of capturing power consumption in scan test
InactiveCN103091620AReduce capture power consumptionElectronic circuit testingSpecial data processing applicationsTest designTest vector
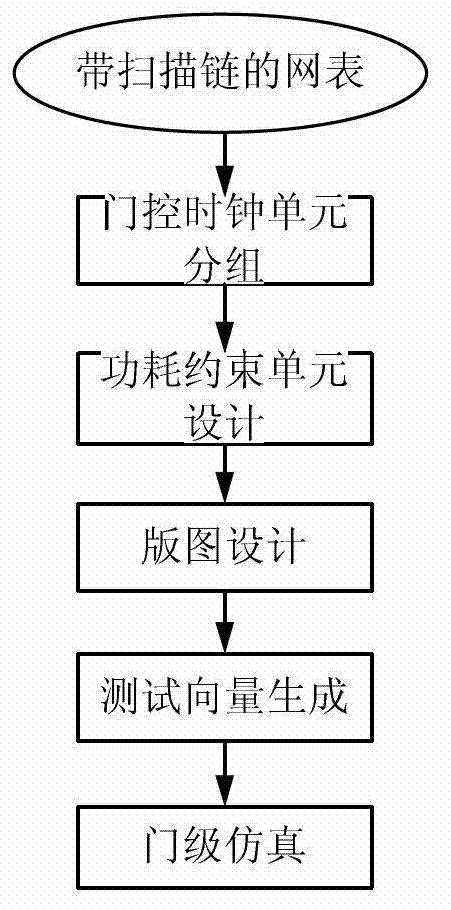
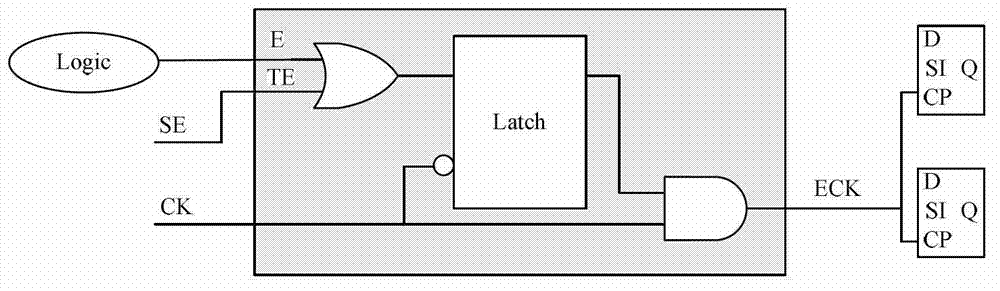
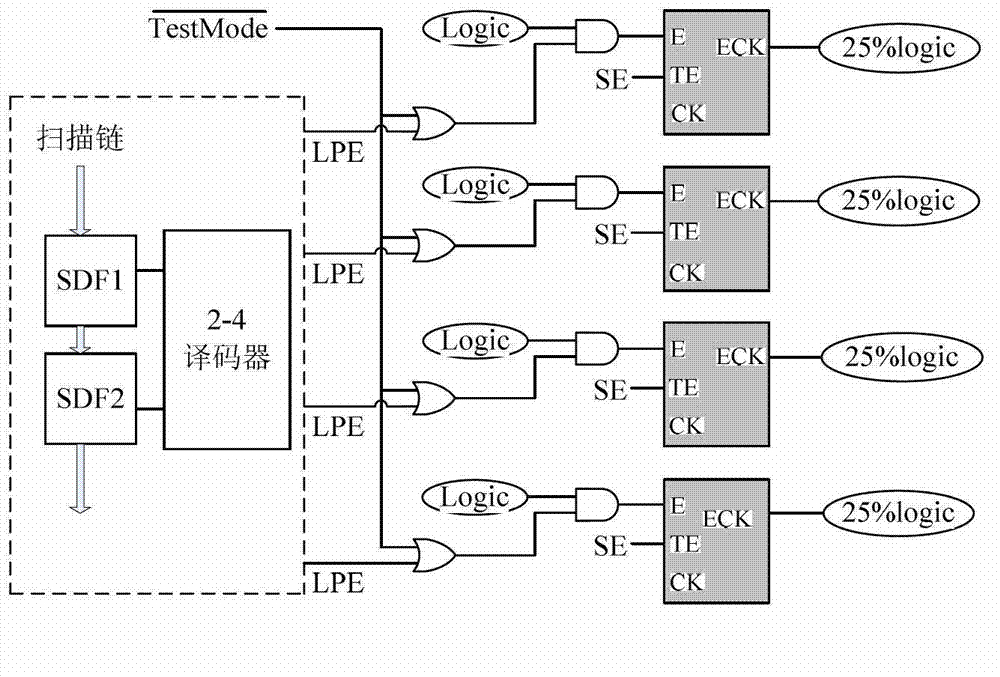
The invention discloses an optimization method of capturing power consumption in a scan test. The optimization method of capturing power consumption in the scan test comprises the following steps: generating a netlist with a scan chain; grouping gating control clock units; designing a power constrain unit; combining with the generated netlist with the scan chain, conducting chip layout design which comprises a floorpan, a layout, a clock tree sythesis and wiring; reading a gate-level netlist with a scan structure, a process library, a timing sequence constrain file and a test protocol into an automatic test vector generating tool after the chip layout design is completed, conducting testability design rule checking, and generating a test vector; and conducting gate-level simulation to the test vector generated. By means of the optimization method of capturing the power consumption in the scan test, the capturing power consumption in a test process can be reduced significantly, the reduction of coverage or the sharp increase of the quantity of test vectors is not generated, changing of a test design process is needless, and realization is easy.
Owner:JIANGSU SEUIC TECH CO LTD
Programmable Design Rule Checking
InactiveUS20090106715A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringDesign rule checking
An analog design-rule-check tool analyzes a microdevice design, such as an integrated circuit design, to identify occurrences of geometric elements that share a specified relationship. When the tool identifies such an occurrence of these geometric elements, it will associate or “cluster” these geometric elements together into an identifiable unit. For specified “clusters” of geometric elements, the analog design-rule-check tool will then determine the value of a measurement or measurements required by a user. Once the analog design-rule-check tool has determined the necessary measurement values, it will use those values to evaluate the function describing a model.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Pattern forming method and pattern verifying method
InactiveUS20080184183A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGuidelineEngineering
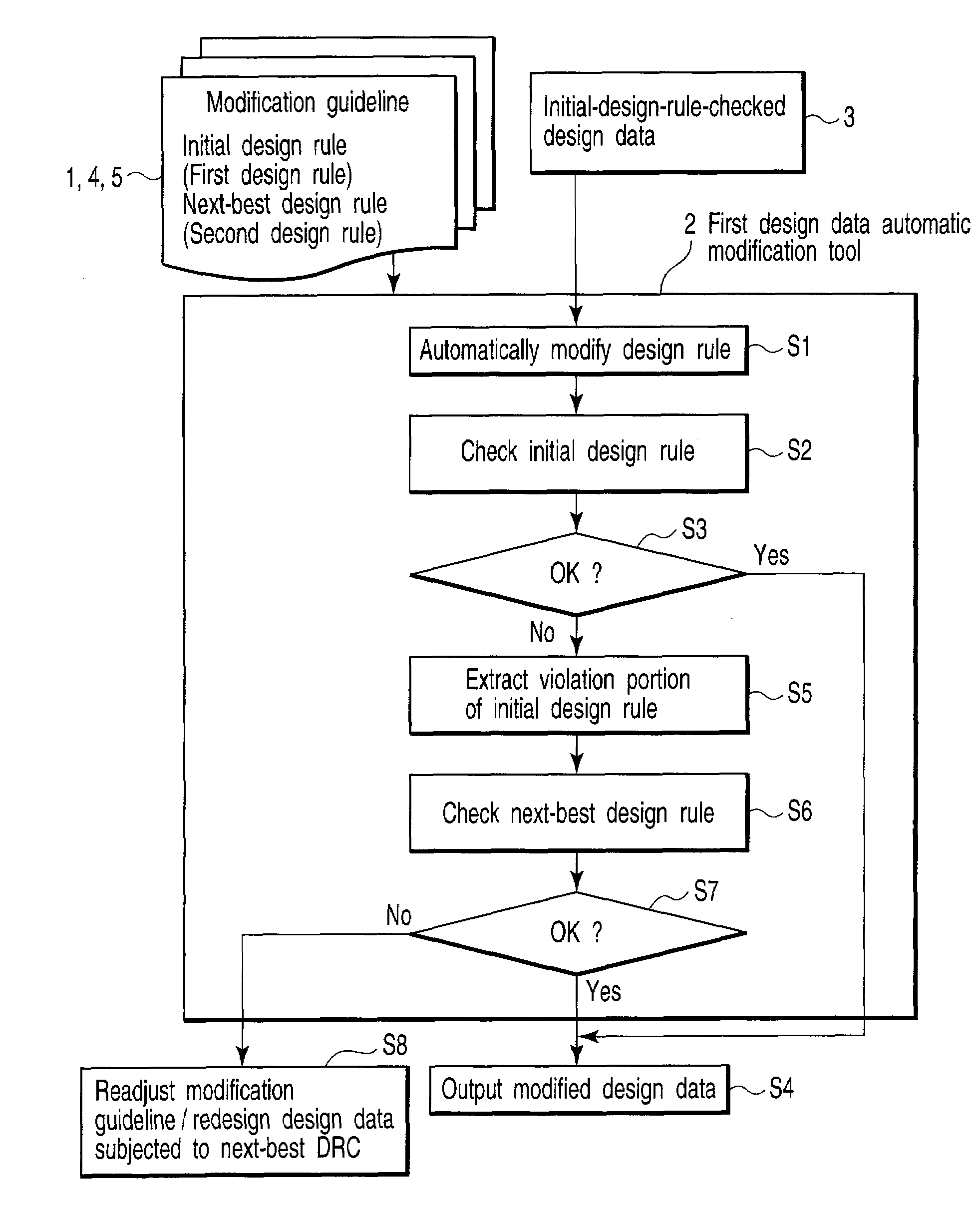
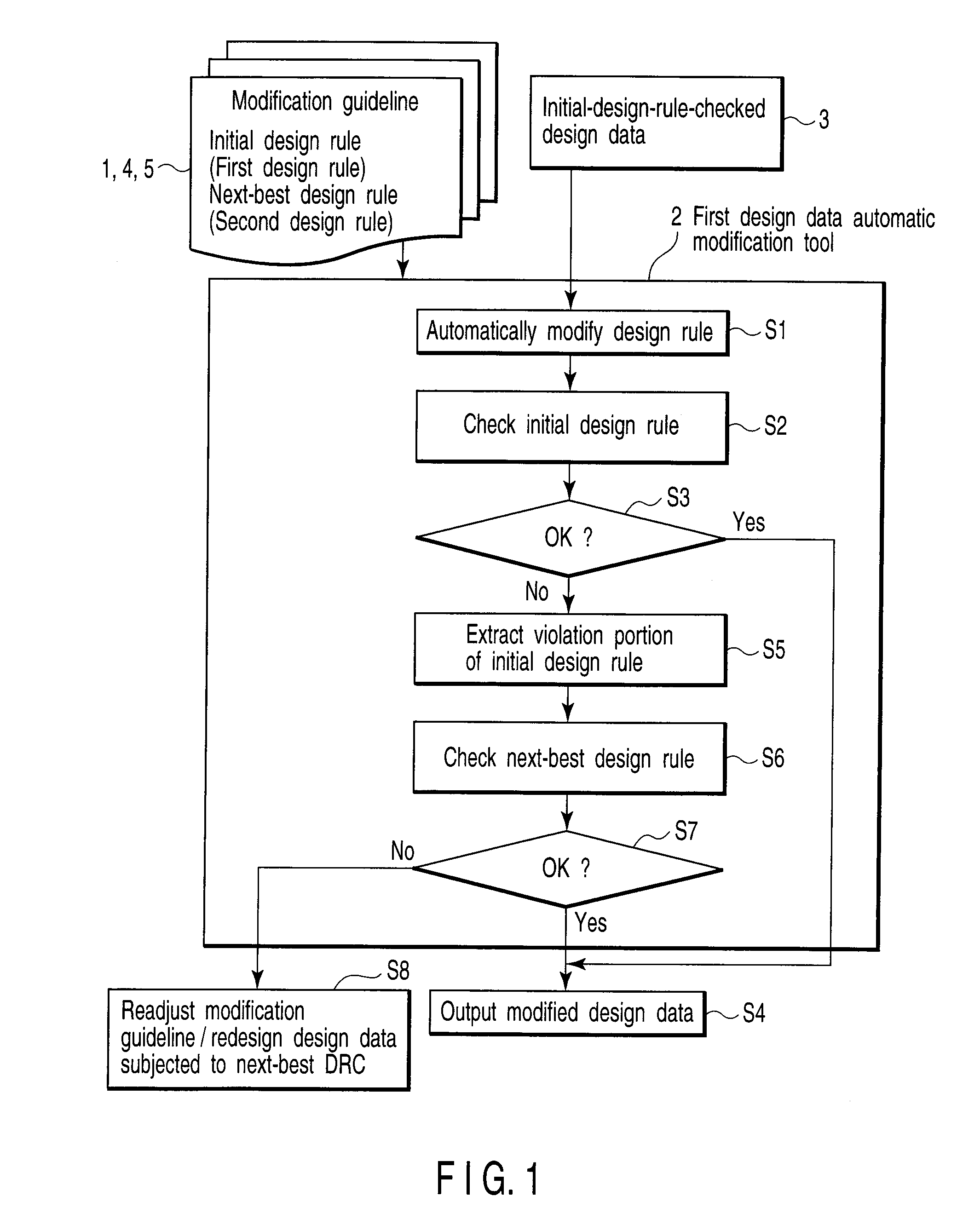
A pattern forming method including modifying design data subjected to a first design rule check in design data of a pattern to be formed in a semiconductor substrate, performing the first design rule check to the modified design data again, outputting the modified design data which does not violate the first design rule as pattern forming design data used in actual pattern formation, and performing a second design rule check having an allowable range wider than that of the first design rule to the modified design data which violates the first design rule, and outputting the modified design data which does not violate the second design rule as the pattern forming design data, and redesigning the pattern to satisfy the second design rule or adjusting the modification guideline such that the modified design data which violates the second design rule satisfies the second design rule.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Via enclosure rule check in a multi-wide object class design layout
InactiveUS6883149B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProgramming languageObject Class
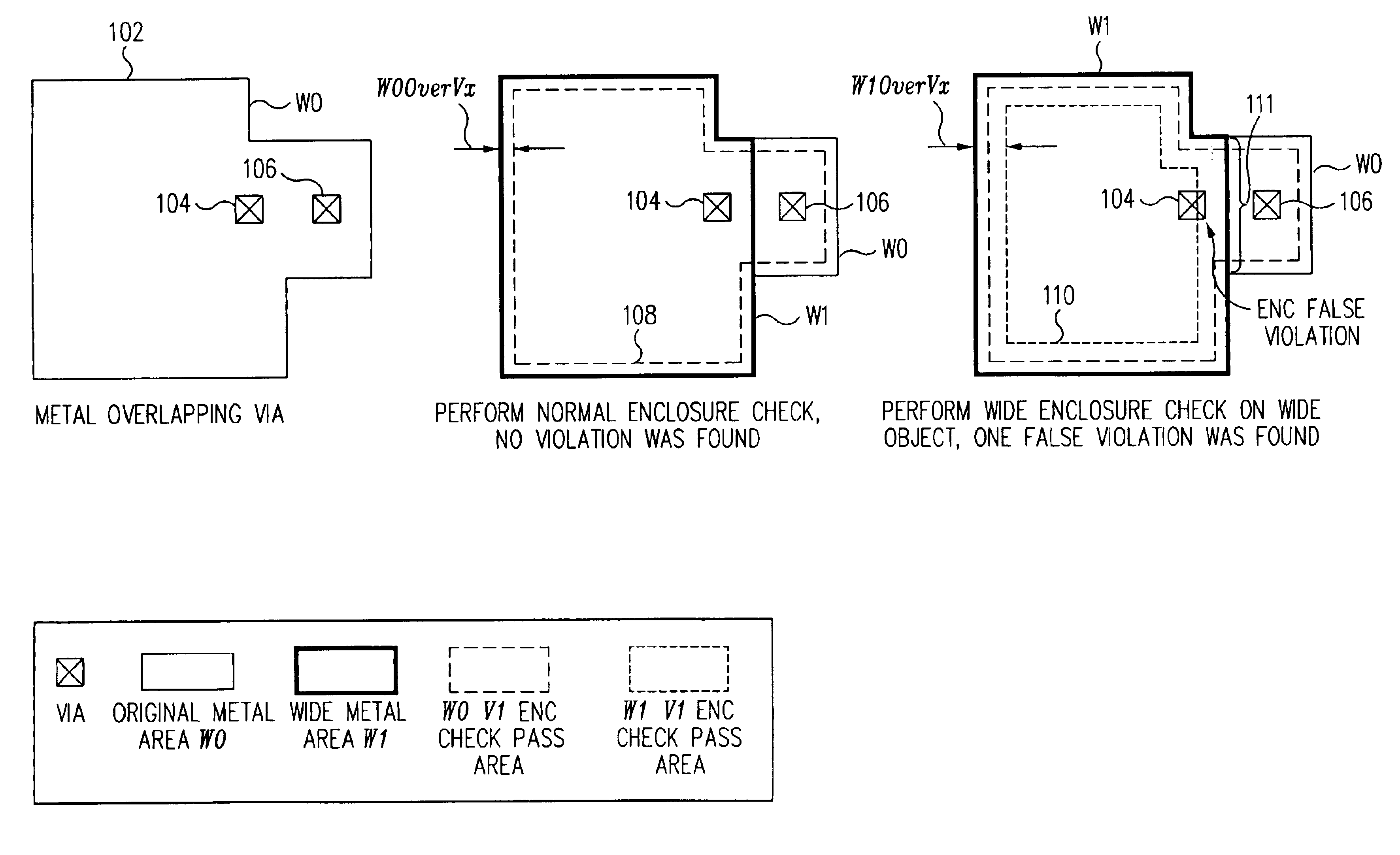
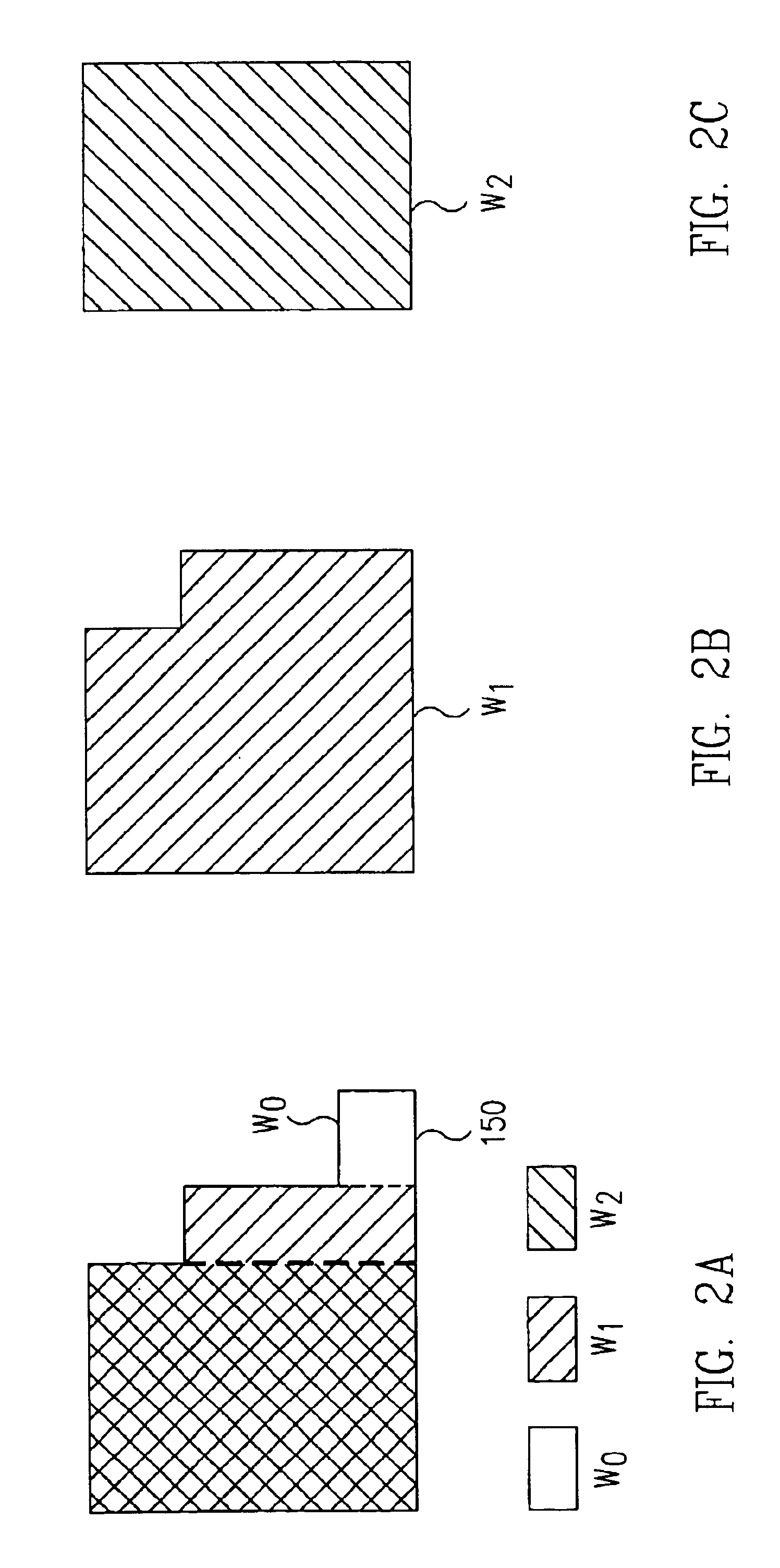
In a multi-wide class design layout, design rule checks for enclosure of multi wide class objects prevent false errors or false passes by performing such checks against the non-virtual boundaries of a wide class object, and not against the virtual boundaries. An exemplary embodiment provides a method for identifying as a violation, for each wide class wi object, any geometry on another layer which is located at least partially inside the wi object and has any portion thereof located within a distance encli of any non-virtual boundary of the wi object. The exemplary method is preferably performed using effective wide class objects.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com