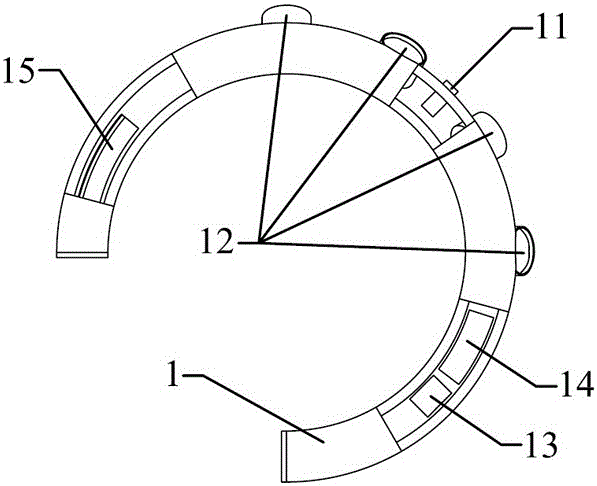
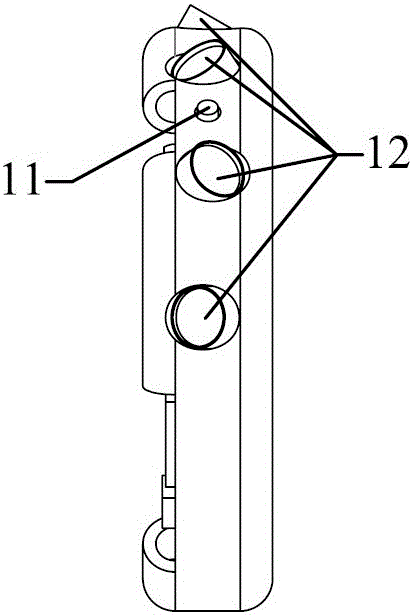
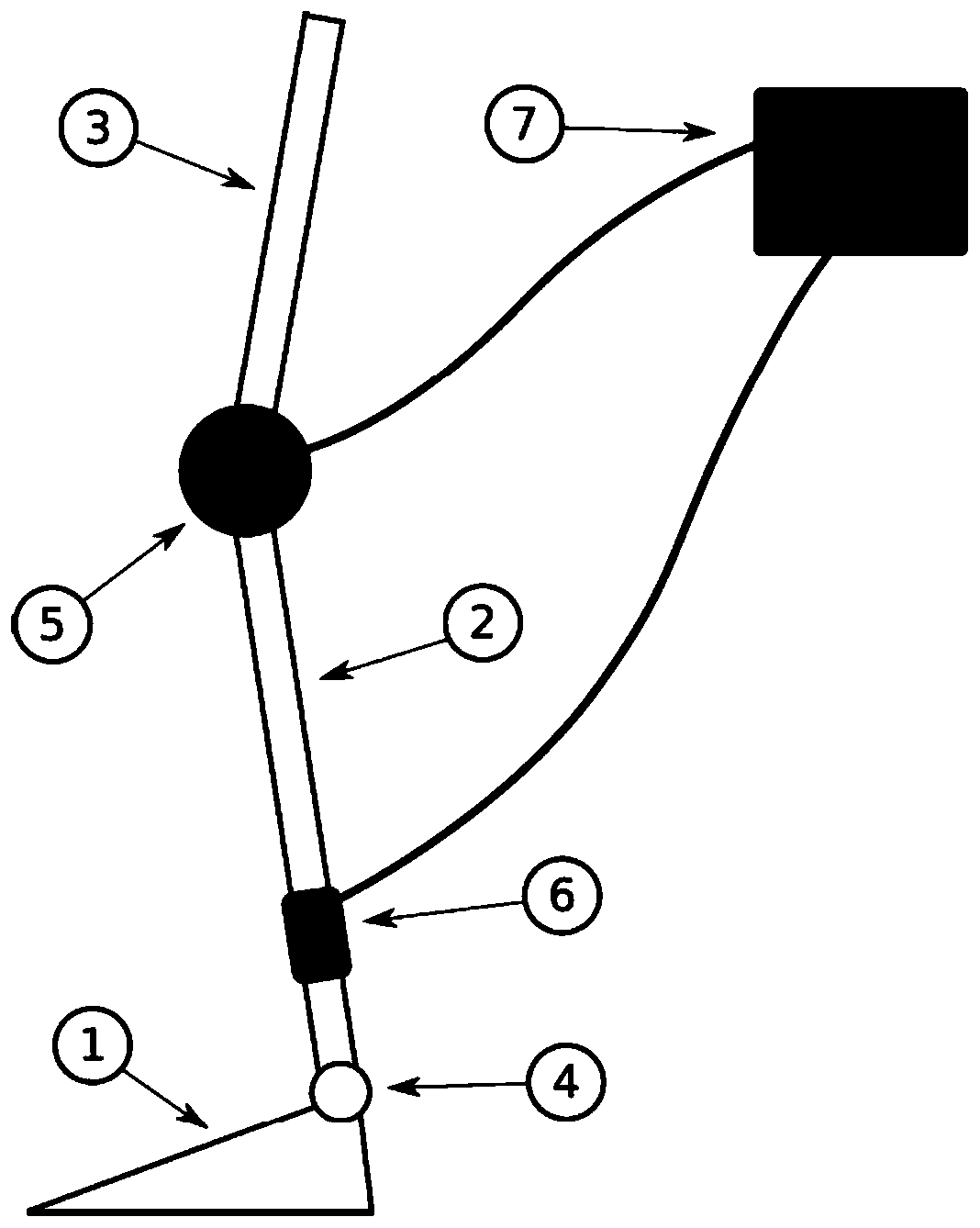
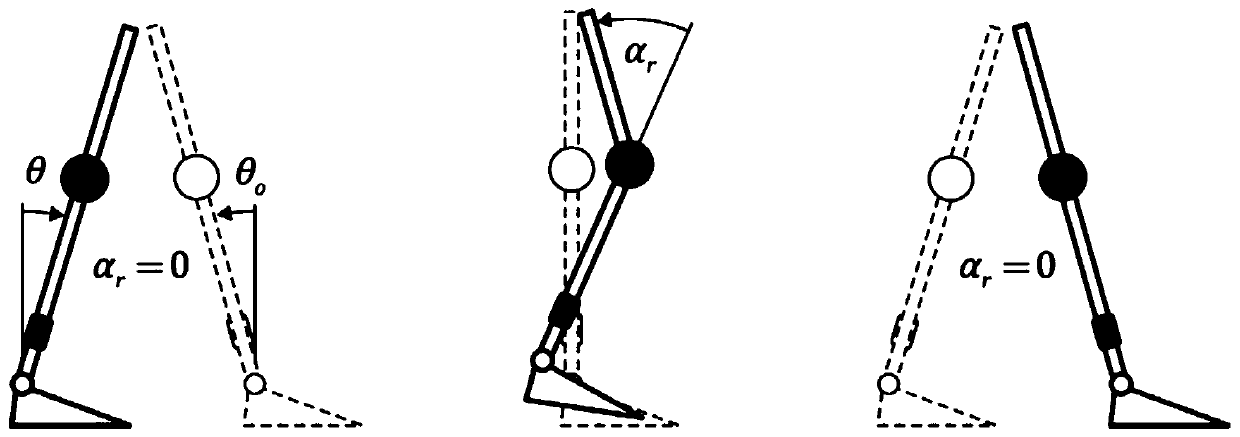
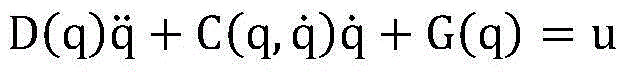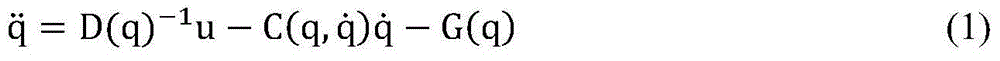Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Walking cycle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
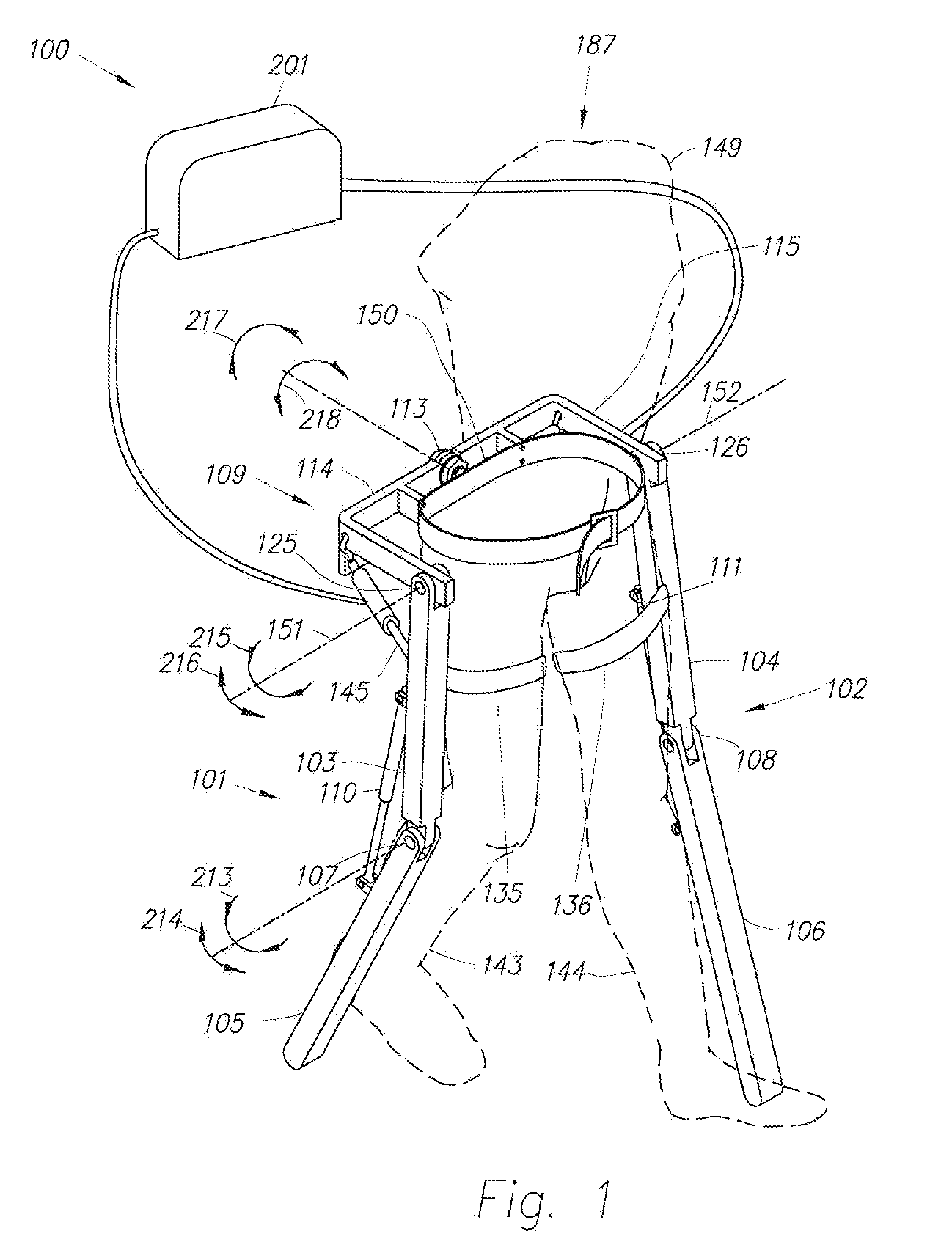
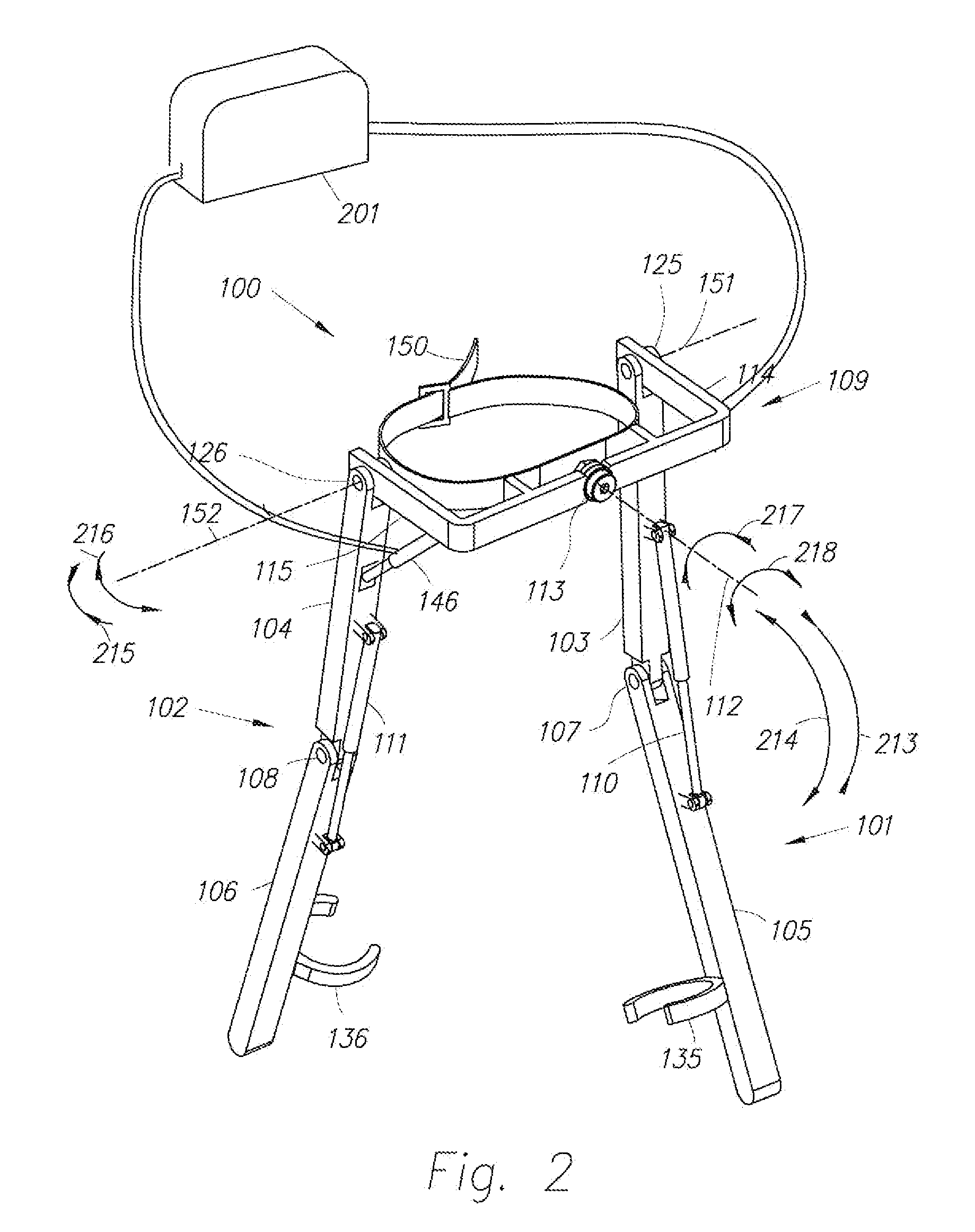
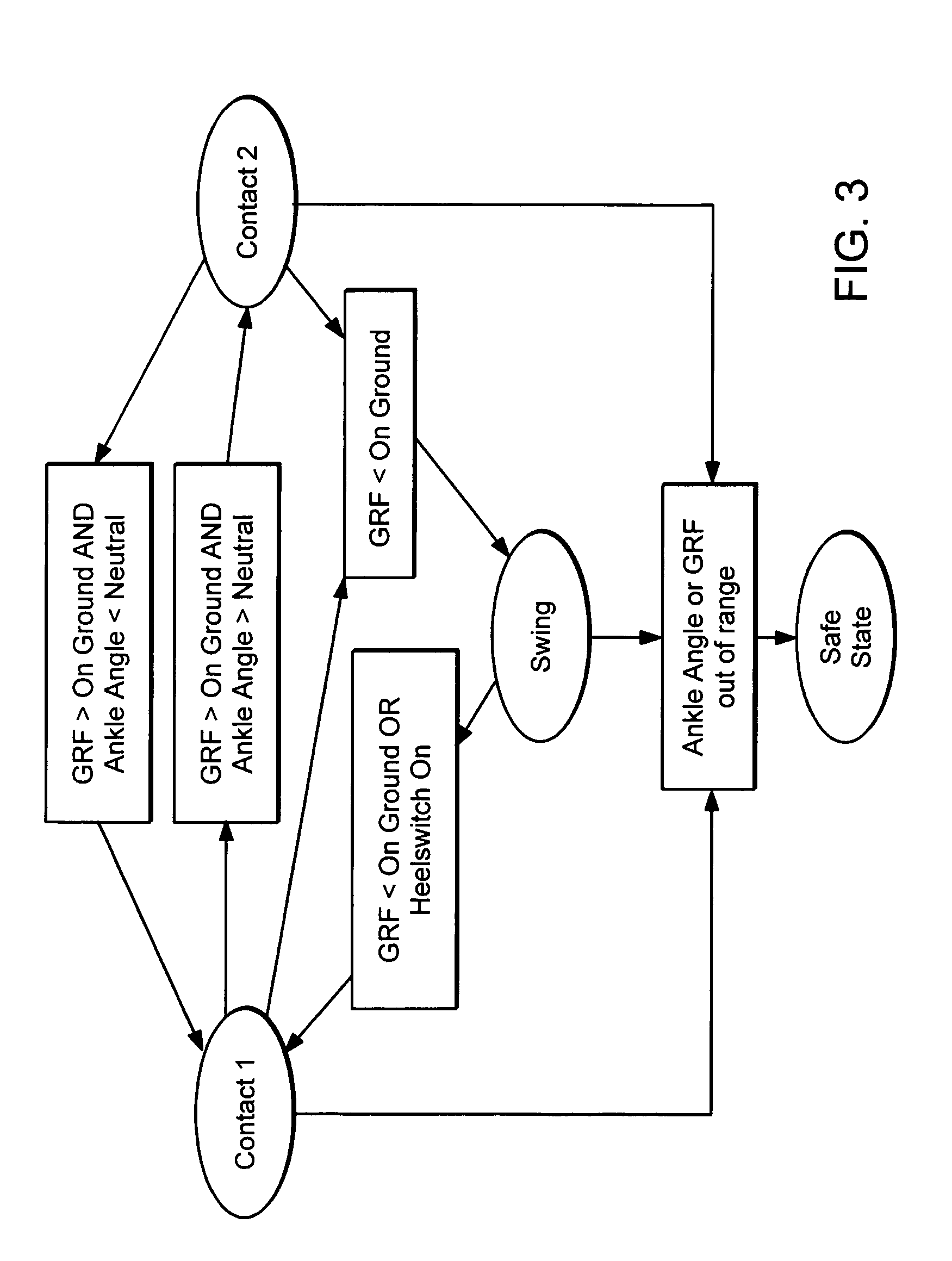
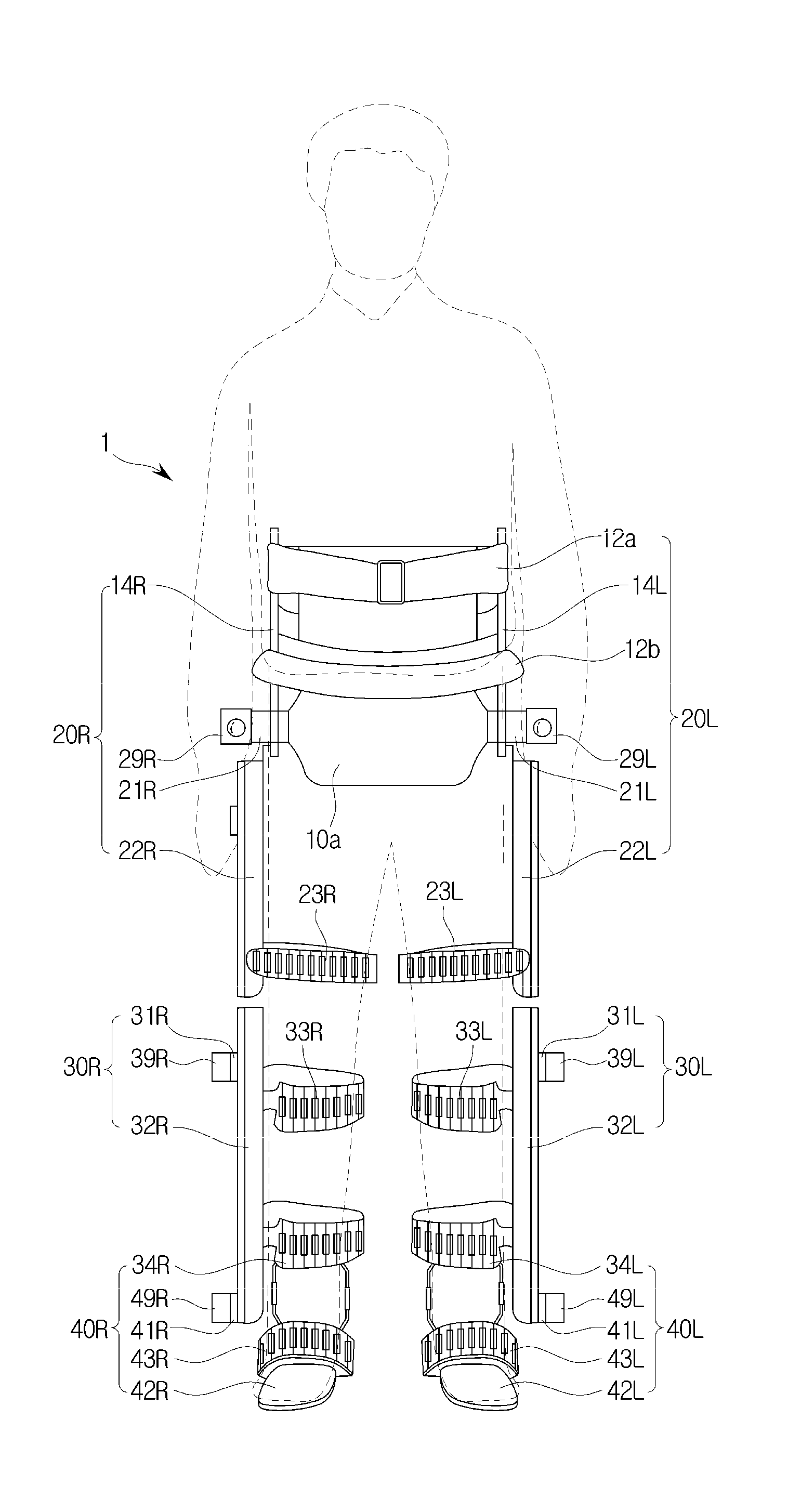
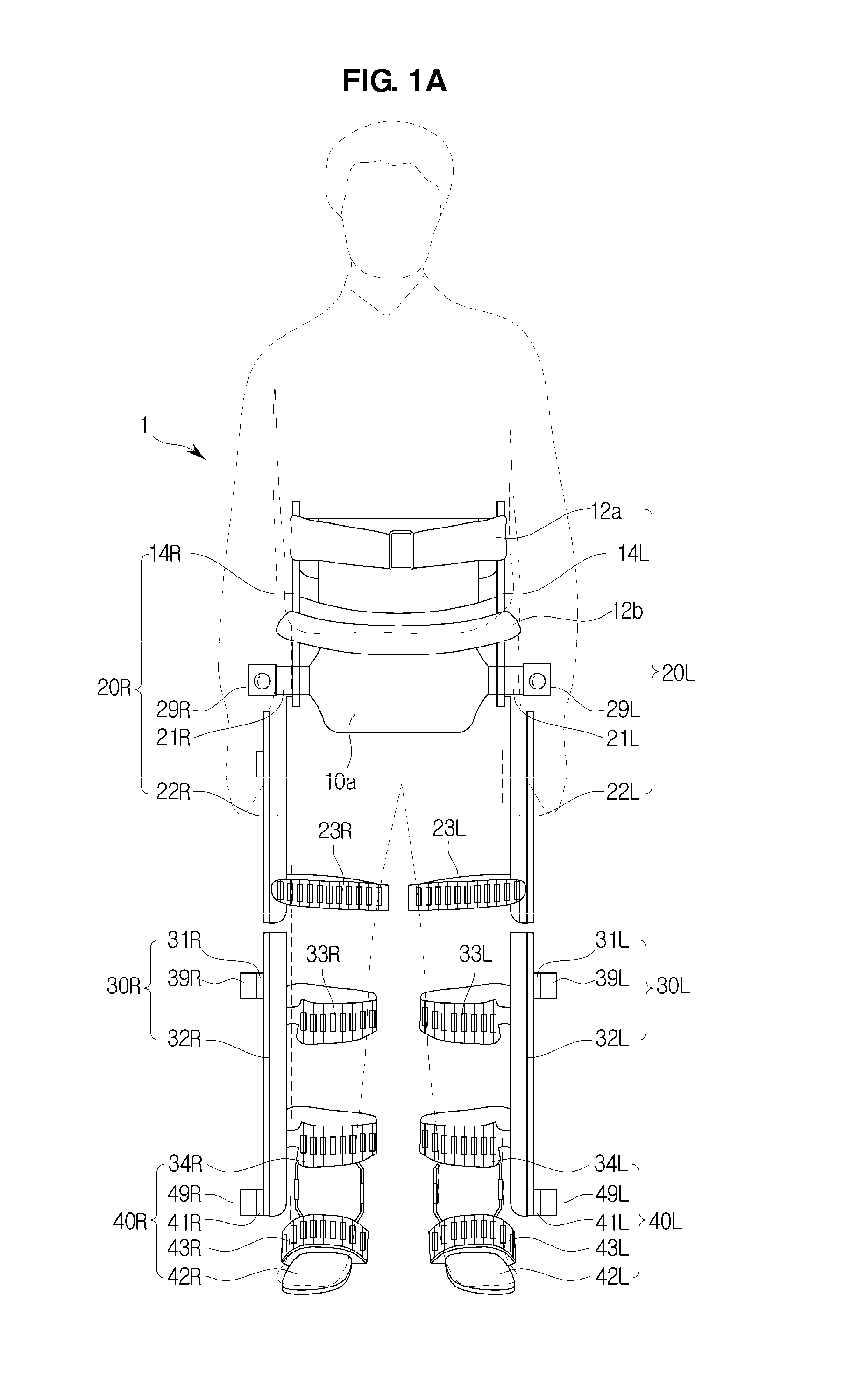
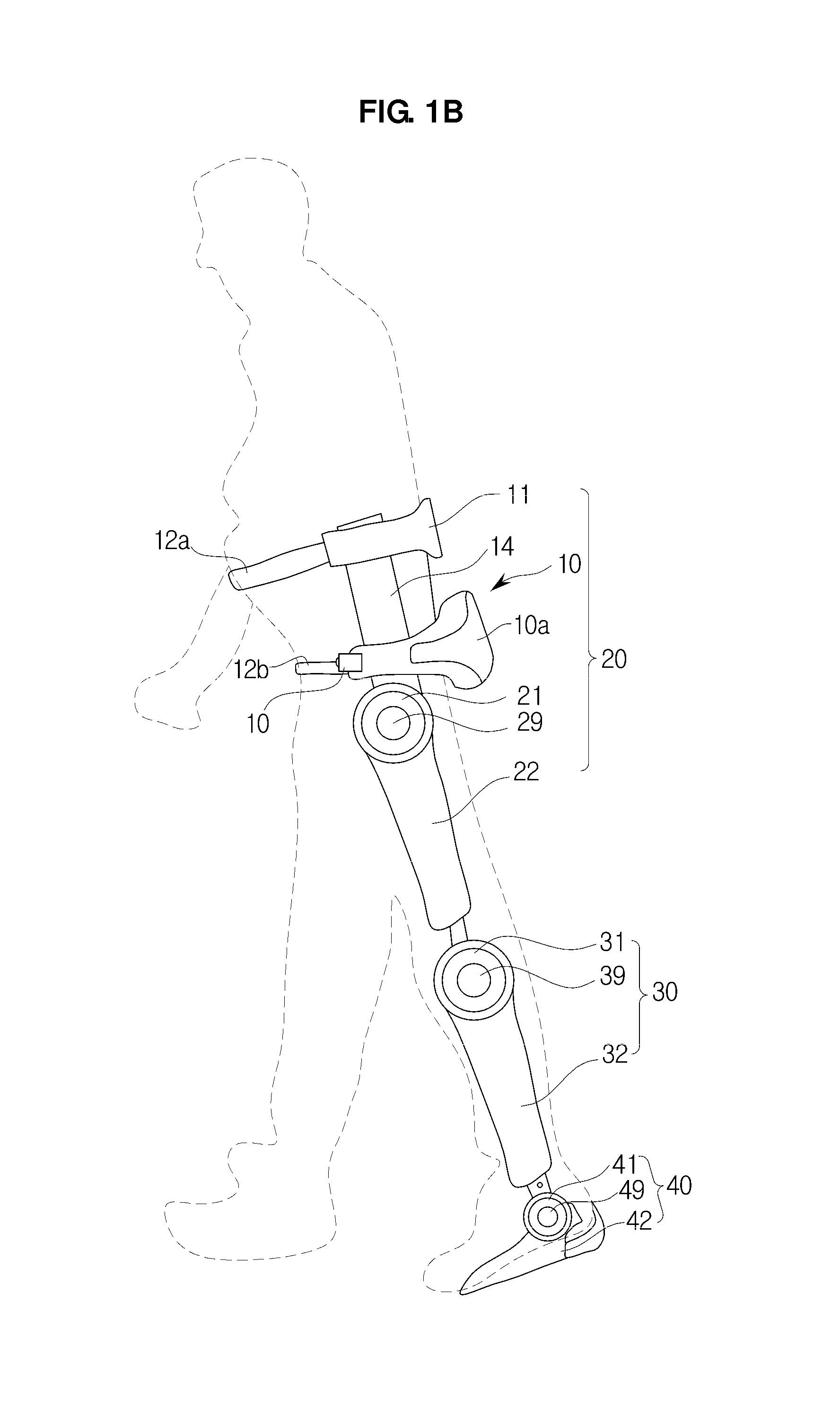
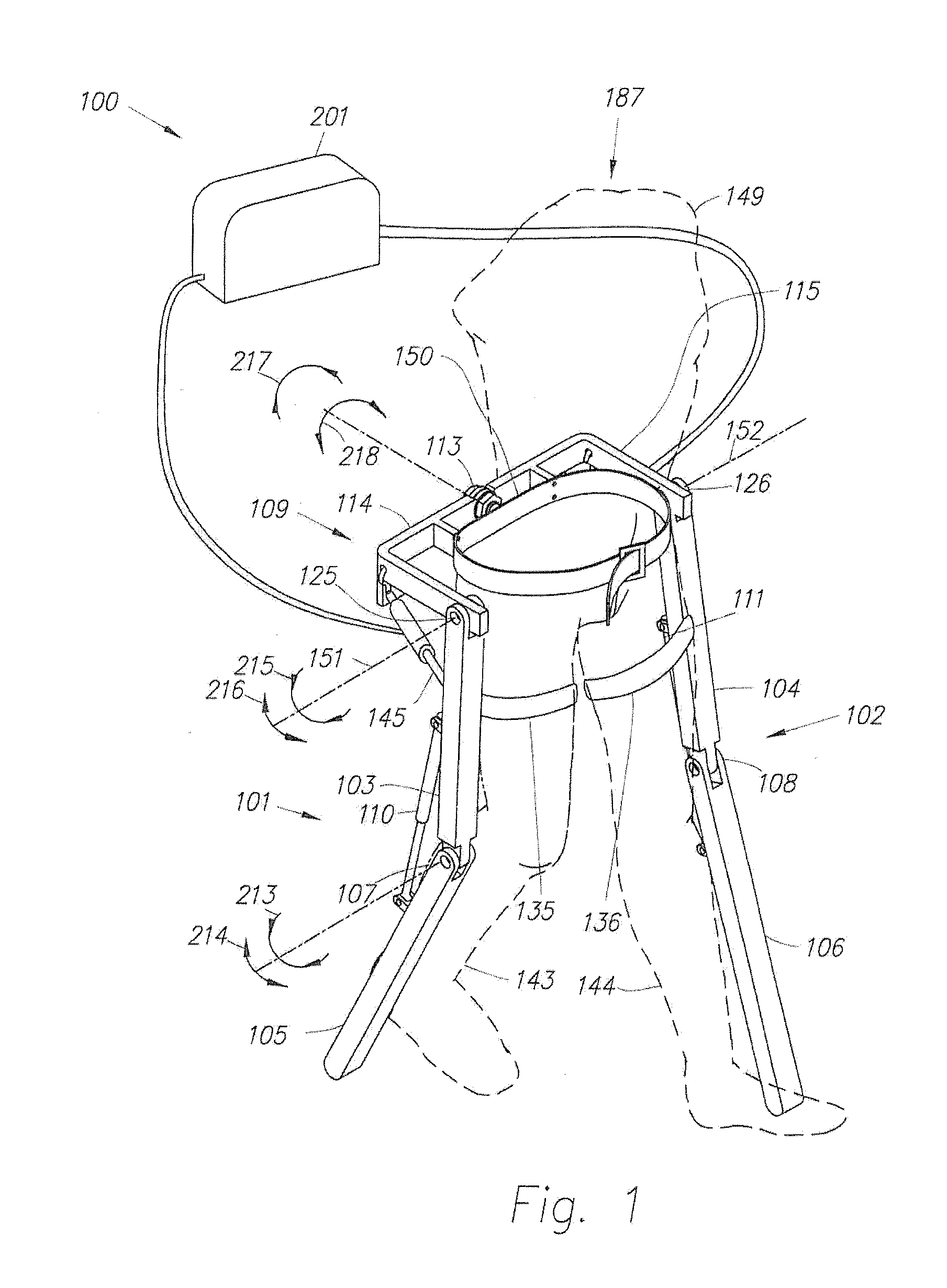
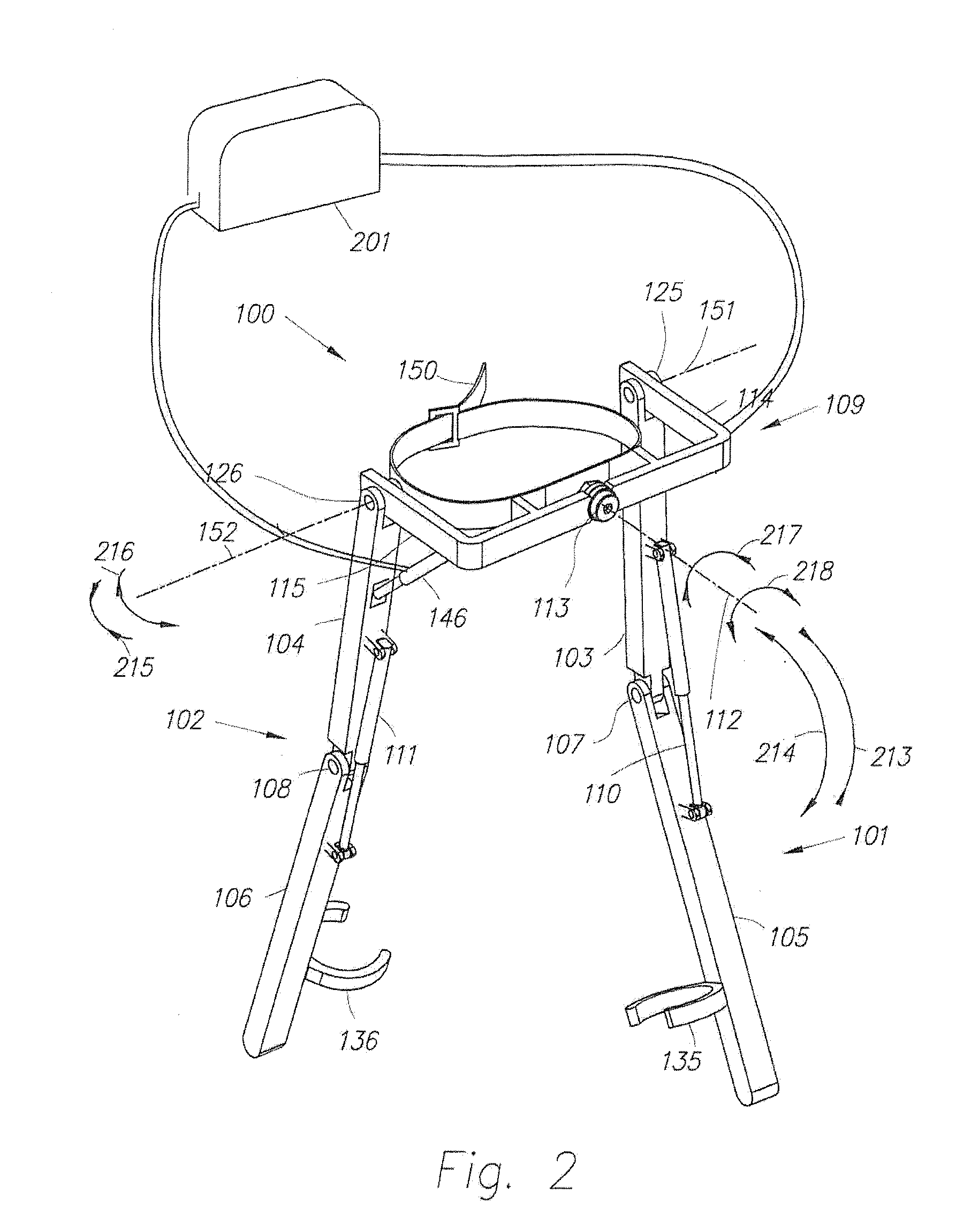
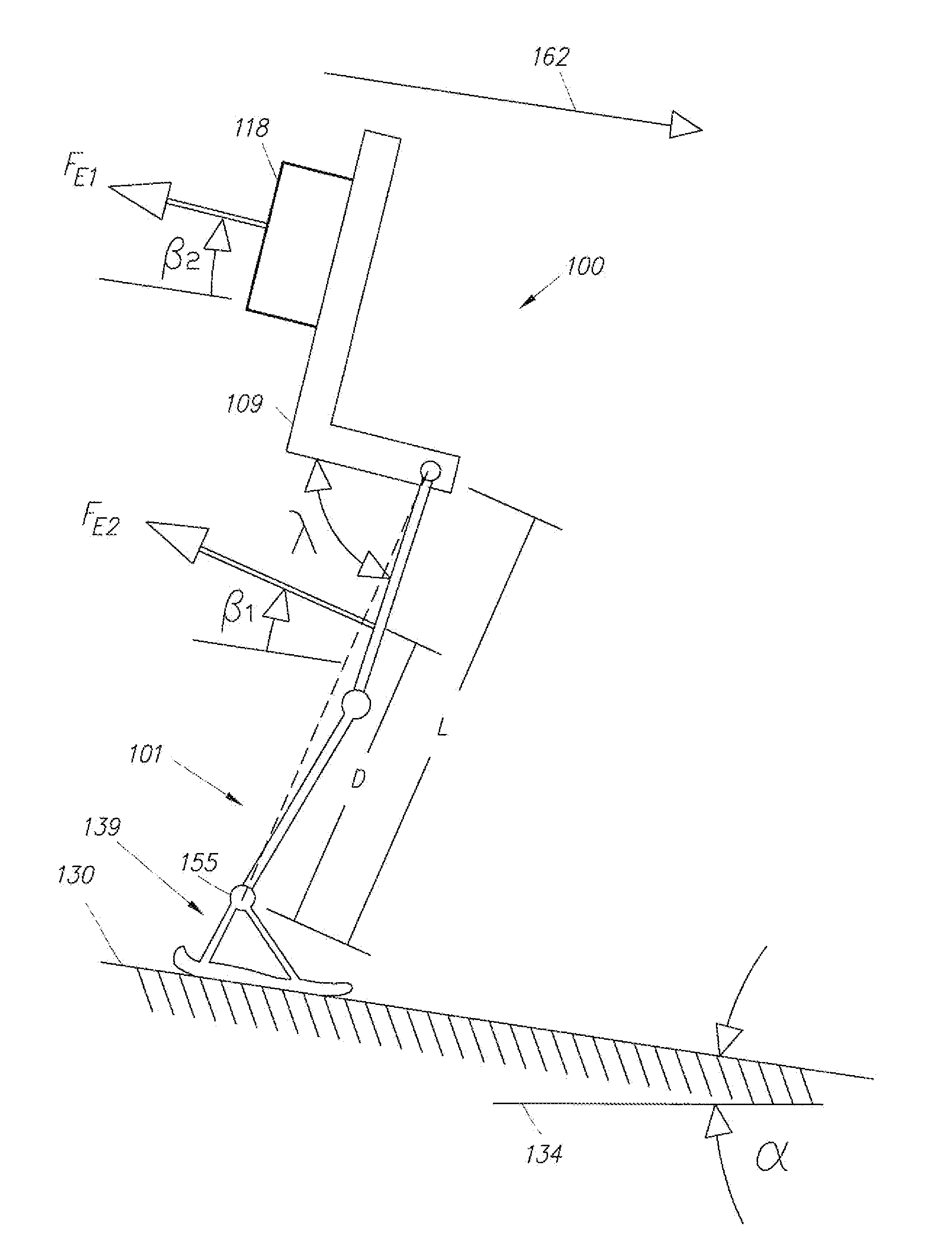
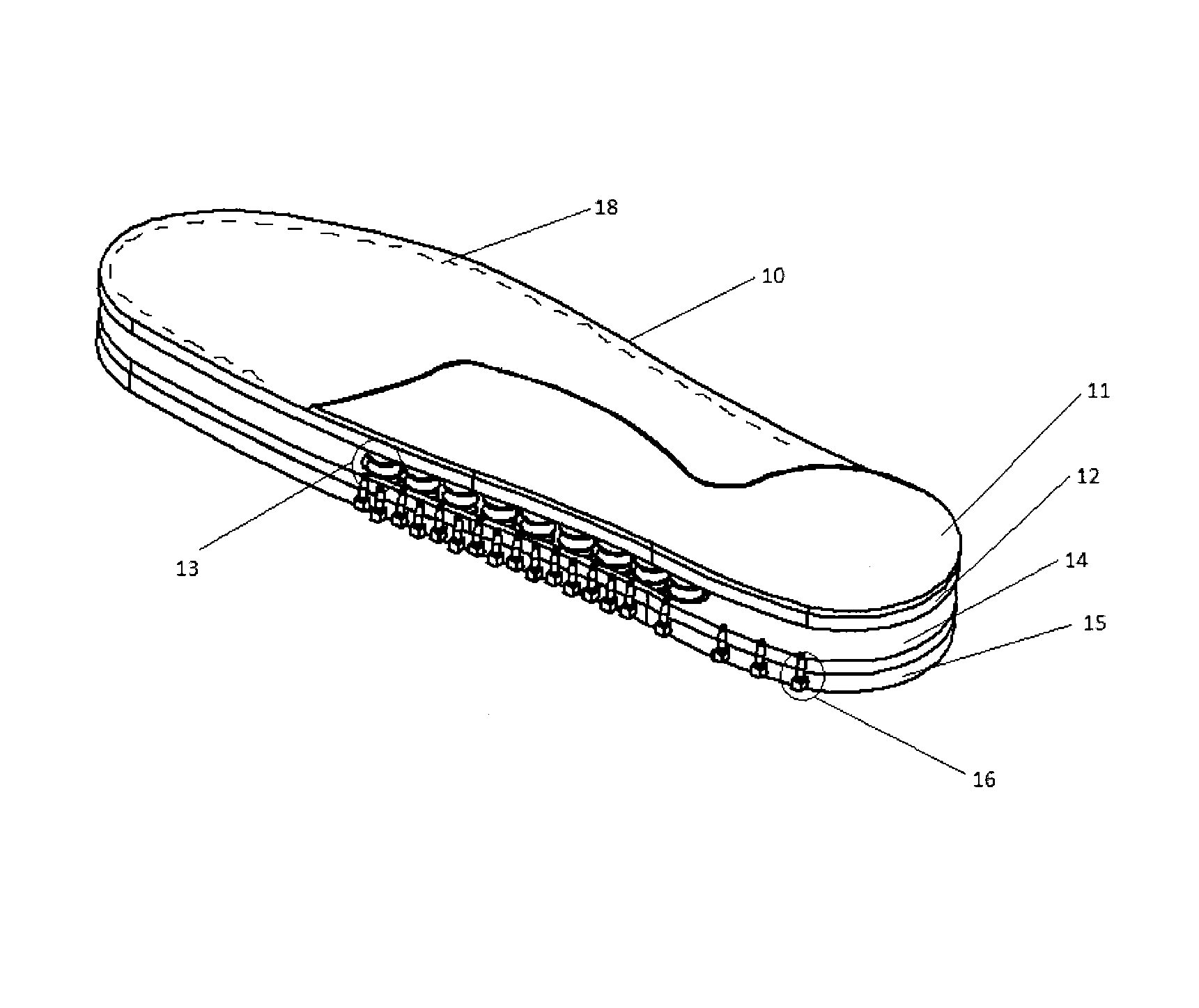
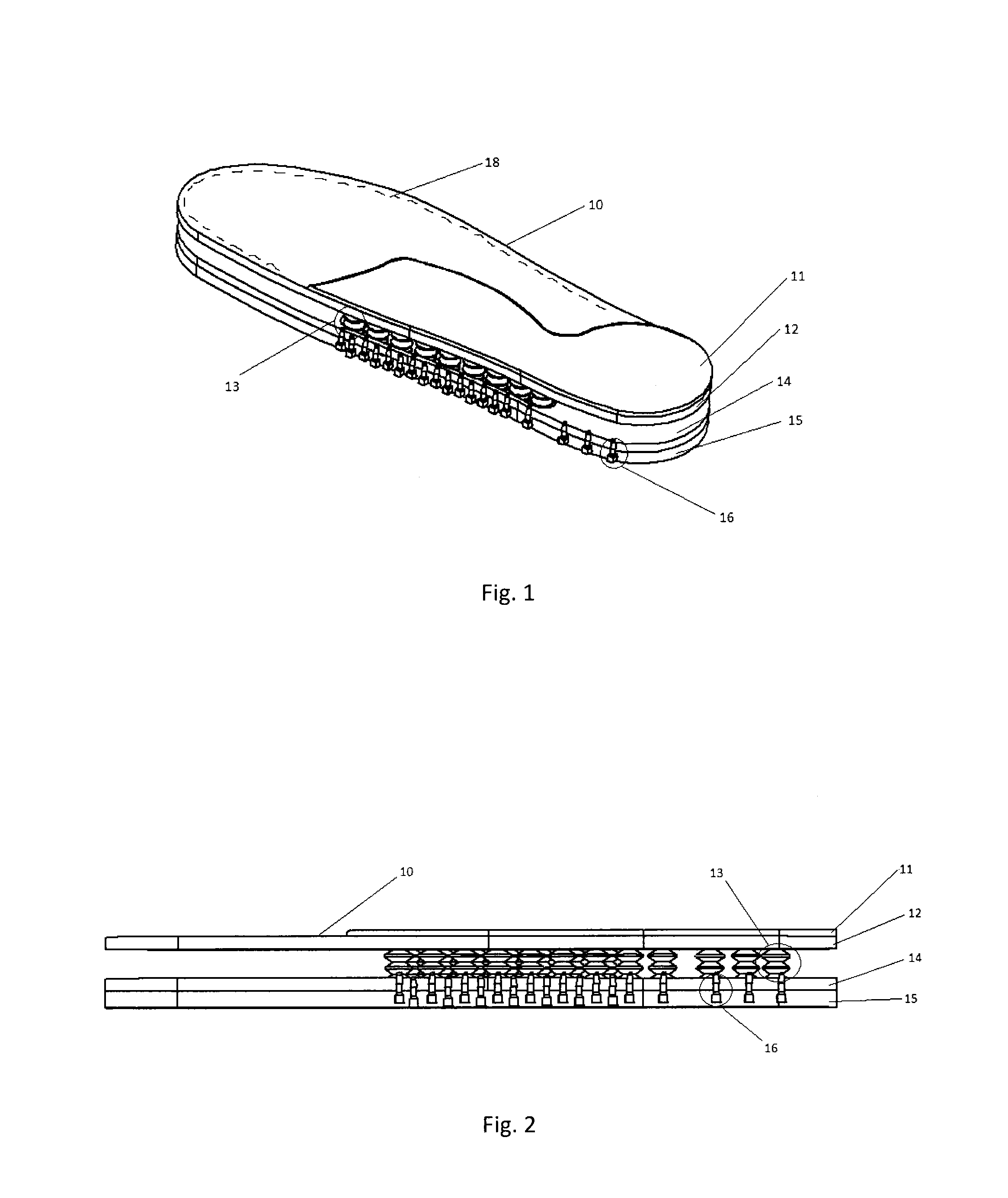
Active Ankle Foot Orthosis
ActiveUS20050070834A1Less kinematic differenceIncrease independenceWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePathology diagnosis
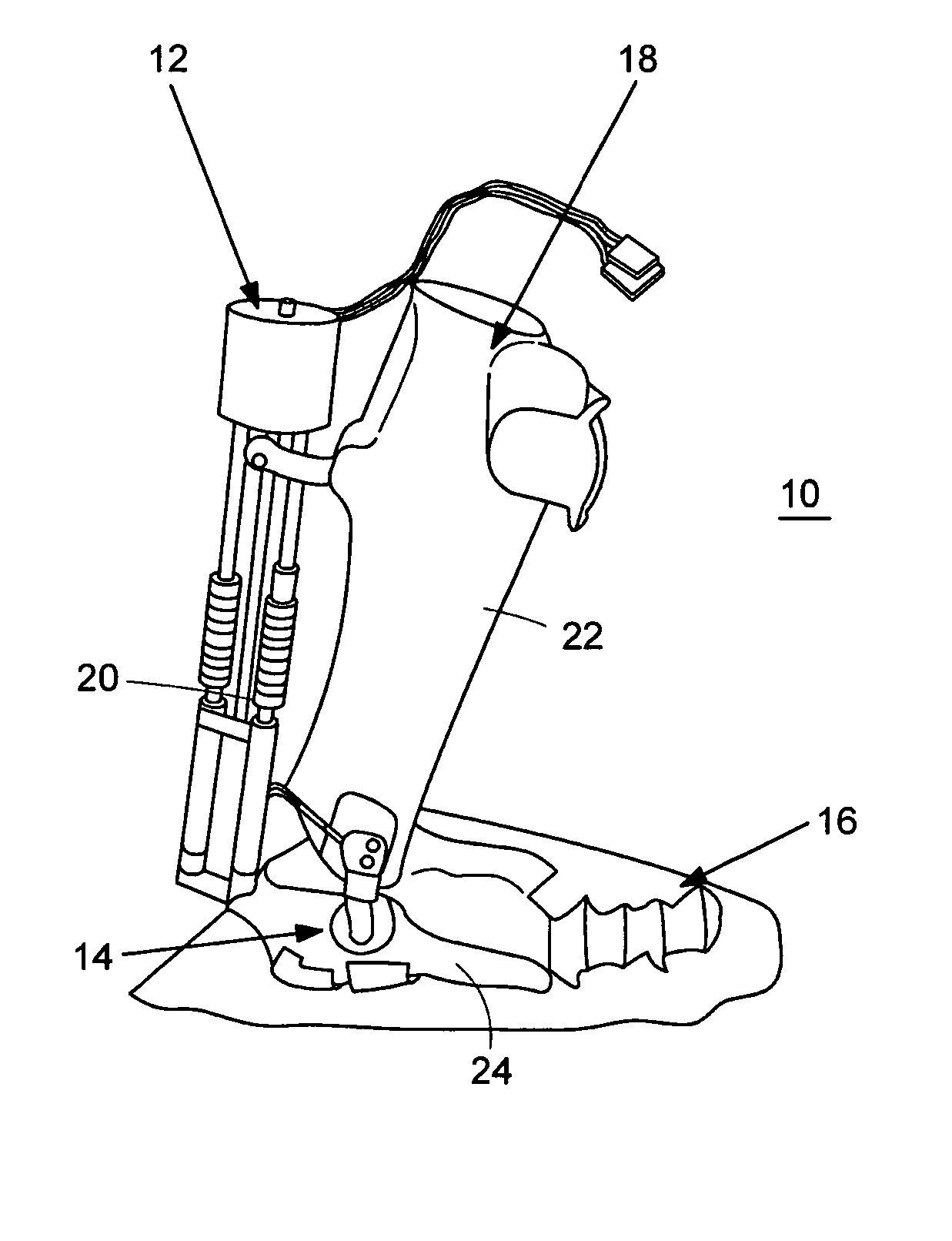
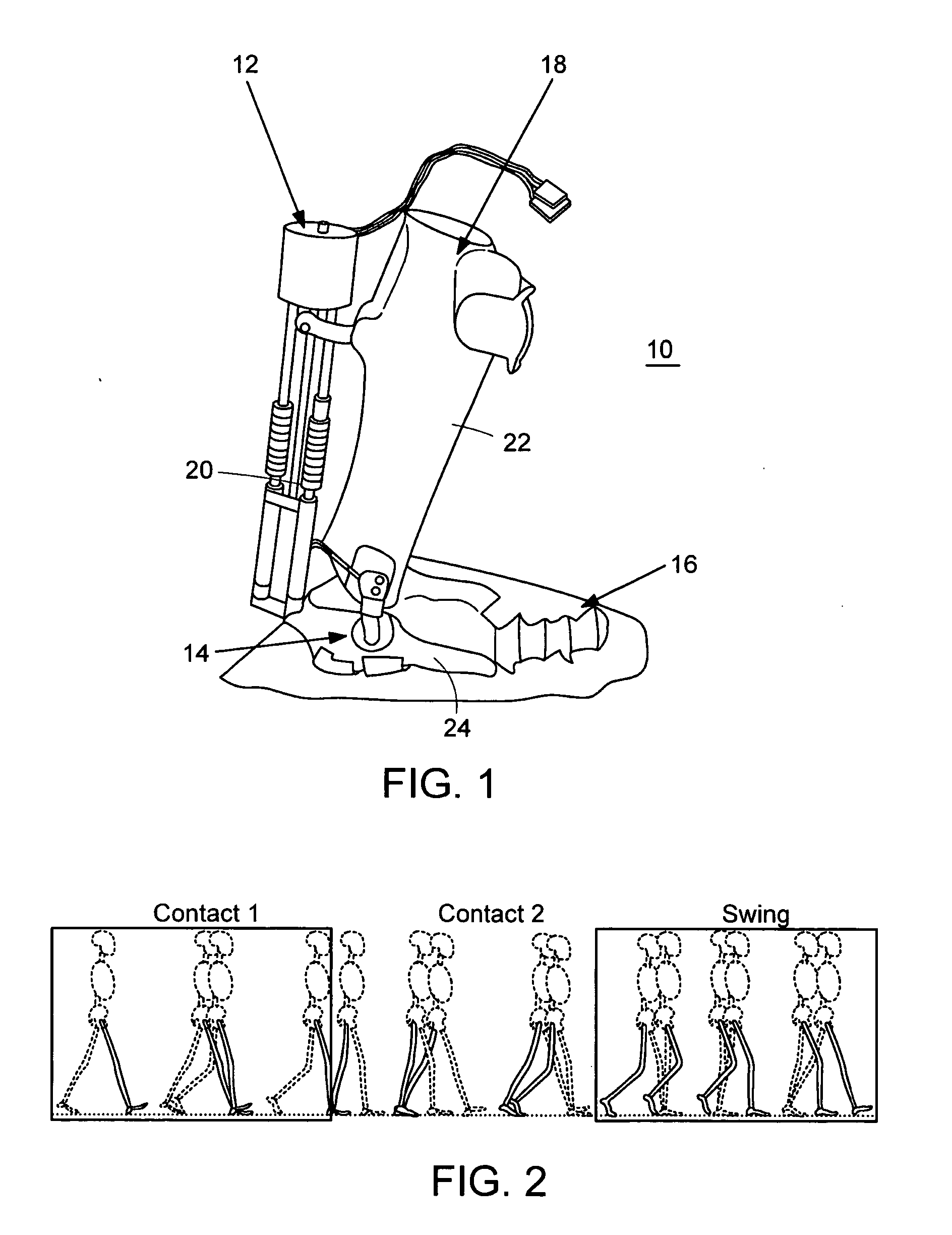
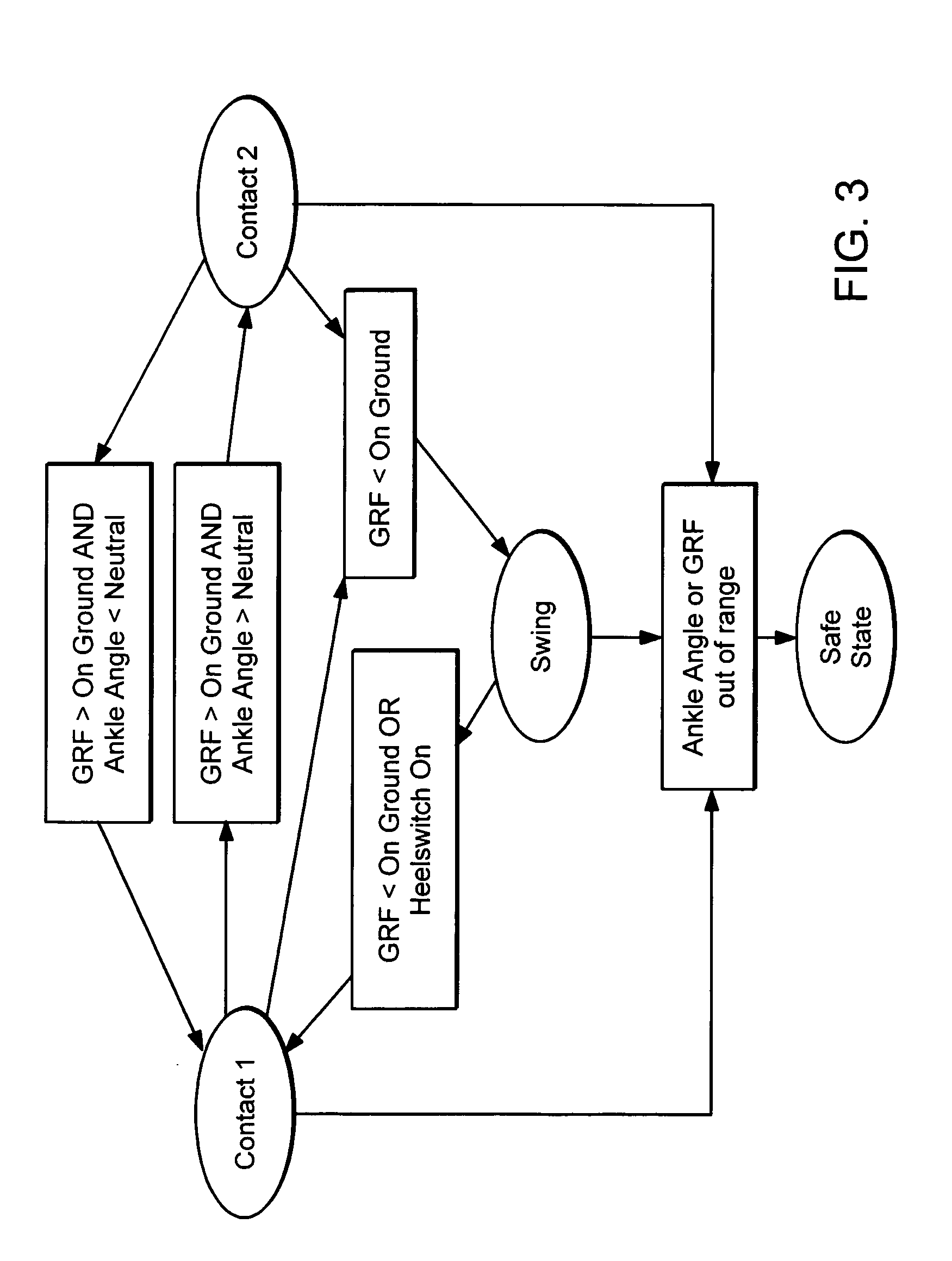
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
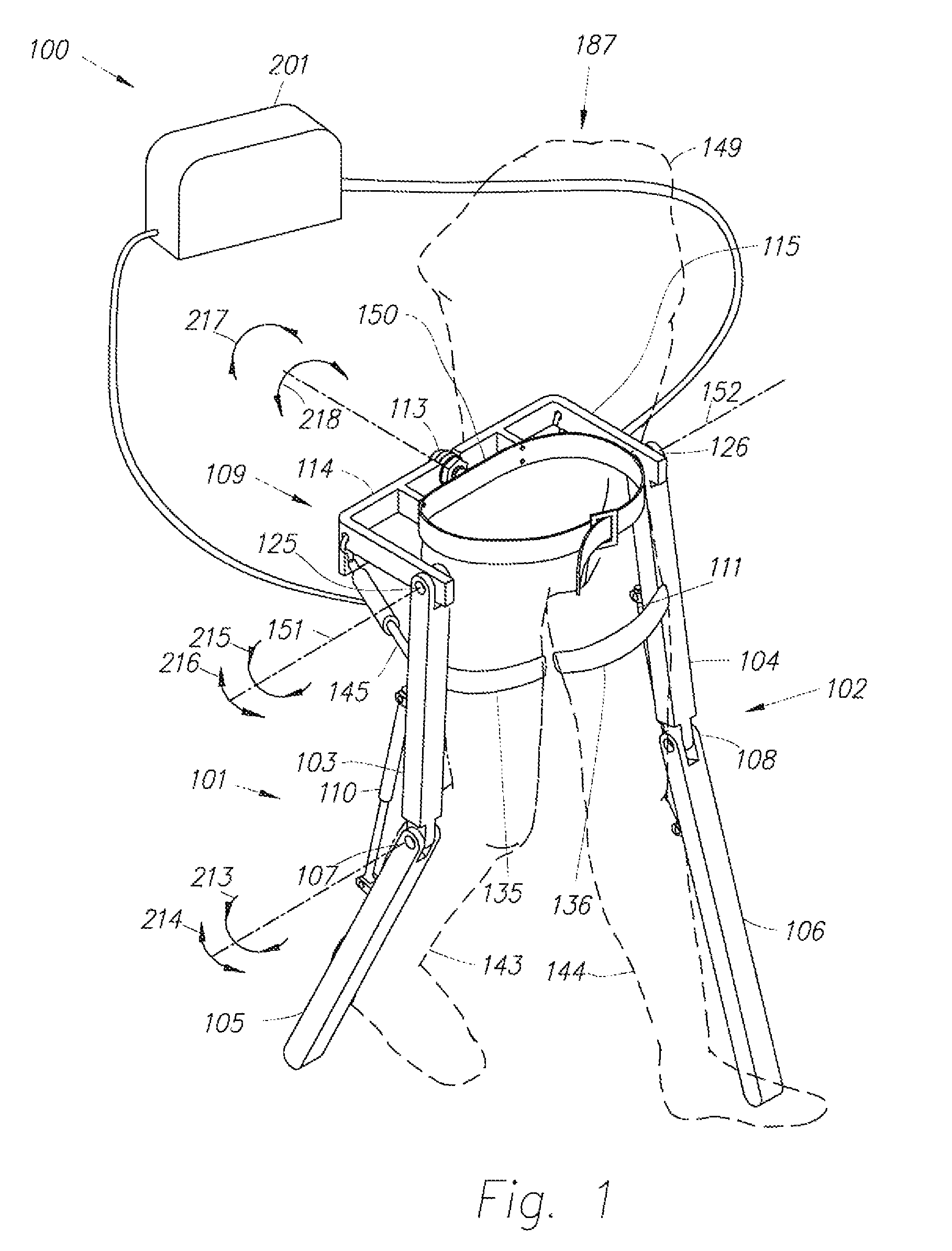
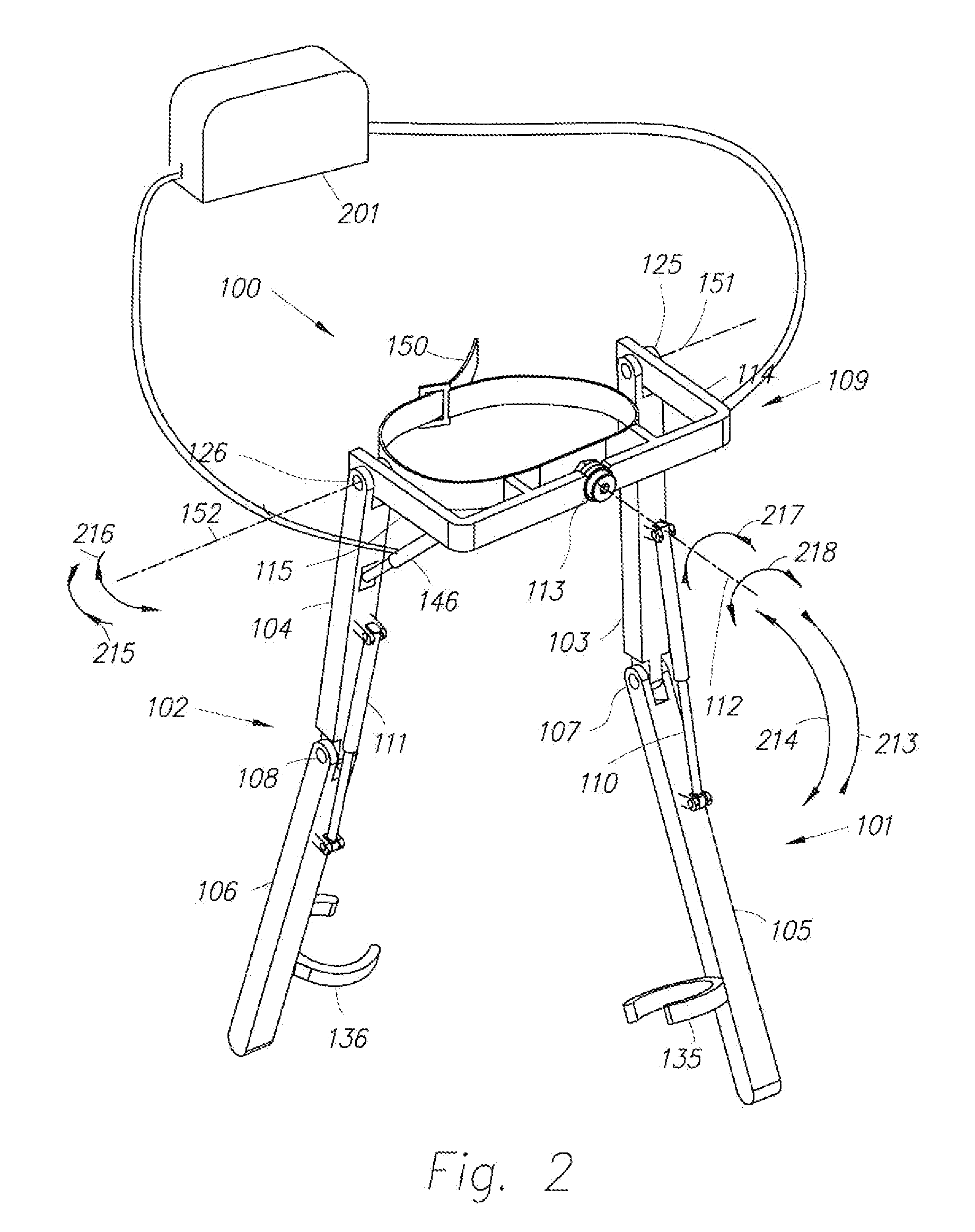
Device and Method for Decreasing Energy Consumption of a Person by Use of a Lower Extremity Exoskeleton
A lower extremity exoskeleton, configurable to be coupled to a person, includes: leg supports configurable to be coupled to the person's lower limbs and designed to rest on the ground during stance phases, with each leg support having a thigh link and a shank link; two knee joints, each configured to allow flexion and extension between respective shank and thigh links; an exoskeleton trunk configurable to be coupled to the person's upper body, rotatably connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports, allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk; two hip actuators configured to create torques between the exoskeleton trunk and the leg supports; and at least one power unit capable of providing power to the hip actuators. In use, power is supplied to the hip actuators in an amount to reduce the energy consumed by a user during a walking cycle.
Owner:EKSO BIONICS
Active ankle foot orthosis
ActiveUS8075633B2Increase independenceGreat easeWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePostural orientation
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
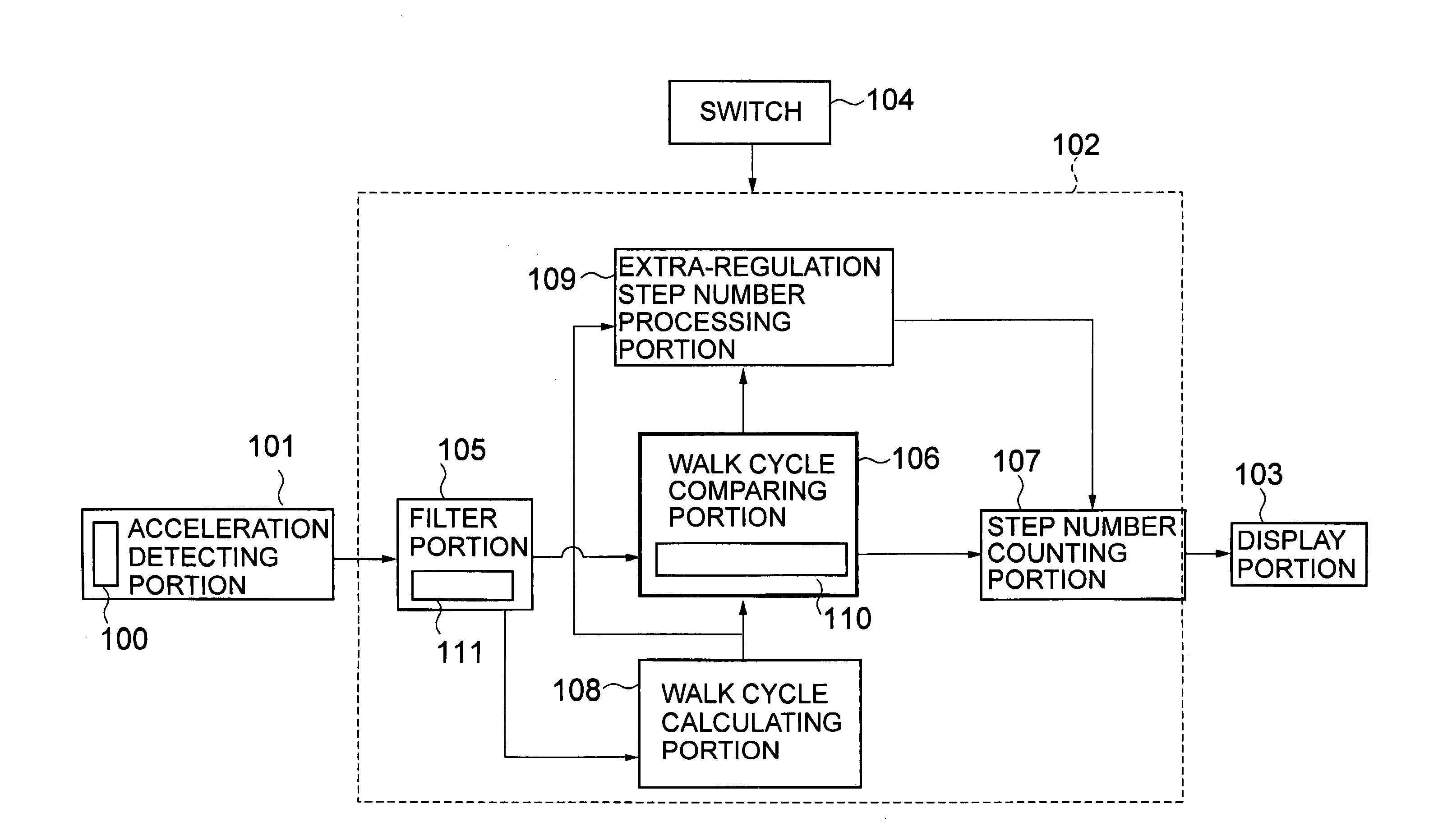
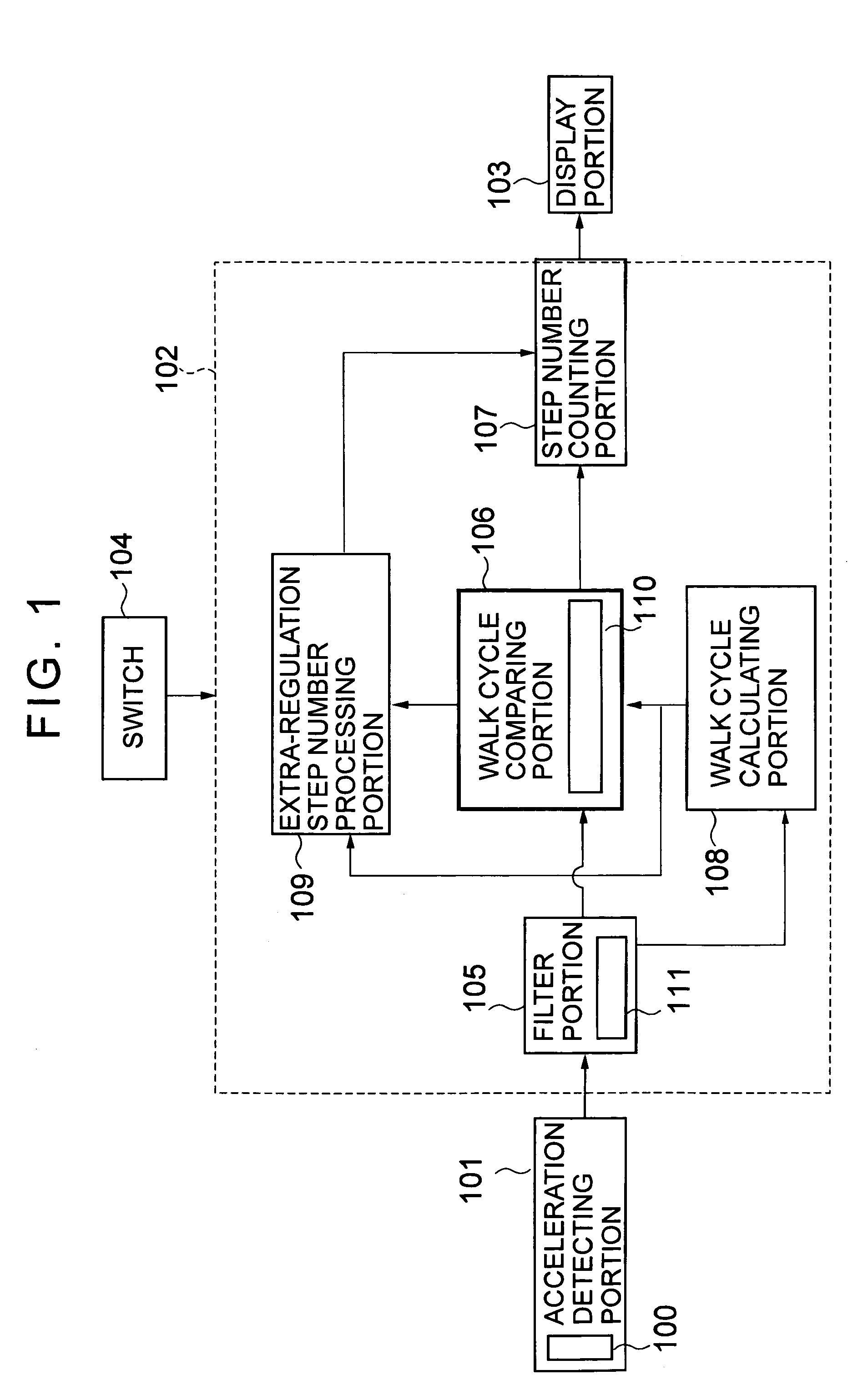
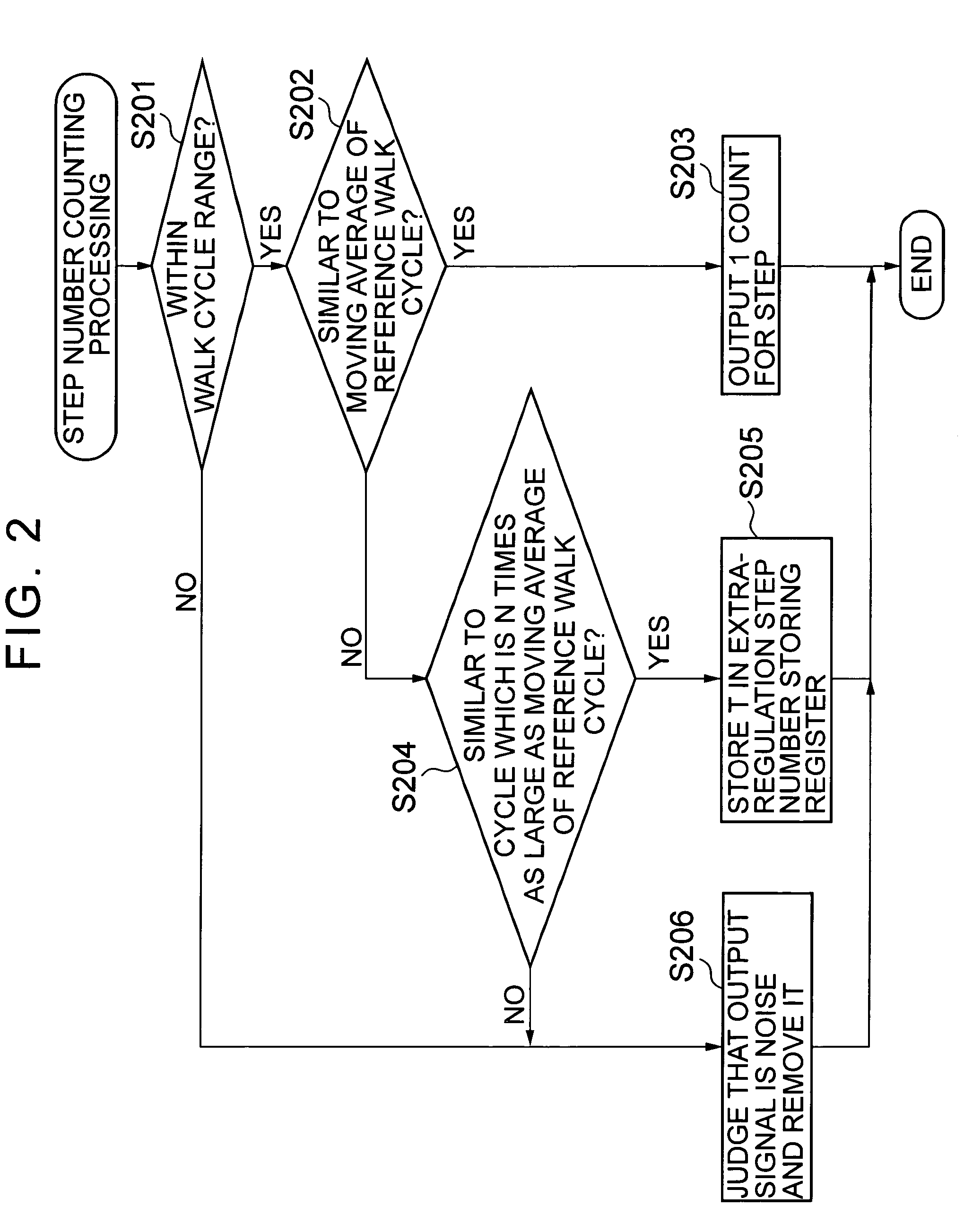
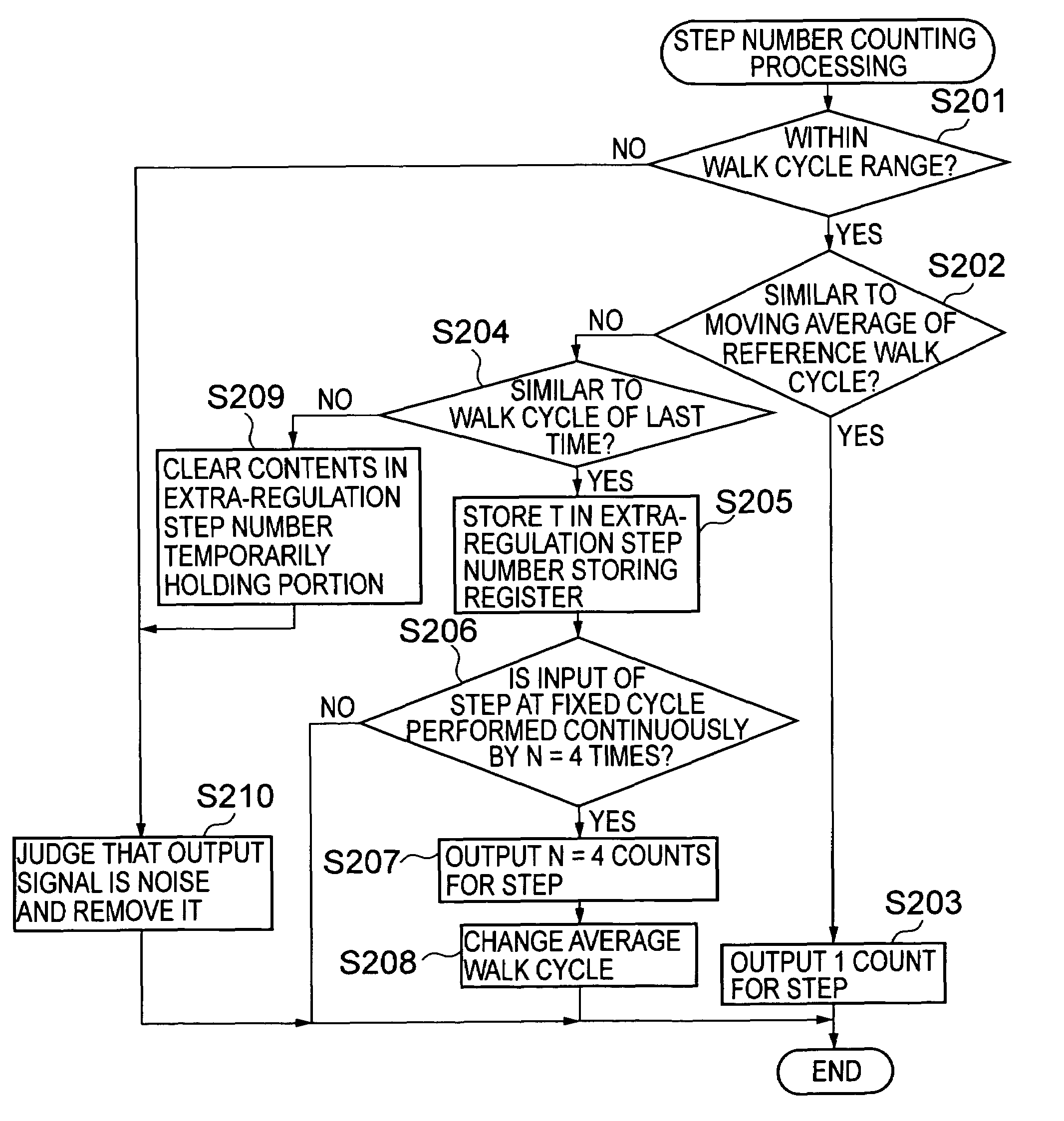
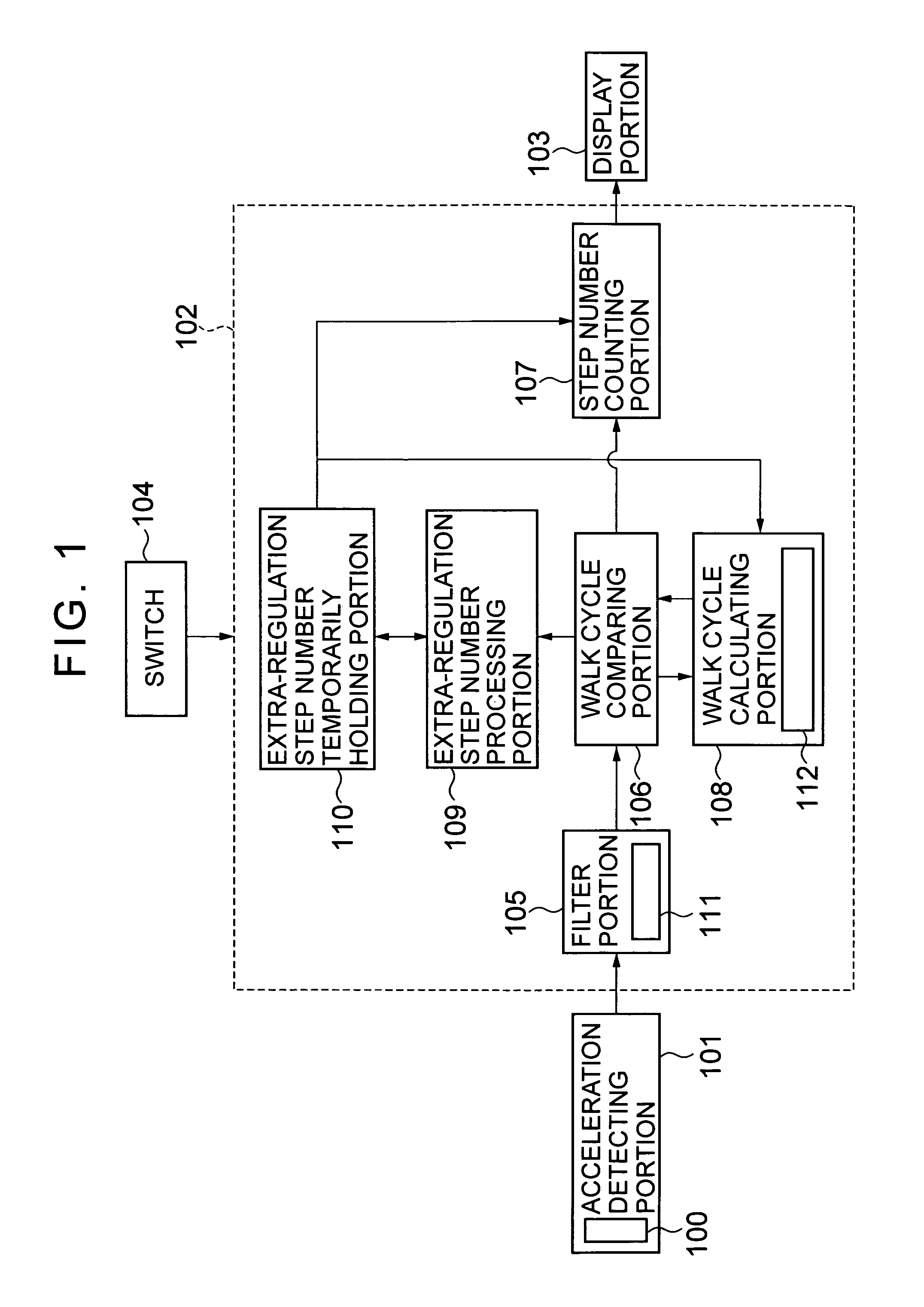
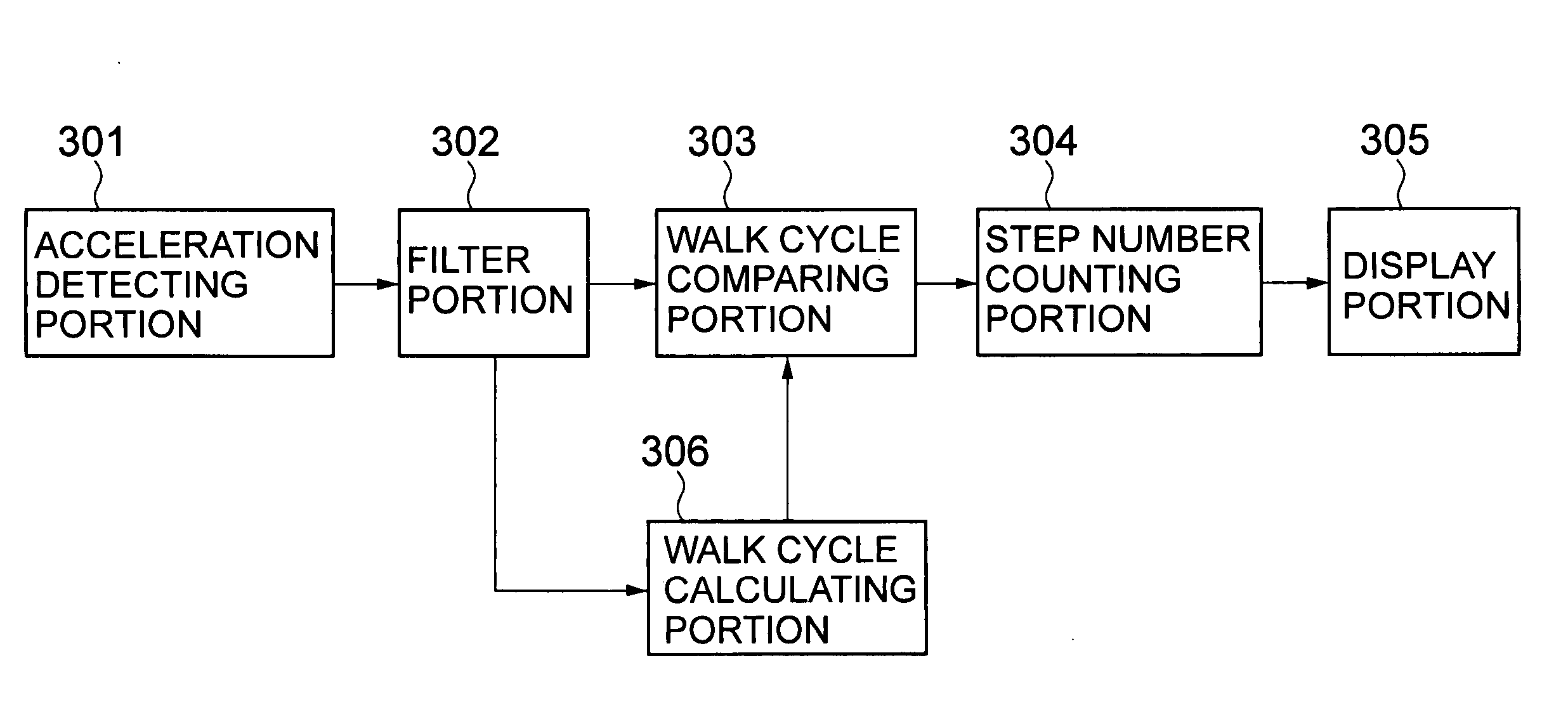
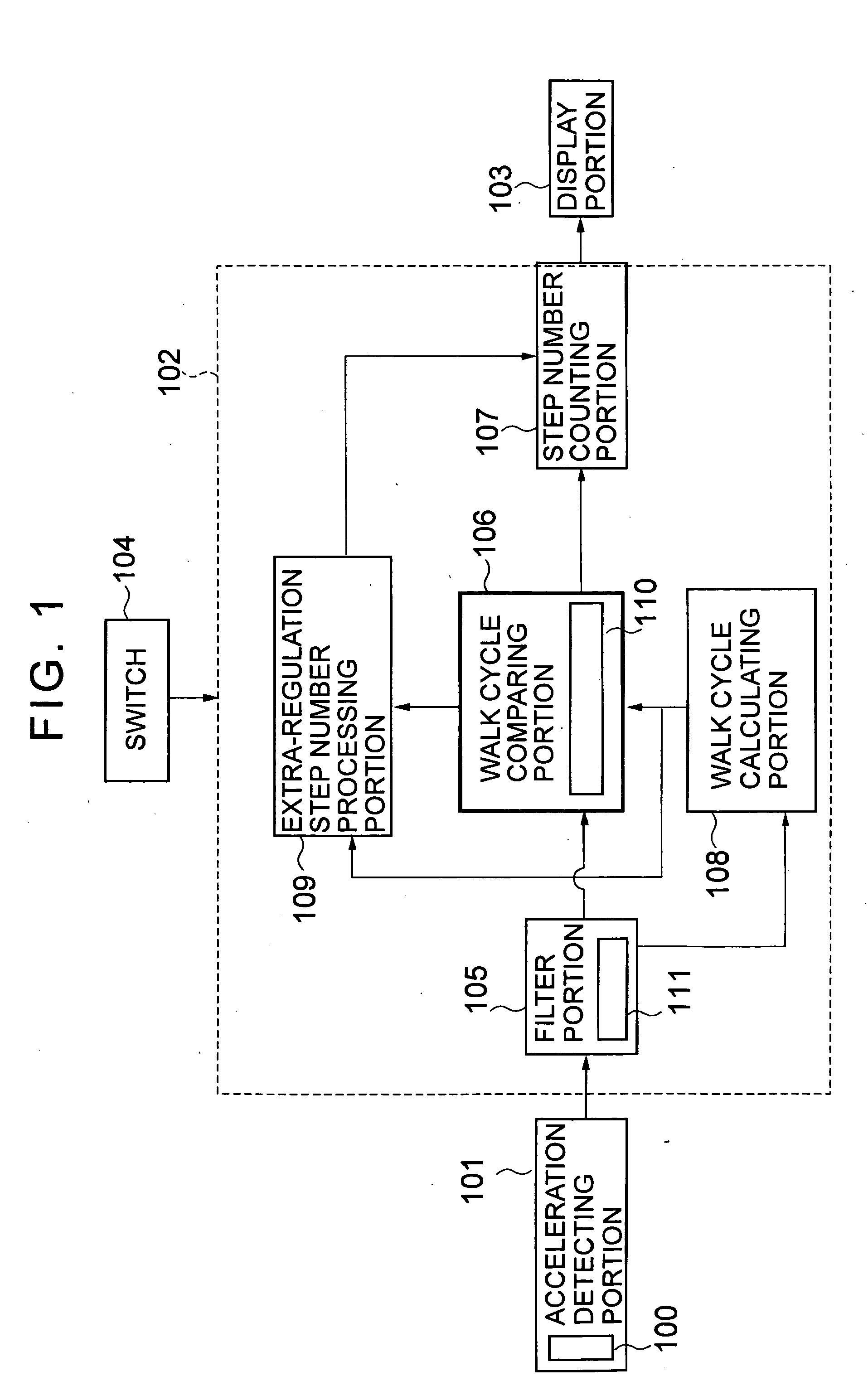
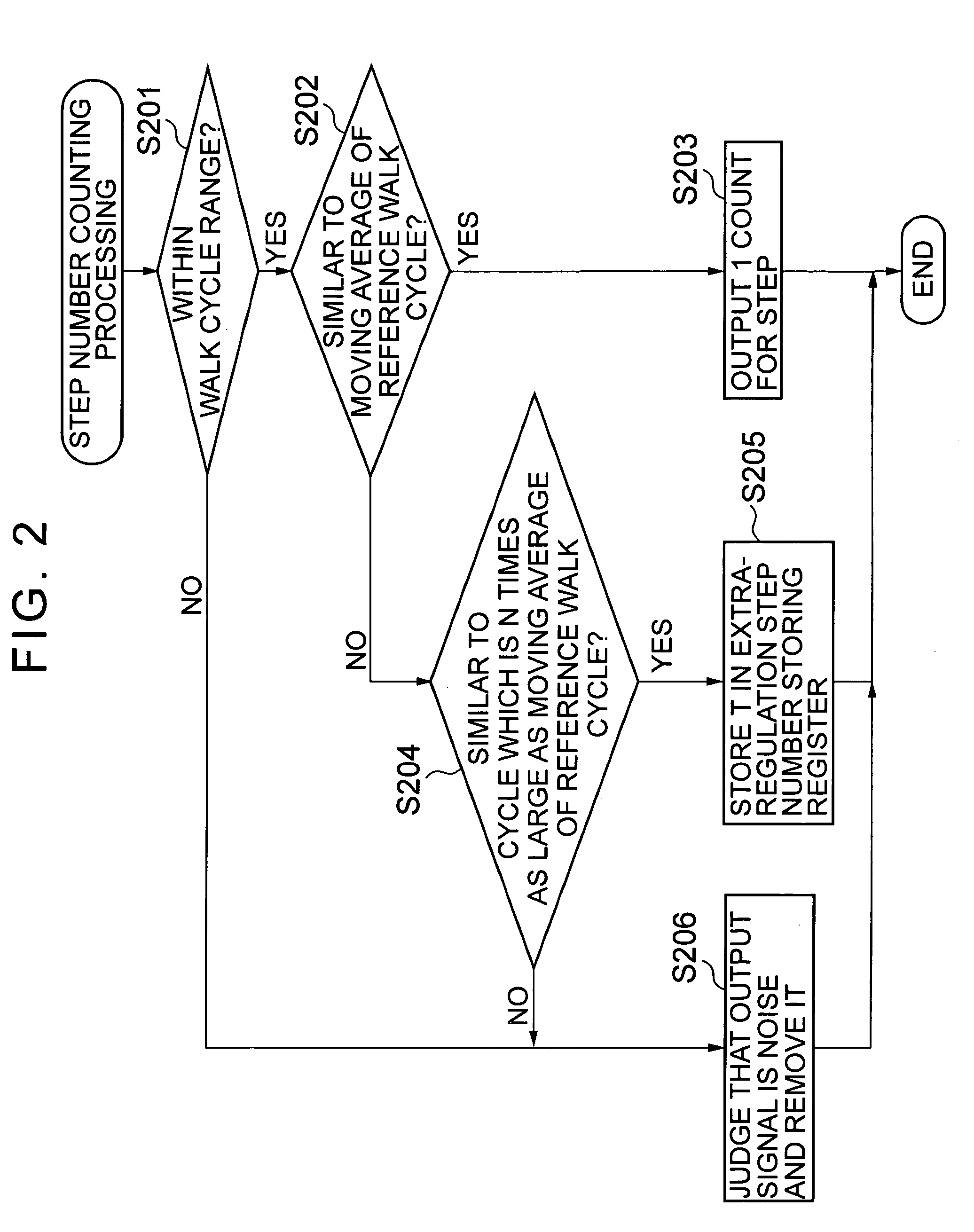
Electronic pedometer
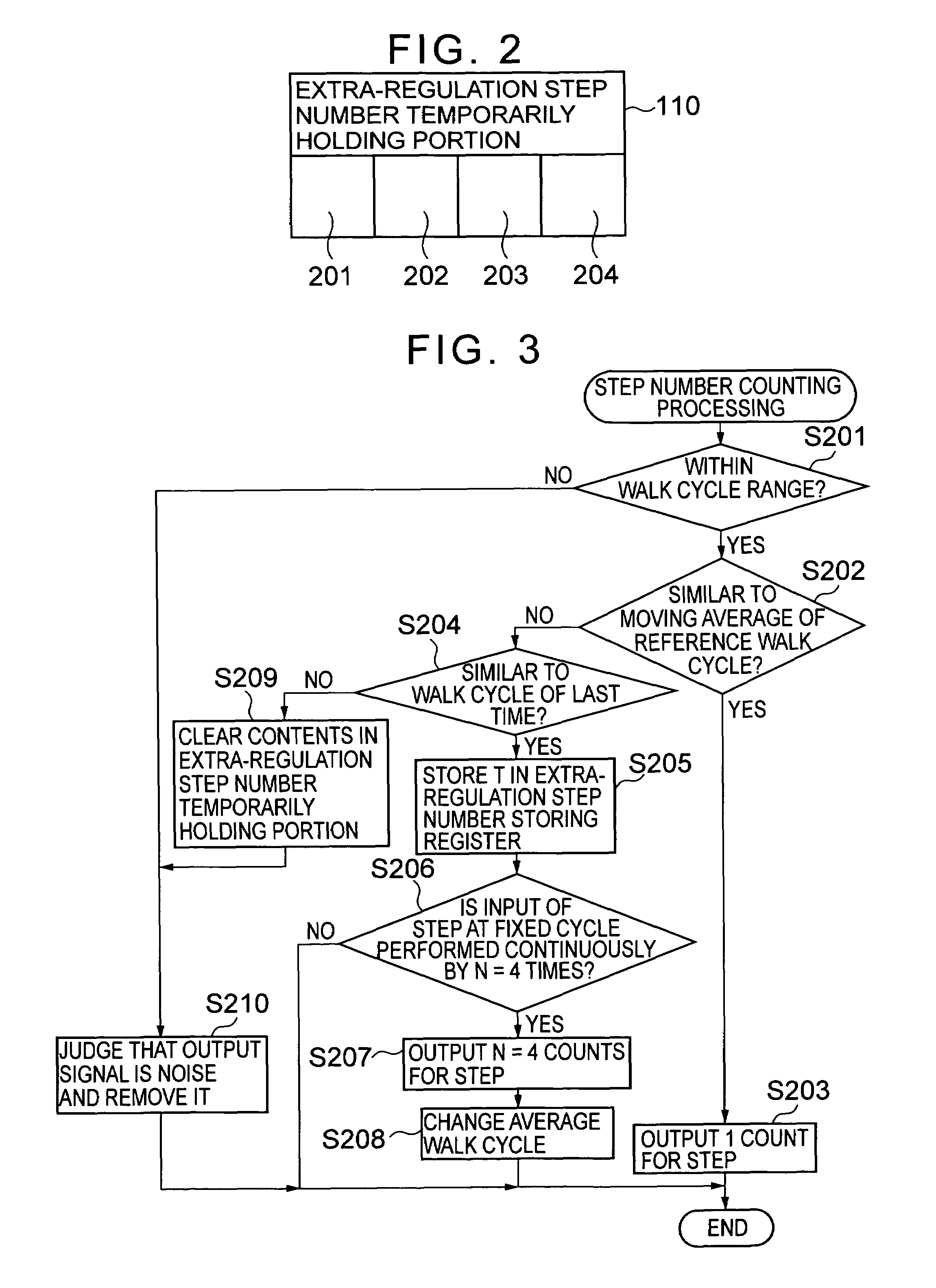
To carry out step number measurement more precisely even when a walk signal enough to be detected is not obtained. After a fixed noise of a signal detected by an acceleration detecting portion having an acceleration sensor is removed by a filter portion of a counting portion, a walk cycle comparing portion compares a cycle of the resultant signal with a moving average value calculated by a walk cycle calculating portion, and each signal within a predetermined cycle range is counted as the number of steps for one step by a step number counting portion. A signal within a range similar to a cycle n times as large as a predetermined cycle of the signals each beyond the predetermined cycle range is judged as the number of steps for n steps by an extra-regulation step number processing portion and is counted as the number of steps for n steps by the step number counting portion. Data on the number of steps obtained through the counting in the step number counting portion is displayed on a display portion.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Walking assistant device and method of controlling walking assistant device
ActiveUS20150190923A1Minimize the numberProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsEngineeringWalking cycle
A walking assistant device may calculate a walking cycle by measuring only motion of a specific joint without a force / torque sensor (F / T sensor) of a foot, and a method of controlling the walking assistant device. The method may include measuring motion of a hinge to which different support frames are connected; overlapping a reference trajectory corresponding to the measured motion and modulation trajectories that have been modulated from the reference trajectory; correcting the overlapping trajectory to correspond to the measured motion; determining assistant torque corresponding to a phase of the corrected trajectory; and providing the determined assistant torque to the support frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and Method for Decreasing Energy Consumption of a Person by Use of a Lower Extremity Exoskeleton
A lower extremity exoskeleton, configurable to be coupled to a person, includes: leg supports configurable to be coupled to the person's lower limbs and designed to rest on the ground during stance phases, with each leg support having a thigh link and a shank link; two knee joints, each configured to allow flexion and extension between respective shank and thigh links; an exoskeleton trunk configurable to be coupled to the person's upper body, rotatably connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports, allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk; two hip actuators configured to create torques between the exoskeleton trunk and the leg supports; and at least one power unit capable of providing power to the hip actuators. In use, power is supplied to the hip actuators in an amount to reduce the energy consumed by a user during a walking cycle.
Owner:EKSO BIONICS
Electronic pedometer
To enhance precision in measurement of the number of steps even when a walk cycle changes. An acceleration detecting portion outputs a walk signal corresponding to a walk of a user detected by a walk sensor. A step number counting portion of a counting portion counts each signal which is judged to be beyond a first reference cycle range by a walk cycle comparing portion among signals from the acceleration detecting portion as the number of steps for one step, and when an extra-regulation step number processing portion judges that a predetermined number of signals each within a second reference cycle range among the signals each beyond the first reference cycle range is continuously outputted, counts the predetermined number of signals as the predetermined number of steps.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Pneumatic lower extremity gait rehabilitation training system
InactiveUS20180071580A1Substantial rigidityBig impactGymnastic exercisingWalking aidsWalking cycleGravity center
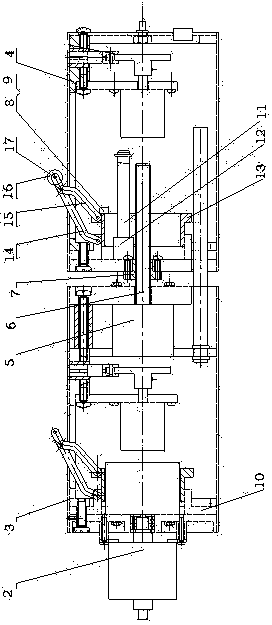
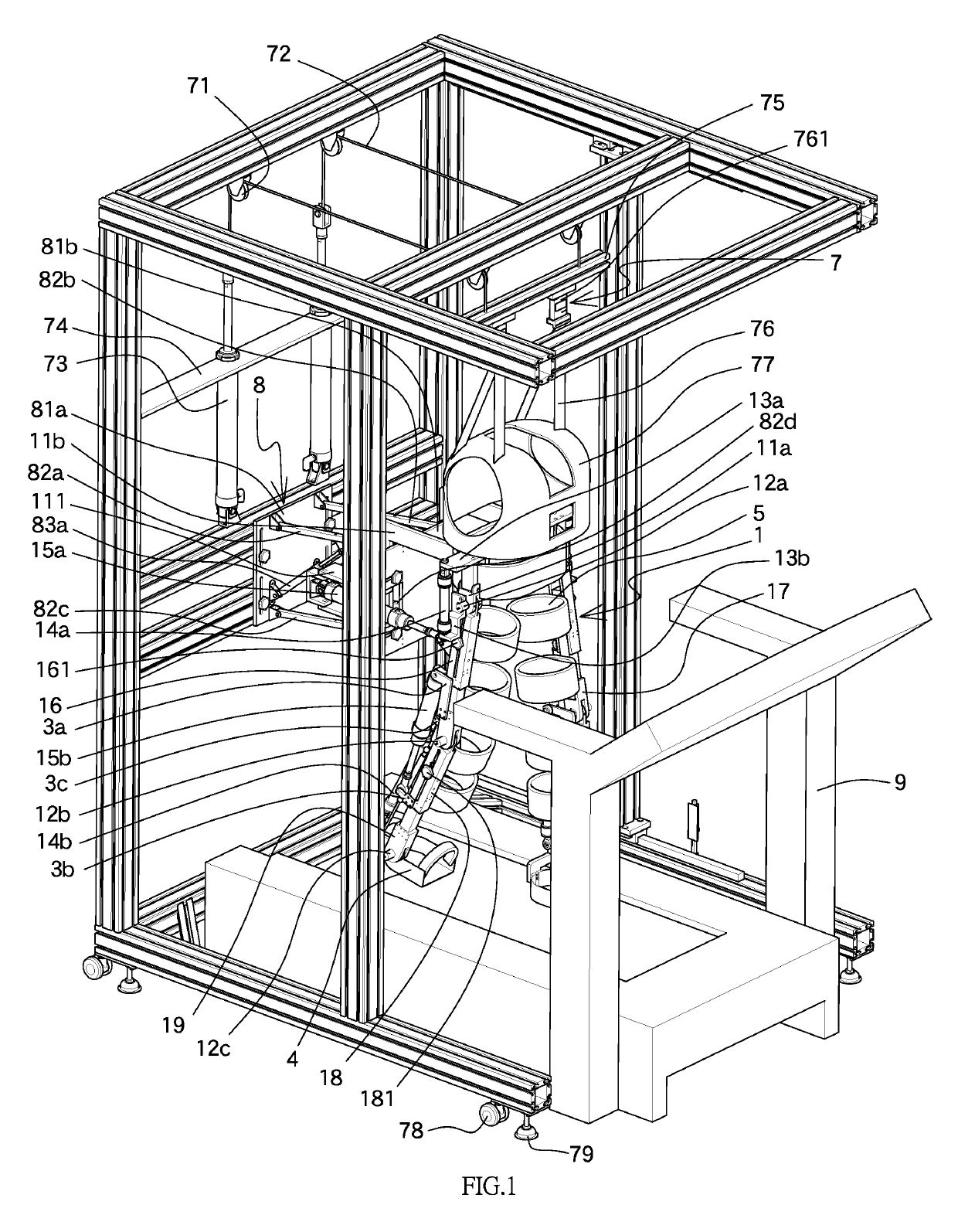
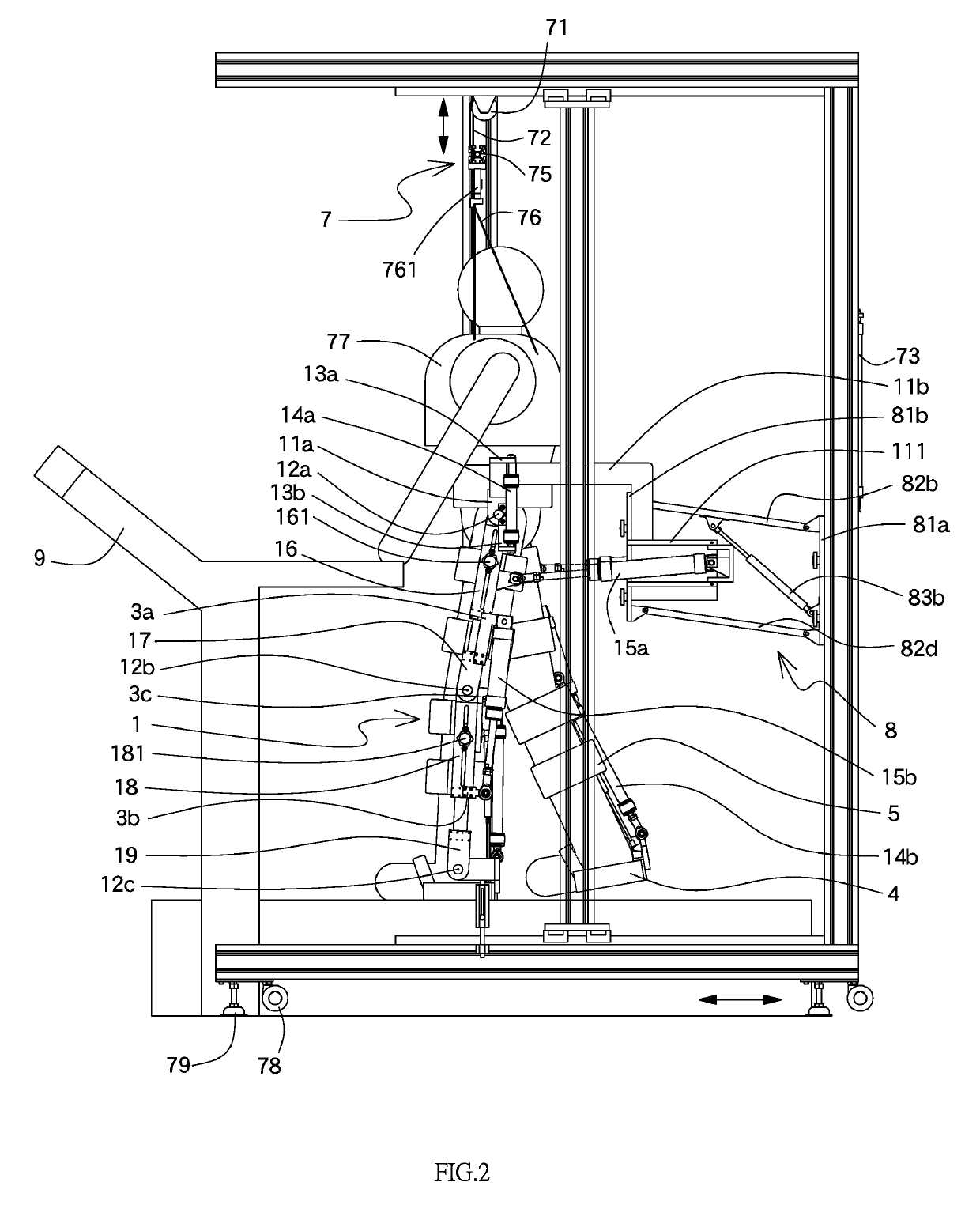
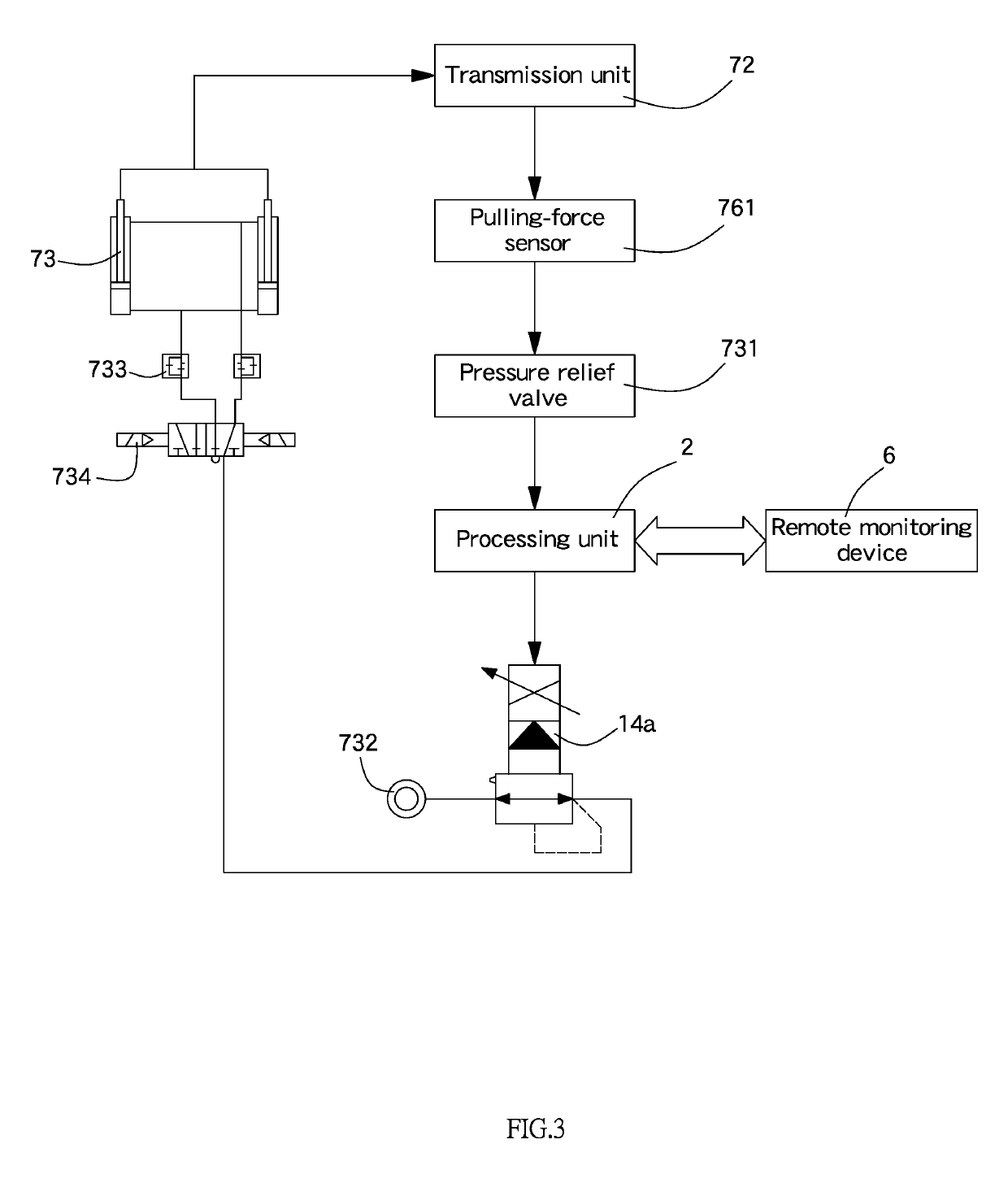
A pneumatic lower extremity gait rehabilitation training system includes a support device for reducing the burden of supporting a user's body weight by lower extremity in a walking therapy, an exoskeleton rehabilitation device for adjusting the user's walking coordination at a treadmill, a center-of-gravity adjusting device for adjusting a change of upper and lower centers of gravity, and a remote monitoring device for receiving and capturing a signal of an angle displacement of a joint mechanism in a walking cycle. The user may support her / his body weight by the support device and the center-of-gravity adjusting device to reduce the gravity exerted onto the user's legs. The exoskeleton rehabilitation device improves the flexibility, safety and lightweight of walking and requires fewer driving elements. The remote monitoring device sends analyzed signals to the treadmill to adjust the user's walking speed, so as to improve the rehabilitation effect.
Owner:LUNGHWA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Device and method for decreasing energy consumption of a person by use of a lower extremity exoskeleton
A lower extremity exoskeleton, configurable to be coupled to a person, includes: leg supports configurable to be coupled to the person's lower limbs and designed to rest on the ground during stance phases, with each leg support having a thigh link and a shank link; two knee joints, each configured to allow flexion and extension between respective shank and thigh links; an exoskeleton trunk configurable to be coupled to the person's upper body, rotatably connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports, allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk; two hip actuators configured to create torques between the exoskeleton trunk and the leg supports; and at least one power unit capable of providing power to the hip actuators. In use, power is supplied to the hip actuators in an amount to reduce the energy consumed by a user during a walking cycle.
Owner:EKSO BIONICS
Electronic pedometer
To carry out step number measurement more precisely even when a walk signal enough to be detected is not obtained. After a fixed noise of a signal detected by an acceleration detecting portion having an acceleration sensor is removed by a filter portion of a counting portion, a walk cycle comparing portion compares a cycle of the resultant signal with a moving average value calculated by a walk cycle calculating portion, and each signal within a predetermined cycle range is counted as the number of steps for one step by a step number counting portion. A signal within a range similar to a cycle n times as large as a predetermined cycle of the signals each beyond the predetermined cycle range is judged as the number of steps for n steps by an extra-regulation step number processing portion and is counted as the number of steps for n steps by the step number counting portion. Data on the number of steps obtained through the counting in the step number counting portion is displayed on a display portion.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Acceleration transducer-based gait identification method
The invention discloses an acceleration transducer-based gait identification method, which comprises the following steps: (1) acquisition of a human gait acceleration sequence; (2) walk cycle segmentation and length normalization; (3) extraction and description of key points in a gait acceleration signal sequence; (4) classification of key points; and (5) identification. The acceleration transducer-based gait identity identification method can effectively utilize key information in a human gait acceleration signal to identify a walker who wears an accelerometer.
Owner:浙江浙大西投脑机智能科技有限公司
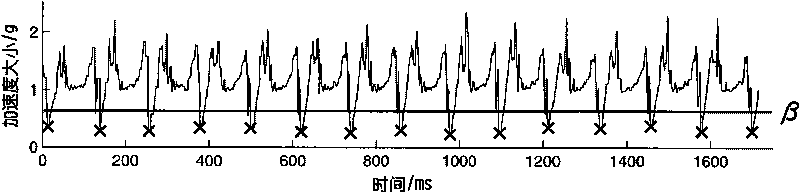
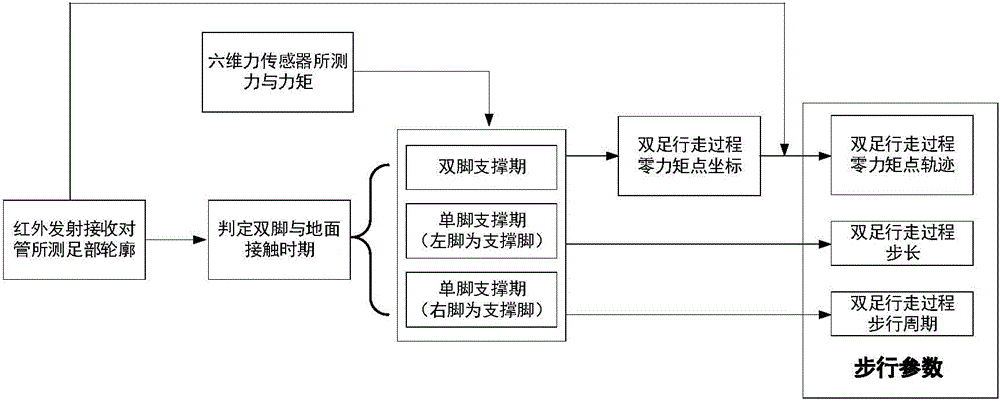
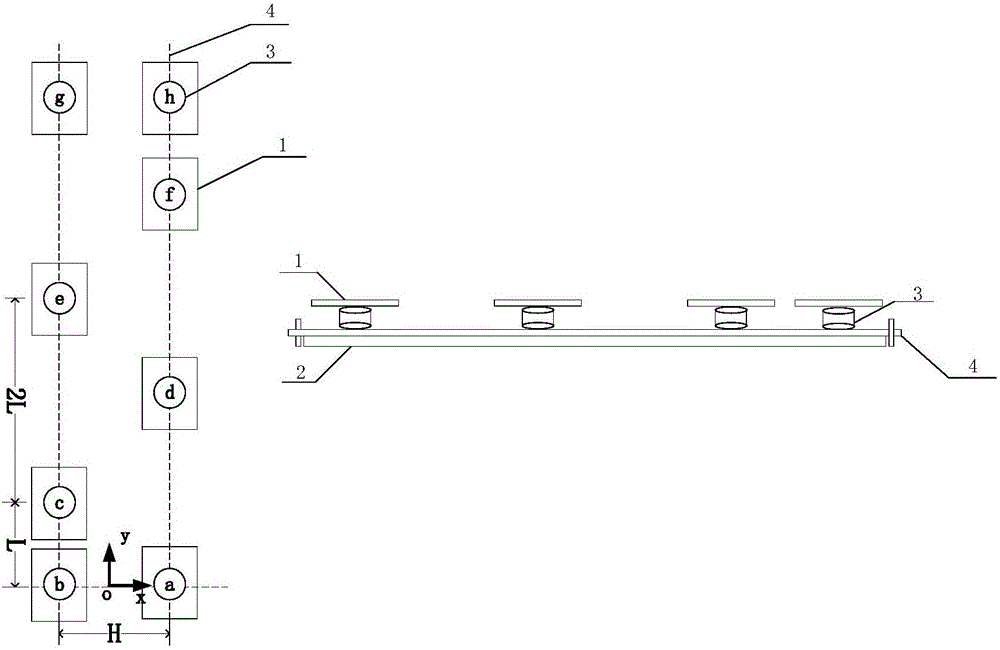
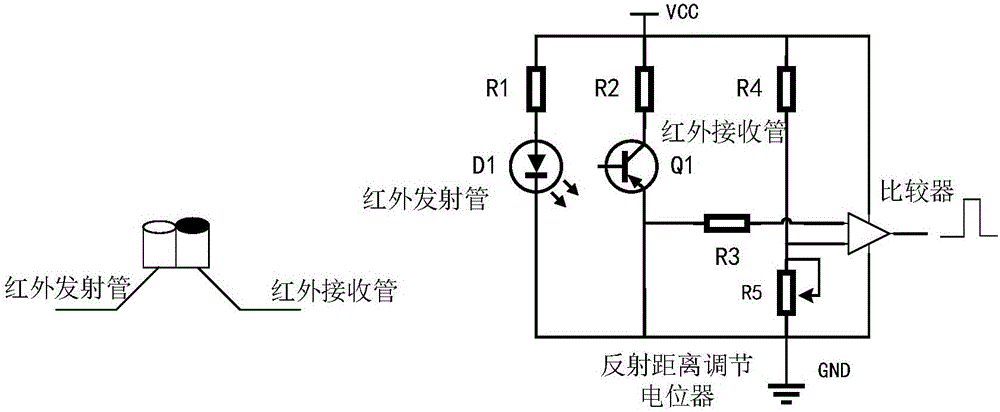
Biped walking parameter measuring method and apparatus
ActiveCN105973143AWalking smoothlyDiagnostic recording/measuringUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceState parameter
The invention provides biped walking parameter measurement and belongs to the technical field of robots. A biped walking parameter measuring apparatus is provided and comprises a zero moment point measuring system, a foot contour measuring system and a walking parameter calculating system. A biped walking parameter measuring method provided can accurately and effectively measure biped walking parameters including stand state parameter before walking, step, step period, zero moment point track, and the contours of feet contacting the ground. The method for measuring biped walking parameters of a human being is of great importance to analysis of walking gaits of the human being, thereby providing important basis for planning track of a biped robot. The method is used for measuring the walking parameters of a biped robot, and feedback parameters of biped robot walking gaits, walking track on-line adjusting, and enclosed control of a host computer and each joint of leg portions are provided. The method is of great significance to stable walking of a biped robot.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
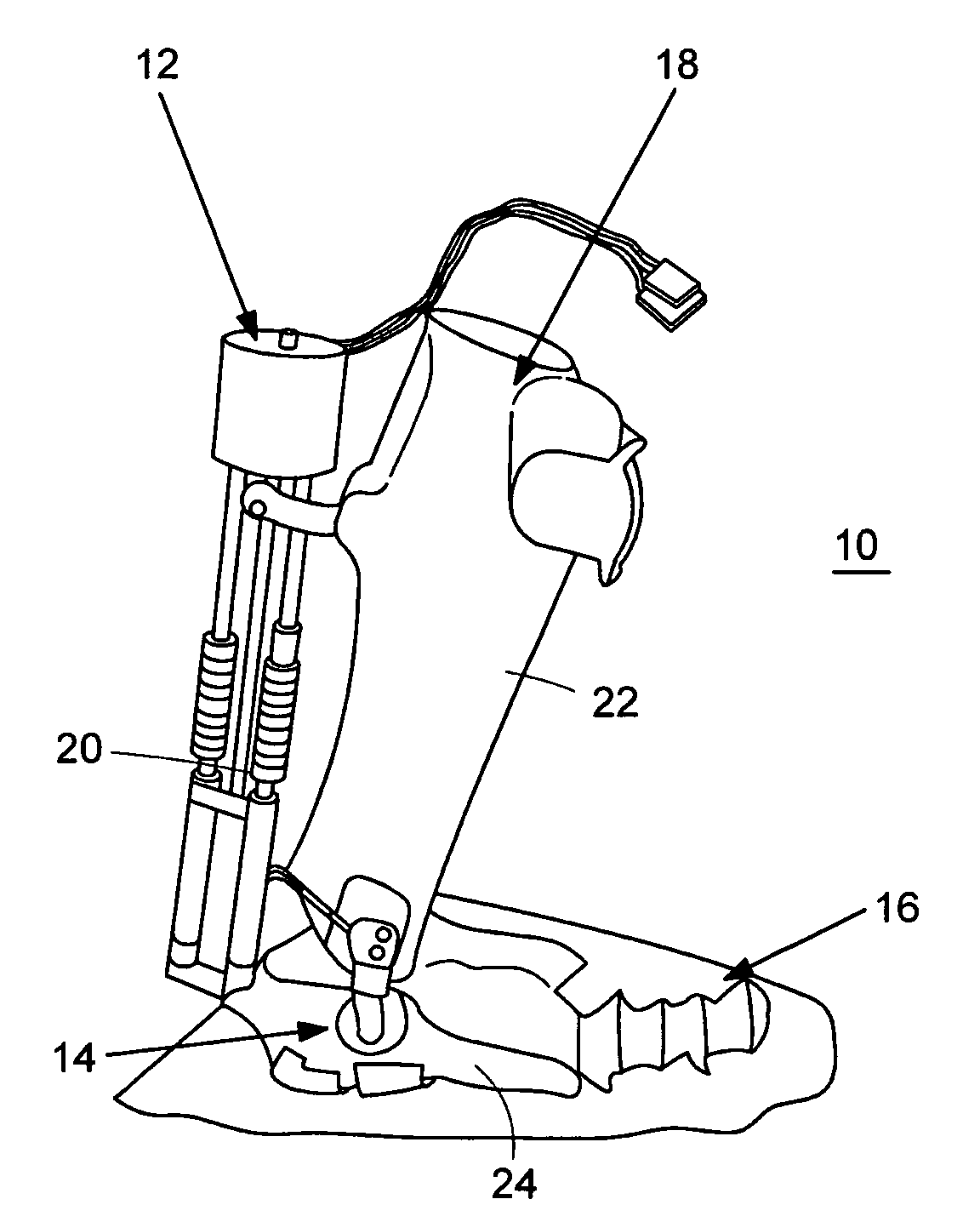
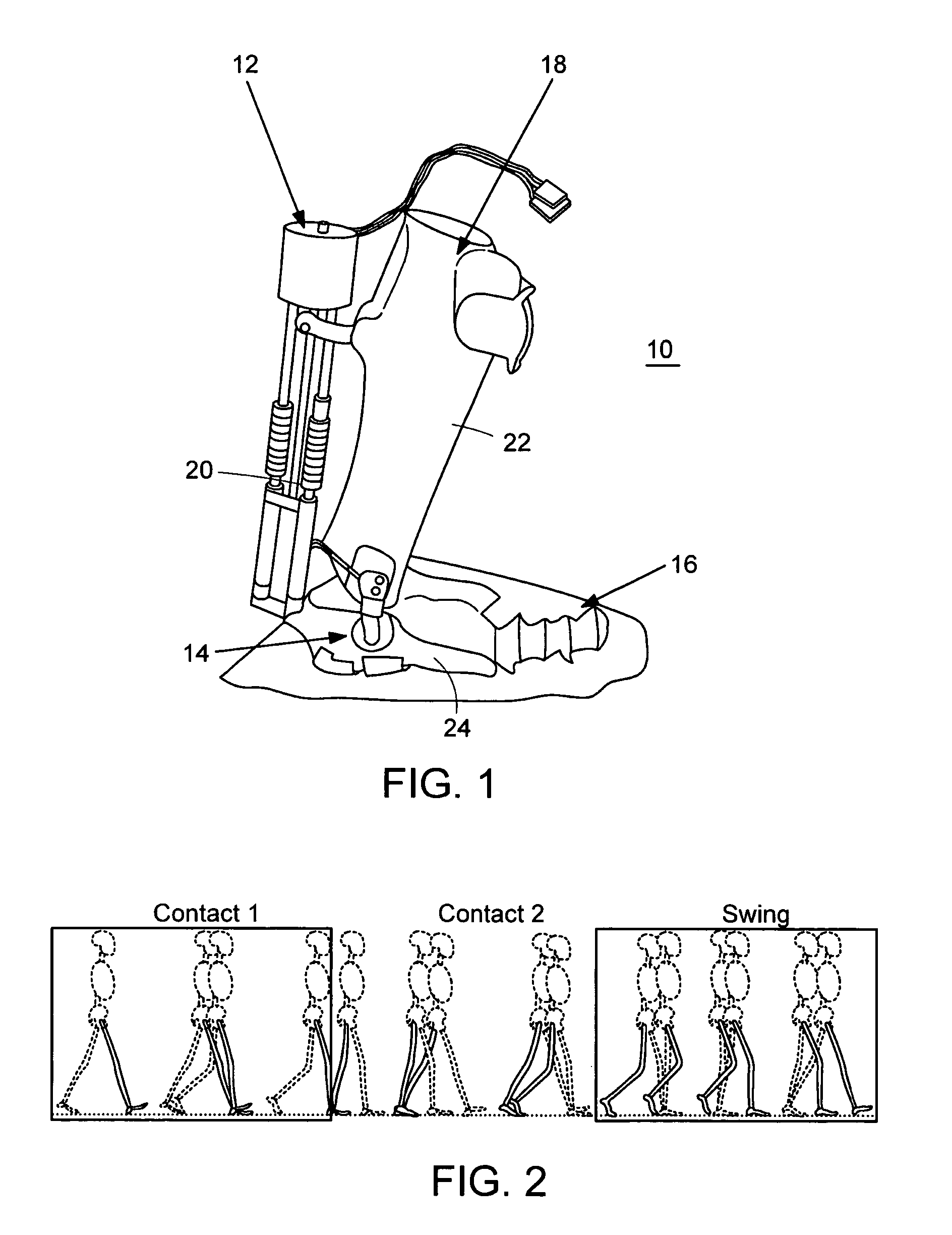
Hydraulic system for a knee-ankle assembly controlled by a microprocessor
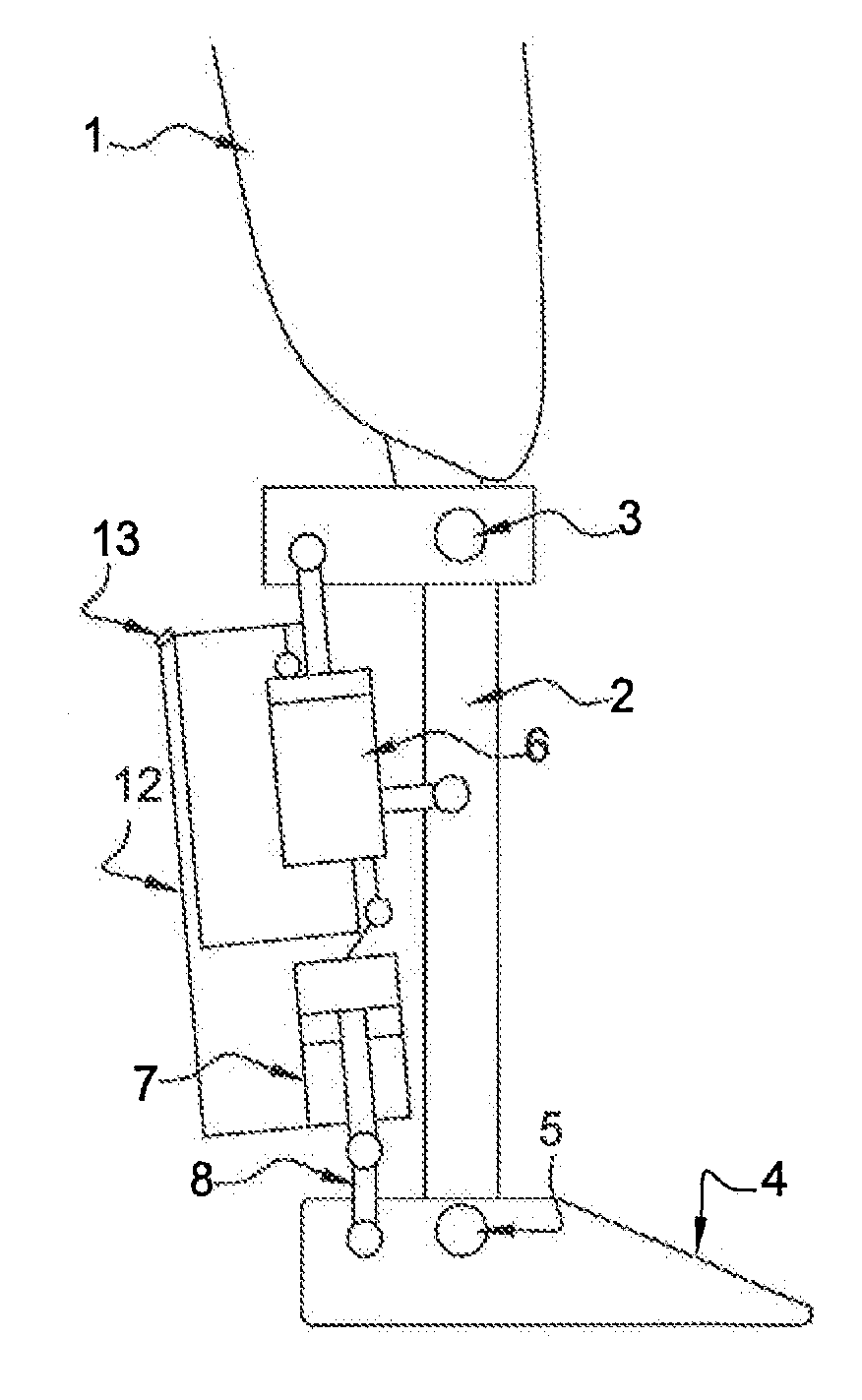
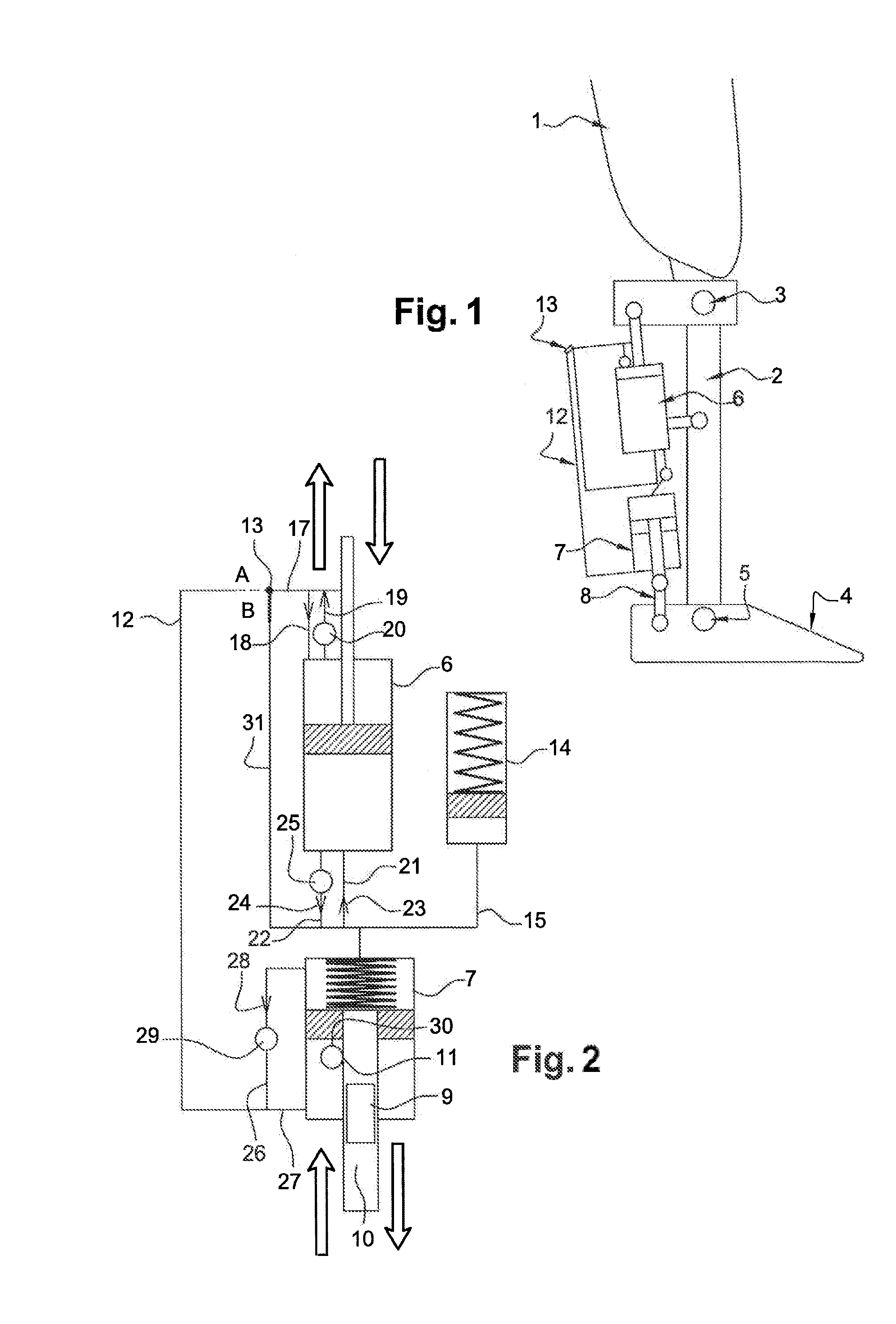
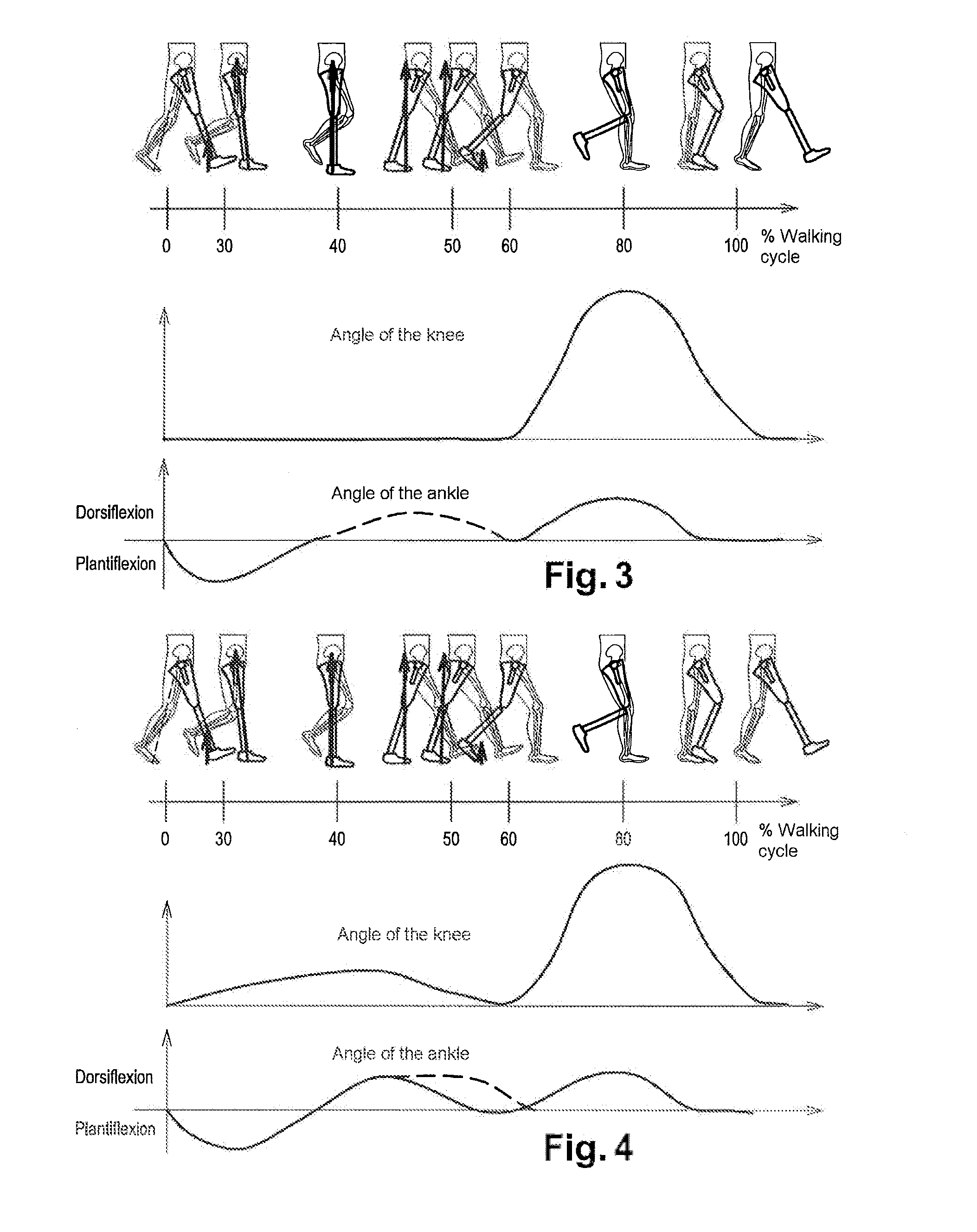
The present invention pertains to a femoral knee-ankle prosthesis intended for persons who are lower-limb amputees but still have a segment suitable for a femoral connection and a tibial connection connected to the femoral segment based on an articulation which reproduces the movements of the knee, the said tibial segment being articulated on one foot based on an articulation reproducing the movements of the ankle, an initial damper the ends of which are joined respectively with the femoral and tibial segments, and another hydraulic damper of which the ends are joined respectively with the tibial and foot segment; the said prosthesis is remarkable in that the chamber of the first hydraulic damper is connected to the chamber of the second hydraulic damper and in that it consists of the means of controlling the first and / or second hydraulic damper depending on the phase of the walking cycle such as the stance phase or the swing phase and / or real-life situations such as stairs, slopes or standing, etc., in such a manner that the flexion of the knee allows the dorsiflexion of the ankle in proportion to the movement of the knee during the stance phase and such that the flexion of the knee results in the dorsiflexion of the ankle during the swing phase.
Owner:PROTEOR
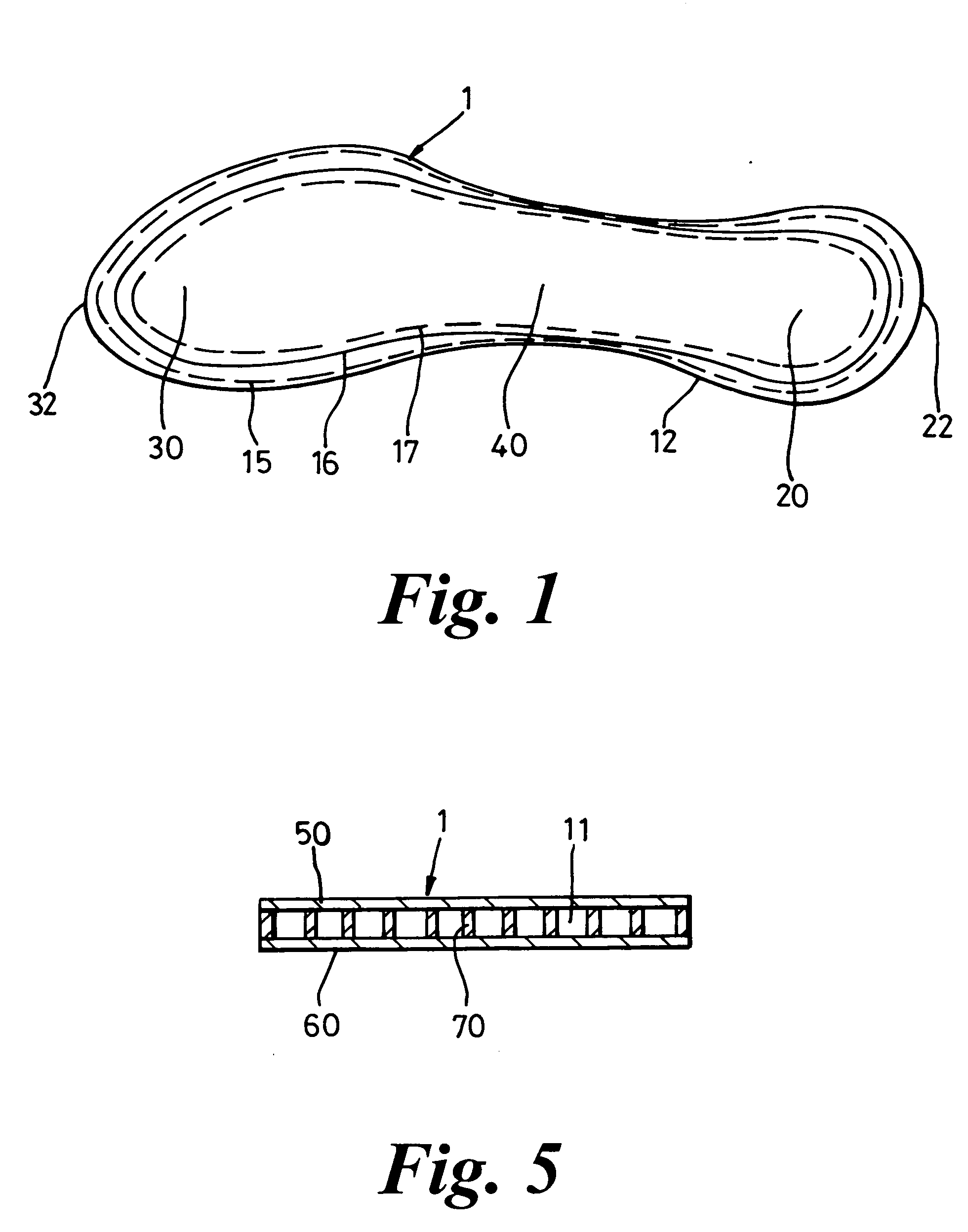
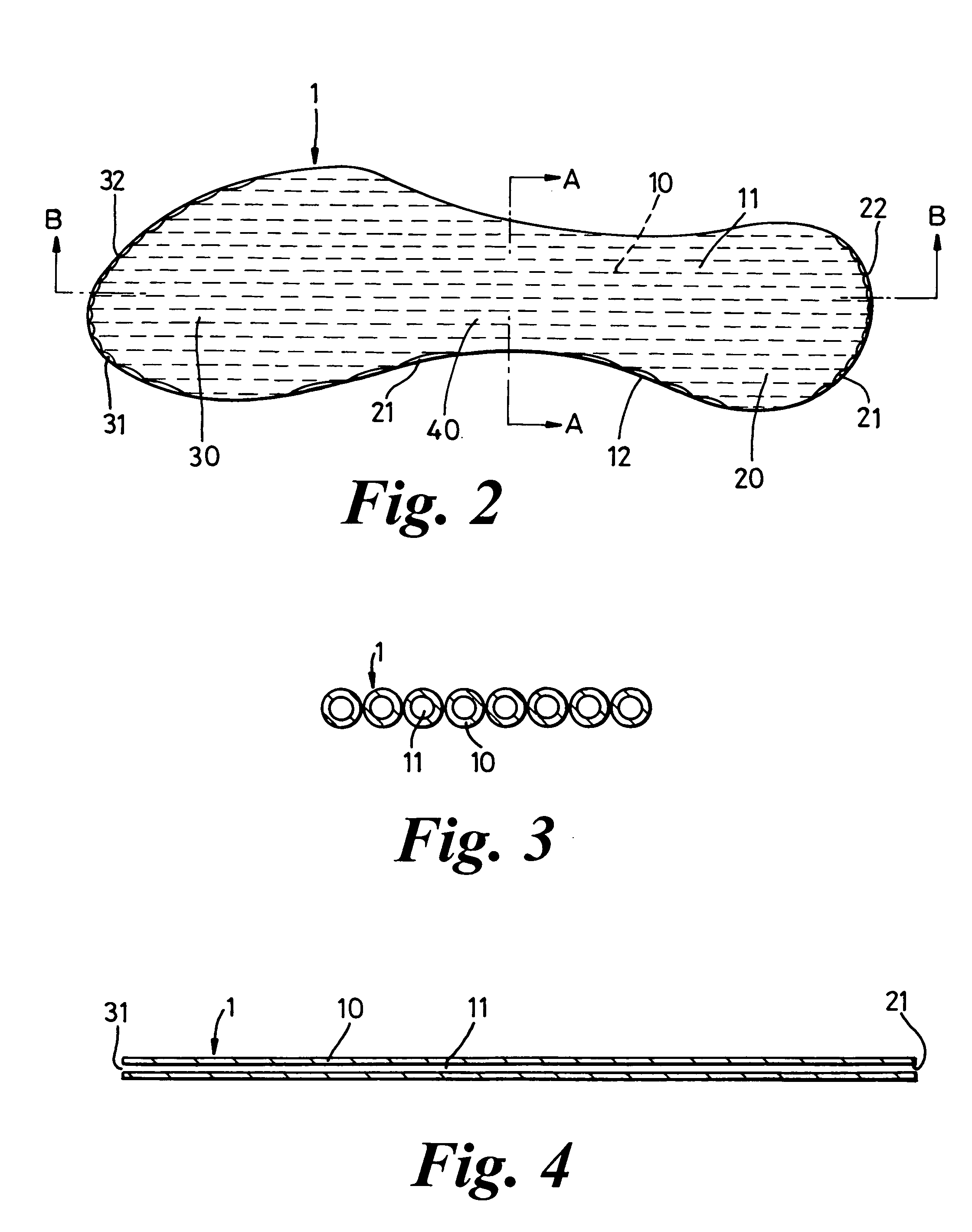
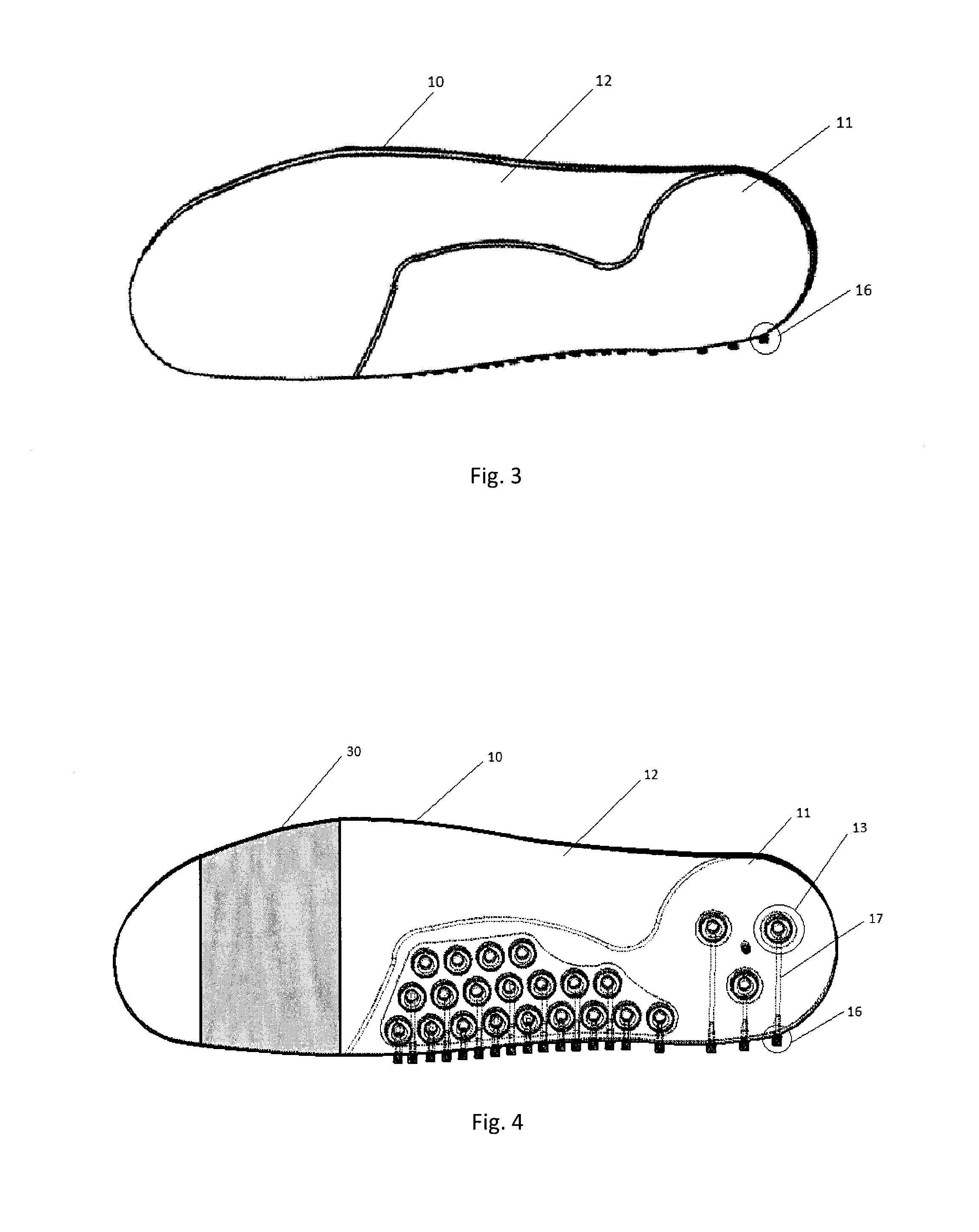
Footwear
InactiveUS20050120591A1Without adversely affecting a wearer's comfortComponent usedSolesInsolesEngineeringWalking cycle
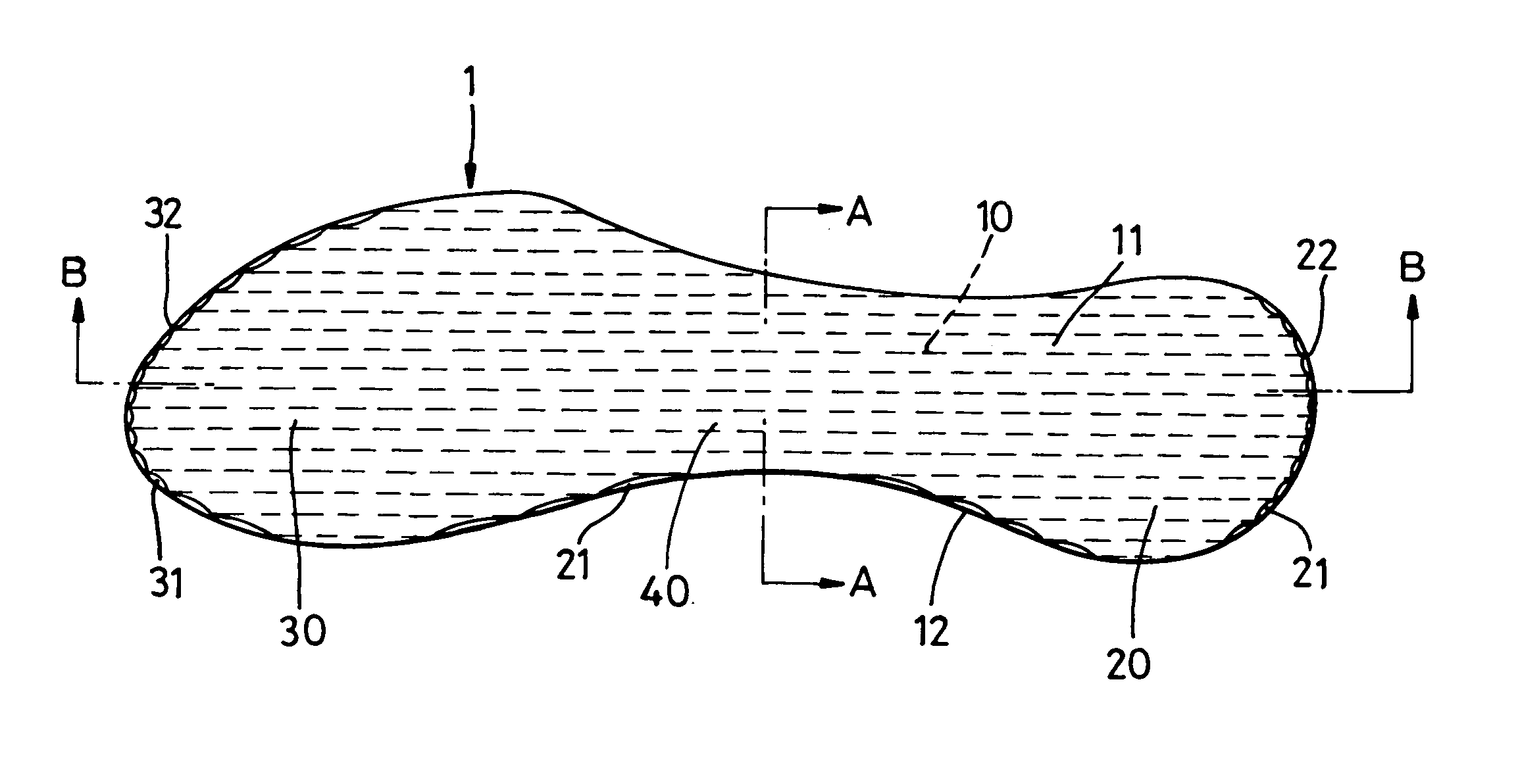
The invention relates to a footwear sole component and to an article of footwear 2 comprising such a sole component. A sole component is suitably an insole 1 with toe and heel portions 30, 20 connected by an arch portion 40, the sole component being arranged to form part of a sole of a closed article of footwear 2 having a foot chamber 90. The sole component includes at least one compressible passage 11 arranged, in use, to have an opening into a first region of the foot chamber 90 and an opening into a second region of the foot chamber 90 such that air can be caused to travel from passage 11 into a second region of the foot chamber 90, by a pumping effect caused by compression of the passage 11 along at least a part of its extent during a stage of a wearers walking cycle.
Owner:ANDREW TERENCE SIDNEY
Walking Device
An orthotic device that includes an active mechanism to modify the curvature of the arch support and a mechanism to tilt the heel while performing varied activities is provided. The system functions by using both a plantar pressure sensor to measure the reaction forces felt on the device by the foot and determine the position in the walking cycle. A fluid sensor is typically used to determine the pressure in each hydraulic chamber to determine if the pressure in each chamber corresponds with the distribution pattern in the plantar pressure sensor. This device hardens the insole at the point before push-off to create a rigid lever that increases the user's transfer of energy to the ground.
Owner:MORENO COLLADO EDUARDO
Computer-aided discrimination method for Parkinson's disease symptoms based on KINECT bone data
InactiveCN107330249AReduce complexityEnsure normal behaviorDiagnostic signal processingSensorsFrame sequenceComputer-aided
The invention discloses a non-contact detection method for Parkinson's disease. The problem of interference with the normal walking of the detected person that may be caused by the contact type is solved, and the hardware cost and the complexity of the device are reduced. The method includes: collecting bone data through kinect; extracting the central point, and performing low-pass filtering on the point coordinate sequence to obtain a new sequence; extracting "the shortest point of the human body in the walking cycle" to calculate the walking cycle; calculating kinematic parameters and stride parameters. One-way analysis of variance was performed on the six groups of parameter sequences, and the experimental data were selected according to the results and box plots to obtain the normal walking data of the tested subjects. A. From the new data, calculate the displacement sequence of the adjacent frames of the left and right feet, and calculate the correlation coefficient to judge the symmetry; if the symmetry conforms to PD, it is suspected PD; B. For the center point movement acceleration sequence, the observation sequence is calculated through the patient's HMM model parameters. probability to determine whether it is a PD patient. If A and B are satisfied at the same time, PD is diagnosed.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
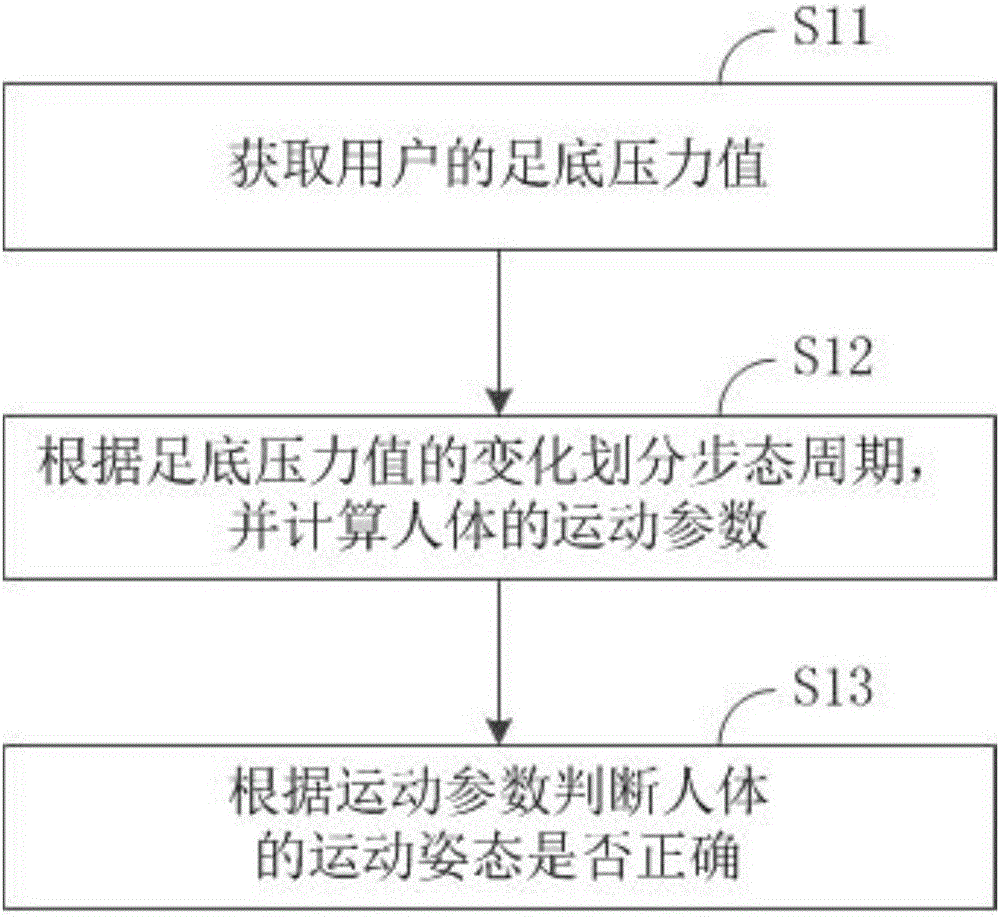
Judgment method, device and system for exercise postures of lower limbs
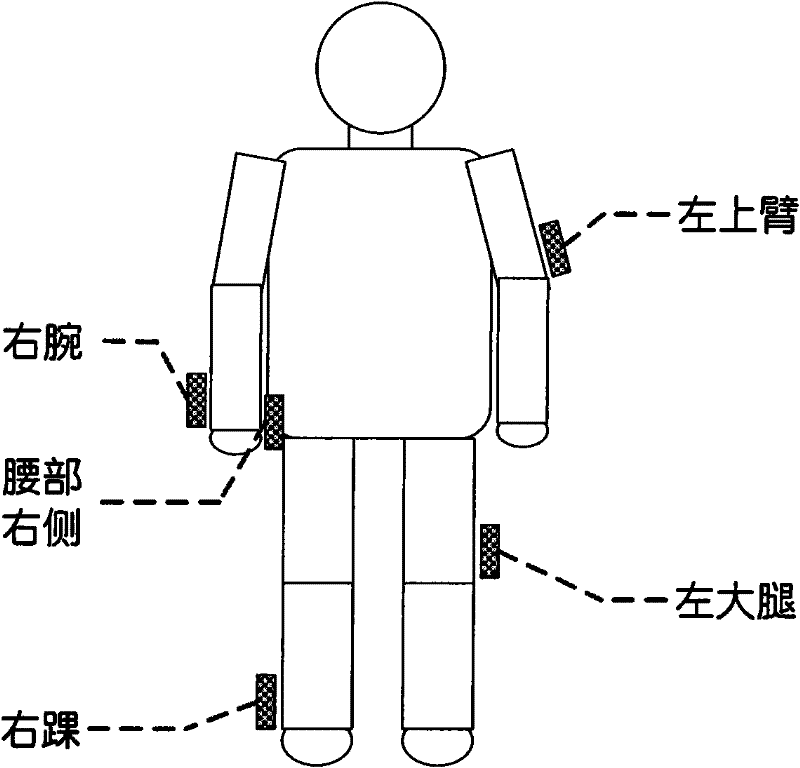
ActiveCN107174253ASo as not to damageImprove exercise effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsWalking cyclePostural orientation
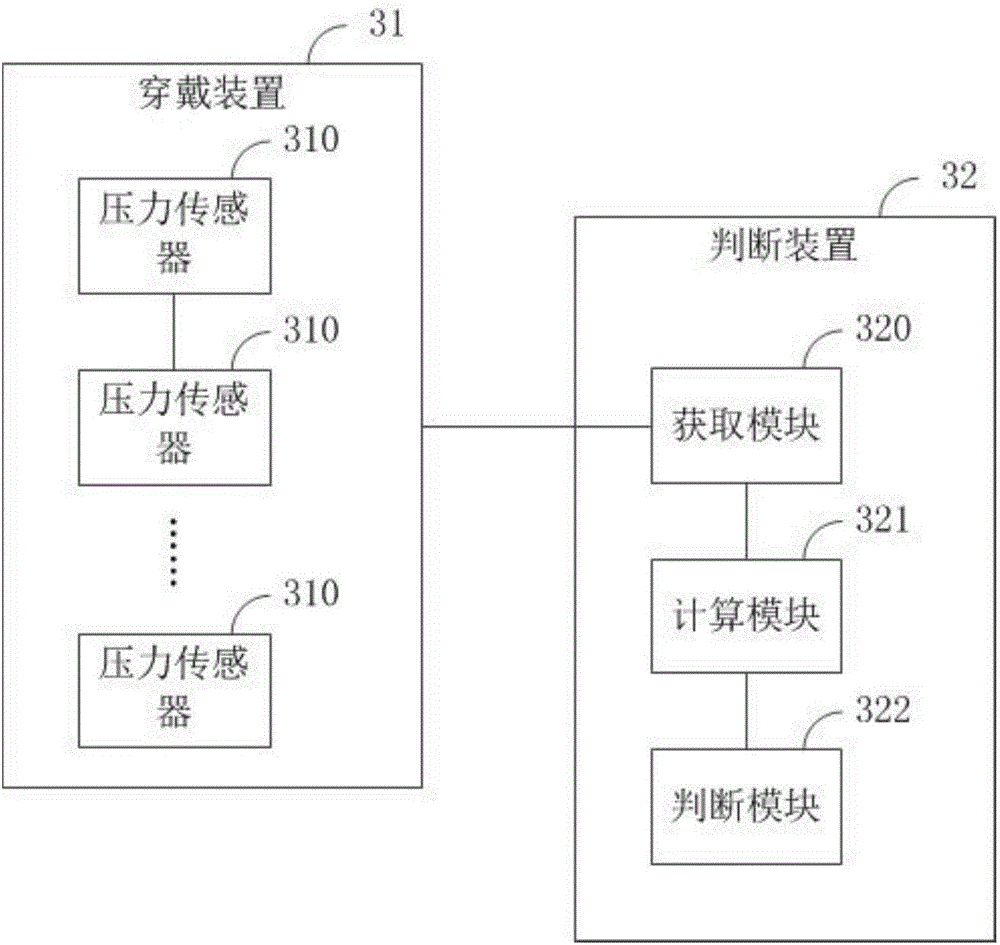
The invention discloses a judgment method, device and system for the exercise postures of lower limbs, and relates to the field of intelligent wearable equipment. The judgment method comprises the following steps: acquiring the sole pressure value of a human body; dividing the walking cycle according to the change of the sole pressure value, and calculating the exercise parameters of the human body; and judging whether the exercise posture of the human body is right according to the exercise parameters. The judgment device is used for executing the judgment method, and the judgment system comprises the judgment device and a wearable device. In the exercise process of a user, through acquiring the sole pressure value of the human body, calculating the exercise parameters of the human body, and judging whether the exercise posture of the human body is right according to the exercise parameters, the judgment method, device and system can instruct the user to exercise in compliance with the right exercise method and exercise posture, thereby achieving a preferable exercise effect and ensuring that the limbs are not injured.
Owner:GUANGDONG COROS SPORTS TECH JOINT CO
Zero-speed detection method based on hidden Markov model and indoor pedestrian inertial navigation system
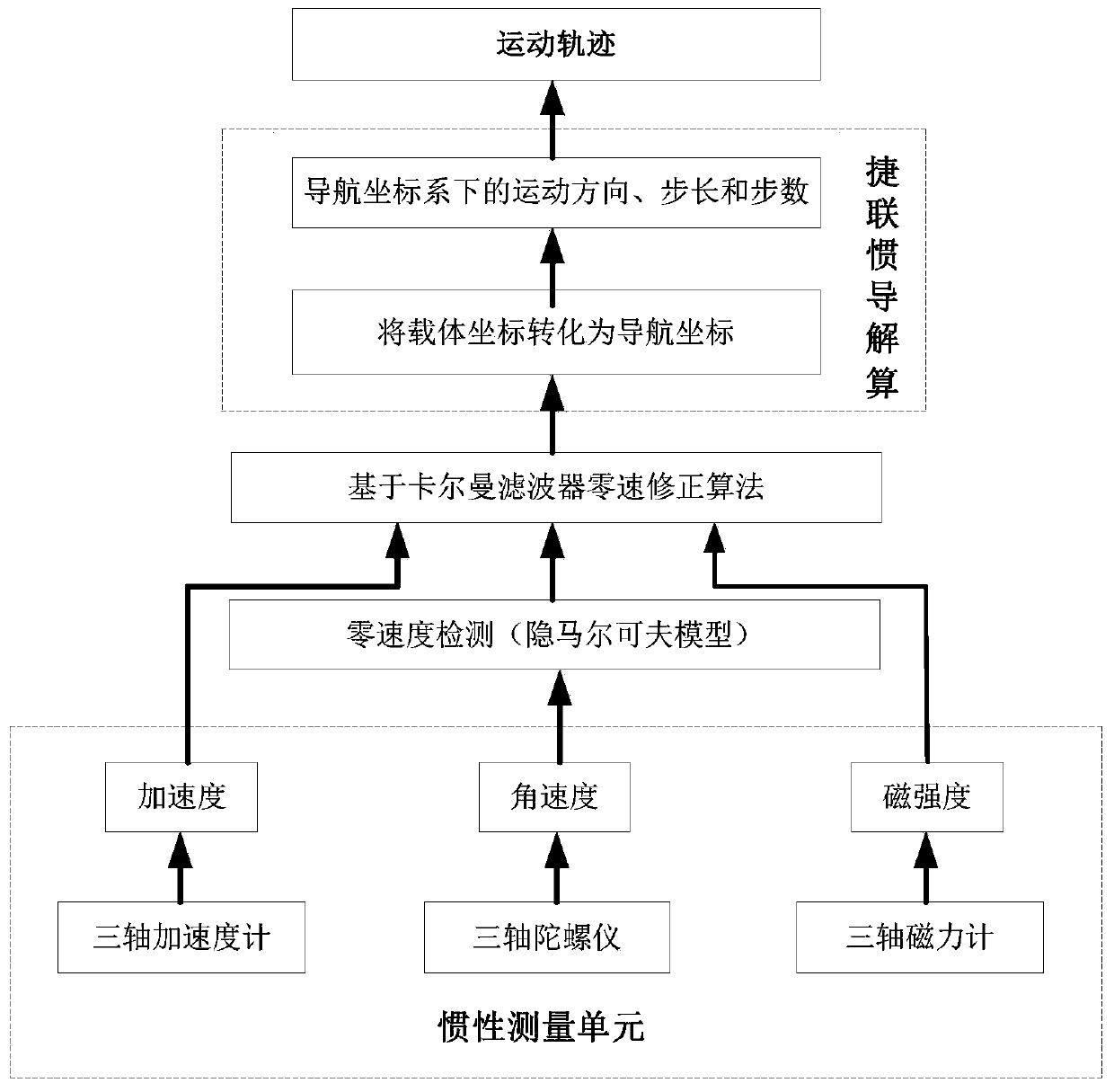
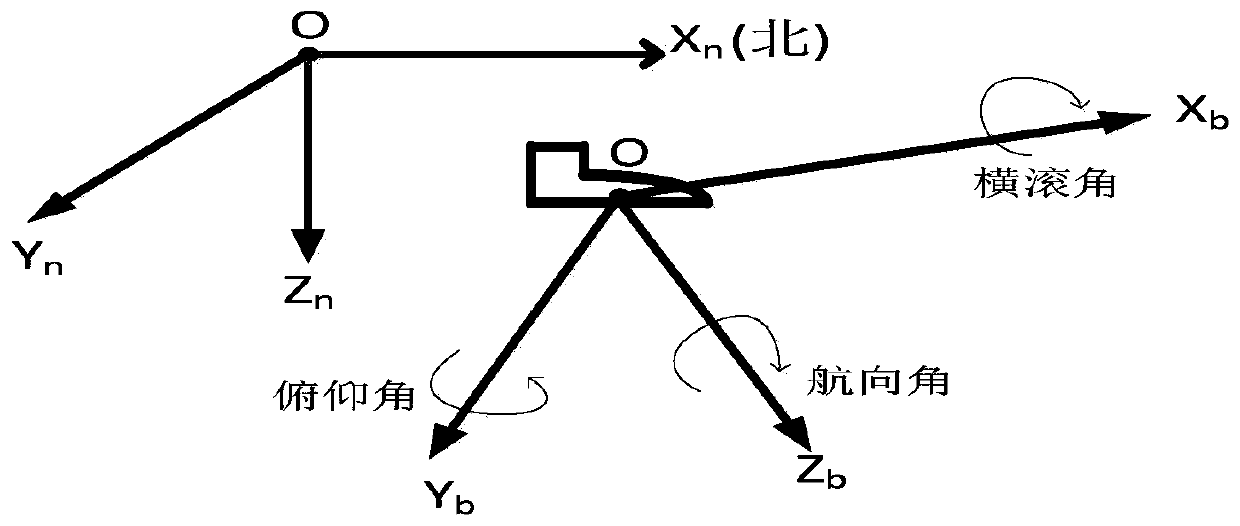
InactiveCN109883429AEstimating and Correcting Navigation ErrorsAccurate gait statusNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsCorrection algorithmHuman body
The invention provides a zero-speed detection method based on a hidden Markov model and an indoor pedestrian inertial navigation system. The method comprises the steps of carrying out periodic division on a gait of a human body; obtaining acceleration data, triaxial angular velocity data and triaxial magnetic force intensity of three axes in a walking process of a pedestrian; defining a state value and an observation value of the gait of the human body, initializing a state transition probability matrix, and abstracting zero-speed detection of the pedestrian in the walking process into the hidden Markov model; and optimizing the hidden Markov model by a zero-speed correction algorithm based on a Kalman filter, detecting the angular velocity of the pedestrian in a standing stage to be a zero moment, and predicting a state of the pedestrian at the next stage of walking exercise. According to a zero-speed detection algorithm provided by the technical scheme, the hidden Markov model is adopted, and the walking cycle of the human body is accurately divided, so that the situations of false detection and missing detection are avoided. Optimal estimation is carried out on a system state byusing the zero-speed correction algorithm based on the Kalman filter.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Optimized control method of humanoid robot walking track
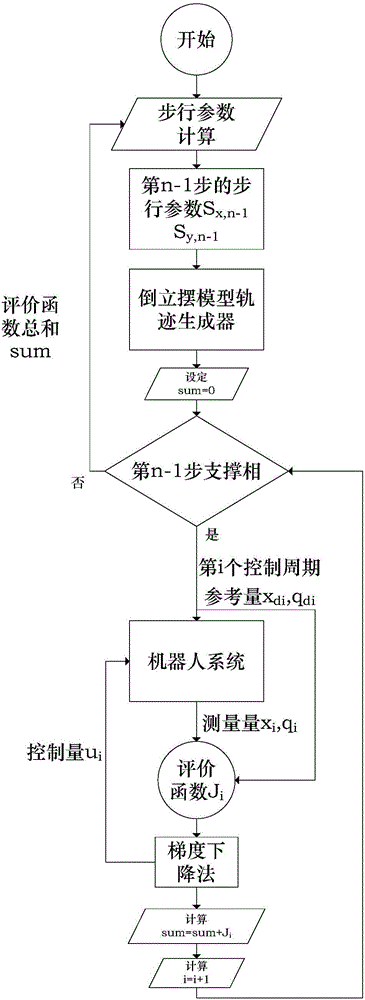
ActiveCN104898672AGuaranteed stabilityGuaranteed TrackingPosition/course control in two dimensionsWalking cycleControl theory
The present invention provides an optimized control method of a humanoid robot walking track. Through the accumulation of complete walk cycle optimization effects, a track correction amount is generated, when each walk cycle is ended, the walk parameter of a humanoid robot is corrected, and the stability of humanoid robot walking is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Indoor and outdoor positioning method, positioning system, and positioning foot rings
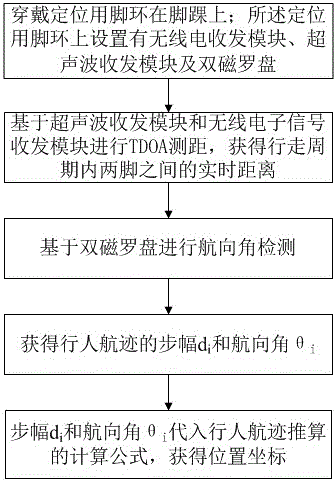
InactiveCN105783920AEasy to assemble and disassembleEasy to carryNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLeft ankleWalking cycle
The invention discloses an indoor and outdoor positioning method, a positioning system and positioning foot rings. The method comprises the following steps: (1) separately putting on the foot rings on a left ankle and a right ankle, wherein radio receiving and transmitting modules, ultrasonic wave receiving and transmitting modules and double magnetic compasses are arranged on the foot rings; (2) performing TDOA distance measurement based on the ultrasonic wave receiving and transmitting modules and the radio receiving and transmitting modules, so as to obtain a real-time distance between two feet within a walking cycle; (3) performing course angle detection based on the double magnetic compasses; (4) acquiring the stride di and the course angle theta i of a track based on the step (2) and the step (3); (5) substituting the stride di and the course angle theta i obtained in the step (4) into a calculating formula for reckoning the pedestrian track, namely a north coordinate shown in the description, an east coordinate shown in the description, so as to obtain the current pedestrian position coordinate. According to the indoor and outdoor positioning method, the positioning system and the positioning foot rings disclosed by the invention, hardware is integrated on the foot rings, and the foot rings are convenient to disassemble, assemble and carry, high in capacity of resisting disturbance, reliability, stability and generality, and free from complicated mounting and connecting, and is directly disassembled and assembled, so that the foot rings are suitable for any people.
Owner:李明科
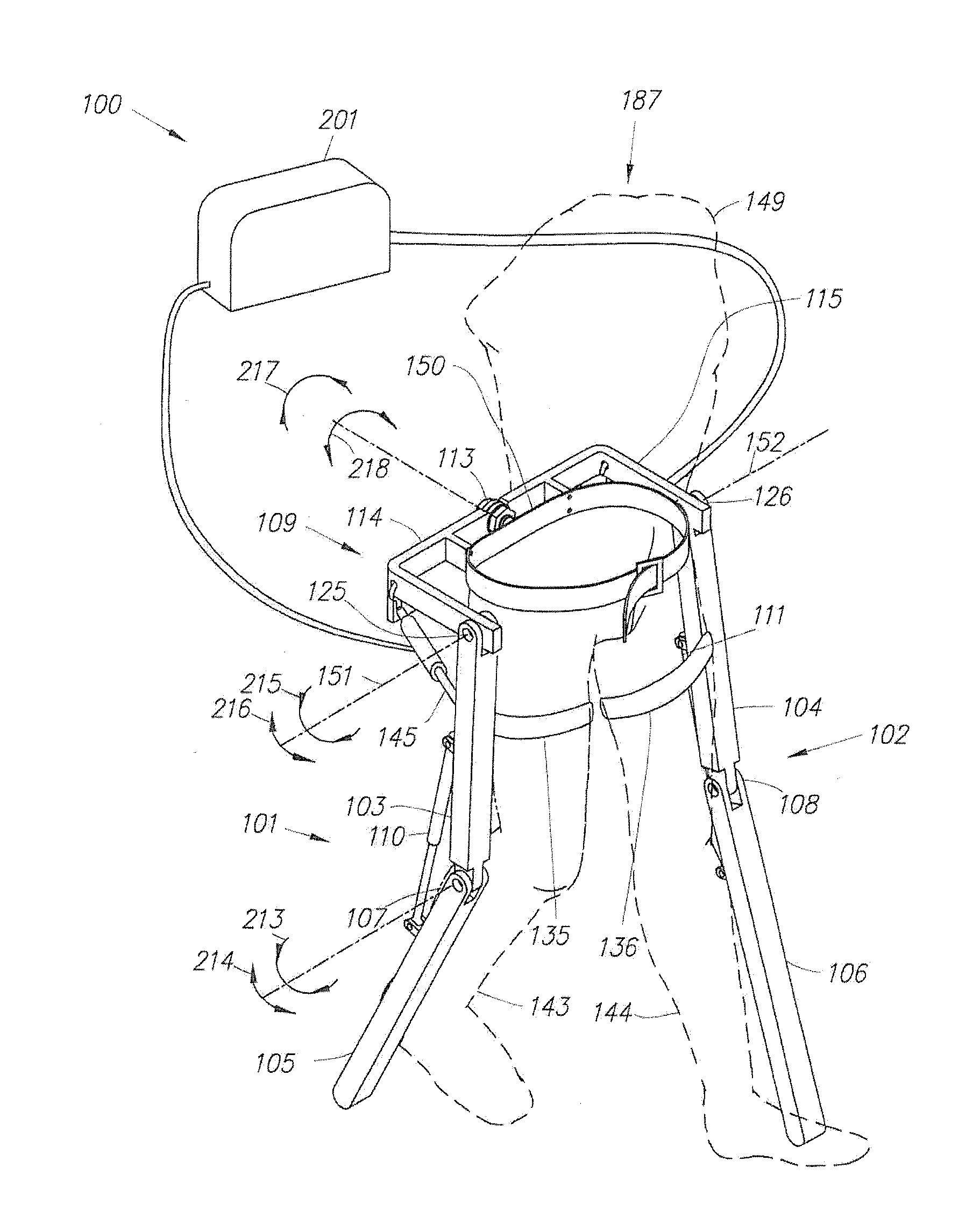
System to assist walking
PendingCN110418626APreserve hip flexionProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesHip flexionSpinal cord lesion
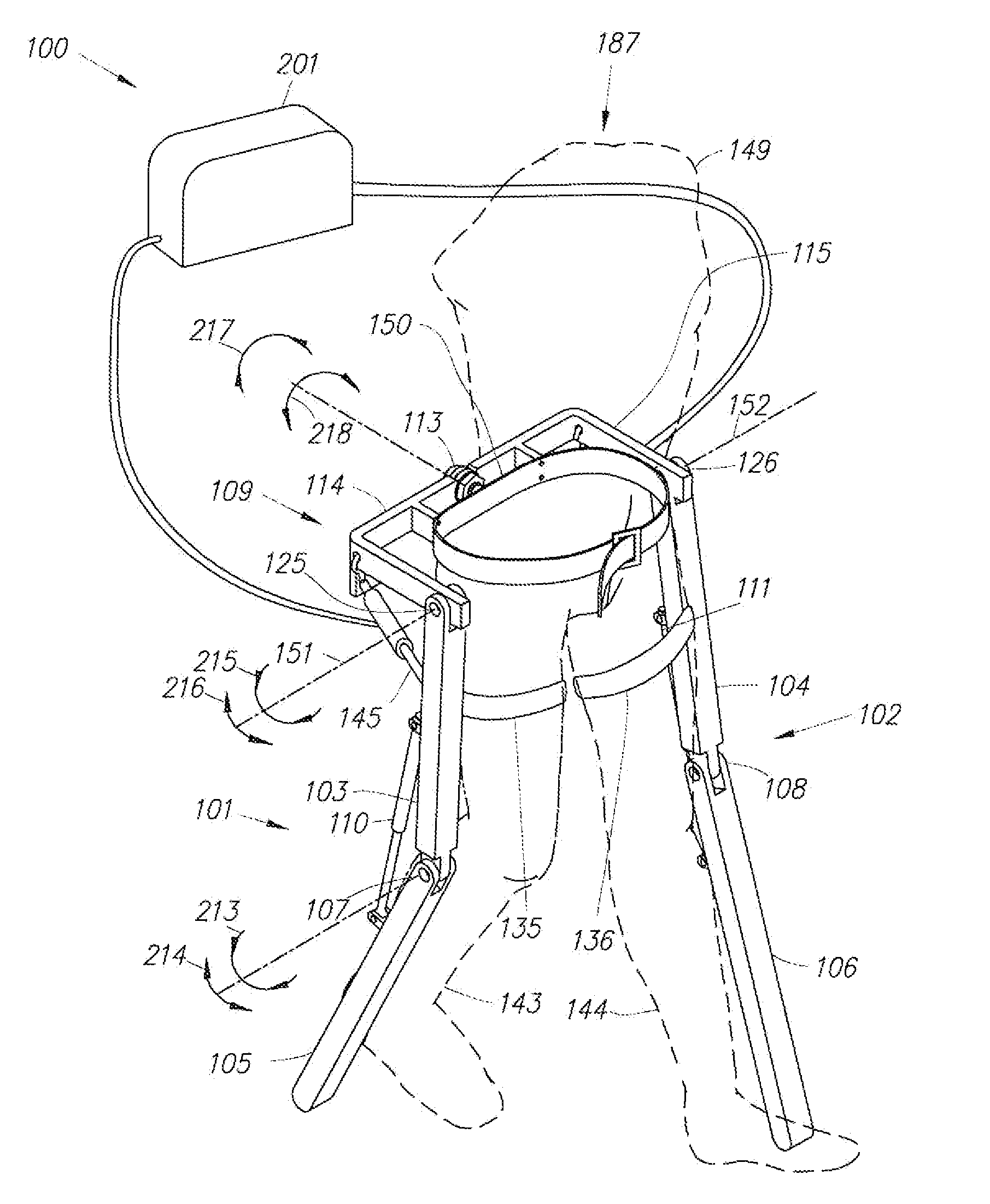
The invention relates to a system to assist walking in spinal cord injured people, who preserve hip flexion capacity, the system comprising a pair of KAFO-type orthoses with: (a) an angular actuator (5) in each knee; (b) an orientation and acceleration sensor (6) on each leg; (c) a power supply and control system (7) to which all the sensors and actuators are connected; (d) a control algorithm deciding when to flex or extend the knee depending on the walking cycle, using information from the sensors.
Owner:UNIV DA CORUNA +2
Height and motion property based comprehensive measuring method of pedestrian step length
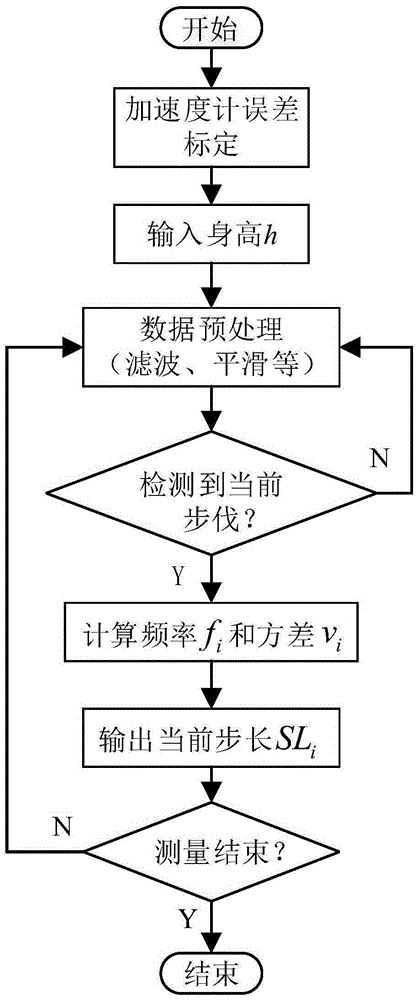
ActiveCN106767807AReduce missed detection rateHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEngineeringWalking cycle
The invention provides a height and motion property based comprehensive measuring method of pedestrian step length. The method is on the basis of three factors, namely, different height, different walking frequency, and acceleration variance within each walking cycle; the vertical acceleration information of a human body is mainly utilized for step length measuring. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the acceleration at the center of body weight when the human walks through an inertial measurement nit (IMU) worn at the waist of the human body; then calculating the walking frequency and the acceleration variance within each walking cycle according to the acceleration data; finally realizing the step length measuring through the relation between the walking frequency, the acceleration variance, the height and the step length. According to the method, the body properties and the motion properties of different people are comprehensively considered, so that the method has the characteristics of being high in reliability and accuracy, and is applicable to step length measuring and navigation positioning in indoor autonomous pedestrian navigation, and can be applied to the fields such as the gait analysis field, the exercise training field and the health monitoring field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Power exoskeleton control method, device, computer device and storage medium
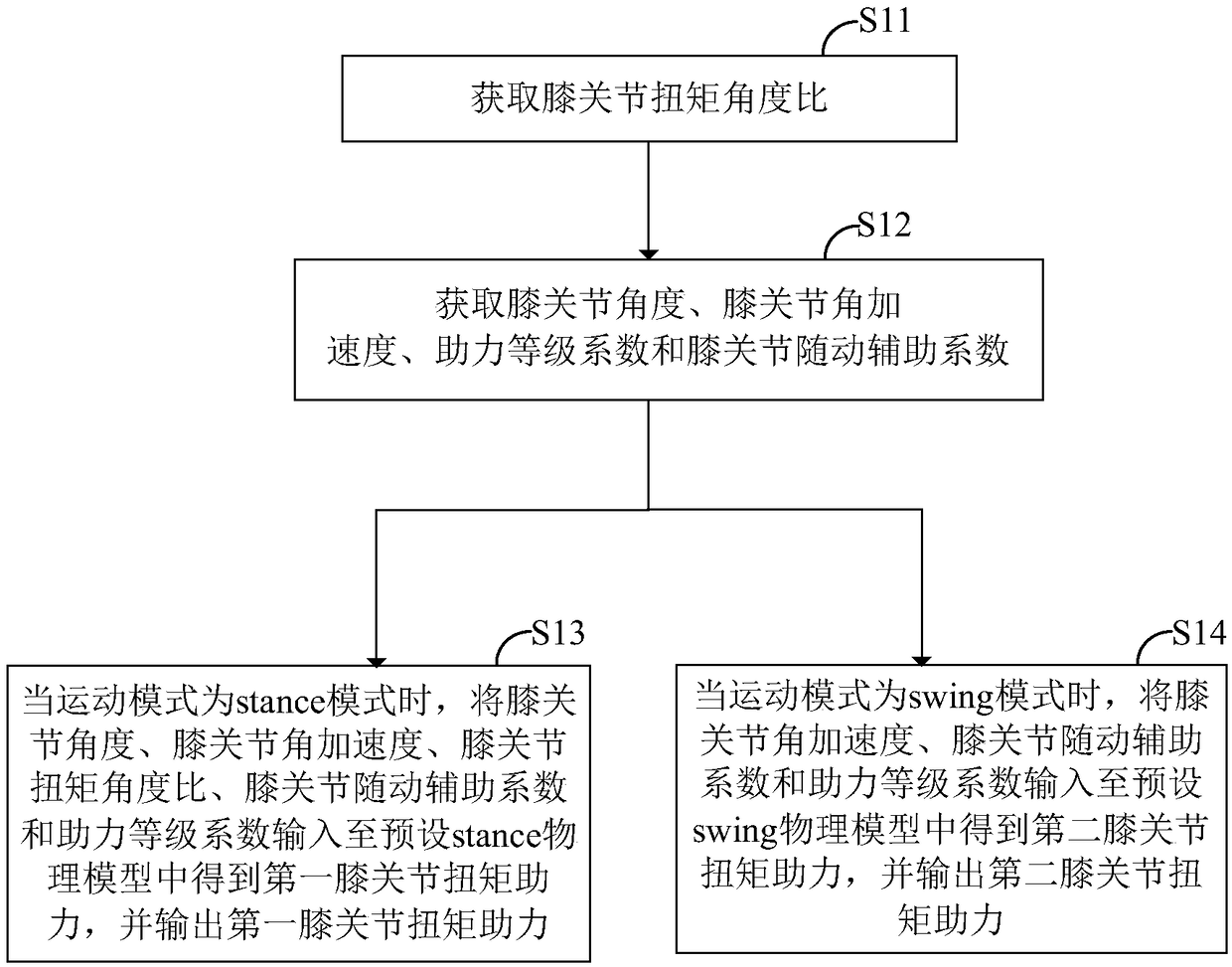
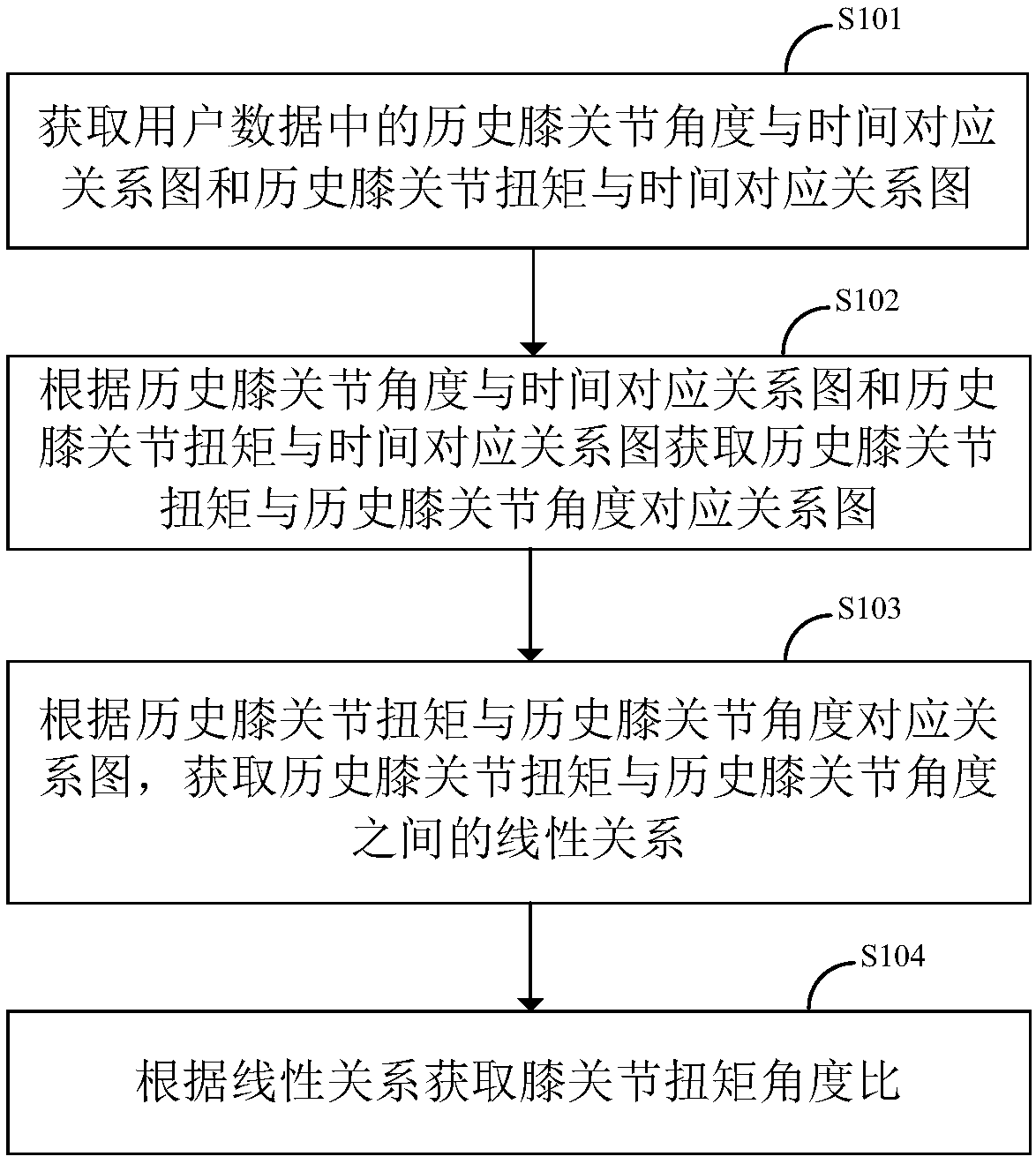
ActiveCN109124998ASimplify complexityImprove stabilityDiagnosticsWalking aidsPhysical modelKnee Joint
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical rehabilitation assisted walking, and particularly relates to a power exoskeleton control method, device, computer equipment and storage medium.The power exoskeleton control method includes the steps of obtaining torque-angle ratio of knee joint, obtaining torque-angle ratio of knee joint, the current angle of knee joint, angular accelerationof knee joint, coefficient of assisting power and coefficient of assisting knee joint; when the walking cycle is stand mode, inputting the knee joint angle value, the knee joint torque angle ratio, the knee joint follow-up assist coefficient ratio and the assist level coefficient into the stand physical model to obtain the knee joint torque assist force; when the walking cycle is swing mode, inputting the knee angular acceleration, knee follow-up assist coefficient and assist grade coefficient into the swing physical model to obtain the knee torque assist. By using the dynamic exoskeleton control method, the human motion is enhanced by torque control without planning the trajectory, and the algorithm complexity is simplified.
Owner:东莞英汉思机器人科技有限公司
Step-length-fixed telescopic automatic walking mechanism
ActiveCN104165257AAccurate surface qualityImprove surface qualityPigs/molesWalking distanceLocking mechanism
The invention discloses a step-length-fixed telescopic automatic walking mechanism, belongs to the technical field of automatic walking and particularly relates to a step-length-fixed telescopic automatic walking technology used for detecting the inner wall of a pipeline. The step-length-fixed telescopic automatic walking mechanism is composed of a front shell and a rear shell, wherein the front shell and the rear shell are respectively provided with an elastic supporting structure and a locking mechanism. The front shell and the rear shell are connected together through a threaded rod motor, a threaded sleeve and a guide pillar. In the process of advancing, the locking mechanism of the front shell is unlocked, the locking mechanism of the rear shell is locked, the threaded rod motor rotates to drive the front shell to advance partially by a regulated distance, then the locking mechanism of the front shell is locked, the locking mechanism of the rear shell is unlocked, the threaded rod motor rotates to drive the rear shell to advance partially, and in this way a walking cycle is finished. The maintaining performance and interchangeability are good, automatic walking can be performed well, the walking distance is high in uniformity each time, the automation degree is high, positioning precision is high, and reliability is high. Meanwhile, time, efforts and labor are saved, and it is guaranteed that the surface quality of the inner wall of the photoelectric instrument detection pipeline is accurate and comprehensive.
Owner:SHANDONG NORTH OPTICAL & ELECTRONICS
Pneumatic lower extremity gait rehabilitation training system
A pneumatic lower extremity gait rehabilitation training system includes a support device for reducing the burden of supporting a user's body weight by lower extremity in a walking therapy, an exoskeleton rehabilitation device for adjusting the user's walking coordination at a treadmill, a center-of-gravity adjusting device for adjusting a change of upper and lower centers of gravity, and a remote monitoring device for receiving and capturing a signal of an angle displacement of a joint mechanism in a walking cycle. The user may support her / his body weight by the support device and the center-of-gravity adjusting device to reduce the gravity exerted onto the user's legs. The exoskeleton rehabilitation device improves the flexibility, safety and lightweight of walking and requires fewer driving elements. The remote monitoring device sends analyzed signals to the treadmill to adjust the user's walking speed, so as to improve the rehabilitation effect.
Owner:LUNGHWA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Stride calculation system
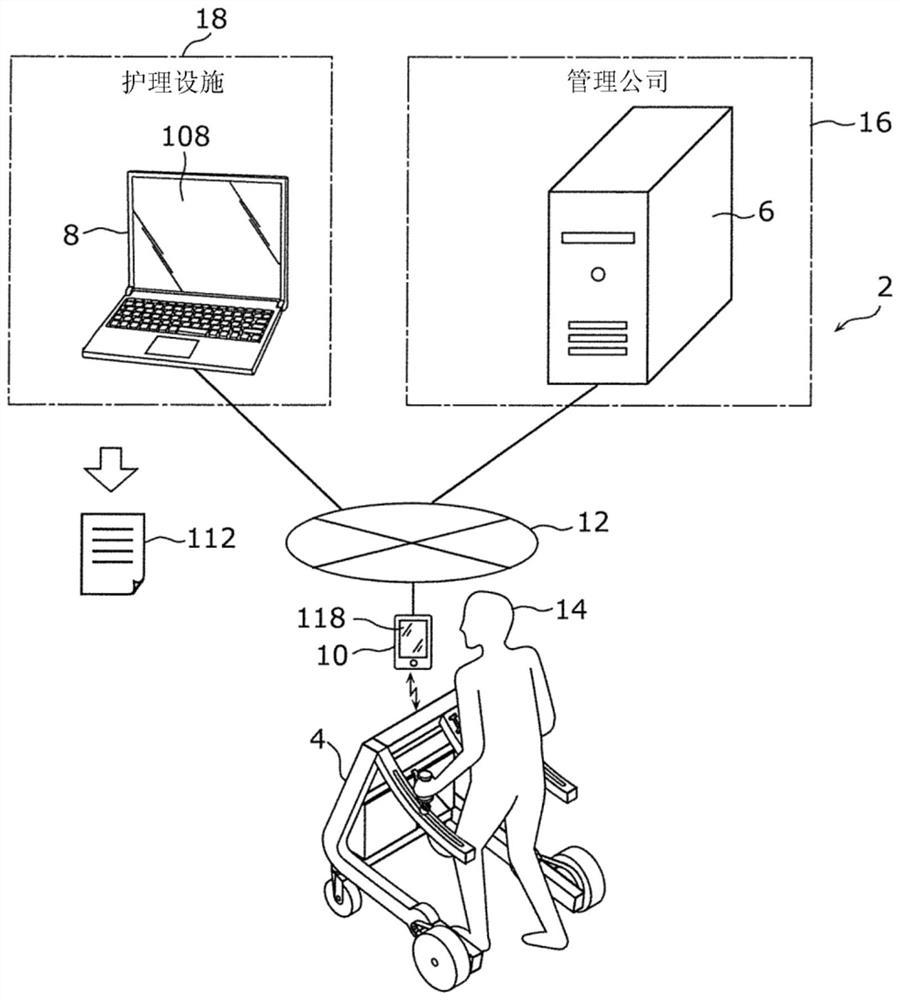
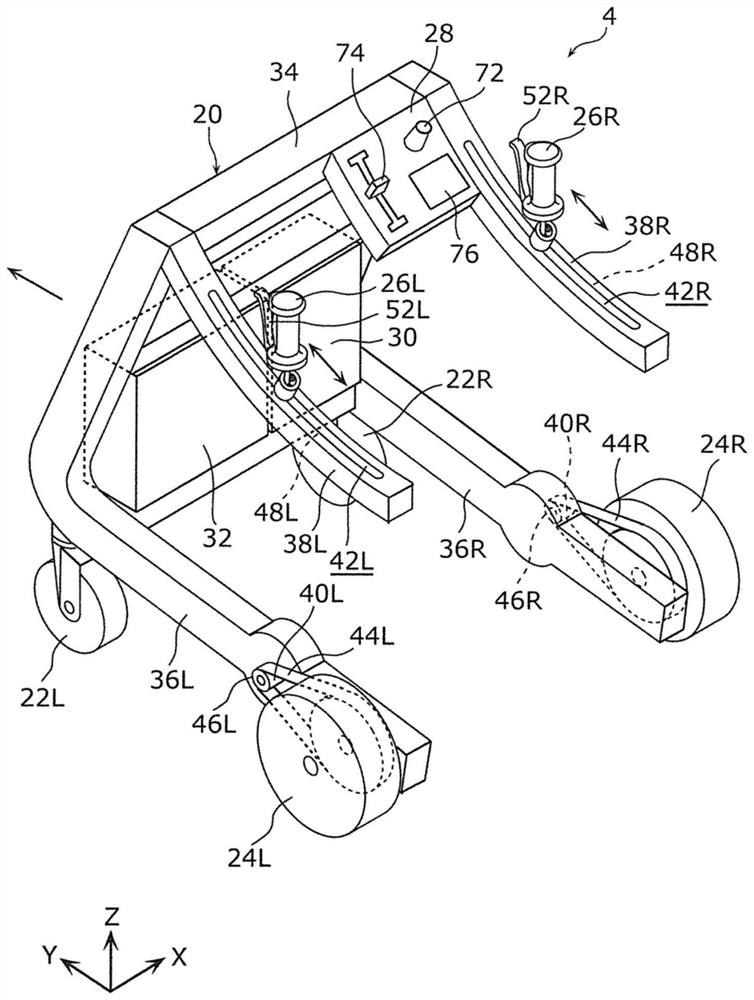
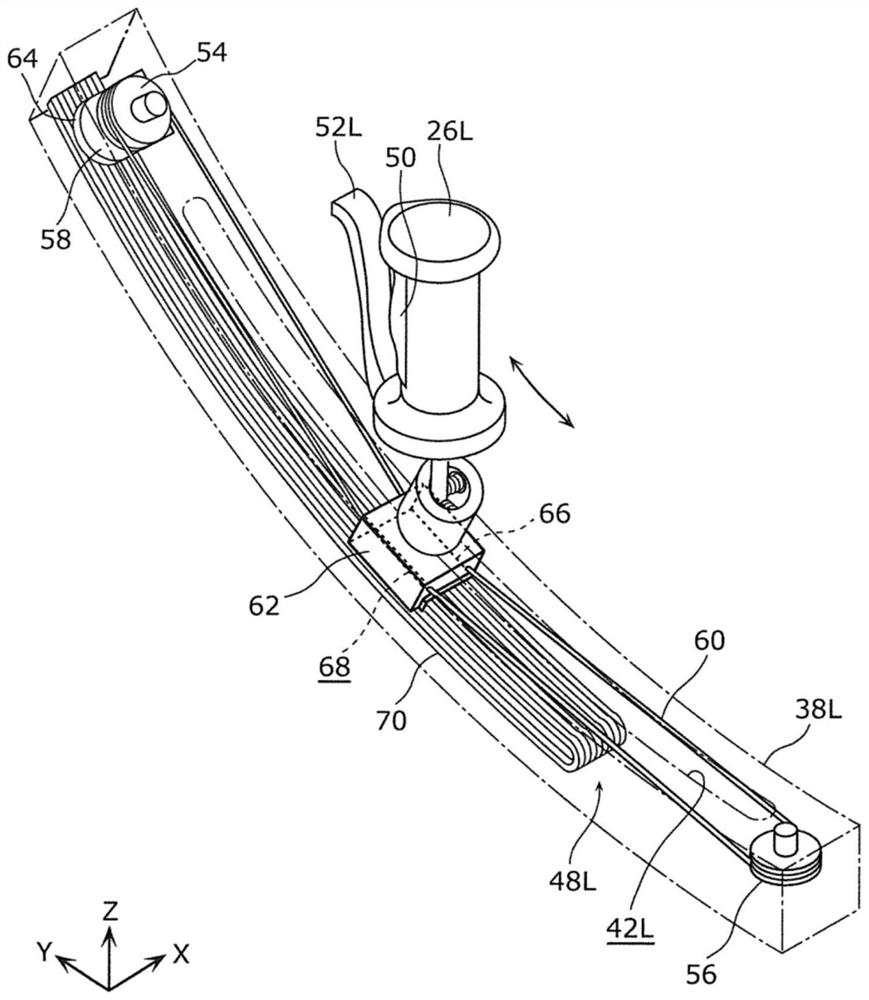
The invention provides a stride calculation system. The stride calculation system is provided with a walker configured to assist a user in walking, and a calculation device. The walker is provided with a walking-related data acquisition unit that acquires walking-related data relating to walking of the user using the walker, and the calculation device acquires walking cycle data relating to a walking cycle of the user on the basis of the walking-related data, and calculates the stride of the user on the basis of the walking-related data and the walking cycle data. The stride calculation systemaccording to this configuration is capable of accurately determining the degree of improvement in the walking ability of a user.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Walking motion display system and program
ActiveCN108348195ASimple compositionImprove convenienceMedical imagingInertial sensorsWalking cycleVertical displacement
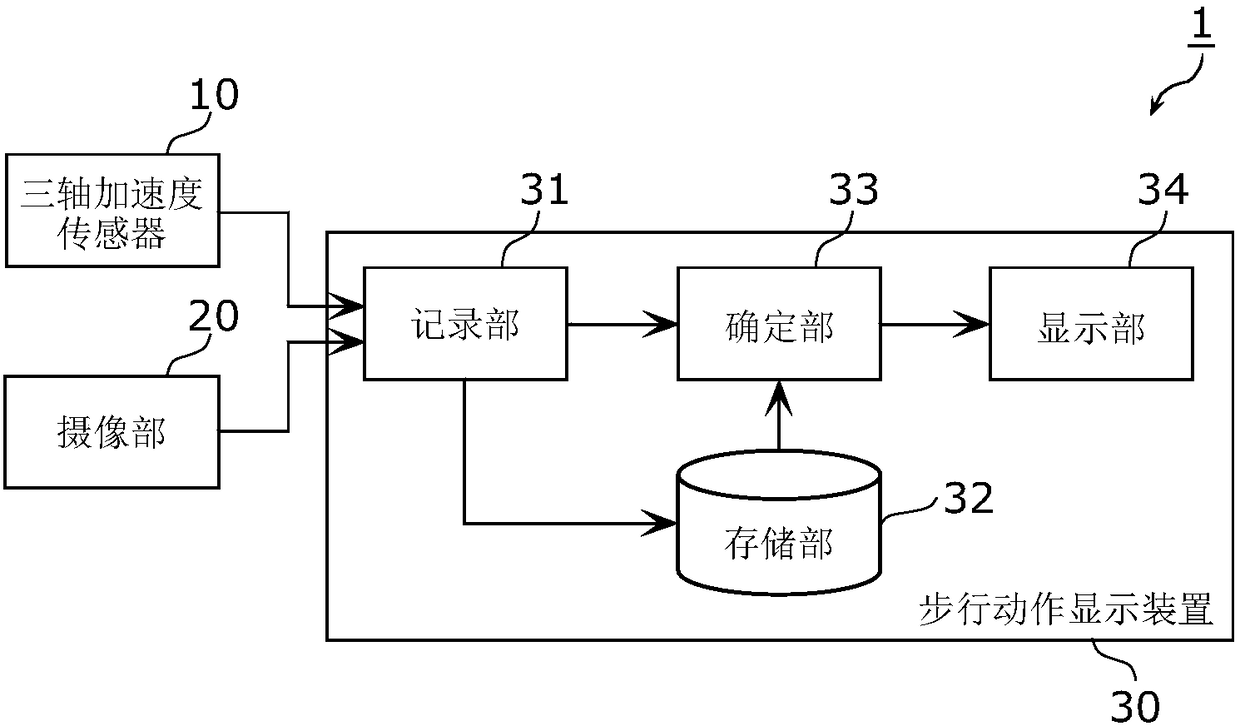
The walking motion display system (1) is provided with: a 3-axis acceleration sensor (10) that is attached to a subject (2) and measures acceleration data of the subject (2) while the subject (2) is walking; an imaging unit (20) that obtains video data showing the walking motion of the subject (2) by imaging the walking subject (2); a recording unit (31) that synchronizes and records the acceleration data and the video data; an identifying unit (33) that converts the acceleration data recorded by the recording unit (31) into horizontal displacement data and vertical displacement data and identifies an image corresponding to a representative motion during a walking cycle from the video data on the basis of the horizontal displacement data or the vertical displacement data; and a display unit (34) that also displays the image identified by the identifying unit (33) in the graphical view of the representative motion during the walking cycle.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
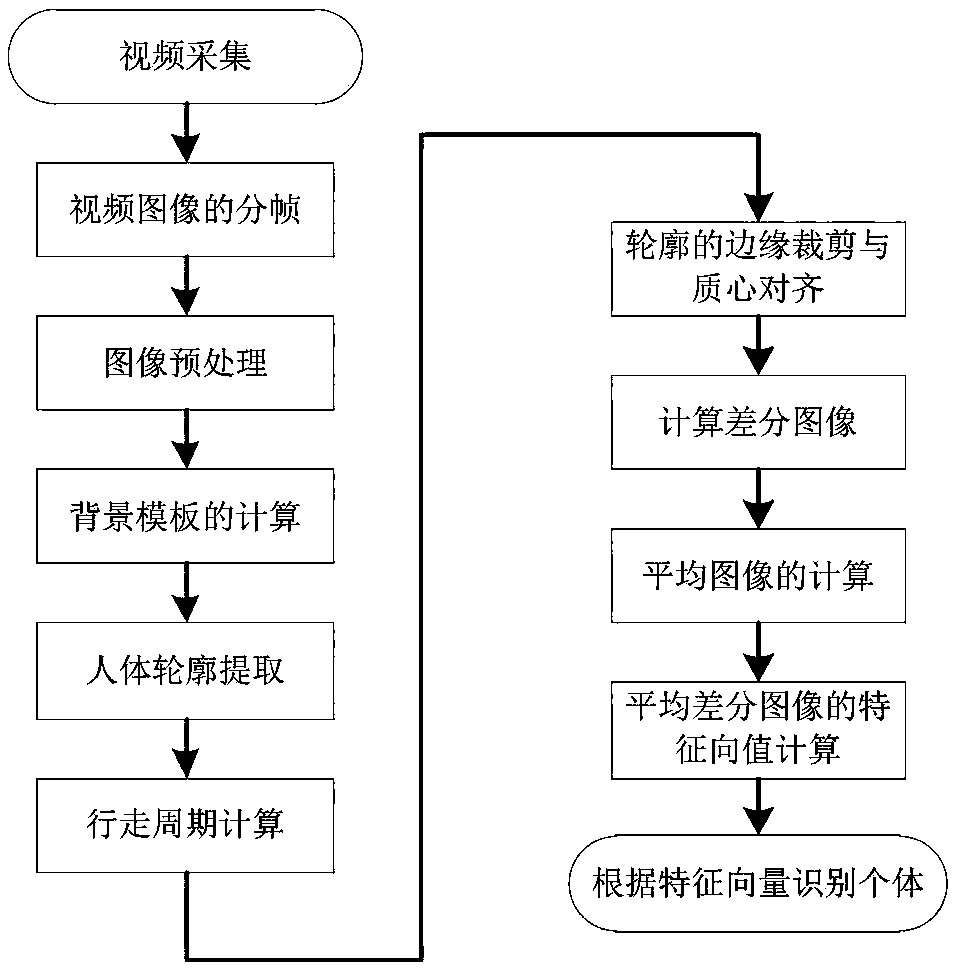
Gait recognition method based on average differential image
InactiveCN108830259AAvoid exact segmentationAvoid the problem of finding corresponding pointsCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyFeature vector
The invention relates to a gait recognition method based on an average differential image, which is applied to gait recognition in a fixed background when a single person walks pass a camera successively. The method comprises following steps: image framing is carried out; a background image is obtained; the contour of a human body is extracted; after each frame of human body contour binary image is subjected to edge clipping, the centroid of each frame of contour is calculated, centroid alignment is carried out, and a centroid alignment contour is obtained; a walking cycle is calculated; in view of the centroid alignment contour in each walking cycle, a differential image between adjacent two frames is calculated; the differential images in multiple walking cycles are overlapped, an average value is obtained, and an average differential image is obtained; features of the average image are extracted; a principal component analysis method is used to calculate the feature value of each average image, the feature values are sorted by absolute values from large to small, and former d feature values with the maximum absolute value are obtained to form a feature vector; and through a nearest neighbor algorithm, gait recognition is carried out.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
An ecological cycle walking animal husbandry house
ActiveCN105359985BAvoid spreadingPrevent proliferationLivestock managementAnimal housingGrazingWalking cycle
The invention discloses an ecological cycle self-propelled stockbreeding room. The ecological cycle self-propelled stockbreeding room comprises a one-section breeding room or a multi-section breeding room which is arranged in a line, wherein the breeding room is provided with a crawler-type or a wheel-track type travel mechanism; a hydraulic lifting mechanism is mounted on the travel mechanism; the travel mechanism is used for supporting the breeding room through the hydraulic lifting mechanism; the breeding room adopts a triangular steel cage structure to form a spanning framework of the breeding room, and a plurality of yards for breeding captive animals are partitioned on a base plate for bearing the animals; manure drain holes or manure drain grooves are formed in the base plate of the yards; two working passages are arranged in the front and at the back of each yard; and a movable grass mowing and cutting mechanism and movable guide rails thereof are arranged in front of the working passage which is arranged in the front of each yard. The technical scheme is integrated with machinery, solar energy electrical appliances, rooms and breeding tool equipment, and is integrated with advantages and functions of captive breeding and grazing.
Owner:李艳辉
Acceleration transducer-based gait identification method
The invention discloses an acceleration transducer-based gait identification method, which comprises the following steps: (1) acquisition of a human gait acceleration sequence; (2) walk cycle segmentation and length normalization; (3) extraction and description of key points in a gait acceleration signal sequence; (4) classification of key points; and (5) identification. The acceleration transducer-based gait identity identification method can effectively utilize key information in a human gait acceleration signal to identify a walker who wears an accelerometer.
Owner:浙江浙大西投脑机智能科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com