Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Resolution enhancement technologies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
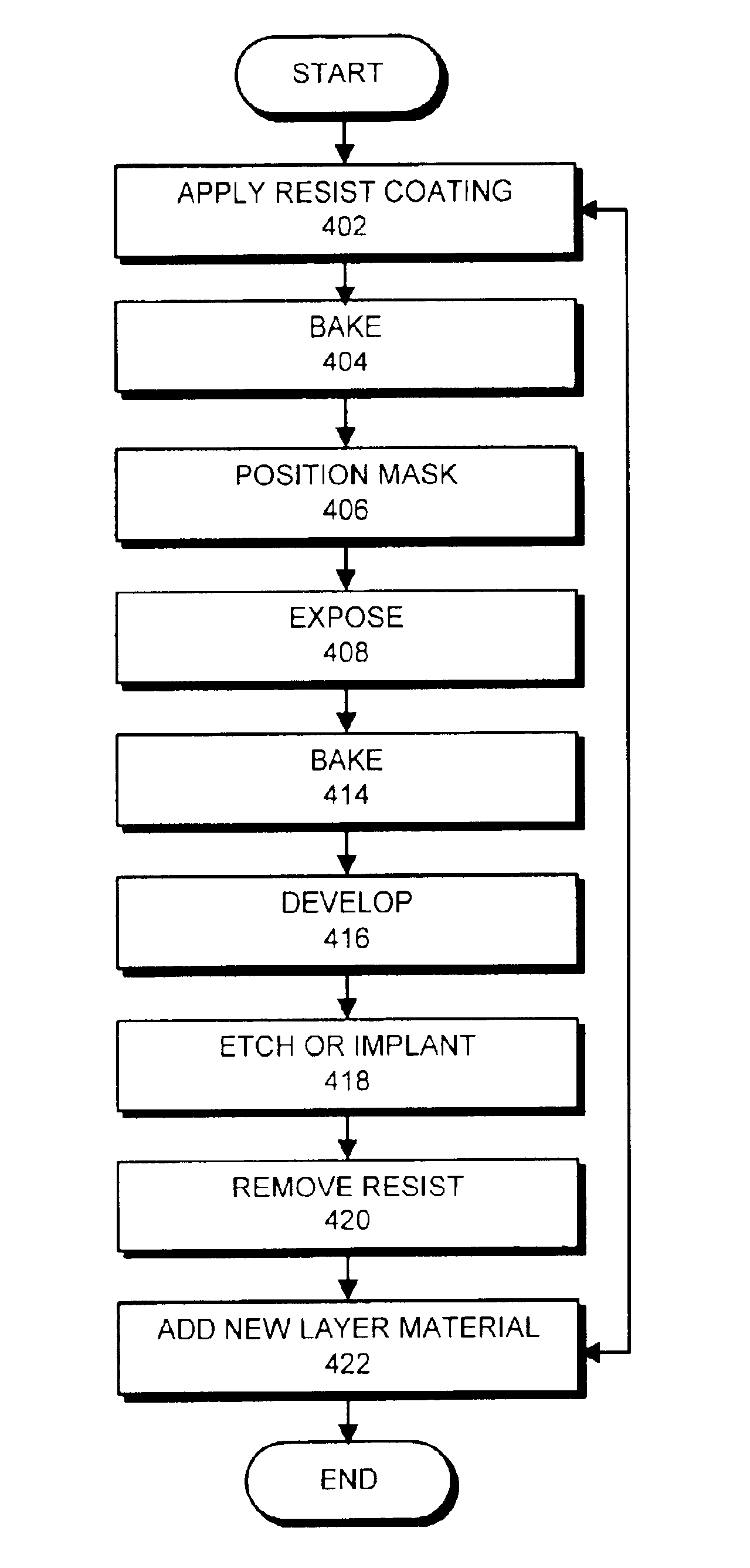
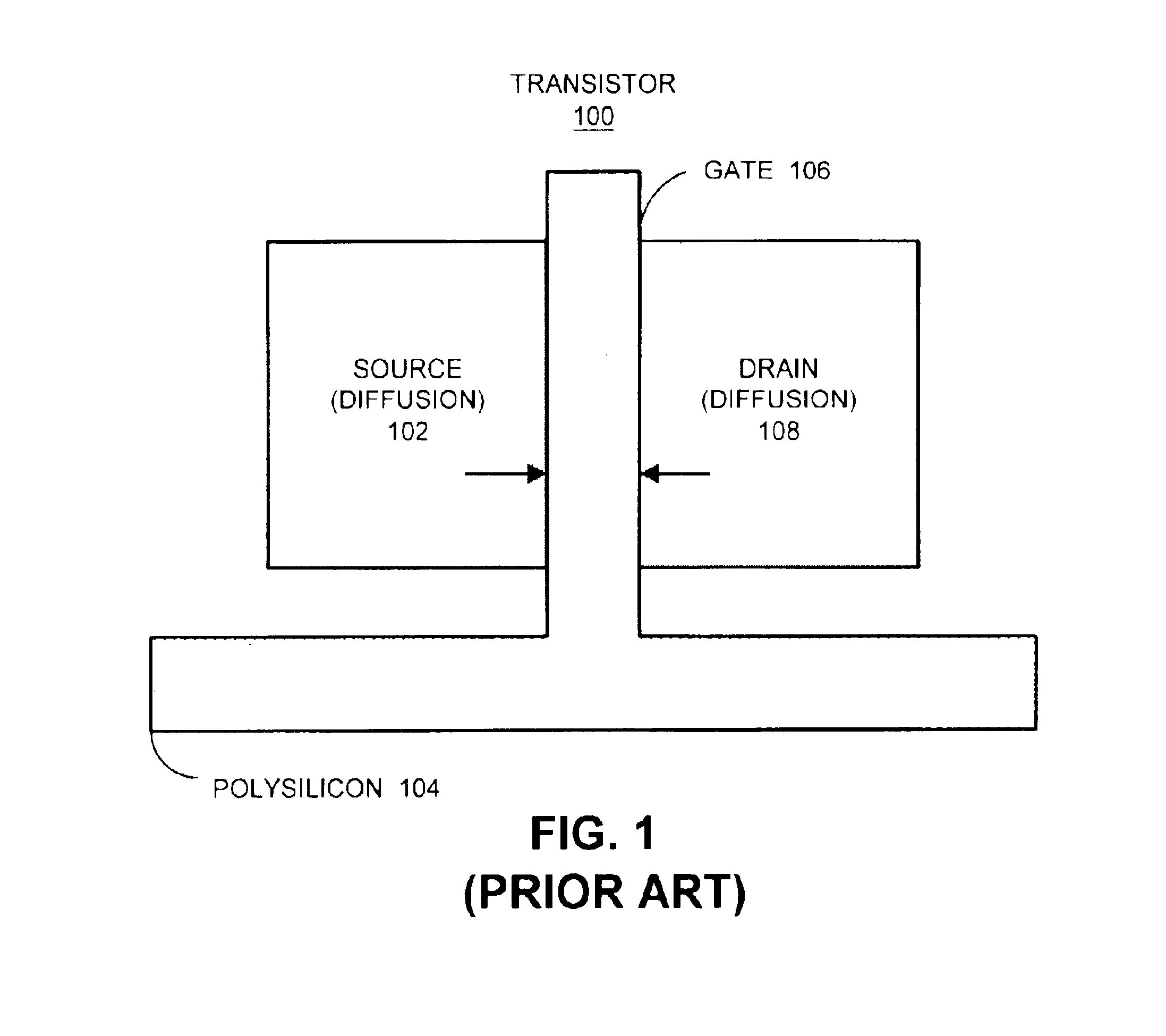
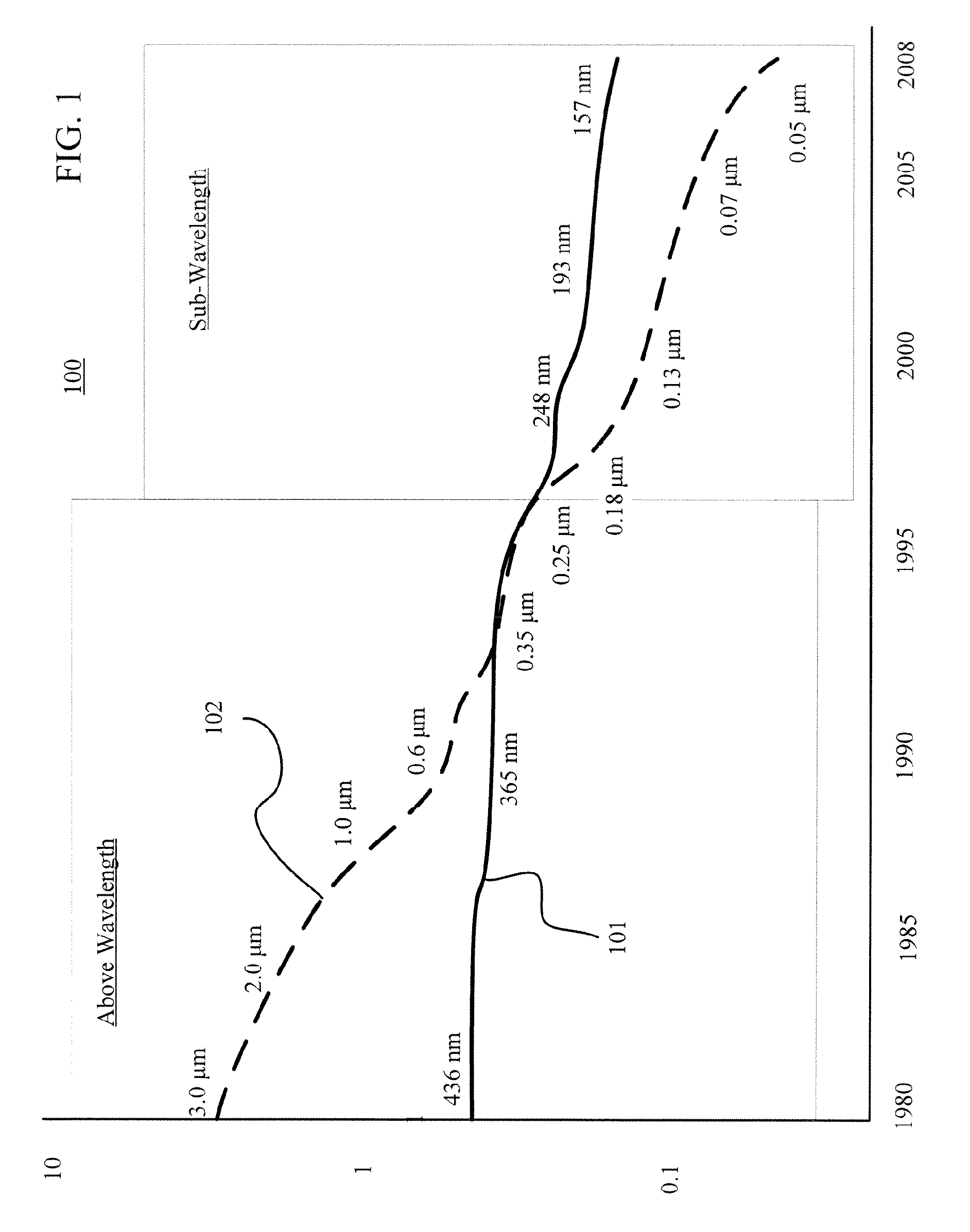
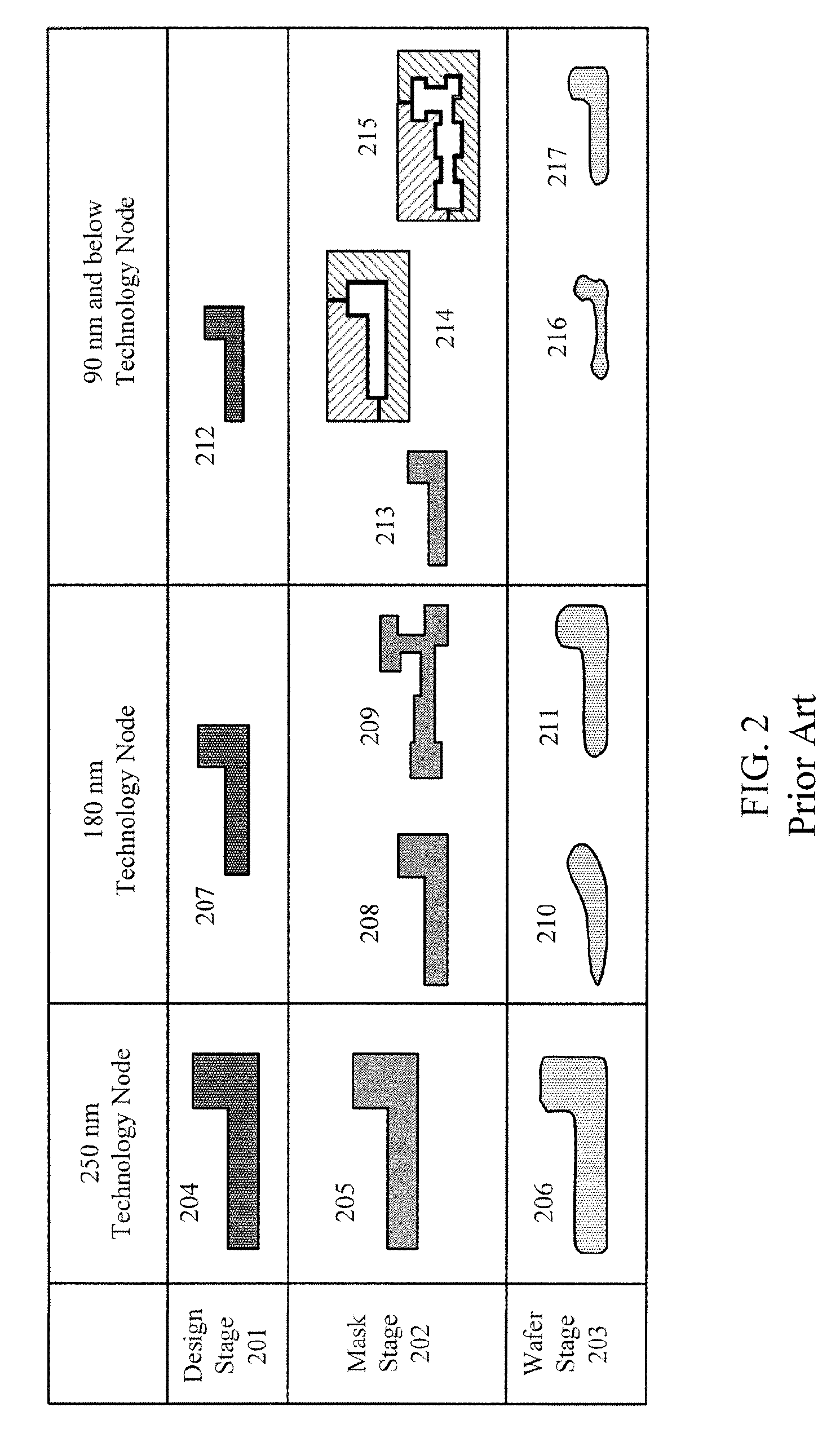
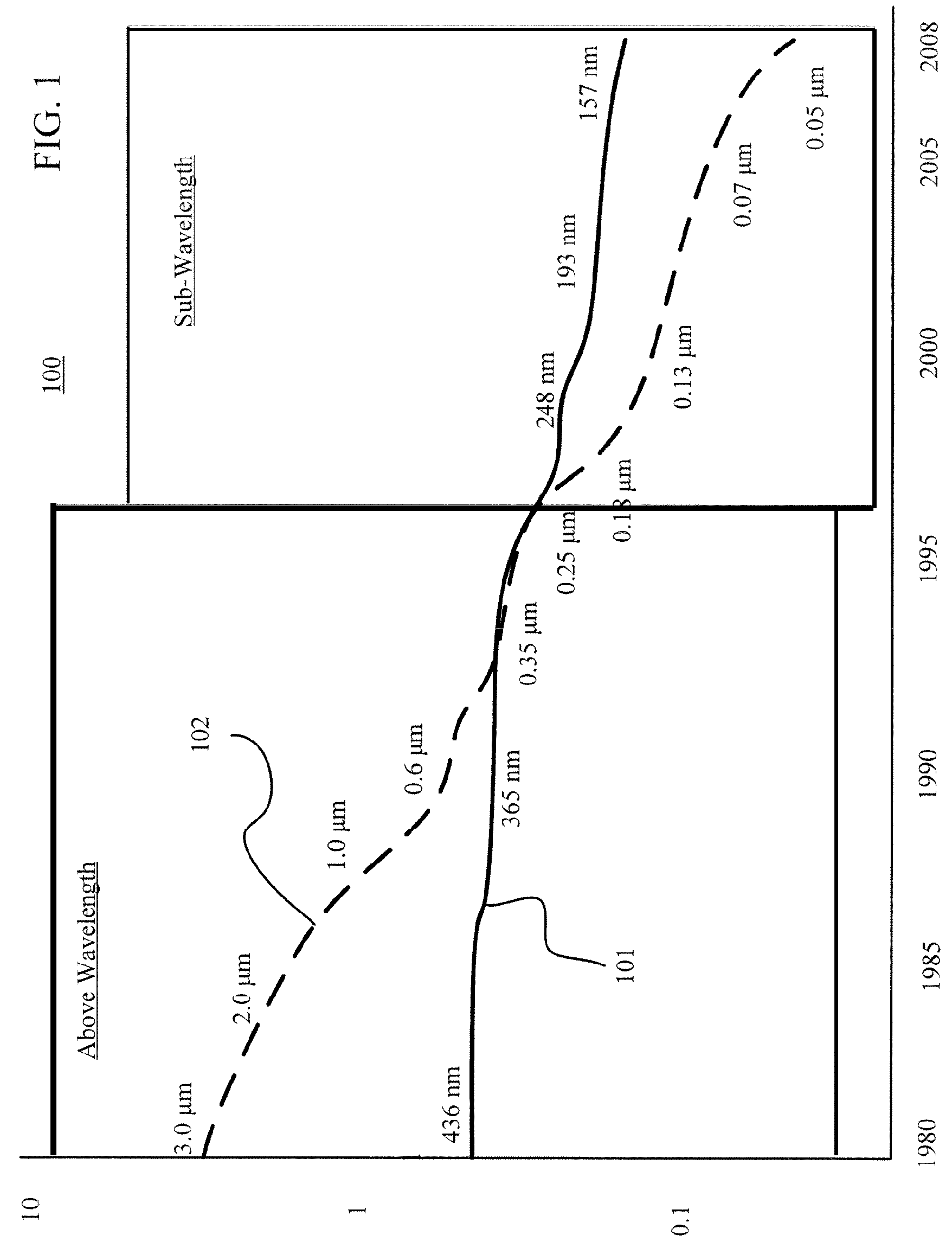
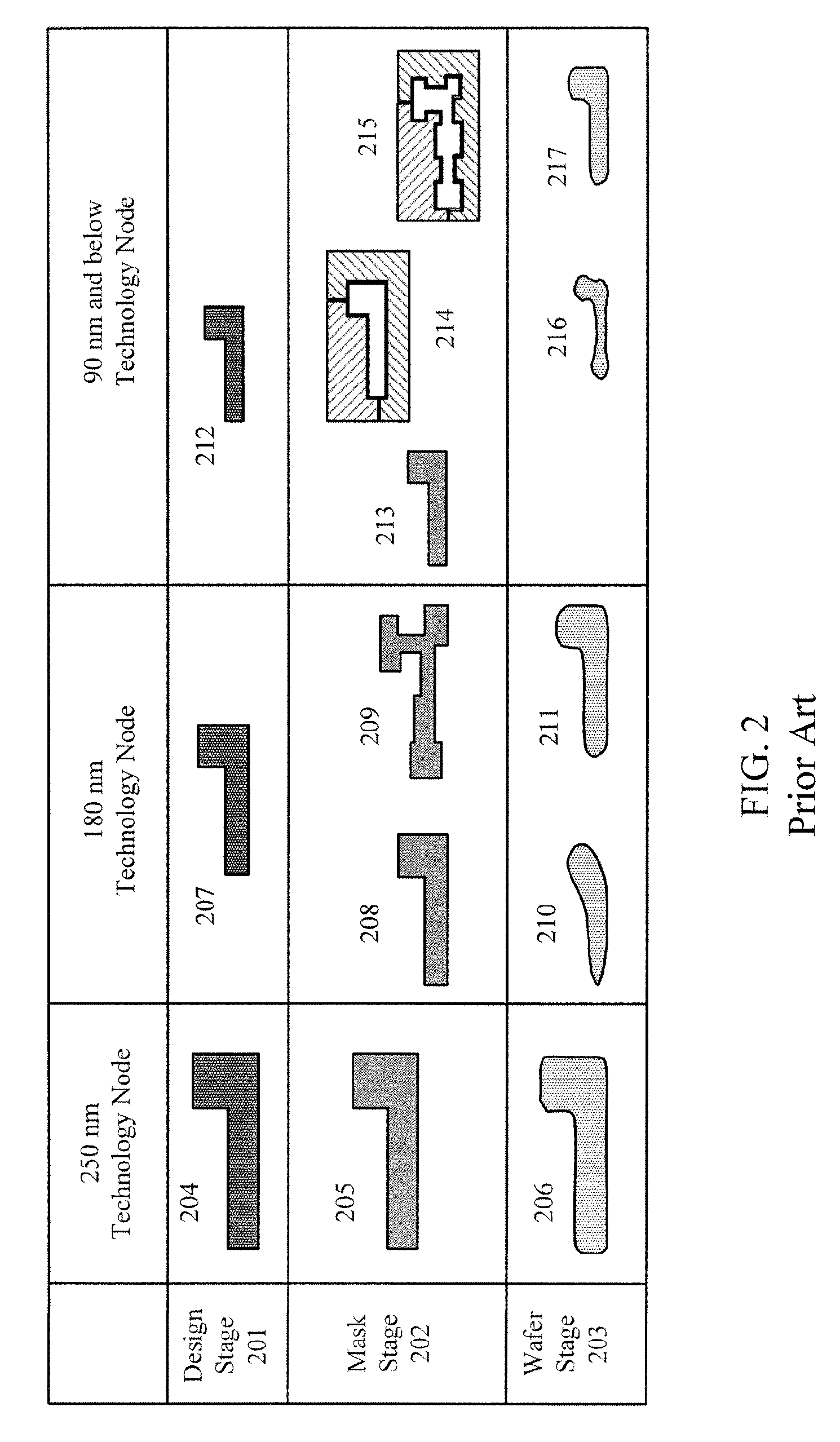
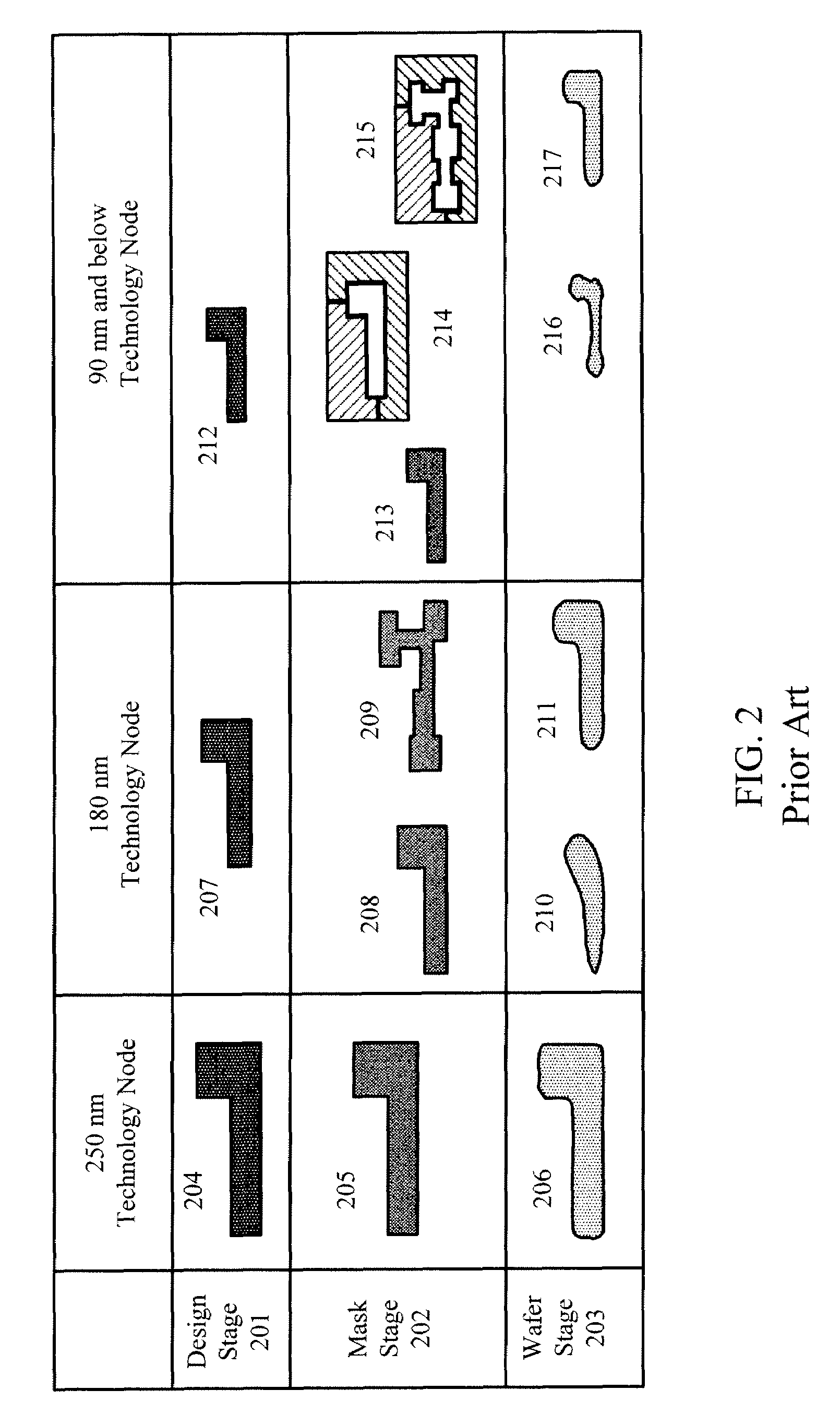
Resolution enhancement technologies are methods used to modify photomasks for integrated circuits (ICs) to compensate for limitations in the lithographic processes used to manufacture the chips. Traditionally, after an IC design has been converted into a physical layout, the timing verified, and the polygons certified to be DRC-clean, the IC was ready for fabrication. The data files representing the various layers were shipped to a mask shop, which used mask-writing equipment to convert each data layer into a corresponding mask, and the masks were shipped to the fab where they were used to repeatedly manufacture the designs in silicon. In the past, the creation of the IC layout was the end of the involvement of electronic design automation.
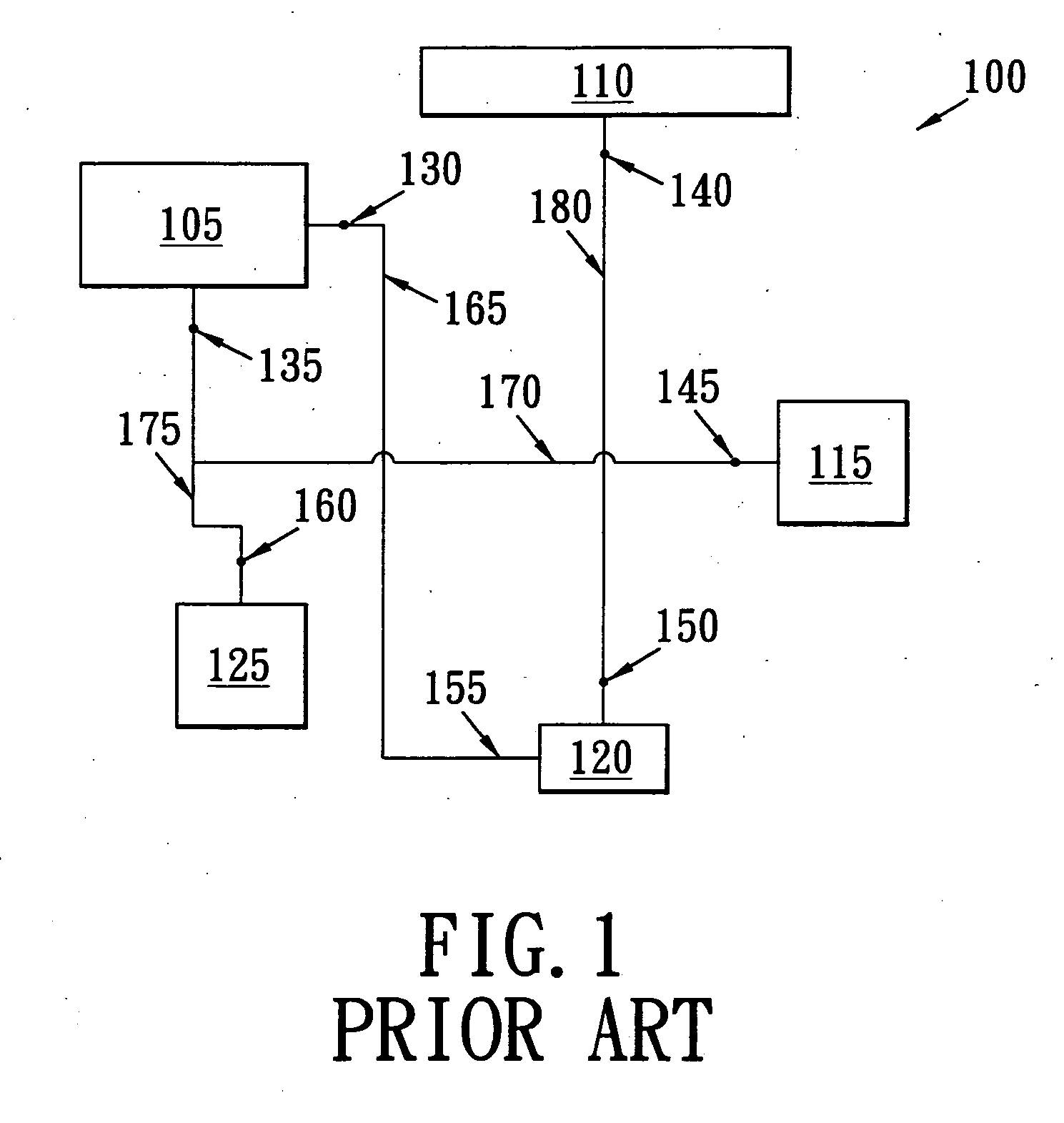
Selectively applying resolution enhancement techniques to improve performance and manufacturing cost of integrated circuits
InactiveUS6928635B2Reduce delaysReduction of gate lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
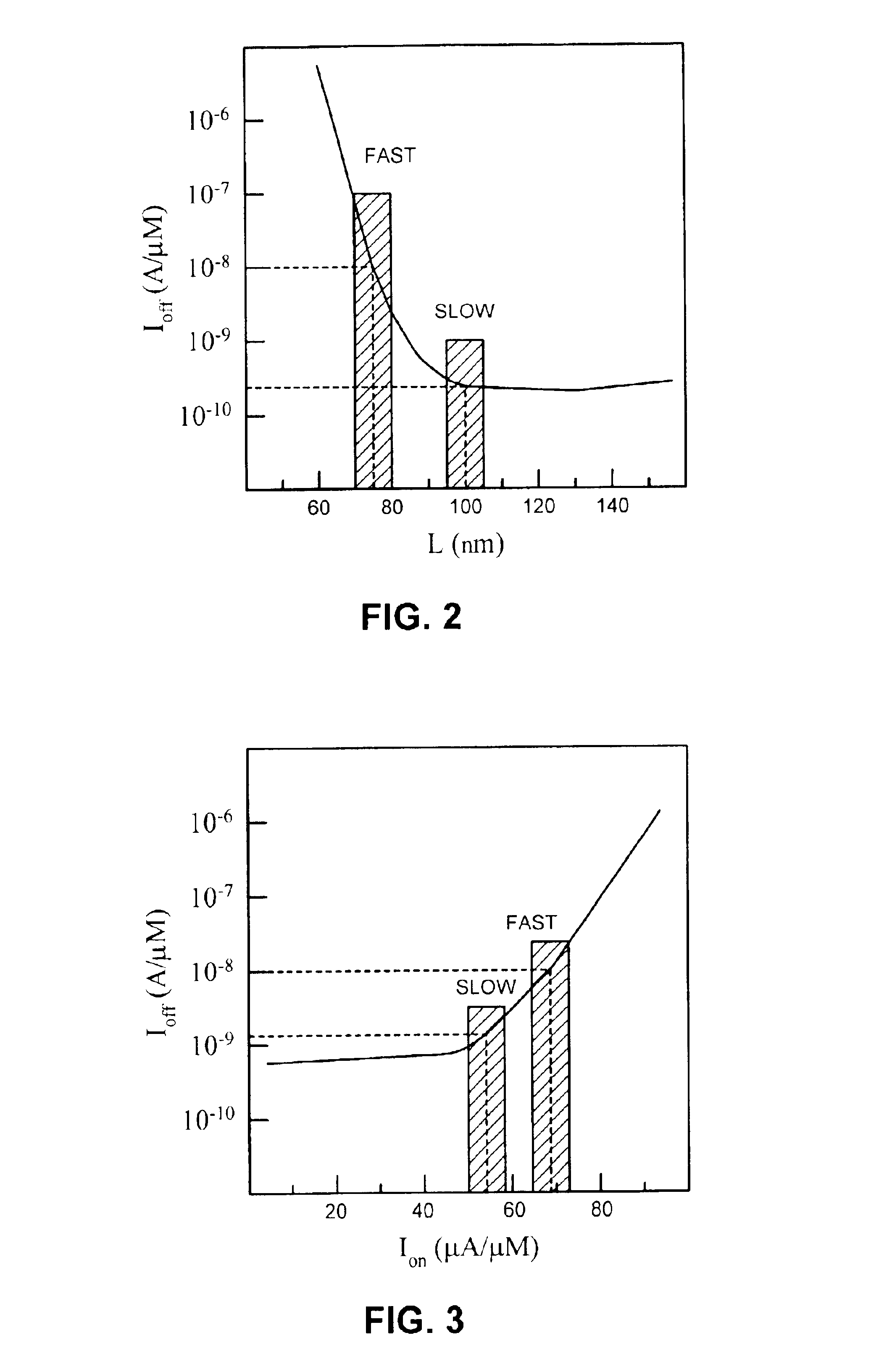
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that applies resolution enhancement techniques (RETs) selectively to a layout of an integrated circuit. Upon receiving the layout of the integrated circuit, the system identifies a plurality of critical regions within the layout based on an analysis of one or more of, timing, dynamic power, and off-state leakage current. The system then performs a first set of aggressive RET operations on the plurality of critical regions. The system also performs a second set of less aggressive RET operations on other non-critical regions of the layout.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Apparatus for a routing system
InactiveUS20070106971A1Reduce violationsReduce processComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designAlgorithmGrid based
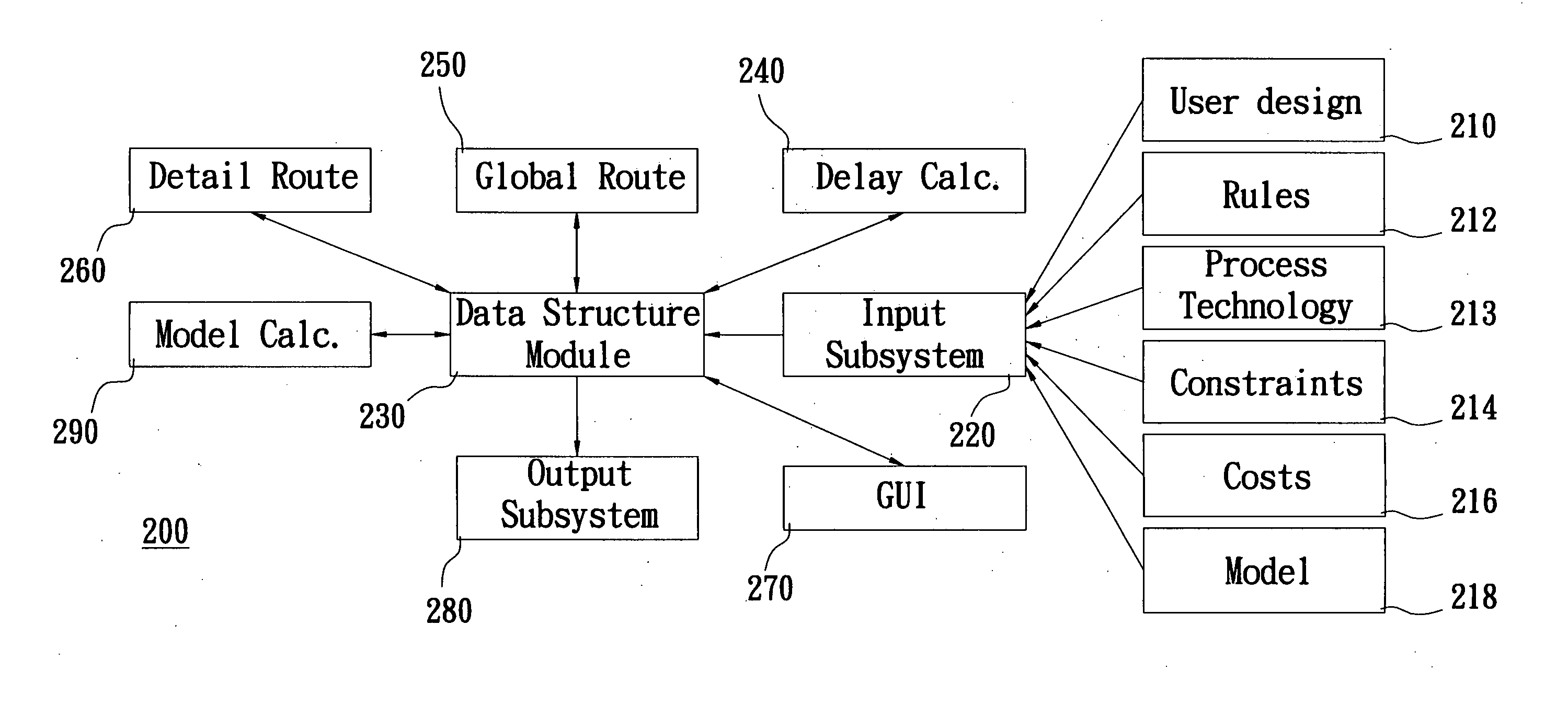
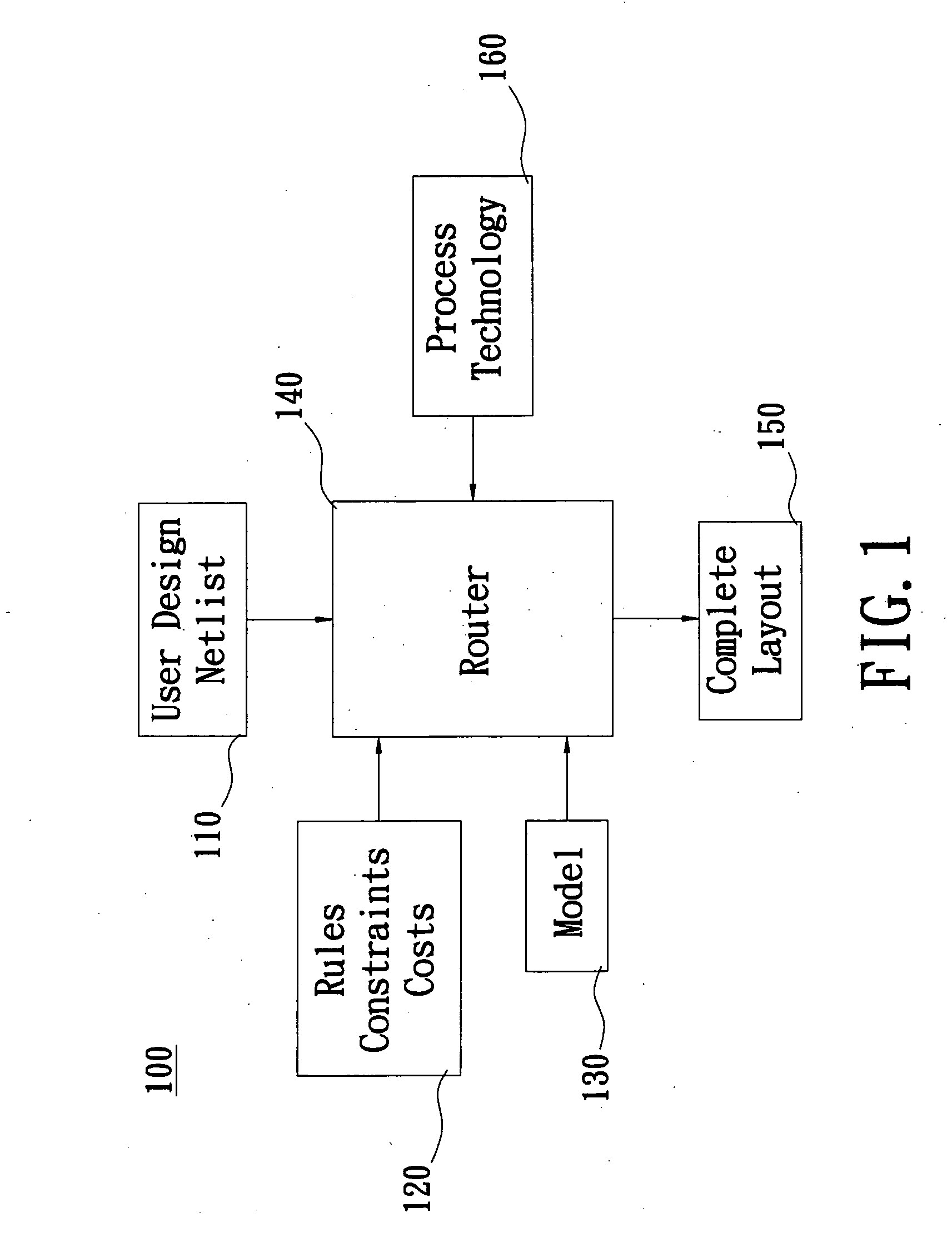
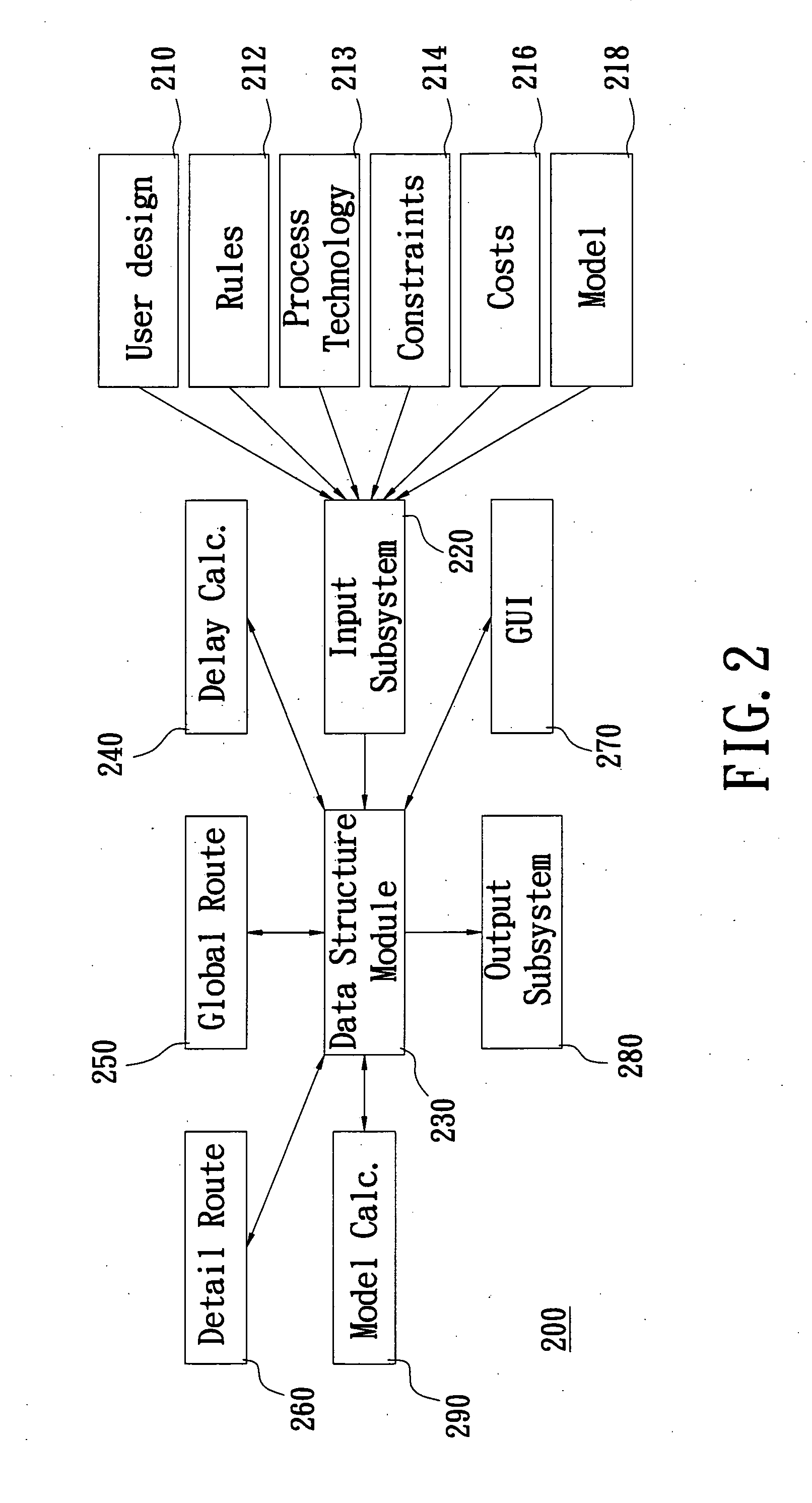
The invention details methods and apparatus for a routing system or router that includes a model. The model can be in many different forms including but not limited to: resolution enhancement technologies such as OPC; lithography model including but not limited to aerial image; pattern-dependent functions; functions for timing / signal integrity / power; manufacturing process variations; and measured silicon data. In one embodiment, the model can be described as input to the system and the model calculator can interact either with the data structure or the query engine of the detail router or both. The model calculator can accept input as a set of geometry description and produce output to guide the query functions. An example technique called set intersection is disclosed herein to combine multiple models in the system. A preferred embodiment of this invention includes a full chip grid-based router being aware of manufacturability.
Owner:LIZOTECH
Rectangular contact lithography for circuit performance improvement and manufacture cost reduction
ActiveUS20050196685A1Reduce manufacturing costLot of restrictionPhoto-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
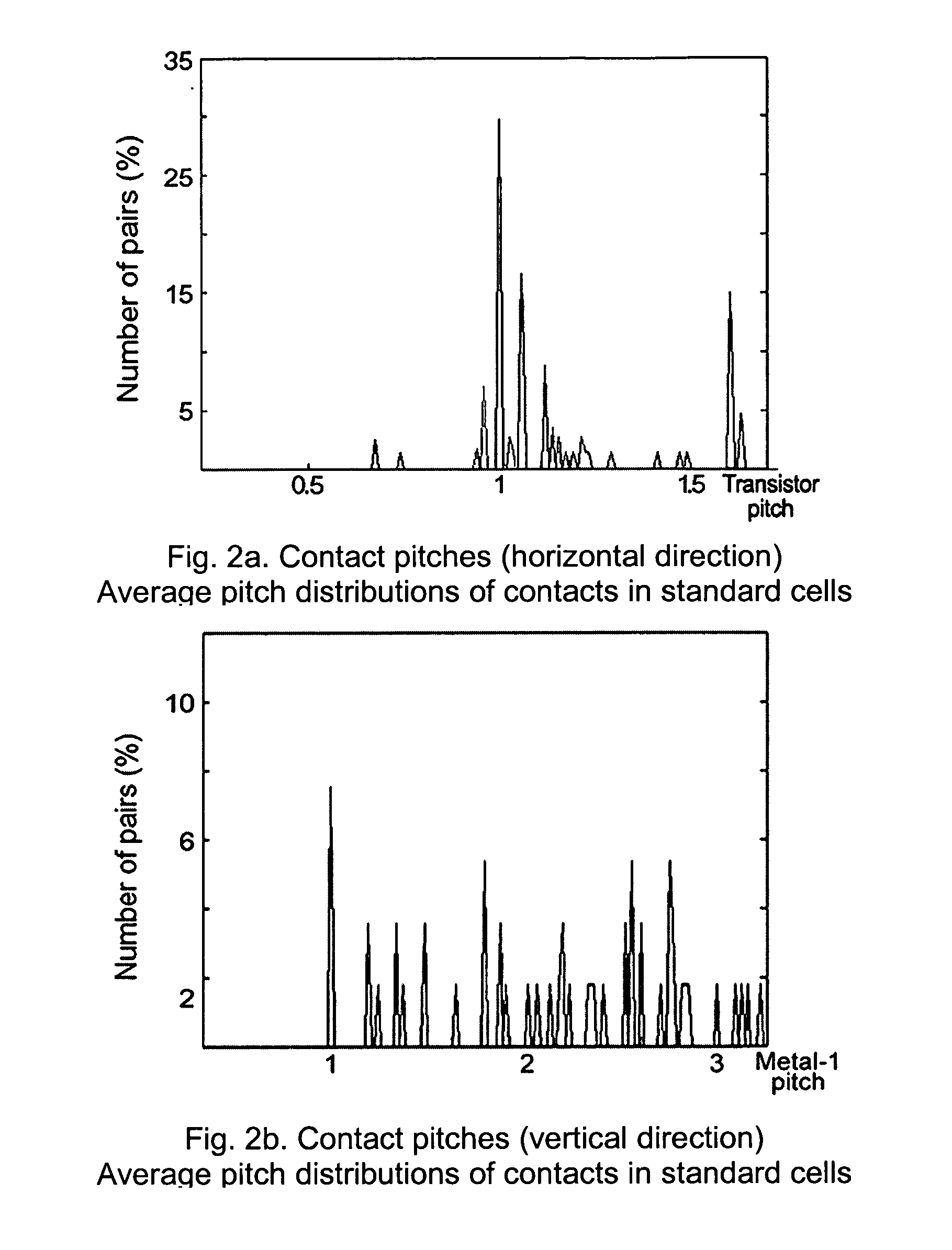
An optical lithography method is disclosed that uses double exposure of a reusable template mask and a trim mask to fabricate regularly-placed rectangular contacts in standard cells of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). A first exposure of the reusable template mask with periodic patterns forms periodic dark lines on a wafer and a second exposure of an application-specific trim mask remove the unwanted part of the dark lines and the small cuts of the dark lines left form the rectangular regularly-placed contacts. All contacts are placed regularly in one direction while unrestrictedly in the perpendicular direction. The regular placement of patterns on the template mask enable more effective use of resolution enhancement technologies, which in turn allows a decrease in manufacturing cost and the minimum contact size and pitch. Since there is no extra application-specific mask needed comparing with the conventional lithography method for unrestrictedly-placed contacts, the extra cost is kept to the lowest. The method of the invention can be used in the fabrication of standard cells in application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) to improve circuit performance and decrease circuit area and manufacturing cost.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Patterning A Single Integrated Circuit Layer Using Multiple Masks And Multiple Masking Layers
ActiveUS20070275309A1Increase productionEasy to useSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResolution enhancement technologiesLength wave
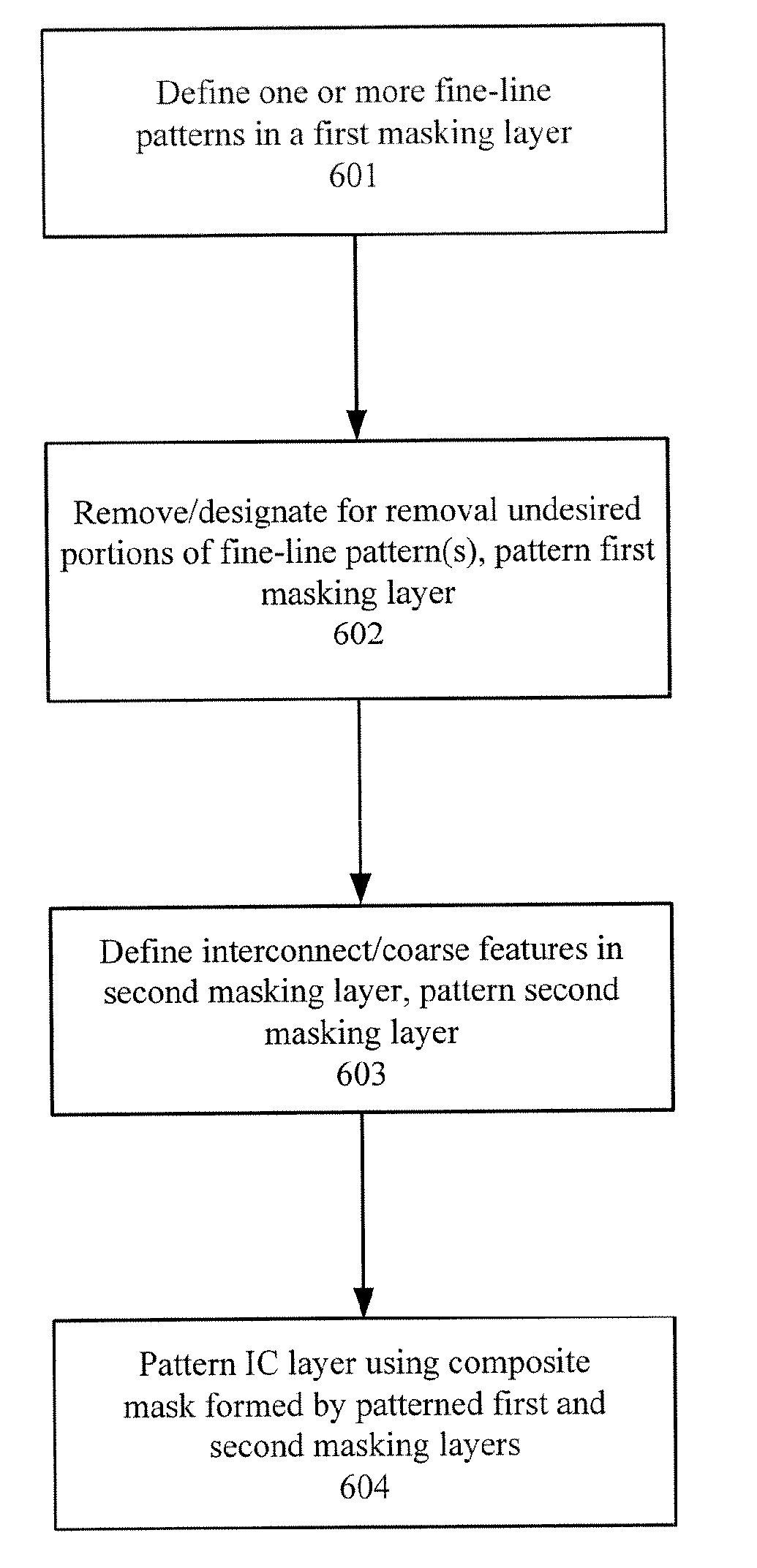
A multiple mask and a multiple masking layer technique can be used to pattern a single IC layer. A resolution enhancement technique can be used to define one or more fine-line patterns in a first masking layer, wherein each fine-line feature is sub-wavelength. Moreover, the pitch of each fine-line pattern is less than or equal to that wavelength. The portions of the fine-line features not needed to implement the circuit design are then removed or designated for removal using a mask. After patterning of the first masking layer, another mask can then be used to define coarse features in a second masking layer formed over the patterned first masking layer. At least one coarse feature is defined to connect two fine-line features. The IC layer can be patterned using the composite mask formed by the patterned first and second masking layers.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Patterning a single integrated circuit layer using multiple masks and multiple masking layers
ActiveUS7537866B2Low costEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResolution enhancement technologiesWavelength
A multiple mask and a multiple masking layer technique can be used to pattern a single IC layer. A resolution enhancement technique can be used to define one or more fine-line patterns in a first masking layer, wherein each fine-line feature is sub-wavelength. Moreover, the pitch of each fine-line pattern is less than or equal to that wavelength. The portions of the fine-line features not needed to implement the circuit design are then removed or designated for removal using a mask. After patterning of the first masking layer, another mask can then be used to define coarse features in a second masking layer formed over the patterned first masking layer. At least one coarse feature is defined to connect two fine-line features. The IC layer can be patterned using the composite mask formed by the patterned first and second masking layers.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
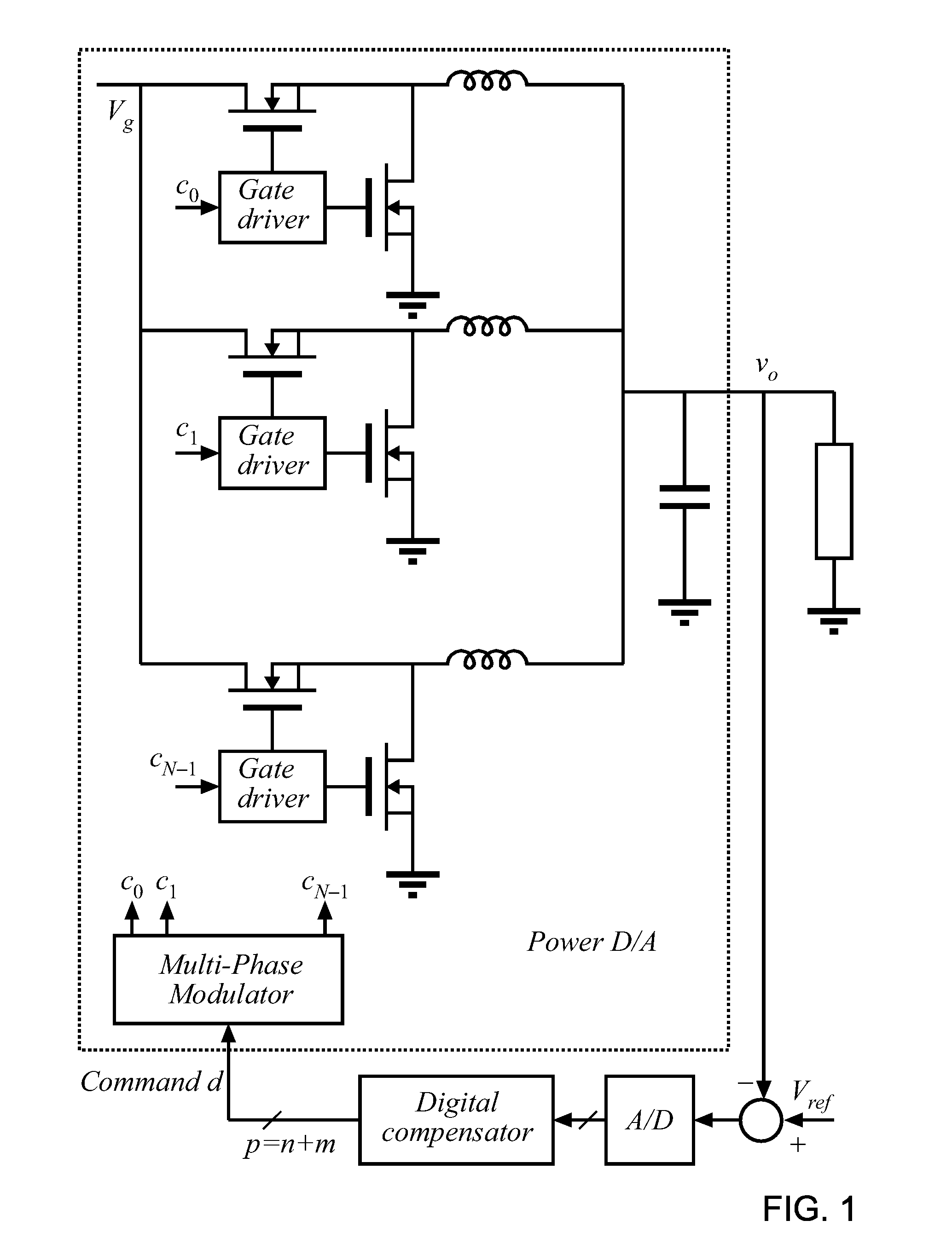
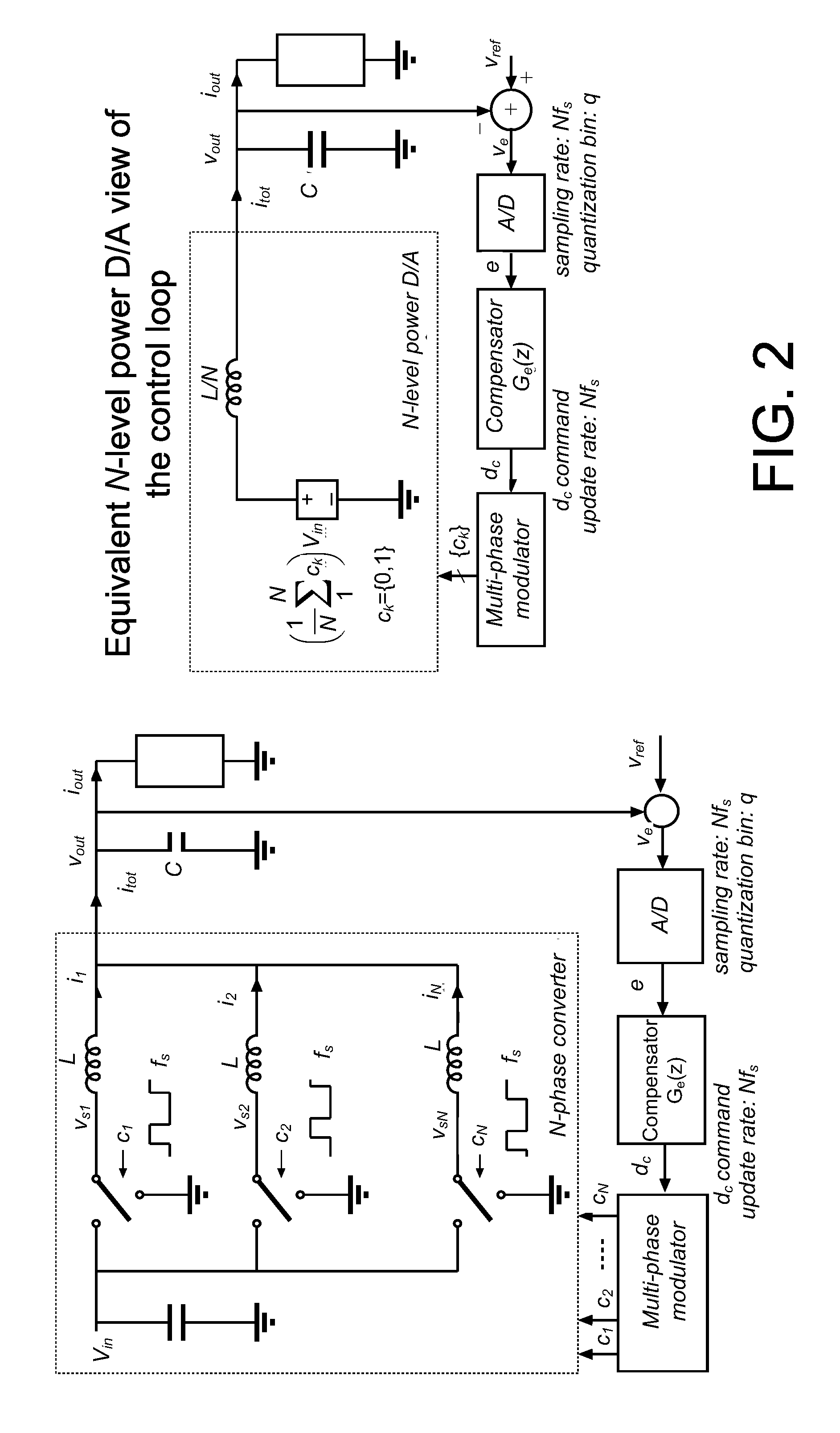
Multi-phase modulator
ActiveUS20080310200A1Dc-dc conversionDc source parallel operationResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
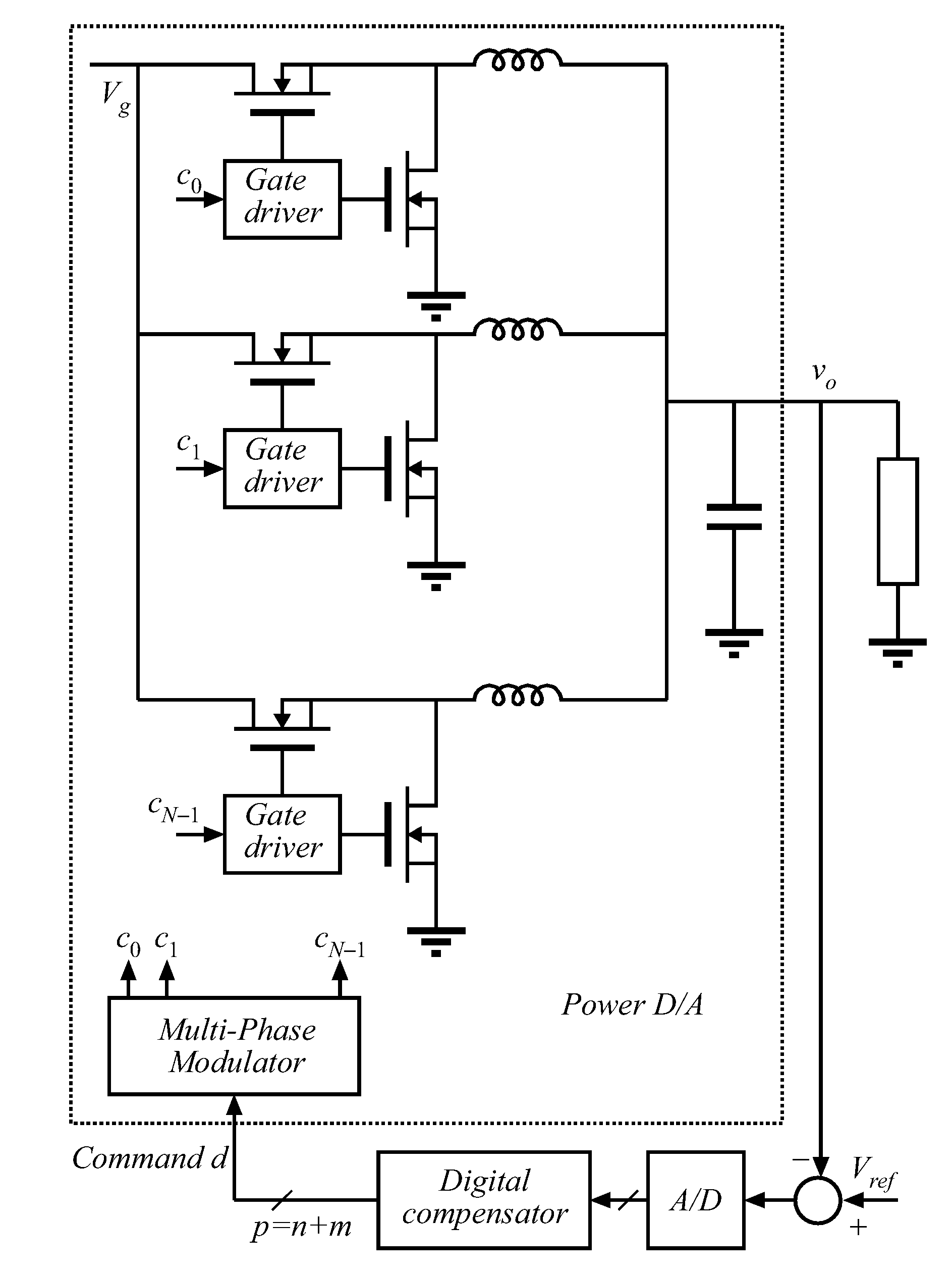
An architecture is described for digital multi-phase modulators (MPM) that leads to an efficient, high performance hardware realization. The combined modulator, switching phases and output filter can be viewed as a multi-level digital to analog converter with high power output, or a power D / A, and concepts used in D / A converters are leveraged to achieve high performance and hardware efficiency. The modulator can be split into three functional blocks including a decoder that determines how many phases are on at any time, a selector that determines which phases are on at any time, and a single high resolution module that is time shared among all phases. The resulting architecture scales favorably with a large number of phases, fs, facilitates fast update rates of the input command well above the single phase switching frequency and is compatible with a wide range of known DPWM techniques for the LSB module and resolution-enhancement techniques such as dithering or Σ-Δ modulation.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
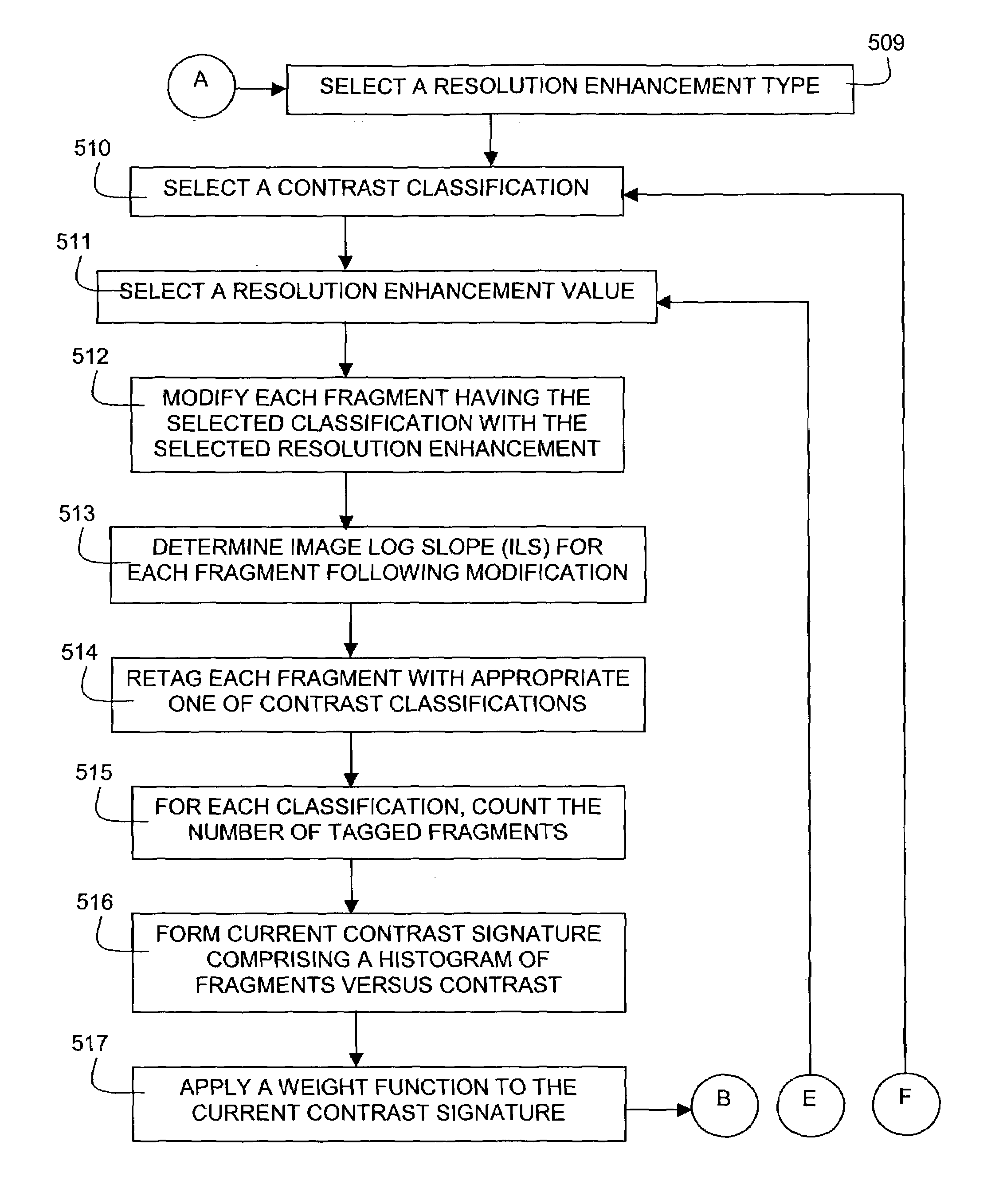
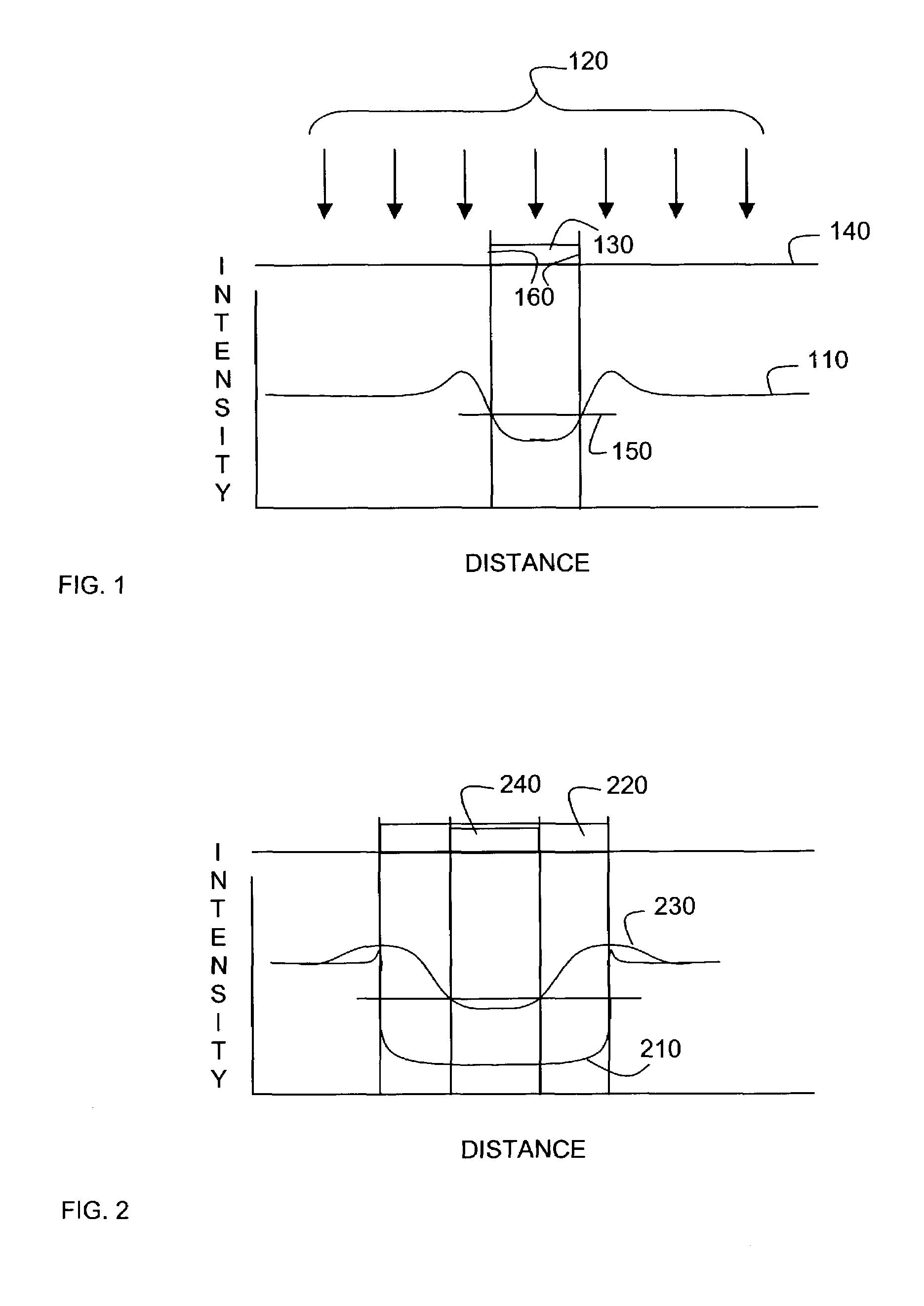
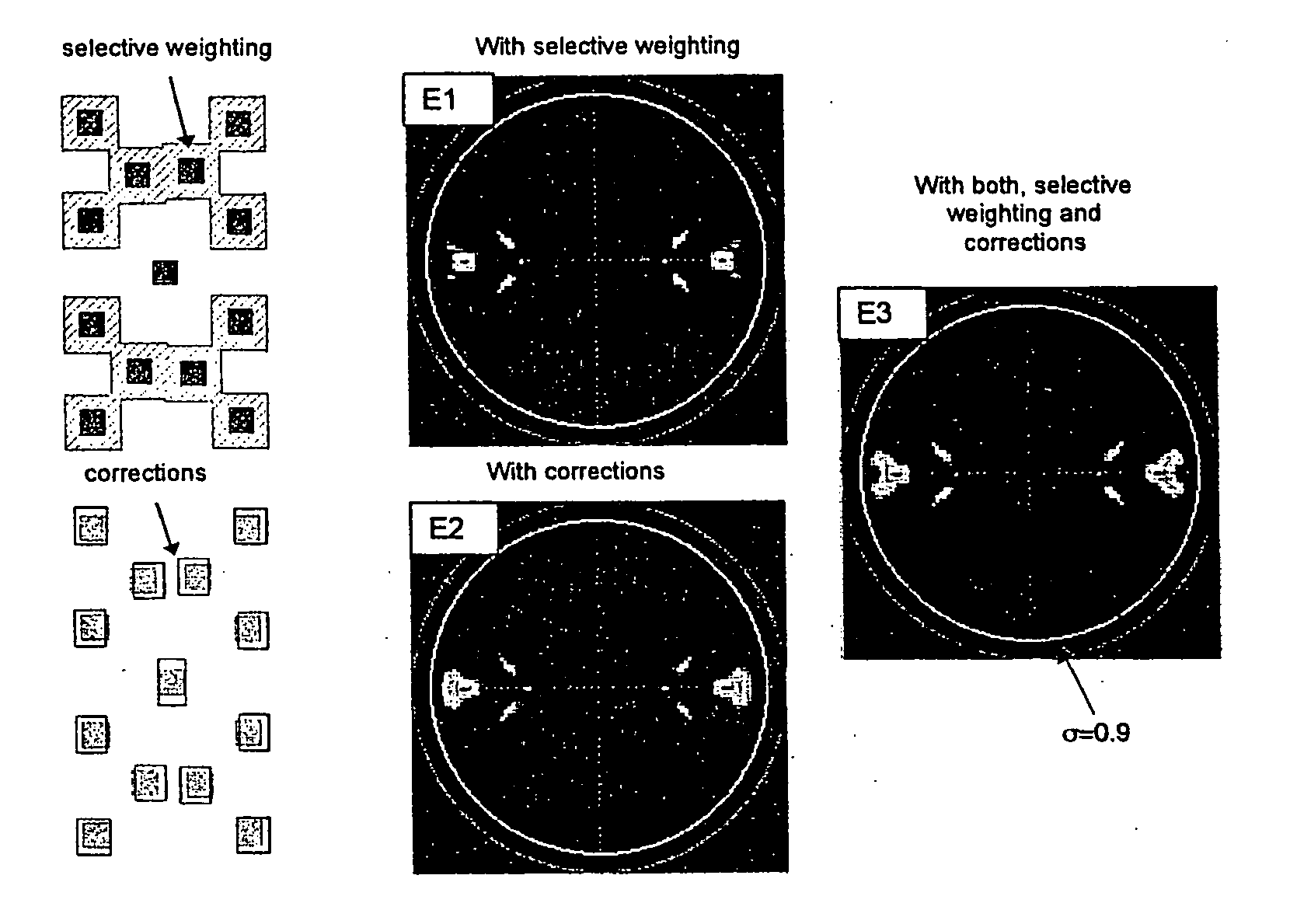
Contrast based resolution enhancing technology
InactiveUS7013439B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusCharacter and pattern recognitionResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Contrast based resolution enhancement for photolithographic processing
InactiveUS20070124708A1Improve manufacturabilityIncrease contrastElectric discharge tubesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
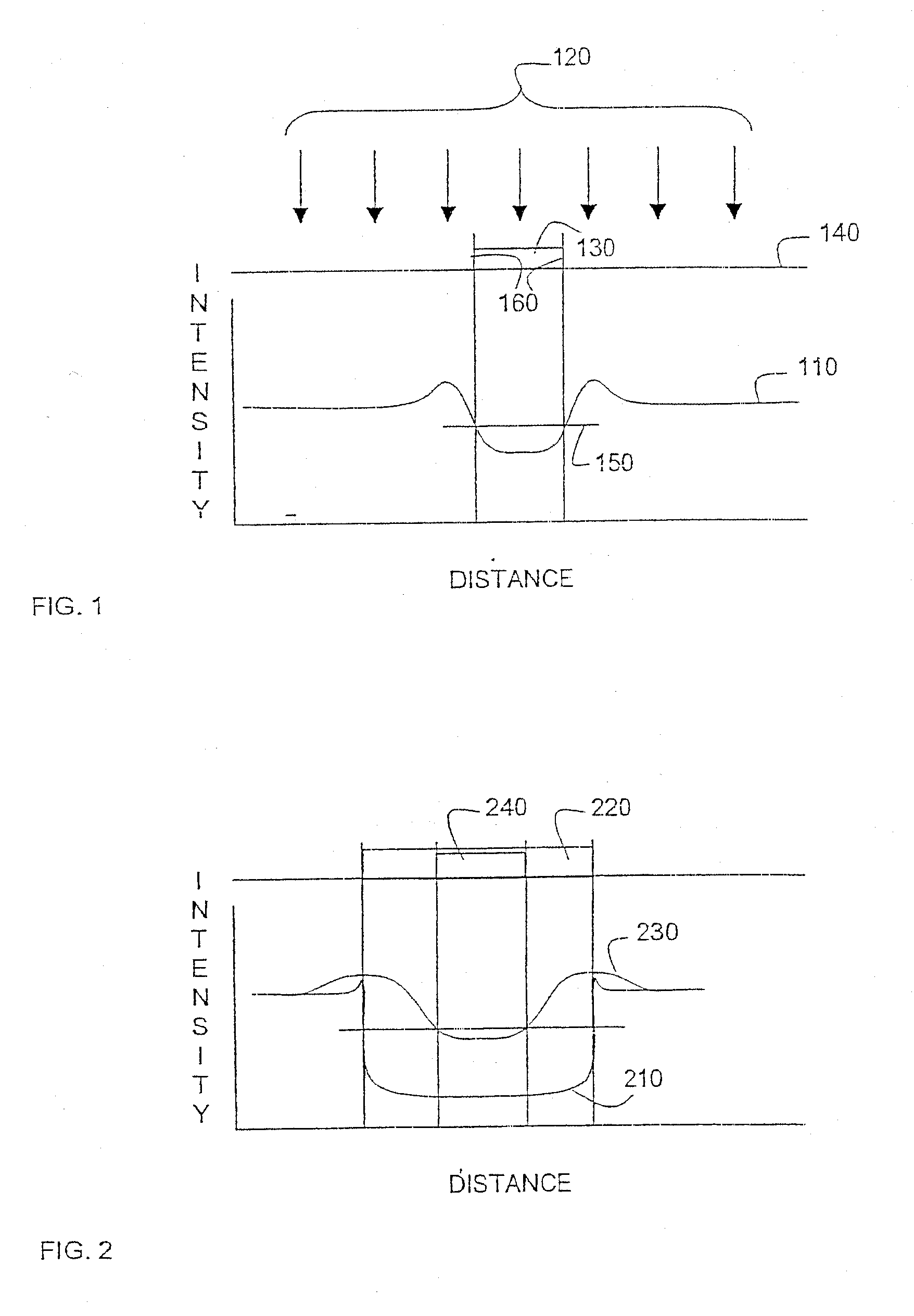
A contrast-based resolution enhancing technology (RET) determines a distribution of contrast values for edge fragments in a design layout or portion thereof. Resolution enhancement is applied to the edge fragments in a way that increases the number of edge fragments having a contrast value that exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Selective promotion for resolution enhancement techniques
InactiveUS7240321B2Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
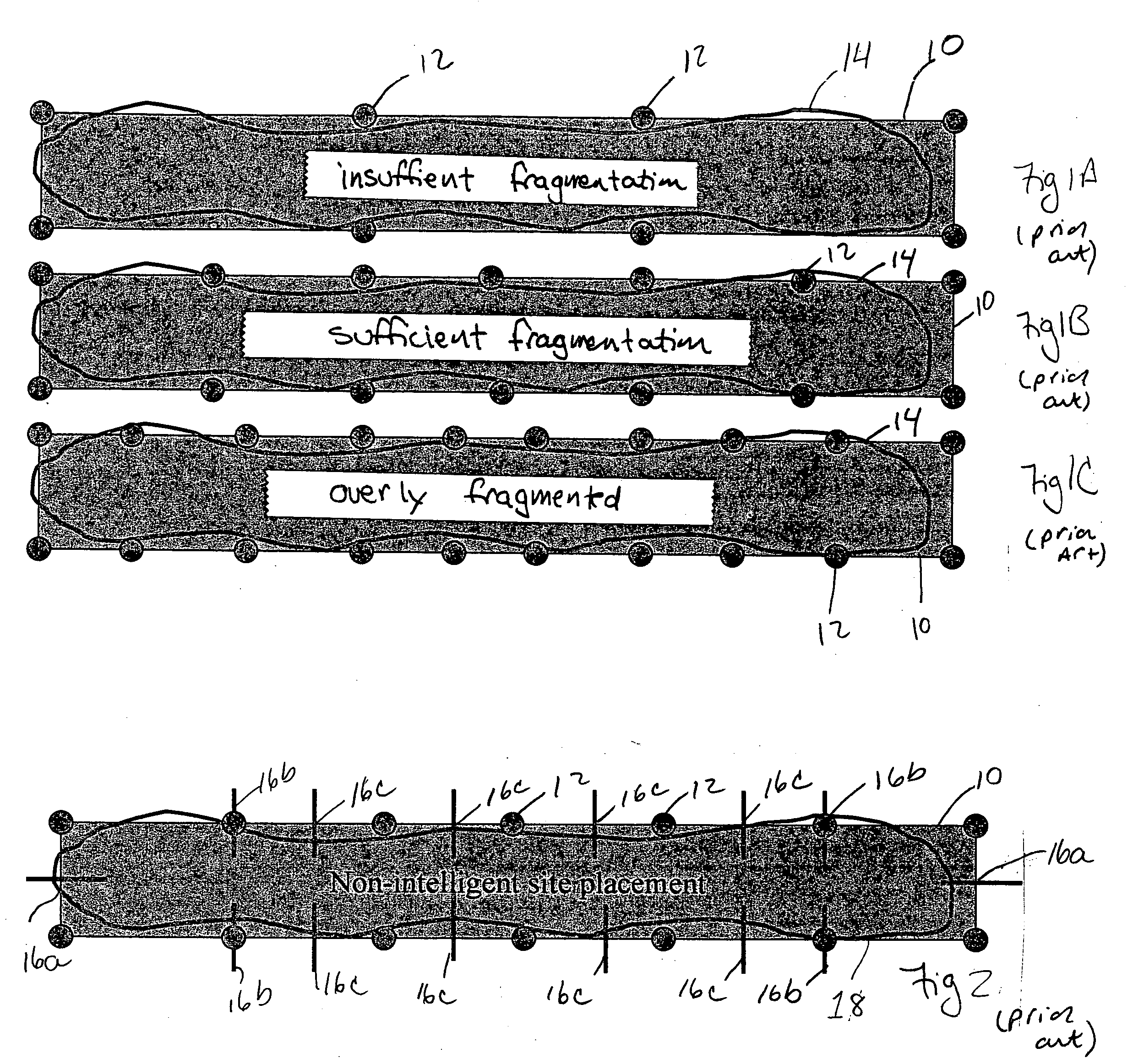
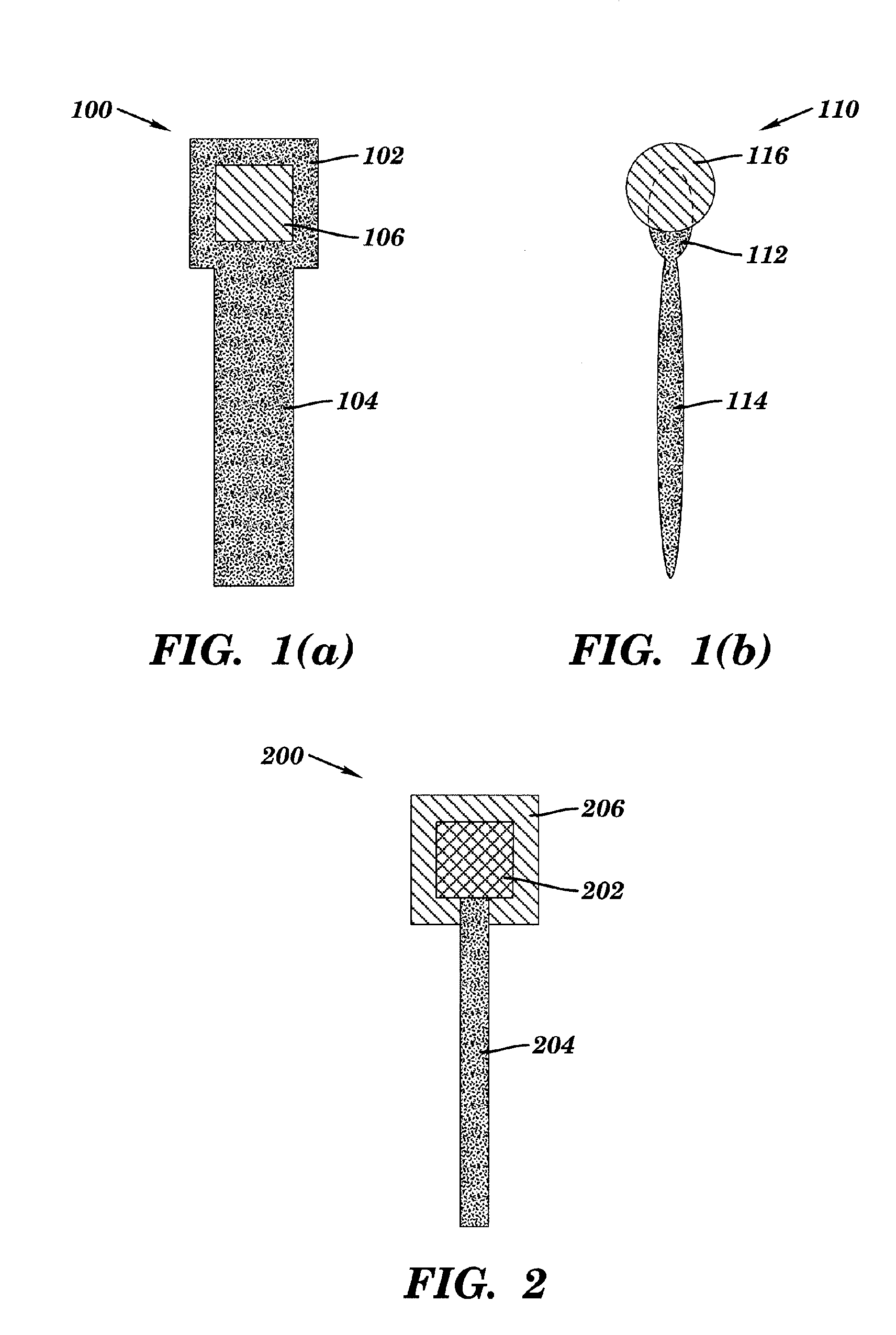
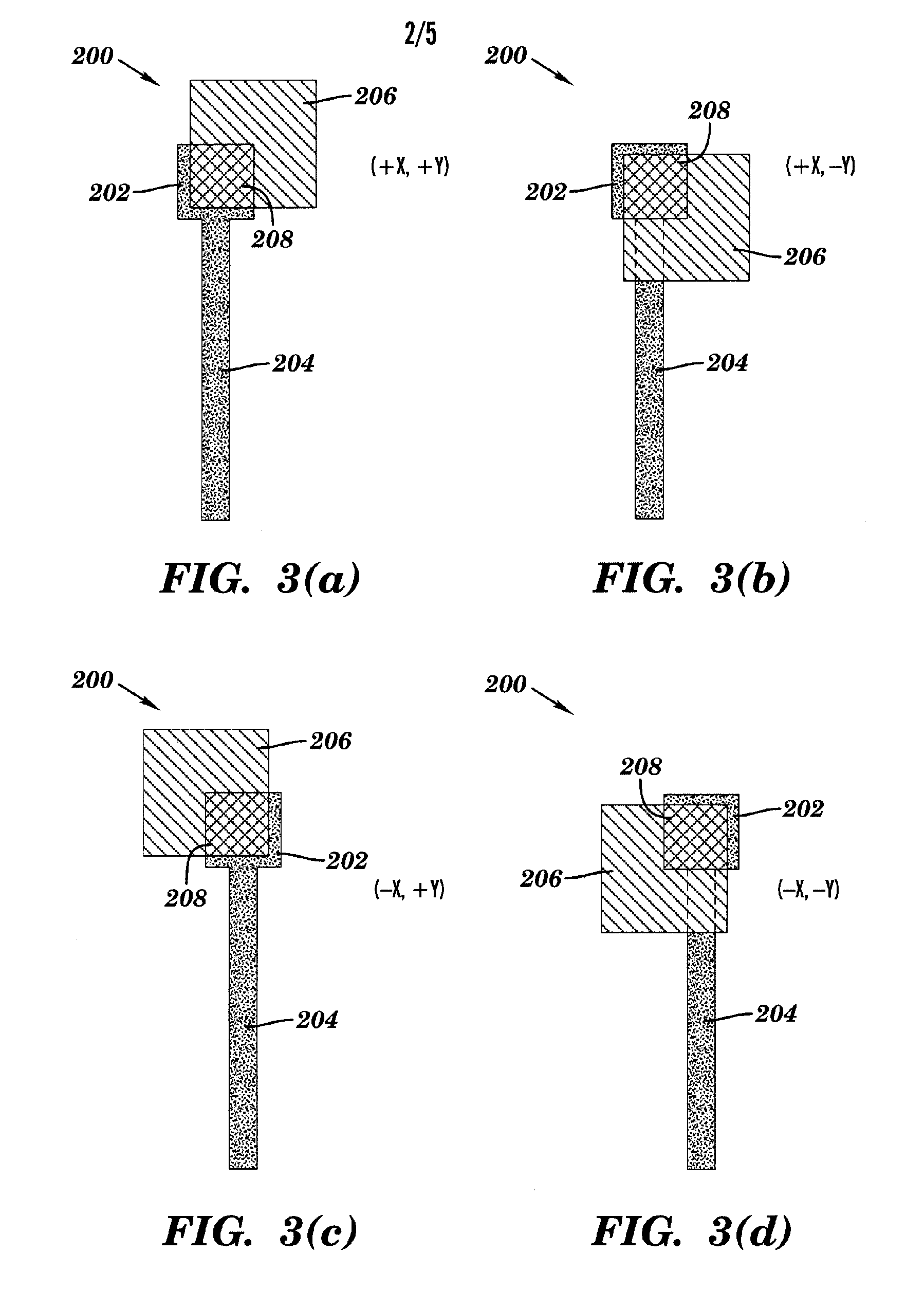
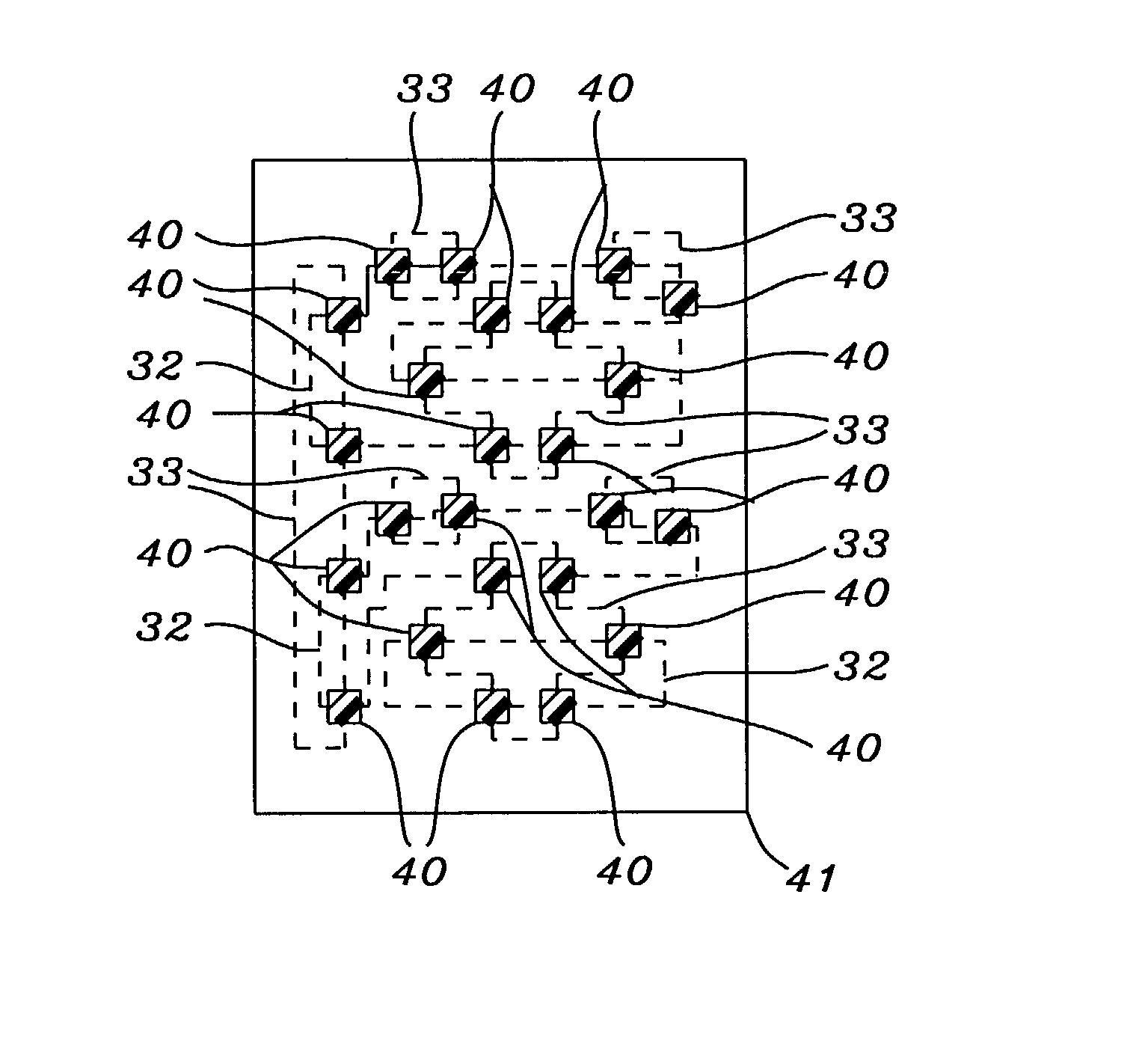
A tool for optimizing the layout of a microdevice adds fragmentation points to polygons in a first hierarchical database layer in a manner suitable for application of a tool to apply a resolution enhancement technique (RET) such as optical and process correction (OPC). Portions of polygons in a database level that interact with polygons of a second level in the database are promoted to the second database level, and refragmented. The RET operates on the polygons of the first and second levels of the database to determine how polygons of each of the first and second levels should be adjusted, if necessary, such that the layout is optimized.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Method and apparatus for integrated circuit layout optimization
InactiveUS20070101303A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designResolution enhancement technologiesLithographic artist
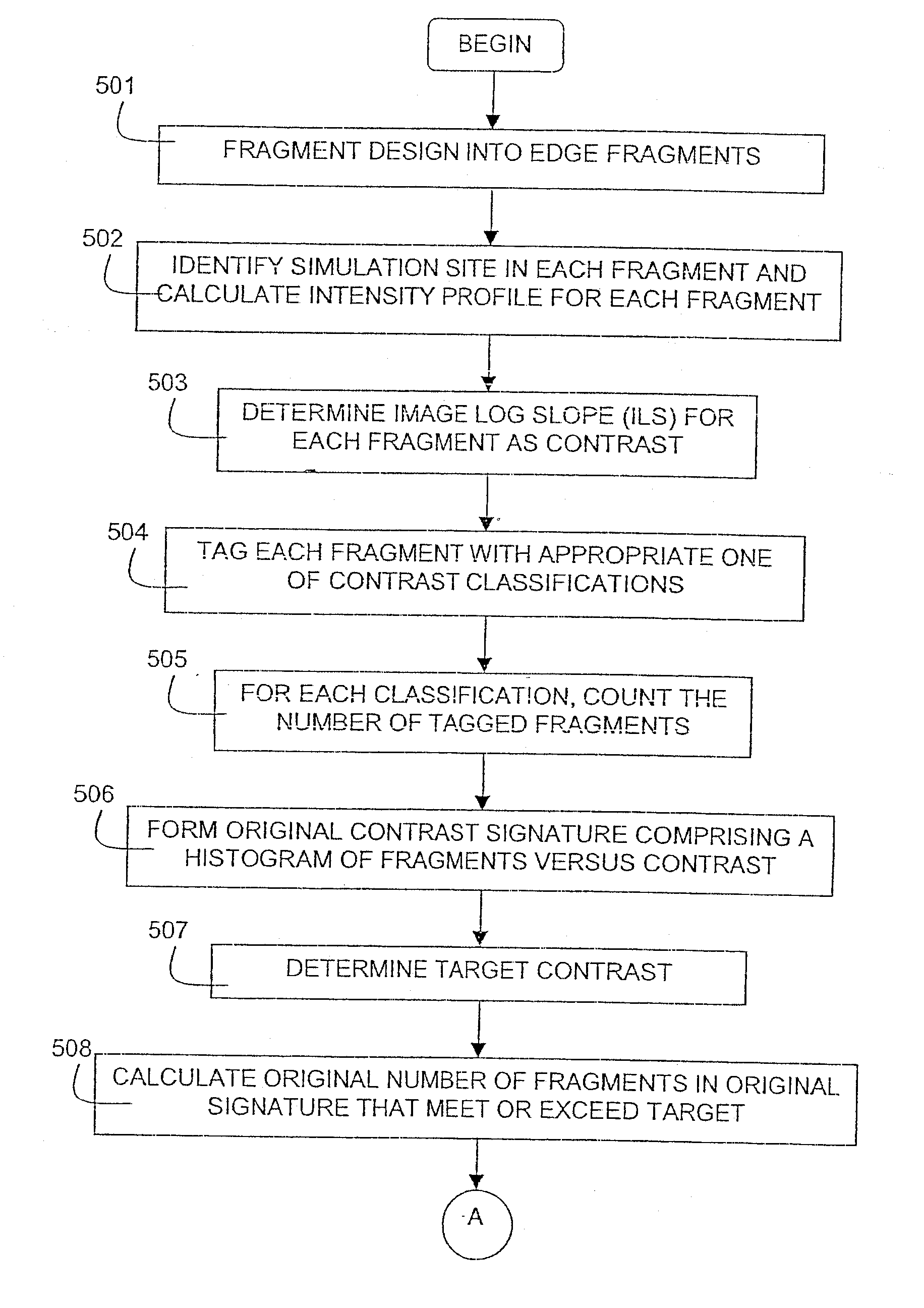
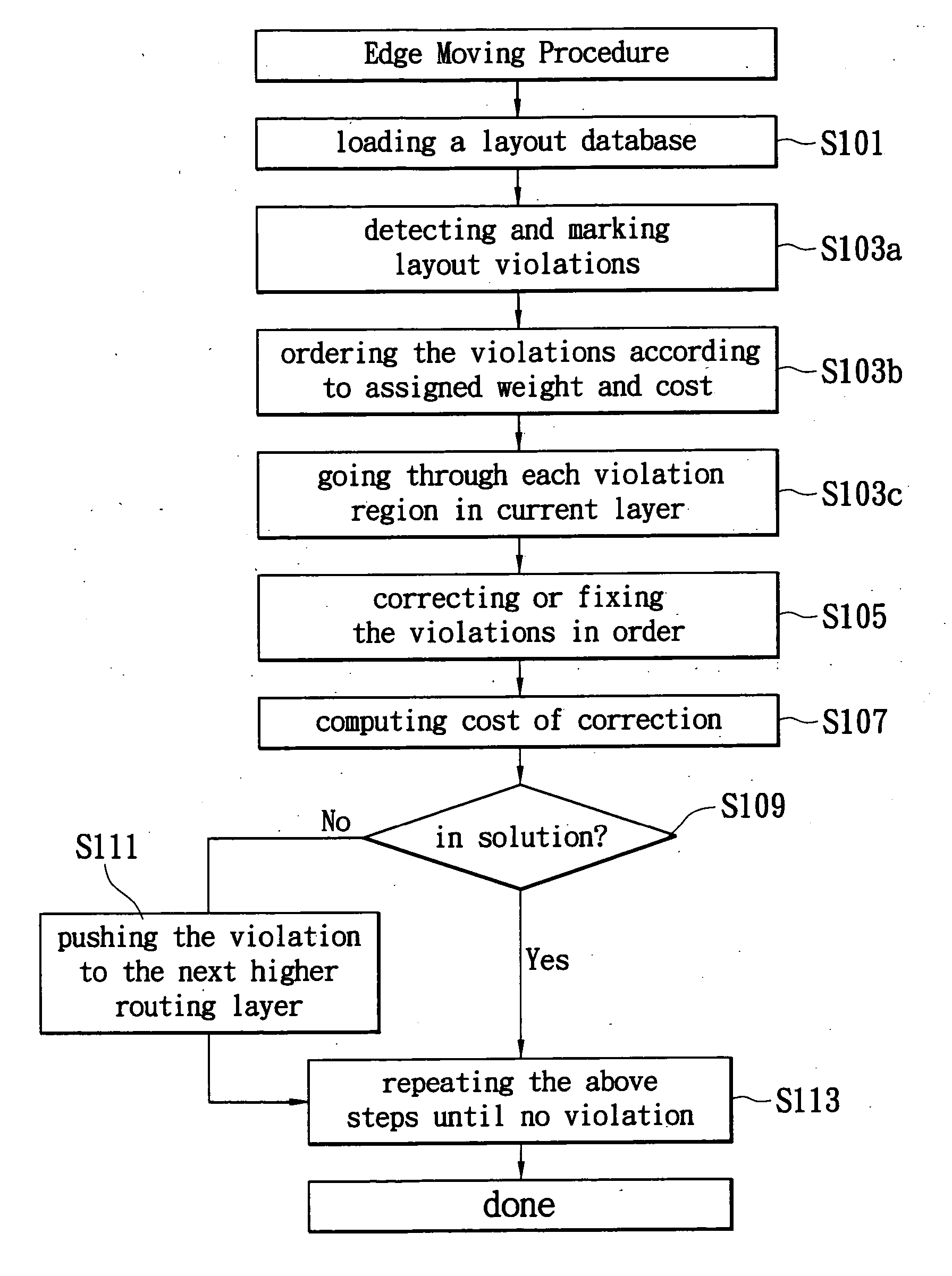
A method and apparatus for integrated circuit layout optimization are provided. In the conventional art, the major challenges in building integrated circuits (IC) at sub-wavelength geometries include i) to ensure the design intent is faithfully transferred onto silicon; ii) to ensure the design is manufacturable, or with acceptable yield subject to process variations. The present invention provides the method to process a layout database to optimize or correct or fix layout violations or enhancements. The layout violations are identified through various means such as design rules, recommended rules, timing / signal integrity / power constraints, lithography rules, Resolution Enhancement Technologies (RET) requirements and preferences, and process and manufacturing constraints. Particularly, the method, techniques and procedures of creating software tools of the present invention used to perform the layout violations or enhancements are disclosed.
Owner:LIZOTECH
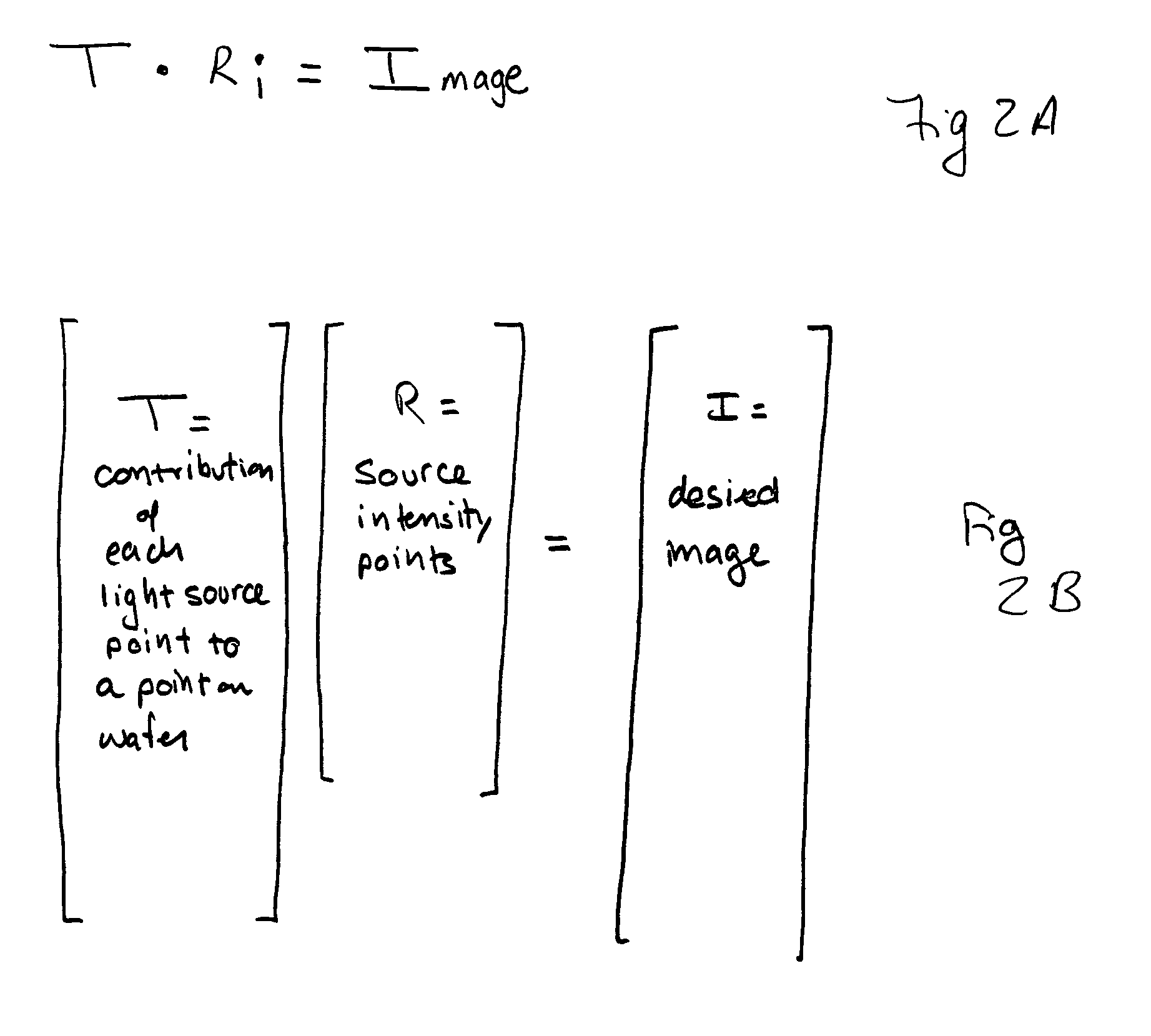
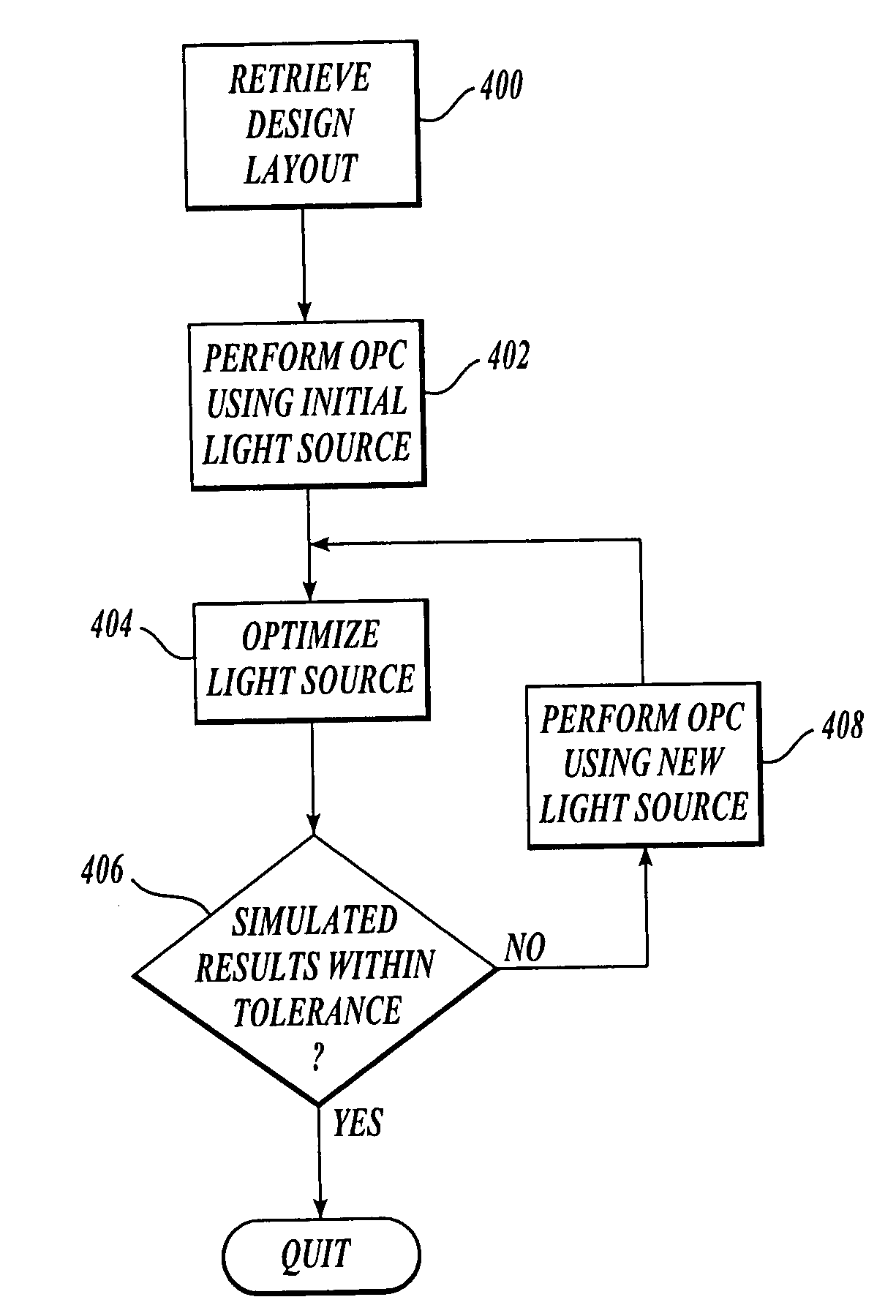
Source optimization for image fidelity and throughput
ActiveUS20050168498A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCathode-ray tube indicatorsResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
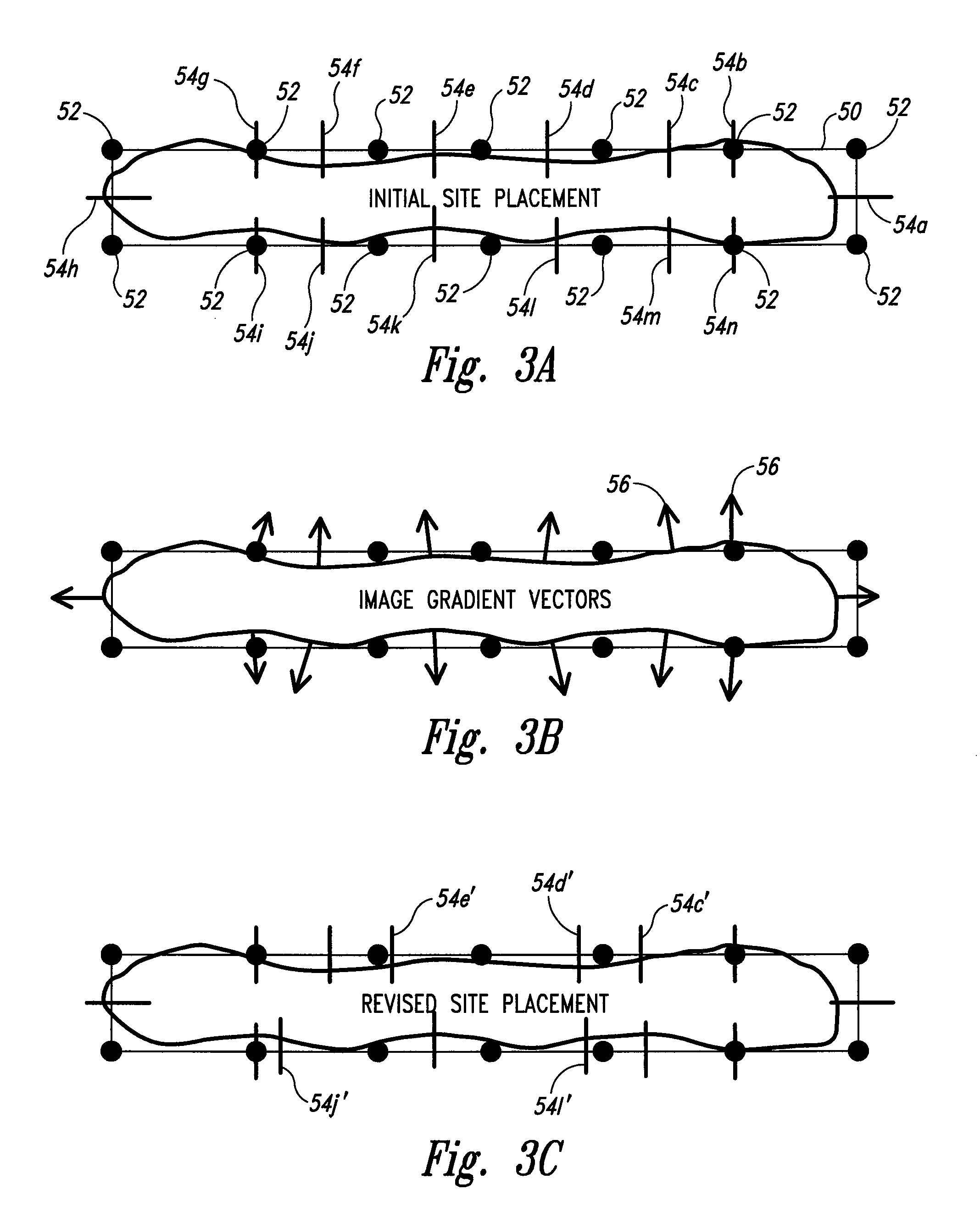
Fragmentation point and simulation site adjustment for resolution enhancement techniques
ActiveUS20050278686A1Electrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisDesign optimisation/simulationResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
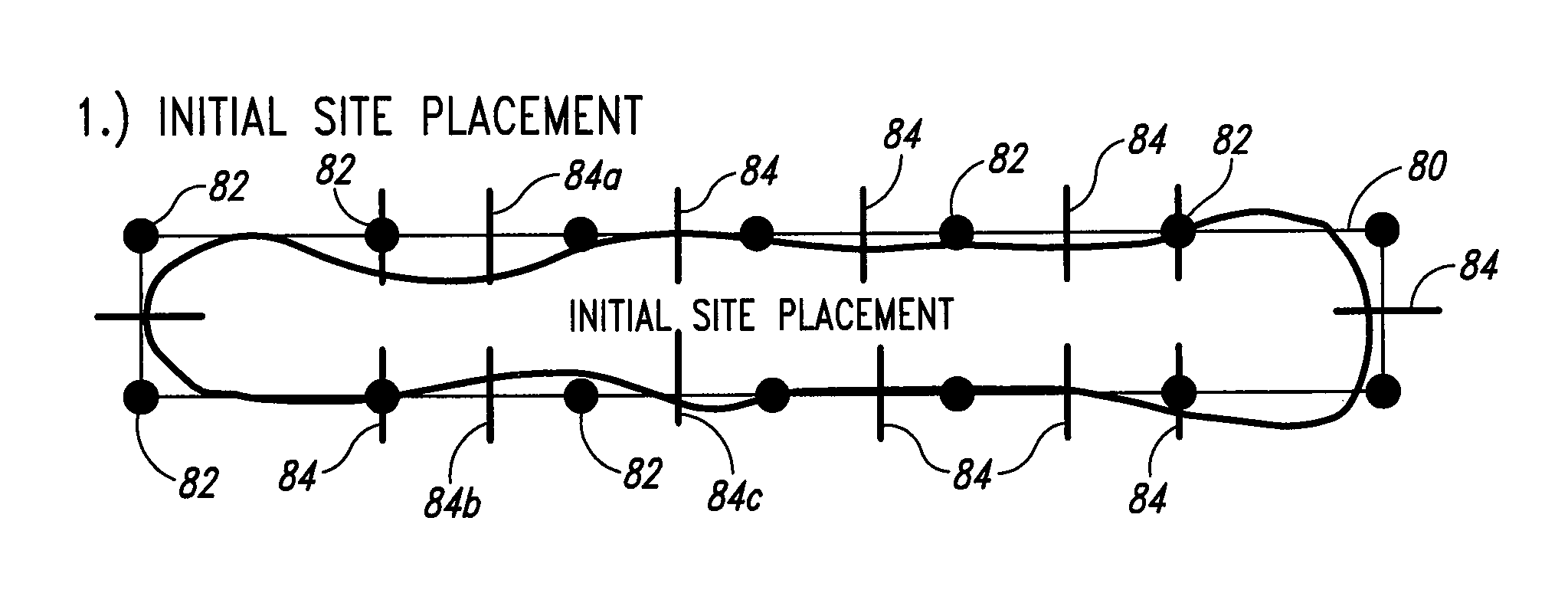
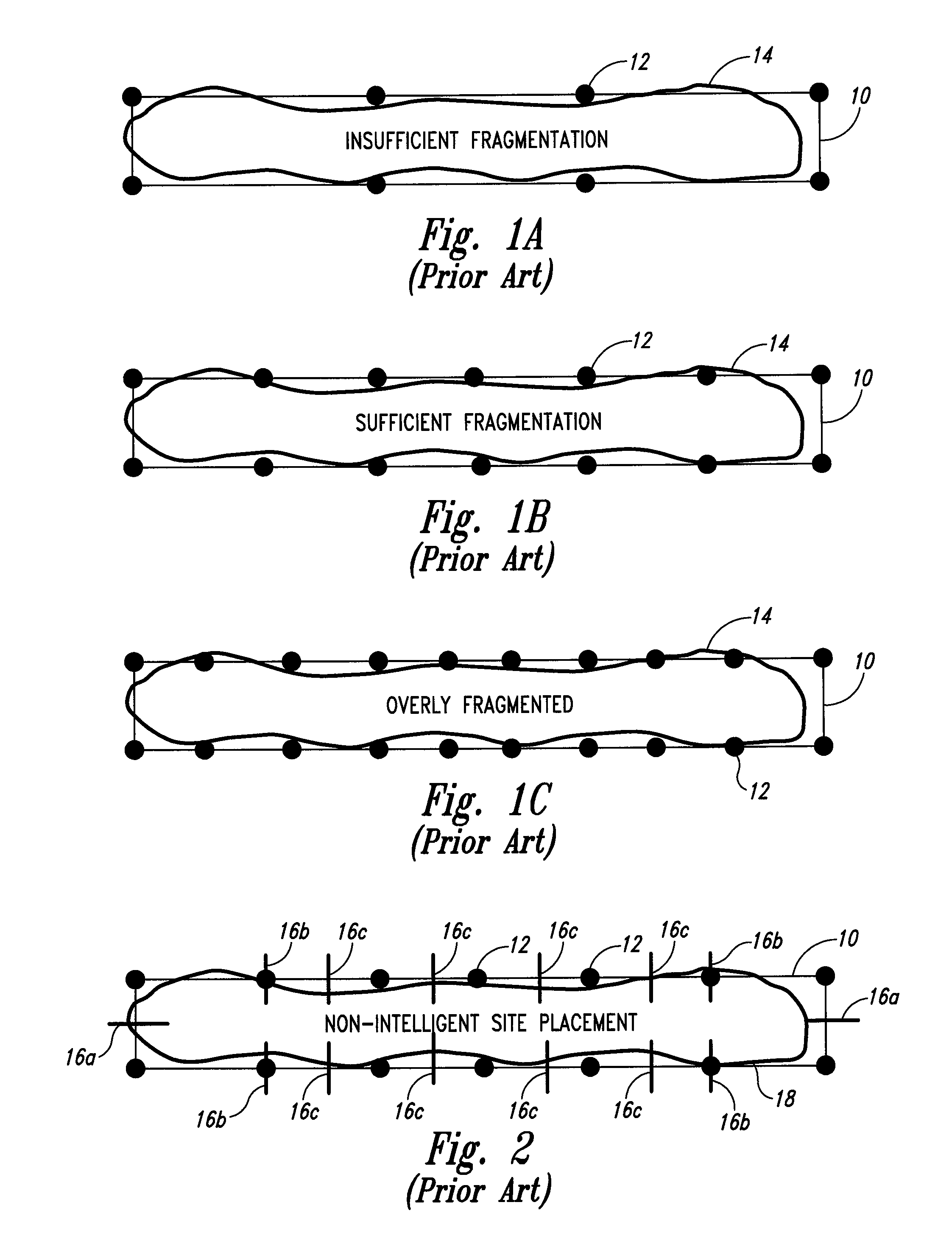
A method of performing a resolution enhancement technique such as OPC on an initial layout description involves fragmenting a polygon that represents a feature to be created into a number of edge fragments. One or more of the edge fragments is assigned an initial simulation site at which the image intensity is calculated. Upon calculation of the image intensity, the position and / or number of initial simulation sites is varied. New calculations are made of the image intensity with the revised placement or number of simulation sites in order to calculate an OPC correction for the edge fragment. In other embodiments, fragmentation of a polygon is adjusted based on the image intensities calculated at the simulation sites. In one embodiment, the image intensity gradient vector calculated at the initial simulation sites is used to adjust the simulation sites and / or fragmentation of the polygon.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Resolution enhancing technology using phase assignment bridges
InactiveUS20060240342A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
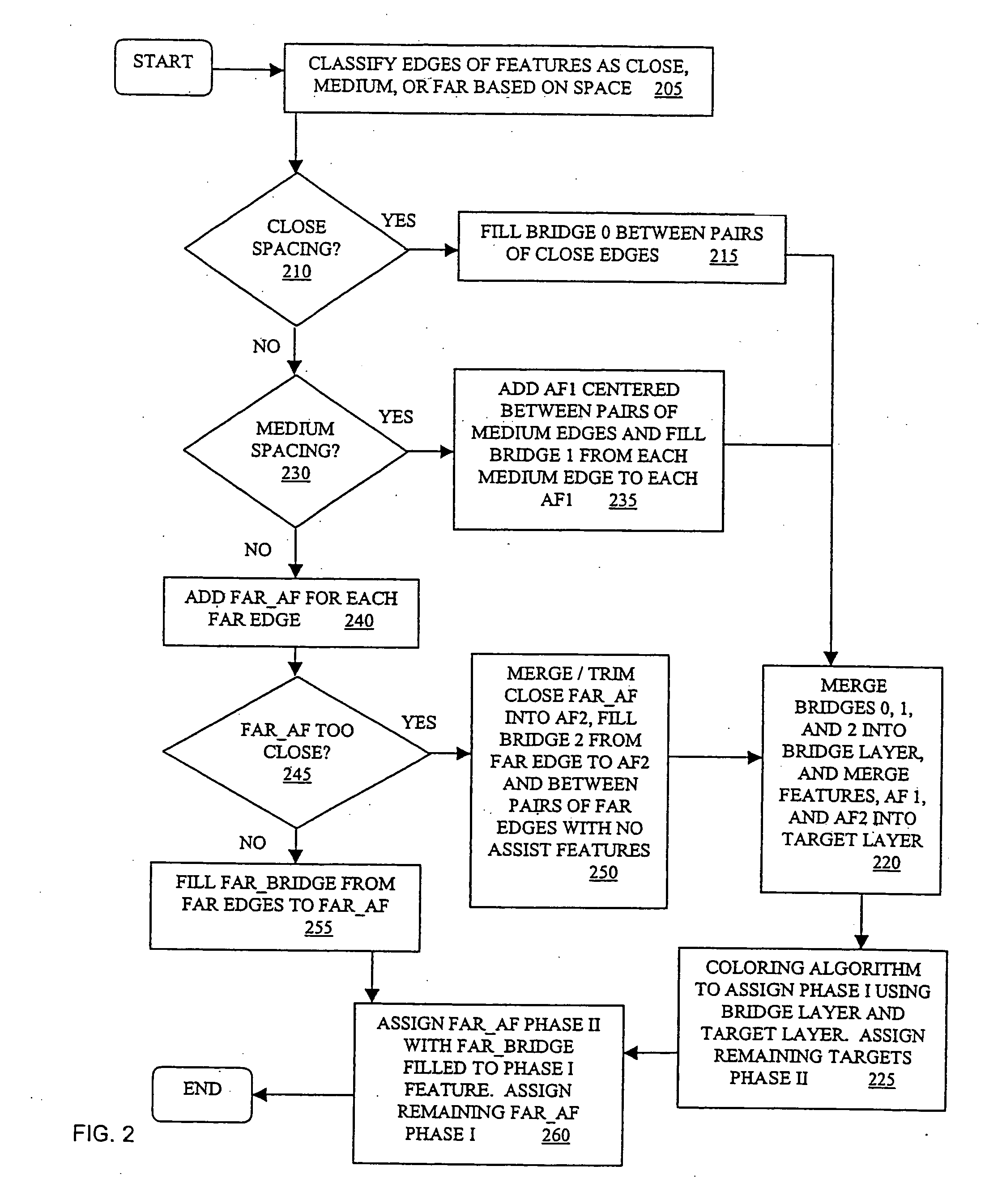
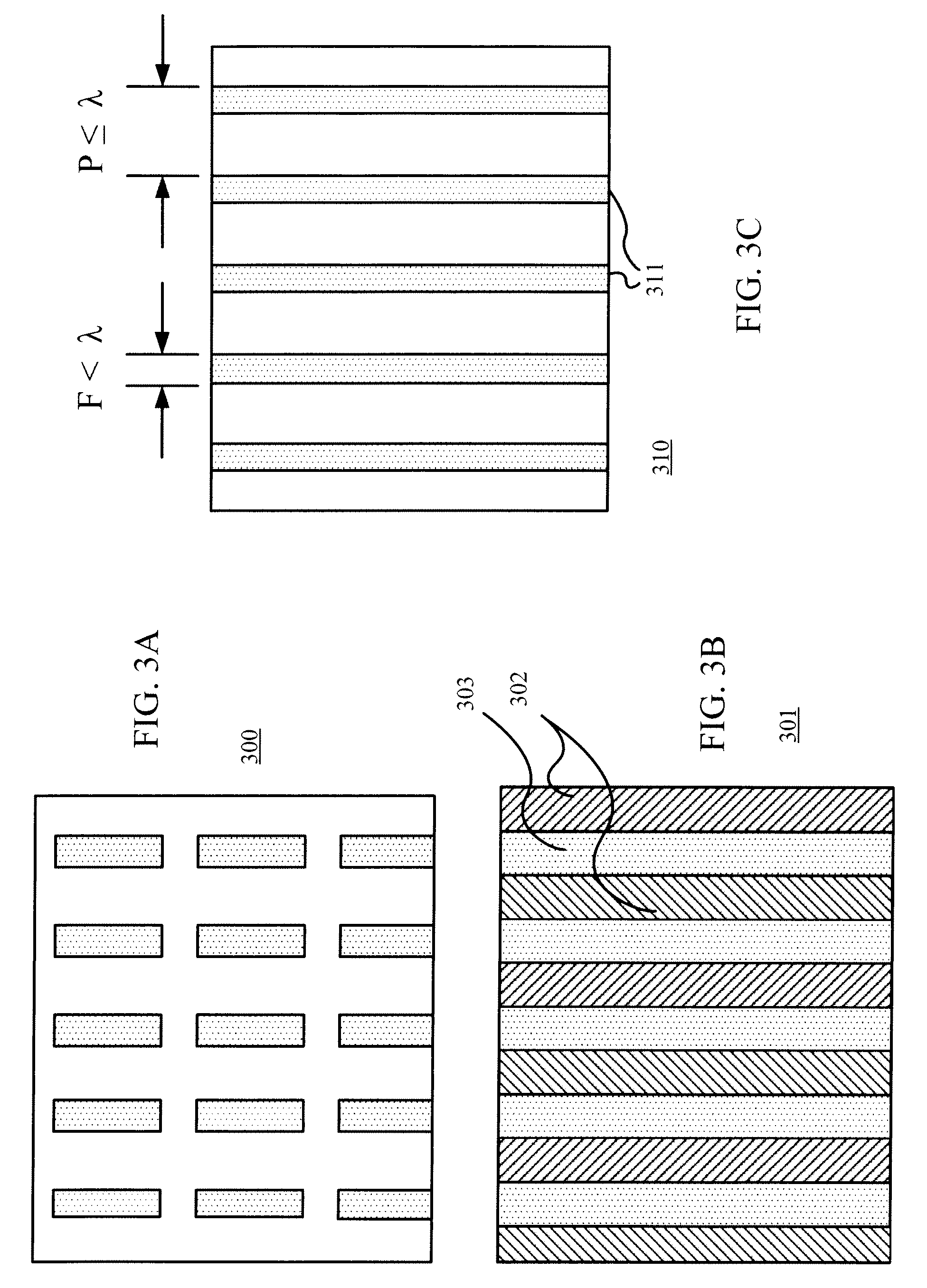
In one embodiment, a spacing is determined for each edge of a number of features in a photolithographic design. The edges have at least a partially predictable layout. Based on the spacing and the predictable layout, a bridge structure is generated. Each bridge of the bridge structure connects one of the edges to an edge of a neighboring feature. Then, the features and the bridge structure are provided for a phase assignment. The phase assignment assigns features at opposite ends of each bridge in the bridge structure to opposite phases. In another embodiment, a sub-resolution assist feature (SRAF) is introduced for an edge of a feature and a bridge is generated from the feature to the SRAF. Then, the feature and the SRAF are assigned to opposite phases based on the relationship defined by the bridge.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Contrast based resolution enhancement for photolithographic processing
InactiveUS7293249B2Improve manufacturabilityIncrease contrastAnalogue computers for electric apparatusCharacter and pattern recognitionResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
A contrast-based resolution enhancing technology (RET) determines a distribution of contrast values for edge fragments in a design layout or portion thereof. Resolution enhancement is applied to the edge fragments in a way that increases the number of edge fragments having a contrast value that exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
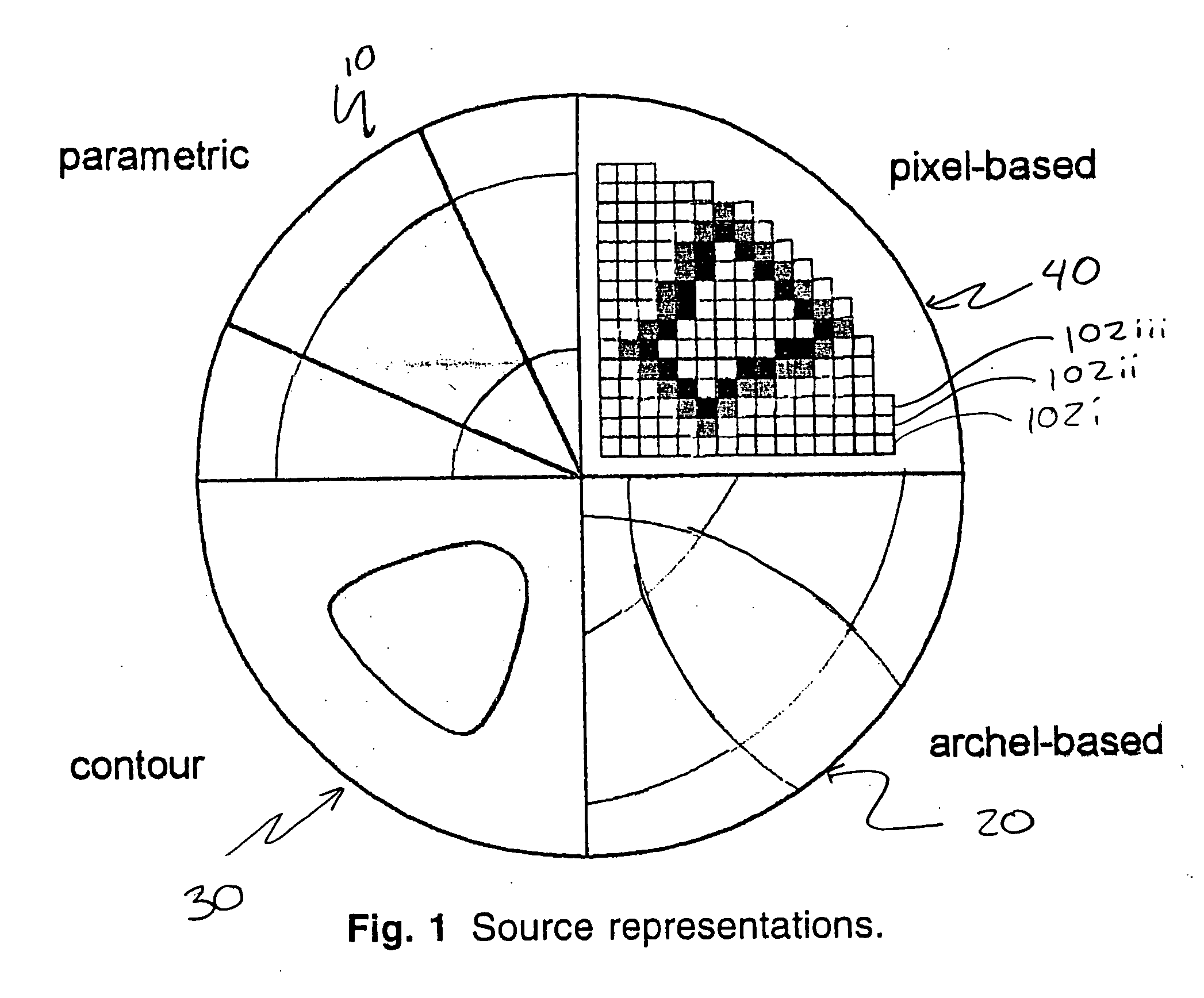
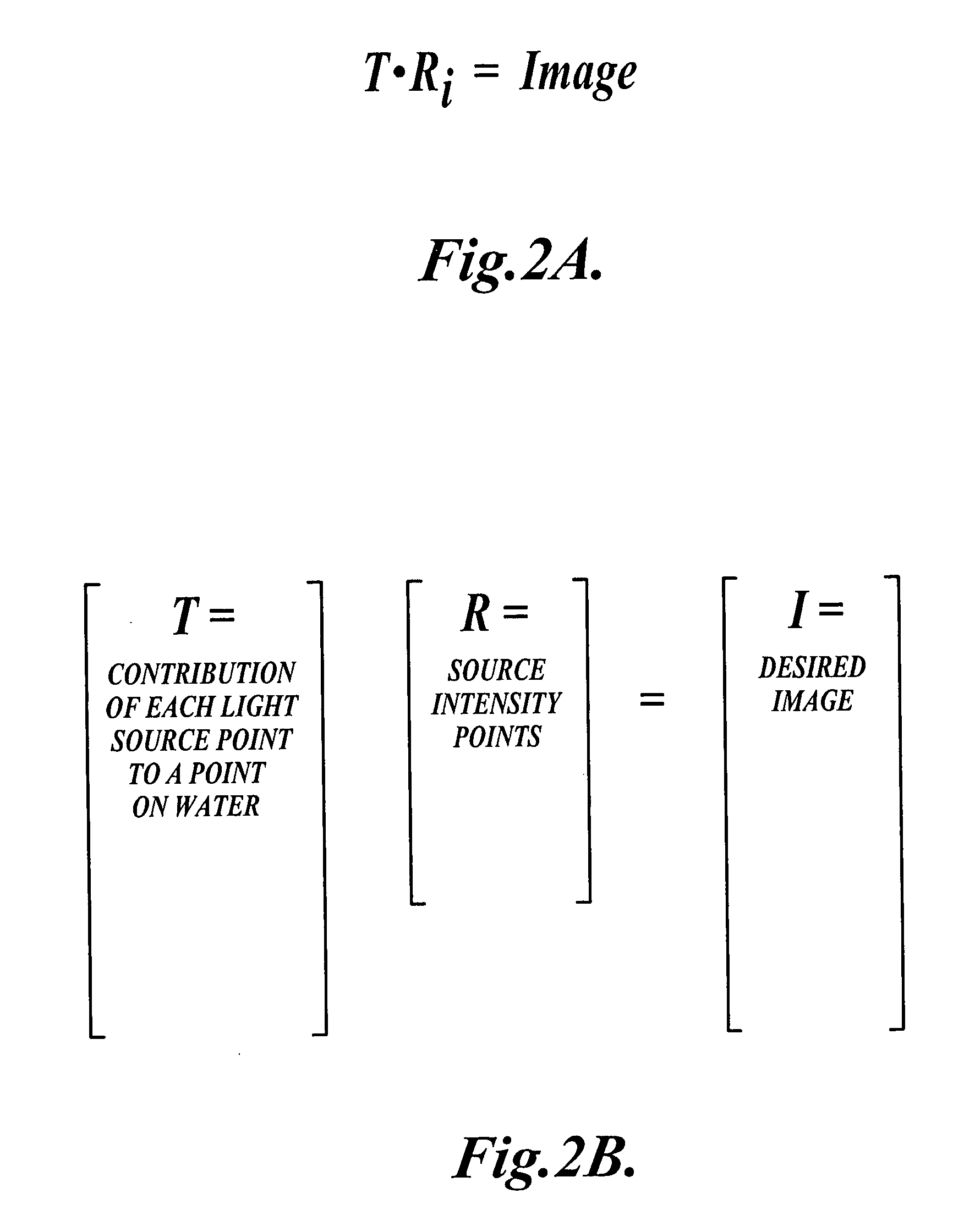
Calculation system for inverse masks
ActiveUS20060269875A1Improve fidelityAvoid makingPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
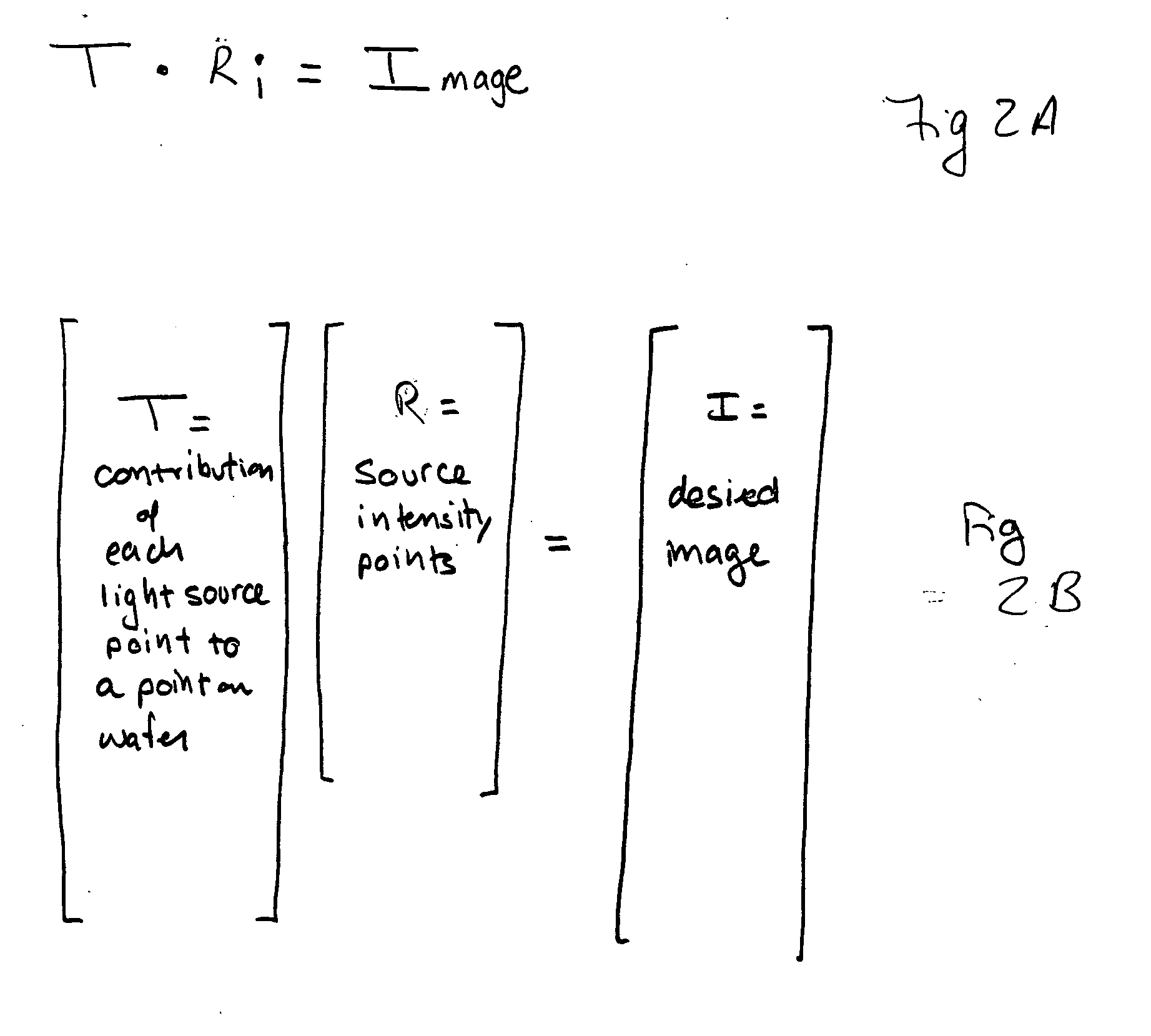
A system for calculating mask data to create a desired layout pattern on a wafer reads all or a portion of a desired layout pattern. Mask data having pixels with transmission characteristics is defined along with corresponding optimal mask data pixel transmission characteristics. An objective function is defined having one or more penalty functions that promote solutions representing a desired resolution enhancement technique. Optimization of the objective function determines the transmission characteristics of the pixels in the mask data that is used to create one or more corresponding masks or reticles.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Contrast based resolution enhancement for photolithographic processing
InactiveUS20050044513A1Improve manufacturabilityIncrease contrast of edgeAnalogue computers for electric apparatusCharacter and pattern recognitionResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
A contrast-based resolution enhancing technology (RET) determines a distribution of contrast values for edge fragments in a design layout or portion thereof. Resolution enhancement is applied to the edge fragments in a way that increases the number of edge fragments having a contrast value that exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
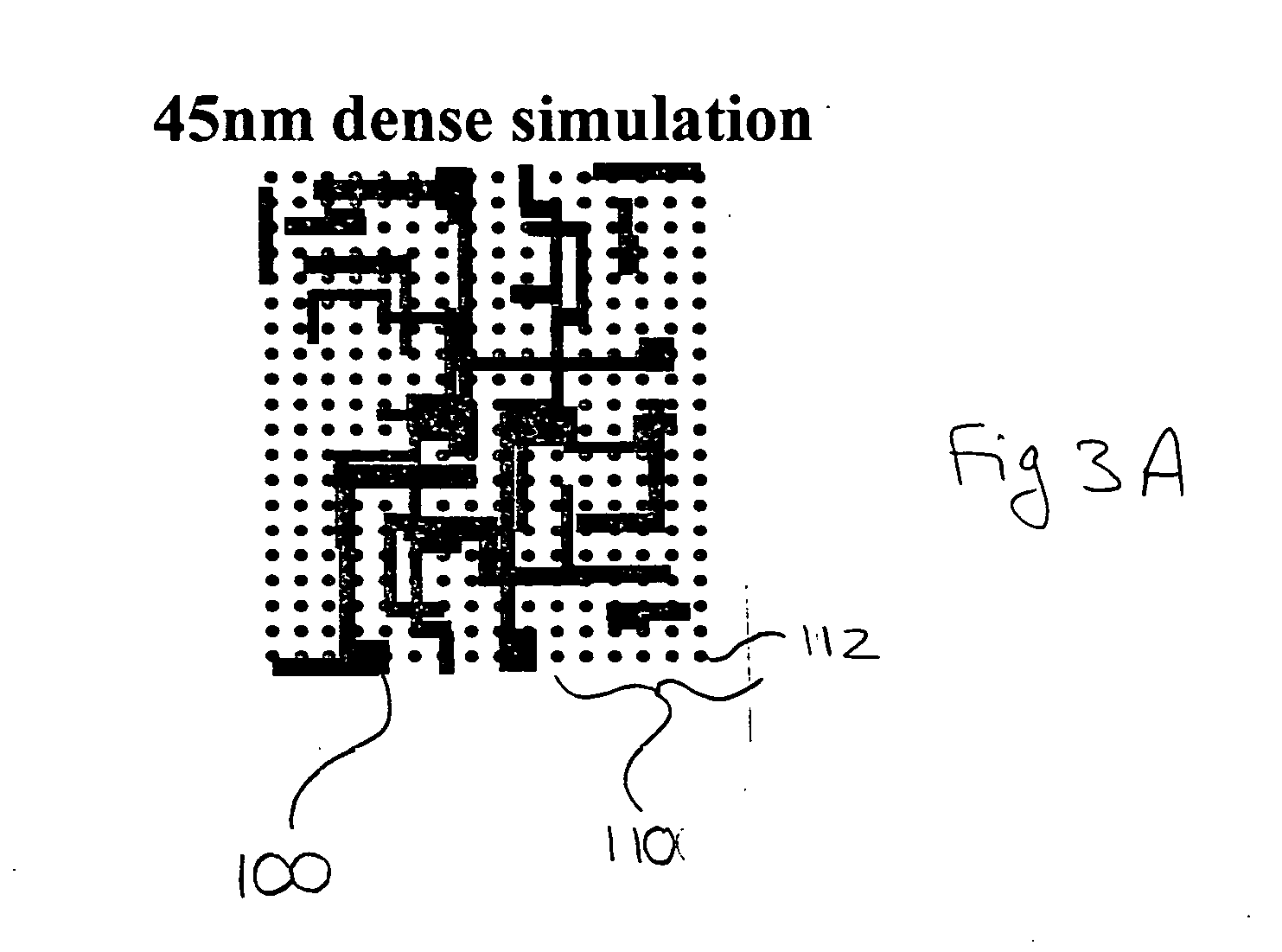
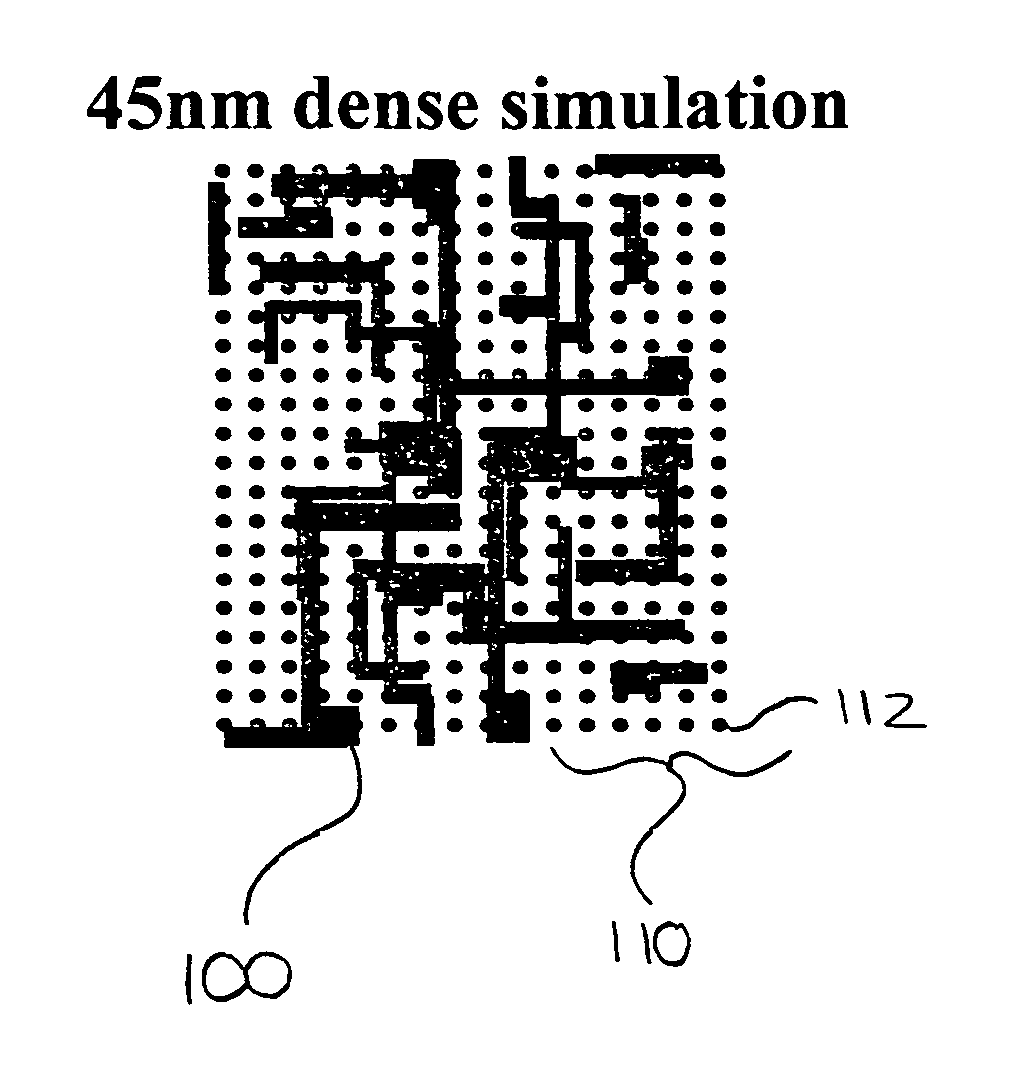
Dense OPC
ActiveUS20070074143A1Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResolution enhancement technologiesAlgorithm
A method of calculating process conditions for performing optical and process correction (OPC) or other resolution enhancement techniques on a layout design. Process conditions are estimated on a layout database on a substantially uniform grid. Contour curves are created from the estimated process conditions. The contour curves are then compared against the features in the layout to determine edge placement errors. From the edge placement errors, OPC or other corrections for the features can be made.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Resolution enhancing technology using phase assignment bridges
InactiveUS20050149901A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
In one embodiment, a spacing is determined for each edge of a number of features in a photolithographic design. The edges have at least a partially predictable layout. Based on the spacing and the predictable layout, a bridge structure is generated. Each bridge of the bridge structure connects one of the edges to an edge of a neighboring feature. Then, the features and the bridge structure are provided for a phase assignment. The phase assignment assigns features at opposite ends of each bridge in the bridge structure to opposite phases. In another embodiment, a sub-resolution assist feature (SRAF) is introduced for an edge of a feature and a bridge is generated from the feature to the SRAF. Then, the feature and the SRAF are assigned to opposite phases based on the relationship defined by the bridge.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Performing OPC on structures with virtual edges
ActiveUS20060188796A1Improve fidelityImprove positionOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPhotographic processesResolution enhancement technologiesEdge segment
A method for compensating for optical distortions occurring in regions associated with non-phase-shifting regions in a mask or reticle. OPC or other resolution enhancement techniques are performed on one or more edge segments associated with adjacent phase-shifting regions in order to compensate for edge position errors occurring in areas corresponding to non-phase-shifting regions.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Source optimization for image fidelity and throughput
ActiveUS7245354B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCathode-ray tube indicatorsResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
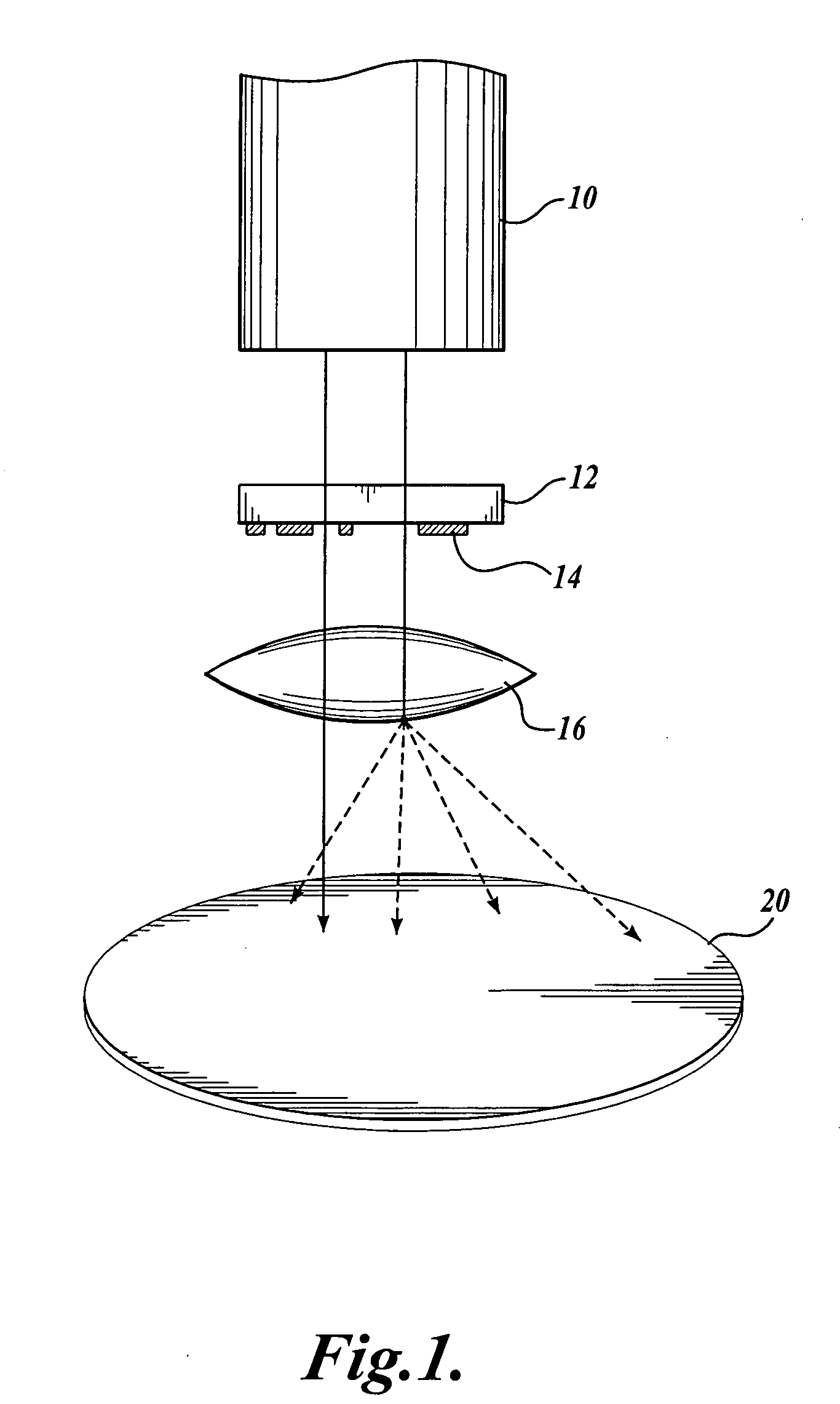
A system and method for optimizing an illumination source to print a desired pattern of features dividing a light source into pixels and determining an optimum intensity for each pixel such that when the pixels are simultaneously illuminated, the error in a printed pattern of features is minimized. In one embodiment, pixel solutions are constrained from solutions that are bright, continuous, and smooth. In another embodiment, the light source optimization and resolution enhancement technique(s) are iteratively performed to minimize errors in a printed pattern of features.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Calculation system for inverse masks
ActiveUS7487489B2Improve fidelityPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
A system for calculating mask data to create a desired layout pattern on a wafer reads all or a portion of a desired layout pattern. Mask data having pixels with transmission characteristics is defined along with corresponding optimal mask data pixel transmission characteristics. An objective function is defined having one or more penalty functions that promote solutions representing a desired resolution enhancement technique. Optimization of the objective function determines the transmission characteristics of the pixels in the mask data that is used to create one or more corresponding masks or reticles.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
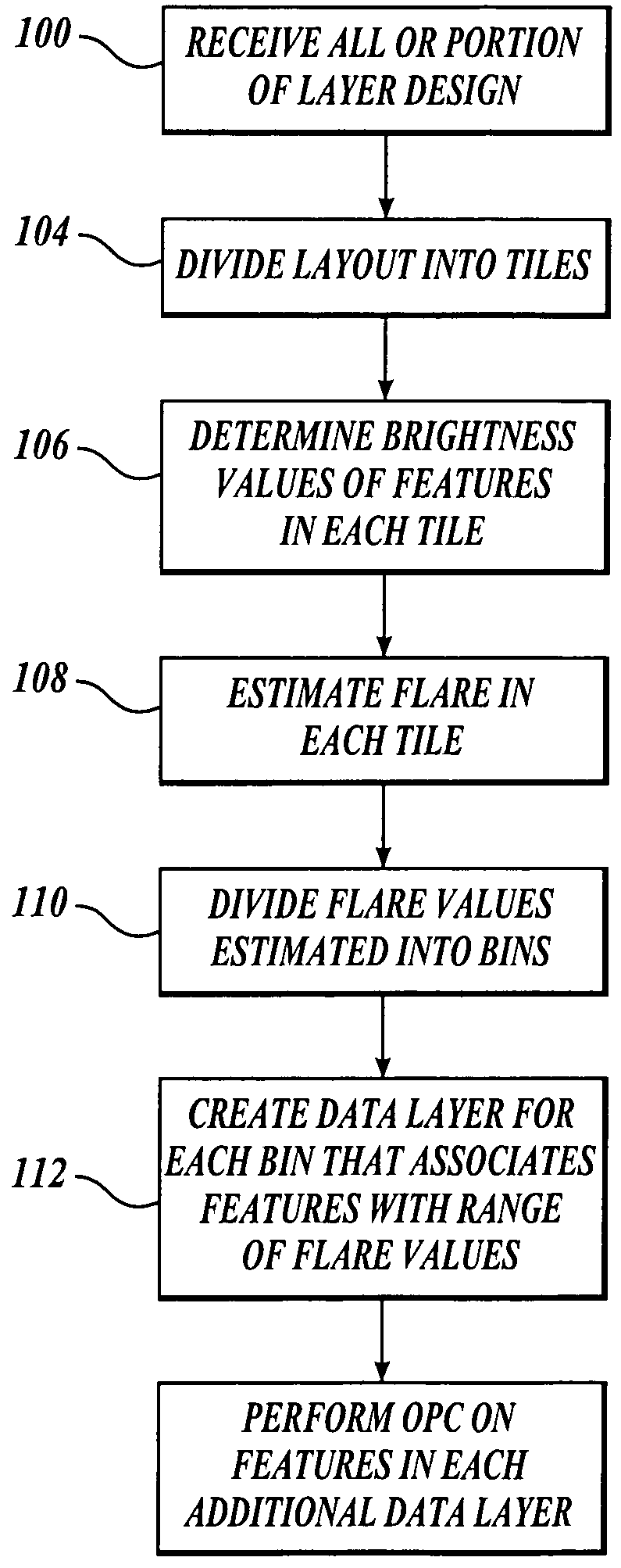
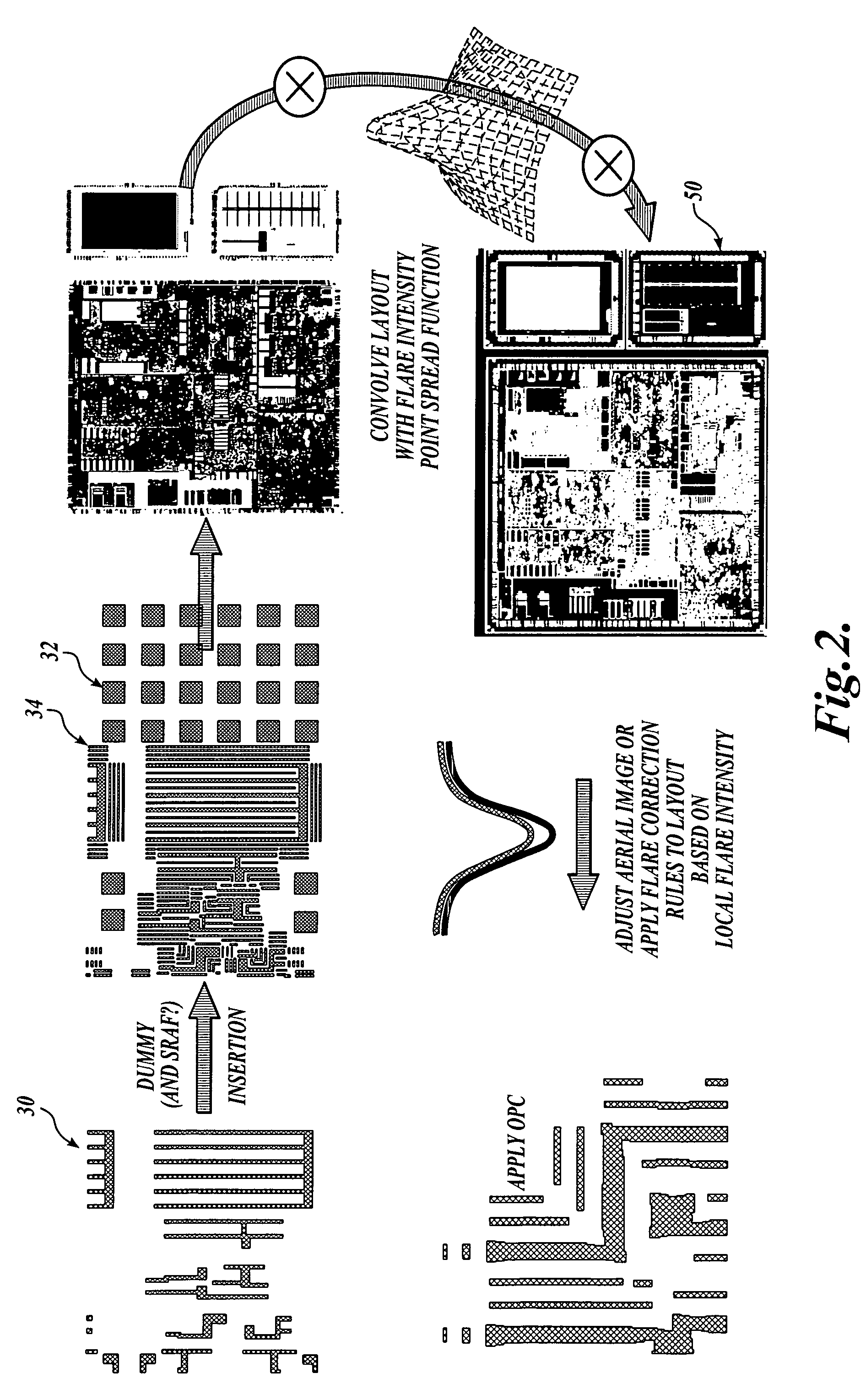
Long range corrections in integrated circuit layout designs
ActiveUS7234130B2CAD circuit designOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
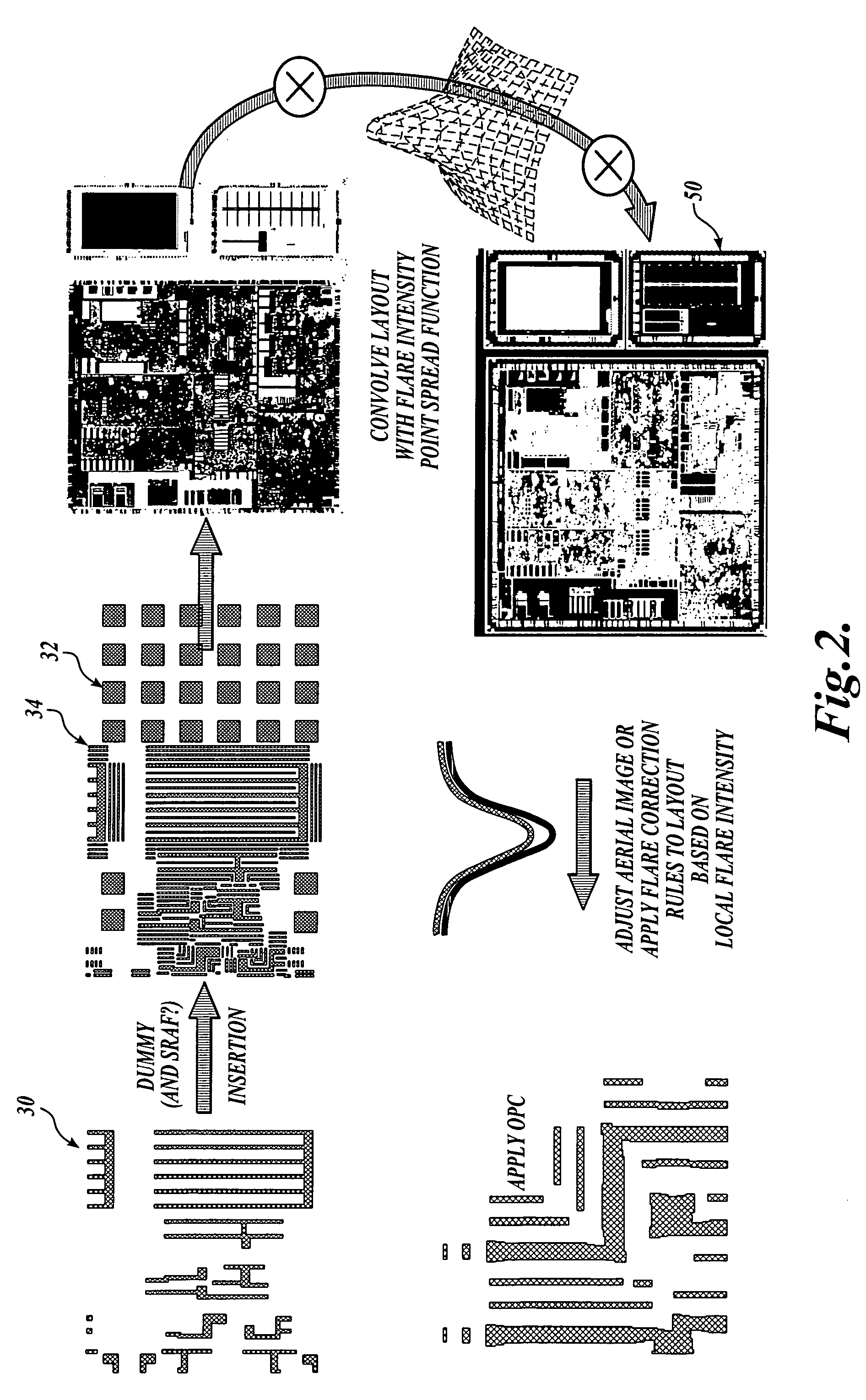
A method and apparatus for compensating for flare intensity variations across an integrated circuit. A layout description for a physical layer of an integrated circuit or portion thereof is divided into a number of regions such as adjacent tiles. An estimate of the flare intensity in each region is determined. The flare intensity values calculated are divided into a number of ranges. In one embodiment, a data layer in a layout description is defined for each range of flare values computed. Features to be printed in an area having a flare value in a particular range are associated with a corresponding additional data layer. The features associated with each additional data layer are analyzed with a resolution enhancement technique that is selected or adjusted to compensate for differing flare values occurring in the integrated circuit.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Source optimization for image fidelity and throughput
ActiveUS20080174756A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
A system and method for optimizing an illumination source to print a desired pattern of features dividing a light source into pixels and determining an optimum intensity for each pixel such that when the pixels are simultaneously illuminated, the error in a printed pattern of features is minimized. In one embodiment, pixel solutions are constrained from solutions that are bright, continuous, and smooth. In another embodiment, the light source optimization and resolution enhancement technique(s) are iteratively performed to minimize errors in a printed pattern of features.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Method for verification of resolution enhancement techniques and optical proximity correction in lithography
InactiveUS6996797B1Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designResolution enhancement technologiesLithographic artist
A method for model-based verification of resolution enhancement techniques (RET) and optical proximity correction (OPC) in lithography includes scaling shapes of a drawn mask layout to their corresponding intended wafer dimensions so as to create a scaled image. A first feature of the scaled image is shifted with respect to a second feature thereof in accordance with a predetermined maximum overlay error. An intersection parameter of the first and said second features of the scaled image is calculated so as to determine a yield metric of an ideal layout. A first feature of a simulated wafer image is shifted with respect to a second feature thereof in accordance with the predetermined maximum overlay error. An intersection parameter of the first and said second features of the simulated wafer image is calculated so as to determine a yield metric of a simulated layout, and the yield metric of the simulated wafer image is compared to the yield metric of the scaled image.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fragmentation point and simulation site adjustment for resolution enhancement techniques
ActiveUS7861207B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Dense OPC
ActiveUS7434199B2Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResolution enhancement technologiesAlgorithm
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Patterning a single integrated circuit layer using multiple masks and multiple masking layers
ActiveUS7560201B2Low costEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
A multiple mask and a multiple masking layer technique can be used to pattern a single IC layer. A resolution enhancement technique can be used to define one or more fine-line patterns in a first masking layer, wherein each fine-line feature is sub-wavelength. Moreover, the pitch of each fine-line pattern is less than or equal to that wavelength. The portions of the fine-line features not needed to implement the circuit design are then removed or designated for removal using a mask. After patterning of the first masking layer, another mask can then be used to define coarse features in a second masking layer formed over the patterned first masking layer. At least one coarse feature is defined to connect two fine-line features, wherein the coarse feature(s) can be derived from a desired layout using a shrink / grow operation. The IC layer can be patterned using the composite mask formed by the patterned first and second masking layers.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Complementary replacement of material
InactiveUS7399709B1Increase contrastMinimized roughnessDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesResistResolution enhancement technologies
An image reversal method is described that removes the etch resistance requirement from a resist. A high resolution resist pattern comprised of islands, lines, or trenches is formed with a large process window by exposing through one or more masks including phase edge masks and optionally with resolution enhancement techniques. A complementary material replacement (CMR) layer comprised of an organic polymer or material such as fluorosilicate glass which has a lower etch rate than the resist is coated over the resist pattern. CMR and resist layers are etched simultaneously to provide an image reversed pattern in the CMR layer which is etch transferred into a substrate. The method avoids edge roughness like bird's beak defects in the etched pattern and is useful for applications including forming contact holes in dielectric layers, forming polysilicon gates, and forming trenches in a damascene process. It is also valuable for direct write methods where an image reversal scheme is desired.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Long range corrections in integrated circuit layout designs
ActiveUS20050216878A1CAD circuit designOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResolution enhancement technologiesImage resolution
A method and apparatus for compensating for flare intensity variations across an integrated circuit. A layout description for a physical layer of an integrated circuit or portion thereof is divided into a number of regions such as adjacent tiles. An estimate of the flare intensity in each region is determined. The flare intensity values calculated are divided into a number of ranges. In one embodiment, a data layer in a layout description is defined for each range of flare values computed. Features to be printed in an area having a flare value in a particular range are associated with a corresponding additional data layer. The features associated with each additional data layer are analyzed with a resolution enhancement technique that is selected or adjusted to compensate for differing flare values occurring in the integrated circuit.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Method for verification of resolution enhancement techniques and optical proximity correction in lithography
InactiveCN1776695AOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designPattern recognitionResolution enhancement technologies
A method for model-based verification of resolution enhancement techniques (RET) and optical proximity correction (OPC) in lithography, the method comprising: scaling the shape of a drawn mask layout to its corresponding intended wafer dimensions to generate a scaled image. The first feature thereof is offset relative to the second feature of the scale image according to a predetermined maximum overlay error. Intersection parameters of said first and said second features of said scale image are calculated to determine a yield measure of an ideal layout. The first feature thereof is offset relative to the second feature of the simulated wafer image according to the predetermined maximum overlay error. calculating an intersection parameter of said first and said second features of said simulated wafer image to determine a yield metric of a simulated layout, and comparing said yield metric of said simulated wafer image to said yield of said scaled image measure.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com