Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
873 results about "Impedance control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
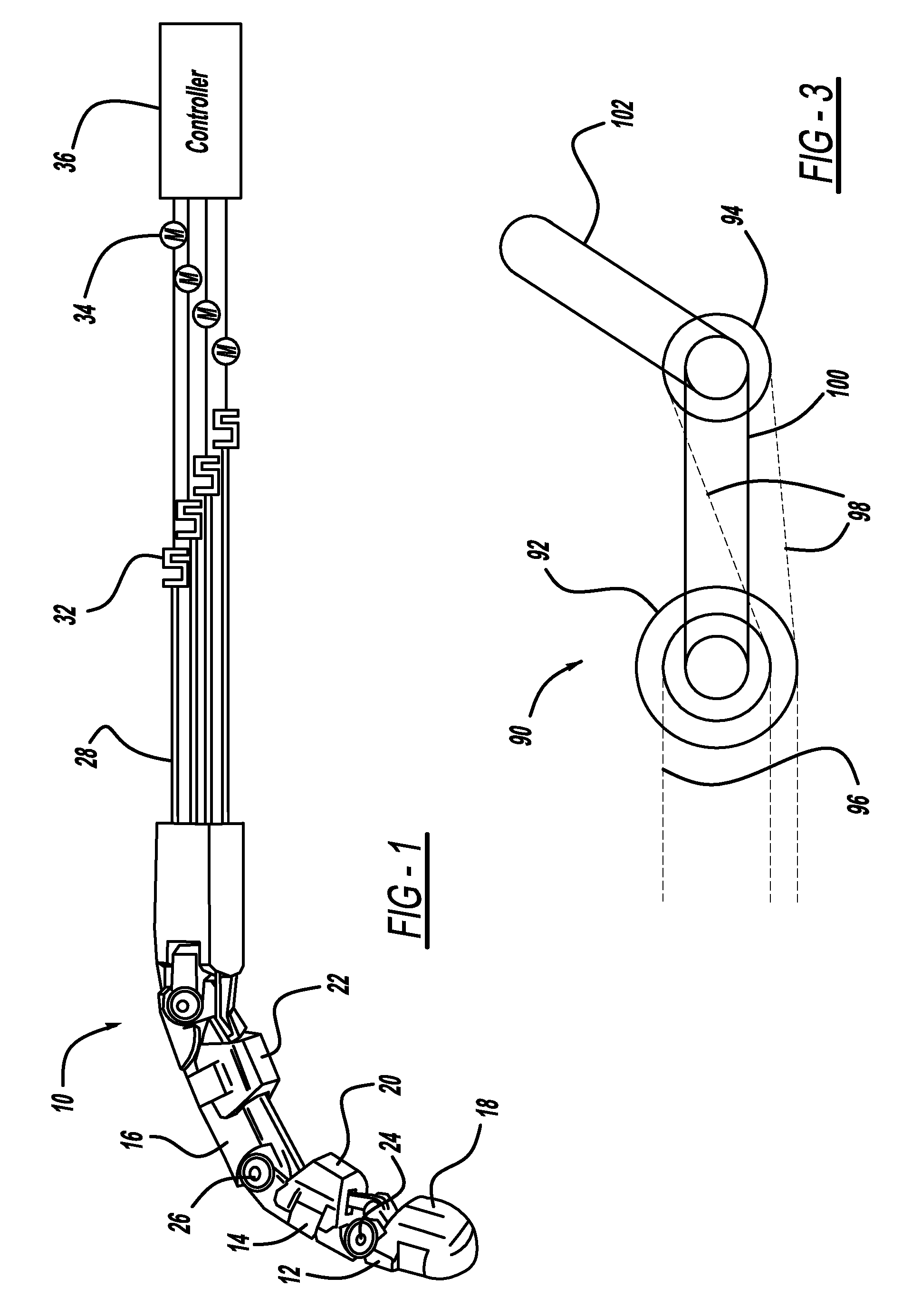
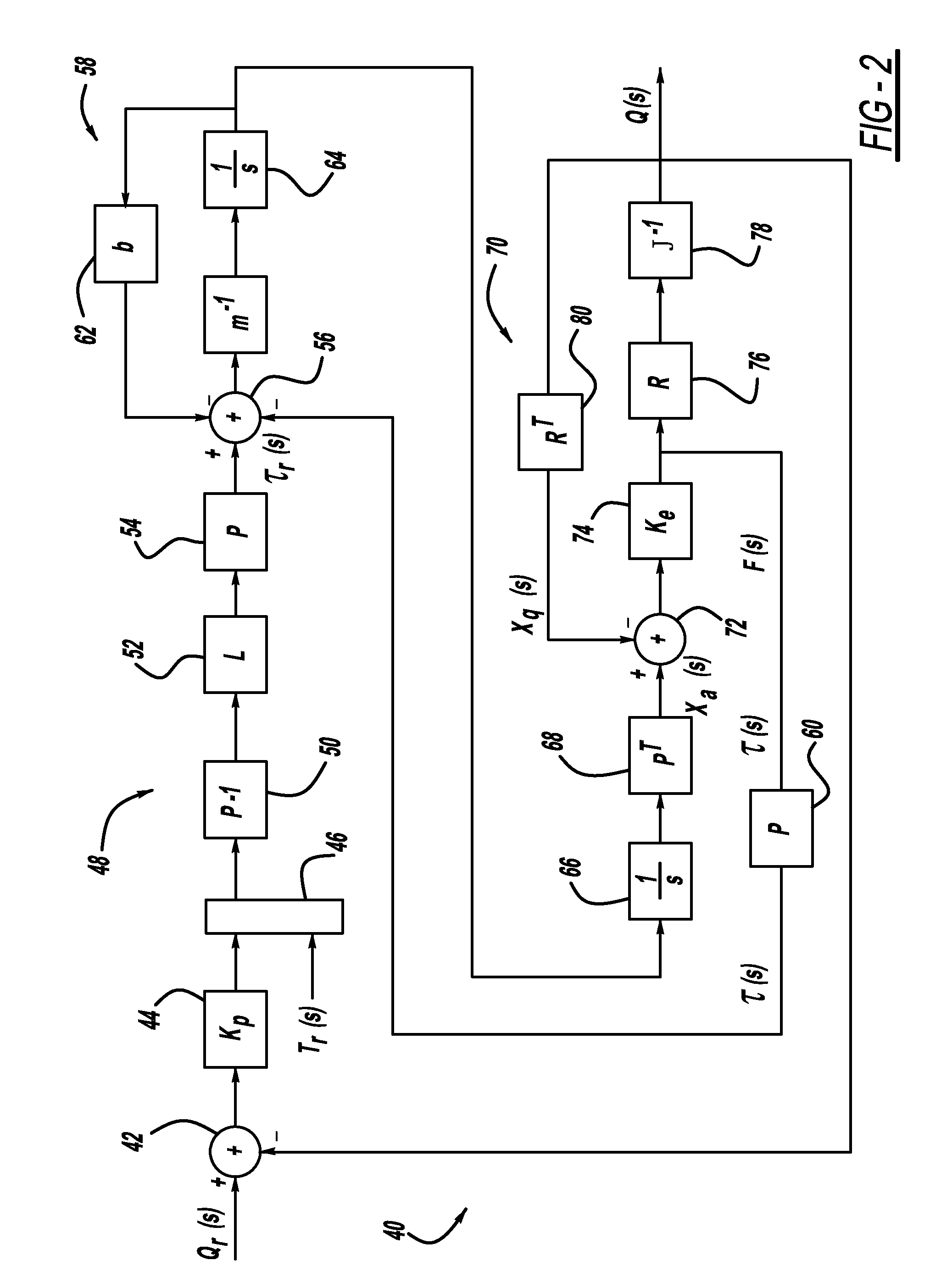
Impedance control is an approach to dynamic control relating force and position. It is often used in applications where a manipulator interacts with its environment and the force position relation is of concern. Examples of such applications include humans interacting with robots, where the force produced by the human relates to how fast the robot should move/stop.
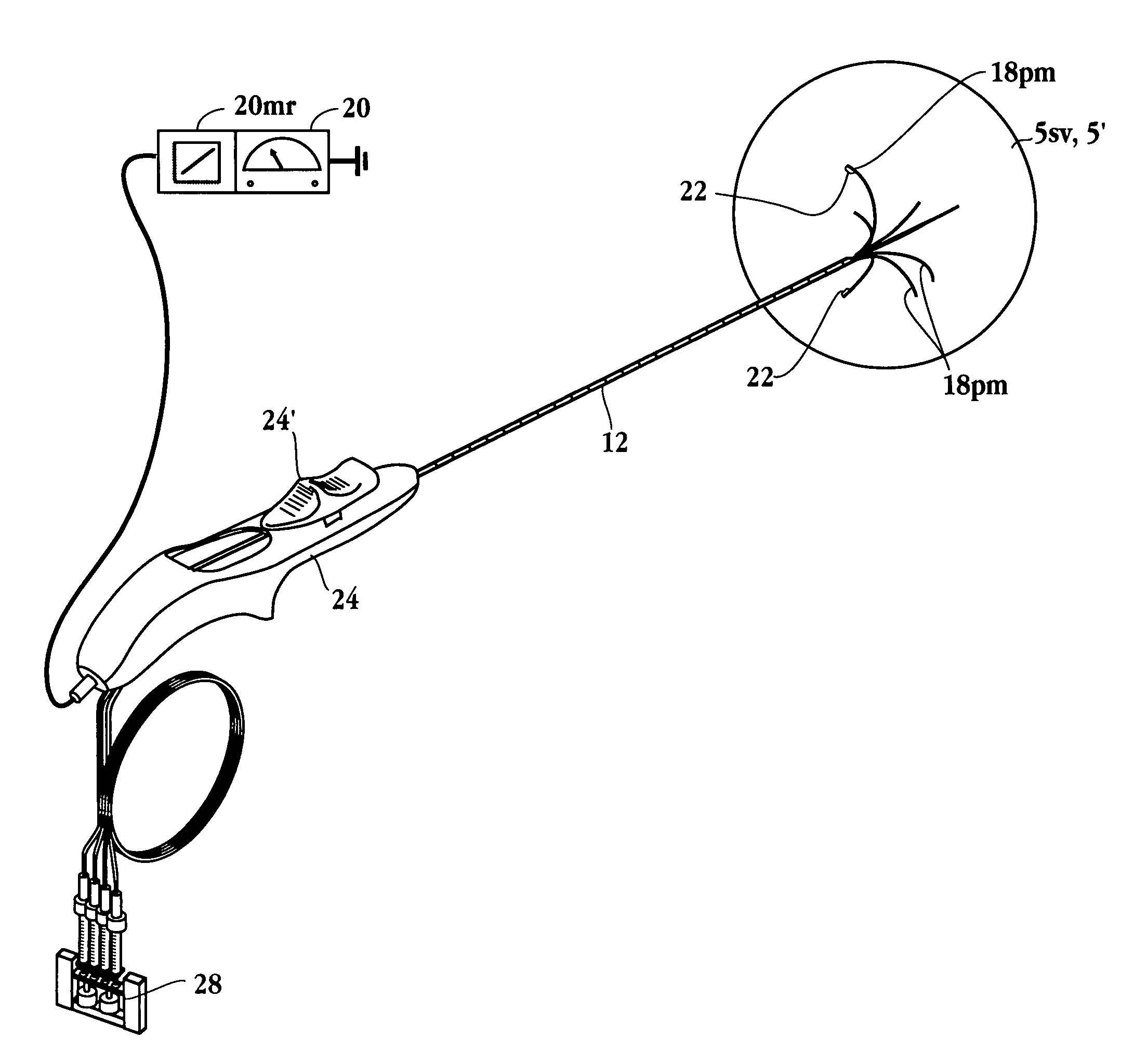
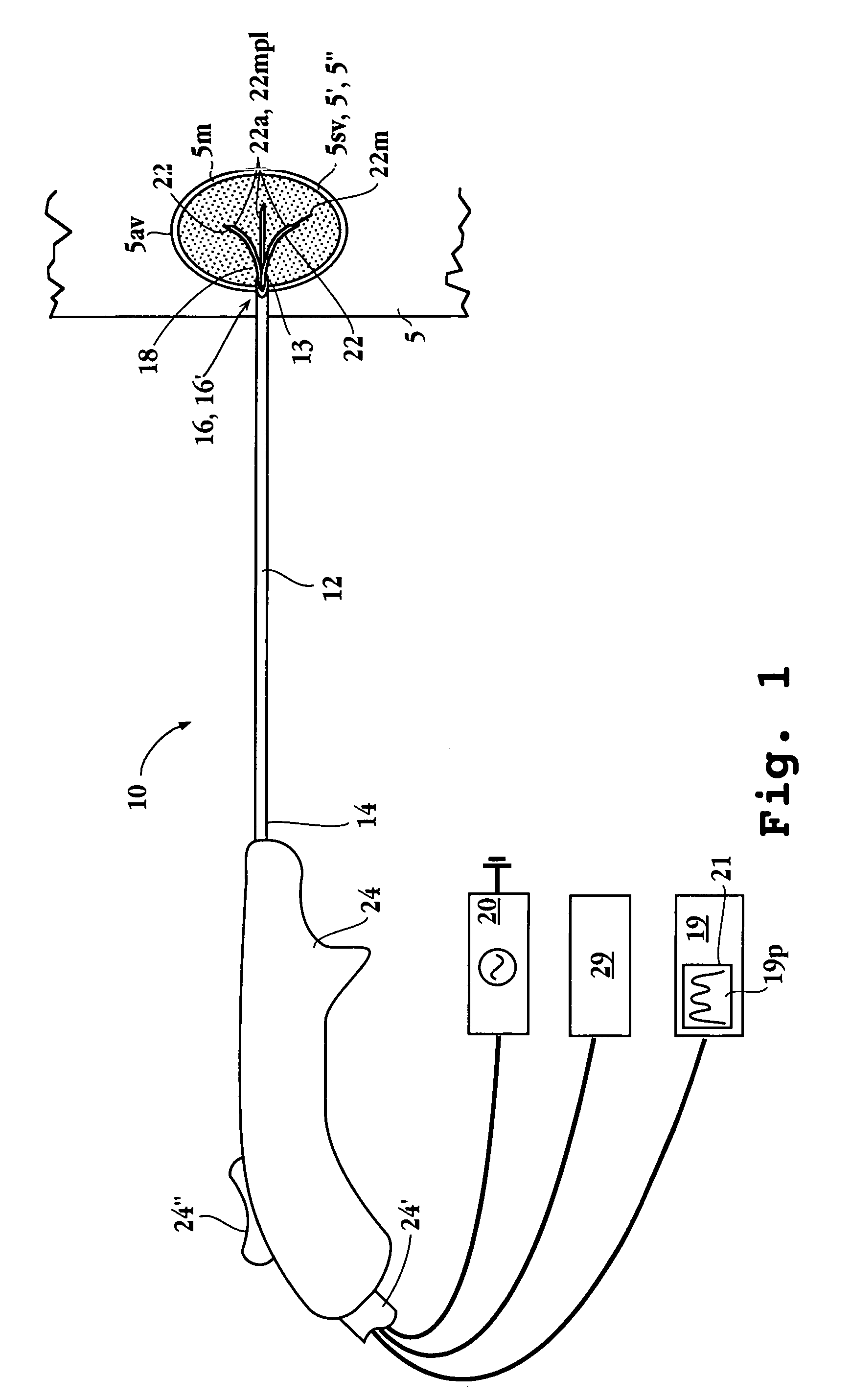
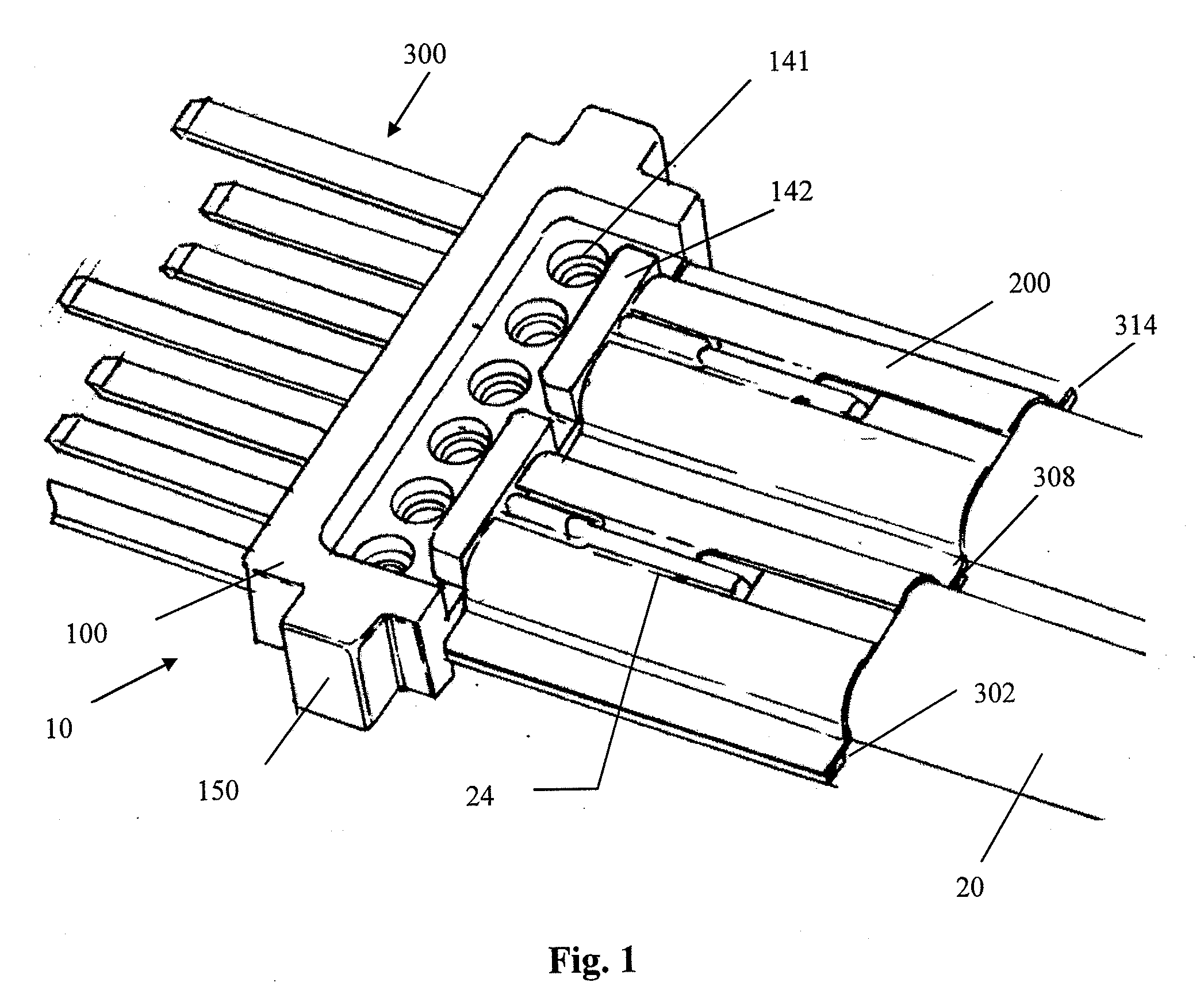
Impedance controlled tissue ablation apparatus and method
InactiveUS7344533B2Improve the level ofIncrease in sizeSurgical needlesDiagnostic recording/measuringRf ablationControl cell
A method and apparatus for carrying our thermal ablation of target tissue is disclosed. The apparatus includes an RF ablation device having a multi-electrode electrode assembly designed to be deployed in target tissue, defining a selected-volume tissue region to be ablated, and having infusion channels for infusing a liquid into the target tissue during the ablation process. A control unit in the apparatus is operably connected to an RF energy source, for controlling the RF power level supplied to the electrodes, and to an infusion device, for controlling the rate of infusion of a liquid through the device into the tissue. During both electrode deployment and tissue ablation, impedance and or temperature measurements made within the tissue are used to control the RF source and infusion device, for optimizing the time and extent of tissue ablation.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
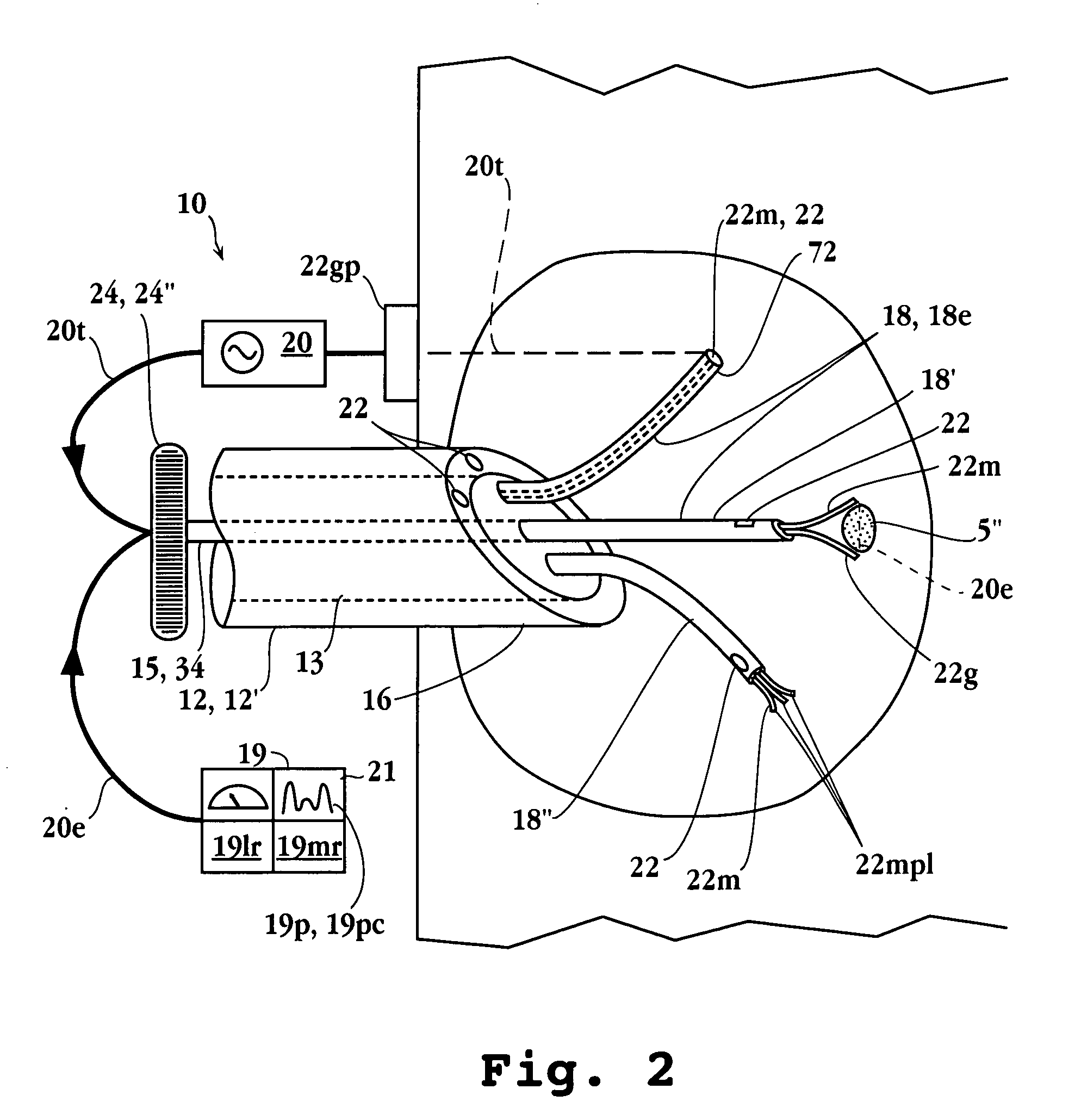
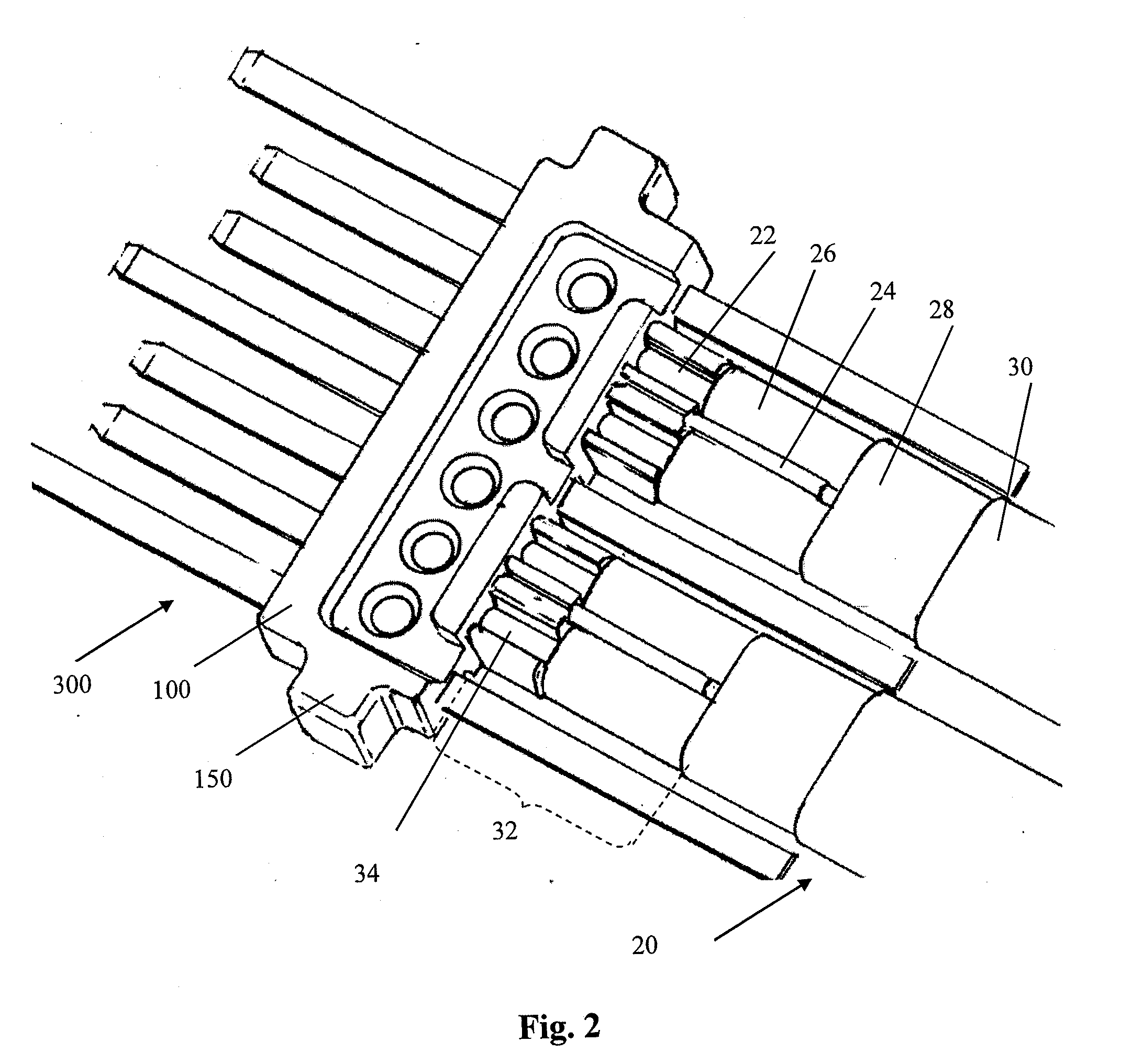
Surgical instrument
InactiveUS20050021078A1Difficult to sterilizeUse reliably and inexpensivelyDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsLess invasive surgeryActuator
The invention relates to an instrument for surgery, in particular minimally invasive surgery. The instrument includes means for feeding back a force which is exerted on the working element of the instrument to the operating element. These means include at least a first force sensor for measuring the force which is exerted on the working element, a control unit and a first actuator. On the basis of a signal which originates from the first force sensor, the control unit controls at least the first actuator in order to control the operating element. Furthermore, the means preferably include a first position sensor for measuring a position of the working element with respect to the frame. The control unit advantageously determines an impedance which the working element is subject to as a result of the presence of a tissue or the like, on the basis of which impedance the control unit controls at least the first actuator.
Owner:VLEUGELS HLDG
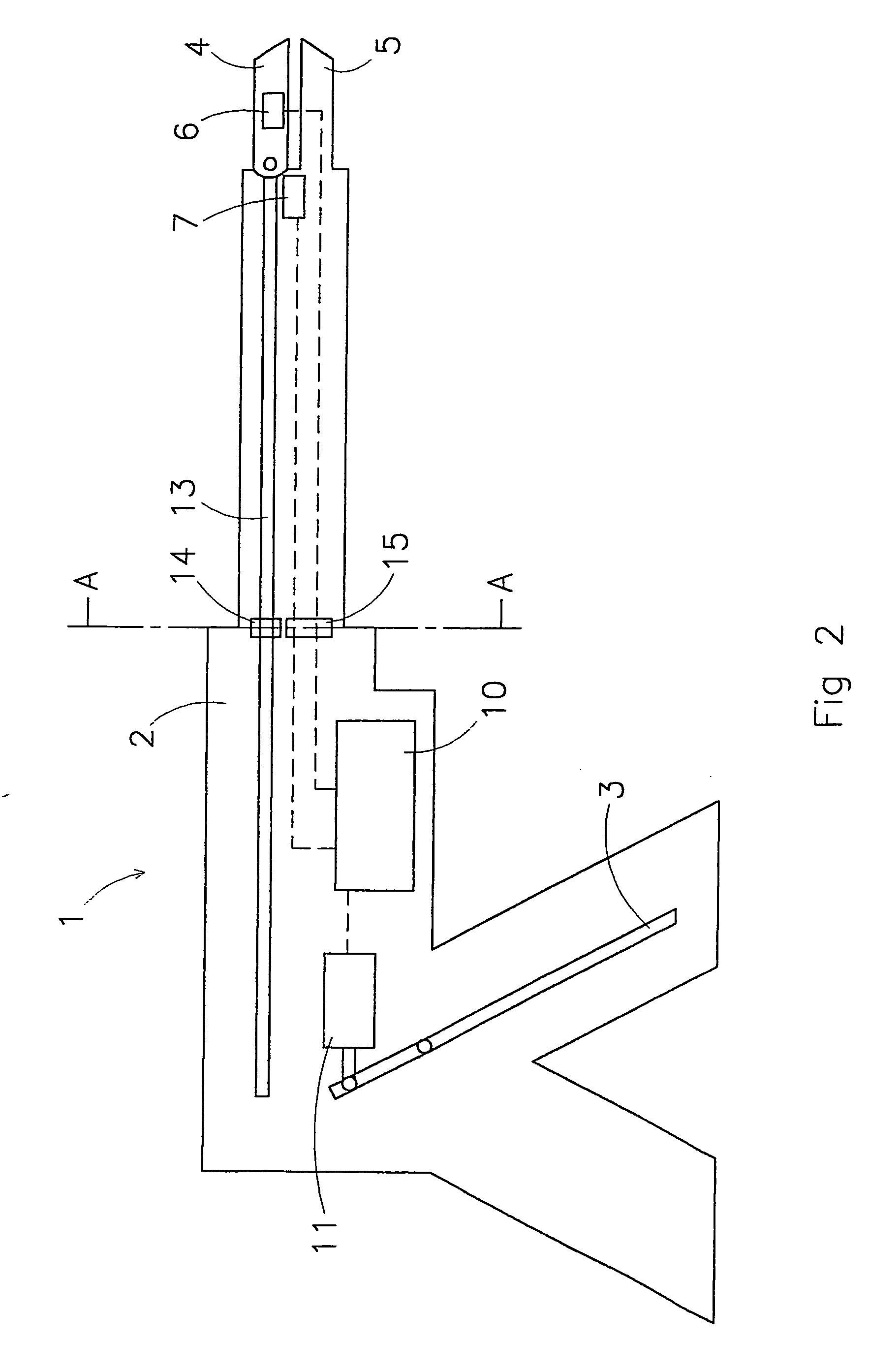
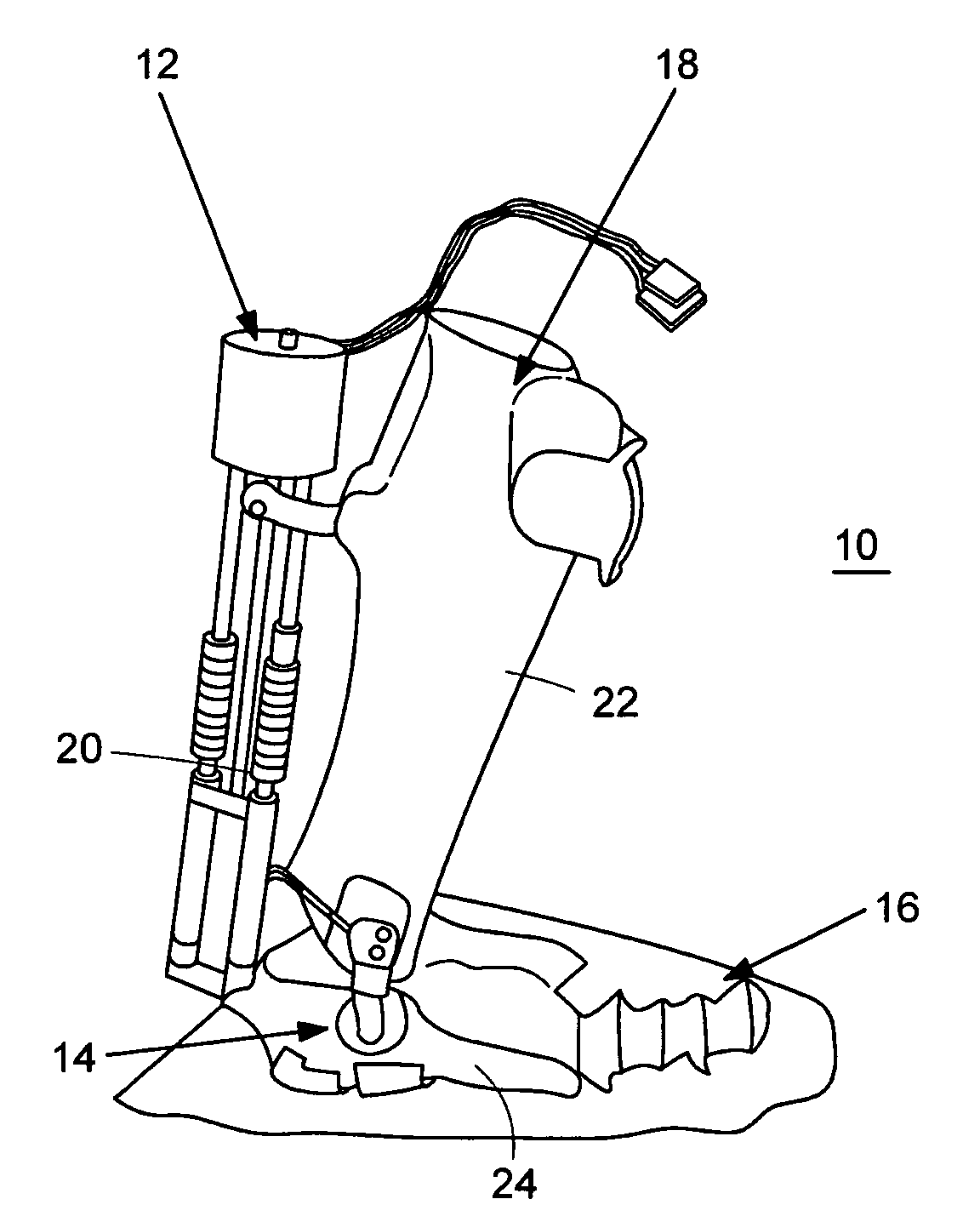
Active Ankle Foot Orthosis
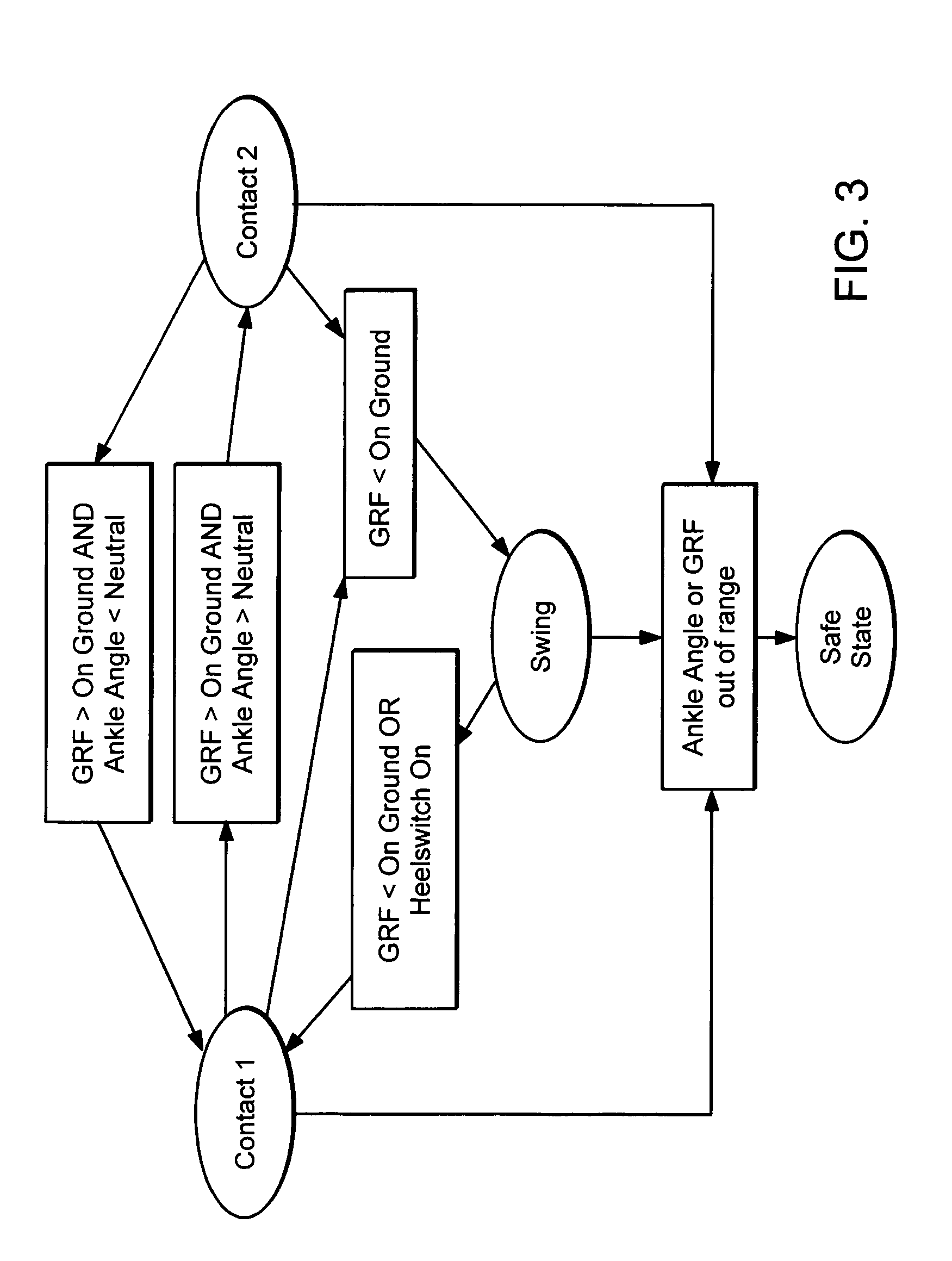
ActiveUS20050070834A1Less kinematic differenceIncrease independenceWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePathology diagnosis
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
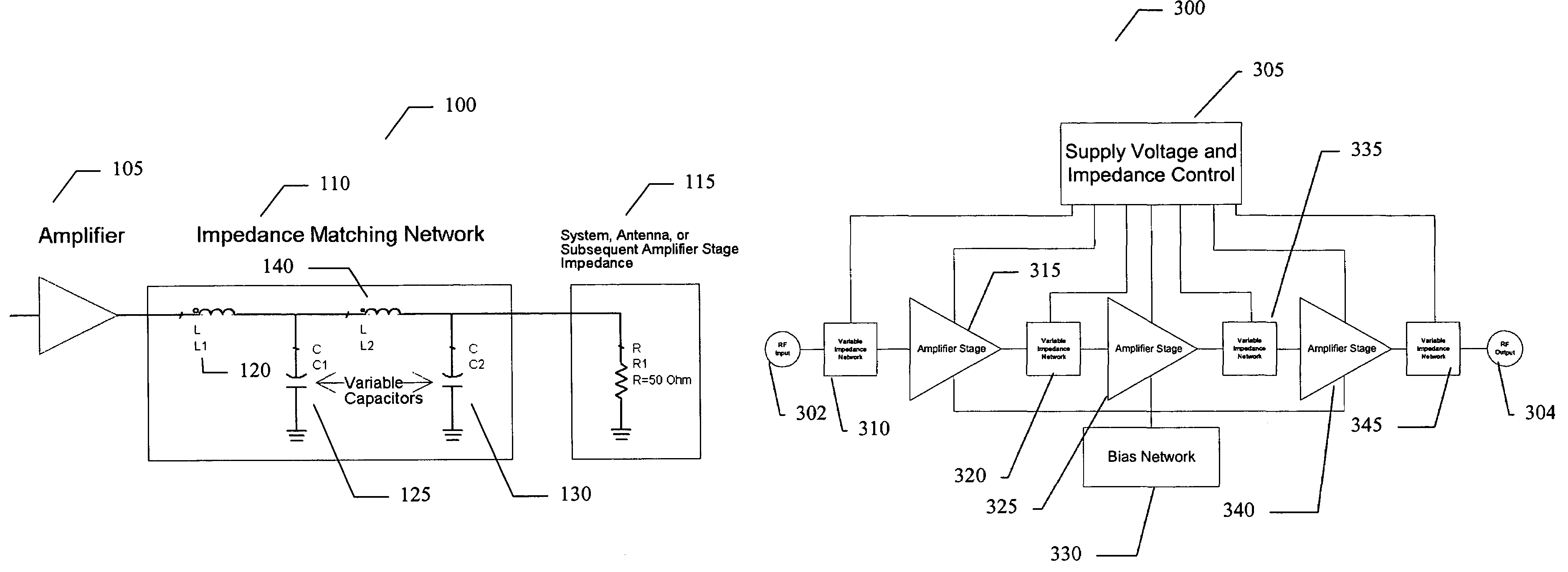
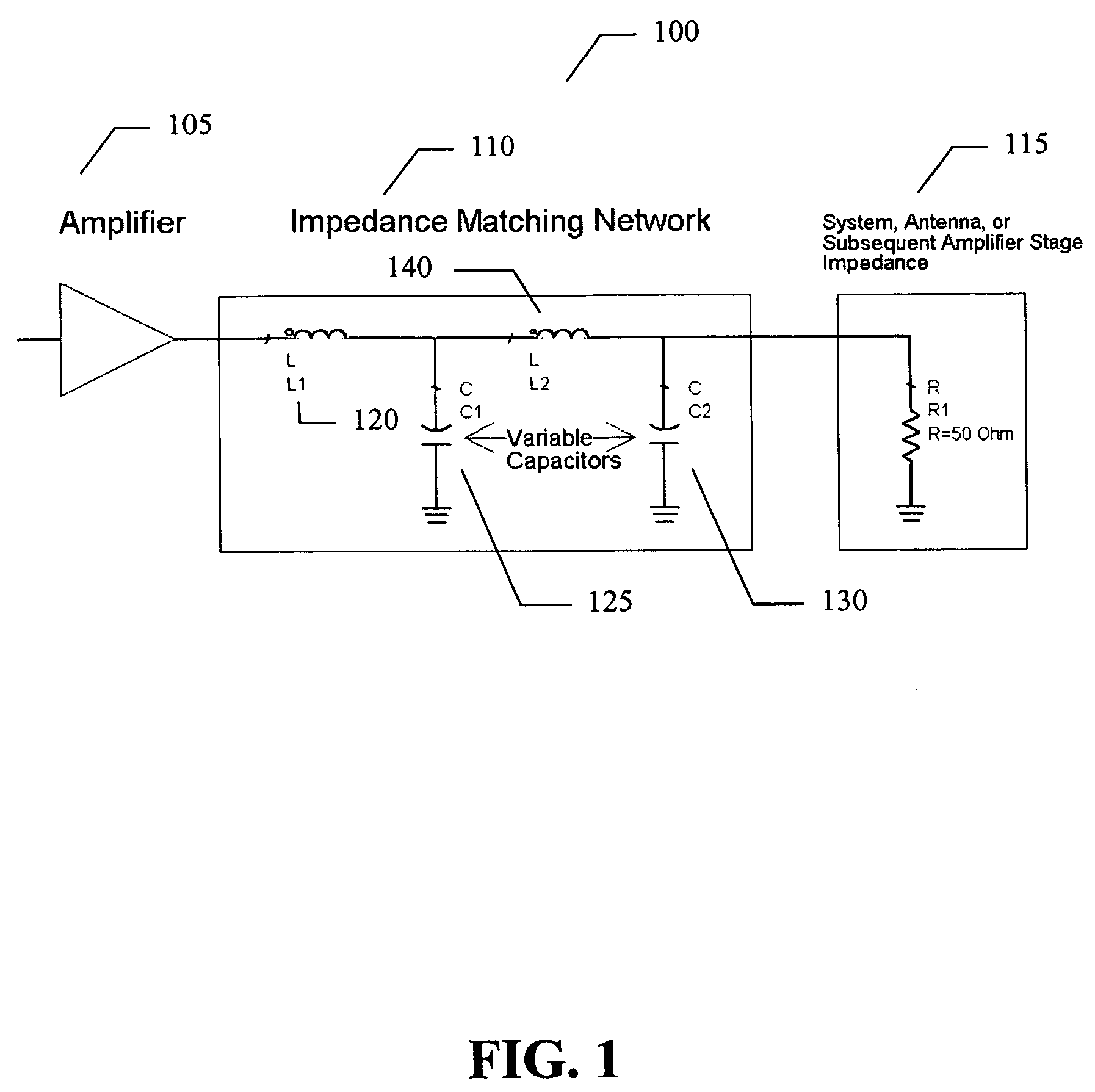
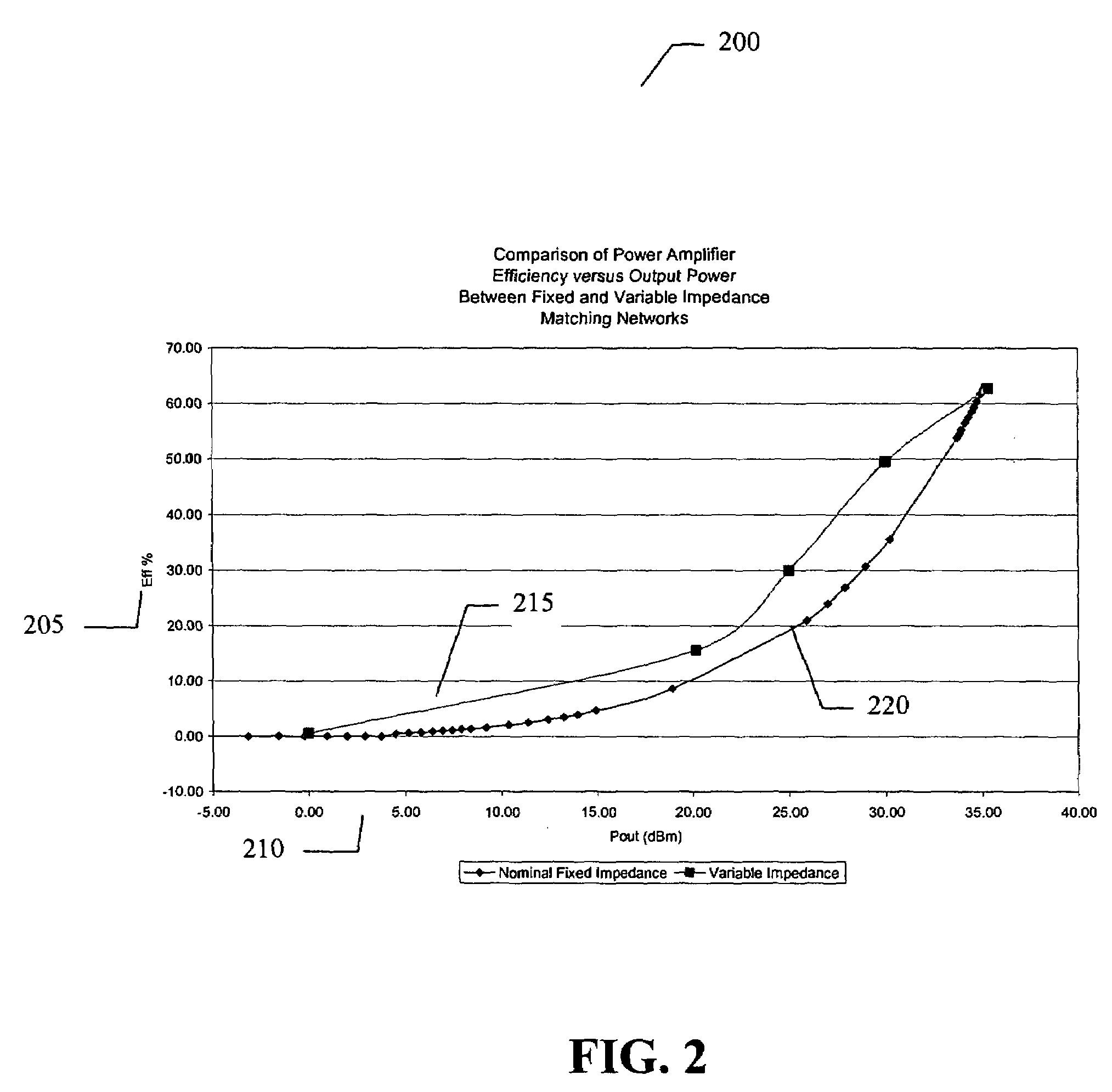
Amplifier system and method
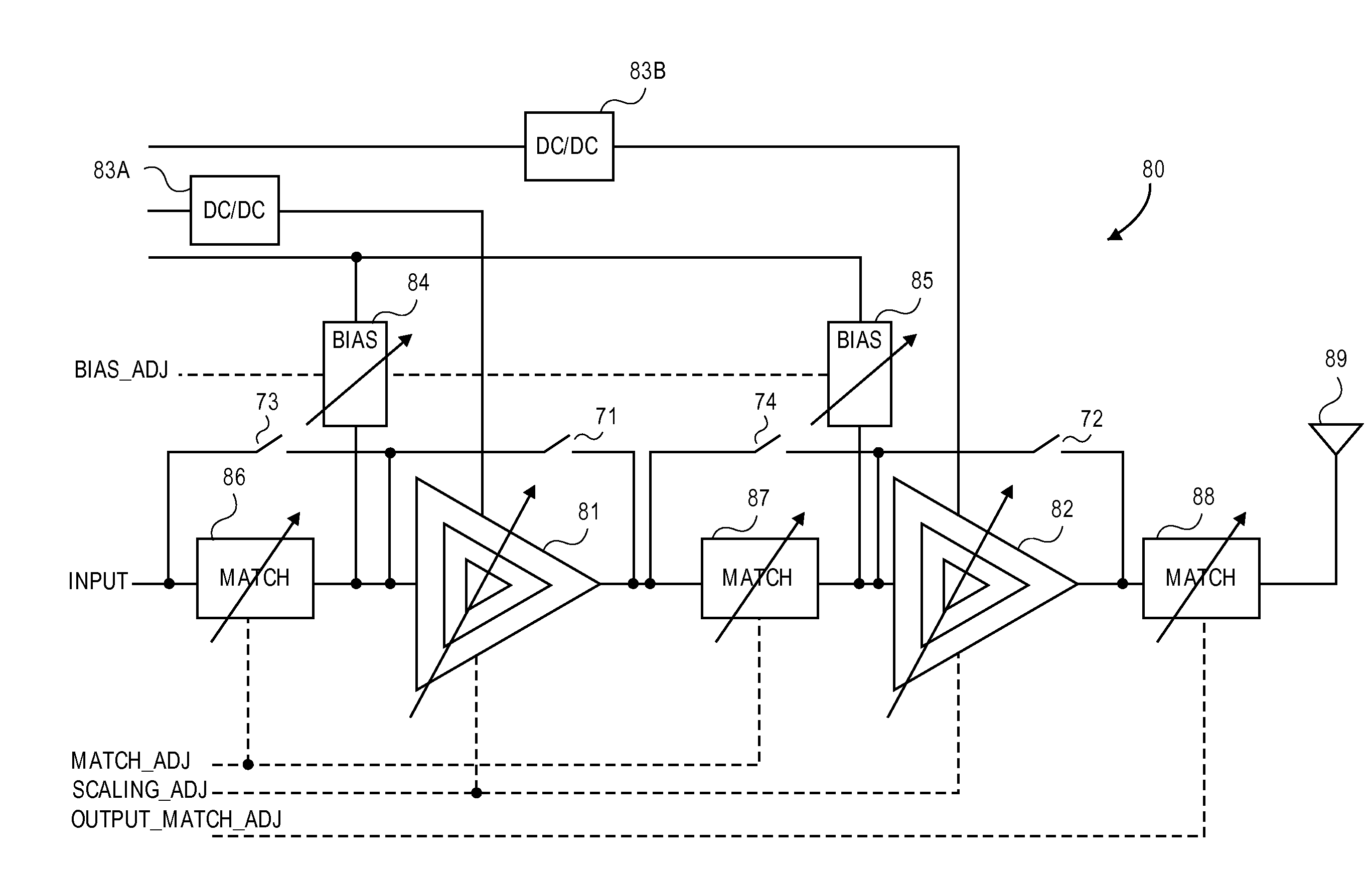
ActiveUS7151411B2High frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierImpedance matching
An embodiment of the present invention provides an amplifier system, comprising at least one variable impedance matching network, the output of which provides the input to at least one amplifier stage or provides an output of the power amplifier itself, and a bias network associated with the at least one amplifier stage. The amplifier system may further comprise a controller enabling impedance control to the at least one variable impedance matching network and a supply voltage provided to the at least one variable impedance network and / or the at least one amplifier stage and wherein the at least one variable impedance network and the at least one amplifier stage may be a plurality of impedance networks connected to a plurality of amplifier stages. The at least one variable impedance network may include at least one variable capacitor and the at least one variable capacitor may be a voltage tunable dielectric capacitor which may include Parascan® voltage tunable dielectric material.
Owner:NXP USA INC
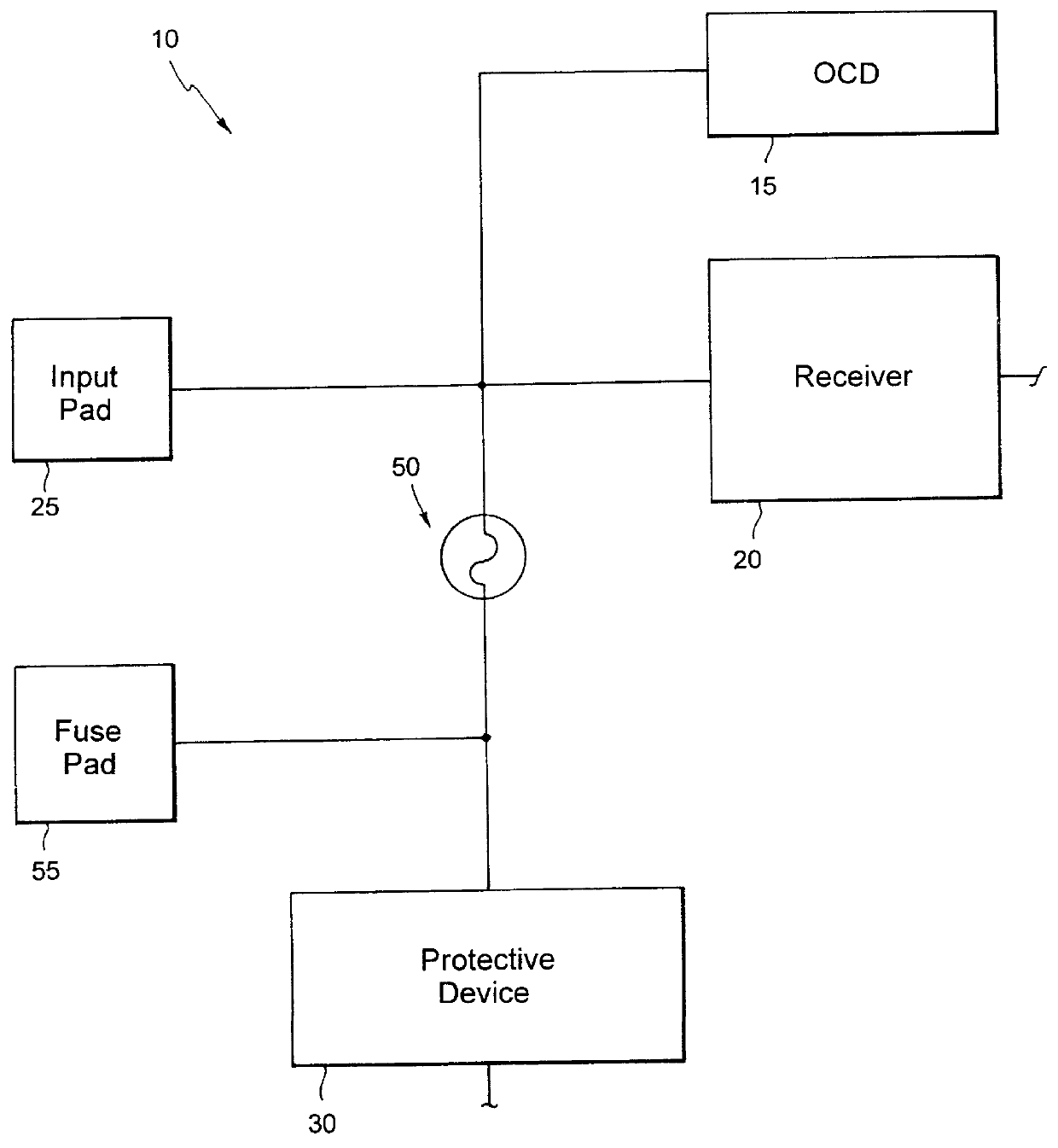
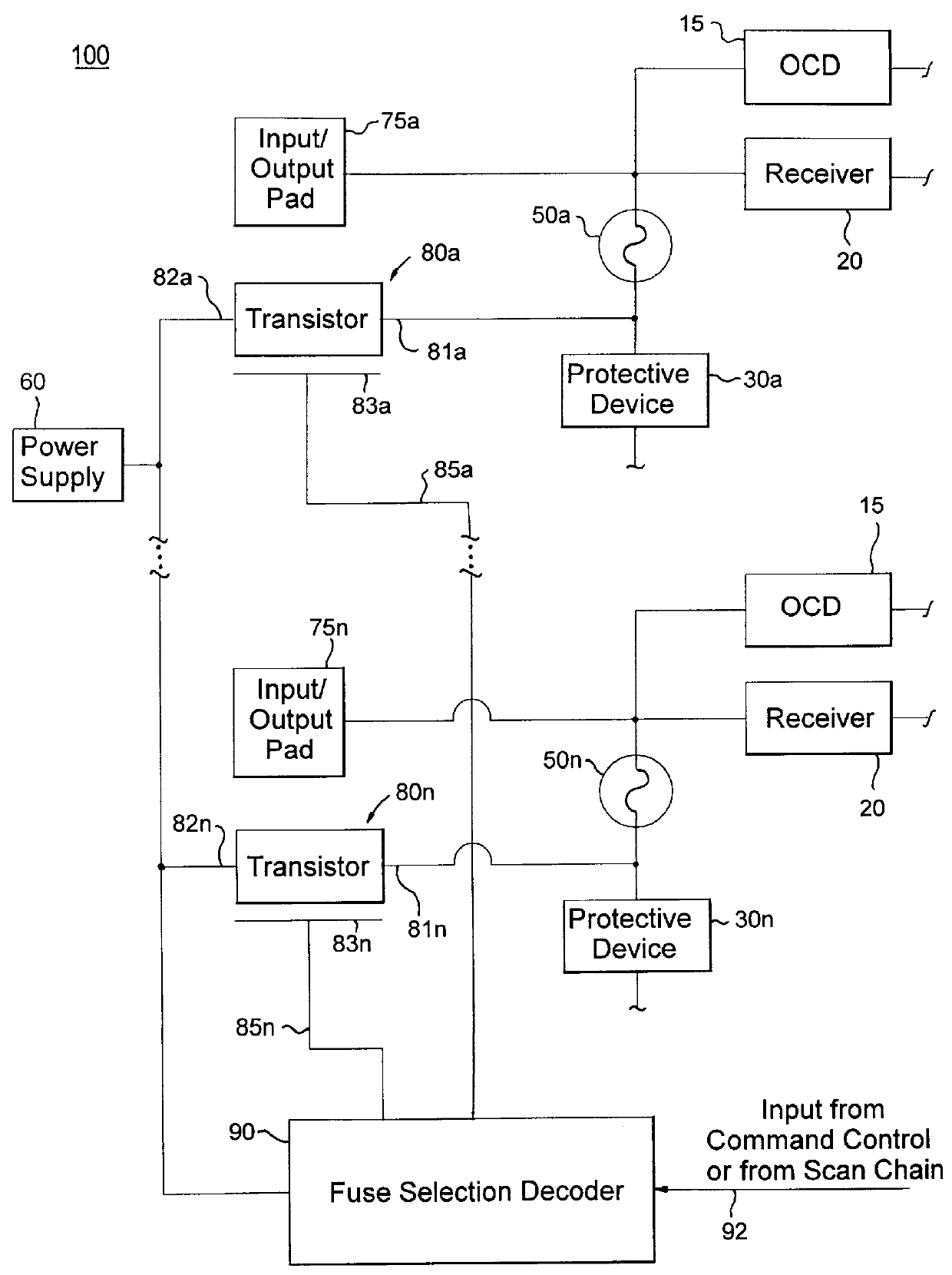
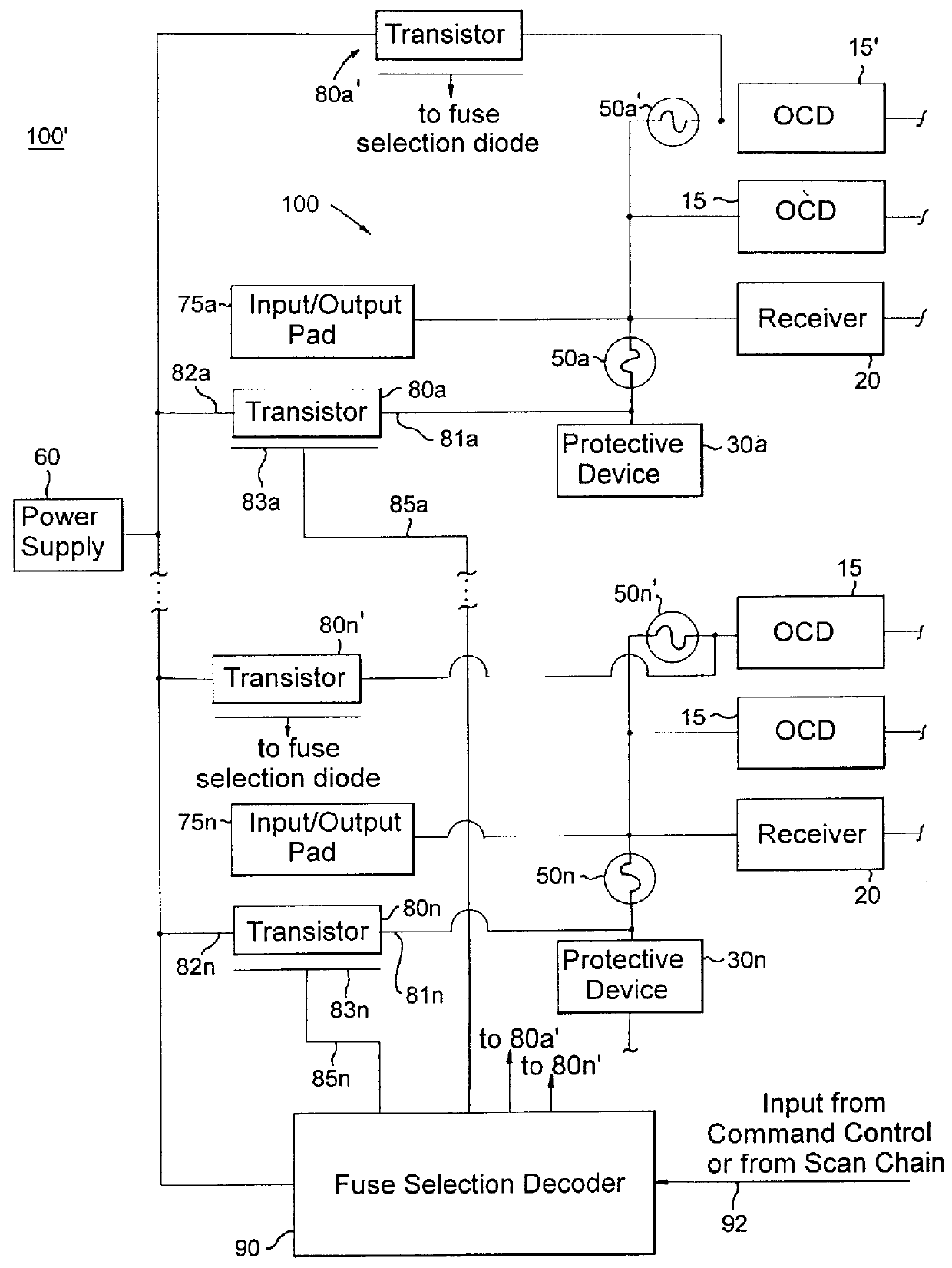
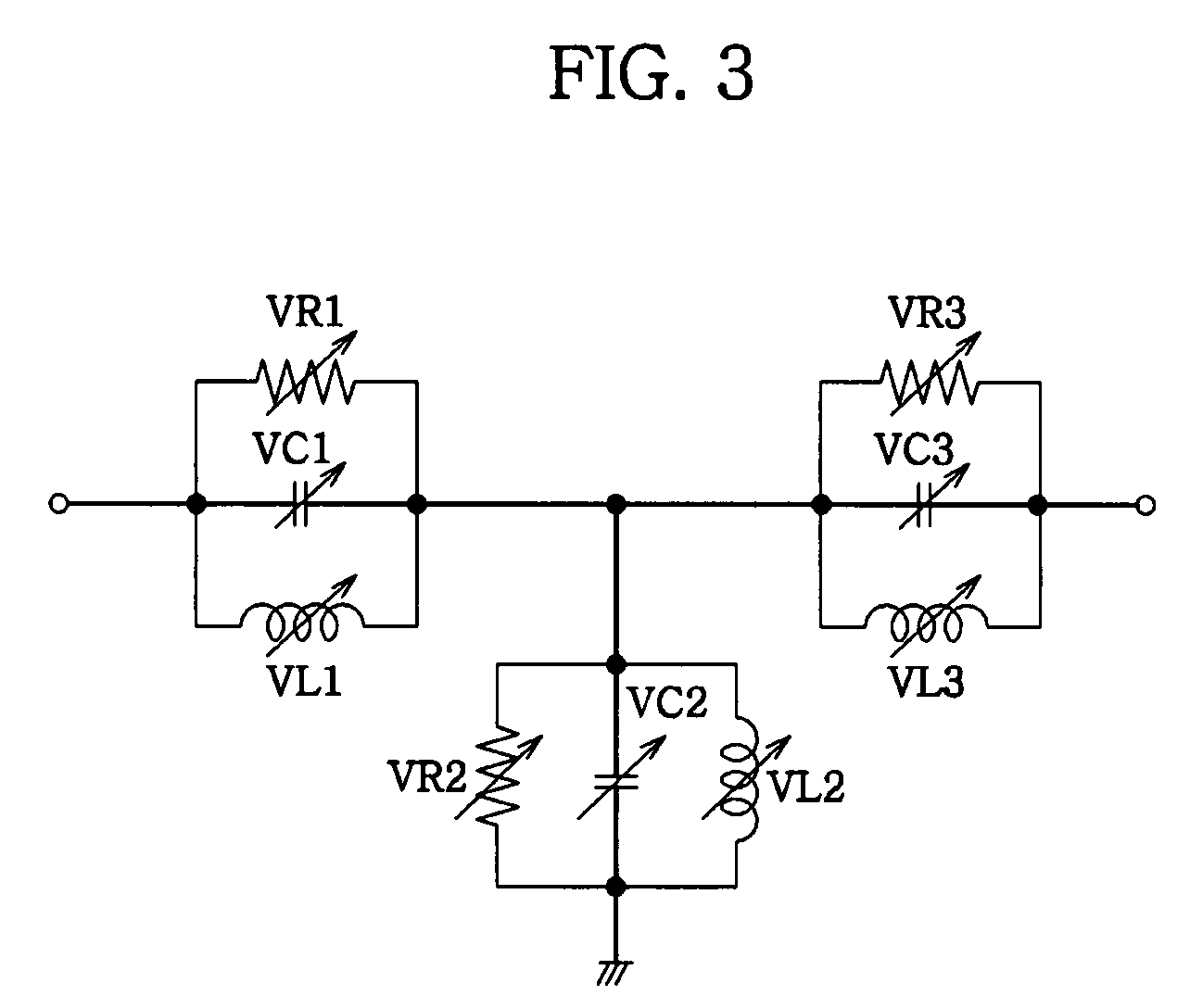
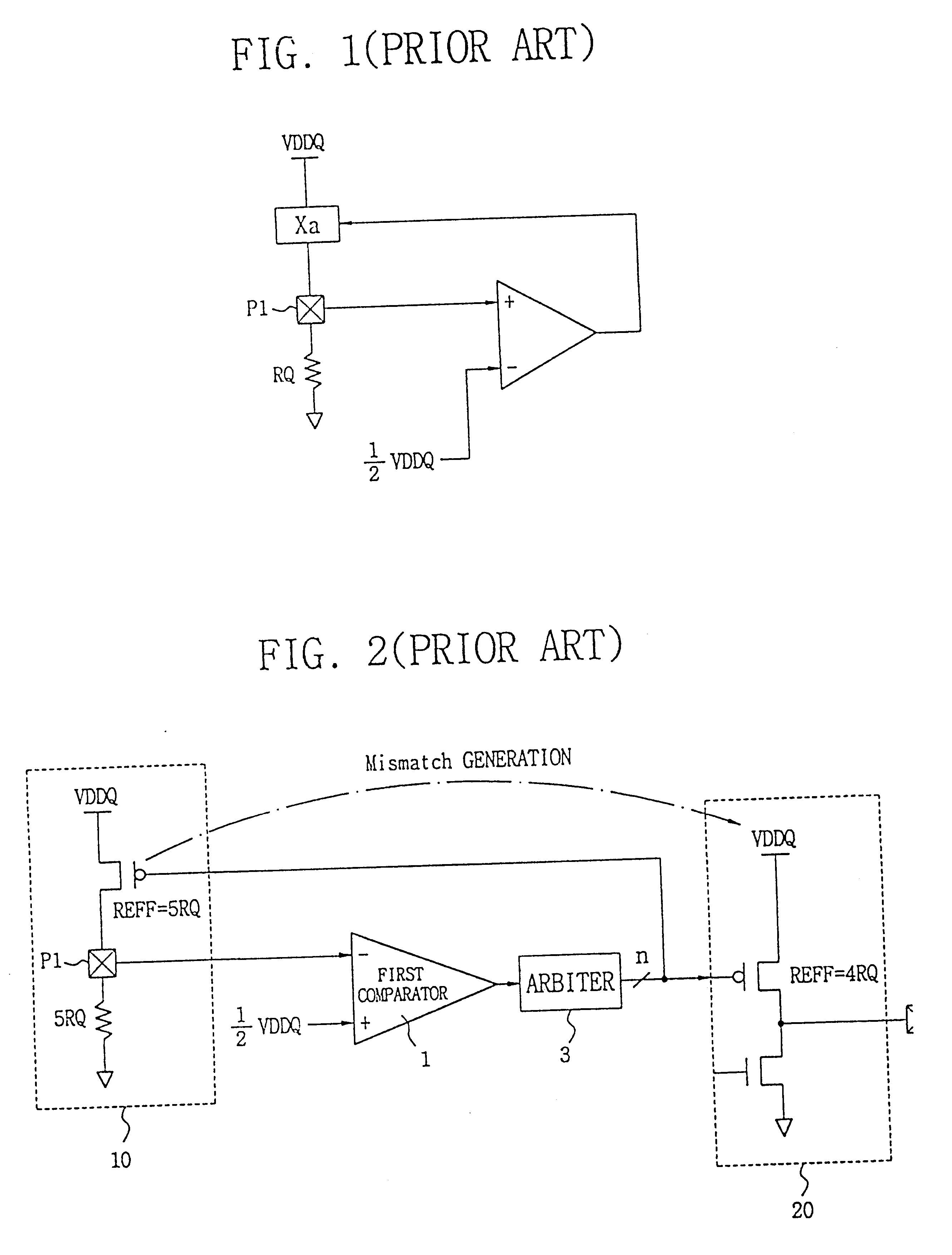
Impedance control using fuses
InactiveUS6141245ALower latencyHigher-bandwidth operationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipElectricity
A system and method for reducing impedance loading of semiconductor integrated circuit devices implementing protective device structures that contributes to impedance loading at an I / O pad connection. The method comprises providing a fuse device between the I / O pad connection and the protective device; connecting a current source device associated with each fuse device in the integrated circuit, the current source device connected to one end of the fuse device; providing fuse selection circuit for activating current flow through a selected fuse device between the current source and the I / O connection, the current flow being of an amount sufficient for blowing the fuse and disconnecting the protective device from the circuit structure, thereby reducing impedance loading at the I / O connection. Such a system and method is employed in a memory system comprising integrated circuit chips disposed in a stacked relation, with each chip including: a layer of active circuitry formed at a first layer of each chip; a plurality of through conducting structures disposed substantially vertically through each chip for enabling electronic connection with active circuitry at the first layer; second conducting device disposed at an end of the through conducting structure at an opposite side of a chip for connection with a corresponding through conductive structure of an adjacent stacked chip, the stacked chip structure formed by aligning one or more through conducting structures and second conducting devices of adjacent chips, whereby a chip of the stack is electronically connected to active circuitry formed on other chips of the stack. The stacked chip structure is ideal for reducing data access latency in memory systems employing memory chips such as DRAM.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
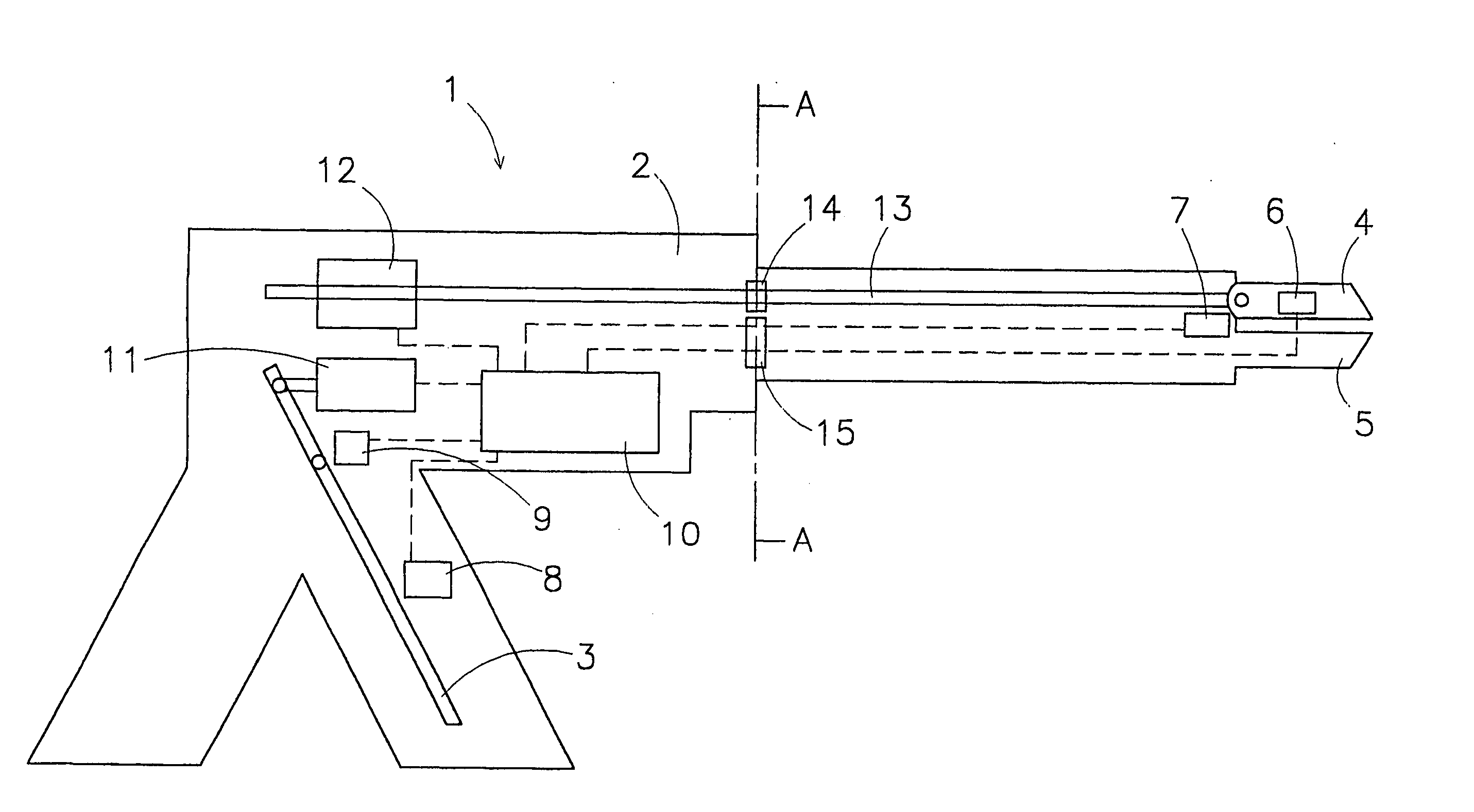
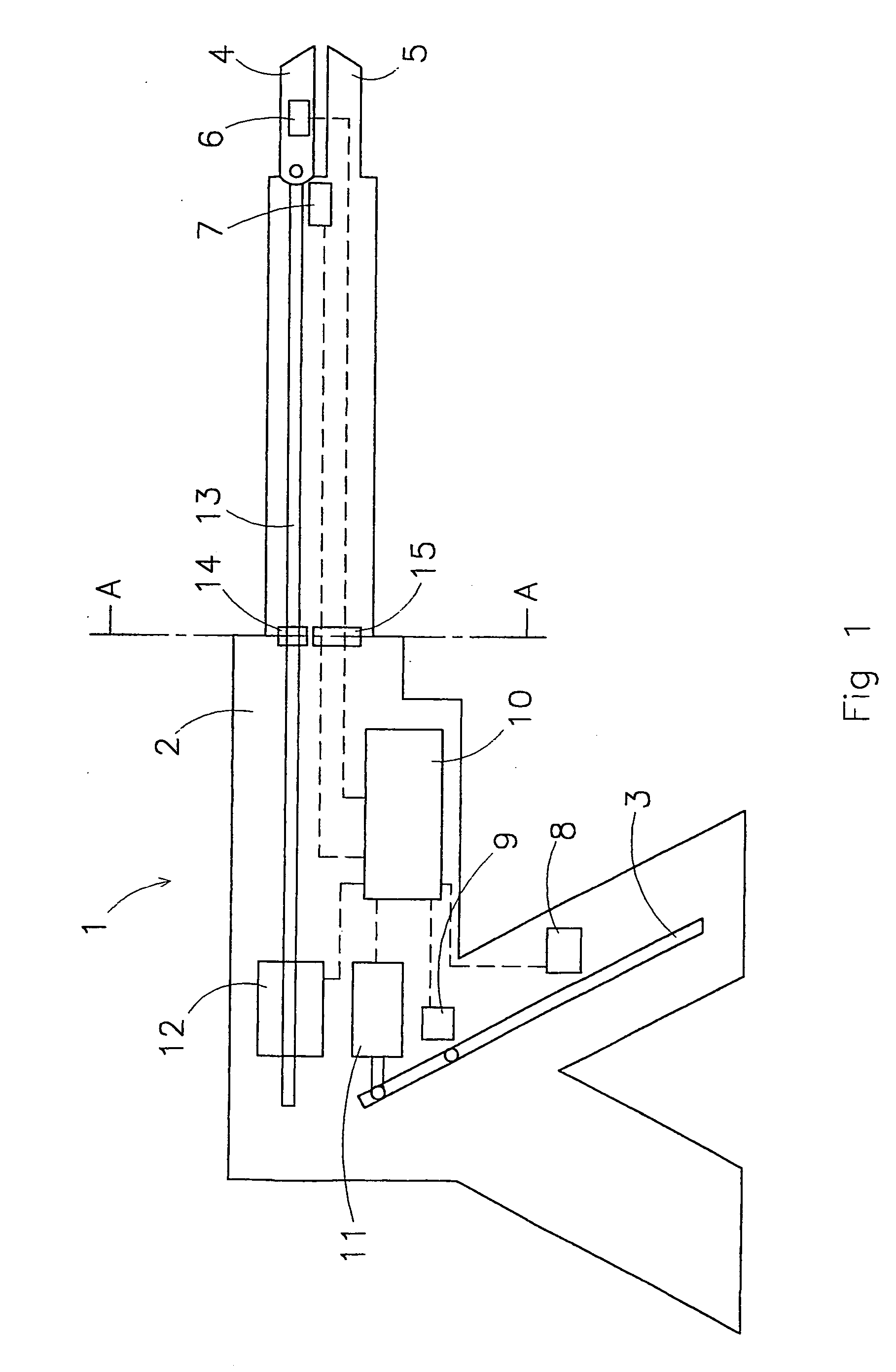
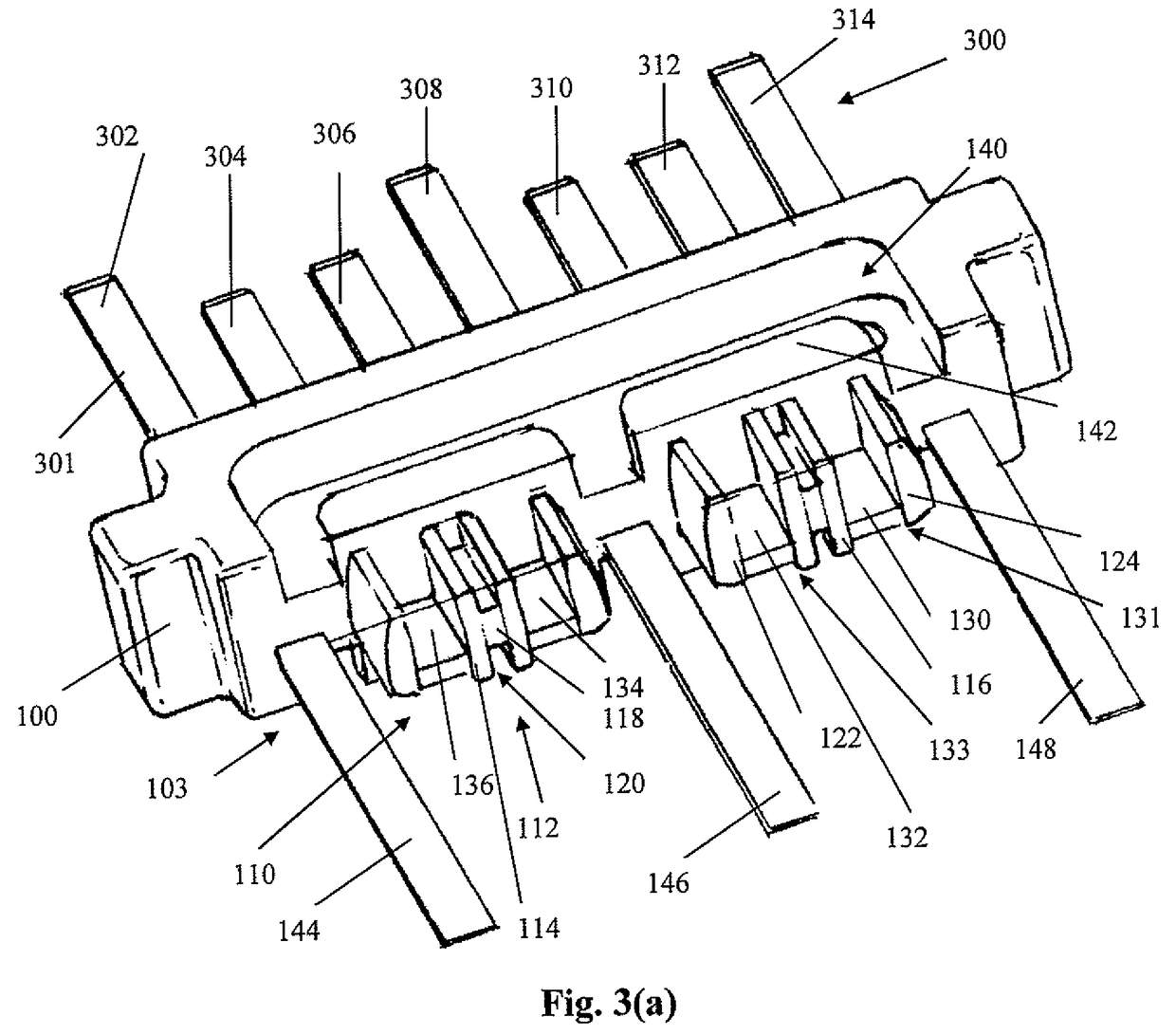
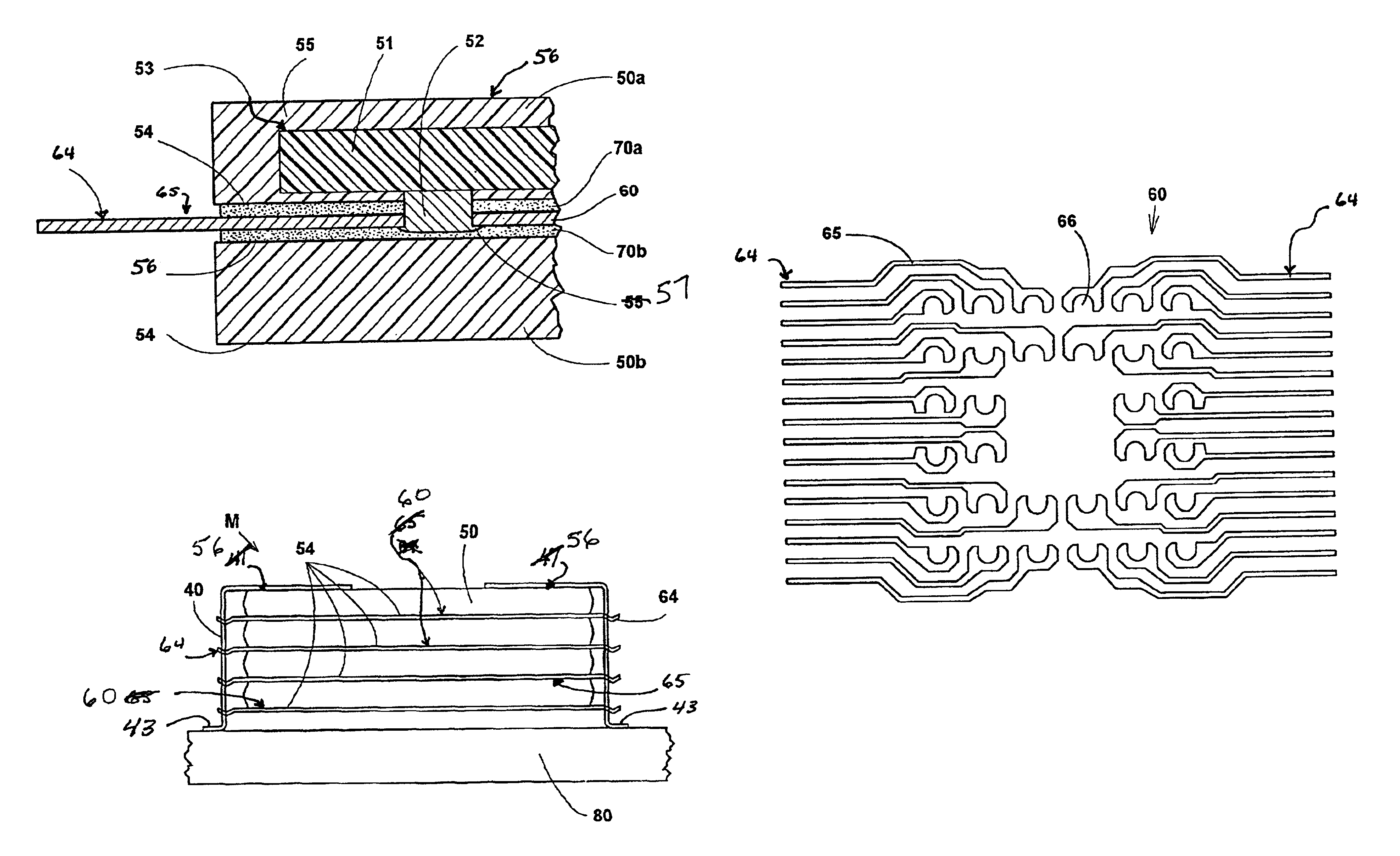
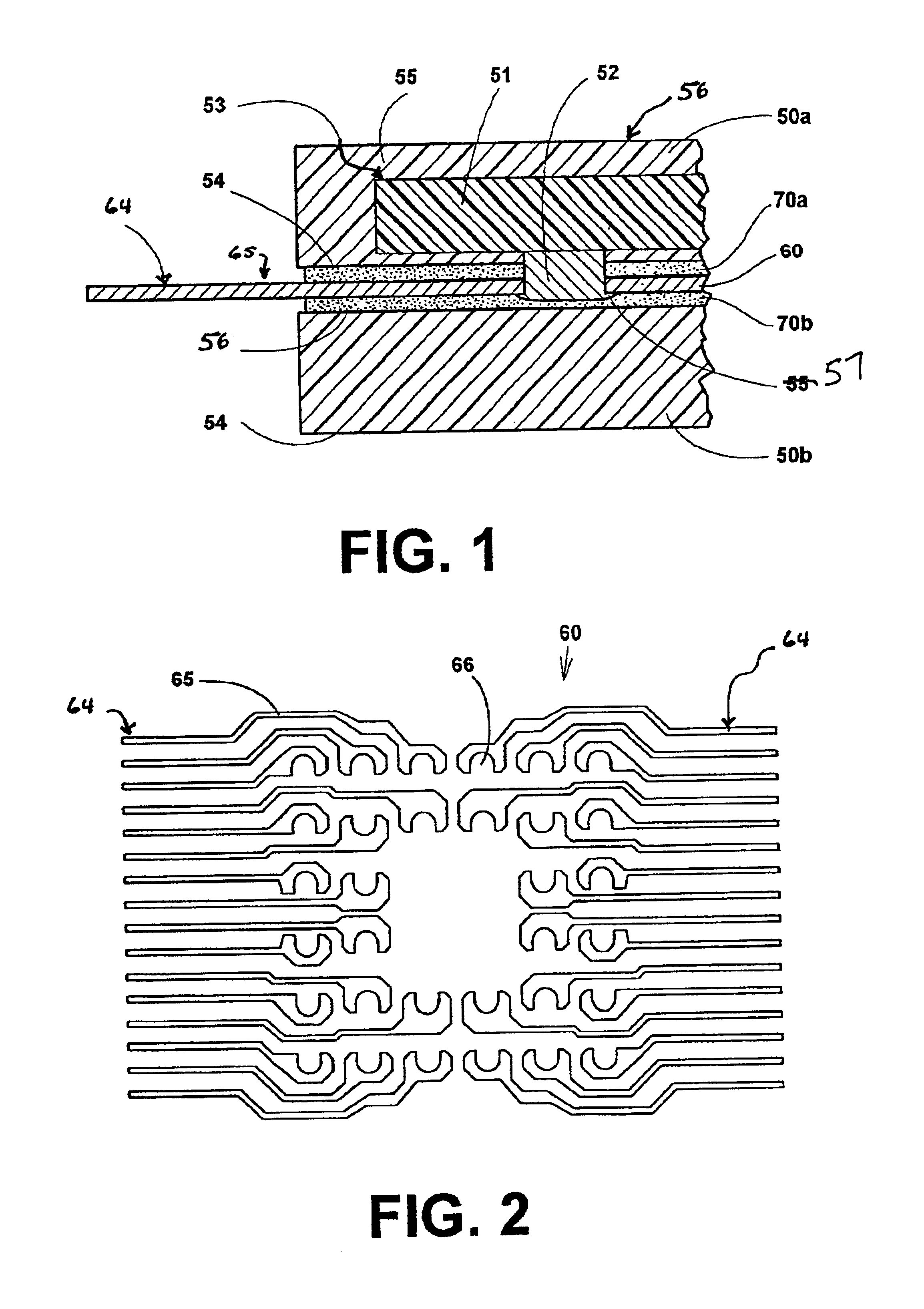
Ground sleeve having improved impedance control and high frequency performance
A waferized connector connects to two twinax cables. The connector includes a molded lead frame, ground sleeve, twinax cable, and overmolded strain relief. The lead frame is molded to retain a lead frame containing both differential signal pins and ground pins. Termination sections are provided at the rear of the lead frame to terminate each of the signal wires of the cables to respective signal lands. The ground sleeve has two general H-shape structures connected together by a center cross-support member. Each of the H-shaped structures having curved legs, each of which fits over the signal wires of one of the twinax cables. The wings of the ground sleeve are terminated to the ground lands of the lead frame and the drain wire of the cable is terminated to the ground sleeve to terminate the drain wire to a ground reference. The ground sleeve controls the impedance in the termination area of the cables, where the twinax foil is removed to expose the wires for termination to the lands. The ground sleeve also shields the cables to reduce crosstalk between themselves and adjacent wafers when arranged in a connector housing. A conductive slab member is formed over the sleeve to provide a capacitive coupling with the conductive foil of the signal cable.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
Impedance control in electrical connectors
InactiveUS6981883B2Coupling contact membersTwo-part coupling devicesDifferential signalingElectrical connector
The invention provides a high speed connector wherein differential signal pairs are arranged so as to limit the level of cross talk between adjacent differential signal pairs. The connector comprises lead frame assembly having a pair of overmolded lead frame housings. Each lead frame housing has a respective signal contact extending therethrough. The lead frame housings may be operatively coupled such that the signal contacts form a broadside-coupled differential signal pair. The contacts may be separated by a gap having a gap width that enables insertion loss and cross talk between signal pairs to be limited.
Owner:FCI AMERICAS TECH LLC
Cross talk reduction and impedance-matching for high speed electrical connectors
InactiveUS6976886B2Reduce weightReduced insertion lossTwo-part coupling devicesPrinted circuitsGround contactInterference (communication)
Lightweight, low cost, high density electrical connectors are disclosed that provide impedance controlled, high-speed, low interference communications, even in the absence of shields between the contacts, and that provide for a variety of other benefits not found in prior art connectors, such as low insertion loss. Signal contacts and ground contacts within the connectors can be scaled and positioned relative to one another such that a differential signal in a first differential signal pair produces a high field in the gap between the contacts that form the signal pair and a low field near an adjacent signal pair. Consequently, cross talk between adjacent signal contacts can be limited to acceptable levels for the particular application. In such connectors, the level of cross talk between adjacent signal contacts can be limited to the point that the need for (and cost of) shields between adjacent contacts is unnecessary, even in high speed, high signal integrity applications.
Owner:FCI USA LLC
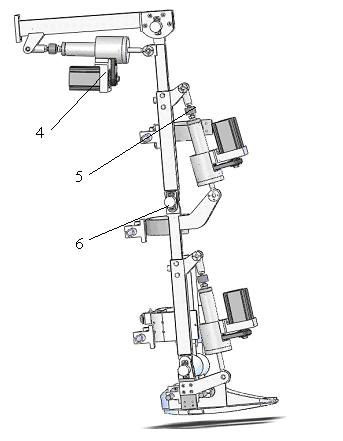
Motion control method of lower limb rehabilitative robot
InactiveCN102058464ARealize tracking controlEnhanced awareness of initiativeChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesEngineeringActive participation
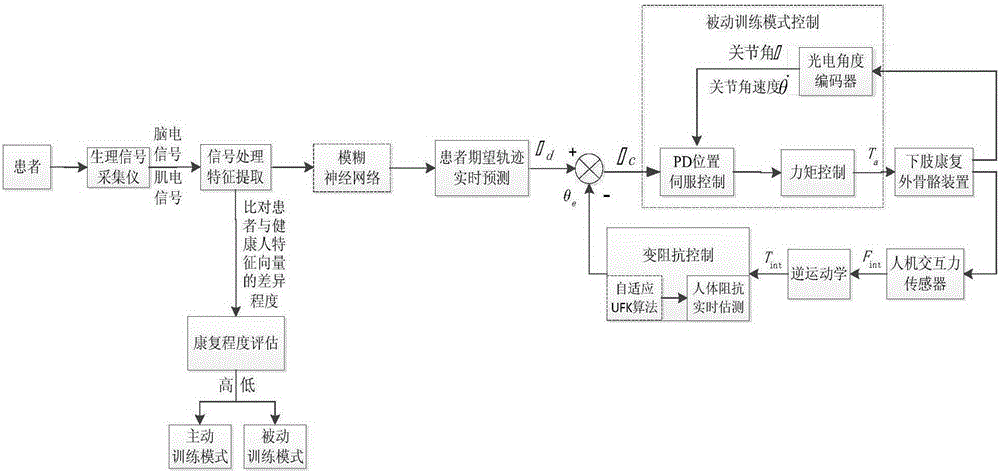
The invention relates to a motion control method of a lower limb rehabilitative robot. In the method, aiming at different rehabilitation stages of a patient, two working modes of passive training and active training are carried out: under the mode of passive training, the patient is driven by controlling the robot to finish specific motions or motion according to a right physiological gait track; abnormal motions of the patient are completely restrained; and the patient passively follows the robot to do walking rehabilitation training; under the mode of active training, limited abnormal motions of the patient are restrained by the robot; through a real-time detection on joint driving forces generated when the patient acts on the robot in the motion process, human-computer interaction moment is extracted by utilizing an inverse dynamic model to judge the active motion intention of lower limbs of the patient; and the interaction moment is converted into correction value of gait track by utilizing an impedance controller to directly correct or generate the gait training track the patient expects through an adaptive controller, therefore, the purpose that the robot can provide auxiliary force and resistant force for the rehabilitation training can be indirectly realized. By means of the motion control method of the lower limb rehabilitative robot, rehabilitation training motions suitable for different rehabilitation stages can be provided for a dysbasia patient, thereby enhancing active participation degree of the rehabilitation training of the patient, building confidence of the rehabilitation and positivity of the motion, and then enhancing effect of the rehabilitation training.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
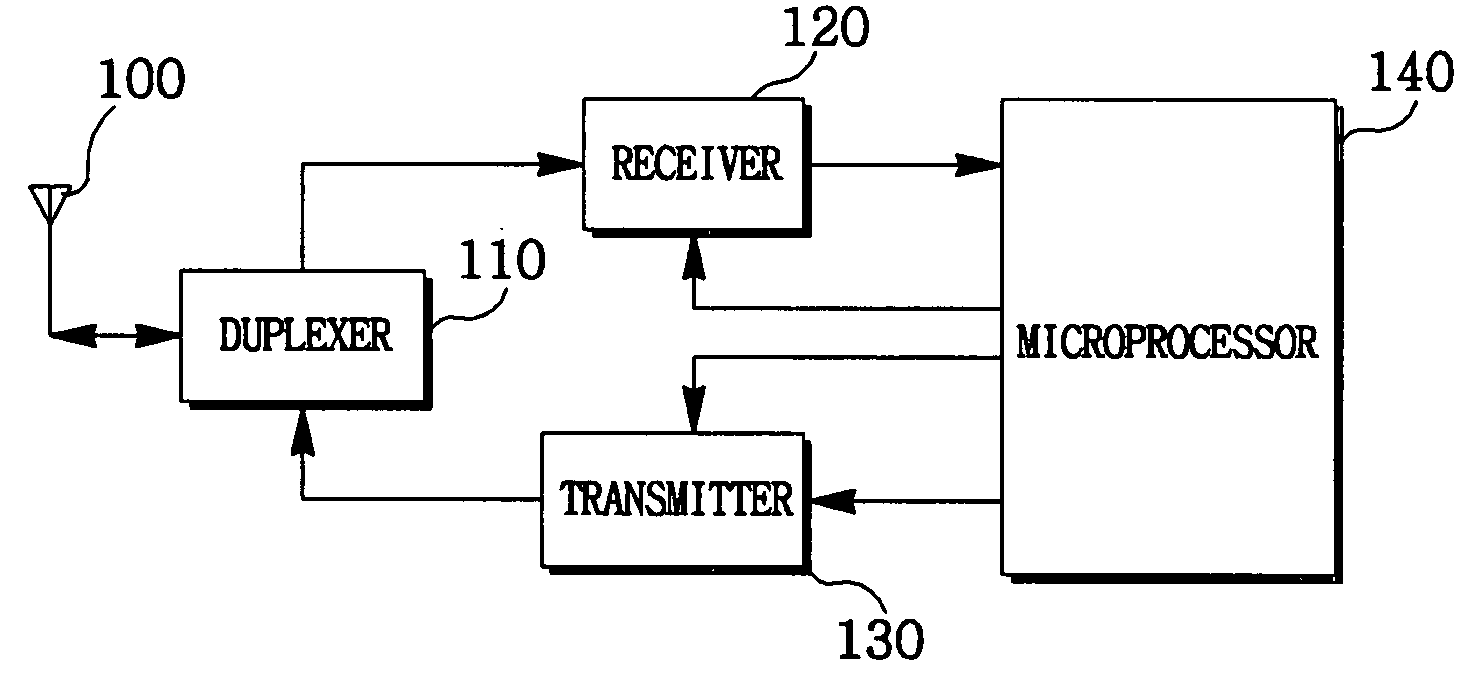
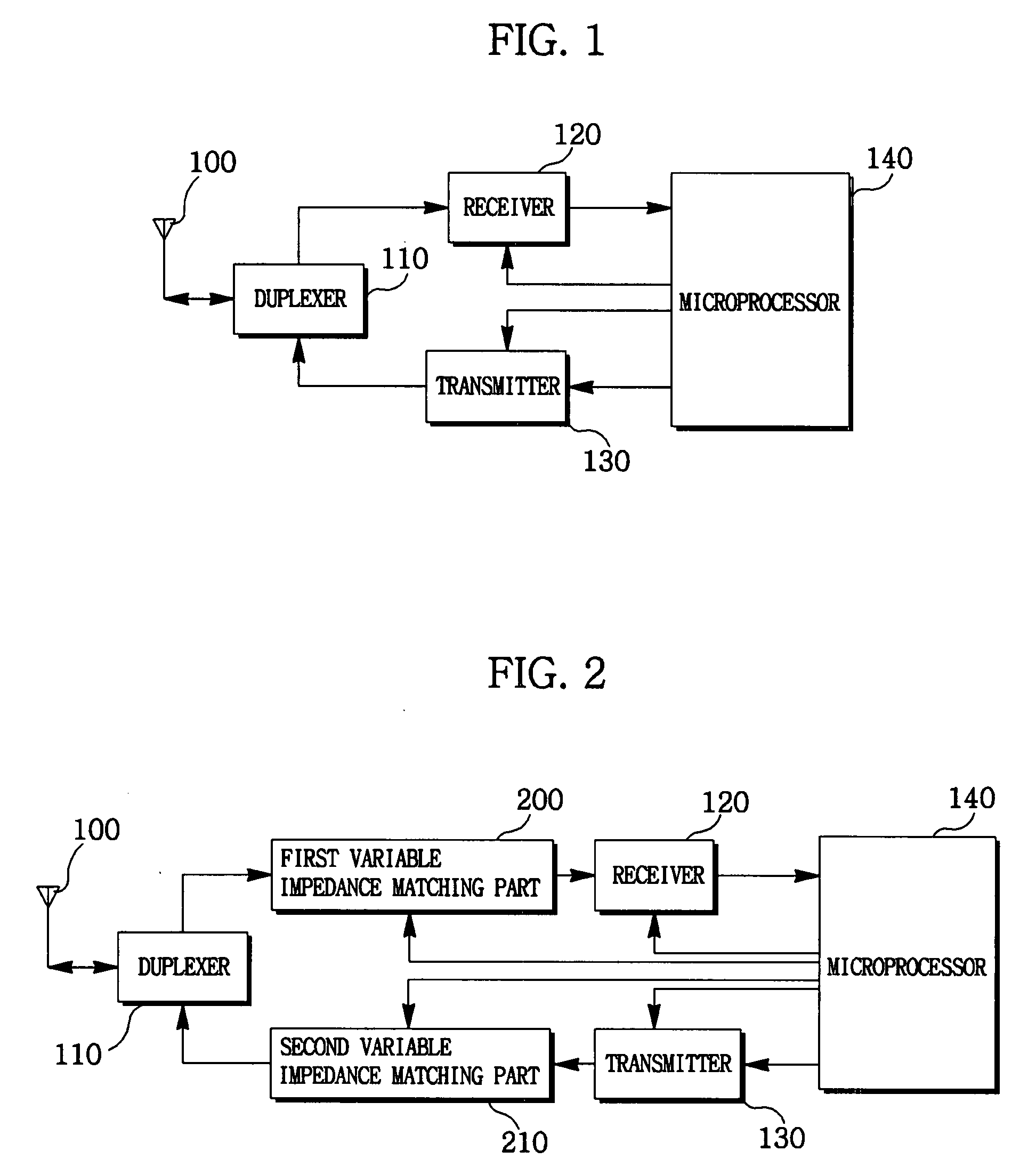
Impedance control apparatus and method for portable mobile communication terminal
ActiveUS20090109880A1Impedance mismatchingTransmission control/equalisingModulation with suppressed carrierImpedance matchingImpedance control
An impedance control apparatus and method for portable mobile communication terminal is disclosed capable of accurately adjusting impedances relative to environment when the portable mobile communication terminal is being used, wherein an impedance of a first variable impedance matching part is varied to receive a reception impedance correction signal transmitted by a base station and to detect a reception strength, an impedance of the first variable impedance matching part is set by a impedance value of the largest reception strength out of the reception strengths, the portable mobile communication terminal varies the impedance of a second variable impedance matching part to transmit a transmission impedance correction signal to a base station and to allow the base station to detect the reception strength, and the impedance setting of the second variable impedance matching part is performed using the reception strength detected by the base station.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
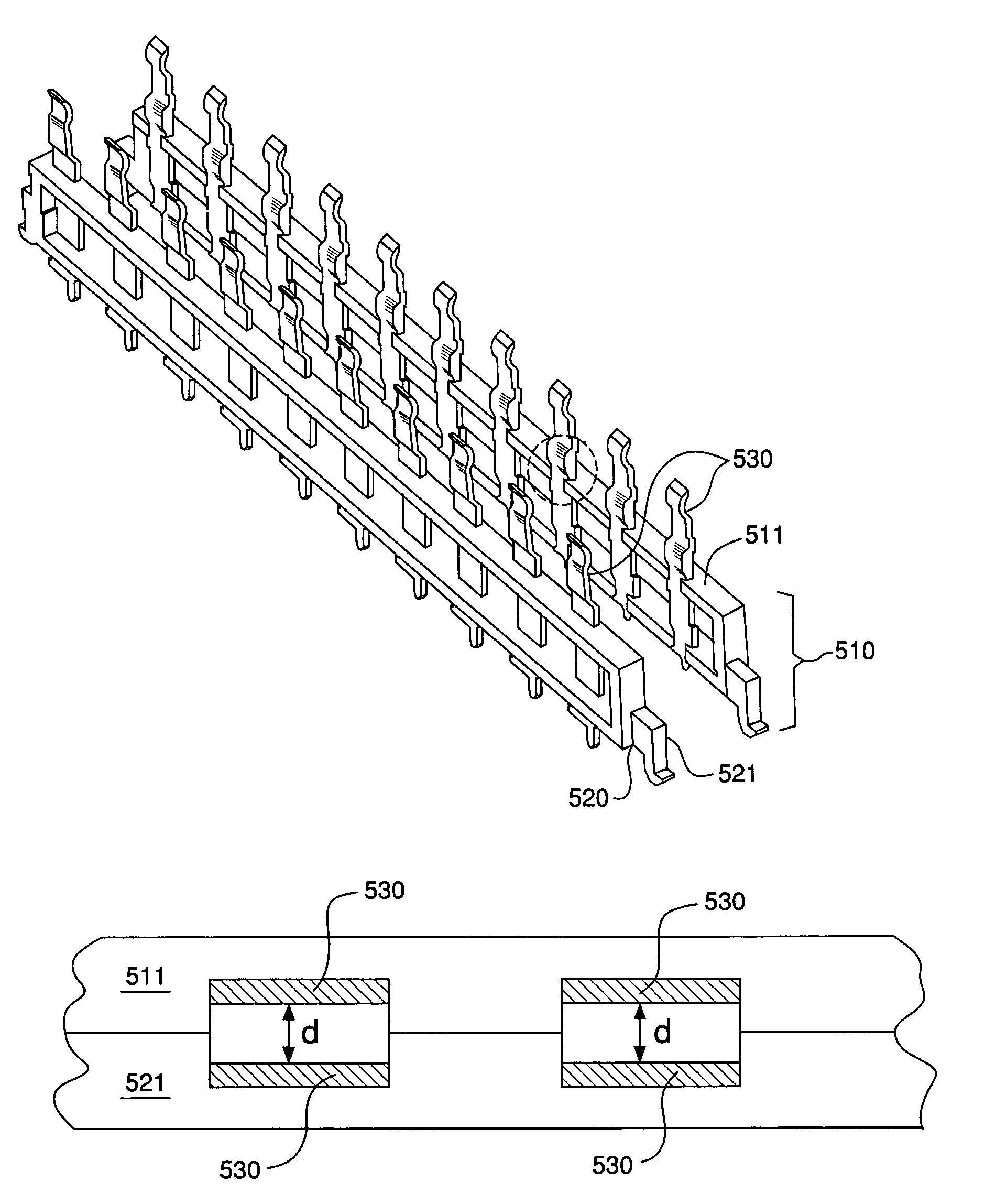
Impedance control in connector mounting areas
ActiveUS7731537B2Reduce crosstalkIncrease their edge-to-edgeElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsDielectricDifferential signaling
A high speed connector with reduced crosstalk utilizes individual connector support frames that are assembled together to form a block of connector units. Each such unit supports a column of conductive terminals in two spaced-apart columns. The columns have differential signal terminal pairs separated from each other by larger intervening ground shields that serve as ground terminals. The ground shields are arranged in alternating fashion within the pair of columns and they are closely spaced together so as to face a differential signal terminal pair. In areas where the terminals are mounted to the connector units, window-like openings are formed in the large ground shield terminals to reduce the amount of broadside coupling between the differential signal terminal pair and the signal terminal pair are narrowed to increase their edge-to-edge distance to account for the change in dielectric constant of the connector unit material filing in the area between the signal terminal pair.
Owner:MOLEX INC
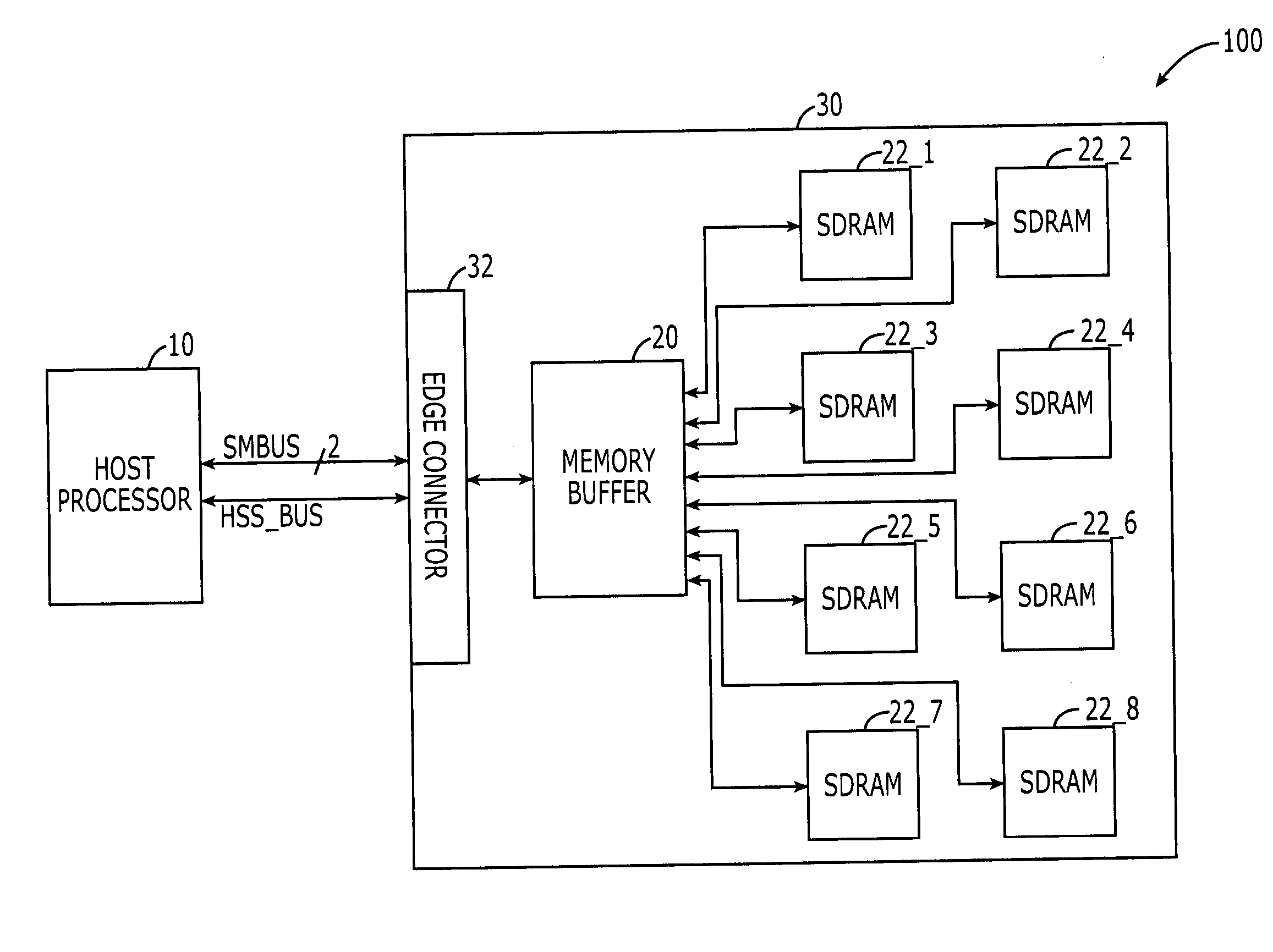
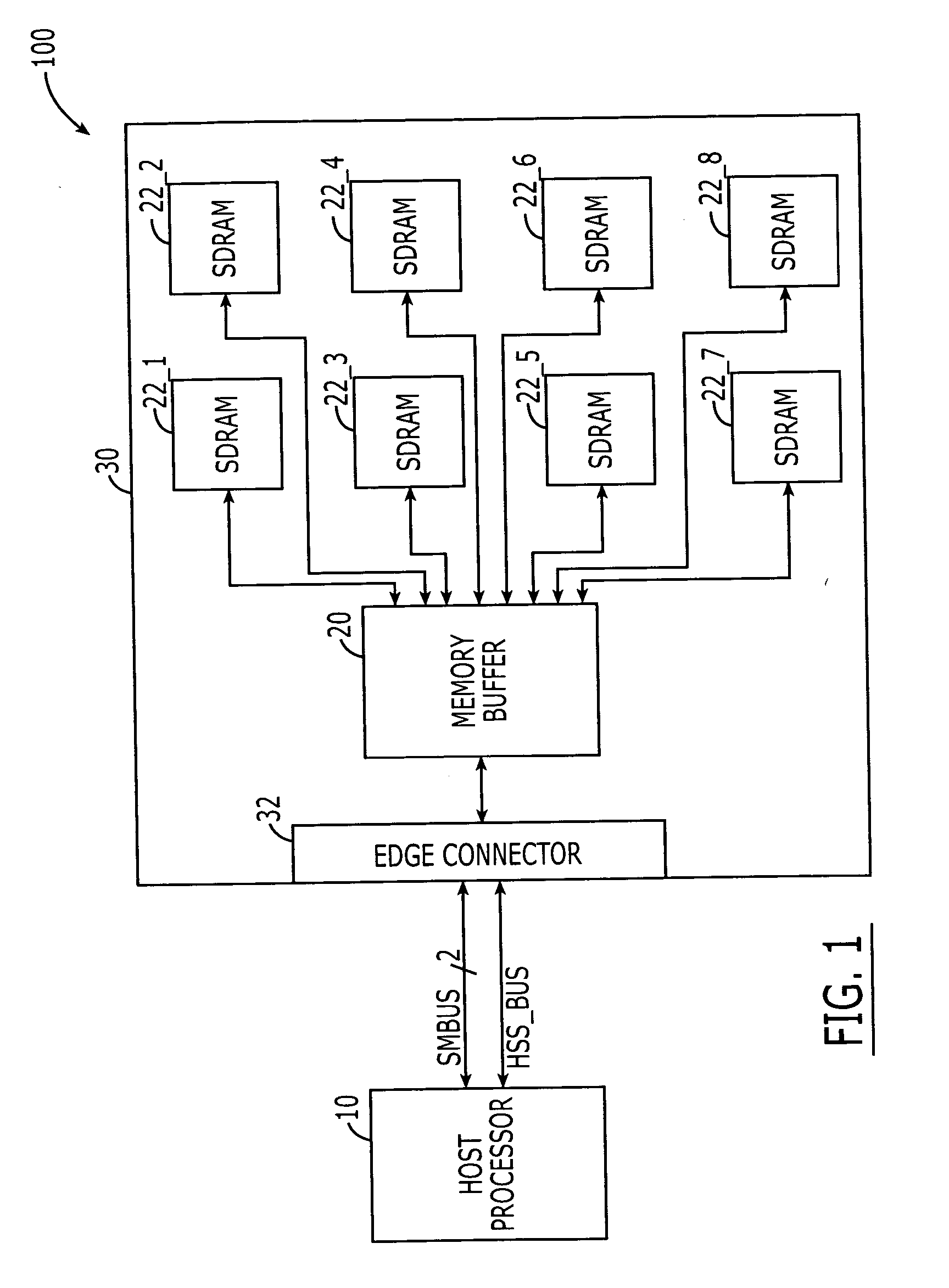
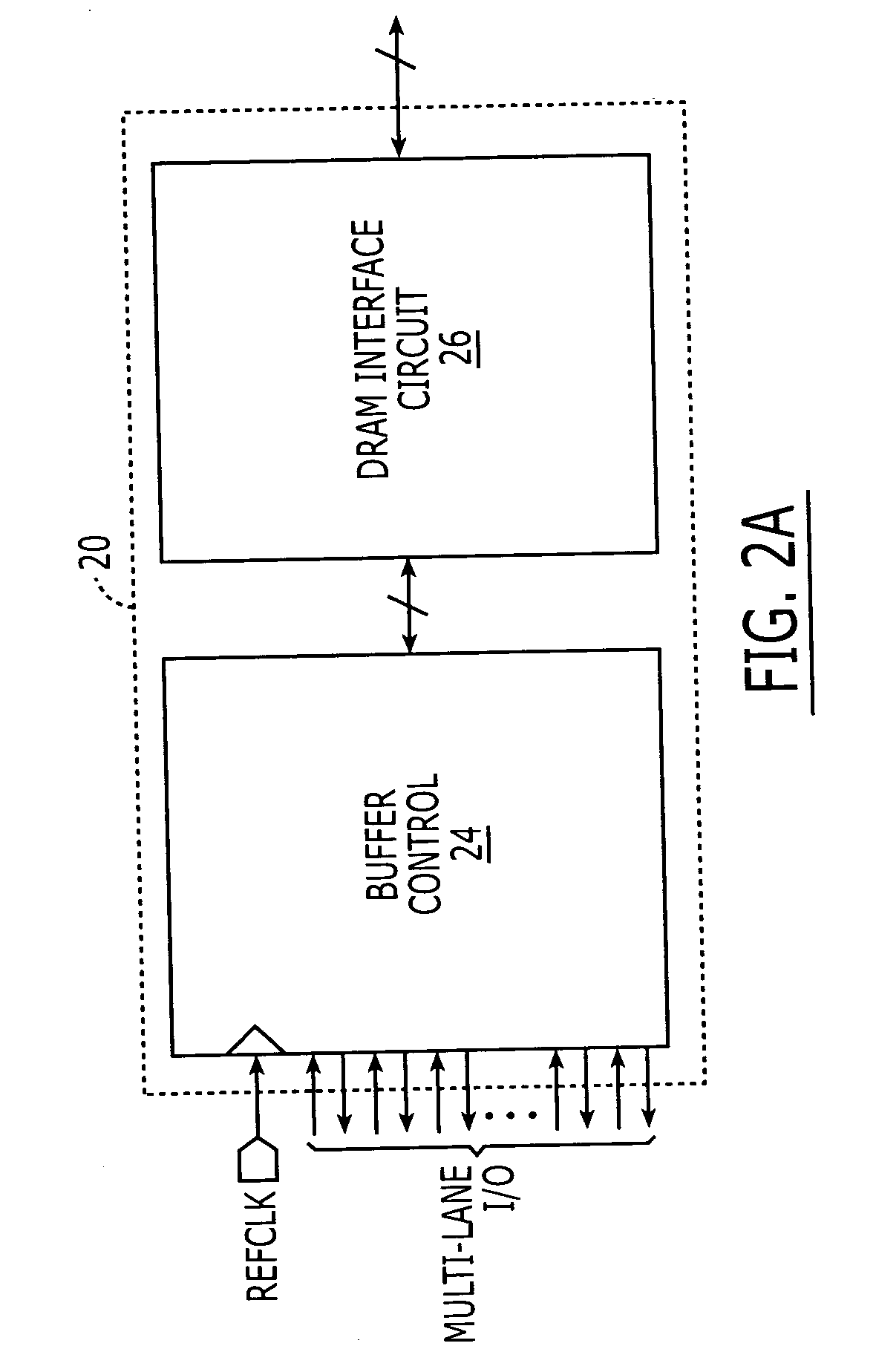
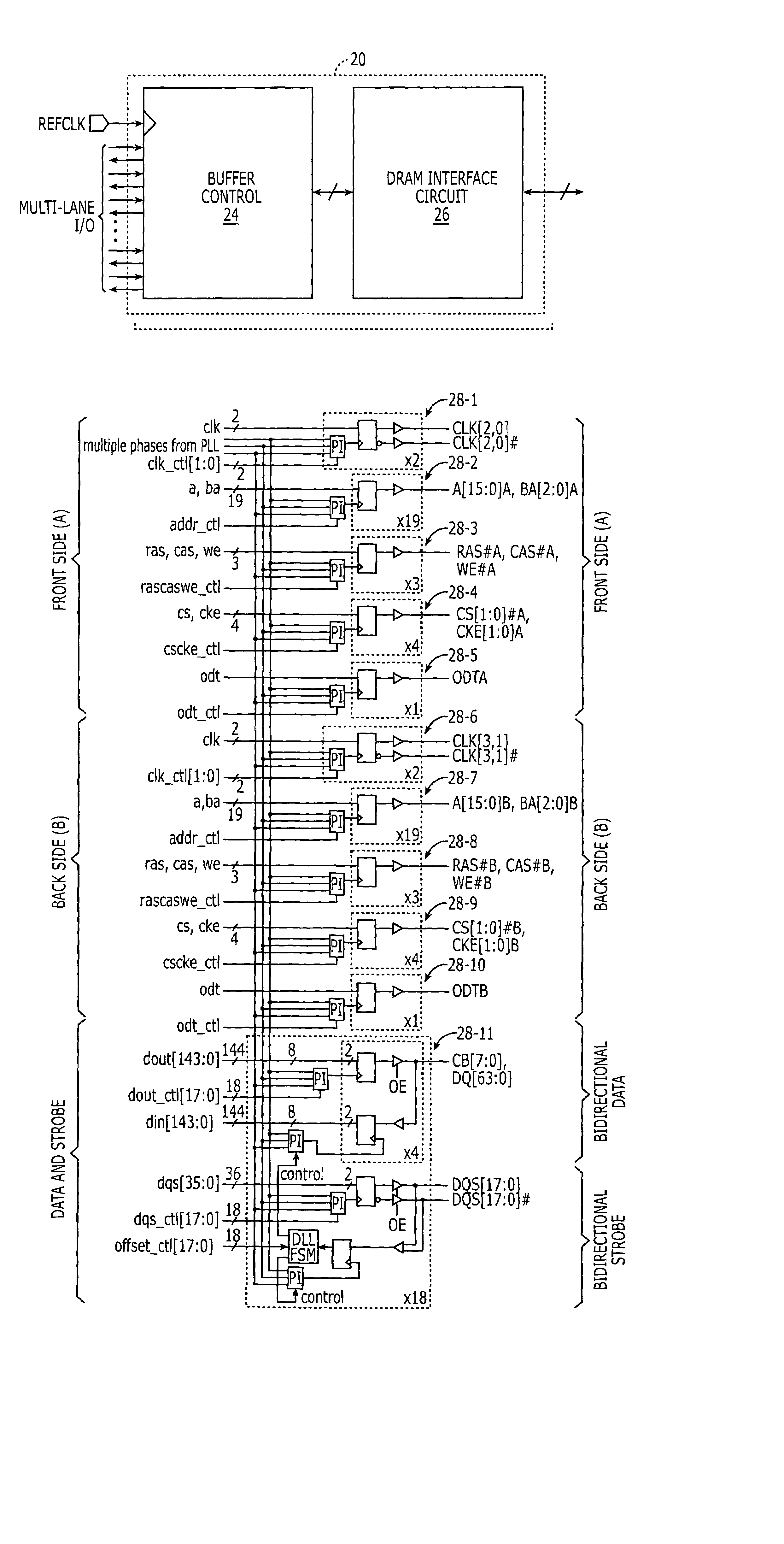
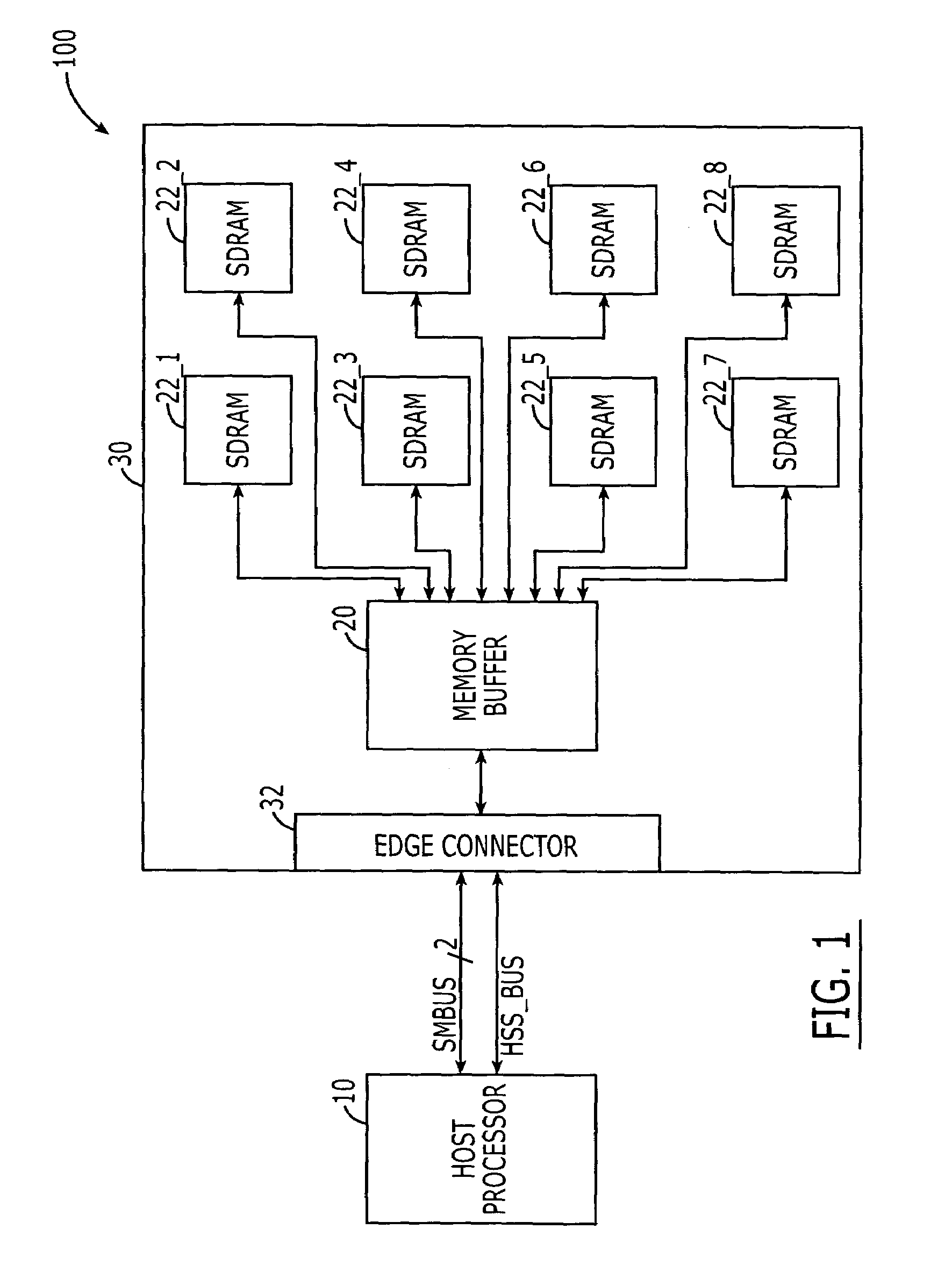
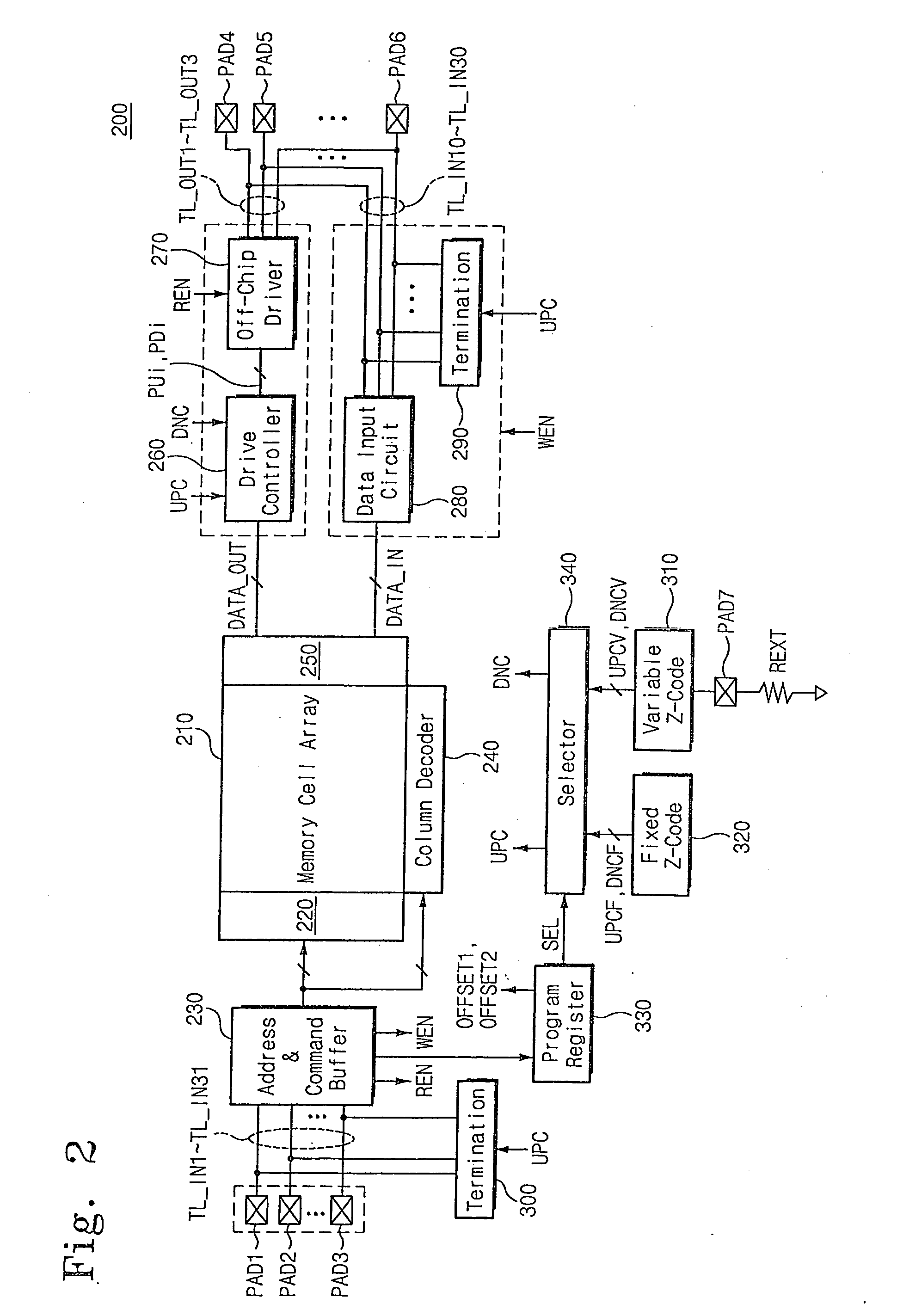
DRAM interface circuits having enhanced skew, slew rate and impedance control
Fully-buffered dual in-line memory modules (FB-DIMM) include advanced memory buffers (AMBs) having enhanced skew, slew rate and output impedance control. The AMB includes user accessible registers that can be programmed to carefully control the edge placement (or phase) of signals generated from the AMB to multiple DRAMs on the module. This control of edge placement, which may be performed independently for each group of signals: clock (CLK, CLK#), command (RAS, CAS, WE), address (including bank address), data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS), provides 360 degrees of control (or one period). This means that any group of signals can be moved independently by one complete period relatively to any other group.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
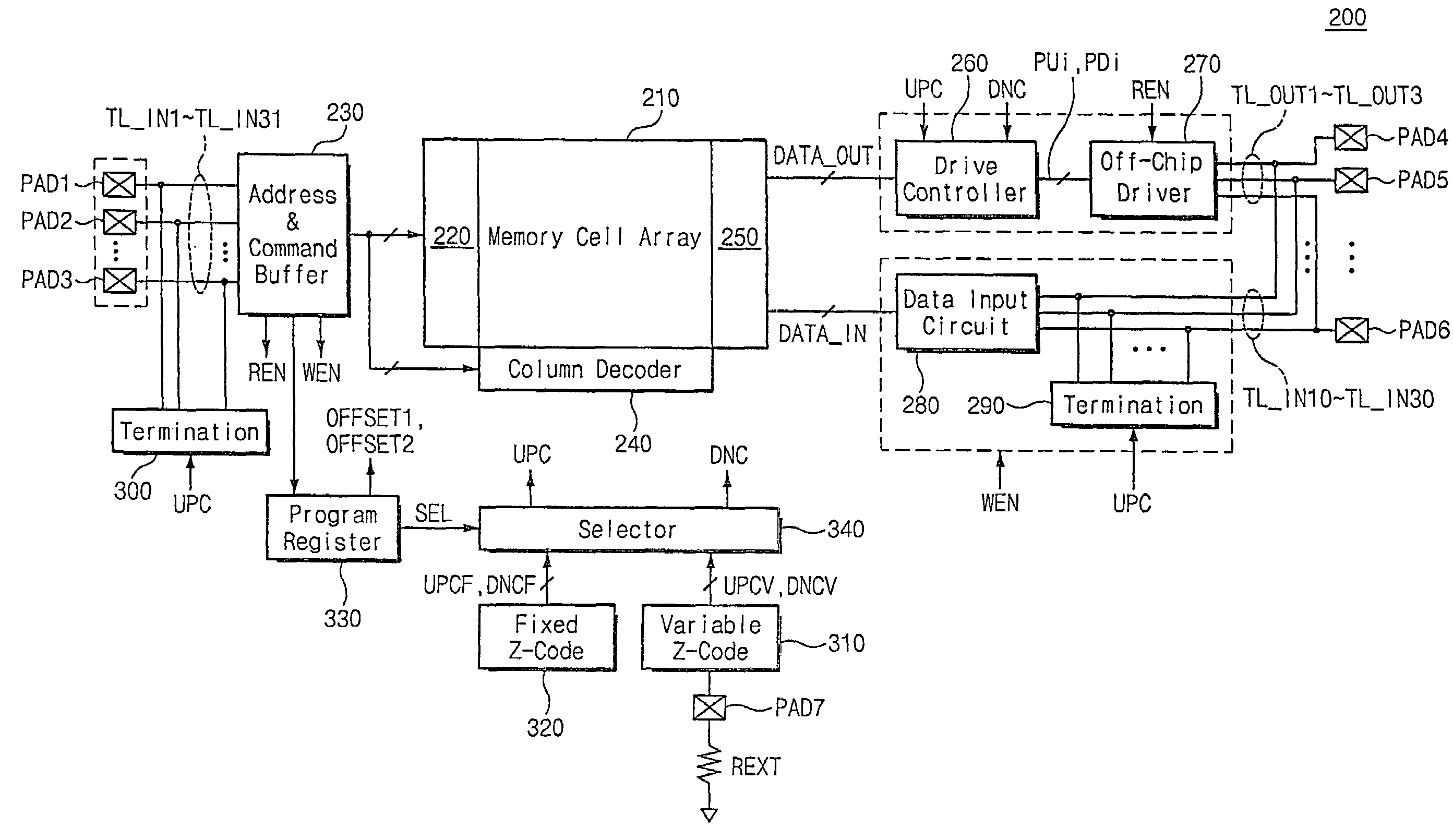
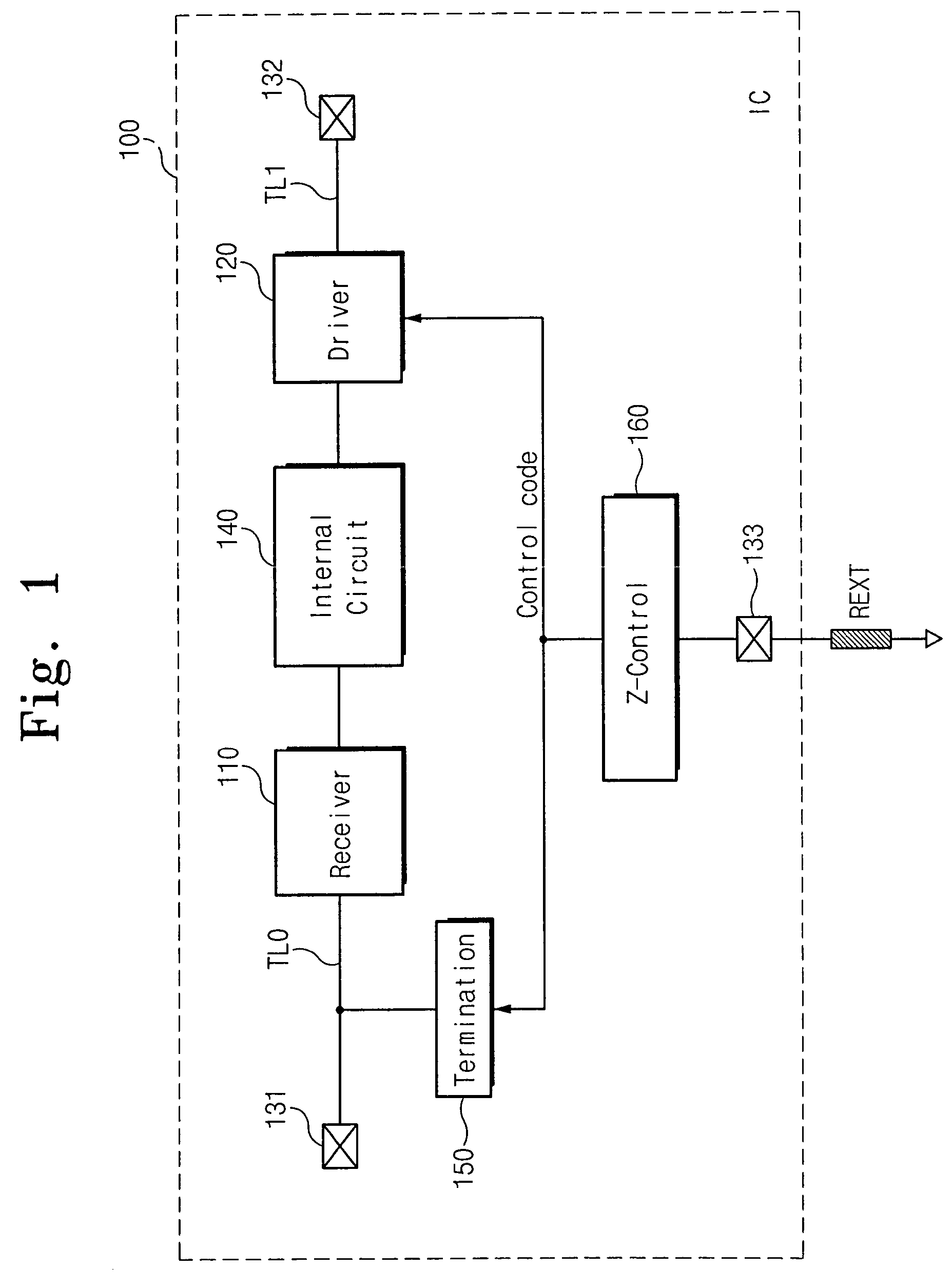
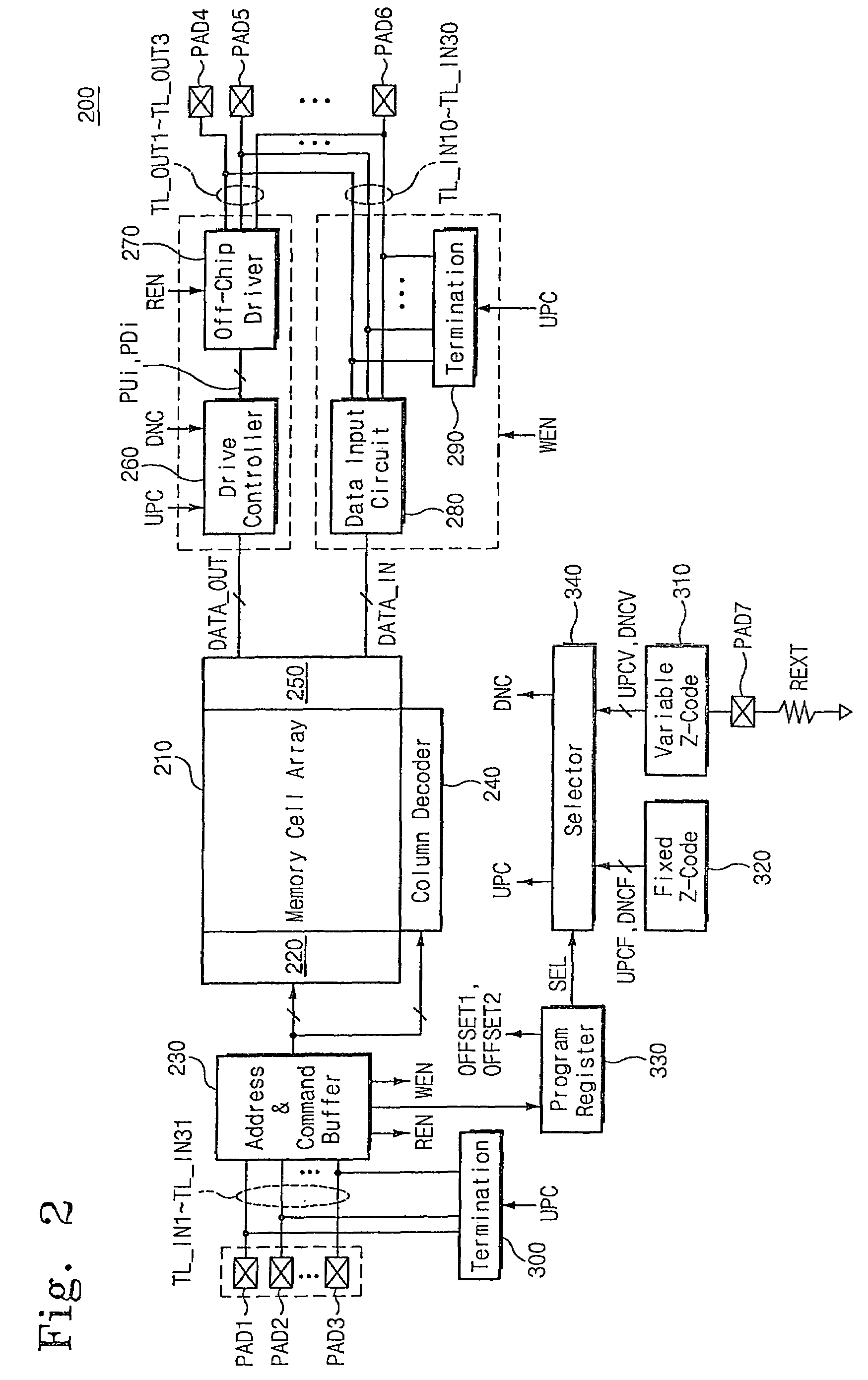
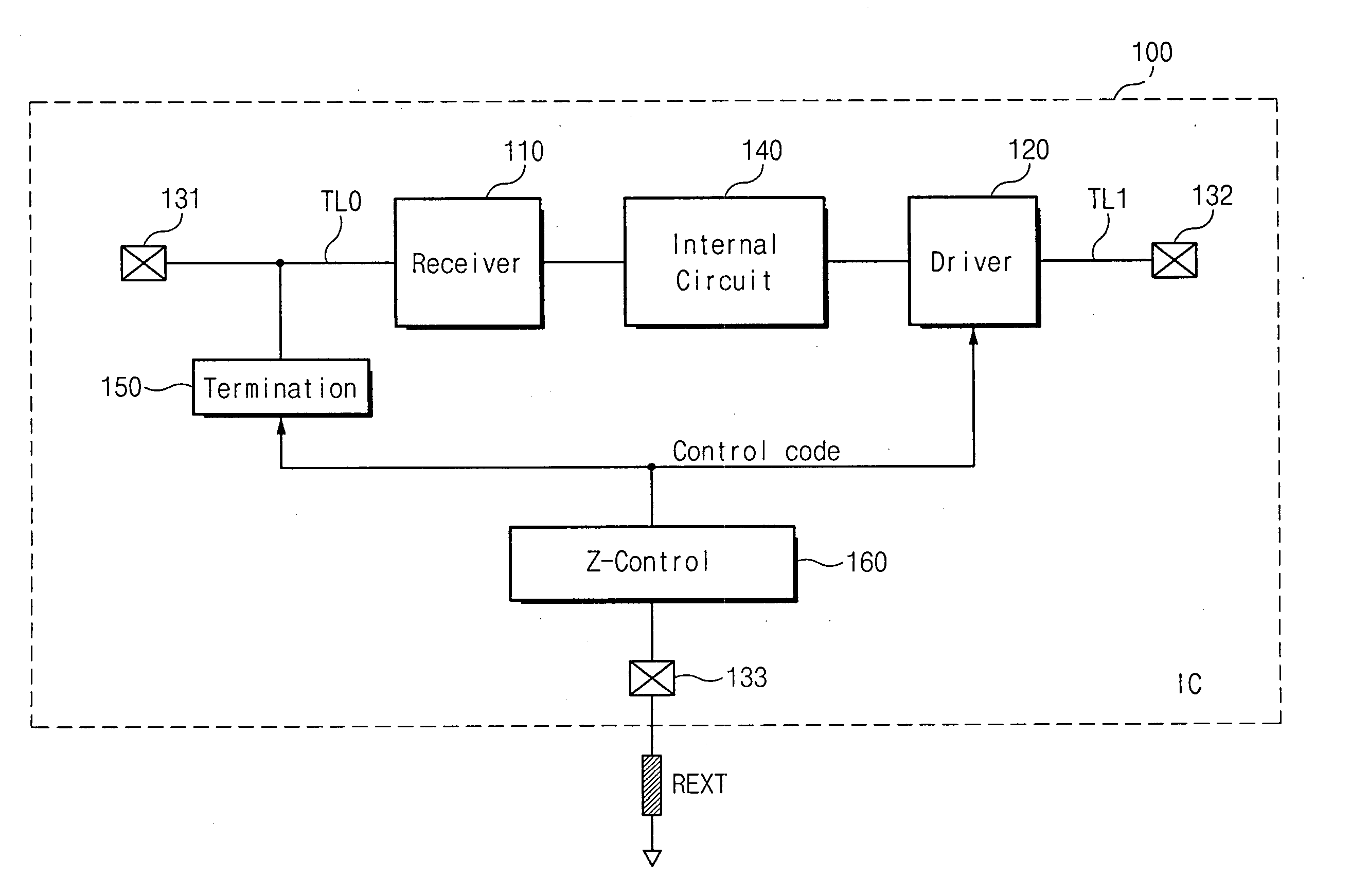
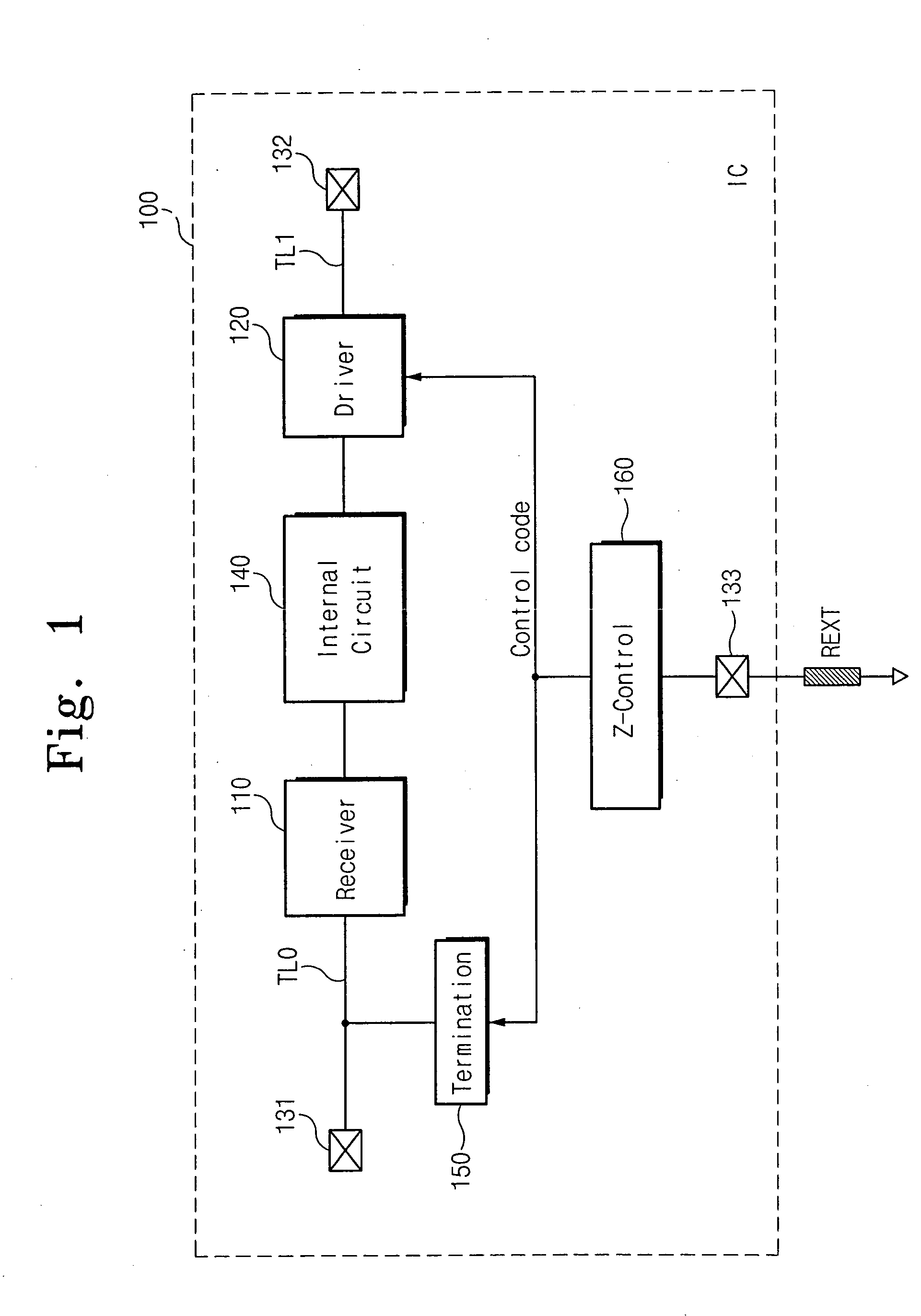
Semiconductor integrated circuit device capable of controlling impedance
ActiveUS7148721B2Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsExternal referenceSemiconductor
A semiconductor integrated circuit device is connected to an external reference resistor, including an impedance control circuit for generating impedance control codes variable with impedances established by the external reference resistor. An input circuit receives an external signal through an input transfer line and forwards the external signal to an internal circuit. A termination circuit terminates the input transfer line in response to at least one of the impedance control code. An output circuit drives an output transfer line in accordance with an output signal. Impedance is variable with the control codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High performance, small form factor connector with common mode impedance control
Techniques for improving electrical performance of a connector. The techniques are compatible with the form factor of a standardized connector, such as an SFP connector or stacked SFP. The resulting connector has reduced insertion loss for high speed signals. Such techniques, which can be used separately or together, include shaping of conductive elements within the connector while still retaining the same mating contact arrangement. Changes may be made at the contact tail portions or in the intermediate portions where engagement to a connector housing occurs. The techniques also include the incorporation of lossy bridging members between conductive elements designated to be ground conductors. For connectors according to the stacked SFP configuration, multiple bridging members may be incorporated at multiple locations within the connector.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
Ground sleeve having improved impedance control and high frequency performance
ActiveUS20100294530A1Electrically conductive connectionsCoupling device detailsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A conductive sleeve includes a central portion with a front, a rear, and sides; at least one flange mated with at the sides of the central portion; and capacitive section that extends from a portion of the central portion at the rear of the central portion. The central portion is adapted to be placed over an end of a cable and extend over at least one conductor of the cable. The at least one flange is adapted to connect with a mating conductor. The capacitive section has a width smaller than a width of the central portion and is adapted to be placed immediately adjacent to an insulator of the cable and another conductor of the cable to form substantially a capacitive shorting circuit.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
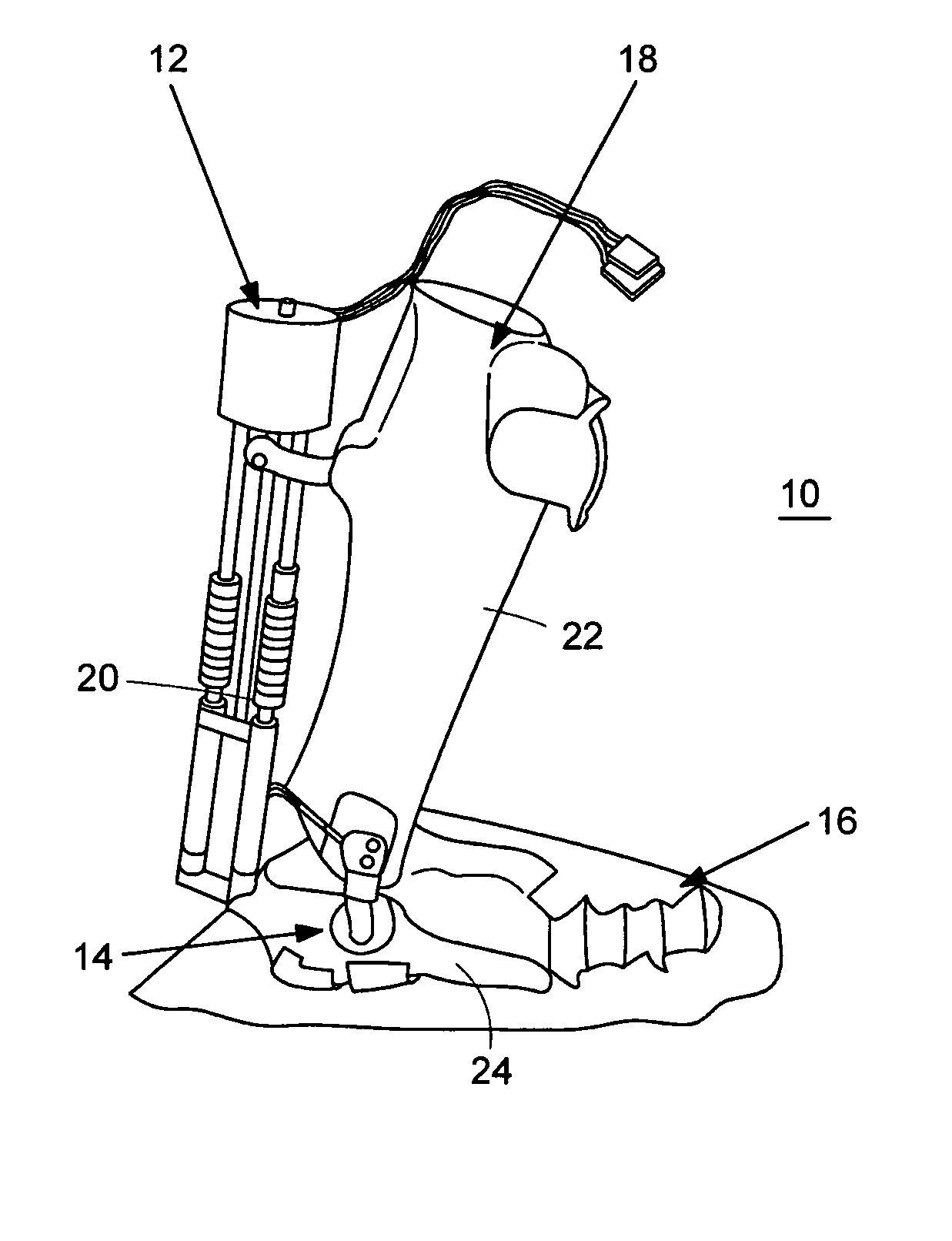
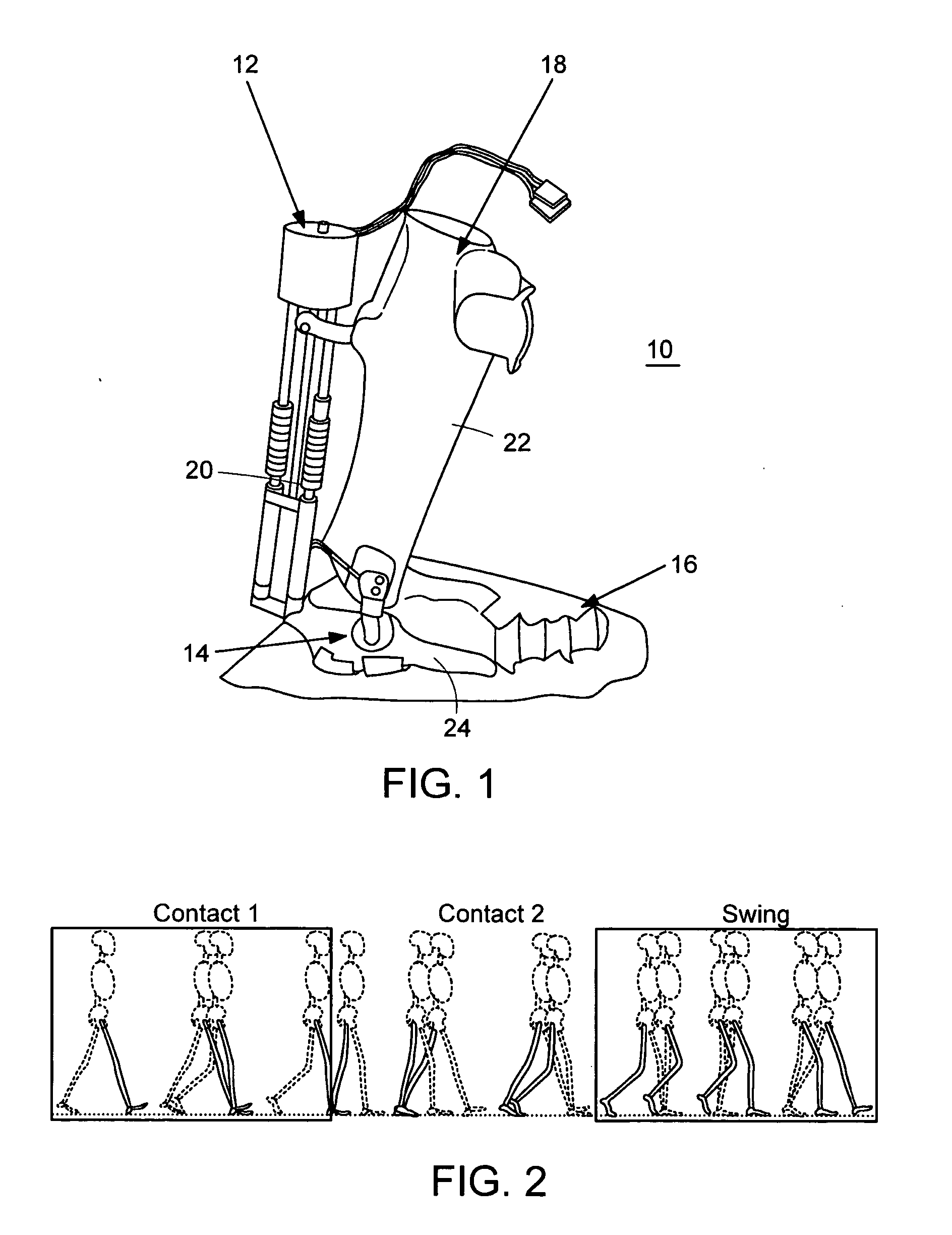
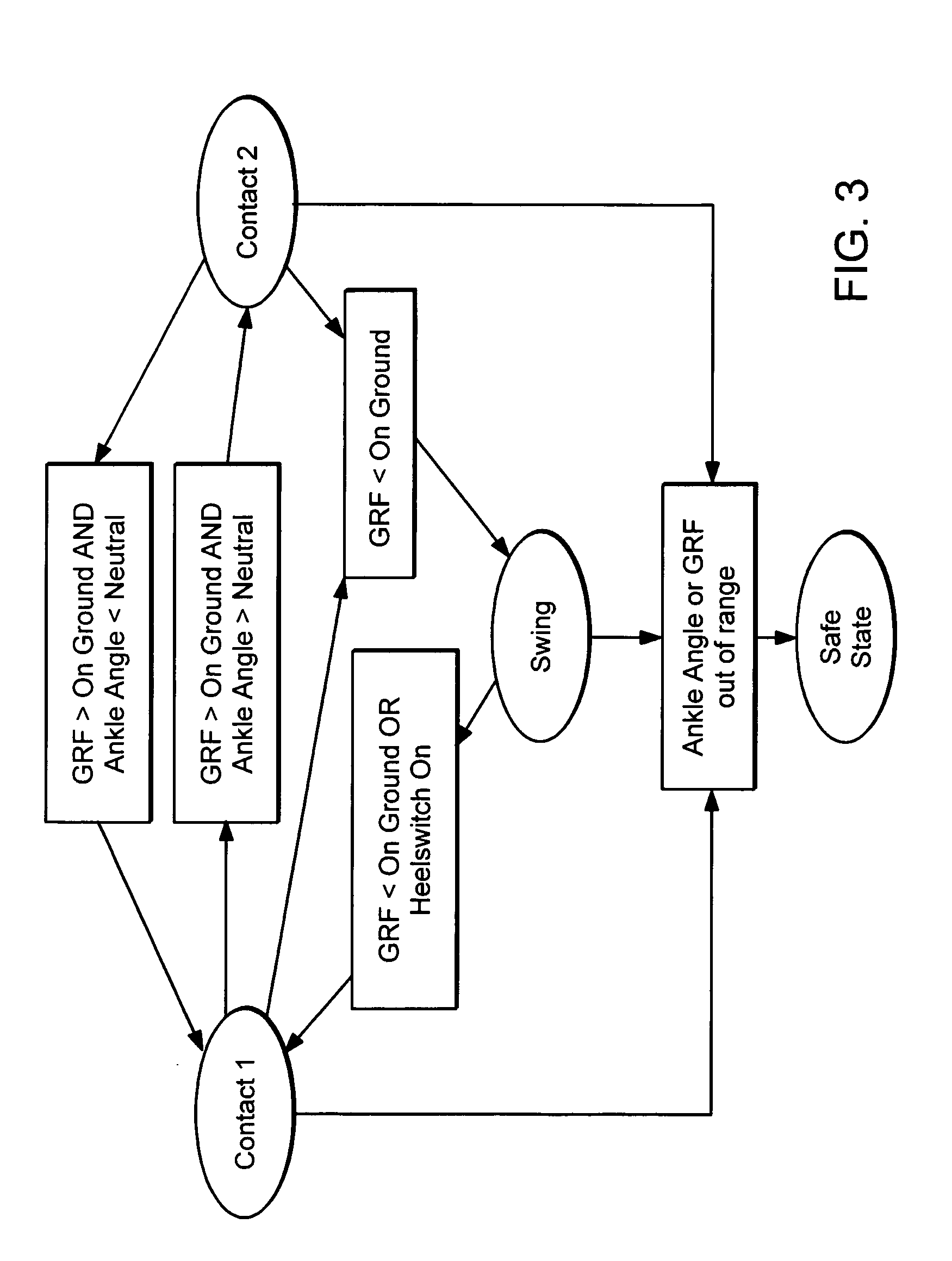
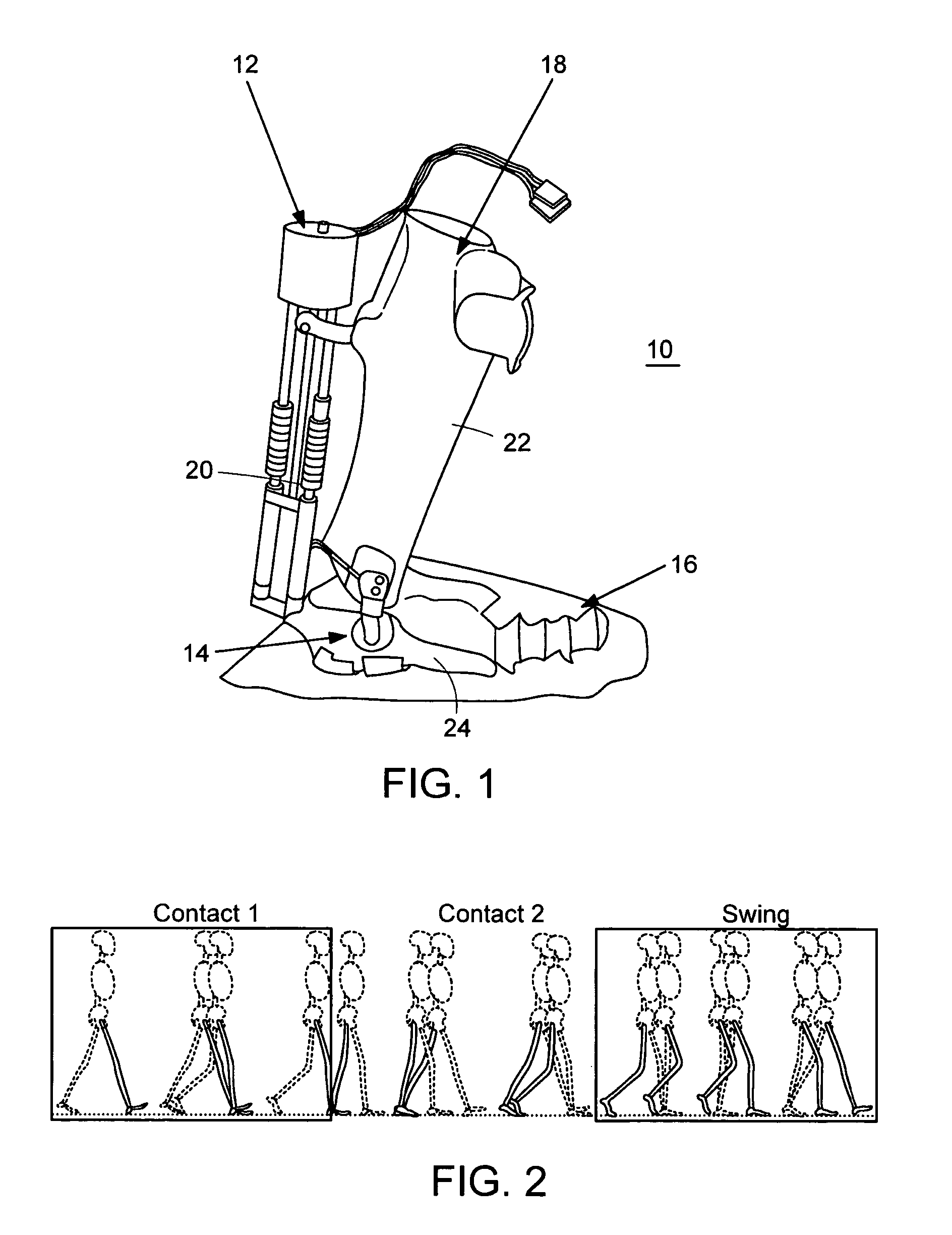
Active ankle foot orthosis
ActiveUS8075633B2Increase independenceGreat easeWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePostural orientation
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
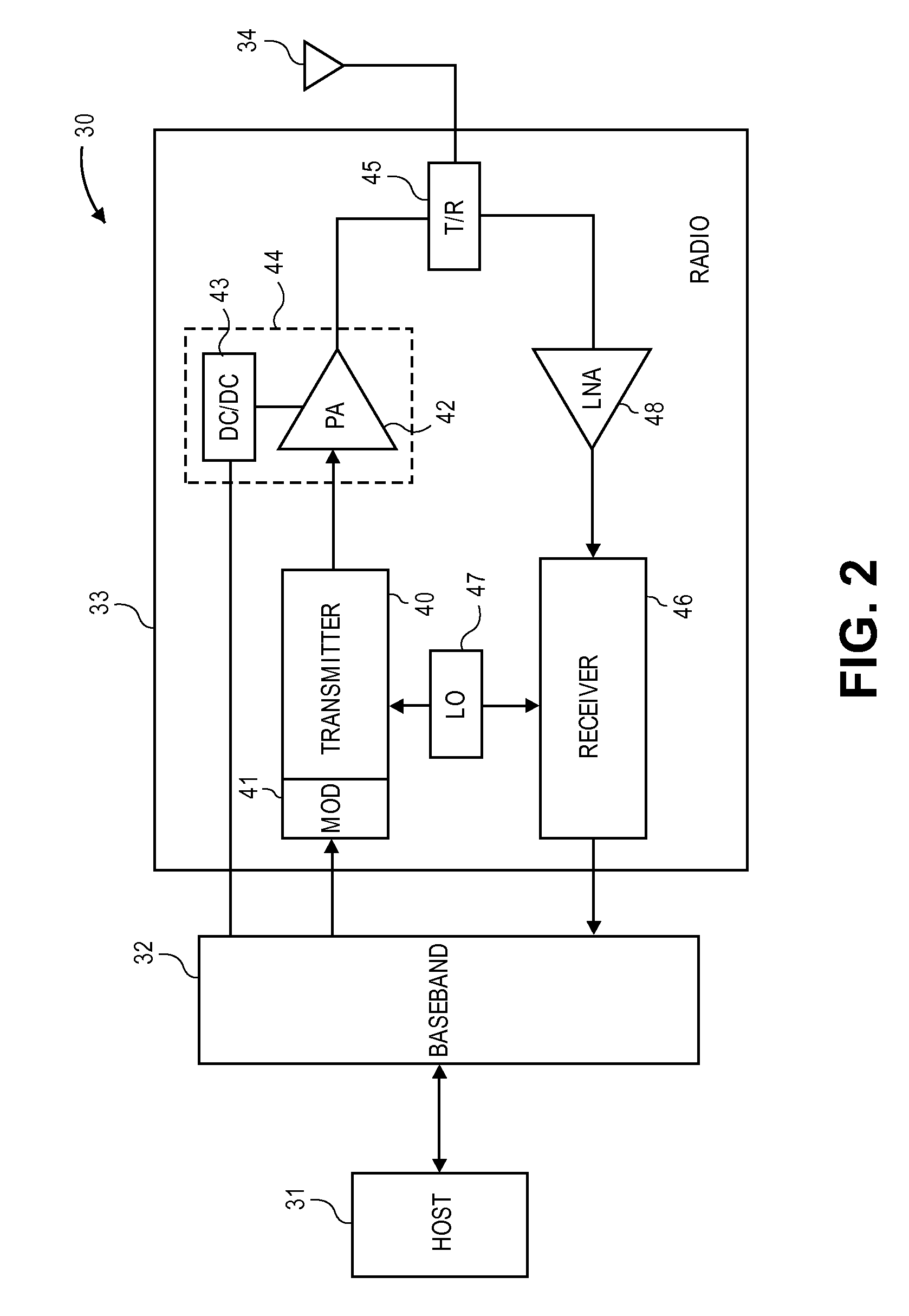
Dynamic stability, gain, efficiency and impedance control in a linear/non-linear CMOS power amplifier
A power amplifier (PA) provides dynamic stability and gain control for linear and non-linear operation. The PA operates with a baseband processor and a transmitter, in which the PA receives a signal from the transmitter for power amplification prior to transmission of the signal. The PA is configured to select between the linear mode of operation and the non-linear mode of operation, in which device scaling within the PA is achieved by changing a device sizing of at least one stage of the PA. Further to changing the device size, the PA changes biasing resistance and impedance of a matching network in response to the changing of the device size to control power output and stability for the PA.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High density integrated circuit module
InactiveUS6919626B2Improve cooling effectImprove space efficiencyPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsAdhesiveFlexible circuits
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for fabricating densely stacked ball-grid-array packages into a three-dimensional multi-package array. Integrated circuit packages are stacked on one another to form a module. Lead carriers provide an external point of electrical connection to buried package leads. Lead carriers are formed with apertures that partially surround each lead and electrically and thermally couple conductive elements or traces in the lead carrier to each package lead. Optionally thin layers of thermally conductive adhesive located between the lead carrier and adjacent packages facilitates the transfer of heat between packages and to the lead carrier. Lead carriers may be formed of custom flexible circuits having multiple layers of conductive material separated by a substrate to provide accurate impedance control and providing high density signal trace routing and ball-grid array connection to a printed wiring board.
Owner:OVID DATA CO
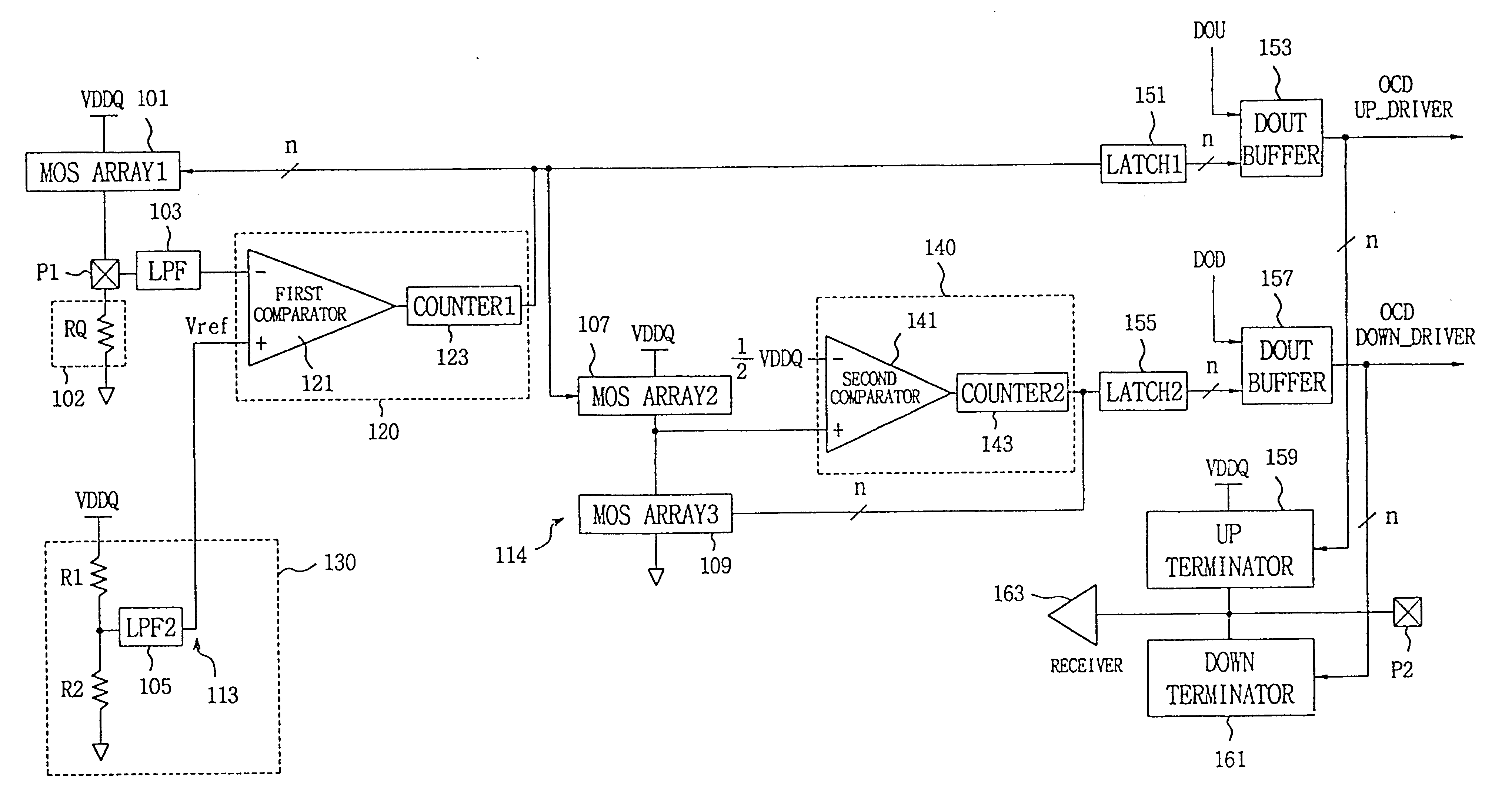
Programmable impedance control circuit
InactiveUS6525558B2Multiple-port networksImpedence matching networksElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
Disclosed is a programmable impedance control circuit, comprising a voltage divider, the voltage divider comprising an MOS array supplied with a first voltage and an external resistance having an external impedance equal to N times said external resistance. The voltage divider outputs a second voltage. A reference voltage generator is provided for generating a third voltage corresponding to N / (N+M) times said first voltage as a reference voltage for said second voltage, and wherein M times internal impedance is used for N times external impedance (N=M or N<> M).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High performance, small form factor connector with common mode impedance control
Techniques for improving electrical performance of a connector. The techniques are compatible with the form factor of a standardized connector, such as an SFP connector or stacked SFP. The resulting connector has reduced insertion loss for high speed signals. Such techniques, which can be used separately or together, include shaping of conductive elements within the connector while still retaining the same mating contact arrangement. Changes may be made at the contact tail portions or in the intermediate portions where engagement to a connector housing occurs. The techniques also include the incorporation of lossy bridging members between conductive elements designated to be ground conductors. For connectors according to the stacked SFP configuration, multiple bridging members may be incorporated at multiple locations within the connector.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
DRAM interface circuits having enhanced skew, slew rate and impedance control
Fully-buffered dual in-line memory modules (FB-DIMM) include advanced memory buffers (AMBs) having enhanced skew, slew rate and output impedance control. The AMB includes user accessible registers that can be programmed to carefully control the edge placement (or phase) of signals generated from the AMB to multiple DRAMs on the module. This control of edge placement, which may be performed independently for each group of signals: clock (CLK, CLK#), command (RAS, CAS, WE), address (including bank address), data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS), provides 360 degrees of control (or one period). This means that any group of signals can be moved independently by one complete period relatively to any other group.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
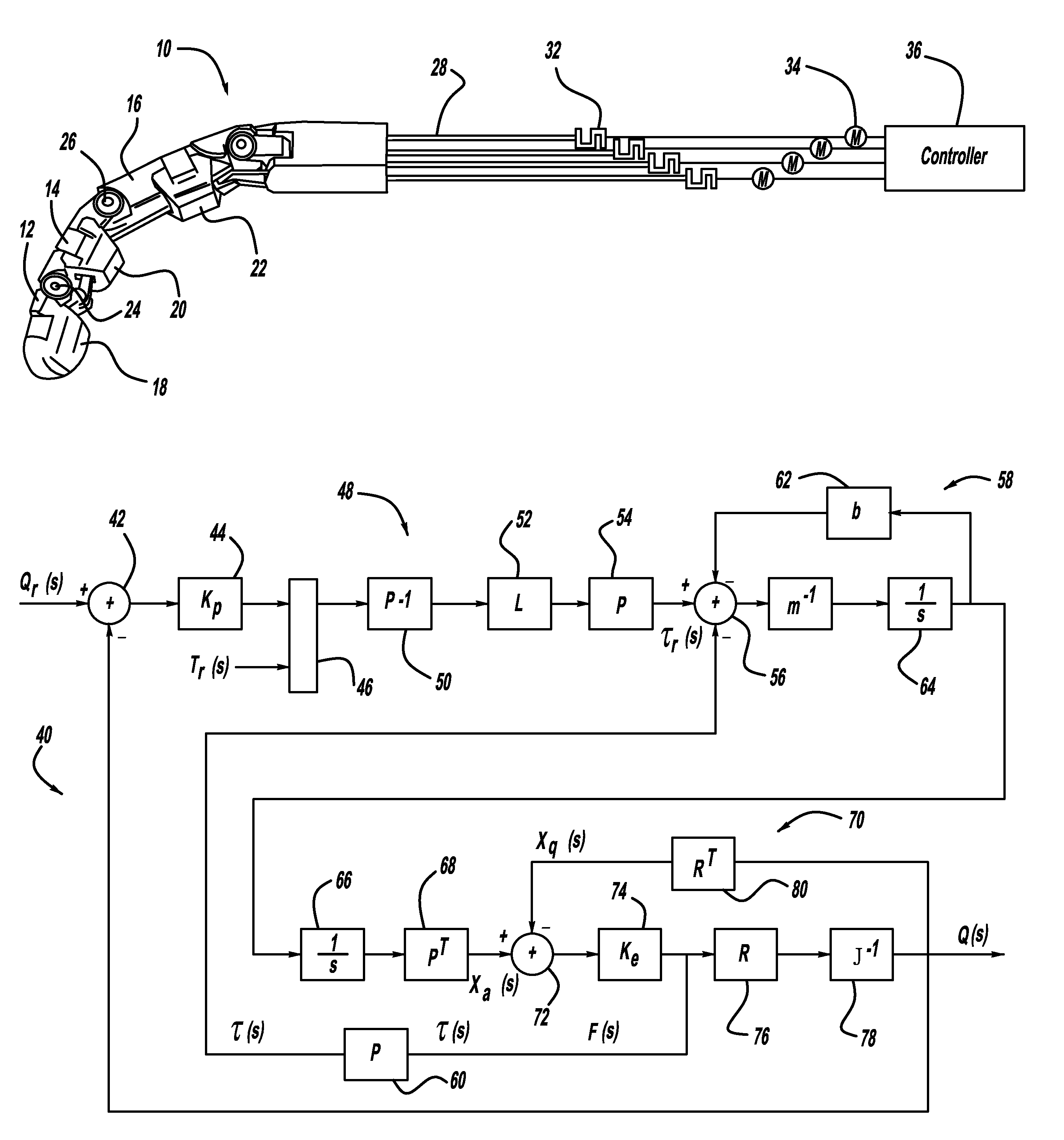
Device and method for controlling robot arm, robot and program
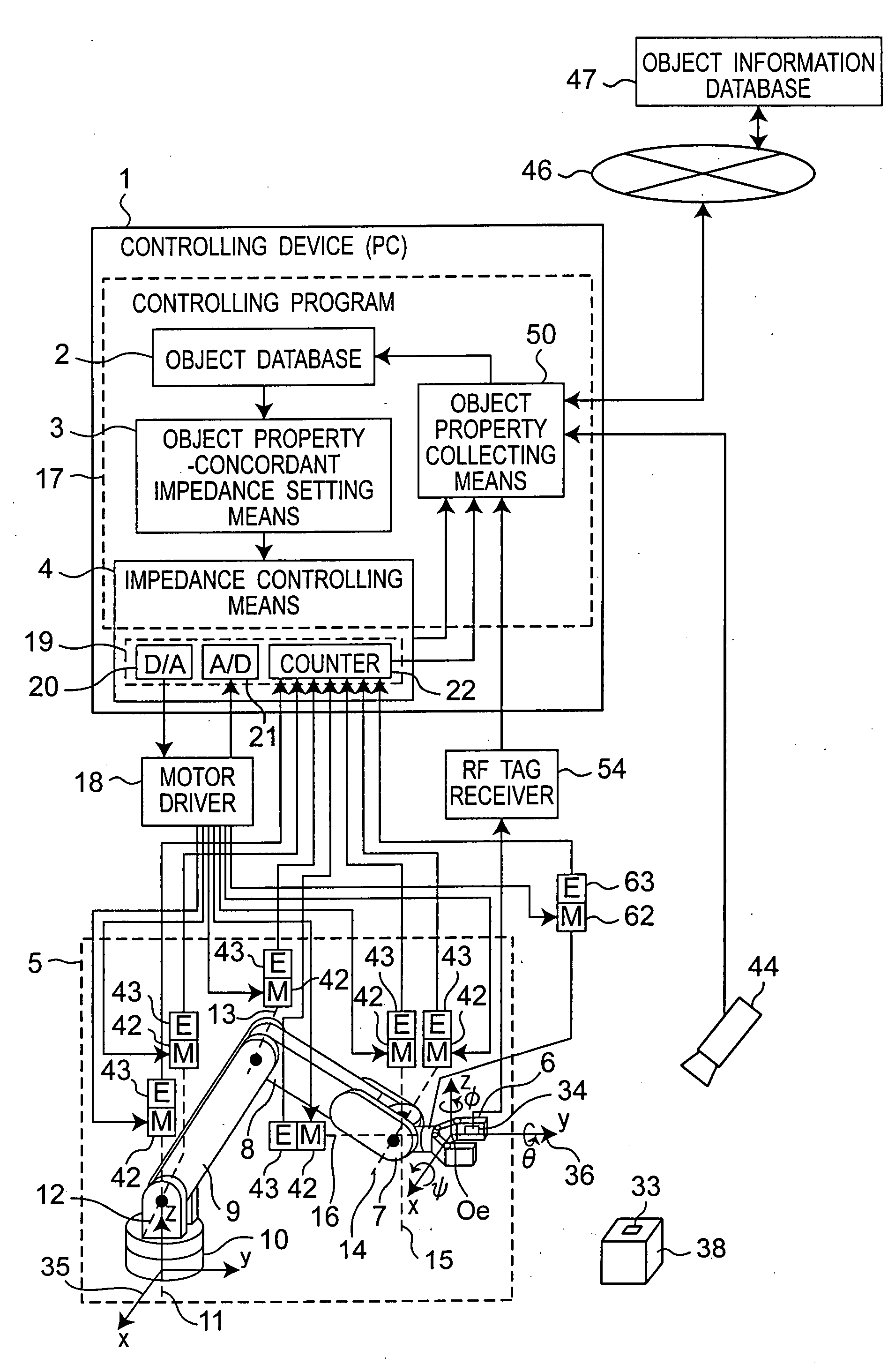
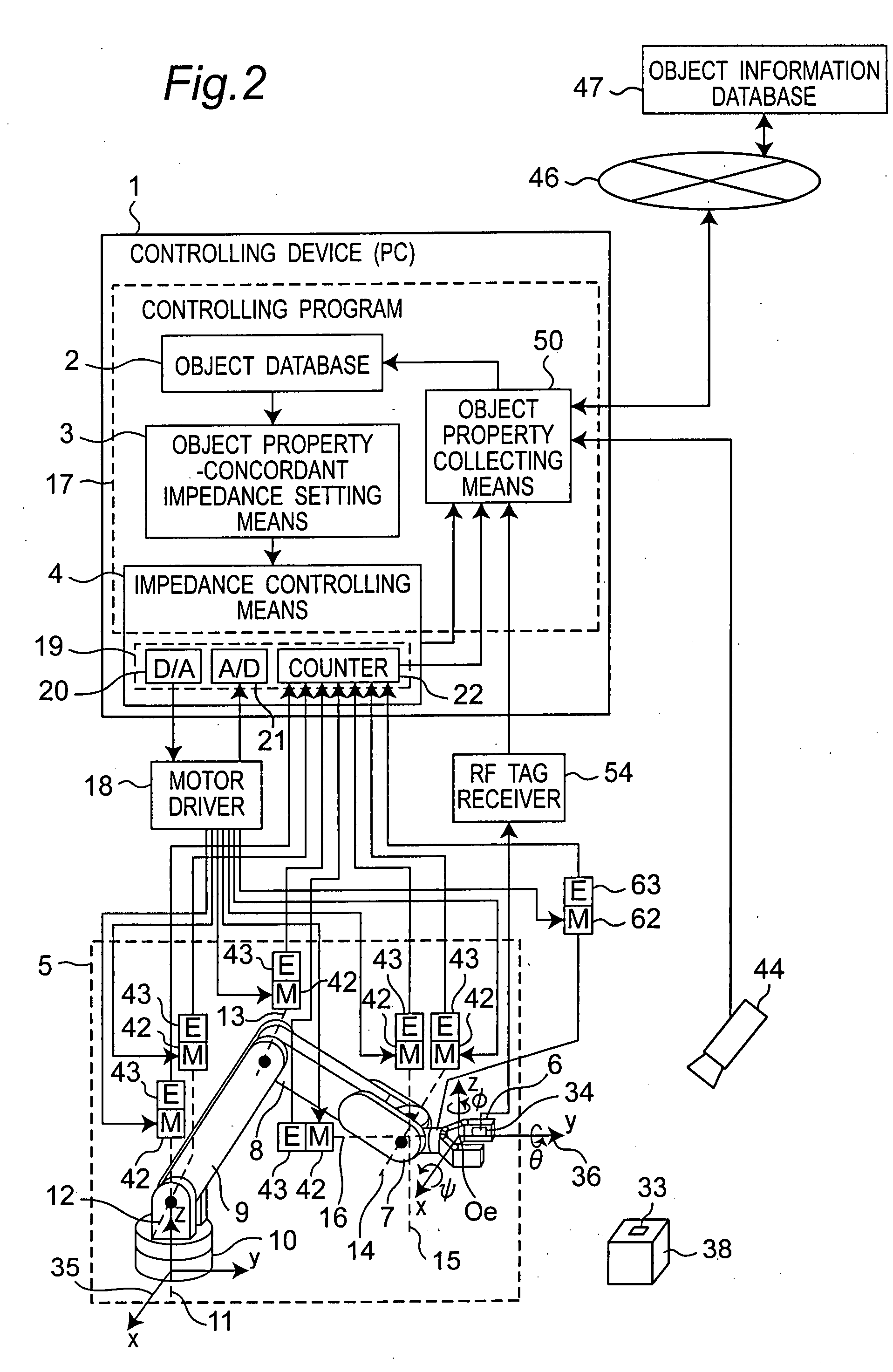
ActiveUS20090105880A1Control be possibleProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringControl theory
In a robot arm controlling device, a mechanical impedance set value of the arm is set by an object property-concordant impedance setting device based on information of an object property database in which information associated with properties of an object being gripped by the arm is recorded, and a mechanical impedance value of the arm is controlled to the set mechanical impedance set value by an impedance controlling device.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
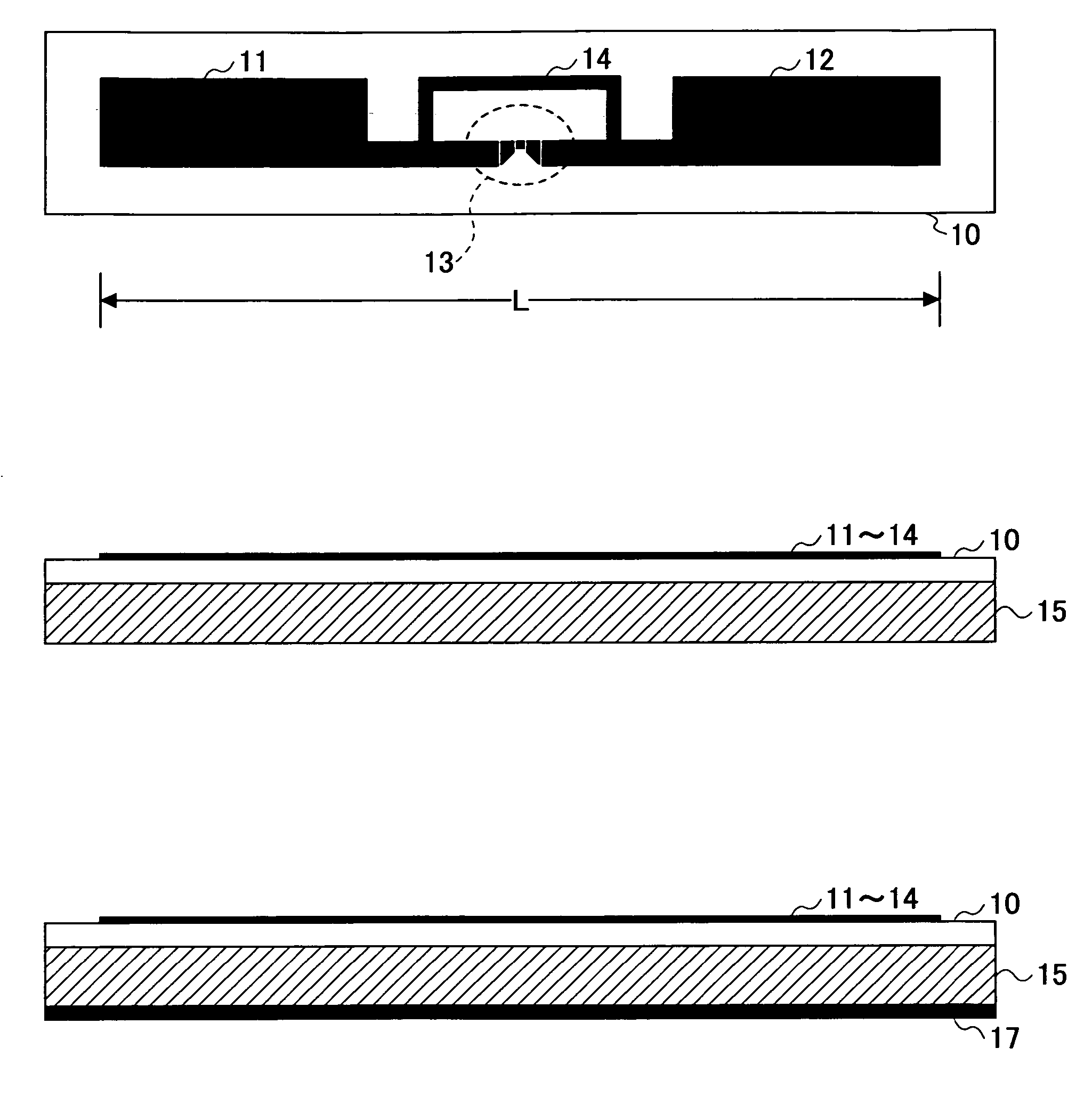
RF tag and method of manufacturing the RF tag
InactiveUS20080111695A1Small sizeRadiating elements structural formsSubscribers indirect connectionEffective lengthLength wave
An RF tag to accompany a conductive object is disclosed that includes an antenna and an integrated circuit connected to the antenna. The antenna includes a first radiating element, a second radiating element, a feeding part connected in series between the first and second radiating elements, and an impedance control part connected parallel to the feeding part. The antenna has an effective length shorter than half of a wavelength used in communication.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
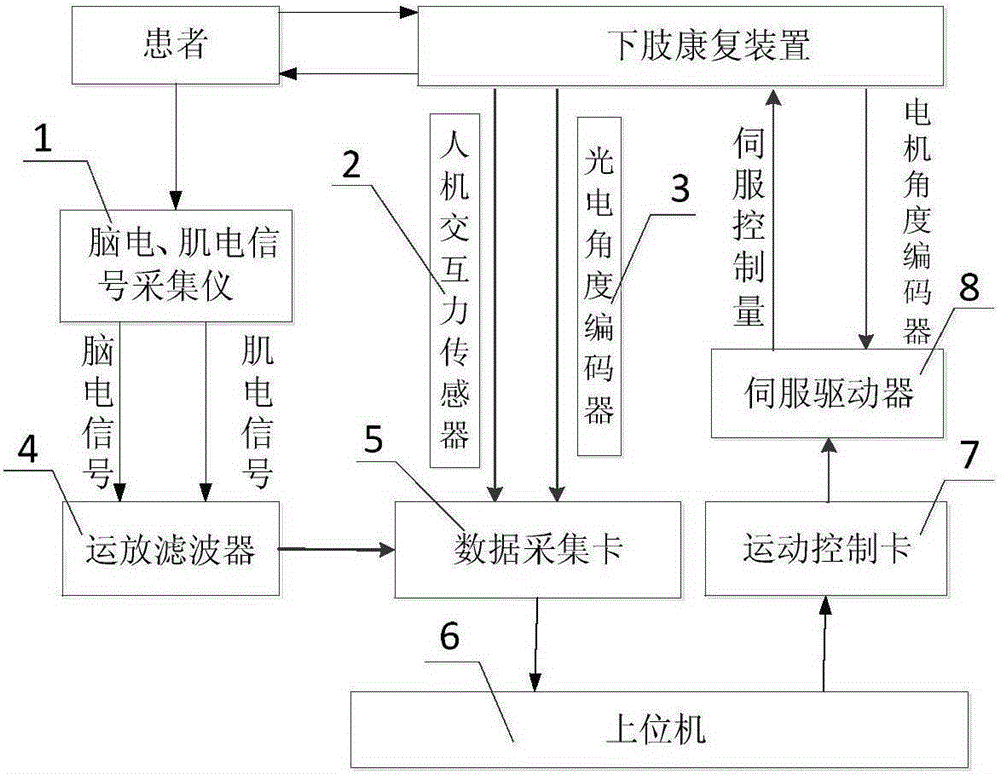
Variable-impedance lower limb rehabilitation robot control method based on brain muscle information
ActiveCN105213153AHigh precisionReal-time recovery assessmentGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesFeature vectorMan machine
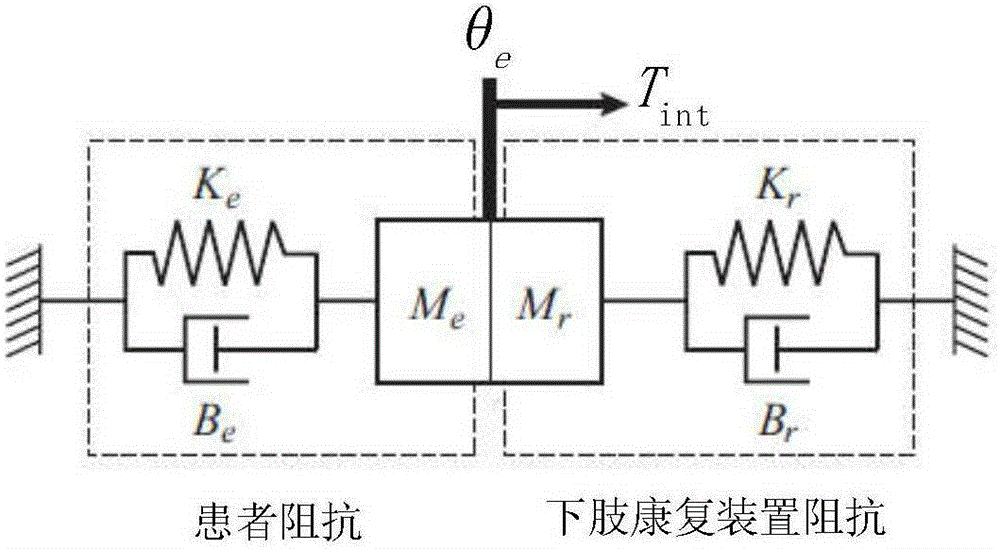
The invention discloses a variable-impedance lower limb rehabilitation robot control method based on brain muscle information. The method includes: collecting electroencephalogram and surface electromyogram signals of a patient in real time through an electroencephalogram and surface electromyogram signal collector, and monitoring and evaluating rehabilitation degree of the patient; adopting different rehabilitation training strategies; when the rehabilitation degree is low, implementing passive training control, adopting a PD position servo control method, and controlling a lower limb rehabilitation device to enable the patient to move with a correct physiological gait track; when the rehabilitation degree is high, adopting an active control mode, and predicting a movement intention of the patient by extracting feature vectors of electroencephalogram signals and surface electromyogram signals of the patient in real time; using a fuzzy neutral network algorithm to integrate the electroencephalogram signals and the surface electromyogram signals to generate a movement gait track curve expected by the patient in real time; utilizing a variable-impedance control method to realize active, realtime and synergistic control of a lower limb rehabilitation robot man-machine system.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
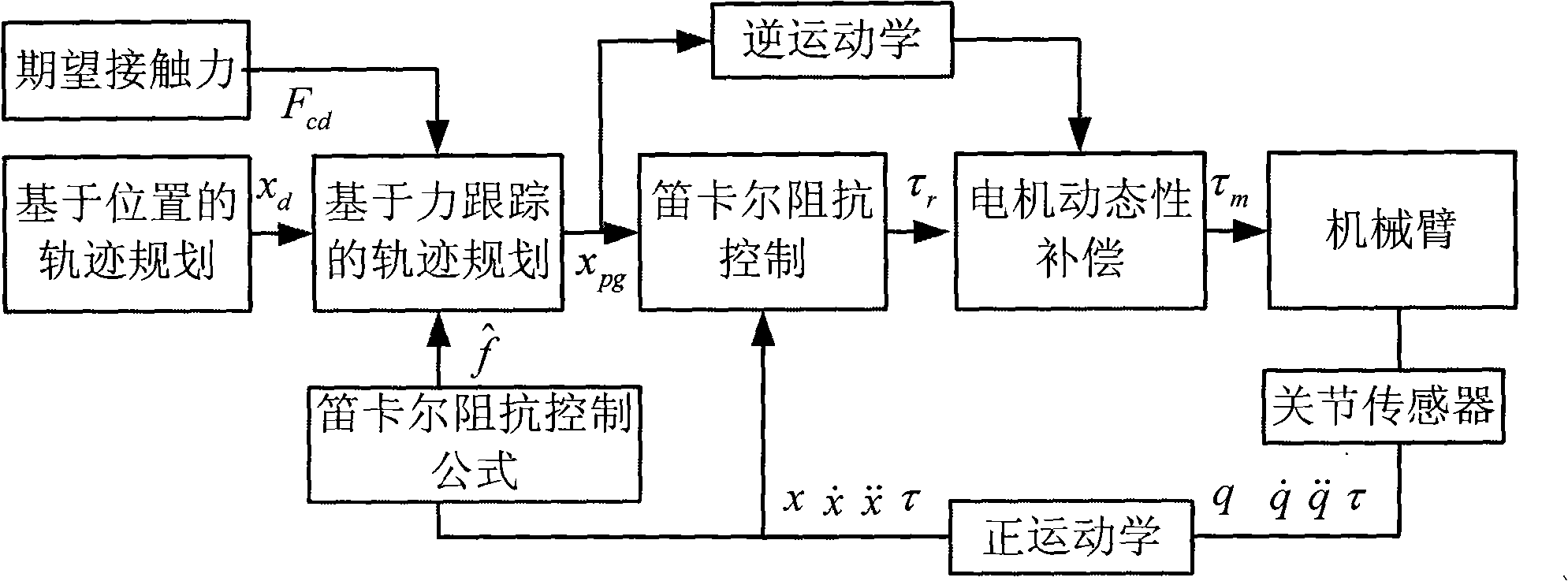
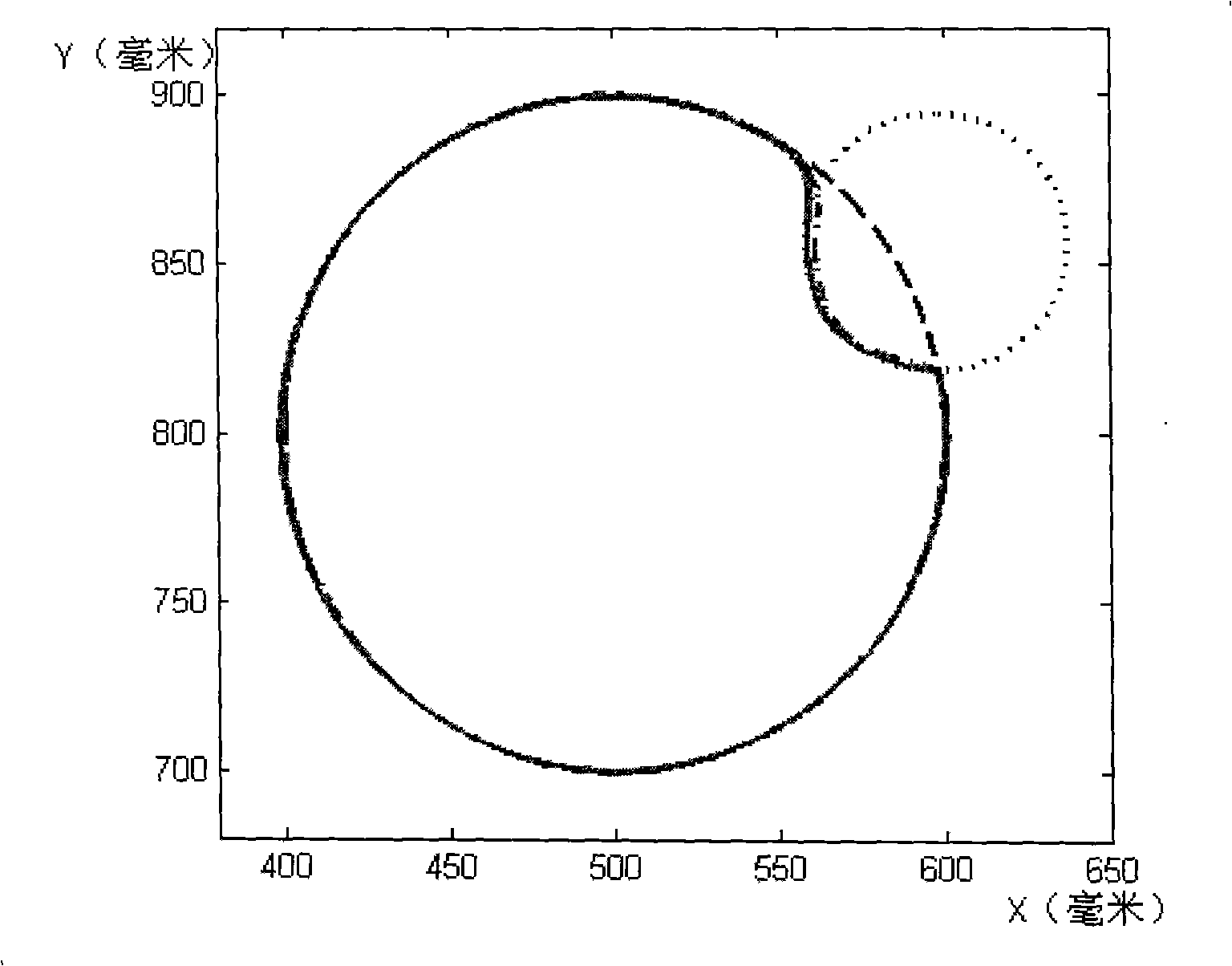
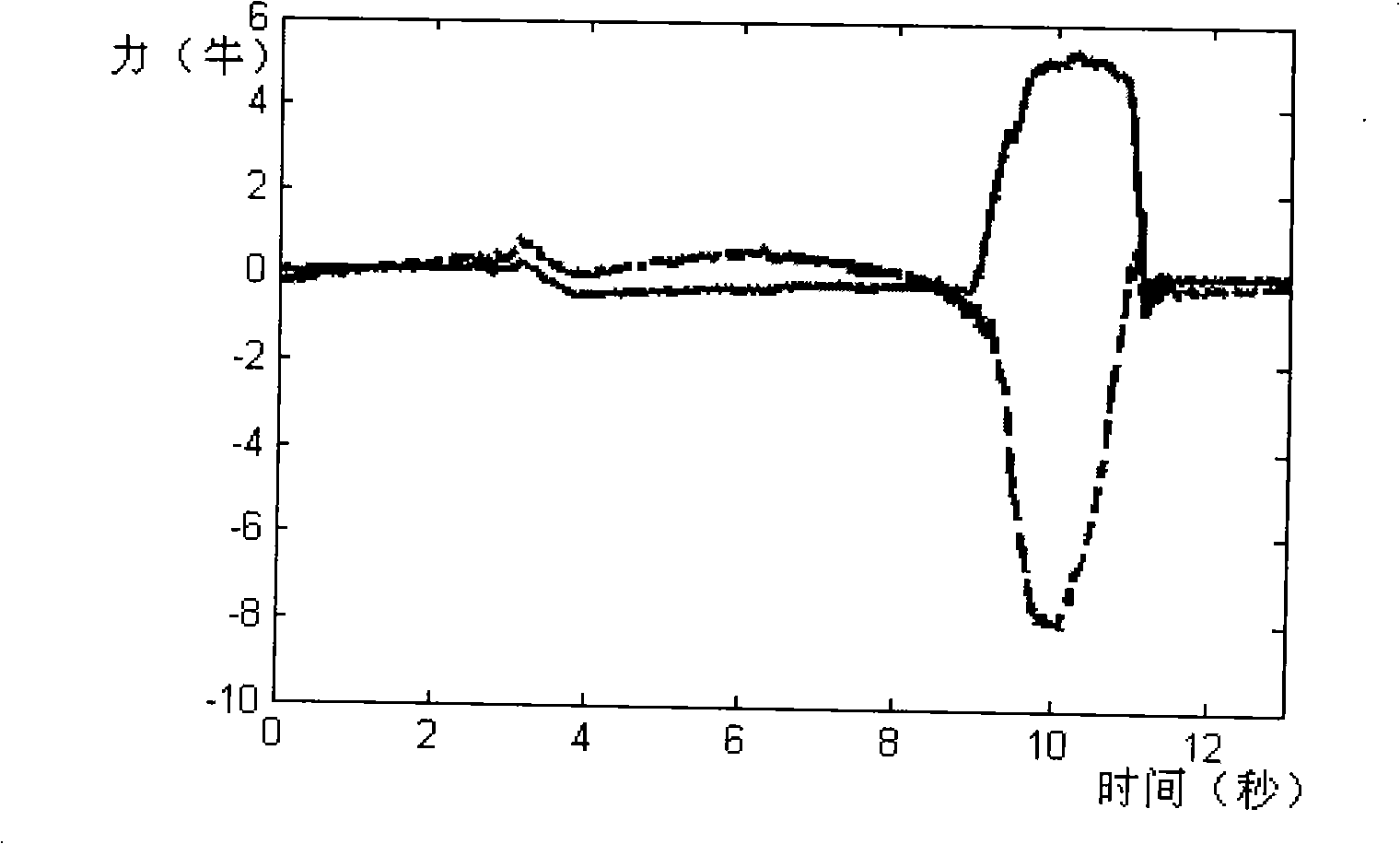
Control method of man machine interaction mechanical arm
InactiveCN101332604AEnsure safetySoft touchProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsElectric machinery
The invention provides a control method of a human-machine interaction mechanical arm, which relates to a safe control method of a mechanical arm working under an unknown environment and solves the problem that an operator accidentally injured due to failure of the existing mechanical arm to accurately model the working environment when the mechanical arm works in close contact with the operator. A mechanical arm controller of the invention collects a joint position in a real time manner by a joint sensor and transforms the joint position q to a Descartes position x by the positive kinematics, and calculates the real-time trajectory planning xpg which is provided with a feedback of the Descartes force; the mechanical arm controller also collects the torque Tau by the joint sensor in a real time manner, calculates the expected torque Taur by Descartes impedance control, and calculates the input torque Taum of the mechanical arm joint by the dynamic compensation of a motor. The control method can effectively detect the force from each joint of the mechanical arm; when contacting an object, the mechanical arm can carry out a soft contact; when a collision happens, the mechanical arm can ensure that the contact force from each direction is within the range of the expected force, thus ensuring the safety of the mechanical arm and the operator.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
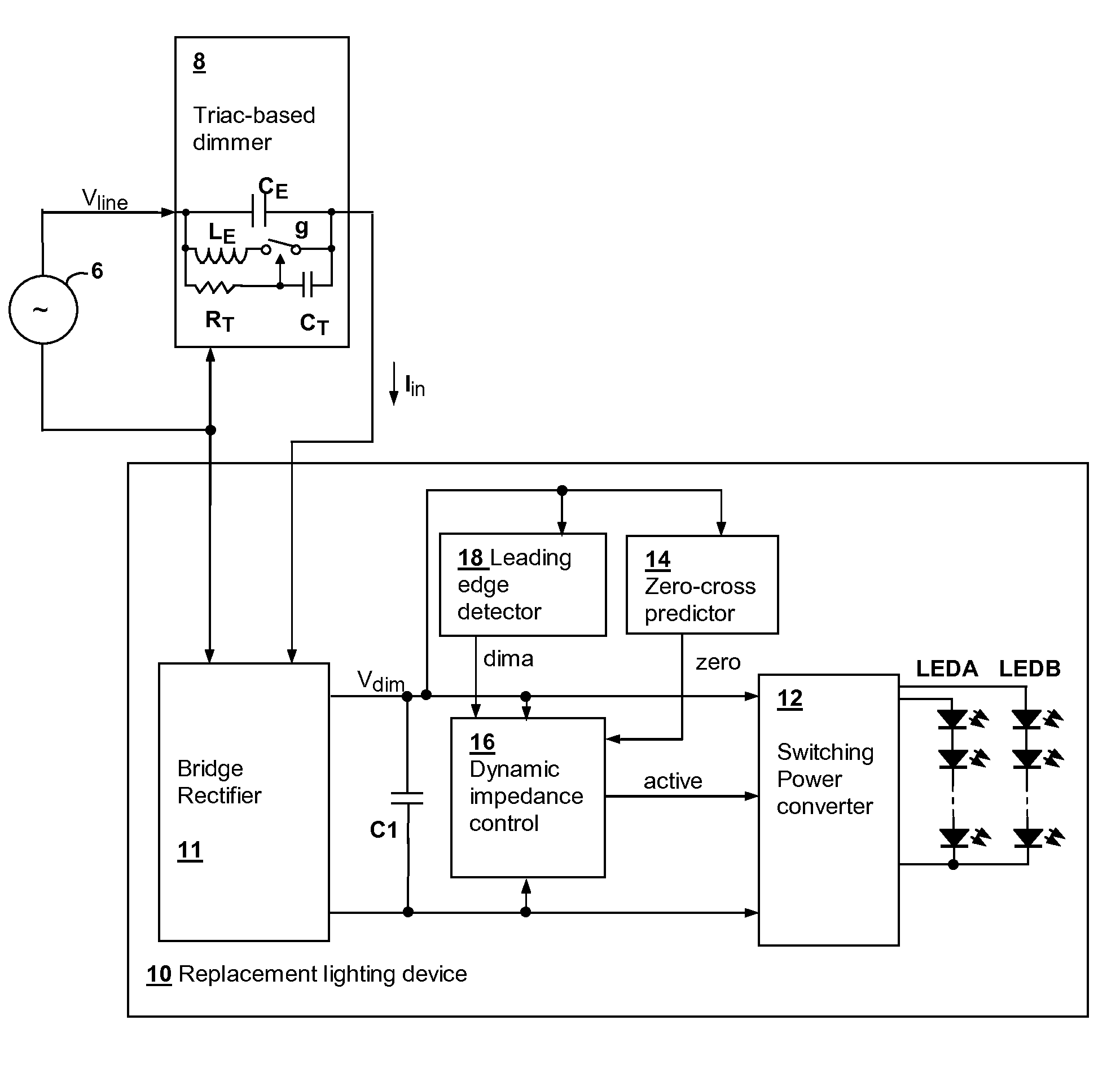
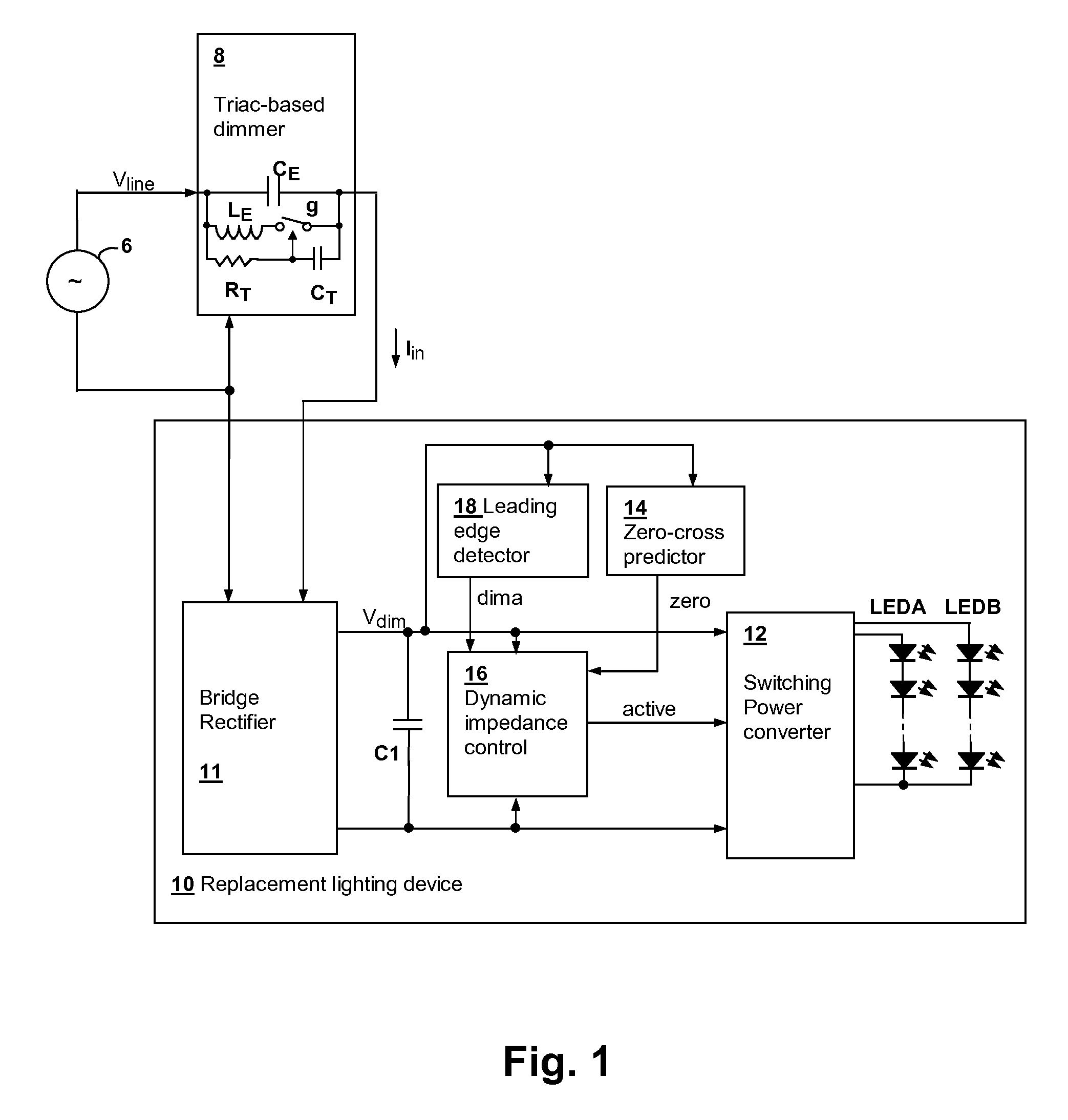
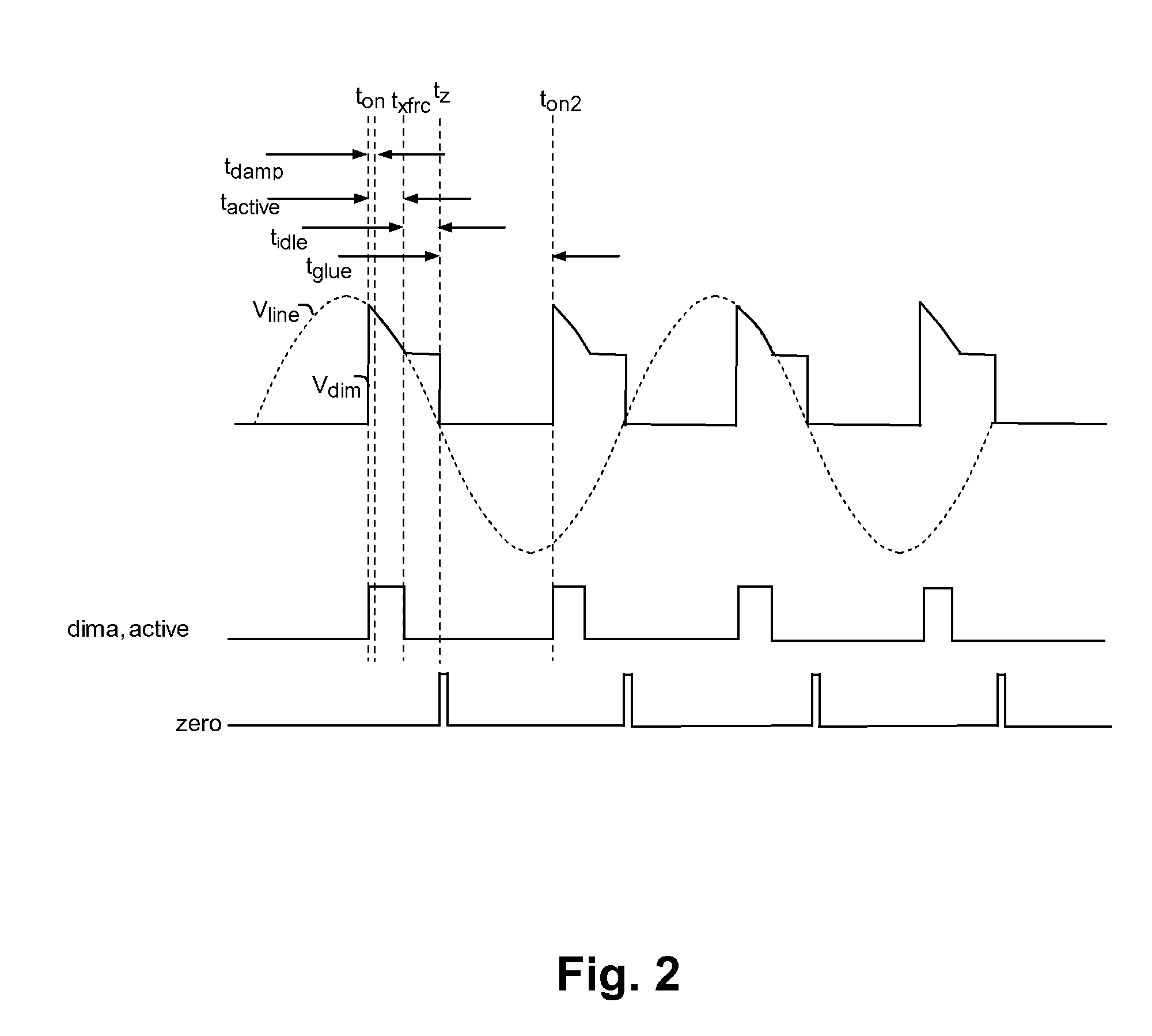
Powering high-efficiency lighting devices from a triac-based dimmer
ActiveUS20120025729A1Preventing false triggeringDissipative loadingElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesTRIACThyratron
A circuit for powering high-efficiency lighting devices from a thyristor-controlled dimmer predicts a zero-crossing time of the AC power line supplying the dimmer and causes a glue impedance to be imposed at the output of the dimmer starting at the time of the zero-crossing, so that the timer in the dimmer will operate properly to generate the turn-on event at the correct time. At turn-on, a lower level of impedance is presented to absorb the energy associated with the turn-on event. A higher level of impedance may be presented after the energy is absorbed until all of the energy needed for the cycle is transferred. Then, a high impedance state is maintained until the next zero-crossing time. The impedance control may be provided by non-uniform operation of a power converter that supplies the lighting devices, or by a combination of non-uniform power converter operation and dissipative loading.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Semiconductor integrated circuit device capable of controlling impedance
ActiveUS20050040845A1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsExternal referenceEngineering
A semiconductor integrated circuit device is connected to an external reference resistor, including an impedance control circuit for generating impedance control codes variable with impedances established by the external reference resistor. An input circuit receives an external signal through an input transfer line and forwards the external signal to an internal circuit. A termination circuit terminates the input transfer line in response to at least one of the impedance control code. An output circuit drives an output transfer line in accordance with an output signal. Impedance is variable with the control codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
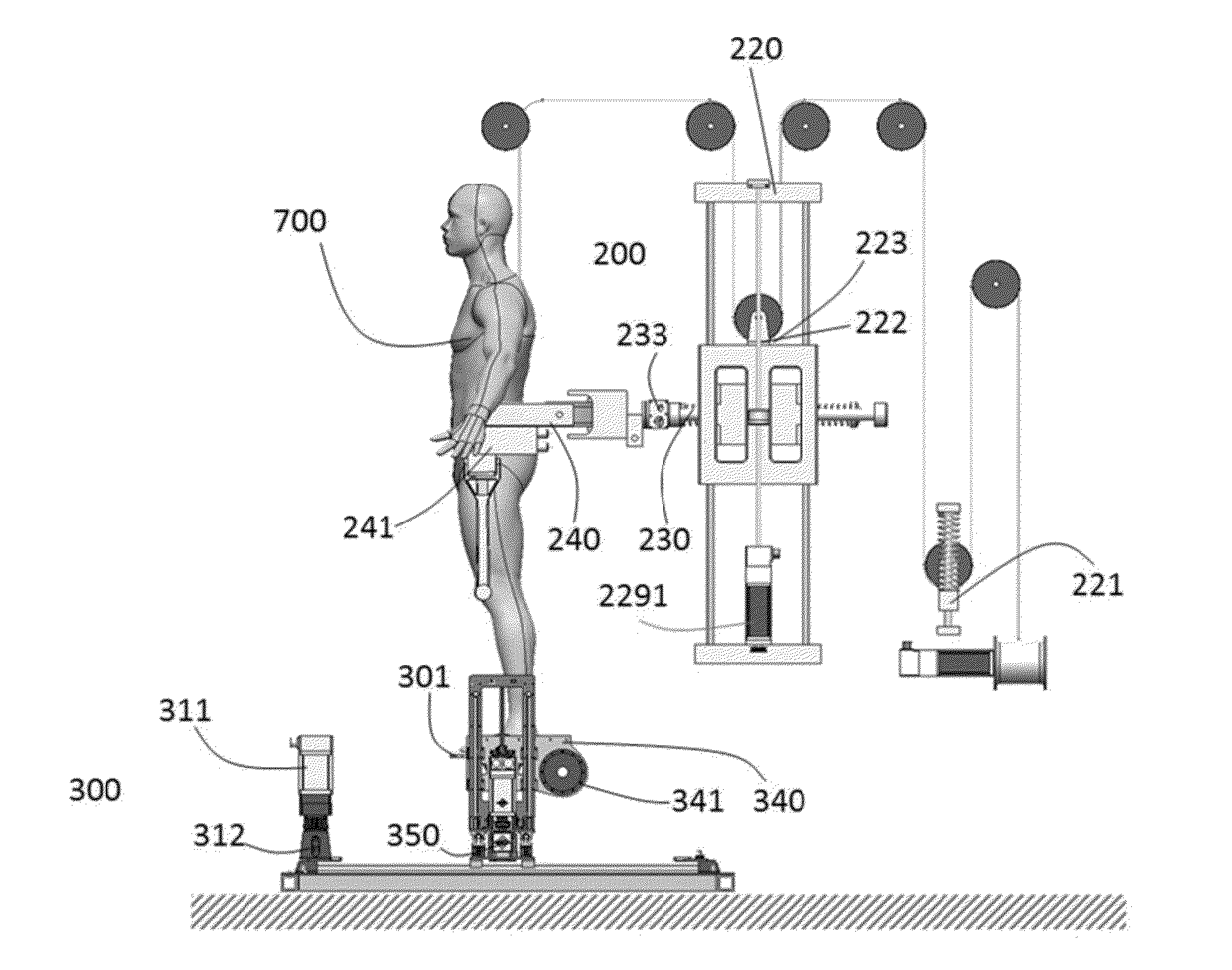
Lower Extremity Robotic Rehabilitation System
To achieve “ecological” robotic rehabilitation therapy, the present invention provides the system capacity of training of patients in different ambulatory tasks utilizing motorized footplates that guide the lower limbs according to human gait trajectories generated for different ambulatory tasks of interest. A lower extremity robotic rehabilitation system comprises an active pelvic / hip device which applies series elastic actuation to achieve an intrinsically safe and desirable impedance control. A robotic unit features the telepresence operation control that allows a patient stay at home or nursing home to continue his or her rehabilitation training under a physician's remote supervision and monitoring. The robot unit utilizes an affective patient-robot interface to capture emotional information of the patient, to allow for real-time adaptation of the robotic system and adjustments of treatment protocol, and to enhance the quality and effectiveness of rehabilitation
Owner:HU JIANJUEN +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com