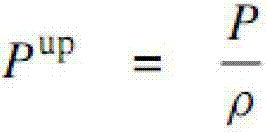Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71results about How to "Improve chip yield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
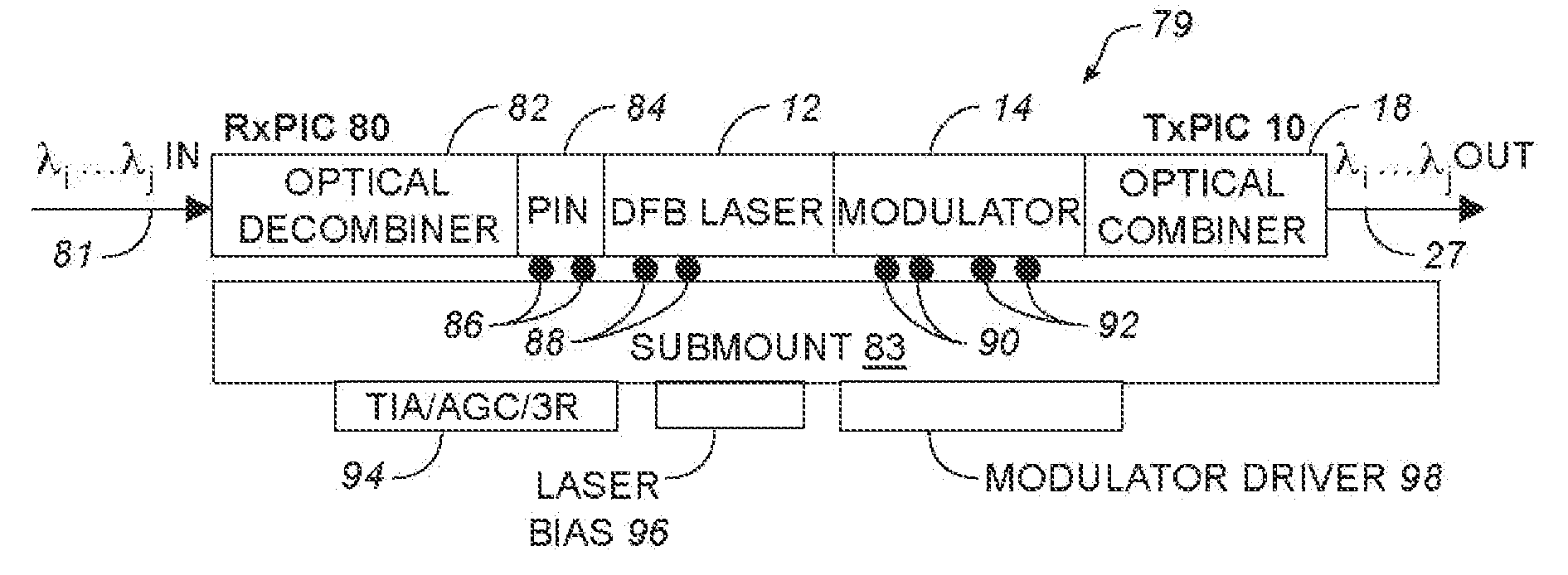
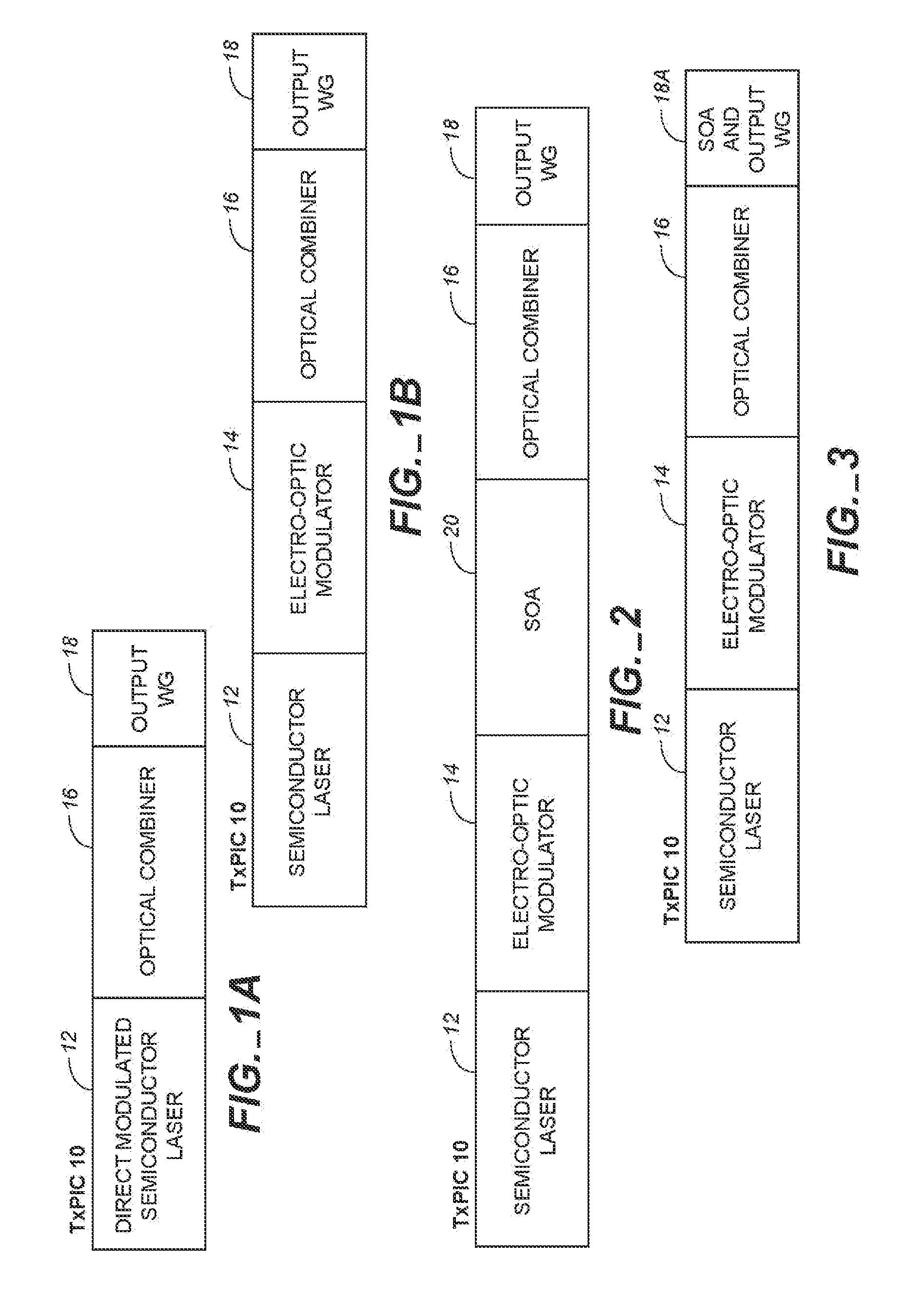
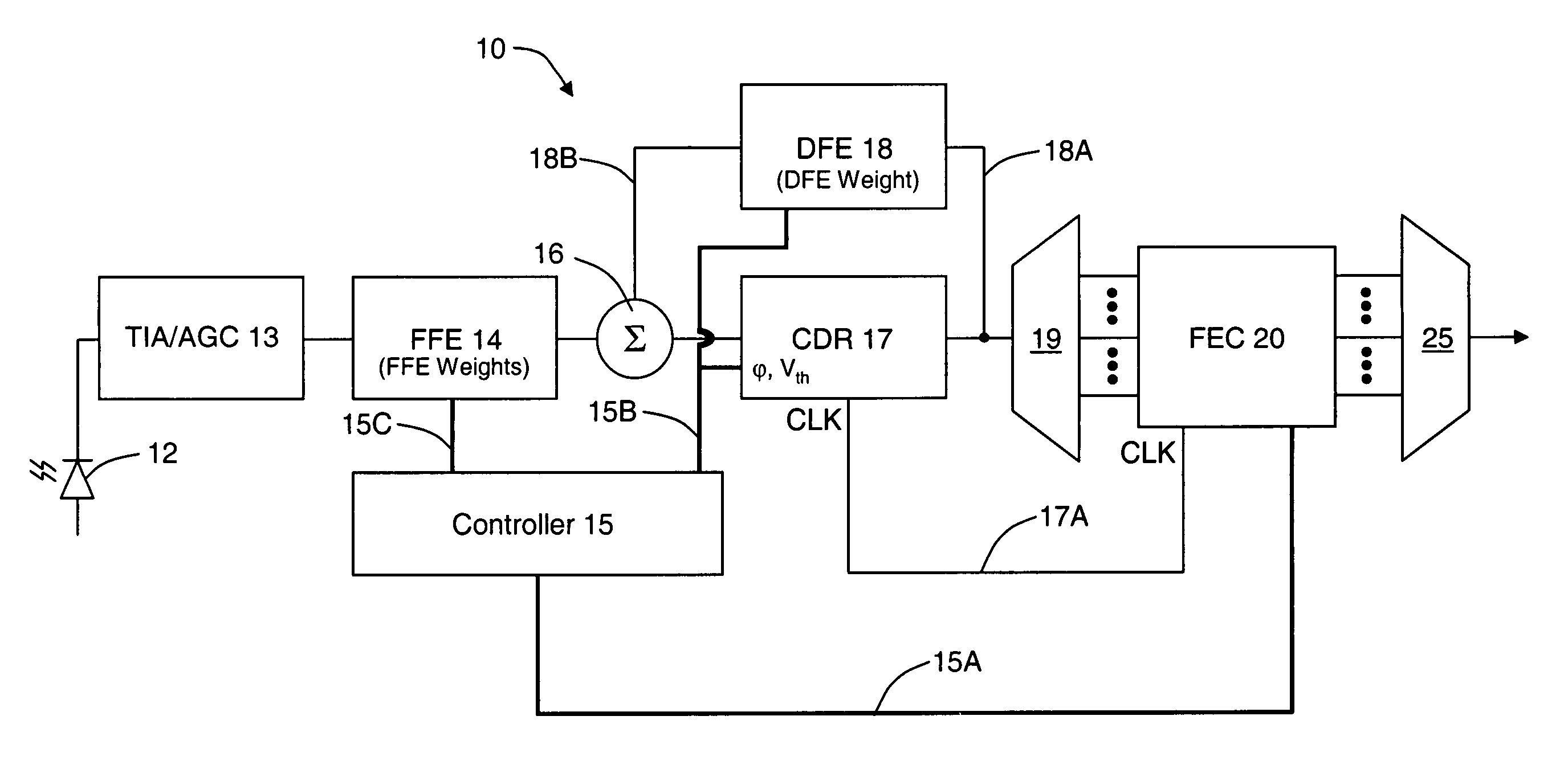
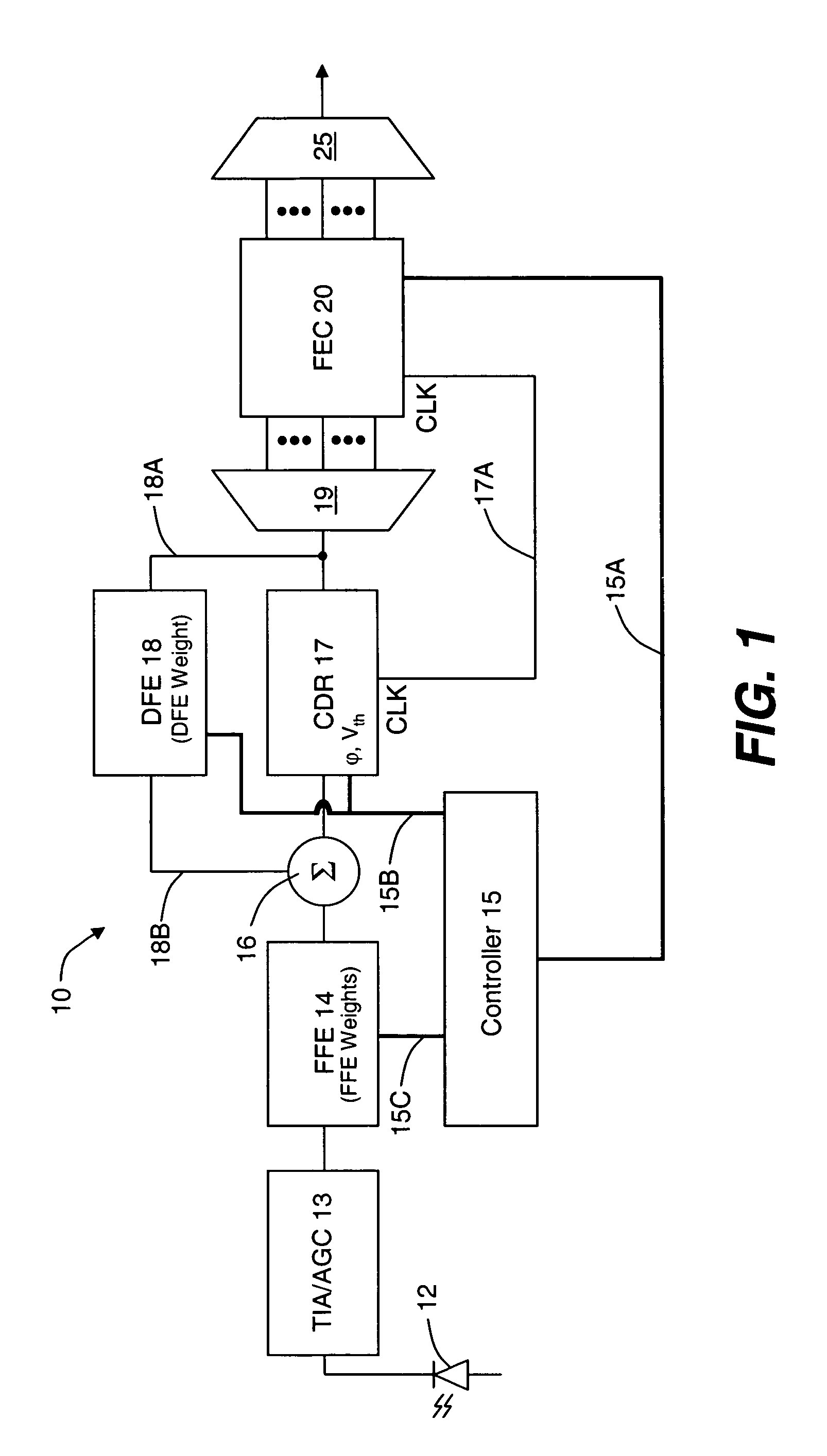
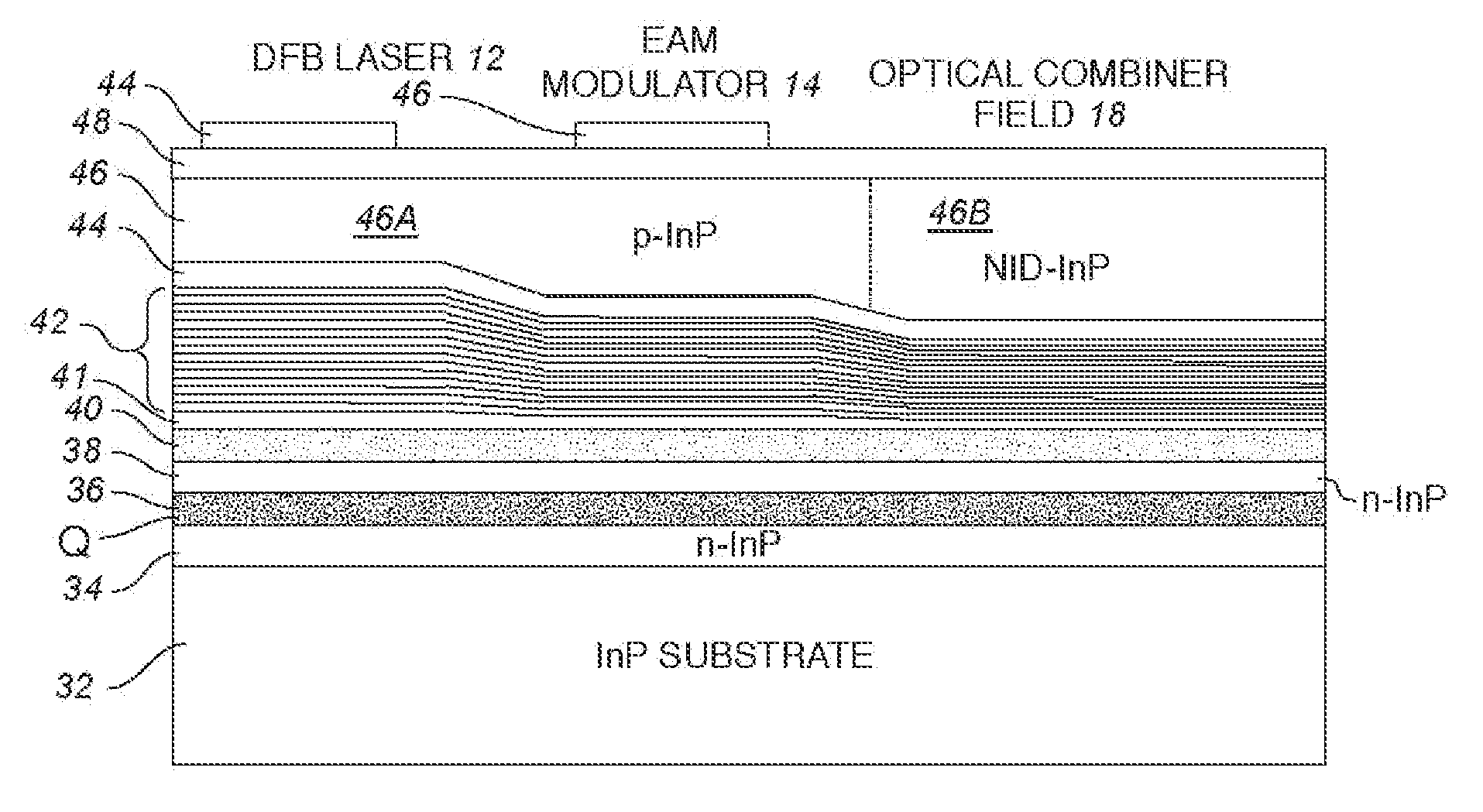
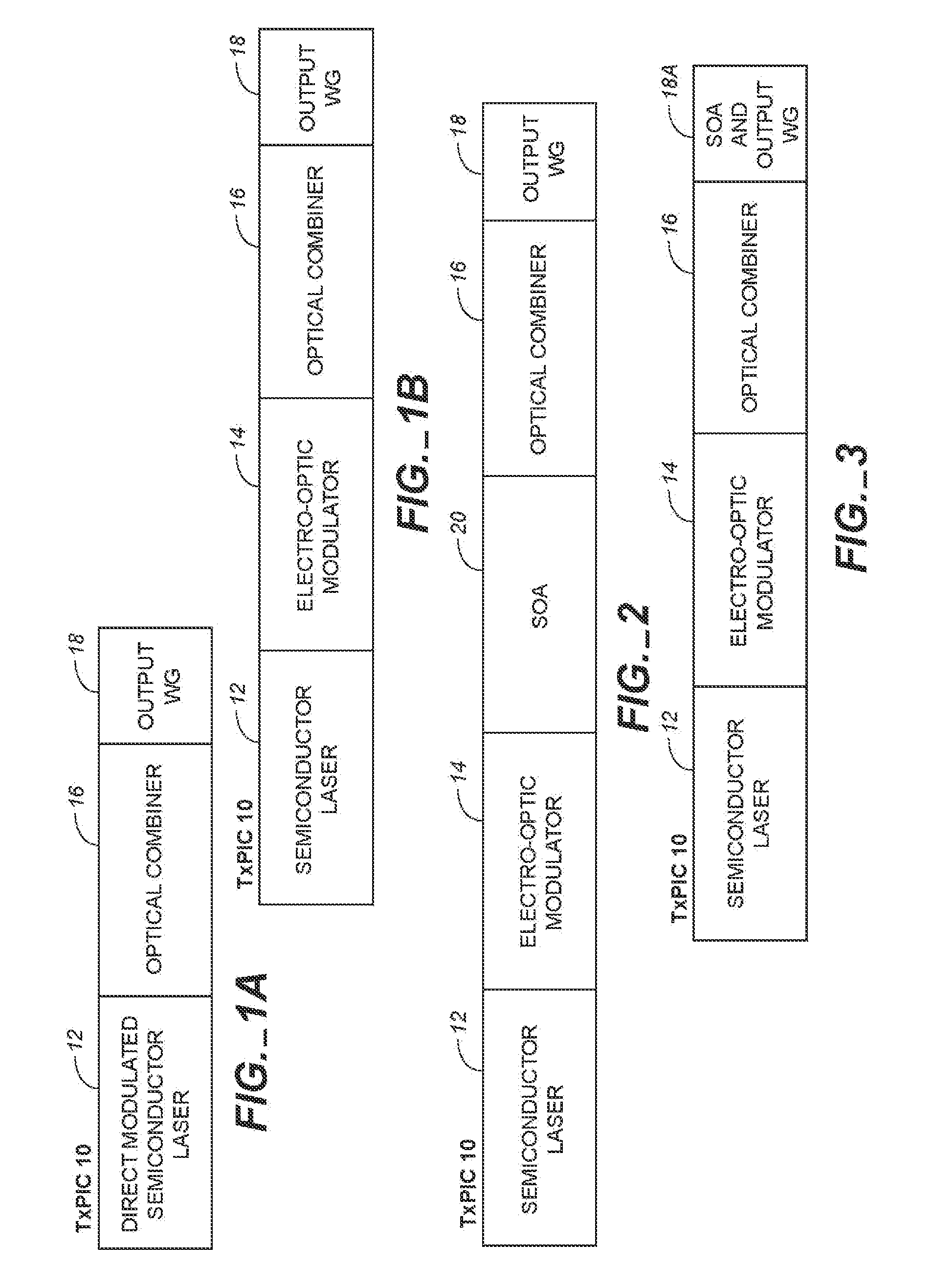
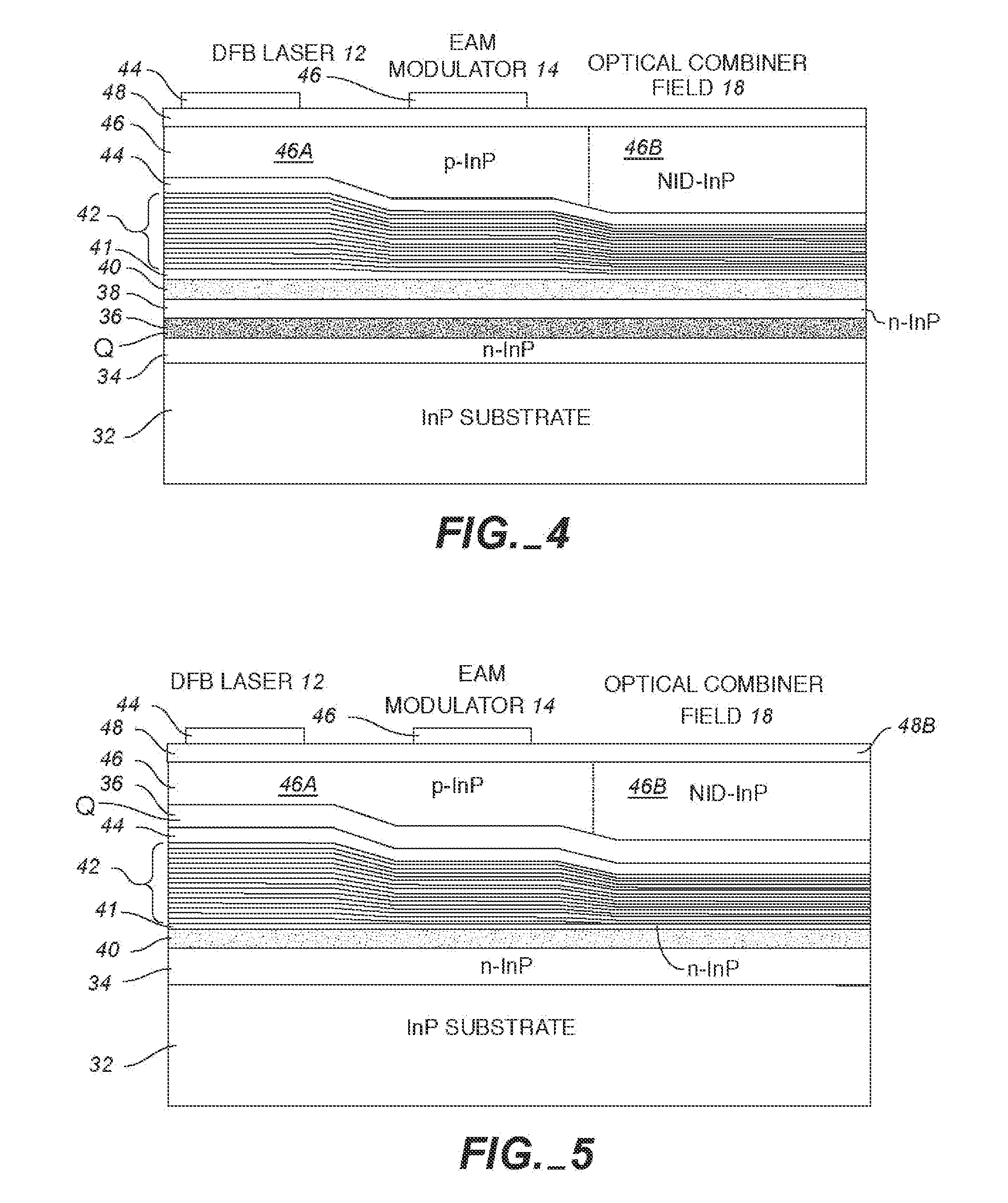
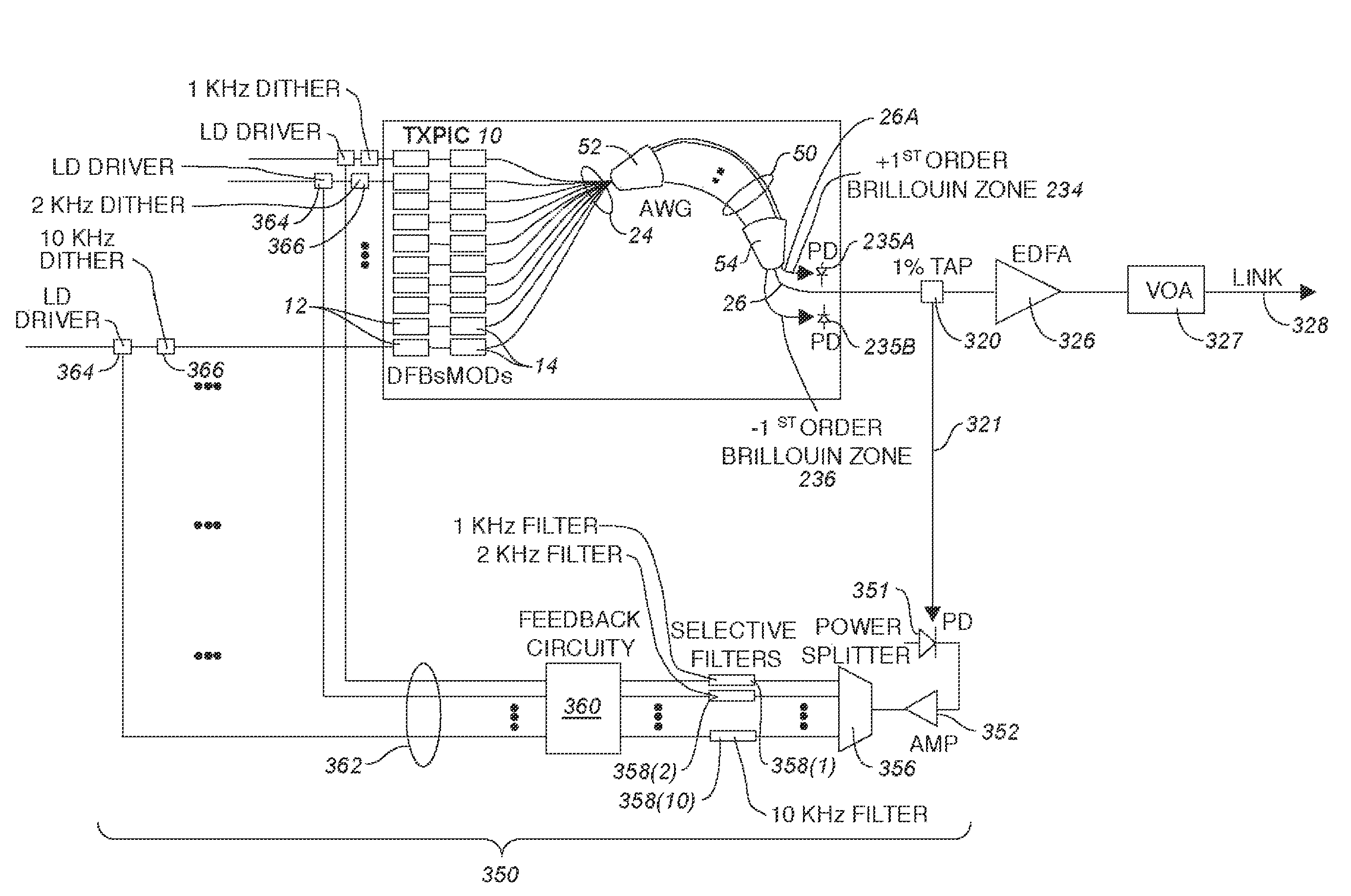
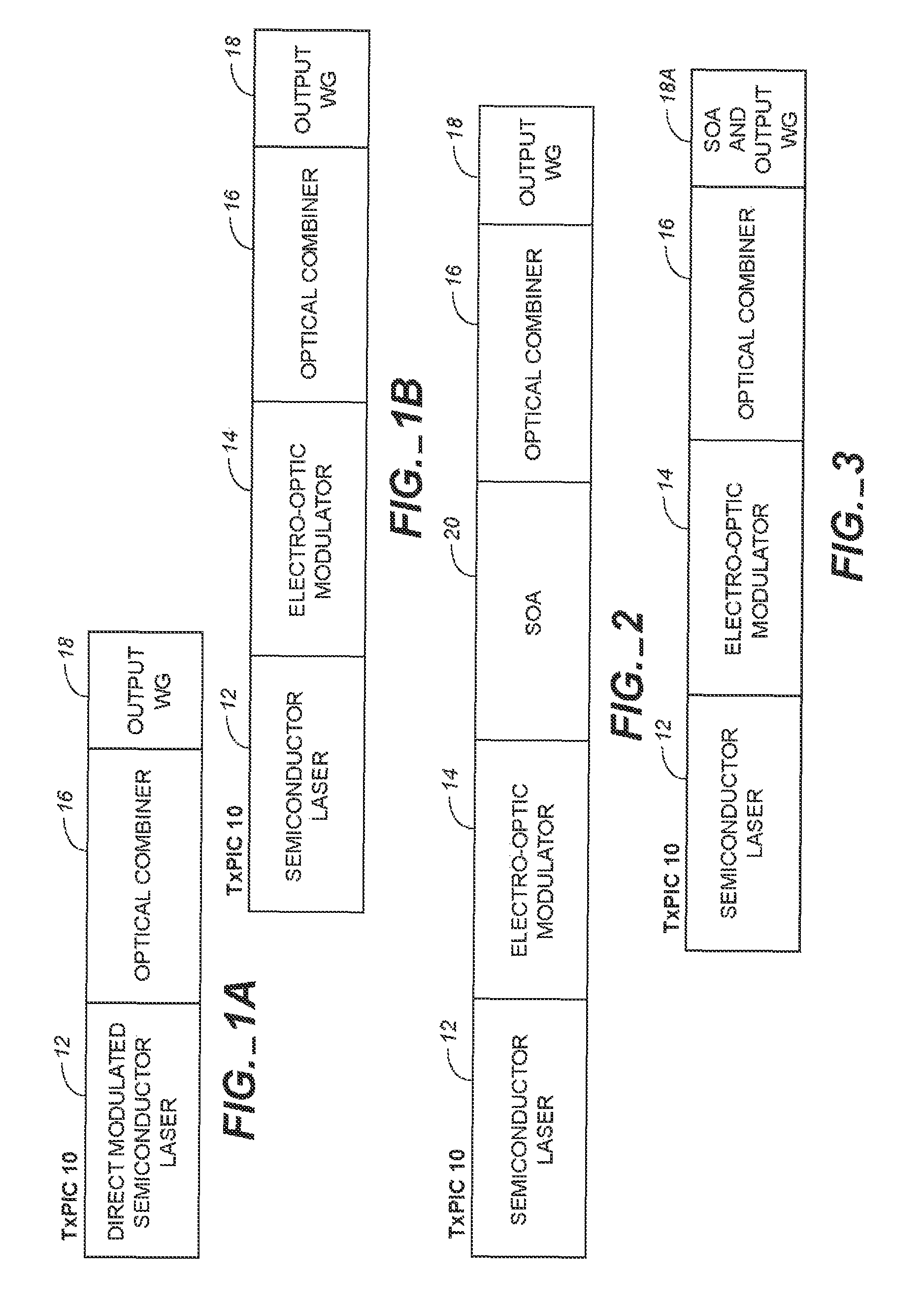
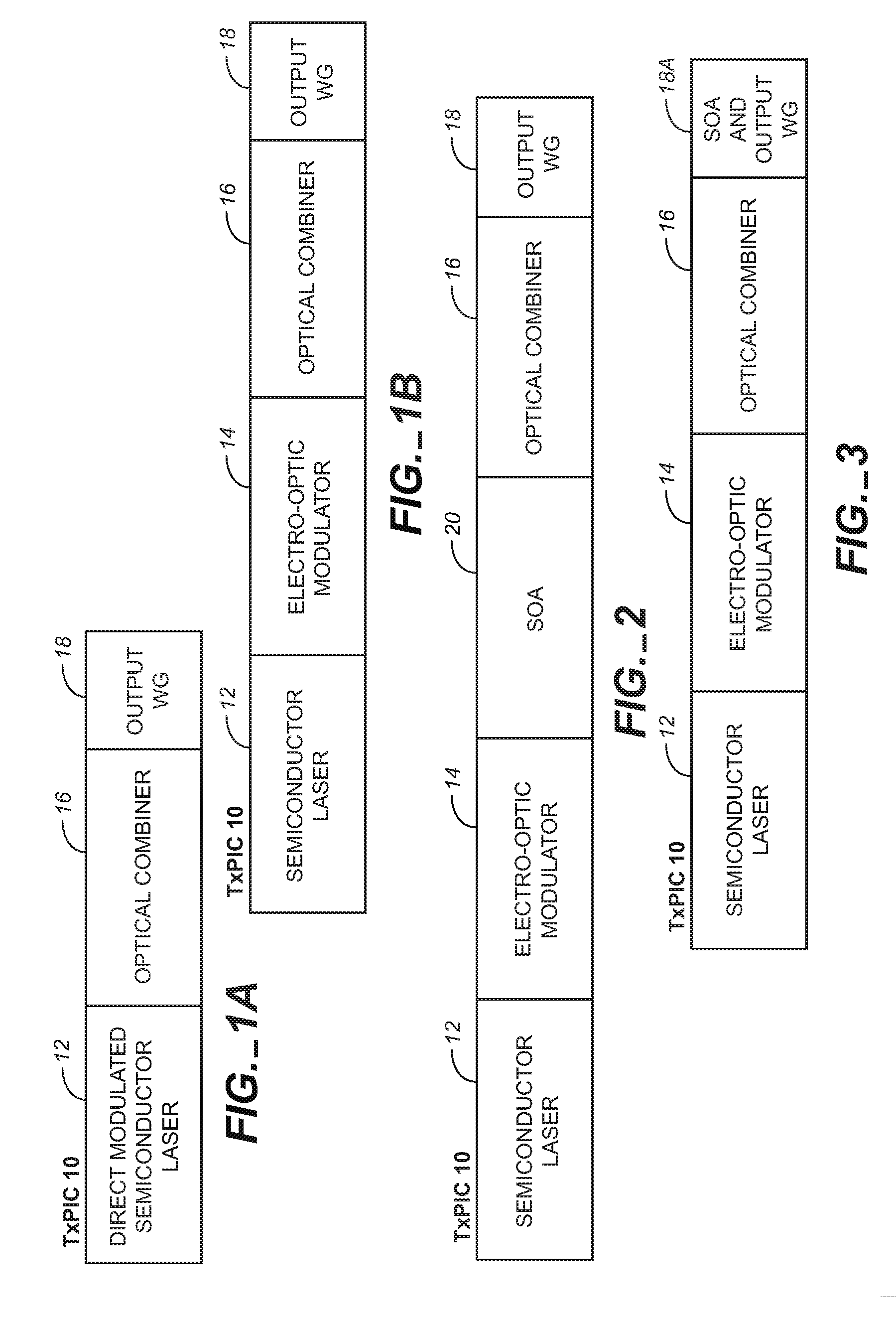
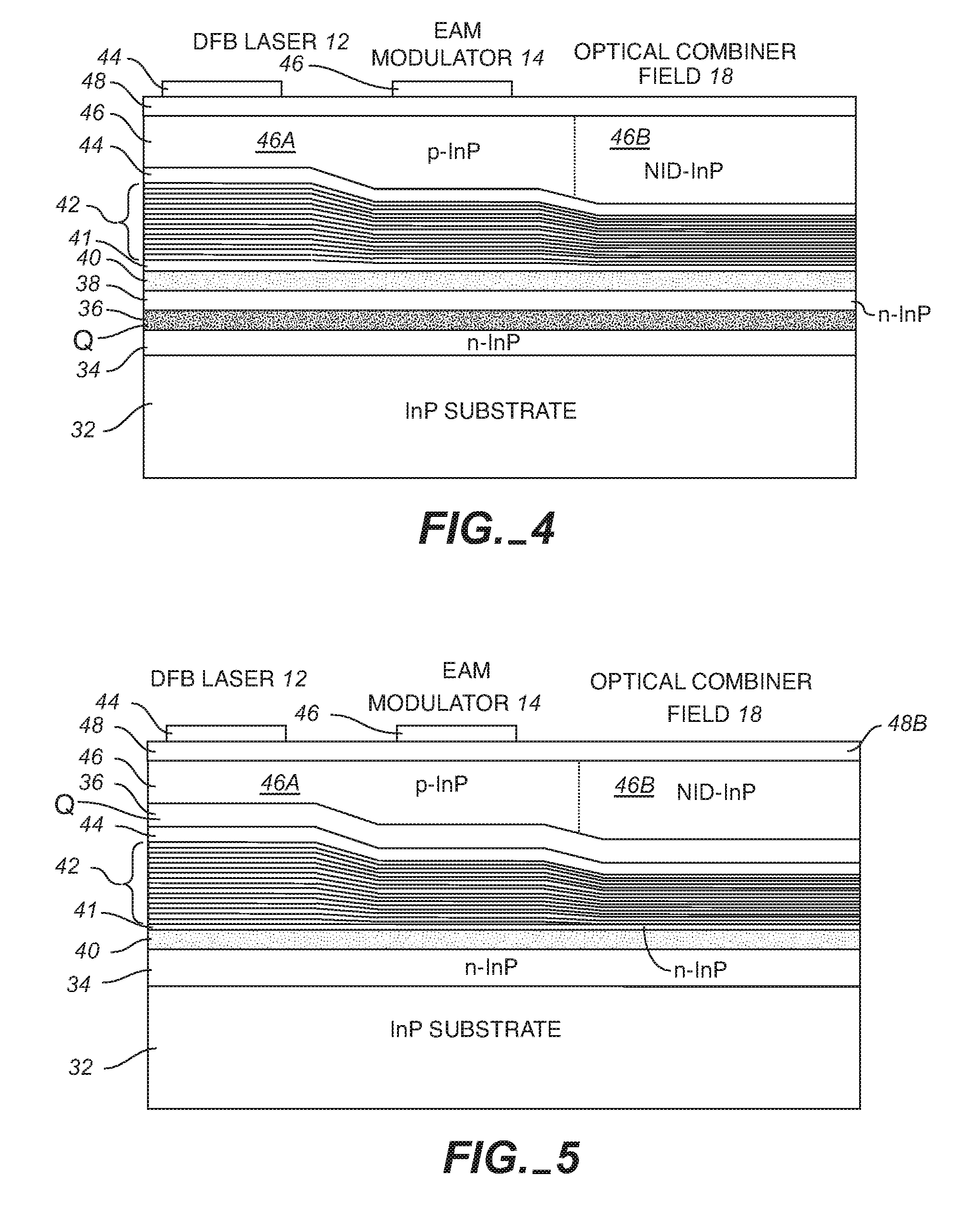
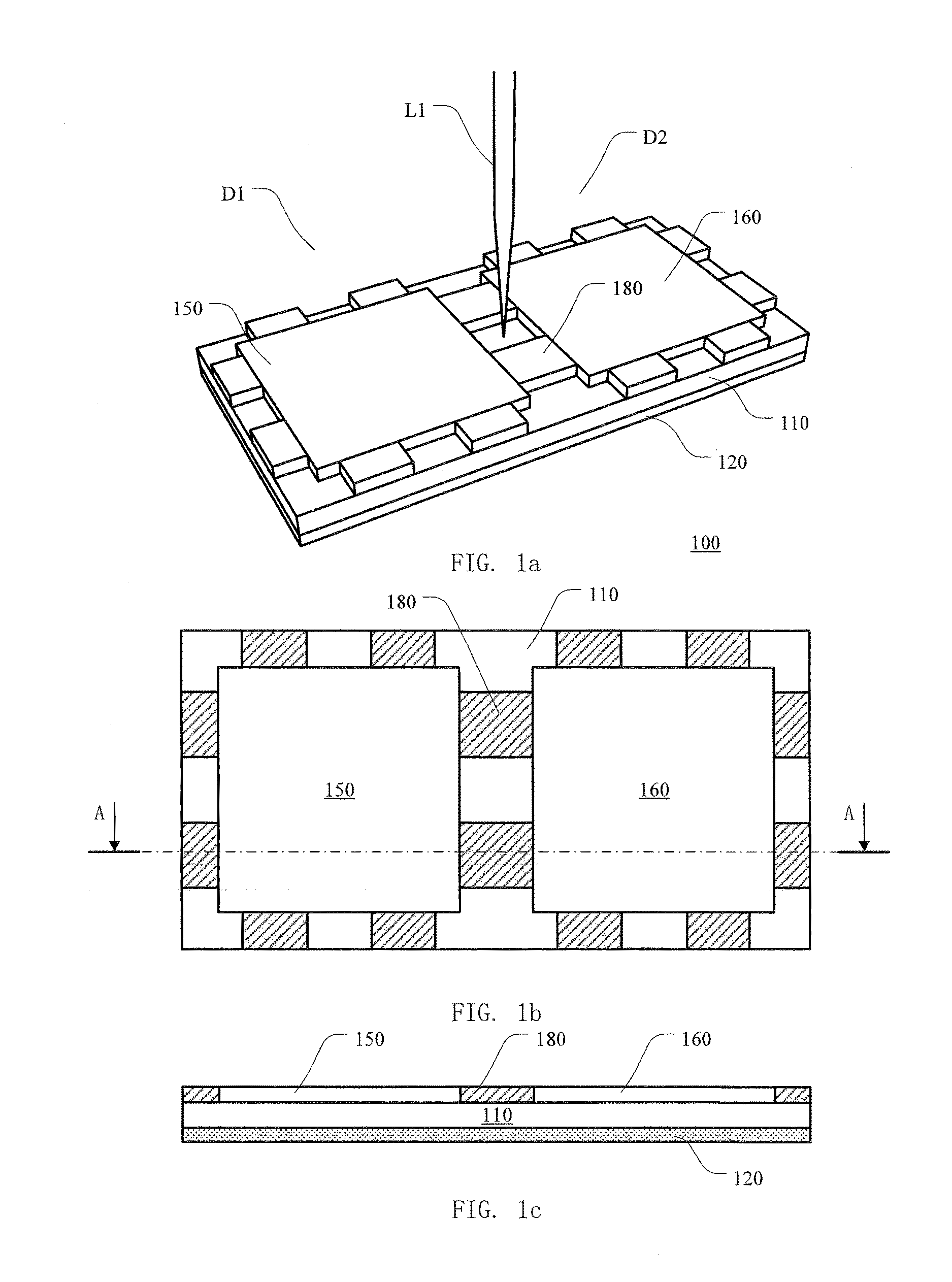
Monolithic transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TXPIC) having tunable modulated sources with feedback system for source power level or wavelength tuning
InactiveUS20080138088A1Reduce in quantityImprove chip yieldLaser optical resonator constructionElectromagnetic transmittersSignal onWavelength
A photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip comprising an array of modulated sources, each providing a modulated signal output at a channel wavelength different from the channel wavelength of other modulated sources and a wavelength selective combiner having an input optically coupled to received all the signal outputs from the modulated sources and provide a combined output signal on an output waveguide from the chip. The modulated sources, combiner and output waveguide are all integrated on the same chip.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
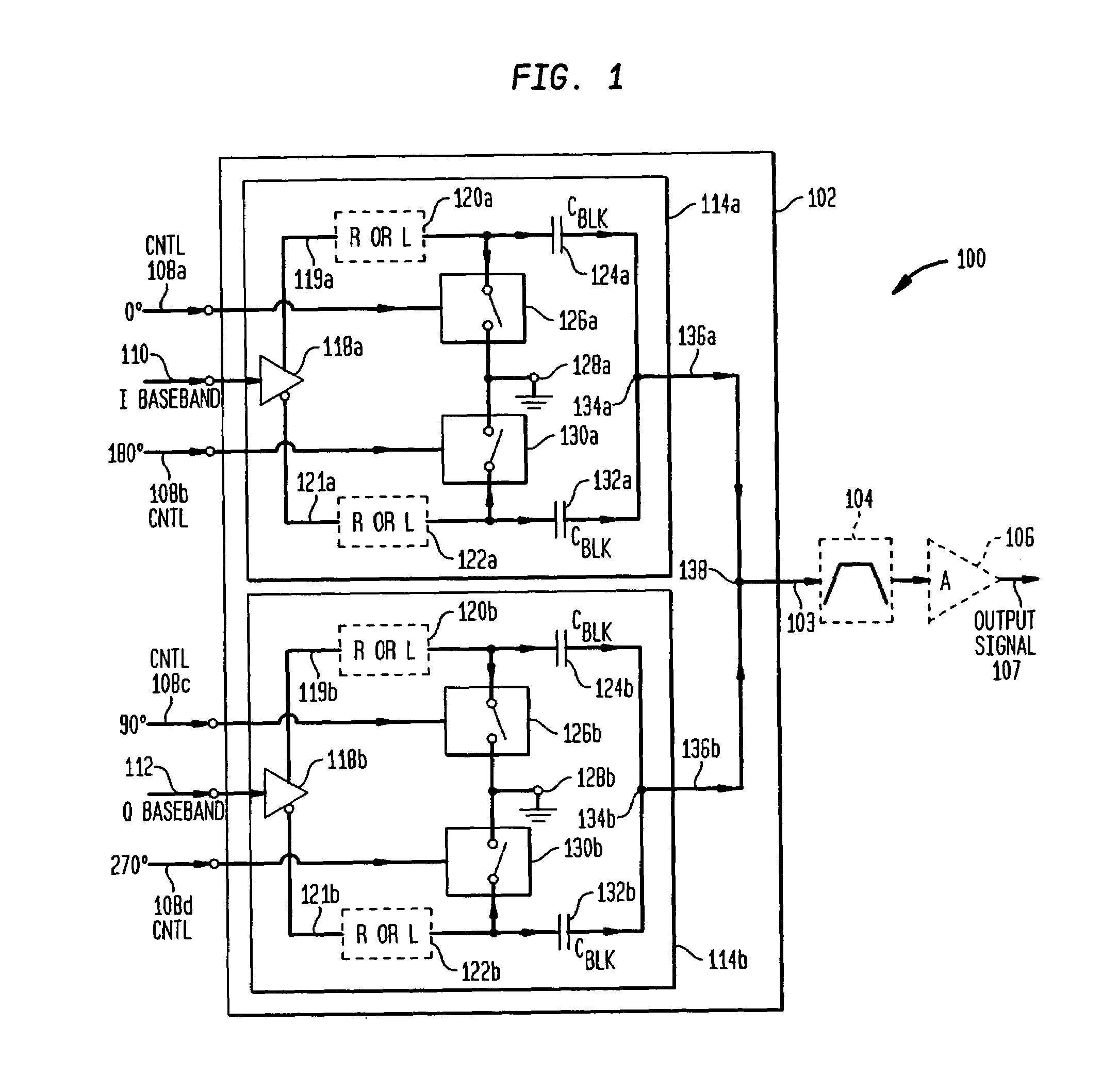
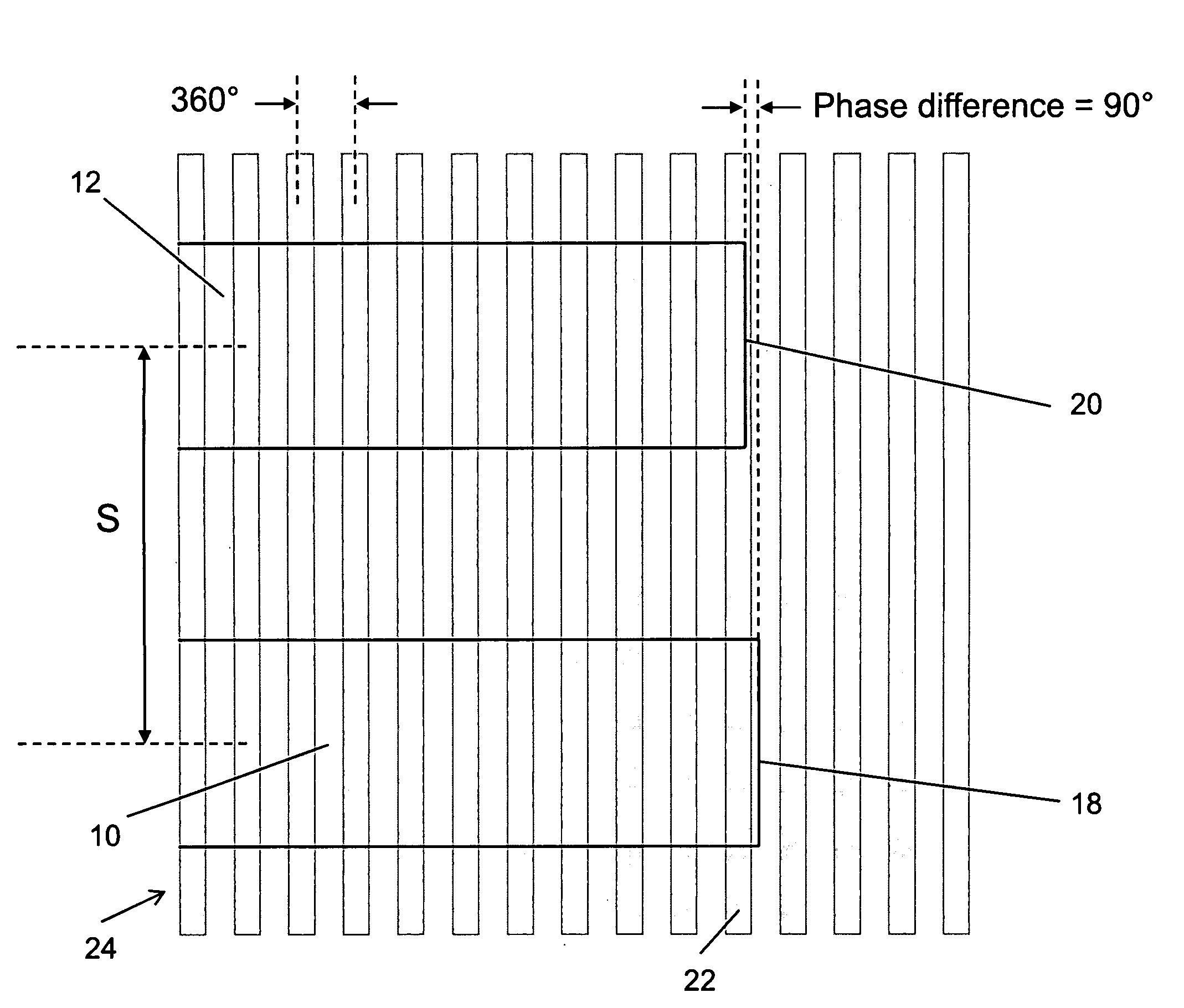
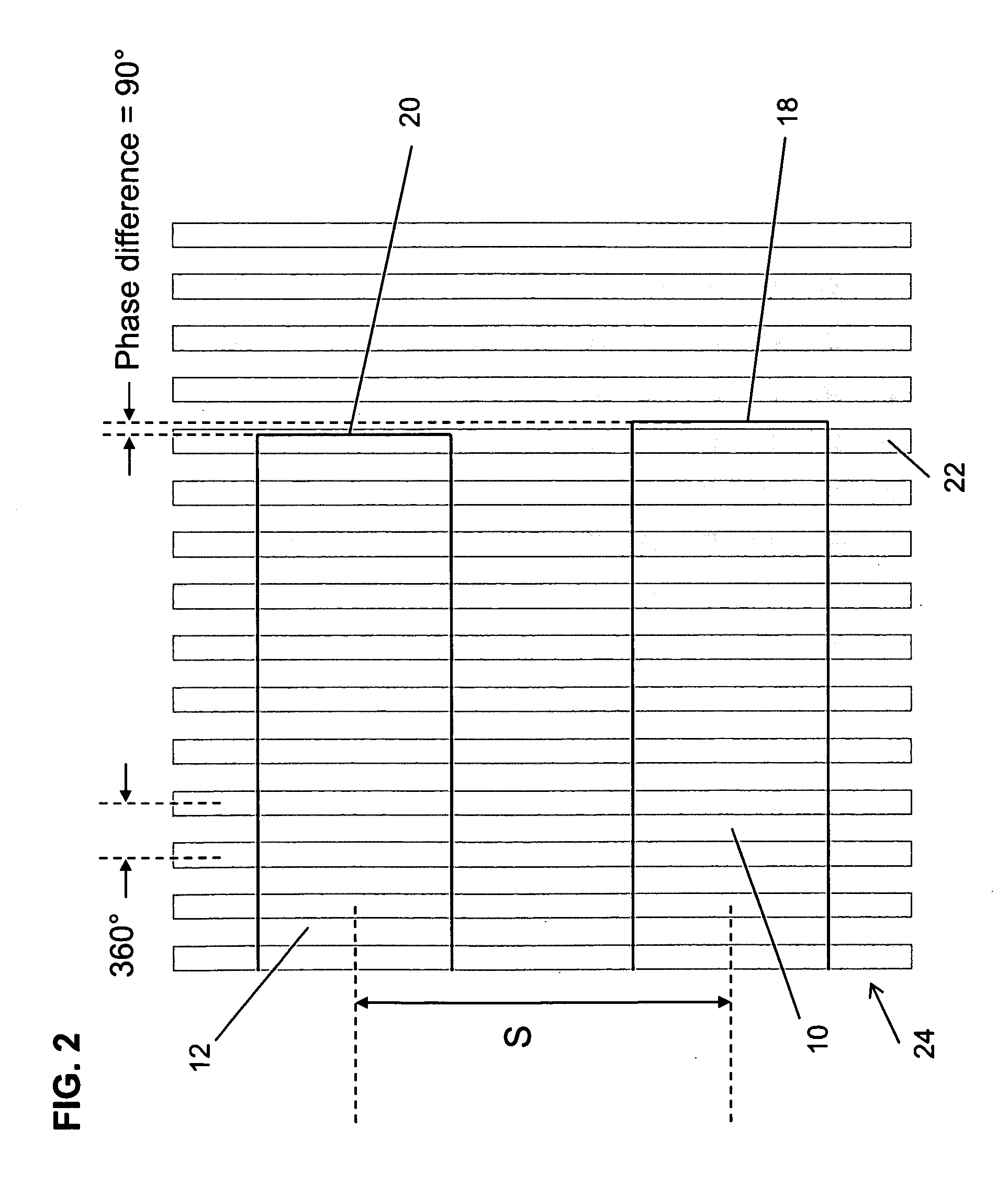
Active polyphase inverter filter for quadrature signal generation
InactiveUS7321640B2Improve phase accuracyIncrease overall chip yieldAngle modulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCMOSOut of phase
A quadrature signal generator receives a differential input signal and generates quadrature output signals that are 90 degrees out-of-phase with each other. The quadrature generator includes a coarse stage and a plurality of refinement stages. The coarse stage generates quadrature signals that may have some phase error, and the refinement stages process the quadrature signals to reduce any phase error. The refinement stages receive quadrature signals from the output of the coarse stage, and processes the quadrature signals to reduce the phase errors. The coarse stage and the refinement stages are configured using delay circuits that can be implemented with inverter circuits, such as, for example, CMOS inverter circuits. In the refinement stages, corresponding outputs of the delay stages are averaged together to reduce the quadrature phase error.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
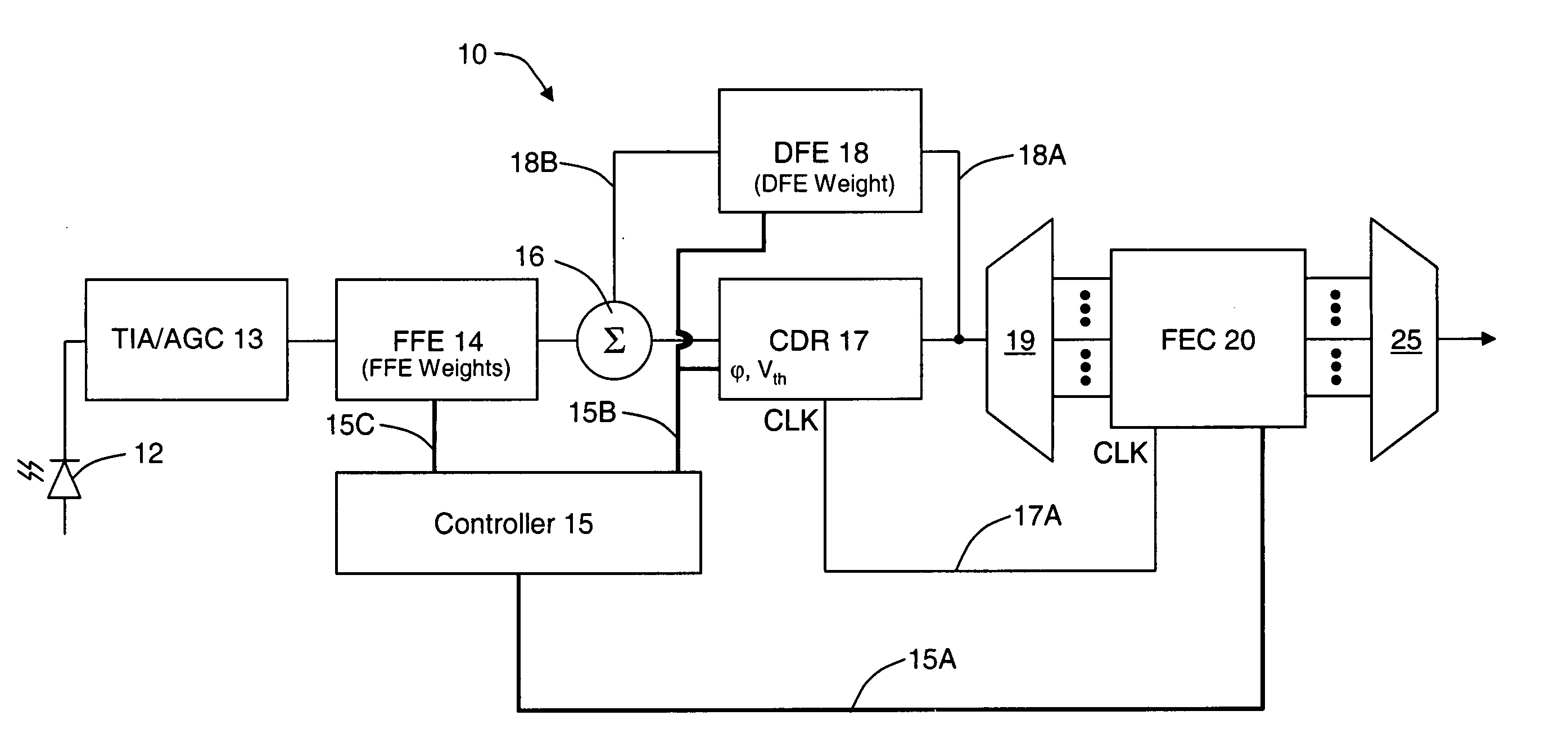
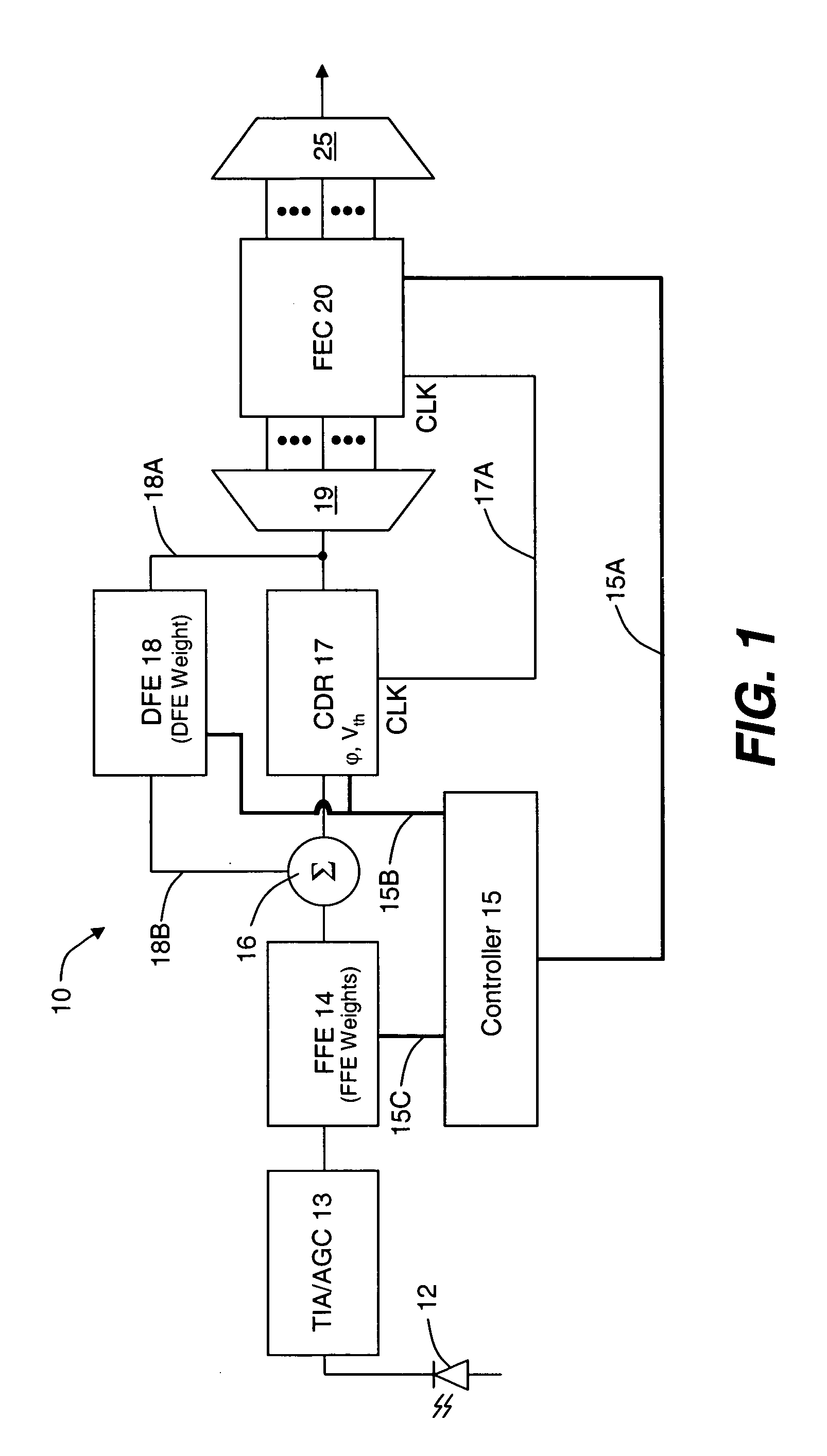
Pattern-dependent error counts for use in correcting operational parameters in an optical receiver
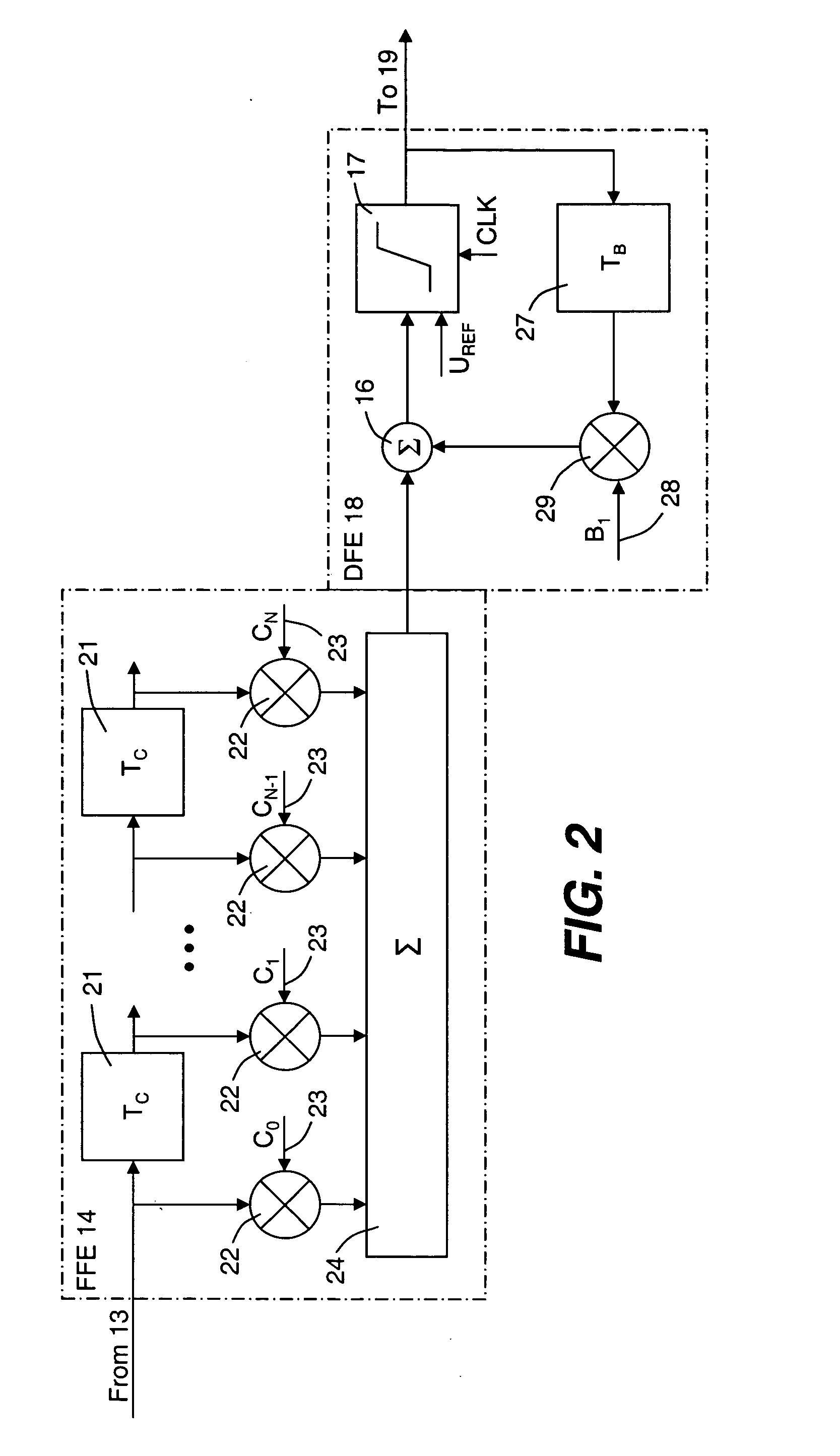
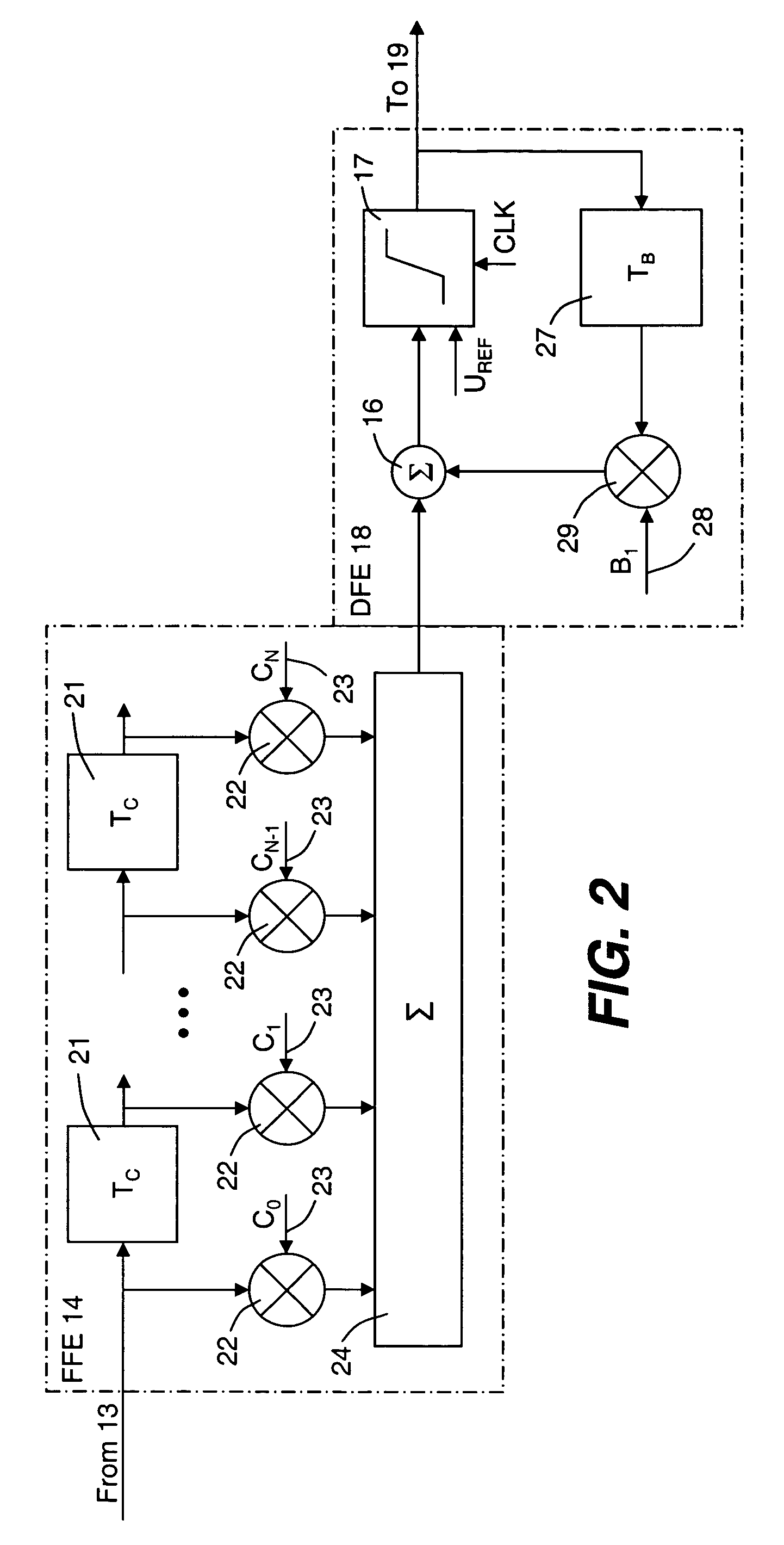
ActiveUS20060008279A1Accurate methodReduce manufacturing costMultiple-port networksError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorWeight coefficientSemiconductor chip
An optical transmission network includes an optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC) chip, utilized in an optical transmitter and has a plurality of monolithic modulated sources integrated for multiple signal channels on the same semiconductor chip is provided with channel equalization at the optical receiver side of the network that permits one or more such integrated modulated sources in the TxPIC chip to be out of specification thereby increasing the chip yield and reducing manufacturing costs in the deployment of such TxPIC chips. FEC error counts at the FEC decoder on the optical receiver side of the network includes counters that accumulate a plurality of bit pattern-dependent error counts based on different N-bit patterns in the received data bit stream. The accumulated counts of different N-bit patterns are utilized to provide for corrections to threshold and phase relative to the bit eye pattern as well as provided for weight coefficients for the optical receiver equalization system. The deployment of this type of equalization in a digital OEO REGEN network substantially reduces, if not eliminates, the need for dispersion compensating fiber (DCF) or EDFAs in an optical link of the network and enhances the optical receiver tolerance to chromatic dispersion (CD) so that an increase in chip yield is realized for TxPIC chips not operating with acceptable operational parameters, particularly with a desired frequency chirp parameter relative to at least one of the TxPIC modulated sources.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Pattern-dependent error counts for use in correcting operational parameters in an optical receiver
ActiveUS7574146B2Accurate methodReduce manufacturing costMultiple-port networksError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorWeight coefficientSemiconductor chip
An optical transmission network includes an optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC) chip, utilized in an optical transmitter and has a plurality of monolithic modulated sources integrated for multiple signal channels on the same semiconductor chip is provided with channel equalization at the optical receiver side of the network that permits one or more such integrated modulated sources in the TxPIC chip to be out of specification thereby increasing the chip yield and reducing manufacturing costs in the deployment of such TxPIC chips. FEC error counts at the FEC decoder on the optical receiver side of the network includes counters that accumulate a plurality of bit pattern-dependent error counts based on different N-bit patterns in the received data bit stream. The accumulated counts of different N-bit patterns are utilized to provide for corrections to threshold and phase relative to the bit eye pattern as well as provided for weight coefficients for the optical receiver equalization system. The deployment of this type of equalization in a digital OEO REGEN network substantially reduces, if not eliminates, the need for dispersion compensating fiber (DCF) or EDFAs in an optical link of the network and enhances the optical receiver tolerance to chromatic dispersion (CD) so that an increase in chip yield is realized for TxPIC chips not operating with acceptable operational parameters, particularly with a desired frequency chirp parameter relative to at least one of the TxPIC modulated sources.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Monolithic Transmitter Photonic Integrated Circuit (TxPIC) with a Traversely Disposed Output
InactiveUS20080013881A1Reduce in quantityImprove chip yieldLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsSignal onLength wave
A photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip comprising an array of modulated sources, each providing a modulated signal output at a channel wavelength different from the channel wavelength of other modulated sources and a wavelength selective combiner having an input optically coupled to received all the signal outputs from the modulated sources and provide a combined output signal on an output waveguide from the chip. The modulated sources, combiner and output waveguide are all integrated on the same chip.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
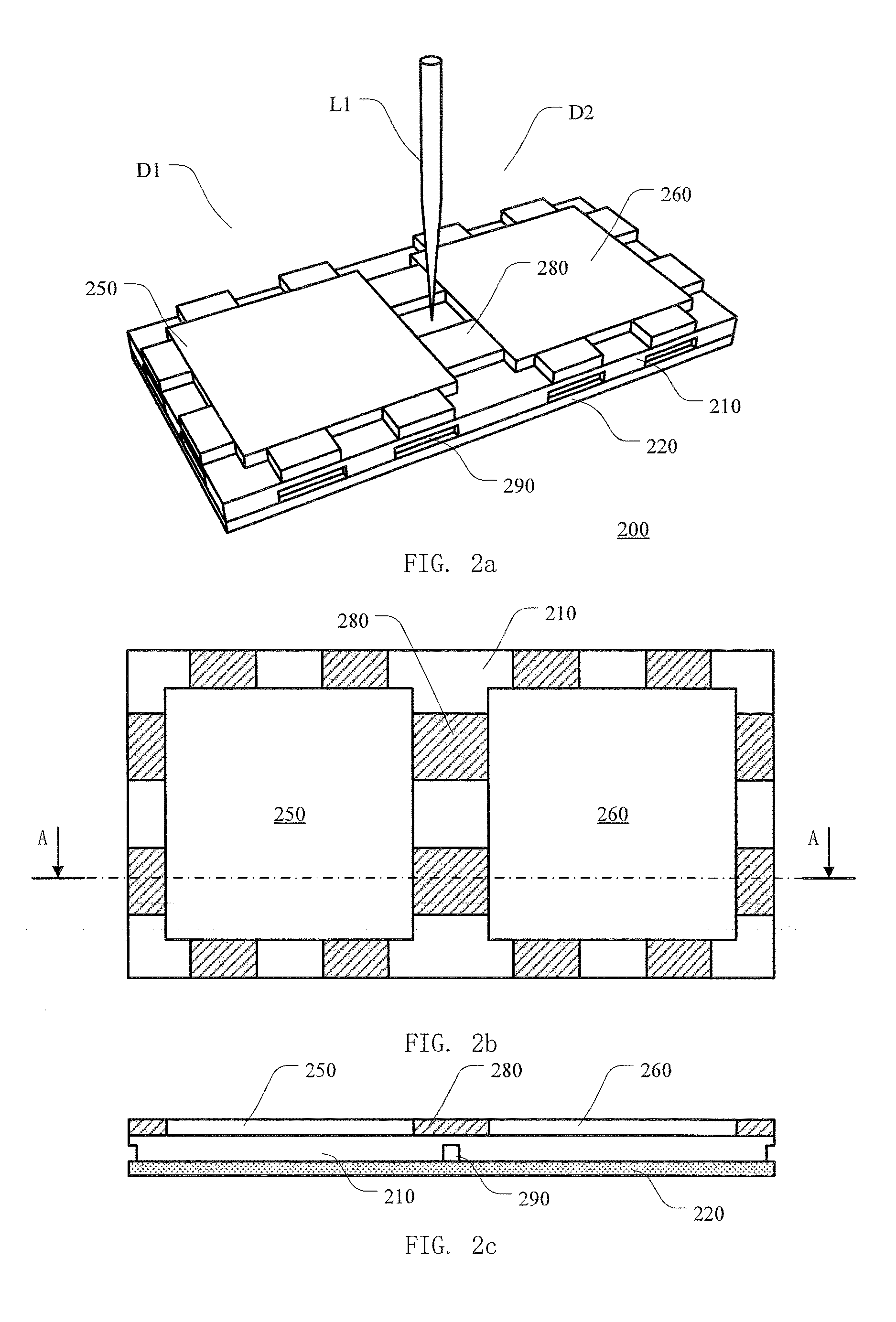
Monolithic transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC) having tunable modulated sources with feedback system for source power level or wavelength tuning
InactiveUS7751658B2Improve chip yieldInhibit outputLaser optical resonator constructionCoupling light guidesSignal onLength wave
Owner:INFINERA CORP
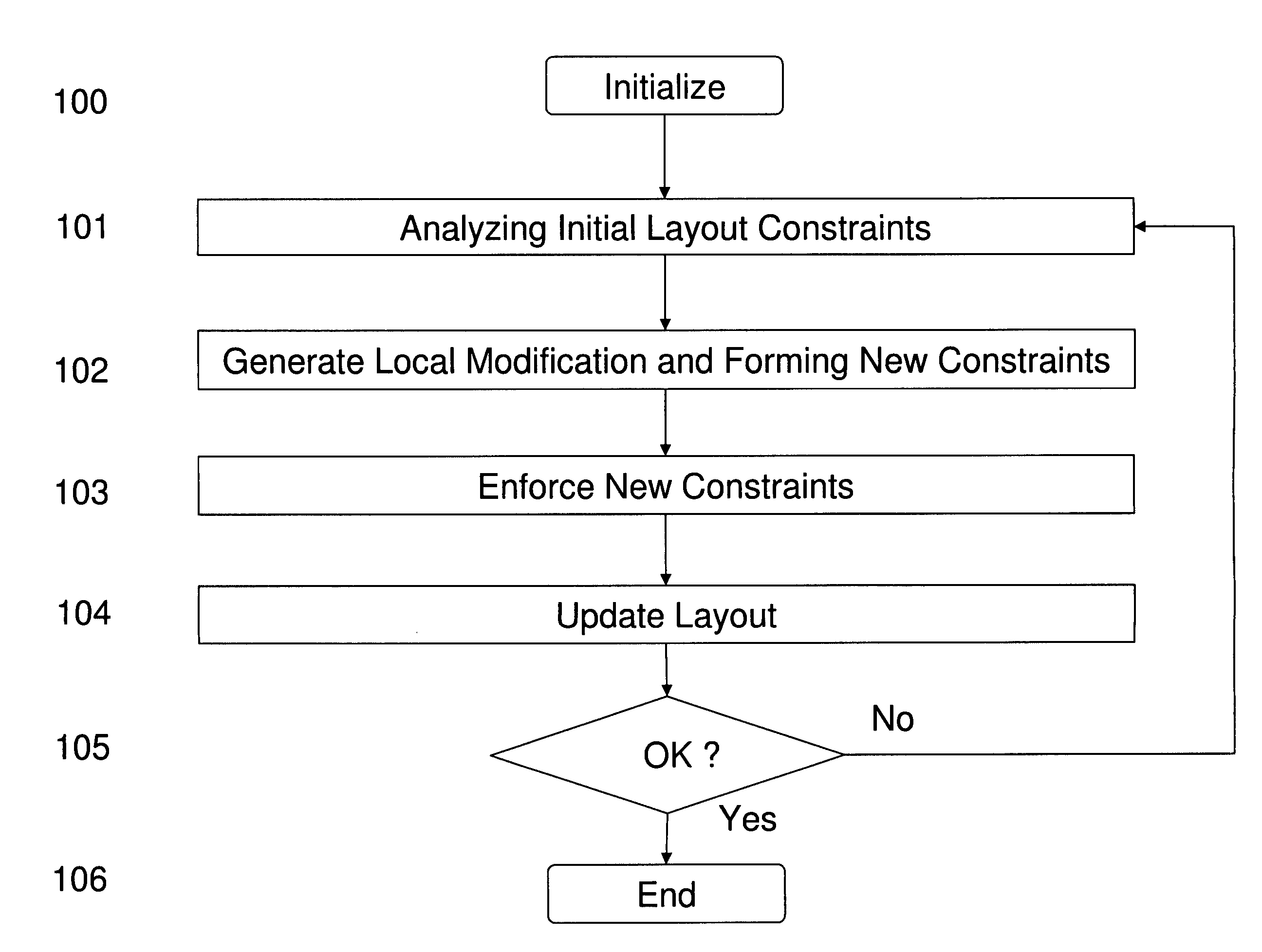
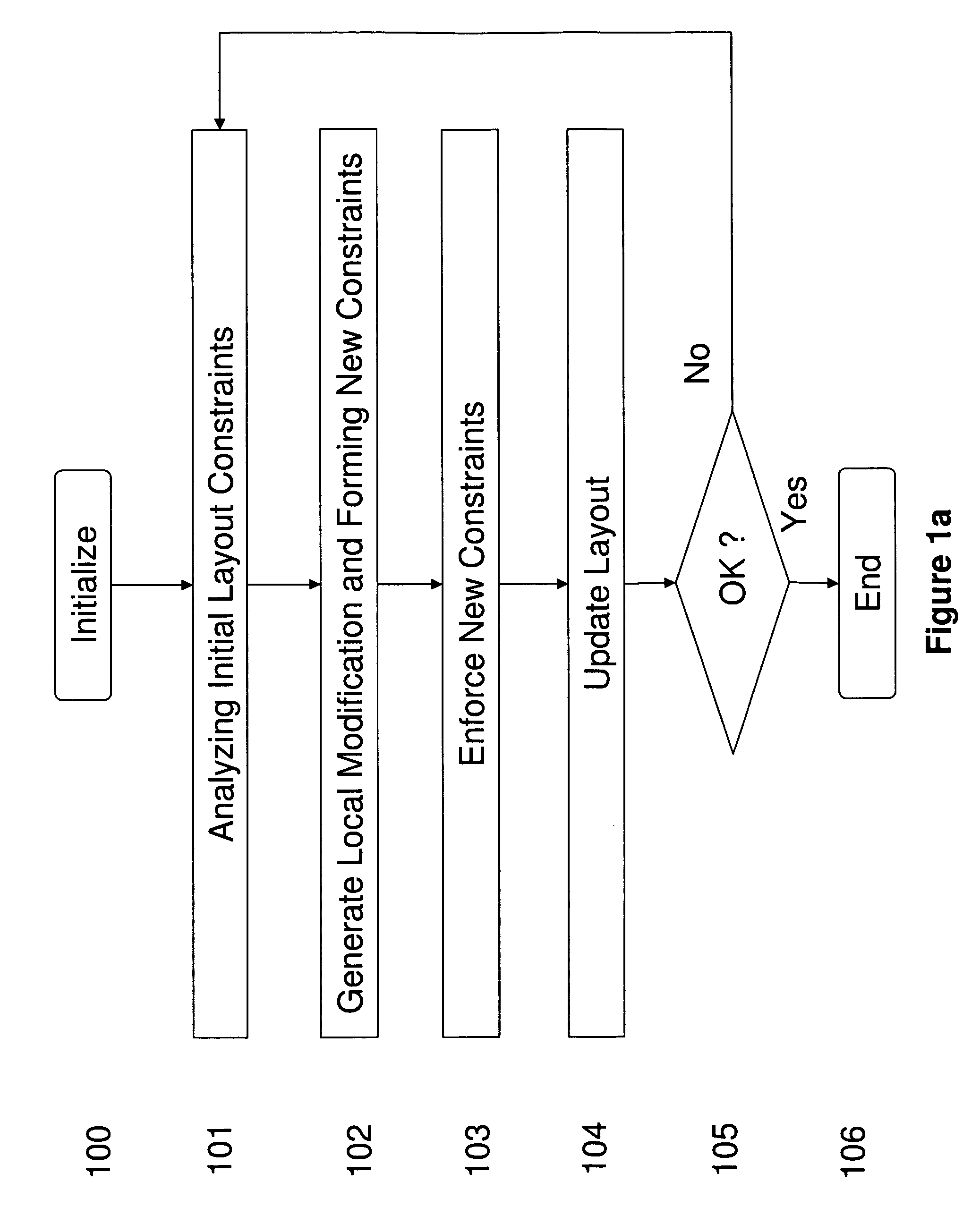
Method and system for optimizing integrated circuit layout
ActiveUS8176445B1Reduce sensitivityReduce in quantityCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureIntegrated circuit layout
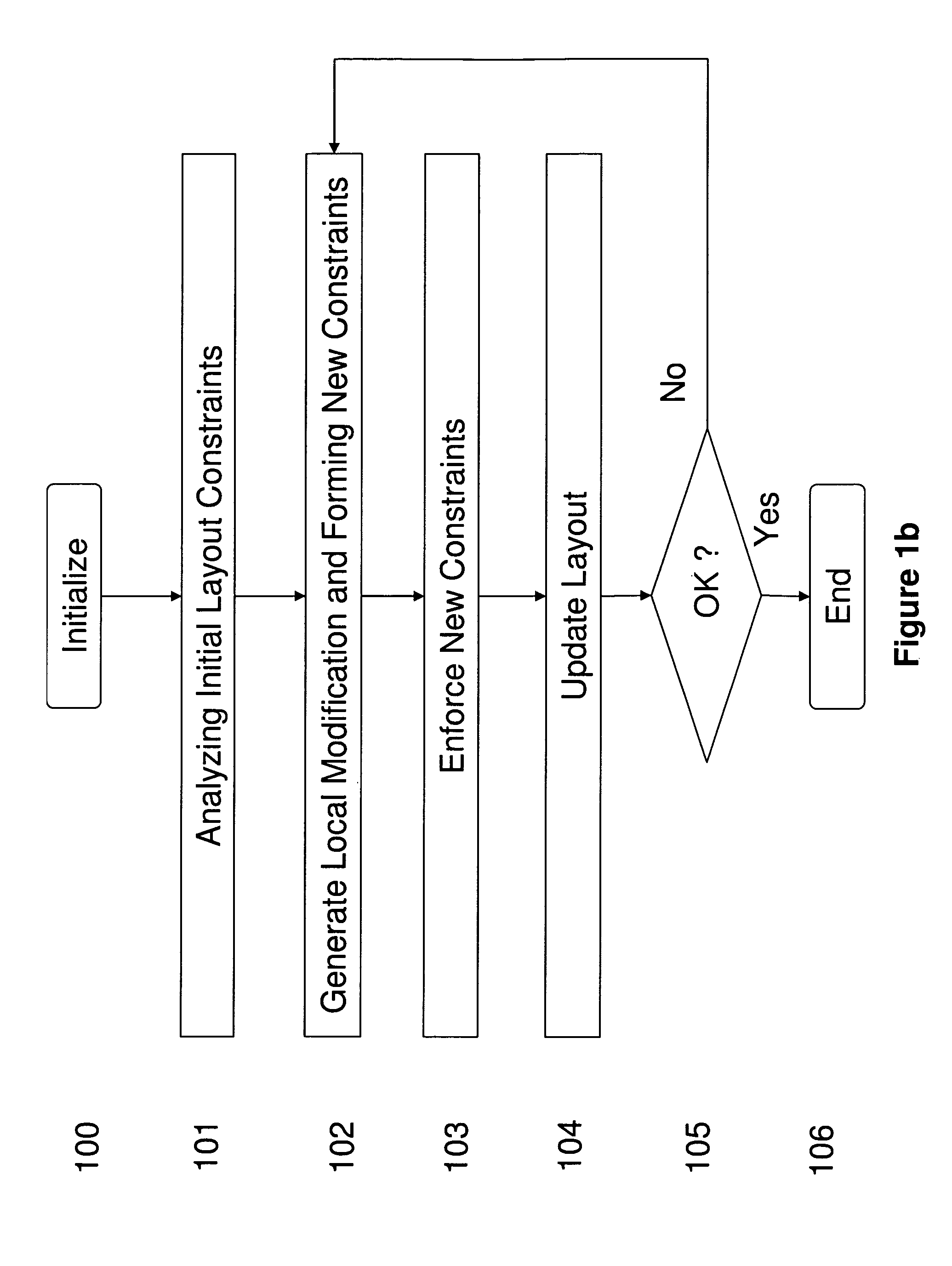
We disclose a method for optimizing integrated circuit layout which comprises analyzing constraint relationship among objects in an initial layout; constructing local modifications to the constraint relationship; forming new constraint relationships by combining initial constraint relationships with their local modifications; and producing a new layout by implementing the new constraint relationships. Local modification to constraints provides a framework for bringing detailed local information into the design process in a highly automated manner, which can be applied to a wide range of situations. We disclose preferred embodiments on improving lithography printability, reducing defect susceptibility, and improving circuit performance such as reducing layout variability and leakage.
Owner:IYM TECH
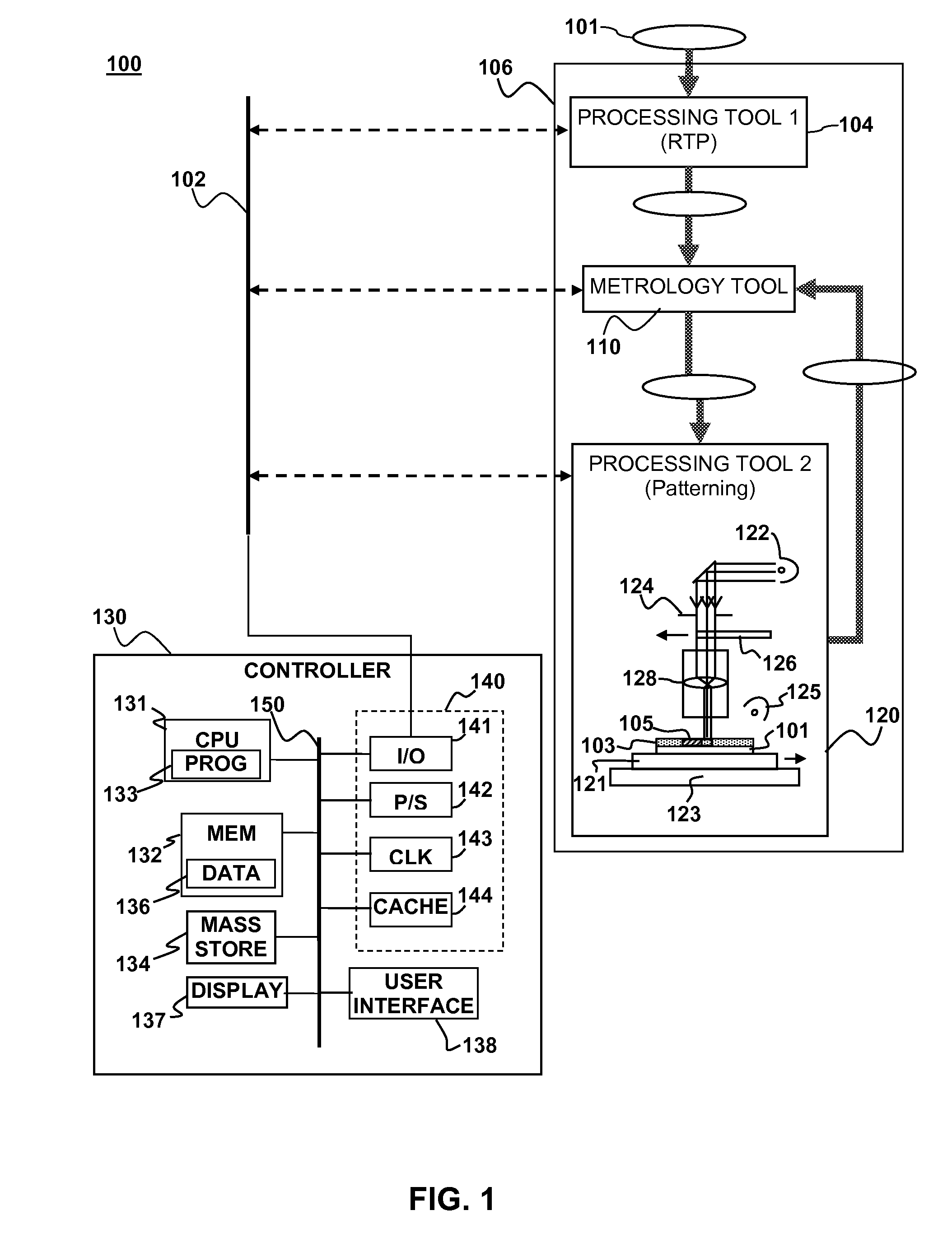
Method and device for using substrate geometry to determine optimum substrate analysis sampling
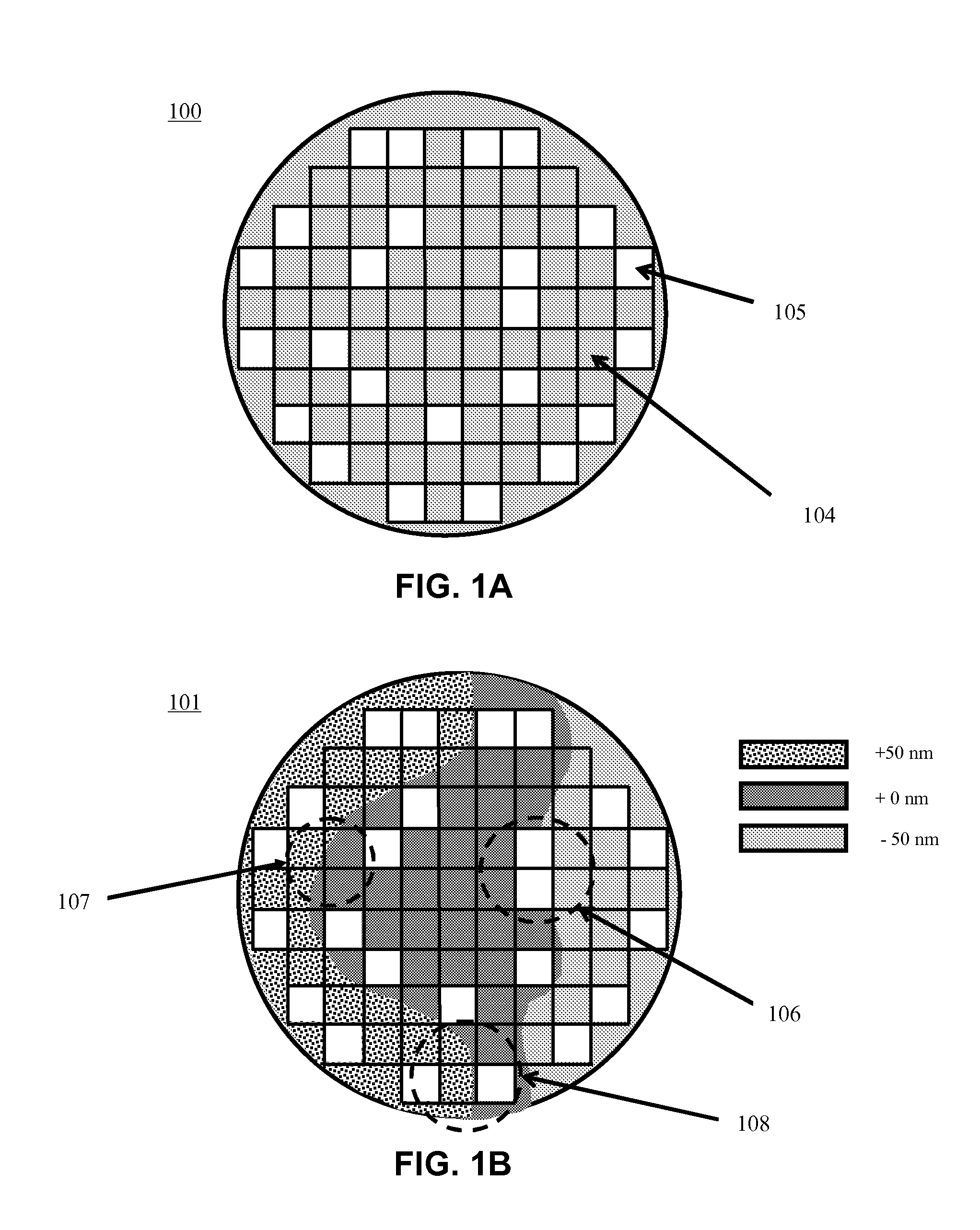
ActiveUS20130310966A1Improve chip yieldHigh yieldProgramme controlPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringProcess control
A method and apparatus for process control in the processing of a substrate is disclosed in the present invention. Embodiments of the present invention utilize a first analysis tool to determine changes in a substrate's geometry. The substrate geometry data is used to generate sampling plan that will be used to check areas of the substrate that are likely to have errors after processing. The sampling plan is fed forwards to a second analysis tool that samples the substrate after it has been processed. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
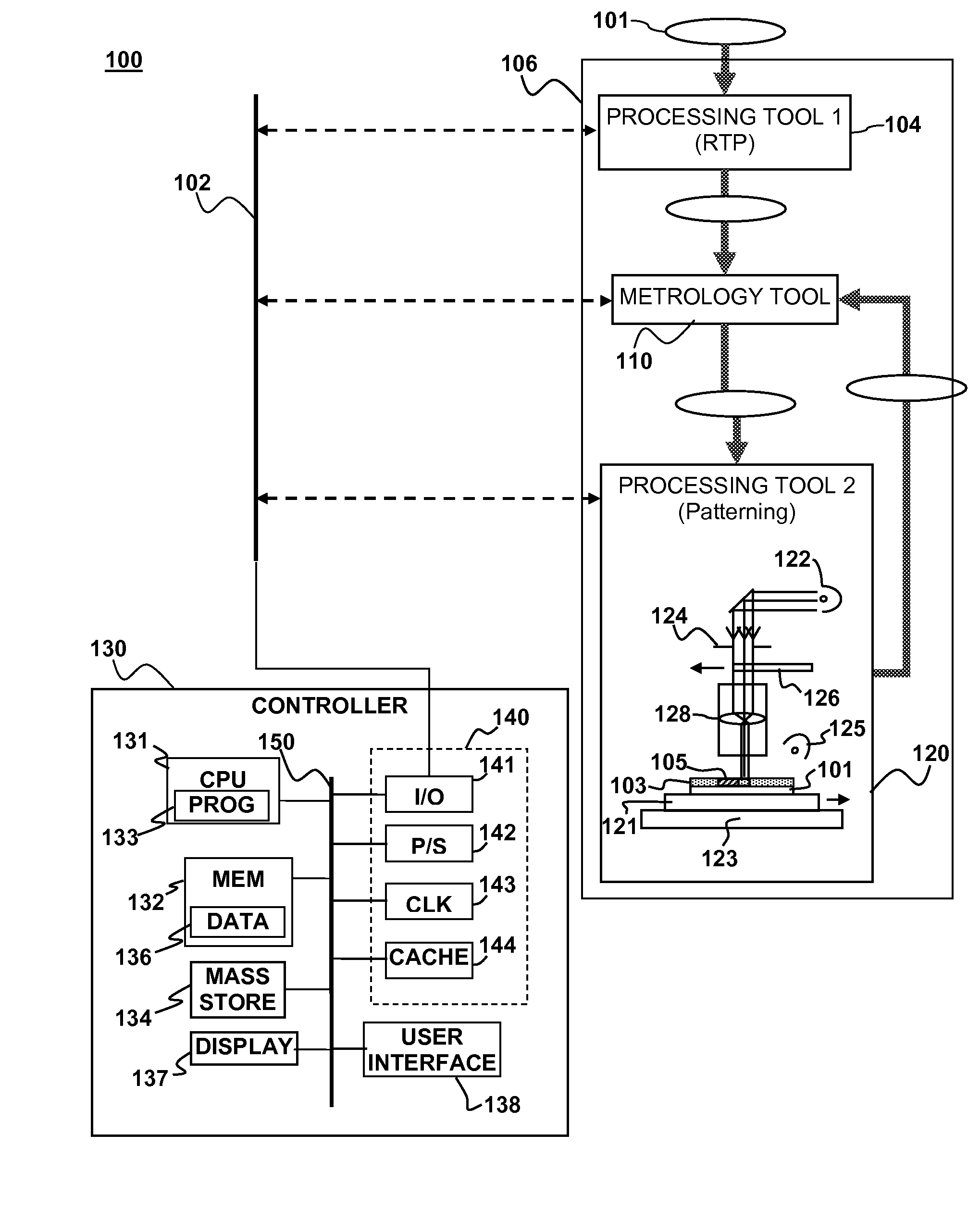
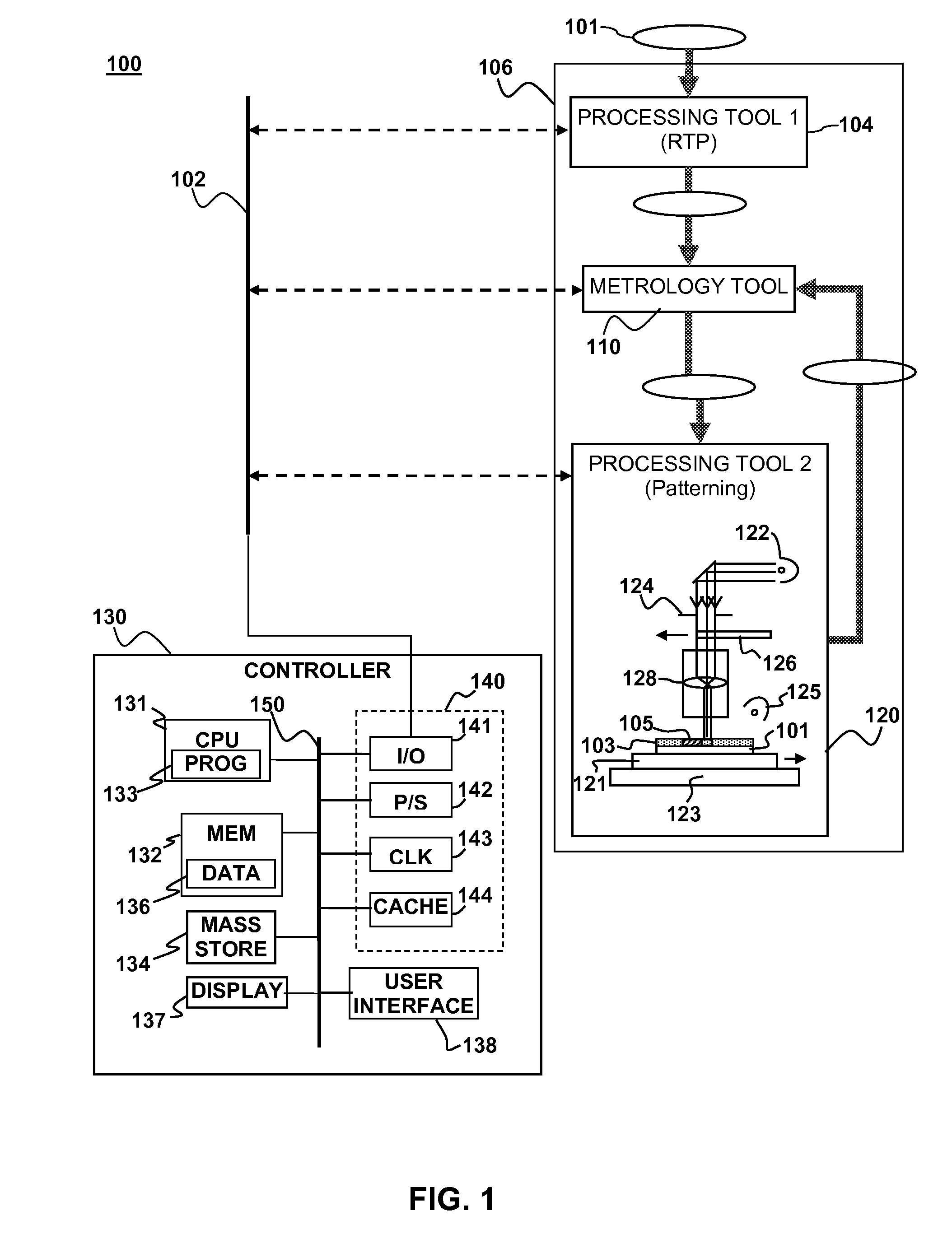
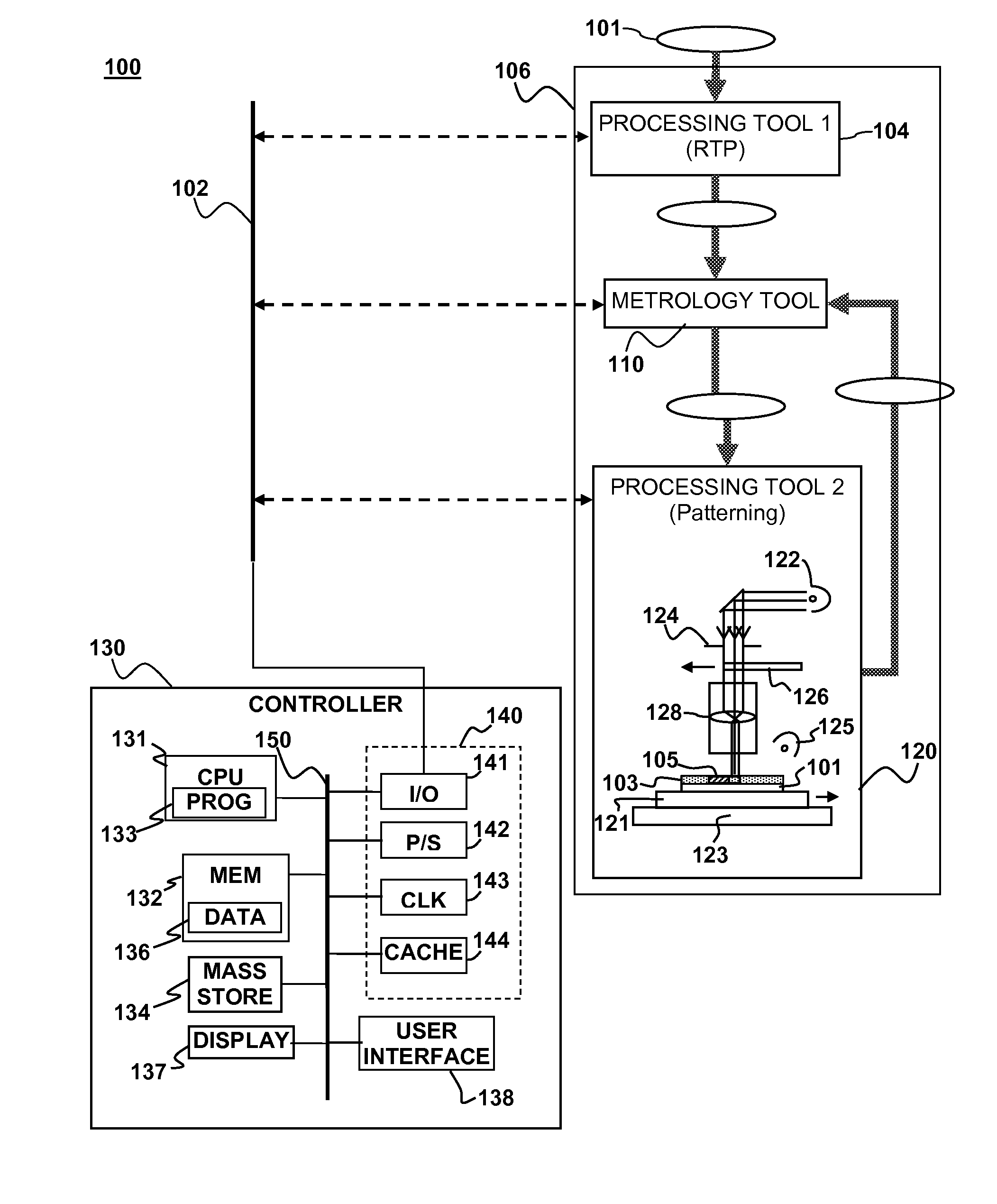
Feedforward/feedback litho process control of stress and overlay
ActiveUS20080316442A1Reduce patterning errorIncrease productionPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLithography processSoftware engineering
A method and apparatus for process control in a lithographic process are described. Metrology may be performed on a substrate either before or after performing a lithographic patterning process on the substrate. One or more correctables to the lithographic patterning process may be generated based on the metrology. The lithographic patterning process performed on the substrate (or a subsequent substrate) may be adjusted with the correctables.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Logic drive using standard commodity programmable logic IC chips
ActiveUS20190363715A1Reduce manufacturing costManufacturing cost to minimumProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsCAD circuit designInterconnectionField-programmable gate array
An expandable logic scheme based on a chip package, includes: an interconnection substrate comprising a set of data buses for use in an expandable interconnection scheme, wherein the set of data buses is divided into a plurality of data bus subsets; and a first field-programmable-gate-array (FPGA) integrated-circuit (IC) chip comprising a plurality of first I / O ports coupling to the set of data buses and at least one first I / O-port selection pad configured to select a first port from the plurality of first I / O ports in a first clock cycle to pass a first data between a first data bus subset of the plurality of data bus subsets and the first field-programmable-gate-array (FPGA) integrated-circuit (IC) chip.
Owner:ICOMETRUE CO LTD
Hybrid bulk/silicon-on-insulator multiprocessors
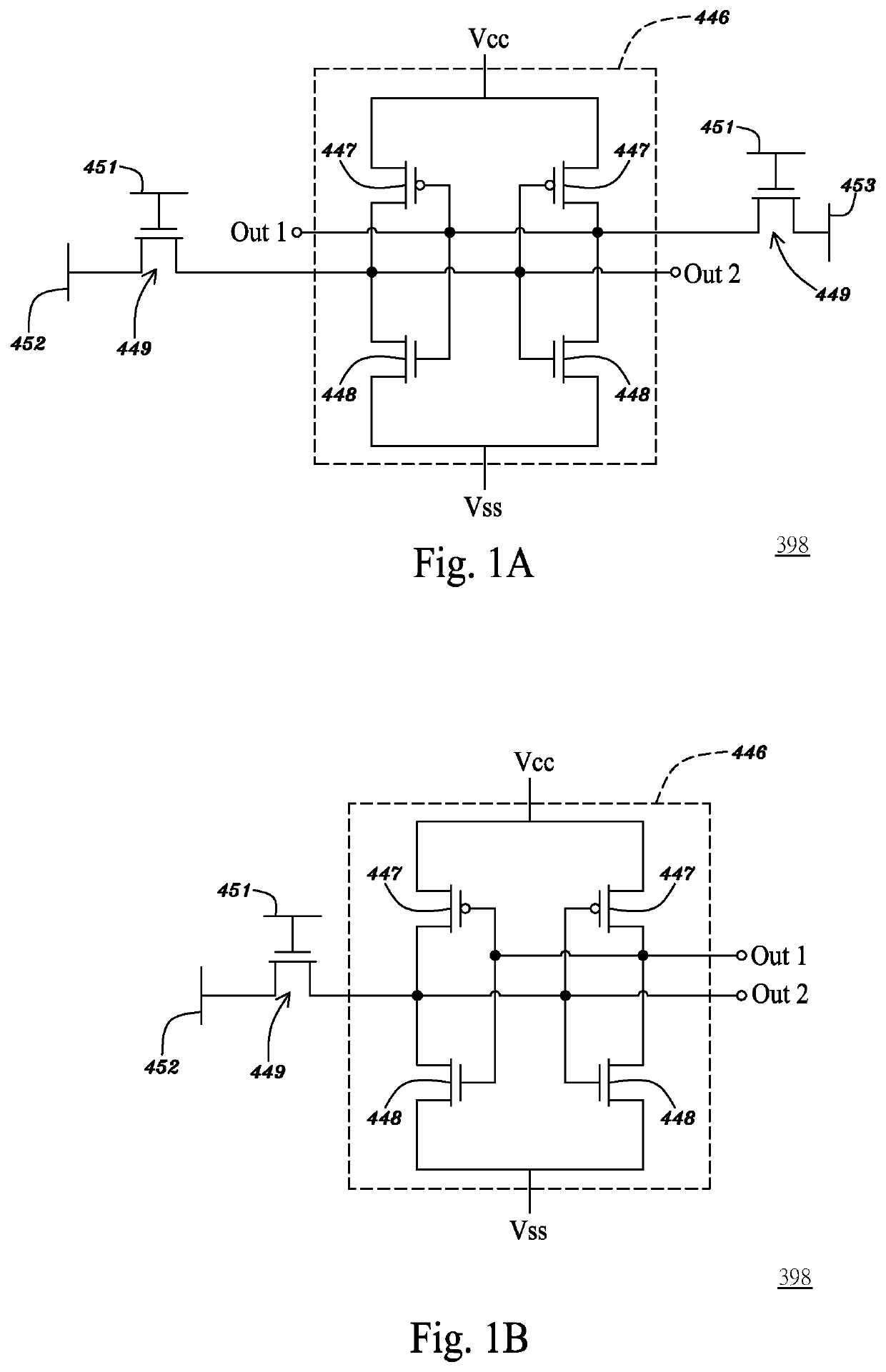
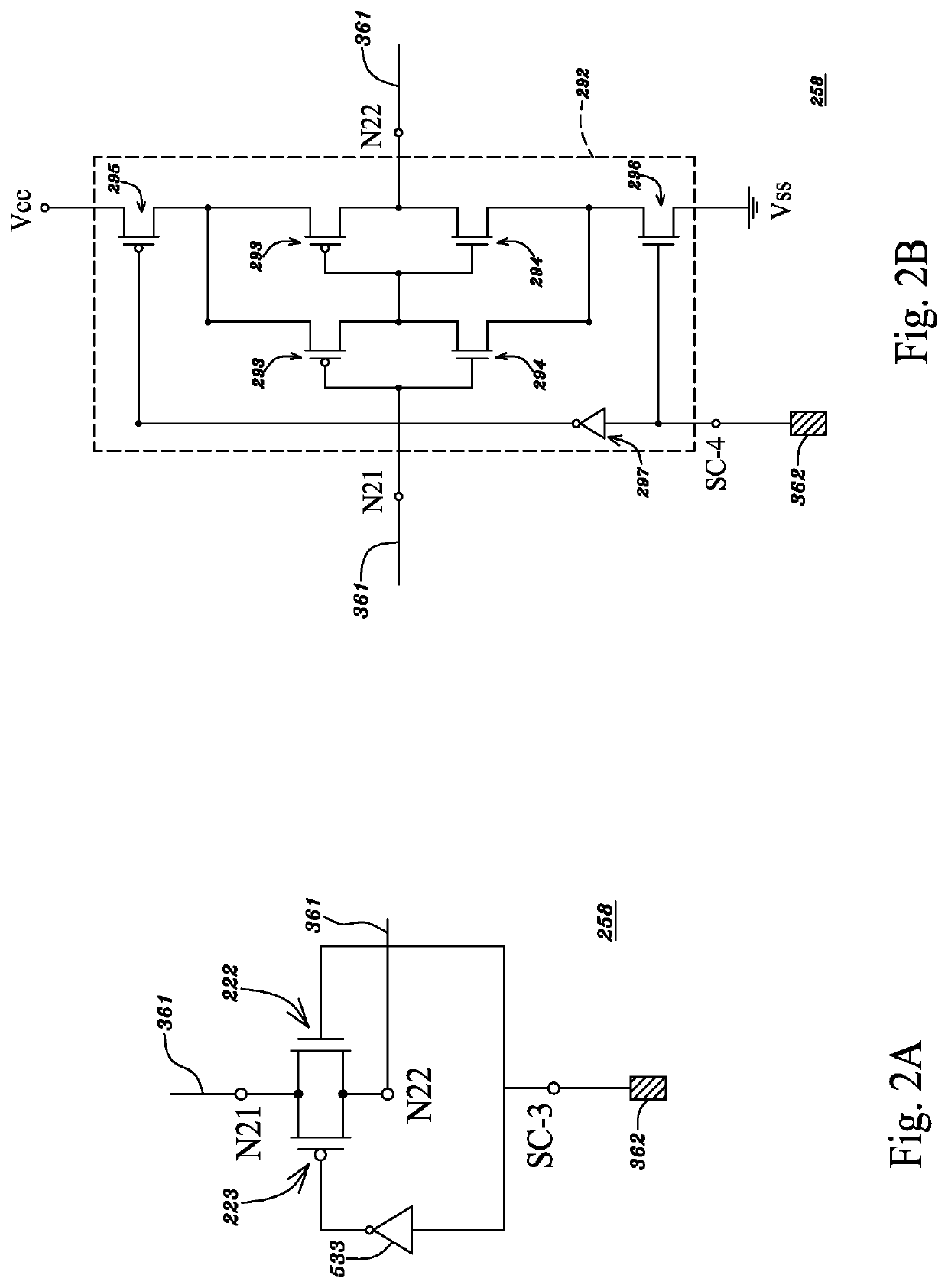
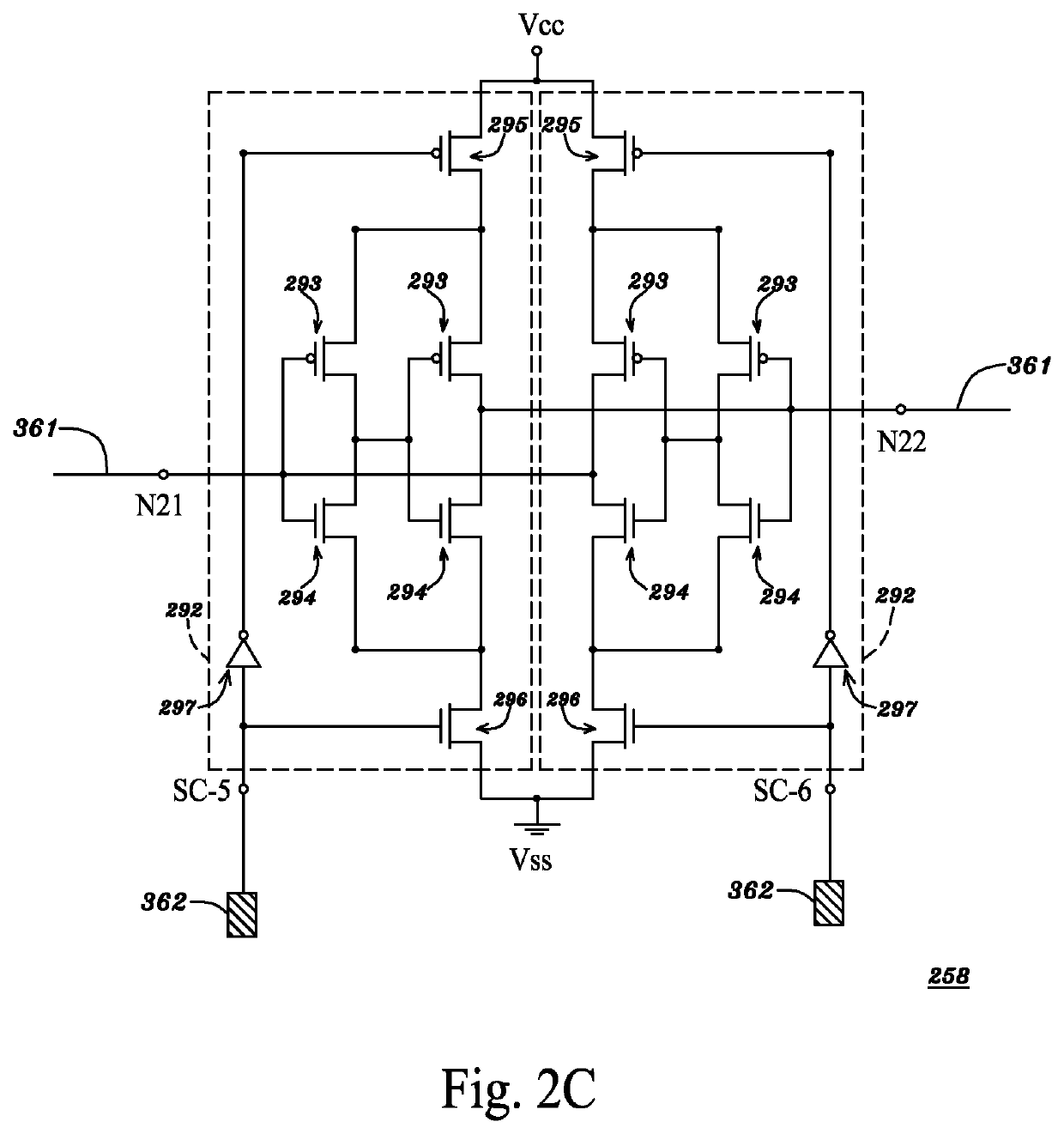
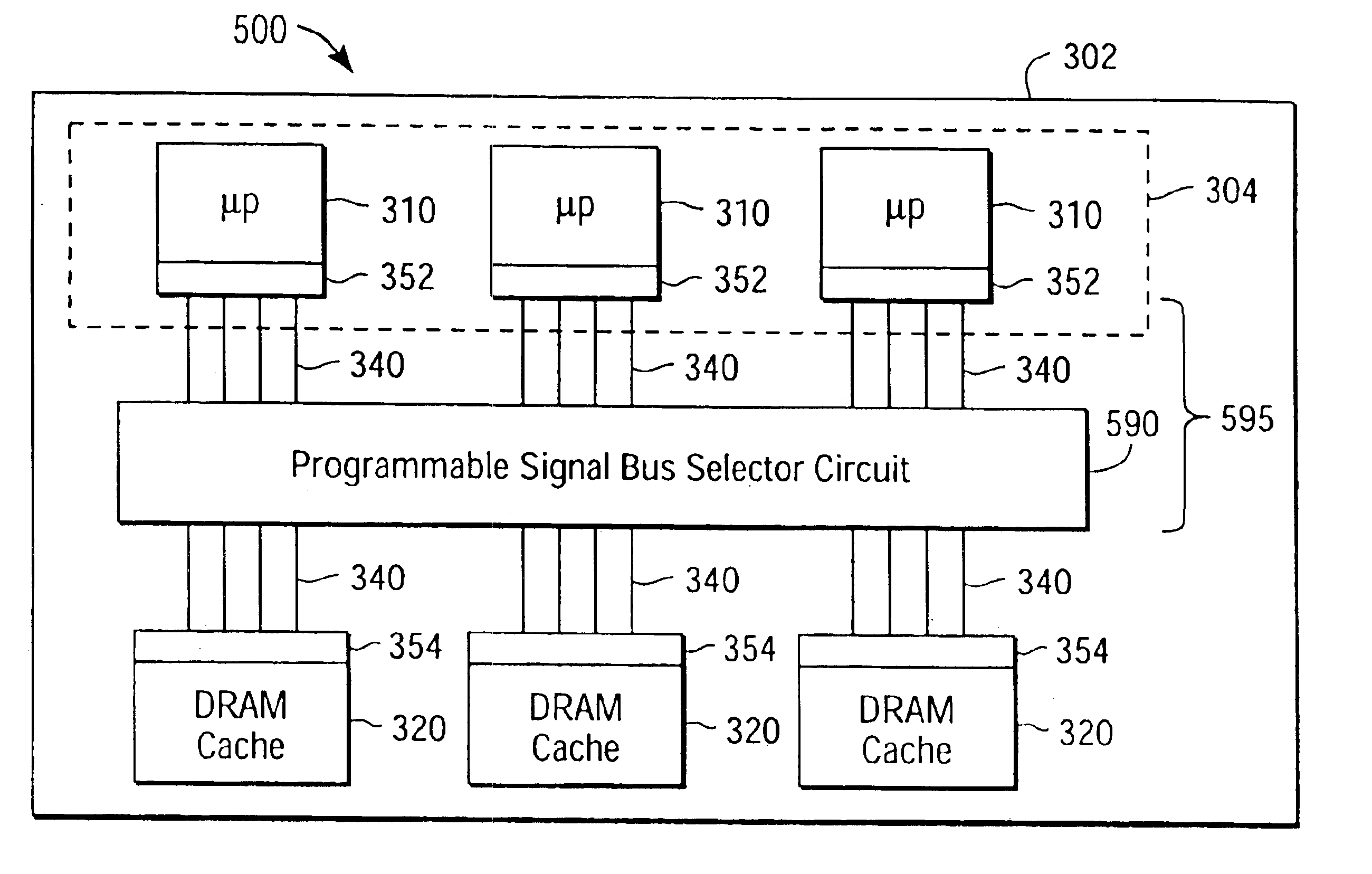
InactiveUS6864524B2Improve chip yieldReduce deleterious diffusionTransistorMemory loss protectionMulti processorParallel computing
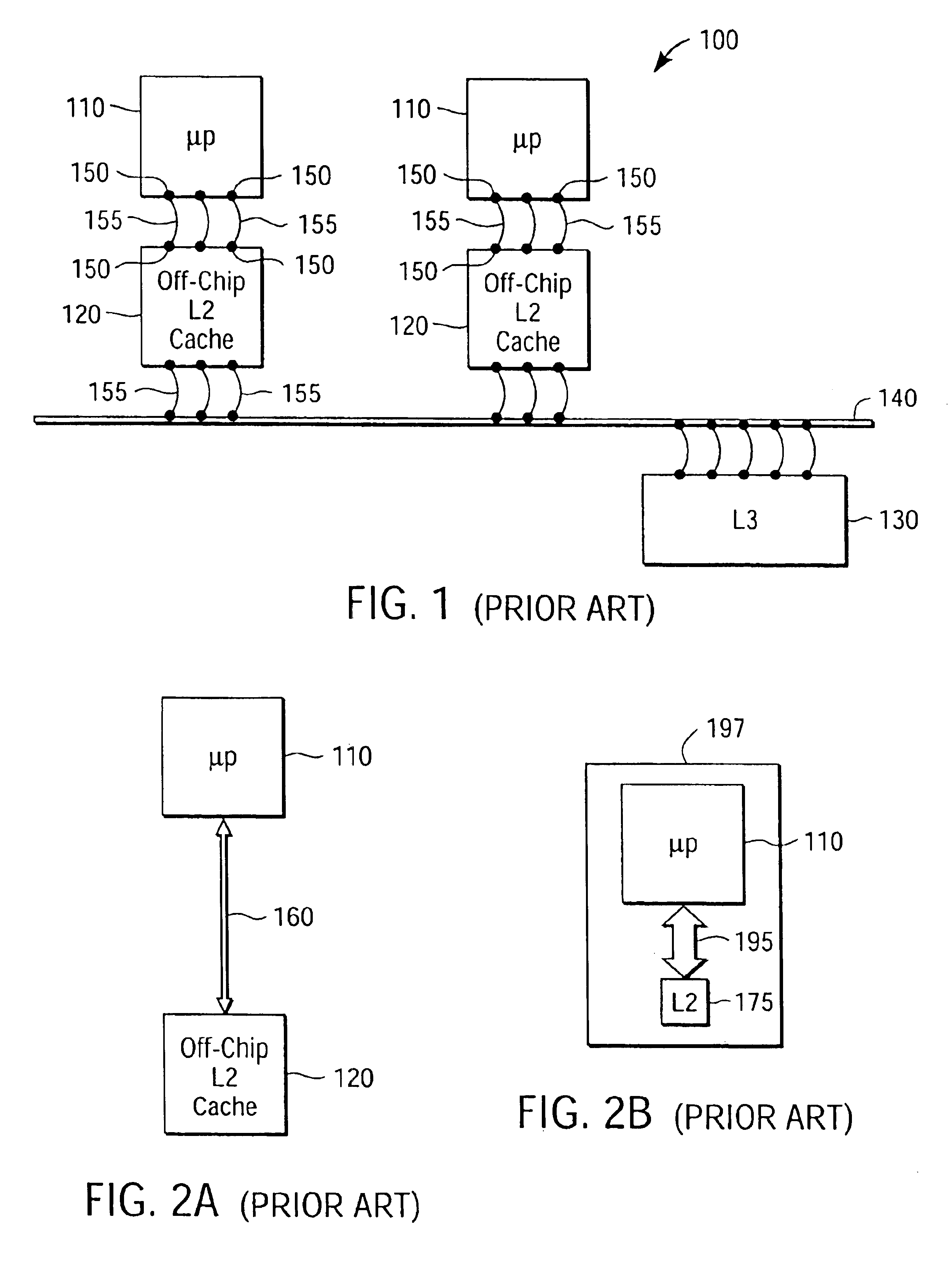
A multiprocessor integrated circuit is disclosed. A preferred embodiment of a multiprocessor chip has microprocessors formed on silicon-on-insulator regions and dynamic random access memory level-2cache memories or level-3 cache memories formed on bulk regions of the chip. A preferred embodiment includes a redundant architecture having a signal bus for coupling the microprocessors to the level-2 or level-3 cache memories in which the signal bus includes a programmable selector circuit for bypassing defective microprocessors or defective level-2 or level-3 cache memories.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Timing calibration for on-chip interconnect
ActiveUS20140070862A1Reduce wire delay mismatchImprove chip yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOxide semiconductorCMOS
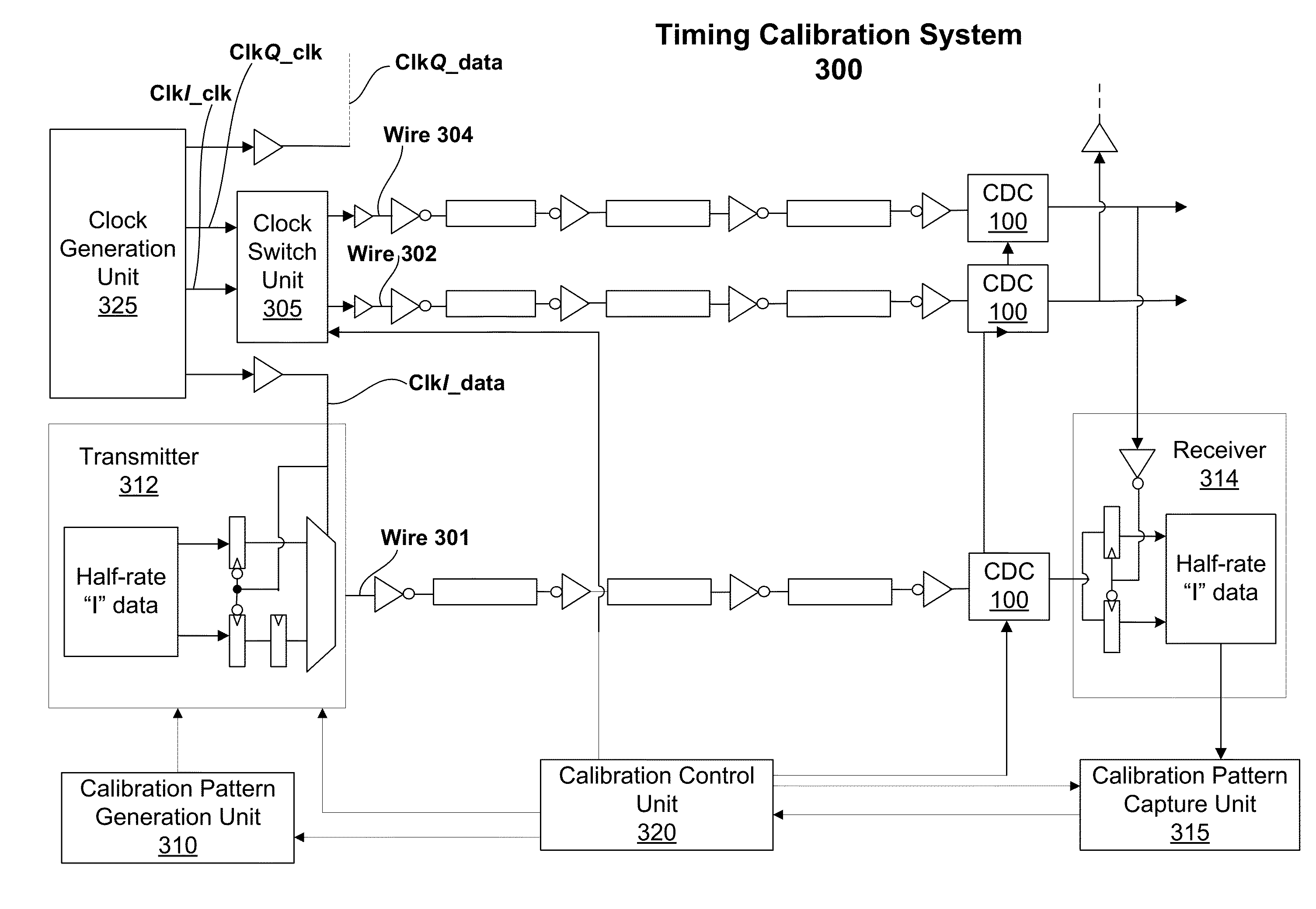
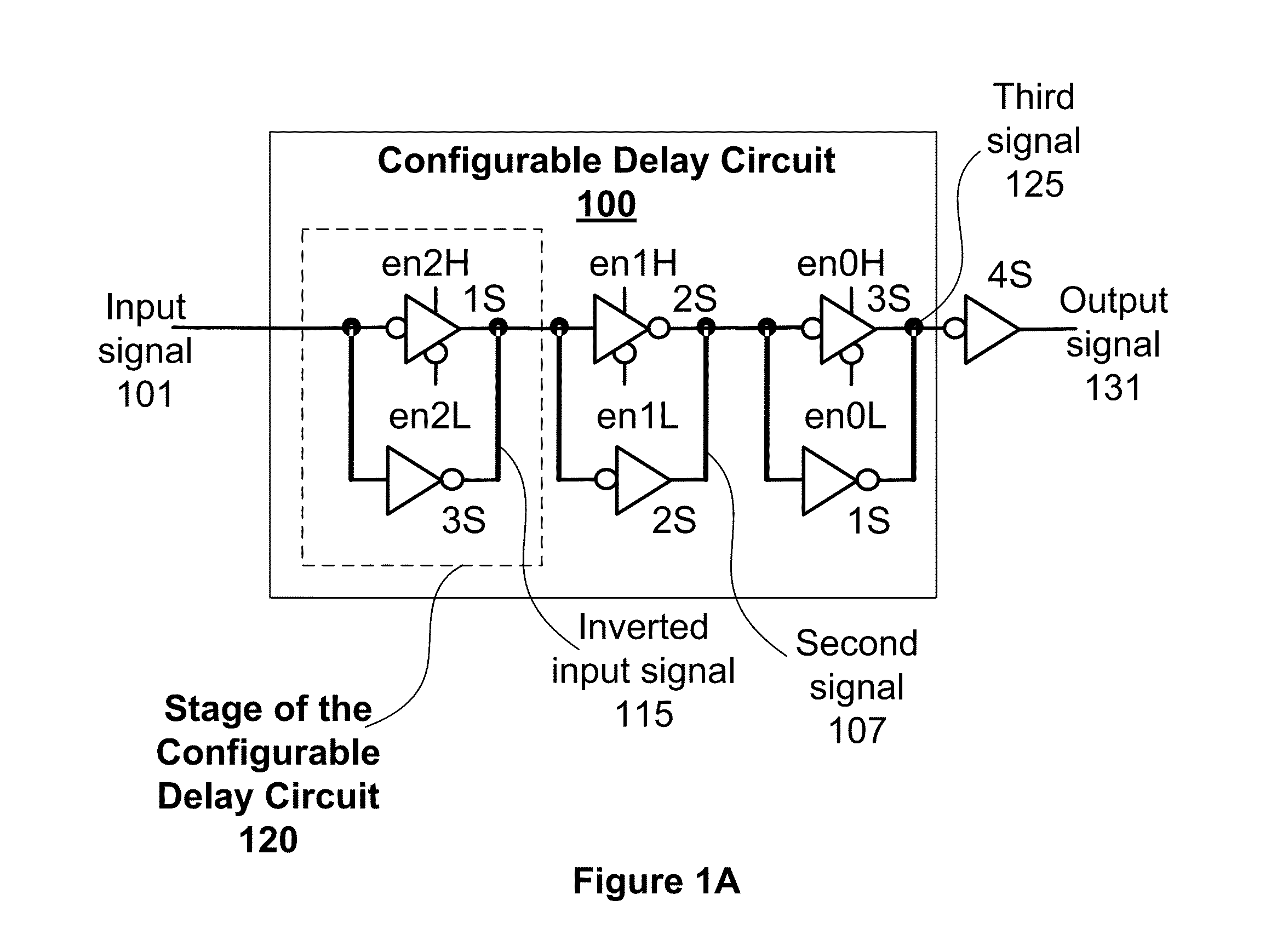
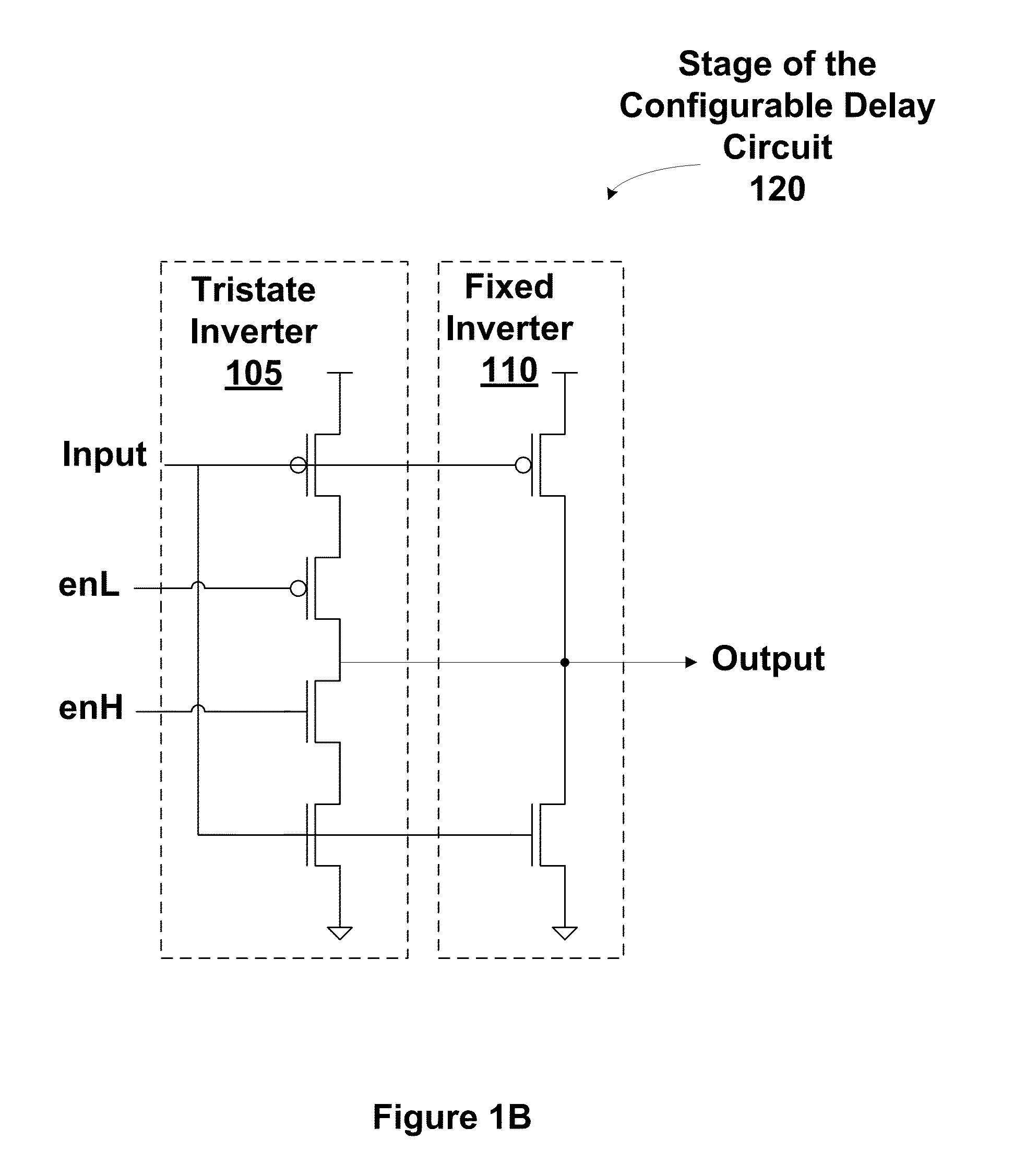
One embodiment sets forth a timing calibration technique for on-chip source-synchronous, complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) repeater-based interconnect. Two transition patterns may be applied to calibrate the delay of an on-chip data or clock wire. Calibration logic is configured to apply the transition patterns and then trim the delays of the clock and data wires based on captured calibration patterns. The trimming adjusts the delay of the clock and data wires using a configurable delay circuit. Timing errors may be caused by crosstalk, power-supply-induced jitter (PSIJ), or wire delay variation due to transistor and wire metallization mismatch. Chip yields may be improved by reducing the occurrence of timing errors due to mismatched delays between different wires of an on-chip interconnect.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
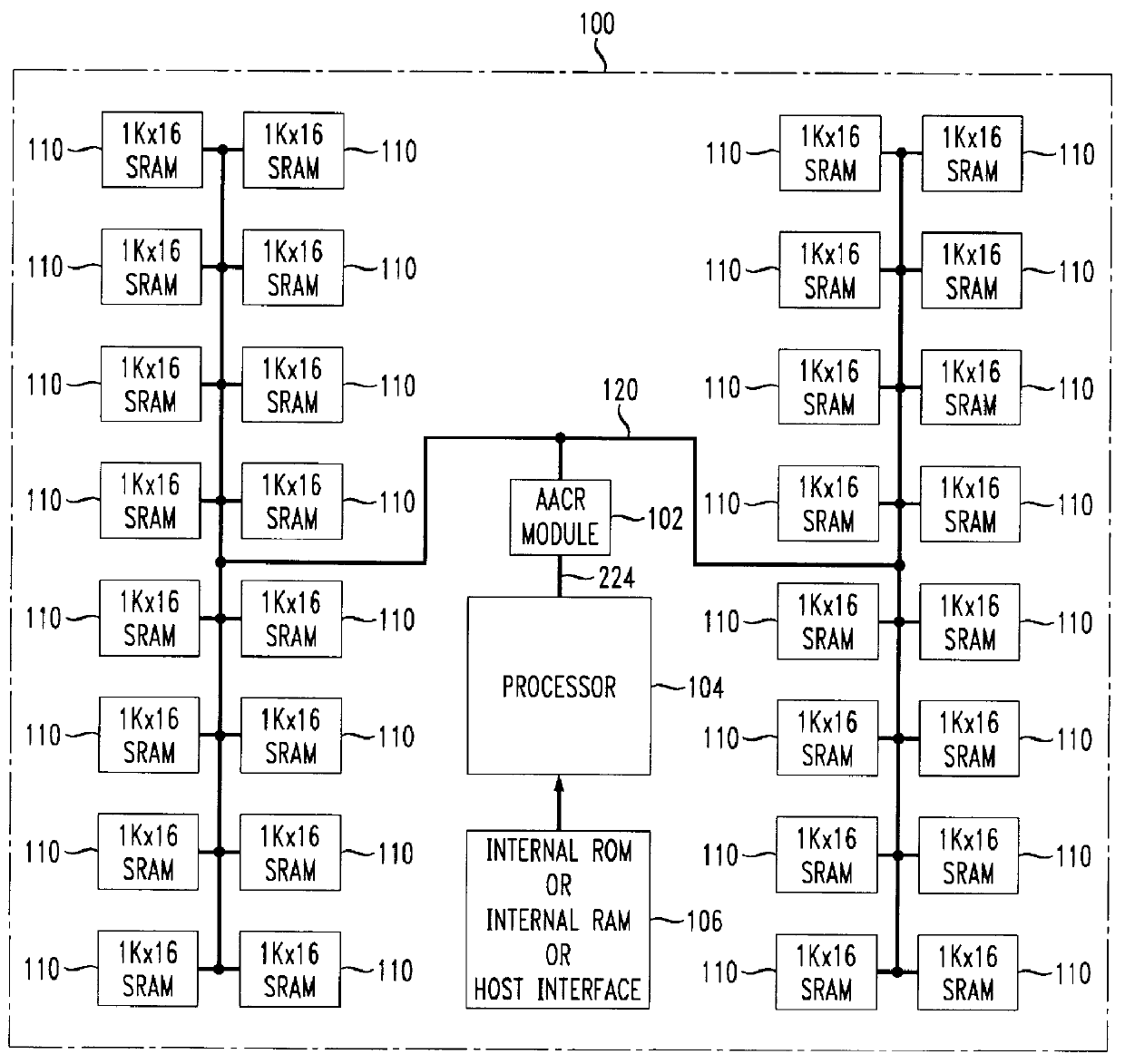
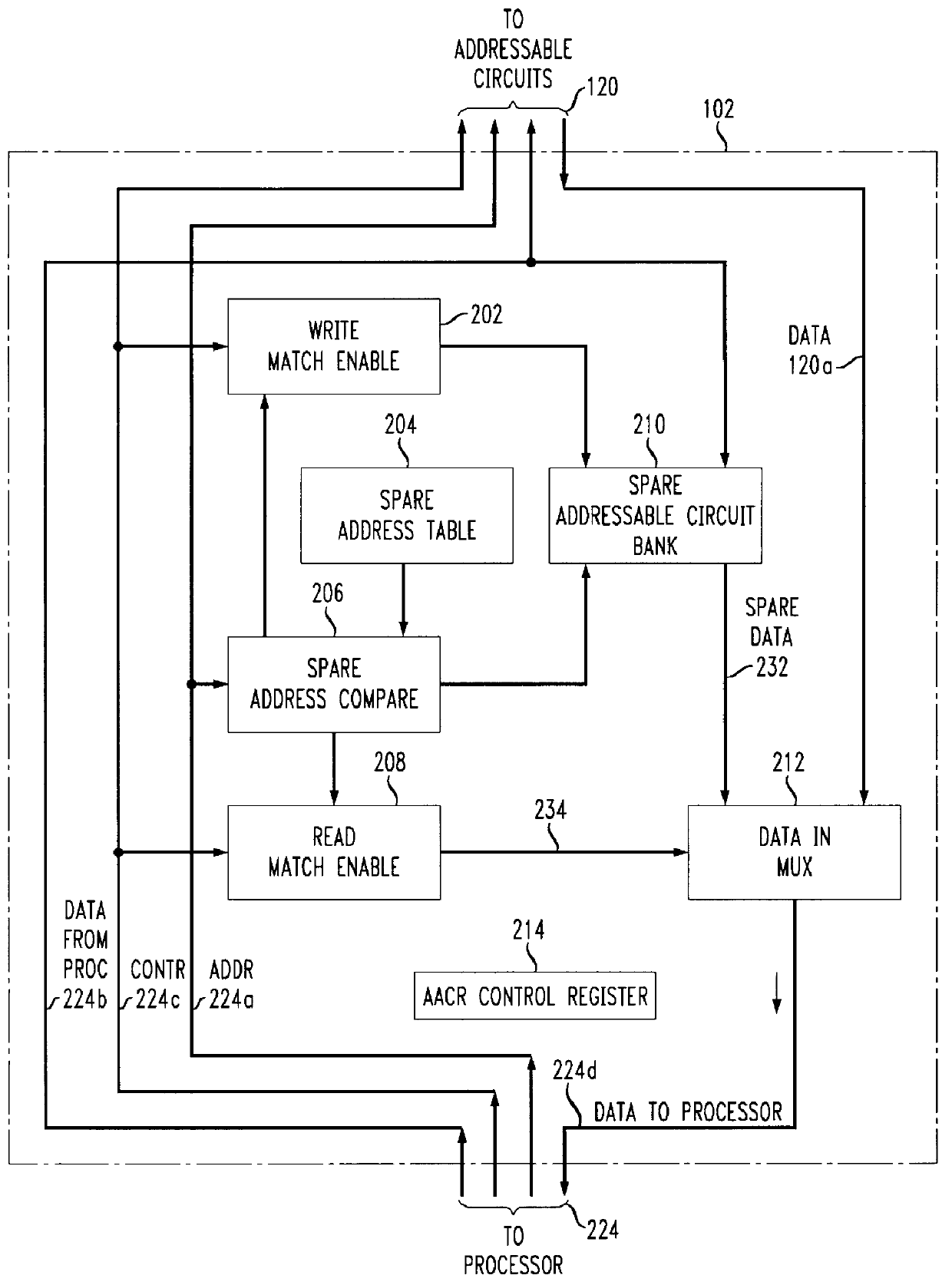
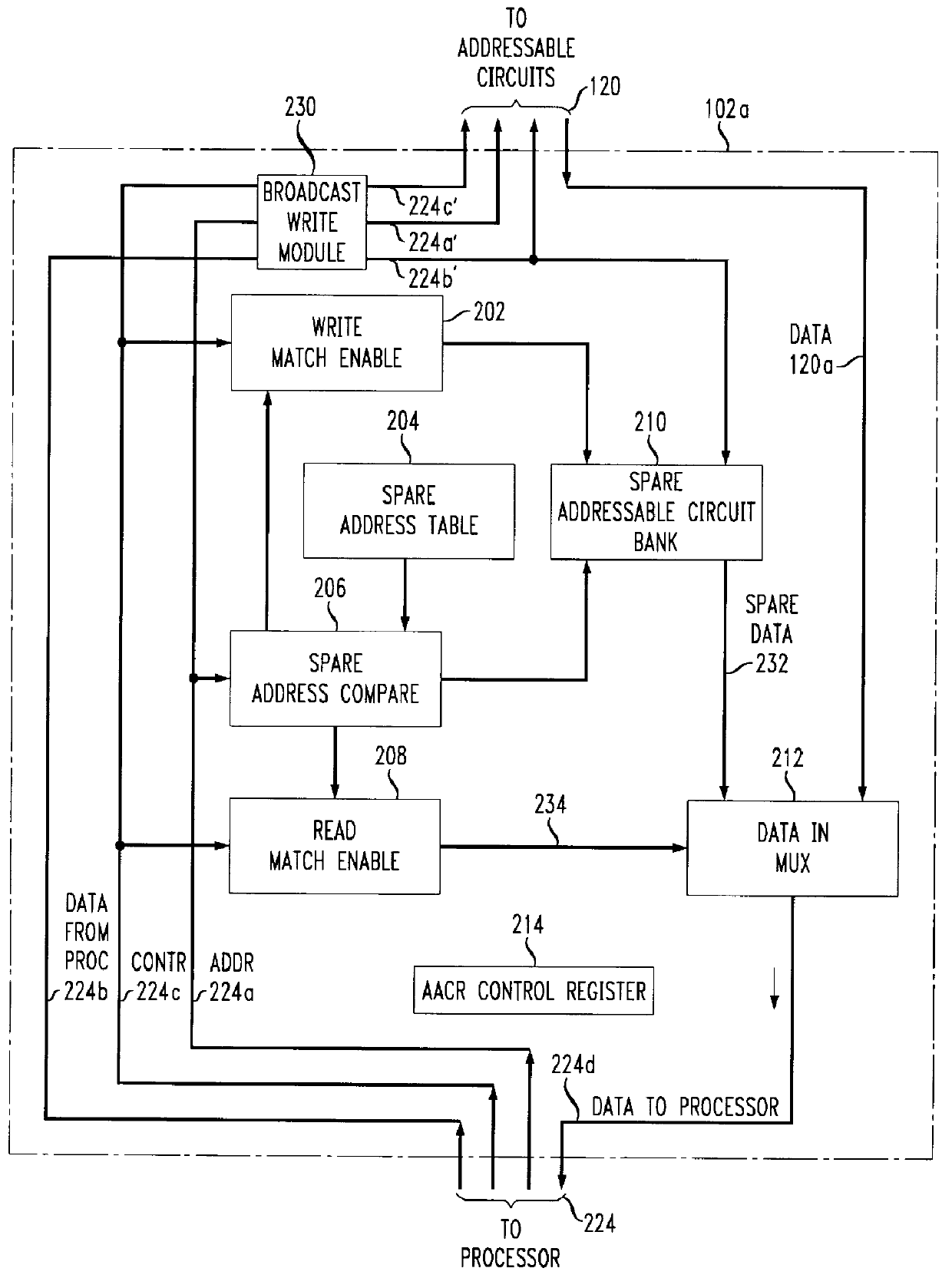
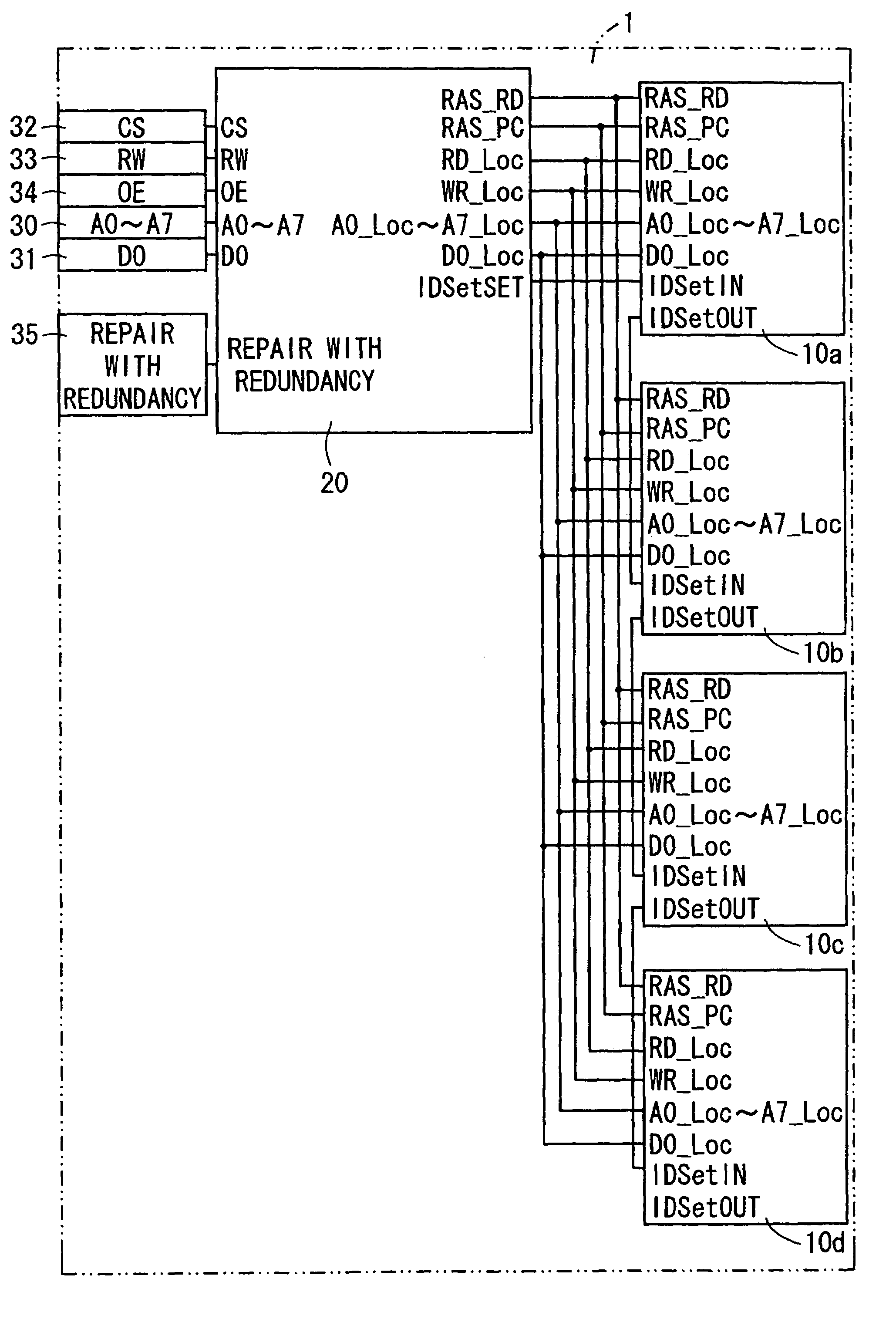
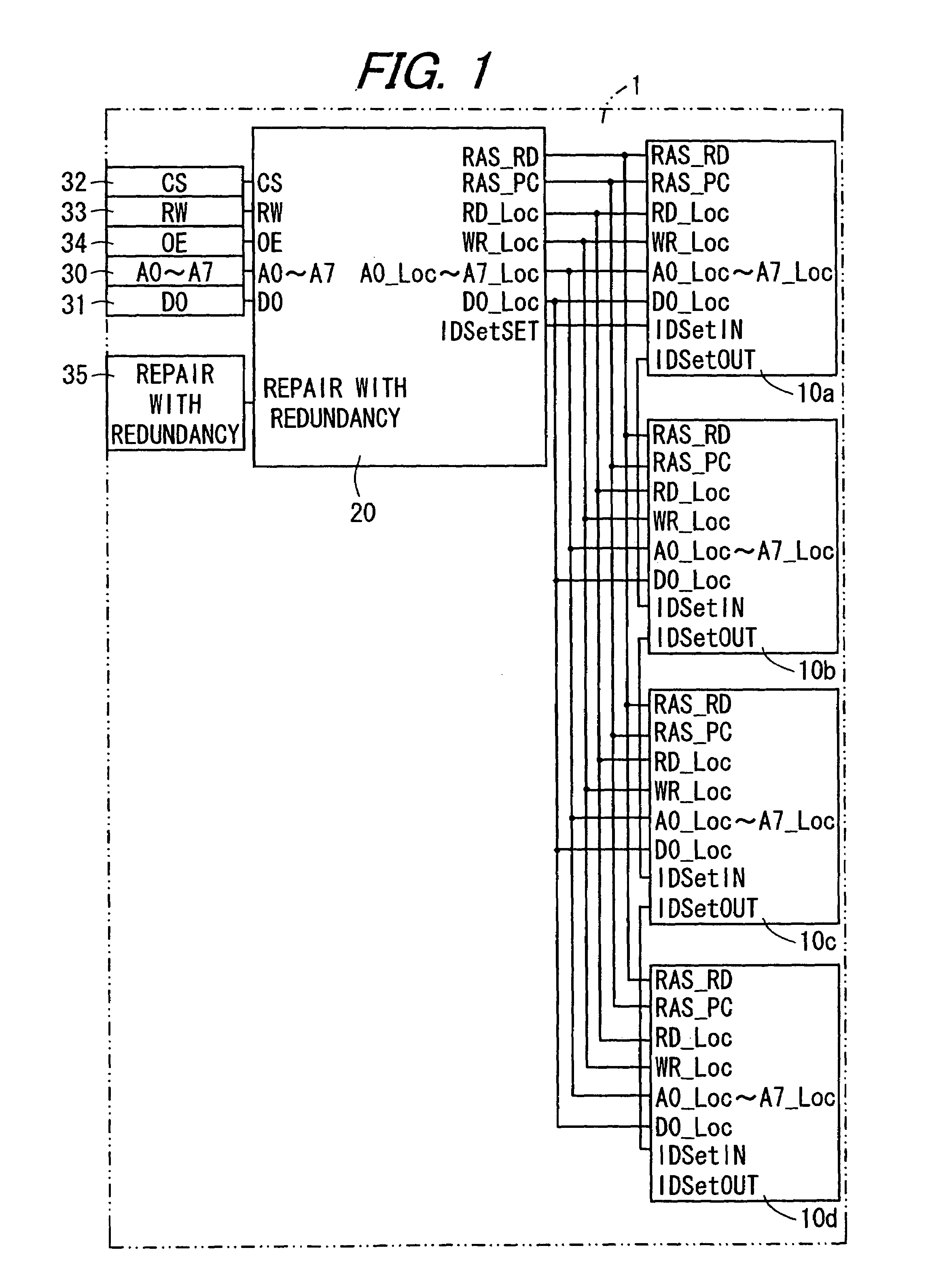
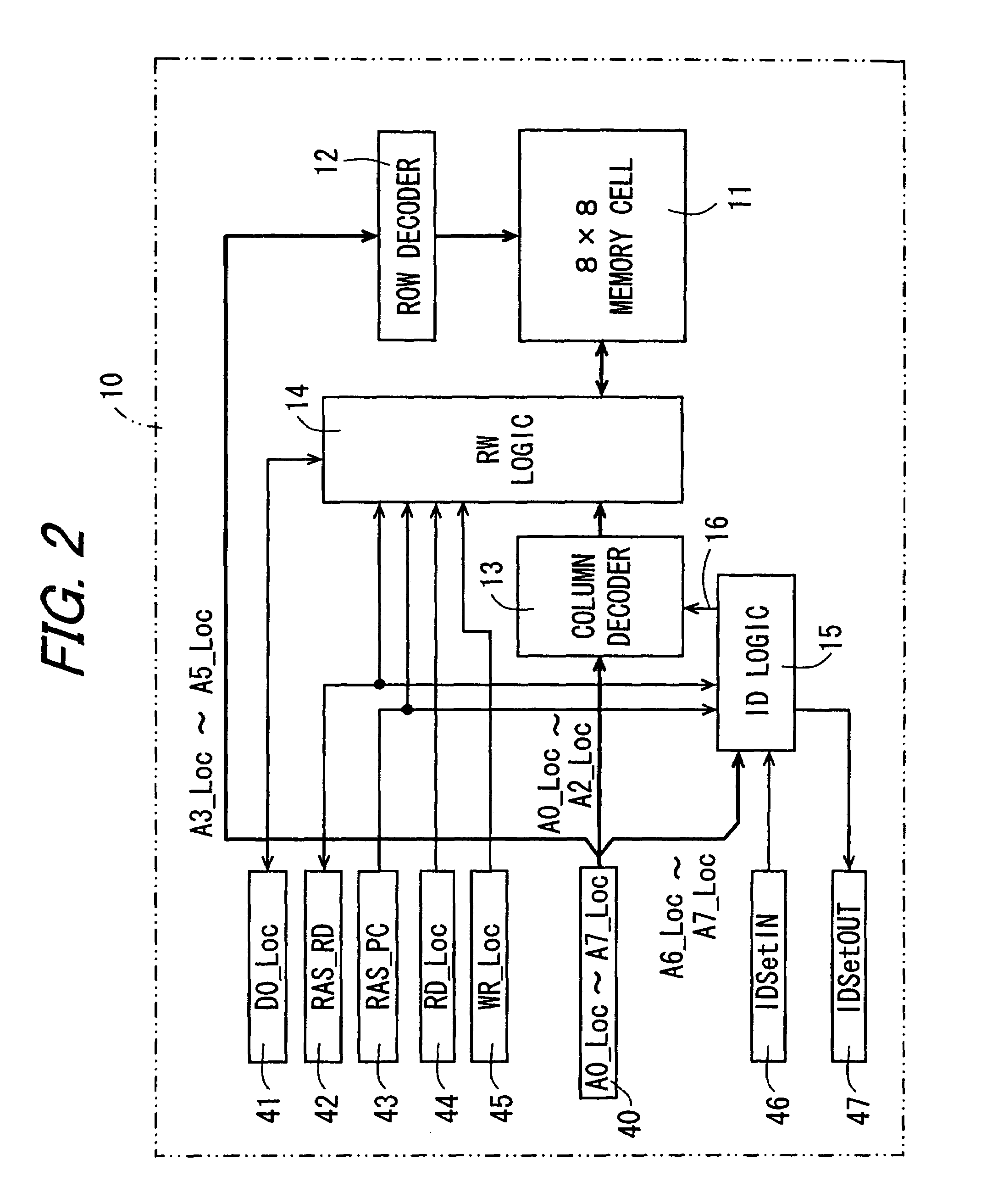
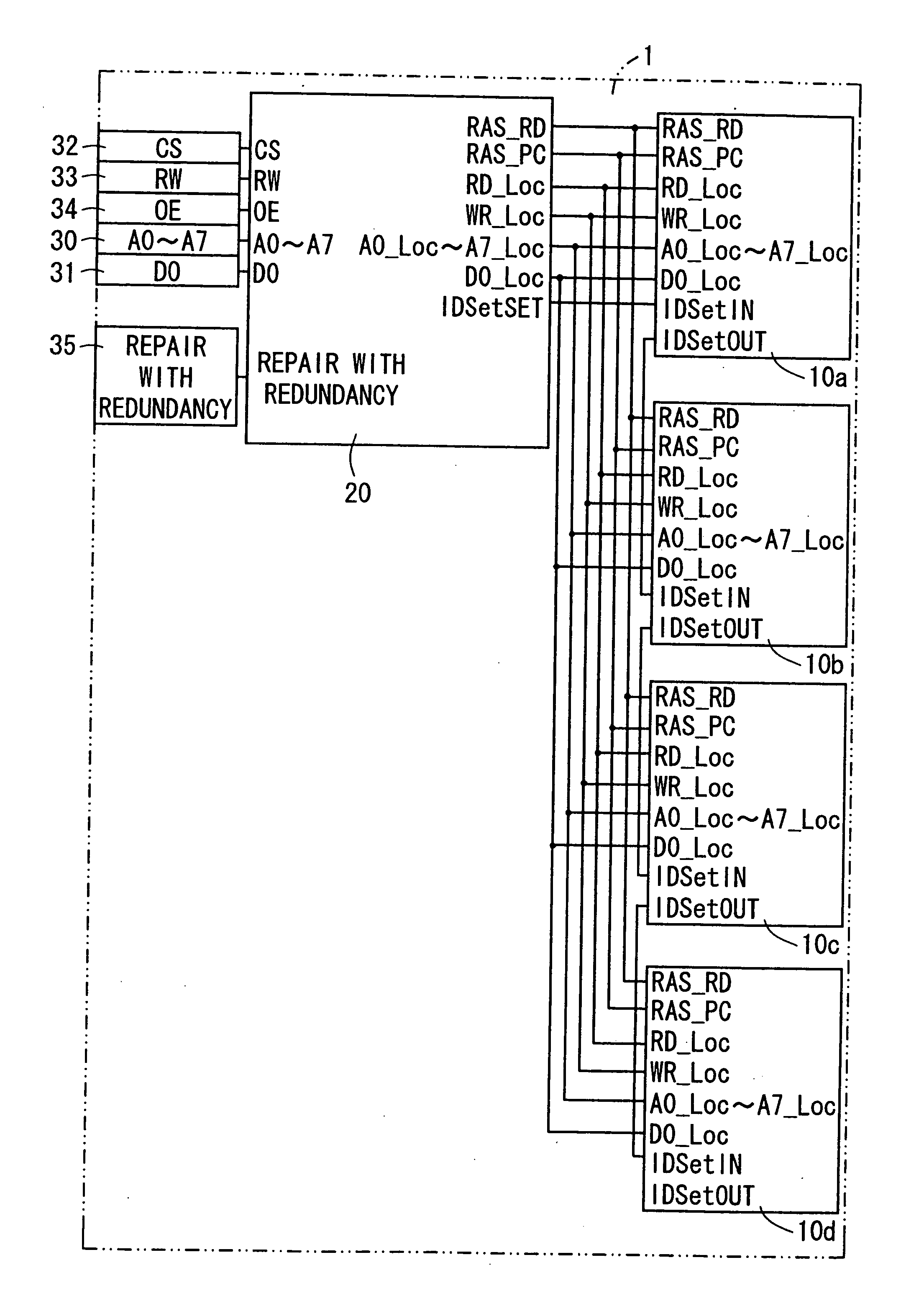
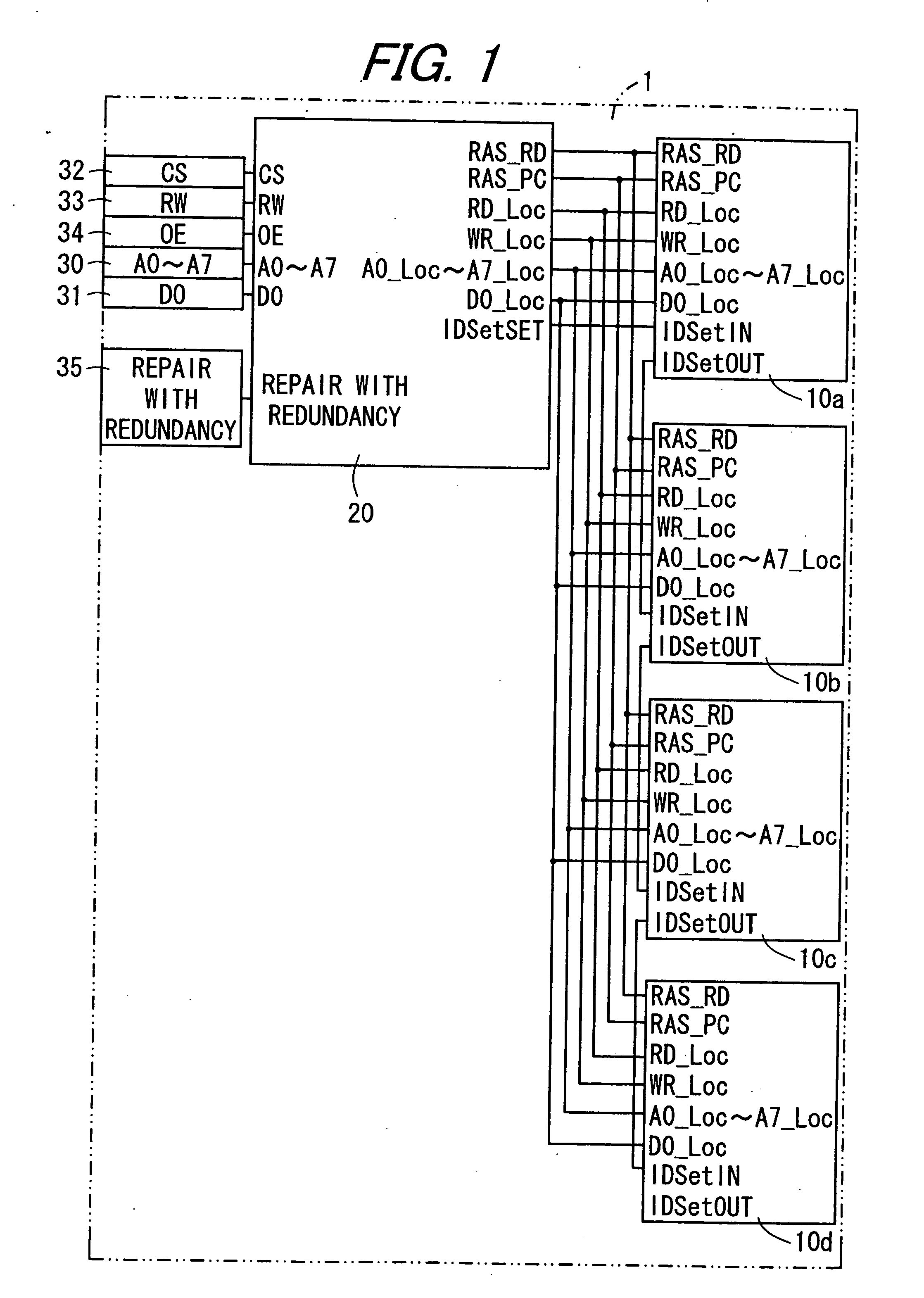
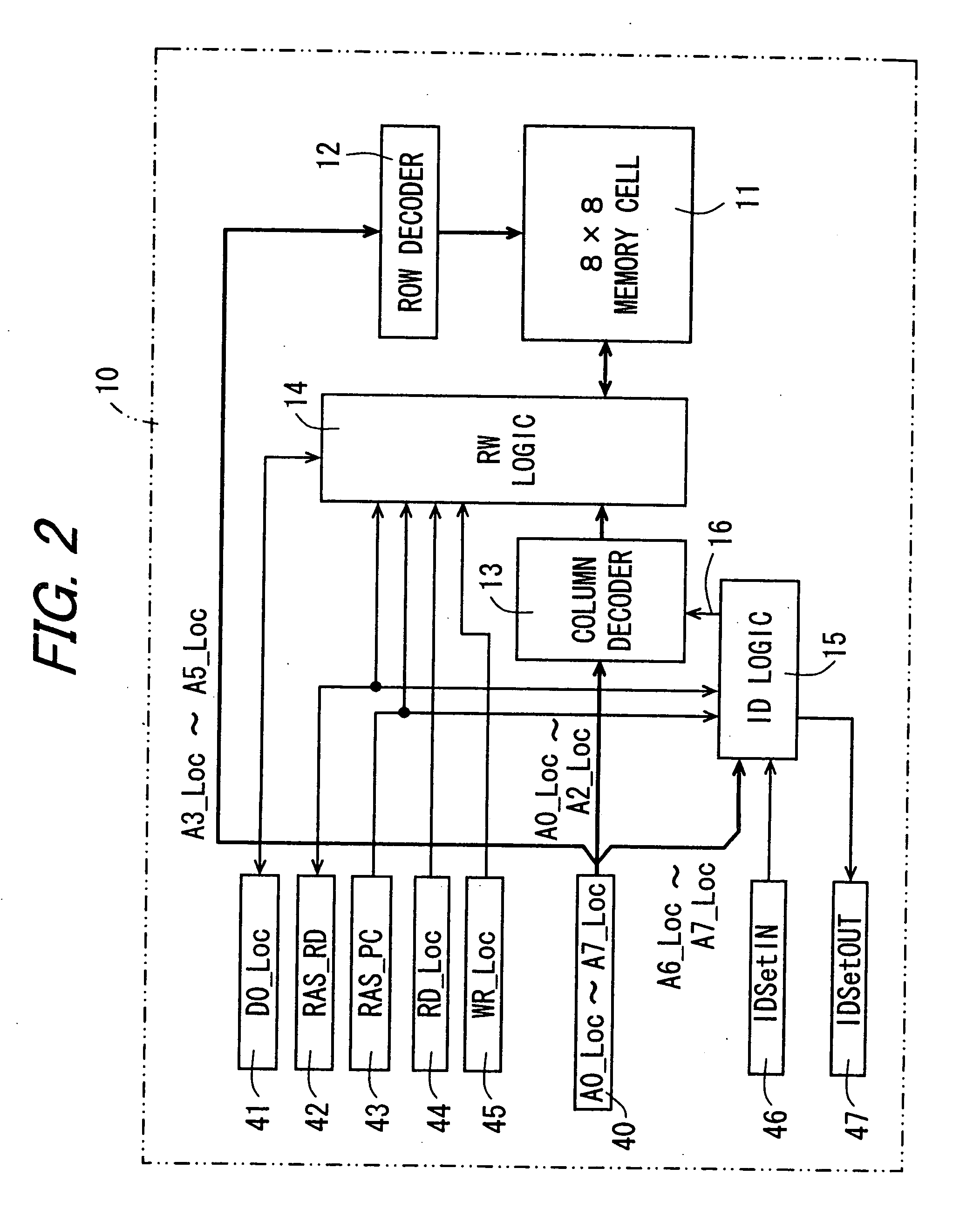
Adaptive addressable circuit redundancy method and apparatus
An adaptive addressable circuit redundancy method and apparatus, e.g., an adaptive memory redundancy method and apparatus, utilizes an on-chip processor to test, analyze and reassign spare addressable circuits to replace defective or intermittent addressable circuits. The present invention is applicable both in a manufacturing environment and / or in a field environment wherein the integrated circuit is operational. An adaptive addressable circuit redundancy module intercepts a data path between the on-chip processor and the addressable circuits to reassign defective addresses as necessary to utilize a spare addressable circuit bank. In another embodiment of the present invention, a broadcast write module cuts memory test time almost in half by writing a same data pattern to a significant portion or all of the addressable circuits, e.g., memory, substantially simultaneously.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
Memory device having redundant memory for repairing defects
First memory chips each have a memory cell as storage means for storing data and do not have a redundant memory cell as redundant storage means for repairing an erroneous bit in the memory cell. Furthermore, a logic minimal in degree is solely provided for operation on a control logic of a second memory chip. The second memory chip has a control logic for effecting memory control of the memory cells, the redundant memory cells, etc. and a redundant memory cell for repairing an error bit of the first memory chips. The memory device is structured by stacking the first and second memory chips.
Owner:SHARP KK
Feedforward/feedback litho process control of stress and overlay
ActiveUS8111376B2Improve chip yieldReduce probabilityPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingProcess engineering
A method and apparatus for process control in a lithographic process are described. Metrology may be performed on a substrate either before or after performing a lithographic patterning process on the substrate. One or more correctables to the lithographic patterning process may be generated based on the metrology. The lithographic patterning process performed on the substrate (or a subsequent substrate) may be adjusted with the correctables.
Owner:KLA CORP
Programming verification method of nonvolatile memory cell, semiconductor memory device, and portable electronic apparatus having the semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS7170791B2Suppression of short channel effectsFacilitates discriminationTransistorSolid-state devicesMemory cellComputational physics
Owner:SHARP KK
Memory device
First memory chips each have a memory cell as storage means for storing data and do not have a redundant memory cell as redundant storage means for repairing an erroneous bit in the memory cell. Furthermore, a logic minimal in degree is solely provided for operation on a control logic of a second memory chip. The second memory chip has a control logic for effecting memory control of the memory cells, the redundant memory cells, etc. and a redundant memory cell for repairing an error bit of the first memory chips. The memory device is structured by stacking the first and second memory chips.
Owner:SHARP KK
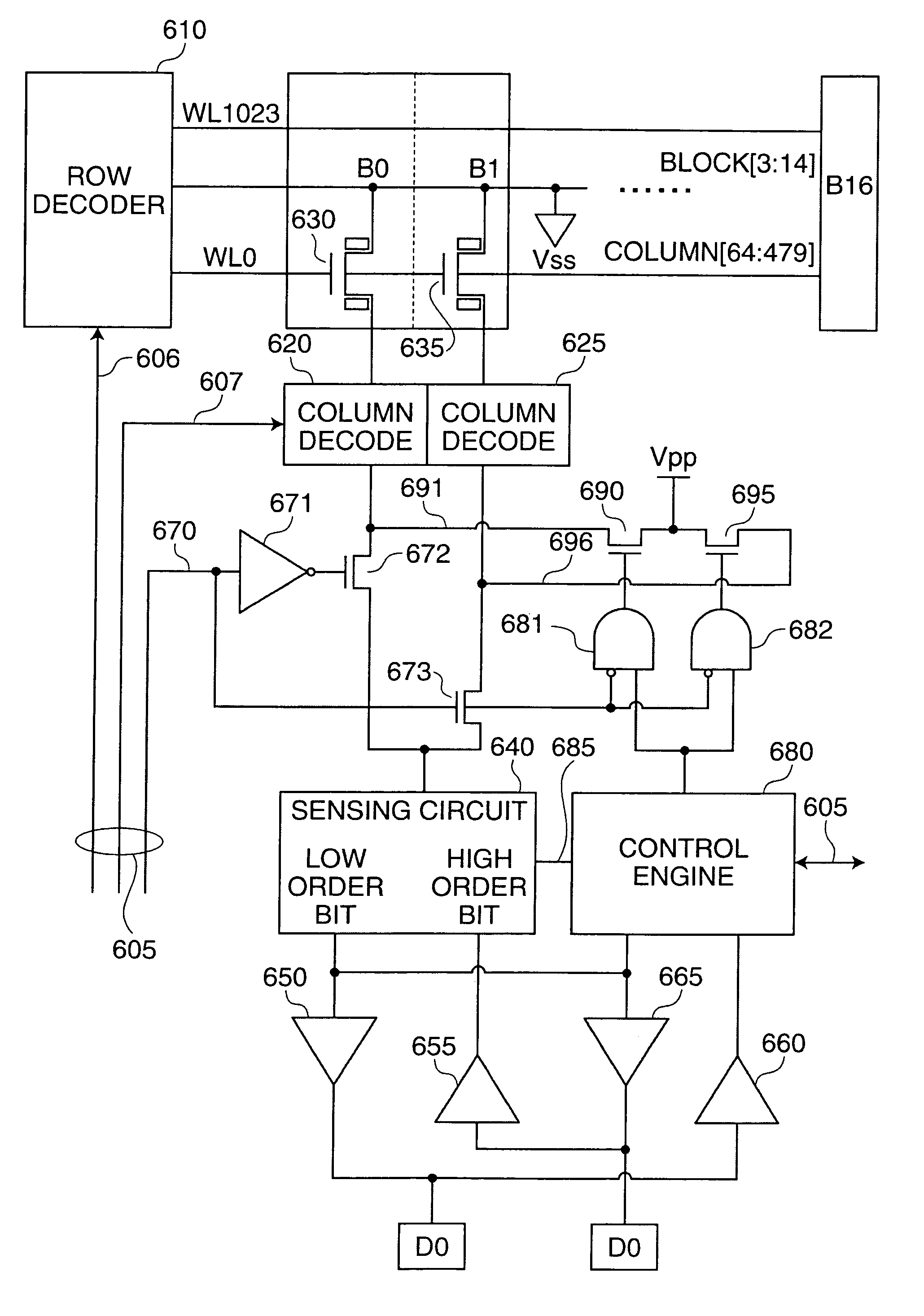
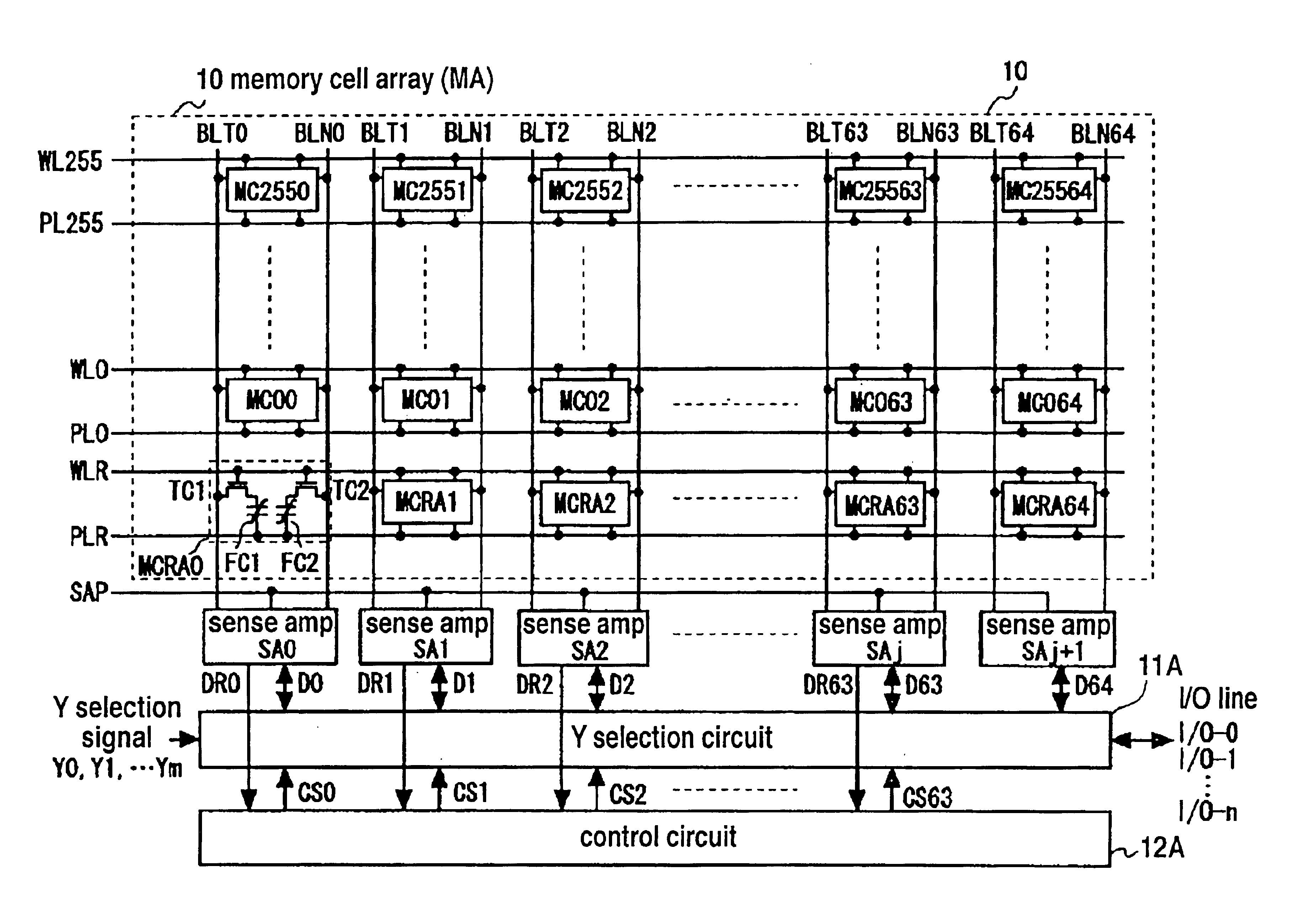
Semiconductor memory having a defective memory cell relieving circuit
InactiveUS6879529B2Minimized area overhead and access time overheadImprove chip yieldDigital storageComputer architectureAccess time
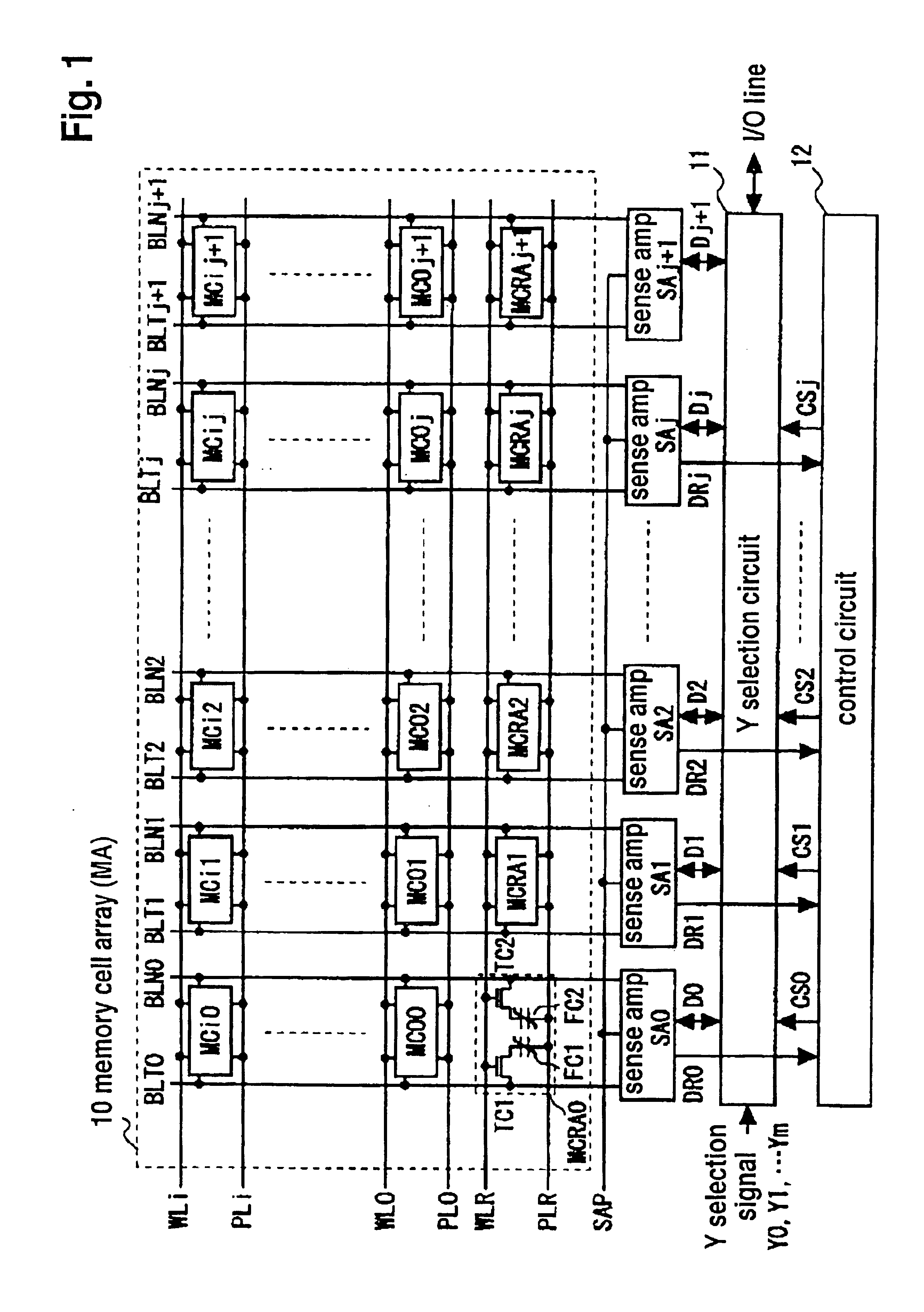
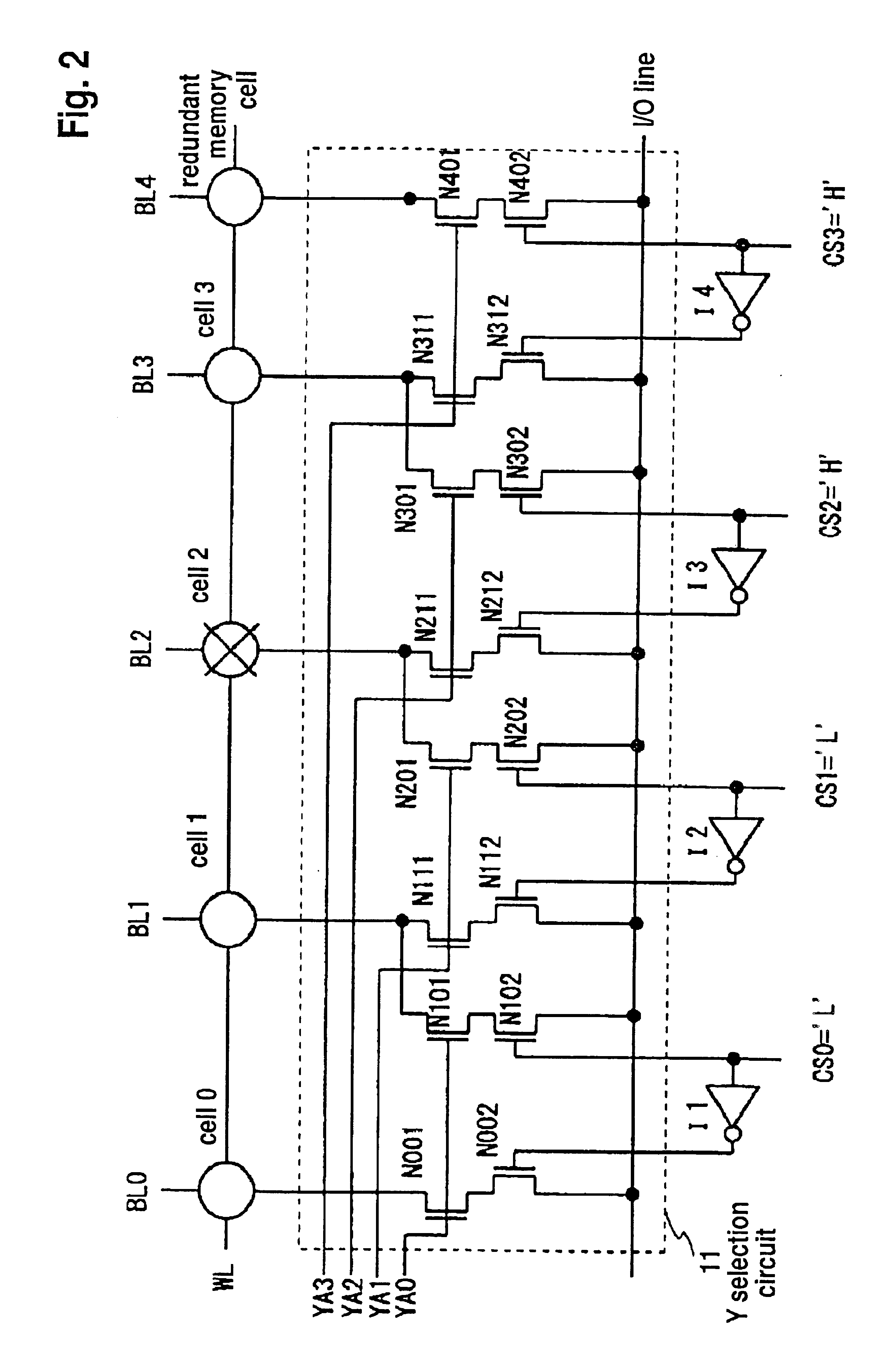
In a semiconductor memory incorporating therein a circuit for relieving a defective memory cell, a memory cell array constituted of a number of main memory cells MC00 to MCij is added with one column of redundant memory cells MC0j+1 to MCij+1 and one word line of substitution information storing memory cells MCRA0 to MCRAj+1. In only a first cycle after the power supply is turned on, the substitution information DR0 to DRj is read out from the substitution information storing memory cells by use of a writing / reading circuit associated with the main memory cells, and is transferred to and held in a control circuit. In a second and succeeding cycles, the control circuit generates Y selection circuit control signals CS0 to CSj on the basis of the substitution information held in the control circuit, and a Y selection circuit is controlled by the control signals CS0 to CSj so as to selectively connect the columns other than a defective column to an input / output line. Thus, a chip area overhead attributable to the installation of the defective memory cell relief circuit is minimized. In addition, an address comparing circuit for a defective memory cell substitution is no longer necessary, and an access time overhead attributable to the address substitution operation does not occur.
Owner:NEC CORP
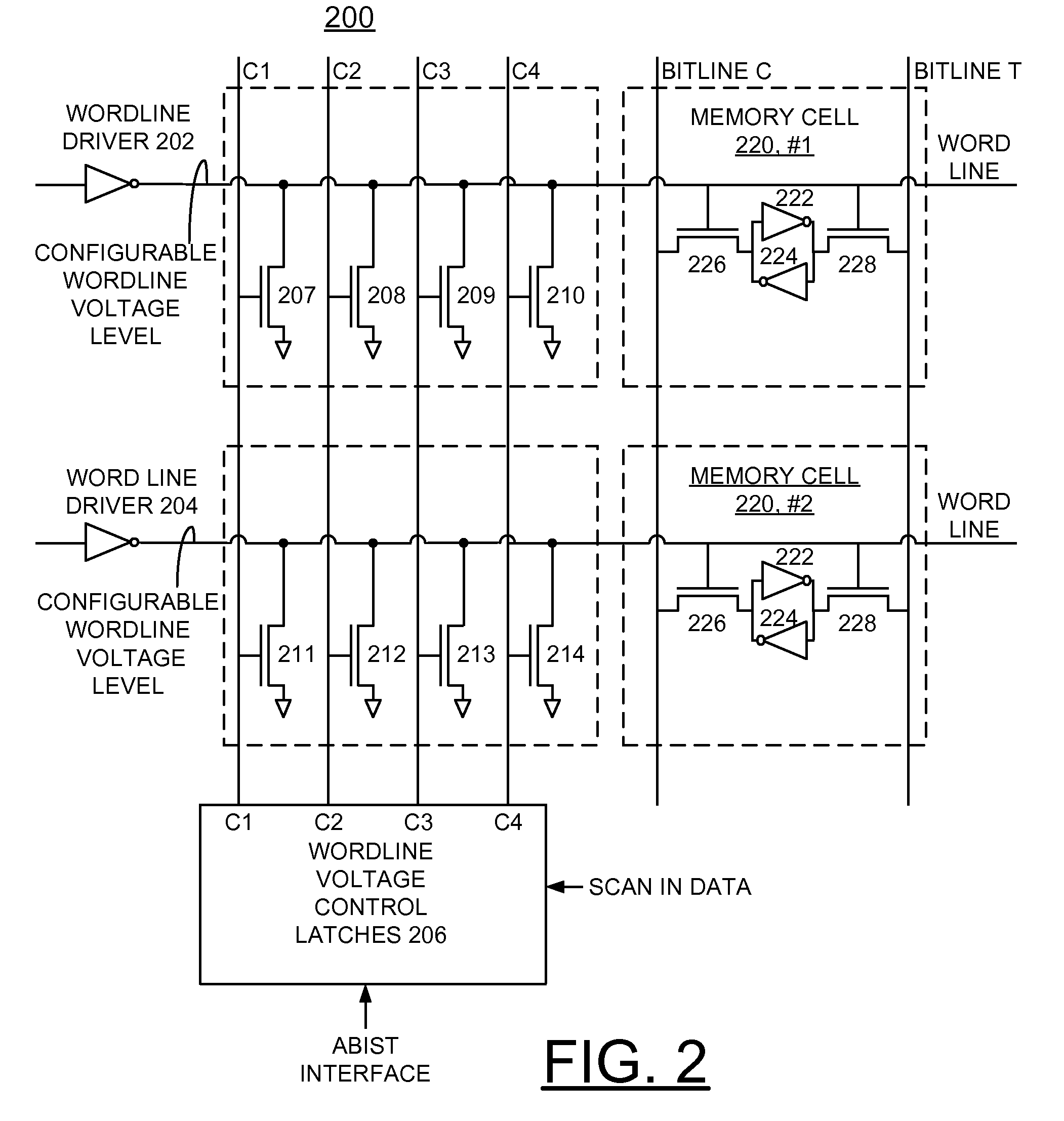
Implementing Enhanced SRAM Stability and Enhanced Chip Yield With Configurable Wordline Voltage Levels
ActiveUS20100188886A1Easy accessImprove chip yieldDigital storageStatic random-access memoryHemt circuits
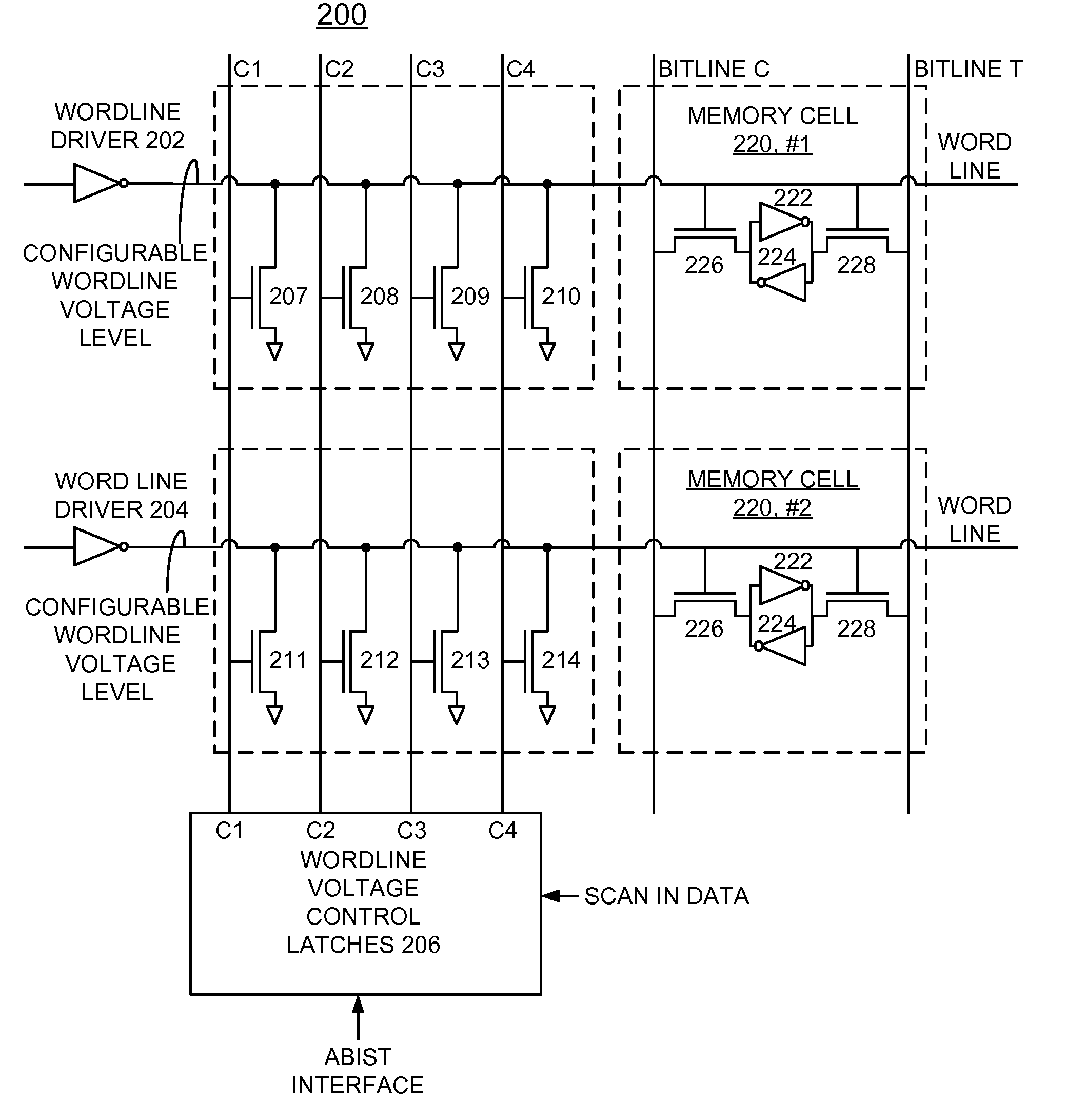
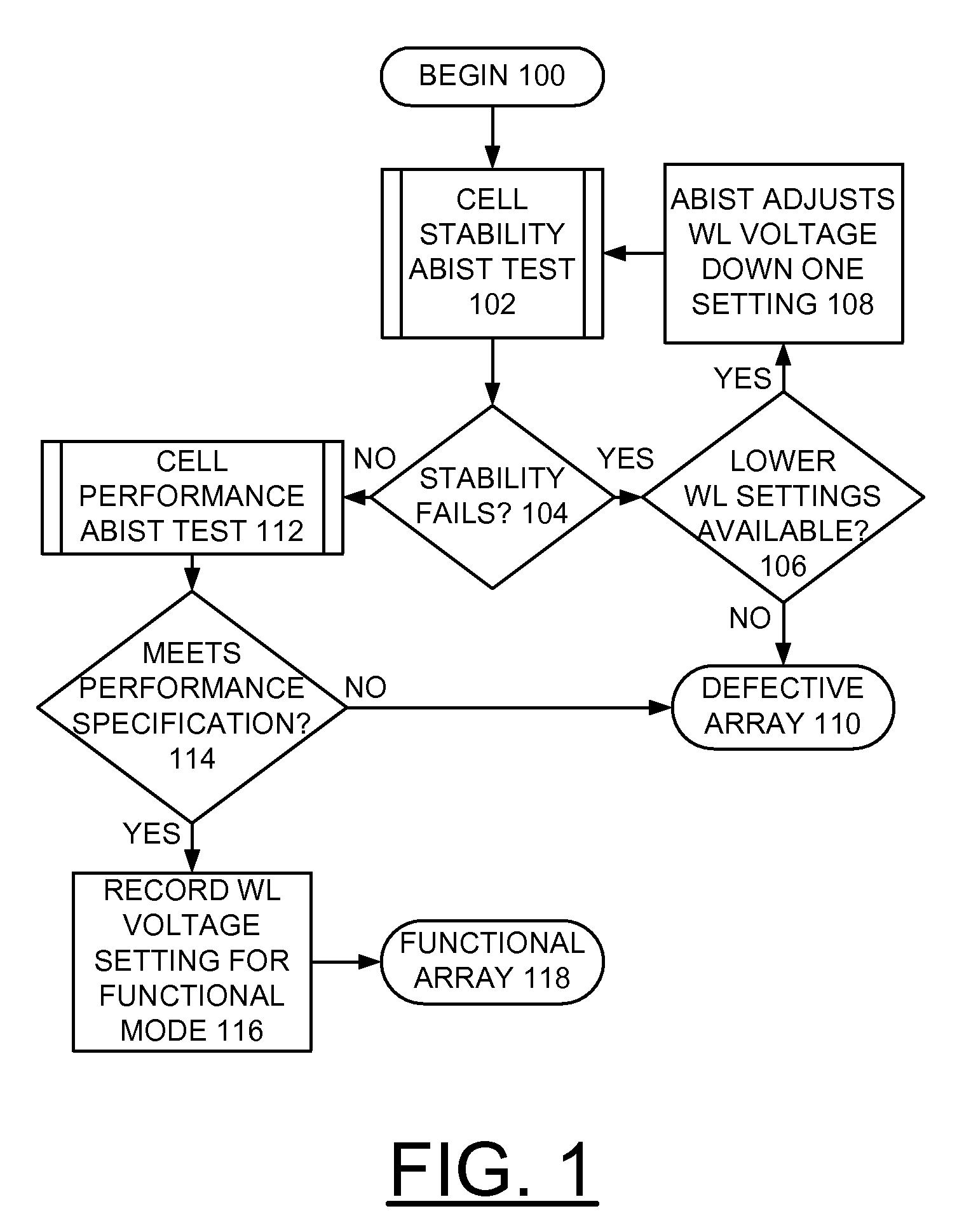
An array built in self test (ABIST) method and circuit for implementing enhanced static random access memory (SRAM) stability and enhanced chip yield using configurable wordline voltage levels, and a design structure on which the subject circuit resides are provided. A wordline is connected to a SRAM memory cell. A plurality of wordline voltage pulldown devices is connected to the wordline. A respective wordline voltage control input signal is applied to each of the plurality of wordline voltage pulldown devices to selectively adjust the voltage level of the wordline.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090090925A1Well formedLow priceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsMonocrystalline siliconDielectric
There are a silicon laser device having a IV-group semiconductor such as silicon or germanium equivalent to the silicon as a basic constituent element on a substrate made of the silicon, and the like by a method capable of easily forming the silicon laser device by using a general silicon process, and a manufacturing method thereof. The silicon laser device is an ultrathin silicon laser that includes a first electrode unit injecting electrons, a second electrode unit injecting holes, a light emitting unit electrically connected to the first electrode unit and the second electrode unit, wherein the light emitting unit is made of single-crystal silicon and has a first surface (top surface) and a second surface (bottom surface) opposed to the first surface, a waveguide made of a first dielectric, which is disposed in the vicinity of the light emitting unit, by setting surface directions of the first and second surfaces as a surface (100) and thinning a thickness of the light emitting unit in a direction perpendicular to the first and second surfaces, and a mirror formed by alternately adjoining the first dielectric and a second dielectric.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Laser diode chip, laser diode, and method for manufacturing laser diode chip
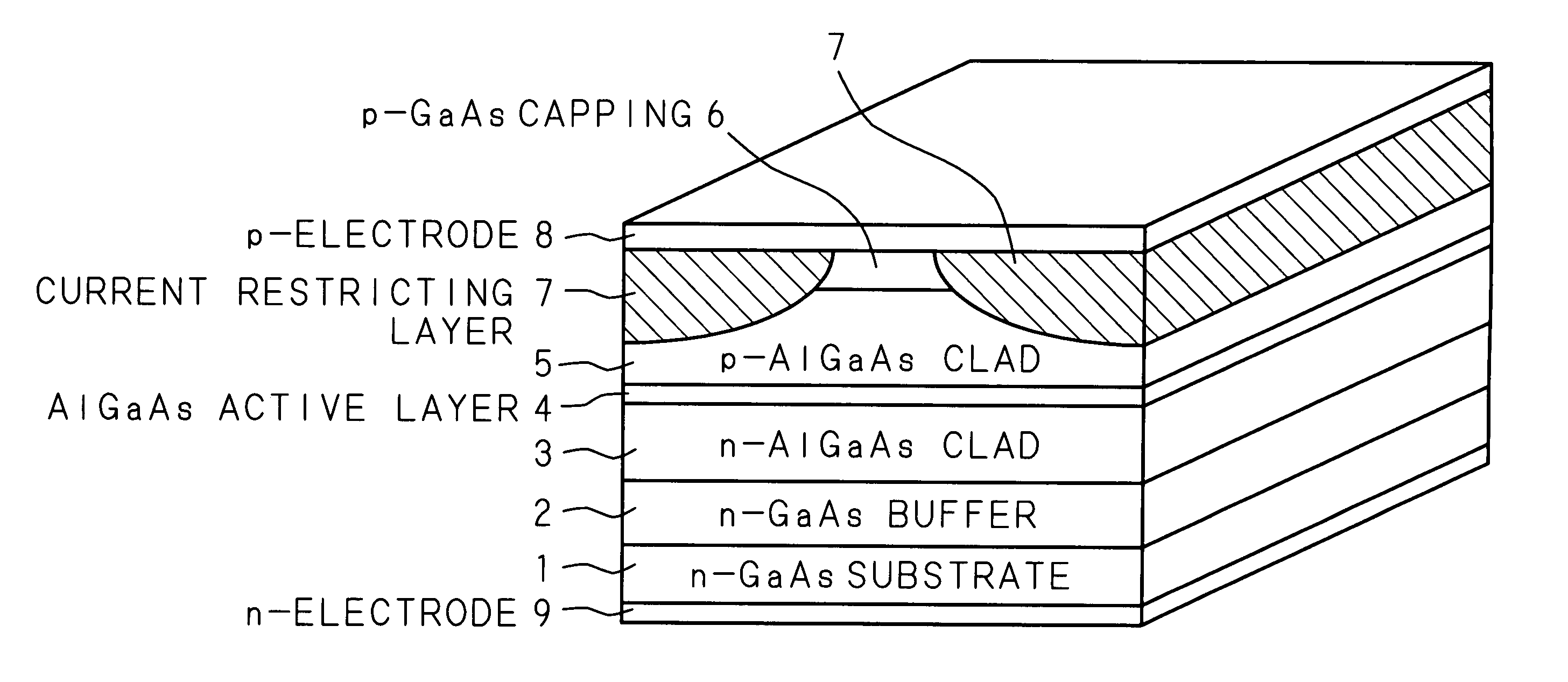
InactiveUS20060203867A1Threshold currentSmall differenceSemiconductor lasersLaser cooling arrangementsCurrent limitingActive layer
Both lateral side portions of a laser diode chip separated by the central portions of a p-type capping layer and a p-type clad layer and parallel to the horizontal edges of the cleavage planes of the chip are cut away by etching, so that the p-type capping layer and the p-type clad layer take the shape of a mountain in cleavage planes which are the end faces of an active layer. The cut portions are provided with current restricting layers of oxide film made by baking a liquid oxide film. The thicknesses of the current restricting layers are increased with distance from the central portion of the laser diode chip.
Owner:PHENITEC SEMICON CORP +1
Optical transport network having a plurality of monolithic photonic integrated circuit (PIC) semiconductor chips
InactiveUS20080025726A1Improve chip yieldInhibit outputLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsSignal onSemiconductor chip
A photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip comprising an array of modulated sources, each providing a modulated signal output at a channel wavelength different from the channel wavelength of other modulated sources and a wavelength selective combiner having an input optically coupled to received all the signal outputs from the modulated sources and provide a combined output signal on an output waveguide from the chip. The modulated sources, combiner and output waveguide are all integrated on the same chip.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Integrated circuit (IC) with on-chip programmable fuses
InactiveUS20060267136A1Improve chip yieldReducing and eliminating damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
An Integrated Circuit (IC) chip with fused circuits and method of making the IC. Fuses in an upper wiring layer are formed using a multi-tone mask to define rounded bottom corners on the fuses, while wiring in the upper wiring layer maintain a rectangular cross-section.
Owner:IBM CORP
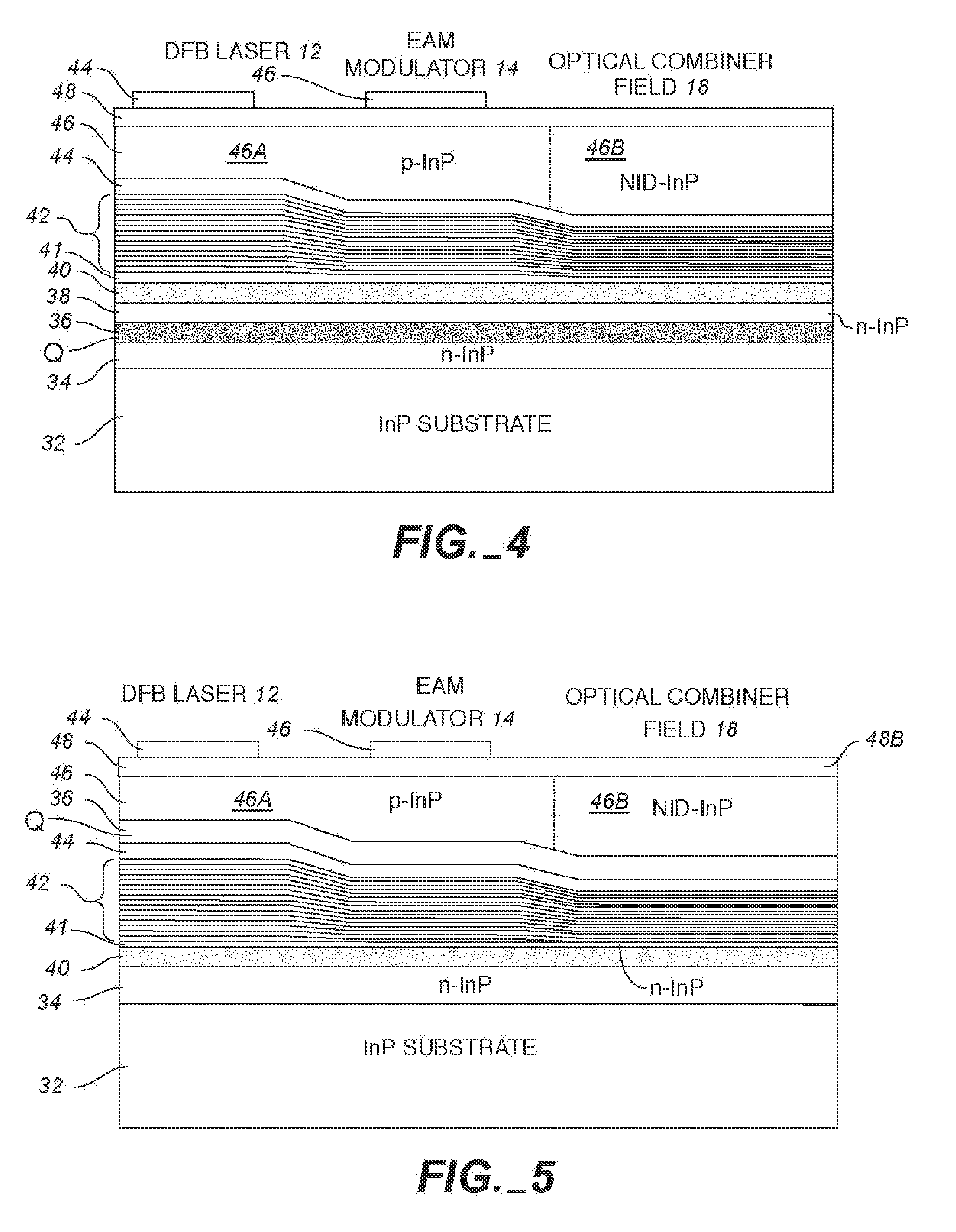
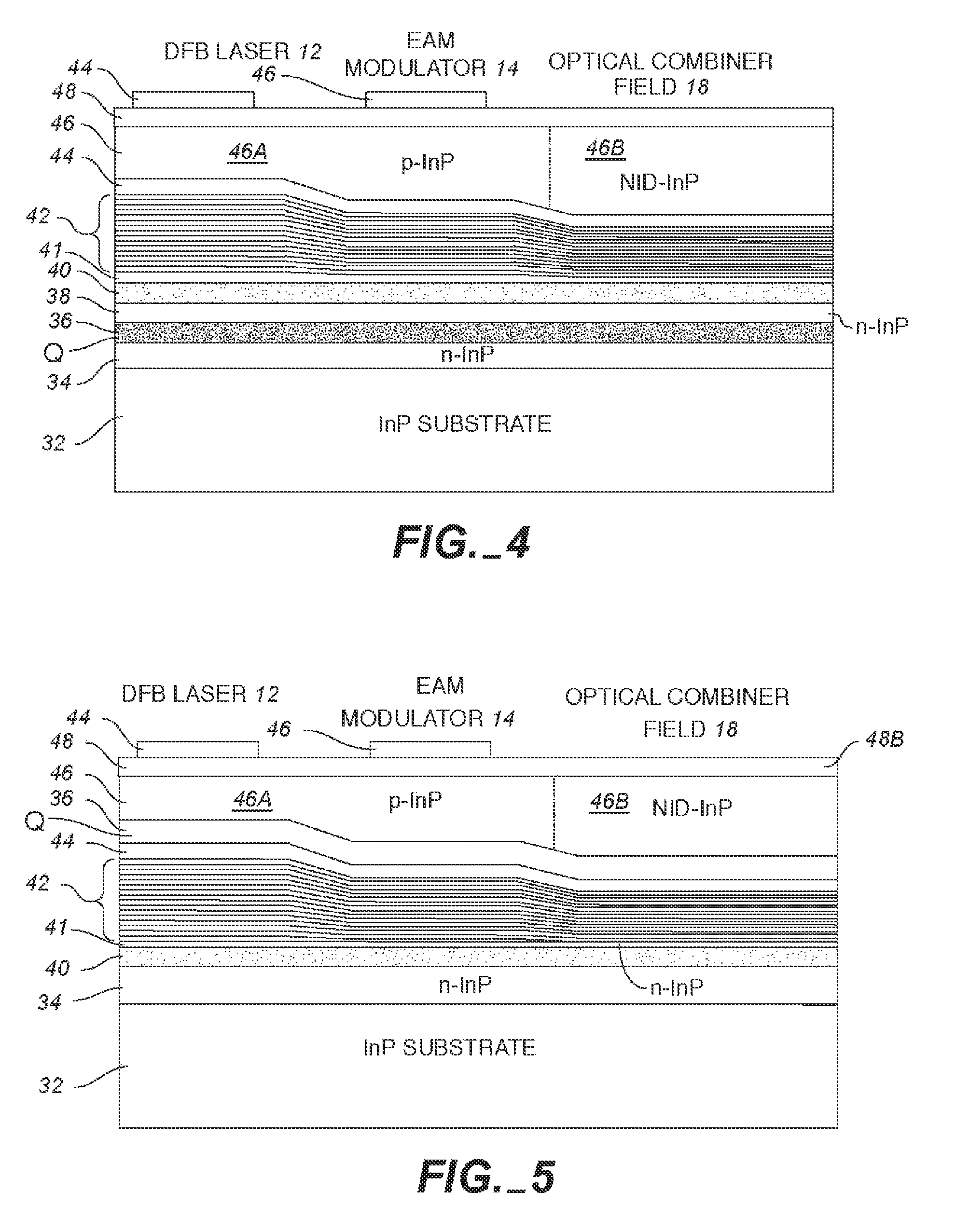
Multiple cavity etched-facet dfb lasers
ActiveUS20090067465A1Accurately determineImprove methodLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor chip has at least two DFB etched facet laser cavities with one set of facets with AR coatings and a second set of etched facets with HR coatings that have a different relative position with respect to the gratings. This creates a difference in the phase between each of the etched facets and the gratings which changes the operational characteristics of the two laser cavities such that at least one of the lasers provides acceptable performance. As a result, the two cavity arrangement greatly improves the yield of the fabricated chips.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
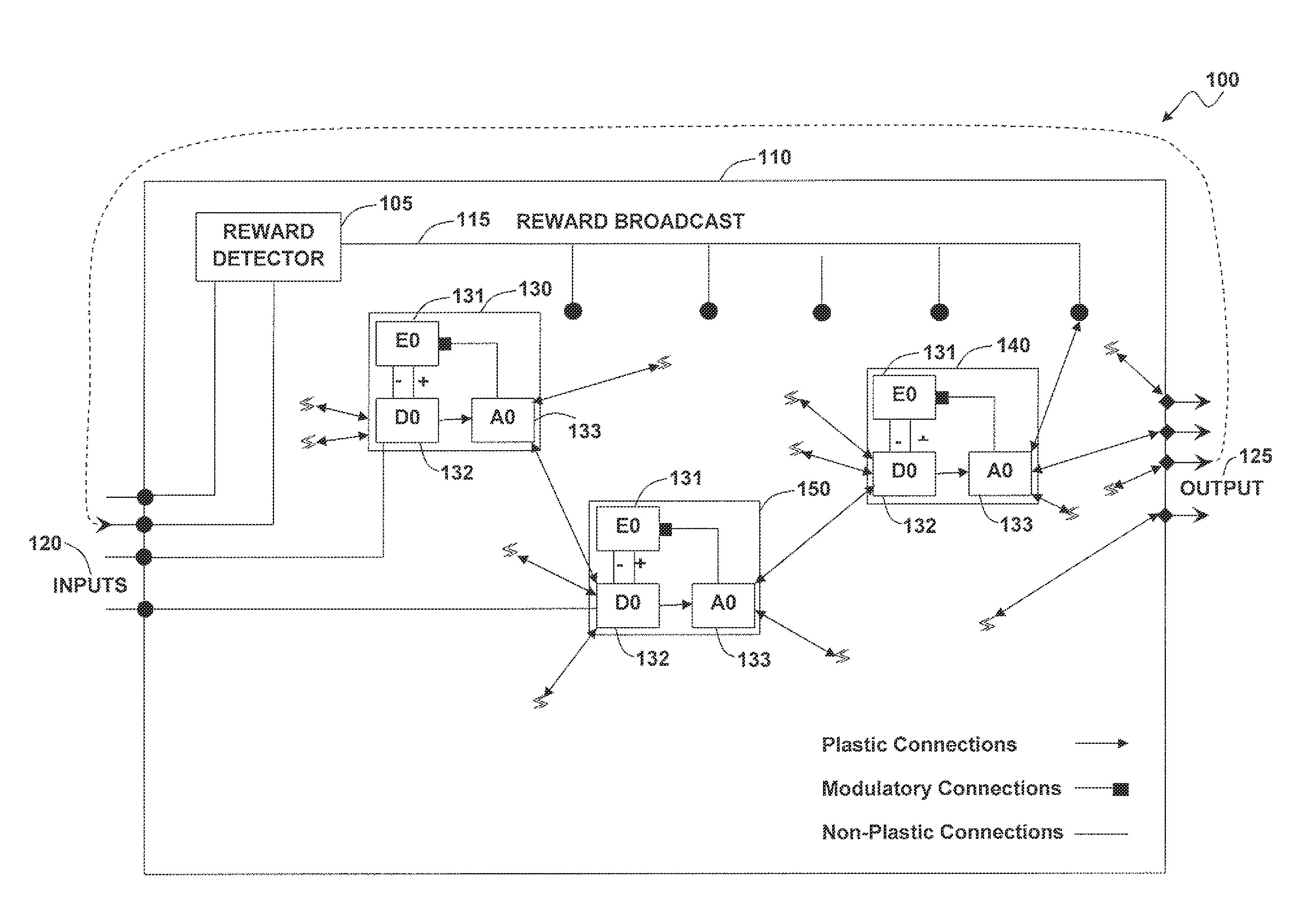
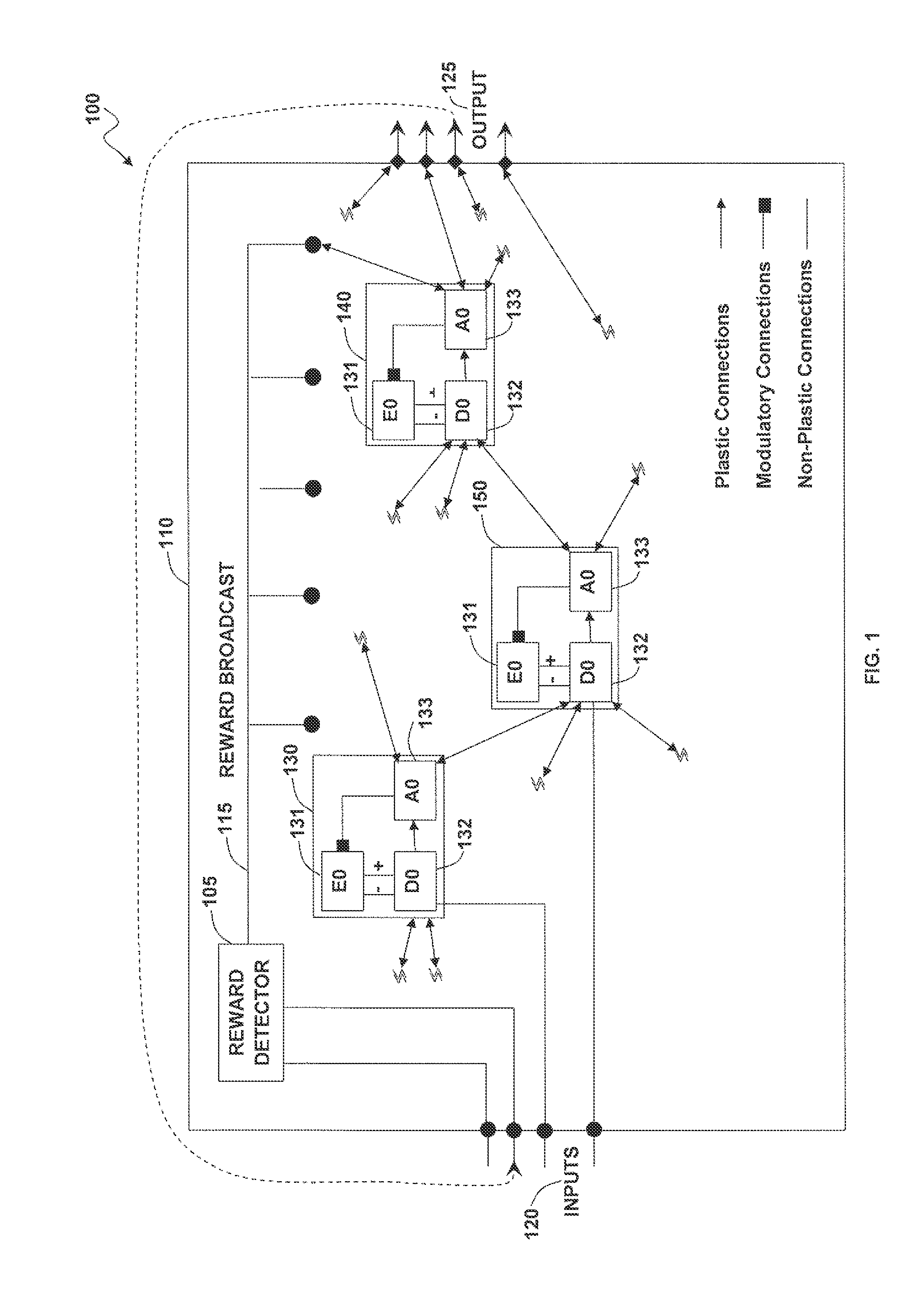
Self-organizing circuits
InactiveUS20110302119A1Reduce needImprove the level ofDigital computer detailsDigital dataSelf-healingElectronic systems
A self-organizing electronic system and method that organizes and repairs itself. A number circuit of modules can be embedded in a fabric. Each circuit module can calculate some function of its inputs and produces an output, which is encoded on volatile memory held together by a plasticity rule. The plasticity rule allows circuit modules to converge to any possible functional state defined by the structure of the information being processed. Flow through the system gates energy dissipation of the individual circuit modules. Circuit modules receiving high flow become locked in their functional states while circuit modules receiving little or no flow mutate in search of better configurations. These principles can be utilized to configure the state of any functional element within the system, and can be abstracted to higher levels of organization. Far from expending energy on state configurations, a volatile system only expends energy stabilizing successful configurations. Continuous stabilization coupled with redundancy results in a circuit capable of healing itself from the bottom-up.
Owner:KNOWM TECH
Liquid crystal display device
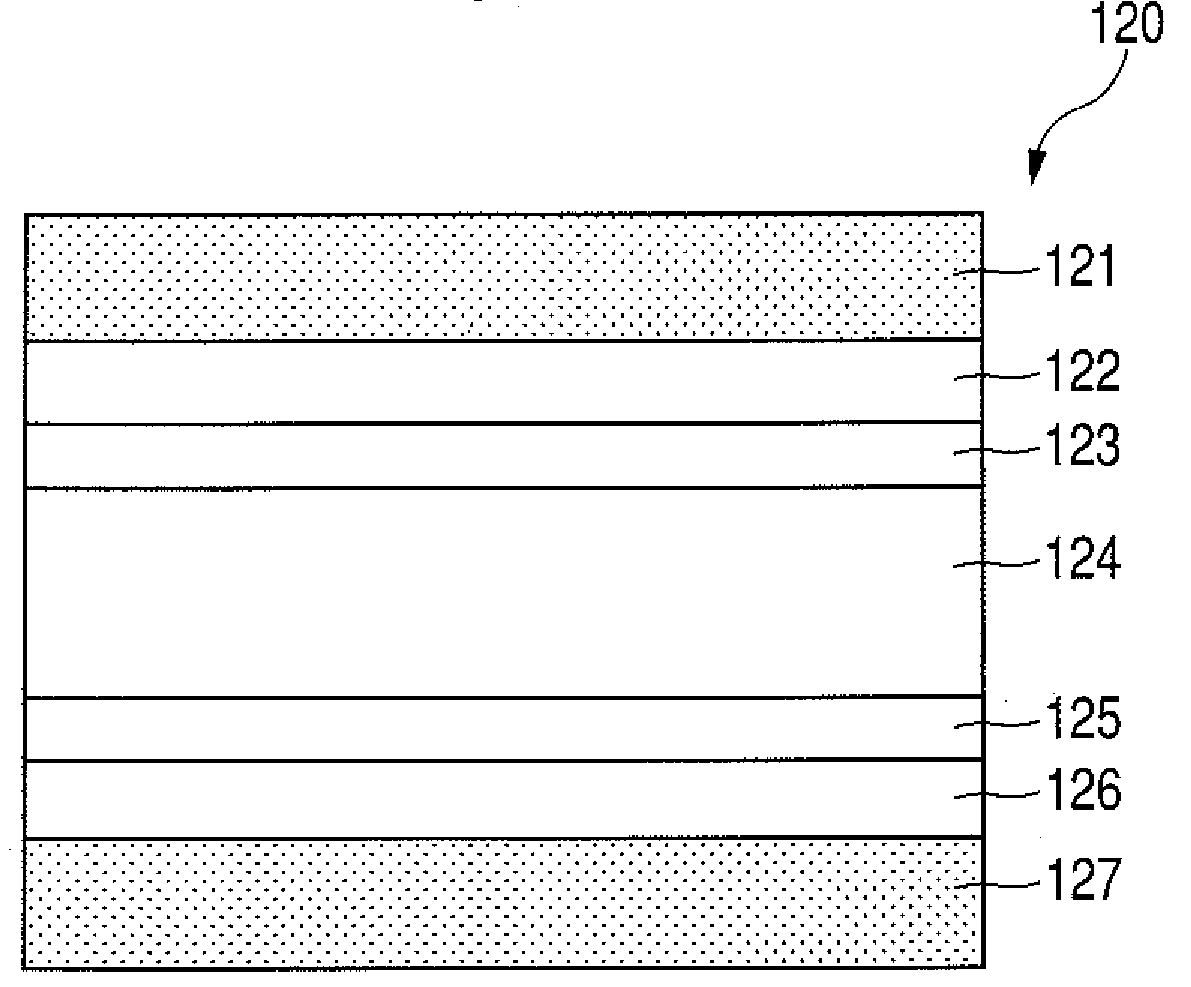
InactiveUS20090079912A1Reduce contrastVariationNon-linear opticsCold cathode manufactureLiquid-crystal displayGas phase
An inorganic alignment film including an inclined columnar structure is used as an alignment film 123, 125 of a liquid crystal element 120, and a light L1 emitted from a light source 50 for incidence on the liquid crystal element 120 is irradiated to the liquid crystal element 120 through a circularly polarizing means 53. Thereby, variations in optical characteristics which are caused by conventional oblique vapor deposition can be reduced.
Owner:CANON KK
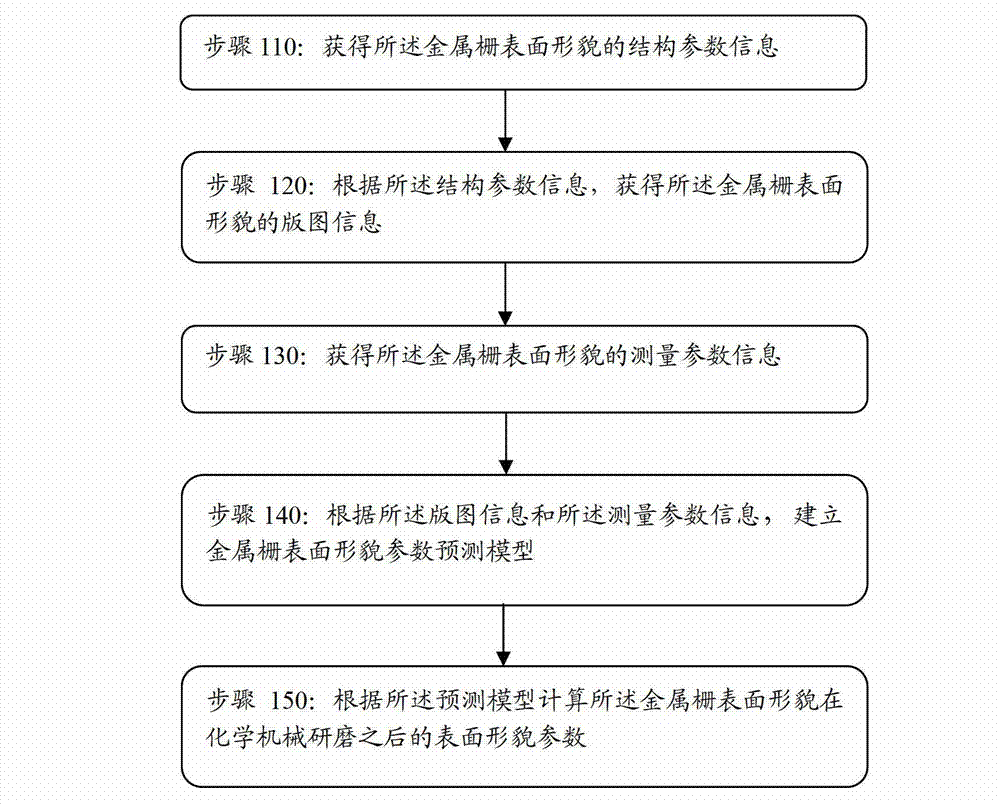
Computing method for meal gate surface appearance
ActiveCN102930101AImprove chip yieldImprove yieldSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringIntegrated circuit manufacturing
The invention discloses a computing method for metal gate surface appearance and belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit manufacturing and electronic design automation. The method includes acquiring map information and measure parameter information of the metal gate surface appearance, then establishing a parameter prediction model of the metal gate surface appearance, and performing a prediction for the surface appearance on the back of a designed metal gate structure corrugated metal pipe (CMP) in a chip design process through the prediction model to obtain dish-shaped appearance of the metal gate and erosion appearance of dielectrics among metal gates. Accordingly, area which is probable to generate problems after the CMP processing step in the design can be found out, the area is provided for designers to improve, the corresponding problems occurring in the manufacturing process are avoided, and thereby the yield of products is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wafer structure and processing method thereof
InactiveUS20170053832A1Increase productionHigh strengthMicrophonesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringLaser cutting
A wafer structure and a processing method of a wafer structure are disclosed here. The wafer structure, which is used for forming a plurality of dies, comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first one; at least one first functional layer and at least one second functional layer at the first surface of the semiconductor substrate, wherein the at least one second functional layer is located in a scribe lane of the wafer; and a plurality of scribing marks in the scribe lane, for singulating adjacent ones of the plurality of dies during a laser cutting process, wherein the plurality of dies each include the at least one first functional layer and a portion of the semiconductor substrate. The wafer structure can provide a functional layer in the scribe lane, while it facilitates to singulate the adjacent ones of the plurality of dies.
Owner:ACUTI MICROSYST
Gas injection system for etching profile control
InactiveUS20110203735A1Effective controlCompensation differenceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPlasma etching
A gas injection system provided in a plasma etching equipment is provided. The system includes a top gas injector for supplying a reaction gas at a top of a chamber, and a side gas injector for supplying a tuning gas from a side surface of the chamber or a backside gas injector upward jetting a tuning gas from a lower side of a wafer. The side gas injector or backside gas injector forms a plurality of jets in a radial shape and simultaneously installs the jets adjacently to an edge part of a wafer such that a tuning gas is jetted adjacently to the edge part of the wafer, thereby being capable of easily controlling a an etch rate or CD uniformity or profile of the edge part.
Owner:DMS CO LTD
Semiconductor wafer polishing apparatus, and method of polishing semiconductor wafer
InactiveUS7303463B2Prevent penetrationImprove chip yieldEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesProduct gasYield ratio
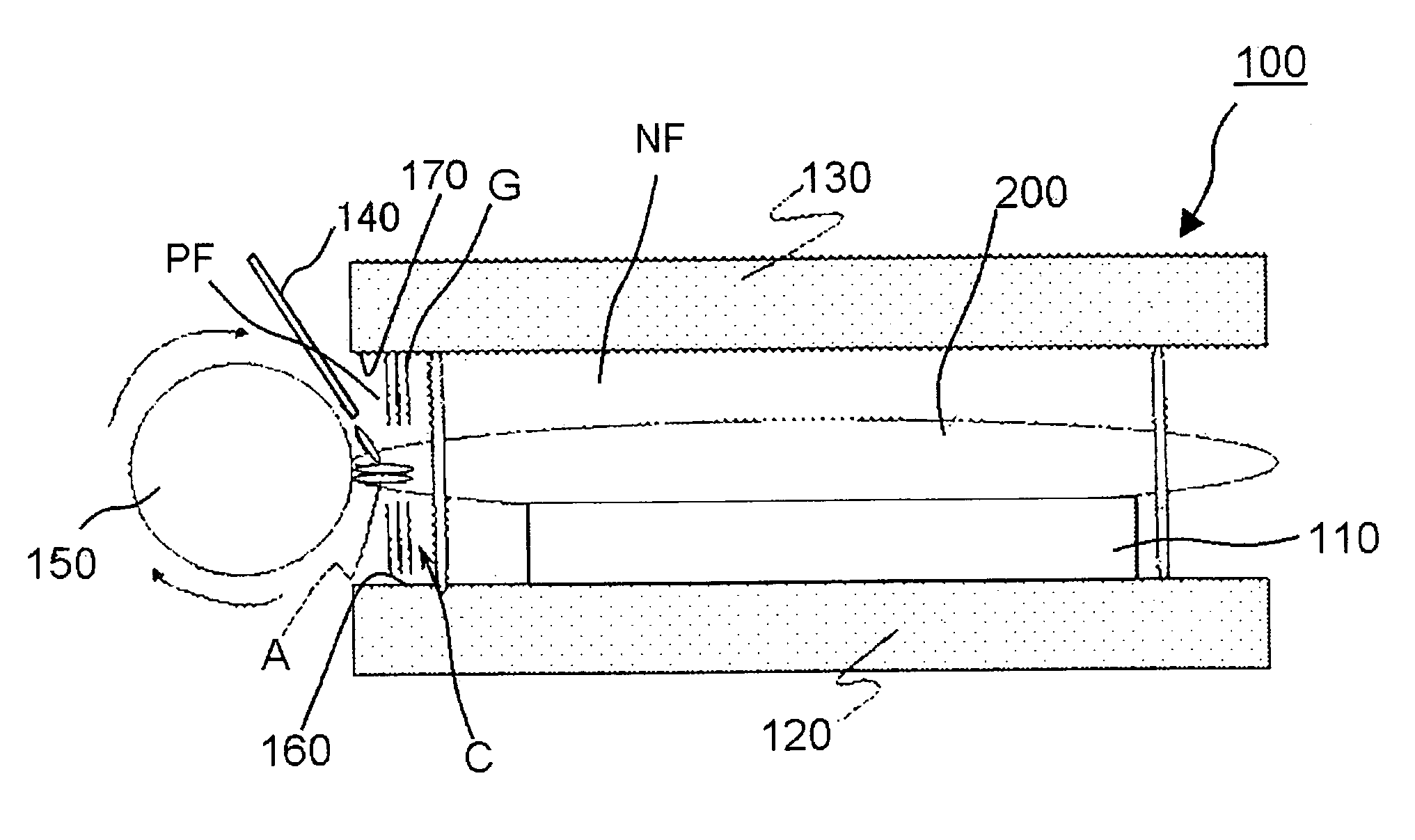
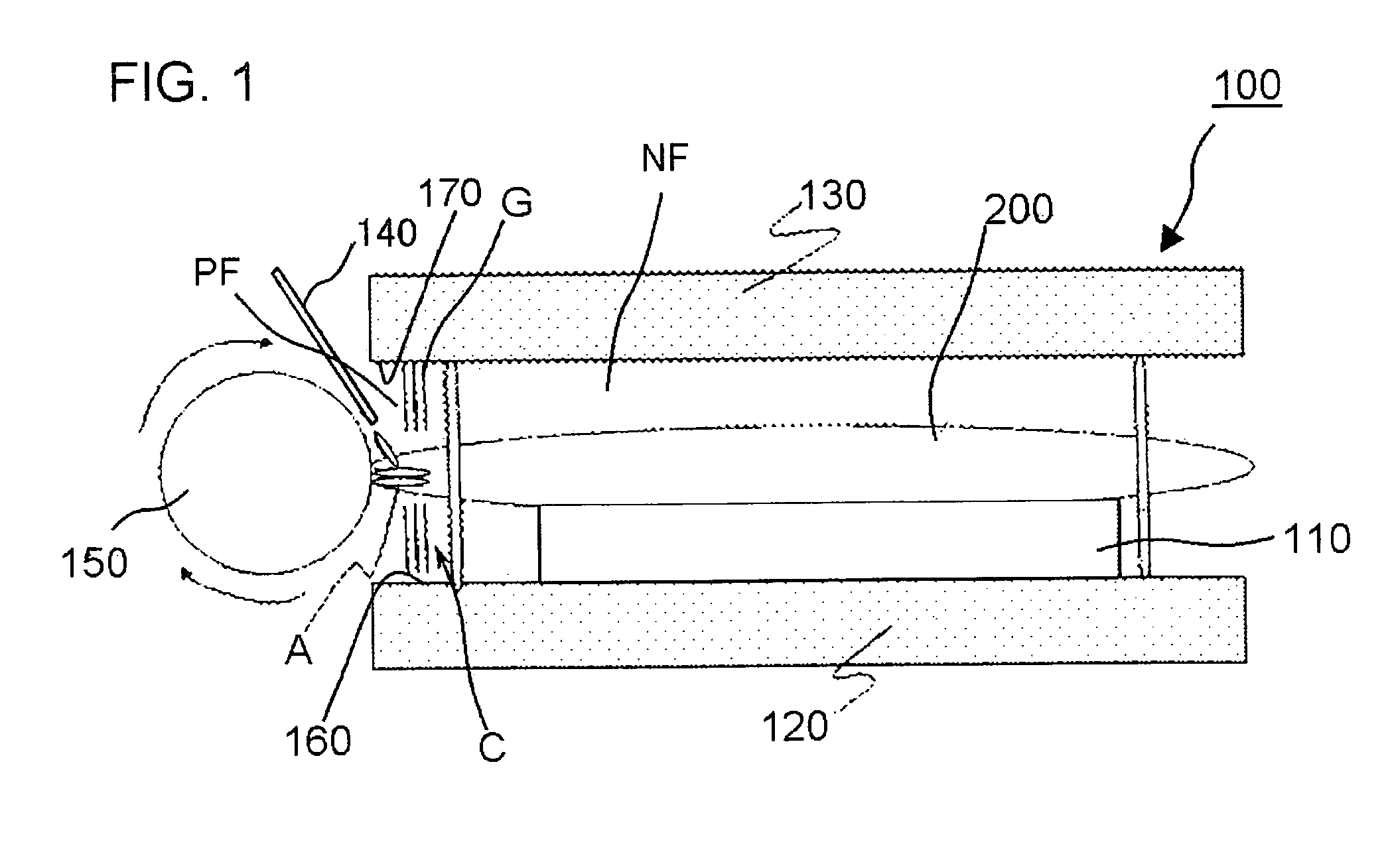
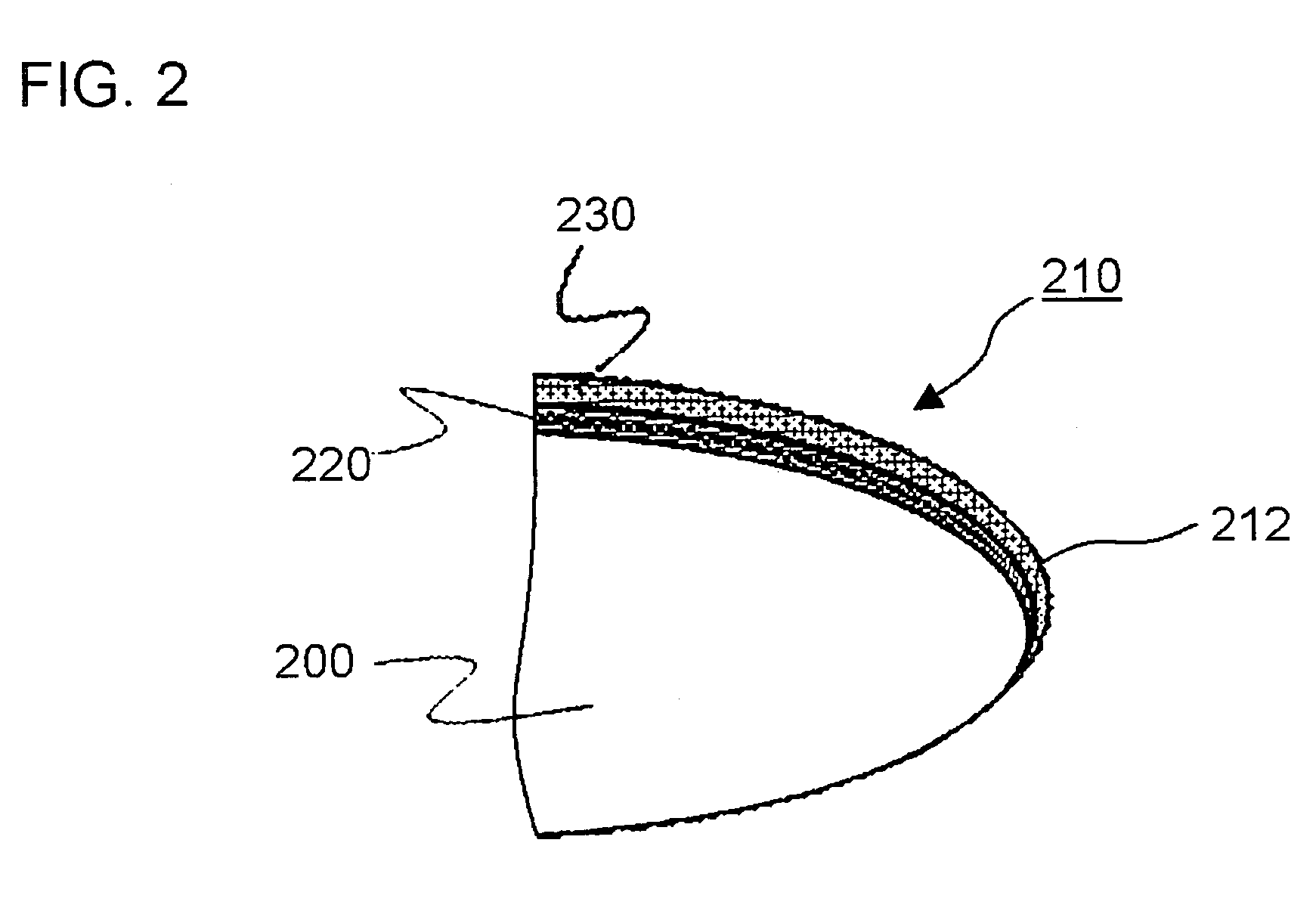
Aimed at thoroughly preventing abrasive and dusts from adhering onto the circuit-forming region of a wafer, improving yield ratio of semiconductor devices, and thereby improving operation rates of the individual manufacturing apparatuses in the succeeding stage, a semiconductor wafer polishing apparatus of the present invention has a polishing unit polishing the circumferential edge side of a disc-formed wafer; and a gas blowing unit blowing a gas G against the surface of the wafer, so as to separate the space over the wafer by a curtain C of the gas G between a polishing field PF in which the wafer is polished by the polishing unit and a normal field NF except the polishing field PF.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com