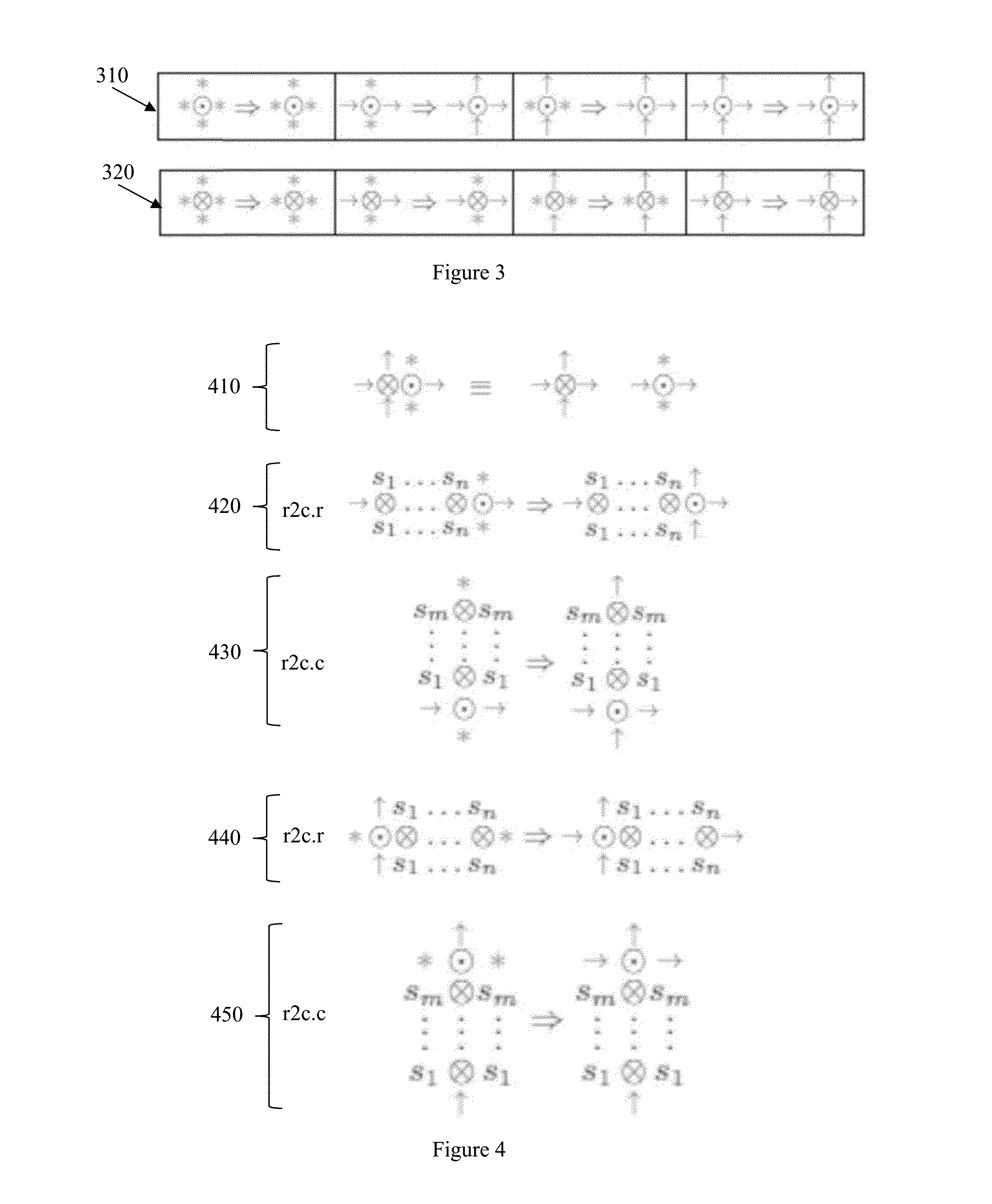Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
250results about "Programmable logic circuit arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
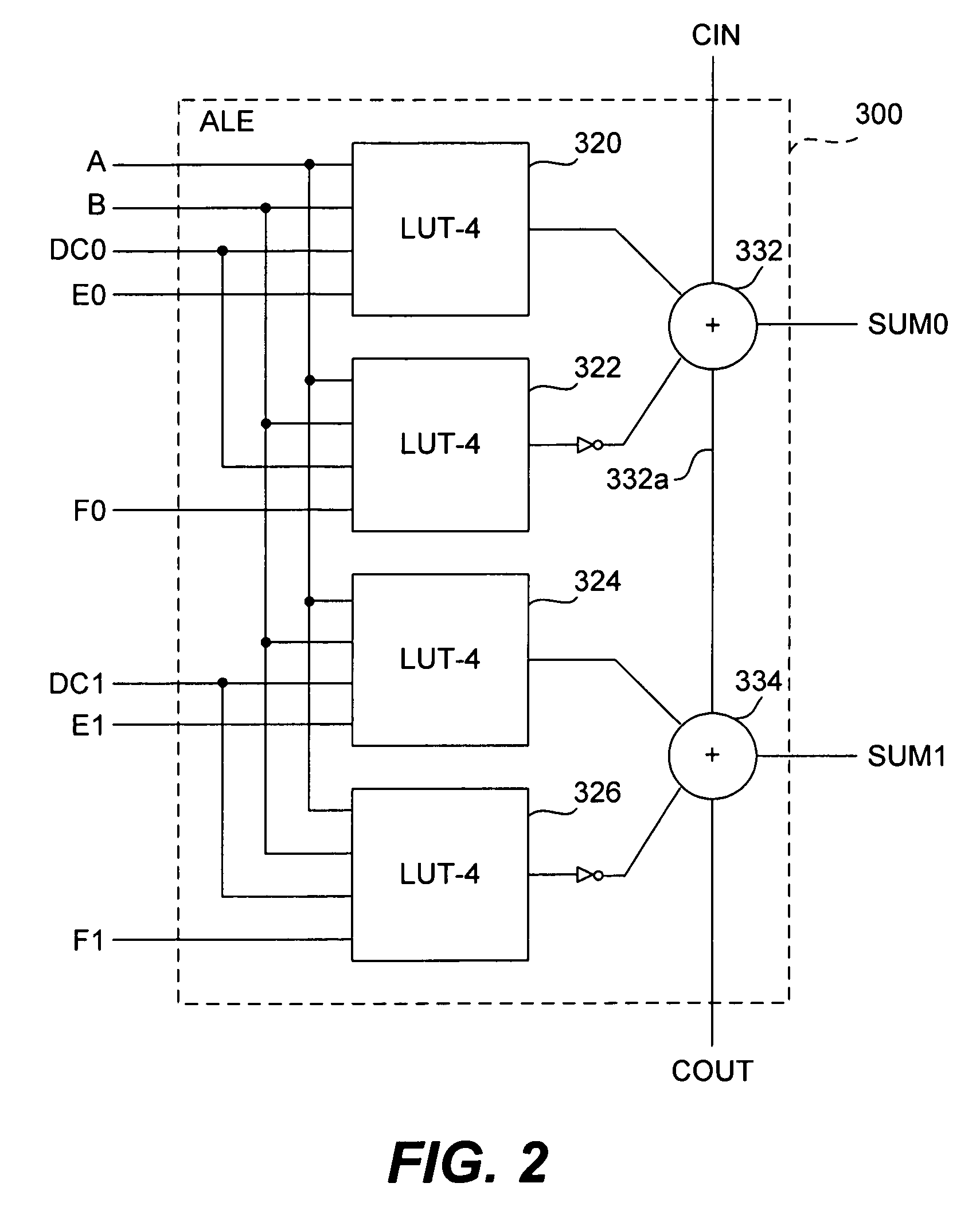
Field Programmable Gate-Array with Embedded Network-on-Chip Hardware and Design Flow
InactiveUS20150109024A1Raise the level of abstractionDesign integration of large systems simpler and more automatedProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesComputer moduleNetworks on chip
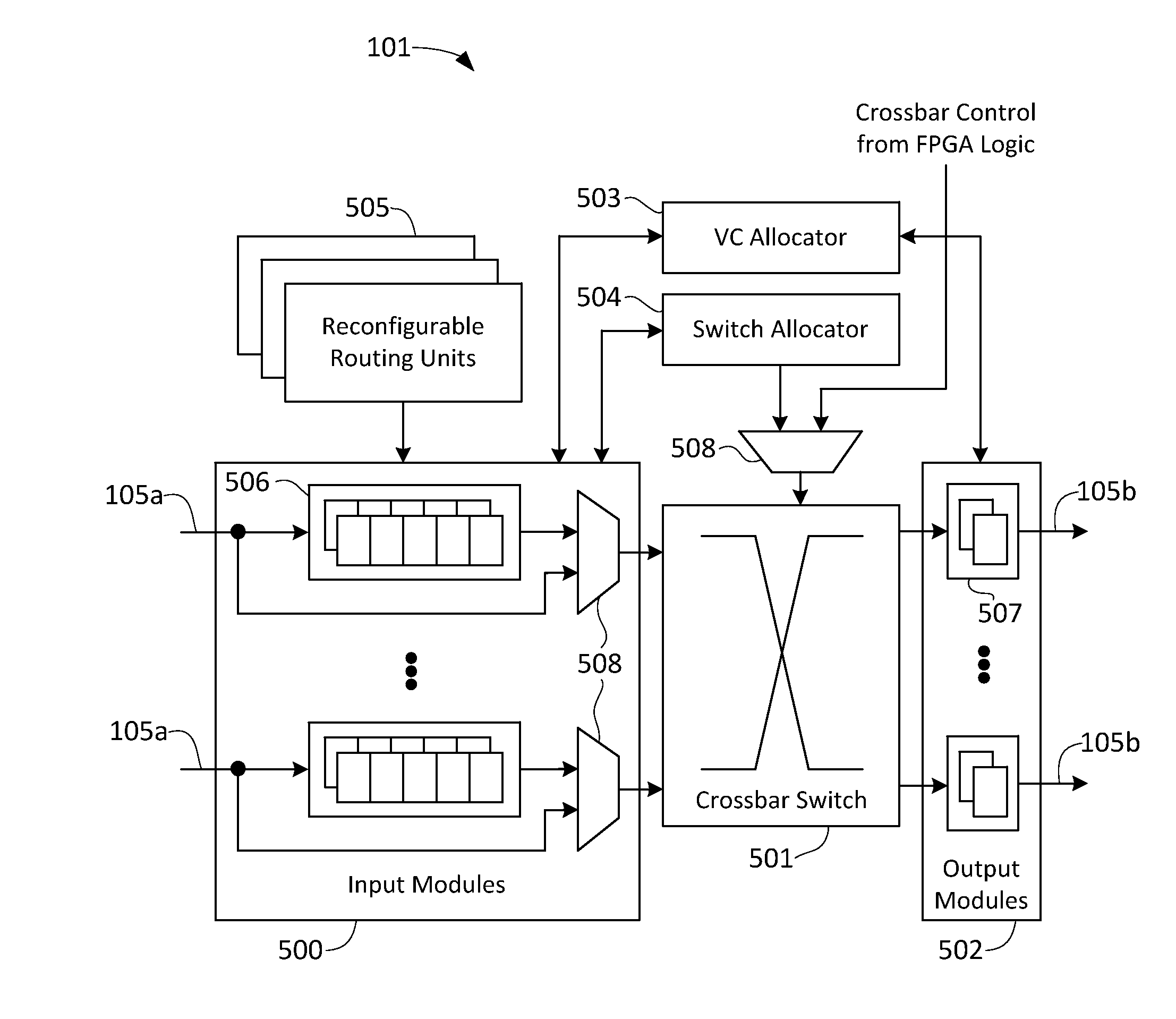
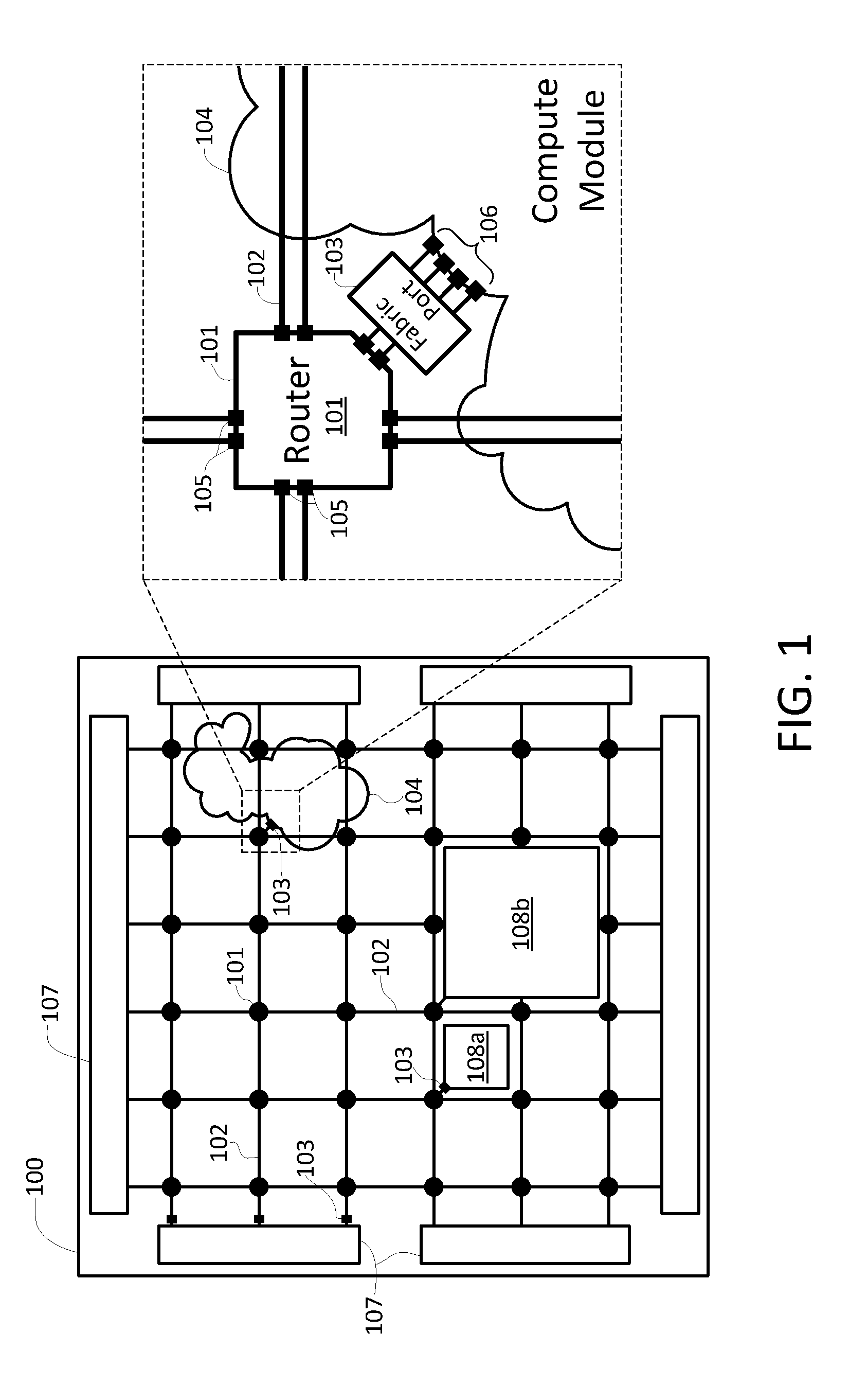
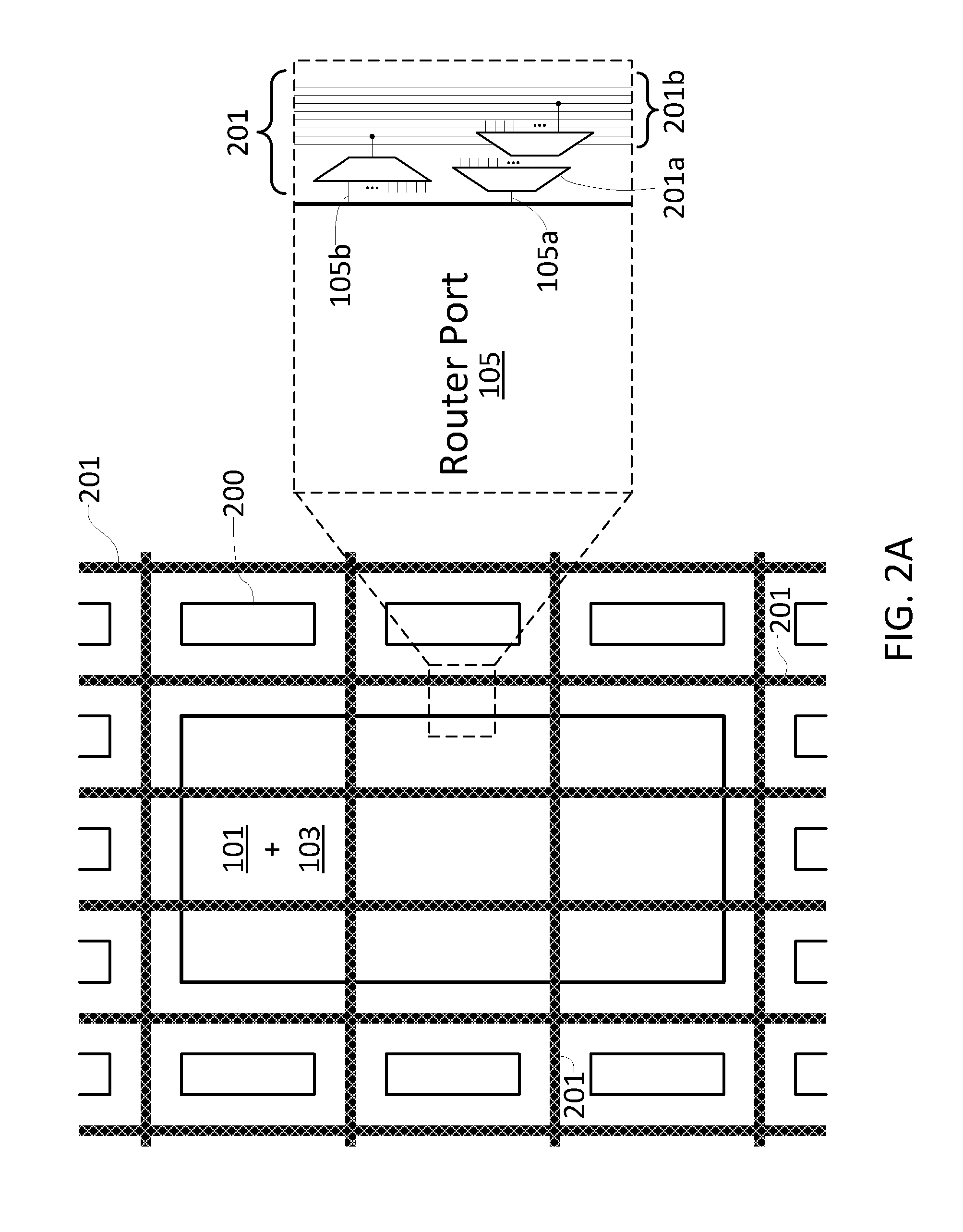
An enhanced field programmable gate-array (FPGA) incorporates one or more programmable networks-on-chip (NoCs) or NoC components integrated within the FPGA fabric. This NoC interconnect augments the existing FPGA interconnect. In one embodiment, the NoC is used as system-level interconnect to connect compute and communication modules to one another and integrate large systems on the FPGA. The NoC components include a “fabric port”, which is a configurable interface that bridges both data width and frequency between the embedded NoC routers and the FPGA fabric components such as logic blocks, block memory, multipliers, processors or I / Os. Finally, the FPGA design flow is modified to target the embedded NoC components either manually through designer intervention, or automatically.
Owner:VAUGHN TIMOTHY BETZ +1
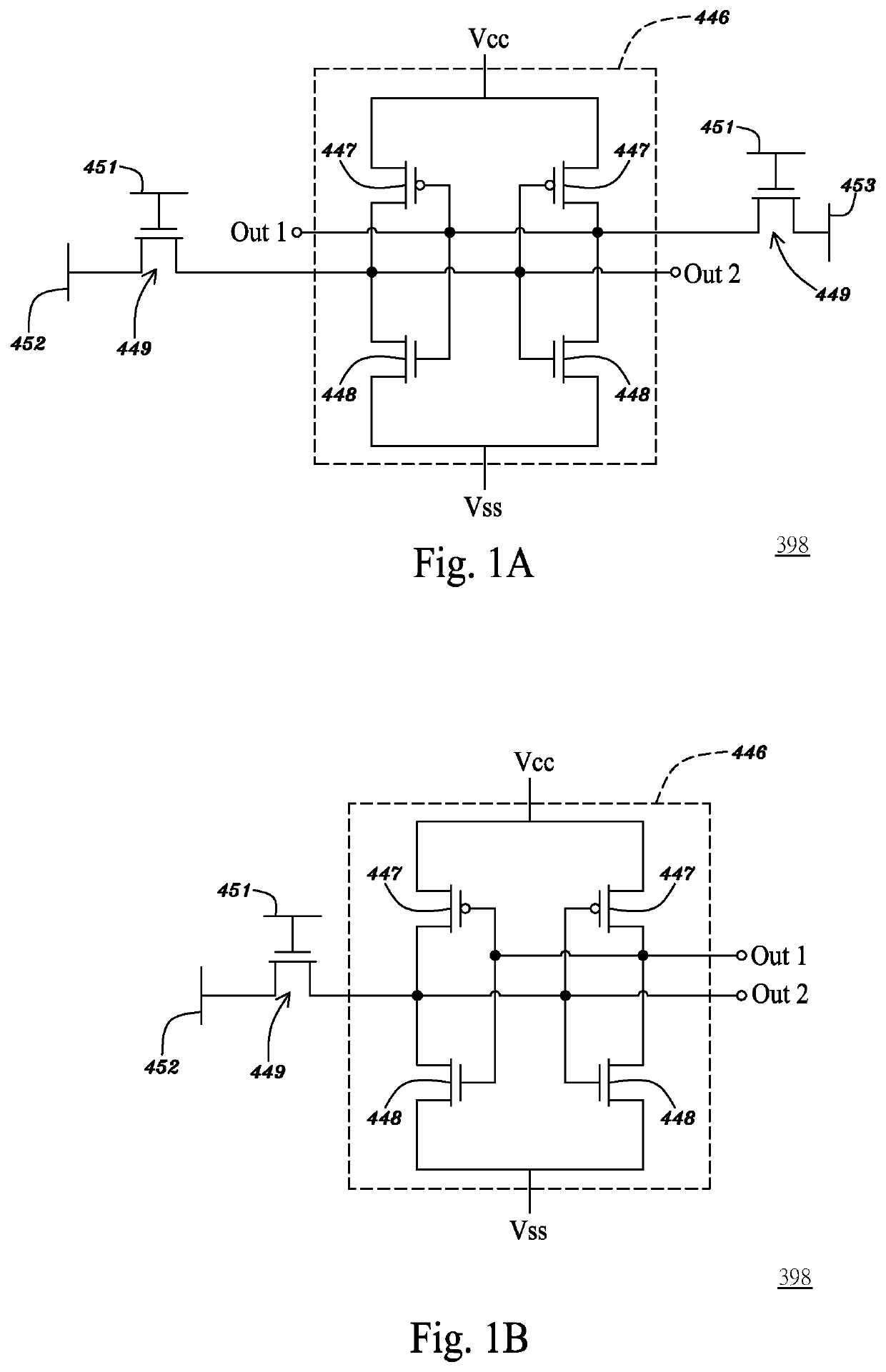
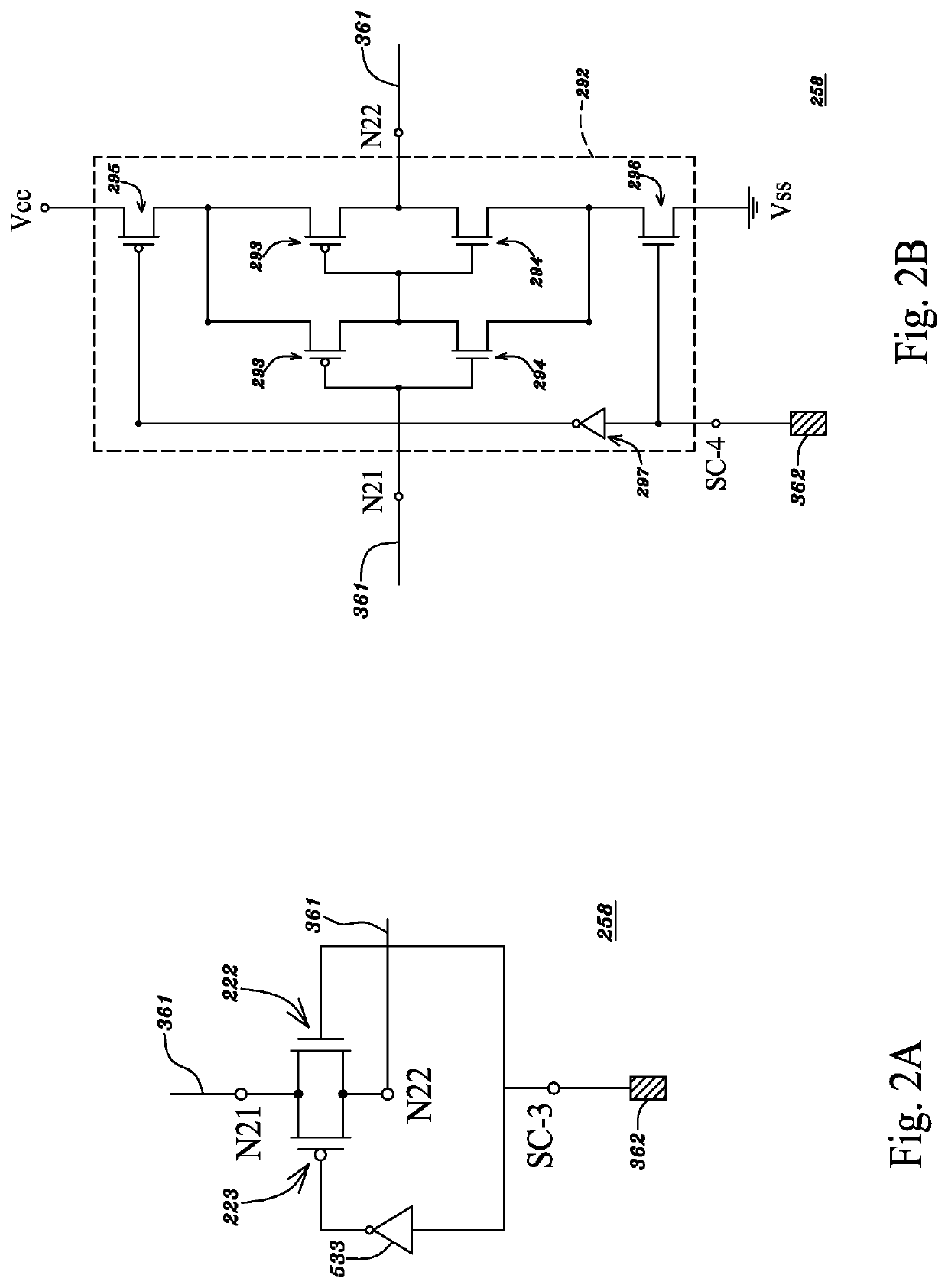
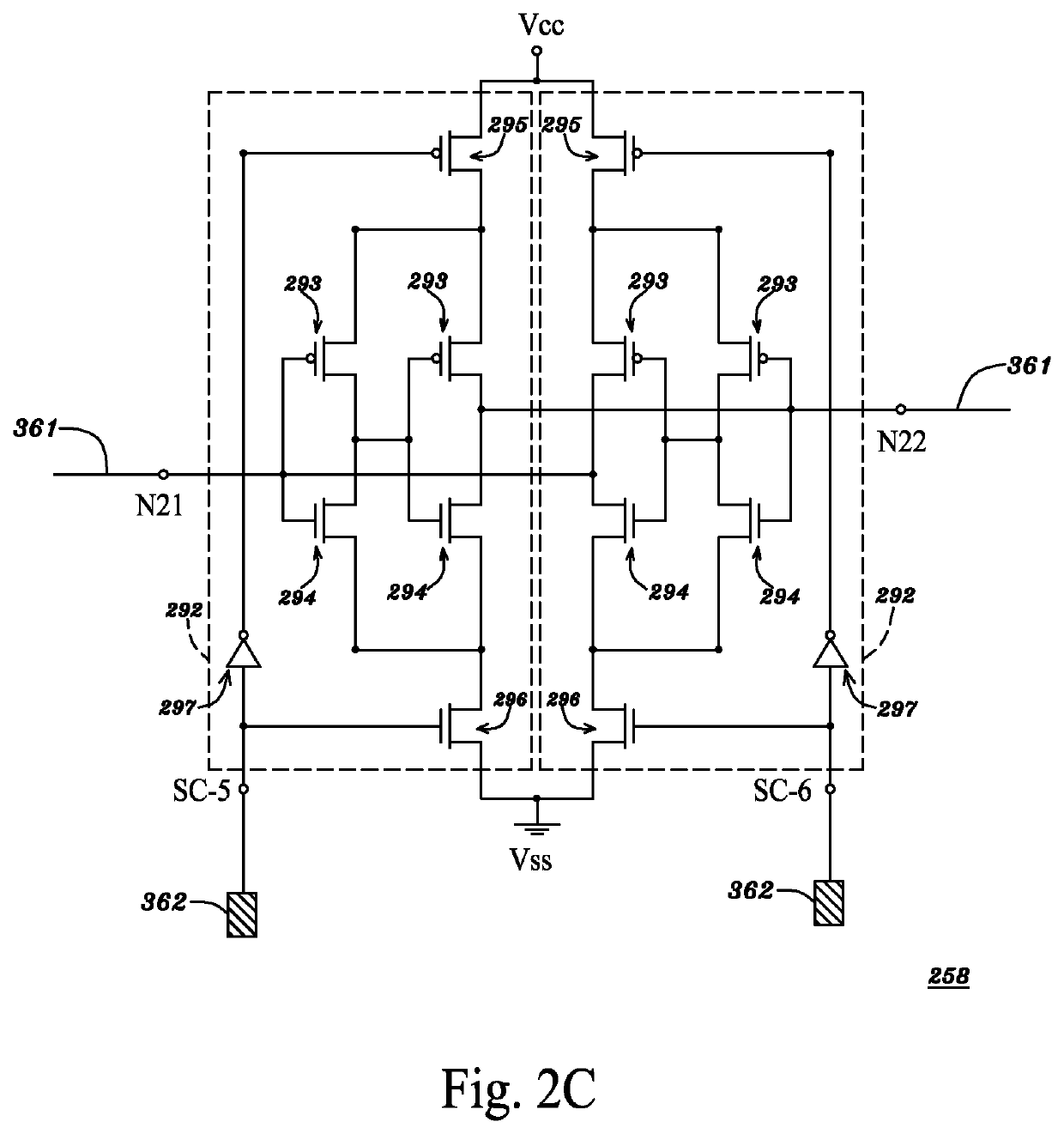
Trigger circuits and event counters for an IC
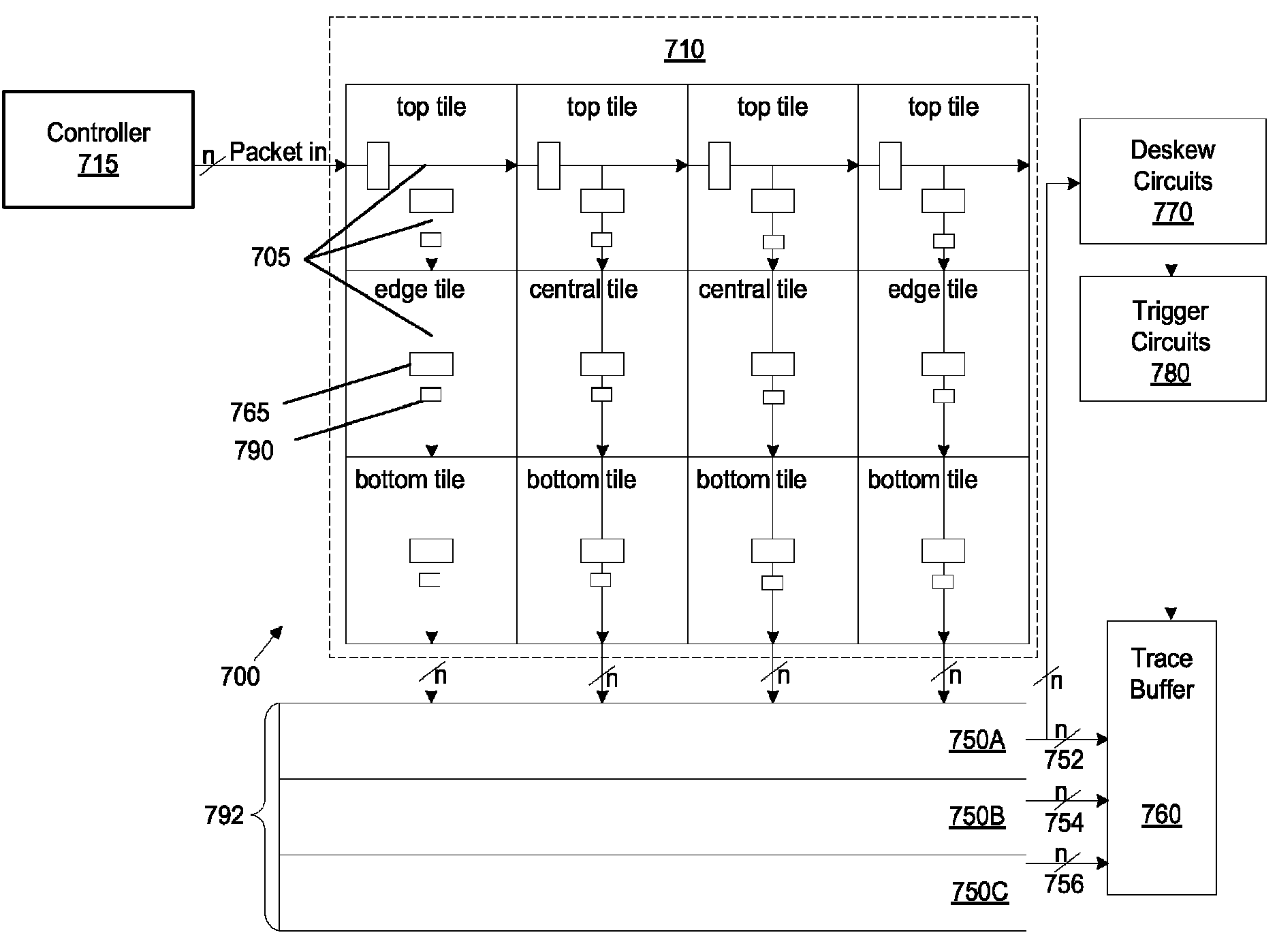
ActiveUS20110199117A1Easy to useProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesComputer hardwareHemt circuits
Some embodiments provide an integrated circuit (‘IC’). The IC includes multiple configurable circuits that configurably perform operations of a user design based on configuration data. The IC also includes a configurable trigger circuit that receives a set of configuration data that specifies an operational event. The configurable trigger circuit also determines whether the operational event has occurred during implementation of the user design of the IC. Additionally, the operational trigger event outputs a trigger signal upon determining that the operational trigger event has occurred.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Omnibus logic element including look up table based logic elements
InactiveUS7167022B1Flexible and efficient to useProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerComputer science
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Logic drive using standard commodity programmable logic IC chips
ActiveUS20190363715A1Reduce manufacturing costManufacturing cost to minimumProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsCAD circuit designInterconnectionField-programmable gate array
An expandable logic scheme based on a chip package, includes: an interconnection substrate comprising a set of data buses for use in an expandable interconnection scheme, wherein the set of data buses is divided into a plurality of data bus subsets; and a first field-programmable-gate-array (FPGA) integrated-circuit (IC) chip comprising a plurality of first I / O ports coupling to the set of data buses and at least one first I / O-port selection pad configured to select a first port from the plurality of first I / O ports in a first clock cycle to pass a first data between a first data bus subset of the plurality of data bus subsets and the first field-programmable-gate-array (FPGA) integrated-circuit (IC) chip.
Owner:ICOMETRUE CO LTD
Configurable Voltage Mode Transmitted Architecture With Common-Mode Adjustment And Novel Pre-Emphasis
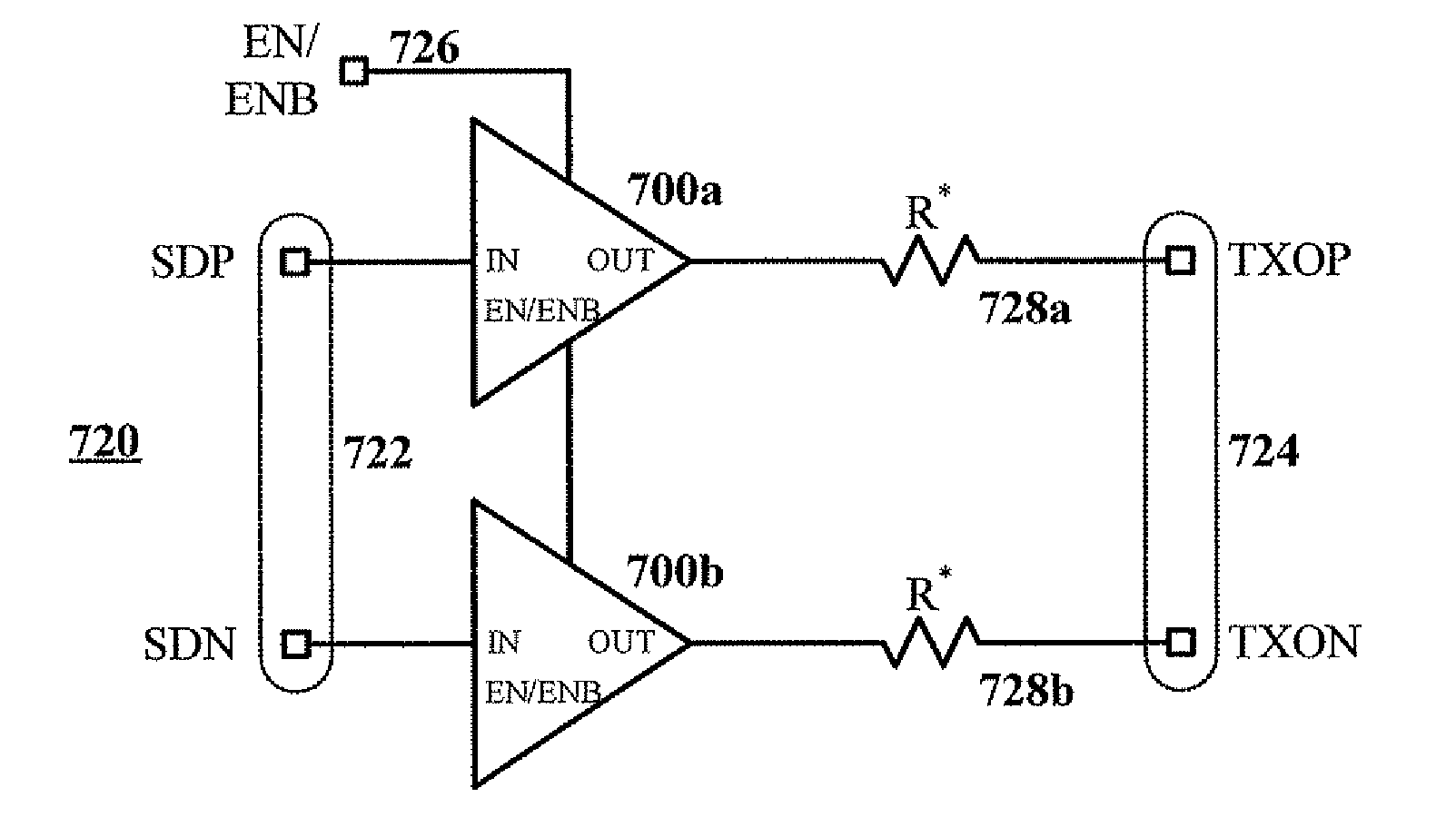
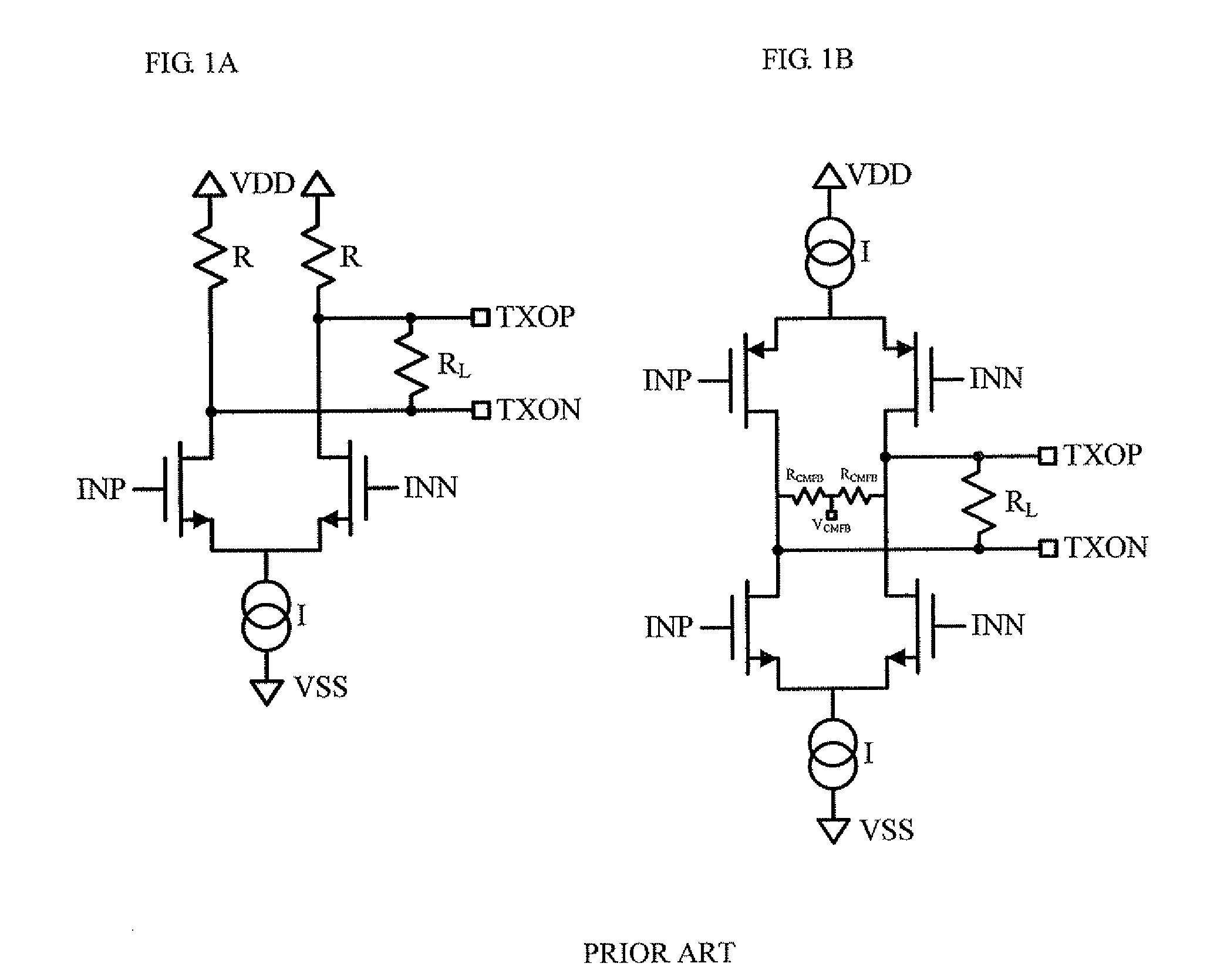
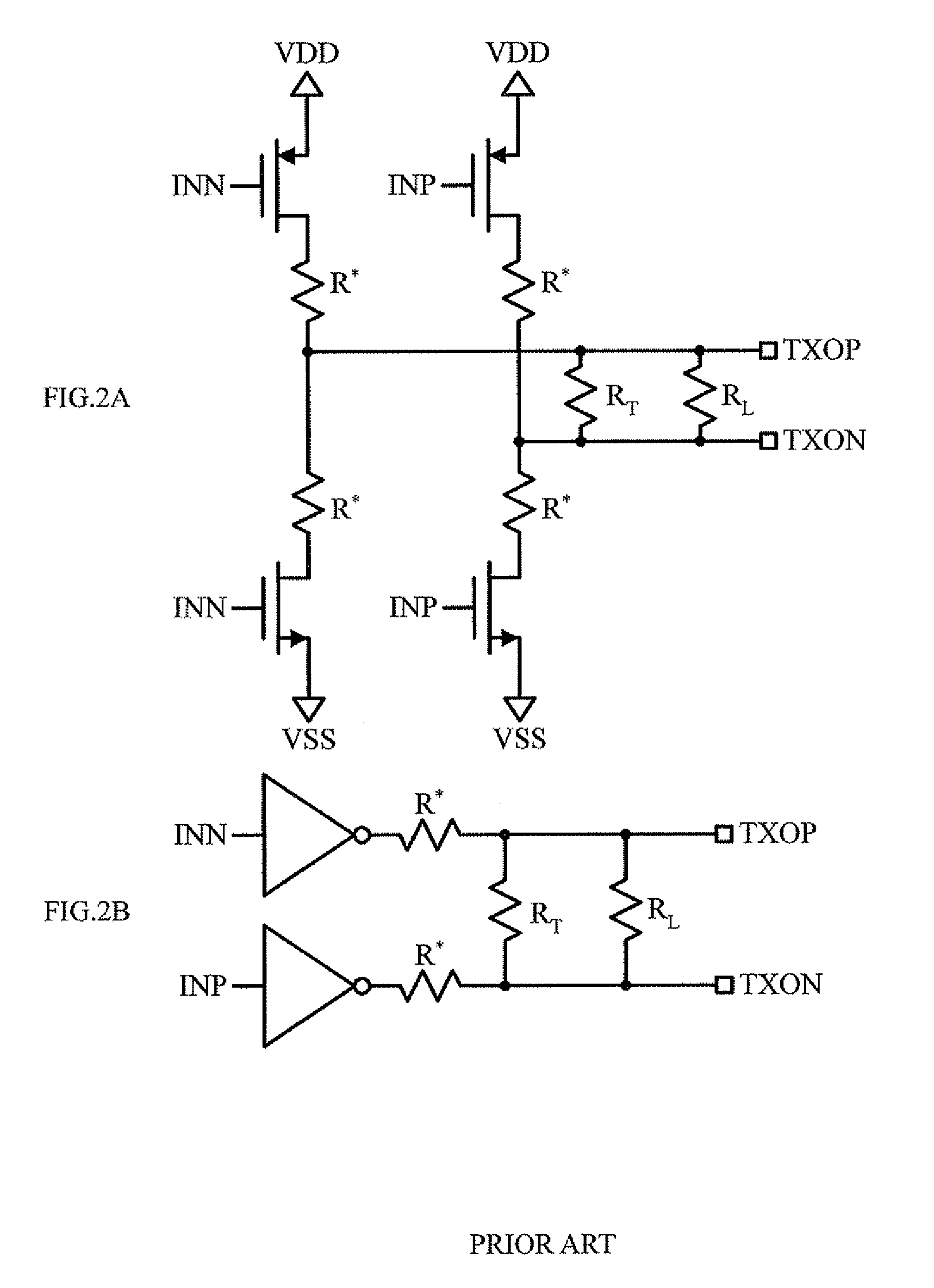
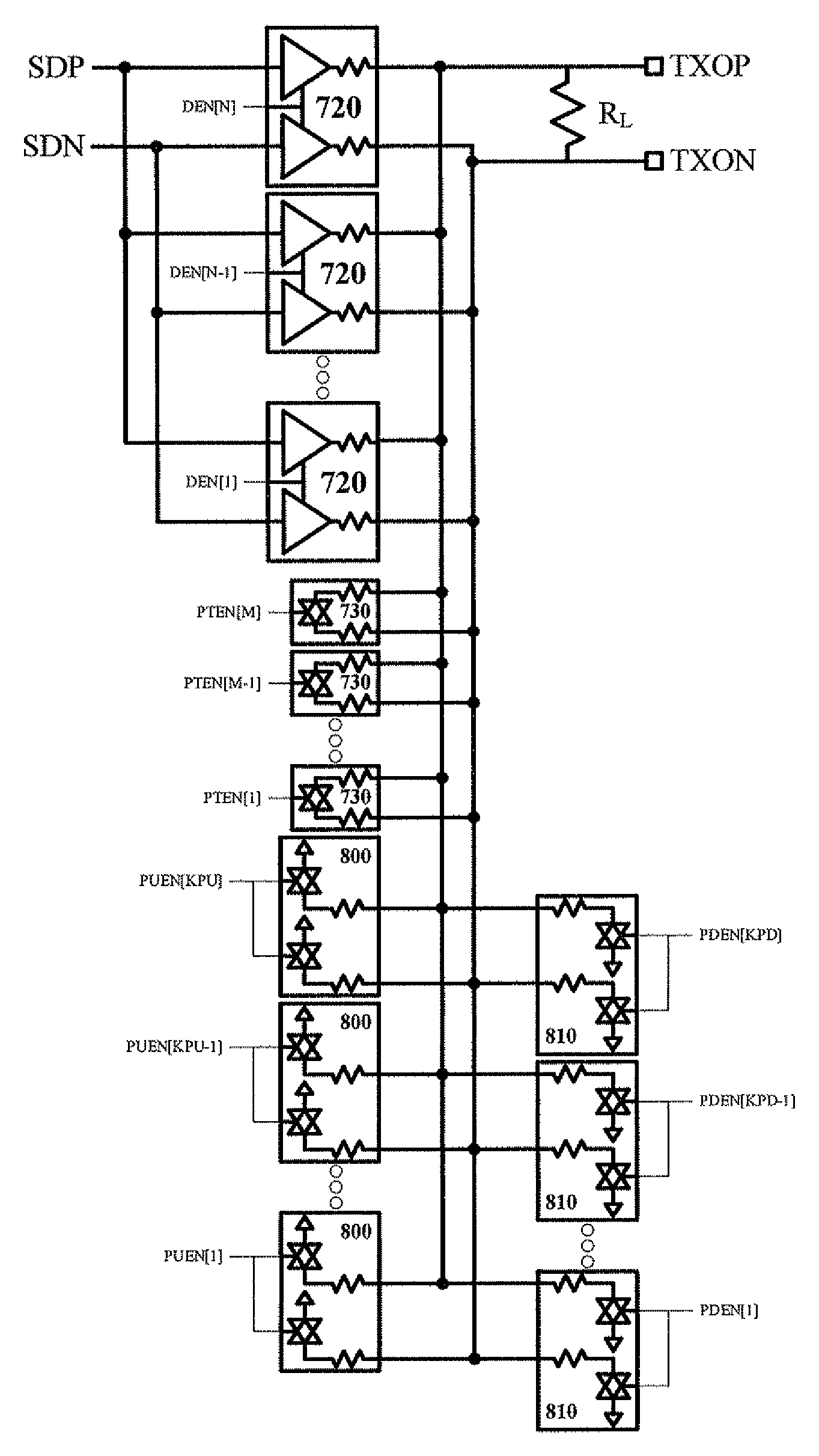
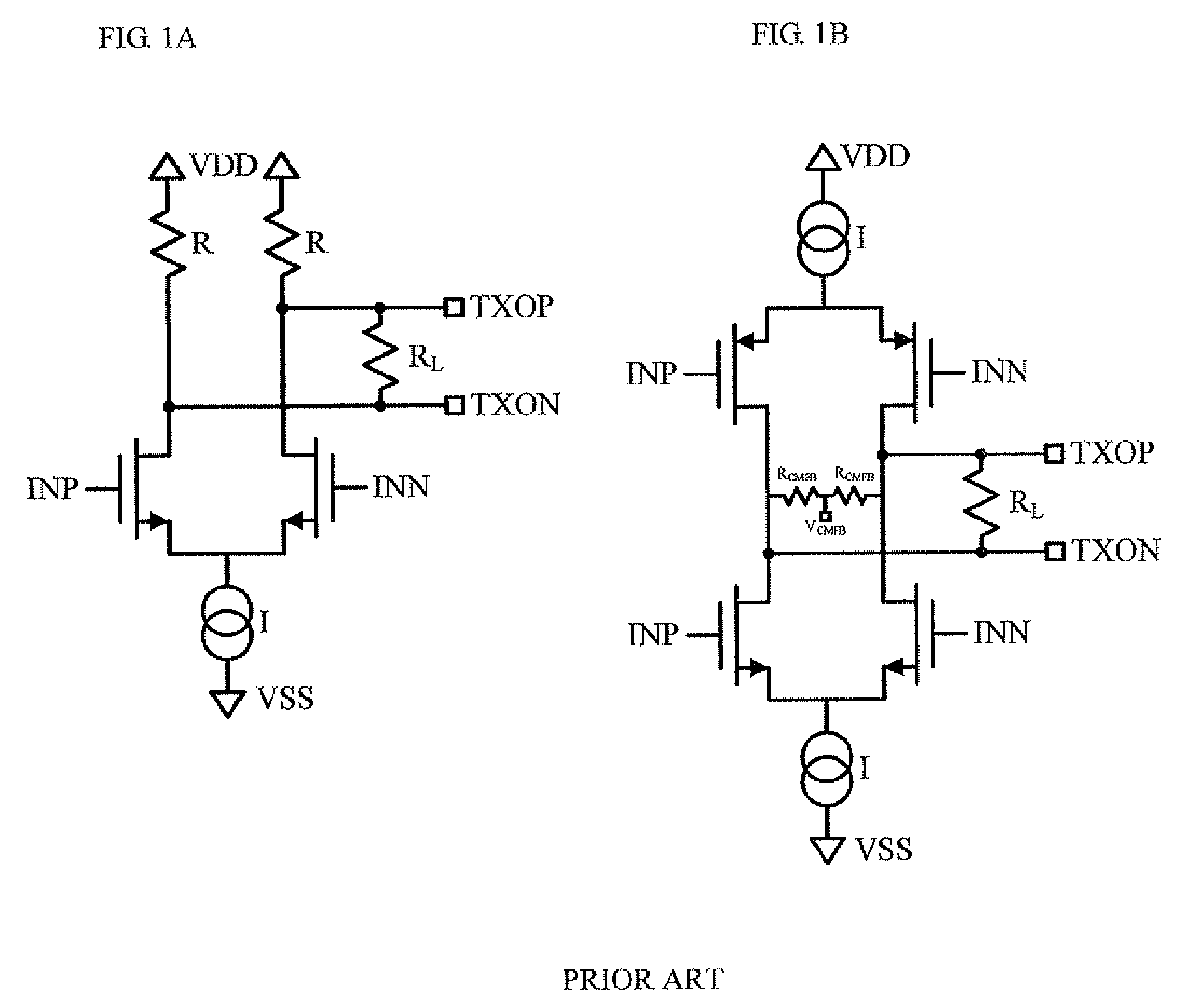
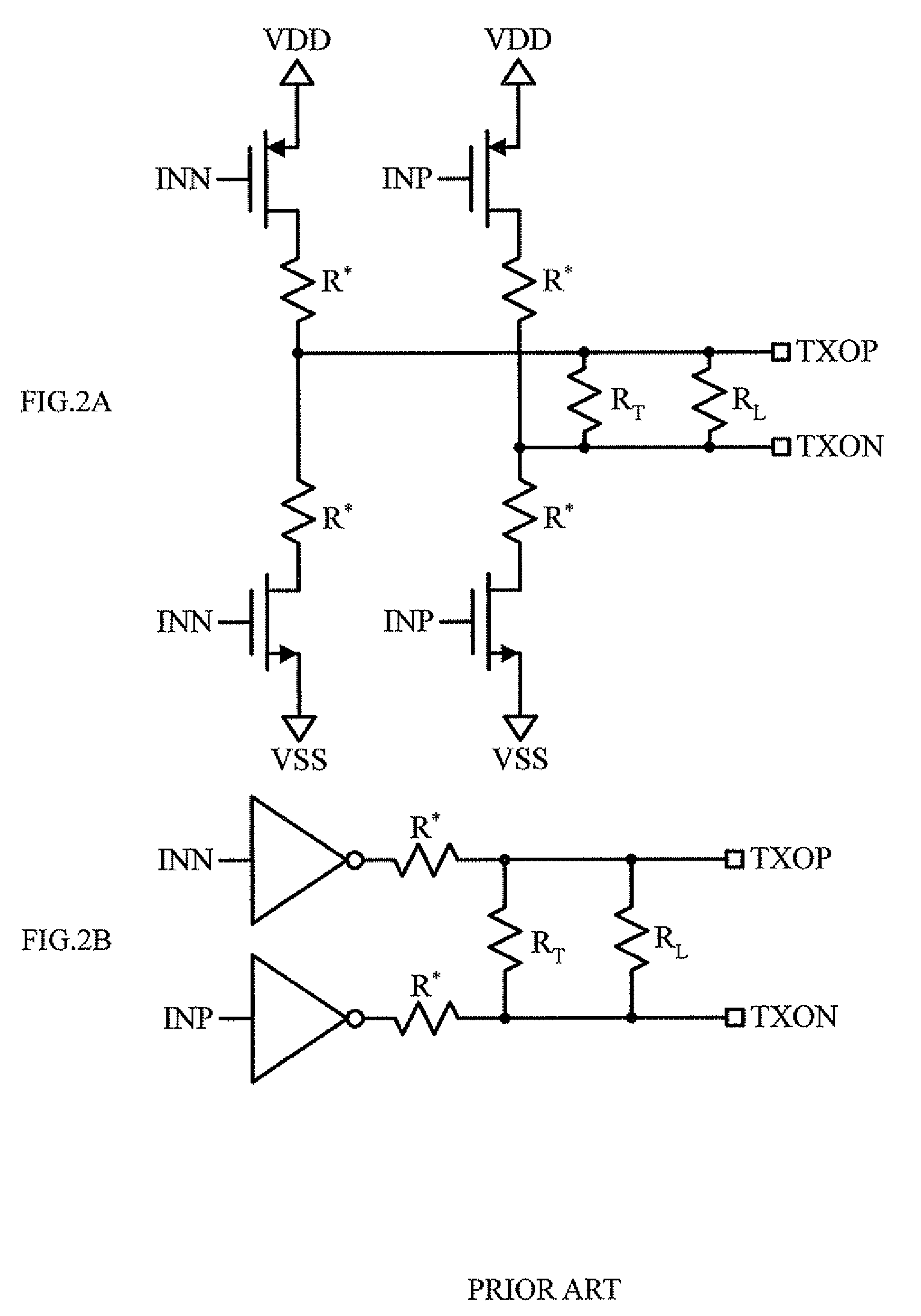
ActiveUS20070285120A1Efficient pre-emphasis implementationConfigurabilityReliability increasing modificationsProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsEngineeringTransmitter
Configurable voltage mode transmitter architectures are based on combinations of drive cells and parallel termination cells connected in parallel across an external load to provide configurable output characteristics. Each drive cell and parallel termination can be individually enabled, various configurations of enabled cells providing the output characteristics configurability. In some embodiments, dedicated or configured pre-emphasis drive cells with individual enablement capability are added. In some embodiments, pull-down and pull-up cells with individual enablement capability are added to provide additional configurability options. When present, the pre-emphasis, pull-down and pull-up cells are connected in parallel across the external load to provide pre-emphasis features to the output.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
Logic circuit
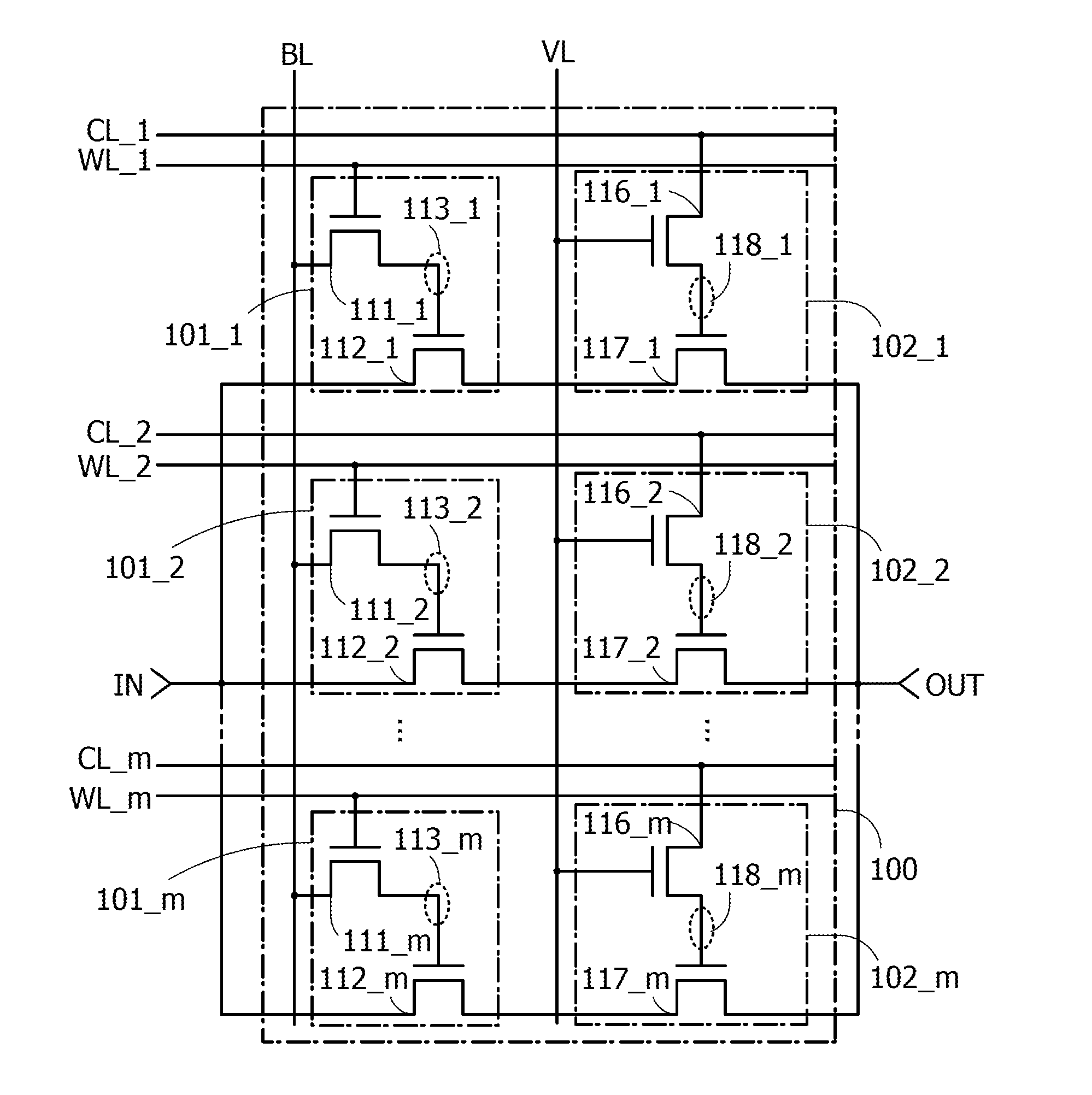
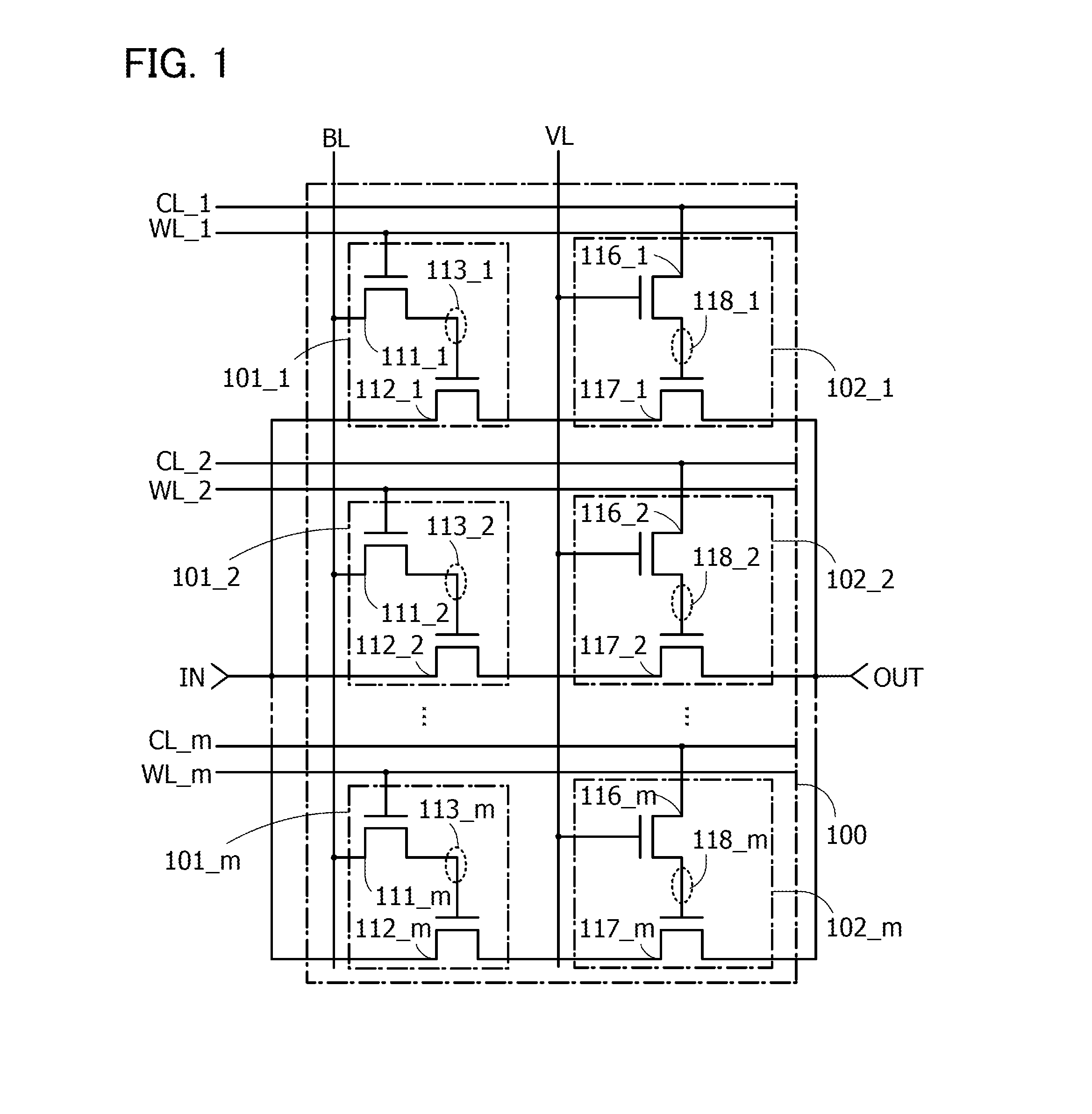
InactiveUS20120293209A1Reduce power consumptionEasy to switchProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesStart up timeState of charge
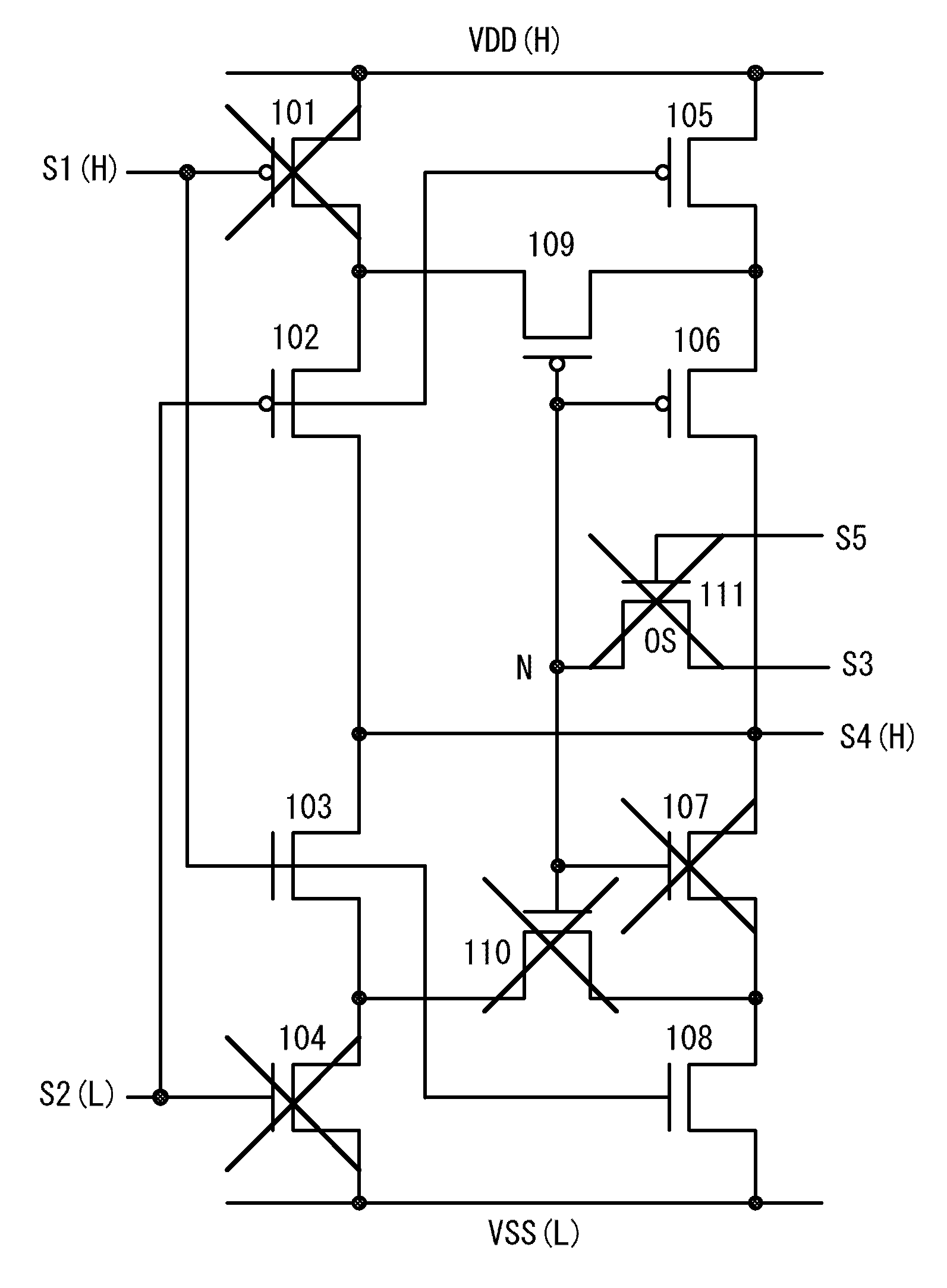
A logic circuit is provided which can hold a switching state of the logic circuit even when a power supply potential is not supplied, has short start-up time of a logic block after the power is supplied, can operate with low power consumption, and can easily switch between a NAND circuit and a NOR circuit. Switching between a NAND circuit and a NOR circuit is achieved by switching a charge holding state at a node through a transistor including an oxide semiconductor. With the use of an oxide semiconductor material which is a wide bandgap semiconductor for the transistor, the off-state current of the transistor can be sufficiently reduced; thus, the state of charge held at the node can be non-volatile.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Configurable voltage mode transmitted architecture with common-mode adjustment and novel pre-emphasis
ActiveUS7501851B2Reliability increasing modificationsProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsEngineeringTransmitter
Configurable voltage mode transmitter architectures are based on combinations of drive cells and parallel termination cells connected in parallel across an external load to provide configurable output characteristics. Each drive cell and parallel termination can be individually enabled, various configurations of enabled cells providing the output characteristics configurability. In some embodiments, dedicated or configured pre-emphasis drive cells with individual enablement capability are added. In some embodiments, pull-down and pull-up cells with individual enablement capability are added to provide additional configurability options. When present, the pre-emphasis, pull-down and pull-up cells are connected in parallel across the external load to provide pre-emphasis features to the output.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
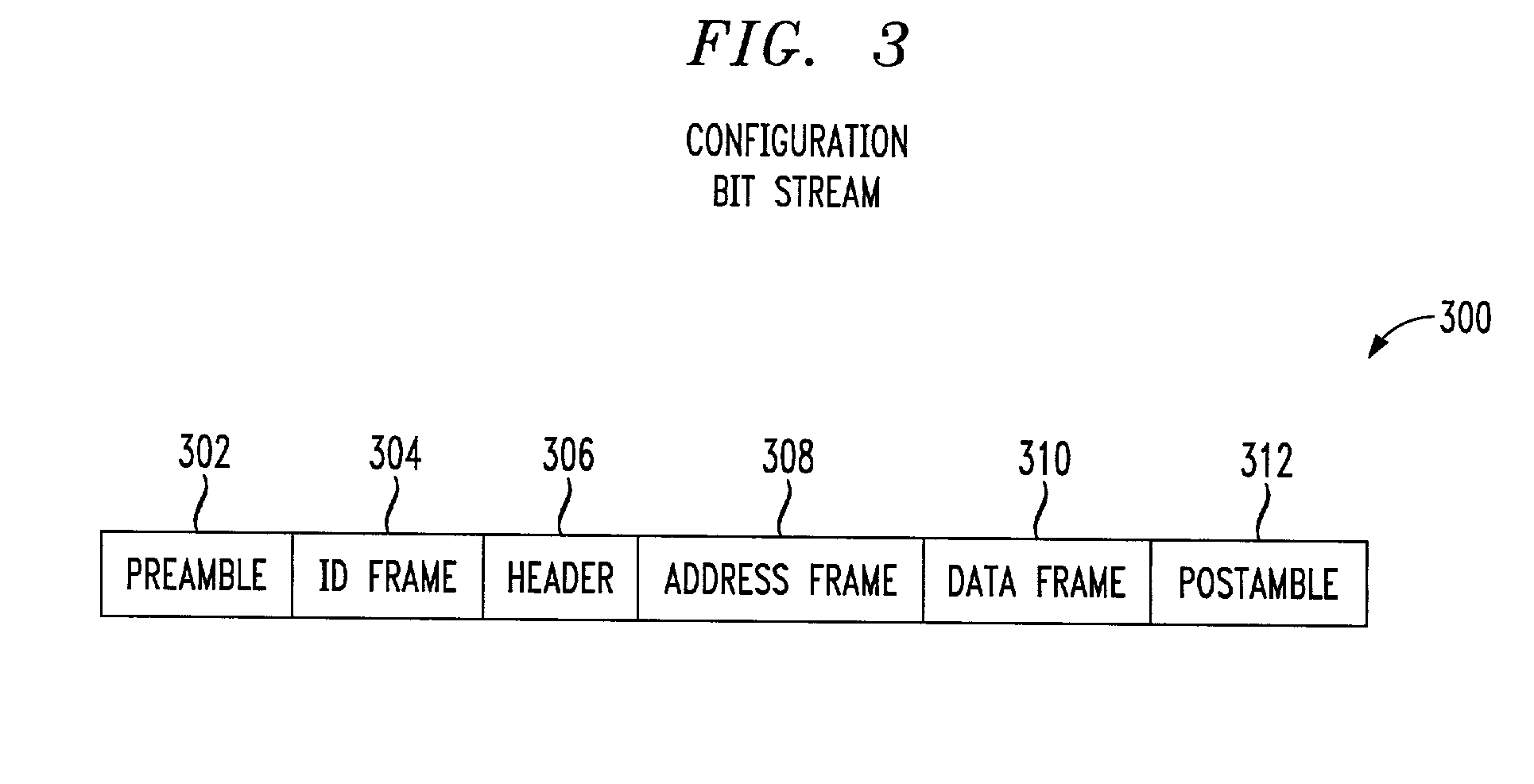
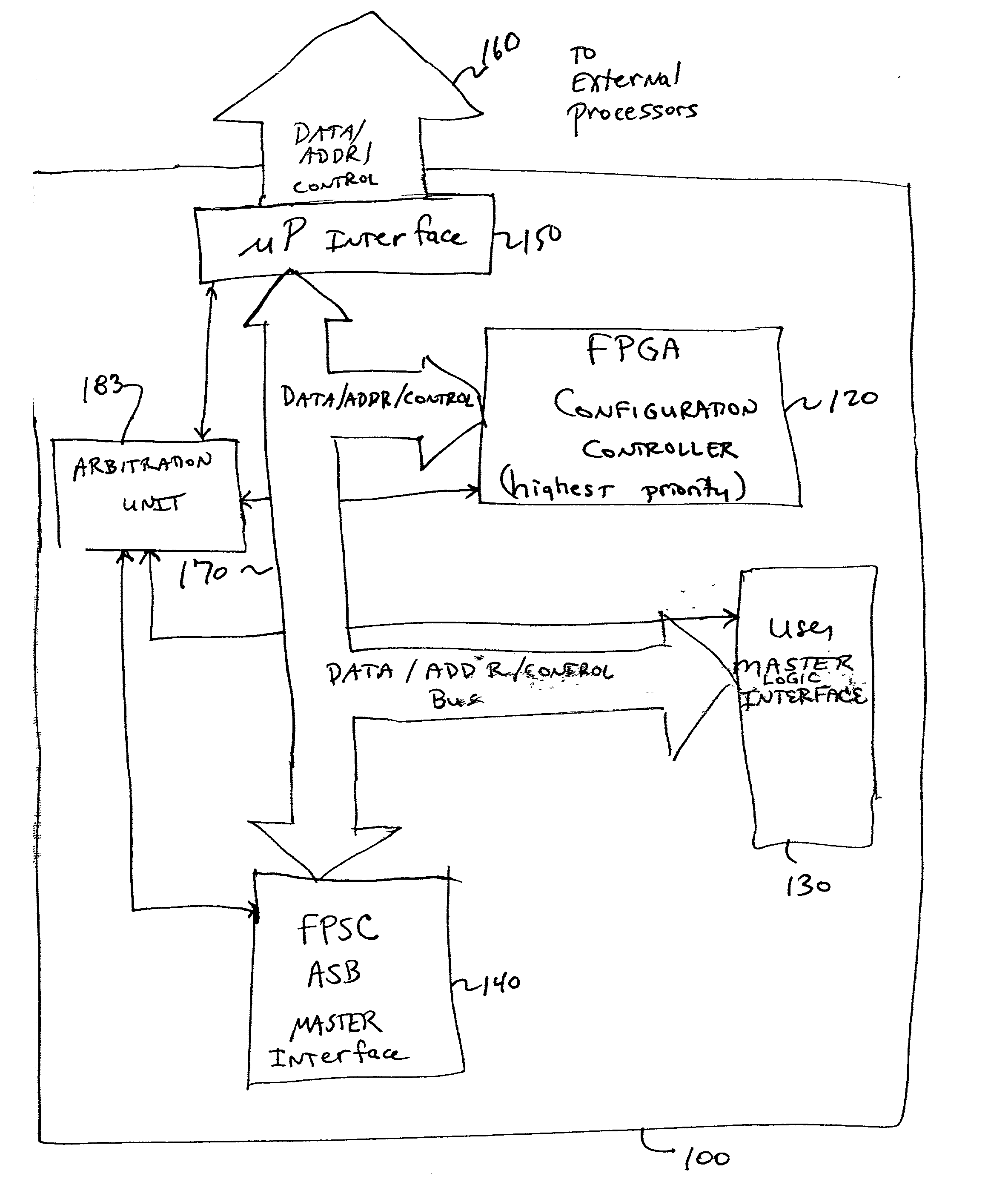
Field programmable gate array (FPGA) bit stream cormat
InactiveUS20020010902A1Programmable logic circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlData streamField-programmable object array
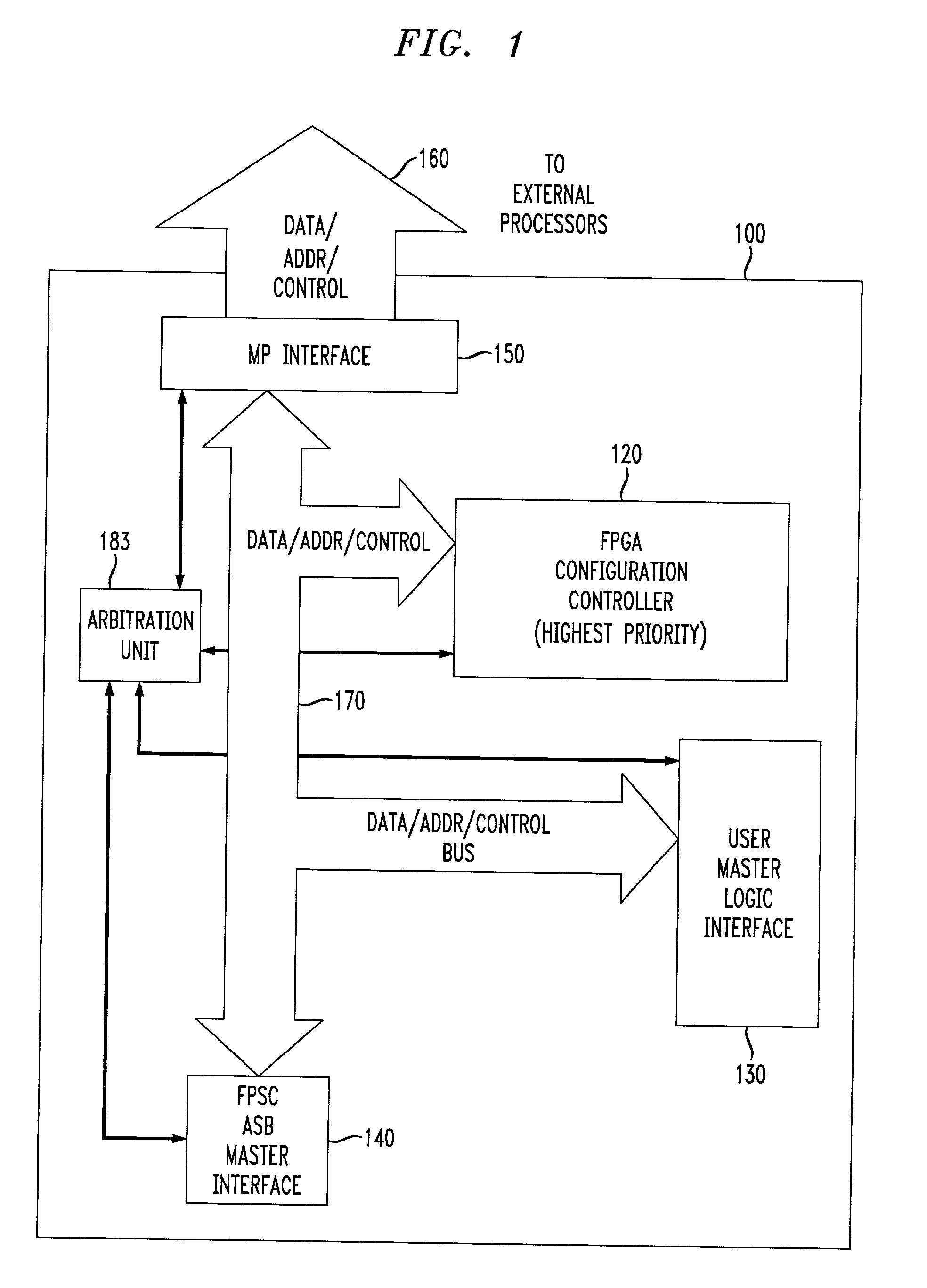
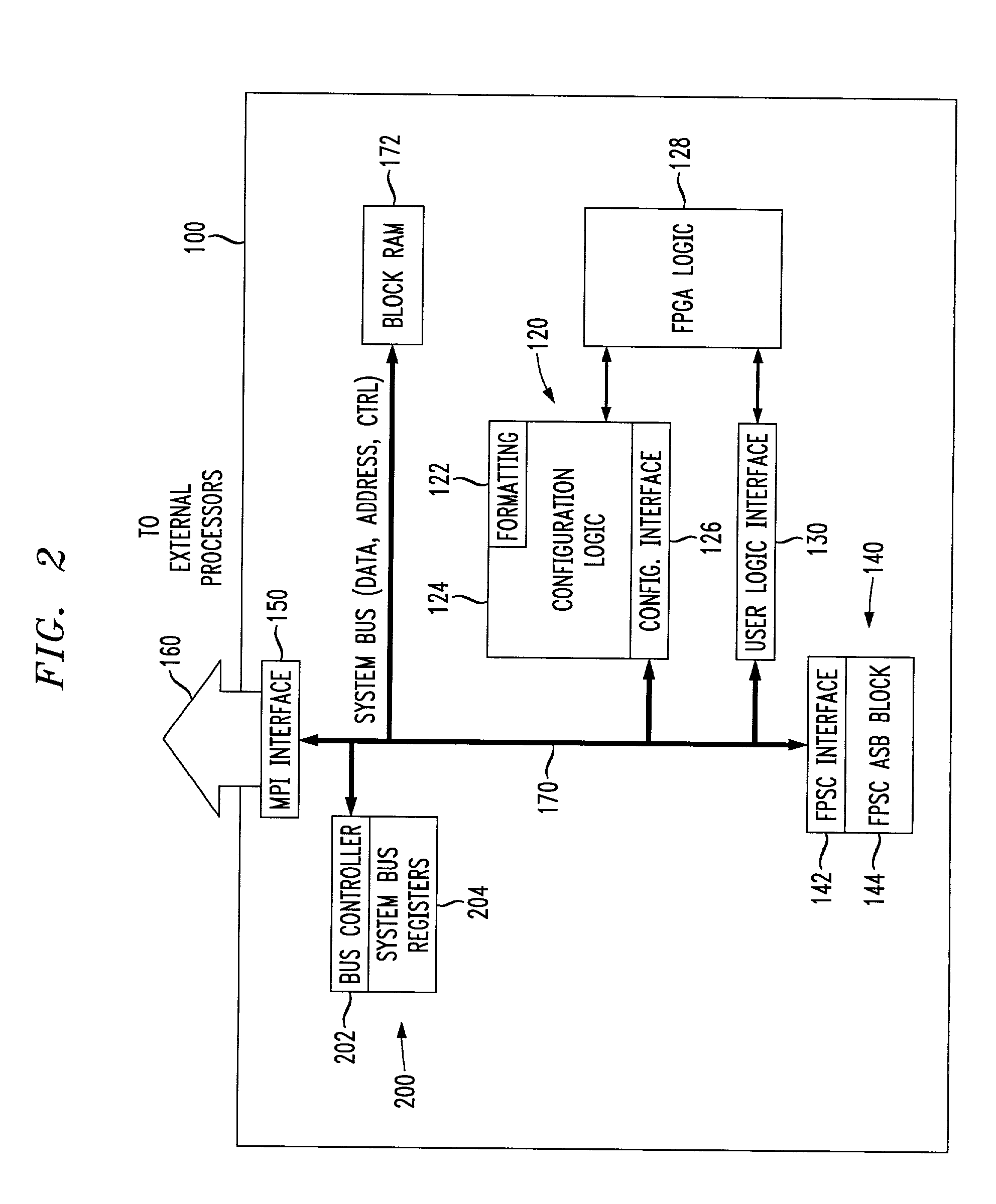
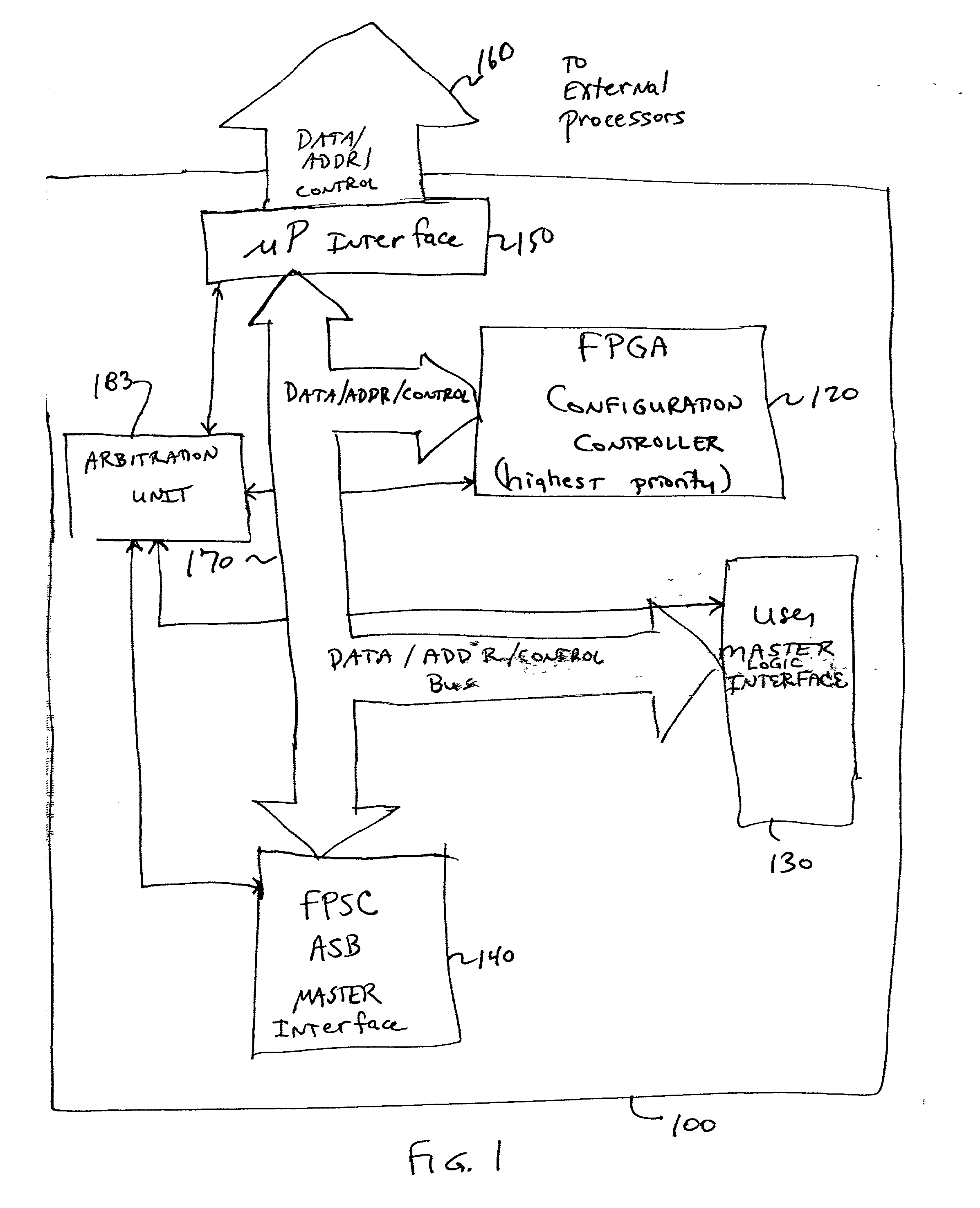
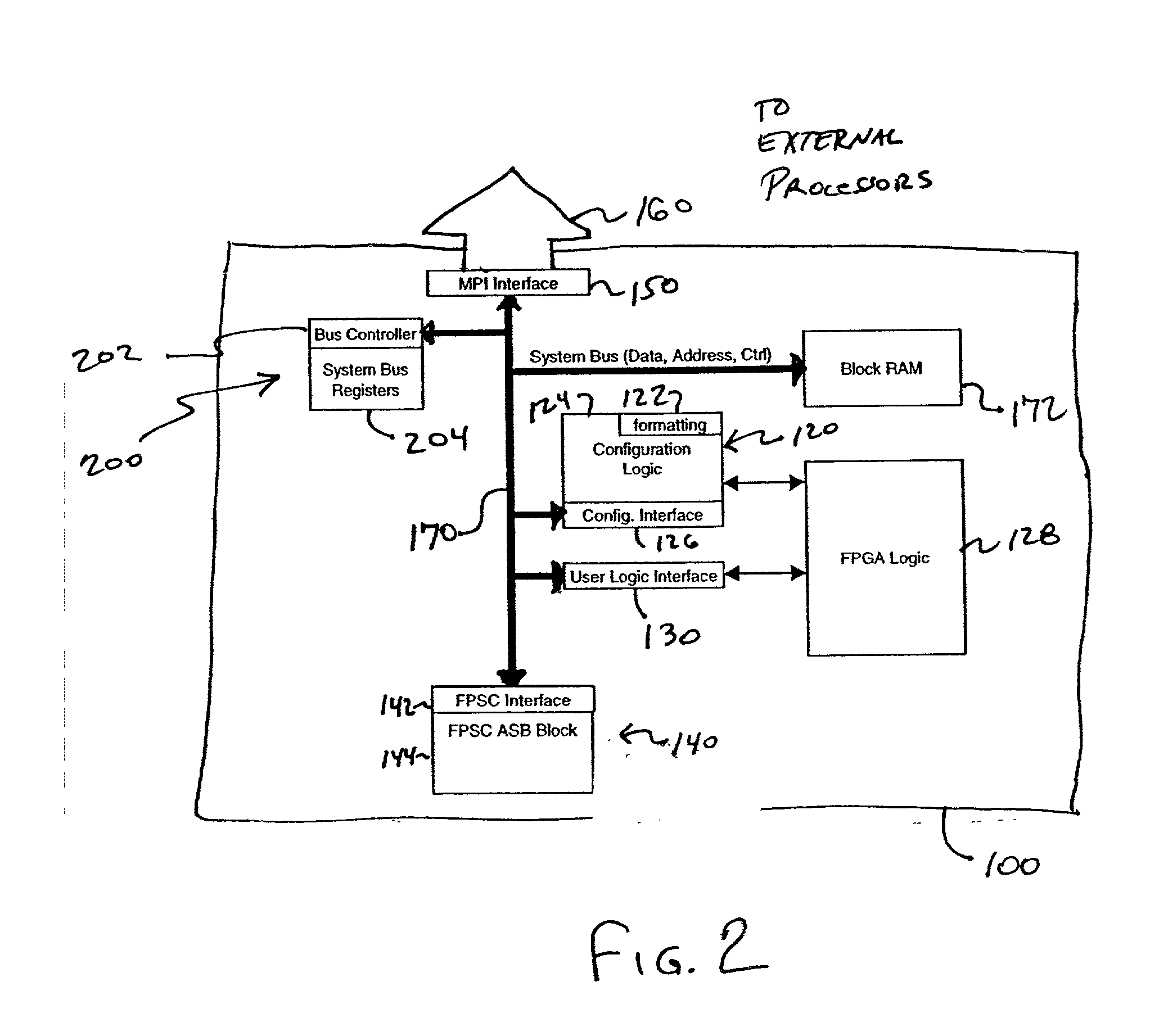
An embedded system bus is woven between a plurality of embedded master elements and at least one slave element within the FPGA device, and provides an external processor interface allowing direct access to any of the plurality of embedded slave elements. Using the embedded system bus, any of a plurality of masters may be allowed to program an embedded element, e.g., embedded FPGA logic, whereas conventional FPGAs allowed only a single master (e.g., a processor) to program the embedded FPGA logic. The embedded system bus is a group of signals, typically data, address and control, that connects system elements together and provides a basic protocol for the flow of data. The embedded system bus allows for control, configuration and status determination of the FPGA device. The embedded system bus is preferably a dedicated function available at all times for arbitrated access to allow communication between the various embedded system components.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Programmable high speed I/O interface
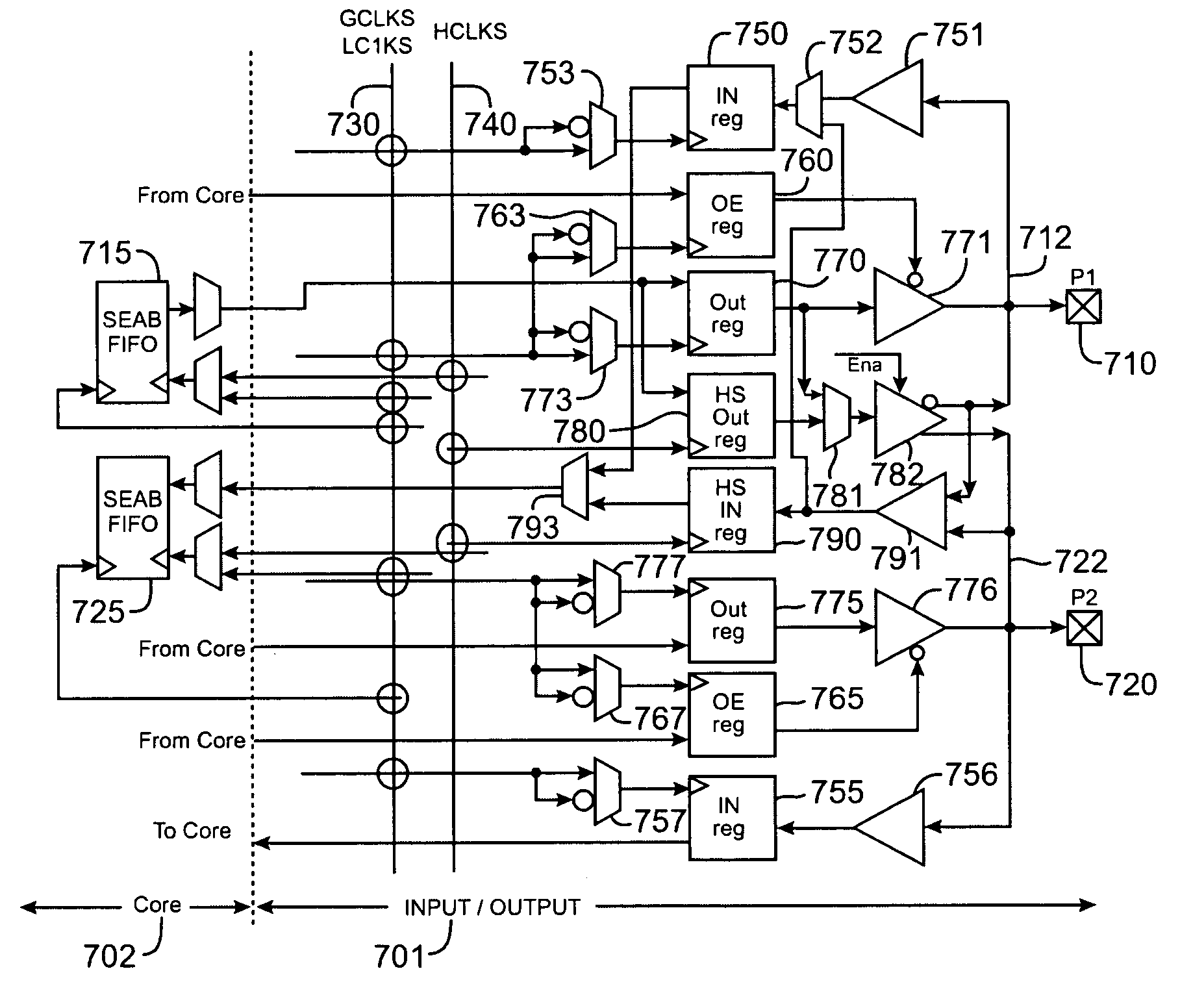
InactiveUS7116135B2High-speed inputHigh-speed outputProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsElectric pulse generatorBoundary testingLow speed
Methods and apparatus for providing either high-speed, or lower-speed, flexible inputs and outputs. An input and output structure having a high-speed input, a high-speed output, a low or moderate speed input, and an low or moderate speed output is provided. One of the input and output circuits are selected and the others are deselected. The high-speed input and output circuits are comparatively simple, in one example having only a clear signal for a control line input, and are able to interface to lower speed circuitry inside the core of an integrated circuit. The low or moderate speed input and output circuits are more flexible, for example, having preset, enable, and clear as control line inputs, and are able to support JTAG boundary testing. These parallel high and lower speed circuits are user selectable such that the input output structure is optimized between speed and functionality depending on the requirements of the application.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Systems and methods for interfacing between hard logic and soft logic in a hybrid integrated device
ActiveUS20120319730A1Speed up the processProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesComputer moduleLogic module
Systems and methods are disclosed for interfacing between hard logic elements and soft logic elements implemented on an integrated device. In particular, a configurable interface is provided that includes interconnects between hard logic and soft logic, which enable signals to be selectively routed between the inputs and outputs of hard logic blocks and soft logic modules. The interconnects allow for certain hard logic blocks to be bypassed in favor of soft logic functionality. Moreover, the interconnects allow soft logic to augment the processing of hard logic blocks, e.g., by providing additional signals to the hard logic block.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
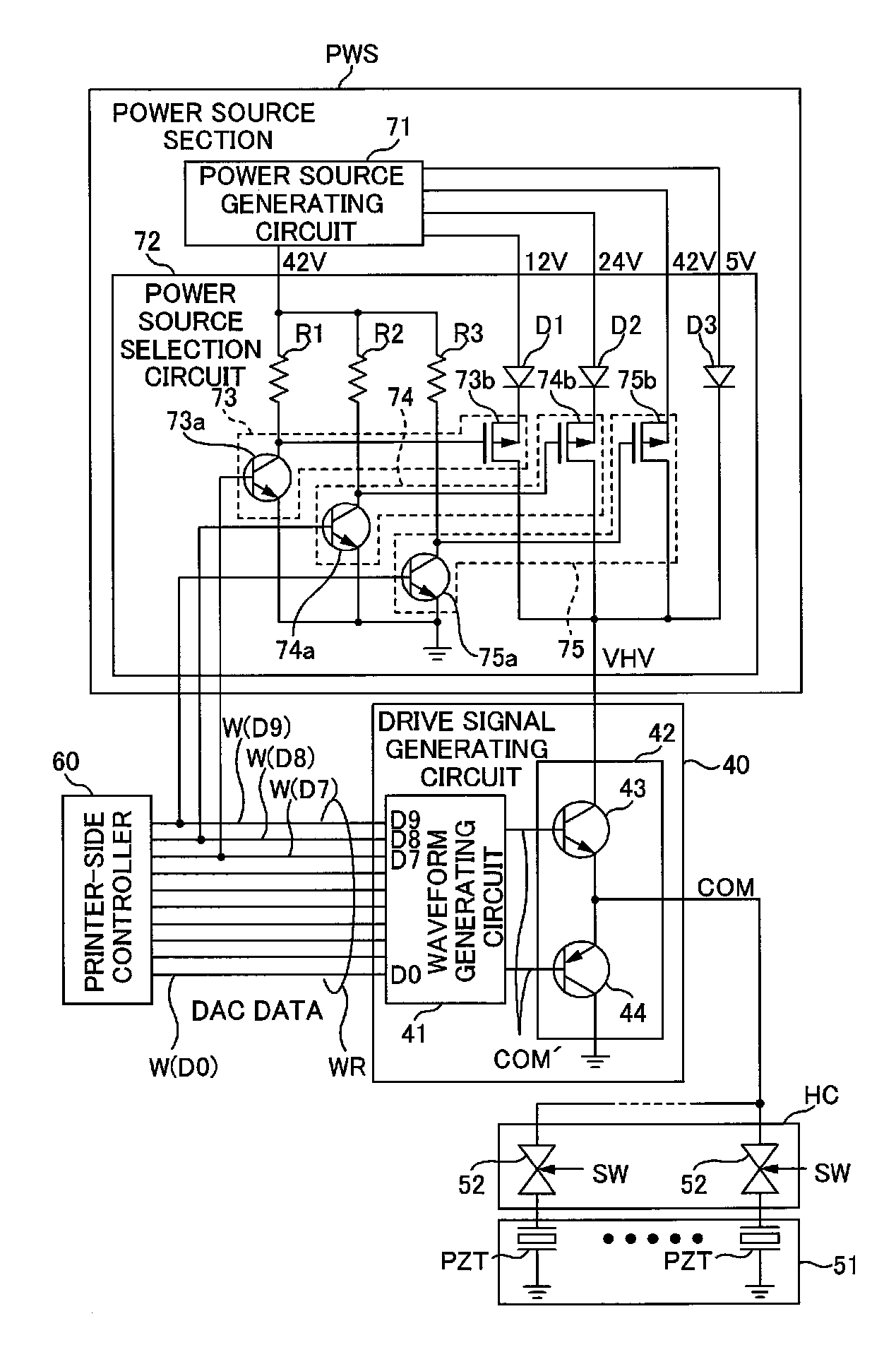
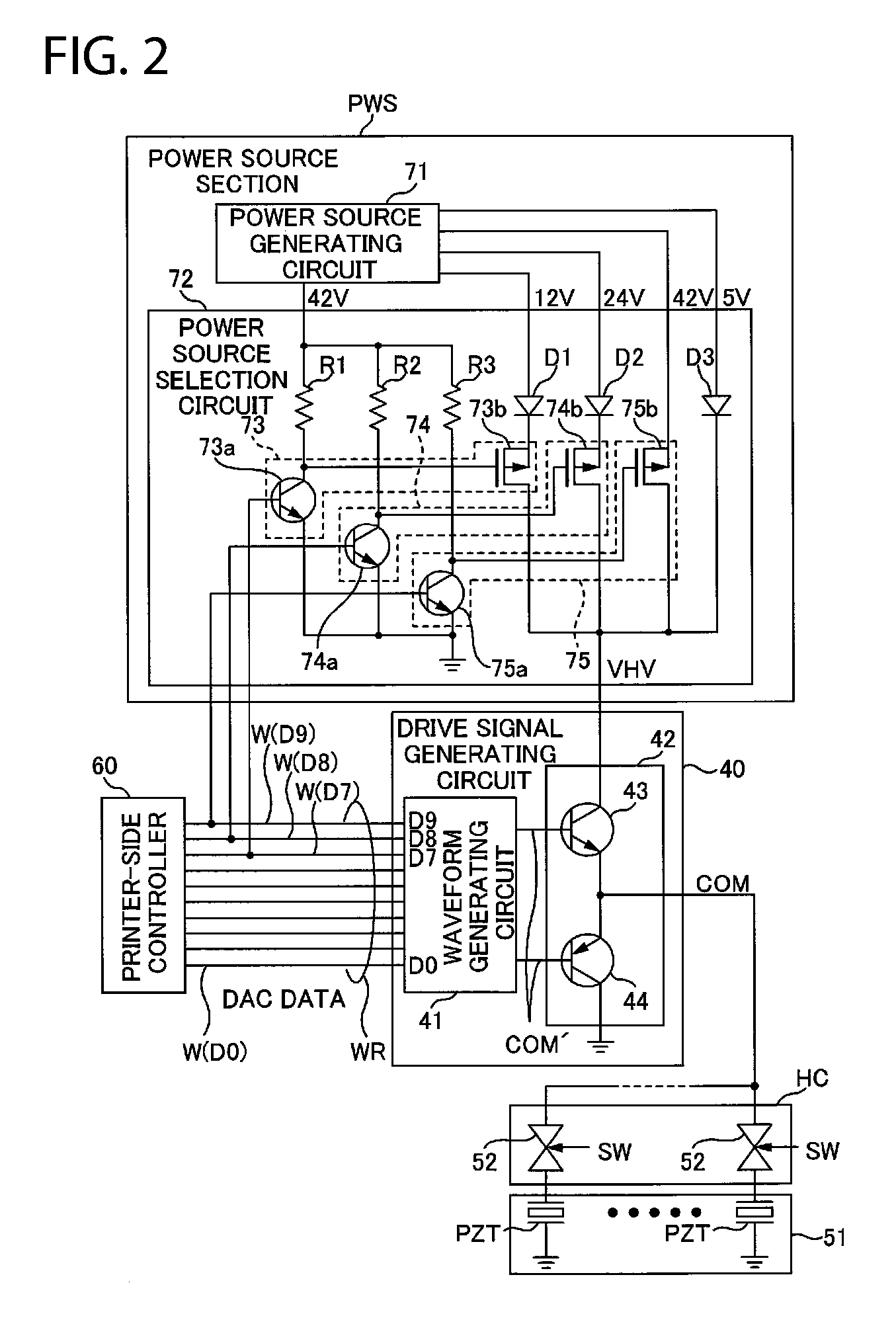
Drive signal generating apparatus, liquid ejecting apparatus, and drive signal generating method
InactiveUS20080238964A1Increase speedProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsElectric pulse generatorDigital dataAnalog signal
A drive signal generating apparatus is provided with an analog signal converting section, a current amplification section, and a power source generating section. The analog signal converting section converts digital data to an analog signal. The current amplification section is provided with a current amplification transistor and generates a drive signal by amplifying a current of the analog signal using the current amplification transistor. The power source generating section is a power source having a voltage determined based on the digital data and generates a power source to be supplied to the current amplification transistor.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Multi-master multi-slave system bus in a field programmable gate array (FPGA)
InactiveUS20020008540A1Programmable logic circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlData streamField-programmable object array
An embedded system bus is woven between a plurality of embedded master elements and at least one slave element within the FPGA device, and provides an external processor interface allowing direct access to any of the plurality of embedded slave elements. Using the embedded system bus, any of a plurality of masters may be allowed to program an embedded element, e.g., embedded FPGA logic, whereas conventional FPGAs allowed only a single master (e.g., a processor) to program the embedded FPGA logic. The embedded system bus is a group of signals, typically data, address and control, that connects system elements together and provides a basic protocol for the flow of data. The embedded system bus allows for control, configuration and status determination of the FPGA device. The embedded system bus is preferably a dedicated function available at all times for arbitrated access to allow communication between the various embedded system components.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Trigger circuits and event counters for an IC
ActiveUS8295428B2Easy to useProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesComputer scienceIntegrated circuit
Some embodiments provide an integrated circuit (“IC”). The IC includes multiple configurable circuits that configurably perform operations of a user design based on configuration data. The IC also includes a configurable trigger circuit that receives a set of configuration data that specifies an operational event. The configurable trigger circuit also determines whether the operational event has occurred during implementation of the user design of the IC. Additionally, the operational trigger event outputs a trigger signal upon determining that the operational trigger event has occurred.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Omnibus logic element
ActiveUS7538579B1Flexible and efficient to useProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerComputer science
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Programmable logic device and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20140225644A1High speedReduce circuit areaProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceProgrammable logic device
To provide a PLD having a reduced circuit area and an increased operation speed. In the circuit structure, a gate of a transistor provided between an input terminal and an output terminal of a programmable switch element is in an electrically floating state in a period when a signal is input to the programmable switch element. The structure enables the voltage of a gate to be increased by a boosting effect in response to a signal supplied from programmable logic elements, suppressing a reduction in amplitude voltage. This can reduce a circuit area by a region occupied by a booster circuit such as a pull-up circuit and increase operation speed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
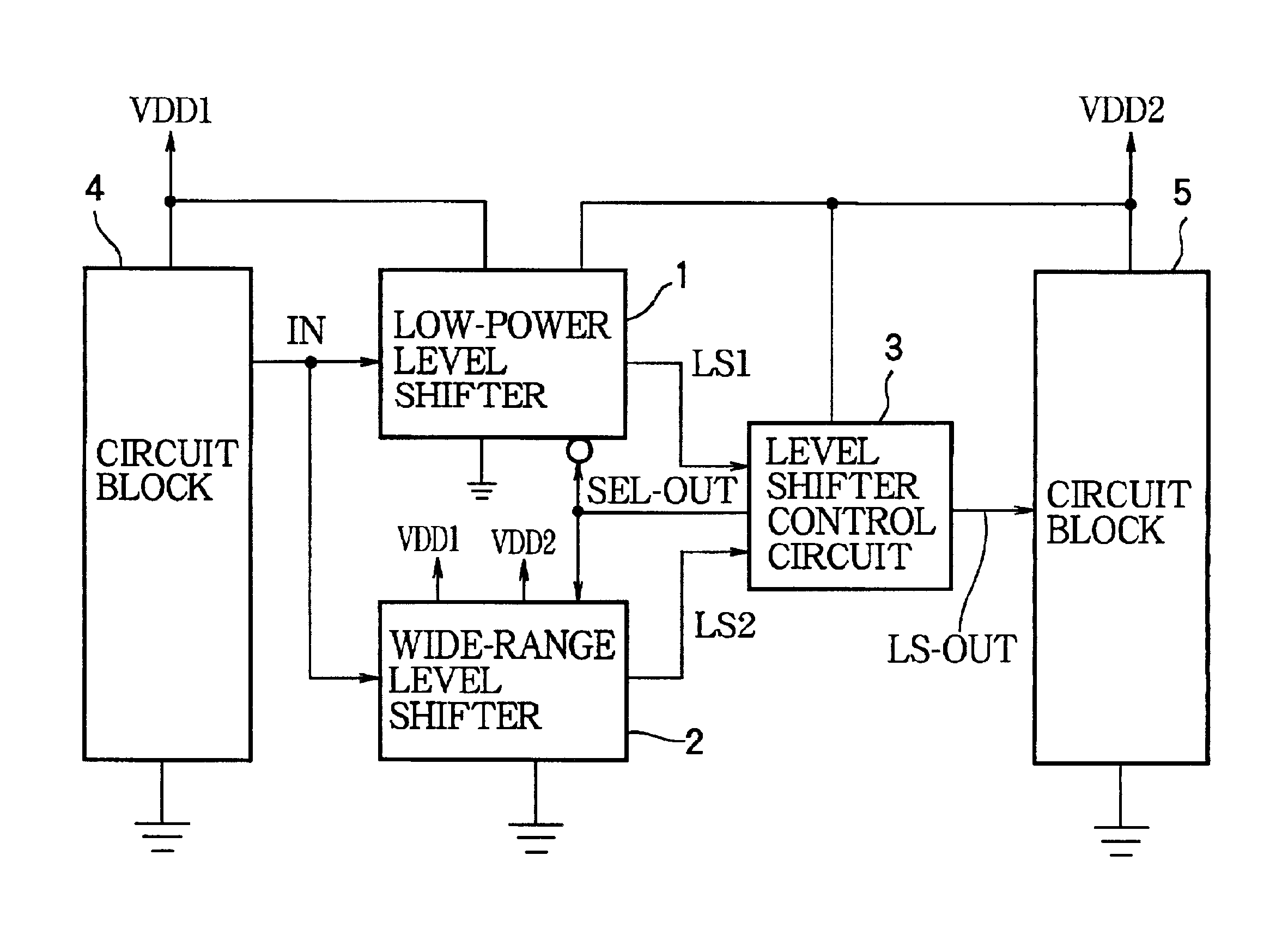
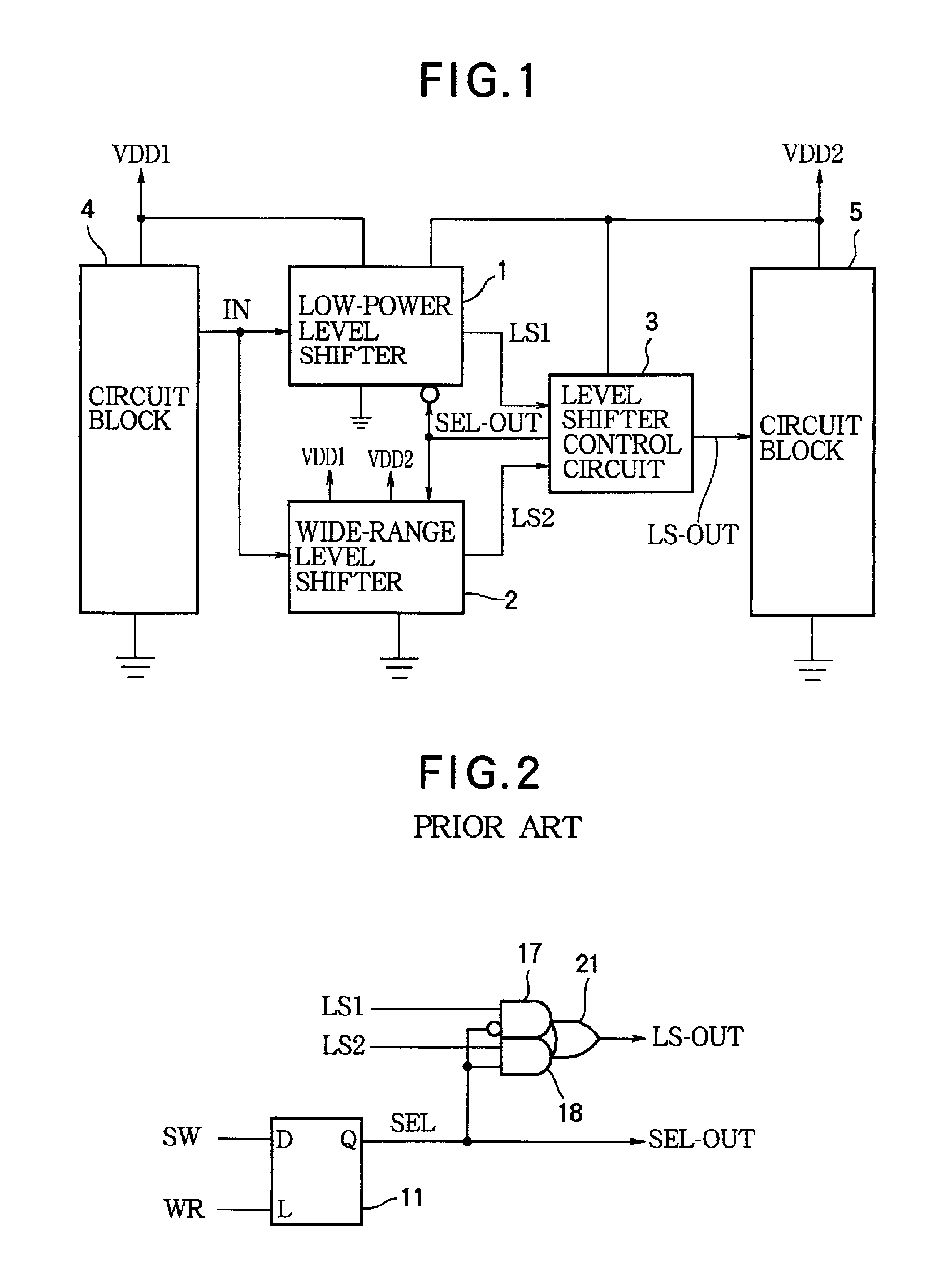
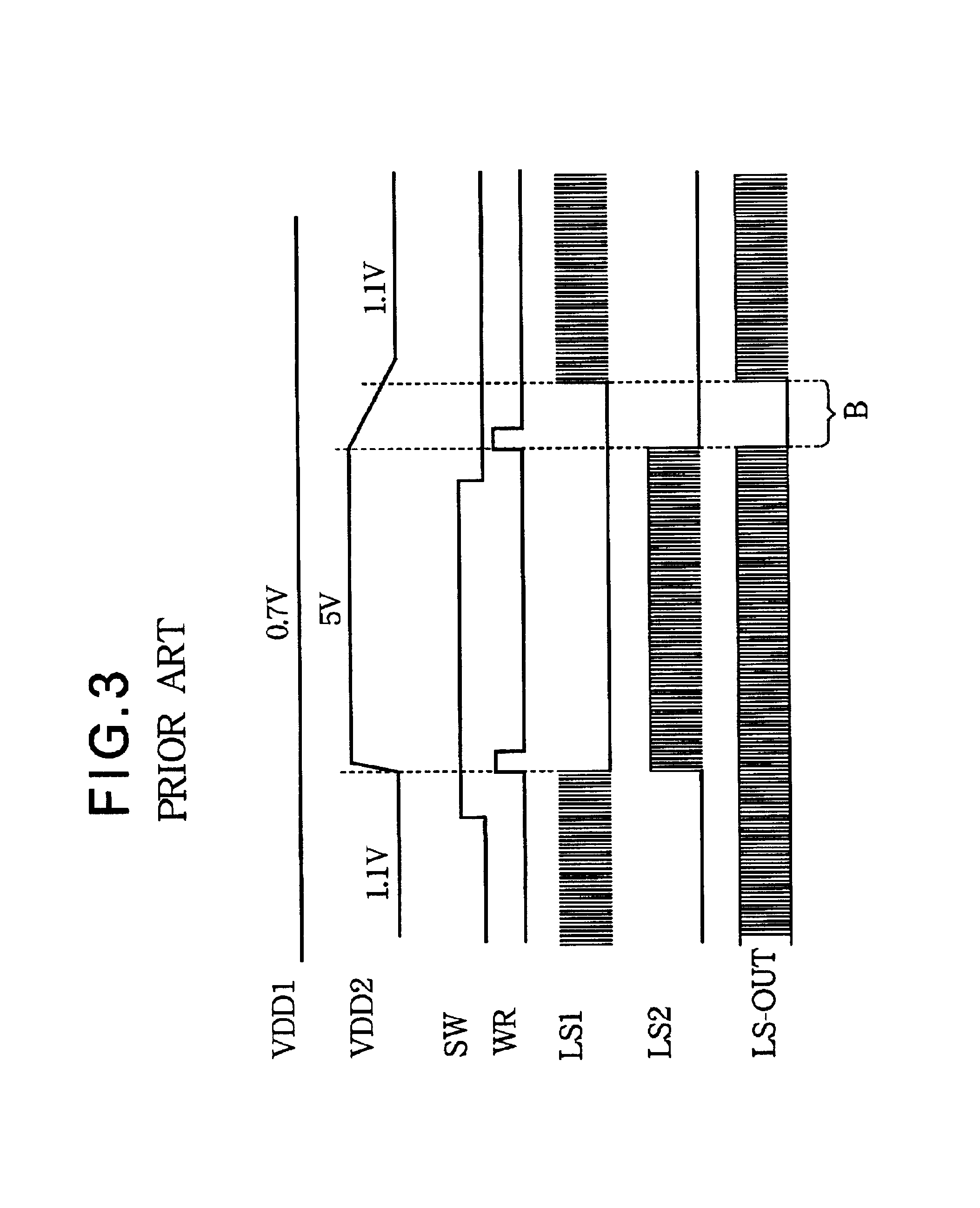
Level shifter control circuit with delayed switchover to low-power level shifter
InactiveUS6920570B2Guaranteed continuous outputProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementLevel shiftingPotential difference
A level shifter control circuit selects one of two level shifters for converting a signal output from a circuit operating on a first power supply for input to a circuit operating on a second power supply. A low-power level shifter is selected when the difference between the two power-supply potentials is comparatively small. A wide-range level shifter is selected when the difference is greater. The switchover from the wide-range level shifter to the low-power level shifter is delayed to allow the power-supply potential difference to diminish to within the operating range of the low-power level shifter, thereby avoiding gaps in the level-shifted signal.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
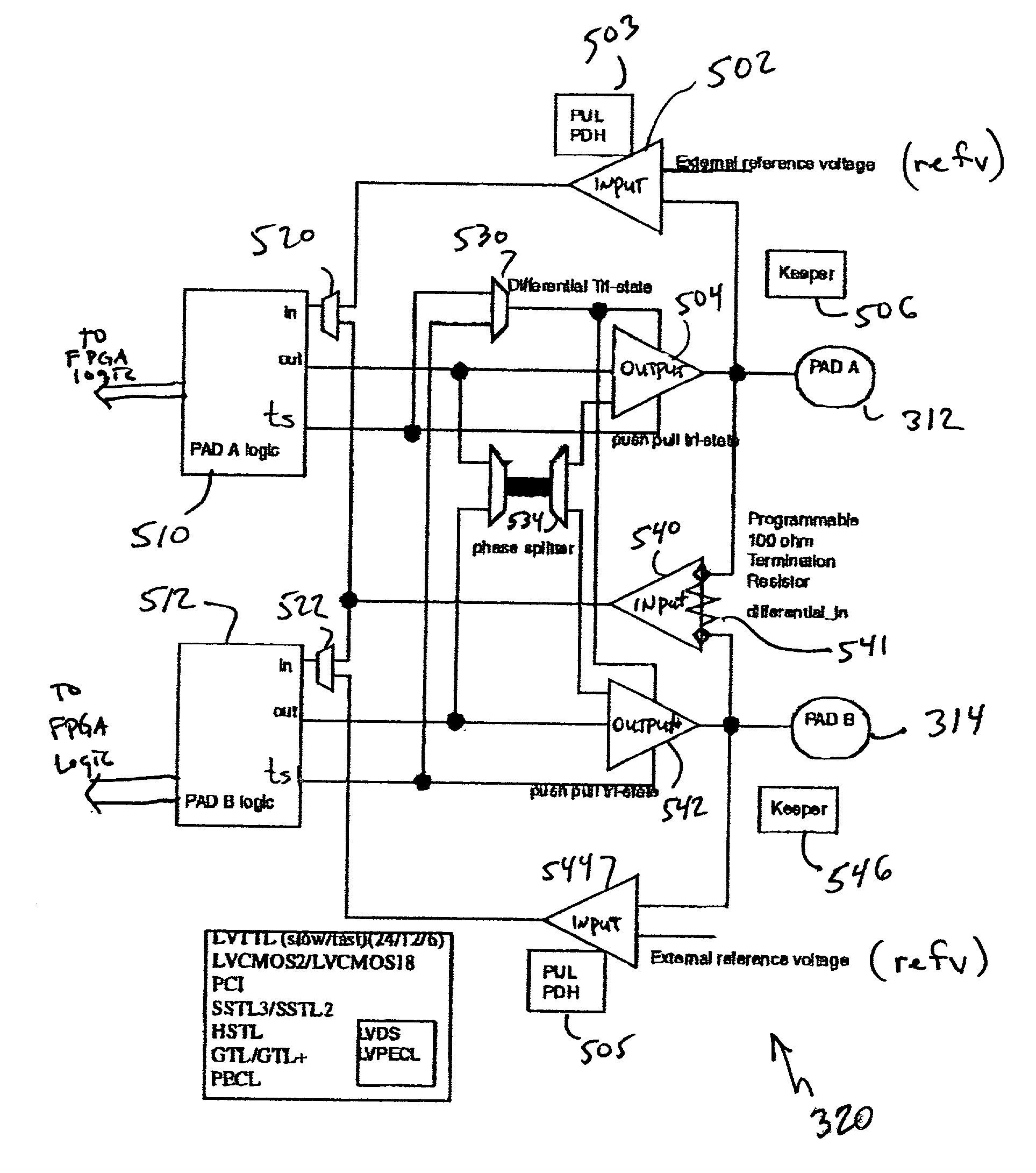
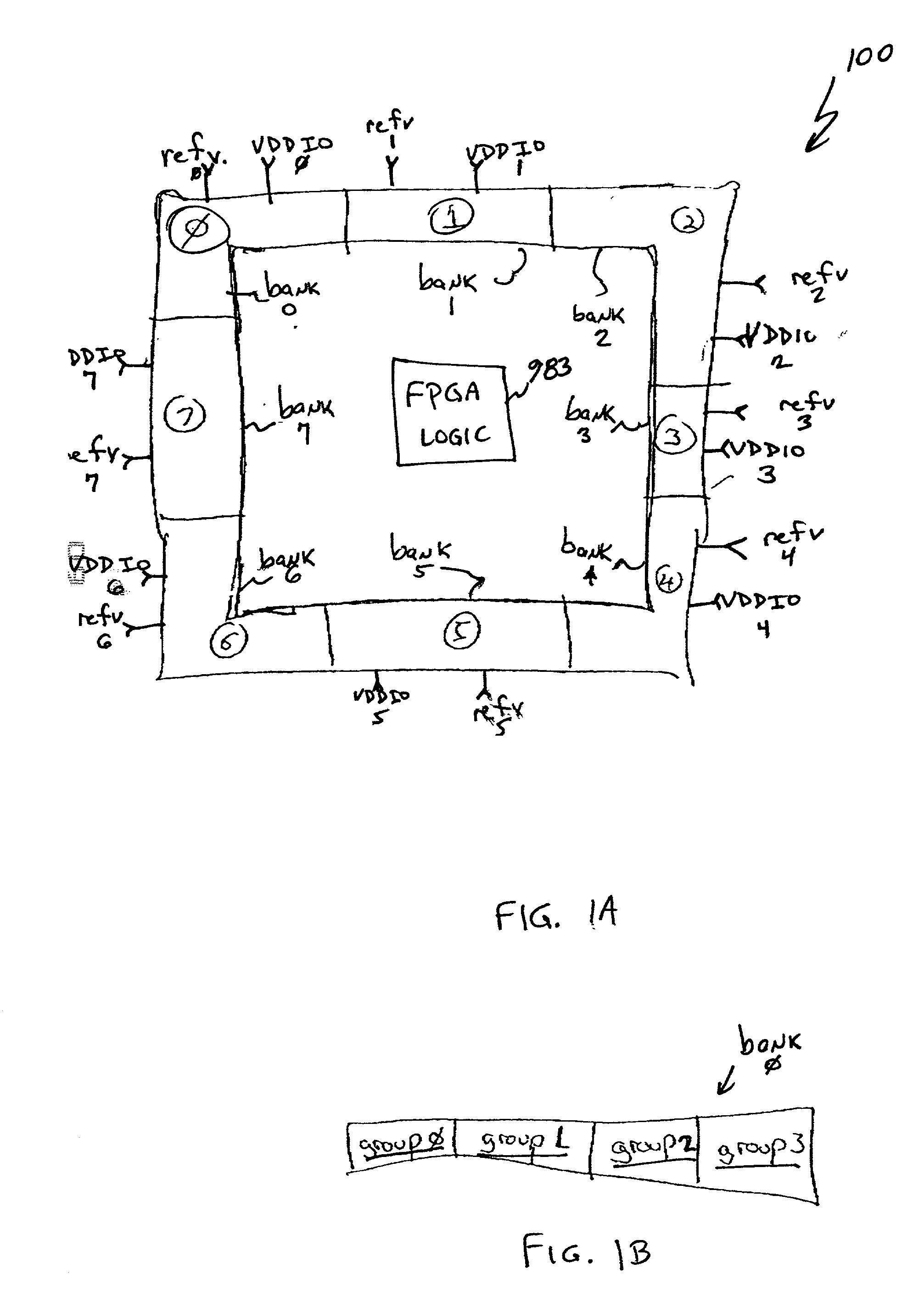
Multi-functional I/O buffers in a field programmable gate array (FPGA)
InactiveUS20020003435A1Programmable logic circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlDouble data rateProgrammable logic device
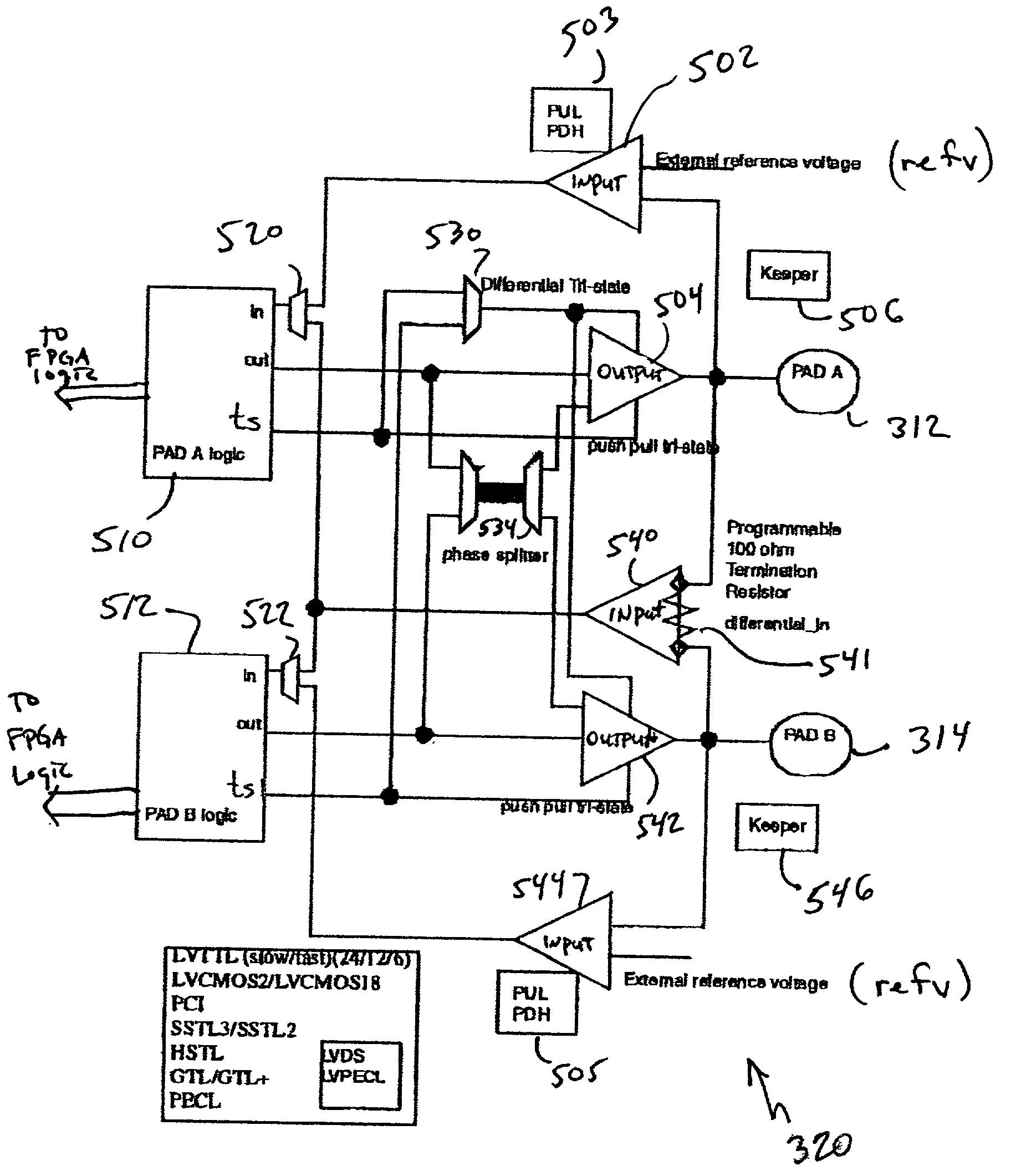
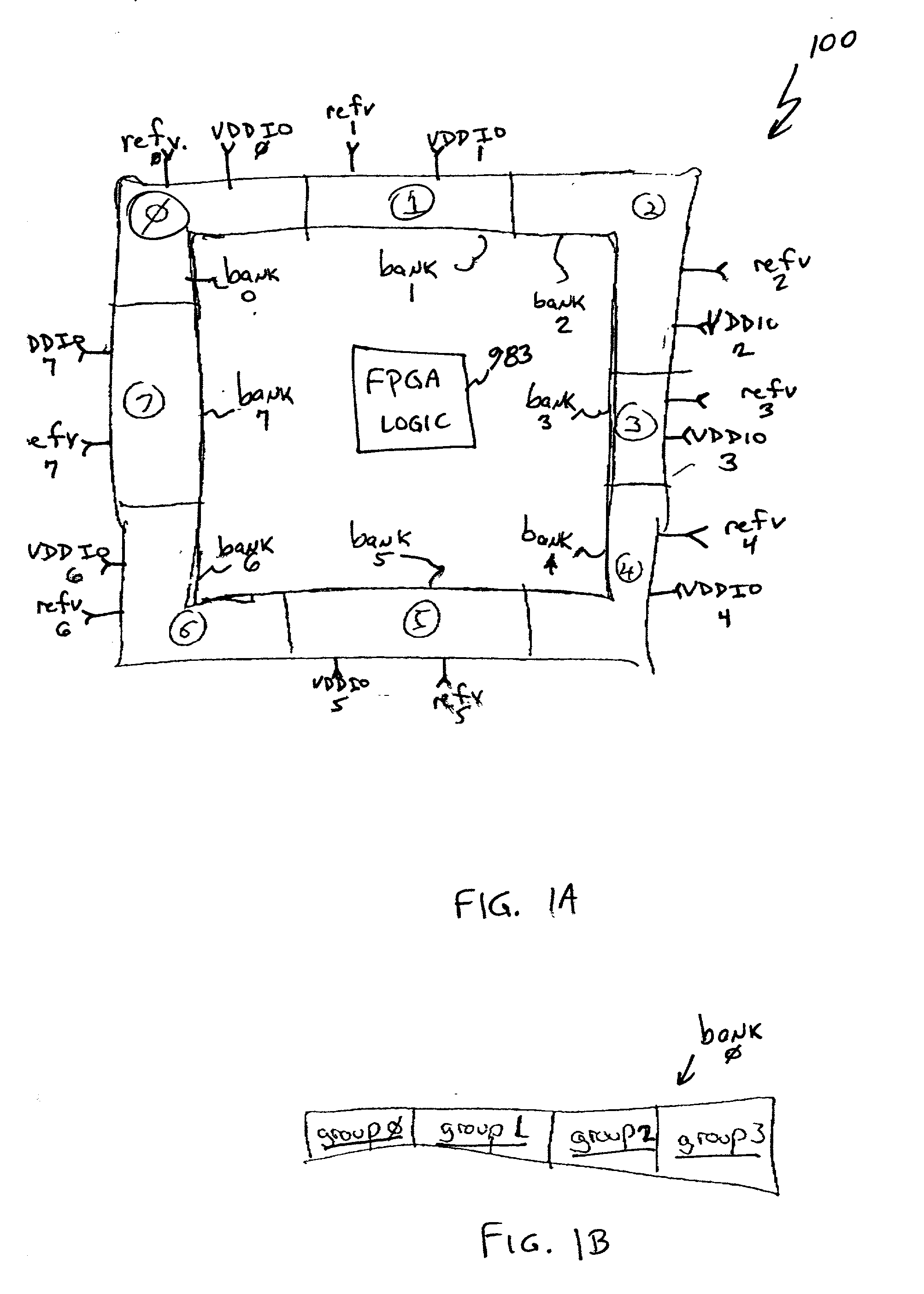
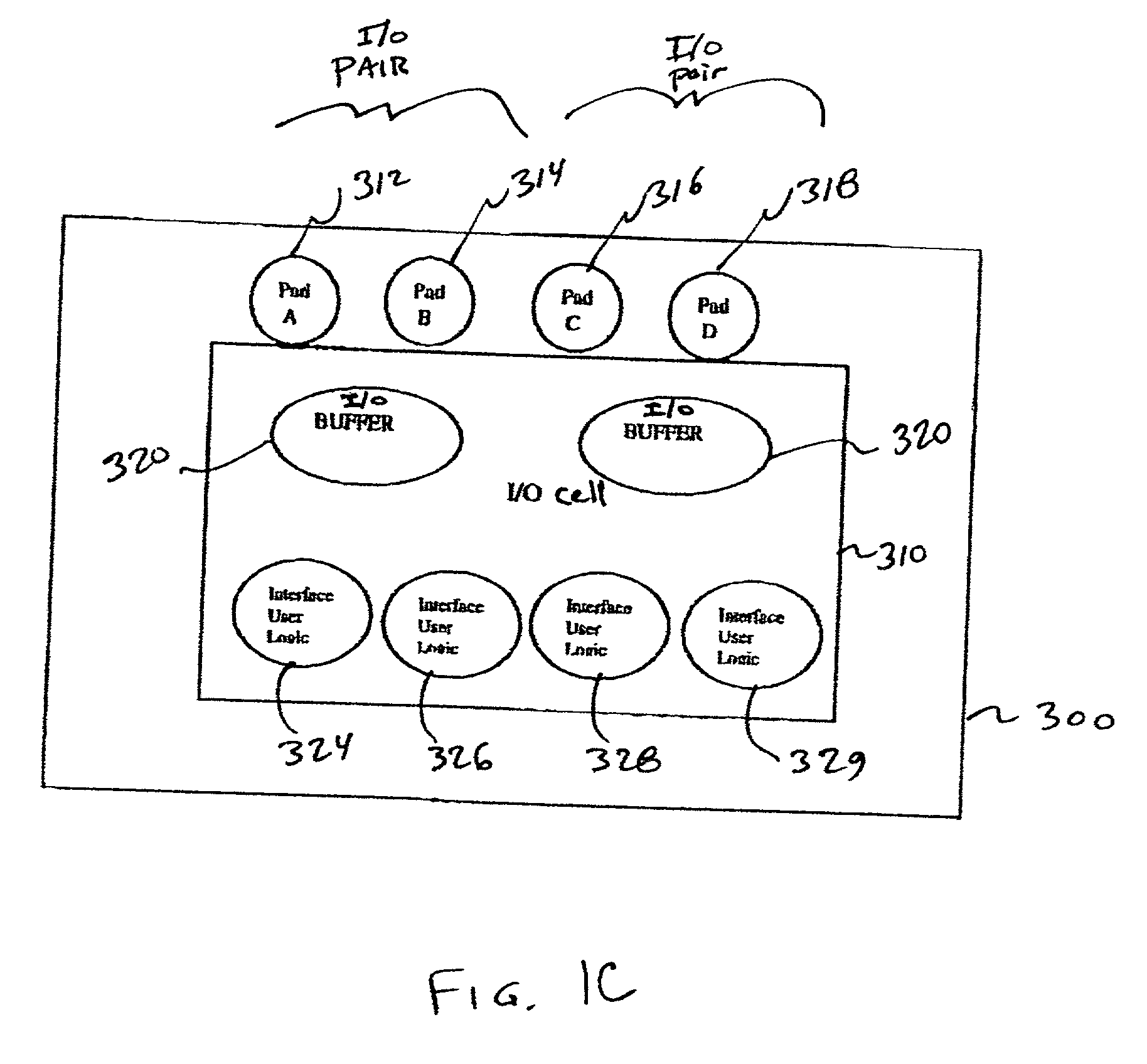
A multi-functional programmable I / O buffer in a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) device. The I / O buffer is programmably configurable to meet any of a wide range of I / O standards, be it single ended or differential, 5V, 3.3V, 2.5V or 1.5V logic, without the need for implementing multiple I / O buffers to properly handle each different iteration of I / O requirements. An embedded, internal programmable resistor (e.g., a programmable 100 ohm resistor) is programmably selected for use in differential I / O applications, thus eliminating the conventional requirement for the use of an external resistor connected to each differential receiver I / O pin. The present invention also separates I / O pads into groups in each of a plurality of banks in a programmable device (e.g., PLD, FPGA, etc.), with each group being separately powered by the user. The disclosed multi-functional I / O buffer may be programmably configured by the user to be, e.g., a single ended receiver or transmitter, a reference receiver or transmitter, or a differential receiver or transmitter. The pad logic of the multi-functional I / O buffer may include a double data rate input and output mode, each of which includes two flip-flop devices operating on opposite sides of a data clock signal. One of the two flip-flop devices may be borrowed from another logic element, e.g., from a shirt register logic element.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Multiple data rate interface architecture
InactiveUS7167023B1Facilitate efficient pin migrationEasily be scaled in sizeProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesComputer architectureProcessor register
Method and circuitry for implementing high speed multiple-data-rate interface architectures for programmable logic devices. The invention partitions I / O pins and their corresponding registers into independent multiple-data rate I / O modules each having at least one pin dedicated to the strobe signal DQS and others to DQ data signals. The modular architecture facilitates pin migration from one generation of PLDs to the next larger generation.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Adjustable data drivers and methods for driving data signals
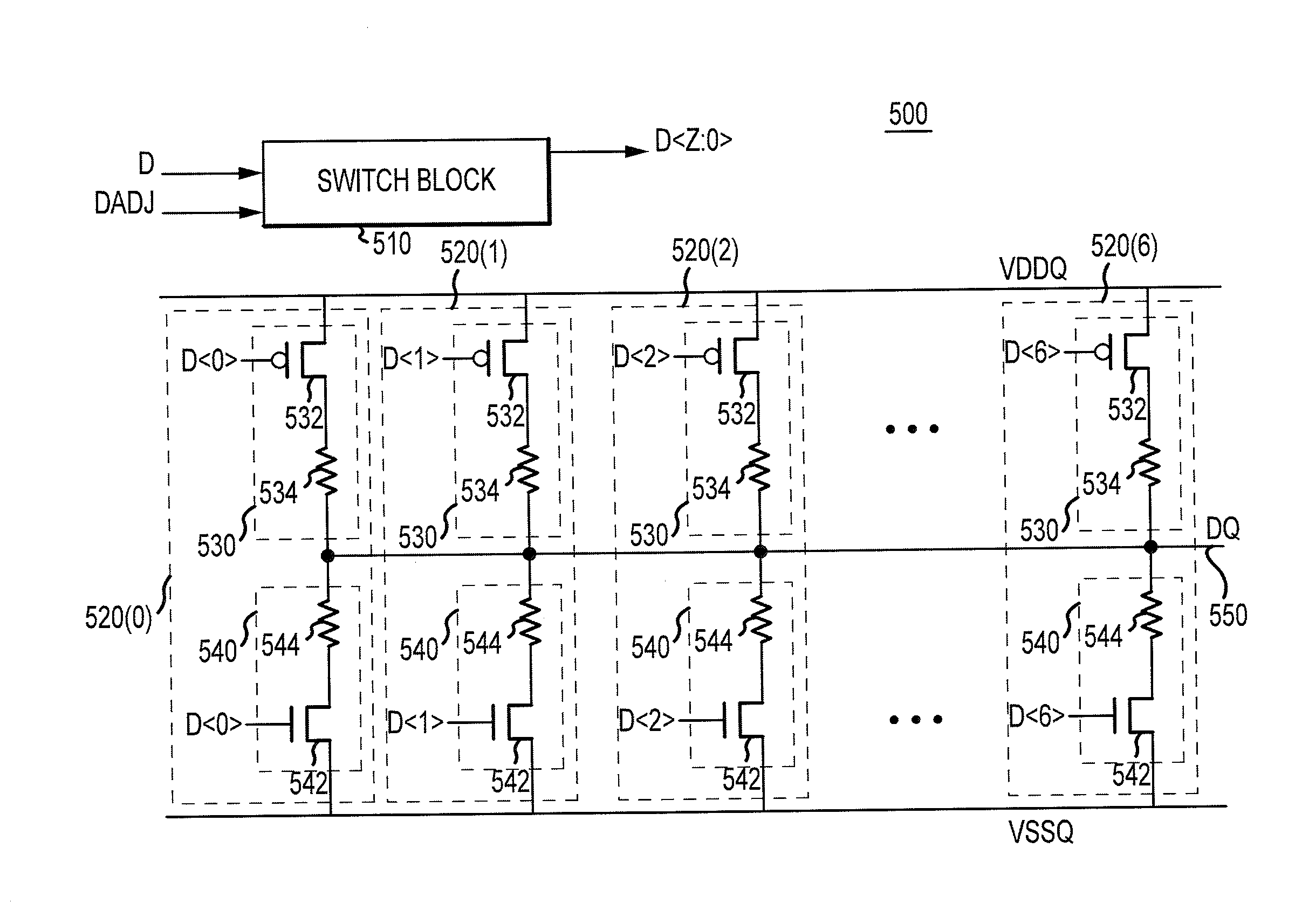
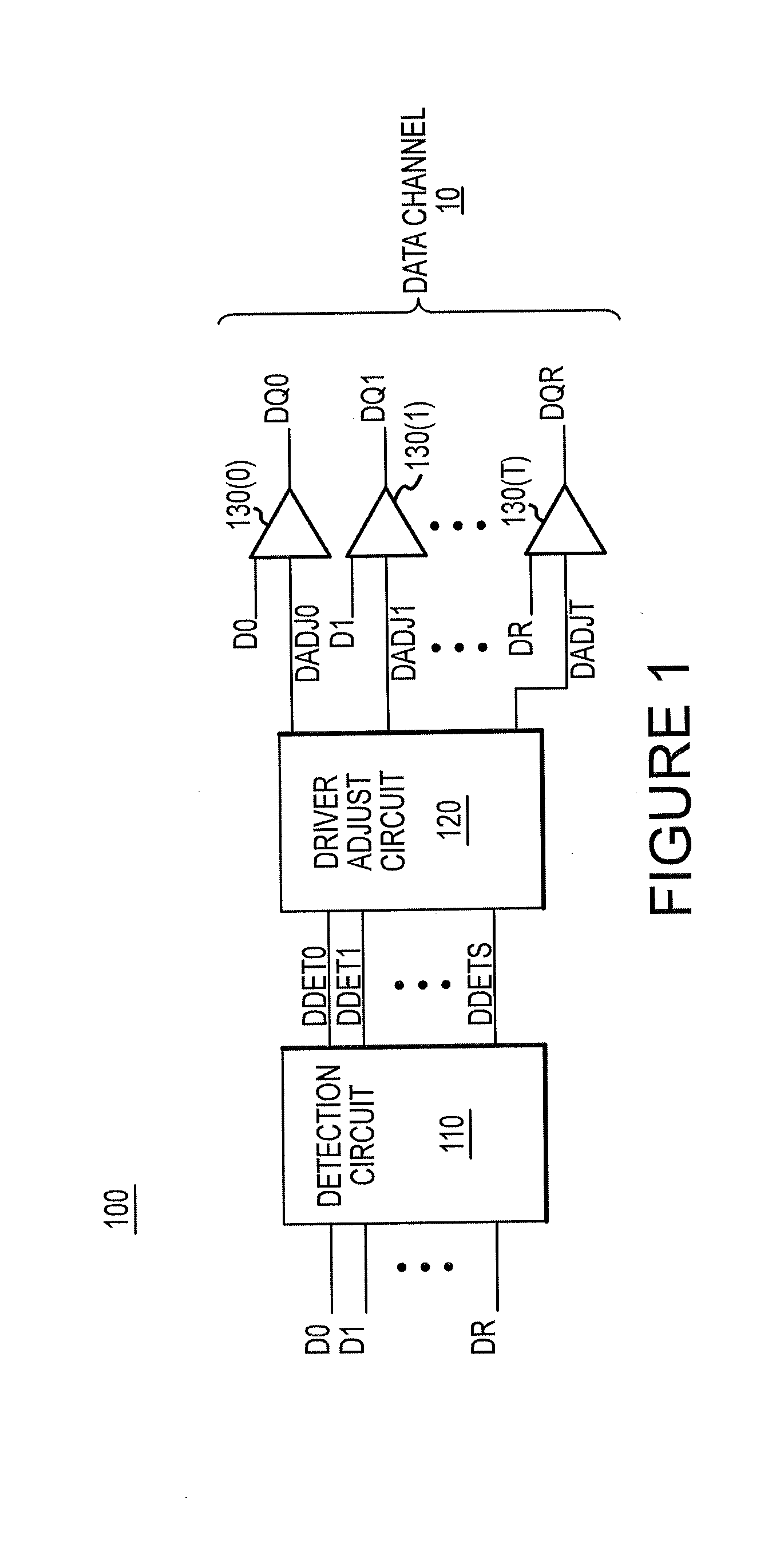
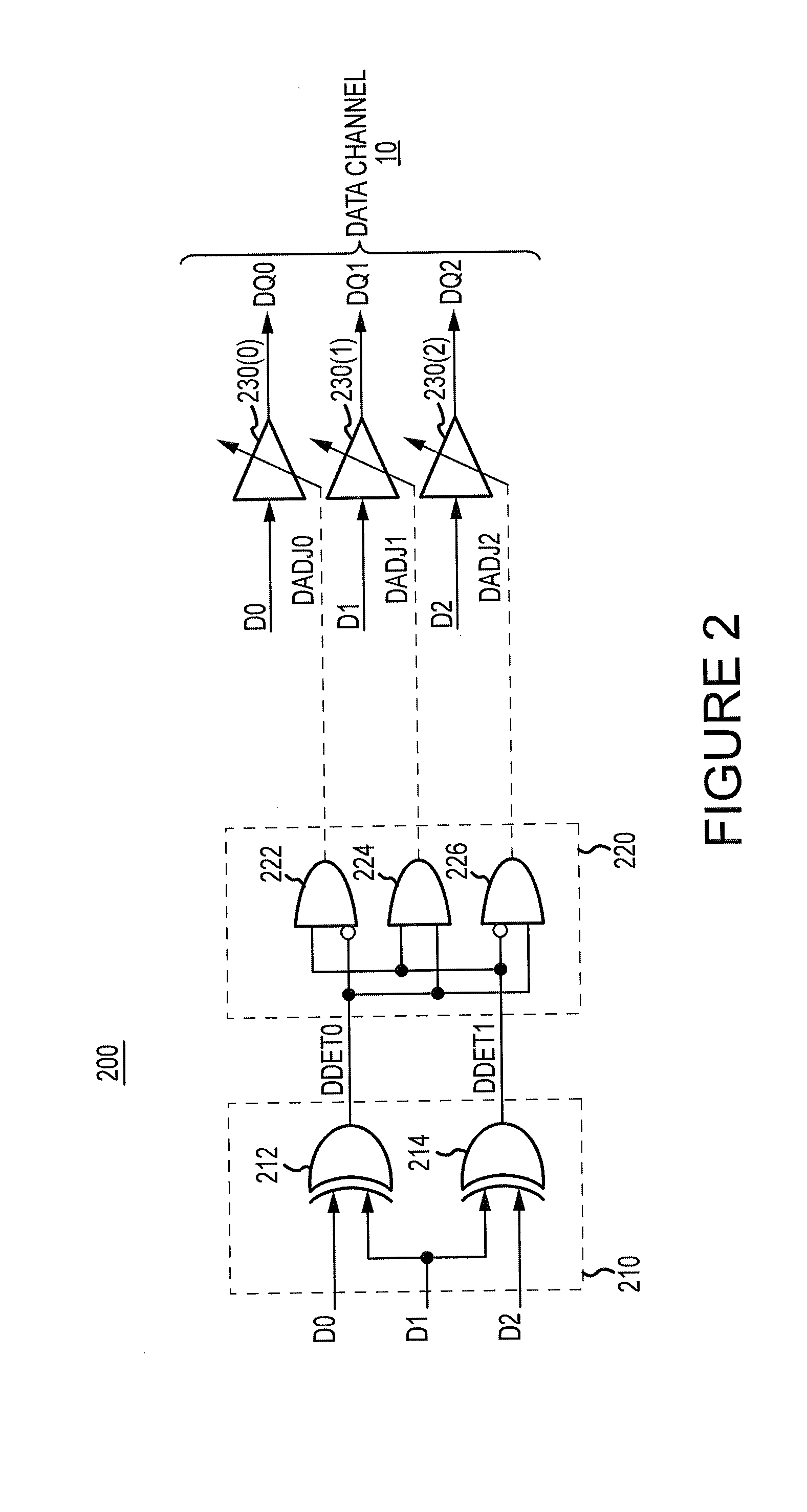
ActiveUS20130043900A1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsData signalEngineering
Apparatuses and methods for driving input data signals onto signal lines as output data signals are disclosed. An example apparatus includes a detection circuit, a driver adjust circuit, and a data driver. The detection circuit is configured to detect a characteristic(s) of a group of input data signals to be driven onto adjacent signal lines. A characteristic could be, for example, a particular combination of logic levels and / or transitions for, the group of input data signals. The driver adjust circuit is configured to provide a driver adjustment signal based at least in part on a detection signal, that is provided by the detection circuit. A data driver is configured to drive a respective one of the group of input data signals as a respective one of the output data signals, wherein the data driver is adjusted based at least in part on the driver adjustment signal.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Computation of boolean formulas using sneak paths in crossbar computing
ActiveUS20150171868A1Programmable logic circuit arrangementsLogic circuits using semiconductor devicesGeneral purposeTheoretical computer science
Memristor-based nano-crossbar computing is a revolutionary computing paradigm that does away with the traditional Von Neumann architectural separation of memory and computation units. The computation of Boolean formulas using memristor circuits has been a subject of several recent investigations. Crossbar computing, in general, has also been a topic of active interest, but sneak paths have posed a hurdle in the design of pervasive general-purpose crossbar computing paradigms. Various embodiments are disclosed which demonstrate that sneak paths in nano-crossbar computing can be exploited to design a Boolean-formula evaluation strategy. Such nano-crossbar designs are also an effective approach for synthesizing high performance customized arithmetic and logic circuits.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE +1
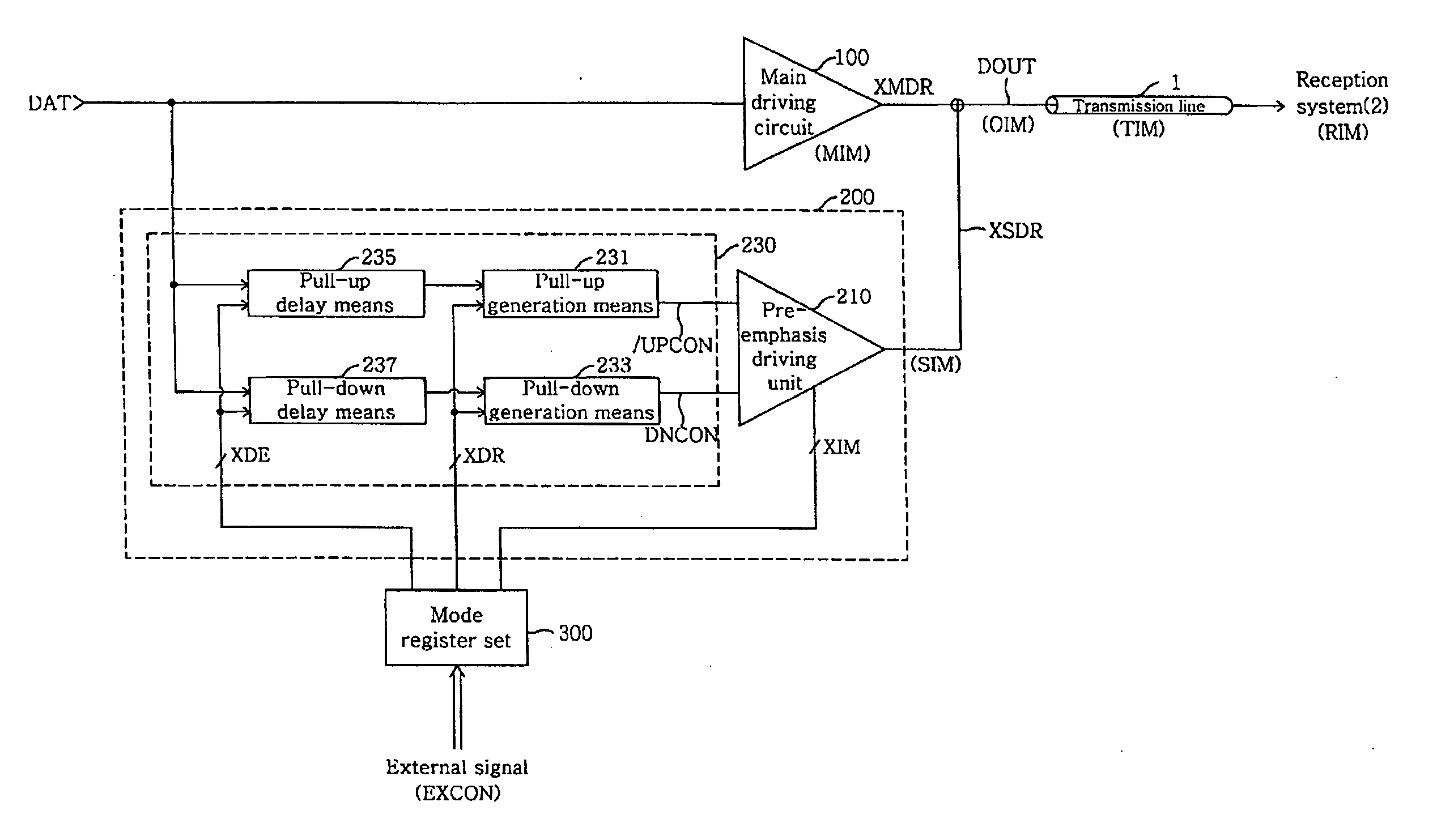
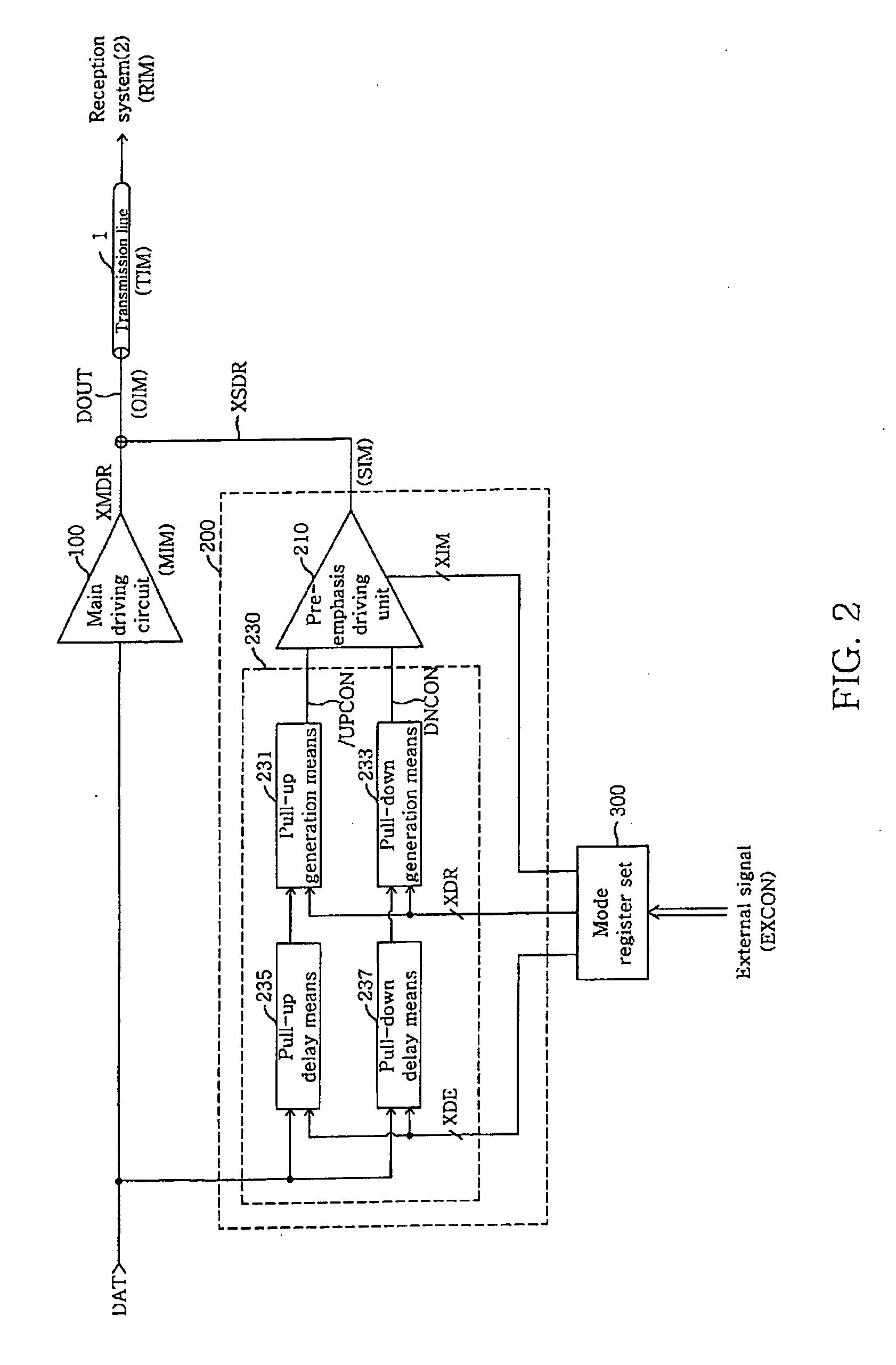
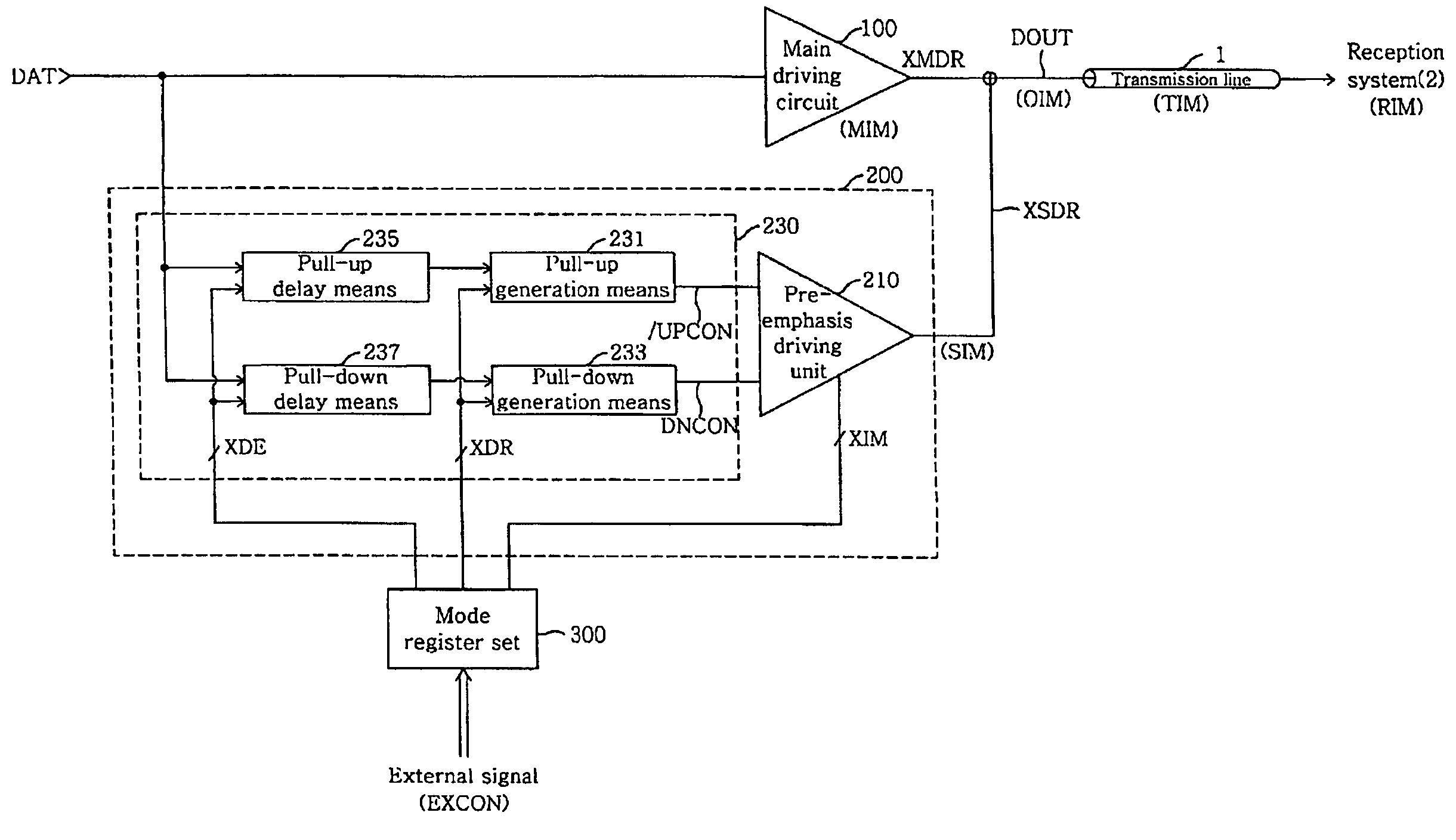
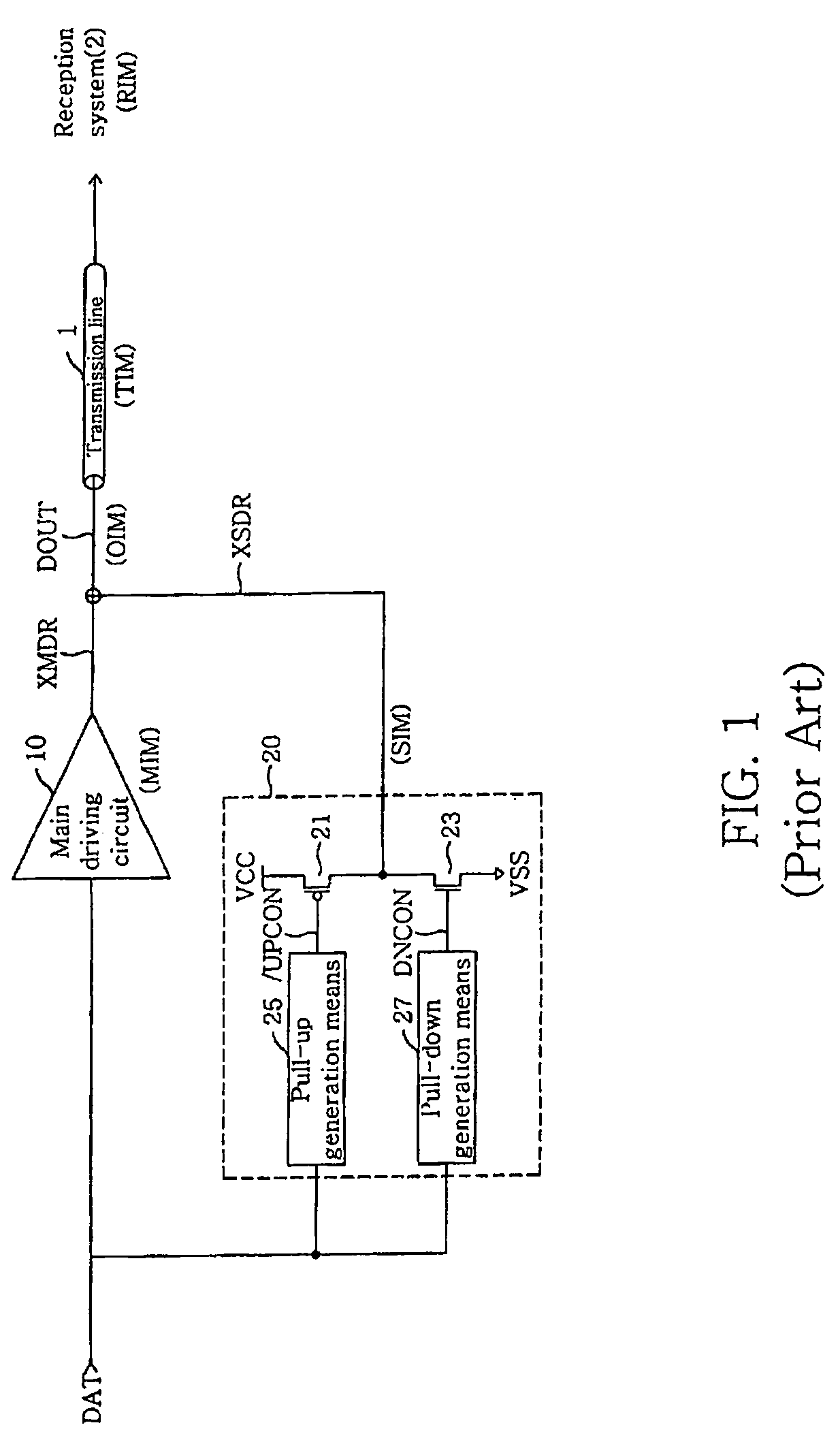
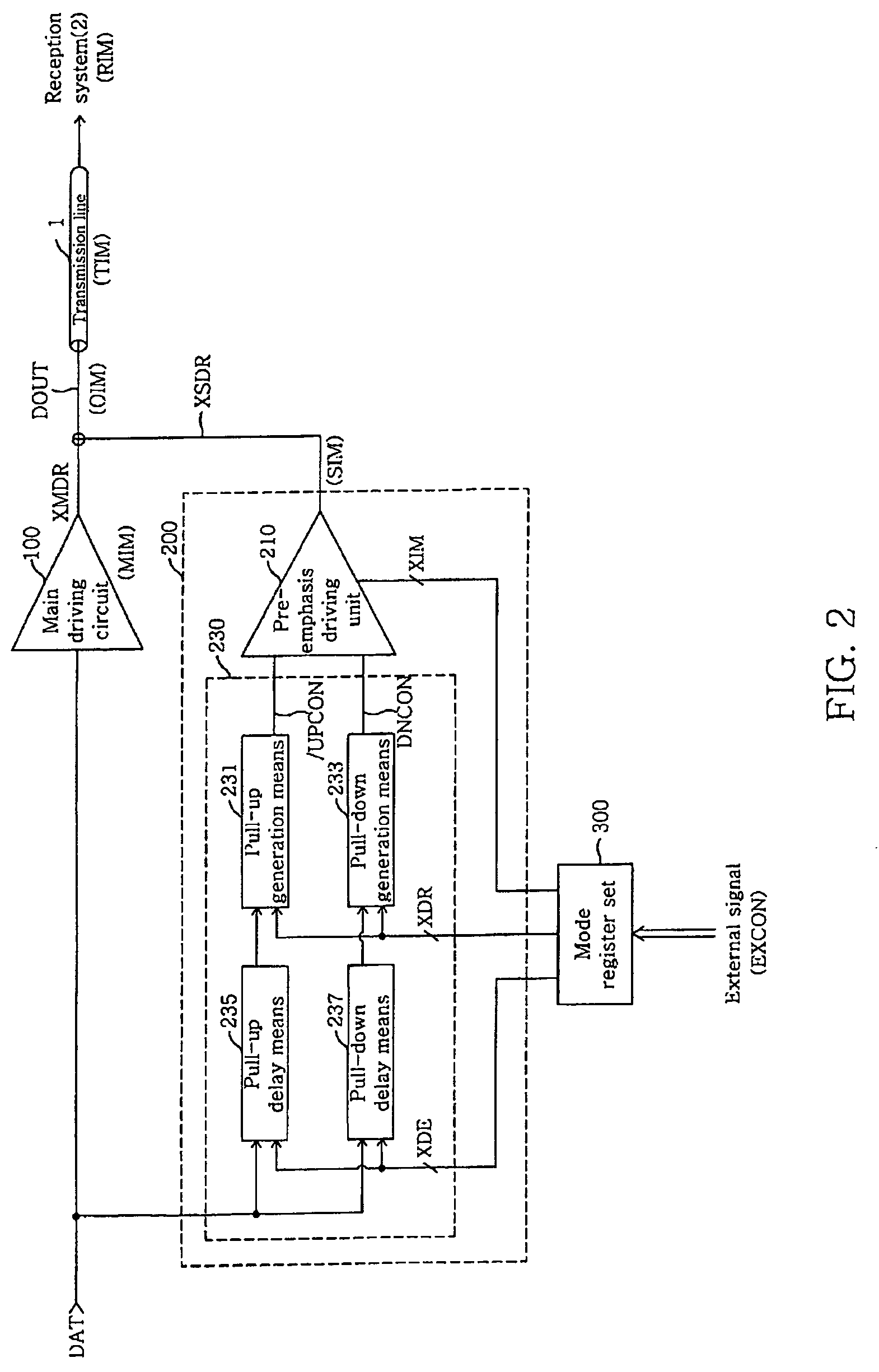
Output driver for controlling impedance and intensity of pre-emphasis driver using mode register set
ActiveUS20070075745A1Efficient receptionEfficiently match output impedanceLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitControl signal
An output driver controls impedance using a mode register set. The output driver includes a main driving circuit that outputs and drives a main signal based on a data signal to a predetermined transmission line, an auxiliary driving circuit that outputs and drives an auxiliary signal to the transmission line, and a mode register set. The mode register set generates an impedance control signal group, a driving width control signal group and a delay control signal group. The amount of an auxiliary impedance (SIM), and the driving width and driving time point of an auxiliary signal (XSDR) can be controlled using the impedance control signal group, the driving width control signal group and the delay control signal group. Therefore, in accordance with the output driver of the present invention, the amount of output impedance (OIM), a pre-emphasis width and a pre-emphasis time point can be readily controlled, and the efficiency of the transmission of an output signal to a reception system is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Double data rate input and output in a programmable logic device
InactiveUS20020003436A1Programmable logic circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlDouble data rateProgrammable logic device
A multi-functional programmable I / O buffer in a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) device. The I / O buffer is programmably configurable to meet any of a wide range of I / O standards, be it single ended or differential, 5V, 3.3V, 2.5V or 1.5V logic, without the need for implementing multiple I / O buffers to properly handle each different iteration of I / O requirements. An embedded, internal programmable resistor (e.g., a programmable 100 ohm resistor) is programmably selected for use in differential I / O applications, thus eliminating the conventional requirement for the use of an external resistor connected to each differential receiver I / O pin. The present invention also separates I / O pads into groups in each of a plurality of banks in a programmable device (e.g., PLD, FPGA, etc.), with each group being separately powered by the user. The disclosed multi-functional I / O buffer may be programmably configured by the user to be, e.g., a single ended receiver or transmitter, a reference receiver or transmitter, or a differential receiver or transmitter. The pad logic of the multi-functional I / O buffer may include a double data rate input and output mode, each of which includes two flip-flop devices operating on opposite sides of a data clock signal. One of the two flip-flop devices may be borrowed from another logic element, e.g., from a shirt register logic element.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
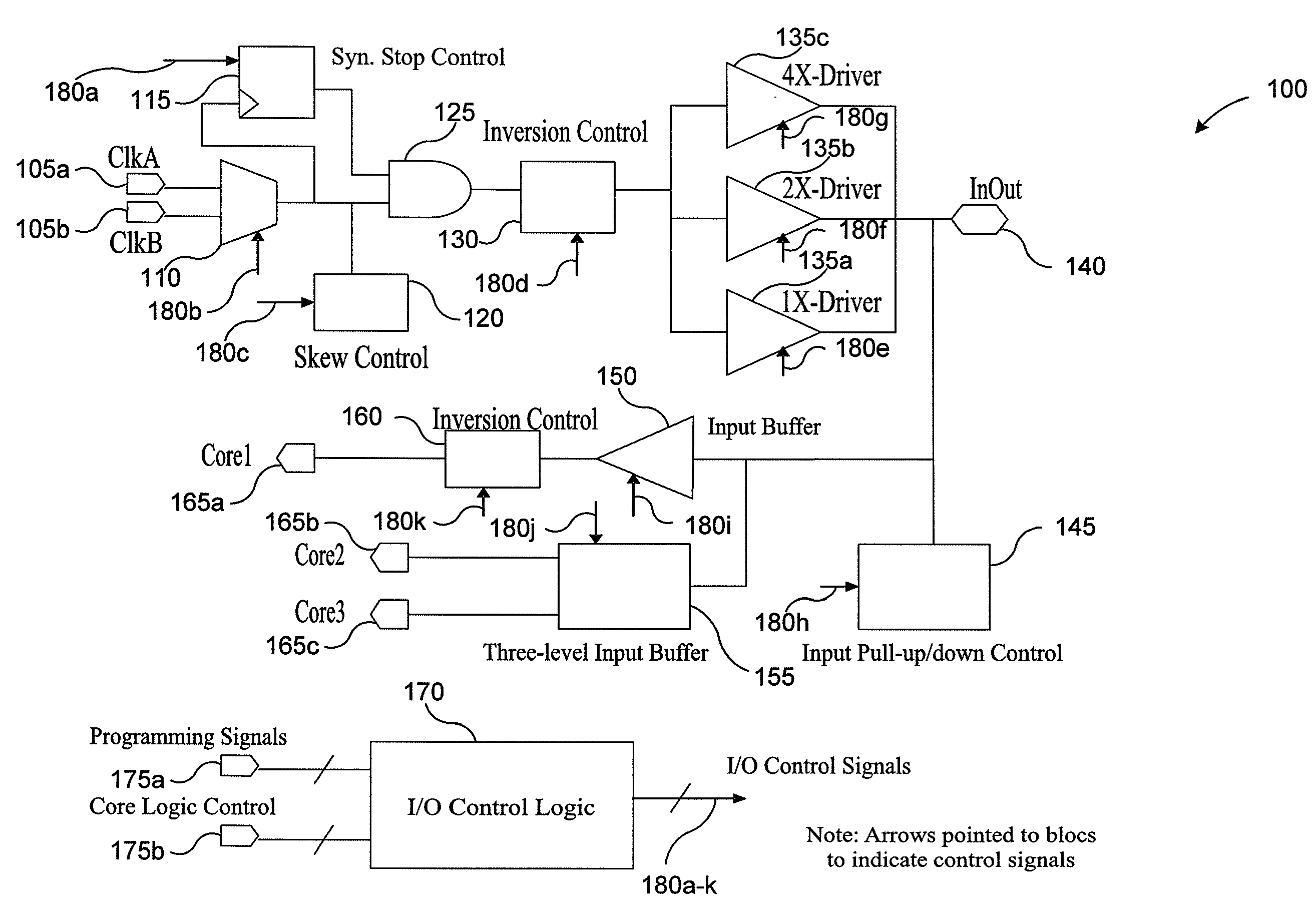
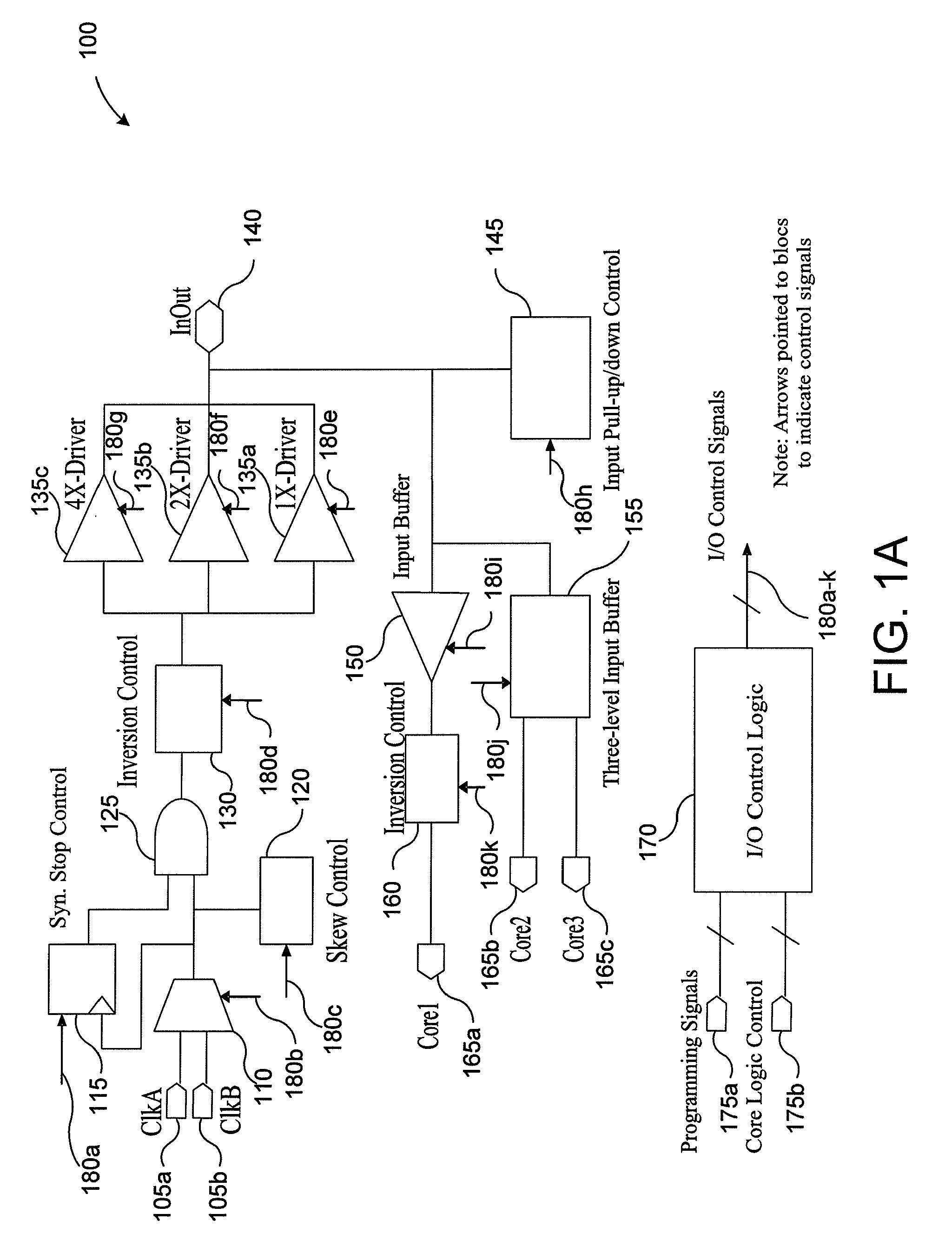
Selectable inversion of differential input and/or output pins in programmable logic devices
ActiveUS7242221B1Effectively reverse polarityProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsDifferential signalingProgrammable logic device
Programmable logic device circuitry for receiving and / or transmitting a differential signal includes controllable invert circuitry that effectively reverses the polarity of the differential signal. The controllable invert circuitry operates on a single-ended (non-differential) signal that has either been derived from a differential input signal or from which a differential output signal will be derived.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Programmable logic device and semiconductor device
InactiveUS8952723B2Reduce circuit areaNovel structureProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesDevice materialProgrammable logic device
To provide a PLD having a reduced circuit area and an increased operation speed. In the circuit structure, a gate of a transistor provided between an input terminal and an output terminal of a programmable switch element is in an electrically floating state in a period when a signal is input to the programmable switch element. The structure enables the voltage of a gate to be increased by a boosting effect in response to a signal supplied from programmable logic elements, suppressing a reduction in amplitude voltage. This can reduce a circuit area by a region occupied by a booster circuit such as a pull-up circuit and increase operation speed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
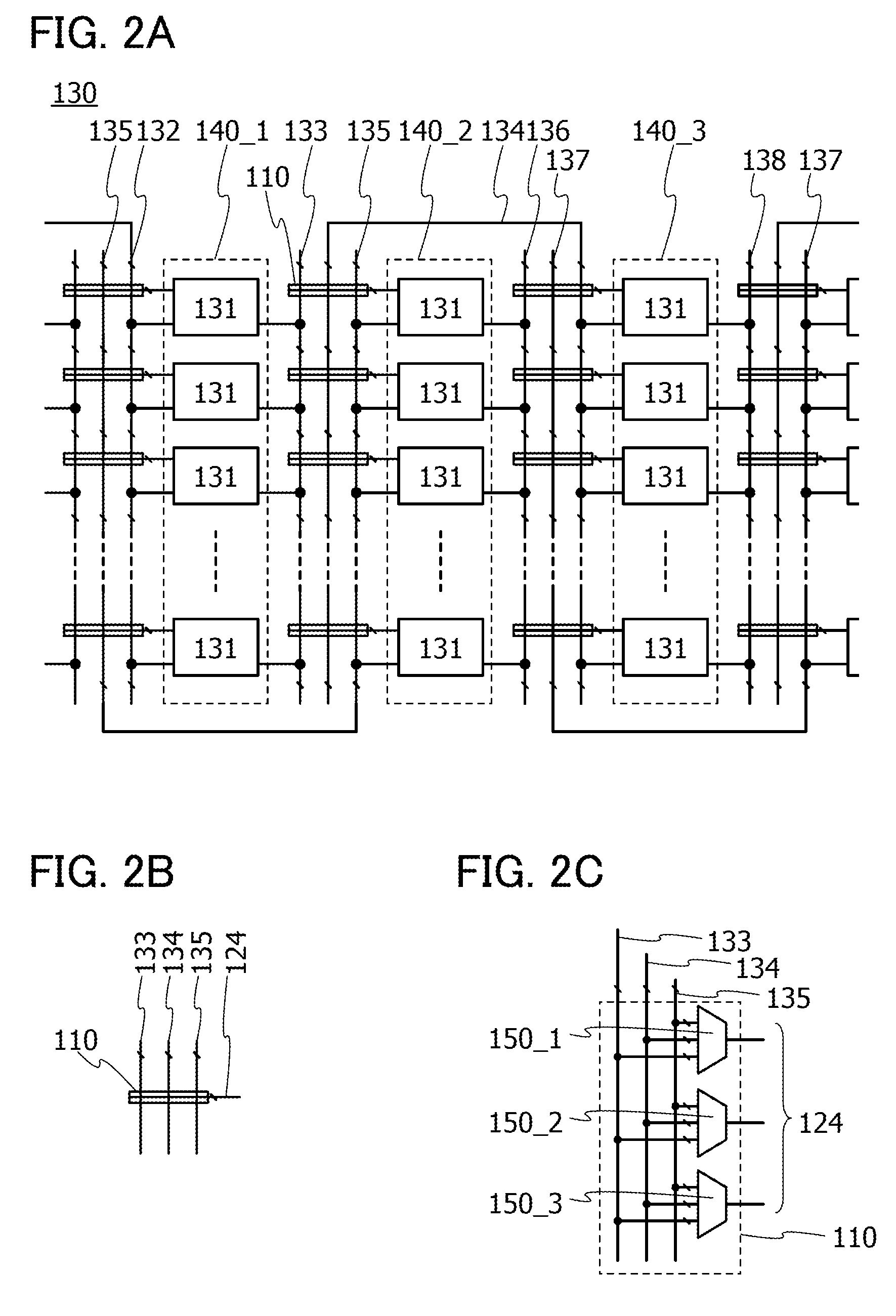
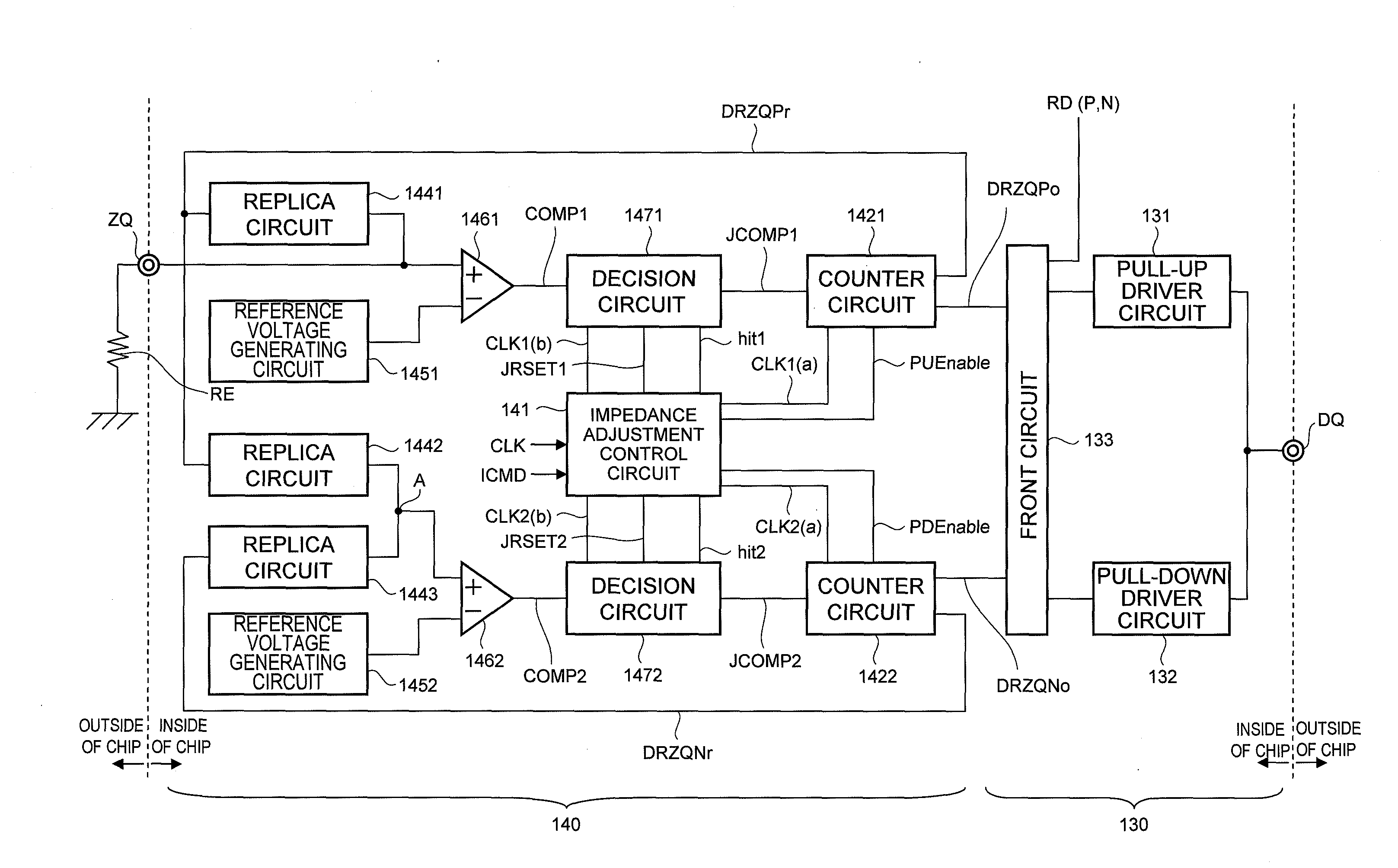
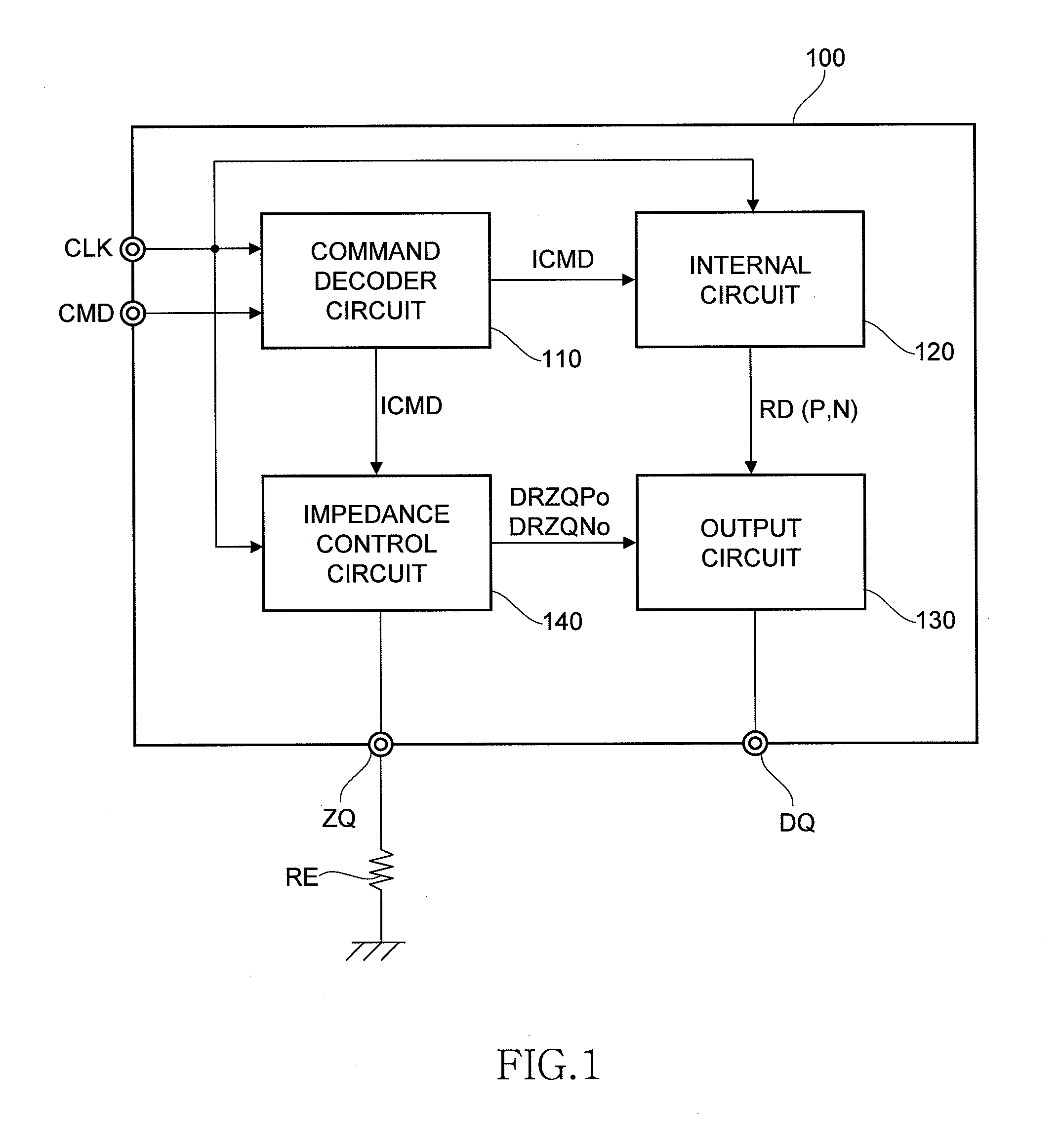
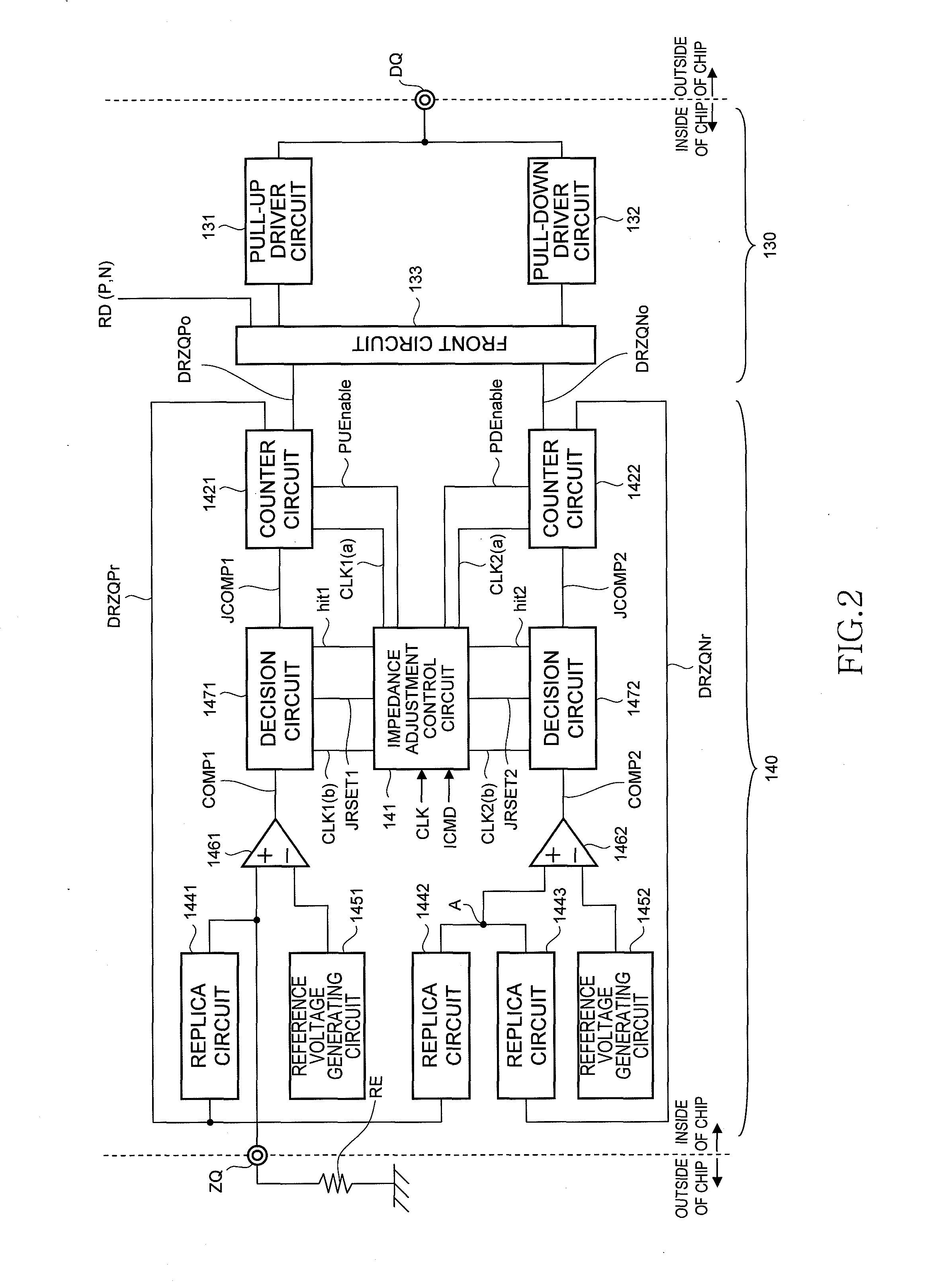
Impedance control circuit and semiconductor device including the same
ActiveUS20100207680A1Reduce impedance adjust errorAccurate impedance control operationInput/output impedence modificationProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsControl circuitSemiconductor
To include two counter circuits that change impedances of two replica circuits, respectively, and an impedance adjustment control circuit that controls the counter circuits to update count values of the counter circuits. The impedance adjustment control circuit controls one of the counter circuits to finish updating the count value of the counter circuit in response to a change of the impedance of the corresponding replica circuit from a state of being lower than an impedance of an external resistor to a state of being higher than the impedance of the external resistor, and controls the other counter circuit to finish updating the count value of the other counter circuit in response to a change of the impedance of the other replica circuit from a state of being higher than the impedance of the former replica circuit to a state of being lower than the impedance of the former replica circuit. With this configuration, the adjust errors generated in the replica circuits are canceled.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Programmable high speed I/O interface
InactiveUS20050134332A1High-speed inputHigh-speed outputProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsElectronic switchingBoundary testingLow speed
Methods and apparatus for providing either high-speed, or lower-speed, flexible inputs and outputs. An input and output structure having a high-speed input, a high-speed output, a low or moderate speed input, and an low or moderate speed output is provided. One of the input and output circuits are selected and the others are deselected. The high-speed input and output circuits are comparatively simple, in one example having only a clear signal for a control line input, and are able to interface to lower speed circuitry inside the core of an integrated circuit. The low or moderate speed input and output circuits are more flexible, for example, having preset, enable, and clear as control line inputs, and are able to support JTAG boundary testing. These parallel high and lower speed circuits are user selectable such that the input output structure is optimized between speed and functionality depending on the requirements of the application.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Buffer circuit having multiplexed voltage level translation
ActiveUS7498860B2Reduce chip areaSmall sizeProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsLogic circuits coupling/interface with bidirectional operationControl signalEngineering
A buffer circuit is selectively operative in one of at least a first mode and a second mode as a function of a first control signal supplied to the buffer circuit. The buffer circuit includes interface circuitry operative to receive at least second and third control signals referenced to a first voltage level, and to generate an output signal referenced to a second voltage level, the second voltage level being greater than the first voltage level. The output signal is a function of the second control signal in the first mode and is a function of the third control signal in the second mode. The buffer circuit further includes at least first and second circuit portions coupled to the interface circuitry, each of the first and second circuit portions including at least one control input operative to receive the output signal generated by the interface circuitry.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
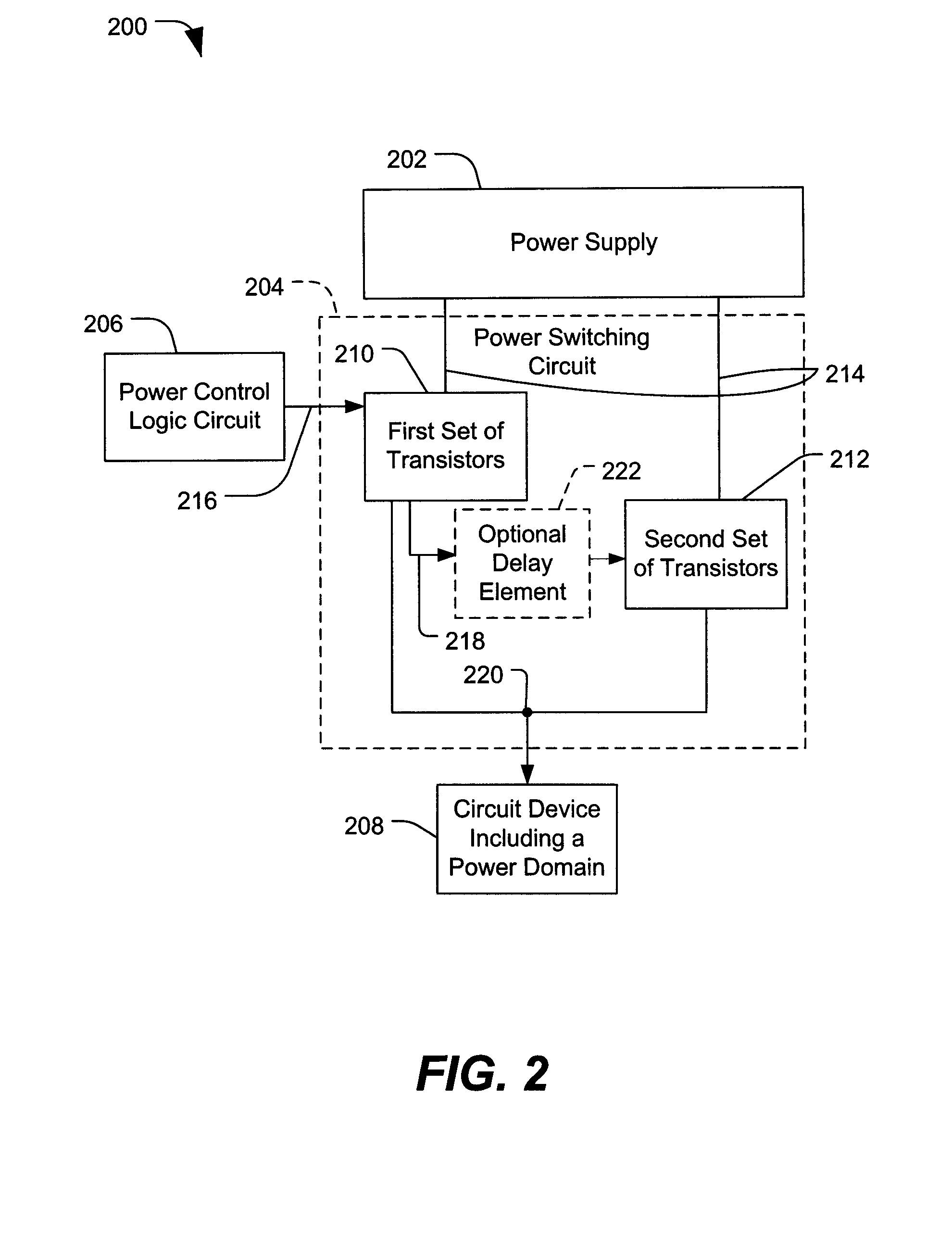
System and Method of Providing Power Using Switching Circuits
ActiveUS20090160253A1Total current dropLow powerProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsConstant-current supply dc circuitElectricityPower switching
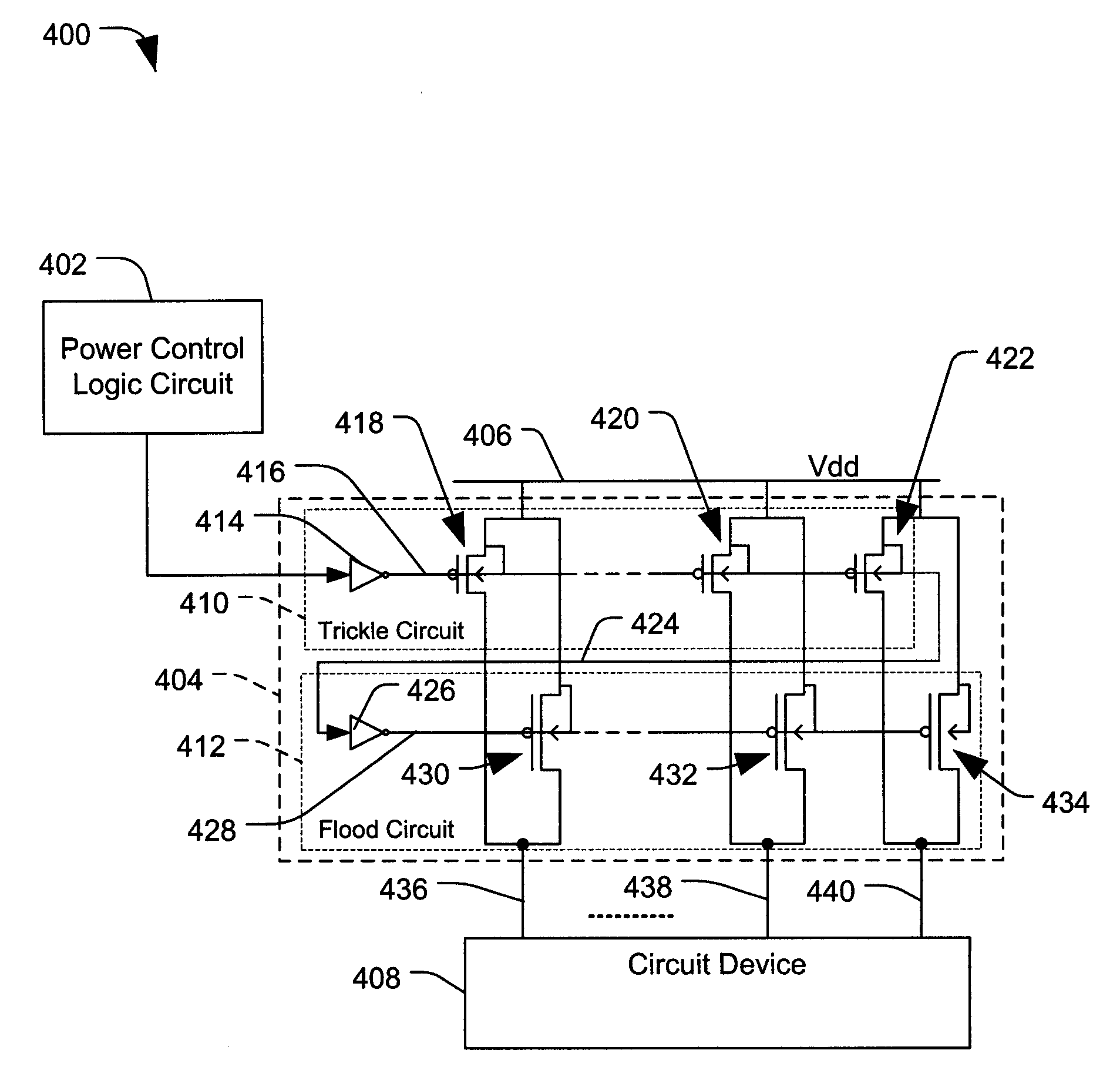
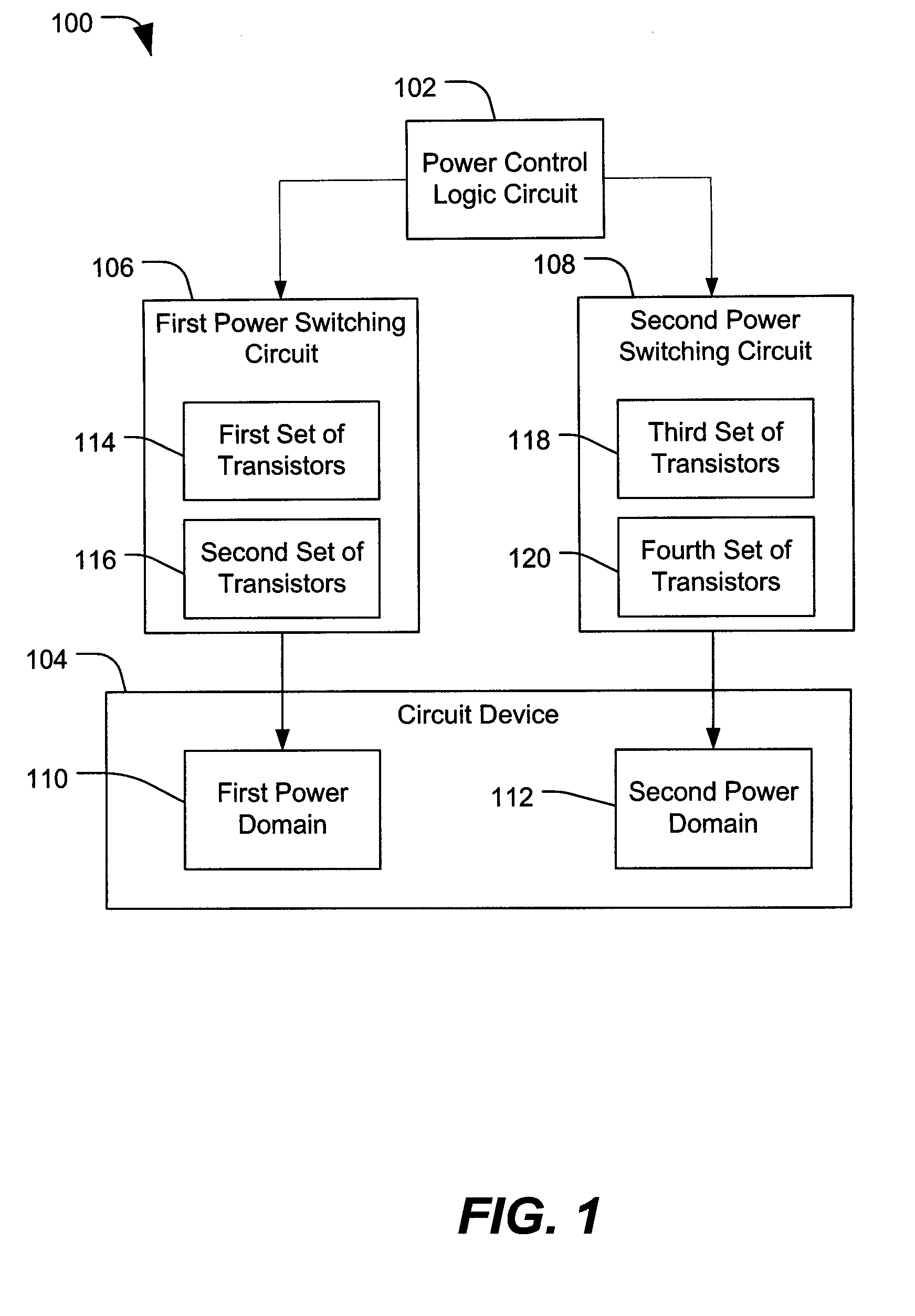
In a particular illustrative embodiment, a system is disclosed that includes a first power domain that is responsive to a first power switching circuit and a second power domain that is responsive to a second power switching circuit. The system also includes a logic circuit adapted to selectively activate the first power switching circuit and the second power switching circuit. At least one of the first power switching circuit and the second power switching circuit includes a first set of transistors adapted for activation during a first power up stage and a second set of transistors adapted for activation during a second power up stage after at least one of the first set of transistors are activated.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Programmable io architecture
ActiveUS20090206875A1Minimize biasWide rangeProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsElectric pulse generatorComputer architectureIntegrated circuit
A buffer device coupled to at least one input / output port of an integrated circuit has a plurality of control inputs configured to receive configuration programming information. The at least one input / output circuit is capable of: (a) being configured in a directional sense of communication by the configuration programming information, (b) being configured as an input circuit which can be further configured to provide input logic switching level thresholds according to the configuration programming information, and (c) being configured as at least one output circuit which can be further configured to provide an output drive strength according to the configuration programming information.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Output driver for controlling impedance and intensity of pre-emphasis driver using mode register set
ActiveUS7545164B2Efficiently match output impedanceReduce widthLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitControl signal
An output driver controls impedance using a mode register set. The output driver includes a main driving circuit that outputs and drives a main signal based on a data signal to a predetermined transmission line, an auxiliary driving circuit that outputs and drives an auxiliary signal to the transmission line, and a mode register set. The mode register set generates an impedance control signal group, a driving width control signal group and a delay control signal group. The amount of an auxiliary impedance (SIM), and the driving width and driving time point of an auxiliary signal (XSDR) can be controlled using the impedance control signal group, the driving width control signal group and the delay control signal group. Therefore, in accordance with the output driver of the present invention, the amount of output impedance (OIM), a pre-emphasis width and a pre-emphasis time point can be readily controlled, and the efficiency of the transmission of an output signal to a reception system is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Popular searches
Special data processing applications Semiconductor devices Counters with additional facilities Generating/distributing signals Computation using denominational number representation Data conversion Read-only memories Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Single output arrangements Input/output processes for data processing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com