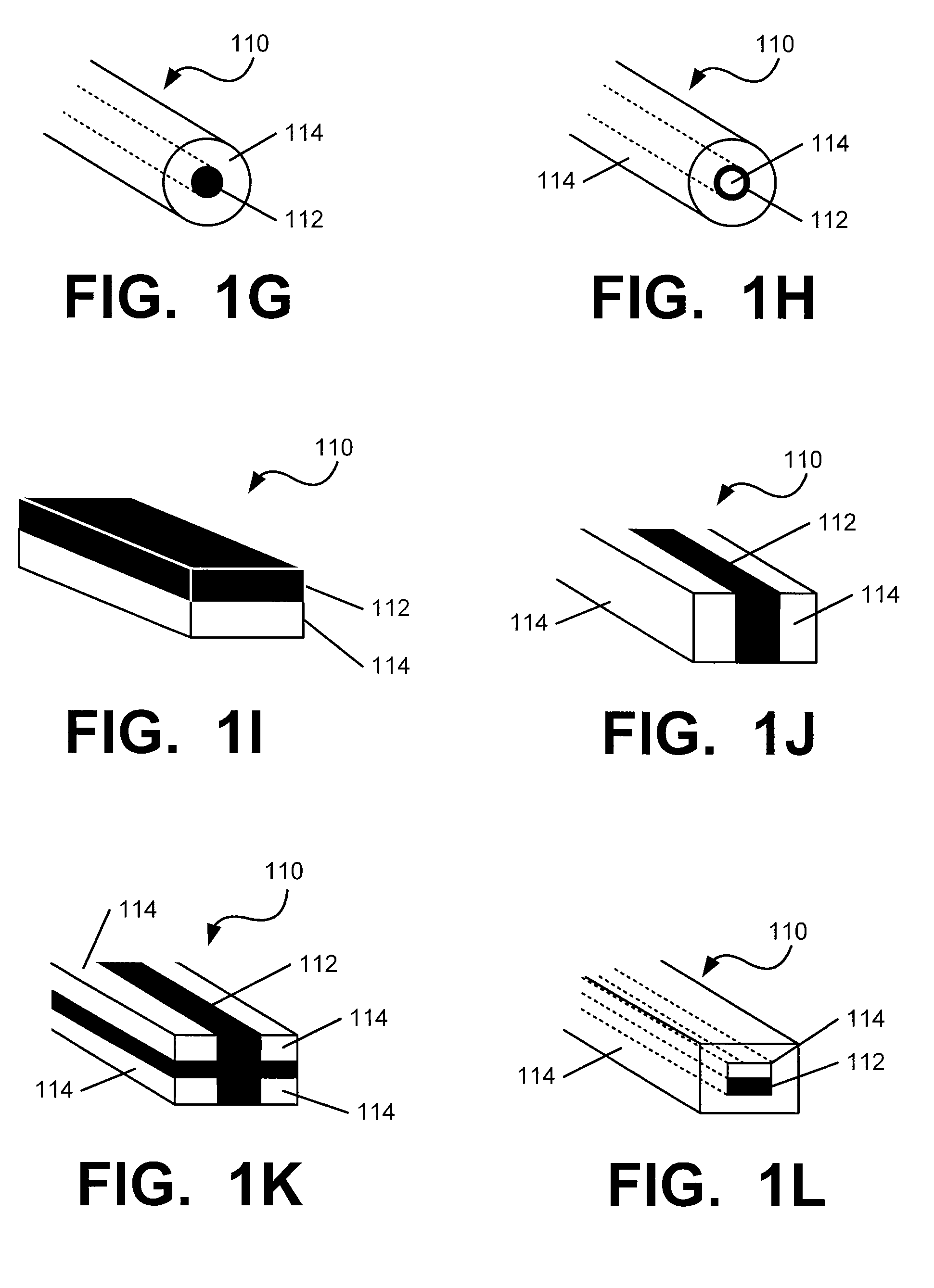
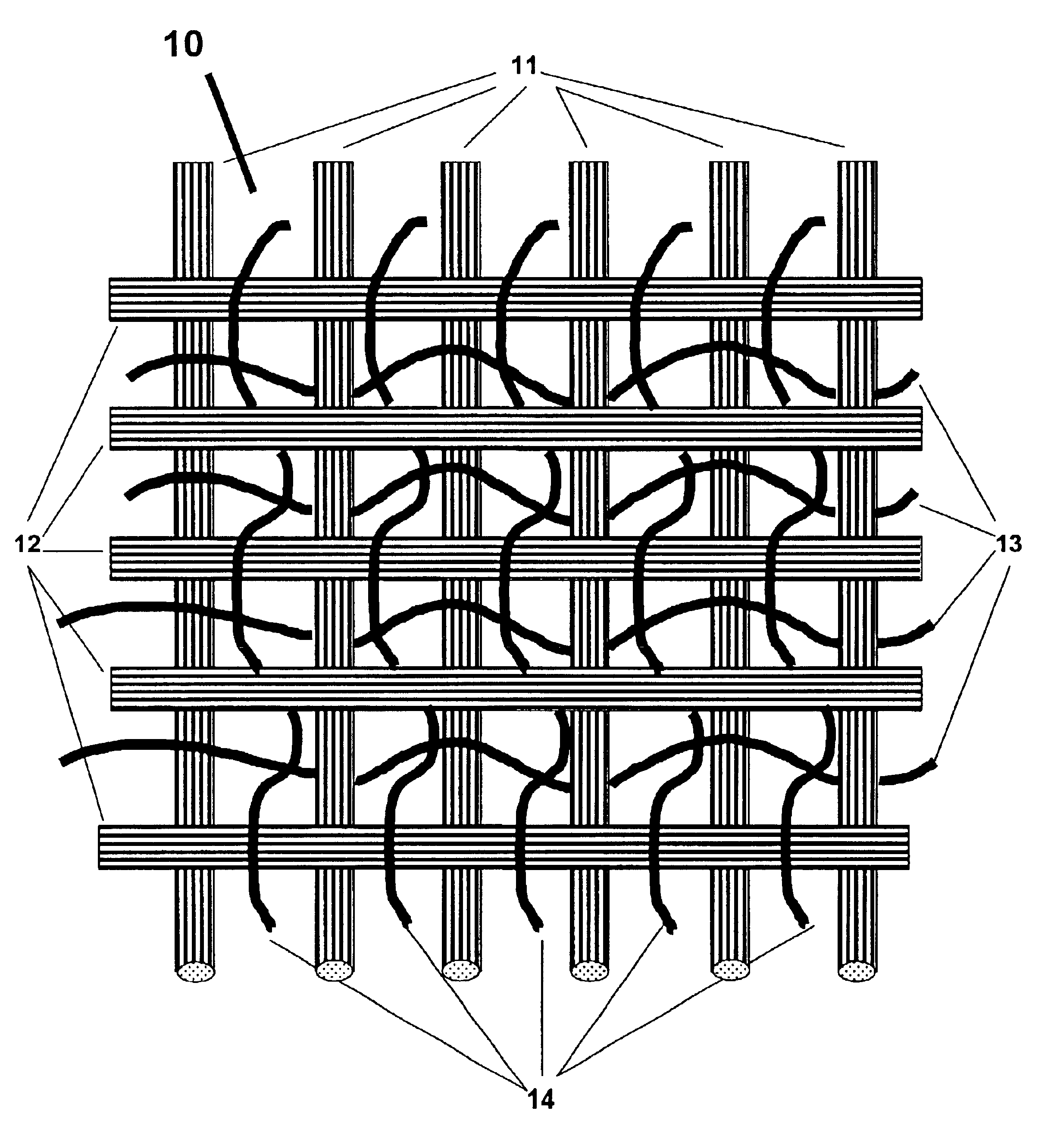
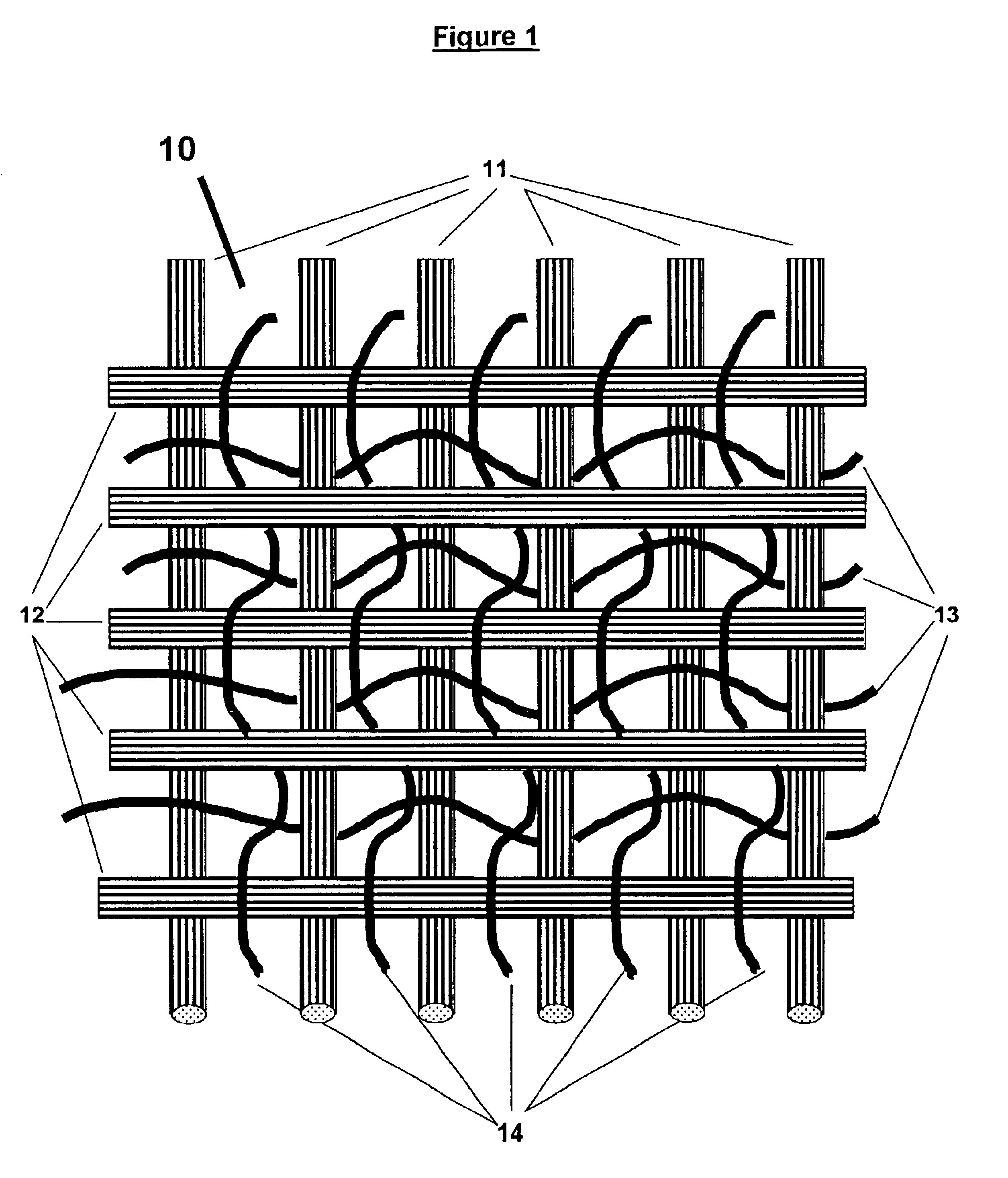
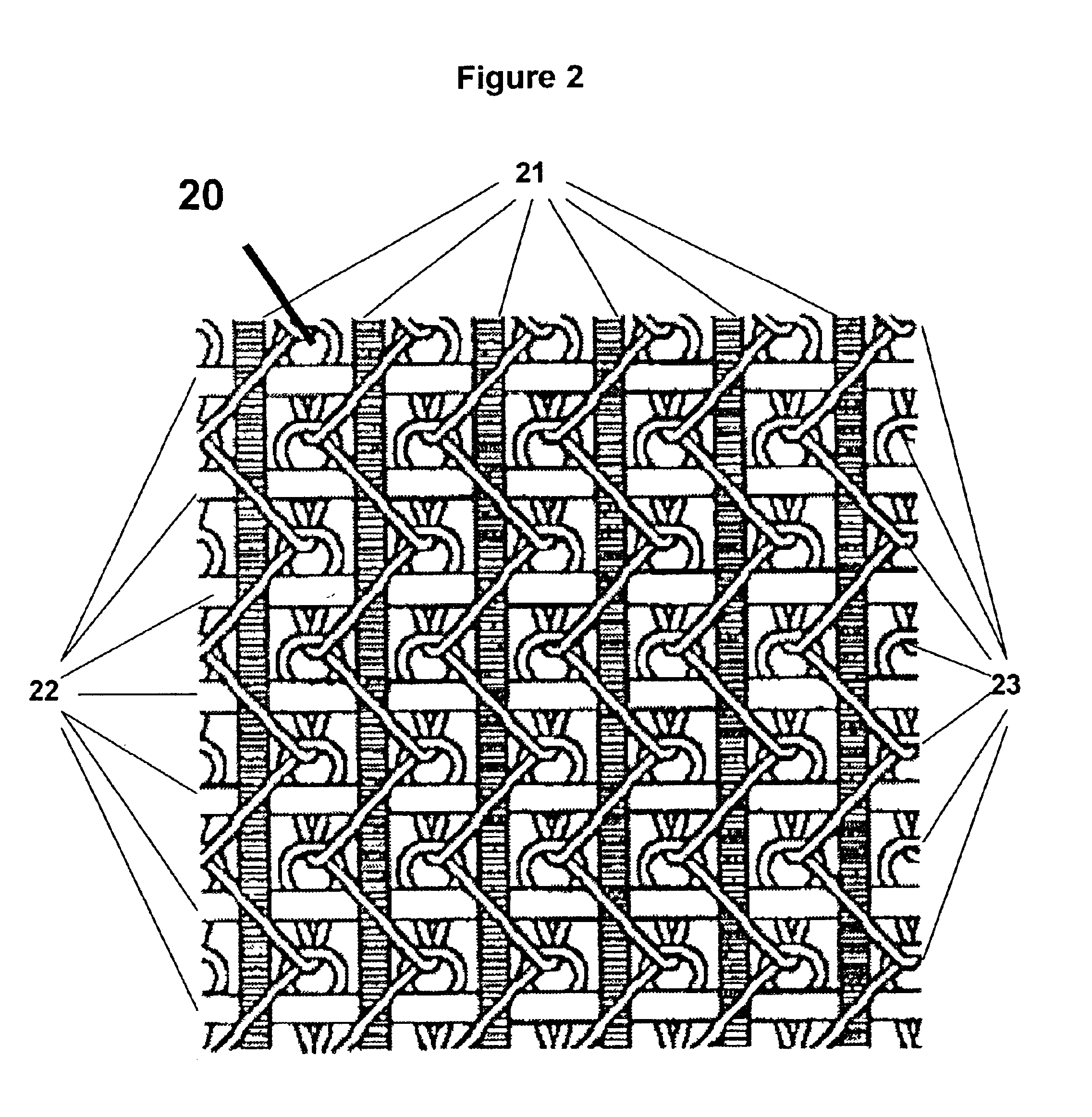
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
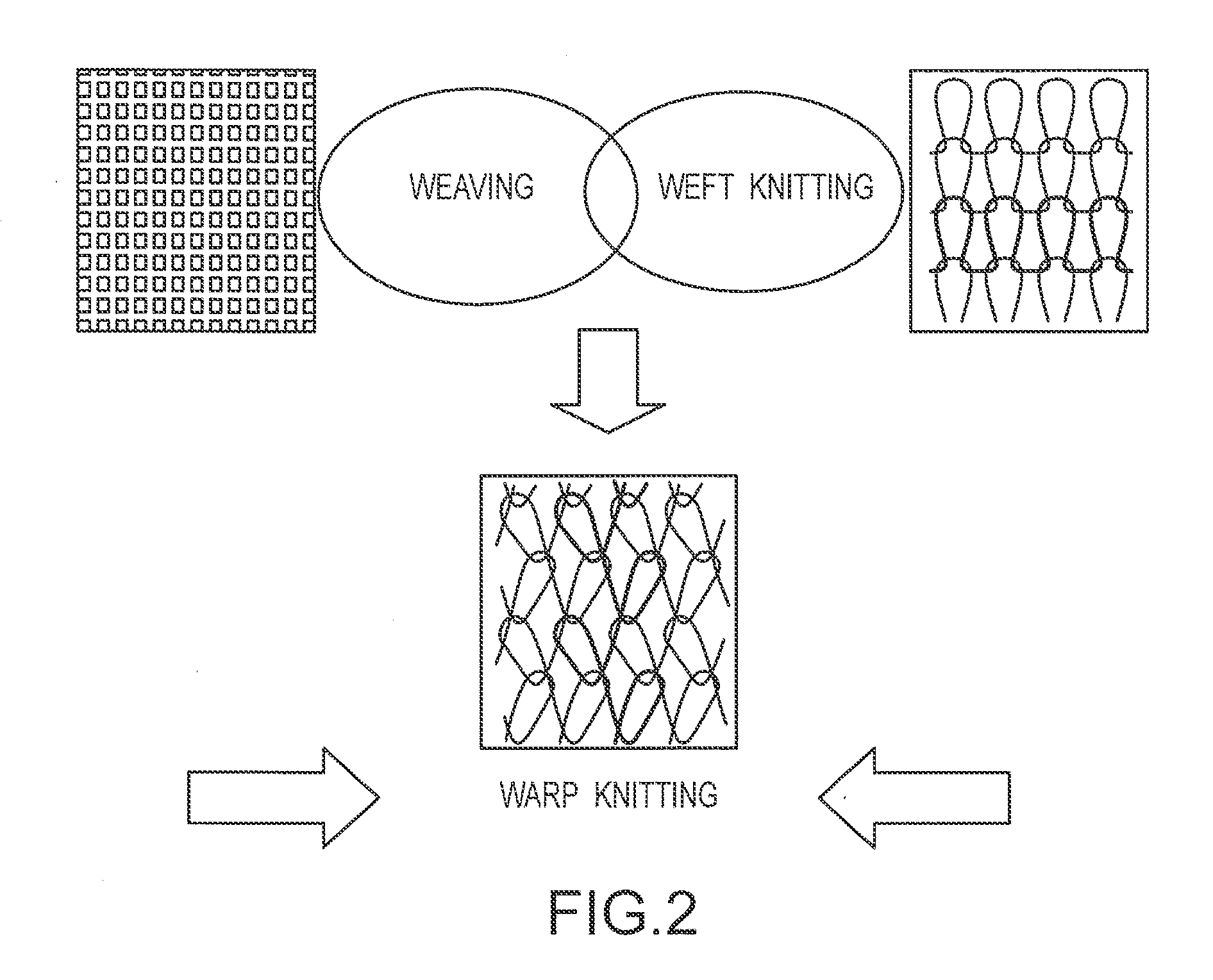
7002results about "Warp knitting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
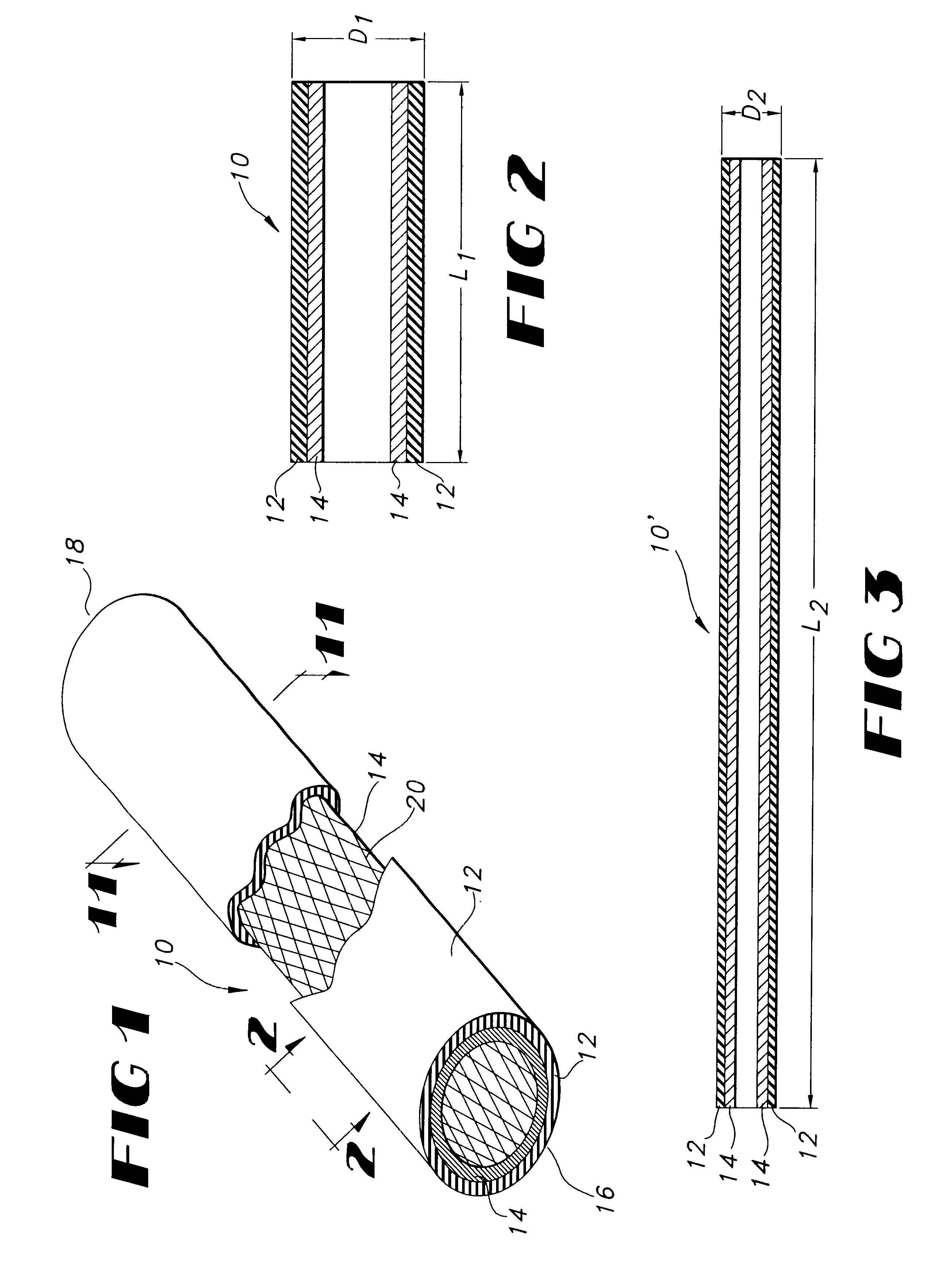
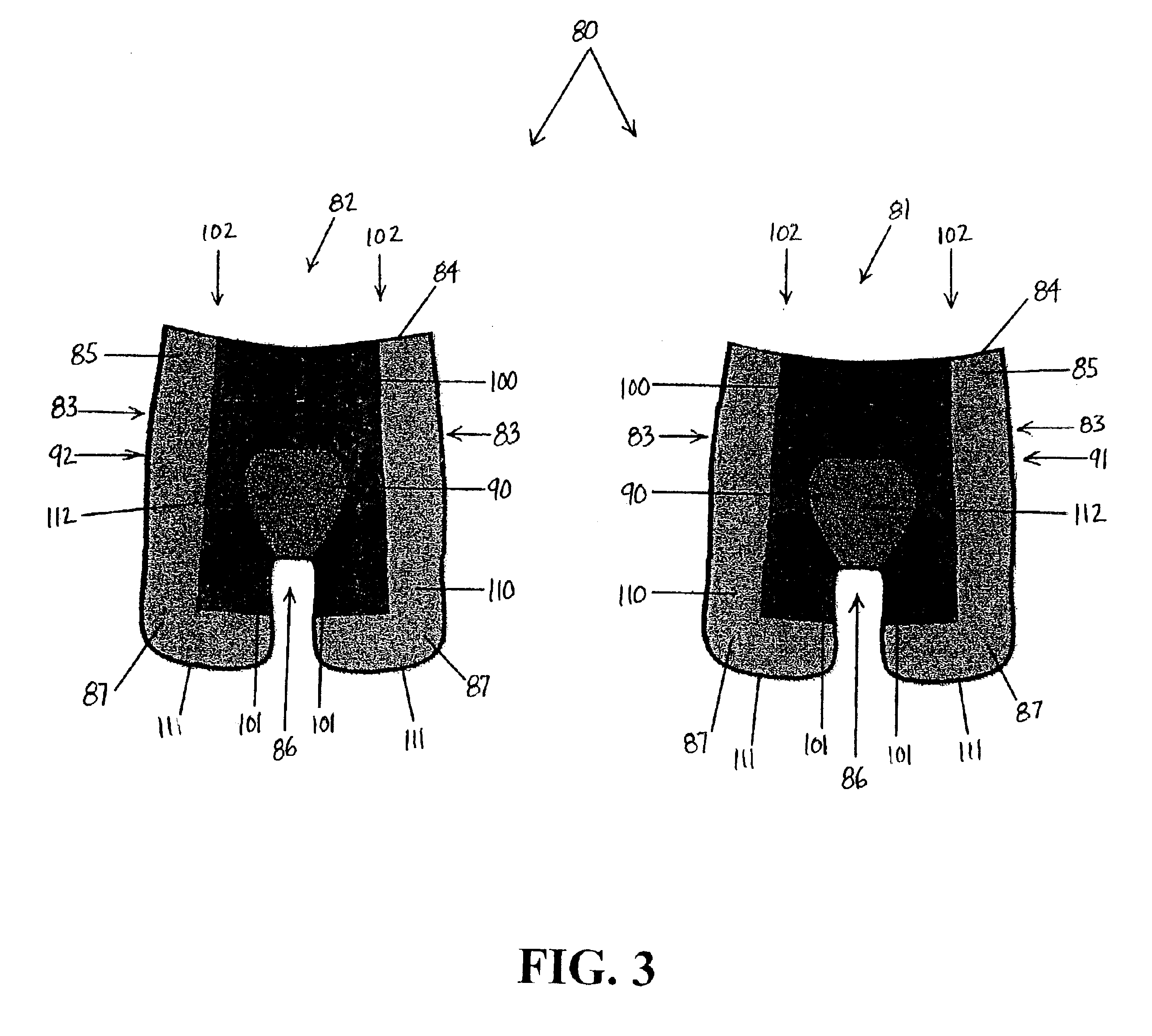
Medical film
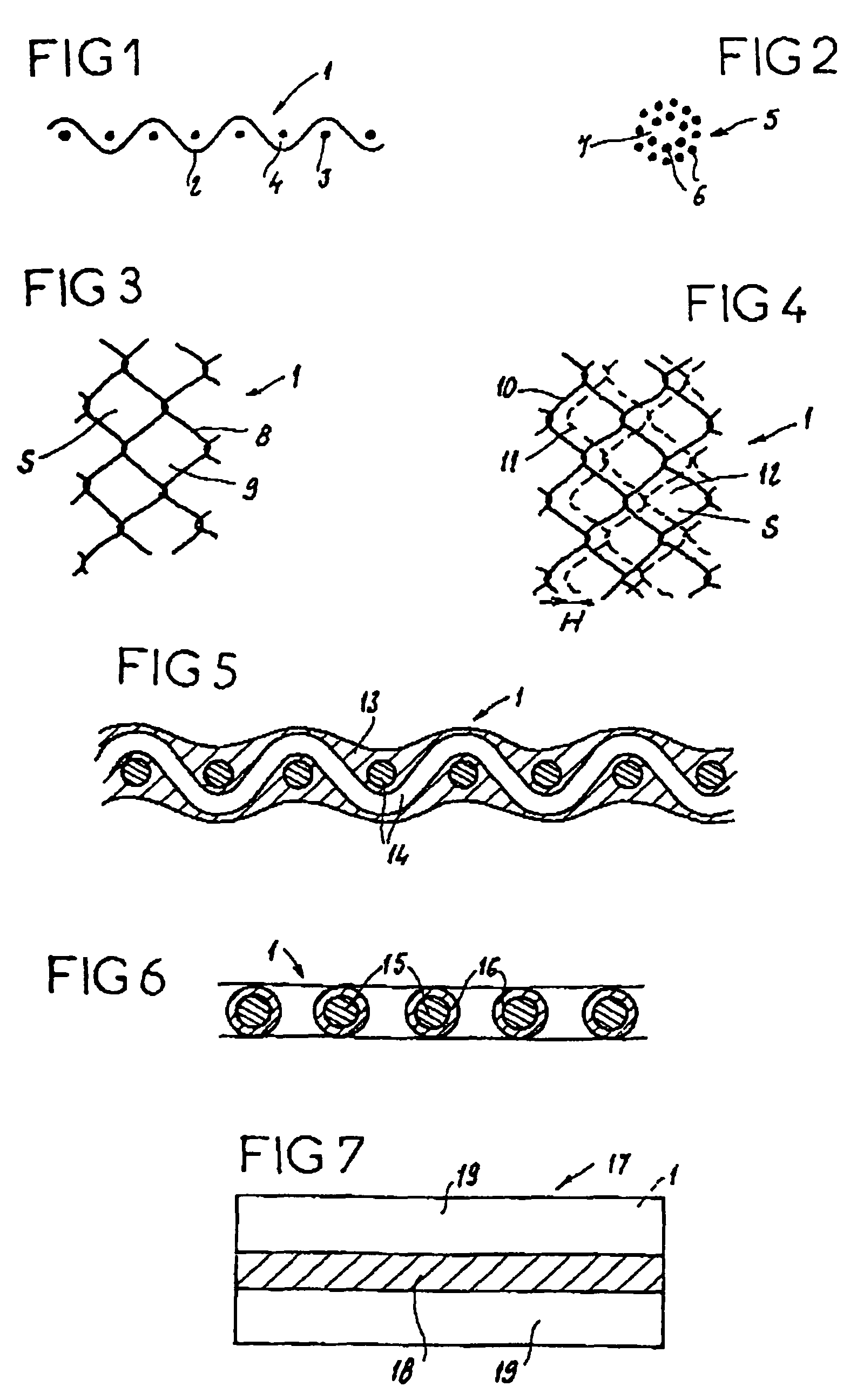
InactiveUS7718556B2Good biocompatibilityHigh strengthSuture equipmentsBiocideGelatin filmThin membrane
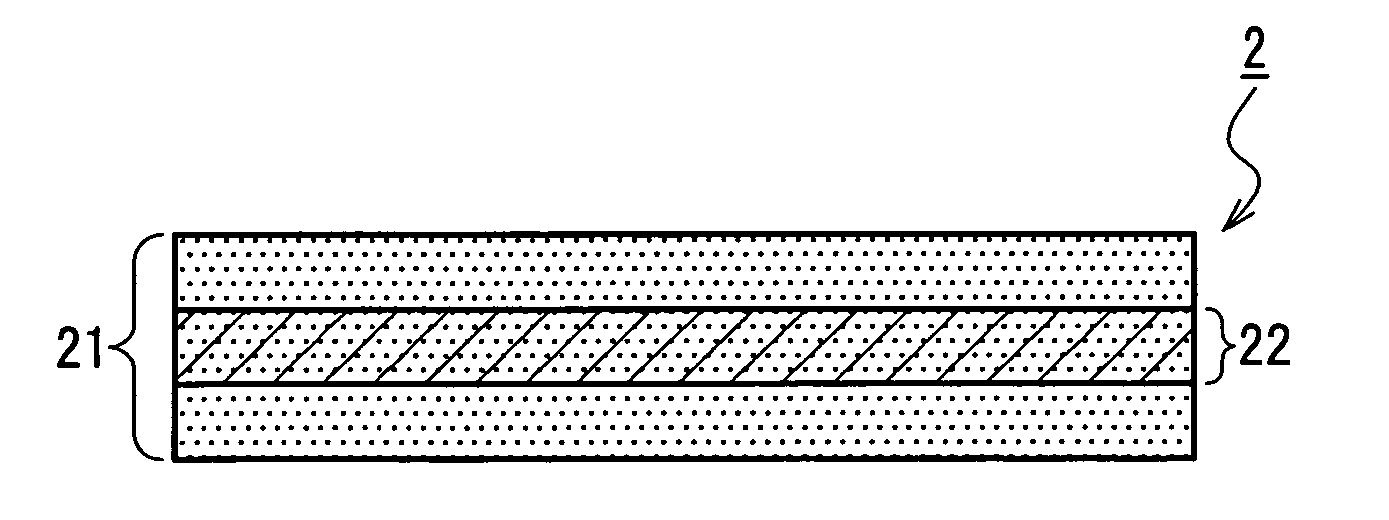
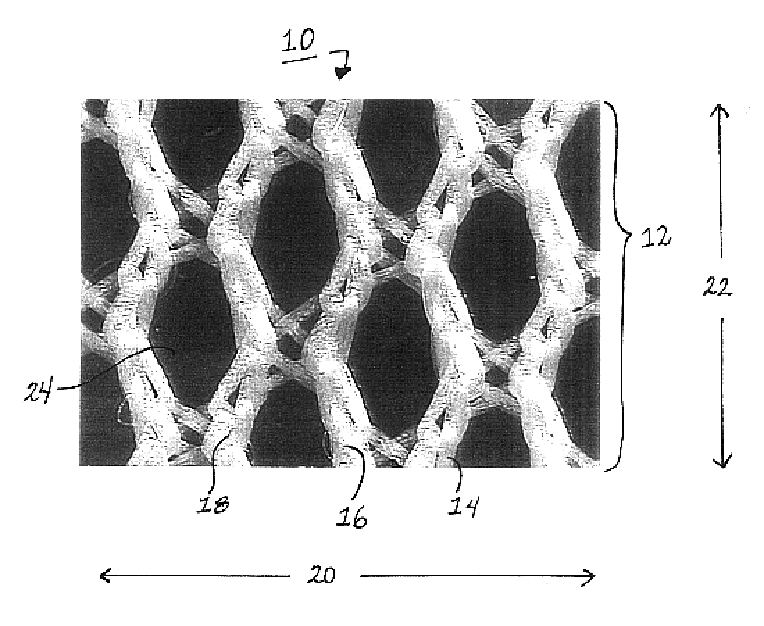
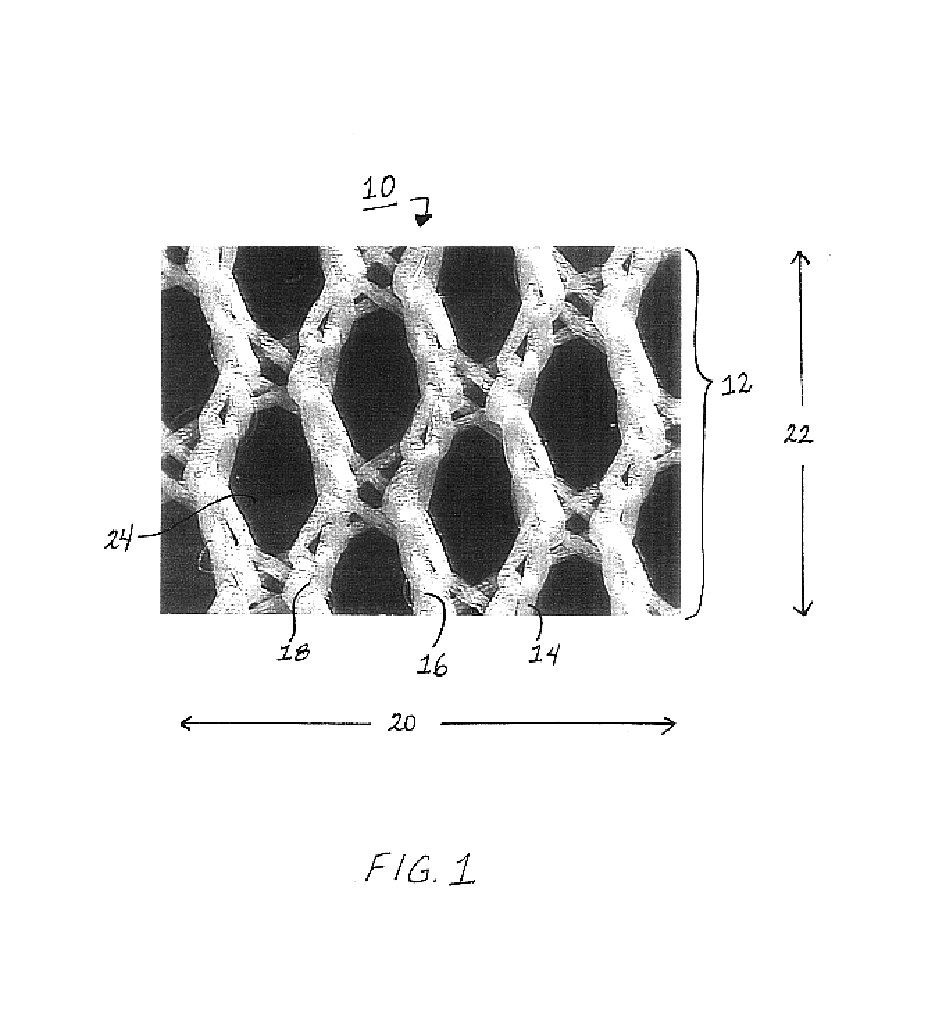
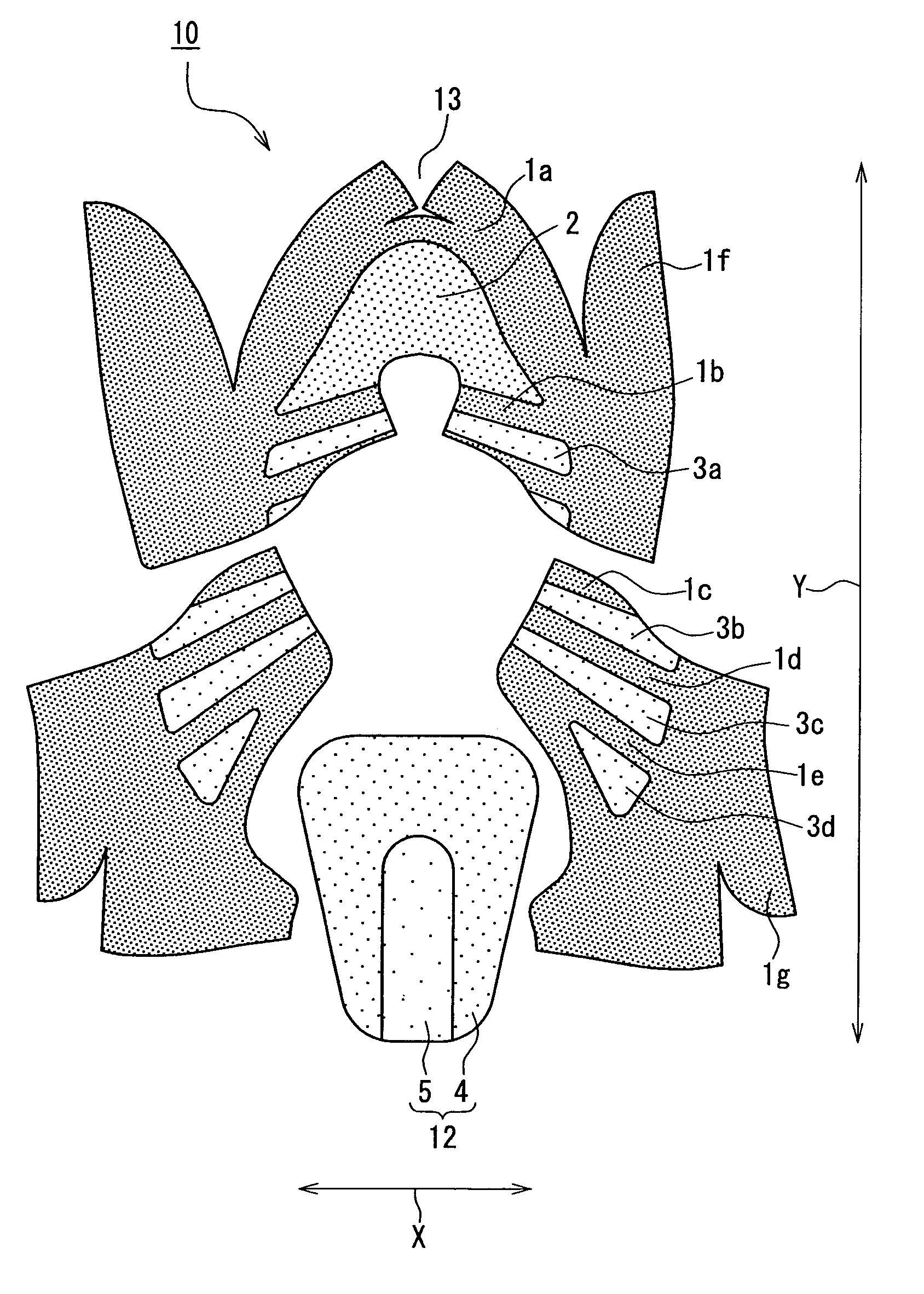
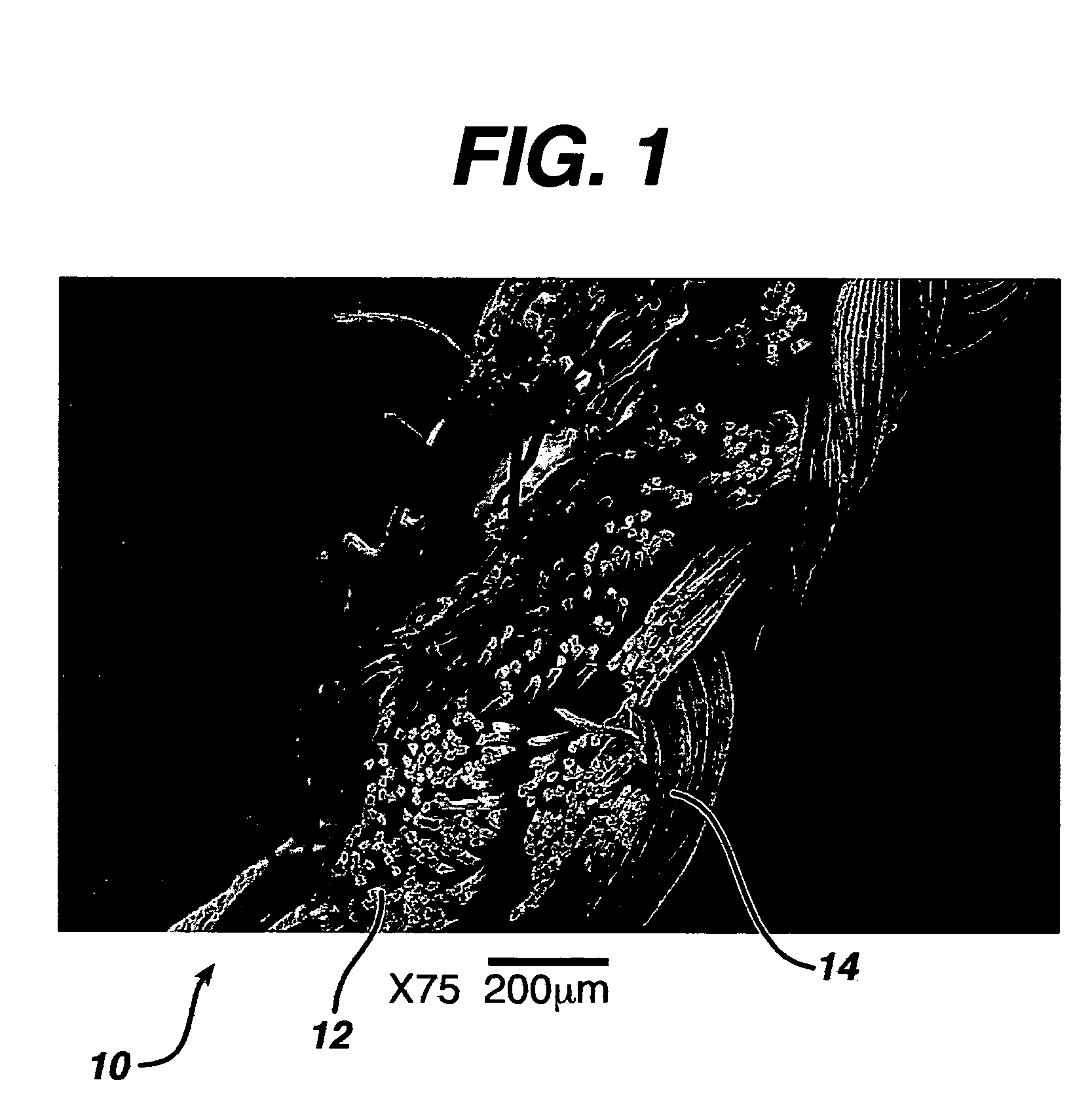
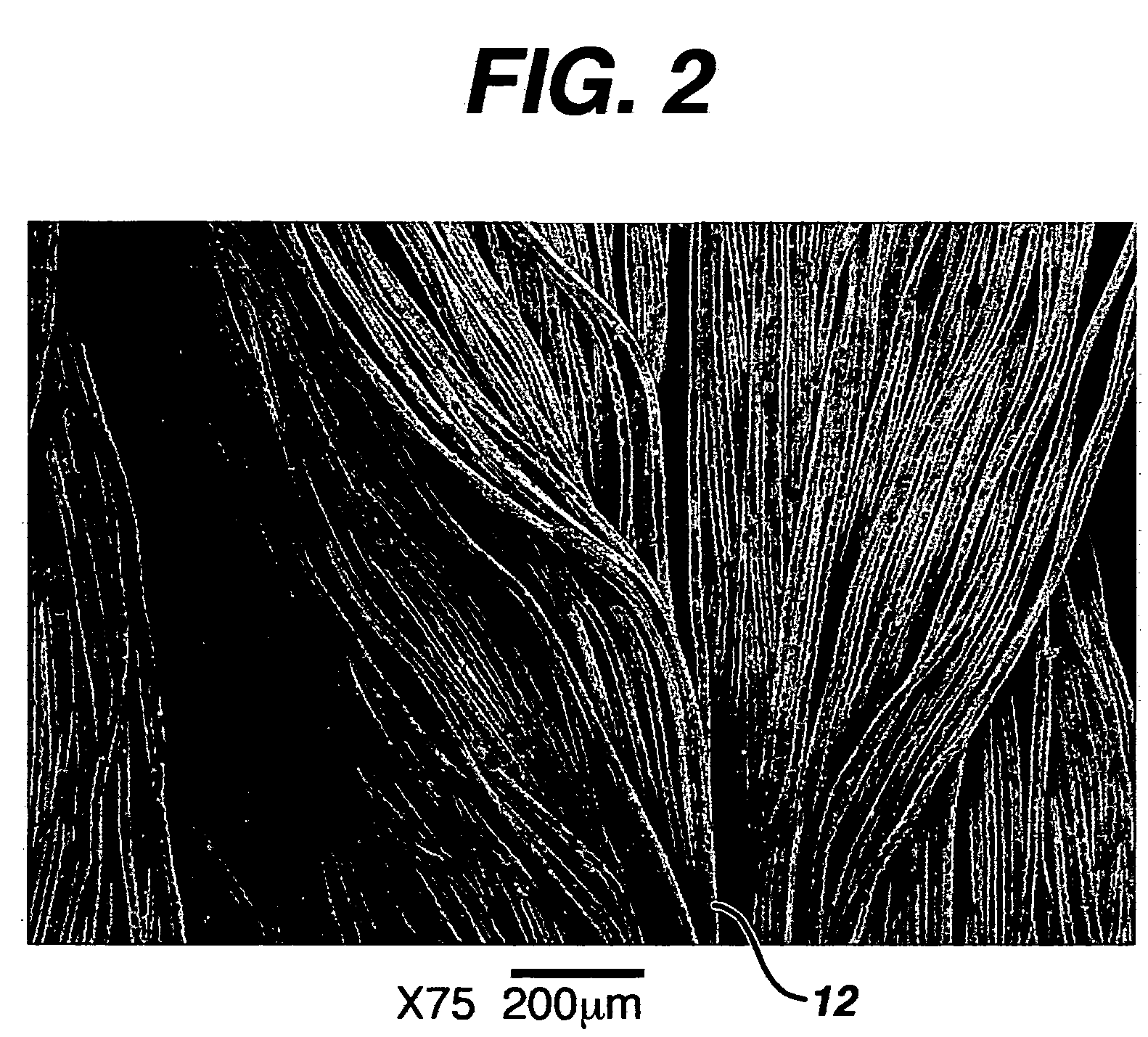
A medical film that is excellent in biocompatibility and bioabsorbability and has an excellent strength in suturing and bonding is provided. A reinforcing material 12 made of a biodegradable polymer is placed in a gelatin solution so as to allow the solution to infiltrate in the reinforcing material 12 and then the gelatin is dried. This allows the gelatin that has infiltrated entirely in an internal part of the reinforcing material 12 to gel, thereby forming a gelatin film 11. Thus, a medical film 1 in which the reinforcing material 12 and the gelatin film 11 are integrated is obtained. The gelatin film 11 preferably is a cross-linked gelatin film.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Prosthesis for reinforcement of tissue structures
The present invention relates to a composite prosthesis for reinforcement of a tissue structure, including a porous textile support which includes an arrangement of threads each composed of at least one filament of nonabsorbable polymer material, said textile support defining a microporous texture including the interstices located between at least two threads at the sites of contact of one thread with at least one other thread, wherein, in at least one protected zone of the textile support, a hydrophilic absorbable material coats the textile support, forming a film enveloping and penetrating into the arrangement of threads, occluding at least the microporous texture, but without forming a plane layer covering at least one face of the textile support.It also relates to a process for preparing such a composite reinforcement prosthesis.
Owner:SOFRADIM PROD SAS
Selectively absorbable/biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs and applications thereof
A family of selectively absorbable / biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs includes different combinations of biostable and absorbable / biodegradable yarns assembled as initially interdependent, load-bearing components, transitioning to exhibit independent functional properties during in vivo end-use. The family of constructs consists of two groups, one group is made of fiber-reinforced composites of high compliance, absorbable matrices of segmented polyaxial copolyesters reinforced with multifilament yarn constructs, which are combinations of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers and at least one absorbable / biodegradable fiber selected from silk fibers and multifilament yarns made from linear segmented, l-lactide copolyesters and poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates, are useful in orthopedic, maxillofacial, urological, vascular, hernial repair and tissue engineering applications. The second group is made of coated and uncoated, warp-knitted mesh constructs for use in hernial, vascular, and urological tissue repair and tissue engineering.
Owner:POLY MED
Implantable devices having swellable grip members
The present disclosure relates to implantable medical devices including swellable tissue gripping elements and methods of forming such devices. The implantable medical device may comprise a biocompatible substrate having a surface comprising at least one swellable grip member. The implantable medical device may take on the form of a surgical mesh, patch, buttress, or pledget and the swellable member may comprise spikes and / or spiked naps. The implantable medical device may also contain a bioactive agent.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
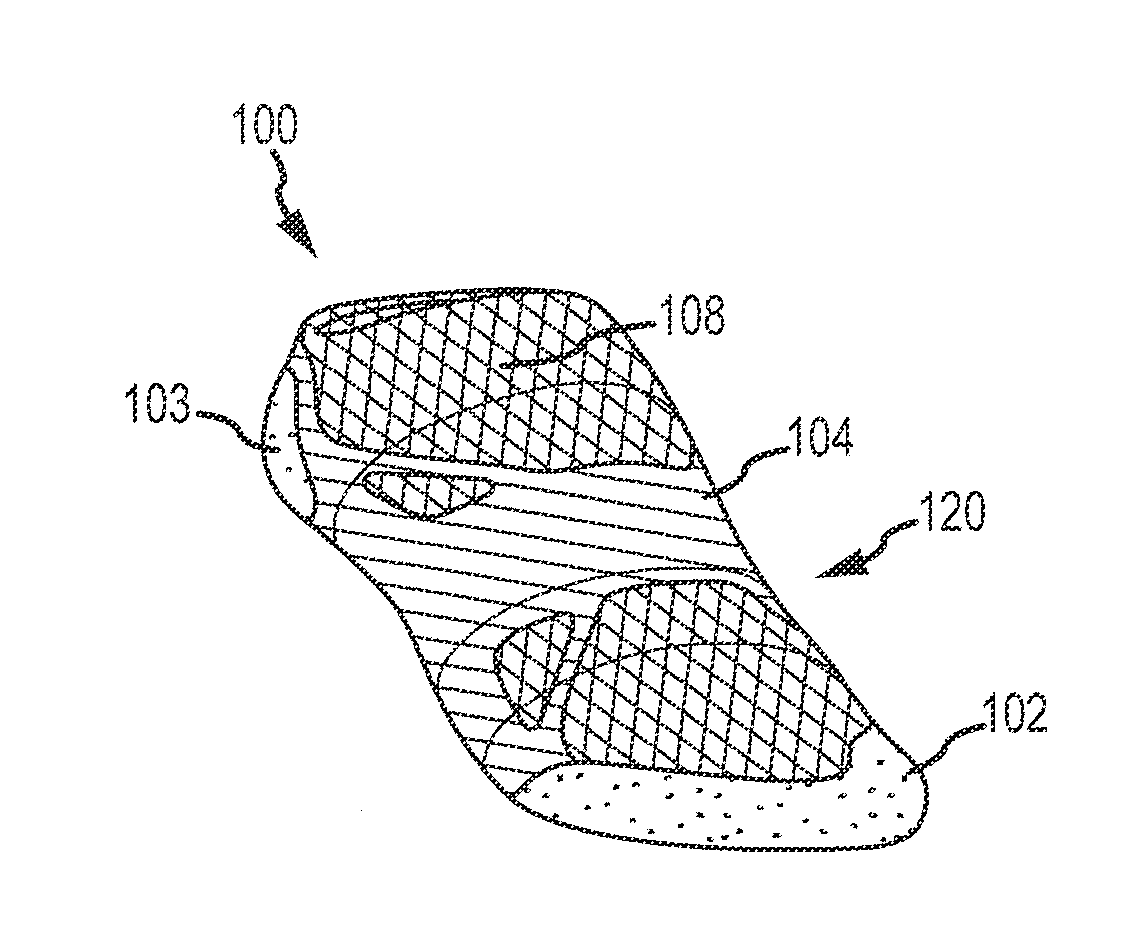
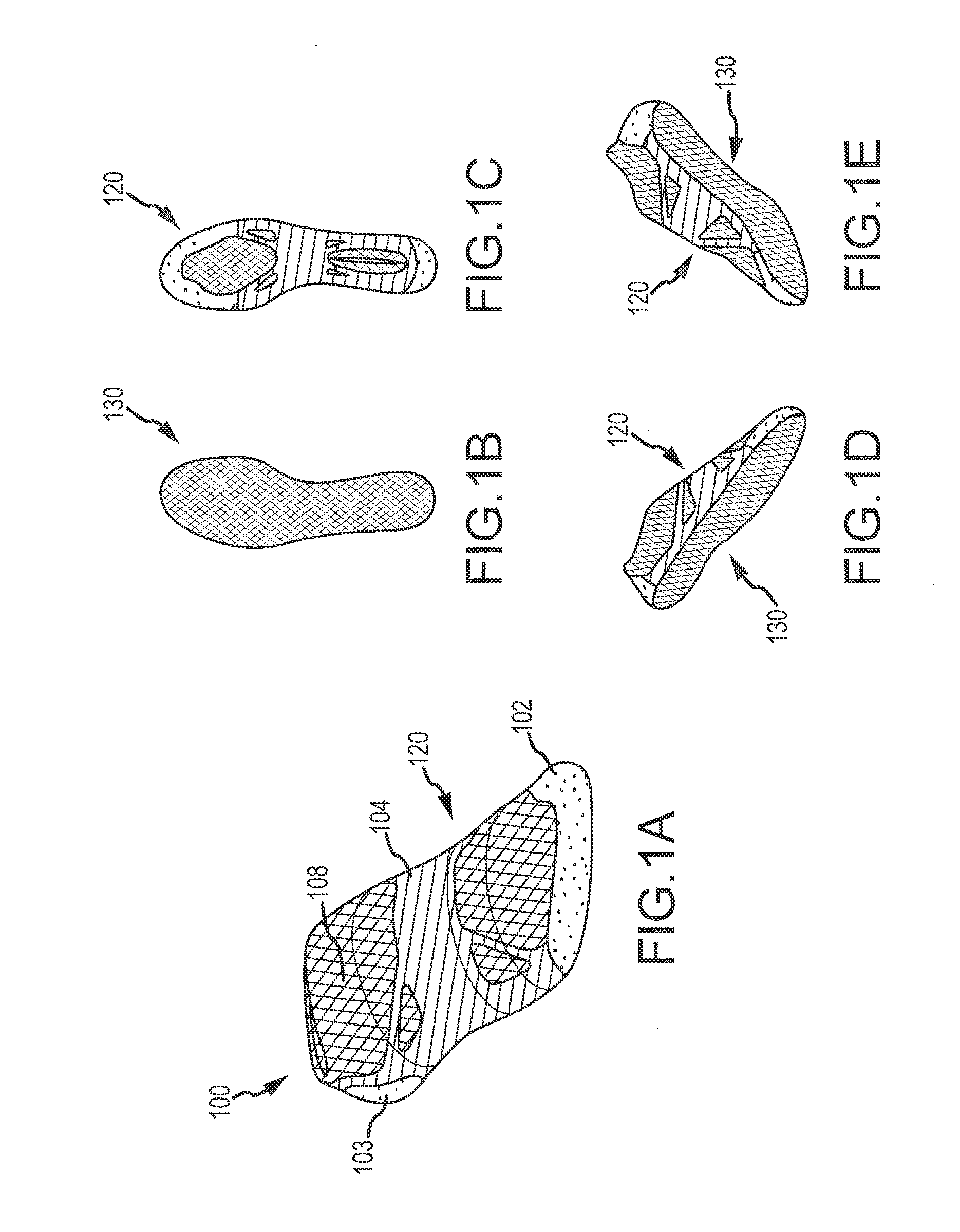
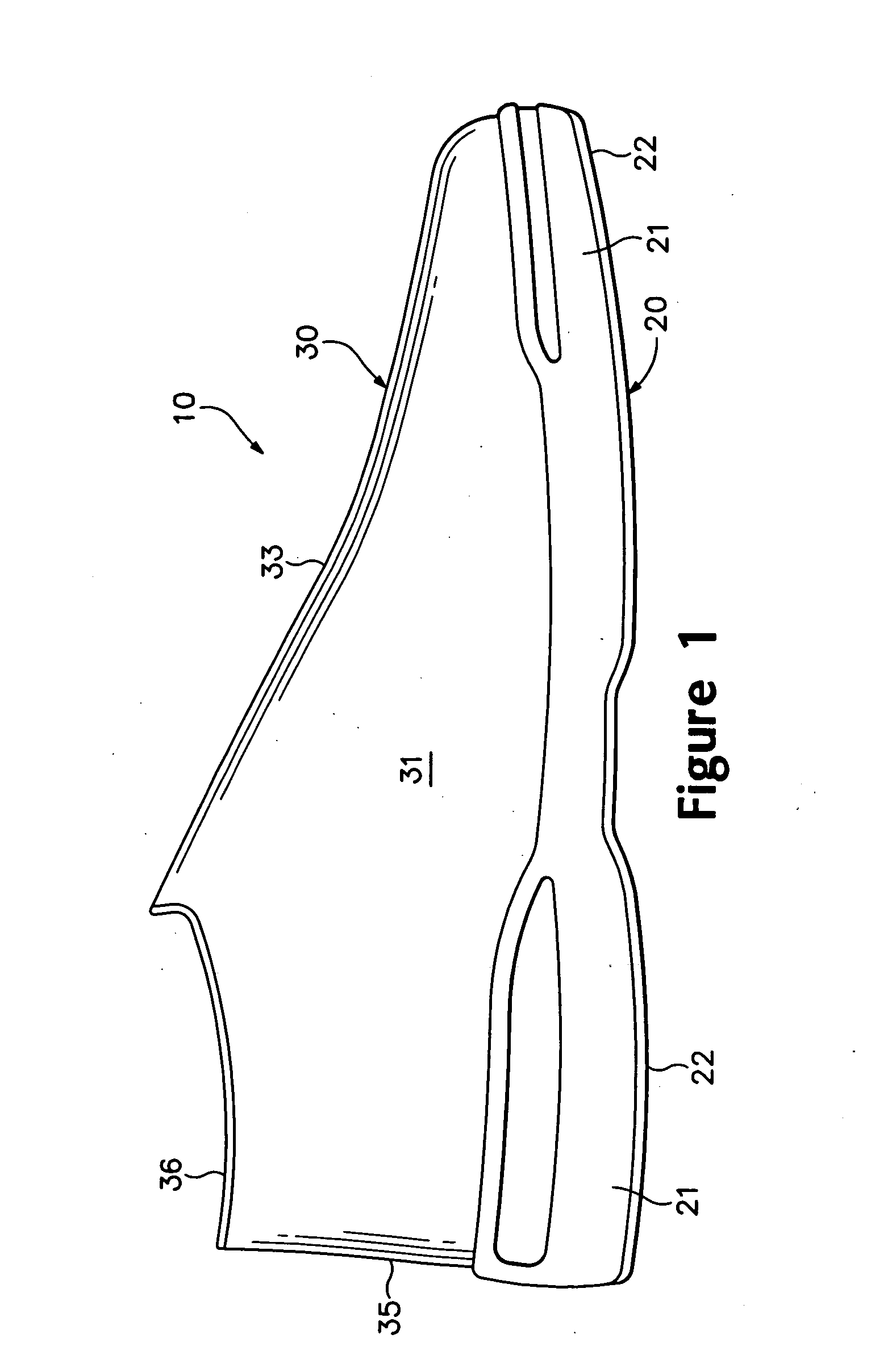
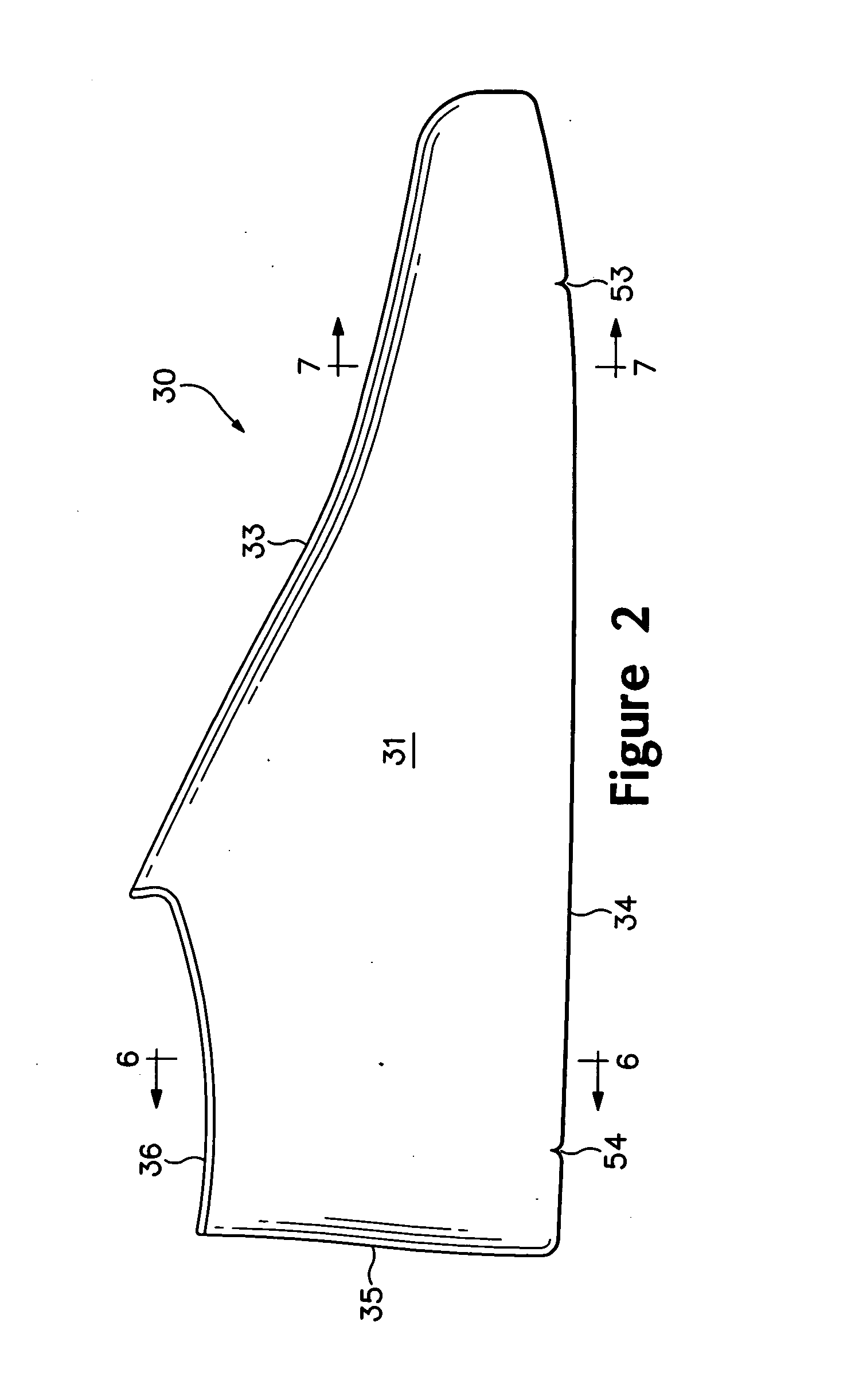
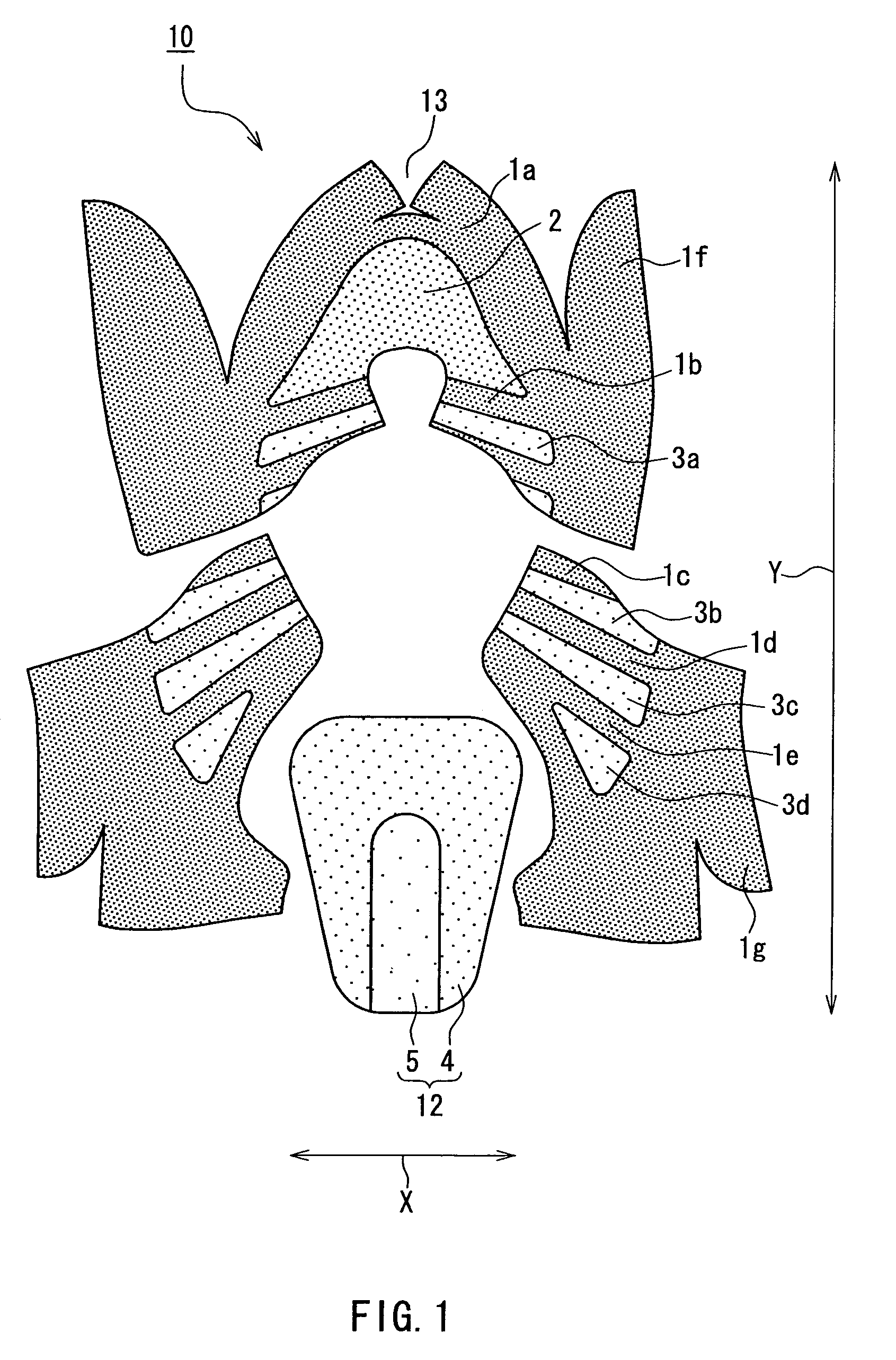
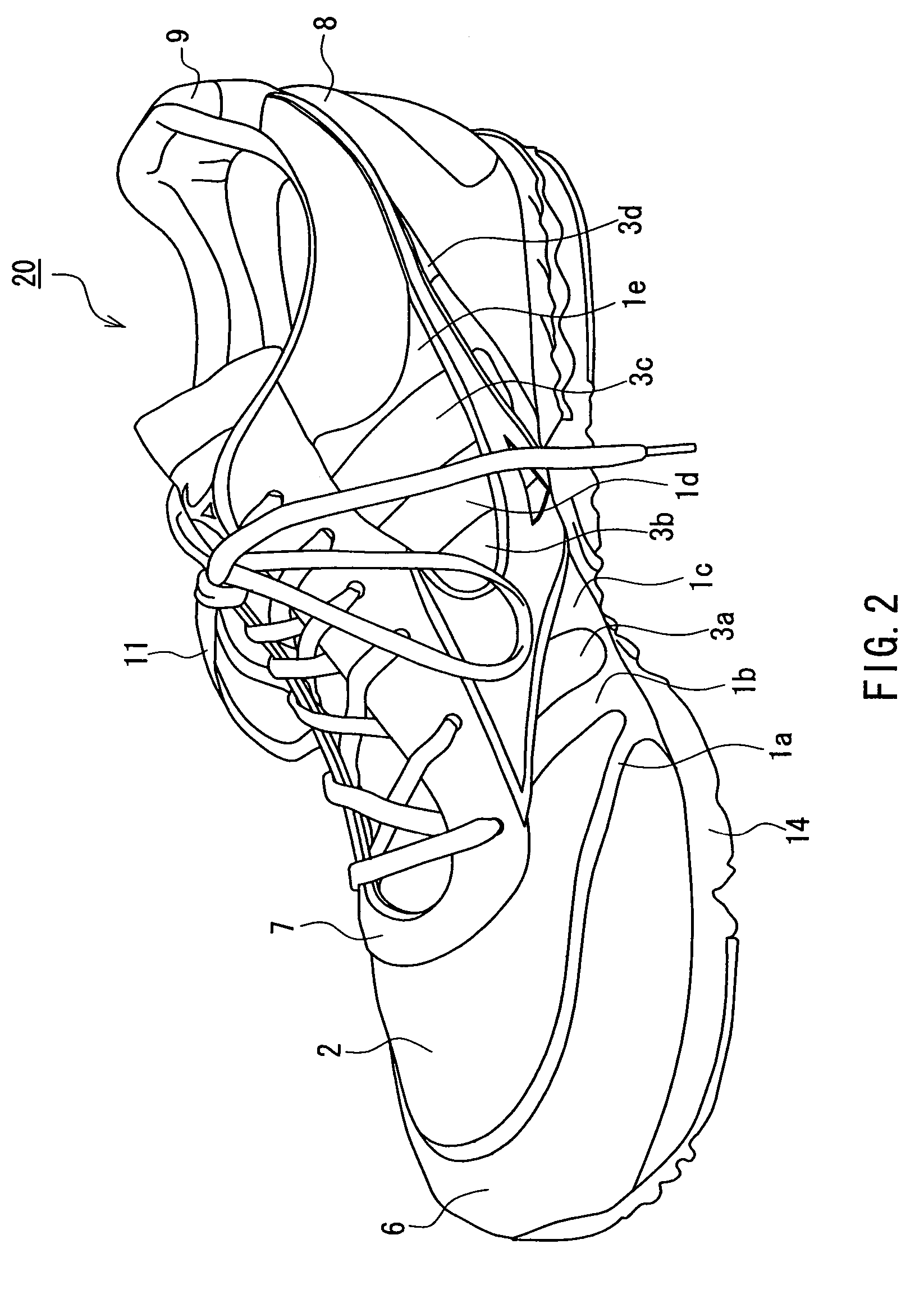
Article of footwear having a textile upper
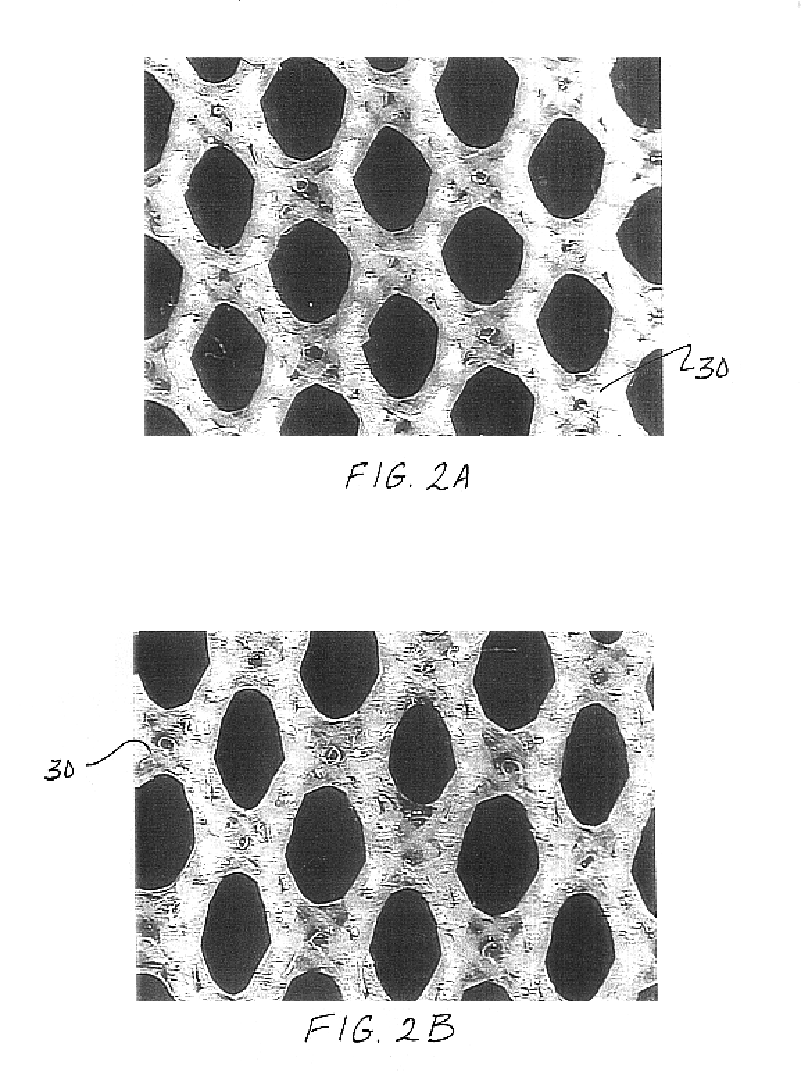
An article of footwear and a method of manufacturing the article of footwear are disclosed. The footwear may include an upper and a sole structure. The upper incorporates a textile element with edges that are joined together to define at least a portion of a void for receiving a foot. The textile element may also have a first area and a second area with a unitary construction. The first area is formed of a first stitch configuration, and the second area is formed of a second stitch configuration that is different from the first stitch configuration to impart varying textures to a surface of the textile element. Various warp knitting or weft knitting processes may be utilized to form the textile element.
Owner:NIKE INC
Seamless upper for footwear and method for making the same
InactiveUS20120255201A1Ease and efficiency of productionShorten assembly timeShoemaking devicesLastingInterior spaceEngineering
Owner:DASHAMERICA INC D B A PEARL IZUMI USA
Article of footwear having a textile upper
ActiveUS20050193592A1Improve understandingShoemaking devicesWeft knittingEngineeringMechanical engineering
An article of footwear and a method of manufacturing the article of footwear are disclosed. The footwear may include an upper and a sole structure. The upper incorporates a textile element with edges that are joined together to define at least a portion of a void for receiving a foot. The textile element may also have a first area and a second area with a unitary construction. The first area is formed of a first stitch configuration, and the second area is formed of a second stitch configuration that is different from the first stitch configuration to impart varying textures to a surface of the textile element. Various warp knitting or weft knitting processes may be utilized to form the textile element.
Owner:NIKE INC
Coated sling material
InactiveUS7025063B2Minimize complexityGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesUrethraShort urethra
The present invention relates to a sling, methods of making and using a sling, and kits comprising a sling for treating urinary incontinence. The sling has multiple elongation properties that serve to improve the support of the urethra. The sling may comprise a coated material adapted for urethral suspension. The coated sling has properties that appear to enhance the sling elongation characteristics. The coated sling further includes properties that reduce its susceptibility to bacterial infections. The sling further includes properties to enhance the proper tensioning of the sling.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Cardiac disease treatment method
A jacket of biological compatible material has an internal volume dimensioned for an apex of the heart to be inserted into the volume and for the jacket to be slipped over the heart. The jacket has a longitudinal dimension between upper and lower ends sufficient for the jacket to surround a lower portion of the heart with the jacket surrounding a valvular annulus of the heart and further surrounding the lower portion to cover at least the ventricular lower extremities of the heart. The jacket is adapted to be secured to the heart with the jacket surrounding at least the valvular annulus and the ventricular lower extremities. The jacket is adjustable on the heart to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and assume a maximum adjusted volume for the jacket to constrain circumferential expansion of the heart beyond the maximum adjusted volume during diastole and to permit unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole.
Owner:MARDIL
Method of thermoforming a bladder structure
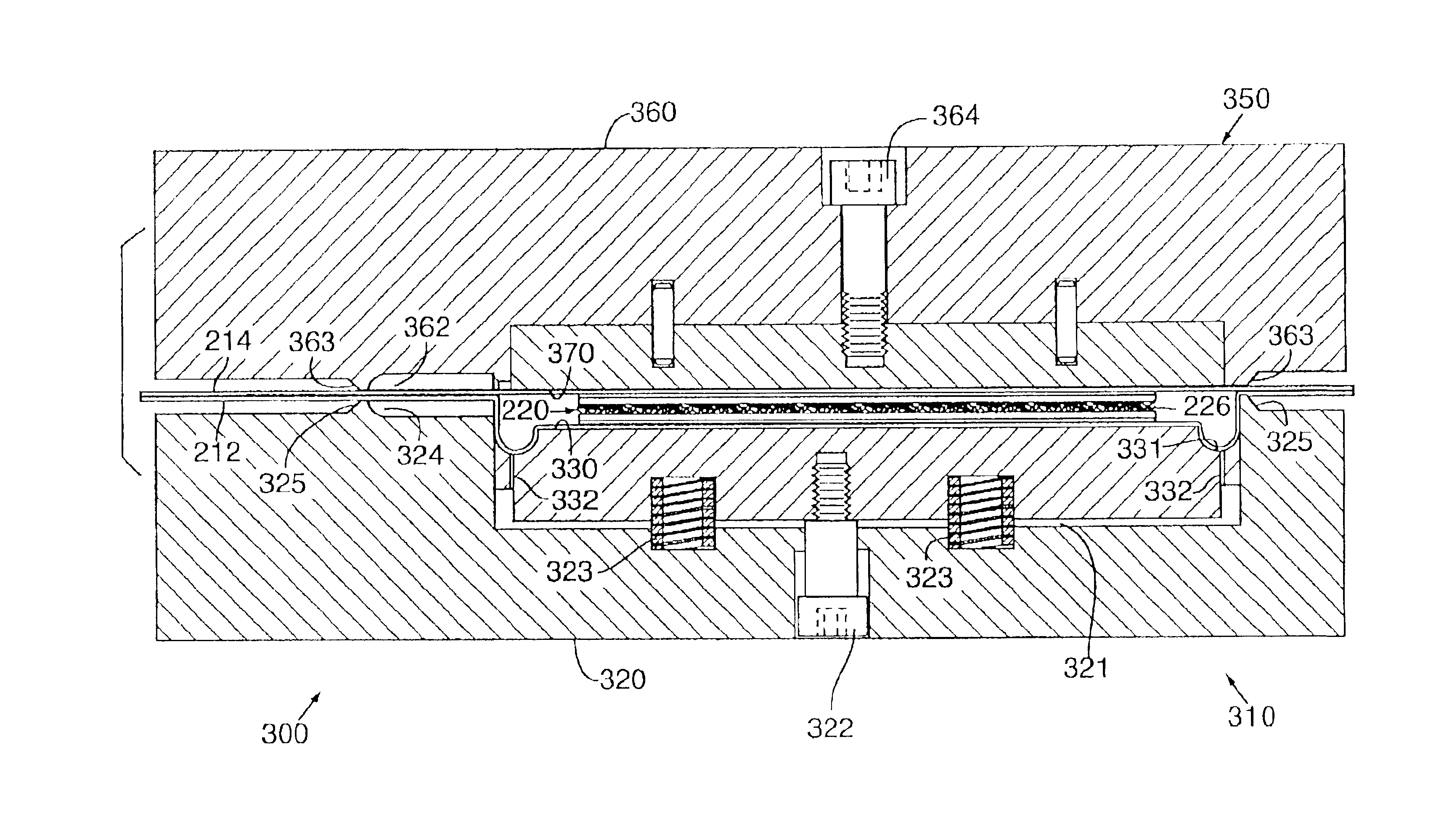
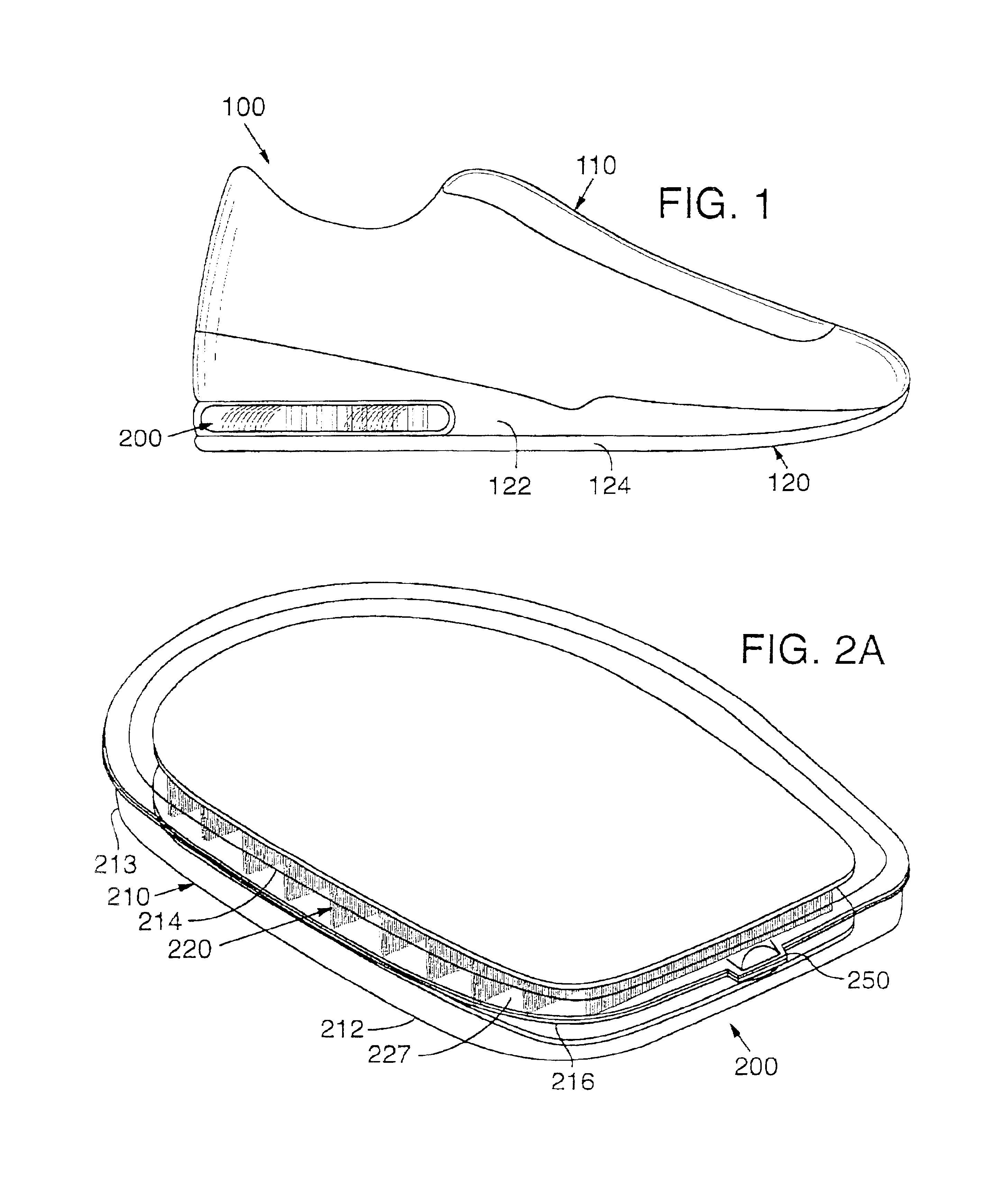
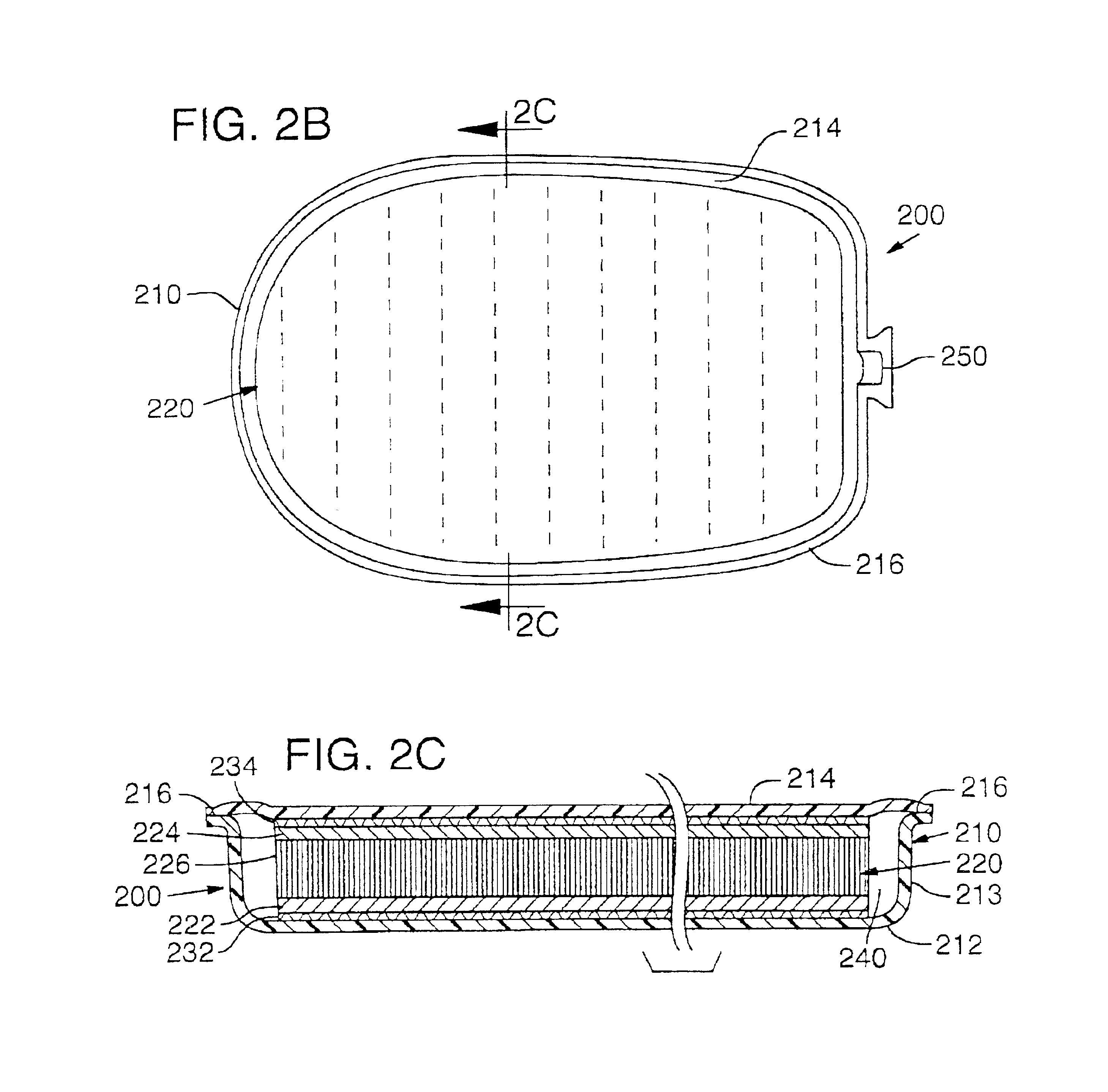
InactiveUS6837951B2Increase awarenessImprove efficiencySolesOrnamental textile articlesBladder structureThermal contact
A method for thermoforming a resilient, fluid-filled bladder structure with thermal contact molding is disclosed. The bladder includes two sheets of thermoplastic material that are separated by at least one core formed of two spaced outer layers connected together by a plurality of connecting members. The bladder is formed by bonding the sheets to the core, bonding the sheets to each other around the periphery of the core and forming a sidewall between the sheets in a single mold. A fluid is then inserted into the space bounded by the peripheral bond and the two sheets such that the connecting members are extended.
Owner:NIKE INC
Isoelastic prosthetic filet stitch fabric
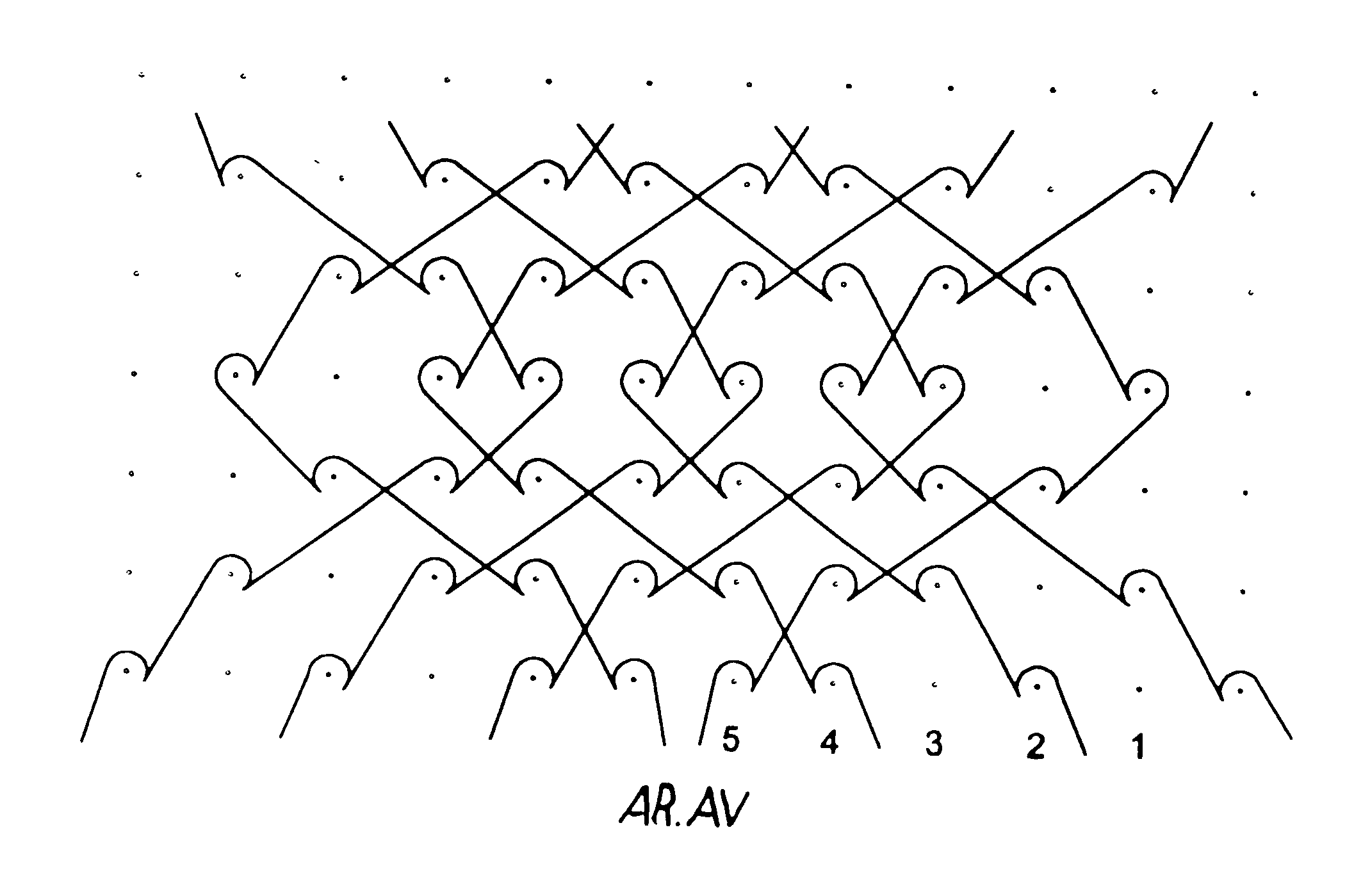
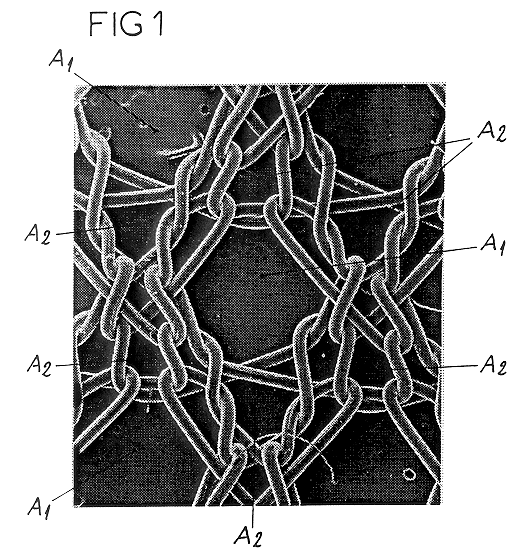
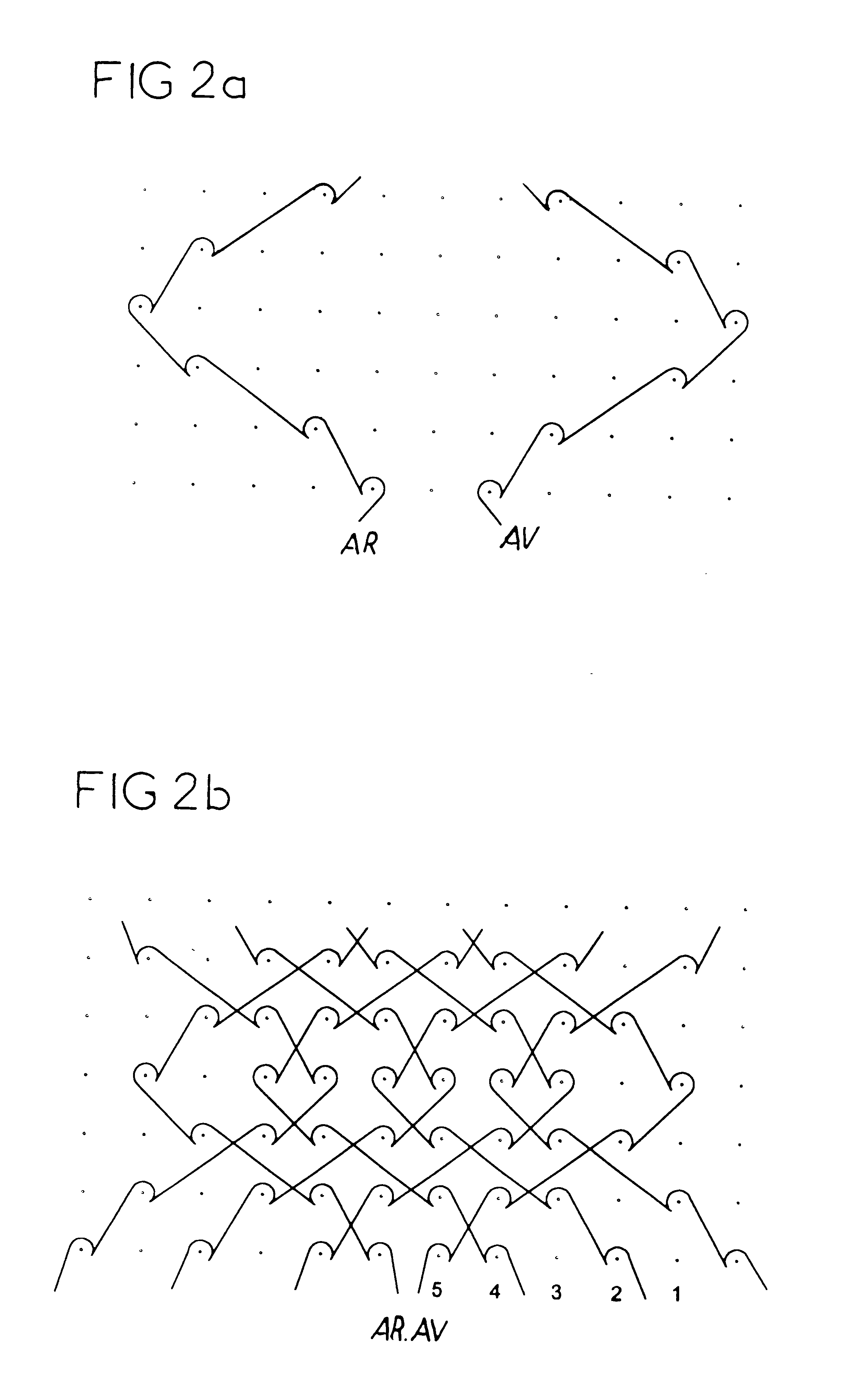
This knit is produced on the basis of a biocompatible polymer material monofilament, whose pattern is defined by a front lap and a rear lap of yarns knitted together and determines a plurality of cells each having a substantially polygonal shape. The pattern gives the knit a multidirectional tensile behavior such as obtained by a front lap capable of being obtained by knitting according to a scheme 5-4 / 4-3 / 2-1 / 0-1 / 1-2 / 3-4 and by a rear lap capable of being obtained by knitting according to a scheme 0-1 / 1-2 / 3-4 / 5-4 / 4-3 / 2-1.
Owner:SOFRADIM PROD SAS
Light weight shoes
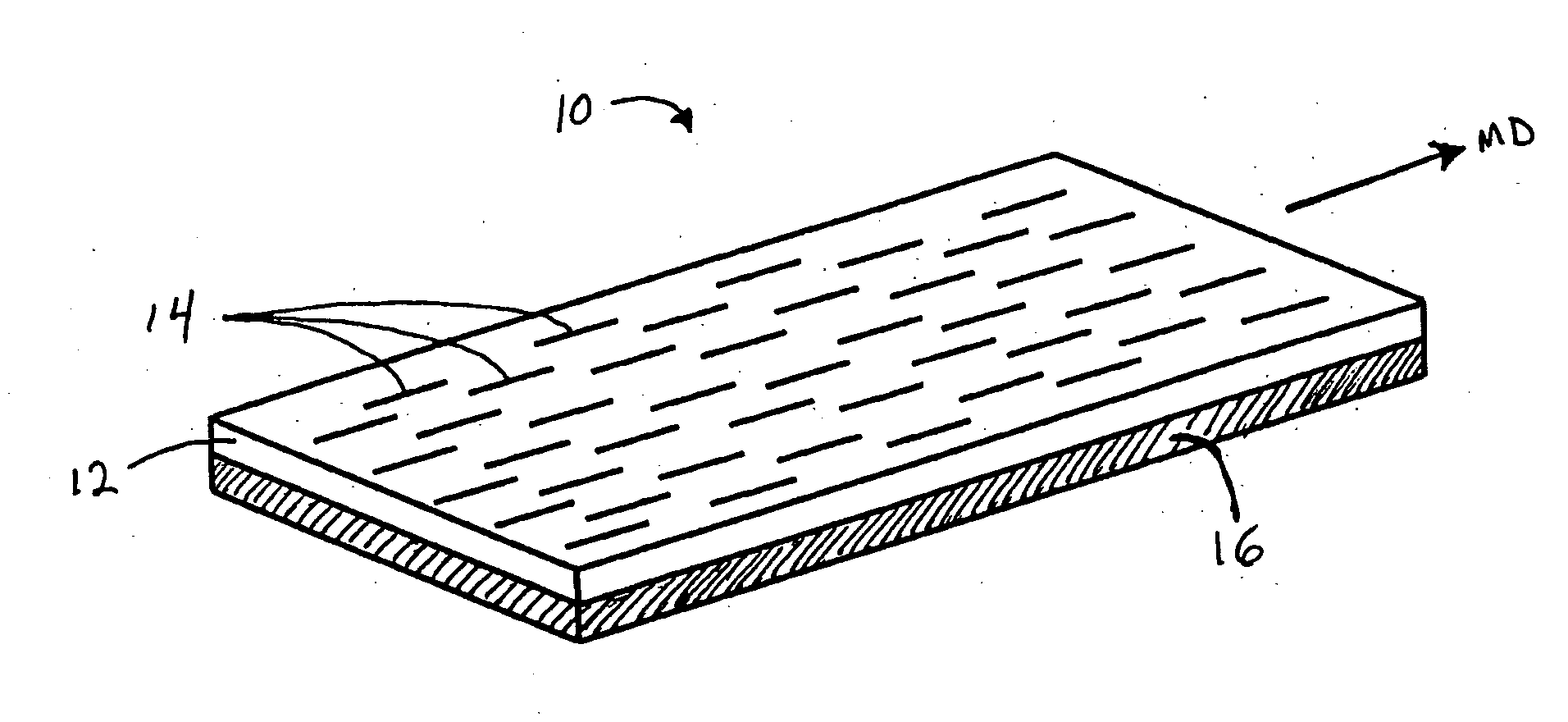
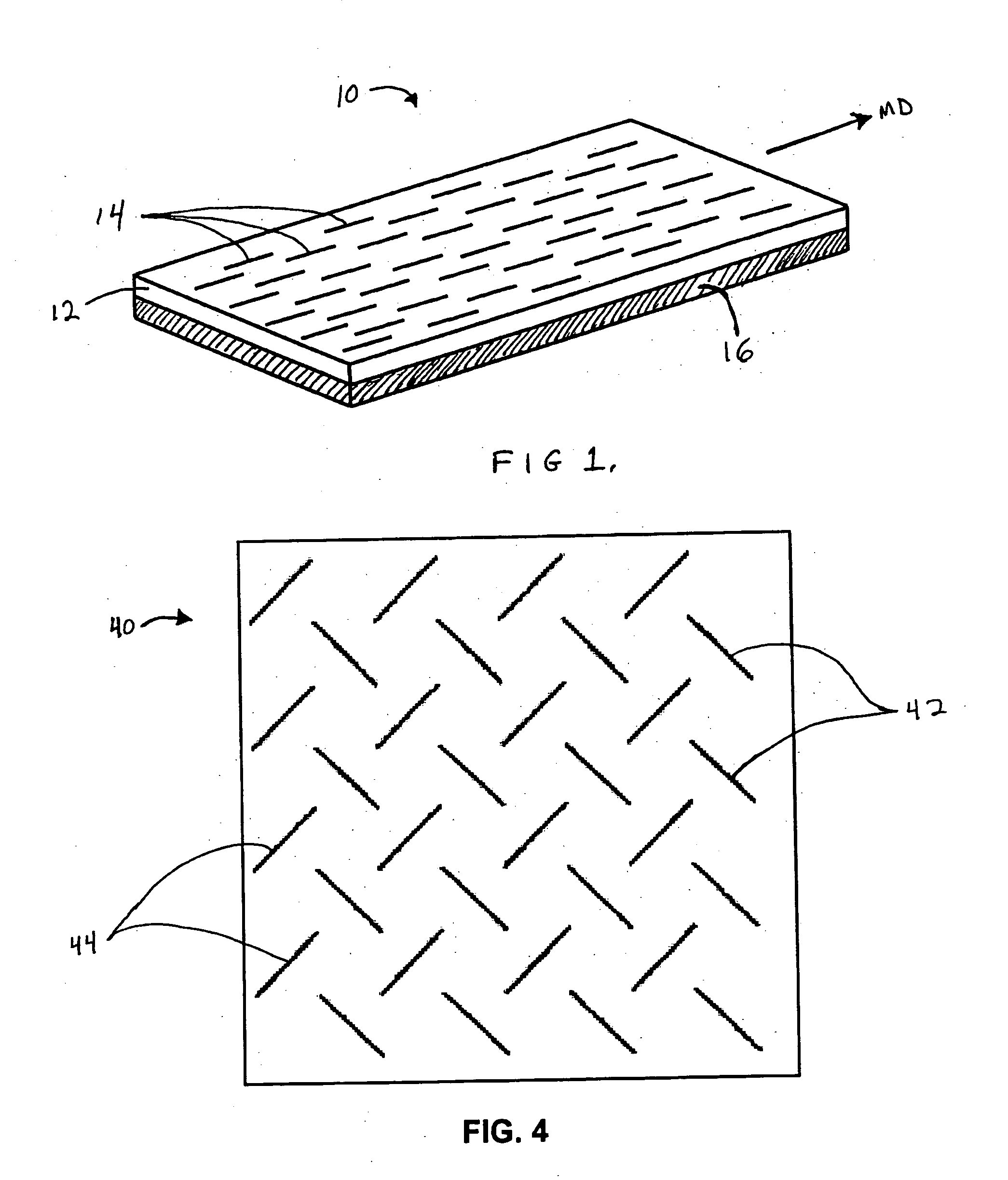
ActiveUS7051460B2Increased durabilityOrnamental textile articlesWarp knittingBursting strengthEngineering
A shoe including an upper material using a double raschel warp knitted fabric is provided. The upper material includes a first surface having a non-mesh structure and a second surface having a non-mesh structure part (A) and mesh structure parts (B, C). The burst strengths burst strengths A, B and C of the parts (A, B and C) satisfy the relationship: A>B>C. The non-mesh structure part (A) is disposed in a part surrounding the tiptoe, a part connecting to a shoe sole and disposed in both sides of the foot for example, in a stripe. The mesh structure part (B) is disposed in the vicinity of the surface of the toe and the mesh structure part (C) is disposed in the both sides of the foot for example, in a stripe. Thus, a shoe having lightweight, air permeability and durability and a double raschel knitted fabric used for the shoe are provided.
Owner:MIZUNO CORPORATION
Fabrics and Garments with Information Infrastructure
Fabrics, articles of apparel, and / or garment structures include infrastructure for transmitting information, such as signals produced by a wearer or from another source. Such fabrics may include: a textile formed through a knitting or weaving process, wherein at least one yarn used in the knitting or weaving process is electrically conductive to form sensor regions and / or other integrated electrically conductive infrastructure for transmitting electrical signals. Additional information is provided relating to methods for forming fabrics, articles of apparel, and / or garment structures of the types described above, as well as methods of using such products, e.g., for monitoring and / or displaying information regarding one or more physical and / or physiological parameters.
Owner:SENSATEX
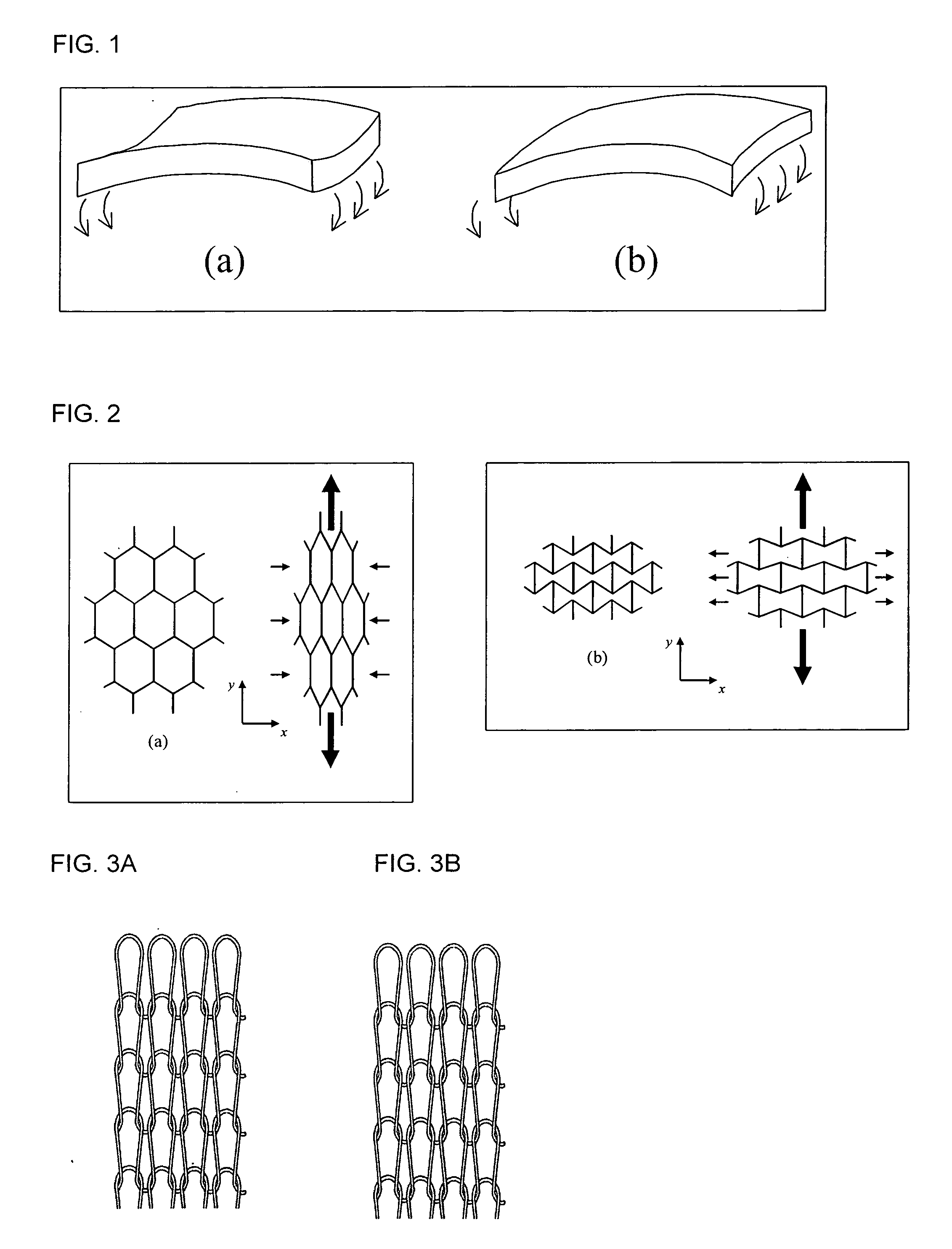
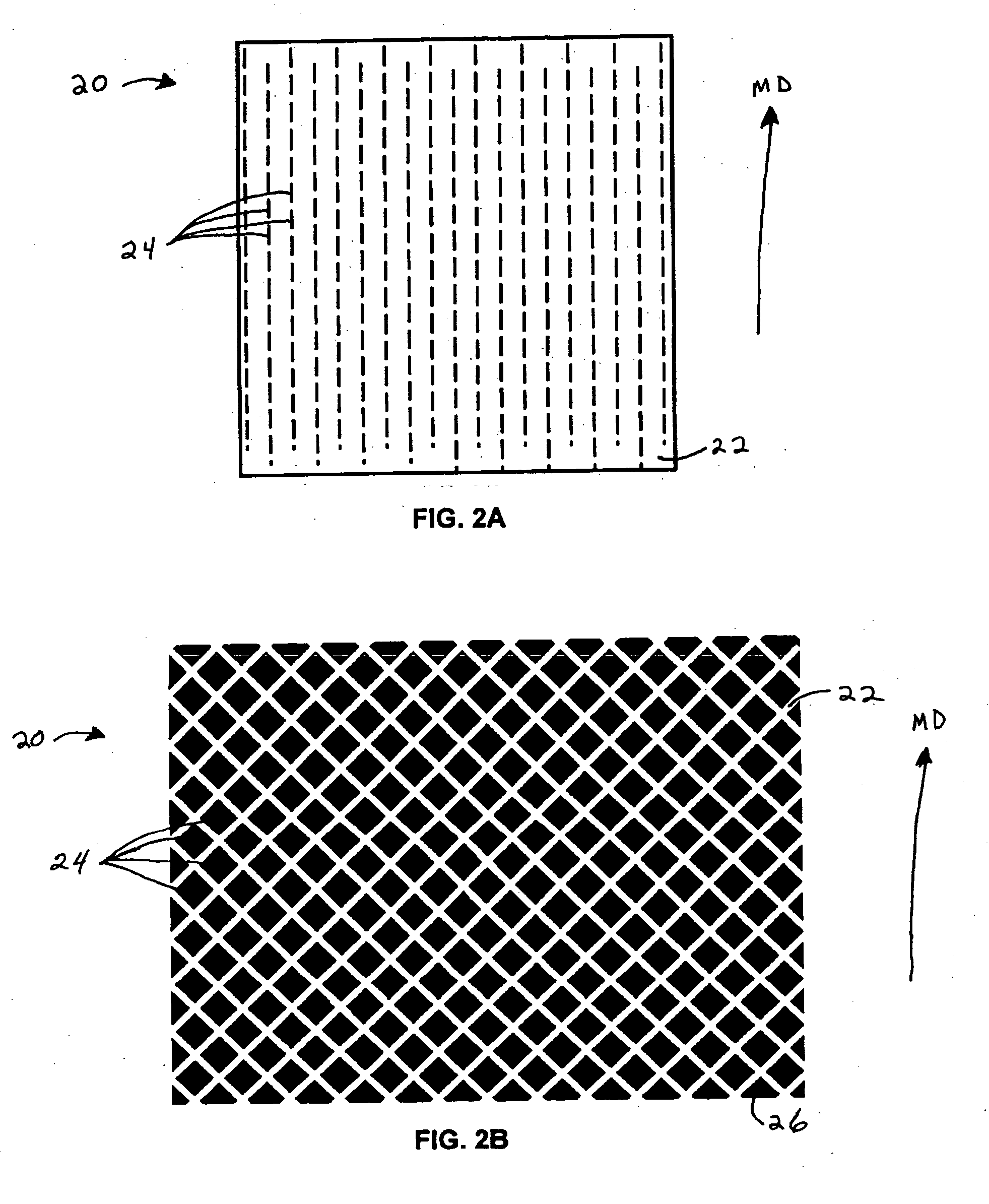
Bi-directional and multi-axial fabrics and fabric composites
InactiveUS6841492B2Increase resistanceImprove effectivenessOrnamental textile articlesProtective fabricsYarnEngineering
Bi-directional and multi-axial fabrics, fabric composites, ballistically resistant assemblies thereof, and the methods by which they are made. The fabrics are comprised of sets of strong, substantially parallel, unidirectional yarns lying in parallel planes, one above the other, with the direction of the yarns in a given plane rotated at an angle to the direction of the yarns in adjacent planes; and one or more sets of yarns having lower strength and higher elongation interleaved with the strong yarns. The fabrics of the invention provide superior ballistic effectiveness compared to ordinary woven and knitted fabrics but retain the ease of manufacture on conventional looms and knitting machines.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
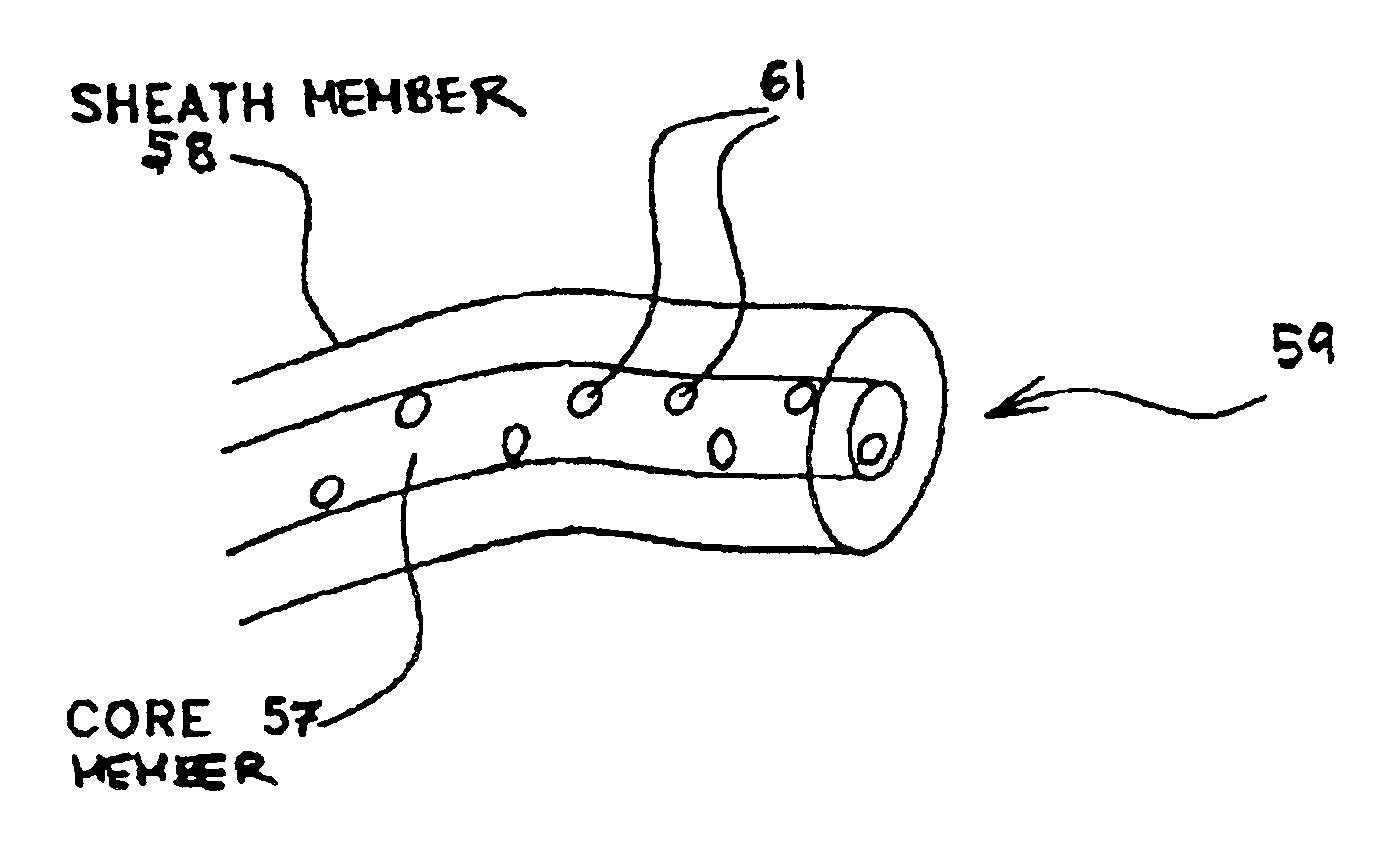
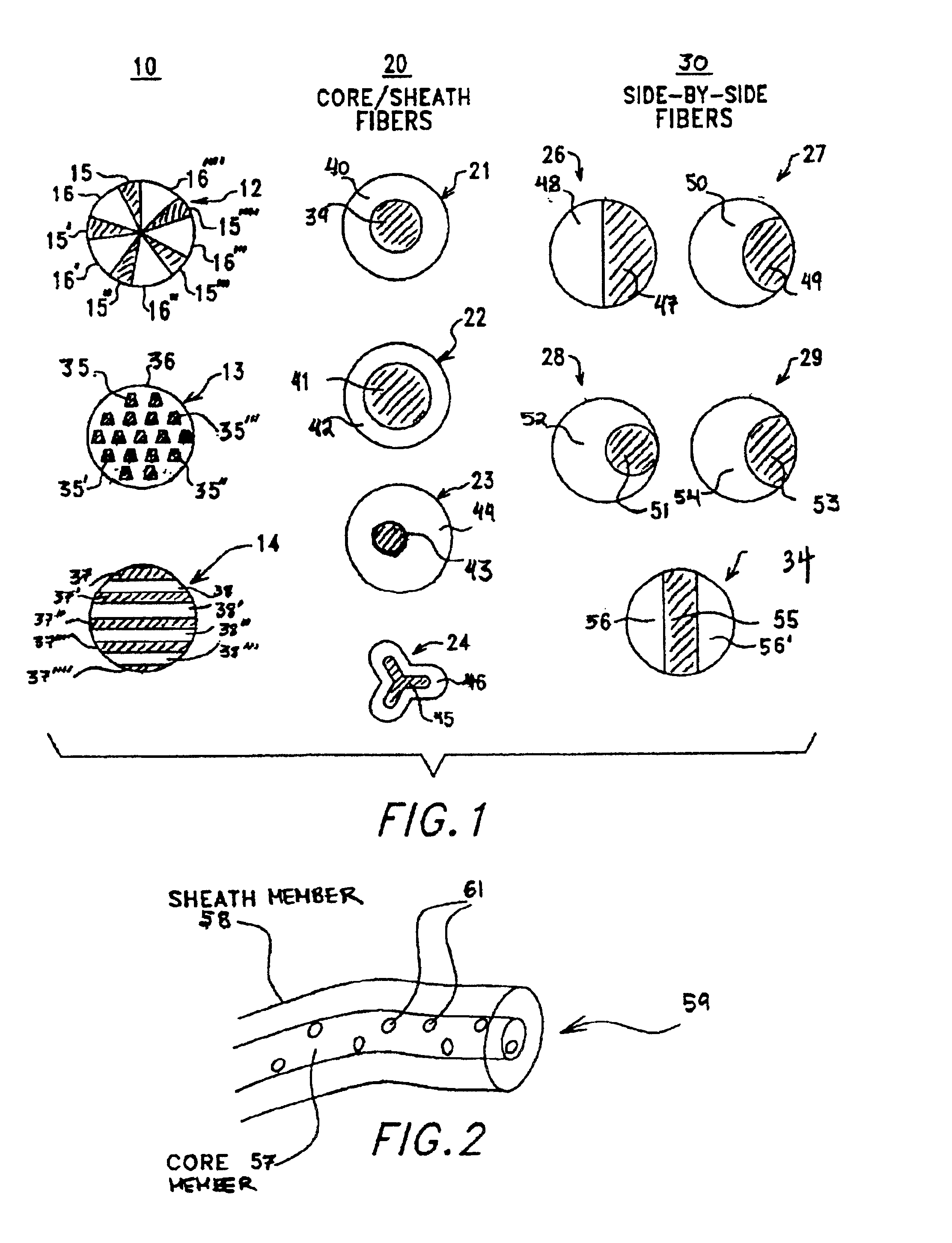
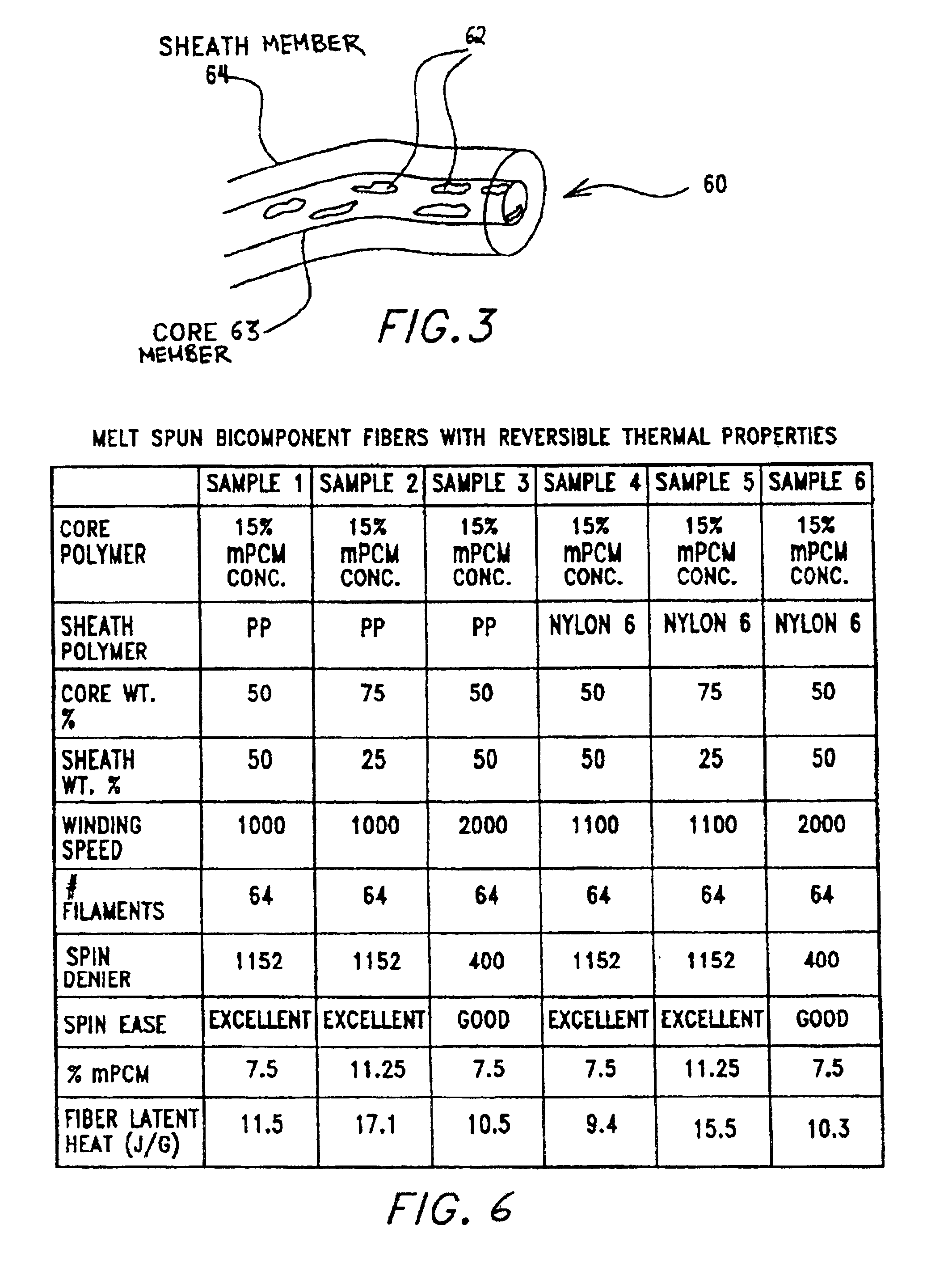
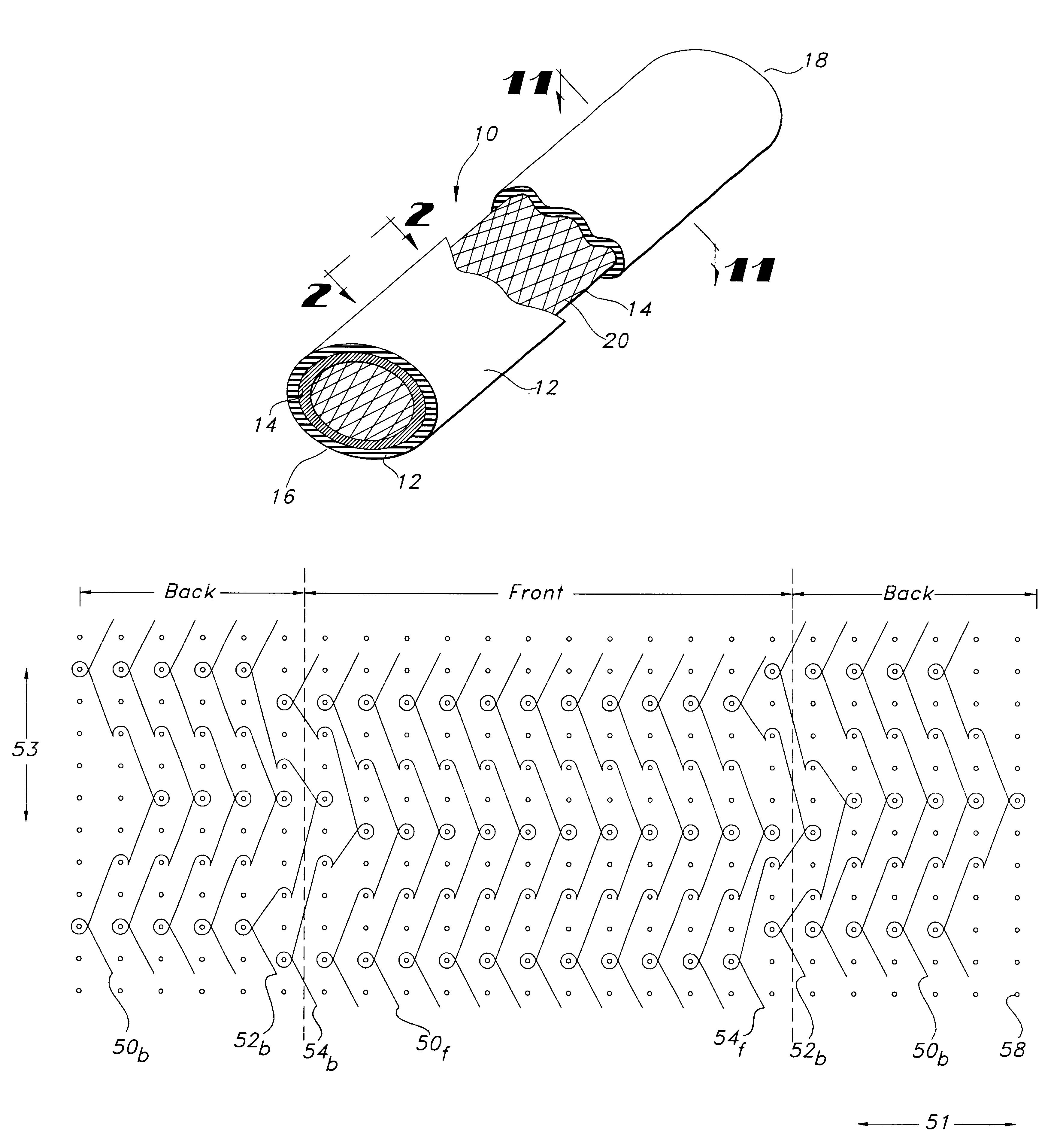
Multi-component fibers having enhanced reversible thermal properties and methods of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS6855422B2Easy to processImprove propertiesHeat storage plantsWarp knittingMedical productPhase-change material
The invention relates to a multi-component fiber having enhanced reversible thermal properties and methods of manufacturing thereof. The multi-component fiber comprises a fiber body formed from a plurality of elongated members, at least one of the elongated members comprising a temperature regulating material dispersed therein. The temperature regulating material comprises a phase change material. The multi-component fiber may be formed via a melt spinning process or a solution spinning process and may be used or incorporated in various products where a thermal regulating property is desired. For example, the multi-component fiber may be used in textiles, apparel, footwear, medical products, containers and packagings, buildings, appliances, and other products.
Owner:HILLS CO
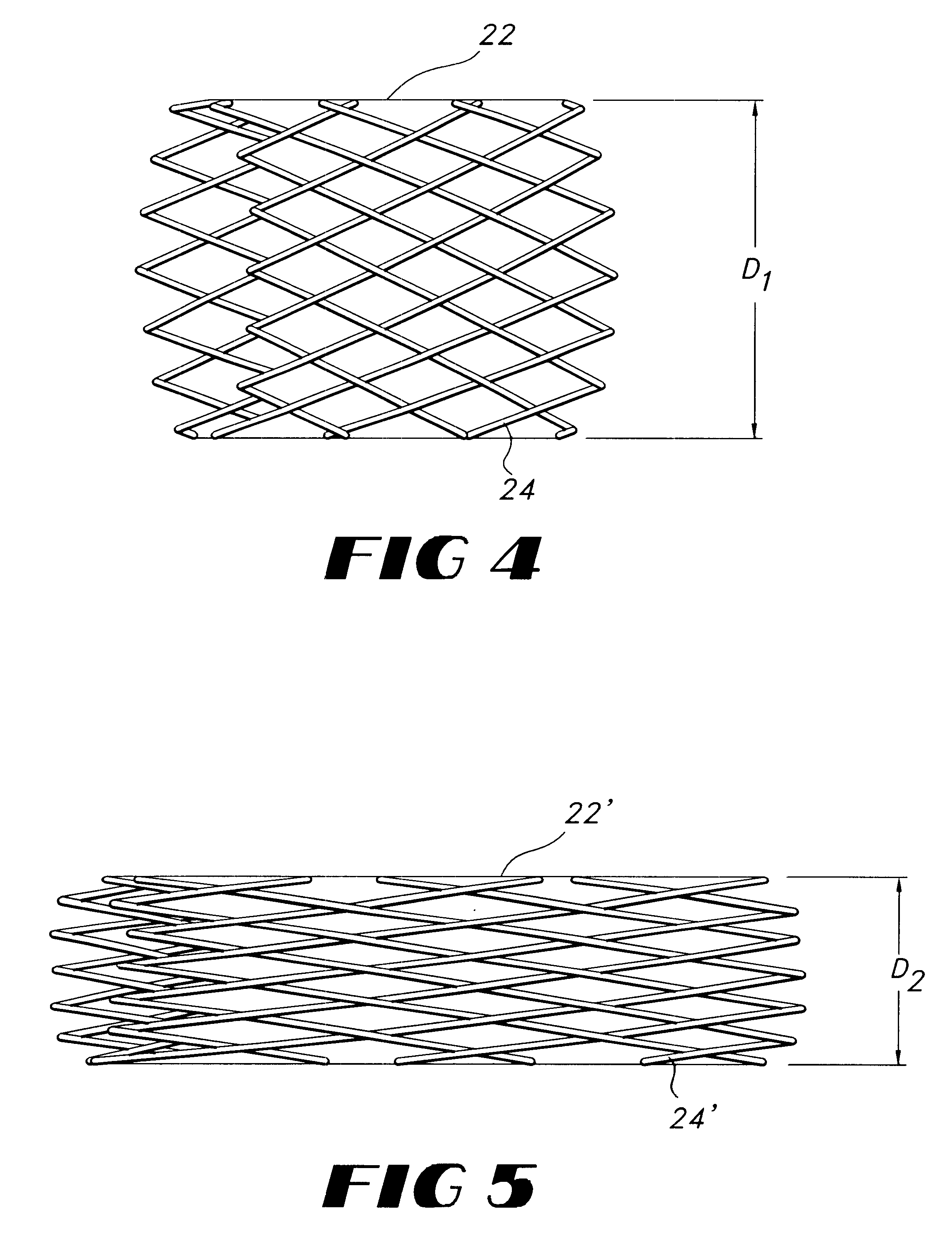
Low profile, high stretch knit prosthetic device
InactiveUS6540773B2High degree of flexibilityHigh degree of stretchabilityStentsWeft knittingYarnInsertion stent
A radially expandable stent-graft endoprosthesis is provided. The graft included in the stent-graft is a knitted tubular structure circumferentially disposed and securably attached to the stent. The knitted tubular structure has a knit pattern of interlacing yarns in an Atlas or a modified-Atlas pattern to provide greater than 150 percent longitudinal stretchability. A knitted tubular graft and a knitted medical fabric with greater than 150 percent longitudinal stretchability are also provided.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Composite medical textile material and implantable devices made therefrom
InactiveUS20050240261A1Improve complianceImprove the immunityStentsOrnamental textile articlesYarnImplanted device
An implantable composite medical device having a longitudinal length a woven textile portion having yarns interlaced in a woven pattern, a knitted textile portion having yarns interlooped in a knitted pattern. The woven and knitted portions are securably attached to one and the other to provide a composite woven and knitted textile surface along the longitudinal length of the device. The woven portion may have a permeability from about 30 to about 500 ml / min / cm2, and the knitted portion may have a permeability from about 30 to about 15,000 ml / min / cm2. Further, a crimped woven portion with a resiliently longitudinal stretchability from about 10 to about 100 linear percent over its quiescent longitudinal dimension or an uncrimped woven portion with a resiliently longitudinal stretchability of less than about 10 linear percent over its quiescent longitudinal dimension are useful. A knitted portion with a resiliently longitudinal stretchability from about 5 to about 200 linear percent over its quiescent longitudinal dimension is also useful.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Low profile, high stretch, low dilation knit prosthetic device
A radially expandable stent-graft endoprosthesis is provided. The graft included in the stent-graft is a knitted tubular structure circumferentially disposed and securably attached to the stent. The knitted tubular structure has a warp knit pattern of interlacing yarns with at least a two-needle underlap to provide greater than 150 percent longitudinal stretchability while substantially inhabiting dilation. A knitted tubular graft and a knitted medical fabric with greater than 150 percent longitudinal stretchability are also provided.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
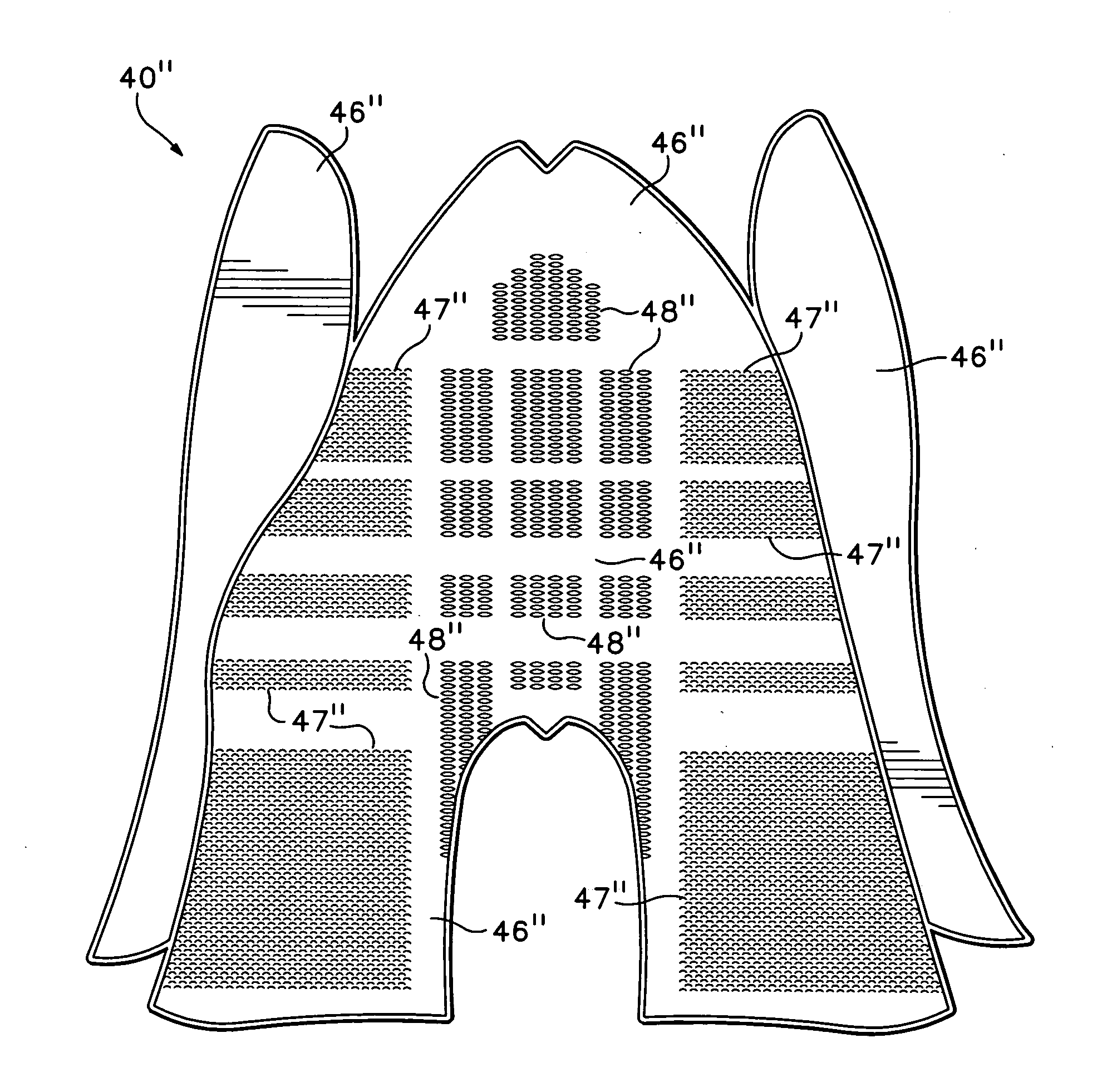
Article of apparel incorporating a zoned modifiable textile structure
ActiveUS20050204449A1Improve understandingGarment special featuresWeft knittingEngineeringE-textiles
An article of apparel is disclosed that includes zones with a textile having a structure that changes or is otherwise modified by a physical stimulus, such as the presence of water or a temperature change, to modify a property of the textile. The zones may be along a center back area and side areas of the apparel, and the textile may increase in air permeability when exposed to water. The zones may also be in an upper area of the torso and in a lower back area, and the textile may increase in texture when exposed to water. In some embodiments, slits are formed in the textile.
Owner:NIKE INC
Low density lightning strike protection for use in airplanes
ActiveUS20090227162A1Minimize micro-crackingWeight optimizationConductive materialWarp knittingFiberEpoxy
Surface films, paints, or primers can be used in preparing aircraft structural composites that may be exposed to lightning strikes. Methods for making and using these films, paints or primers are also disclosed. The surface film can include a thermoset resin or polymer, e.g., an epoxy resin and / or a thermoplastic polymer, which can be cured, bonded, or painted on the composite structure. Low-density electrically conductive materials are disclosed, such as carbon nanofiber, copper powder, metal coated microspheres, metal-coated carbon nanotubes, single wall carbon nanotubes, graphite nanoplatelets and the like, that can be uniformly dispersed throughout or on the film. Low density conductive materials can include metal screens, optionally in combination with carbon nanofibers.
Owner:ROHR INC +1
Three dimensional random looped structures made from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins and uses thereof
Cushioning net structures comprise random loops, such as three-dimensional random loops, bonded with one another, wherein the loops are formed by allowing continuous fibers, made of ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers, to bend to come in contact with one another in a molten state and to be heat-bonded at most contact points. The structures provided herein have desirable heat resistance, durability and cushioning property. The cushioning structures are used in furniture, vehicle seats etc.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Flame resistant fabrics and garments made from same
InactiveUS20080057807A1Inexpensive and comfortable to wearerCotton-low durability-isWarp knittingAnimal housingPolymer scienceNatural fiber
Unique blends of fibers that incorporate synthetic cellulosic fibers to render fabrics made with such blends more durable than fabrics made with natural cellulosic fibers such as cotton. While more durable than cotton, the synthetic cellulosic fibers used in the blends are still inexpensive and comfortable to the wearer. Thus, the benefits of cotton (affordability and comfort) are still attained while a drawback of cotton—low durability—is avoided. In one embodiment, the fiber blend includes FR modacrylic fibers and synthetic cellulosic fibers, preferably, but not necessarily non-FR lyocell fibers such as TENCEL™ and TENCEL A100™. Other fibers may be added to the blend, including, but not limited to, additional types of inherently FR fibers, anti-static fibers, anti-microbial fibers, stretch fibers, and / or high tenacity fibers. The fiber blends disclosed herein may be used to form various types of FR fabrics. Desired colors may be imparted in a variety of ways and with a variety of dyes to the fabrics disclosed herein. Fabrics having the fibers blends disclosed herein can be used to construct the entirety of, or various portions of, a variety of protective garments for protecting the wearer against electrical arc flash and flames, including, but not limited to, coveralls, jumpsuits, shirts, jackets, vests, and trousers.
Owner:SOUTHERN MILLS
Wound treatment device
InactiveUS8376972B2Promote healingIncrease displacementOrnamental textile articlesLayered productsSurface layerWound surface
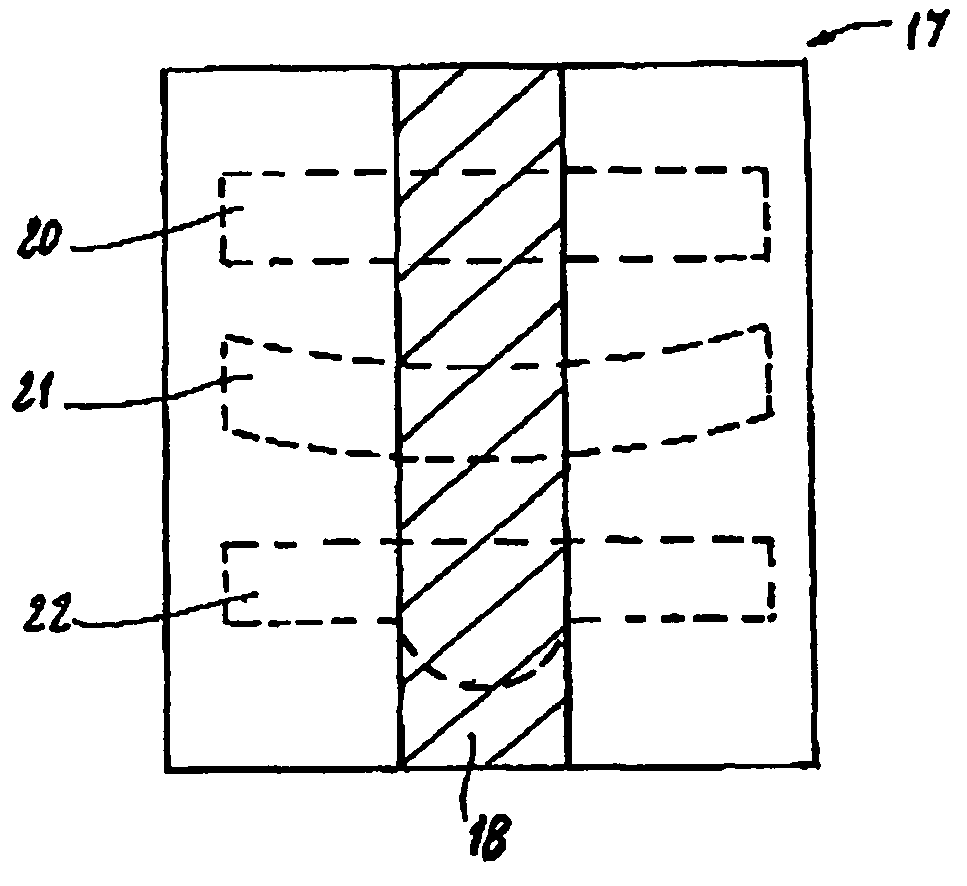
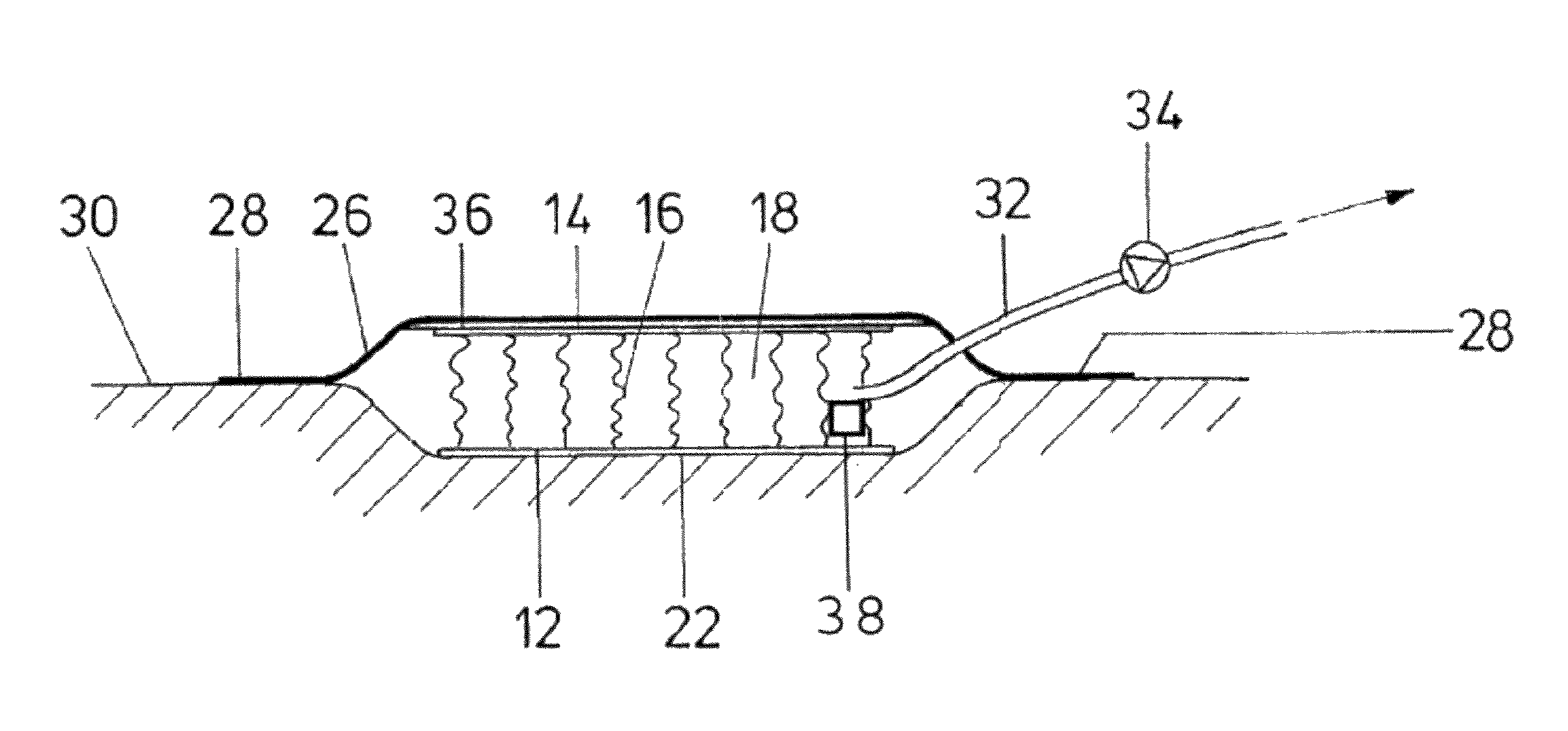
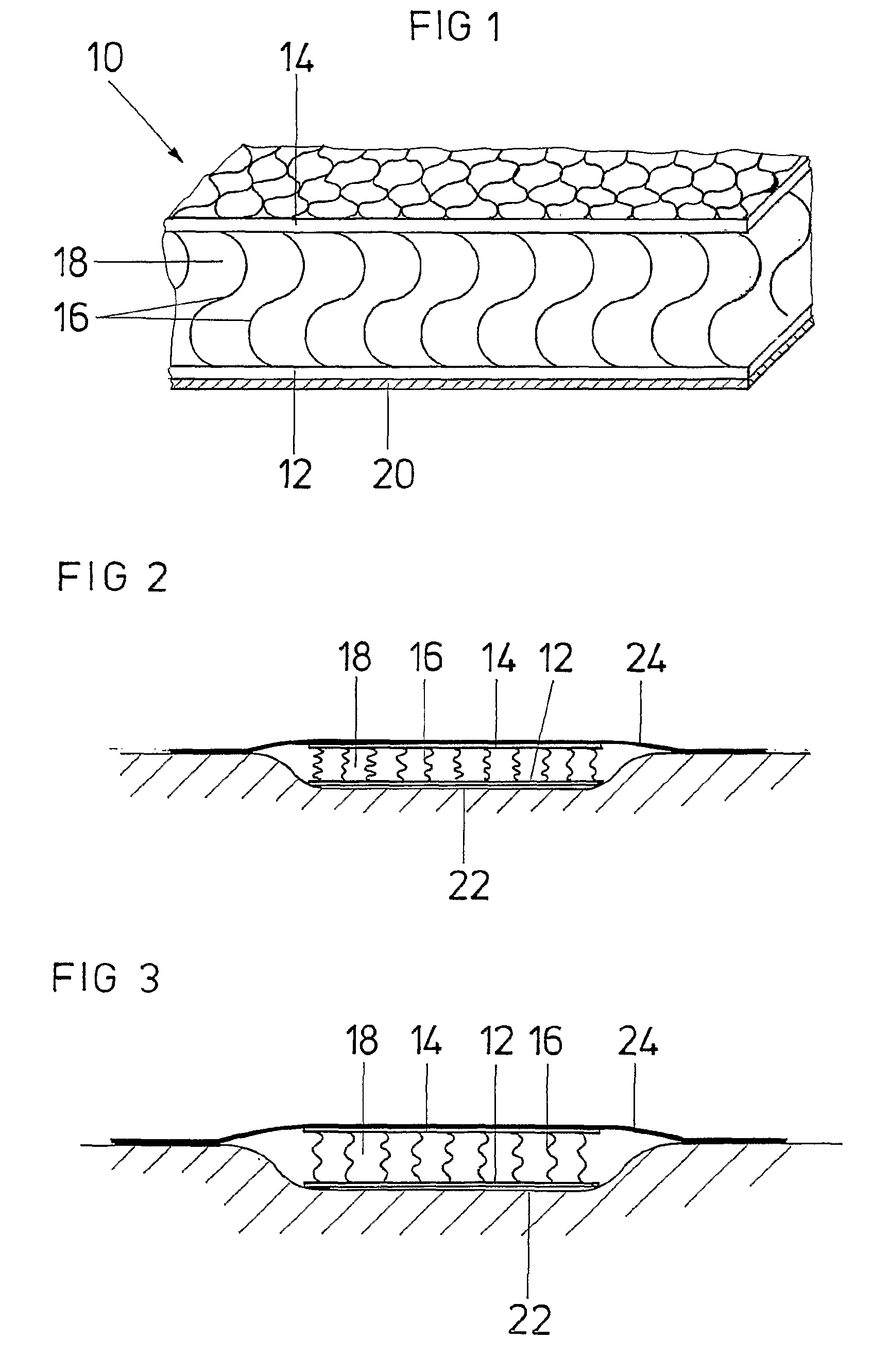
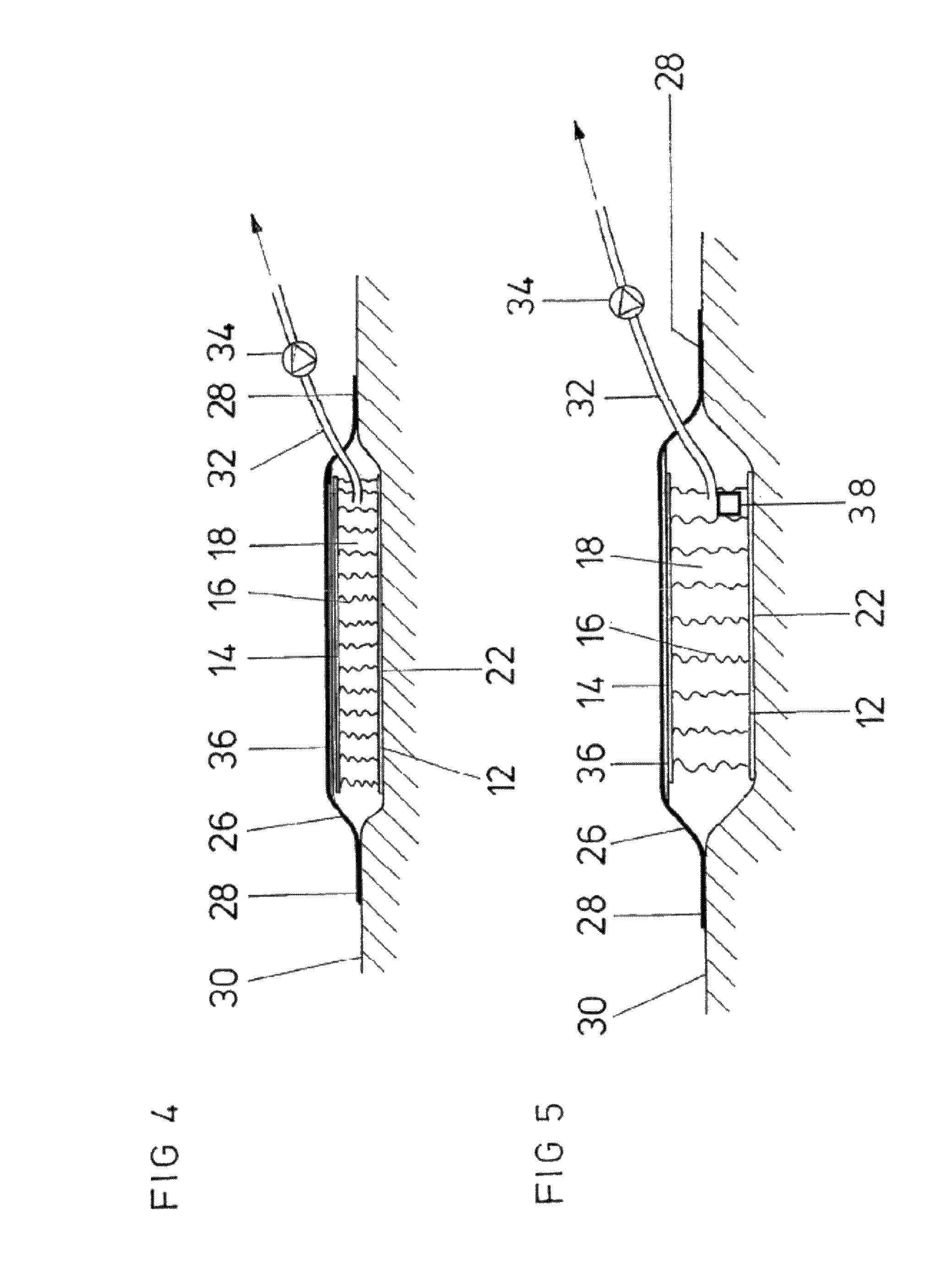
A wound treatment device comprises a wound surface contacting plug (10) and a cover (24) for covering the wound surface (22) and the plug (10), wherein said plug (10) consists of a flat textile isolating material comprising at least one first surface layer (12), one second surface layer (14) and one intermediate space (18) arranged between said surface layers (12, 14). At least the first surface layer (12) is provided with a biocompatible surface and a structure which enables a liquid to pass and prevents a wound tissue from growing in said structure. The intermediate space (18) is provided with isolating threads (16) elastically holding the first surface layer (12) and the second surface layer at a certain distance from each other.
Owner:T J SMITH & NEPHEW
Ballistic fabrics with improved antiballistic properties
ActiveUS20060062944A1Good physical propertiesImprove propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyWarp knittingFiberYarn
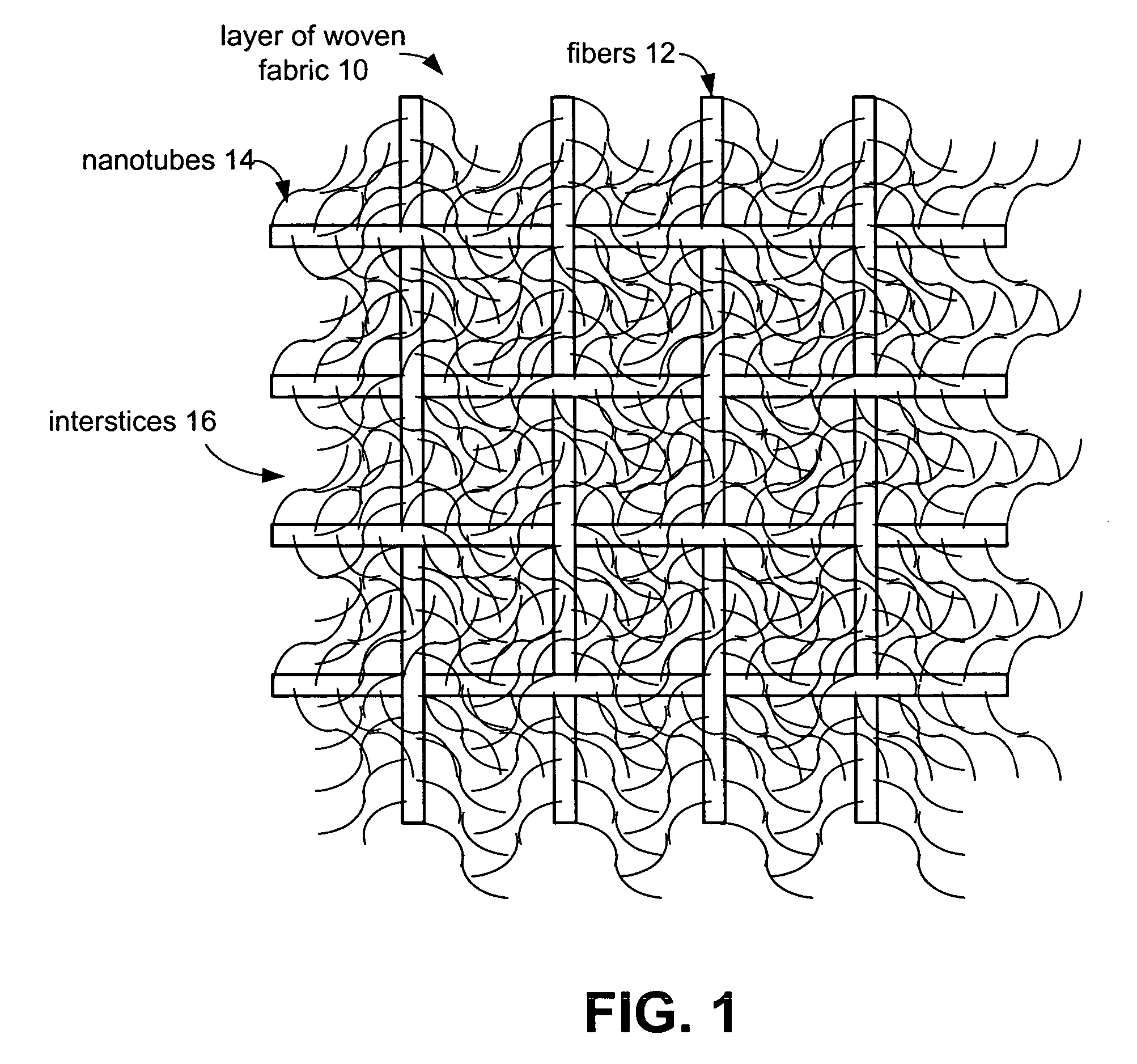
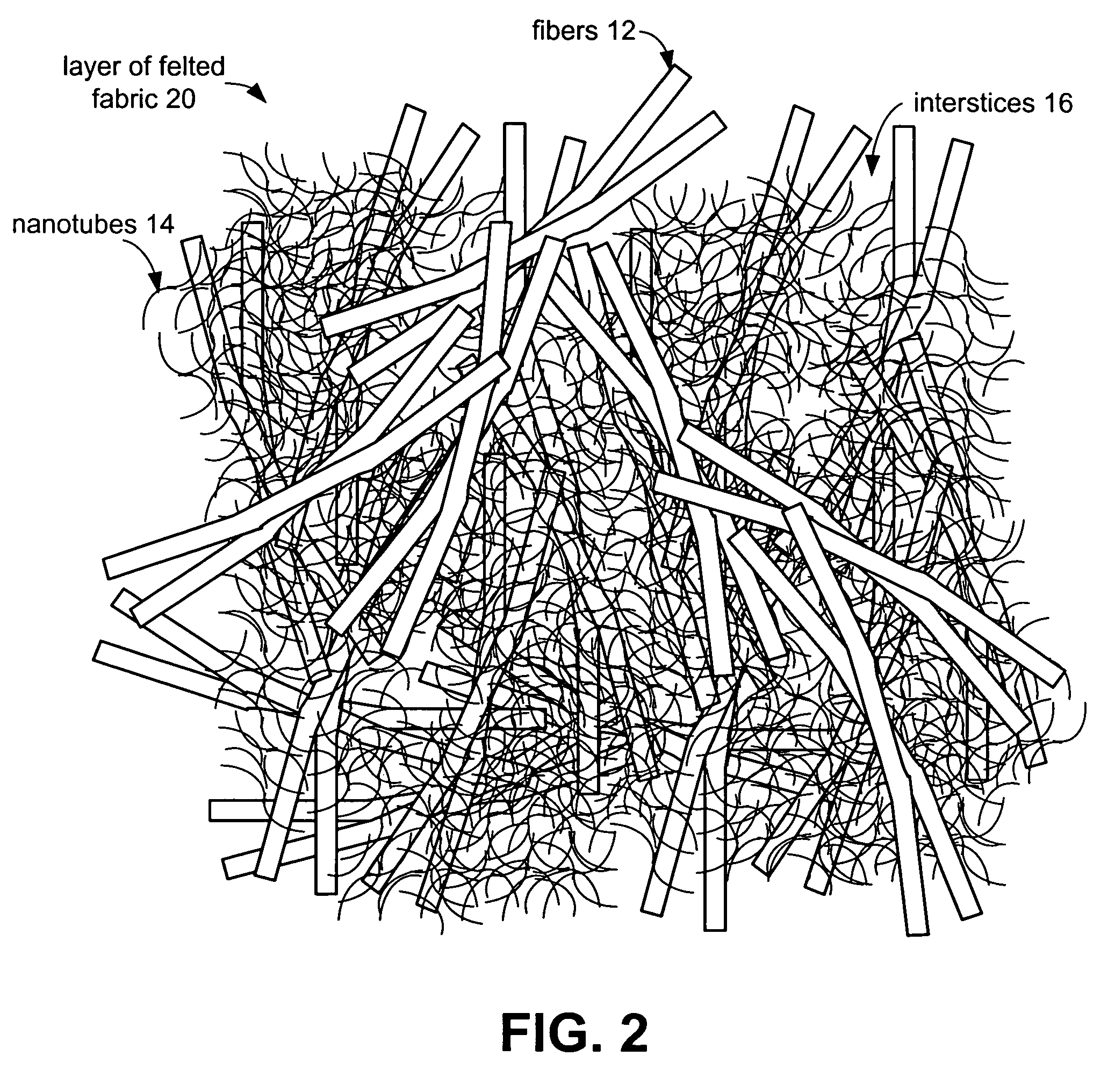
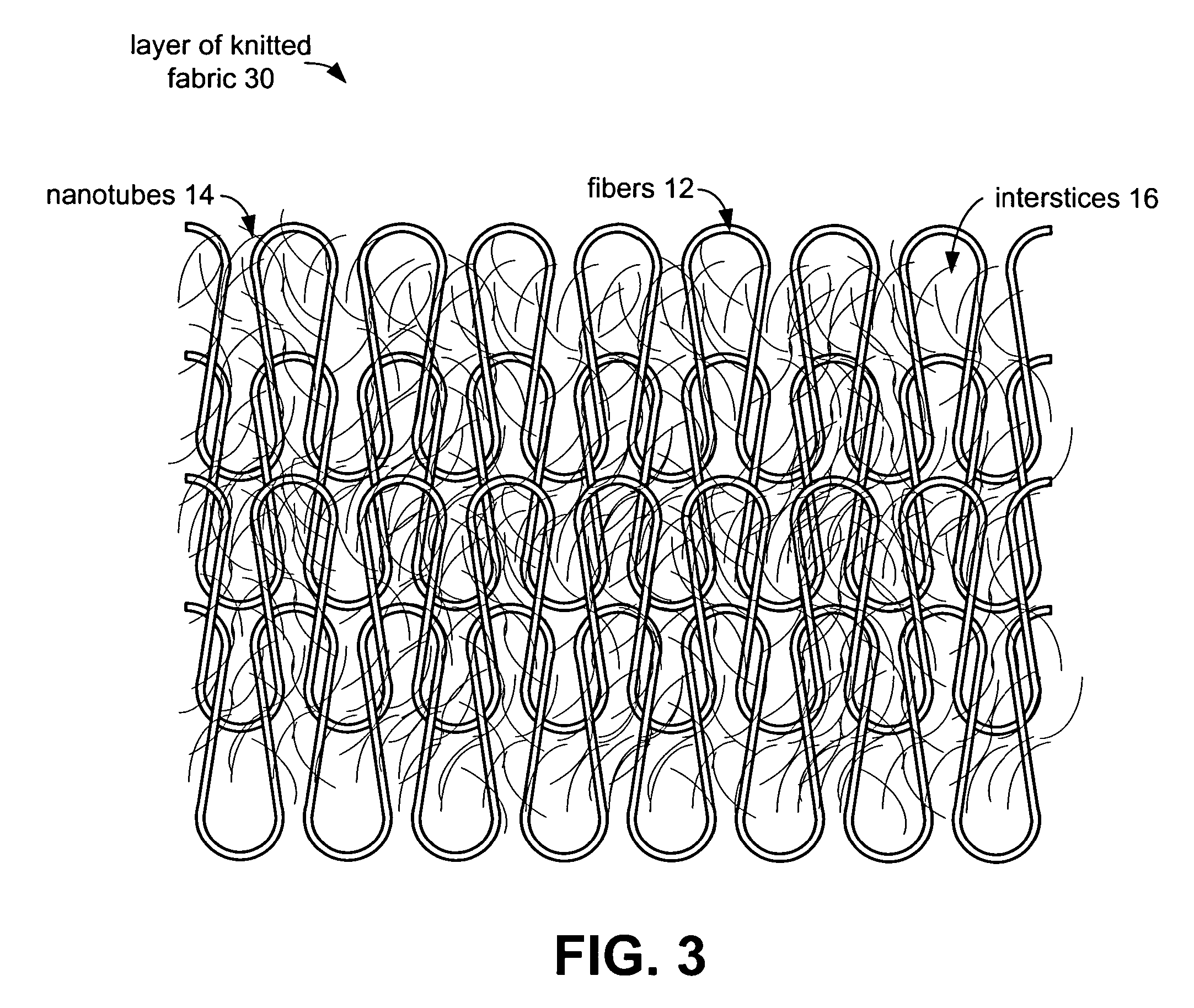
The present invention provides fabrics that have unique mechanical, chemical, electrical, and thermal properties. The fabrics comprise layers of woven, knit or felted fibers, yarns or tow. Interstitially synthesized nanotubes, such as single-walled or multi-walled carbon nanotubes, enhance the fabric's antiballistic properties. These nanotubes may also insulate, semi-conduct or super-conduct electrical charges, or provide enhanced thermal properties of these fabrics which can be layered to form unique garments or structures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Adhesive-containing wound closure device and method
InactiveUS20060009099A1Enlarging woundShorten operation timeWeft knittingWarp knittingPolymerizationChemistry
An article, such as a tissue bonding article, includes a flexible material, a polymerization initiator or rate modifier disposed in or on the flexible material, and a polymerizable adhesive composition permeated throughout at least a portion of the flexible material, where the polymerization initiator or rate modifier is a polymerization initiator or rate modifier for the polymerizable adhesive composition.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Fabrics having knit structures exhibiting auxetic properties and garments formed thereby
Owner:HBI BRANDED APPAREL ENTERPRISES
Protective fabric and apparel systems
InactiveUS6918140B1Remove moistureReduce contact stressOrnamental textile articlesTrousersCushioningYarn
A multi-layer protective fabric includes an inner layer, an middle layer, and an outer wicking layer. The outer fabric layer includes an inside layer of hydrophobic material, an outside layer of hydrophilic material, and an intermediate layer of hydrophobic monofilament yarns extending between and knitted together with the outside and inside layers, and promotes wicking of moisture from a wearer's skin to the outer layer. The multi-layer protective fabric middle layer includes a porous, cushioning material. The multi-layer protective fabric inner layer includes a cushioning, abrasion-resistant material, such as doeskin. Articles of apparel, for example cycling shorts, can include such a multi-layer protective fabric either alone or in combination with other moisture-managing, cushioning fabrics. Such protective fabric and apparel systems provide improved removal of moisture from skin, reduction of contact stress, and decrease in abrasion.
Owner:DEFEET INT
Color change laminate material
Disclosed herein are color change laminate materials suitable for a variety of uses. The color change laminate materials include at least two layers of extensible materials having visually distinct coloration, and indicate a stretched or extended state by exposing the previously covered coloration of a lower layer. The color change laminate materials may also indicate the amount of stretching or extension is applied to the laminate. When the laminate includes elastic materials capable of stretch and recovery, the color change laminate materials may further be reversible color change laminate materials that can display color change upon extension and then recover the extension and return to the original coloration. Such color change laminate materials and reversible color change laminate materials are highly useful for use in garments or other textile type applications, in or on personal care products, protective wear products, health care and medical care products, bandages and the like.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Composite mesh devices and methods for soft tissue repair
InactiveUS20100318108A1Reduce adhesionDifferent and simple configurationCovering/liningsWarp knittingComposite meshSoft tissue repair
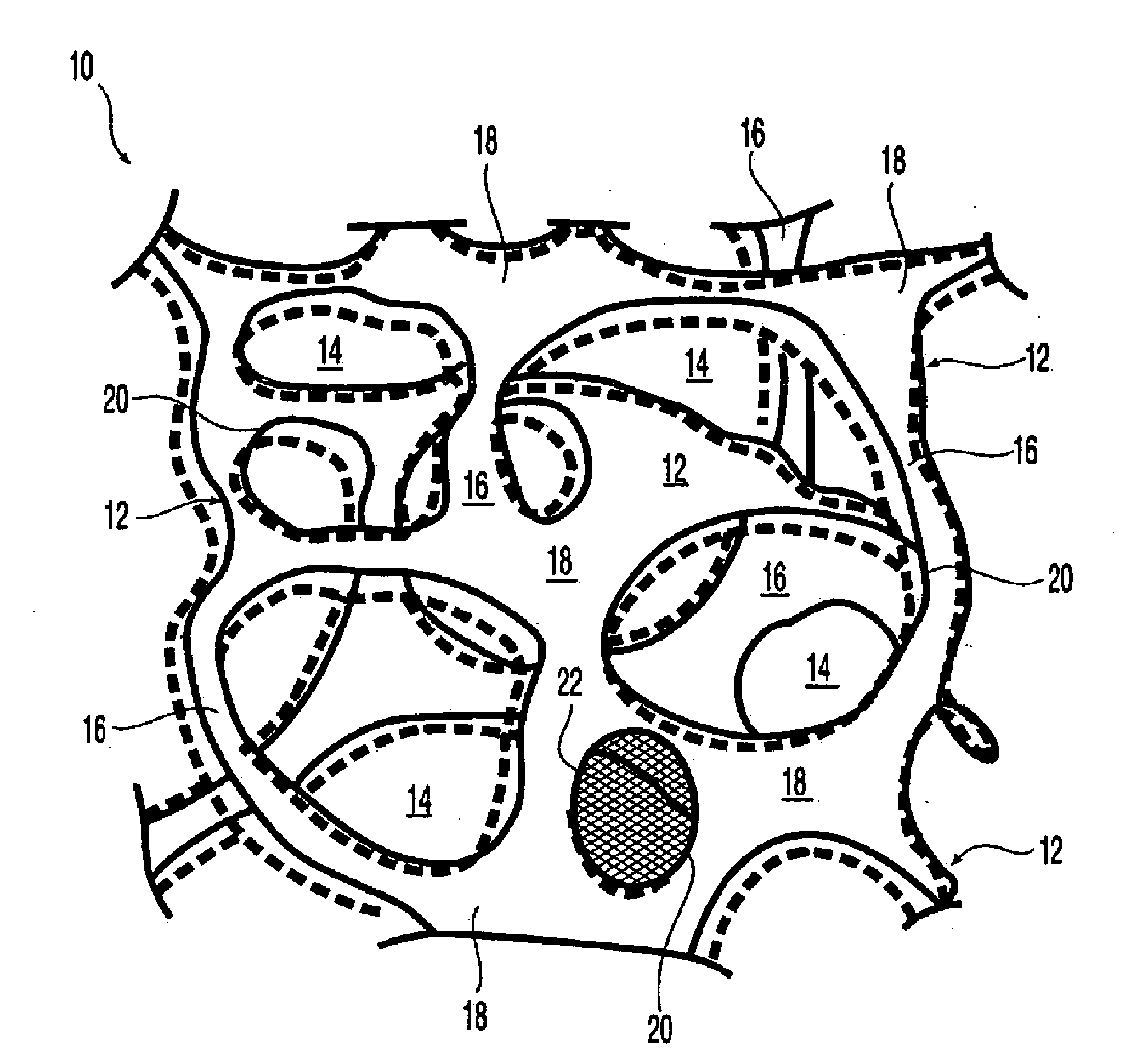
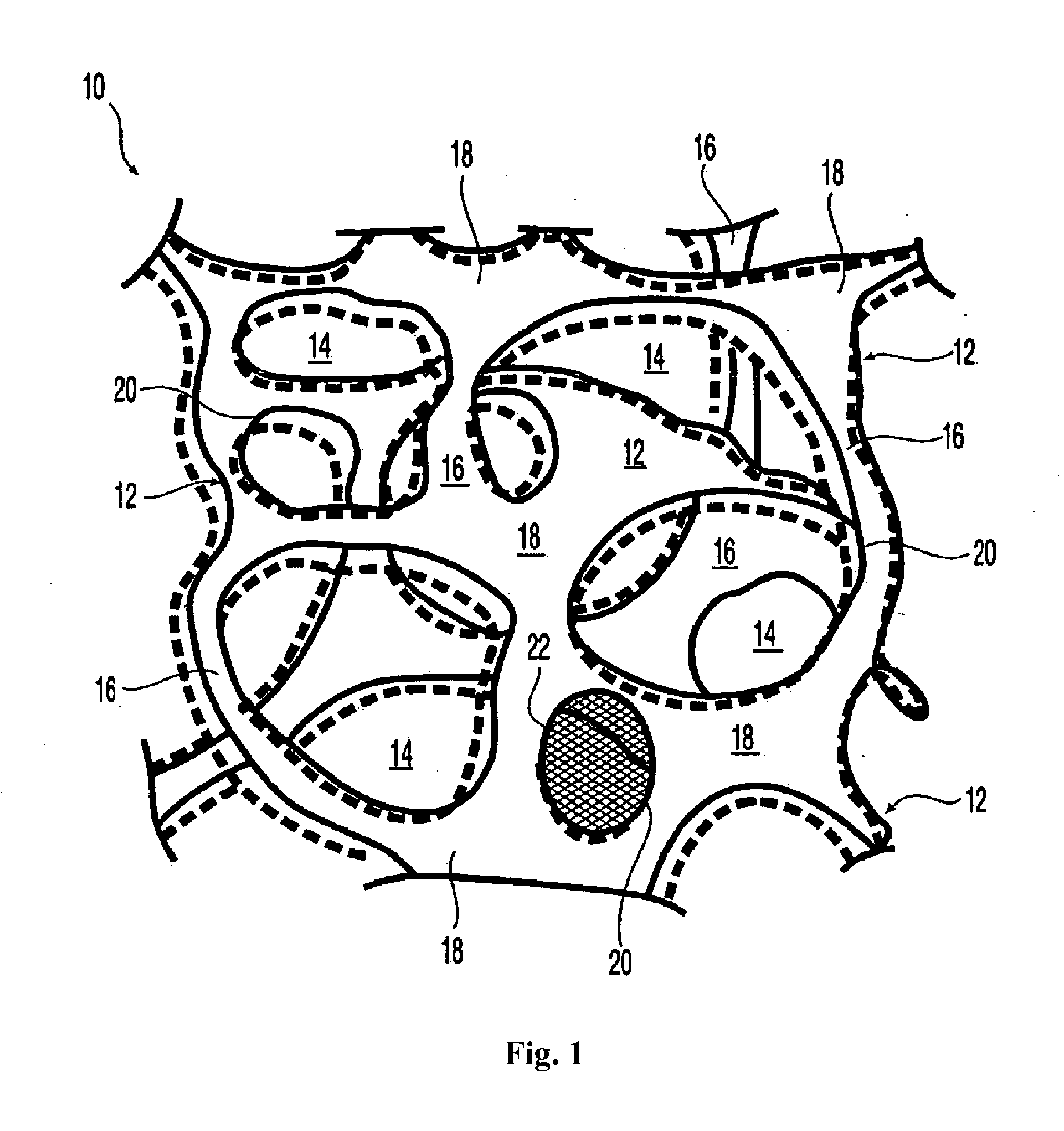
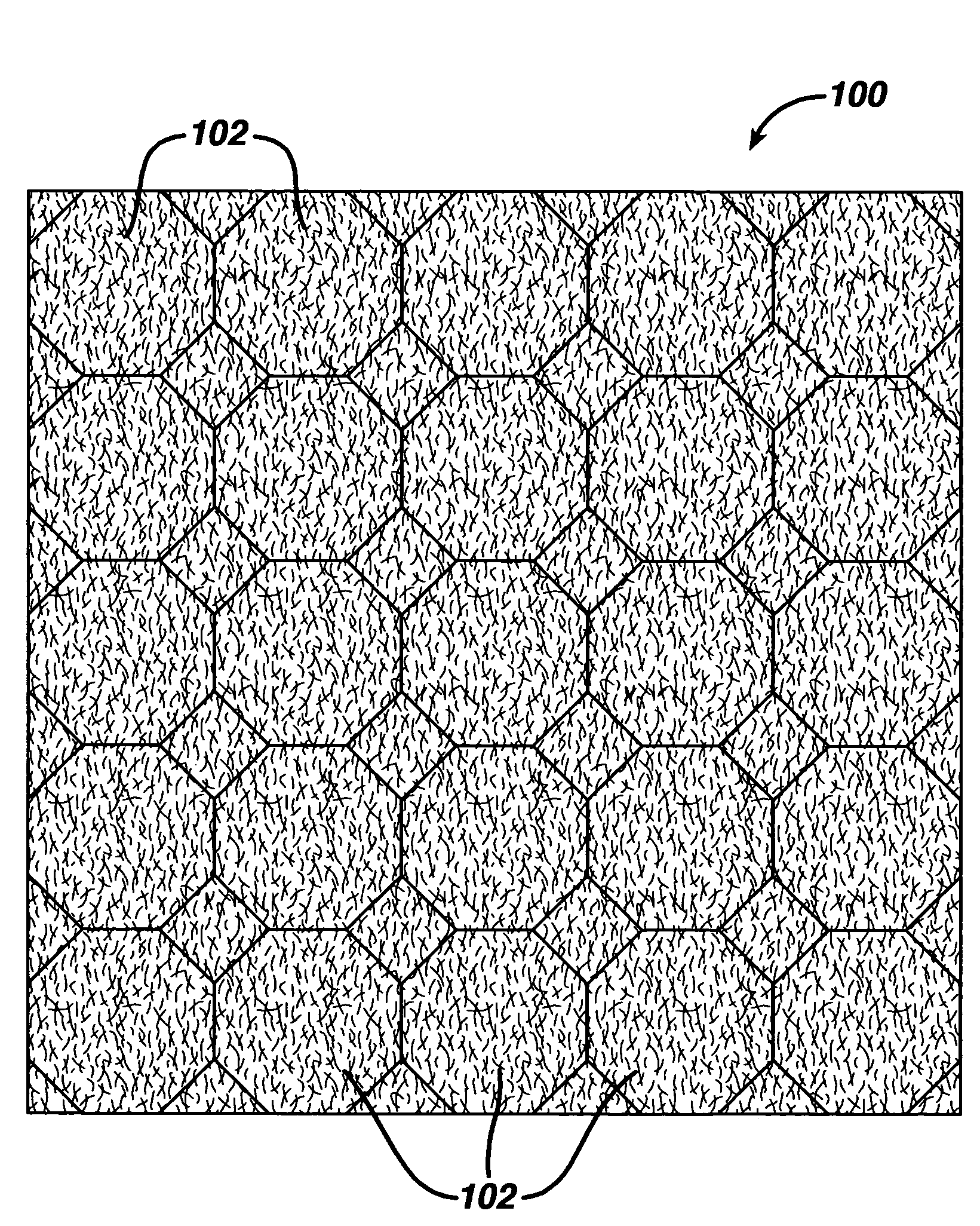
A composite implantable device for promoting tissue ingrowth therein comprising a biodurable reticulated elastomeric matrix having a three-dimensional porous structure having a continueous network of interconnected and intercommunicating open pores and a support structure is disclosed. The support structure may be a polymeric surgical mesh comprising a plurality of intersecting one-dimensional reinforcement elements, wherein said mesh is affixed to a face of said first matrix. Methods of making and using the implantable device are also provided.
Owner:BIOMERIX CORP
Hemostatic wound dressings and methods of making same
The present invention is directed to a hemostatic wound dressing that utilizes a fibrous, fabric substrate made from carboxylic-oxidized cellulose and containing a first surface and a second surface opposing the first surface, the fabric having flexibility, strength and porosity effective for use as a hemostat; and further having a porous, polymeric matrix substantially homogeneously distributed on the first and second surfaces and through the fabric, the porous, polymeric matrix being made of a biocompatible, water-soluble or water-swellable cellulose polymer, wherein prior to distribution of the polymeric matrix on and through the fabric, the fabric contains about 3 percent by weight or more of water-soluble oligosaccharides.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com