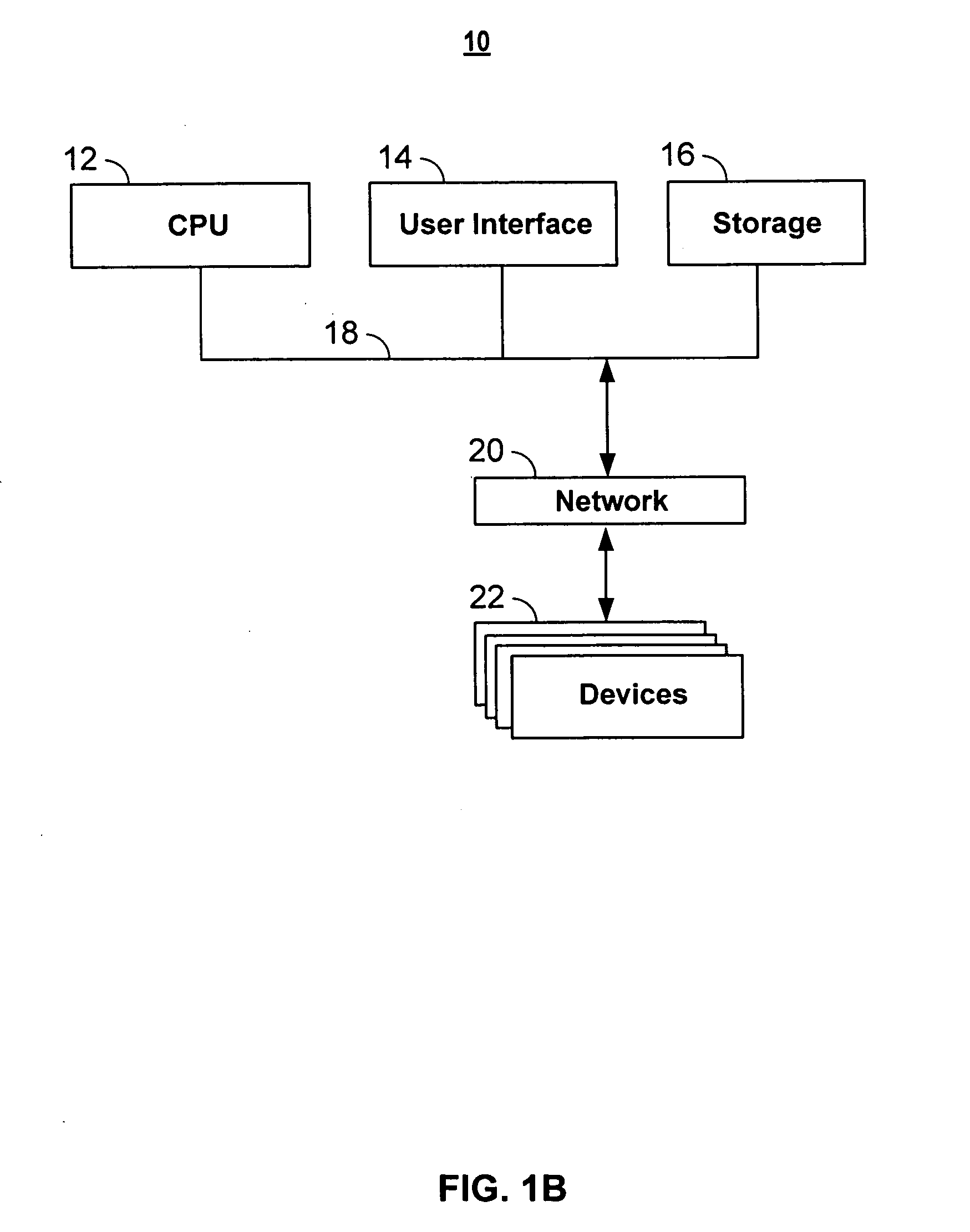
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
115 results about "Design intent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
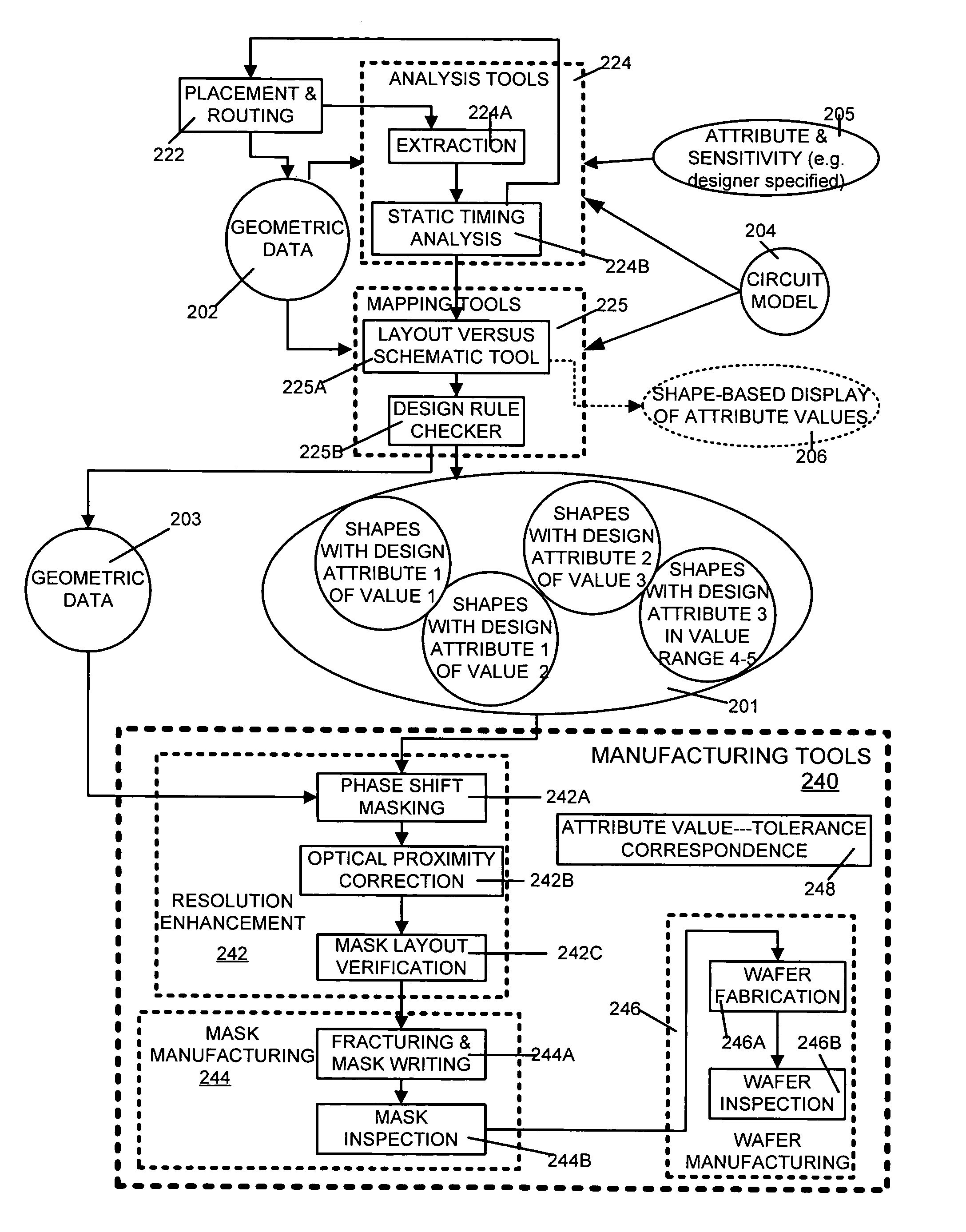
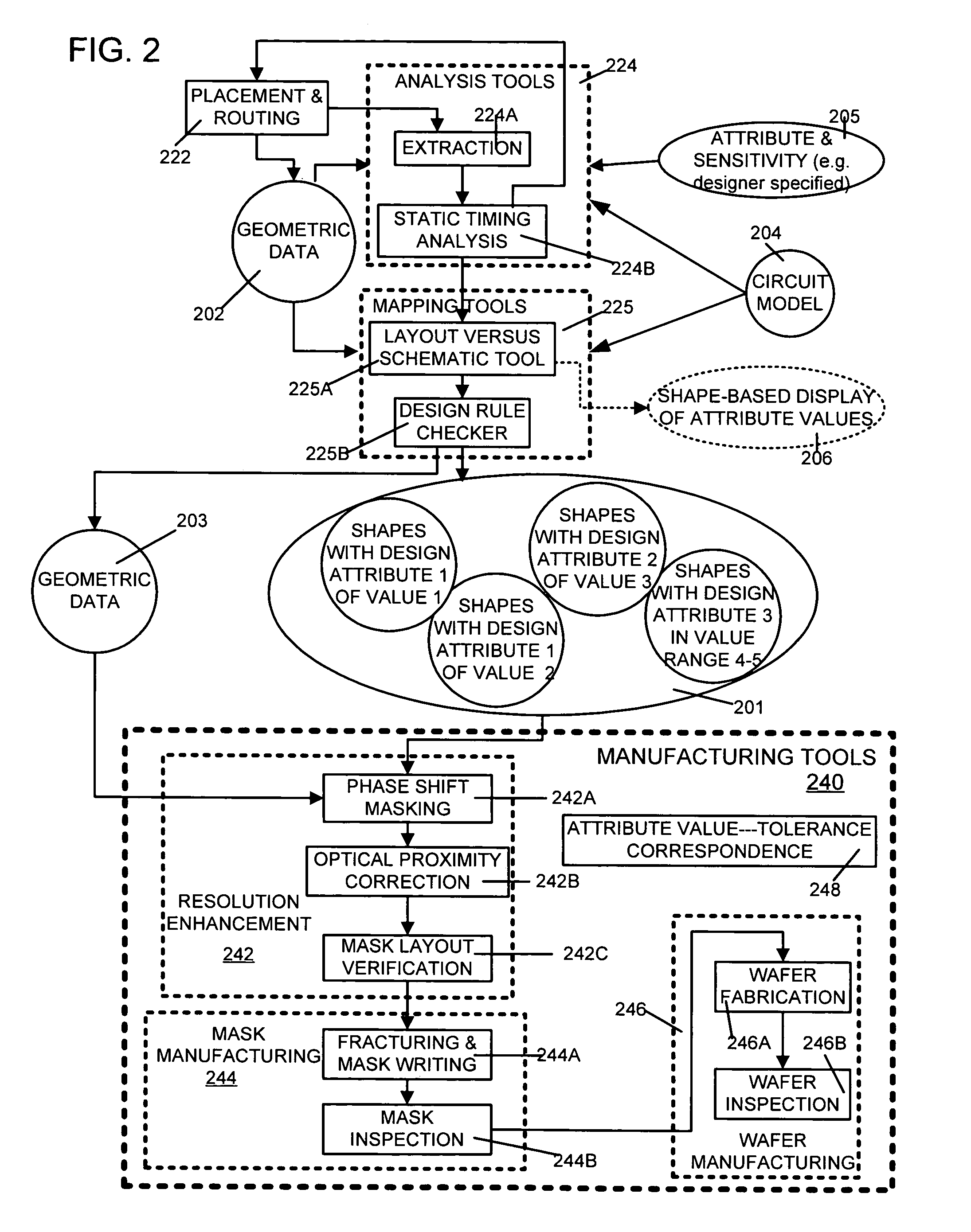
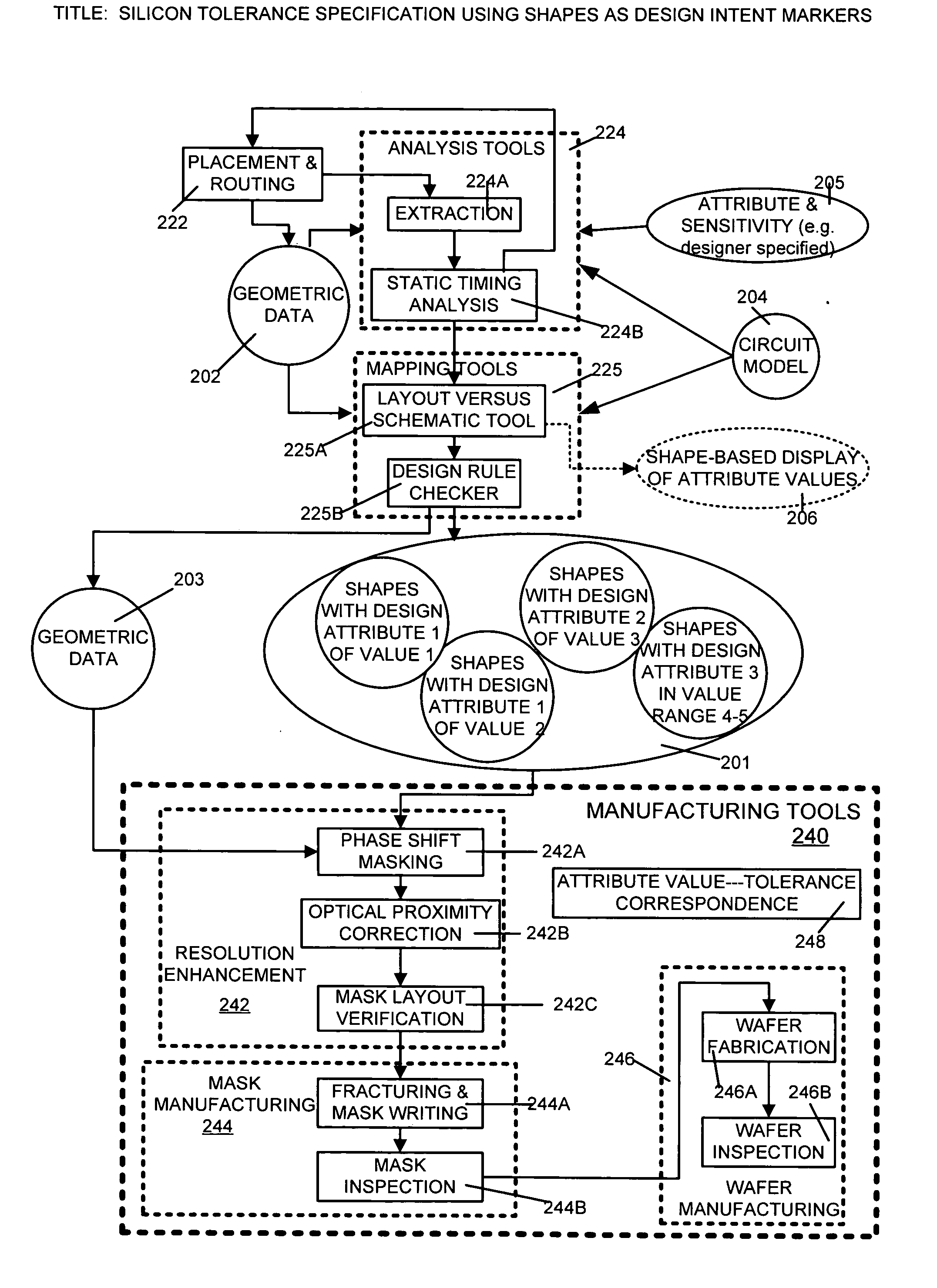
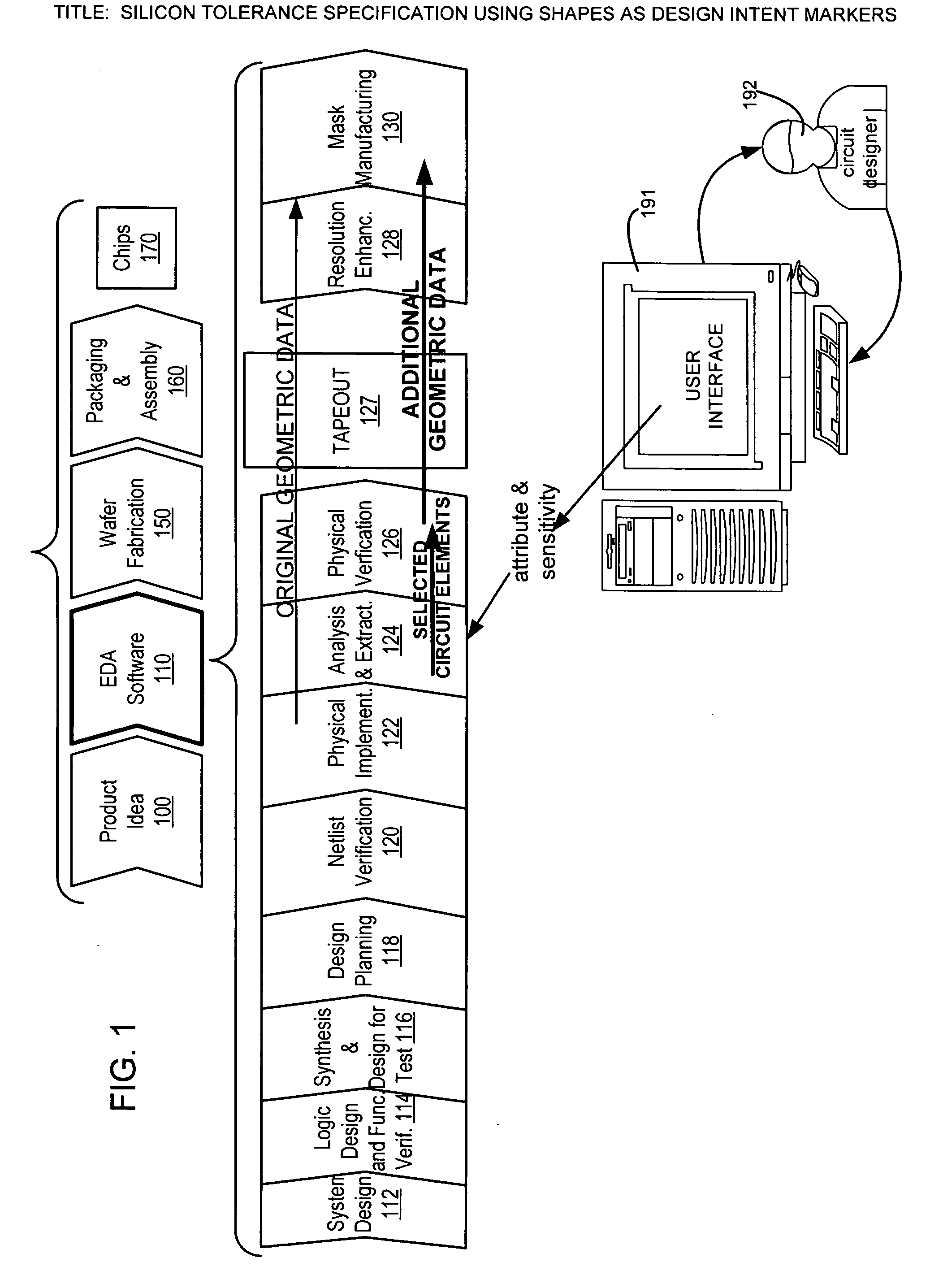
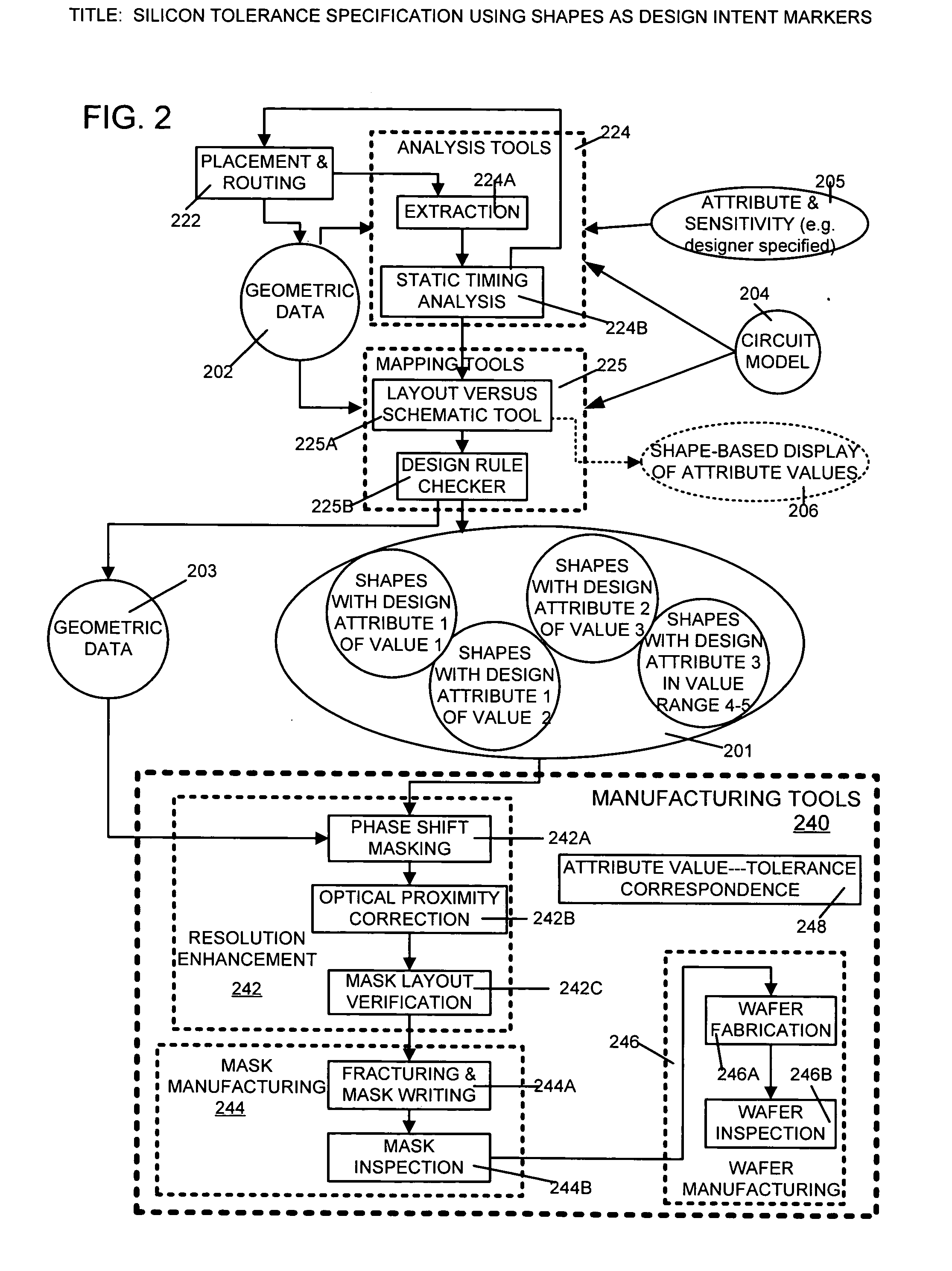
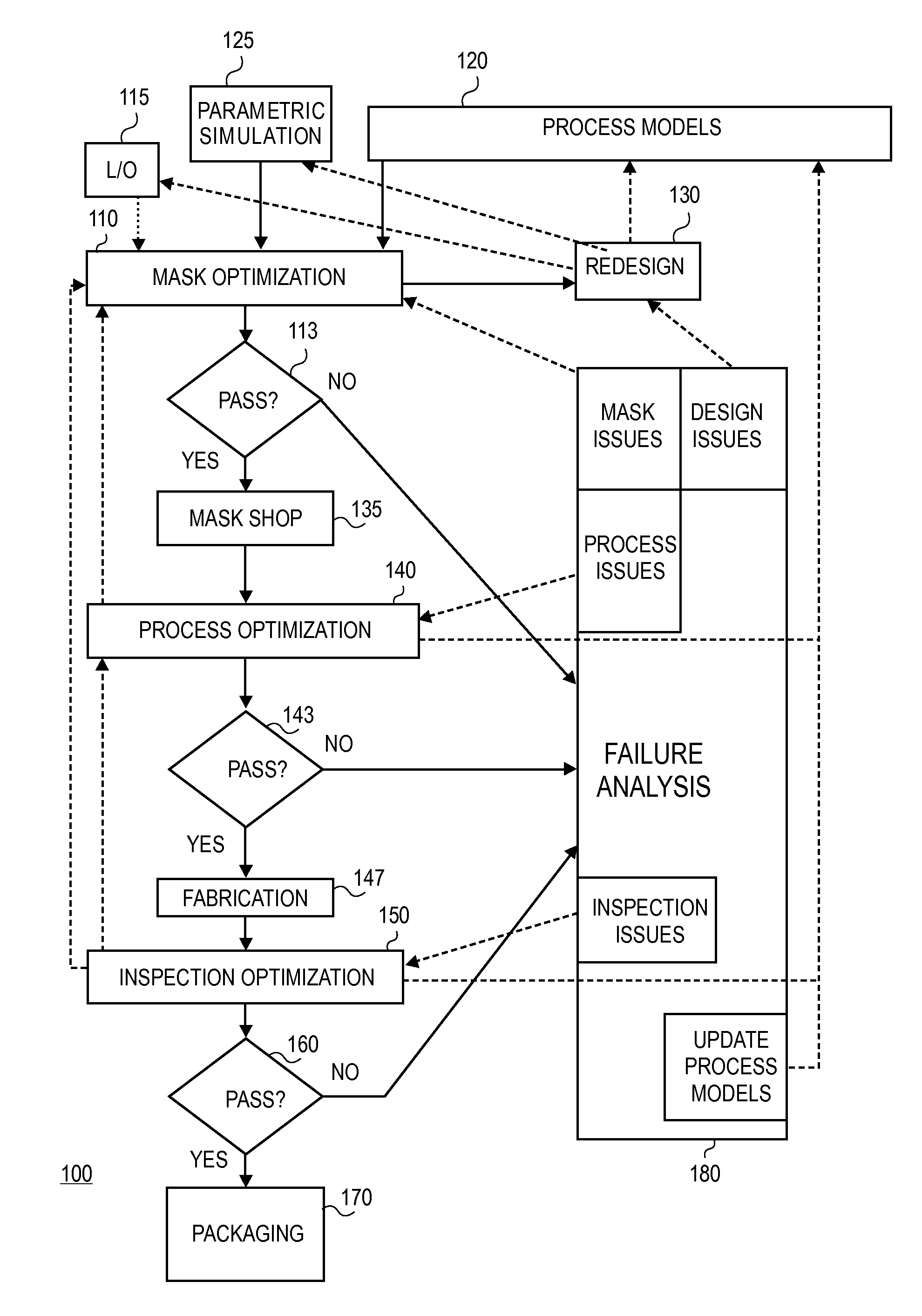
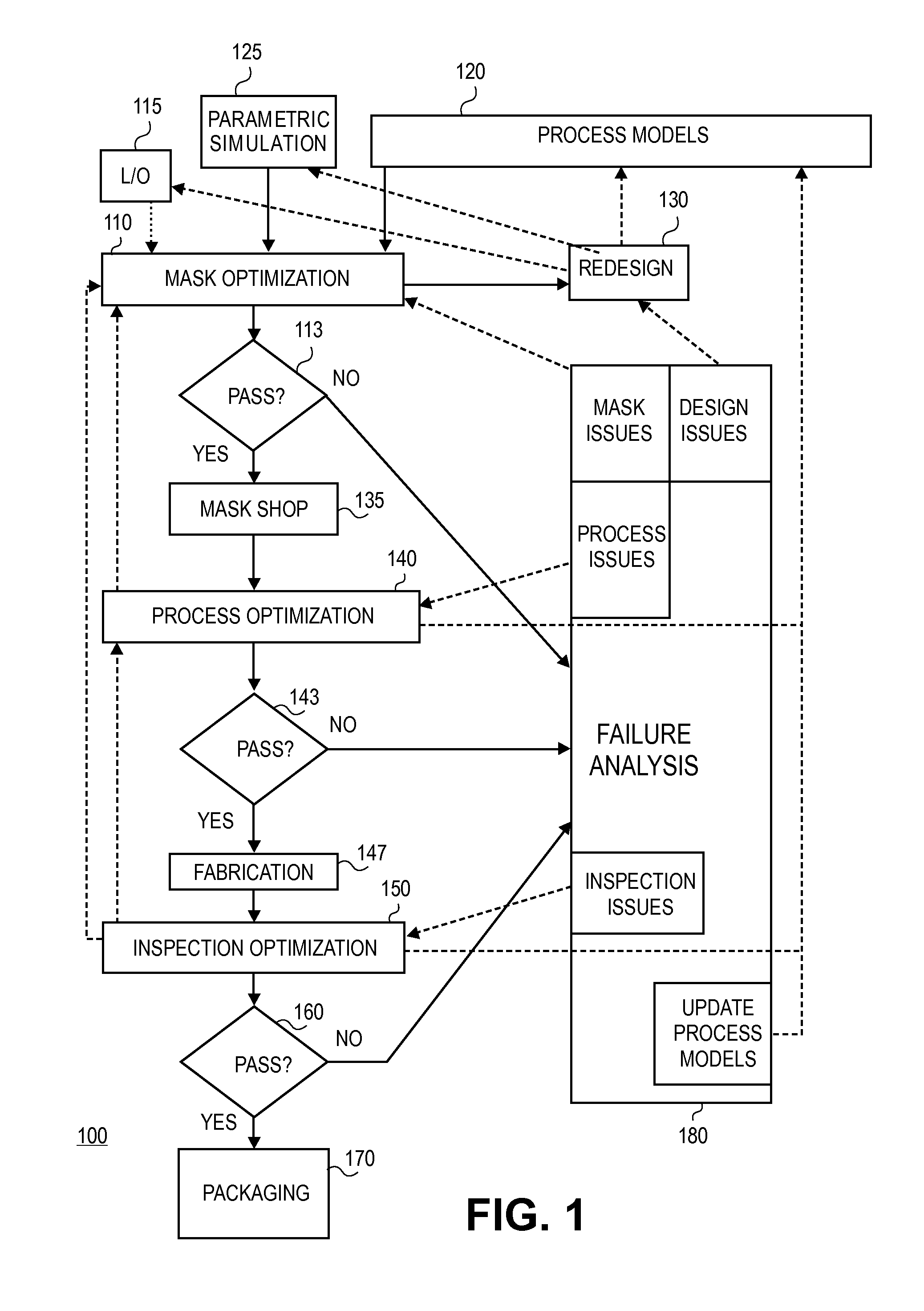
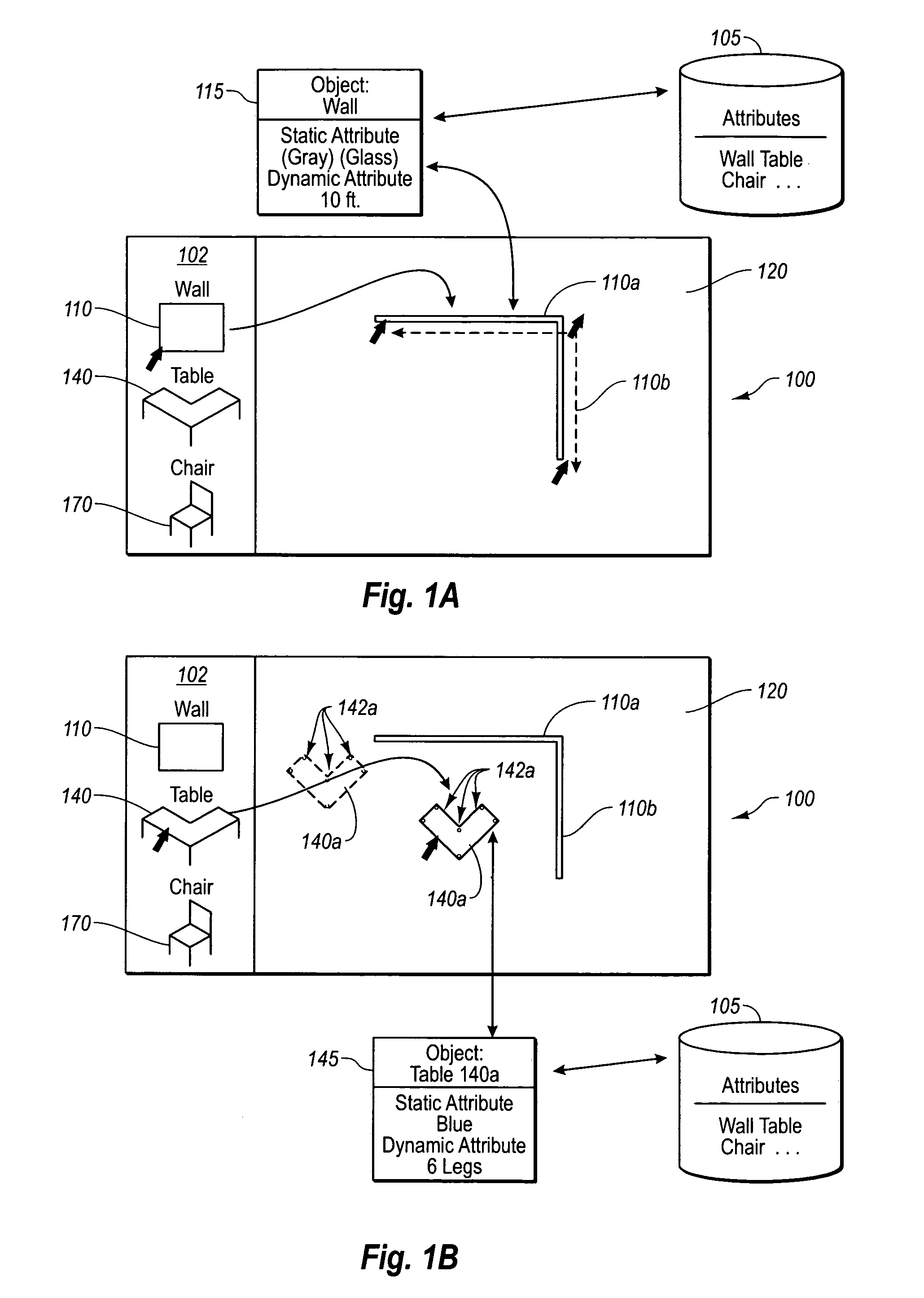
Silicon tolerance specification using shapes as design intent markers
ActiveUS7458045B2High yieldCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringSilicon
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System and method for browsing graphically an electronic design based on a hardware description language specification
InactiveUS6366874B1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGraphicsProgramming language
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
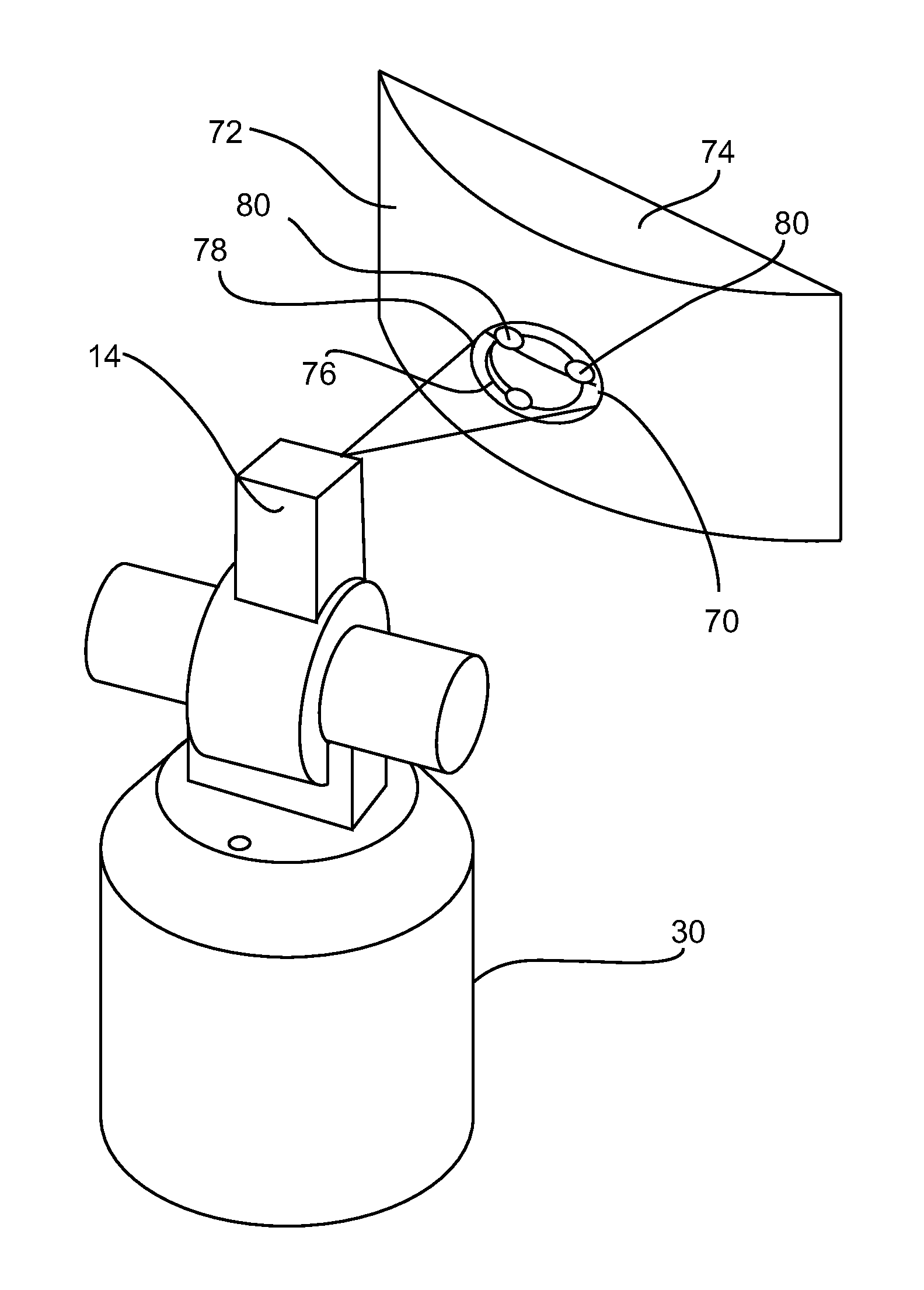
Laser scanner or laser tracker having a projector
Owner:FARO TECH INC
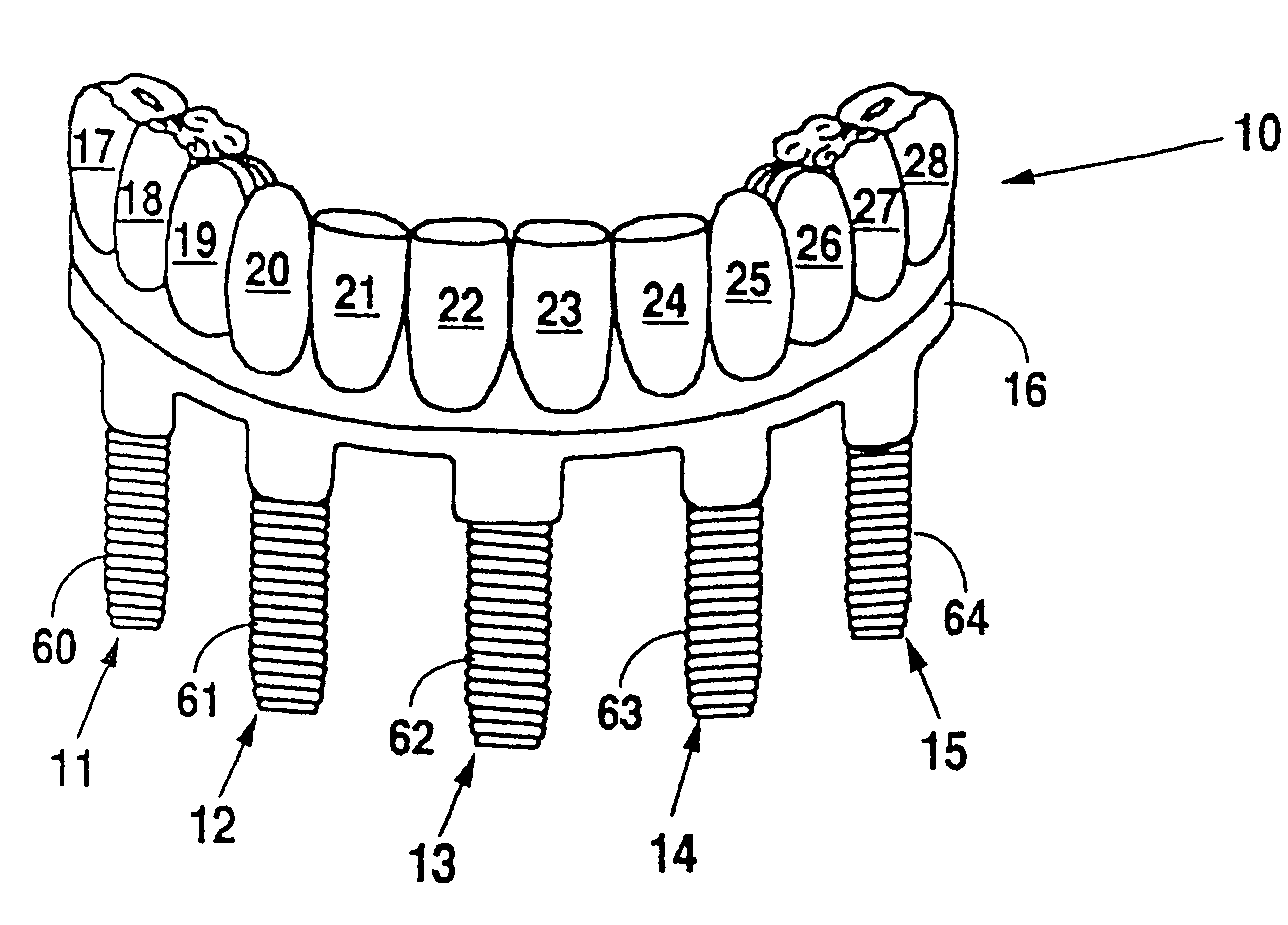
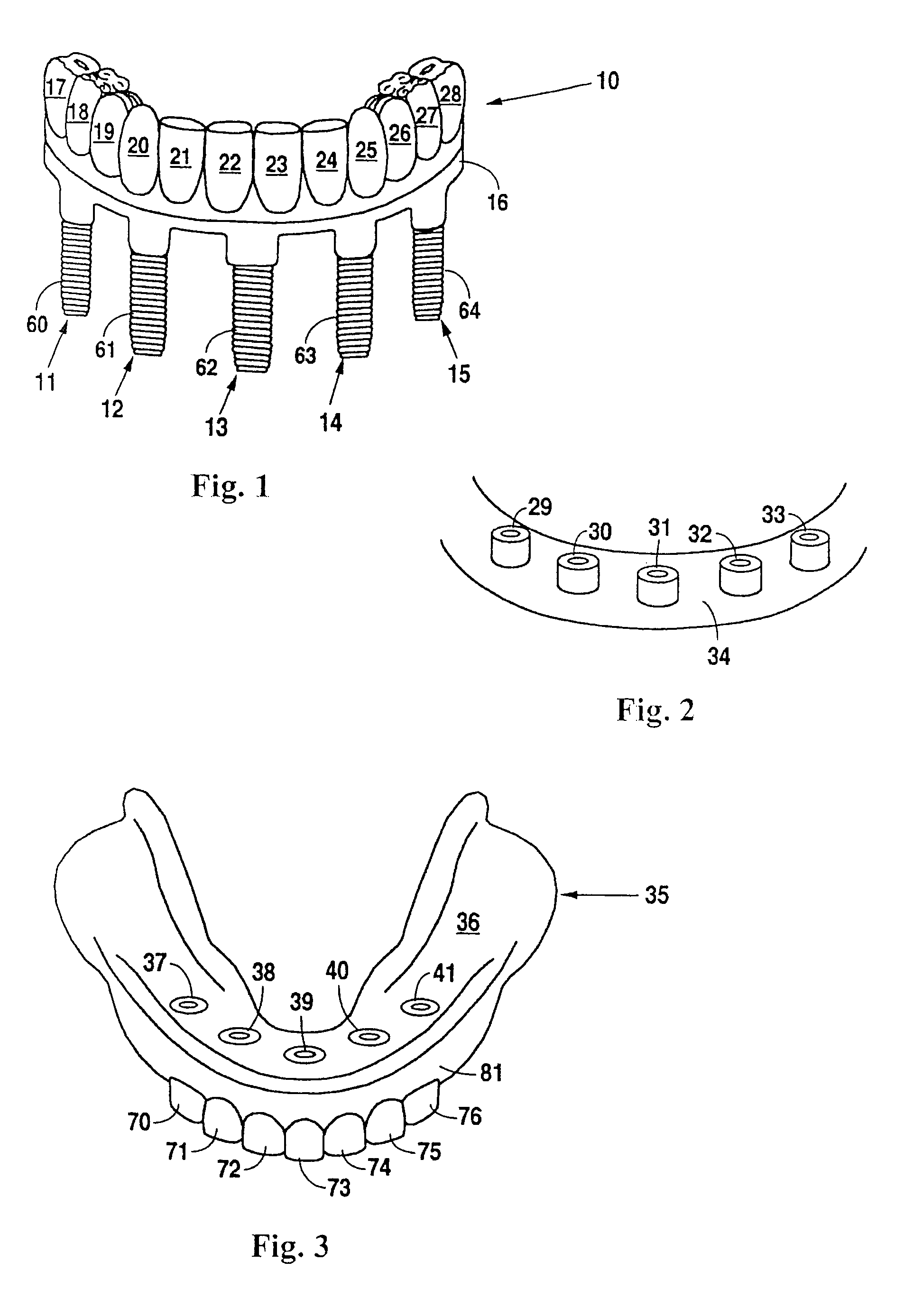
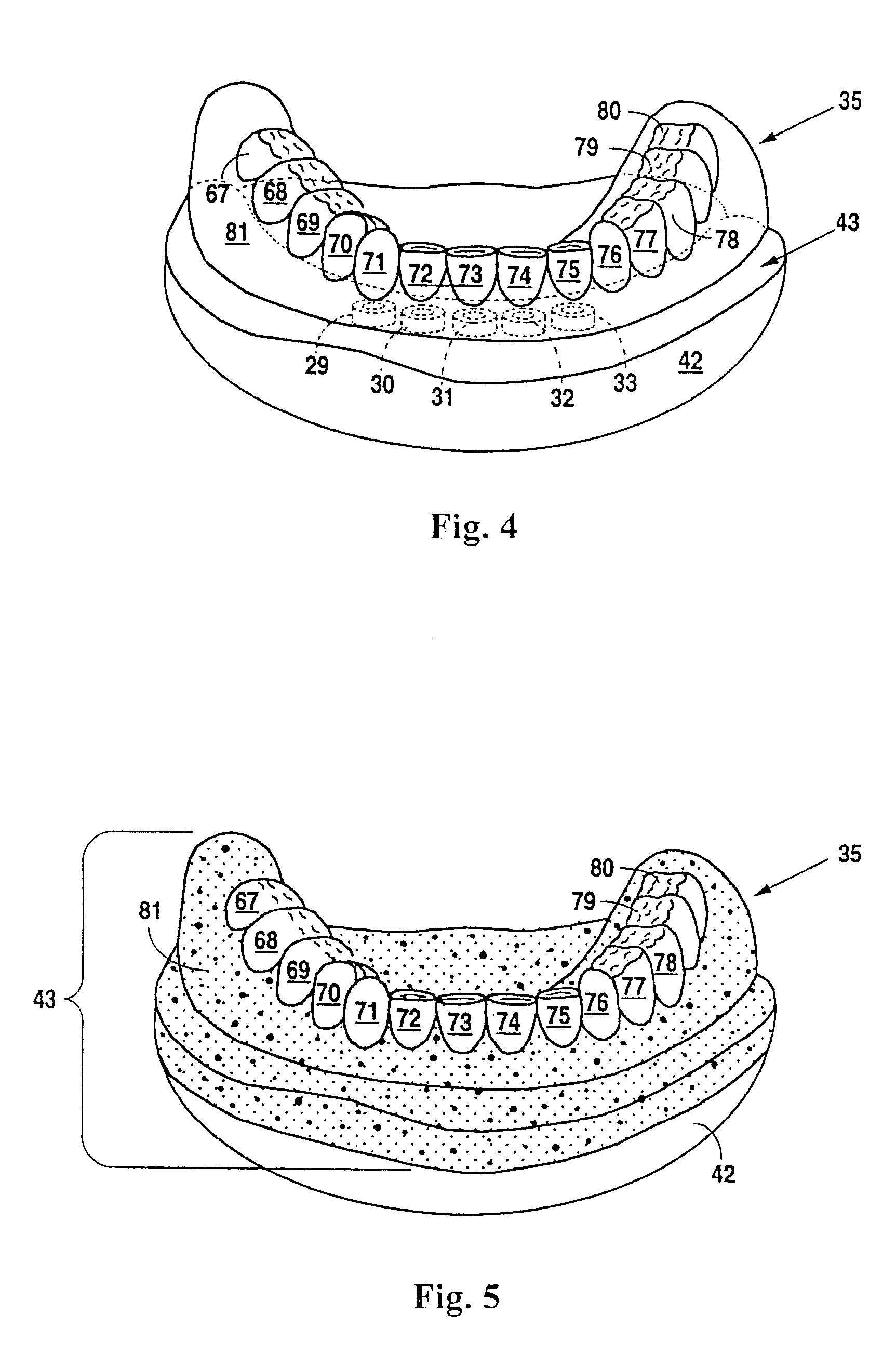
Design and manufacture of dental implant restorations
Owner:VOXELOGIX CORP
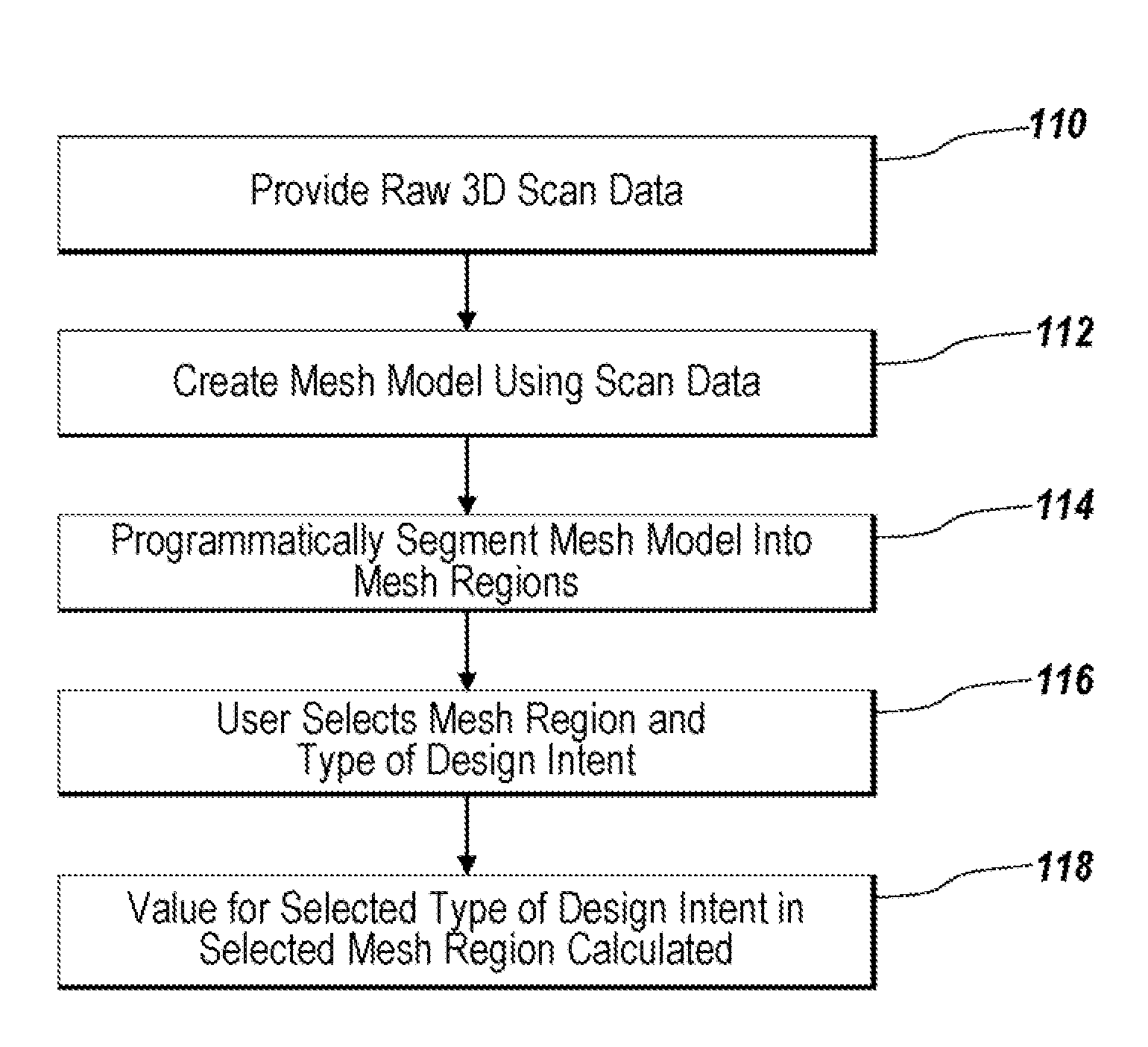
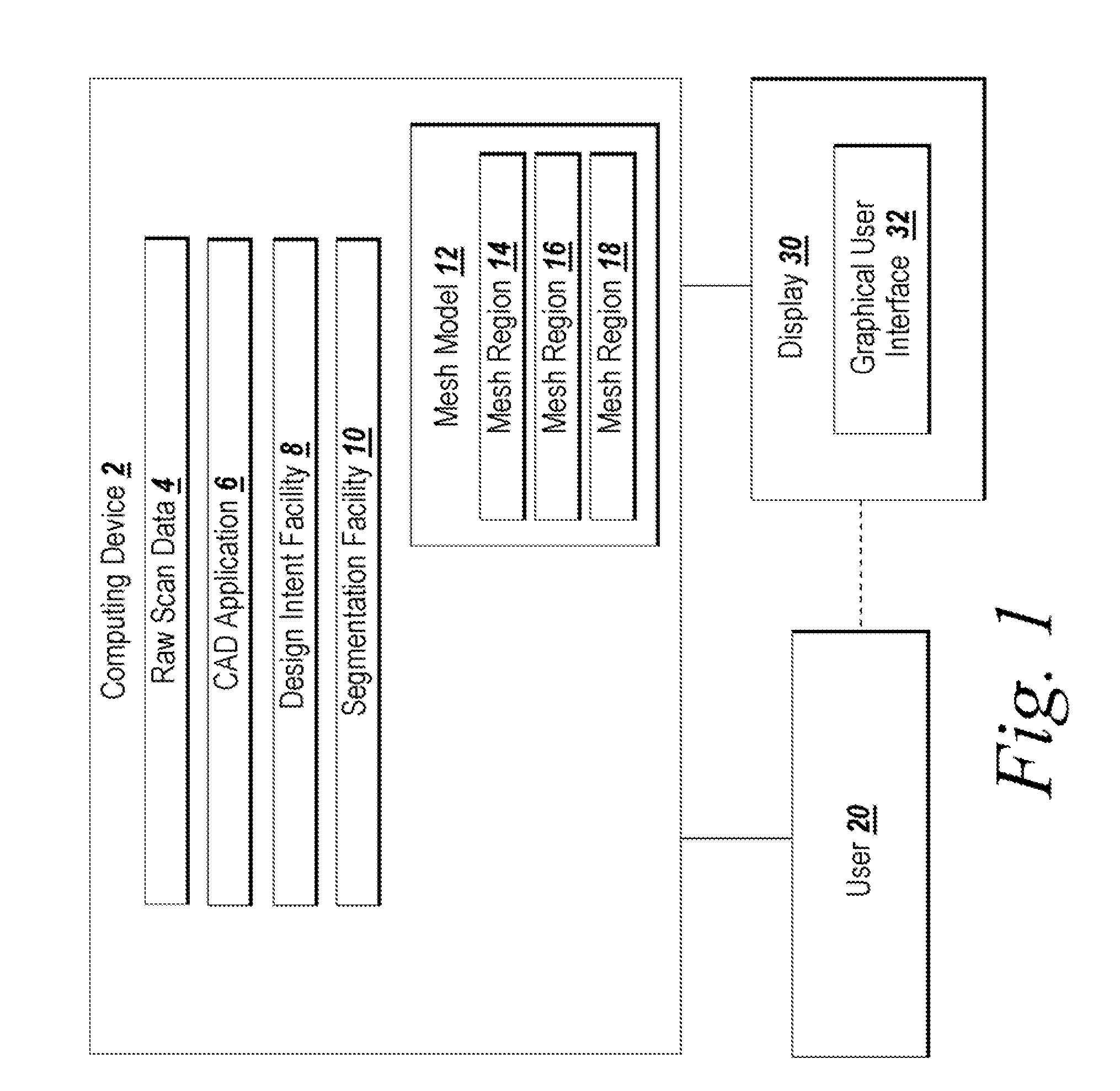
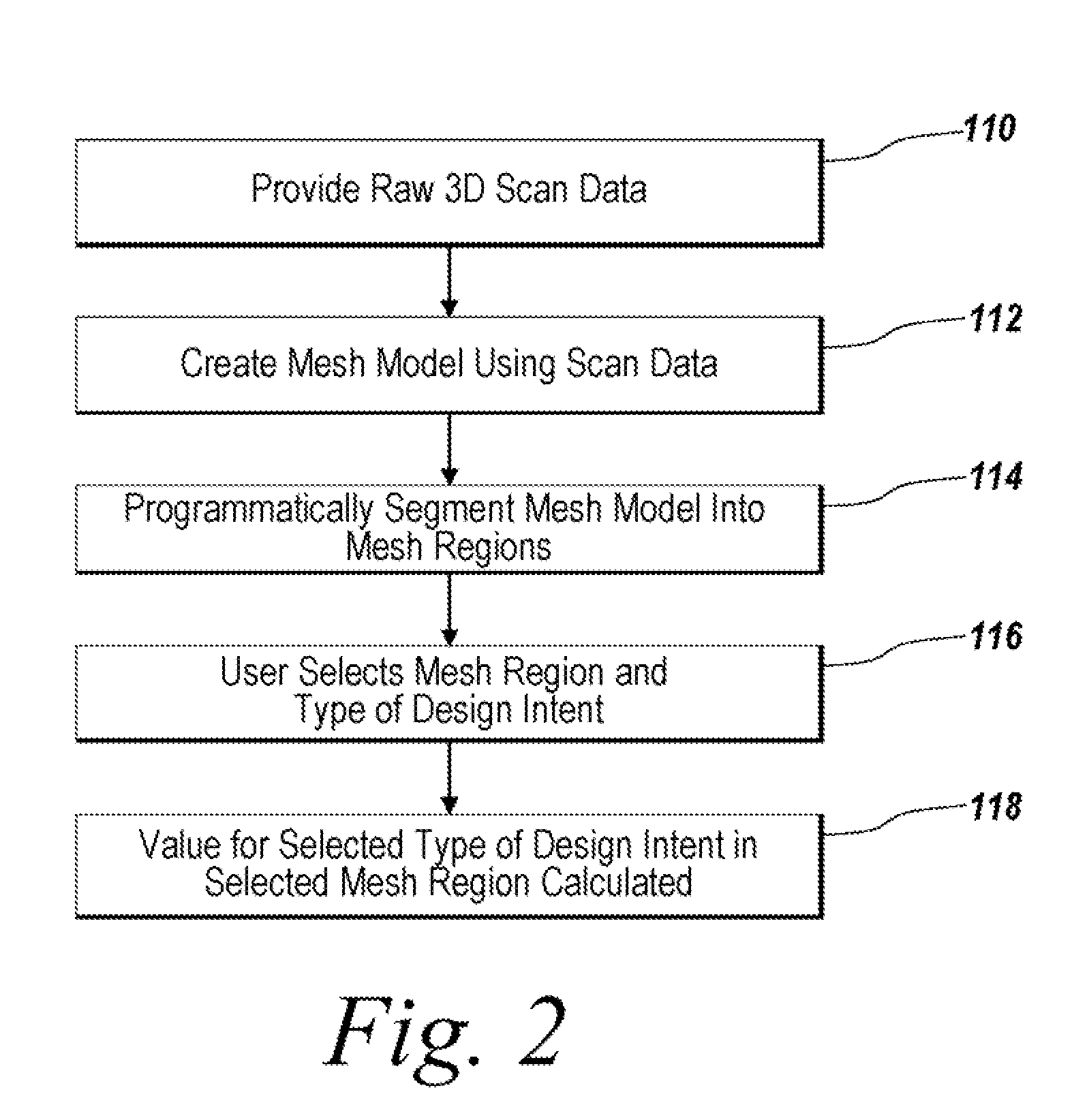
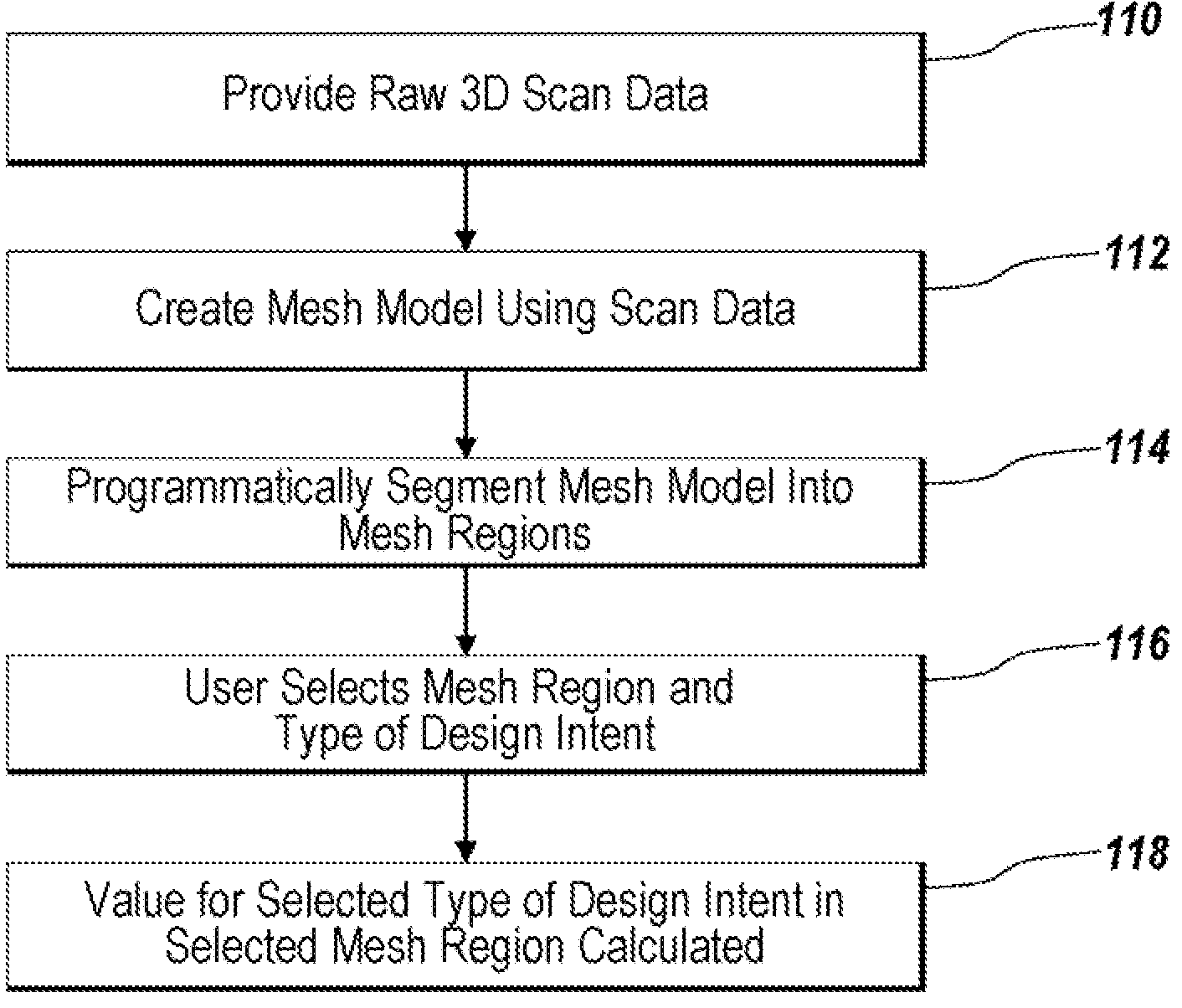
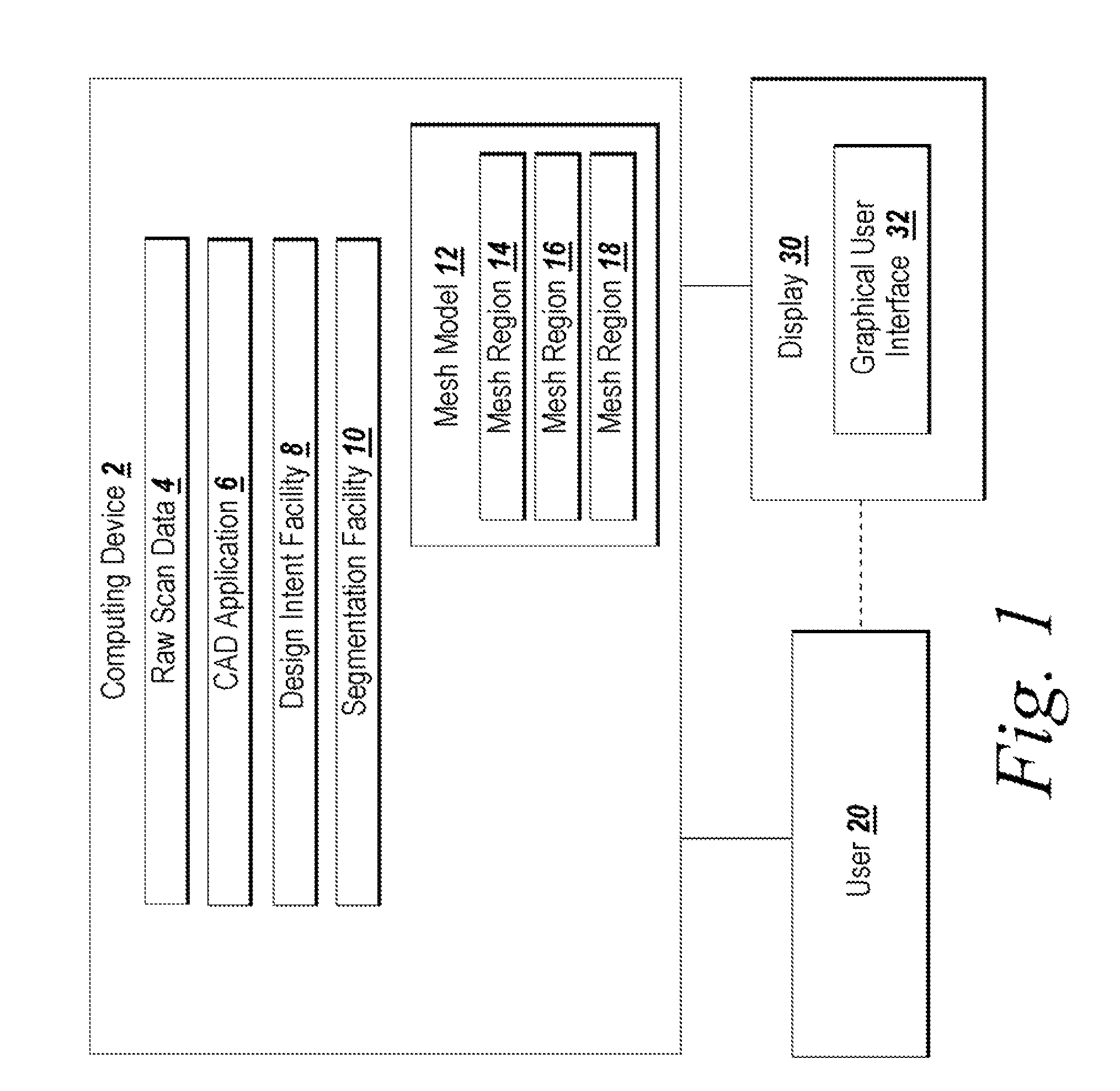
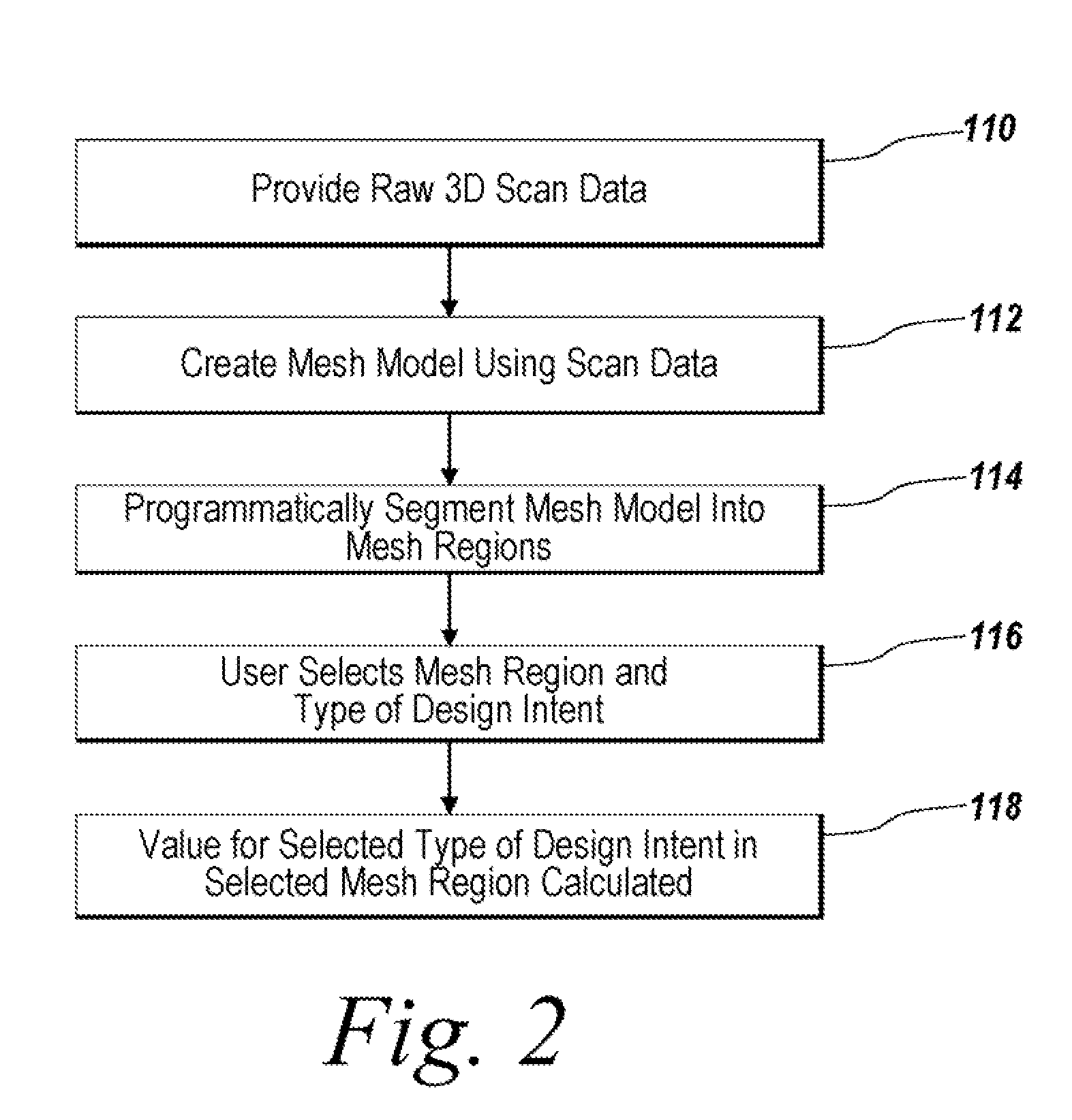
System and Method for Identifying Original Design Intents Using 3D Scan Data
ActiveUS20080040080A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
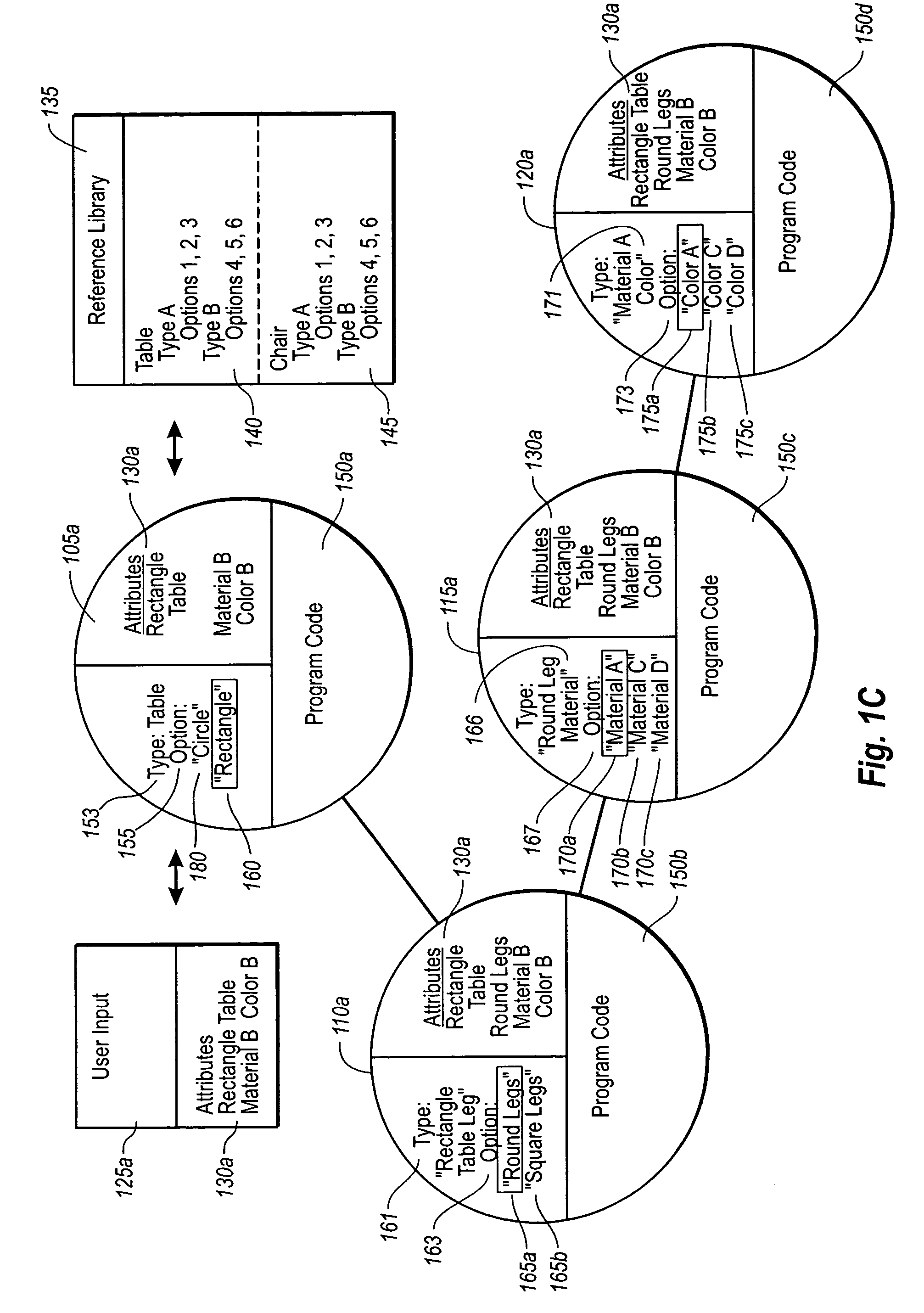
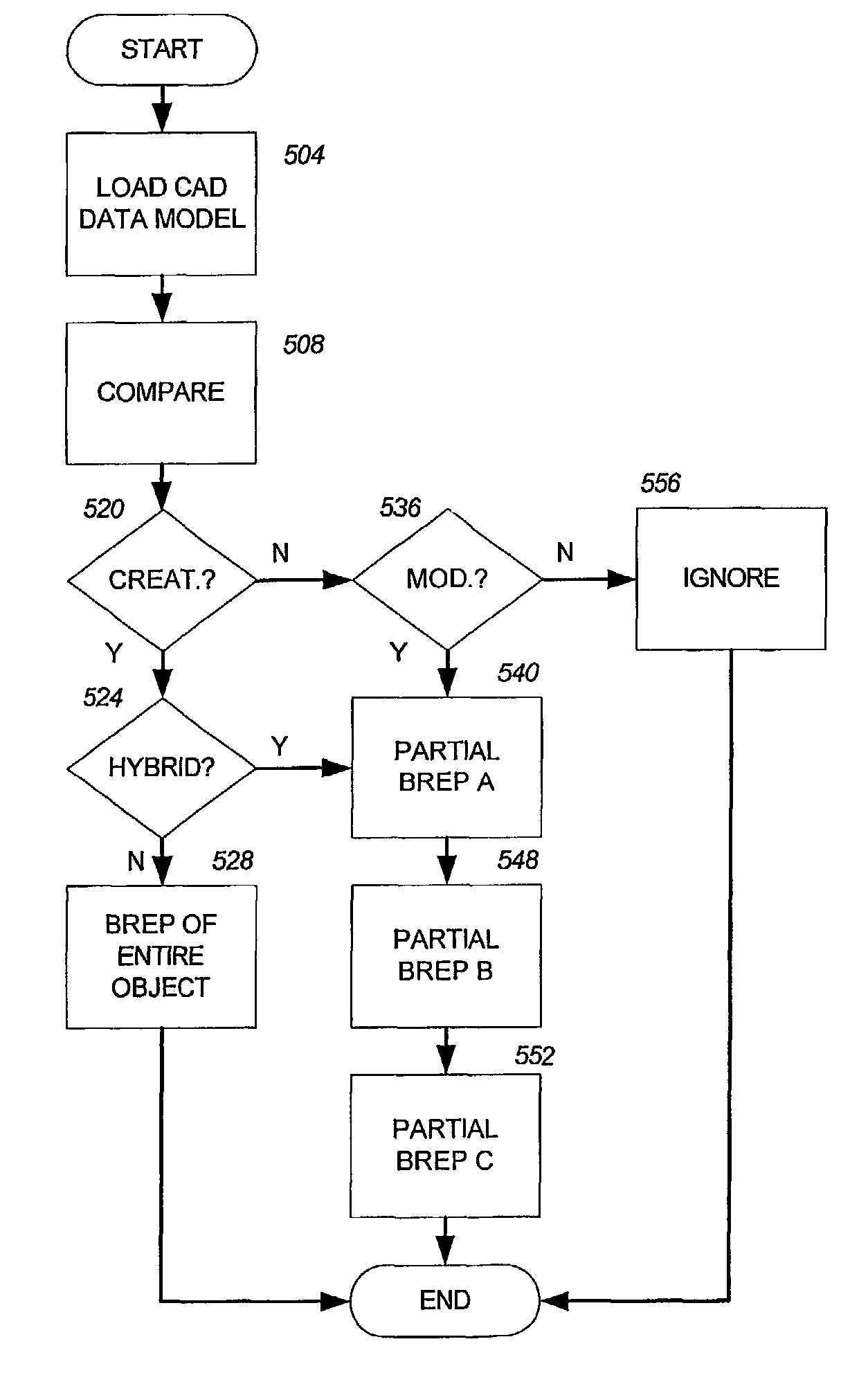
Programmatic extraction and management of solid and surface modeling parameters from raw 3D scan data is discussed. An automated process reads raw 3D scan data and works in communication with a CAD system able to perform CAD part modeling. The user is provided with an automatic function to segment a mesh model (formed from the raw 3D scan data) into dozens of mesh regions. A graphical user interface is provided which enables a user to choose a type of the design intent along with the mesh regions from which the design intent is calculated. Each design intent is represented in a vector, a plane or a poly-line depending upon the type of design intent. In response to a user demand for the parameters of a modeling feature, a best approximation of the requested parameter value is calculated by processing the raw 3D scan data using a set of functions.
Owner:INUS TECH
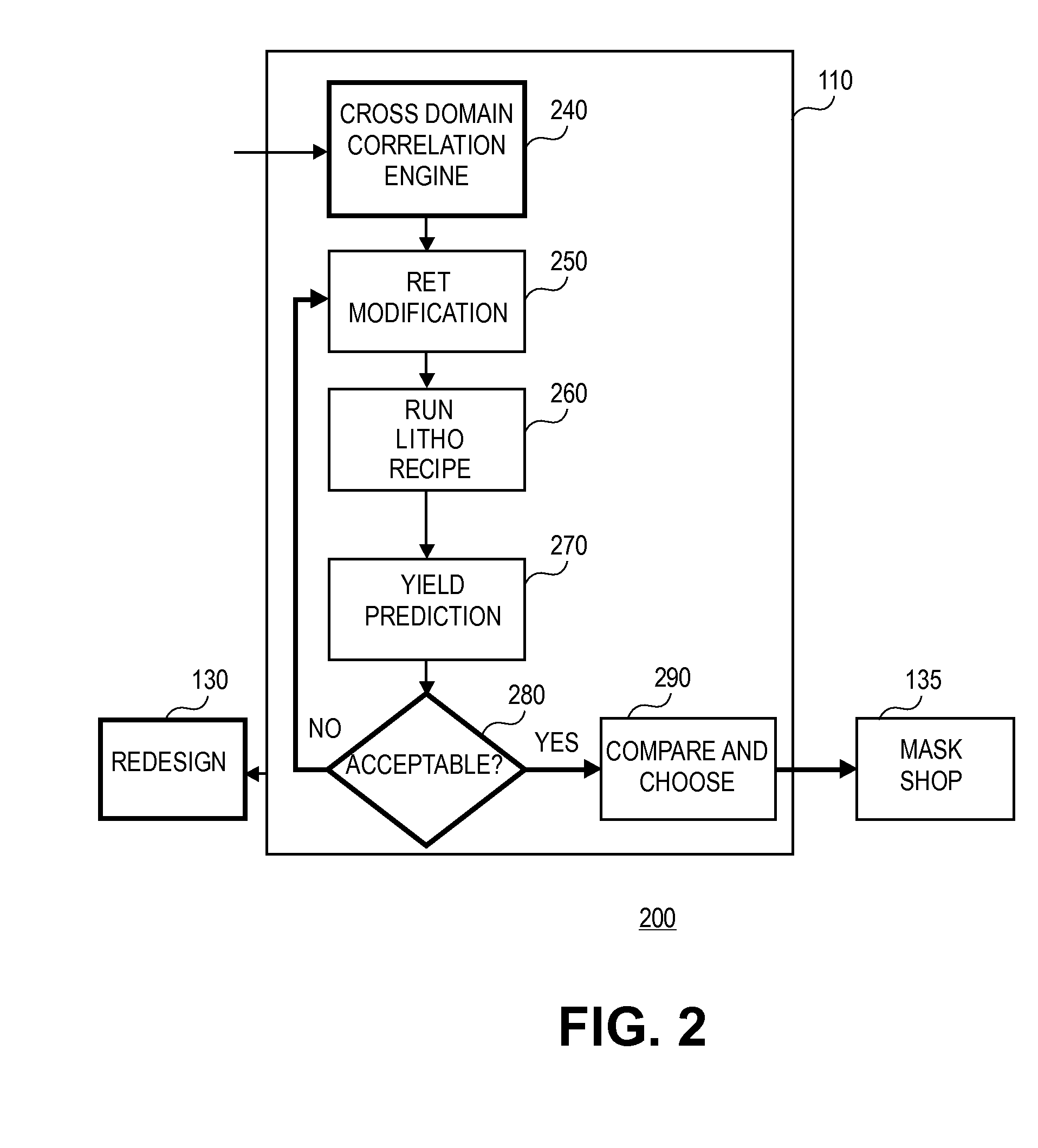
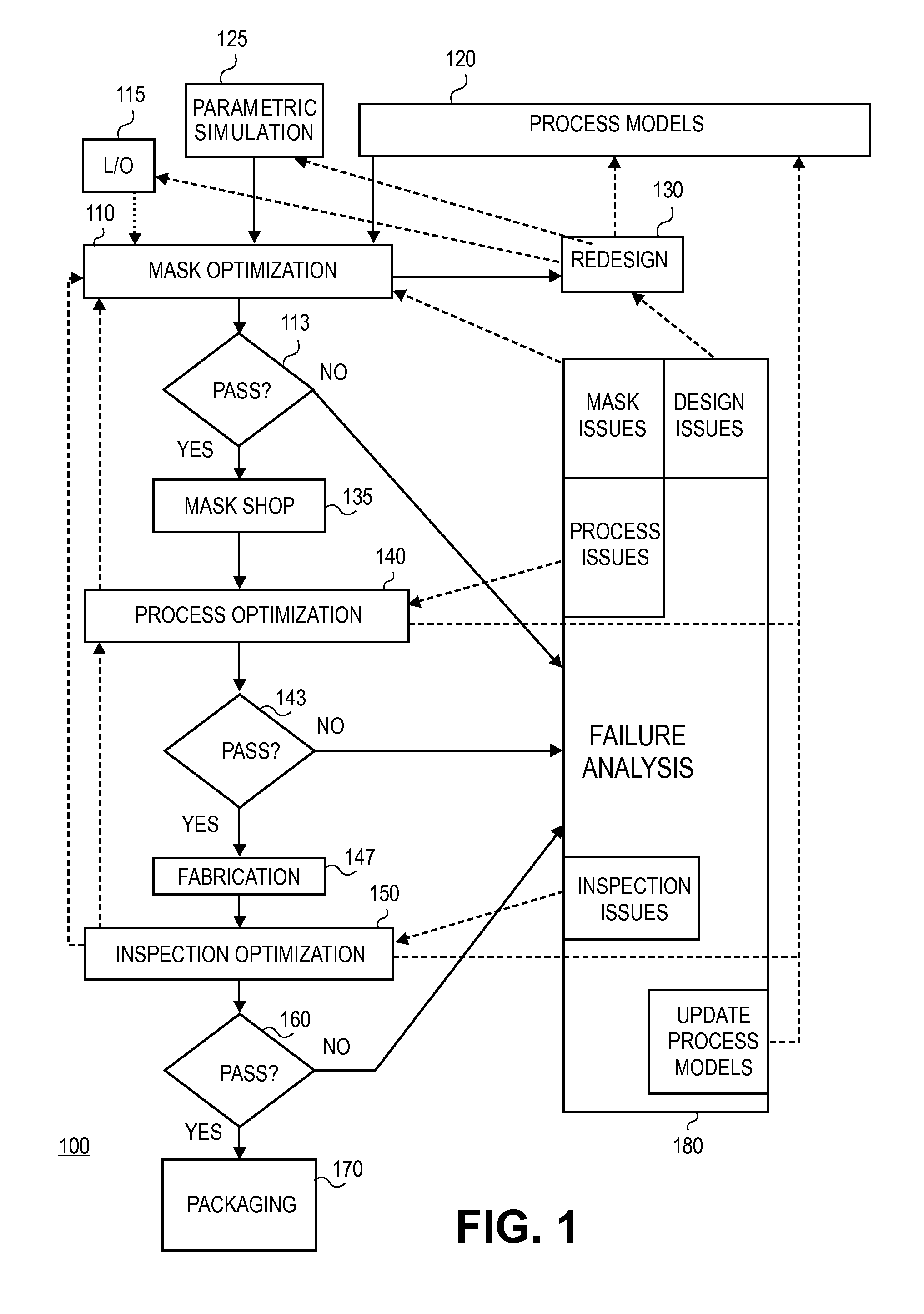
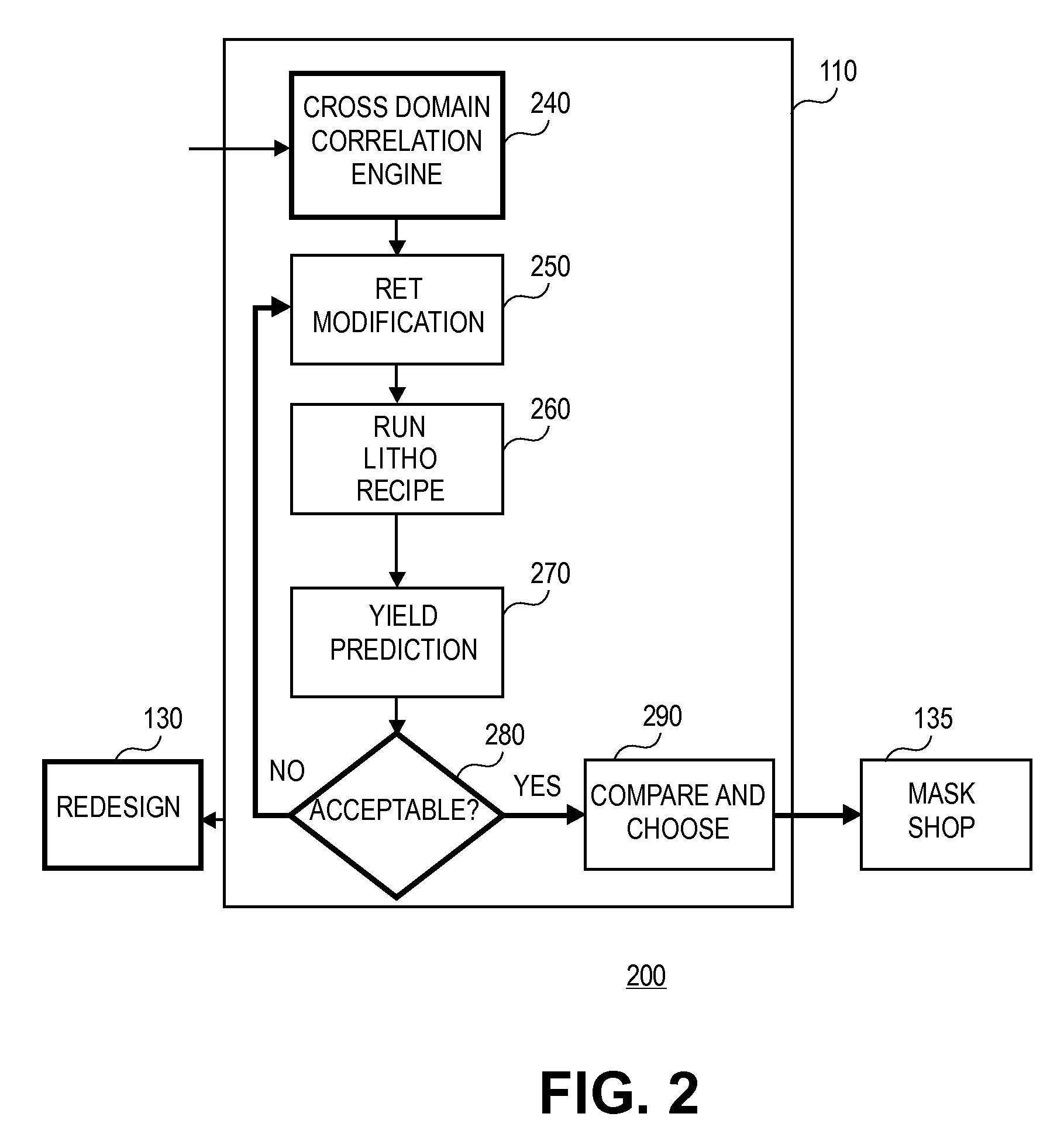
Method and apparatus for integrated circuit layout optimization
InactiveUS20070101303A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designResolution enhancement technologiesLithographic artist
Owner:LIZOTECH
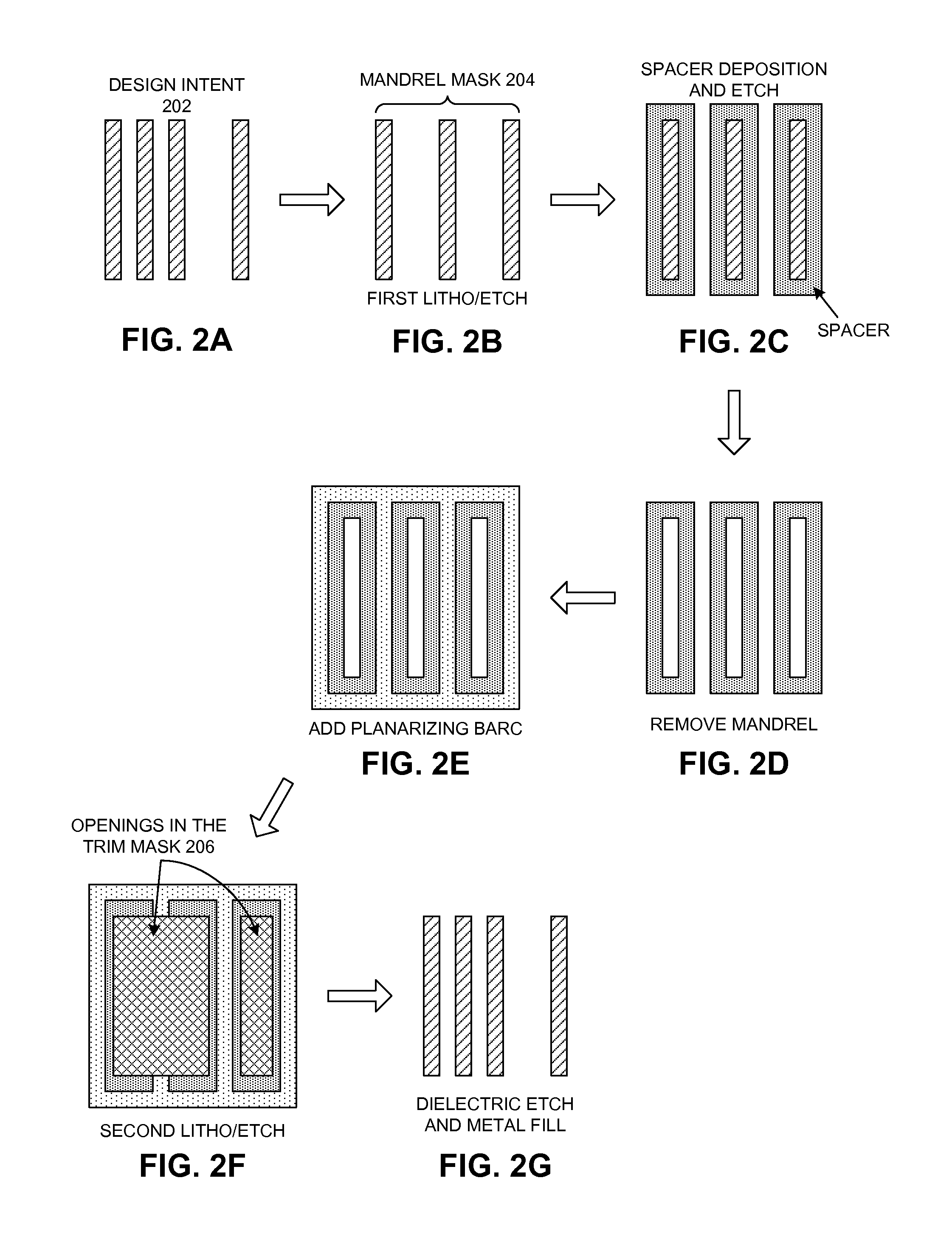
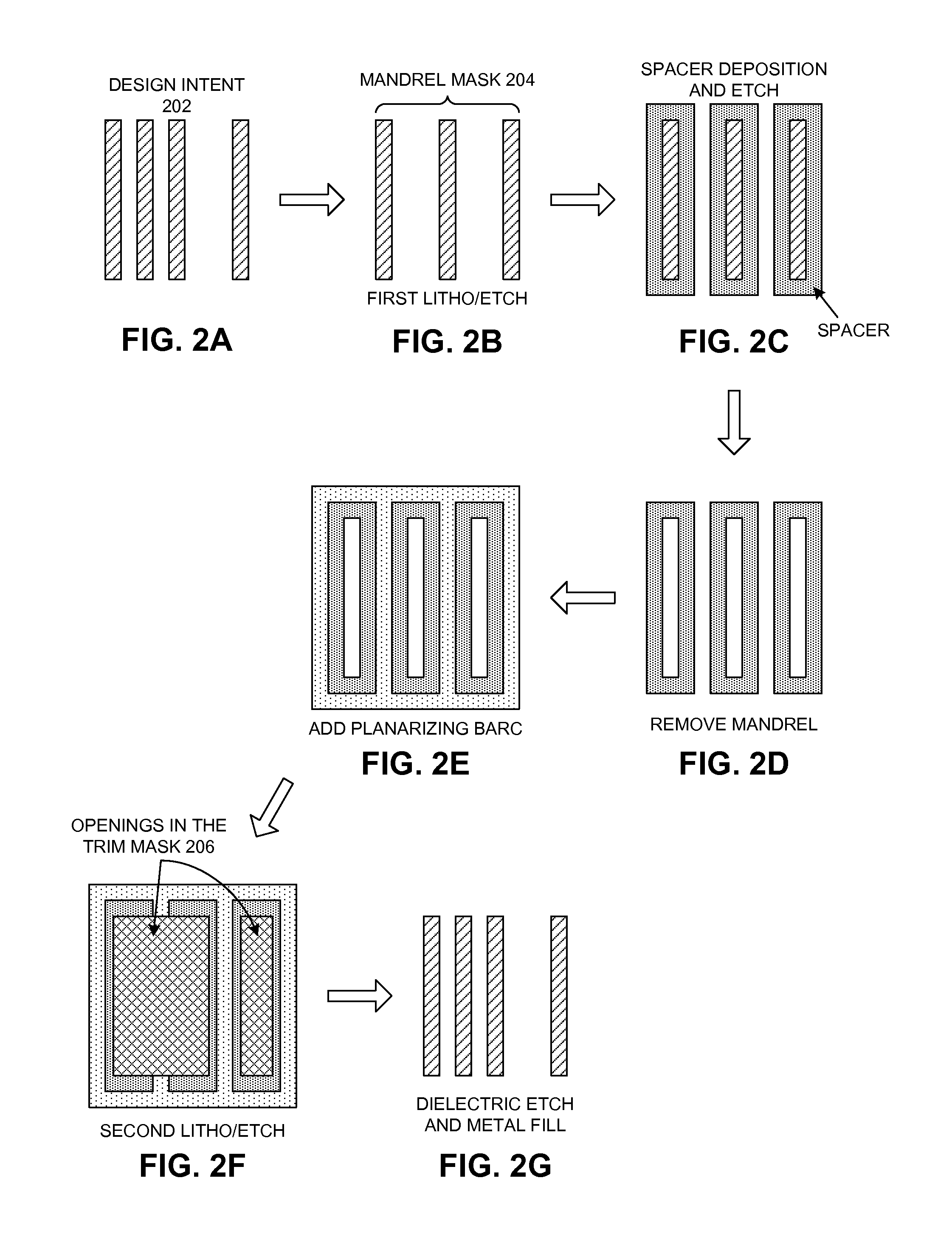
Method and apparatus for determining mask layouts for a spacer-is-dielectric self-aligned double-patterning process
ActiveUS8312394B2Improve manufacturabilityMinimum run lengthCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsEngineering
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Silicon tolerance specification using shapes as design intent markers
ActiveUS20060095889A1High yieldIncrease costCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringSilicon
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
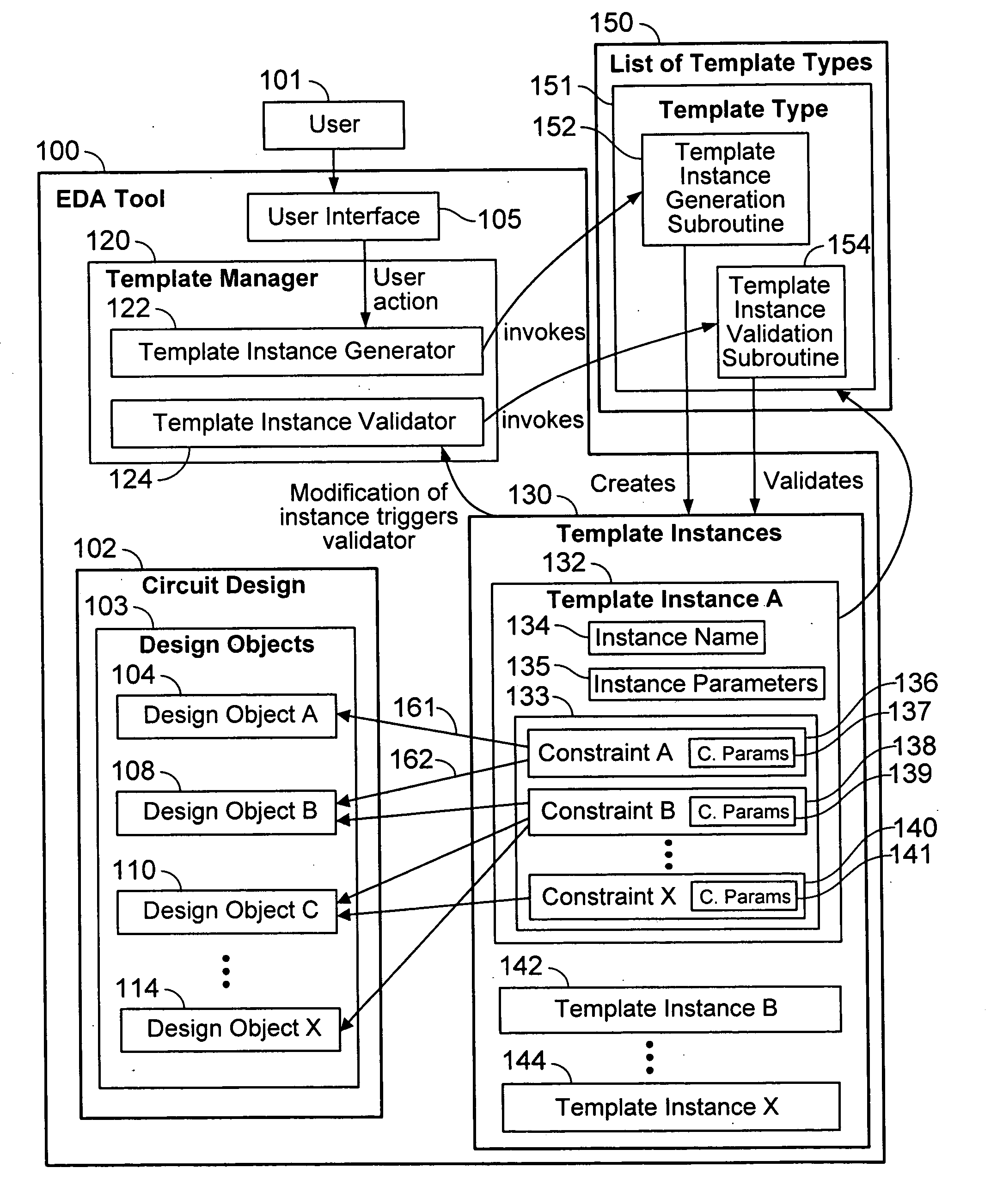
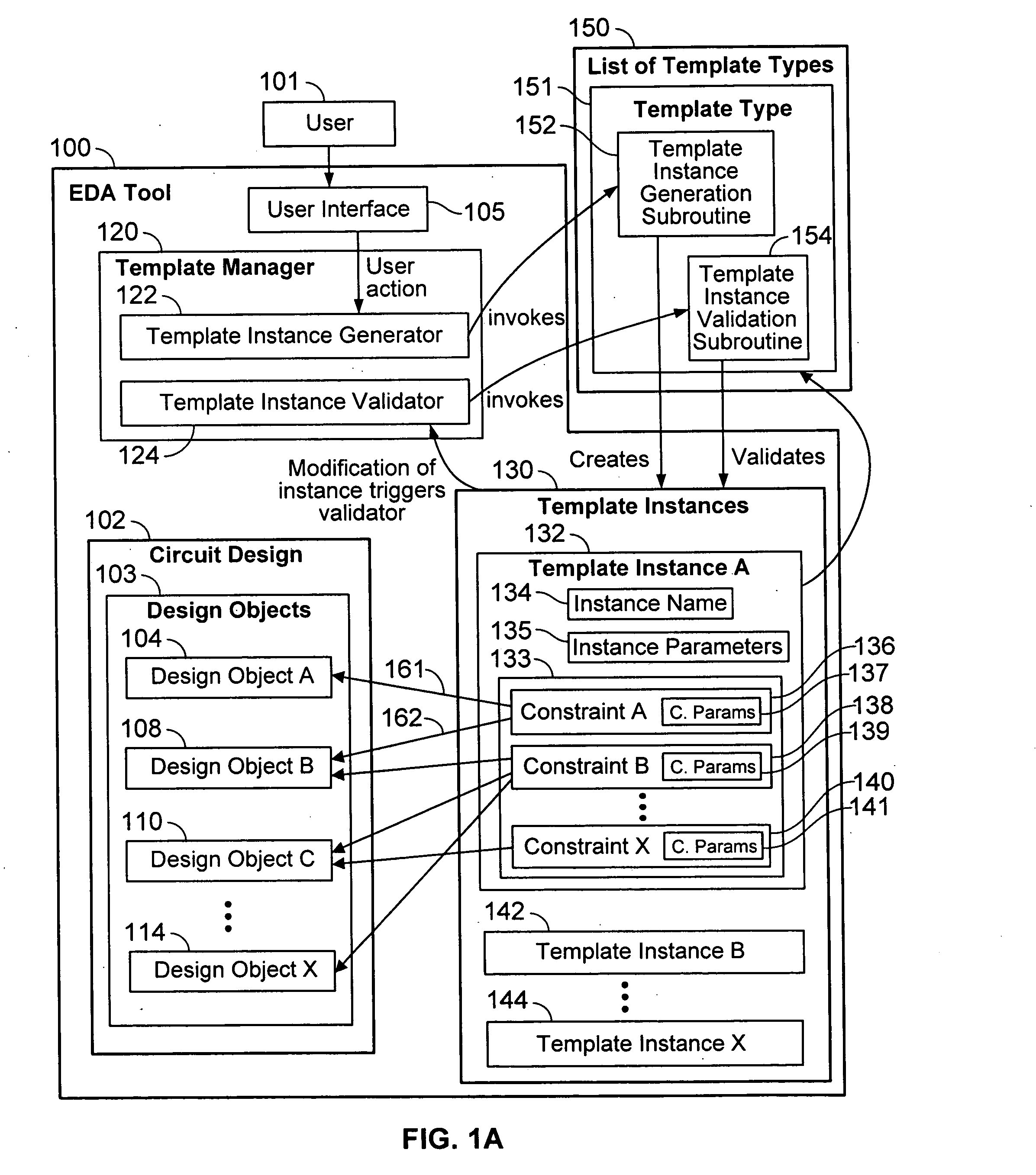
Generalized constraint collection management method
ActiveUS20080077901A1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designCollection managementElectronic design automation
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method and apparatus for determining mask layouts for a spacer-is-dielectric self-aligned double-patterning process
ActiveUS20120137261A1Improve manufacturabilityMinimum run lengthCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsEngineering
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method and apparatus to determine if a pattern is robustly manufacturable
ActiveUS7739651B2Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsGenerative DesignEngineering
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Methods and system for improving integrated circuit layout
ActiveUS7448012B1Reduce guard bandImprove chip yieldSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designPresent methodIntegrated circuit layout
Owner:IYM TECH
Capturing a user's intent in design software
ActiveUS20060041842A1Efficient constructionAccurate representationGeometric CADCAD network environmentInterior spaceUser input
Owner:ARMSTRONG WORLD INDUSTRIES
Dynamic layout system and processes
InactiveUS20070028165A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Free form
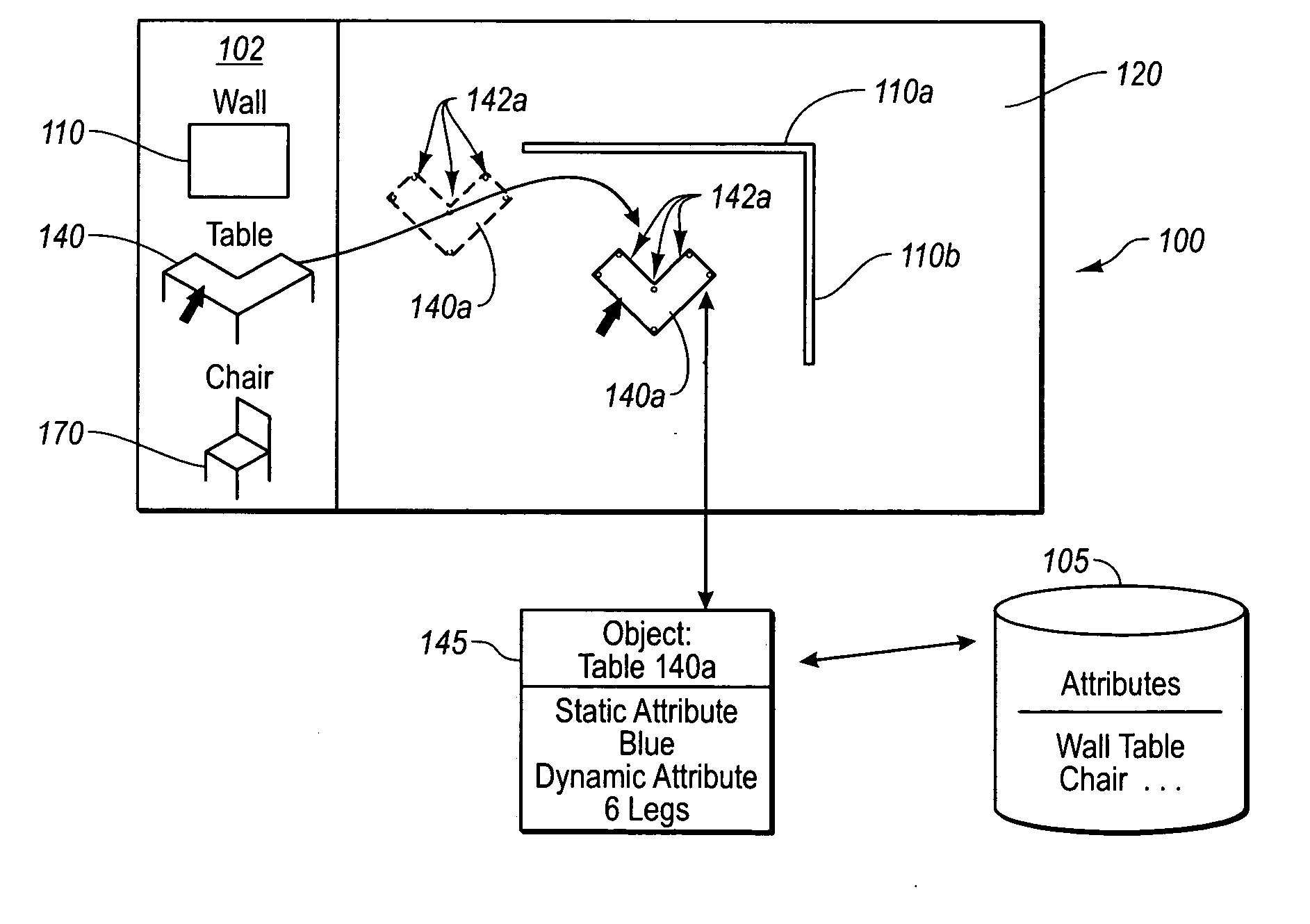
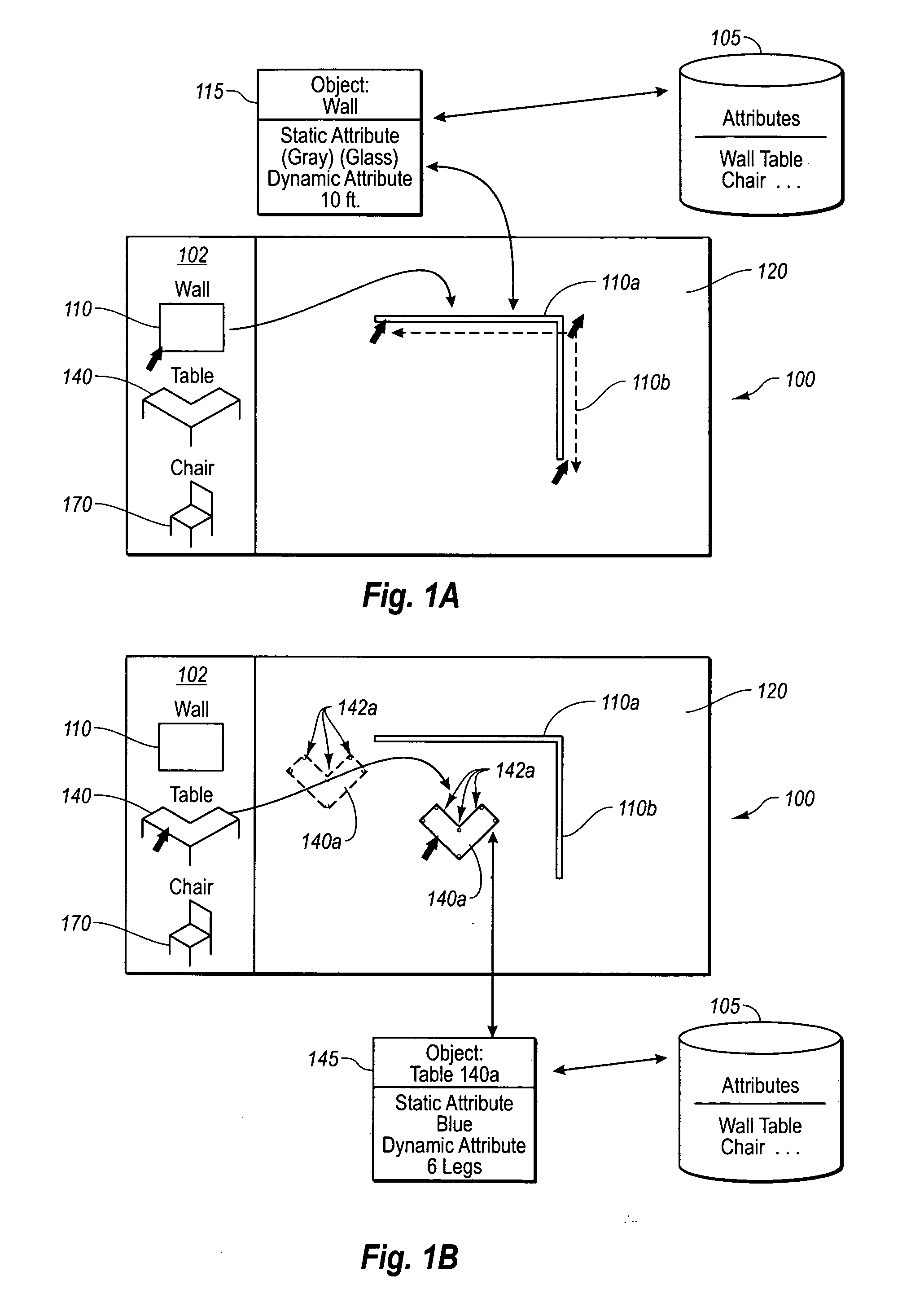
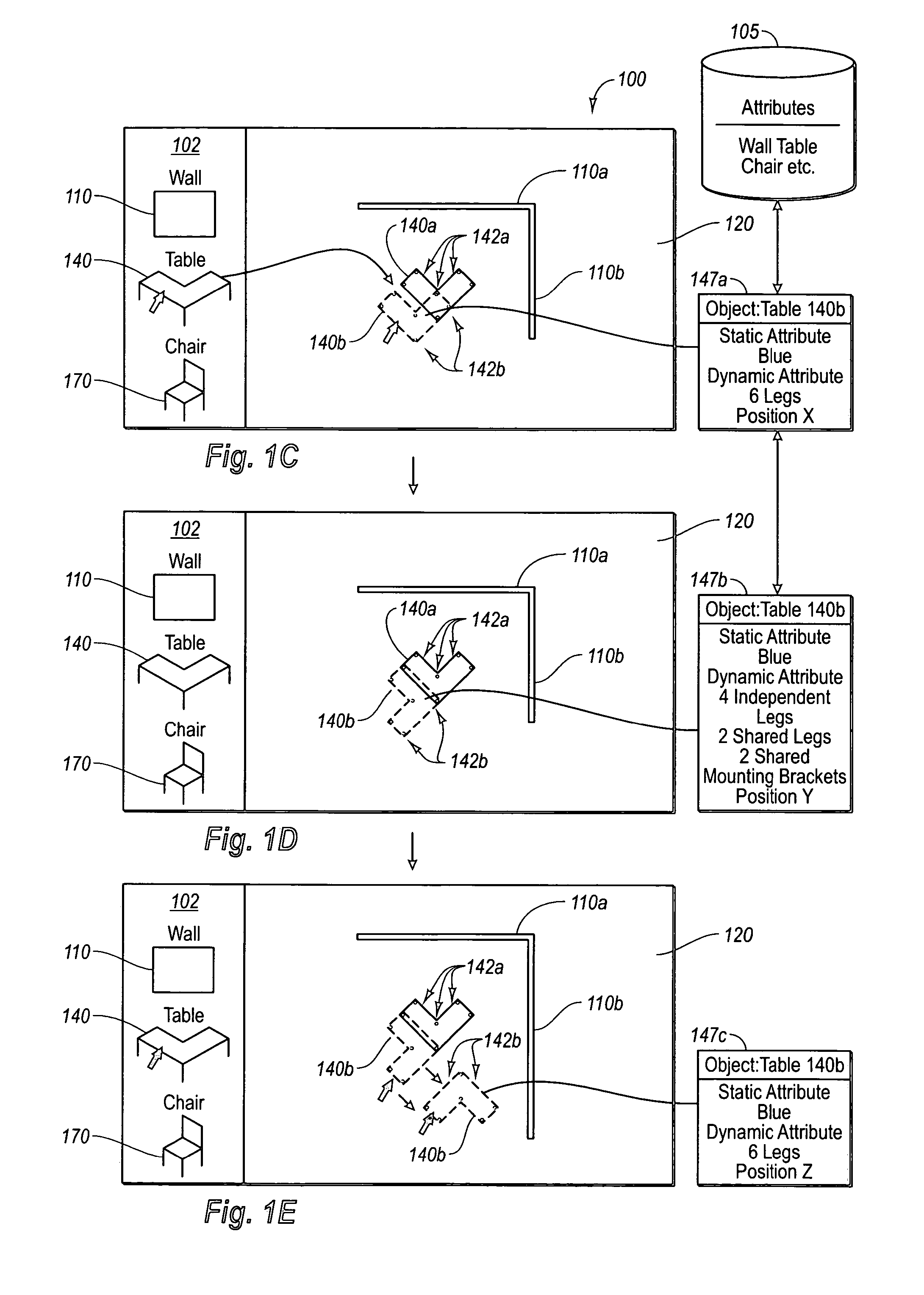
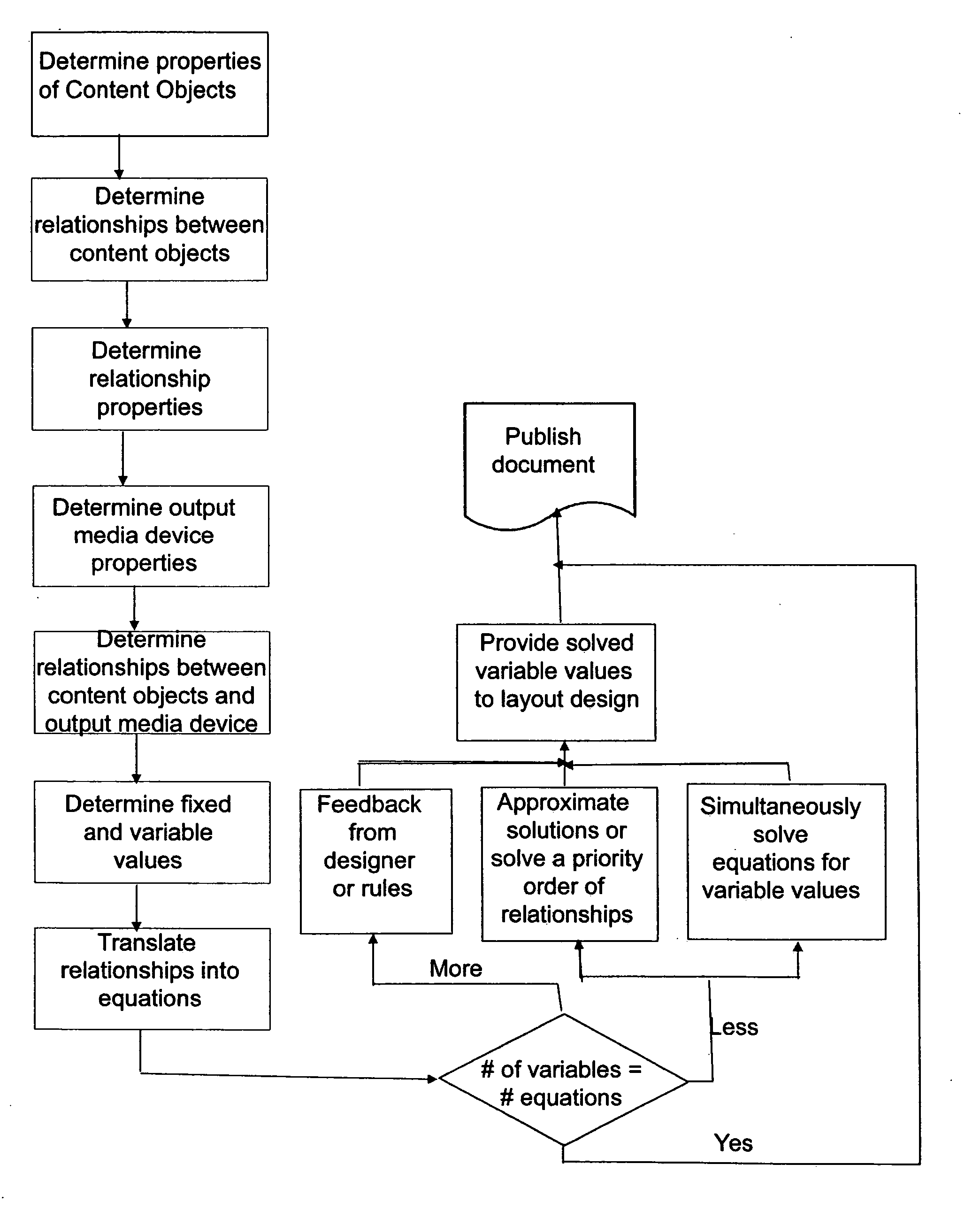
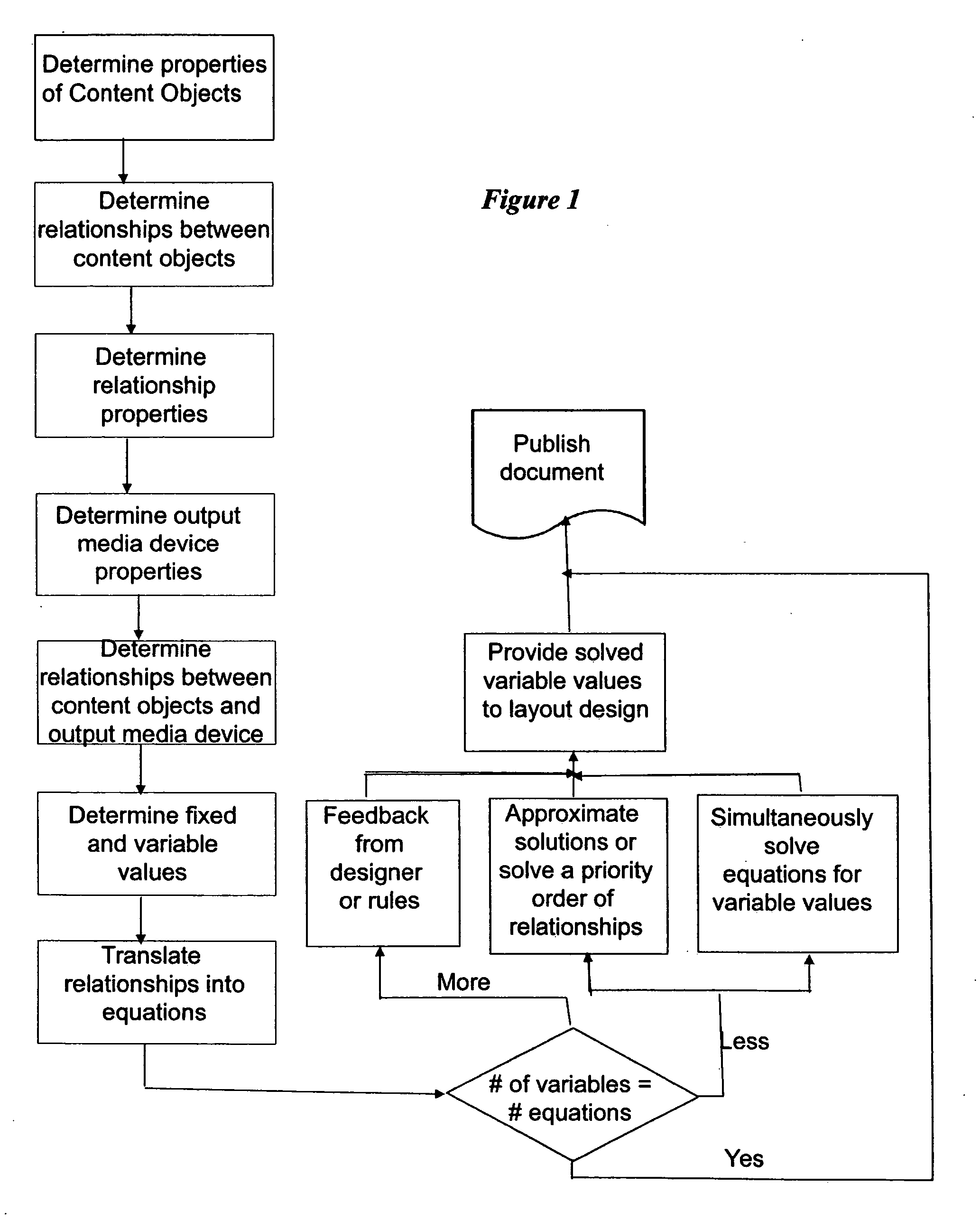
A completely free form layout of the physical content of a publication. The publication is represented as an unstructured set of content objects whose design relationships are specified as separate relationship objects, all of which interact with objects representing the properties of the display media. Through this representation, the present invention is better able to capture, represent and display the design intent of a designer throughout the entire design process.
Owner:QUARK INC
Capturing a user's design intent with resolvable objects
Owner:ARMSTRONG WORLD IND INC
Apparatus and Method For Measurement of the Film Cooling Effect Produced By Air Cooled Gas Turbine Components
InactiveUS20110119020A1Reduce the impactQuality improvementRadiation pyrometryMaterial heat developmentInfrared signatureCooling effect
Owner:MEYER TOOL
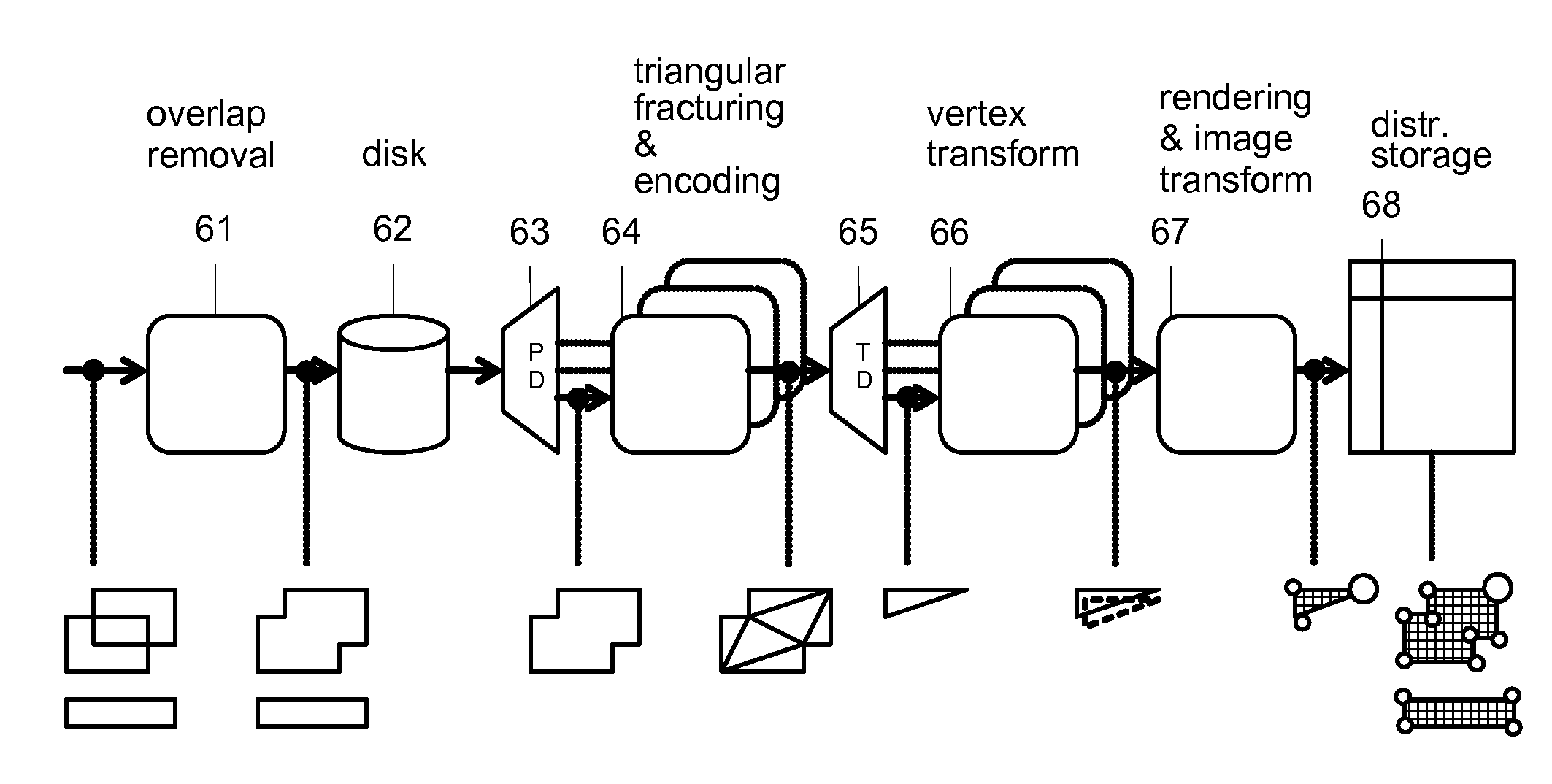
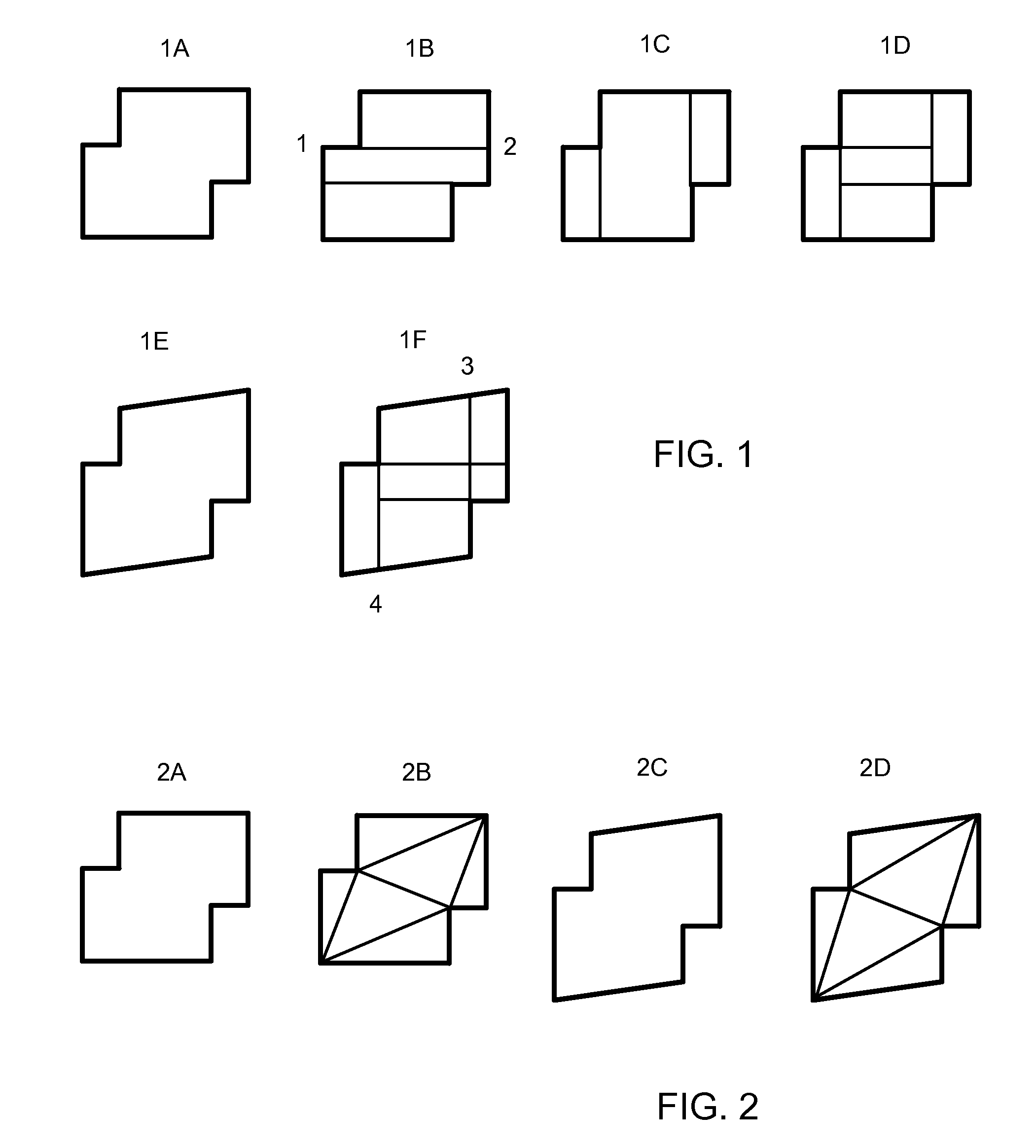
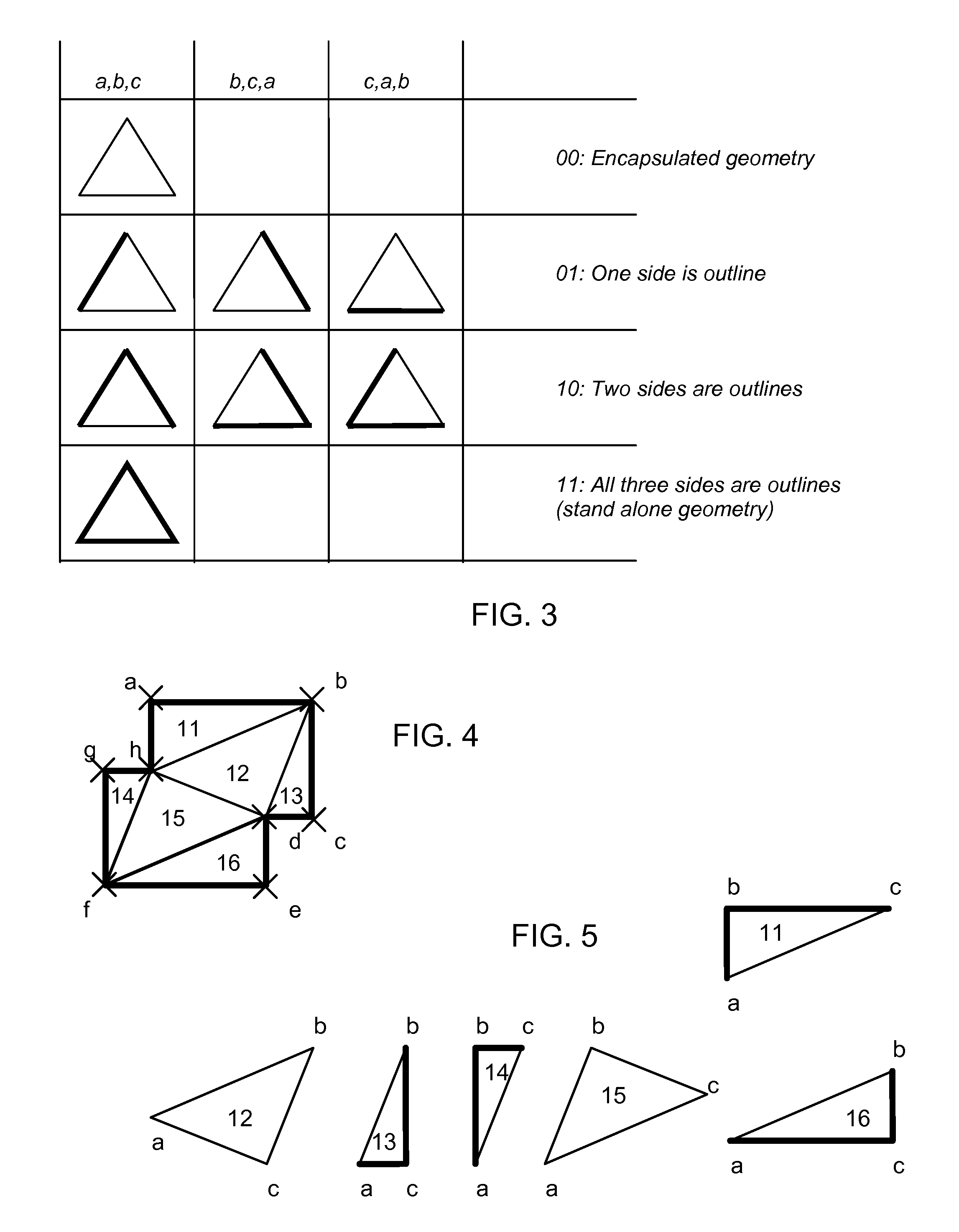
Triangulating Design Data and Encoding Design Intent for Microlithographic Printing
ActiveUS20080260283A1Electric discharge tubesGeometric image transformationTriangulationComputer science
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
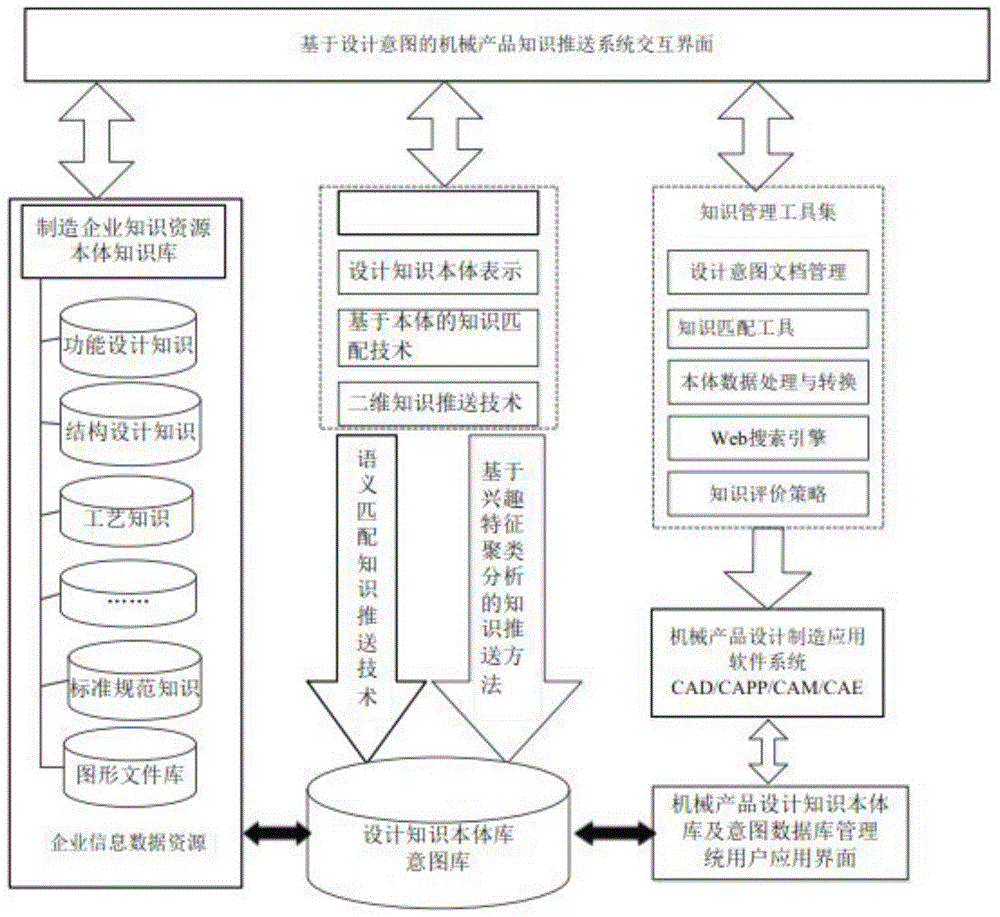
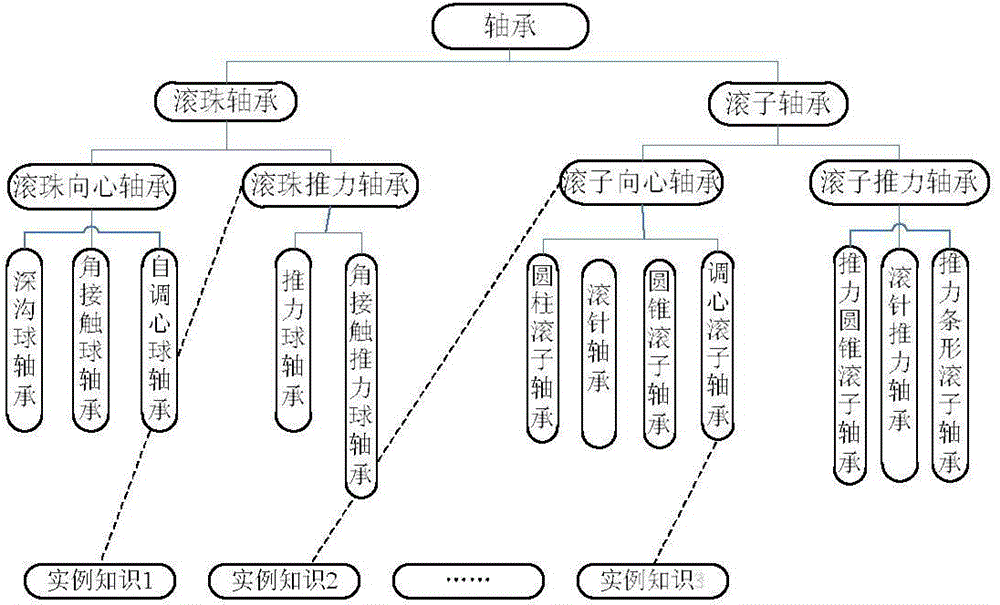
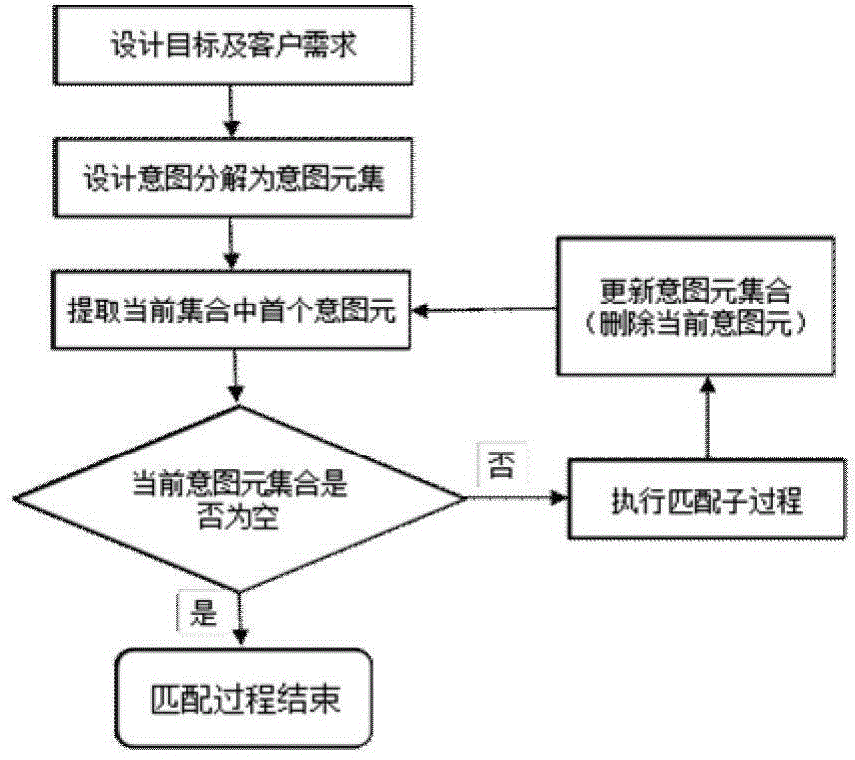
Mechanical product design two-dimensional knowledge pushing method based on design intent
ActiveCN104899242ARich knowledge push resultsAdapt to the needs of deepening developmentSpecial data processing applicationsInformatizationConcept Attribute
The present invention discloses a mechanical product design two-dimensional knowledge pushing method based on design intents. The mechanical product design two-dimensional knowledge pushing method mainly comprises: establishing a mechanical product design intent database, establishing a design intent acquisition and decomposition method, constructing a design intent attribute table by a rough set theory and performing reduction to obtain the simplest design intent set; establishing a mechanical product design knowledge ontology database; and calculating similarity degrees between intent elements and a compared knowledge ontology in a sequential traversing manner by using an improved similarity degree matching algorithm based on a knowledge ontology concept semantic distance and a concept attribute, sequentially carrying out matching on each intent element, of which the similarity degree is greater than a threshold value, in an intent element set from large to small according to the similarity degrees until completing all the matching, and completing matching of the knowledge ontologies by utilizing a text semantic similarity degree calculating method. The mechanical product design two-dimensional knowledge pushing method can solve the problem of low knowledge intelligent degree of knowledge pushing in the mechanical product design, can improve efficiency of mechanical product design and is suitable for the requirement of the manufacturing information engineering technology for deepening development.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for determining mask layouts for a multiple patterning process
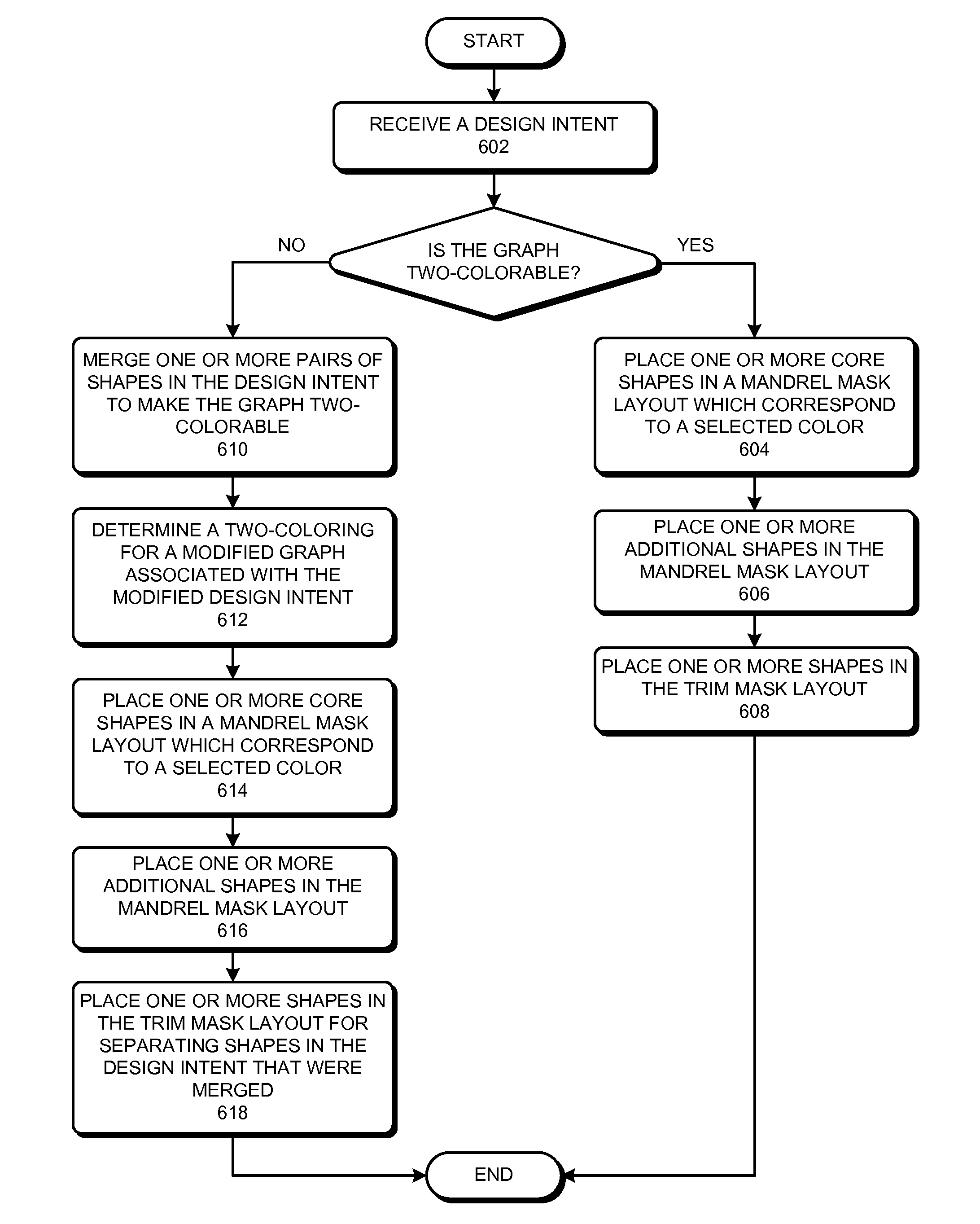
ActiveUS20080244504A1Improve toleranceIncreasing trenchOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringDesign intent
One embodiment provides a method for determining mask layouts. During operation, the system can receive a design intent. Next, the system can determine a set of critical edges in the design layout, and select a first edge and a second edge. The system can then determine a first trench and a second trench using the first edge and the second edge, respectively. Note that an edge of the first trench may substantially overlap with the first edge, and an edge of the second trench may substantially overlap with the second edge. Next, the system may assign the first trench and the second trench to the first mask layout and the second mask layout, respectively. The system can then increase the first trench and the second trench, thereby improving pattern fidelity. The resulting mask layouts may be used in a double patterning process.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
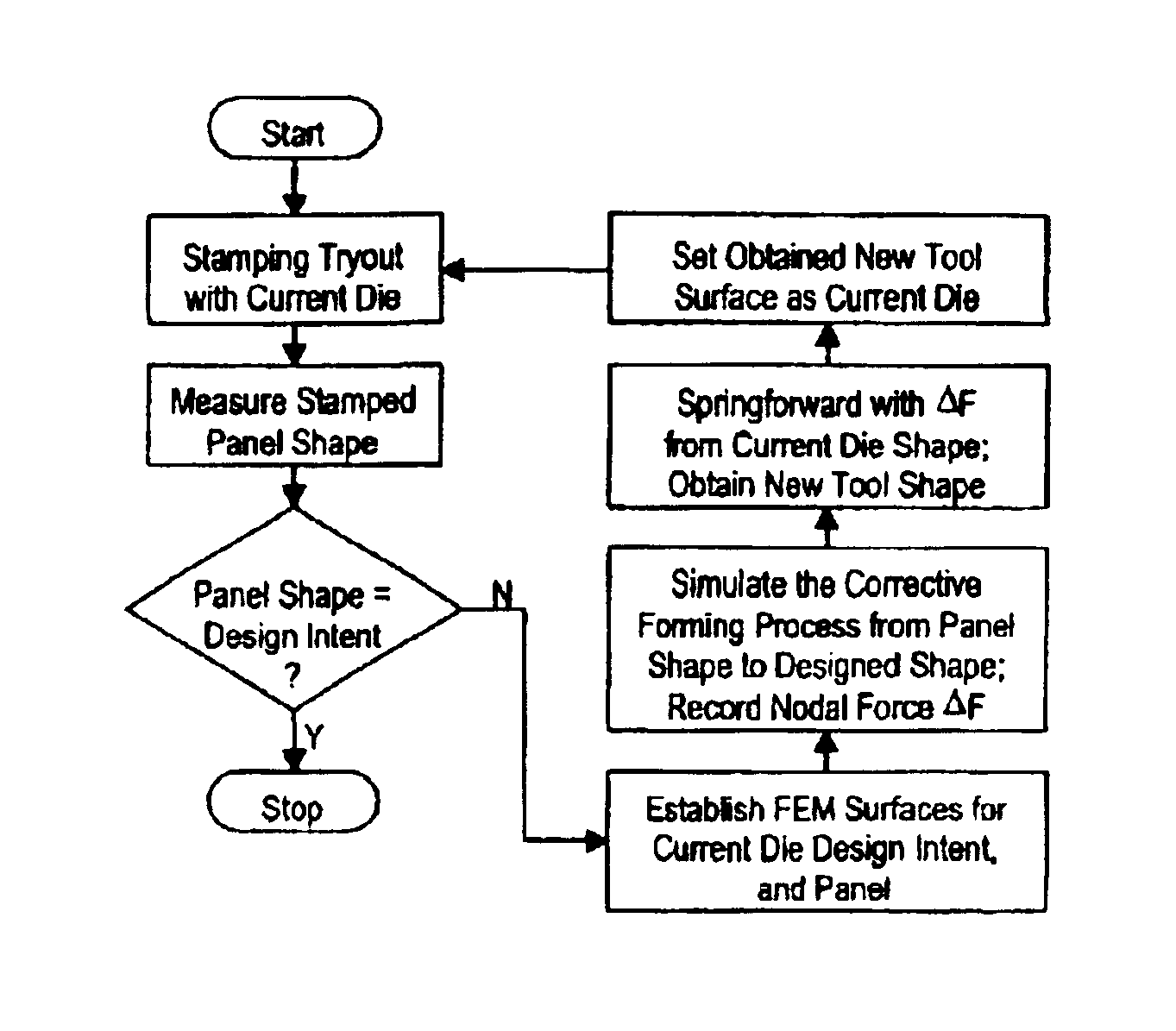
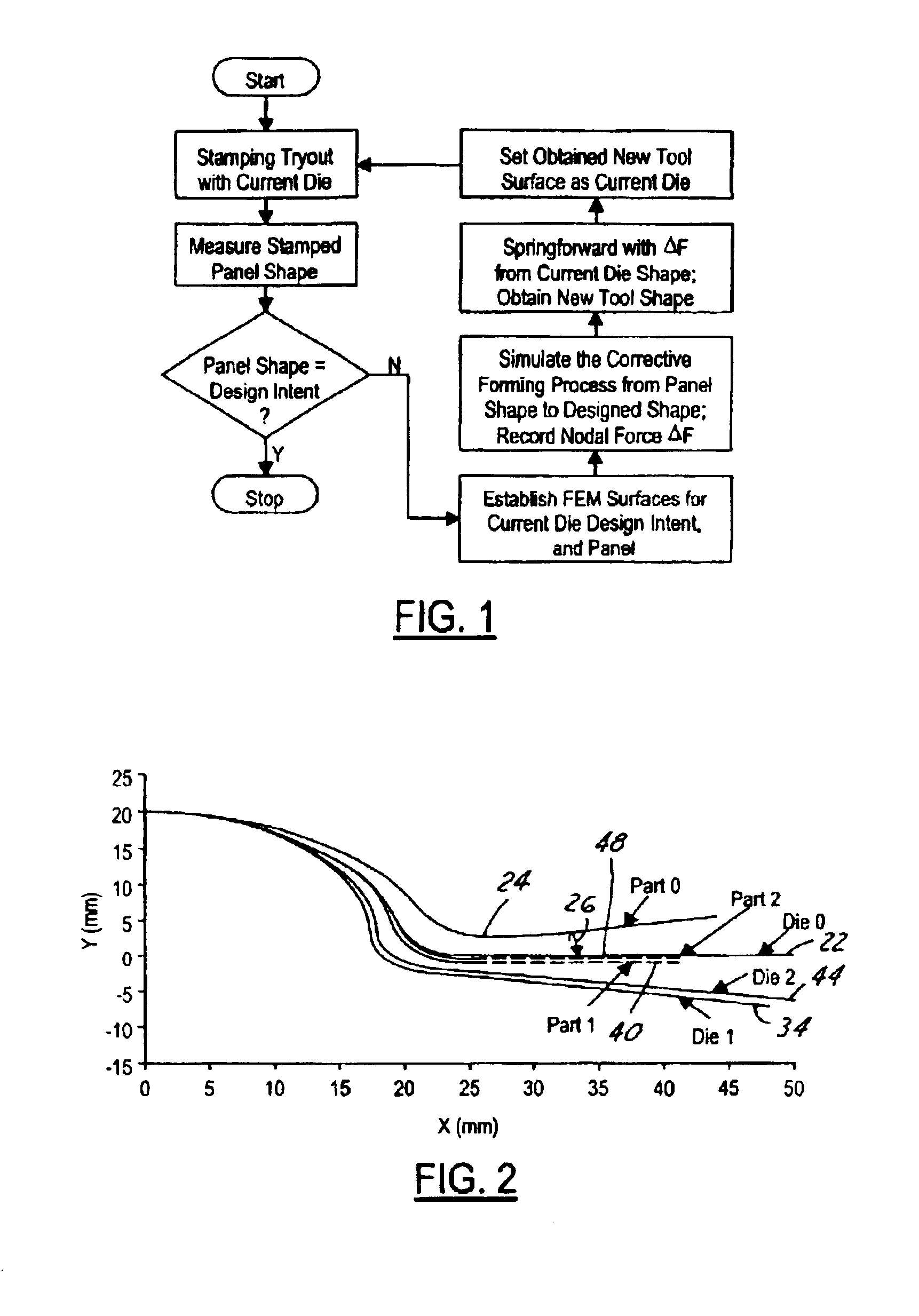
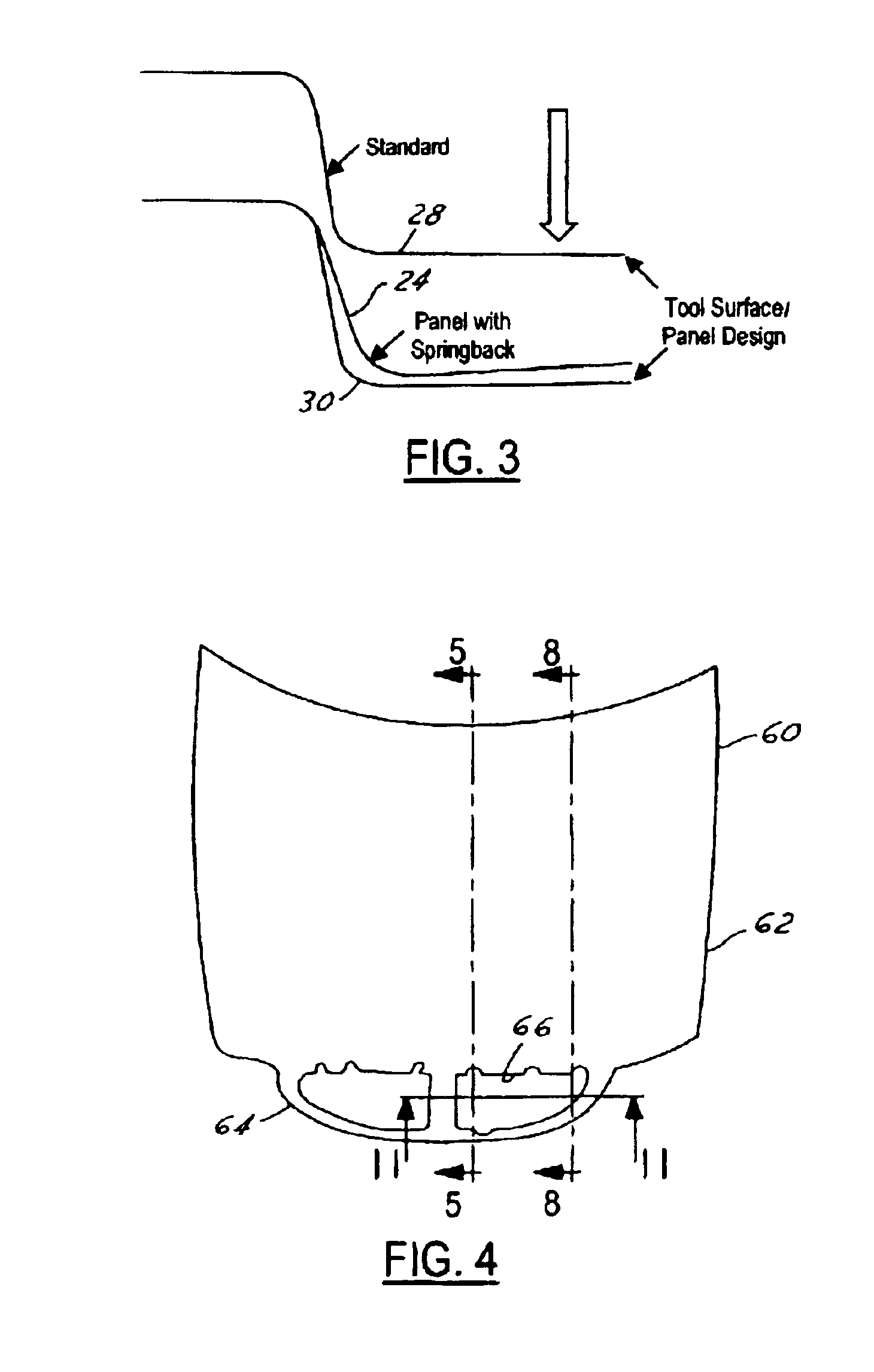
Method of modifying stamping tools for spring back compensation based on tryout measurements
InactiveUS6947809B2Apparent advantageShaping toolsSpecial data processing applicationsIndustrial engineeringDesign intent
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
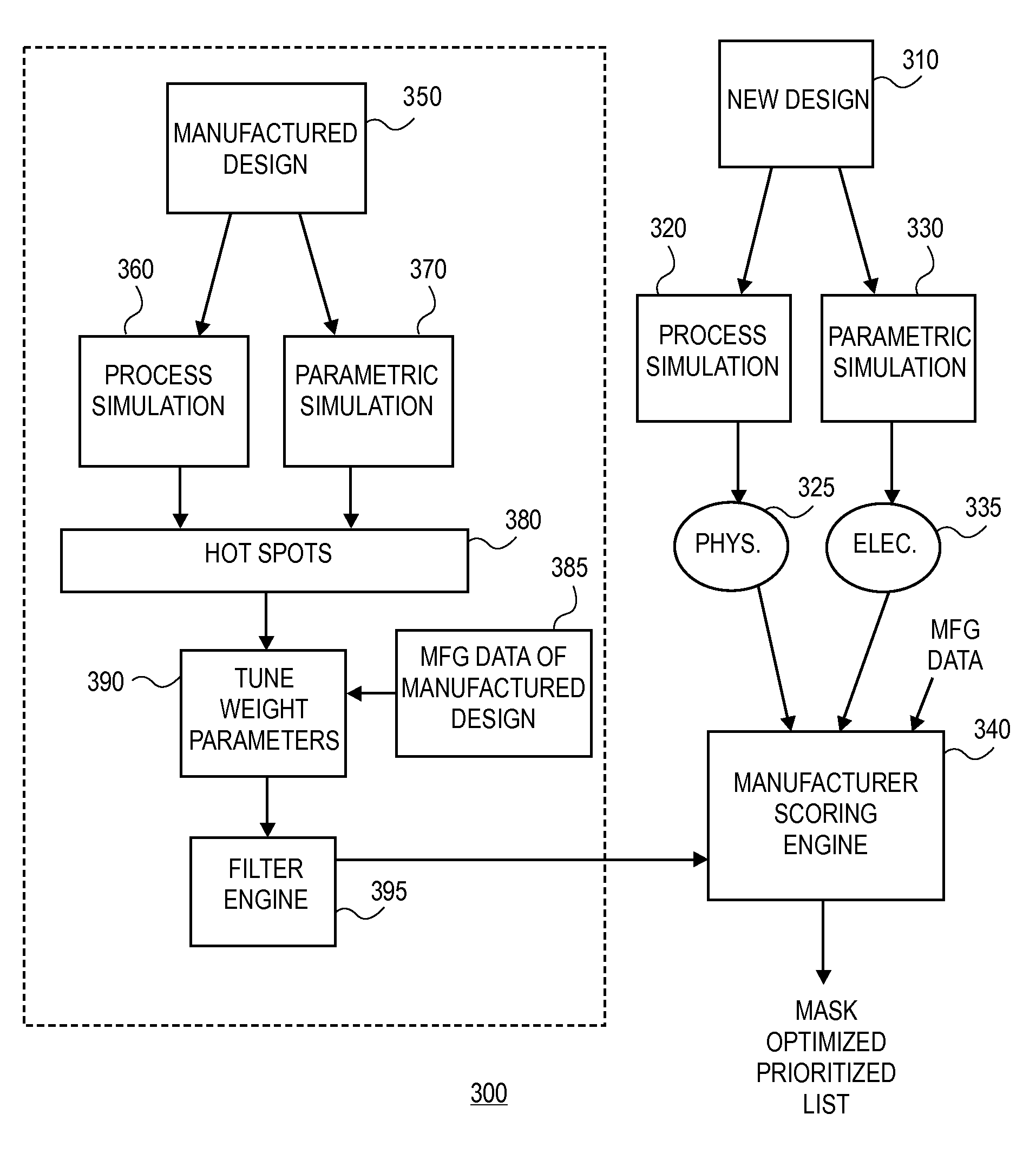
Modeling and cross correlation of design predicted criticalities for optimization of semiconductor manufacturing
InactiveUS20080147374A1CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsMetrologyInformation sharing
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
System and method for identifying original design intents using 3D scan data
ActiveUS7814441B2Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Owner:INUS TECH
Integrated method for measurement and reconstruction of three-dimensional model and system thereof
InactiveCN101630418ASimplify the reverse engineering processFully consider the design intentUsing optical meansStereoscopic photographySurface markerComputer vision
Owner:白晓亮 +2
Boundary representation per feature methods and systems
InactiveUS7277835B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsComputation using non-denominational number representationPattern matchingData exchange
Owner:PROFICIENCY
Capturing a user's intent in design software
ActiveUS8751950B2Efficient constructionAccurate representationGeometric CADCAD network environmentInterior spaceUser input
Owner:ARMSTRONG WORLD IND INC
Modeling and cross correlation of design predicted criticalities for optimization of semiconductor manufacturing
InactiveUS7694244B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMetrologyInformation sharing
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method and system for designing objects using design intent merge
ActiveUS7155375B1Computation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designFistDigital mockup
Owner:IMPACTXOFT
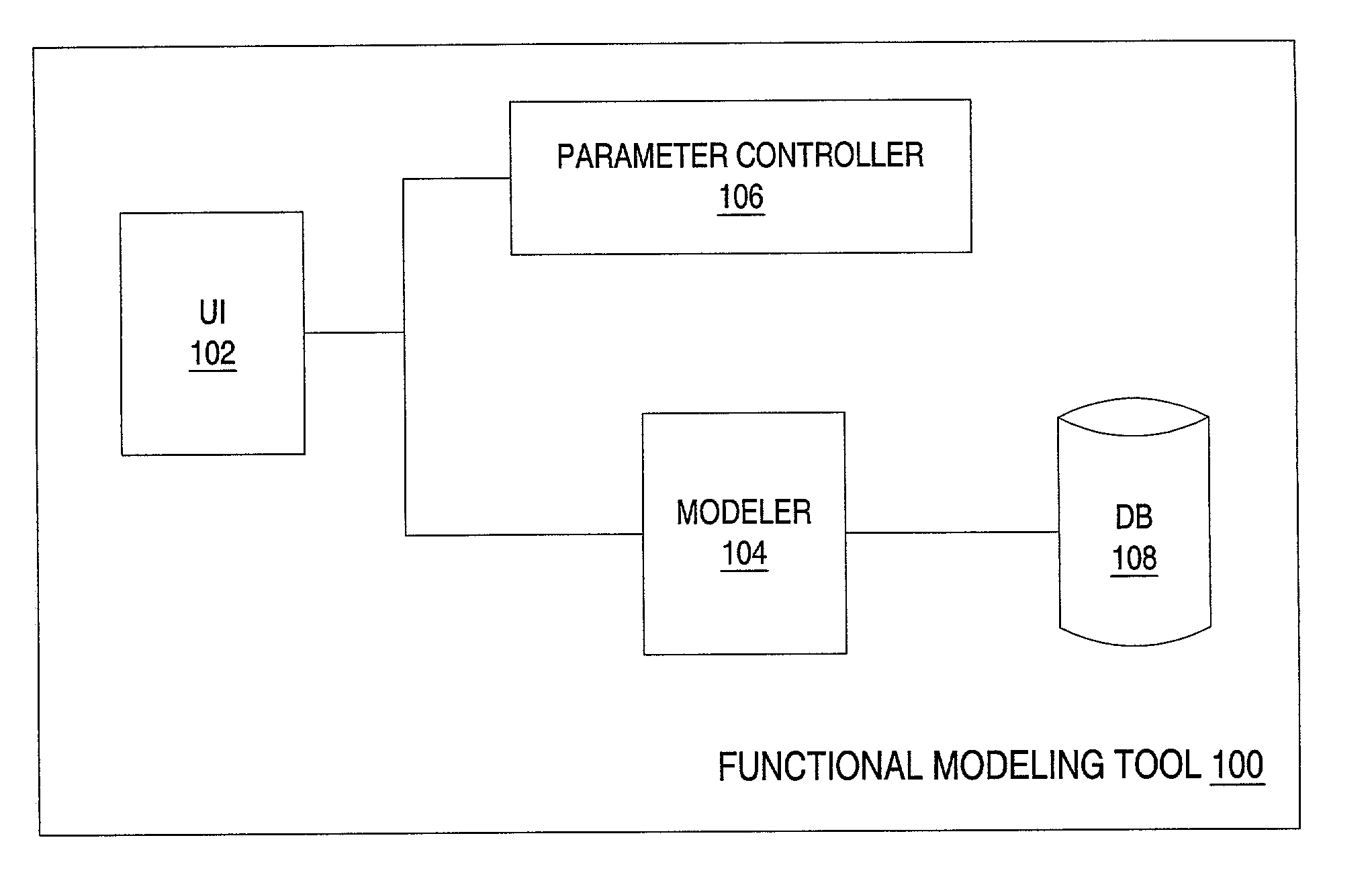
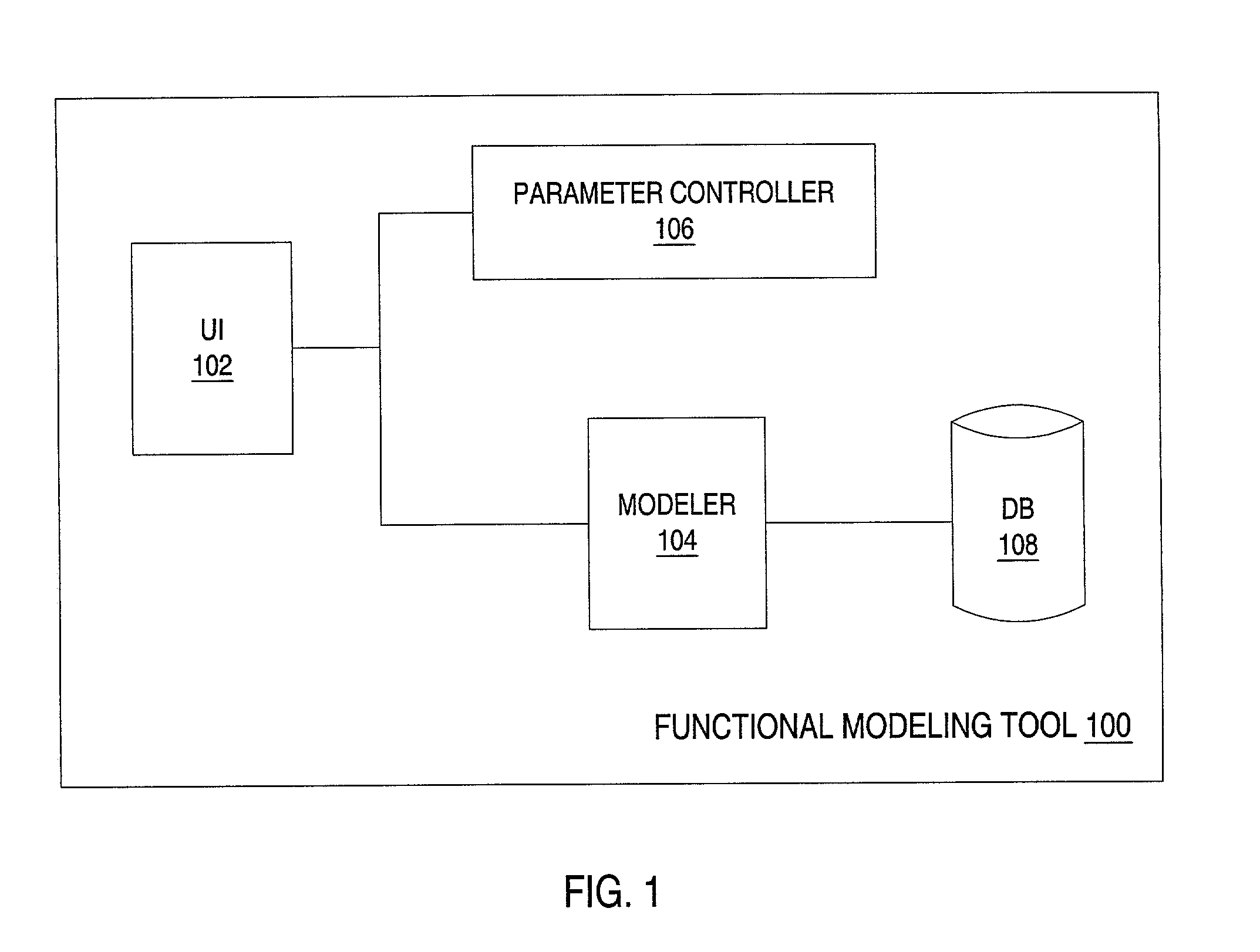
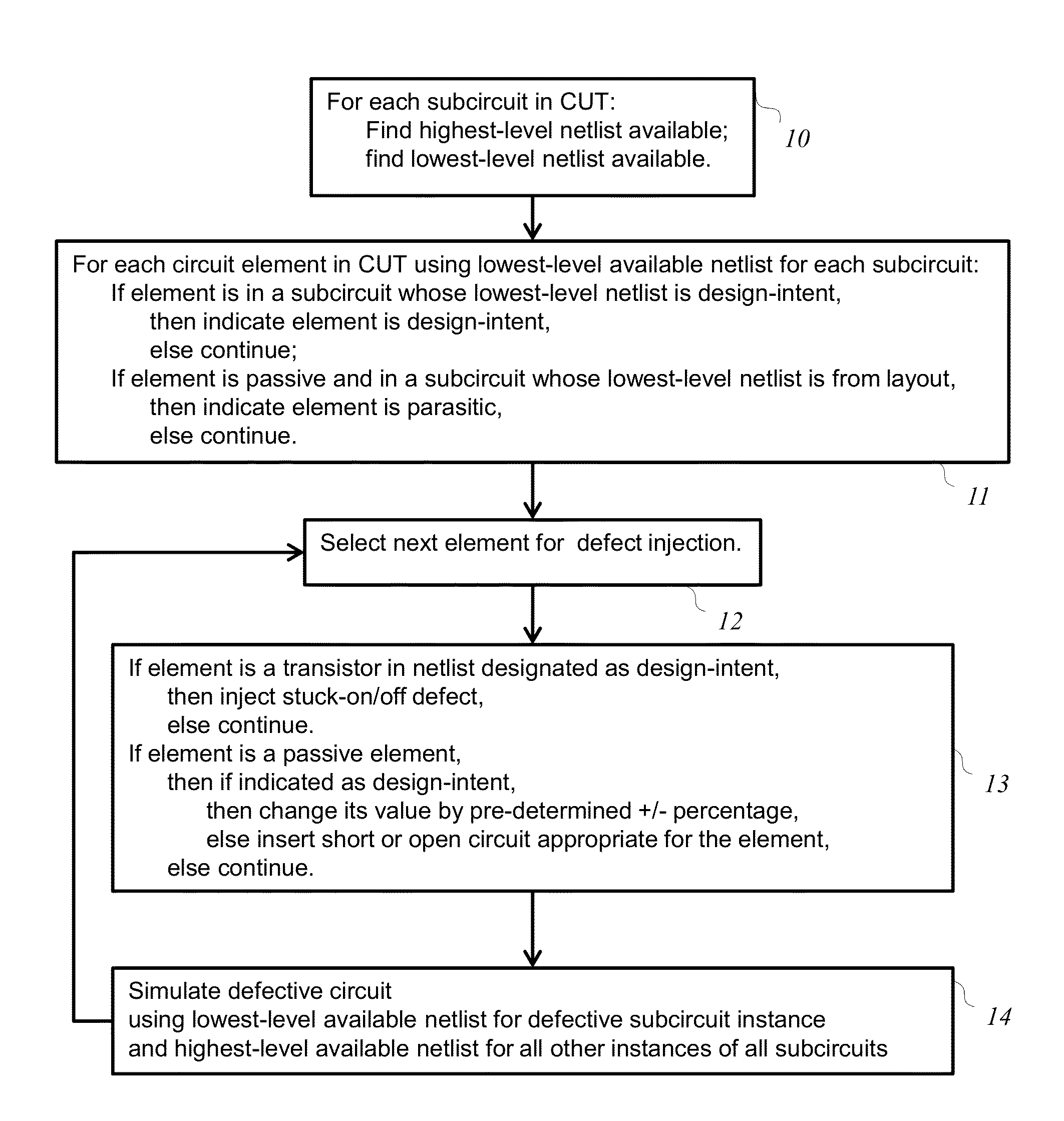
Defect Injection For Transistor-Level Fault Simulation
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Laser scanner or laser tracker having a projector
Owner:FARO TECH INC
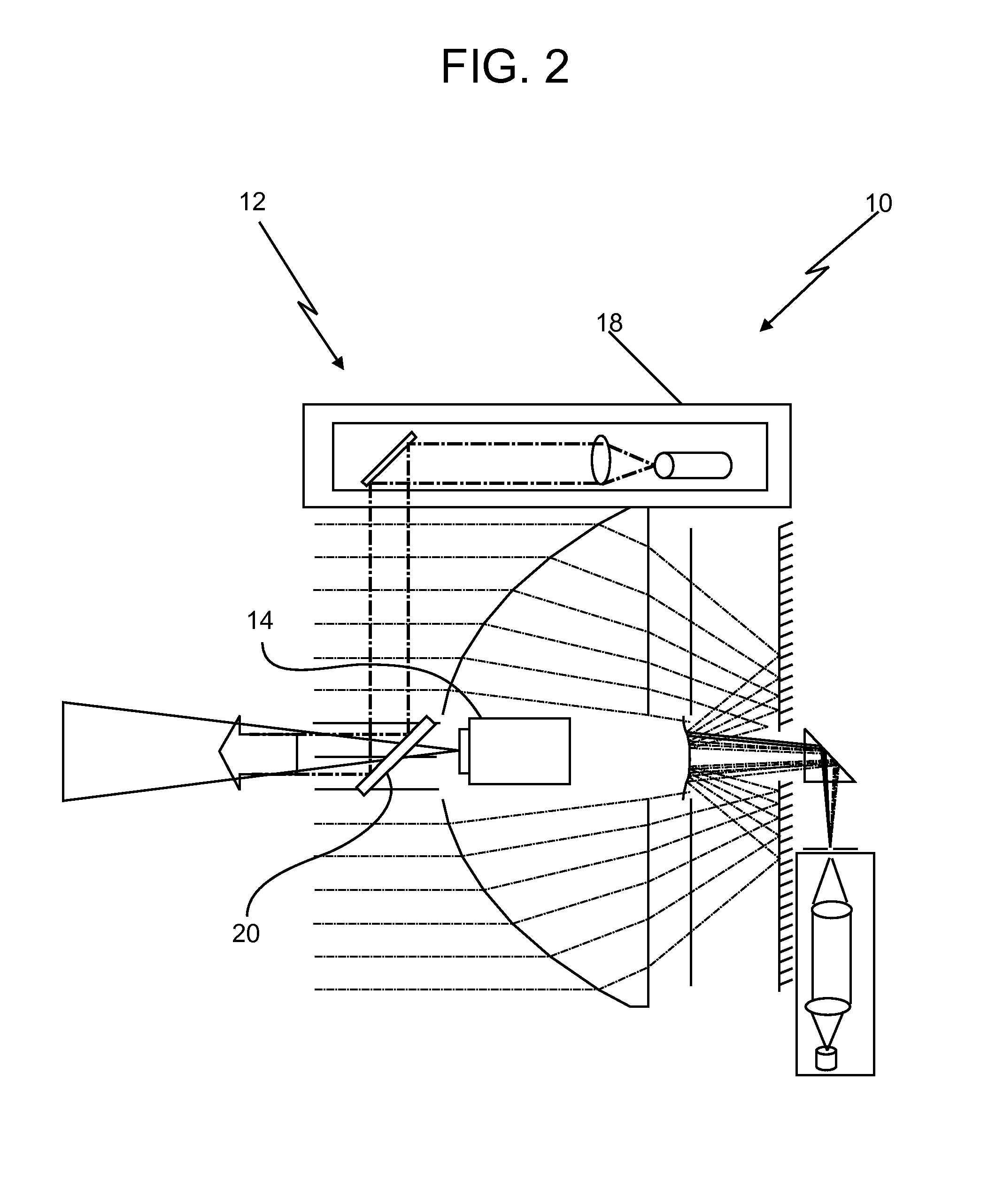
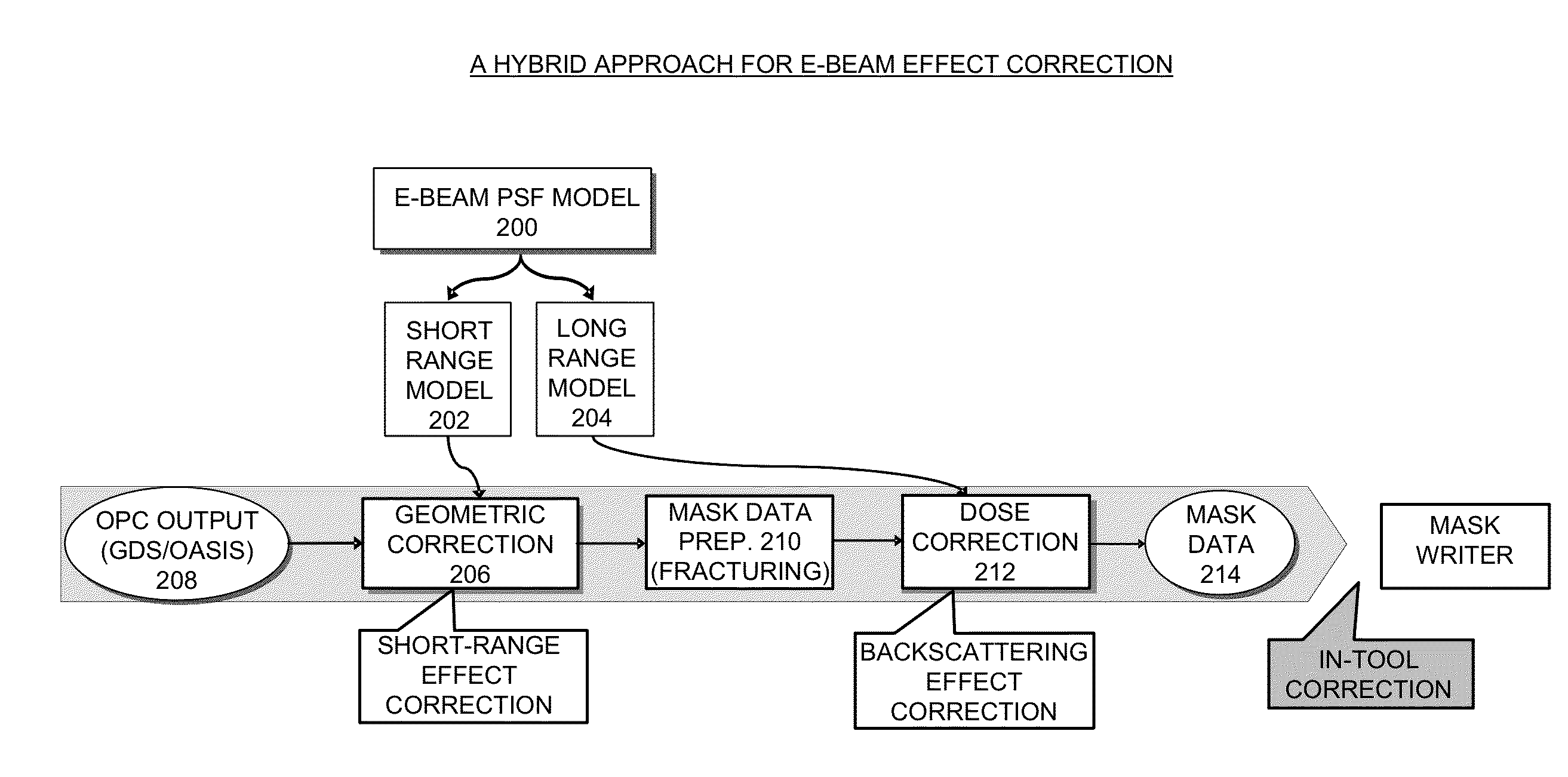
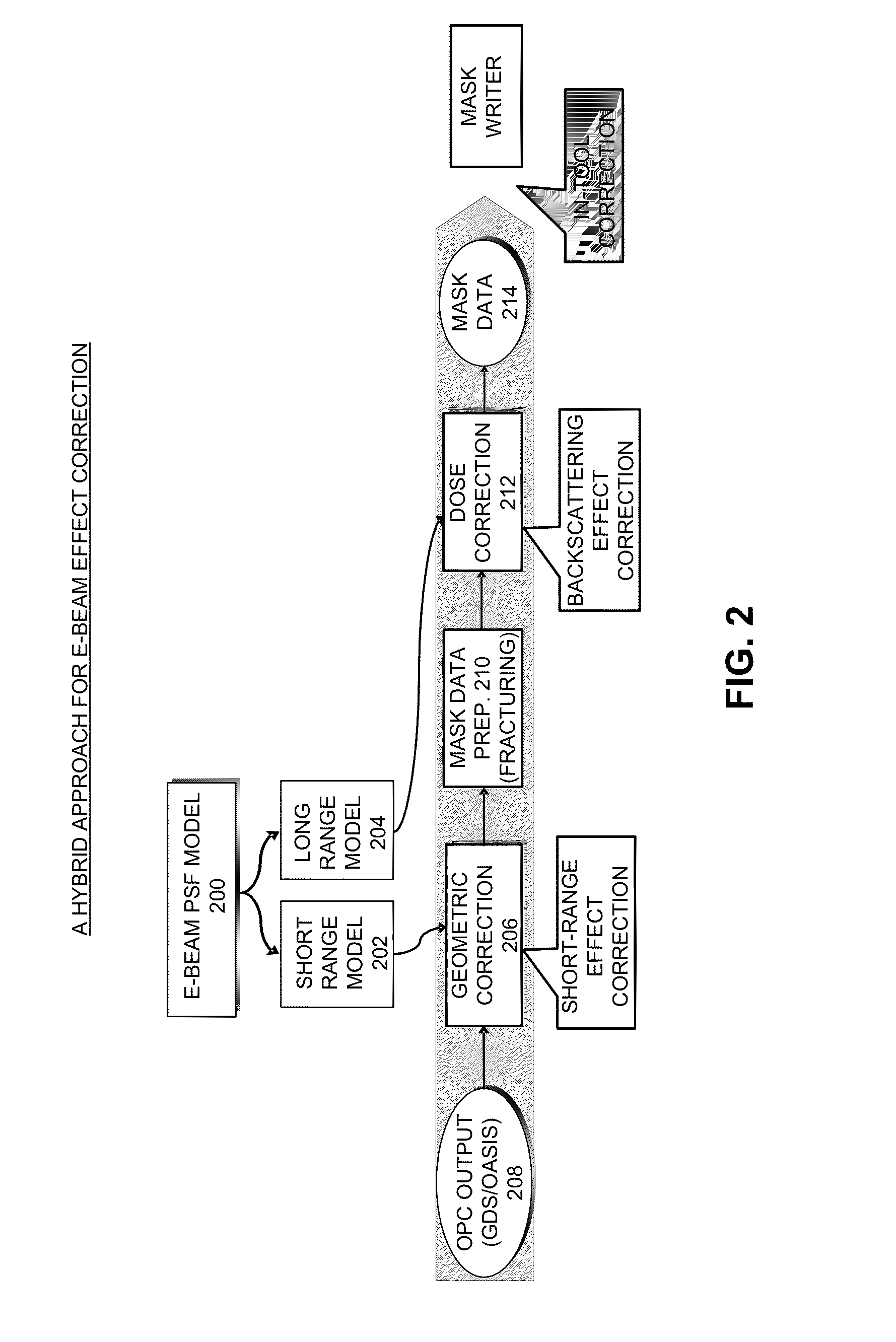
Modeling and correcting short-range and long-range effects in e-beam lithography
ActiveUS20140114634A1Increase weightReduce weightElectric discharge tubesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusLithography processLithographic artist
Processes and apparatuses are described for modeling and correcting electron-beam (e-beam) proximity effects during e-beam lithography. An uncalibrated e-beam model, which includes a long-range component and a short-range component, can be calibrated based on one or more test layouts. During correction, a first resist intensity map can be computed based on the long-range component of the calibrated e-beam model and a mask layout. Next, a target pattern in the mask layout can be corrected by, iteratively: (1) computing a second resist intensity map based on the short-range component of the calibrated e-beam model and the target pattern; (2) obtaining a combined resist intensity map by combining the first resist intensity map and the second resist intensity map; and (3) adjusting the target pattern based on the combined resist intensity map and the design intent.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap