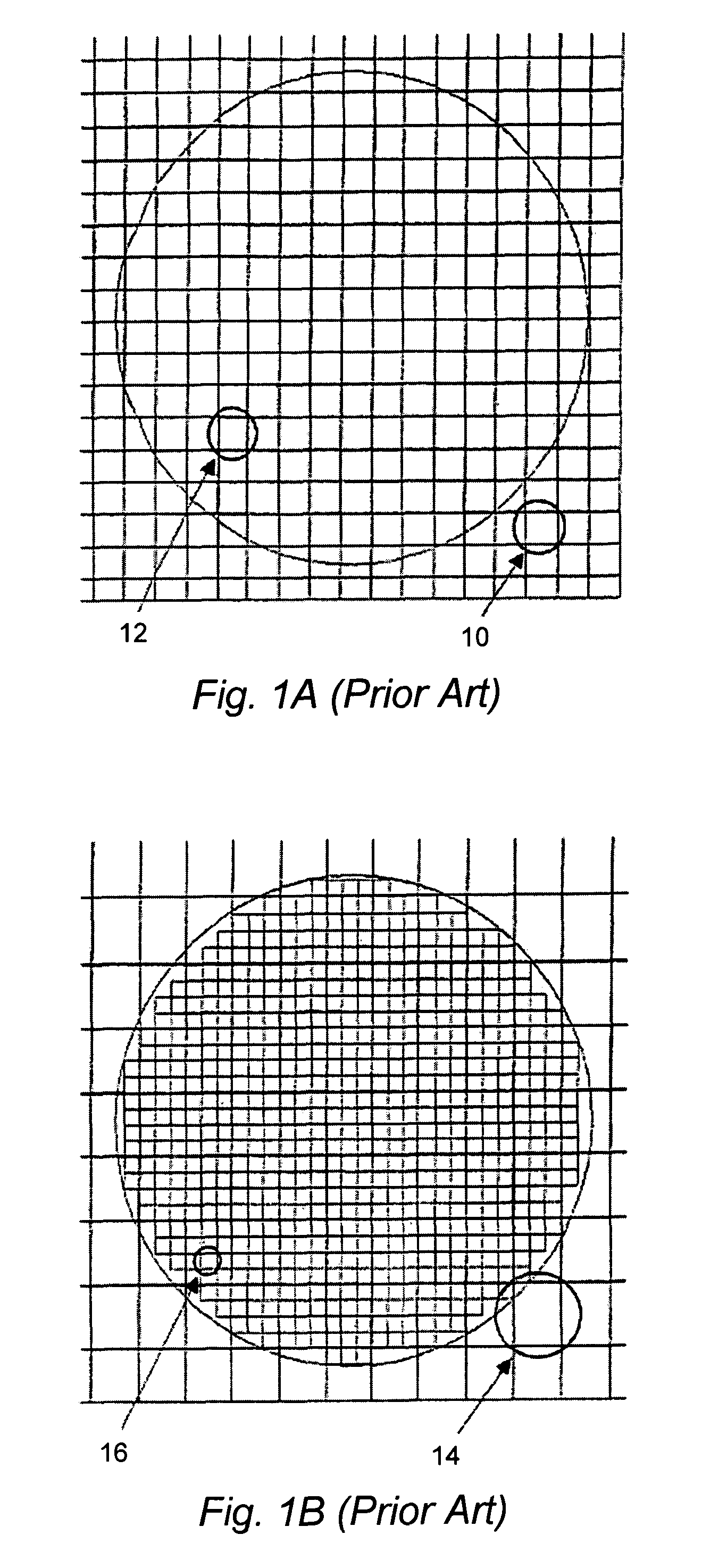
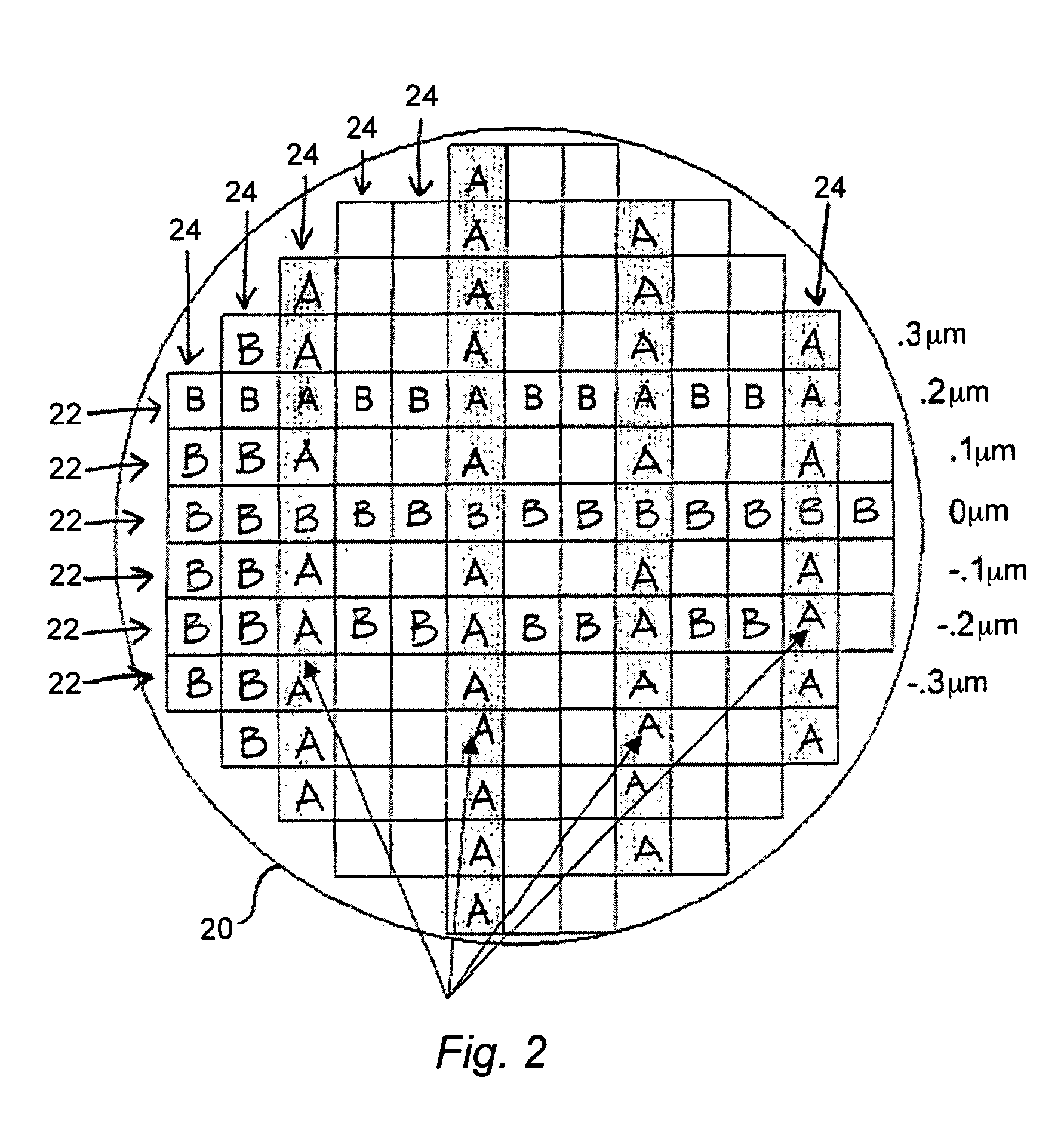
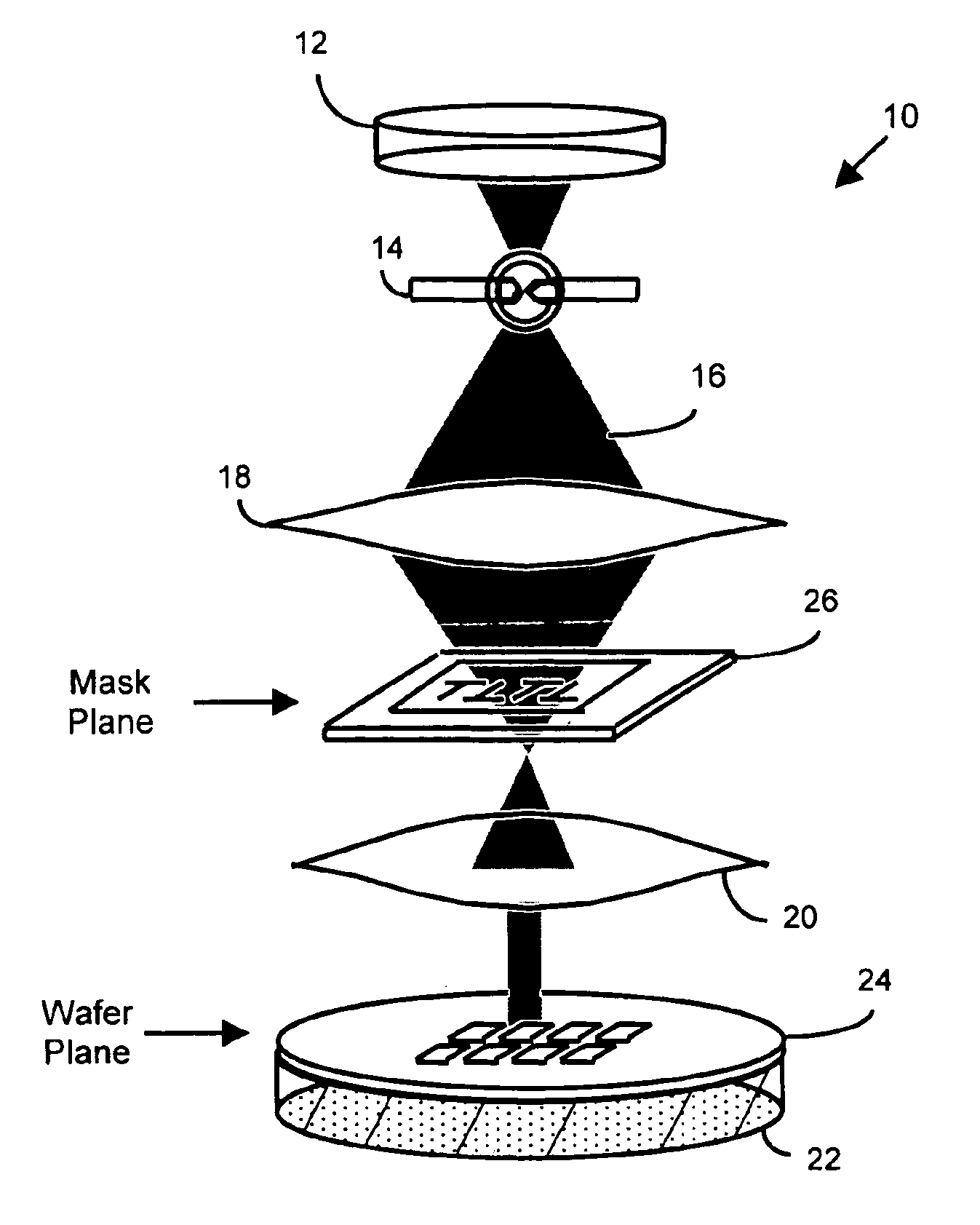
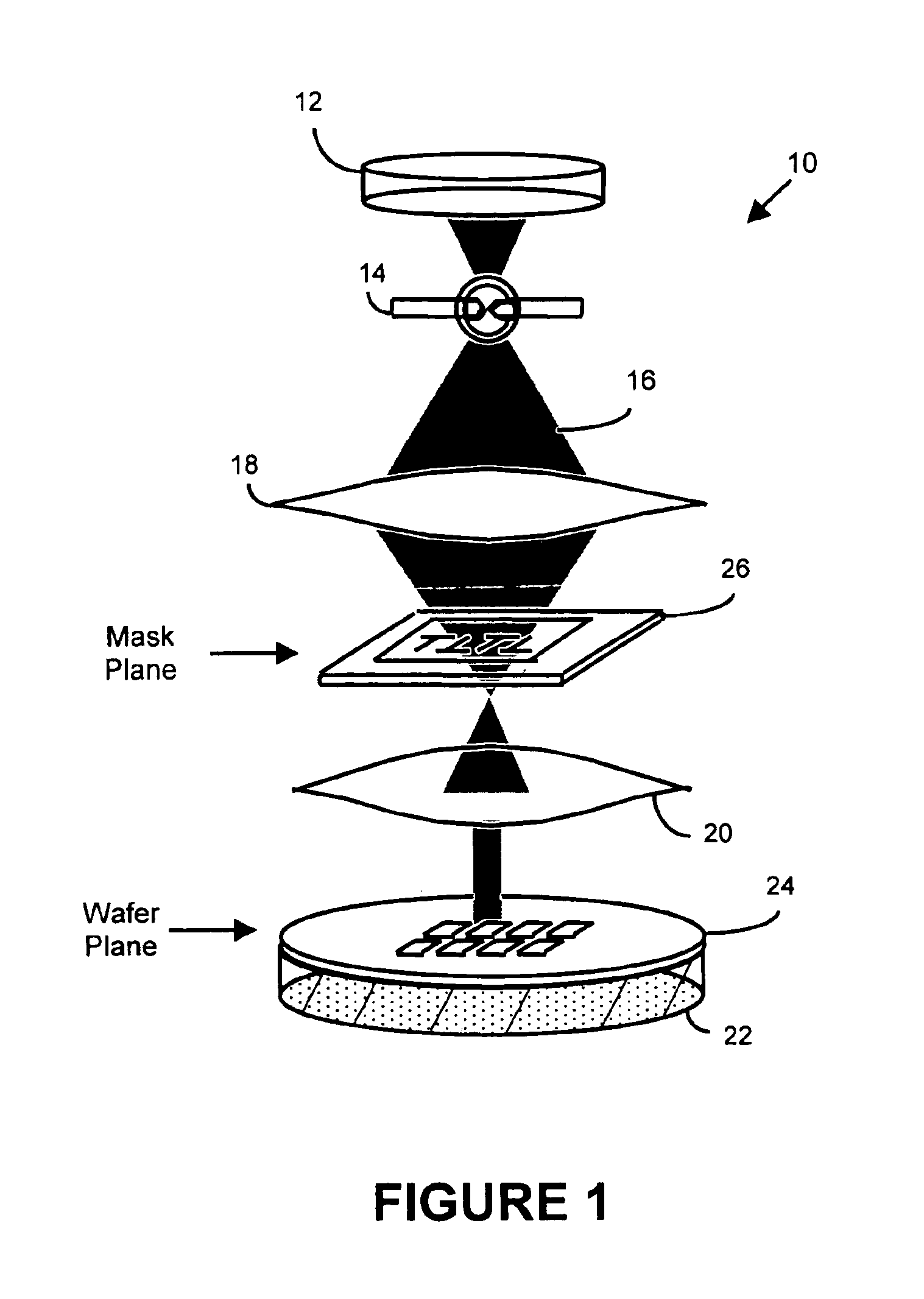
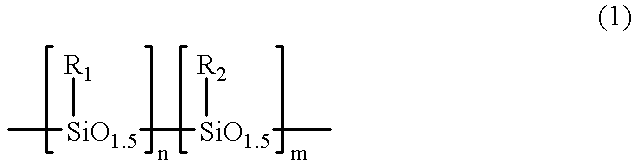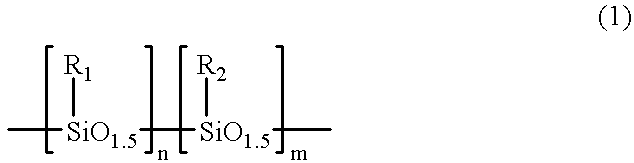Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2366 results about "Lithography process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
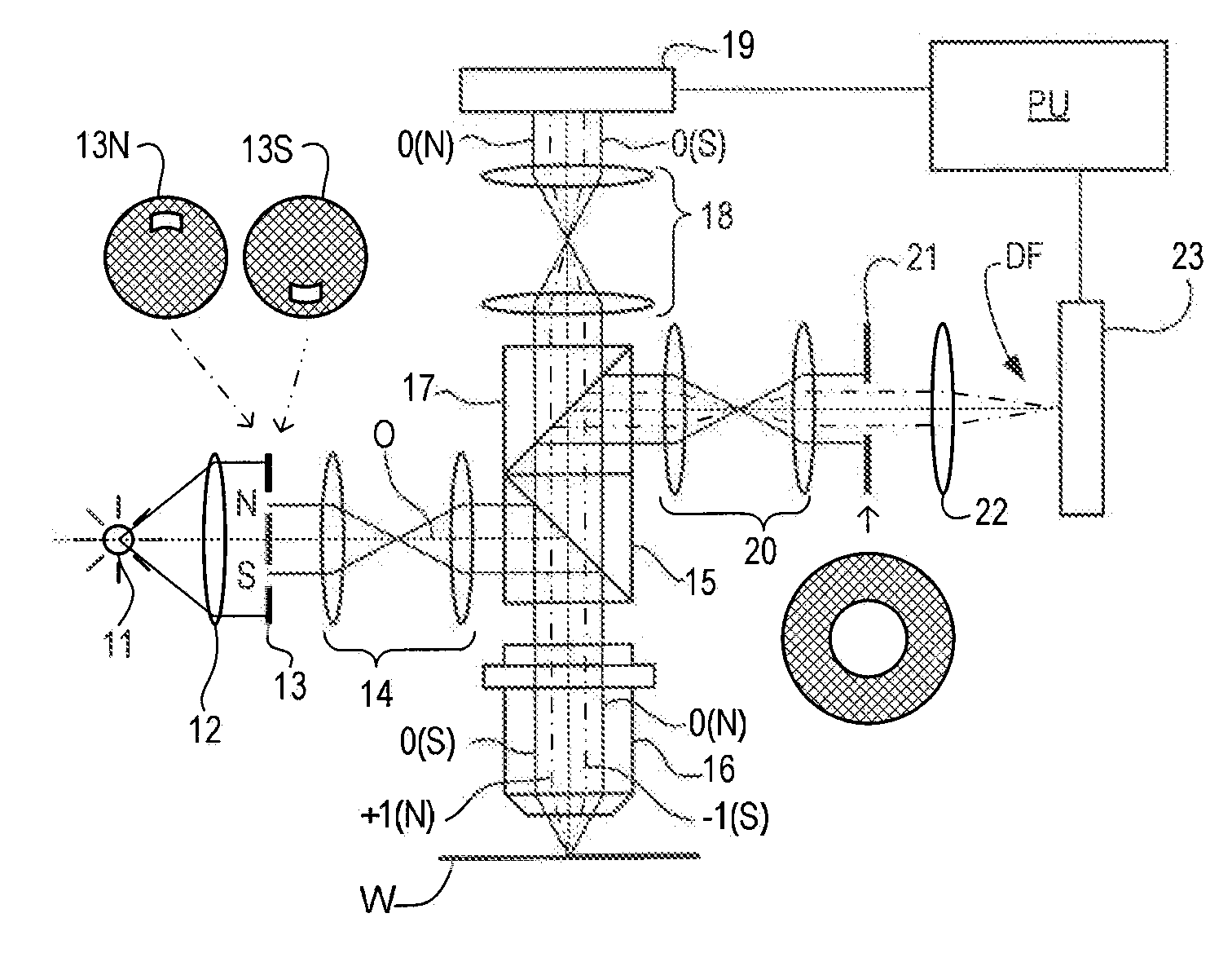
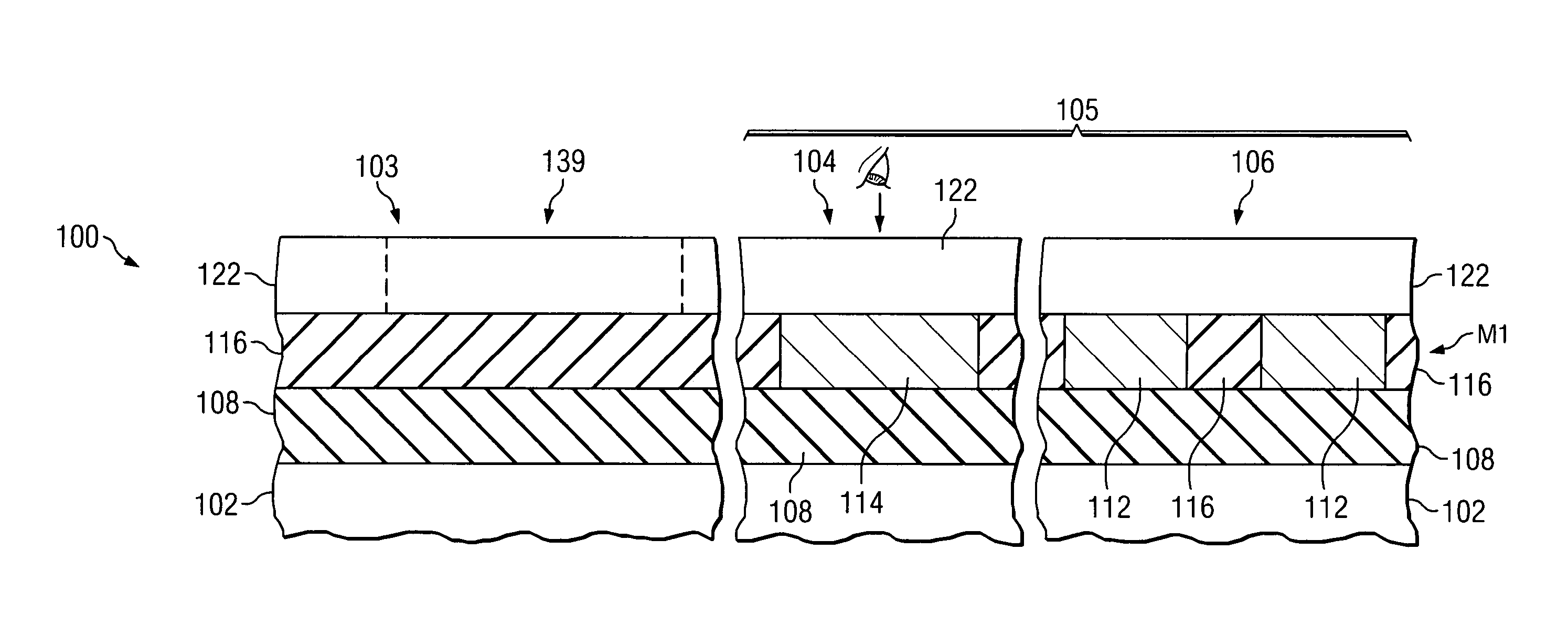
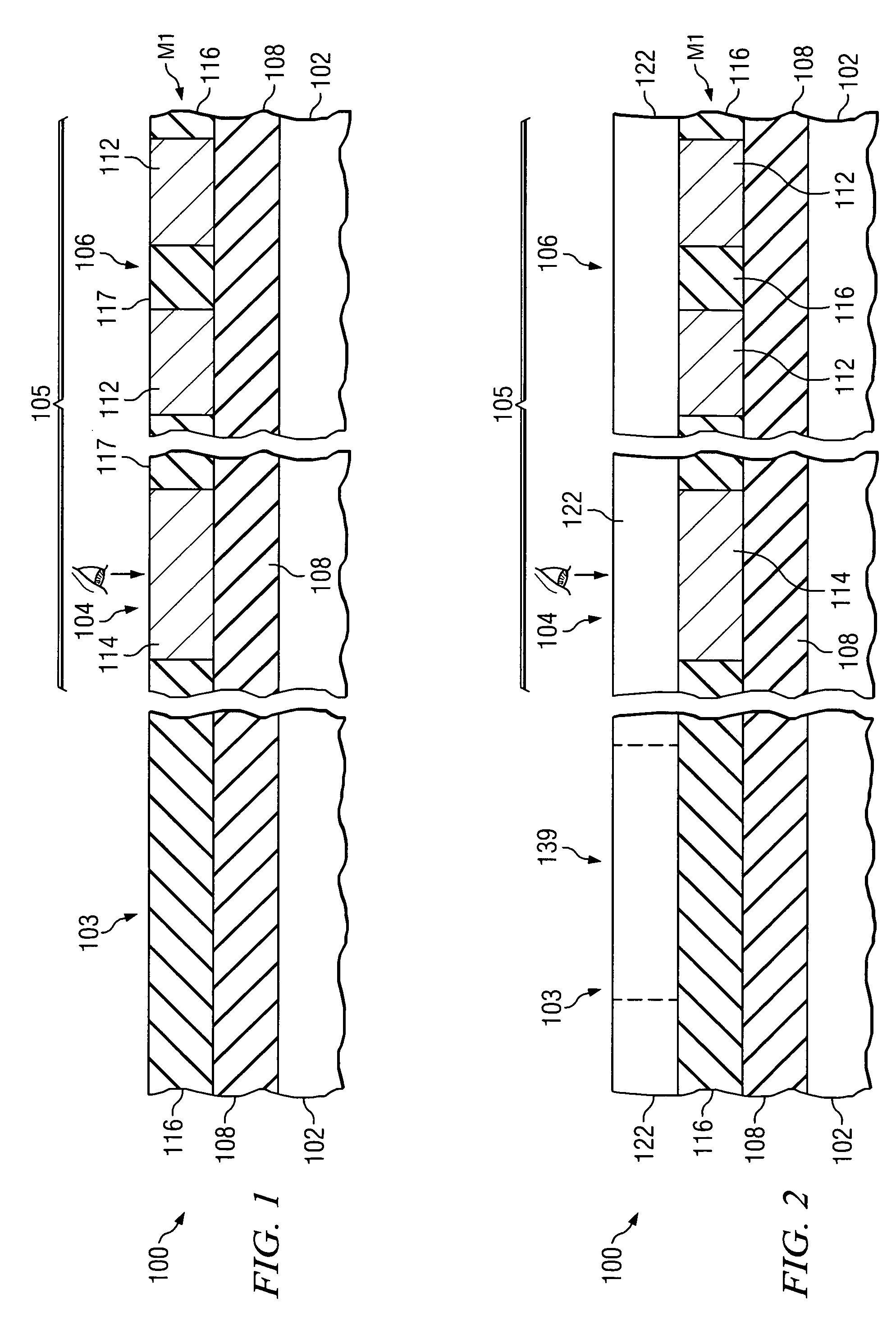
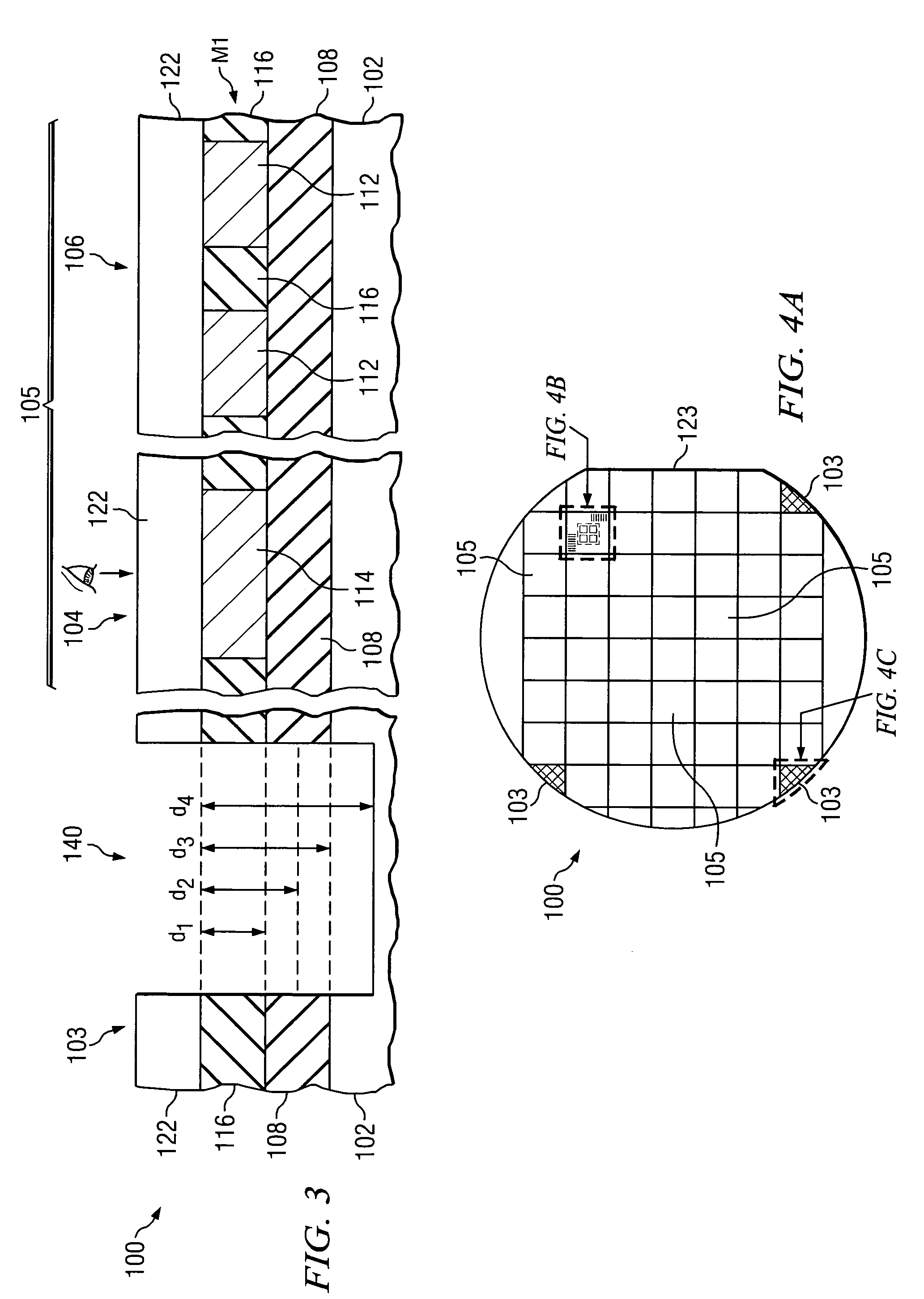
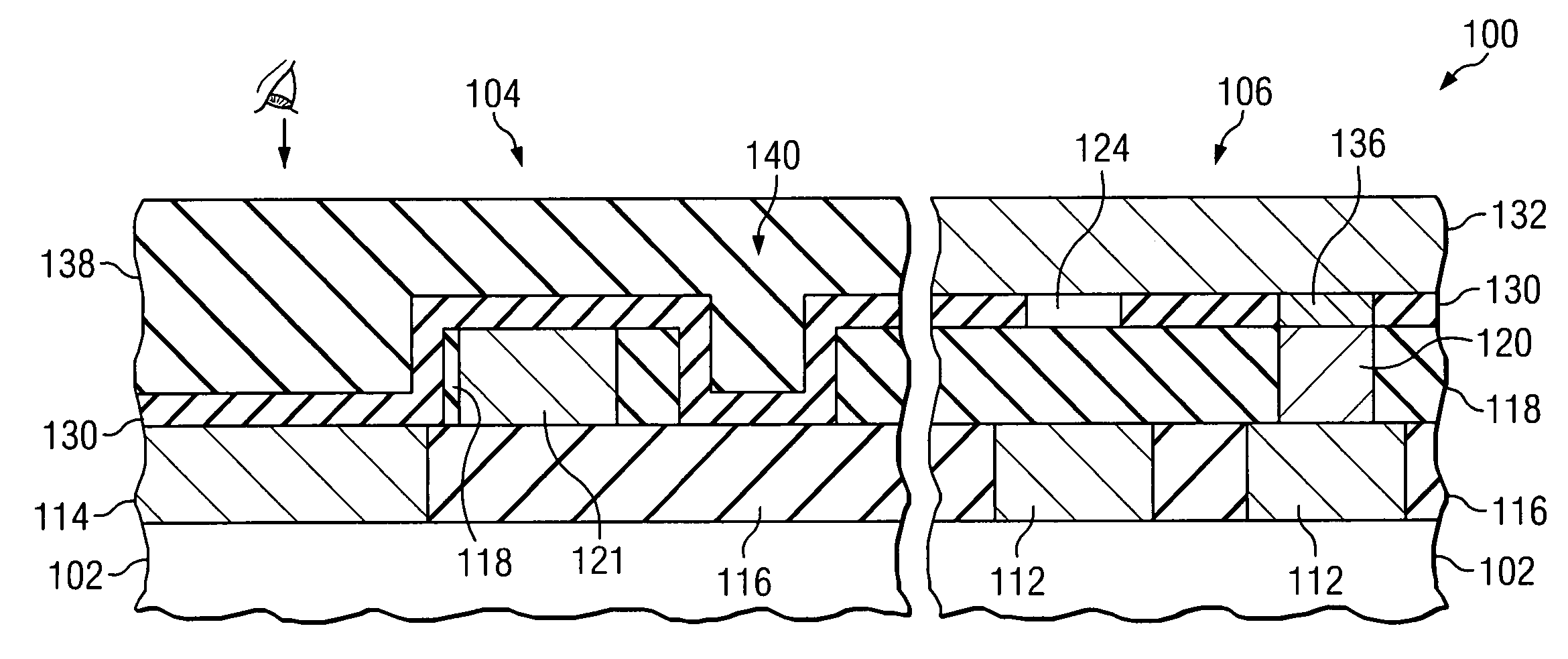
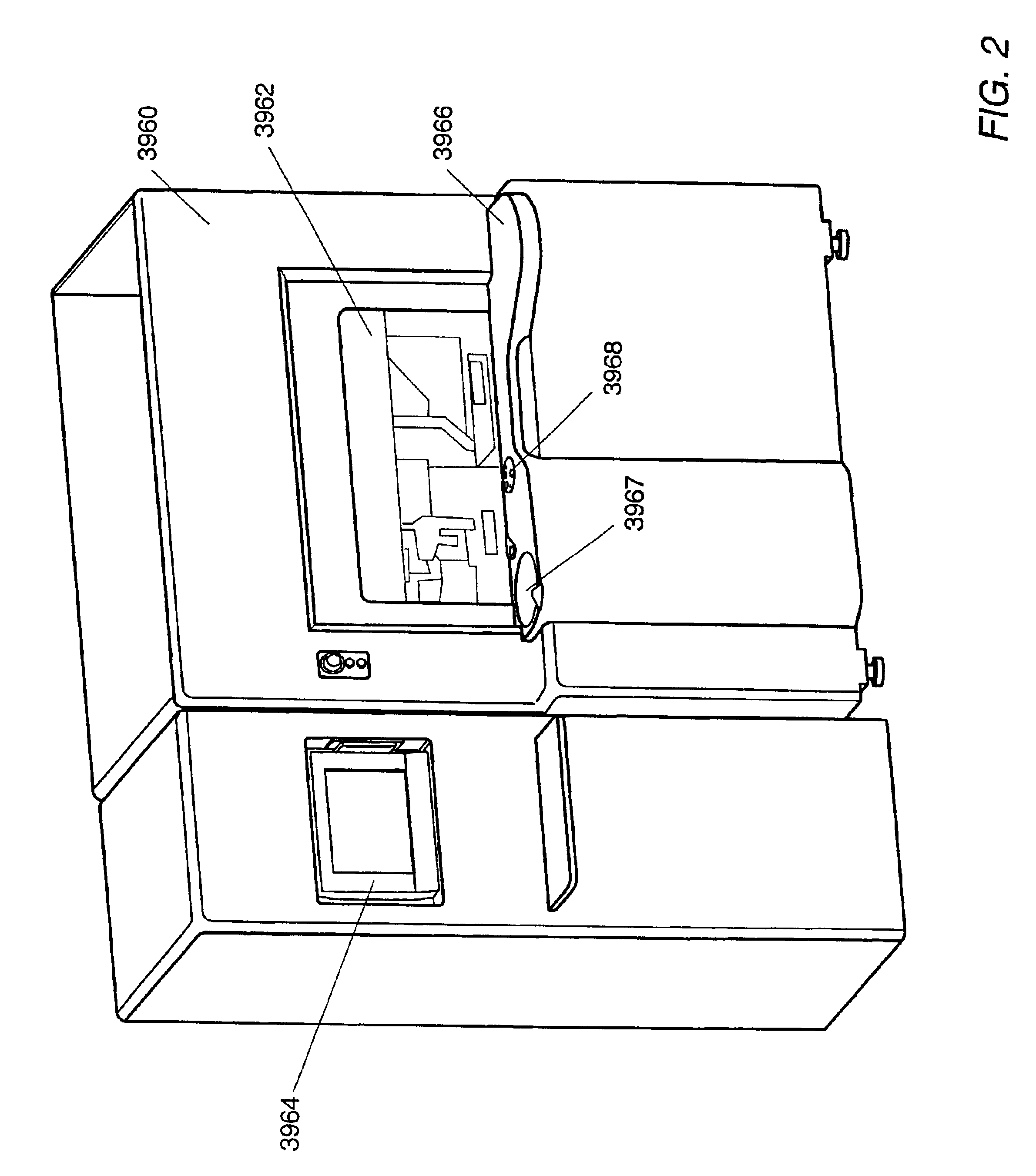
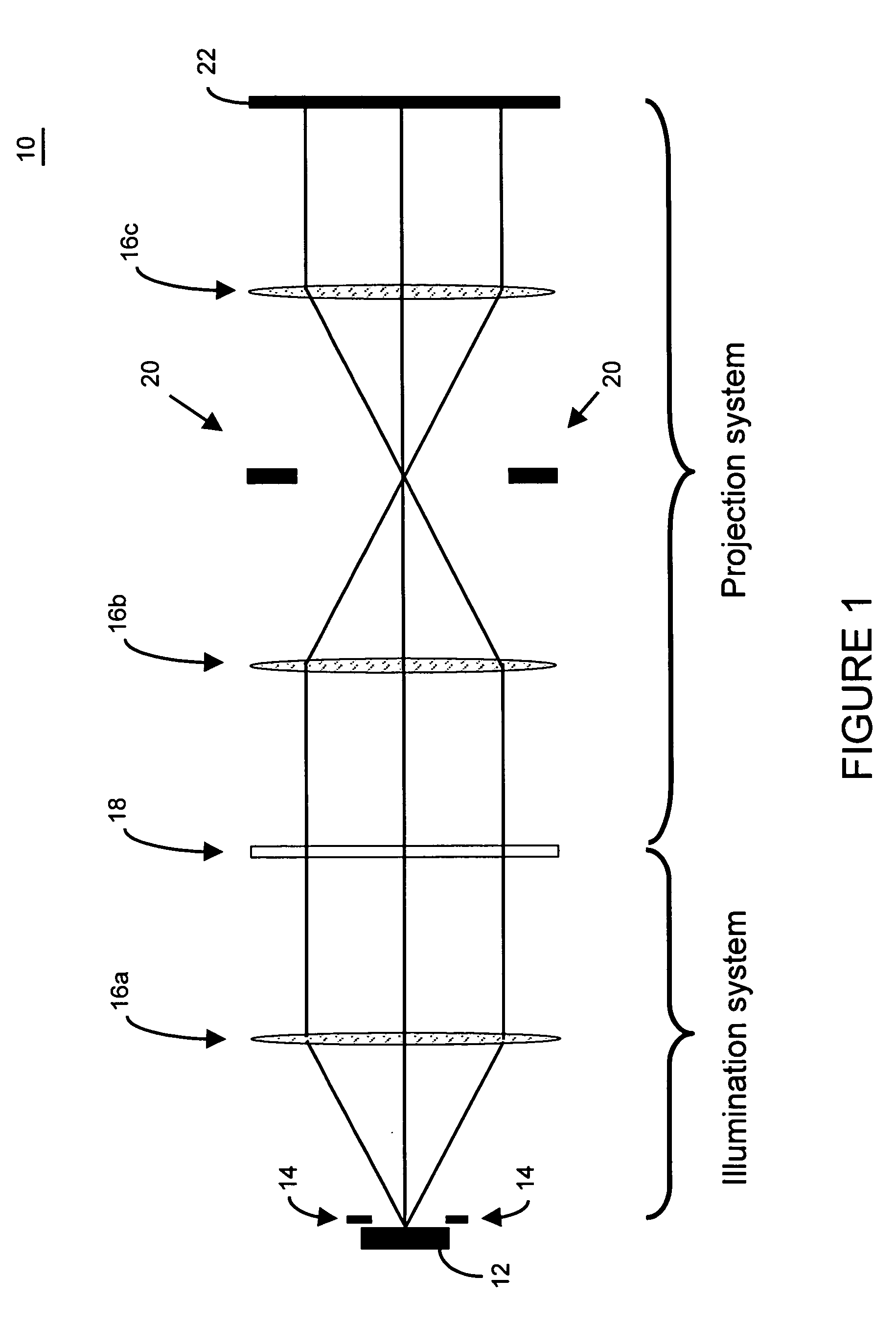
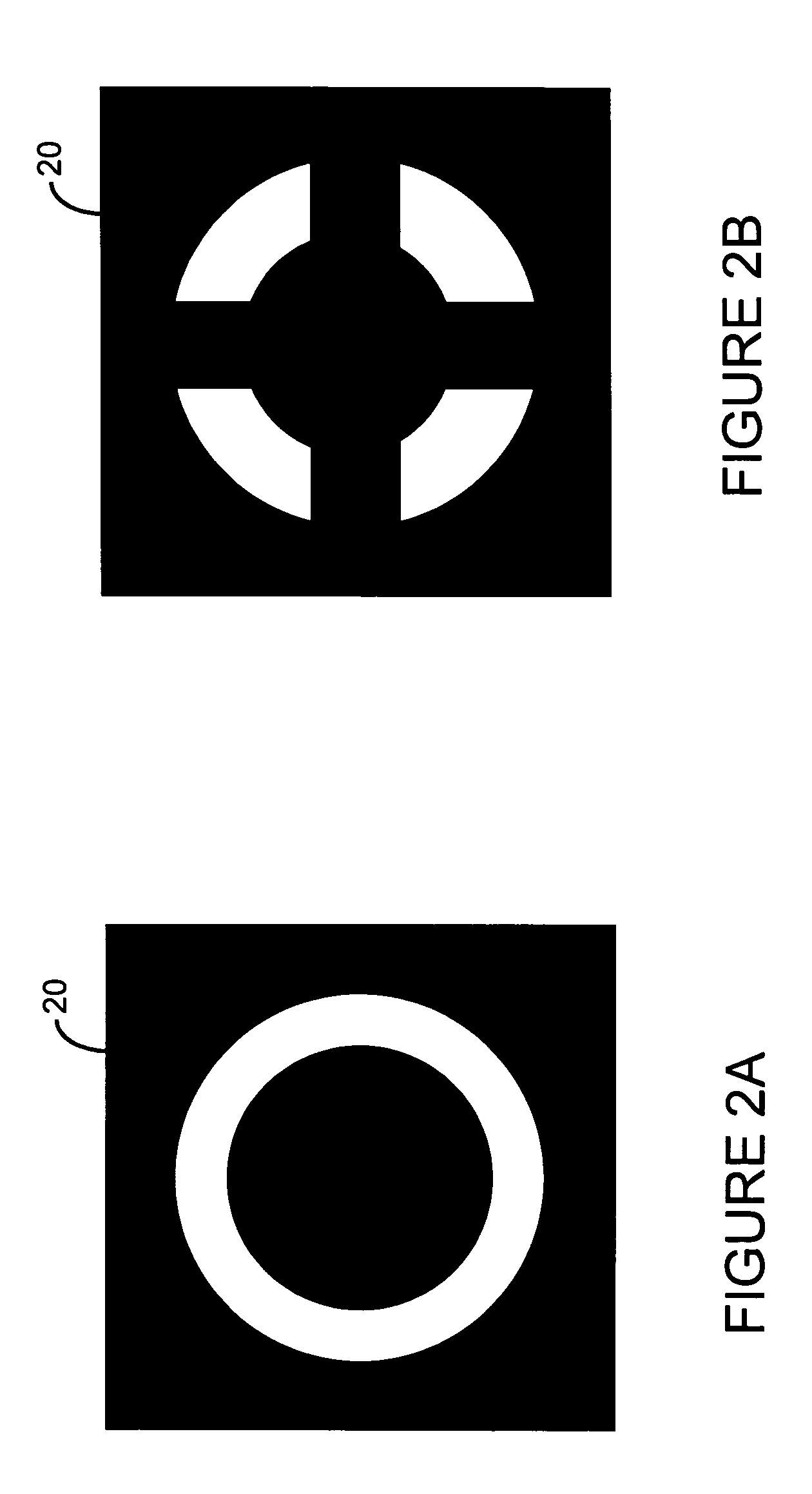
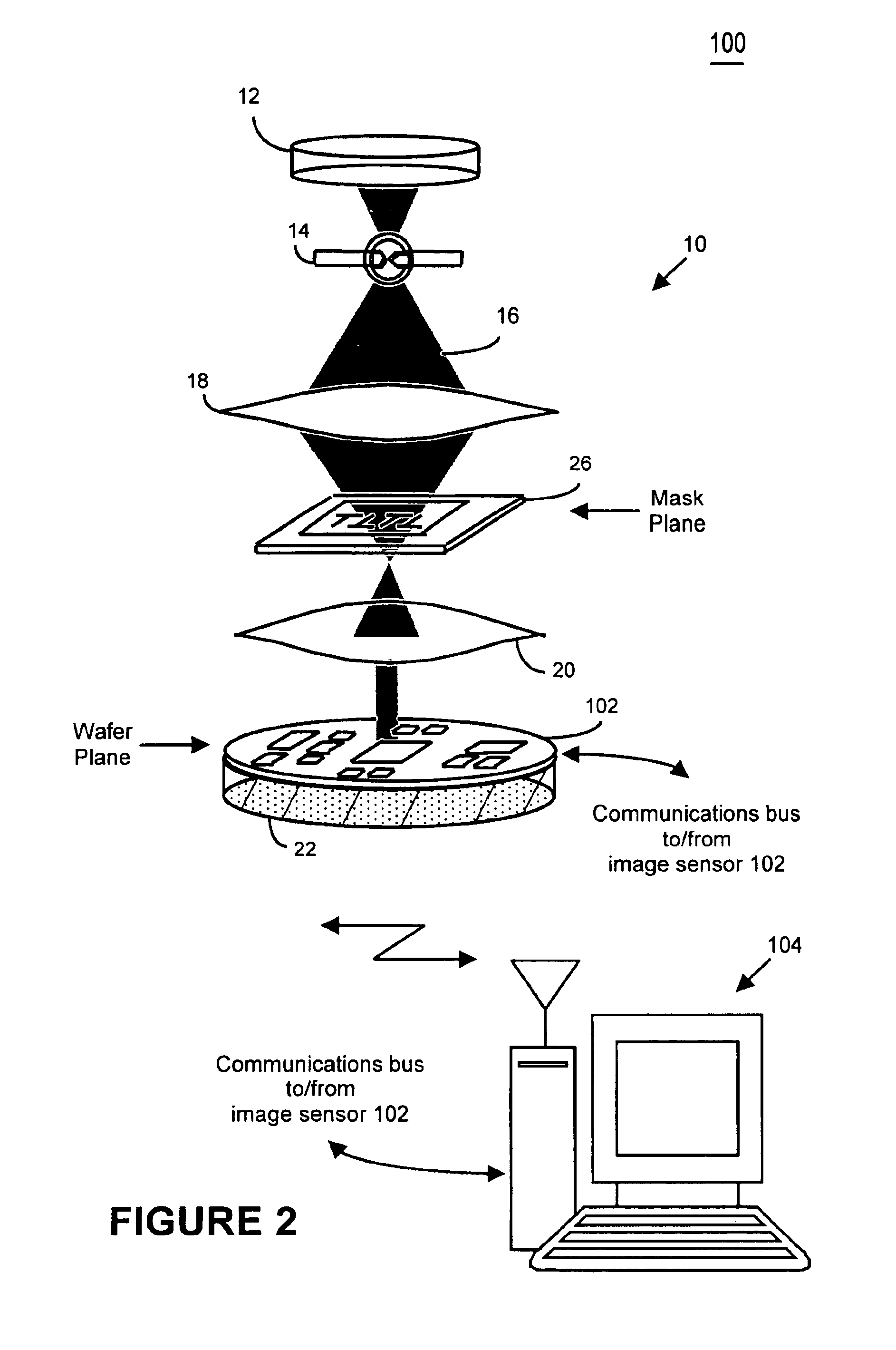
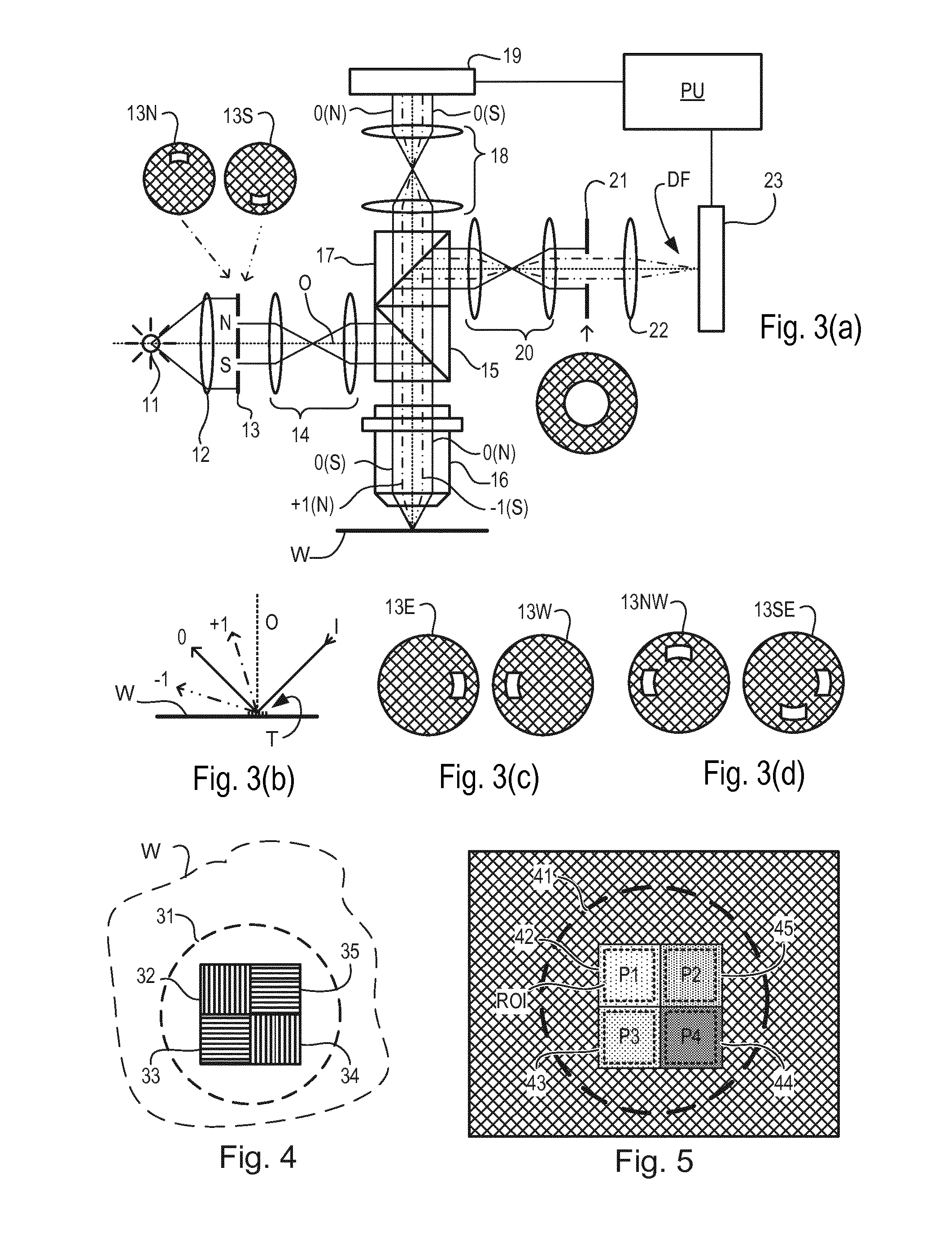
Metrology Method and Apparatus, and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20120242970A1Improve accuracyImprove throughputPhotomechanical apparatusOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMetrologyGrating
Methods are disclosed for measuring target structures formed by a lithographic process on a substrate. A grating or other structure within the target is smaller than an illumination spot and field of view of a measurement optical system. The position of an image of the component structure varies between measurements, and a first type of correction is applied to reduce the influence on the measured intensities, caused by differences in the optical path to and from different positions. A plurality of structures may be imaged simultaneously within the field of view of the optical system, and each corrected for its respective position. The measurements may comprise first and second images of the same target under different modes of illumination and / or imaging, for example in a dark field metrology application. A second type of correction may be applied to reduce the influence of asymmetry between the first and second modes of illumination or imaging, for example to permit a more accurate overly measurement in a semiconductor device manufacturing process.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
High precision orientation alignment and gap control stages for imprint lithography processes
InactiveUS6873087B1Achieve separationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesNanoinformaticsLithography processEngineering
Processes and associated devices for high precision positioning of a template an substrate during imprint lithography includes a calibration system with a course calibration stage and a fine orientation stage capable of maintaining a uniform gap between the template and substrate. The fine orientation stage includes a pair of flexure members having flexure joints for motion about a pivot point intersected by first and second orientation axes. Actuators lengthen or shorten to expand or contract the flexure members. Separation of the template is achieved using a peel-and-pull method that avoids destruction of imprinted features from the substrate.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Formation of discontinuous films during an imprint lithography process
ActiveUS6932934B2Low viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLithography processLithographic artist
The present invention is directed to methods for patterning a substrate by imprint lithography. An imprint lithography method includes placing a curable liquid on a substrate. A template may be contacted with the curable liquid. Surface forces at the interface of the curable liquid and the template cause the curable liquid to gather in an area defined by a lower surface of the template. Alternately, the curable liquid may fill one or more relatively shallow recesses in the template and the area under the template lower surface. Activating light is applied to the curable liquid to form a patterned layer on the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Step and repeat imprint lithography processes
The present invention is directed to methods for patterning a substrate by imprint lithography. Imprint lithography is a process in which a liquid is dispensed onto a substrate. A template is brought into contact with the liquid and the liquid is cured. The cured liquid includes an imprint of any patterns formed in the template. In one embodiment, the imprint process is designed to imprint only a portion of the substrate. The remainder of the substrate is imprinted by moving the template to a different portion of the template and repeating the imprint lithography process.
Owner:CANON KK
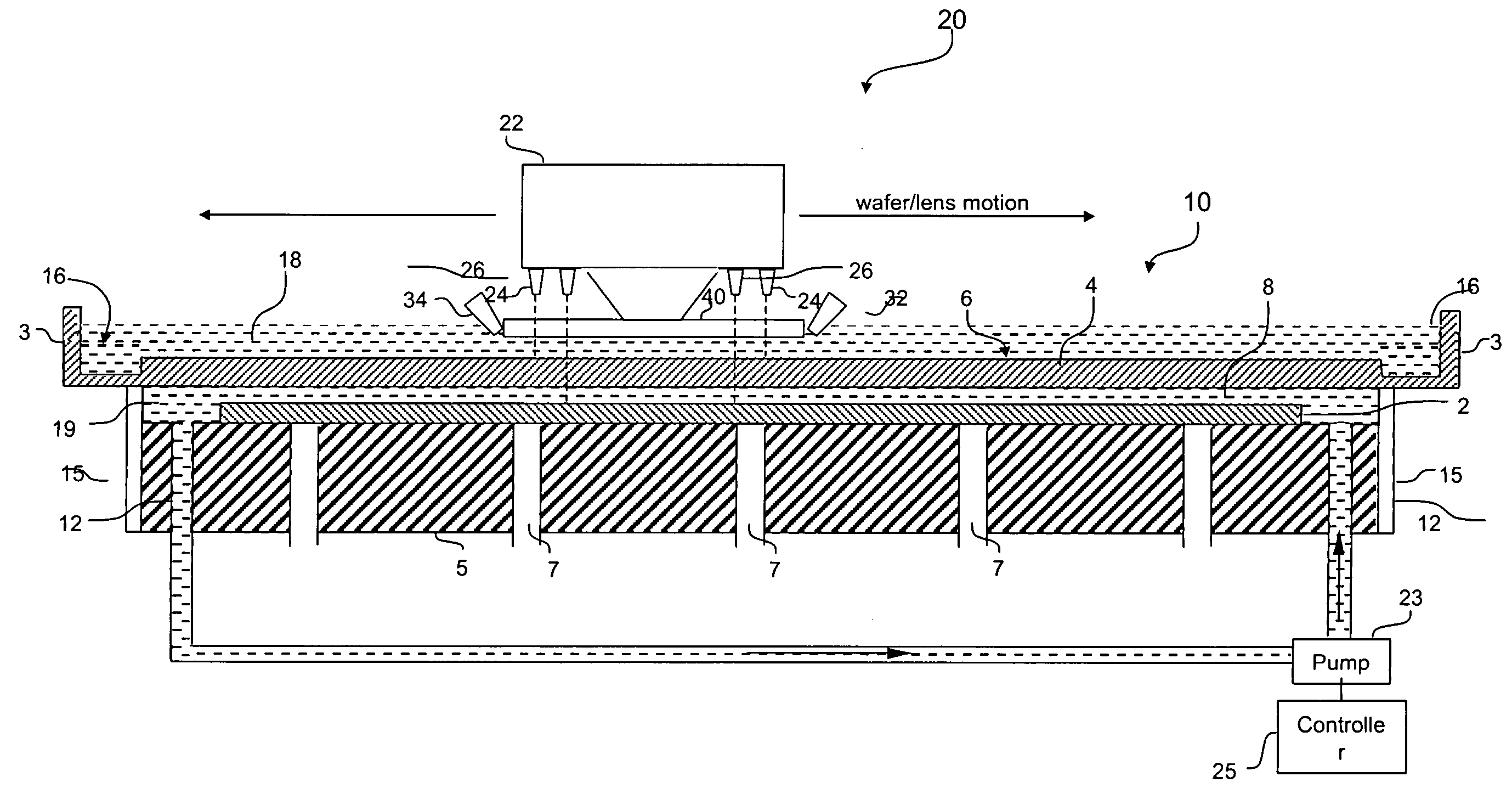
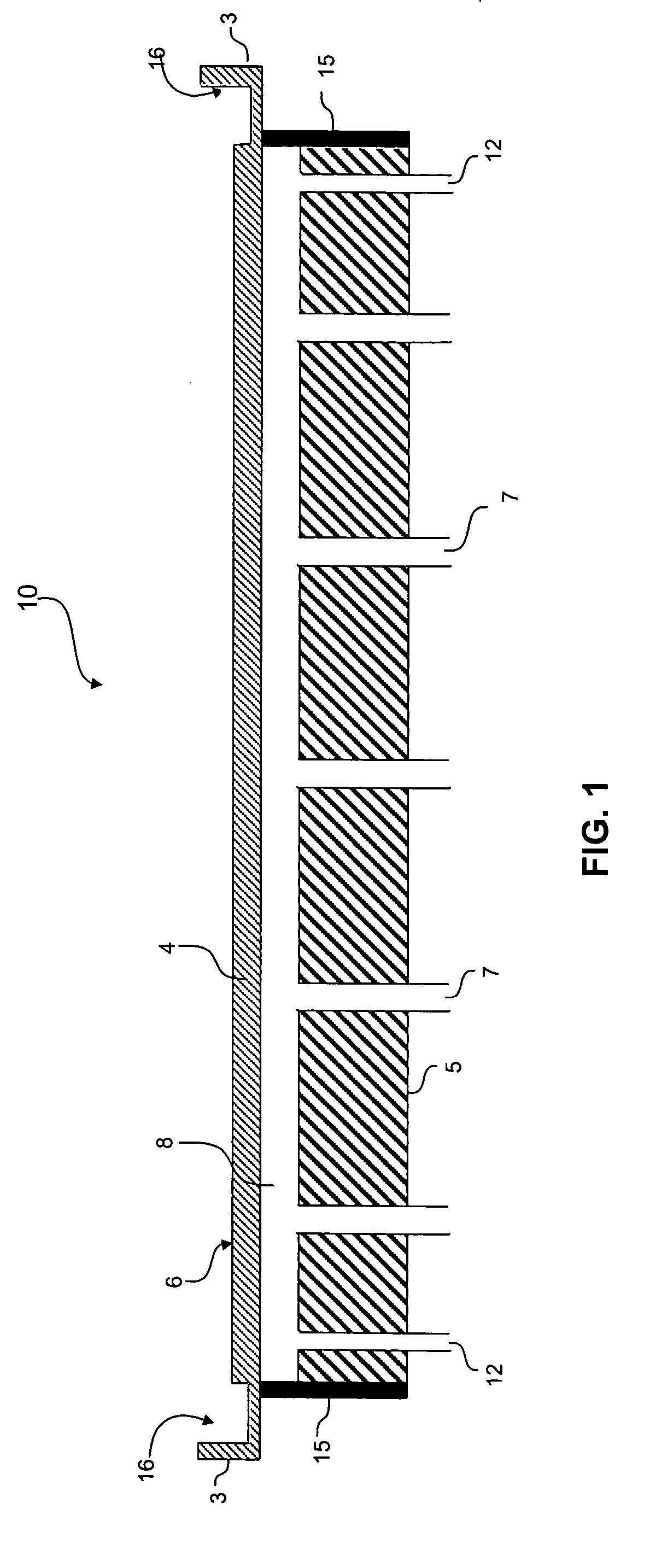
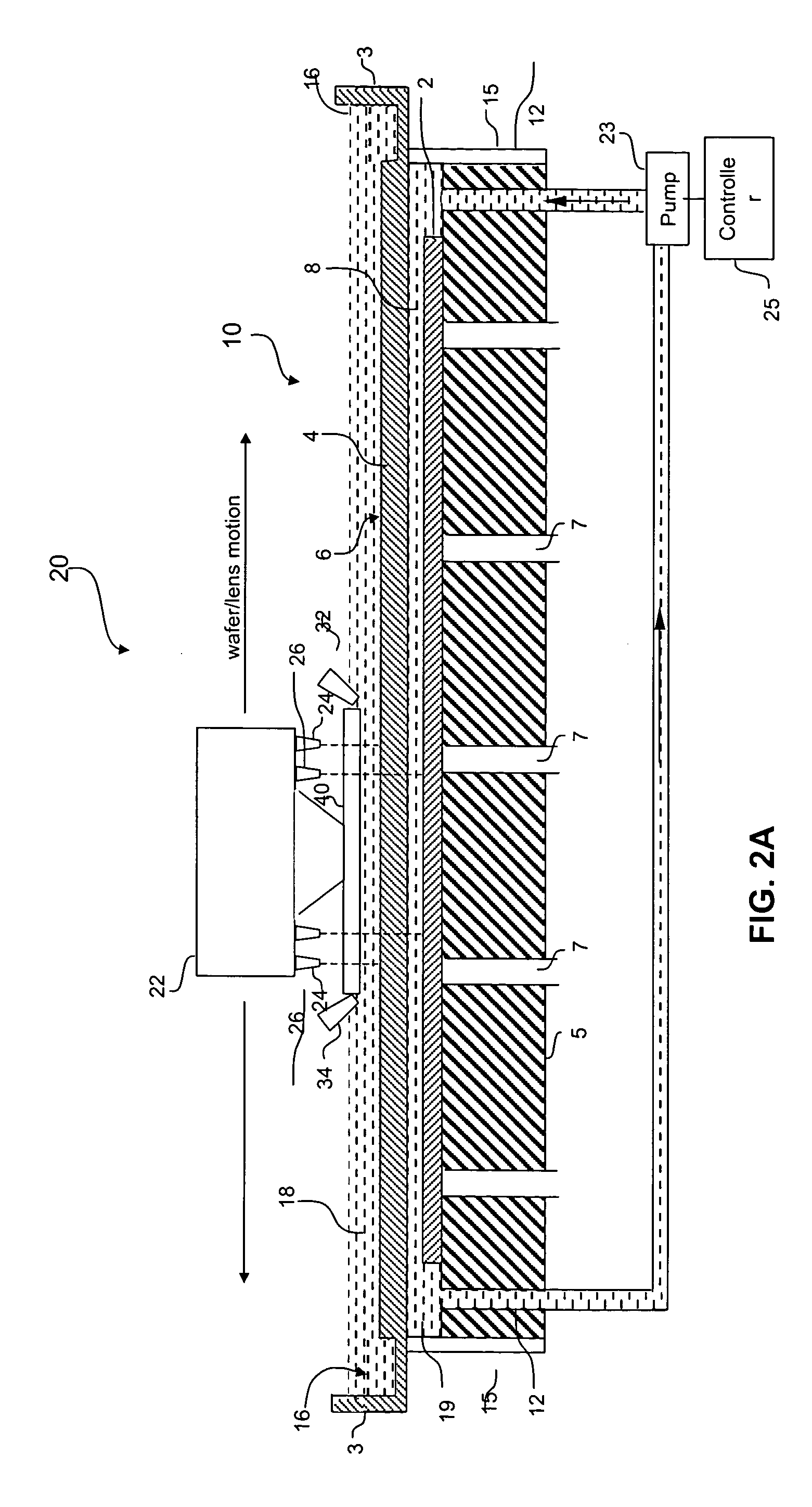
Wafer cell for immersion lithography
InactiveUS20050237501A1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithography processSemiconductor
An apparatus, system and method for use with a photolithographic system. In accordance with one embodiment, the photolithographic system of the present invention includes a workpiece support member for supporting a semiconductor wafer. A substantially transparent cover member is disposed over the workpiece support member to form a substantially enclosed workpiece cell therebetween. The enclosed workpiece cell is filled with a first immersion fluid having suitable refractive properties. The cover member, having suitable refractive properties, includes an upper surface contoured to form an open reservoir containing a second immersion fluid, having suitable refractive properties, and in which a final lens element may be immersed during a lithography process.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Polymers for photoresist and photoresist compositions using the same
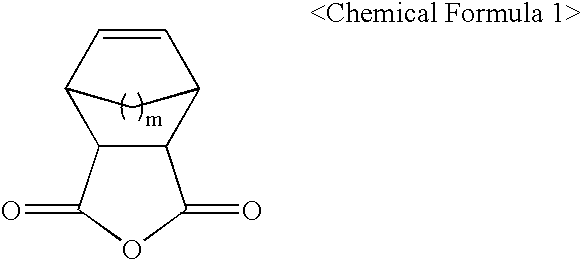
InactiveUS6987155B2Improve the immunityExcellent etching resistance and adhesiveness and photosensitivityElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistX-ray
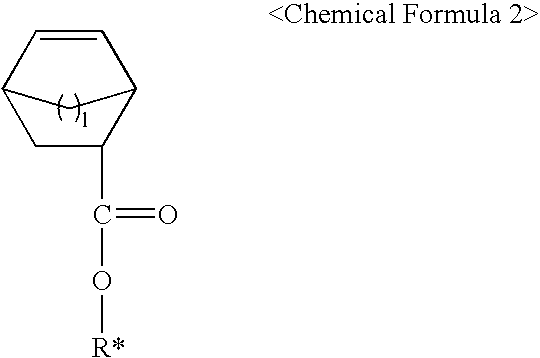
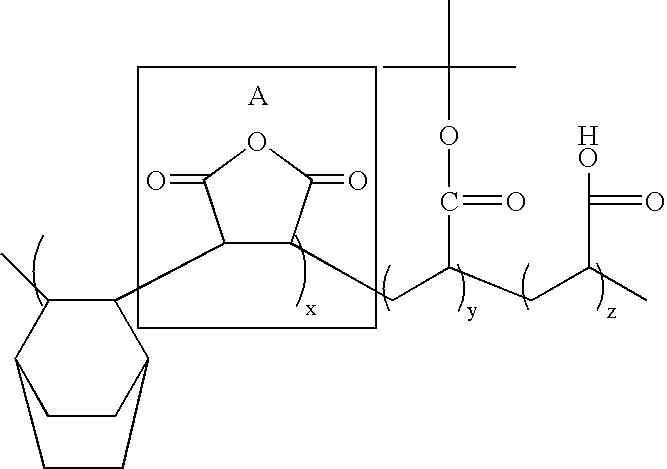
The present invention relates to photoresist monomers, polymers formed therefrom and photoresist compositions suitable for photolithography processes employing a DUV light source, such as KrF (249 nm) and ArF(193 nm); EUV; VUV; E-beam; ion-beam; and X-ray. Photoresist monomers of the present invention are represented by the following Chemical Formula 1: wherein, m is 1 or 2.Polymers of the present invention comprise repeating units derived from the comonomer of Chemical Formula 1, preferably together with monomers of the following Chemical Formula 2: wherein,R* is an acid-labile group, andl is 1 or 2.
Owner:HYUNDAI ELECTRONICS IND CO LTD
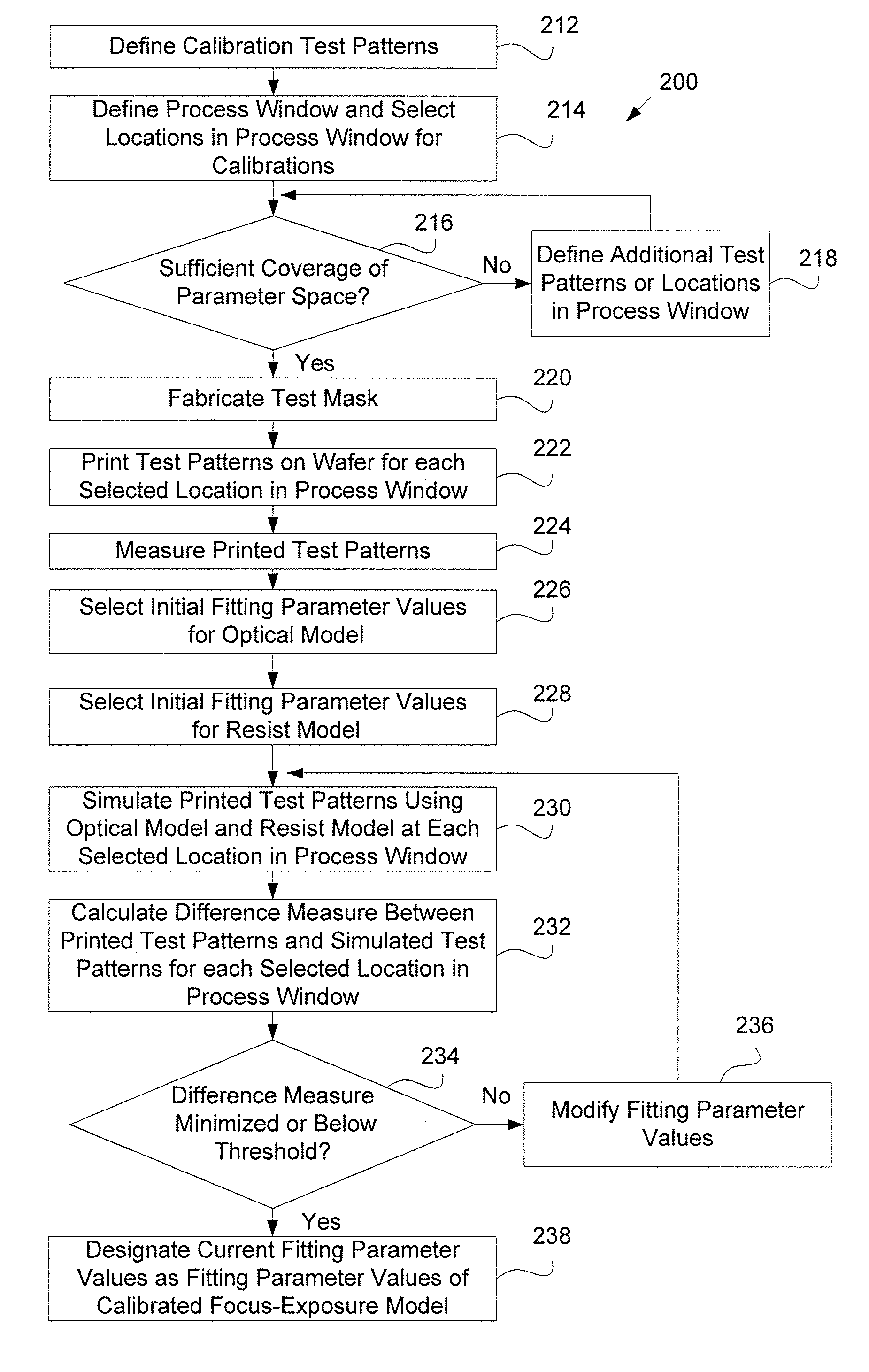
System and method for creating a focus-exposure model of a lithography process
ActiveUS20070031745A1Good accuracy and robustnessPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithography processAlgorithm
A system and a method for creating a focus-exposure model of a lithography process are disclosed. The system and the method utilize calibration data along multiple dimensions of parameter variations, in particular within an exposure-defocus process window space. The system and the method provide a unified set of model parameter values that result in better accuracy and robustness of simulations at nominal process conditions, as well as the ability to predict lithographic performance at any point continuously throughout a complete process window area without a need for recalibration at different settings. With a smaller number of measurements required than the prior-art multiple-model calibration, the focus-exposure model provides more predictive and more robust model parameter values that can be used at any location in the process window.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Composition for forming resist overlayer film for EUV lithography
ActiveUS20130209940A1High resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoatingsLithographic artistLithography process
There is provided a composition for forming an EUV resist overlayer film that is used in an EUV lithography process, that does not intermix with the EUV resist, that blocks unfavorable exposure light for EUV exposure, for example, UV light and DUV light and selectively transmits EUV light alone, and that can be developed with a developer after exposure. A composition for forming an EUV resist overlayer film used in an EUV lithography process including a resin containing a naphthalene ring in a main chain or in a side chain and a solvent, in which the resin may include a hydroxy group, a carboxy group, a sulfo group, or a monovalent organic group having at least one of these groups as a hydrophilic group.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Deep alignment marks on edge chips for subsequent alignment of opaque layers
InactiveUS20060024923A1Easy alignmentIncrease patternSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLithographic artistLithography process
A method of forming alignment marks on edge chips in a kerf region of a semiconductor workpiece. The alignment marks are formed in at least one material layer of the semiconductor device. The alignment marks are formed using a separate lithography mask, and may extend into lower layers, including the workpiece, of the semiconductor device. An opaque material layer is deposited, and depressions are formed in the opaque layer over the deep alignment mark trenches. The depressions in the opaque material layer are used to align a lithography process to open the opaque material layer over alignment marks in an underlying metallization layer. The alignment marks in the metallization layer are then used to align the lithography process used to pattern the opaque material layer.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Alignment of MTJ stack to conductive lines in the absence of topography
InactiveUS7223612B2Convenient lengthIncrease patternSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLithography processLithographic artist
A scheme for aligning opaque material layers of a semiconductor device. Alignment marks are formed in a via level of the semiconductor device. The alignment marks are formed using a separate lithography mask, and may have about the same length as vias formed in the via layer. The alignment marks comprise trenches that are not filled with material and are not exposed to a CMP process. An opaque material layer is deposited, and depressions are formed in the opaque material layer over the alignment mark trenches. The depressions in the opaque material layer are used to align a lithography process to open the opaque material layer over alignment marks in an underlying metallization layer. The alignment marks in the metallization layer are then used to align the lithography process used to pattern the opaque material layer.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Method for imprint lithography using an electric field
InactiveUS6908861B2High aspect ratioDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsLithographic artistLithography process
A lithography process for creating patterns in an activating light curable liquid using electric fields followed by curing of the activating light curable liquid is described. The process involves the use of a template that is formed of non-conductive and electrically conductive portions. The template is brought into close proximity to the activating light curable liquid on the substrate. An external electric field is applied to the template-substrate interface while maintaining a uniform, carefully controlled gap between the template and substrate. This causes the activating light curable liquid to be attracted to the raised portions of the template. Activating light is applied to the curable liquid while an electric field is applied to the template to create a patterned layer on the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
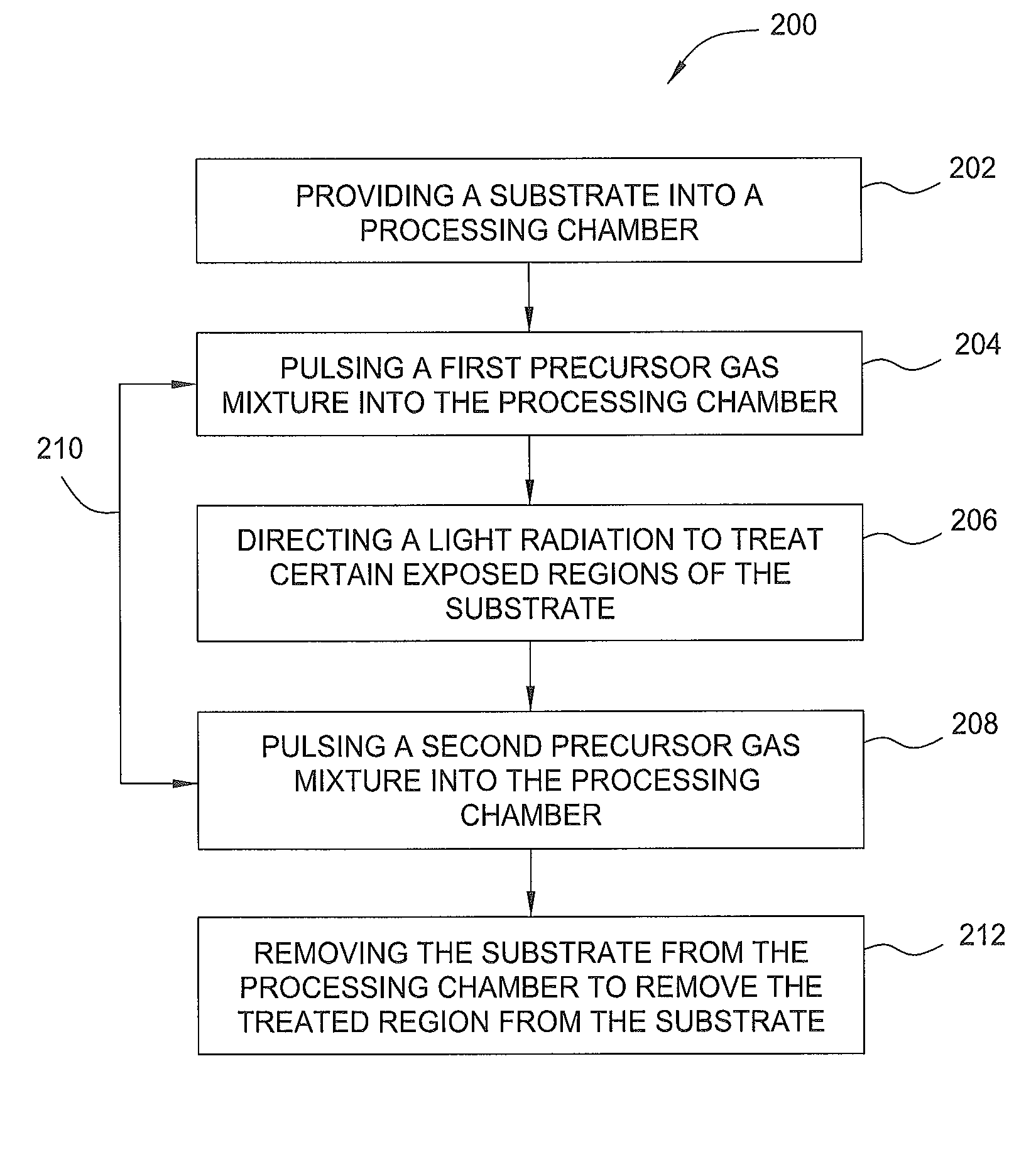
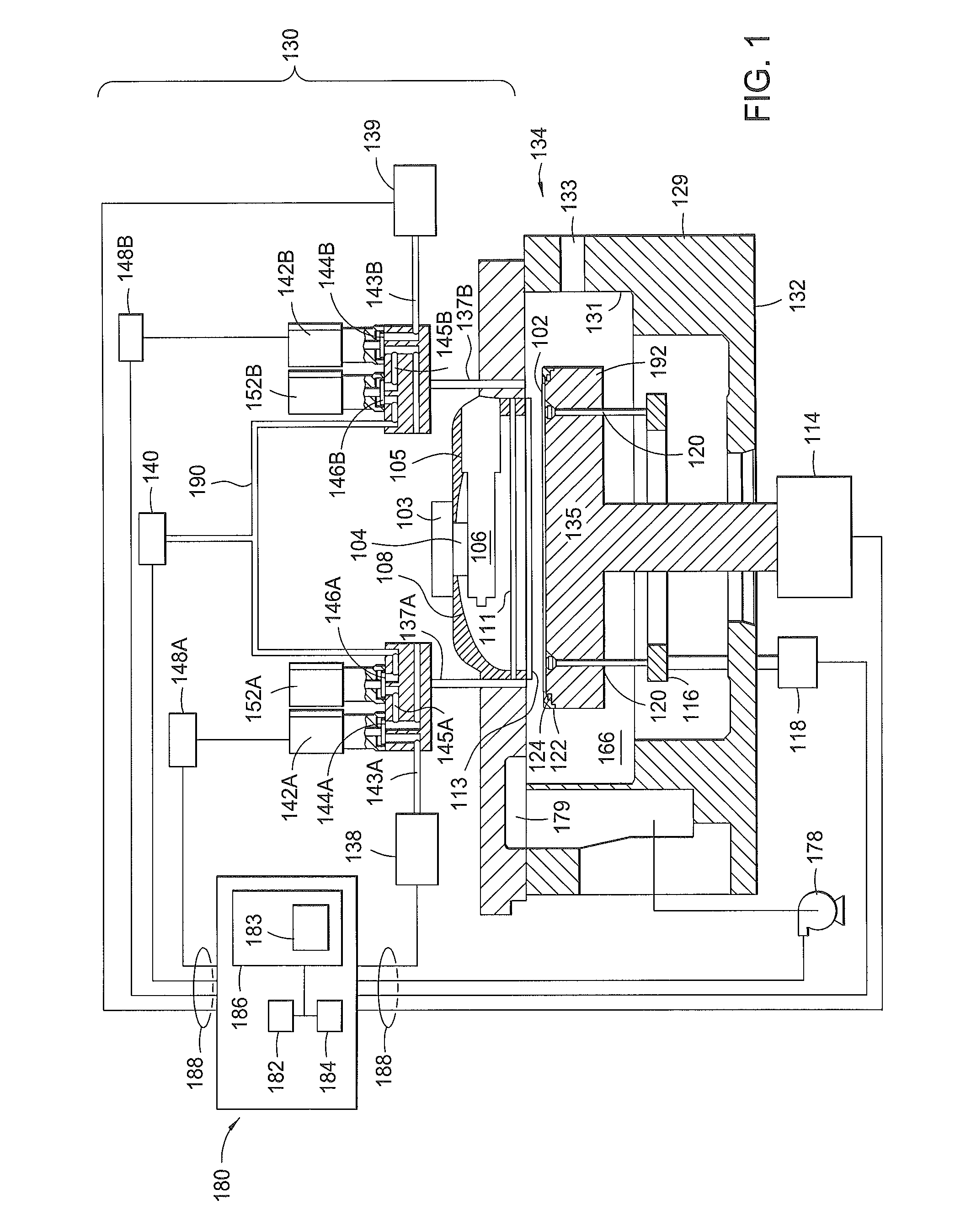
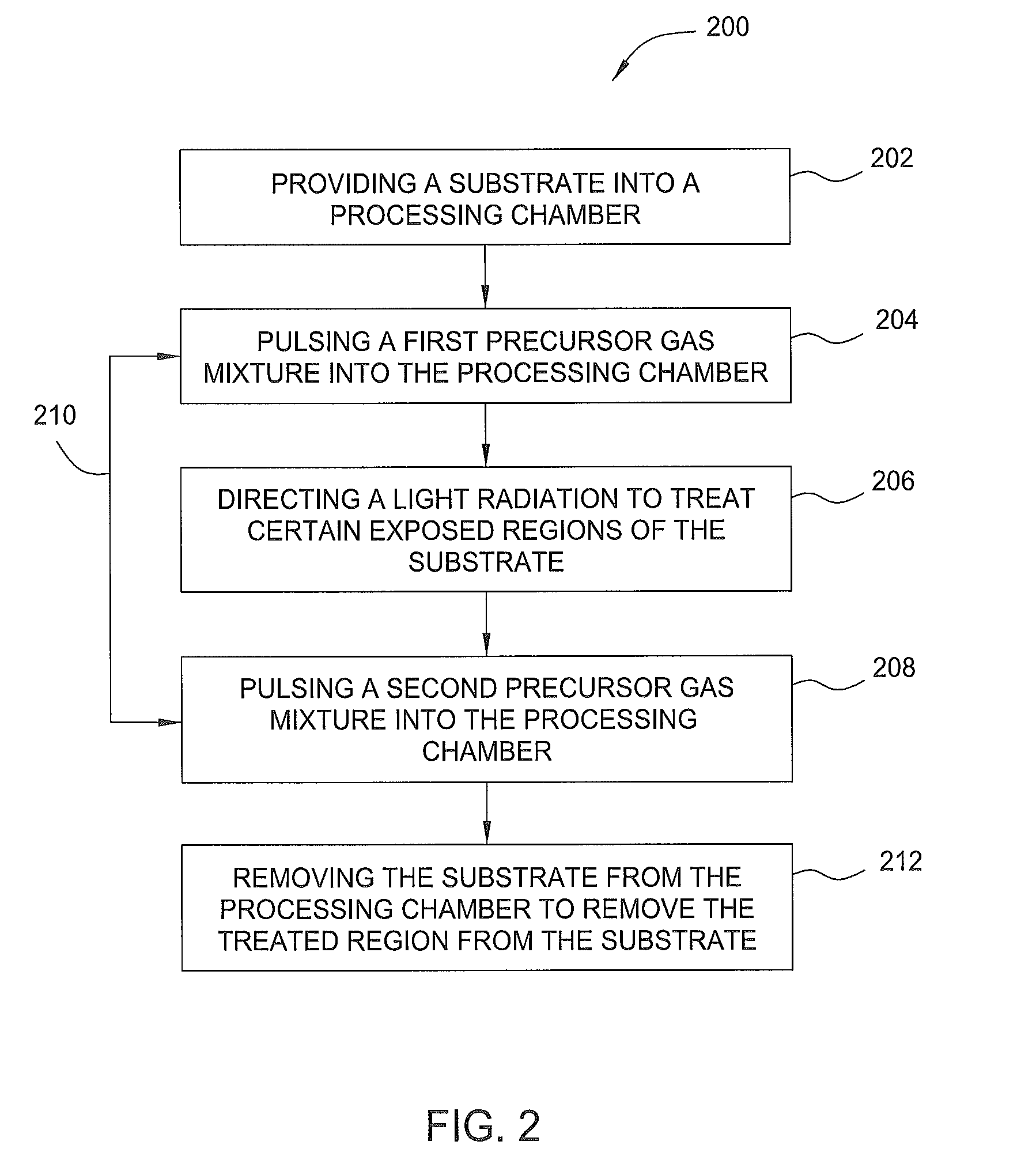
Atomic layer deposition lithography
InactiveUS8932802B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical coating apparatusLithography processLithographic artist
Methods and apparatus for performing an atomic layer deposition lithography process are provided in the present disclosure. In one embodiment, a method for forming features on a material layer in a device includes pulsing a first reactant gas mixture to a surface of a substrate disposed in a processing chamber to form a first monolayer of a material layer on the substrate surface, directing an energetic radiation to treat a first region of the first monolayer, and pulsing a second reactant gas mixture to the substrate surface to selectively form a second monolayer on a second region of the first monolayer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
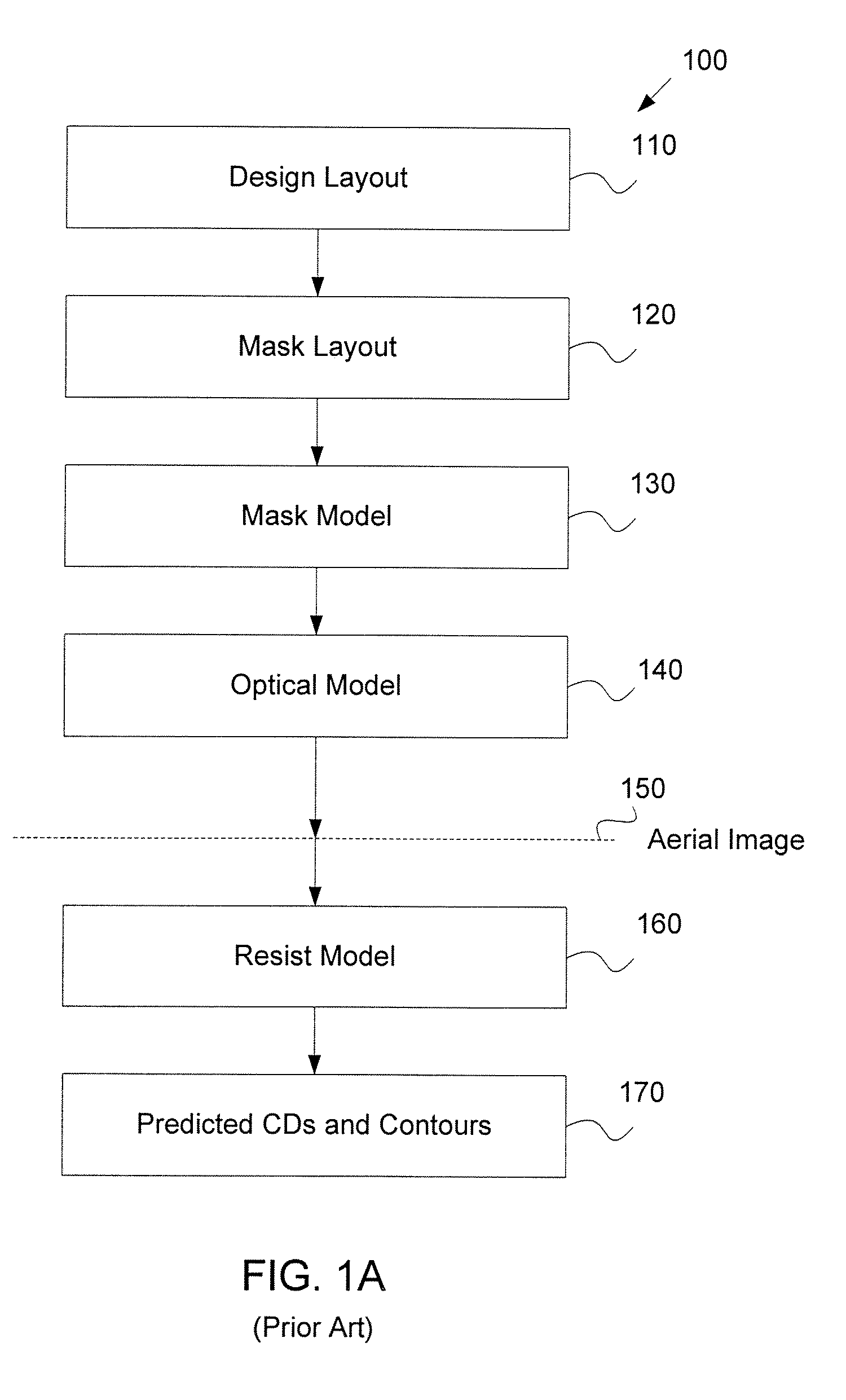
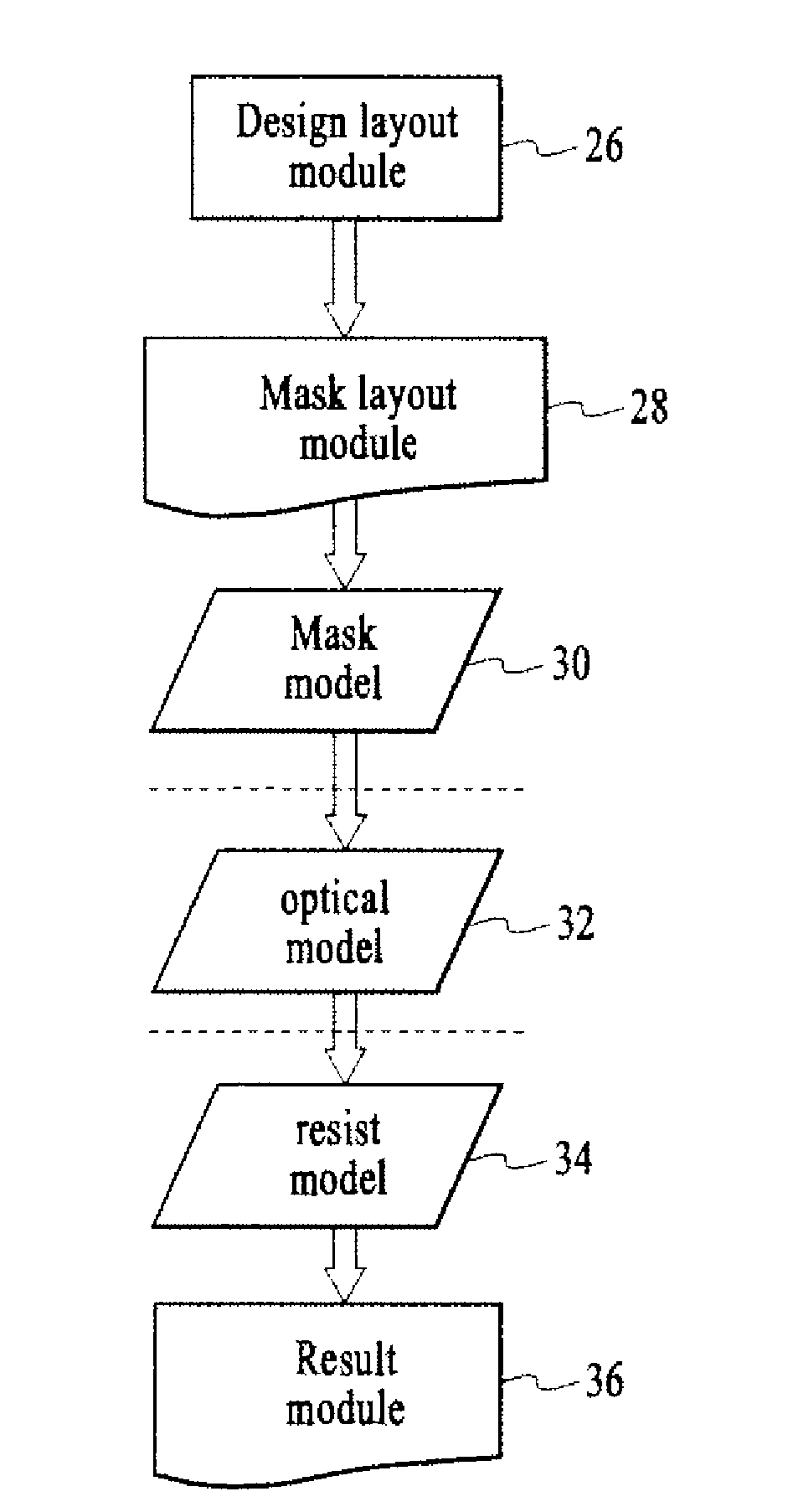
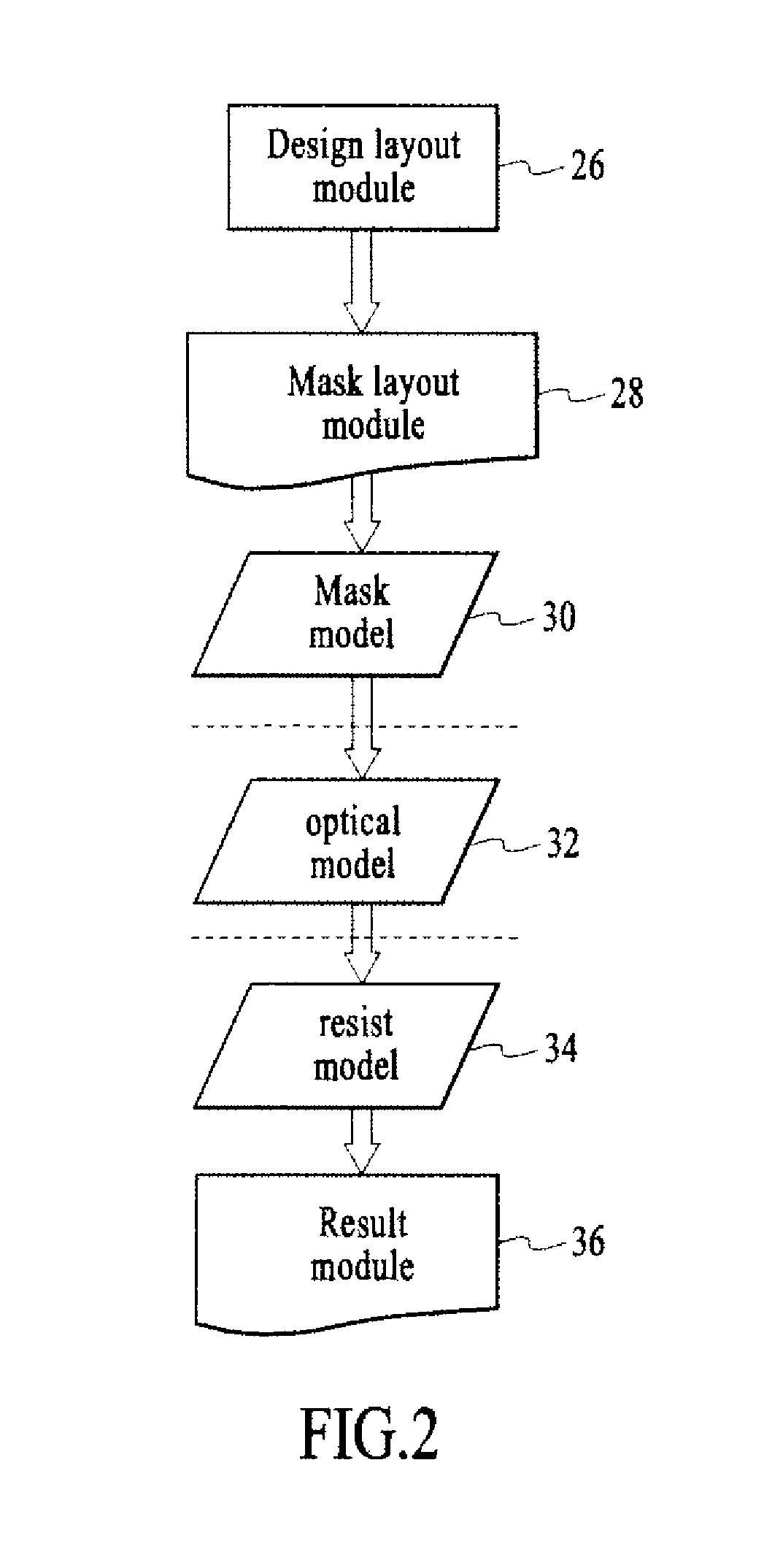
Method for lithography model calibration
ActiveUS20070032896A1Easy CalibrationImprove predictabilityPhotomechanical apparatusCalibration apparatusLithography processLithographic artist
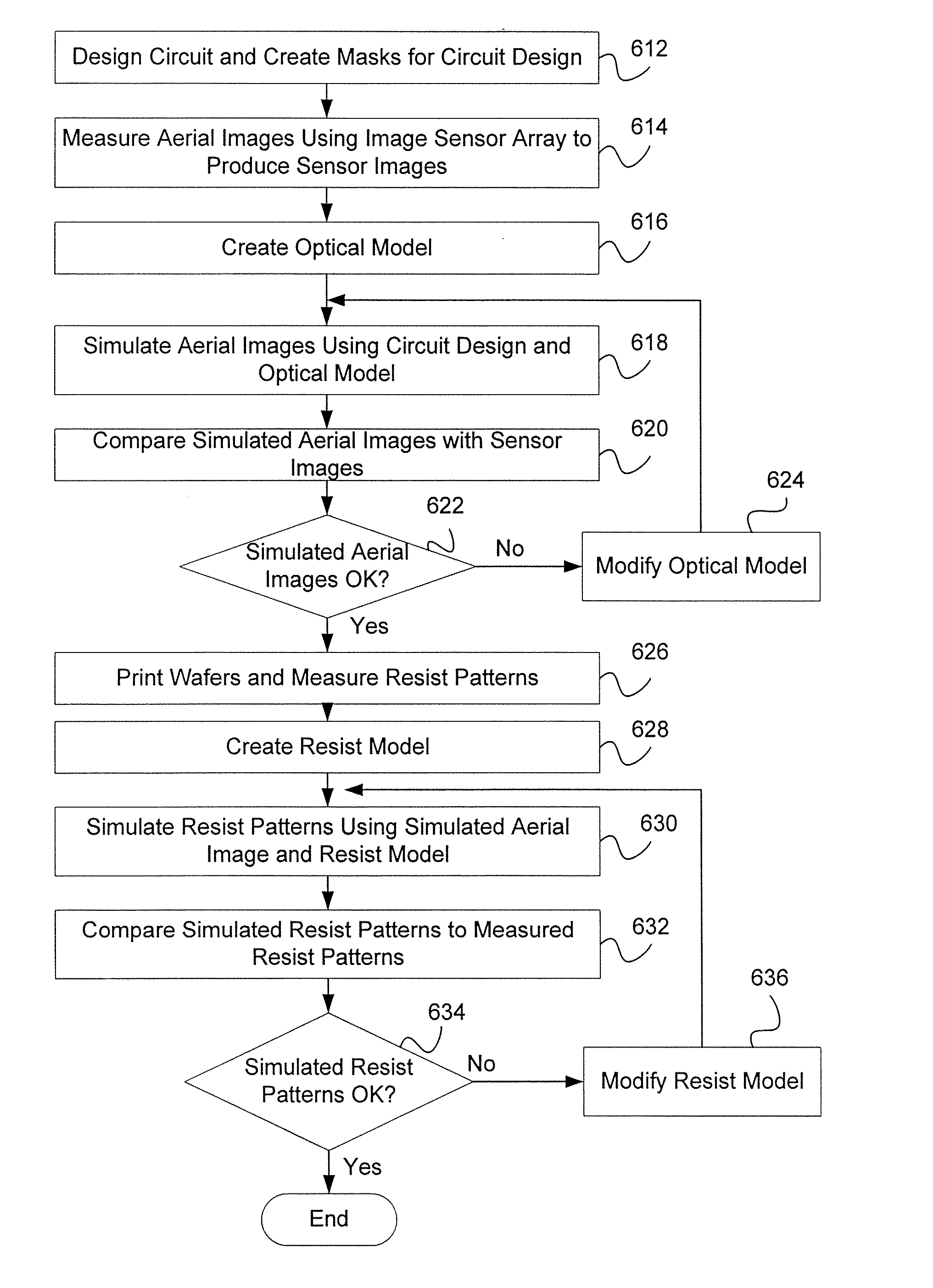
A method for separately calibrating an optical model and a resist model of lithography process using information derived from in-situ aerial image measurements to improve the calibration of both the optical model and the resist model components of the lithography simulation model. Aerial images produced by an exposure tool are measured using an image sensor array loaded into the exposure tool. Multiple embodiments of measuring aerial image information and using the measured aerial image information to calibrate the optical model and the resist model are disclosed. The method of the invention creates more accurate and separable optical and resist models, leading to better predictability of the pattern transfer process from mask to wafer, more accurate verification of circuit patterns and how they will actually print in production, and more accurate model-based process control in the wafer fabrication facility.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
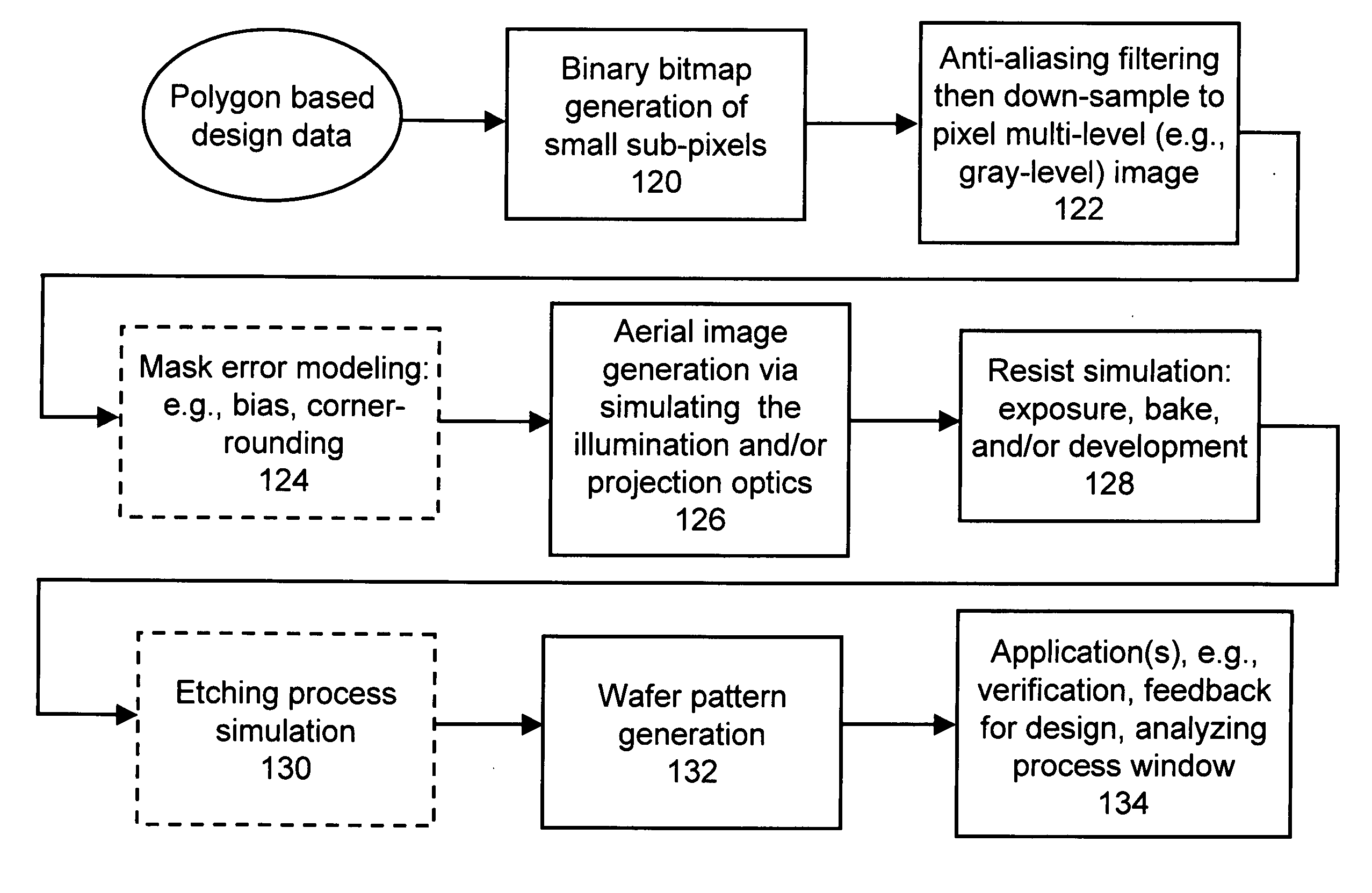
System and method for lithography simulation
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a technique of, and system for simulating, verifying, inspecting, characterizing, determining and / or evaluating the lithographic designs, techniques and / or systems, and / or individual functions performed thereby or components used therein. In one embodiment, the present invention is a system and method that accelerates lithography simulation, inspection, characterization and / or evaluation of the optical characteristics and / or properties, as well as the effects and / or interactions of lithographic systems and processing techniques. In this regard, in one embodiment, the present invention employs a lithography simulation system architecture, including application-specific hardware accelerators, and a processing technique to accelerate and facilitate verification, characterization and / or inspection of a mask design, for example, RET design, including detailed simulation and characterization of the entire lithography process to verify that the design achieves and / or provides the desired results on final wafer pattern. The system includes: (1) general purpose-type computing device(s) to perform the case-based logic having branches and inter-dependency in the data handling and (2) accelerator subsystems to perform a majority of the computation intensive tasks.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
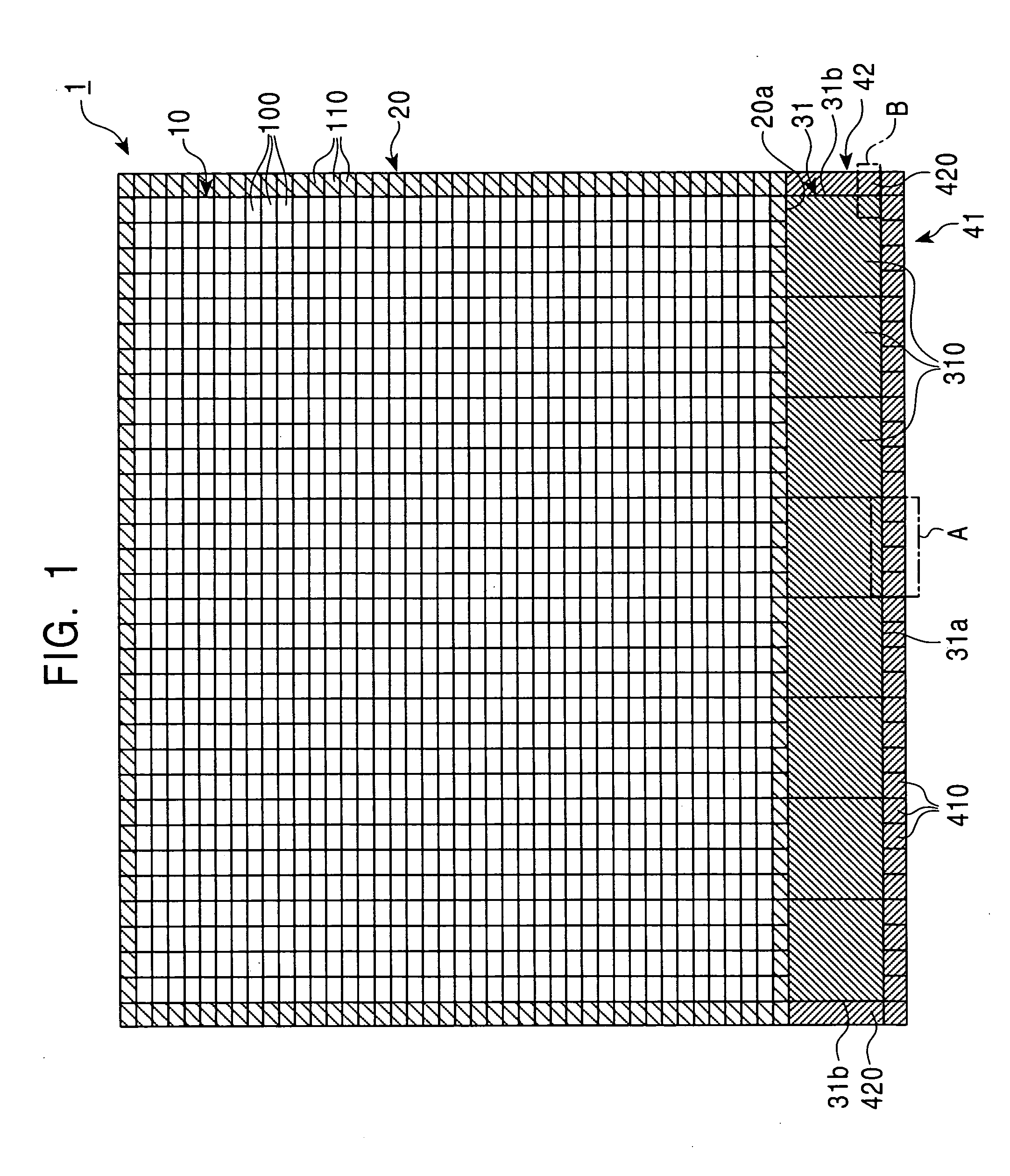
Layout structure of semiconductor integrated circuit and method for forming the same
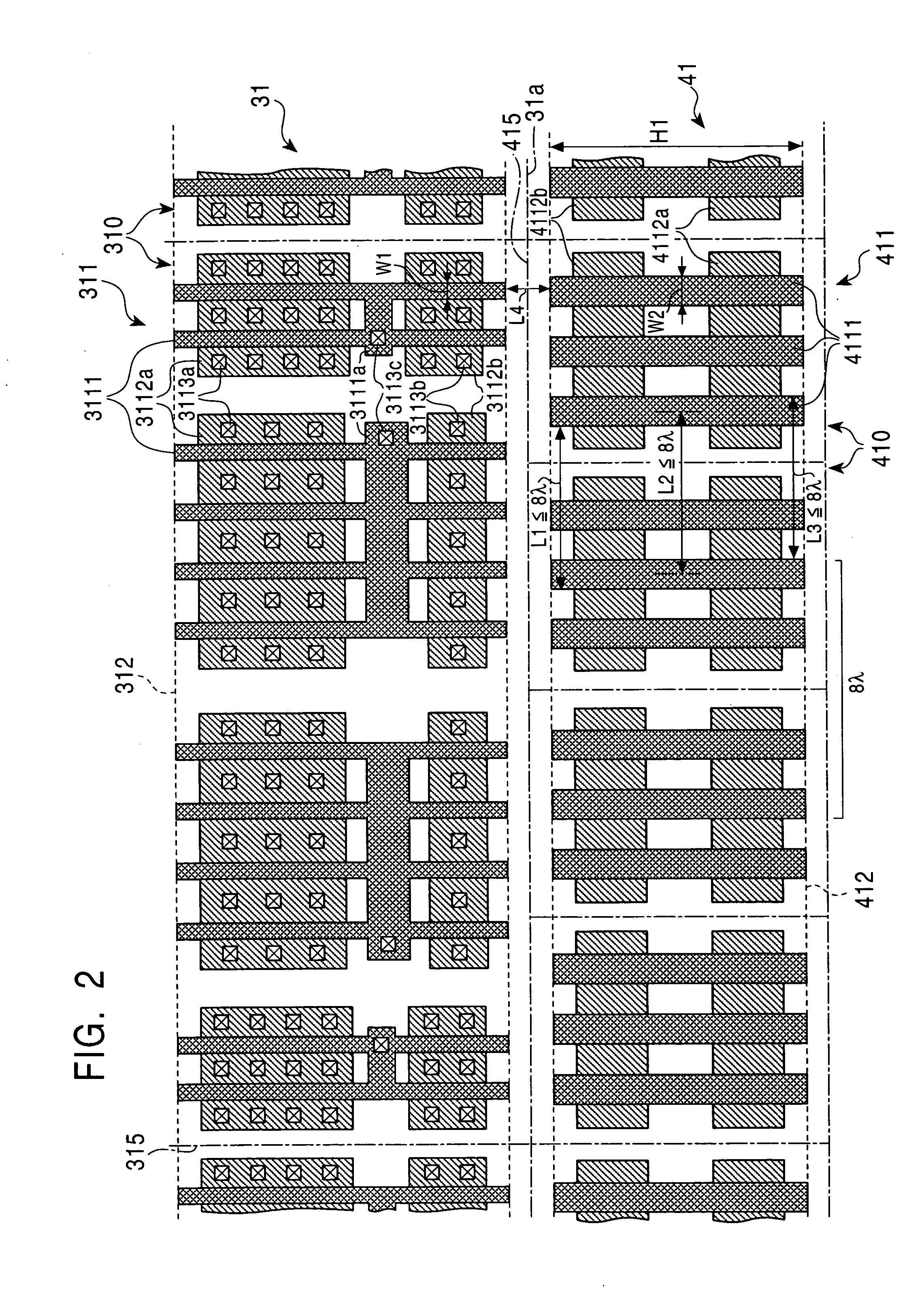
ActiveUS20050076320A1Improve regularityGood pattern uniformityTransistorSolid-state devicesLength wavePhotolithography
In an exemplary layout structure of a semiconductor integrated circuit manufactured by a photolithographic process using an exposing light having a wavelength λ, a peripheral circuit region is formed by arranging a plurality of peripheral circuit cells, each having peripheral circuit patterns, along a side of an internal circuit region. A proximity dummy region is formed by arranging a plurality of proximity dummy cells, each having a proximity dummy pattern, along at least one side of the peripheral circuit region. The proximity dummy region includes a line-and-space repetition structure including, and having the regularity of, two or more pairs of lines and spaces between the lines every 8λ. The repetition structure in the proximity dummy region reduces the dimensional deviation in the outermost portion of the peripheral circuit region.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
Formation of discontinuous films during an imprint lithography process
The present invention is directed to a template having a body including a surface with first and second regions. The first region has first wetting characteristics for a given material and the second region has second wetting characteristics for the given material. The first wetting characteristics differ from the second wetting characteristics. Specifically, the first region is formed from a surface treatment layer with a first surface energy to provide the first wetting characteristics. The second region is exposed portions of the body, typically quartz of fused silica, having a second surface energy associated therewith. The second surface energy is greater than the first surface energy to provide the second region with the second wetting characteristics.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Method and system for lithography process-window-maximixing optical proximity correction
ActiveUS20100162197A1MaximizesOvercome deficienciesPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithography processGray level
The present invention relates to an efficient OPC method of increasing imaging performance of a lithographic process utilized to image a target design having a plurality of features. The method includes the steps of determining a function for generating a simulated image, where the function accounts for process variations associated with the lithographic process; and optimizing target gray level for each evaluation point in each OPC iteration based on this function. In one given embodiment, the function is approximated as a polynomial function of focus and exposure, R(ε, f)=P0+f2·Pb with a threshold of T+Vε for contours, where P0 represents image intensity at nominal focus, f represents the defocus value relative to the nominal focus, ε represents the exposure change, V represents the scaling of exposure change, and parameter “Pb” represents second order derivative images. In another given embodiment, the analytical optimal gray level is given for best focus with the assumption that the probability distribution of focus and exposure variation is Gaussian.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method of design and fabrication of integrated circuits using regular arrays and gratings
InactiveUS6818389B2Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingRounding
A circuit fabrication and lithography process utilizes a mask including dense repetitive structures of features that result in a wide array of fine densely populated features on the exposed substrate film. Following this, a trimming procedure is performed to remove any unwanted fine patterned features providing multiple trimmed patterns on the substrate. An optional final step adds additional features as well as the interconnect features thus forming a circuit pattern. In this manner, all fine features may be generated using the exact same density of intensity patterns, and therefore, maximum consistency between features is established without the need for optical proximity correction. The secondary exposures are substantially independent from the initial dense-feature exposure in that the exposure of one set of features and the subsequent exposure of another set of features result in separate independent resist or masking layer reactions, thus minimizing corner rounding, line end shortening and other related spatial frequency effects and unwanted exposure memory effects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods and systems for lithography process control
InactiveUS6987572B2High performance bin distributionReduce yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesLithography processProcess module
Methods and systems for evaluating and controlling a lithography process are provided. For example, a method for reducing within wafer variation of a critical metric of a lithography process may include measuring at least one property of a resist disposed upon a wafer during the lithography process. A critical metric of a lithography process may include, but may not be limited to, a critical dimension of a feature formed during the lithography process. The method may also include altering at least one parameter of a process module configured to perform a step of the lithography process to reduce within wafer variation of the critical metric. The parameter of the process module may be altered in response to at least the one measured property of the resist.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Imprint lithography template comprising alignment marks
InactiveUS6842229B2Accurately determineTimely processingLiquid crystal compositionsNanoinformaticsLithography processComputer engineering
A system of determining and correcting alignment during imprint lithography process is described. During an imprint lithographic process the template may be aligned with the substrate by the use of alignment marks disposed on both the template and substrate. The alignment may be determined and corrected for before the layer is processed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Overcoating composition for photoresist and method for forming photoresist pattern using the same
InactiveUS6916594B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingLithography processPhotoresist
Overcoating compositions for photoresist and methods for reducing linewidth of the photoresist patterns are disclosed. More specifically, an overcoating composition containing acids is coated on a whole surface of a photoresist pattern formed by a common lithography process to diffuse the acids into the photoresist pattern. The photoresist in the portion where the acids are diffused is developed with an alkali solution to be removed. As a result, the linewidth of positive photoresist patterns can be reduced, and the linewidth of negative photoresist patterns can be prevented from slimming in a subsequent linewidth measurement process using SEM.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Step and repeat imprint lithography processes
ActiveUS20060076717A1Enhance lithography processLow viscosity liquidMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLithography processEngineering
The present invention is directed to methods for patterning a substrate by imprint lithography. Imprint lithography is a process in which a liquid is dispensed onto a substrate. A template is brought into contact with the liquid and the liquid is cured. The cured liquid includes an imprint of any patterns formed in the template. In one embodiment, the imprint process is designed to imprint only a portion of the substrate. The remainder of the substrate is imprinted by moving the template to a different portion of the template and repeating the imprint lithography process.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Apparatus and methods for detection of systematic defects
ActiveUS7280945B1Electrical testingComputation using non-denominational number representationResistSystem failure
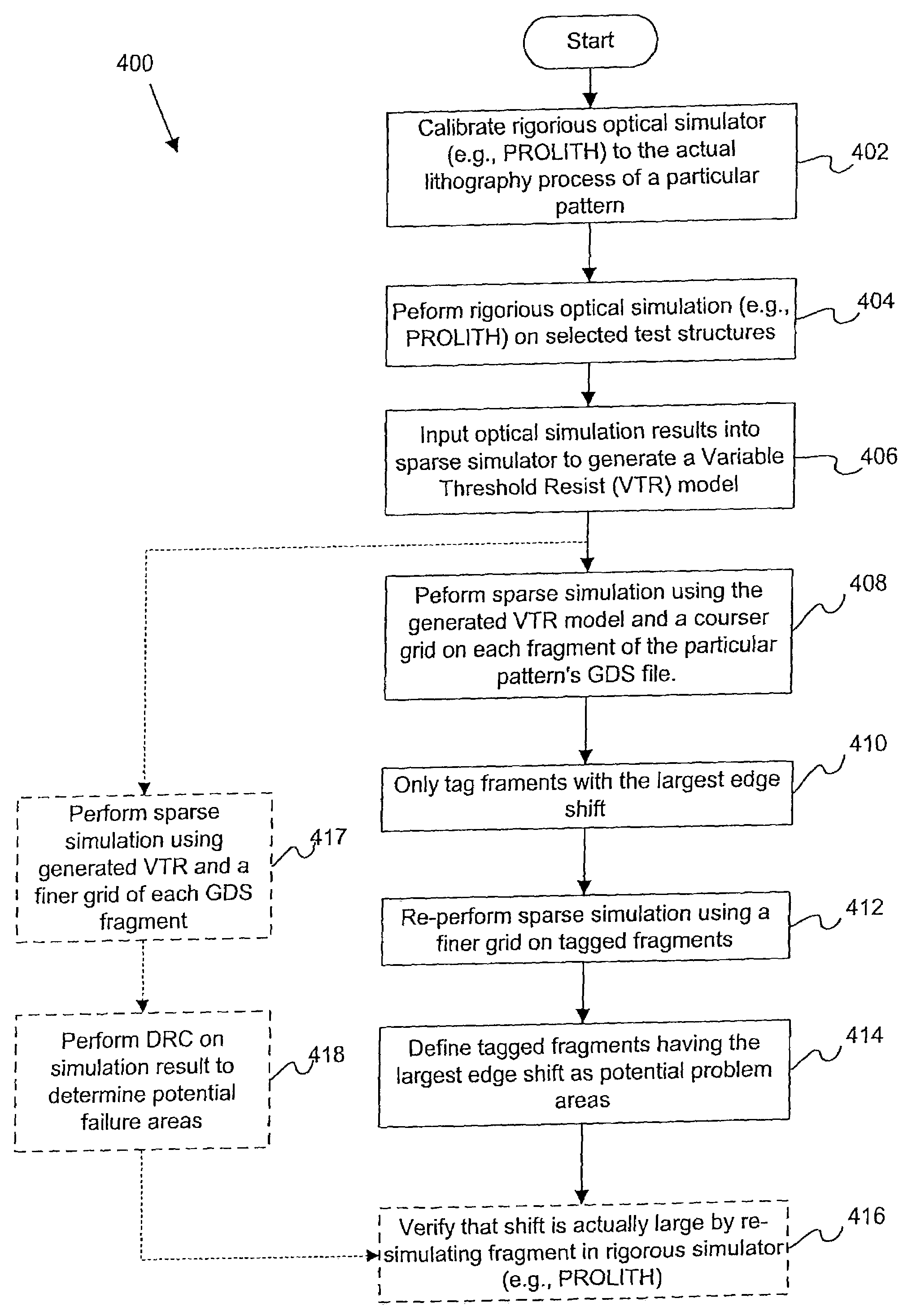
Disclosed are mechanisms are provided for determining whether a particular integrated circuit (IC) pattern is susceptible to systematic failure, e.g., due to process fluctuations. In one embodiment, final resist patterns for such IC pattern are simulated using a sparse type simulator under various process settings. The sparse type simulator uses a model (e.g., a variable threshold resist model) for a particular photolithography process in which the IC pattern is to be fabricated. The model is generated from measurements taken from a plurality of simulated structures output from a rigorous type simulator. The simulated final resist patterns may then be analyzed to determine whether the corresponding IC pattern is susceptible to systematic failure. After an IC pattern which is susceptible to systematic failure has been found, a test structure may be fabricated from a plurality of IC patterns or cells. The cells of the test structure are arranged to have a particular pattern of voltage potential or brightness levels during a voltage contrast inspection. Mechanisms for quickly inspecting such test structures to thereby predict systematic yield of a product device containing patterns similar to the test structure cells are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Formation of discontinuous films during an imprint lithography process
The present invention is directed to a template having a body including a surface with first and second regions. The first region has first wetting characteristics for a given material and the second region has second wetting characteristics for the given material. The first wetting characteristics differ from the second wetting characteristics. Specifically, the first region is formed from a surface treatment layer with a first surface energy to provide the first wetting characteristics. The second region is exposed portions of the body, typically quartz of fused silica, having a second surface energy associated therewith. The second surface energy is greater than the first surface energy to provide the second region with the second wetting characteristics.
Owner:CANON KK +1
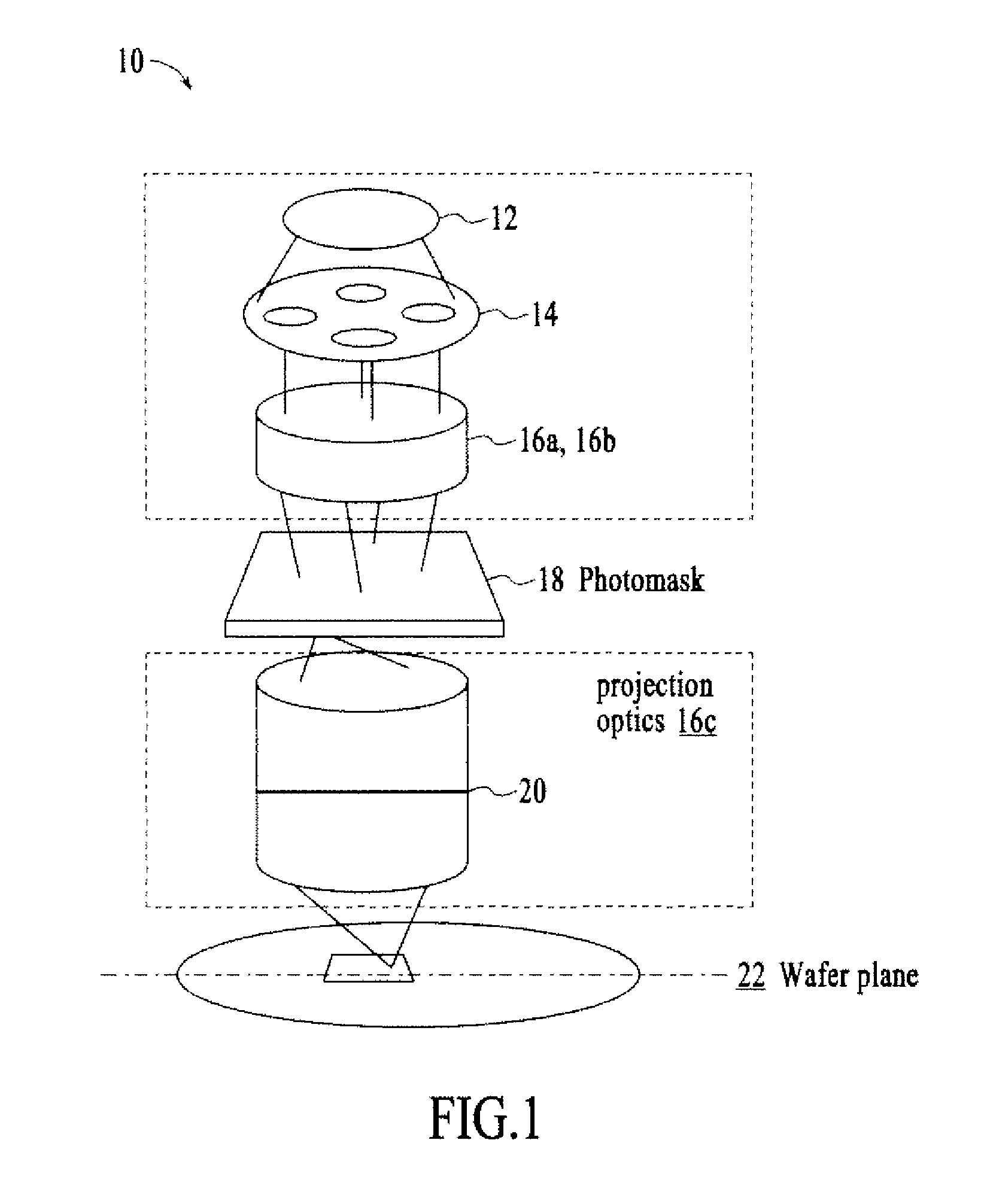
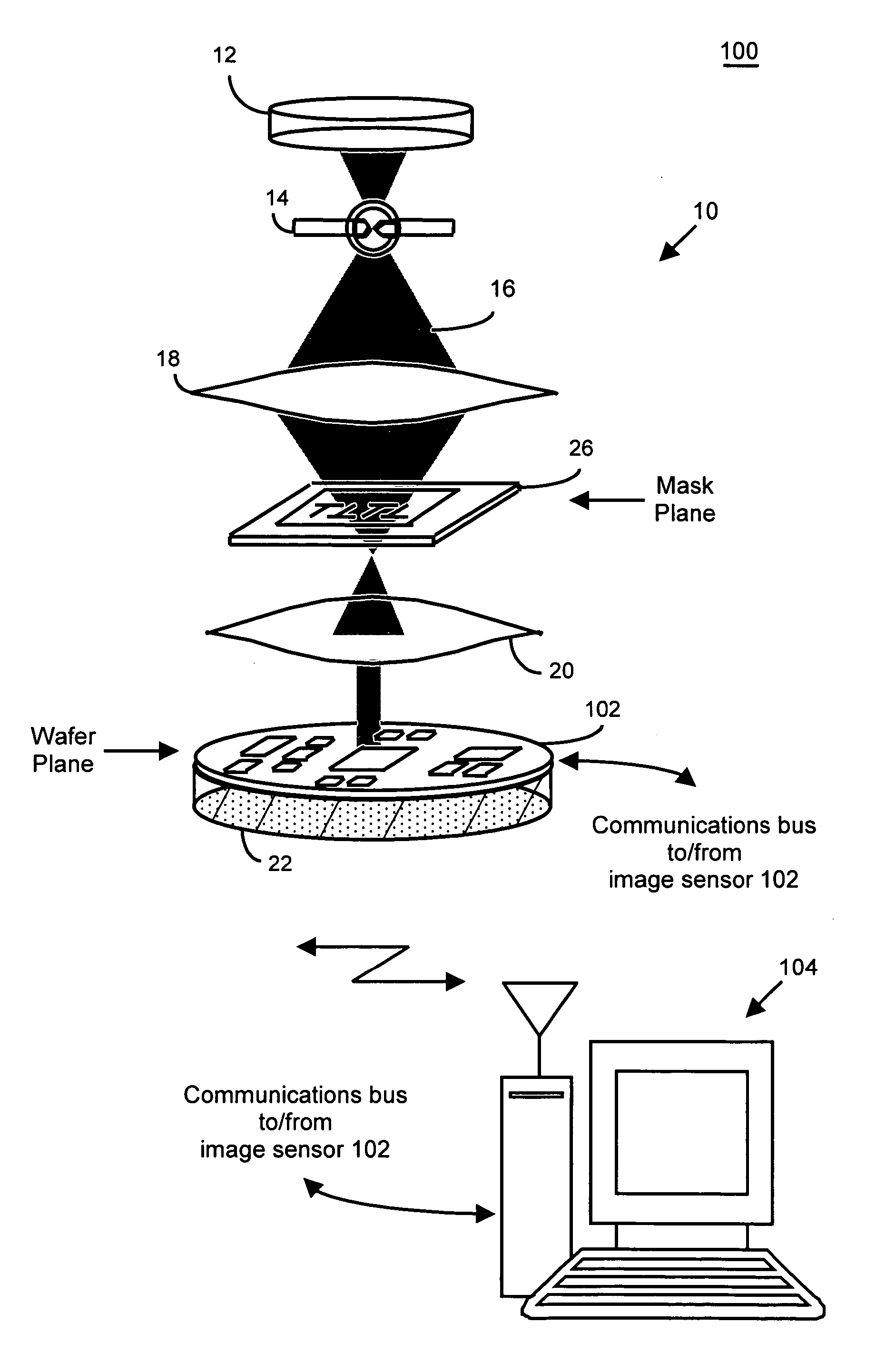
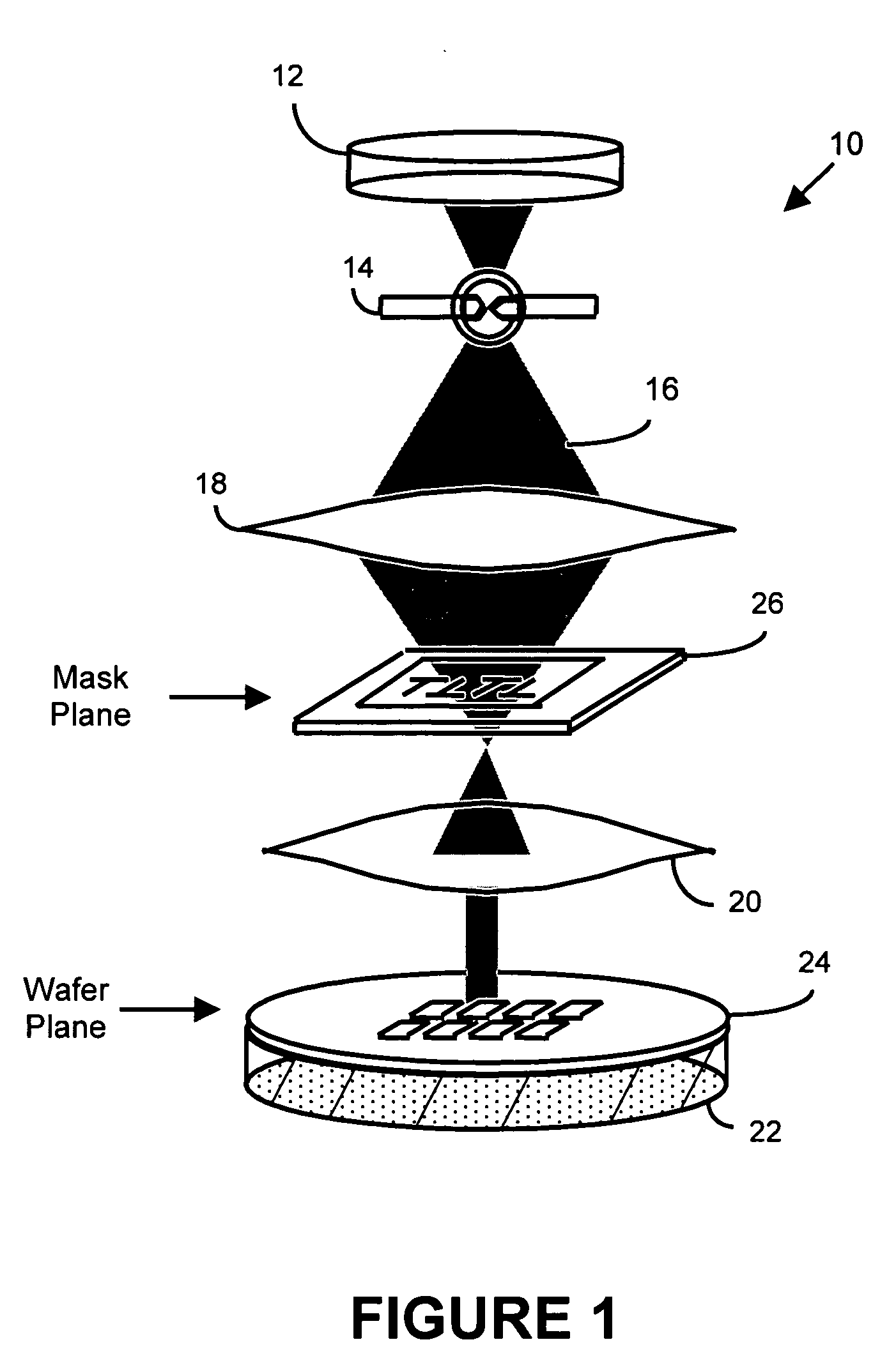
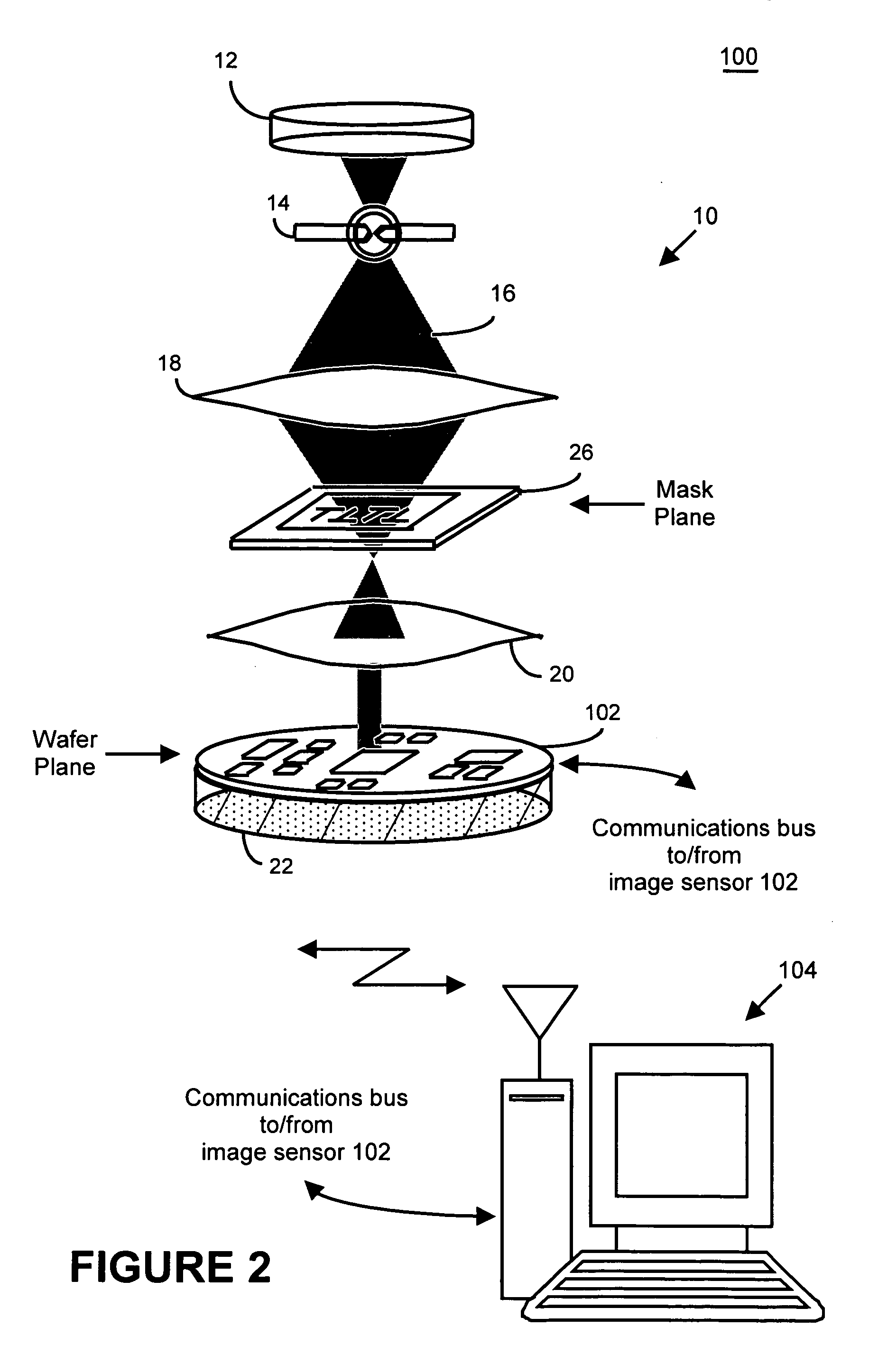
System and method for lithography process monitoring and control
InactiveUS20060000964A1Highly precise moveable platformSolid-state devicesPhotomechanical apparatusIntegrated circuit manufacturingLithography process
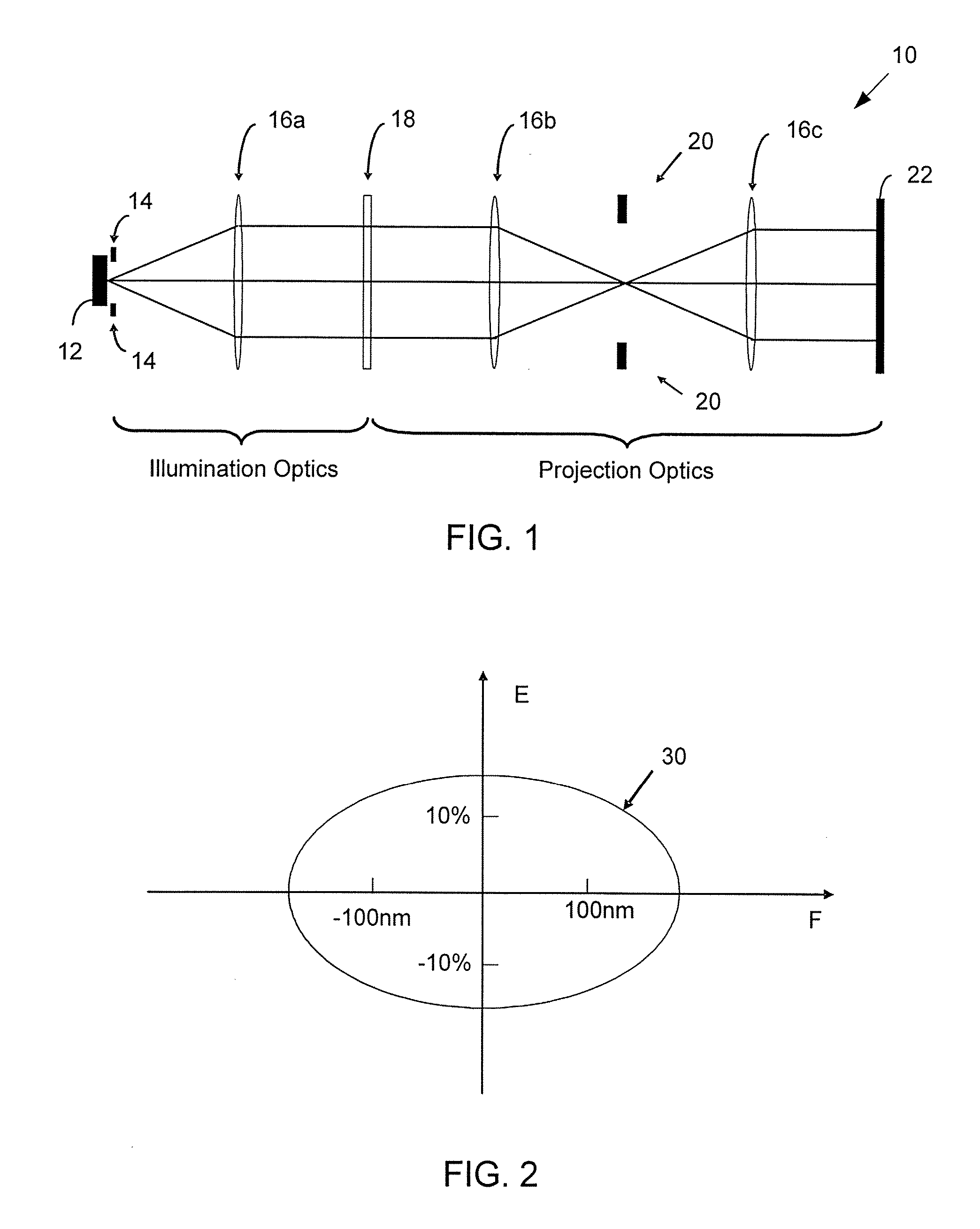
In one aspect, the present invention is a technique of, and a system and sensor for measuring, inspecting, characterizing and / or evaluating optical lithographic equipment, methods, and / or materials used therewith, for example, photomasks. In one embodiment, the system, sensor and technique measures, collects and / or detects an aerial image produced or generated by the interaction between the photomask and lithographic equipment. An image sensor unit may measure, collect, sense and / or detect the aerial image in situ—that is, the aerial image at the wafer plane produced, in part, by a product-type photomask (i.e., a wafer having integrated circuits formed during the integrated circuit fabrication process) and / or by associated lithographic equipment used, or to be used, to manufacture of integrated circuits. In this way, the aerial image used, generated or produced to measure, inspect, characterize and / or evaluate the photomask is the same aerial image used, generated or produced during wafer exposure in integrated circuit manufacturing. In another embodiment, the system, sensor and technique characterizes and / or evaluates the performance of the optical lithographic equipment, for example, the optical sub-system of such equipment. In this regard, in one embodiment, an image sensor unit measures, collects, senses and / or detects the aerial image produced or generated by the interaction between lithographic equipment and a photomask having a known, predetermined or fixed pattern (i.e., test mask). In this way, the system, sensor and technique collects, senses and / or detects the aerial image produced or generated by the test mask—lithographic equipment in order to inspect, evaluate and / or characterize the performance of the lithographic equipment.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method of varying template dimensions to achieve alignment during imprint lithography
InactiveUS6916585B2Minimize focusing problemAccurately determineDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsLithography processComputer engineering
A method of determining and correcting alignment during imprint lithography process is described. During an imprint lithographic process the template may be aligned with the substrate by the use of alignment marks disposed on both the template and substrate. The alignment may be determined and corrected for before the layer is processed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Silsesquioxane polymers, method of synthesis, photoresist composition, and multilayer lithographic method
InactiveUS6340734B1Reduce usageAvoid pollutionSilicon organic compoundsRadiation applicationsResistPolymer science
Novel silsesquioxane polymers are formed by methods which avoid the use of BBr3. The novel silsesquioxane polymers are especially useful in negative photoresist compositions and photolithographic processes. Alternatively, improved silsesquioxane polymer-containing negative photoresist compositions are obtained by using a polymer component containing a blend of silsesquioxane polymer and non-silsesquioxane polymer. The photoresist compositions provide improved dissolution characteristics enabling the use of 0.26N TMAH developer. The photoresist compositions also provide improved thermal characteristics enabling use of higher processing temperatures. The photoresist compositions are especially useful in a multilayer photolithographic processes and are capable of producing high resolution.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Qualifying patterns, patterning processes, or patterning apparatus in the fabrication of microlithographic patterns
ActiveUS7418124B2MaximizeIncrease catch rateAnalogue computers for electric apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithography processComputer science
Methods that include acquiring aerial images of a reticle for different values of a member of a set of lithographic variables are provided. One method also includes determining a presence of an anomaly in a design pattern of the reticle by comparing at least one pair of the aerial images corresponding to at least two of the different values. A different method includes comparing at least one pair of the aerial images corresponding to at least two of the different values and determining an area on the reticle where a lithography process using the reticle is most susceptible to failure based on the results of the comparison. Another embodiment includes determining a presence of transient repeating defects on the reticle by subtracting non-transient defects from the aerial images and comparing at least one pair of the aerial images corresponding to at least two of the different values.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
System and method for lithography process monitoring and control
InactiveUS6884984B2Highly precise moveable platformPhotometrySolid-state devicesLithography processEngineering
In one aspect, the present invention is a technique of, and a system and sensor for measuring, inspecting, characterizing and / or evaluating optical lithographic equipment, methods, and / or materials used therewith, for example, photomasks. In one embodiment, the system, sensor and technique measures, collects and / or detects an aerial image (or portion thereof) produced or generated by the interaction between the photomask and lithographic equipment. An image sensor unit may measure, collect, sense and / or detect the aerial image in situ—that is, the aerial image at the wafer plane produced, in part, by a production-type photomask (i.e., a wafer having integrated circuits formed during the integrated circuit fabrication process) and / or by associated lithographic equipment used, or to be used, to manufacture of integrated circuits. A processing unit, coupled to the image sensor unit, may measure the critical dimensions of features of the photomask, using data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the image sensor unit, to control at least one operating parameter of the lithographic equipment.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
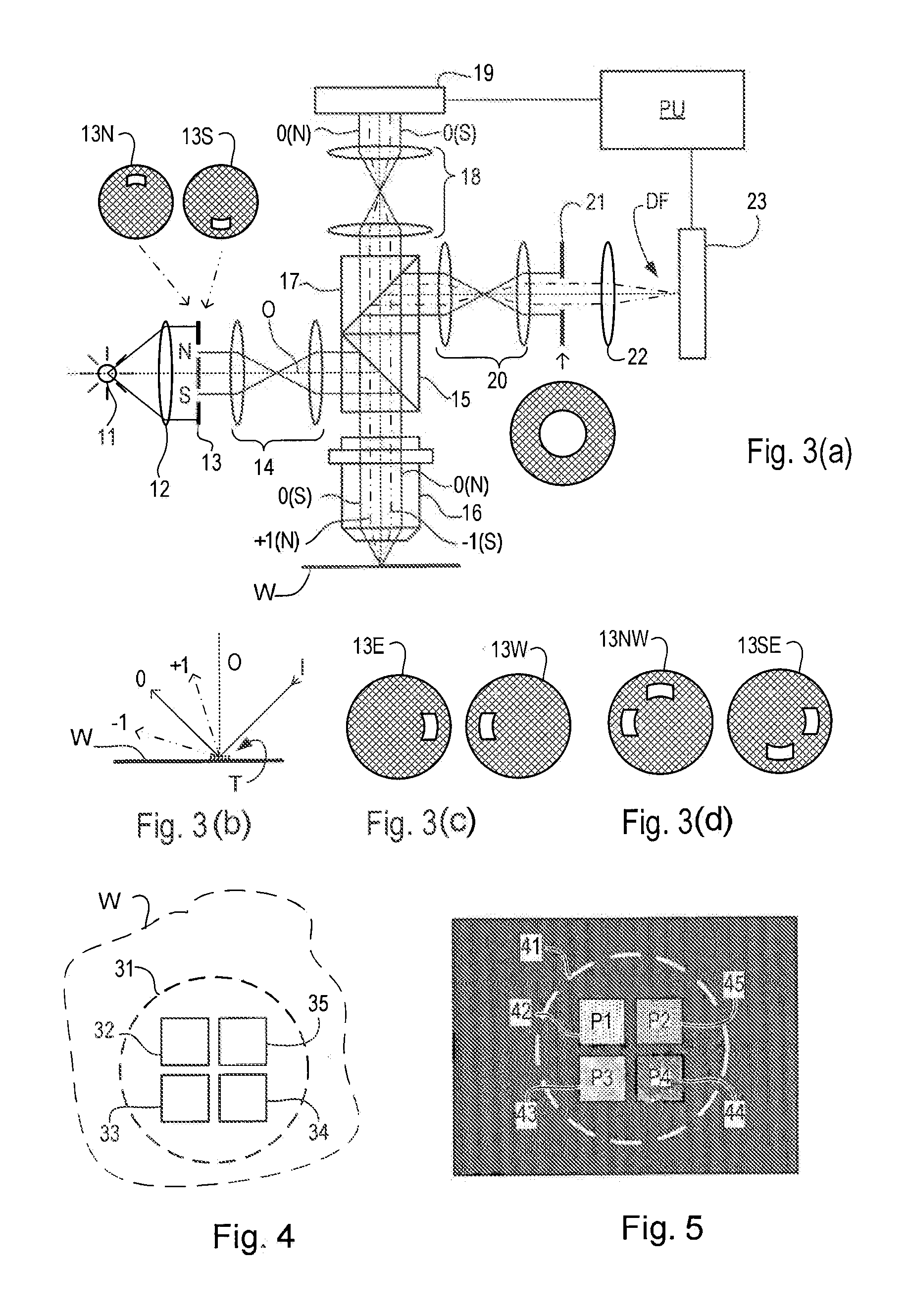
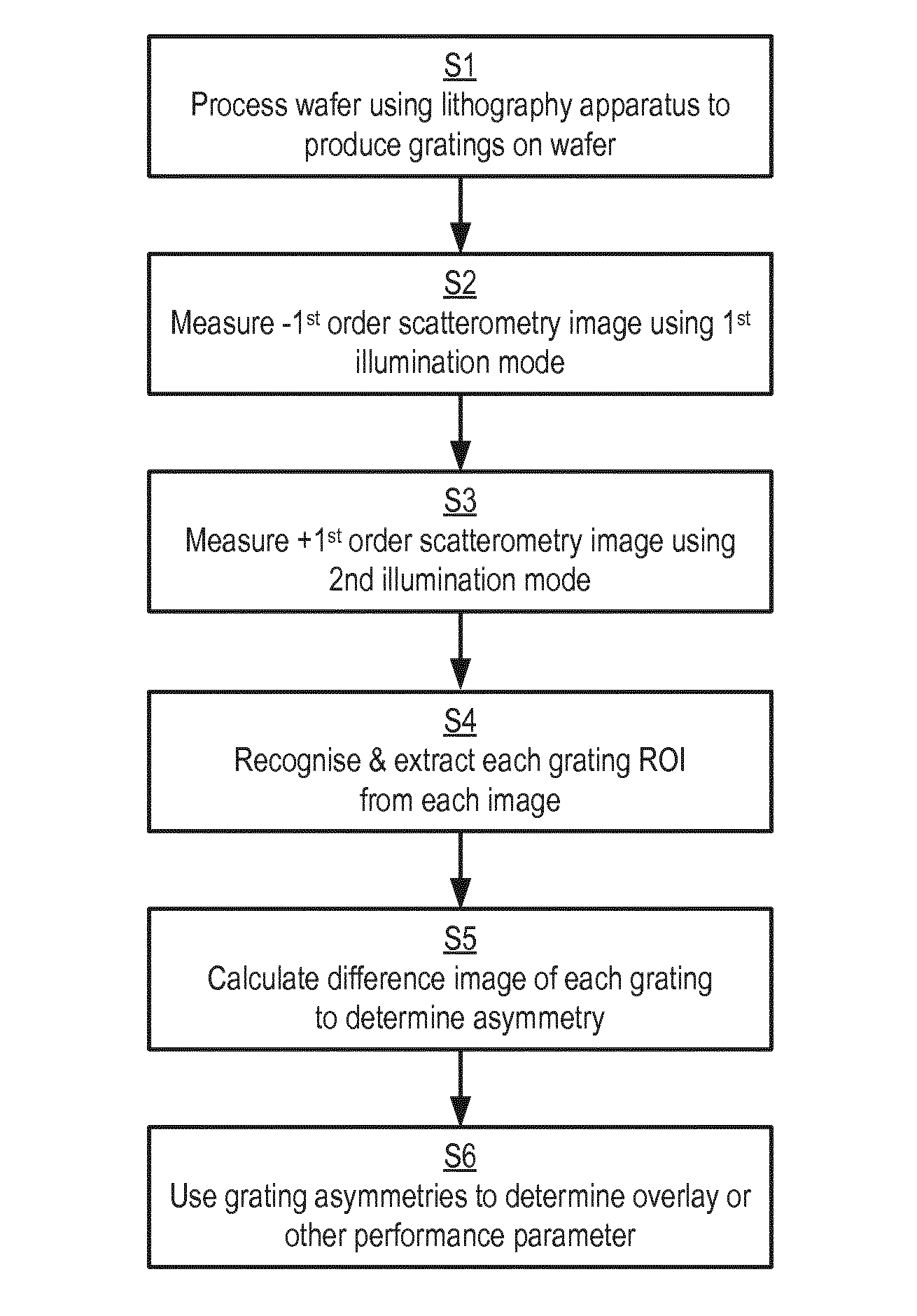
Metrology Method and Apparatus, Lithographic System and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20160161864A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithography processRegression analysis
Disclosed is a method of measuring a parameter of a litho-graphic process, and associated inspection apparatus. The method comprises measuring at least two target structures on a substrate using a plurality of different illumination conditions, the target structures having deliberate overlay biases; to obtain for each target structure an asymmetry measurement representing an overall asymmetry that includes contributions due to (i) the deliberate overlay biases, (ii) an overlay error during forming of the target structure and (iii) any feature asymmetry. A regression analysis is performed on the asymmetry measurement data by fitting a linear regression model to a planar representation of asymmetry measurements for one target structure against asymmetry measurements for another target structure, the linear regression model not necessarily being fitted through an origin of the planar representation. The overlay error can then be determined from a gradient described by the linear regression model.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com