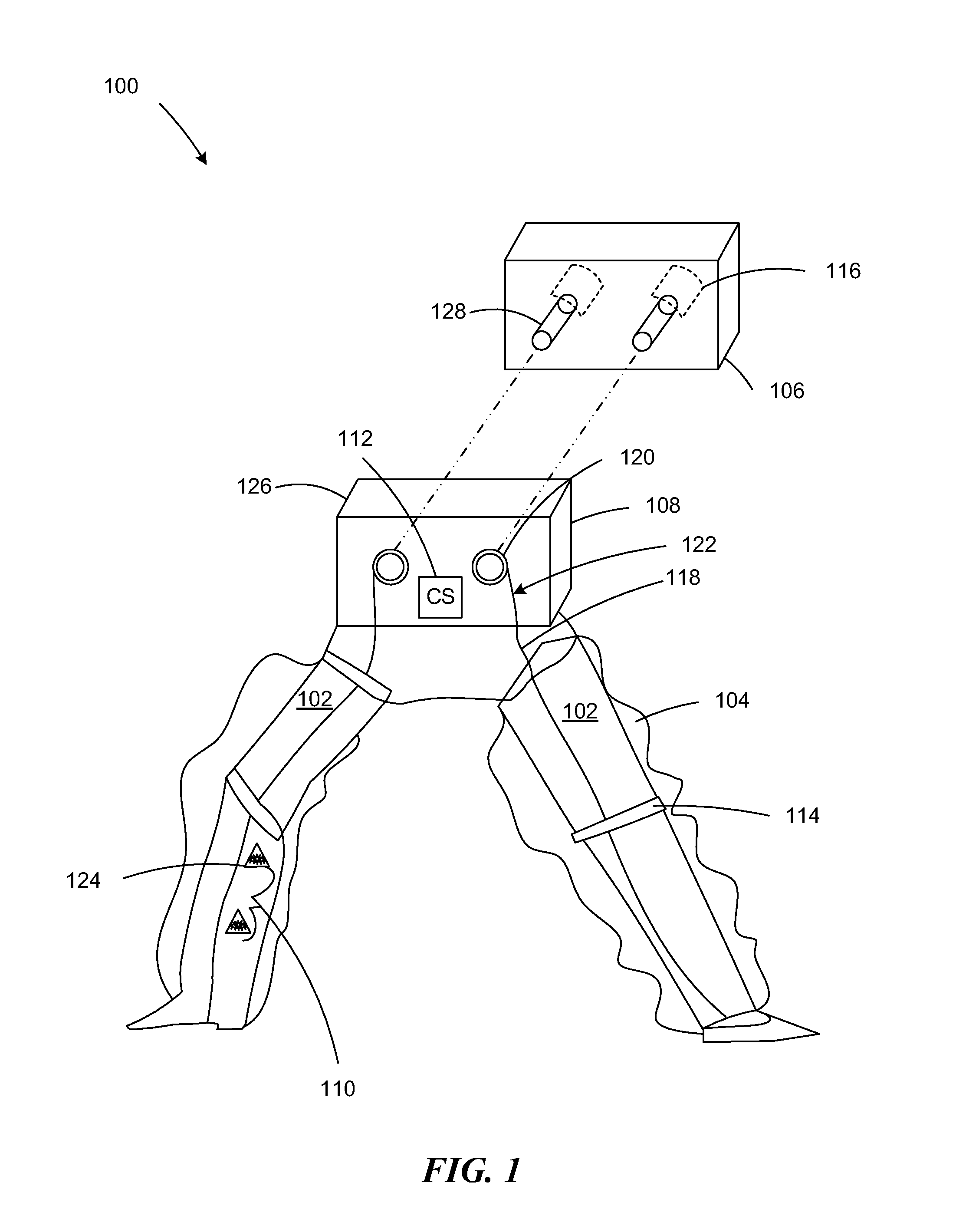
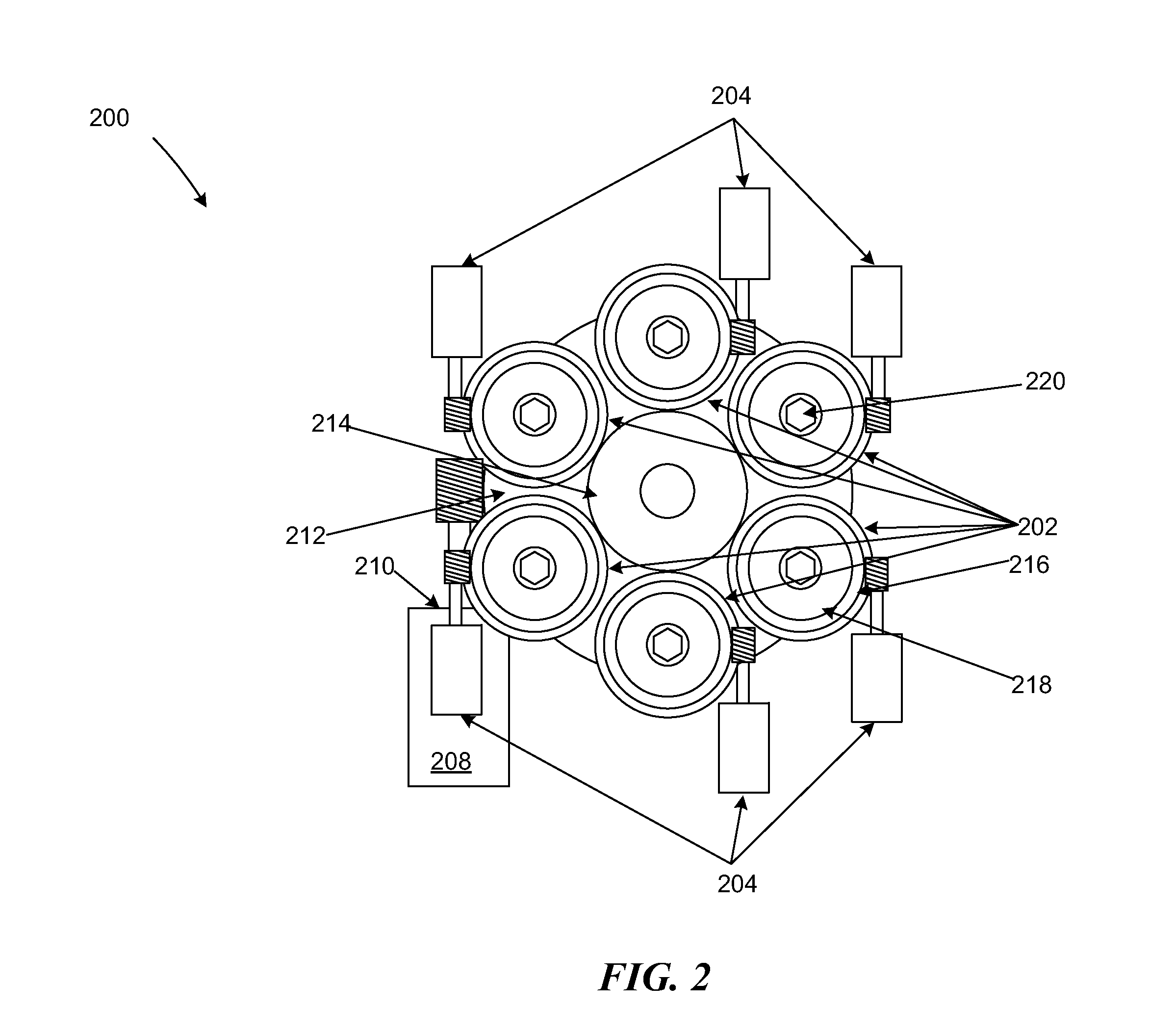
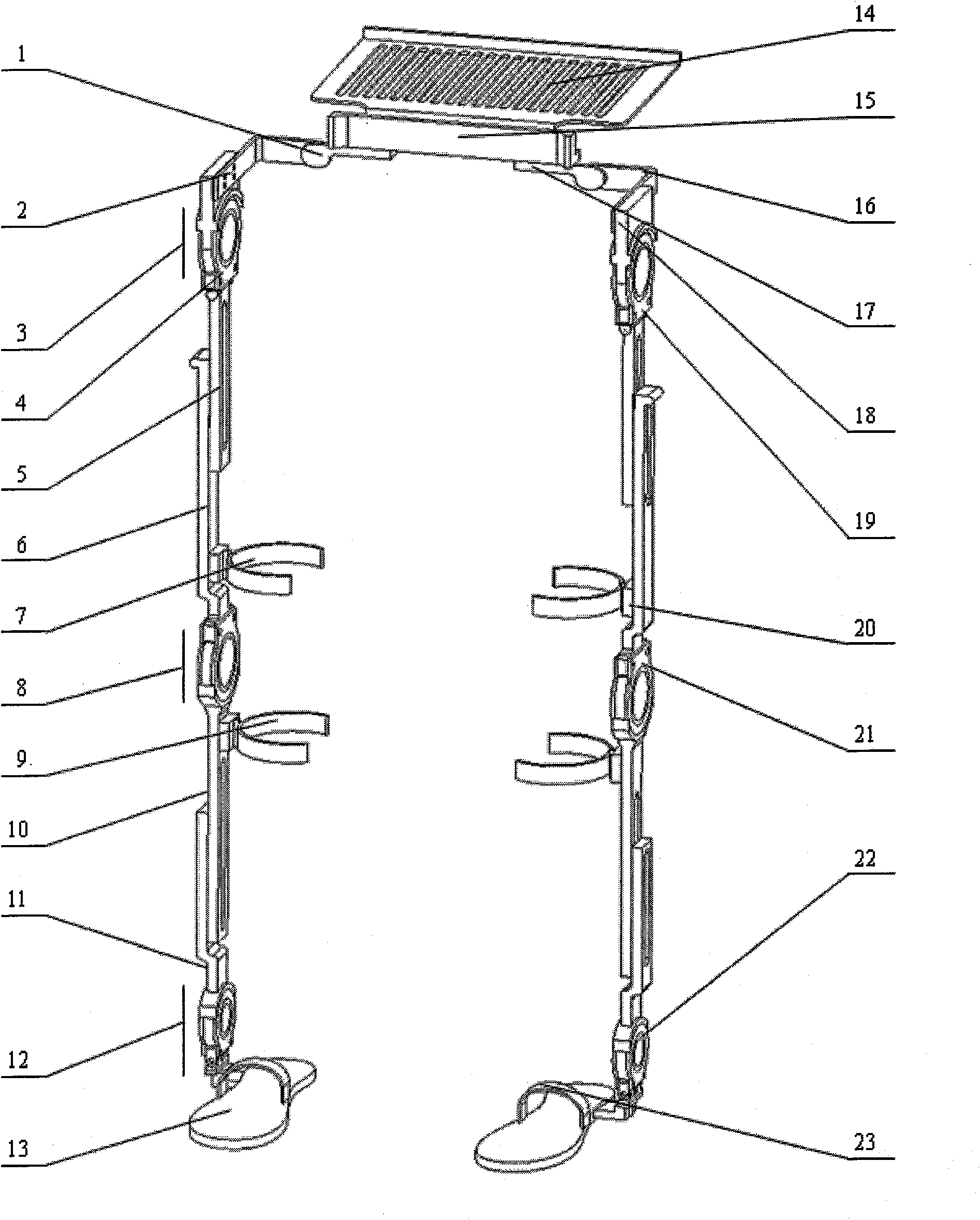
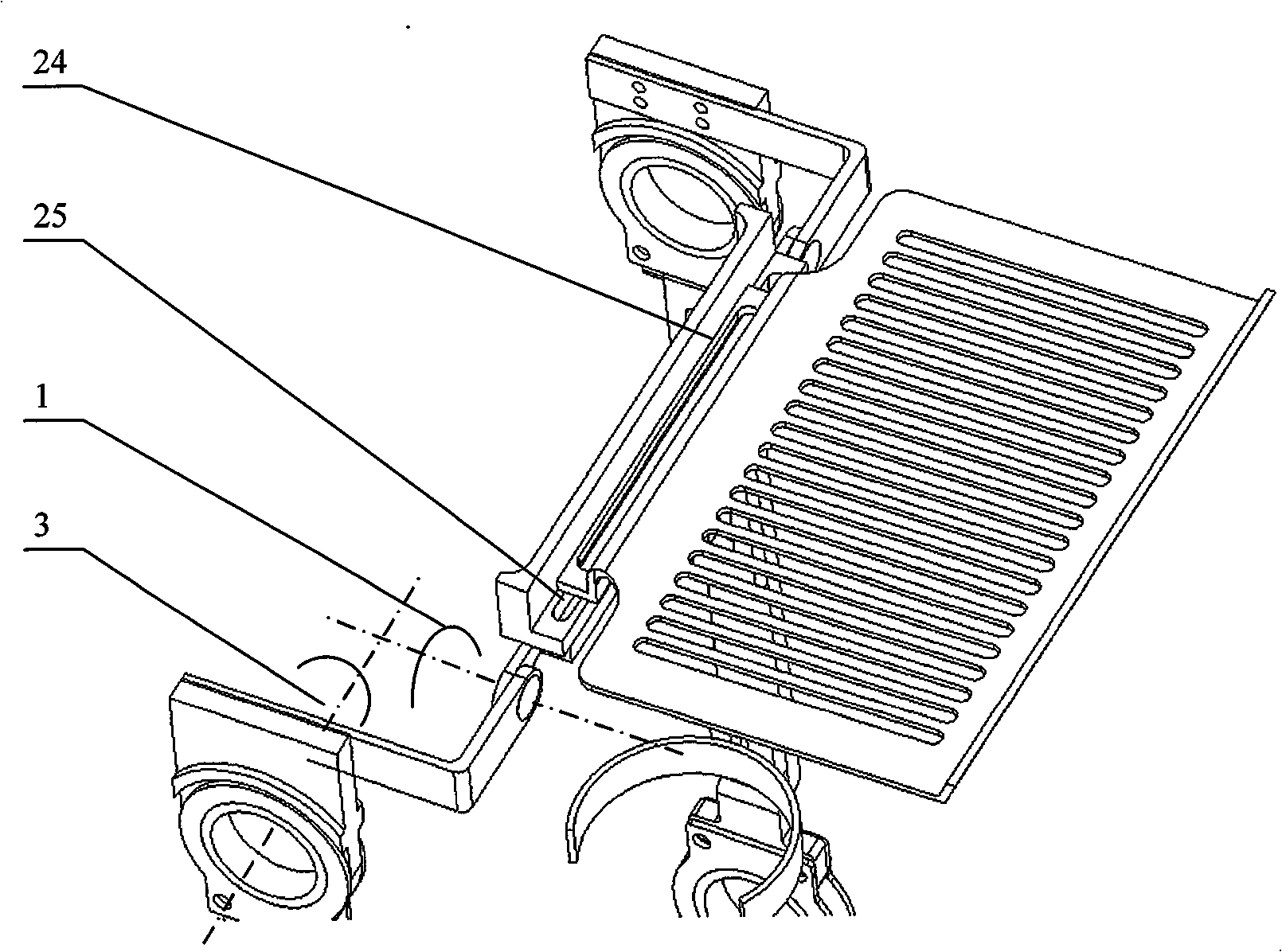
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7220results about "Walking aids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
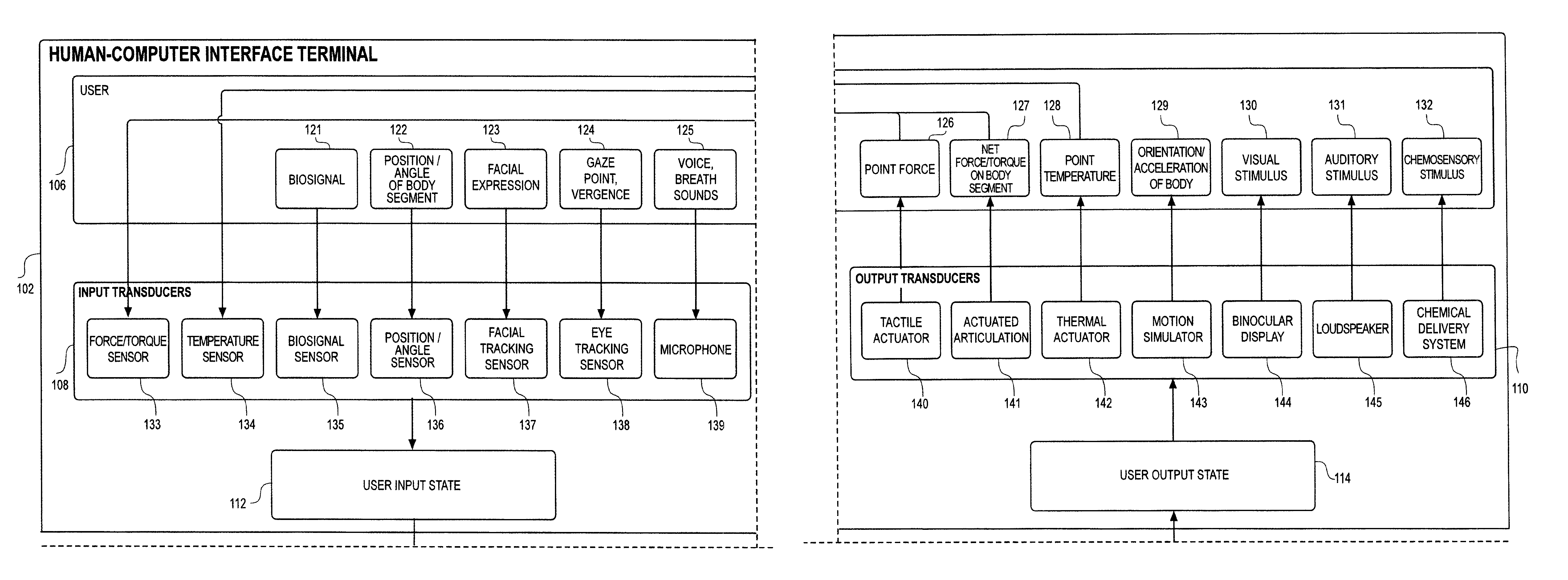
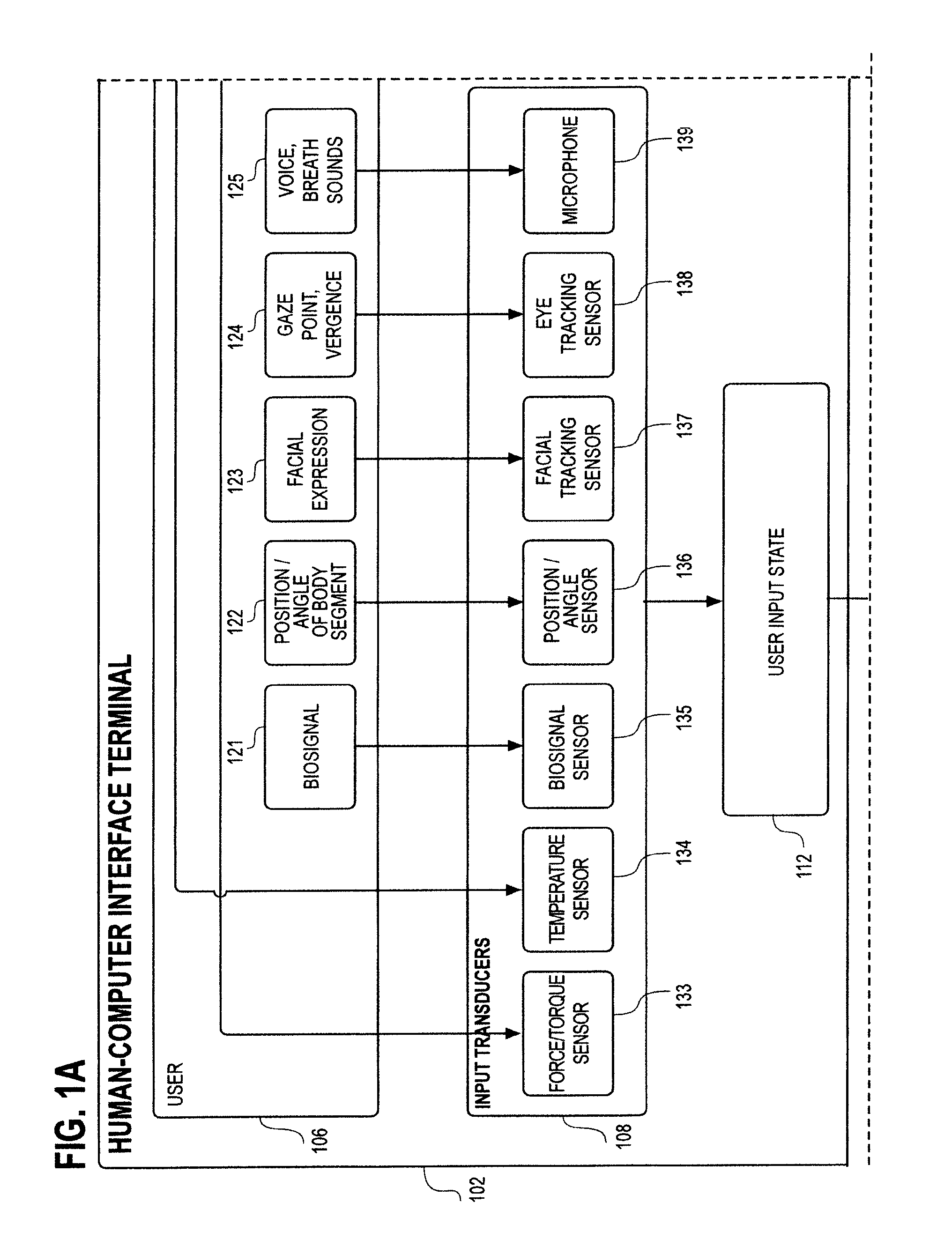
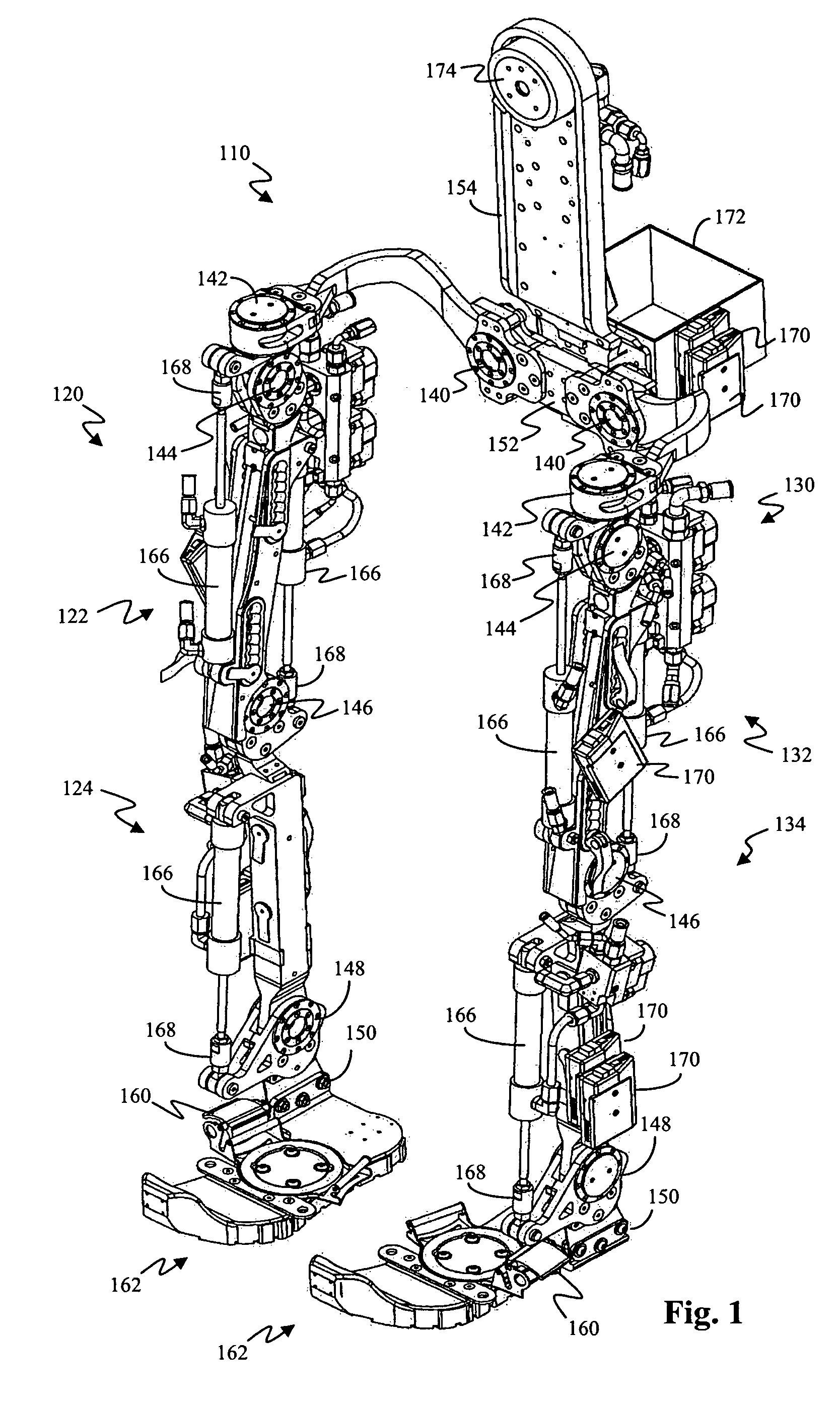
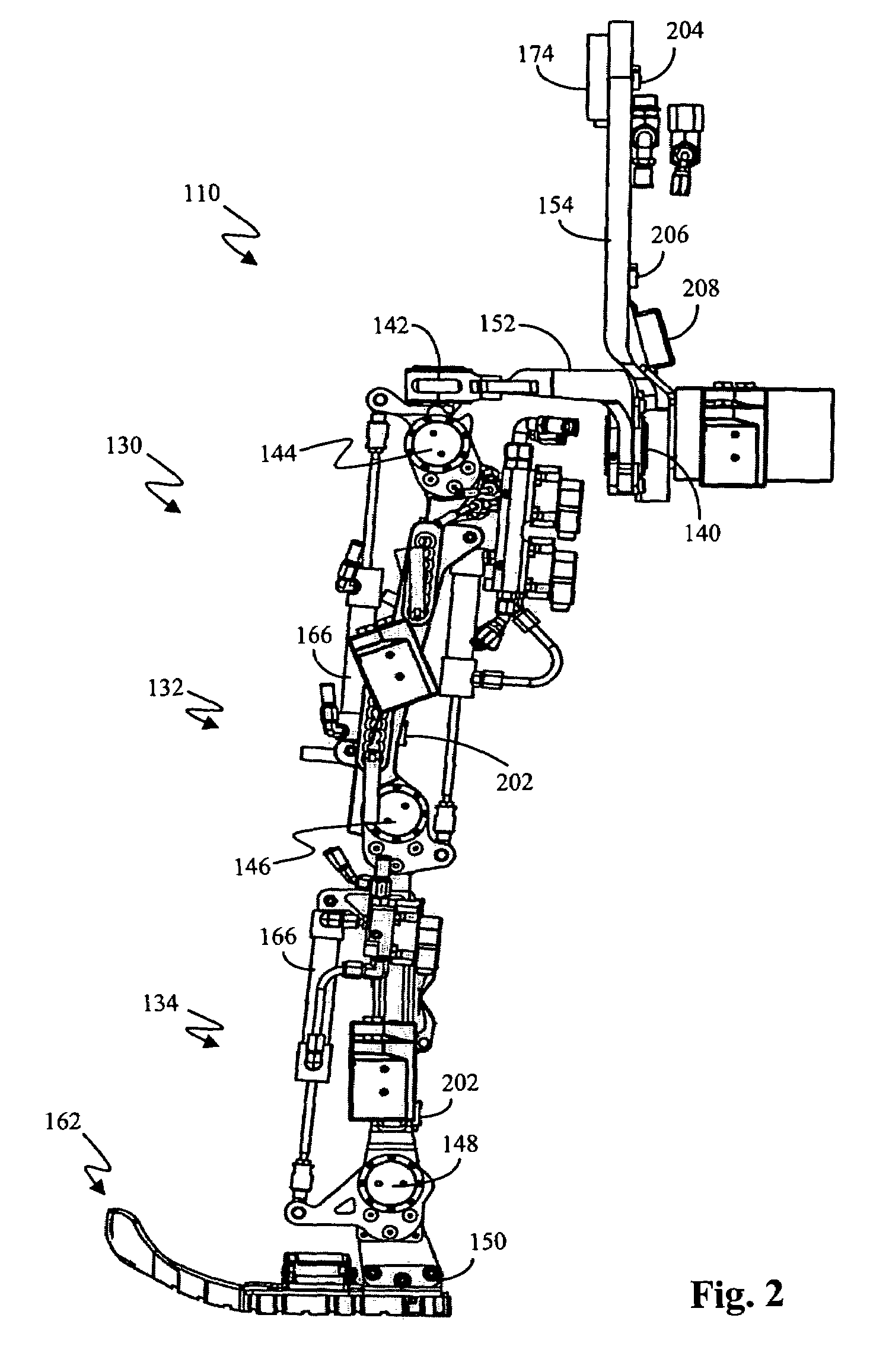
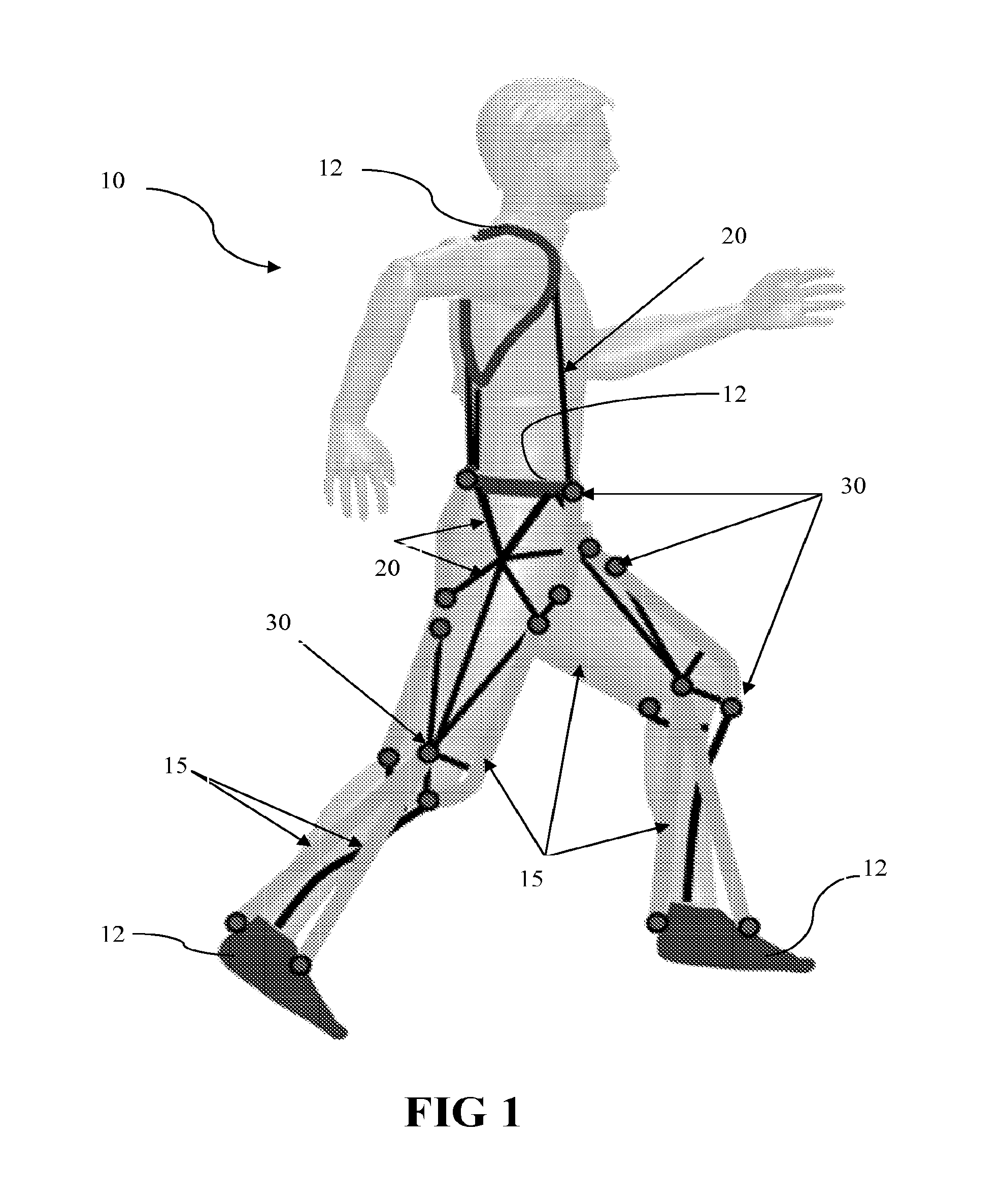
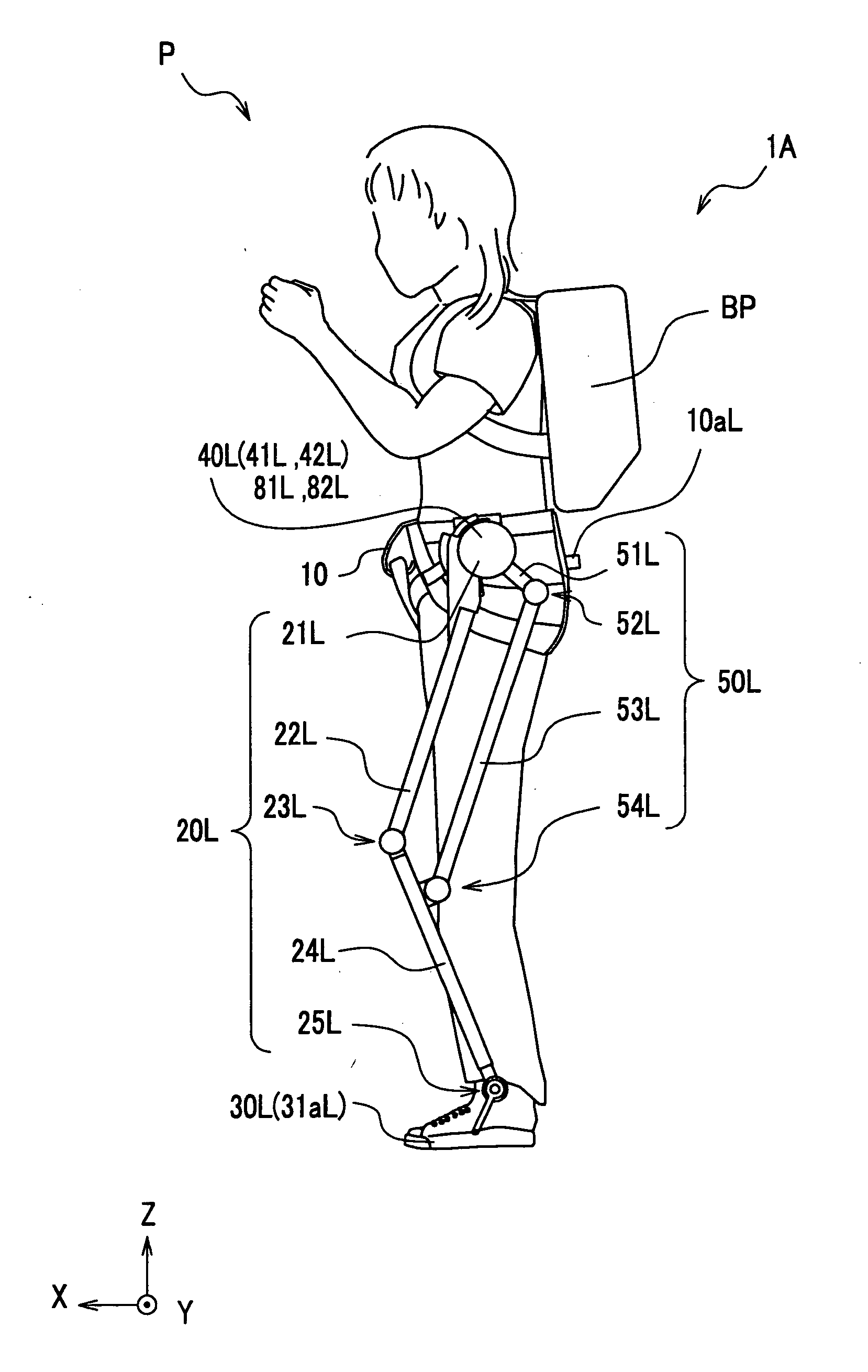
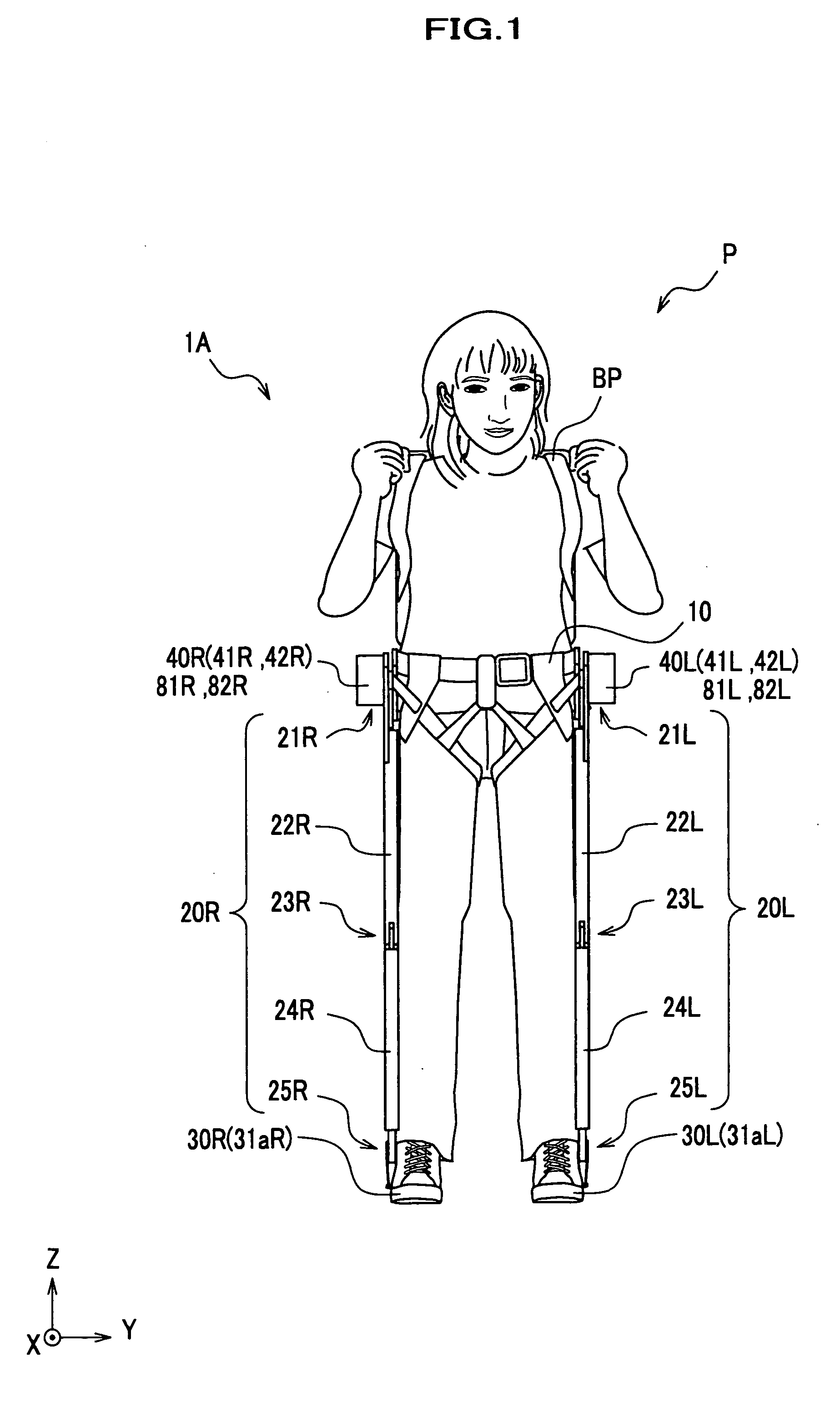
Whole-body human-computer interface
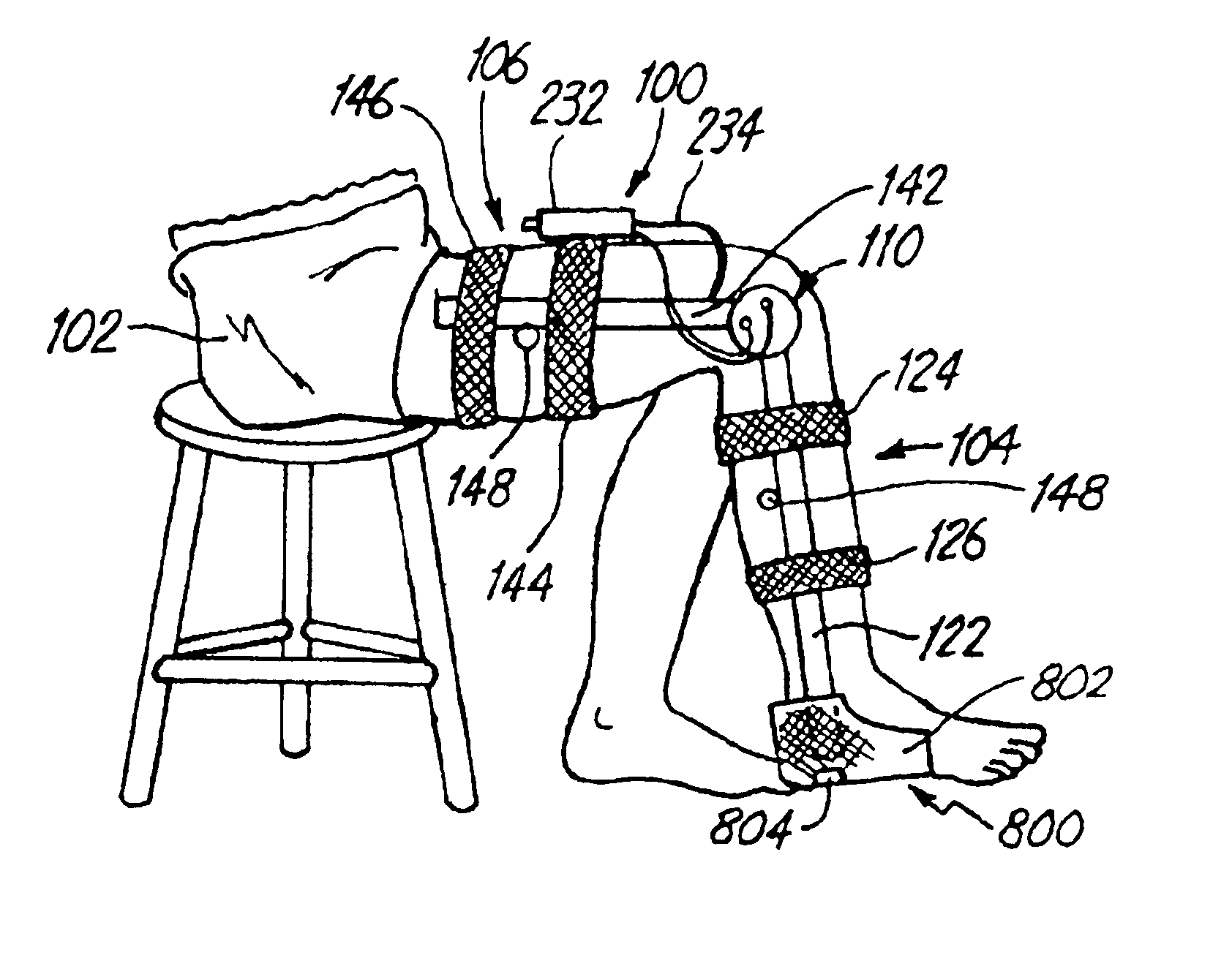
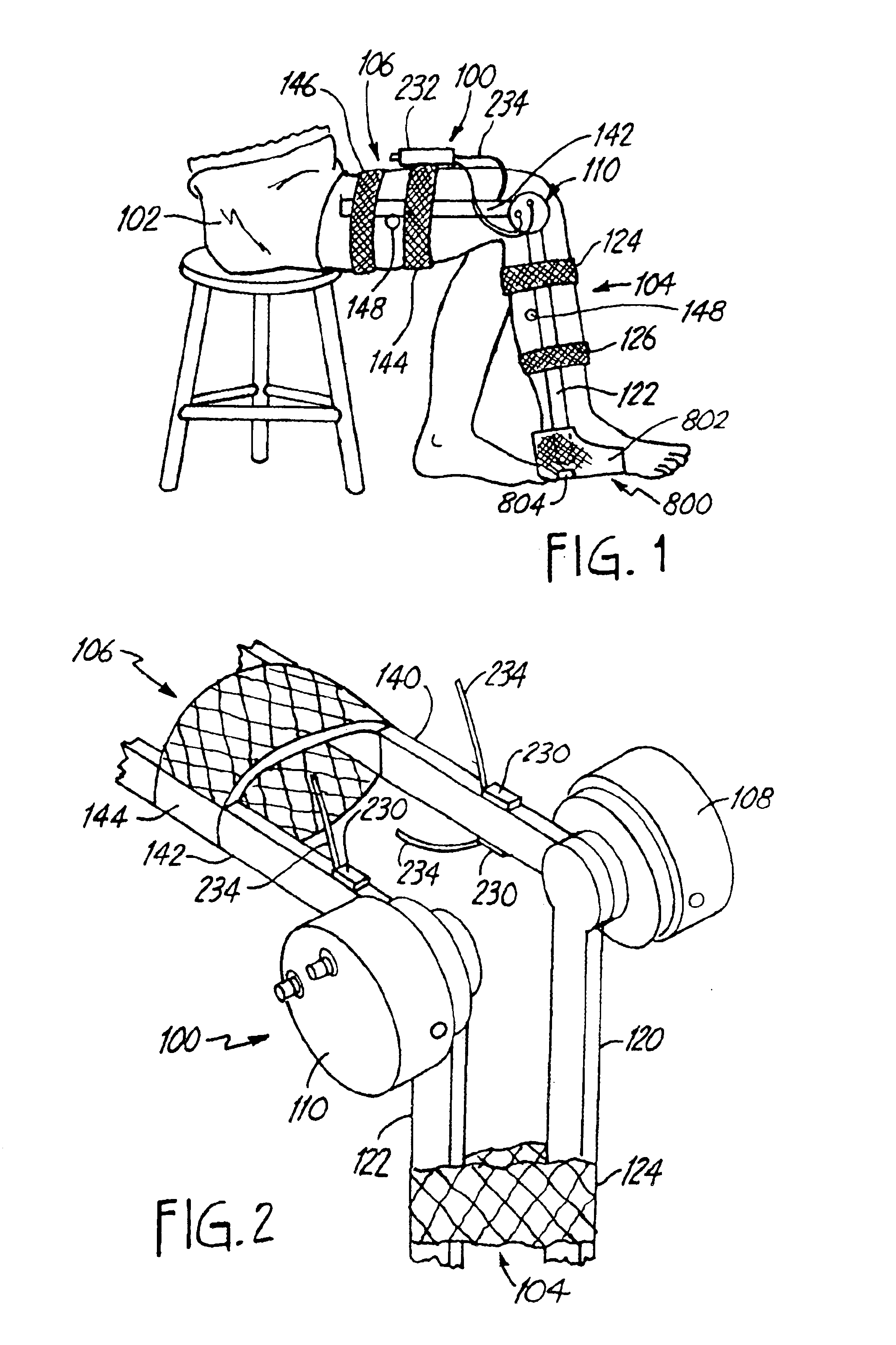
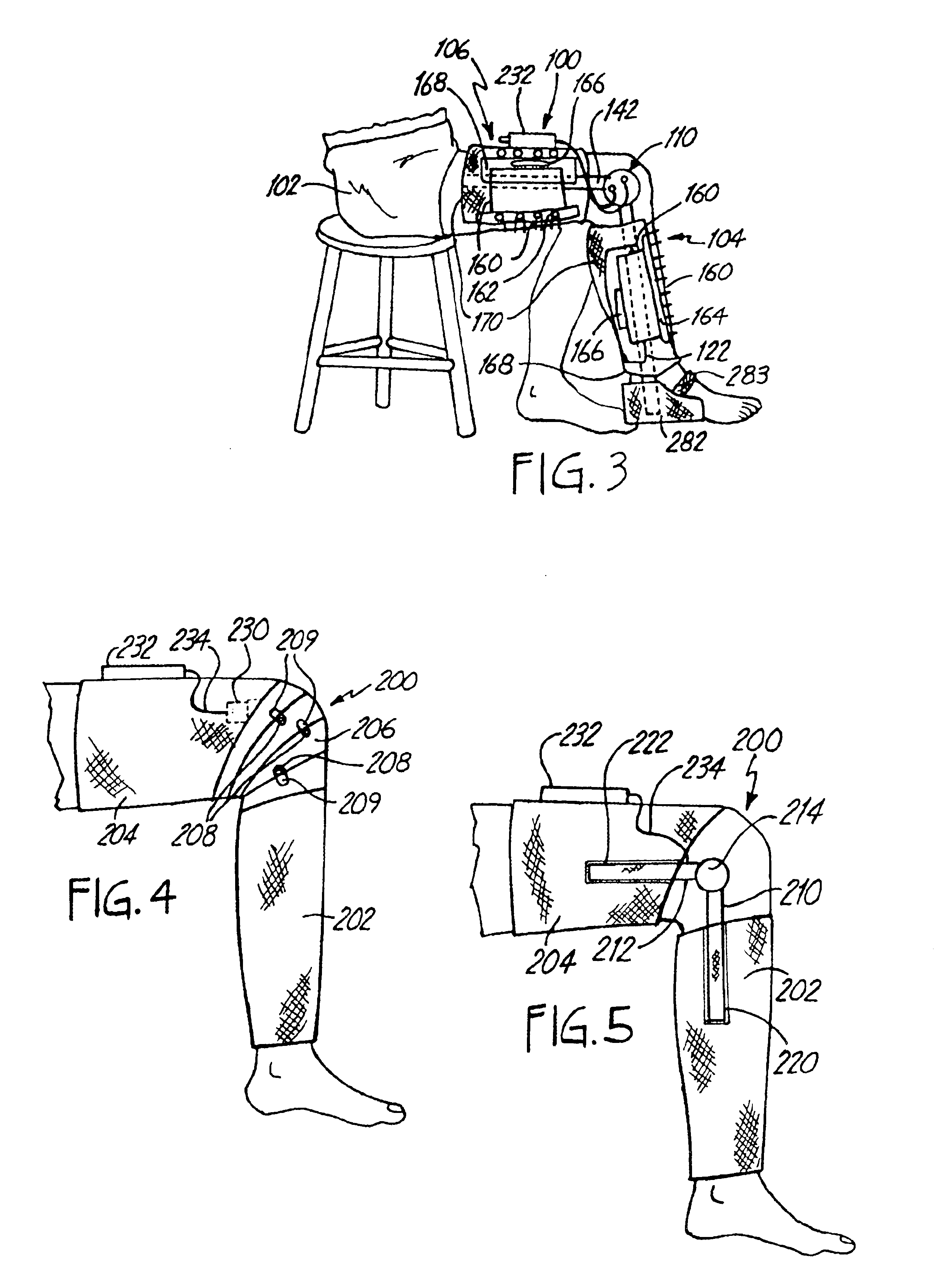
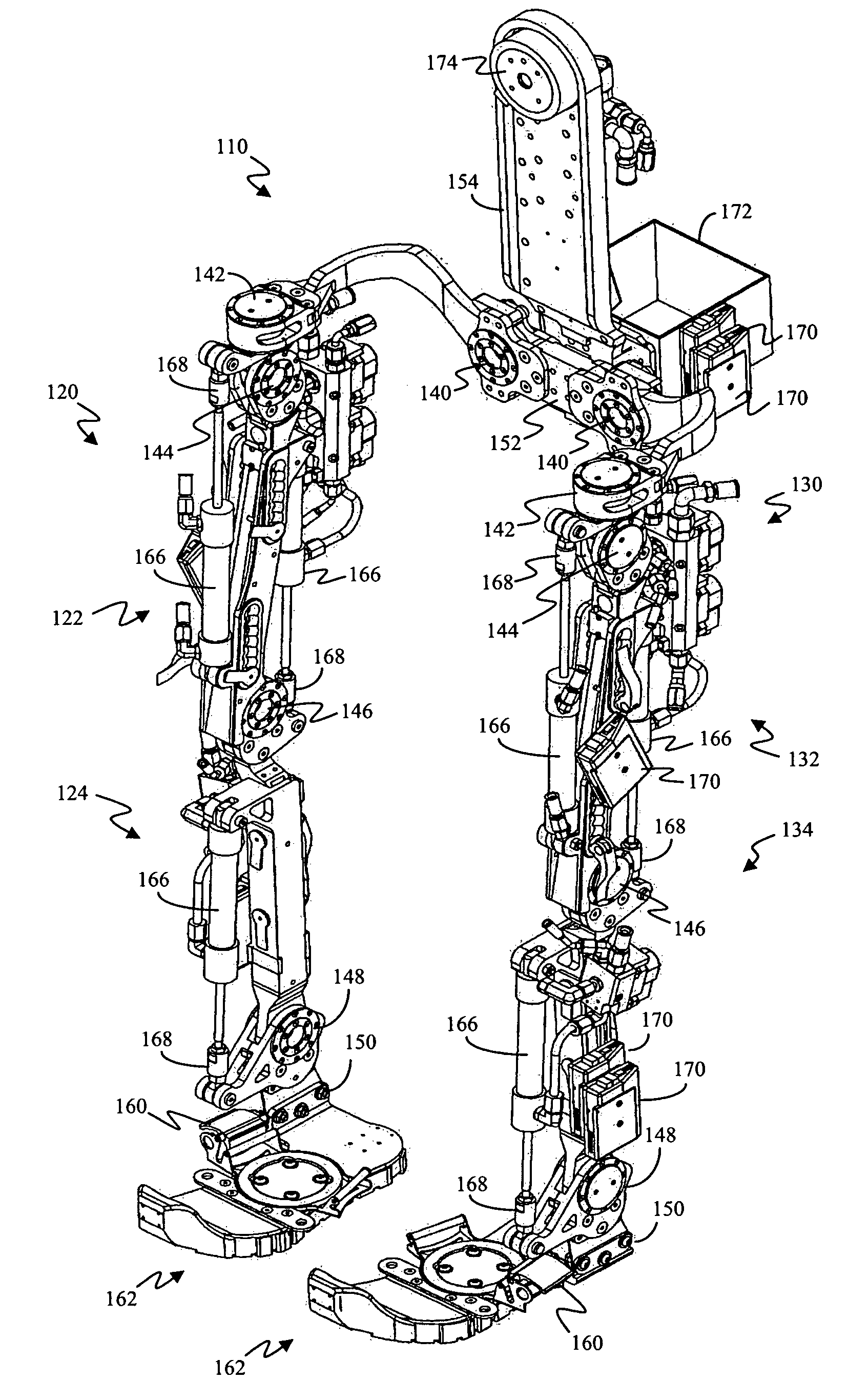
ActiveUS20160139666A1Input/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorWhole bodyComputer module
A human-computer interface system having an exoskeleton including a plurality of structural members coupled to one another by at least one articulation configured to apply a force to a body segment of a user, the exoskeleton comprising a body-borne portion and a point-of-use portion; the body-borne portion configured to be operatively coupled to the point-of-use portion; and at least one locomotor module including at least one actuator configured to actuate the at least one articulation, the at least one actuator being in operative communication with the exoskeleton.
Owner:HAPTX INC
Haptic button and haptic device using the same
InactiveUS20070152974A1Easy to operateInput/output for user-computer interactionSingle unit pavingsActive polymerEngineering
A haptic button providing various stimulations to a user according to a current application and a haptic device using the same are provided. The haptic button includes an electro-active polymer having a flat shape, a pair of electrodes contacting two sides of the electro-active polymer, an electric circuit applying a predetermined voltage to the pair of electrodes, and a sensor sensing a button input from a user, wherein stimulation provided from the electro-active polymer to the user is changed by changing a waveform of the voltage according to a current application status.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Management and navigation system for the blind
InactiveUS20060129308A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlCouplingTransducer
A computer-aided communication and navigation system that uses a computer or other processor in wireless communication with Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags to aid a blind person. A communication module worn by the user receives information from one or more RFID tags readers and provides audio and, optionally, stimulatory information to the blind person. In one embodiment, a tag reader is provided in a walking cane. In one embodiment, tag readers are provided in one or more ankle bracelets or shoes. In one embodiment, a wireless (or wired) earpiece is provided to provide audio information to one or both ears. In one embodiment, audio information is provided through one or more transducers that couple sound through bones. The use of bone coupling allows the blind person to hear the sound information from the communication module in concert with normal hearing. The tag readers provided to the ankles or shoes communicate with the communication module to allow the blind user to navigate by following a “trail” of RFID tags.
Owner:NEST LABS
Orthoses for joint rehabilitation
InactiveUS6872187B1Physical therapies and activitiesPerson identificationImpaired proprioceptionRange of motion
Orthoses with microprocessor control placed around the joint of a patient are used to perform and to monitor isometric, range-of-motion, proprioception and isotonic exercises of the joint. A variety of improved hardware elements result in an orthosis that is easier to use and interacts more efficiently with the controller to allow the monitoring of a greater range of motions while holding down cost and provide suitable accurate evaluation of the exercises. Efficient ways of programming the exercises, monitoring the exercises and evaluating the exercise provide a comprehensive program for the rehabilitation of an injured or weakened joint.
Owner:IZEX TECH
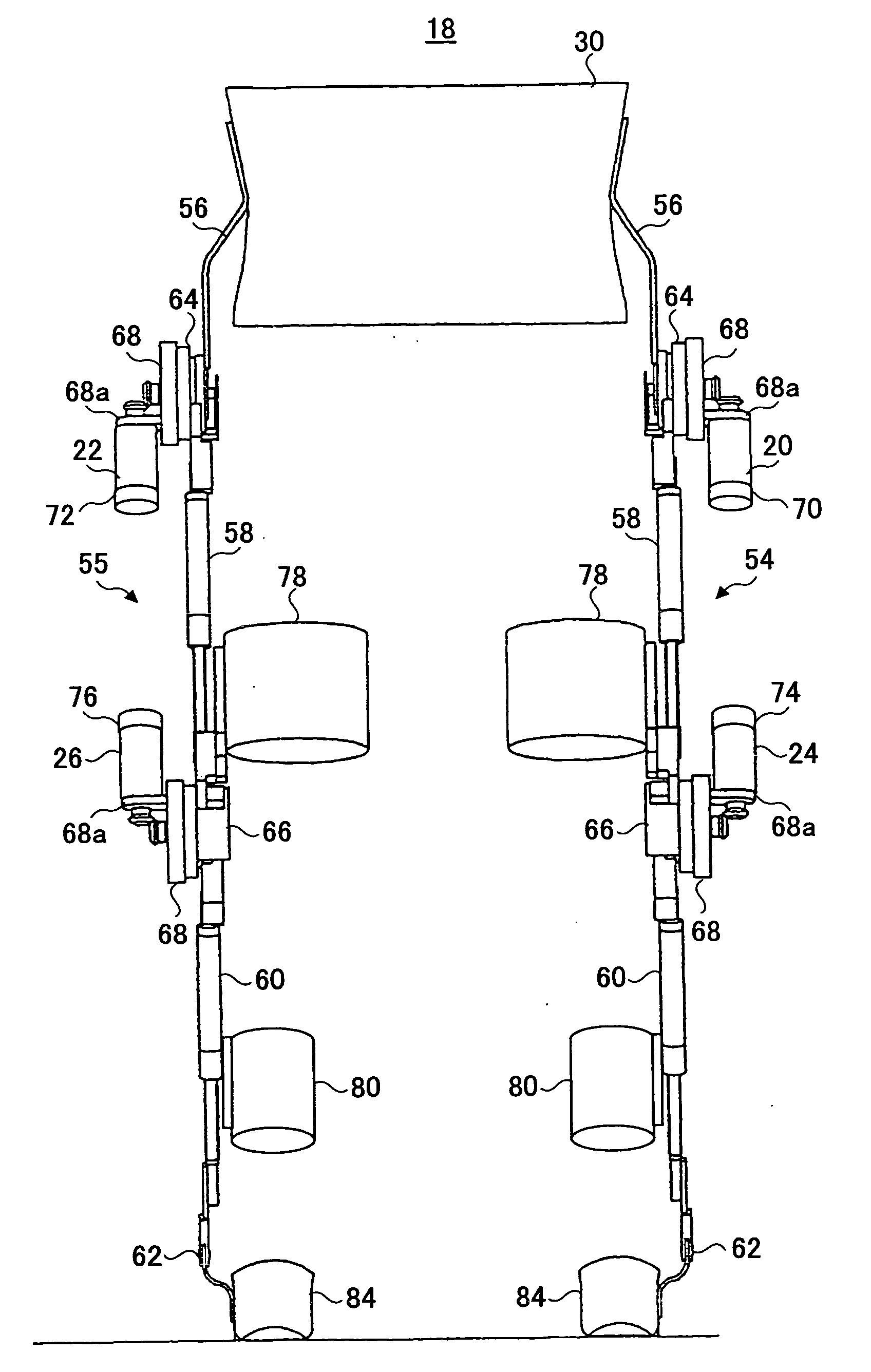
Lower extremity enhancer
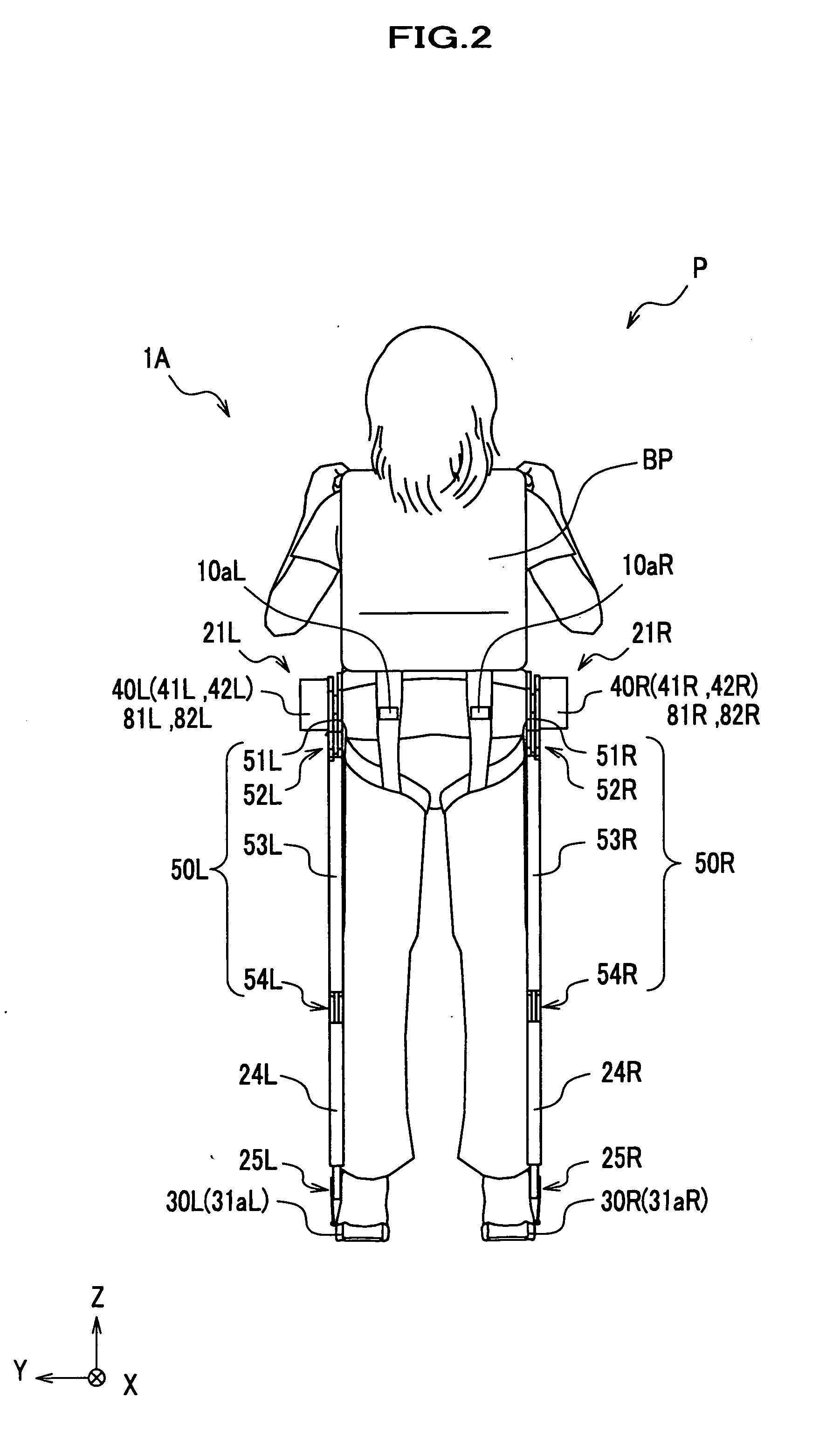
A lower extremity enhancer to be worn by a user to enable the user to carry a load includes two leg supports having a plurality of jointed links. Proximal ends of the leg supports are connected to a back frame adapted to carry the load. Distal ends of the leg supports are connected to two foot links. The leg supports are powered by a plurality of actuators adapted to apply torques to the leg supports in response to movement of the user's legs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
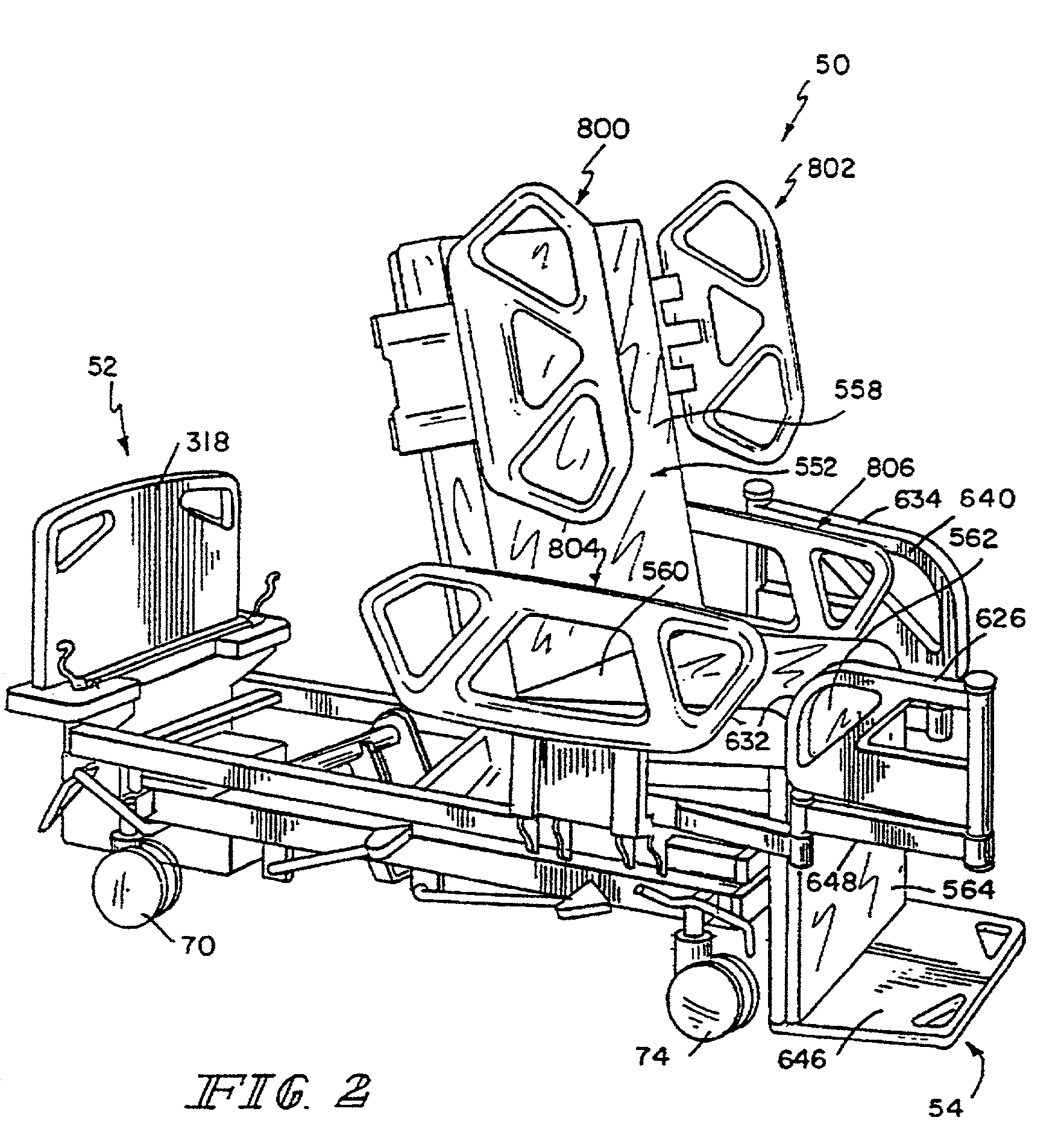
Hospital bed
InactiveUS7017208B2Improved upgradeabilityEasy to addDiagnosticsKids bedsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method is provided for permitting a module which is configured to perform a dedicated function on a bed to use a graphical interface. Graphic format data used by the module is downloaded, if necessary, and stored in a memory of the graphical interface.
Owner:HILL ROM SERVICES
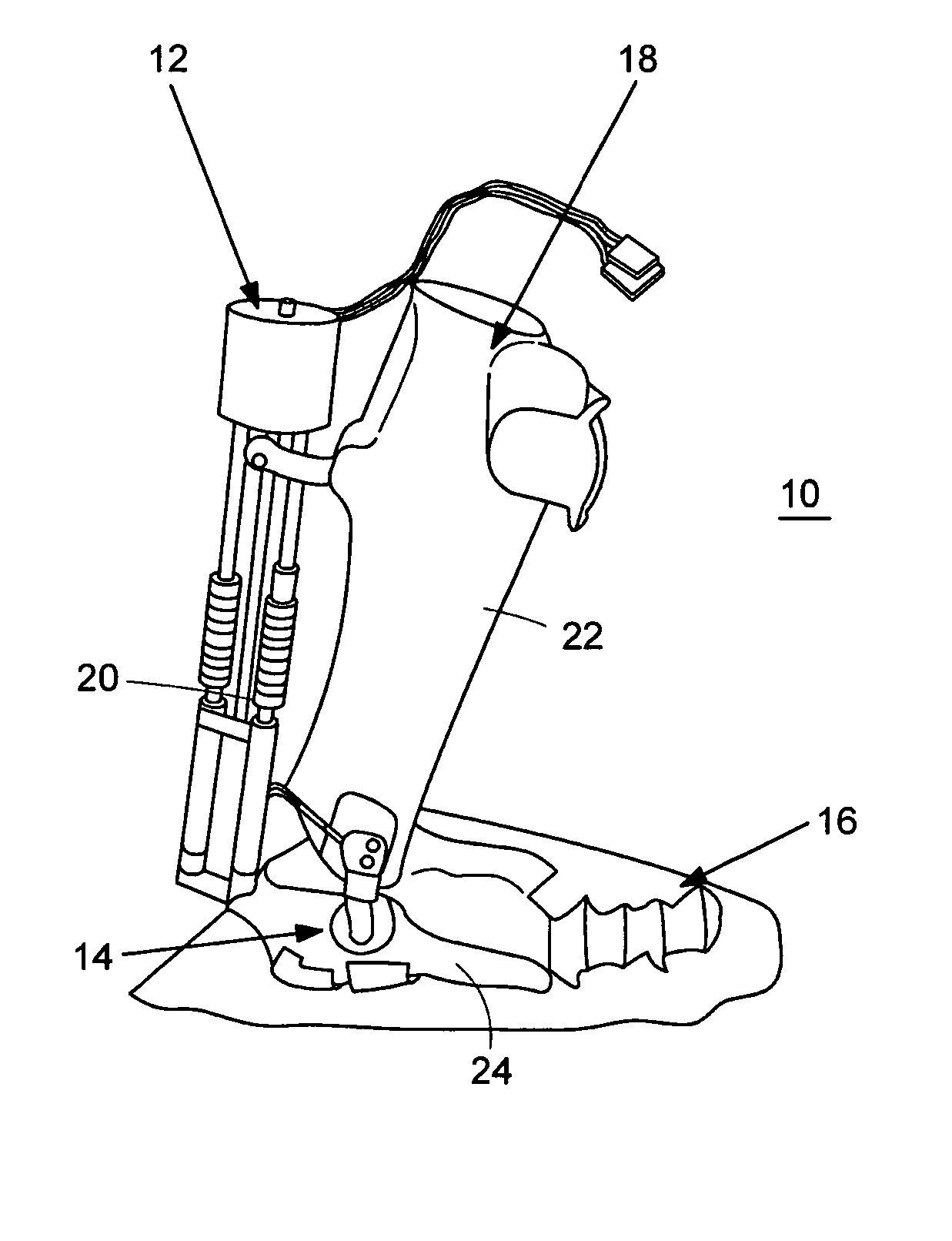
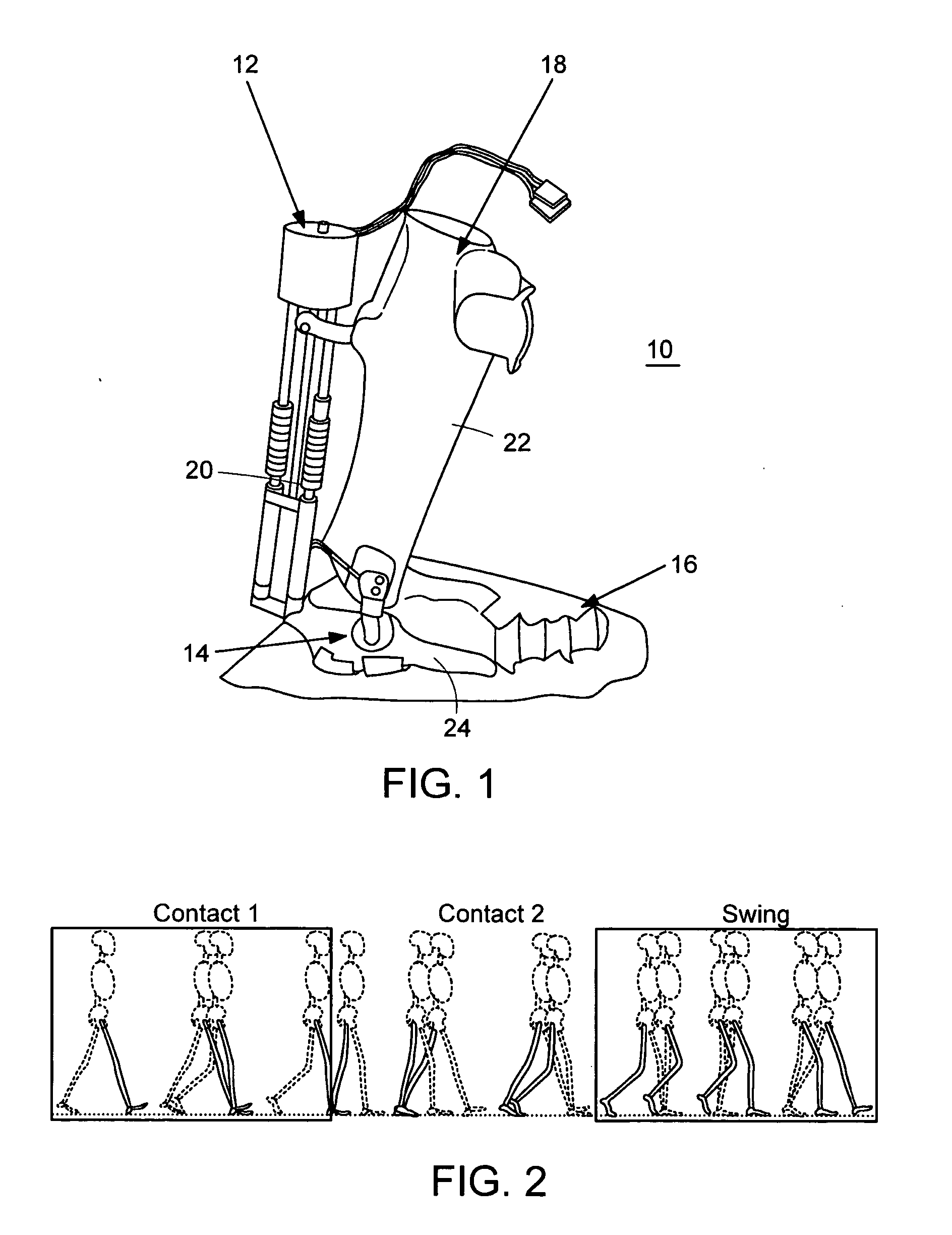
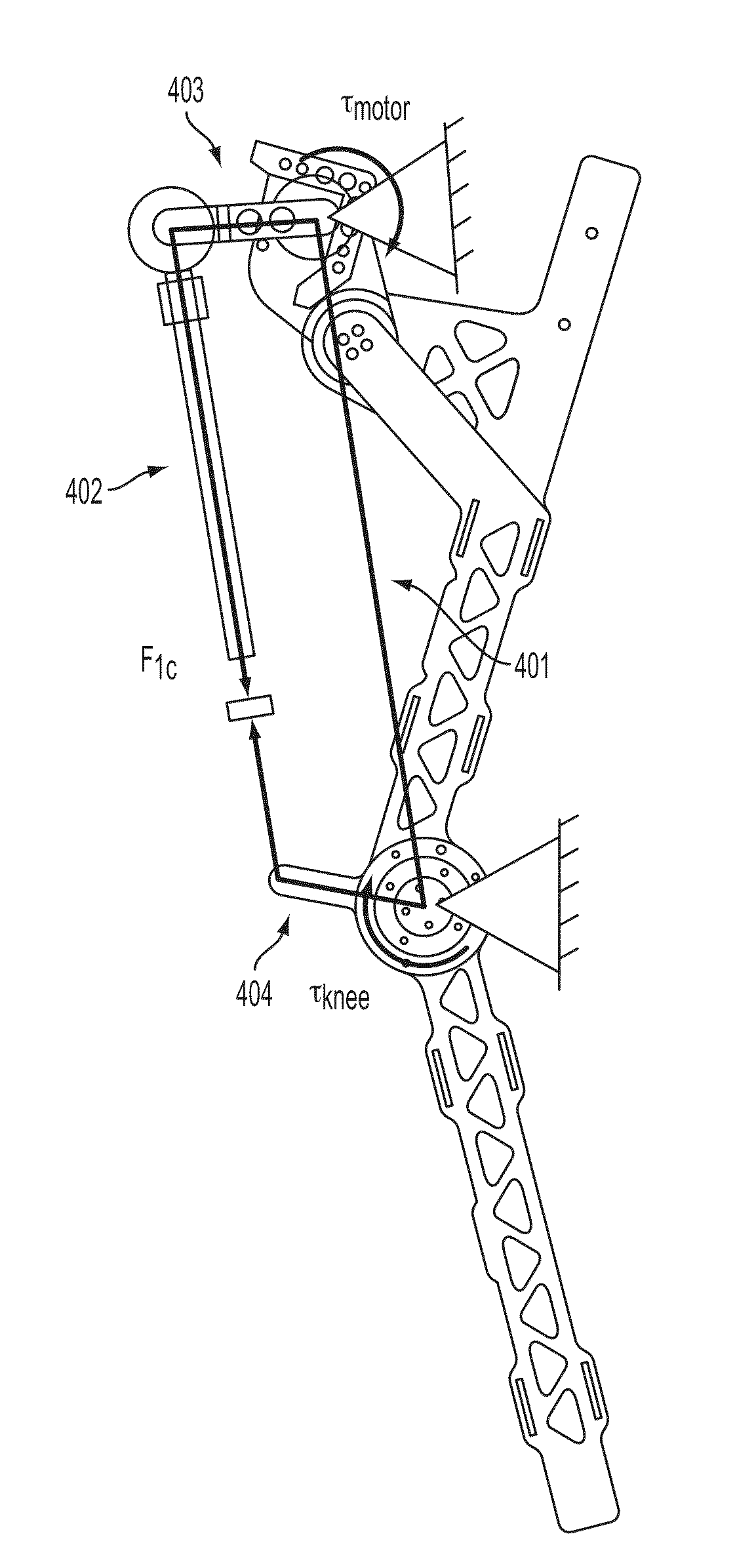
Semi-powered lower extremity exoskeleton
ActiveUS20070056592A1Drag minimizationProgramme-controlled manipulatorOperating chairsKnee JointEngineering
The lower extremity exoskeleton comprises two leg supports connectable to person's lower limbs and configured to rest on the ground during their stance phase. Each leg support comprises a thigh link and a shank link; a knee joint configured to allow flexion and extension between the shank link and the thigh link. The lower extremity exoskeleton further comprises an exoskeleton trunk connectable to the person'supper body. The exoskeleton trunk is connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk. Two torque generators are coupled to each of the knee joints. A power unit, capable of providing power, is coupled to the torque generators. In operation when a leg support is in a stance phase and climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit injects power into the respective torque generator thereby extending the respective knee angle. When a leg support is in stance phase and not climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to resist flexion of the respective knee joint. When a leg support is in a swing phase, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to minimize its resistance to knee flexion and extension.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
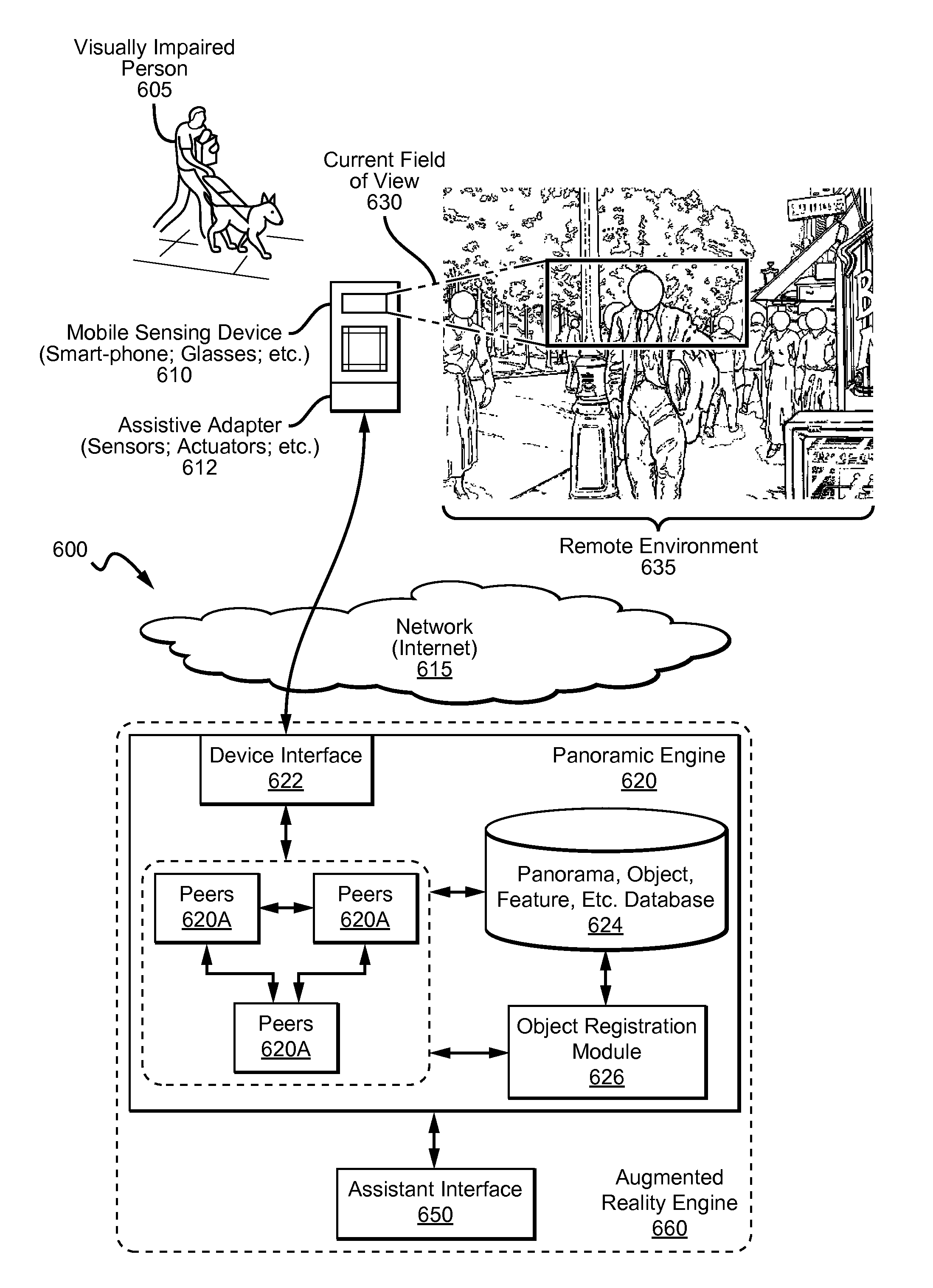
Augmented reality panorama supporting visually impaired individuals
There is presented a system and method for providing real-time object recognition to a remote user. The system comprises a portable communication device including a camera, at least one client-server host device remote from and accessible by the portable communication device over a network, and a recognition database accessible by the client-server host device or devices. A recognition application residing on the client-server host device or devices is capable of utilizing the recognition database to provide real-time object recognition of visual imagery captured using the portable communication device to the remote user of the portable communication device. In one embodiment, a sighted assistant shares an augmented reality panorama with a visually impaired user of the portable communication device where the panorama is constructed from sensor data from the device.
Owner:NANT HLDG IP LLC
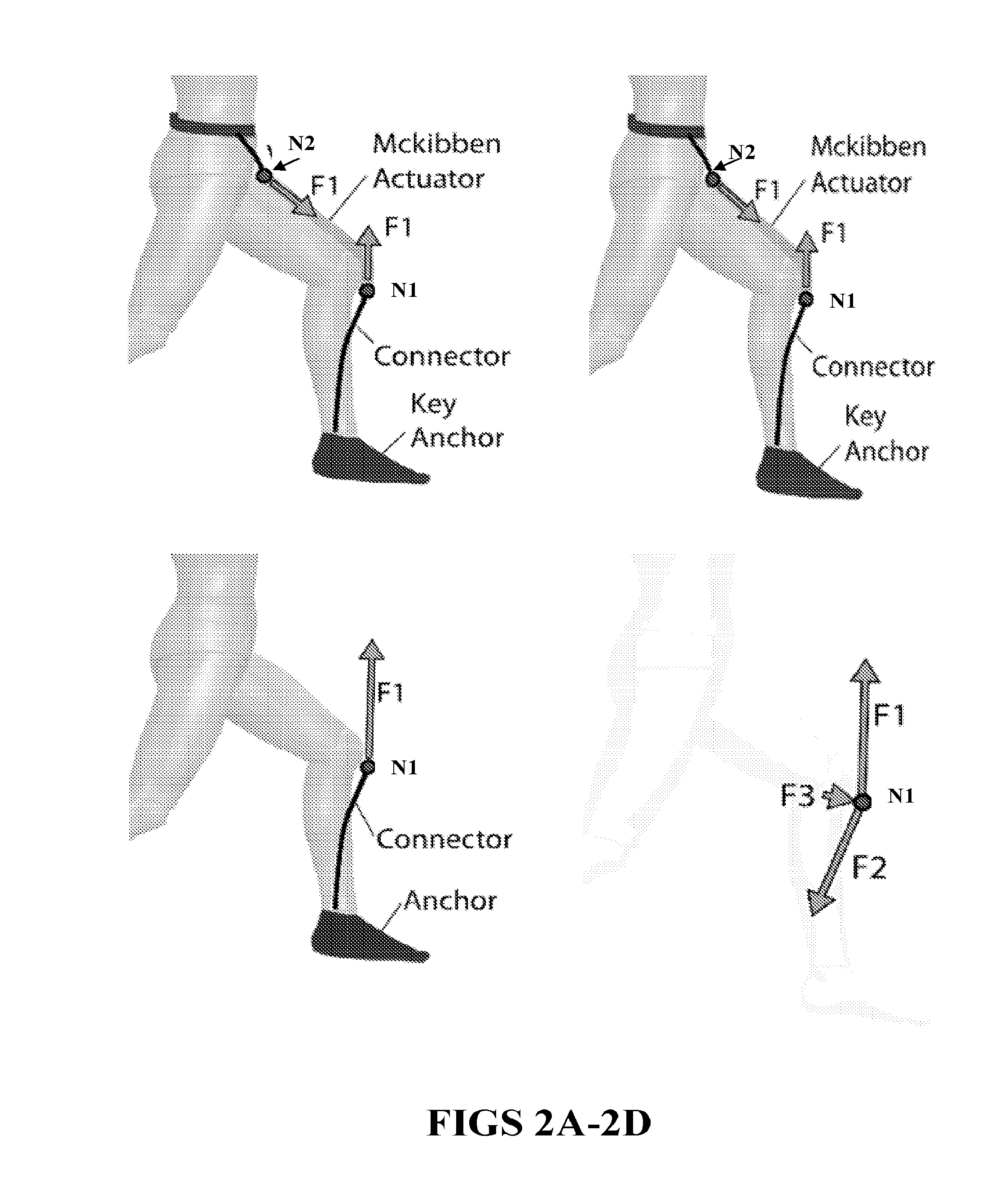
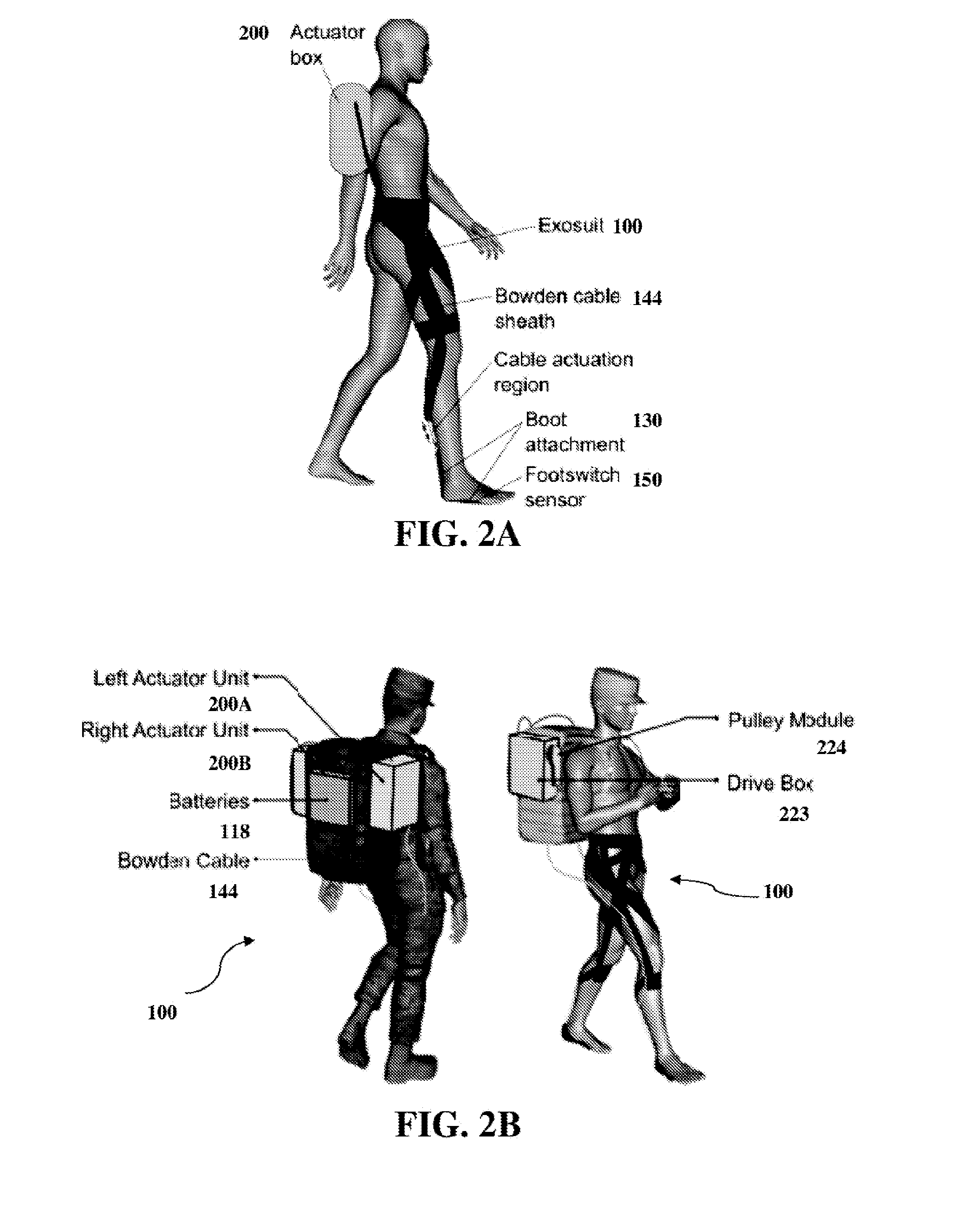
Soft exosuit for assistance with human motion
ActiveUS20150173993A1Complete, and more natural, range of joint(s) motion(s)Comfortable to wearProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsHuman motionEngineering
In at least one aspect, there is provided a system for generating force about one or more joints including a soft exosuit having a plurality of anchor elements and at least one connection element disposed between the plurality of anchor elements. The system also includes at least one sensor to determine a force the at least one connection element or at least one of the plurality of anchor elements and to output signals relating to the force, at least one actuator configured to change a tension in the soft exosuit and at least one controller configured to receive the signals output from the at least one sensor and actuate the at least one actuator responsive to the received signals.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Active Ankle Foot Orthosis
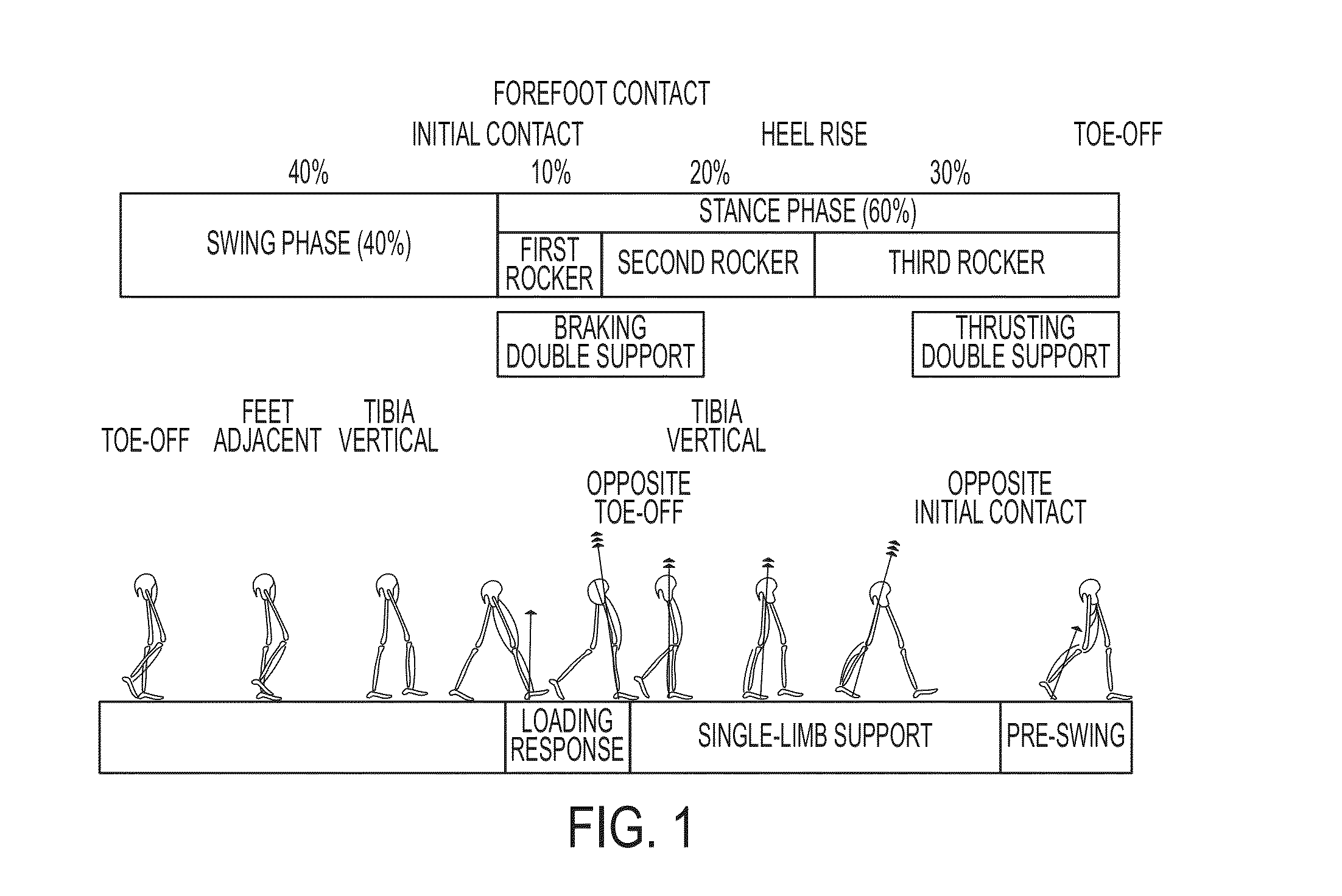
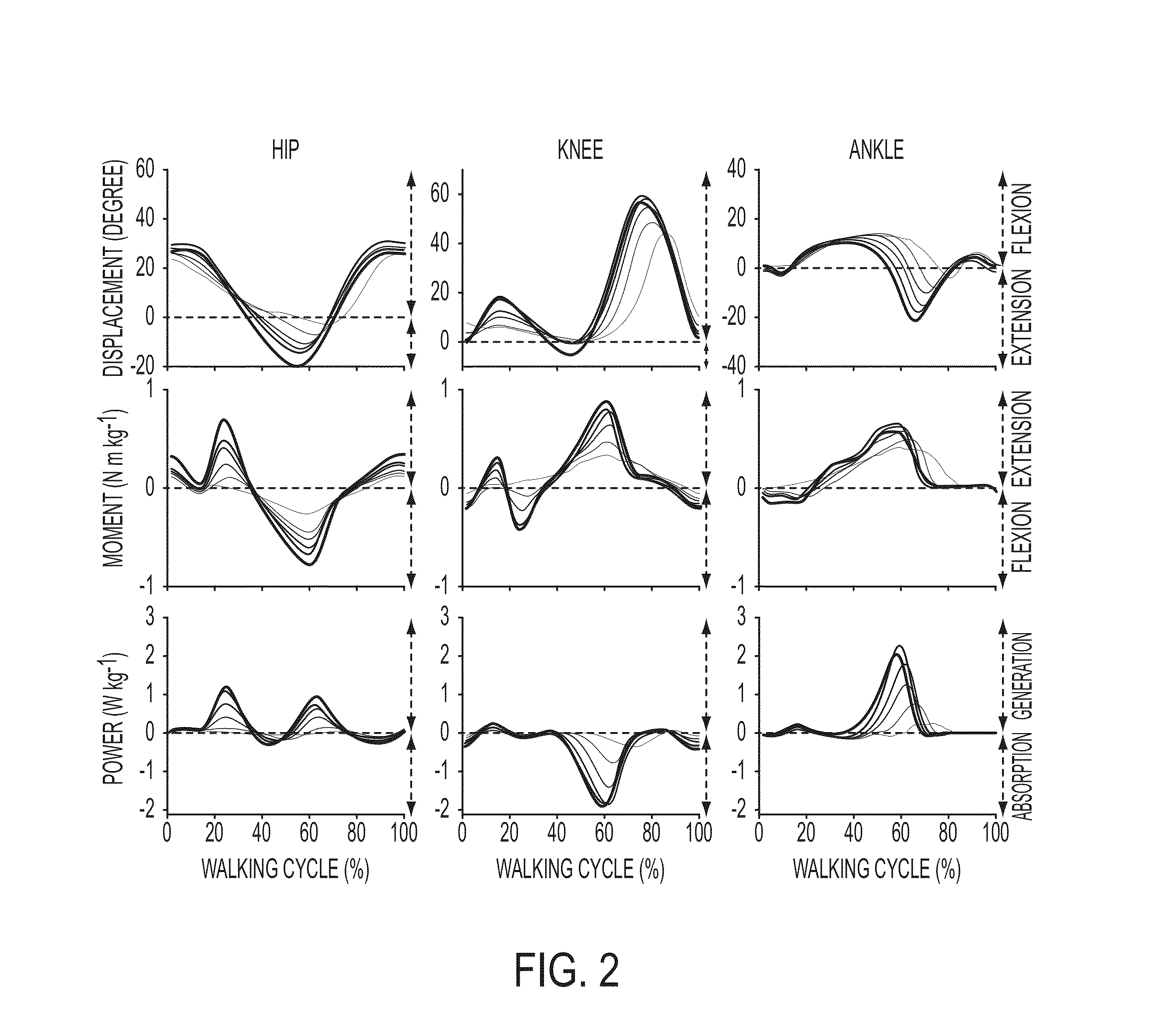
ActiveUS20050070834A1Less kinematic differenceIncrease independenceWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePathology diagnosis
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Walking assistance system
ActiveUS20060064047A1Uncomfortable sensationEliminate uncomfortable sensationChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighCoxal joint
A walking assistance system includes an upper leg fitting which is attached along a user's upper leg. The upper leg fitting is formed from an upper leg frame that forms a framework of the upper leg fitting, and an upper leg coupling member that is vertically slidably supported on a guide rail provided on the upper leg frame, rotatably supported around a support shaft, and joined to the upper leg. When the upper leg fitting is made to swing in the fore-and-aft direction relative to the user's hip by a hip joint actuator, the position of the center of swing of the upper end of the upper leg fitting and the position of the hip joint are displaced, but it is possible to make the upper leg coupling member follow the upper leg by moving the upper leg coupling member relative to the upper leg frame, thus eliminating any uncomfortable sensation.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
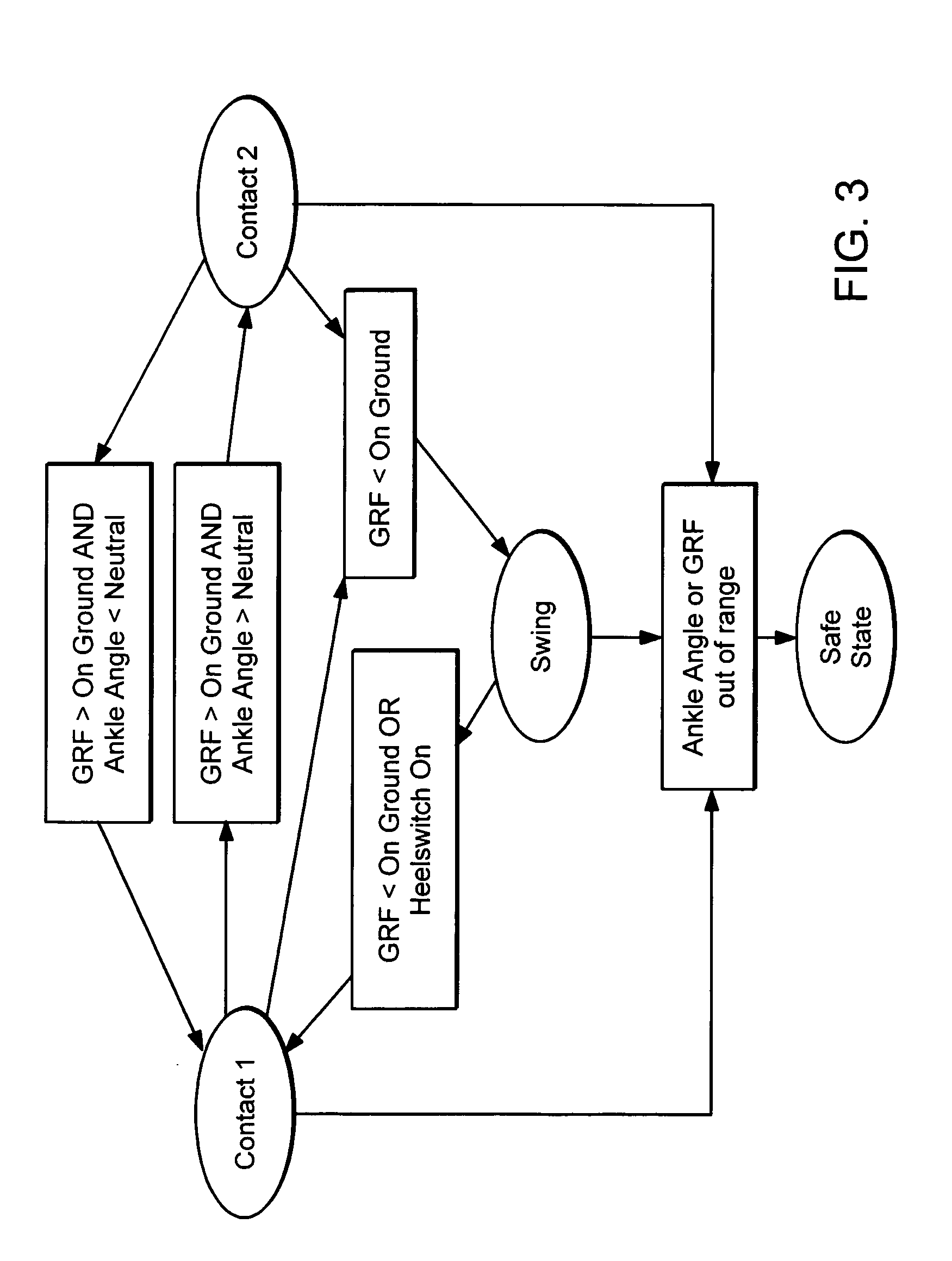
Locomotion assisting device and method
An exoskeleton bracing system includes: a trunk support for affixing to the trunk of a disabled person and leg braces for connecting to the legs of the person, each leg brace including limb segment braces. Motorized joints are adapted to provide relative angular movement between the limb segment braces of the leg braces and between the leg braces and the trunk support. One or more ground force sensors are designed to sense ground force exerted on each of the leg braces. The system also includes a controller for receiving sensed signals from said one or more ground force sensors, with an algorithm for identifying a stance from the sensed signals and, based on the identified stance, actuating the motorized joints to perform an action relating to a mode of locomotion selected from a set of predefined actions corresponding to the identified stance.
Owner:REWALK ROBOTICS LTD
Soft Exosuit for Assistance with Human Motion
ActiveUS20160107309A1Beneficial reduction in metabolic consumption of energyReduce loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesControl systemHuman motion
A motion control system includes an actuator having an actuation member, the actuation member having a proximal end attached to the actuator on a first side of a joint and a distal end attached to an anchor element attachment point on a second side of the joint. A first sensor is configured to output signals defining a gait cycle and a second sensor is configured to output signals representing a tensile force in the at least one actuation member. A controller receives the output signals from the sensors and actuates the actuator, during a first portion of the gait cycle, to apply a force greater than a predetermined threshold tensile force to the anchor element attachment point via the actuation member to generate a beneficial moment about the joint and to automatically actuate the actuator.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
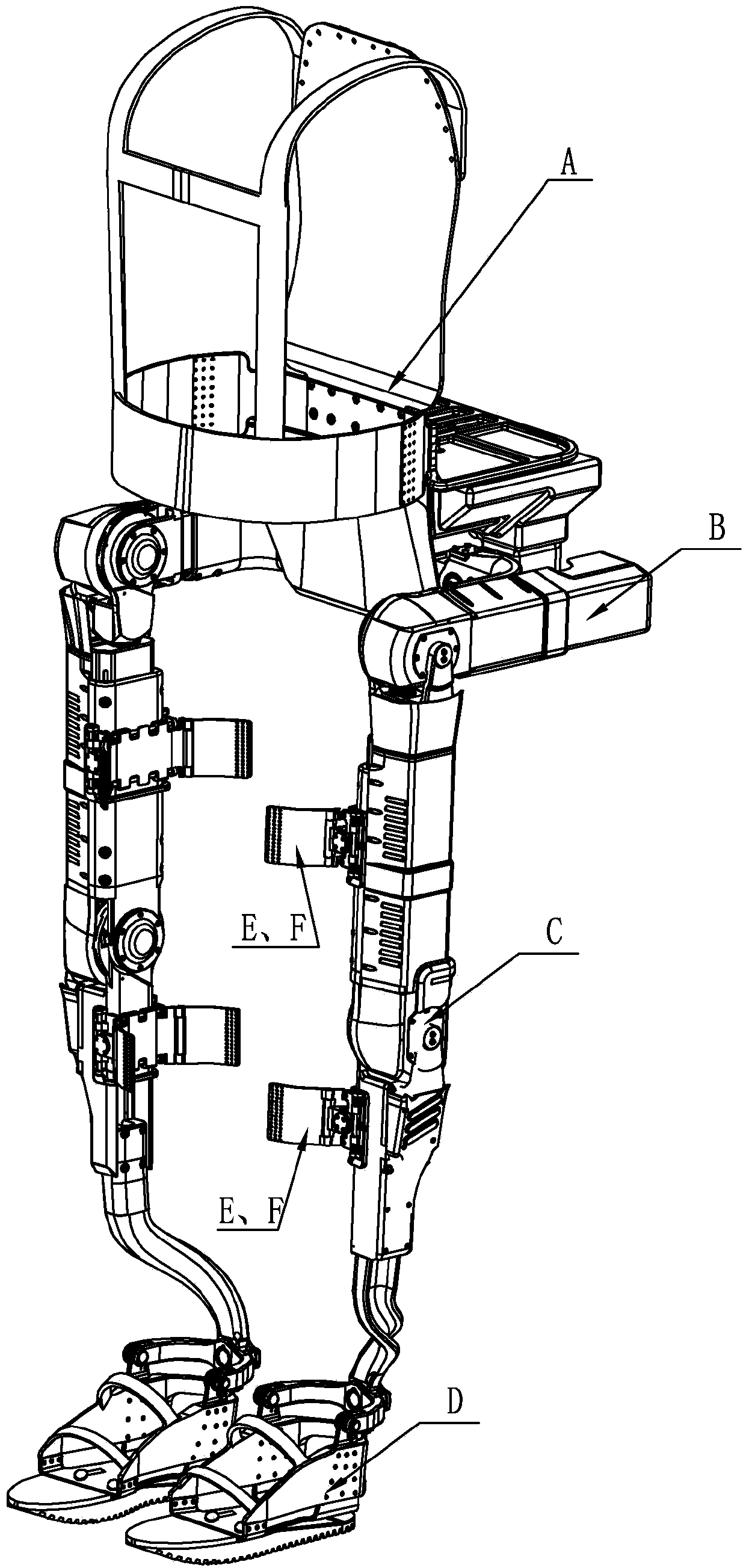
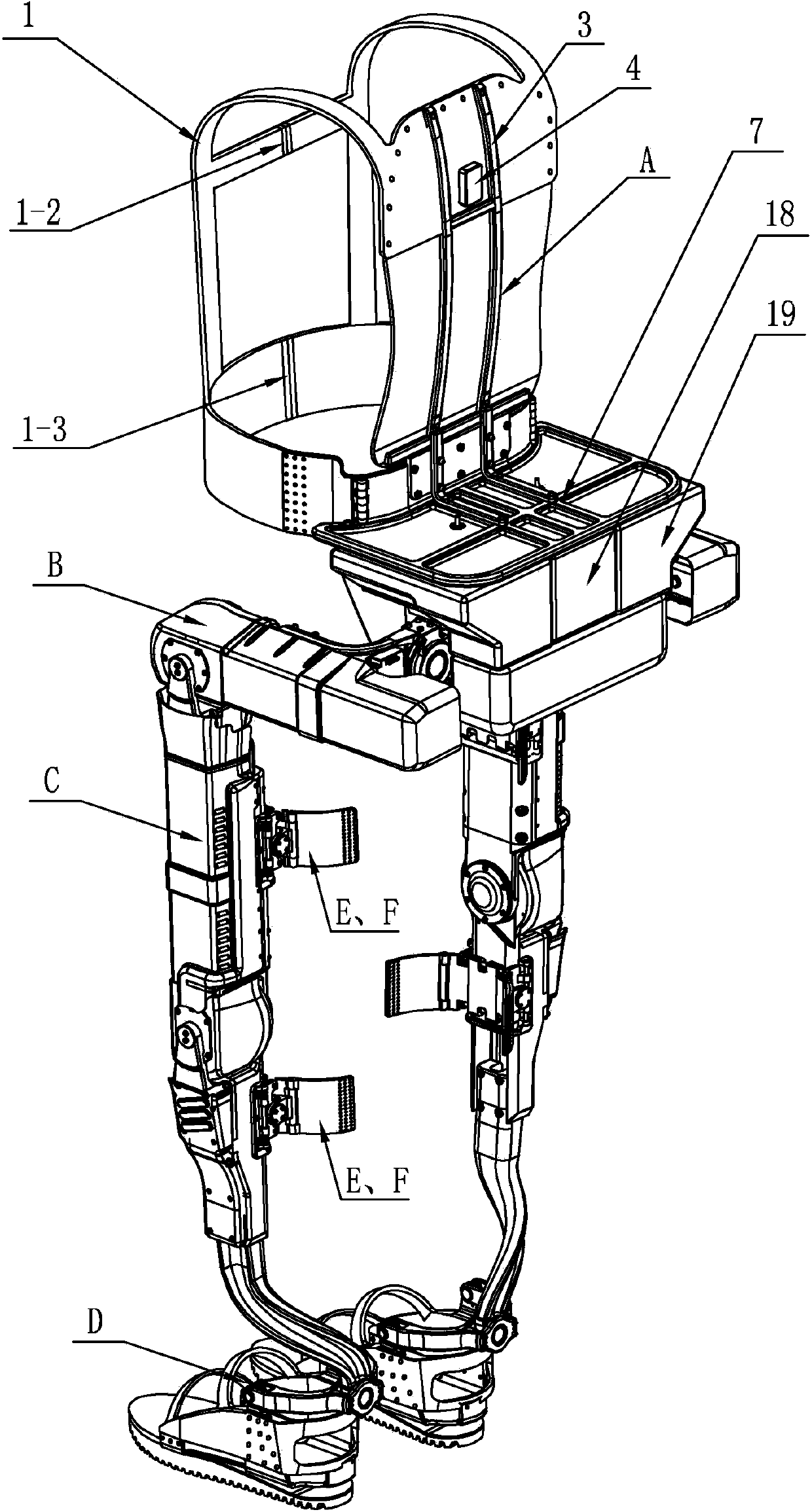
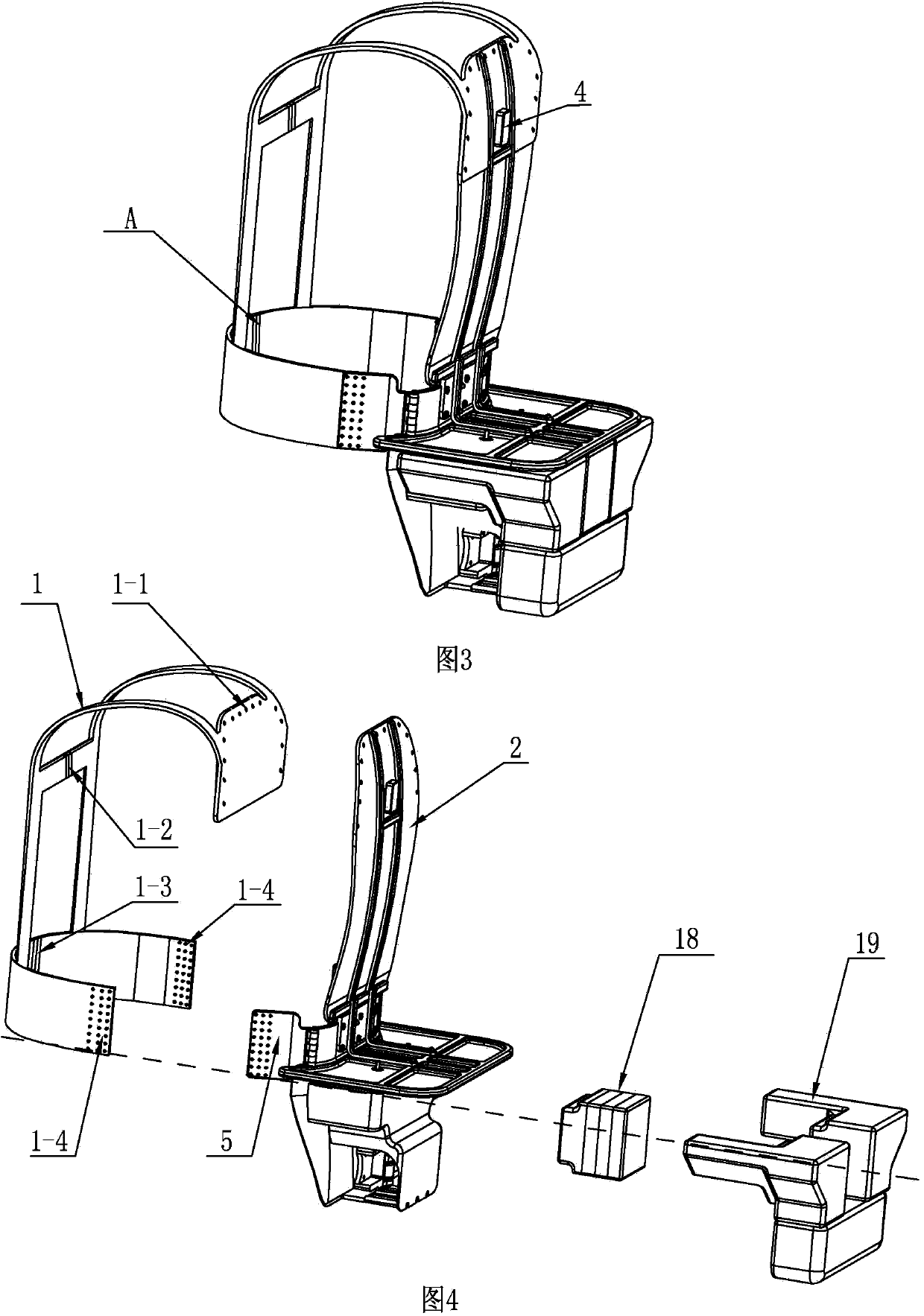
Human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting lower limbs
ActiveCN103610568ARealize the safety requirements of mechanical limitConvenient and accurate adjustment of telescopic lengthChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighExoskeleton robot
The invention relates to an external skeleton robot, in particular to a human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs aims to solve the problems that an existing external skeleton robot is low in coupling degree of motion space and poor in wearing comfort, reliability and adaptation, and power needed by a motor is large. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs comprises an upper body back part, a left leg and a right leg. The left leg and the right leg respectively comprise a hip drive system, a knee drive system and a foot wearing system. A rear side connection board of the waist is in rotating connection with a load installation board. Each hip joint supporting board is provided with a first motor and a first reducer, wherein the first motor is provided with an encoder, and the output end of the first motor provided with the encoder is connected with the input end of the first reducer. Each hip joint connecting board can rotate in the vertical plane. Each thigh stretching board is in detachable connection with the corresponding hip joint connecting board. The output end of a main drive mechanism is connected with each crus connecting board. The lower surfaces of elastic boards are bonded with the upper surfaces of the rubber soles of the feet. The human-simulated external skeleton robot assisting the lower limbs can assist in walking.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
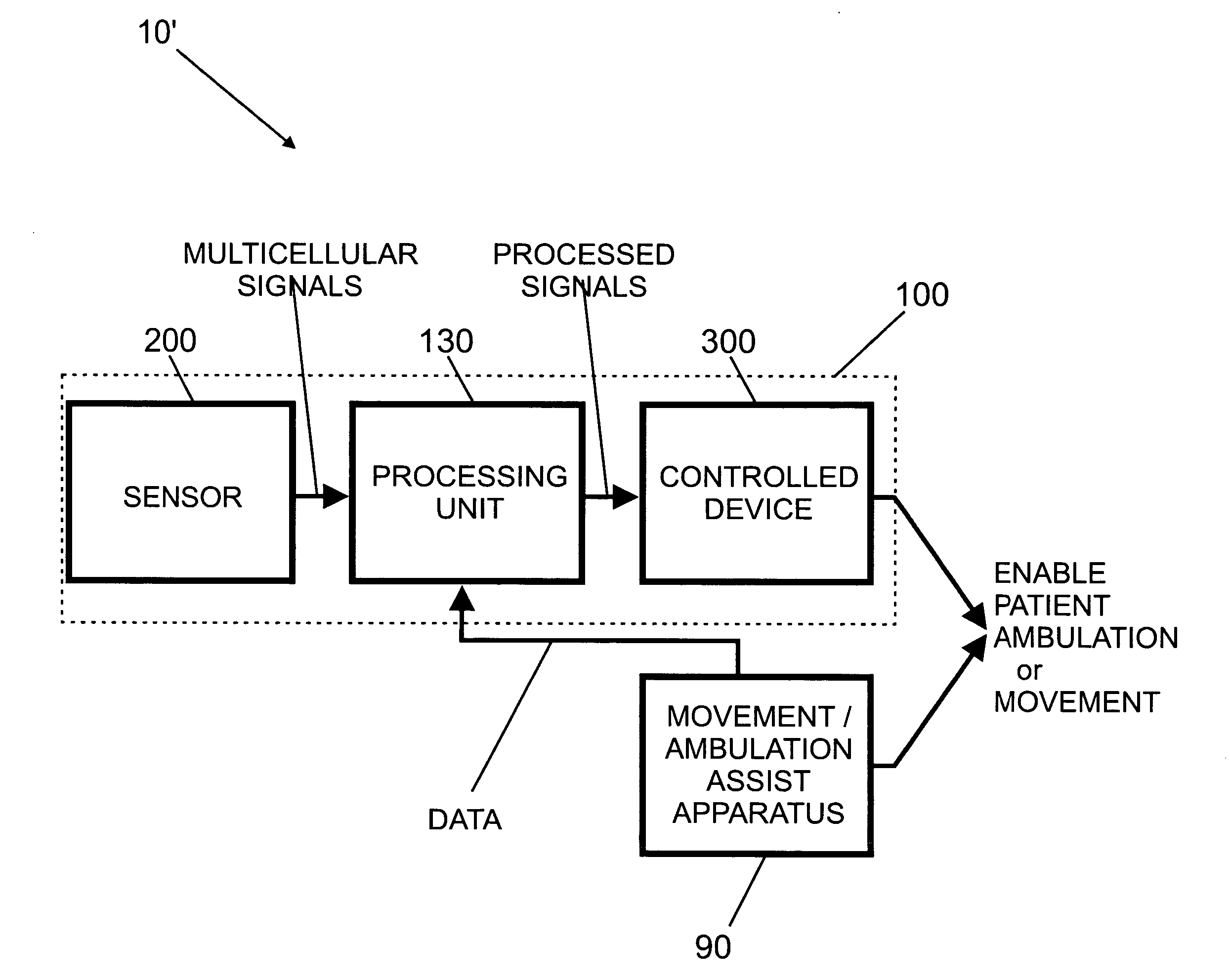
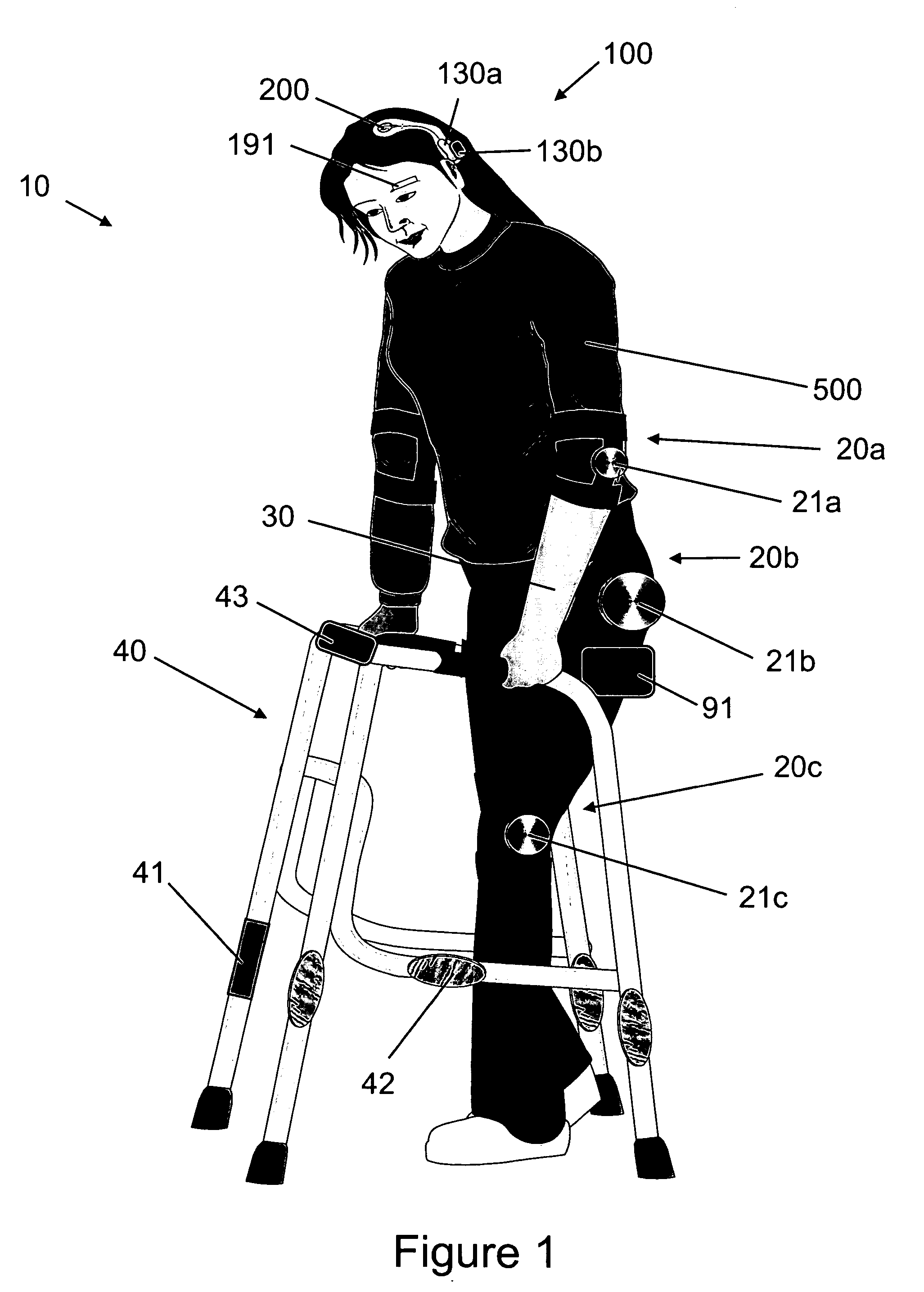
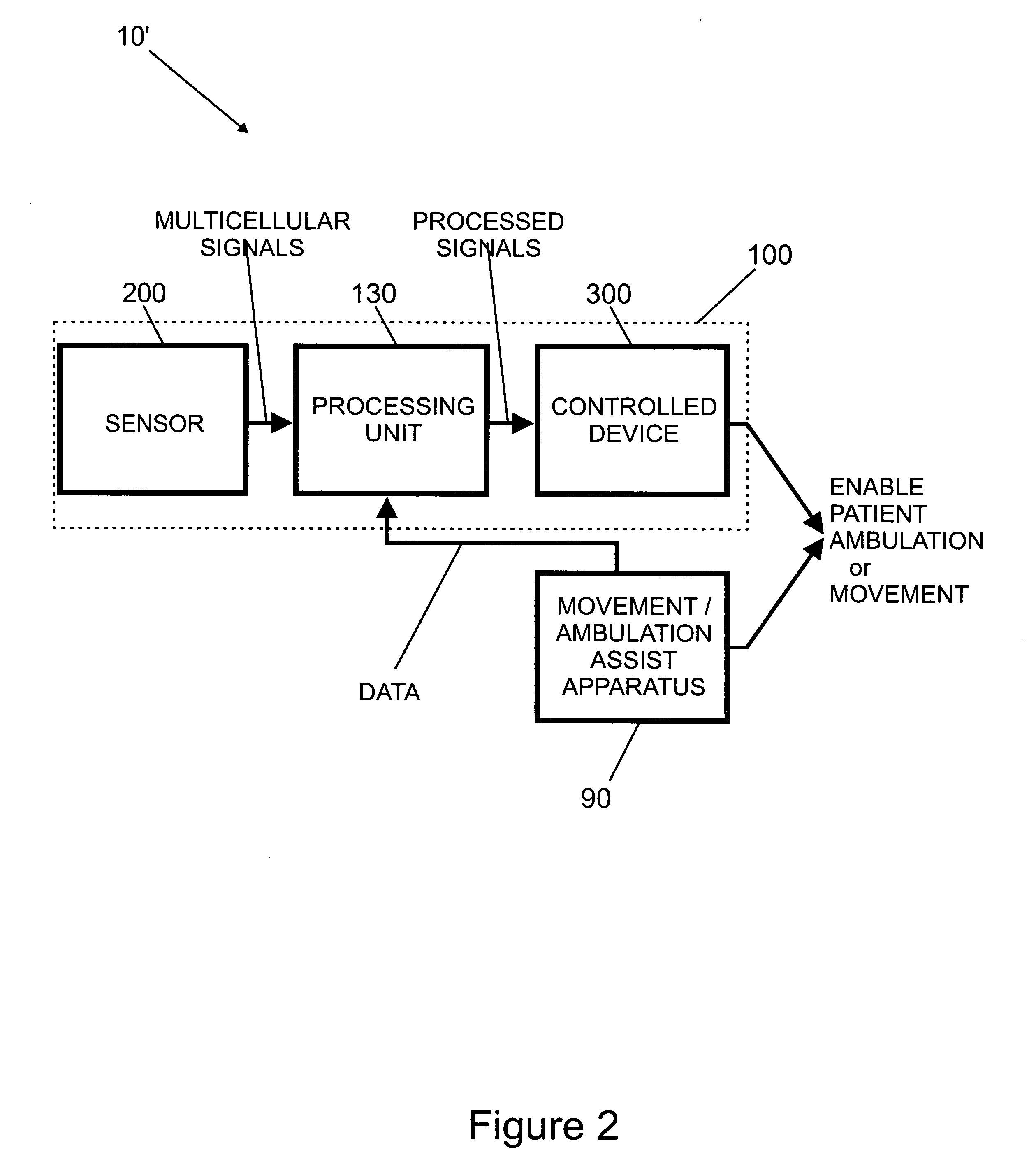
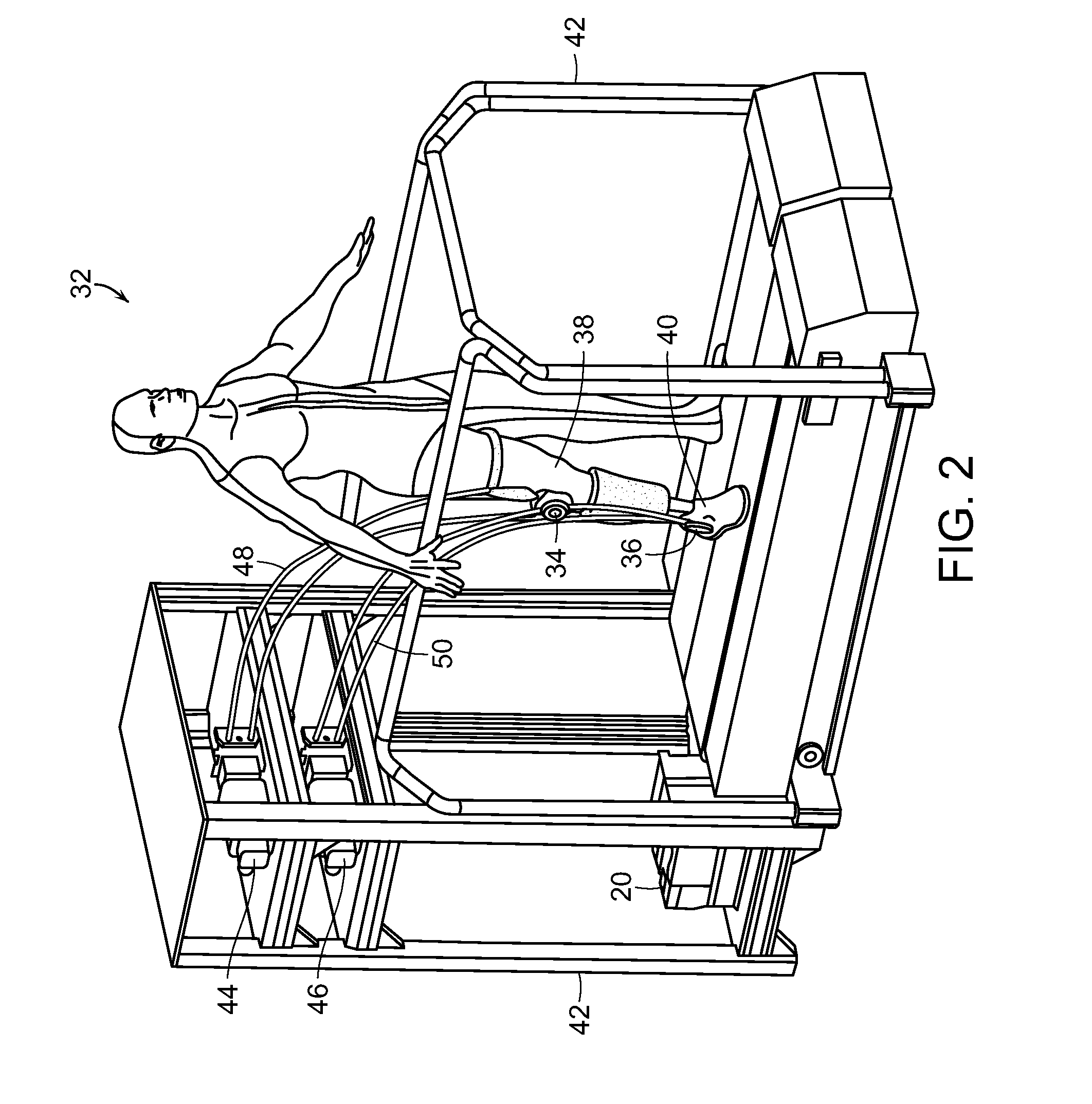
Multi-device patient ambulation system
InactiveUS20060206167A1Improve performanceImprove securityProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectrotherapyEngineeringProcessing element
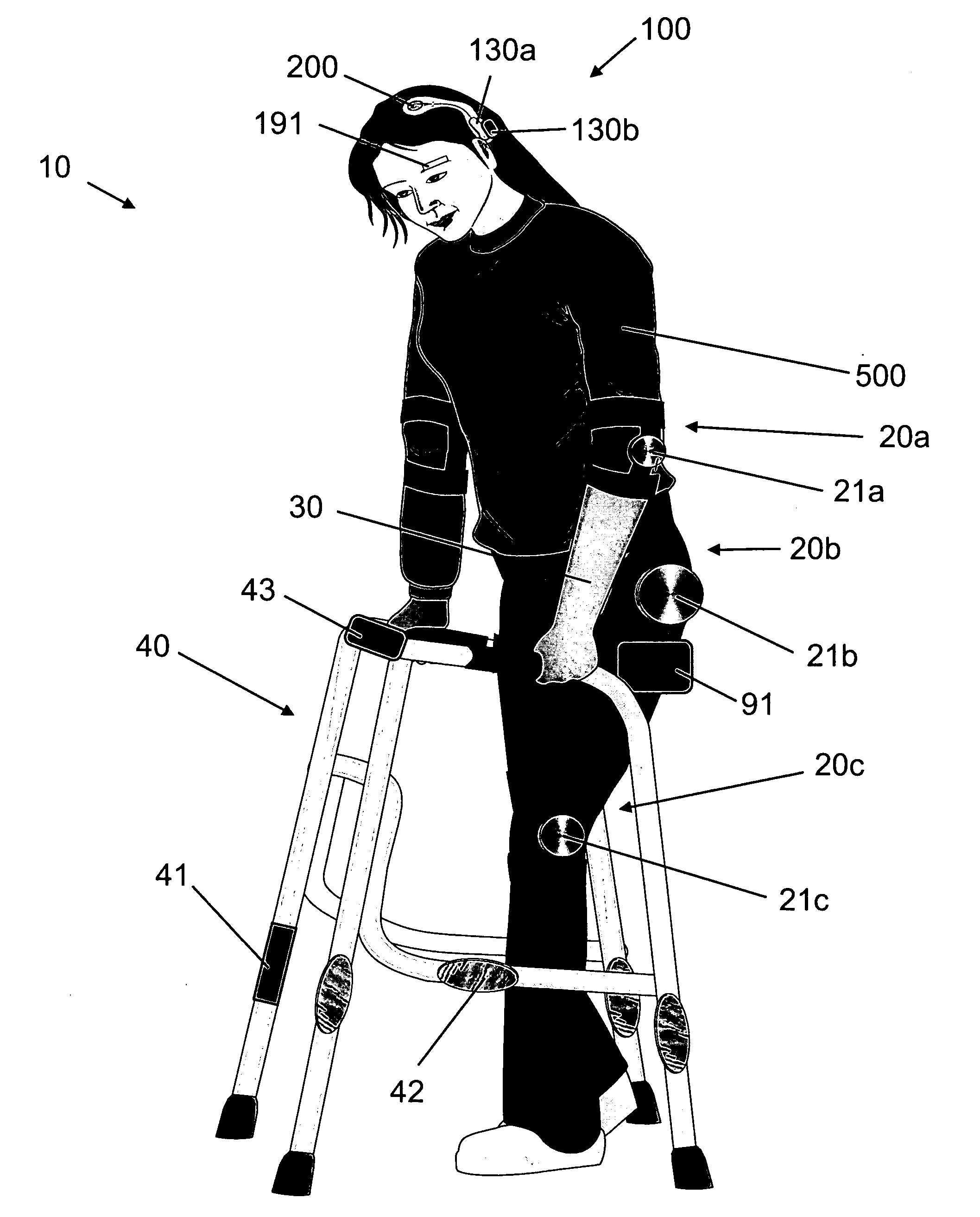
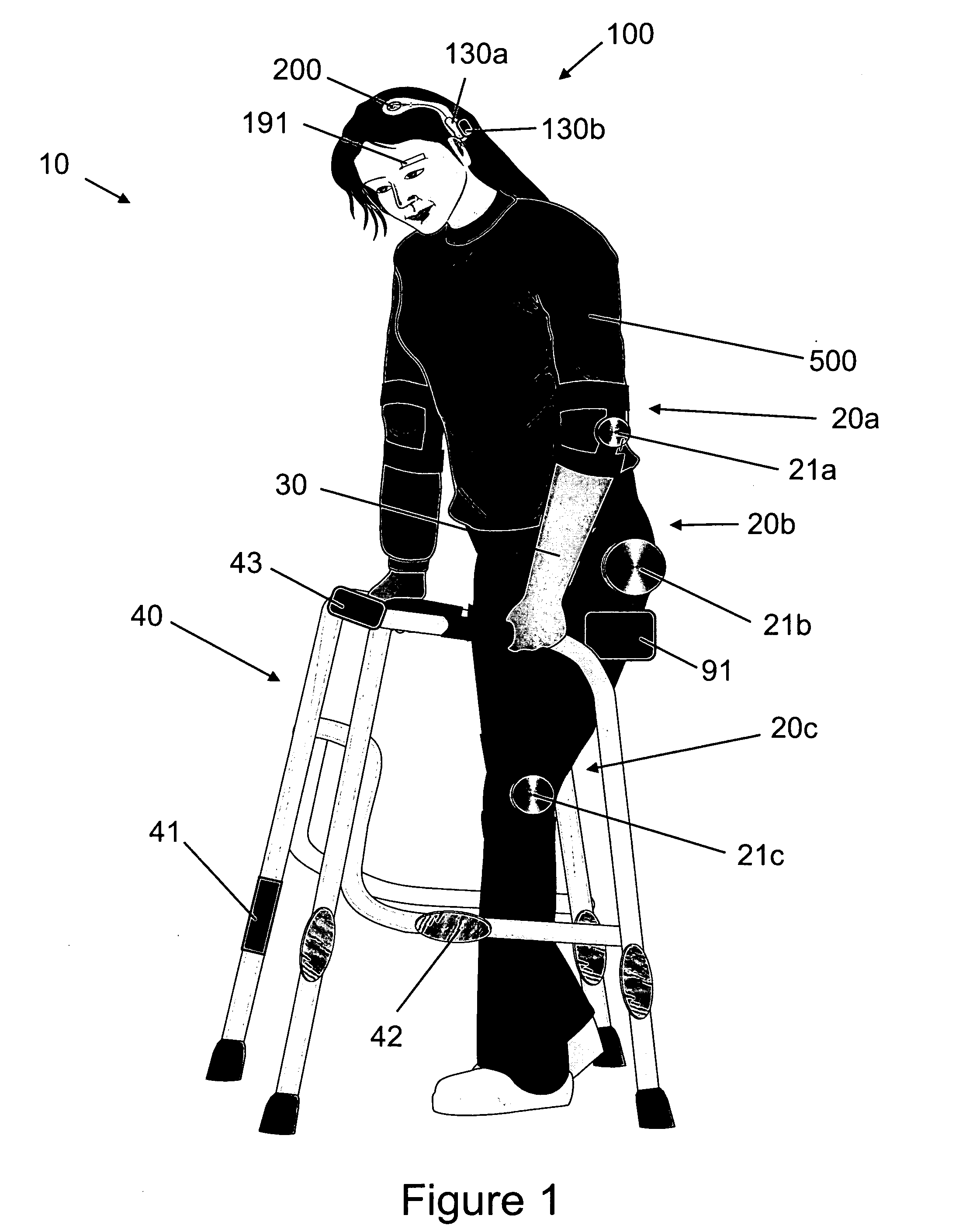
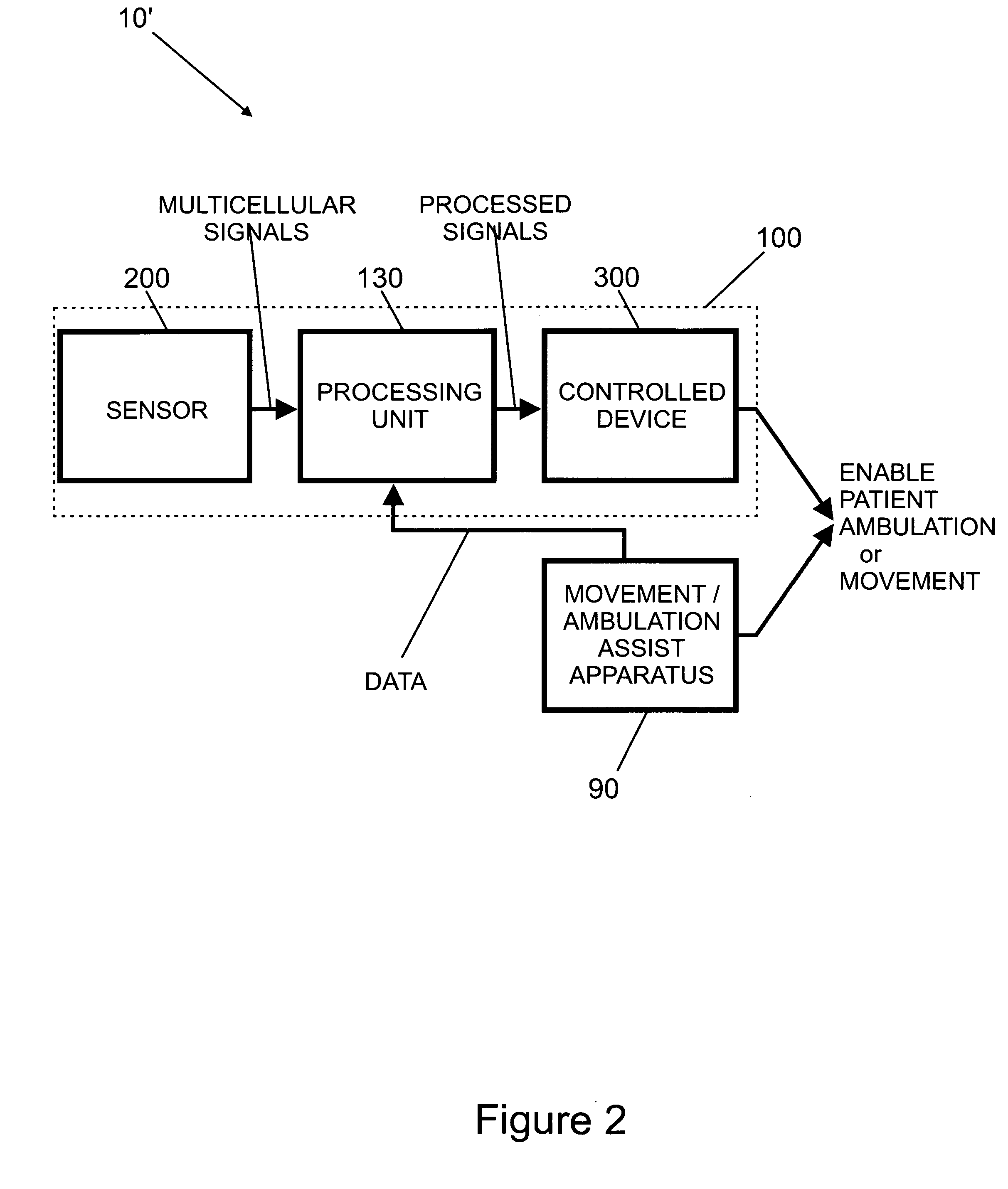
Various embodiments of an ambulation and movement assist system are disclosed. For example, an ambulation system for a patient may comprise an exoskeleton device attached to the patient, an FES device at least partially implanted in the patient, and a biological interface apparatus. The biological interface apparatus comprises a sensor having a plurality of electrodes for detecting multicellular signals, a processing unit configured to receive the multicellular signals from the sensor, process the multicellular signals to produce a processed signal, and transmit the processed signal to a controlled device. At least one of the exoskeleton device and the FES device is the controlled device of the biological interface apparatus.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD +1
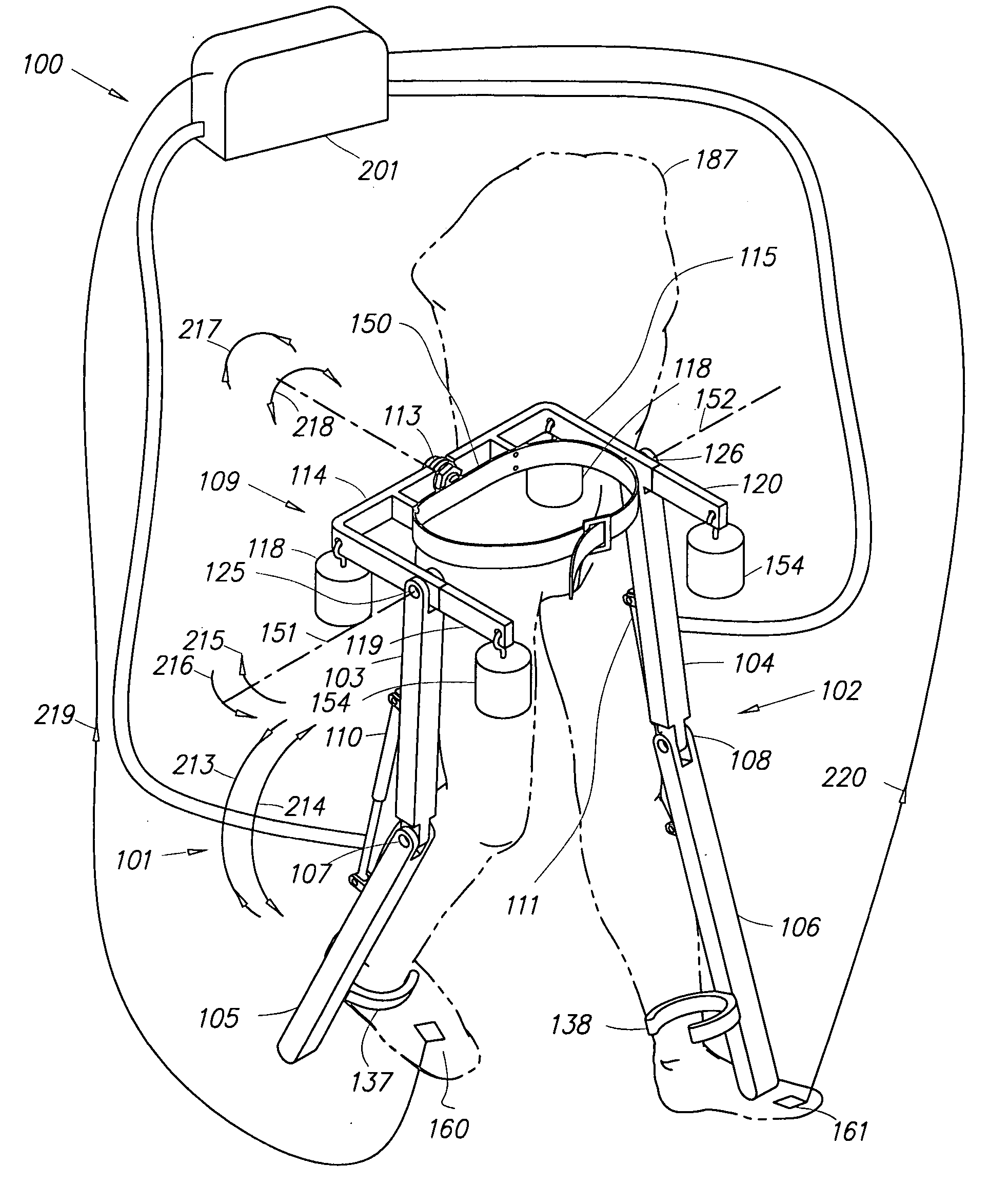
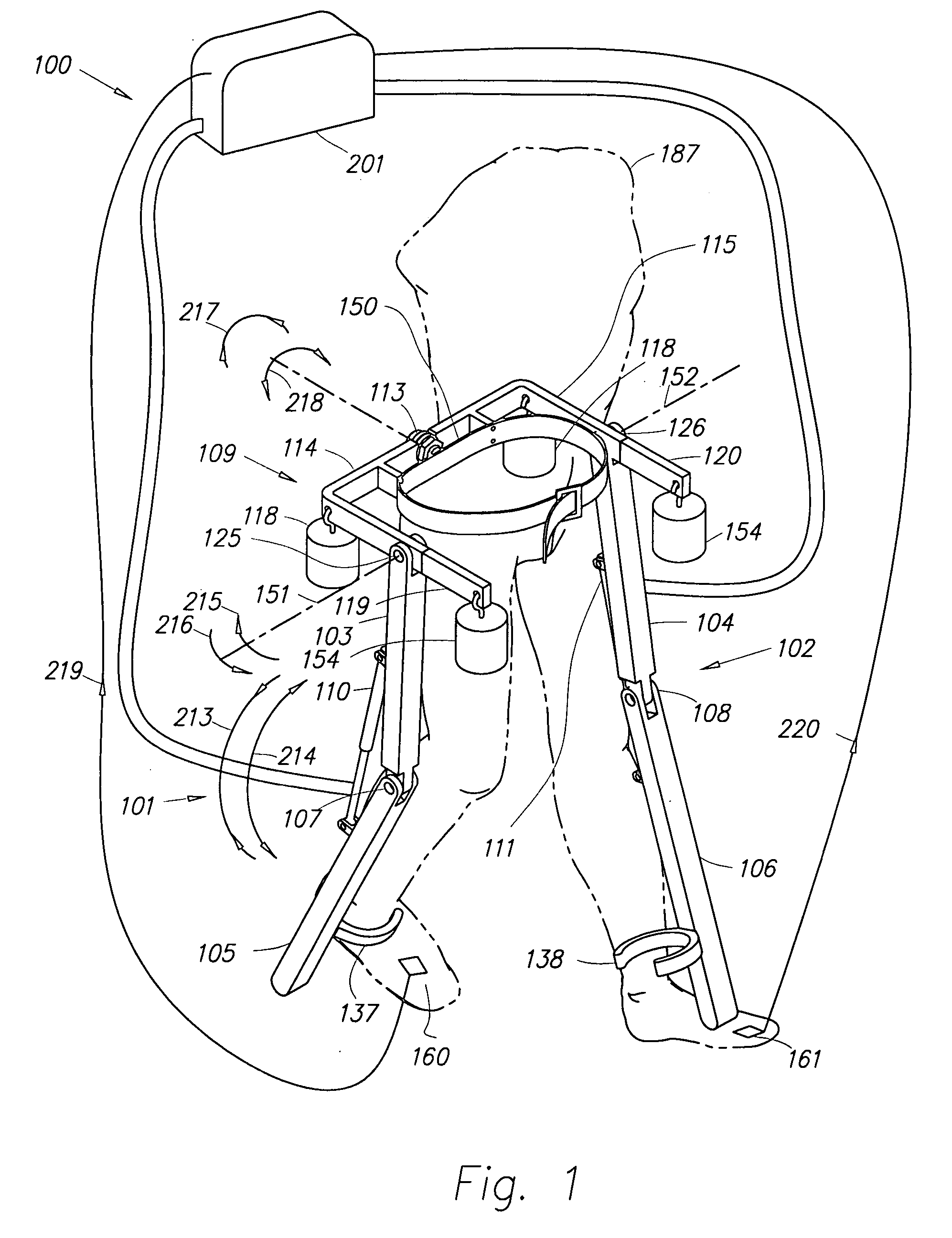
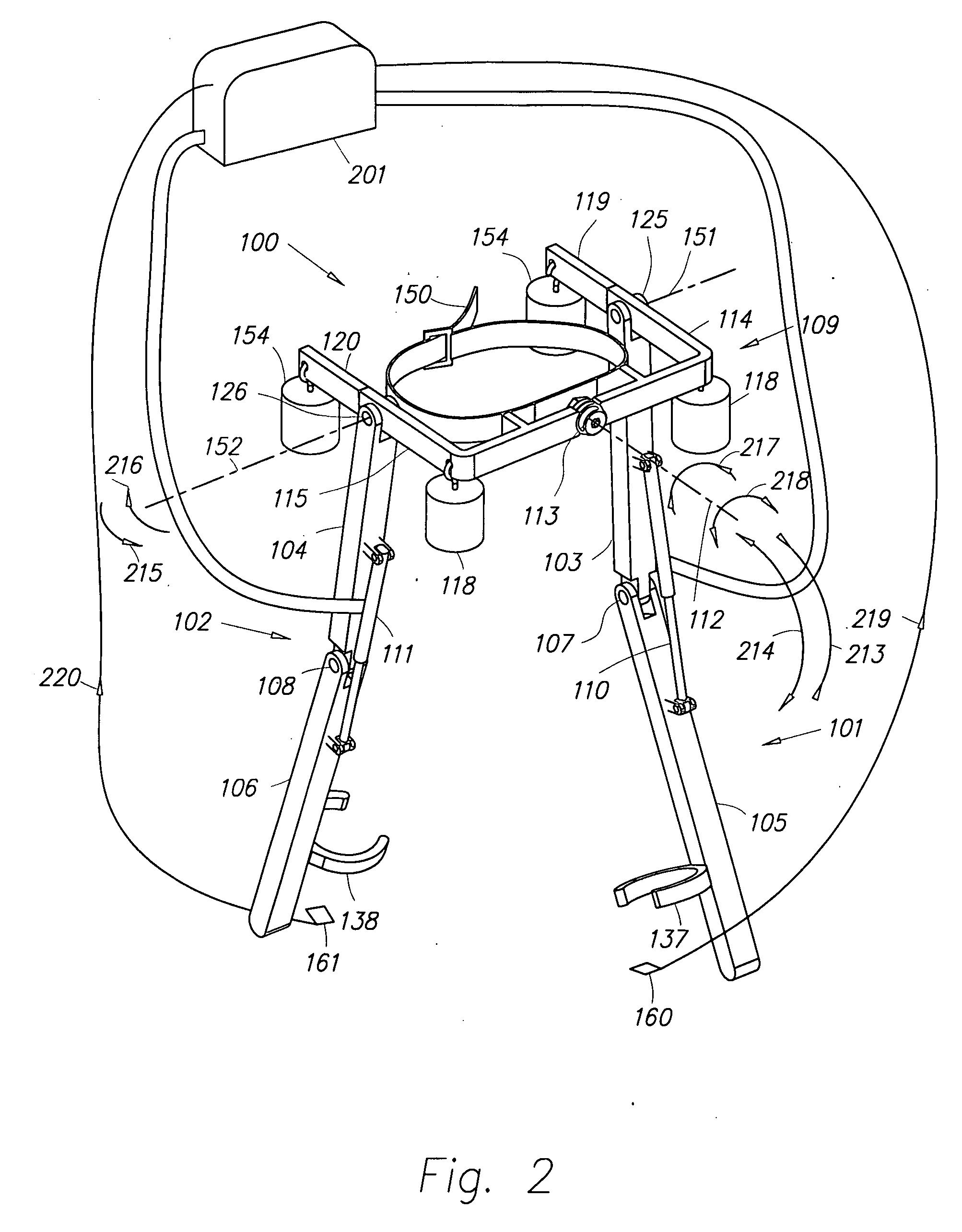
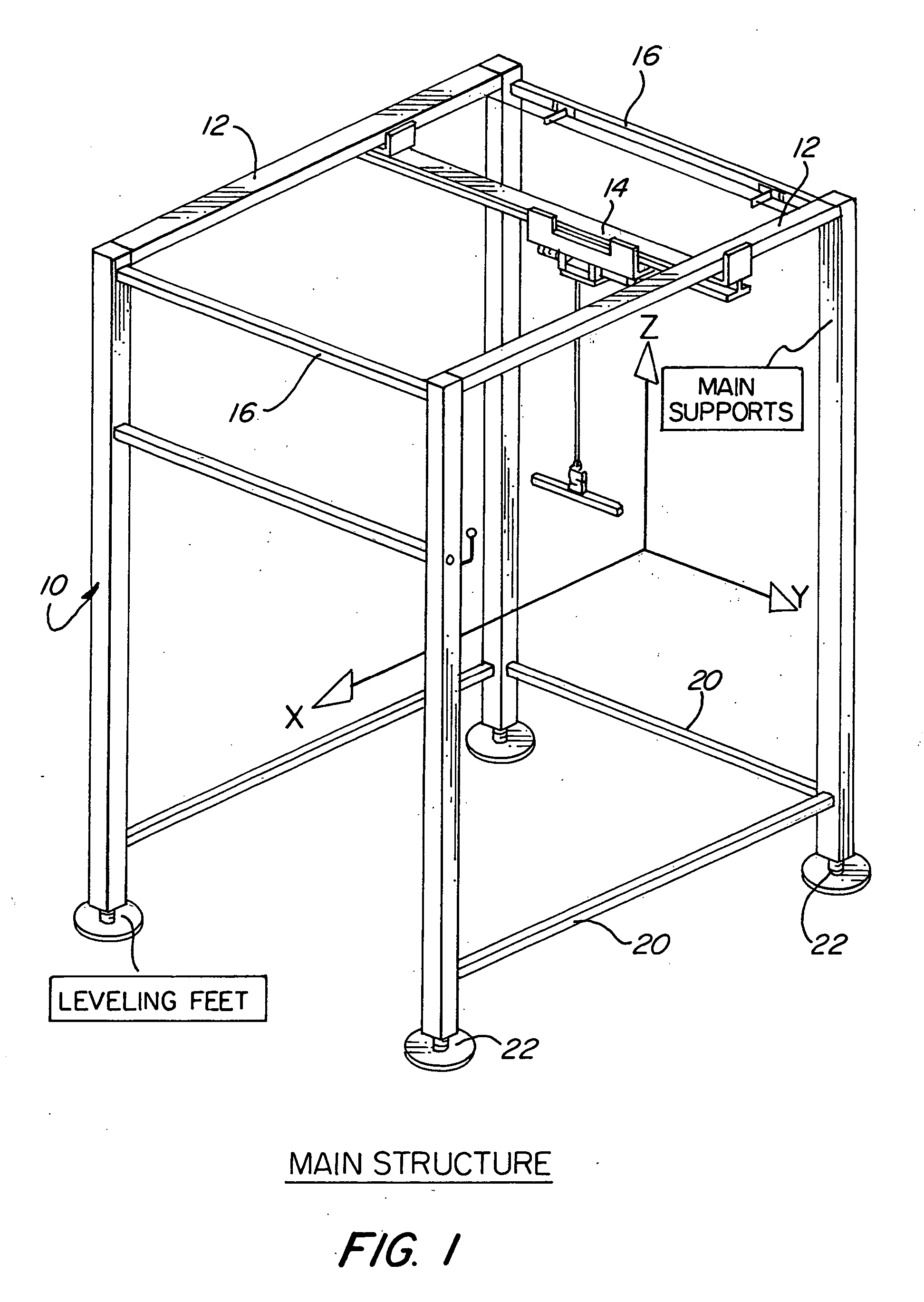
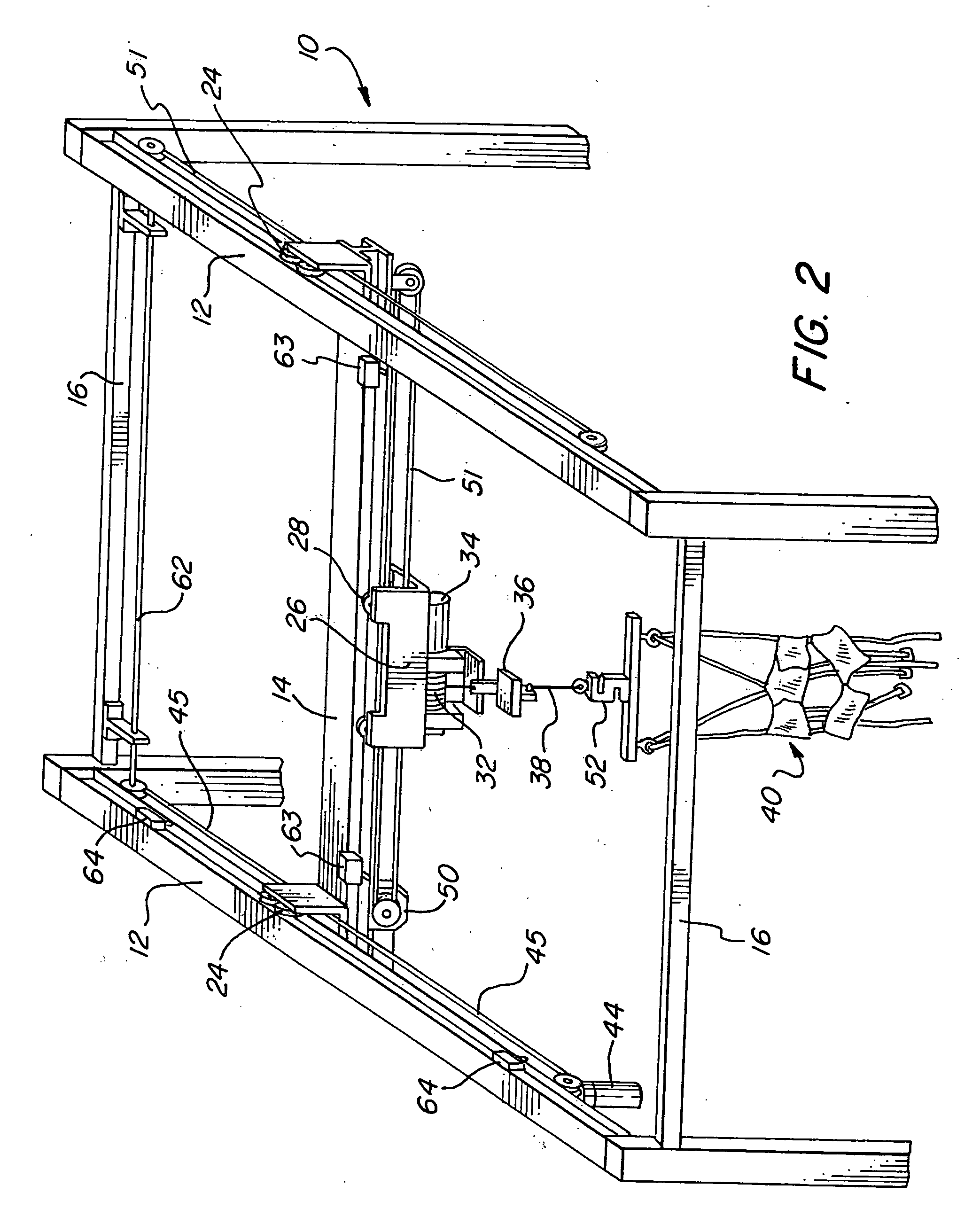
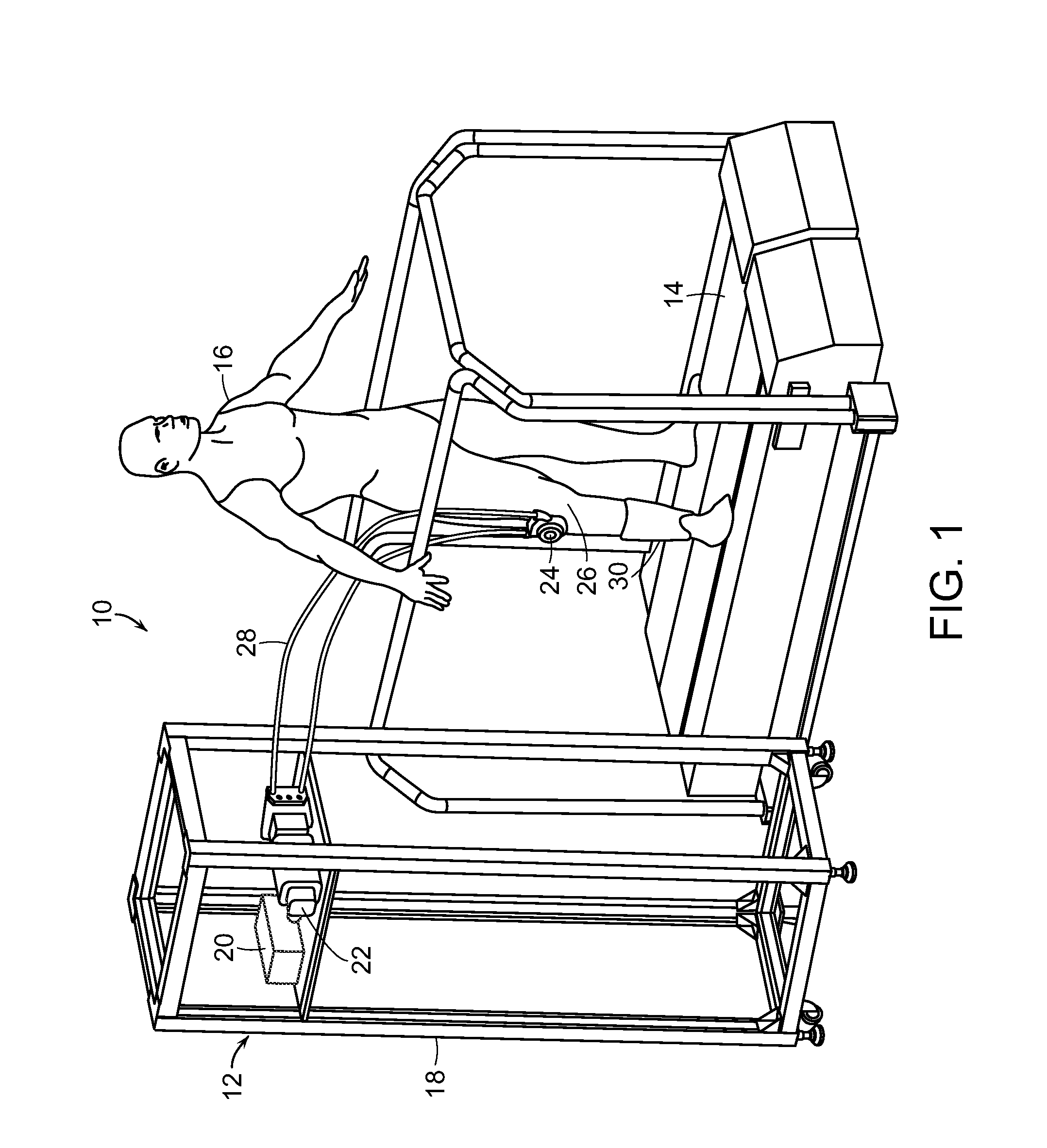
Ambulatory suspension and rehabilitation apparatus
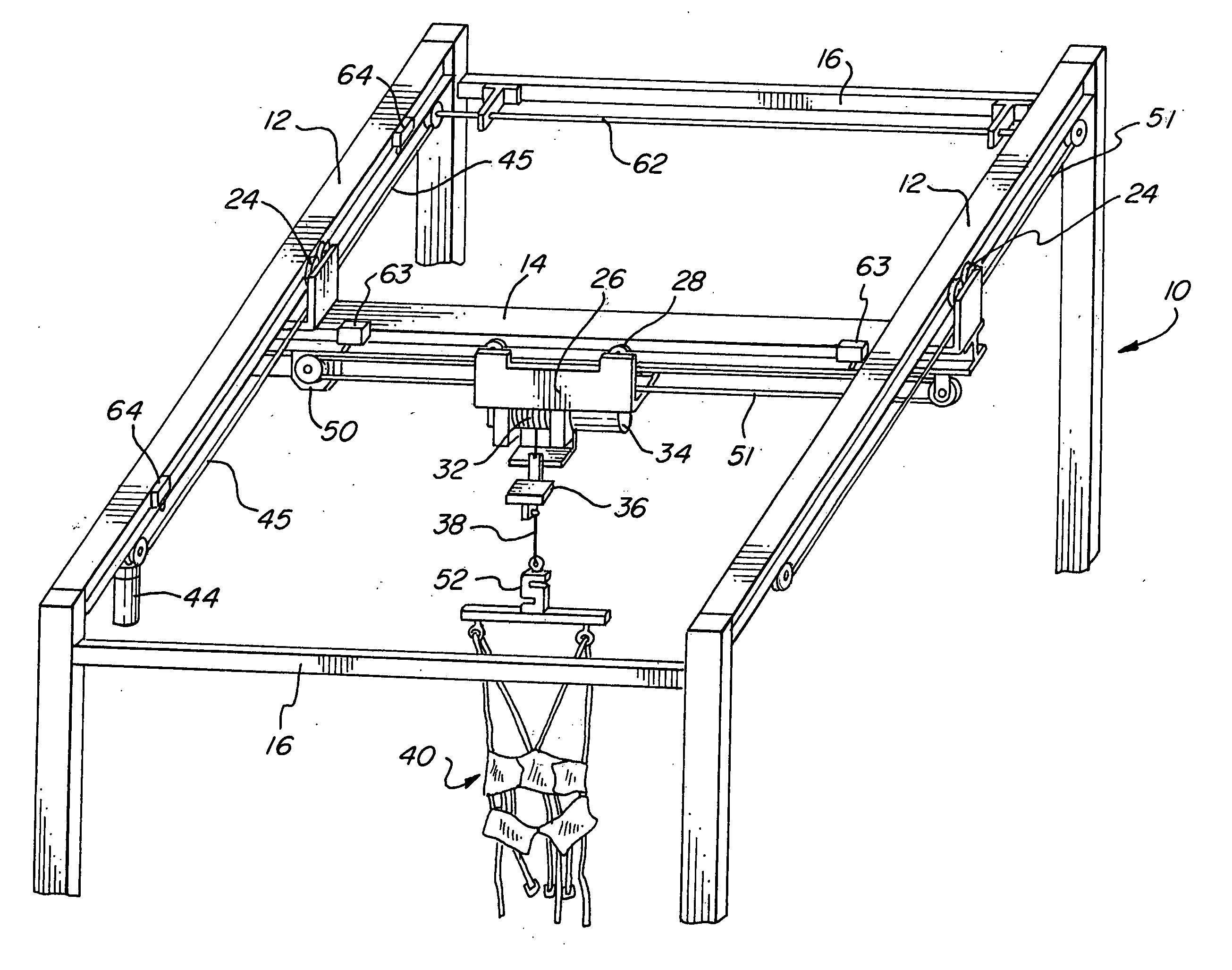
An ambulatory suspension system for gait rehabilitation has a parallel pair of rails bordering the sides of a training area and a bridge extending between and movable along the rails. A trolley is movable along the bridge and includes a motor driven hoist with a cable extending thereabout and depending from the trolley. The hoist is operable to vary the length of the cable depending from the trolley, and a harness is suspended by the cable. Motors move the bridge along the rails and the trolley along the bridge as the sensors sense the direction of movement of the patient in X and Y directions. The falling motion of a patient supported in the harness is sensed and will immediately disable the system. A computer control receives signals from the sensors and operates the motors so that the patient is held in an upright position.
Owner:HARTFORD THE UNIV OF +1
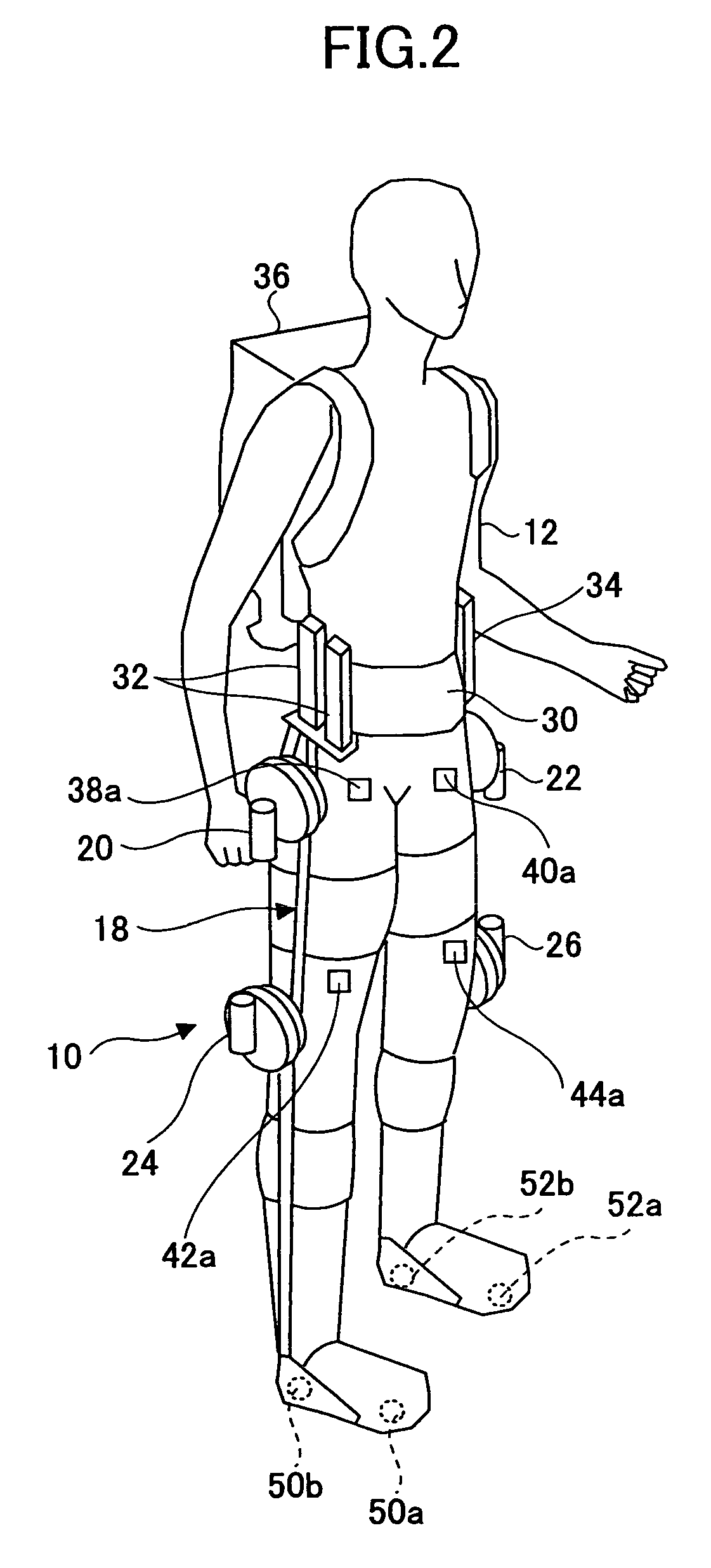
Apparatus for assisting limb and computer program
InactiveUS20060276728A1Applied load reductionStrengthen restrictionsProgramme-controlled manipulatorWalking sticksThighKnee Joint
An apparatus for assisting limb includes a body attachment, a link for upper leg, and a knee joint unit, a link for lower leg, a lower limb attachment, a drive unit and a knee joint actuator. The body attachment is attached to a trunk of a user. The link for upper leg is placed alongside with an upper leg of the user and coupled with the body attachment. The link for lower leg is placed alongside with a lower leg of the user and coupled with the link for the upper leg via the knee joint unit. The lower limb attachment is attached to one of the lower leg and a foot of the user, and coupled with the link for lower leg. The knee joint actuator is placed in the body attachment so as to apply rotational torque to the knee joint unit via the drive unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Lower Extremity Exoskeleton for Gait Retraining
InactiveUS20130226048A1Facilitate overground locomotionPromote sportsChiropractic devicesWalking aidsNervous systemAnkle foot orthoses
The Active Knee Rehabilitation Orthotic System (ANdROS) is a wearable and portable assistive tool for gait rehabilitation and monitoring of people with motor control deficits due to a neurological ailment, such as stroke. ANdROS reinforces a desired gait pattern by continually applying a corrective torque around the knee joint, commanded by a impedance controller. A sensorized yet unactuated brace worn on the unimpaired leg is used to synchronize the playback of the desired trajectory based on the user's intent. The device is mechanically grounded through two ankle foot orthoses (AFOs) rigidly attached to the main structure, which helps reduce the weight perceived by the user.
Owner:SPAULDING REHABILITATION HOSPITAL CORP +1
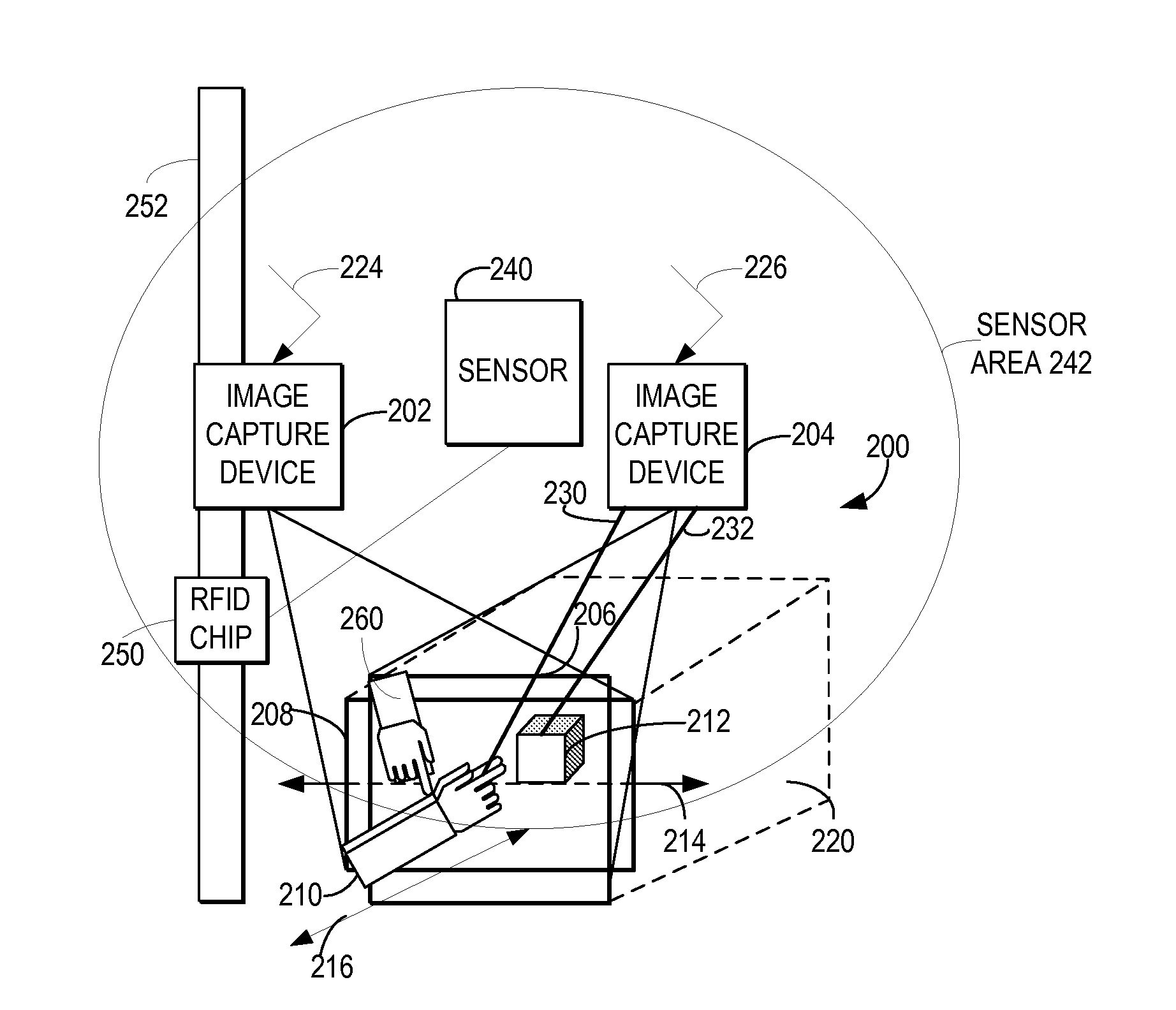
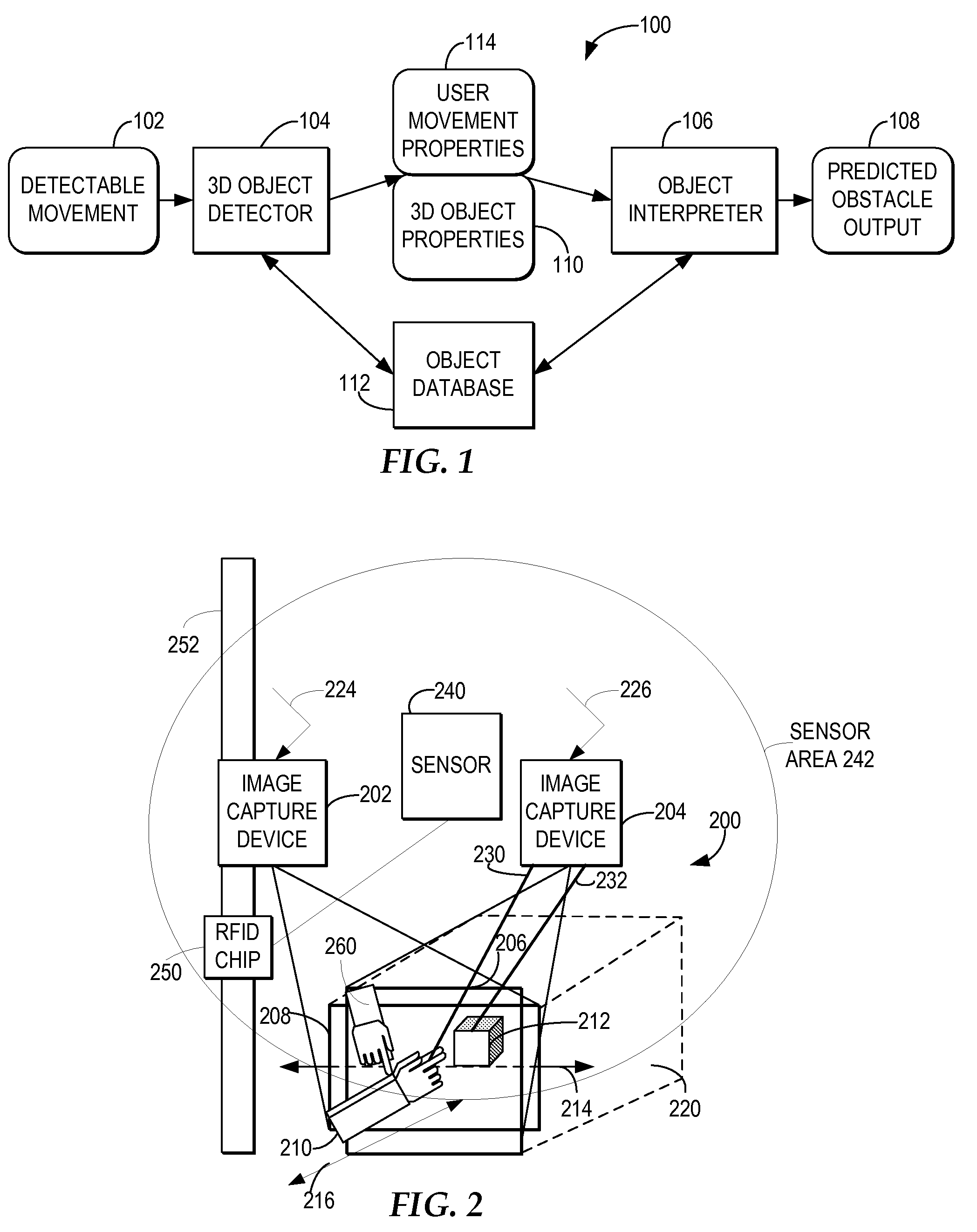
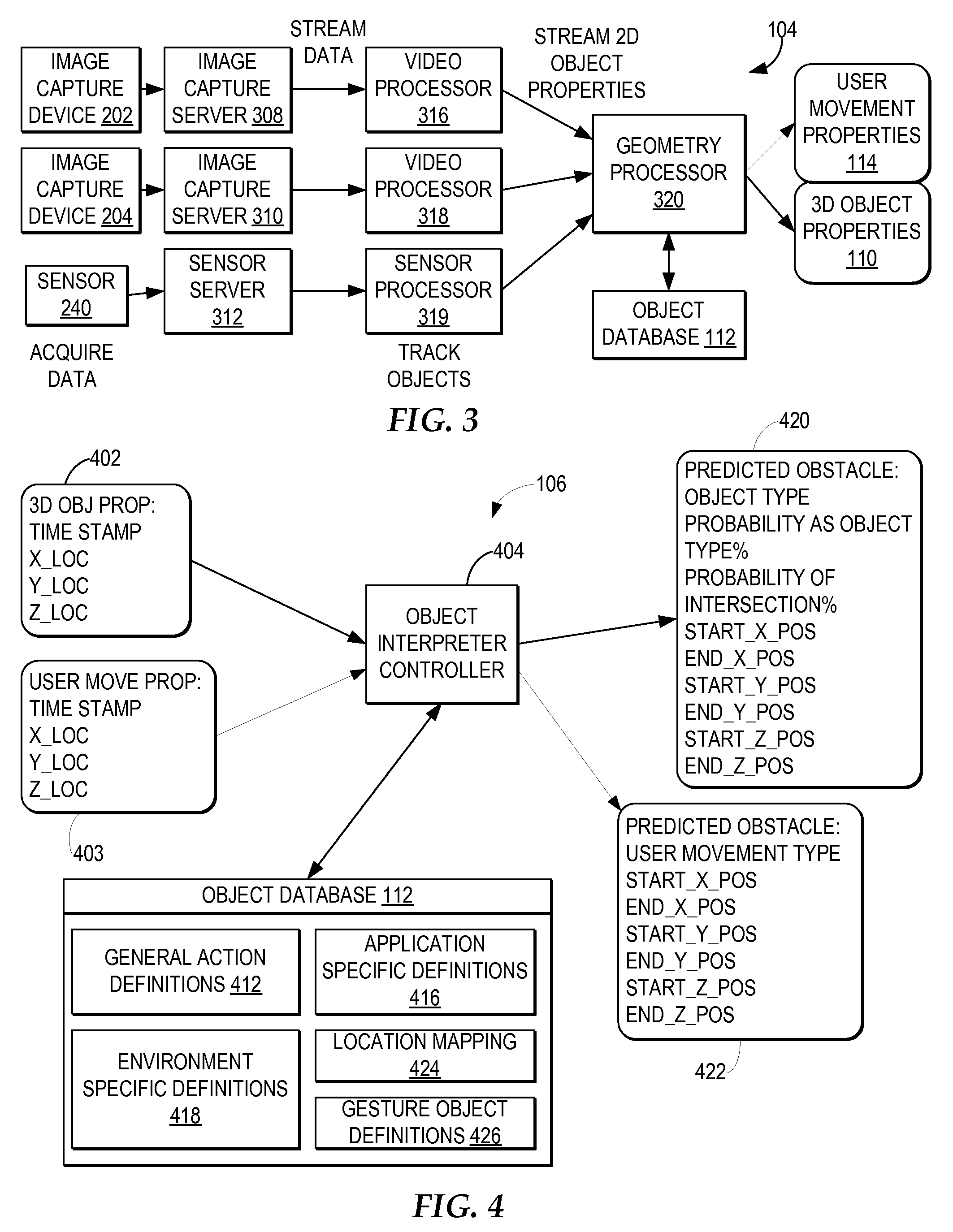
Assisting a vision-impaired user with navigation based on a 3D captured image stream
An object-enabled navigation system assists a vision-impaired user in navigating an environment. The system captures 3D movement of a moving object within the environment, wherein the three-dimensional movement is determined using at least one image capture device aimed at the moving object. The system predicts a mobile path of the visually-impaired user. The system determines whether the movement of the moving object will intersect with the mobile path of the vision-impaired user and informs the vision-impaired user whether the movement of the moving object will intersect the mobile path of the vision-impaired user.
Owner:IBM CORP
Neurally controlled patient ambulation system
ActiveUS20060149338A1Improve performanceImprove securityProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectrotherapyEngineeringProcessing element
Various embodiments of an ambulation system and a movement assist system are disclosed. For example, an ambulation system for a patient may comprise a biological interface apparatus and an ambulation assist apparatus. The biological interface apparatus may comprise a sensor having a plurality of electrodes for detecting multicellular signals, a processing unit configured to receive the multicellular signals from the sensor, process the multicellular signals to produce a processed signal, and transmit the processed signal to a controlled device. The ambulation assist apparatus may comprise a rigid structure configured to provide support between a portion of the patient's body and a surface. Data may be transferred from the ambulation assist apparatus to the biological interface apparatus.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD +1
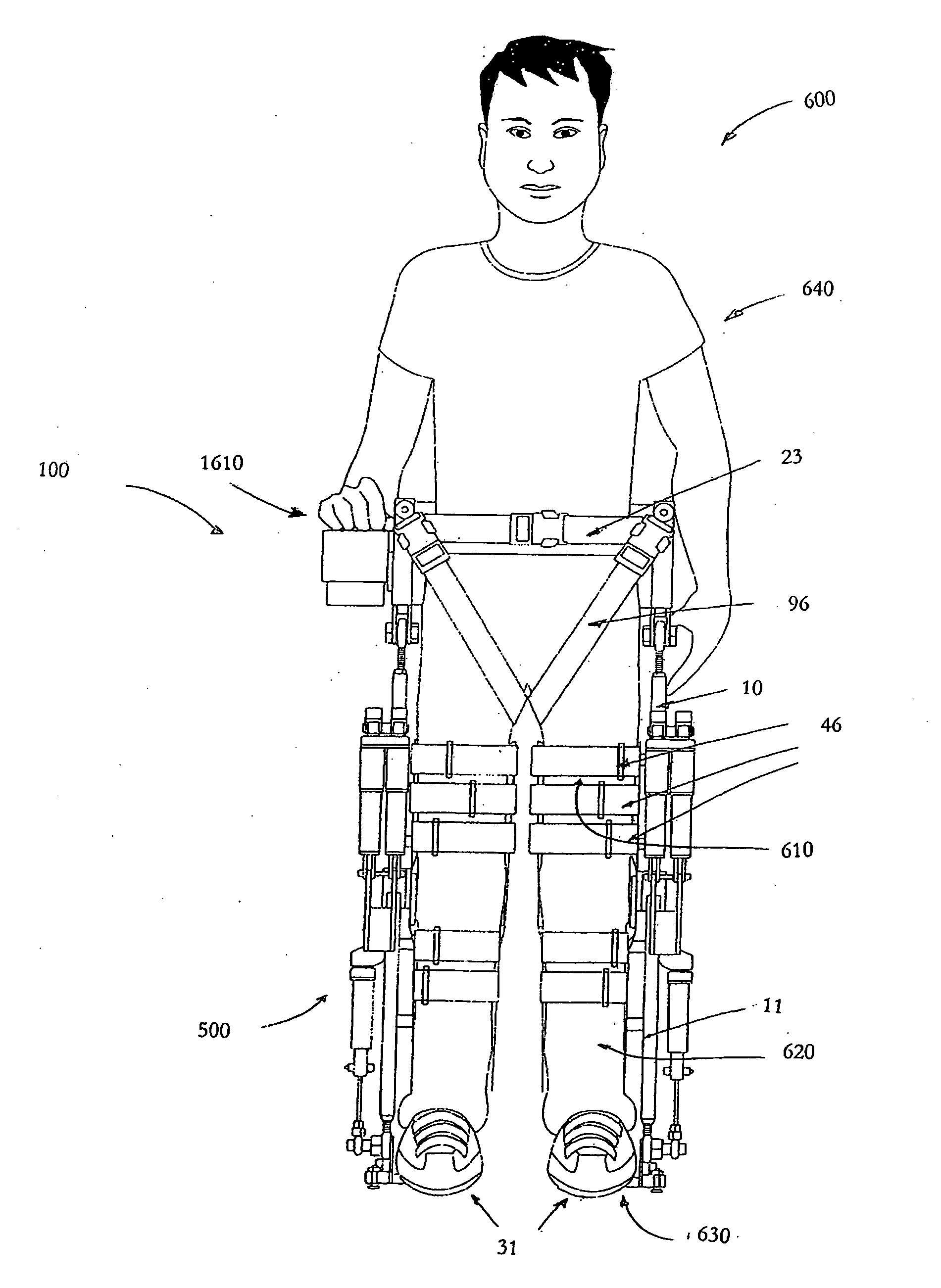
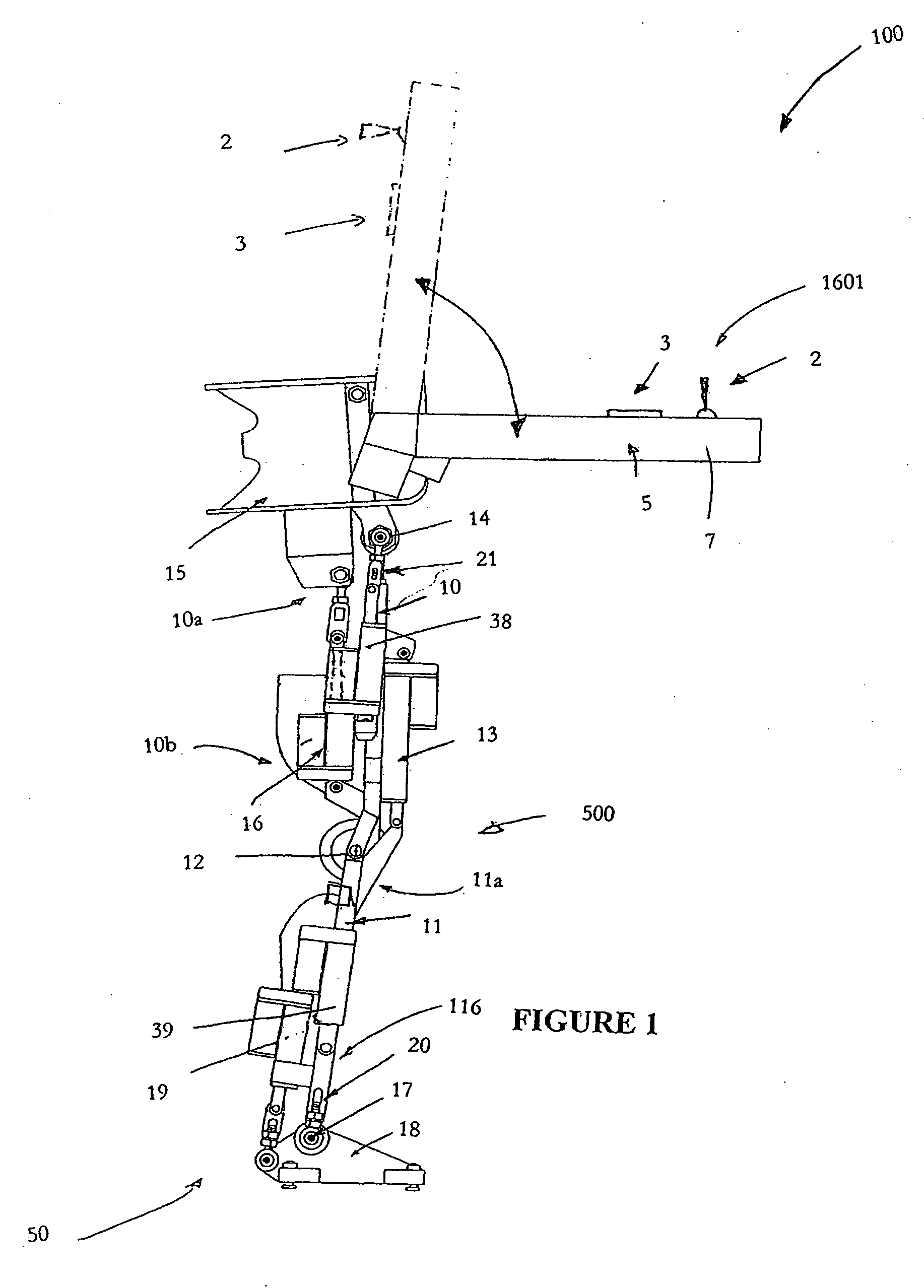
Self contained powered exoskeleton walker for a disabled user
InactiveUS20110066088A1Programme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesPowered exoskeletonControl system
A walker by a mobility impaired disabled user while moving through a set of movements correlating to a walking motion. The walker comprises an exoskeleton, a power source in the form of a battery pack or other similar onboard power pack together with its associated power supply cables, and a control systemThe exoskeleton comprises a rigid pelvic support member including a pelvic harness and a pair of leg structures Each of the leg structures comprise an upper leg structural member, a lower leg structural member, a foot member, a main hip actuator, a knee actuator and a main foot actuator.
Owner:REX BIONICS
Semi-powered lower extremity exoskeleton
The lower extremity exoskeleton comprises two leg supports connectable to person's lower limbs and configured to rest on the ground during their stance phase. Each leg support comprises a thigh link and a shank link; a knee joint configured to allow flexion and extension between the shank link and the thigh link. The lower extremity exoskeleton further comprises an exoskeleton trunk connectable to the person'supper body. The exoskeleton trunk is connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk. Two torque generators are coupled to each of the knee joints. A power unit, capable of providing power, is coupled to the torque generators. In operation when a leg support is in a stance phase and climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit injects power into the respective torque generator thereby extending the respective knee angle. When a leg support is in stance phase and not climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to resist flexion of the respective knee joint. When a leg support is in a swing phase, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to minimize its resistance to knee flexion and extension.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
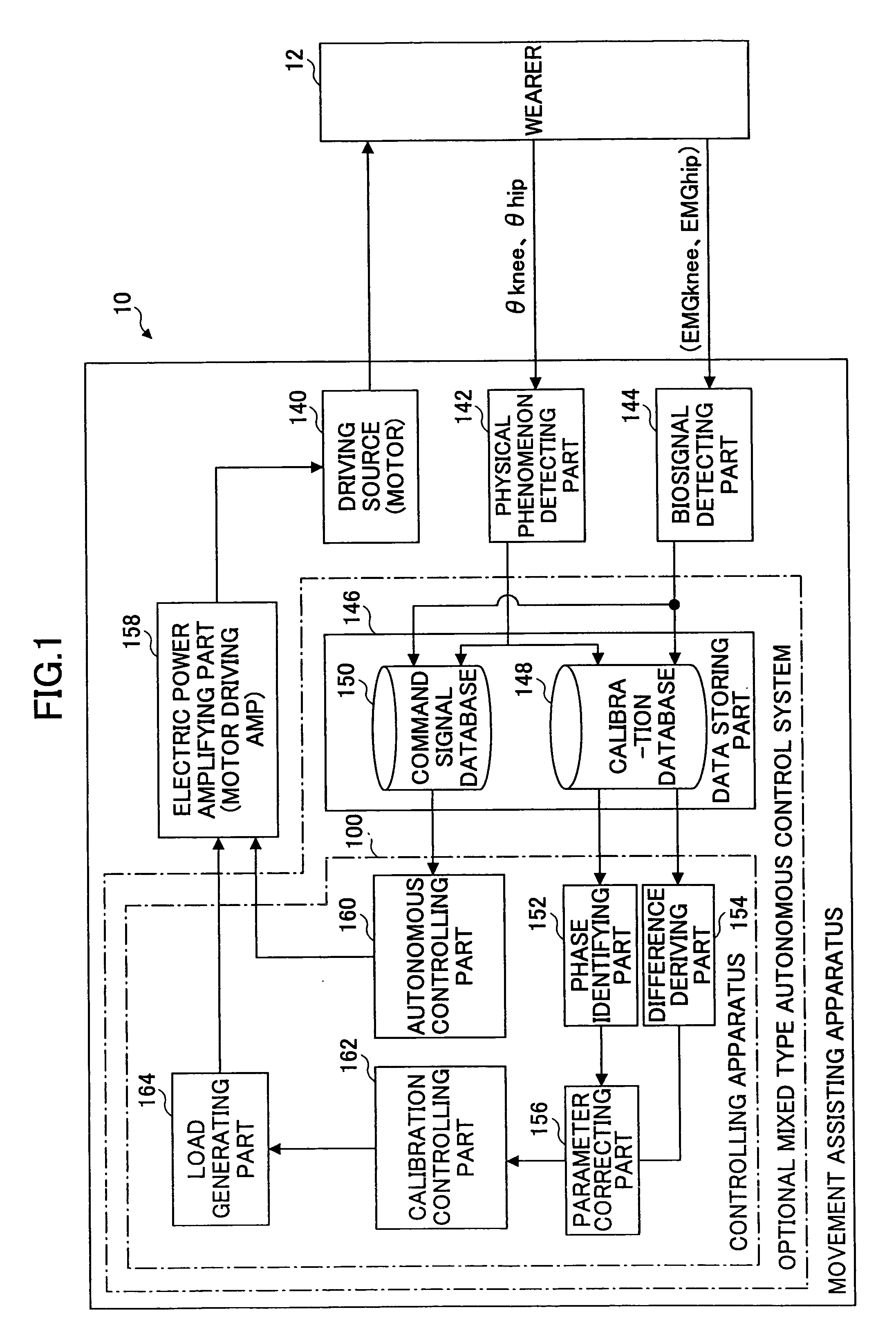
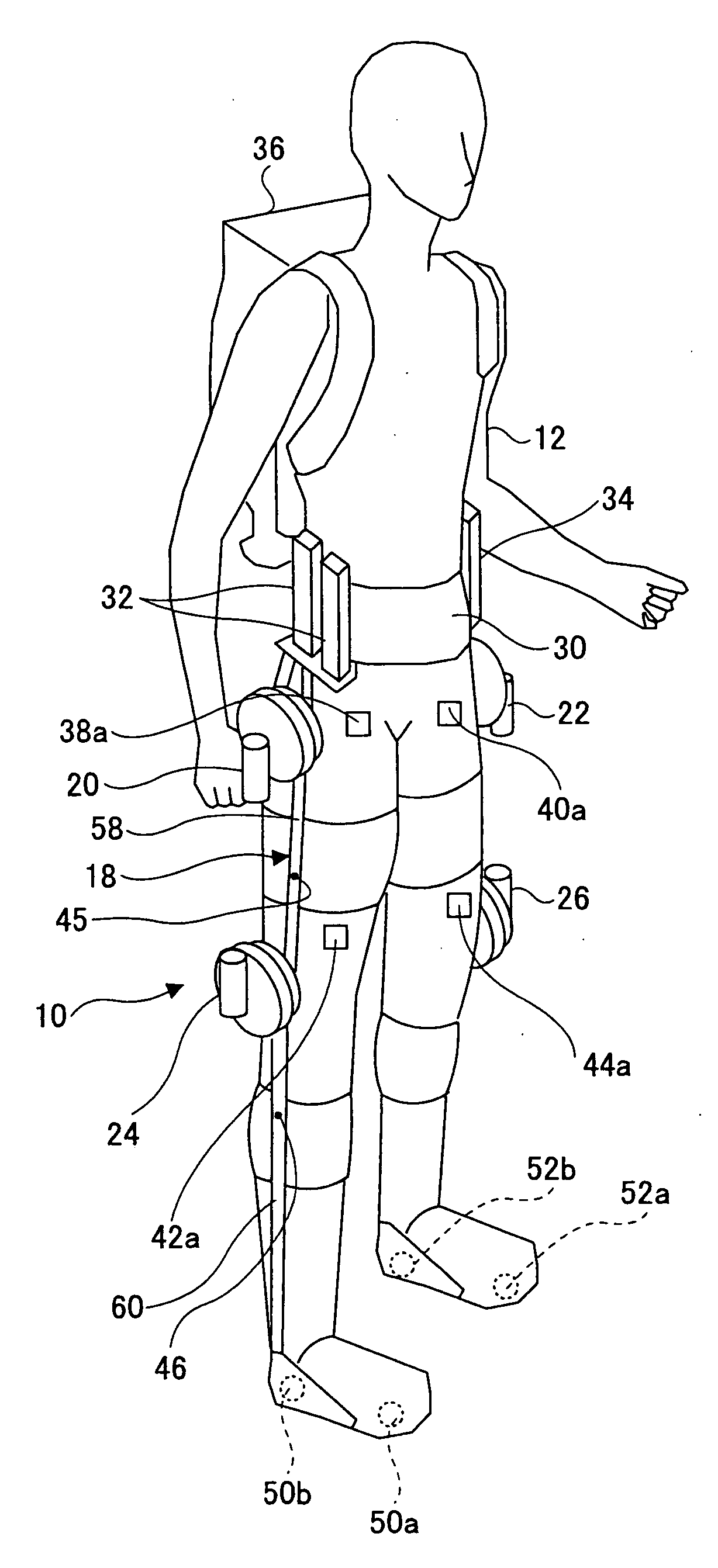
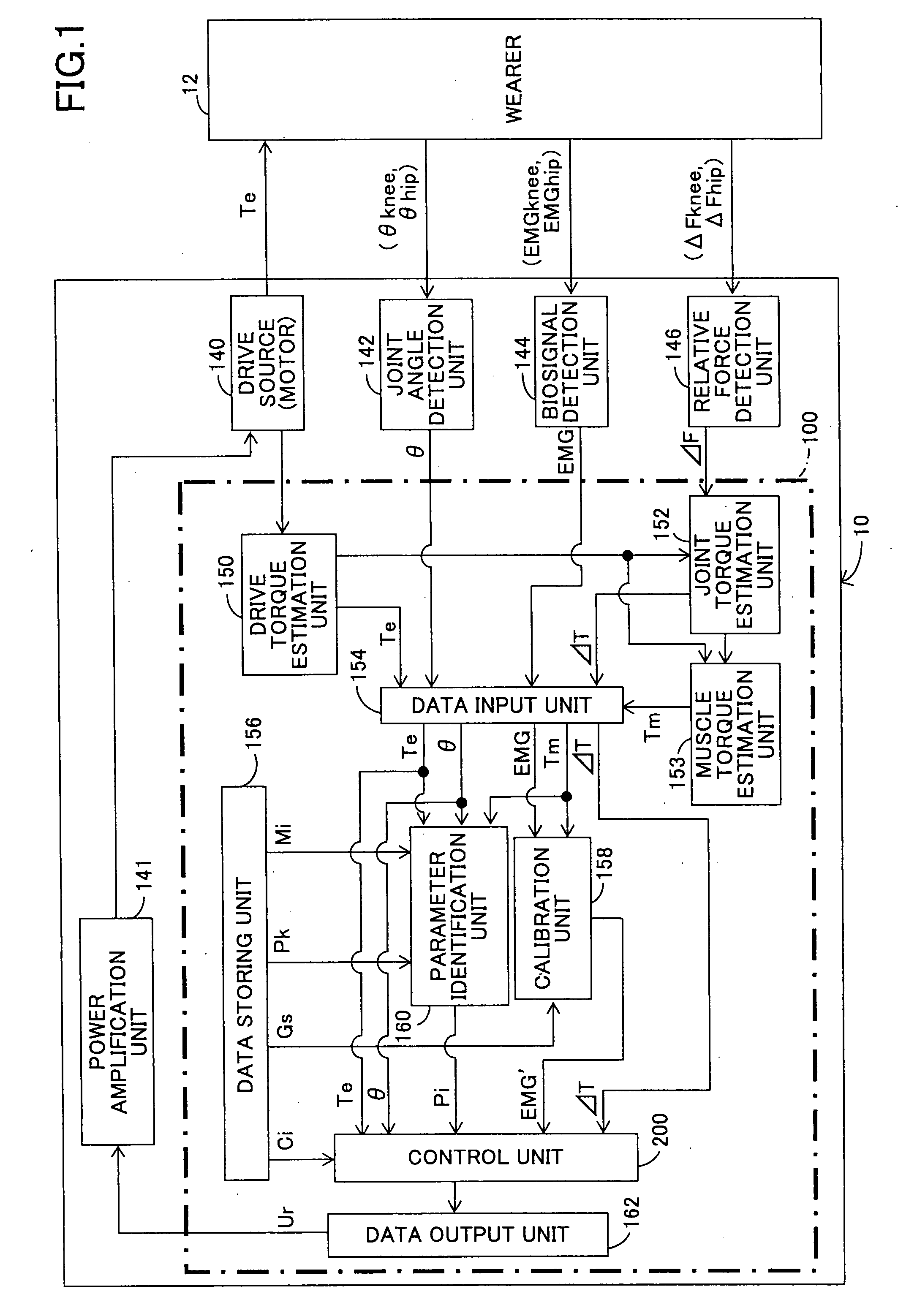
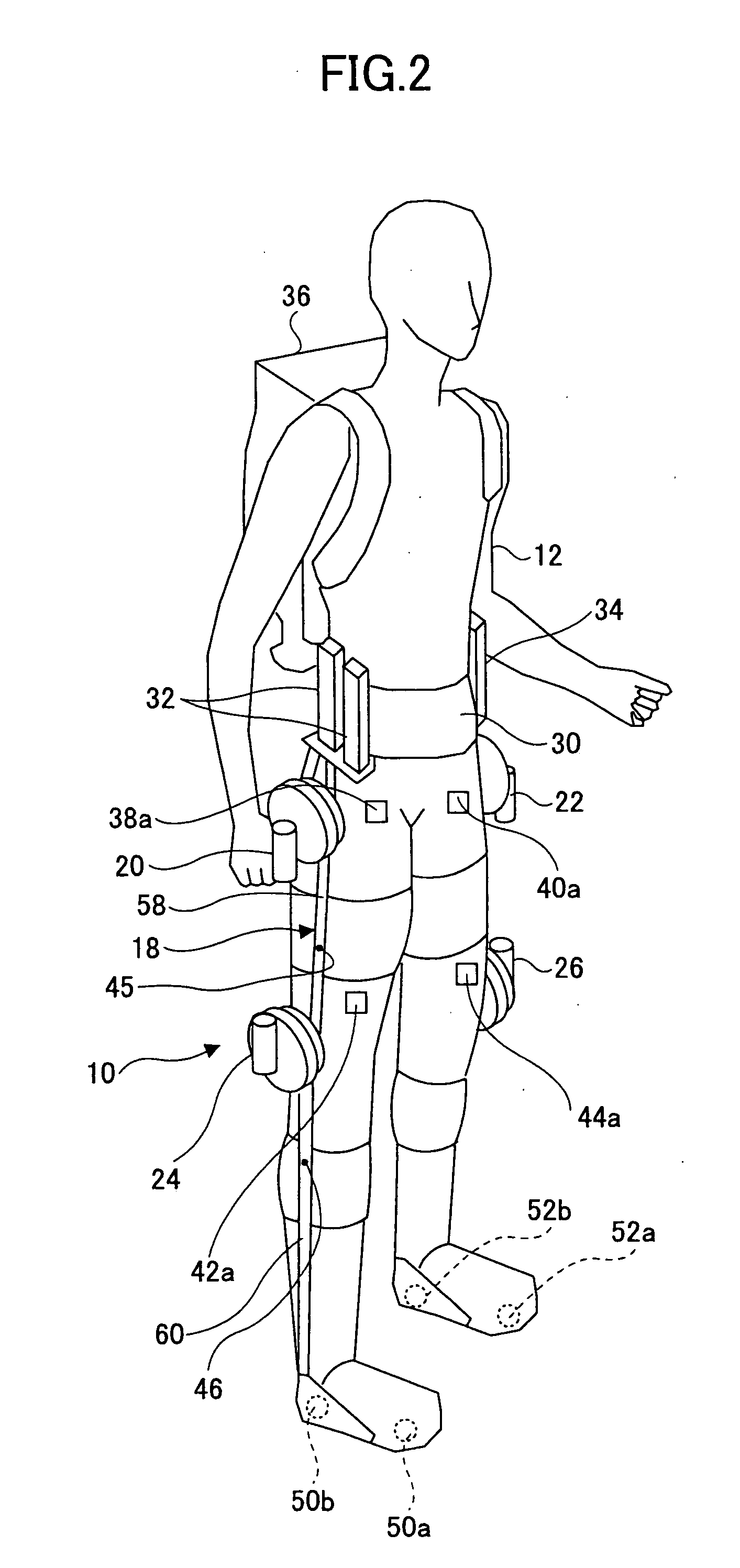
Wearing Type Behavior Help Device, Wearing Type Behavior Help Device Calibration Device, and Calibration Program
ActiveUS20080234608A1Precise applicationReliable typeProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectromyographyEngineeringSkeletal muscle
[Problem to be Solved]The problem to be solved by the present invention is to reduce the load applied to the wearer by correcting a parameter in correspondence with detectivity of biosignals.[Means to Solve Problem]The calibration controlling part 162 of the movement assisting apparatus 10 enables the power amplifying part 158 to apply a driving force of the driving source 140 as a load (input torque) from the load generating part 164 to the wearer 12 when the wearer 12 wears the movement assisting wearing device. Then, the wearer 12 applied with the driving force of the driving source 140 generates power from the skeletal muscles by performing a predetermined calibration operation. Accordingly, the physical phenomenon detecting part 142 detects joint angle along with the calibration operation, and the biosignal detecting part 144 detects myoelectric signals. In the parameter correction part 156, a parameter K is corrected based on the difference between the load (input torque) and the driving force (muscular strength) being calculated by the difference deriving part 154 with respect to the phase identified by the phase identifying part 152.
Owner:TSUKUBA UNIV OF +1
Robotic System for Simulating a Wearable Device and Method of Use
ActiveUS20130158444A1Reduce weightAccurately and rapidly modelProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsRobotic systemsControl system
A robotic system for simulating a wearable device actuation delivery mechanism and the source removed from the actuation delivery mechanism that is linked to the actuation delivery mechanism by at least one cable. A sensing system detects a physiological feature of the subject and, based on feedback from the sensing system, a control system linked to both the sensing system and the actuation source modulates the actuation source, and thereby modulating actuation of the joint of a subject in response to the physiological future sensed by the sensing system. A method for simulating a wearable robotic system employs the robotic system of the invention to thereby provide a model on which to base design of an ambulatory prosthetic for a subject.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Device for providing perception of the physical environment
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG
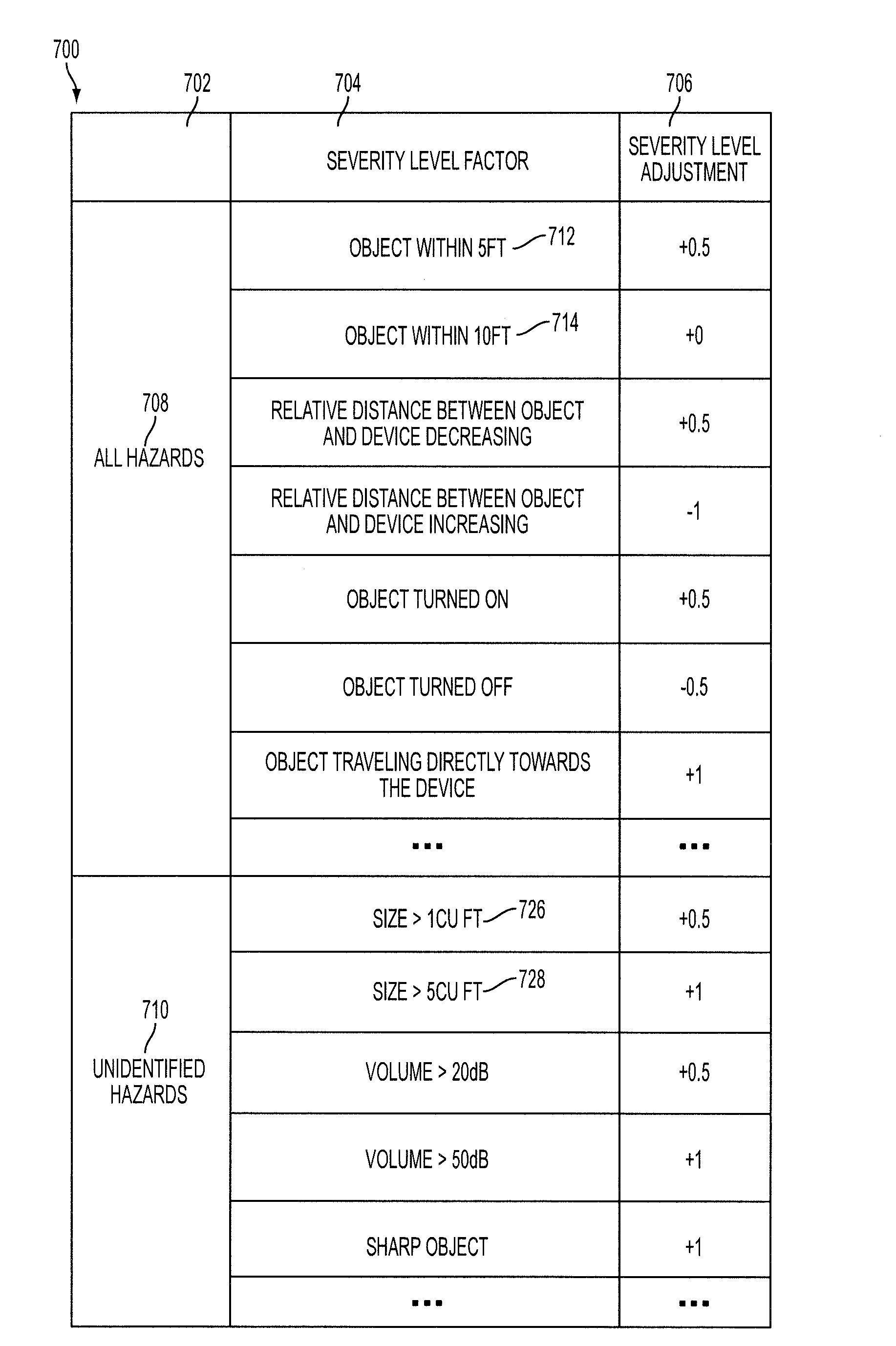
Wearable smart device for hazard detection and warning based on image and audio data
ActiveUS20160210834A1Television system detailsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsHazard potentialEmbedded system
A wearable smart device for providing hazard warning information to a user. The wearable smart device includes a microphone configured to detect audio data associated with a potential hazard. The wearable smart device also includes a camera configured to detect image data associated with the potential hazard. The wearable smart device also includes a processor coupled to the microphone and the camera and configured to determine whether the potential hazard presents a real hazard based on the detected audio data and the detected image data.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Exoskeleton for gait assistance and rehabilitation
A method of operating an exoskeleton device includes: receiving sensor information; connecting a clutch system to a pulley system in; determining whether to engage a drive train gear to the clutch system based on the sensor information; engaging the drive train gear through the clutch system when determined to engage the drive train gear; and powering a first motor to drive the drive train gear for controlling a joint or segment of exoskeleton device.
Owner:LEONIS MEDICAL CORP
Wearable lower limb exoskeleton device
InactiveCN101589983AImprove consistencySmall coaxialityWalking aidsInvalid friendly devicesHuman bodyKnee Joint
The invention discloses a wearable lower limb exoskeleton device, which comprises a waist supporting frame, a waist object carrier, an adjustable hip mechanism, a connecting rod adjustable knee joint mechanism, a connecting rod adjustable ankle joint mechanism, pressure detection shoes, a leg connecting rod, a constraint part and various connecting pieces. Both lower limbs have twelve rotational freedoms, the single lower limb has six degrees of freedom respectively, a hip has two degrees of freedom which finish bending and stretching as well as adduction and abduction movements of a hip joint, two joint axes always intersects at the center of the hip joint of a human body through the adjustment of the hip mechanism, and a knee joint has one degree of freedom which is coaxial with the knee joint of the human body and corresponds to the bending and stretching movement of the knee joint of the human body; and an ankle joint has three degrees of freedom. The device has good consistency of the movement of the hip joint and the movement of the human body during the walking of people; human-machine knee joints have small coaxality and position deviation; and the ankle joint has a compact structure. The device can be used for strengthening the abilities of walking with load and walking for a long time of wearers and detecting walking information of the wearers, and can also be used for helping people with slight obstacle of lower limb movement to normally walk and gradually rehabilitate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
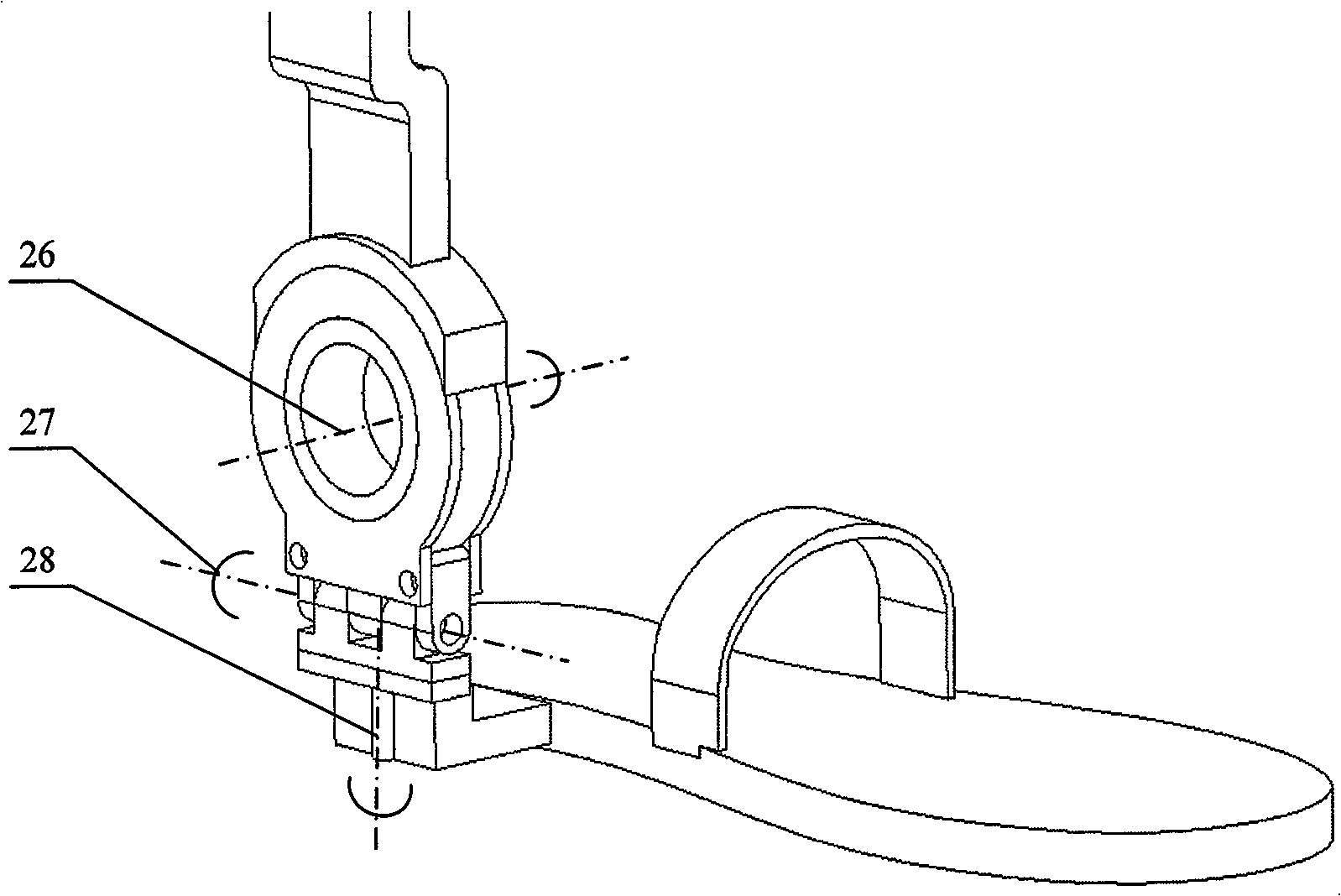
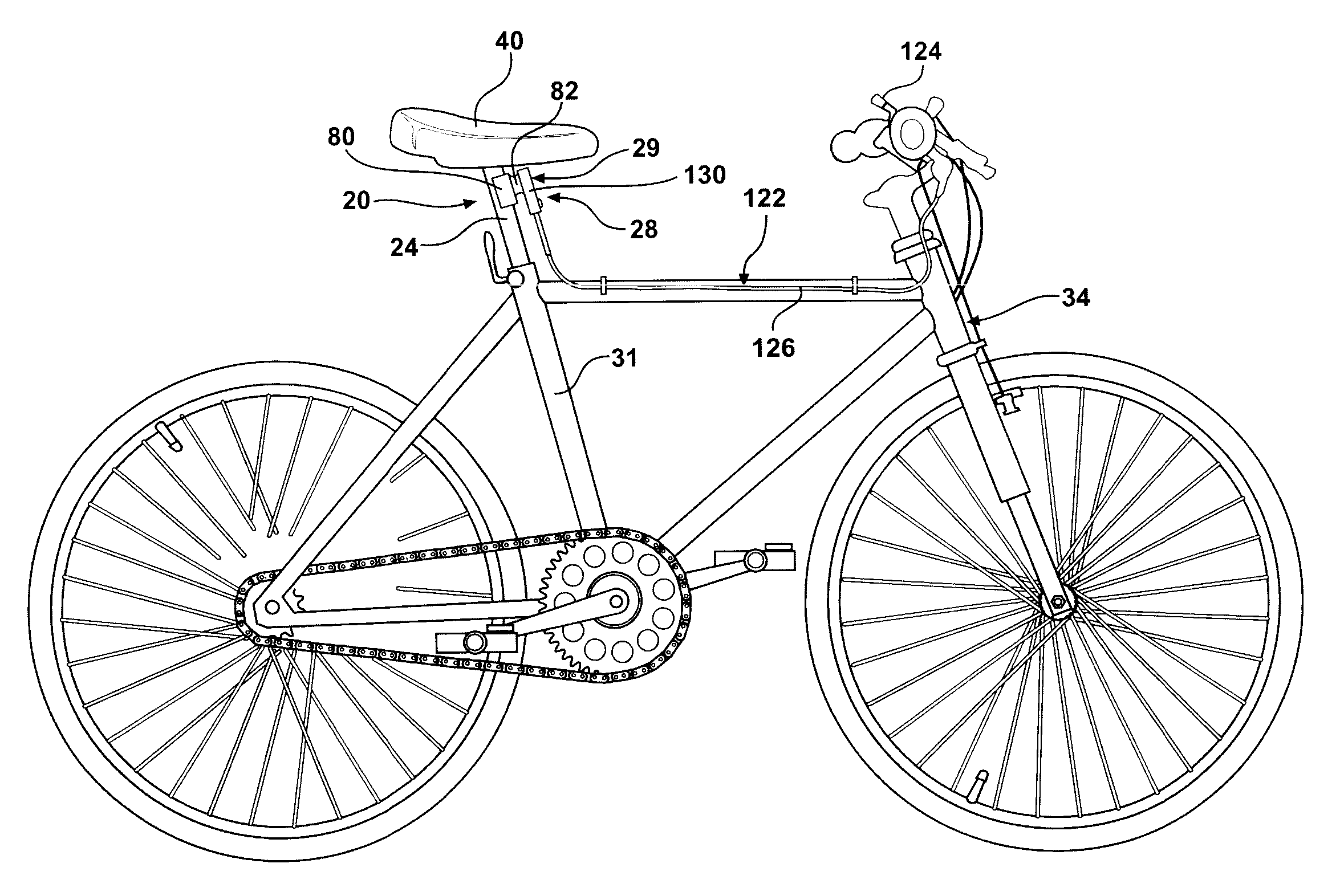
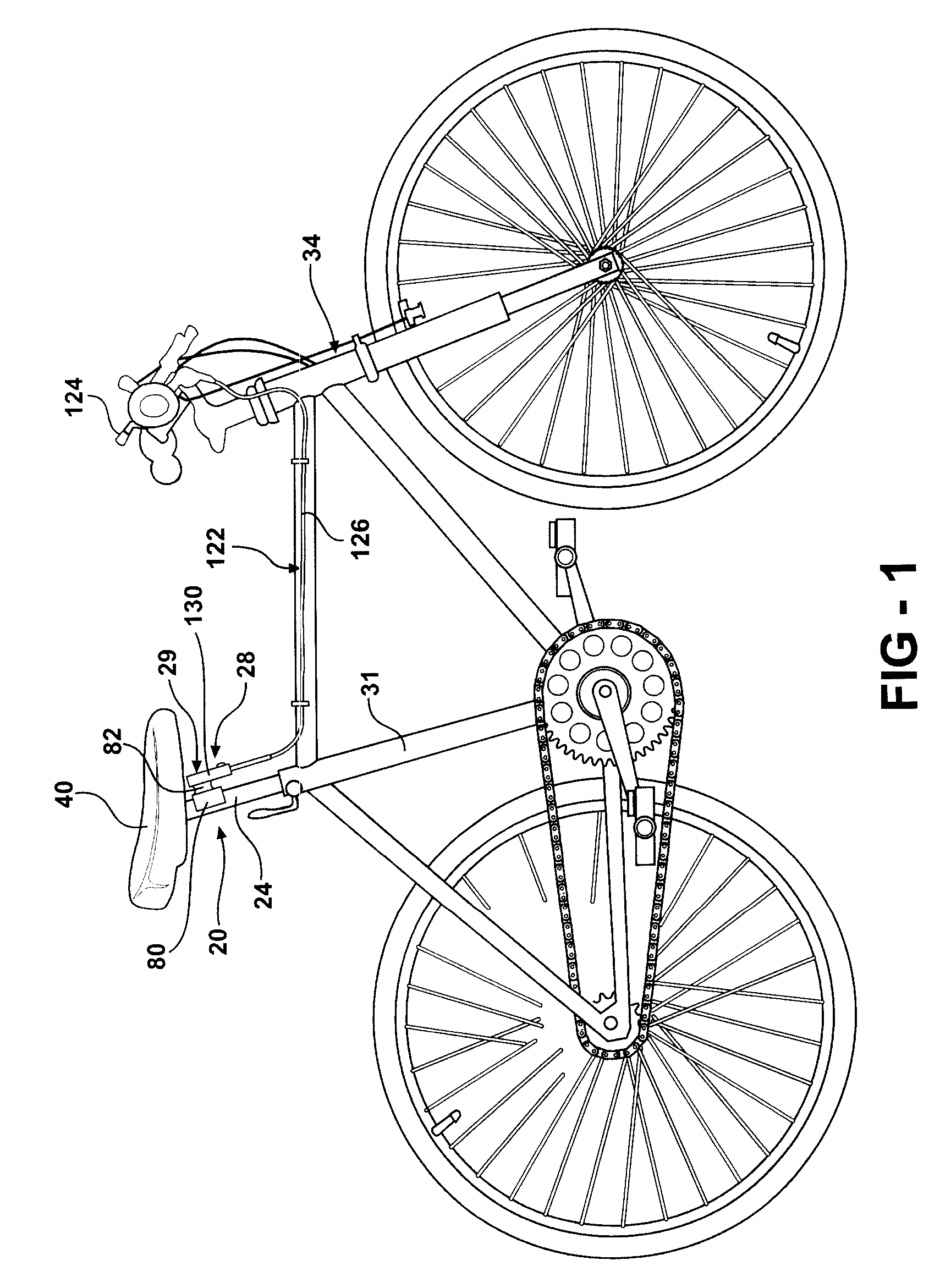
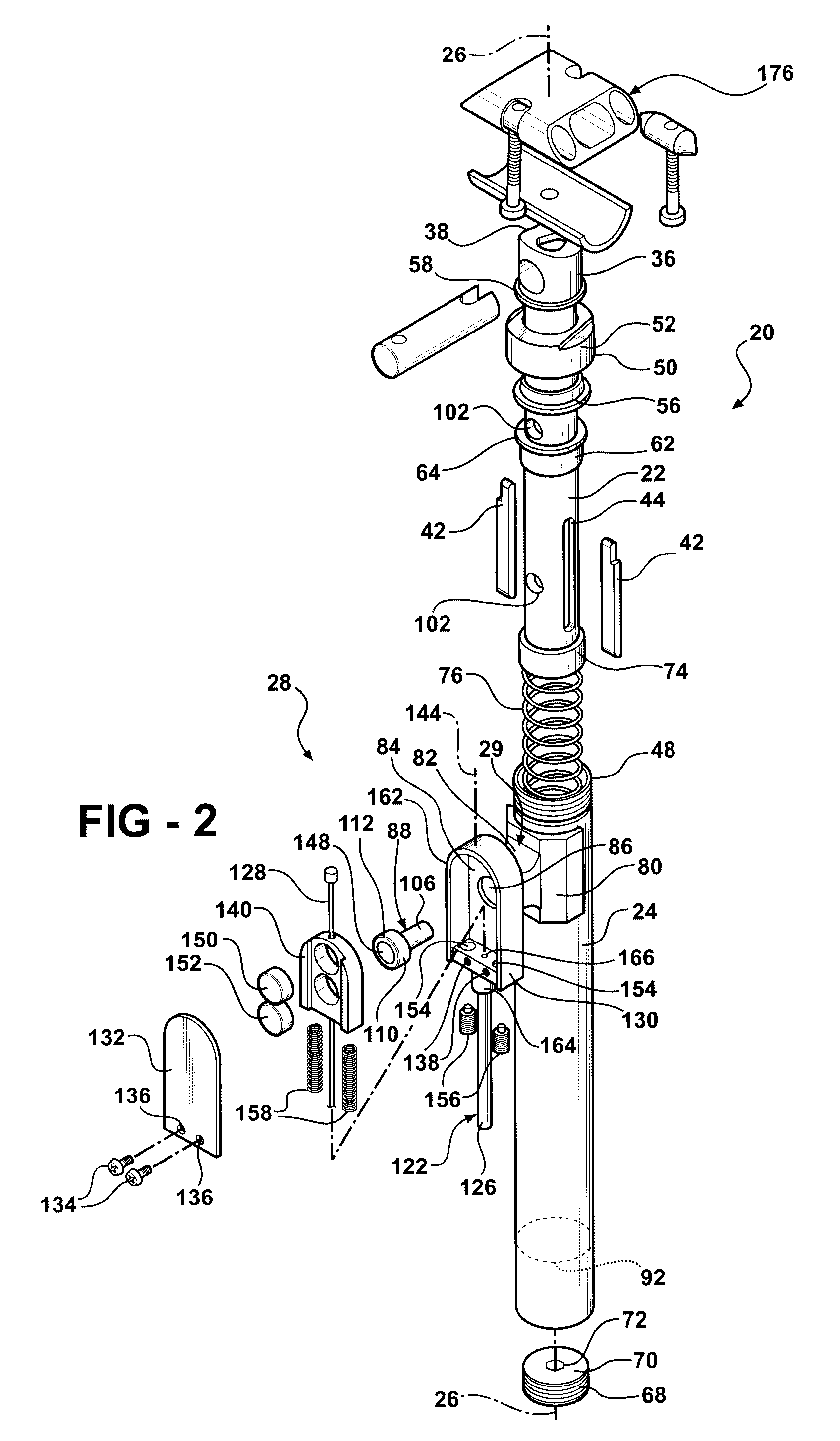
Adjustable Bicycle Seat Post Assembly
InactiveUS20060175792A1Enhanced bicycle experienceEasy to handlePassenger cyclesWheel based transmissionCouplingLocking mechanism
An adjustable-height bicycle seat post assembly comprises a hollow seat post for supporting a bicycle seat slidably on plastic guides or shims inside a hollow tube. The hollow tube clamps into the frame of a bicycle. A mainspring forces the post upward, but a locking mechanism interconnects the post with the tube in various fixed positions relative to the tube. The locking mechanism includes a housing, which supports a plunger for reciprocating movement into and out of engagement with holes on the post. The locking mechanism is affixed to the outside of the tube to bear shearing forces on the plunger. An endcap on the locking mechanism and a topcap on the tube protect the assembly from foreign debris. The locking mechanism may be manipulated remotely using a magnetic switch assembly or manually using a mechanical assembly. A lost motion coupling is integrated into the locking mechanism and / or actuator assembly to enable the remote actuator to be moved or deployed while the latch remains trapped under the influence of a dominant shear load. The lost motion coupling is also effective to allow an operator to deploy the remote actuator at any convenient time prior to a desired change in seat height.
Owner:KIMIR SEATPOST
Wearing-Type Motion Assistance Device and Program for Control
ActiveUS20080161937A1Sufficient effect in conformityAvoid it happening againProgramme-controlled manipulatorGymnastic exercisingEngineeringParametric identification
A motion assistance device has a biological signal detection means for detecting a biological signal from the wearer of the device; a motion assistance device installation member having a drive source for applying torque acting to the wearer by use of each joint of the wearer as a rotating shaft; a control means for controlling the drive source to generate torque corresponding to the biological signal detected by the biological signal detection mean; a drive torque estimation means for estimating the drive torque generated by the drive source; a joint angle detection means for detecting angular displacement of a joint; and a parameter identification means for substituting the drive torque estimated by the drive torque estimation means and the angular displacement detected by the joint angle detection means into an equation of motion to specify the wearer-specific dynamics parameter, the equation relating to the entire system and including wearer-specific dynamics parameter. The control means controls the drive source according to a predetermined control method, based on the equation of motion into which the dynamics parameter identified by the parameter identification means is substituted.
Owner:CYBERDYNE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com