Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5720results about How to "Comfortable to wear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
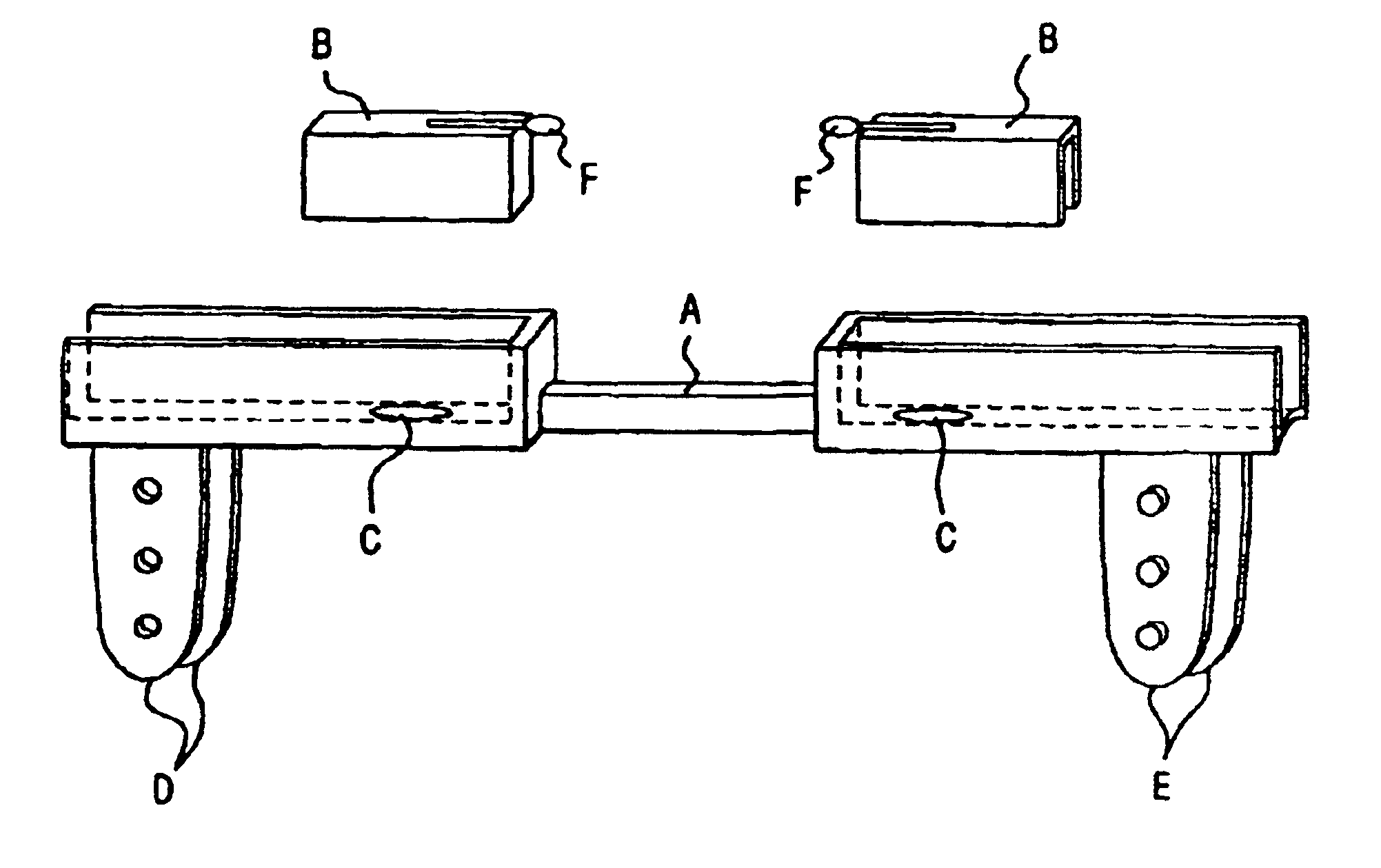
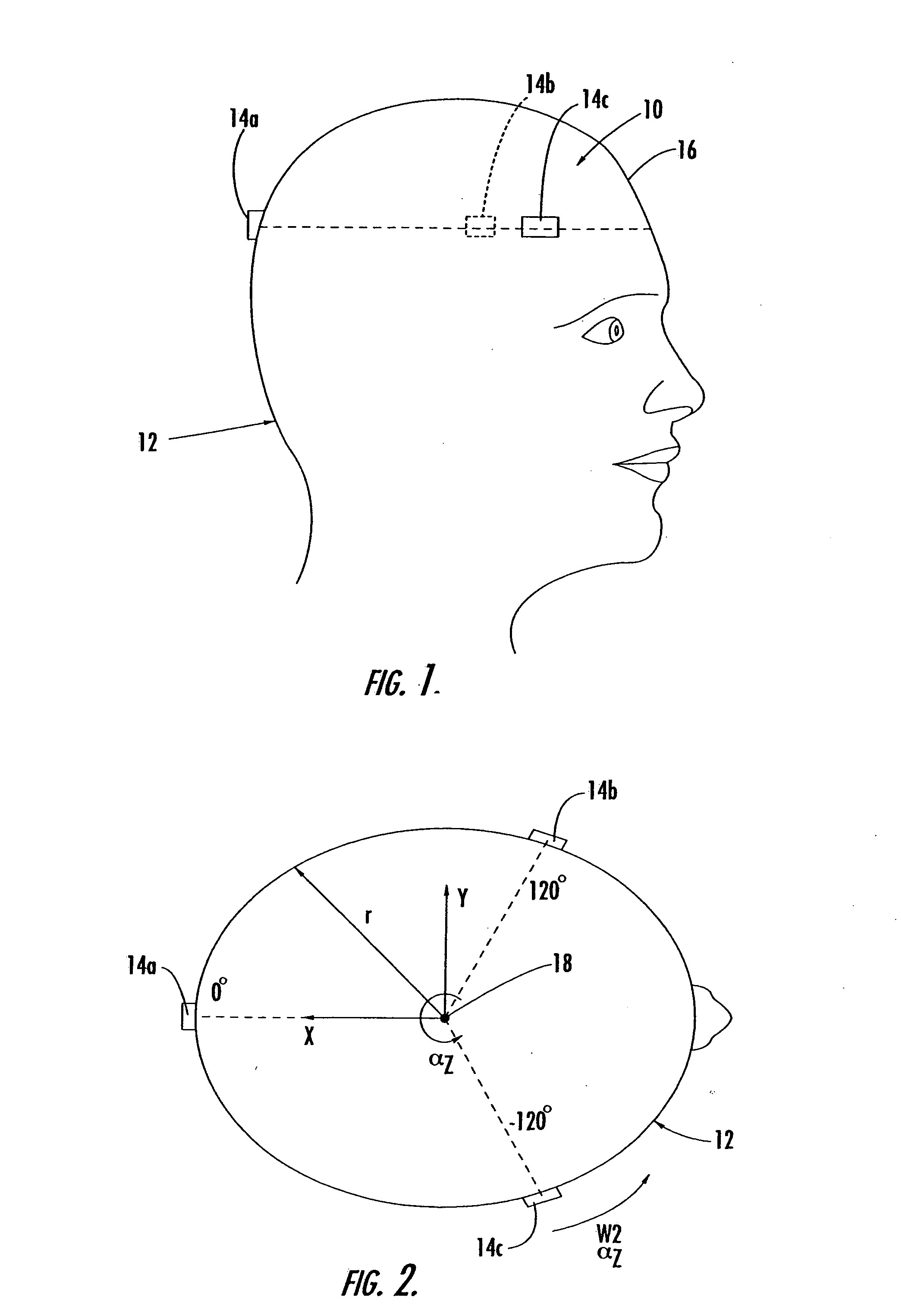
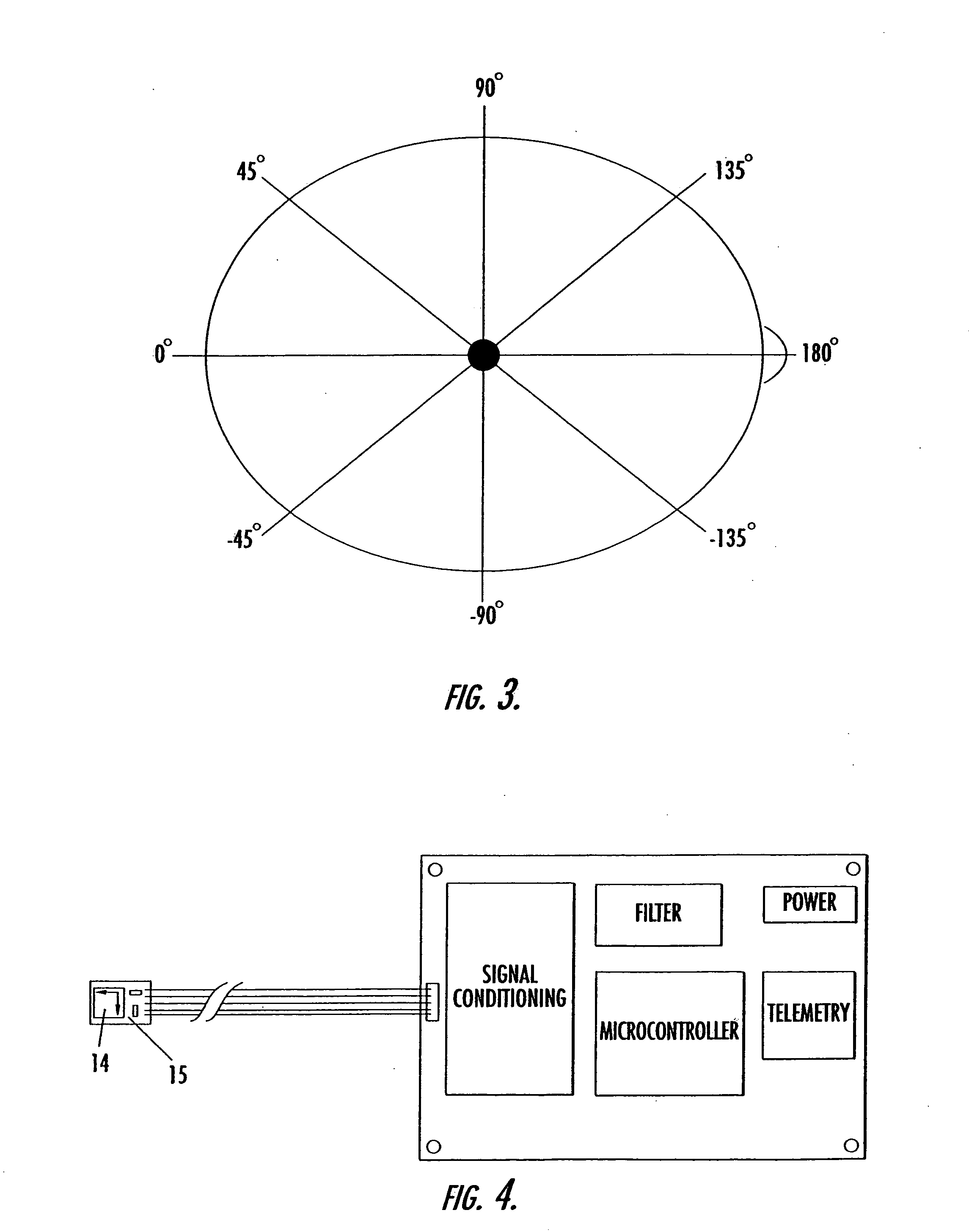
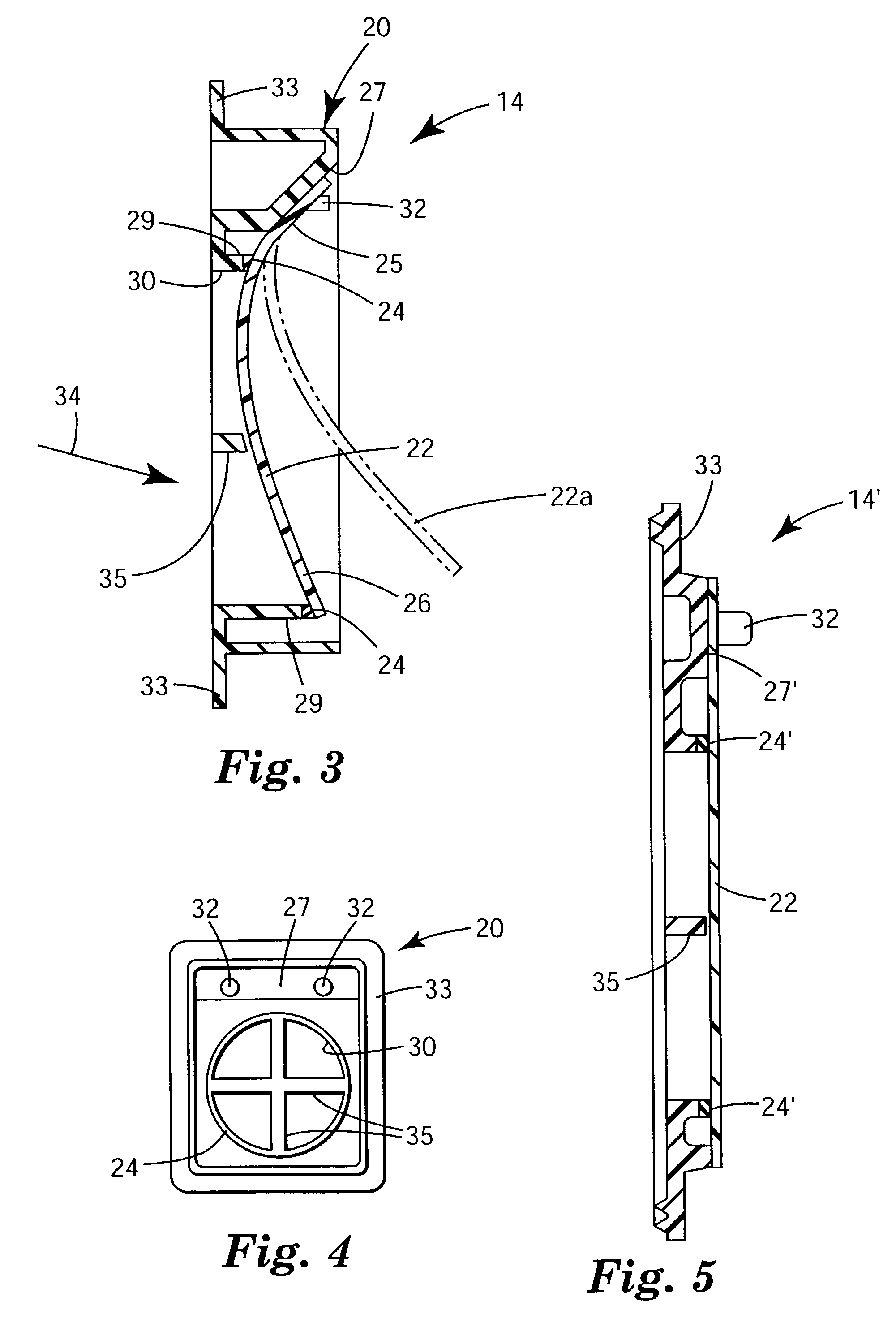
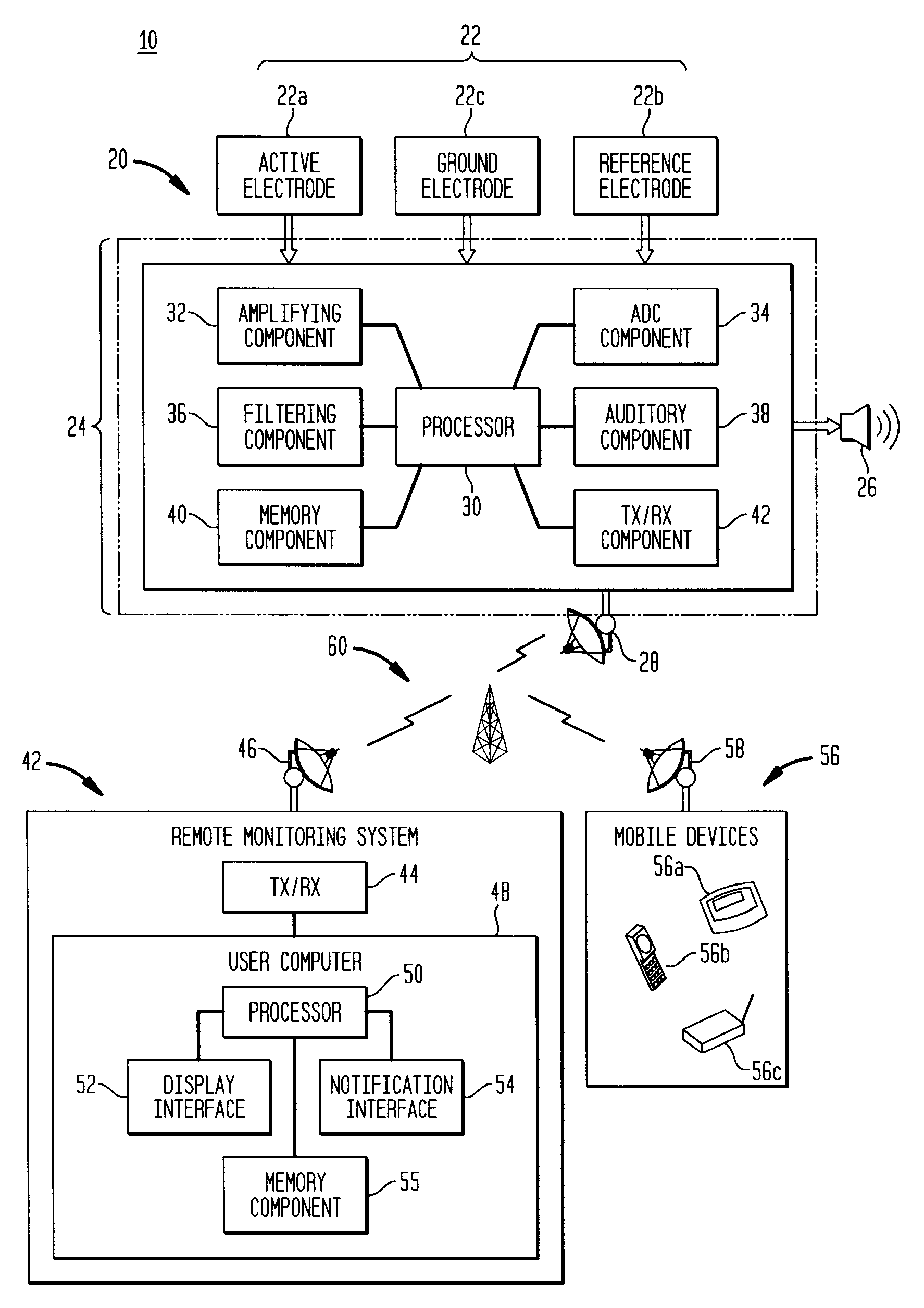
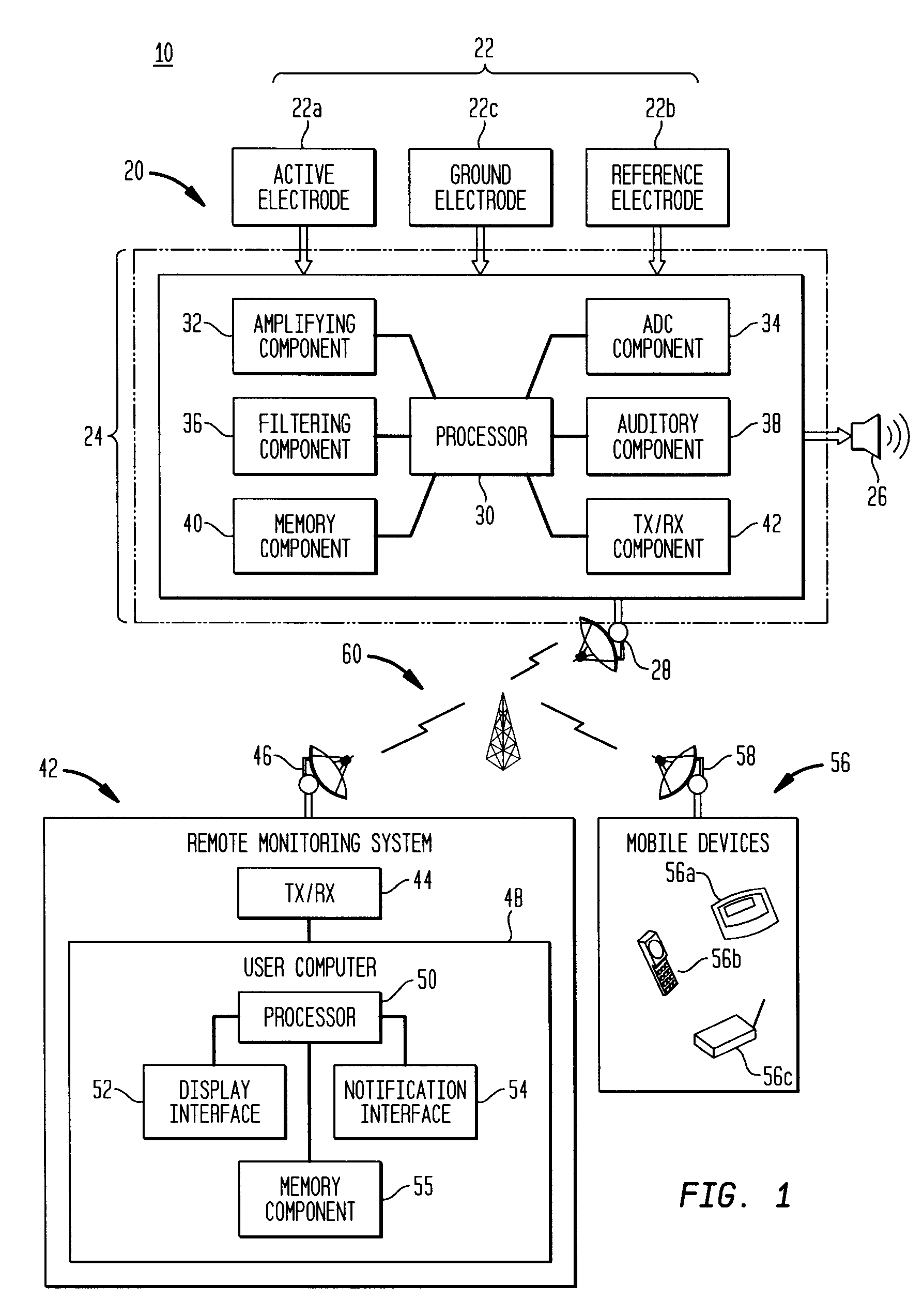
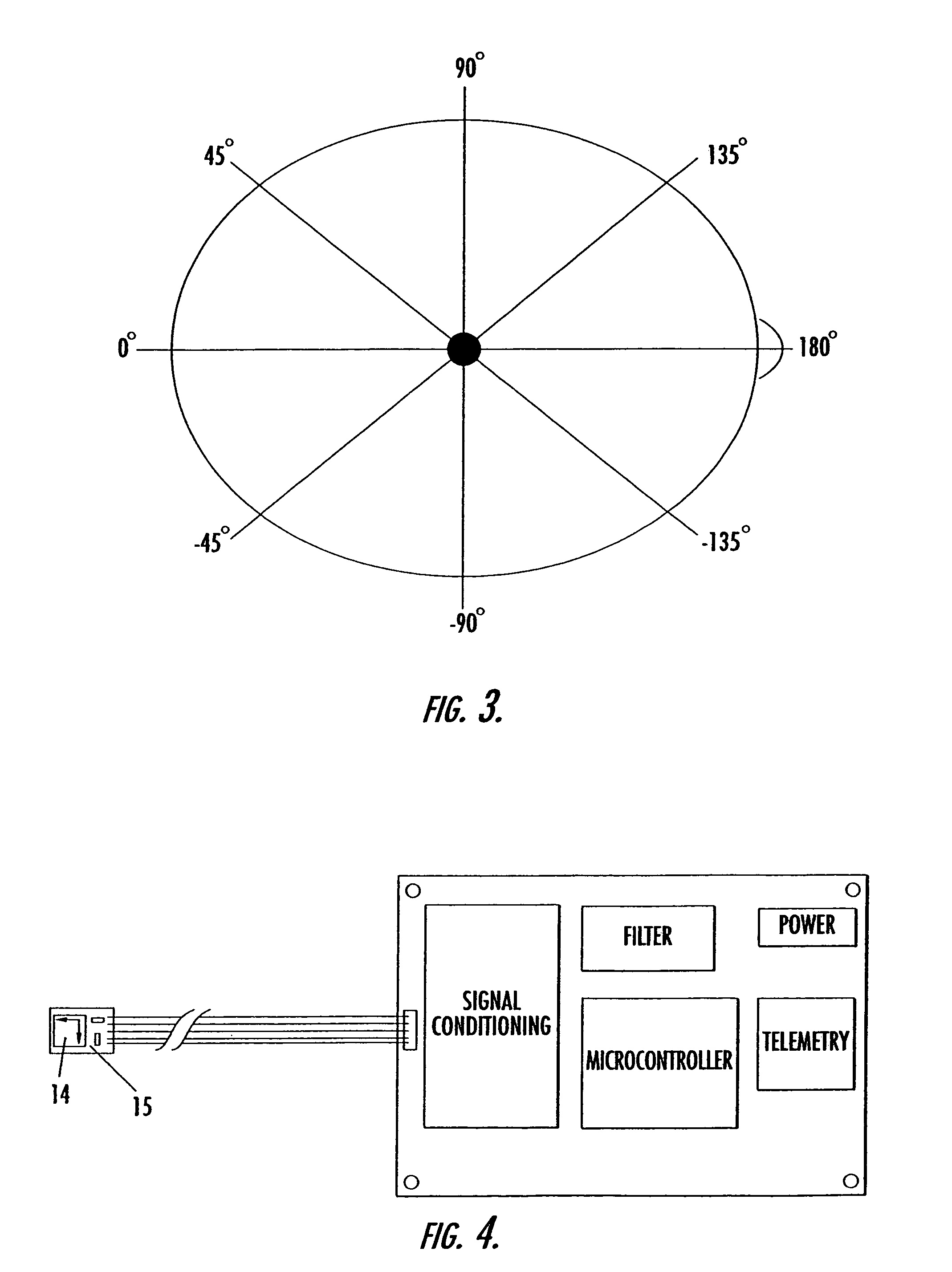
Universal modular pulse oximeter probe for use with reusable and disposable patient attachment devices
InactiveUSRE41317E1Easy to transportImprove fitDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiomedical engineeringPulse oxymetry
A system and method of standardizing modular probe housings so that the standardized probe housings may be incorporated into probes adapted to work with at least one of a multiplicity of manufacturers' oximeters. The probe housings are adapted to matingly engage at least a disposable bandage apparatus and a reusable finger attachment device.A pulse oximeter system comprises a finger attachment device having first and second probe couplers, the first and second probe couplers are configured to be matingly engageable with probe housings of a pulse oximeter probe.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
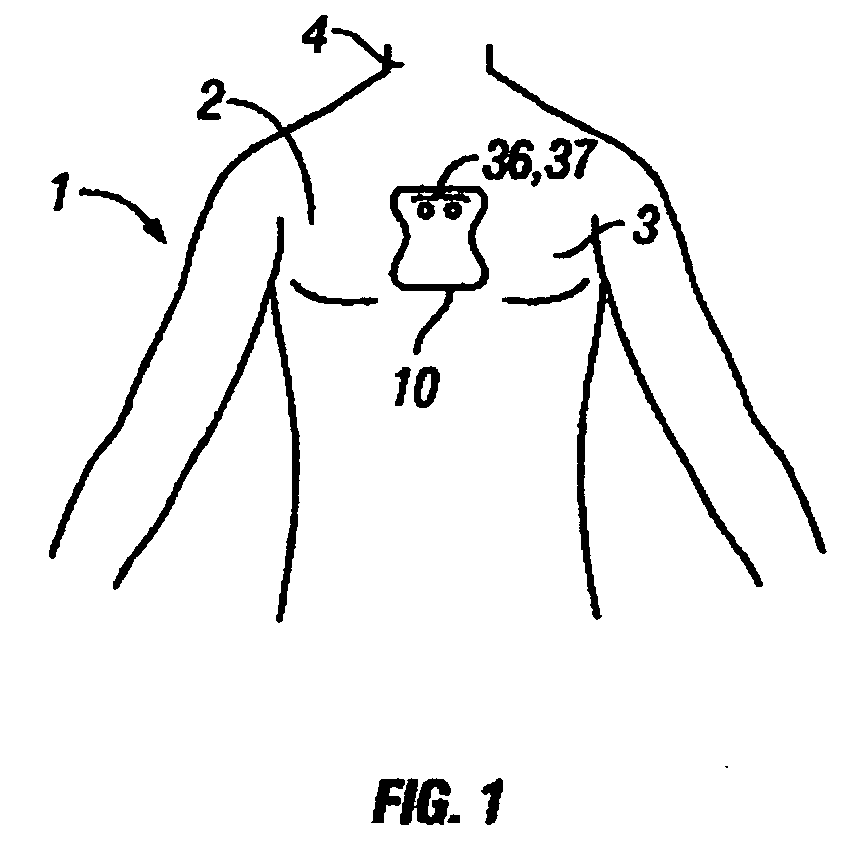
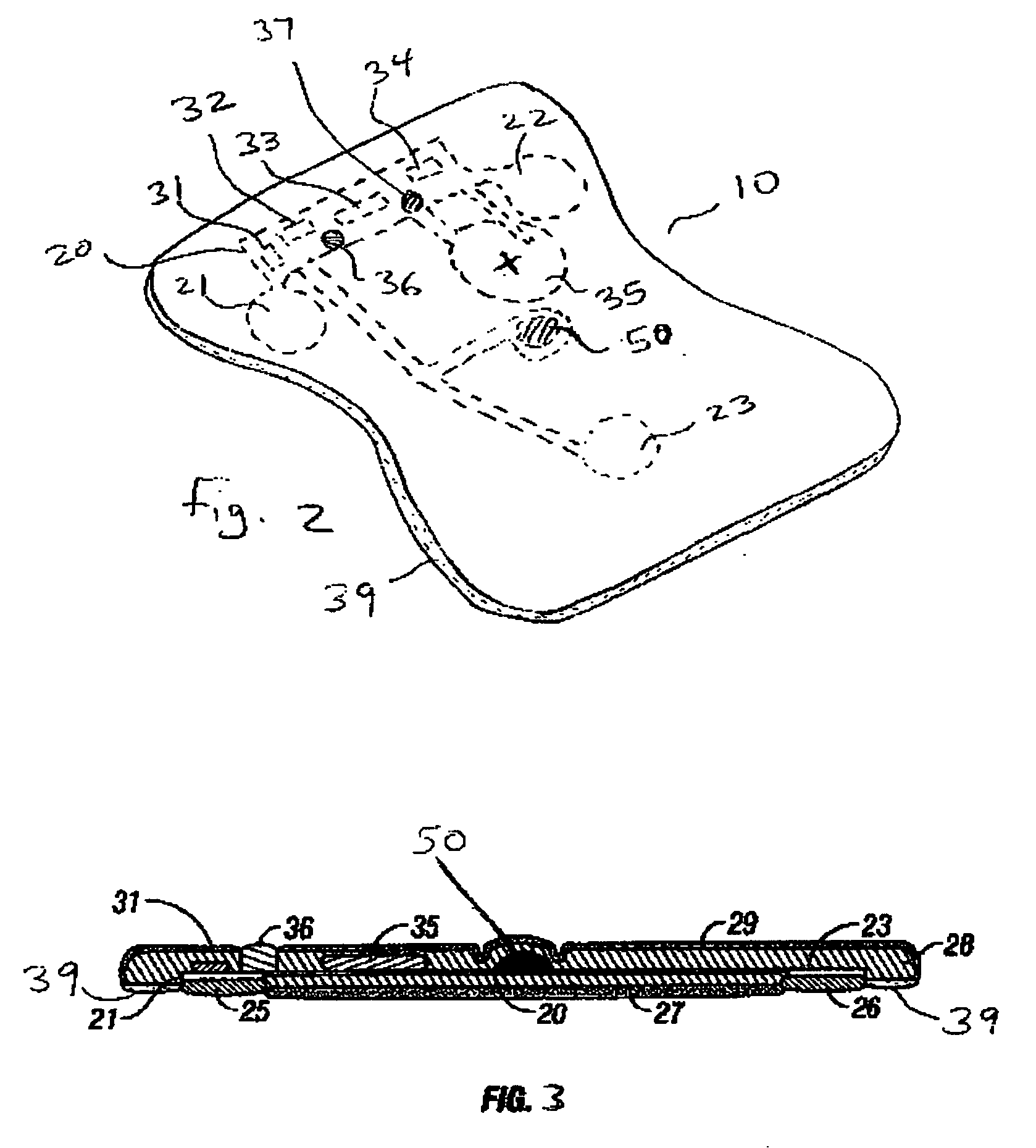
Disposable extended wear heart monitor patch
InactiveUS20060224072A1Easy diagnosisMinimizing contaminationElectrocardiographySensorsWireless transmissionNon invasive
The invention provides a disposable sensor patch for non-invasive monitoring and recording of infrequent cardiac events. The patch is thin and flexible for comfortable wear on the person's chest for automatic analysis and recording of ECG. The patch is inexpensive and simple for self-administration. The patch incorporates a battery, ECG amplifier, and a processor for analyzing ECG waveform and recording events. A software algorithm searches for a cardiac abnormality. The patch is designed for continuous long-term wear exceeding 3 days for diagnostic monitoring and exceeding 14 days for event detection. In one embodiment a preformatted report is automatically generated by the patch for wireless transmission to a reporting device such as a generic printer or a wireless network system. The patch may also incorporate a marker switch to correlate recorded ECG data with the patient's perception of a cardiac event.
Owner:CARDIOVU
Portable wound treatment apparatus
A portable wound treatment apparatus, for stimulating the healing of superficial wounds, comprises a housing containing a suction pump and a canister for containing fluids drawn from the wound. The housing is supported on a harness or belt worn by the patient. The canister is connected to a porous wound dressing at the wound site via a plurality of tubes, a multi-lumen tube or a combination thereof. A rechargeable battery pack may be incorporated within the housing or externally thereto. The external battery pack may be shaped to balance the housing on the harness or belt. Pressure transducers are provided to monitor and report pressures at the wound site or internal to the canister. Monitored pressures may also be utilized to determine the filled state of the canister and, thereafter, either report this state to the operator or automatically discontinue suction from the wound, or both.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
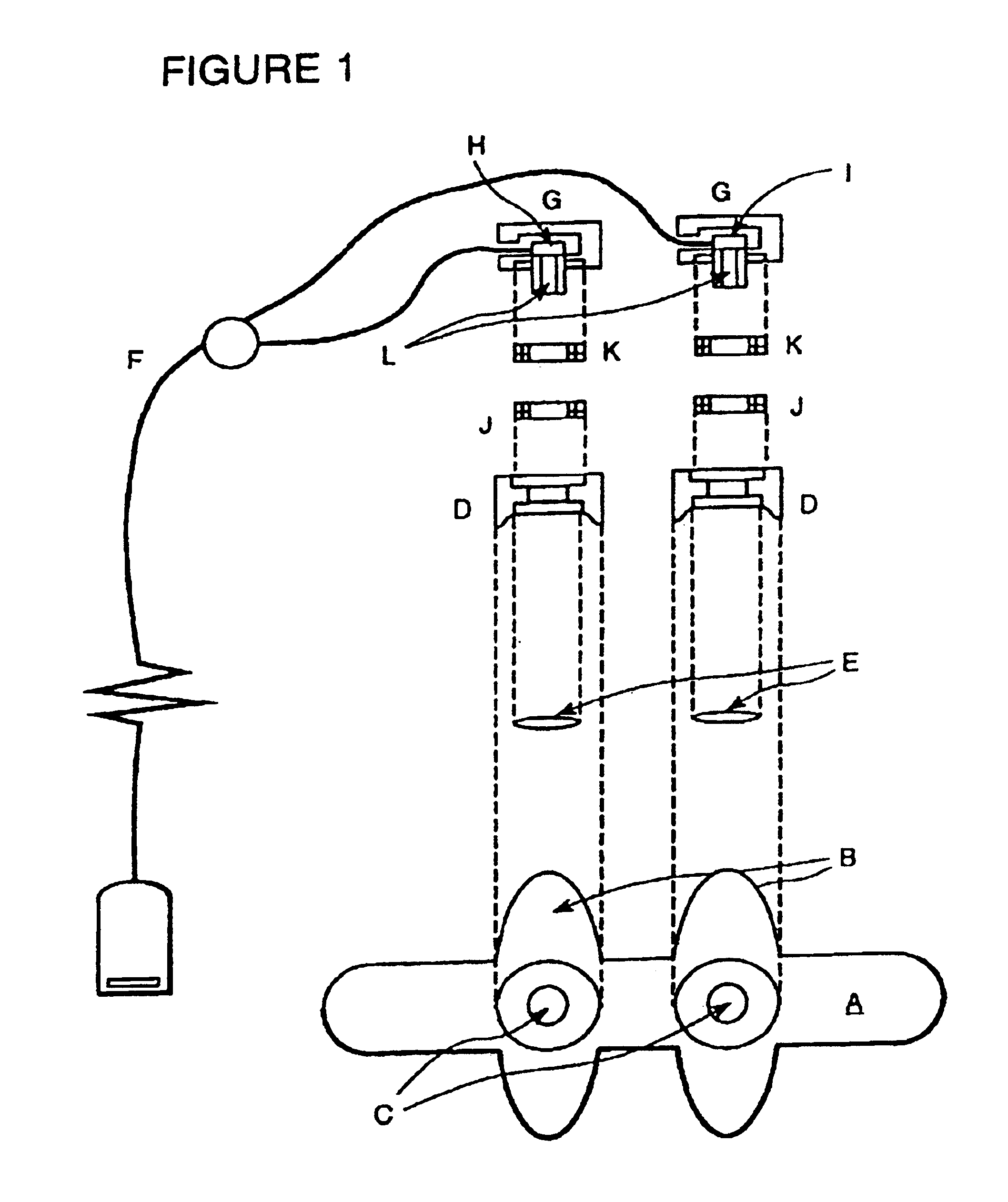
Monitoring device with an accelerometer, method and system
ActiveUS8172761B1Light weightComfortable to wearCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerPhotodetector
A monitoring device for monitoring the vital signs of a user is disclosed herein. The monitoring device is preferably comprises an article, an optical sensor, an accelerometer and processor. The optical sensor preferably comprises a photodetector and a plurality of light emitting diodes. A sensor signal from the optical sensor is processed with a filtered accelerometer output signal from the accelerometer to create a filtered vital sign signal used to generate a real-time vital sign for a user.
Owner:FRX POLYMERS LLC +1
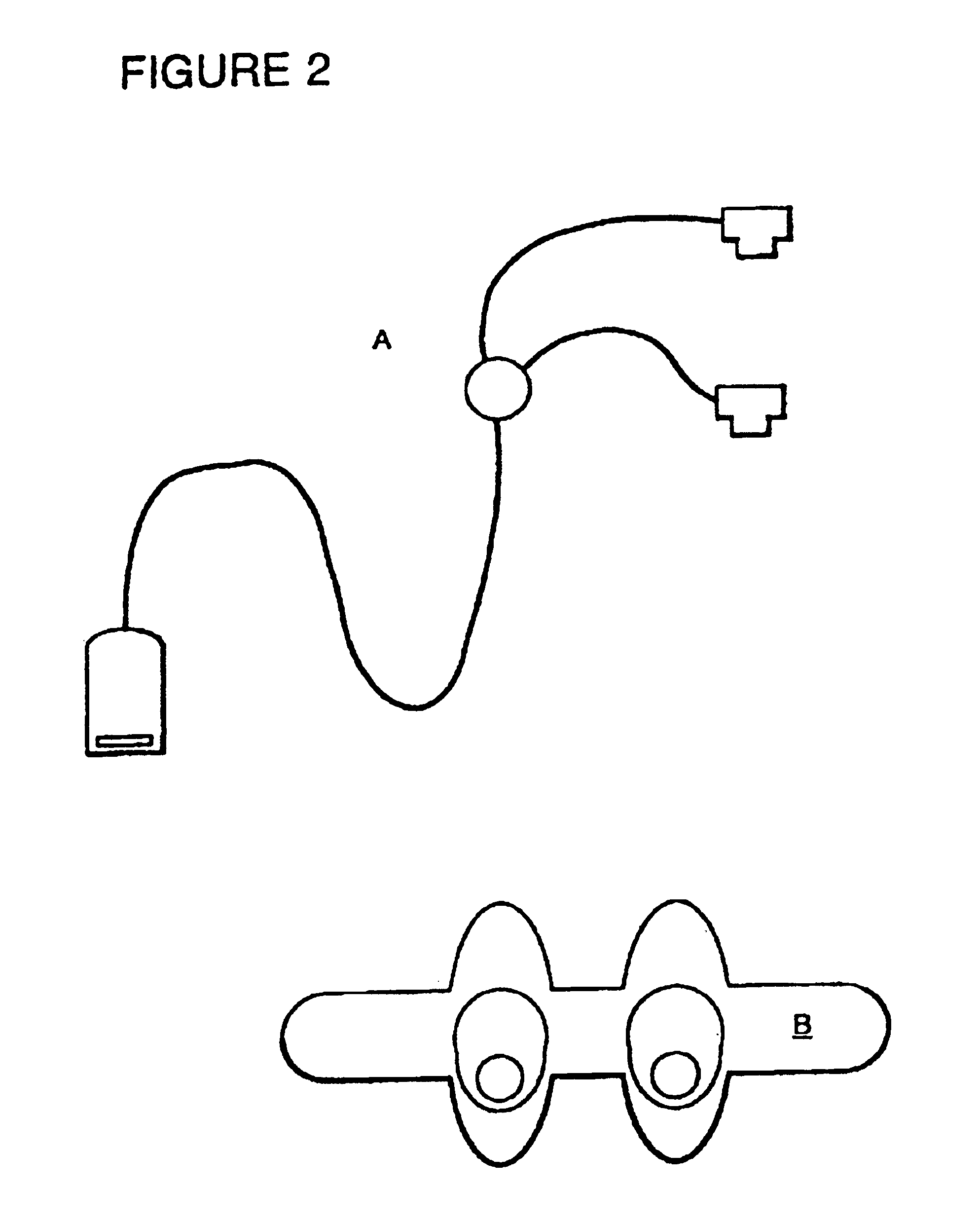
Monitoring device, method and system
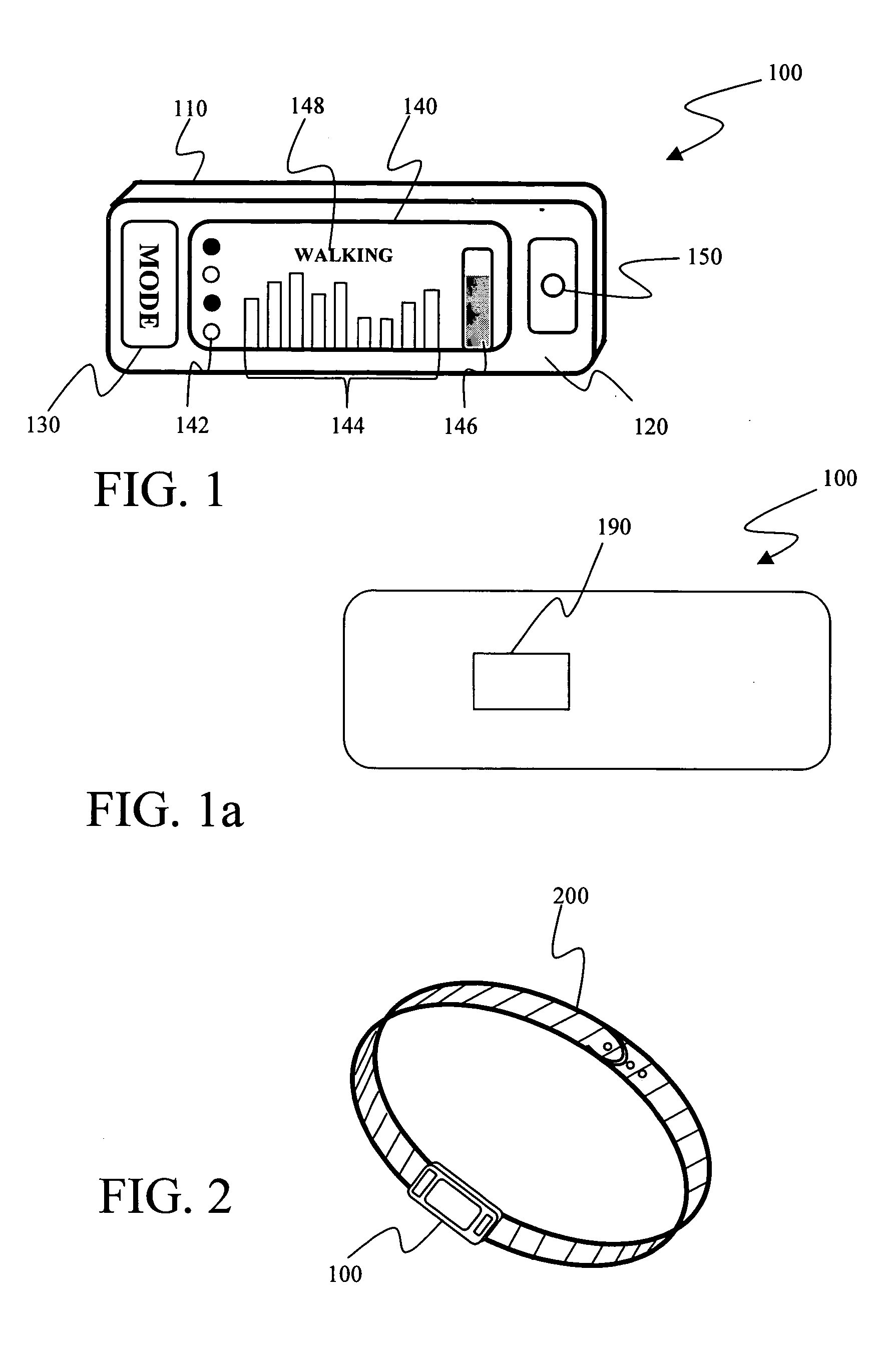
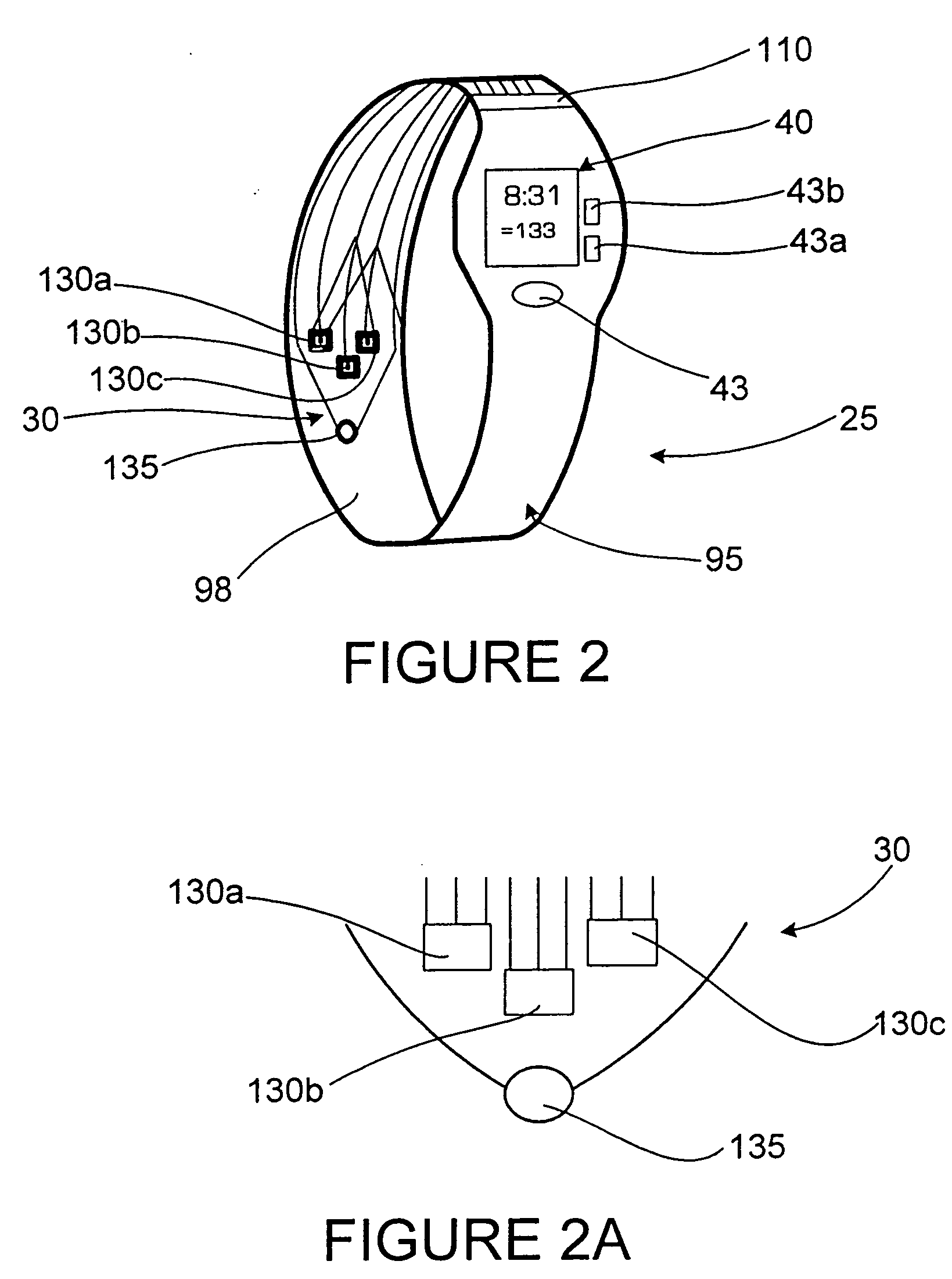
InactiveUS20060253010A1Light weightExpand the amount of informationTime-pieces with integrated devicesSensorsBlood oxygenationPulse rate
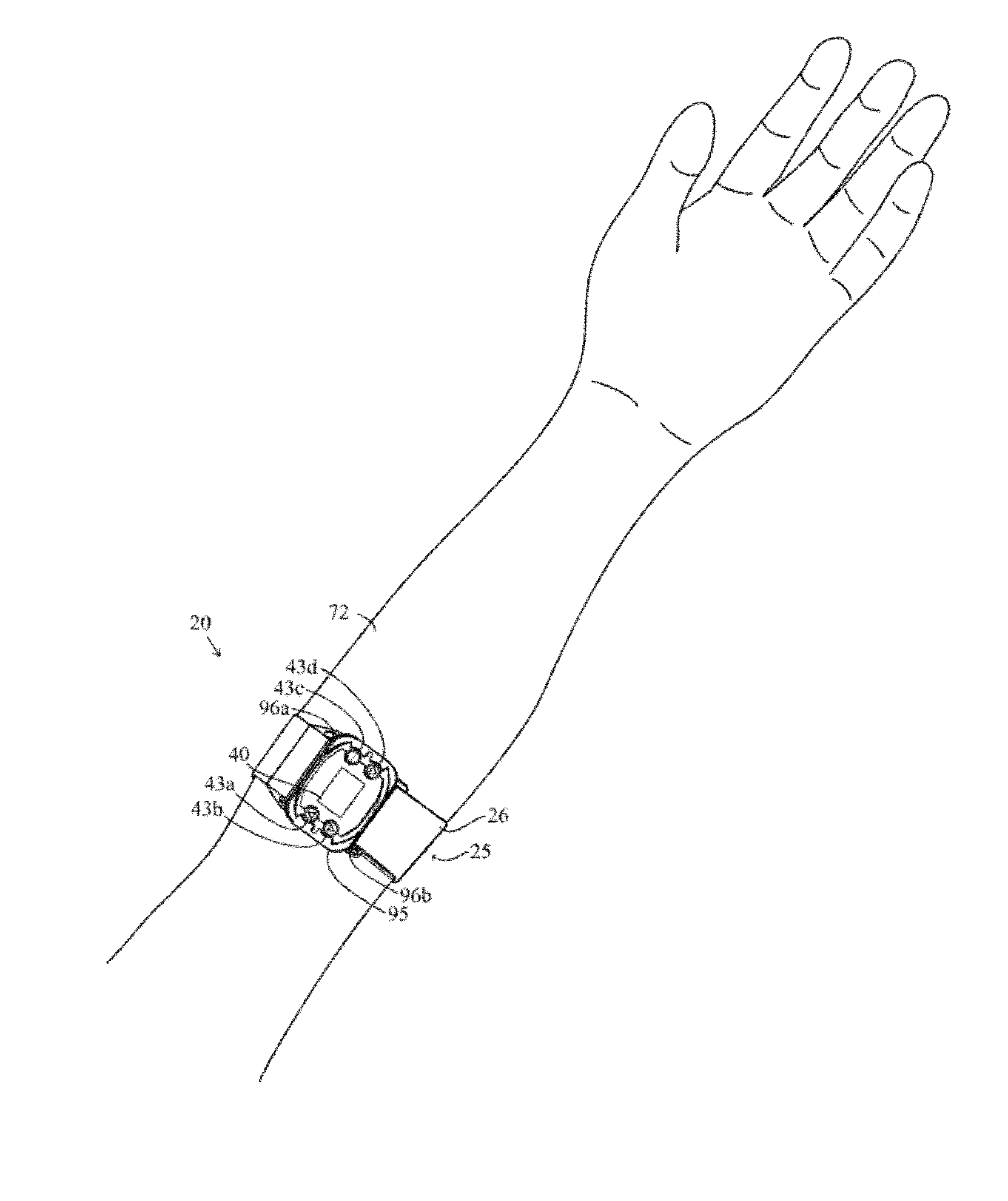
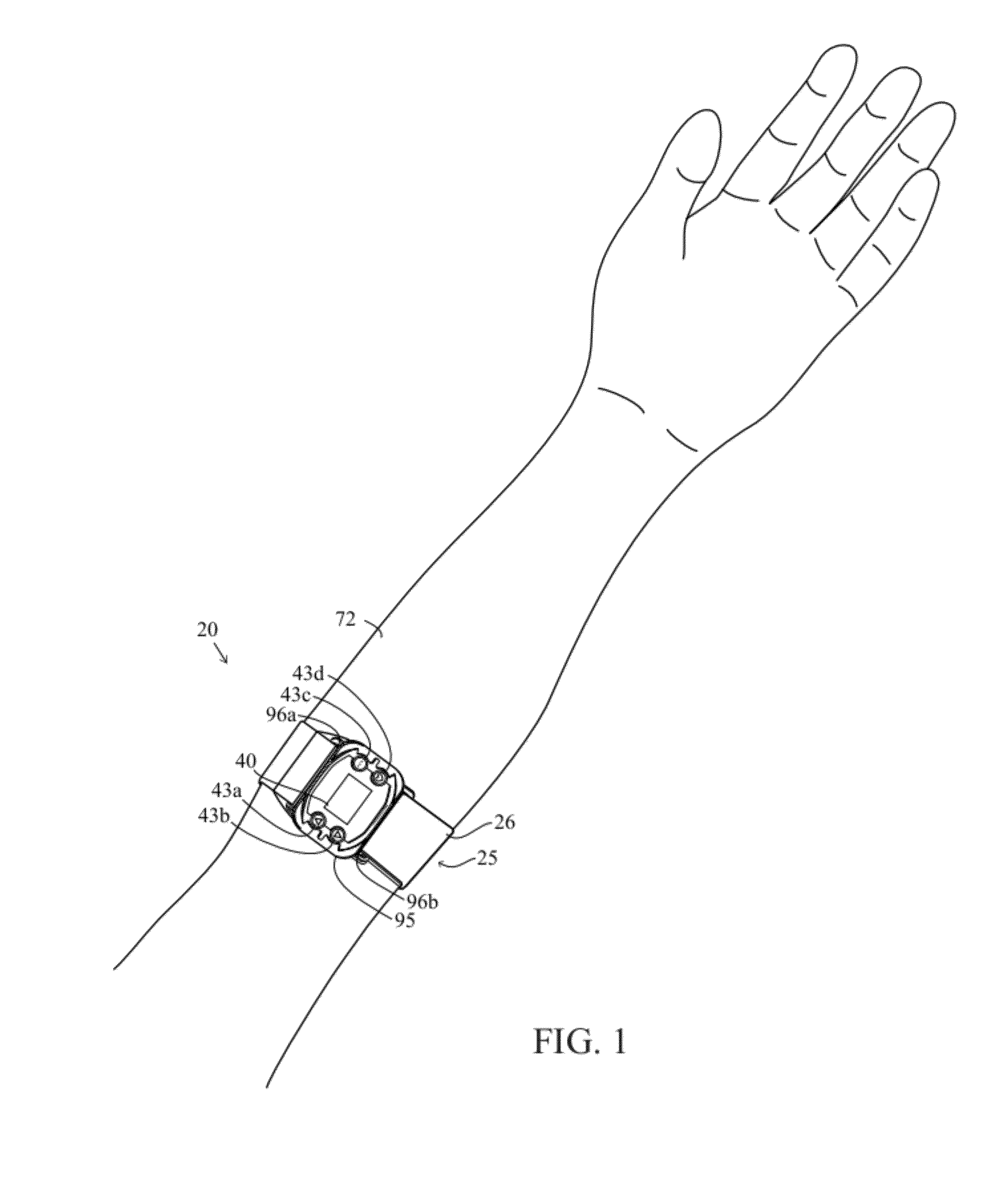
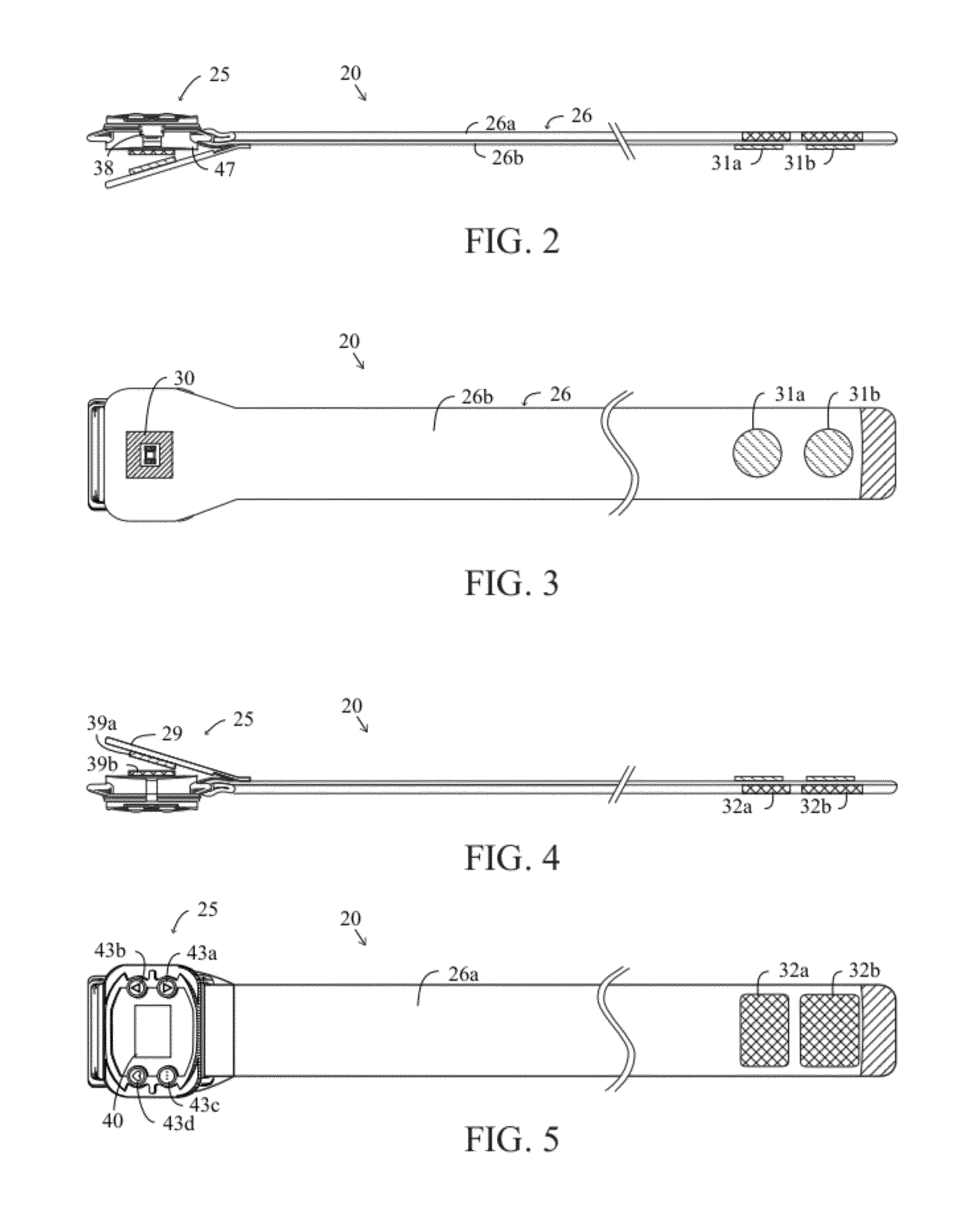
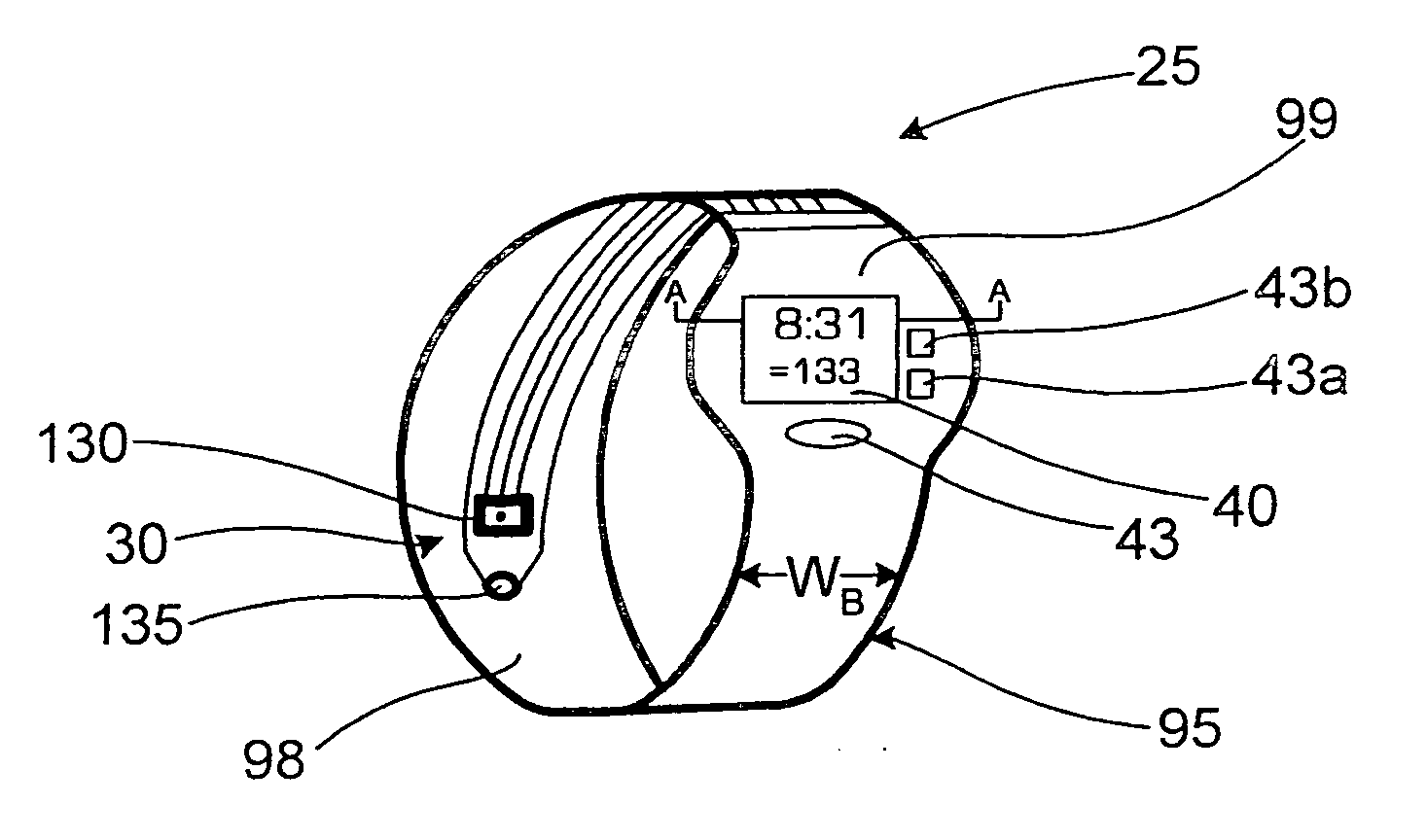
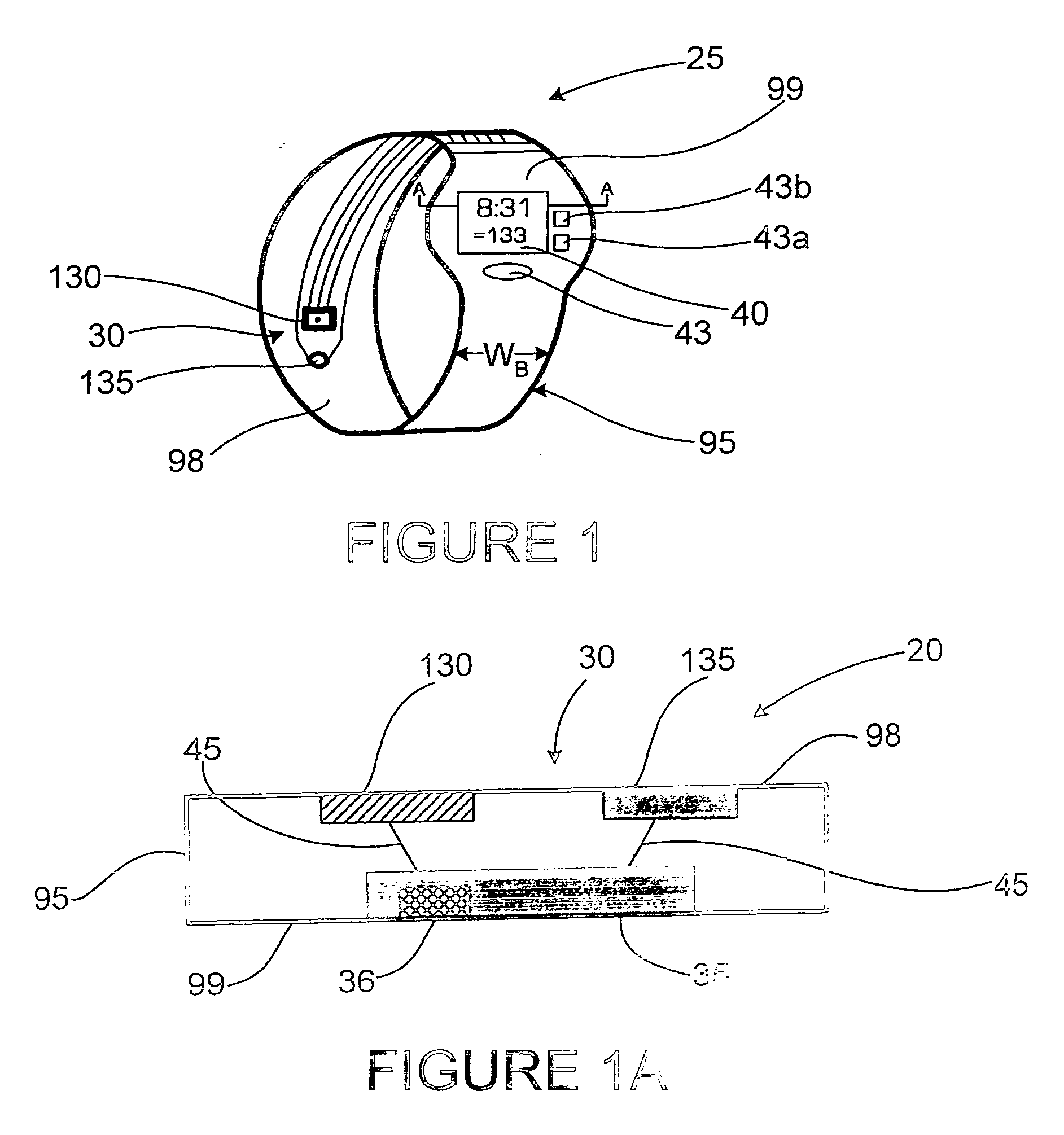
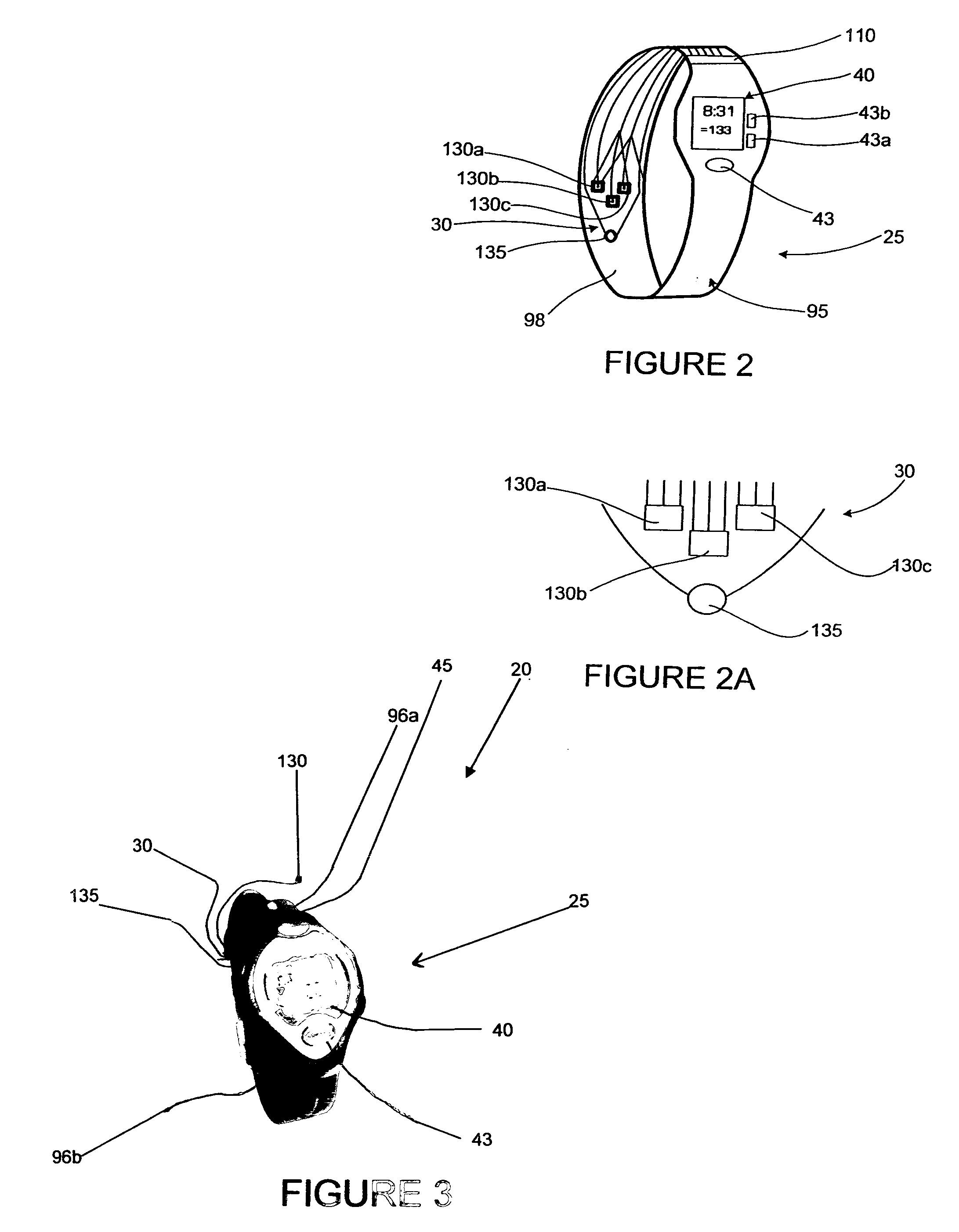
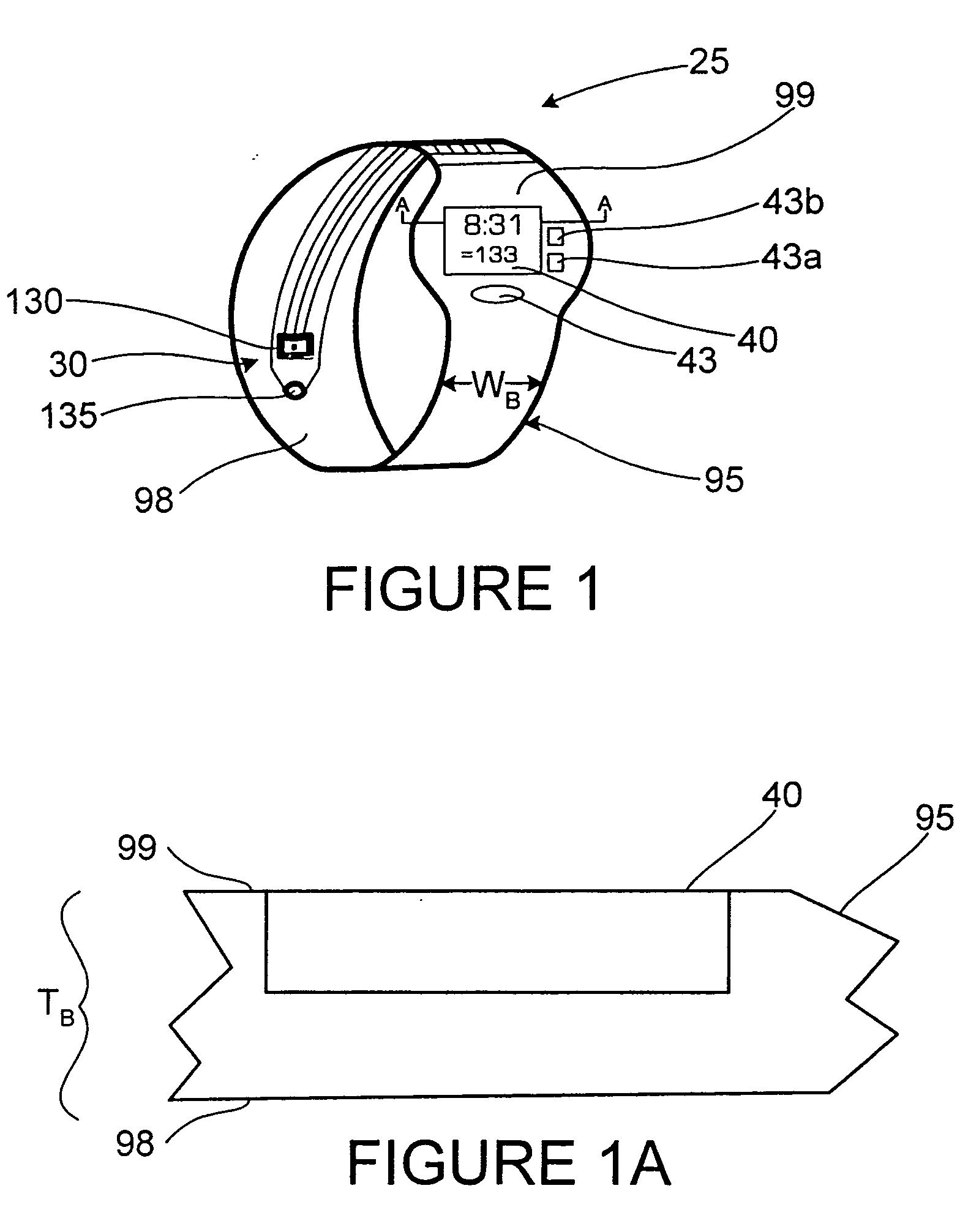
A monitoring device (20) and method (200) for monitoring the health of a user is disclosed herein. The monitoring device (20) is preferably a watch (25), an optical sensor (30) disposed on a band of the watch (25), a circuitry assembly (35) embedded within a main body of the watch (25), a display member (40) disposed on an exterior surface of the main of the watch, and a control component (43). The monitoring device (20) preferably displays the following information about the user: pulse rate; blood oxygenation levels; calories expended by the user of a pre-set time period; target zones of activity; time; distance traveled; and dynamic blood pressure. The watch (25) also displays the time of day on the display member (40).
Owner:BRADY DONALD +2
Power management of a system for measuring the acceleration of a body part
InactiveUS20050177929A1Small sizeConvenient lightingFlow propertiesInertial sensorsAccelerometerUltrasonic sensor
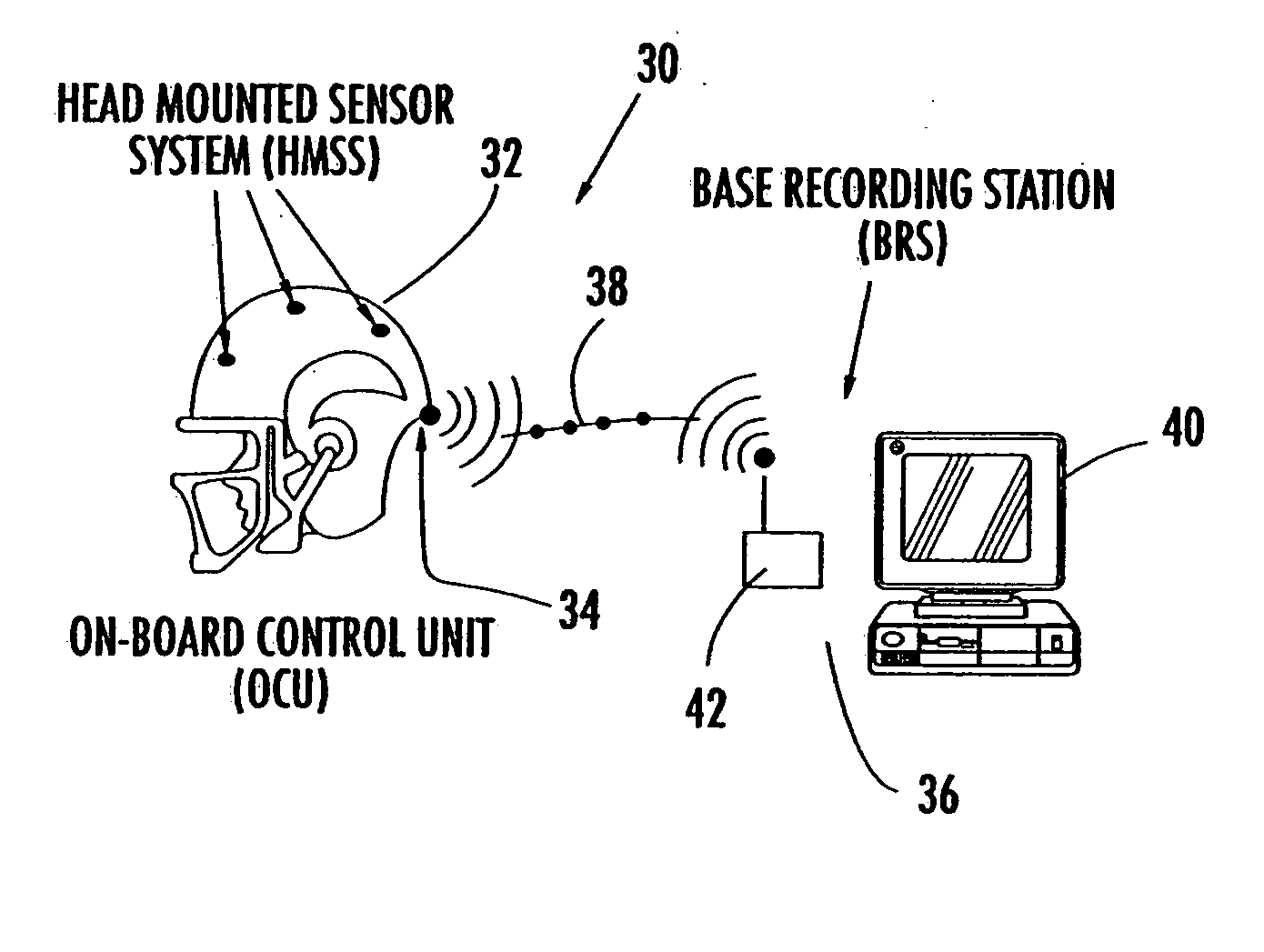
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for determining the magnitude of linear and rotational acceleration of an impact to a body part. The apparatus can be used with protective sports equipment, such as a sports helmet, wherein the apparatus includes a battery, a number of accelerometers positioned proximate to the outer surface of the head, and an electronic device with a processor and a transmitter to transmit data received from the accelerometers. To maximize the battery life and minimize power consumption by the electronic device, the apparatus includes a power management system with a sensor assembly. The sensor assembly sends a first signal to the electronic device to initiate operation when the sensor assembly detects the presence of an object within the helmet, and a second signal to the electronic device to cease operation when the sensor assembly detects the absence of the object. The sensor assembly may be a proximity sensor, more specifically an inductive, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensor.
Owner:RIDDELL
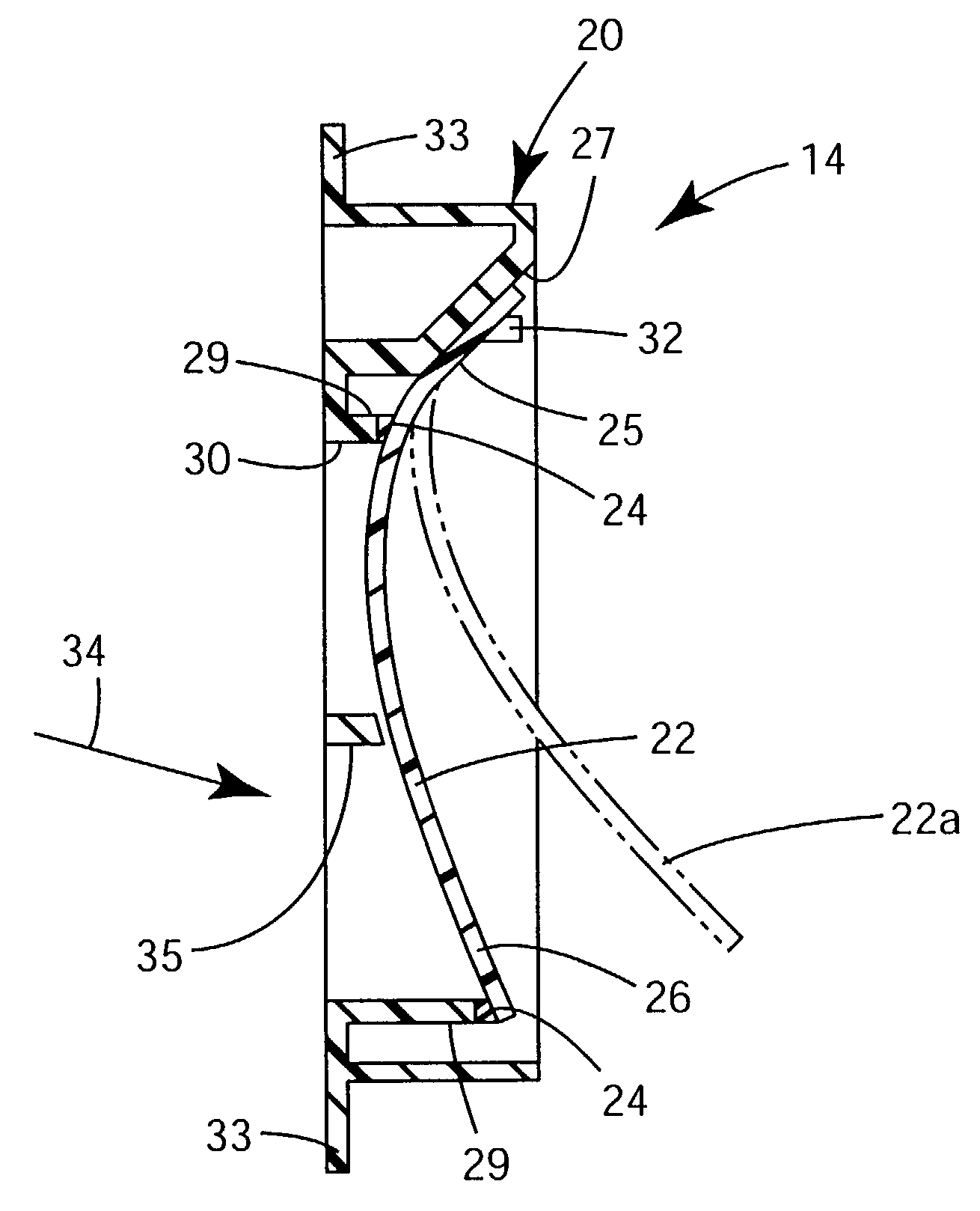
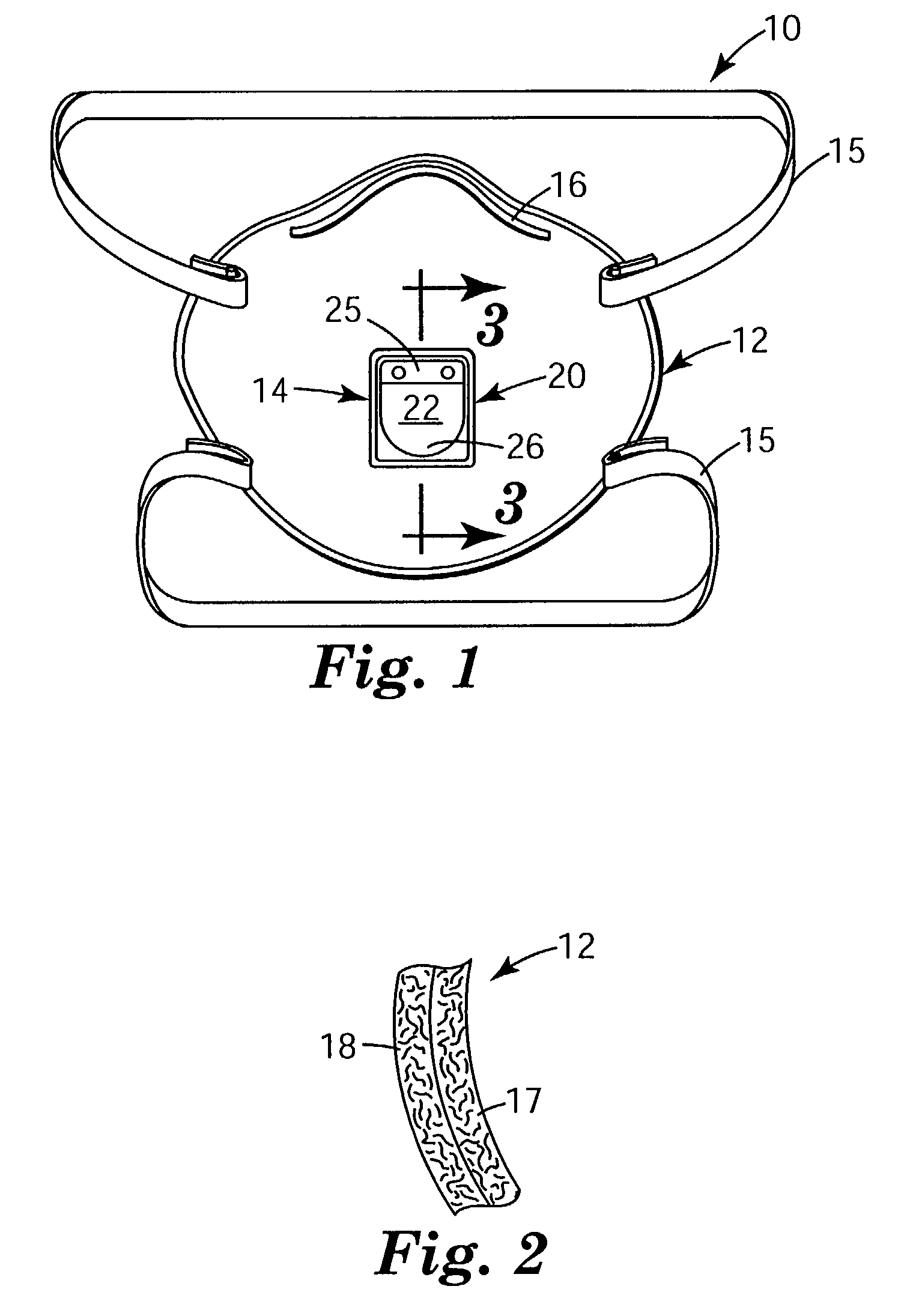
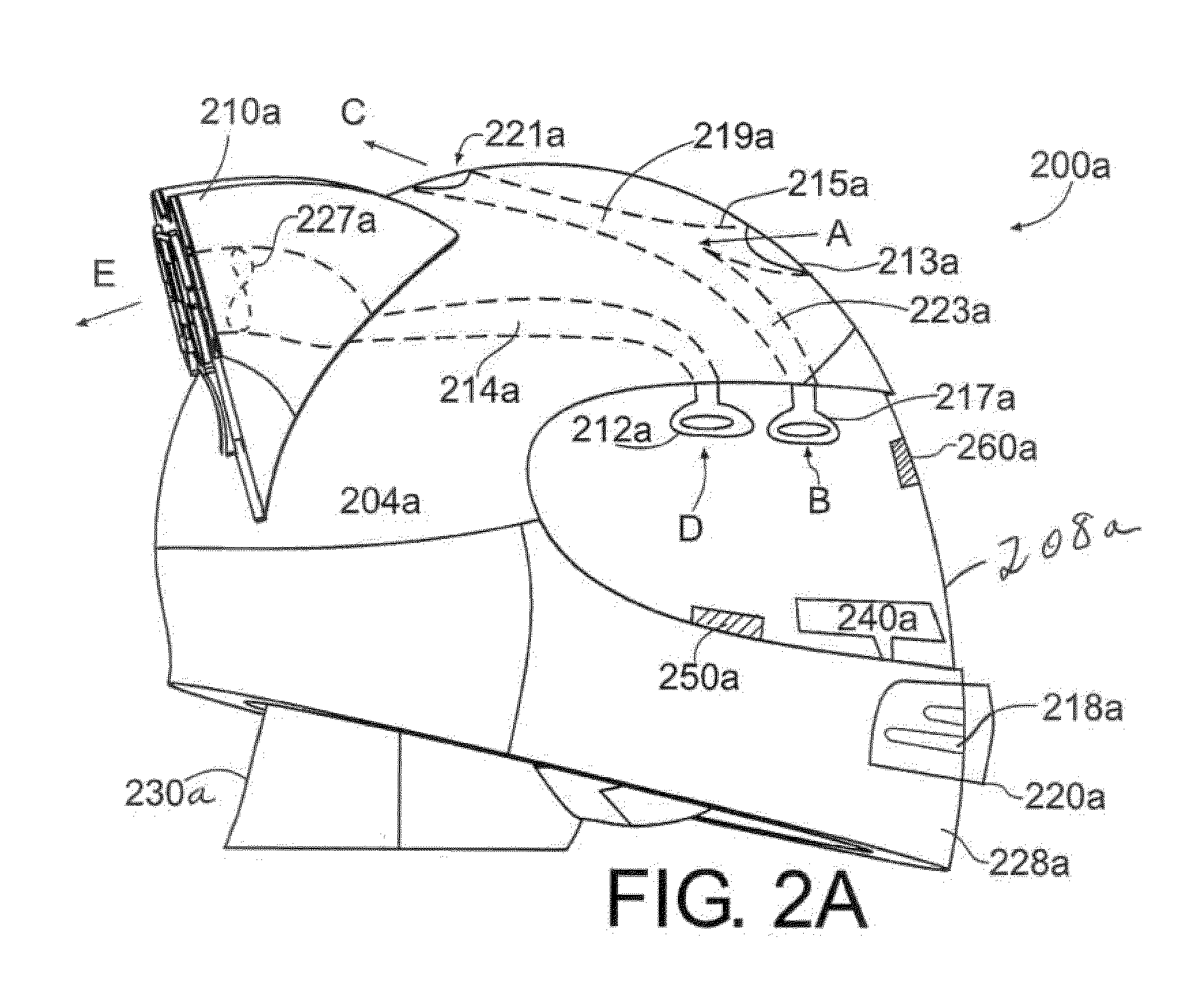
Filtering face mask that has a resilient seal surface in its exhalation valve
ActiveUS7188622B2More rigidLess force or pressureRespiratorsBreathing filtersExhalationDuring expiration
A filtering face mask 10 that has a mask body and a new exhalation valve 14. The mask body is adapted to fit at least over the nose and mouth of a person to help define an interior gas space when the mask is worn. The exhalation valve 14 permits fluid communication between the interior gas space and an exterior gas space. The exhalation valve 14 has a valve seat 20 and a flap 22. The valve seat 20 includes a resilient seal surface 24 and an orifice 30 through which exhaled air may pass to leave the interior gas space. The flap 22 is mounted to the valve seat 20 such that the flap 22 makes contact with the resilient seal surface 24 when the valve is in its closed position and such that the flap 22 can move away from the seal surface 24 in response to an exhalation to allow exhaled air to pass through the orifice 30 to ultimately enter the exterior gas space. A filtering face mask that utilizes an exhalation valve that has a resilient seal surface can enable the valve to open under substantially less pressure, which, in turn, may improve wearer comfort.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Wetness monitoring system
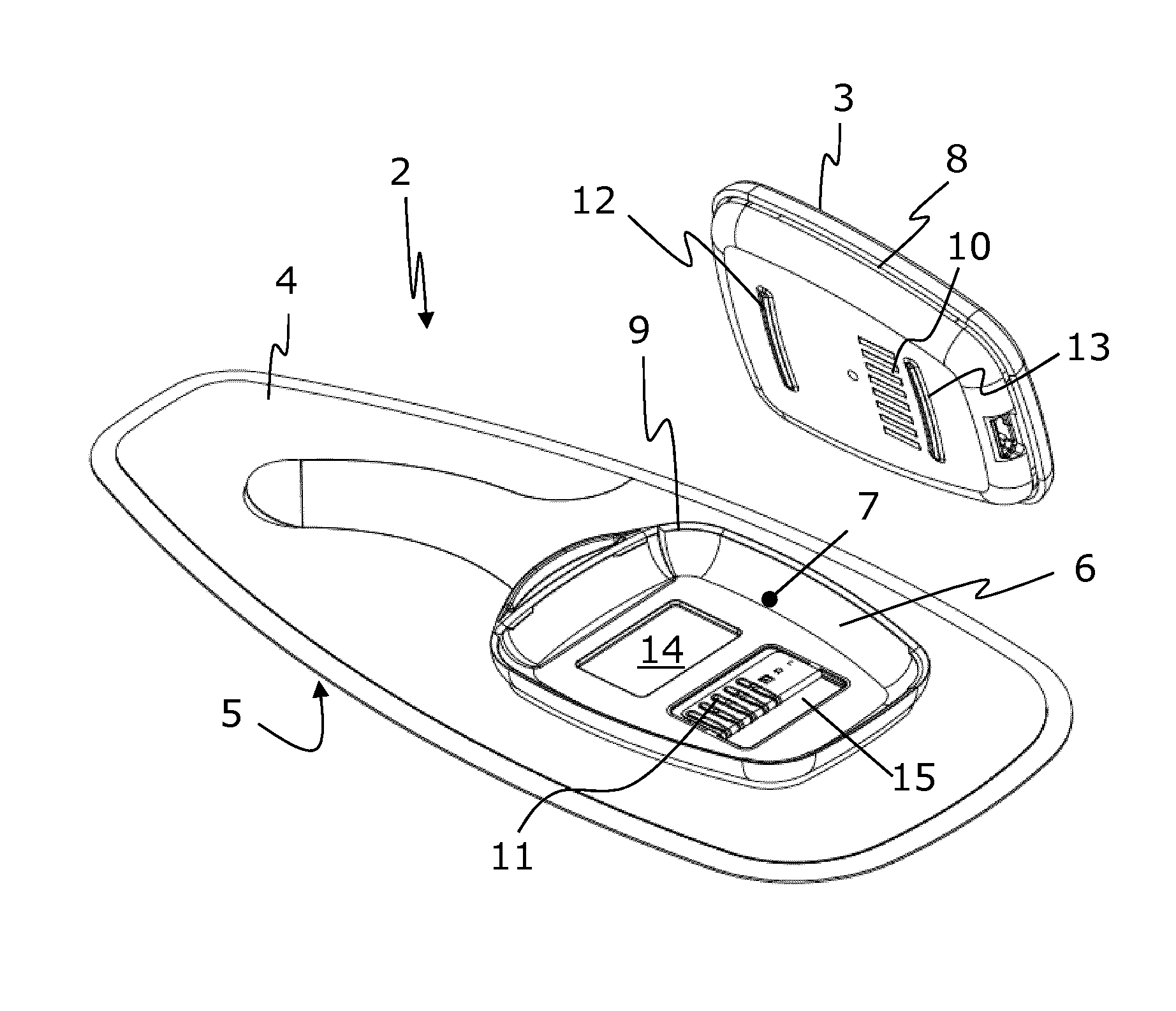
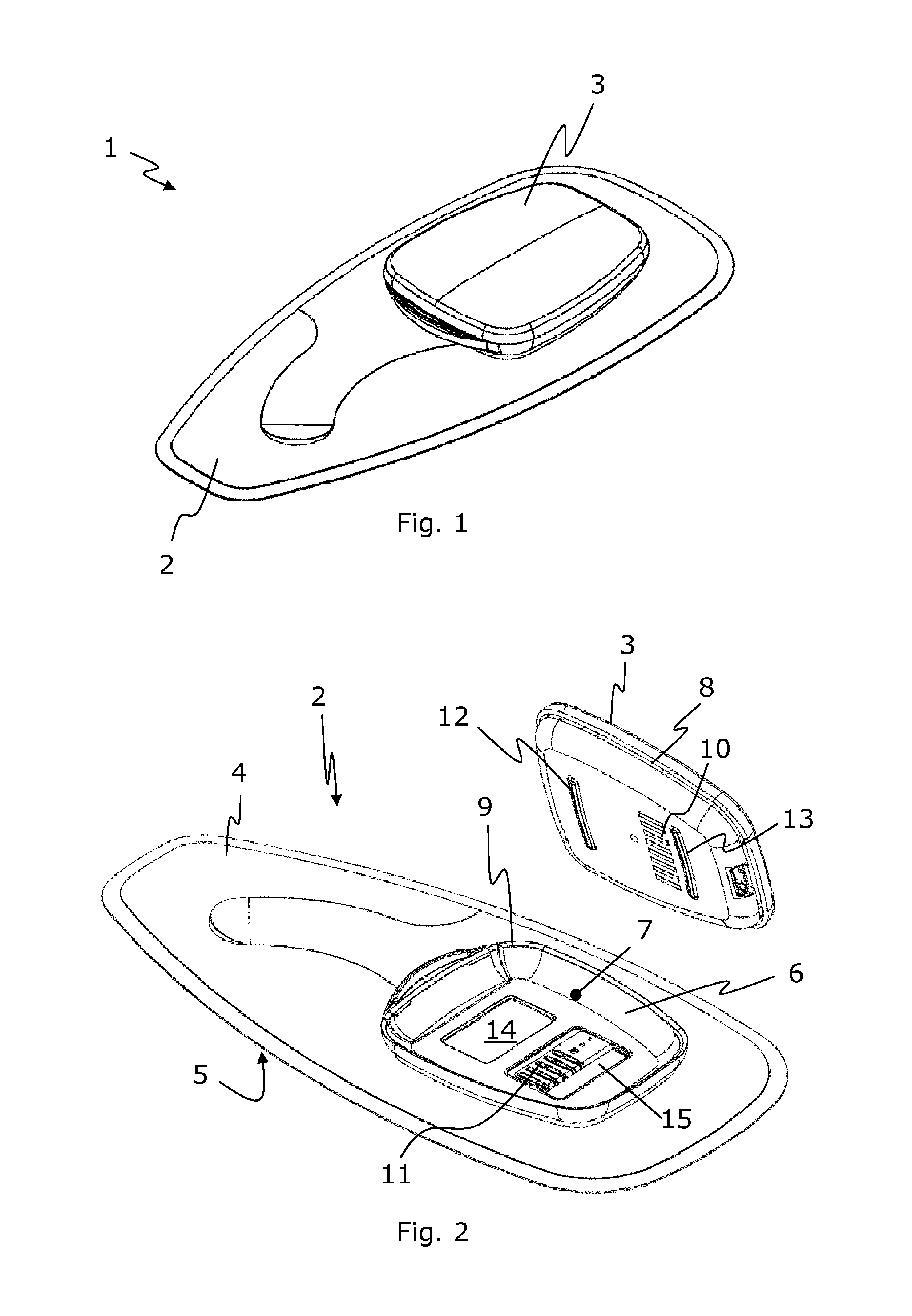
InactiveUS7250547B1Reduce operating costsLower annual operating costsBaby linensAlarmsData acquisitionMonitoring system
The present invention relates to a wetness monitoring system that includes a data collection device that sends wetness measurement data to a central computer that detects changes in wetness measurement data caused by the presence of urine or other dielectric fluids. The data collection device includes a semi-reusable sensor and reusable data collector that are worn on a garment of the person. The data collector includes an internal power source so that the person can live a normal ambulatory life. The data collector has an electrical circuit that uses the changing resistance characteristics in the sensor to gather wetness measurement data. The data collector periodically generates and transmits a signal containing the actual wetness measurement data. The signals are coded to identify the particular data collector or person sending the signal. The data collector is programmed to conserve power by sending signals less frequently during periods when the sensor is clearly dry. Signals are sent more frequently when the sensor is damp or a wetness event may have occurred. The central computer receives the signals containing the wetness measurement data and compares the measurement data to an adjustable wetness sensitivity level to determine if a wetness event has occurred. When the central computer determines that a wetness event has occurred, the computer displays the name of the particular person wearing the data collector and the approximate time that the wetness event occurred. The system then pages an appropriate healthcare worker to inform them that the particular individual needs attention and tracks the approximate response times to ensure that the patient is continuously receiving prompt care.
Owner:RF TECH
Apparatus and method for the measurement and monitoring of bioelectric signal patterns
InactiveUS20070112277A1Less cumbersomeMinimally invasiveElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyAuditory stimuliMeasurement device
A wireless apparatus and method for the measurement and monitoring of bioelectric signal patterns associated with EEG, EOG and EMG readings is provided. The apparatus is comprised of at least one measurement device employing the use of three bioelectric sensing electrodes, wherein at least one of the electrodes is configured for secure placement within the ear canal of an individual under medical surveillance. Acoustic stimulation may be provided directly into the ear canal of the individual via an auditory stimulus emitted from the measurement device for evoking brain activity and the subsequent measurement of bioelectric signal patterns associated with the evoked activity.
Owner:FISCHER RUSSELL J +3
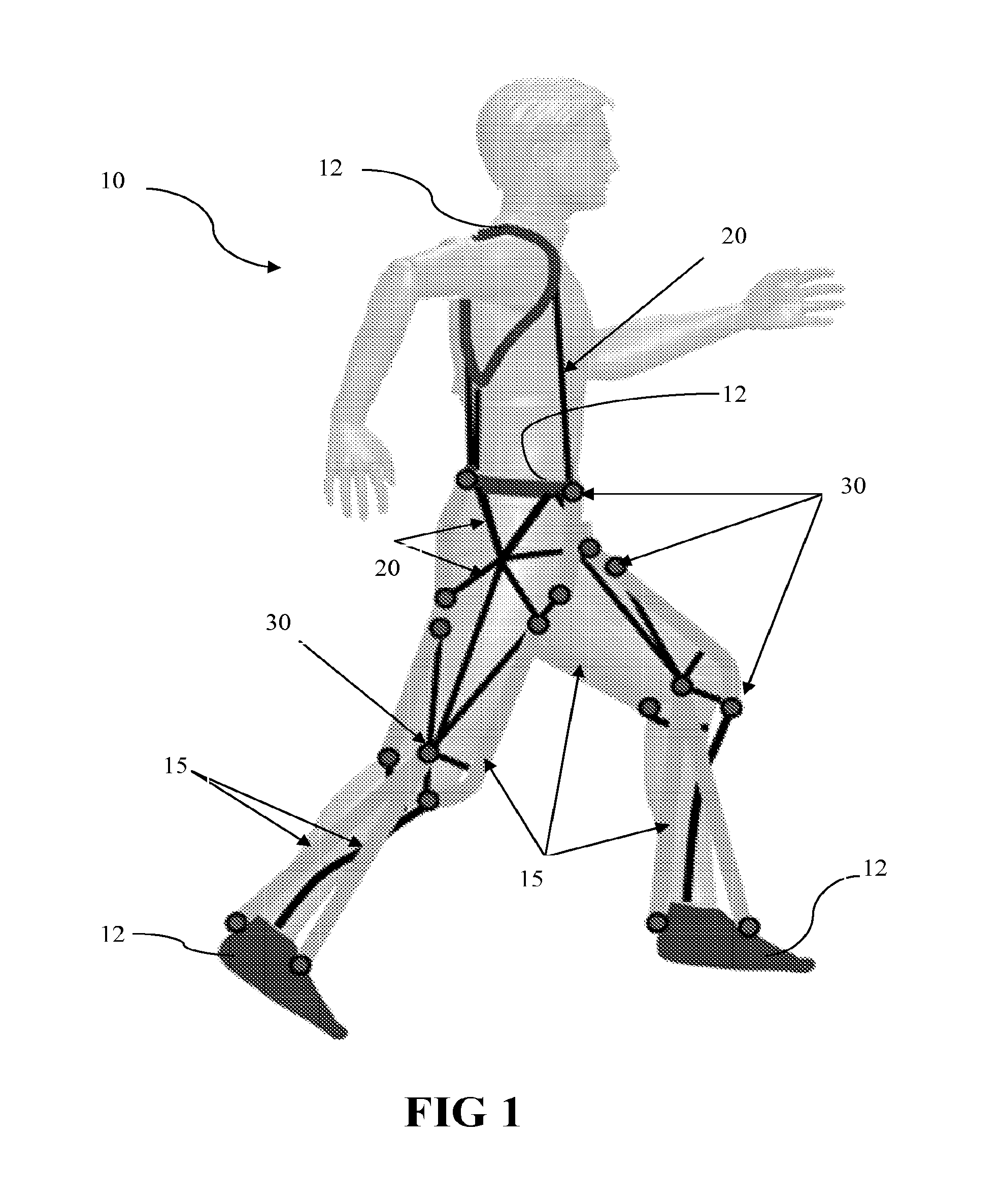
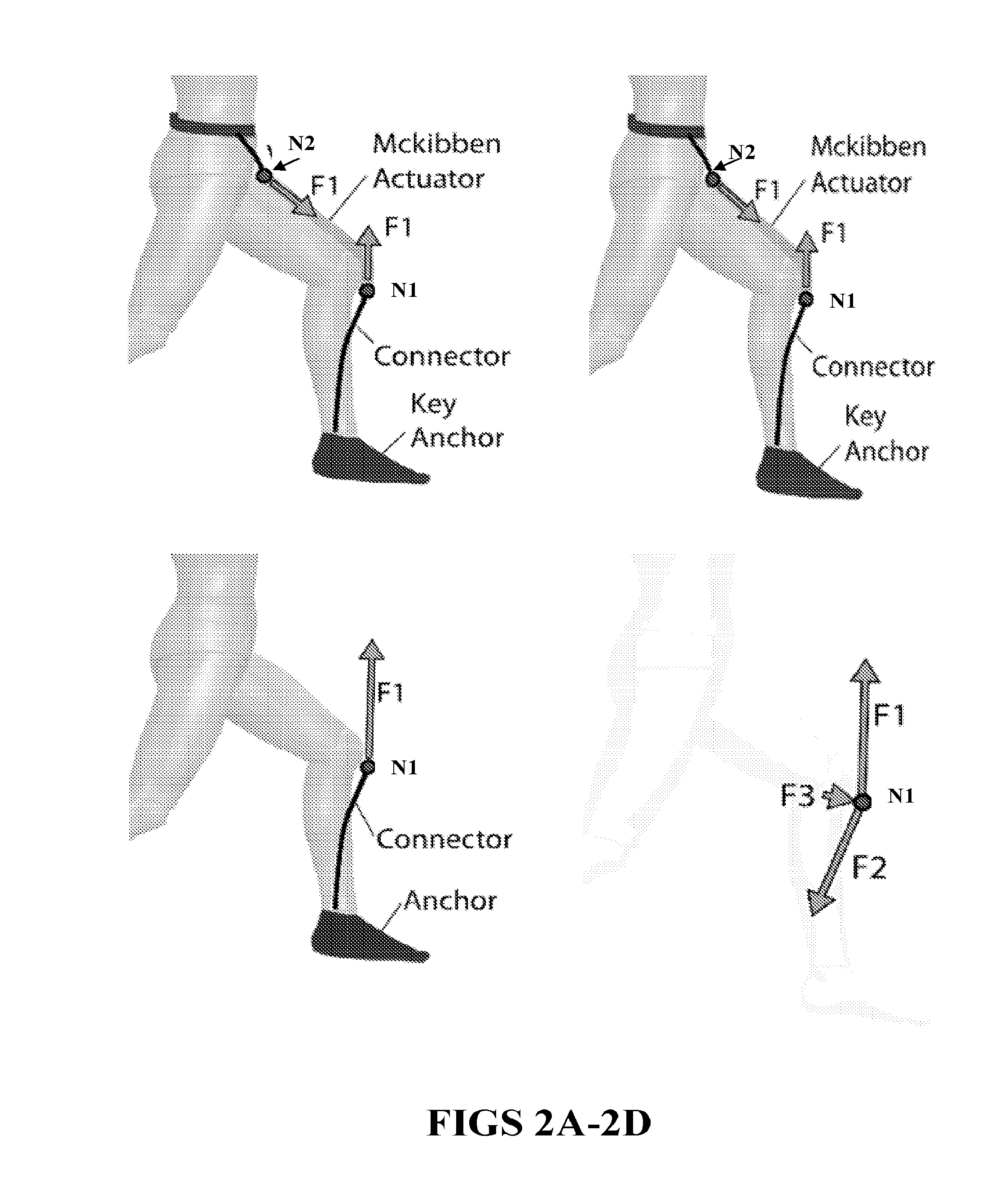
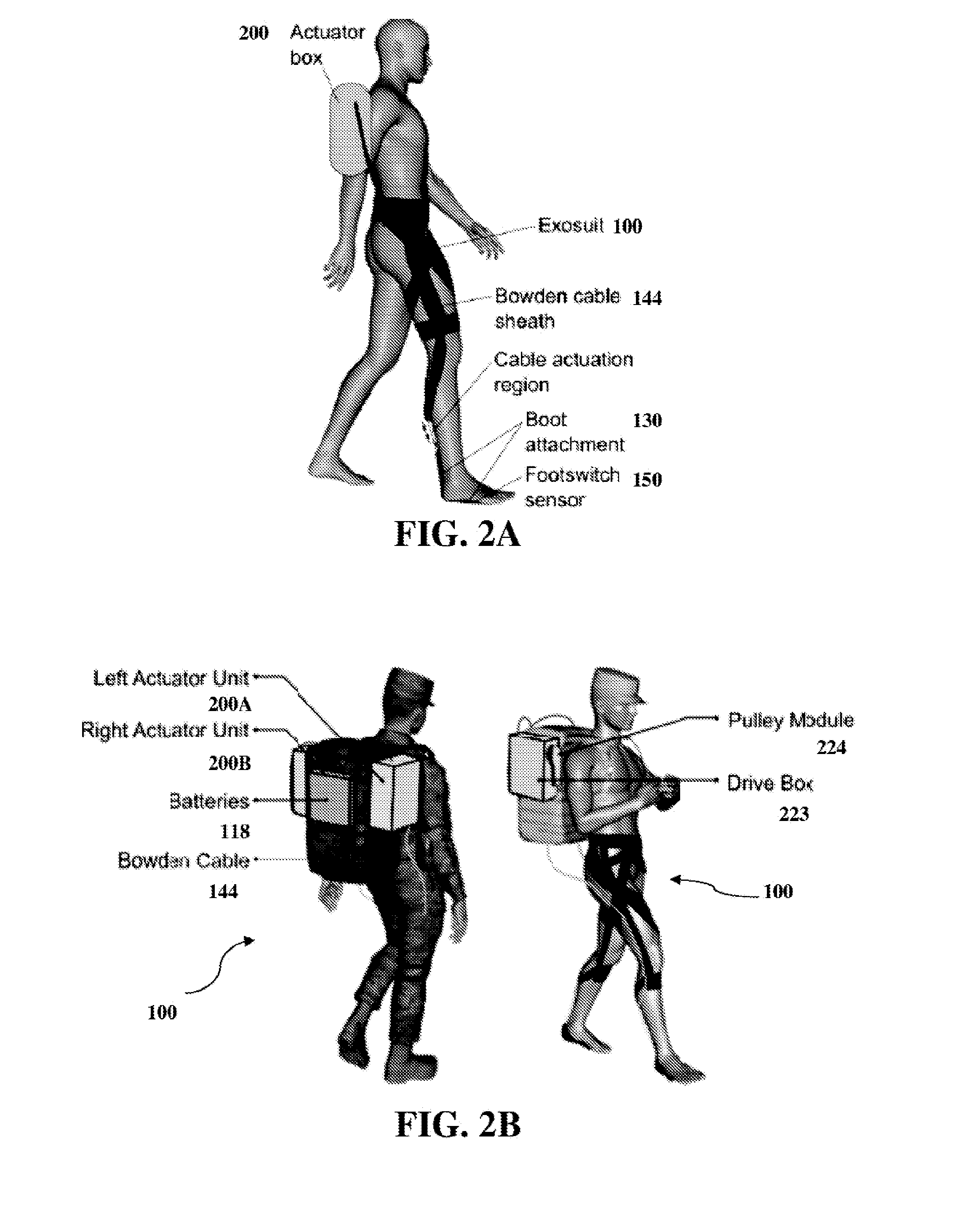
Soft exosuit for assistance with human motion
ActiveUS20150173993A1Complete, and more natural, range of joint(s) motion(s)Comfortable to wearProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsHuman motionEngineering
In at least one aspect, there is provided a system for generating force about one or more joints including a soft exosuit having a plurality of anchor elements and at least one connection element disposed between the plurality of anchor elements. The system also includes at least one sensor to determine a force the at least one connection element or at least one of the plurality of anchor elements and to output signals relating to the force, at least one actuator configured to change a tension in the soft exosuit and at least one controller configured to receive the signals output from the at least one sensor and actuate the at least one actuator responsive to the received signals.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Soft Exosuit for Assistance with Human Motion
ActiveUS20160107309A1Beneficial reduction in metabolic consumption of energyReduce loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesControl systemHuman motion
A motion control system includes an actuator having an actuation member, the actuation member having a proximal end attached to the actuator on a first side of a joint and a distal end attached to an anchor element attachment point on a second side of the joint. A first sensor is configured to output signals defining a gait cycle and a second sensor is configured to output signals representing a tensile force in the at least one actuation member. A controller receives the output signals from the sensors and actuates the actuator, during a first portion of the gait cycle, to apply a force greater than a predetermined threshold tensile force to the anchor element attachment point via the actuation member to generate a beneficial moment about the joint and to automatically actuate the actuator.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Absorbent core having two or more types of superabsorbent
InactiveUS20060069367A1Fast absorbency rateHigh absorbencyBaby linensTamponsAbsorption rateFibrous layer
An absorbent core for use in an absorbent article, including a central fibrous layer having synthetic fibers, and two or more types of superabsorbent material (SAP). The SAP is contained primarily in upper and / or lower layers of the absorbent core. The upper and / or lower layer may be a substantially continuous layer of SAP, or may include a free-form of SAP. The upper and / or lower layers may have a blend of two or more types of SAP, or may have only a virgin, unblended SAP. Each of the types of SAP preferably has a different absorbent property (such as high AUL, or fast absorption rate), so that the resultant absorbent core benefits from having multiple absorbent properties provided by the SAP's. An absorbent article including the absorbent core, and a method of providing an absorbent article including the absorbent core are also described.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY RETAIL SERVICES
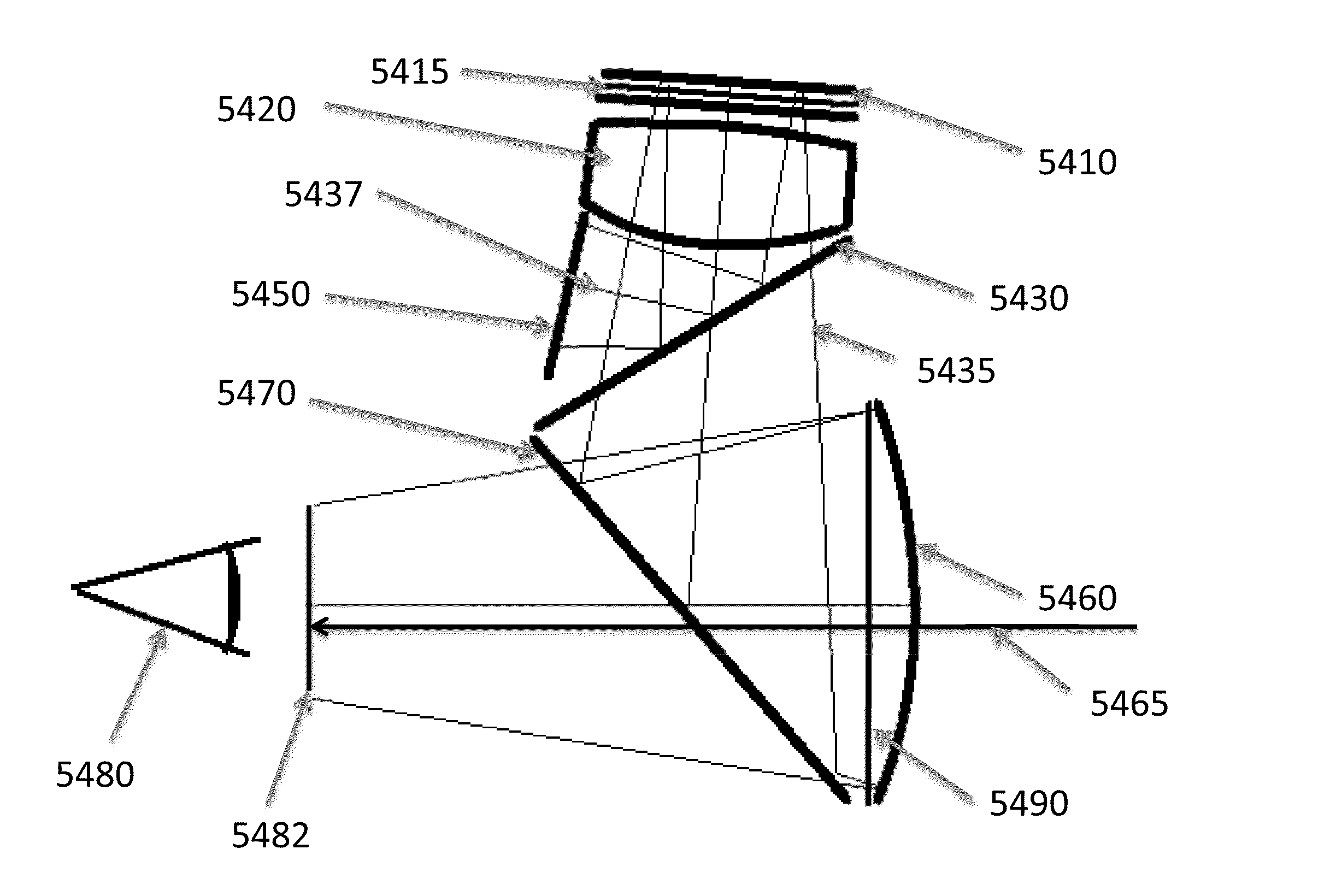
Optical systems for see-through displays
ActiveUS9366867B2Reduce weightComfortable to wearPolarising elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSee-through displayComputer science
Aspects of the present invention relate to methods and systems for providing a high quality display images in see-through head-worn optics.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
Power management of a system for measuring the acceleration of a body part
InactiveUS7526389B2Small sizeConvenient lightingFlow propertiesInertial sensorsAccelerometerProximate
Owner:RIDDELL
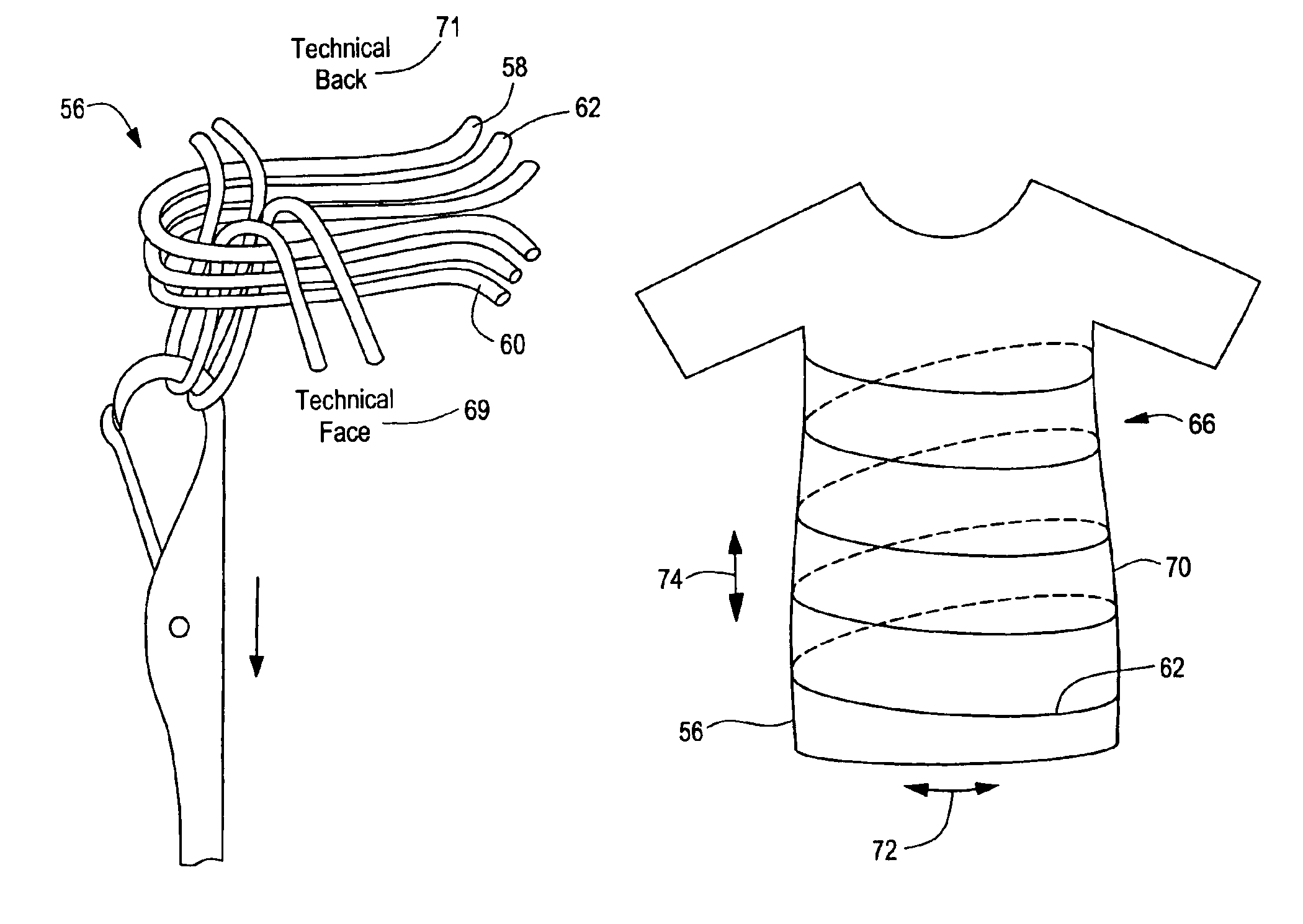
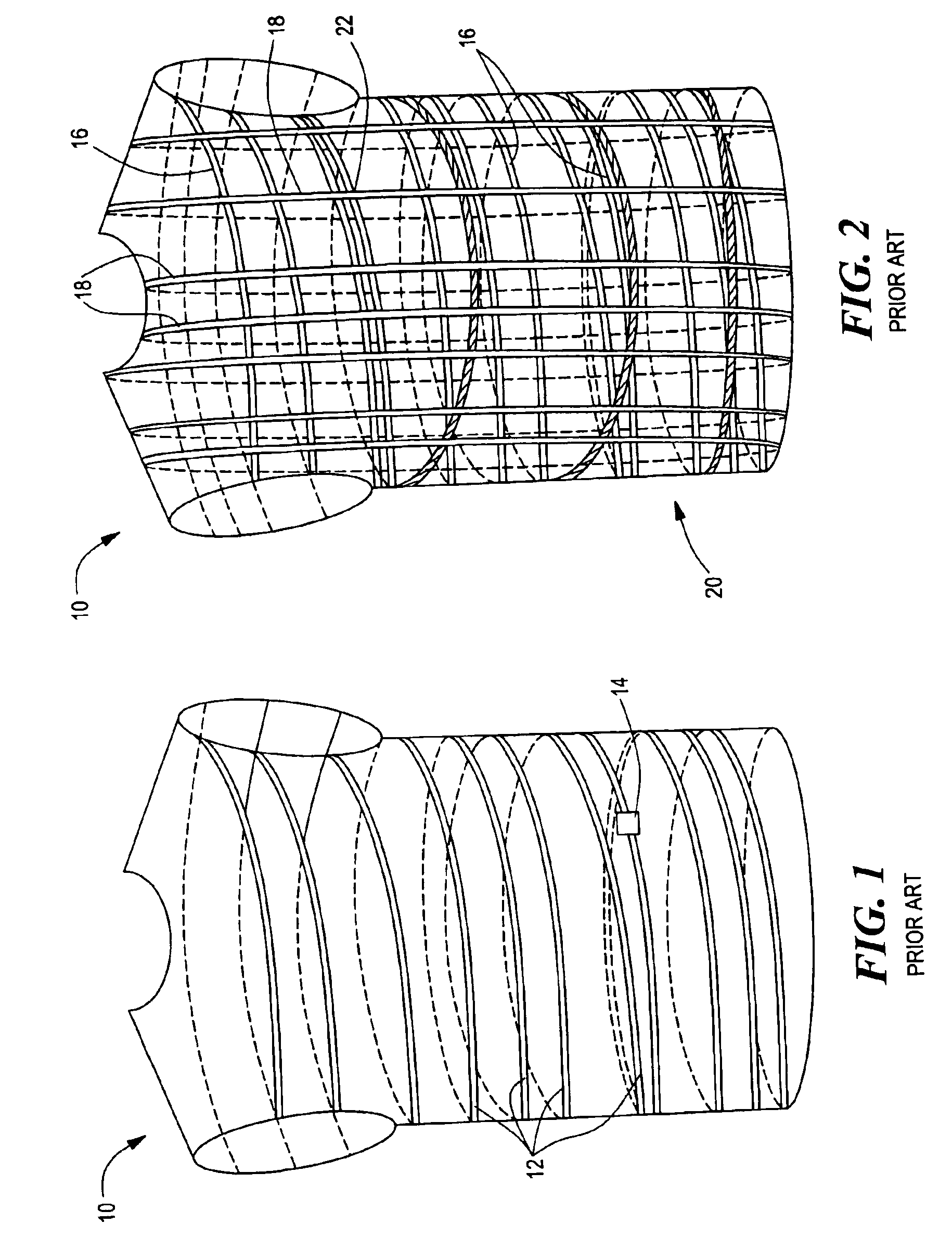
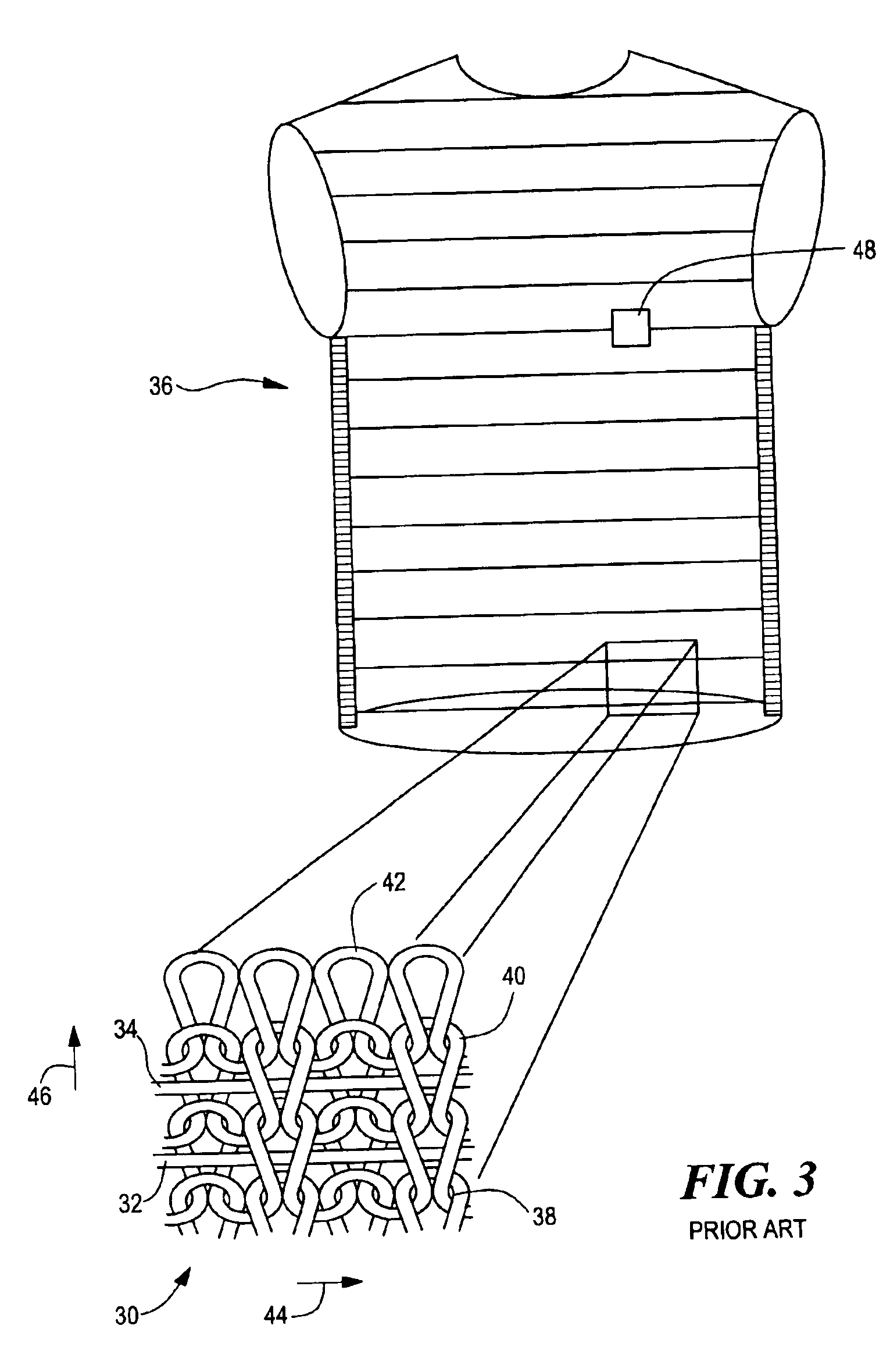
Tubular knit fabric and system
ActiveUS6941775B2Comfortable to wearAccurate and reliableOrnamental textile articlesDiagnostic recording/measuringYarnBiomedical engineering
A tubular knit fabric comprising at least one insulative yarn, at least one stretchable yarn, and at least one functional yarn, the insulating yarn, the stretchable yarn, and the functional yarn knitted together to define a tubular fabric sleeve having the functional yarn embedded in the tubular fabric sleeve in a continuous spiral configuration which longitudinally extends the length of the sleeve.
Owner:MMI IPCO +1
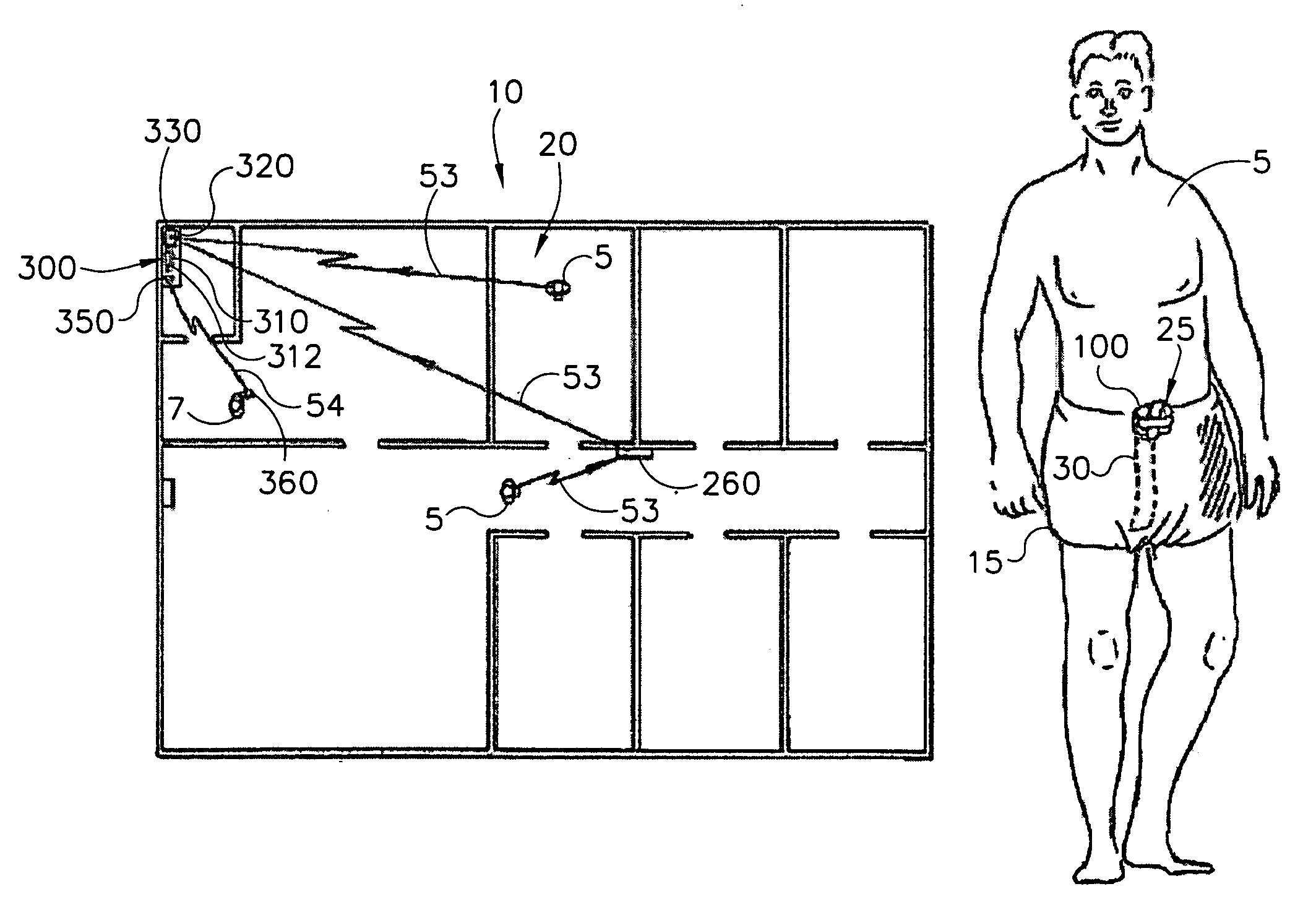
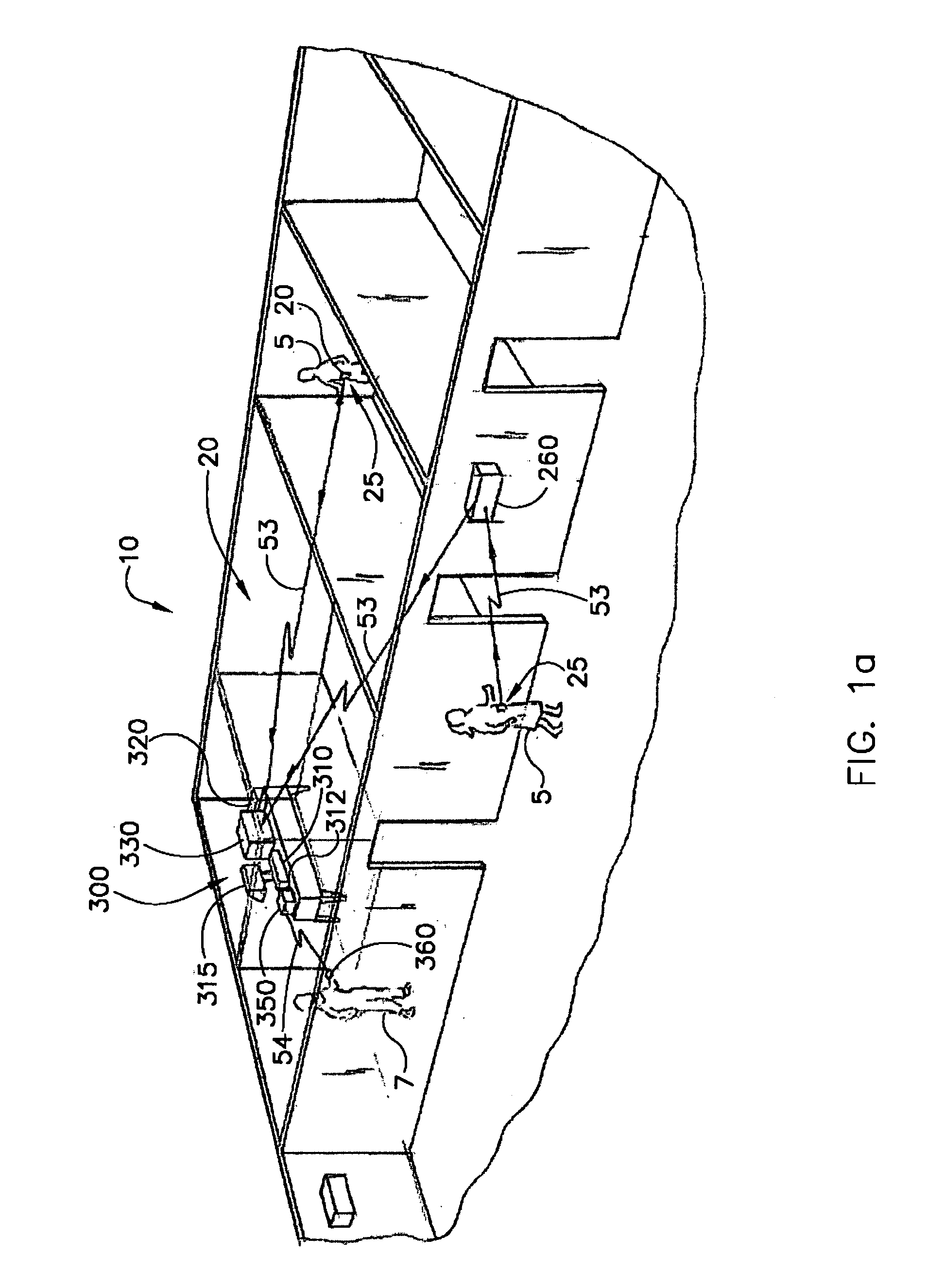
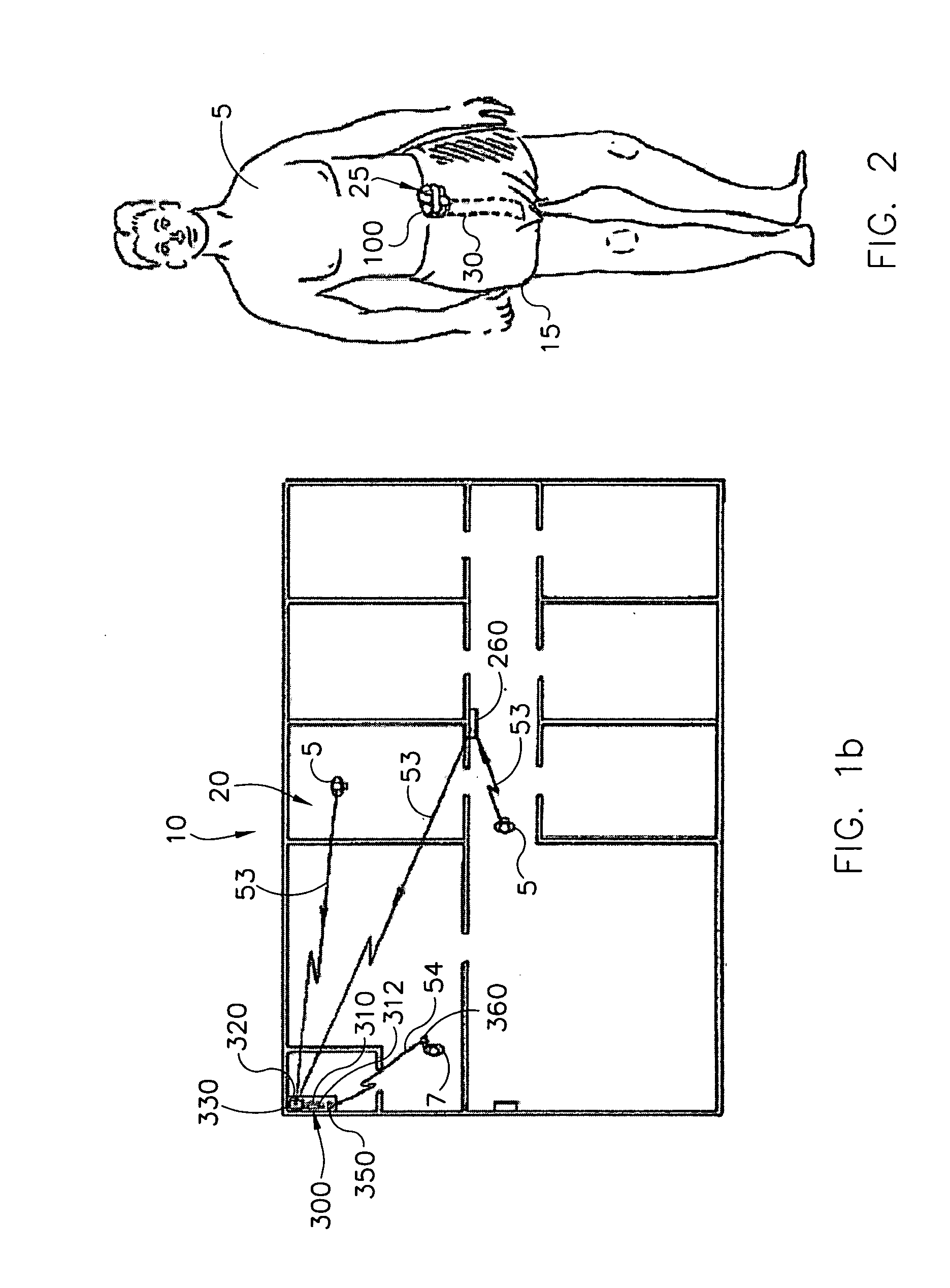
Personal wellness monitor system and process
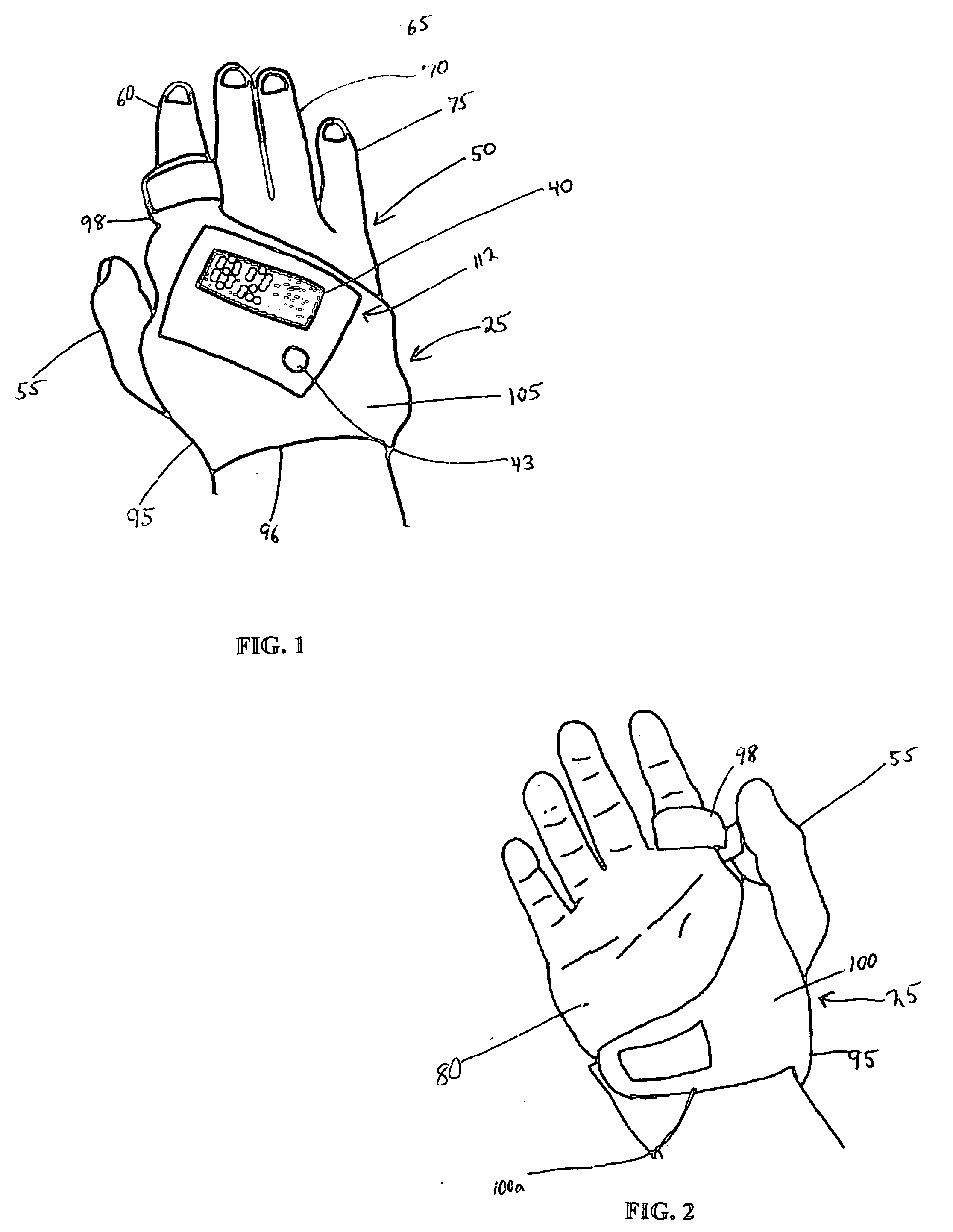
InactiveUS20050245793A1Effectively monitor relatively slowly changing physiological and biometric propertiesComfortable to wearPerson identificationCatheterPersonal health monitoringData center
Disclosed is an apparatus and methodology for providing a personal wellness monitor (PWM) that may be used to measure and store physiological parameters indicative of sustained activity by a User. Data collected by the PWM may be correlated over time with relation to a particular activity mode. Activity modes monitored may include walking, sleeping, exercising, or other activities. The User may be alerted by the PWM as predetermined physiological parameters are reached. Data from the PWM may be uploaded to a Data Center and stored for analysis and historical record in a central database, accessible by the User. The User's historical record may be pertinent in determining changes in health and wellness.
Owner:HILTON THEODORE CRAIG +1
Absorbent core with three-dimensional sub-layer
InactiveUS20050101929A1Improved ability to retain fluidPrevent leakageBaby linensTamponsEngineeringFibrous layer
An absorbent core for use in an absorbent article, having a central fibrous layer having synthetic fibers, and a three-dimensional sub-layer having a plurality of small pockets that contain superabsorbent particles. Superabsorbent particles are deposited and partially enclosed in the discrete small pockets, and are prevented from shifting to other portions of the absorbent core. An absorbent article including the absorbent core, and a method for providing an absorbent article including the absorbent core are also described.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY RETAIL SERVICES
Security and protection device for an ear-mounted audio amplifier or telecommunication instrument
InactiveUS20120057740A1Comfortable to wearLight weightEarpiece/earphone attachmentsHearing aids housingAudio power amplifierEngineering
A security and protection device for an ear-mounted audio amplifier or telecommunication instrument. The device includes a resilient water-pervious hollow sleeve sized and shaped to snugly conform to the shape of an audio amplifier or telecommunication instrument having an earpiece insertable in to the ear of a user when the sleeve is slid over the instrument. The sleeve has a top opening at a top end of the sleeve and a bottom opening at an opposite bottom end of the sleeve. The bottom opening is sized to snugly receive the instrument into the hollow sleeve so as to substantially completely cover the instrument when journalled in the sleeve. The top opening is sized to snugly receive through the top opening a corresponding upper end of the instrument. The upper end of the instrument is connected to the instrument earpiece.
Owner:ROSAL MARK BRYAN
Protective headgear compression member
InactiveUS20100186150A1Comfortable to wearIncrease the gapSpringsHelmetsMechanical engineeringProtective headgear
A protective headgear compression member includes a hollow compression cell having a top wall, a bowed side wall and a bottom wall and a liner element secured to that bottom wall coaxially to said cell. The liner element is composed of a flexible envelope substantially filled with resilient material and the envelope is secured to the bottom wall via an axially flexible connection to prevent the bottoming out of the liner element against the bottom wall of the cell.
Owner:XENITH
Wettable silicone hydrogel contact lenses and related compositions and methods
ActiveUS8231218B2Comfortable to wearPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOptical articlesInterpenetrating polymer networkChemistry
Silicone hydrogel contact lenses having ophthalmically acceptable surface wettabilities are obtained from pre-extracted polymerized silicone hydrogel contact lens products having relatively large amounts of removable or extractable materials. The silicone hydrogel contact lenses can be obtained from non-polar resin based contact lens molds and without surface treatments or an interpenetrating polymeric network of a polymeric wetting agent. Related lens products, polymerizable compositions, and methods are also described.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Method for operating a hearing aid or hearing aid system, and a hearing aid and hearing aid system
InactiveUS6882736B2Comfortable to wearImprove comfortMicrophonesTransmission noise suppressionEngineeringSignal processing
In a method for operating a hearing aid or hearing aid system, and a hearing aid or hearing aid system, wind noises are detected by analyzing the output signals of at least two microphones. If wind noises are present, the signal processing unit of the hearing aid or hearing aid system and / or the signal paths of microphones are adapted in order to reduce such noises.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
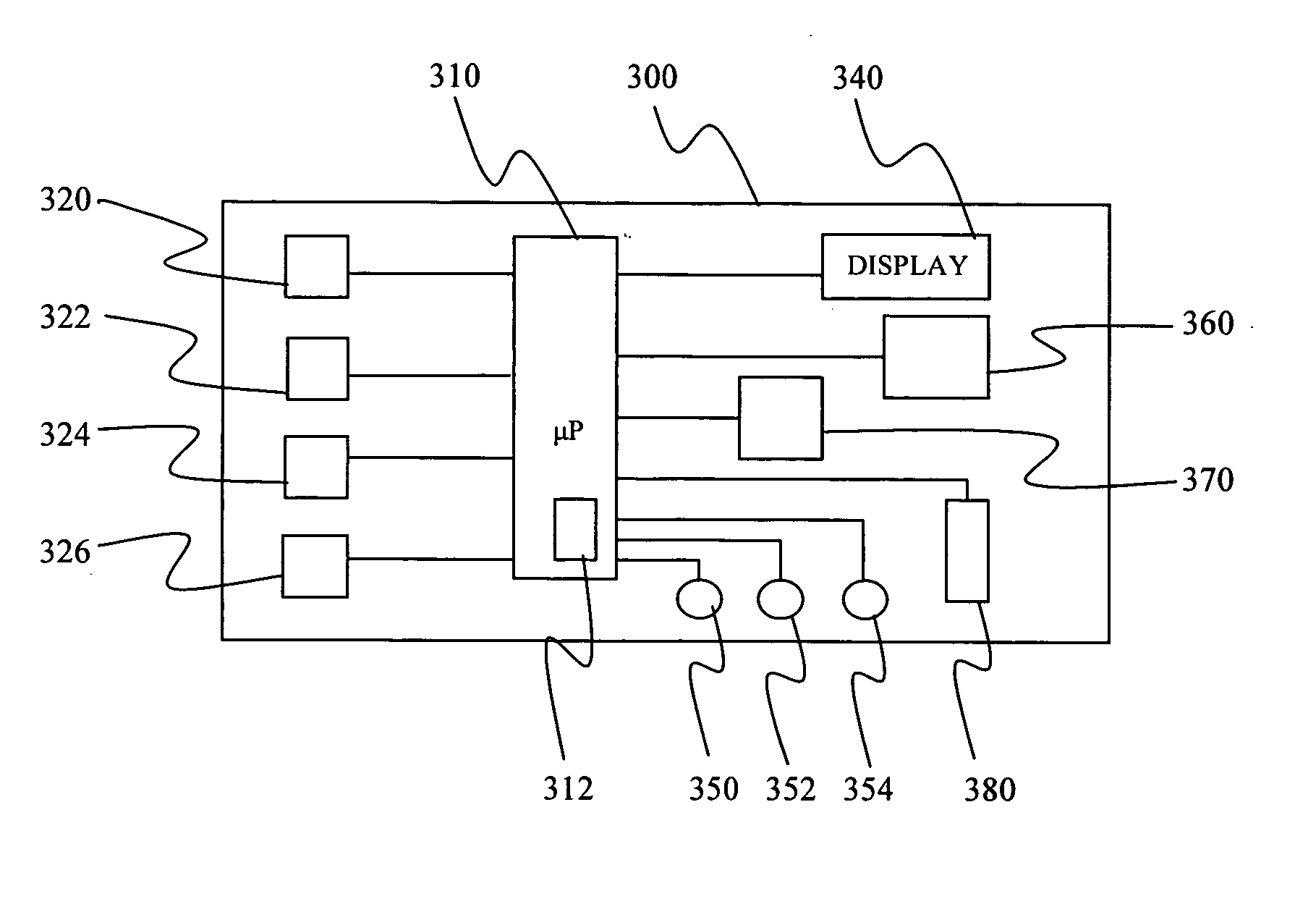
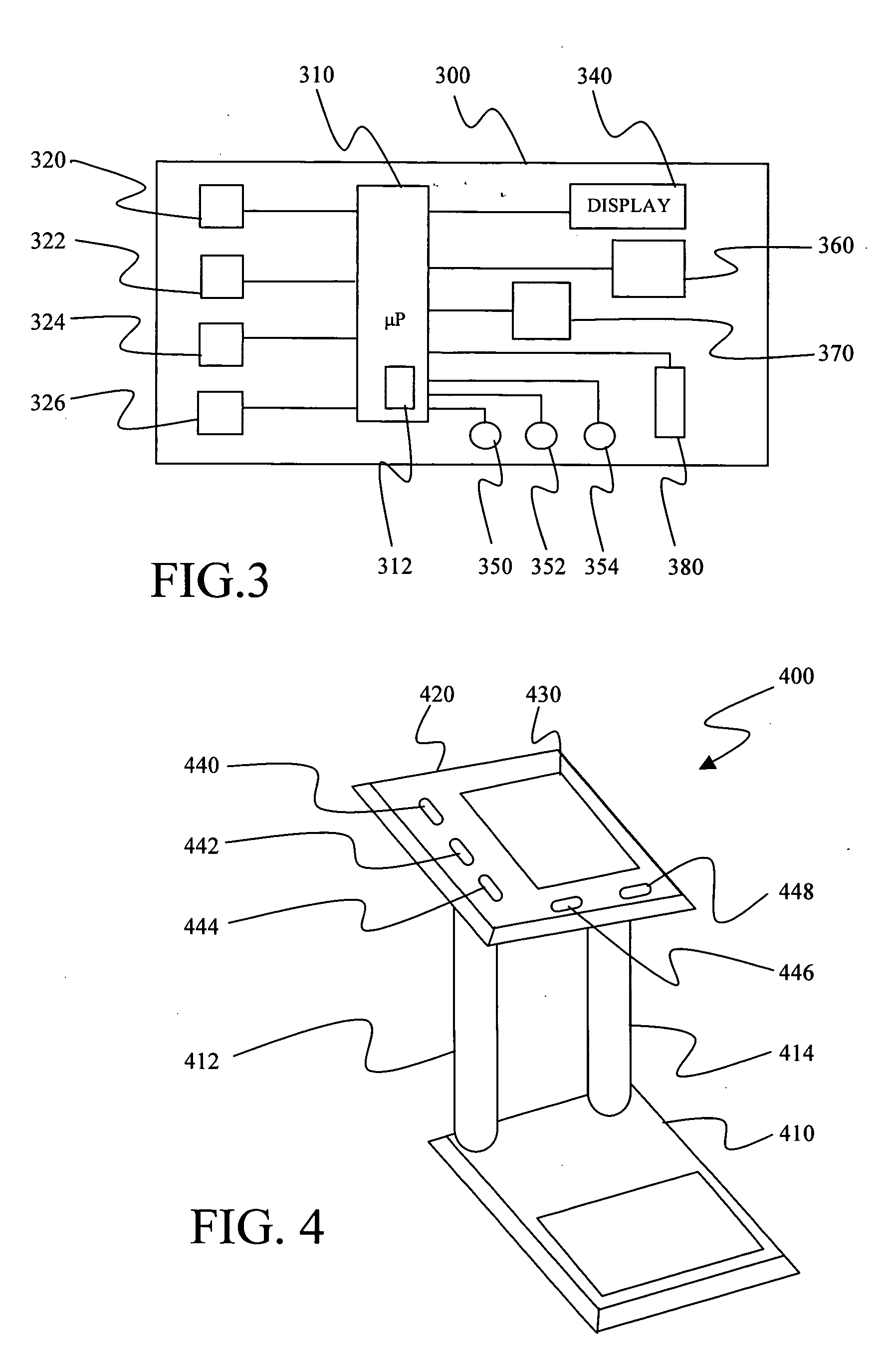
Monitoring device, method and system
InactiveUS20070106132A1Easy to viewLight weightEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterBlood oxygenationPulse rate
A monitoring device (20) and system (50) for monitoring the vital signs of a user is disclosed herein. The monitoring device (20) is preferably an article (25), an optical sensor (30) and a circuitry assembly (35). The monitoring device (20) preferably provides for the display of the following information about the user: pulse rate; blood oxygenation levels; calories expended by the user of a pre-set time period; target zones of activity; time; distance traveled; and dynamic blood pressure. The article (25) is preferably a band worn on a user's wrist, arm or ankle. The system (50) allows for real-time monitoring and display of the vital signs of an athlete or player during a live event.
Owner:ELHAG SAMMY I +2
Monitoring device
ActiveUS20150250422A1Easy to useComfortable to wearElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyElectricityCoupling
A monitoring device suitable for attachment to a surface of a subject, the device having a data collector and a processor. The data collector includes a flexible foil attached to a less flexible socket, where the foil forms a dermal side surface of the data collector for adhesion to a skin surface of a subject to be monitored. To enable communication of electrical signals between the data collector and the processor, the data collector includes a distribution structure formed as a pattern of an electrically conductive material on an outer surface of a foldable sheet. The foldable sheet forms a layer in the flexible foil and having an interface portion which is folded into an aperture in the socket to form a coupling inside the cavity for electrical communication with a matching coupling of the processor when the processor is received in the cavity.
Owner:BRAEMAR MFG +1
Monitoring device, method and system
InactiveUS20060069319A1Light weightComfortable to wearInertial sensorsCatheterBlood oxygenationPulse rate
A monitoring device (20) and method (200) for monitoring the health of a user is disclosed herein. The monitoring device (20) is preferably an article (25), an optical sensor (30), a circuitry assembly (35) a display member (40) and a control component (43). The monitoring device (20) preferably displays the following information about the user: pulse rate; blood oxygenation levels; calories expended by the user of a pre-set time period; target zones of activity; time; distance traveled; and dynamic blood pressure.
Owner:IMPACT SPORTS TECH
Electro-mechanical sexual stimulation device to be worn during intercourse
ActiveUS7931605B2Comfortable to wearCreate vibrationChiropractic devicesVibration massageClitorisVagina
A device for use by a female for sexual stimulation comprising an inner arm dimensioned for insertion into a vagina, to contact the wall of the vagina at or near the G-spot, an outer arm dimensioned to contact the clitoris, and a resilient U-shaped member connecting the inner and outer arms.
Owner:WOW TECH CANADA LTD
Actively ventilated helmet systems and methods
ActiveUS20100095439A1Prevent and remove condensationExcellent fit for eyeglass wearersEye treatmentHatsEngineeringMoisture sensor
Helmet systems and methods reduce the formation of vapor condensation within the helmet interior, and inhibit fogging of the helmet visor. Exemplary embodiments include a helmet shell having a venting tube, a visor coupled with the helmet shell, a humidity sensor that senses humidity within the helmet interior cavity, and a ventilation system that removes moist air from the helmet interior.
Owner:HABERVISION
Absorbent articles containing absorbent cores having zoned absorbency and methods of making same
InactiveUS7759540B2Improved ability to retain fluidPrevent leakageBaby linensTamponsAdhesiveEngineering
The present invention relates generally to an absorbent core for an absorbent article, and more particularly to an absorbent core having zoned absorbency due to specific placement of adhesives or specific lack of adhesive. Such absorbent cores provide the flexibility of creating precise zoning of particular properties throughout the core, and they provide improved comfort and fit.
Owner:PARAGON TRADE BRANDS
Flame-resistant fiber blend, yarn, and fabric, and method for making same
InactiveUS20060292953A1Improve flame retardant performanceReduce weightWarp knittingWoven fabricsYarnAramid
A fiber blend, a yarn spun from the fiber blend, and a fabric made from the yarn, wherein the fiber blend comprises: (a) about 40 wt.% to about 65 wt.% modacrylic fibers containing antimony, or FR acrylic fibers; (b) about 10 wt.% to about 50 wt.% cotton fibers or FR cotton fibers; (c) up to about 25 wt.% nylon fibers; and (d) greater than about 3 wt.% and less than 10 wt.% para-aramid fibers. The fabric is over 90 percent dyeable and is capable of achieving ASTM F1506 certification with an Arc Thermal Performance Value greater than 8.0 cal / cm2. The fabric is woven or knitted, and has a weight of about 4.0 oz. / yd.2 to about 10.5 oz. / yd.2. The fabric is suitable for garments worn during activities in which there is potential for exposure to flame and / or electrical arc.
Owner:SPRINGFIELD
Optical configurations for head-worn see-through displays
ActiveUS20170023790A1Reduce weightComfortable to wearPolarising elementsSee-through displayDisplay device
Aspects of the present invention relate to methods and systems for providing high quality display images in see-through head-worn optics.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
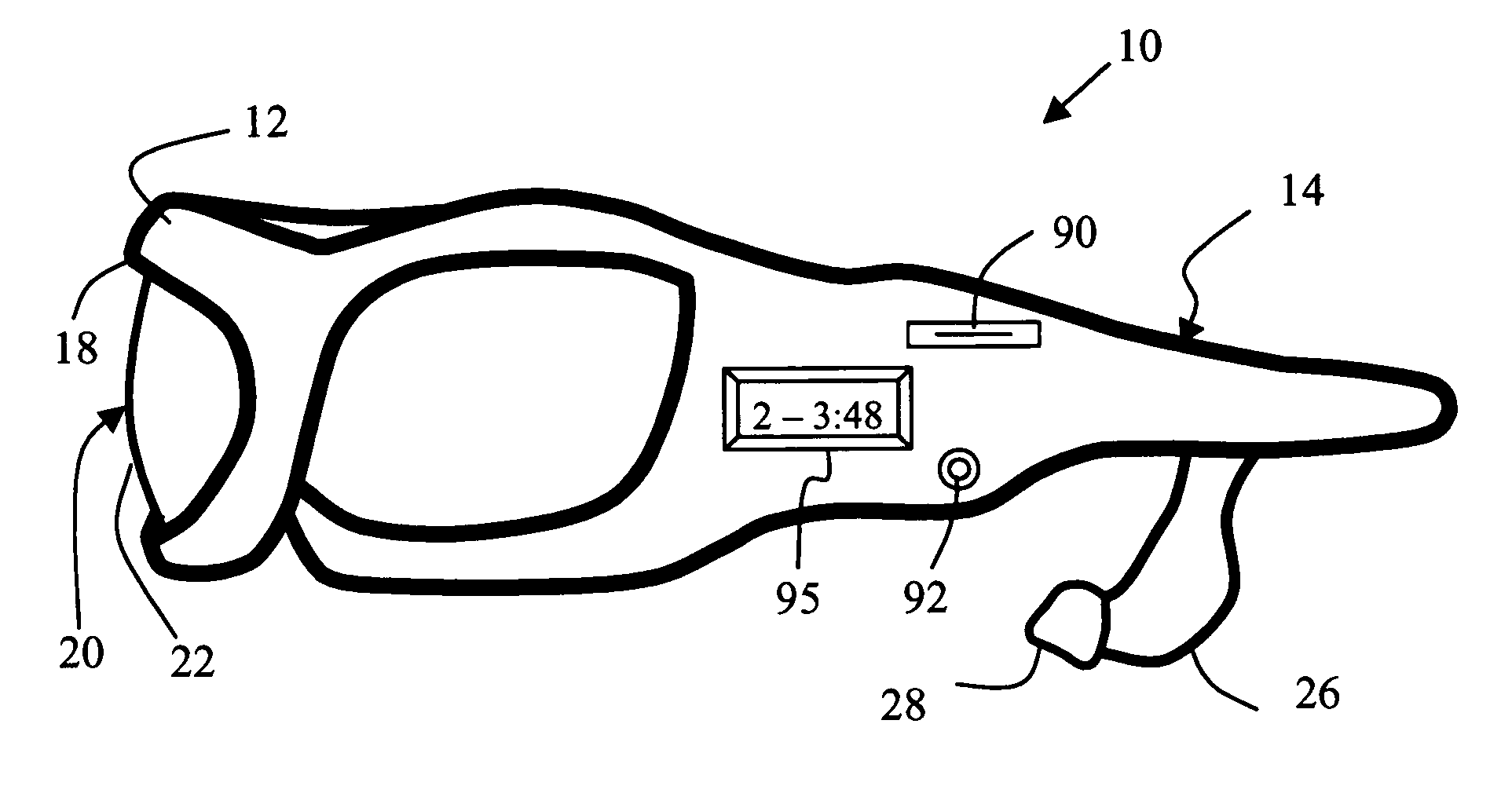
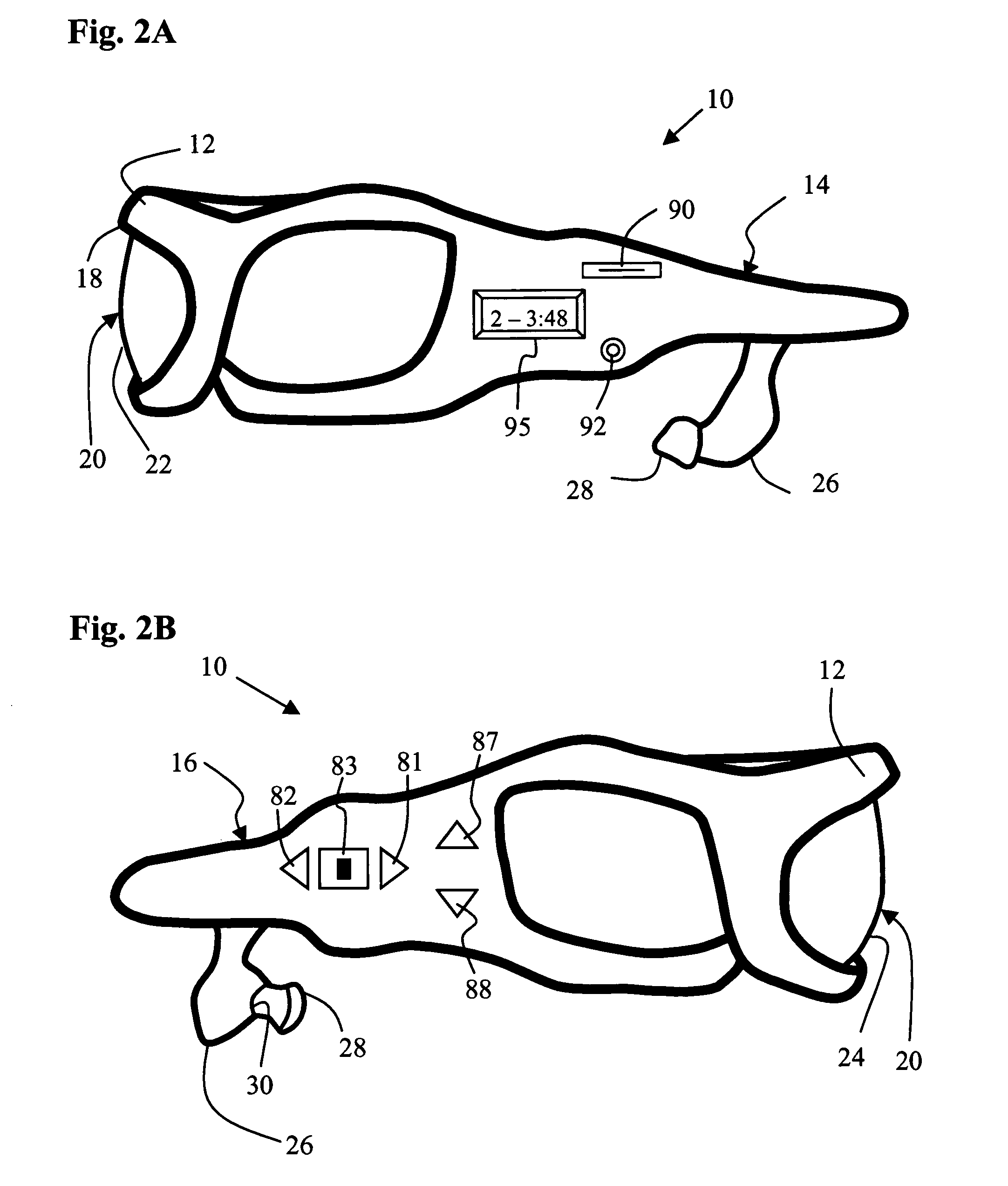
Audio eyeglasses
InactiveUS20060034478A1Easily program and operateConveniently wearMicrophonesHeadphones for stereophonic communicationRight templeTransducer
Audio eyeglasses comprise: a frame assembly having left and right temples and a front; a lens assembly secured to the frame assembly; and an audio unit disposed in the frame assembly. The audio unit comprises: (i) mass storage means for storing a plurality of digital audio files and selectively outputting at least one of said digital audio files; (ii) a playback unit adapted to receive said at least one digital audio file from said mass storage means and convert it to an electrical audio output signal; and (iii) control means for enabling said user to select said at least one audio file for output and control the playback thereof by said playback unit. At least one, and preferably two, audio transducers are attached to the frame assembly and proximate an ear of the user. The transducers are operably connected to the audio unit to receive the electrical audio output signal and convert it to a sound wave transmitted to the user's ears. Further provided is a personal audio system incorporating the audio eyeglasses and a docking station adapted to receive the eyeglasses and be connected to a computer for download of digital audio files.
Owner:DAVENPORT KEVIN E
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com