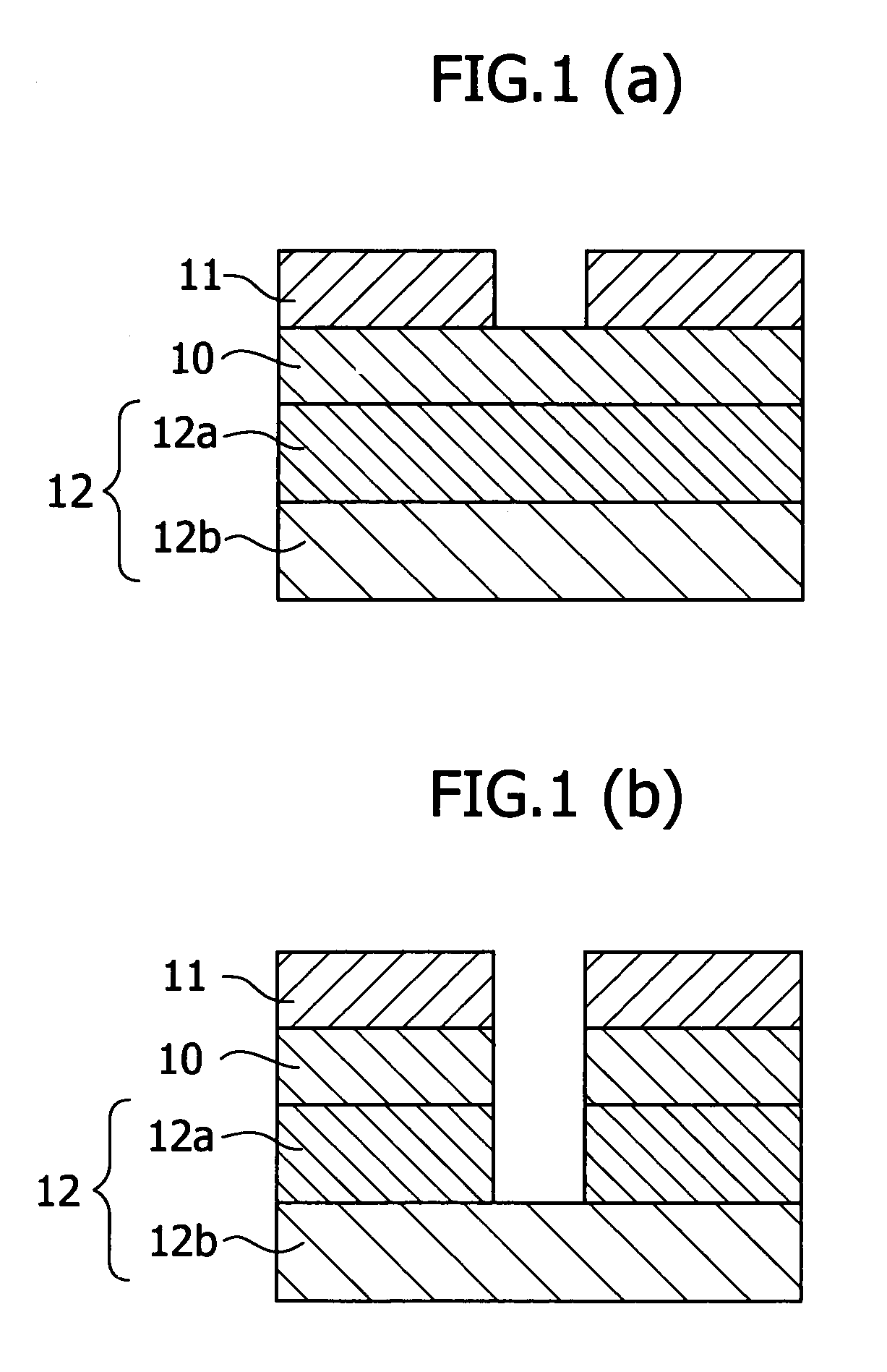
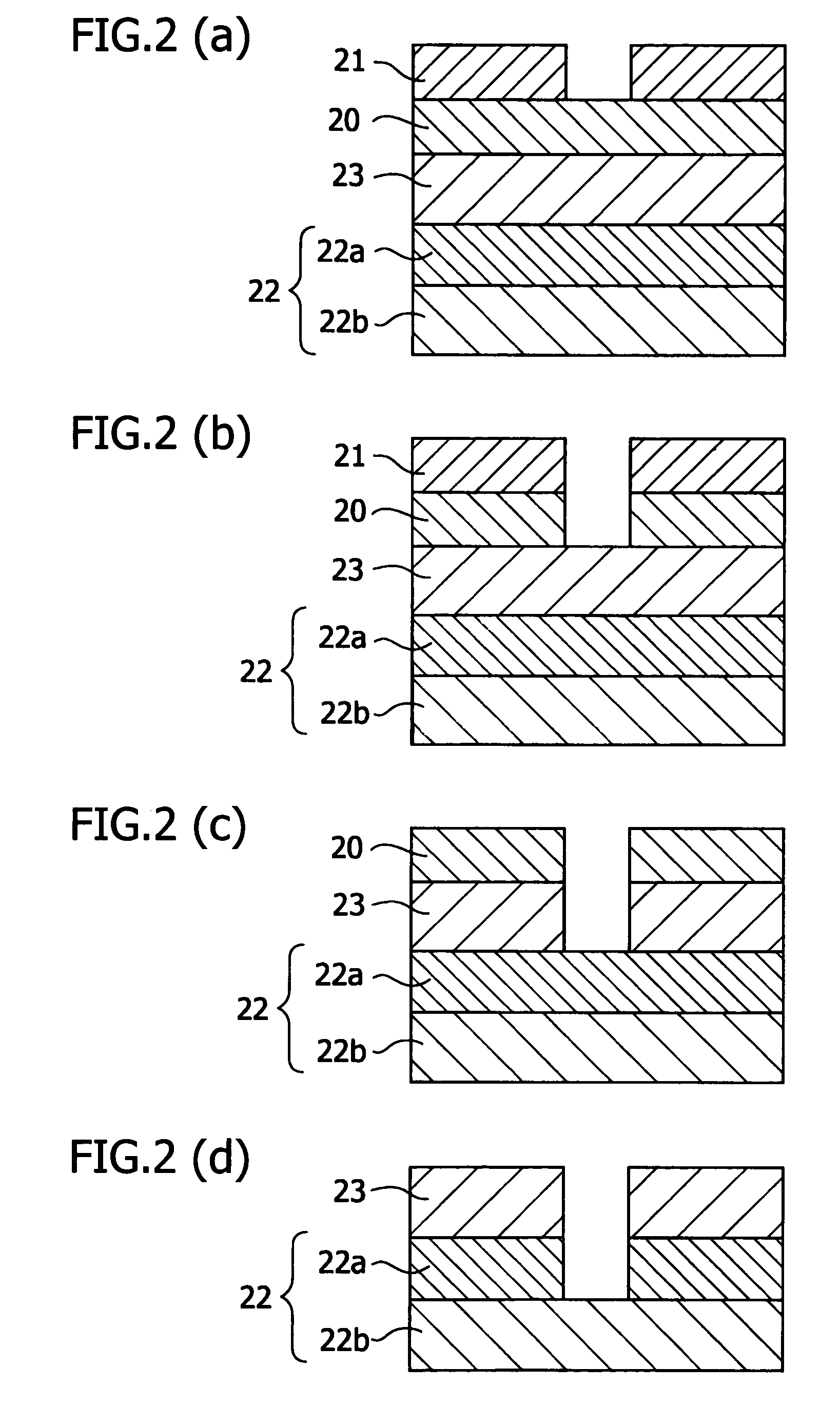
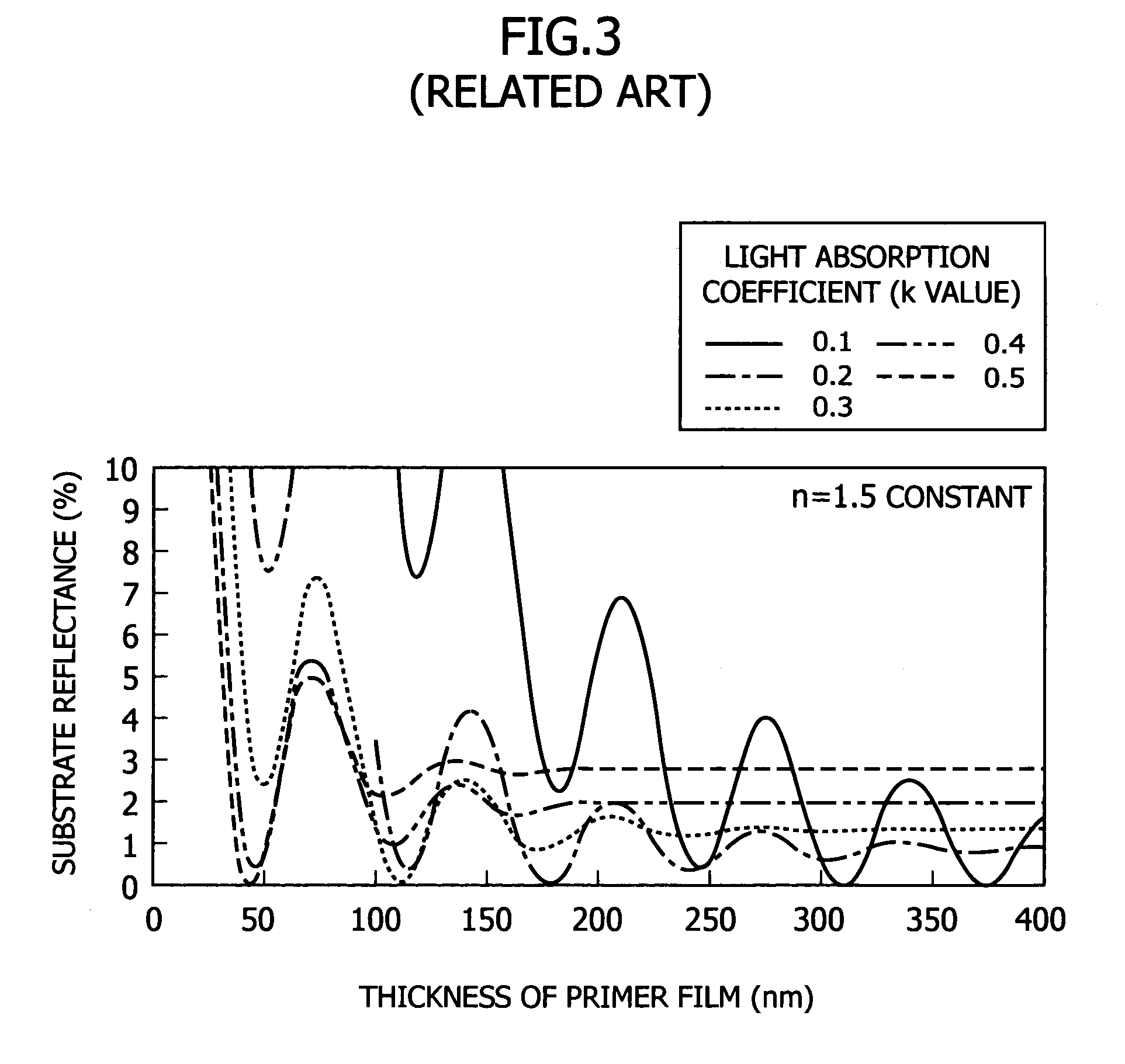
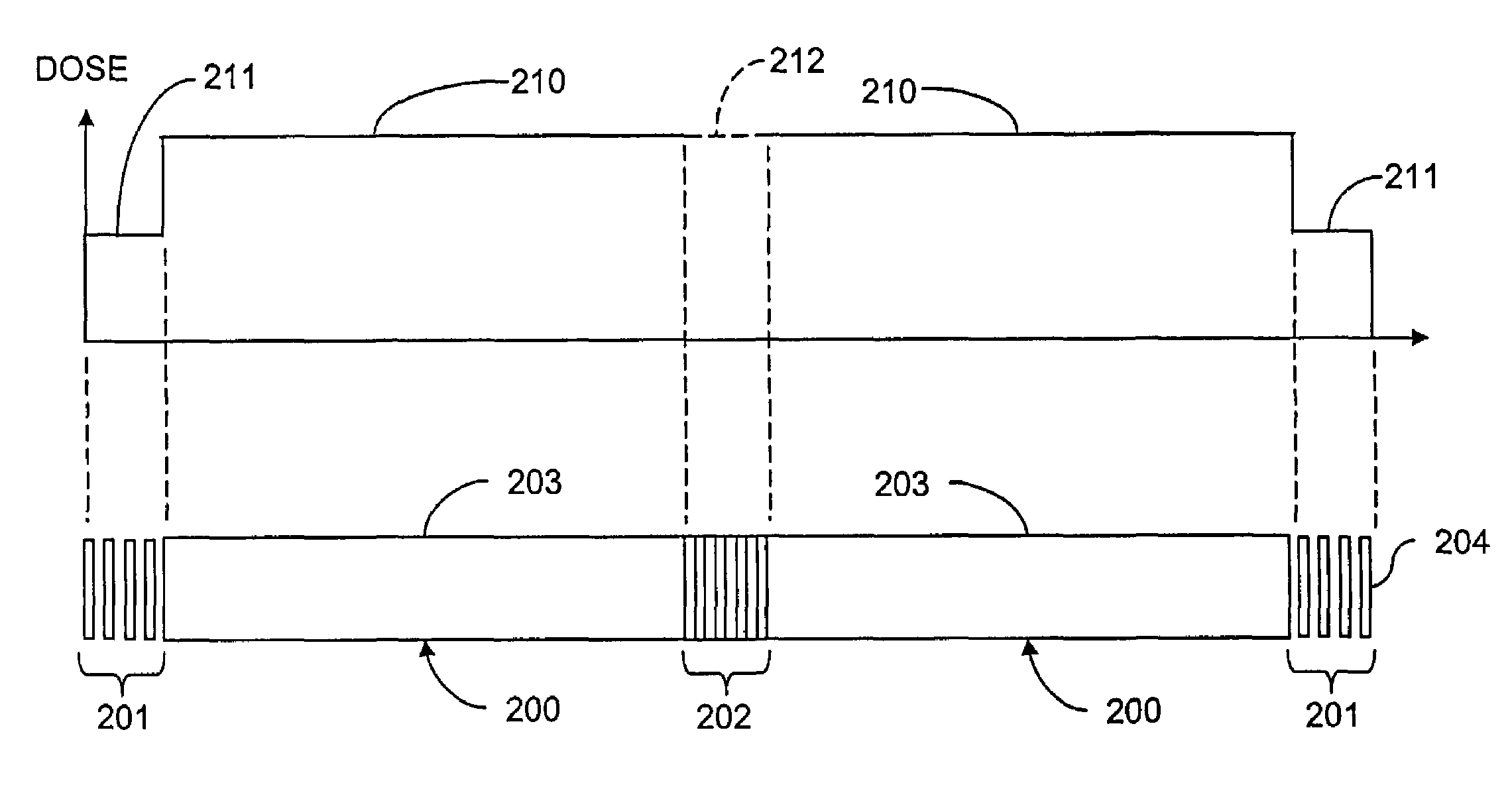
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
573results about "Photo-taking processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
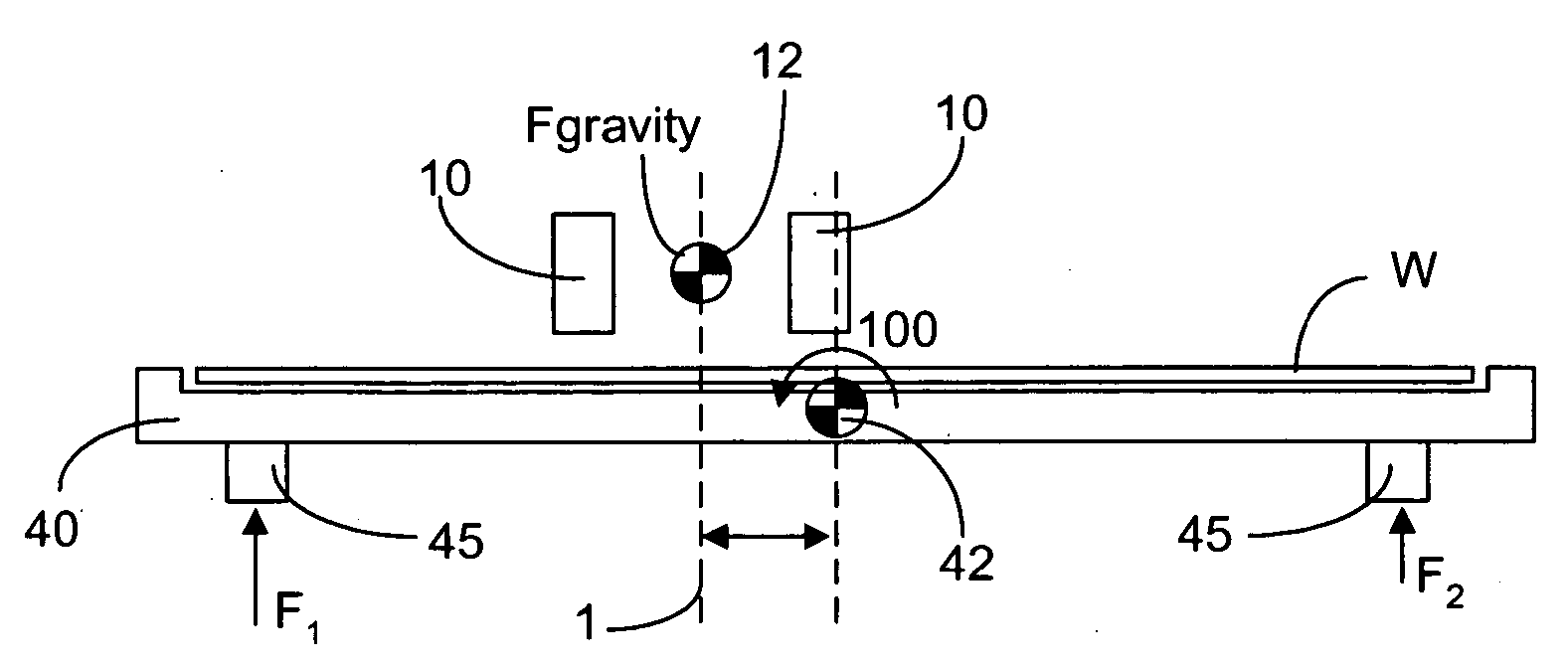
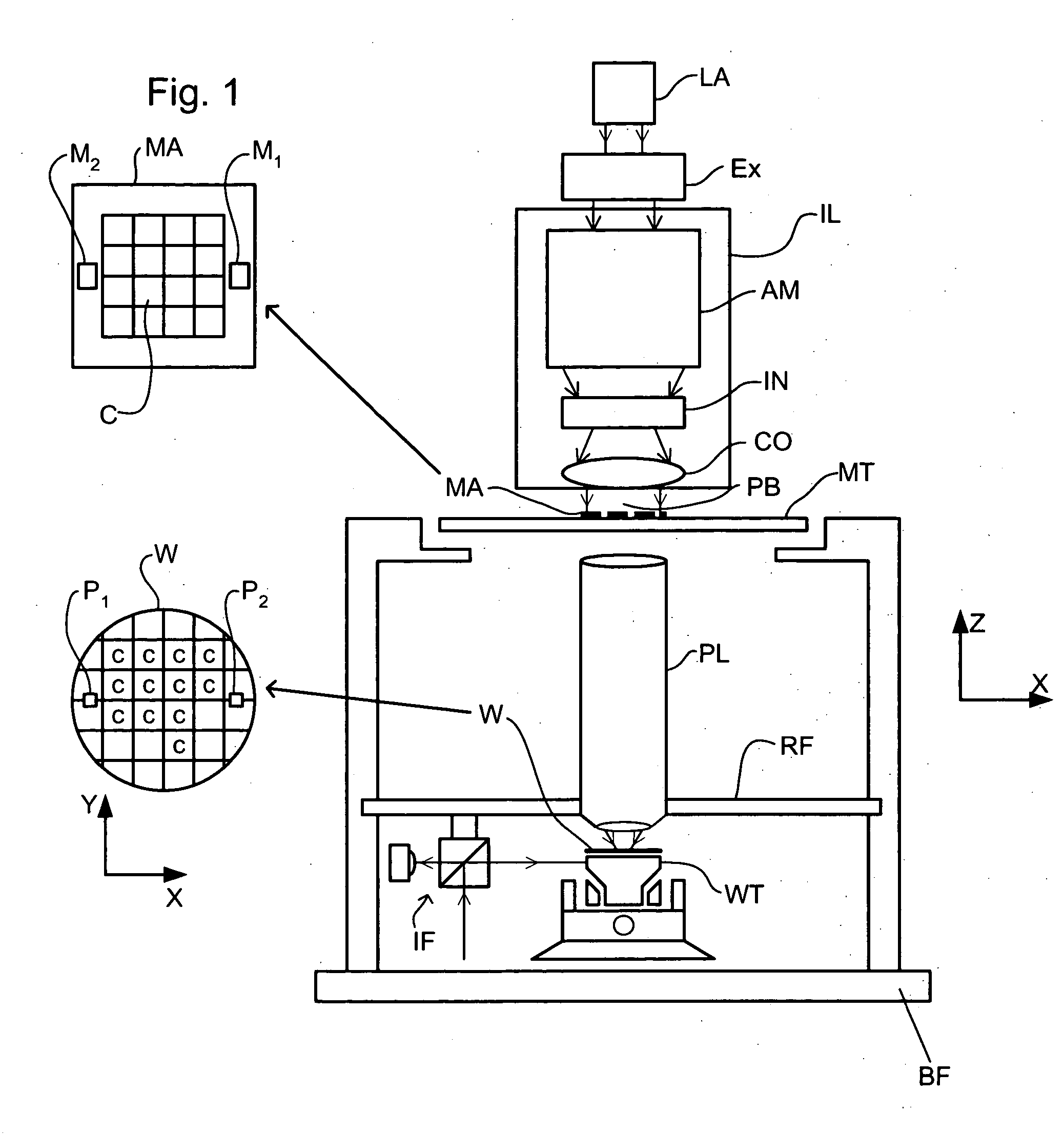
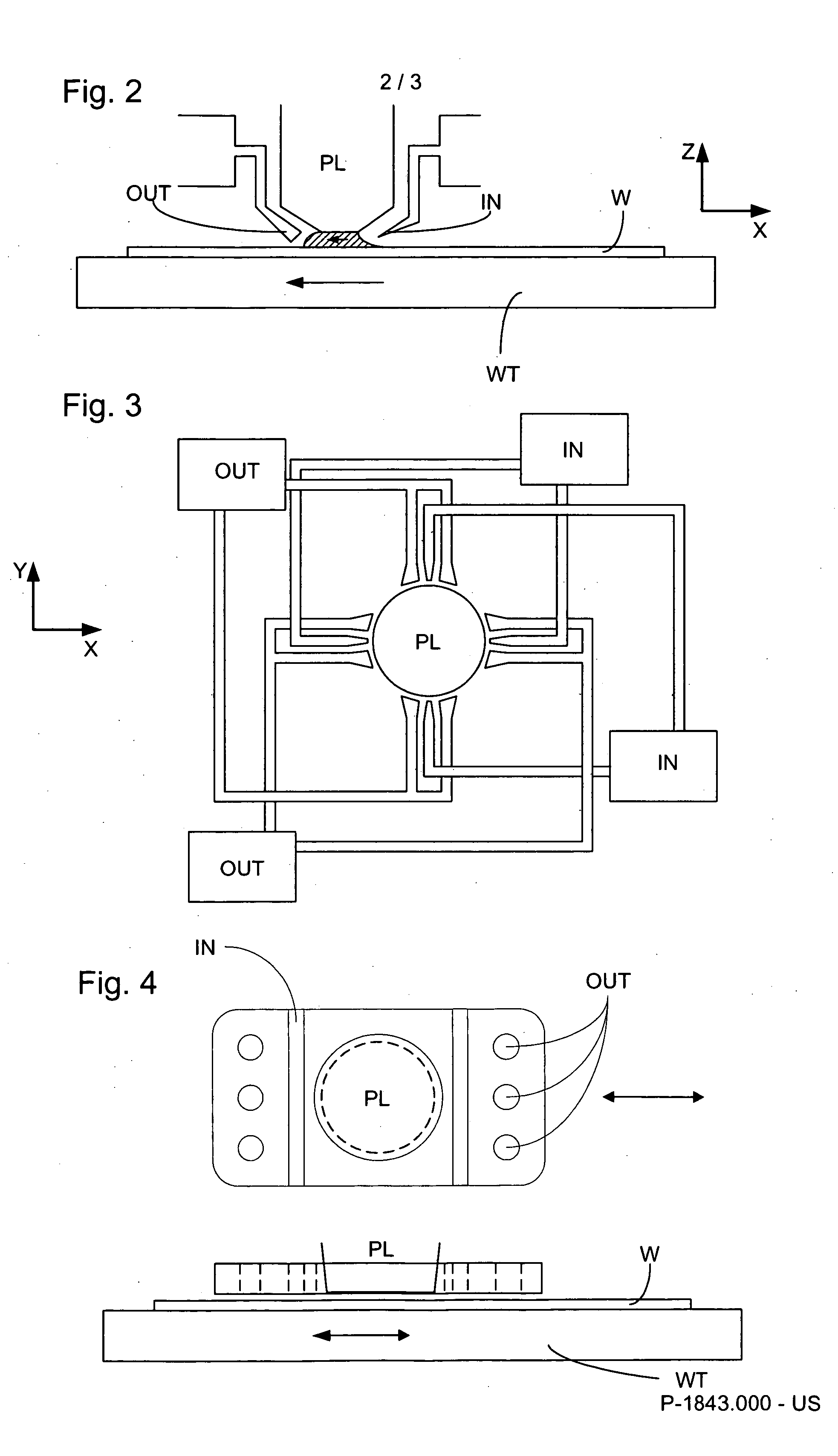
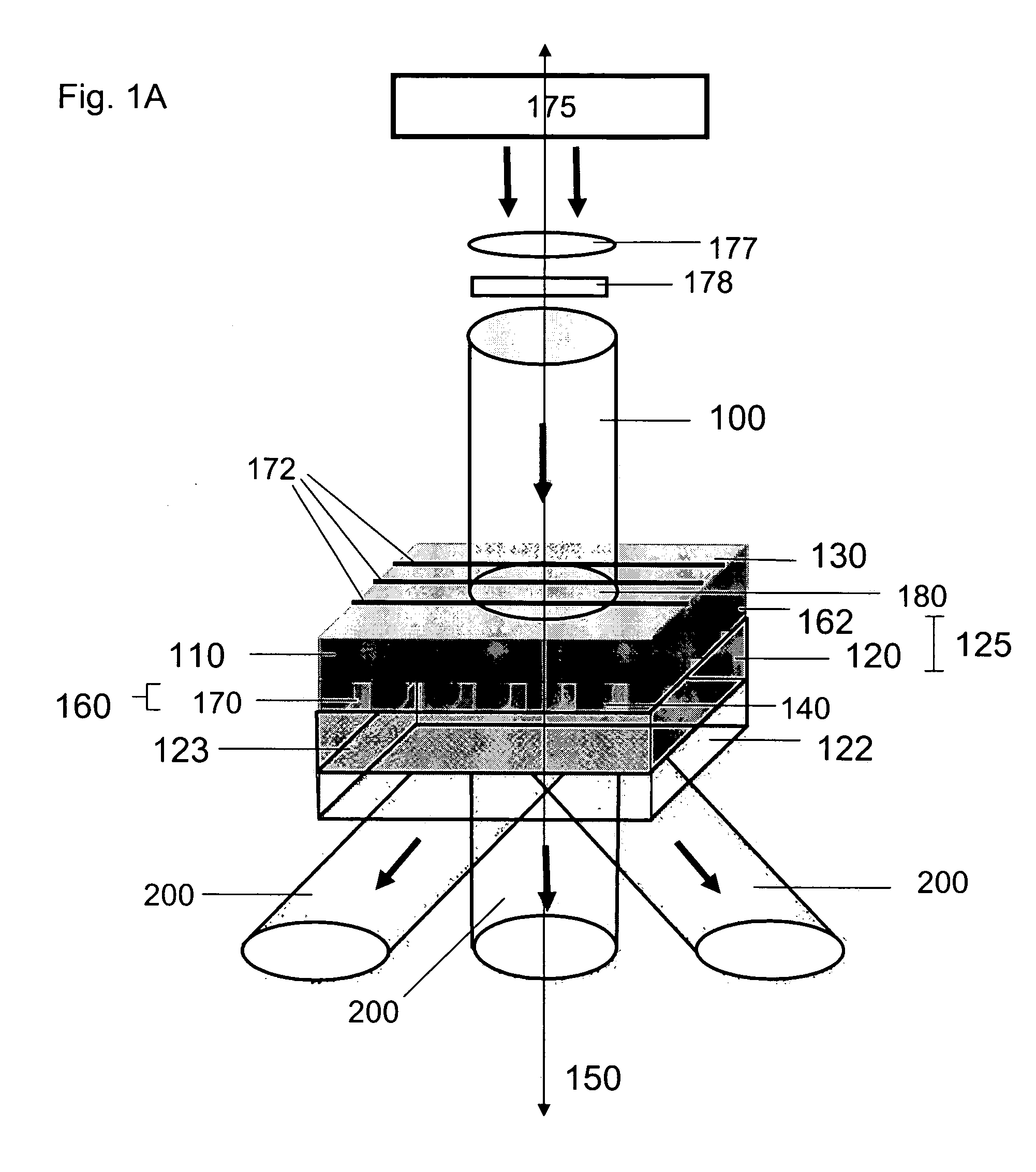
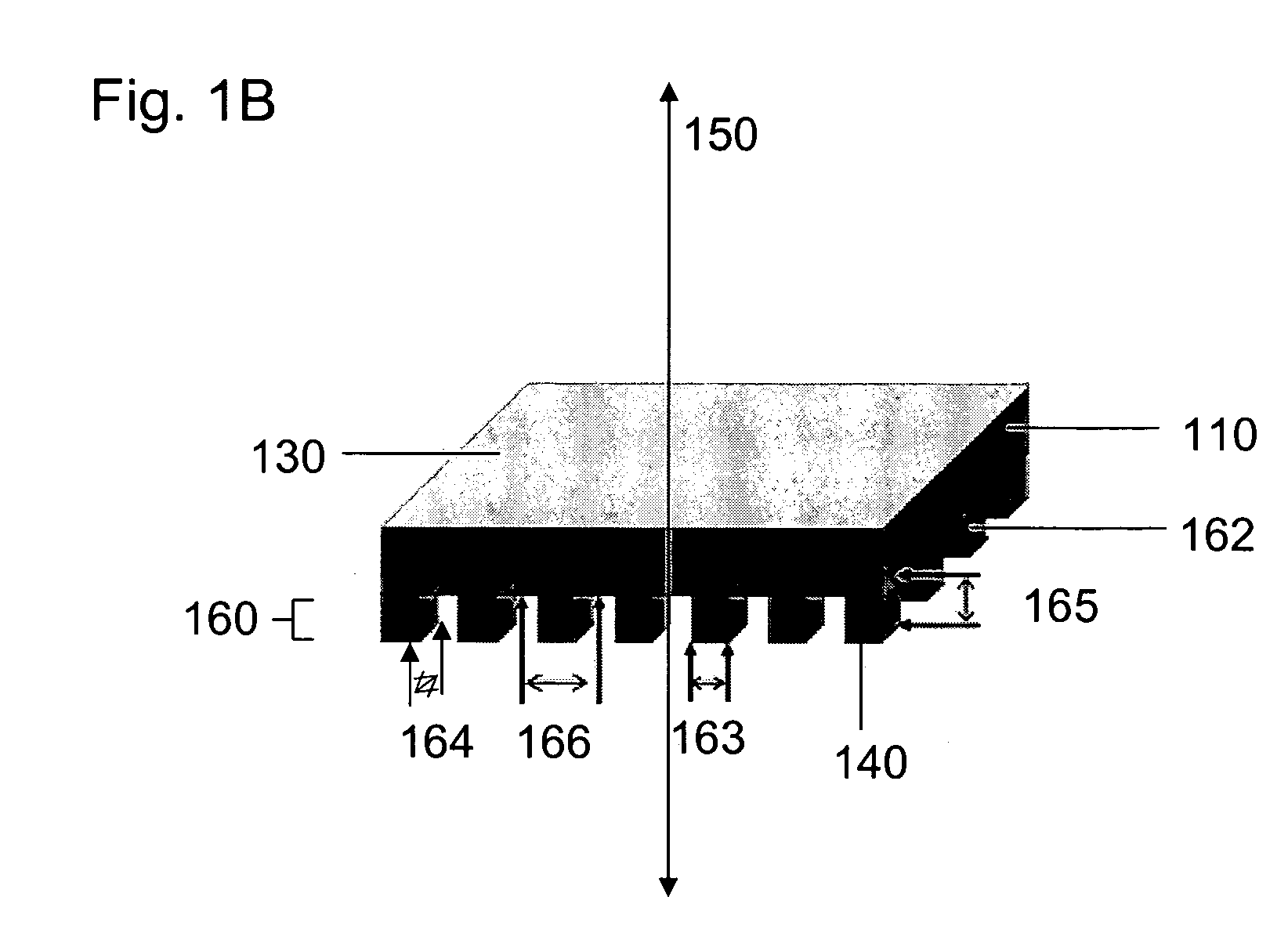
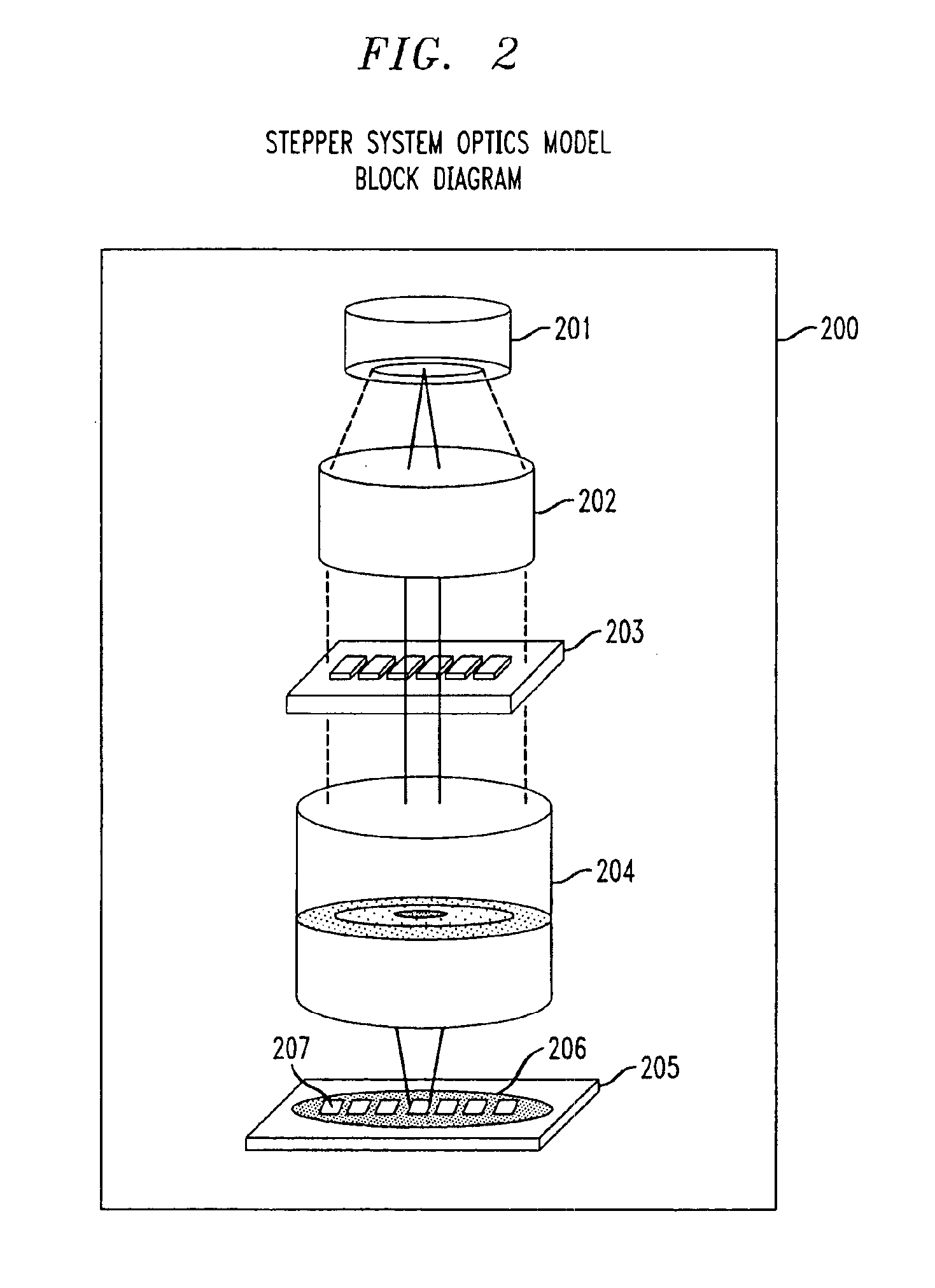
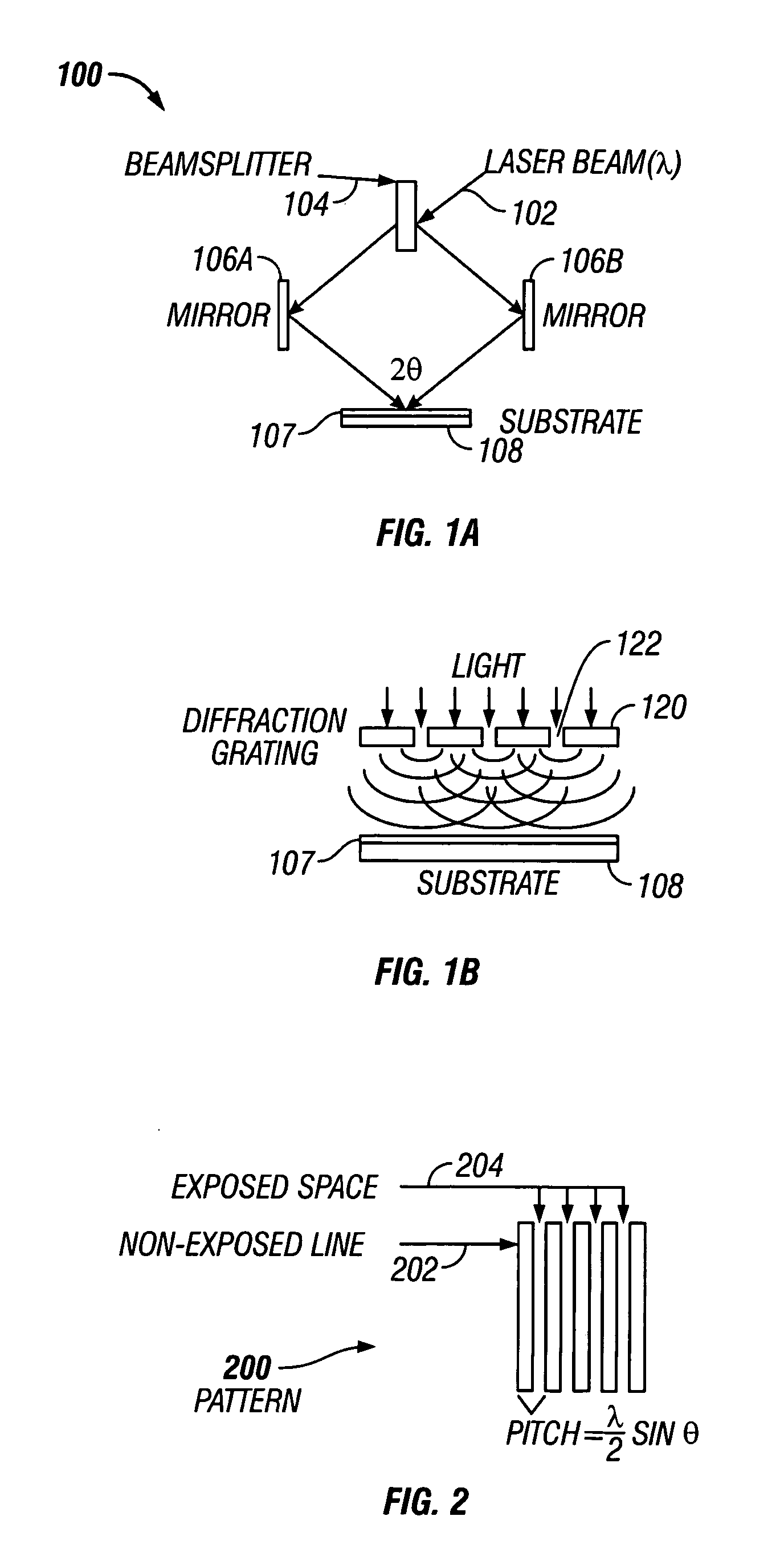
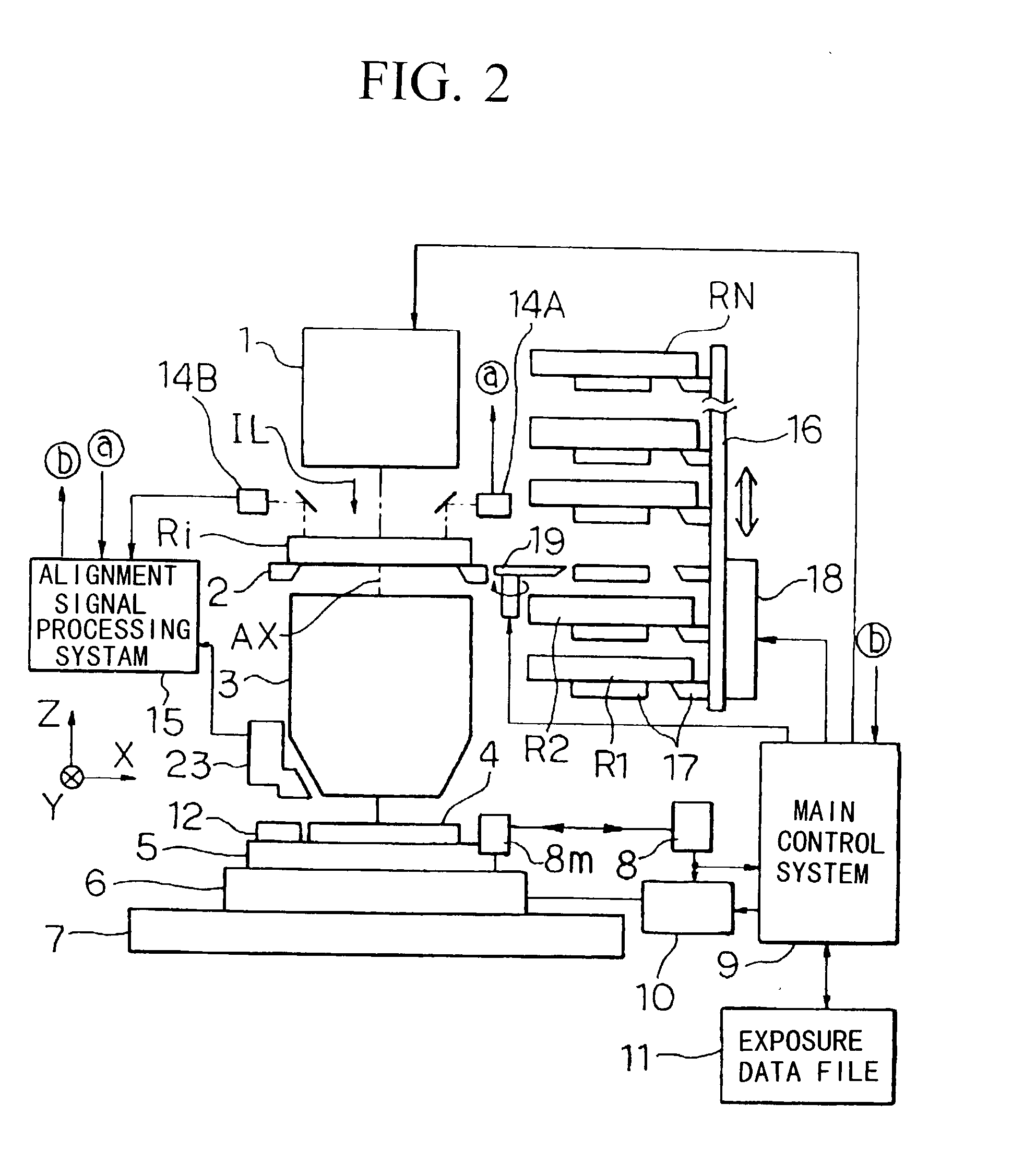
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
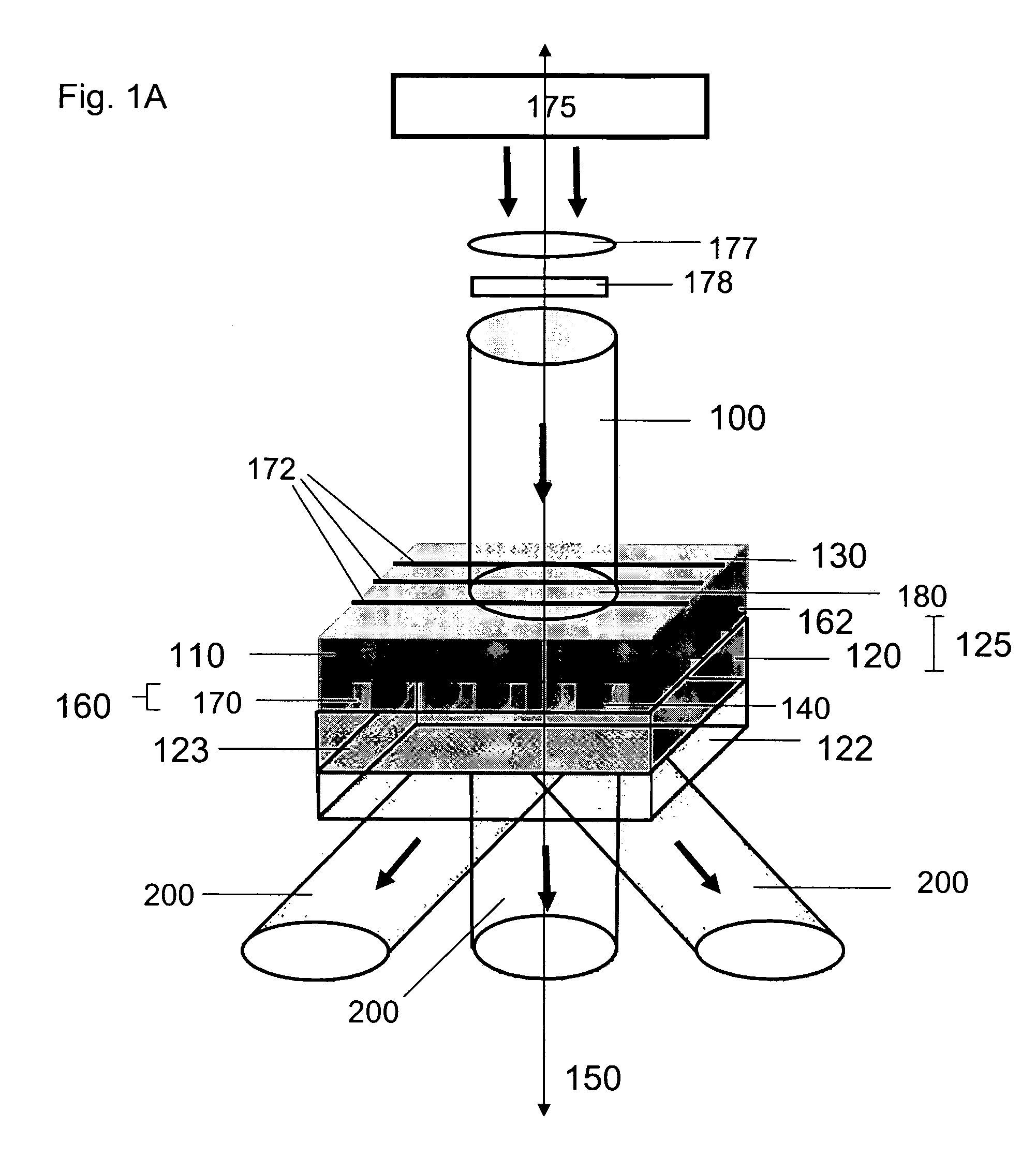
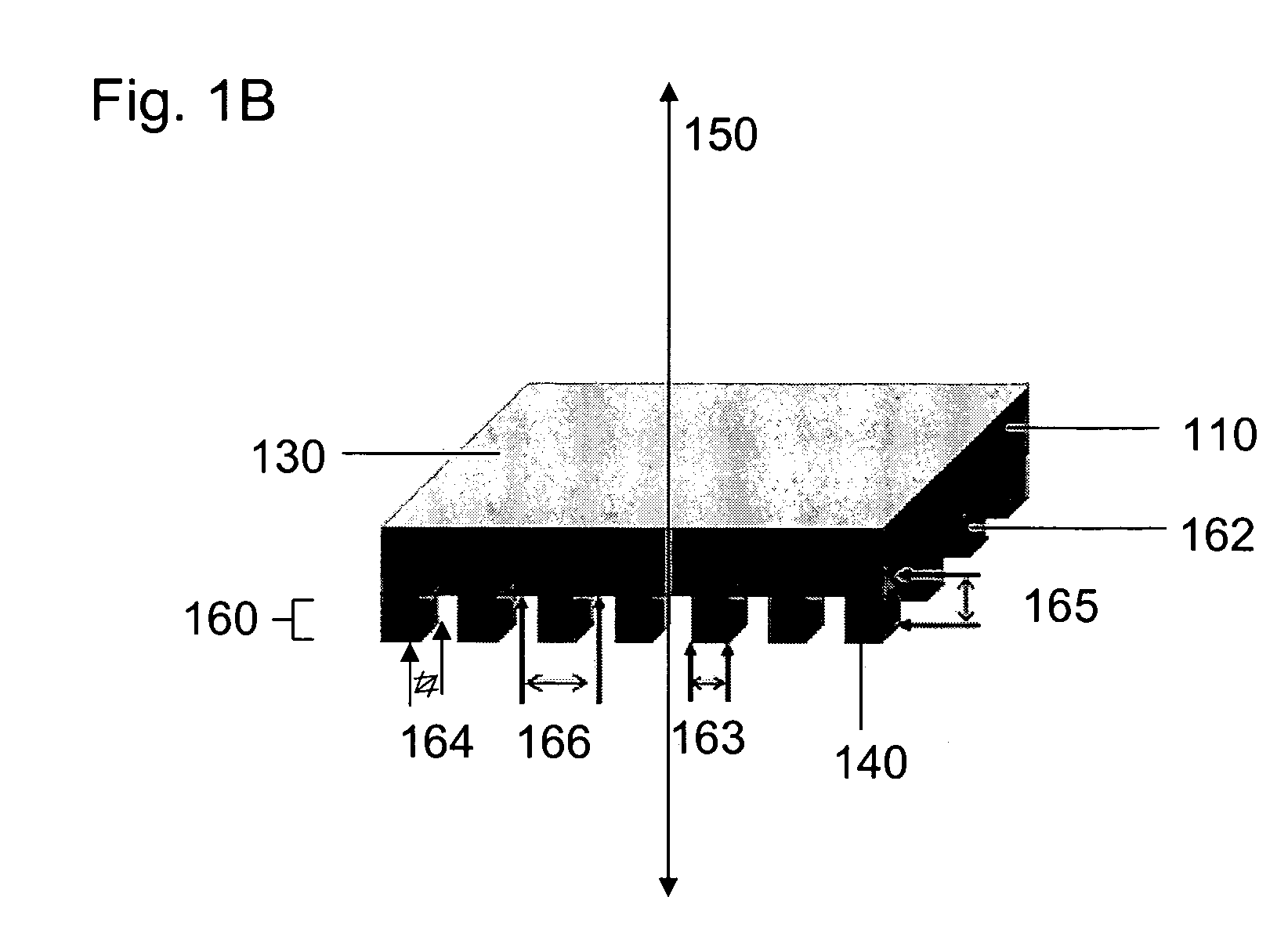
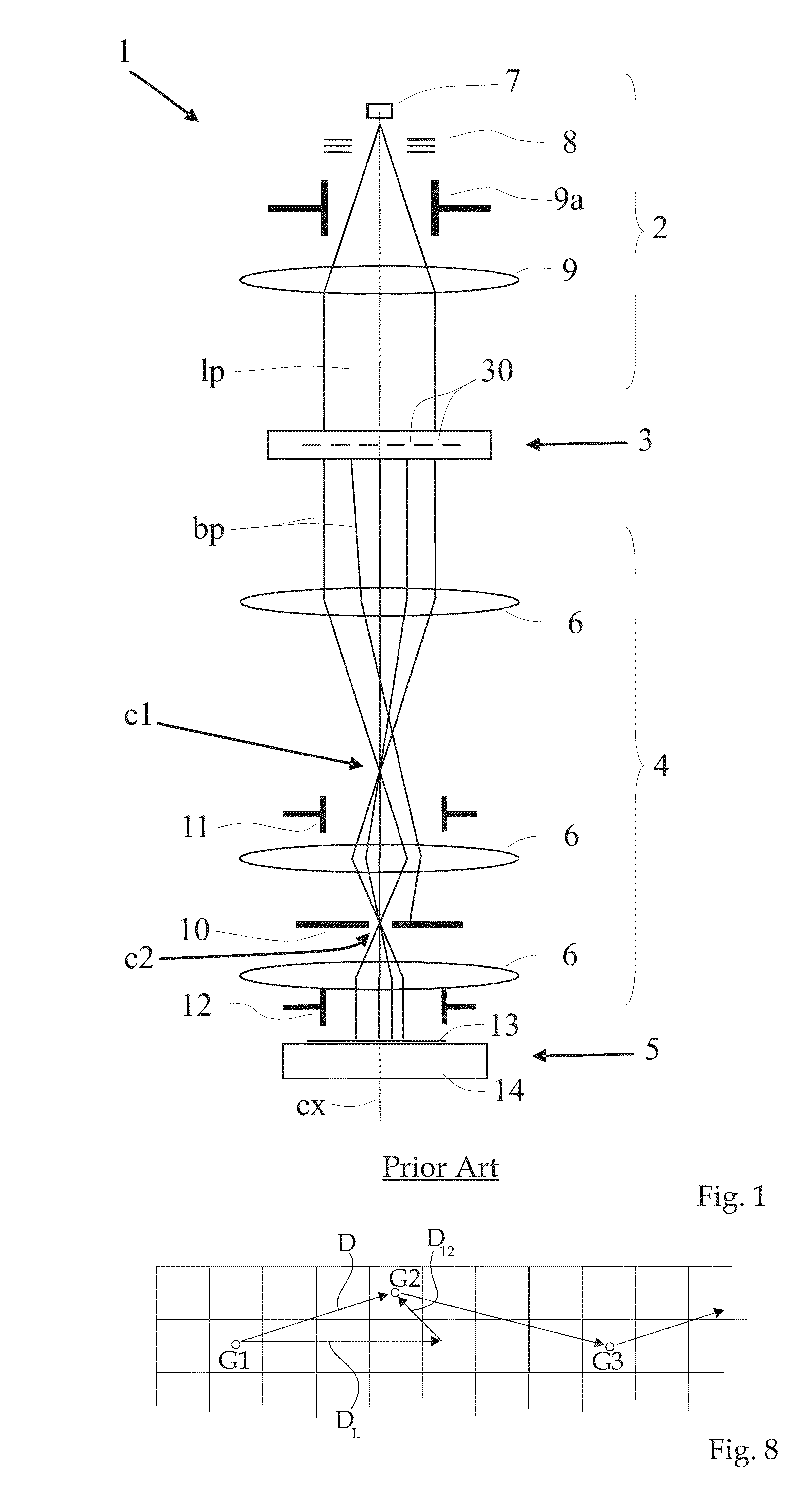
ActiveUS20050219481A1Improve throughputEasy to stackPhoto-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProjection systemActuator
A lithographic apparatus for immersion lithography is described in which a compensation controller controls actuators to apply forces to the substrate equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to forces which are applied to the substrate by a liquid supply system which supplies liquid between the projection system and the substrate.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
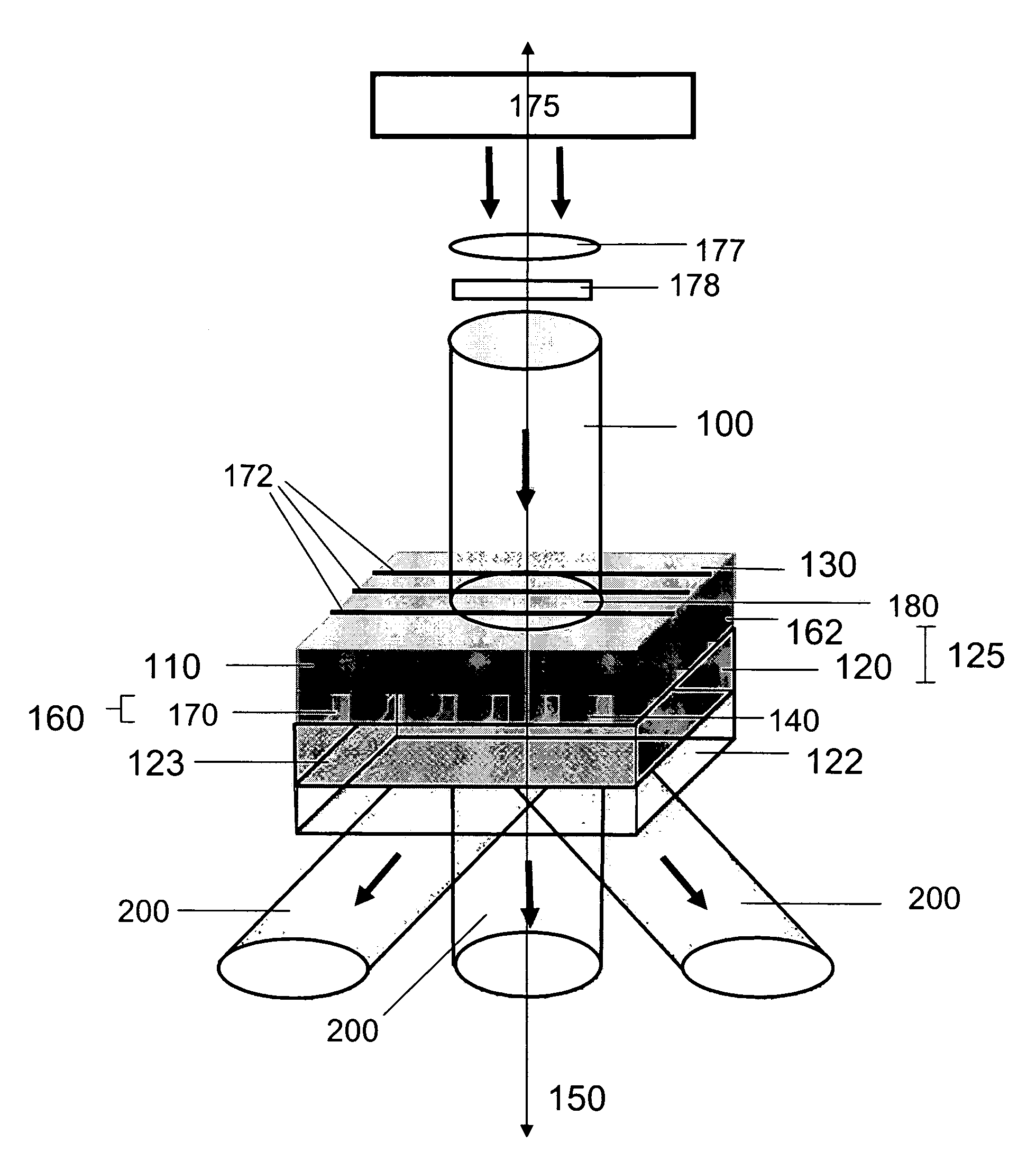
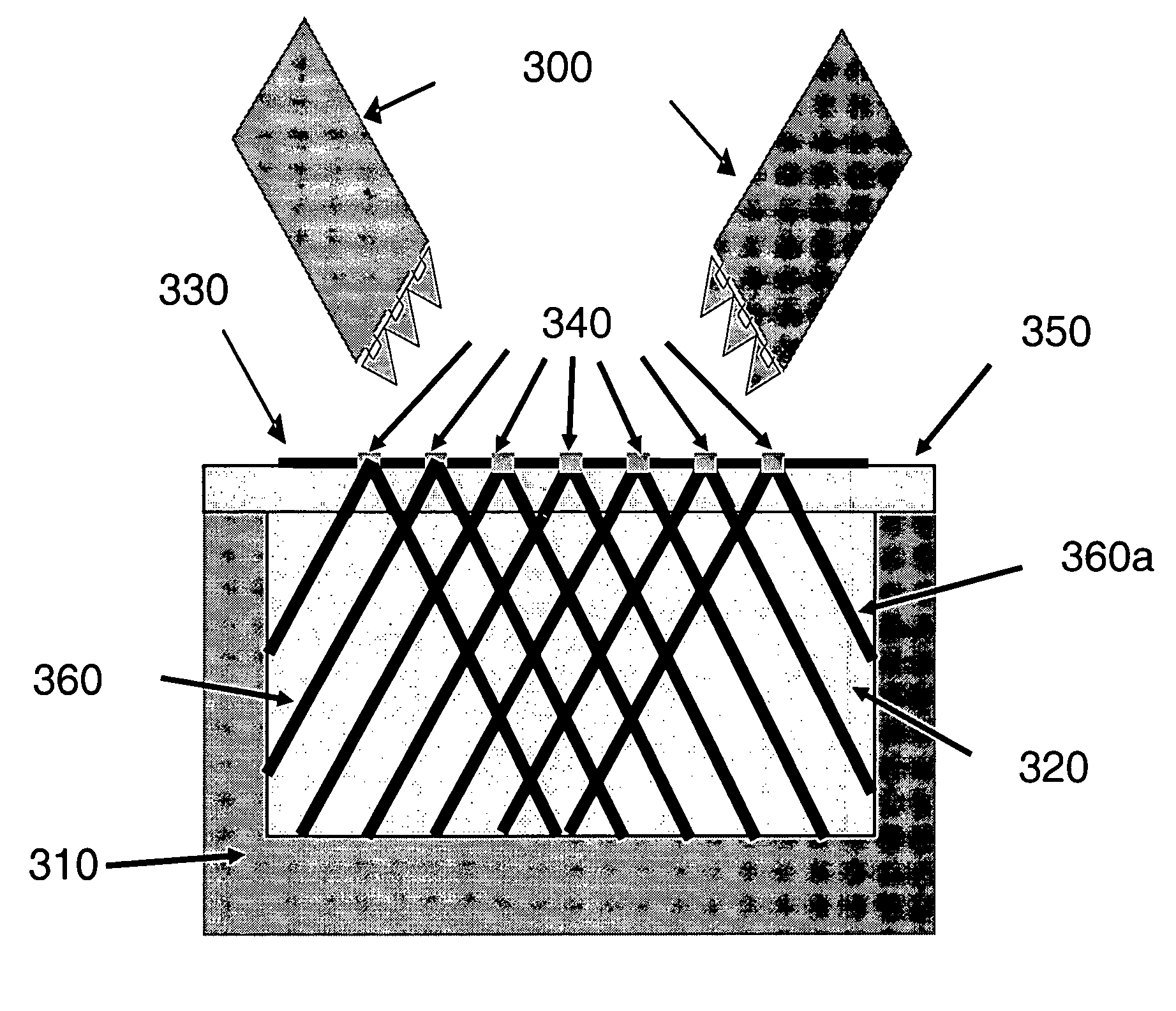
Methods and devices for fabricating three-dimensional nanoscale structures
ActiveUS7704684B2Convenient ArrangementEfficiently patternMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention provides methods and devices for fabricating 3D structures and patterns of 3D structures on substrate surfaces, including symmetrical and asymmetrical patterns of 3D structures. Methods of the present invention provide a means of fabricating 3D structures having accurately selected physical dimensions, including lateral and vertical dimensions ranging from 10s of nanometers to 1000s of nanometers. In one aspect, methods are provided using a mask element comprising a conformable, elastomeric phase mask capable of establishing conformal contact with a radiation sensitive material undergoing photoprocessing. In another aspect, the temporal and / or spatial coherence of electromagnetic radiation using for photoprocessing is selected to fabricate complex structures having nanoscale features that do not extend entirely through the thickness of the structure fabricated.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Optically oriented three-dimensional polymer microstructures
A method and system of creating one or more waveguides and / or patterning these waveguides to form a 3D microstructure that uses mask and collimated light. In one embodiment, the system includes at least one collimated light source selected to produce a collimated light beam; a reservoir having a photo-monomer adapted to polymerize by the collimated light beam; and a mask having at least one aperture and positioned between the at least one collimated light source and the reservoir. Here, the at least one aperture is adapted to guide a portion of the collimated light beam into the photo-monomer to form the at least one polymer waveguide through a portion of a volume of the photo-monomer.
Owner:HRL LAB
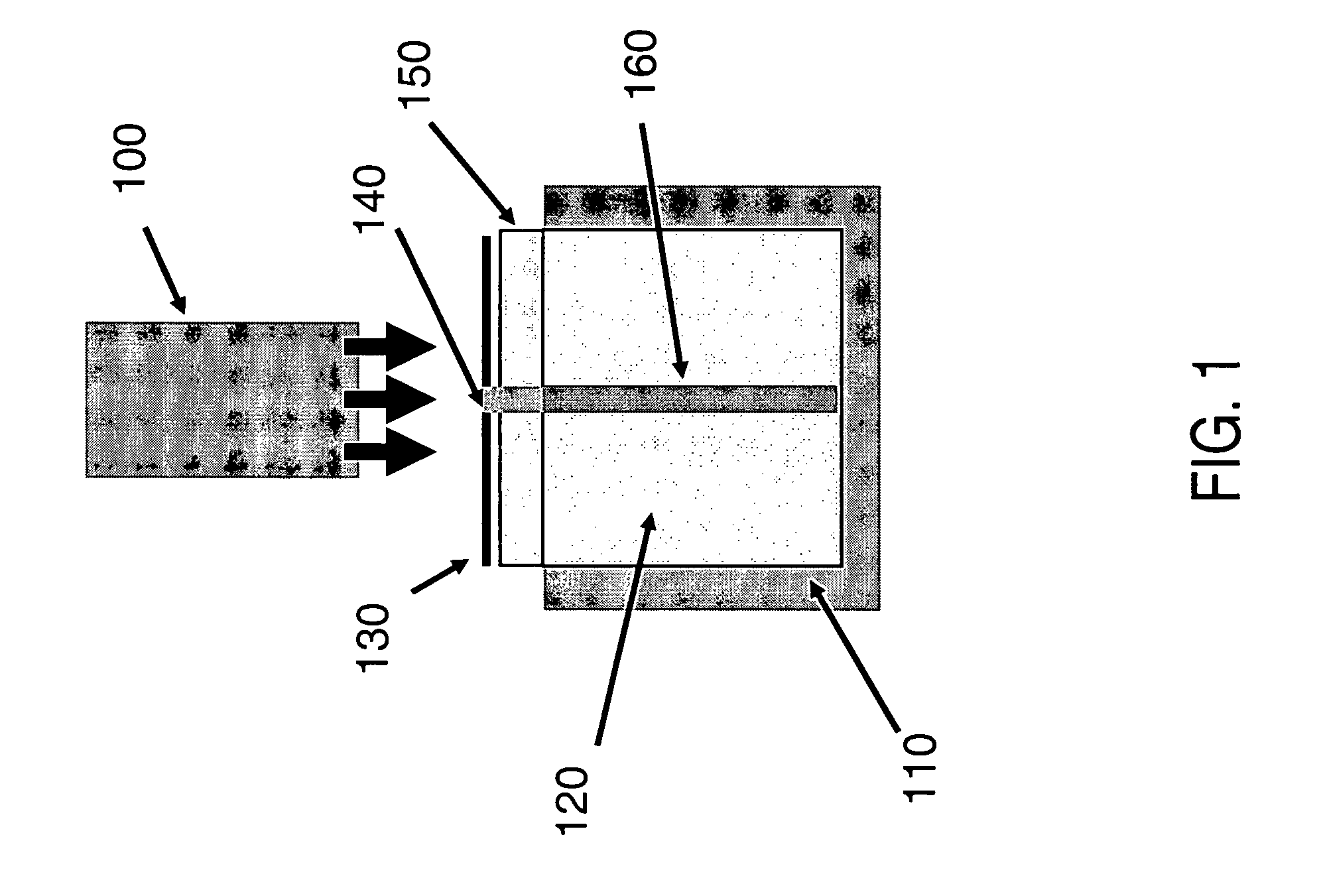
Process for roll-to-roll manufacture of a display by synchronized photolithographic exposure on a substrate web
InactiveUS20020182544A1High aspect ratioWell-defined shapePhoto-taking processesPhotomechanical apparatusDisplay deviceRefractive index
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> This invention relates to an electrophoretic display or a liquid crystal display and novel processes for its manufacture. The electrophoretic display (EPD) of the present invention comprises microcups of well-defined shape, size and aspect ratio and the microcups are filled with charged pigment particles dispersed in an optically contrasting dielectric solvent. The liquid crystal display (LCD) of this invention comprises well-defined microcups filled with at least a liquid crystal composition having its ordinary refractive index matched to that of the isotropic cup material. A novel roll-to-roll process and apparatus of the invention permits the display manufacture to be carried out continuously by a synchronized photo-lithographic process. The synchronized roll-to-roll process and apparatus permits a pre-patterned photomask, formed as a continuous loop, to be rolled in a synchronized motion in close parallel alignment to a web which has been pre-coated with a radiation sensitive material, so as to maintain image alignment during exposure to a radiation source. The radiation sensitive material may be a radiation curable material, in which the exposed and cured portions form the microcup structure. In an additional process step, the radiation sensitive material may be a positively working photoresist which temporarily seals the microcups. Exposure of a selected subset of the microcups via the photomask image permits selective re-opening, filling and sealing of the microcup subset. Repetition with additional colors permits the continuous assembly of a multicolor EPD or LCD display.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Rectangular contact lithography for circuit performance improvement and manufacture cost reduction
ActiveUS20050196685A1Reduce manufacturing costLot of restrictionPhoto-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
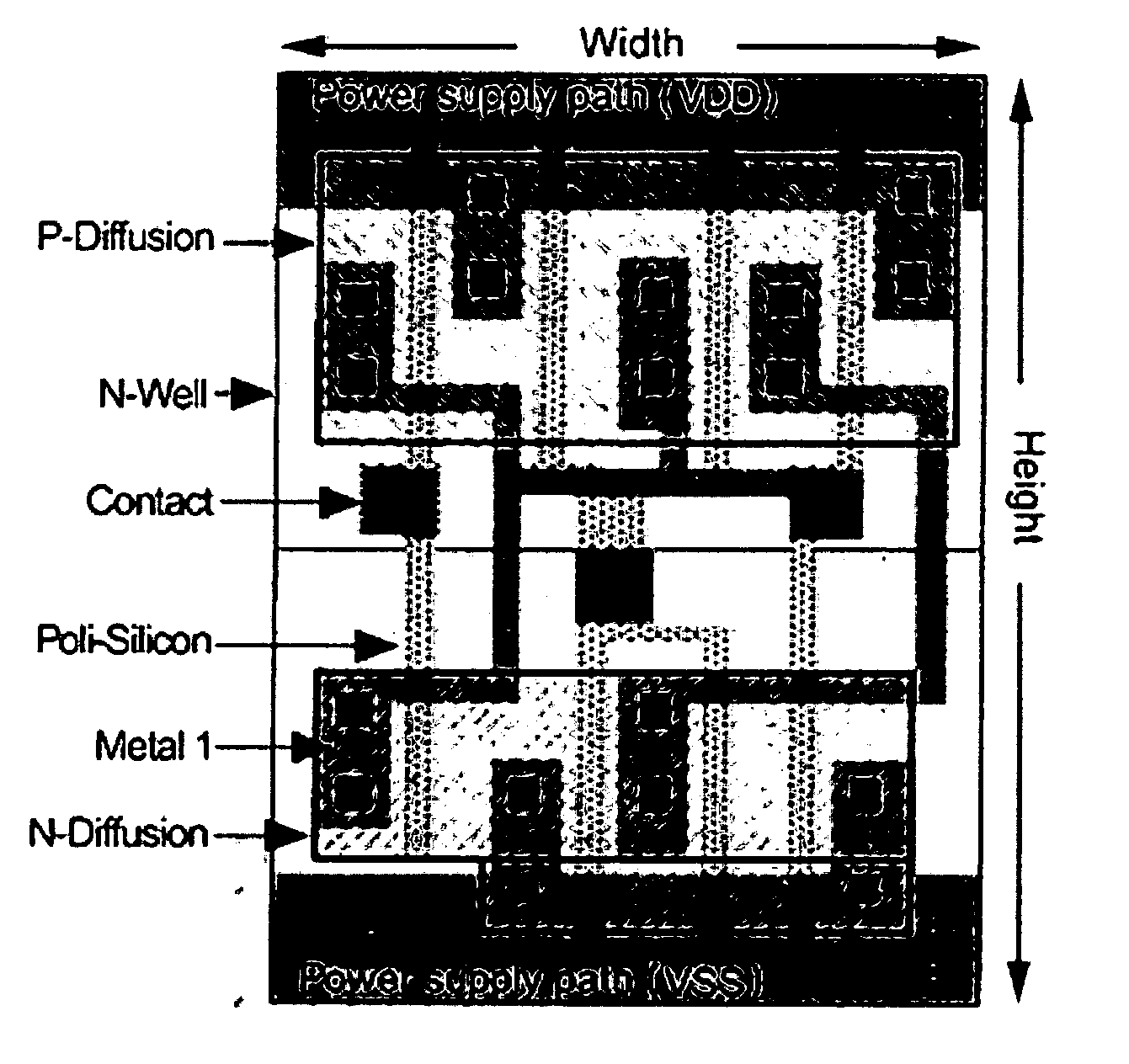
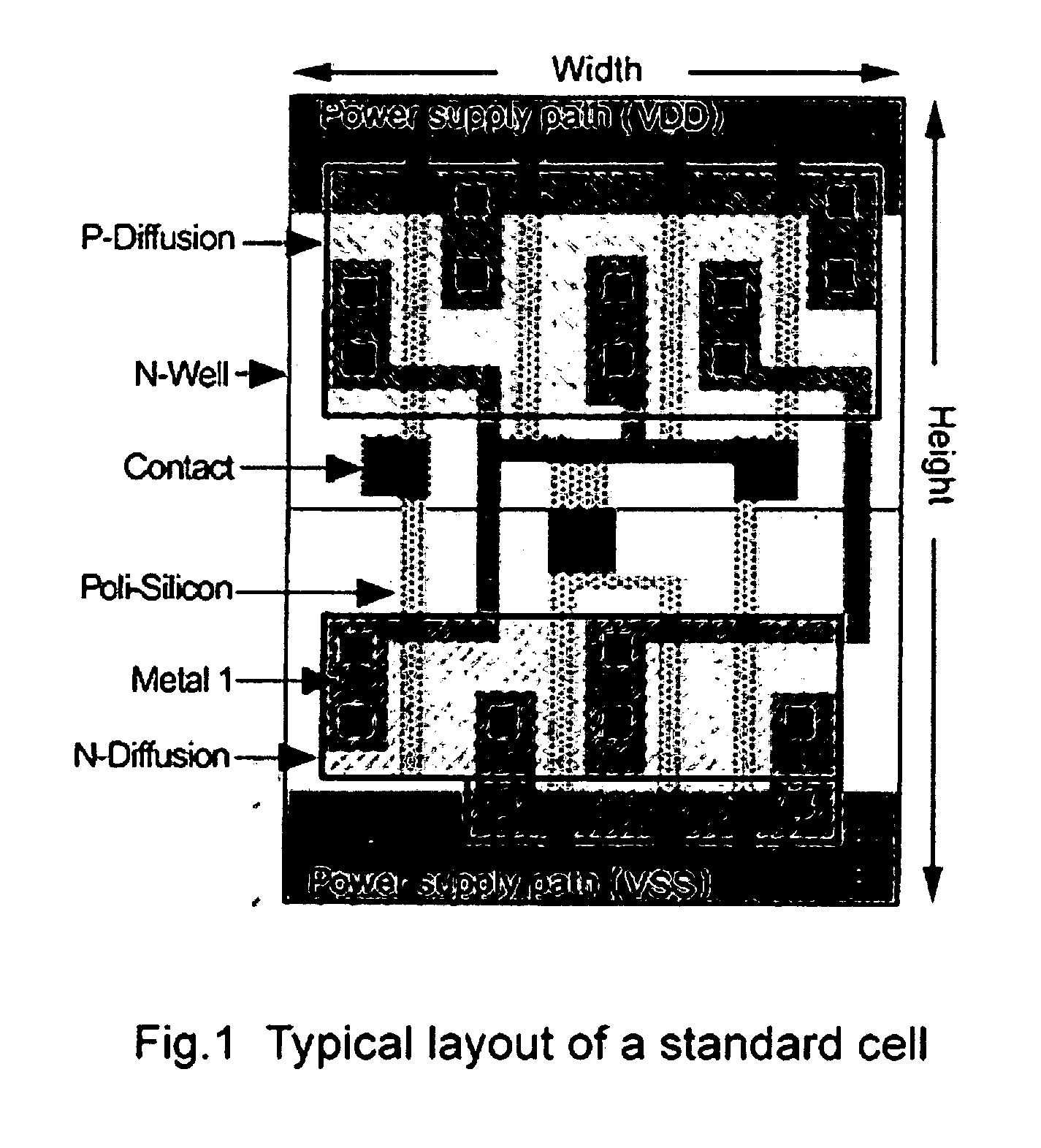
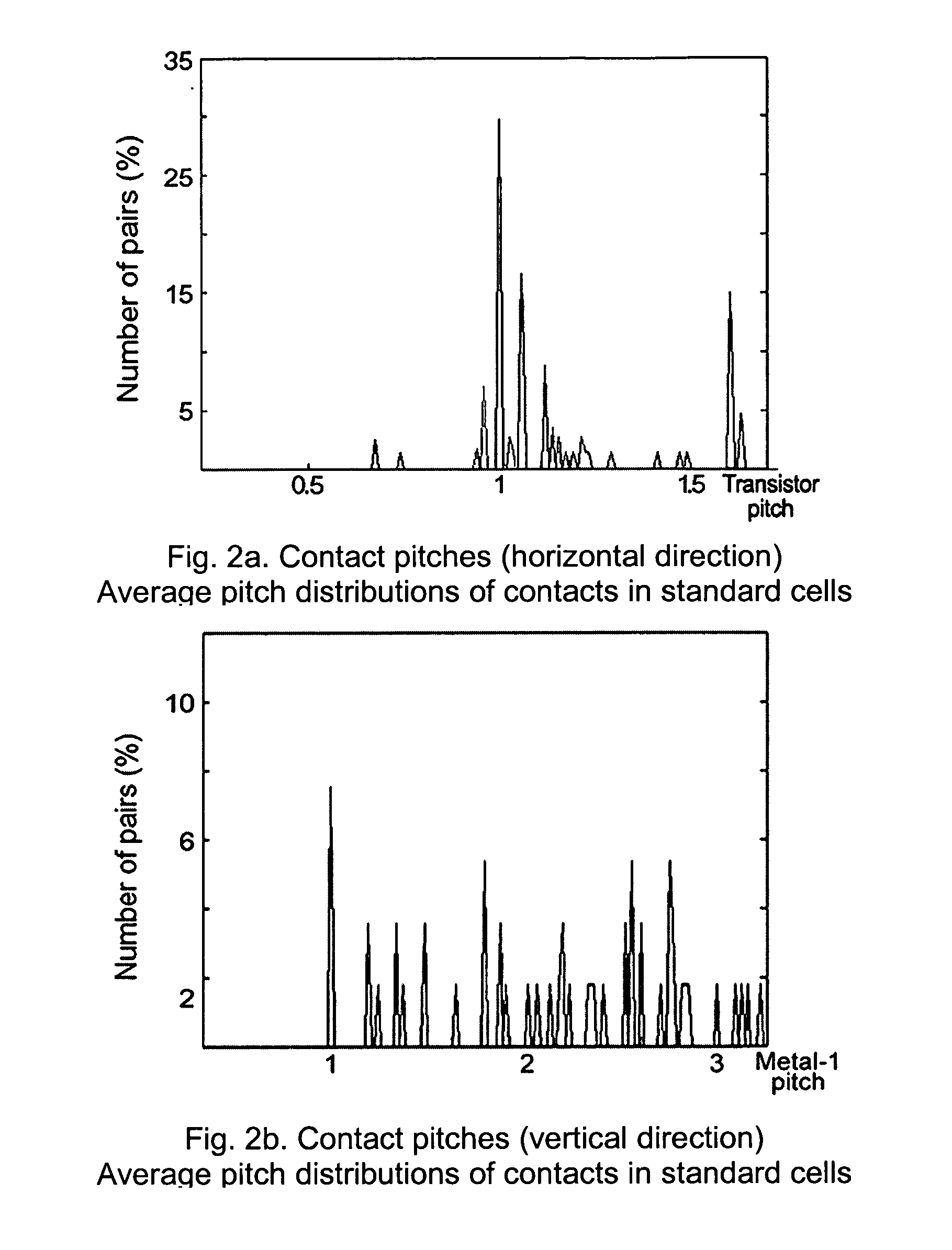
An optical lithography method is disclosed that uses double exposure of a reusable template mask and a trim mask to fabricate regularly-placed rectangular contacts in standard cells of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). A first exposure of the reusable template mask with periodic patterns forms periodic dark lines on a wafer and a second exposure of an application-specific trim mask remove the unwanted part of the dark lines and the small cuts of the dark lines left form the rectangular regularly-placed contacts. All contacts are placed regularly in one direction while unrestrictedly in the perpendicular direction. The regular placement of patterns on the template mask enable more effective use of resolution enhancement technologies, which in turn allows a decrease in manufacturing cost and the minimum contact size and pitch. Since there is no extra application-specific mask needed comparing with the conventional lithography method for unrestrictedly-placed contacts, the extra cost is kept to the lowest. The method of the invention can be used in the fabrication of standard cells in application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) to improve circuit performance and decrease circuit area and manufacturing cost.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods and devices for fabricating three-dimensional nanoscale structures
ActiveUS20060286488A1Simple optical arrangementConvenient ArrangementMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention provides methods and devices for fabricating 3D structures and patterns of 3D structures on substrate surfaces, including symmetrical and asymmetrical patterns of 3D structures. Methods of the present invention provide a means of fabricating 3D structures having accurately selected physical dimensions, including lateral and vertical dimensions ranging from 10 s of nanometers to 1000 s of nanometers. In one aspect, methods are provided using a mask element comprising a conformable, elastomeric phase mask capable of establishing conformal contact with a radiation sensitive material undergoing photoprocessing. In another aspect, the temporal and / or spatial coherence of electromagnetic radiation using for photoprocessing is selected to fabricate complex structures having nanoscale features that do not extend entirely through the thickness of the structure fabricated.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Manufacturing methods for printed circuit boards
InactiveUS6902869B2Improve rigidityEasy to handleLine/current collector detailsWave amplification devicesDielectric substratePhotoresist
A method of forming a plurality of solid conductive bumps for interconnecting two conductive layers of a circuit board with substantially coplanar upper surfaces. The method comprises the steps of applying a continuous homogenous metal layer onto a dielectric substrate, applying a first photoresist and exposing and developing said first photoresist to define a pattern of conductive bumps; etching the metal layer exposed by said development to form said plurality of conductive bumps; removing said first photoresist; applying a second photoresist onto the metal layer; exposing and developing said second photoresist to define a pattern of conductive bumps and circuit lines; etching the metal layer exposed by said development to form a pattern of circuit lines in said metal layer; and removing said second photoresist. The methods of the present invention also provides for fabricating a multilayer circuit board and a metallic border for providing rigidity to a panel.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
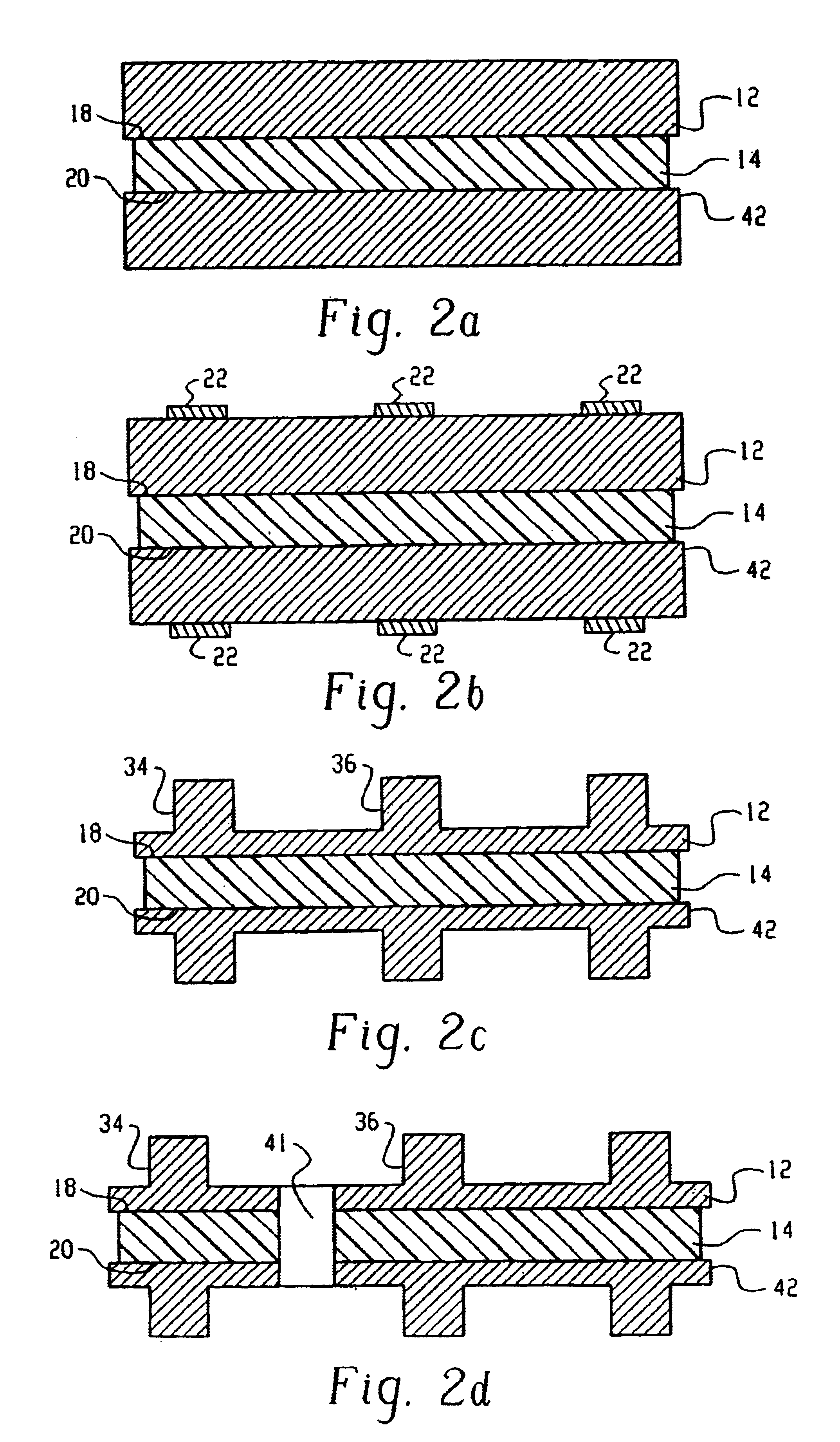
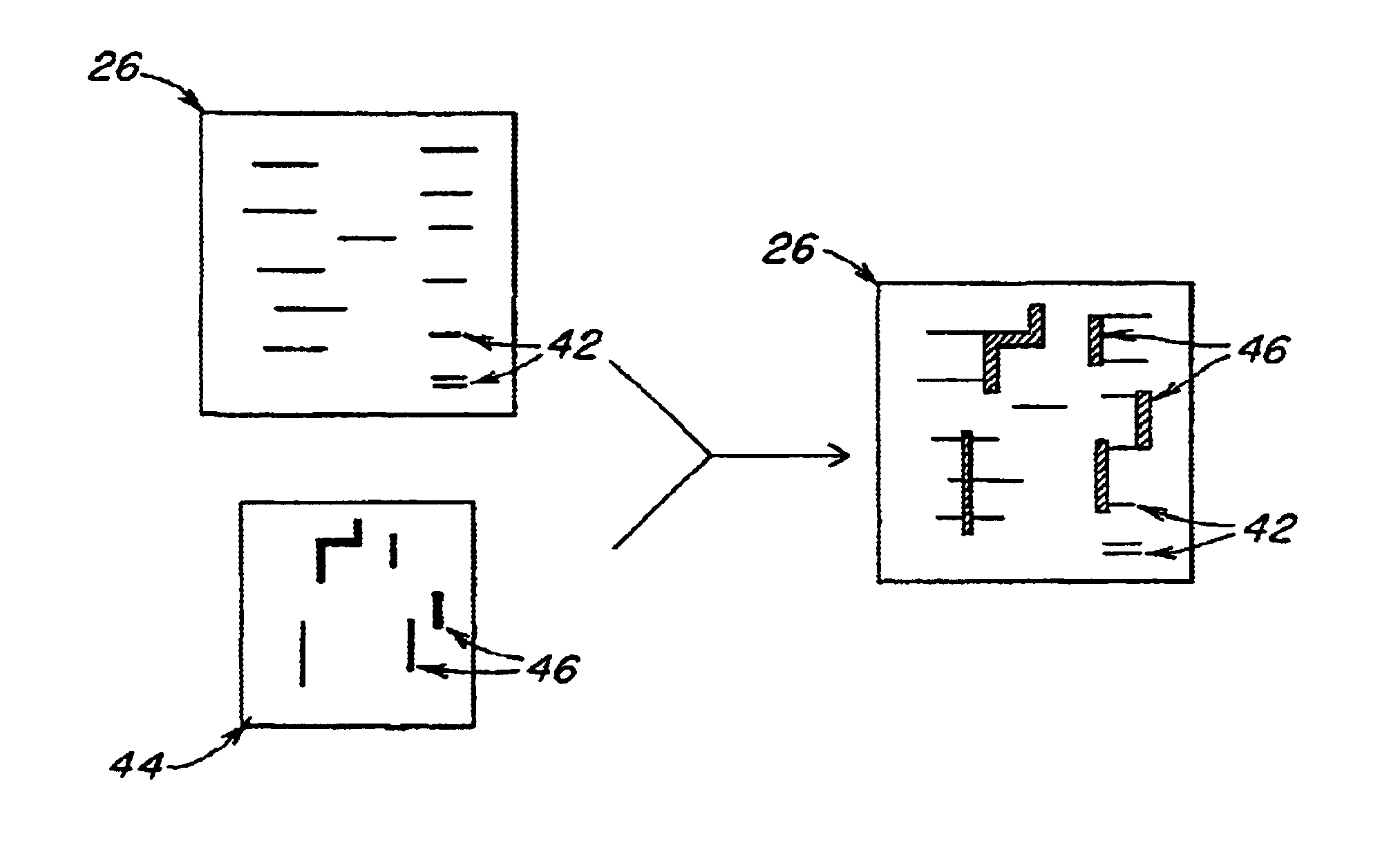
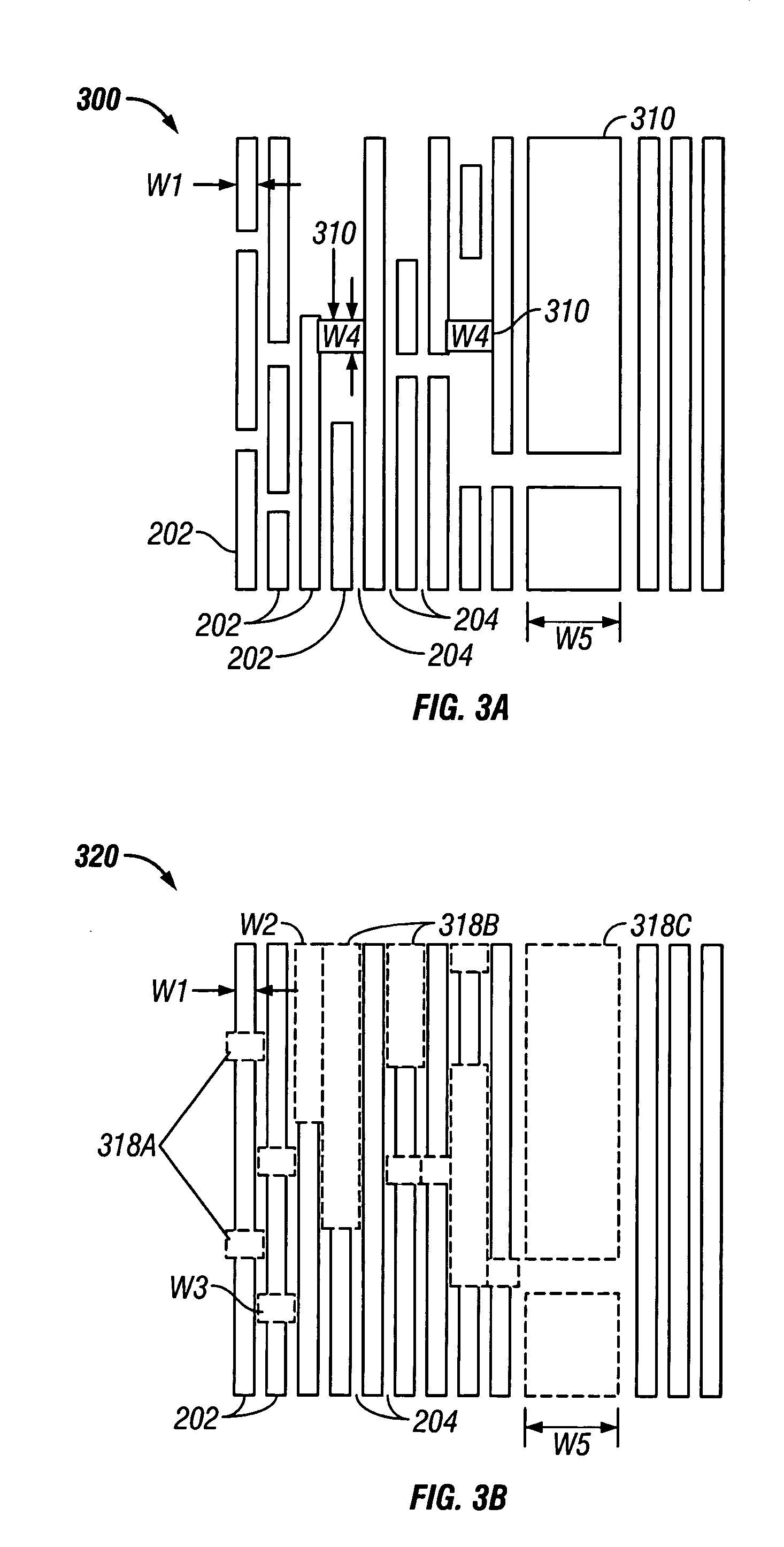
Method of design and fabrication of integrated circuits using regular arrays and gratings
InactiveUS6818389B2Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingRounding
A circuit fabrication and lithography process utilizes a mask including dense repetitive structures of features that result in a wide array of fine densely populated features on the exposed substrate film. Following this, a trimming procedure is performed to remove any unwanted fine patterned features providing multiple trimmed patterns on the substrate. An optional final step adds additional features as well as the interconnect features thus forming a circuit pattern. In this manner, all fine features may be generated using the exact same density of intensity patterns, and therefore, maximum consistency between features is established without the need for optical proximity correction. The secondary exposures are substantially independent from the initial dense-feature exposure in that the exposure of one set of features and the subsequent exposure of another set of features result in separate independent resist or masking layer reactions, thus minimizing corner rounding, line end shortening and other related spatial frequency effects and unwanted exposure memory effects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
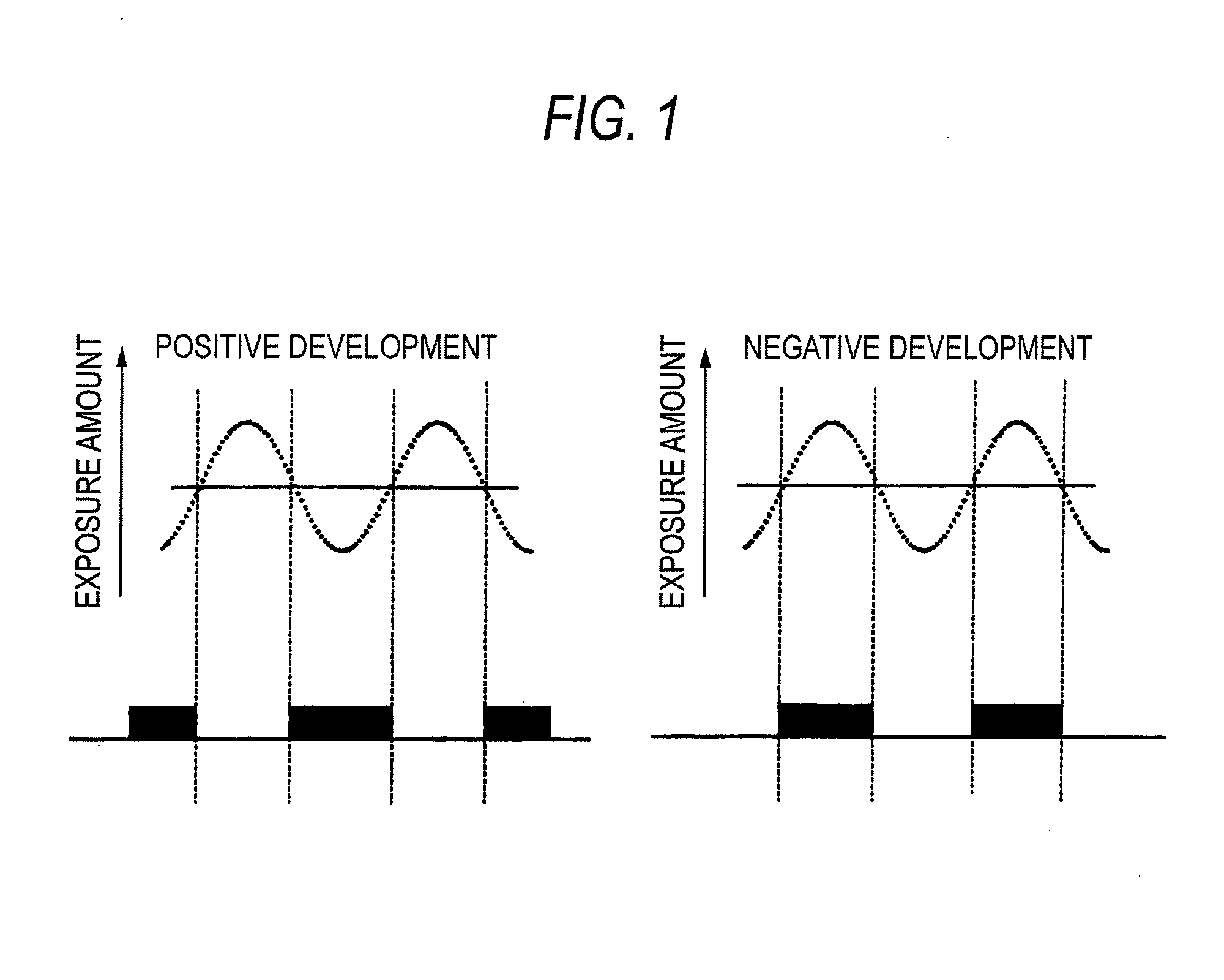
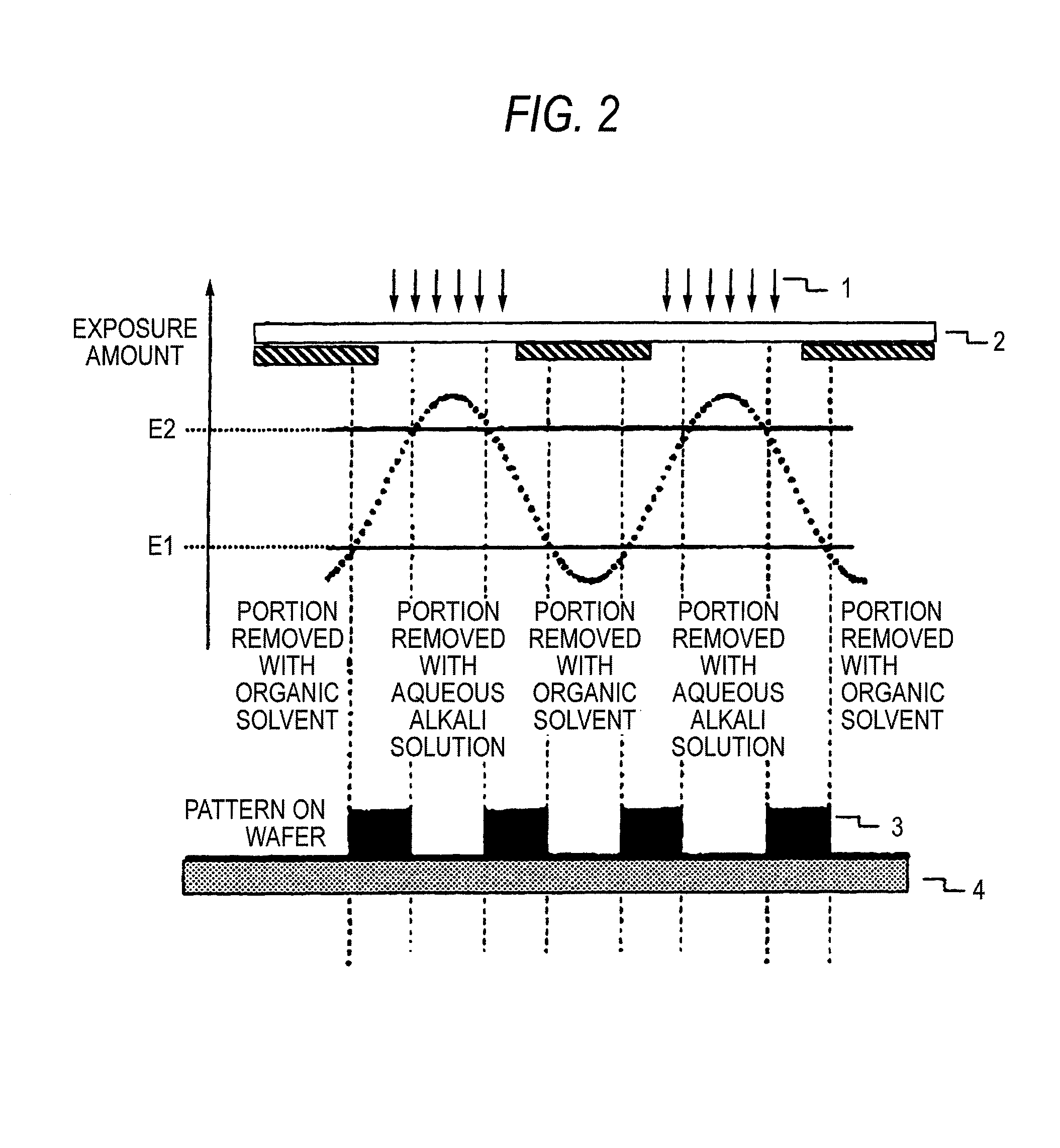
Method of forming patterns
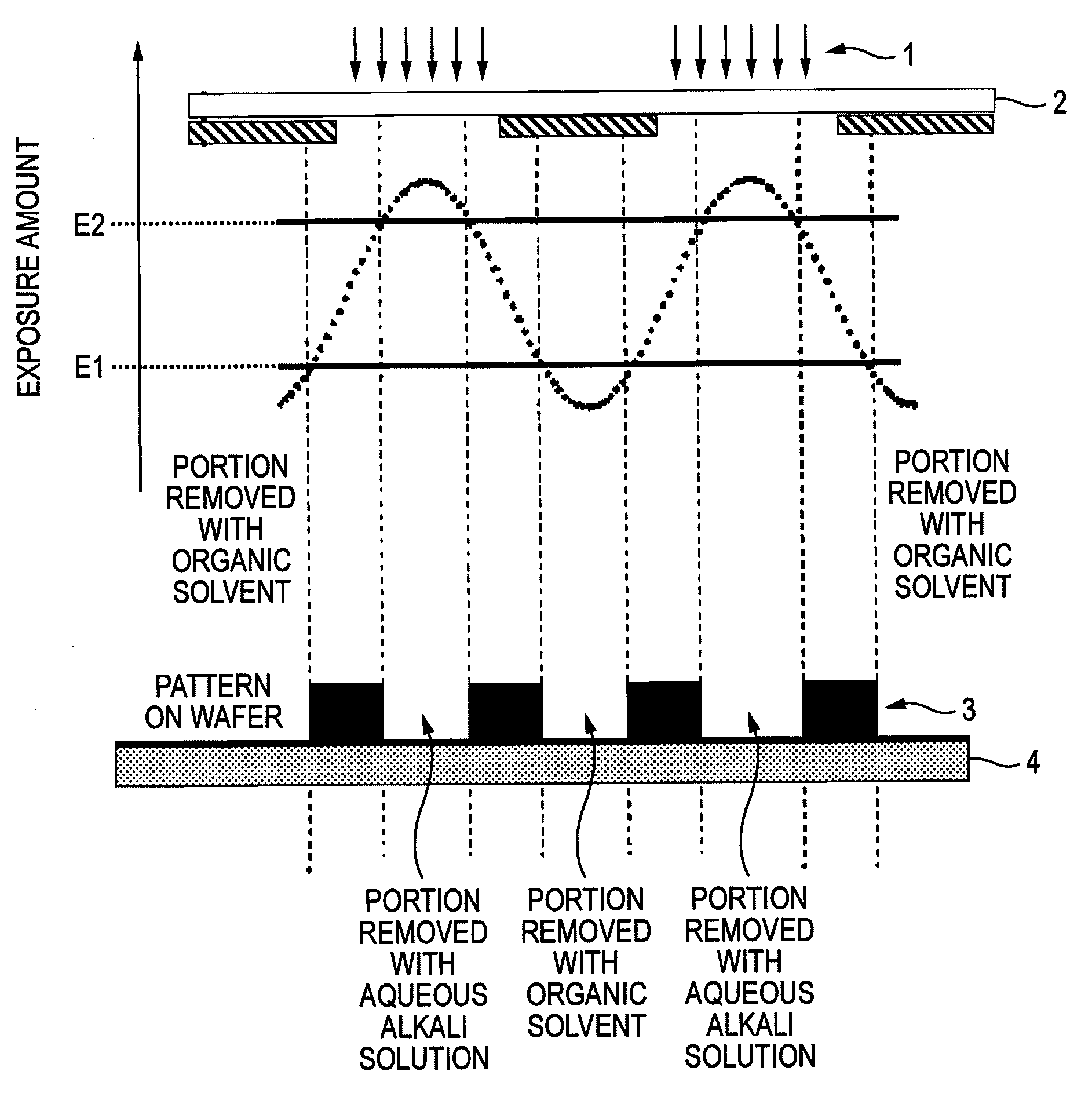
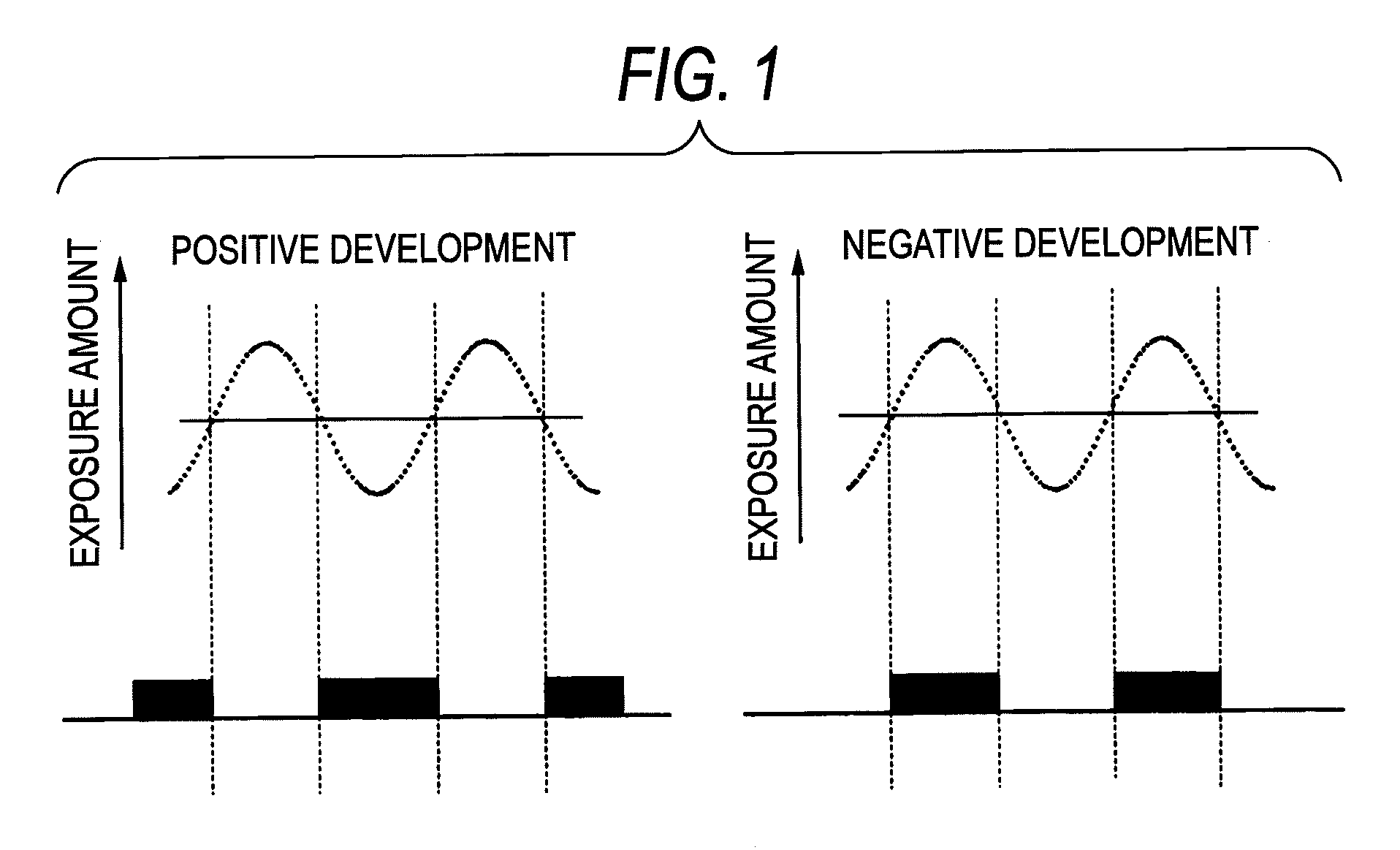
ActiveUS20090042147A1Development defect can be reducedReduced line edge roughnessPhotosensitive materialsPhoto-taking processesActinic RaysChemistry
A method of forming patterns includes (a) coating a substrate with a resist composition for negative development to form a resist film, wherein the resist composition contains a resin capable of increasing the polarity by the action of the acid and becomes more soluble in a positive developer and less soluble in a negative developer upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation, (b) forming a protective film on the resist film with a protective film composition after forming the resist film and before exposing the resist film, (c) exposing the resist film via an immersion medium, and (d) performing development with a negative developer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for maskless particle-beam exposure
ActiveUS8222621B2Inhibition effectThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticle beamLight beam
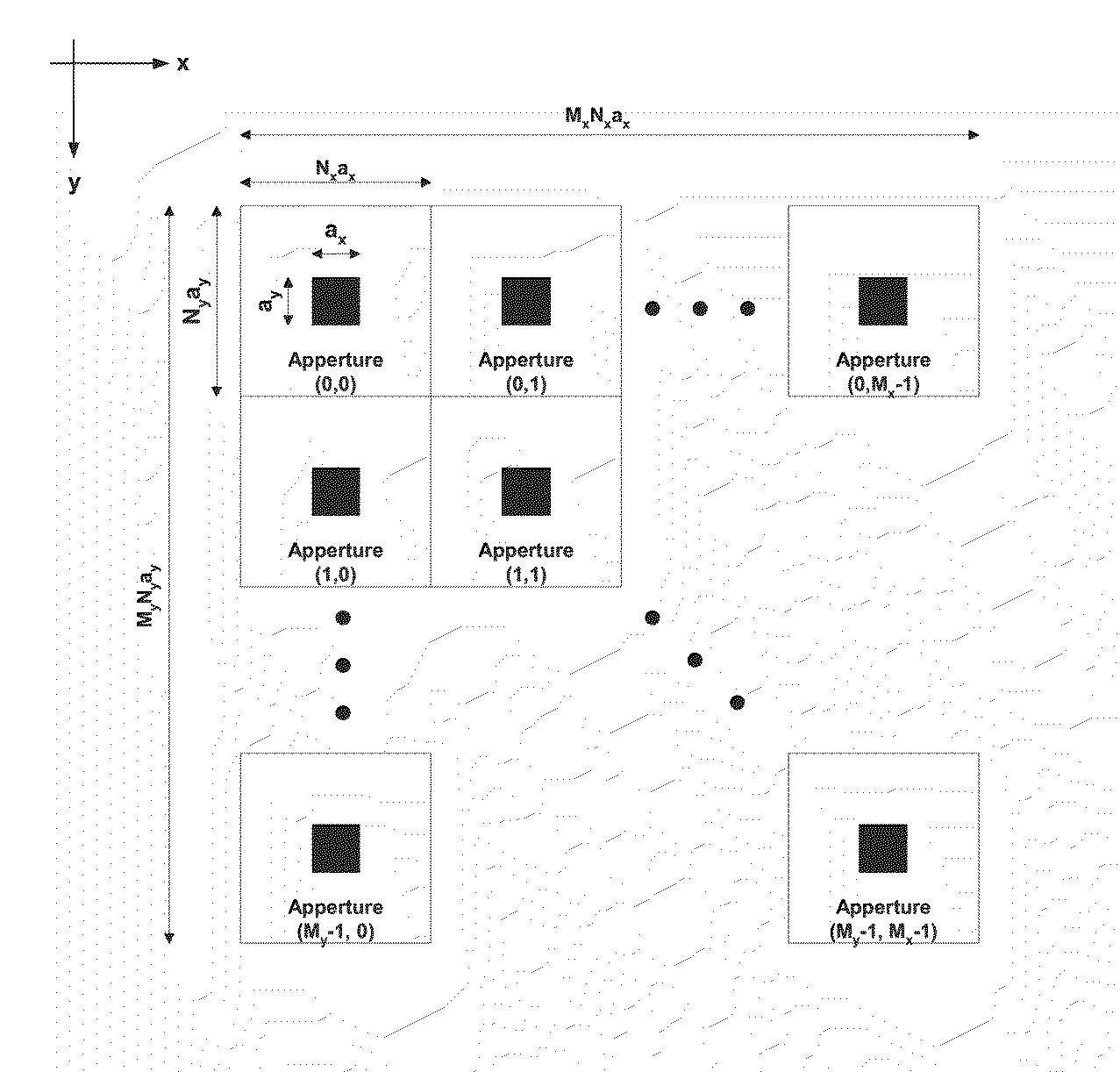
In a maskless particle multibeam processing apparatus, a particle beam is projected through a pattern definition system producing a regular array of beamlets according to a desired pattern, which is projected onto a target which moves at continuous speed along a scanning direction with respect to the pattern definition system. During a sequence of uniformly timed exposure steps the beam image is moved along with the target along the scanning direction, and between exposure steps the location of the beam image is changed with respect to the target. During each exposure step the target covers a distance greater than the mutual distance of neighboring image elements on the target. The location of the beam image at consecutive exposure steps corresponds to a sequence of interlacing placement grids, and after each exposure step the beam image is shifted to a position associated with a different placement grid, with a change of location generally including a component across the scanning direction, thus cycling through the set of placement grids.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
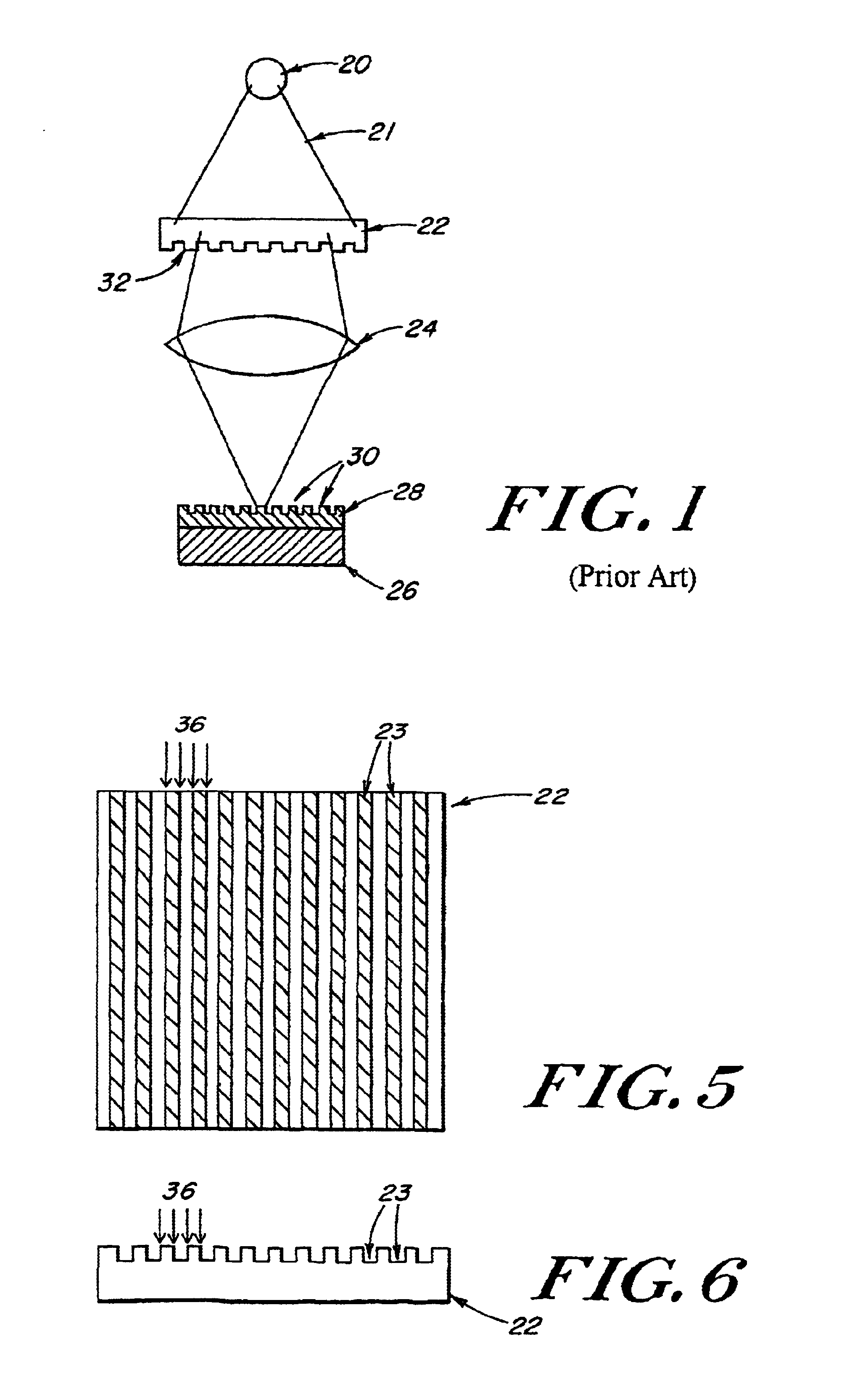
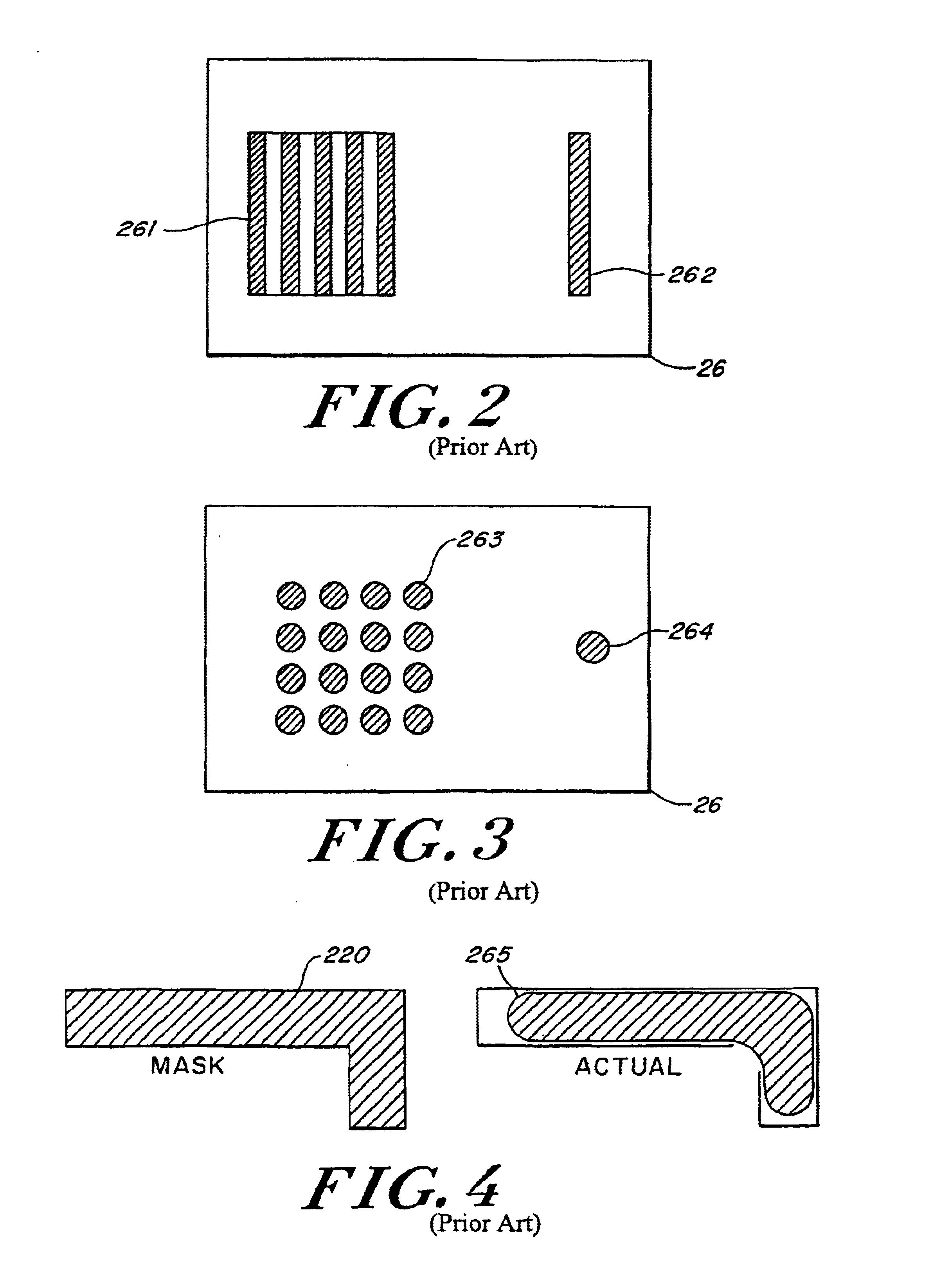
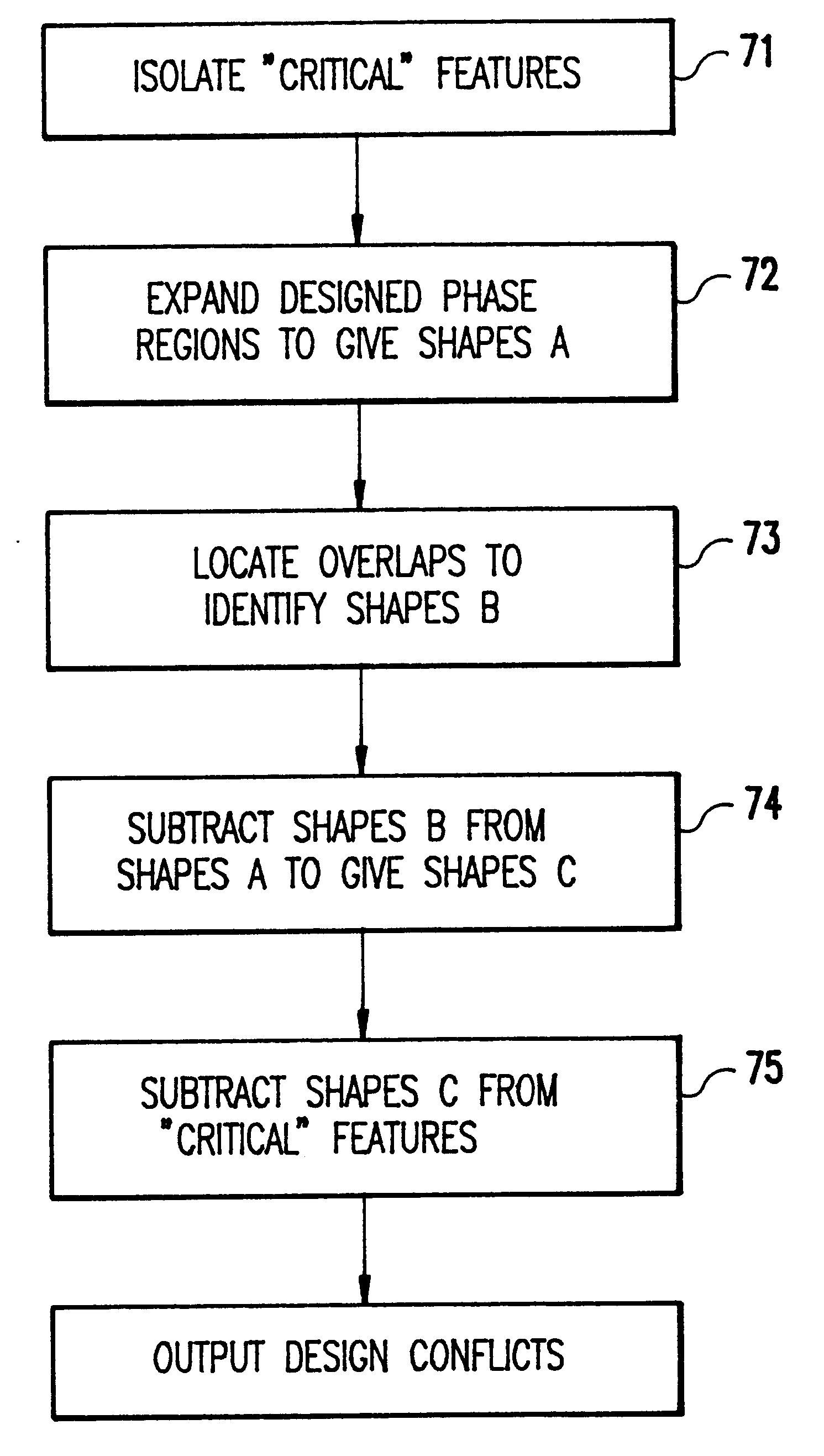
Design verification for asymmetric phase shift mask layouts
InactiveUS6185727B1Photo-taking processesOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer Aided DesignPhase shifted
A checking routine verifies a phase shifted mask (PSM) design based on fundamental principles of PSM and utilizing only basic shape manipulation functions and Boolean operations found in most computer aided design (CAD) systems. The design verification system checks complete chip designs for the two possible design errors that can cause defective masks by eliminating the phase transition; namely, placing a 180° phase region on both sides of a critical feature or completely omitting the phase region adjacent to certain critical features.
Owner:IBM CORP
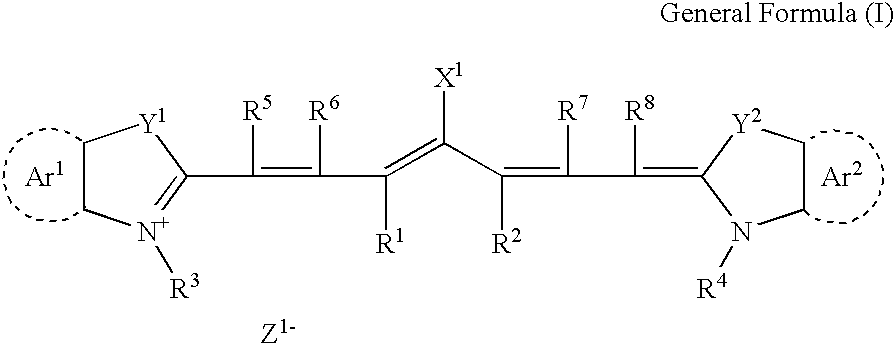
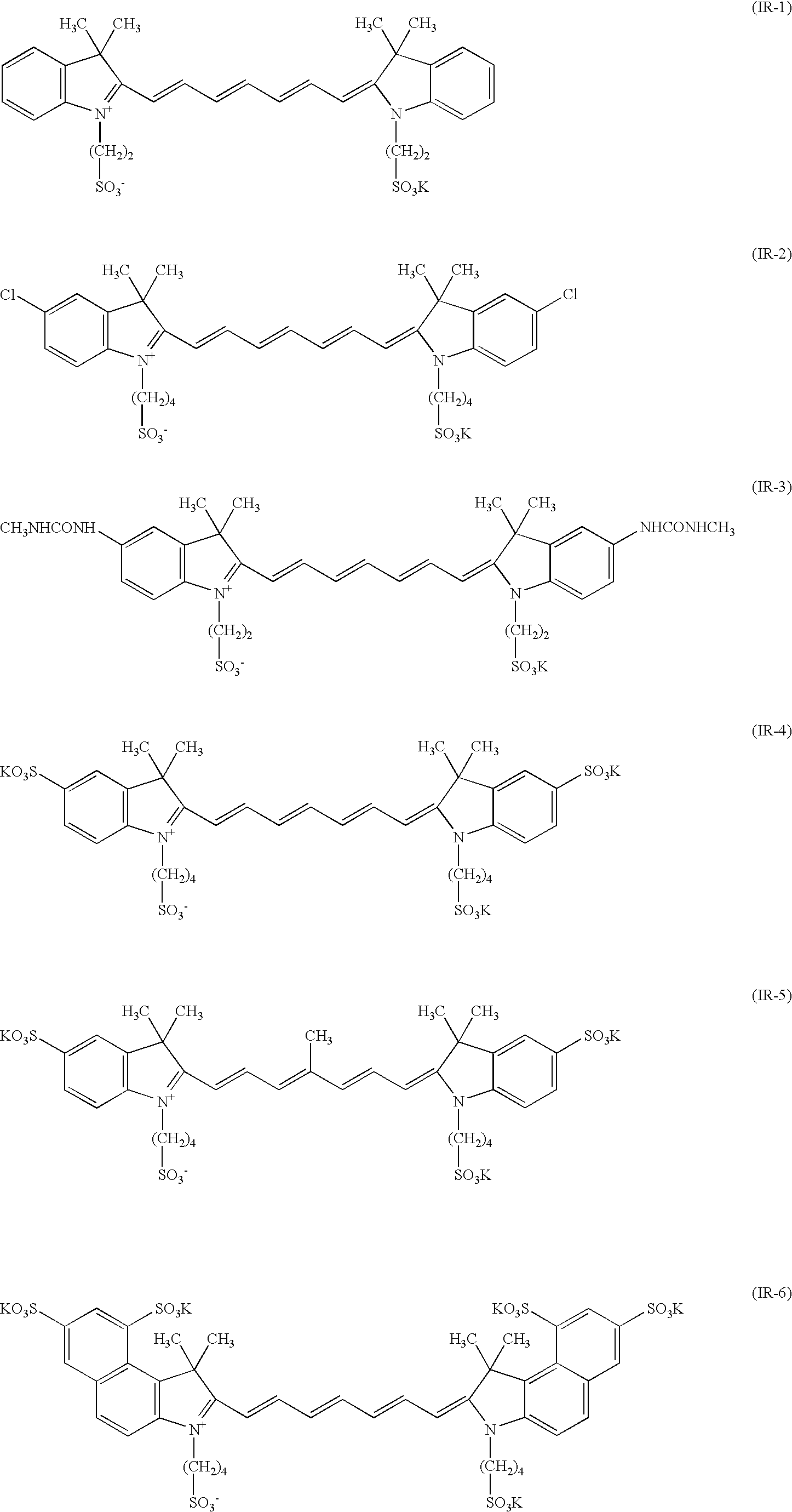
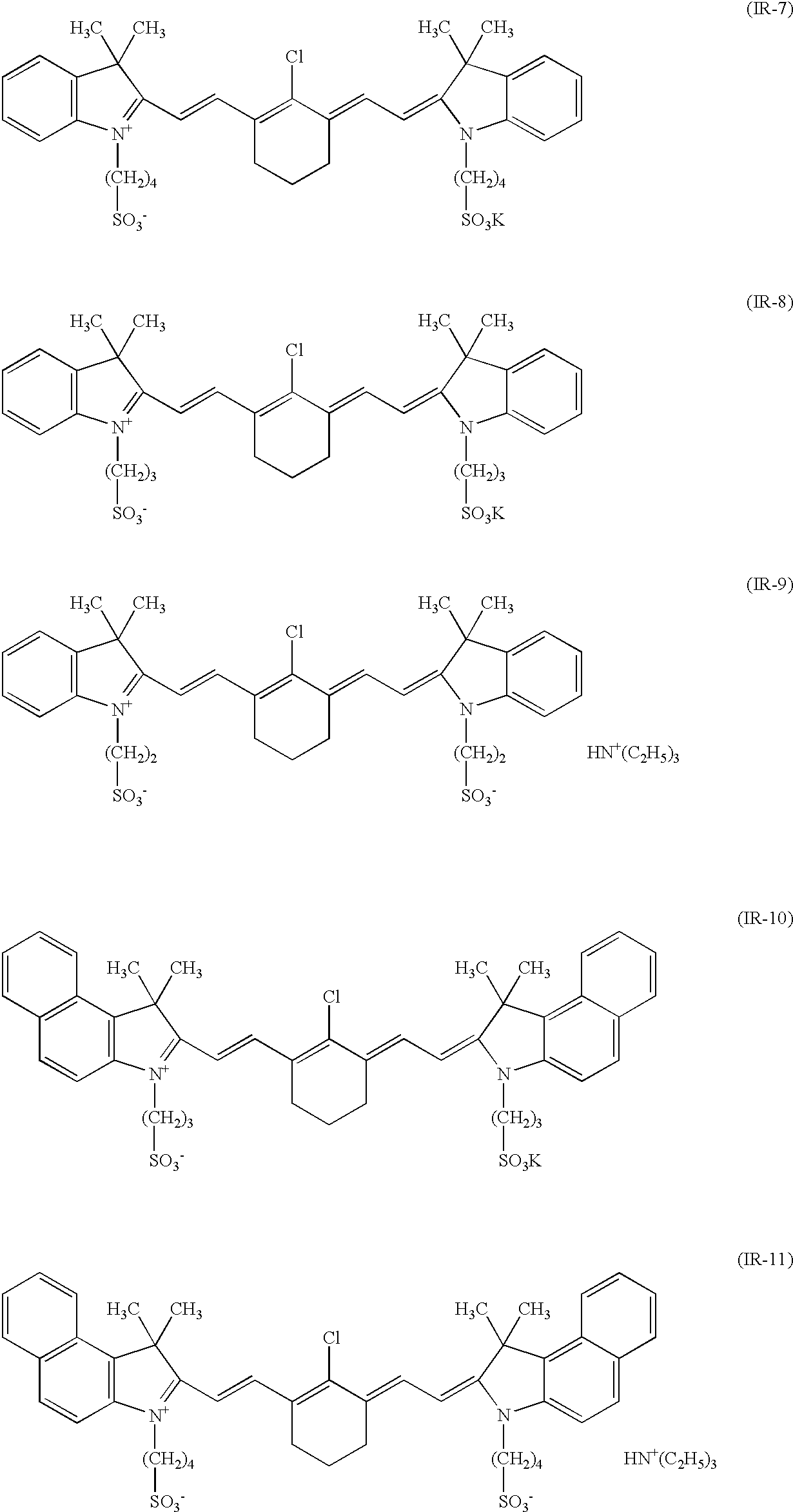
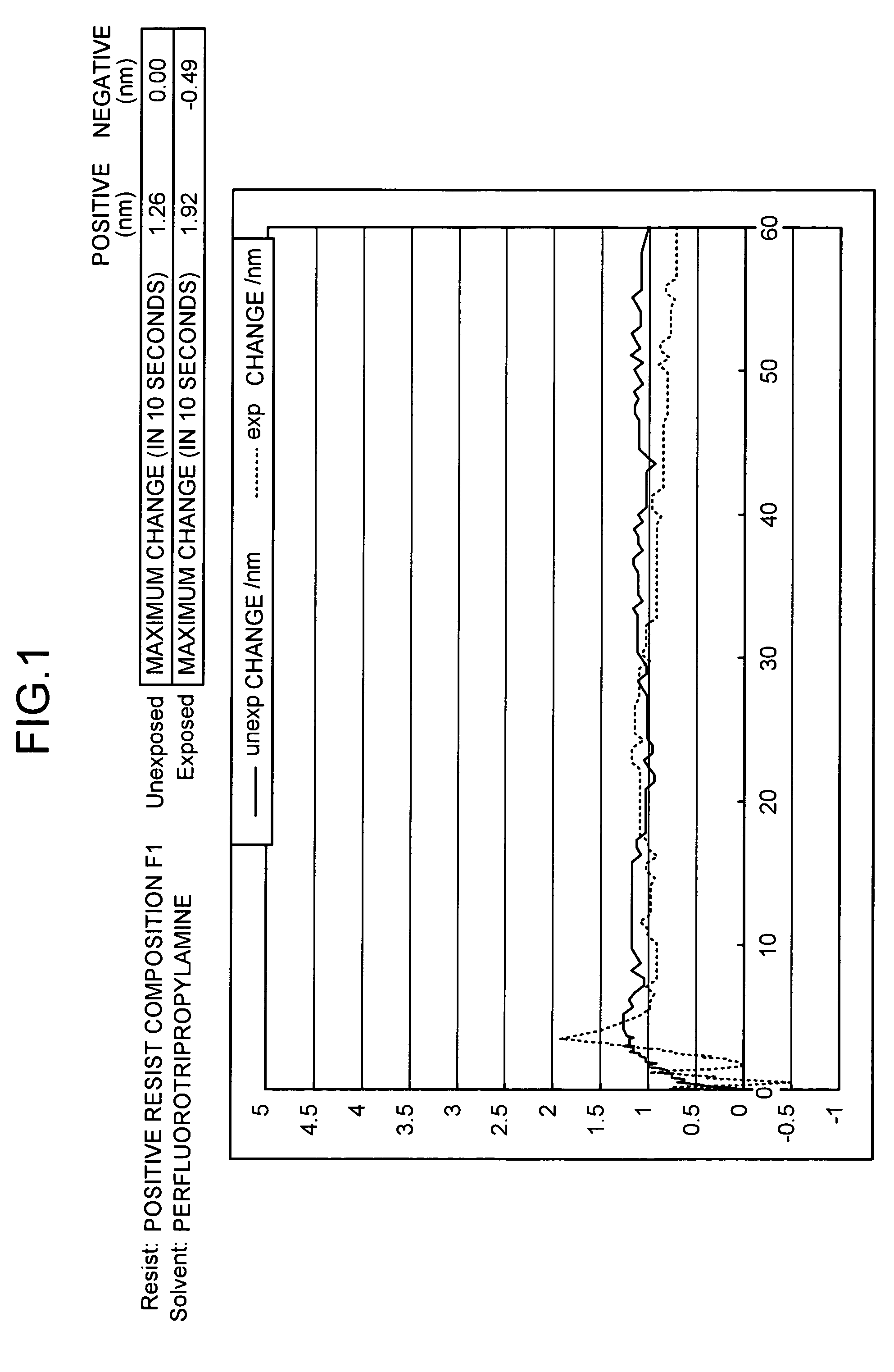
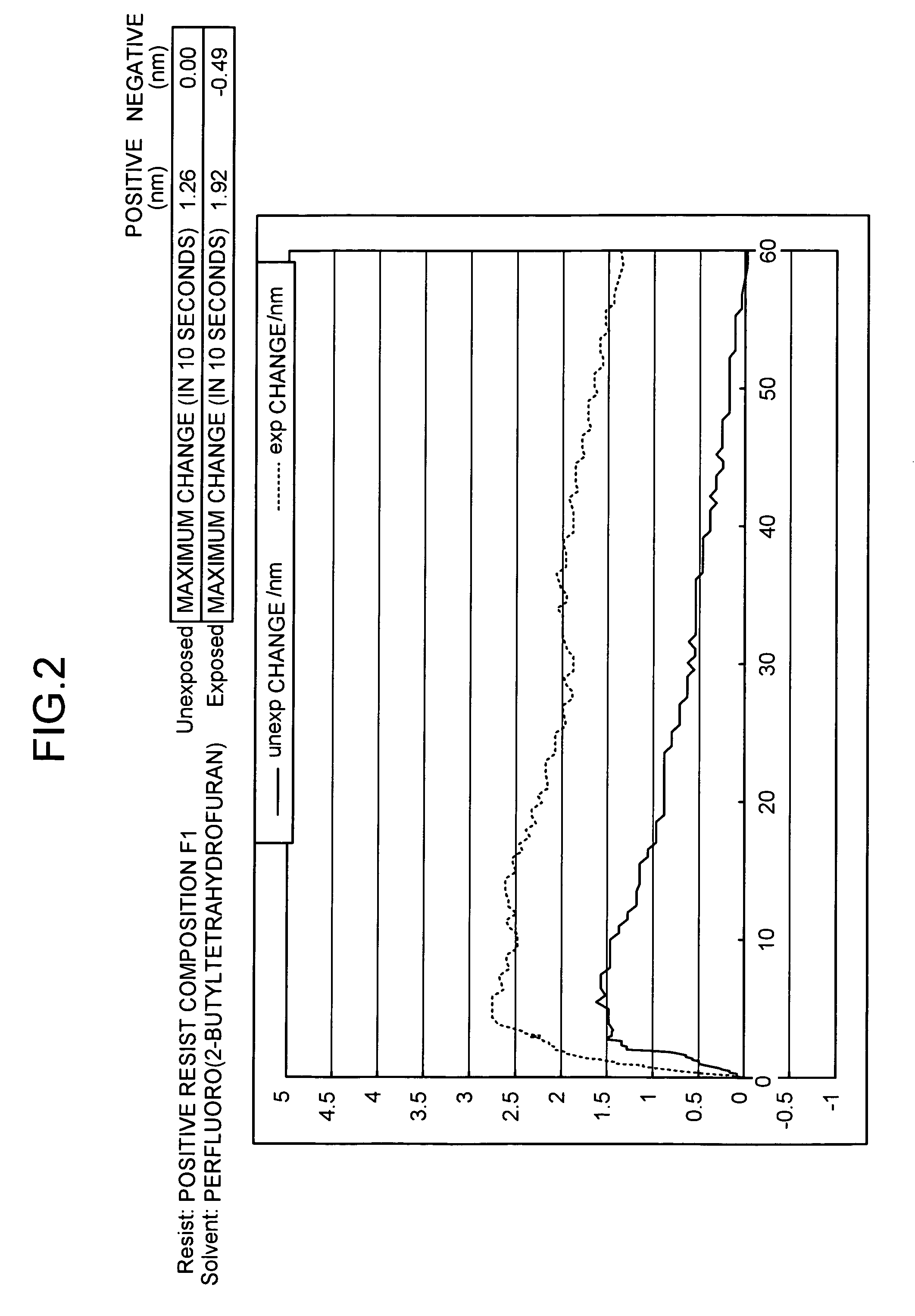
Novel photoacid generator, resist composition, and patterning process
ActiveUS20090274978A1Addressing Insufficient ControlInhibits the formation of defectsPhotosensitive materialsPhoto-taking processesResistHigh energy
Photoacid generators generate sulfonic acids of formula (1a) or (1b) upon exposure to high-energy radiation.R1—COOCH2CF2SO3−H+ (1a)R1—O—COOCH2CF2SO3−H+ (1b)R1 is a monovalent C20-C50 hydrocarbon group of steroid structure which may contain a heteroatom. The bulky steroid structure ensures adequate control of acid diffusion. The photoacid generators are compatible with resins and suited for use in chemically amplified resist compositions.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Multiple step printing methods for microbarcodes
A method of forming a plurality of encoded microparticles with a lithography process to define codes for identifying the particles is disclosed herein.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method for masking and exposing photosensitive printing plates
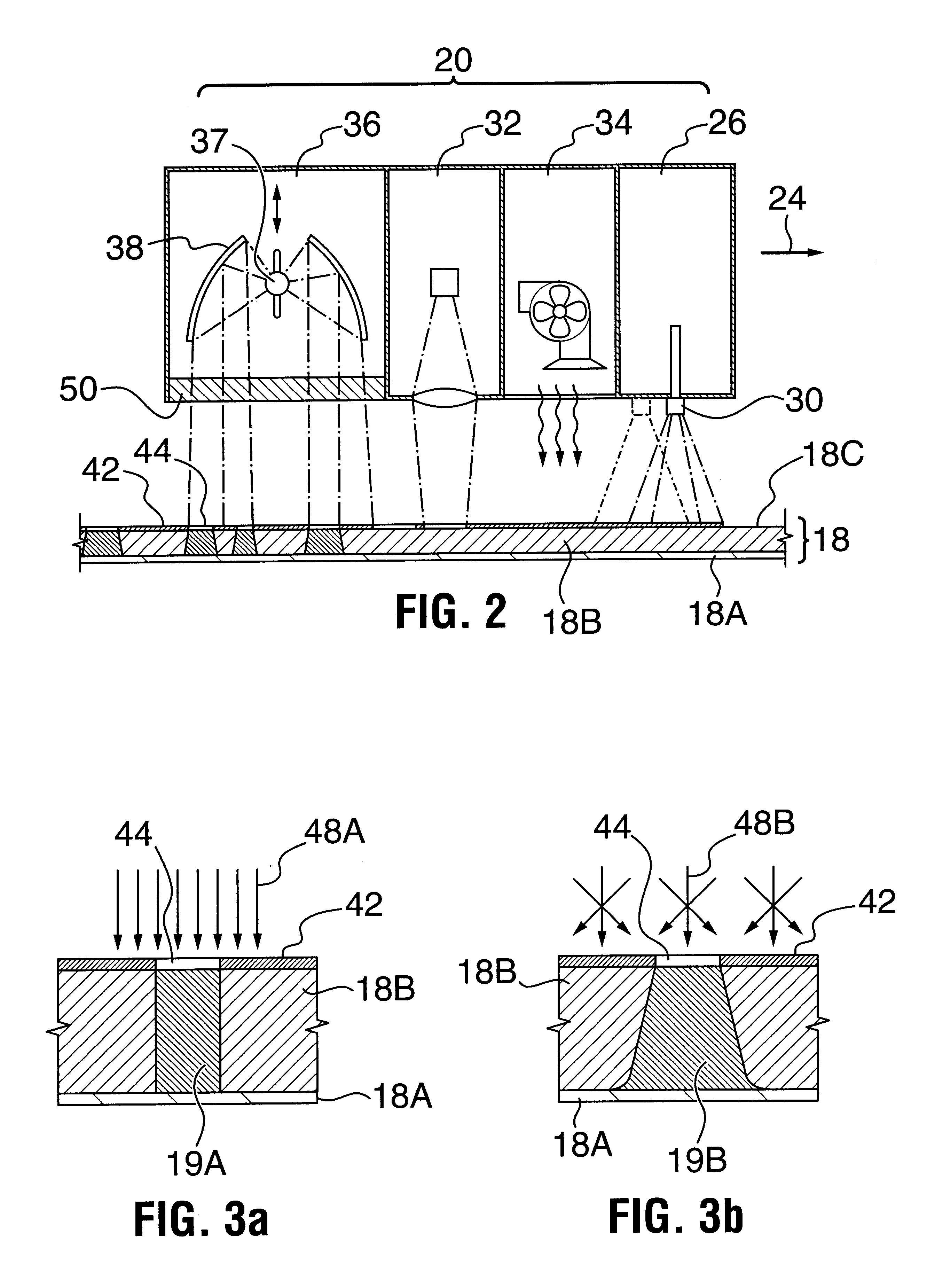
InactiveUS6180325B1Avoid disadvantagesAvoid problemsX-ray/infra-red processesPhotosensitive materialsEngineeringLaser ablation
A method for exposing photo-sensitive printing plates comprises applying a patterned coating to the printing plate to form a mask. The coating may be sprayed onto the printing plate and patterned by laser ablation. The method avoids the need to stock printing plates with integral masking layers. In preferred implementations the printing plate is exposed to actinic radiation without dismounting it from the apparatus in which the coating is applied. This minimizes the likelihood that the coating could be damaged in handling. The coating may be a thin sprayed on layer of carbon in a suitable binder.
Owner:CREO SRL
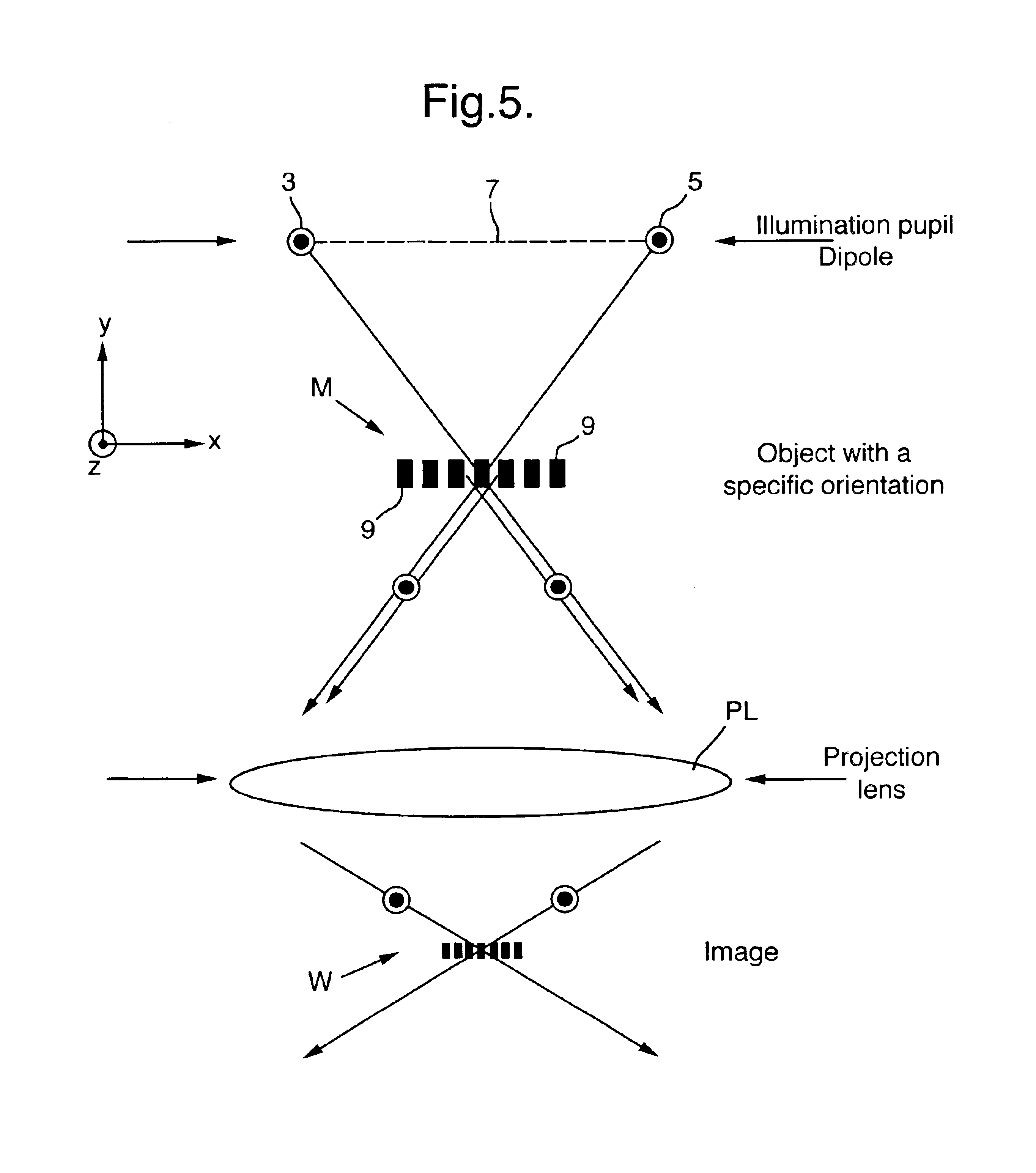
Lithographic method and apparatus
InactiveUS6855486B1Small feature sizeOptimizing Process ParametersPhoto-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle exposureMethod of images
A method of imaging a pattern in a microlithographic exposure apparatus includes performing two exposures, each with a different mask, the superposition of the images defined by the two masks produces the complete circuit pattern. A dipolar illumination mode is used for each exposure, the dipoles of the two exposures being mutually perpendicular. The dipolar illumination mode of the first exposure is used to image mask features parallel to a first direction, and the dipolar illumination mode of the second exposure is used to image mask features perpendicular to the first direction.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
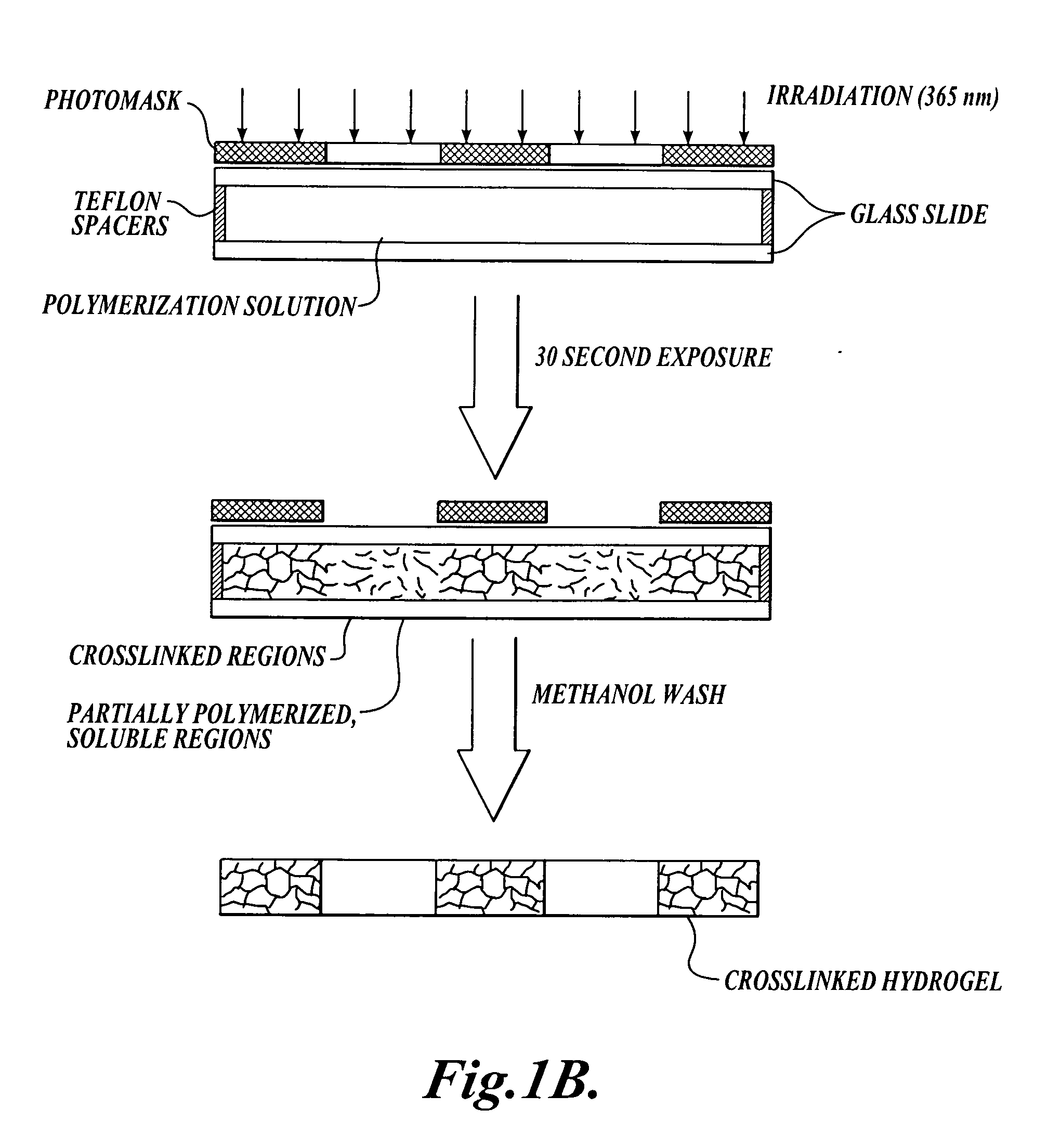
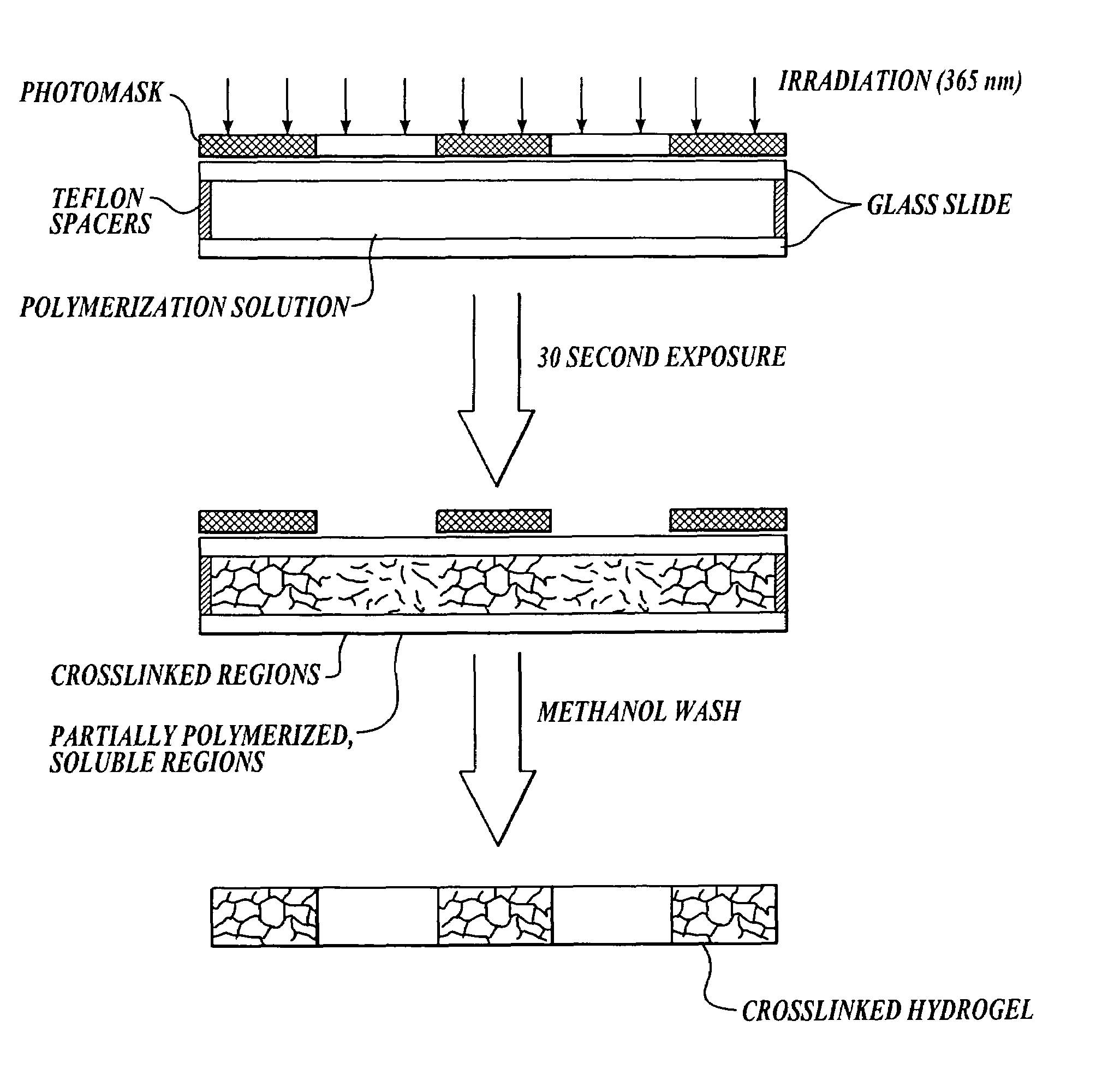
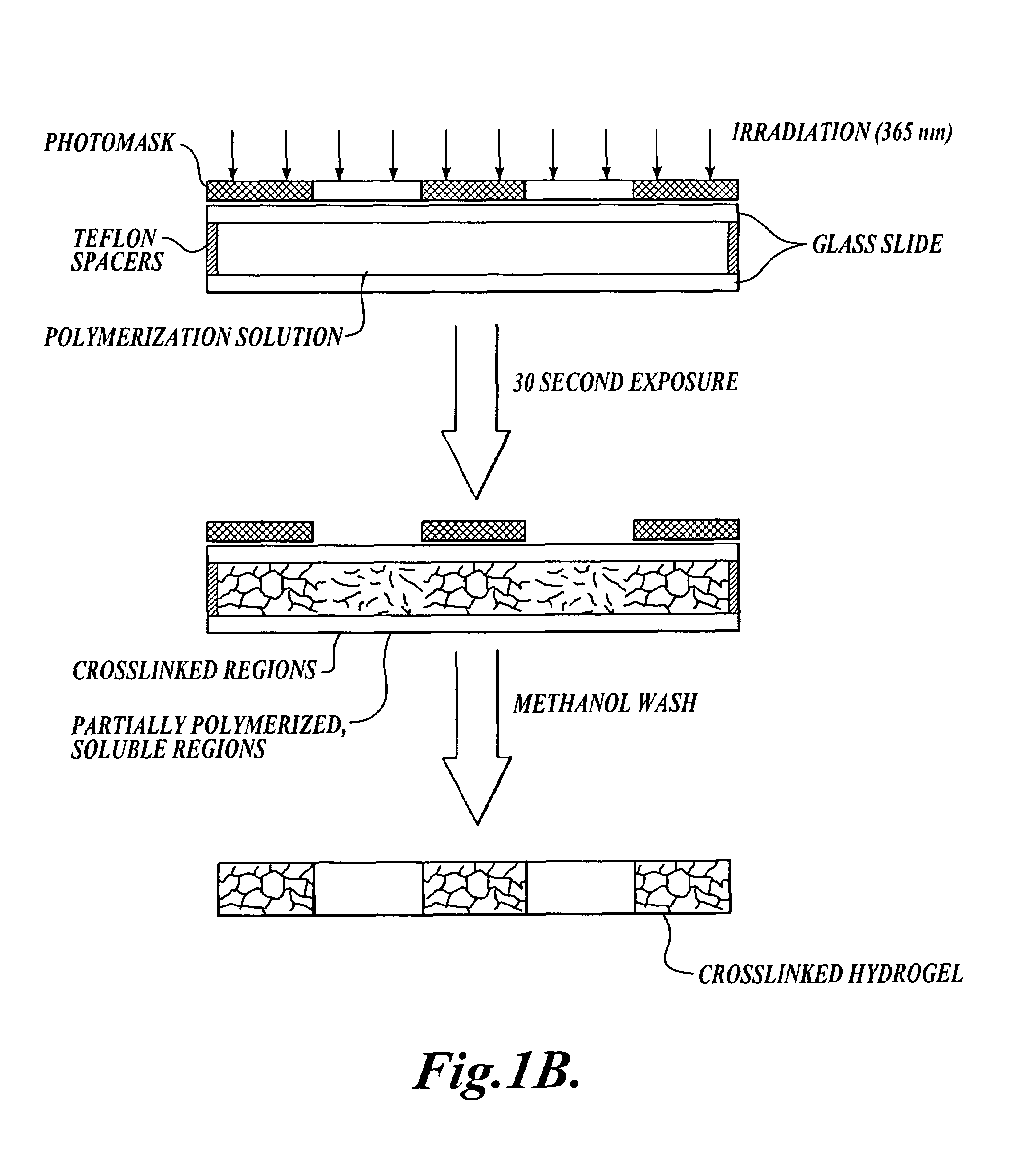
Methods for photopatterning hydrogels
In one aspect, the invention provides methods for forming a photopatterned hydrogel. In some embodiments, the methods comprise the step of exposing a solution comprising a monomer, a crosslinking agent, and a photoinitiator to a pattern of light comprising a first and a second light intensity for a period of time and under suitable conditions for the first light intensity to induce essentially complete conversion of polymerizable groups on the monomer and the crosslinking agent to form a patterned hydrogel, and for the second light intensity to induce partial conversion of the polymerizable groups on the monomer and the crosslinking agent to form partially polymerized polymers that remain soluble. In some embodiments, the first light intensity is lower than the second light intensity. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for forming porous, photopatterned hydrogels.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Planographic printing plate precursor and planographic printing method
ActiveUS7005234B2Excellent plate-wear resistanceAvoid small quantitiesPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsPlanographic printingPhotochemistry
The present invention provides a planographic printing plate precursor comprising a photosensitive layer on a support, the photosensitive layer including an infrared absorbent, a radical polymerization initiator and a radical polymerizing compound, the photosensitive layer being recordable with irradiation with an infrared ray, and being at least one of soluble and dispersible in water.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Resist composition for liquid immersion exposure process and method of forming resist pattern therewith
ActiveUS7264918B2Large investment in equipmentLow costPhotosensitive materialsPhoto-taking processesSolubilityStructural unit
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
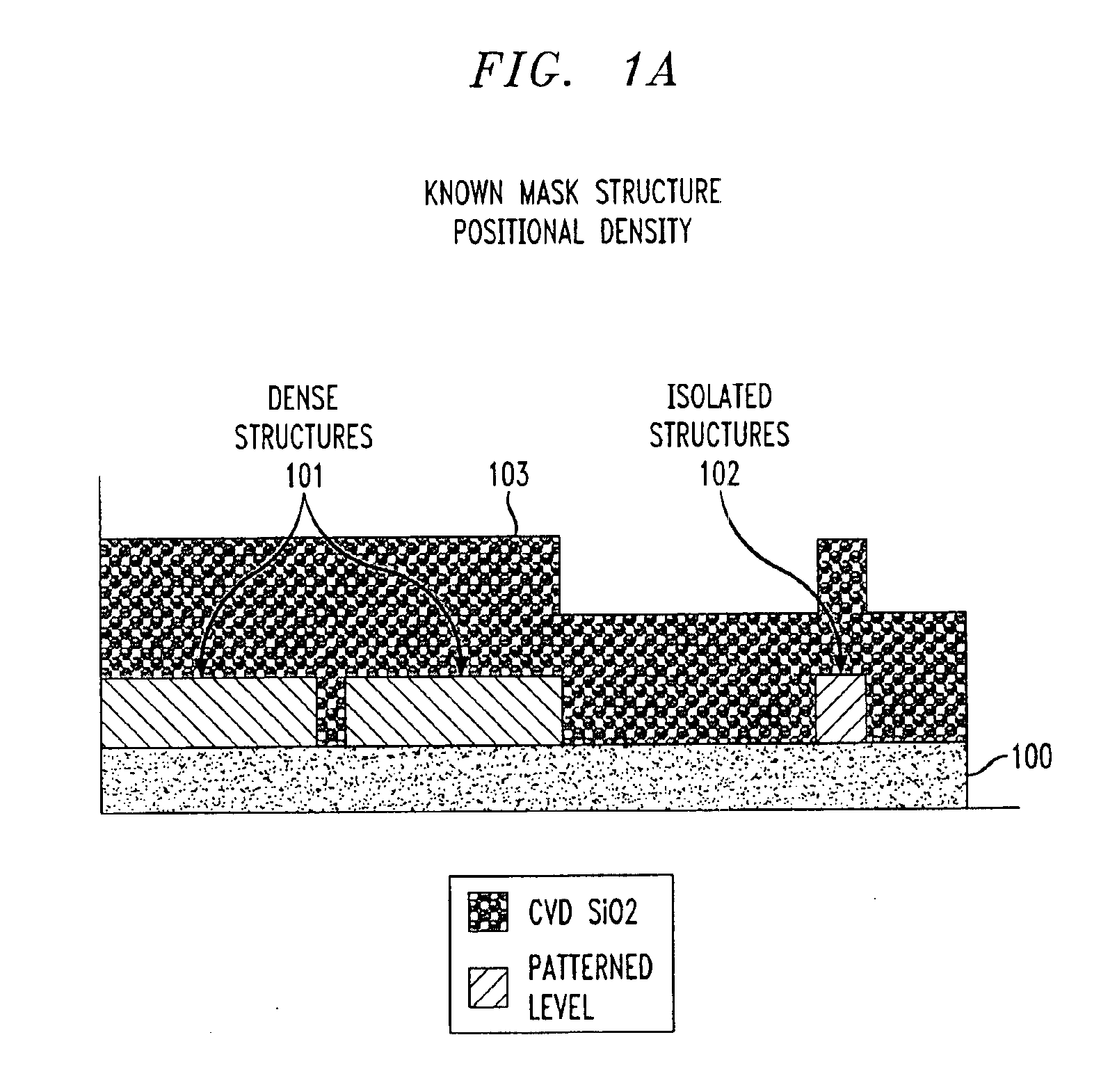
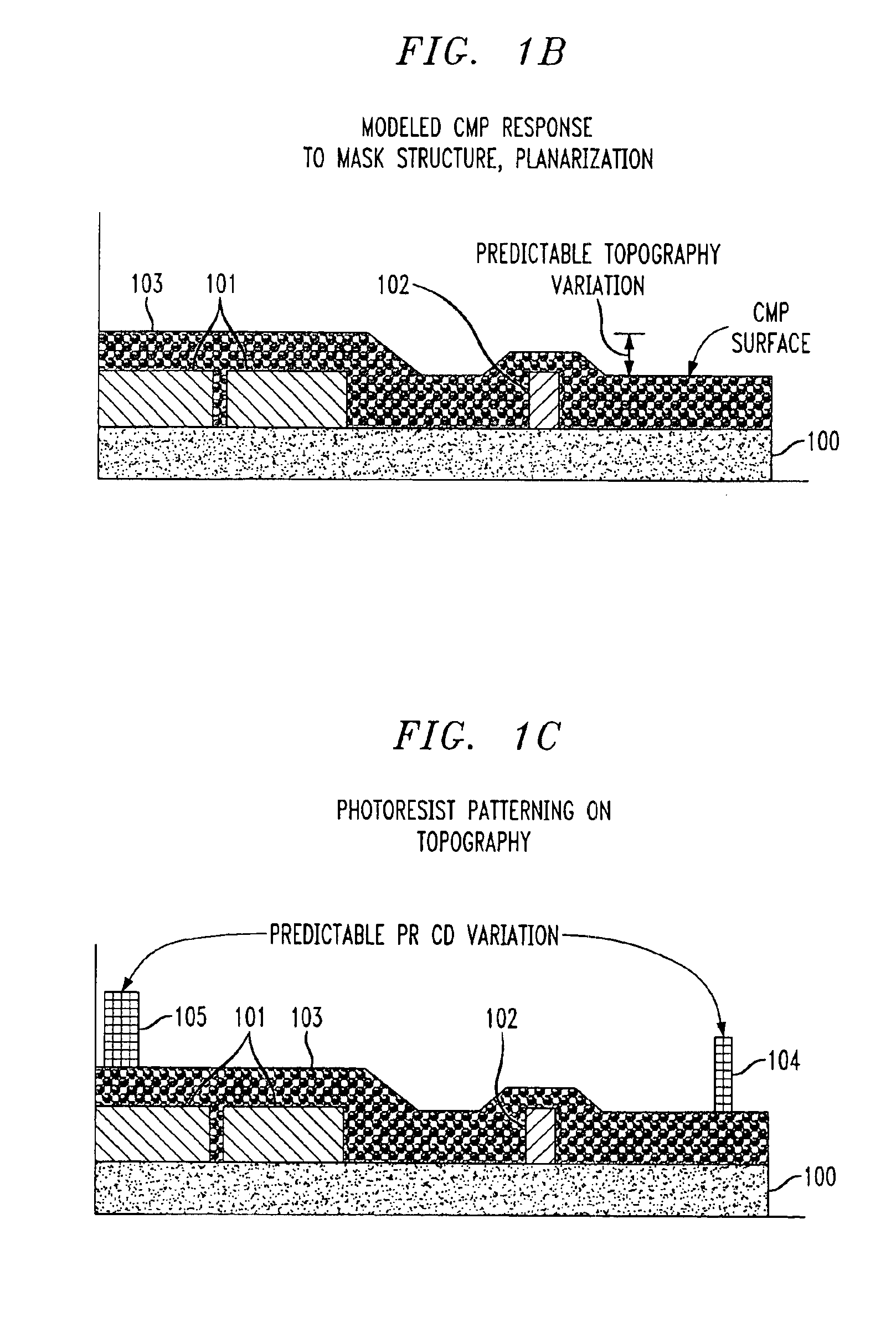
Substrate topography compensation at mask design: 3D OPC topography anchored
InactiveUS6893800B2Improve production yieldAvoid low process precisionPhoto-taking processesDecorative surface effectsResistEngineering
A semiconductor manufacturing method analyzes topography variations in three dimensions for each photolithographic level and determines critical dimension (CD) bias compensation as inputs to mask layout creation. Accurate predictions of topography variation for a specific mask design are made at the die level using known pattern density and CMP planarization length characteristics for a specific pattern. Exhaustive characterization of the photoresist response to de-focus and mask bias is determined by artificially expanding loss of CD through focus. Mask compensation to an expanded range of focus over all lines and spaces is maintained within the specification. 3D mask density data is obtained to determine the height component at each pixel location in the die. The resulting 3D OPC model is then utilized for mask creation.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
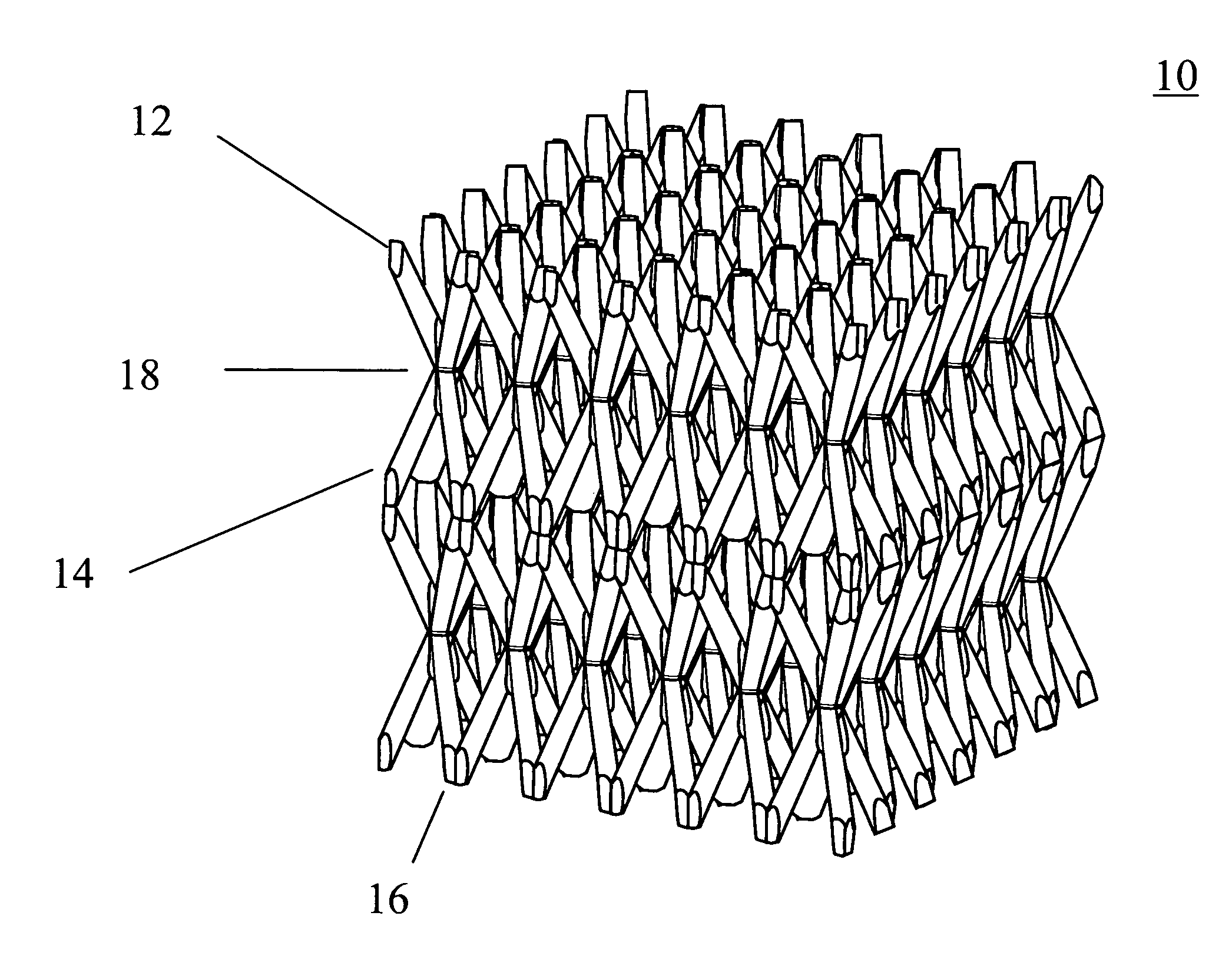
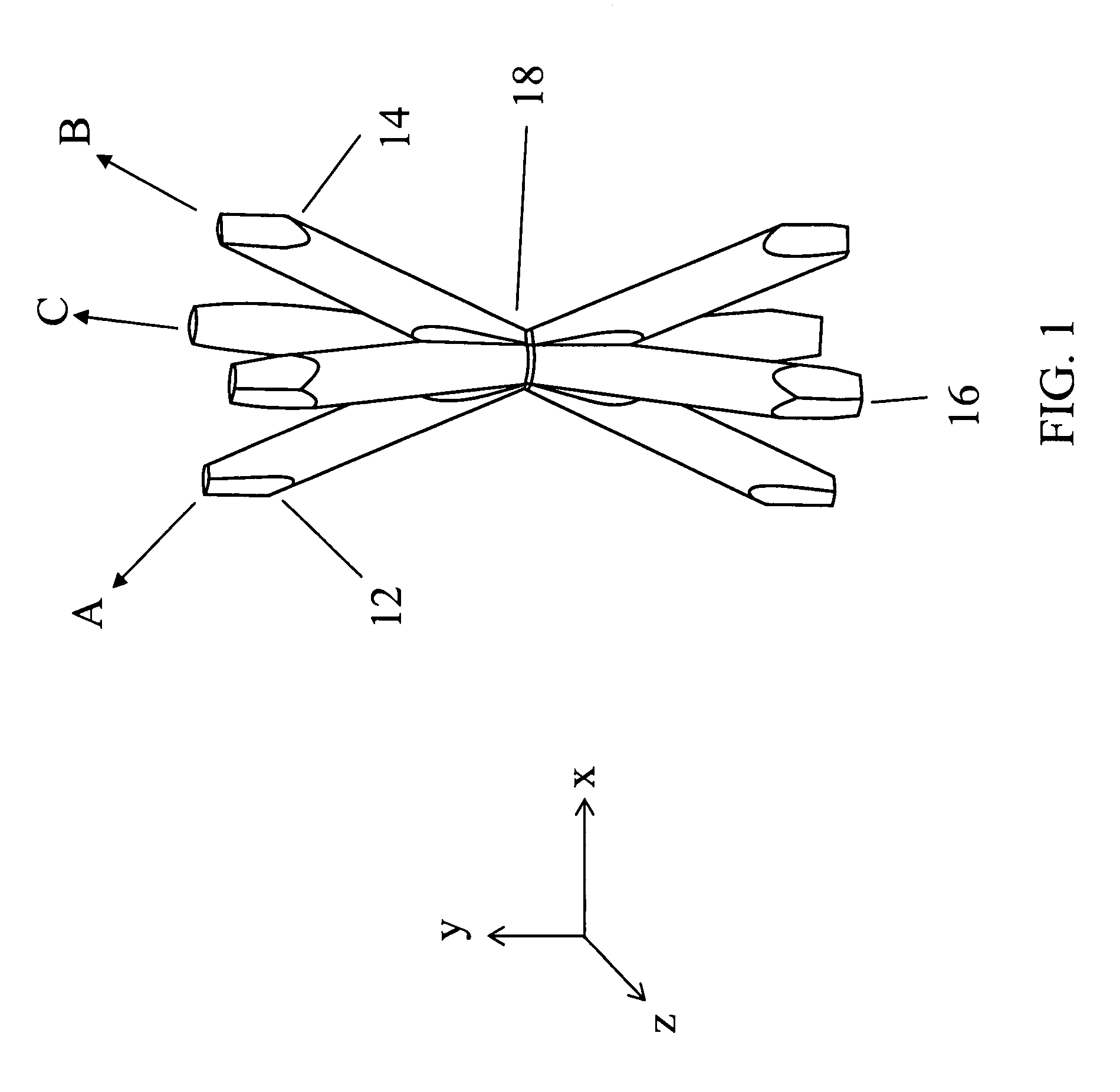
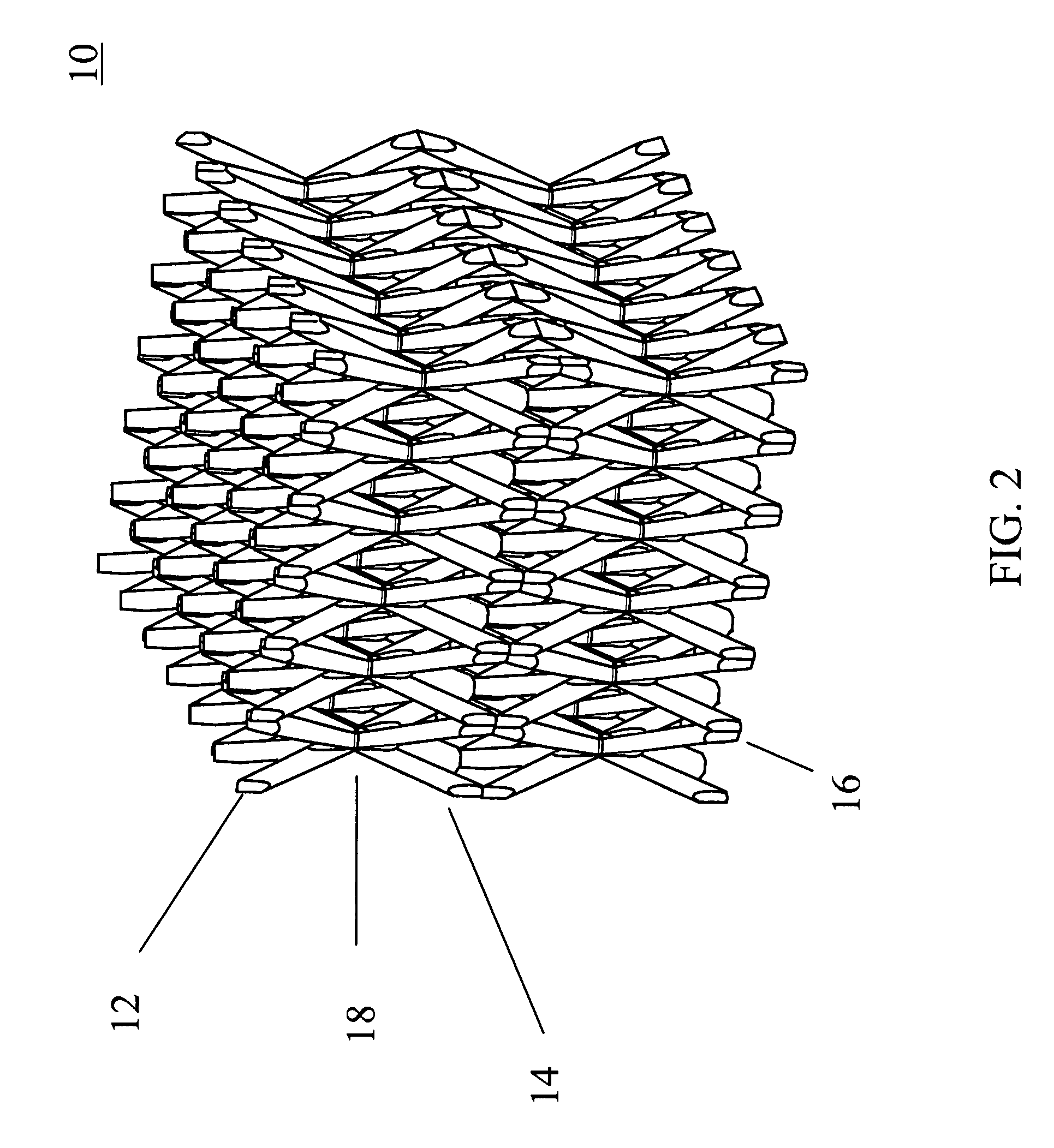
Three-dimensional ordered open-cellular structures
ActiveUS8197930B1Overcome the small stiffnessHigh strengthPhoto-taking processesLayered productsEngineeringPolymer
A three-dimensional ordered open-cellular structure. In one embodiment, the structure includes: a plurality of first truss elements defined by a plurality of first self-propagating polymer waveguides and extending along a first direction; a plurality of second truss elements defined by a plurality of second self-propagating polymer waveguides and extending along a second direction; and a plurality of third truss elements defined by a plurality of third self-propagating polymer waveguides and extending along a third direction. The first, second, and third truss elements interpenetrate each other at a plurality of nodes to form a continuous material, and the three-dimensional structure is self-supporting.
Owner:HRL LAB
Methods for photopatterning hydrogels
In one aspect, the invention provides methods for forming a photopatterned hydrogel. In some embodiments, the methods comprise the step of exposing a solution comprising a monomer, a crosslinking agent, and a photoinitiator to a pattern of light comprising a first and a second light intensity for a period of time and under suitable conditions for the first light intensity to induce essentially complete conversion of polymerizable groups on the monomer and the crosslinking agent to form a patterned hydrogel, and for the second light intensity to induce partial conversion of the polymerizable groups on the monomer and the crosslinking agent to form partially polymerized polymers that remain soluble. In some embodiments, the first light intensity is lower than the second light intensity. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for forming porous, photopatterned hydrogels.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
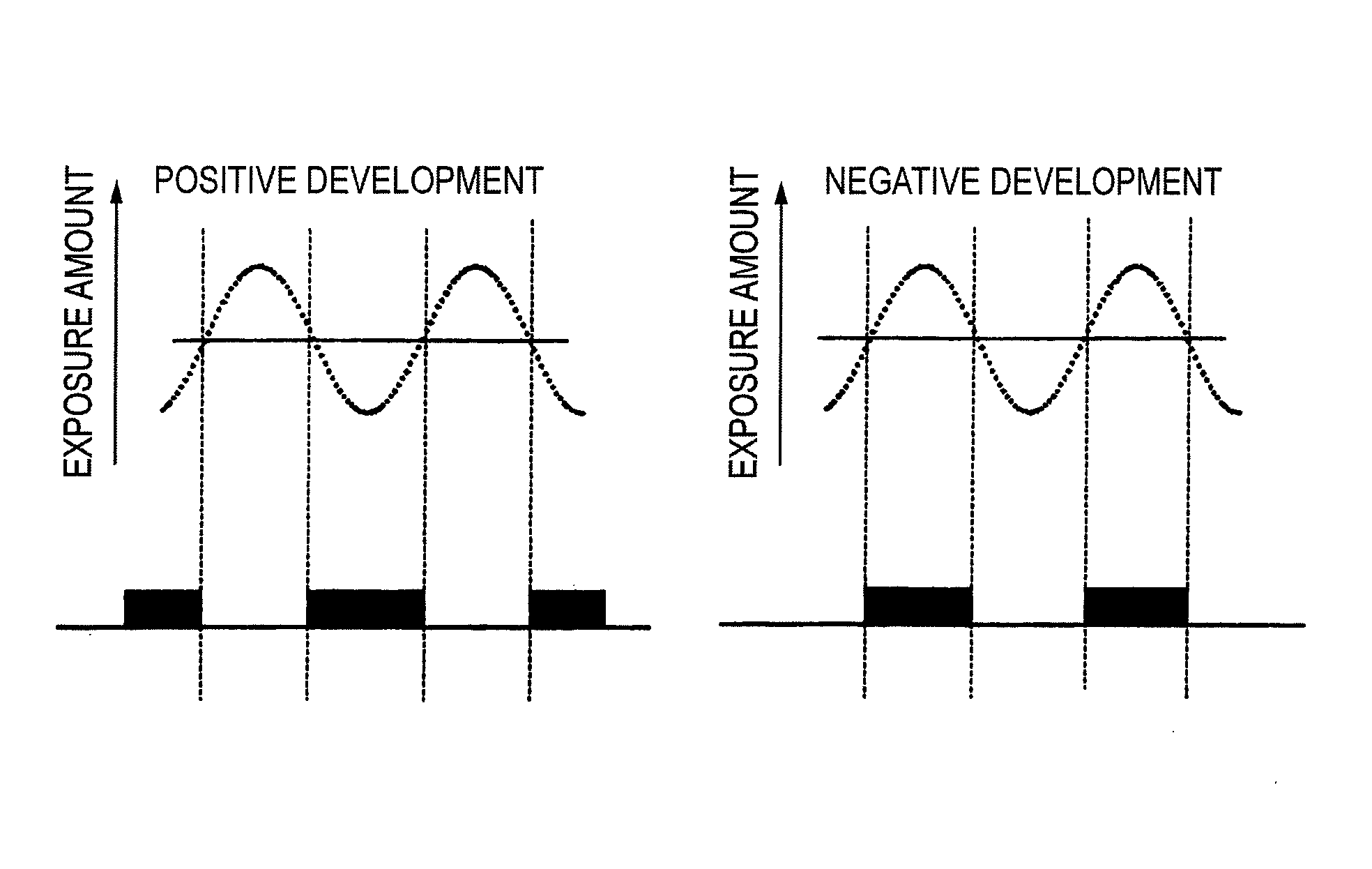
Method of forming patterns
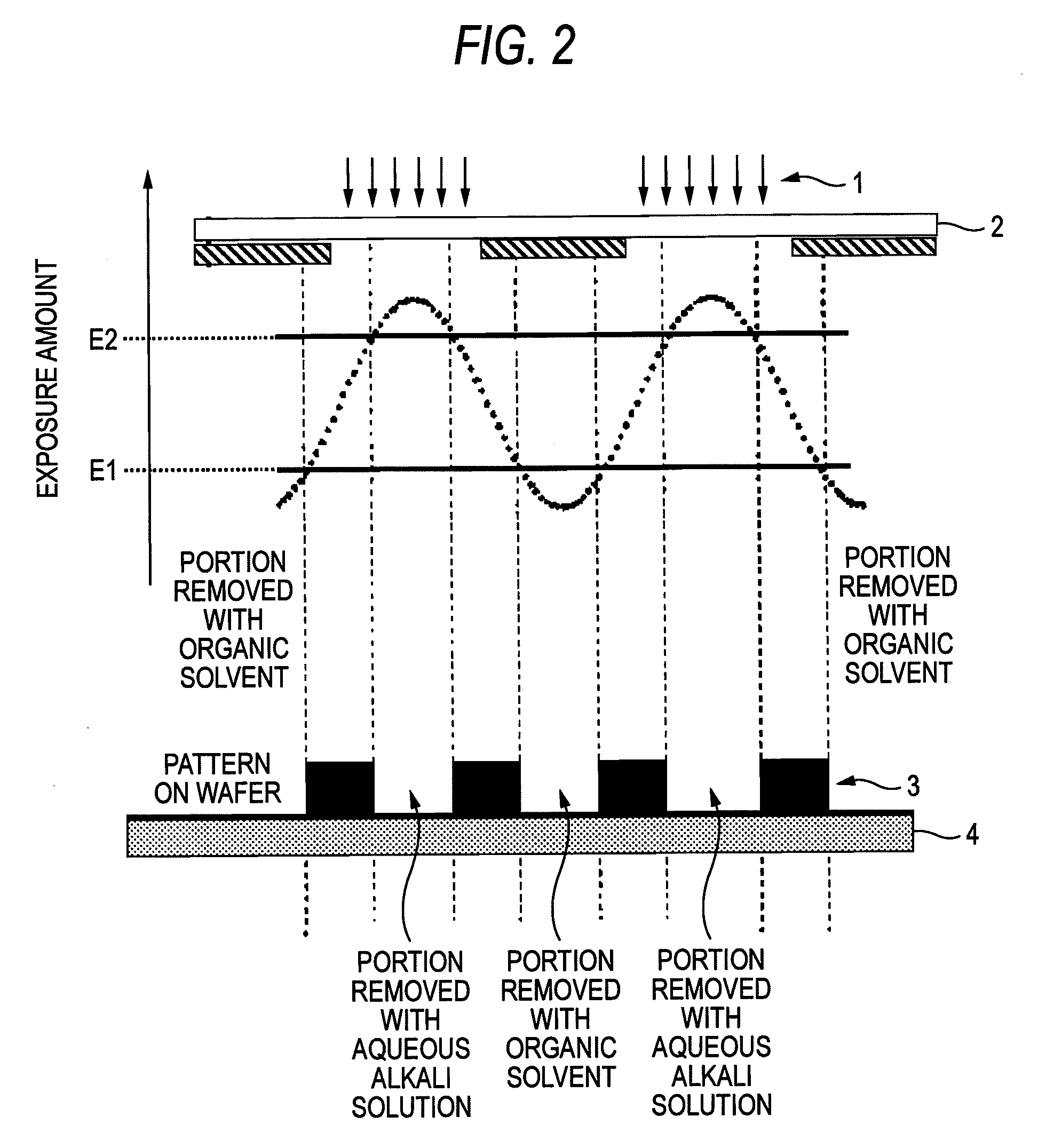
ActiveUS20080318171A1Enhanced in-plane uniformity of line widthReduced line edge roughnessPhotosensitive materialsPhoto-taking processesActinic RaysRadiation exposure
A method of forming patterns includes (a) coating a substrate with a resist composition for negative development to form a resist film having a receding contact angle of 70 degrees or above with respect to water, wherein the resist composition for negative development contains a resin capable of increasing the polarity by the action of an acid and becomes more soluble in a positive developer and less soluble in a negative developer upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation, (b) exposing the resist film via an immersion medium, and (c) performing development with a negative developer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
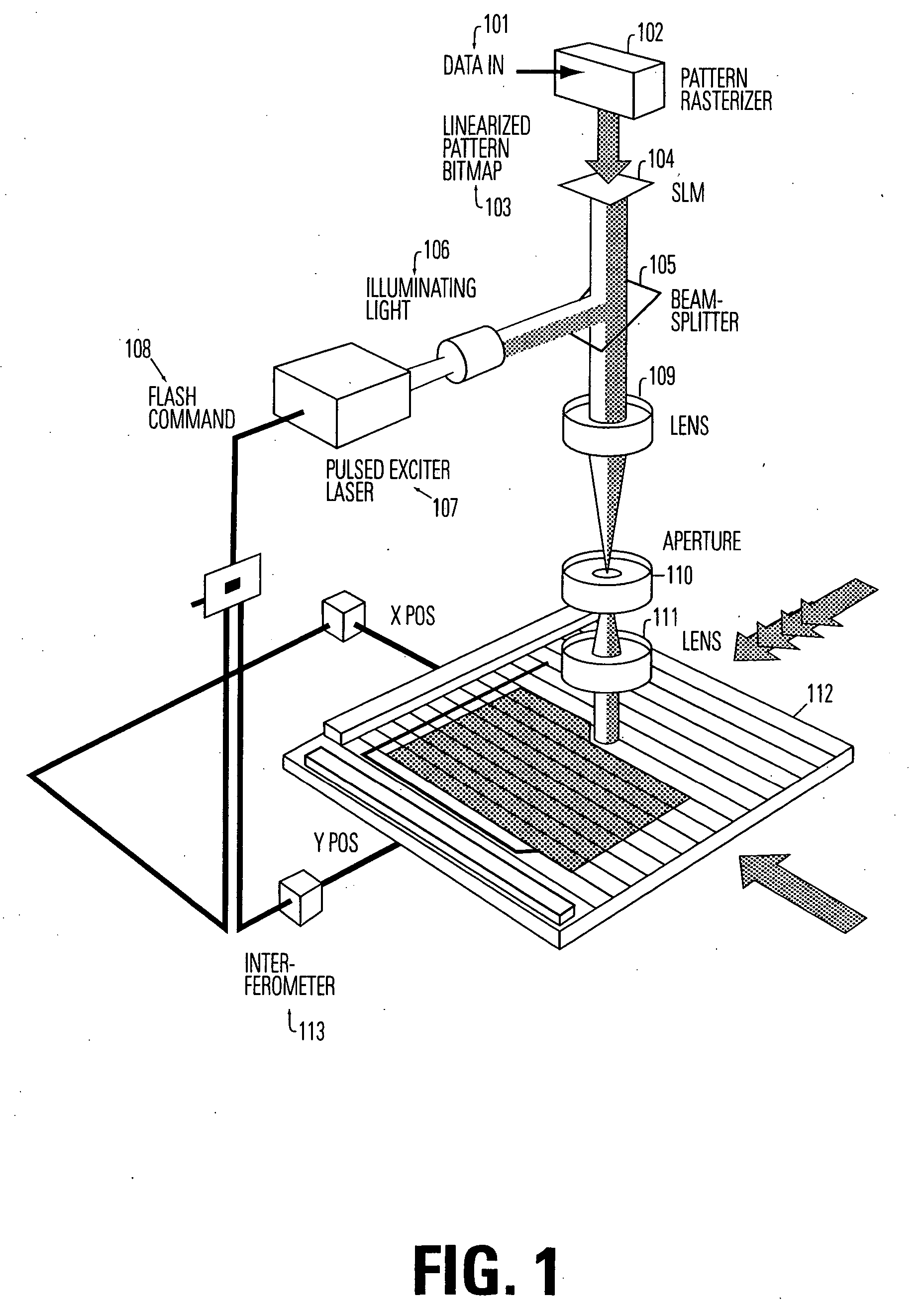
RET for optical maskless lithography
The present invention relates to Optical Maskless Lithography (OML). In particular, it relates to providing OML with a recognizable relationship to mask and phase-shift mask techniques.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
Optical fluids, and systems and methods of making and using the same
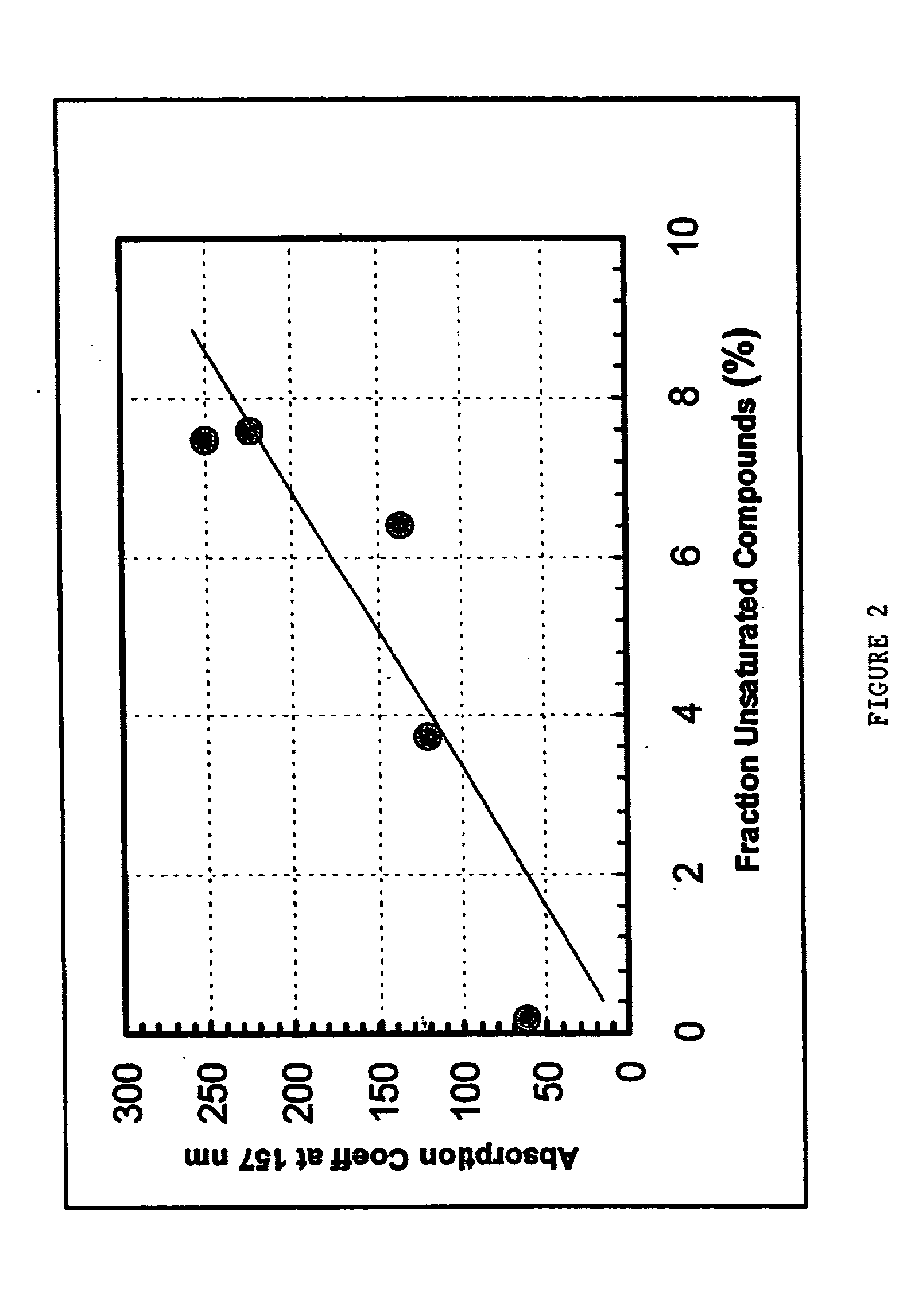
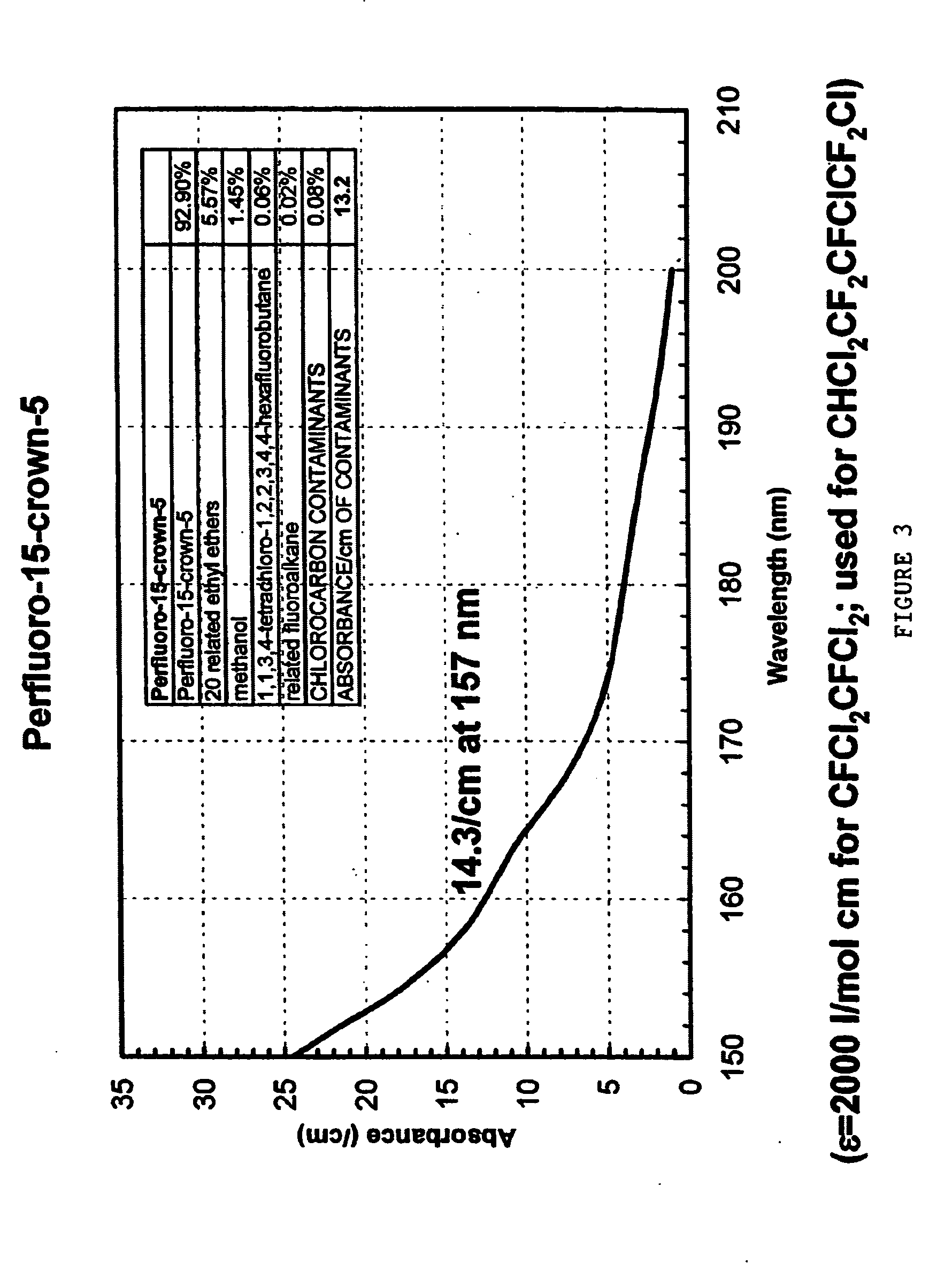
In part, the present invention is directed towards a fluid composition, and systems and methods of making and using the same, wherein the fluid composition has an absorbance of less than about 2 cm−1.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Composite optical lithography method for patterning lines of significantly different widths
InactiveUS20050074698A1Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithography processInterference lithography
A composite patterning technique may include three lithography processes. A first lithography process forms a periodic pattern of alternating continuous lines of substantially equal width and spaces on a first photoresist. A second lithography process uses a non-interference lithography technique to break continuity of the patterned lines and form portions of desired integrated circuit features. The first photoresist may be developed. A second photoresist is formed over the first photoresist. A third lithography process uses a non-interference lithography technique to expose a pattern on the second photoresist and form remaining desired features of an integrated circuit pattern.
Owner:INTEL CORP
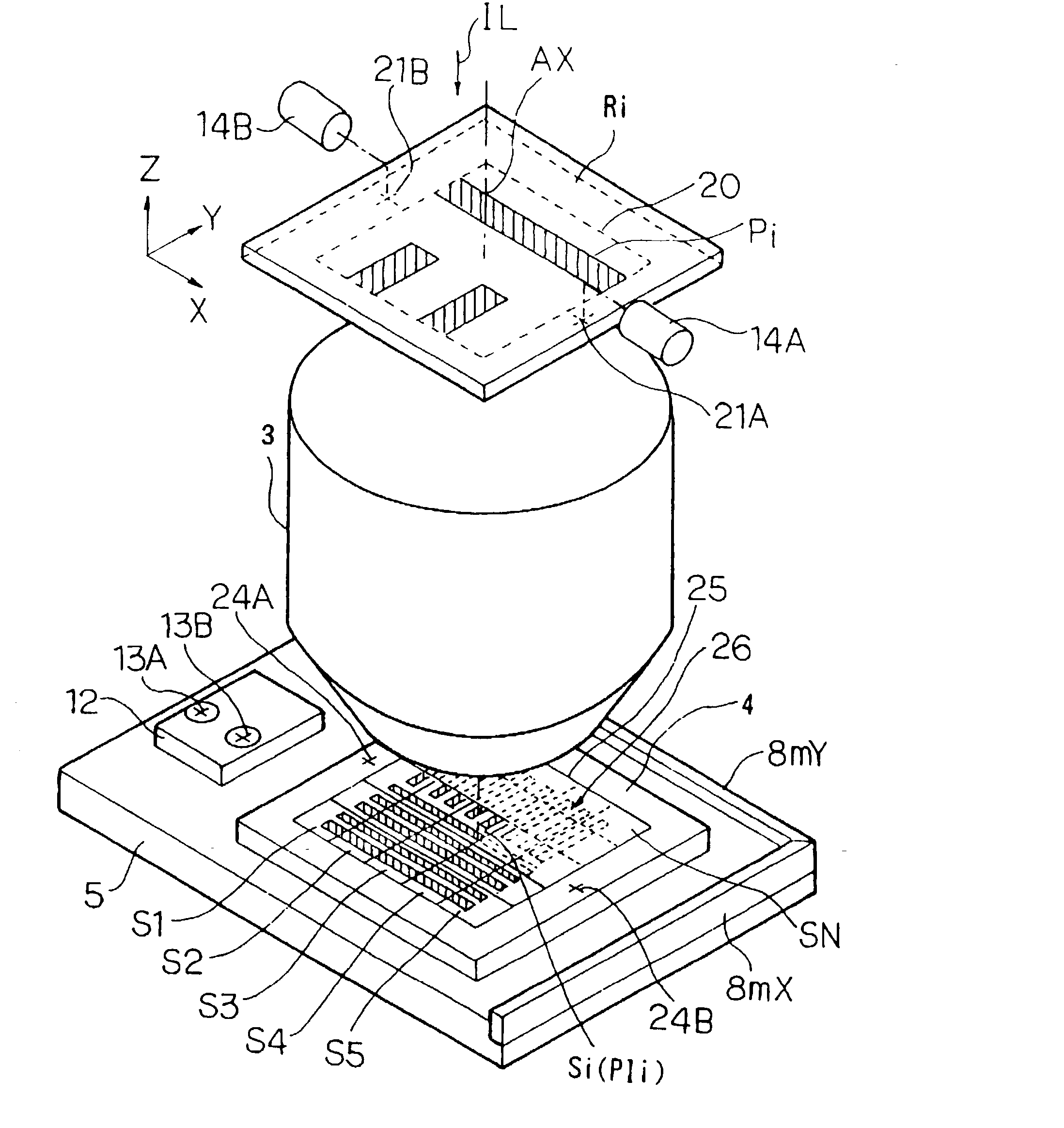
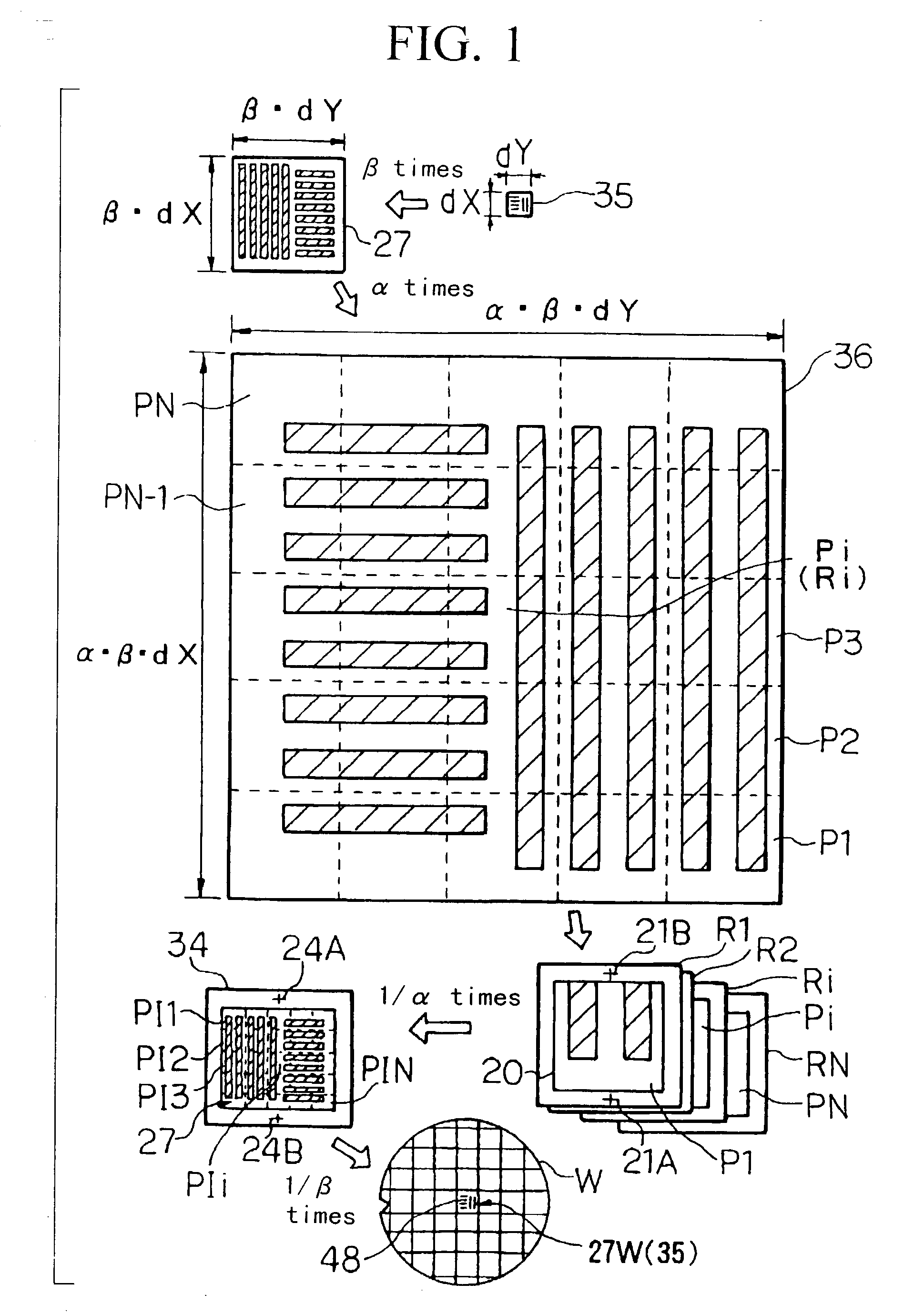
Photomask producing method and apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20020187406A1Photo-taking processesElectric discharge tubesComputational physicsPhotolithography
A photomask producing method according to the present invention segments a parent pattern which is an alpha-magnification of an original pattern which is a beta-magnification of a circuit pattern into alpha lengthwise and breadthwise, thereby forming parent patterns on data. The parent patterns are written on a substrate at equal magnification by using an electron beam lithography system, thereby producing master reticles. Reduced images of the parent patterns of the master reticles are transferred on a substrate while performing screen linking, thereby producing working reticle. This photomask producing method can form an original pattern with a high precision and in a short period of time.
Owner:NIKON CORP
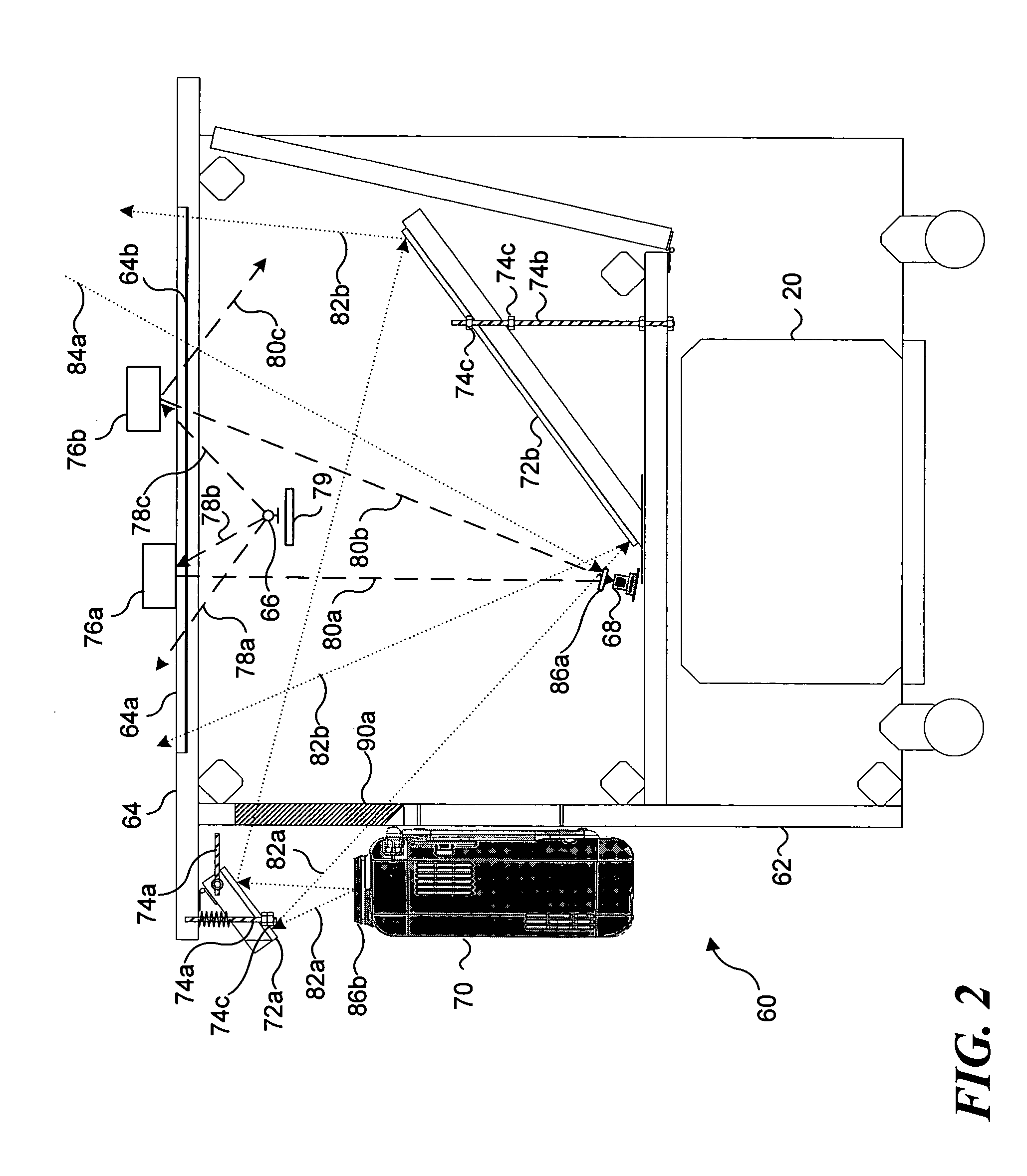
Method for controlling an intensity of an infrared source used to detect objects adjacent to an interactive display surface
InactiveUS20050277071A1Improve the level ofAdequate levelTelevision system detailsPhoto-taking processesInteractive displaysComputer science
In an interactive display table that uses infrared (IR) light to detect an object on an interactive display surface, IR light sources within the table are controlled in response to the level of ambient IR light passing through the interactive display surface. Light from the IR light sources that is reflected the regions disposed inside the table and peripherally around the interactive display surface is captured in an image that also includes the ambient IR light passing through the interactive display surface. A signal corresponding to the image is processed, so that the relative levels of the IR light can be compared. The IR light sources are then controlled so that the level of IR light reflected from the regions exceeds the level of ambient IR light by at least a predefined amount.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Antireflective film material, and antireflective film and pattern formation method using the same
ActiveUS7202013B2Sufficient antireflective effectImprove etch selectivityPhotosensitive materialsPhoto-taking processesResistOrganic solvent
It is an object of the present invention to provide a material for an antireflective film that has high etching selectivity with respect to the resist, that is, that has a faster etching speed than the resist, a pattern formation method for forming an antireflective film layer on a substrate using this antireflective film material, and a pattern formation method using this antireflective film as a hard mask for substrate processing.The present invention provides an antireflective film material comprising a polymer (A) comprising copolymerized repeating units expressed by the Formula (1) and / or the Formula (2), an organic solvent (B), an acid generator (C) and an optional crosslinking agent (D)
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Pattern compensation for stitching
InactiveUS6982135B2Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGray levelData file
A method for transferring a pattern from a mask to a substrate (or wafer), comprises dividing a mask generation data file into a plurality of segments. The segments include a main pattern area and a stitching area. Each stitching area contains a respective common pattern. An image of an illuminated portion of the main pattern area is formed. Connection ends of the segments in a substrate area (or wafer area) are illuminated with an illumination beam. An image of the illuminated portion of the main pattern area is formed, and a halftone gray level dosage distribution is produced in the substrate area (or wafer area) corresponding to the common pattern. The common patterns of adjacent segments substantially overlap in the substrate area (or wafer area).
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Contact or proximity printing using a magnified mask image
InactiveUS20050007567A1Avoid stickingElectric discharge tubesPhoto-taking processesLithographic artistImage resolution
Improvements in the fabrication of integrated circuits are driven by the decrease of the size of the features printed on the wafers. Current lithography techniques limits have been extended through the use of phase-shifting masks, off-axis illumination, and proximity effect correction. More recently, liquid immersion lithography has been proposed as a way to extend even further the limits of optical lithography. This invention described a methodology based on contact or proximity printing using a projection lens to define the image of the mask onto the wafer. As the imaging is performed in a solid material, larger refractive indices can be obtained and the resolution of the imaging system can be increased.
Owner:TAKUMI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com